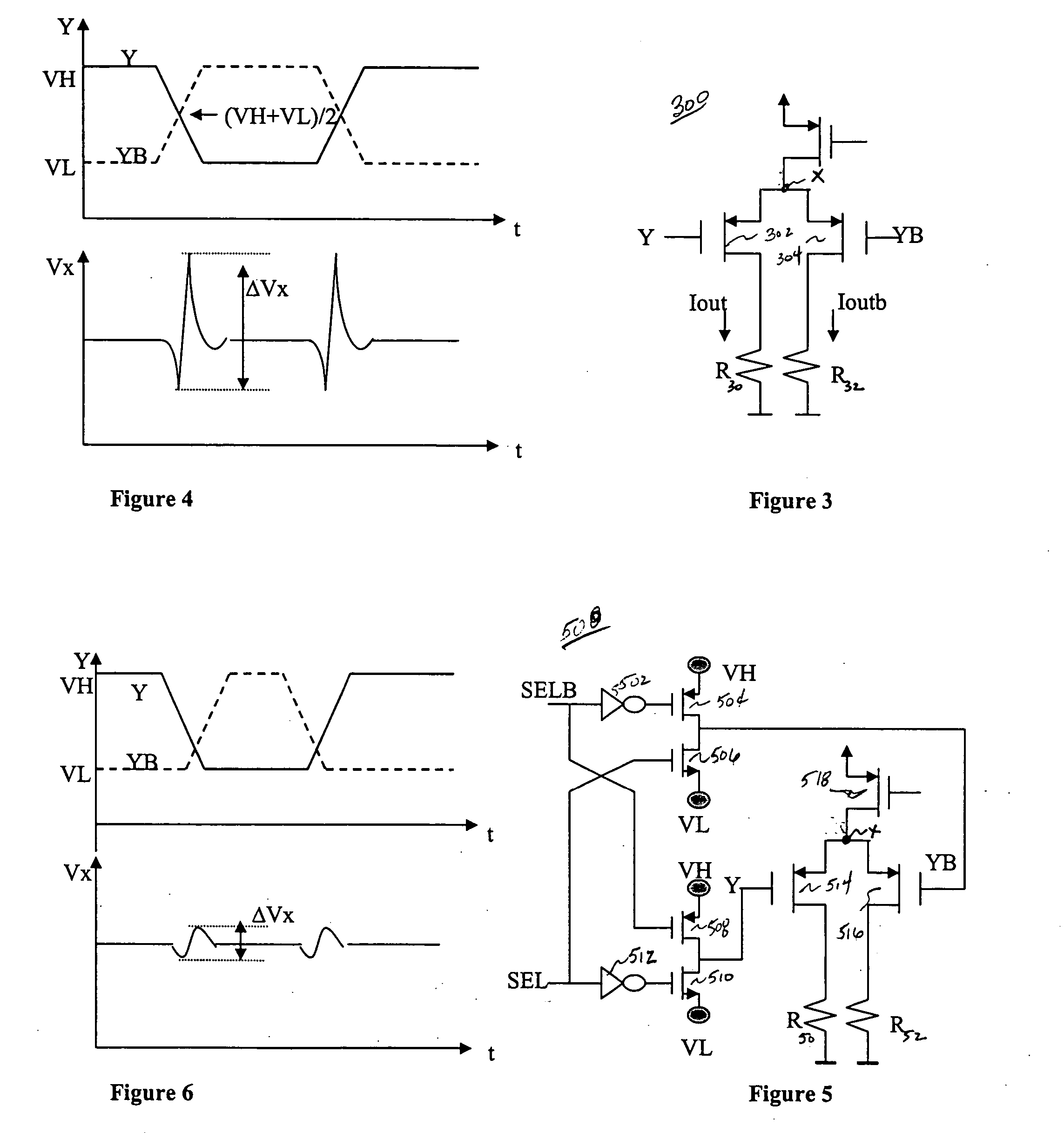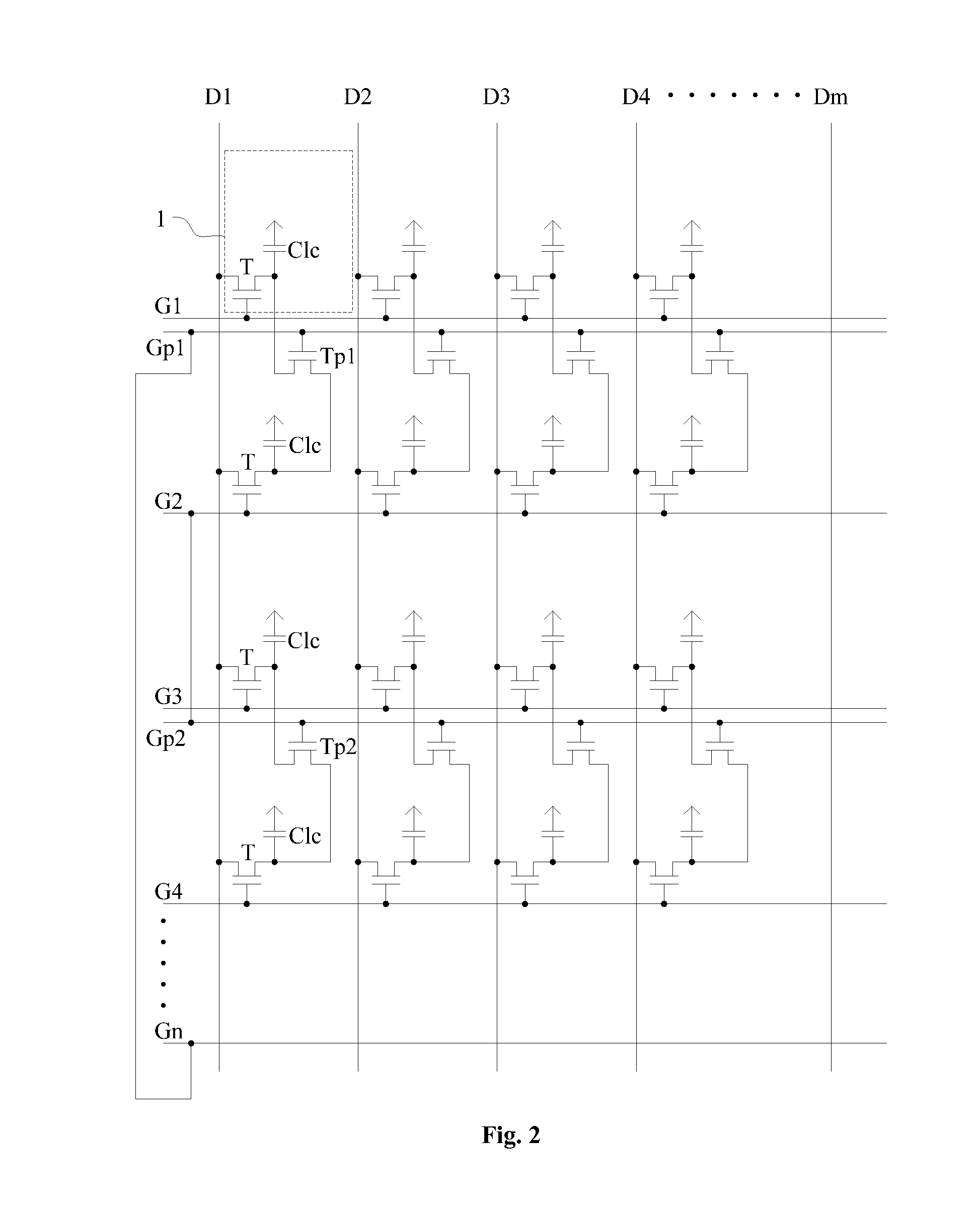Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "Reduce voltage variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
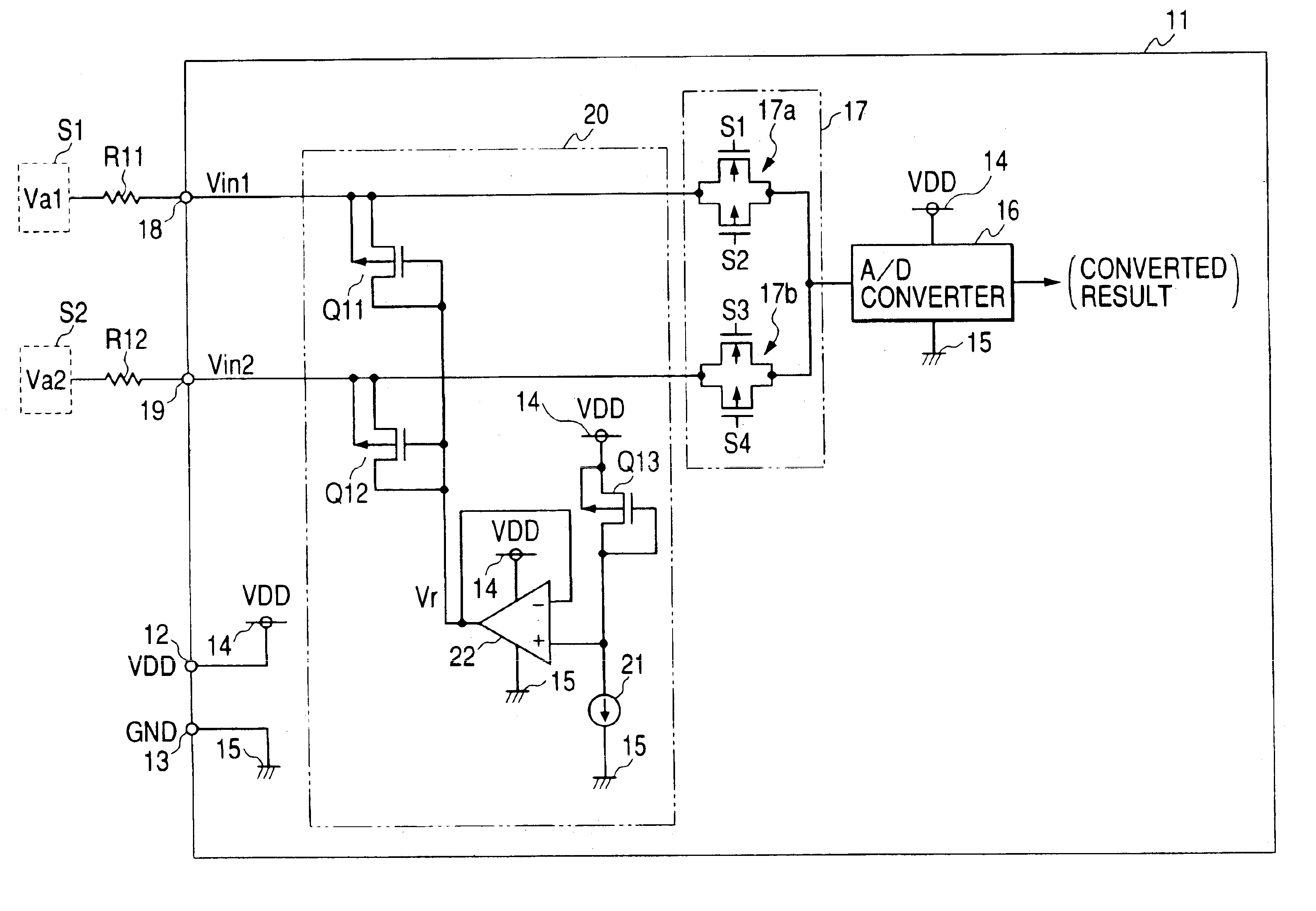
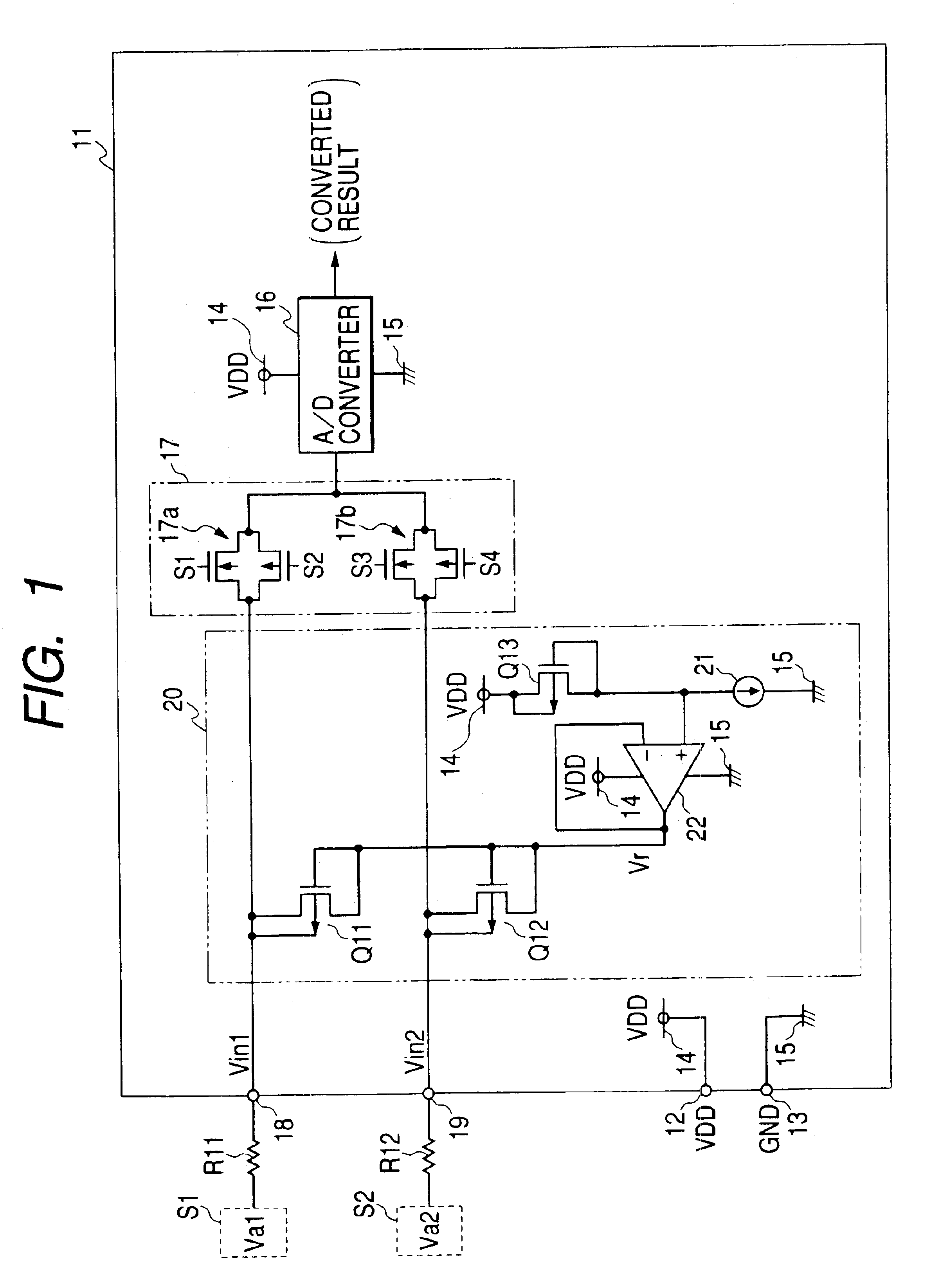
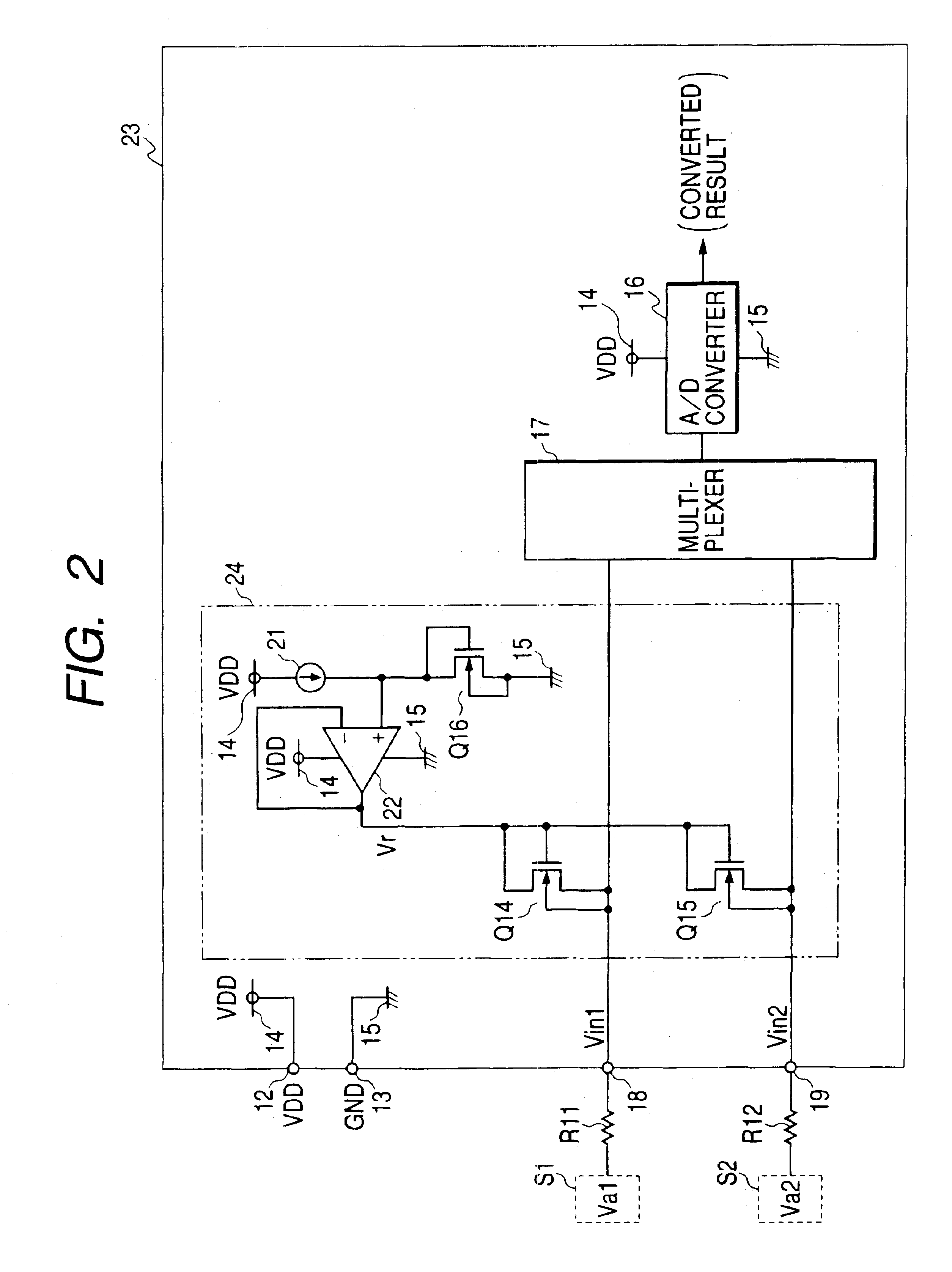
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS6794921B2Reduce voltage variationPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesTerminal voltageEngineering
In the clamp circuit, the first transistor shifts a target clamp voltage by a gate-source voltage to output the target clamp voltage. The buffer circuit inputs the shifted voltage and output a reference voltage on the inputted shifted voltage. The gate of the second transistor is connected to the output terminal of the buffer circuit. The source of the second transistor is connected to the input terminal of the first transistor. In this structure, the reference voltage is supplied to the gate of the second transistor so that, when a terminal voltage of the input terminal of the IC is not less than a clamp voltage corresponding to the sum of the reference voltage and a threshold voltage of the second transistor, the second transistor turns on, whereby the terminal voltage is clamped to a clamp voltage related to the target clamp voltage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
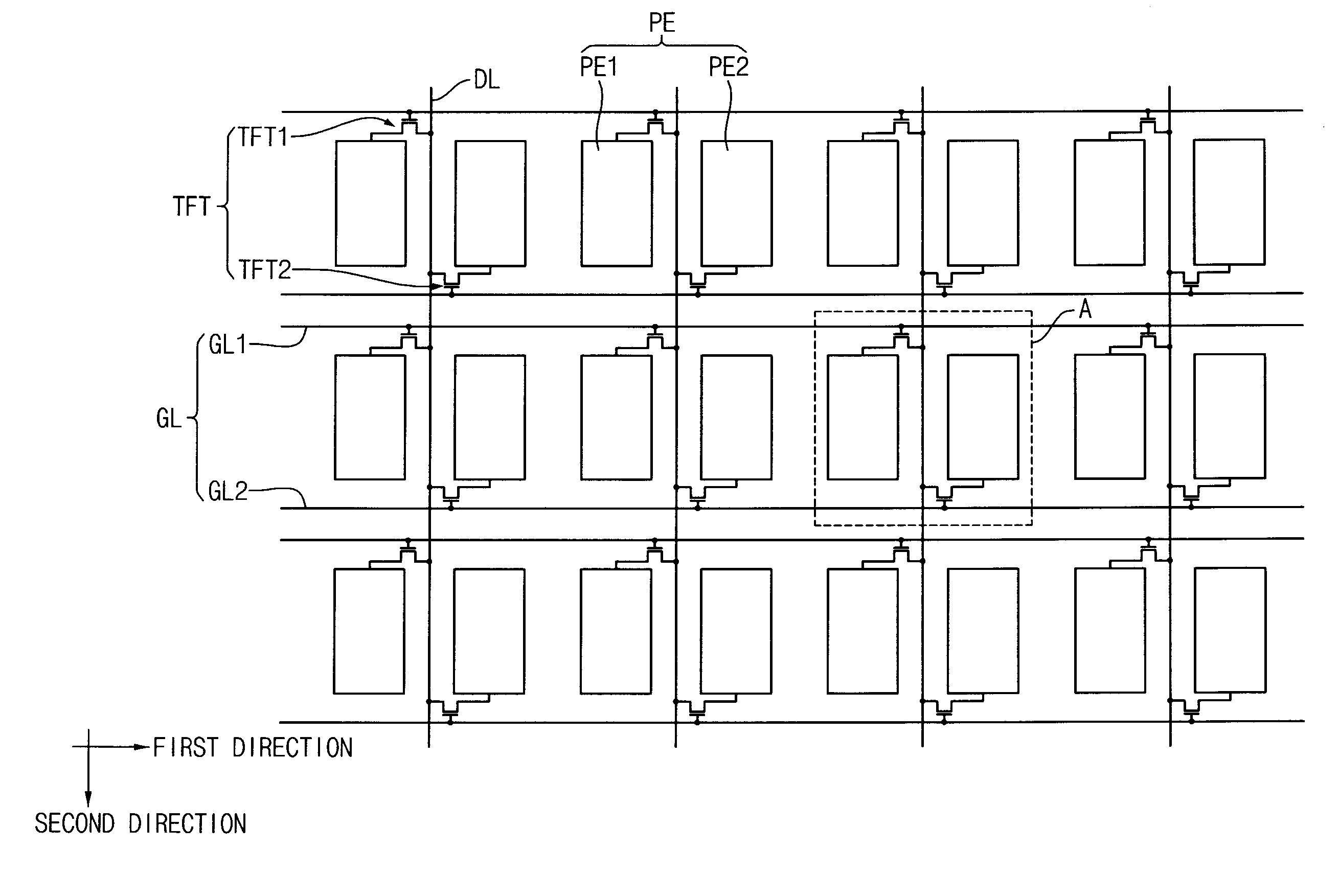
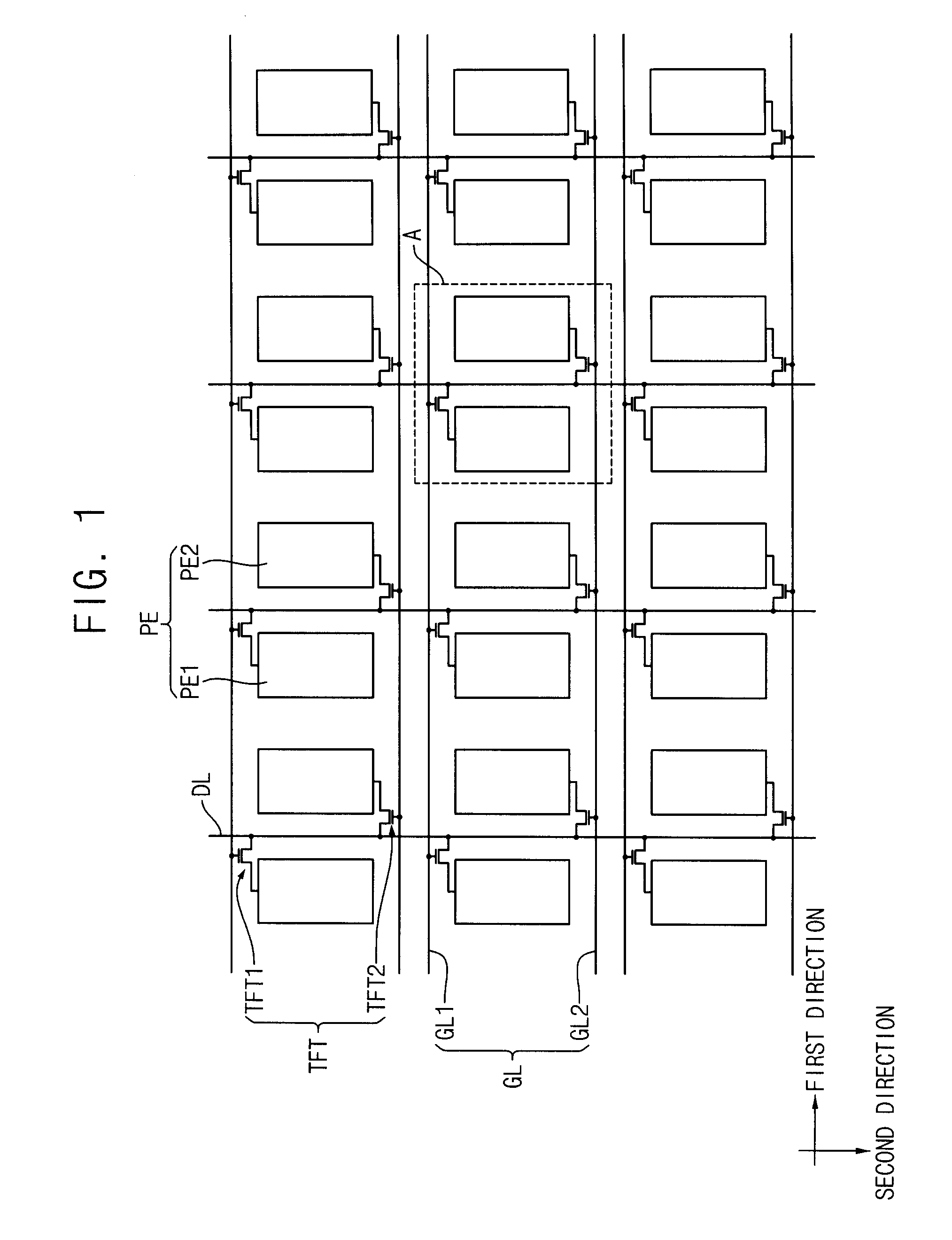
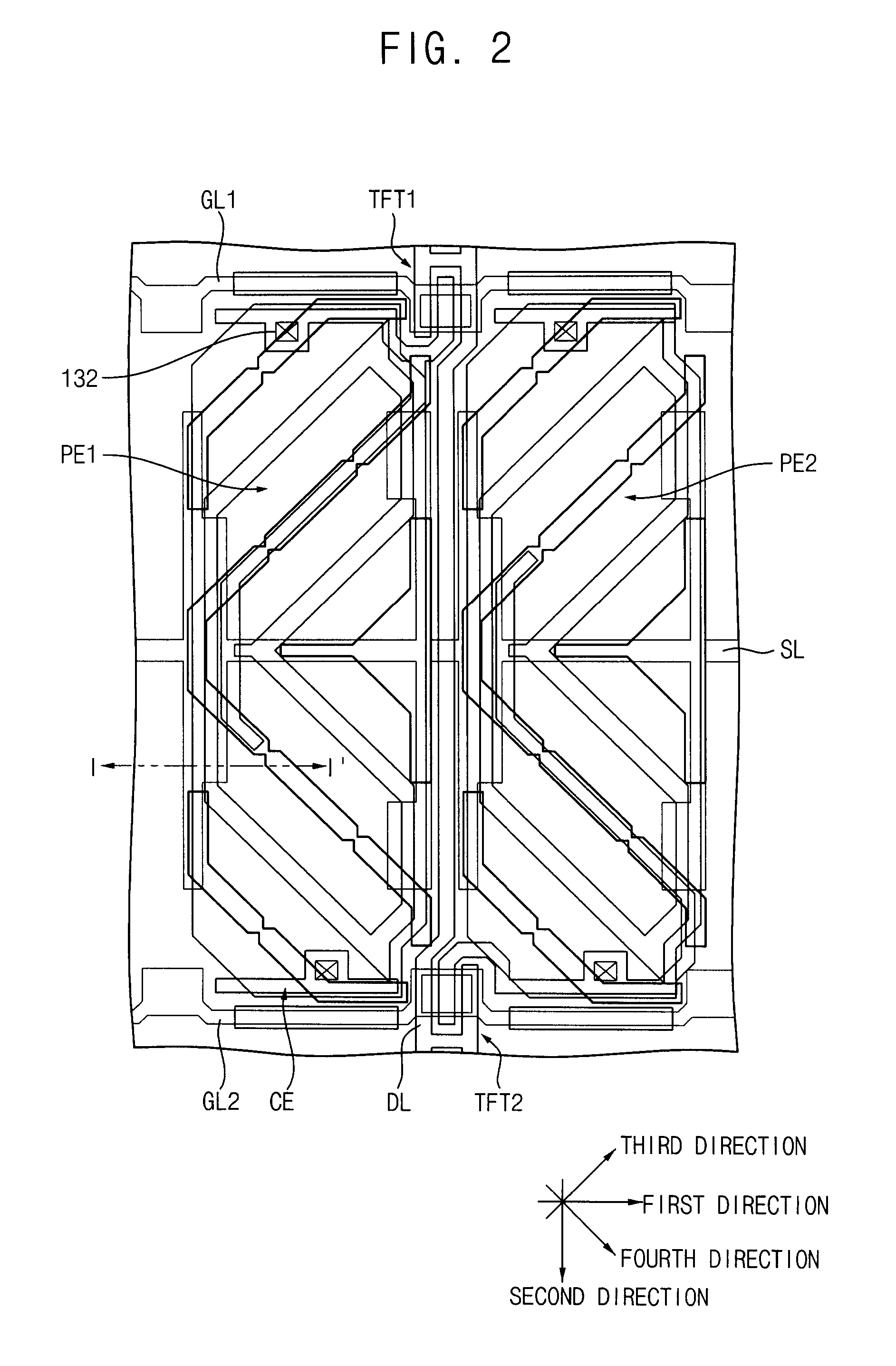
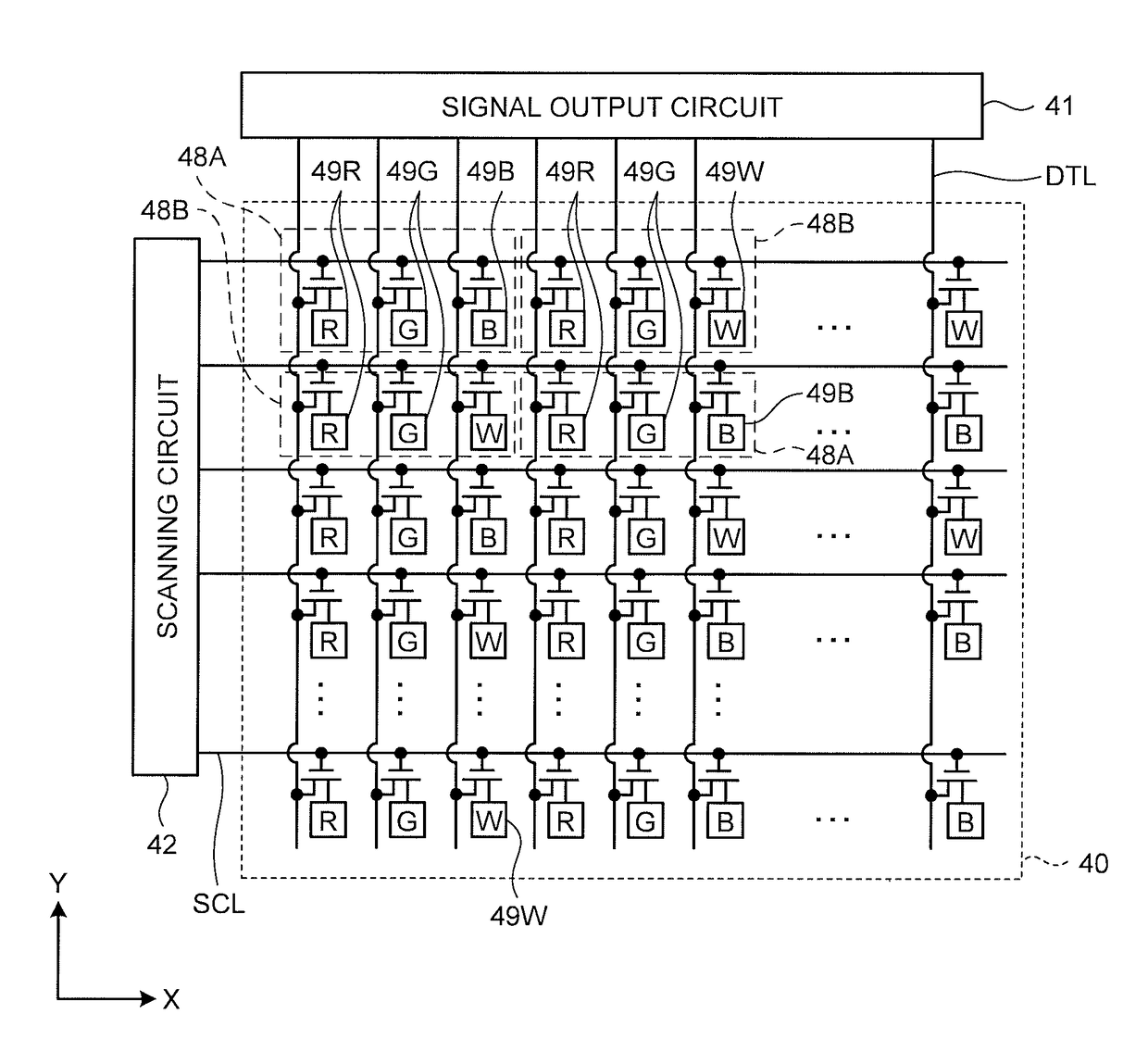
Array substrate and display panel having the same
ActiveUS20080100555A1Reduce voltage variationImprove display qualityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsTransistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
An array substrate includes a gate line, a data line, a thin film transistor (TFT), a pixel electrode and a storage line. The pixel electrode includes a main pixel electrode and a sub pixel electrode partly surrounding at least a portion of the main pixel electrode. The storage line includes a main storage line that extends substantially parallel to the gate line and across the pixel electrode, a sub storage line that extends from the main storage line and substantially parallel to the data line to overlap the sub pixel electrode, and a protruding storage line that extends from the sub storage line and substantially parallel to the gate line to overlap the main pixel electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
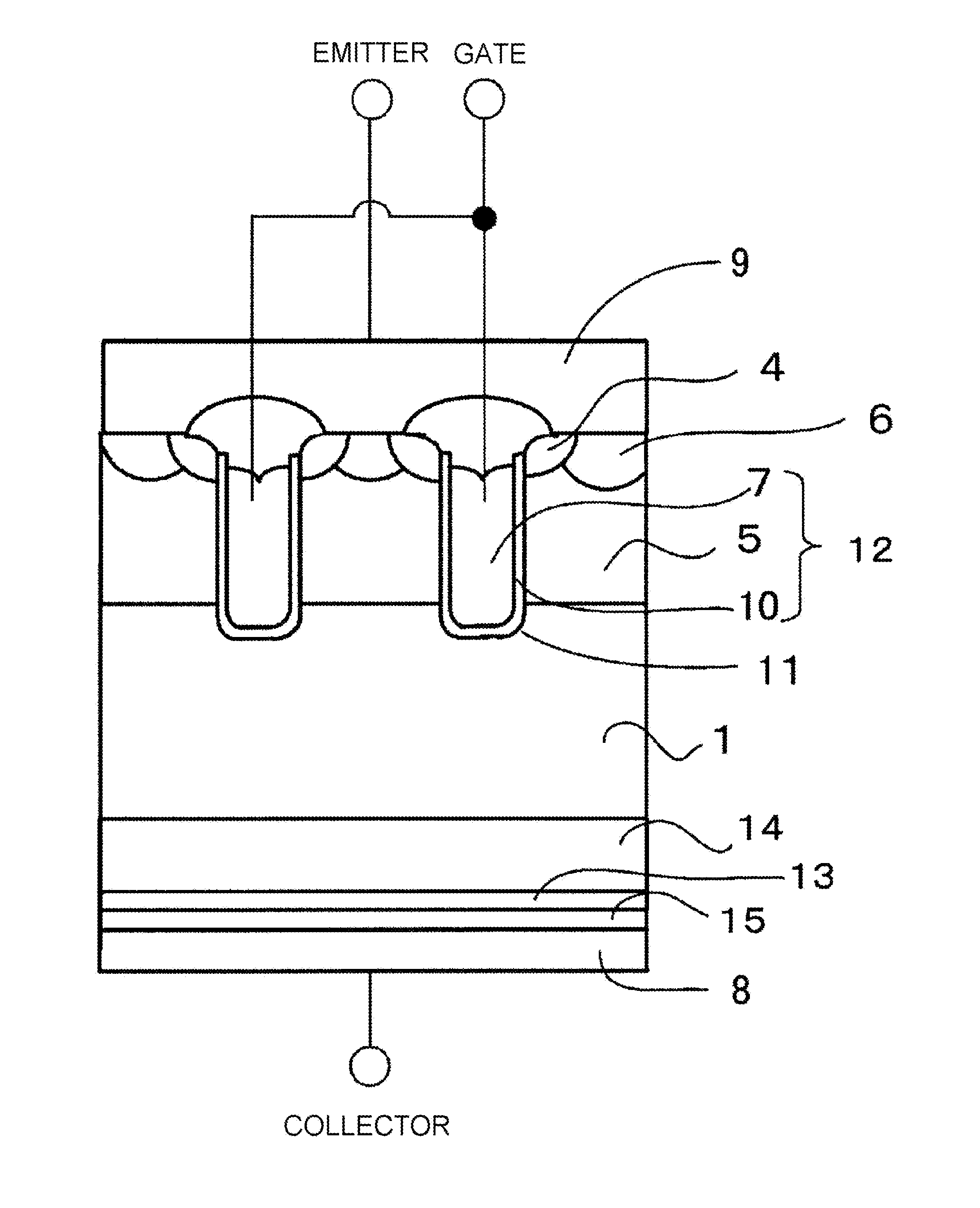
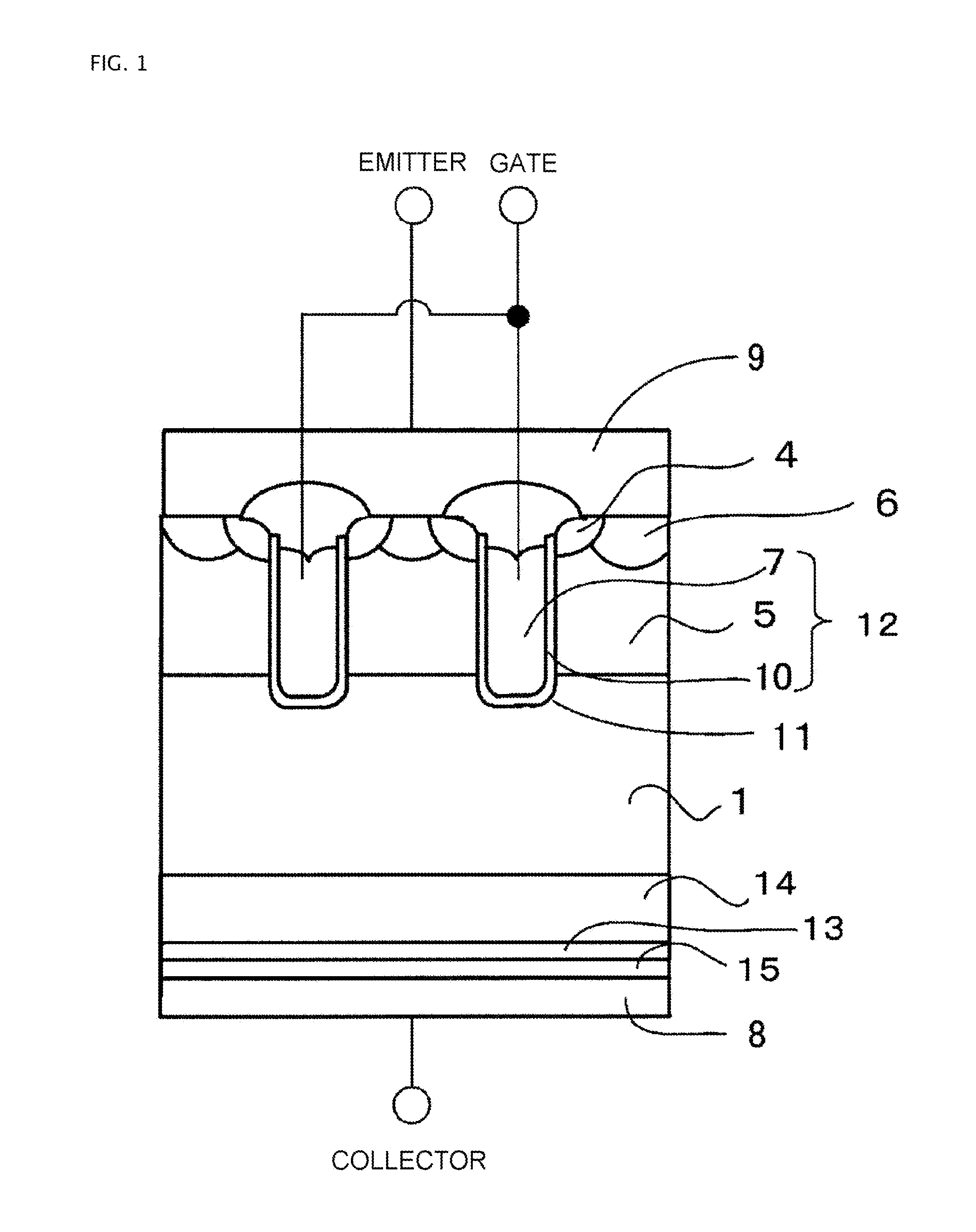
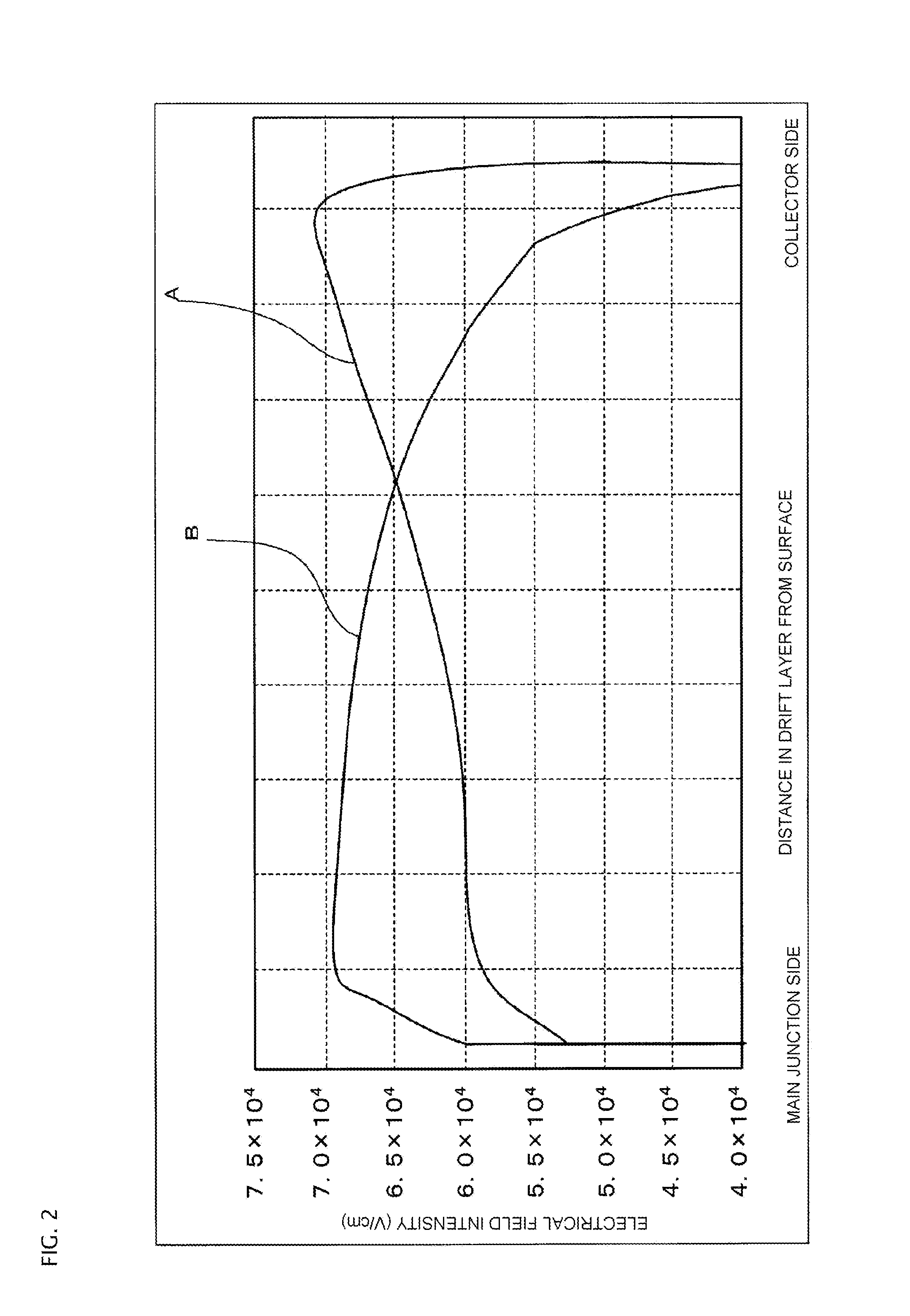
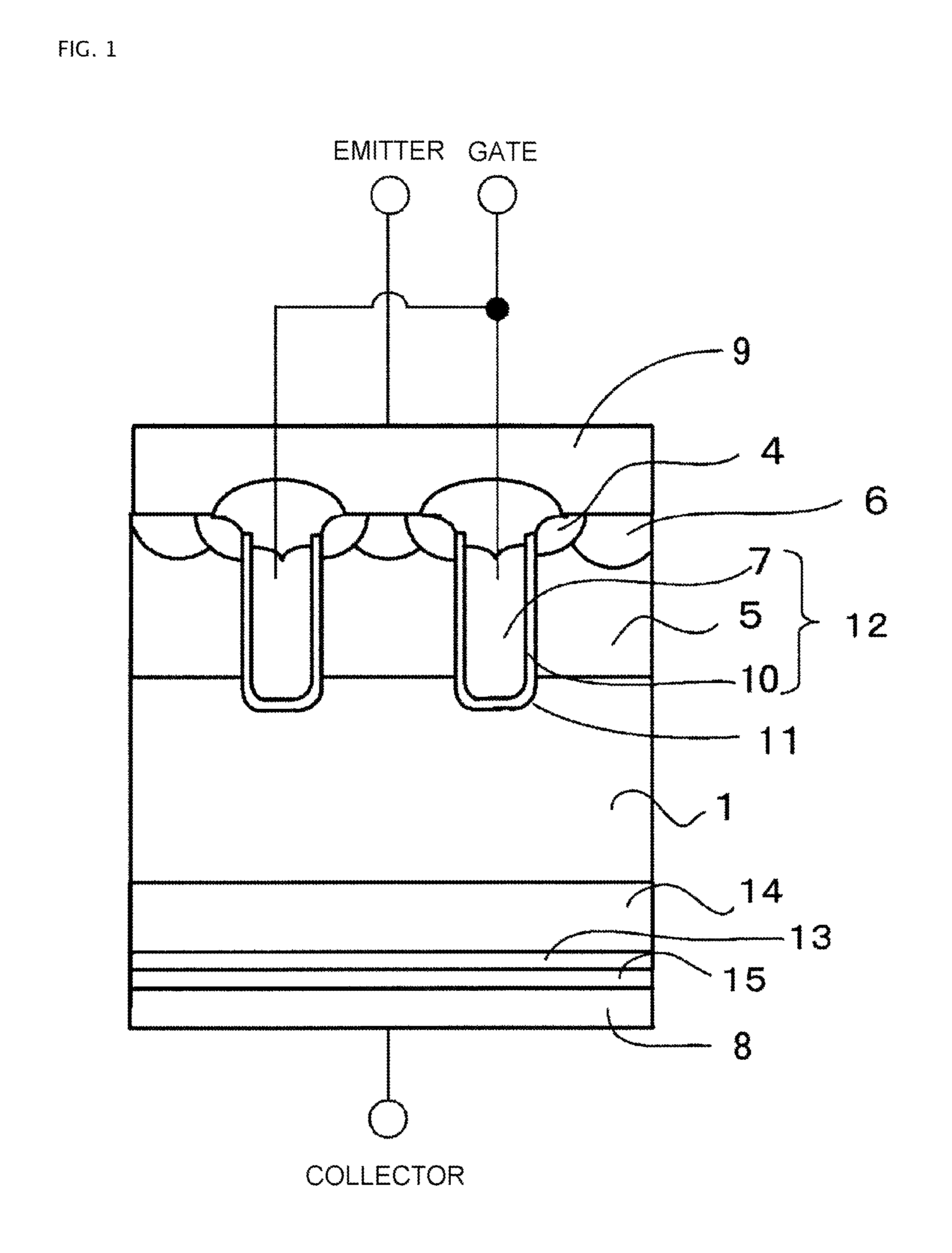
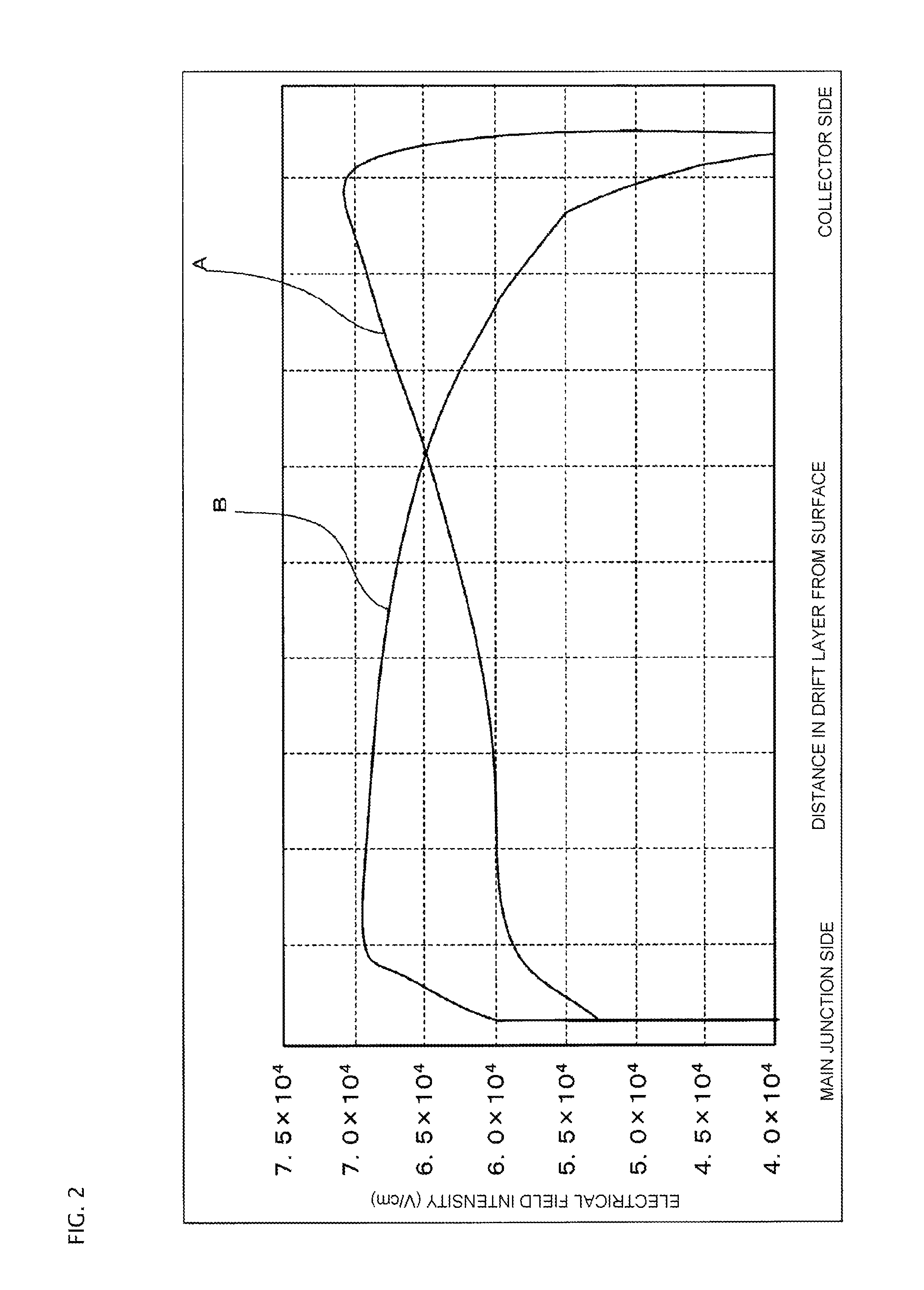
ActiveUS20140070268A1Rise of magnetic field intensityReduce on-state voltage variationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceConcentration gradient
In some aspects of the invention, an n-type field-stop layer can have a total impurity of such an extent that a depletion layer spreading in response to an application of a rated voltage stops inside the n-type field-stop layer together with the total impurity of an n− type drift layer. Also, the n-type field-stop layer can have a concentration gradient such that the impurity concentration of the n-type field-stop layer decreases from a p+ type collector layer toward a p-type base layer, and the diffusion depth is 20 μm or more. Furthermore, an n+ type buffer layer of which the peak impurity concentration can be higher than that of the n-type field-stop layer at 6×1015 cm−3 or more, and one-tenth or less of the peak impurity concentration of the p+ type collector layer, can be included between the n-type field-stop layer and p+ type collector layer.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
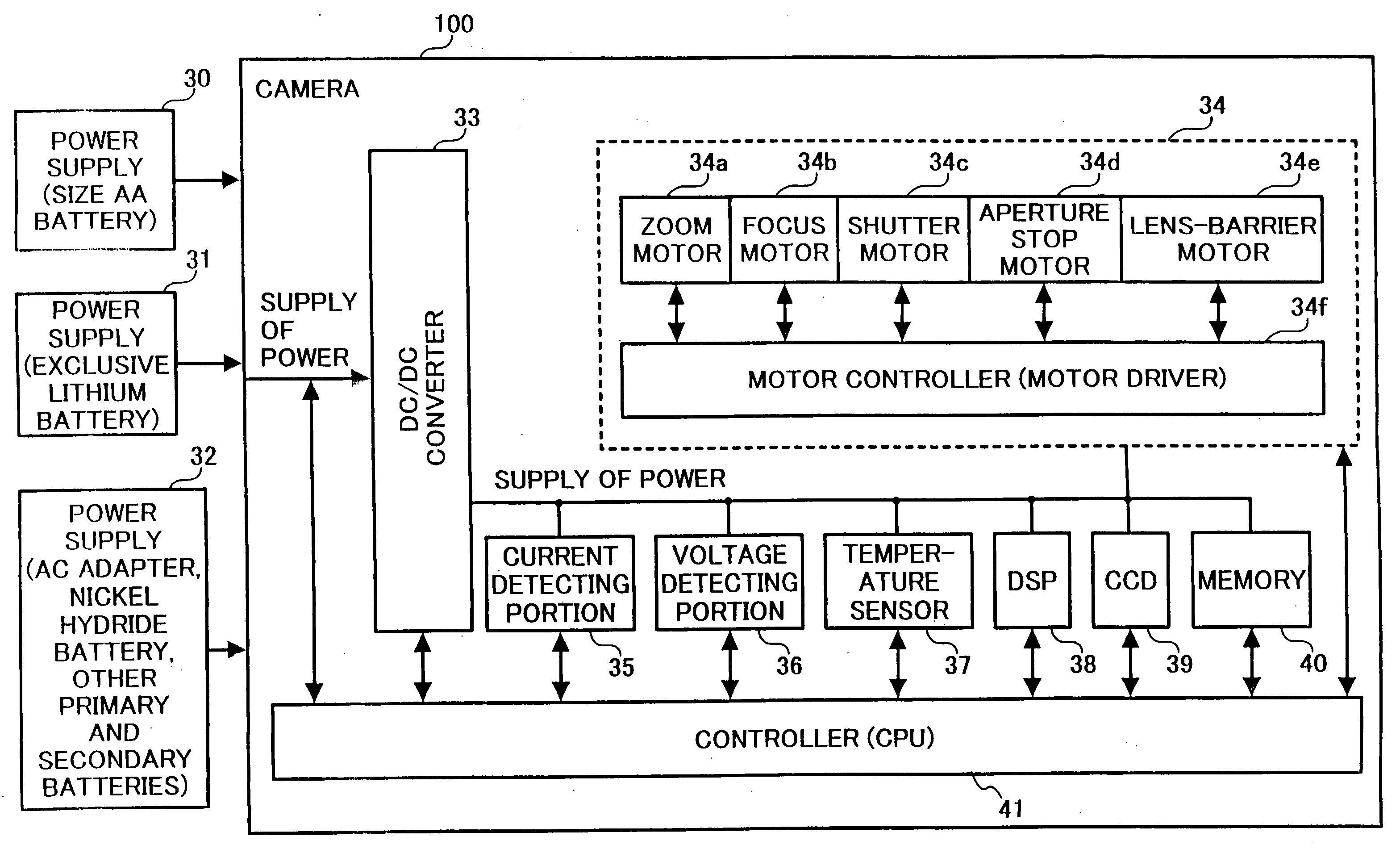
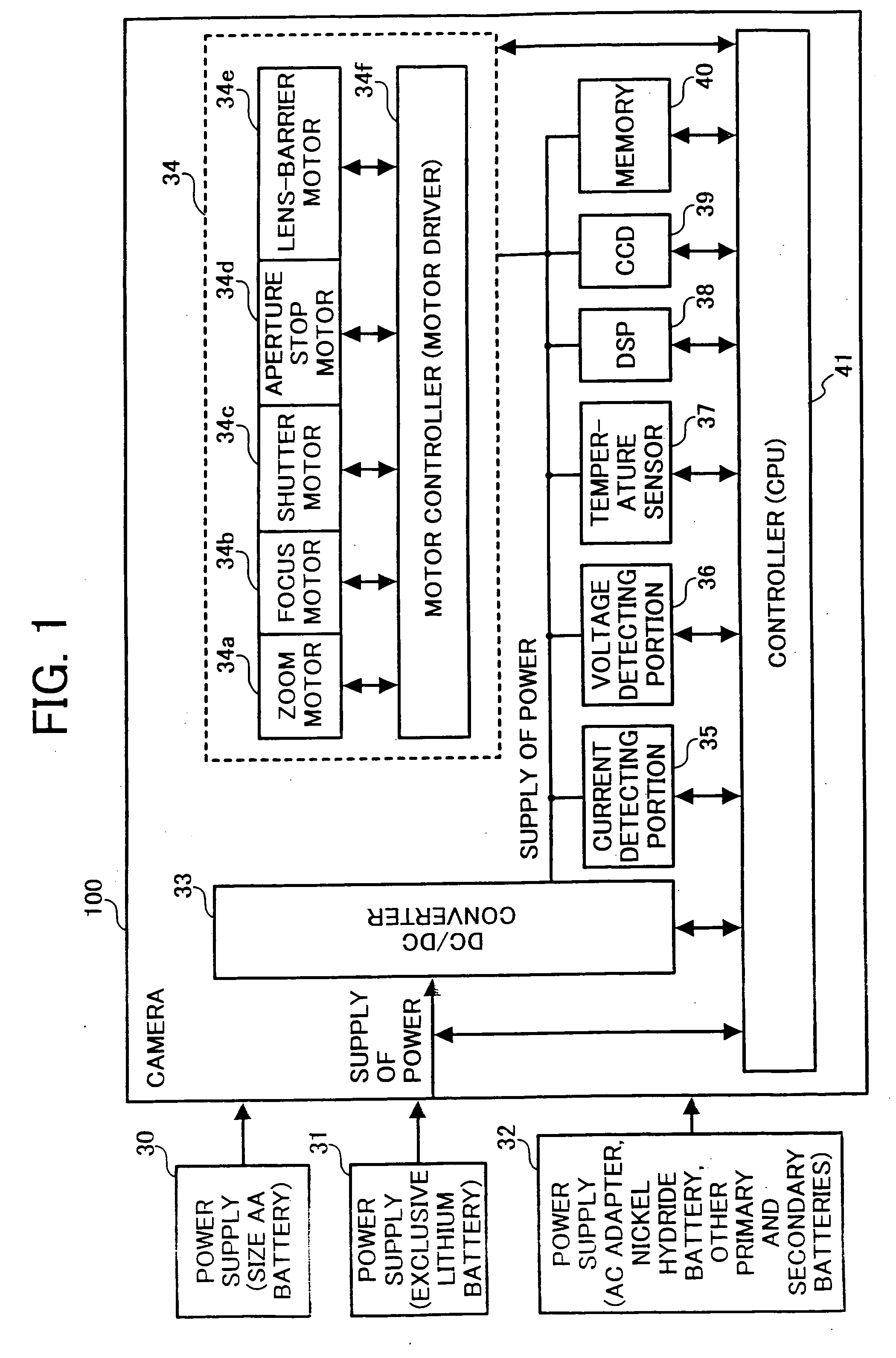
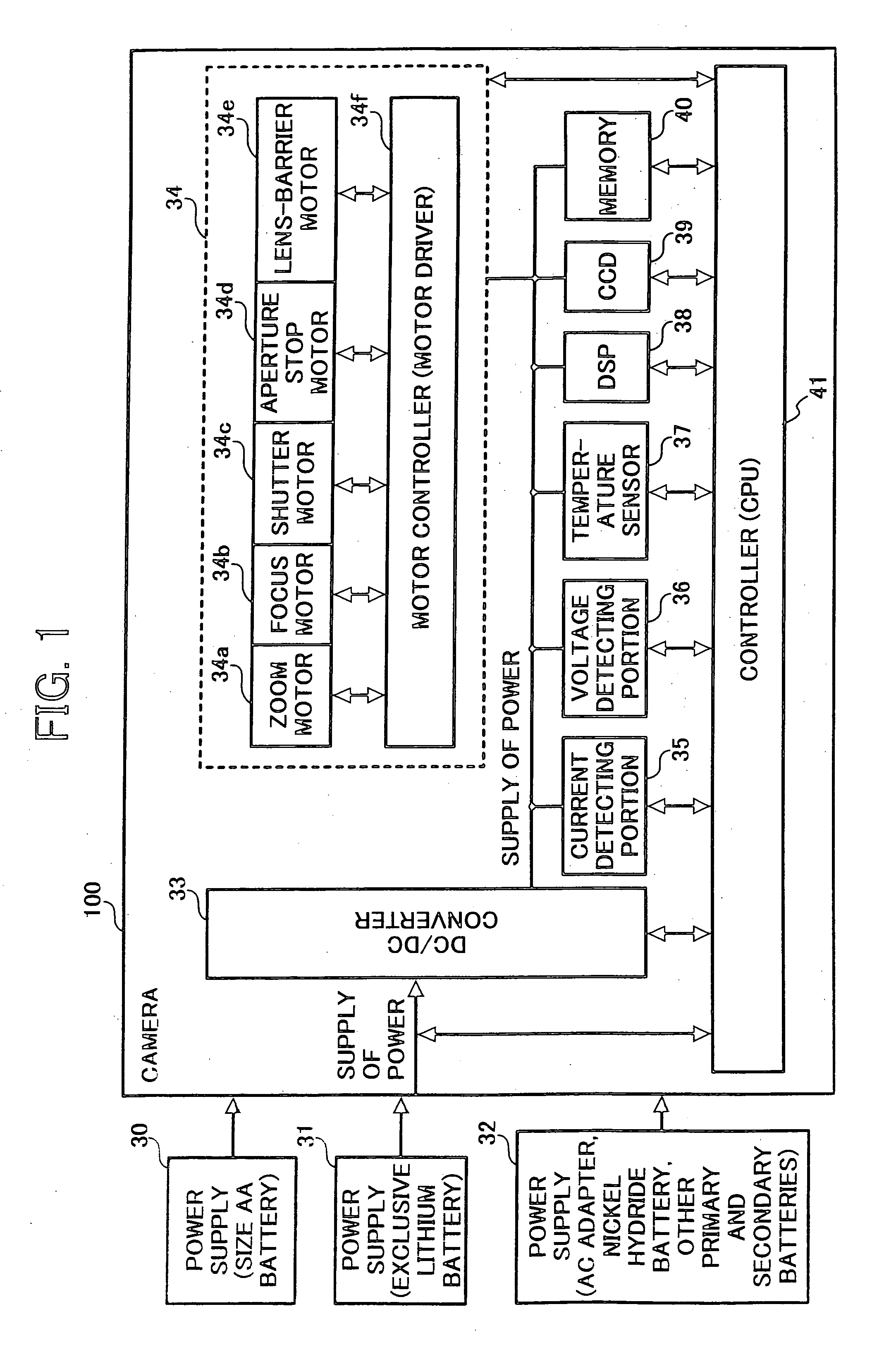
Digital camera and power supply apparatus used therefor
InactiveUS7123829B2Shortened battery lifeAvoid powerTelevision system detailsDc network circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectrical current
Owner:RICOH KK
Current-steering digital-to-analog converter having a minimum charge injection latch
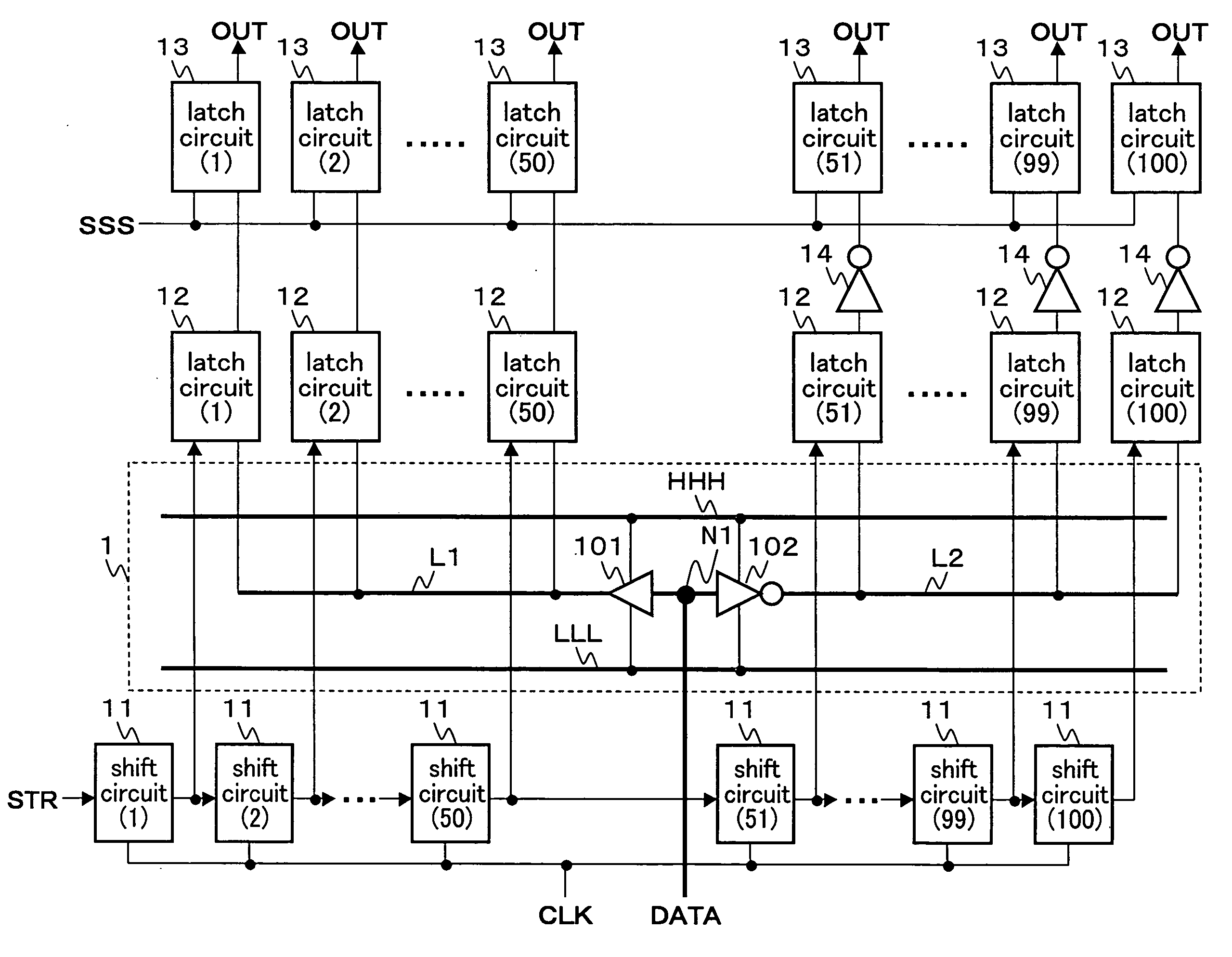
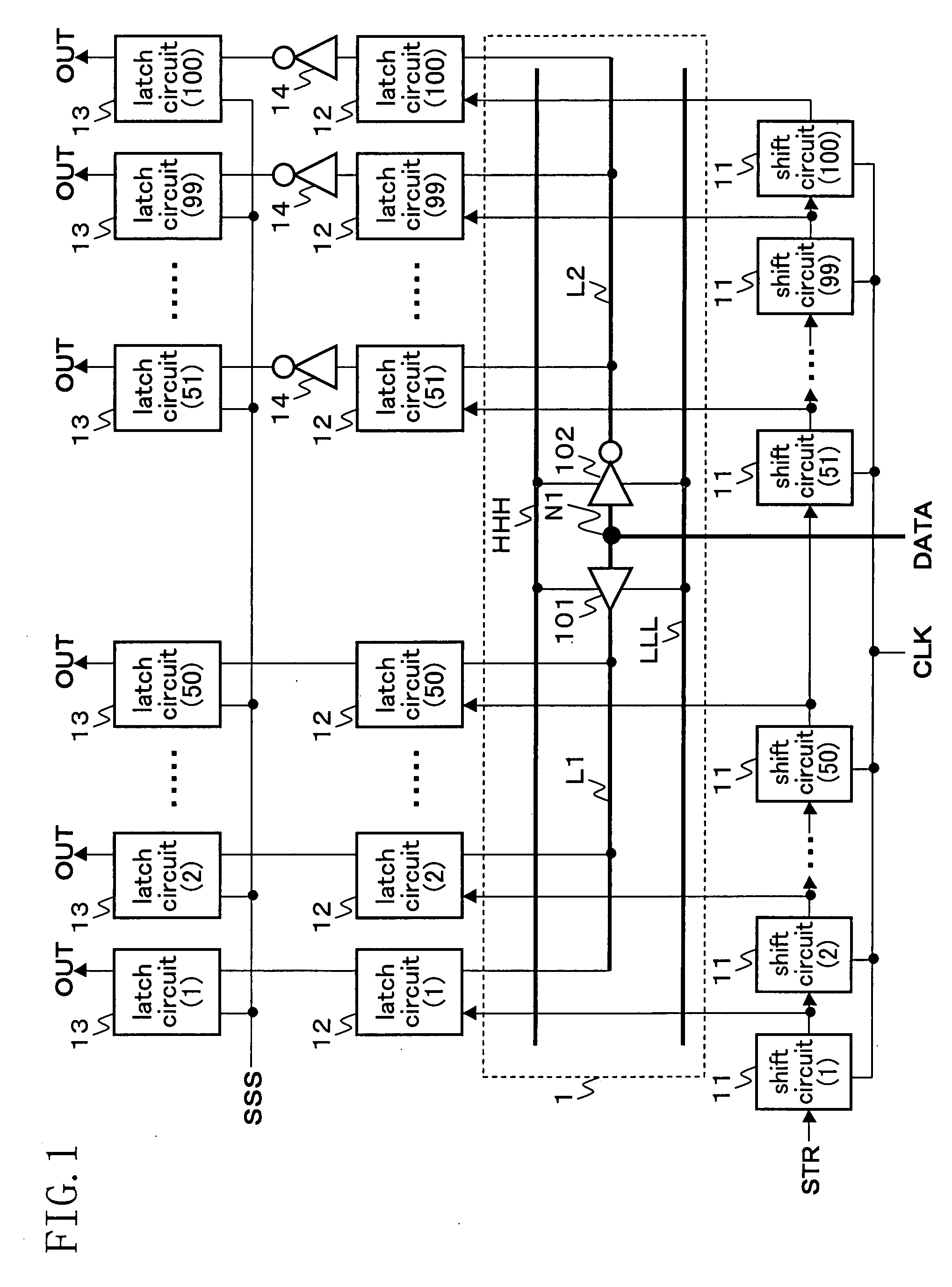
ActiveUS20050225465A1Reduce couplingReduce voltage variationElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsCurrent cellControl signal
A latch architecture for driving unit current cell of a current-steering digital-to-analog converter (DAC) which reduces the drain-source voltage variation of the output current-source transistors and reduces the coupling of unwanted injection of input digital signals as well as clock signals is presented herein. Moreover, this latch helps to achieve lower glitch during code transition with improved dynamic performance. The latch effectively uses the intrinsic RC delay of most transistors within the latch architecture in order to achieve optimal crossing points of complementary control signals. Unwanted input injection or cross-talk is reduced by introducing transistors (904, 906, 932 and 934) that are off during code transitions without compromising the DAC update speed. Conflicts between currently held and new inputs are avoided in an effort to reduce the harmonic distortion. Furthermore, the distortion as a result of the clock signal fed through each transistor in the first and second subcircuit portions cancel each other.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving circuit
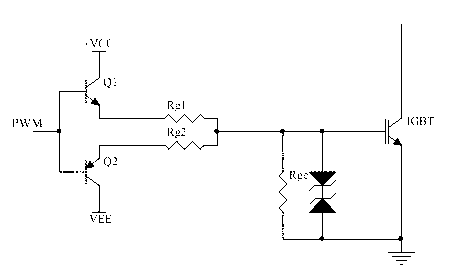
ActiveCN102324835AReduce voltage variationReduce discharge ratePower conversion systemsHigh resistanceVoltage variation
The invention provides an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving circuit, which comprises a switching-on resistor with a relatively higher resistance value, a switching-off resistor with a relatively lower resistance value and a switching input circuit, wherein the switching input circuit is connected to the gate of an IGBT by the switching-on resistor; and one end of the switching-off resistor is connected to the gate of the IGBT. The IGBT driving circuit further comprises an over-voltage detection circuit and a rapid switching-off control circuit. The rapid switching-off control circuit controls the other end of the switching-off resistor to be switched off when the switching input circuits inputs a switching-on level, controls the other end of the switching-off circuit to be grounded when the switching input circuit inputs a switching-off level, and controls the other end of the switching-off resistor to be switched off when the voltage, detected by the over-voltage detection circuit, of the collector of the IGBT is higher than a preset value. The IGBT driving circuit provided by the invention can rapidly realize the rapid switching-off of the IGBT and simultaneously suppress the excessive voltage variations of the IGBT.
Owner:EAST GRP CO LTD
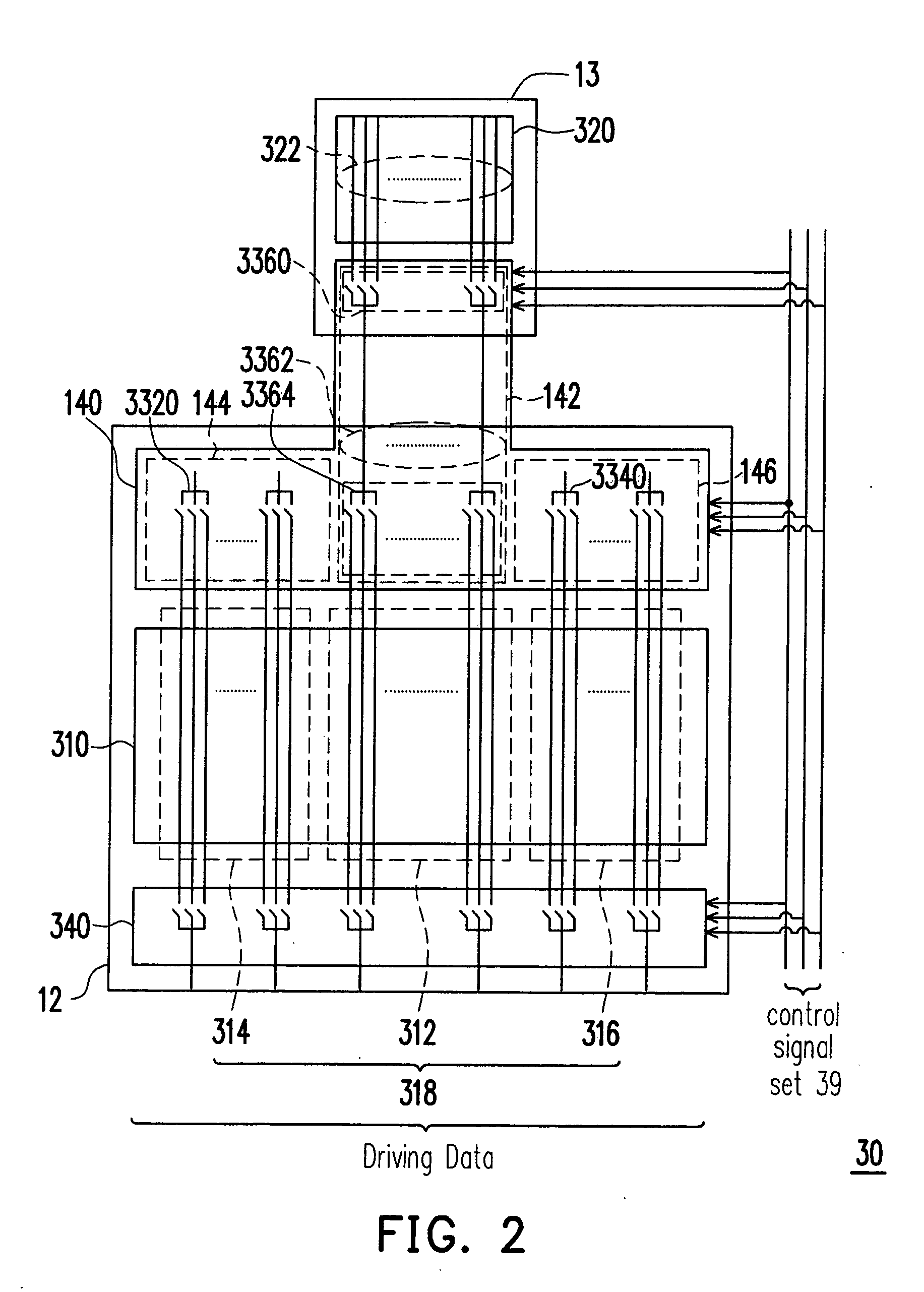
Array substrate, touch display panel and touch display device
ActiveCN104699318AReduce voltage variationSlow down the degree of coupled mutationInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDisplay device
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Display Drives Circuits and Techniques
InactiveUS20130082912A1Quick switchReduce flickerStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsDriver circuitActive matrix
A pixel driver architecture for an active matrix OLED display, the pixel driver architecture comprising a voltage-programmed master pixel programming circuit, and a first plurality of current-programmed slave pixel driver circuits, each coupled to said master pixel programming circuit.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
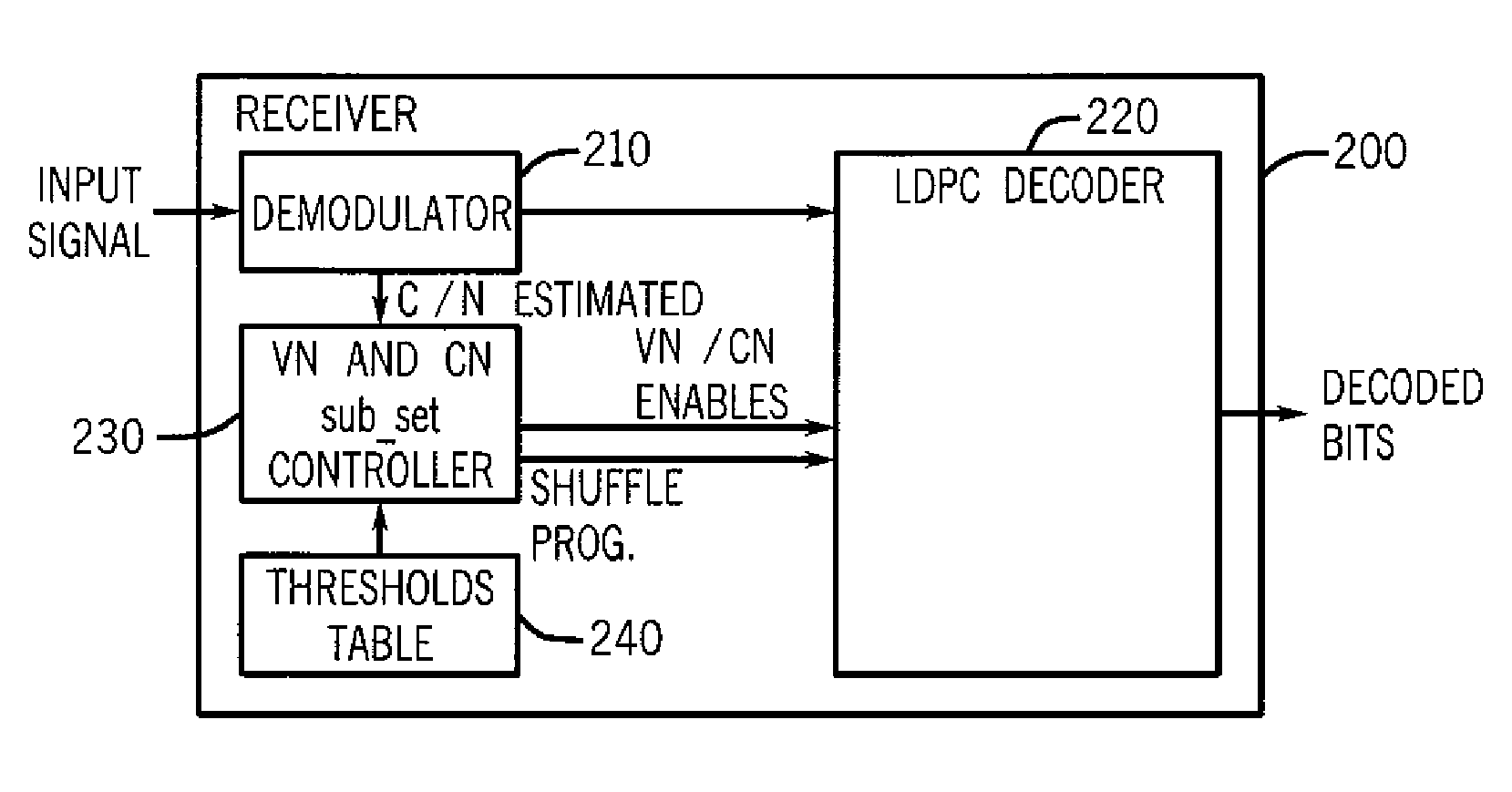
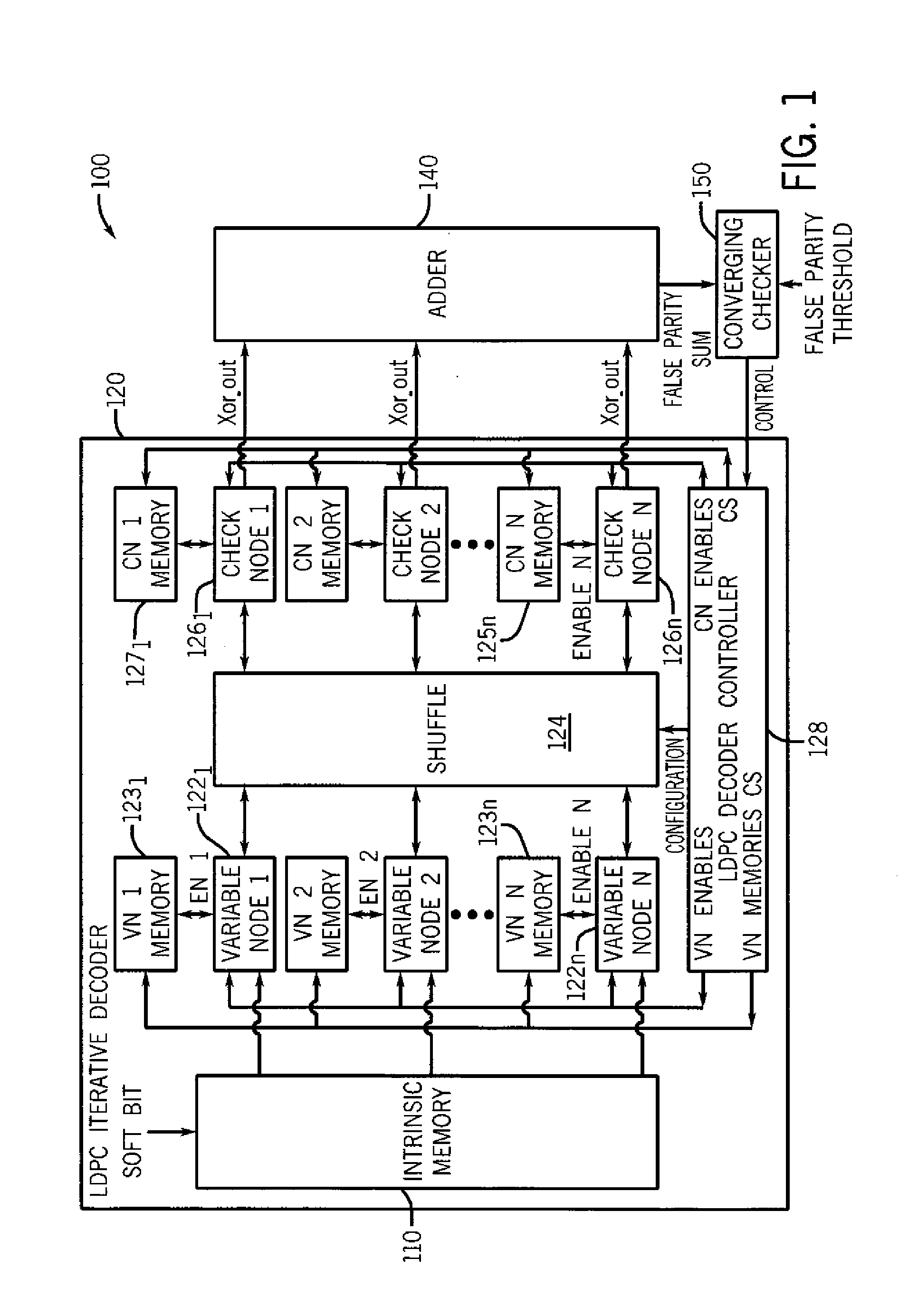
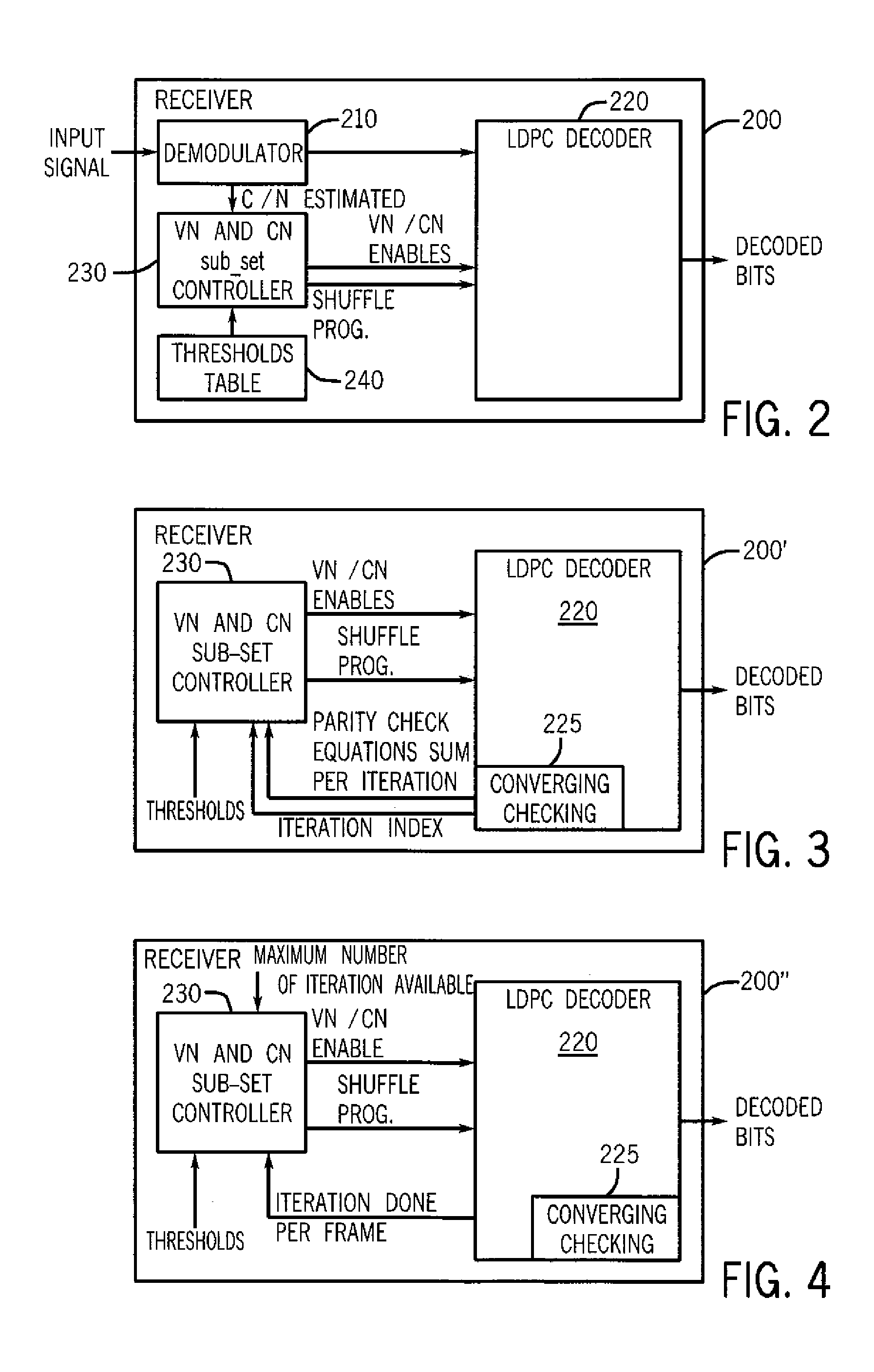
Techniques to control power consumption in an iterative decoder by control of node configurations
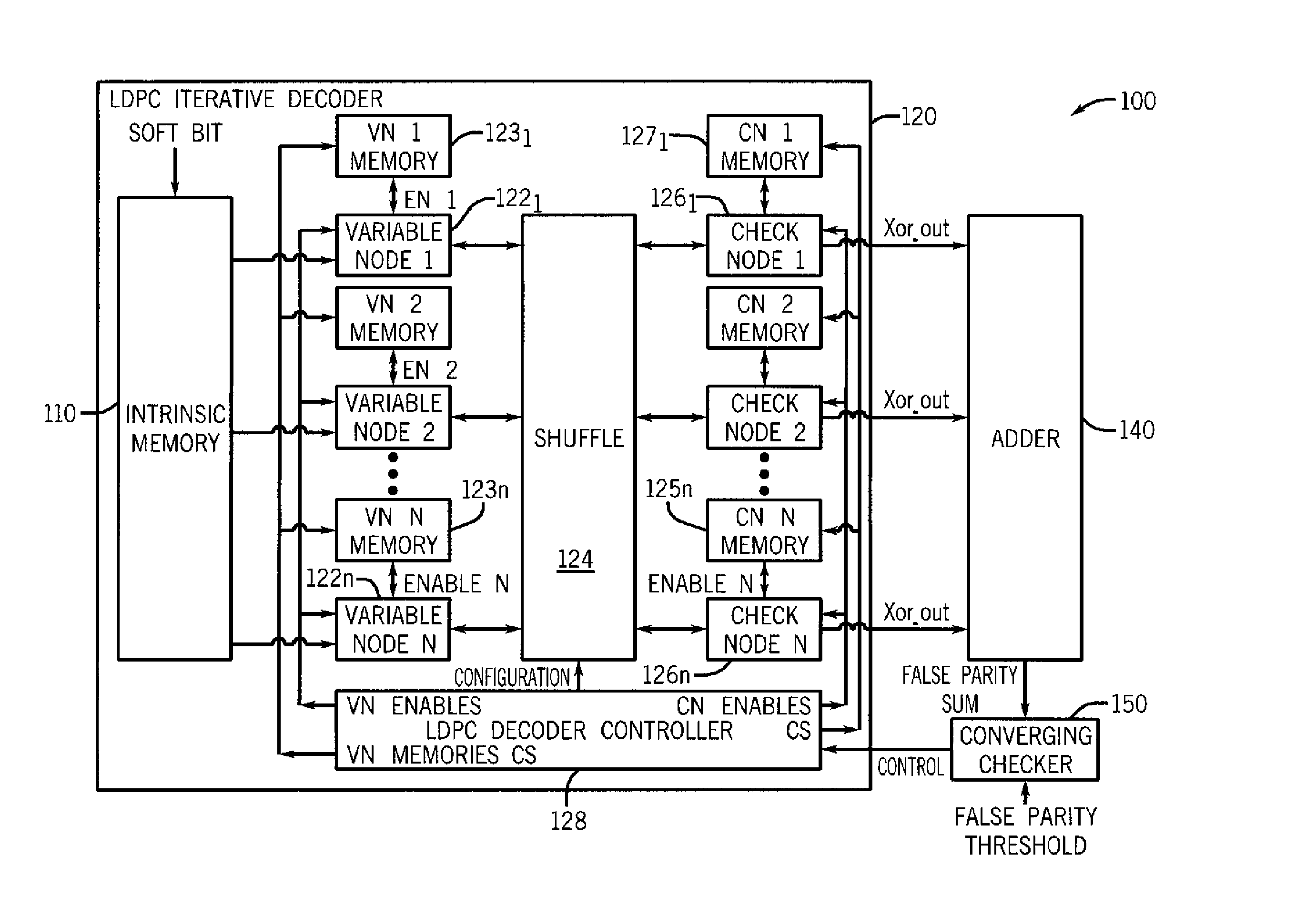
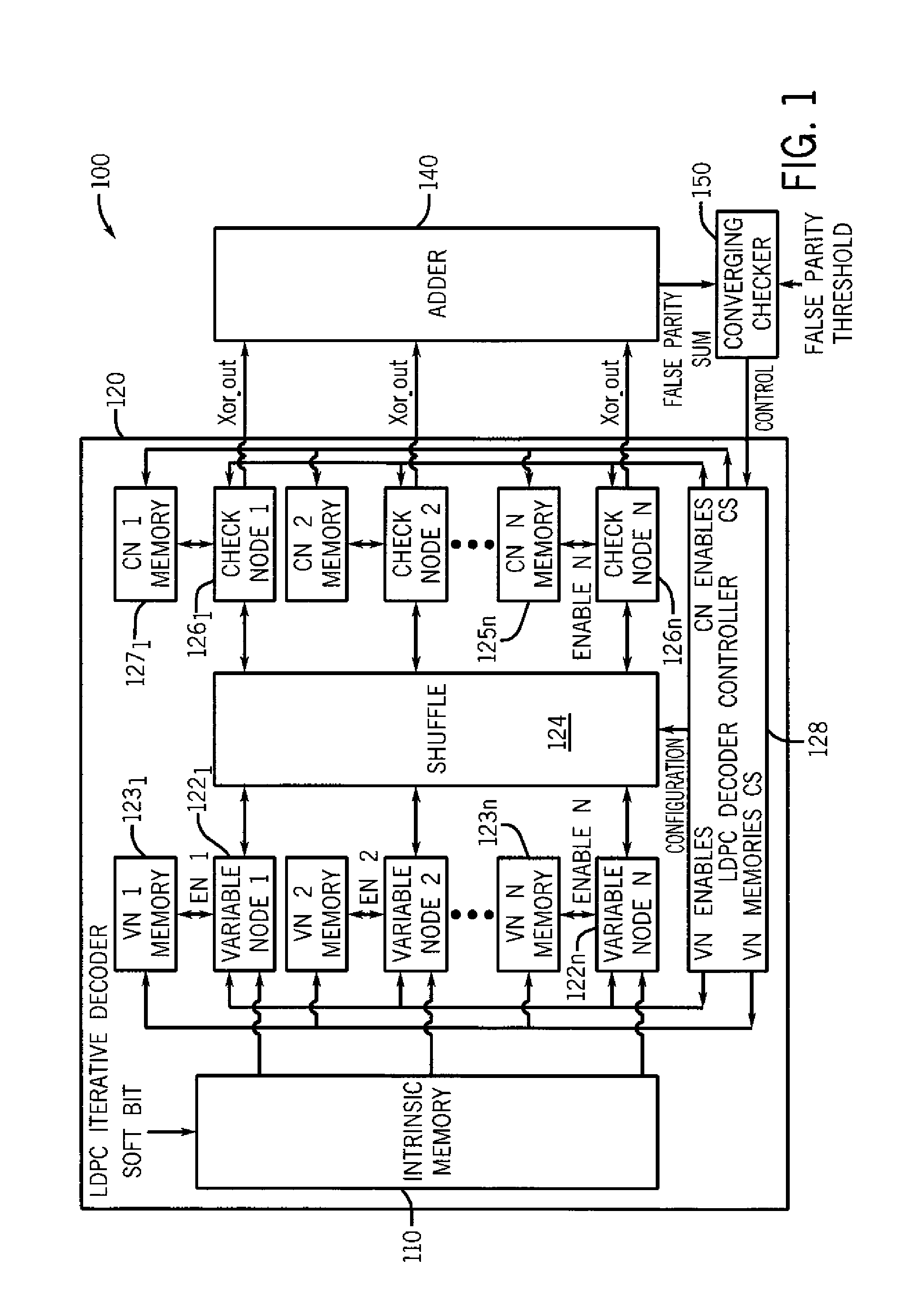
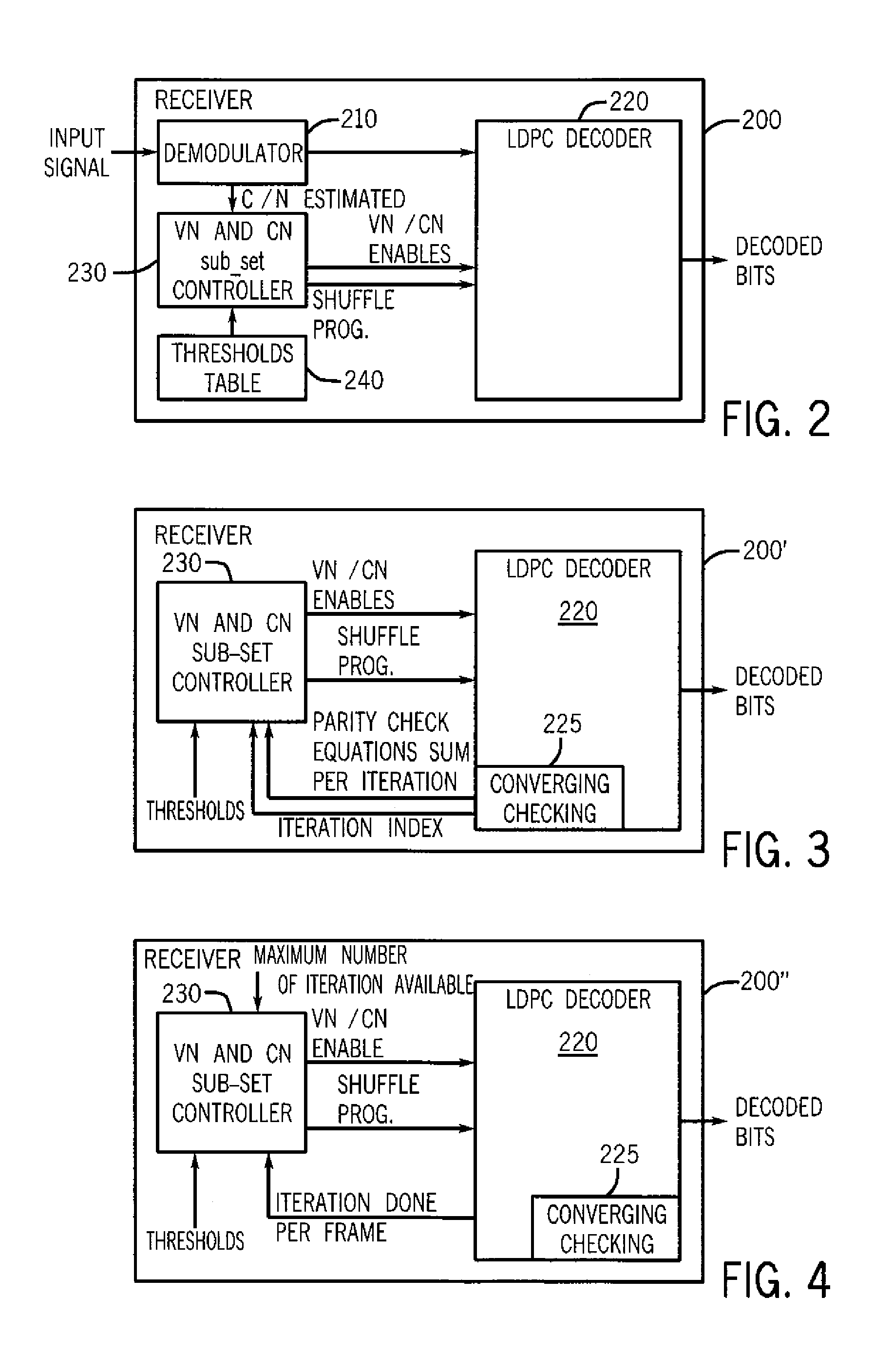
ActiveUS8555131B2Reduce voltage variationDigital data processing detailsCode conversionControl powerVoltage variation
A method for controlling power consumption of an iterative decoder based on one or more criteria is described. The method may include progressively enabling and disabling nodes of the iterative decoder to perform iterative decoding on a demodulated signal to provide a decoded signal with minimal variation of a supply voltage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
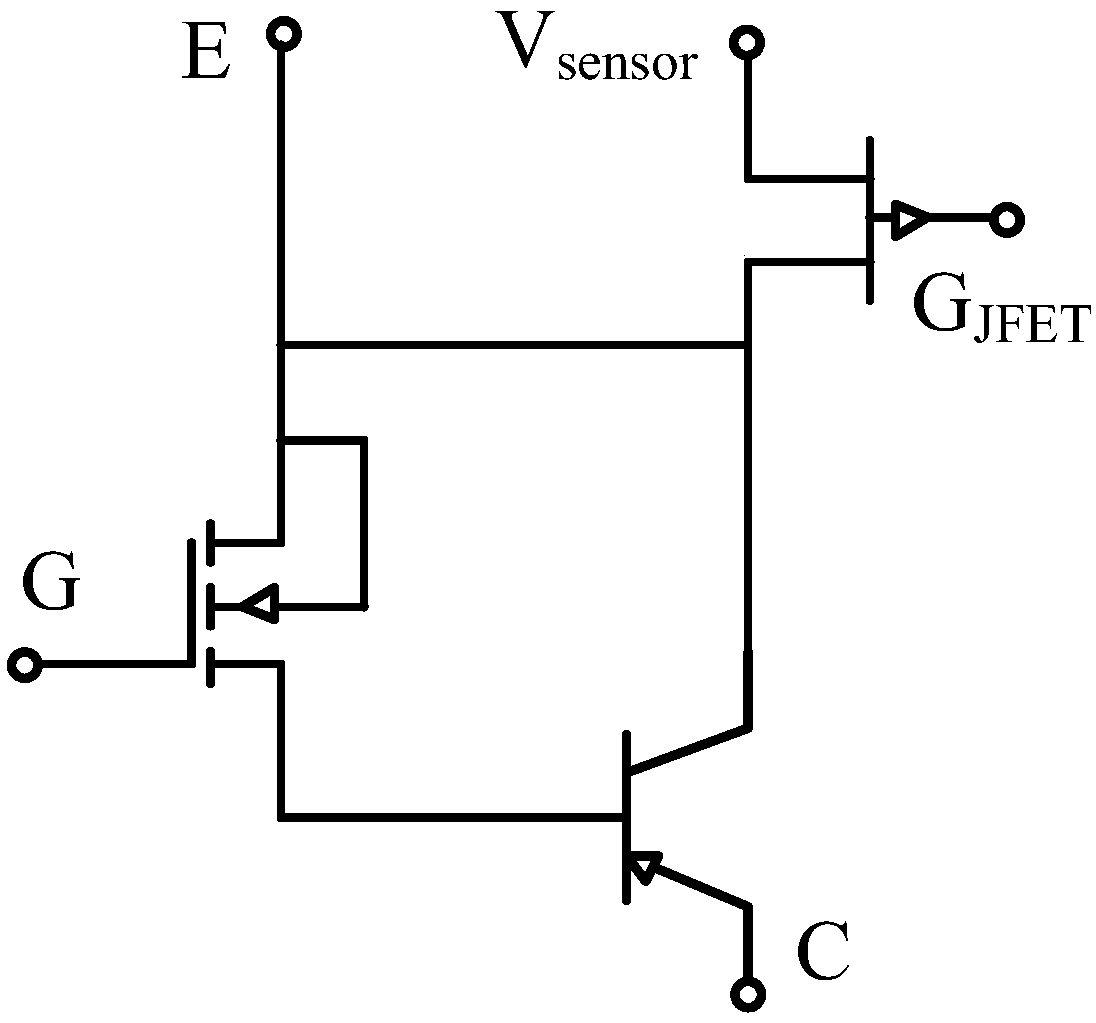
IGBT device with integrated voltage sampling function
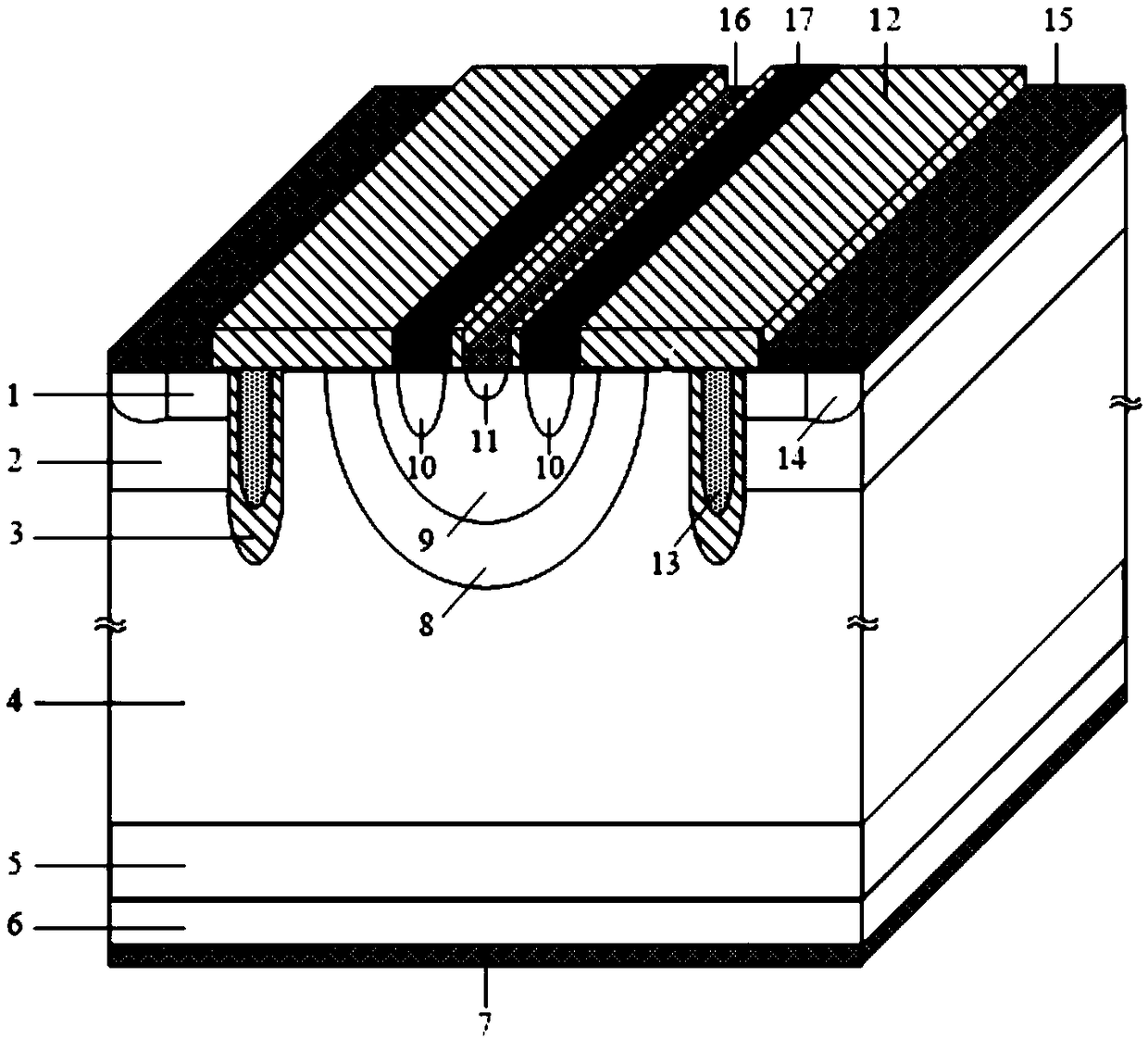
ActiveCN108767006AMeet voltage sampling requirementsSimple sampling structureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIsolation effectEngineering
The invention provides an IGBT device with an integrated voltage sampling function, and belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. A channel in which a JFET structure is introducedin a body region is in a normally-closed state, the device is in a forward turning-on state, and carriers are stored in the body region, so that an electric conductance modulating action is strengthened, and the saturated turning-on voltage drop of the device is reduced; in a turning-off state of the device, the body region plays a floating field limiting ring role, so that an electric field aggregation phenomena at the bottom of a groove gate is weakened, and the voltage withstand reliability of the device is improved; the grid electrode and the source electrode of the introduced JFET structure are connected with a peripheral control circuit and a sampling port respectively, a voltage sampling function can be realized by using a mapping reaction between the voltage change of the source electrode of the JFET structure and withstanding voltage of an IGBT, and the forward blocking characteristic of the device cannot be damaged while an electric isolation effect is reached; and the adjustment for voltage sampling rate is realized by changing the grid electrode bias voltage of the JFET structure, so that the requirement of different application conditions on voltage sampling is met. The IGBT device is simple in sampling structure, and is compatible with an existing technology.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Techniques To Control Power Consumption In An Iterative Decoder By Control Of Node Configurations
ActiveUS20120036410A1Reduce supply voltage variationReduce voltage variationDigital data processing detailsCode conversionControl powerComputer science
A method for controlling power consumption of an iterative decoder based on one or more criteria is described. The method may include progressively enabling and disabling nodes of the iterative decoder to perform iterative decoding on a demodulated signal to provide a decoded signal with minimal variation of a supply voltage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Digital camera and power supply apparatus used therefor
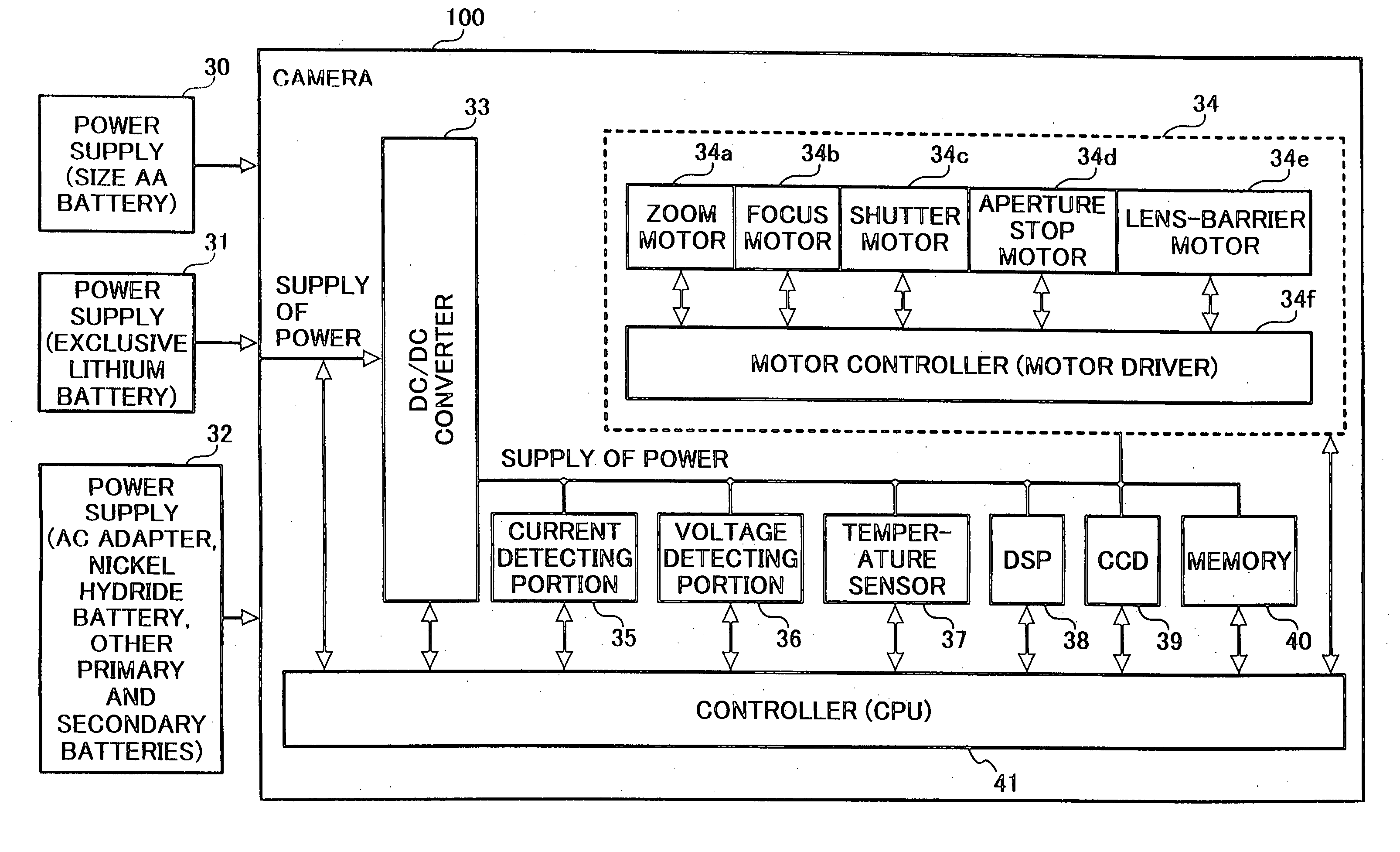
InactiveUS20050062879A1Avoid excessive application of loadShortened battery lifeTelevision system detailsDc network circuit arrangementsElectric machineEngineering
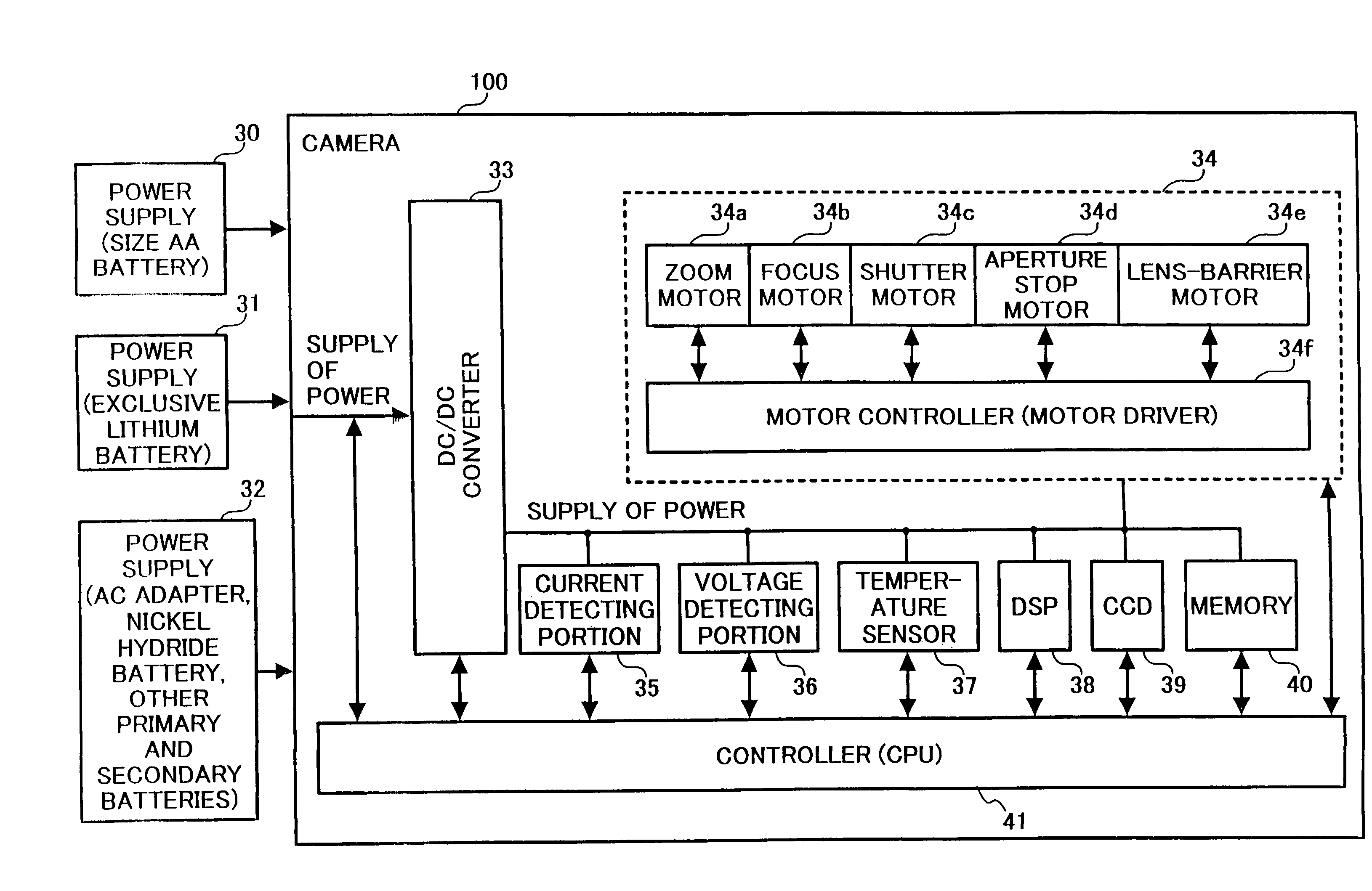
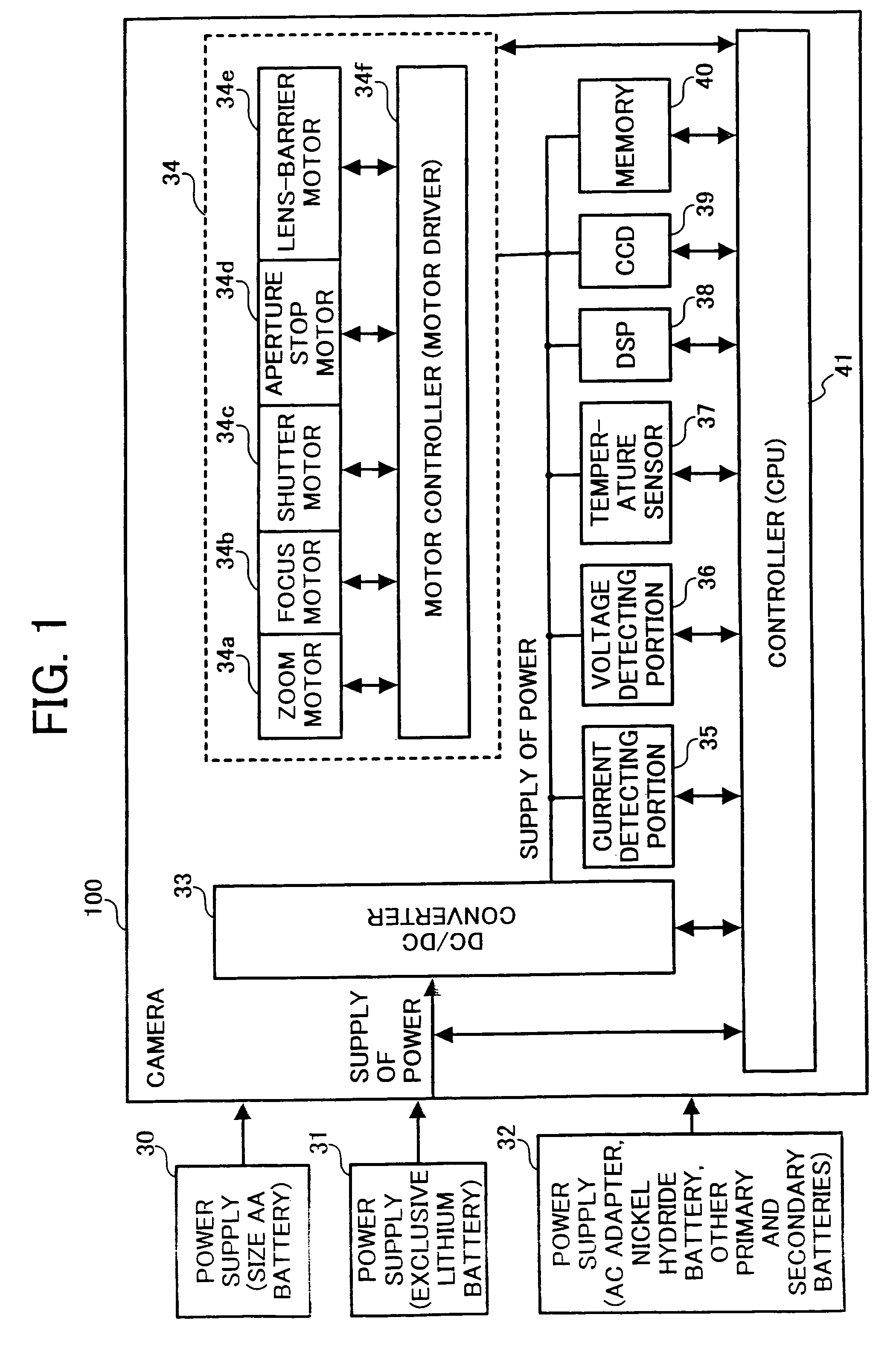
A digital camera, including a common power supply for supplying power; a plurality of motors sharing the power supply and driven by the power supplied from the power supply; and a current detector for detecting load current supplied to the plurality of motors, wherein, when either one of the plurality of motors is operated, other motor is driven not to overlap with a maximum value of the load current detected by the current detector.
Owner:RICOH KK
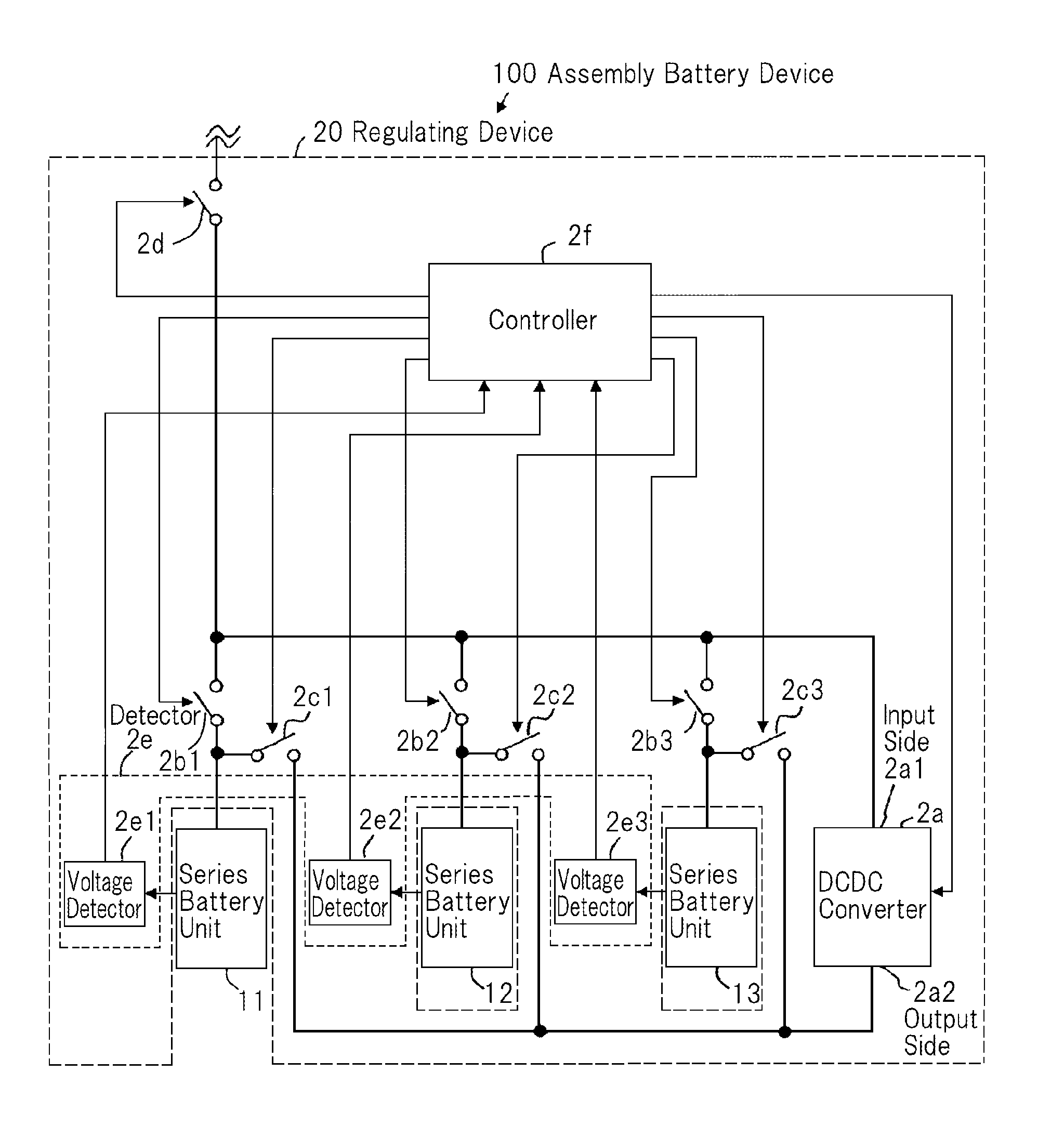
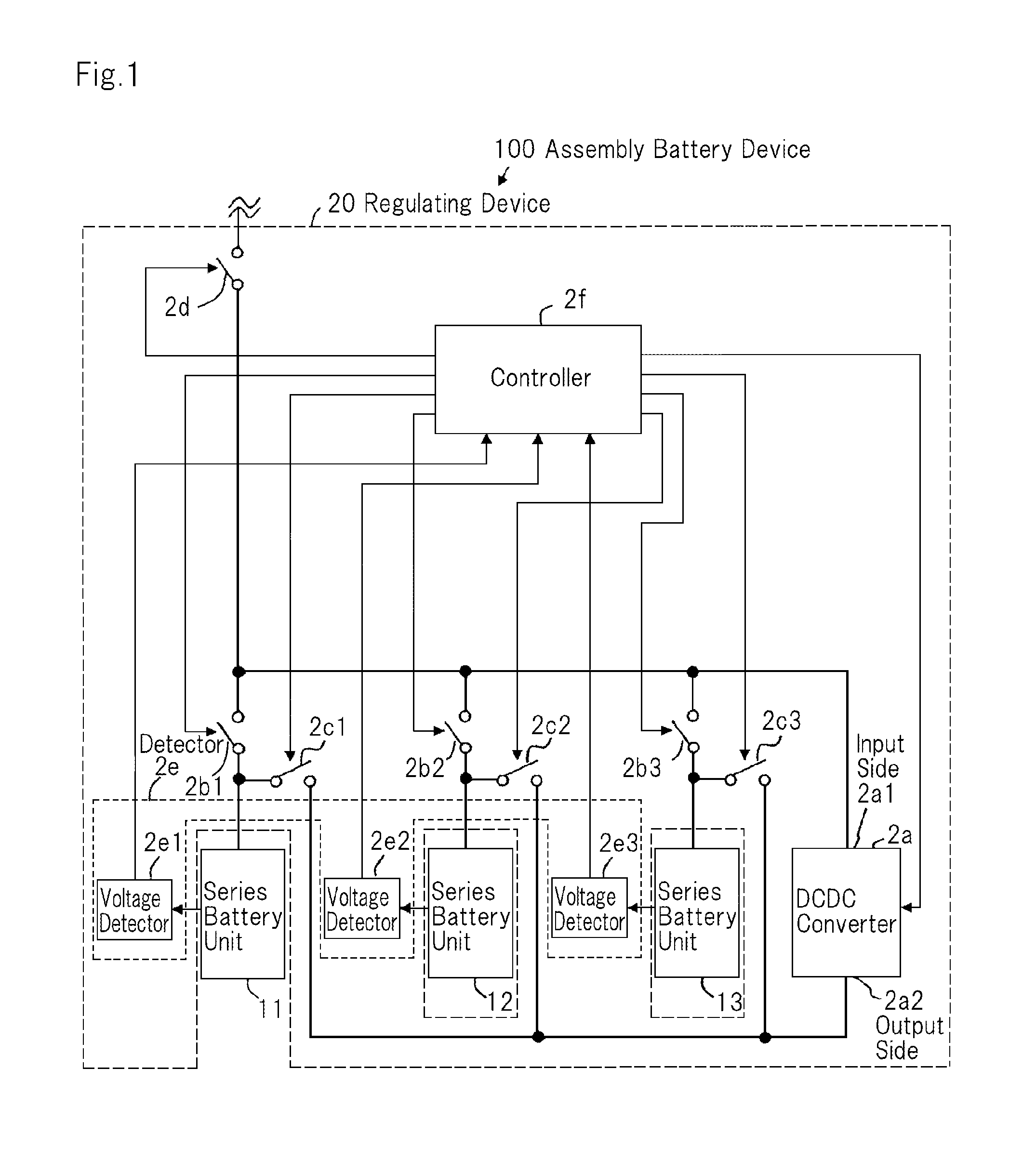
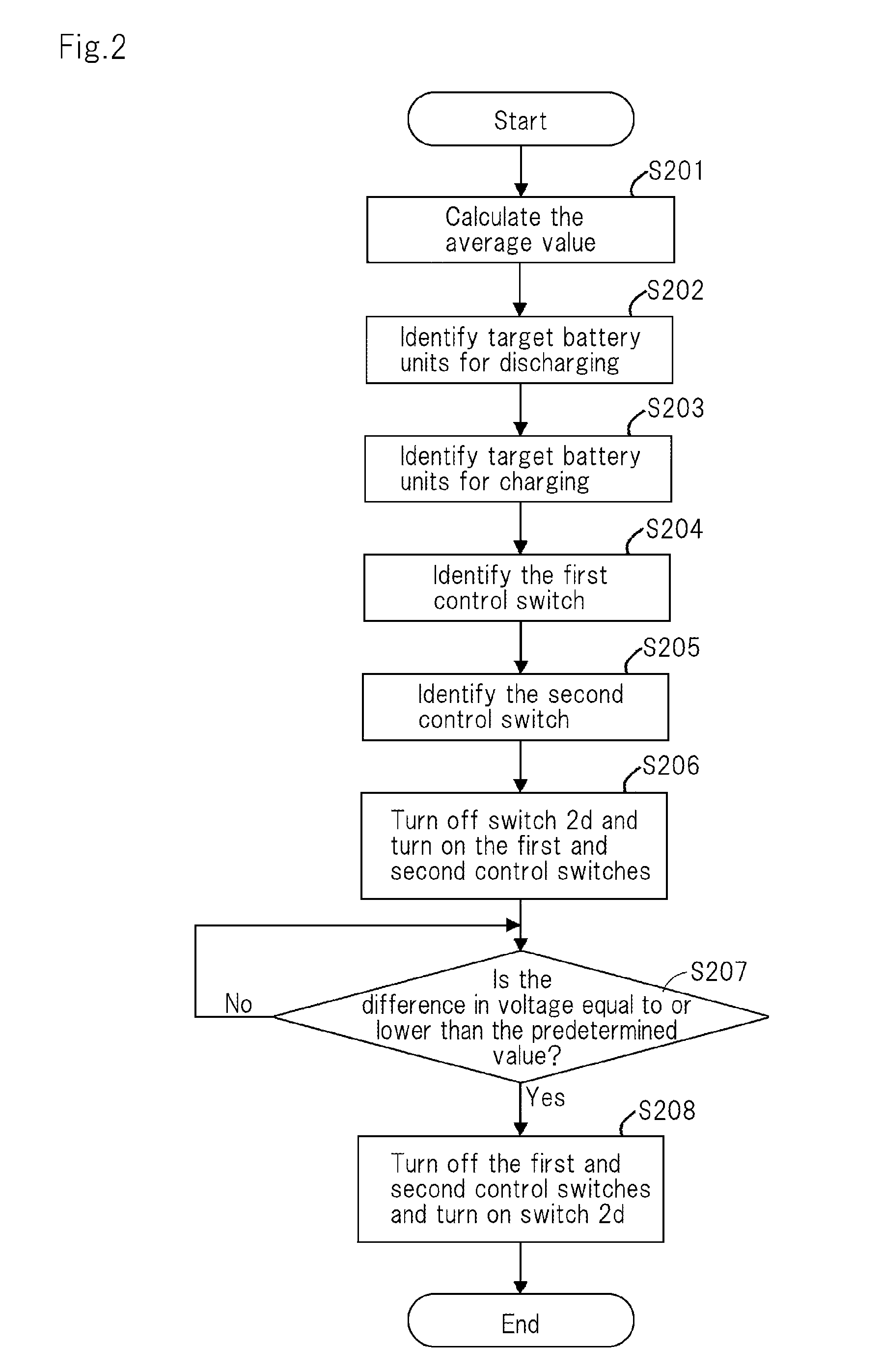
Regulating device, battery assembly device and regulating method
ActiveUS20150077061A1Reduce voltage variationCircuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitEngineeringVoltage
A regulating device includes: a generating means for generating an output voltage from an input voltage; a plurality of first switches, respectively corresponding to the plural storage battery units connected in parallel, with each of said first switches interposed between the corresponding storage battery unit and the input side of the generating means; a plurality of second switches, respectively corresponding to the plural storage battery units, with each of said second switches interposed between the corresponding storage battery unit and the output side of the generating means; a detecting means for detecting the voltage of each of the plural storage battery units; and, a control means that, referring to the result of detection from the detecting means, identifies first storage battery units whose voltages are higher than the average value of voltage of the plural storage battery units and second storage battery units whose voltages are lower than the average value, from the plural storage battery units, and turns on the first control switches corresponding to the first storage battery units from among the plural first switches and the second control switches corresponding to the second storage battery units from among the second switches.
Owner:NEC CORP
Array substrate and preparation method thereof, and display device
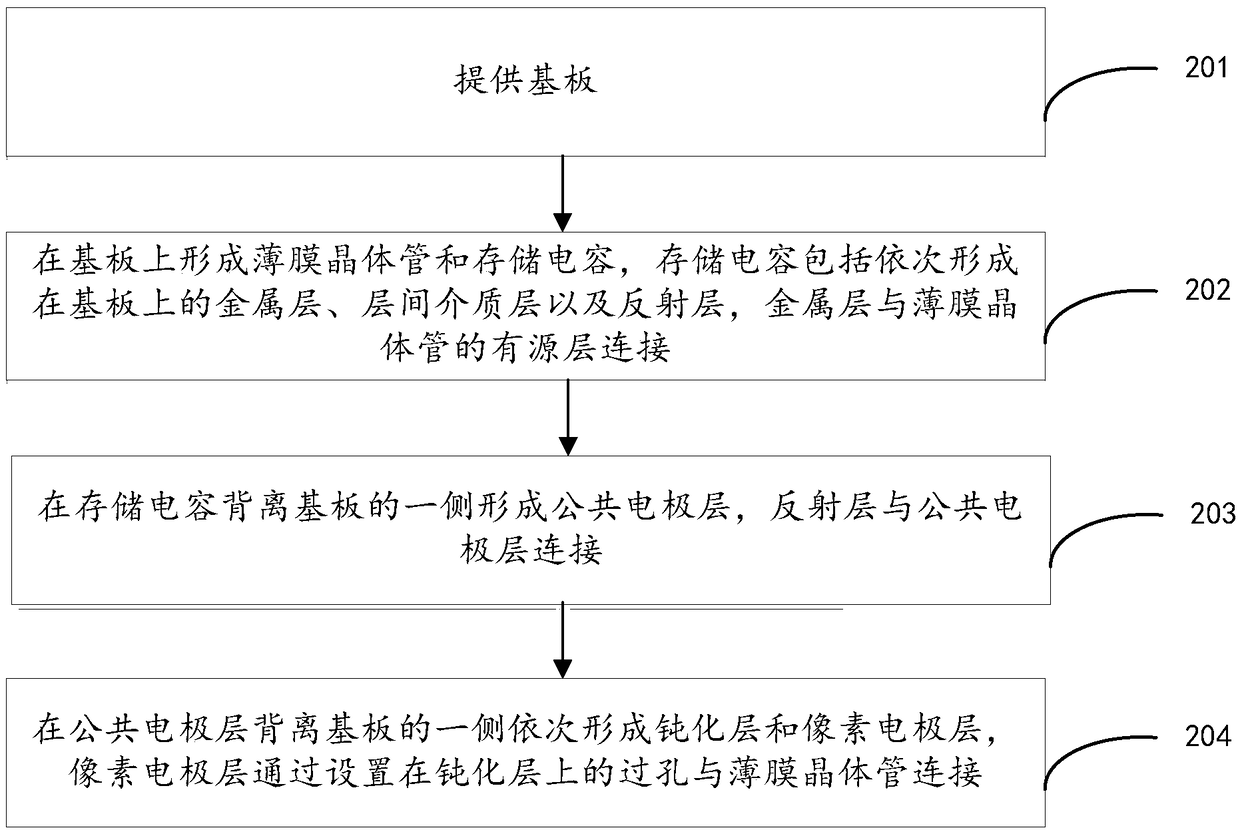
ActiveCN109116647AReduce power consumptionIncrease potential holding capacitySolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsCapacitanceDisplay device
The application provides an array substrate and a preparation method thereof, and a display device. The array substrate comprises multiple pixel units and a public electrode layer, wherein the pixel units are divided into a transmitting region and a reflecting region; the array substrate of the reflecting region comprises a substrate, a thin-film transistor and a storage capacitor, wherein the thin-film transistor and the storage capacitor are arranged on the substrate, the storage capacitor comprises a metal layer, an interlayer dielectric layer and a reflecting layer laminated at one side ofthe substrate, and the metal layer is close to the substrate; and the public electrode layer is arranged at one side, far away from the substrate, of the storage capacitor, wherein the reflecting layer is connected with the public electrode layer, and the metal layer is connected with an active layer of the thin-film transistor. Since the ambient light can be reflected through the arrangement ofthe reflecting layer in the reflecting region, the power consumption of the backlight source is reduced; and meanwhile, the storage capacitor formed between the metal layer and the reflecting layer can store the liquid crystal pixel voltage, the voltage variation caused by leakage current is reduced, the liquid crystal pixel potential holding capacity can be effectively increased, and a display effect is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
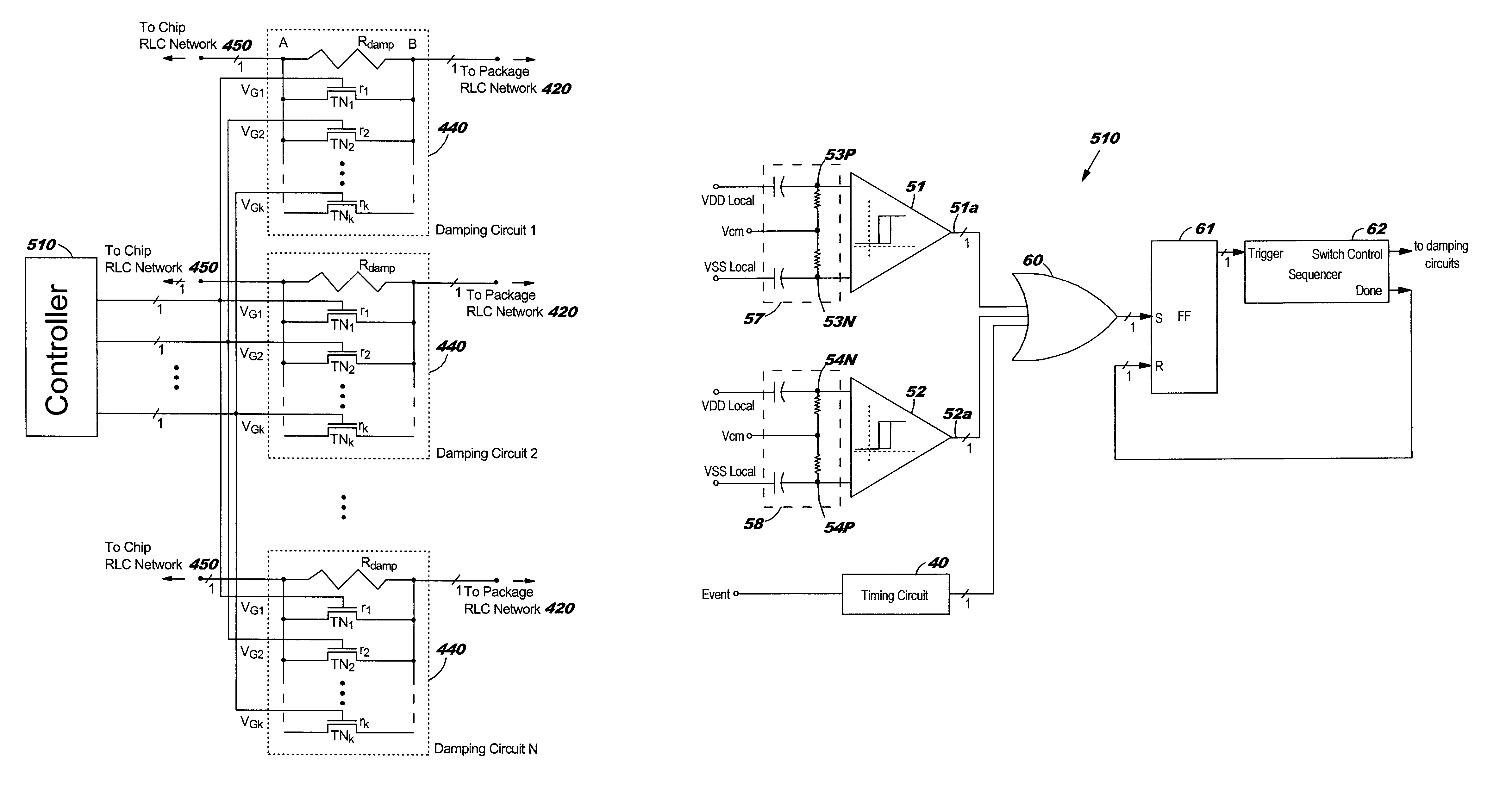
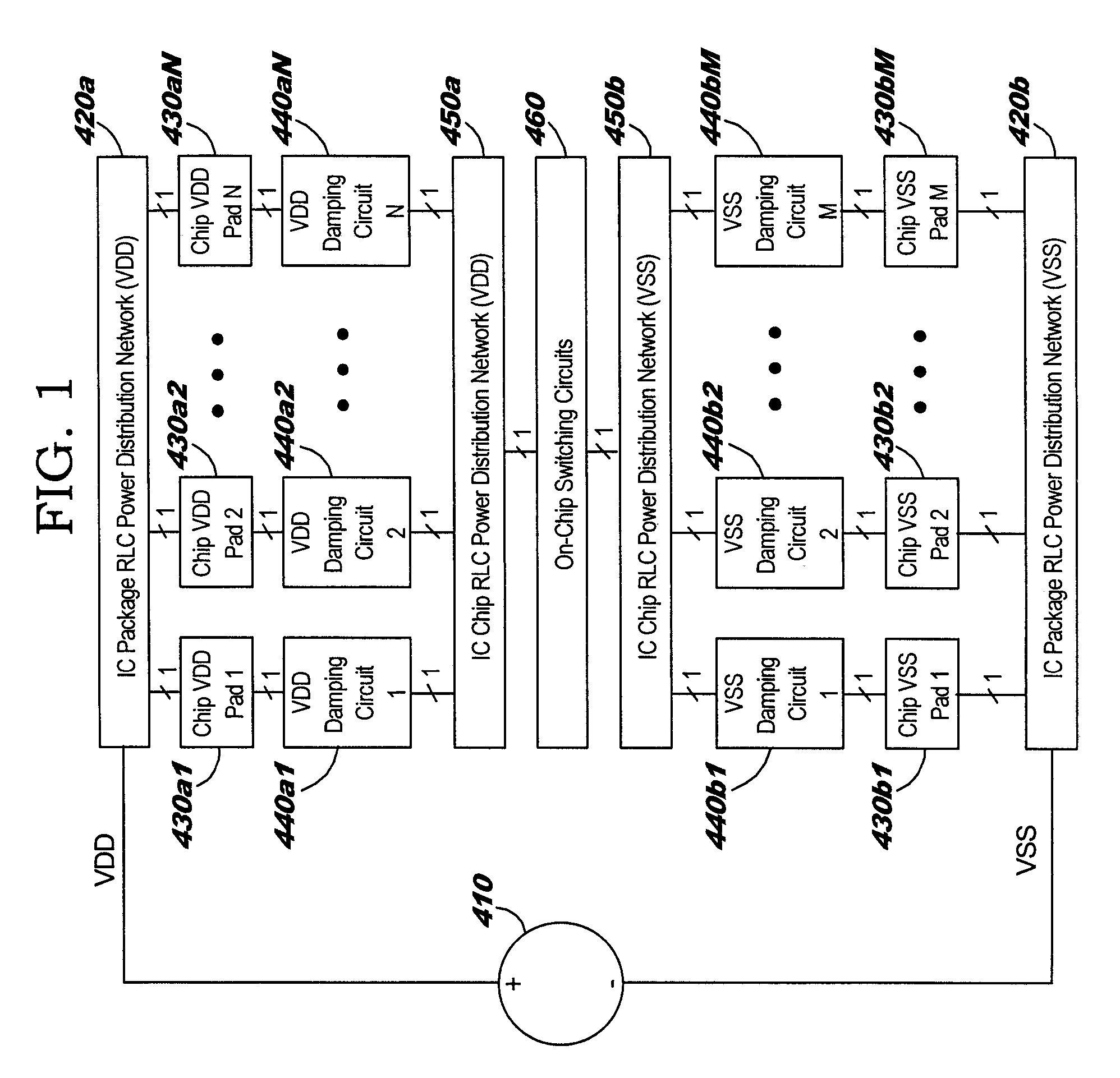
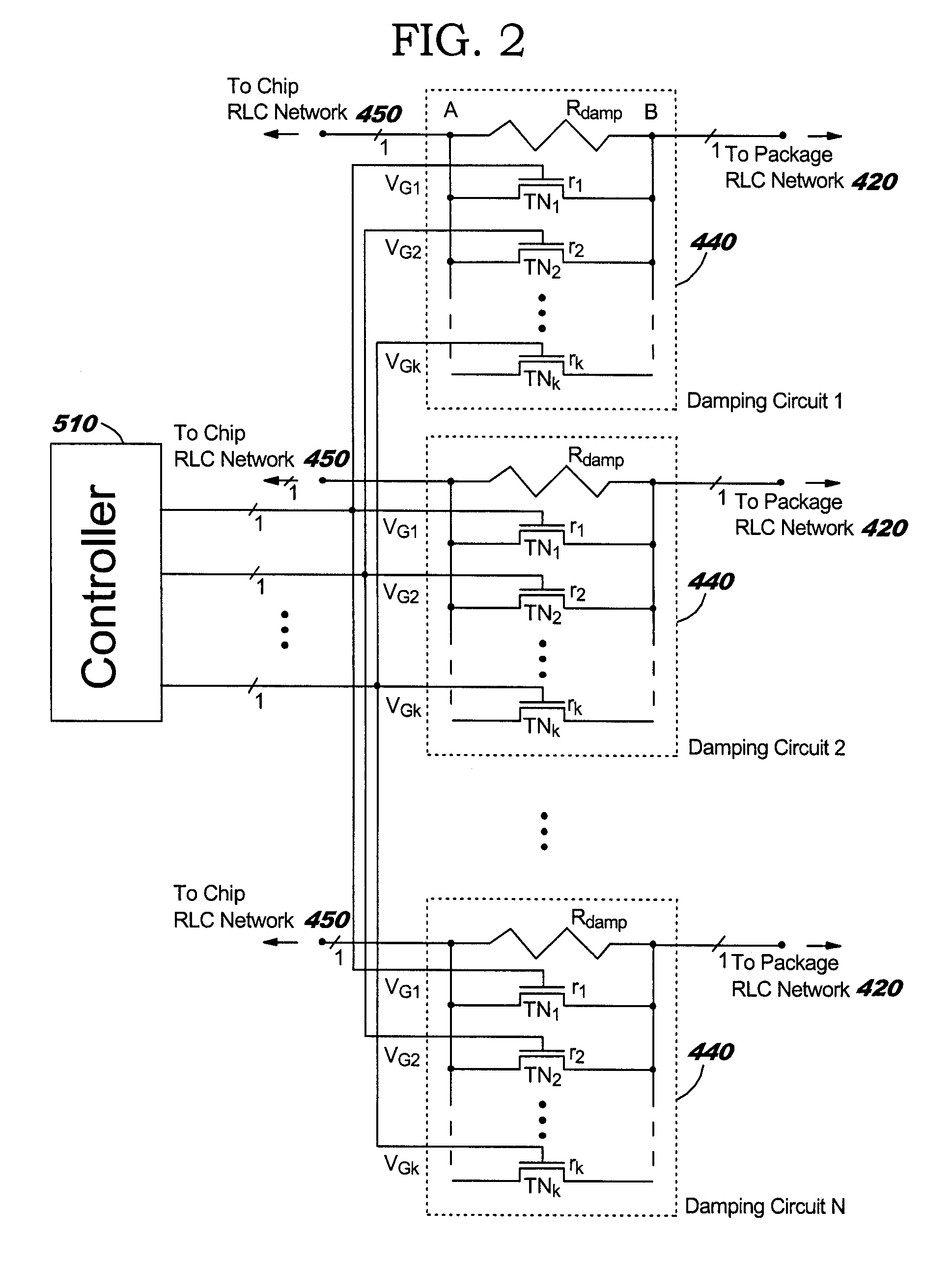
Damping of LC Ringing in IC (Integrated Circuit) Power Distribution Systems
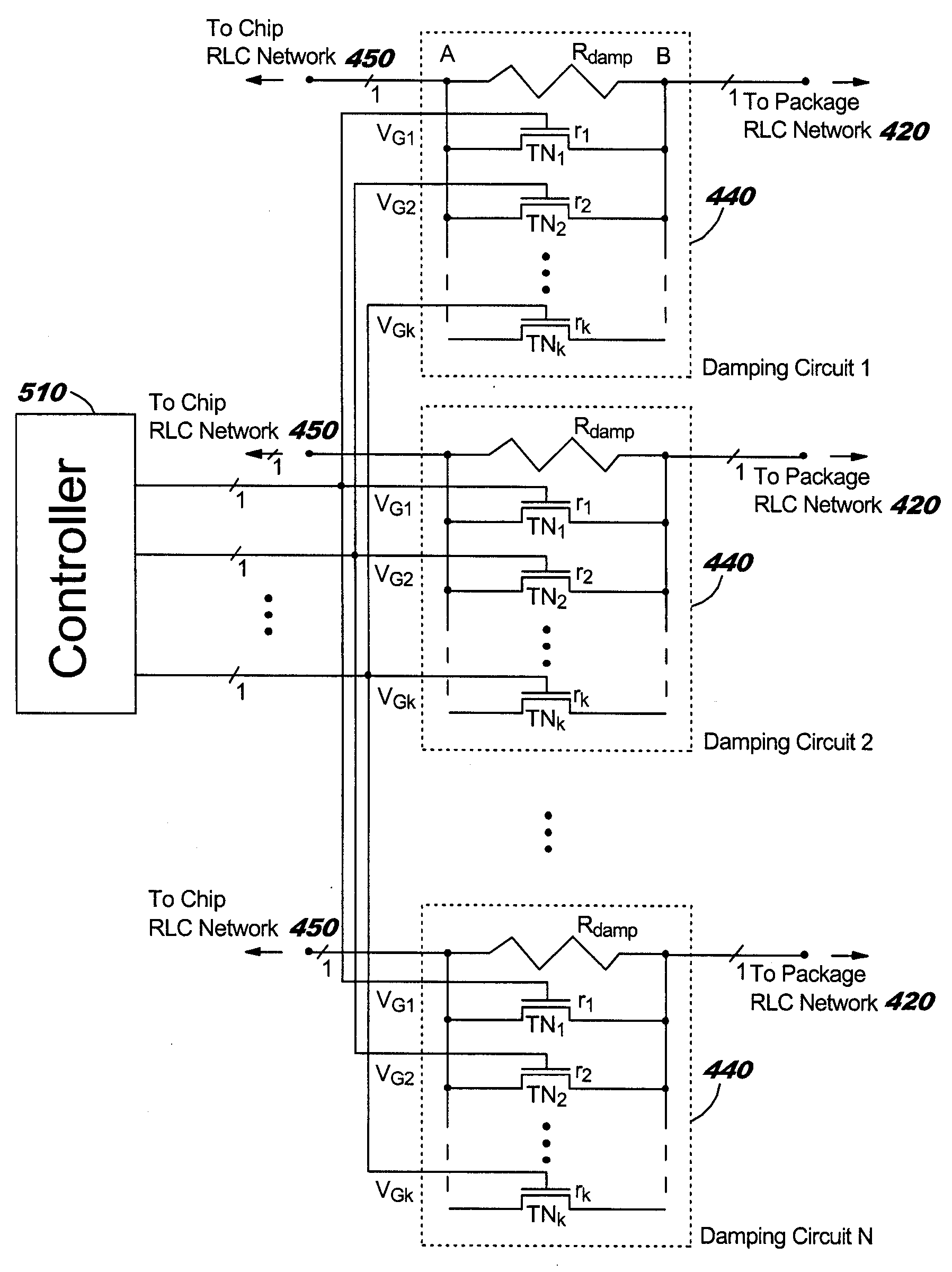
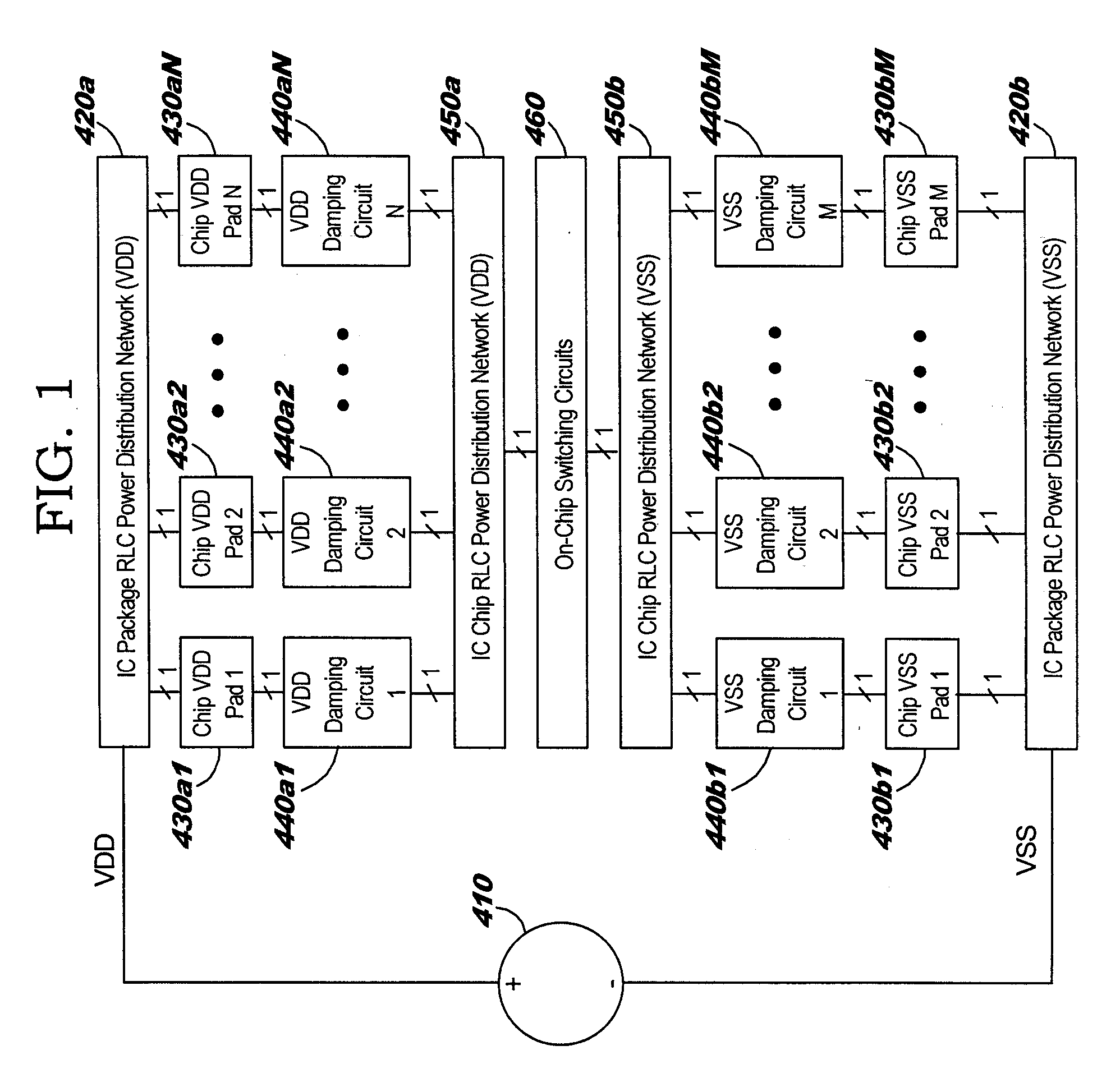
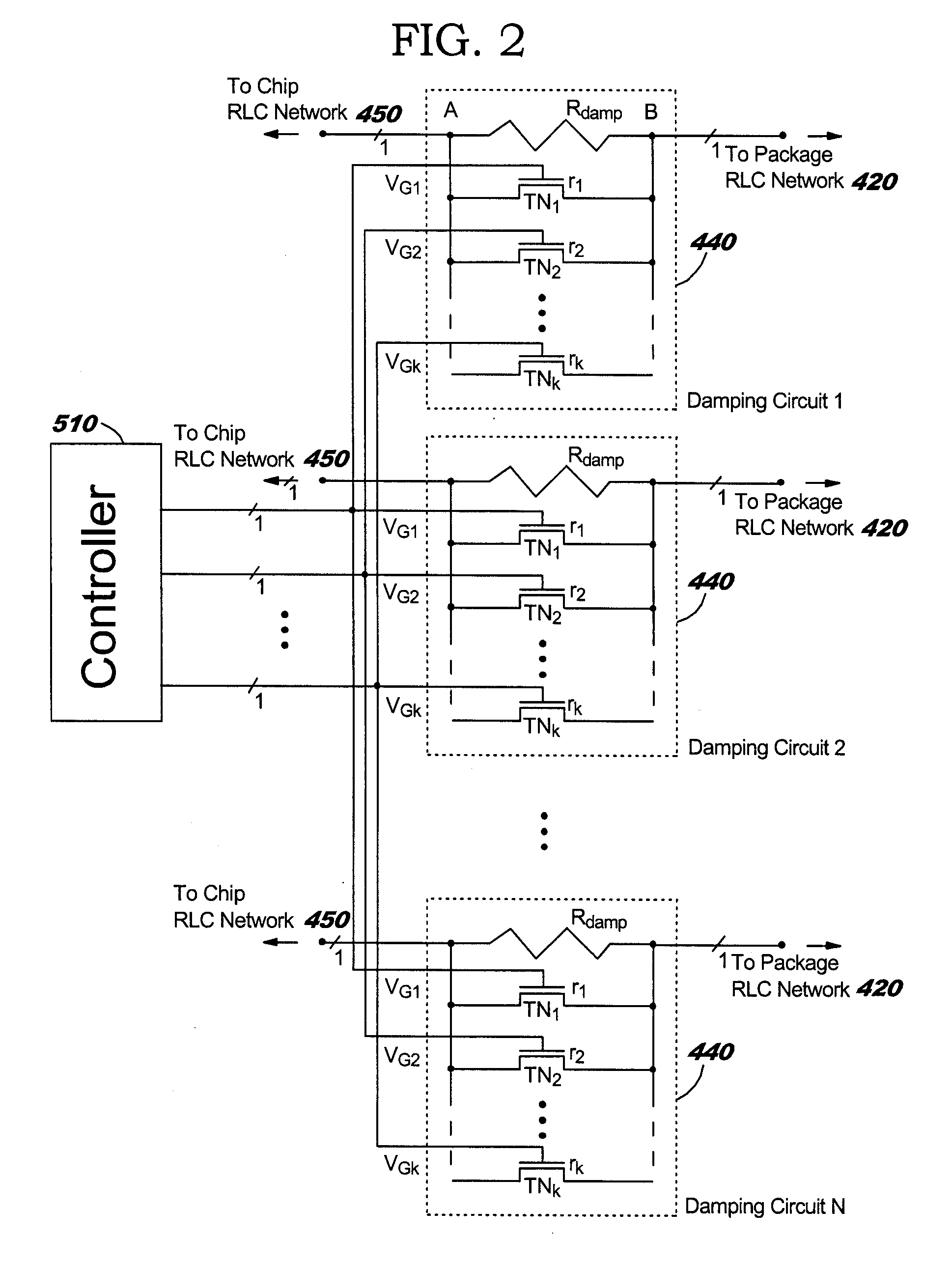
InactiveUS20050110551A1Avoid changeReduce voltage variationPulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceElectricity
A structure and method for damping LC (inductance-capacitance) ringing in integrated circuit (IC) power distribution systems. The structure comprises a resistance electrically connected in parallel with a plurality of electrical switches. The resistance and electrical switches are electrically connected in series with the package and on-chip power distribution circuit. When on-chip switching activity creates a sudden and appreciable change in IC power demand the electrical switches are opened to temporarily increase the resistance in series with the power supply. This serves to dampen the power-distribution LC ringing. Later, the electrical switches are closed to shunt the series resistance and reduce the level of steady-state voltage drop in the power structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fuel Cell System
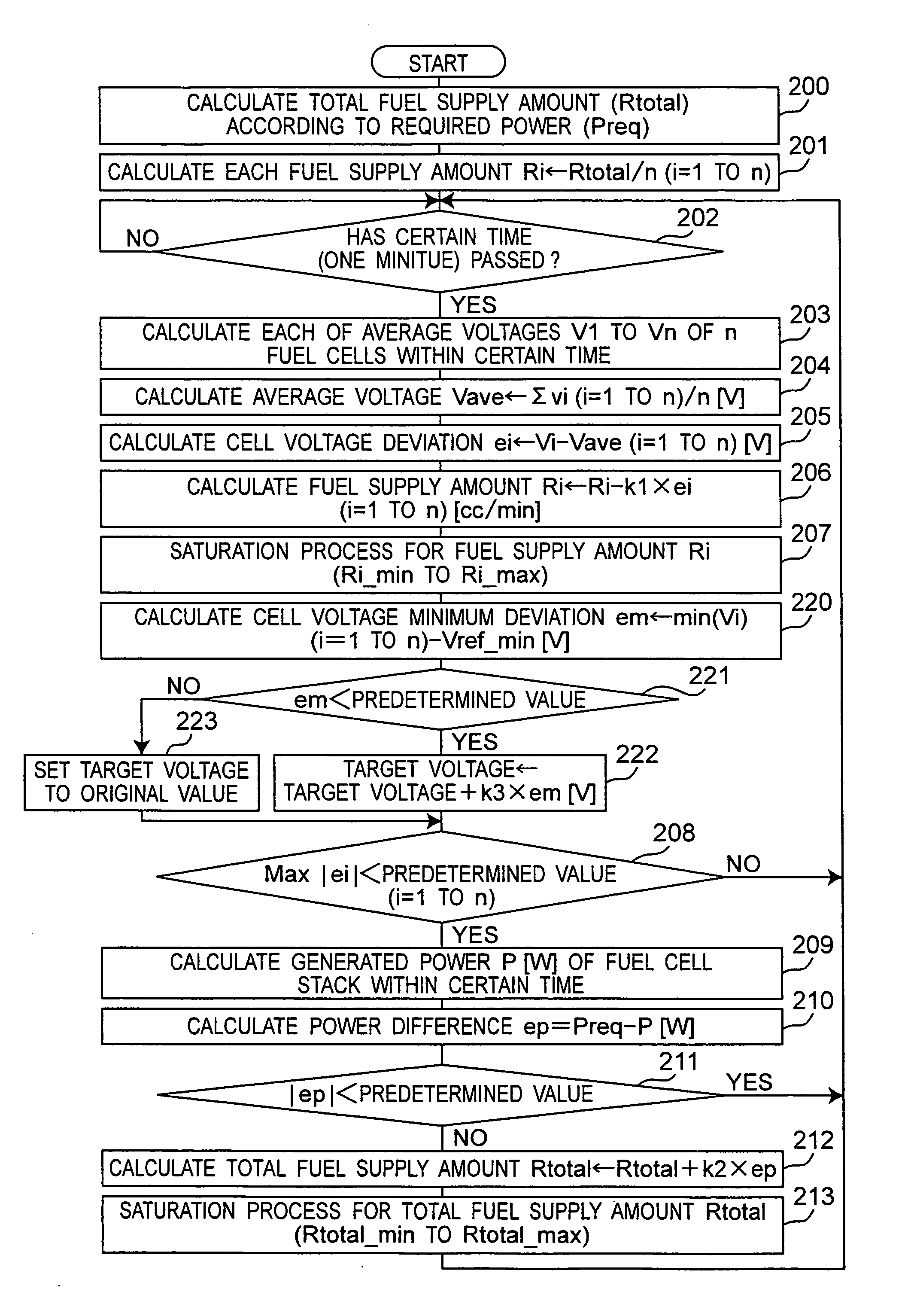
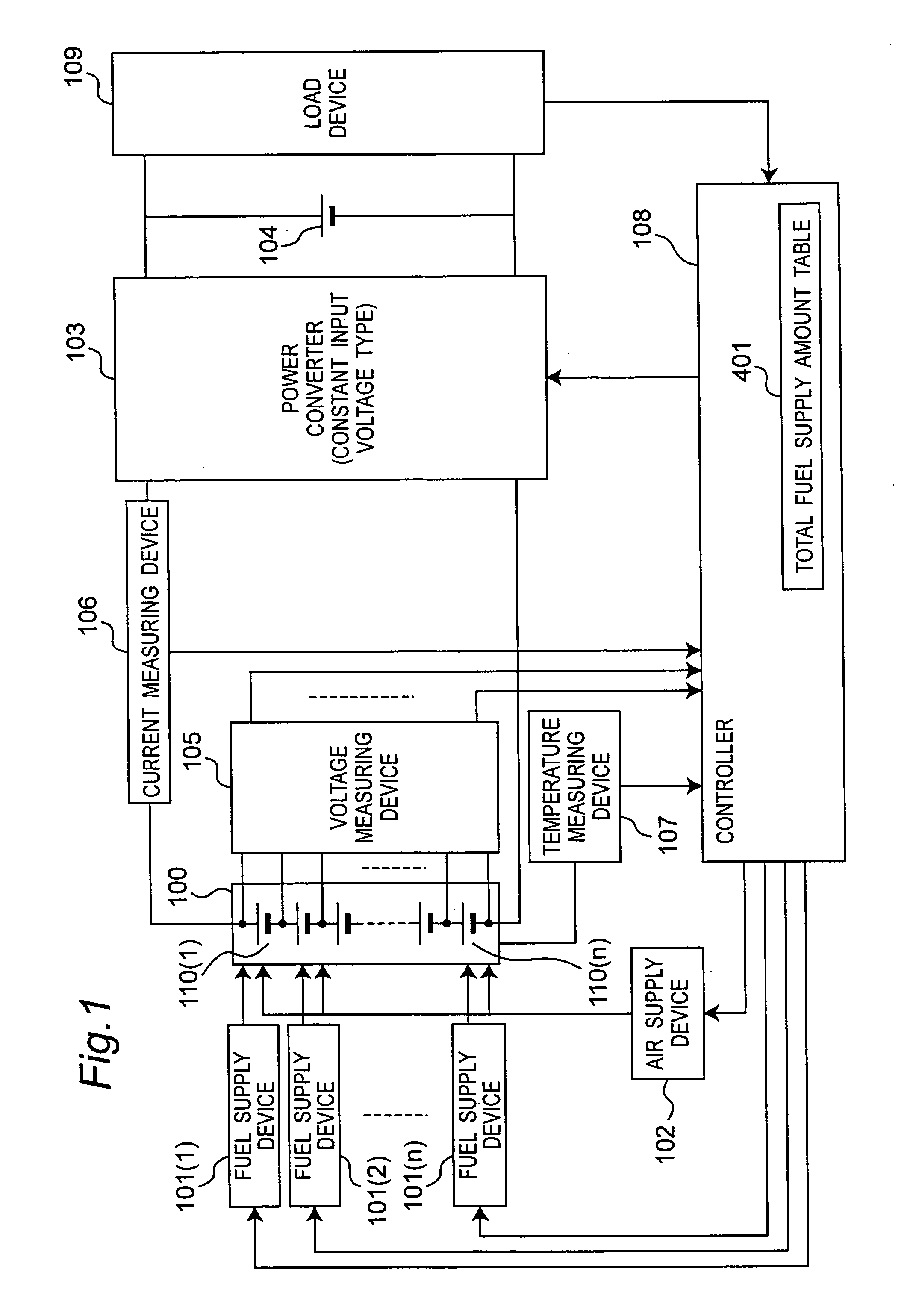
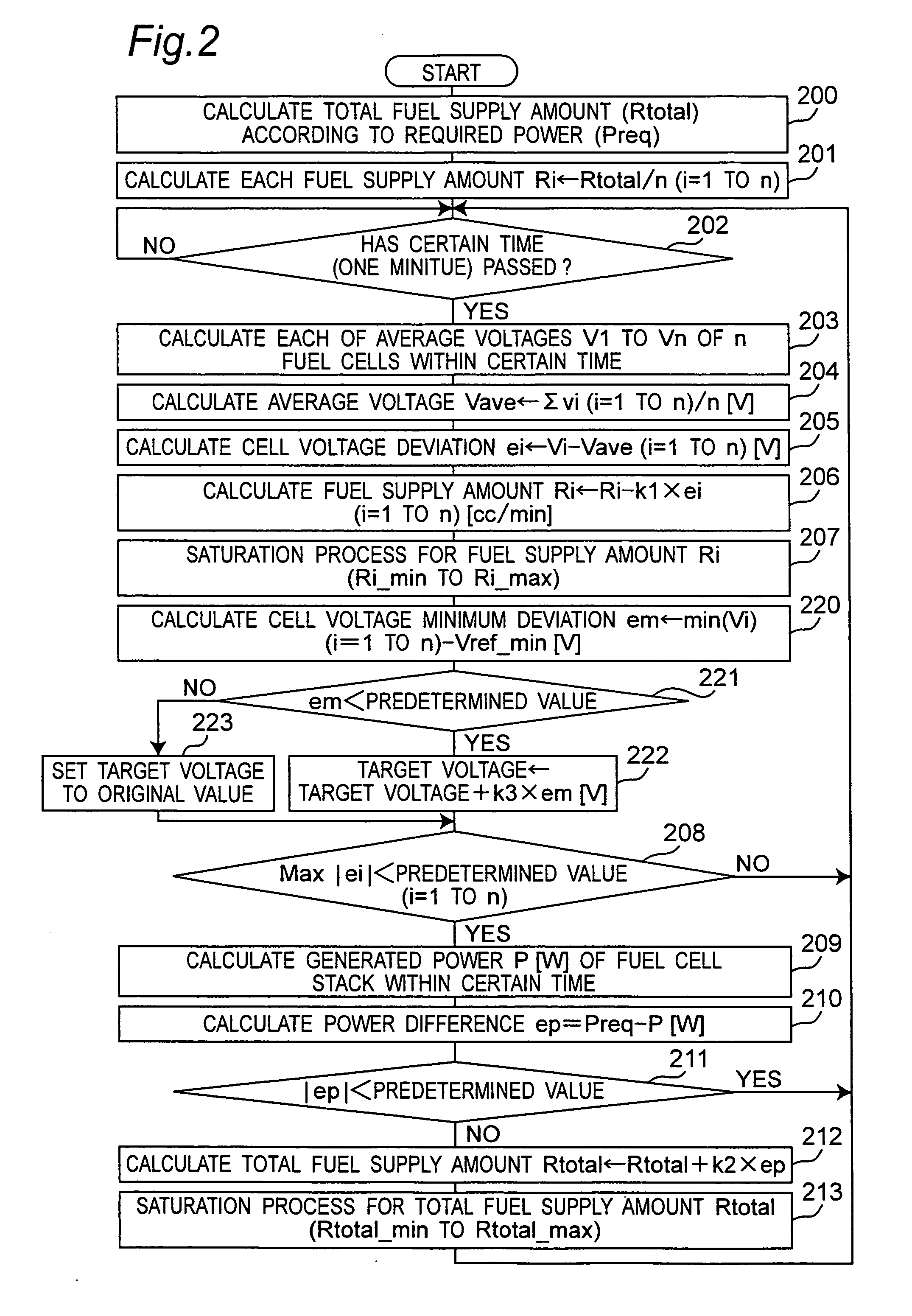
InactiveUS20070212579A1Stabilize generated powerReduce voltage variationFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel supplyVoltage variation
There is provided a fuel cell system which reduces voltage variations of a plurality of fuel cells and stabilizes a generated power of a fuel cell stack. A fuel cell system according to the invention includes a fuel cell stack having a plurality of fuel cells connected in series, a fuel supply device, an air supply device and a controller. The controller sets at least one of a fuel supply amount and an air supply amount for each fuel cell based on each voltage of the plurality of fuel cells so that each voltage variation of the plurality of fuel cells may be minimized, and the fuel supply device supplies fuel to each of the fuel cells based on the fuel supply amount of each fuel cell, and / or the air supply device supplies air to each of the fuel cells based on the air supply amount of each fuel cell.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Digital camera and power supply apparatus used therefor
InactiveUS20070003271A1Shortened battery lifeAvoid powerTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectric forceEmbedded system
Owner:RICOH KK
Driving circuit and multi-display apparatus and electronic device using the same
InactiveUS20060077170A1Reduce voltage variationCompensation effectStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsCouplingDisplay device
A driving circuit for multi-panel display and a multi-panel display apparatus and system using the same is provided. The driving circuit comprises a plurality of first driving lines formed on a main panel, a plurality of second driving lines formed on a sub panel and a coupling device. The coupling device comprises an effective coupling module and a dummy coupling module, wherein the effective coupling module electrically couples between each of the second driving lines and a corresponding one of a first part of the first driving lines, and the dummy coupling module electrically couples to a second part of the first driving lines.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
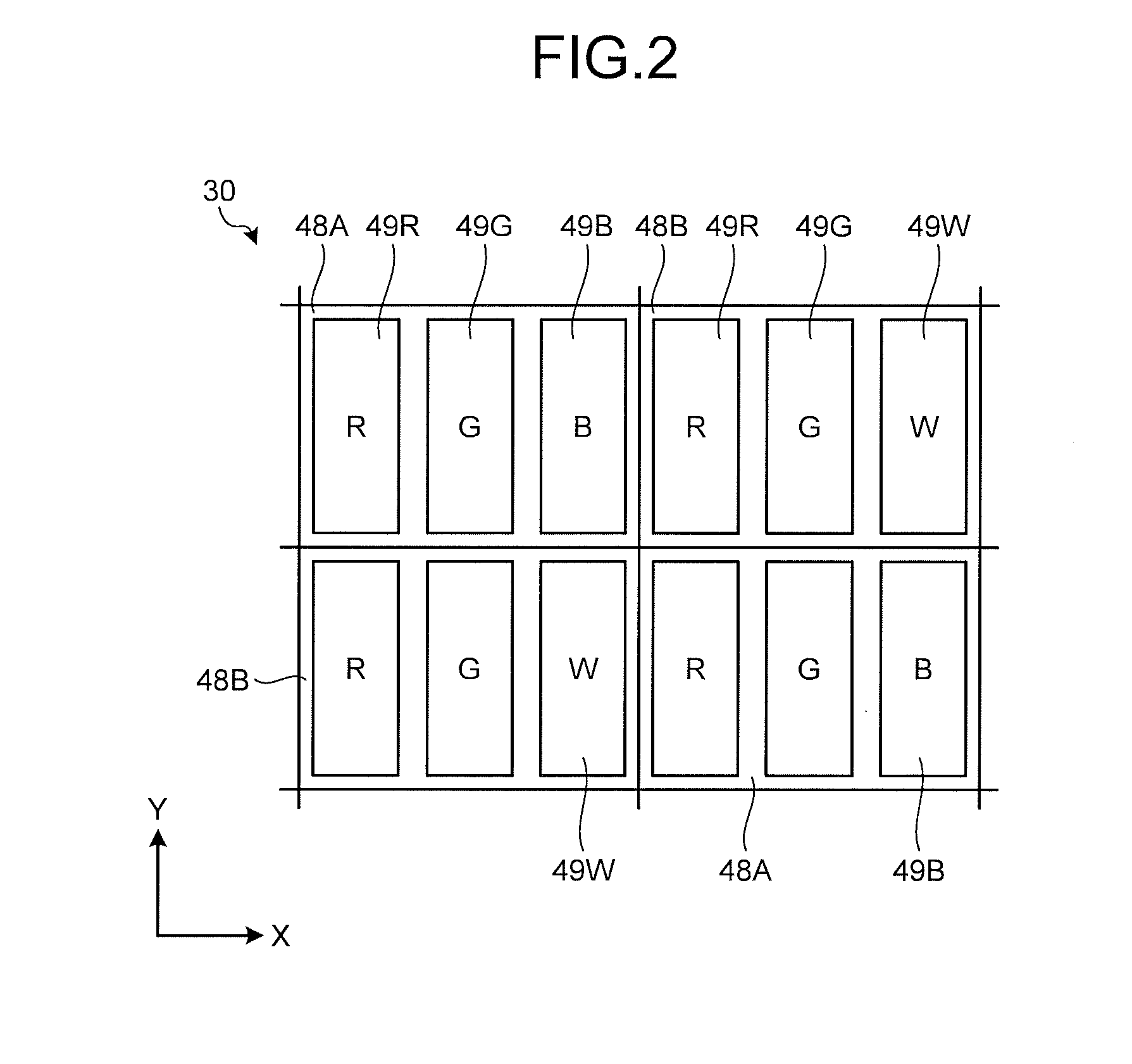
Display device
ActiveUS20150348489A1Increase brightnessTotal current dropCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical polarityDisplay device
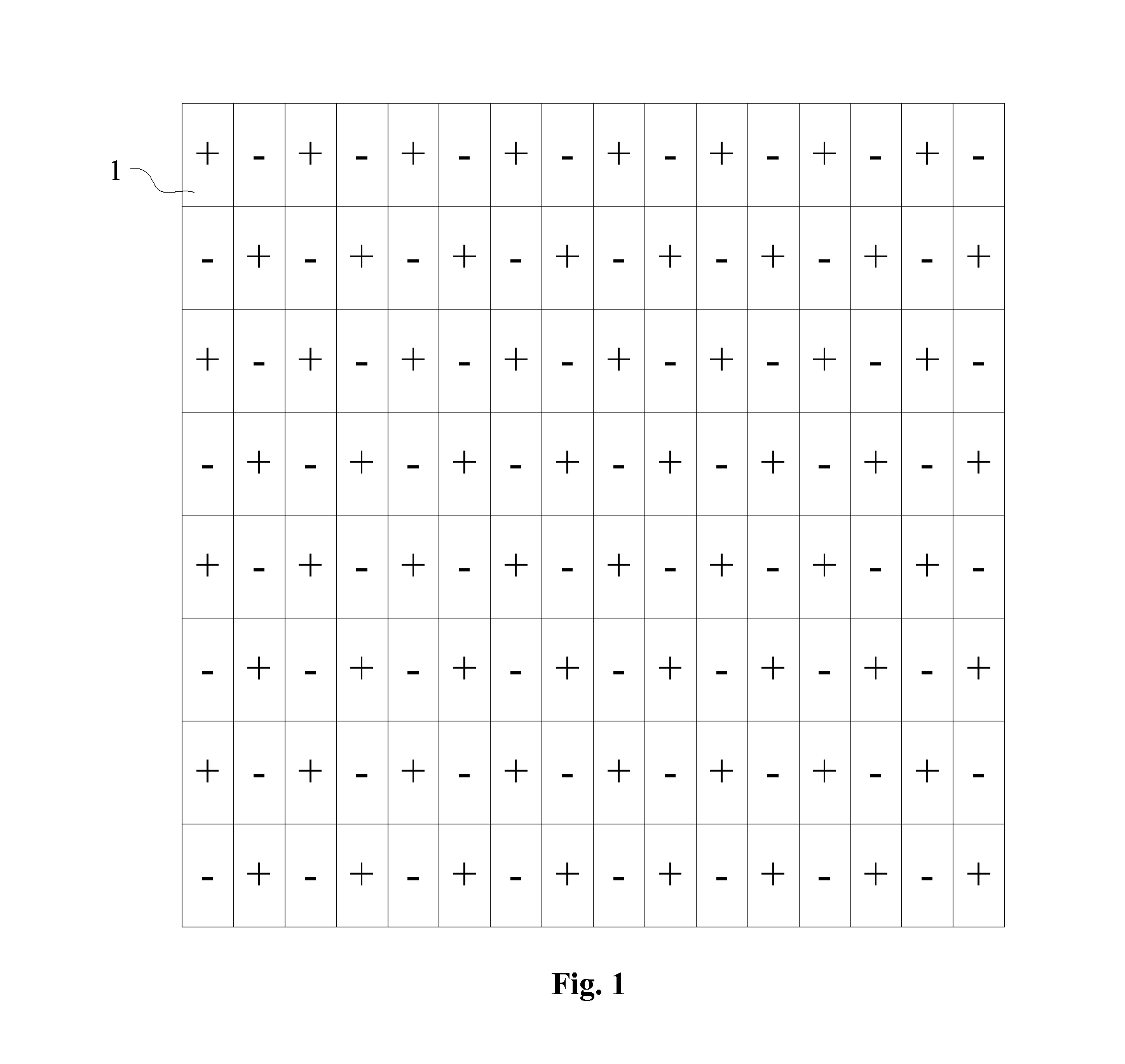
A display device includes an image display panel and a control device. The image display panel includes first sub-pixels, second sub-pixels, third sub-pixels, and fourth sub-pixels in which a specified sub-pixel column including the third sub-pixels and the fourth sub-pixels and at least one other sub-pixel column arranged next to the specified sub-pixel column are periodically arranged. The control device performs column inversion driving to apply a voltage having the same polarity to signal lines of a first specified sub-pixel column belonging to the specified sub-pixel columns and the other sub-pixel column adjacent to the first specified sub-pixel column, apply a voltage having the same polarity as the first specified sub-pixel column to one of the signal lines of a second specified sub-pixel column and a third specified sub-pixel column adjacent to the first specified sub-pixel column, and invert the polarities of the voltages to be applied at predetermined cycles.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Controllable delay line and regulation compensation circuit thereof
A controllable delay line includes an anti-jitter unit, a dependent current source, a first current mirror, a second current mirror, a regulation capacitor, a compensation capacitor and an output buffer unit. The anti-jitter unit receives a first bias voltage and produces a second bias voltage based on the first bias voltage. When the voltage source used in the controllable delay line has a variation, the second bias voltage varies therewith. The regulation capacitor is used for reducing the variation of the voltage difference between the voltage source and a node voltage of the first current source. The compensation capacitor is used for reducing the influence of a transition of the input signal of the output buffer unit on the node voltage, so as to lower the jitter amount of the output signal of the output buffer unit.
Owner:FARADAY TECH CORP
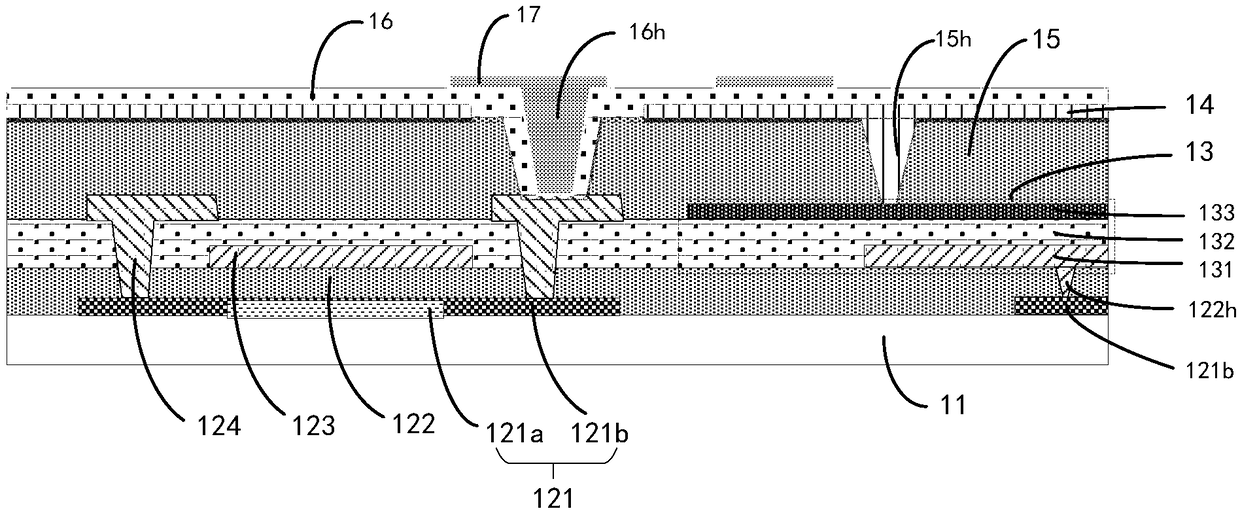
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS9324847B2Reduce variationImprove the immunitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPeak valueConcentration gradient
In some aspects of the invention, an n-type field-stop layer can have a total impurity of such an extent that a depletion layer spreading in response to an application of a rated voltage stops inside the n-type field-stop layer together with the total impurity of an n− type drift layer. Also, the n-type field-stop layer can have a concentration gradient such that the impurity concentration of the n-type field-stop layer decreases from a p+ type collector layer toward a p-type base layer, and the diffusion depth is 20 μm or more. Furthermore, an n+ type buffer layer of which the peak impurity concentration can be higher than that of the n-type field-stop layer at 6×1015 cm−3 or more, and one-tenth or less of the peak impurity concentration of the p+ type collector layer, can be included between the n-type field-stop layer and p+ type collector layer.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
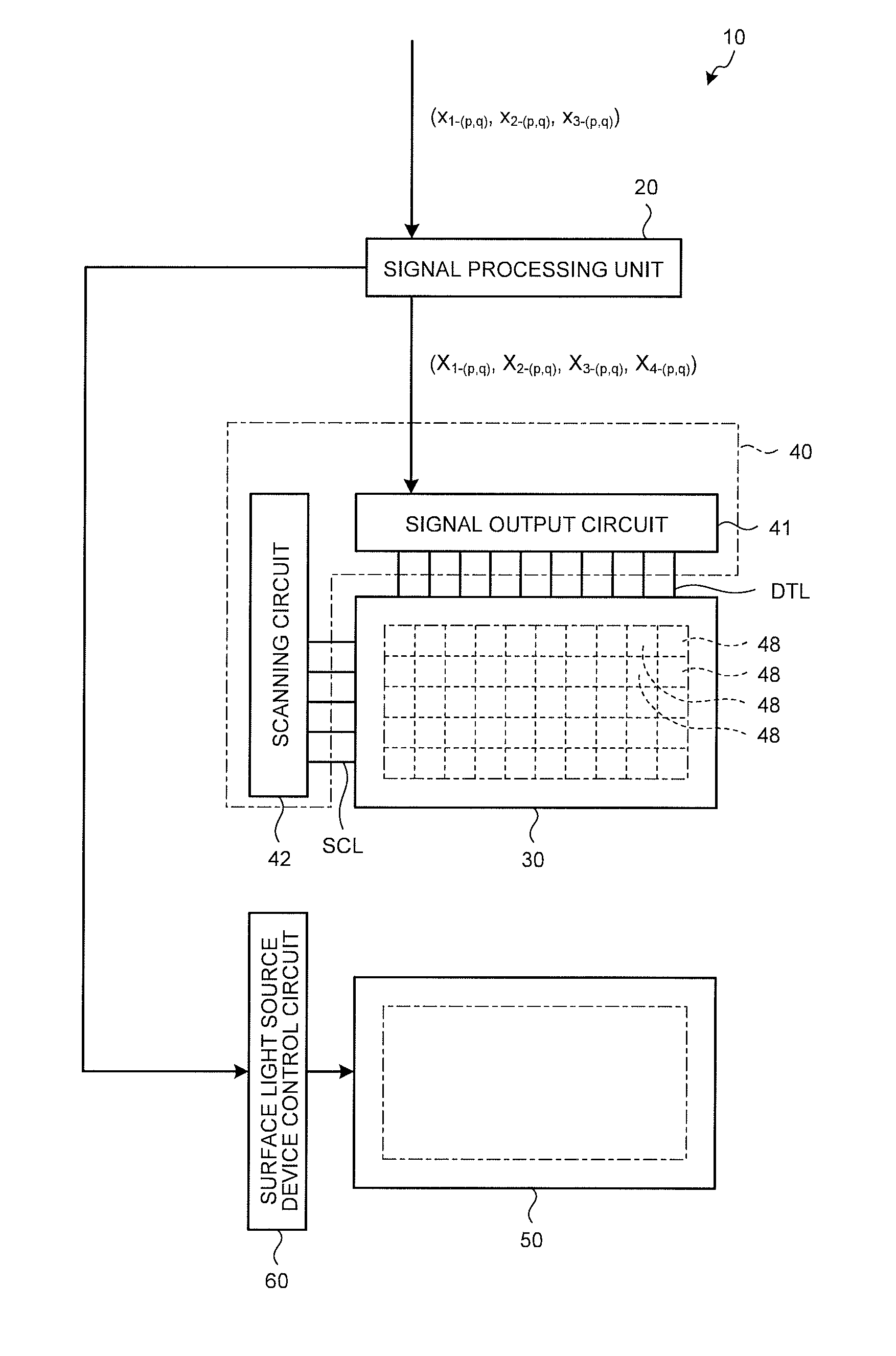
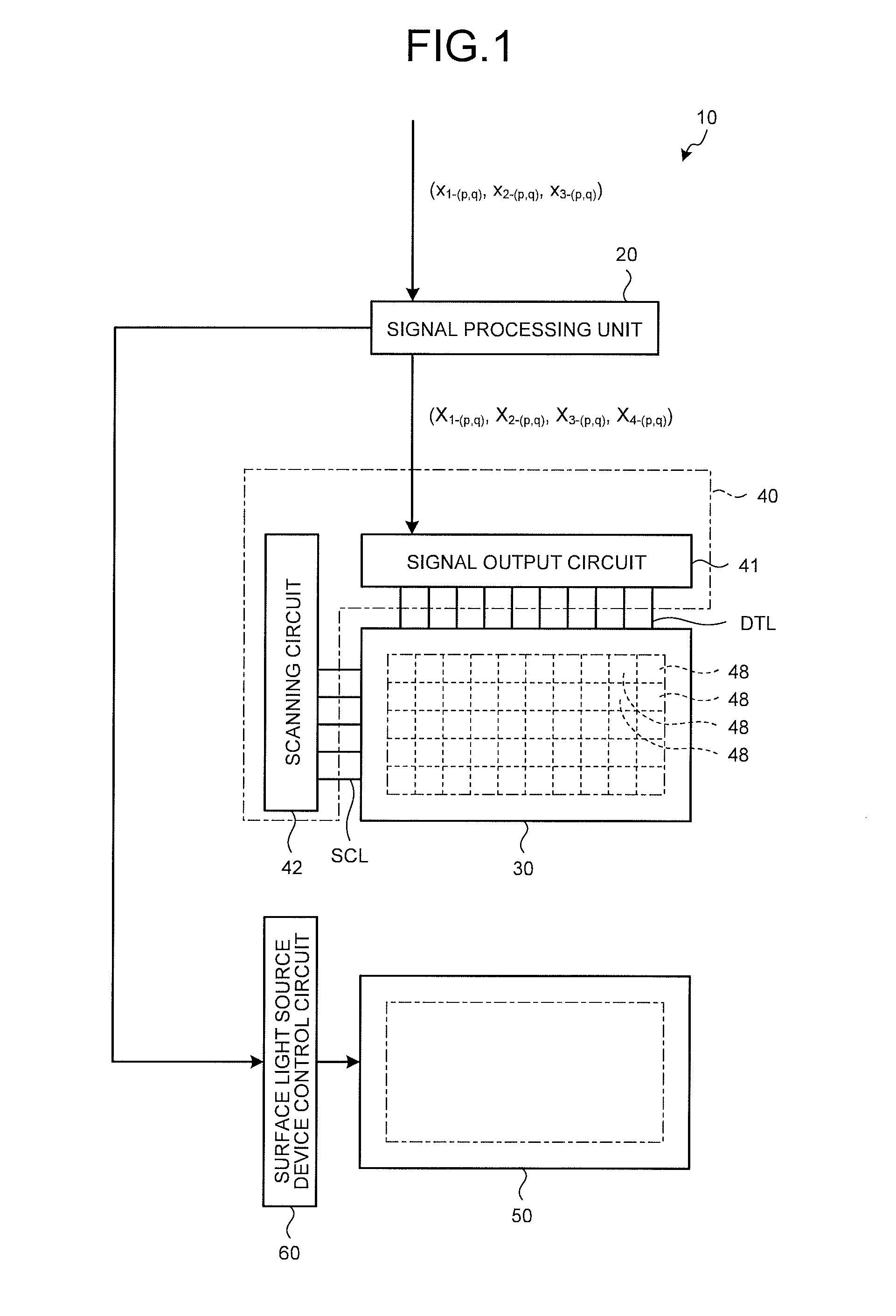
Signal transfer circuit, display data processing apparatus, and display apparatus
InactiveUS20080079707A1Reduce voltage variationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical polarityInput/output
First and second input / output circuits each have an input terminal connected to the input node. A first power supply wiring supplies a first voltage. A second power supply wiring supplies a second voltage. The first and second input / output circuits each select any one of the first and second power supply wirings, depending on the polarity of an input signal, to output an output signal. The first and second input / output circuits each have any one of a first characteristic in which an output signal having the same polarity as that of the input signal is output and a second characteristic in which an output signal having a polarity opposite to that of the input signal is output. The characteristics possessed by the first and second input / output circuits are different from each other.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Power grid and bump pattern with reduced inductance and resistance
ActiveUS6961247B2Reduce resistanceReduce inductanceElectrically conductive connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductancePower grid
Disclosed are novel methods and apparatus for efficiently providing power buses and bump patterns with reduced inductance and / or resistance. In an embodiment, an apparatus is disclosed. The apparatus includes a plurality of power and ground bus pairs. Each power and ground bus pair may have a power bus and a ground bus. The apparatus further includes a first power bus from a first pair of the plurality of power and ground bus pairs. The first power bus may include a plurality of power bumps. The apparatus also includes a first ground bus from the first pair of the plurality of power and ground bus pairs. The first ground bus may include a plurality of ground bumps. Each of the plurality of power / ground bumps may be substantially equidistance from any immediately neighboring ground bump of the first ground bus.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Display device
ActiveUS10019961B2Increase brightnessTotal current dropCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical polarityDisplay device
A display device includes an image display panel and a control device. The image display panel includes first sub-pixels, second sub-pixels, third sub-pixels, and fourth sub-pixels in which a specified sub-pixel column including the third sub-pixels and the fourth sub-pixels and at least one other sub-pixel column arranged next to the specified sub-pixel column are periodically arranged. The control device performs column inversion driving to apply a voltage having the same polarity to signal lines of a first specified sub-pixel column belonging to the specified sub-pixel columns and the other sub-pixel column adjacent to the first specified sub-pixel column, apply a voltage having the same polarity as the first specified sub-pixel column to one of the signal lines of a second specified sub-pixel column and a third specified sub-pixel column adjacent to the first specified sub-pixel column, and invert the polarities of the voltages to be applied at predetermined cycles.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Damping of LC ringing in IC (integrated circuit) power distribution systems
InactiveUS6963240B2Reduce voltage variationDampen variationPulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A structure and method for damping LC (inductance-capacitance) ringing in integrated circuit (IC) power distribution systems. The structure comprises a resistance electrically connected in parallel with a plurality of electrical switches. The resistance and electrical switches are electrically connected in series with the package and on-chip power distribution circuit. When on-chip switching activity creates a sudden and appreciable change in IC power demand the electrical switches are opened to temporarily increase the resistance in series with the power supply. This serves to dampen the power-distribution LC ringing. Later, the electrical switches are closed to shunt the series resistance and reduce the level of steady-state voltage drop in the power structure.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
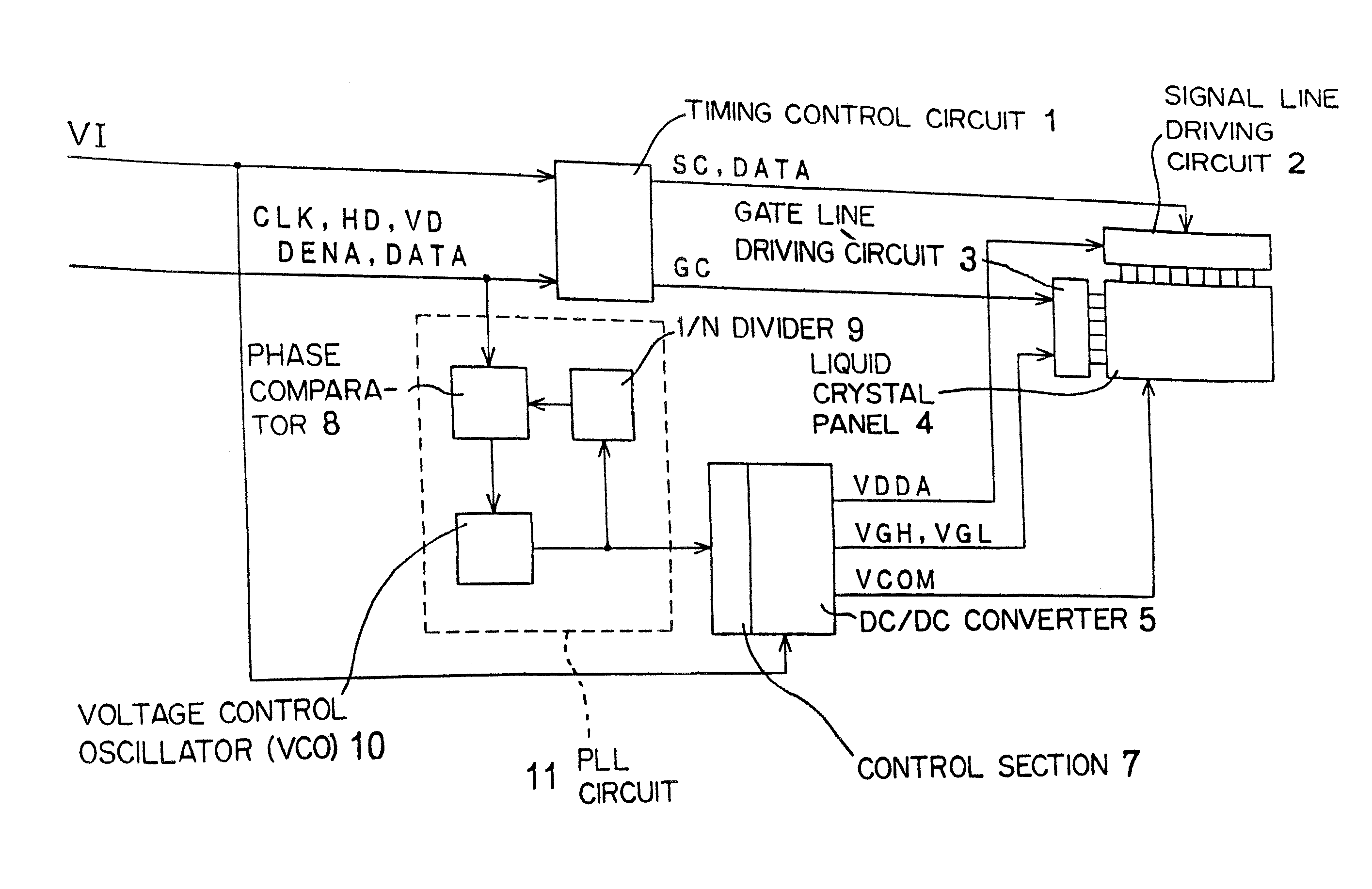
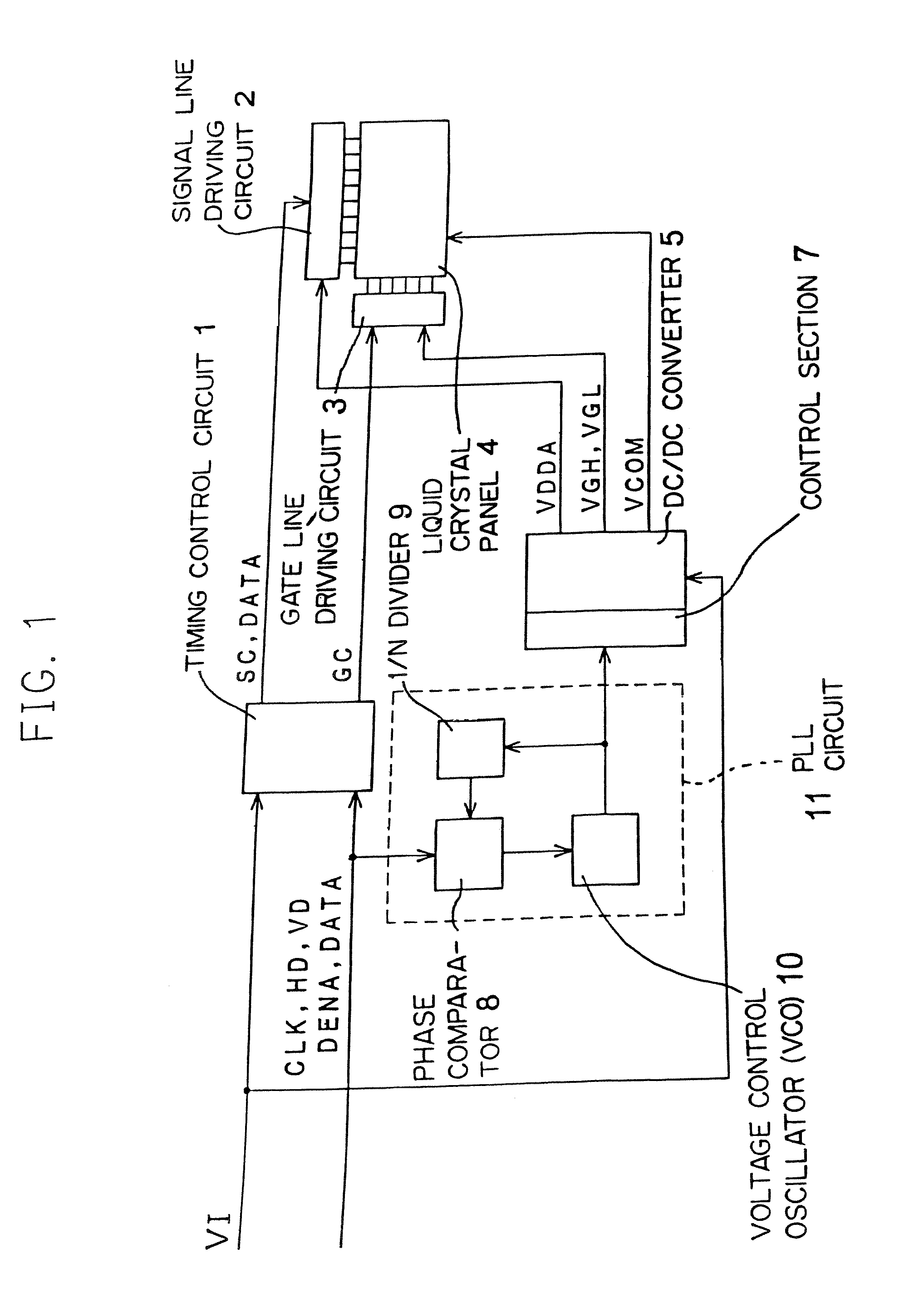
Liquid crystal display
InactiveUS7362302B2Reduce voltage variationSwitching noise effectivelyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayControl signal
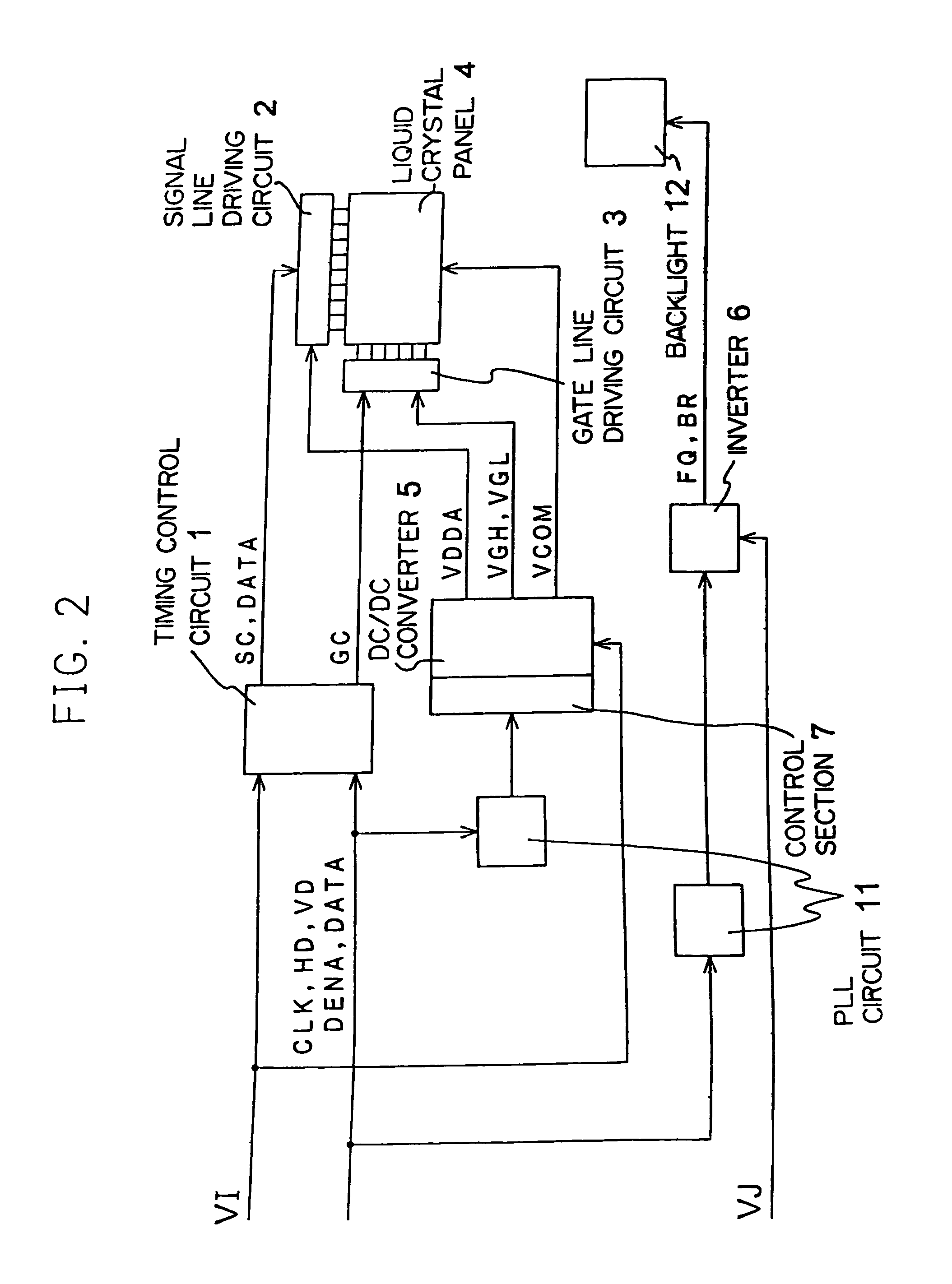
A liquid crystal display according to the present invention can prevent interference fringe on a display panel due to a switching noise of a DC / DC converter, therefore a high-quality image can be displayed. Either of input signals for a timing control circuit is also supplied to a PLL circuit and the DC / DC converter is controlled by an output signal of the PLL circuit, thereby enables to synchronize a switching frequency of the DC / DC converter and control signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Display device and method for driving the same
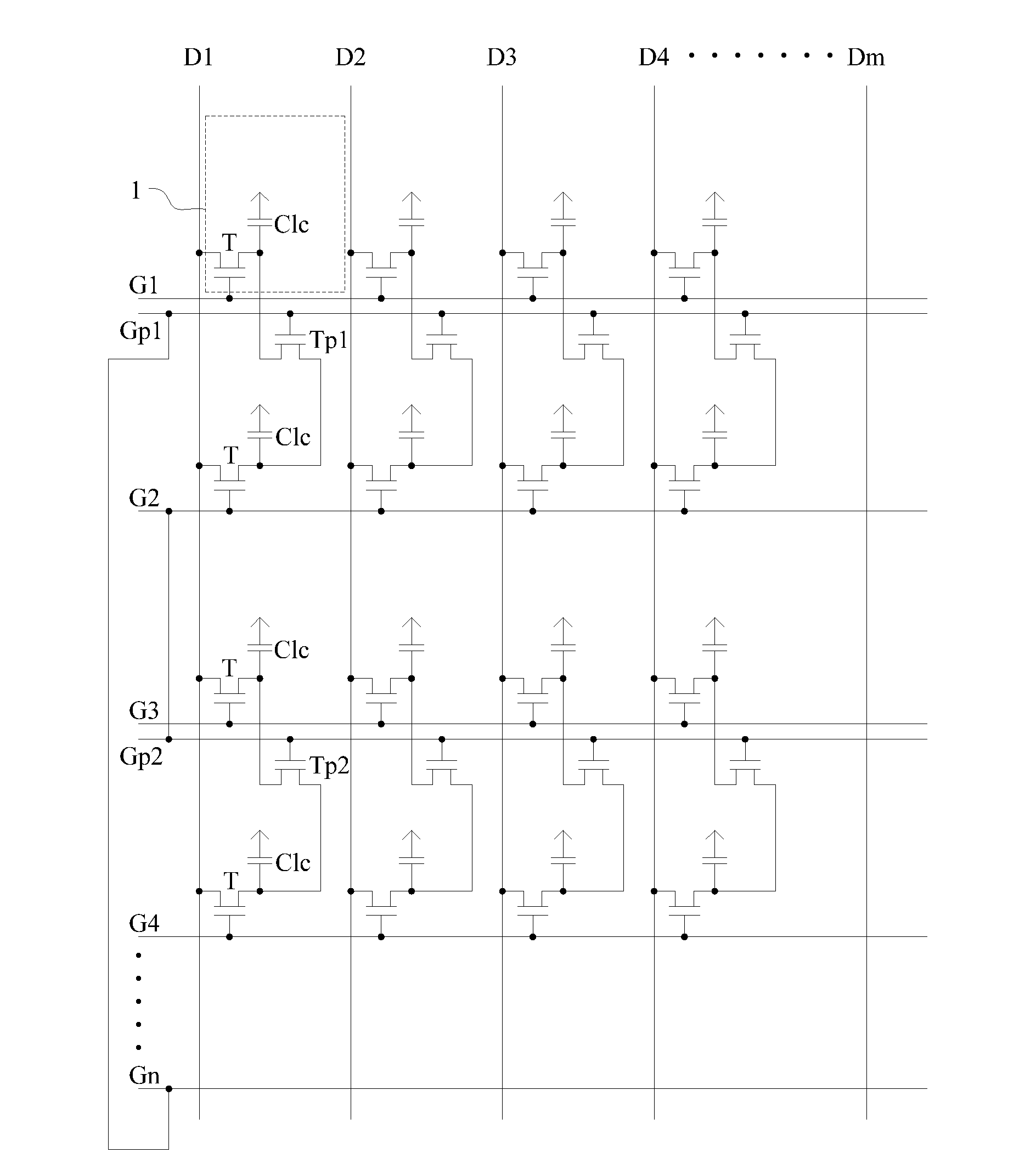
InactiveUS20160042710A1Reduce voltage variationIncrease the speed of chargingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayScan line
The present disclosure discloses a display device and a method for driving the same, which belongs to the field of display technology and therefore solves the technical problem of low charging speed of a liquid crystal display in the prior art.The display device comprises a plurality of scan lines and data lines that are staggered with each other vertically and horizontally, a plurality of sub-pixel units defined by the scan lines and data lines, an additional scan line, and an additional TFT, wherein the additional TFT has its gate connected to the additional scan line, its source connected to the pixel electrode of a first sub-pixel unit, and its drain connected to the pixel electrode of a second sub-pixel unit, and wherein the polarities of voltages on the pixel electrodes of the first sub-pixel unit and the second sub-pixel unit are opposite to each other.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Preparation method for electronic components with an alloy electrode layer
InactiveUS20160293300A1Improve reliabilityReduce voltage variationResistor manufactureConductive pattern formationElectronic componentElectron
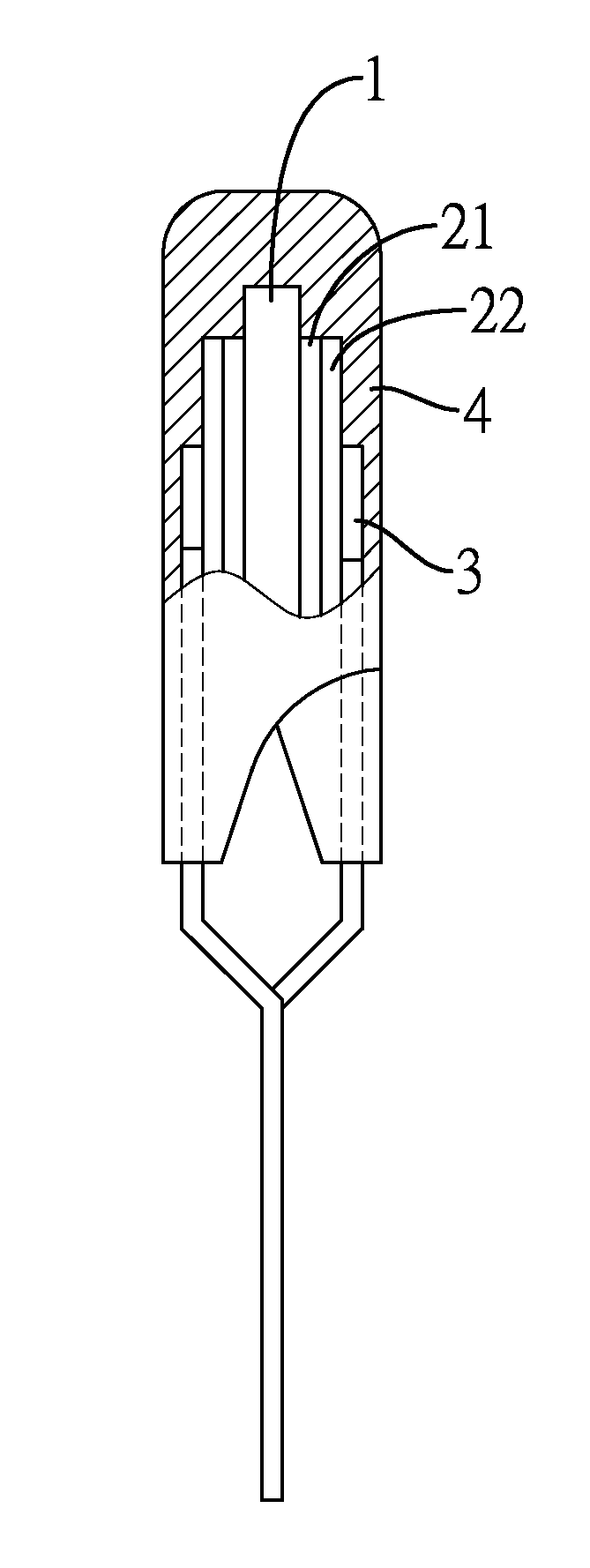
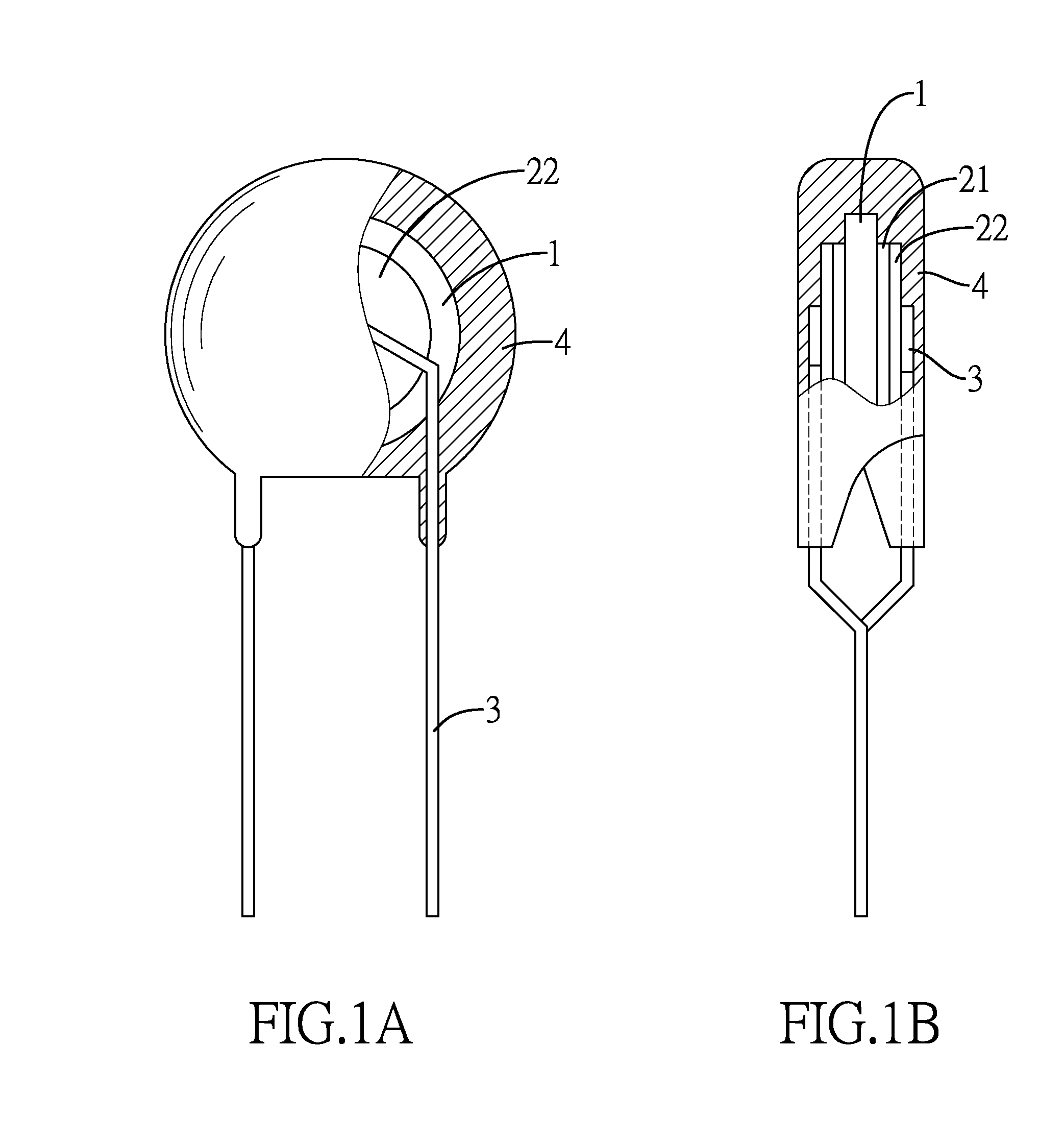
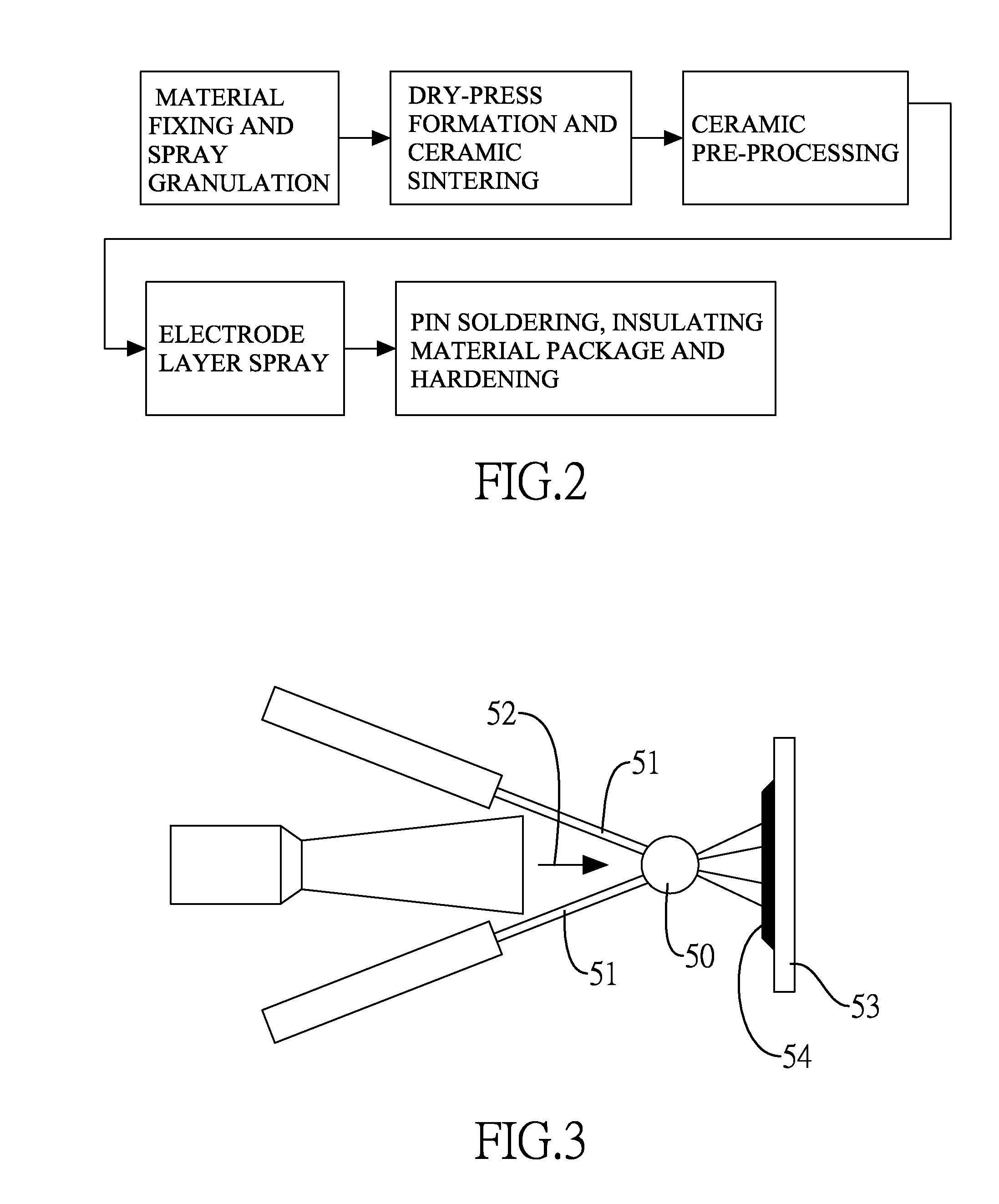
A preparation method for an electronic component with an alloy electrode layer includes steps of printing a metal layer on each of the two opposite surfaces of a ceramic substrate with the metal layer made from aluminum, spraying an alloy layer being a copper alloy layer on an outer surface of each metal layer, connecting a pin to each alloy layer, and enclosing the ceramic substrate, the metal layers, the alloy layers and a portion of each pin with an insulating layer. With the adoption of copper alloy for the alloy layer, the preparation method has the advantages of low production cost and high reliability of the electronic component produced by the method.
Owner:THINKING ELECTRONICS INDAL
Insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving circuit
ActiveCN102324835BReduce voltage variationReduce discharge ratePower conversion systemsOvervoltageHemt circuits
The invention provides an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) driving circuit, which comprises a switching-on resistor with a relatively higher resistance value, a switching-off resistor with a relatively lower resistance value and a switching input circuit, wherein the switching input circuit is connected to the gate of an IGBT by the switching-on resistor; and one end of the switching-off resistor is connected to the gate of the IGBT. The IGBT driving circuit further comprises an over-voltage detection circuit and a rapid switching-off control circuit. The rapid switching-off control circuit controls the other end of the switching-off resistor to be switched off when the switching input circuits inputs a switching-on level, controls the other end of the switching-off circuit to be grounded when the switching input circuit inputs a switching-off level, and controls the other end of the switching-off resistor to be switched off when the voltage, detected by the over-voltage detection circuit, of the collector of the IGBT is higher than a preset value. The IGBT driving circuit provided by the invention can rapidly realize the rapid switching-off of the IGBT and simultaneously suppress the excessive voltage variations of the IGBT.
Owner:EAST GRP CO LTD
Synchronous rectification control circuit and power converter
PendingCN112398315AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTerminal voltageVoltage regulation
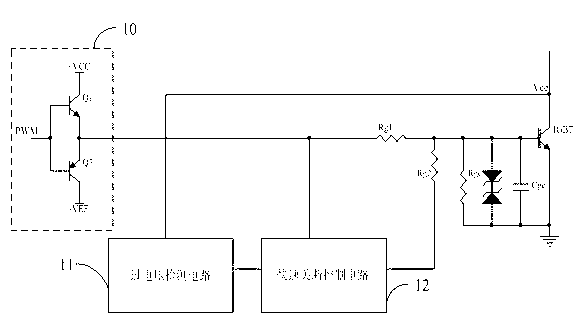
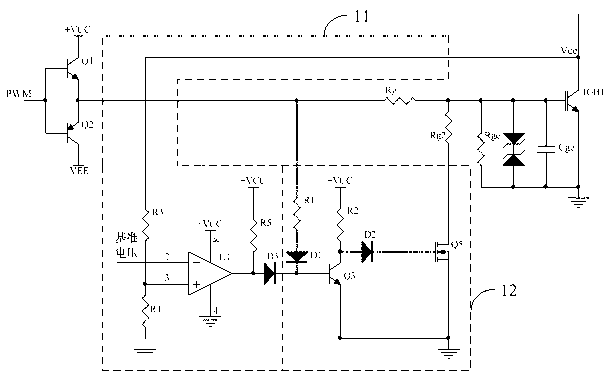
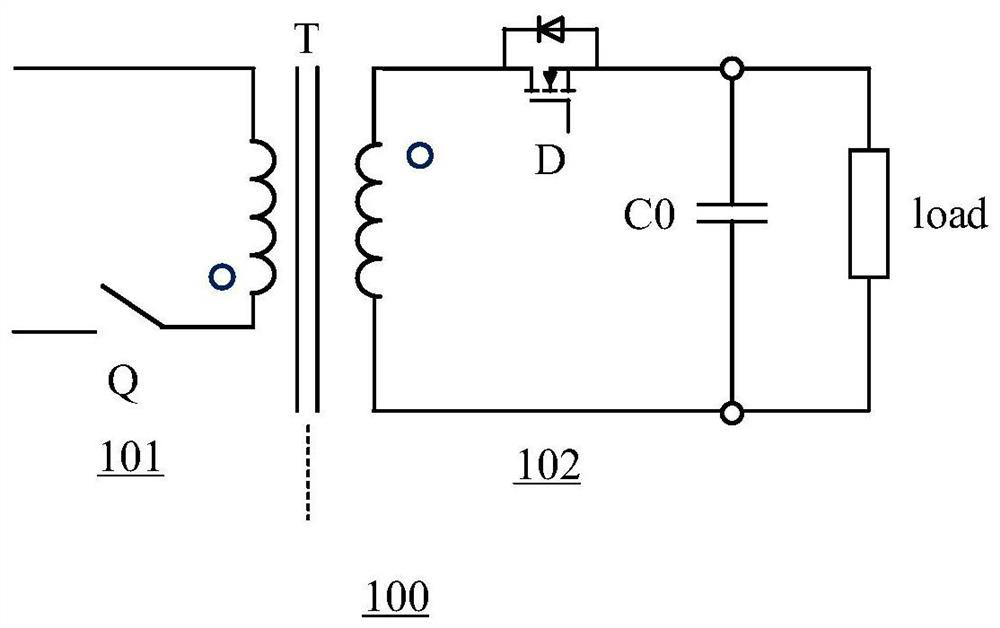
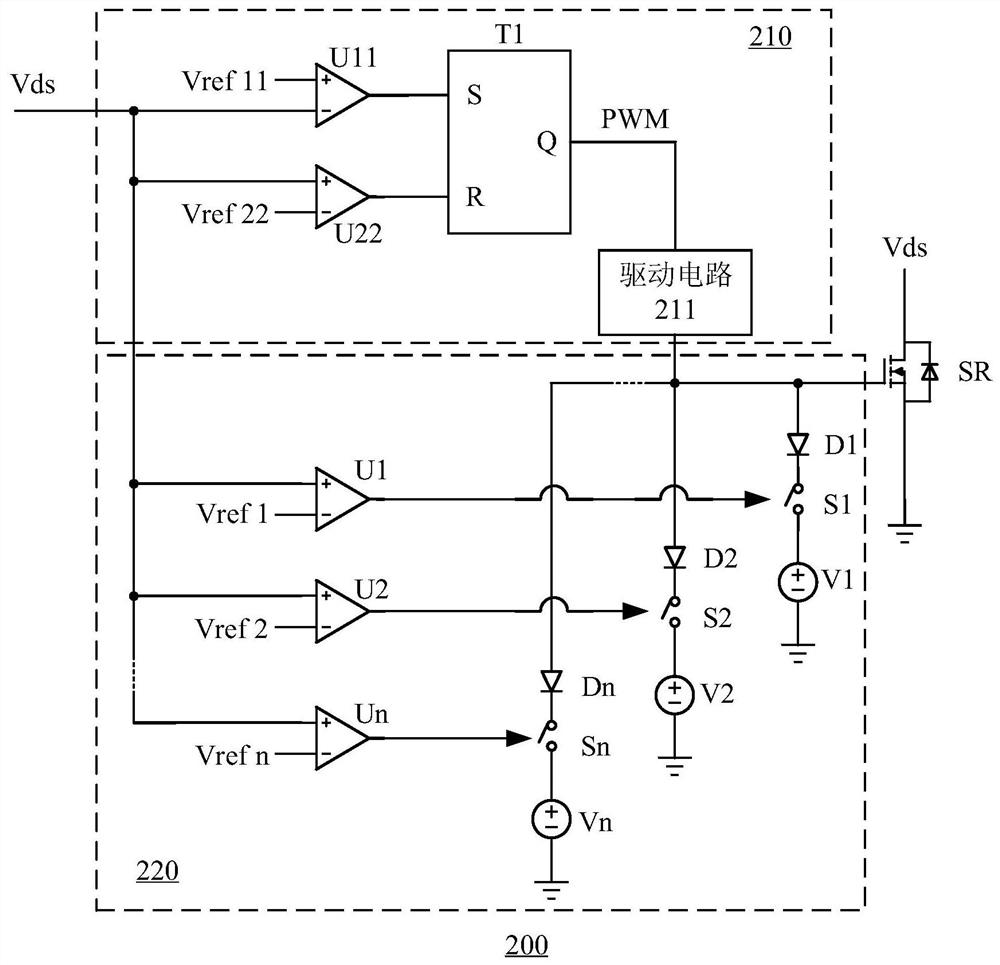
Disclosed are a synchronous rectification control circuit and a power converter. The power converter comprises the synchronous rectification control circuit, and the synchronous rectification controlcircuit comprises a main control circuit for controlling the on and off of a synchronous rectifier tube; and a voltage regulating circuit which is used for regulating the voltage output end to be connected to the control end of the synchronous rectifier tube and reducing the voltage at the control end of the synchronous rectifier tube before the synchronous rectifier tube is turned off within theturn-on time of the synchronous rectifier tube. According to the synchronous rectification control circuit and the power converter provided by the invention, the voltage variation when the synchronousrectification tube is turned off can be reduced, the turn-off delay of the synchronous rectification tube is reduced, and the reliability and stability of synchronous rectification control are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN KIWI MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com