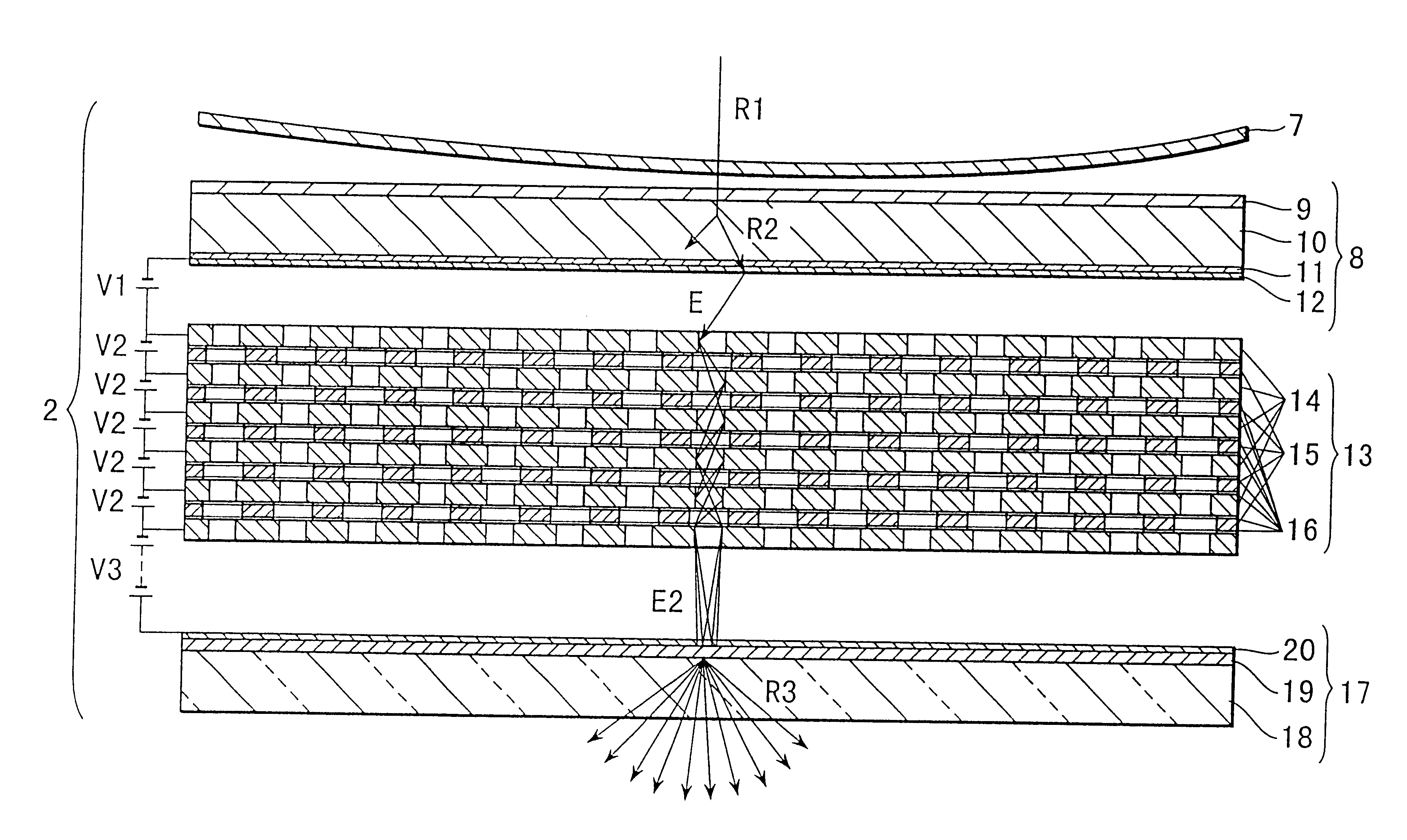
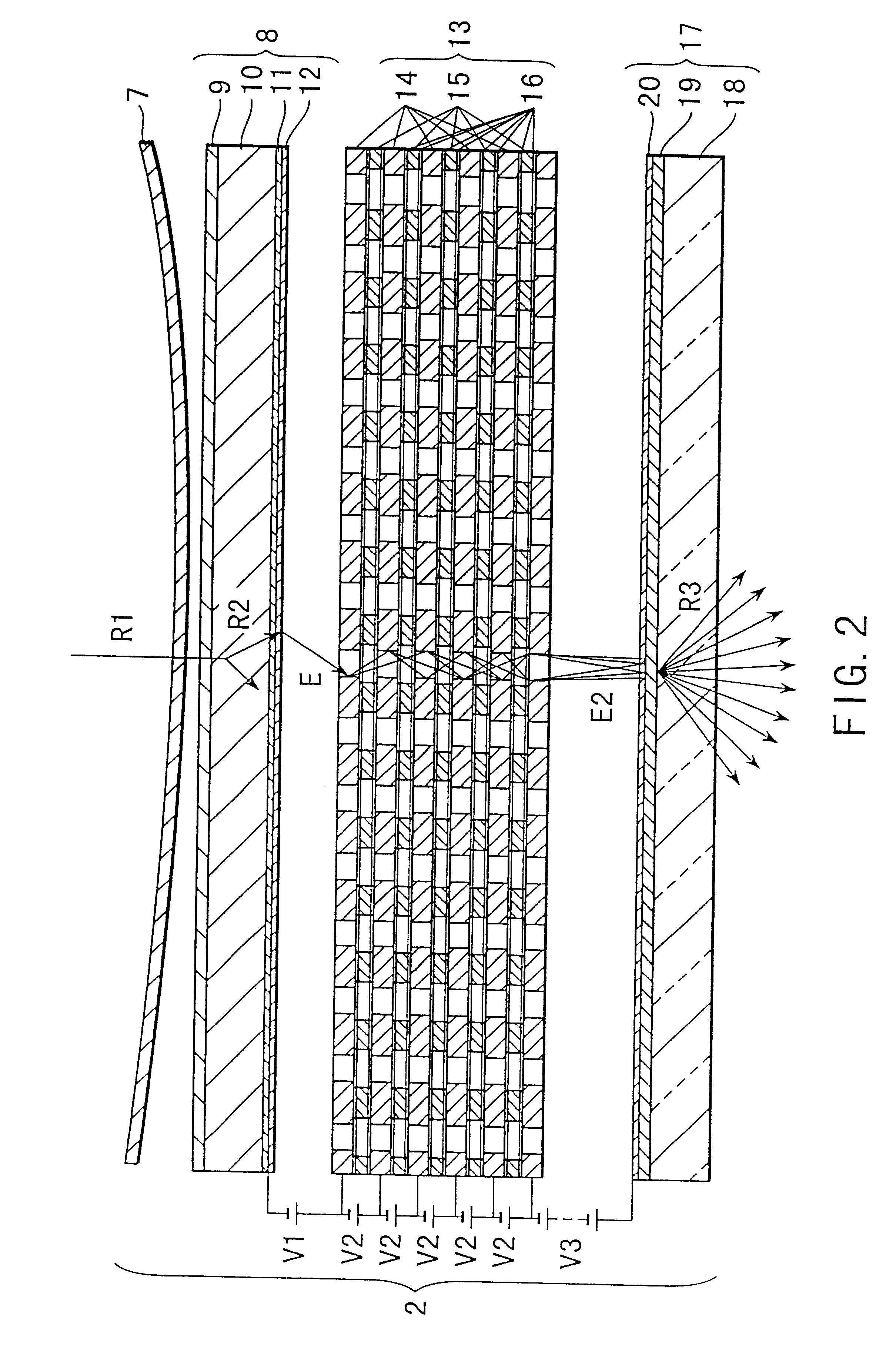
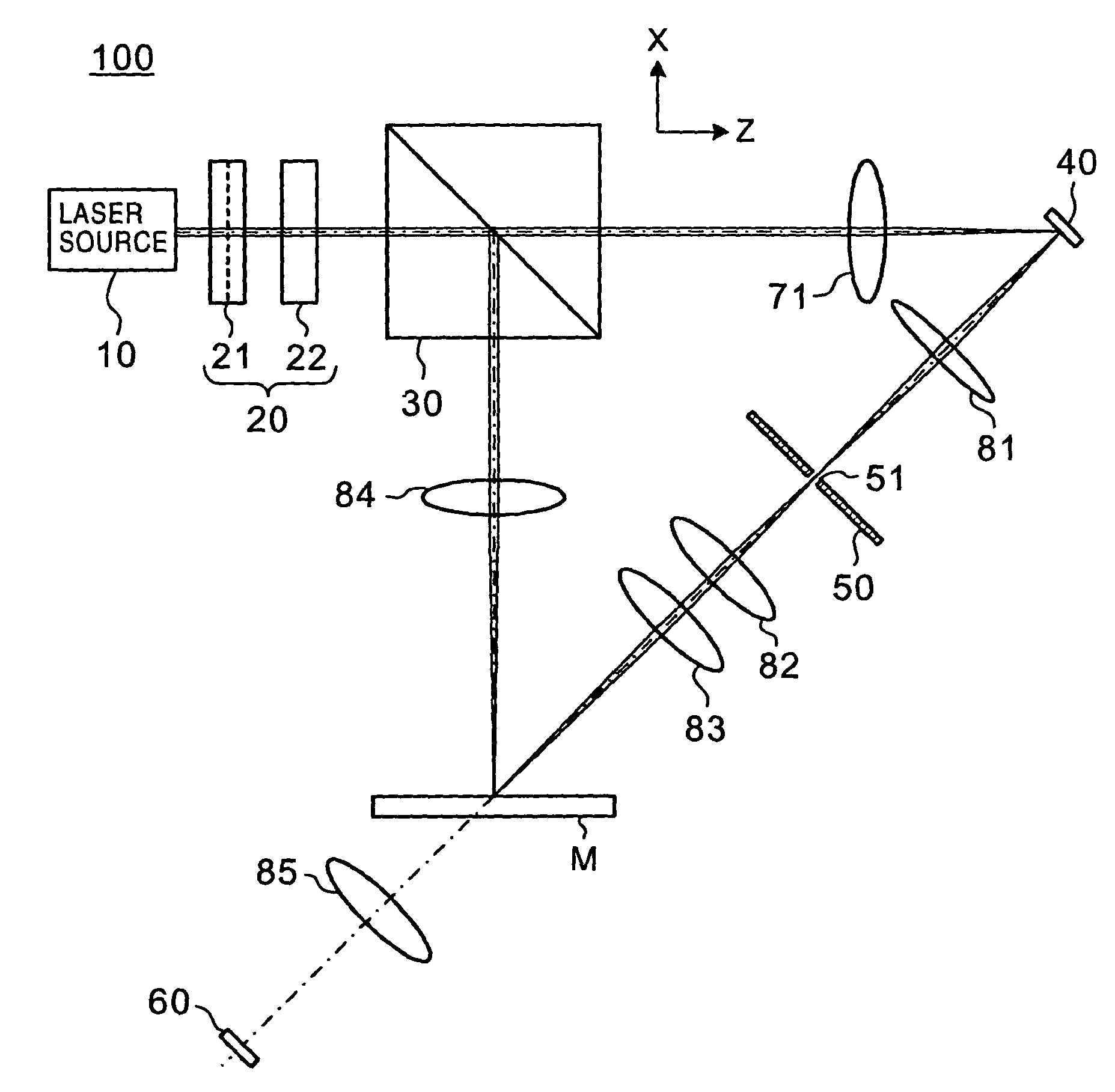
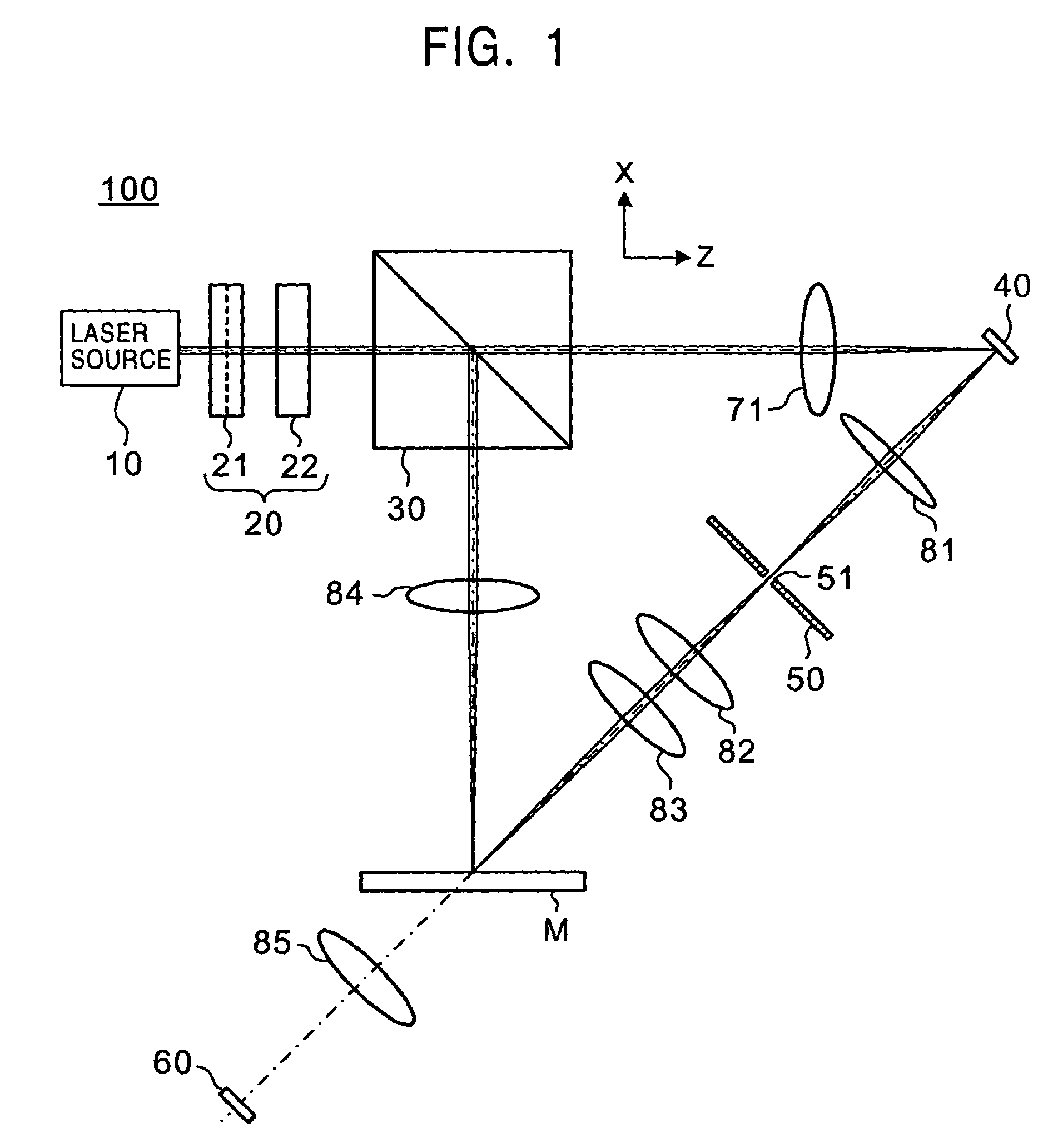
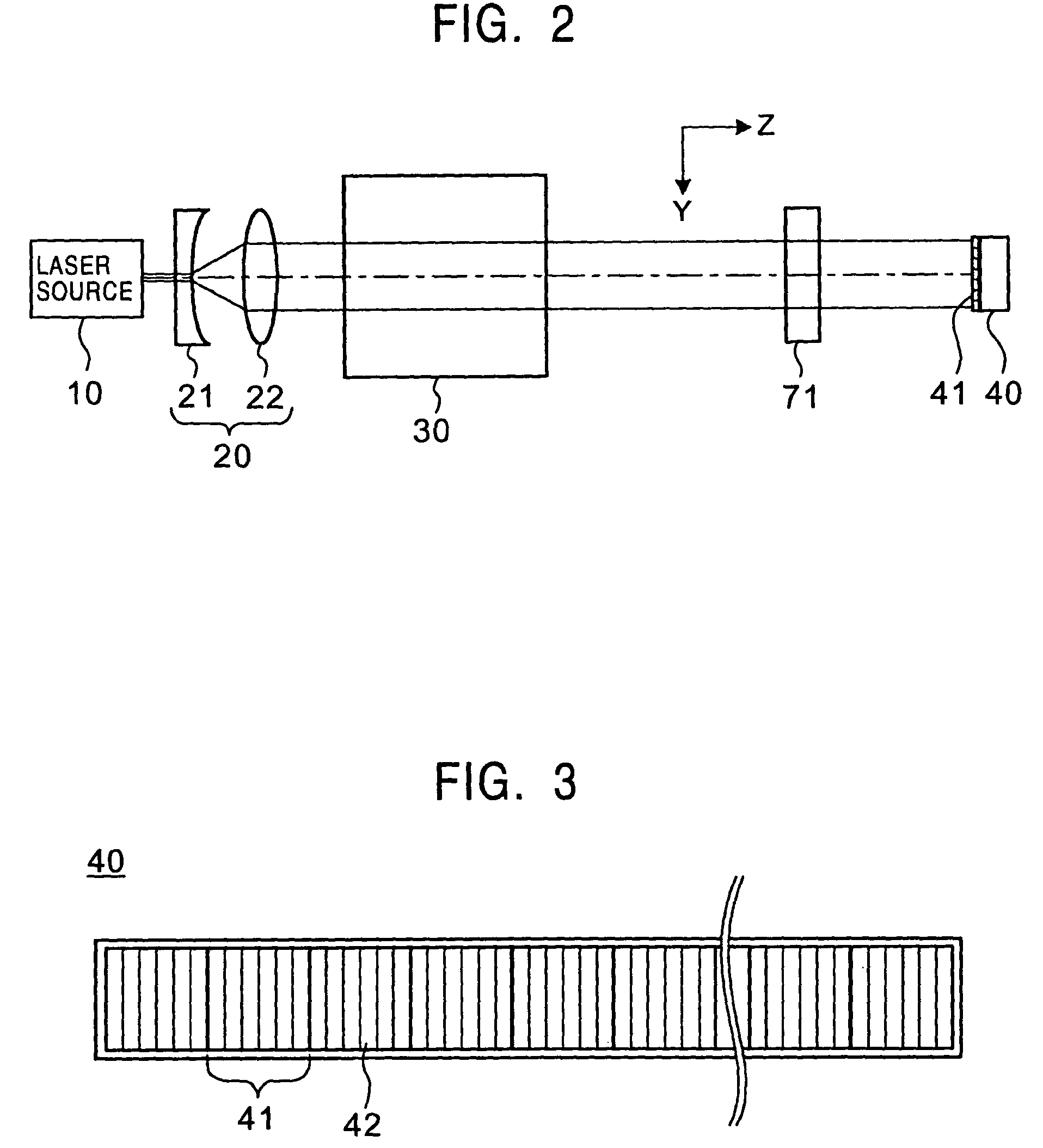
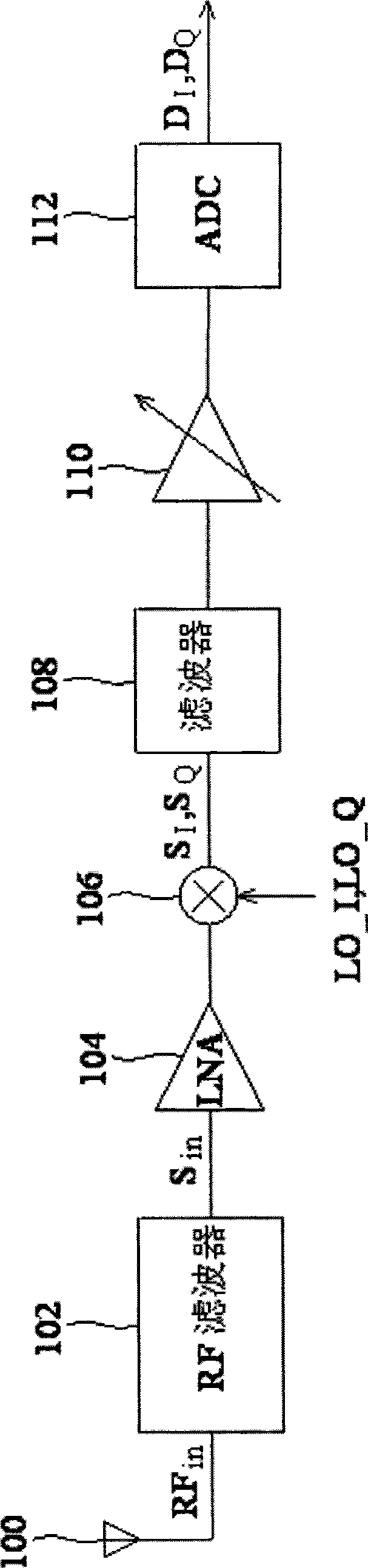
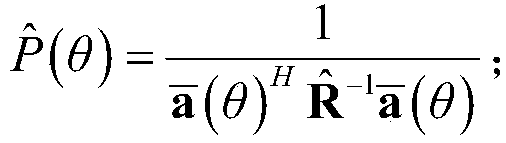Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97results about How to "Reduce noise components" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
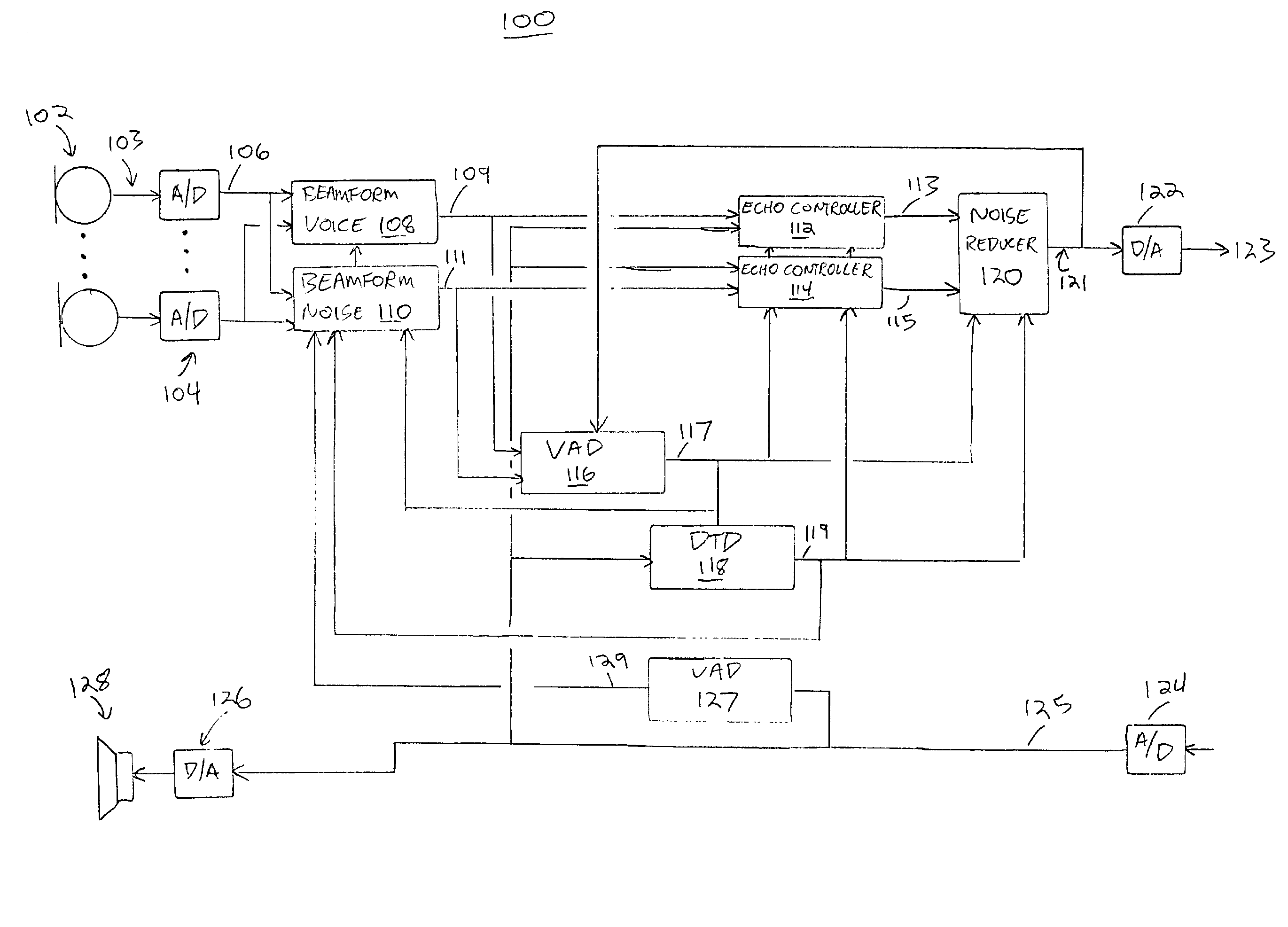
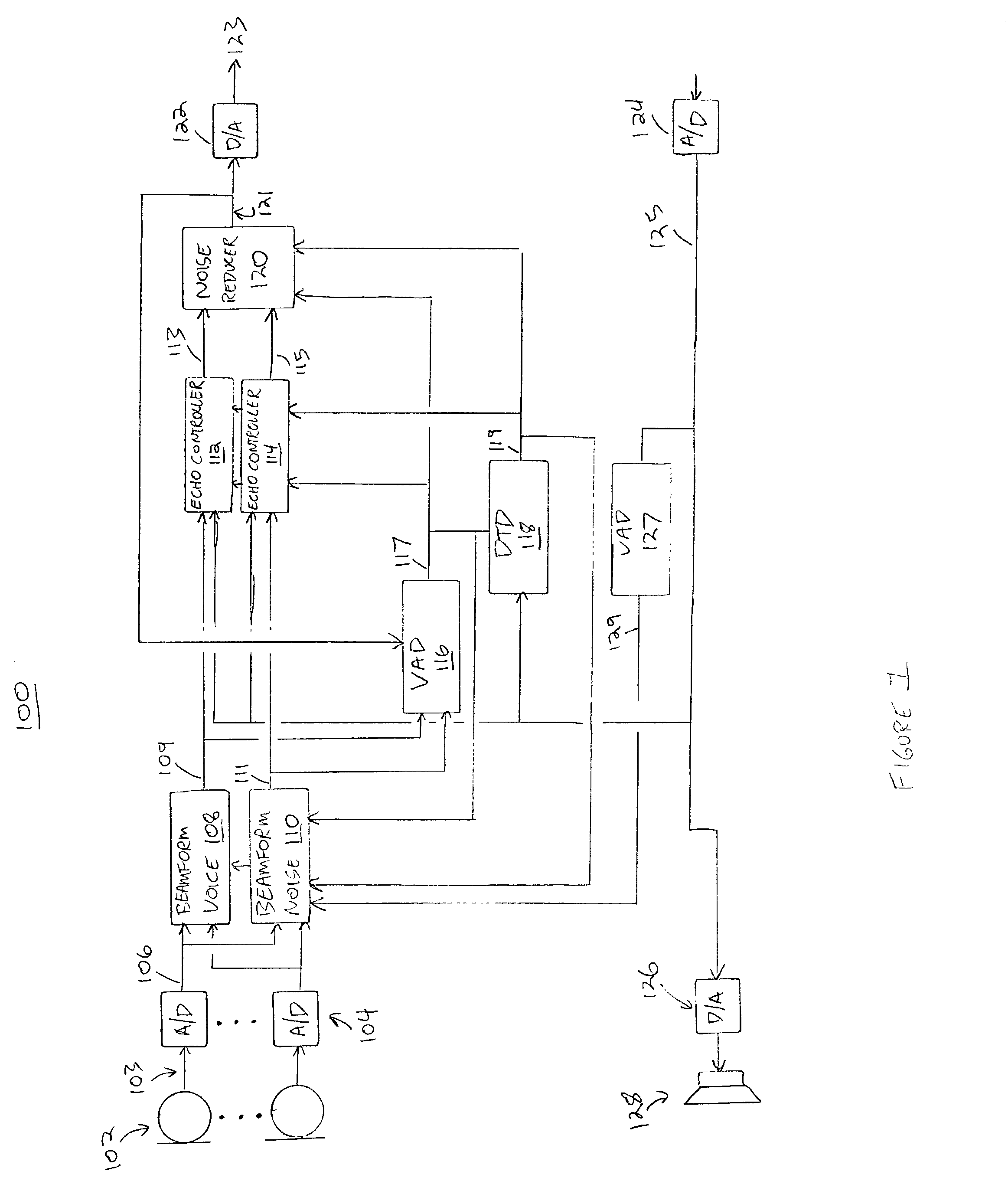
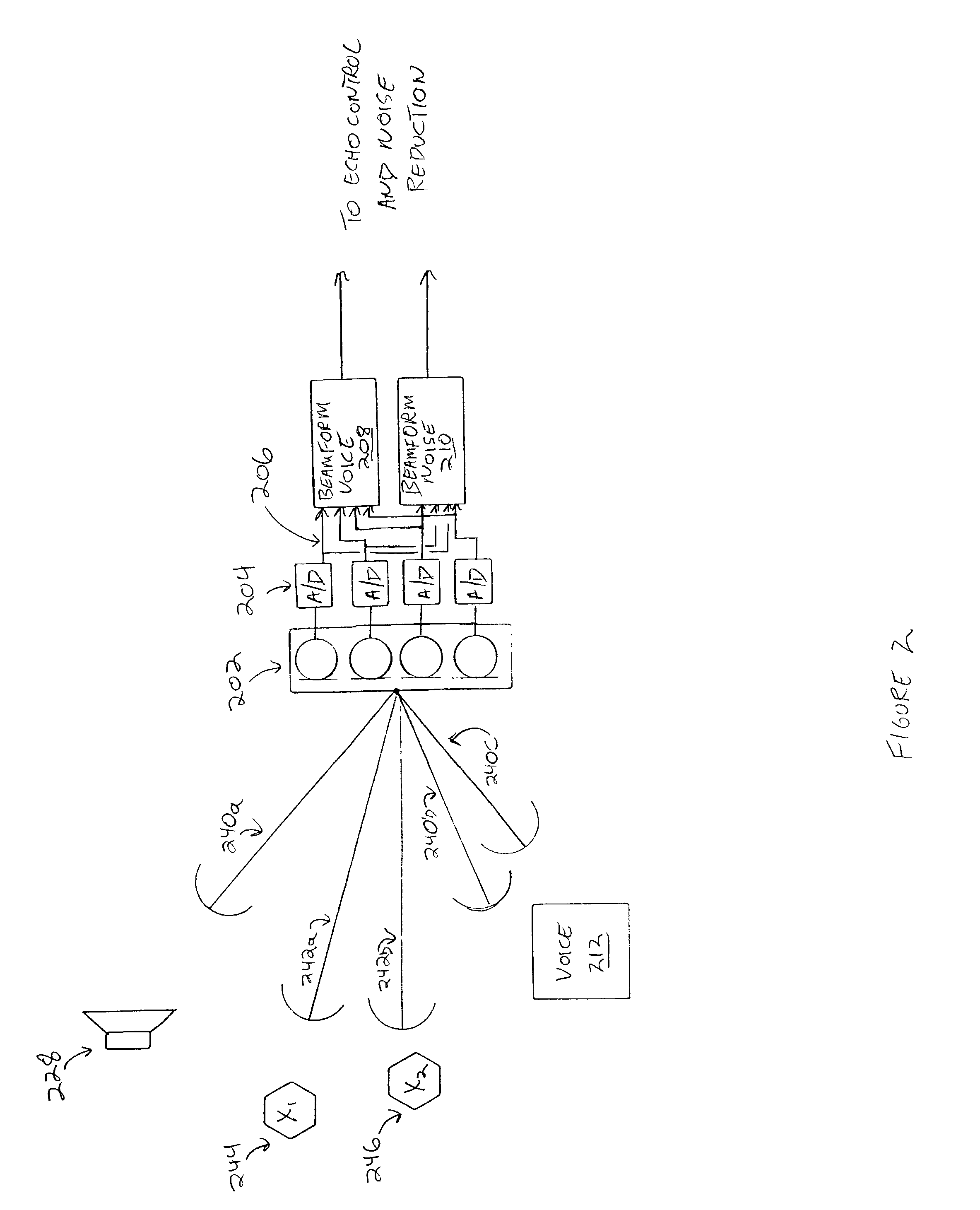
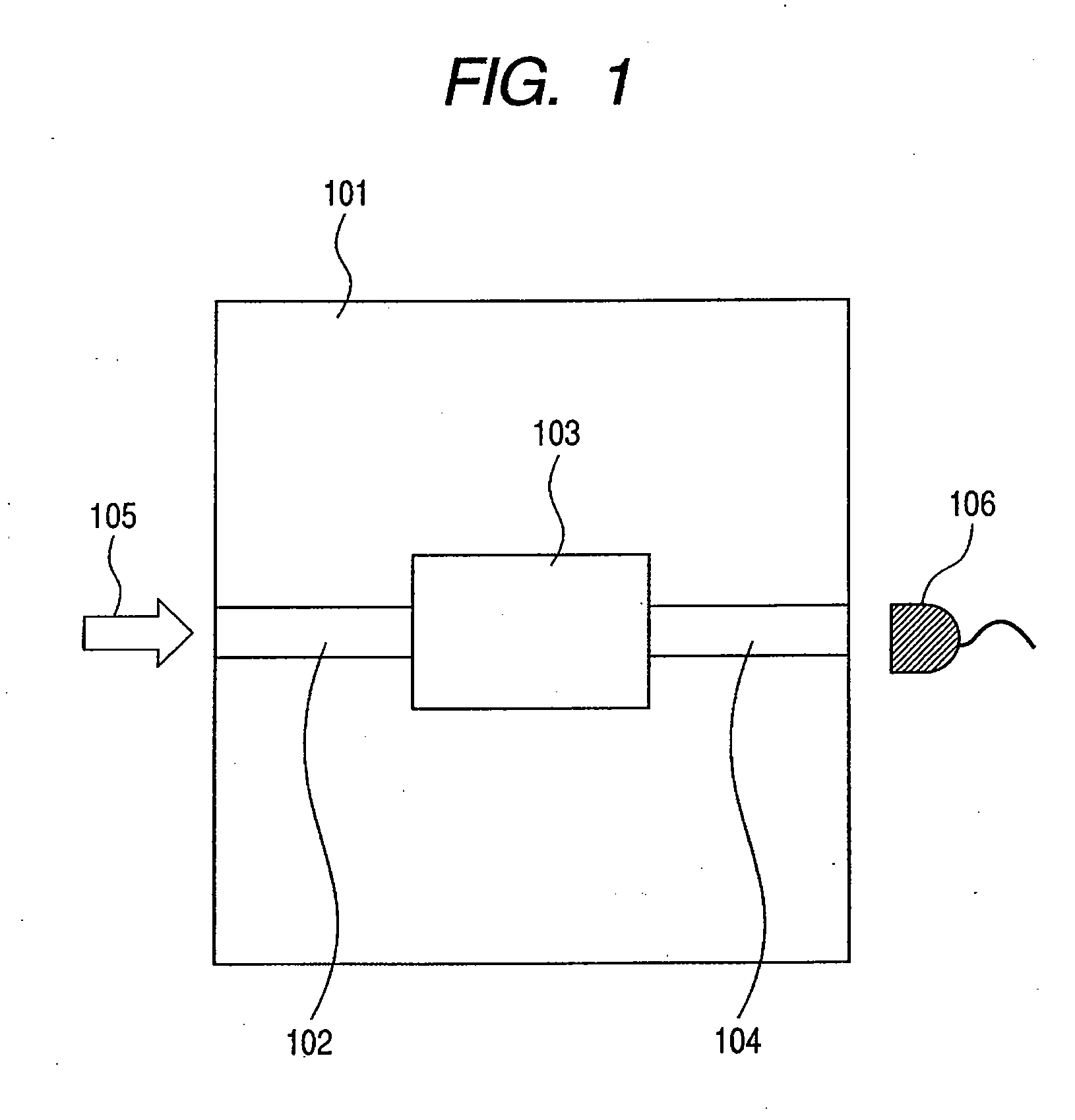
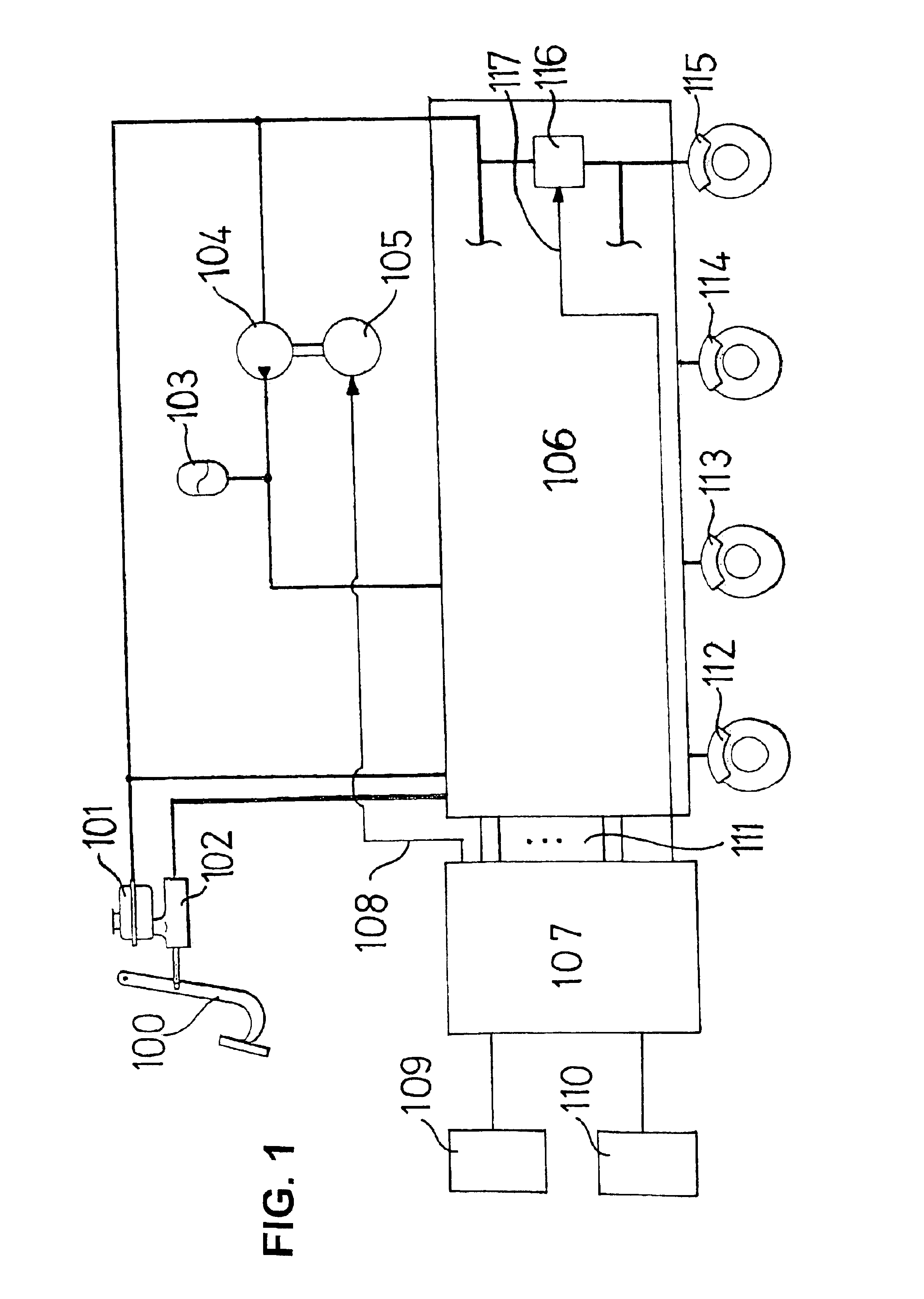
Method and apparatus for reducing echo and noise
InactiveUS7359504B1Reducing acoustic echoReduce background noiseTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsReducerComputer science
The present invention provides a solution to the needs described above through a method and apparatus for reducing echo and noise. The apparatus includes a microphone array for receiving and audio signal, the audio signal including a voice signal component and a noise signal component. The apparatus further includes a voice processing path having an input coupled to the microphone array and a noise processing path having an input coupled to the microphone array. The voice processing path is adapted to detect voice signals and the noise processing path is adapted to detect noise signals. A first echo controller is coupled to the voice processing path and a second echo controller is coupled to the noise processing path. A noise reducer is coupled to the output of the first echo controller and second echo controller.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
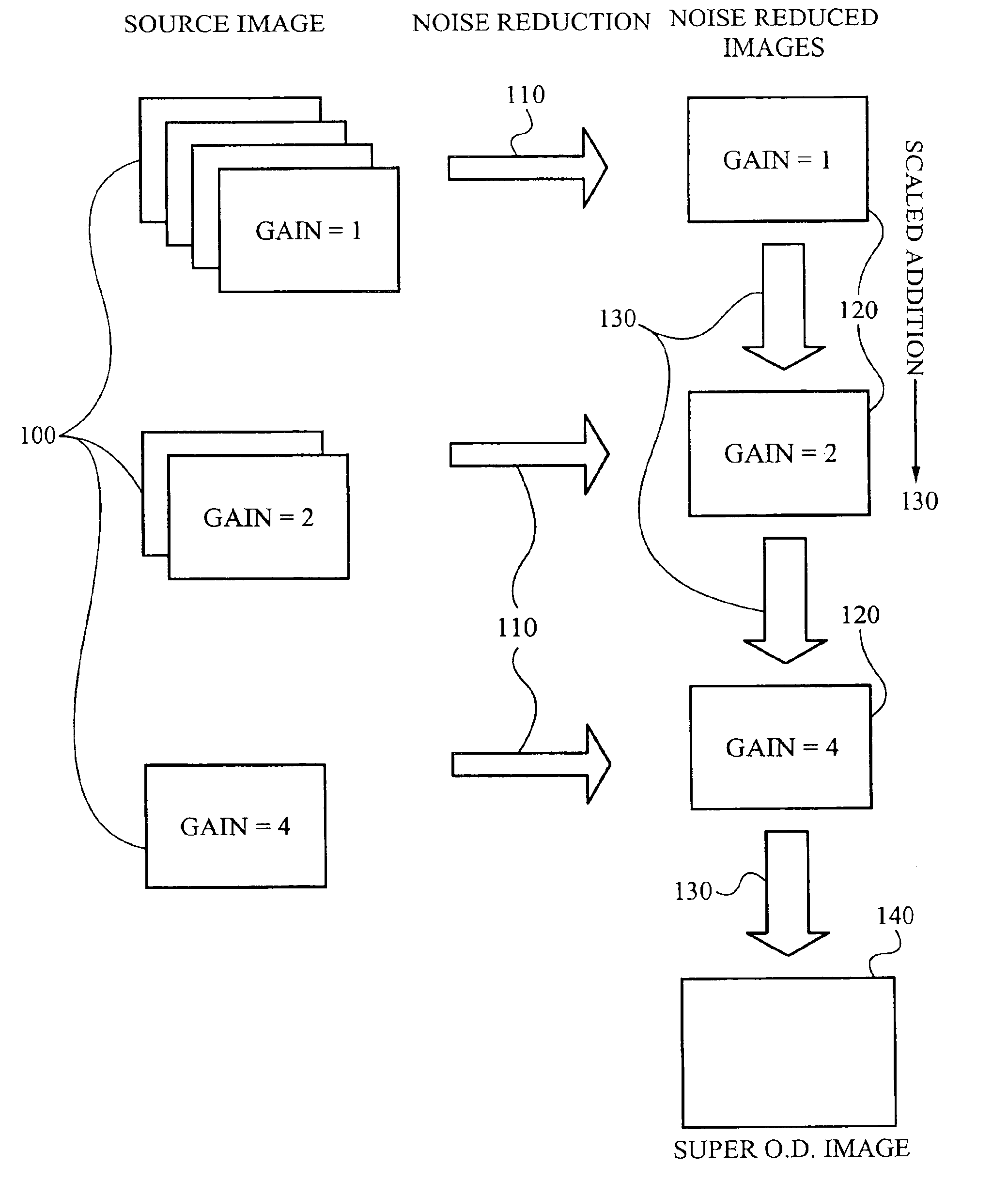
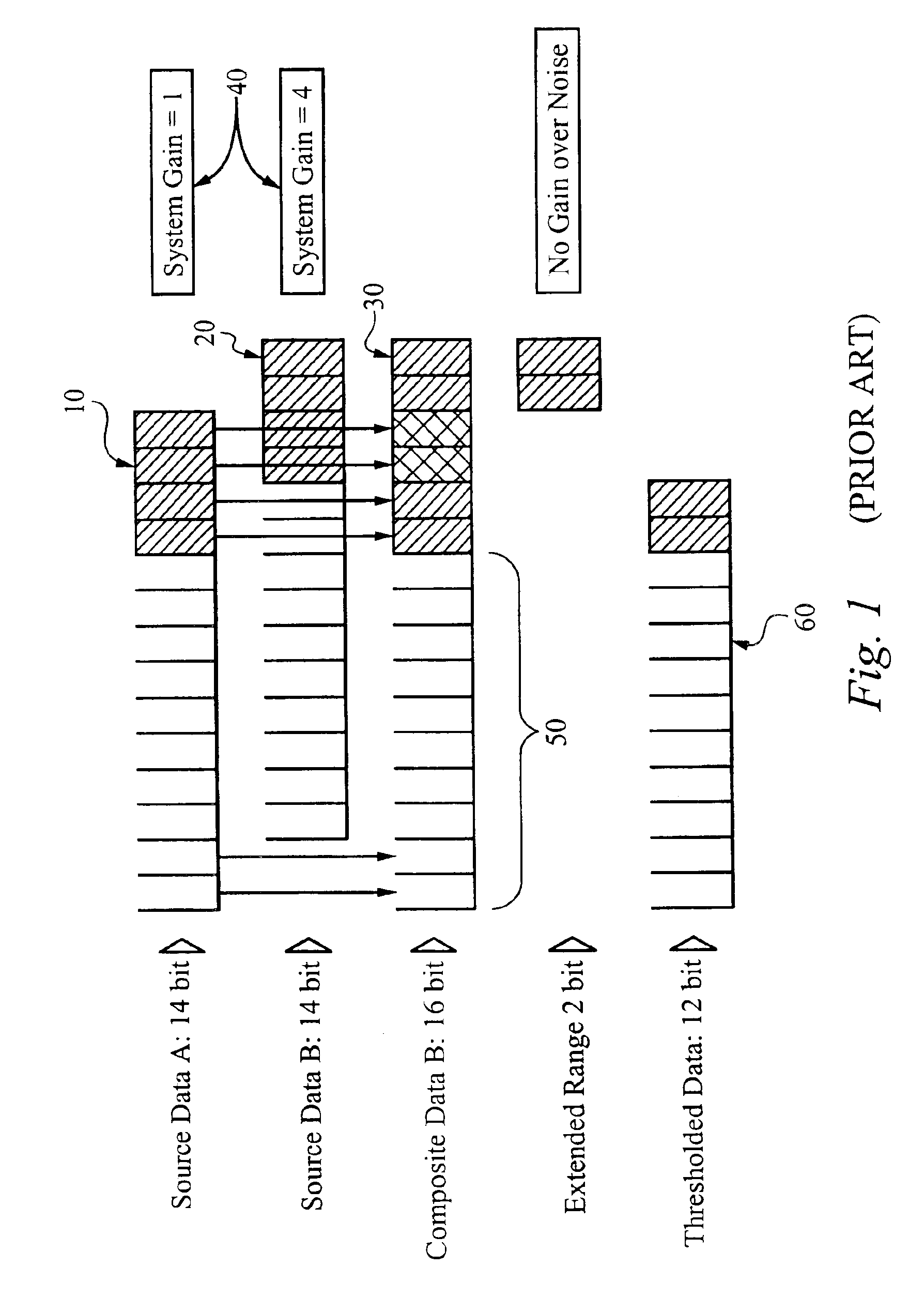
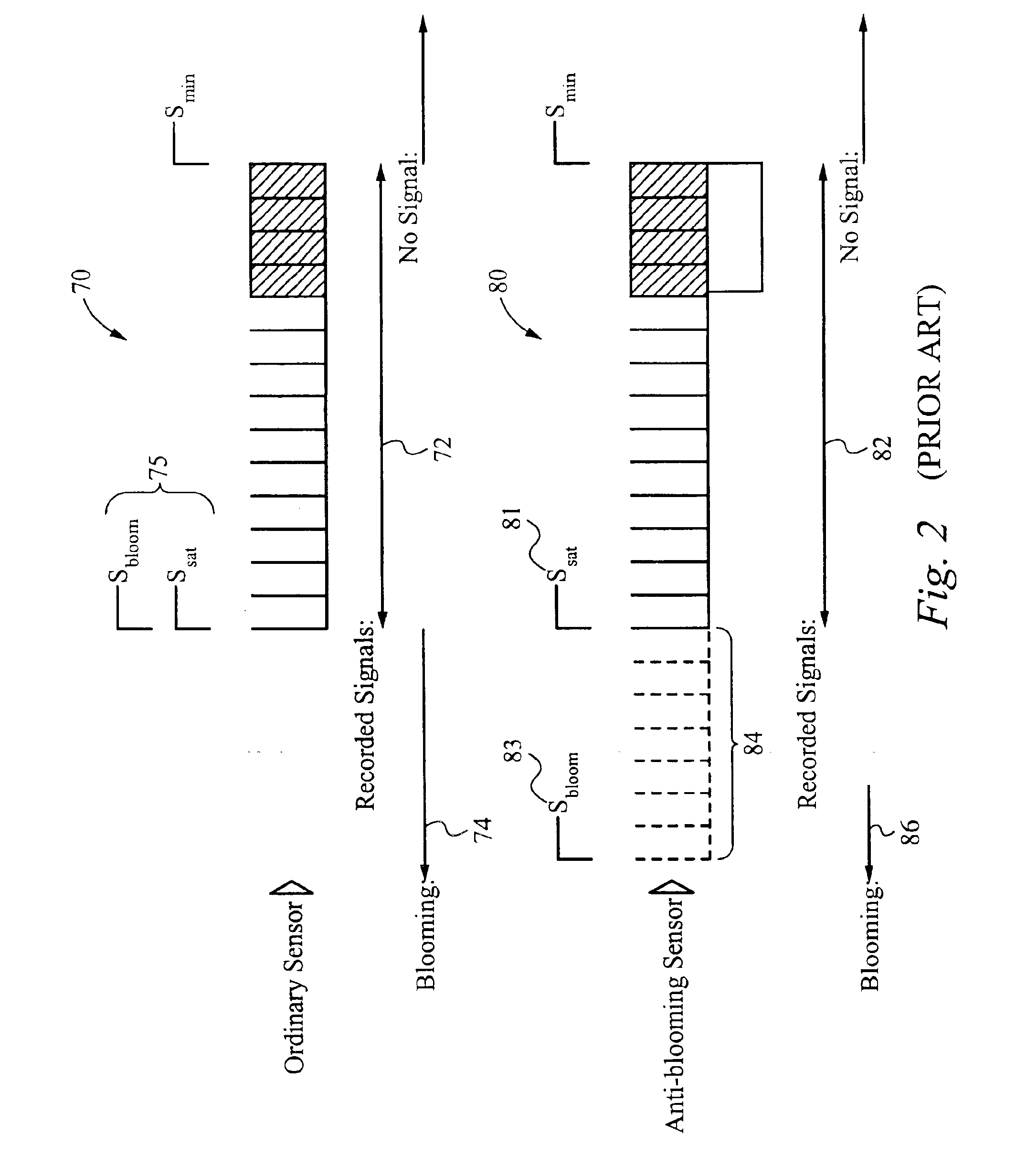
Method of and apparatus for extending signal ranges of digital images
ActiveUS6909459B2Reduce noise componentReduce componentsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSource dataImage content
The invention is a method and apparatus to extend the signal range of a digital image beyond the nominal sensor or data format range. The method and apparatus automatically acquires a scaled series of source data, applies noise reduction to the source data, and constructs a scaled composite with usable signal ranges greater than that of the individual data sources. Applied to digital images, the invention permits presentation and analysis of all signals from a subject in a single composite or an image resulting from the method and apparatus of the present invention. The present invention overcomes two defects in prior art systems: increased noise in the resultant composite image arising from rescaling of component images and dependence on evaluating image content to determine image scaling. Because this invention can be automated, it can be applied in numerous fields requiring high throughput.
Owner:PROTEINSIMPLE +1
Methods and devices for denoising in video coding and decoding,
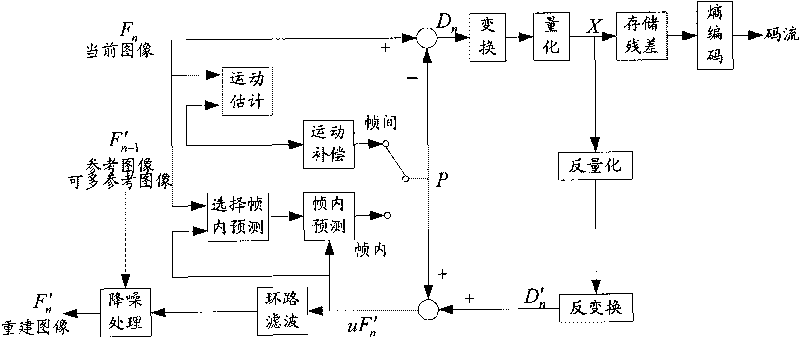
ActiveCN101742290AGuaranteed spatial and temporal correlationHigh precisionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMotion estimationVideo decoding
The invention discloses methods and devices for denoising in video coding and decoding. The method for denoising in video coding comprises the following steps of: in the process of video coding, performing full pixel denoising treatment on a reconstructed picture of the current coding picture; and taking the denoised and reconstructed picture as a reference picture of other coding pictures. The method for denoising in video decoding comprises the following steps of: in the process of video decoding, performing the full pixel denoising treatment on the reconstructed picture of the current decoding picture; and taking the denoised reconstructed picture as the reference picture of other decoding pictures and the final reconstructed picture. The technical scheme disclosed by invention can suppress noises in the acquired video pictures, and improve the precision of a block matching result in the process of motion estimation.
Owner:VIMICRO ELECTRONICS CORP +1
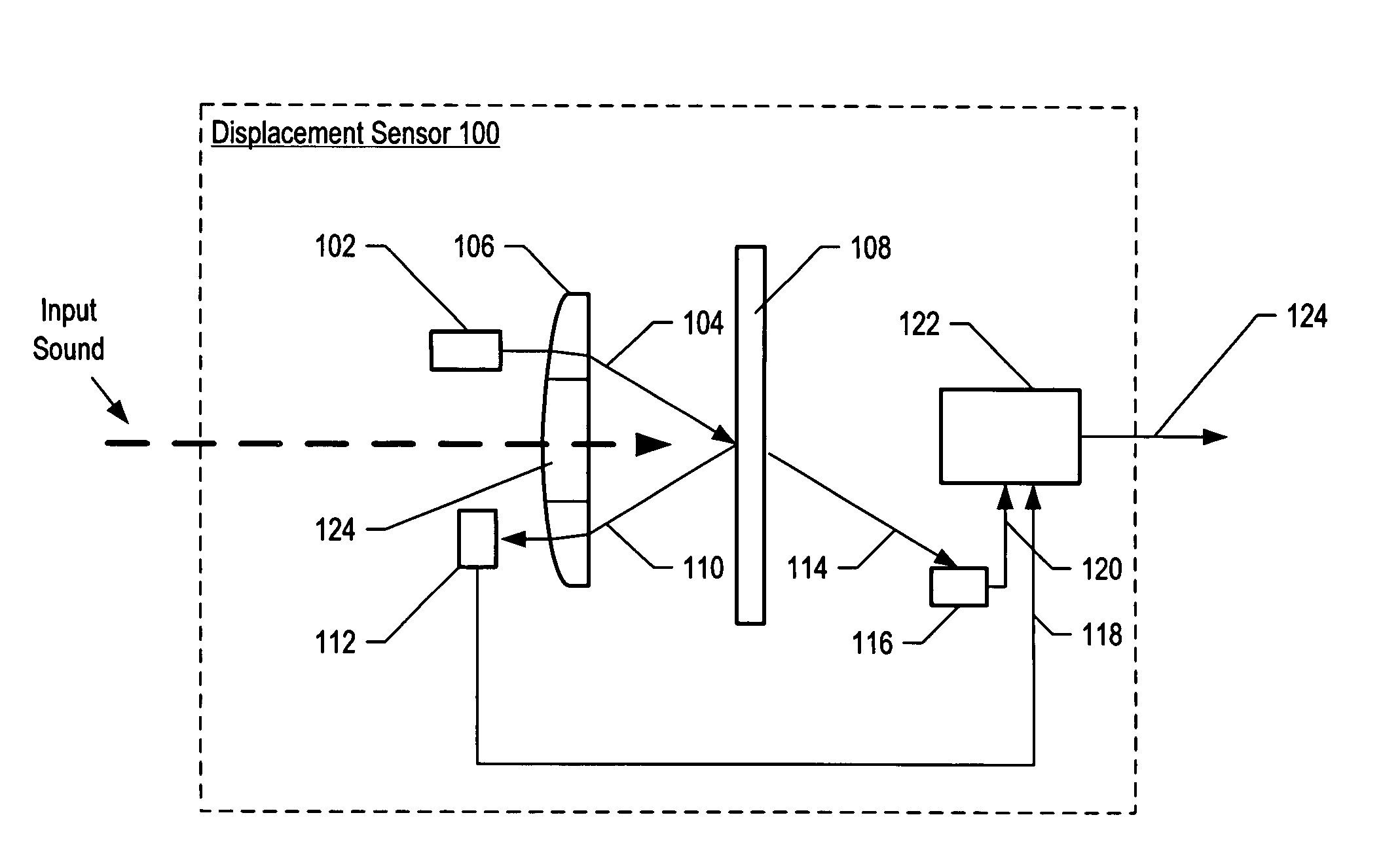
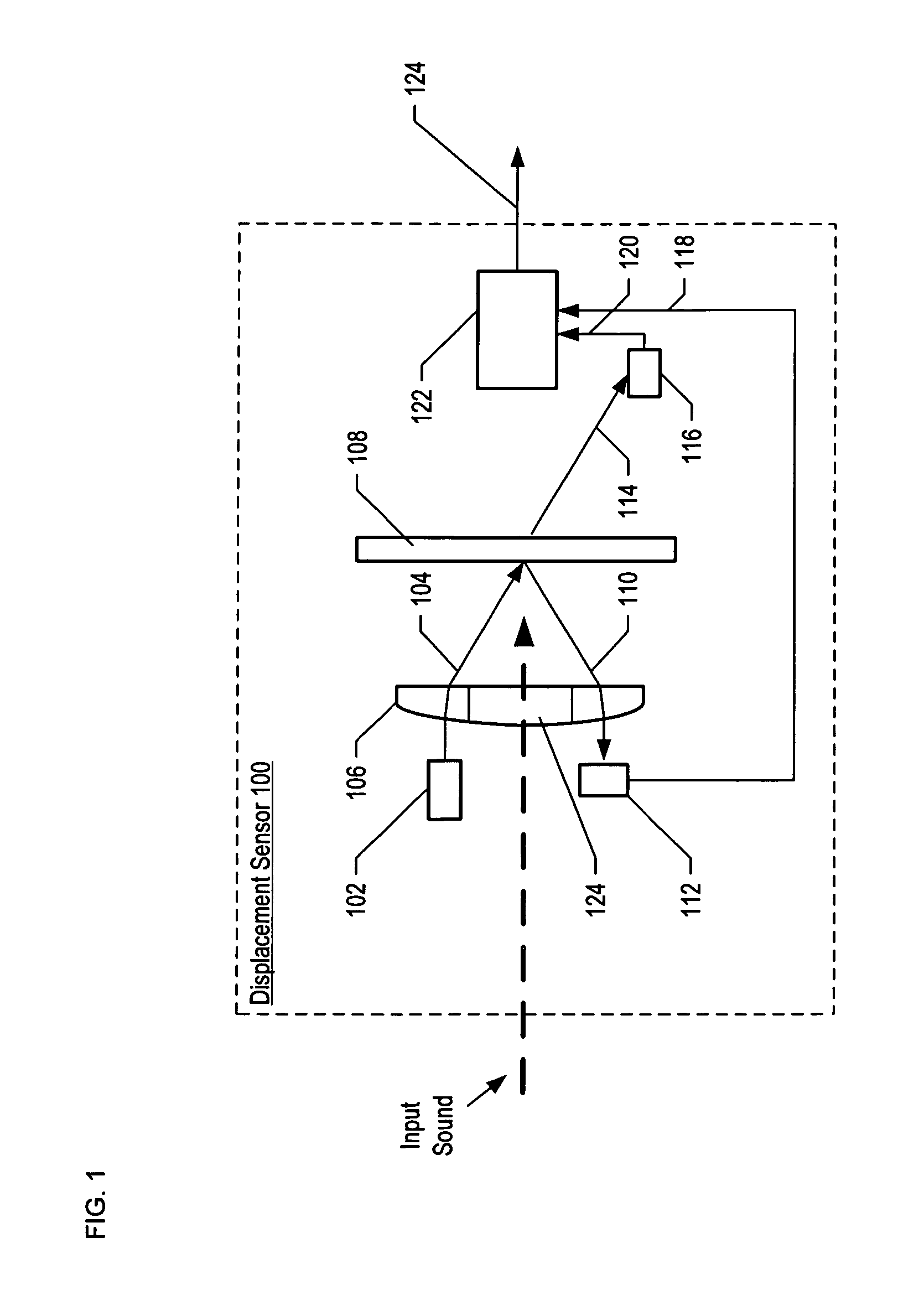
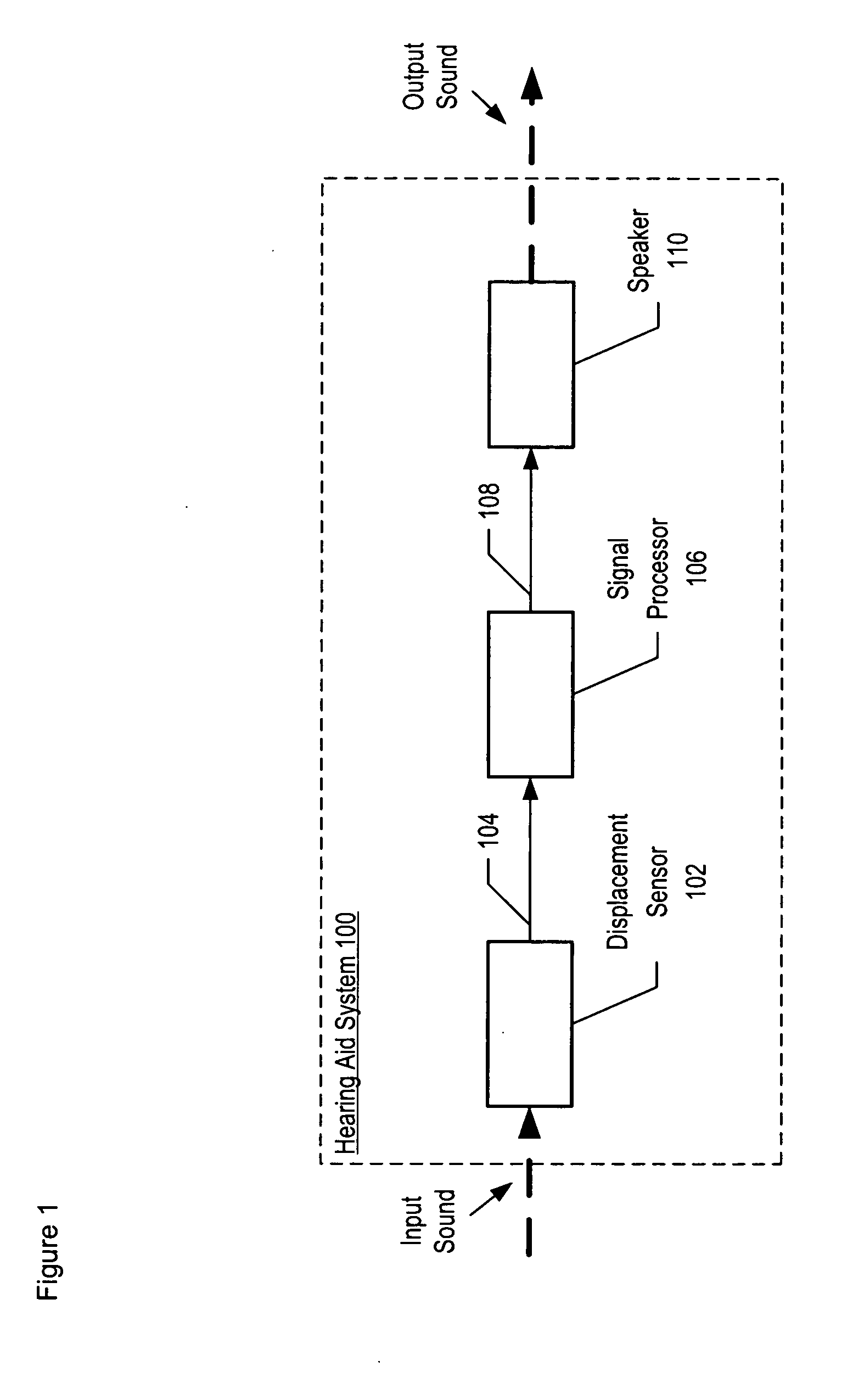
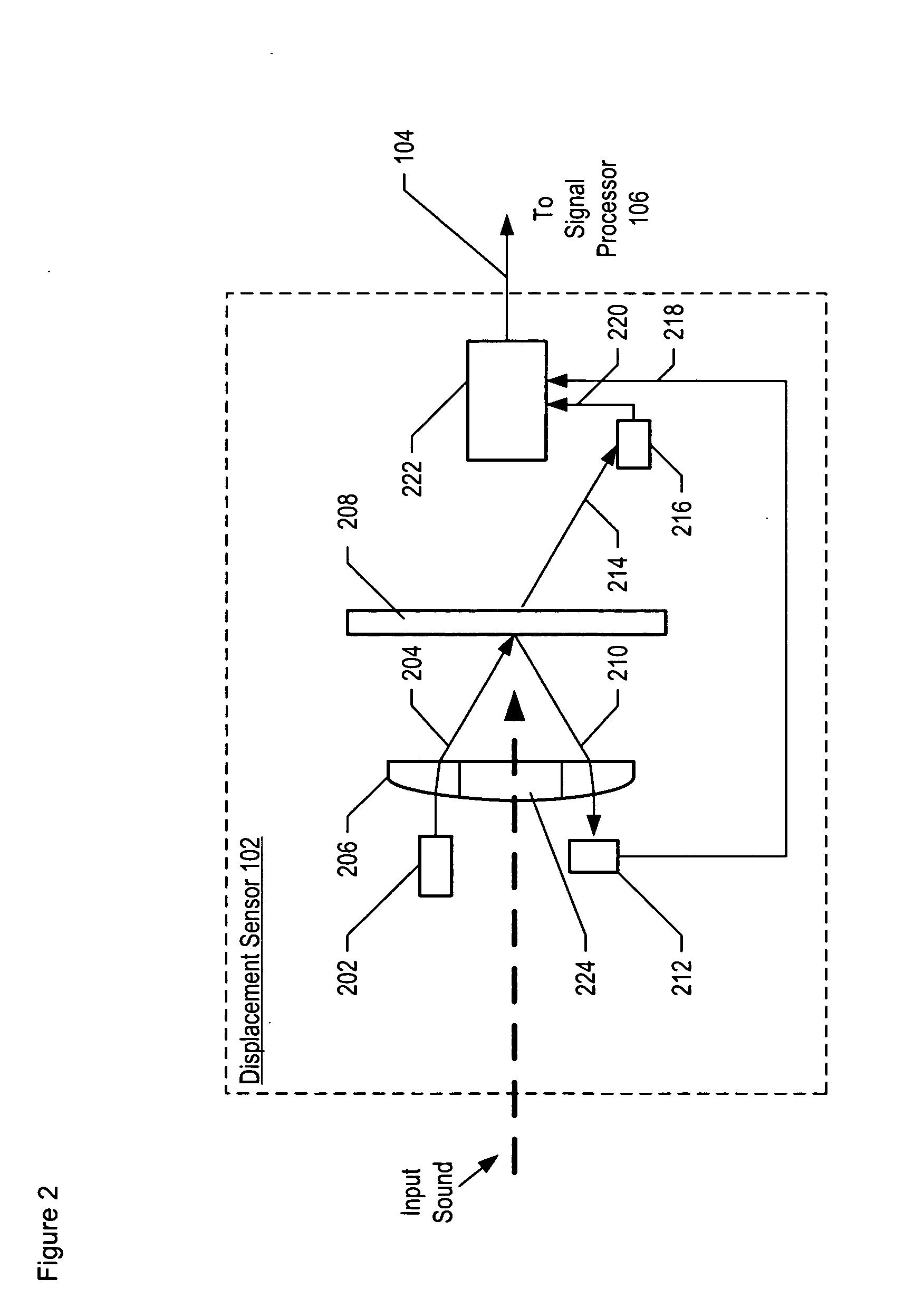
Apparatus comprising a high-signal-to-noise displacement sensor and method therefore
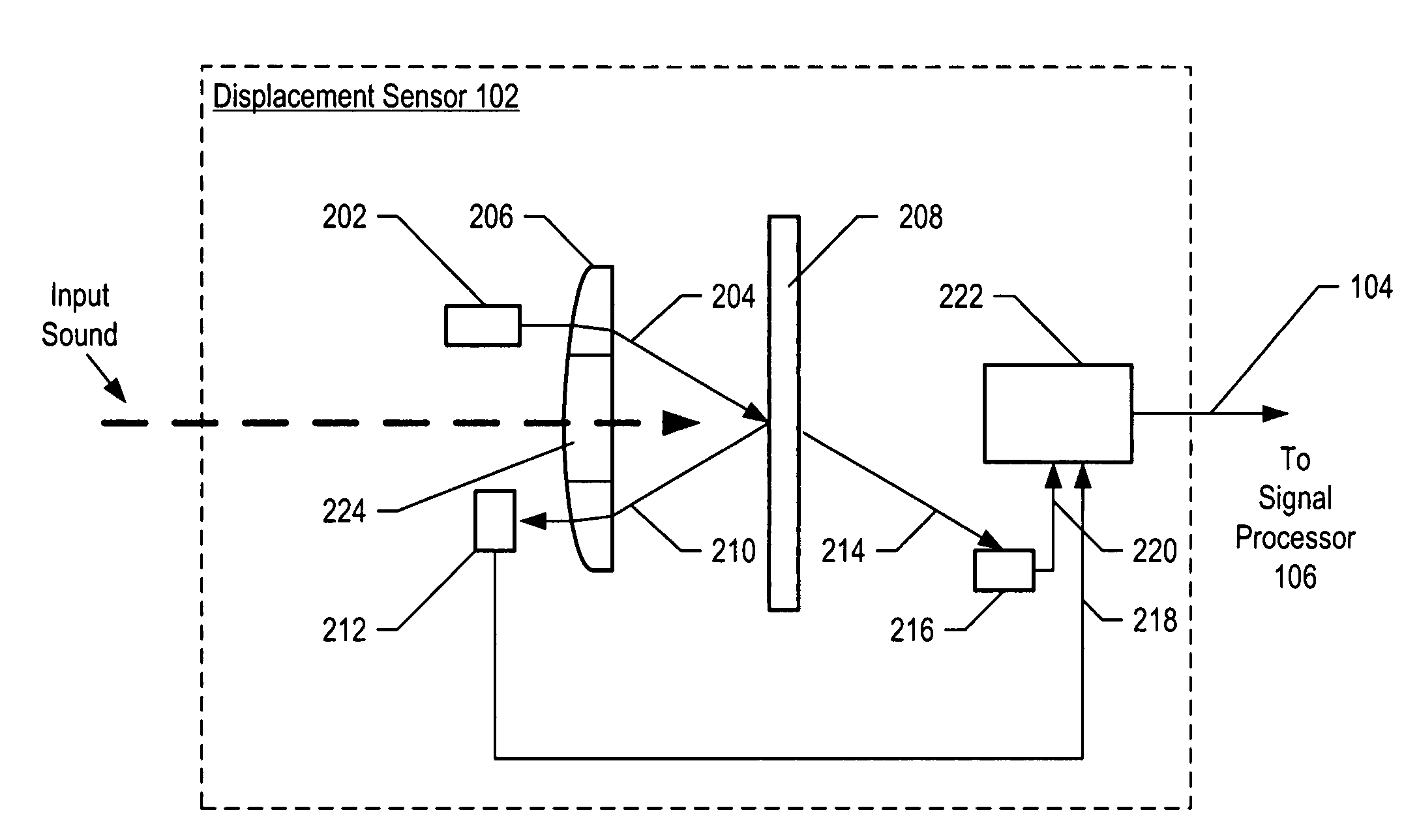
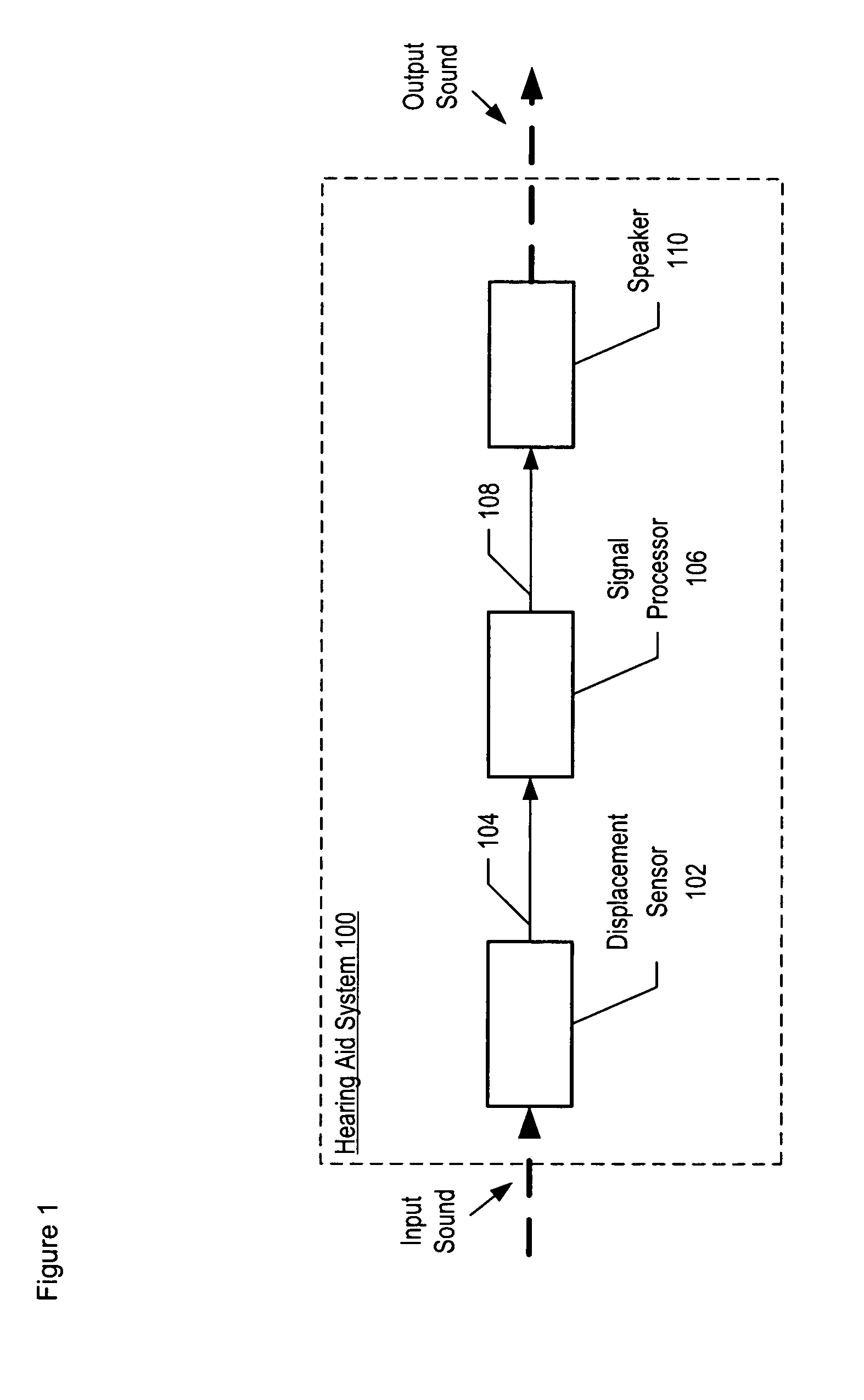
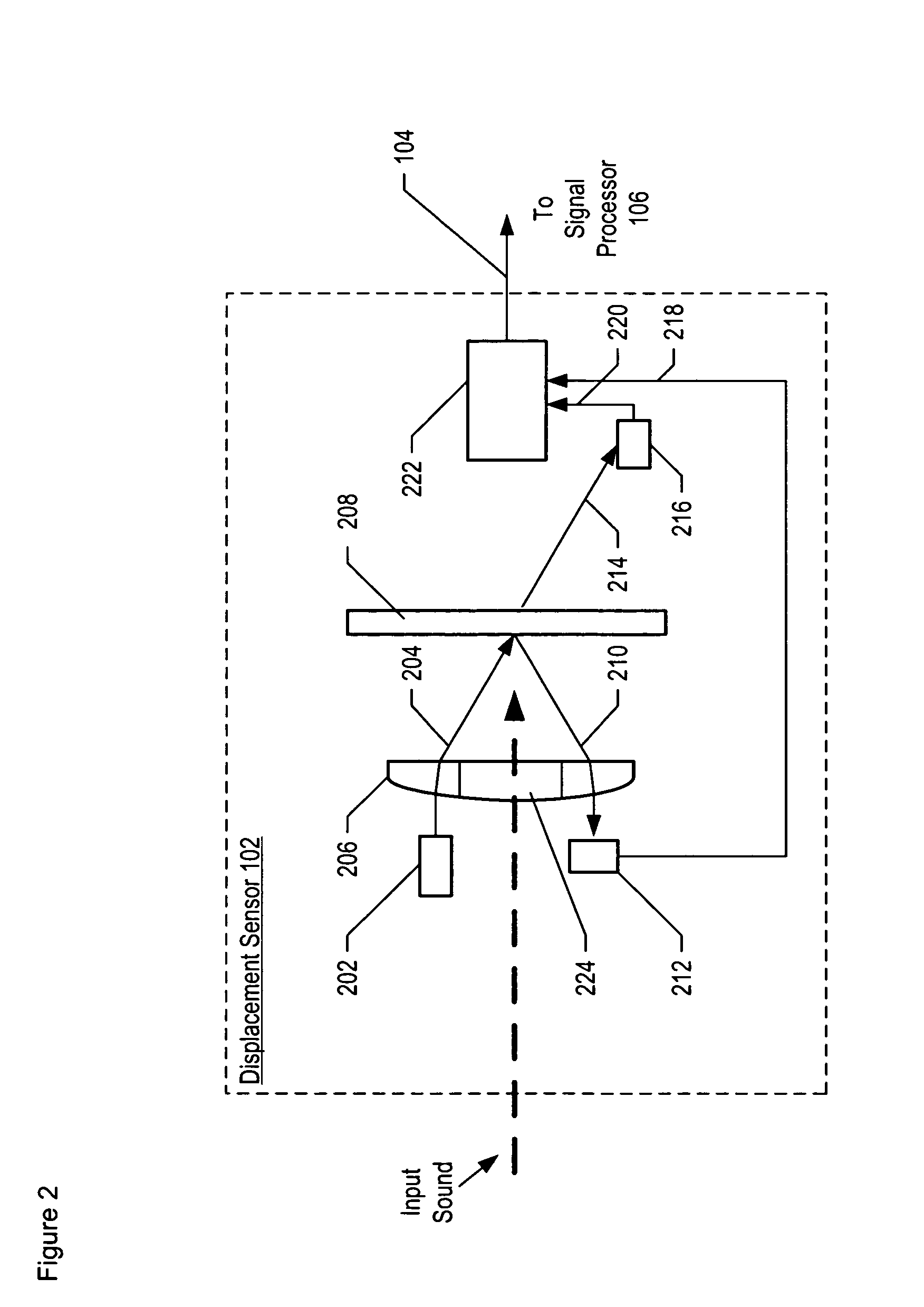
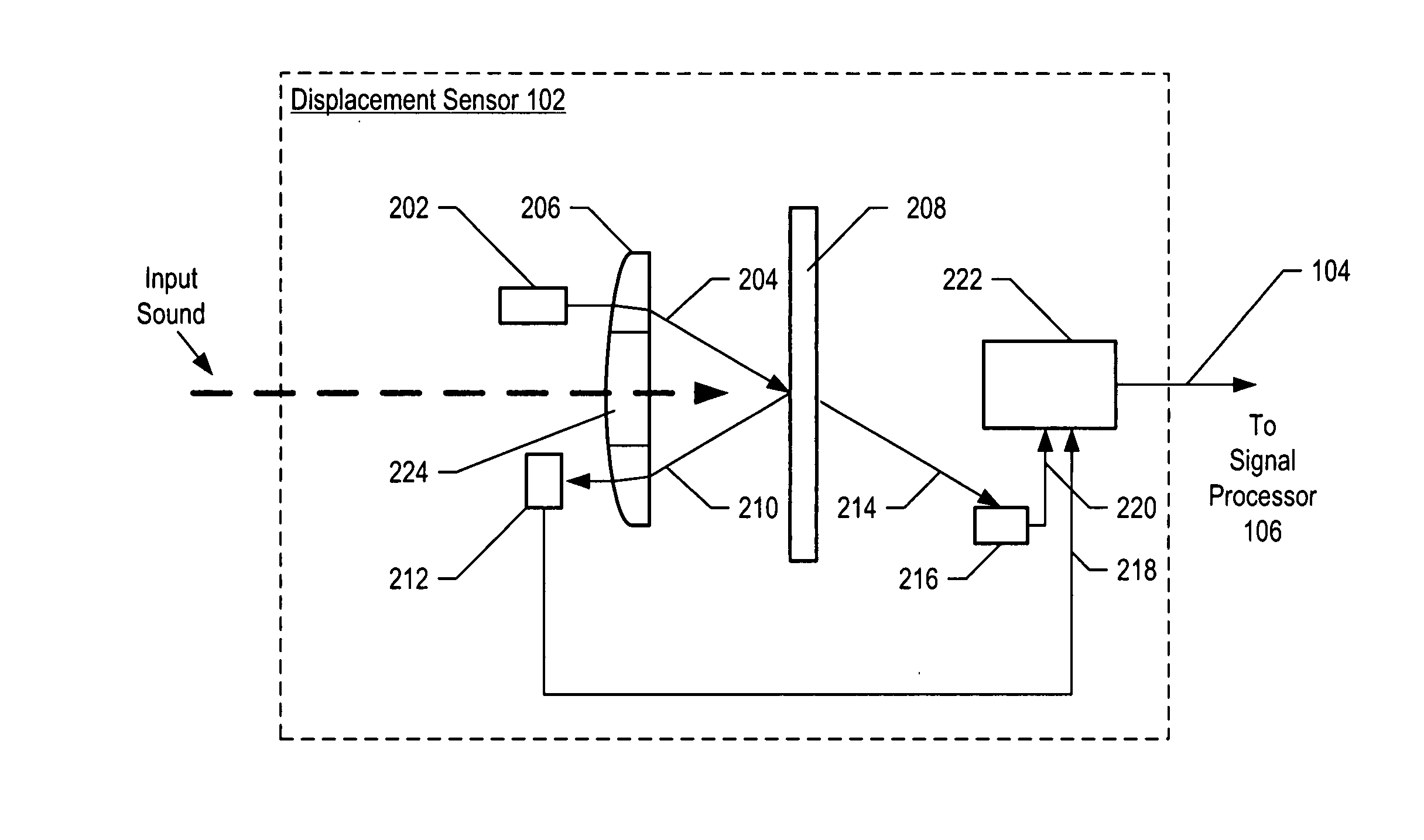
InactiveUS7355723B2Increase signal strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical signal transducersSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
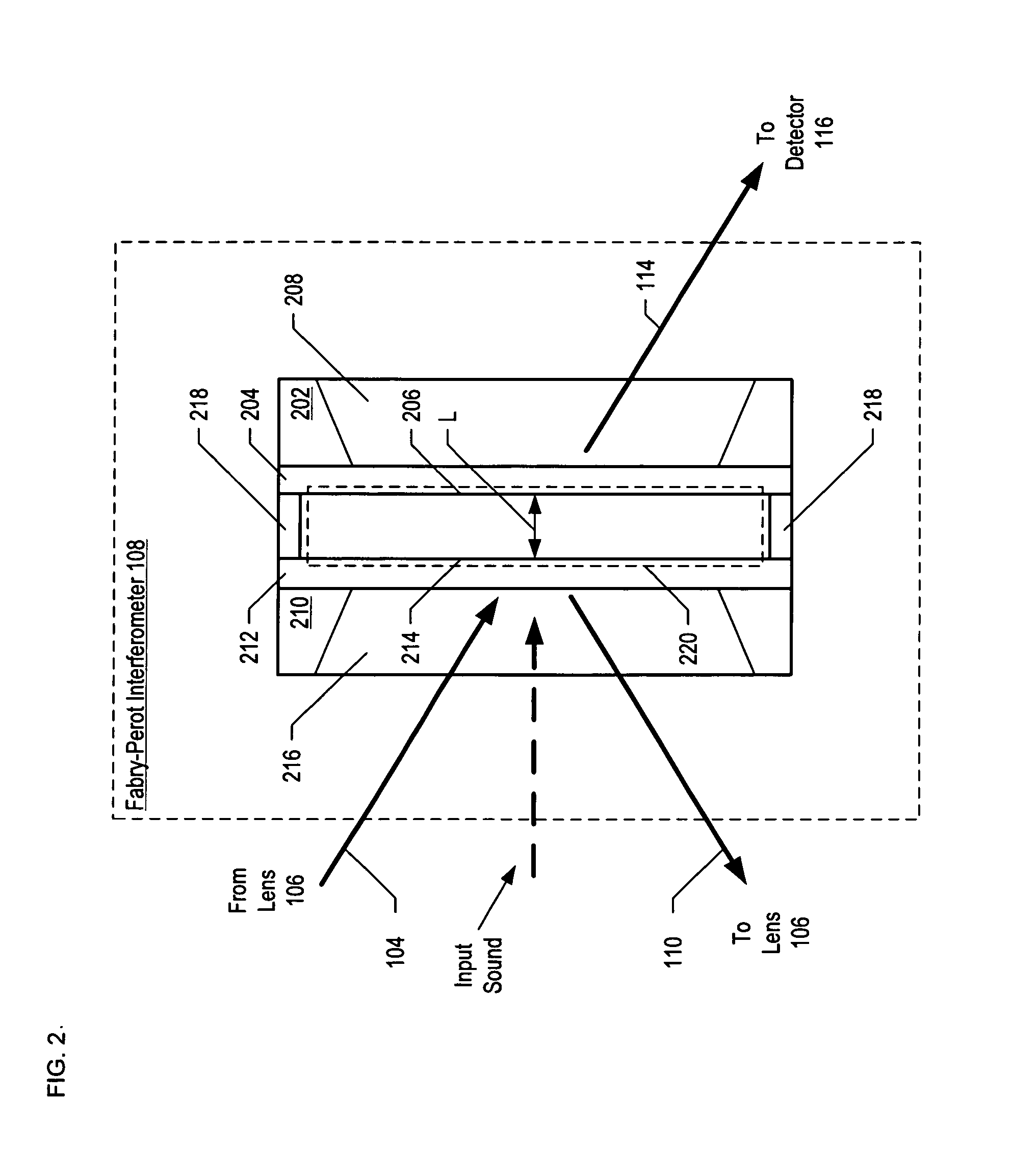
An optical displacement sensor is disclosed that provides a high signal-to-noise ratio output signal without some of the disadvantages for doing so in the prior art. An embodiment of the present invention directs a light beam toward a Fabry-Perot interferometer and detects both the reflected and transmitted optical beams that result from interaction with the Fabry-Perot interferometer. Signal processing techniques are applied to signals based on both the reflected and transmitted beams, resulting in higher signal strength and / or reduced noise in the resulting output signal.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
Switch cabinet fault feature selection method and apparatus
ActiveCN105095675AReduce noise componentsAchieve dimensionality reductionSpecial data processing applicationsFeature DimensionFeature set
The application discloses a switch cabinet fault feature selection method and apparatus. The method comprises: based on a sorting principle of importance degree of fault features, performing sorting on N fault features of a fault feature set to obtain to-be-selected fault feature subsets; based on mRMR criterions, performing screening on the to-be-selected fault feature subsets with an increment search method; and calculating the classification accuracy of each candidate fault feature subset in N candidate fault feature subsets obtained after screening, and determining the candidate fault feature subset with highest classification accuracy as an optimal candidate fault feature subset. According to the switch cabinet fault feature selection method and apparatus, the fault features in the fault feature set are sorted in advance, so that the dimension reduction of the fault features is realized; and then the screening is performed based on the mRNR criterions, so that noise components in a fault feature sample are effectively reduced, the feature dimensions are further reduced, the screening effect is improved, and the degree of matching between the subsequently obtained optimal fault feature subset and an actual fault reason is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TRULY ELECTRIC +4
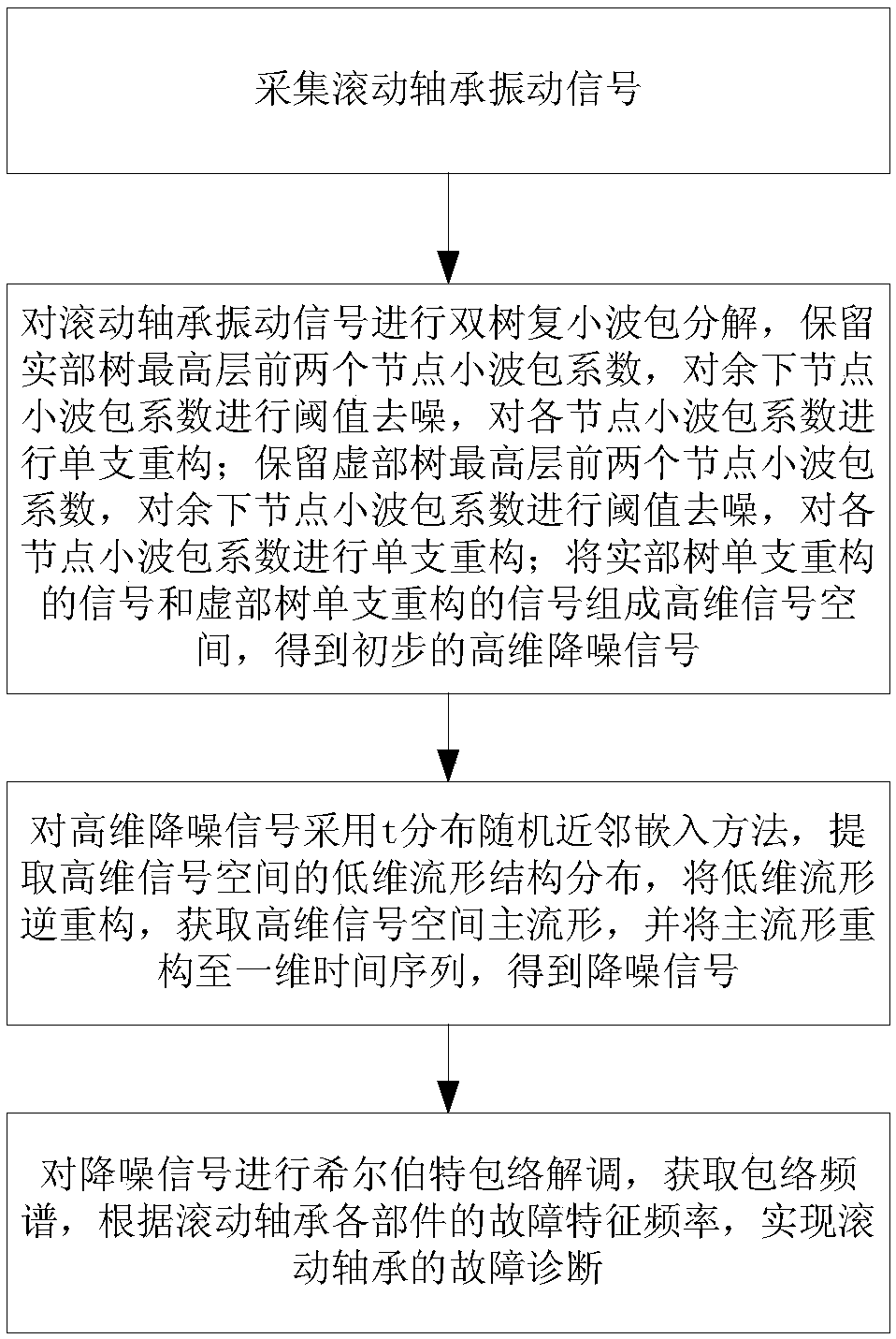
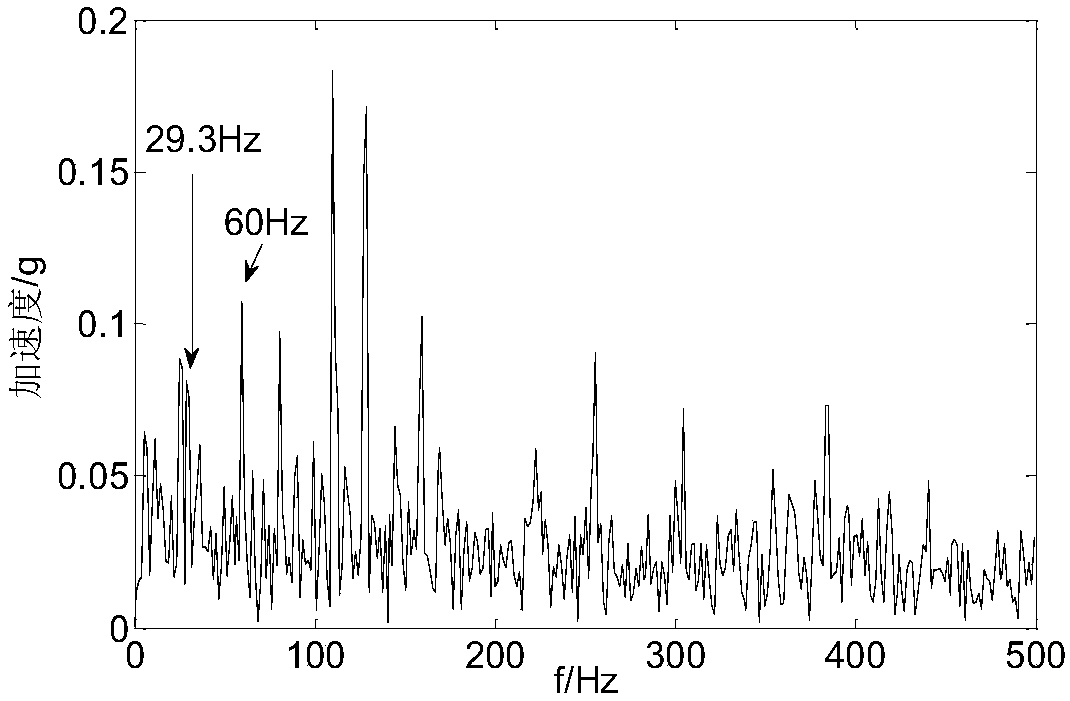
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on dual-tree complex wavelet pack manifold domain noise reduction
ActiveCN107727399AAccurately obtain fault characteristic frequencyImplement fault diagnosisMachine bearings testingComplex mathematical operationsFrequency spectrumDecomposition
The invention relates to a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on dual-tree complex wavelet pack manifold domain noise reduction. The rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on the dual-tree complex wavelet pack manifold domain noise reduction comprises steps of using an accelerated speed sensor to collect a vibration signal of the rolling bearing, performing dual-tree complex wavelet pack decomposition on the vibration signal, maintaining wavelet pack coefficients of first two nodes, performing threshold noise reduction on wavelet coefficients of the rest nodes, performing single branch reconstruction on the wavelet pack coefficient of each node to perform a high dimensional signal space, using a t distribution random neighbor embedding method to extract low a dimensional manifold, performing inverse reconstruction on the low-dimensional manifold to obtain a high-dimensional space main manifold, obtaining a signal after noise reduction, performing Hilbert envelope demodulation on the signal after noise reduction to obtain an envelope frequency spectrum of the vibration signal, and realizing fault diagnosis of the rolling bearing according to an inner ring fault characteristic frequency and an outer ring fault characteristic frequency of the rolling bearing, a rolling body fault characteristic frequency and a retainer fault characteristic frequency.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
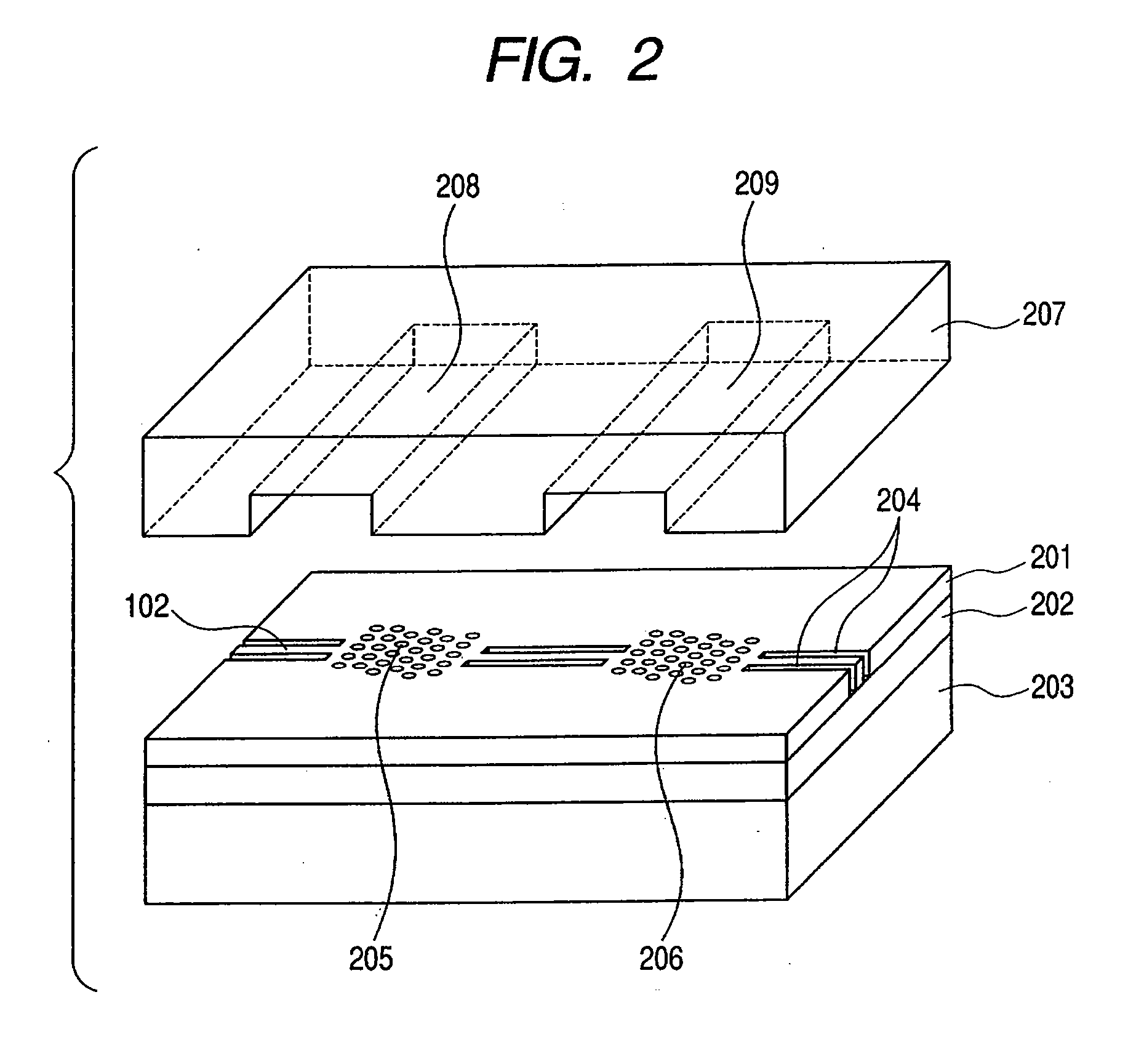
Sensor device
InactiveUS20060193552A1Decrease of noise componentReduce noise componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsOptical detectorsOptical detector
A sensor device for detecting a substance contained in a fluid comprises first and second photonic crystal regions, first and second flow channels, an optical waveguide connected to the first and second photonic crystal regions and an optical detector for detecting the lights transmitted through the first photonic crystal region and the waveguide and transmitted through or reflected by the second photonic crystal region.
Owner:CANON KK
Accelerometer comprising an optically resonant cavity
InactiveUS7583390B2Increase signal strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioAcceleration measurement using interia forcesOptical signal transducersResonant cavityLight beam
An accelerometer based on an optical displacement sensor is disclosed. An embodiment of the present invention directs a light beam toward an optically resonant cavity and detects both the reflected and transmitted optical beams that result from interaction with the optically resonant cavity. The optically resonant cavity has a cavity length that is based on the position of a proof mass that moves in response to an acceleration.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
VCO with power supply rejection enhancement circuit
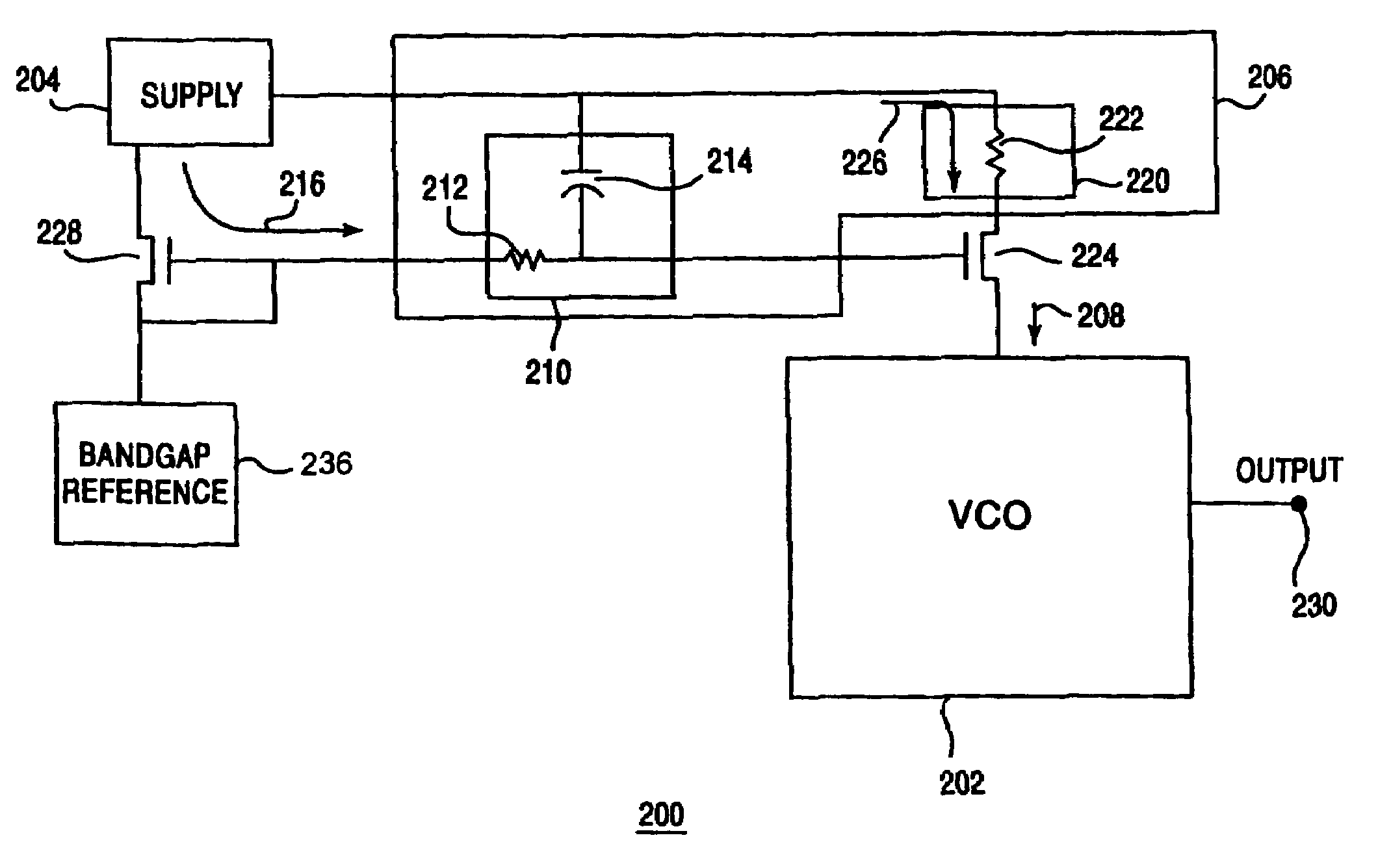
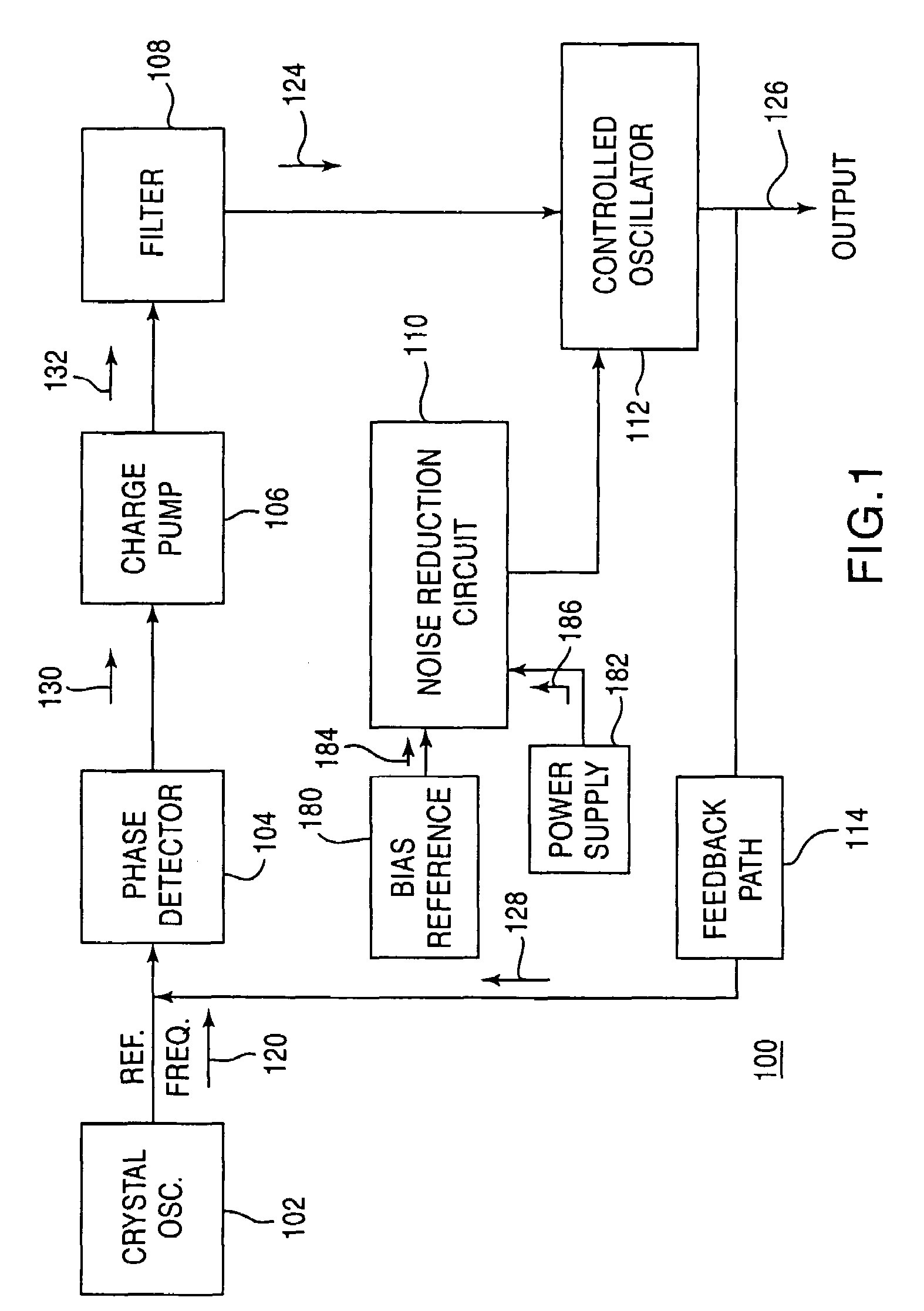
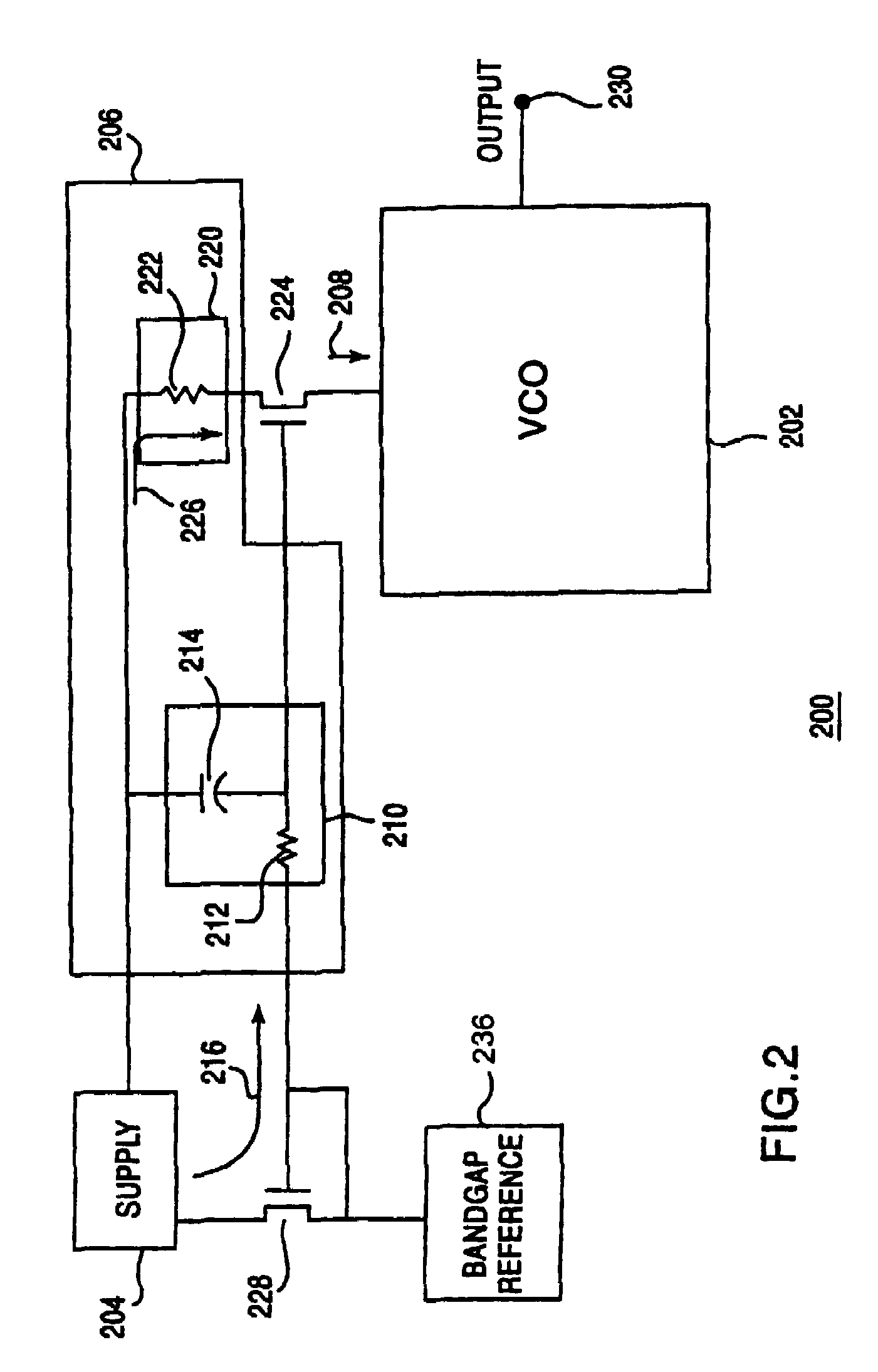
ActiveUS7042302B2Reduce gainReduce noise componentsPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsNoise reductionSupply current
An oscillating circuit having a noise reduction circuit is disclosed. The noise reduction circuit is coupled to the current source for the oscillating circuit. The noise reduction circuit reduces a bias noise component from a bias current, and a supply noise component from a supply current. The noise reduction circuit is coupled to the current source at a gate and a supply for the current source. The noise reduction circuit includes a filter coupled to the gate of the current source that reduces the bias noise component. The noise reduction circuit also includes a degeneration circuit coupled to the supply of the current source that reduces the supply noise component. The current source generates an input signal to control the oscillating circuit with reduced noise.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
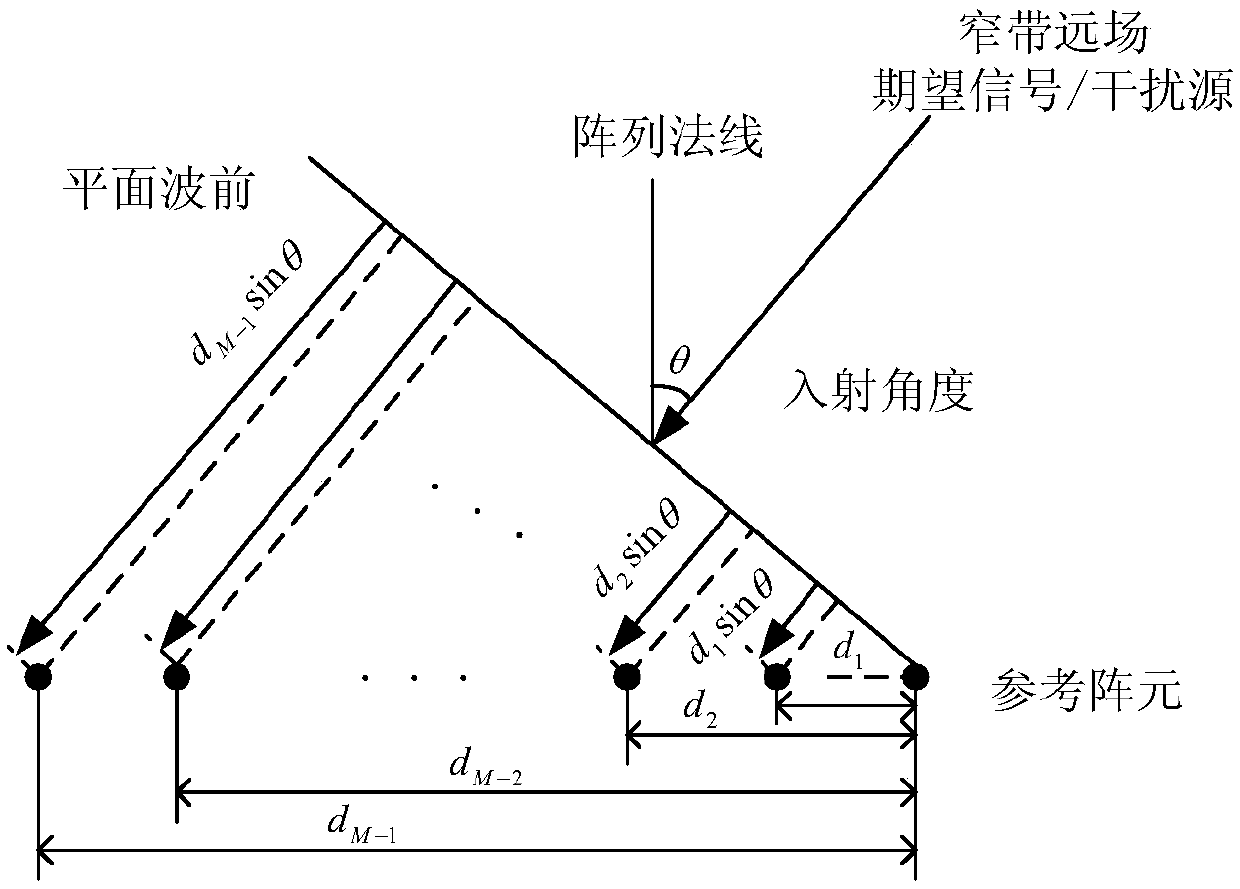
Steady self-adaptive beamforming method based on information source number constraint
ActiveCN108809398AReduce noise componentsImprove accuracySpatial transmit diversitySelf adaptiveAdaptive beamformer
The invention discloses a steady self-adaptive beamforming technology based on information source number constraint and used for reconstructing covariance matrix and accurately estimating expected signal steering vector. The method comprises the following steps: firstly estimating interference source number, expected signal angle region, interference angle region and noise angle region, estimatingnoise average power in the noise angle region to acquire a noise covariance matrix; estimating accurate interference power through the noise average power in the interference region, reconstructing the interference covariance matrix, and modifying the reconstructed interference covariance matrix according to the interference source number constraint to acquire the interference and noise covariance matrix; estimating the accurate expected signal power through the noise average power in the expected signal angle region, reconstructing the expected signal covariance matrix, decomposing the feature of the expected signal covariance matrix to acquire the steering vector of the expected signal, thereby acquiring the weight vector of the steady self-adaptive beam-former, and forming the output of the steady self-adaptive beam-former.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device for controlling units in a vehicle according to the level of noise
InactiveUS6783195B1Reduce noise componentsDistraction disturbing noiseEar treatmentTracheaeEngineeringControl unit
A method, a device, and a control unit are for controlling at least one aggregate in a vehicle, the noise caused by the aggregate and / or at least one variable representing this noise being ascertained. The passenger compartment noises in the vehicle are ascertained, or at least one variable representing these is ascertained. The noise caused by the aggregate and / or the variable representing this is correlated with the passenger compartment noises and / or the variable representing these. As a function of that, the control or a control signal for the aggregate is generated and / or adapted.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
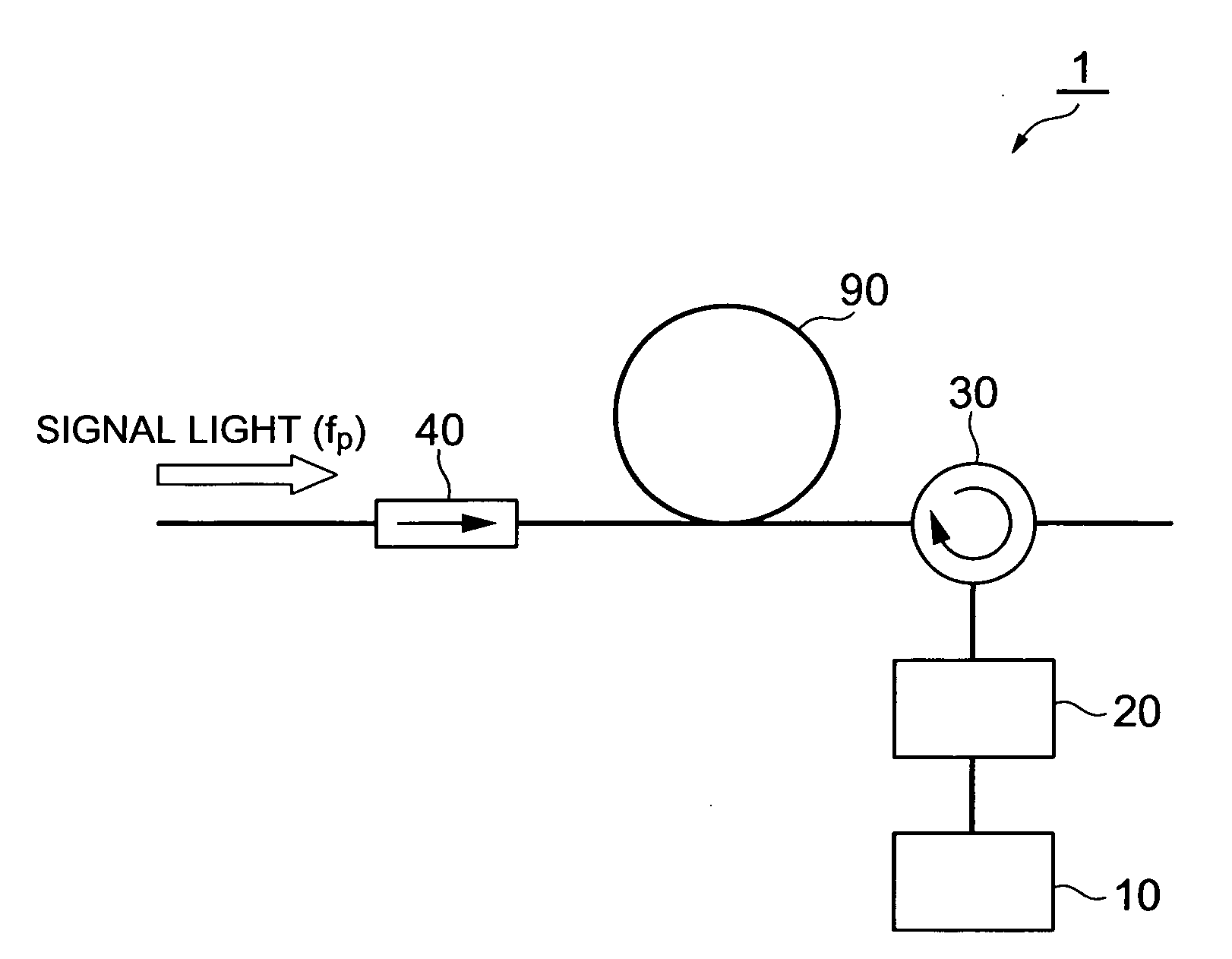
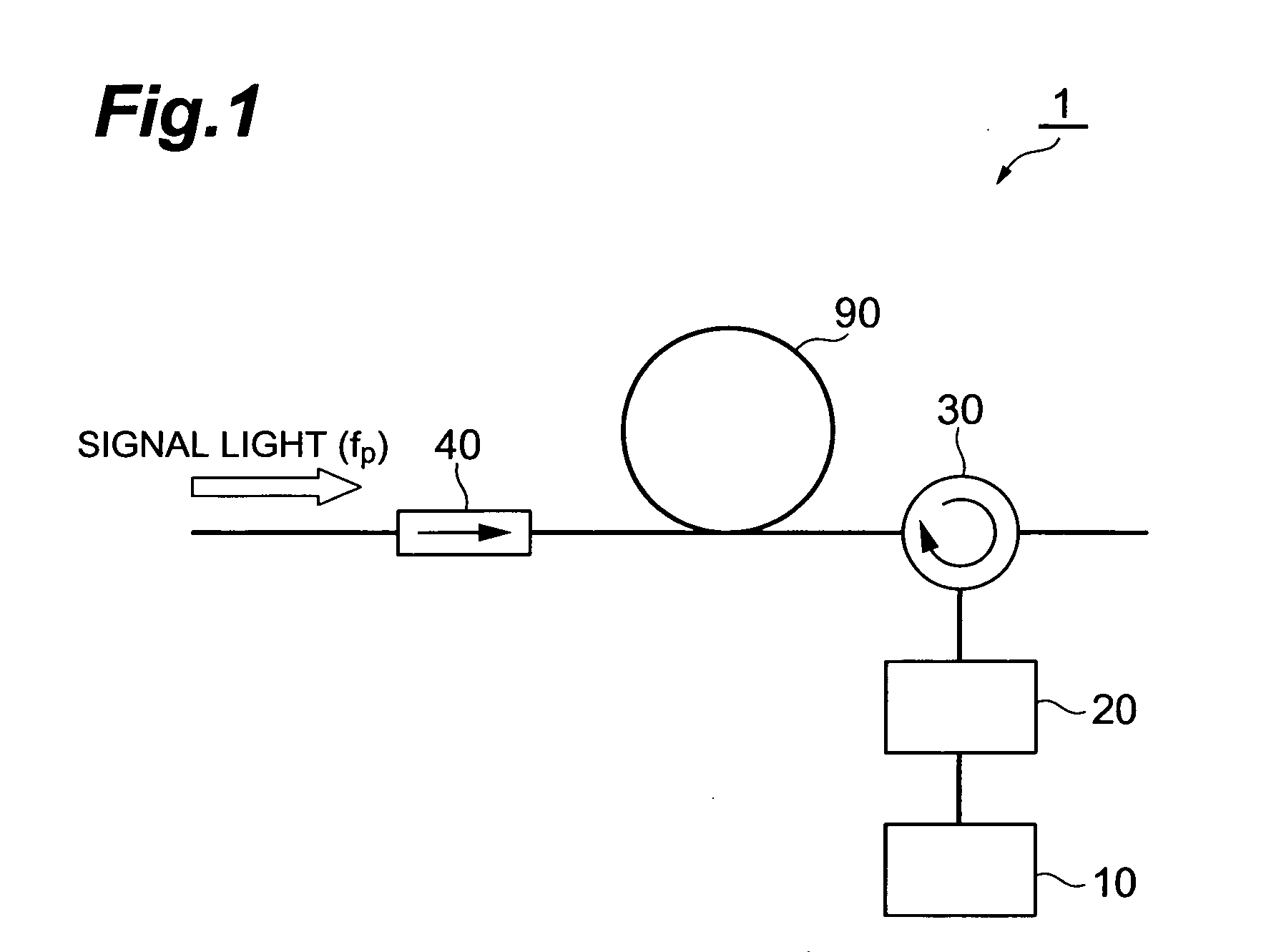
Optical signal noise suppressor and optical signal noise suppressing method
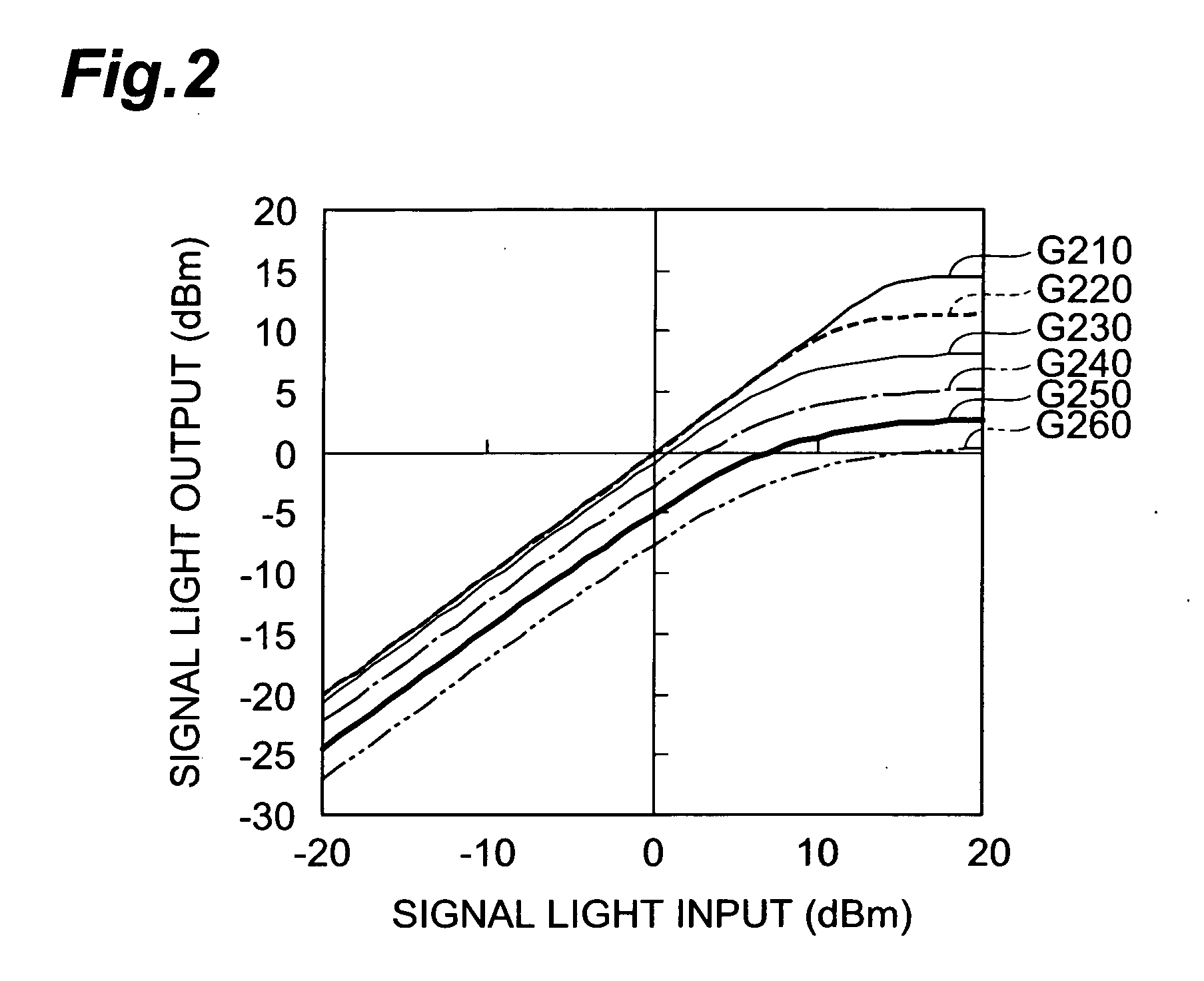
InactiveUS20080144987A1Reduce noise componentsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersLight guideOptical isolator
The present invention provides an optical signal noise suppressor and an optical signal noise suppressing method that can decrease noise components to be superimposed on signal light. The optical signal noise suppressor is a device for suppressing noise caused by SBS which is generated when a signal light propagates from a first end side to a second end side of an optical fiber, and comprises a light source section, an optical attenuator, an optical circulator and an optical isolator. A counter light, outputted from the light source section and passing through the optical attenuator, is guided into the optical fiber via the optical circulator. The counter light guided into the optical fiber is interrupted by the optical isolator, and does not reach the signal light source section. The counter light has the same optical frequency components as the SBS light generated by the propagation of the signal light, and propagates in the optical fiber in an opposite direction of the propagation direction of the signal light.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Sensor device
InactiveUS7391945B2Reduce noise componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPhotonic crystalWaveguide
A sensor device for detecting a substance contained in a fluid comprises first and second photonic crystal regions, first and second flow channels, an optical waveguide connected to the first and second photonic crystal regions and an optical detector for detecting the lights transmitted through the first photonic crystal region and the waveguide and transmitted through or reflected by the second photonic crystal region.
Owner:CANON KK
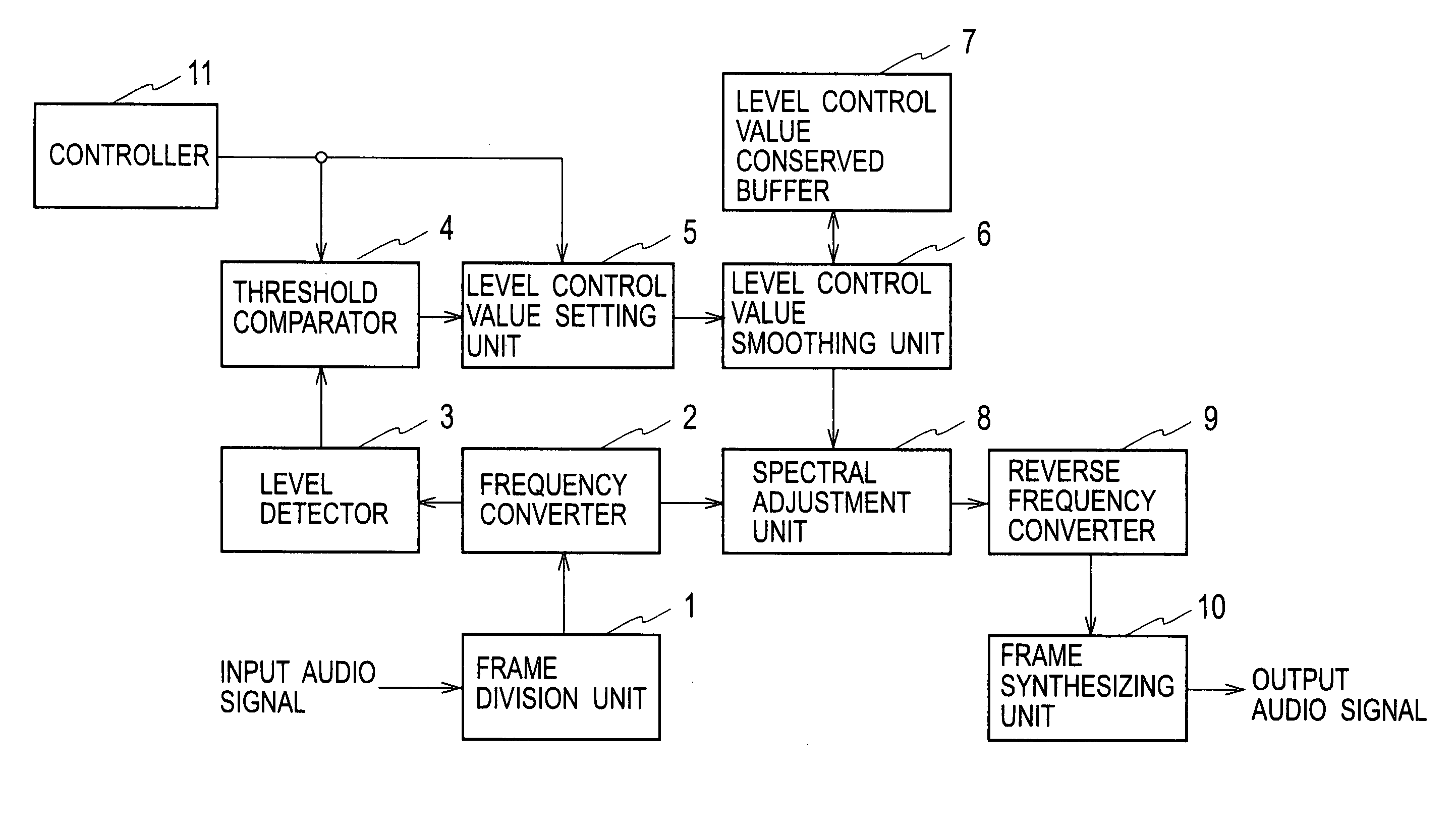
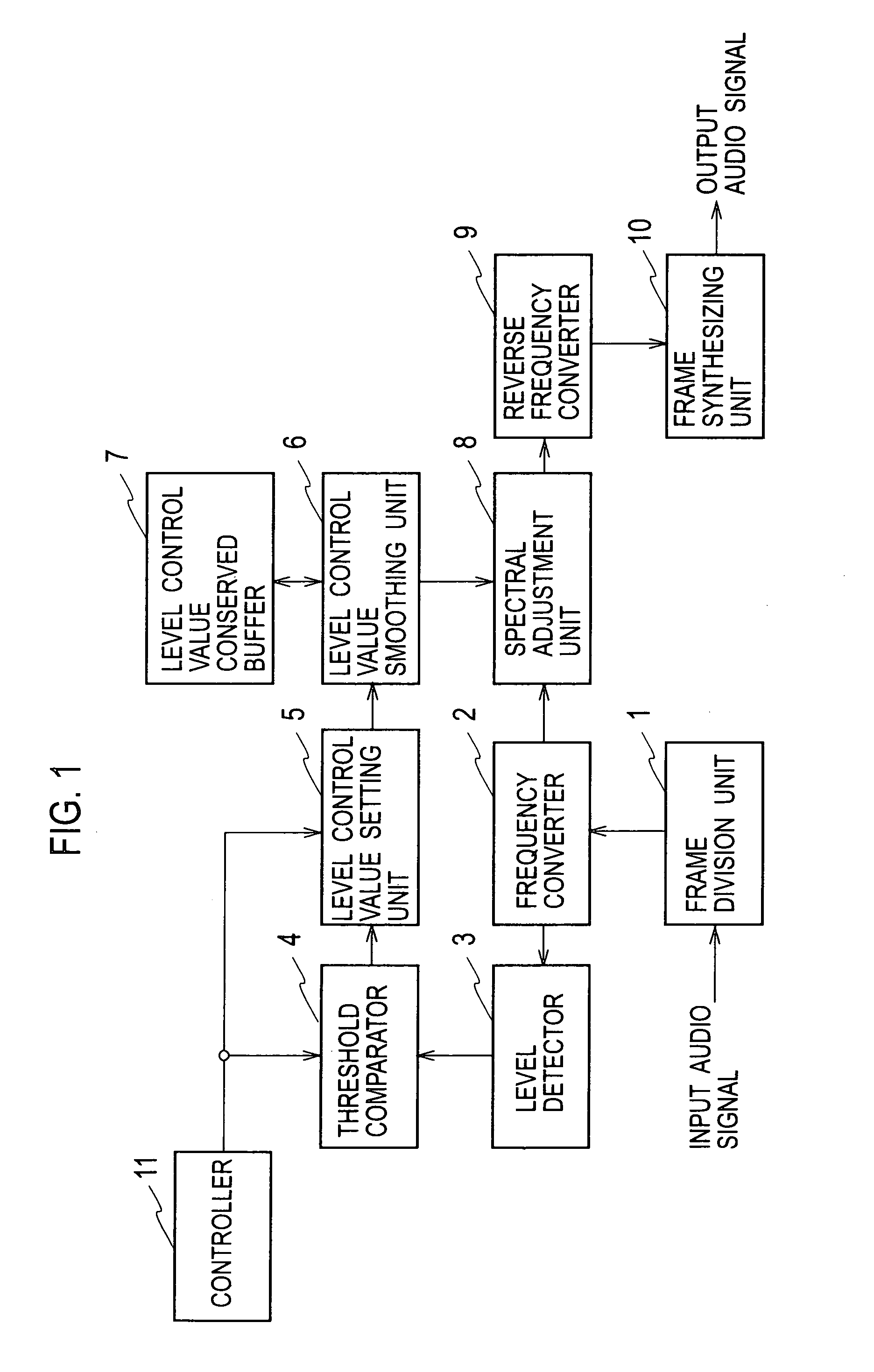
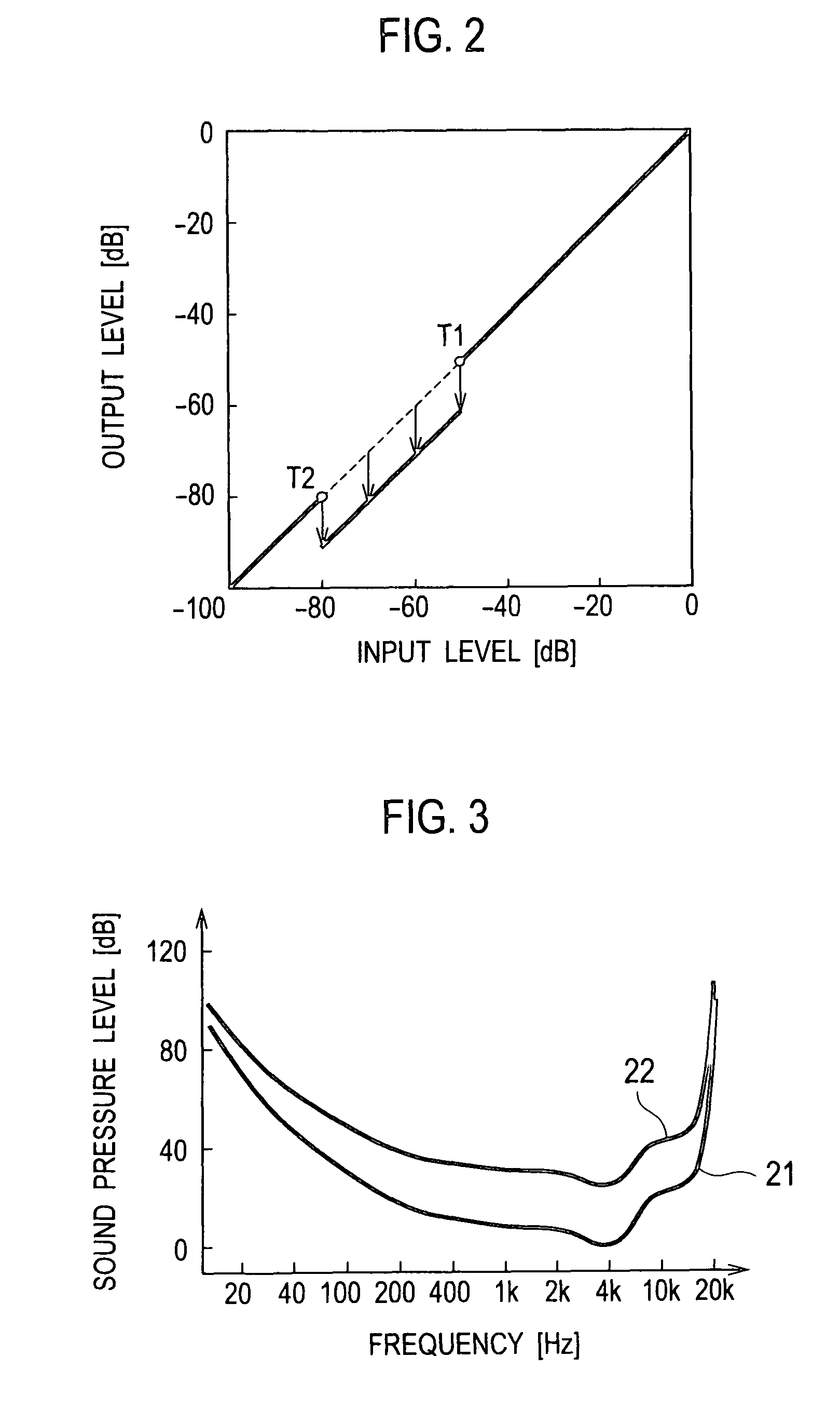
Audio signal processing device and audio signal processing method
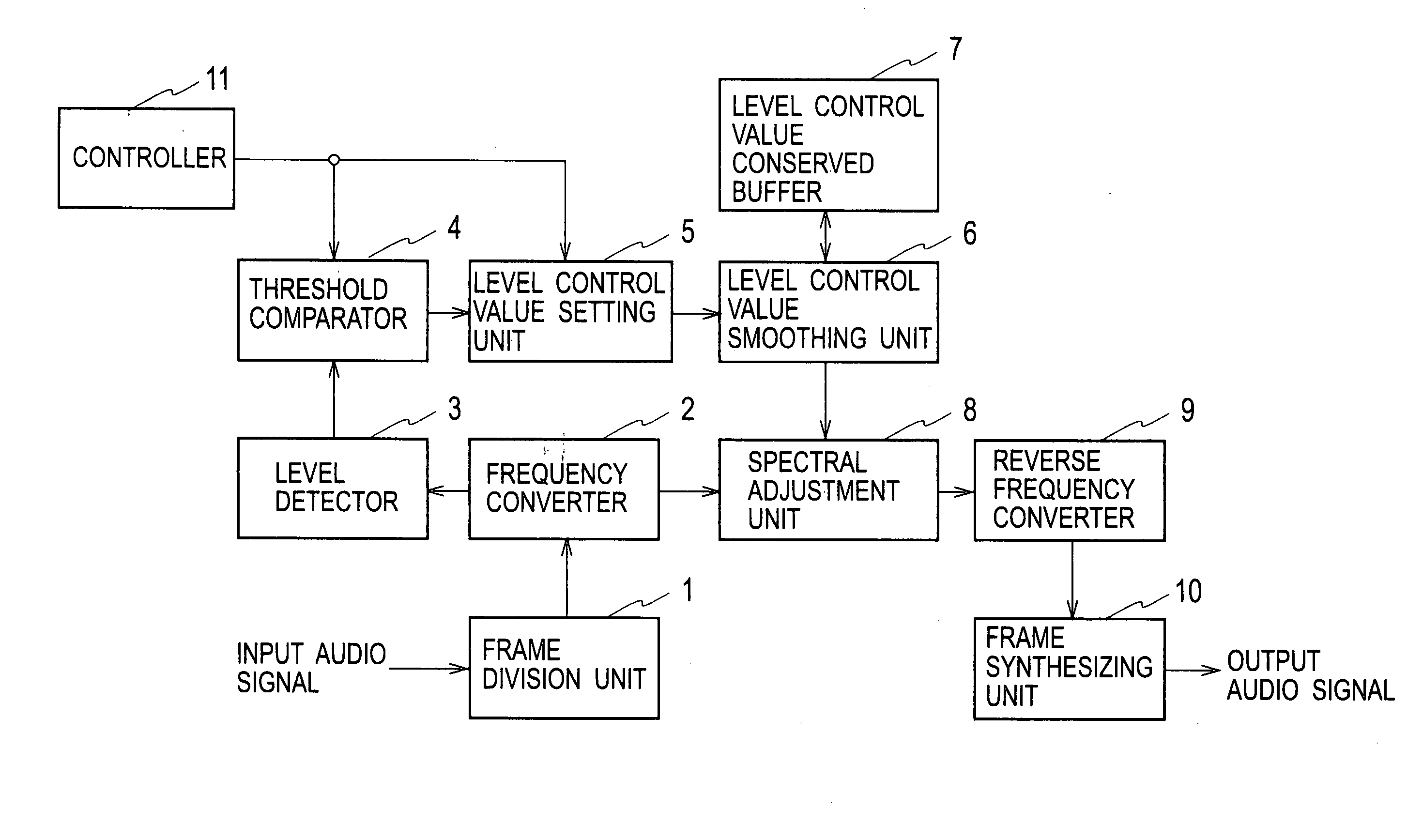
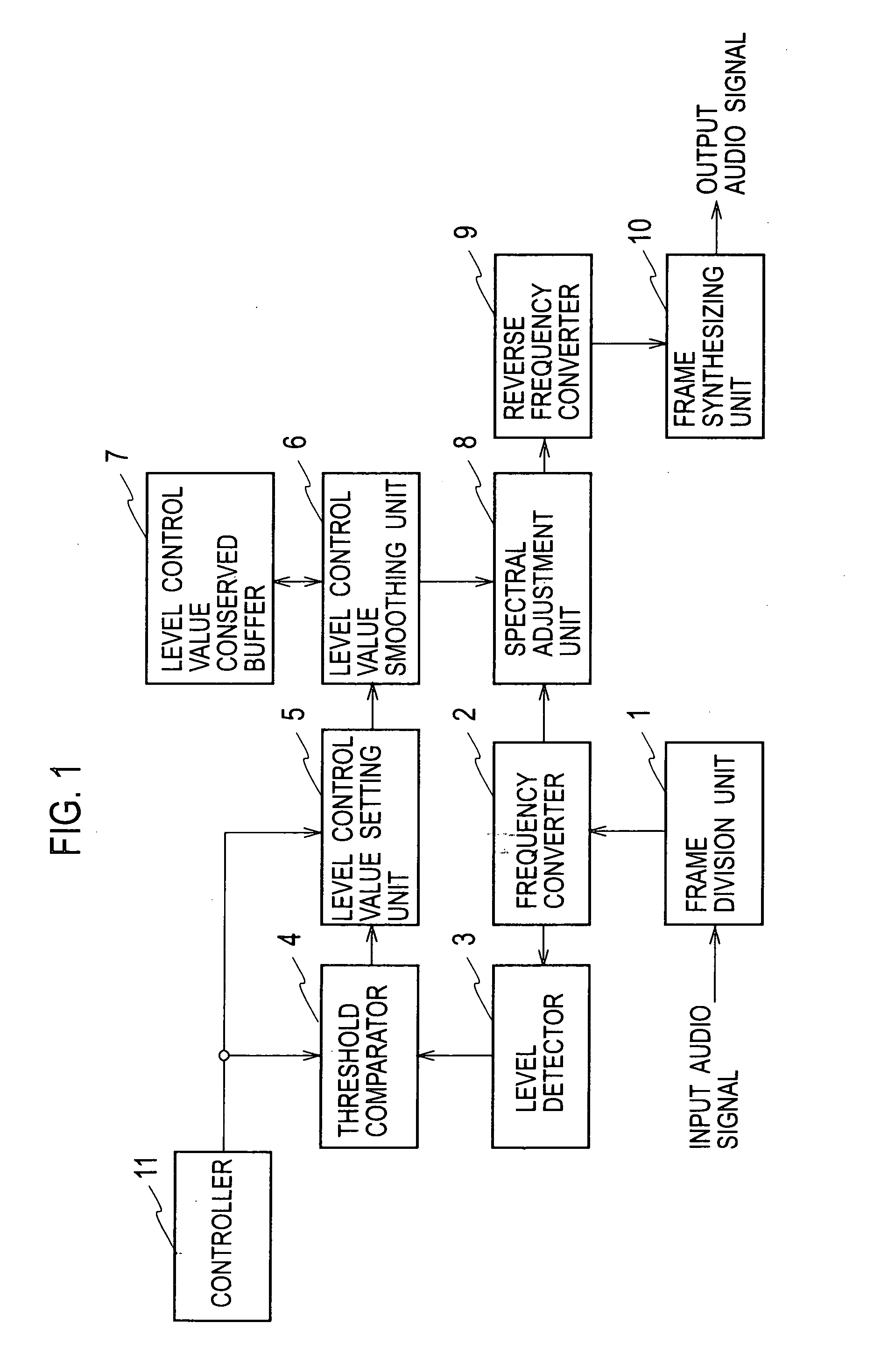
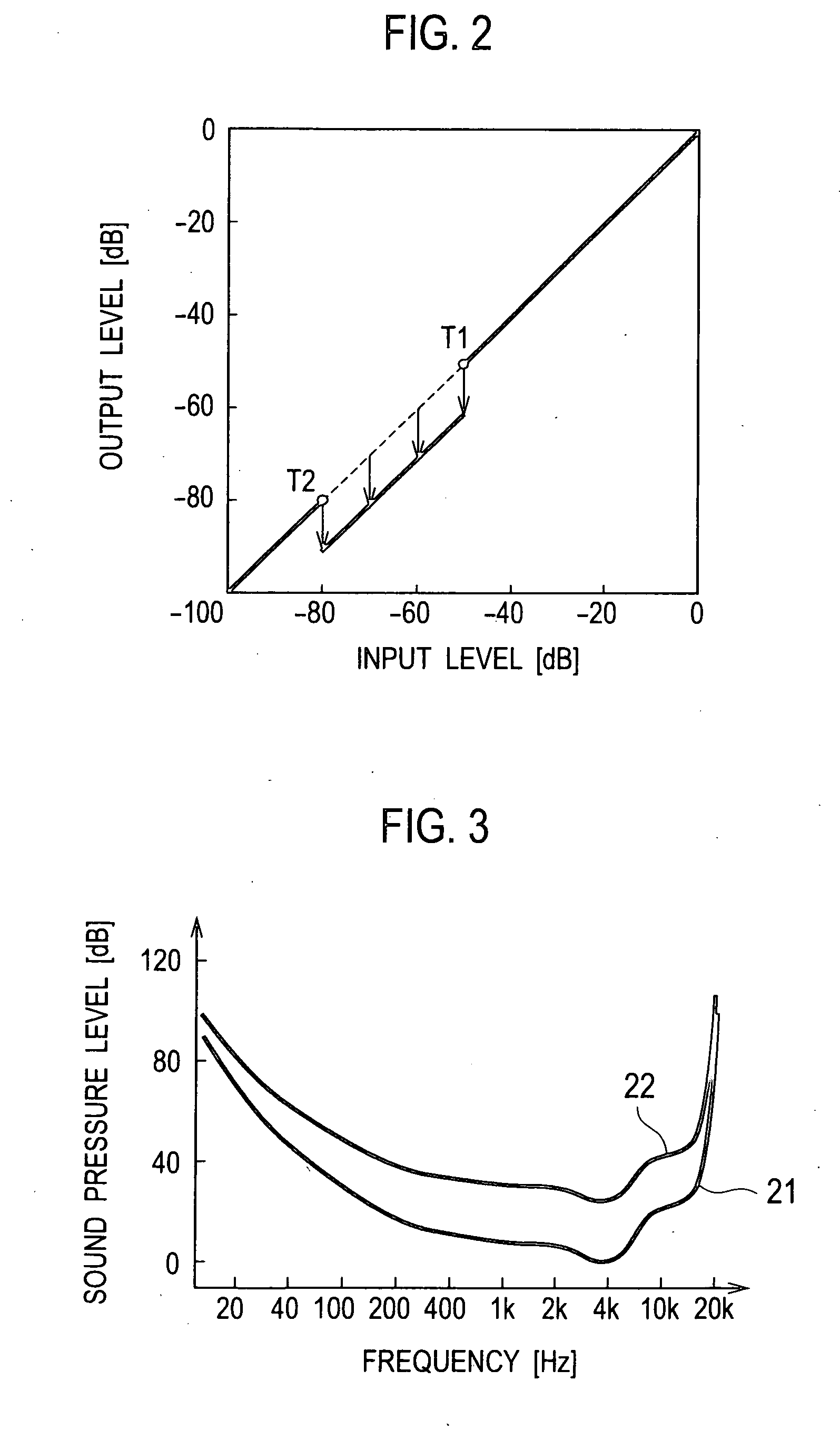
ActiveUS20100128882A1Reduce noise componentSimple computationEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationVIT signalsFrequency domain
In frequency signals obtained by converting input audio signals from time-domain signals to frequency-domain signals, a level control value setting unit 5 establishes a level control value for reducing the levels of spectrums at a noise-components level. A level control value smoothing unit 6 carries out a smoothing process of smoothing the level control value established by the level control value setting unit 5 temporally. A spectral adjustment unit 8 multiplies the level control value after the smoothing process by the frequency signals, performing a level control.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Apparatus comprising a high-signal-to-noise displacement sensor and method therefore
InactiveUS20070206202A1Increase signal strengthImprove signal-to-noise ratioOptical signal transducersSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementLight beamAcoustics
An optical displacement sensor is disclosed that provides a high signal-to-noise ratio output signal without some of the disadvantages for doing so in the prior art. An embodiment of the present invention directs a light beam toward a Fabry-Perot interferometer and detects both the reflected and transmitted optical beams that result from interaction with the Fabry-Perot interferometer. Signal processing techniques are applied to signals based on both the reflected and transmitted beams, resulting in higher signal strength and / or reduced noise in the resulting output signal.
Owner:SYMPHONY ACOUSTICS
Optical semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090230498A1Light receiving can be increasedReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorSignal processing
An optical semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate; a light receiving element formed on the semiconductor substrate; a light absorbing element formed on the semiconductor substrate and located adjacent to the light receiving element; and a semiconductor element formed on the semiconductor substrate and used for signal processing. The light absorbing element includes a fifth semiconductor layer, and a light absorption region in the light receiving element has a different structure from a light absorption region in the light absorbing element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing thereof
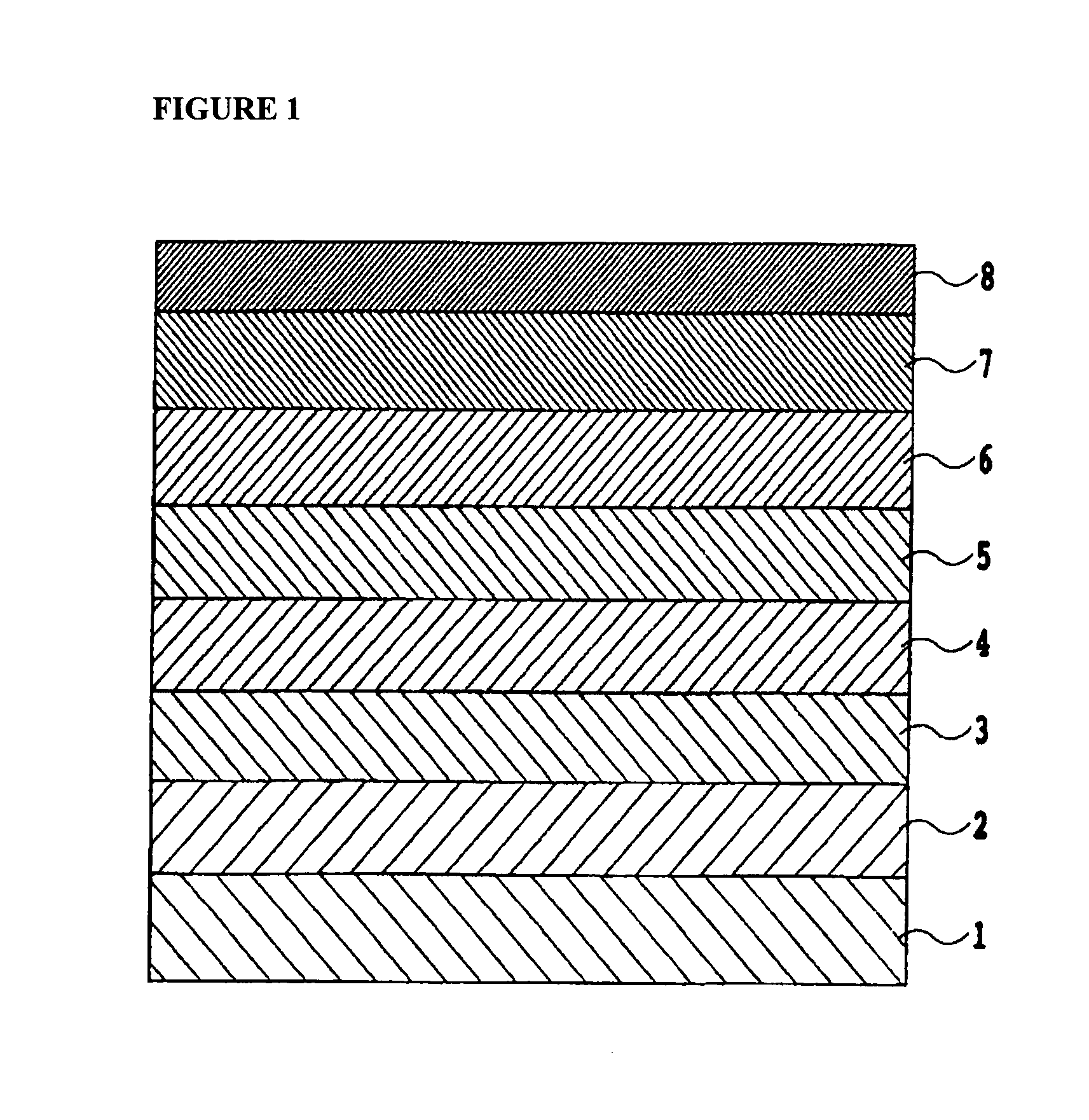
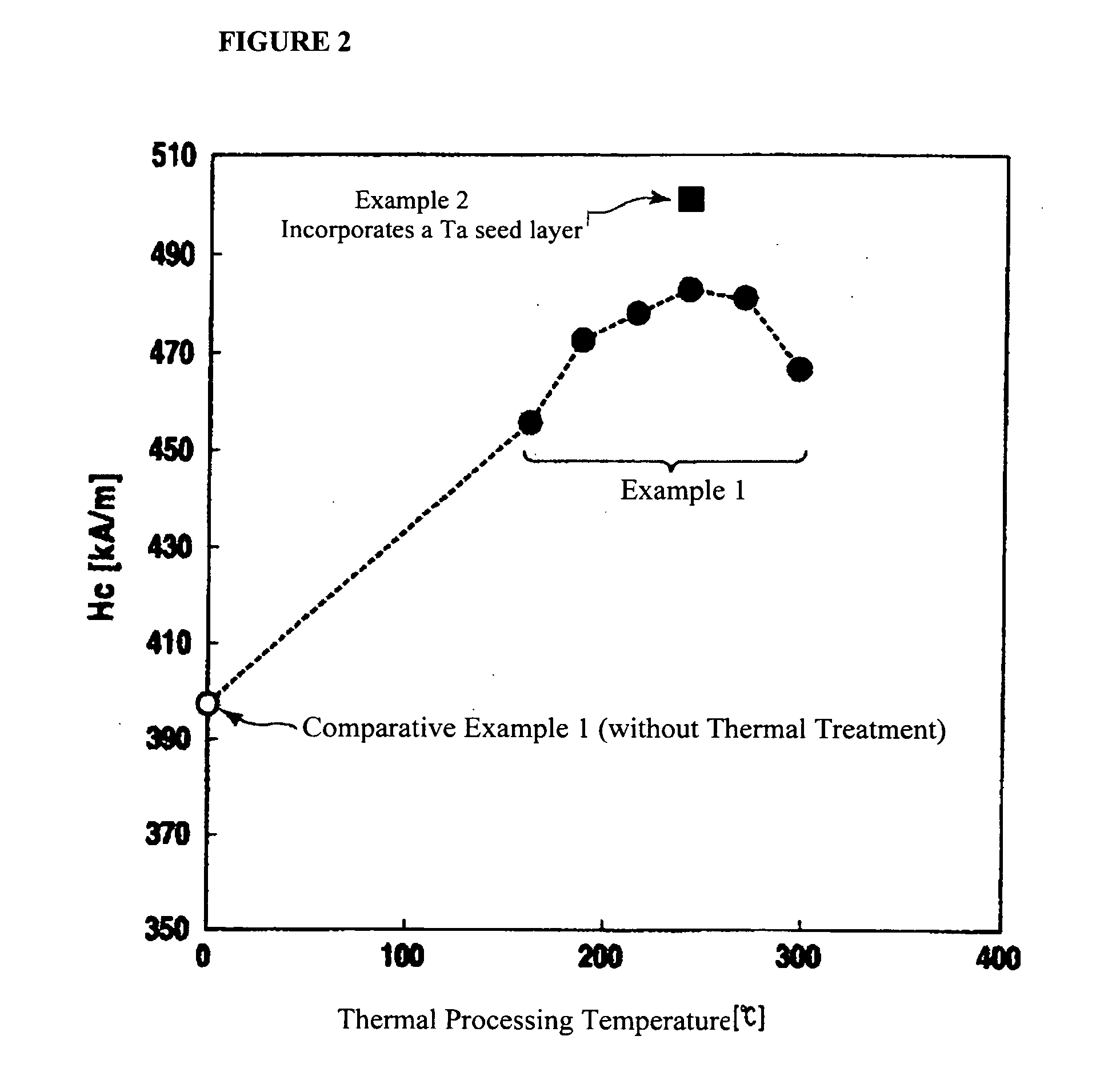
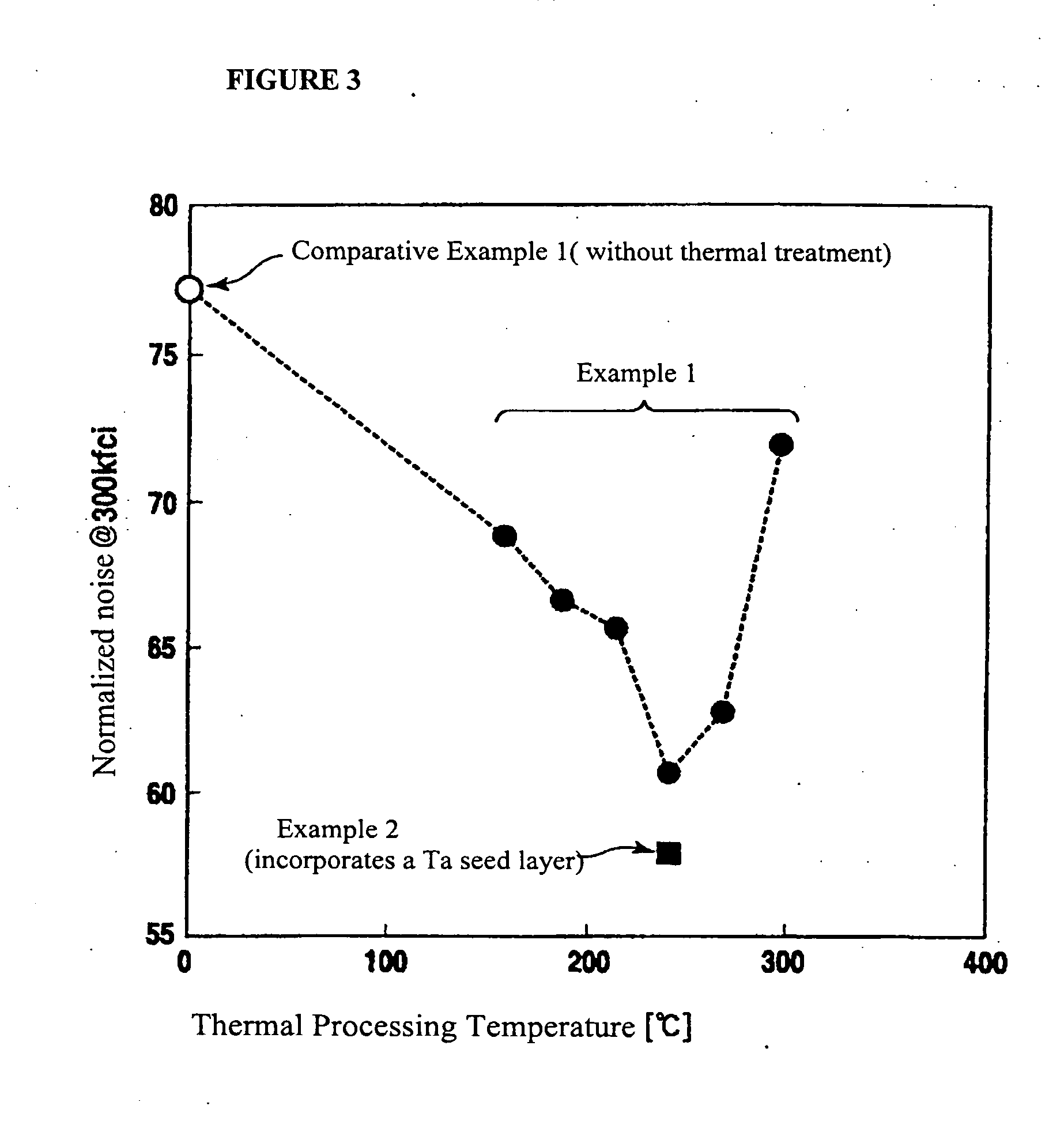
ActiveUS20050014029A1Reduce noise componentsSegregation can be facilitatedProtective coatings for layersBase layers for recording layersHeat stabilityRecording layer
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium is disclosed that is characterized by a lowered noise component and improved thermal stability. The method for making the recording medium includes the serial steps of forming a soft magnetic back-lining layer on a non-magnetic substrate, forming an intermediate layer on the soft magnetic back-lining layer, forming a magnetic recording layer on the intermediate layer, and forming a protective film and then a liquid lubricating layer on the magnetic recording layer. Thermal treatment is executed after the formation of the magnetic recording layer and before the formation of the protective film, or after the formation of the protective film and before the formation of the liquid lubricating layer. The thermal-processing steps are is executed in a vacuum higher than about 0.1 Pa and in a thermal environment within a range from about 200° C. to about 250° C. for a period of less than about 60 seconds.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
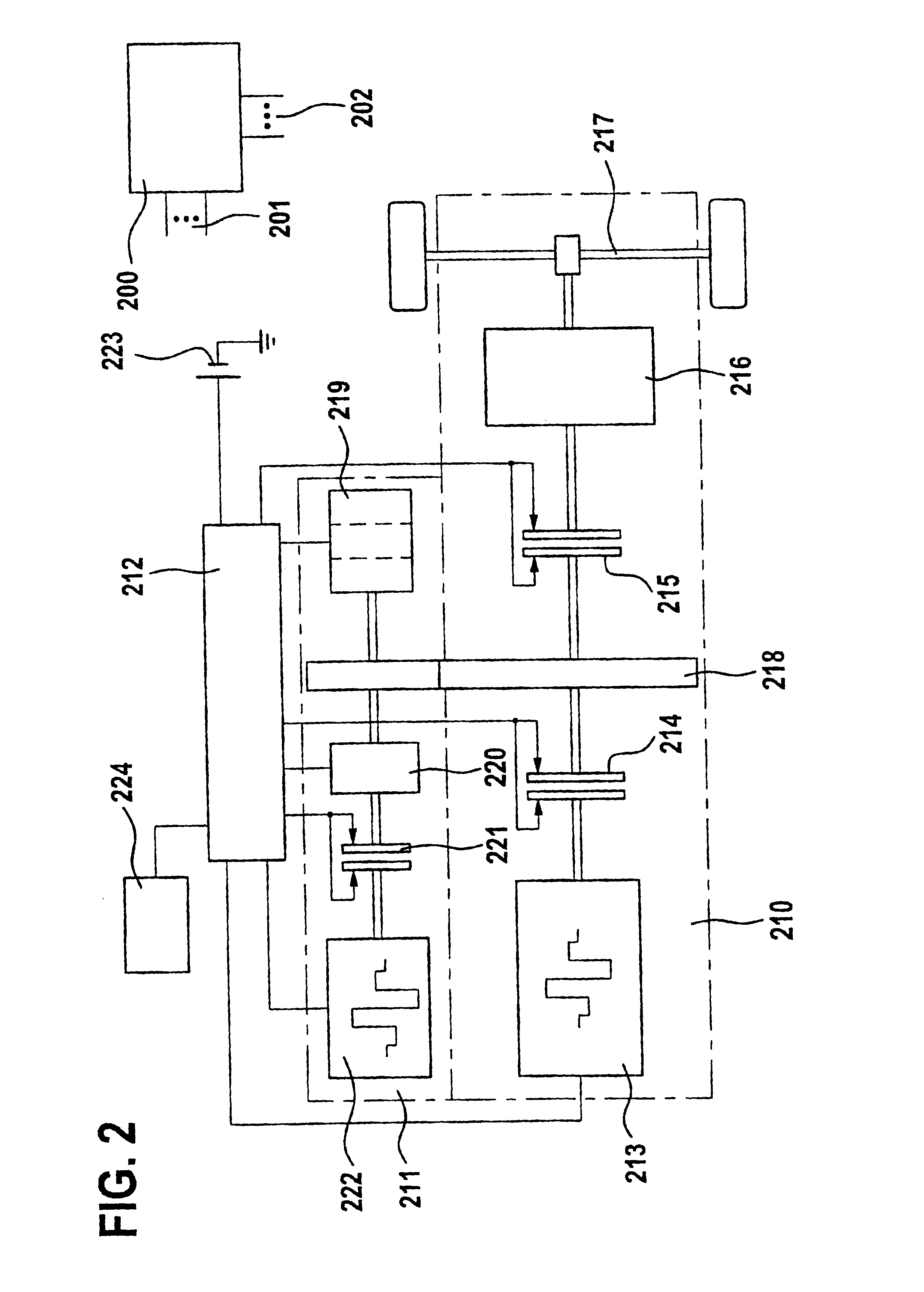
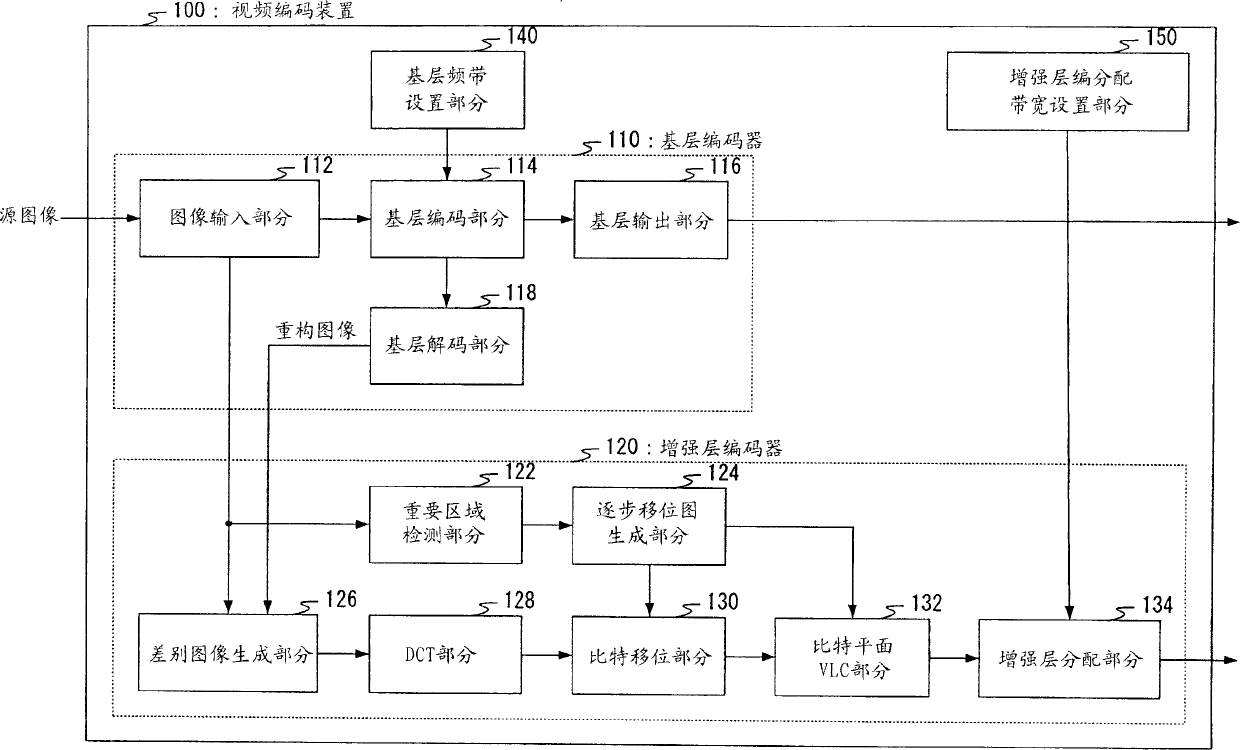
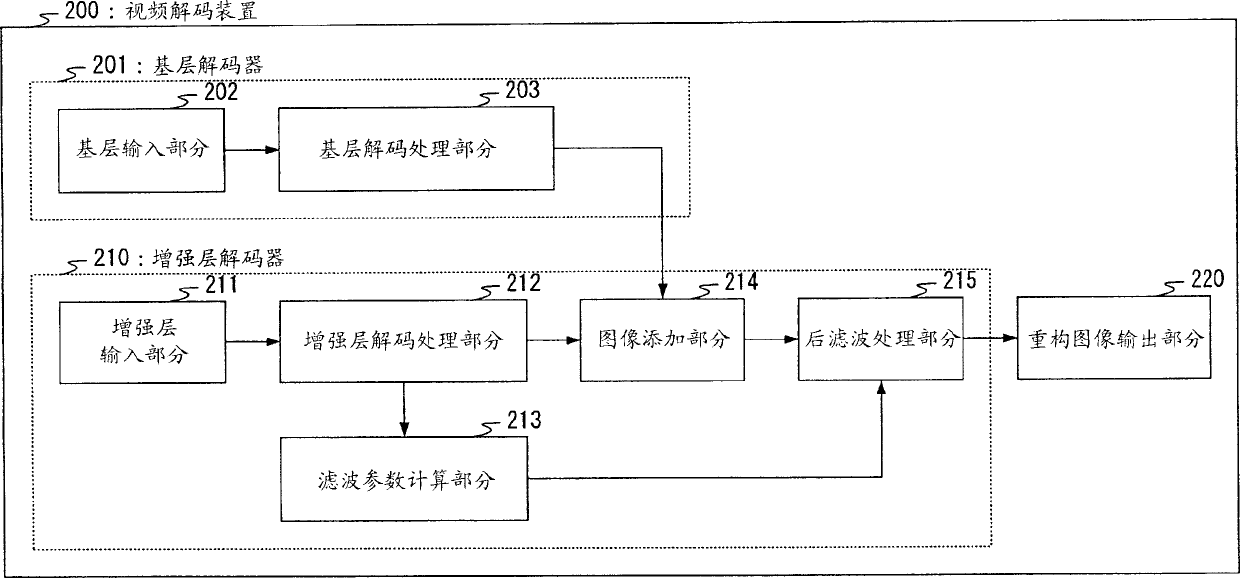
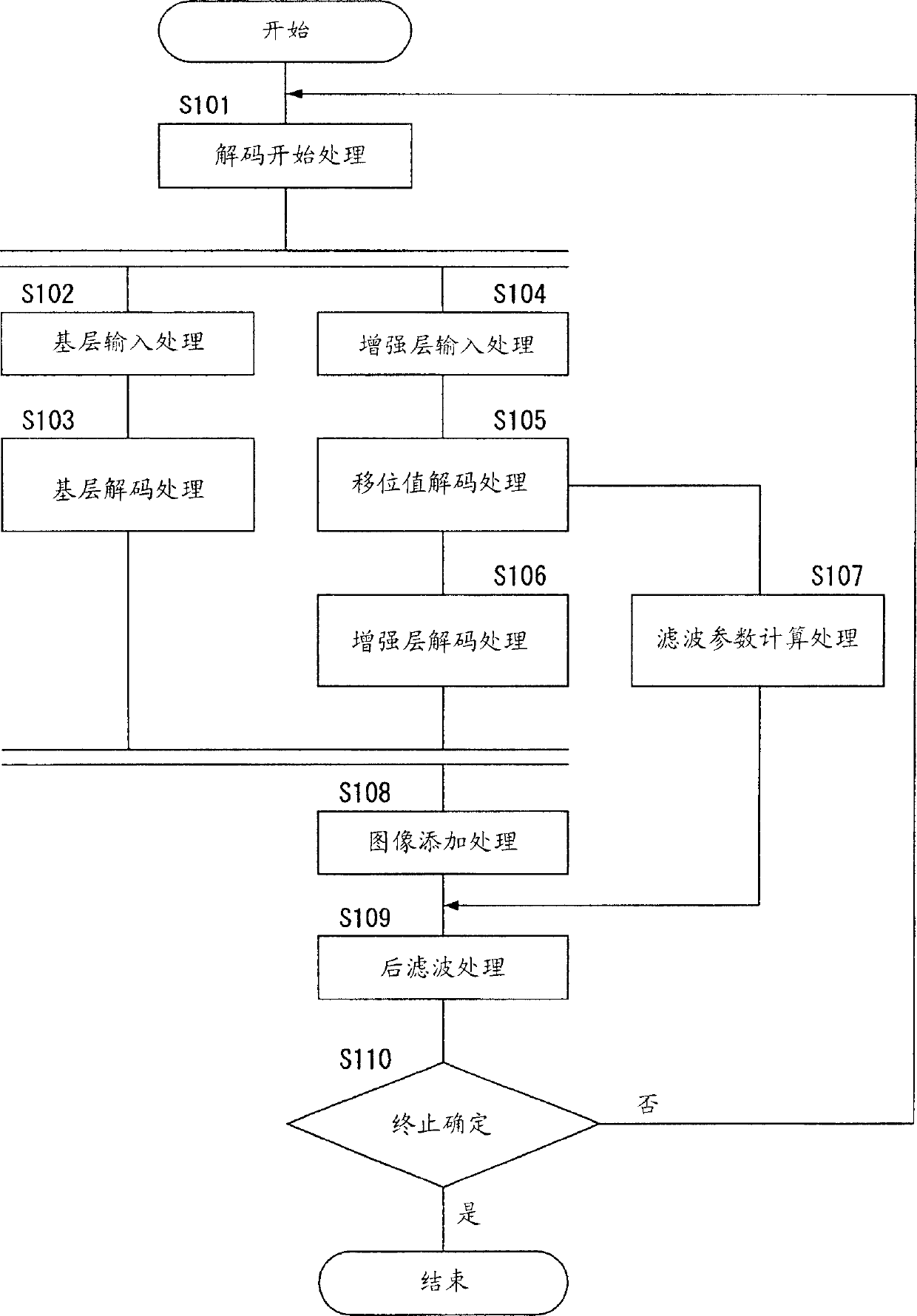
Moving image decoding apparatus and moving image decoding method
InactiveCN1574968AReduce noise componentsTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationVideo encodingImaging quality
A video decoding apparatus that adaptively controls post-filter filter parameters according to a characteristic quantity of priority-coded data priority-coded for individual areas classified by importance within a moving image, and improves the subjective image quality of an overall screen. In a video decoding apparatus 200, a filter parameter calculation section 213 calculates filter parameters that control the noise elimination intensity of a post-filter processing section 215 based on shift values of individual small areas set in a stepwise shift map in which the shift value decreases stepwise from an important area to the peripheral area within a screen in the video coding apparatus, and a post-filter processing section 215 performs post-filter processing of a reconstructed image by applying the calculated filter parameters.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
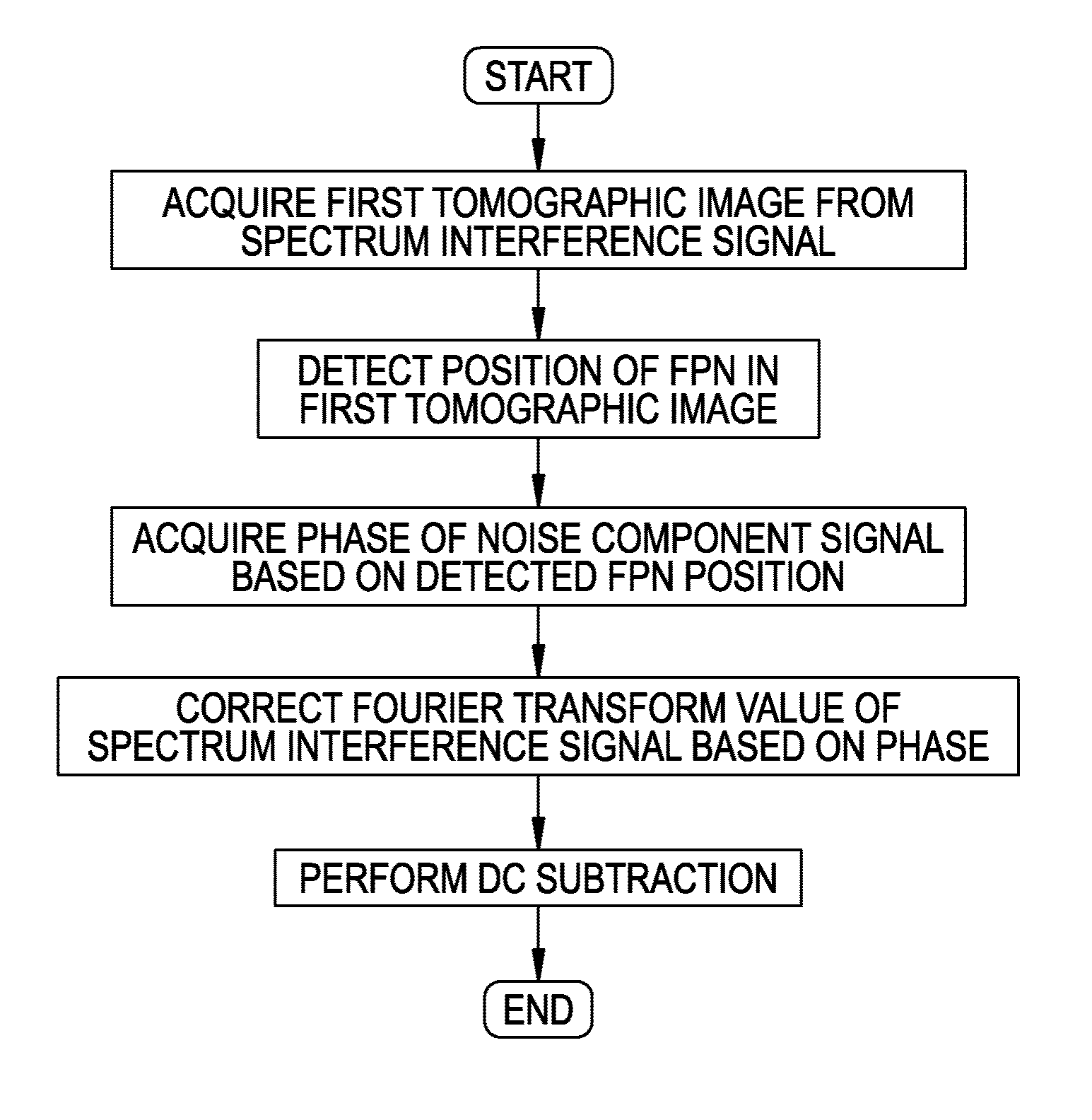
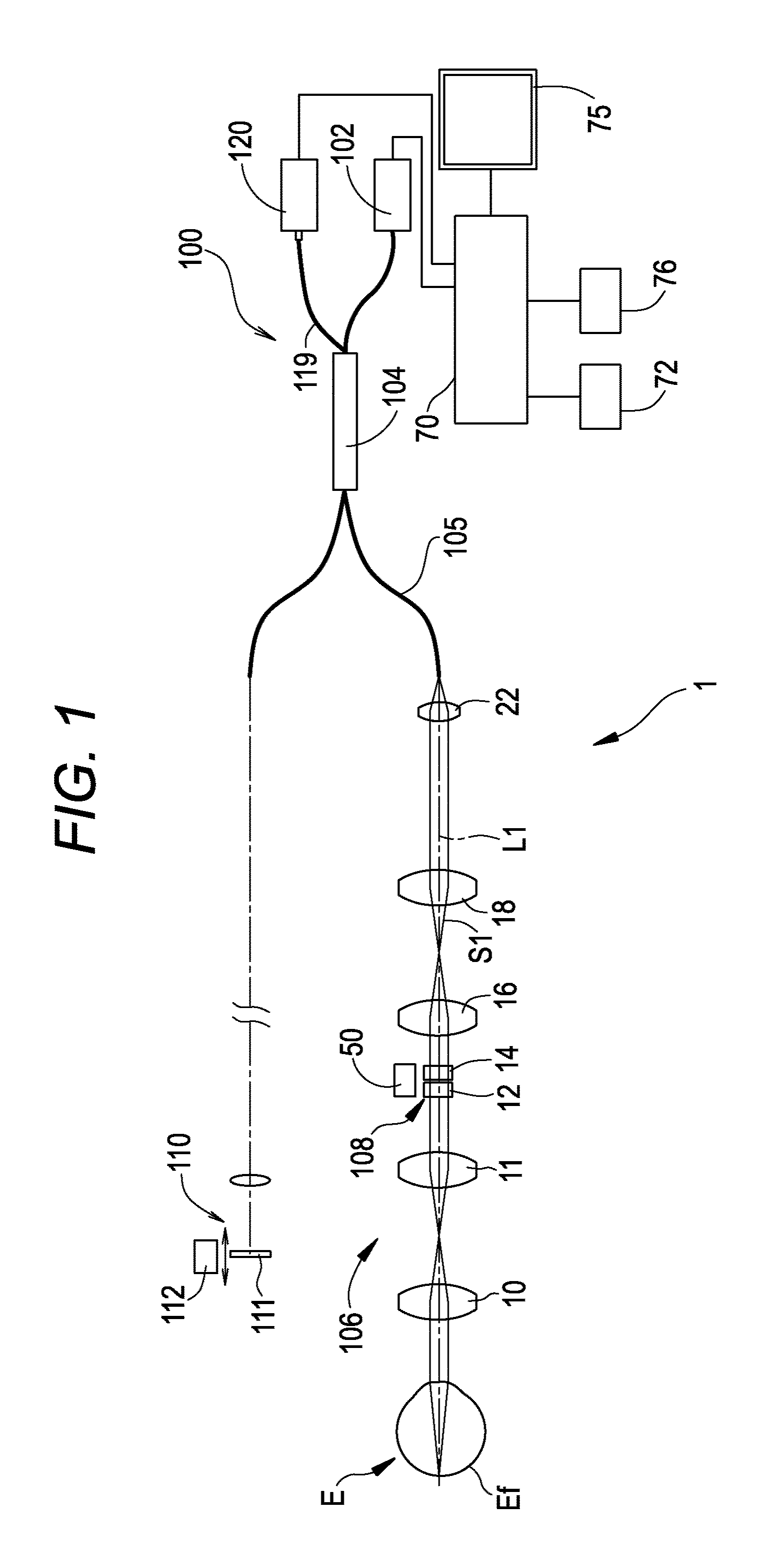
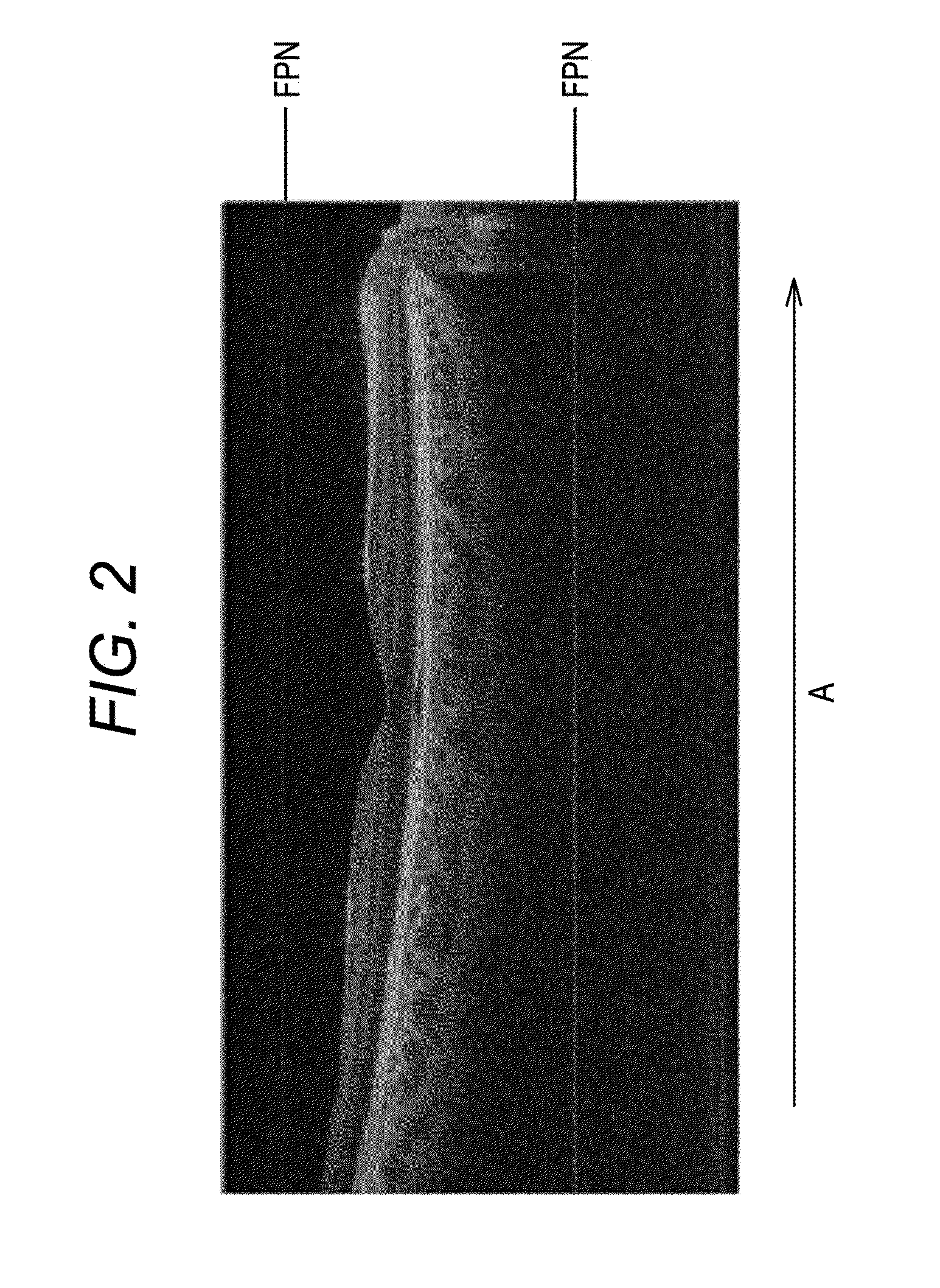
Method for reducing noise in tomographic image and recording medium having noise reducing program stored therein
ActiveUS20130208968A1Reduce noiseReduce componentsImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumTomography
A method for reducing noise in a tomographic image, includes: acquiring phase information of a noise component signal, the signal being provided as a signal corresponding to a noise component of the tomographic image and included in a spectrum interference signal output from a detector of a swept source optical coherence tomography device; acquiring a tomographic image in response to a spectrum interference signal with a corrected phase deviation based on the acquired phase information; and reducing the noise component of this tomographic image.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
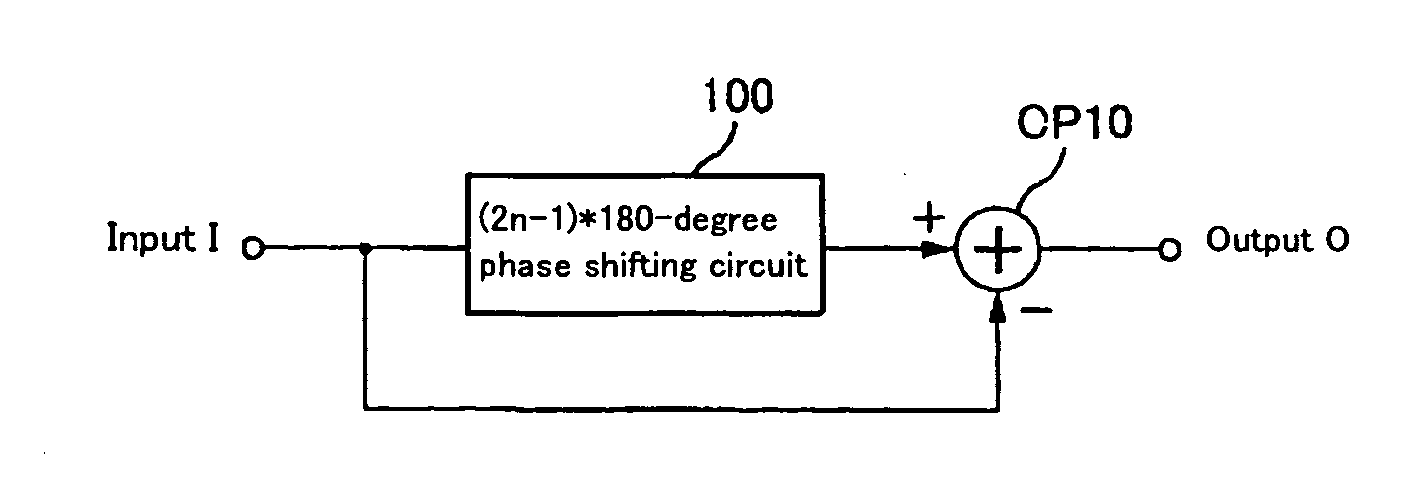
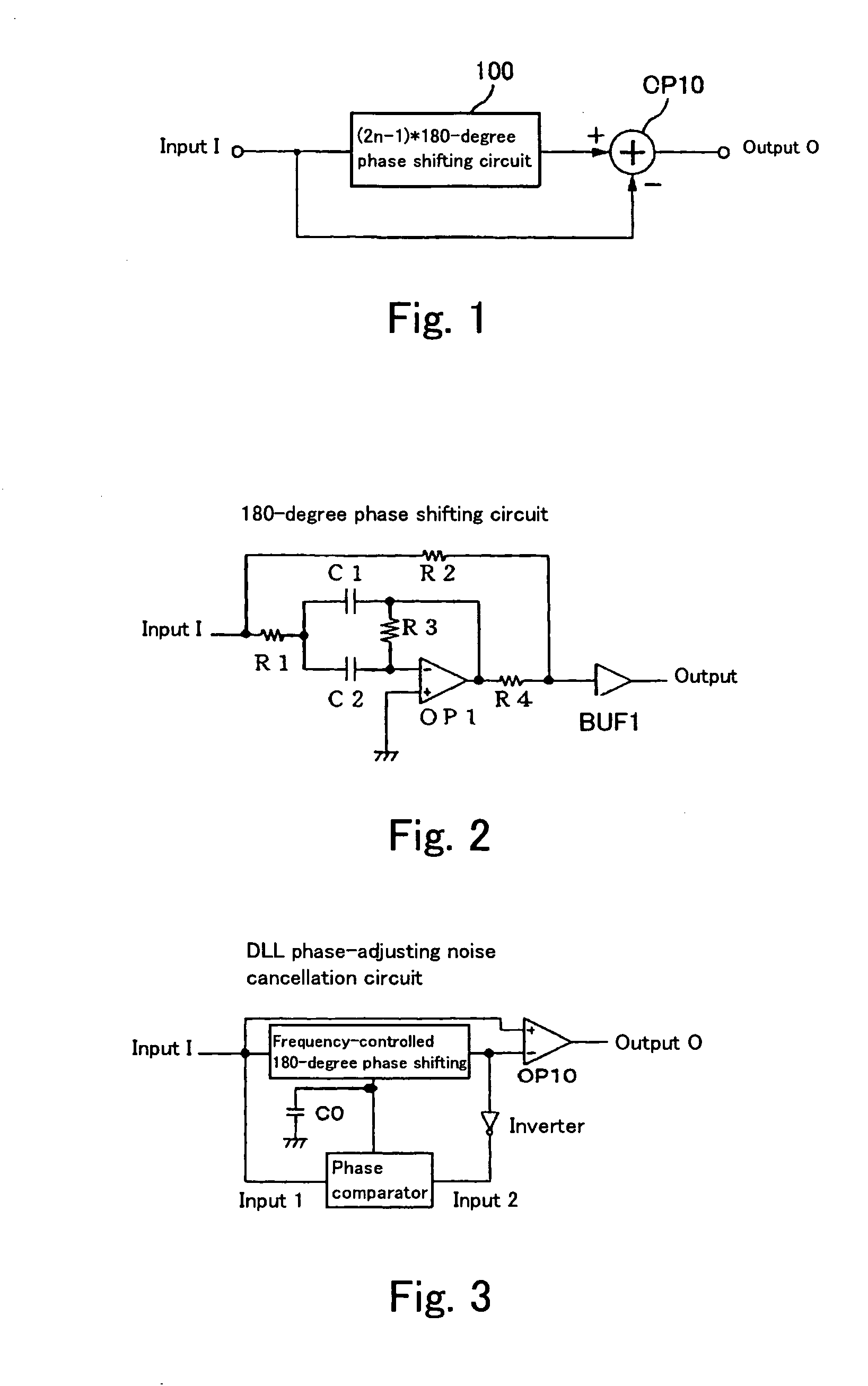
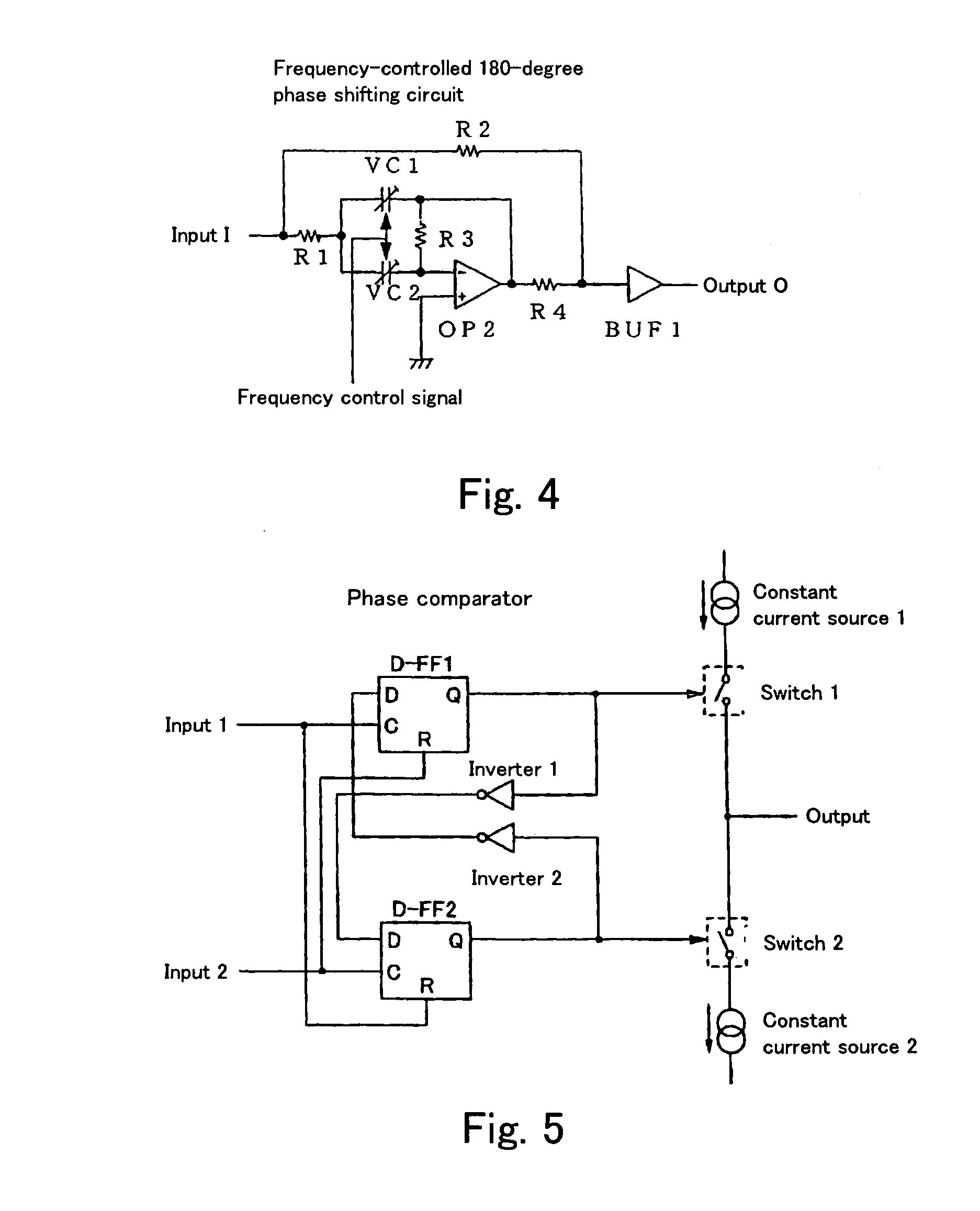
Noise removal using 180-degree or 360-degree phase shifting circuit
ActiveUS7266062B2Reduce noise componentsAvoid it happening againReliability increasing modificationsFilamentary/web record carriersPhase shiftedNoise removal
A noise removal circuit of the present invention comprises a 180-degree odd multiple shifting section for outputting a 180-degree shifted signal that is phase-shifted from an input signal by an odd multiple of 180 degrees and difference output section for outputting a difference between the input signal and the 180-degree shifted signal. The noise removal circuit comprises a 360-degree shifting section for outputting a 360-degree shifted signal that is phase-shifted from an input signal by an integral multiple of 360 degrees and sum output section for outputting a sum of the input signal and the 360-degree shifted signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Audio signal processing device for noise reduction and audio enhancement, and method for the same
ActiveUS8355908B2Reduce noiseIncrease in circuit sizeHearing device active noise cancellationGain controlTime domainFrequency spectrum
In frequency signals obtained by converting input audio signals from time-domain signals to frequency-domain signals, a level control value setting unit 5 establishes a level control value for reducing the levels of spectrums at a noise-components level. A level control value smoothing unit 6 carries out a smoothing process of smoothing the level control value established by the level control value setting unit 5 temporally. A spectral adjustment unit 8 multiplies the level control value after the smoothing process by the frequency signals, performing a level control.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
X-ray image detector
InactiveUS6380674B1Reduce in sizeReduce noise componentElectron multiplier detailsImage pickup tubesPhysicsX ray image
The present invention provides an X-ray image detector (1) which can reduce the size of a whole apparatus associated with an X-ray imaging tube, reduce noise components of an output X-ray image even if an incident X-ray is very weak, and provide a distortion-free visible image or electric image. The X-ray image detector (1) comprises a vacuum container having an input fluorescent screen outputting fluorescent light, a photoelectric screen converting the fluorescent light which is output from the input fluorescent screen to a photoelectron, and an output fluorescent screen outputting a visible light image with the obtained electron, a plurality of image pick-up elements (3) arranged such that partially overlapped areas are outside an image taking area and taking the visible light image in a divided way, image processing circuits (4) so arranged as to correspond to the image pick-up elements and trimming a taken video signal, an output image processing circuit (6) obtaining a composed image and a display device (5) displaying it as one signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
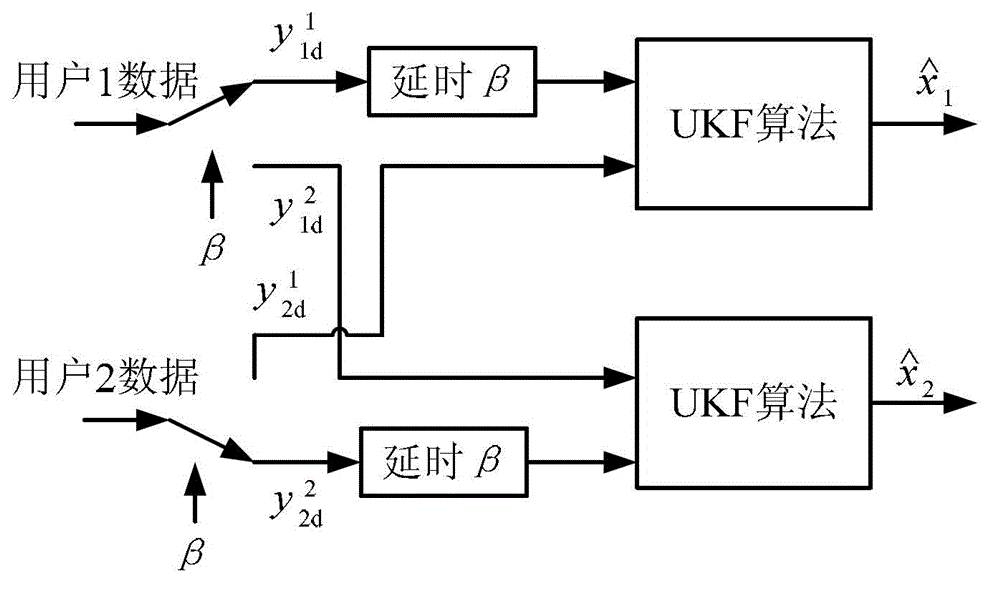
Chaos coordinating communication method based on UKF (unscented Kalman filter)
InactiveCN102868652AImprove efficiencyReduce noise componentsModulated-carrier systemsBaseband system detailsCommunications systemPhase shifted
The invention discloses a chaos coordinating communication method based on a UKF (unscented Kalman filter). On the basis of a chaos difference phase shift keying (PSK) communication system, a UKF algorithm is applied to estimate a carrier signal, and the estimated carrier signal is taken as a reference signal and a subsequently transmitted user information signal after being demodulated. According to the UKF algorithm, a noise component in the reference signal is decreased, bit error property is effectively improved, additionally, according to a changing speed of a channel, a frame number ratio of an appropriate reference signal to the user information signal is selected, and the frame number of required transmitting signals is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
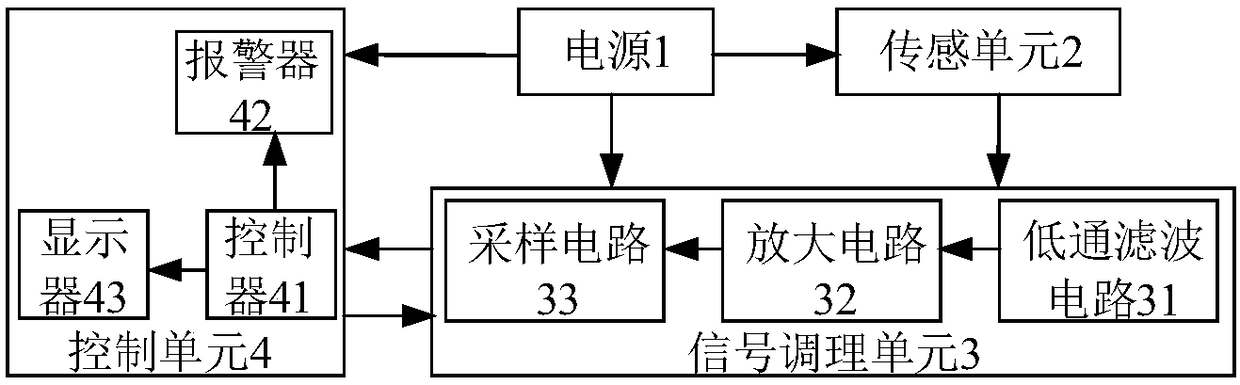
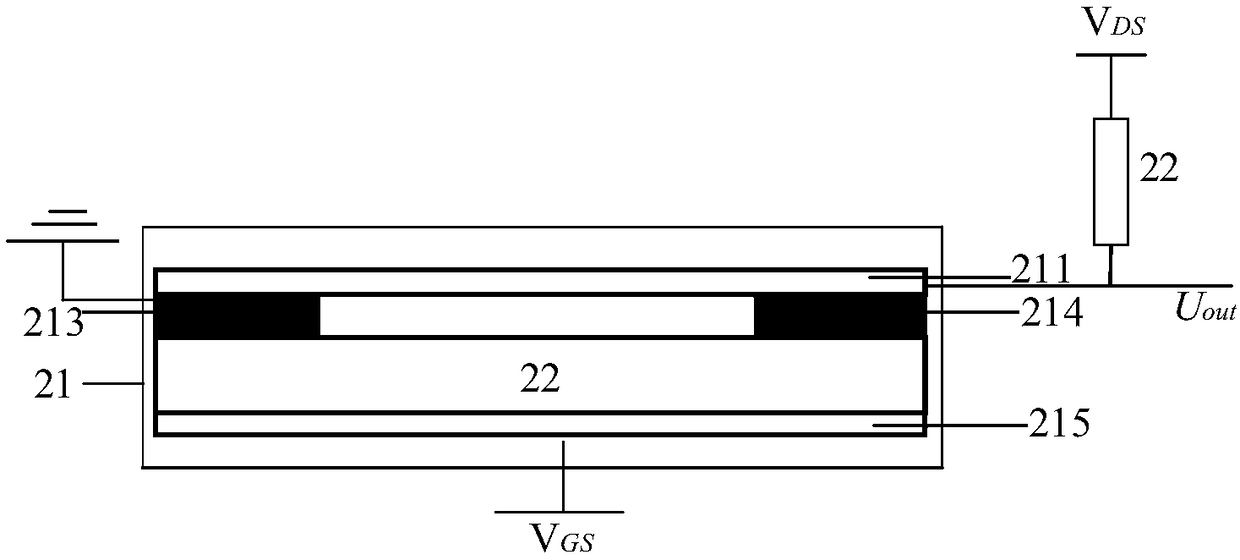
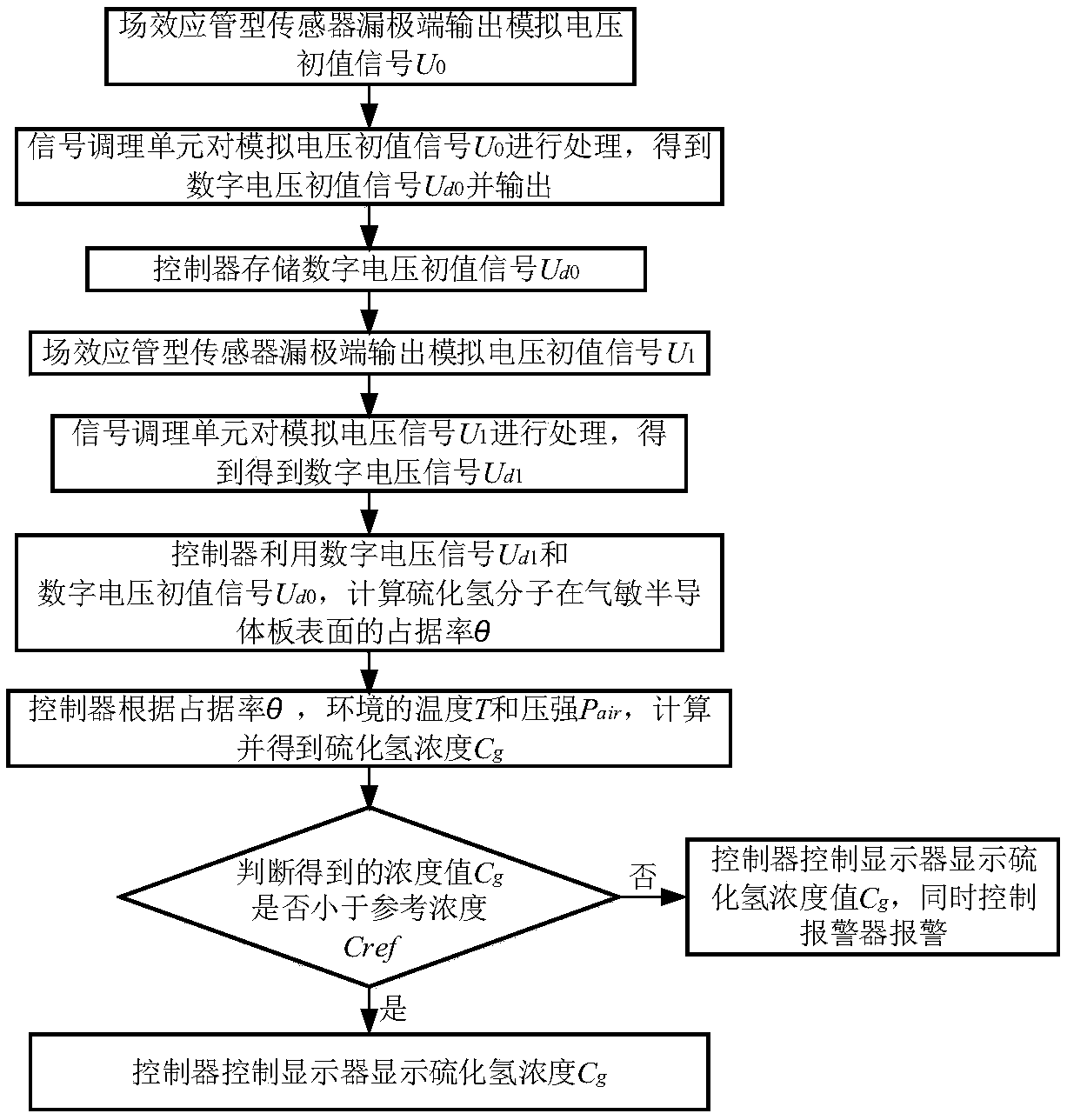
Hydrogen sulfide detection device and method
ActiveCN108267487AHigh sensitivityImprove response speedMaterial resistanceElectrical resistance and conductanceSignal conditioning
The invention provides a hydrogen sulfide detection device and method which are used for improving the detection sensitivity and the response speed of the detection device. The hydrogen sulfide detection method comprises the steps that firstly, outside a to-be-detected environment, a power supply, a field-effect tube type sensor connected with a resistor and a signal conditioning unit are used forobtaining a digital voltage initial value signal, and the digital voltage initial value signal is stored by a controller; secondly, in the to-be-detected environment, the power supply, the field-effect tube type sensor connected with the resistor and the signal conditioning unit are used for obtaining a digital voltage signal, and the digital voltage signal is output; thirdly, the controller calculates the hydrogen sulfide concentration by utilizing the digital voltage initial value signal, the digital voltage signal, the temperature of the to-be-detected environment and the pressure intensity; finally, the controller judges whether the hydrogen sulfide concentration is smaller than a reference concentration or not, if yes, the controller controls a displayer to display the hydrogen sulfide concentration, otherwise, the controller controls the display to display the hydrogen sulfide concentration and controls an alarm device to give an alarm at the same time. The device is relativelyhigh in sensitivity and relatively high in response speed and can be used for detecting the concentration of hydrogen sulfide gas.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hologram recording apparatus, hologram recording method, and hologram recording medium
InactiveUS7085028B2Reduce noise componentsImprove data integrityRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansSpatial light modulatorLight beam
A hologram recording apparatus, a hologram recording method and a hologram recording medium reduce noise components generated by a phase modulation type spatial light modulator, thus permitting improved integrity of data to be achieved. A light beam whose diffraction state has been controlled by a diffraction control element is condensed on a hologram recording medium. With this arrangement, a predetermined diffracted light component is removed from a diffracted light beam emergent from the diffraction control element when recording information, which is based on the diffraction state controlled by the diffraction control element, in a hologram recording medium. Thus, noise components when information is recorded can be reduced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Amplifier and the method thereof
ActiveCN101471625AReduce noise componentsImpedence matching networksAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierChannel thermal noise
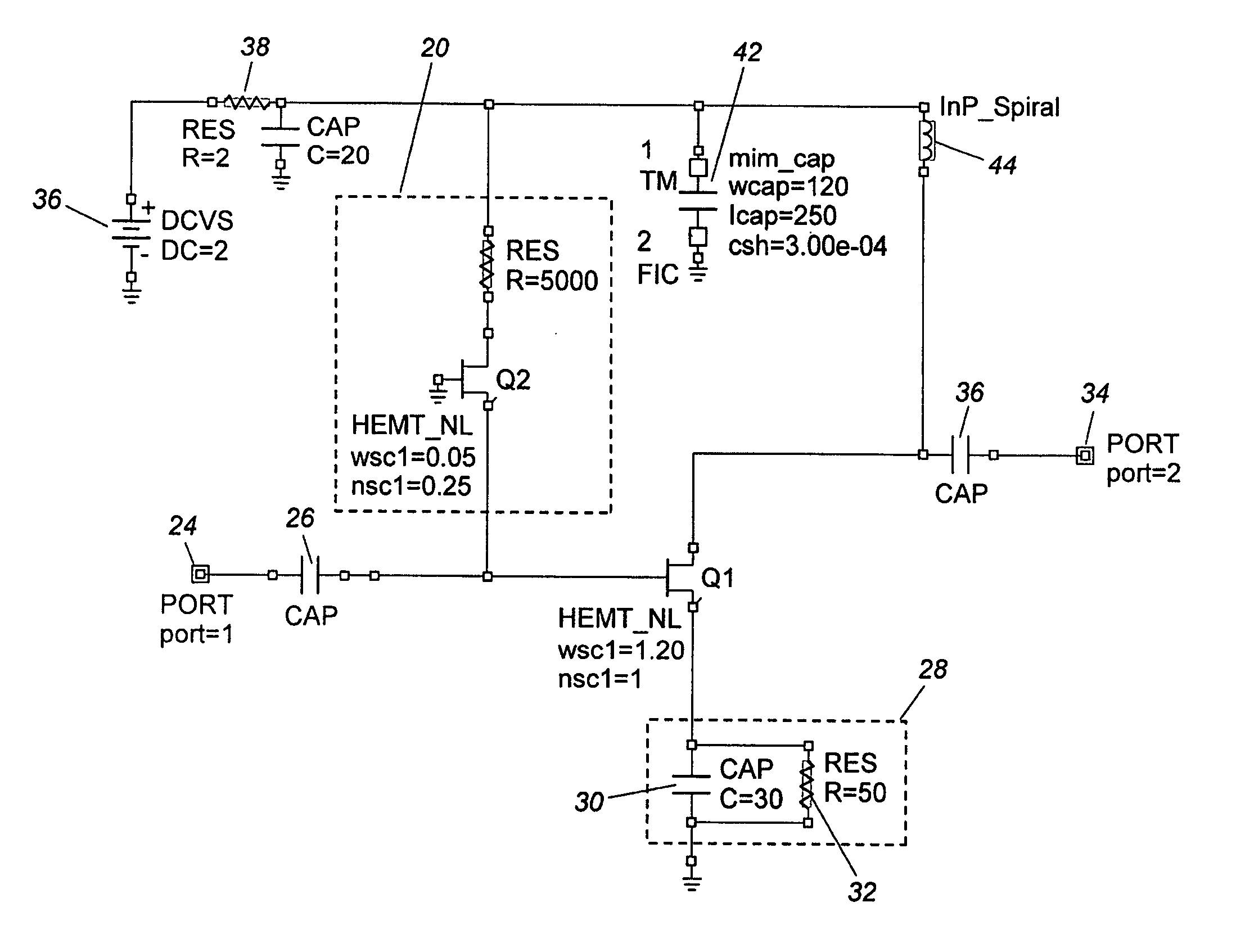
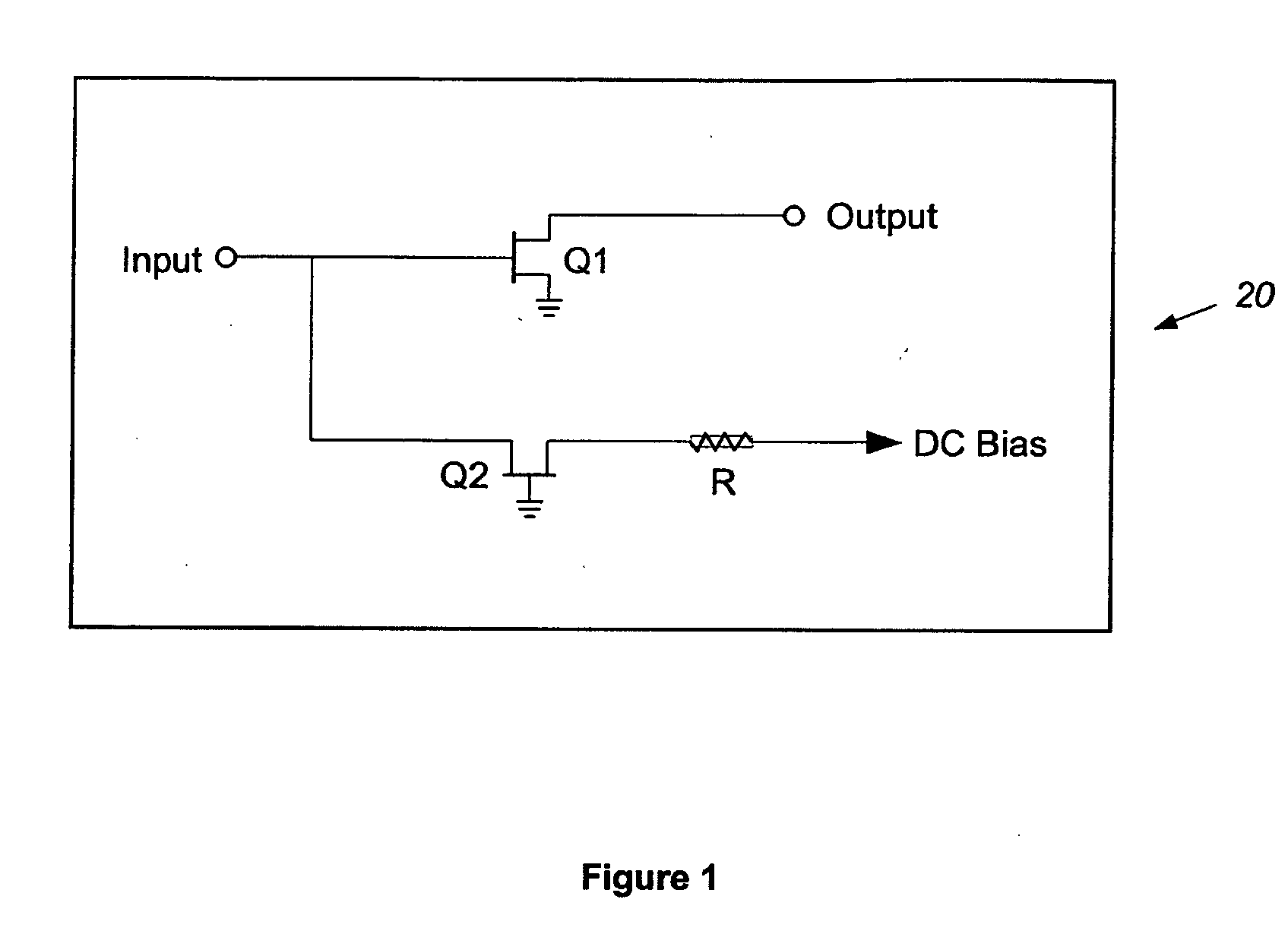
The invention relates to an amplifier for amplifying an input signal to generate an output current, comprising an impedance matching network for receiving the input signal to perform impedance matching; a first resistor for receiving the input signal to generate the matched signal; a first transistor having a channel thermal noise to establish a first noise voltage; a second resistor for receiving the channel thermal noise to establish a second noise voltage; and a transconductance circuit, comprising a first transconductance circuit which has a first transconductance coefficient and receives the first noise voltage to generate a first noise current; a second transconductance circuit which has a second transconductance coefficient and receives the second noise voltage to generate a second noise current such that the first and the second noise currents are counteracted with each other to reduce the noises in the output current. In contrast to the prior art, the invention can efficiently reduce the noises in the output current.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Annular-beam coupling system
ActiveCN109564327AReduce noise componentsReduce autofluorescent componentsCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFiberDouble-clad fiber
Disclosed is an annular-beam coupling system enabling reduction of noise generated from a core of a double-clad fiber. The disclosed annular-beam coupling system comprises: a fiber for transmitting light of a light source; a collimator for receiving input of the light output from the fiber and forming a spherical parallel beam; an annular-beam generation portion for converting the parallel beam into an annular beam; and a double-clad fiber having the annular beam coupled in a cladding region.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
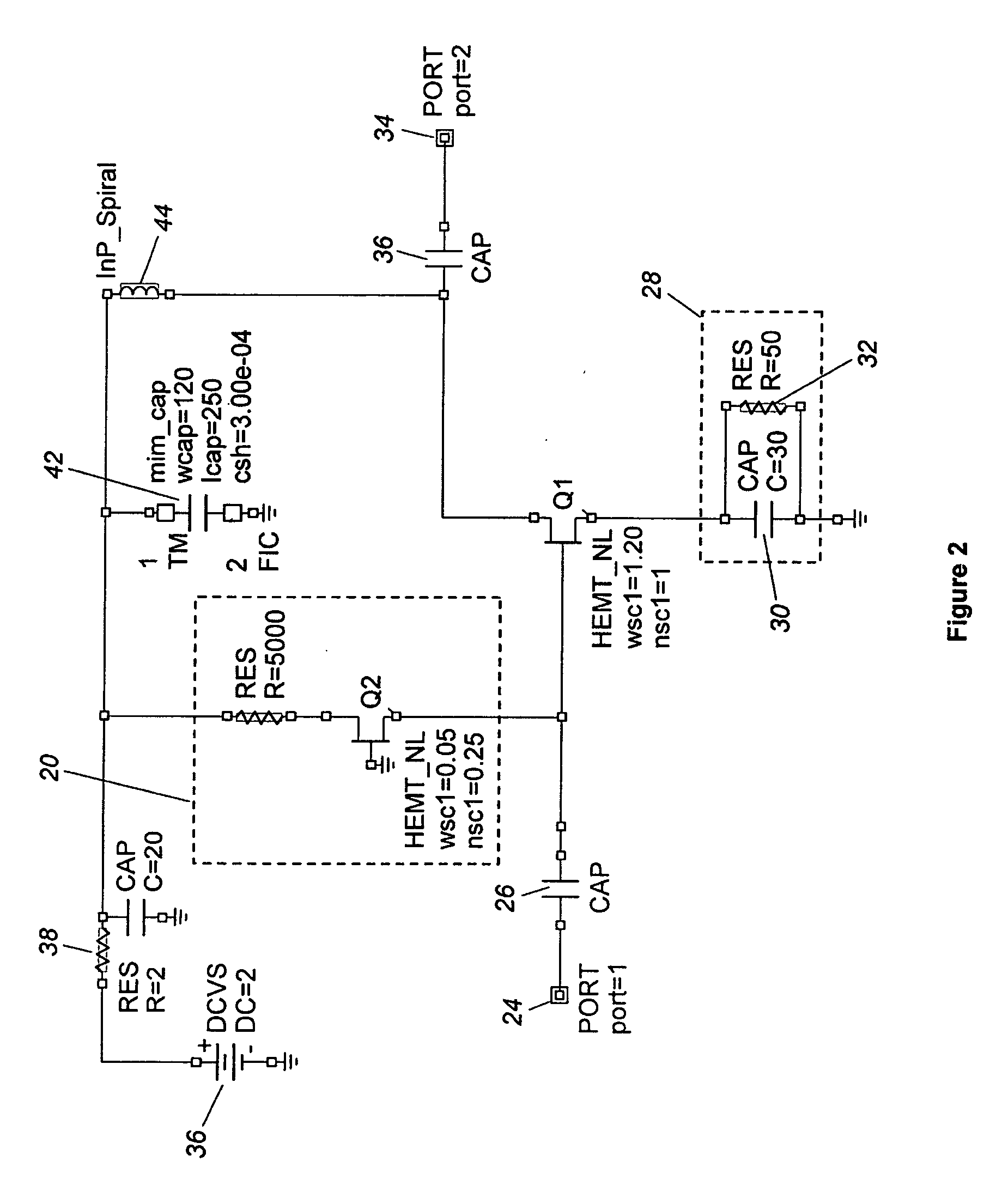
Active input load wide bandwidth low noise hemt amplifier
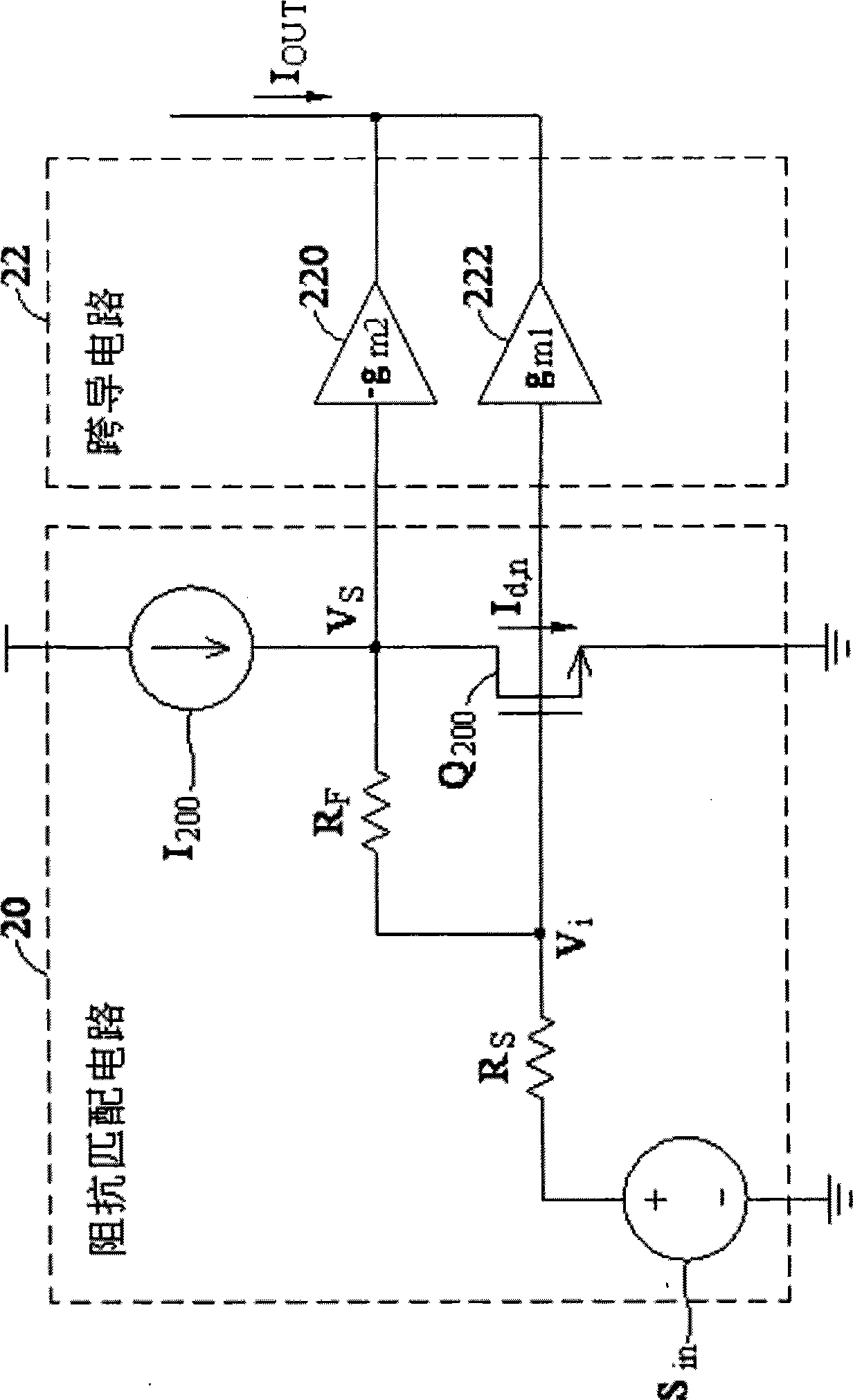
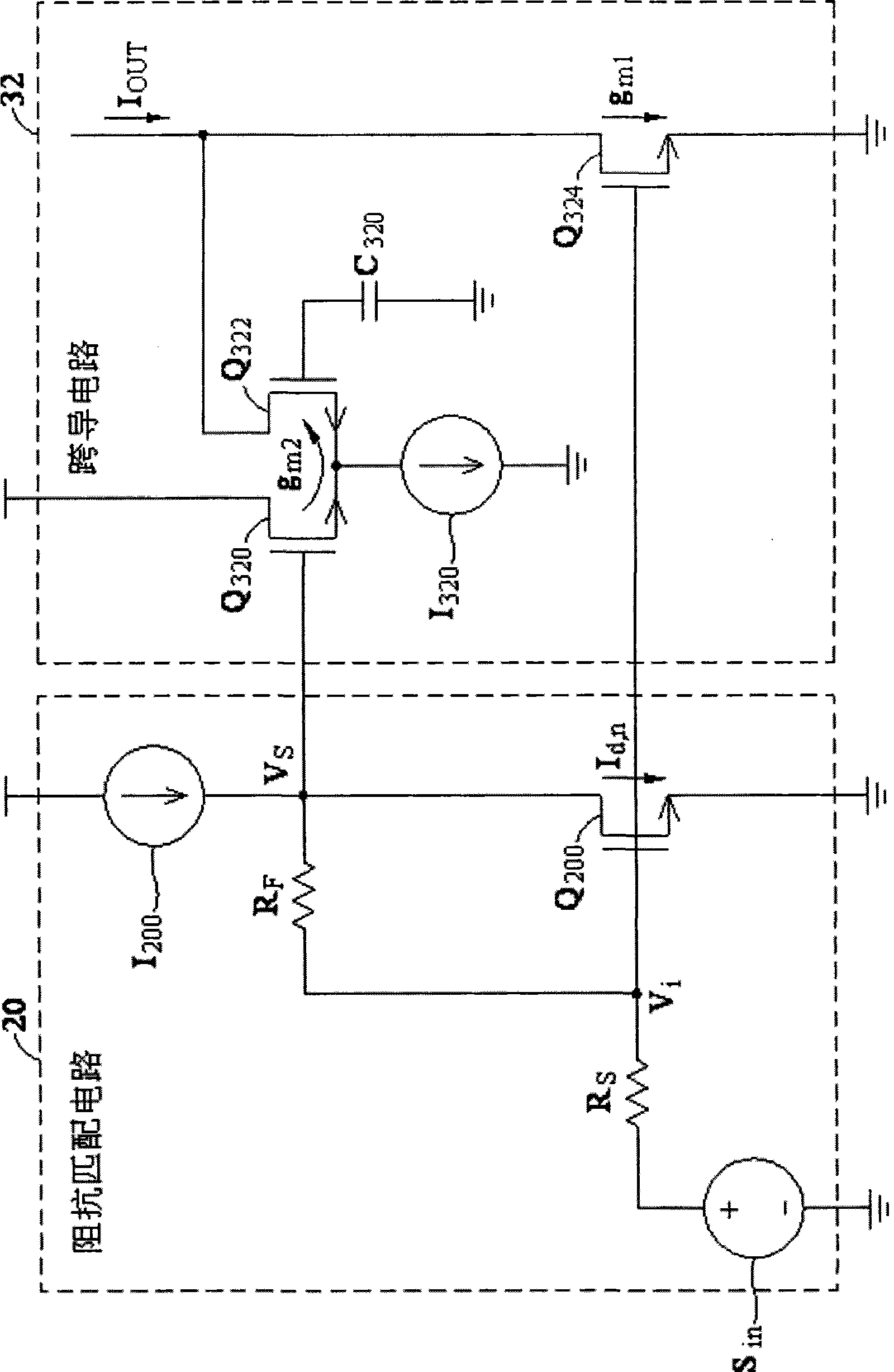
ActiveUS20070090879A1Wide bandwidthReduce noise componentsImpedence matching networksAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCapacitanceTransistor channel
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and device for smoothing of image data ,and smoothing program
InactiveCN1503562AReduce noise componentsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging data
Image data (D0) which includes a plurality of object unit image data arranged in time series, such as field images, is supplied from an image source. The object unit image data subjected to the smoothing process is divided into blocks of a predetermined size. Then, a difference between the object unit image data and preceding unit image data which is immediately before the object unit image data, and a difference between the object unit image data and subsequent unit image data which is immediately after the object unit image data are determined for a plurality of blocks, based on a pixel value. The object unit image data is smoothed with one of the preceding unit image data and the subsequent unit image data having a smaller difference.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
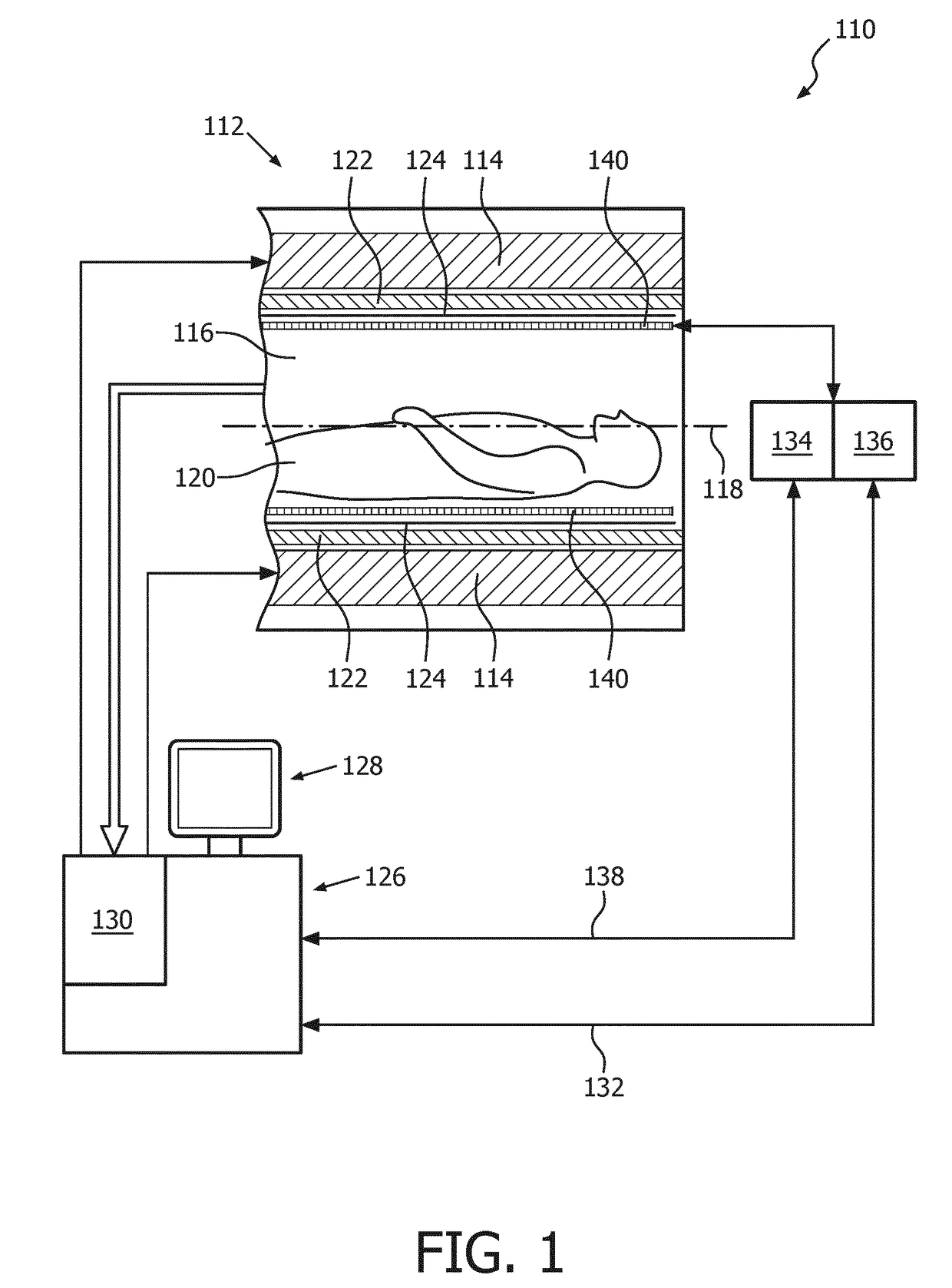
Receive coil unit with integrated noise antennas and magnetic resonance imaging system with such a receive coil unit
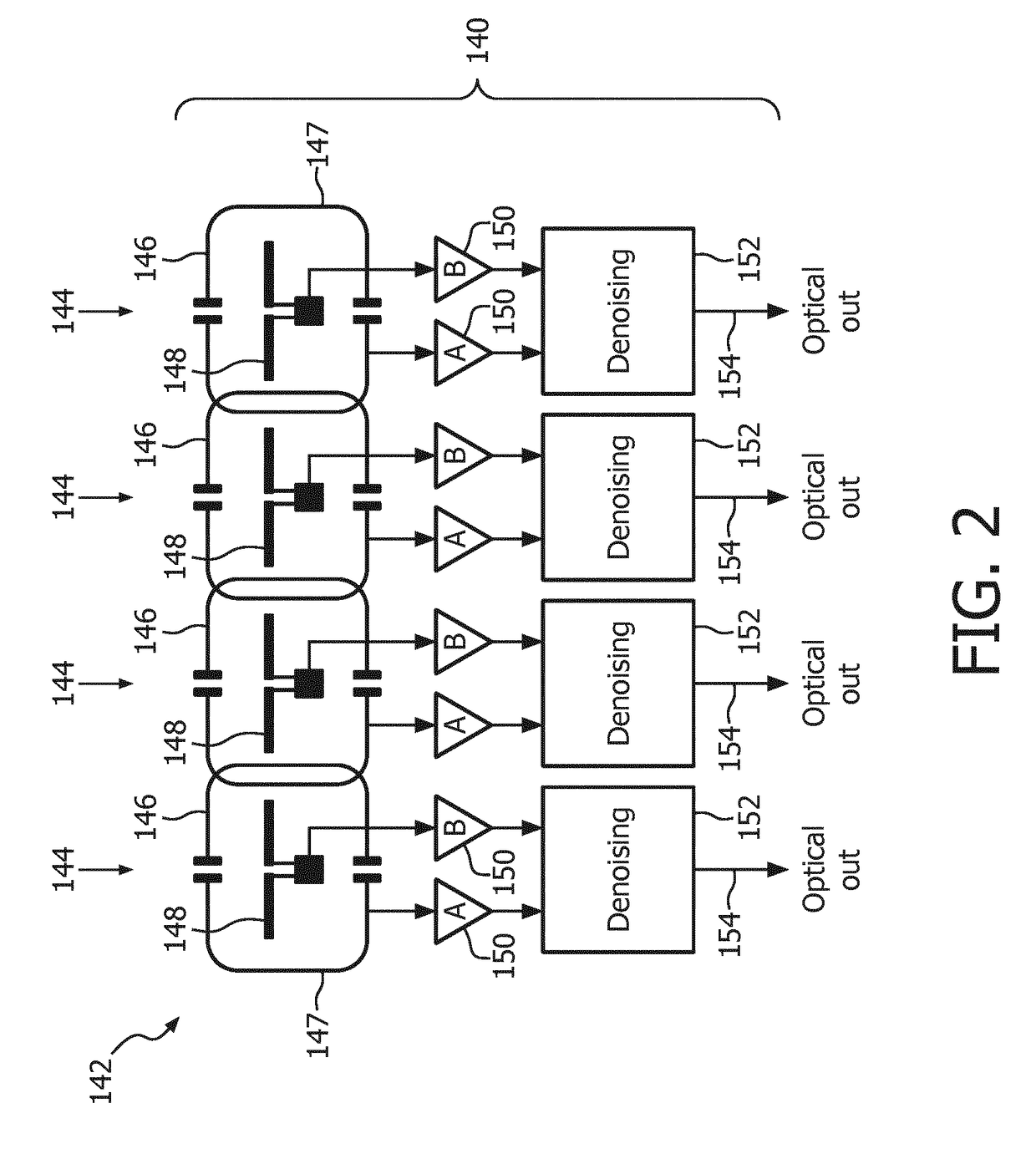
ActiveUS20170307701A1Reduce noise componentsLess susceptible to RF noiseMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCoil arrayReceiver coil
The present invention provides a receive coil unit (140) comprising a receive coil array (142) for use in a magnetic resonance imaging system (110) with multiple antenna units (144) sensitive to magnetic resonance signals, i.e. antenna units (144) sensitive to B-field signals, whereby each antenna unit (144) comprises a coil element (146) sensitive to B-field signals, and each antenna unit (144) comprises an E-field antenna (148) sensitive to E-field signals. The present invention also provides a magnetic resonance imaging system (110) comprising a receive coil unit (140) with a receive coil array (142) having multiple antenna units (144) sensitive to magnetic resonance signals, i.e. antenna units (144) sensitive to B-field signals, whereby the receive coil unit (140) is provided as a receive coil unit (140) as specified above. Still further, the present invention provides a method for magnetic resonance imaging comprising the steps of providing a receive coil unit (140) comprising a receive coil array (142) for use in a magnetic resonance imaging system (110) with multiple antenna units (144) sensitive to magnetic resonance signals, i.e. antenna units (144) sensitive to B-field signals, whereby each antenna unit (144) comprises a coil element (146) sensitive to B-field signals, and each antenna unit (144) comprises an E-field antenna (148) sensitive to E-field signals, and performing de-noising of the B-field signals received from the coil elements (146) of the receive coil unit (140) by filtering noise signals, as received from the E-field antenna (148), from the B-field signals.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com