Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Practical limitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
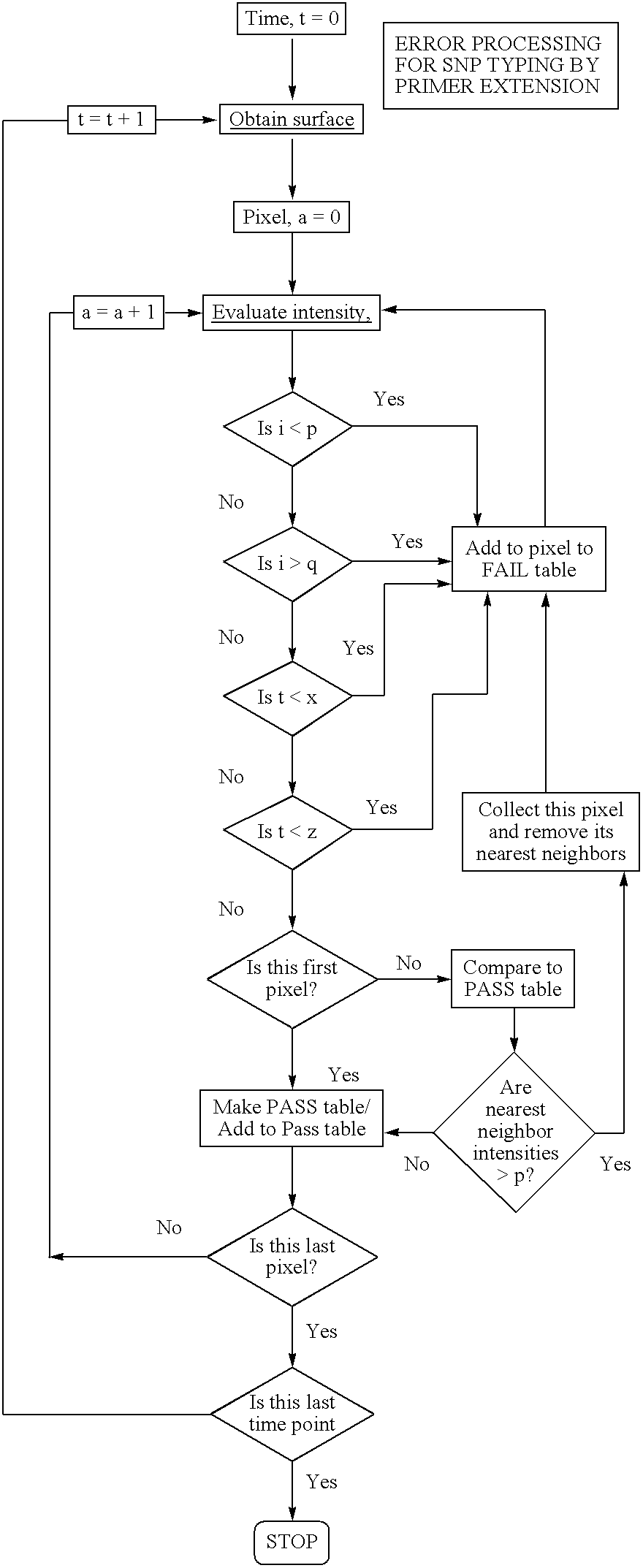
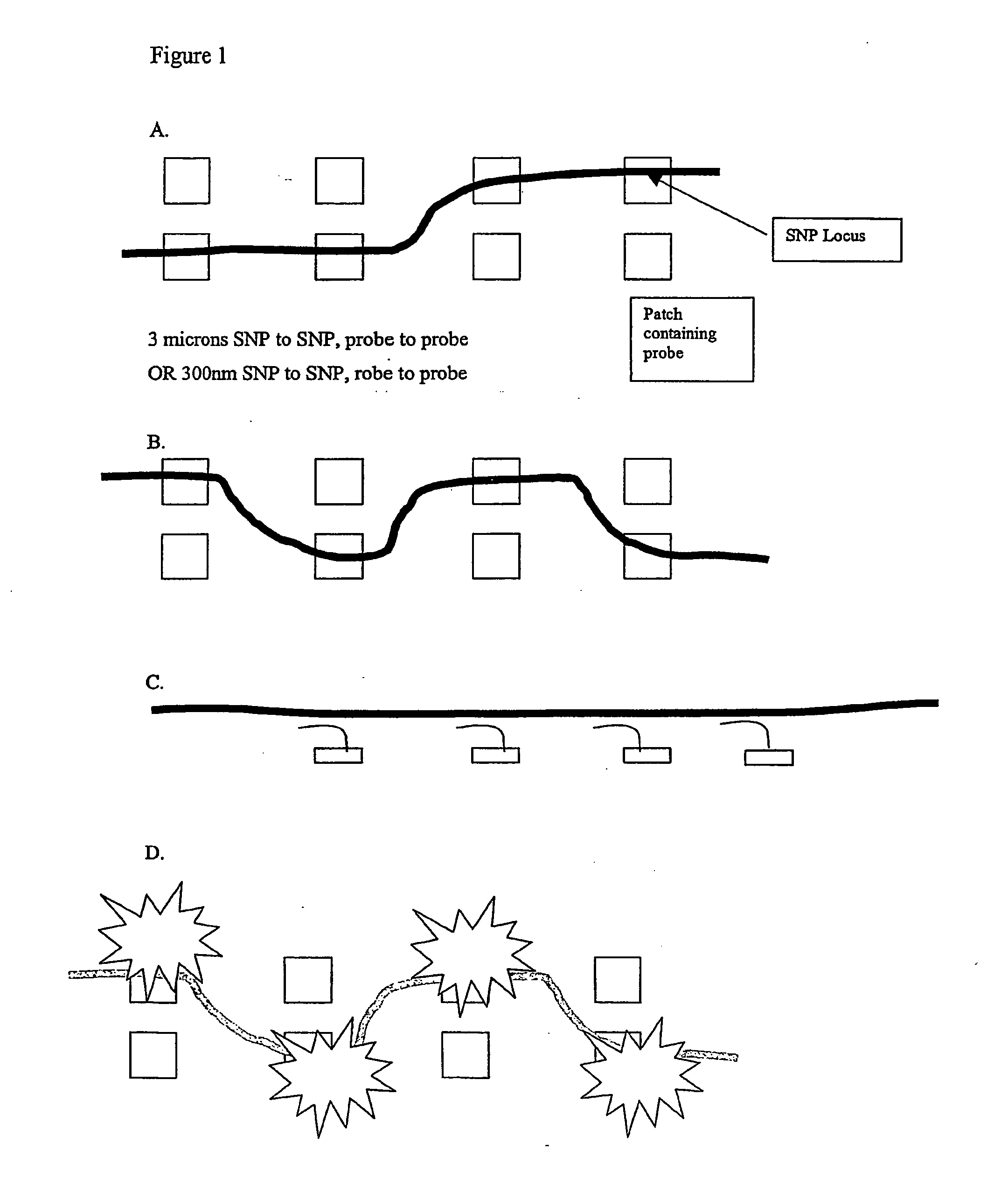
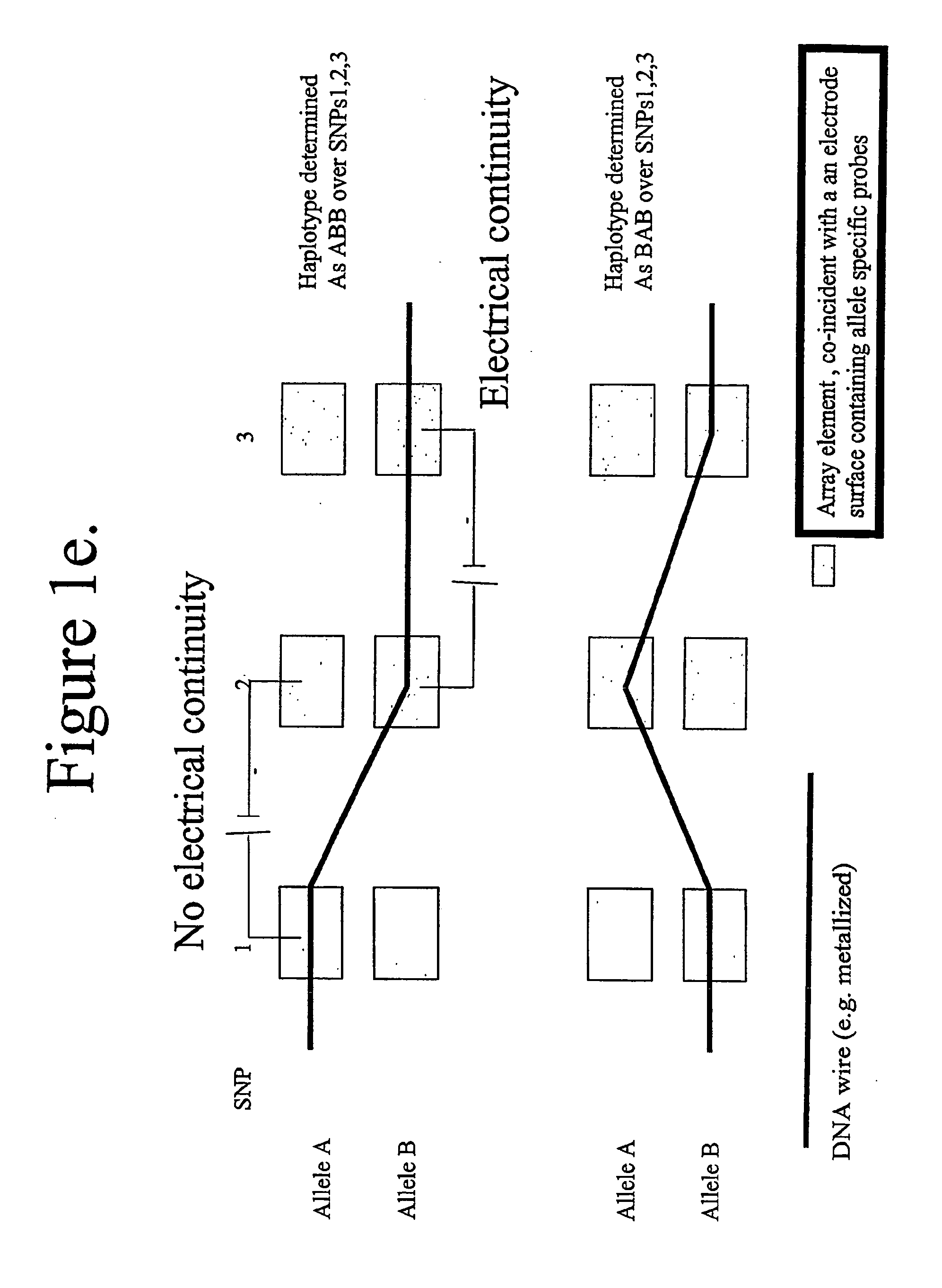
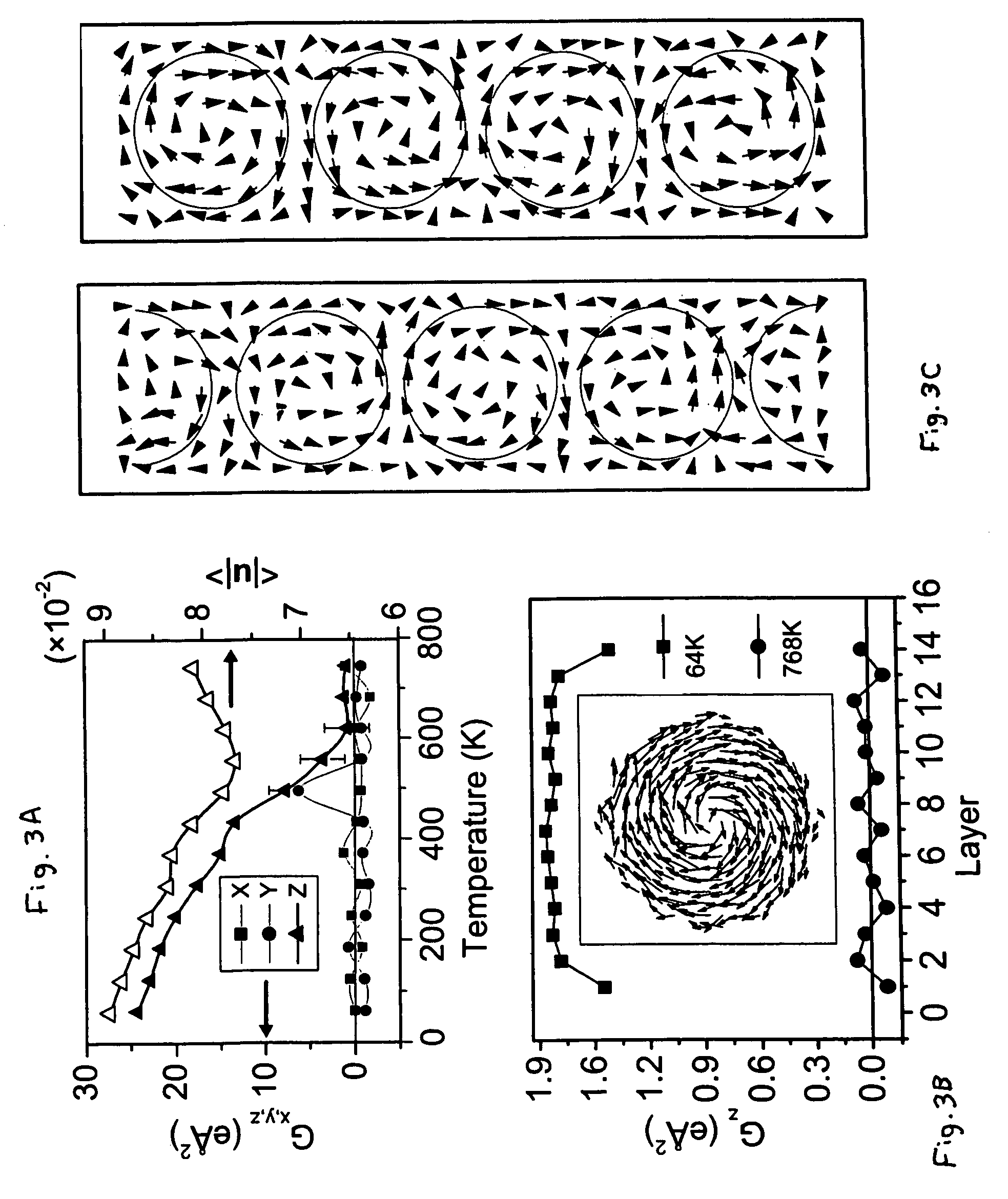
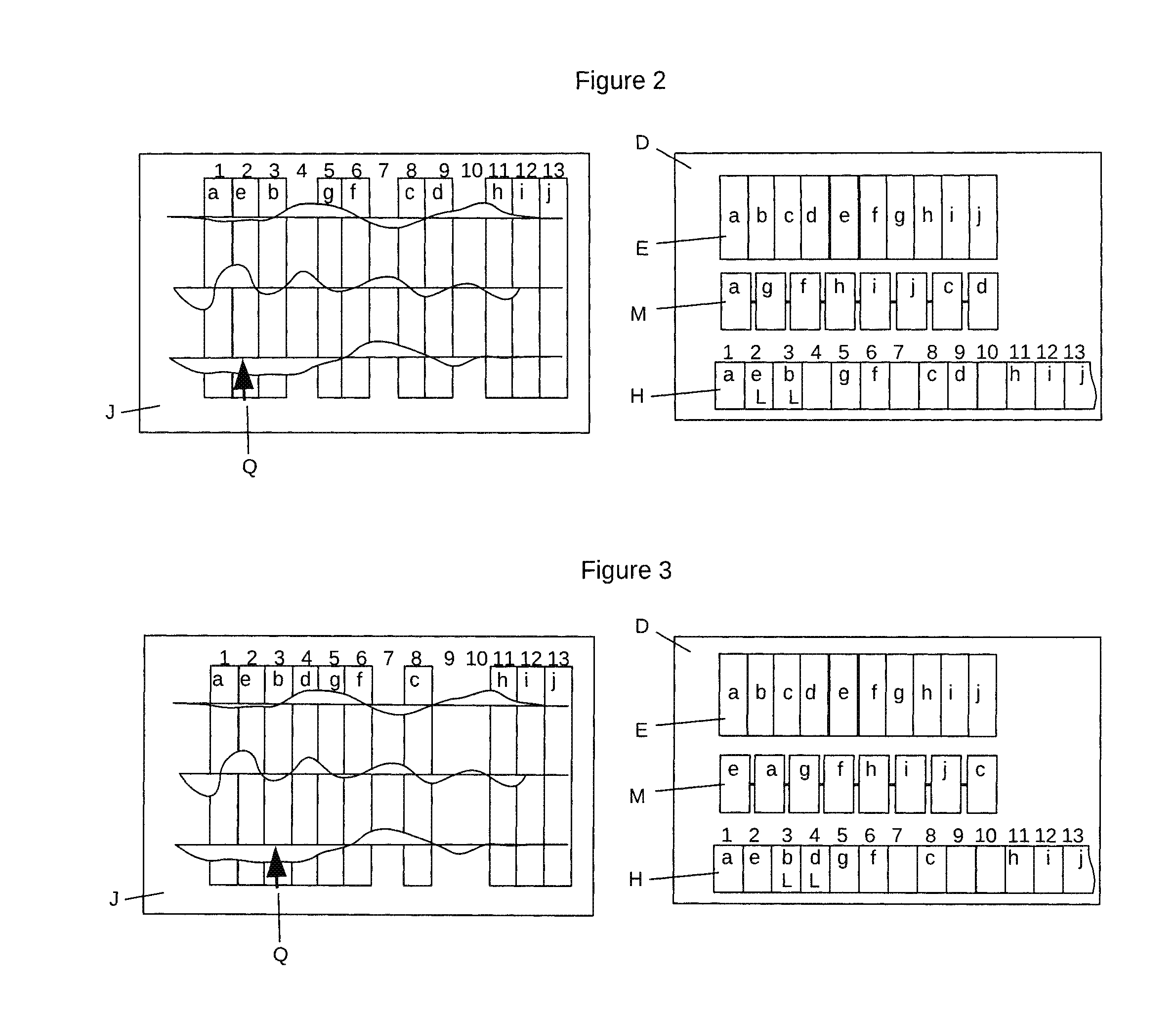
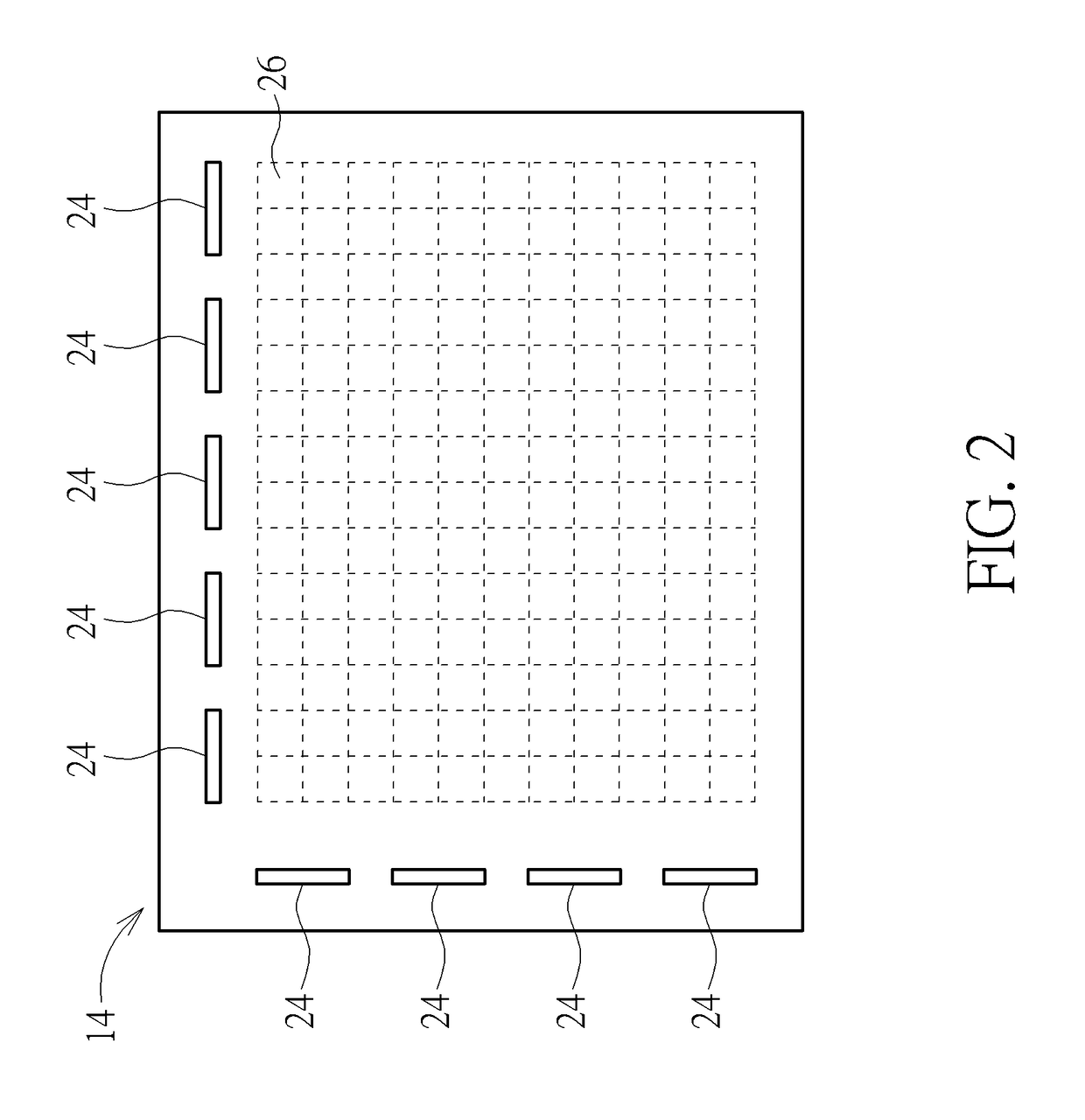
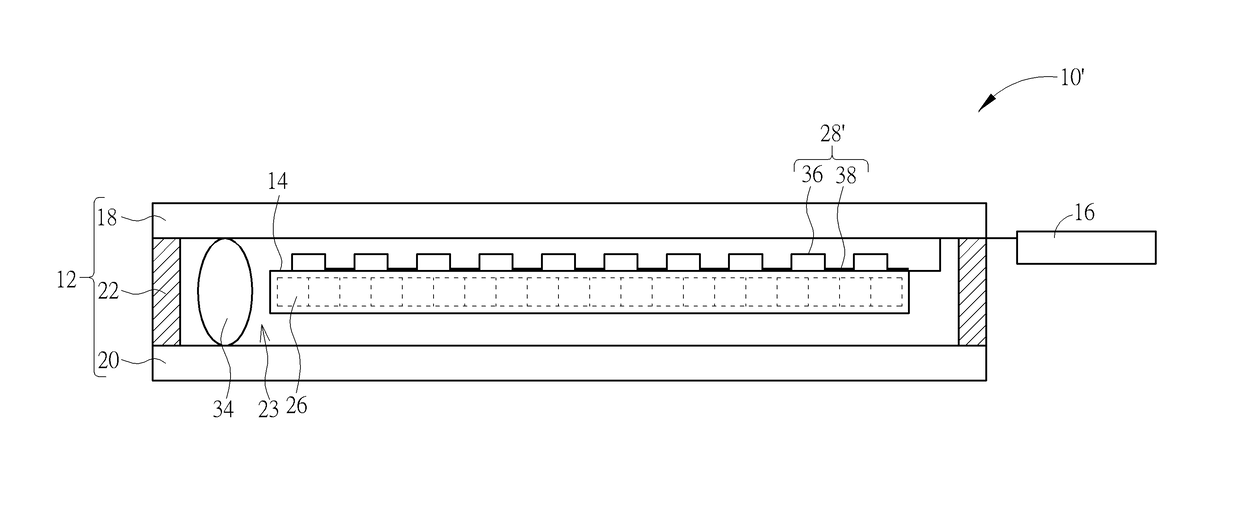
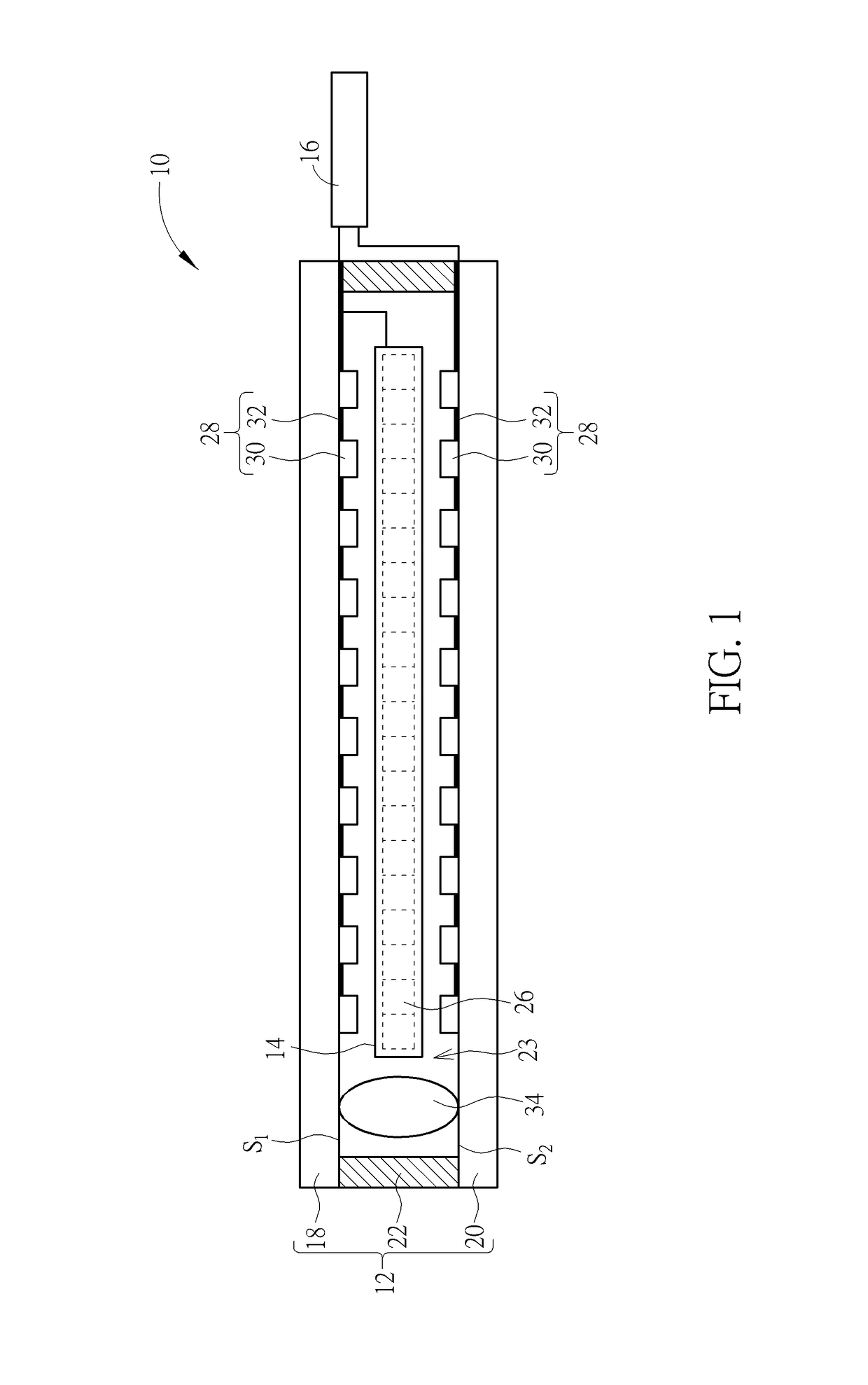
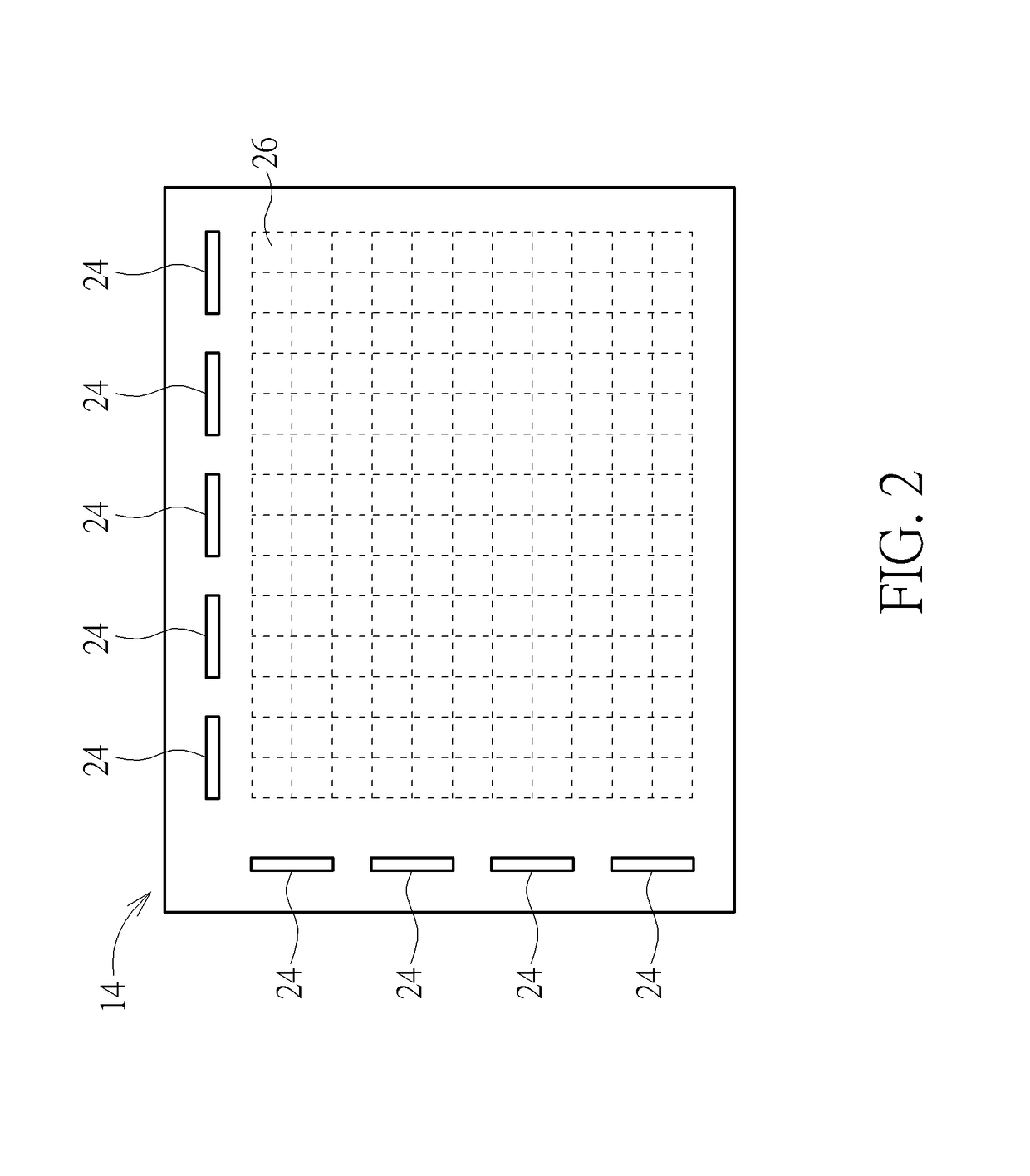
Molecular arrays and single molecule detection
InactiveUS20050244863A1Precision and richness of informationPrecision and richness of and speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical physicsMolecular array
Methods are provided for producing a molecular array comprising a plurality of molecules immobilized to a solid substrate at a density which allows individual immobilized molecules to be individually resolved, wherein each individual molecule in the array is spatially addressable and the identity of each molecule is known or determined prior to immobilisation. The use of spatially addressable low density molecular arrays in single molecule detection techniques is also provided.
Owner:KALIM MIR +2
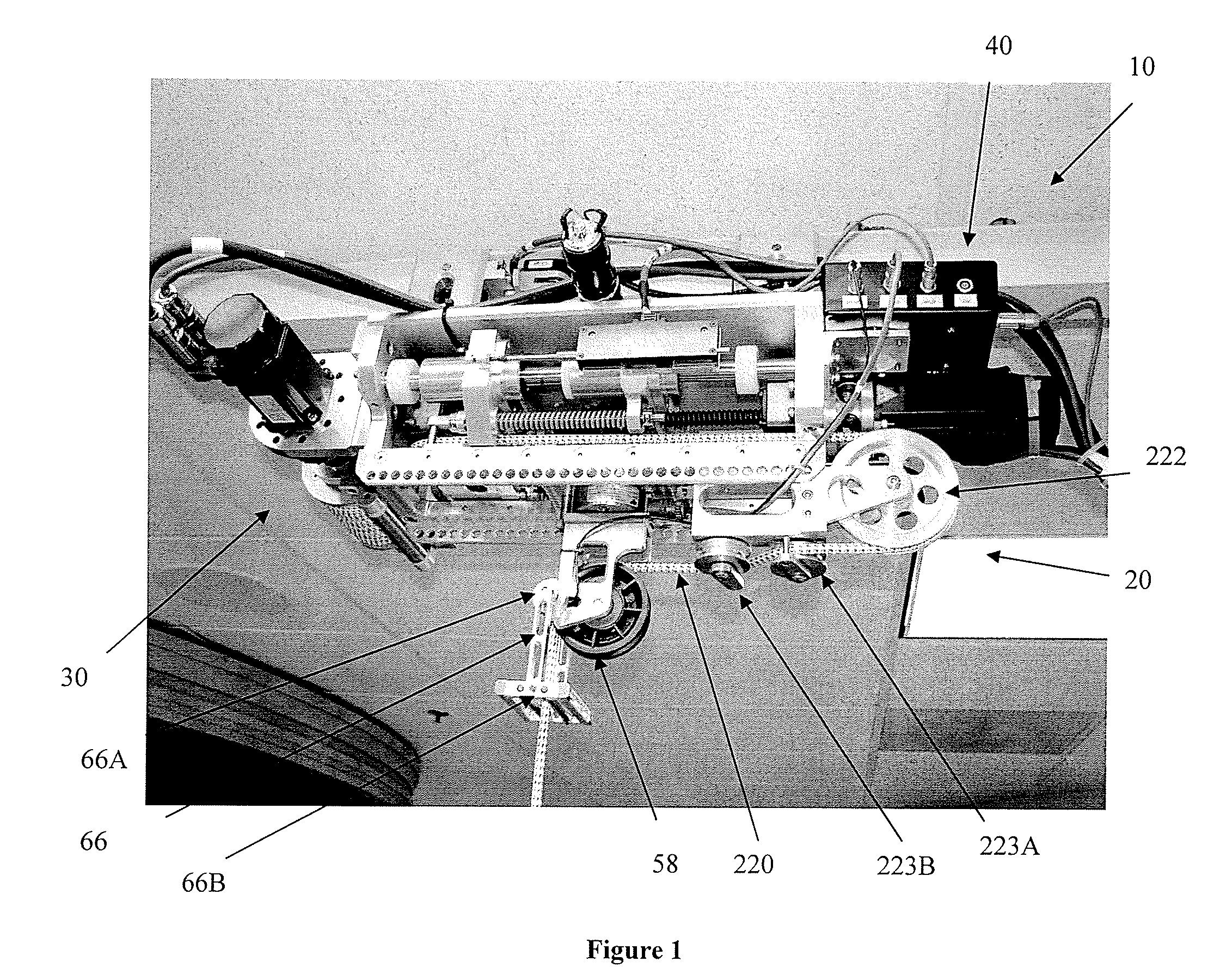
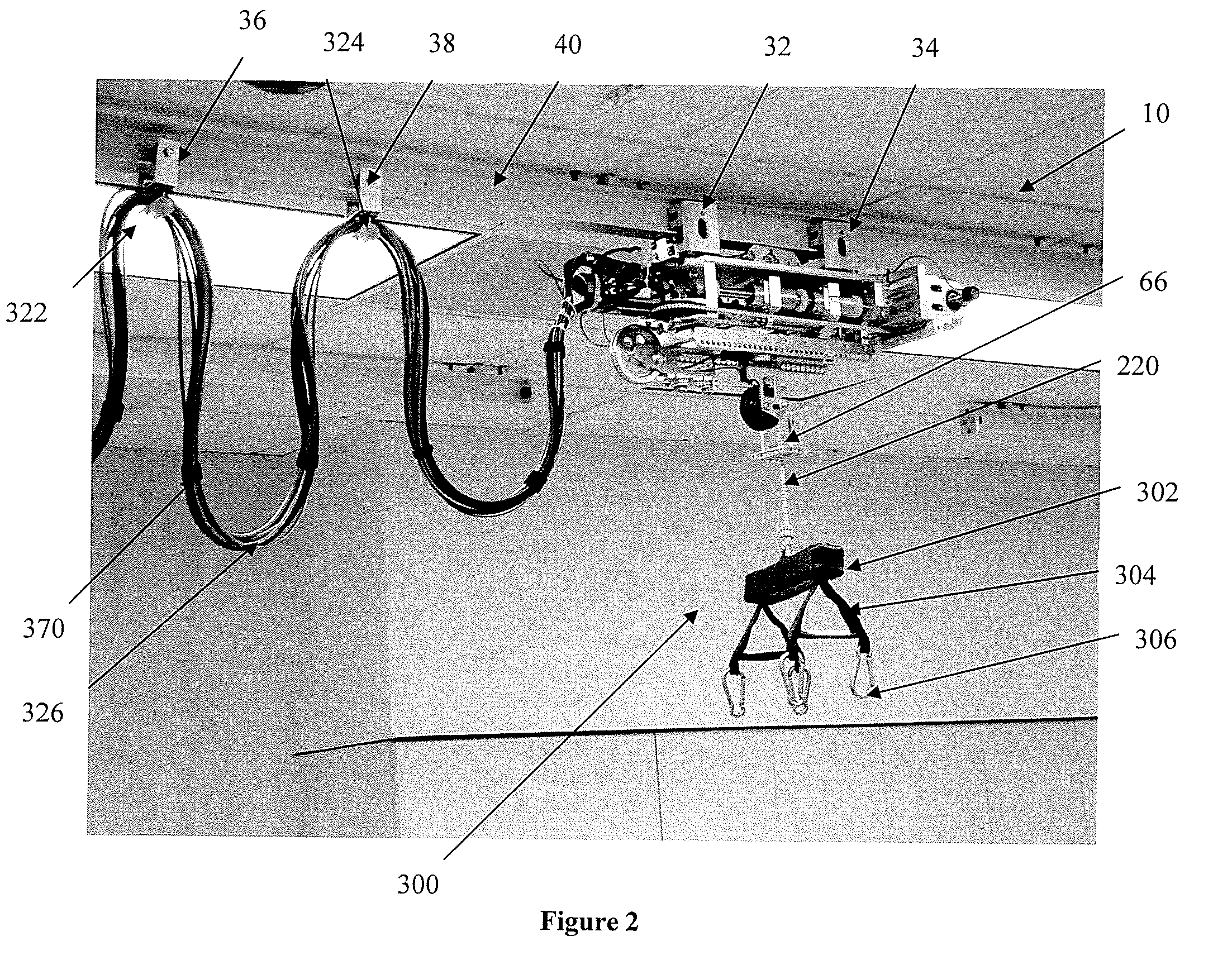
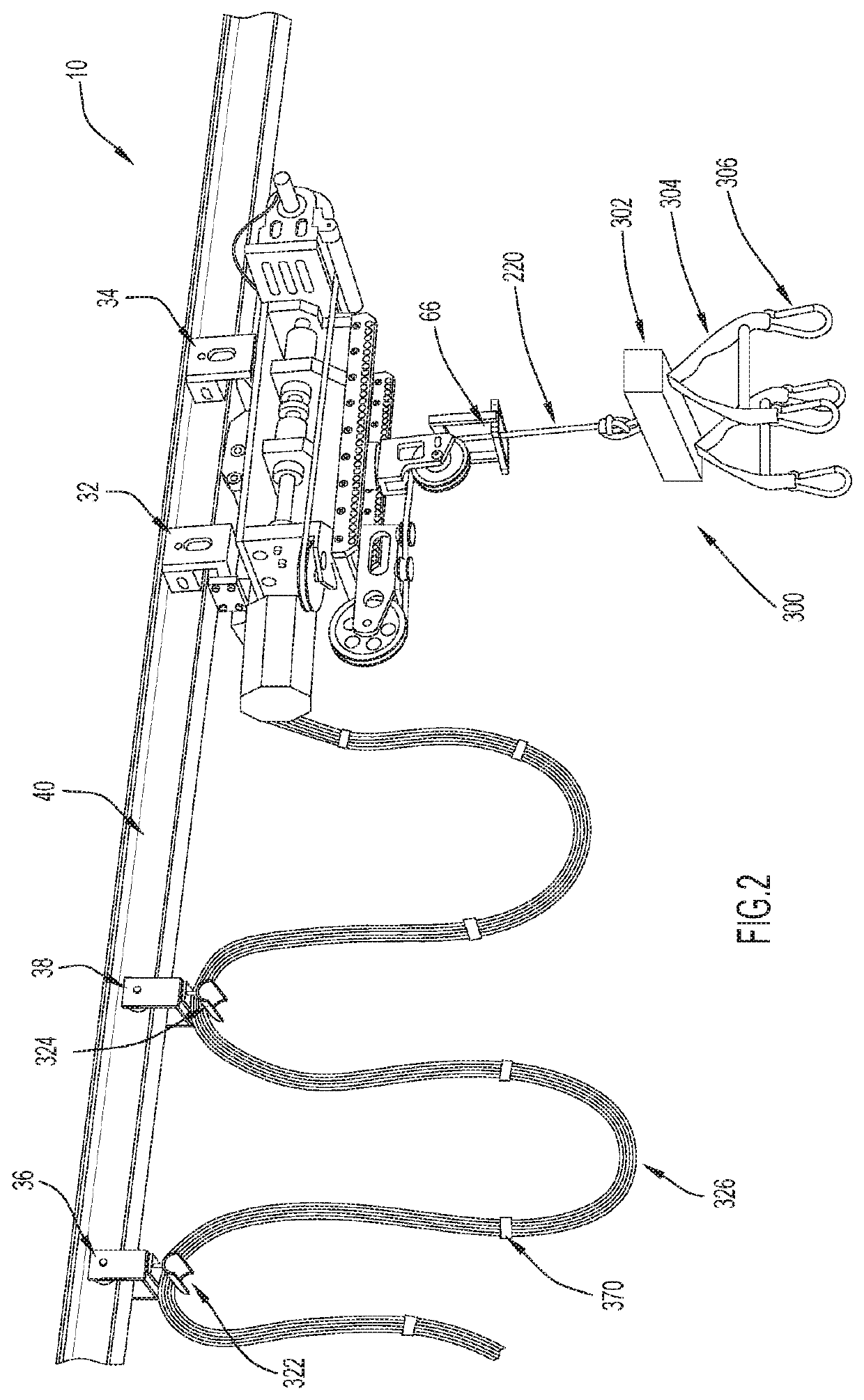
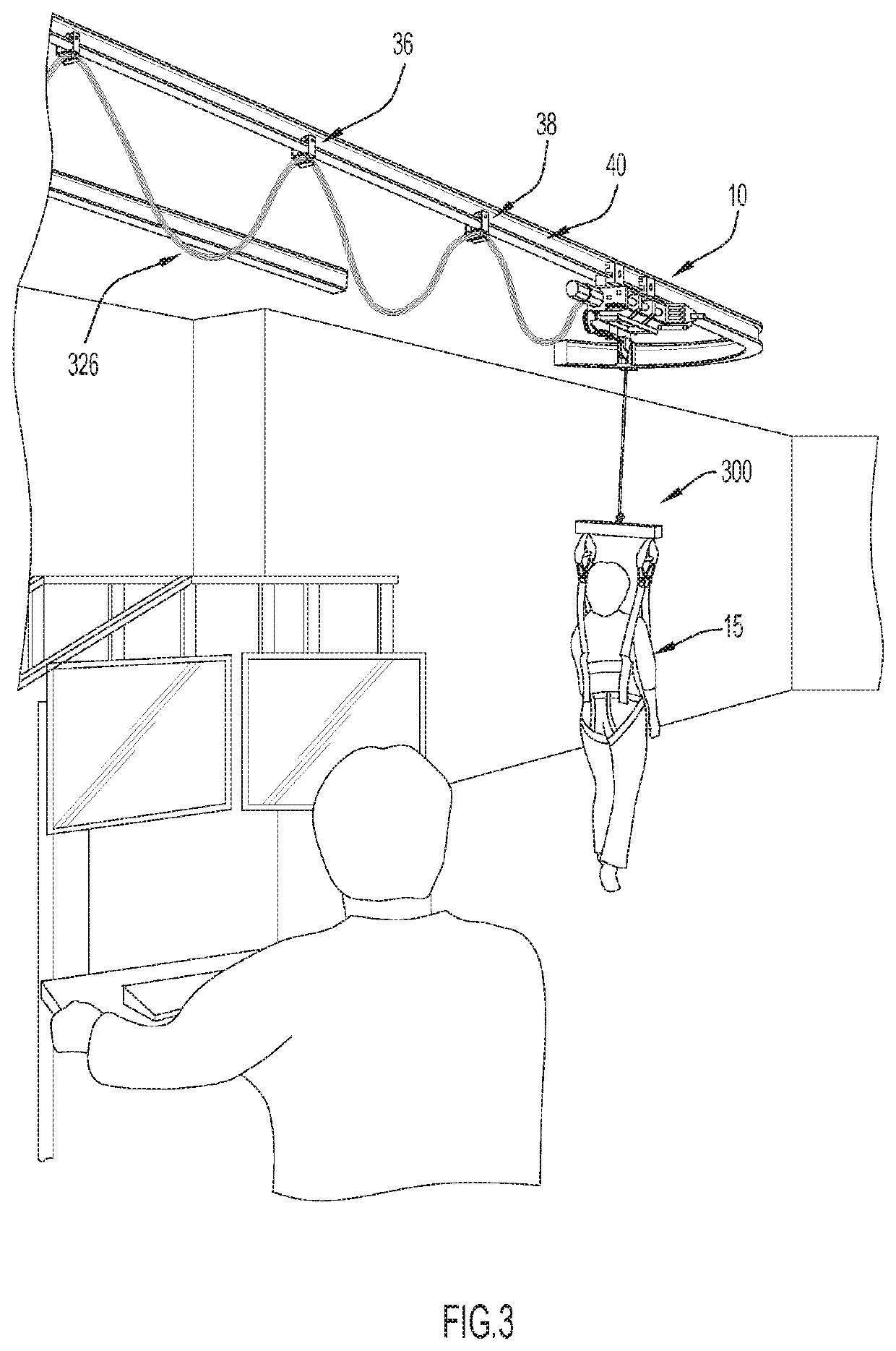
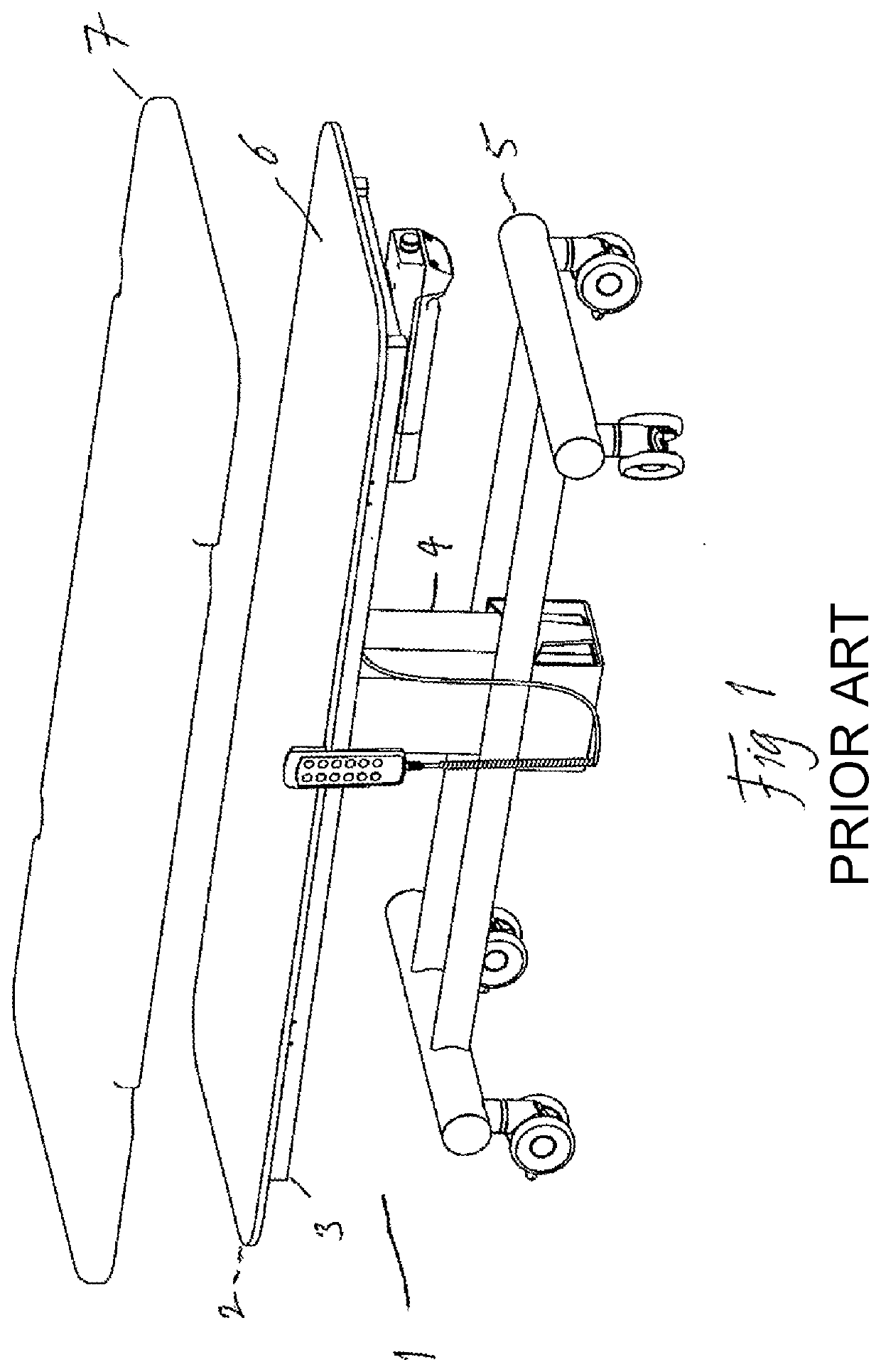
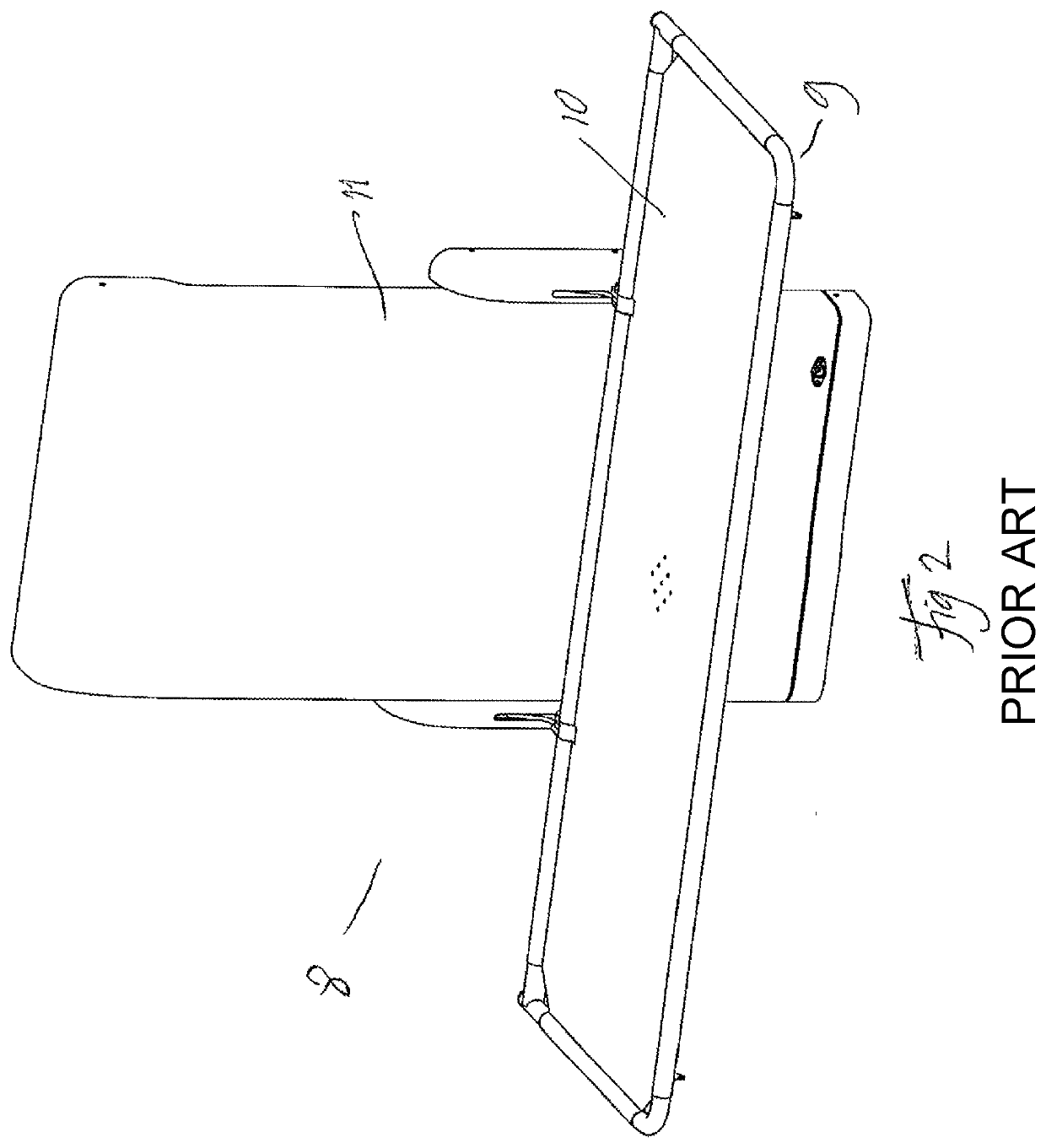
Body Weight Support System and Method of Using the Same
ActiveUS20080287268A1Practical limitationChiropractic devicesWalking aidsSupporting systemControl manner
A body-weight support system that allows individuals with severe gait impairments to practice over-ground walking in a safe, controlled manner is disclosed. The system includes a body-weight support system that rides along a driven trolley and can be controlled in response to the movement of the subject using the system.
Owner:HIDLER JOSEPH
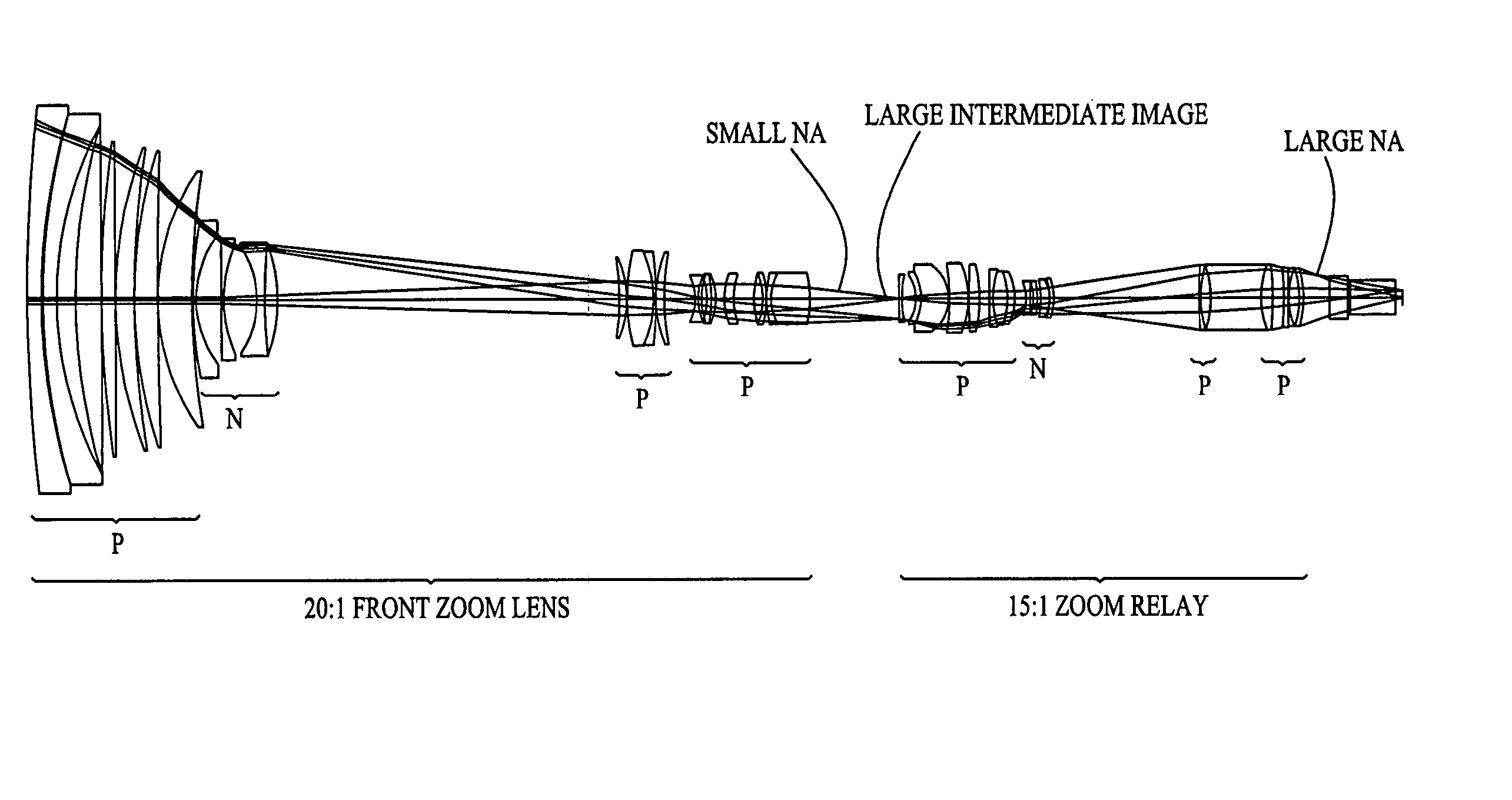
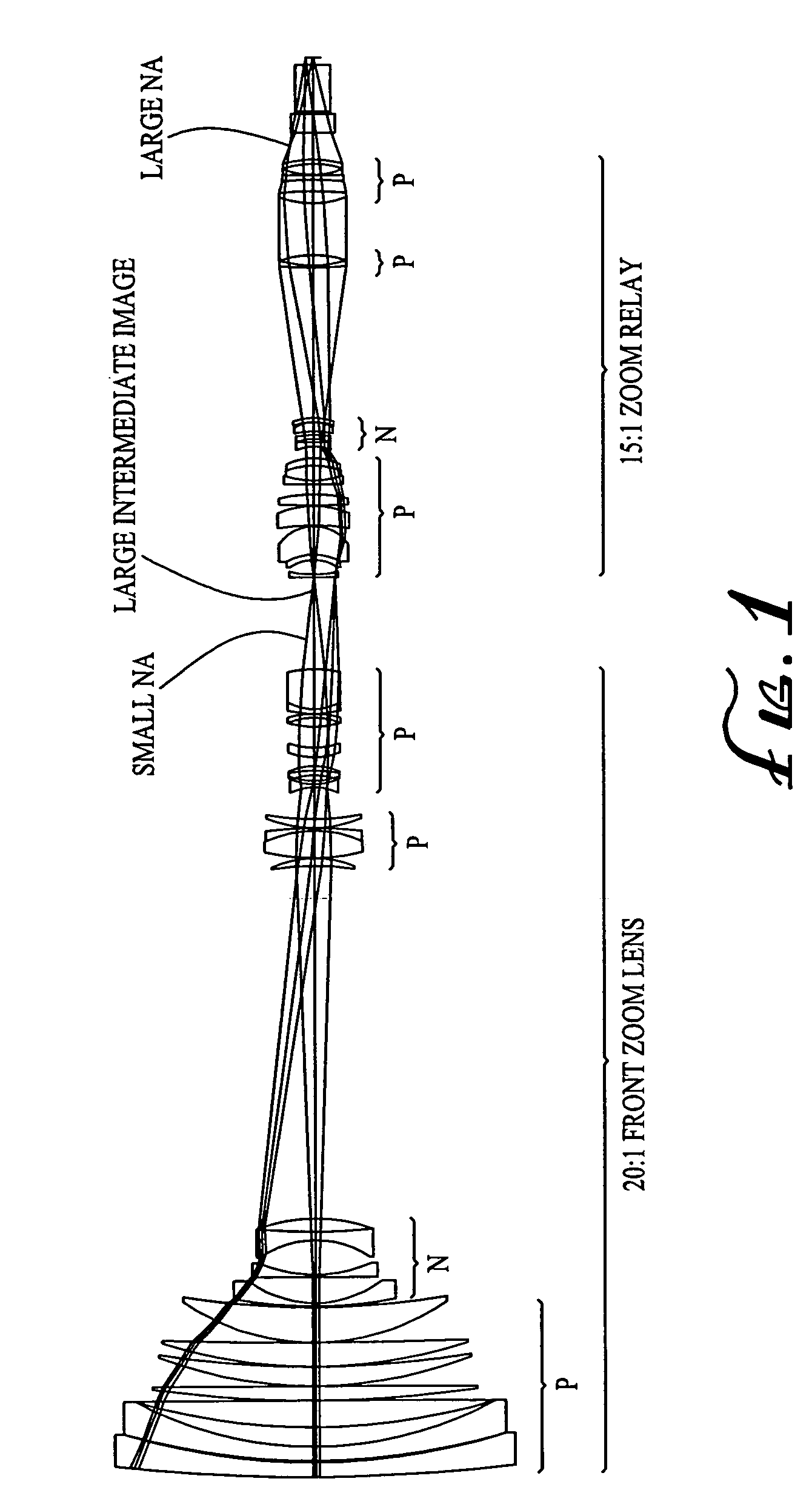
Zoom lens system
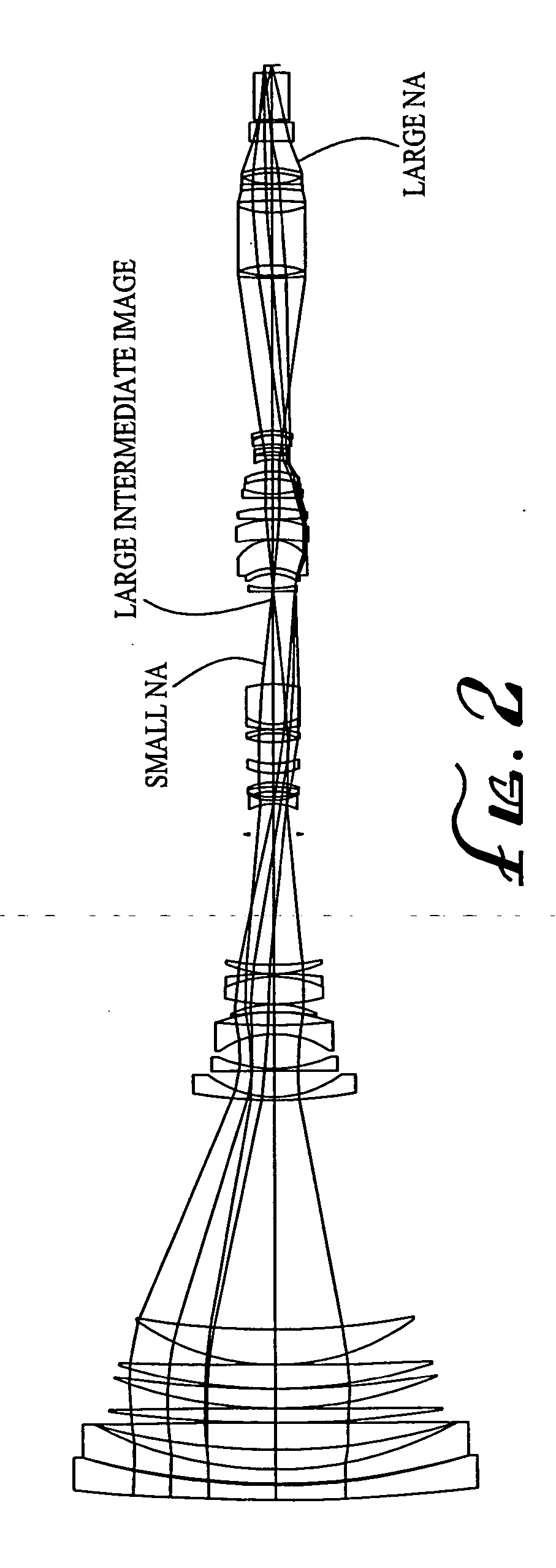
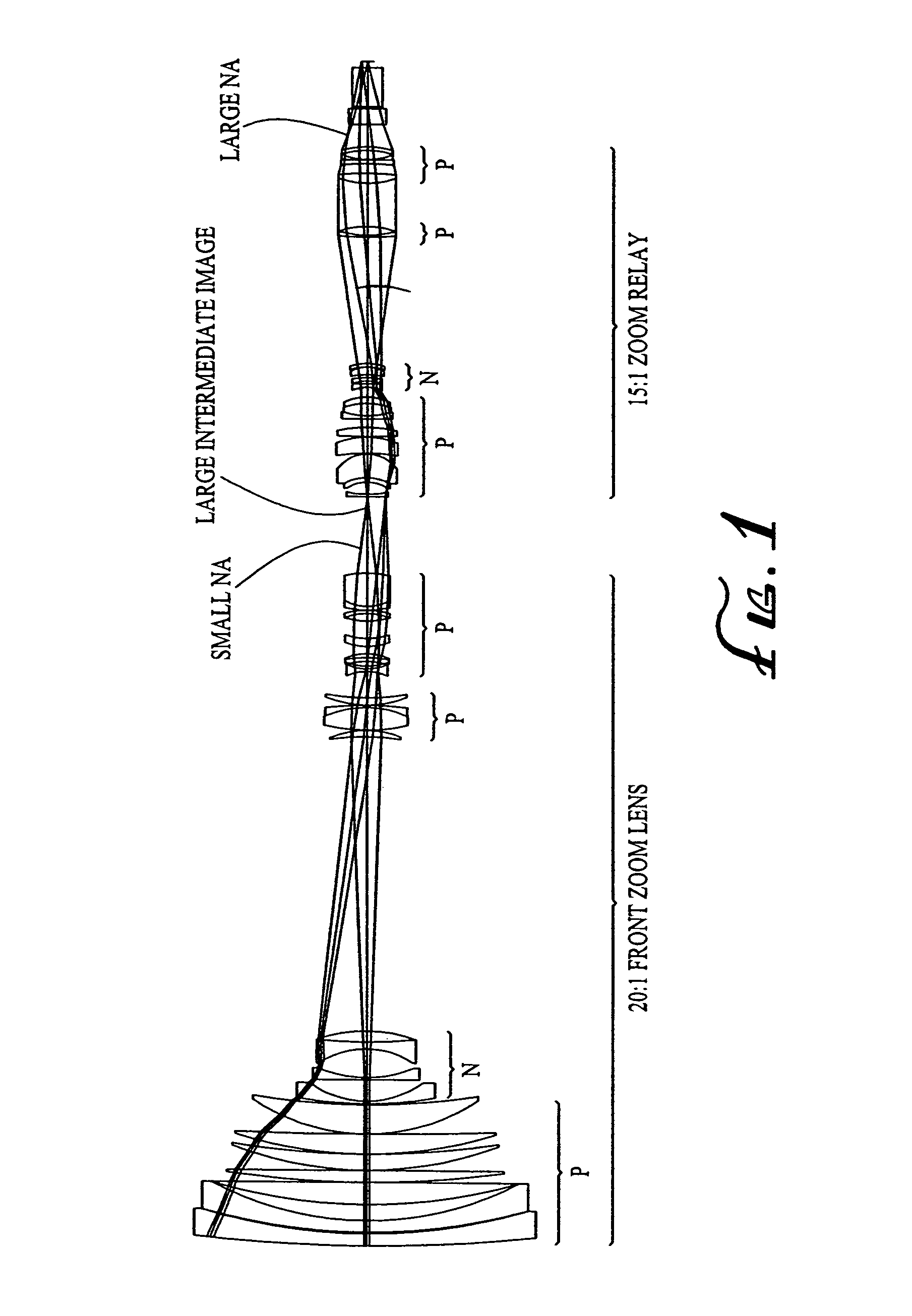
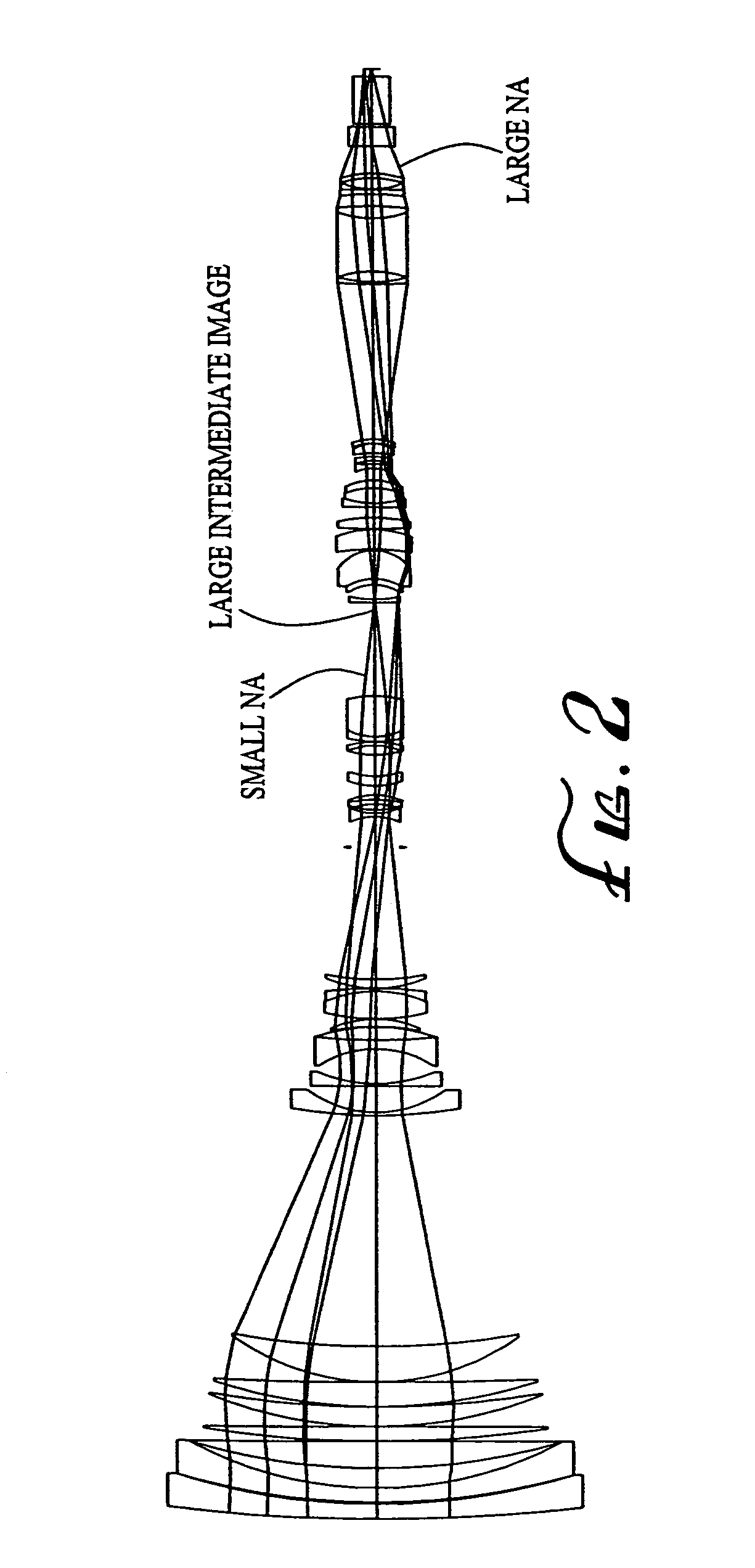
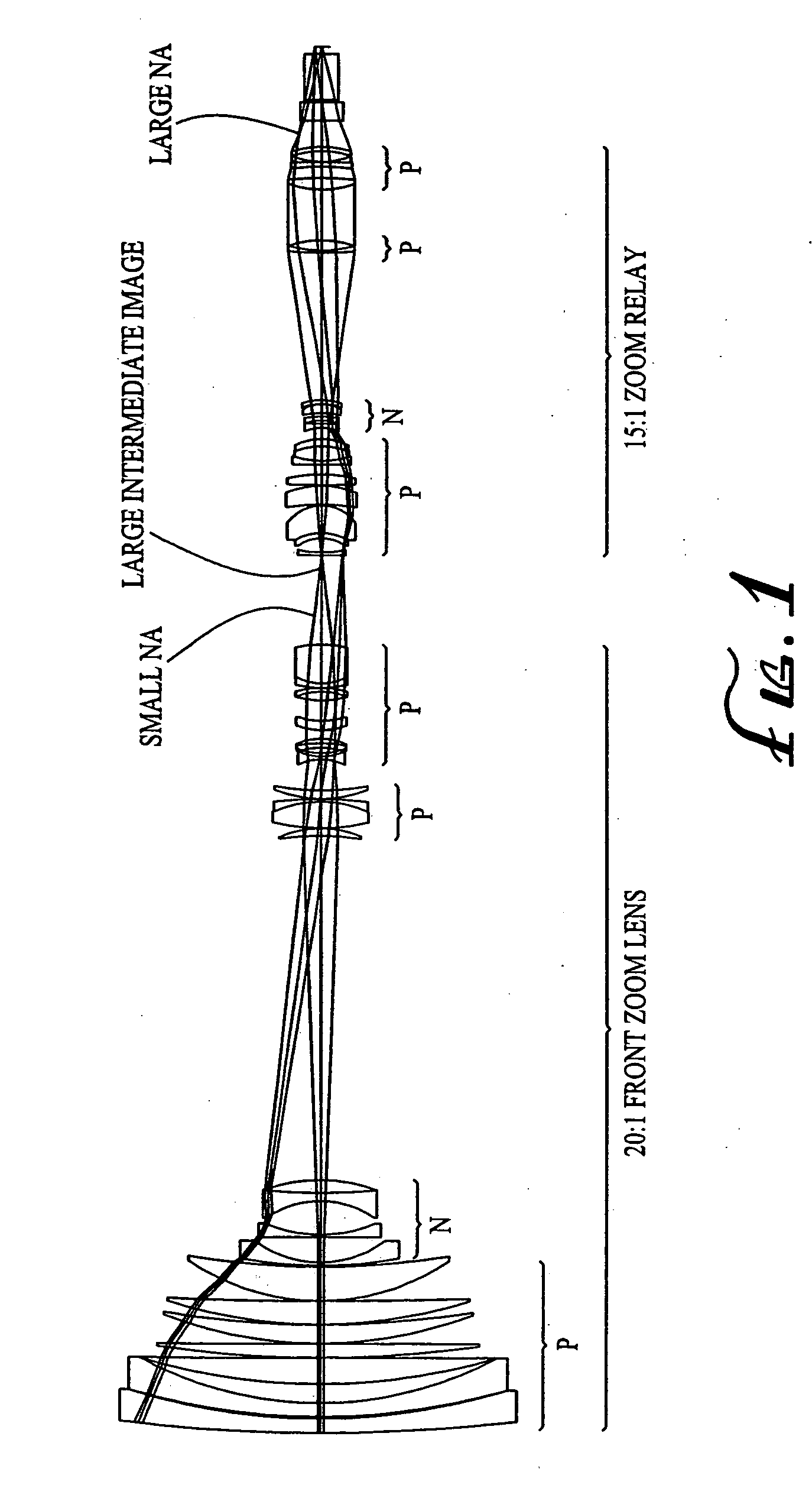
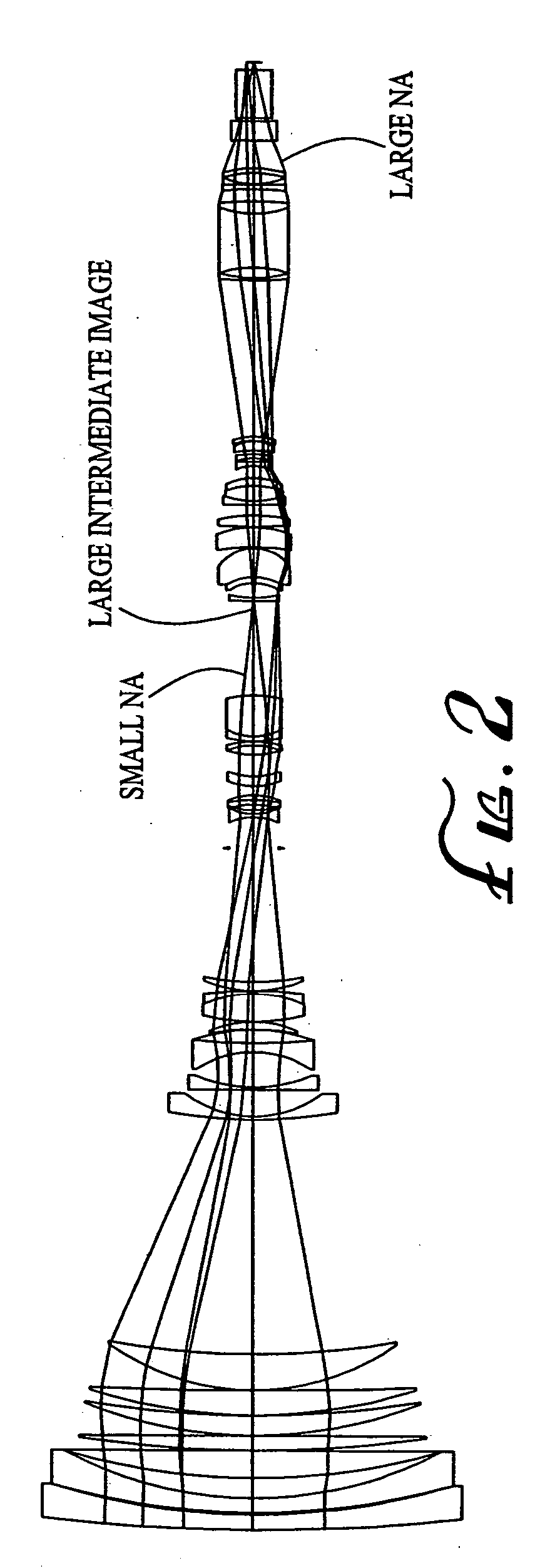
ActiveUS20040021953A1Practical limitationSimple designOptical elementsCamera lensImage stabilization
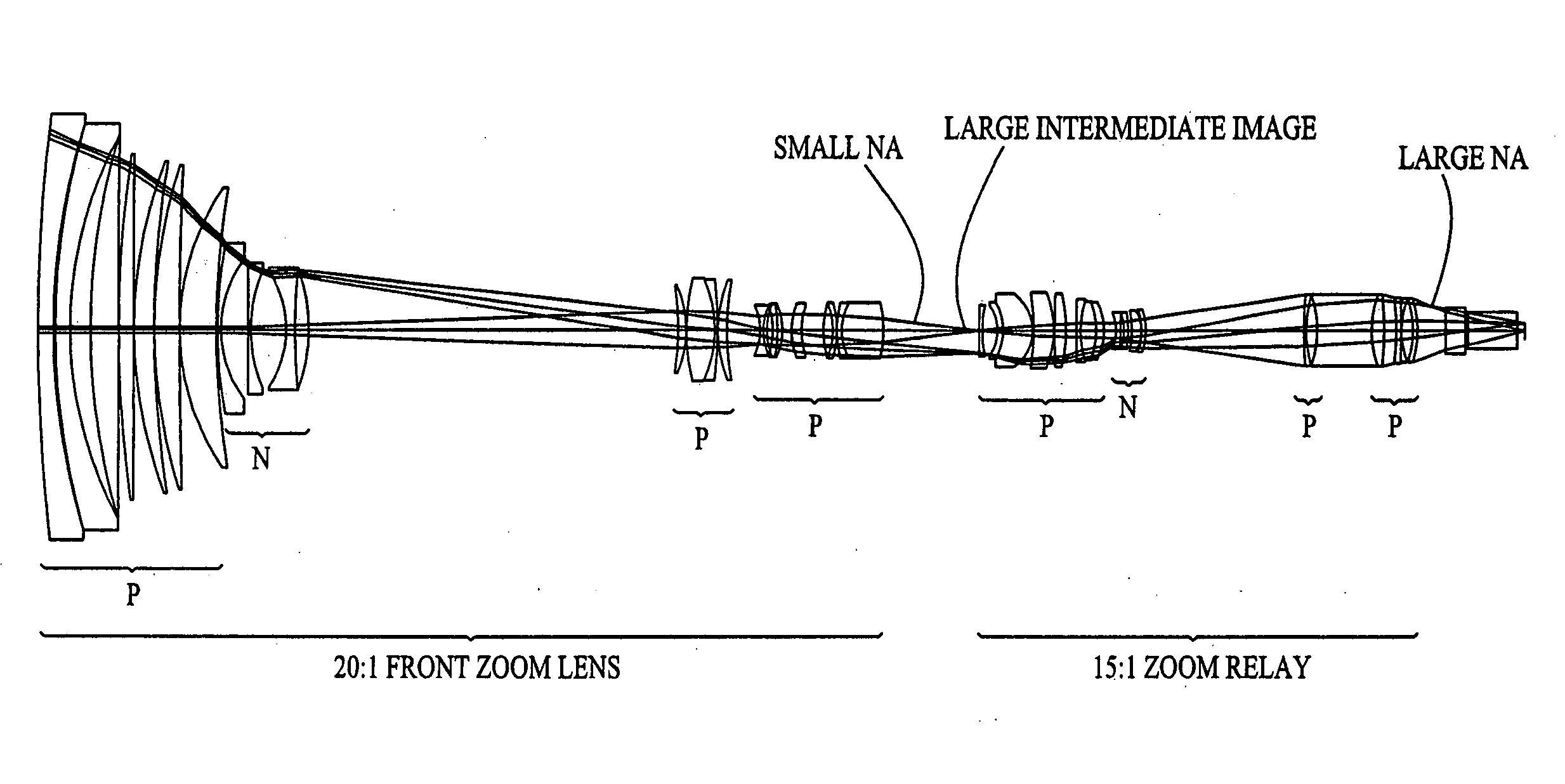
A zoom lens system is disclosed. The zoom lens system forms a final image of an object and a first intermediate real image between the object and the final image. The zoom lens system includes a first optical unit located between the object and the first intermediate real image. The first optical unit comprises at least one optical subunit which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the first intermediate real image. The zoom lens system also includes a second optical unit located between the first intermediate real image and the final image, at least a portion of which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the final image. The zoom lens system provides a wide zoom range of focal lengths with continuous zooming between the focal lengths and optional image stabilization.
Owner:COURTLAND CAPITAL MARKET SERVICES LLC +1
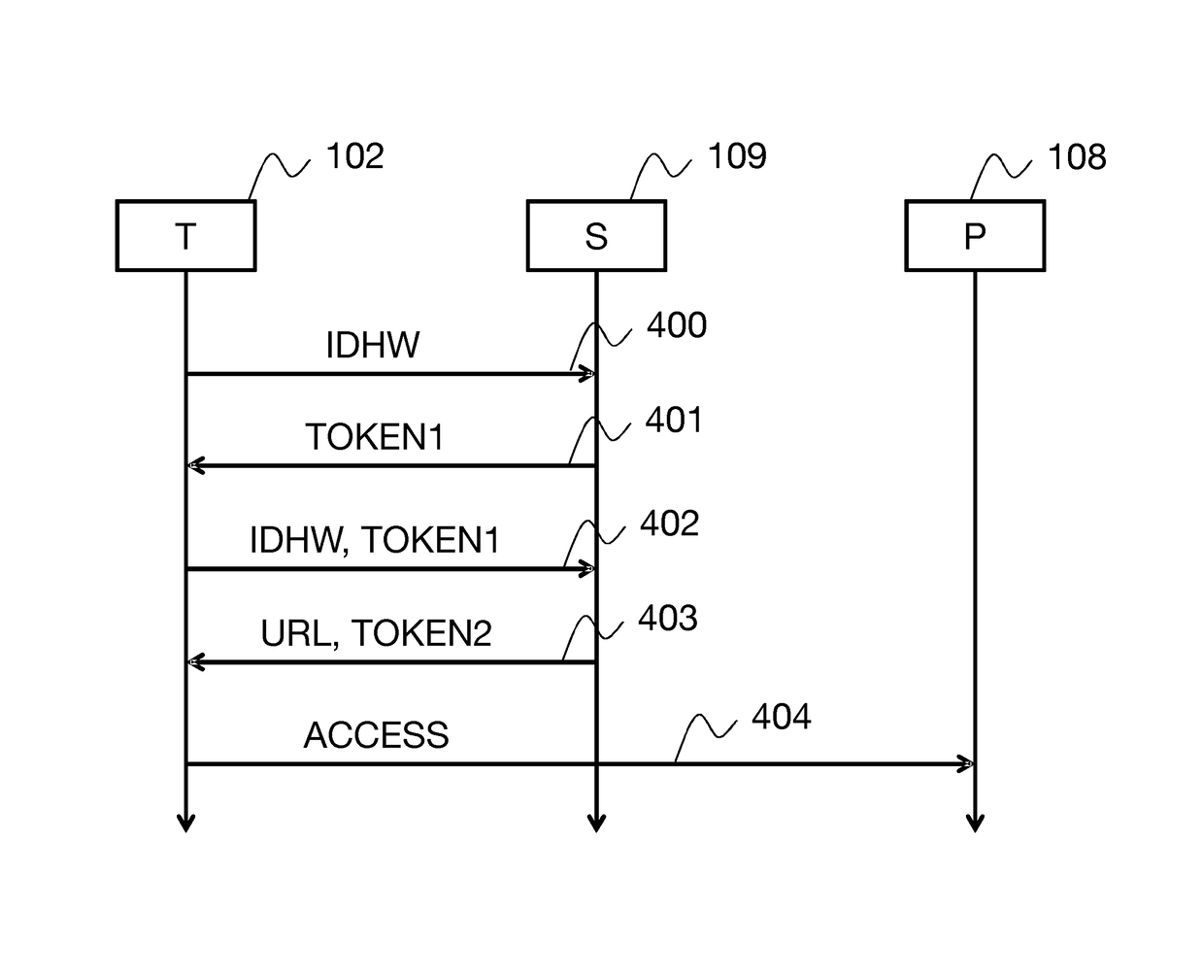
Method of Authentication by Token
ActiveUS20150172283A1Easy to useLimitation on frequencyDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUnique identifierAuthorization
A method is provided for authentication by token for accessing a service from a terminal. The method includes, on receipt of a service access authorization request including at least one unique identifier of the terminal, steps of determining a network access context of the terminal; checking validity of the service access rights, including at least checking an access right associated with the network access context of the terminal; and, if the access rights are valid, generating a valid authentication token on the basis of the unique identifier of the terminal and the network access context, and transmitting the token to the terminal.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Zoom lens system
InactiveUS20050259330A1High performance featuresAccurate focusTelescopesOptical elementsMagnificationComputer science
Owner:COURTLAND CAPITAL MARKET SERVICES LLC +1
Zoom lens system
A zoom lens system is disclosed. The zoom lens system forms a final image of an object and a first intermediate real image between the object and the final image. The zoom lens system includes a first optical unit located between the object and the first intermediate real image. The first optical unit comprises at least one optical subunit which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the first intermediate real image. The zoom lens system also includes a second optical unit located between the first intermediate real image and the final image, at least a portion of which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the final image. The zoom lens system provides a wide zoom range of focal lengths with continuous zooming between the focal lengths.
Owner:COURTLAND CAPITAL MARKET SERVICES LLC +1
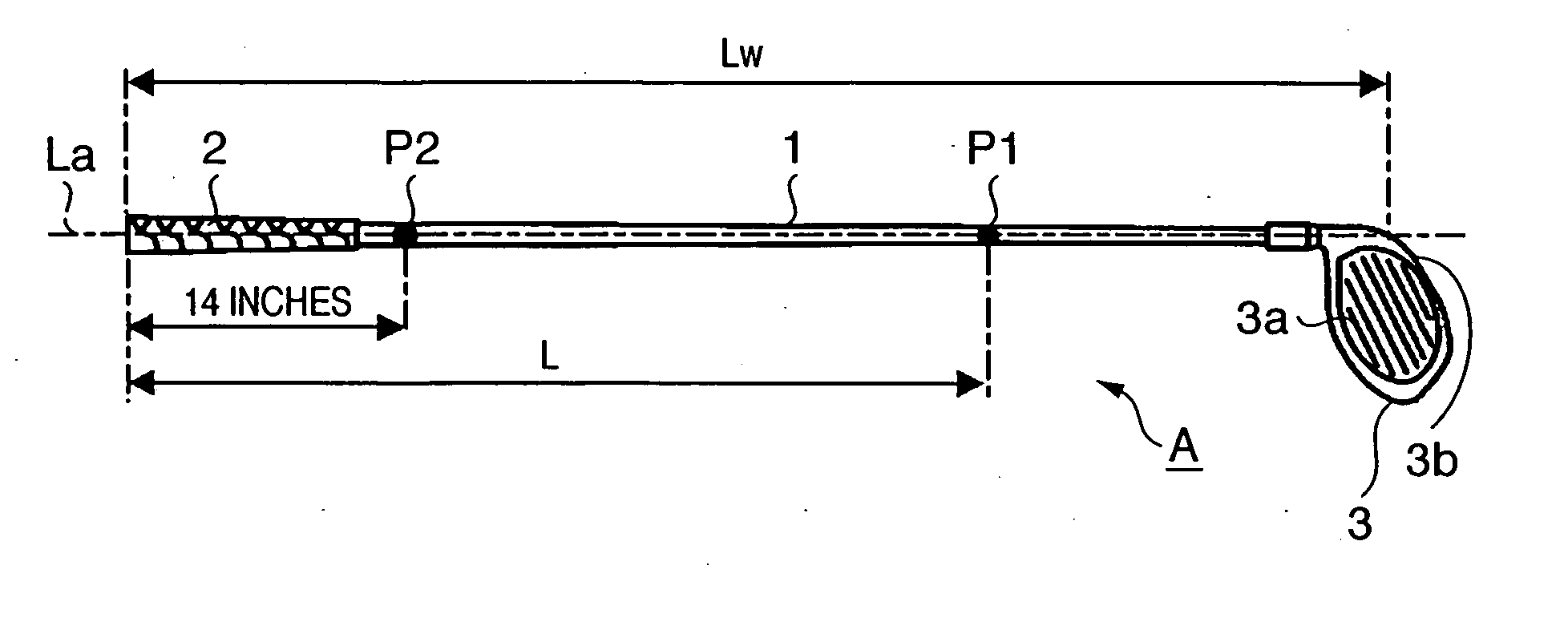
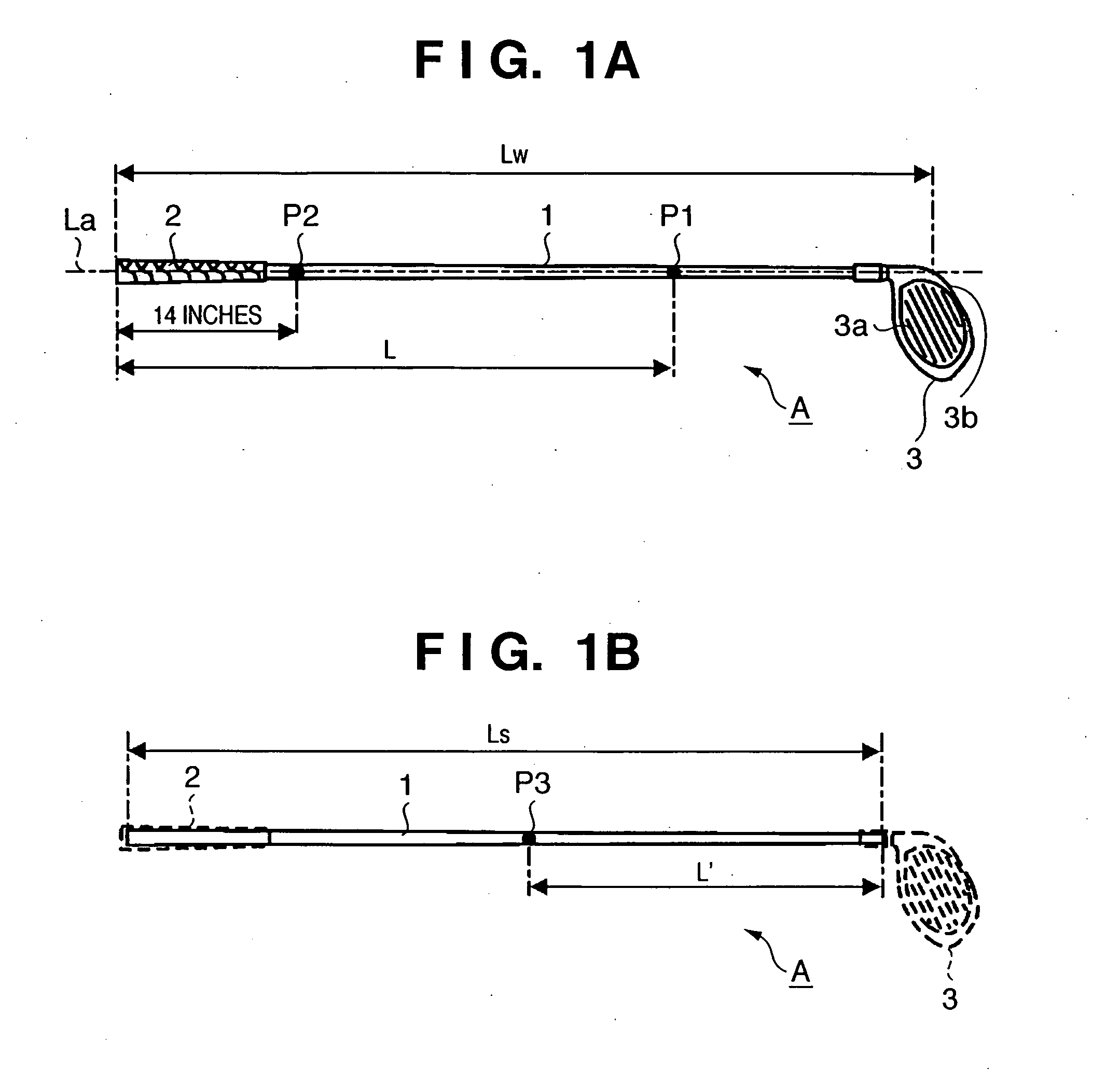
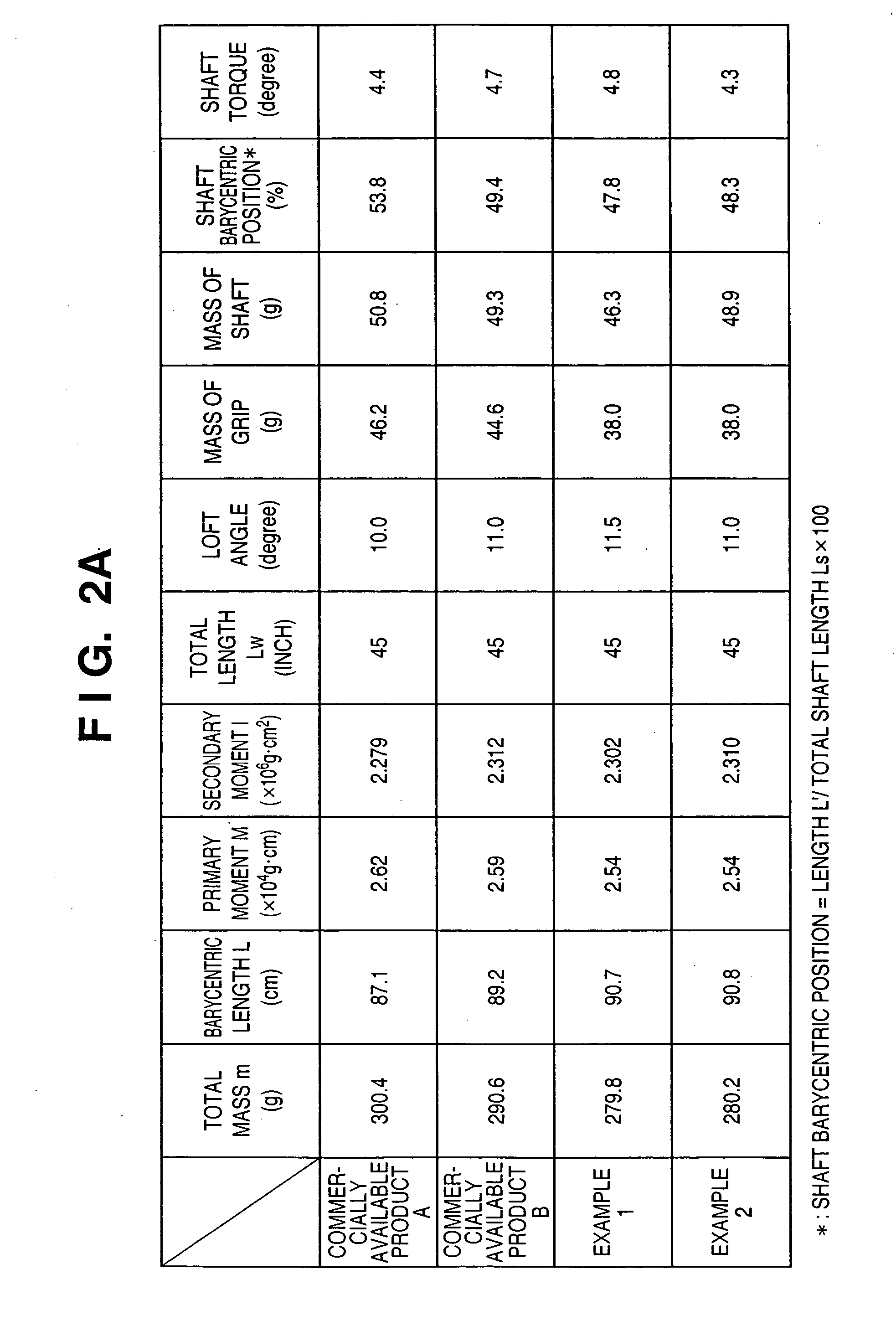
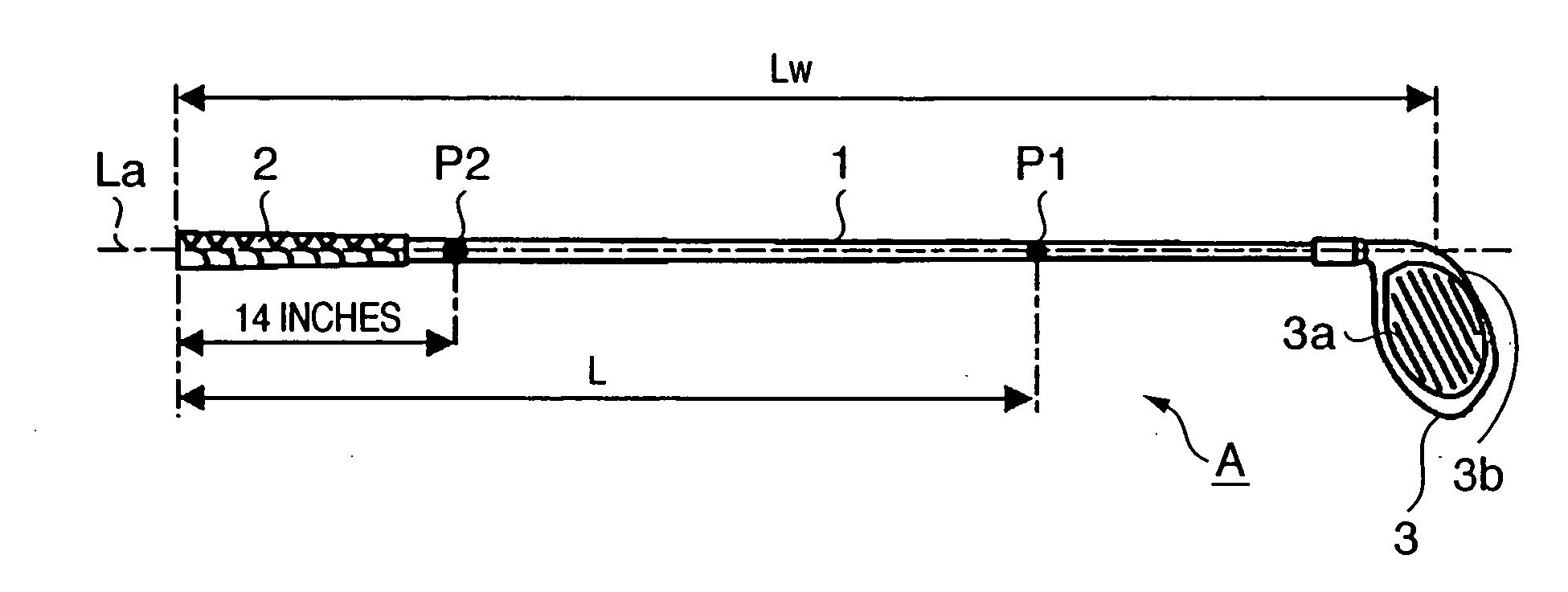
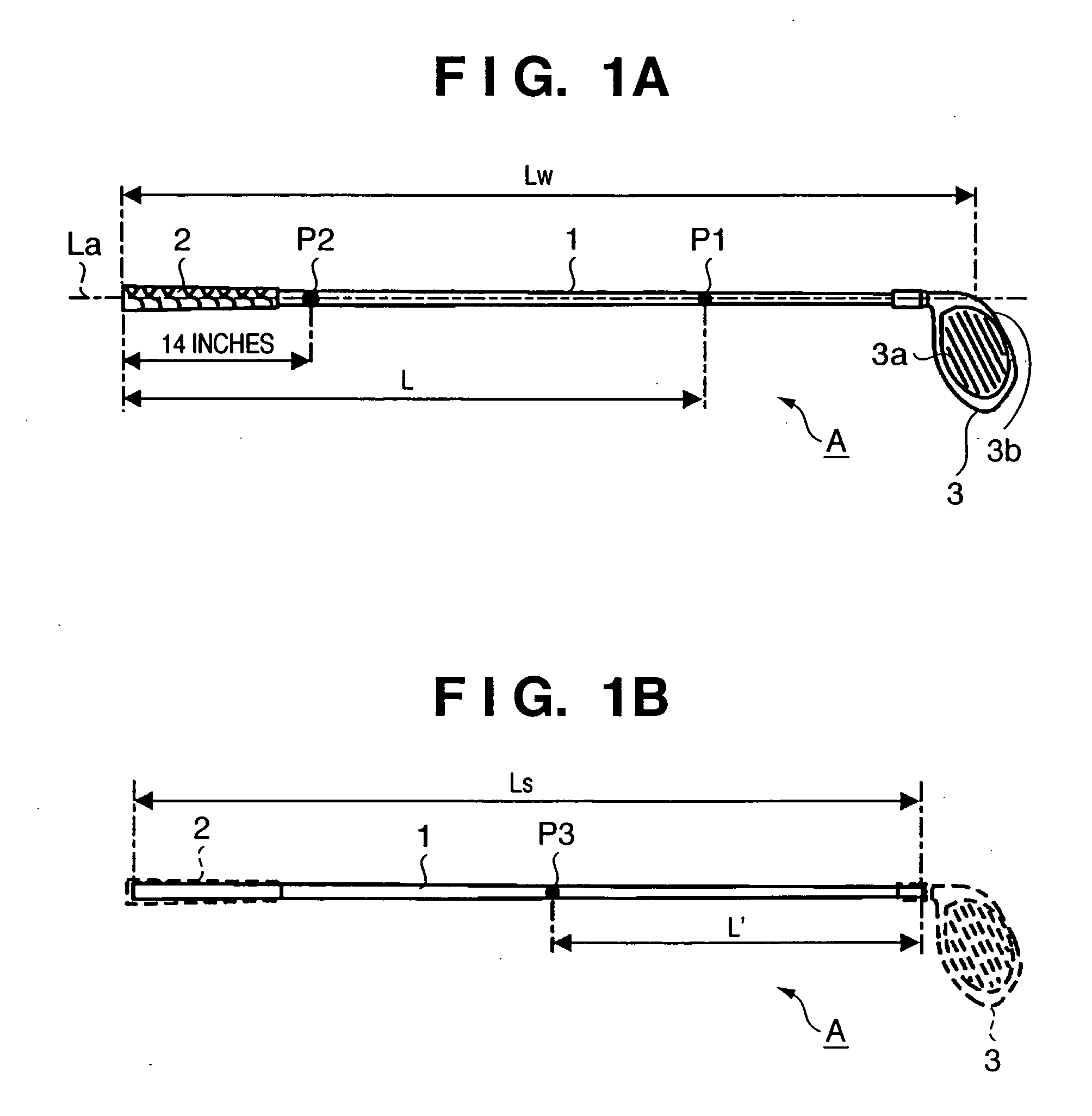
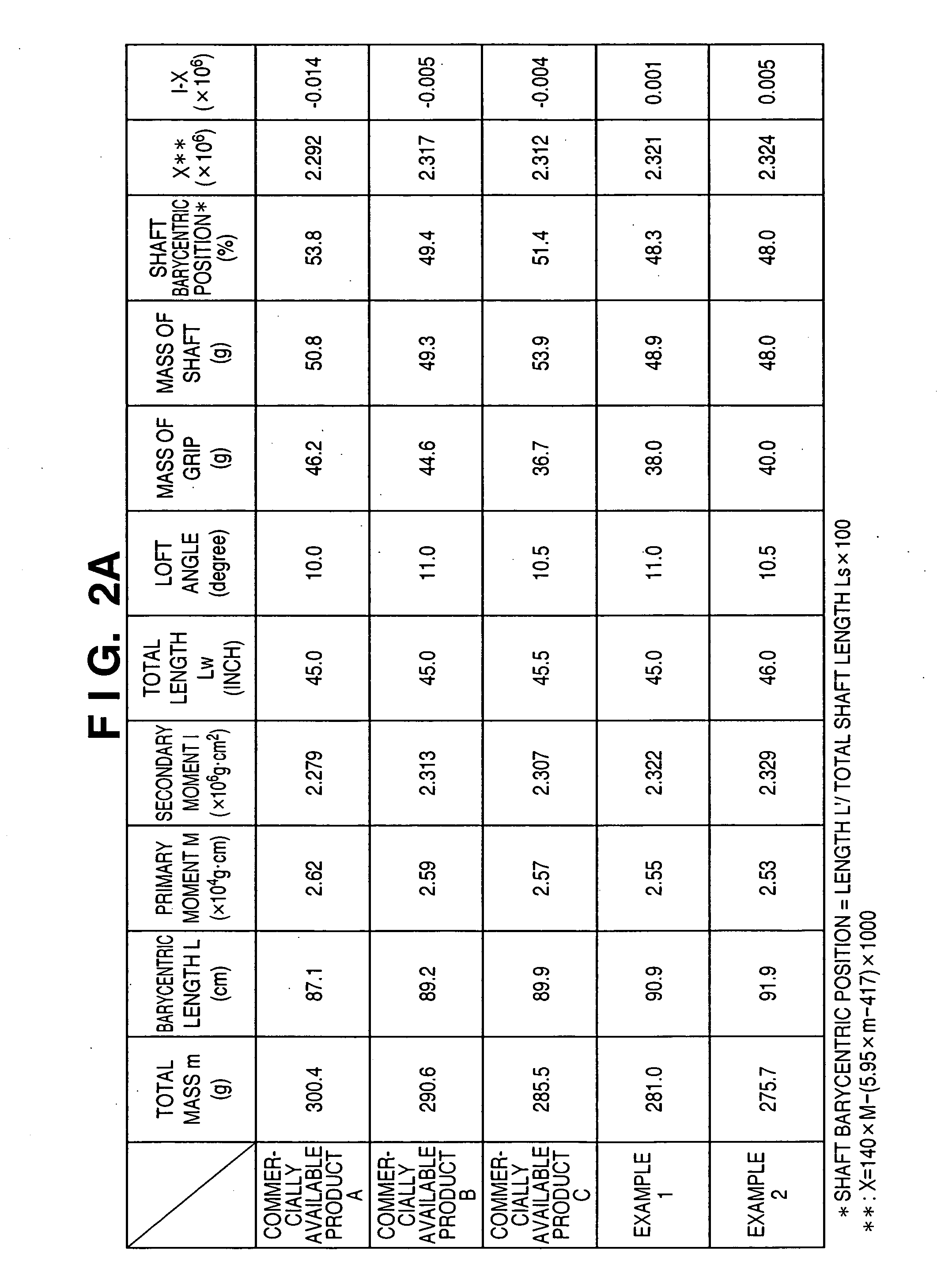
Golf club
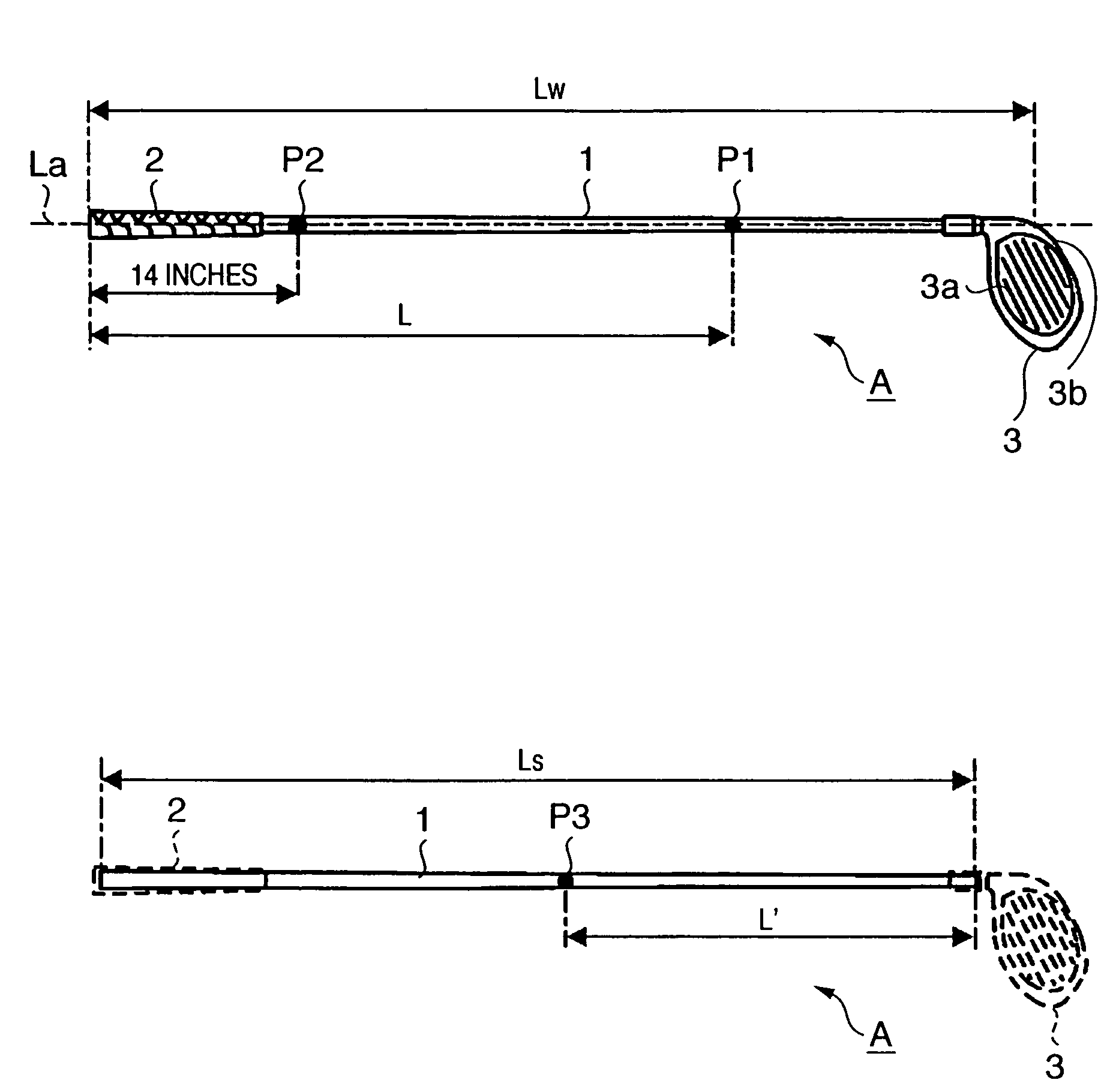
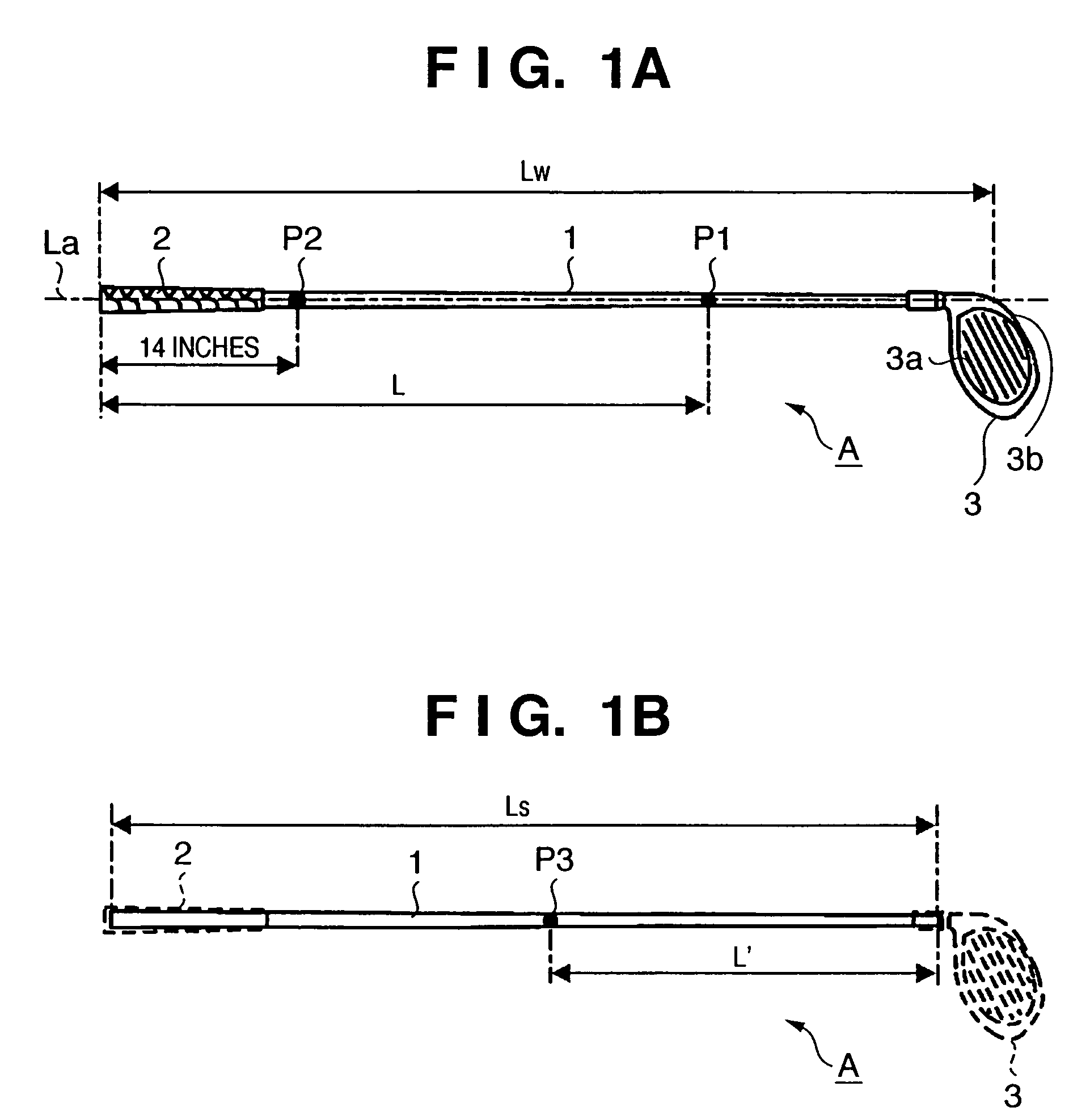
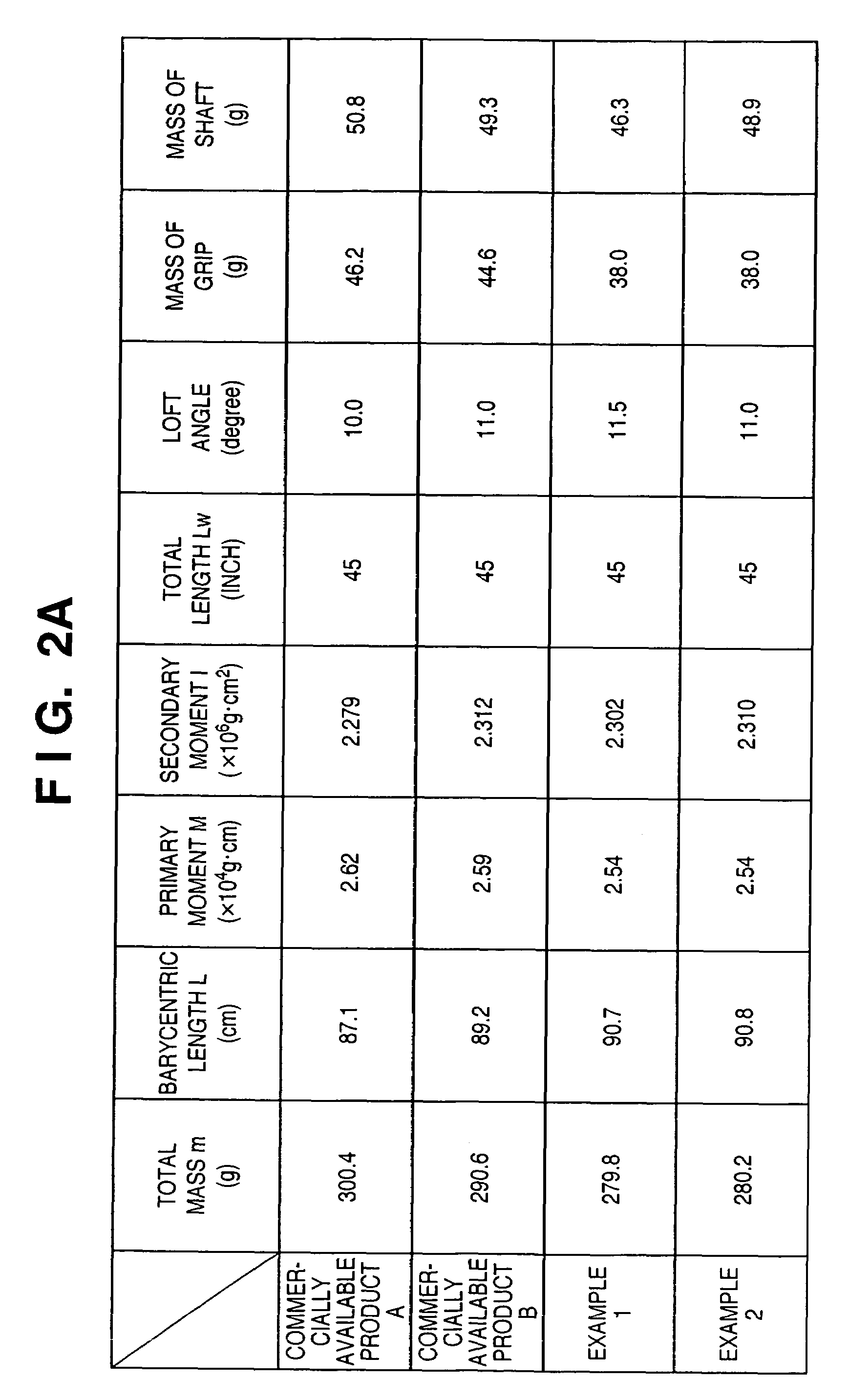
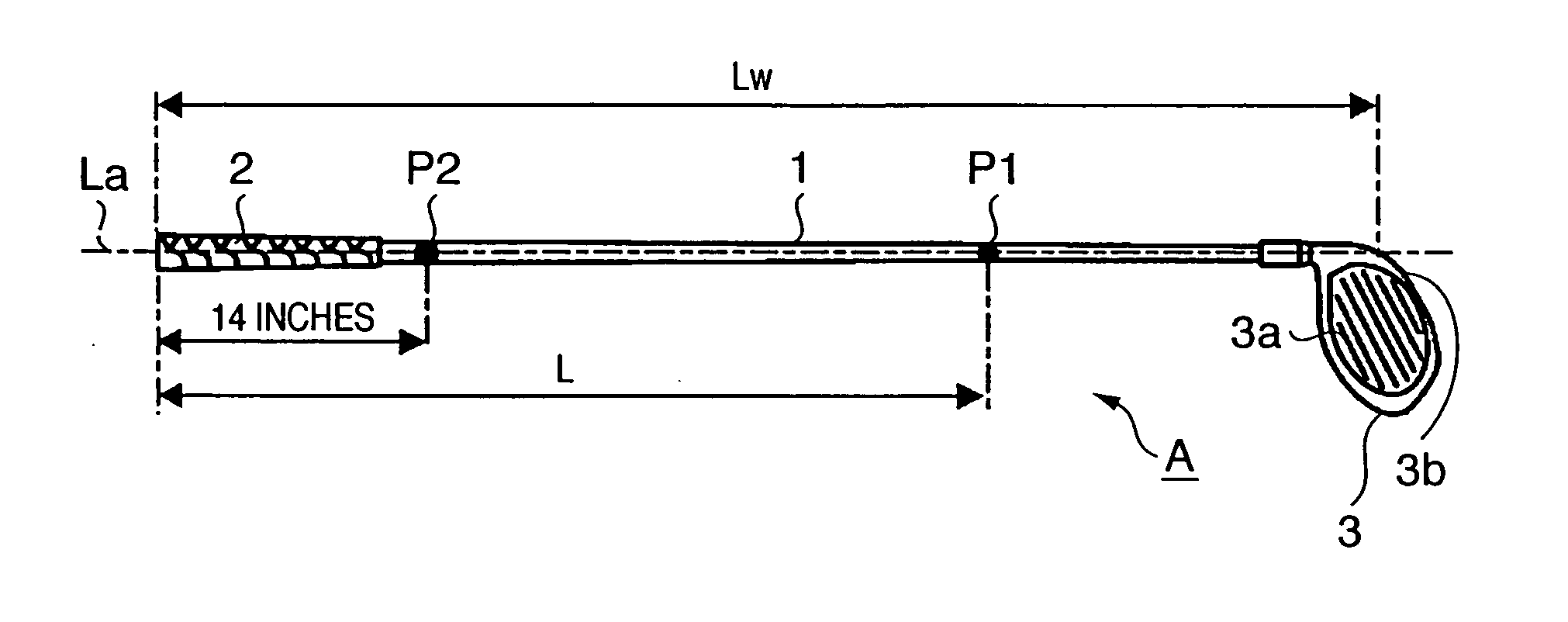
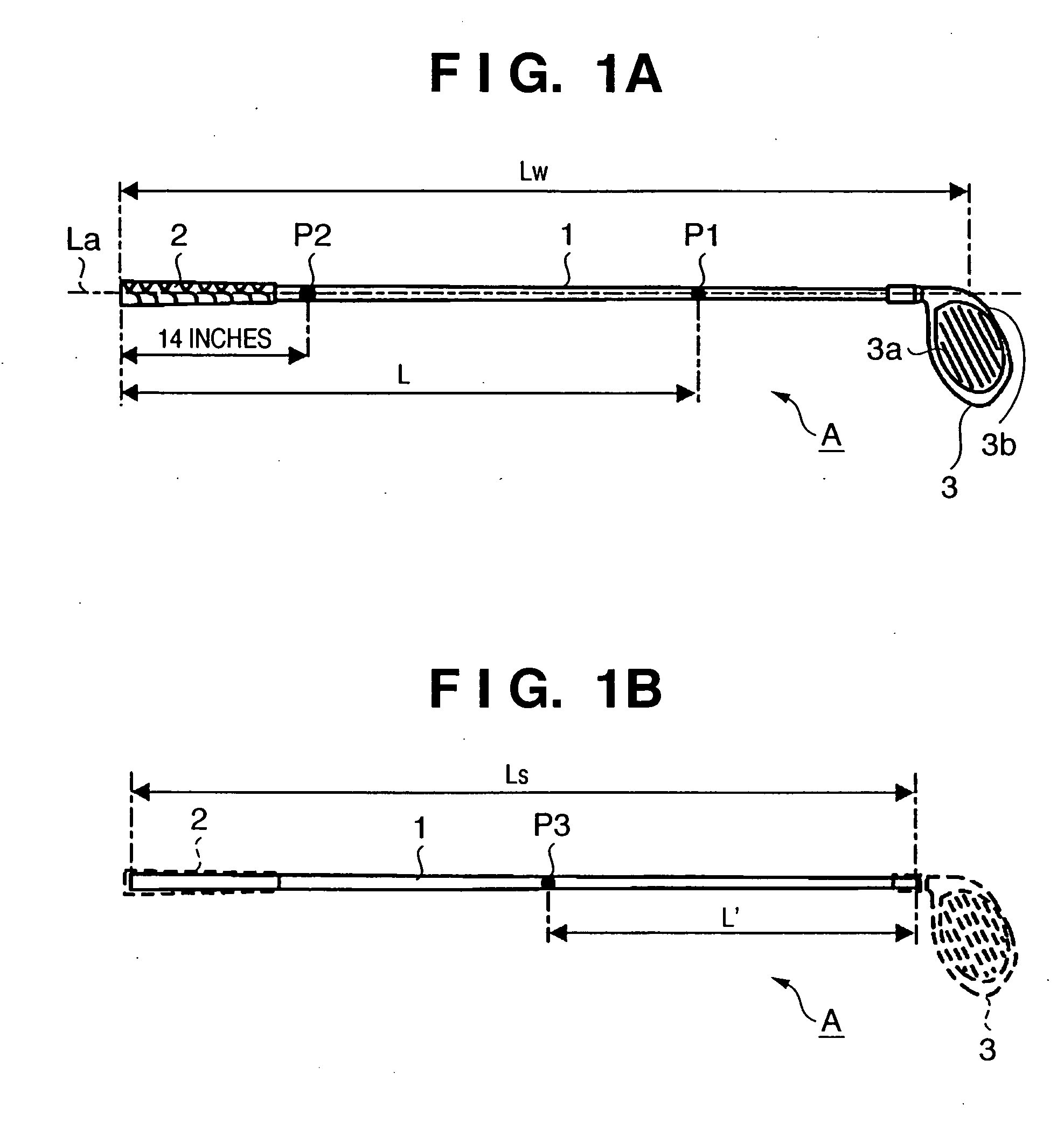
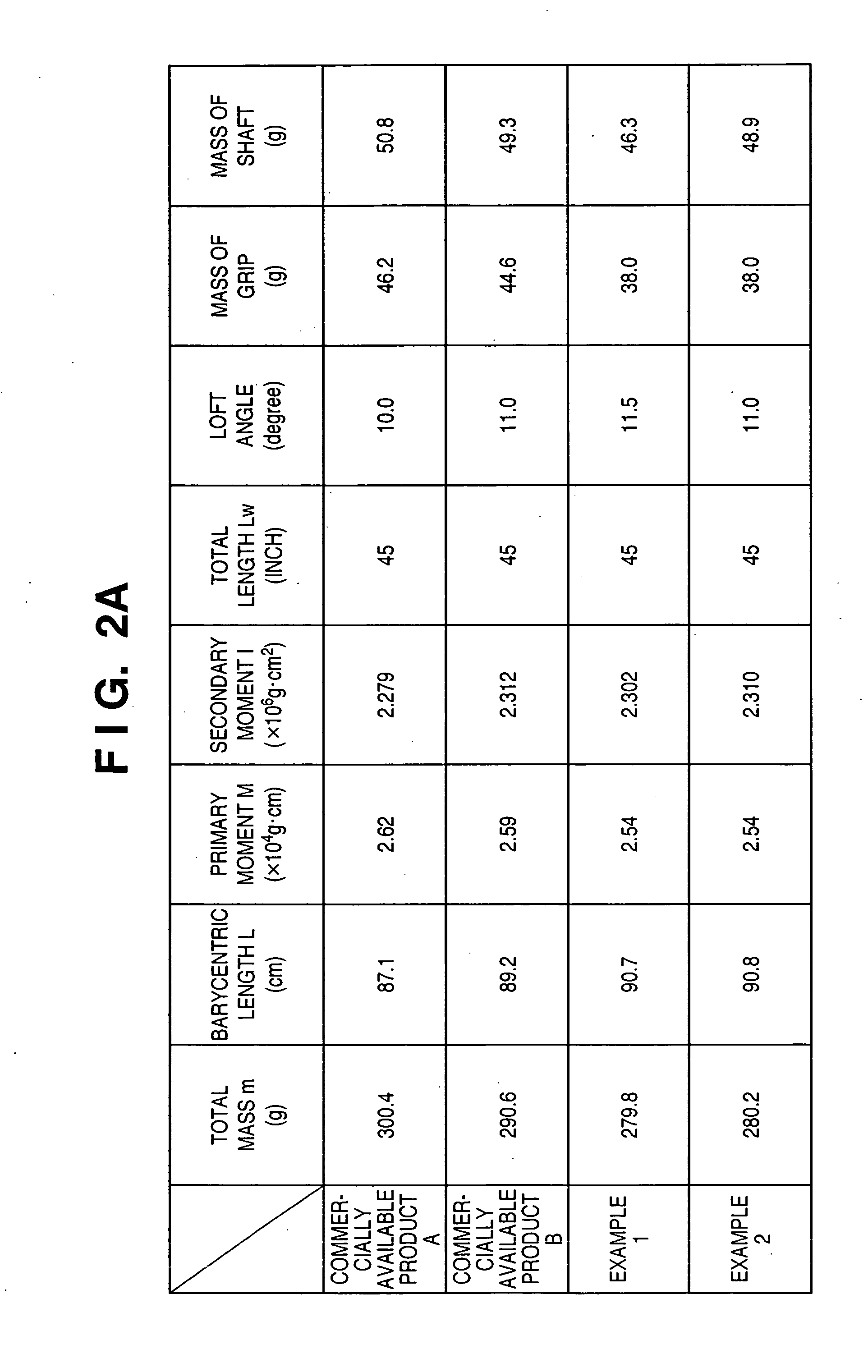
InactiveUS7416495B2Extended driving distanceImprove impactGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
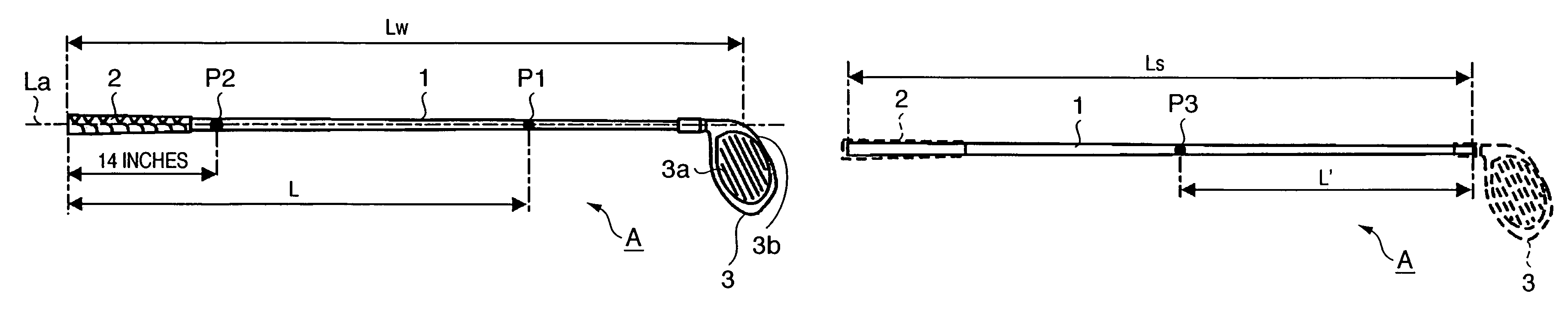
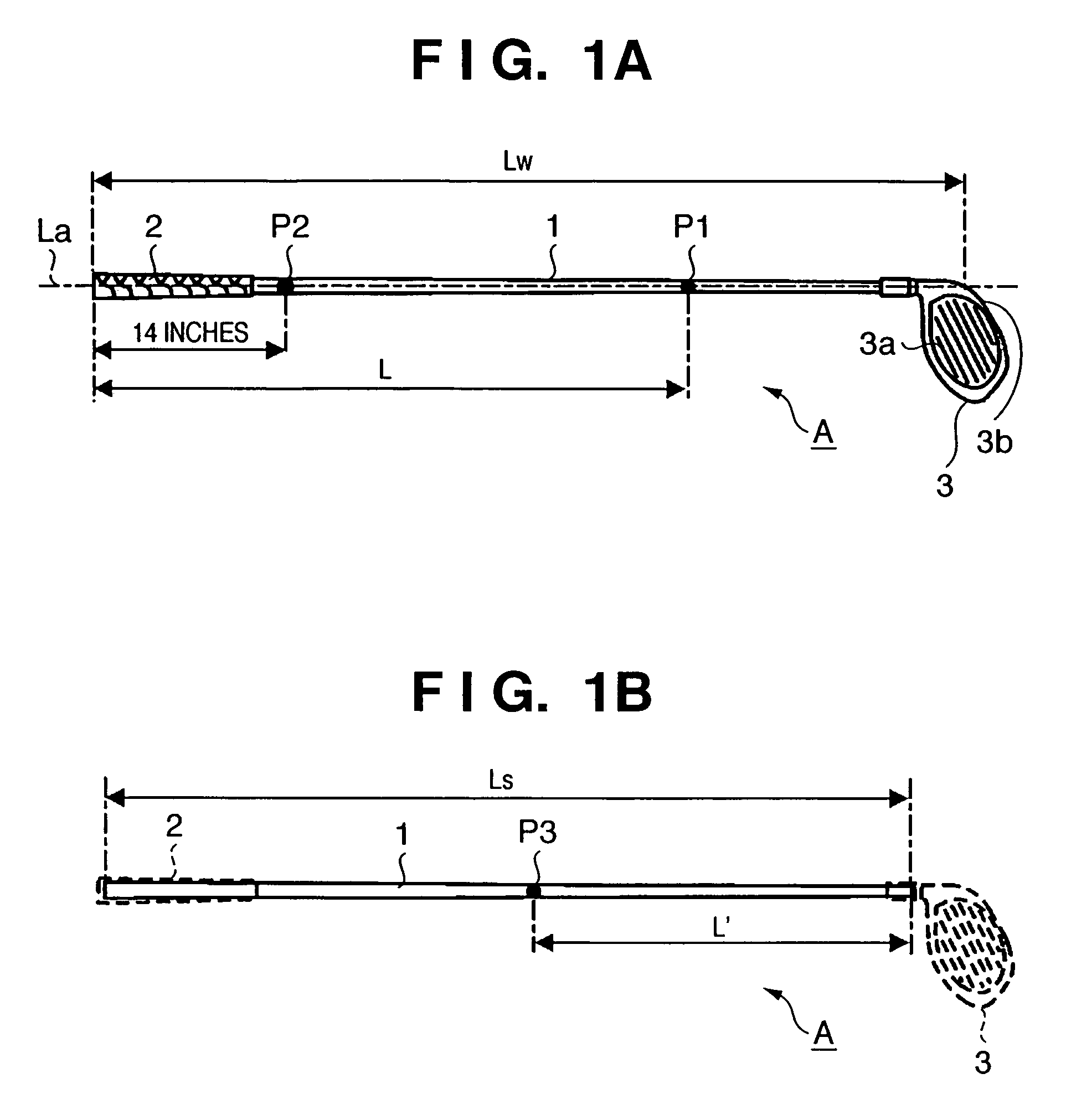
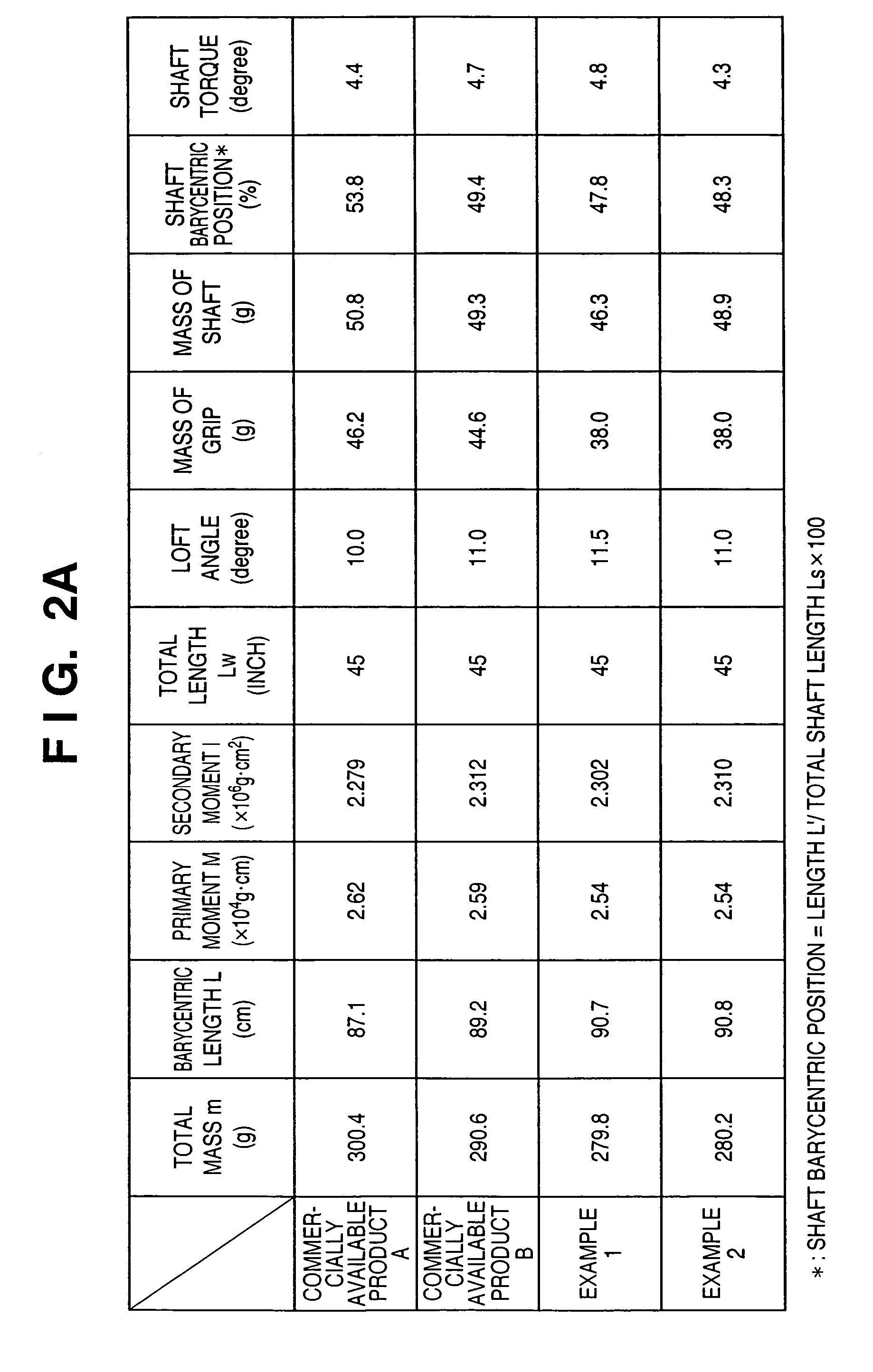
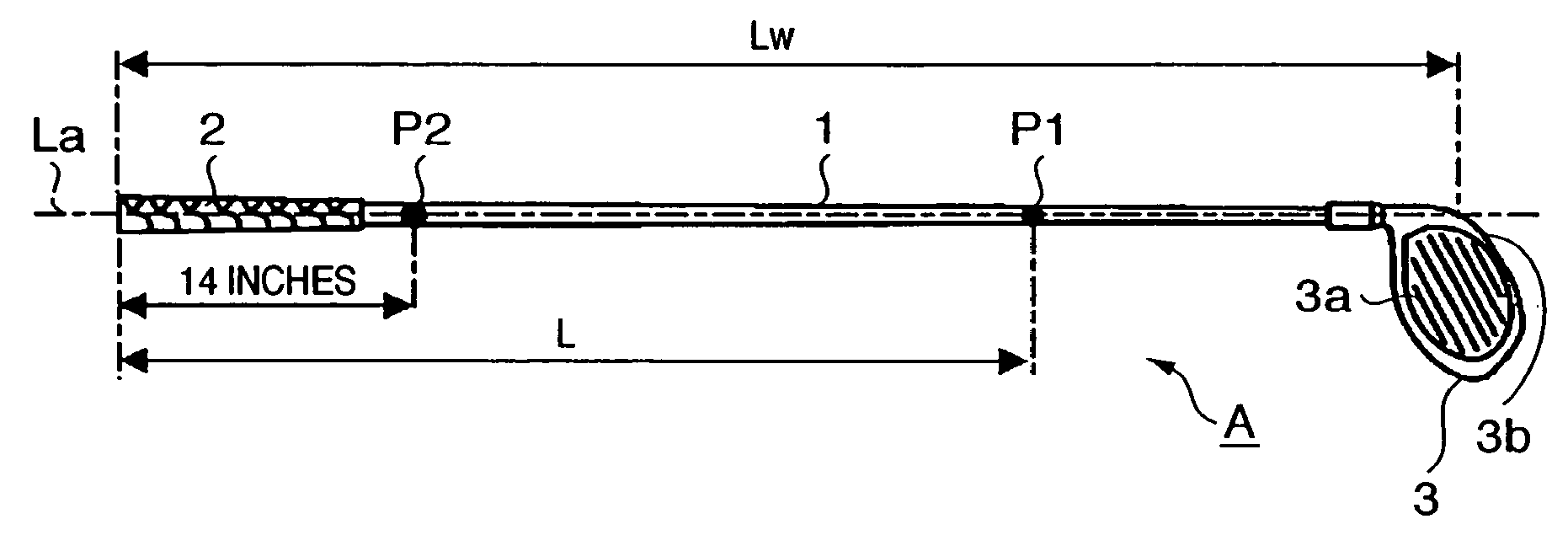
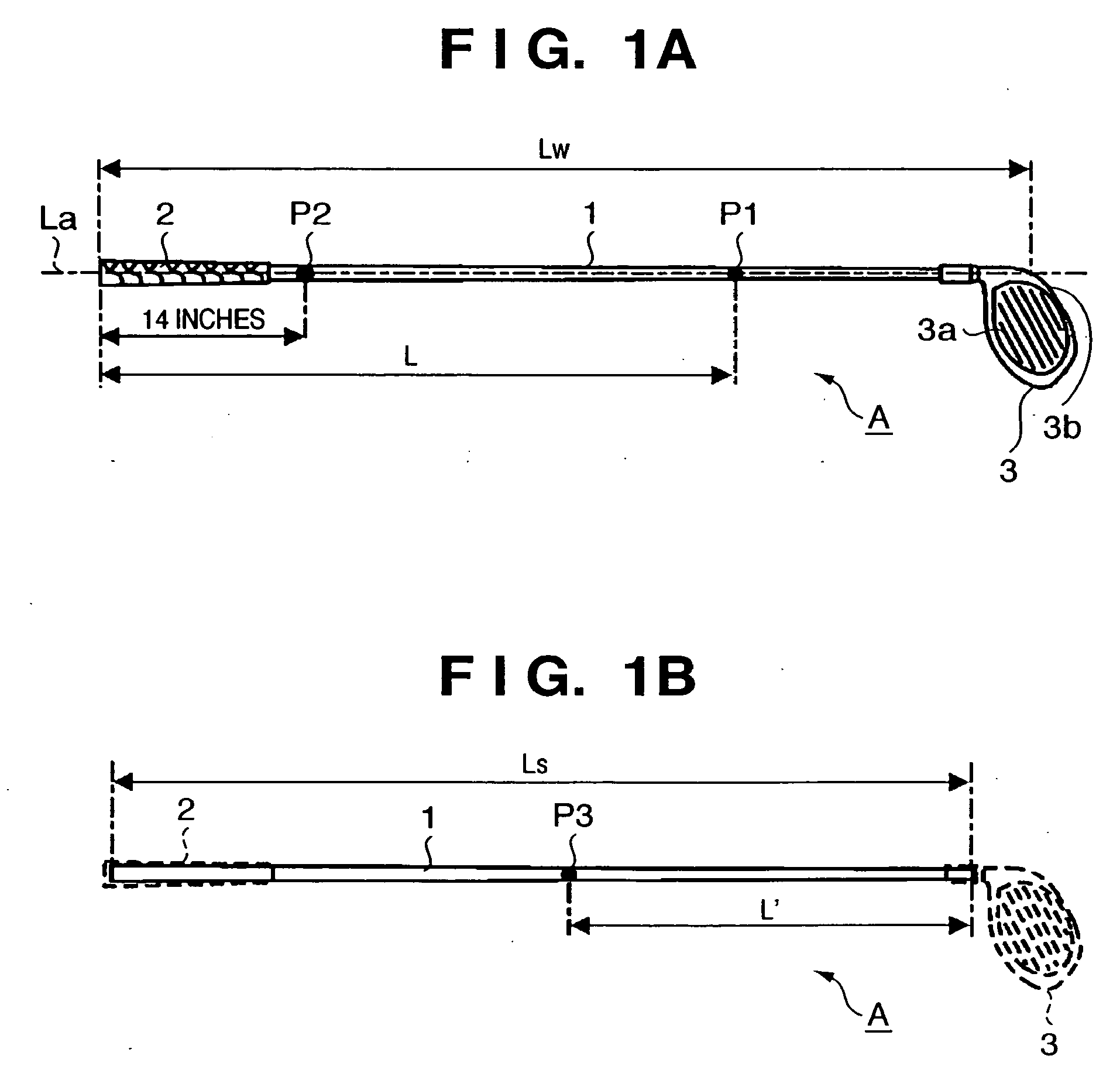
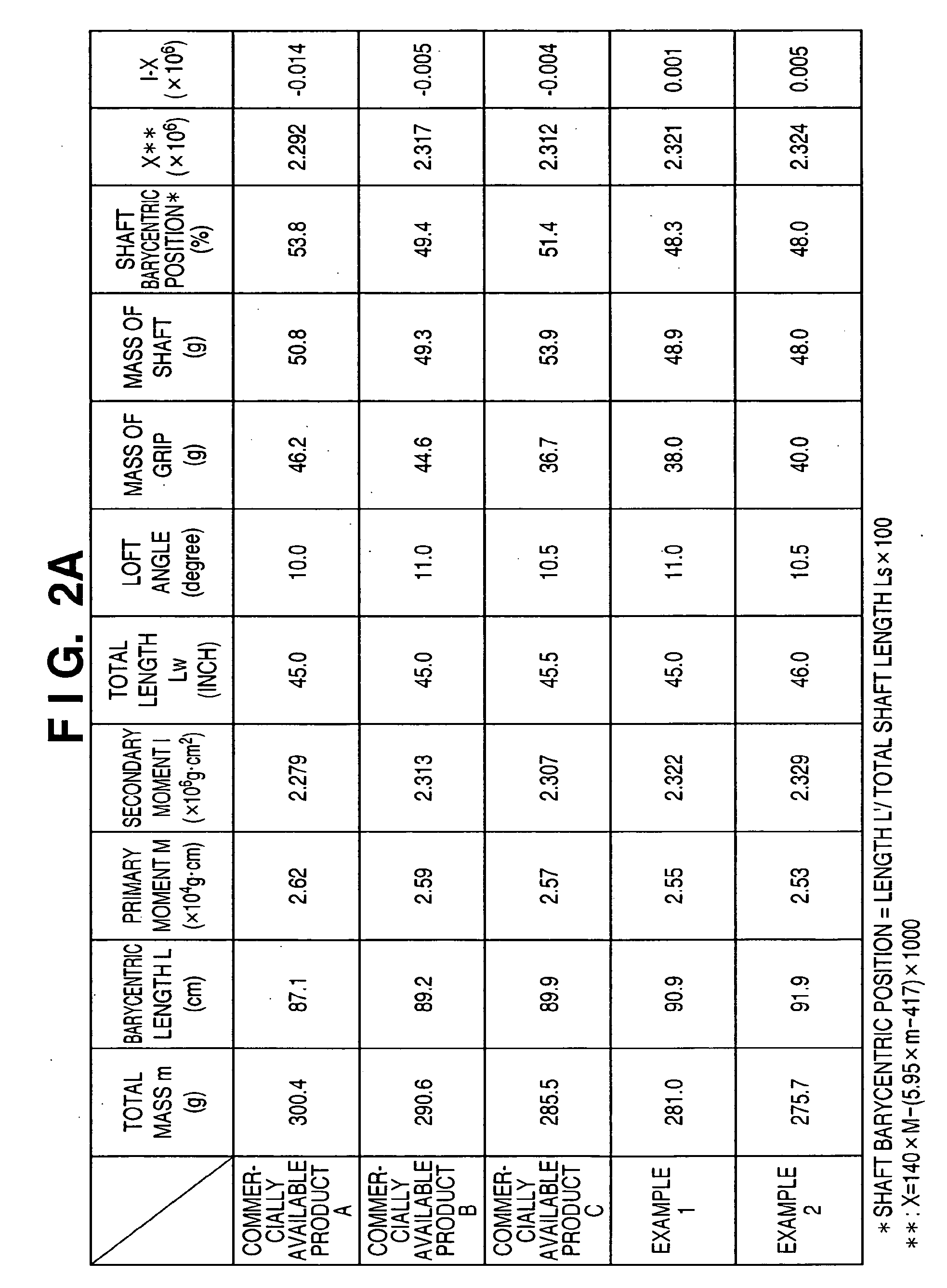
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L≦2.60×104 (g·cm) and m×L2≧2.270×106 (g·cm2), and the barycentric position of the shaft is within a range of 48.5% the total length of the shaft from a head side end of the shaft.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
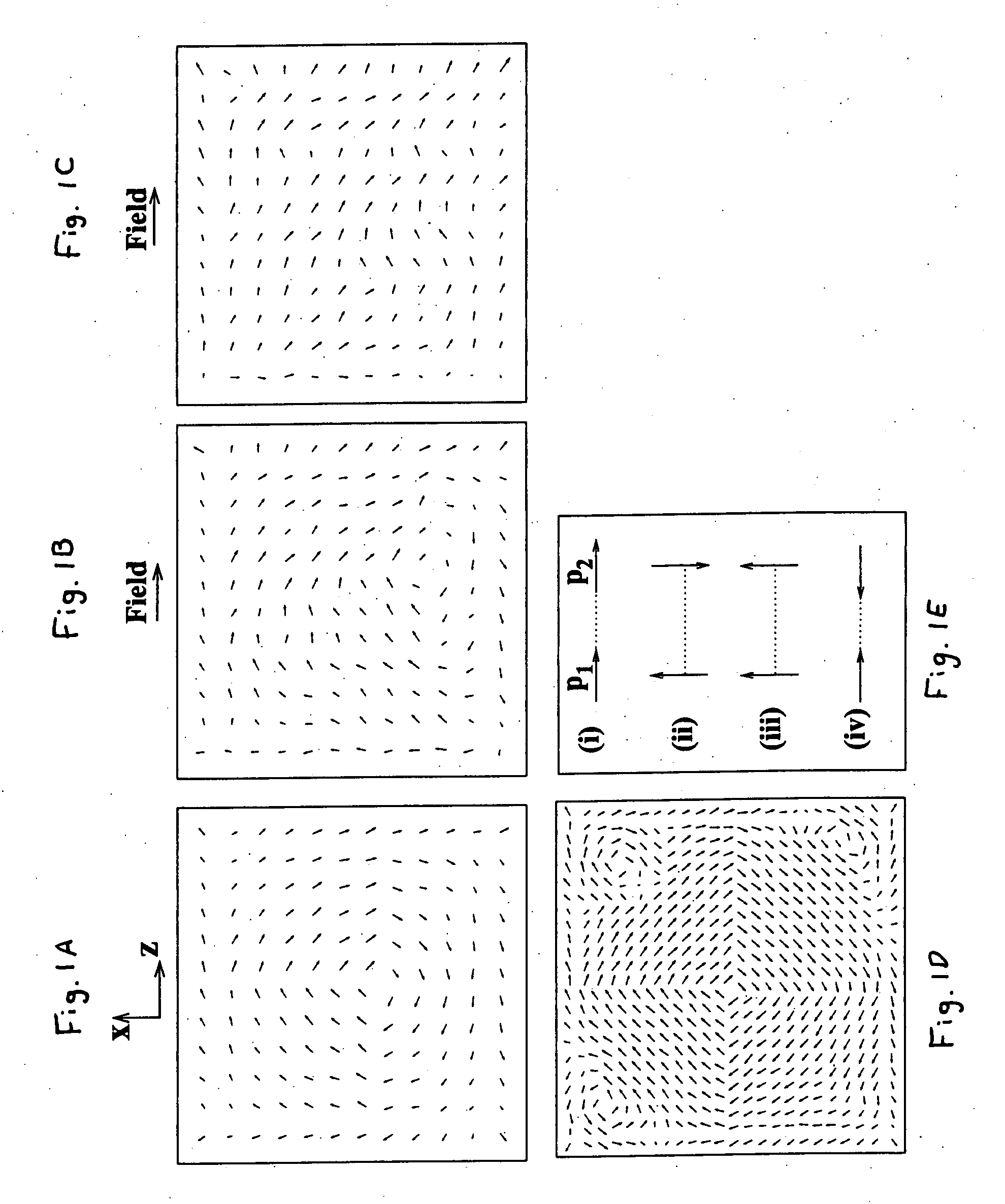
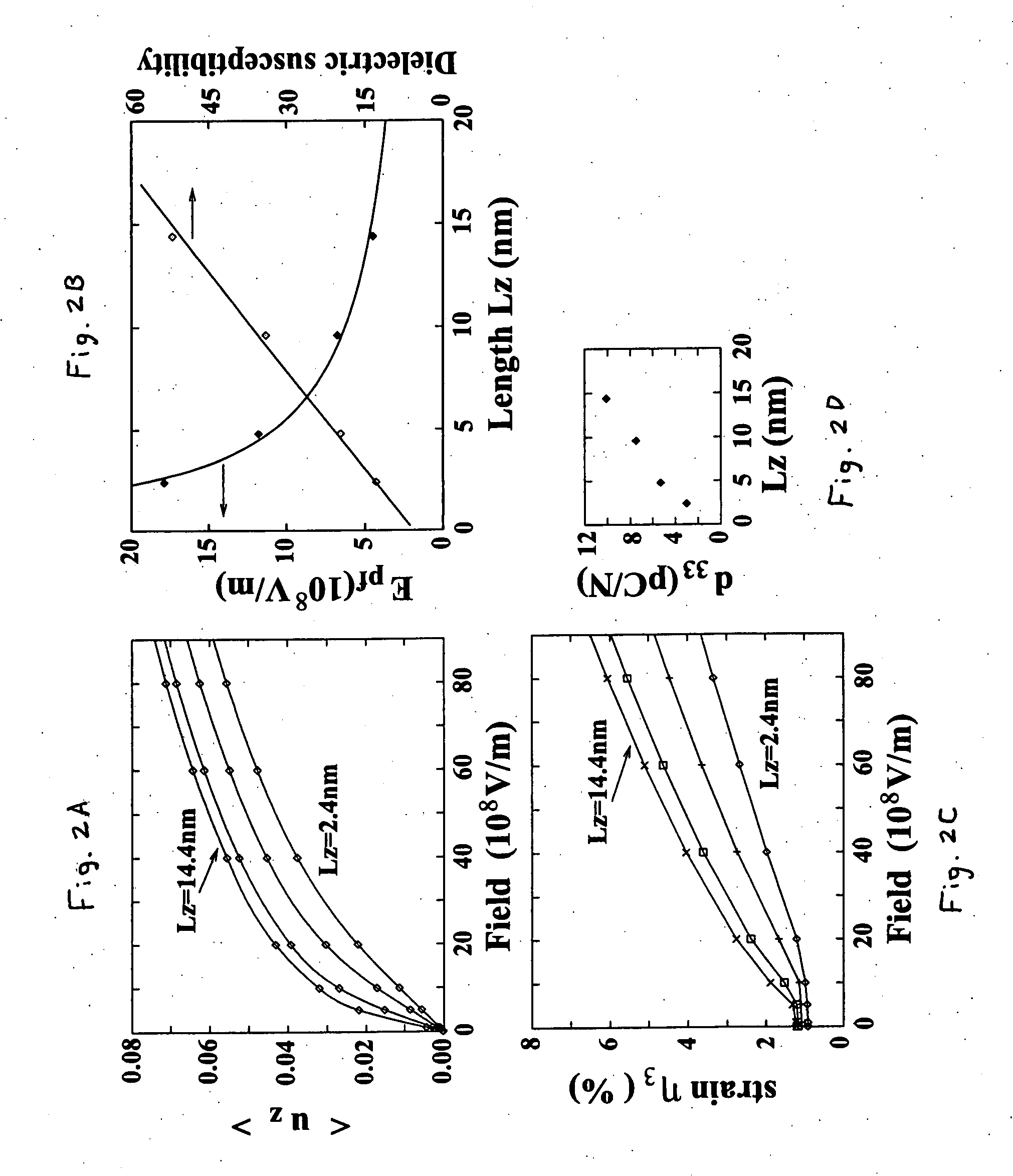
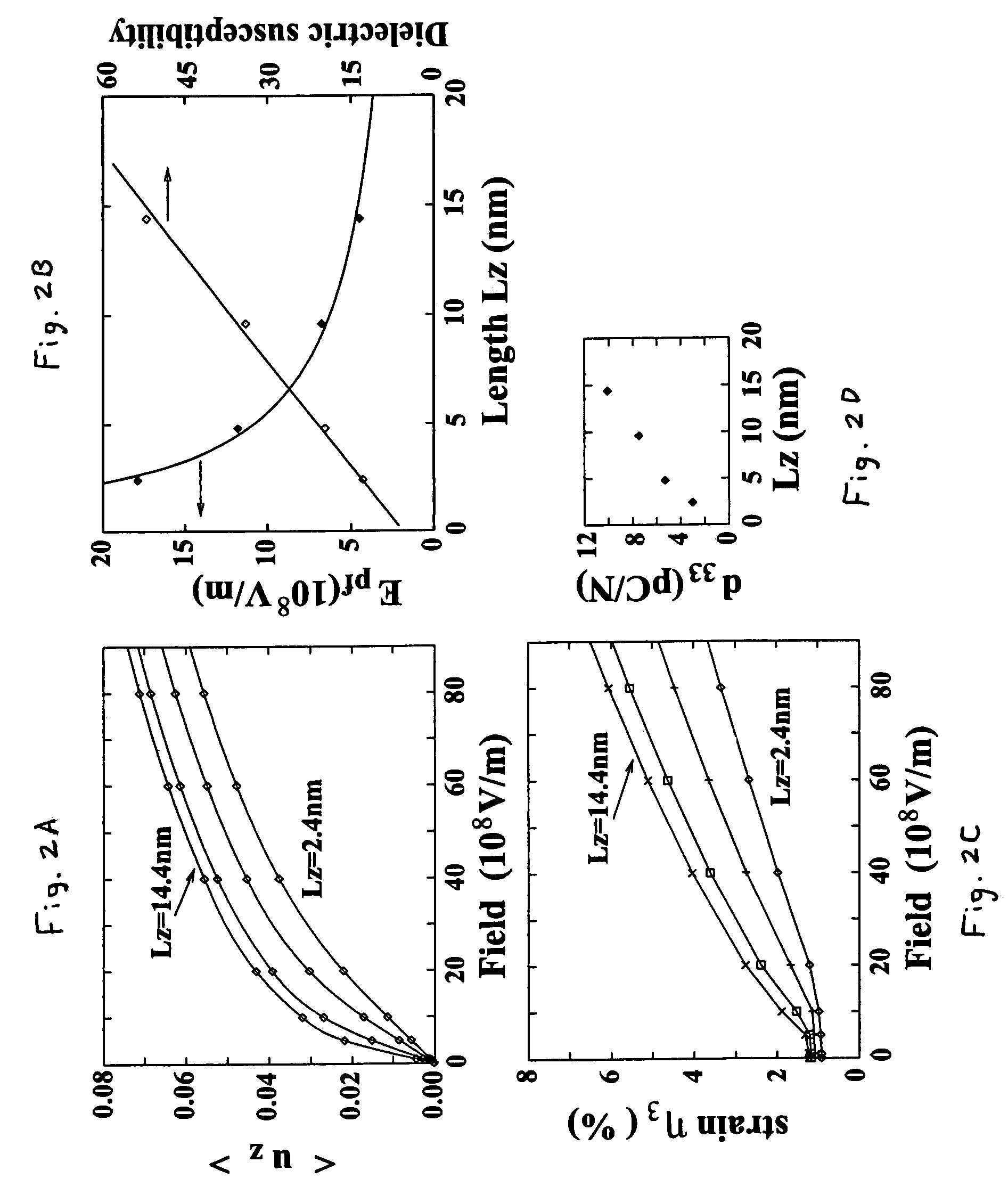
Ferroelectric nanostructure having switchable multi-stable vortex states
InactiveUS20080130346A1Increase data storageEasy to switchFerroelectric carrier recordingDigital storageStable stateNanodot
A ferroelectric nanostructure formed as a low dimensional nano-scale ferroelectric material having at least one vortex ring of polarization generating an ordered toroid moment switchable between multi-stable states. A stress-free ferroelectric nanodot under open-circuit-like electrical boundary conditions maintains such a vortex structure for their local dipoles when subject to a transverse inhomogeneous static electric field controlling the direction of the macroscopic toroidal moment. Stress is also capable of controlling the vortex's chirality, because of the electromechanical coupling that exists in ferroelectric nanodots.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Method of authentication by token
ActiveUS9774595B2Limitation on frequencyPractical limitationTransmissionSecurity arrangementUnique identifierComputer terminal
A method is provided for authentication by token for accessing a service from a terminal. The method includes, on receipt of a service access authorization request including at least one unique identifier of the terminal, steps of determining a network access context of the terminal; checking validity of the service access rights, including at least checking an access right associated with the network access context of the terminal; and, if the access rights are valid, generating a valid authentication token on the basis of the unique identifier of the terminal and the network access context, and transmitting the token to the terminal.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Ferroelectric nanostructure having switchable multi-stable vortex states
InactiveUS7593250B2Increase data storageEasy to switchFerroelectric carrier recordingDigital storageStable stateNanodot
A ferroelectric nanostructure formed as a low dimensional nano-scale ferroelectric material having at least one vortex ring of polarization generating an ordered toroid moment switchable between multi-stable states. A stress-free ferroelectric nanodot under open-circuit-like electrical boundary conditions maintains such a vortex structure for their local dipoles when subject to a transverse inhomogeneous static electric field controlling the direction of the macroscopic toroidal moment. Stress is also capable of controlling the vortex's chirality, because of the electromechanical coupling that exists in ferroelectric nanodots.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
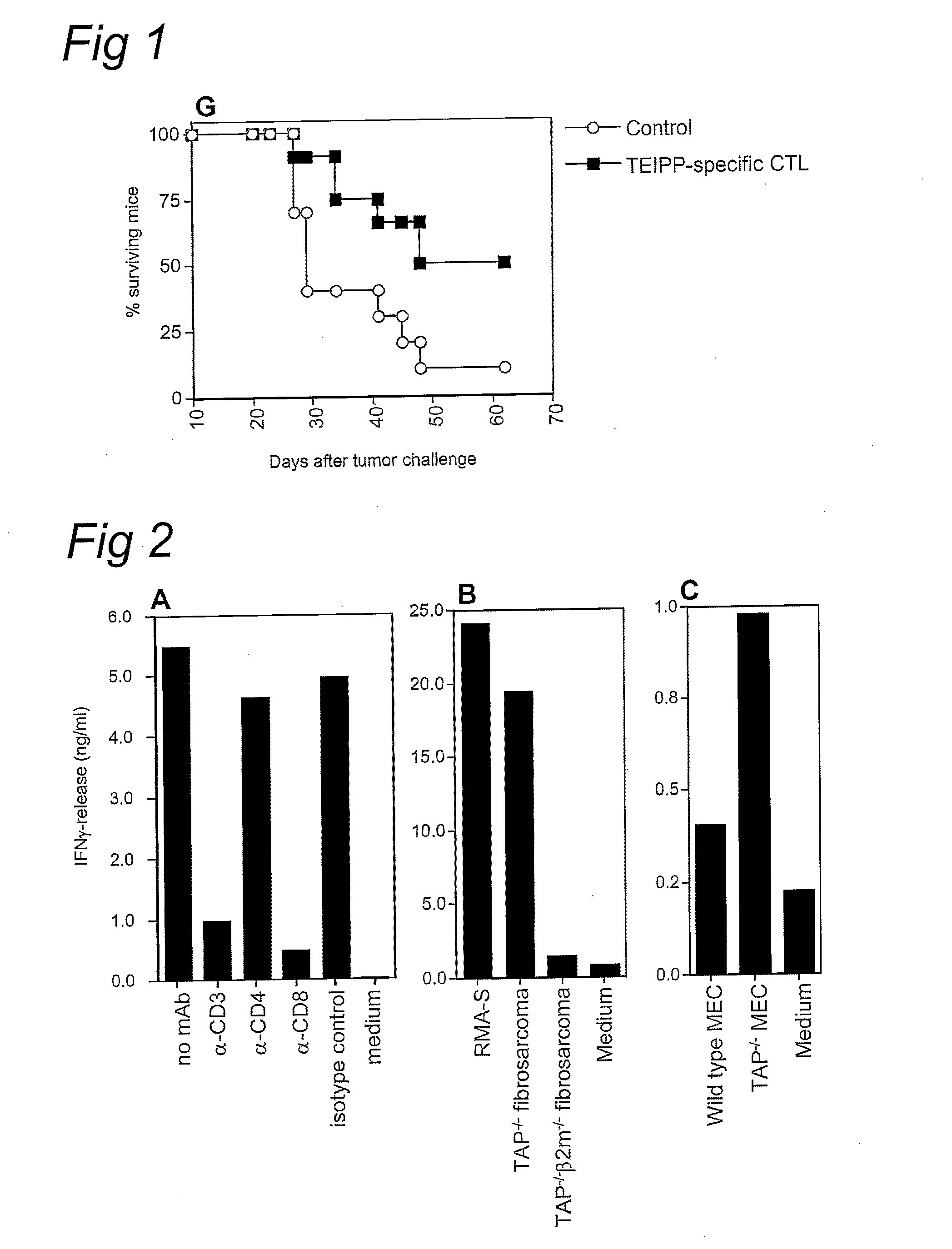
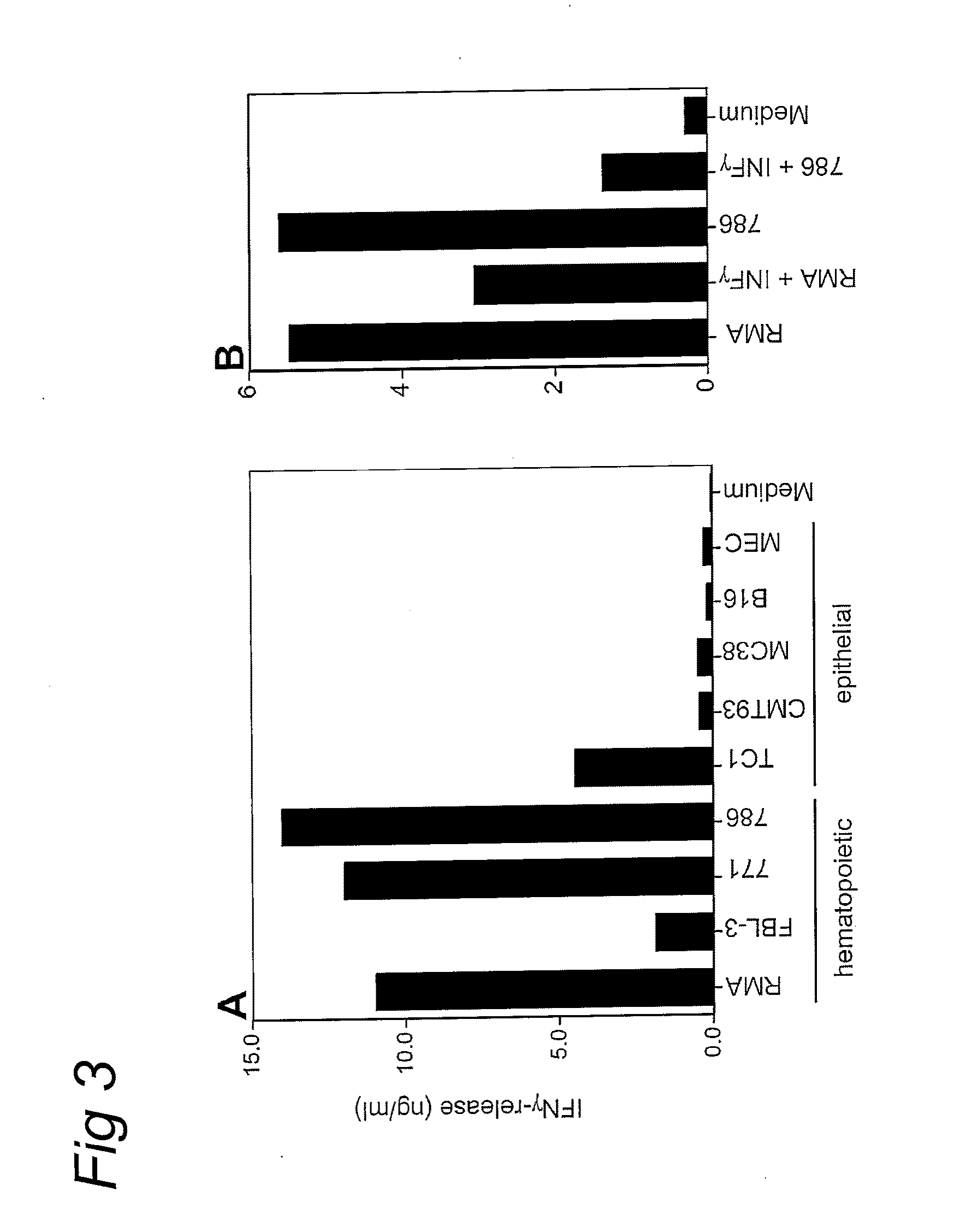
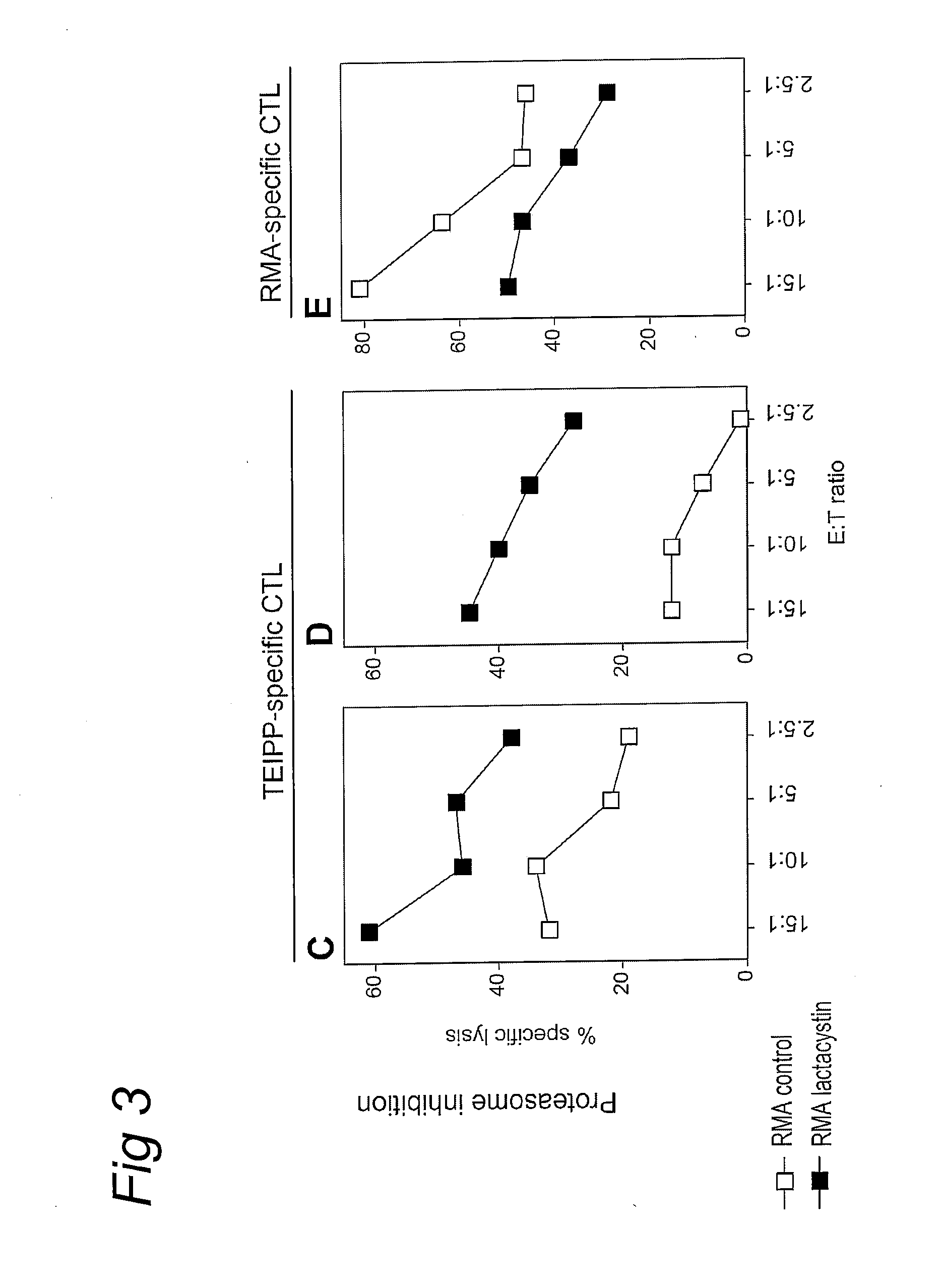
Methods for identifying t-cell epitopes associated with impaired peptide processing and applications of the identified epitopes
InactiveUS20090220534A1Easy to usePoint to optimizationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDifferential displayTumor cells
The current invention provides methods for the identification of antigens and / or epitopes that are differentially displayed on TAP deficient or TAP impaired cells and are not detectably displayed on normal or TAP proficient cells. The identification and applications of these differentially presented antigens, which in this specification are referred to as TEIPP, T cell Epitopes associated with Impaired Peptide Processing, is a prime object of this invention. The invention also provides peptides comprising a TEIPP epitope obtained from the methods of the invention, which may be applied in medicaments and methods of treatment raising a T cell response against TAP deficient tumor cells or virally infected cells.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIV (MEDICAL CENT)
Golf club
InactiveUS20080234065A1Extended driving distanceImprove impactGolf clubsRacket sportsGravity centerEngineering
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L=2.55×104 (g·cm) and m×L2=2.322×106 (g·cm2), and a barycentric position of the shaft is at 48.3% a total length of the shaft from a head side end of the shaft.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Zoom lens system
InactiveUS20050190434A1High performance featuresAccurate focusMicroscopesImage stabilizationMagnification
A zoom lens system is disclosed. The zoom lens system forms a final image of an object and a first intermediate real image between the object and the final image. The zoom lens system includes a first optical unit located between the object and the first intermediate real image. The first optical unit comprises at least one optical subunit which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the first intermediate real image. The zoom lens system also includes a second optical unit located between the first intermediate real image and the final image, at least a portion of which is moved to change the size (magnification) of the final image. The zoom lens system provides a wide zoom range of focal lengths with continuous zooming between the focal lengths and optional image stabilization.
Owner:COURTLAND CAPITAL MARKET SERVICES LLC +1
Golf club
InactiveUS7507165B2Extended driving distanceImprove impactDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringGolf Ball
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L≦2.56×104 (g·cm) and m×L2≧2.300×106 (g·cm2).
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Golf club
InactiveUS20070105642A1Extended driving distanceImprove impactDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusGolf BallGolf club
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L≦2.56×104 (g·cm) and m×L≧2.300×106 (g·cm2).
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Assay method
InactiveUS20130337481A1Avoid the needPractical limitationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical propertyPeroxidase
The invention provides an assay method for determining a level of haptoglobin in a sample comprising the steps of: (i) mixing haemoglobin with the sample to be assayed so as to form a haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex with haptoglobin present in the sample; (ii) contacting the product of step (i) with reagents for generating hydrogen peroxide and one or more chromogens which undergo a spectroscopically detectable change when peroxidase activity is present, in the presence of a buffer, under conditions in which hydrogen peroxide is generated from said reagents and forms a substrate for the peroxidise activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex present, and wherein the pH of the buffer is within a range which is sufficiently low that the peroxidise activity of any uncomplexed haemoglobin is substantially suppressed but sufficiently high that hydrogen peroxide generation occurs; (iii) determining the peroxidase activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex by measuring the change in an optical property of the reaction mixture; and (iv) correlating the level of peroxidise activity of the haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex with the amount of haptoglobin in the sample. A kit for use in such a method is also provided.
Owner:REACTIVLAB
Golf club
InactiveUS20070105640A1Extended driving distanceFeel goodGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L≦2.60×104 (g·cm) and m×L2≧2.270×106 (g·cm2), and the barycentric position of the shaft is within a range of 48.5% the total length of the shaft from a head side end of the shaft.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
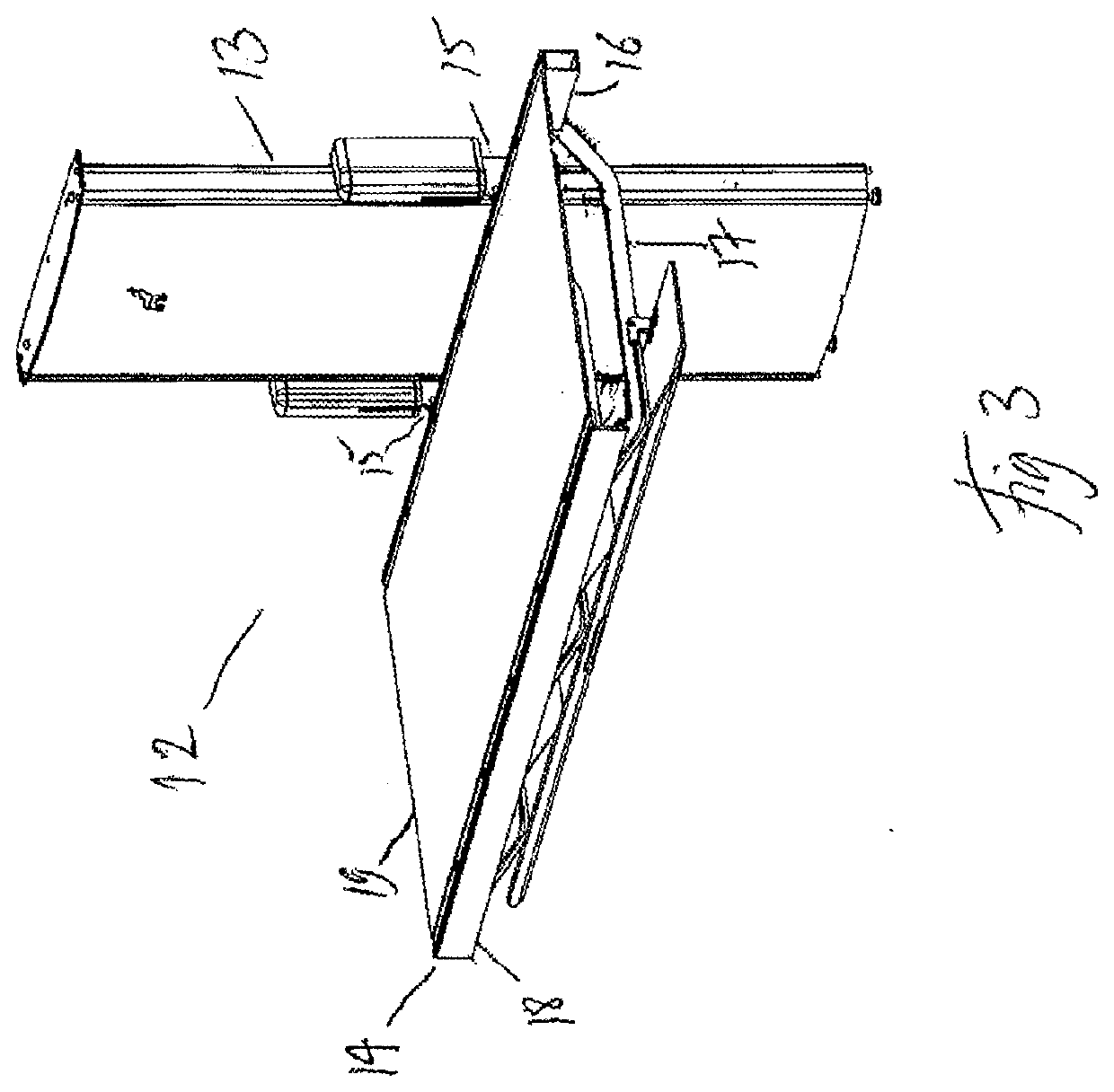
Gait training via perturbations provided by body-weight support system
ActiveUS20200230005A1Practical limitationReduce the risk of fallingWalking aidsNursing bedsControl mannerEngineering
A body-weight support system that allows individuals with severe gait impairments to practice over-ground walking in a safe, controlled manner is disclosed. The system includes a body-weight support system that rides along a driven trolley and can be controlled in response to the movement of the subject using the system. They system is also configured to apply strong, yet brief perturbations to a subject as they are stationary or performing a dynamic task, such as walking, side stepping, etc., via the trolley of a body weight support system.
Owner:HIDLER JOSEPH
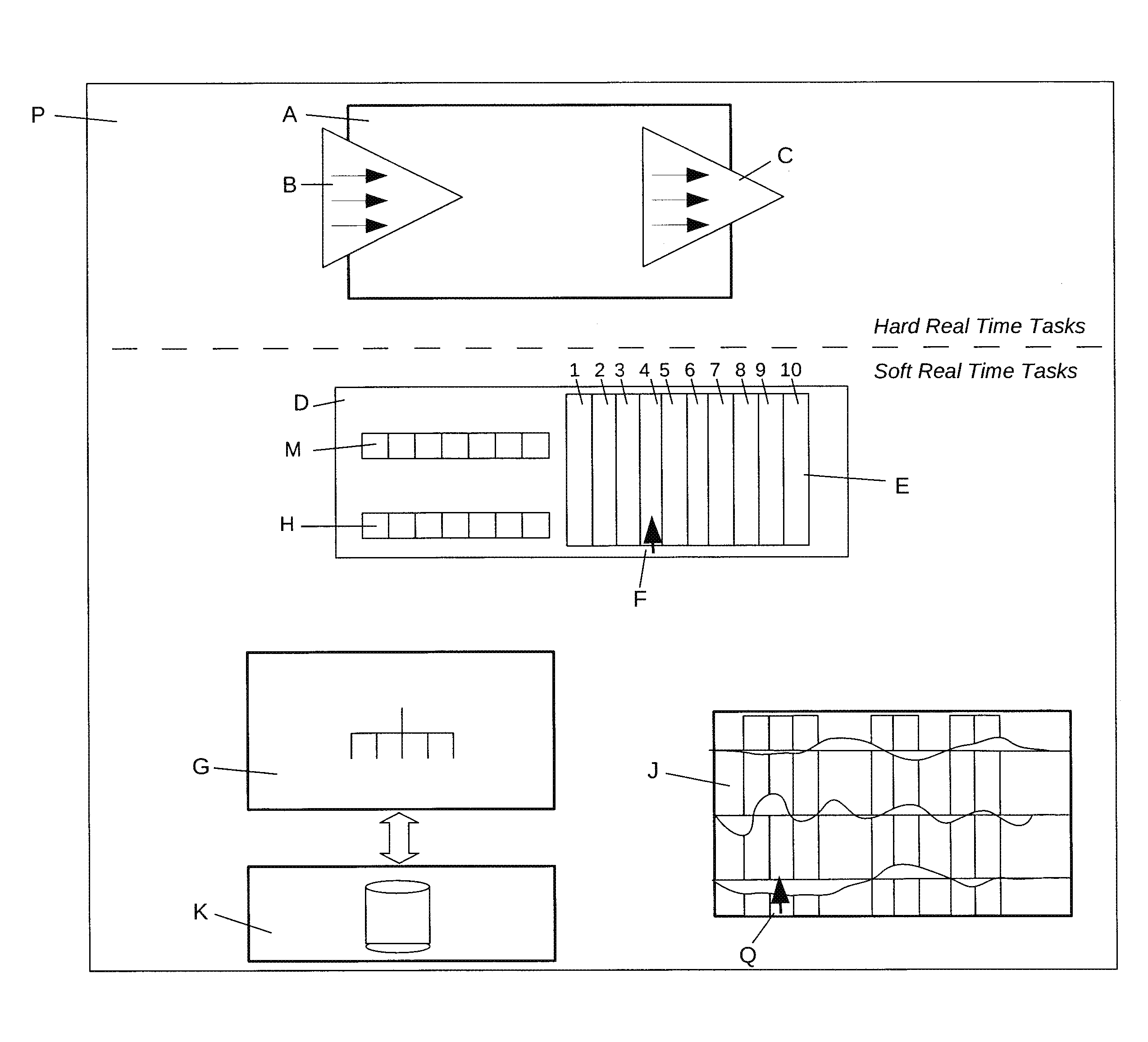
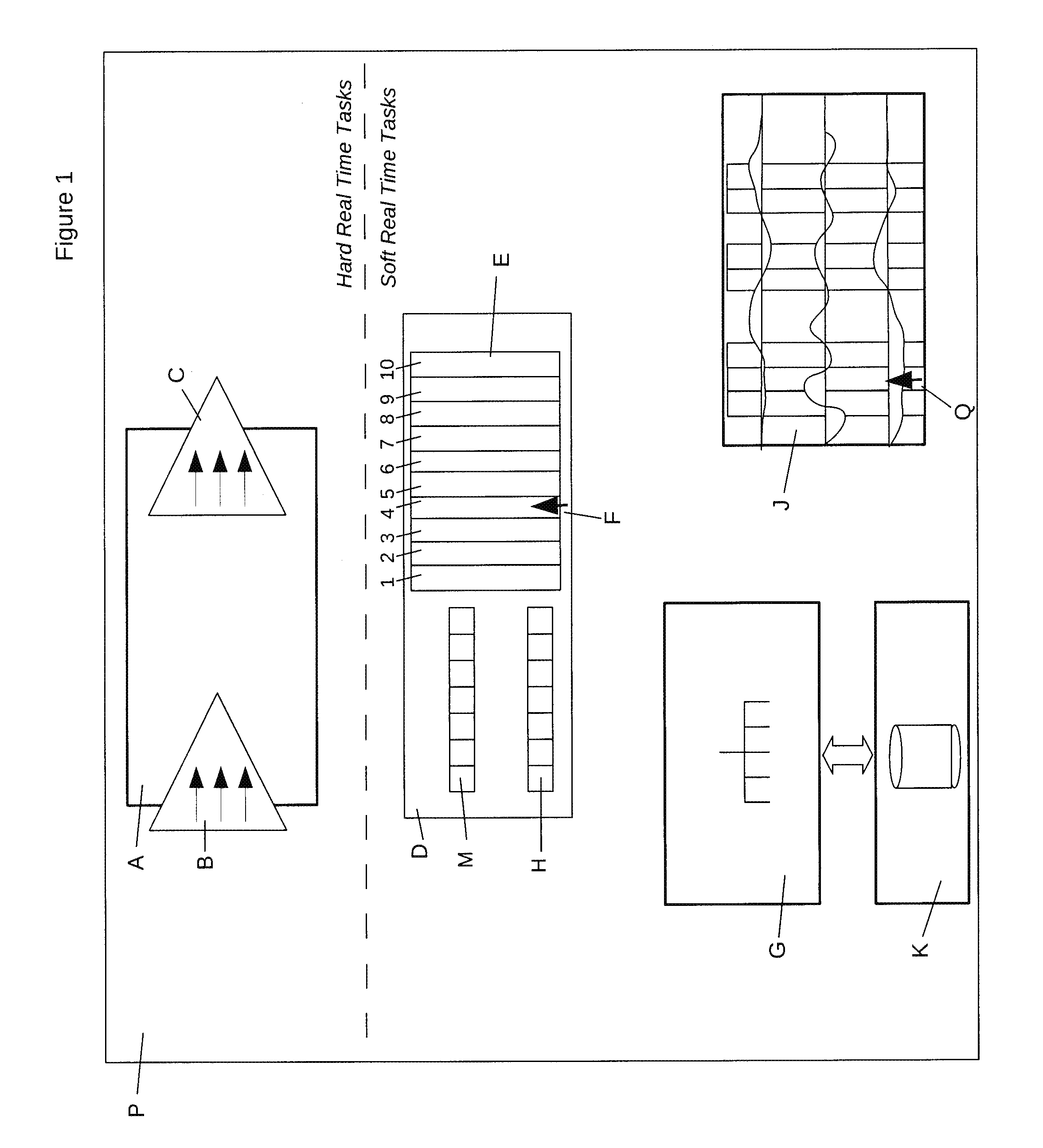
Memory paging system for real time motion data recording, editing, and playback
ActiveUS8654136B1Practical limitationDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsData streamData set
A system and method of capturing, storing, editing and outputting multi-track motion data in a continuous stream on a computer with deterministic timing, where the length of the motion dataset is not limited by computer Random Access Memory. A hard real time periodic motion task takes in data streams from sensors or other computers, stores it in a shared memory area, and streams out the data to other computers so as to actuate motion. A shared memory area stores buffers and flags which indicate what data should be swapped to and from persistent storage. A soft real time periodic task transfers data pages between RAM and persistent storage based on requests from the motion task. Three data pages surround the active point in the motion dataset, four pages are reserved for copying whole blocks of data, and three pages are reserved for data editing. These ten active memory pages define a fixed memory footprint which can handle a deterministic data stream of effectively infinite length. The systems periodic data output can be triggered instantaneously or locked in synchronization with other hard real time equipment such that data is never lost or transmitted late. The system may capture data, control robotic mechanisms, or stream motion via a network into the graphics or data capture environments of other computers.
Owner:CONCEPT OVERDRIVE
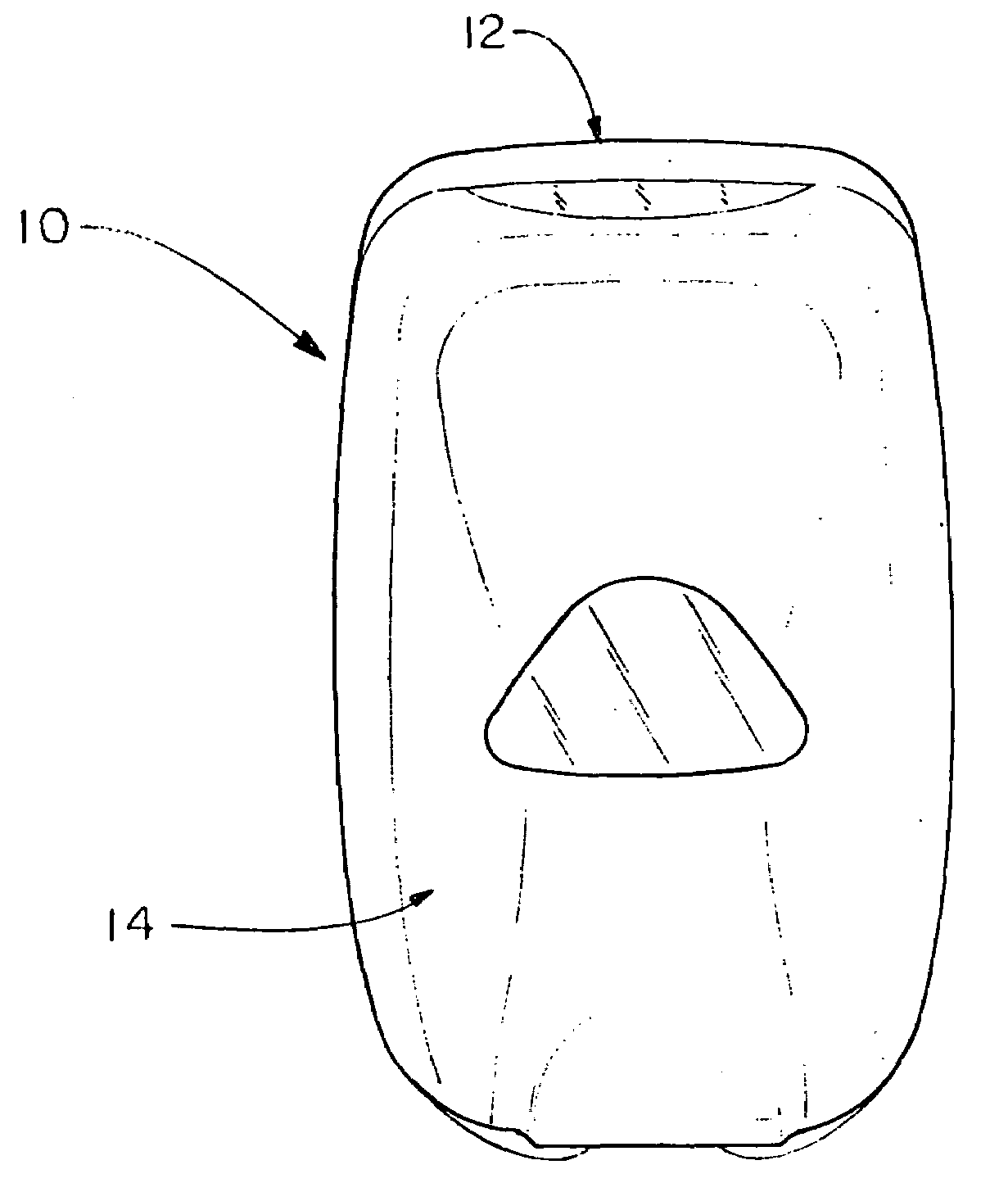
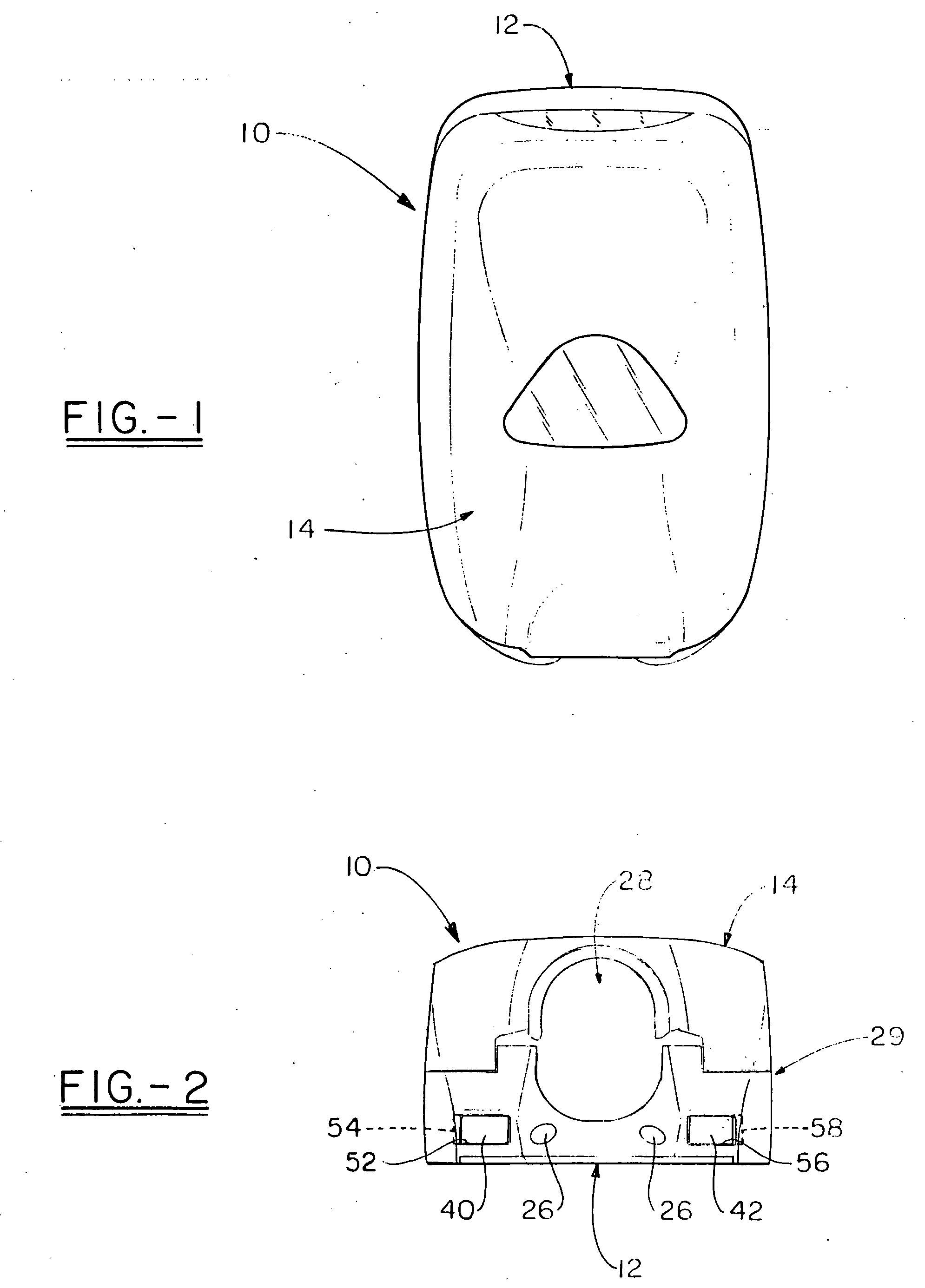
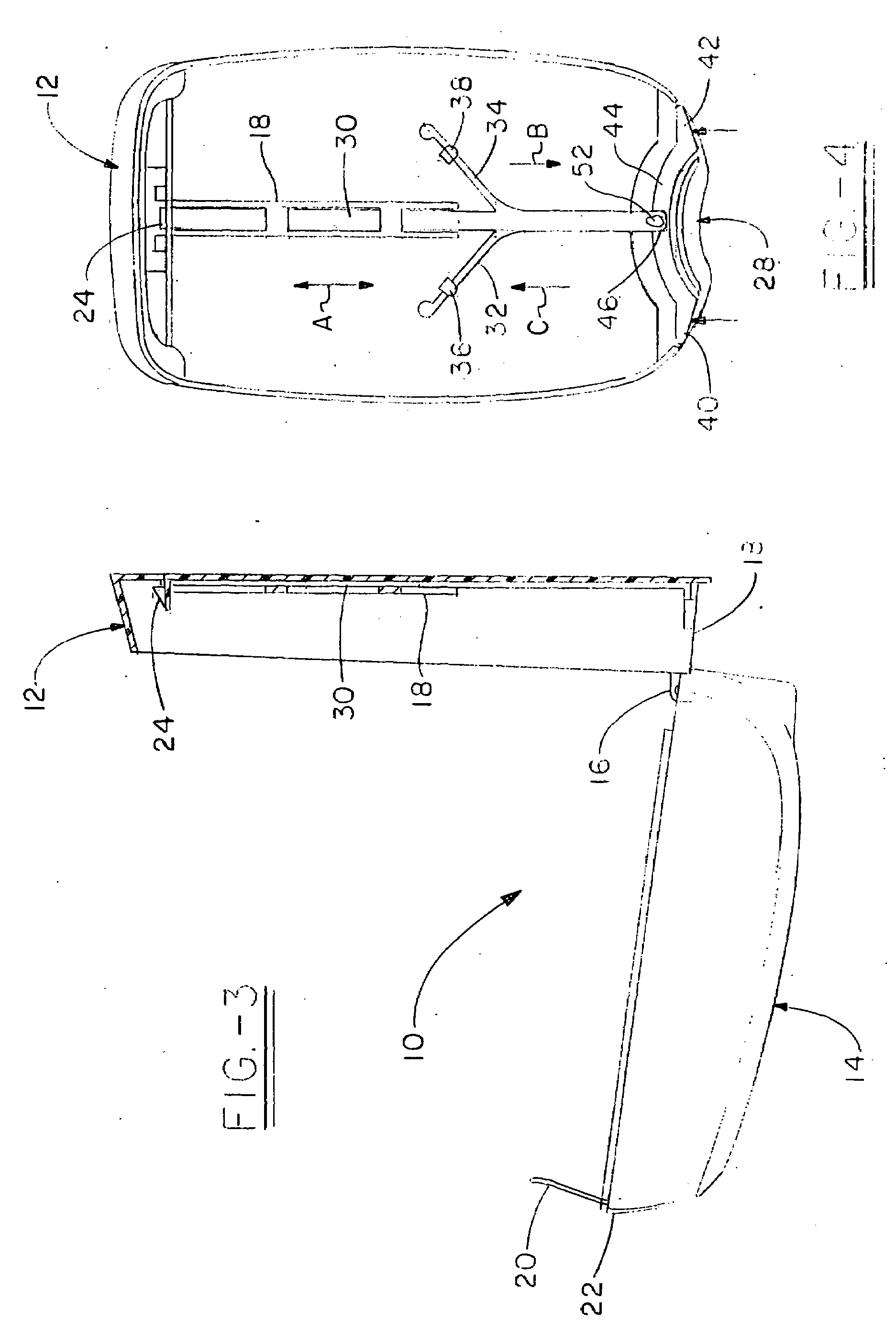
Cover release mechanism for a dispenser
ActiveUS20080054016A1Practical limitationHolders and dispensersLiquid transferring devicesMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:KANFER JOSEPH S
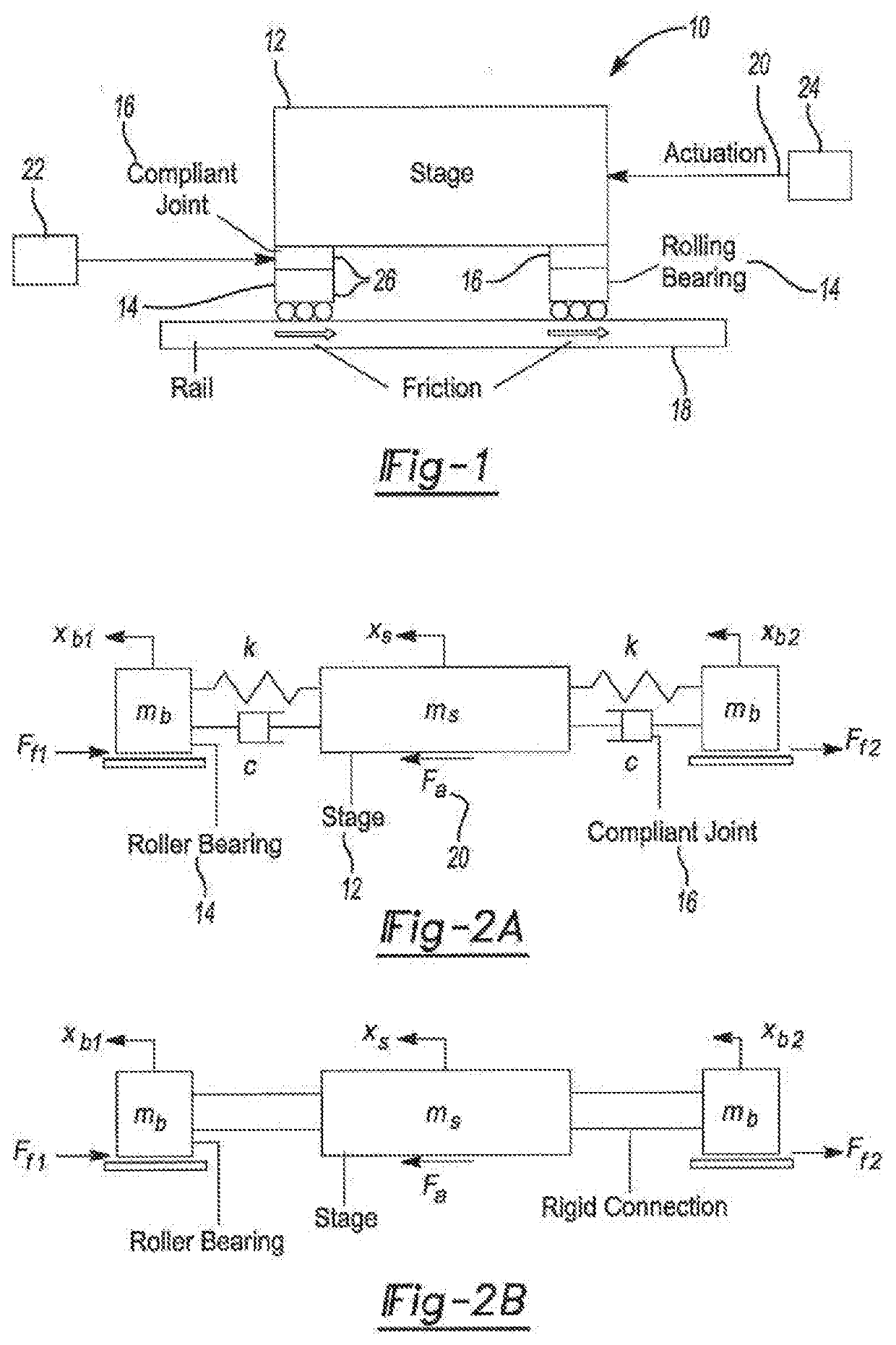
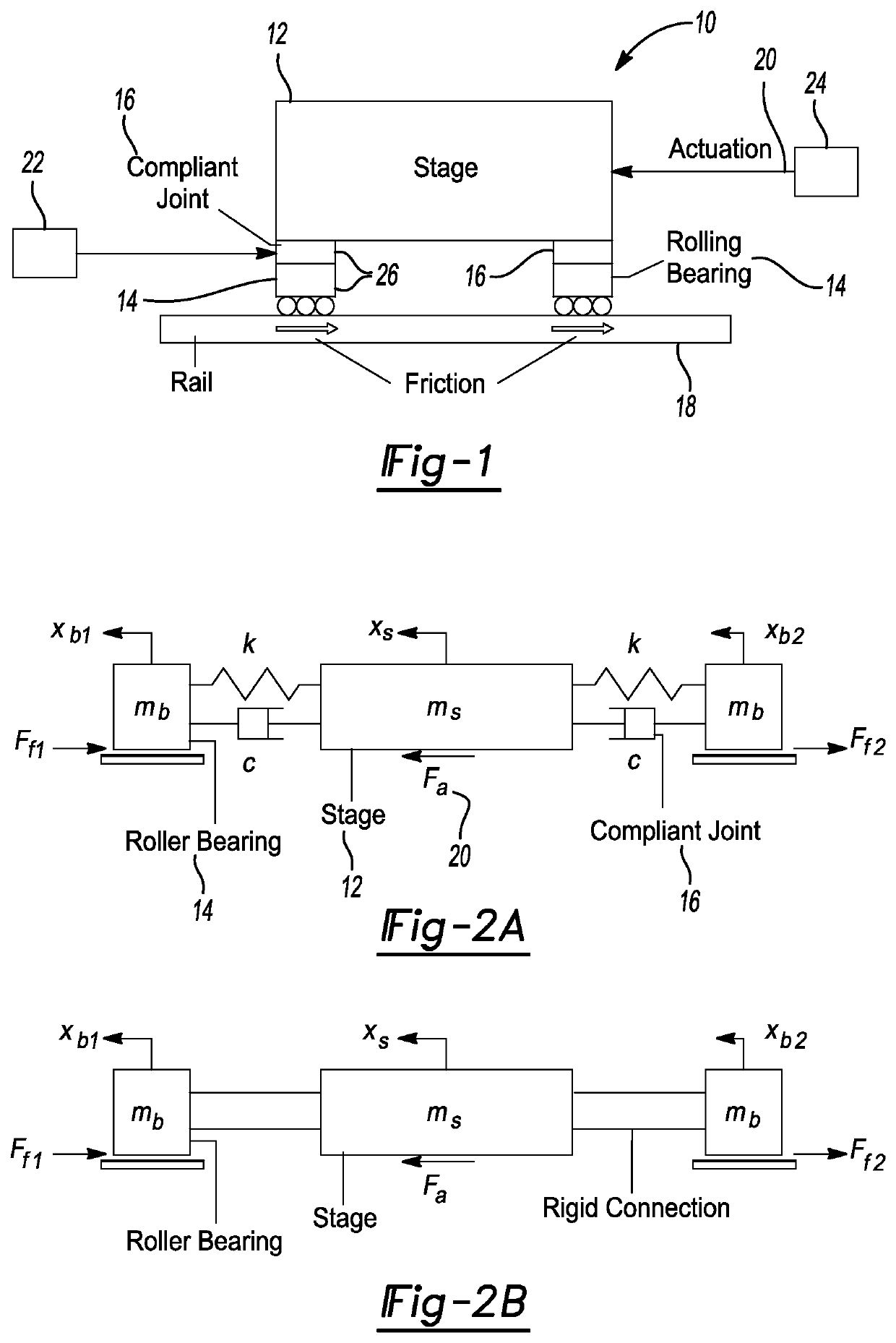
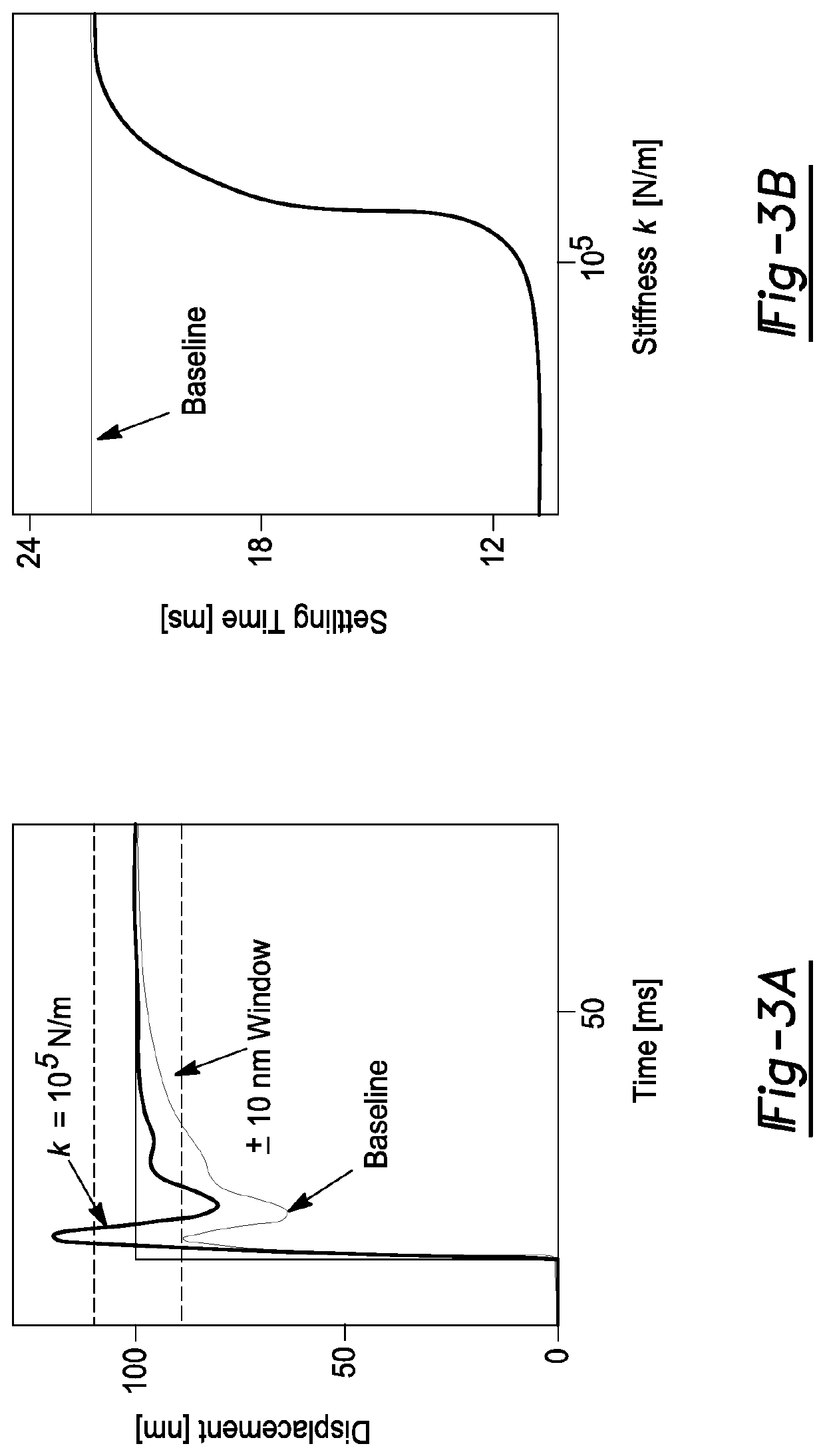
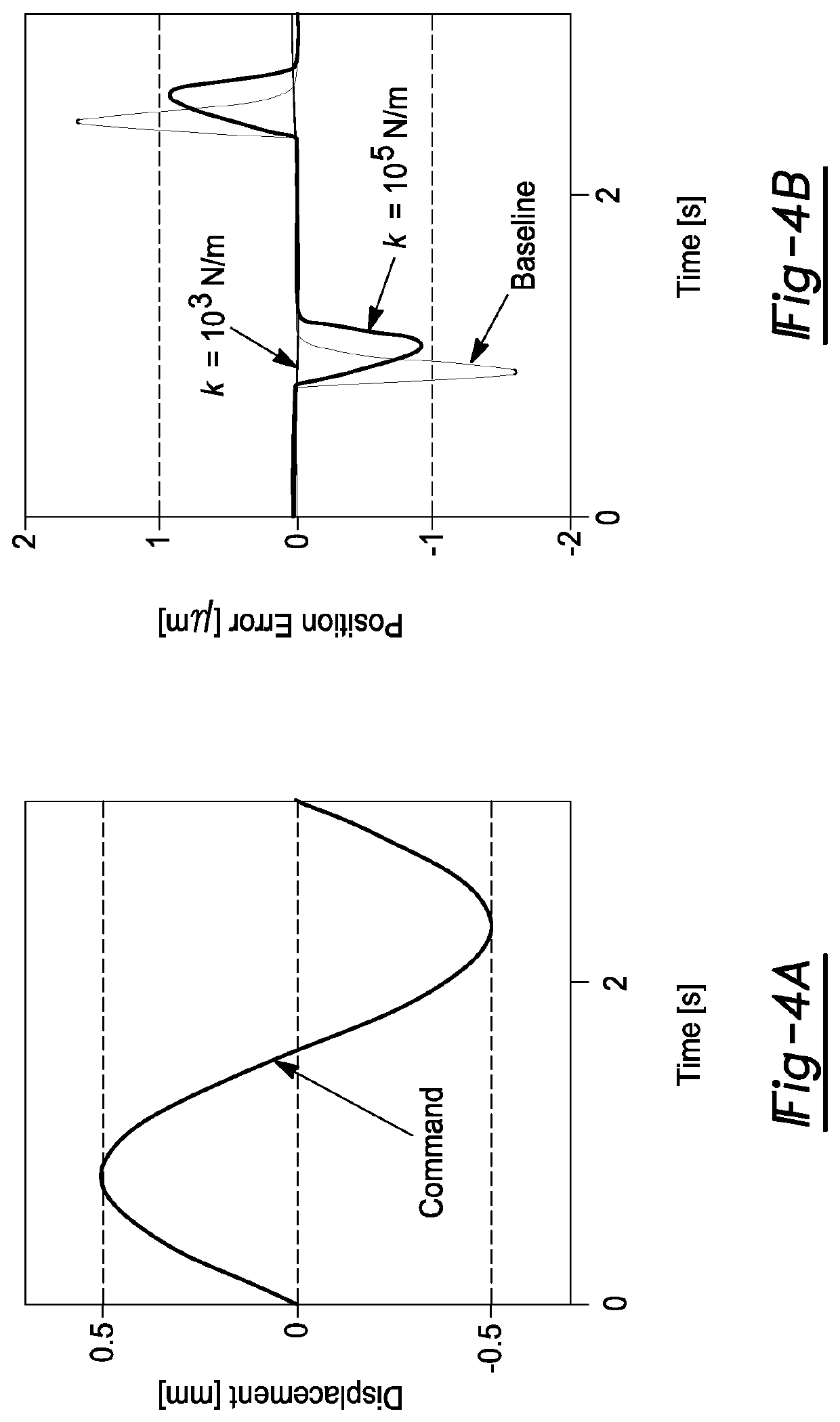
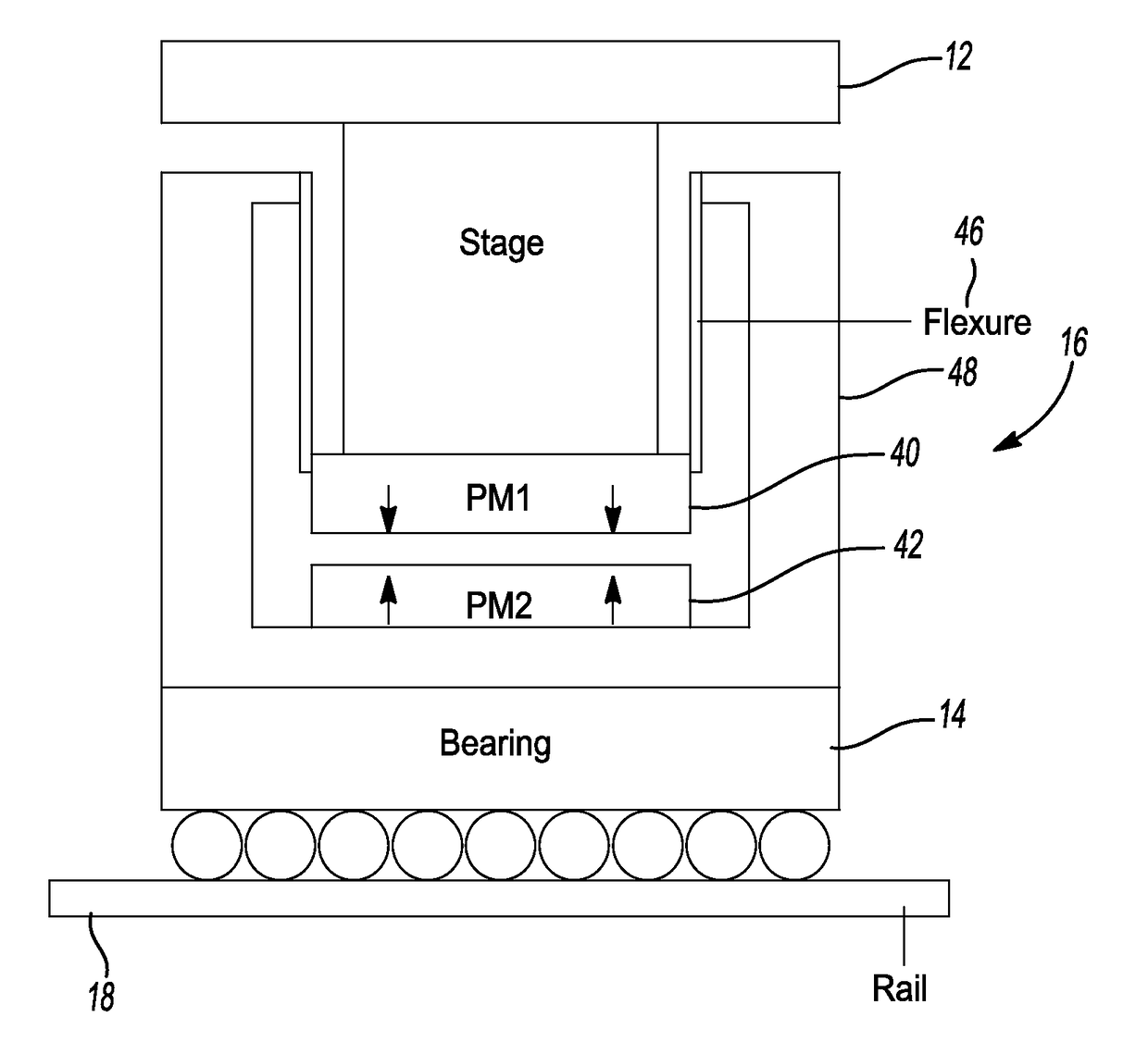
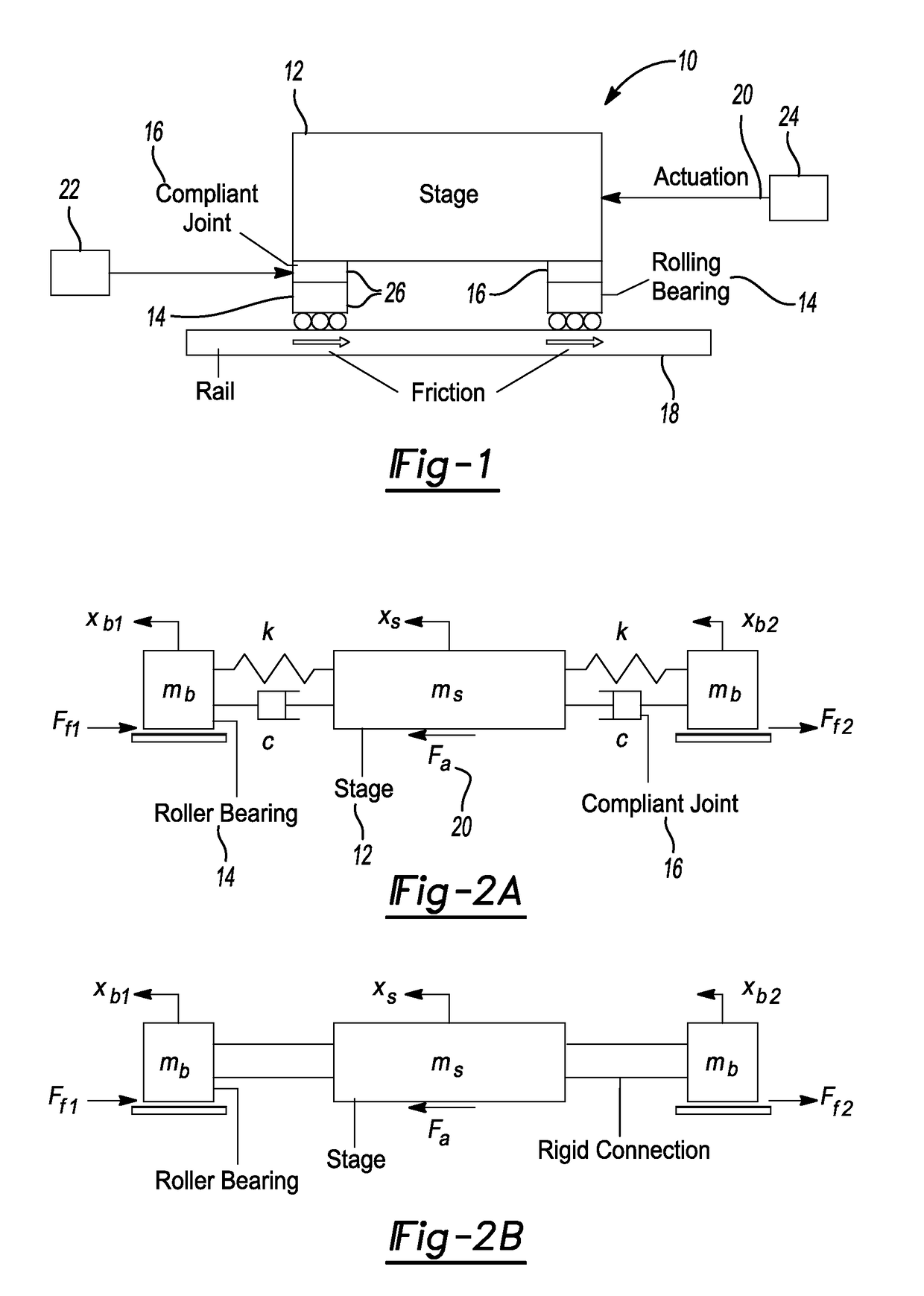
Axially Compliant Bearing For Precision Positioning
ActiveUS20210048067A1Cost effectivePractical limitationRolling contact bearingsNon-rotating vibration suppressionRotational axisClassical mechanics
A rotationally compliant bearing roller assembly having a roller, at least one bearing member operably coupled to a base configured to support rotational movement about a rotational axis; and a rotary compliant joint interconnecting the at least one bearing member to the roller. The rotary compliant joint having a first compliance in a rotational direction about the rotational axis to permit movement of the roller in the rotational direction relative to the at least one bearing member, such that the first compliance being greater than a friction induced compliance of the at least one bearing member in the rotational direction. The compliant joint having a second compliance in a direction orthogonal to the rotational direction, such that the second compliance being less than the first compliance.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Golf club
InactiveUS20070105641A1Extended driving distanceImprove impactGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
This invention provides a wood type golf club including a shaft, a grip at one end of the shaft, and a head at the other end of the shaft, wherein a mass m (g) of the golf club and a length L (cm) from a grip side end of the golf club to a barycentric position of the golf club satisfy m×L2>2.280×106 (g·cm2) and m×L2>140×m×L−(5.95×m−417)×103.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Axially compliant bearing for precision positioning
ActiveUS10837492B2Cost effectivePractical limitationLinear bearingsMagnetic bearingsRolling-element bearingClassical mechanics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Stereoscopic three dimensional projection system with short throw ratio
ActiveUS20190107729A1Short throw-ratioImprove homogeneityProjectorsColor television detailsBeam splittingProjection system
The present invention relates to a time-multiplexed stereoscopic 3d projection system wherein the image-beam from a digital cinema projector is separated by a polarization beam-splitting element into one primary image-beam possessing a first state of polarization and at least one secondary image-beam possessing a second state of polarization. Polarization modulators are provided in order to modulate the polarization state for each of said primary and secondary image-beams thereof and arranged so that all left-eye images possess a first modulated state of polarization and all right-eye images possess a second modulated state of polarization. Additionally, there is provided one uniaxial condensing lens and at least one uniaxial expanding lens in order to minimize the optical path-lengths for each of said primary and secondary image-beams thereof, hence enabling said stereoscopic 3d projection system according to the present invention to operate together with projectors having a shorter throw-ratio as compared to other prior-art technologies.
Owner:VOLFONI R&D EURL
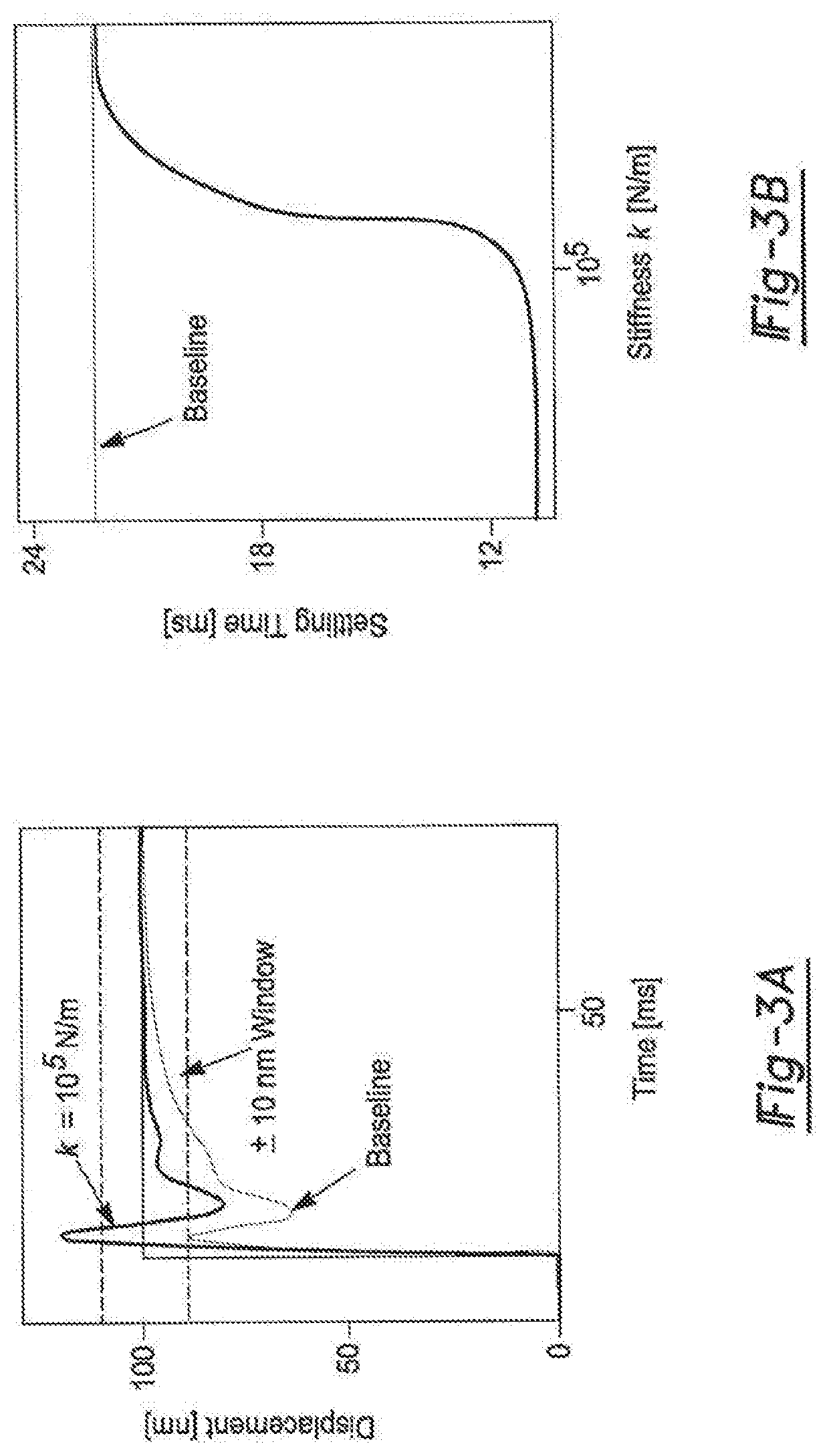
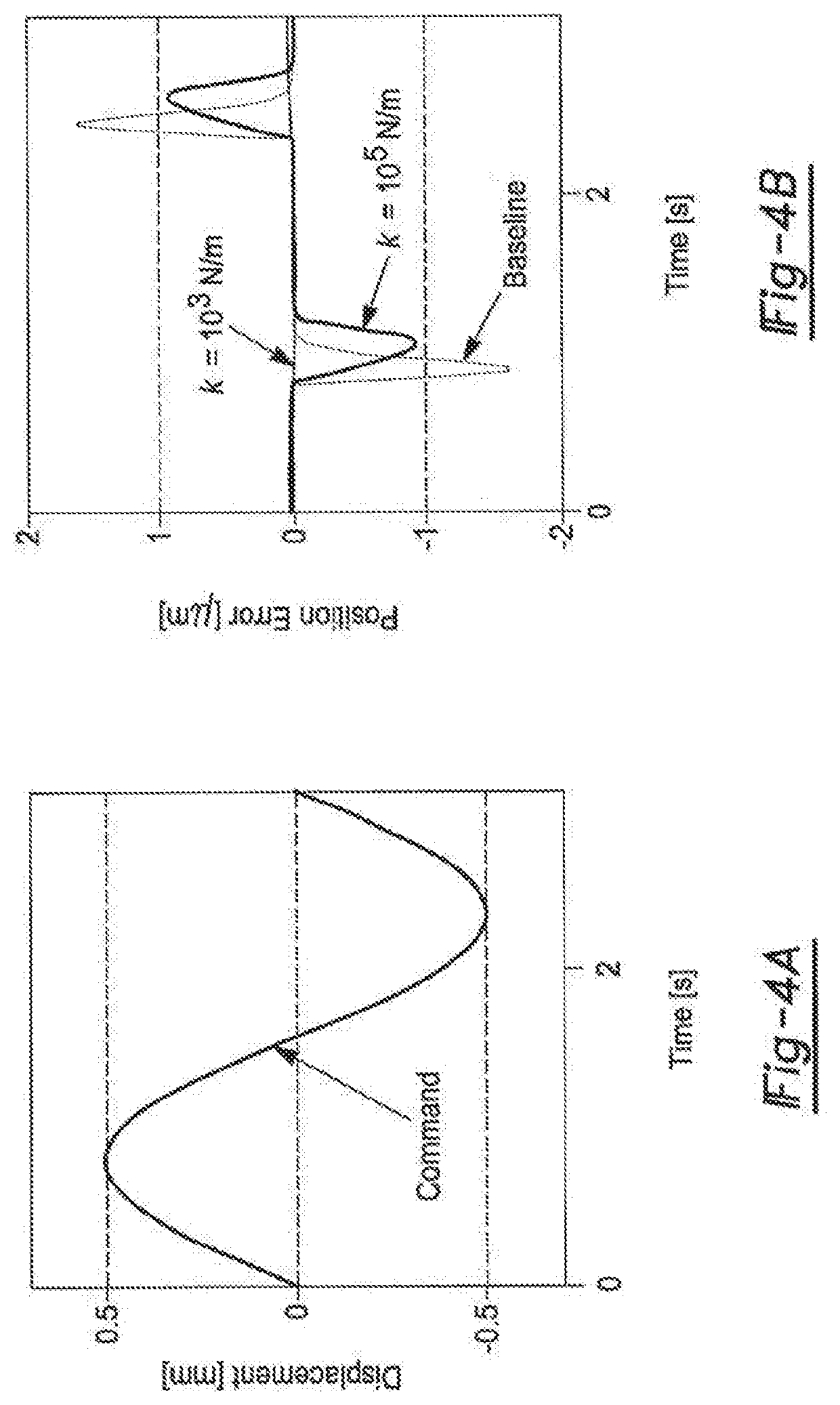
Axially compliant bearing for precision positioning
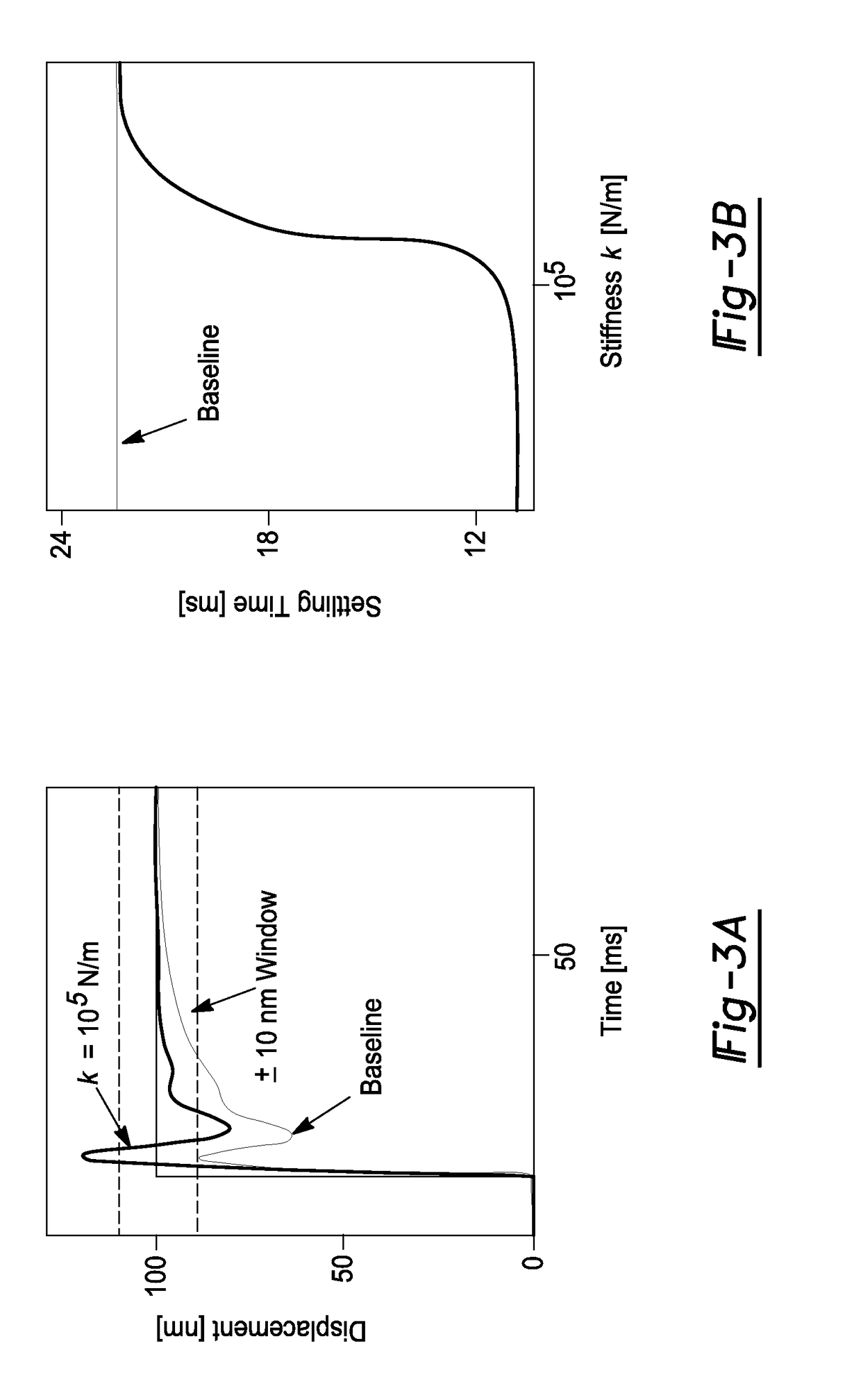
ActiveUS20180320739A1Reduce settling timeReduce track errorLinear bearingsMagnetic bearingsRoller bearingEngineering
An axially compliant rolling bearing for precision motion stages having a stage, at least one bearing member slidably disposed along a rail, and a compliant joint interconnecting the at least one roller bearing to the stage. The compliant joint is sufficiently compliant to permit movement of the stage in the axial direction while remaining stiff in other directions orthogonal to the axial direction.
Owner:THE RGT OF THE UNIV OF MICHIGAN
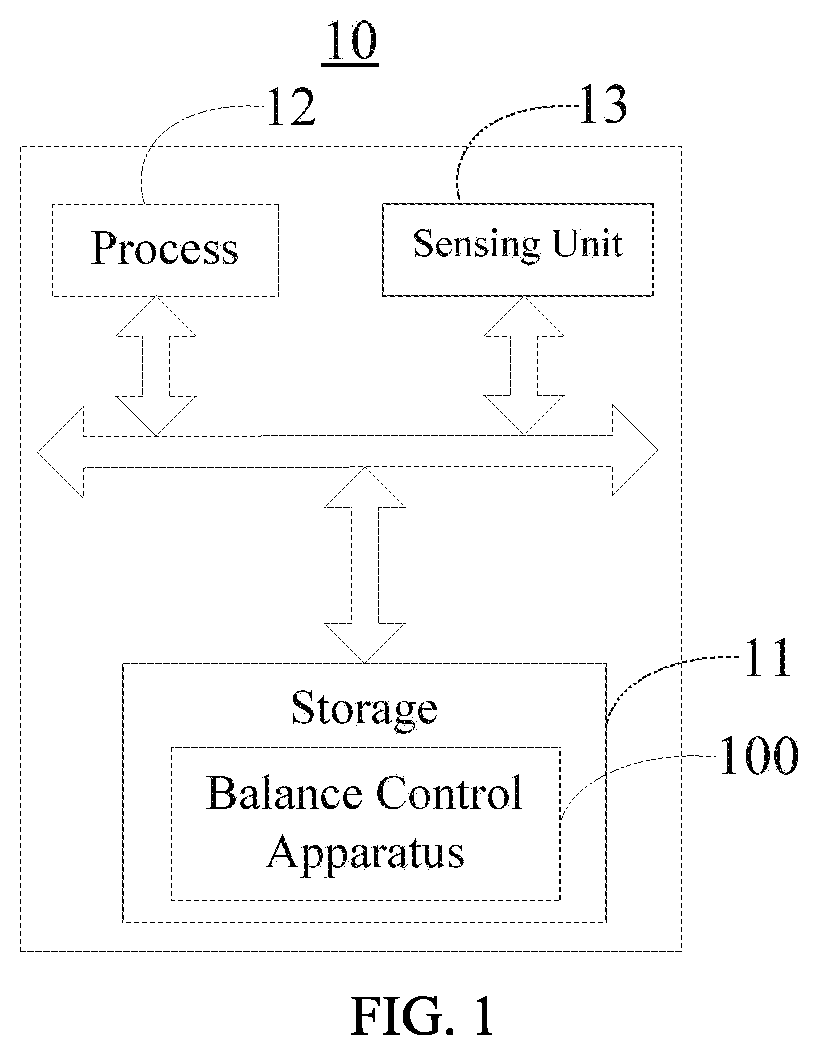
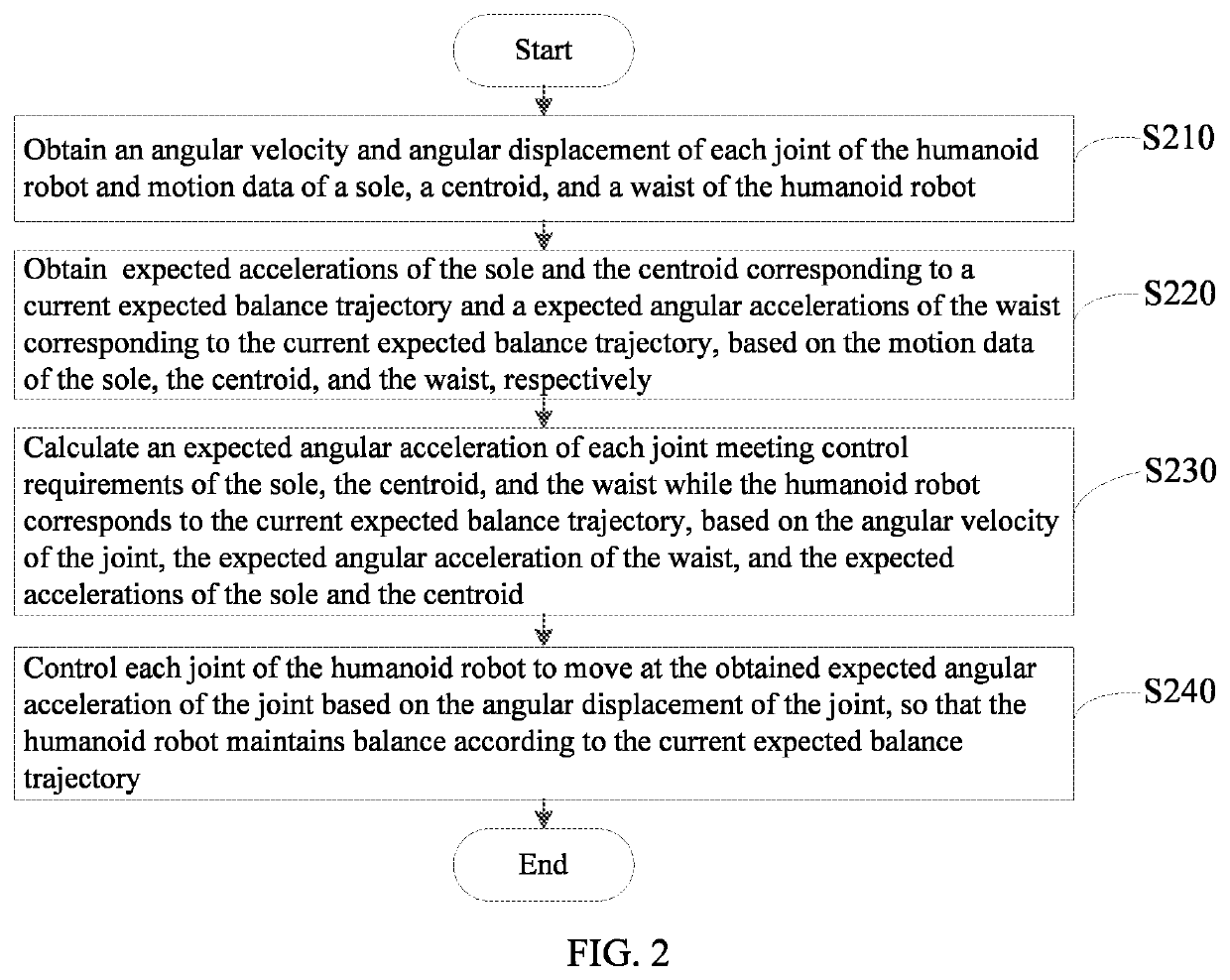
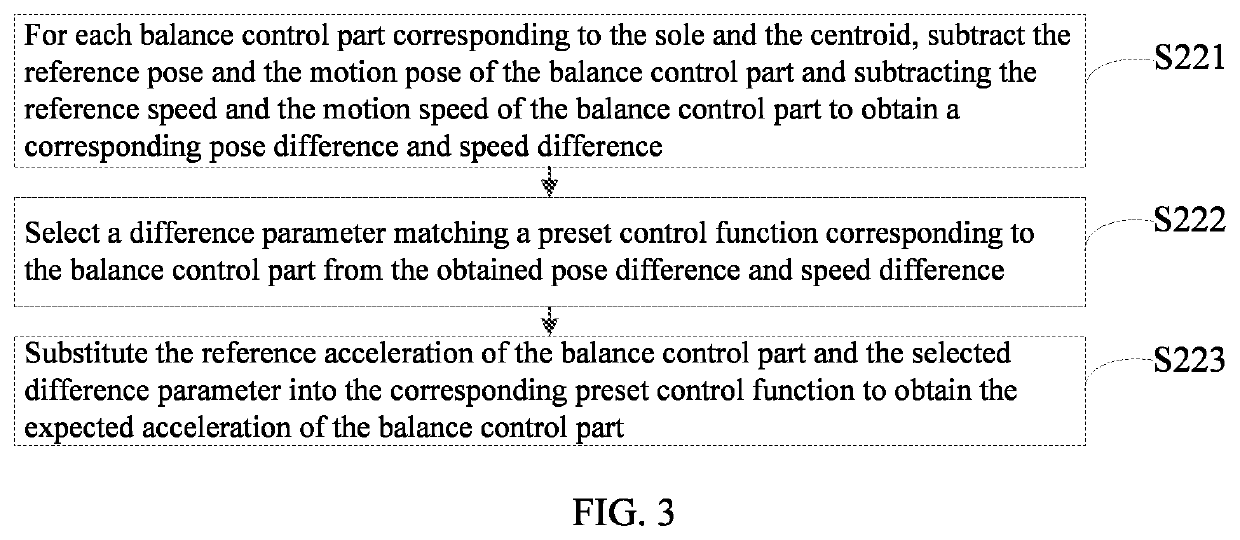
Humanoid robot and its balance control method and computer readable storage medium
ActiveUS20220040857A1Maintain balanceIncreased complexityProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotyHumanoid robot
A humanoid robot and its balance control method and computer readable storage medium are provided. Expected accelerations of each of a sole and centroid of a humanoid robot corresponding to a current expected balance trajectory and an expected angular acceleration of the waist corresponding to the current expected balance trajectory are obtained based on current motion data of the sole, the centroid, and the waist, respectively first, then an expected angular acceleration of each joint meeting control requirements of the sole, the centroid, and the waist while the robot corresponds to the current expected balance trajectory is calculated based on an angular velocity of the joint, the expected accelerations of the waist, the sole, and the centroid, respectively, and then each joint of the robot is controlled to move at the obtained expected angular acceleration of the joint based on the angular displacement of the joint.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Liquid crystal device
ActiveUS10048525B2Improve directivityPractical limitationStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVacuum pumpingLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal device includes a vacuum insulating structure, a liquid crystal panel and a control circuit board. The vacuum insulating structure includes a first glass sheet, a second glass sheet, and a sealant. The sealant is attached between the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet for forming a vacuum space cooperatively with the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet by a vacuum pumping process. The liquid crystal panel is disposed in the vacuum space. The control circuit board is electrically connected to the liquid crystal panel for controlling the liquid crystal panel.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Liquid crystal device
ActiveUS20180101048A1Improve directivityPractical limitationStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVacuum pumpingEngineering
A liquid crystal device includes a vacuum insulating structure, a liquid crystal panel and a control circuit board. The vacuum insulating structure includes a first glass sheet, a second glass sheet, and a sealant. The sealant is attached between the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet for forming a vacuum space cooperatively with the first glass sheet and the second glass sheet by a vacuum pumping process. The liquid crystal panel is disposed in the vacuum space. The control circuit board is electrically connected to the liquid crystal panel for controlling the liquid crystal panel.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Changing table
ActiveUS20220061547A1Shorter unsupported spanImprove comfortDressing tableNursing bedsSupporting systemSupport system
A changing table has a changing surface on which an individual can lie to be changed or washed. The changing surface is formed from a sheet of semi-rigid material having a longitudinal center axis and having also, parallel to the center axis, first and second edges occupying nominal rest positions with respect to each other when there is no load on the surface, the said edges being fixed to first and second longitudinal members, the sheet and longitudinal members forming together a support system having for the first 10 mm of extension between the said center line and the said nominal rest position of the said first edge and between the said center line and the said nominal rest position of the said second edge an average spring rate in extension of more than 300 N / mm and the said semi-rigid sheet having a torsion coefficient of more than 10 Nm / radian.
Owner:ASTOR BANNERMANMEDICAL
Method for determining a position of an object
ActiveUS7440868B2Precise positioningLow technical expenditureFinanceDigital computer detailsAlgorithmComputer vision
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com