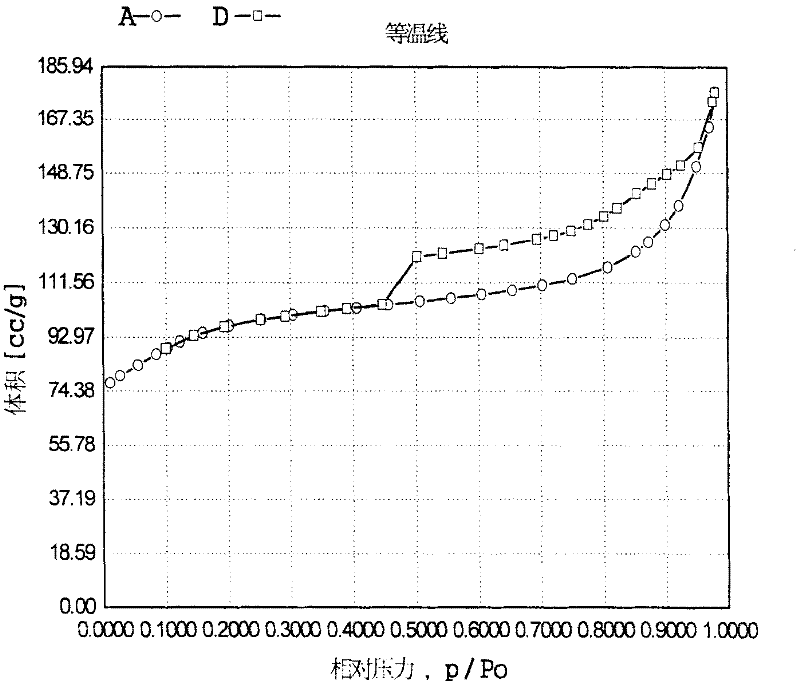
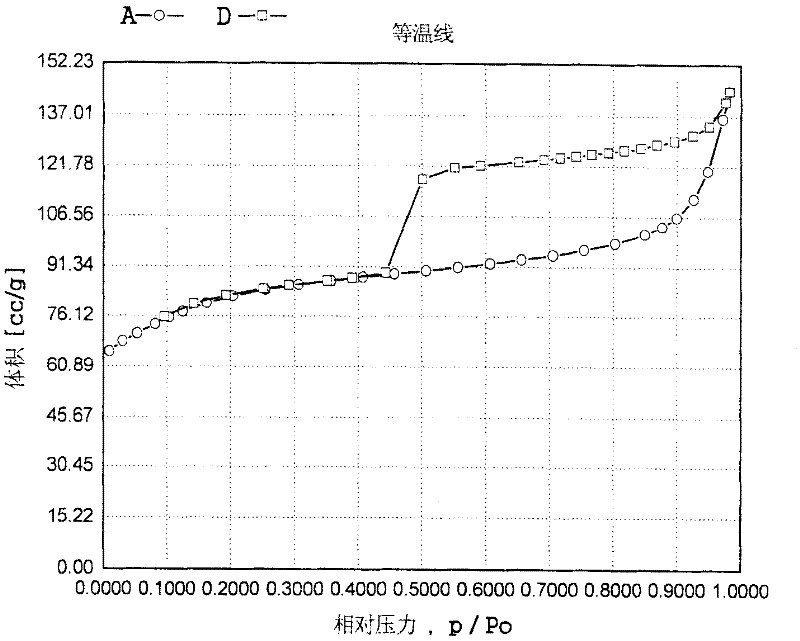
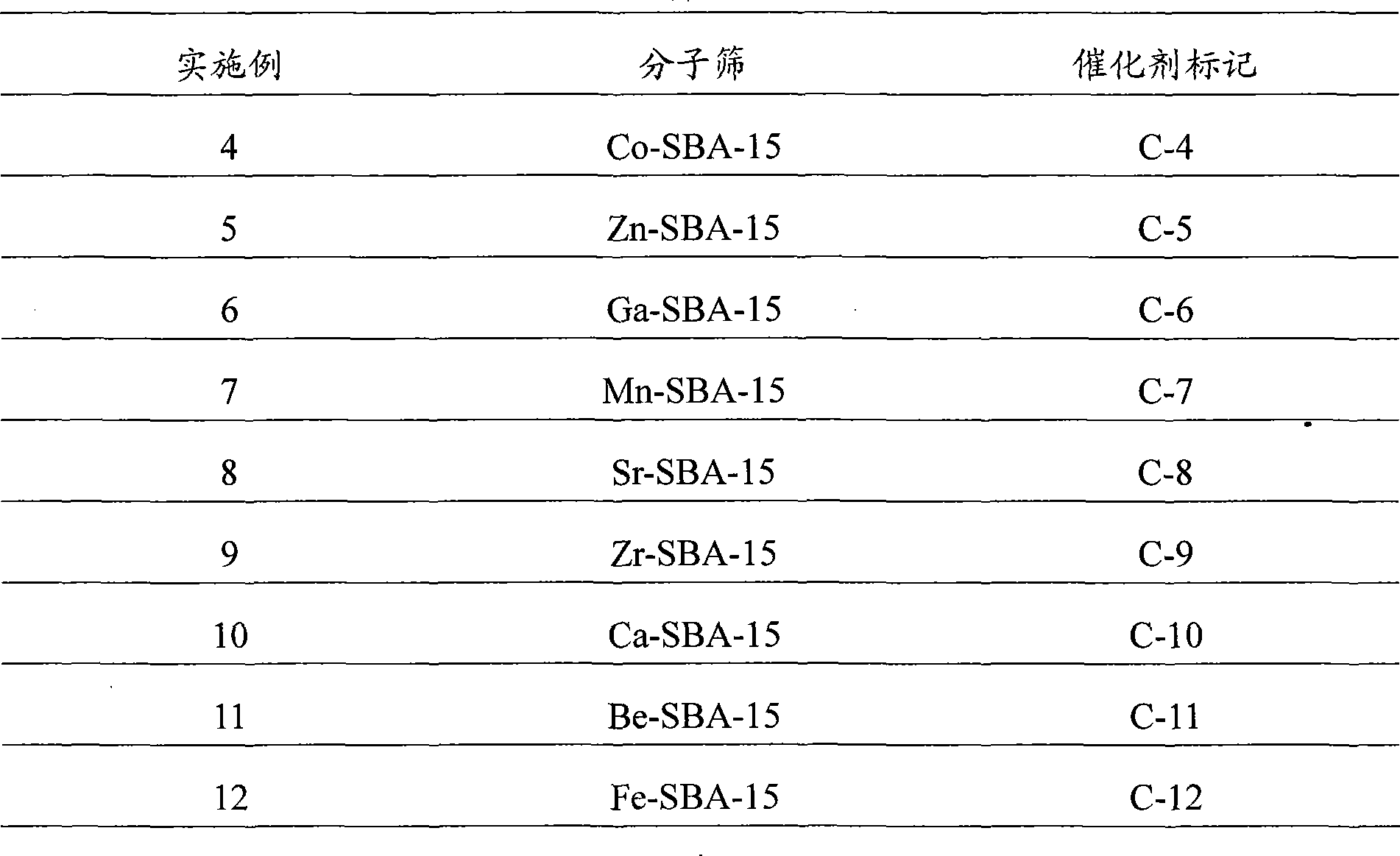
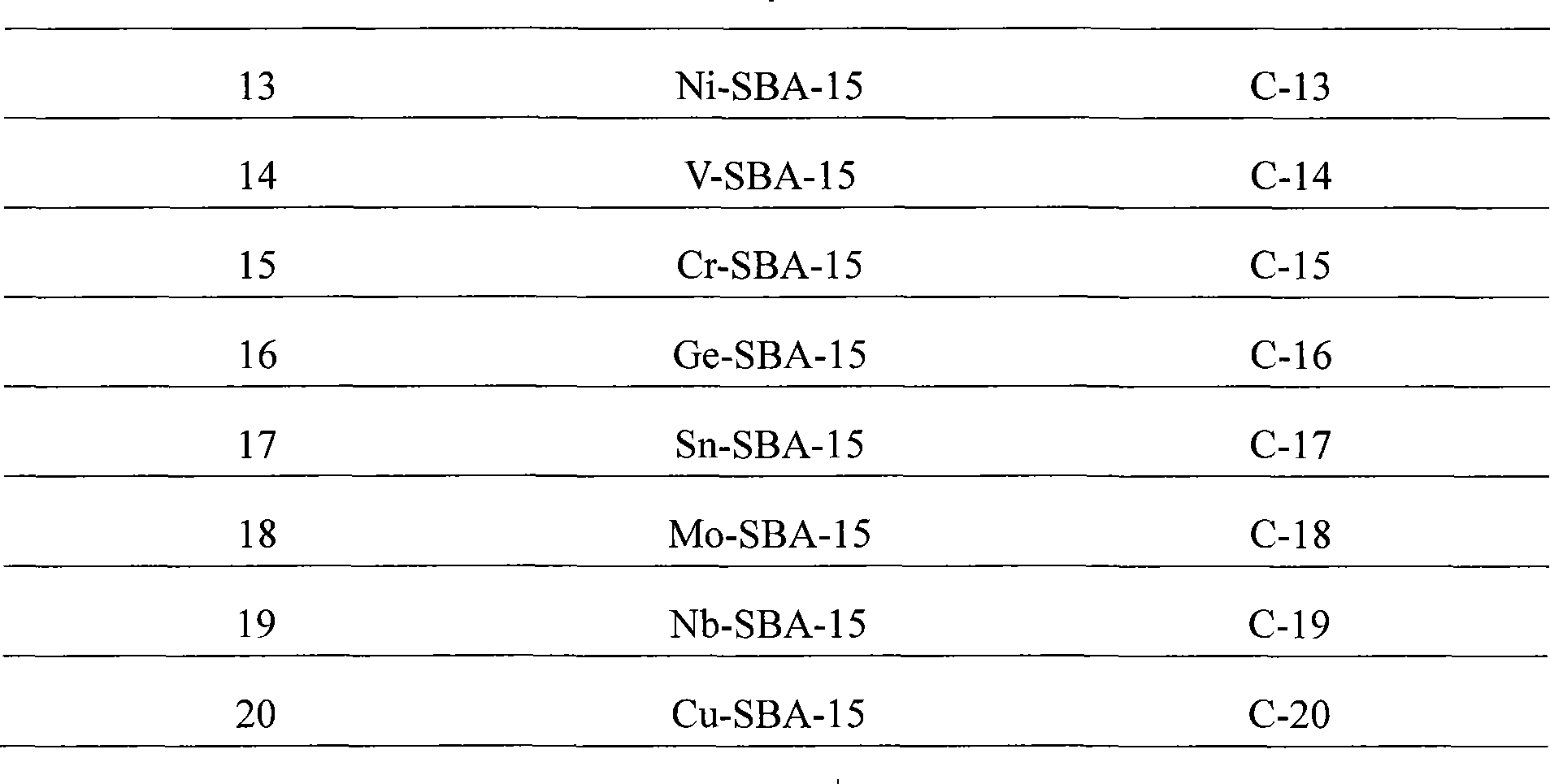
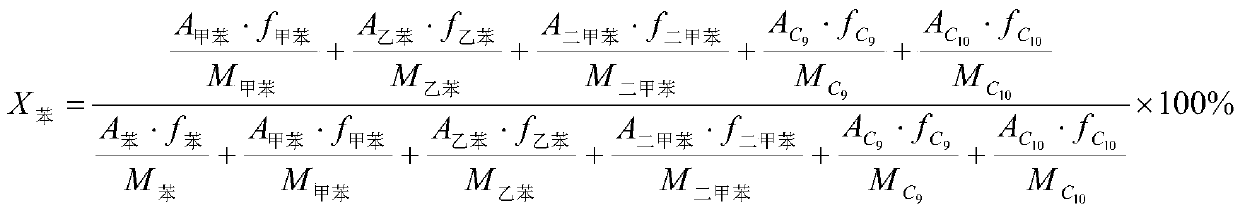
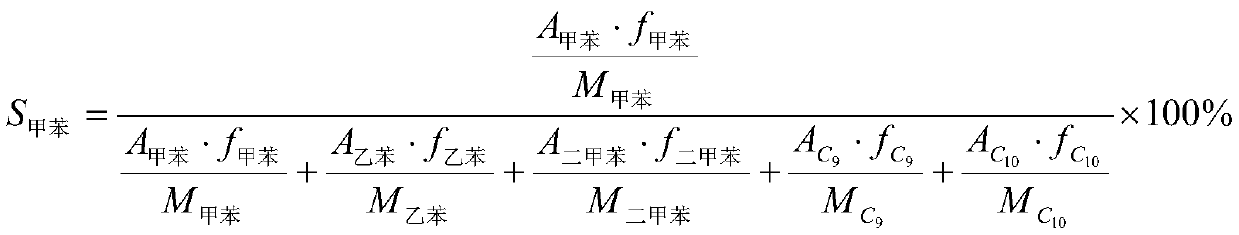
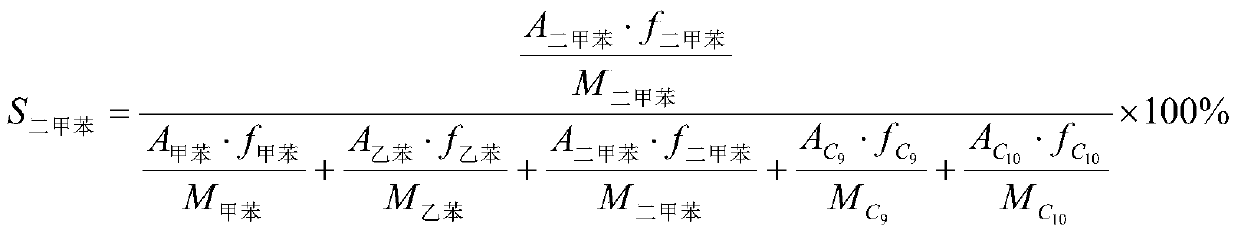
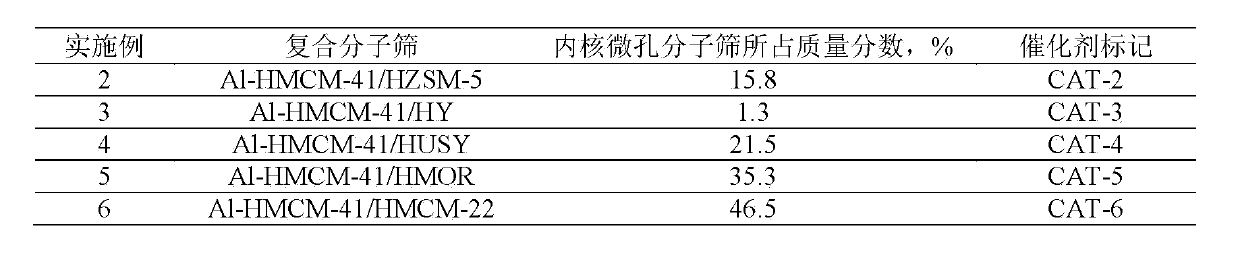
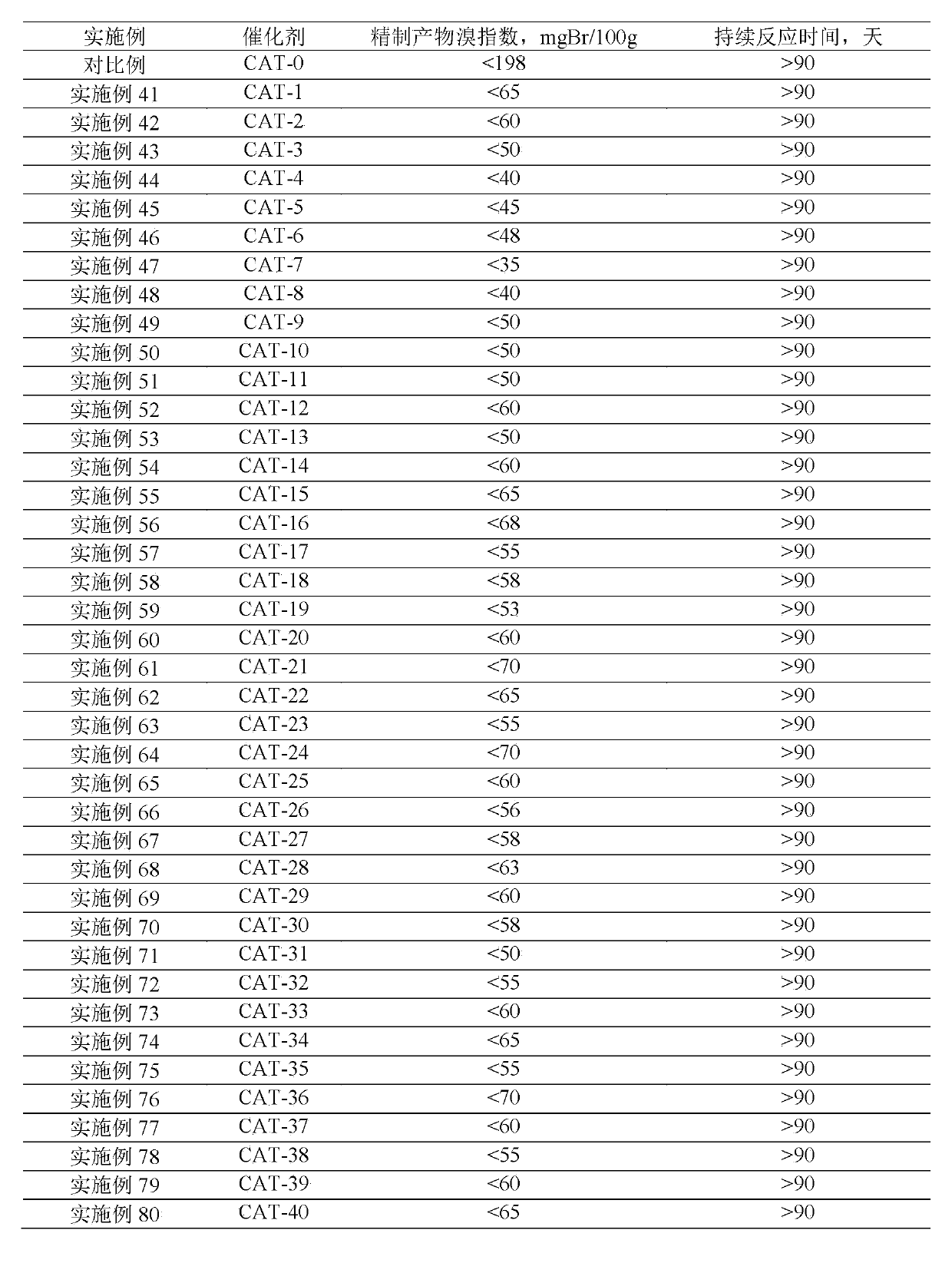
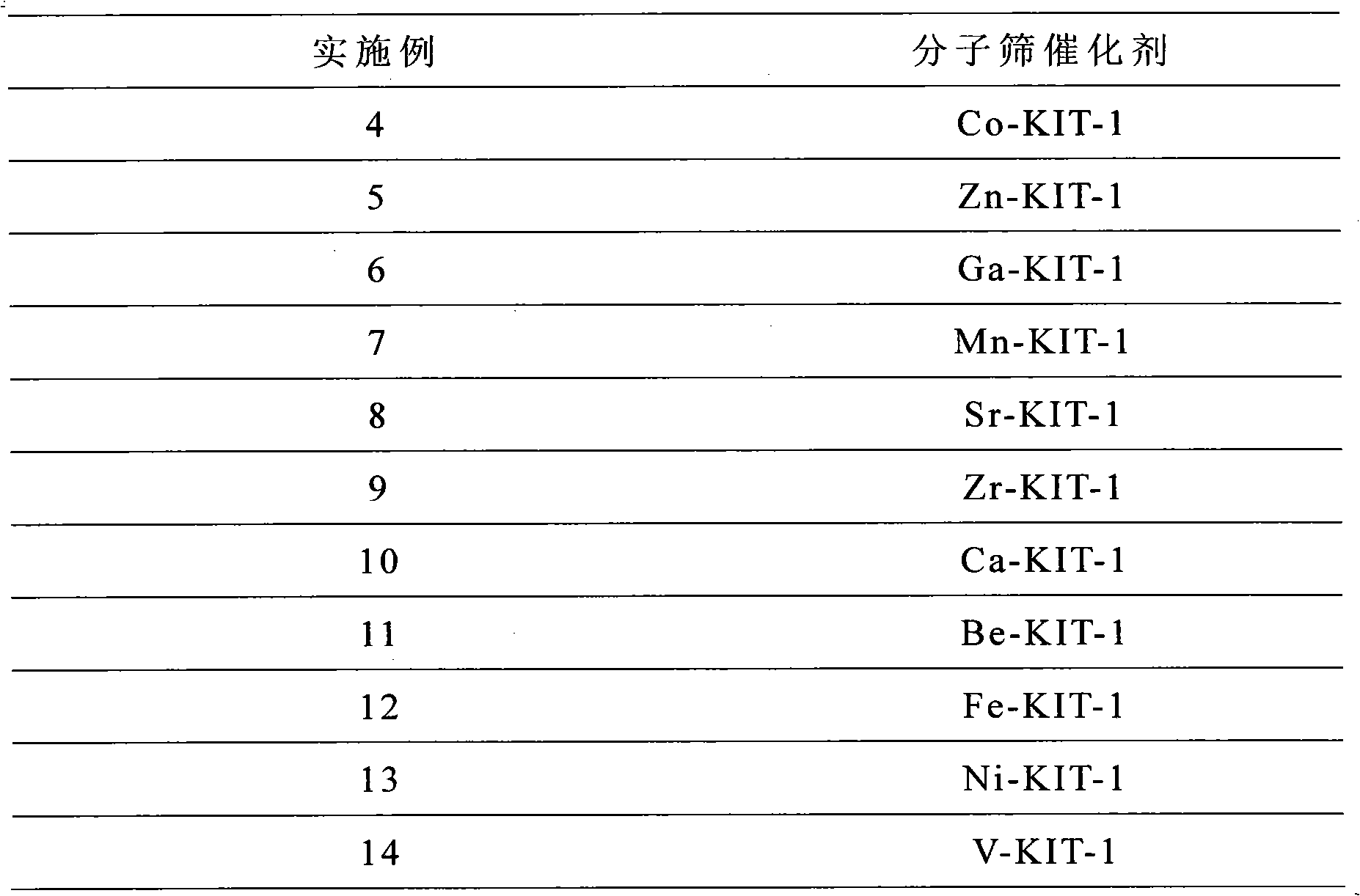
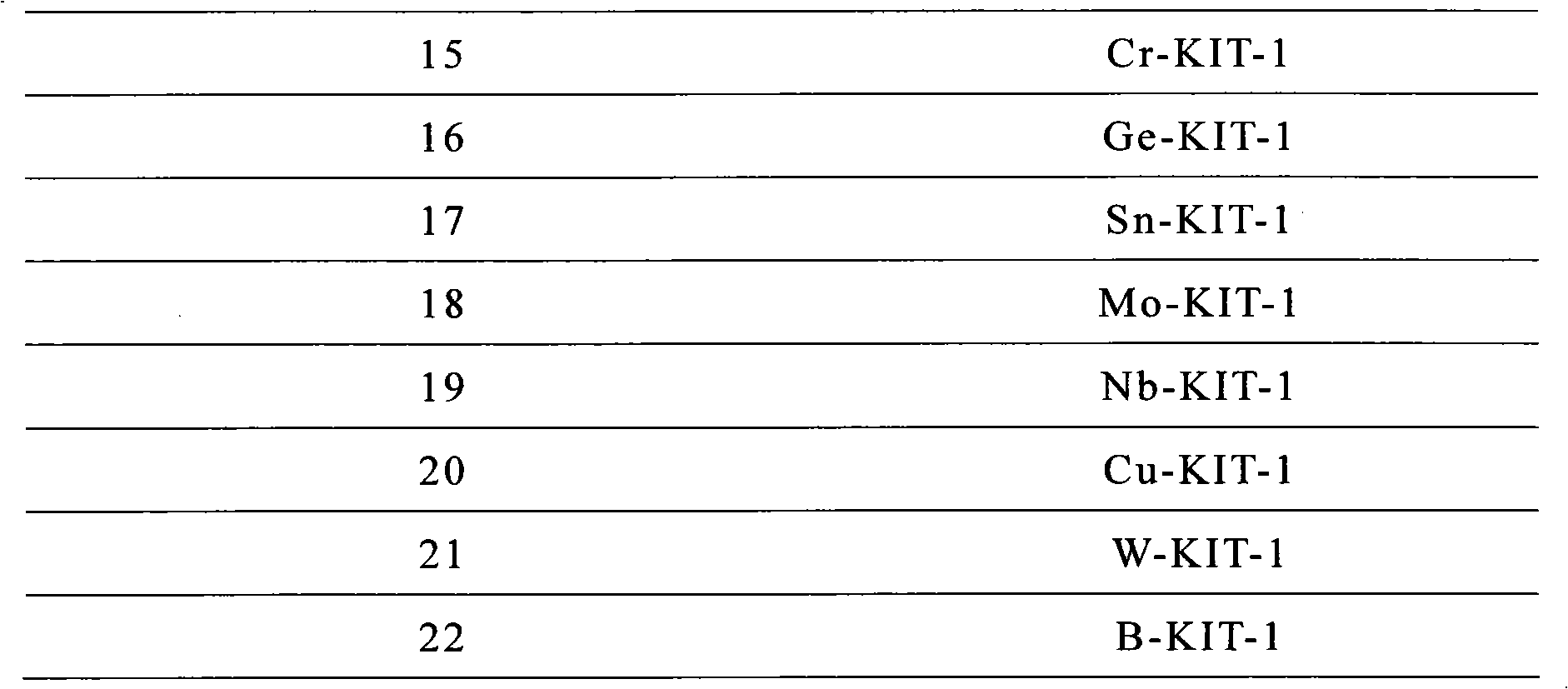
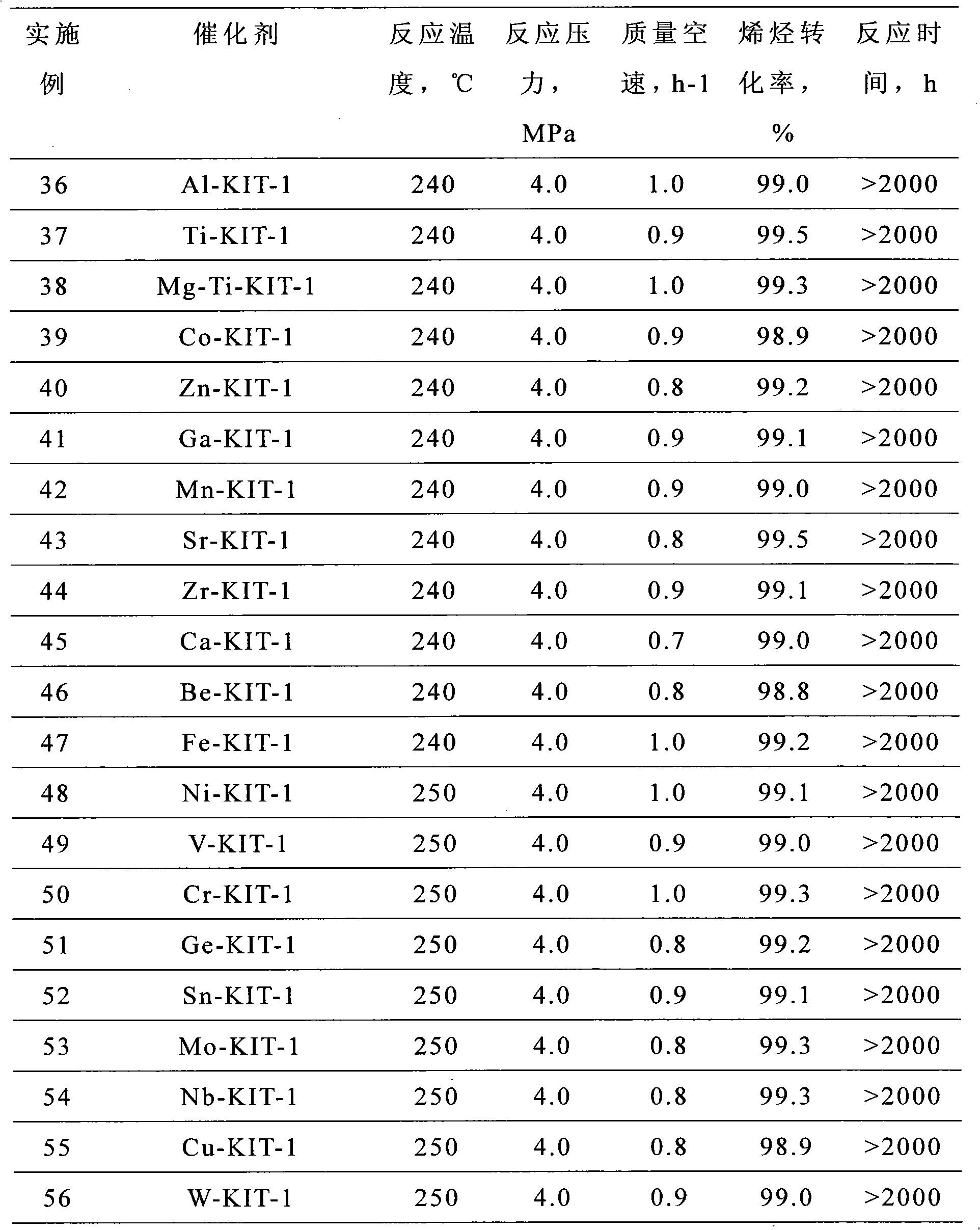
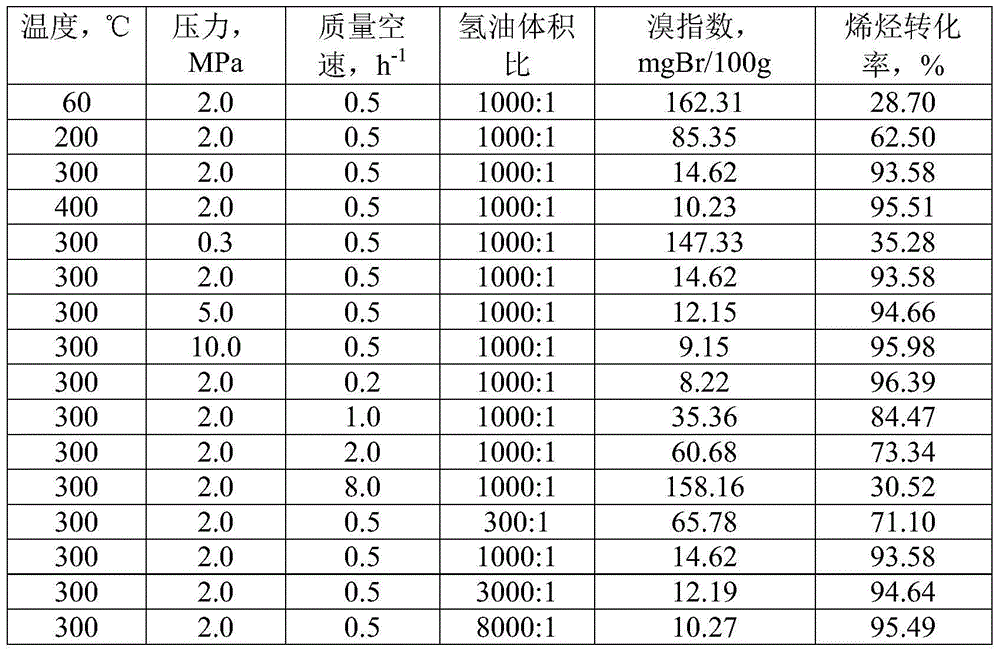
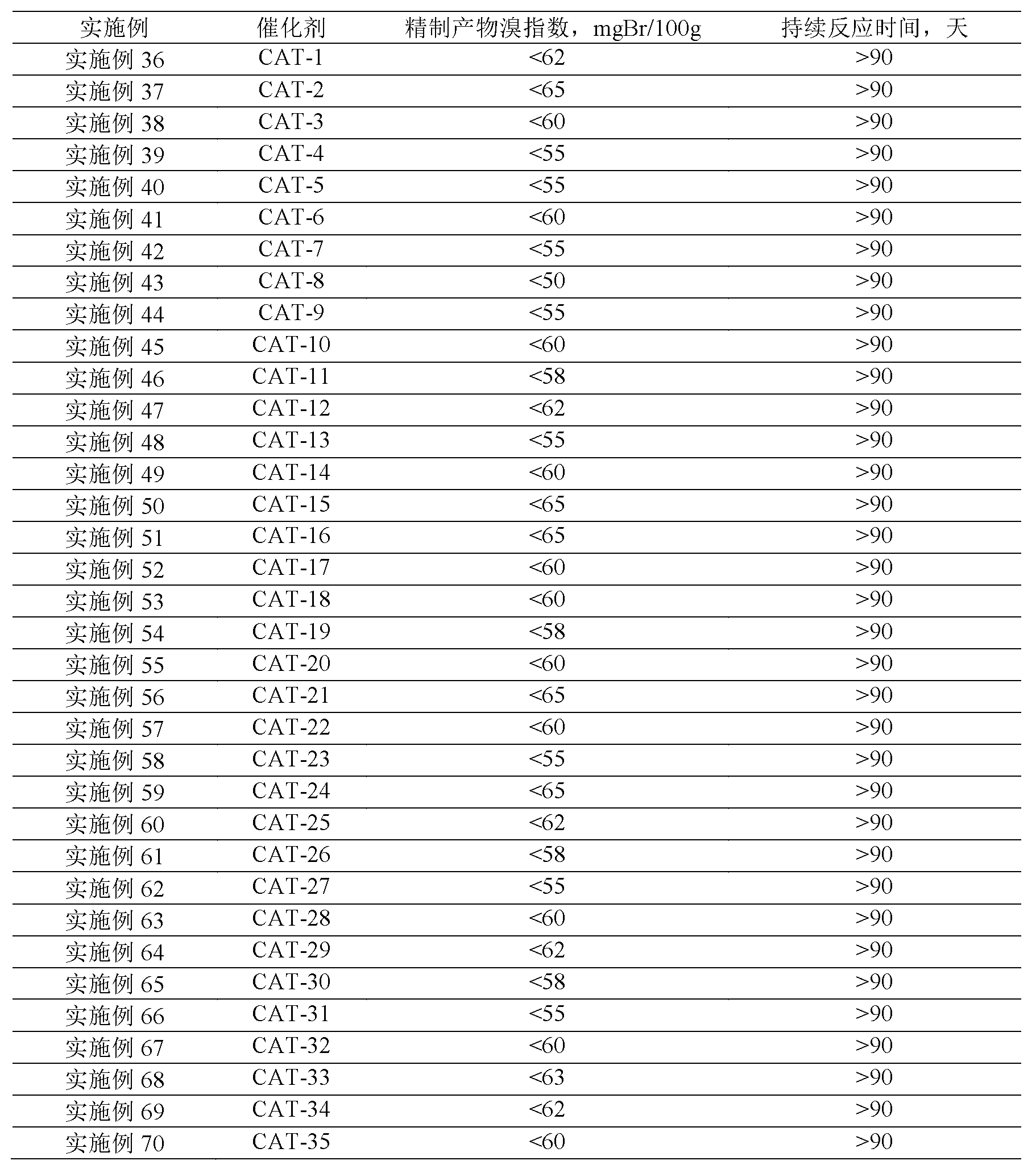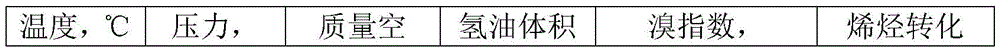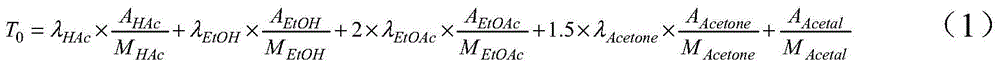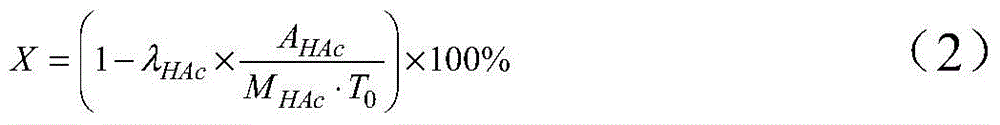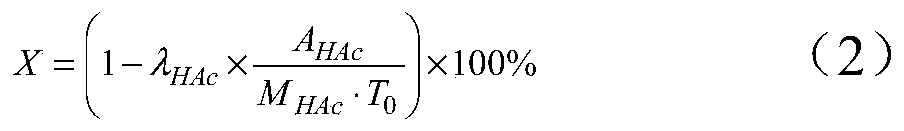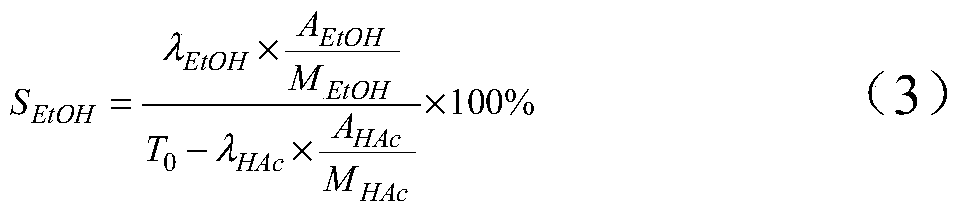Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41results about How to "Long stable operation time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for removing micro-quantity alkene in aromatic hydrocarbon
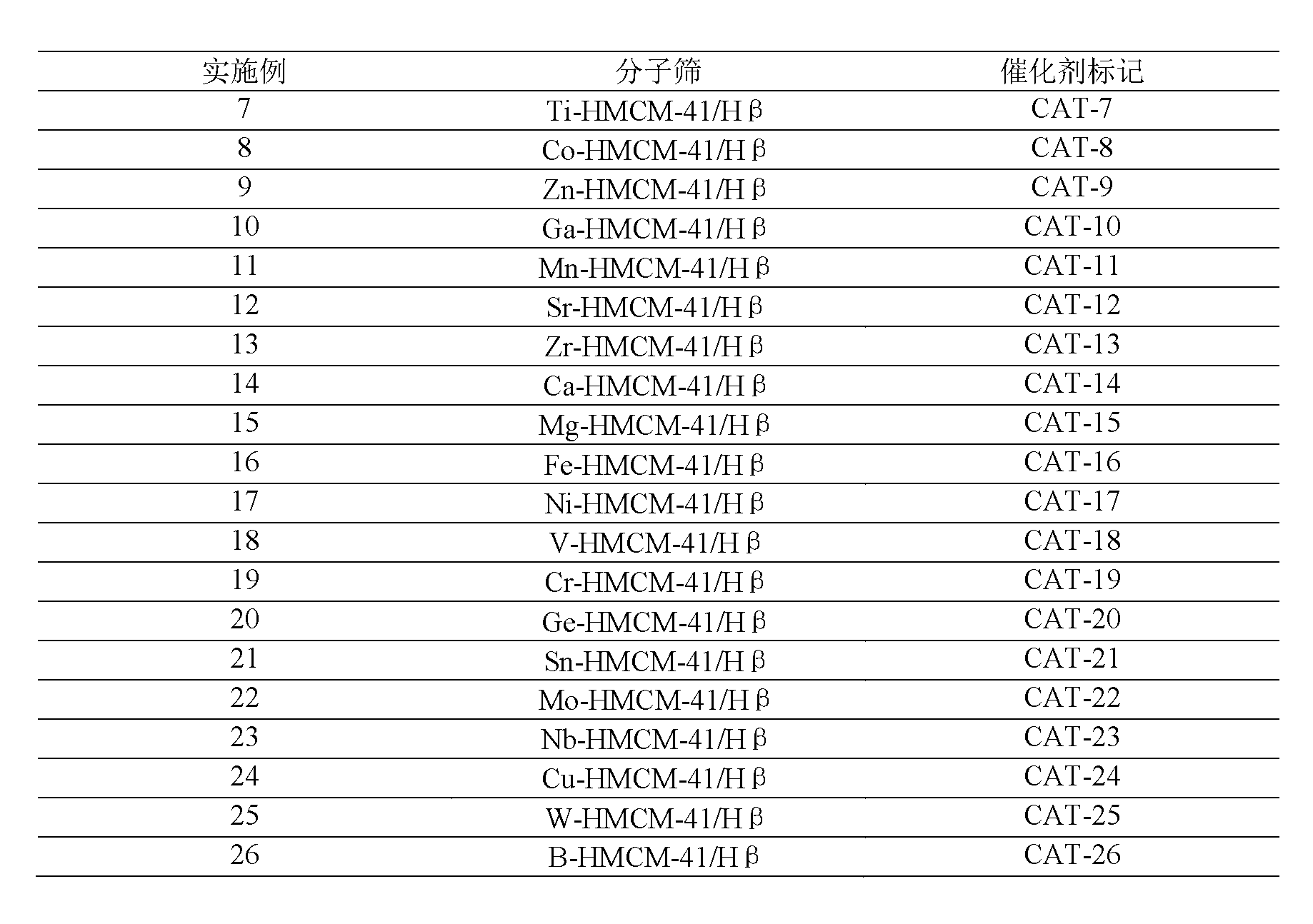
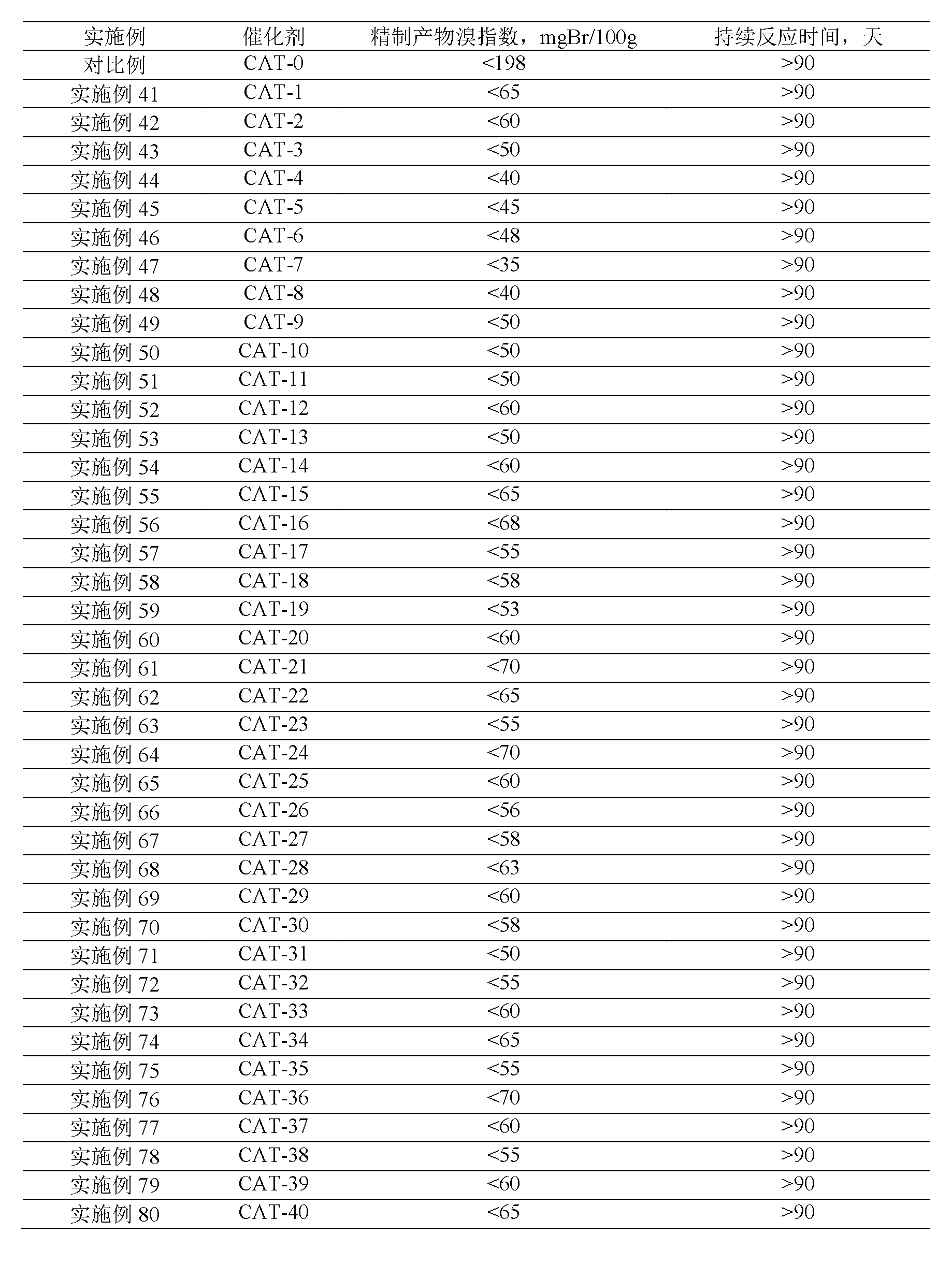
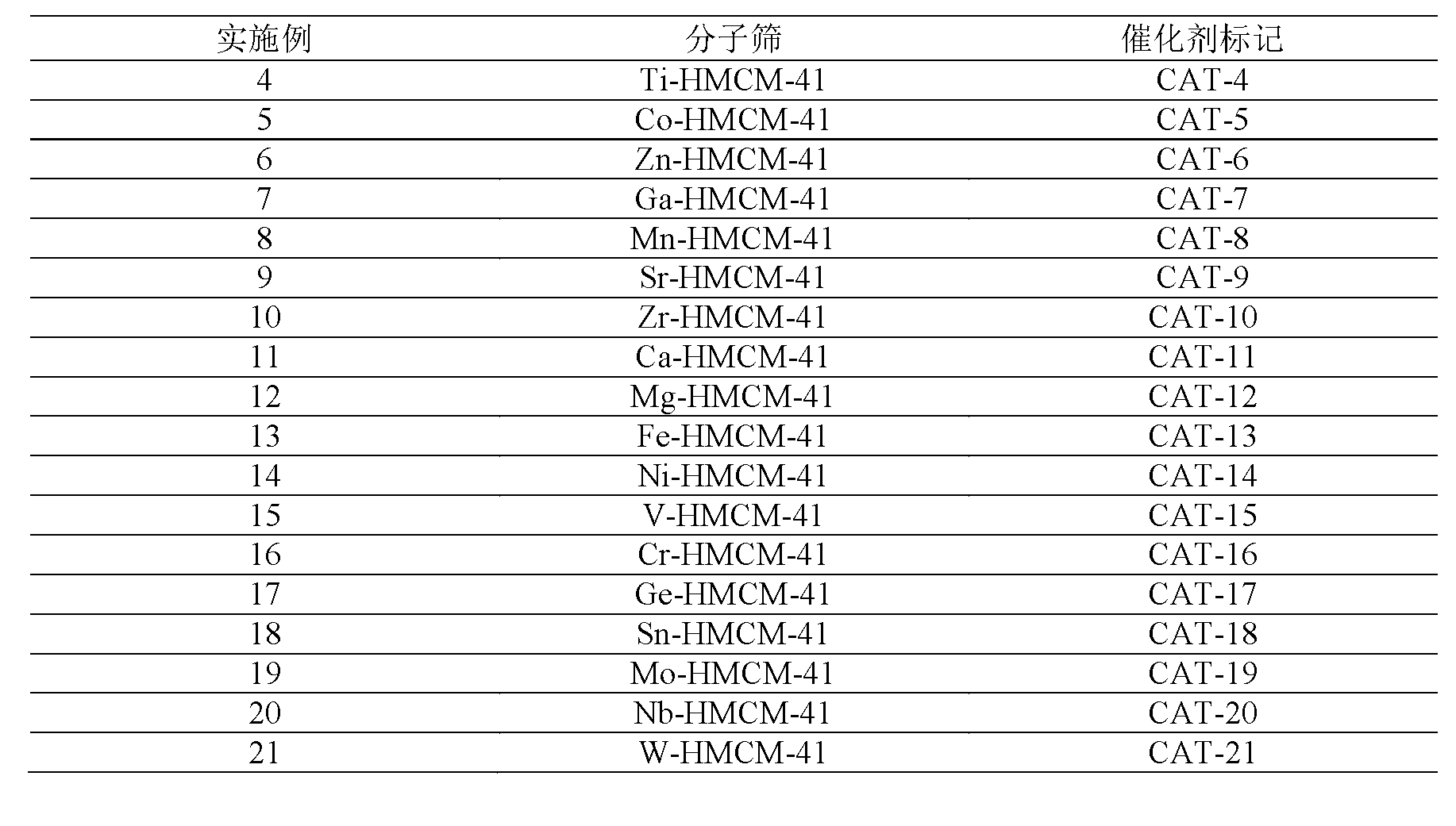
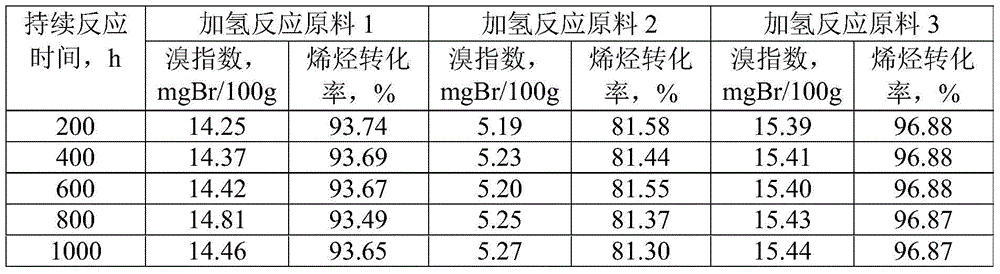
ActiveCN103012034ASimple processDoes not consume hydrogenChemical recyclingChemical modification purification/separationAlkyl transferSolid acid
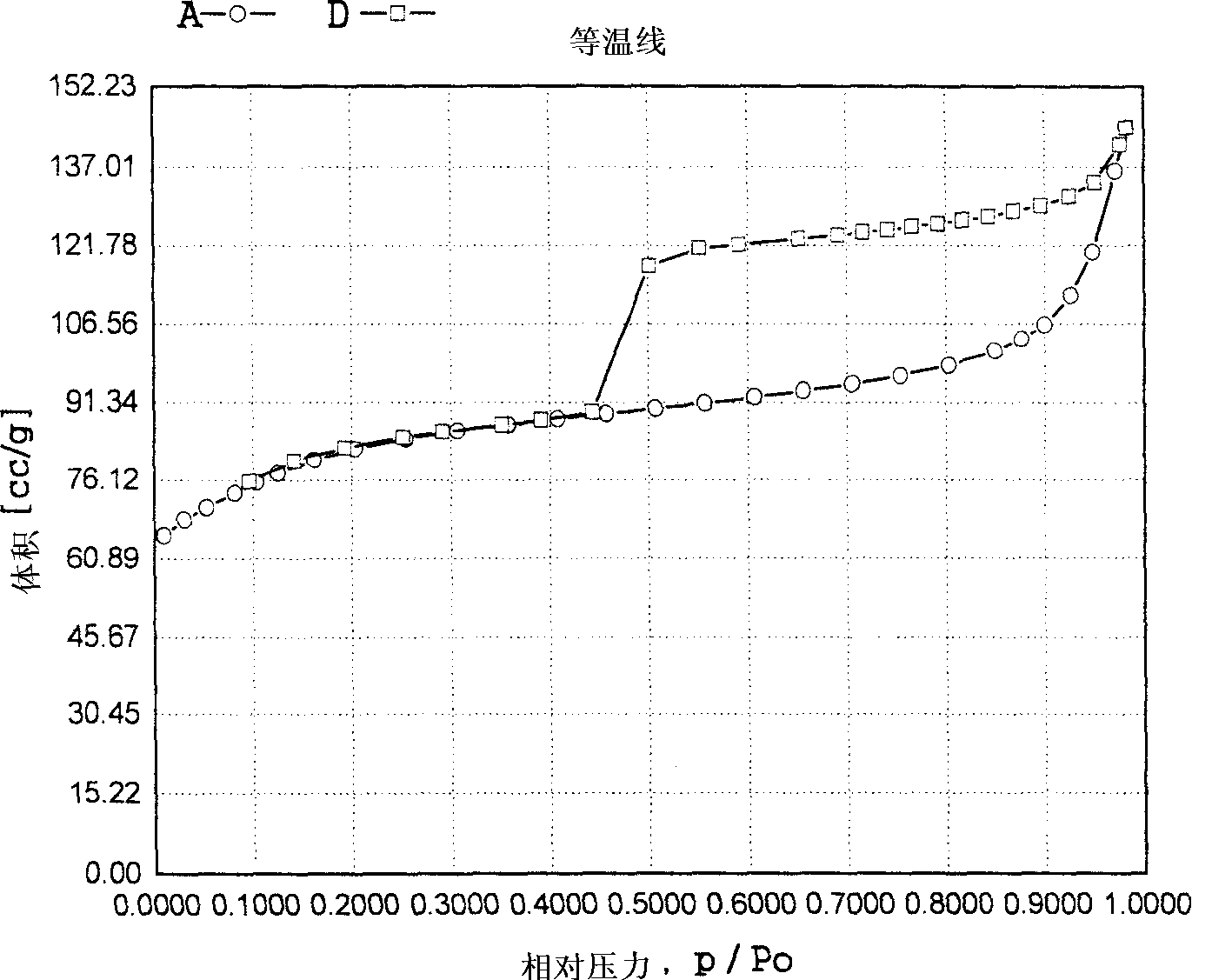
The invention discloses a method for removing micro-quantity alkene in aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the following steps of: contacting and reacting the aromatic hydrocarbon with a solid acid catalyst under the condition of temperature of 30-350 DEG C, pressure of 0.1-12MPa and feeding quality airspeed of 0.1-15 h<-1>, so that micro-quantity alkene in the aromatic hydrocarbon undergoes adsorbing, overlapping and alkylation reaction so as to remove the micro-quantity alkene in the aromatic hydrocarbon. The method is simple in process procedure, free of oxygen consumption and low in device investment and operation expense; and the catalyst is good in activity stability, the device is long in stable operation time, the aromatic hydrocarbon loss is small, the frequent switching operation between reactor reaction and regeneration is avoided, and the catalyst can be regenerated, so that a great deal of waste catalyst is prevented from being buried, and the environment is less polluted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing trace hydrocarbon out of aromatic hydrocarbon by utilizing HMCM-41 type mesoporous molecular sieve
ActiveCN103012035ASimple processLow device investment and operating costsChemical modification purification/separationMolecular sieveAlkene
The invention discloses a method for removing hydrocarbon out of aromatic hydrocarbon by utilizing an HMCM-41 type mesoporous molecular sieve. The method comprises the following steps of allowing aromatic hydrocarbon to contact and react with solid acid catalyst under conditions that the temperature is between 30 and 350 DEG C, the pressure is between 0.1 and 12MPa and the feeding mass space velocity is between 0.1 and 15 hour<-1> to obtain hydrocarbon removed aromatic hydrocarbon, wherein the hydrocarbon is reformed oil, reformed hydrocarbon or aromatic hydrocarbon generated by a steam cracking device. The method is simple in process flow, does not consume hydrogen, and is low in device investment and operation cost; the catalyst is good in activity stability, the device is stable and long in operation time, less hydrocarbon is lost, and operation of frequent switching between reaction and regeneration of the reactor can be avoided; and the catalyst is reproducible to avoid massive waste catalyst accumulation and bury, and has small influence on the environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis method of linear alkylbenzene
InactiveCN1868985AImprove conversion rateEasy to operateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkyl transferMolecular sieve
A process for preparing straight-chain alkylbenzene from C2-C20 straight-chain olefine and benzene features the alkylating reaction between benzene and olefine in the ratio of (2-100):1 in supercritical condition (290-450 deg.C and 5-15 MPa) under the action of solid acid catalyst. Said catalyst is the P-Al molecular sieve with AIPO4-5 crystal structure or the P-Al molecular sieve composition containing substitute element.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of preparing linear alkylbenzene
InactiveCN101058523AGood activity and stabilityImprove conversion rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkyl transferMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of straight-line alkyl benzene, which comprises the following steps: adopting straight-line olefin with carbon atom number between 2 and 20 and benzene as raw material; inputting in the reactor; reacting benzene and olefin with molar rate at 2-100:1 at 290-450 deg. c under 5-15Mpa hypercritical condition; setting the air speed at 0. 1-20h-1; making solid acid as catalyst; adopting one of loaded modified (1) SBA-15 typed molecular sieve, (2) HY typed molecular sieve, (3) USY typed molecular sieve, (4) H beta typed molecular sieve, (5) H-Moderite typed molecular sieve, (6) HZSM-20 typed molecular sieve as composite typed solid acid catalyst. The invention improves transmitting rate of olefin with stable operation, which possesses good using prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing trace hydrocarbon from aromatic hydrocarbon by utilizing AlPO4-5 type Al-P molecular sieve
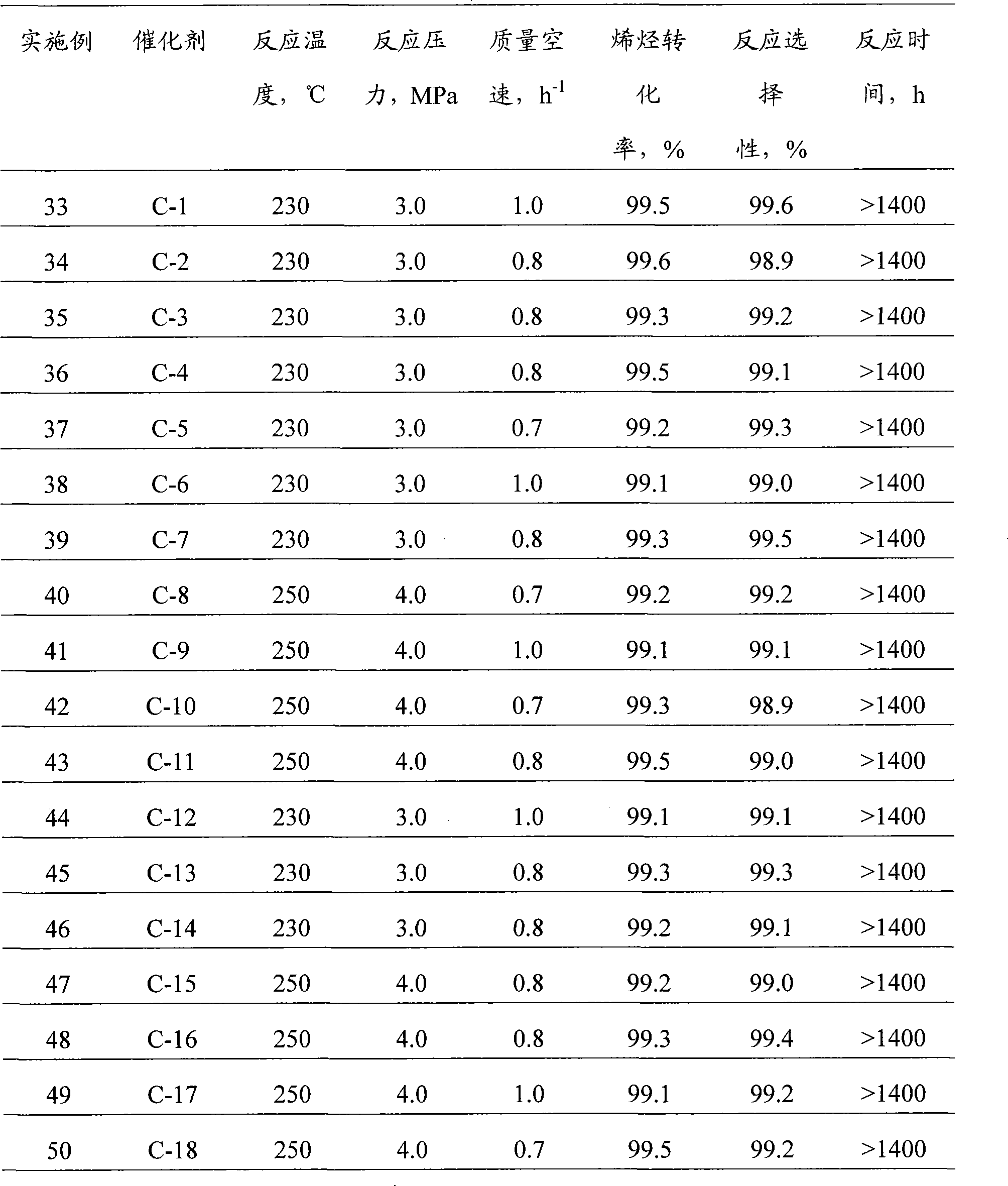
InactiveCN103013556ASimple processDoes not consume hydrogenCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for removing trace hydrocarbon from aromatic hydrocarbon by utilizing an AlPO4-5 type Al-P molecular sieve. The method comprises the following steps: allowing aromatic hydrocarbon to contact and react with solid acid catalyst under conditions that the temperature is between 30 and 350 DEG C, the pressure is between 0.1 and 12MPa and the mass space velocity is between 0.1 and 15 hour<-1> to obtain hydrocarbon removed aromatic hydrocarbon, wherein the hydrocarbon is reformed oil, reformed hydrocarbon or aromatic hydrocarbon generated by steam cracking. The method is simple in process flow, does not consume hydrogen, and is low in device investment and operation cost; the catalyst is good in activity stability, the device is stable and long in operation time, less hydrocarbon is lost, and operation of frequent switching between reaction and regeneration of the reactor can be avoided; and the catalyst is reproducible to avoid massive waste catalyst accumulation and bury, and has small influence on the environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Propylene chloride epoxidation process in the presence of hydrogen and oxygen
ActiveCN101434586AImprove conversion rateIncrease the speed of diffusionOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsSolventOxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing epichlorohydrin by the epoxidation of chloropropene by means of catalyzing, which is characterized in that under the conditions of temperature of 0 DEG C to 180 DEG C and pressure of 0.1 MPa to 3.0 MPa, chloropropene, oxygen, hydrogen, diluents, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed and contacted for reaction; the mole ratio of the chloropropene, the oxygen, the hydrogen, the diluents, the solvent and the catalyst is 1: (0.1 to 10): (0.1 to 10): (0 to 100); the mass ratio of the chloropropene and the catalyst is (0.1 to 50):1; the mass ratio of the solvent and the catalyst is (20 to 1000):1; the catalyst refers to a cellular titanium silicon material or a composite containing the cellular titanium silicon material; the composition of the cellular titanium silicon material expressed in the manner of oxides is xTiO2 question mark 100SiO2 question mark yEm question mark On question mark zE, wherein, the value of X is between 0.001 and 50.0; the value of (y plus z) is between 0.005 and 20.0 and y divided by z is less than 1; E represents one or more noble metals selected out of Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Os, Ir, Pt and Au; m and n are numbers meeting the need of E at oxidation state; and the grains of the material are partially hollow or completely hollow. The method obviously promotes the transformation rate of chloropropene and has high selectivity and hydrogen effective utilization rate and long running period.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Selective hydrogenation catalyst for gasoline and process
InactiveCN1252222CGood choiceHigh selectivityRefining to eliminate hetero atomsActive componentHydrodesulfurization
The present invention relates to a selective hydro-desulfurization catalyst of gasoline and process for using said catalyst. Said invented catayst uses alumina as carrier, uses molybdenum and cobalt as active component, at the same time contains adjuvant potassium and phosphorus, and the optimized atomic ratio of phosphorus and potassium is 1-2. Said invented catalyst has good selectivity and stability, and at the same time has proper activity, and is mainly used for selective hydro-desulfurization of catalytic cracked gasoline.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
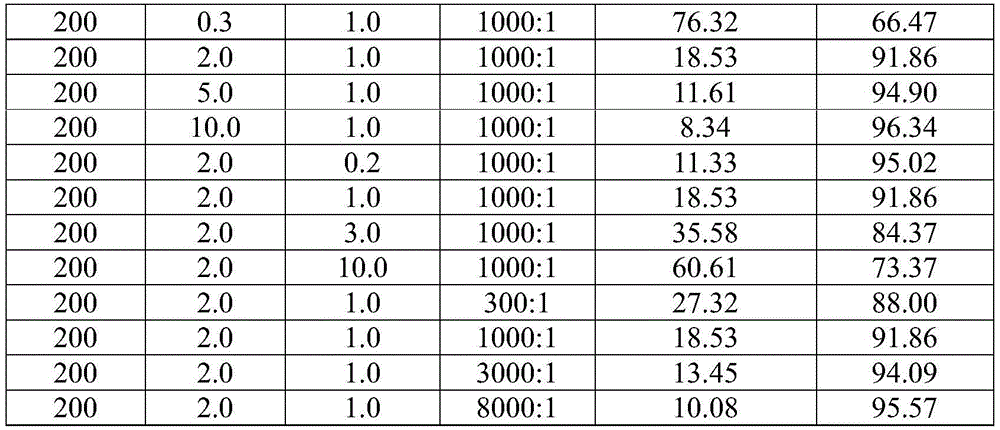
Linear alkylbenzene catalytic hydrofining method
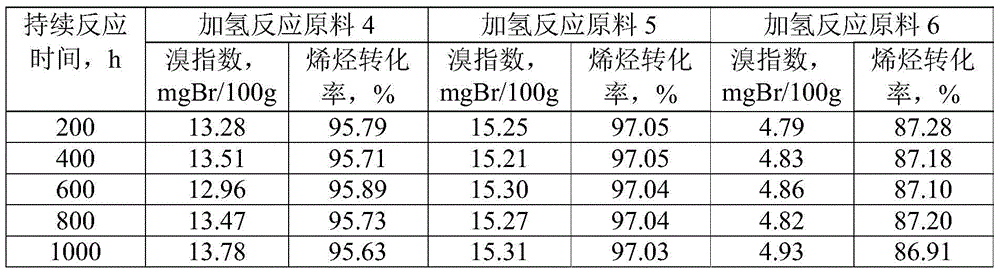
ActiveCN105601463AAvoid pollutionSimple processHydrocarbon purification/separationCatalyst activation/preparationAlkyl transferBenzene
The invention discloses a linear alkylbenzene catalytic hydrofining method. The method comprises the steps that under the conditions that the temperature ranges from 60 DEG C to 350 DEG C, pressure ranges from 0.3 MPa to 10.0 MPa, the mass space velocity ranges from 0.2 h<-1> to 10.0 h<-1>, and the hydrogen and oil volume ratio ranges from 300:1 to 8000:1, a hydrogenation raw material and hydrogen are mixed and react with a palladium supported type catalyst in a contact mode so that olefin can be saturated, and then a trace amount of olefin is removed, the bromine index of linear alkylbenzene is reduced, and the product quality is improved; the hydrogenation raw material is linear alkylbenzene obtained by alkylation of benzene with C10-C14 linear olefins mixture in a distillation separation mode, or is alkylation of benzene with C10-C14 linear olefins mixture. The technological process is simple, the catalyst activity is good in stability, the stable operation time of a device is long, reactor reaction and regeneration frequent switching operation can be avoided, less loss of linear alkylbenzene is realized, the catalyst is reproducible, postprocessing of a large number of catalysts can be avoided, and less influence is caused for an environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for synthesizing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether by continuous reactions in microtube
ActiveCN103304442AReduce operating costsThe concentration is basically constantOximes preparationPotassium hydroxideOil phase
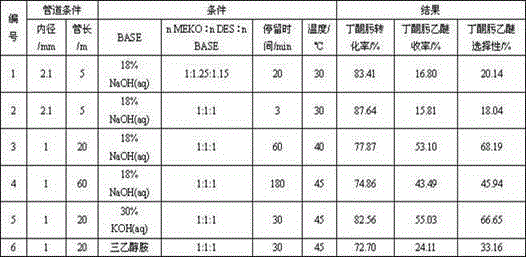
The invention discloses a process for synthesizing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether by continuous reactions in a microtube. In the process, diacetylmonoxime and diethyl sulfate are directly reacted to synthesize diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether in a condition that the temperature is 30-45 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1MPa in the presence of strong base with the adoption of a continuous reaction technology in the microtube, wherein the strong base is sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or an alcamine compound. In the process, diethyl sulfate, the alkali liquor and diacetylmonoxime are respectively fed by a precise micro pump, wherein diacetylmonoxime sequentially mixed with the alkali liquor and diethyl sulfate reacts in a microtube reactor. The product through a heat exchanger is condensed and collected at low temperature, and is stewed and layered by a chromatographic separator. A water phase is extracted and separated by a micro extraction tower, and an oil phase containing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether is rectified and purified by a rectifying tower, so that the final product diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether is obtained. The process is high in selectivity of diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether, mass transfer and heat transfer can be remarkably enhanced, and hydrolysis of diethyl sulfate is effectively avoided. The process is simple in process, long in stable transfer time, low in cost, easy to amplify and suitable for the industrialized production requirement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing phenol
ActiveCN101434515AImprove conversion rateLong stable operation timeOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsOxidation stateOxygen
The invention discloses a preparing method of phenol, which is characterized in that in the conditions that the temperature is 0 to 150 DEG C and the pressure is 0.1 to 3.0MPa, benzene, oxygen, hydrogen, diluent gas, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed for contact reaction. The mol ratio of the benzene to the oxygen to the hydrogen to the diluent gas is equal to 1 : (0.1 to 10) : (0.1 to 10) : (0 to 100); the mass ratio between the benzene and the catalyst is (0.5 to 50) : 1; the mass ratio between the solvent and the catalyst is (20 to 1000) : 1; the catalyst is a millipore titanium silicon material or a composition containing the millipore titanium silicon material; and the component of the millipore titanium silicon material can be expressed by oxide as xTiO2 question mark 100SiO2 question mark yEmOn question mark zE, wherein, x is equal to 0.001 to 50.0, (y plus z) is equal to 0.005 to 20.0, y / z is less than 1, E represents one or a plurality of noble metals such as Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Os, Ir, Pt and Au, m and n are the numbers meeting the oxidation state of E. The crystal grain is completely or partially in hollow-core structure.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
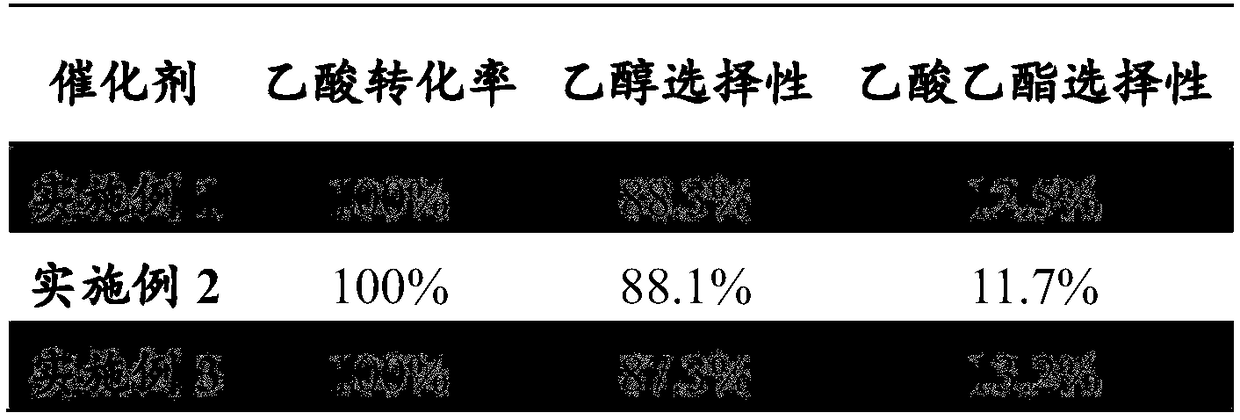
Method for preparing ethanol by hydrogenating acetic acid
ActiveCN105646148ALow priceReduce manufacturing costPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationTransition metal carbidesAcetic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing ethanol by hydrogenating acetic acid. The method comprises the following steps of mixing the acetic acid and hydrogen under the conditions that the temperature is 250 to 400DEG C, the pressure is 0.5 to 10.0MPa, the weight hourly space velocity is 0.2 to 8.0h<-1>, and the feeding mole ratio of the hydrogen to the acetic acid is 1:1 to 20:1; performing contact reaction on a mixture and a loaded transition metal carbide catalyst; hydrogenating the acetic acid to prepare the ethanol. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the process flow is simple, the price of the catalyst is lower, the performance stability of the catalyst is good, and the stable operation time of the device is long; frequent switching operation of reaction and regeneration of a reactor can be avoided, the catalyst can be regenerated, posttreatment of a large amount of waste catalysts can be avoided, and further the influence on the environment is little.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing pyridine N-oxide
ActiveCN101570509AImprove conversion rateLong stable operation timeOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsConvex structurePyridine-N-oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing pyridine N-oxide, which is characterized in that the pyridine N-oxide is prepared by mixing pyridine, oxygen, hydrogen, diluent gas, solvent and catalyst for contact reaction at 0-180 DEG C and 0.1-3.0 MPa, wherein the mol ratio of the pyridine to the oxygen to the hydrogen to the diluent gas is 1:0.1-10:0.1-10:0-100, the mass ratio of the pyridine to the catalyst is 0.5-50:1, and the mass ratio of the solvent to the catalyst is 20-1000:1, and in addition, the catalyst is microporous titanium silicon material or compound containing the microporous titanium silicon material, an oxide formed by the microporous titanium silicon material has the formula of xTio2.100SiO2.yEmOn.zE, wherein x is equal to 0.001-50.0, y+z is equal to 0.005-20.0, y / z is less than 5, E can be one or more of such noble metals as Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Os, Ir, Ag, Pt and Au, and both m and n are the numbers meeting the need of the oxidation of the E. The grains of the epoxy propanol can be in hollow structures or concavo-convex structures, and the method ensures the high conversion rate, the good selectivity and the long operation period of the pyridine.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for removing trace olefin from aromatic hydrocarbon
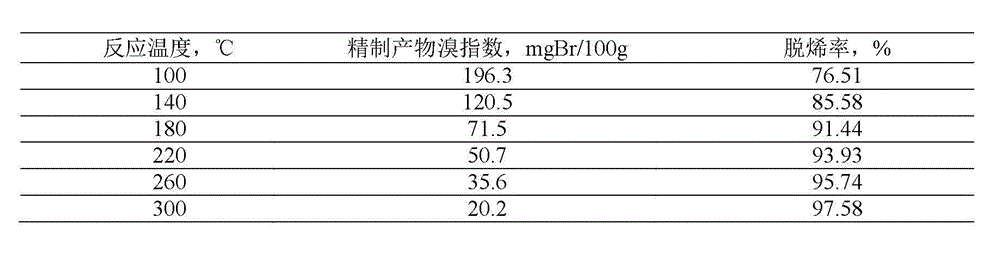
ActiveCN103012037ASimple processLow device investment and operating costsChemical modification purification/separationChemistryEnvironment effect
The invention discloses a method for removing trace olefin from aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the step of carrying out contact reaction on aromatic hydrocarbon and a solid acid catalyst under the conditions that the temperature is 30-400 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-12MPa and the feeding mass space velocity is 0.1-15h<-1> to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon after the olefin is removed. The method is simple in process without consuming hydrogen, low in device investment and operation cost, good in catalyst activity stability, long in device stable operation time and less in aromatic hydrocarbon loss; and reactor reaction and regeneration frequent switching operation can be avoided and a large quantity of waste catalysts can be prevented from being stacked and embedded, and environment influence is little.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Propylene chloride epoxidation process in the presence of hydrogen and oxygen
ActiveCN101434586BImprove conversion rateIncrease the speed of diffusionOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsMass ratioOxidation state
The invention discloses a method for preparing epichlorohydrin by the epoxidation of chloropropene by means of catalyzing, which is characterized in that under the conditions of temperature of 0 DEG C to 180 DEG C and pressure of 0.1 MPa to 3.0 MPa, chloropropene, oxygen, hydrogen, diluents, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed and contacted for reaction; the mole ratio of the chloropropene, the oxygen, the hydrogen, the diluents, the solvent and the catalyst is 1: (0.1 to 10): (0.1 to 10): (0 to 100); the mass ratio of the chloropropene and the catalyst is (0.1 to 50):1; the mass ratio of the solvent and the catalyst is (20 to 1000):1; the catalyst refers to a cellular titanium silicon material or a composite containing the cellular titanium silicon material; the composition of the cellular titanium silicon material expressed in the manner of oxides is xTiO2 question mark 100SiO2 question mark yEm question mark On question mark zE, wherein, the value of X is between 0.001 and 50.0; the value of (y plus z) is between 0.005 and 20.0 and y divided by z is less than 1; E represents one or more noble metals selected out of Ru, Rh, Pd, Re, Os, Ir, Pt and Au; m and n are numbers meeting the need of E at oxidation state; and the grains of the material are partially hollow or completely hollow. The method obviously promotes the transformation rate of chloropropene and has high selectivity and hydrogen effective utilization rate and long running period.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for synthesizing linear alkylbenzene
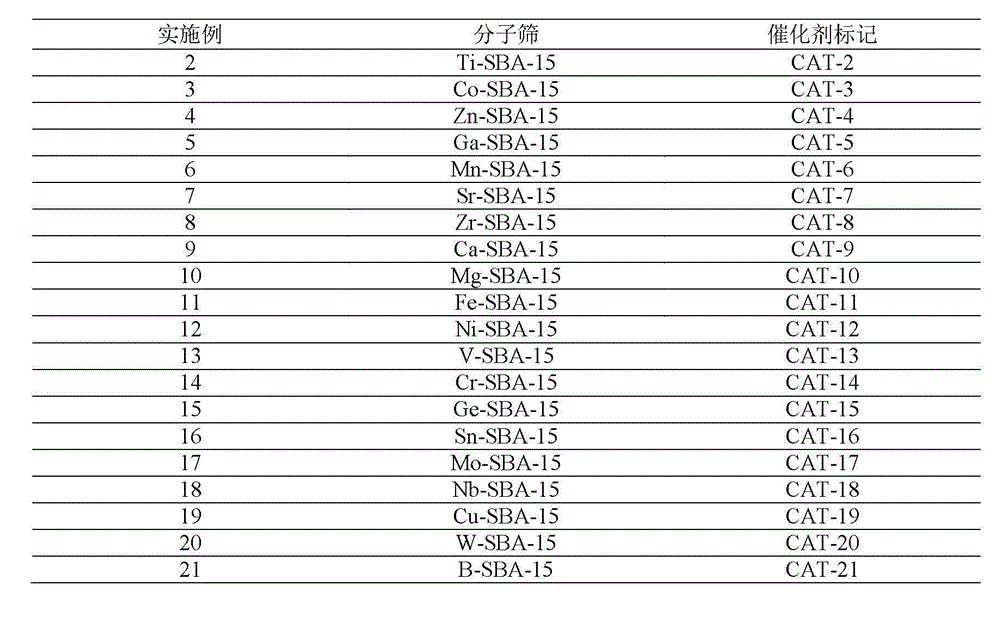
ActiveCN101289358BNot corrosiveEnvironmentally friendlyMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsSolid acidLinear alkylbenzene
The invention provides a synthetic method for linear alkylbenzene. By taking linear olefin containing 2 to 20 carbon atoms and benzene as raw materials under the reaction condition of a temperature being 10 to 450 DEG C, a pressure being 0.1 to 15MPa, the ratio of the amount of substances of benzene and the olefin is 2 to 100:1 and the airspeed of a feeding total mass is 0.1 to 20 h<-1>, and an alkylation reaction is carried out by catalyzing by a solid acid catalyst, the linear alkylbenzene is obtained. The solid acid catalyst is M-SBA-15 typed mesopore molecular sieve catalyst or compound solid acid catalyst which is obtained by modifying the M-SBA-15 typed mesopore molecular sieve catalyst. The catalyst adopted by the invention has no corrosion, is friendly to environment and has good activity stability; therefore, higher olefin conversion and reaction selectivity can also be obtained even under comparatively lower temperature. Furthermore, the device is stable and has long operation time; therefore, frequent switching operation on the reaction and regeneration of the reactor can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing high-octane aromatic gasoline by alkylation of benzene and methanol
InactiveCN111518584AImprove catalytic performanceReduce coking deactivation rateMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention provides a method for producing high-octane aromatic gasoline by alkylation of benzene and methanol, which comprises the following steps: inputting raw materials benzene and methanol into a fixed bed reactor, contacting with a modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst, and carrying out alkylation reaction to generate high-octane aromatic gasoline mainly containing toluene and xylene;the modified HZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst with high catalytic performance is prepared by utilizing the dispersion effect of a penetrant and adopting a permeation impregnation method of a metal compound, so that a metal oxide tends to be uniformly loaded in molecular sieve pores, the surface acidity and the pore diameter are effectively regulated and controlled; the methanol alkylation selectivity reaches 98% or above, and the total selectivity of toluene and xylene is close to 100%; the methanol conversion rate reaches 100%, the benzene conversion rate is close to 40%, the activity stabilization time of the catalyst is longer than 2160 h, and the deactivated catalyst can be regenerated; inert gas or hydrogenated hydrogen does not need to be jointly fed into the reactor, the reaction technological process is simple, and energy consumption is low.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of method of hydrogenation of acetic acid to produce ethanol
ActiveCN105646148BLow priceReduce manufacturing costPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationTransition metal carbidesAcetic acid
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing micro-quantity alkene in aromatic hydrocarbon
ActiveCN103012034BGood activity and stabilityReduce lossesChemical recyclingChemical modification purification/separationAlkyl transferEnvironment effect
The invention discloses a method for removing micro-quantity alkene in aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the following steps of: contacting and reacting the aromatic hydrocarbon with a solid acid catalyst under the condition of temperature of 30-350 DEG C, pressure of 0.1-12MPa and feeding quality airspeed of 0.1-15 h<-1>, so that micro-quantity alkene in the aromatic hydrocarbon undergoes adsorbing, overlapping and alkylation reaction so as to remove the micro-quantity alkene in the aromatic hydrocarbon. The method is simple in process procedure, free of oxygen consumption and low in device investment and operation expense; and the catalyst is good in activity stability, the device is long in stable operation time, the aromatic hydrocarbon loss is small, the frequent switching operation between reactor reaction and regeneration is avoided, and the catalyst can be regenerated, so that a great deal of waste catalyst is prevented from being buried, and the environment is less polluted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing ethanol by hydrogenating acetic acid
InactiveCN108774108AGood activity and stabilityAvoid frequent switchingPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a method for preparing ethanol by hydrogenating acetic acid. A supported transition metal phosphide catalyst takes carbon nanotubes (CNTS) as a carrier, so that the activity and stability of the catalyst are good; a device is stable and long in operation time; the frequent switching operation of reactor reaction and regeneration can be avoided; the conversion rate of the acetic acid is 100%, and the selectivity of the ethanol is 88% or above.
Owner:杨彩花
Aromatic hydrocarbon purifying method
ActiveCN103012036BGood activity and stabilityReduce lossesChemical recyclingChemical modification purification/separationHydrogenEnvironment effect
The invention discloses an aromatic hydrocarbon purifying method which comprises the step of carrying out a contact reaction on aromatic hydrocarbon and a solid acid catalyst under the conditions that the temperature is 50-400 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-12MPa and the feeding mass space velocity is 0.1-15h<-1> to obtain purified aromatic hydrocarbon. The aromatic hydrocarbon purifying method is simple in process without consuming hydrogen, low in device investment and operation cost, good in catalyst activity stability, long in device stable operation time and less in aromatic hydrocarbon loss; and reactor reaction and regeneration frequent switching operation can be avoided, the catalyst can be regenerated, a large quantity of waste catalysts can be prevented from being stacked and embedded, and environment influence is little.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Utilize transition metal phosphide catalyst to catalyze the method for hydrogenation of acetic acid to produce ethanol
ActiveCN105669372BGood activity and stabilityLong stable operation timePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for catalyzing the hydrogenation of acetic acid to produce ethanol by using a transition metal phosphide catalyst. Under the condition that the molar ratio of hydrogen to acetic acid is 1:1 to 20:1, acetic acid and hydrogen are mixed, and contacted and reacted with a supported transition metal phosphide catalyst to hydrogenate acetic acid to produce ethanol; the process of the invention is simple, and the catalyst price Lower, the catalyst performance stability is good, the stable operation time of the device is long, the frequent switching operation of the reactor reaction and regeneration can be avoided, the catalyst can be regenerated, the post-treatment of a large number of spent catalysts can be avoided, and the impact on the environment is small.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
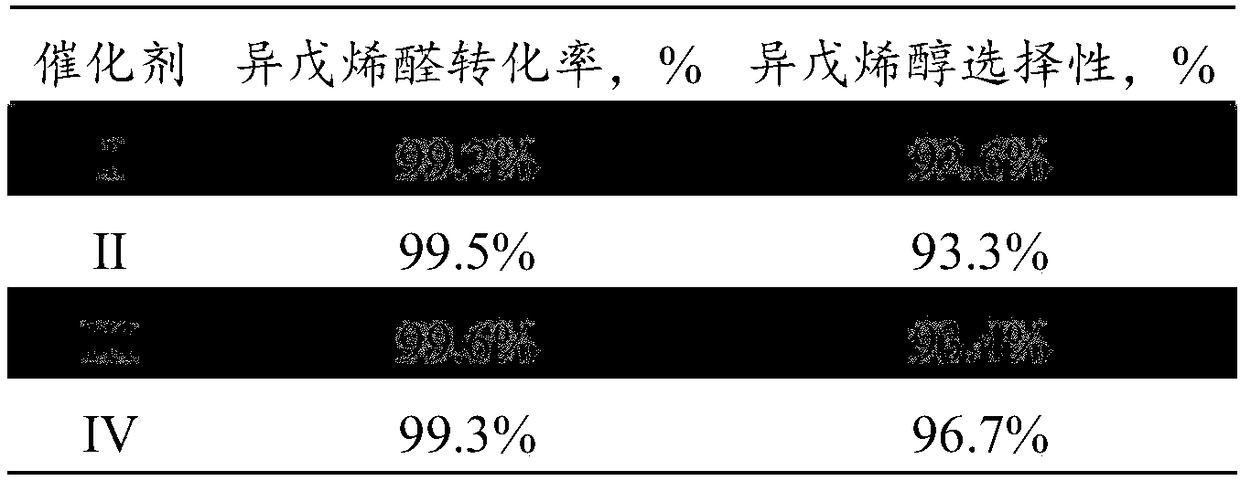
Method for preparing methyl-2-buten-1-ol from 3-methylcrotonaldehyde by selective hydrogenation
InactiveCN109369329AReduce manufacturing costHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydrogenation reactionSubstance amount
The invention discloses a method for preparing methyl-2-buten-1-ol from 3-methylcrotonaldehyde by selective hydrogenation. The method comprises steps as follows: 3-methylcrotonaldehyde and hydrogen are mixed under the conditions of temperature being 50-80 DEG C, pressure being 0.1-3.0 MPa, mass space velocity being 5-8 h<-1> and a ratio of feeding substance amount of hydrogen to 3-methylcrotonaldehyde being 1:1-20:1, a mixture is contacted with a supported Al-Zn / CeO2 catalyst for a hydrogenation reaction, and methyl-2-buten-1-ol is obtained. The catalyst is cheaper and has high selective activity, methyl-2-buten-1-ol can be prepared under the conditions of low temperature, low pressure and high space velocity, and production cost of methyl-2-buten-1-ol is reduced.
Owner:杭州更蓝生物科技有限公司
Method for lowering bromine index of linear alkylbenzene
ActiveCN105503495AAvoid pollutionSimple processHydrocarbon purification/separationCatalystsBenzeneAlkyl transfer
The invention discloses a method for lowering bromine index of linear alkylbenzene, which comprises the following steps: mixing a hydrogenation raw material and hydrogen gas at 60-350 DEG C under the pressure of 0.3-10.0 MPa at the weight hourly space velocity of 0.2-10.0 hour<-1> under the condition that the hydrogen / oil volume ratio is 300:1-8000:1, carrying out contact reaction with a Pt-Sn / SiO2 supported catalyst until olefins are saturated, thereby lowering the bromine index of the linear alkylbenzene and the improving the product quality, wherein the hydrogenation raw material is linear alkylbenzene prepared by carrying out distillation separation on a benzene-C10-C14 linear olefin alkylation mixture, or a benzene-C10-C14 linear olefin alkylation mixture. The method has the advantages of simple technical process, high catalyst activity and stability, long stable operation time of the device, low loss of linear alkylbenzene, renewable catalyst and low influence on the environment, can avoid frequent switching operation between reactor reaction and regeneration, and can avoid abundant spent catalyst after-treatment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Solid-acid-catalyzed method for synthesizing straight-chain alkyl-benzene
ActiveCN102464539BShort processGood activity and stabilityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSolid acidLinear alkylbenzene
The invention relates to a solid-acid-catalyzed method for synthesizing straight-chain alkyl-benzene, comprising the steps of: with straight-chain olefin having 10 to 14 carbon atoms and benzene as raw materials, and carrying out alkylation reaction with catalysis of a solid acid catalyst to obtain the straight-chain alkyl-benzene under the reaction condition that the temperature is 10-450 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-15MPa, the mass ratio of the benzene to olefin substance is (2-100):1 and the total mass airspeed of feedstock is 0.1-20h<-1>, wherein the solid acid catalyst is mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst of M-KIT-1 type or a composite solid acid catalyst obtained by loading a modified compound on the mesoporous molecular sieve catalyst of M-KIT-1 type. The catalyst adopted in the method disclosed by the invention is free of corrosiveness, friendly to environment and has good activity stability. Stable operation time of a device is long so that a reactor is prevented from being switched between reaction and regeneration frequently.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Method of preparing linear alkylbenzene
InactiveCN101058523BGood activity and stabilityImprove conversion rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkyl transferMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of straight-line alkyl benzene, which comprises the following steps: adopting straight-line olefin with carbon atom number between 2 and 20 and benzene as raw material; inputting in the reactor; reacting benzene and olefin with molar rate at 2-100:1 at 290-450 deg. c under 5-15Mpa hypercritical condition; setting the air speed at 0. 1-20h-1; making solid acid as catalyst; adopting one of loaded modified (1) SBA-15 typed molecular sieve, (2) HY typed molecular sieve, (3) USY typed molecular sieve, (4) H beta typed molecular sieve, (5) H-Moderite typed molecular sieve, (6) HZSM-20 typed molecular sieve as composite typed solid acid catalyst. The invention improves transmitting rate of olefin with stable operation, which possesses good using prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of catalytic hydrogenation method that reduces linear alkylbenzene bromide index
ActiveCN105601464BAvoid pollutionSimple processHydrocarbon purification/separationCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystDistillation
The invention discloses a catalytic hydrogenation method for reducing the linear alkylbenzene bromine index. The method is as follows: at a temperature of 60-400°C, a pressure of 0.3-10.0MPa, and a mass space velocity of 0.2-8.0 hours-1, hydrogen Under the condition of oil volume ratio of 300:1~8000:1, the hydrogenation raw material is mixed with hydrogen, and reacted with transition metal phosphide supported catalyst to saturate olefins, thereby reducing the linear alkylbenzene bromide index and improving product quality The raw material for hydrogenation is linear alkylbenzene obtained by distillation and separation of the alkylation mixture of benzene and C10-C14 linear olefins, or the alkylation mixture of benzene and C10-C14 linear olefins; the process flow of the present invention is simple, The catalyst has good activity and stability, and the stable operation time of the device is long, which can avoid the frequent switching operation of reactor reaction and regeneration, the loss of linear alkylbenzene is small, the catalyst can be regenerated, and the post-treatment of a large amount of spent catalyst can be avoided, and the impact on the environment is small.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing olefin in aromatic hydrocarbon by M-SBA-15 type mesoporous molecular sieve
ActiveCN102992932BSimple processDoes not consume hydrogenChemical modification purification/separationMolecular sieveAlkene
The invention discloses a method for removing olefin in aromatic hydrocarbon by an M-SBA-15 type mesoporous molecular sieve. The method comprises the step of carrying out contact reaction of aromatic hydrocarbon with a solid acid catalyst to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon without olefin at 30-350 DEGC, at a pressure of 0.1-10MPa, and at an air speed of 0.1-15 / h for feed quality, wherein the aromatic hydrocarbon is aromatic hydrocarbon generated by reforming generated oil, reforming aromatic hydrocarbon or steam cracking. The method is simple in process flow, free of hydrogen consumption and low in device investment and operating cost. The catalyst activity is good in stability, the stable operation of the device is long and the aromatic hydrocarbon loss is small, so that the frequency switching operation between reaction and regeneration of a reactor is avoided. The catalyst is reproducible, so that a great amount of dead catalysts is not buried, therefore, the environmental influence is small.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing trace olefin from aromatic hydrocarbon
ActiveCN103012037BSimple processDoes not consume hydrogenChemical modification purification/separationEnvironment effectHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for removing trace olefin from aromatic hydrocarbon. The method comprises the step of carrying out contact reaction on aromatic hydrocarbon and a solid acid catalyst under the conditions that the temperature is 30-400 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-12MPa and the feeding mass space velocity is 0.1-15h<-1> to obtain aromatic hydrocarbon after the olefin is removed. The method is simple in process without consuming hydrogen, low in device investment and operation cost, good in catalyst activity stability, long in device stable operation time and less in aromatic hydrocarbon loss; and reactor reaction and regeneration frequent switching operation can be avoided and a large quantity of waste catalysts can be prevented from being stacked and embedded, and environment influence is little.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing ethanol by ethyl acetate hydrogenation
InactiveCN108586196ALow priceHigh activityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationSubstance amountEthyl ester
The invention discloses a method for preparing ethanol by ethyl acetate hydrogenation. The method comprises the steps: mixing ethyl acetate and hydrogen under the conditions that the temperature is 100-200 DEG C, the pressure is 0.1-2.0MPa, the mass space velocity is 10-15h<-1>, and the feeding substance amount ratio of hydrogen to ethyl acetate is 1:1 to 10:1, and contacting the mixture with a supported Co-Sn / Al2O3 catalyst to carry out a hydrogenation reaction to obtain ethanol. The catalyst is relatively low in price and high in activity, ethanol can be obtained under the conditions of lowtemperature, low pressure and high space velocity, and the production cost of ethanol is reduced.
Owner:肖锦
Process for synthesizing diacetylmonoxime ethyl ether by continuous reactions in microtube
ActiveCN103304442BReduce operating costsThe concentration is basically constantOximes preparationPotassium hydroxidePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a process for synthesizing butanone oxime ethyl ether through continuous microtube reaction. The process adopts continuous microtube reaction technology, under the conditions of temperature 30-45℃, pressure 0.1MPa and strong base, butanone oxime and diethyl sulfate are reacted to directly synthesize butanone oxime ethyl ether; the strong base is hydrogen Sodium oxide, potassium hydroxide or alcohol amine compounds. In this process, diethyl sulfate, lye and butanone oxime are respectively fed by precision micropumps, butanone oxime is mixed with lye and diethyl sulfate in turn, and then reacted in a microtube reactor. After the heater, it is condensed and collected at low temperature, the chromatographic separator is left to stand for stratification, the water phase is extracted and separated by a micro-extraction tower, and the oil phase product containing butanone oxime ether is purified by rectification in a rectification tower to obtain the final product butanone oxime ether. The process has high selectivity of butanone oxime ethyl ether, can significantly enhance mass transfer and heat transfer, effectively avoid the hydrolysis of diethyl sulfate, has simple process, long stable operation time, low cost, is easy to scale up, and meets the requirements of industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com