Method for removing micro-quantity alkene in aromatic hydrocarbon
A technology for aromatics and olefins, which is applied in the field of removing trace olefins in aromatics by using solid acid catalysts. It can solve problems such as poor hydrothermal stability, limited application prospects, and weak acidity, and achieves low environmental impact, simple process flow, and high activity. good stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of Al-HMCM-41 mesoporous / Hβ microporous composite molecular sieve catalyst
[0034] 1.0 g of Hβ microporous molecular sieve powder was used as the inner core, and 10.0 g of 15.0 wt % cetyltrimethylammonium bromide aqueous solution was stirred and mixed for 1.0 hour to obtain a mixture A. According to Al 2 o 3 : SiO 2 :CTMAB:NaOH:ETHA:H 2 The raw material molar ratio of O is 1:10.0:1.4:2.4:8.67:140.0, weigh 4.86 grams of alumina monohydrate, and a certain amount of silica sol, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTMAB), hydroxide Sodium, ethanol (ETHA) and deionized water were stirred and mixed at 70°C for 0.5 hours to make mixture B; mixture A was added to mixture B, stirred and mixed at 70°C for 4.5 hours, and the resulting The obtained mixture was added to an autoclave, and crystallized at 150°C and autogenous pressure for 24 hours to obtain a crystallized product, and then the crystallized product was filtered, washed with water, dried, an...
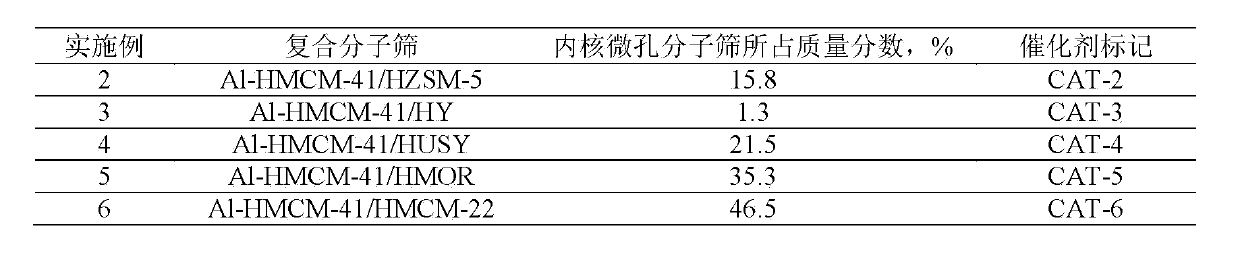
Embodiment 2~6
[0036] Using HZSM-5 molecular sieve, HY molecular sieve, HUSY molecular sieve, HMOR molecular sieve, HMCM-22 molecular sieve respectively as the core microporous molecular sieve, after hydrothermal synthesis, tablet molding, other operations are the same as in Example 1, to obtain mesoporous / microporous core-shell Type composite molecular sieve catalysts are listed in Table 1.
[0037] Table 1
[0038]
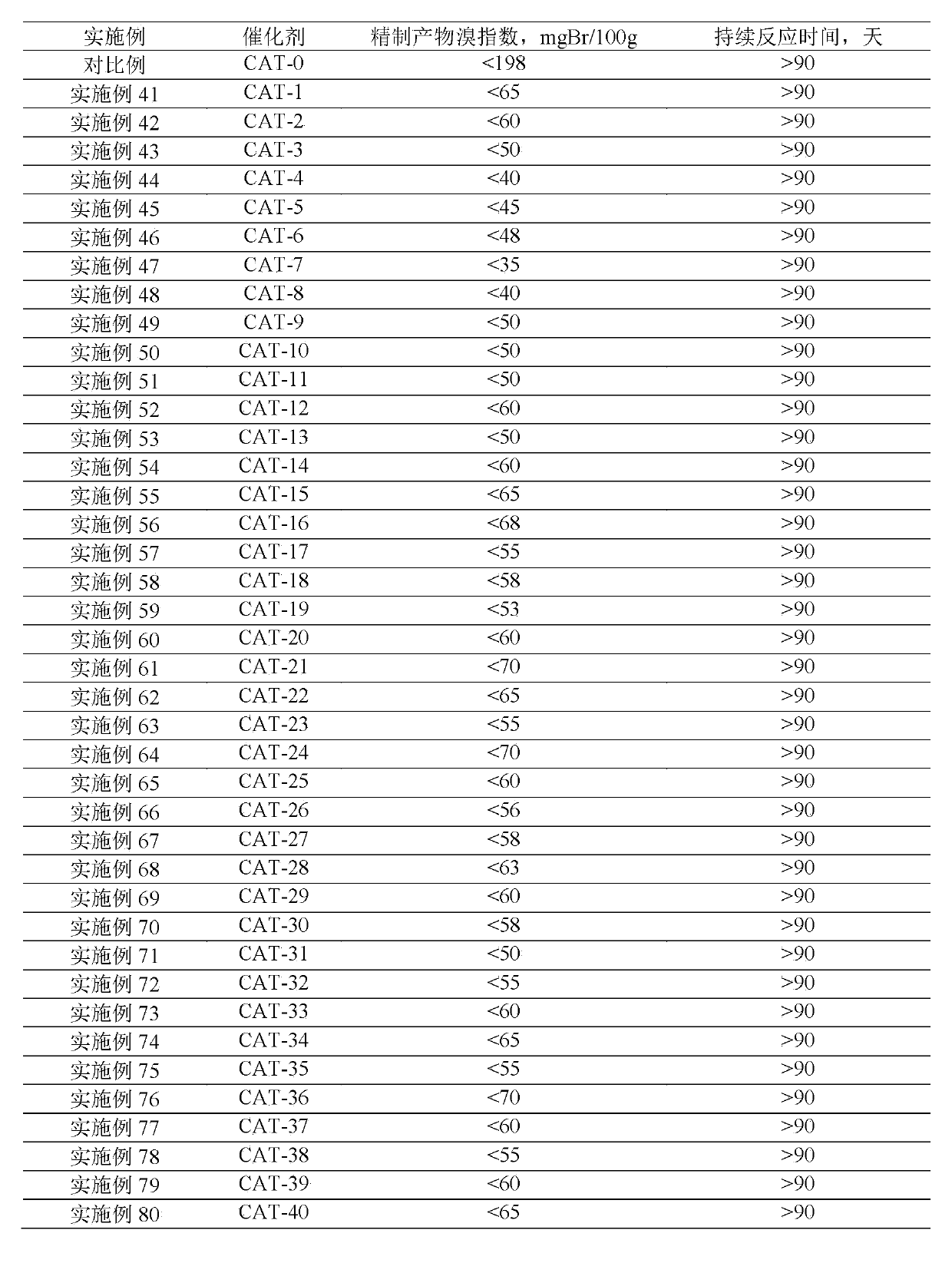
Embodiment 7~26
[0040] Using the same operation as in Example 1, the difference is that butyl titanate, cobalt nitrate, zinc nitrate, gallium nitrate, manganese nitrate, strontium nitrate, zirconium nitrate, calcium nitrate, magnesium nitrate, iron nitrate, nickel nitrate, nitric acid Vanadium, chromium nitrate, germanium nitrate, tin nitrate, molybdenum nitrate, niobic acid, copper nitrate, tungstic acid, and boric acid are used as the precursors of the substituting element M, and the M-HMCM-41 mesoporous / Hβ microporous core-shell containing the substituting element is synthesized Type composite molecular sieve catalyst, the mass fraction of the core Hβ microporous molecular sieve is 15.8%, listed in Table 2.
[0041] Table 2
[0042]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bromine number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com