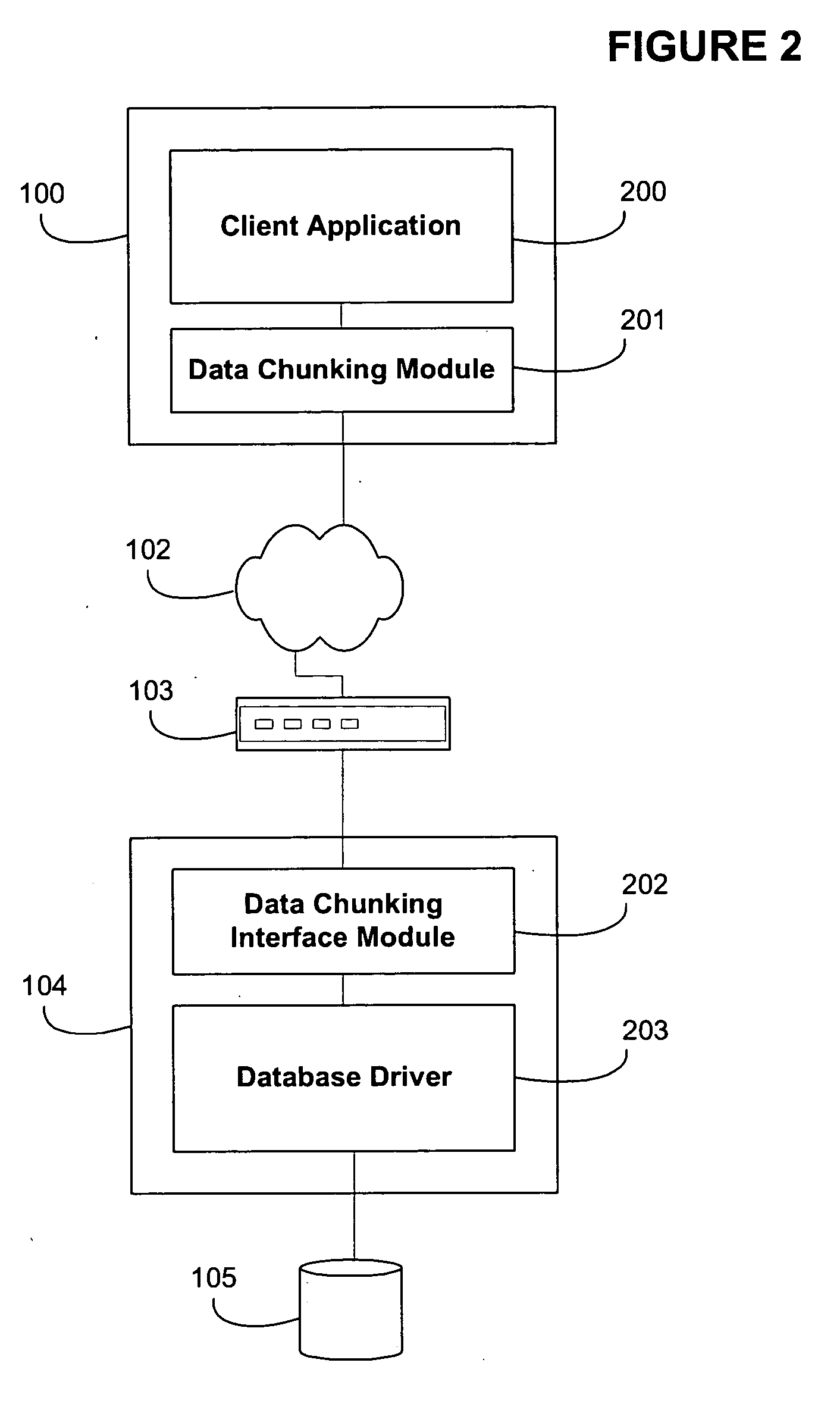
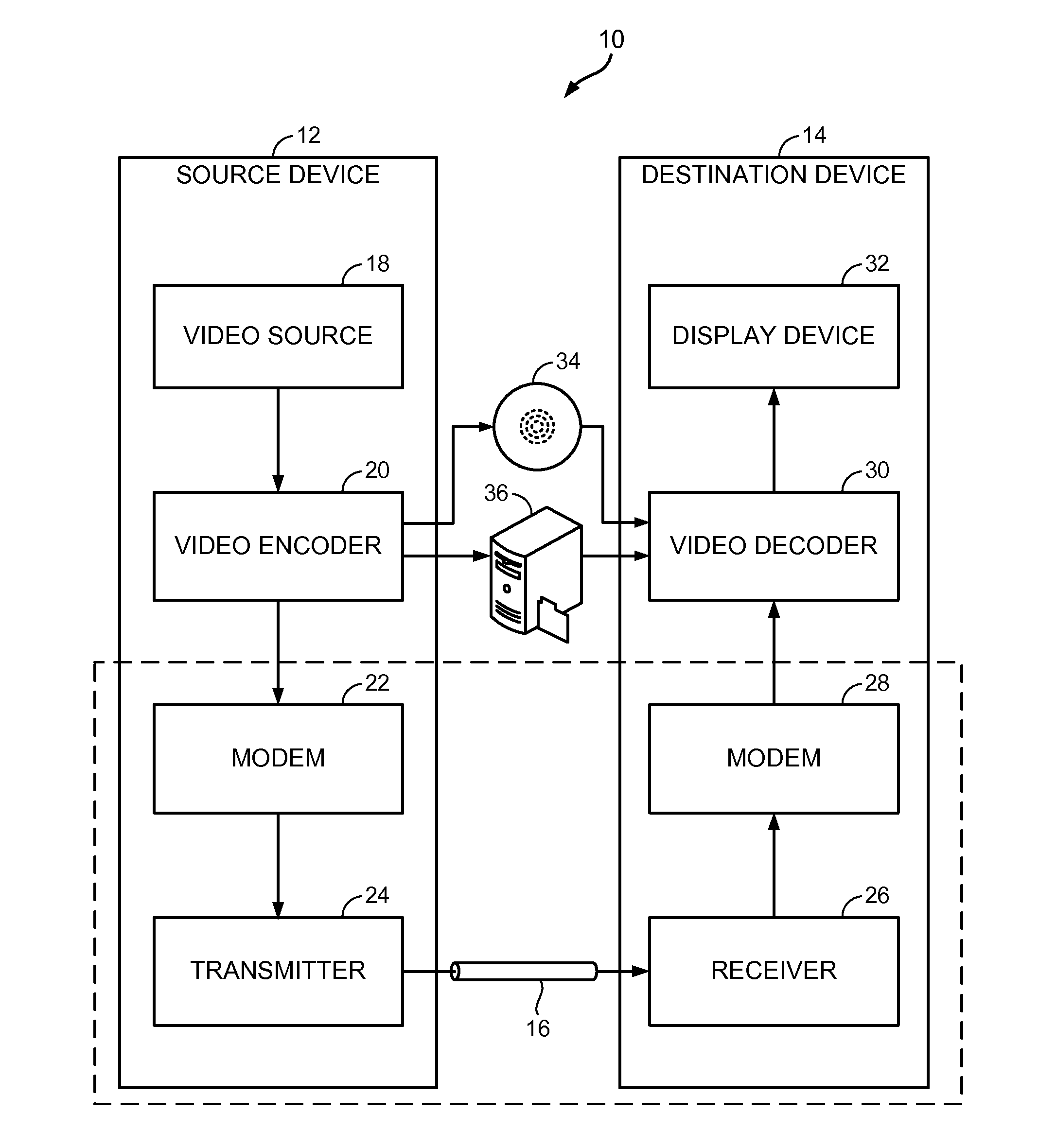
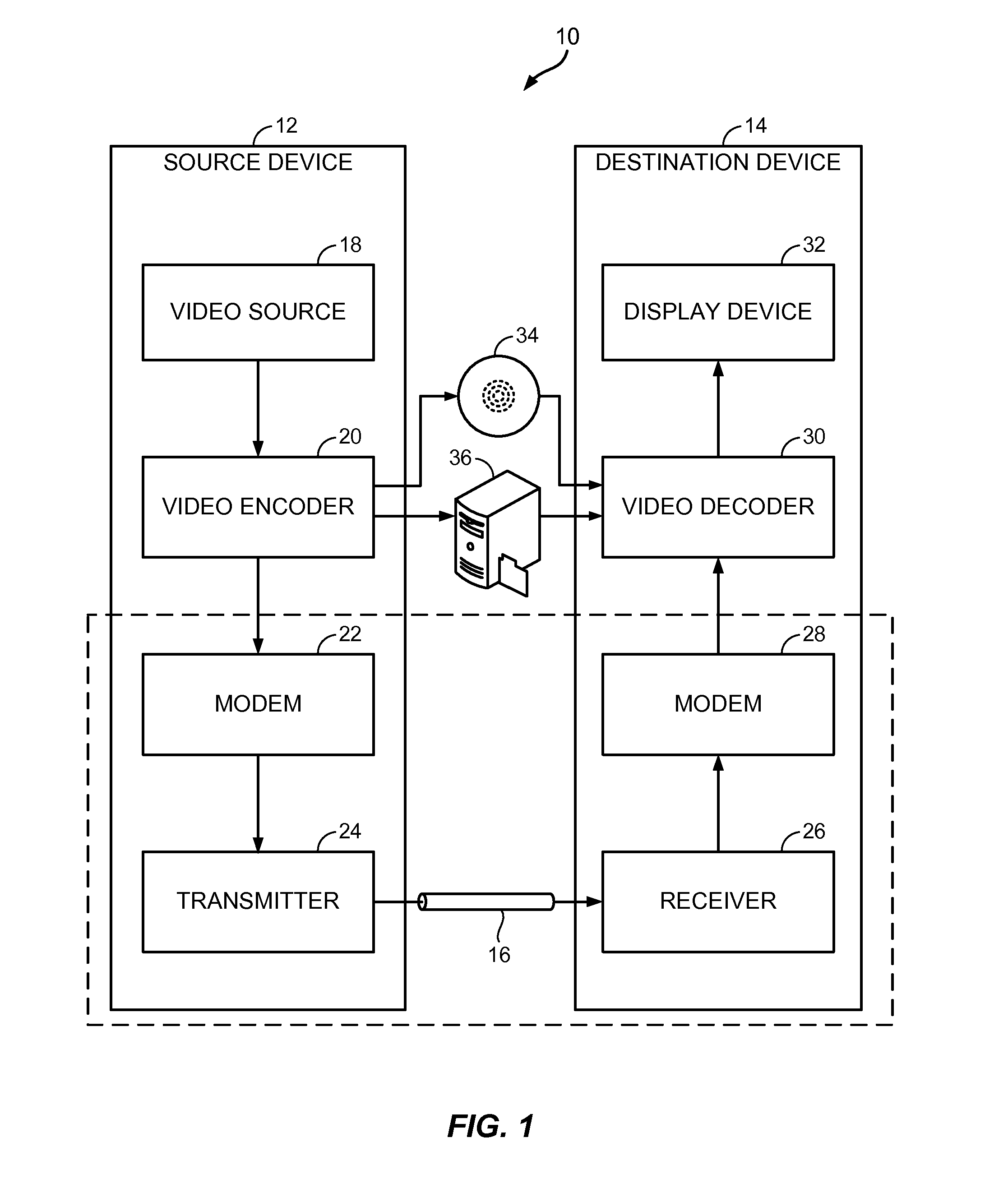
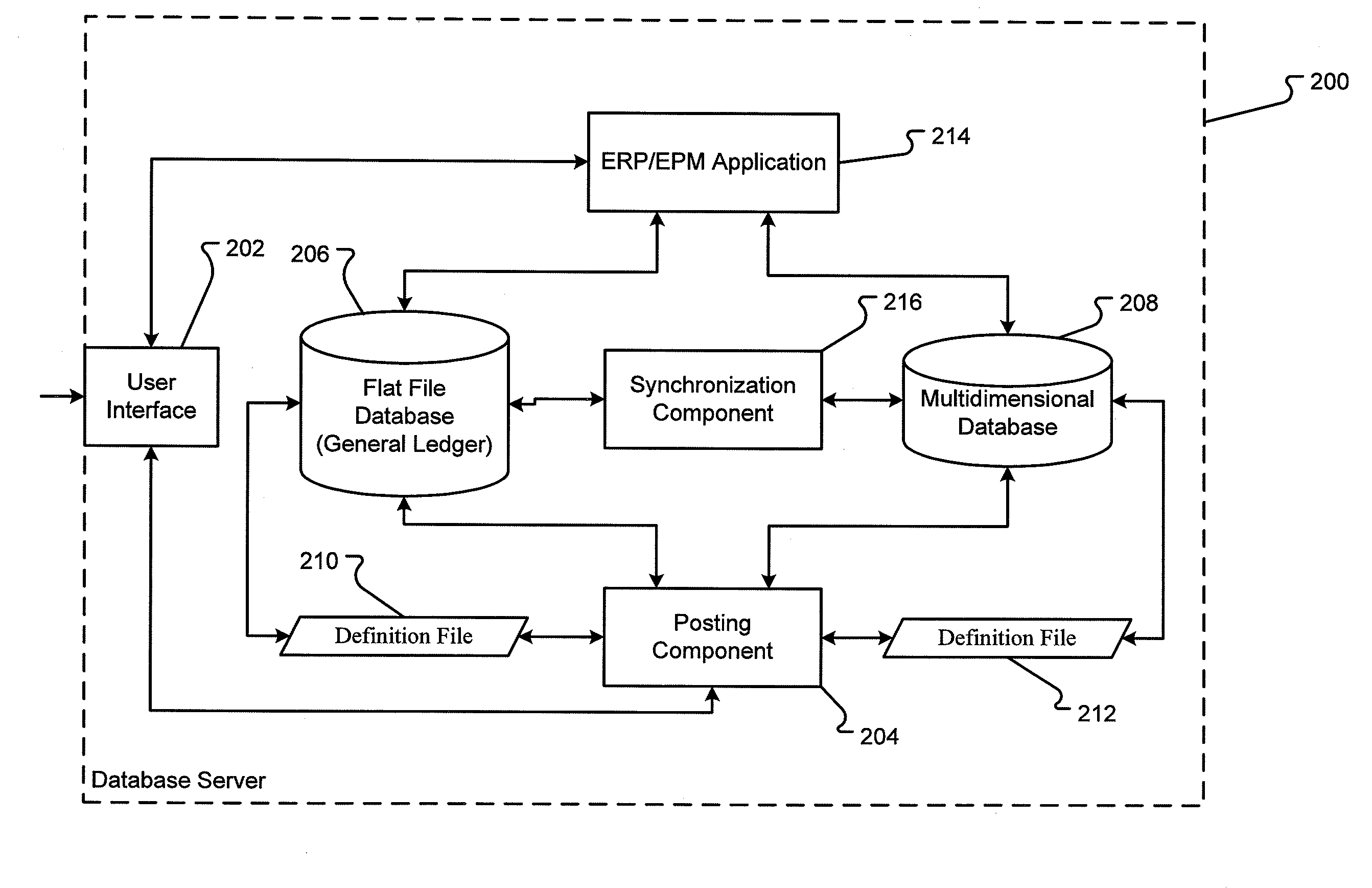
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
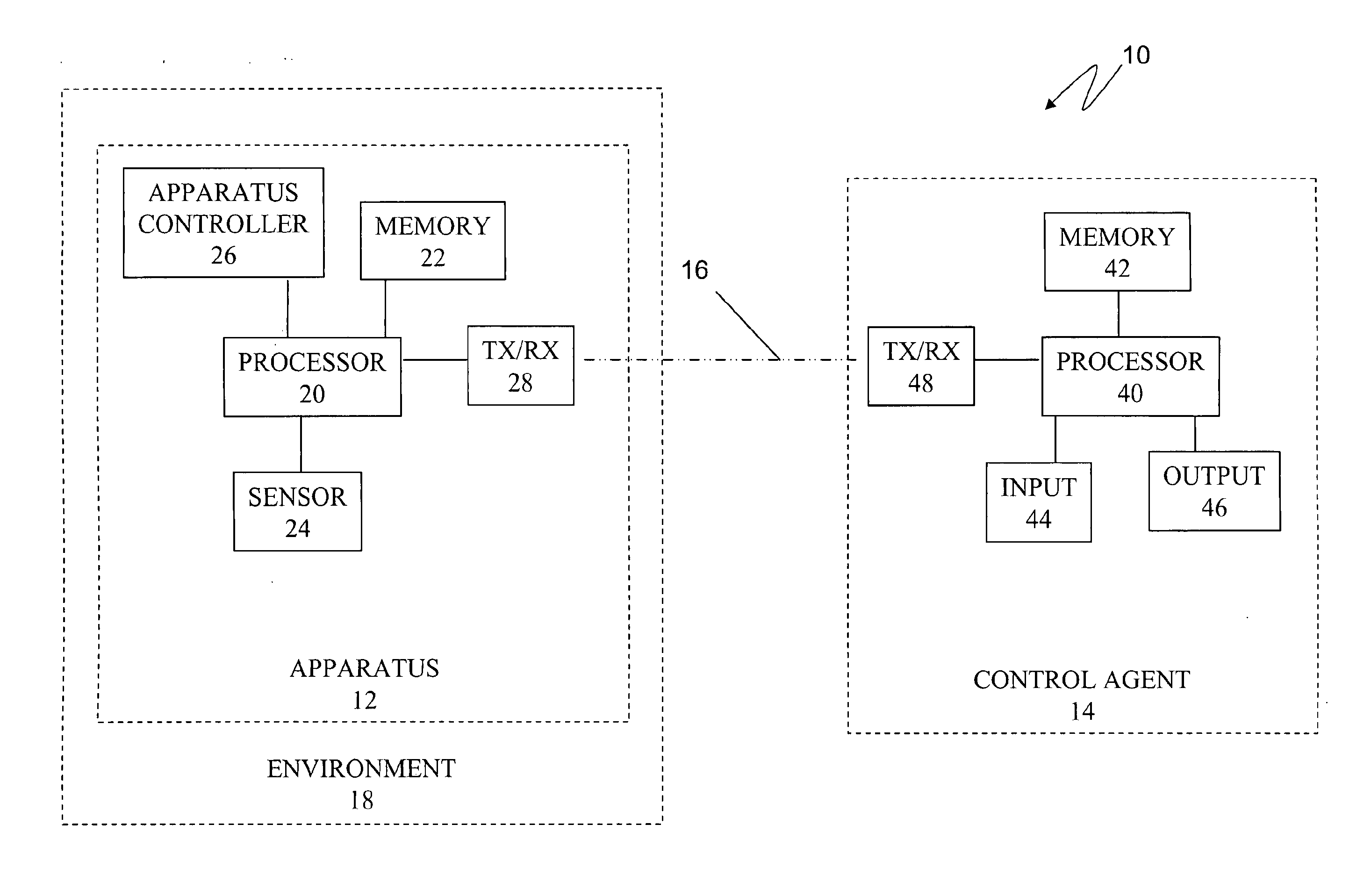
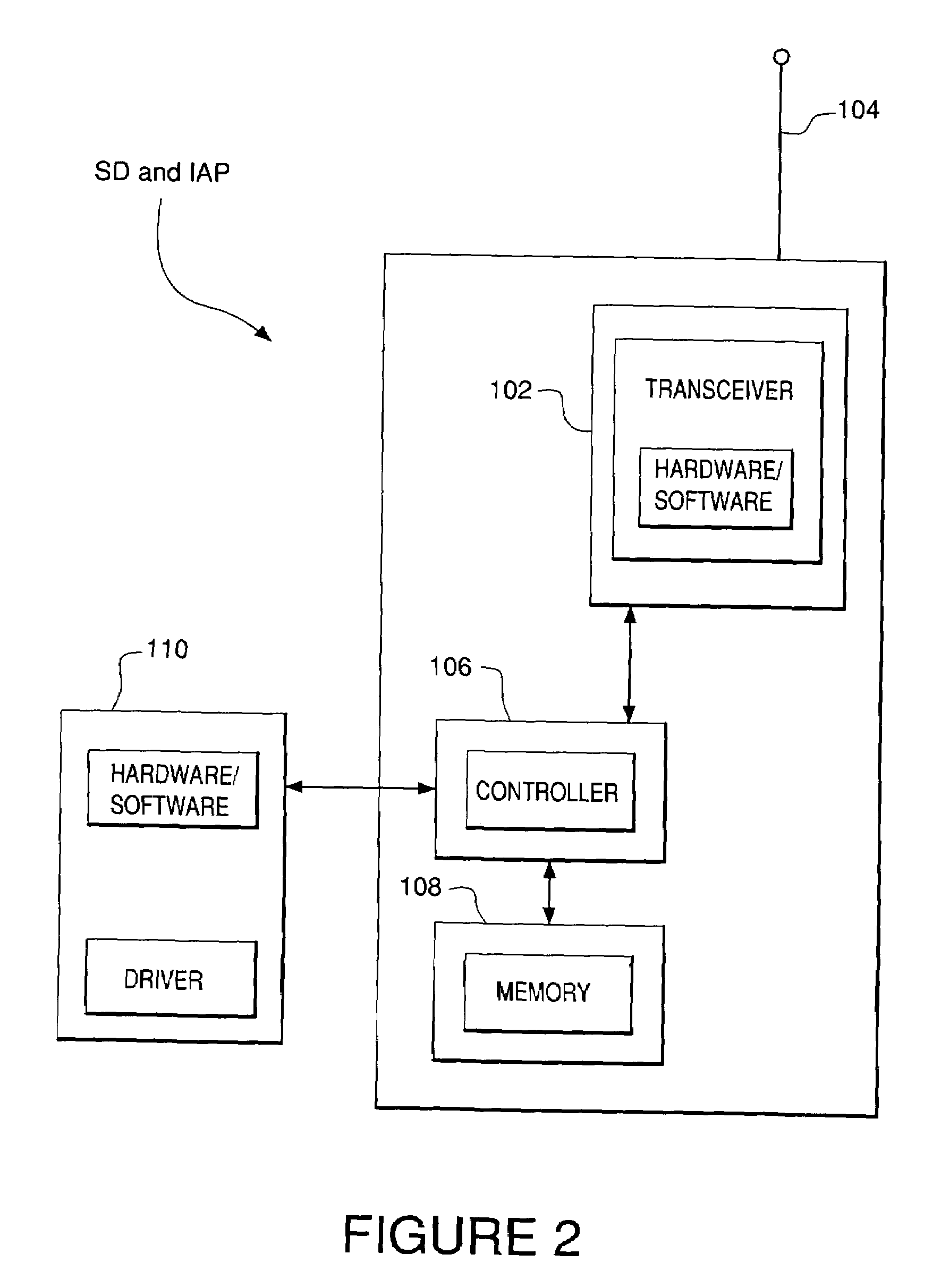
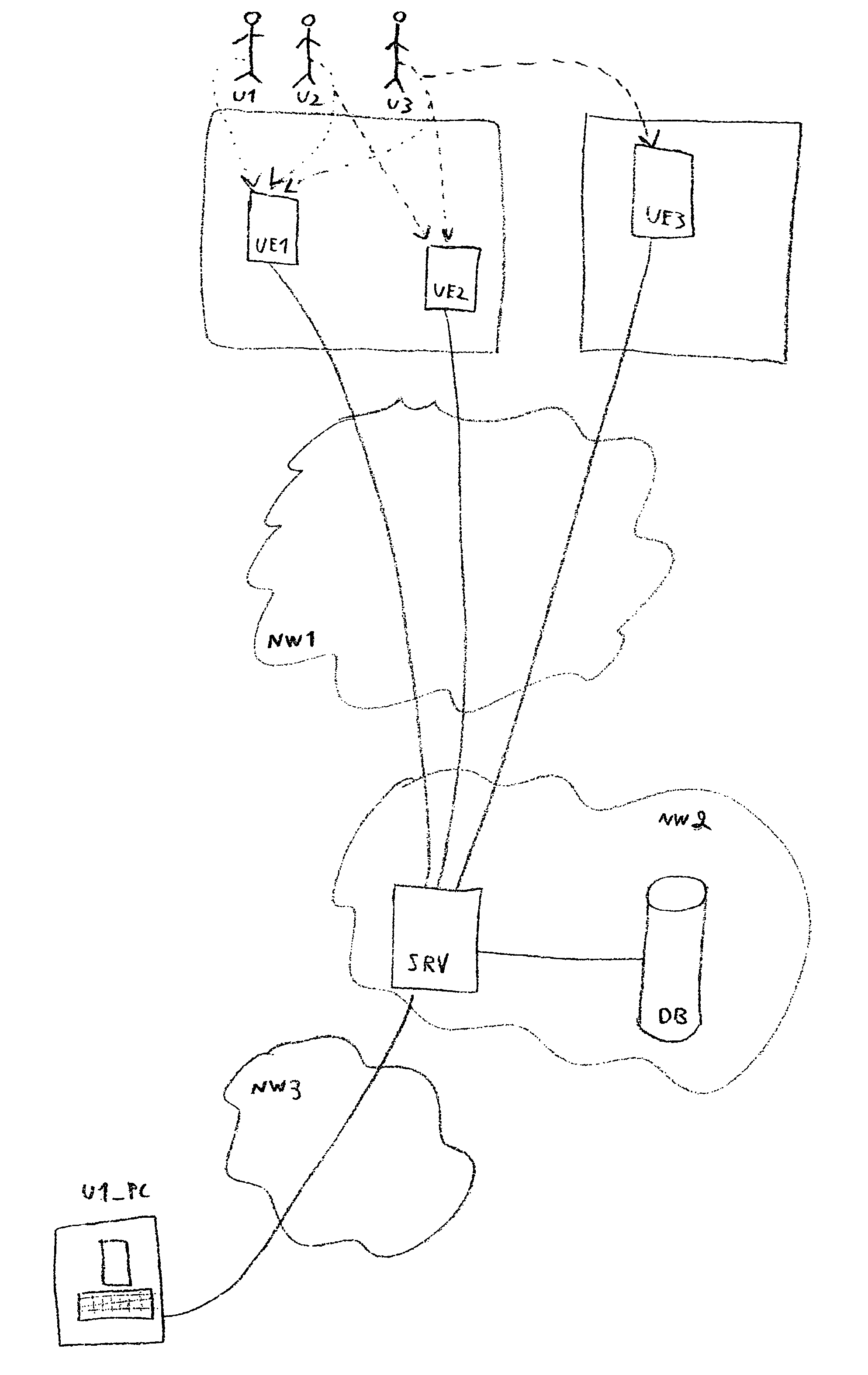
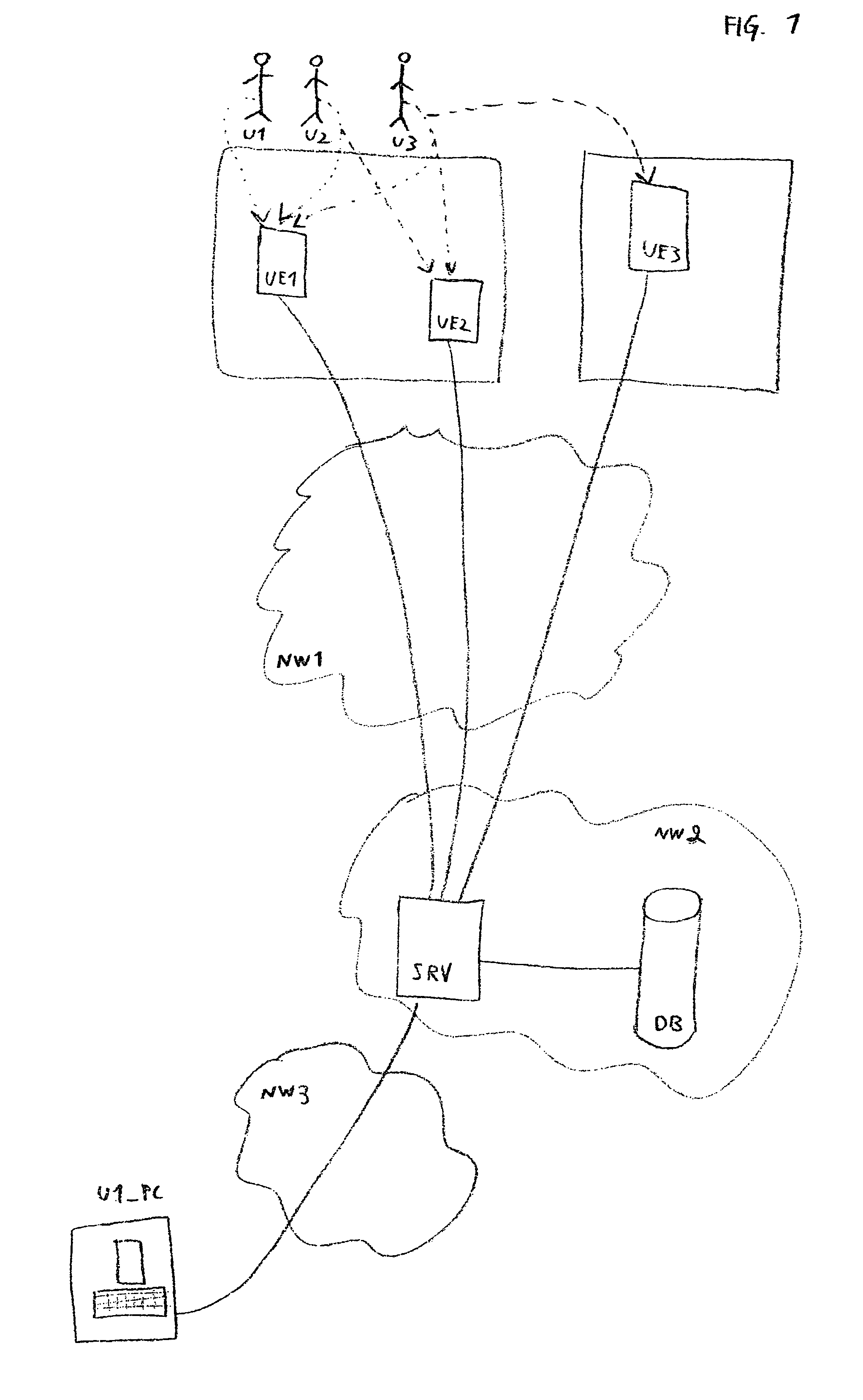
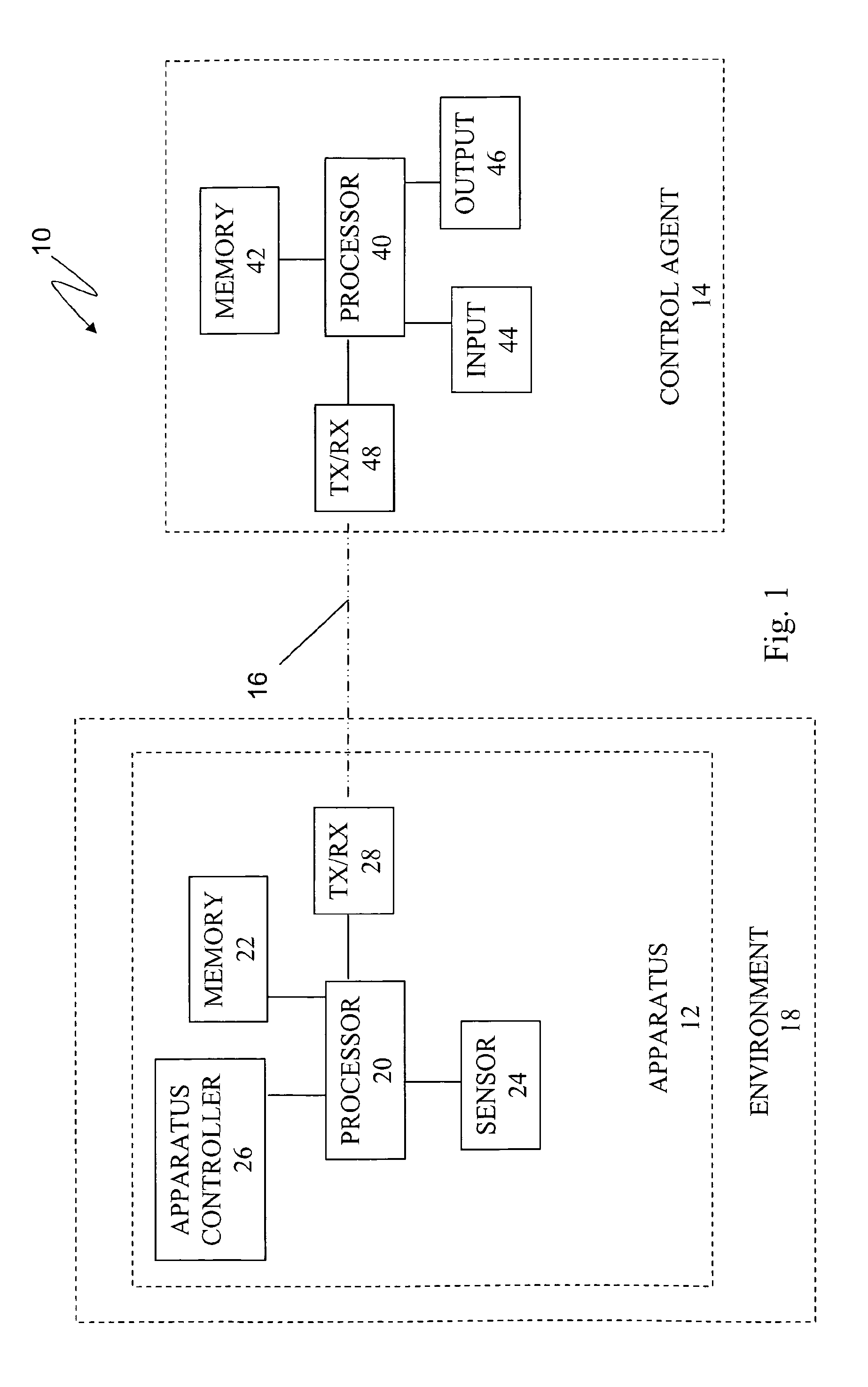
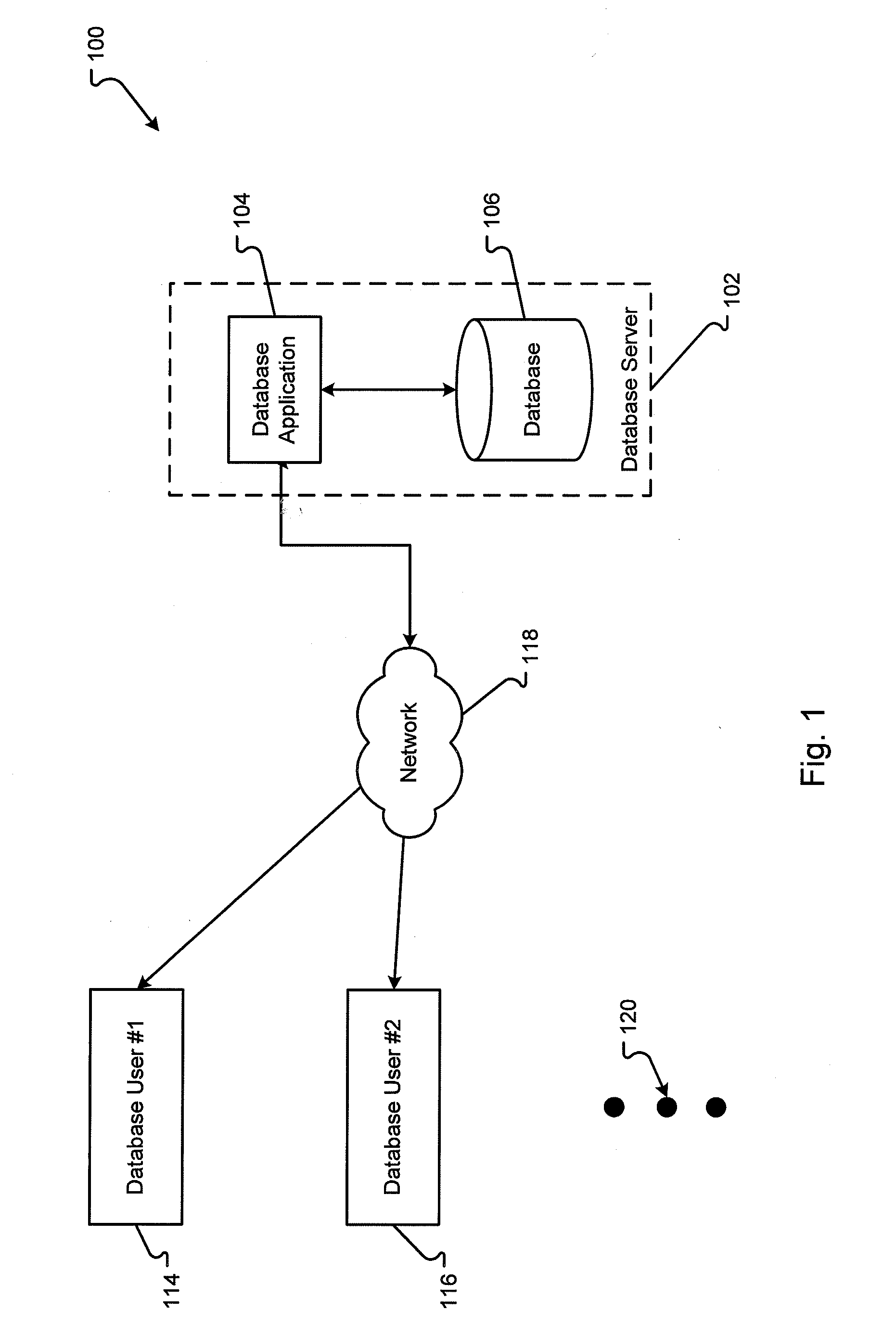
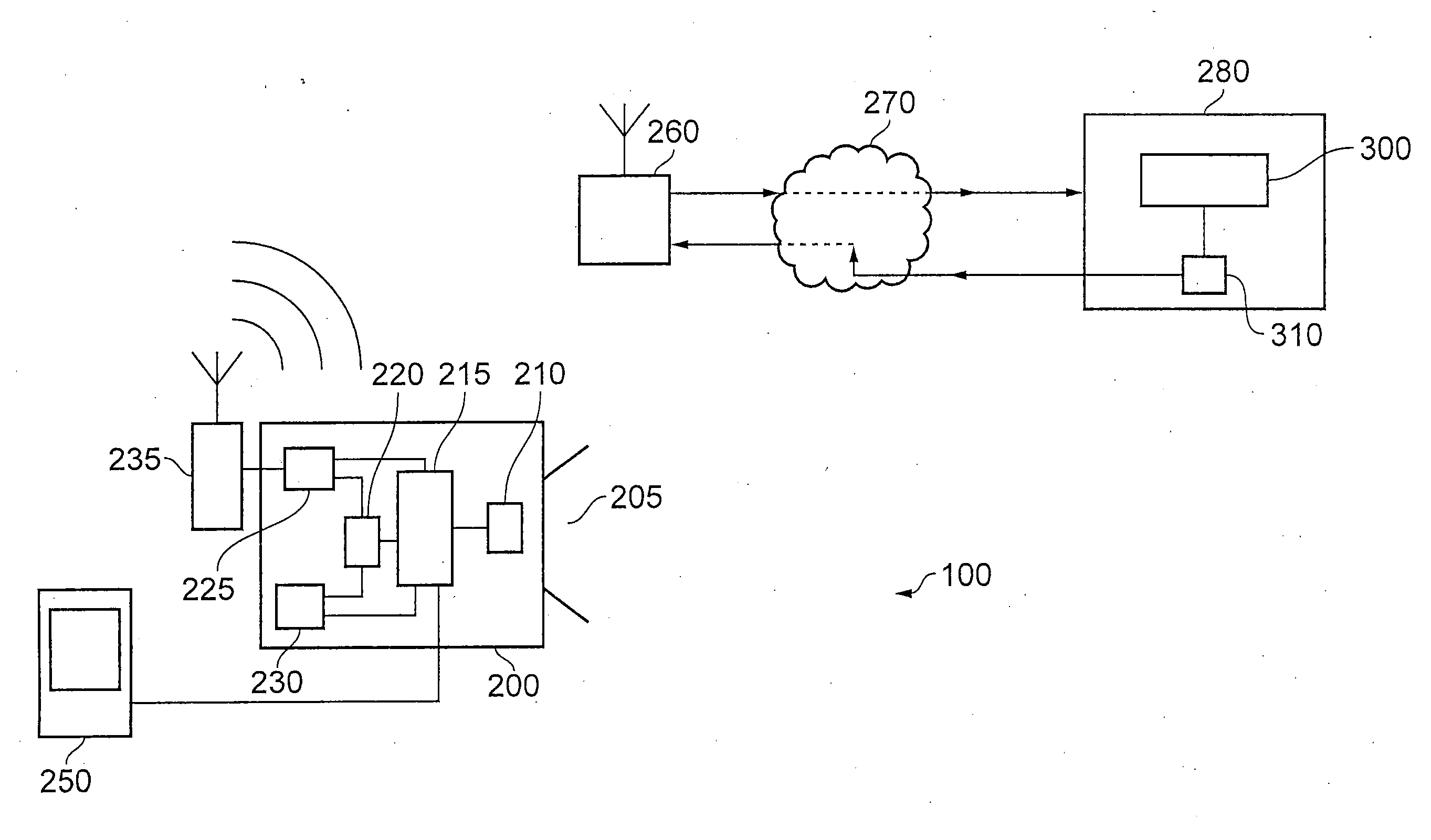
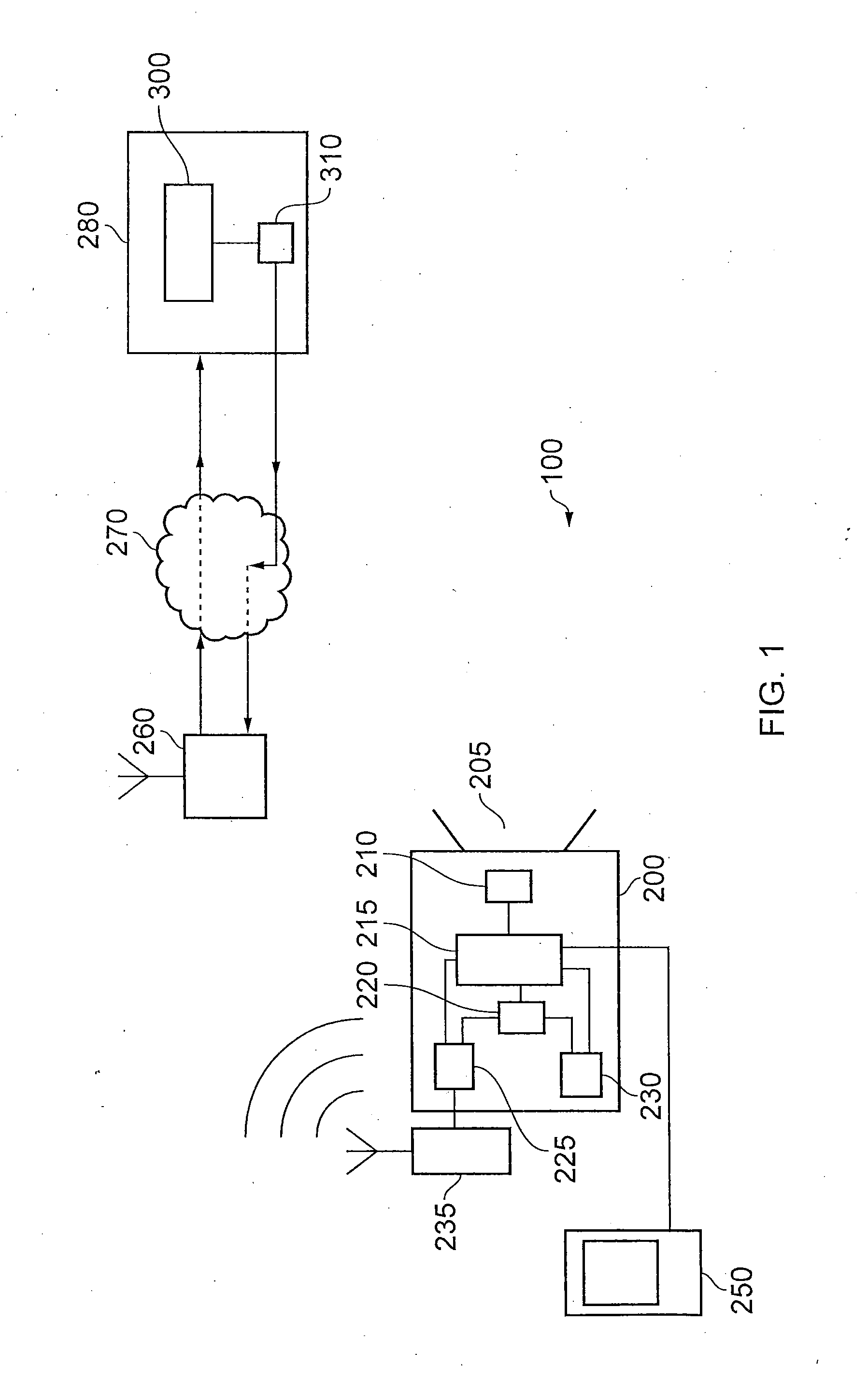
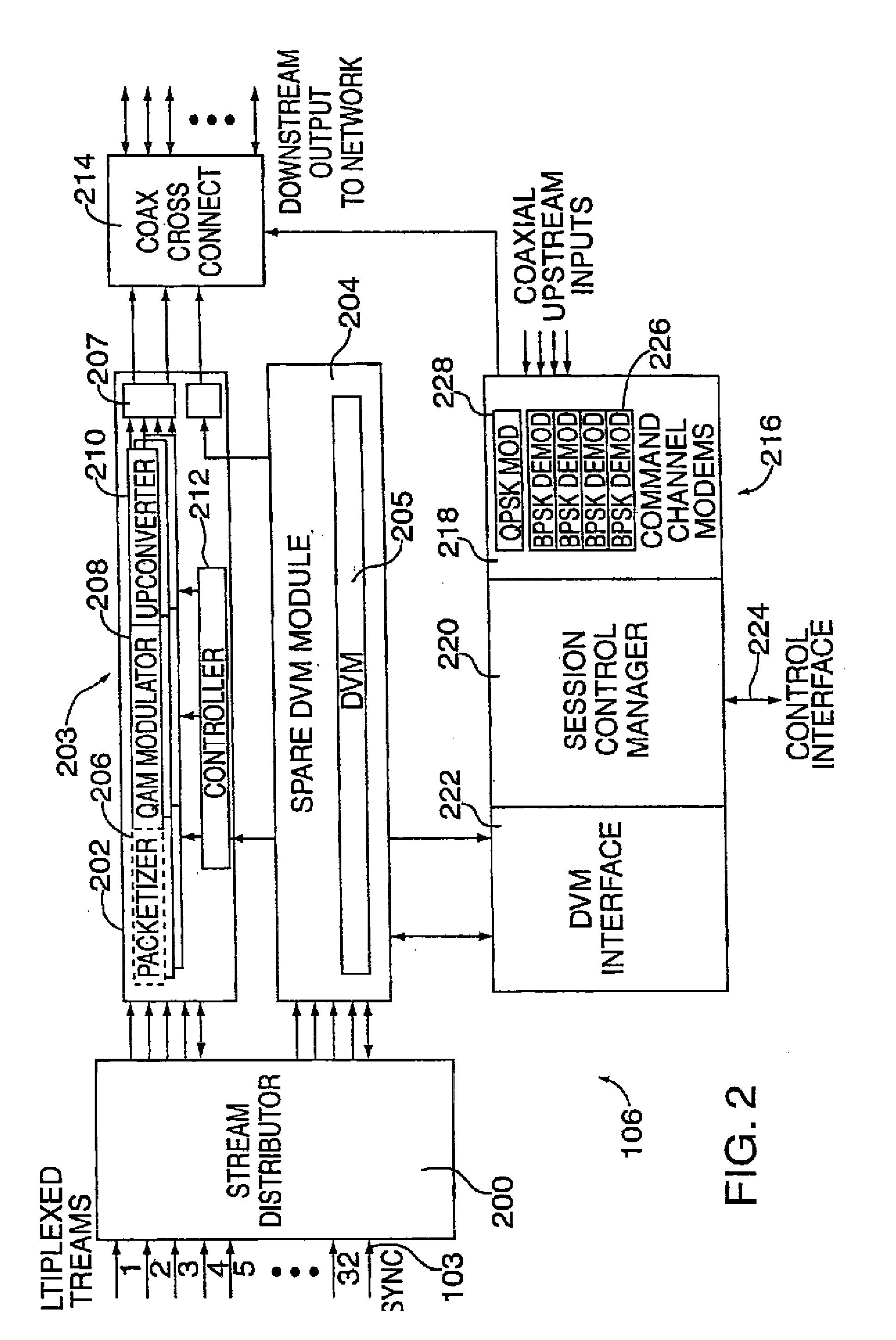
Apparatuses, Systems, and Methods for Apparatus Operation and Remote Sensing
ActiveUS20110066262A1Reduces required bandwidthAttenuation bandwidthTesting/monitoring control systemsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusVirtualizationState of the Environment
A method and system for controlling an apparatus including receiving data indicative of an actual state of the apparatus, defining a first viewpoint relative to at least one of the environment and the apparatus, determining a first predicted state of the apparatus at time T, determining a first predicted state of the environment at time T, producing a first virtualized view from the first viewpoint, sending a first control signal to the apparatus after producing the first virtualized view, defining a second viewpoint relative to at least one of the apparatus and the environment, determining a second predicted state of the apparatus at time T+delta T, determining a second predicted state of the environment at time T+delta T, producing the second virtualized view from the second viewpoint, sending a second control signal to the apparatus after producing the second virtualized view, and changing the actual state of the apparatus based on the first control signal.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
System and method for decreasing latency in locating routes between nodes in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS7061925B2Reduce usageLatencyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesReal-time computingInformation level
A system and method for controlling the dissemination of Routing packets, and decreasing the latency in finding routes between nodes. The system and method provides message exchanges between wireless devices to determine optimized communication routes with a minimum of overhead messages and buffered data. Exchanged messages are reduced to a specific series of exchanges indicating destination, destination node detection, and route, preferably using a series of IAP devices. Routes are discovered in an efficient manner and latency in finding routes between nodes is reduced, thereby reducing buffered information levels at individual devices.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
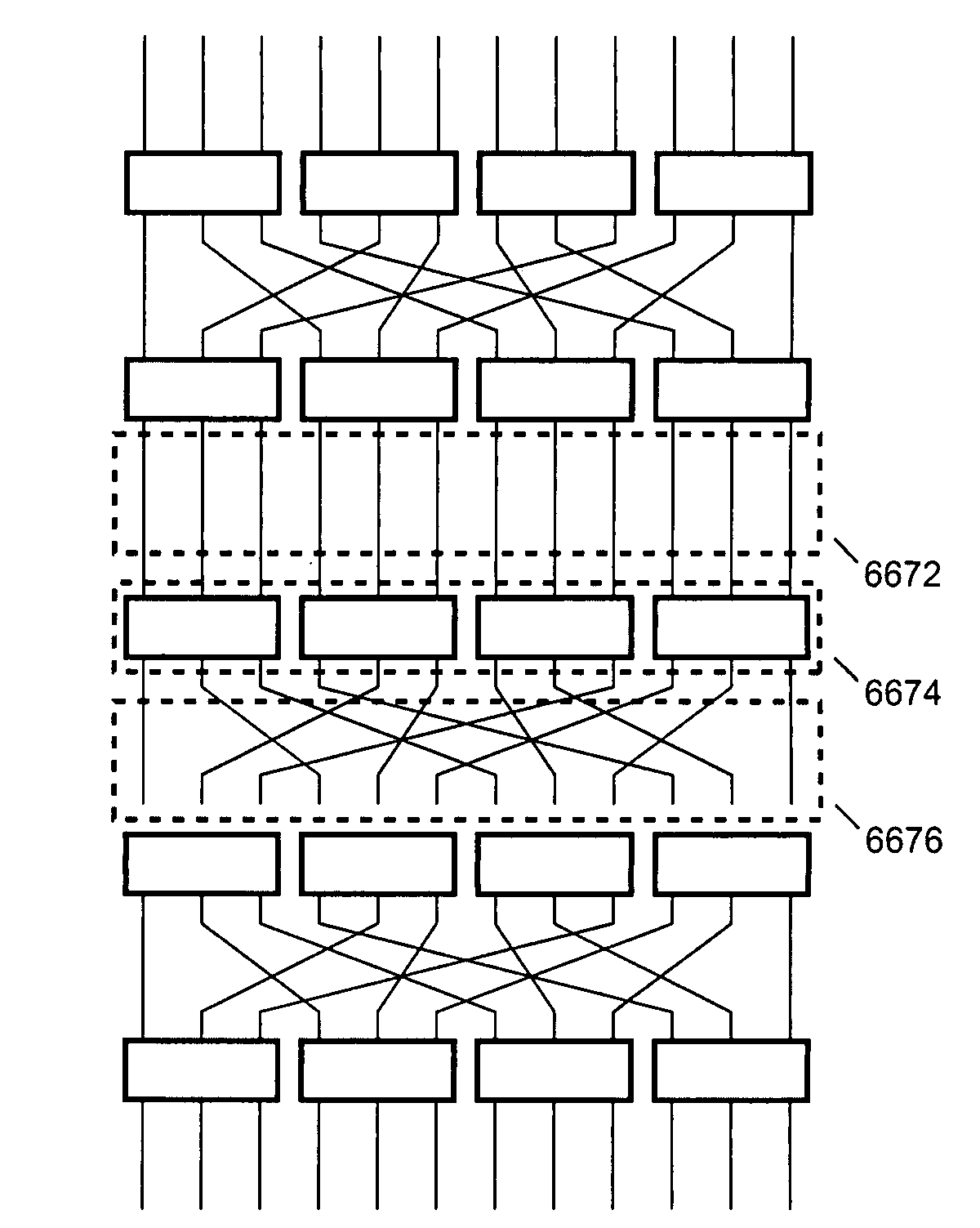
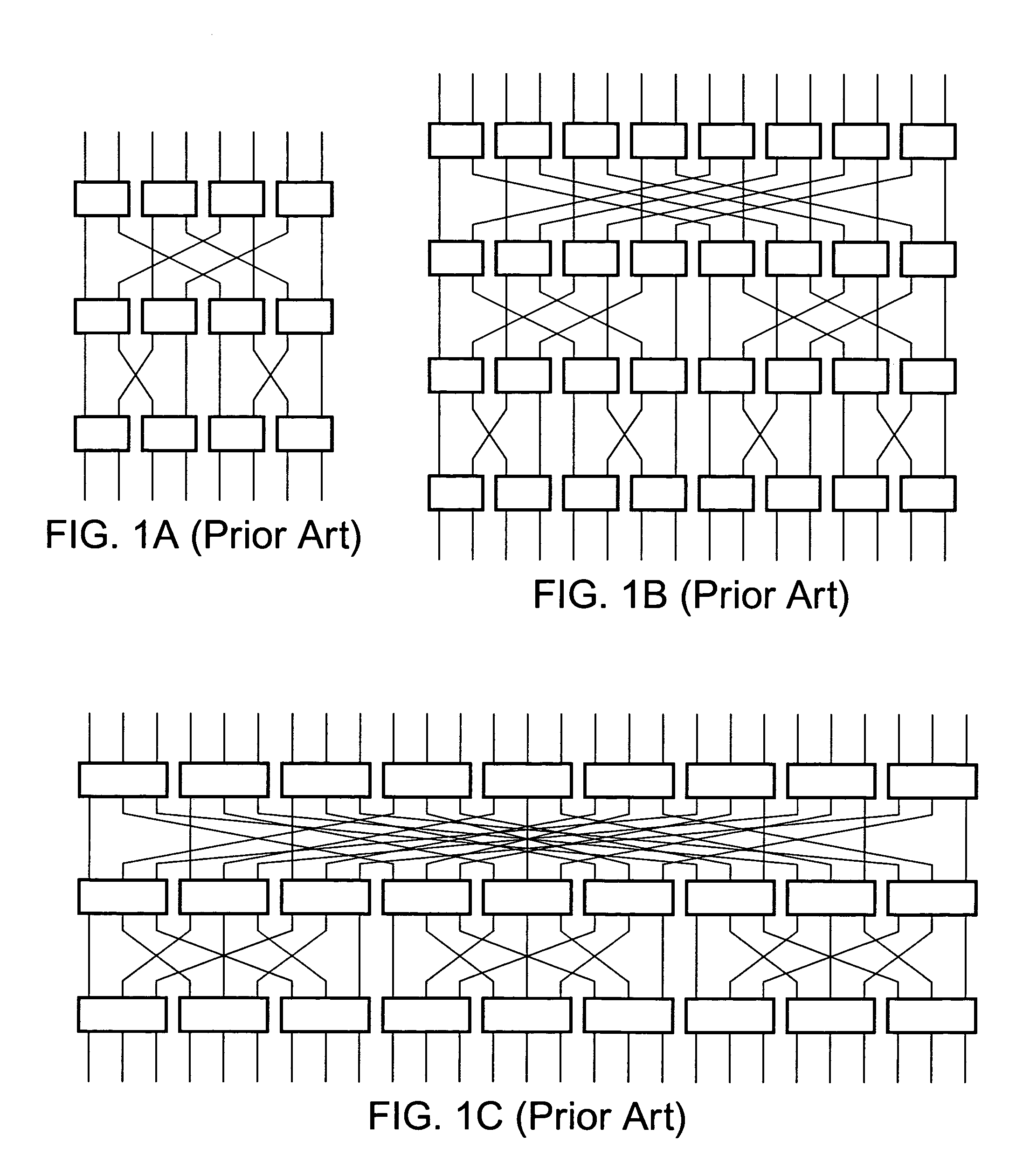
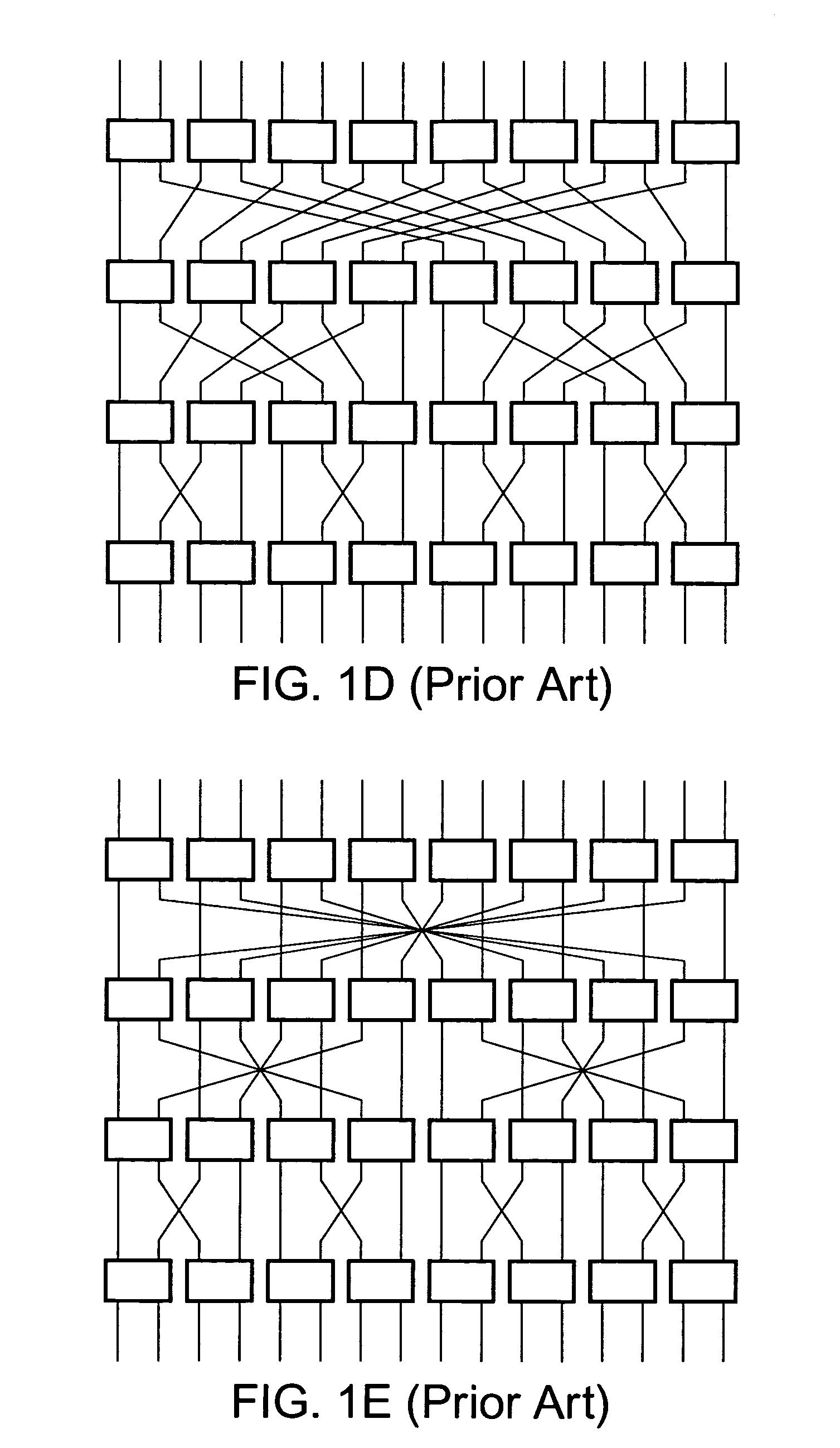
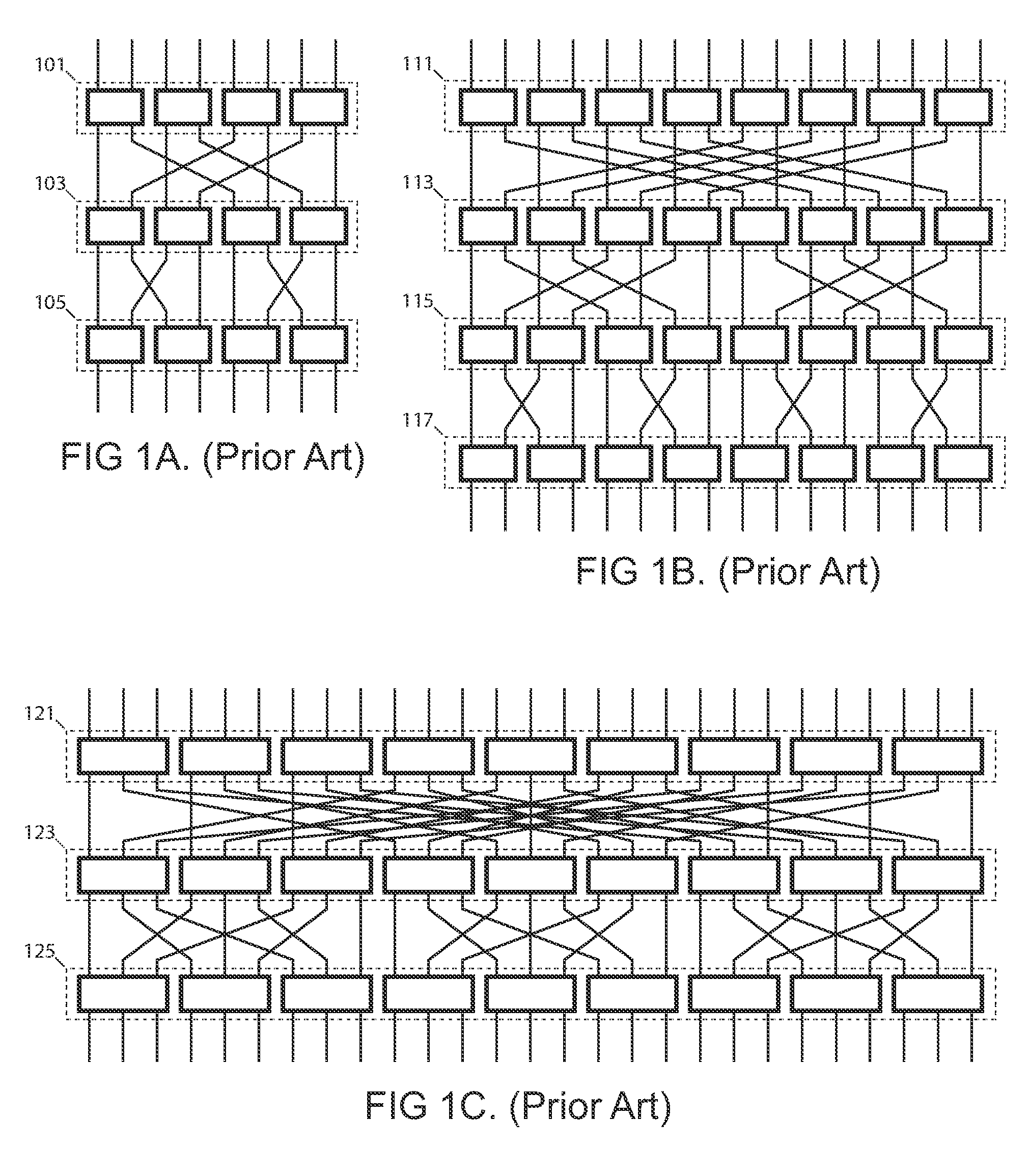
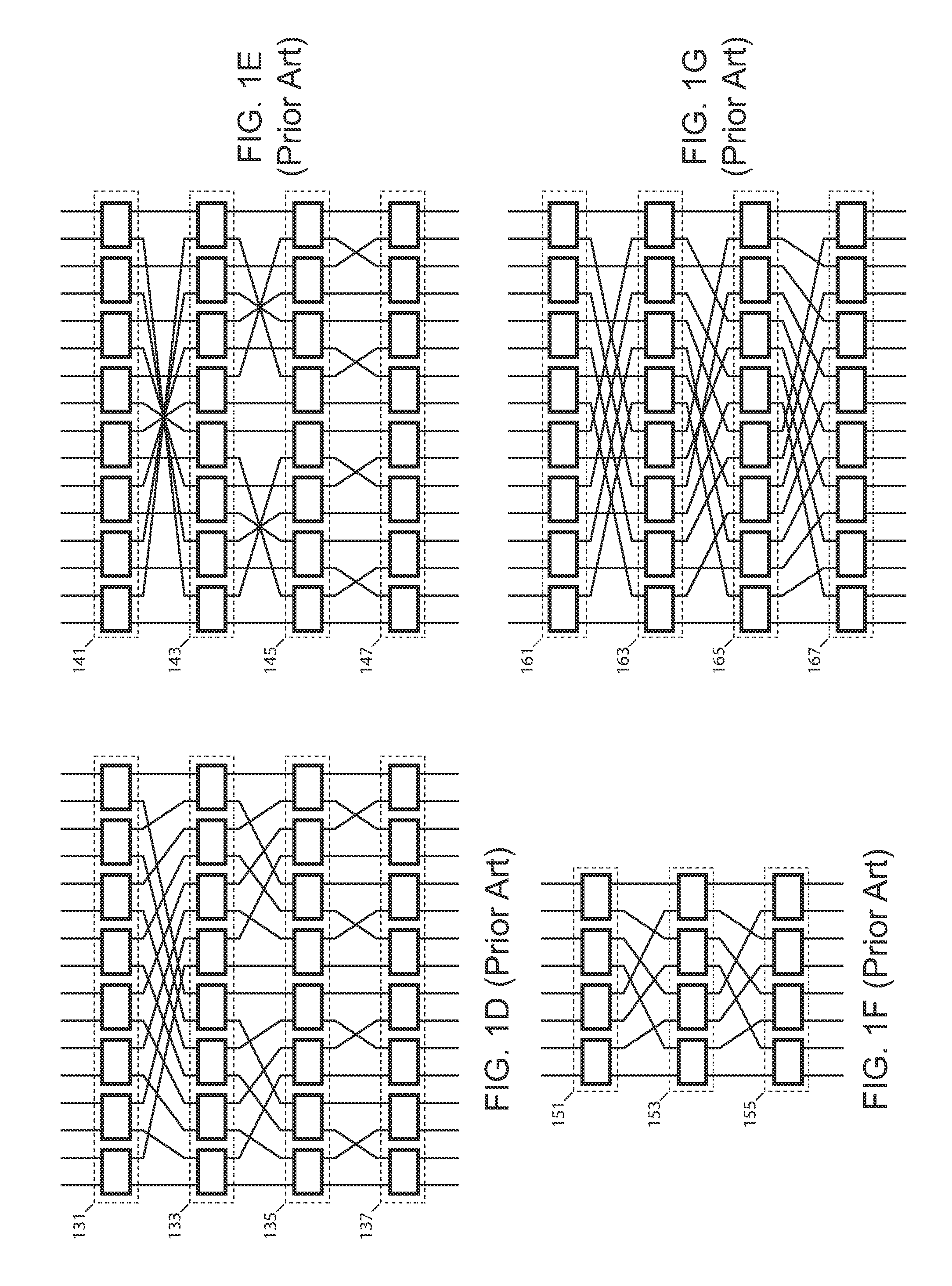
Systems and methods for upgradeable scalable switching
InactiveUS7440448B1Reduce distanceLatencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionFault toleranceExchange network
The creation of a variety of upgradeable scalable switching networks are set forth including multistage switching networks as well as novel multidirectional architectures. Systems and methods exploiting the properties such as fault tolerance, upgradeability with out service disruption and path redundancy are incorporated into a variety of systems. A wide range of methods for upgrading and reconfiguration the scalable switching networks are presented including manifestations of implementations of said networks and said methods. Methods for designing new upgradeable scalable switching and the novel architectures derived thereof including architectures built from the redundant blocking compenstated cyclic group networks are set forth.
Owner:LU HAW MINN
Method for storing exercise performance of user of exercise device and exercise device
ActiveUS7722502B2LatencyPossible to utilizePhysical therapies and activitiesClubsExercise performanceComputer science
Owner:TECHNOGYM SPA +1
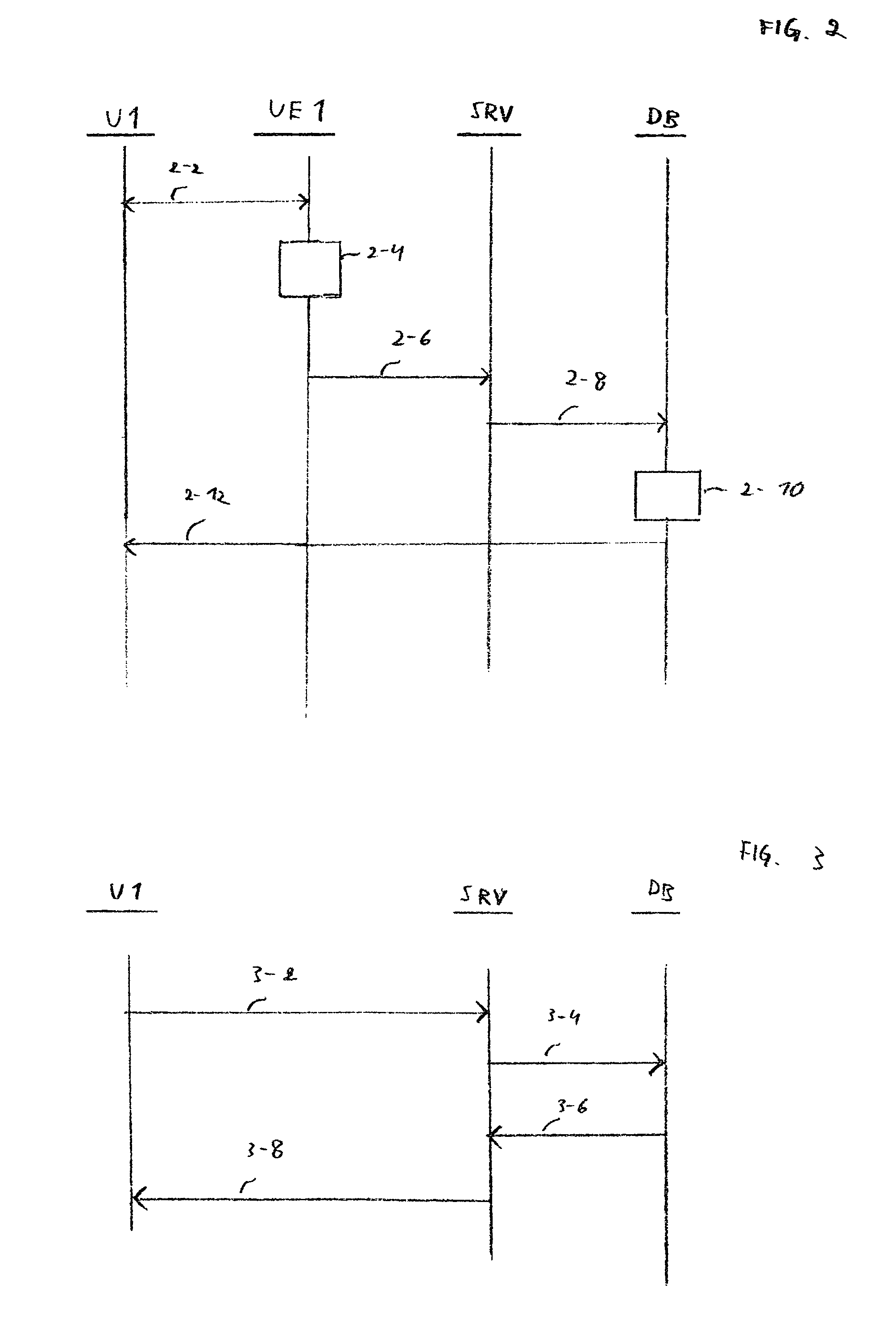
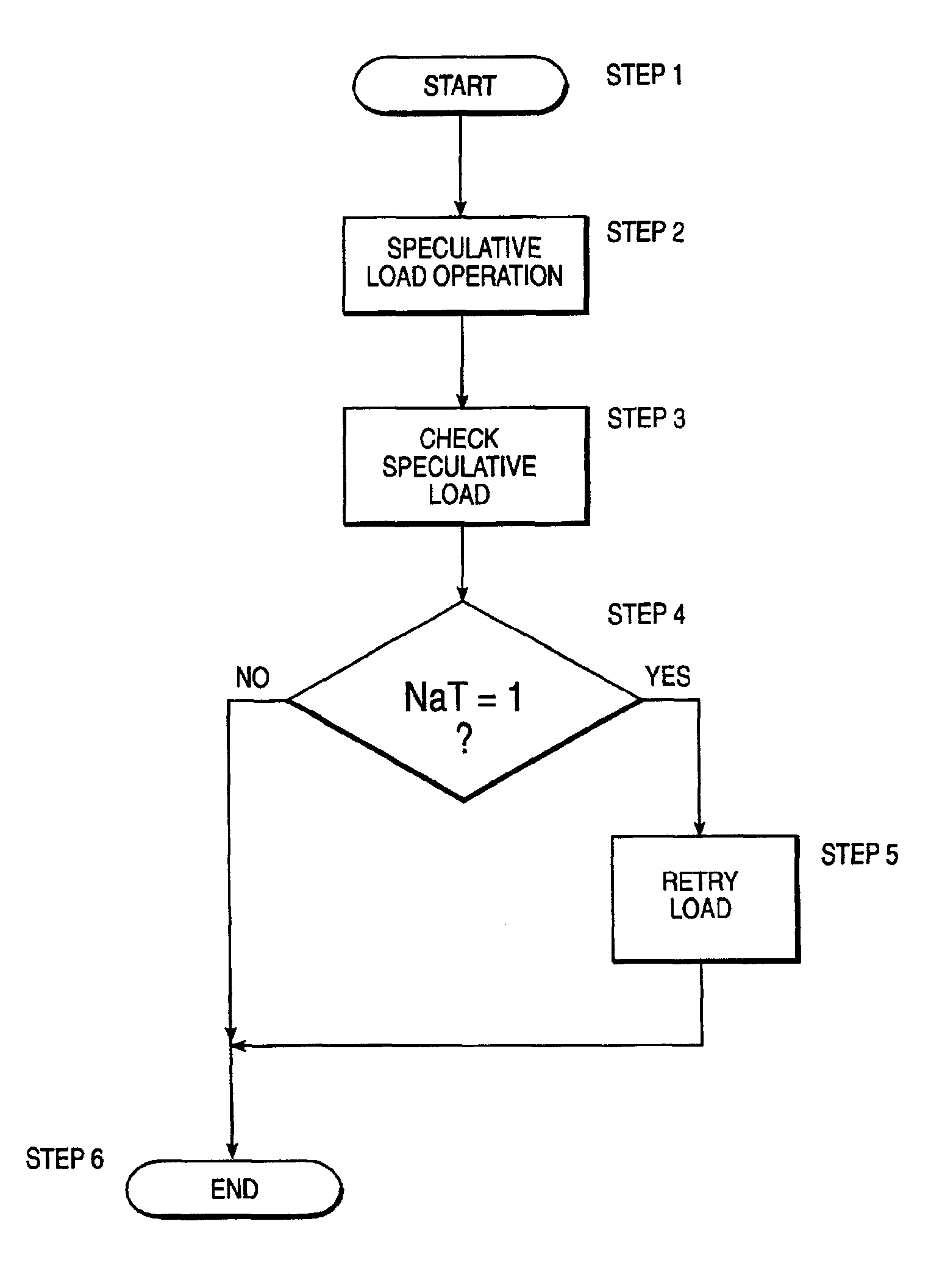
Microprocessor for executing speculative load instructions with retry of speculative load instruction without calling any recovery procedures
InactiveUS6918030B2Gain in efficiency and resource utilizationLatencyDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionCompilerInstruction stream
A system, method and apparatus is provided that splits a microprocessor load instruction into two (2) parts, a speculative load instruction and a check speculative load instruction. The speculative load instruction can be moved ahead in the instruction stream by the compiler as soon as the address and result registers are available. This is true even when the data to be loaded is not actually required. This speculative load instruction will not cause a fault in the memory if the access is invalid, i.e. the load misses and a token bit is set. The check speculative load instruction will cause the speculative load instruction to be retried in the event the token bit was set equal to one. In this manner, the latency associated with branching to an interrupt routine will be eliminated a significant amount of the time. It is very possible that the reasons for invalidating the speculative load operation are no longer present (e.g. page in memory is not present) and the load will be allowed to complete. Therefore, substantial gains in efficiency and resource utilization can be achieved by deferring the branch to recovery routines until after the speculative load is retried.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fast WIFI to LTE handover
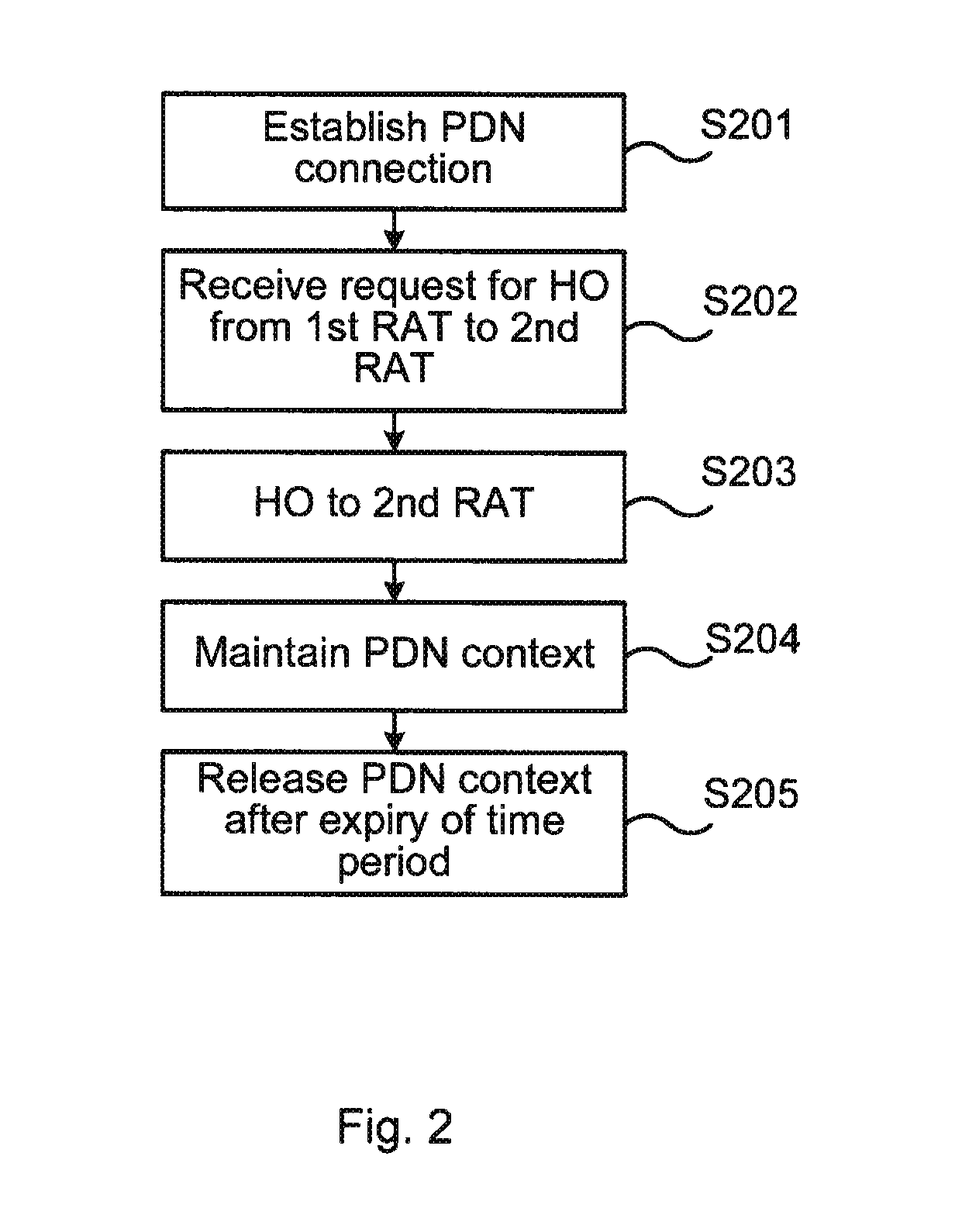
ActiveUS20160080981A1LatencyAvoid signalingWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyComputer science
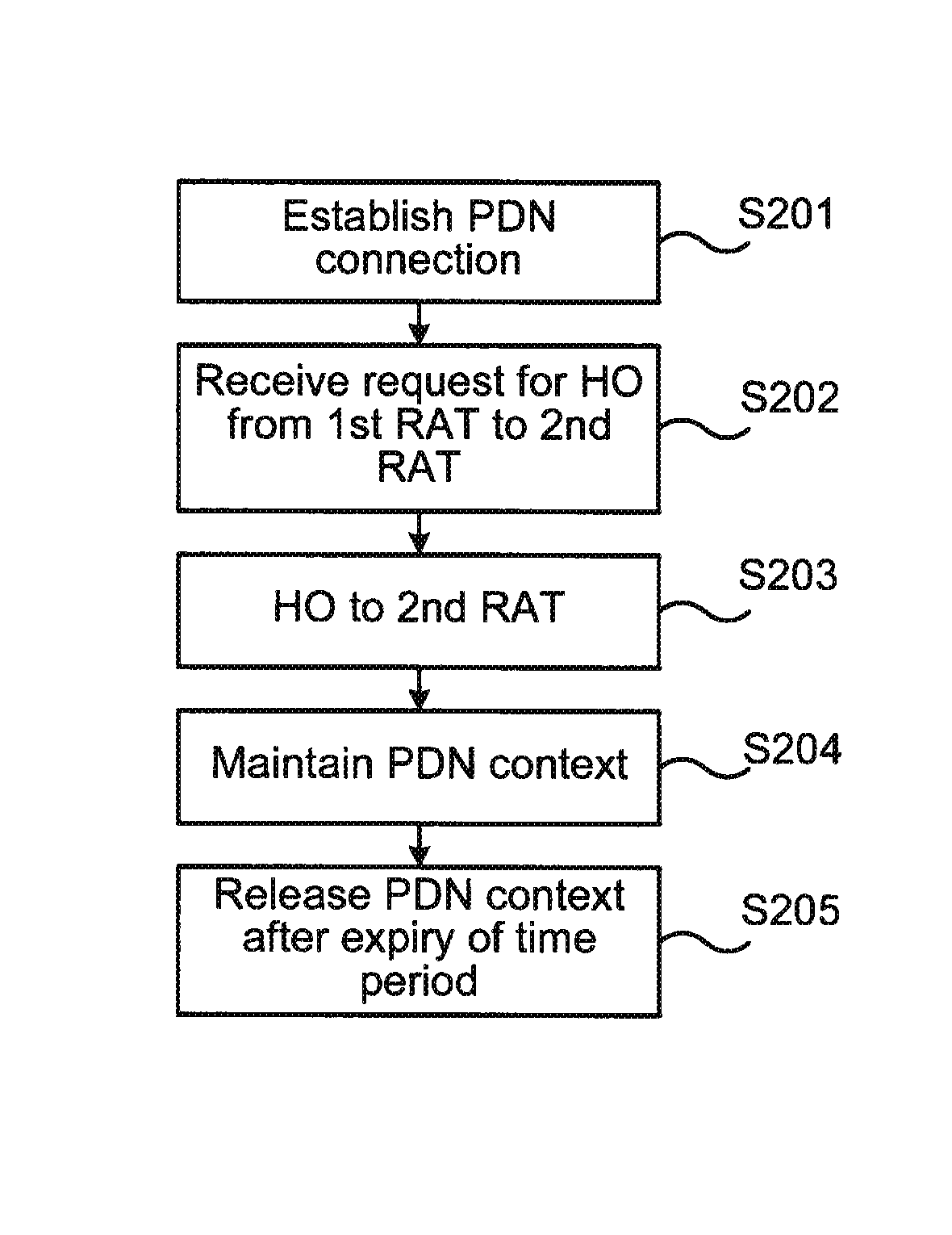
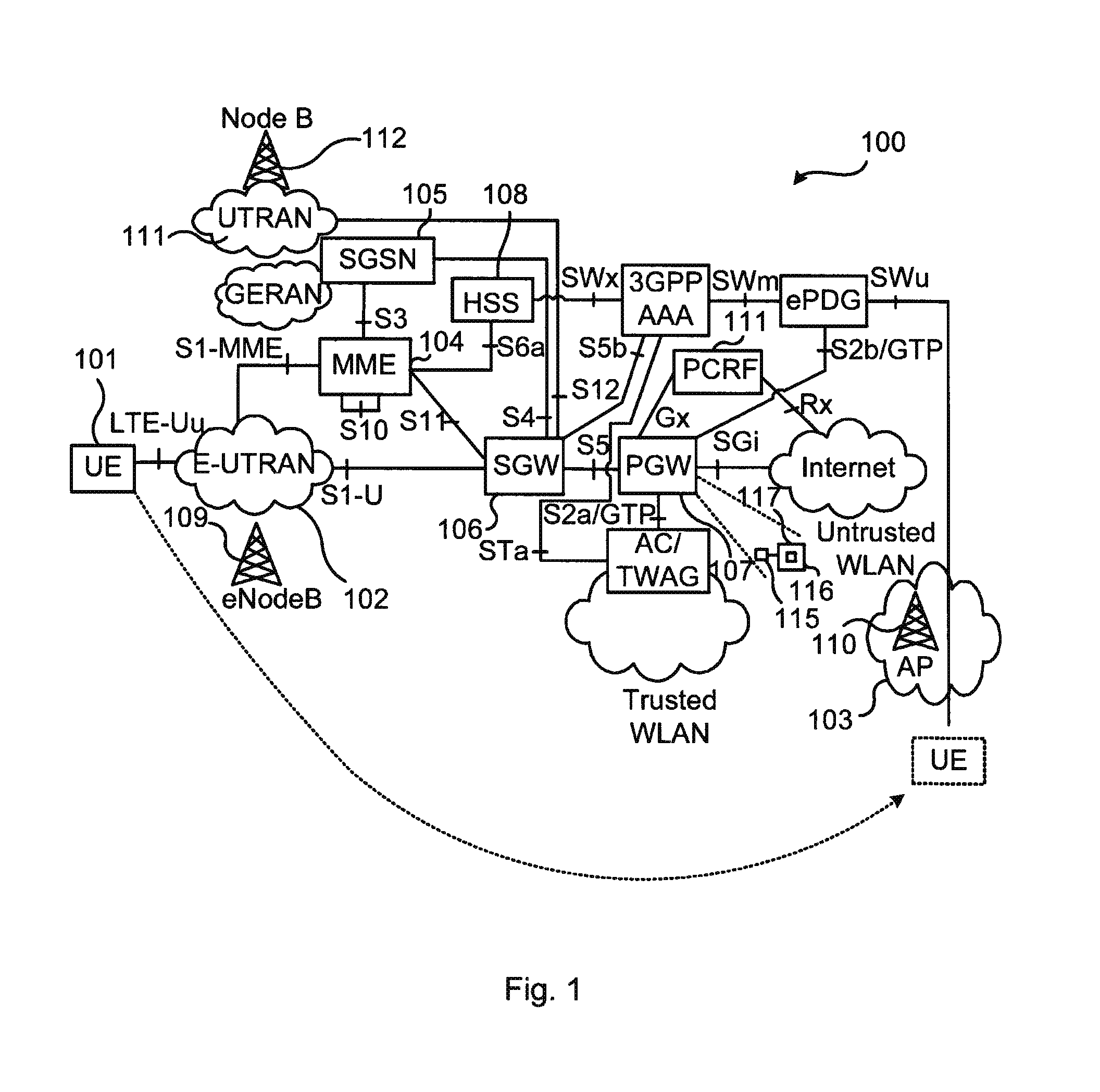
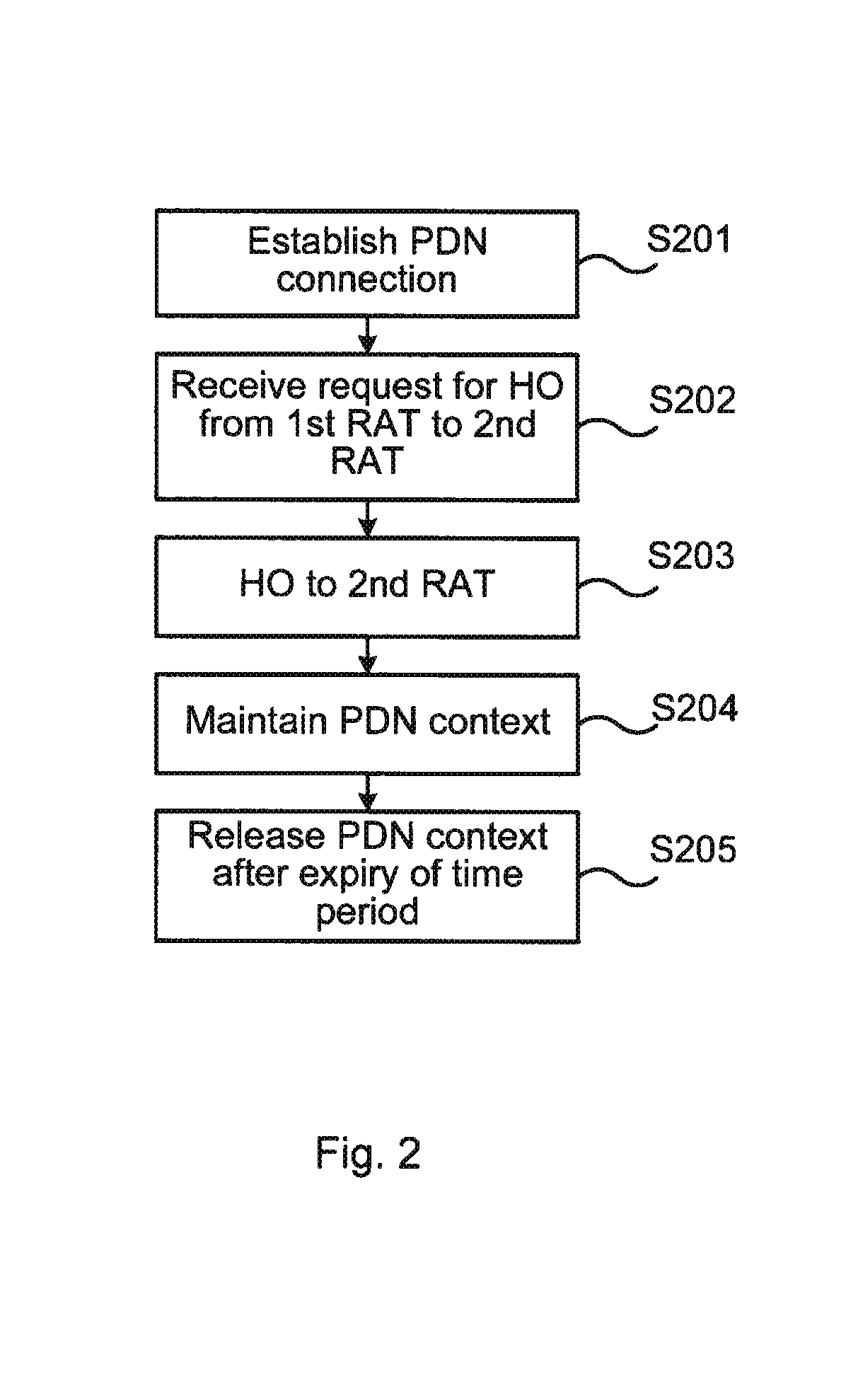
The present invention relates to a network node and a method at the network node of handing over a mobile terminal between a first RAT and a second RAT in a wireless communications network. The invention further relates to a computer program performing the method according to the present invention, and a computer program product comprising computer readable medium having the computer program embodied therein.A method at a network node of a packet core network of performing handover of a mobile terminal between a first Radio Access Technology (RAT), and a second RAT in a wireless communications network is provided in an embodiment of the present invention. The method comprises receiving a request for handover of the mobile terminal to the second RAT, establishing a PDN connection with the mobile terminal via the first RAT, and performing handover of the mobile terminal to the second RAT. The method further comprises maintaining PDN connection context for the PDN connection established via the first RAT for a time period, and releasing the PDN connection context at expiry of the time period.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus and method for communicating between computer systems using a sliding send window for ordered messages in a clustered computing environment
InactiveUS7185099B1Reduce communication trafficEnhance performanceSpecial service provision for substationMultiprogramming arrangementsTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
A clustered computer system includes multiple computer systems (or nodes) coupled together via one or more networks that can become members of a group to work on a particular task. Each node includes a cluster engine, a cluster communication mechanism that includes a sliding send window, and one or more service tasks that process messages. The sliding send window allows a node to send out multiple messages without waiting for an individual acknowledgment to each message. The sliding send window also allows a node that received the multiple messages to send a single acknowledge message for multiple received messages. By using a sliding send window to communicate with other computer systems in the cluster, the communication traffic in the cluster is greatly reduced, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the cluster. In addition, the latency between multiple messages sent concurrently is dramatically reduced.
Owner:IBM CORP
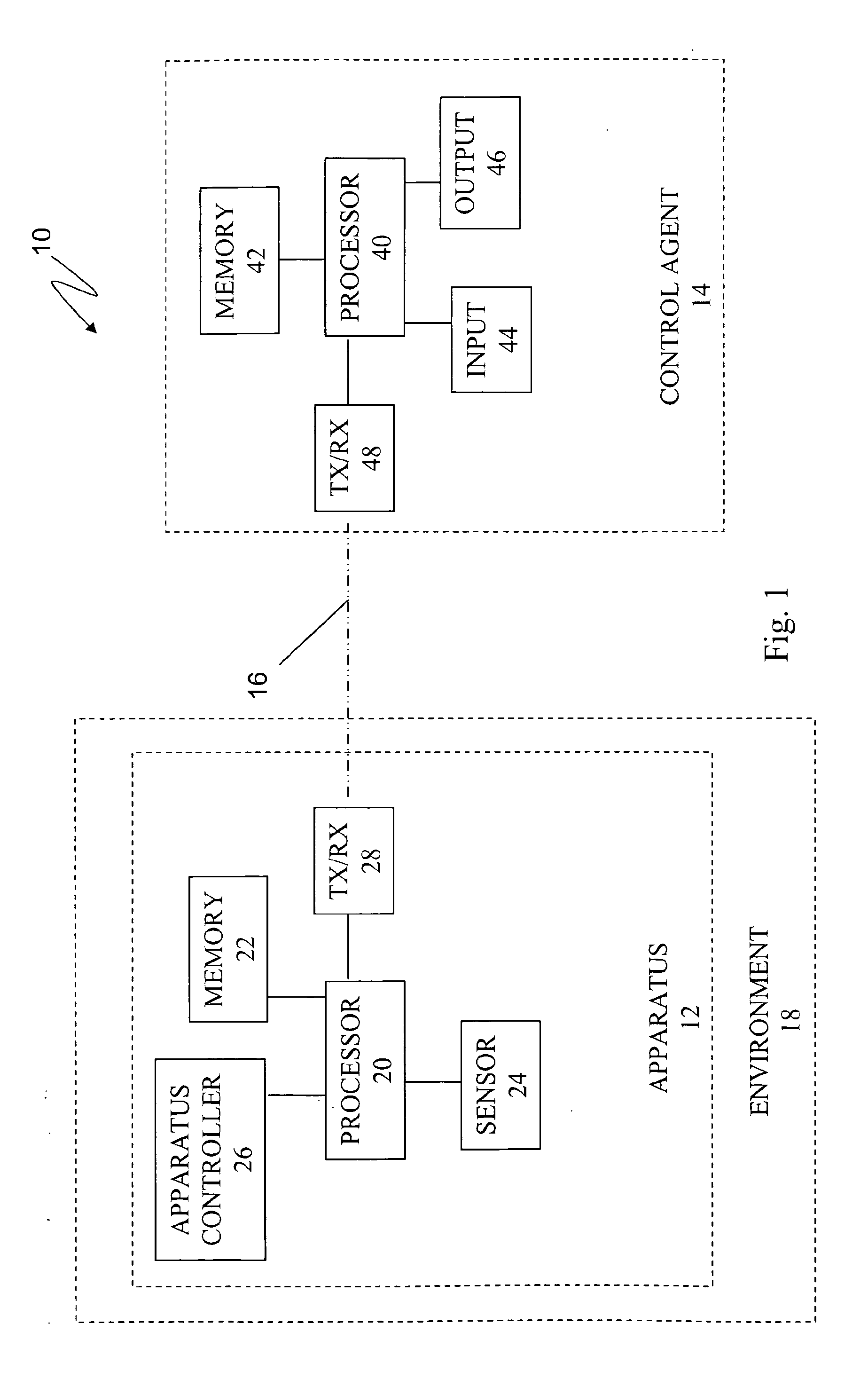
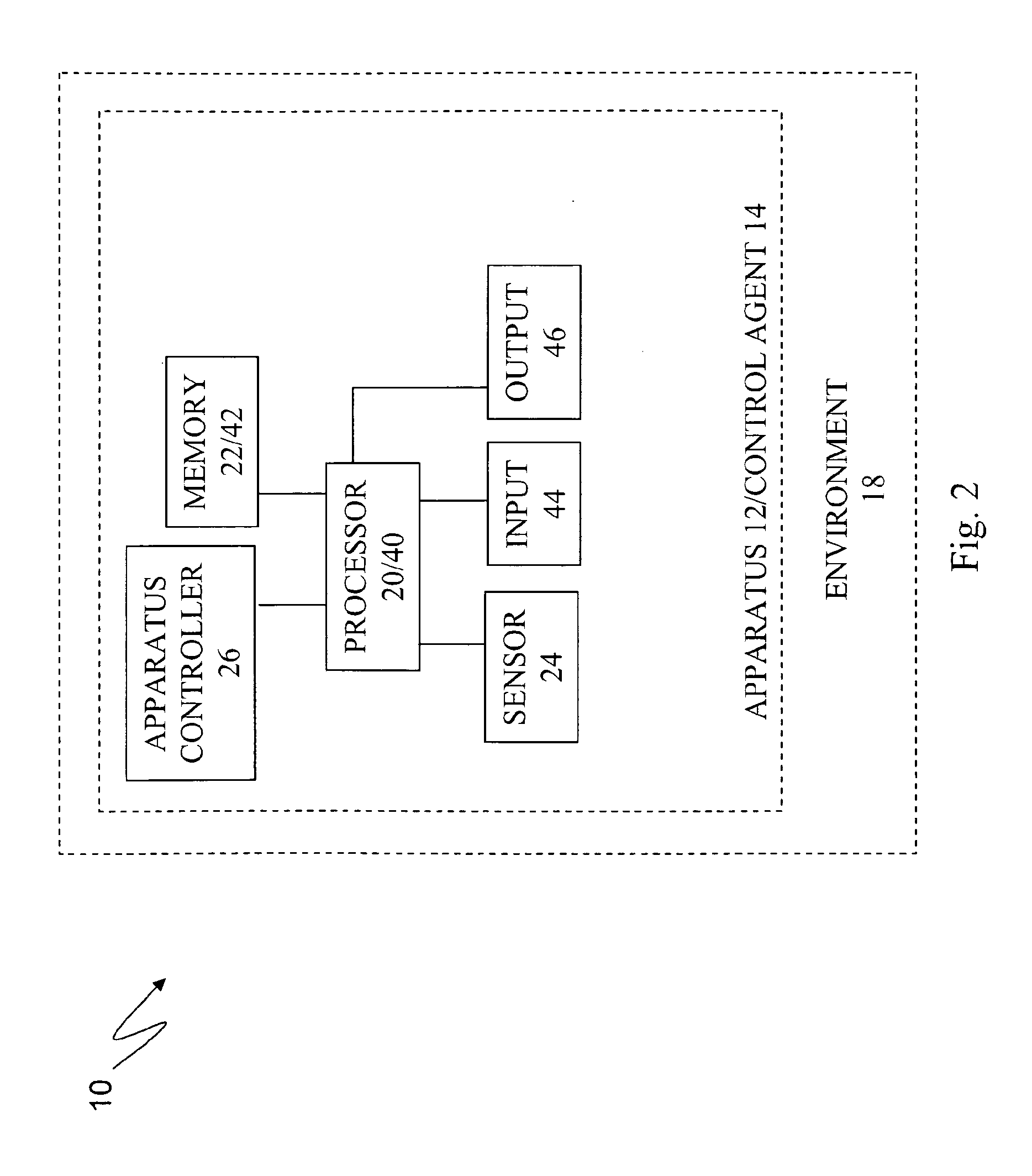
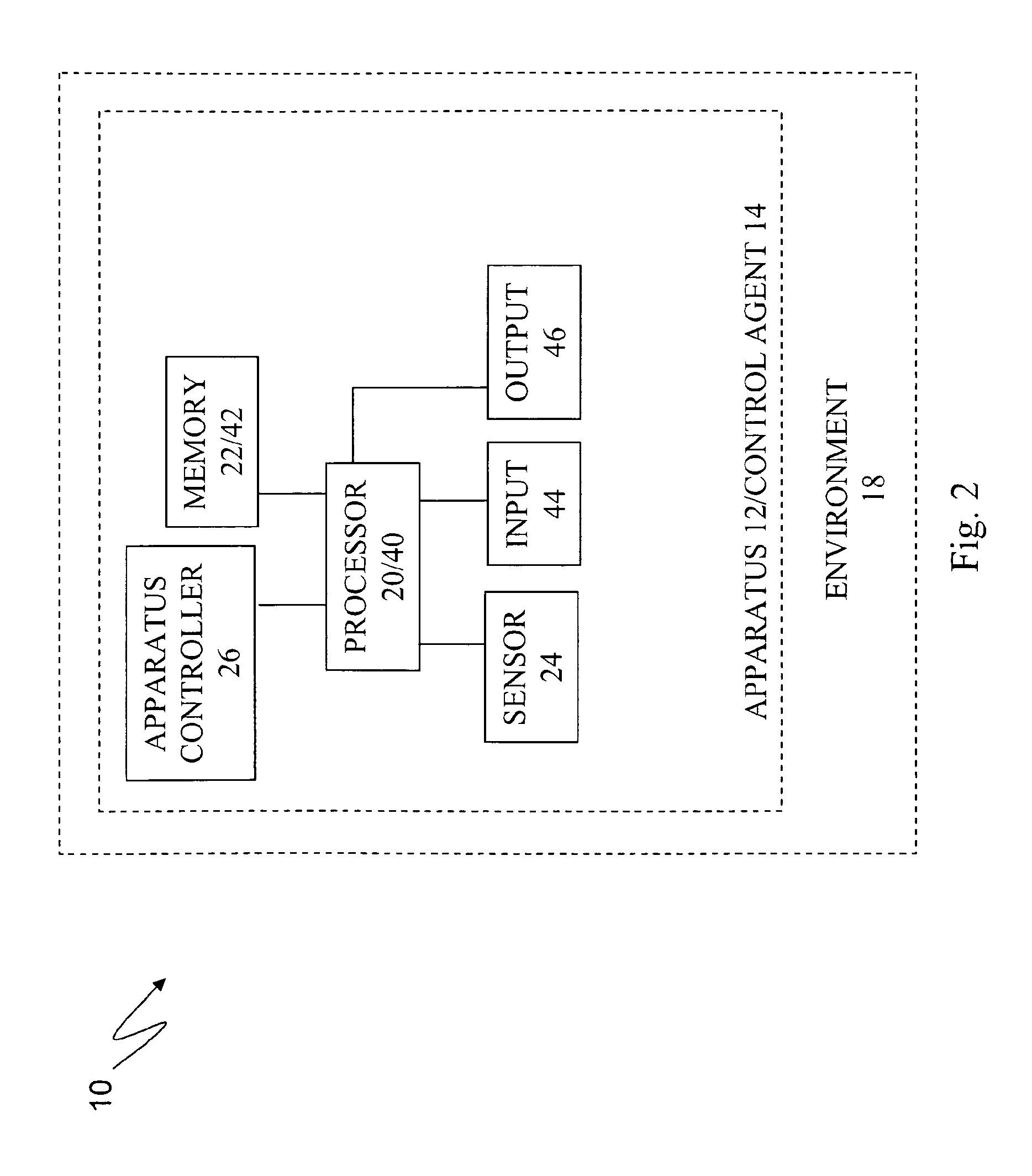
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for apparatus operation and remote sensing
ActiveUS8774950B2Reducing and eliminating apparent latencyLatencyComputer controlSimulator controlVirtualizationViewpoints
A method and system for controlling an apparatus including receiving data indicative of an actual state of the apparatus, defining a first viewpoint relative to at least one of the environment and the apparatus, determining a first predicted state of the apparatus at time T, determining a first predicted state of the environment at time T, producing a first virtualized view from the first viewpoint, sending a first control signal to the apparatus after producing the first virtualized view, defining a second viewpoint relative to at least one of the apparatus and the environment, determining a second predicted state of the apparatus at time T+delta T, determining a second predicted state of the environment at time T+delta T, producing the second virtualized view from the second viewpoint, sending a second control signal to the apparatus after producing the second virtualized view, and changing the actual state of the apparatus based on the first control signal.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
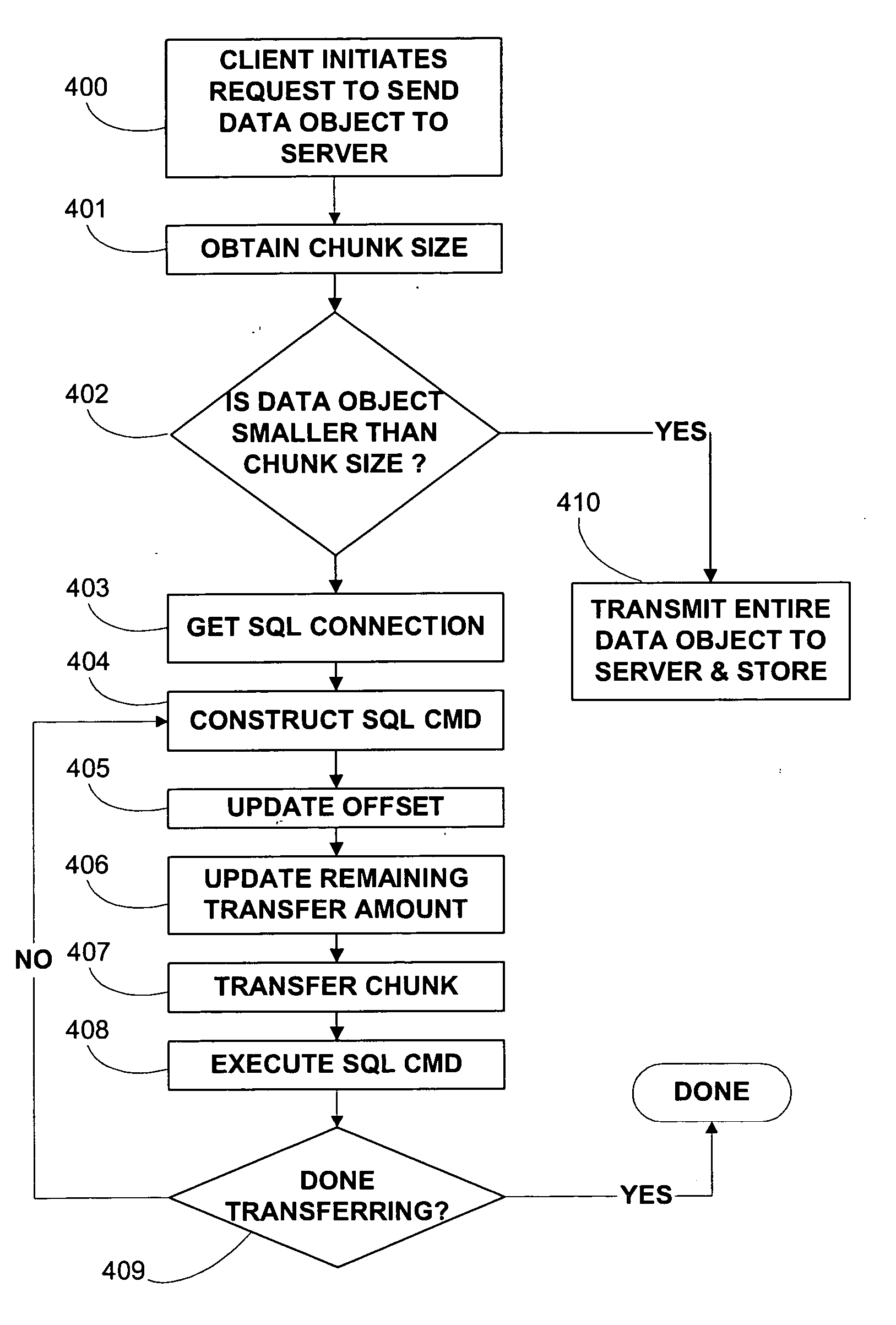
Method and apparatus for managing data object size in a multi-user environment
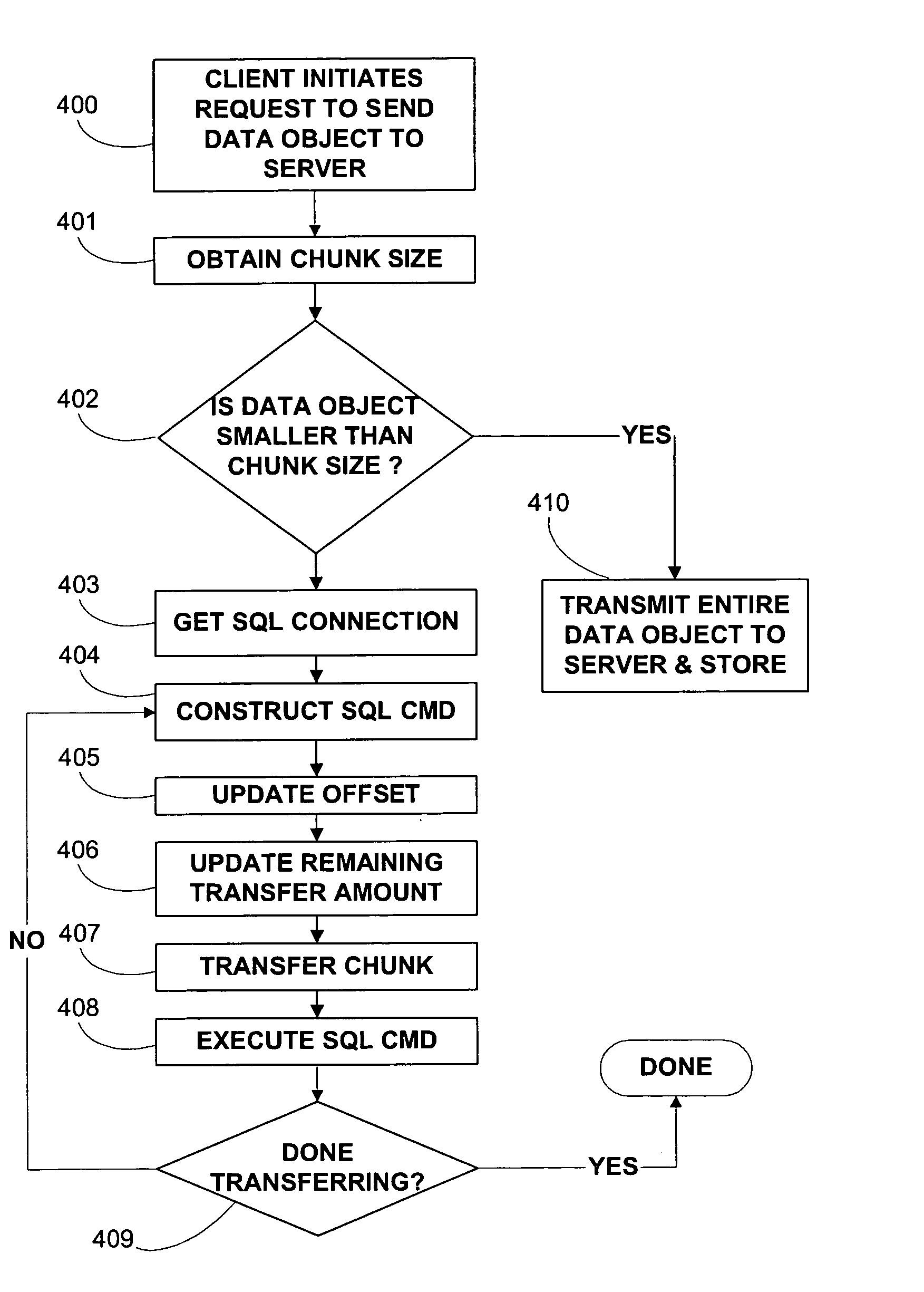
ActiveUS20060167922A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData segmentResource utilization
One or more embodiments of the invention enable improved communication with a database comprising multiple clients utilizing multiple large data objects concurrently. For example when a client system interacts with a server with respect to a data object that is over a threshold size, the system may utilizing a communication methodology that minimizes system resource usage such as CPU utilization and network utilization. In one embodiment of the invention when a client request for an object falls within the relevant size threshold, one or more embodiments of the invention segment the object into smaller size chunks. Hence the server is not required to assemble all data associated with a request at once, but is instead able to immediately start transmitting smaller segments of data. Allowing for the transmission of smaller data chunks prevents the server from allocating large blocks of memory to one object and although the server may be required to handle more memory allocations, each allocation is smaller in size and can therefore be processed much faster. The determination of the chunk size is dependent on inherent system resources such as the amount of server memory, and the available bandwidth of the network. In addition, the determination of chunk size is dependent on environmental factors such as the time of day, the day of the week, the number of users, the number of predicted users for a given time and day based on historical logging, and the current and predicted network utilization for a given time and day. One or more embodiments of the invention obtain the chunk size and optionally obtain a chunk transfer size from a server that may alter these quantities dynamically in order to minimize resource utilization.
Owner:REGIONAL RESOURCES LTD
Pipelined intra-prediction hardware architecture for video coding
ActiveUS20160100191A1Lower latencyLower performance requirementsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingParallel processing
As the quality and quantity of shared video content increases, video encoding standards and techniques are being developed and improved to reduce bandwidth consumption over telecommunication and other networks. One technique to reduce bandwidth consumption is intra-prediction, which exploits spatial redundancies within video frames. Each video frame may be segmented into blocks, and intra-prediction may be applied to the blocks. However, intra-prediction of some blocks may rely upon the completion (e.g., reconstruction) of other blocks, which can make parallel processing challenging. Provided are exemplary techniques for improving the efficiency and throughput associated with the intra-prediction of multiple blocks.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
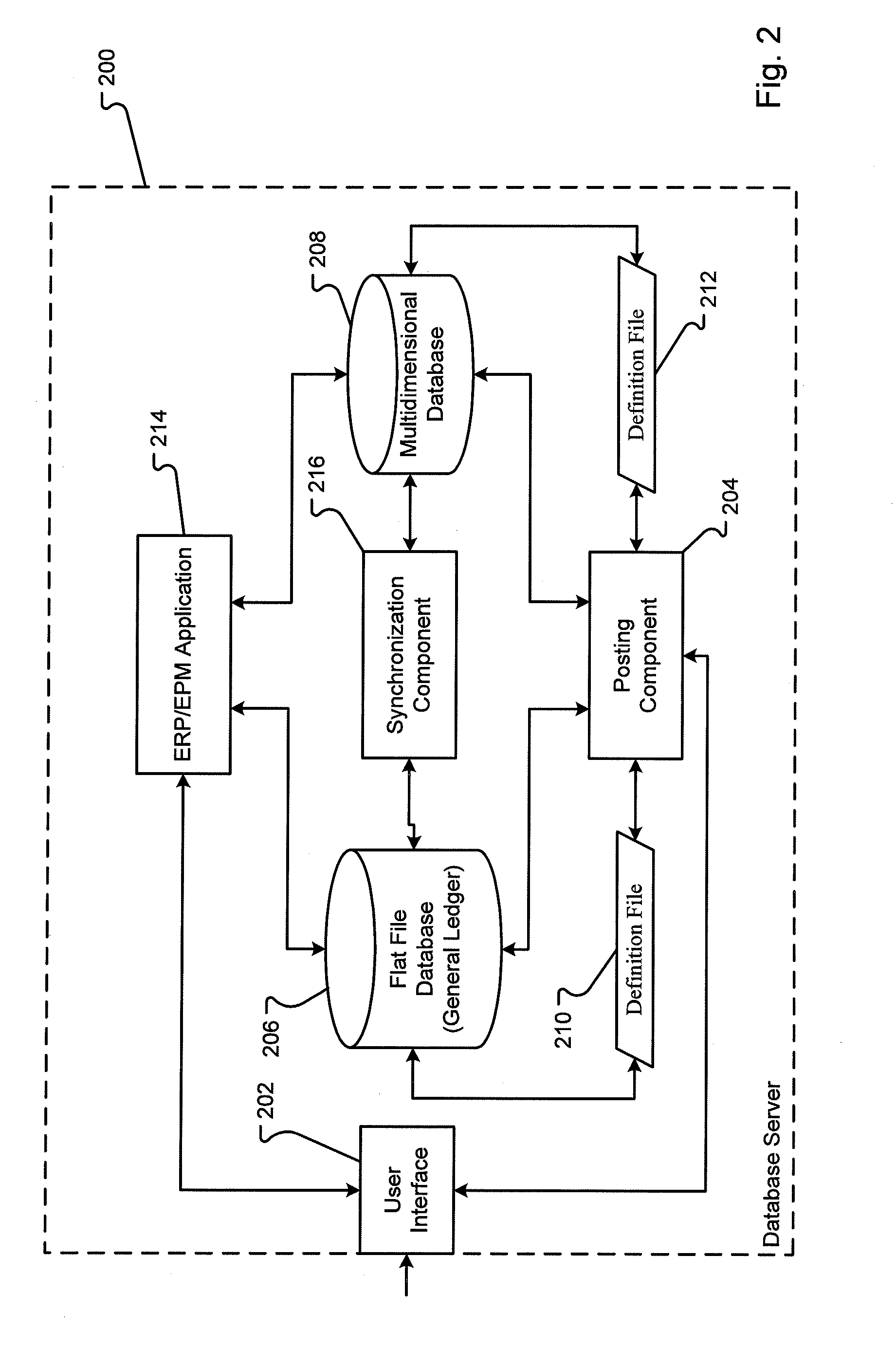
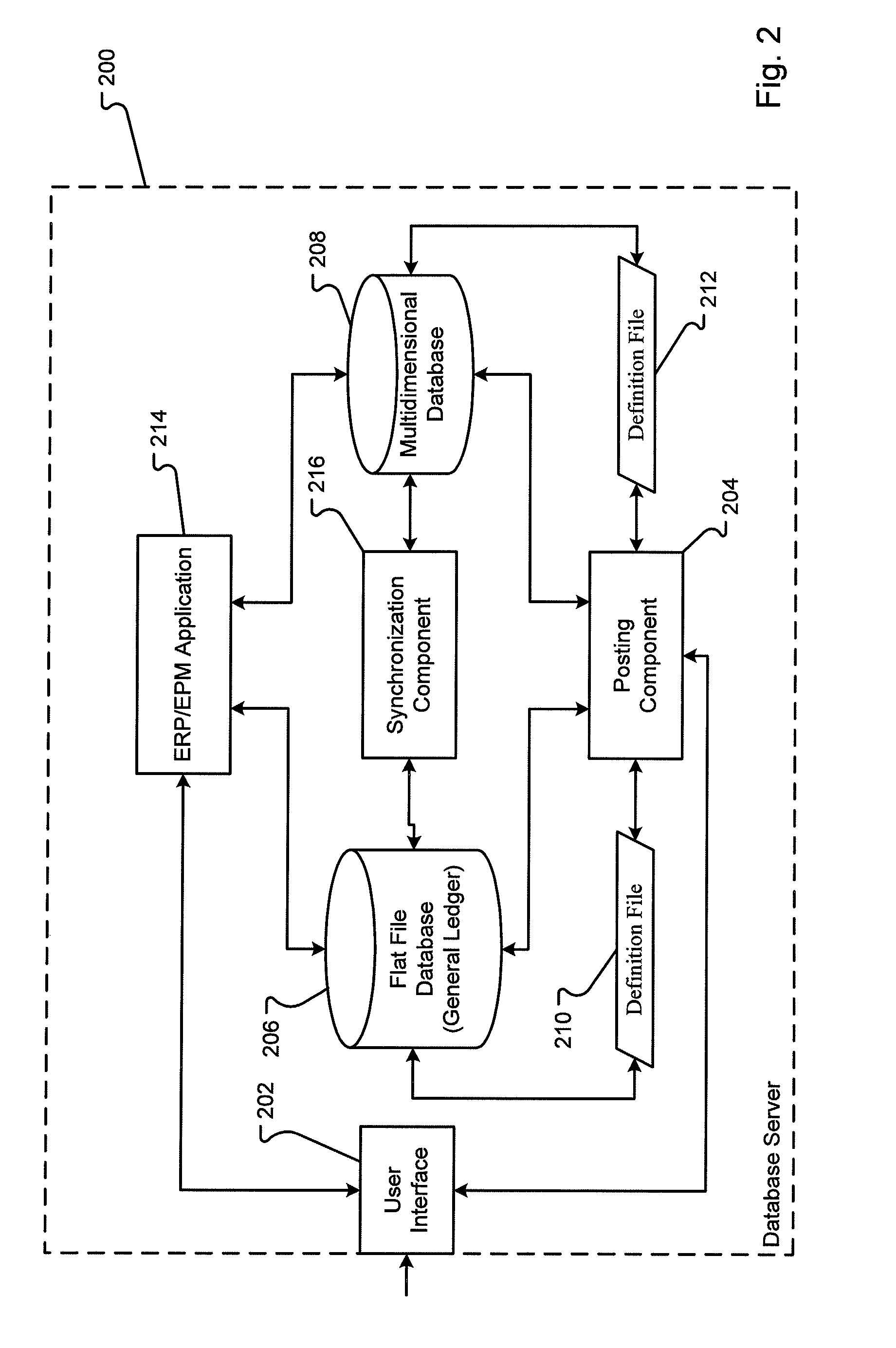
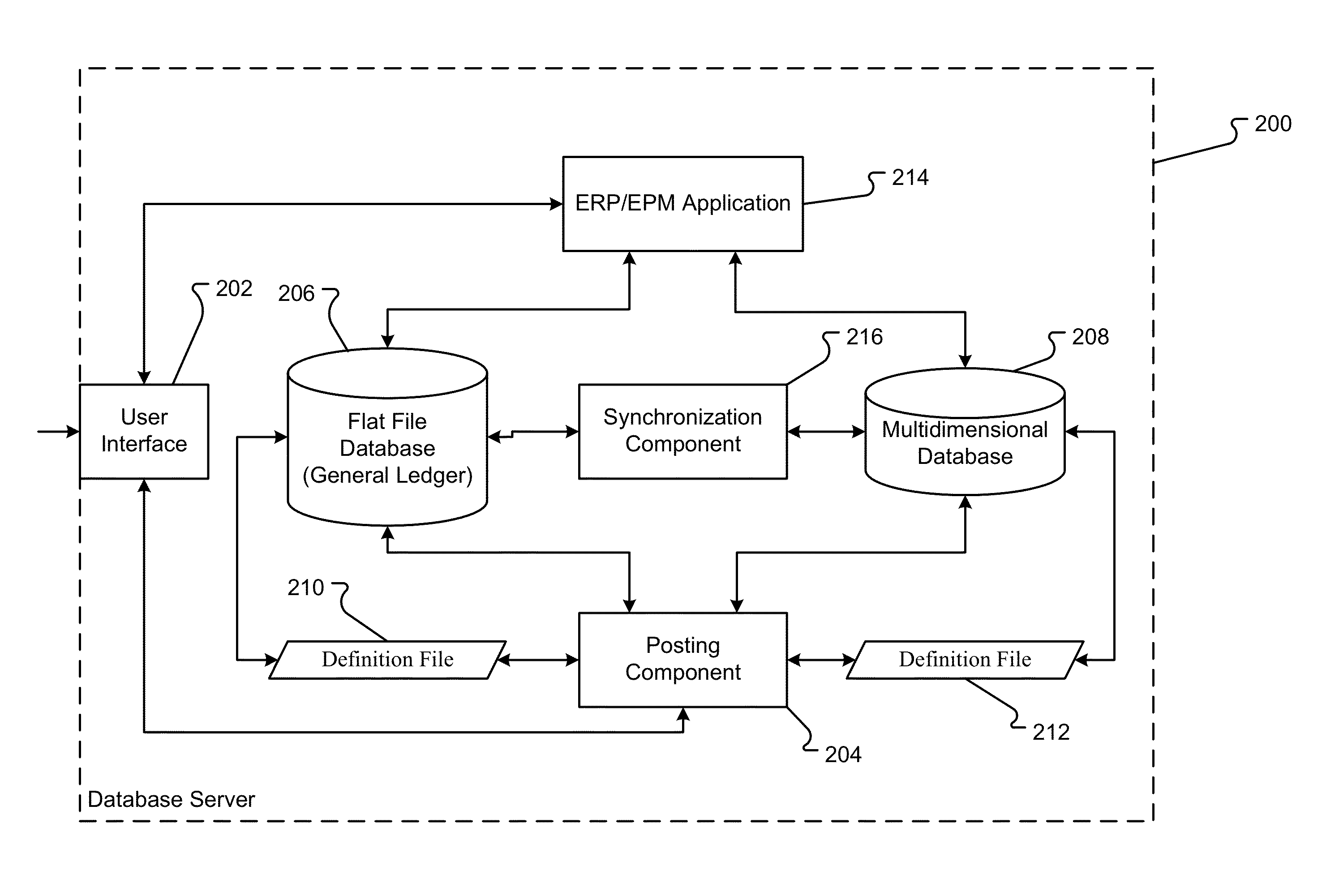
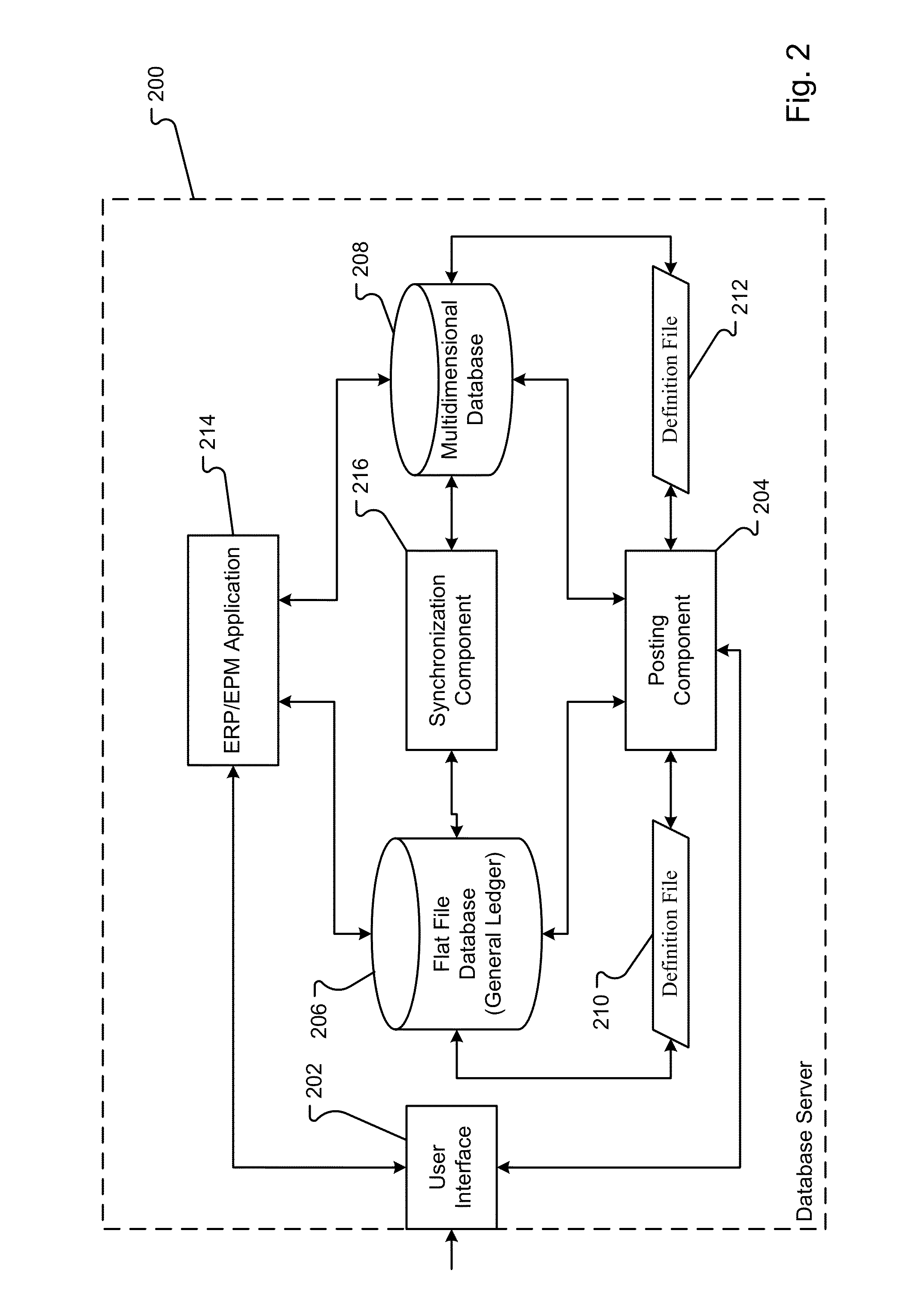
Fusion general ledger
ActiveUS20100318572A1LatencyMinimum delayDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesMulti dimensional dataMulti dimensional
A database system combines a general ledger and a multi-dimensional database. The general ledger and multi-dimensional database are mapped such that relationships between the general ledger and multi-dimensional database are characterized with metadata dimensions. Using the mapping, data can be received into the general ledger and stored in both the general ledger and multi-dimensional database substantially simultaneously. Further, a synchronization of the data copies changes to the data automatically from the general ledger to the multi-dimensional database. Thus, there is no manual copying of data between the general ledger and the database. Further, the latency between the general ledger and database is minimal ensuring accurate analysis even contemporaneous with the input of the data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
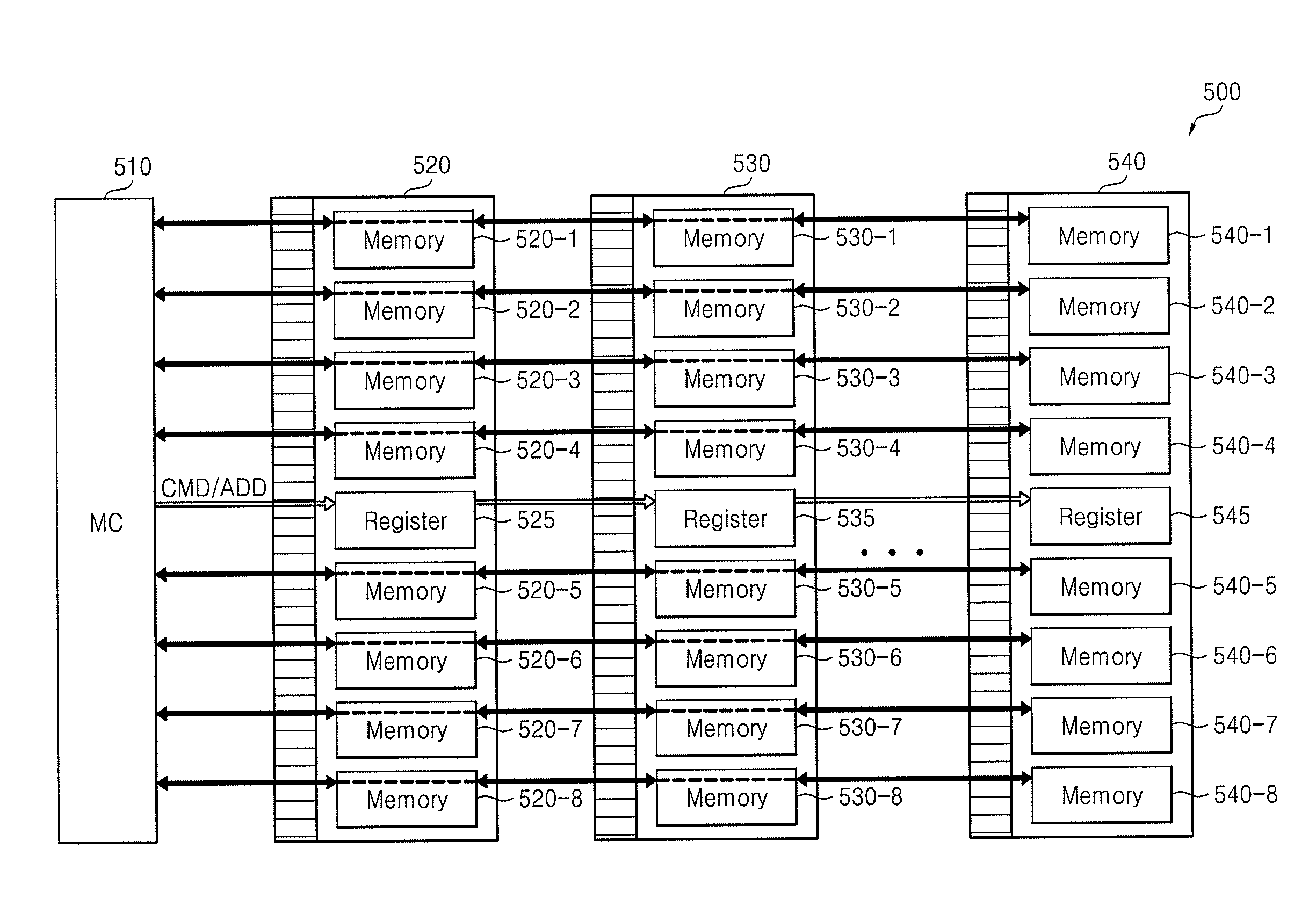
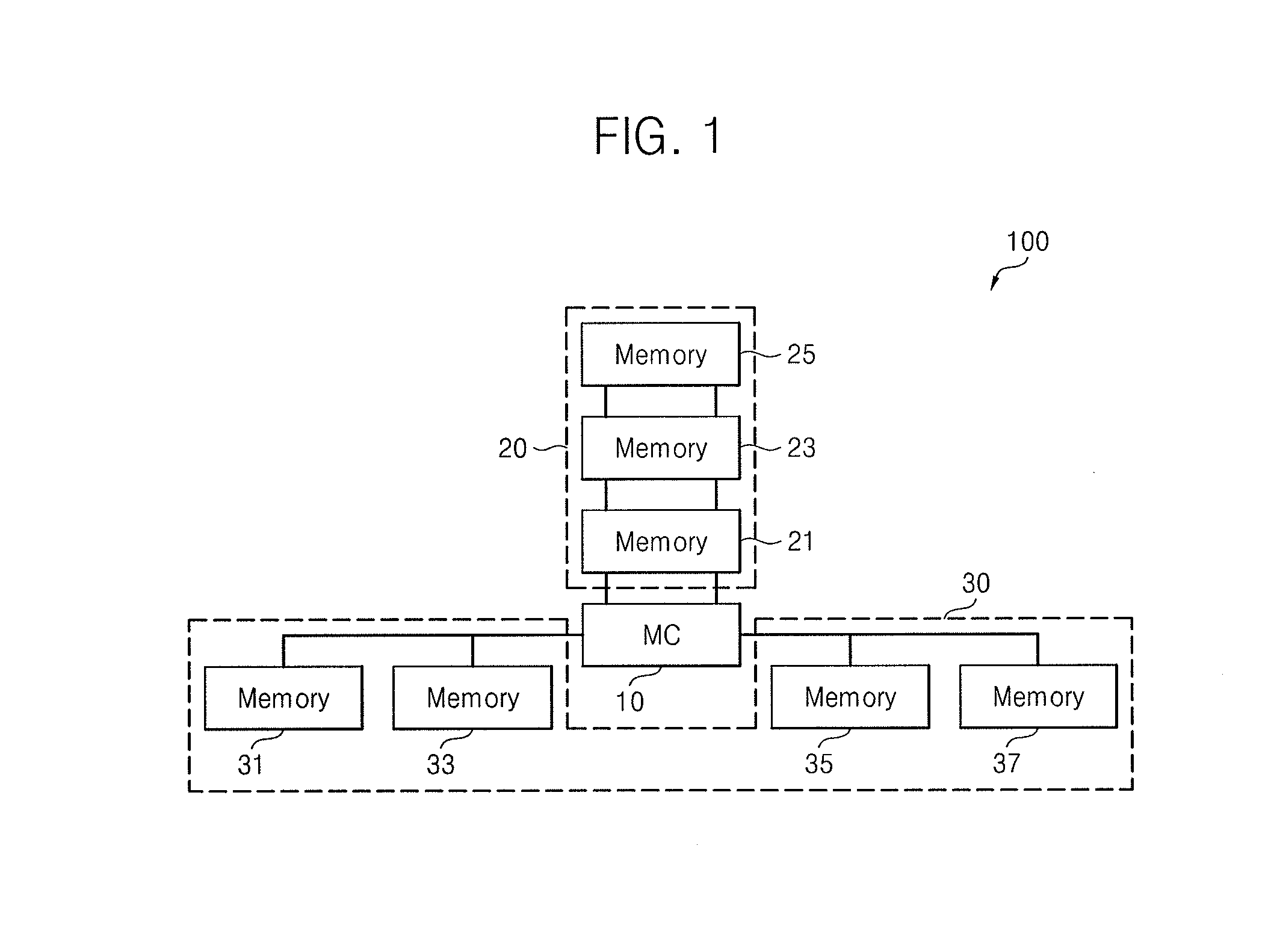
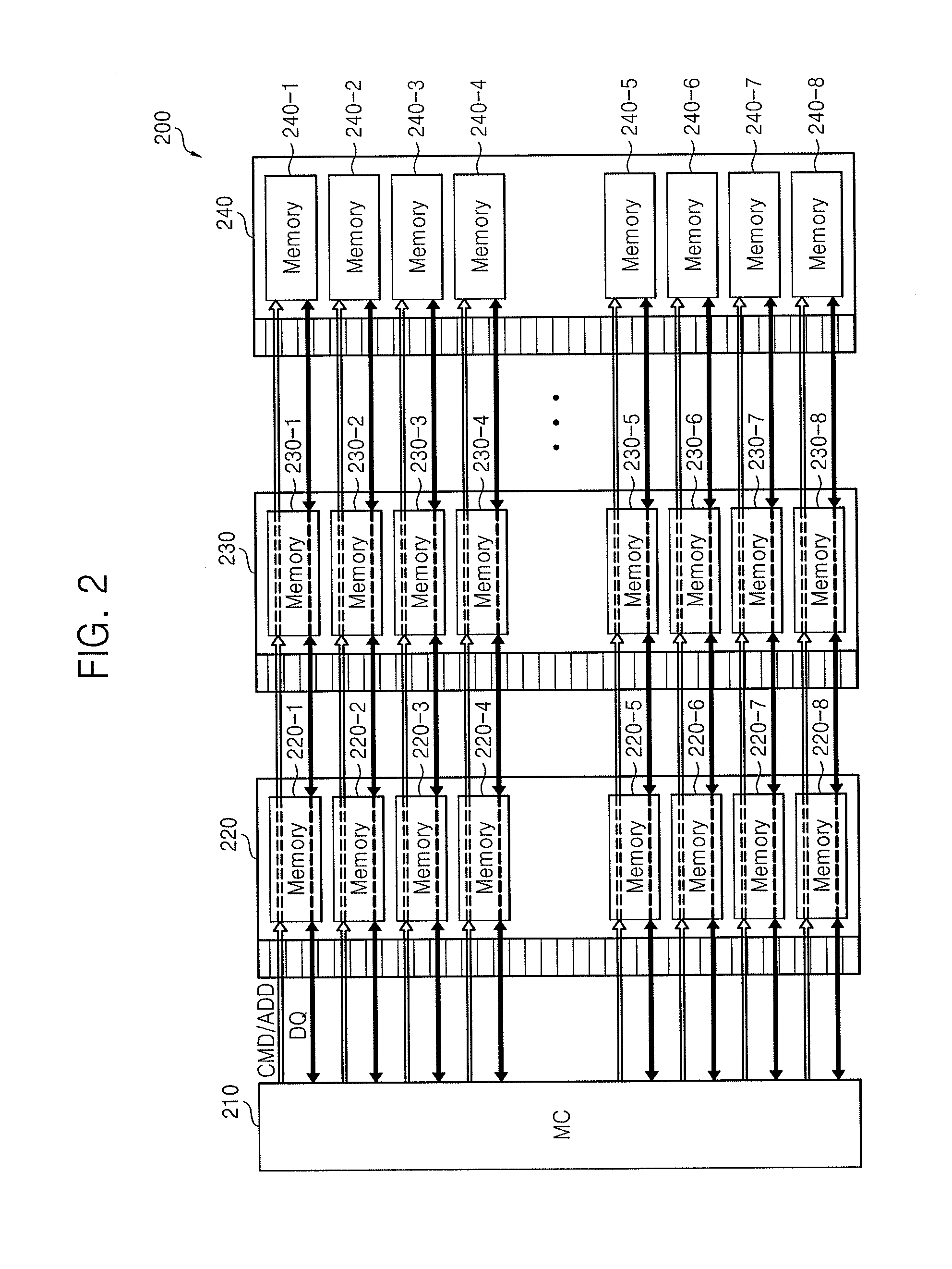
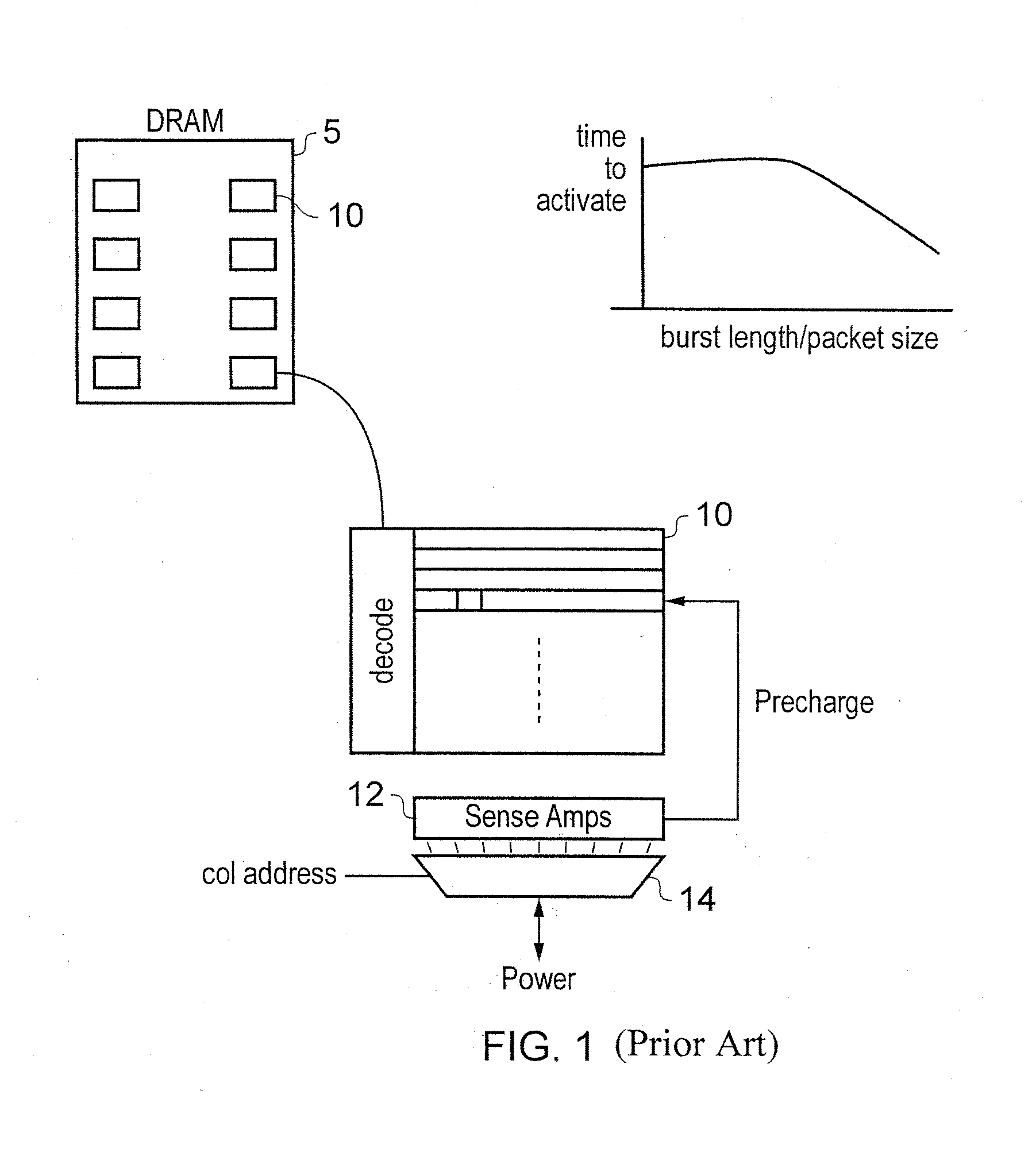
Memory system
InactiveUS20140310481A1Lower latencyCorrection capabilityDigital storageMemory systemsComputer hardwareMemory controller
A memory system includes a memory controller to control a first memory device and a second memory device. The first and second memory devices are different in terms of at least one of physical distance from the memory controller, a manner of connection to the memory controller, error correction capability, or memory supply voltage. The first and second memory devices also have different latencies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
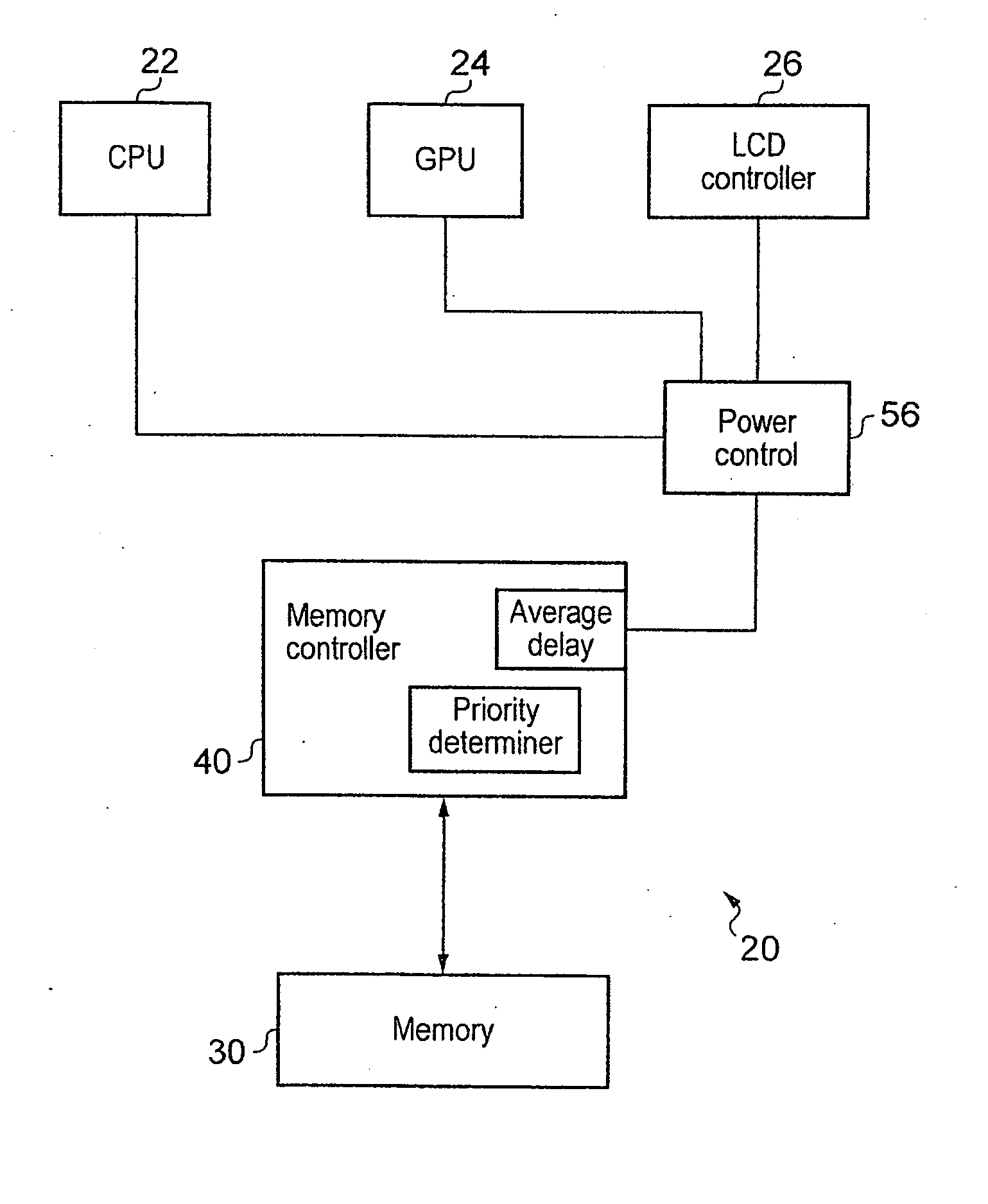
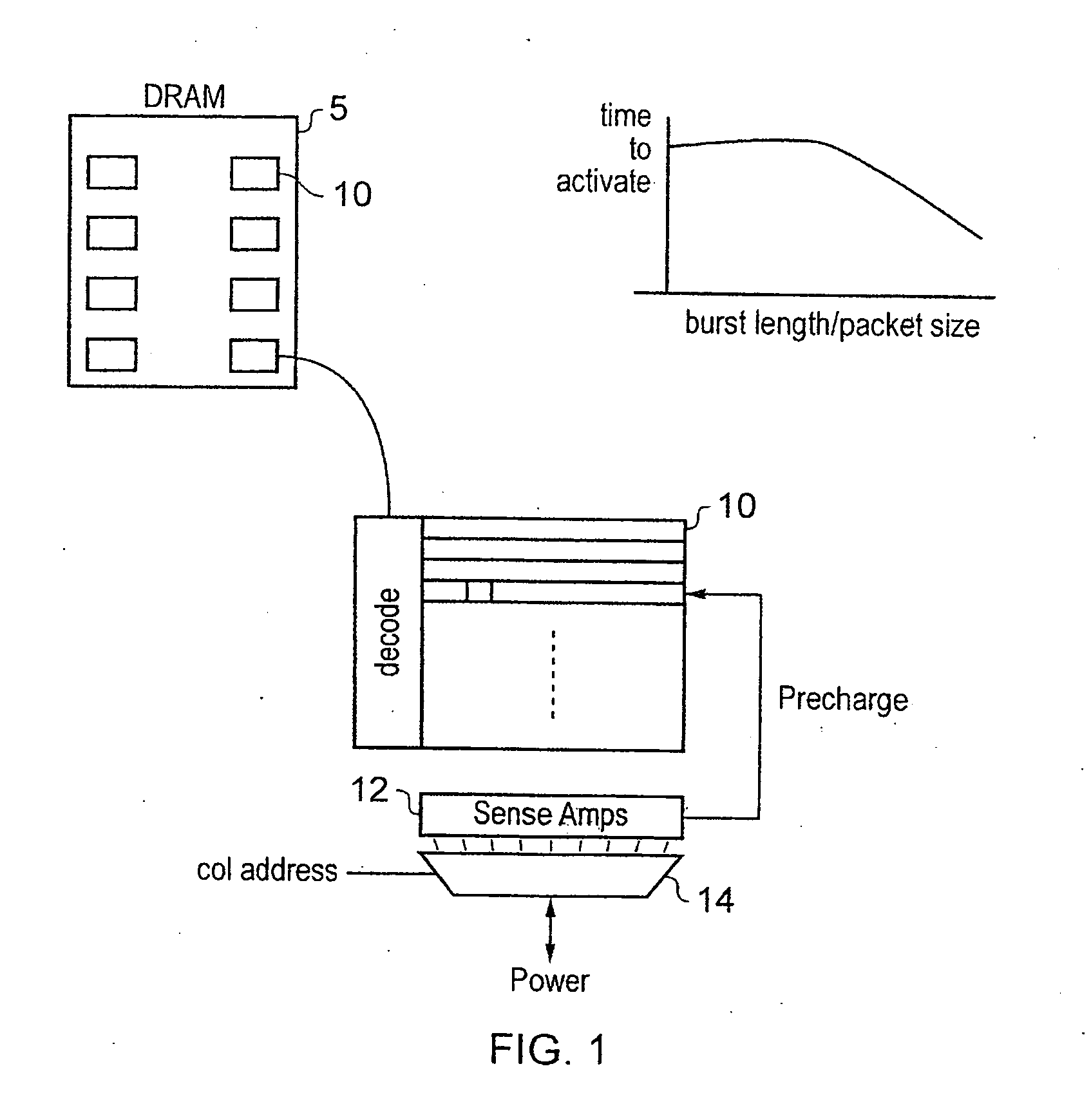
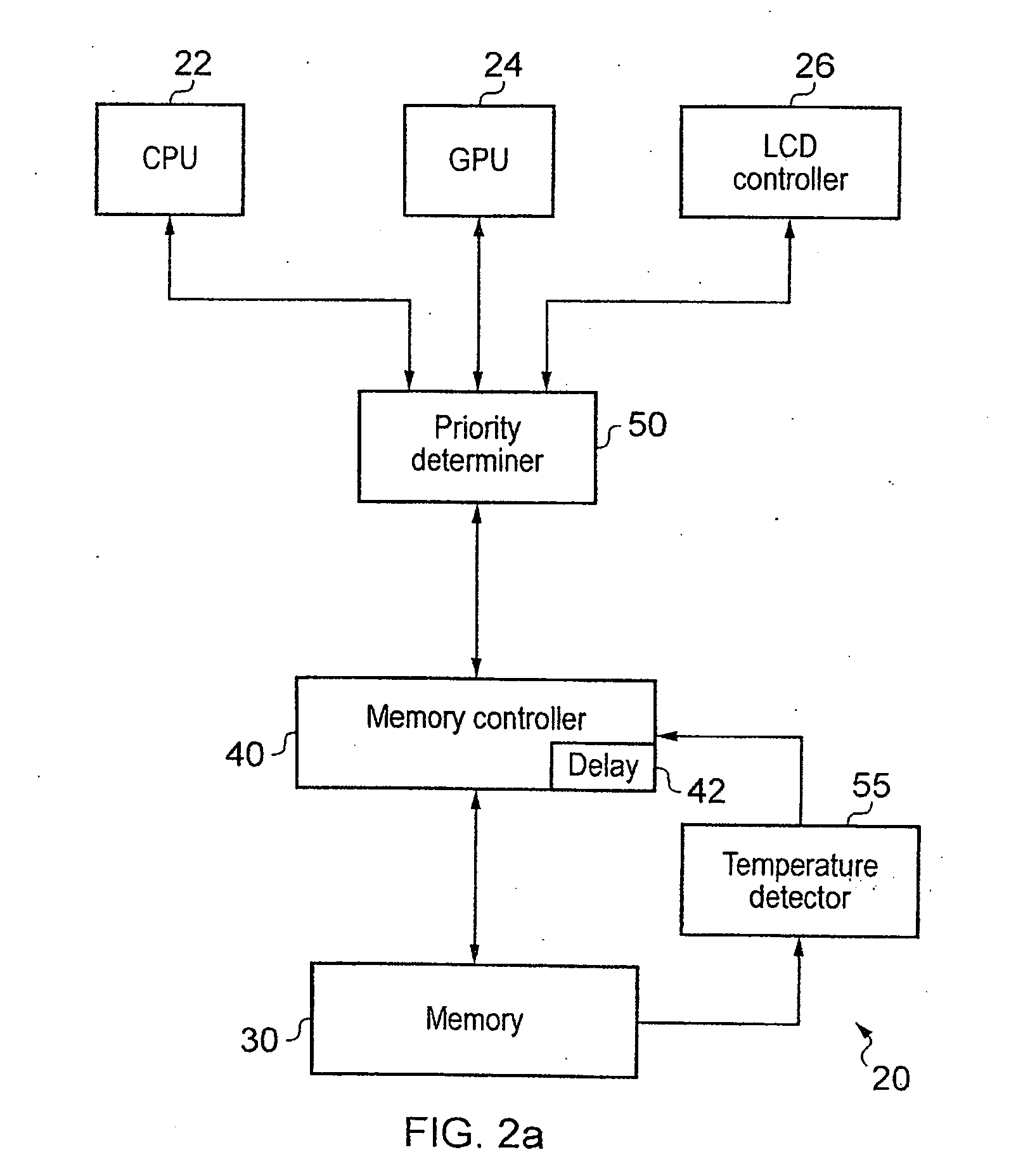
Controlling latency and power consumption in a memory
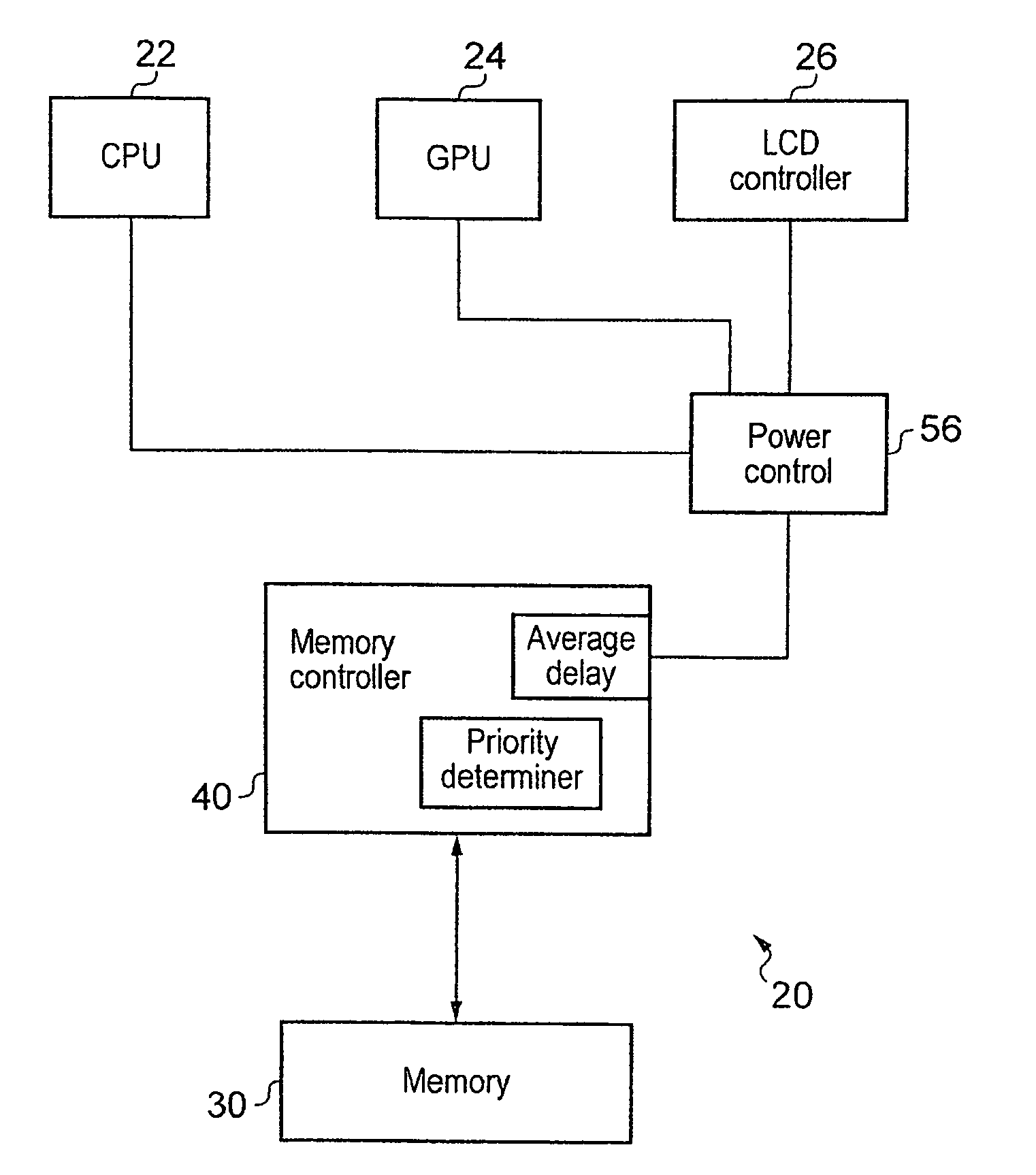
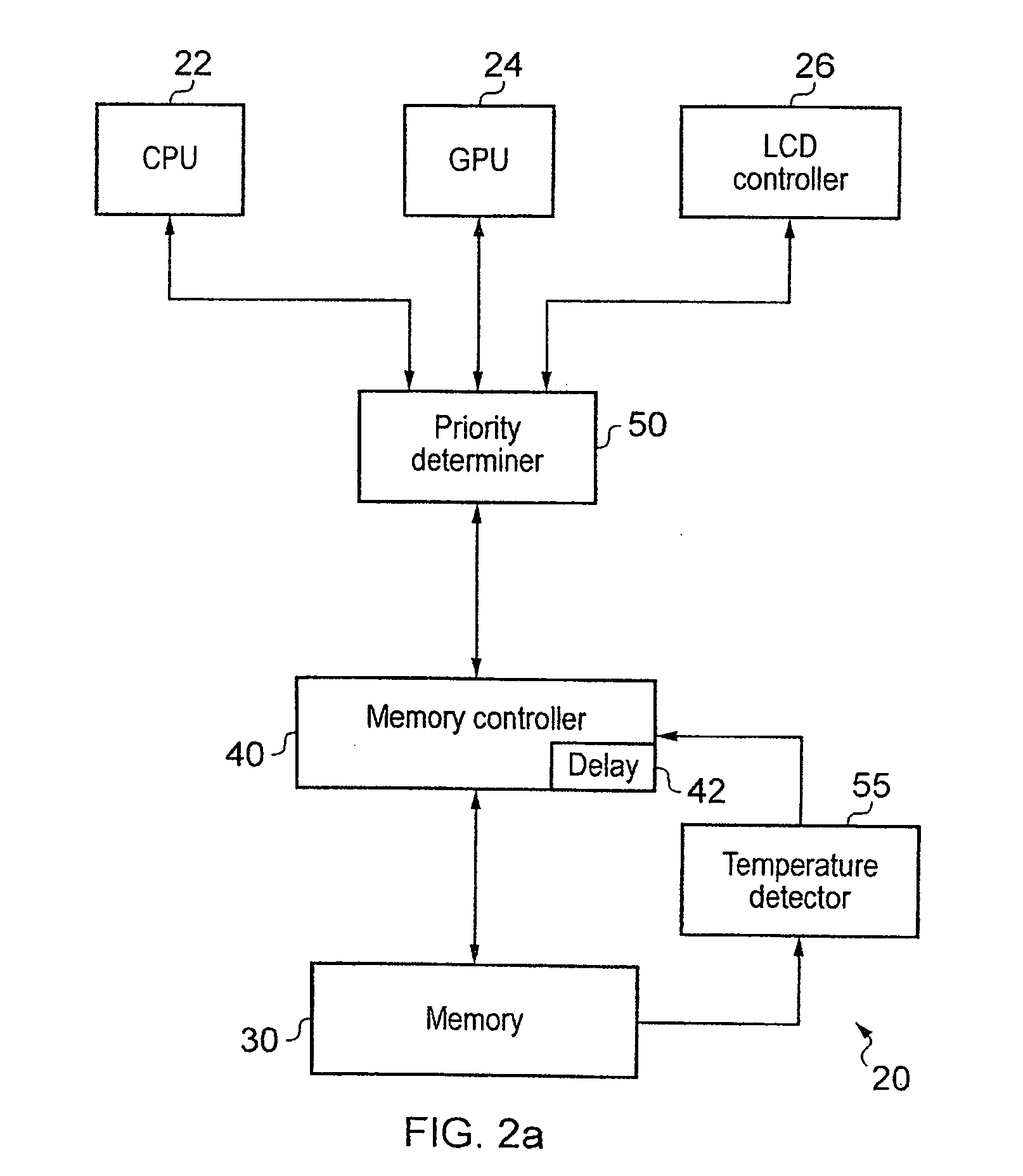
ActiveUS20120210055A1Raise the barRaise priorityDigital data processing detailsMemory systemsControl powerMemory circuits
Memory circuitry, a data processing apparatus and a method of storing data are disclosed. The memory circuitry comprises: a memory for storing the data; and control circuitry for controlling power consumption of the memory by controlling a rate of access to the memory such that an average access delay between adjacent accesses is maintained at or above a predetermined value; wherein the control circuitry is configured to determine a priority of an access request to the memory and to maintain the average access delay at or above the predetermined value by delaying at least some accesses from access requests having a lower priority for longer than at least some accesses from access requests having a higher priority.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method, apparatus and system for prioritising content for distribution
InactiveUS20130120570A1Improve efficiencyLatencyColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsNetwork packetAudio frequency
A method of prioritising content for distribution from a camera to a server over an Internet Protocol (IP) network, the method comprising: storing a plurality of audio and / or video data packages to be distributed to the server over the IP network; obtaining information indicating the priority at which each audio and / or video package is to be distributed over the IP network, the priority being determined in accordance with the content of the audio and / or video package; and sending each audio and / or video data package over the IP network, the order in which each audio and / or video data package is sent being determined in accordance with the indicated priority.
Owner:SONY CORP
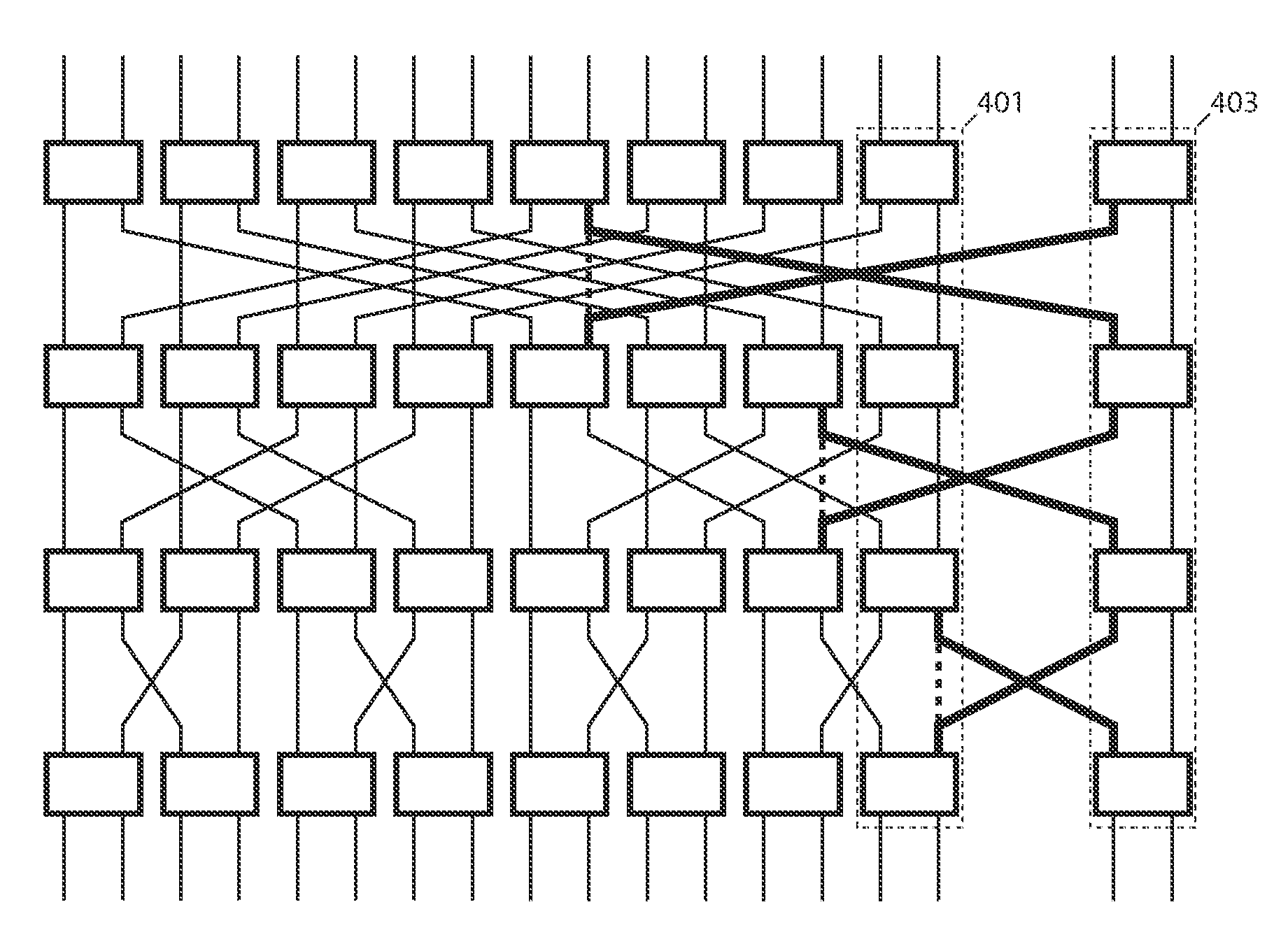
Systems and methods for overlaid switching networks
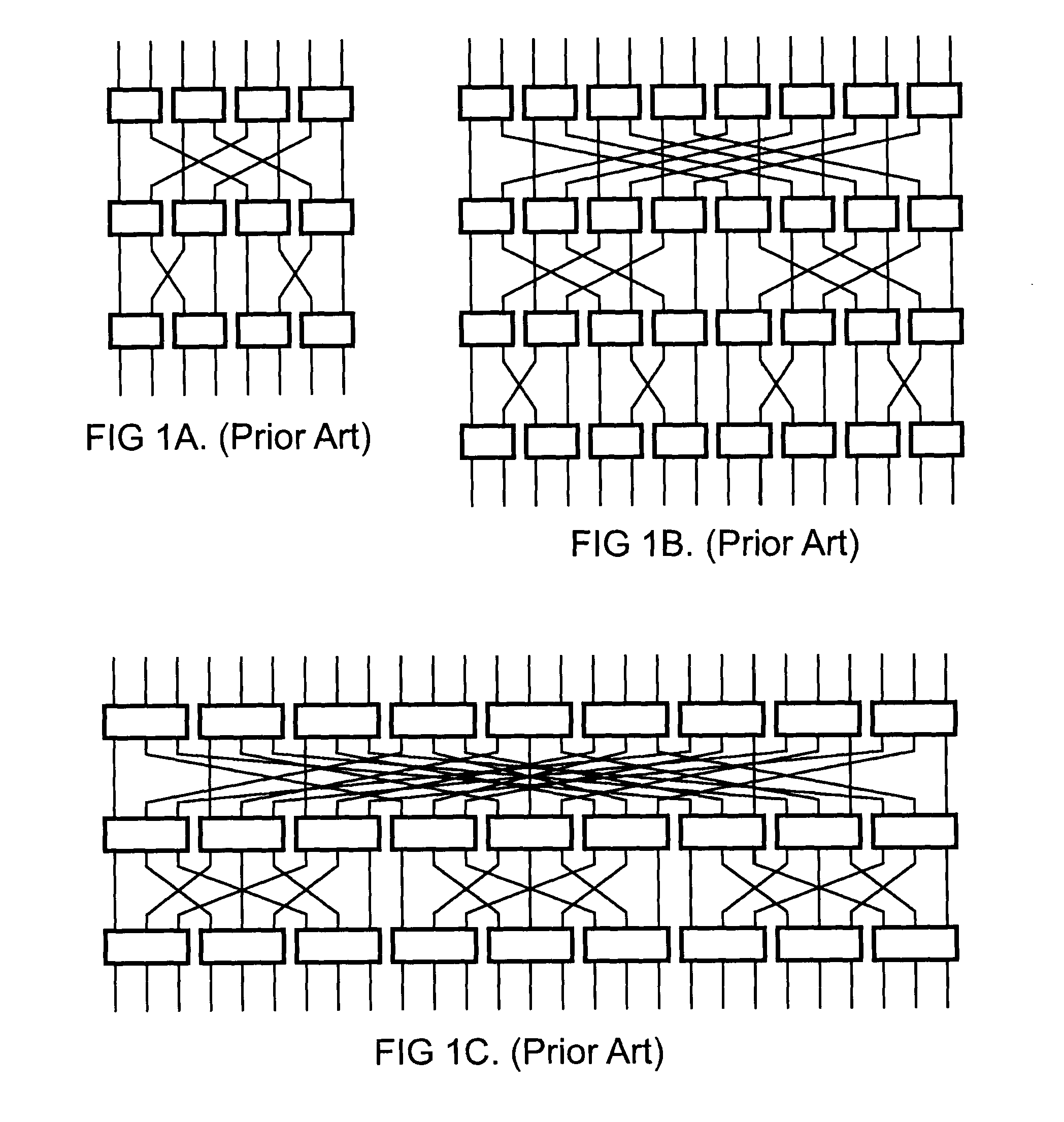
InactiveUS8391282B1Reduce distanceLatencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission systemsExchange networkMultistage interconnection networks
An overlaid switching network is derived by overlaying perpendicularly one multistage interconnection network with a second multistage interconnection network. The new network is formed by placing a switching element corresponding to the position of switching elements in either multistage interconnection network. Each switching element in the overlaid network has the ports defined by the two multistage interconnection networks as does its interconnection networks. A special case occurs when the number of rows and columns of the first multistage interconnection network is the number of columns and rows of the second multistage interconnection network, respectively. The overlaid switching networks also inherit their upgradeability from the multistage interconnection networks from which they are derived, such as in the case of a redundant blocking compensated cyclic group multistage network.
Owner:LU HAW MINN +1
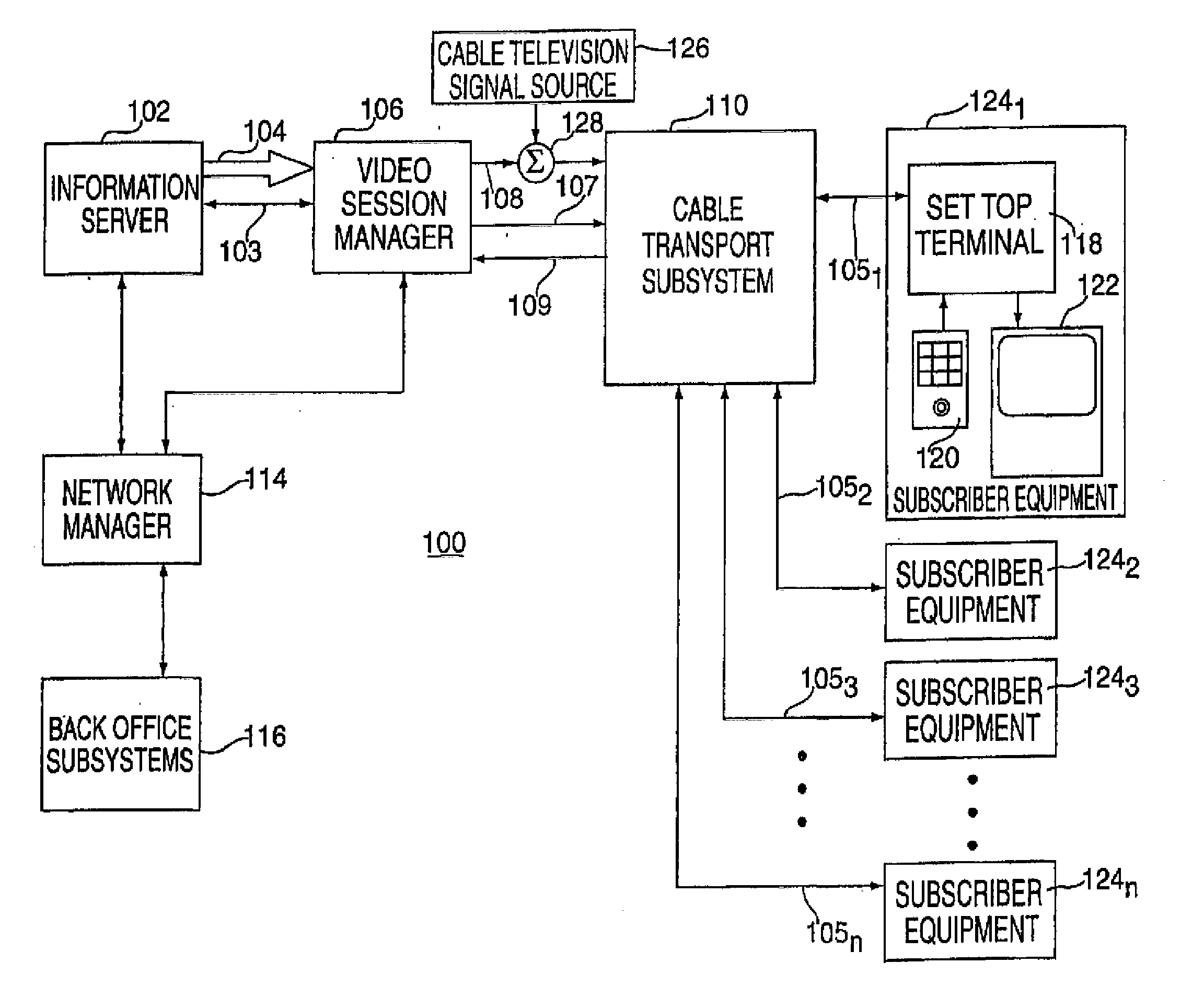
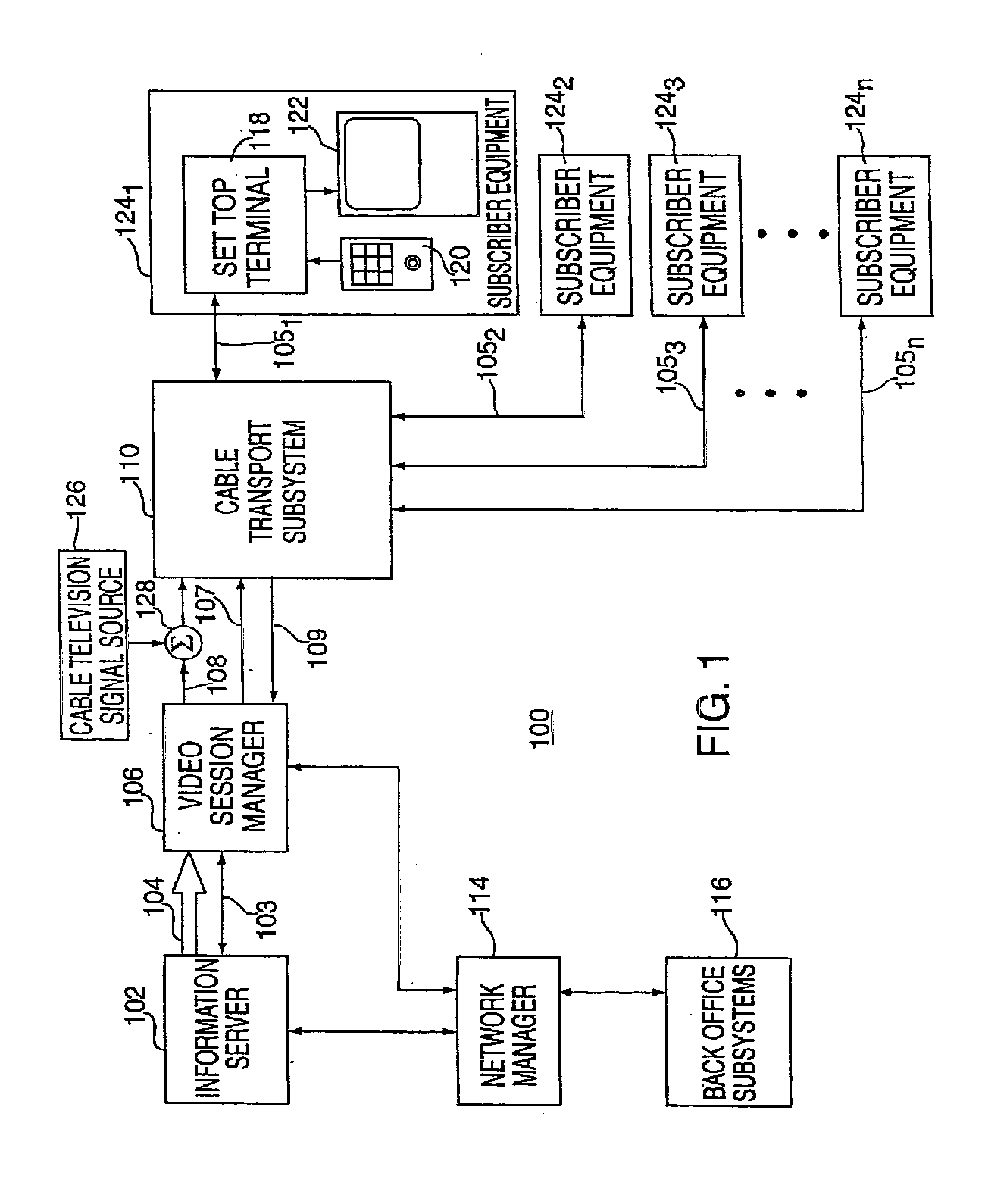
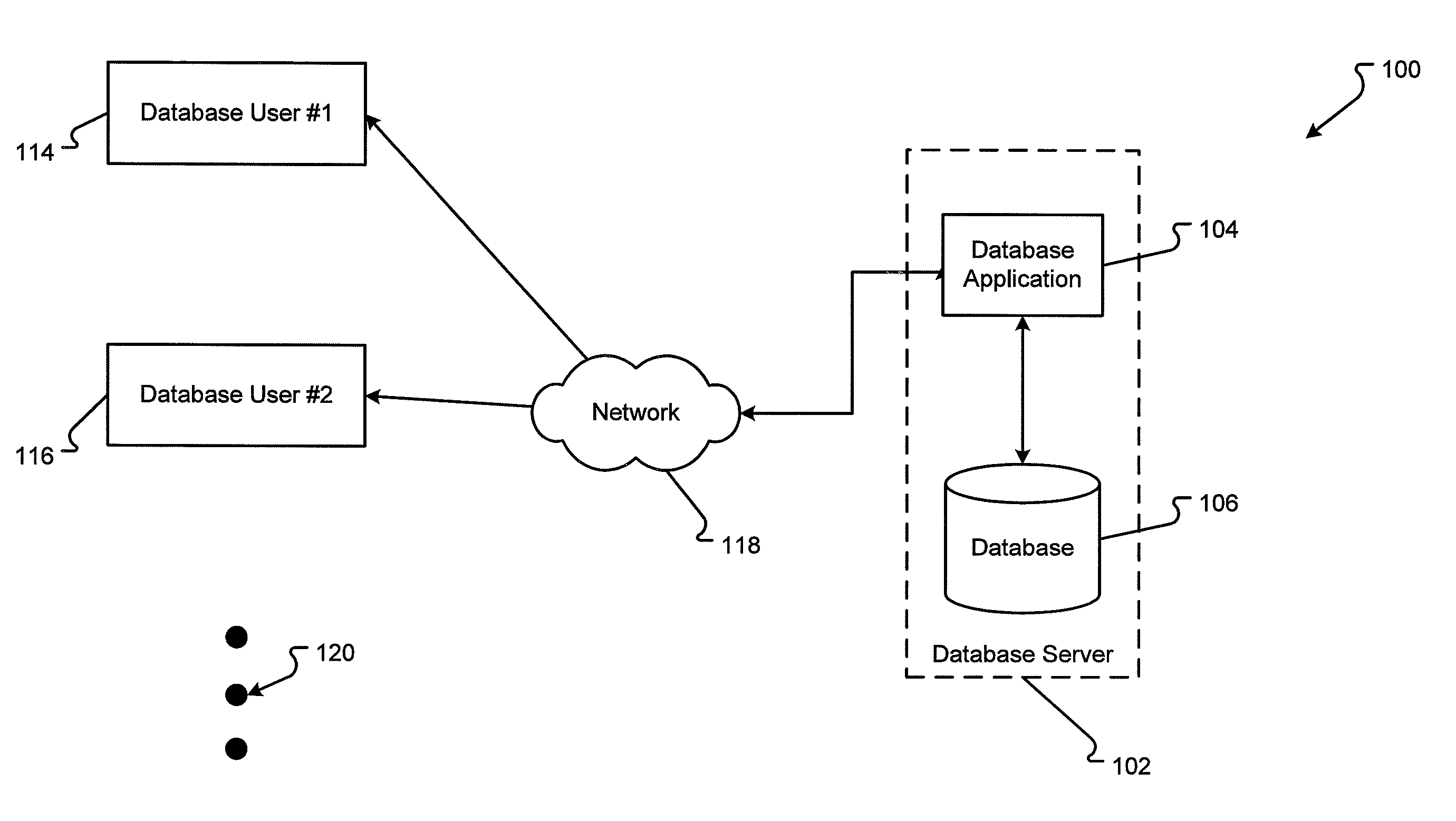
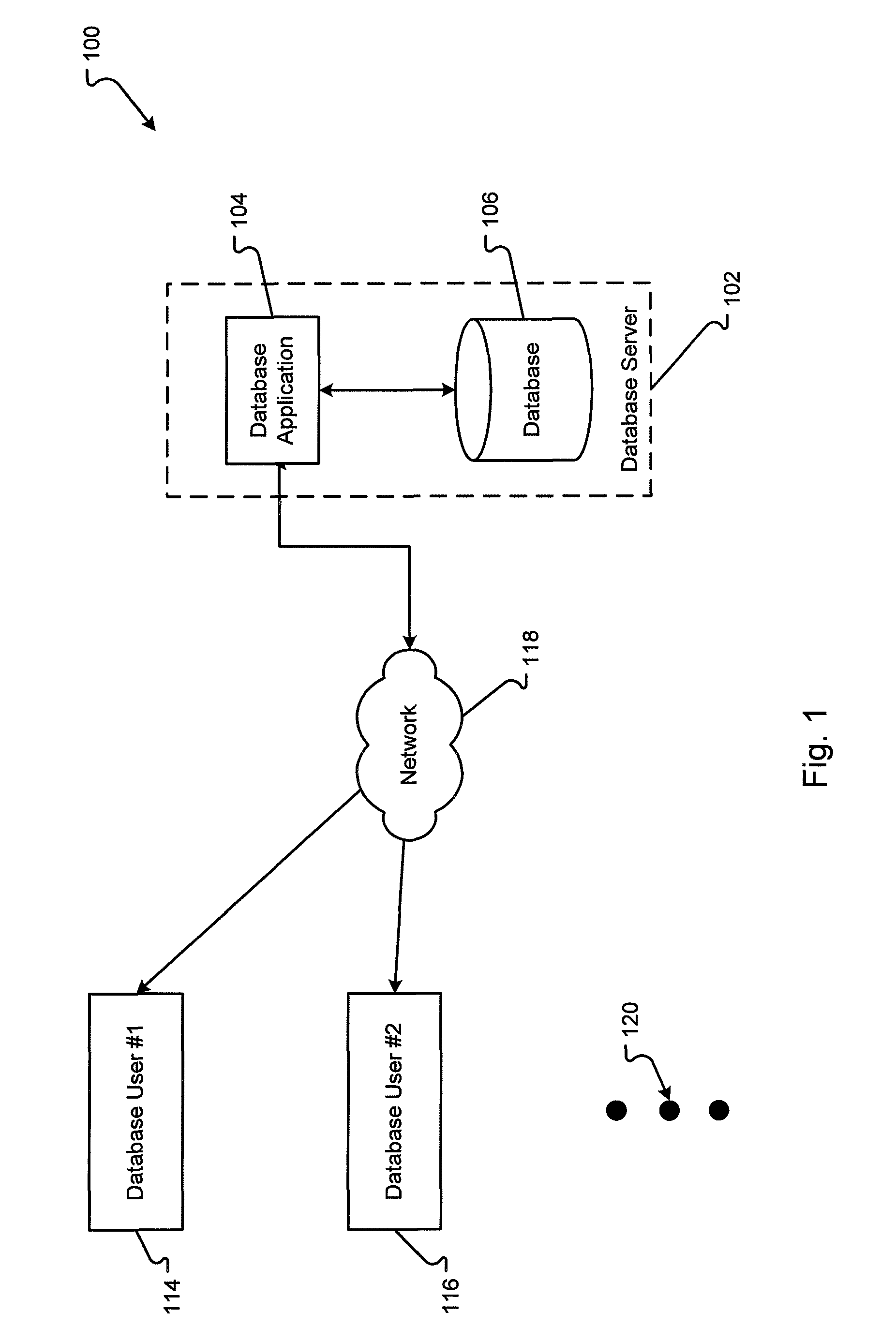
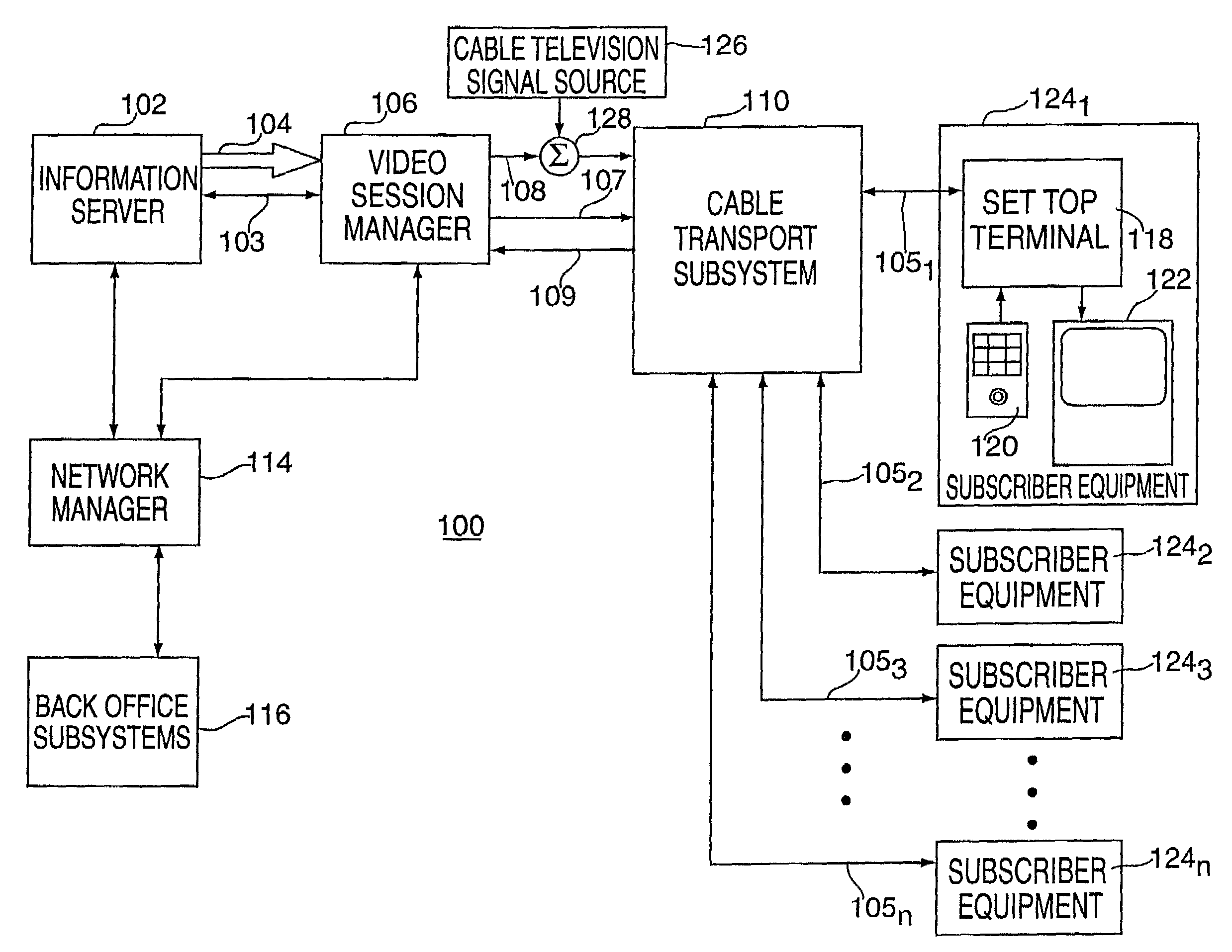
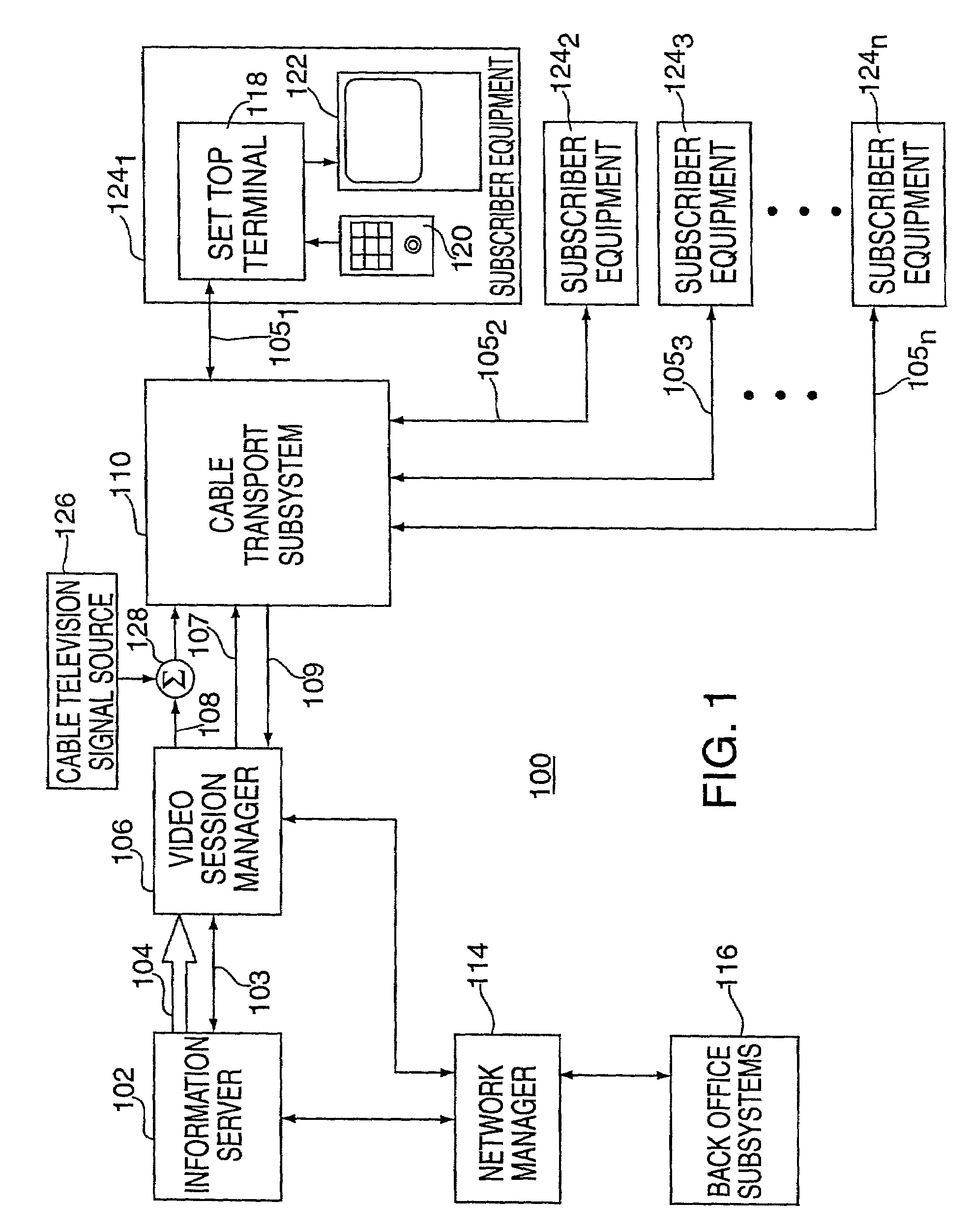
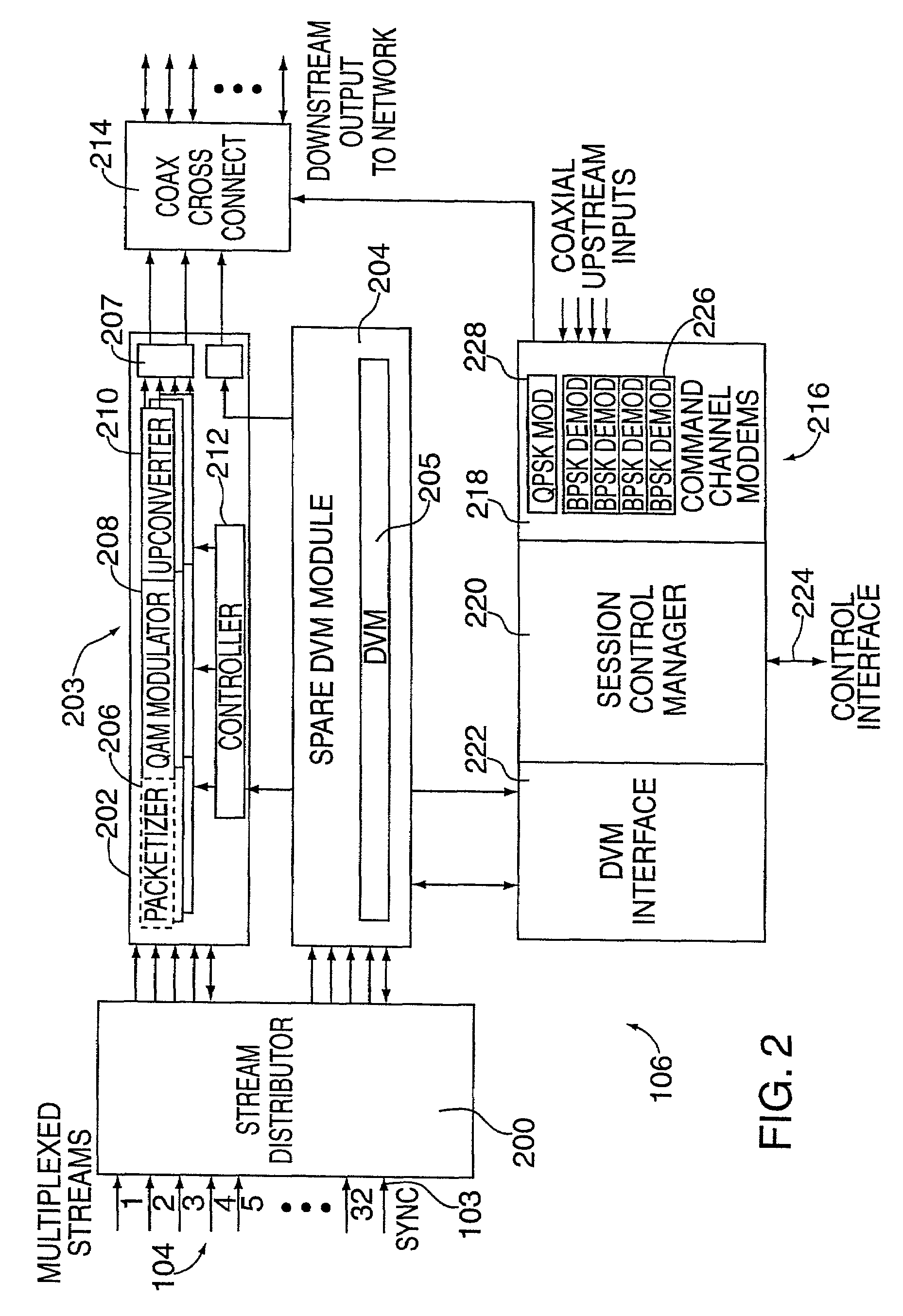
System for Interactively Distributing Information Services
InactiveUS20100095322A1LatencyLow costAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsService provisionDistribution system
An interactive information distribution system includes service provider equipment for generating an information stream that is coupled to an information channel and transmitted to subscriber equipment. The service provider also generates a command signal that is coupled to a command channel and transmitted to the subscriber equipment. The service provider also receives information manipulation requests from the subscriber via a back channel. A communication network supporting the information channel, command channel and back channel is coupled between the service provider equipment and the subscriber equipment.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Fusion general ledger
ActiveUS8156150B2LatencyMinimum delayDigital data processing detailsMulti-dimensional databasesMulti dimensional dataMulti dimensional
A database system combines a general ledger and a multi-dimensional database. The general ledger and multi-dimensional database are mapped such that relationships between the general ledger and multi-dimensional database are characterized with metadata dimensions. Using the mapping, data can be received into the general ledger and stored in both the general ledger and multi-dimensional database substantially simultaneously. Further, a synchronization of the data copies changes to the data automatically from the general ledger to the multi-dimensional database. Thus, there is no manual copying of data between the general ledger and the database. Further, the latency between the general ledger and database is minimal ensuring accurate analysis even contemporaneous with the input of the data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for managing data object size in a multi-user environment
ActiveUS7305387B2Facilitate communicationMinimizing system resourceData processing applicationsRelational databasesMulti user environmentClient-side
Improved communication with database for multiple clients utilizing large date objects concurrently. When interacting with a server with data objects over threshold size, minimizes system resource usage such as CPU and network utilization. Segments objects into smaller size chunks, allowing for transmission of smaller chunks which prevents server from allocating large blocks of memory to one object. Although server handles more memory allocations, each allocation is smaller in size and can therefore be processed much faster. Determination of chunk size is dependent on inherent system resources such as the amount of server memory, available network bandwidth. Chunk size is dependent on environmental factors such as time of day, day of week, number of users, number of predicted users for a given time and day based on historical logging, current and predicted network utilization for given time and day. Chunk size and chunk transfer size may be altered dynamically.
Owner:REGIONAL RESOURCES LTD
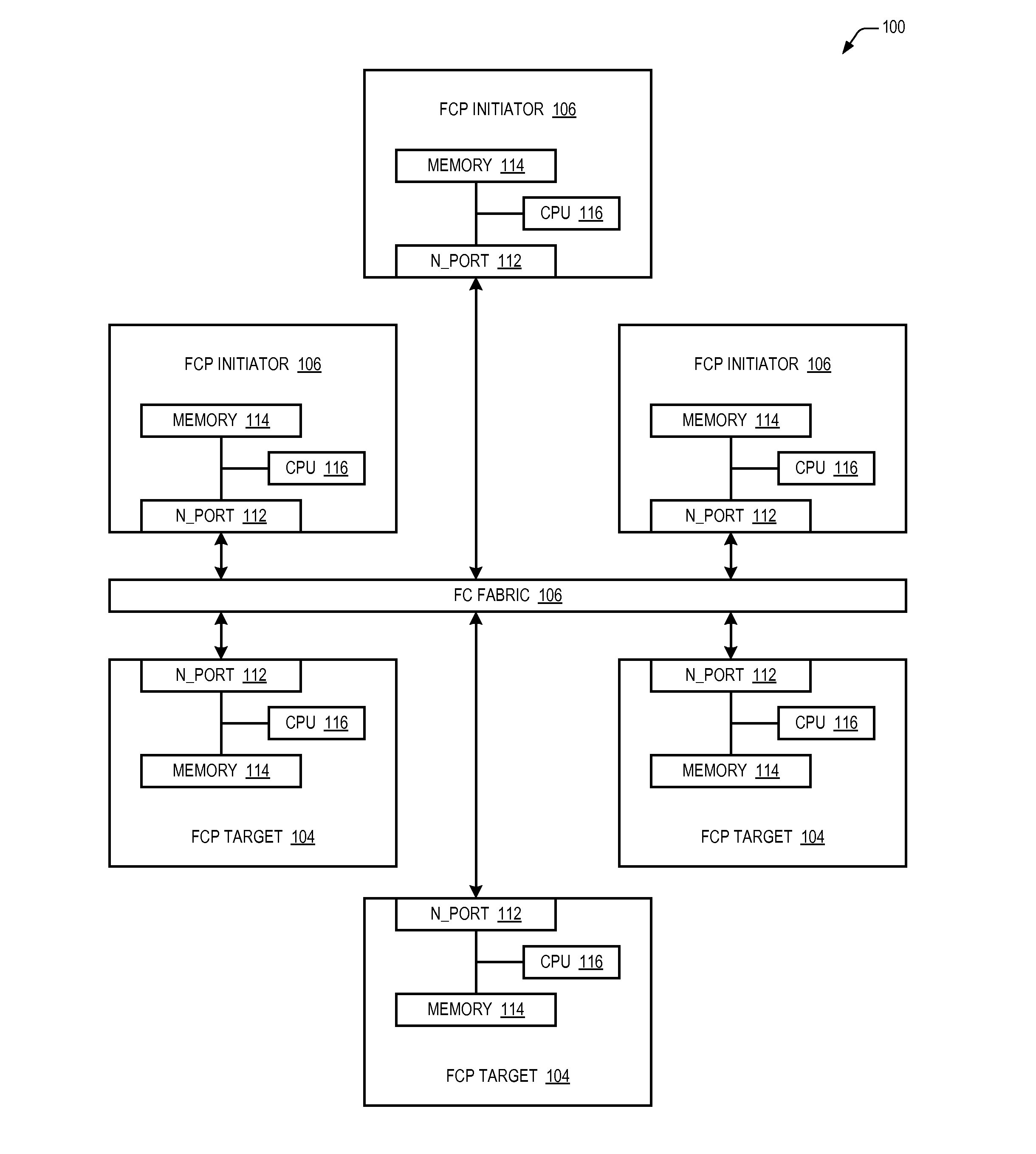
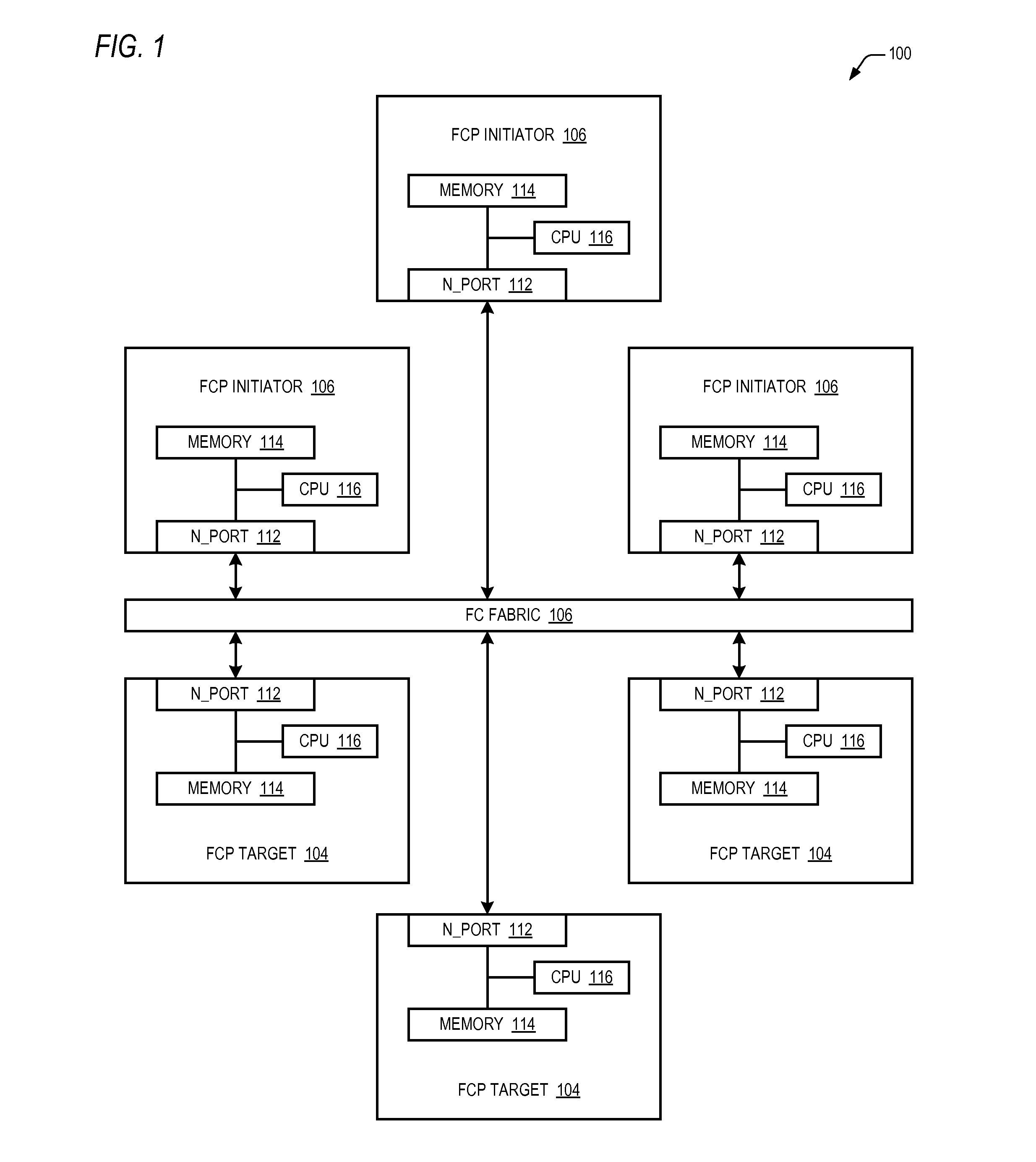
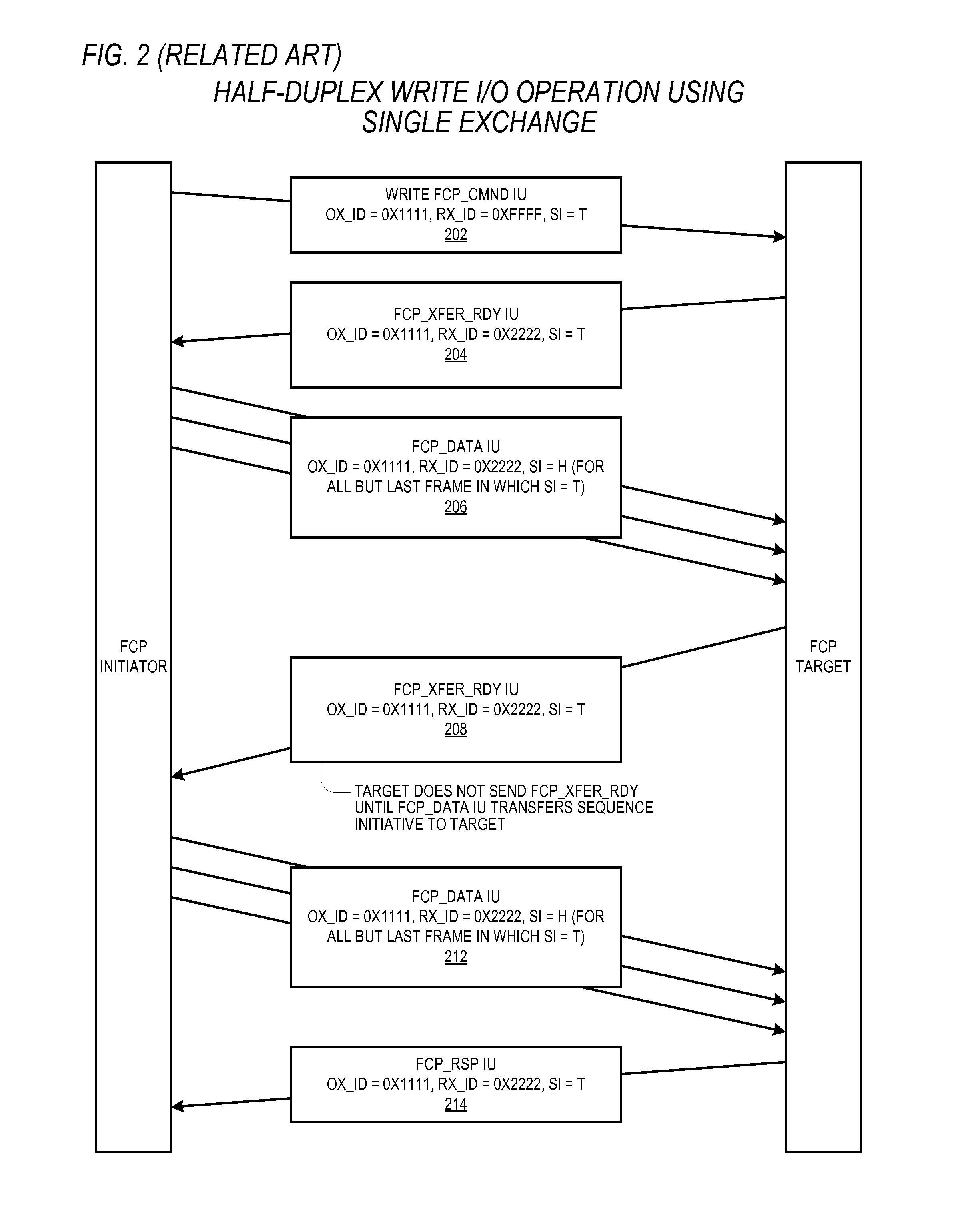
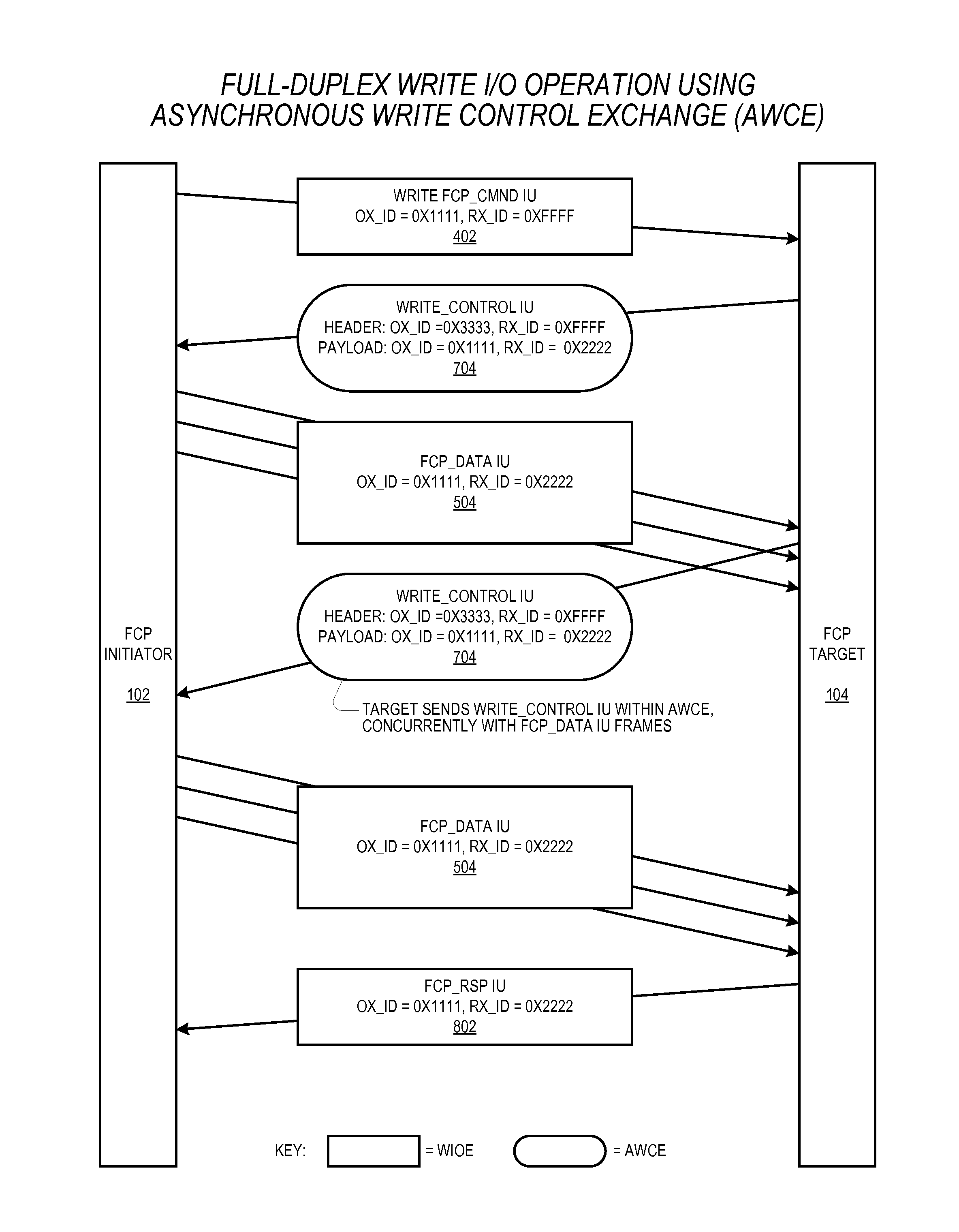
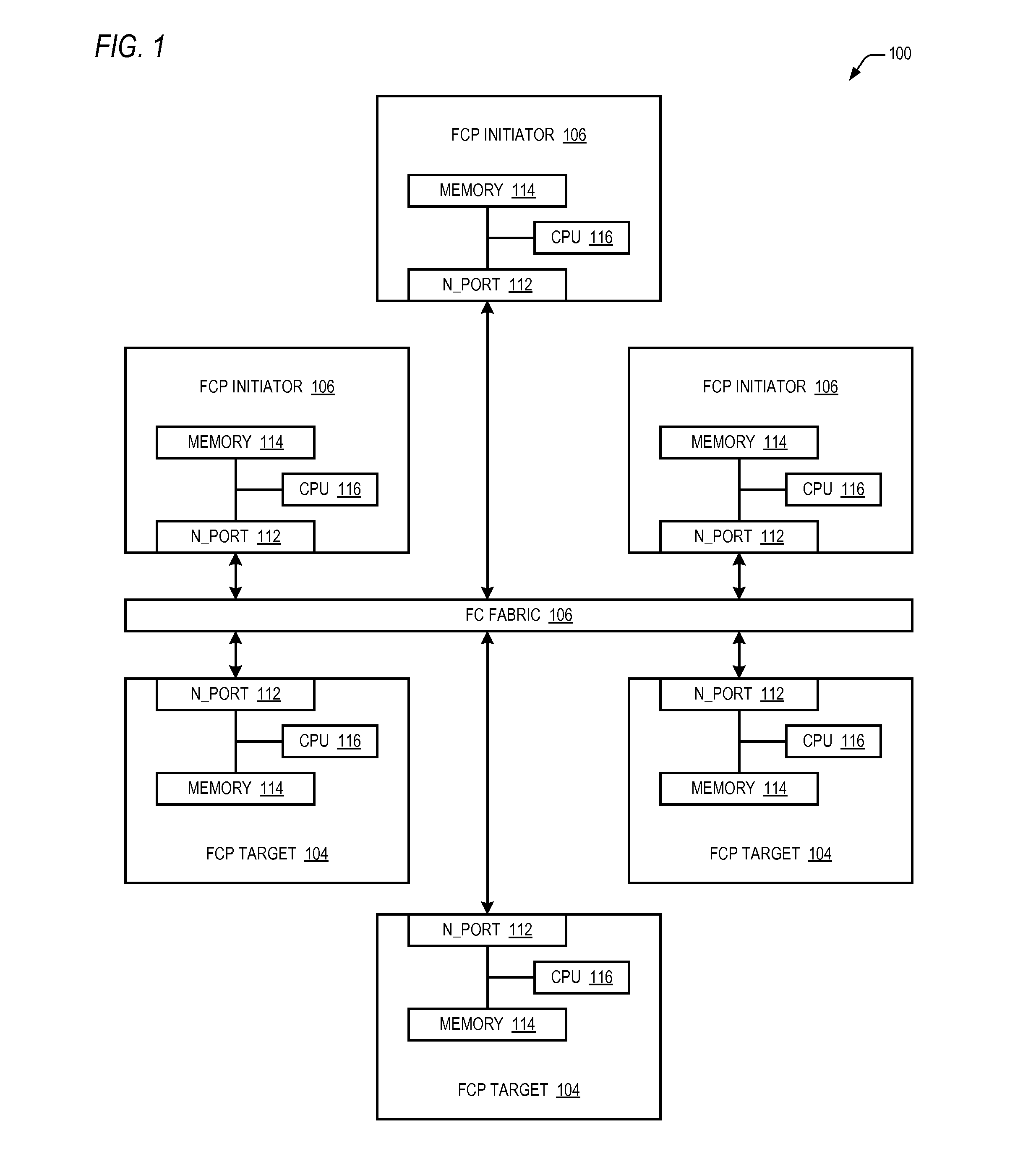
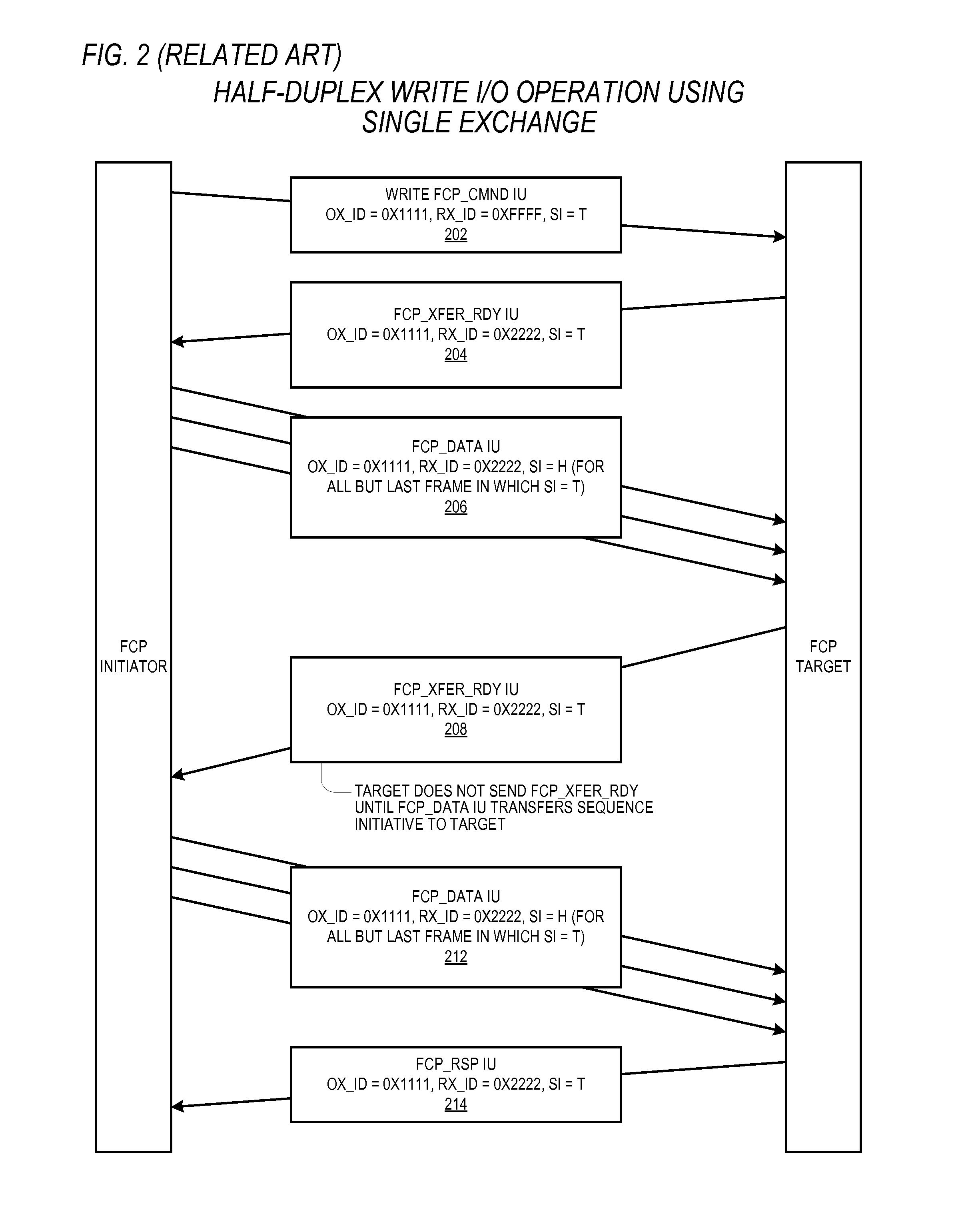
Reducing write I/O latency using asynchronous fibre channel exchange
ActiveUS20140215108A1Lower latencyLatencyInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwarePayload
A FCP initiator sends a FCP write command to a FCP target within a second FC Exchange, and the target sends one or more FC write control IUs to the initiator within a first FC Exchange to request a transfer of data associated with the write command. The first and second FC exchanges are distinct from one another. A payload of each write control IU includes an OX_ID value with which the initiator originated the second Exchange and a RX_ID value assigned by the FCP target for the second exchange. The two Exchanges yield a full-duplex communication environment between the initiator and target that enables the reduction or elimination of latencies incurred in a conventional FCP write I / O operation due to the half-duplex nature of a single FC Exchange. The write control IU may be an enhanced FCP_XFER_RDY IU or a new FC IU previously undefined by the FCP standard.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
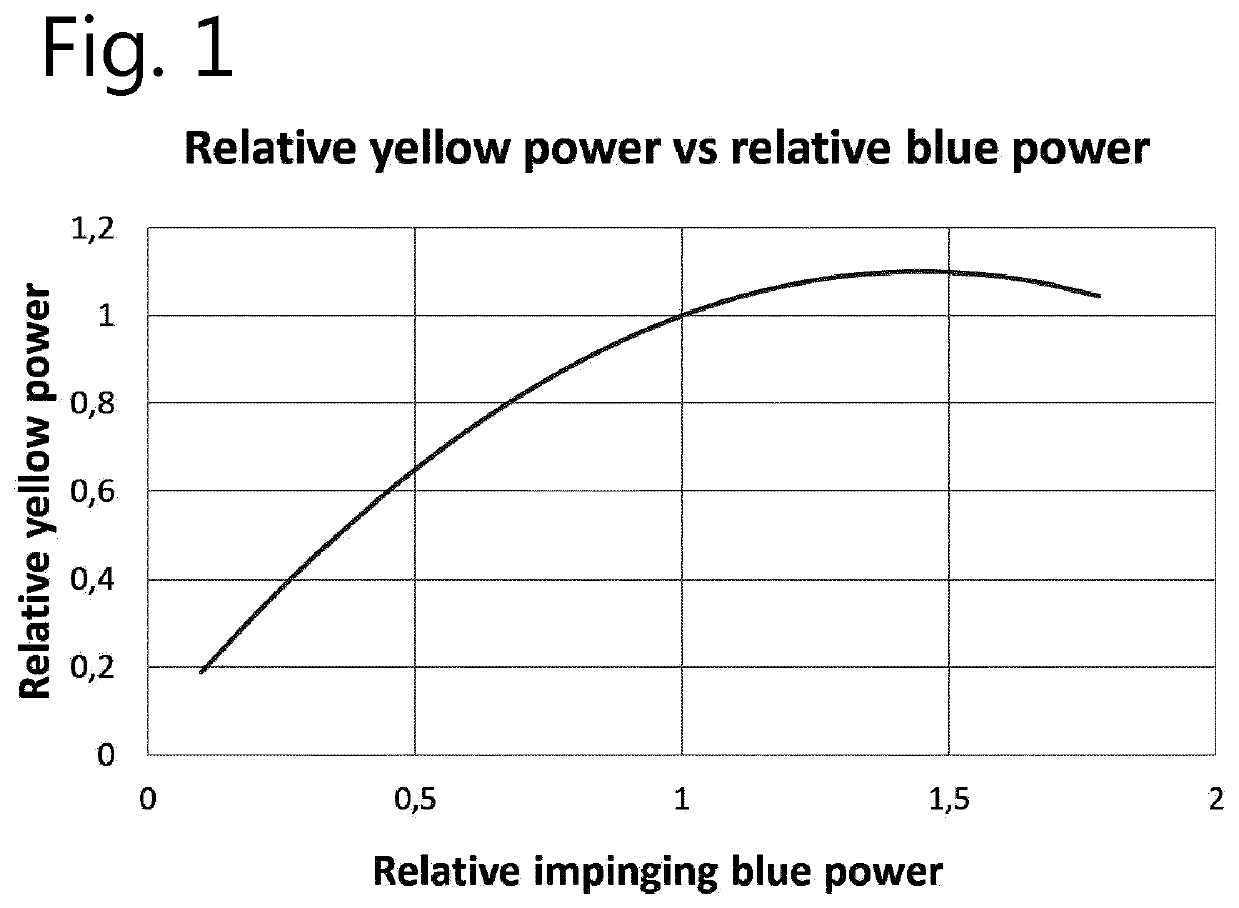
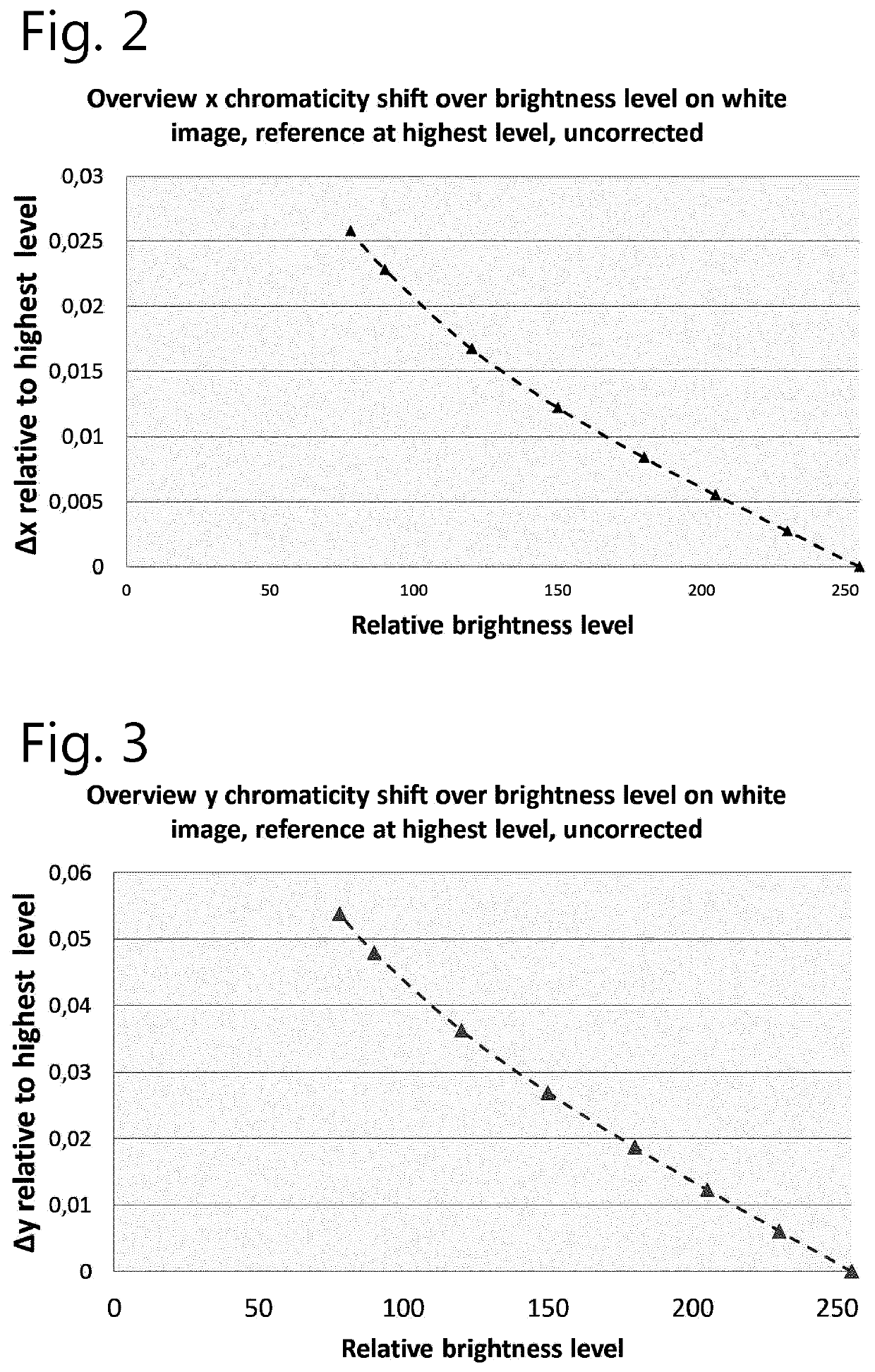
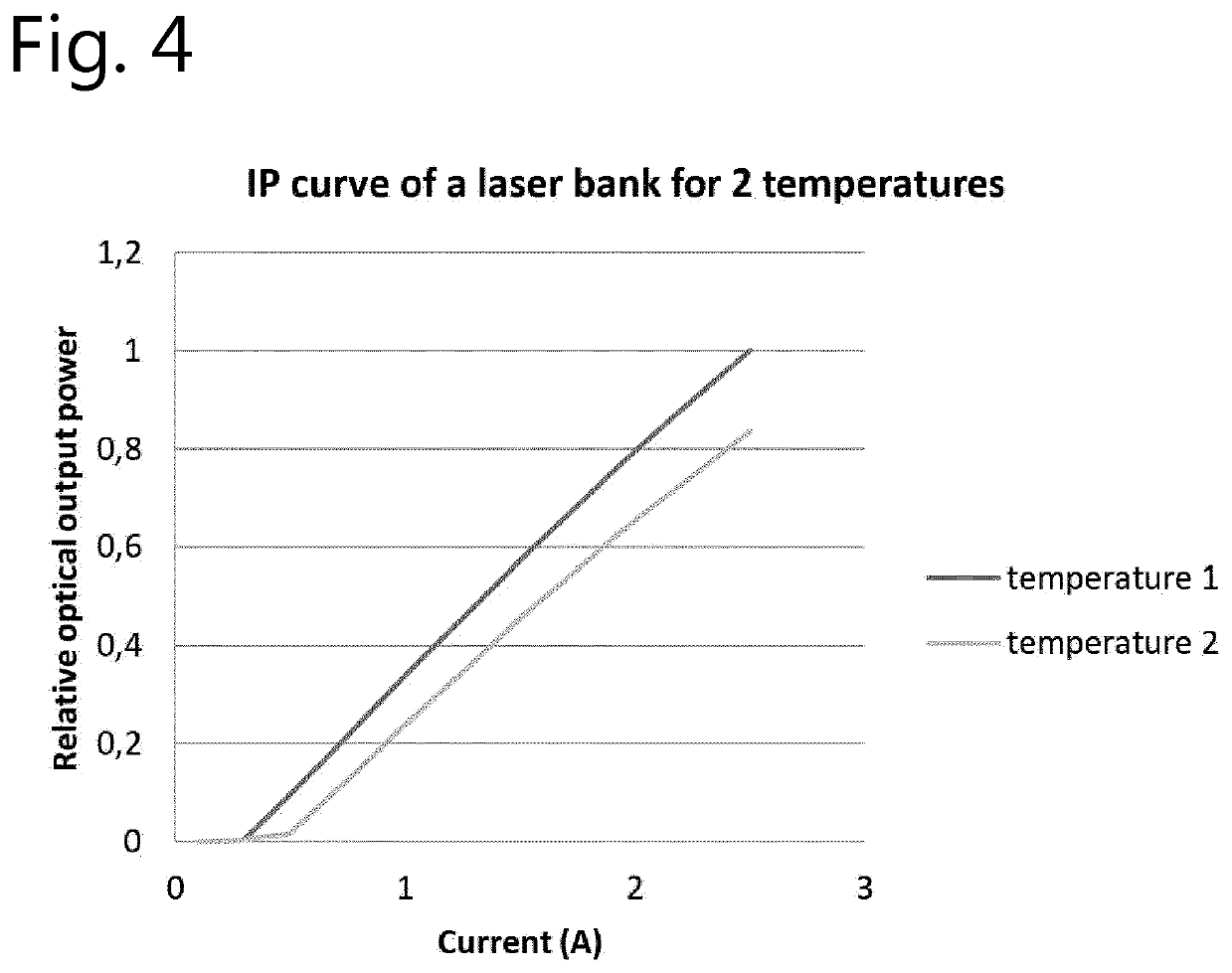
Laser driver
ActiveUS20200218142A1Accurate correctionReduce in quantityProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesProjection systemMechanical engineering
A light projection system and method for generating an image with three primary colors having a module of first blue lasers, second lasers and a wavelength conversion element configured to emit light at a plurality of wavelengths after absorption of a light beam from the second lasers at an excitation wavelength, the output of the module being a combined light beam having a pre-defined chromaticity where the projector is calibrated so as to provide the pre-defined chromaticity of the combined beam over at least a range of laser drive current values to correct for non-linear performance of the wavelength conversion element.
Owner:BARCO NV
Reducing write I/O latency using asynchronous Fibre Channel exchange
A FCP initiator sends a FCP write command to a FCP target within a second FC Exchange, and the target sends one or more FC write control IUs to the initiator within a first FC Exchange to request a transfer of data associated with the write command. The first and second FC exchanges are distinct from one another. A payload of each write control IU includes an OX_ID value with which the initiator originated the second Exchange and a RX_ID value assigned by the FCP target for the second exchange. The two Exchanges yield a full-duplex communication environment between the initiator and target that enables the reduction or elimination of latencies incurred in a conventional FCP write I / O operation due to the half-duplex nature of a single FC Exchange. The write control IU may be an enhanced FCP_XFER_RDY IU or a new FC IU previously undefined by the FCP standard.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Applications of upgradeable scalable switching networks
InactiveUS7912019B1Reduce distanceLatencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionFault toleranceComputer science
The creation of a variety of upgradeable scalable switching networks are set forth including multistage switching networks as well as novel multidirectional architectures. Systems and methods exploiting the properties such as fault tolerance, upgradeability without service disruption and path redundancy are incorporated into a variety of systems. A wide range of methods for upgrading and reconfiguring the scalable switching networks are presented including manifestations of implementations of these networks and methods. Methods for designing new upgradeable scalable switching and the novel architectures derived thereof including architectures built from the redundant blocking compensated cyclic group networks are set forth.
Owner:LU HAW MINN +1
Mechanism for synchronizing OLAP system structure and OLTP system structure
ActiveUS8959050B2LatencyMinimum delayDatabase management systemsDigital data processing detailsRelational databaseMultidimensional data
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System for interactively distributing information services
InactiveUS7657918B2LatencyShort incubation periodData switching by path configurationTwo-way working systemsDistribution systemService provider
An interactive information distribution system includes service provider equipment for generating an information stream that is coupled to an information channel and transmitted to subscriber equipment. The service provider also generates a command signal that is coupled to a command channel and transmitted to the subscriber equipment. The service provider also receives information manipulation requests from the subscriber via a back channel. A communication network supporting the information channel, command channel and back channel is coupled between the service provider equipment and the subscriber equipment.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Controlling latency and power consumption in a memory
ActiveUS9087017B2Increase delayReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingMemory systemsControl powerMemory circuits
Memory circuitry, a data processing apparatus and a method of storing data are disclosed. The memory circuitry comprises: a memory for storing the data; and control circuitry for controlling power consumption of the memory by controlling a rate of access to the memory such that an average access delay between adjacent accesses is maintained at or above a predetermined value; wherein the control circuitry is configured to determine a priority of an access request to the memory and to maintain the average access delay at or above the predetermined value by delaying at least some accesses from access requests having a lower priority for longer than at least some accesses from access requests having a higher priority.
Owner:ARM LTD
Fast WiFi to LTE handover
A network node, and a method at the network node, for handing over a mobile terminal between a first RAT and a second RAT in a wireless communications network. In some embodiments, the method comprises establishing a PDN connection with the mobile terminal via the first RAT, receiving a request for handover of the mobile terminal from the first RAT to the second RAT, performing the requested handover, maintaining PDN connection context for the PDN connection established via the first RAT for a time period, and releasing the PDN connection context at expiry of the time period.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
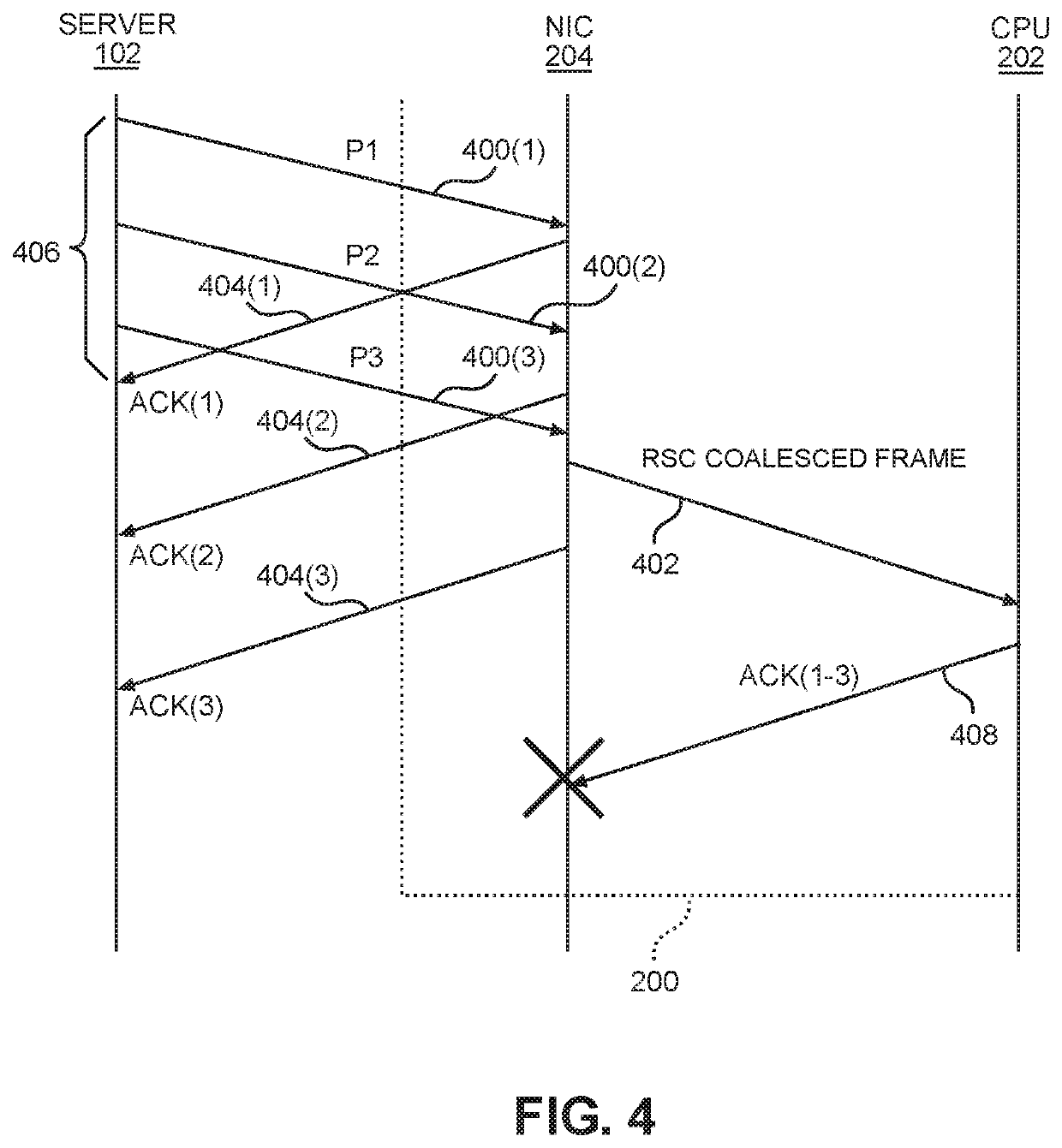
Alternate acknowledgment (ACK) signals in a coalescing transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) system
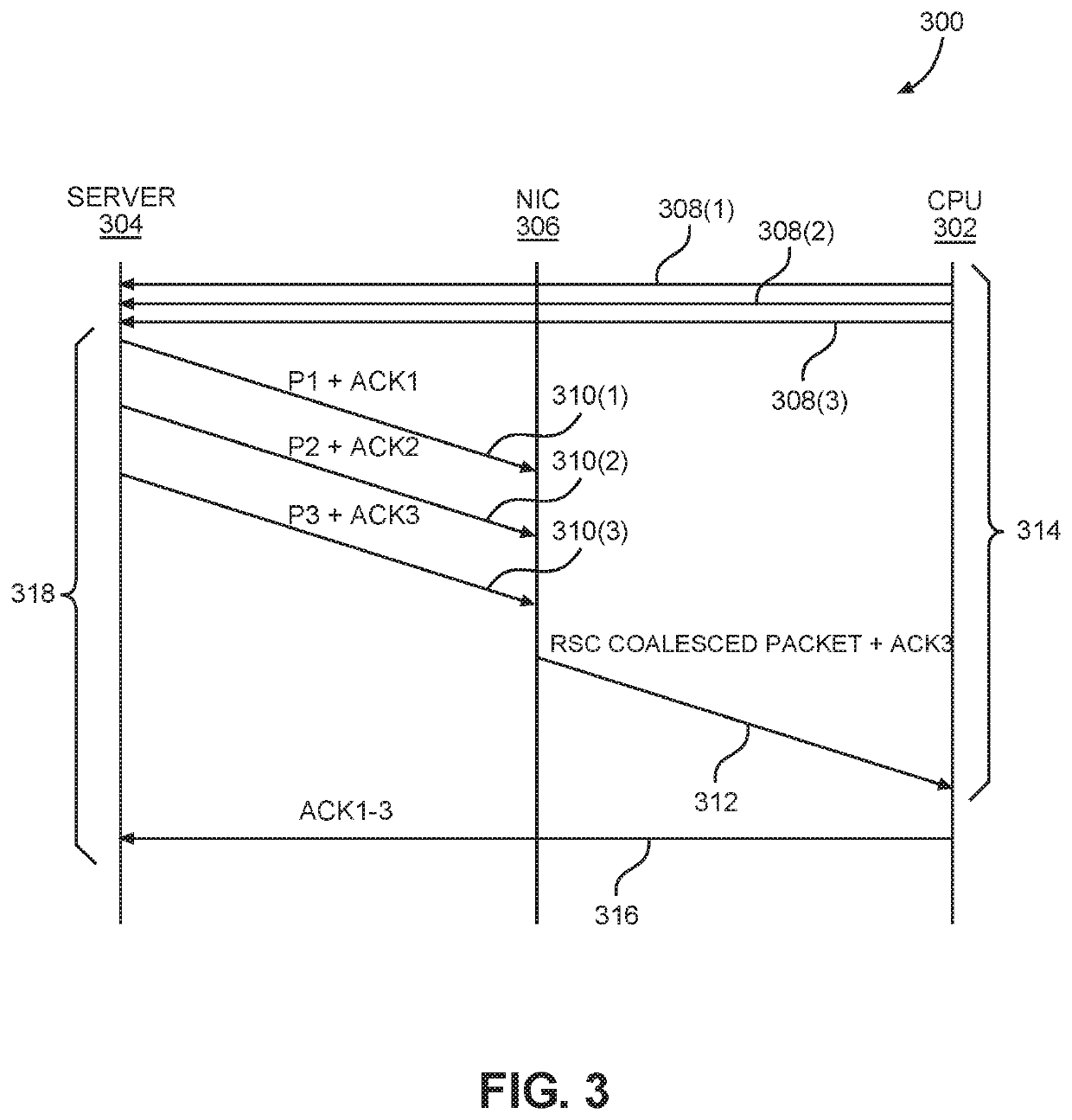
ActiveUS10645200B2LatencyElimination of such latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient computingSignal cancellationServer
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for detection of soft media errors for hard drive
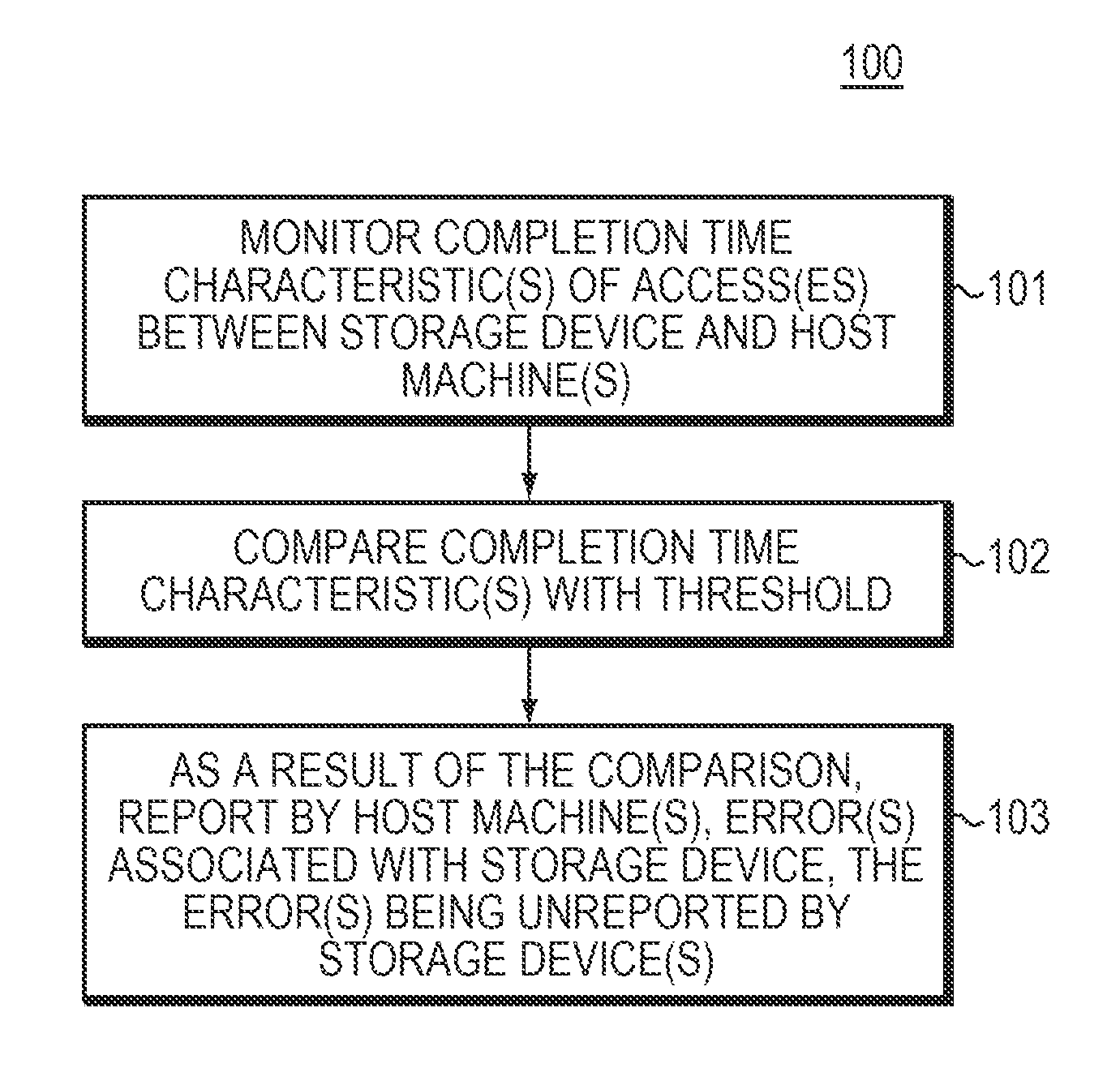
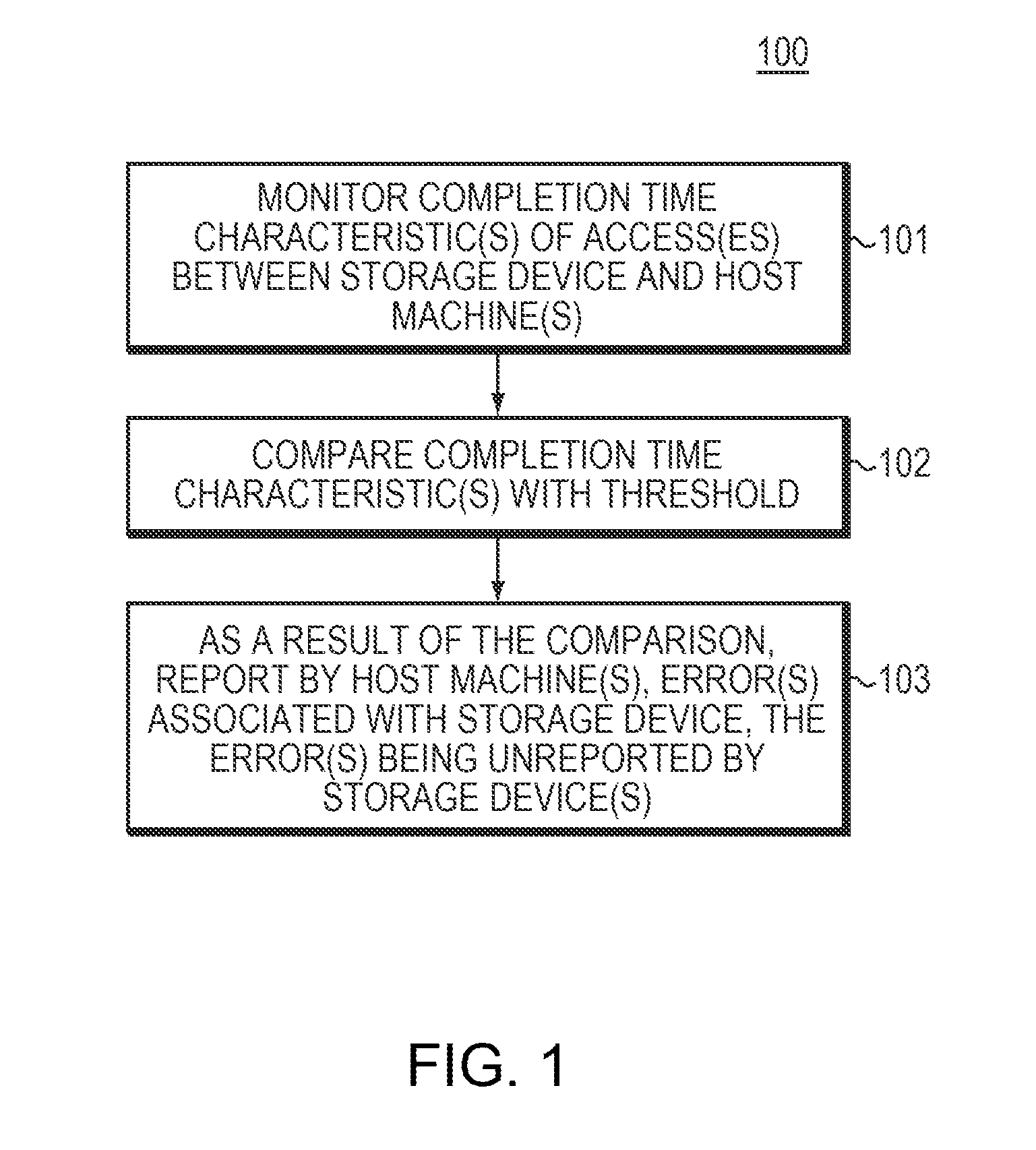
Some embodiments are directed to a method, corresponding system, and corresponding apparatus for detecting unexpectedly high latency, due to excessive retries of a given storage device of a set of storage devices. Some embodiments may comprise a processor and associated memory. Some embodiments may monitor one or more completion time characteristics of one or more accesses between the given storage device and one or more host machines. Some embodiments may then compare the one or more completion time characteristics with a given threshold. As a result of the comparison, some embodiments may report, by the one or more host machines, at least one error associated with the given storage device. The error may be unreported by the set of storage devices.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
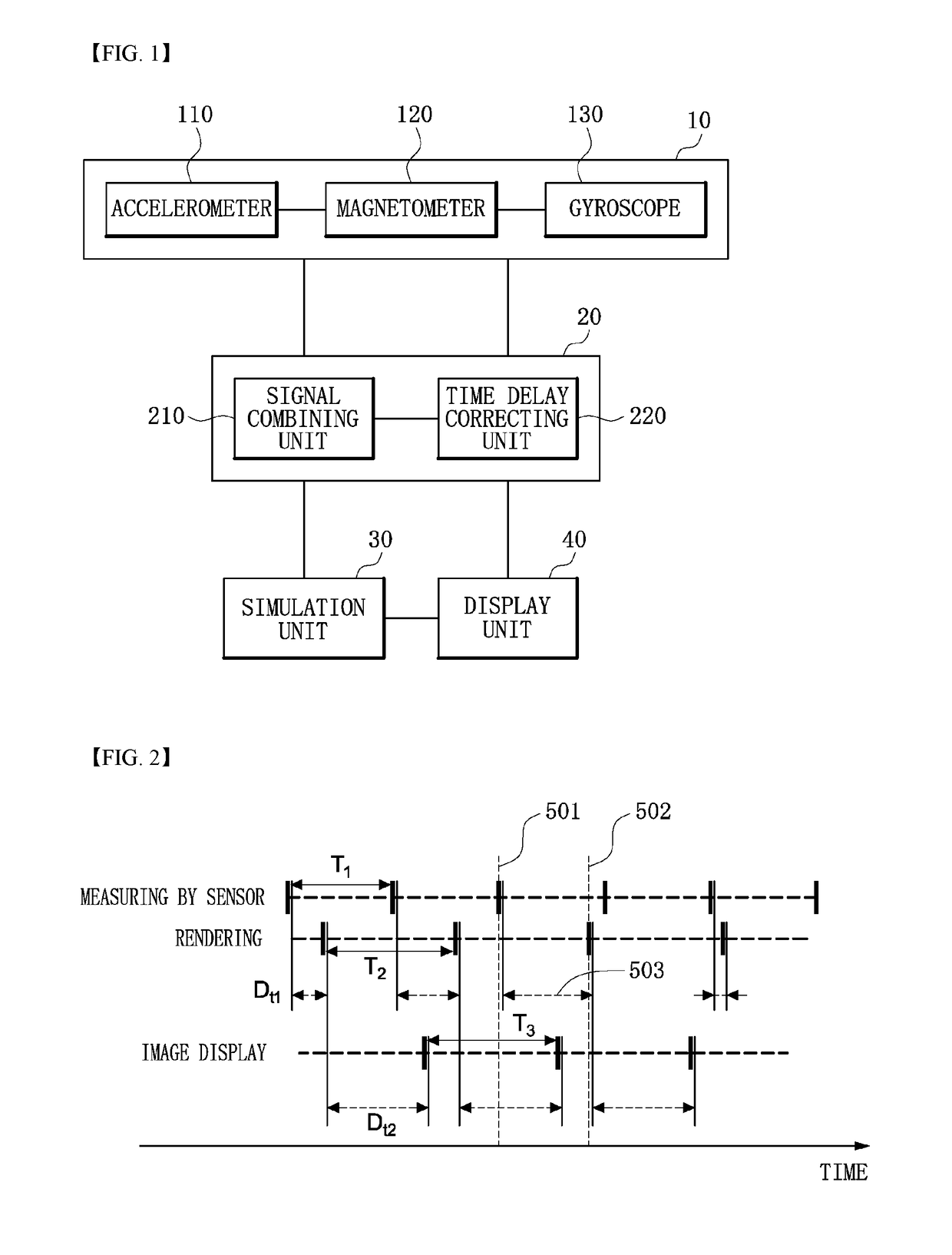
Low latency simulation apparatus and method using direction prediction, and computer program therefor
ActiveUS10204420B2LatencyLower latencyImage analysisGeometric image transformationLatency (engineering)Direction information
A simulation apparatus may comprise: a sensor unit configured to acquire movement information of an object using one or more sensors; a direction calculation unit configured to calculate direction information of the object using the movement information; and a simulation unit configured to simulate a physical object and render an image of the physical object on the basis of the direction information received from the direction calculation unit. The direction calculation unit may include a time delay correction unit configured to correct the direction information using a time difference between the time of acquiring the movement information and the time of rendering the image.
Owner:FXGEAR CO LTD
Method for measuring and eliminating delay between sounding data and positioning data of unmanned ship
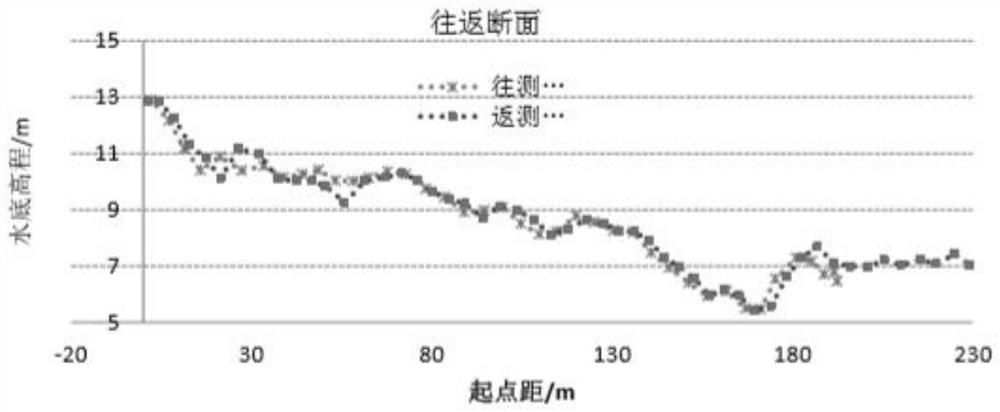
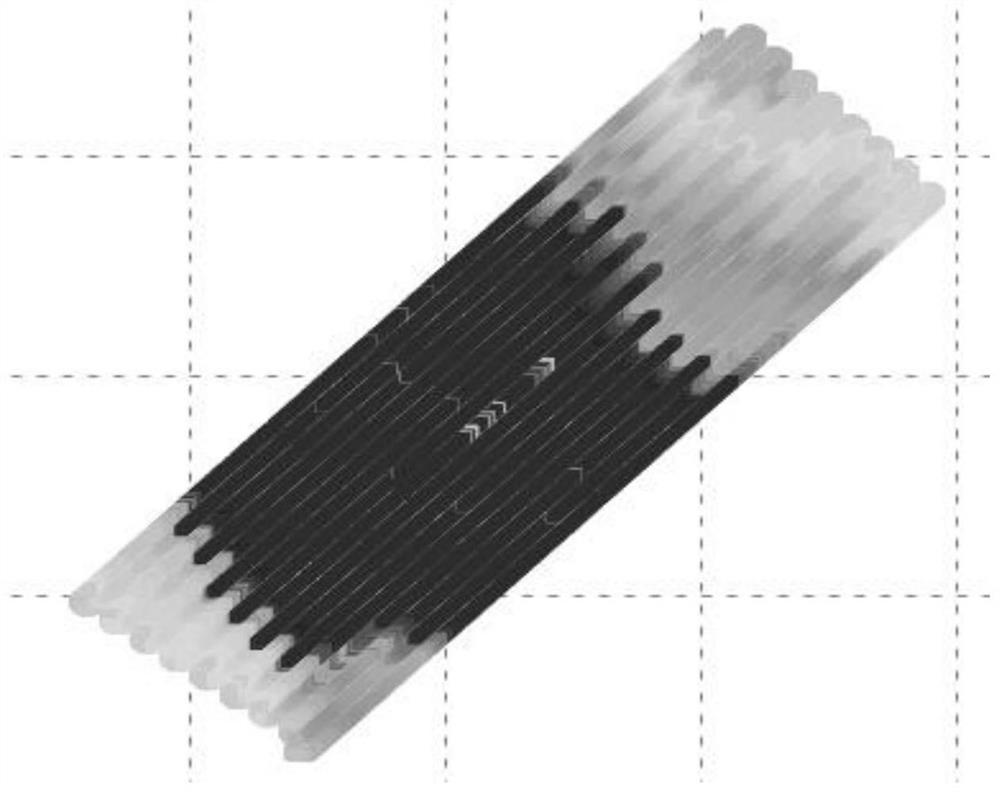
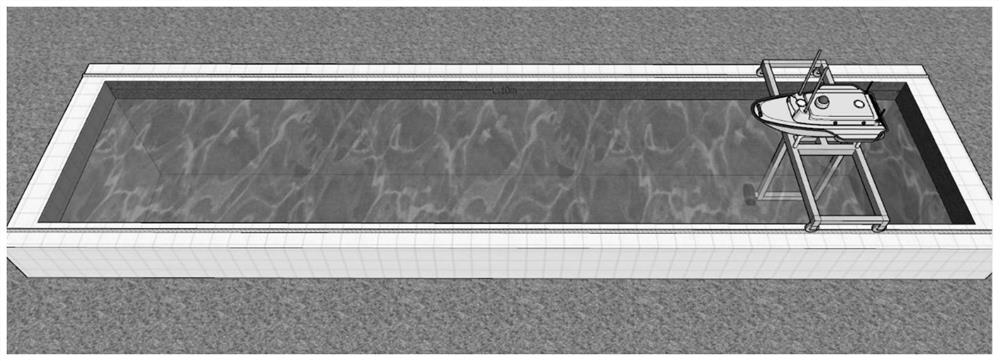
ActiveCN112902931AEliminate sounding delayEliminate propagation timeSynchronisation arrangementMeasuring open water depthTimestampMarine engineering
The invention discloses a method for measuring and eliminating delay between sounding data and positioning data of an unmanned ship. The method comprises the steps: providing an anechoic pool for single-beam precision measurement, installing a transducer of the unmanned ship on a support of the anechoic pool, transversely transmitting beams, and fixing a positioning module of the unmanned ship at the top of the support. Unique corresponding water depth values are positioned for different positions in the movement process of the unmanned ship, and synchronous change of the positioning data and the water depth data under the condition that the precision and the range are known is achieved. The invention realizesthe method for measuring and eliminating delay between sounding data and positioning data of the unmanned ship; and when GNSS data acquisition is carried out, a timestamp signal is transmitted to a depth finder, and after the time of transmitting a ping signal at the moment is recorded, and after the depth finder completes the ping search and returns depth data, packaging with previous waiting positioning data is carried out, so that the propagation time of sound waves and the processing delay of the data of the depth finder are eliminated.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUACE NAVIGATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com