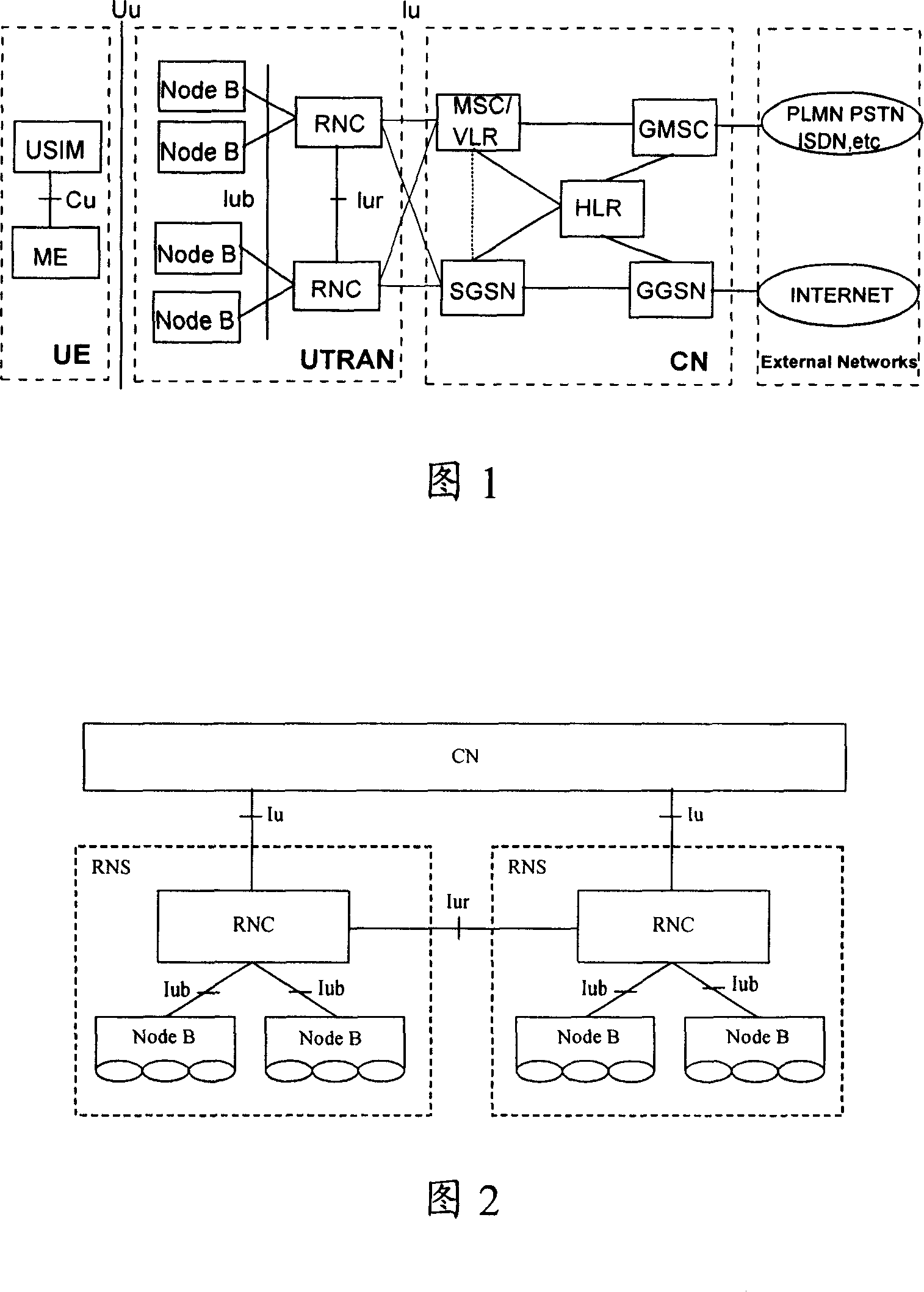
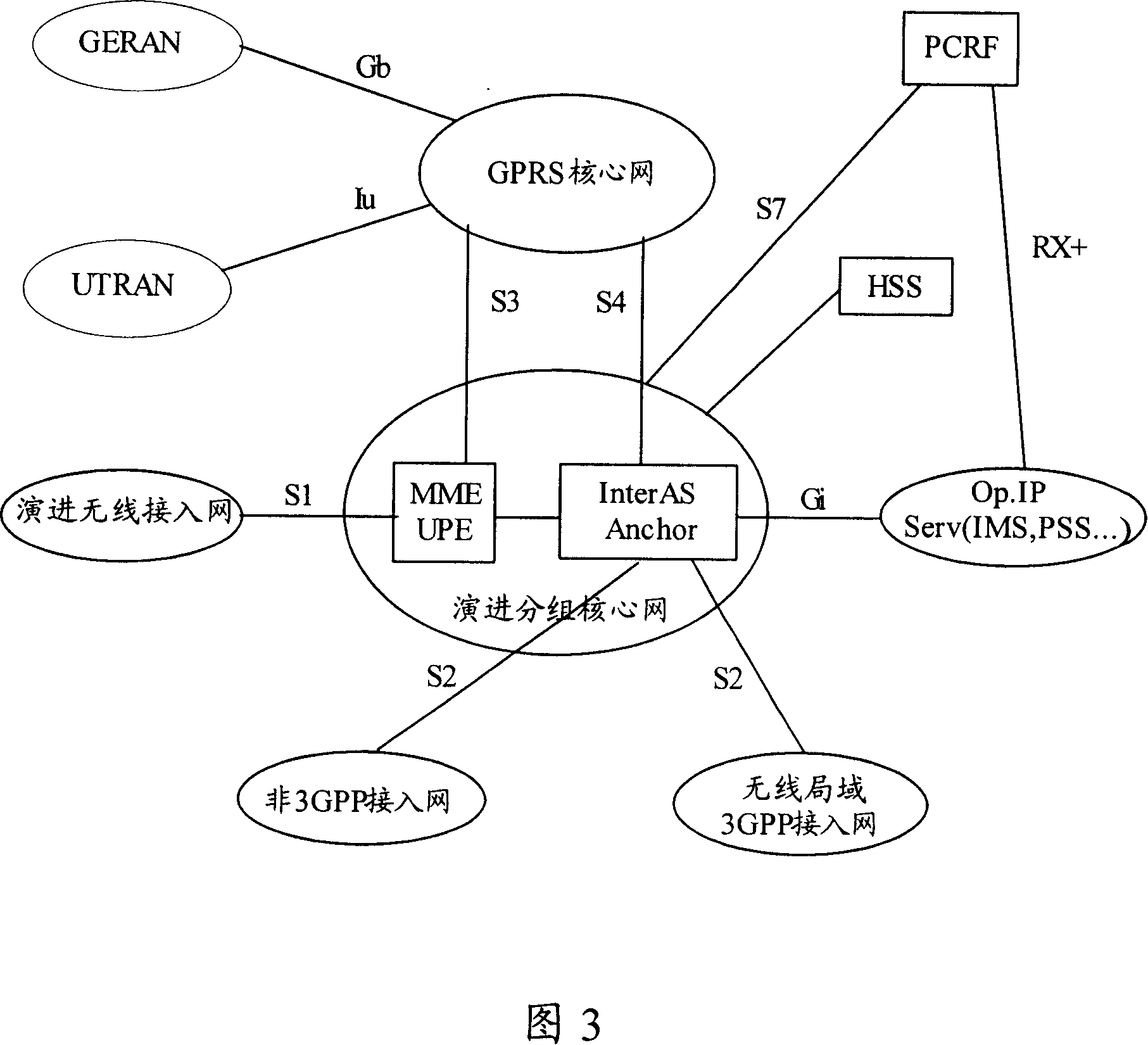
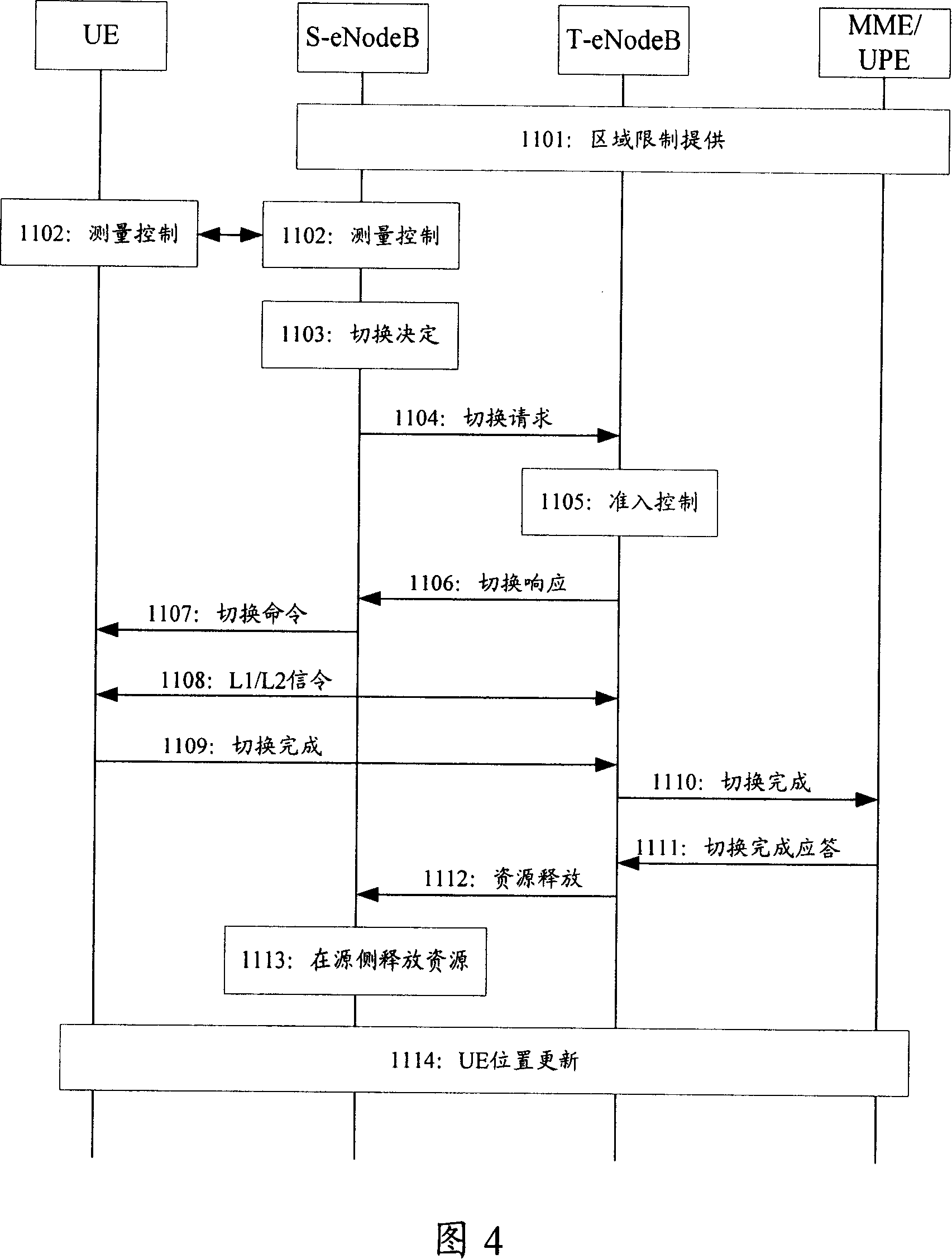
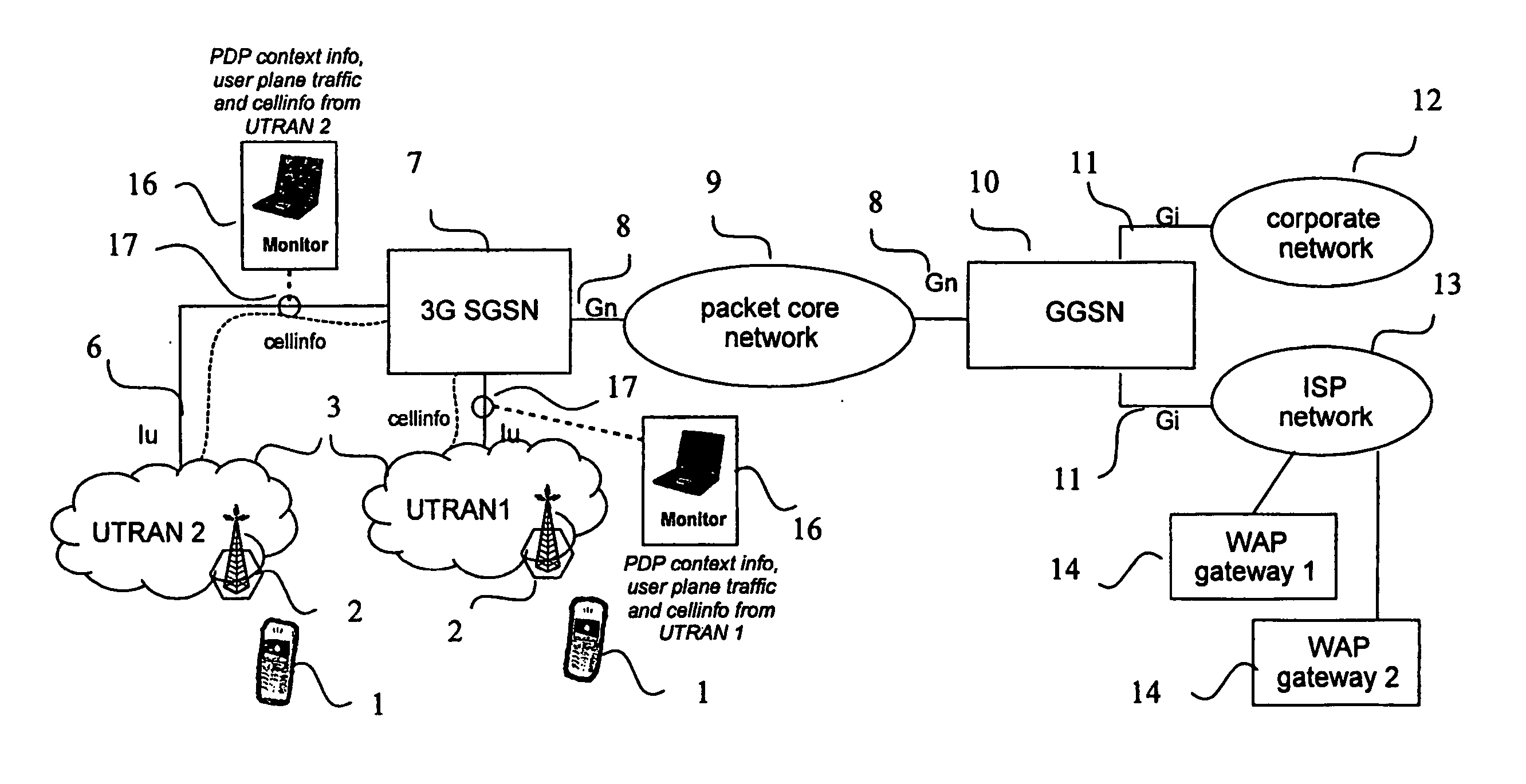
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
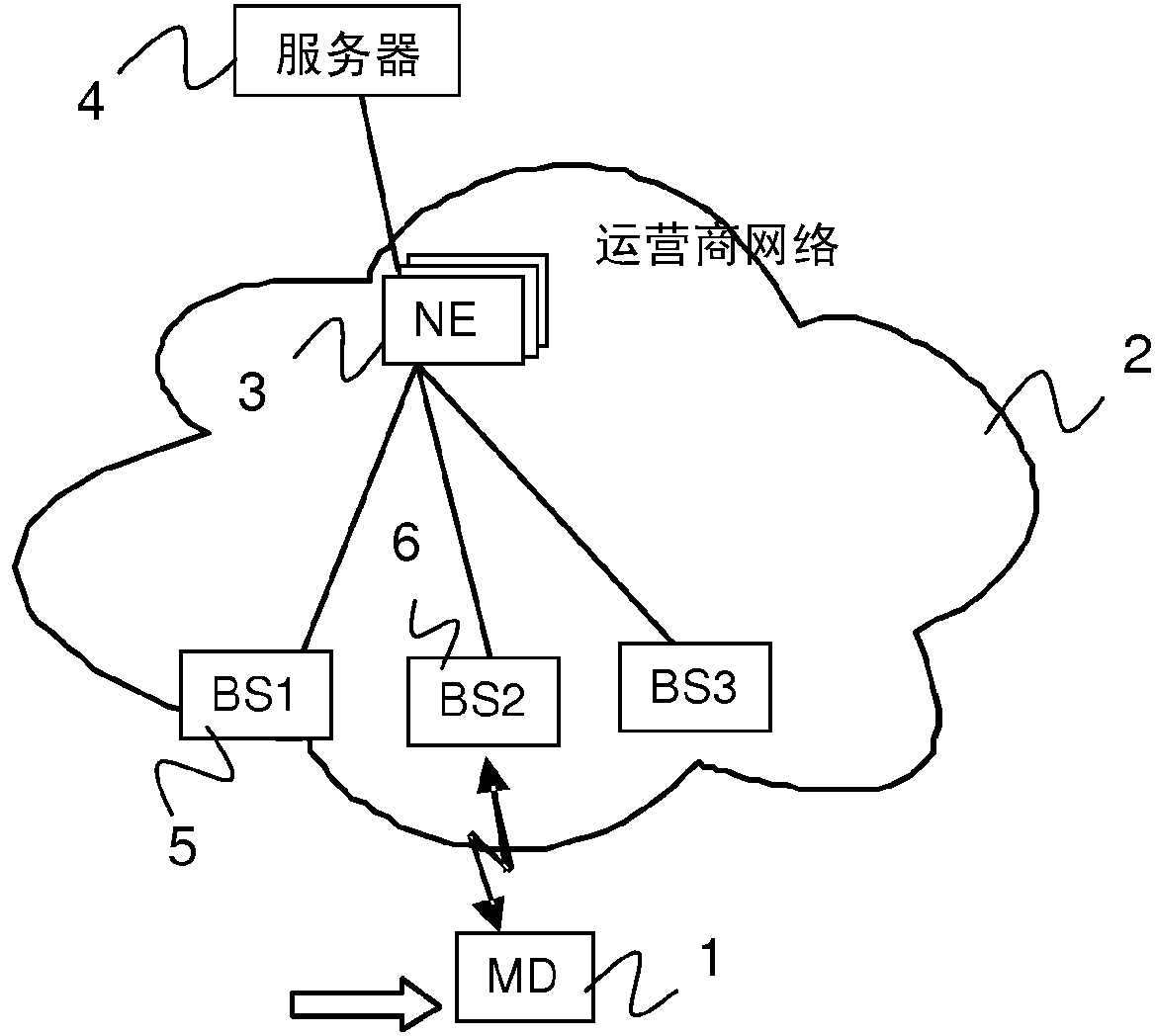
200 results about "Packet core network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
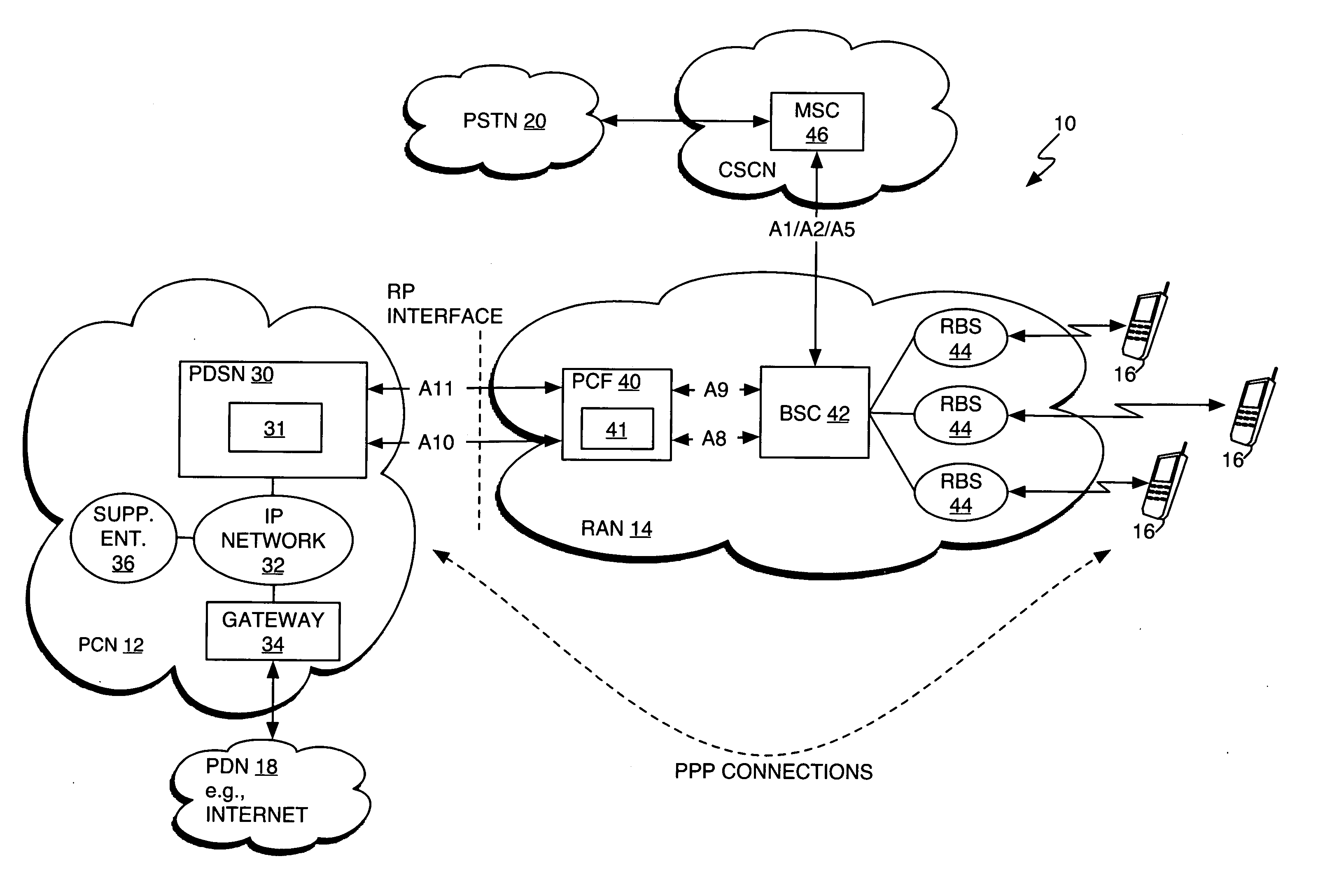
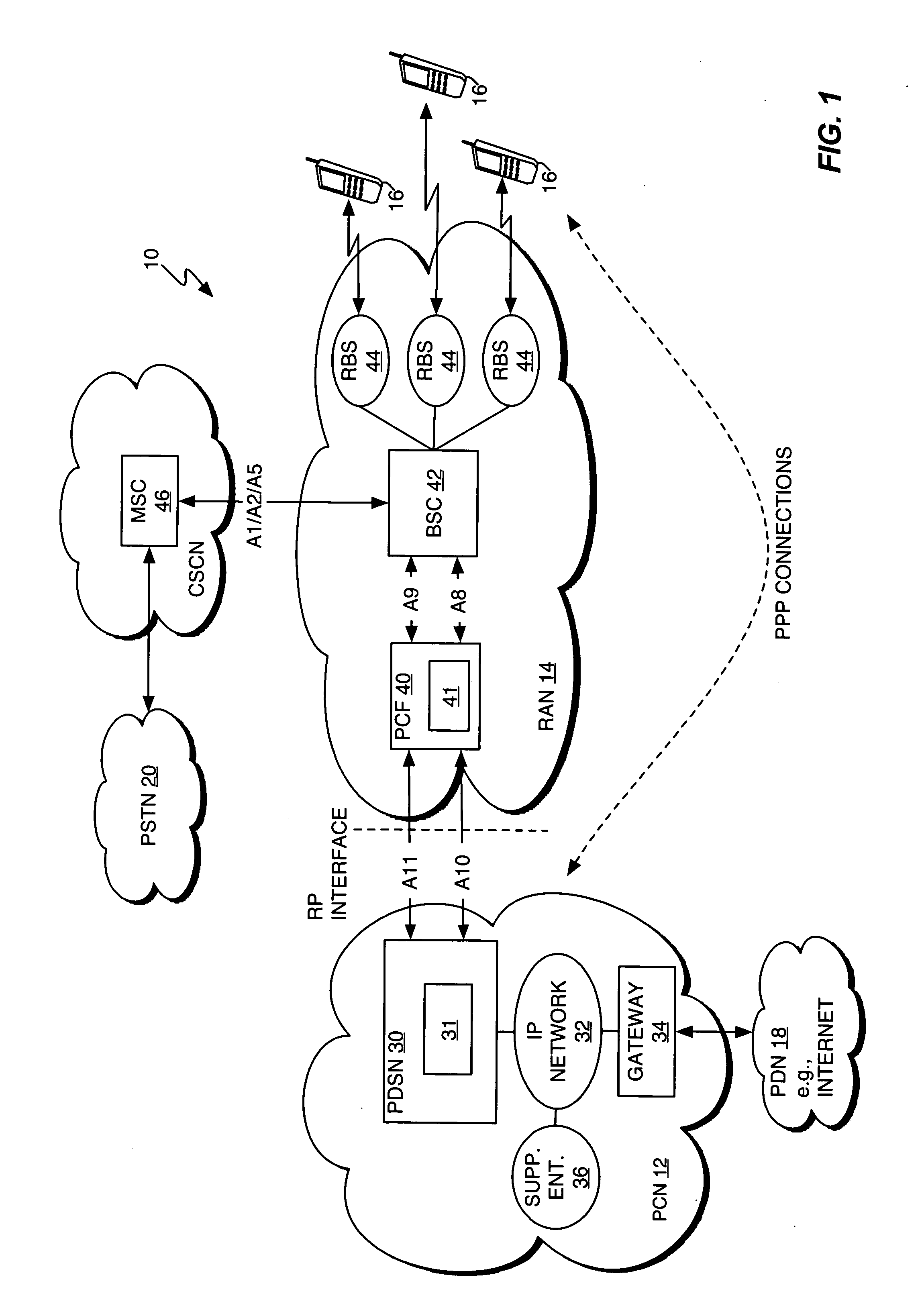
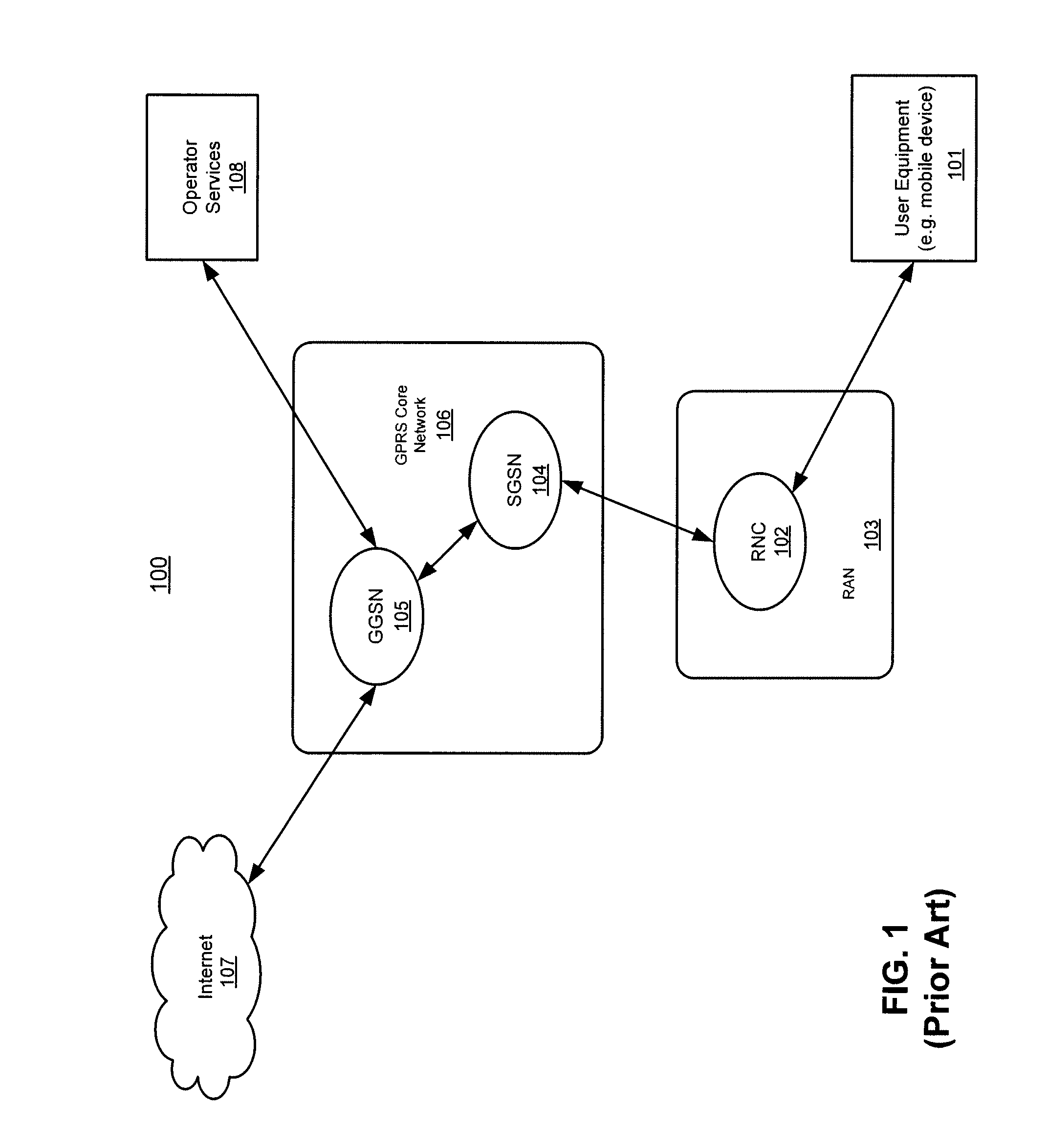
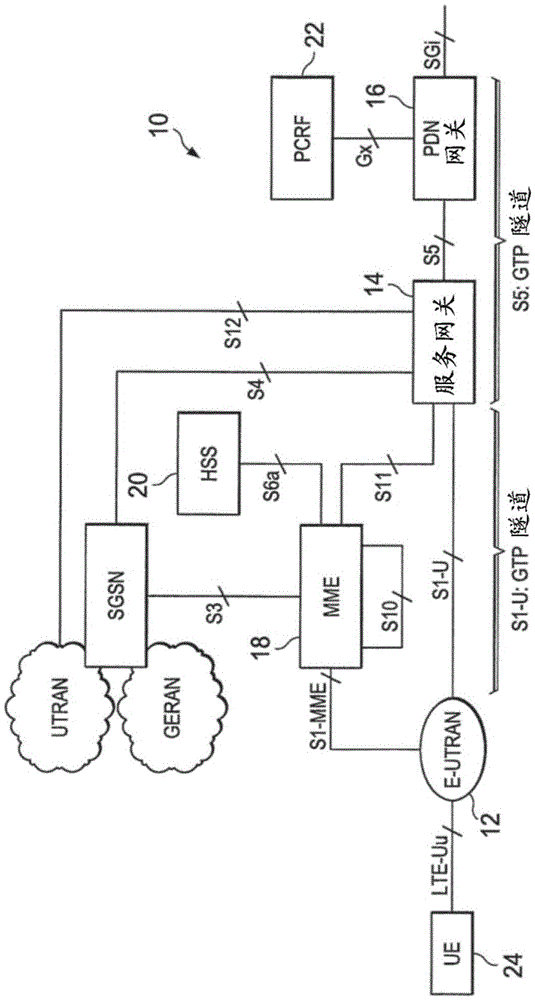
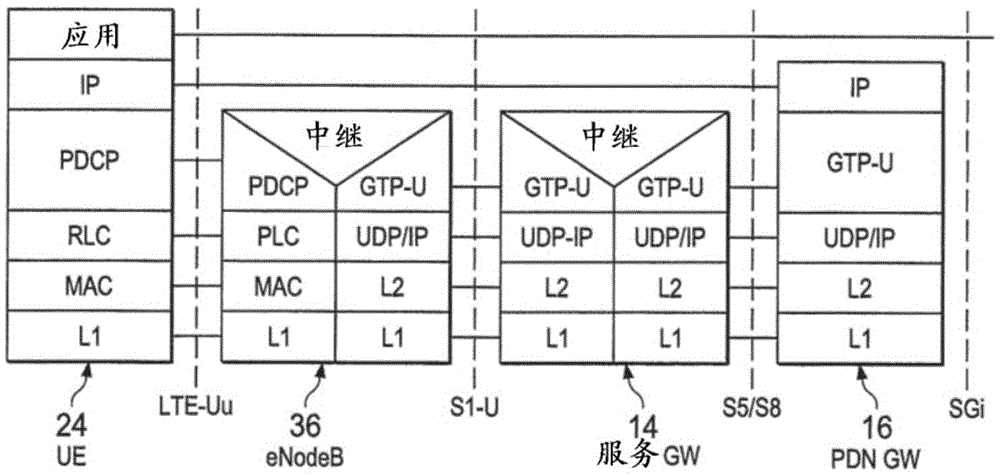
Answer Wiki. "Evolved Packet Core" derives its antecedents from "Packet Core Network" which in turn is derived from "Core Network". Evolved Packet Core is the "Evolution" of this core network! When a User makes a call / uses data, the information is transmitted from the phone to a tower through the air using Radio Frequency.
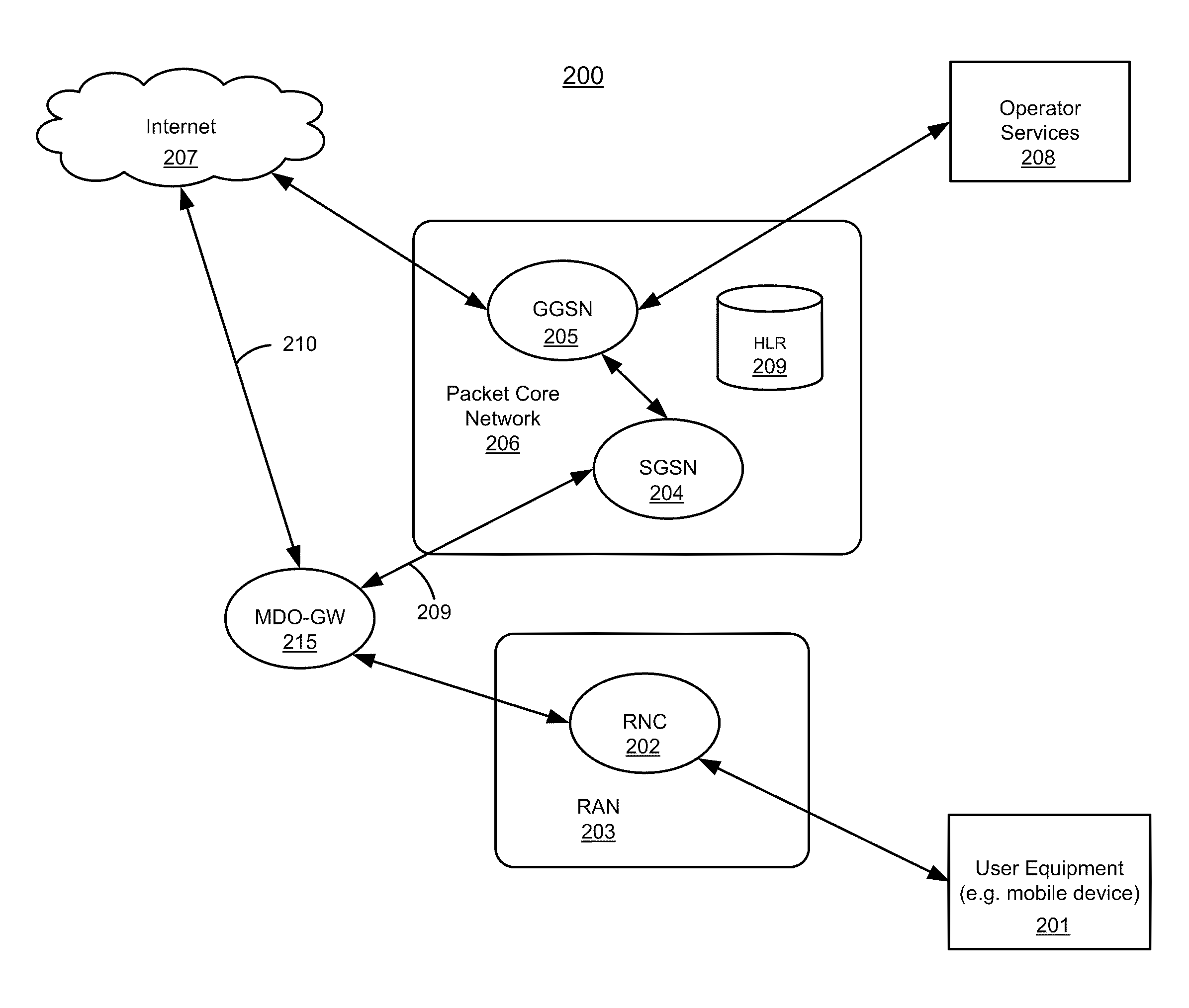
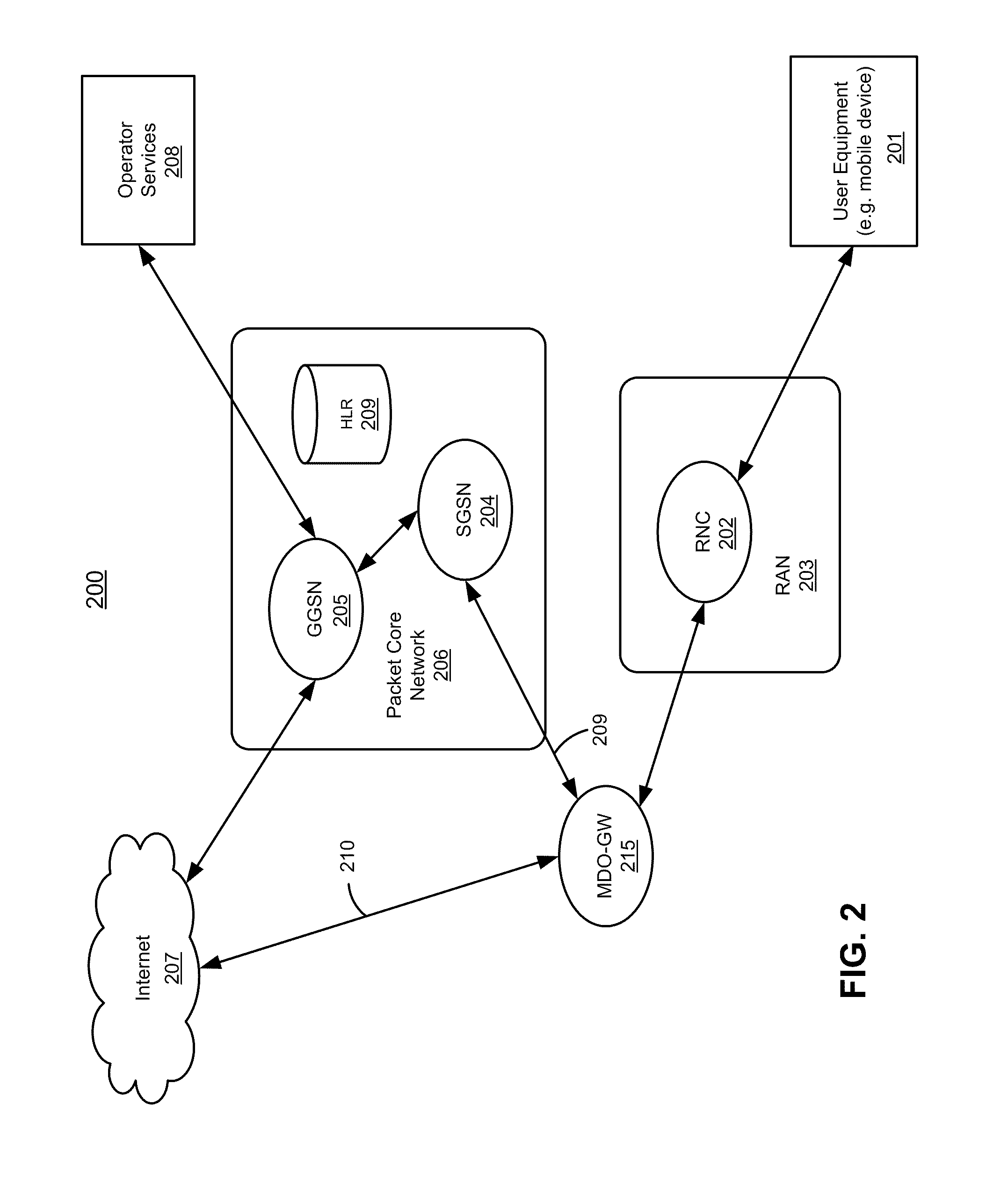
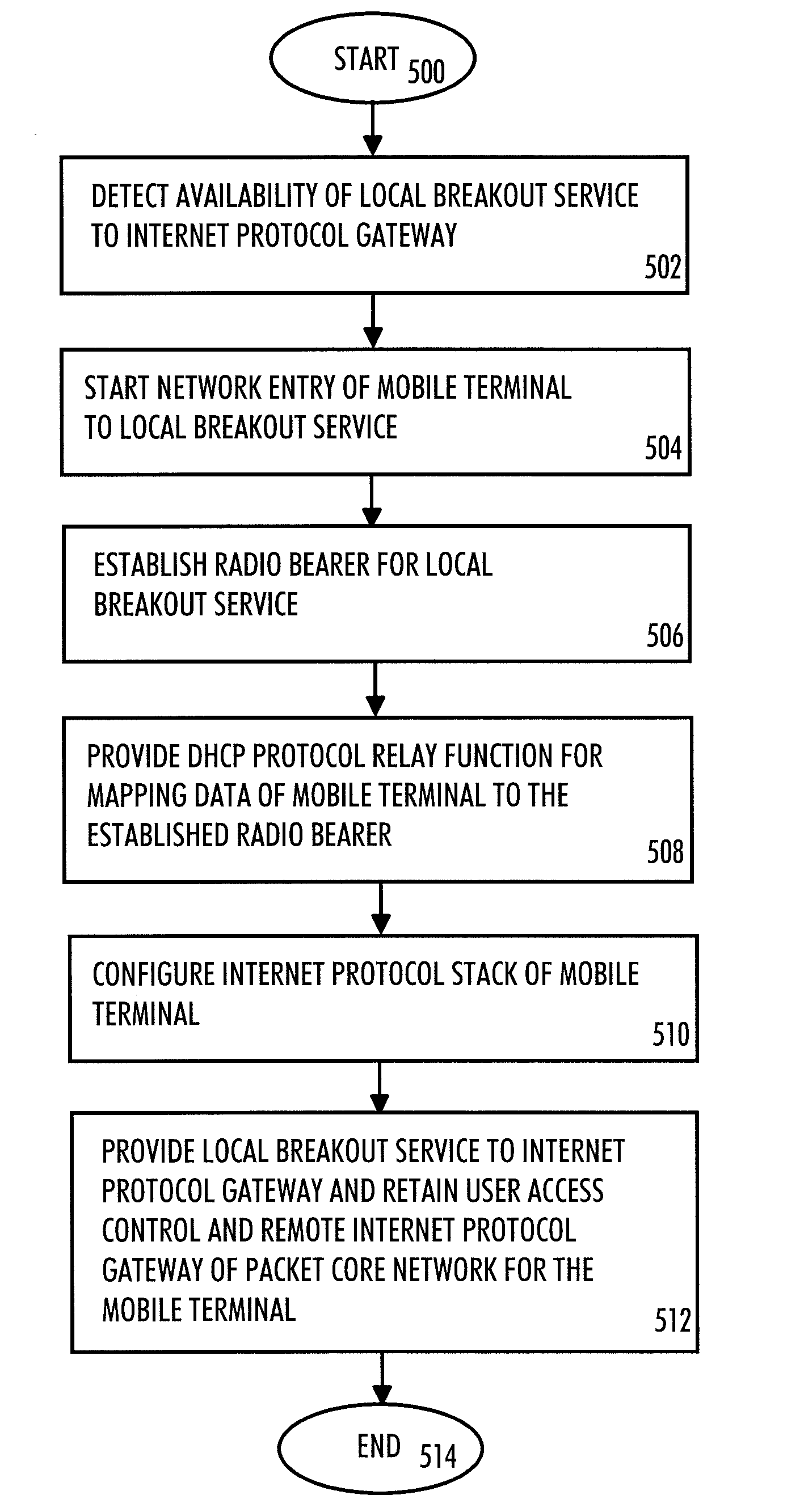
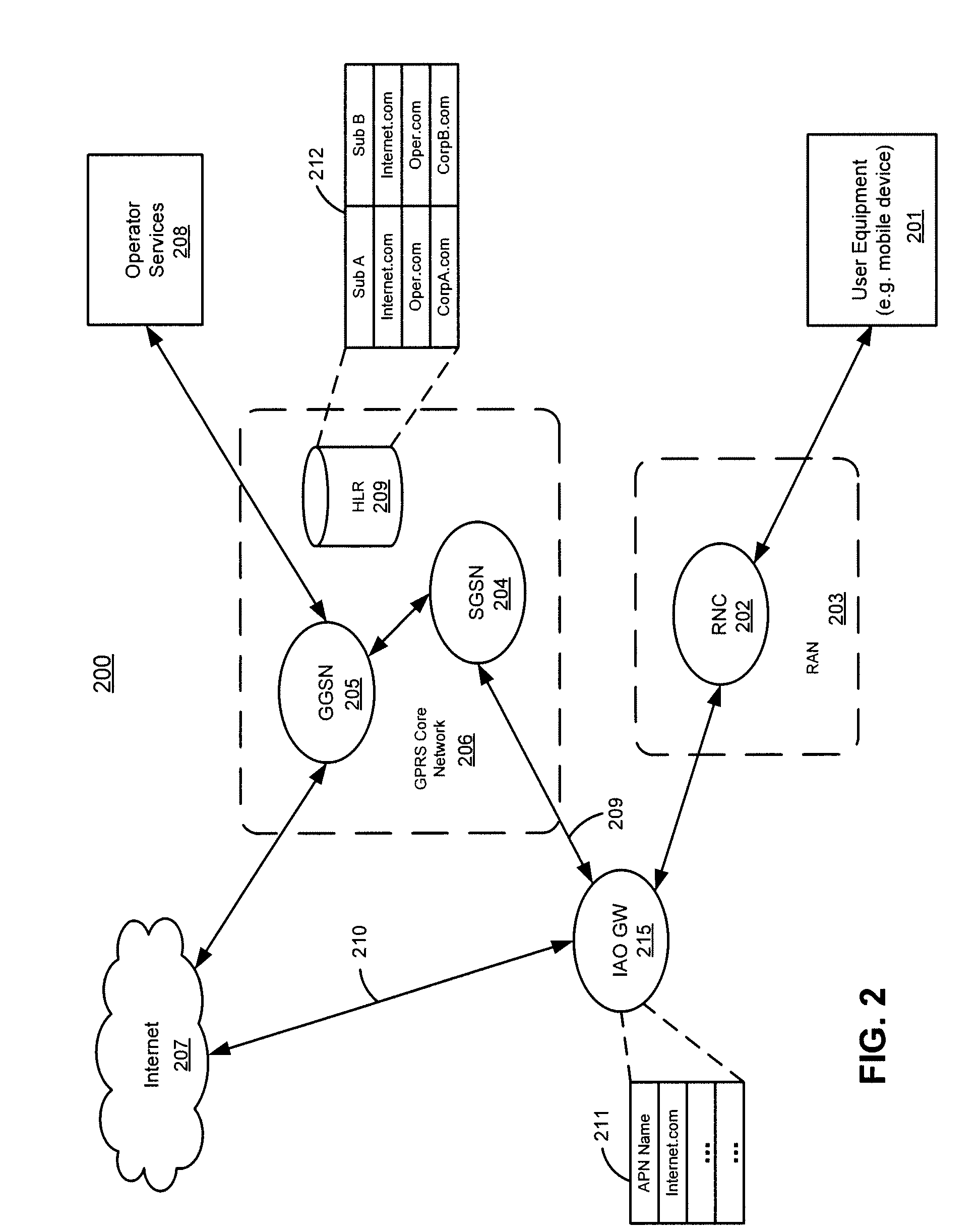
Method, radio system, mobile terminal and base station for providing local breakout service
ActiveUS20120269162A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationPacket core networkUser control
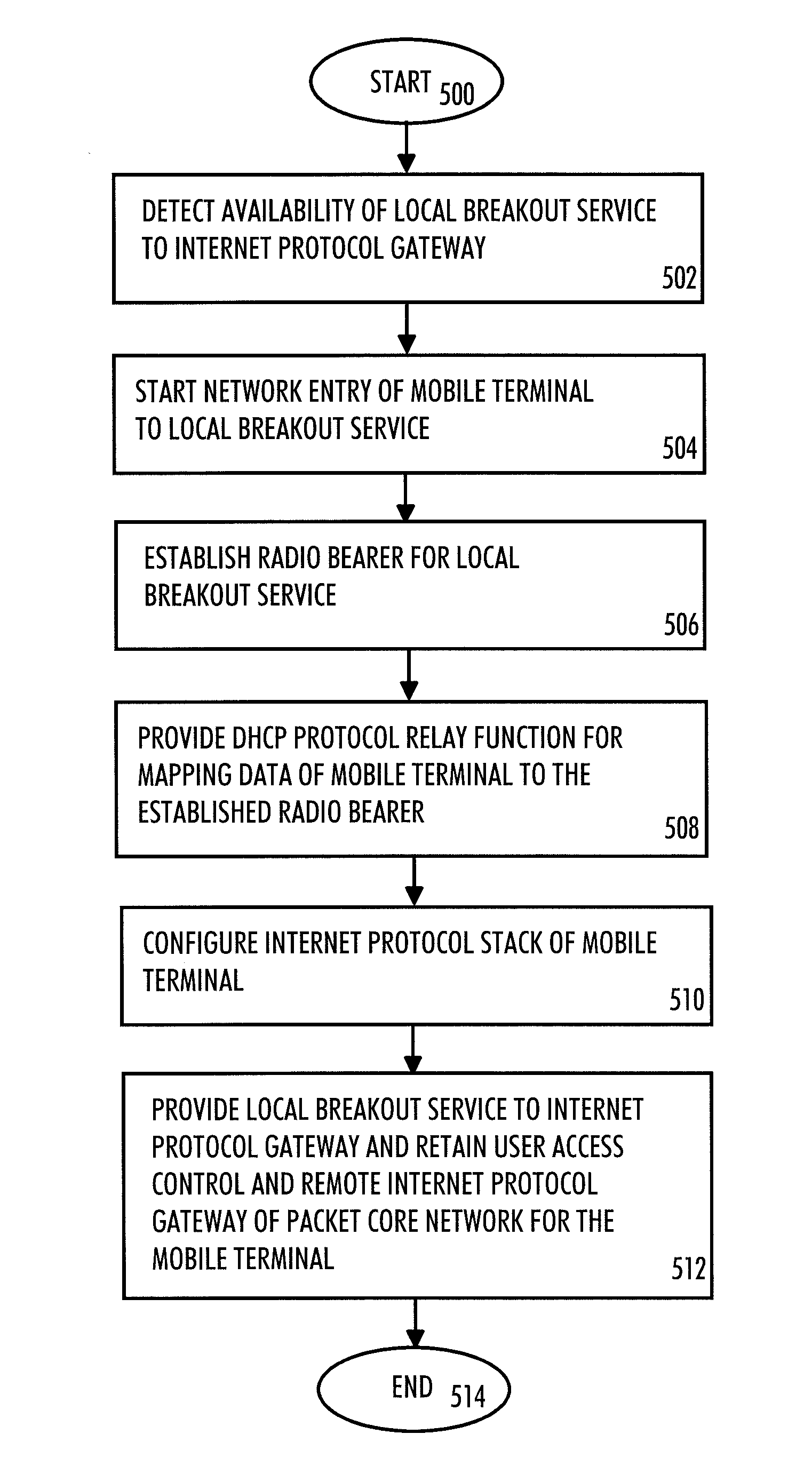
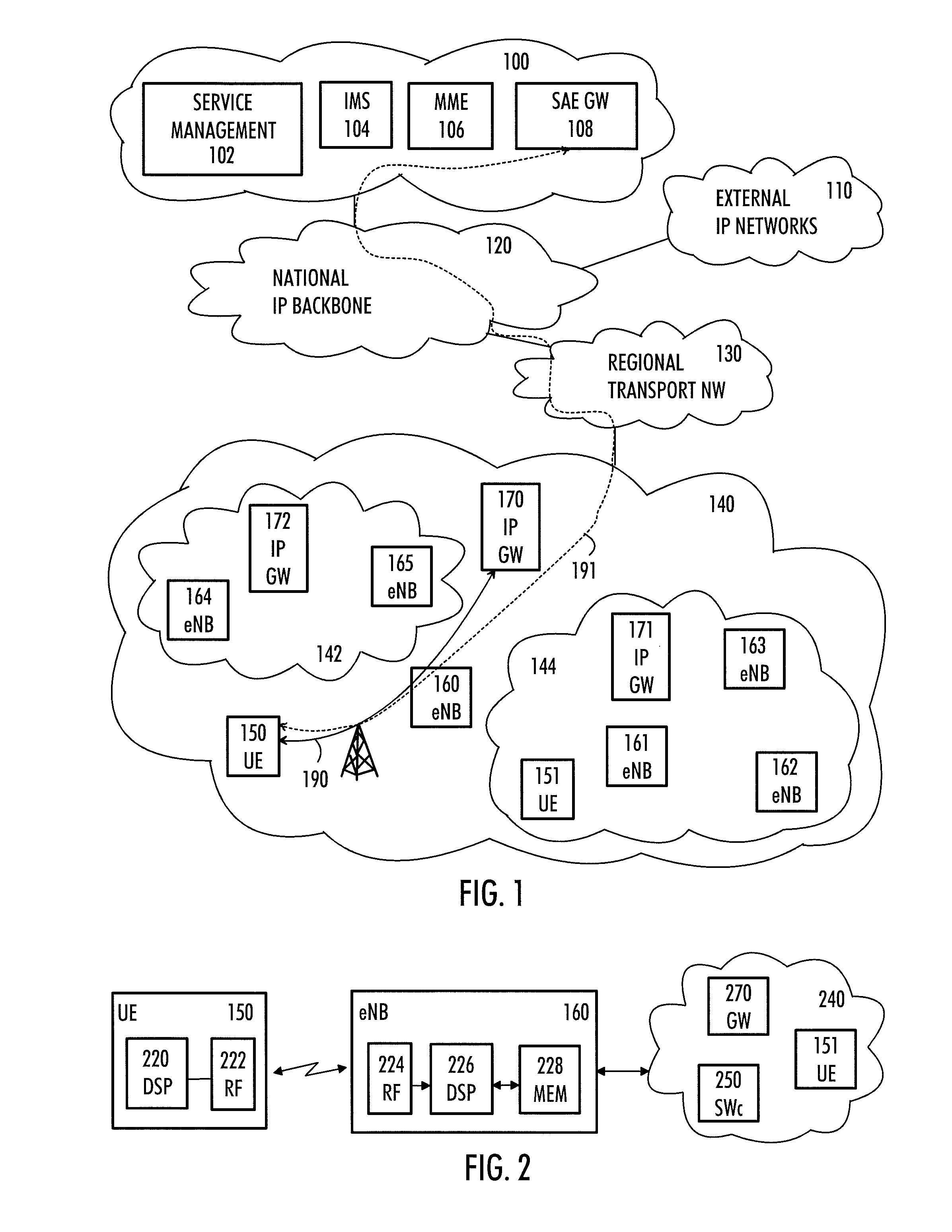
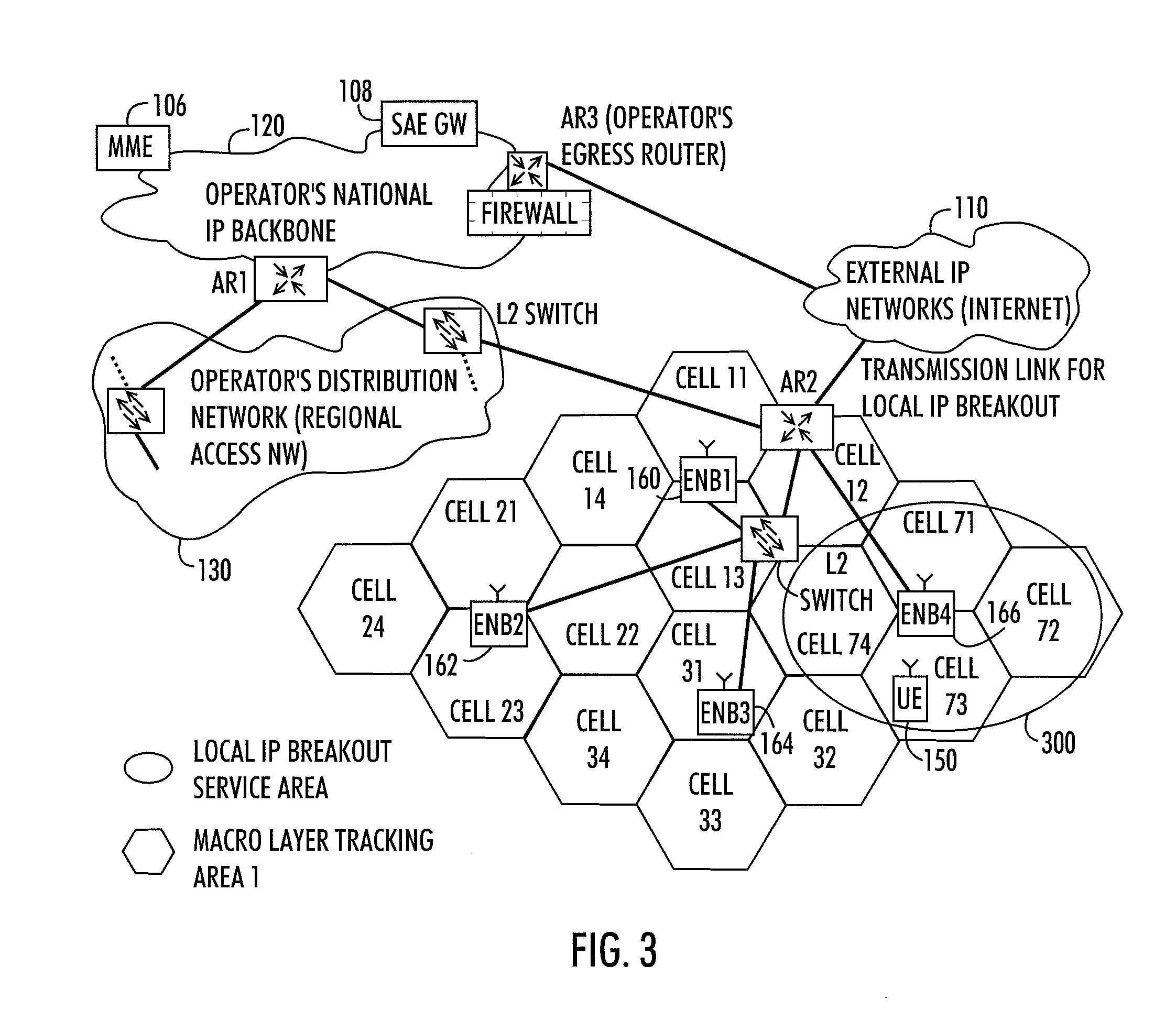
There is provided a radio system wherein a mobile terminal is configured to detect availability of a local breakout service to an Internet protocol gateway; to start a network entry to the local breakout service; and to configure an Internet protocol stack of the mobile terminal on the basis of received configuration data. A serving base station of the mobile terminal is configured to establish a radio bearer for the local breakout service; to provide a dynamic host control protocol relay function for mapping data of the mobile terminal using a local Internet protocol address to the established radio bearer; and to provide the local breakout service to the Internet protocol gateway while retaining user access control and a remote Internet protocol gateway of a packet core network of the public mobile network for the mobile terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
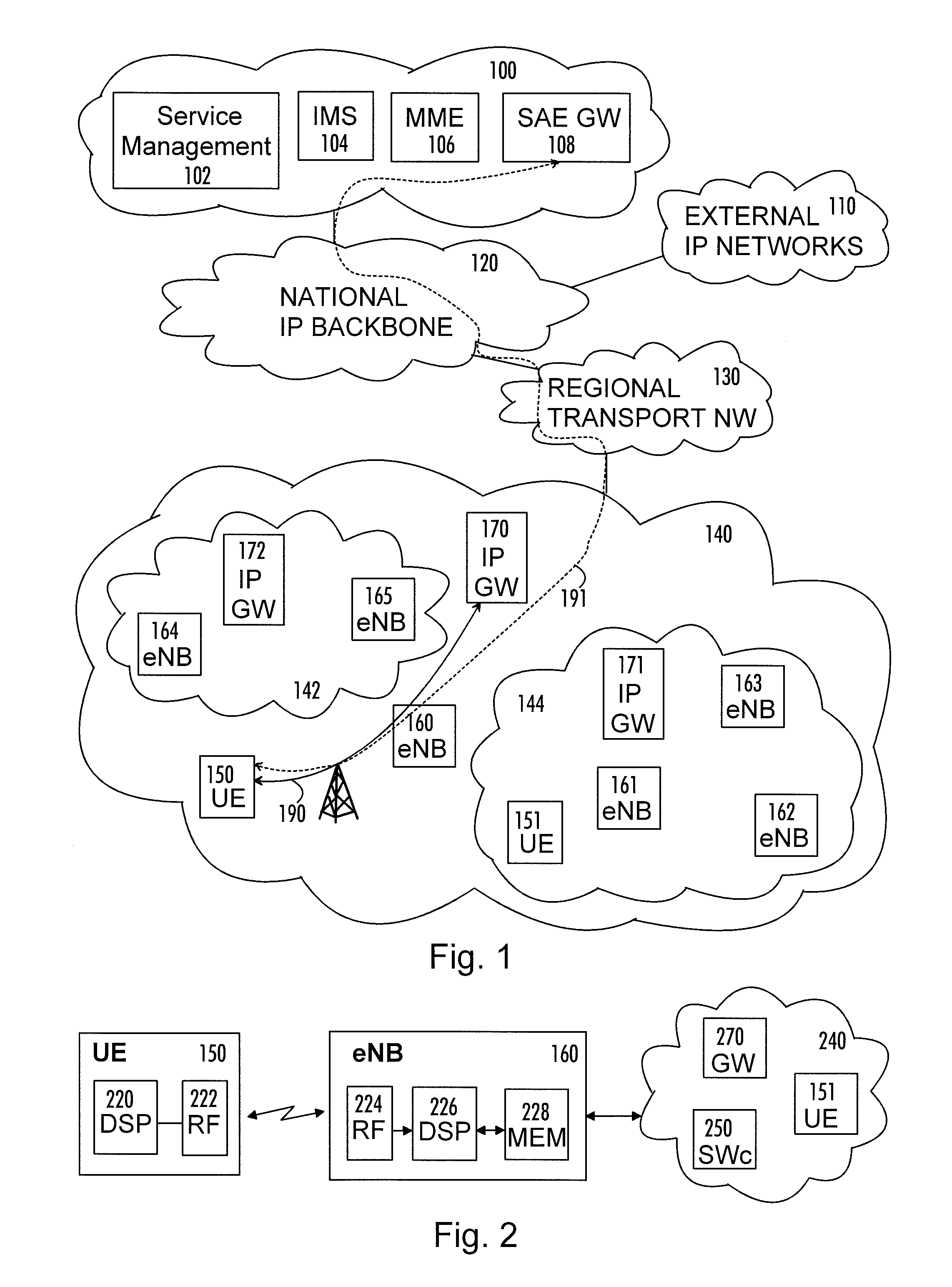
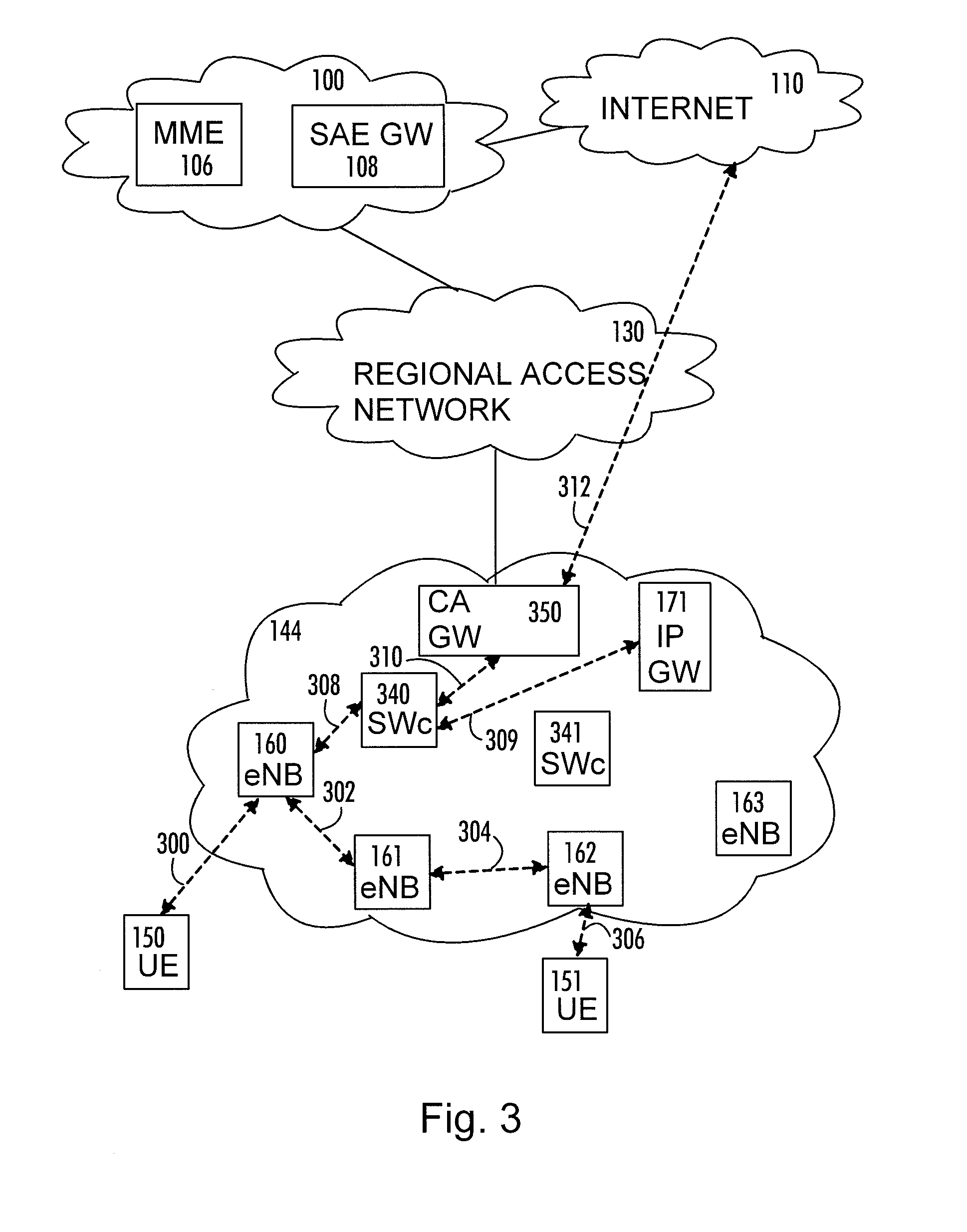
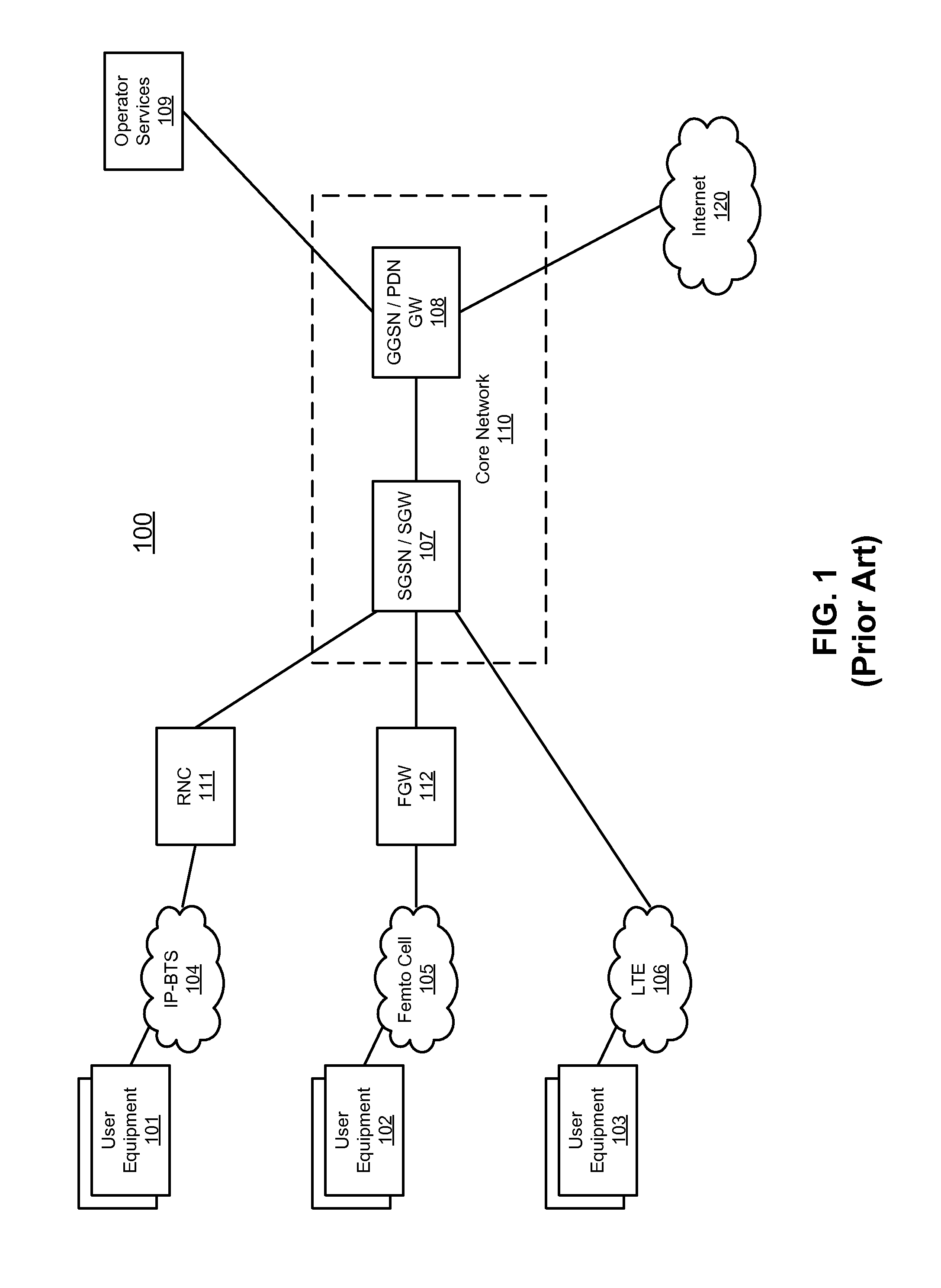
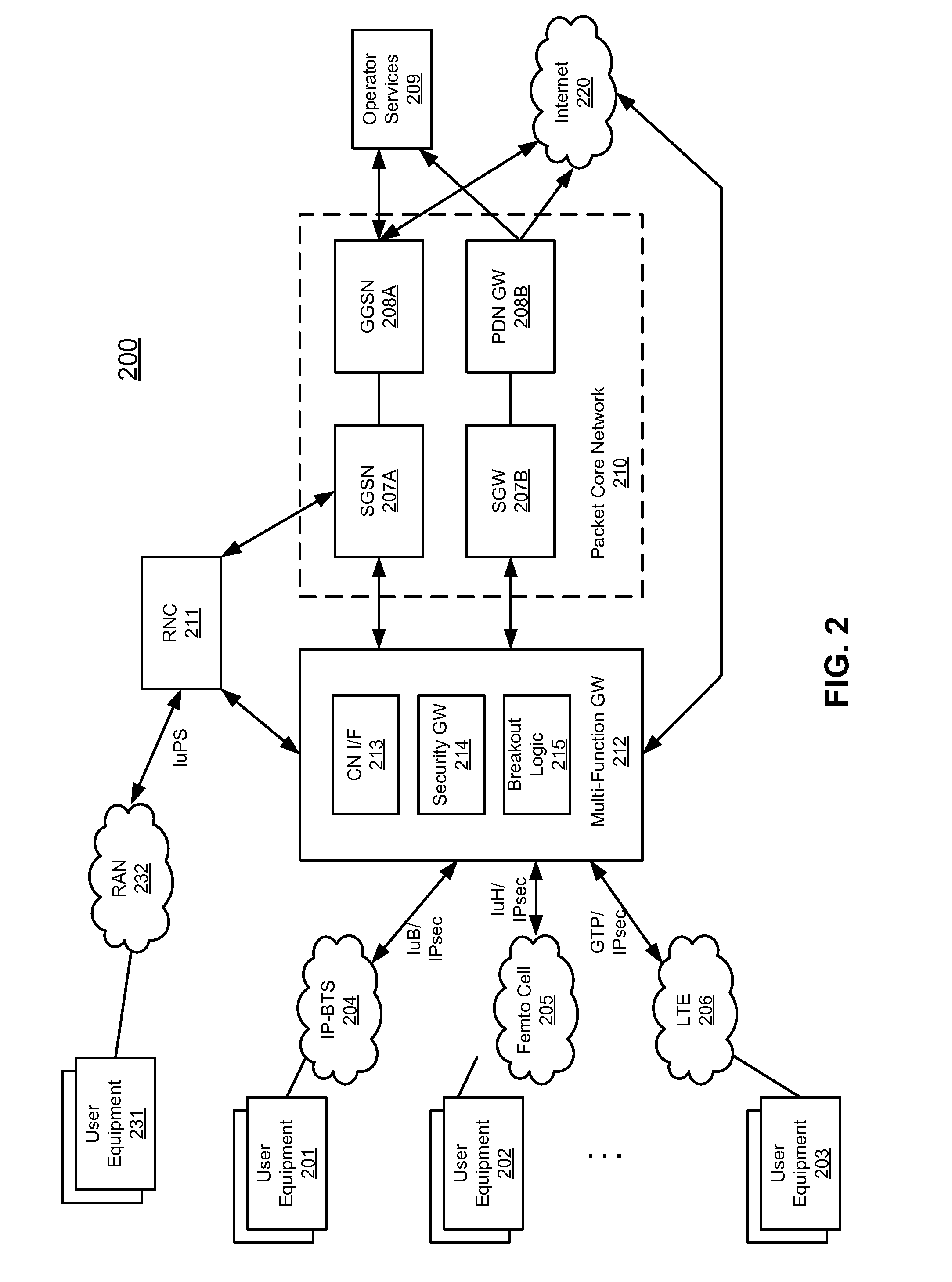
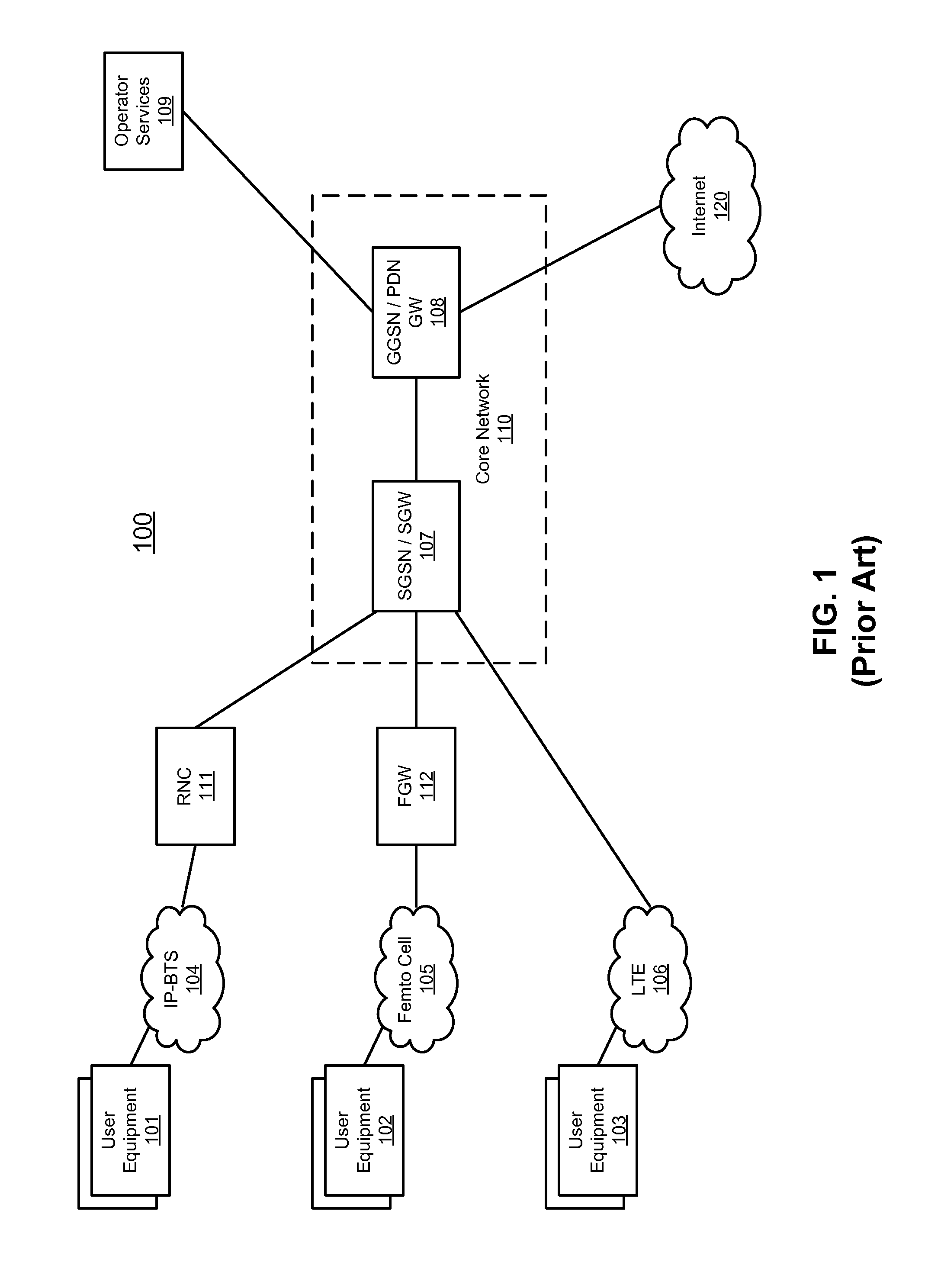
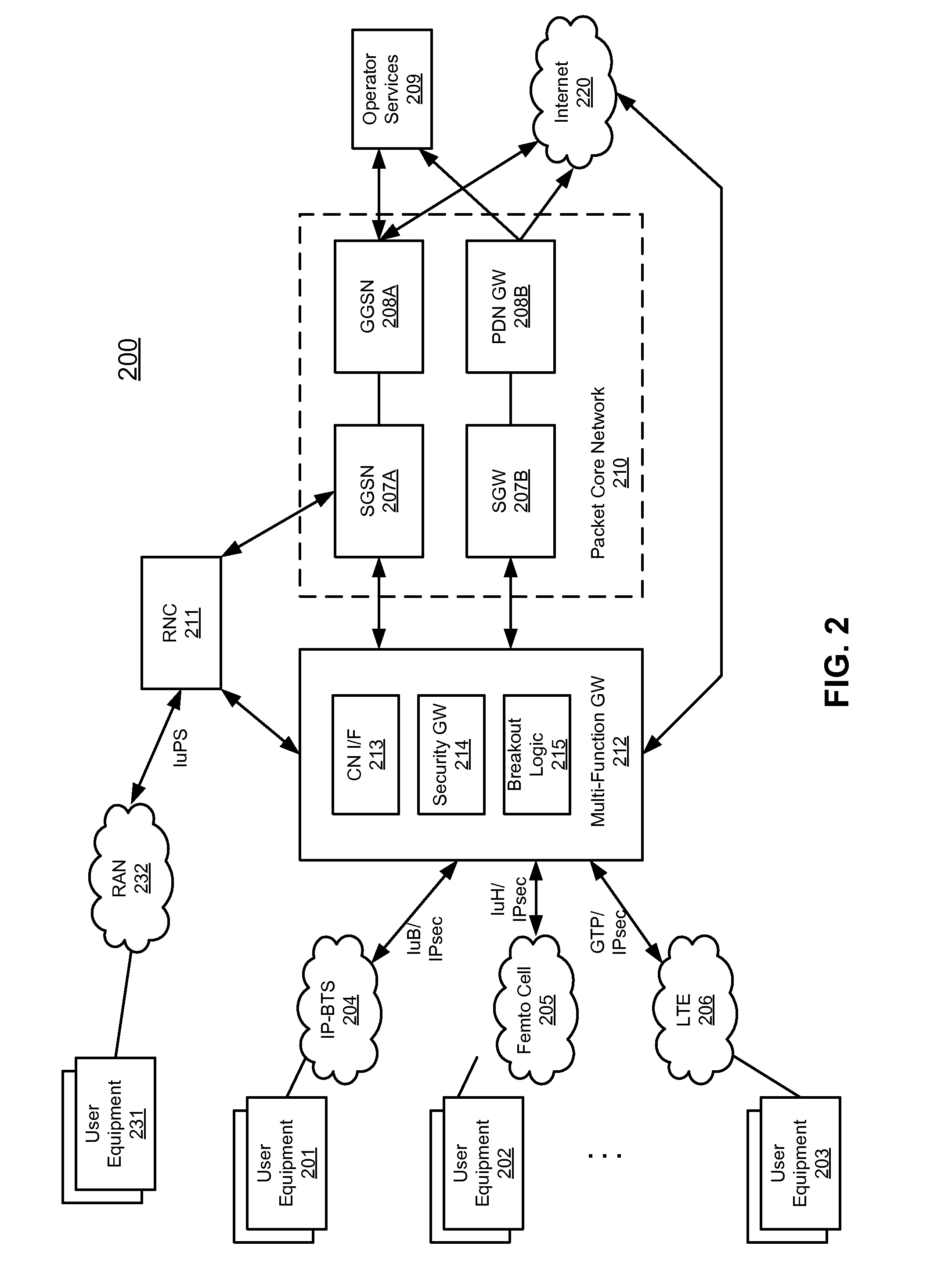
Method and system for bypassing 3gpp packet switched core network when accessing internet from 3gpp ues using ip-bts, femto cell, or LTE access network
A type of network traffic associated with a packet received from a remote node of an access network is determined. A first interface logic routes the packet to a radio network controller (RNC) if the packet is received from an Internet protocol-basestation (IP-BTS) access network and destined to a packet core network. The RNC forwards the packet to a component of the packet core network. A second interface logic routes the packet to the component of the packet core network, including aggregating other packets of the same type received from other remote nodes, if the packet is received from a femto cell and destined to the packet core network. A breakout logic routes the packet to a destination of the Internet directly to enable the packet to reach the Internet without having to route the packet to the component of the packet core network, if the packet is destined to the Internet.
Owner:MAVENIR SYSTEMS
Method, Radio System, and Base Station
ActiveUS20100208658A1Support mobilityNetwork topologiesConnection managementInternet protocol suiteRadio networks
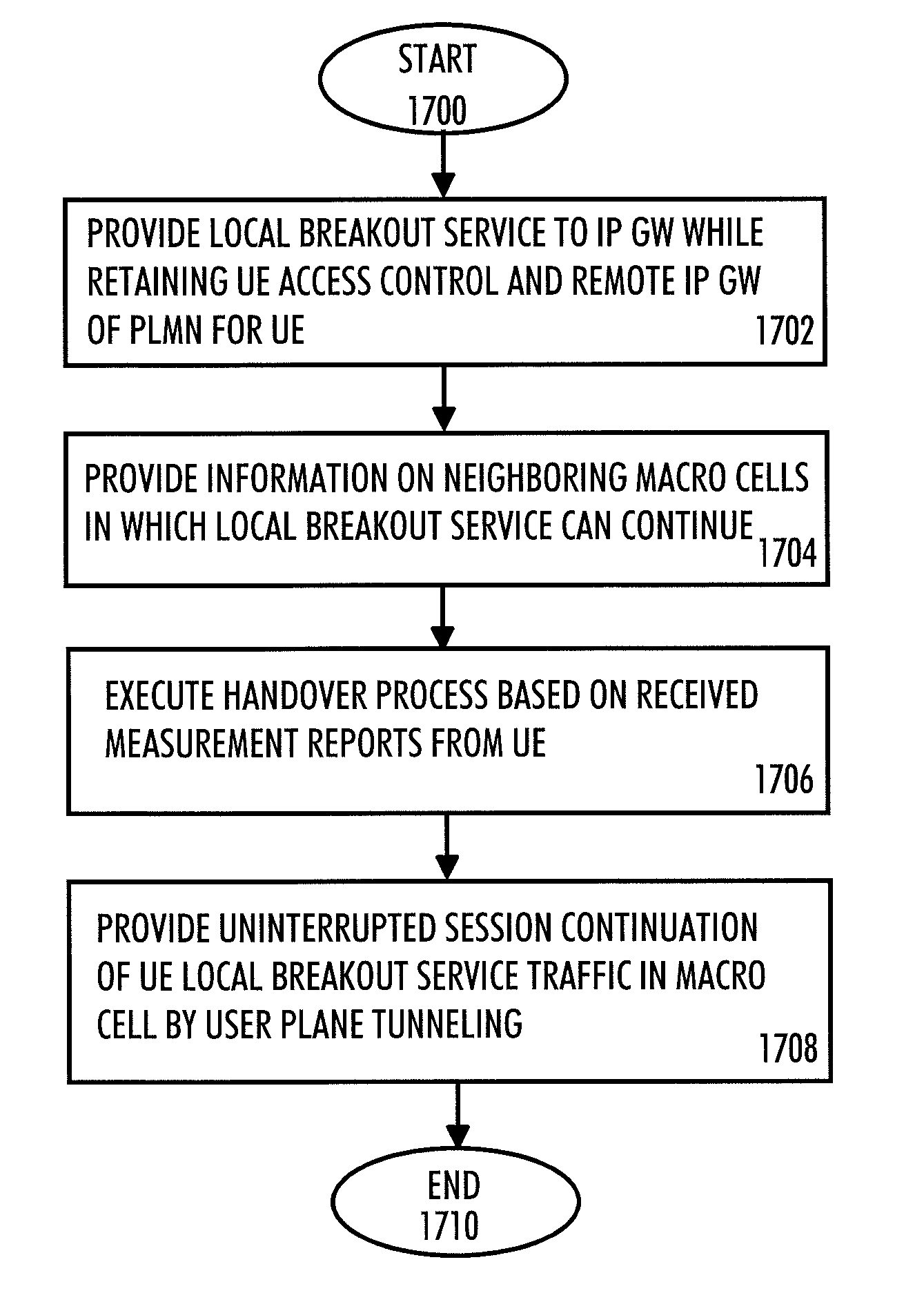
There is provided a method including providing a local breakout service to an Internet protocol gateway while retaining user access control and a remote Internet protocol gateway of a packet core network of a radio network for a mobile terminal; providing information on neighboring macro cells in which the local breakout service can continue, the macro cells belonging to a network using another tracking area than that of the serving cell of the mobile terminal; executing a handover process of the mobile terminal from a source base station in the serving cell of the mobile terminal to a target base station in a neighboring macro cell; and providing session continuation of the mobile terminal local breakout service traffic in the neighboring macro cell by controlling user plane tunneling between the target base station and the local packet switched network from which an Internet protocol address for the local breakout service was assigned.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Streaming video monitoring using cdn data feeds
ActiveUS20150304196A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTelevision systemsData feedVideo monitoring
A method for monitoring streaming video content is provided. Content Delivery Network (CDN) feed sent over one or more CDNs is monitored and analyzed using a first soft probe deployed in the one or more CDNs to generate a first video session record. Video traffic sent over a packet core network (PCN) is monitored and analyzed using a second soft probe deployed in the PCN to generate a second video session record. A third session record is generated by correlating the first session record to the second session record. The third session record corresponds to an end-to-end video streaming session. One or more performance characteristics corresponding to the end-to-end video streaming session are generated based at least in part on the third session record.
Owner:NETSCOUT SYST TEXAS LLC
Method for establishing connection between mobile station and evolution packet core network
InactiveCN101026861AShorten the timeSimplify the control plane protocol stackConnection managementWireless network protocolsTelecommunicationsAccess time
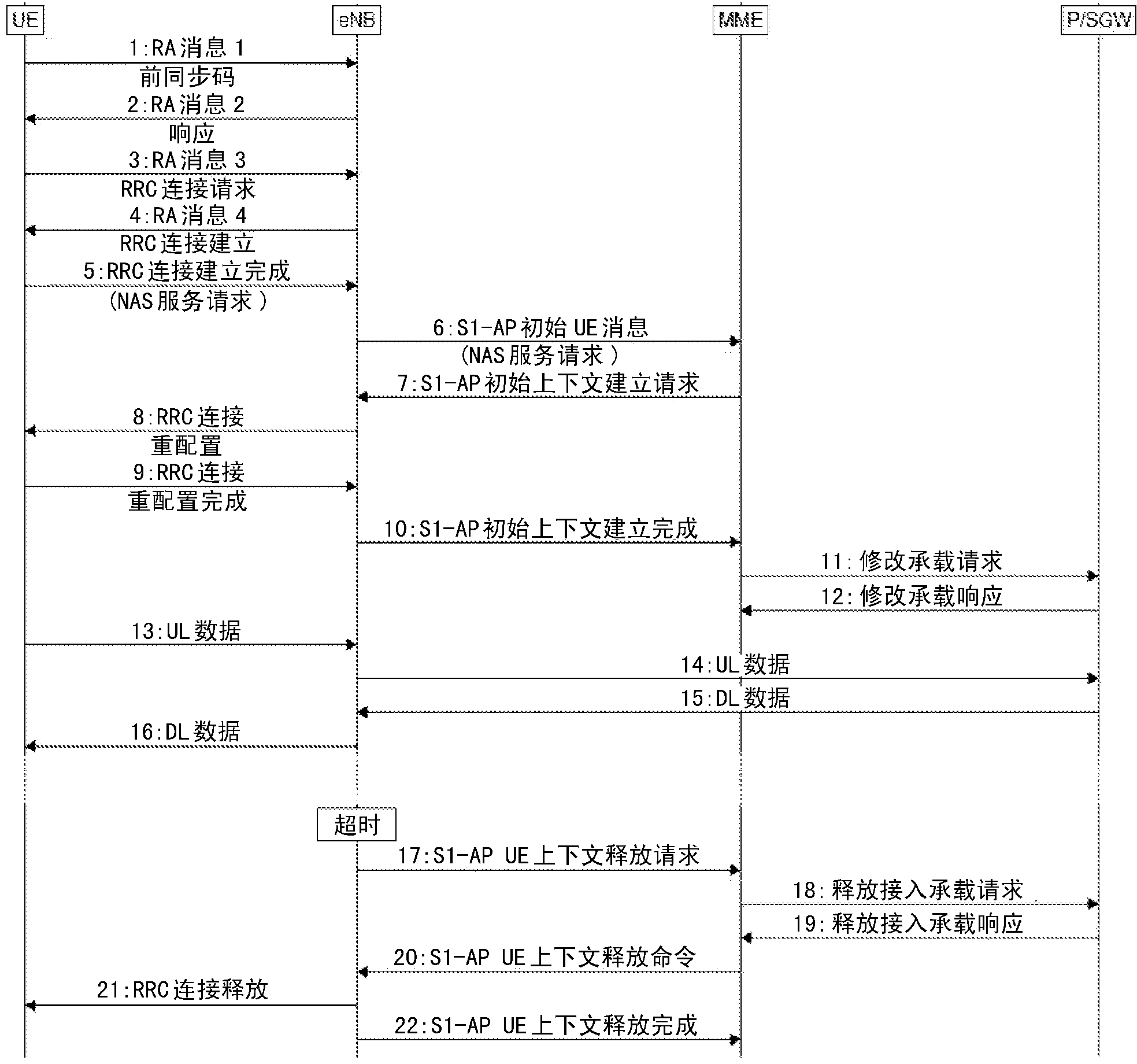
The method includes steps: receiving message from access layer of mobile station (MS), evolution radio access network (ERAN) establishes signaling connection between ERAN and MS based on signaling message of data as data unit of non access layer protocol carried by message from access layer of MS; at same time, ERAN establishes signaling connection between ERAN and evolution packet core network (EPCN) so as to build up signaling connection between MS and EPCN. In procedure for building signaling message between MS and EPCN, the invention builds up signaling message between MS and ERAN as well as signaling message between ERAN and EPCN at same time. Thus, the invention shortens time for building connection between MS and EPCN greatly so as to meet requirement on switching and accessing time put forward by evolution network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Precise geolocation for content caching in evolved packet core networks
InactiveUS20130132544A1Accurately locating a mobile deviceInformation formatDigital computer detailsContent distributionGeolocation
A network element in a network is provided. The network element includes a receiver that receives a content request message. The received content request message indicates content to be transmitted to a device. The network element includes a processor in communication with the receiver. The processor generates a modified content request message by inserting identification data into the content request message. The identification data identifies at least one of a plurality of network nodes in the network. The network element includes a transmitter that transmits the modified content request message to a content distribution network server. The receiver further receives a redirect message that is based on the transmitted modified content request message. The redirect message identifies that a one of the plurality of network nodes is a cache location storing the indicated content.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for selectively bypassing packet core network within a session based on traffic type
According to one aspect of the invention, packets of a first type within a first data flow are routed to a destination through a packet core network. In response to a detection that packets of a second type are to be routed while routing the first data flow, a second data flow is created which is a sub-flow of the first data flow. Packets of the second type are routed via the second data flow to the destination without traversing the packet core network, while packets of the first type are routed via the first data flow traversing the packet core network.
Owner:MAVENIR SYSTEMS
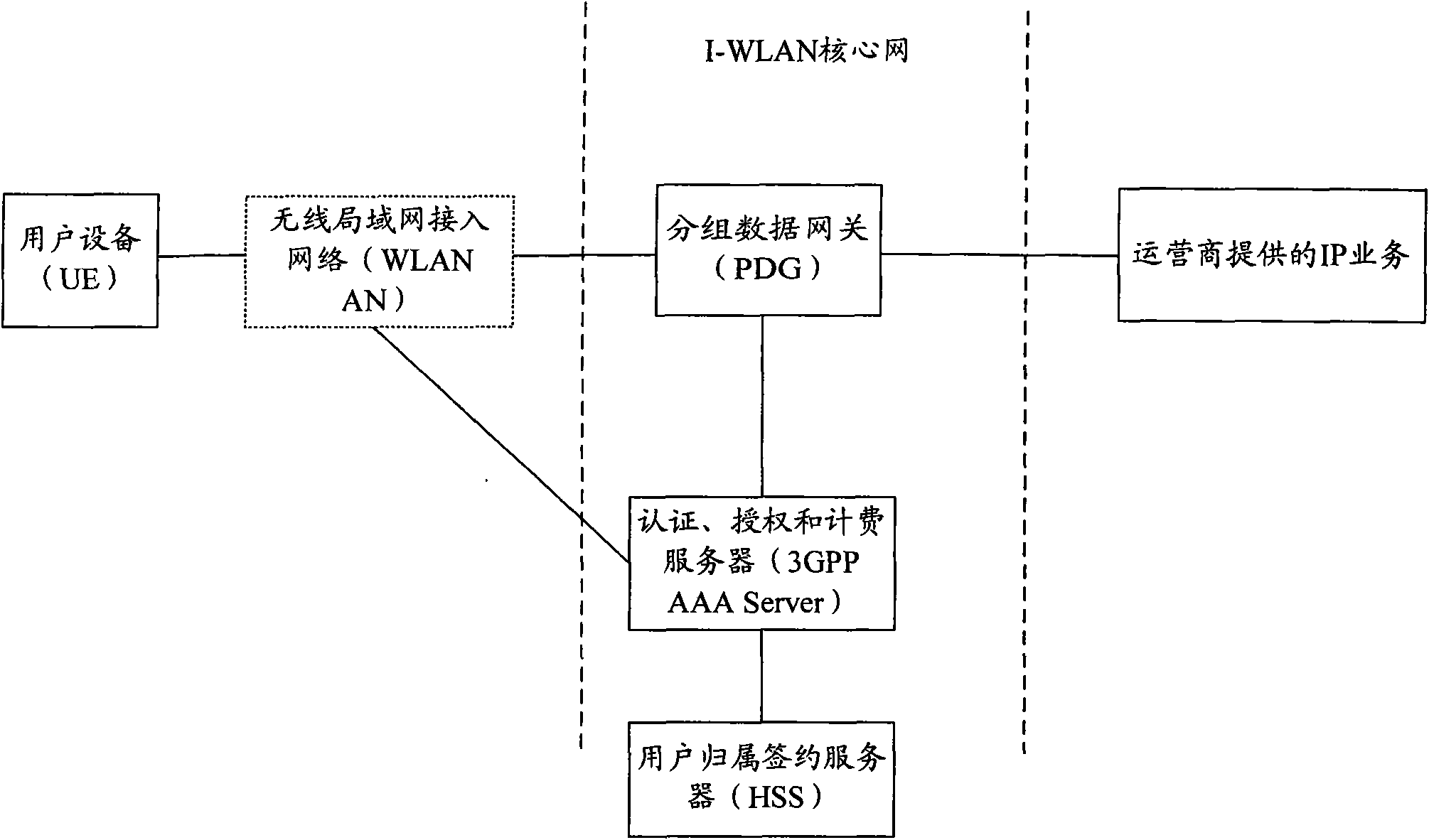
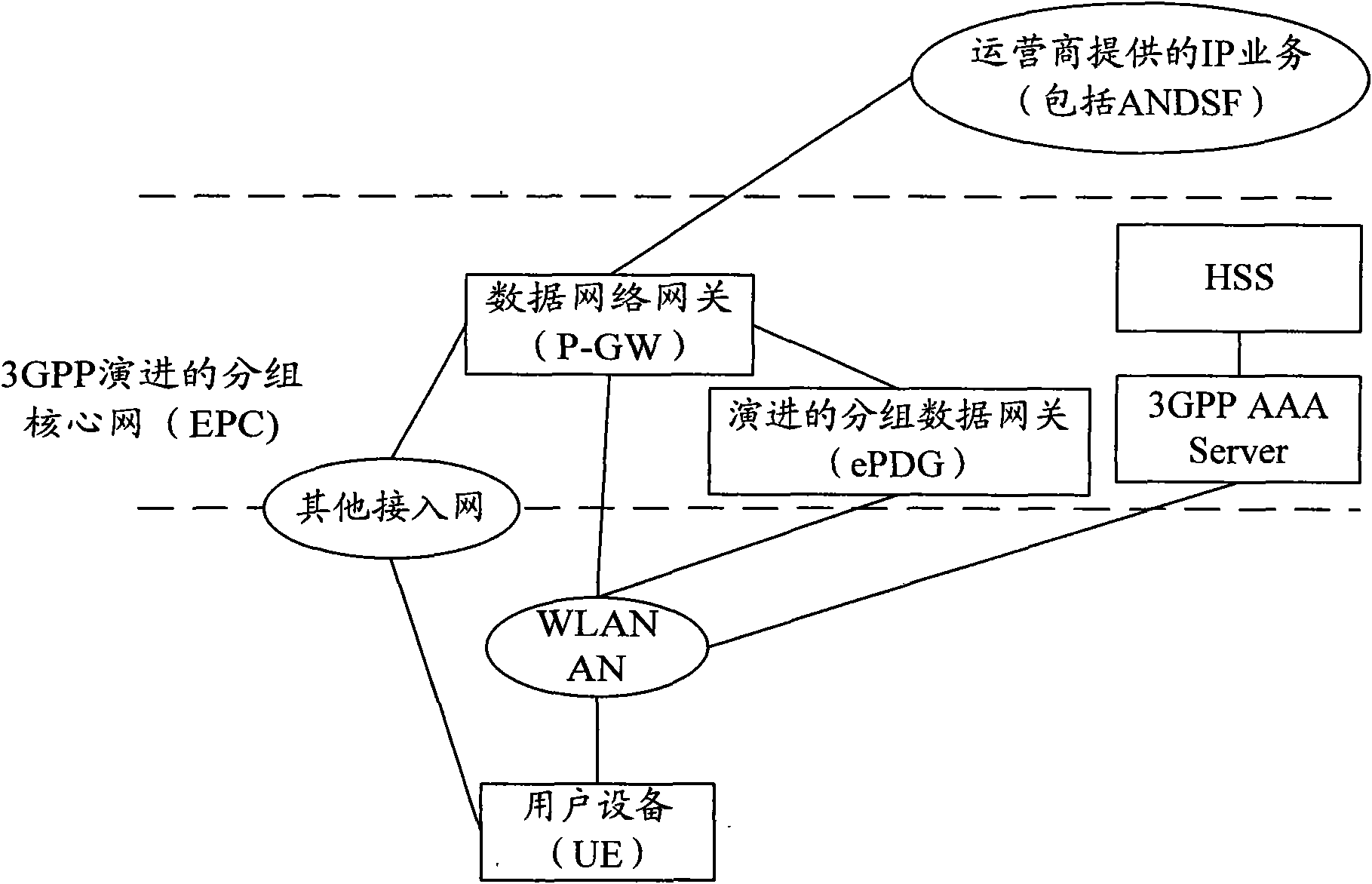
Method and system for realizing accessing through wireless local area network access network
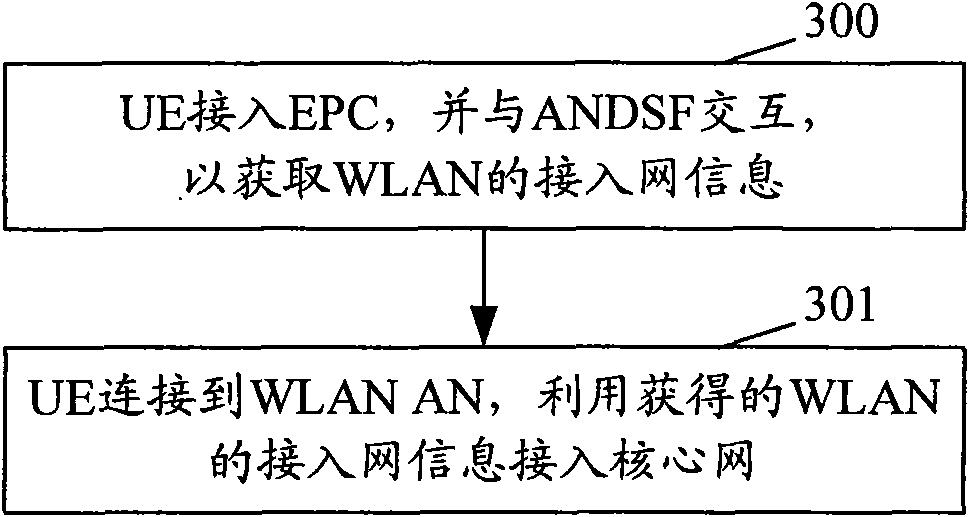
ActiveCN101990274AEasy accessReduce loadAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesAccess networkPacket core network
The invention provides a method and a system for realizing accessing through a wireless local area network (WLAN) access network. The method comprises the following steps that: user equipment (UE) accesses an evolved packet core network (EPC) and interacts with access network discovery and selection function (ANDSF) to acquire access network information of a WLAN; and the UE is connected with the wireless local area network access network (WLANAN) and accesses the core network by using the acquired access network information of the WLAN. Because the UE previously accesses the EPC and interacts with the ANDSF to acquire the access network information of the WLAN, namely the UE knows the wireless core network to which the current WLANAN is connected or can be accessed. Thus, the wireless core network which subsequently participates in access authentication is the wireless core network to which the current WLANAN is connected or can be accessed, successful accessing of the UE is ensured, and the load of the UE and the network is reduced, so that the resource is saved and the user experience is enhanced.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Method and system for selecting service gateway
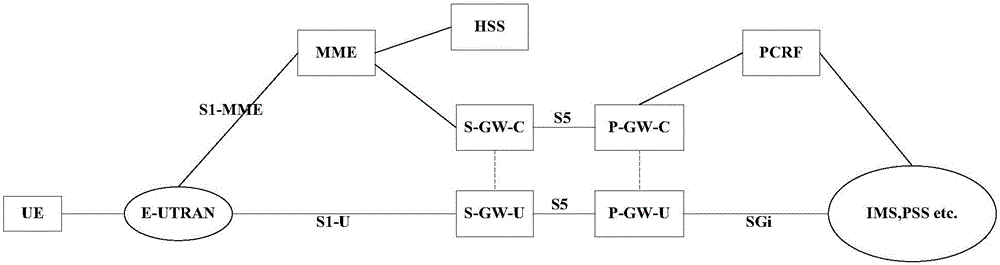
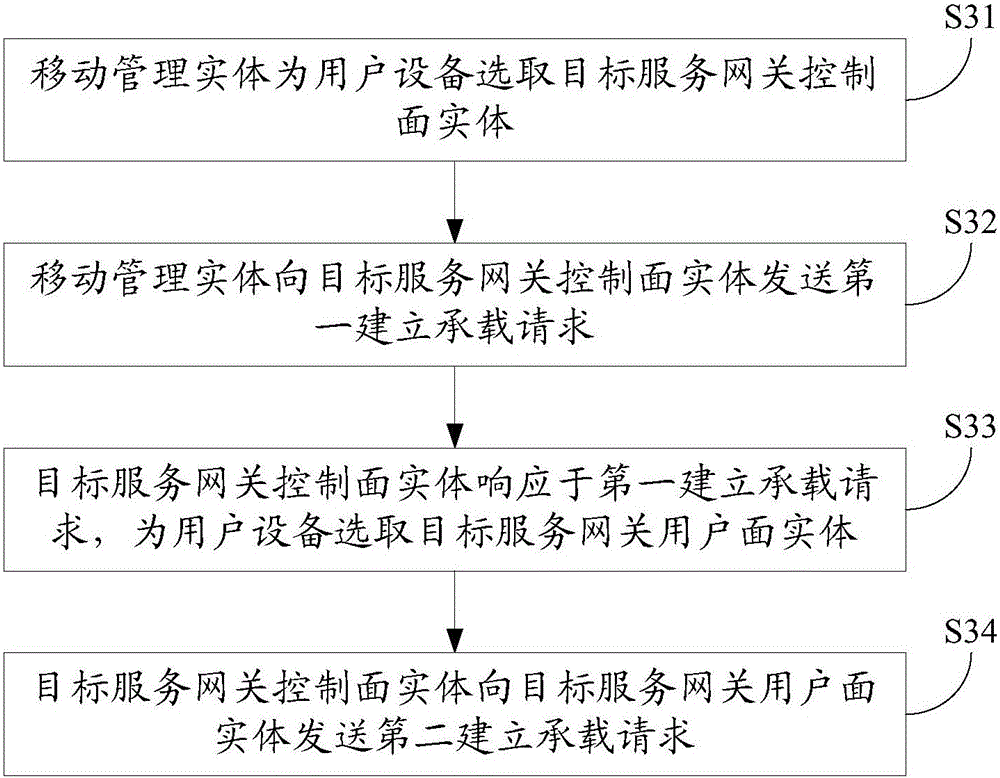
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and system for selecting a service gateway. A mobile management entity selects a proper service gateway control plane entity for user equipment; and the service gateway control plane entity selected by the mobile management entity selects a service gateway user plane entity for the user equipment. Therefore, effective operation of evolved packet core network architecture after separation of an SGW into an SGW-C entity and an SGW-U entity can be guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
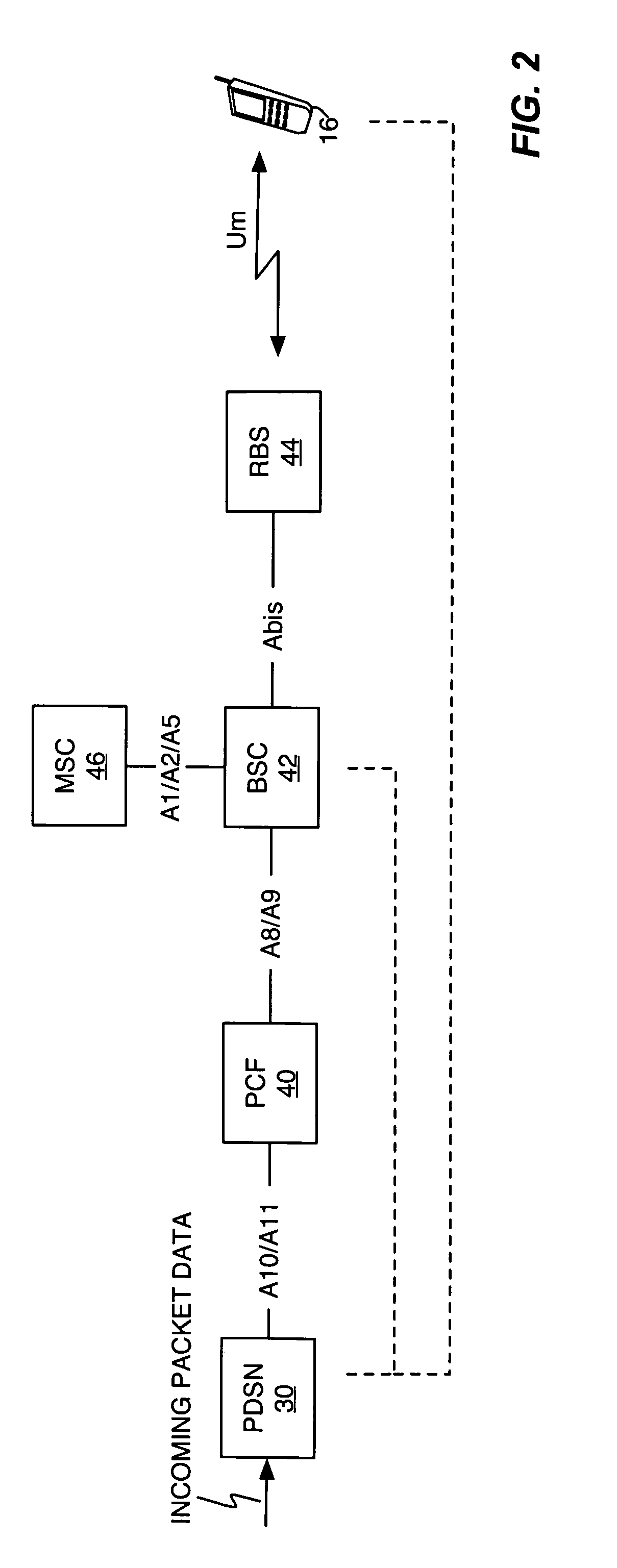
Method and apparatus for network imposed packet data flow control
ActiveUS20050226154A1Shorten the timeError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionPacket data serving node
A method and apparatus provide network-based flow control for mobile station having data connections to the network. In an exemplary embodiment, a Packet Control Function (PCF) in a Radio Access Network (RAN) requests that a Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) in a Packet Core Network (PCN) turn flow control on and off as needed for mobile station data connections. That is, if the PCF receives data from the PDSN for delivery to a mobile station that the PCF determines to be unavailable, the PCF requests that data transfers from the PDSN be suspended for that mobile station. Such suspension avoids needless continued transfer of undeliverable data to the PCF. The PCF monitors or otherwise determines whether a flow-controlled mobile station has become available again and, if so, notifies the PDSN so that it can lift the suspension and resume data transfers as needed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
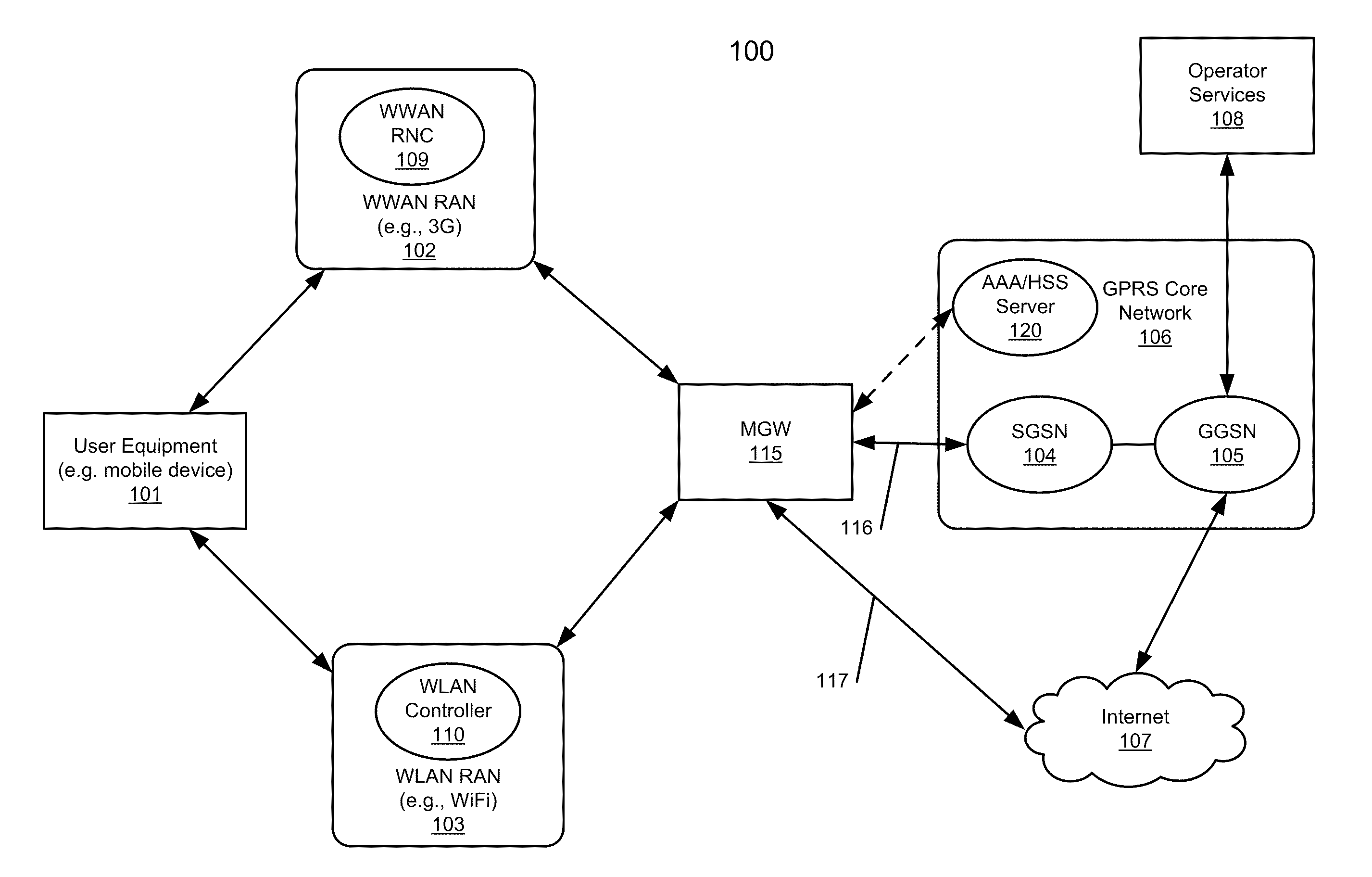
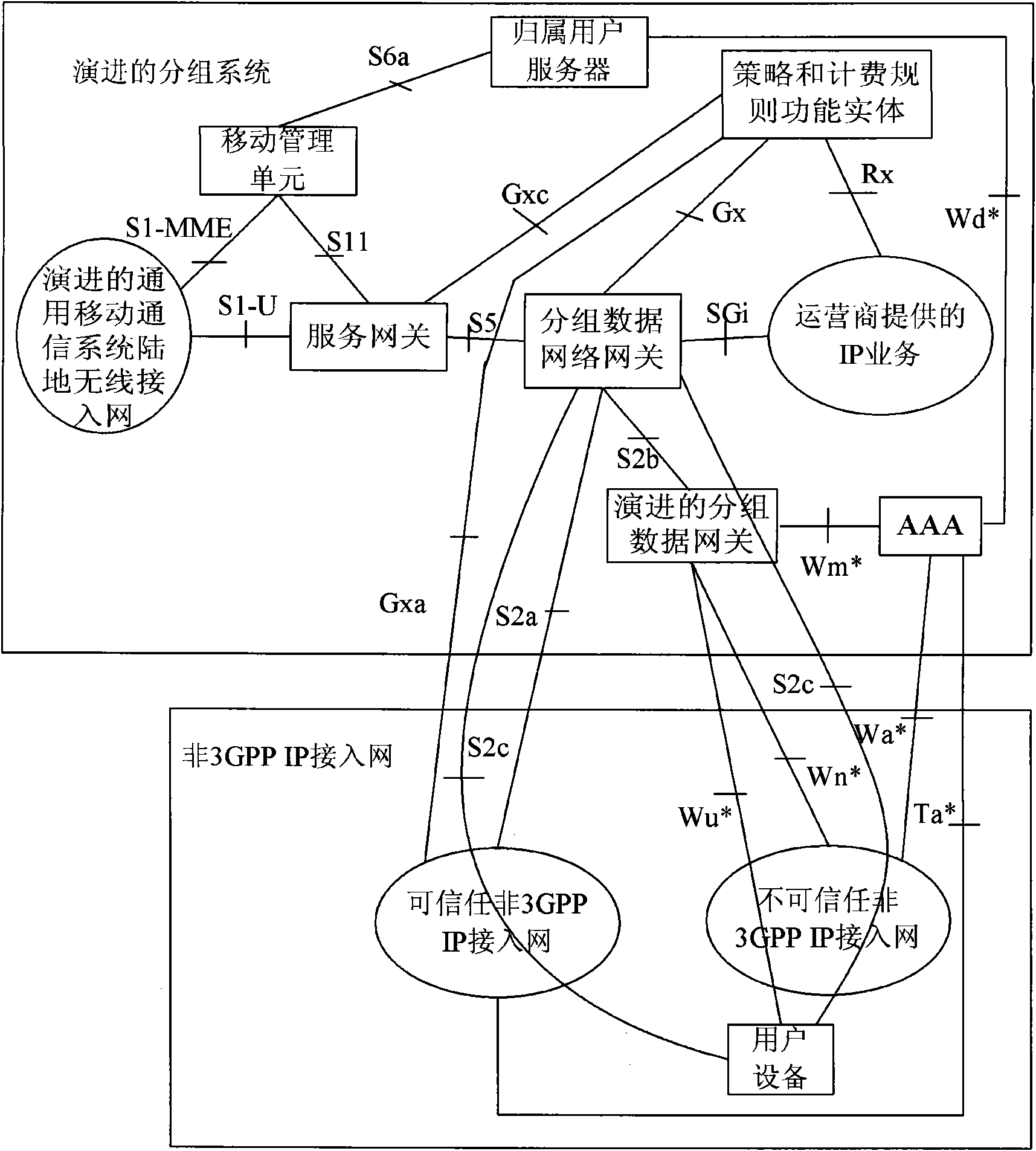
Method and system for interworking a WLAN into a wwan for session and mobility management
ActiveUS20120008578A1Connection managementData switching by path configurationIp addressThe Internet
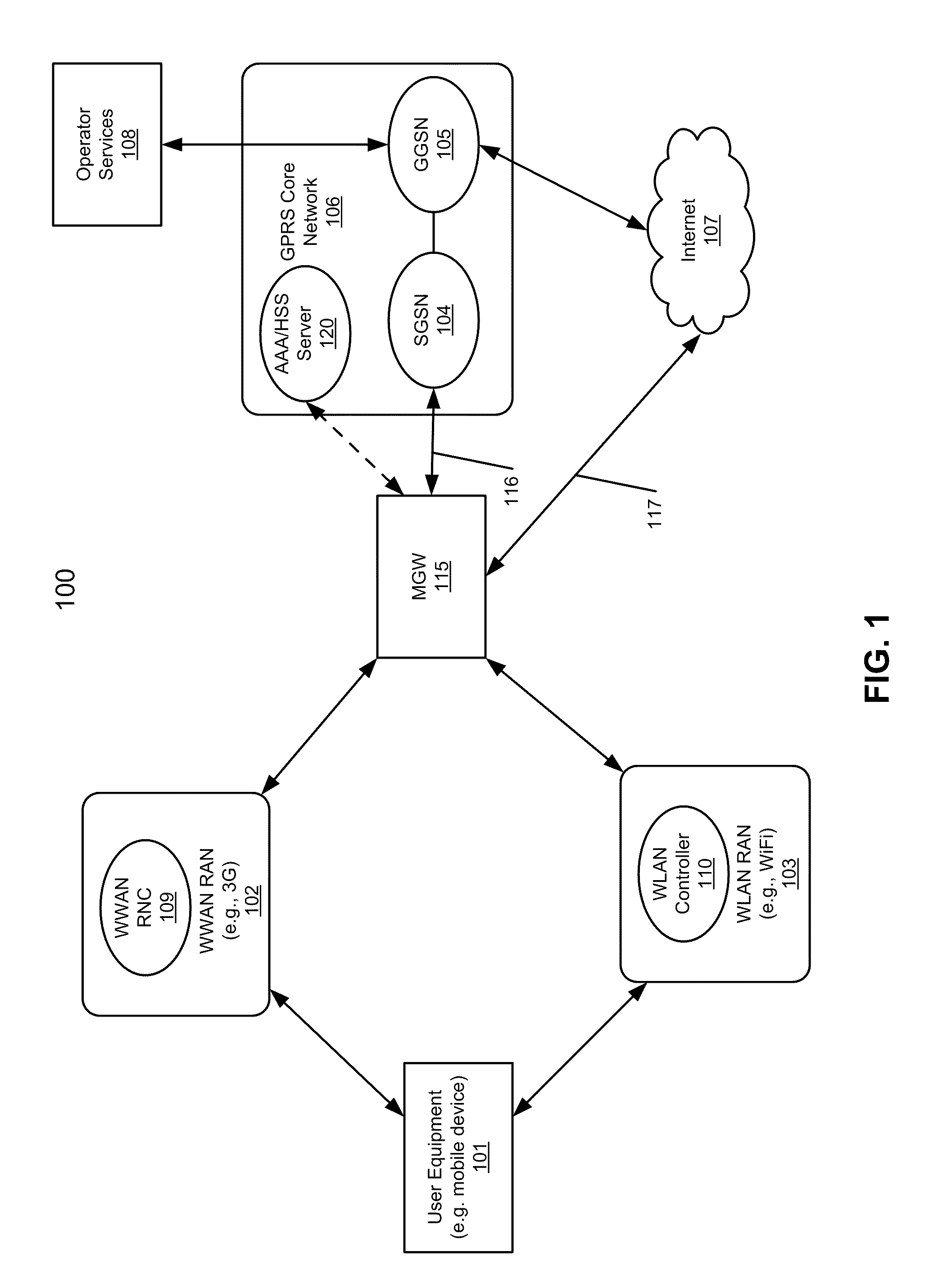
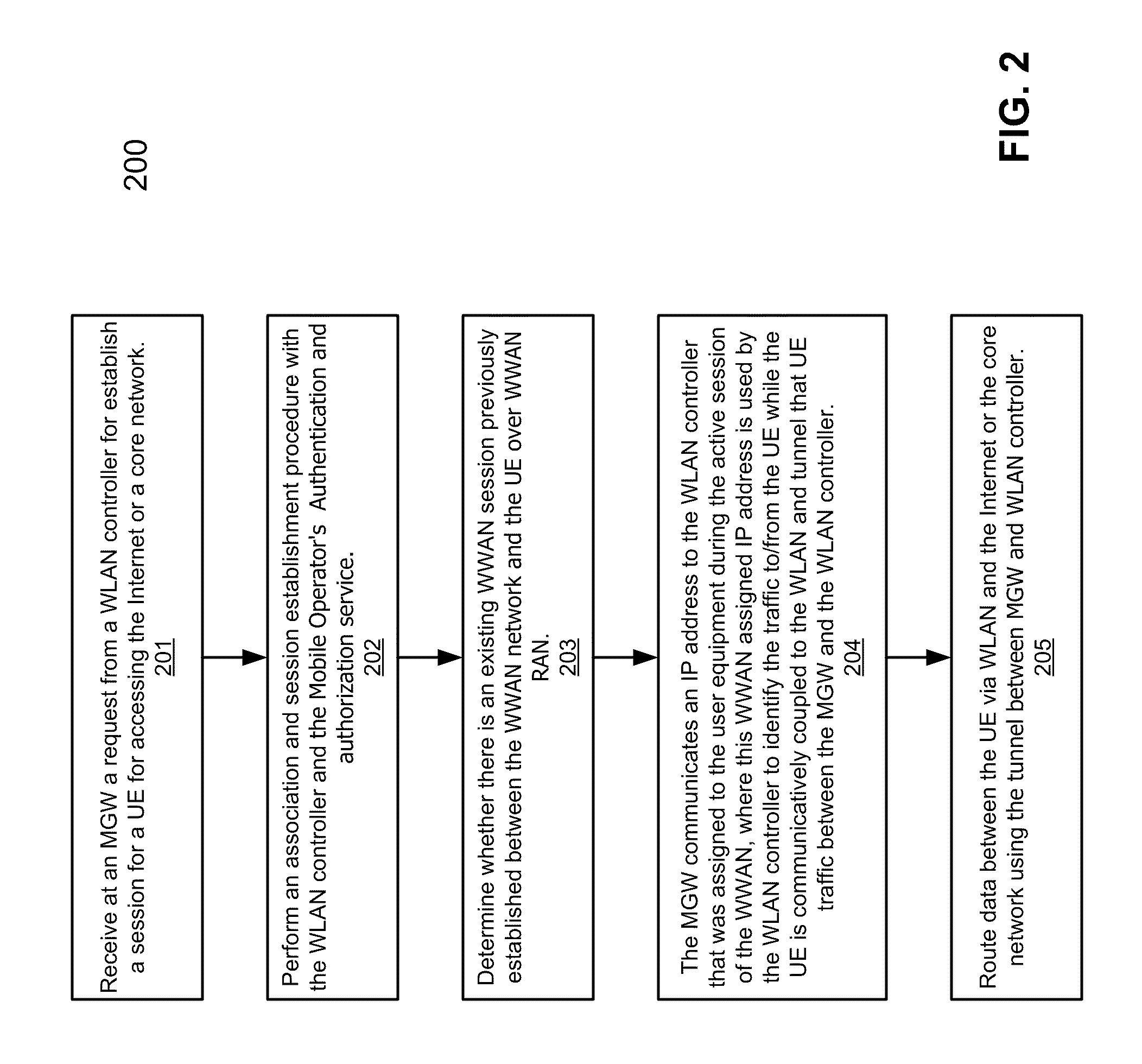
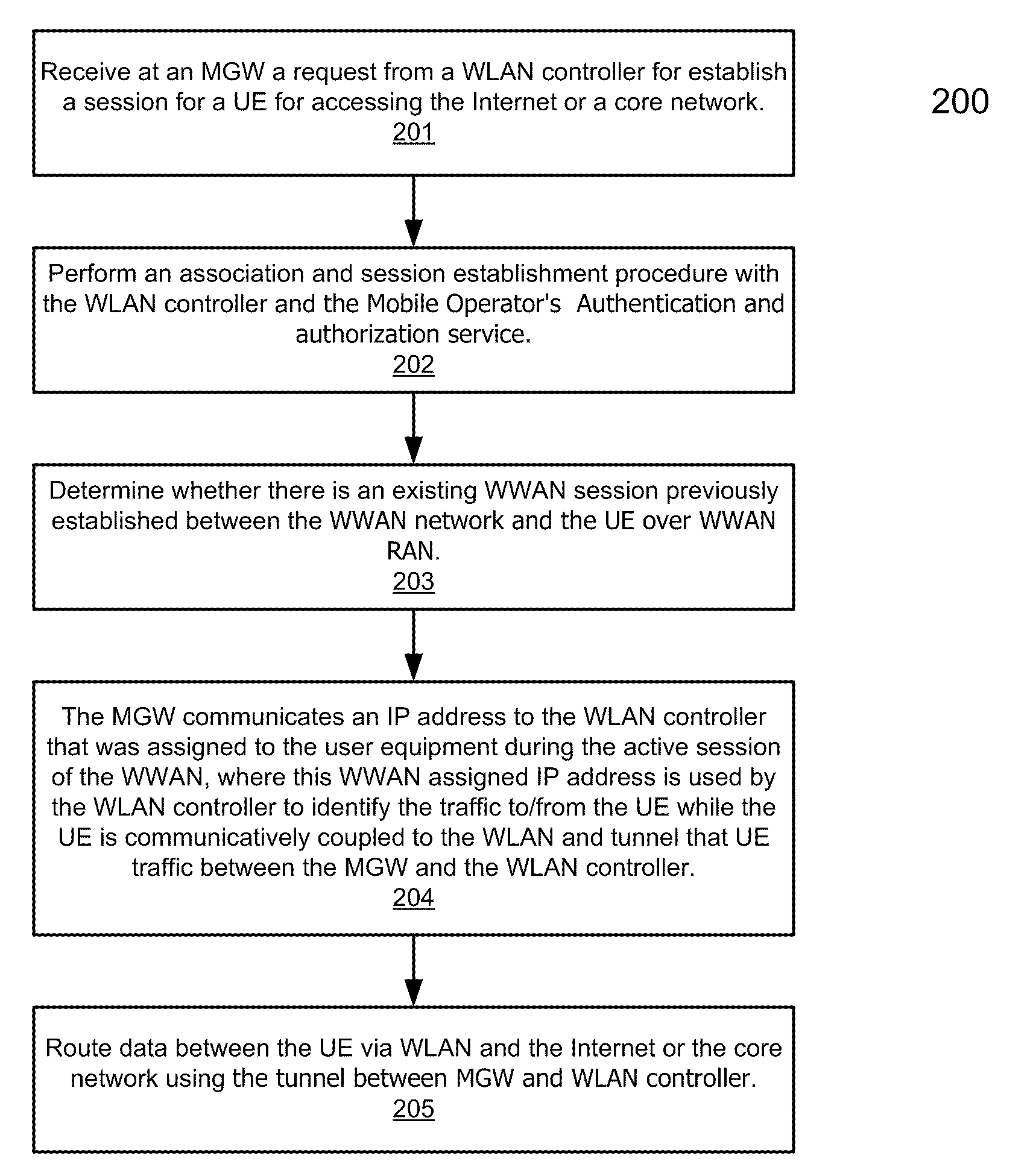
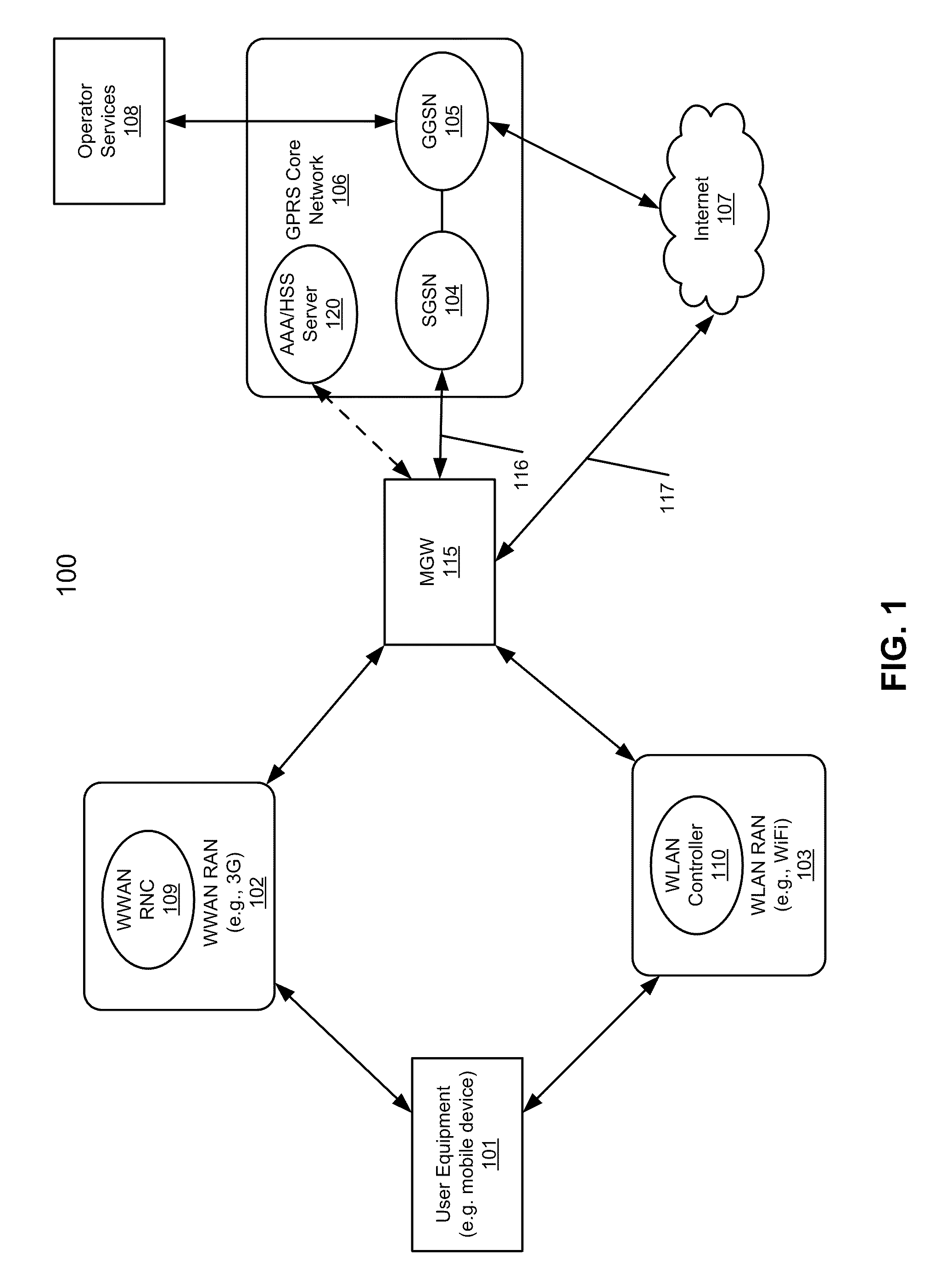
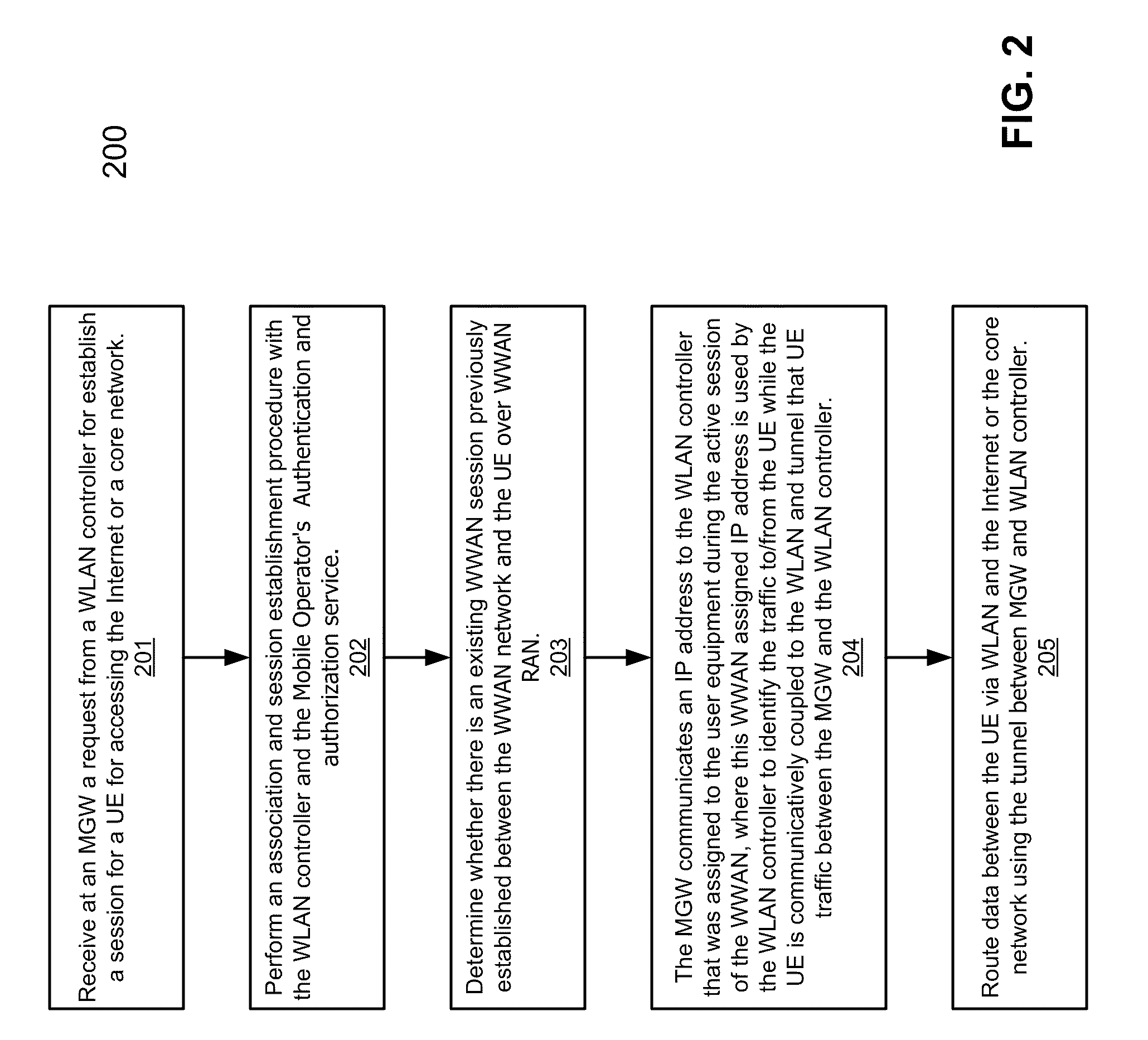
According to one aspect, a mobility gateway device (MGW) receives a request from a wireless local area network (WLAN) controller of a WLAN for accessing the Internet or a packet core network, where the request is originated from a user equipment communicatively coupled to the WLAN. In response to the request, the MGW is configured to determine whether there is an active session associated with the UE over a wireless wide area network (WWAN). If so, the MGW assigns an IP address to the UE that was assigned to the UE during the active session of the WWAN. The assigned IP address is used by the UE to access the Internet or the packet core network over the WLAN.
Owner:MAVENIR SYST INC
Method and system for interworking a WLAN into a WWAN for session and mobility management
According to one aspect, a mobility gateway device (MGW) receives a request from a wireless local area network (WLAN) controller of a WLAN for accessing the Internet or a packet core network, where the request is originated from a user equipment communicatively coupled to the WLAN. In response to the request, the MGW is configured to determine whether there is an active session associated with the UE over a wireless wide area network (WWAN). If so, the MGW assigns an IP address to the UE that was assigned to the UE during the active session of the WWAN. The assigned IP address is used by the UE to access the Internet or the packet core network over the WLAN.
Owner:MAVENIR SYST INC
Method and apparatus of communicating packet data units in a wireless network environment and system using thereof
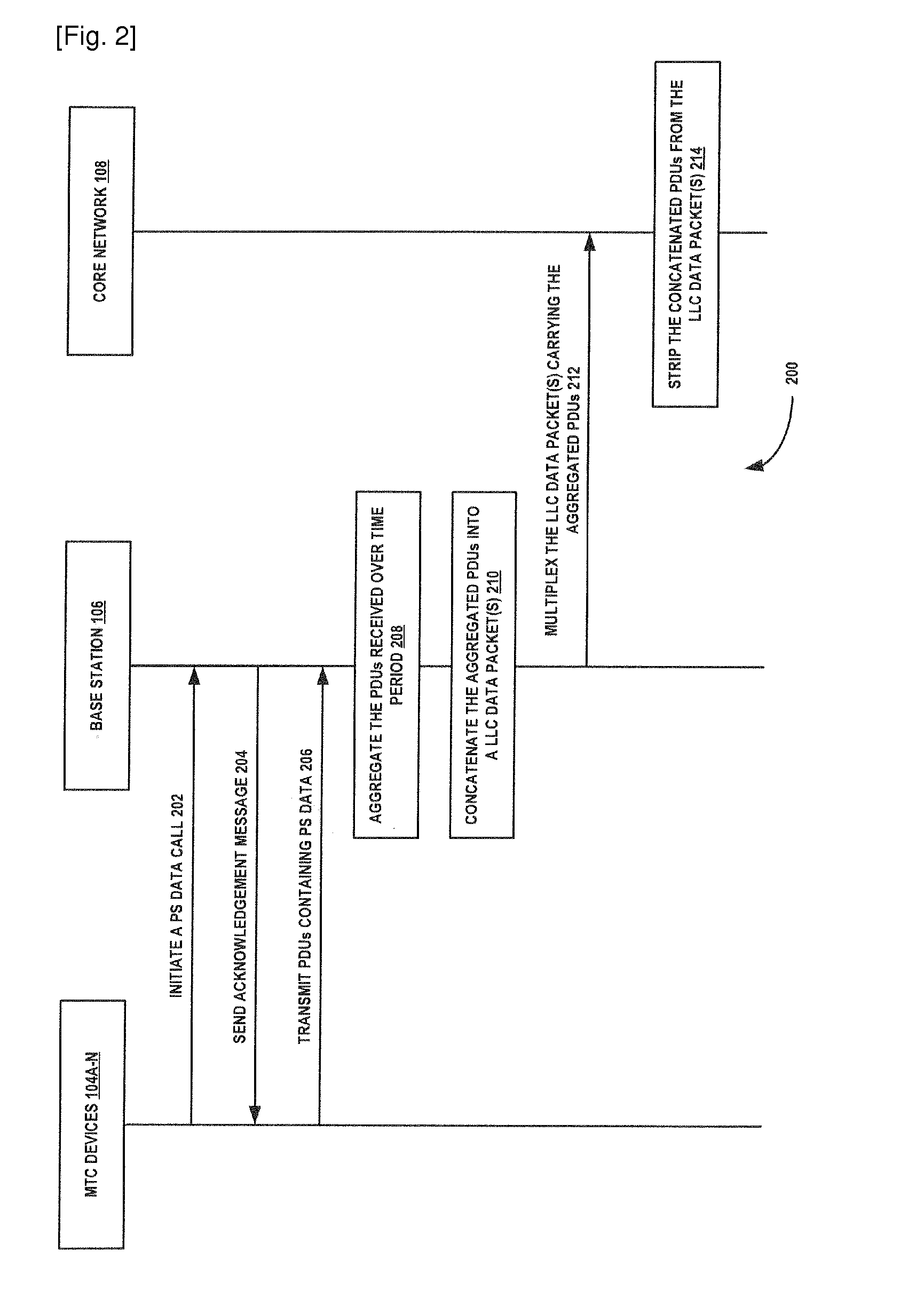
InactiveUS20130136064A1Network traffic/resource managementWireless commuication servicesSingle sessionLogical link control
A method and system for communicating packet data units over a Gb interface in a wireless communication environment is provided. Packed Data Units (PDUs) are received from Machine Type Communication (MTC) device(s) by a base station coupled to the MTC device(s). Then, the PDUs are aggregated over a period of time by the base station. Further, the aggregated PDUs are packed in at least one Logical Link Control (LLC) data packet. The at least one LLC data packet including the aggregated PDUs is multiplexed over a Gb interface in a single session between the base station and a packet core network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flow control method and system for wireless network
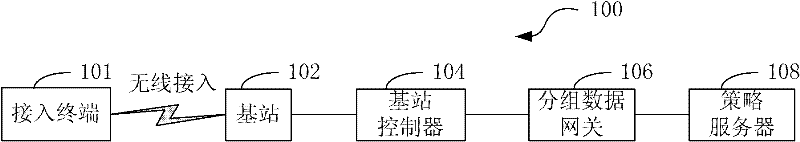
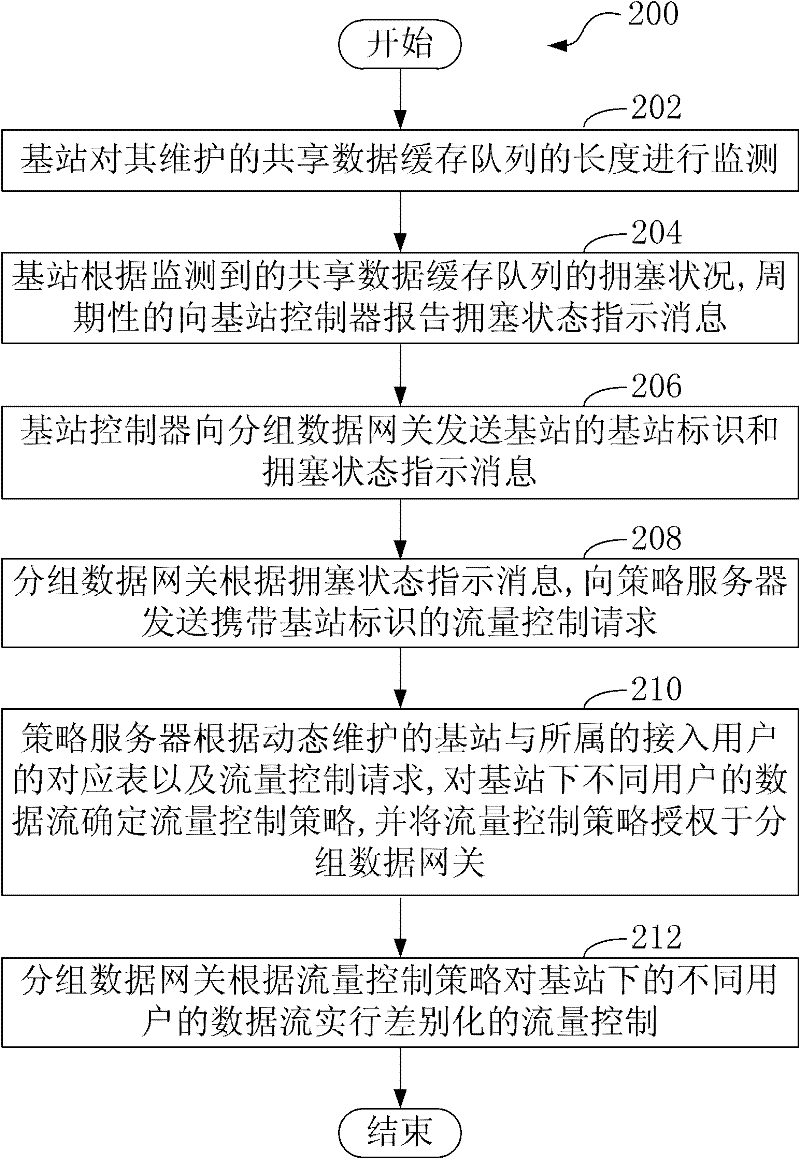
ActiveCN102300264AImprove differentiated service performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementData streamPacket core network
The invention, which relates to the communication technology, provides a flow control method and a system thereof for a wireless network. The flow control method comprises the following steps that: a base station monitors a length of a shared data buffer queue that is maintained by the base station, wherein the shared data buffer queue comprises all downstream user flows that are from a packet core network and belong to the base station; according to a monitored congestion state of the shared data buffer queue, the base station reports indication information on the congestion state to a base station controller; the base station controller transmits a congestion state indication through a signaling protocol of a packet data gateway, wherein the signaling protocol is established between the base station controller and the core network; and the packet data gateway sends a flow control request to a strategy server; the strategy server determines flow control strategies for data flows of different users under the base station; and the packet data gateway carried out flow controls on data flows of the different users according to the flow control strategies. According to the invention, on the basis of monitoring on a congestion state of a shared data buffer queue by a base station, a strategy server and a packet data gateway can carry out differential flow controls on data flows of different users.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Fast WIFI to LTE handover
ActiveUS20160080981A1LatencyAvoid signalingWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyComputer science
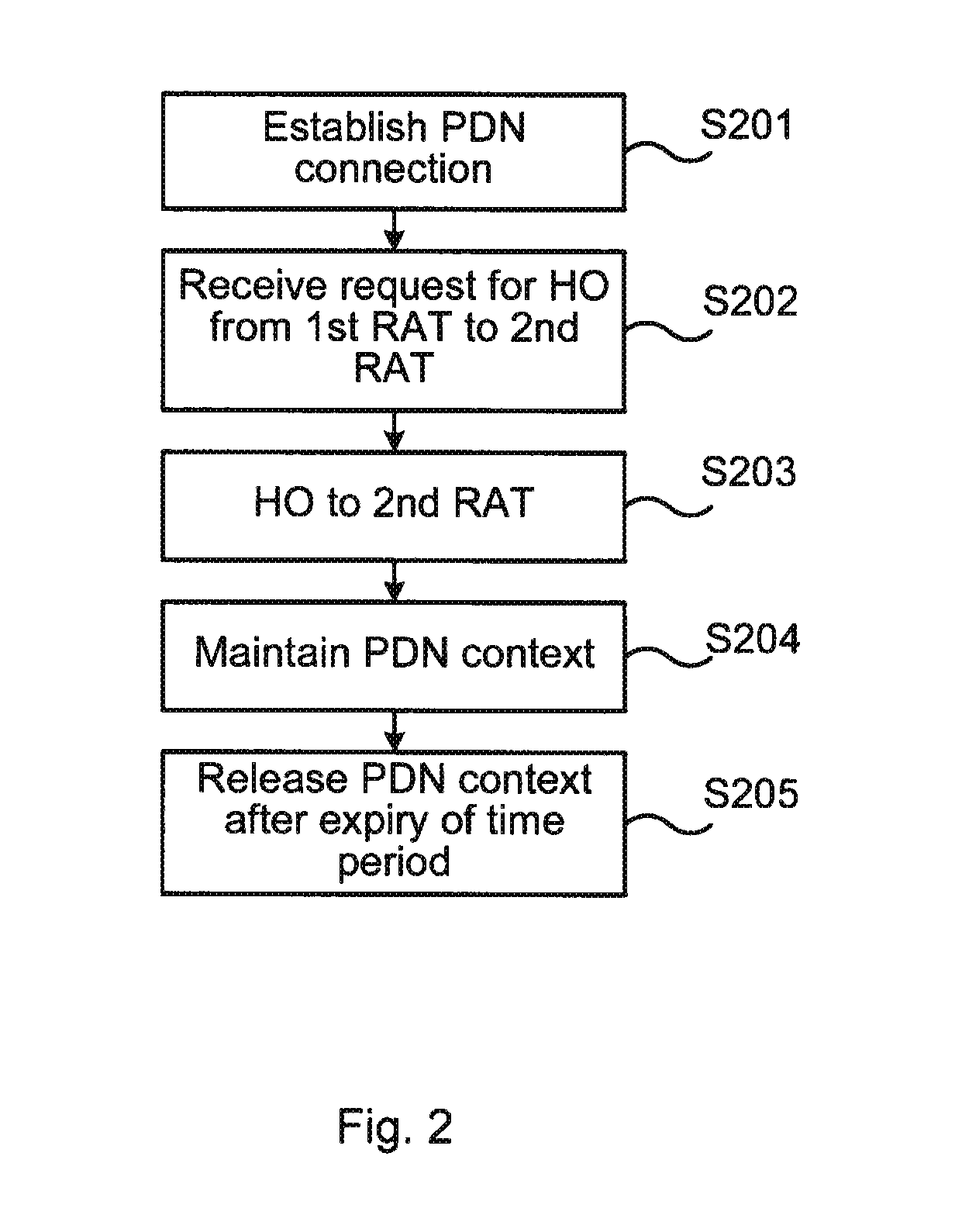
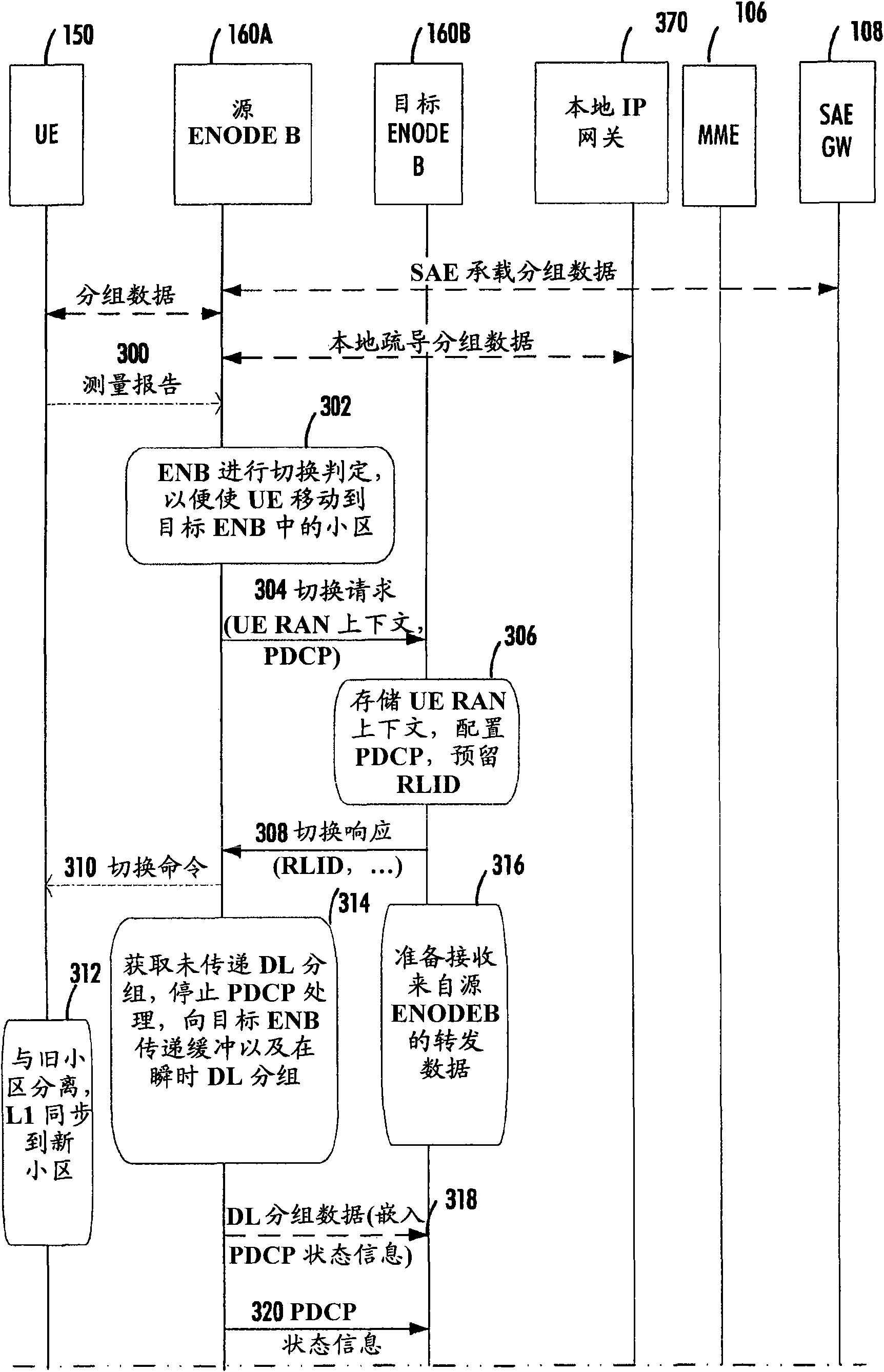
The present invention relates to a network node and a method at the network node of handing over a mobile terminal between a first RAT and a second RAT in a wireless communications network. The invention further relates to a computer program performing the method according to the present invention, and a computer program product comprising computer readable medium having the computer program embodied therein.A method at a network node of a packet core network of performing handover of a mobile terminal between a first Radio Access Technology (RAT), and a second RAT in a wireless communications network is provided in an embodiment of the present invention. The method comprises receiving a request for handover of the mobile terminal to the second RAT, establishing a PDN connection with the mobile terminal via the first RAT, and performing handover of the mobile terminal to the second RAT. The method further comprises maintaining PDN connection context for the PDN connection established via the first RAT for a time period, and releasing the PDN connection context at expiry of the time period.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
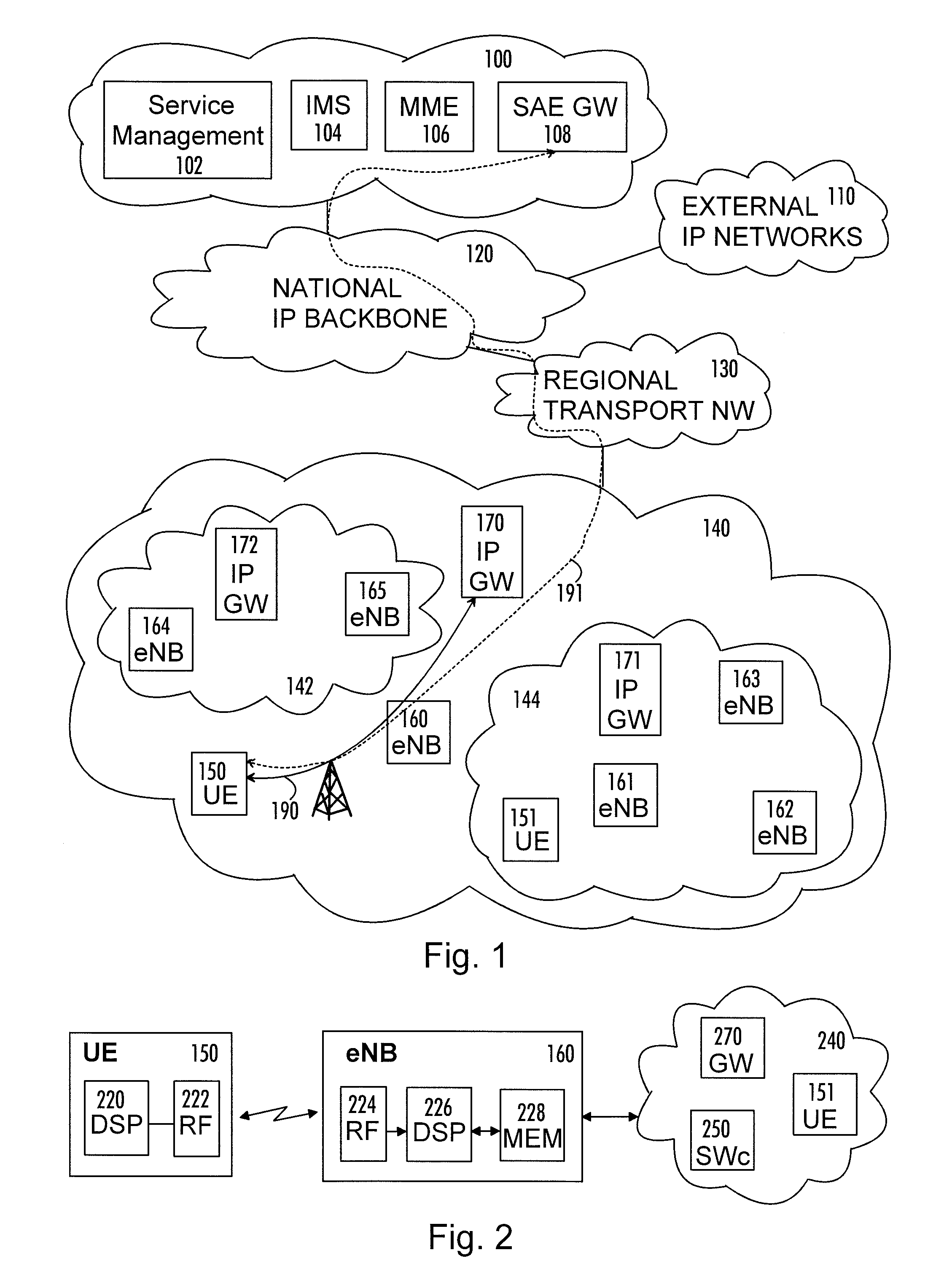
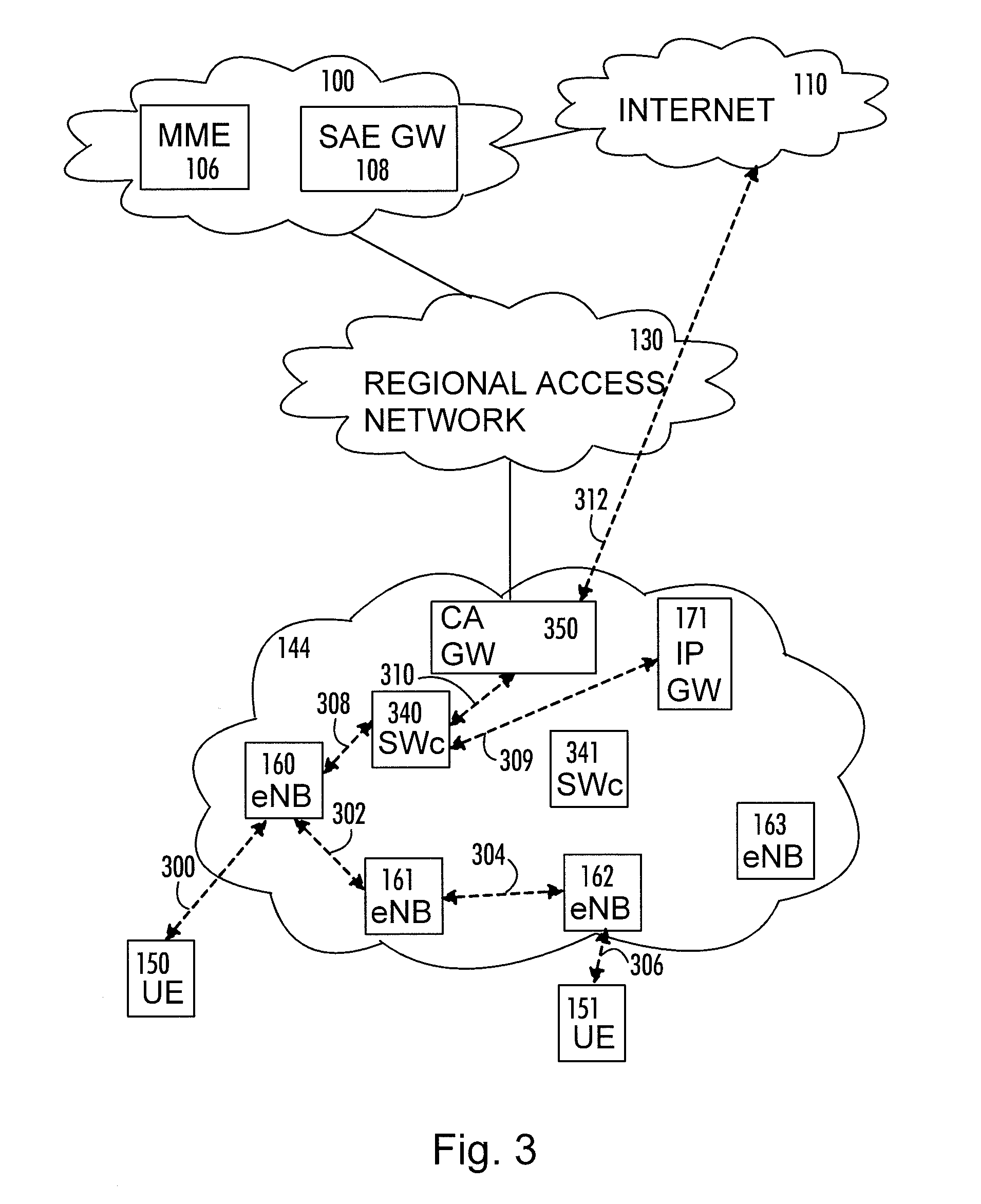
Method, radio system, and base station
There is provided a radio system comprising: one or more base stations of a public mobile network, at least one mobile terminal communicating with the one or more base stations, and a local breakout service network providing Internet protocol gateway services. A serving base station of a mobile terminal is configured to provide the local breakout service to the Internet protocol gateway while retaining user access control and a remote Internet protocol gateway of a packet core network of the public mobile network for the mobile terminal; to provide information on neighboring cells in which the local breakout service can continue; to make a handover decision based on measurement reports received from the mobile terminal; and to transfer user context data including local breakout ser-vice related information to a target base station during handover for providing mobility within the local breakout service area for the mobile terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method, radio system, mobile terminal and base station for providing local breakout service
ActiveUS8462696B2Network topologiesData switching by path configurationTTEthernetPacket core network
There is provided a radio system wherein a mobile terminal is configured to detect availability of a local breakout service to an Internet protocol gateway; to start a network entry to the local breakout service; and to configure an Internet protocol stack of the mobile terminal on the basis of received configuration data. A serving base station of the mobile terminal is configured to establish a radio bearer for the local breakout service; to provide a dynamic host control protocol relay function for mapping data of the mobile terminal using a local Internet protocol address to the established radio bearer; and to provide the local breakout service to the Internet protocol gateway while retaining user access control and a remote Internet protocol gateway of a packet core network of the public mobile network for the mobile terminal.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
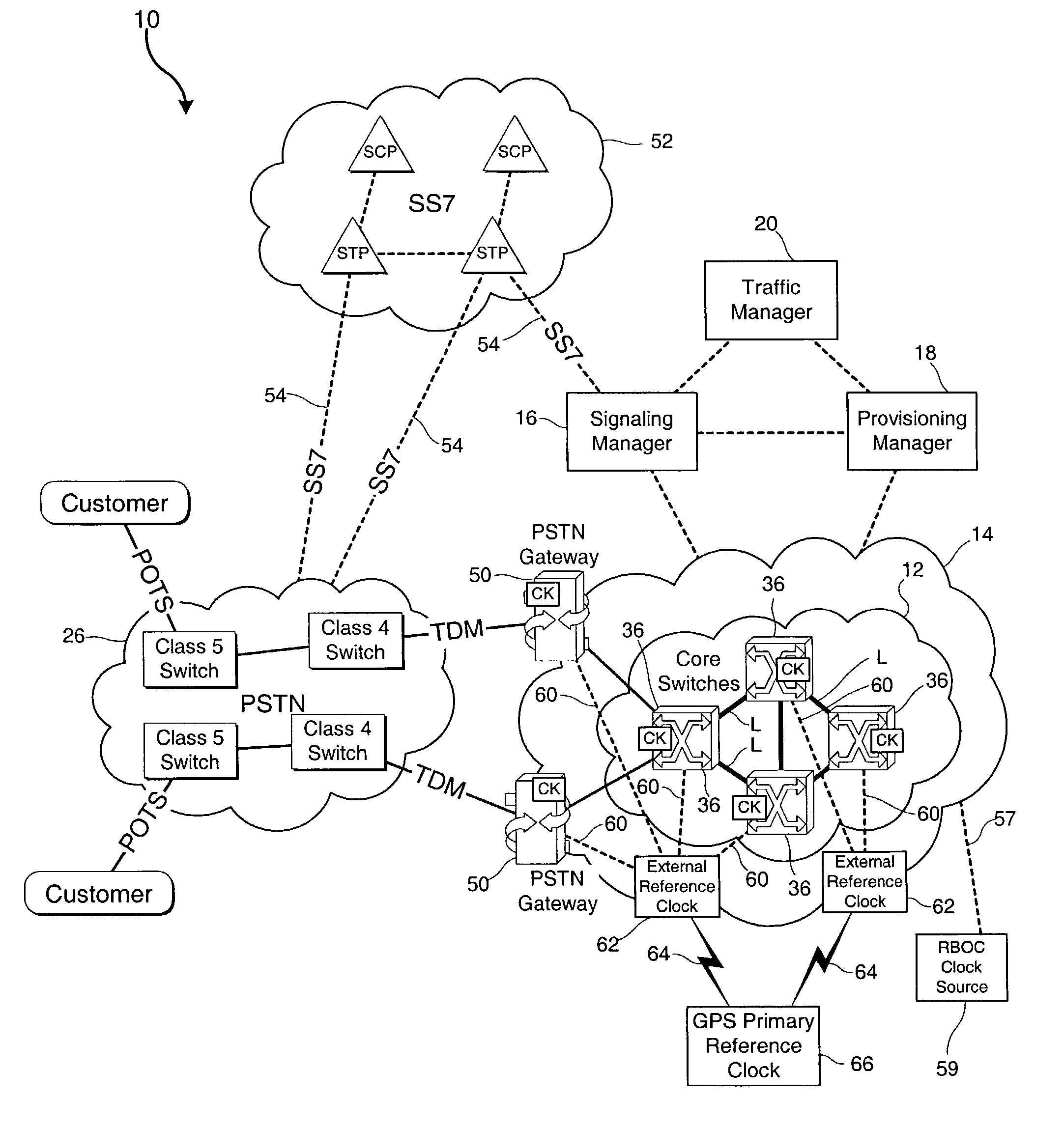
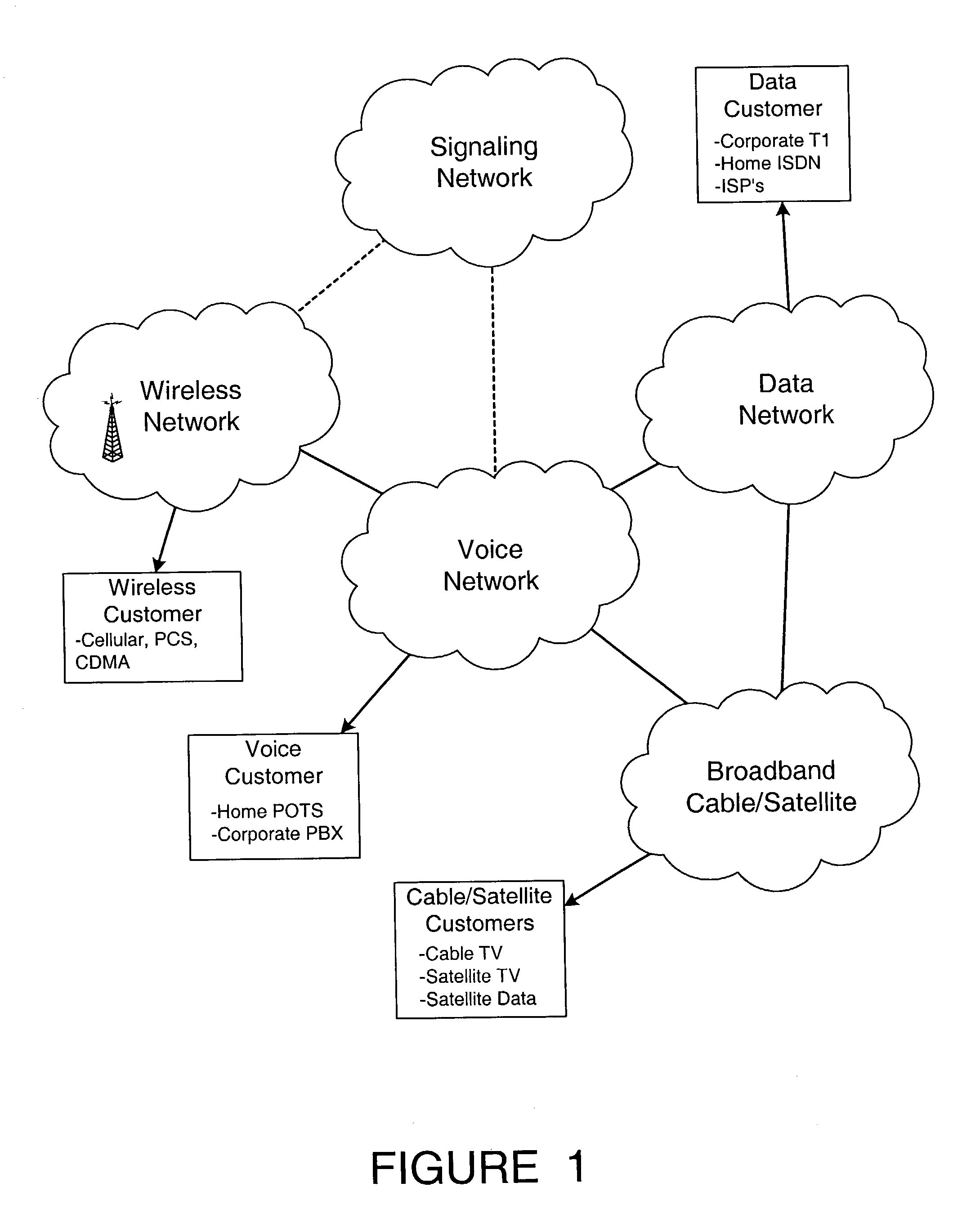
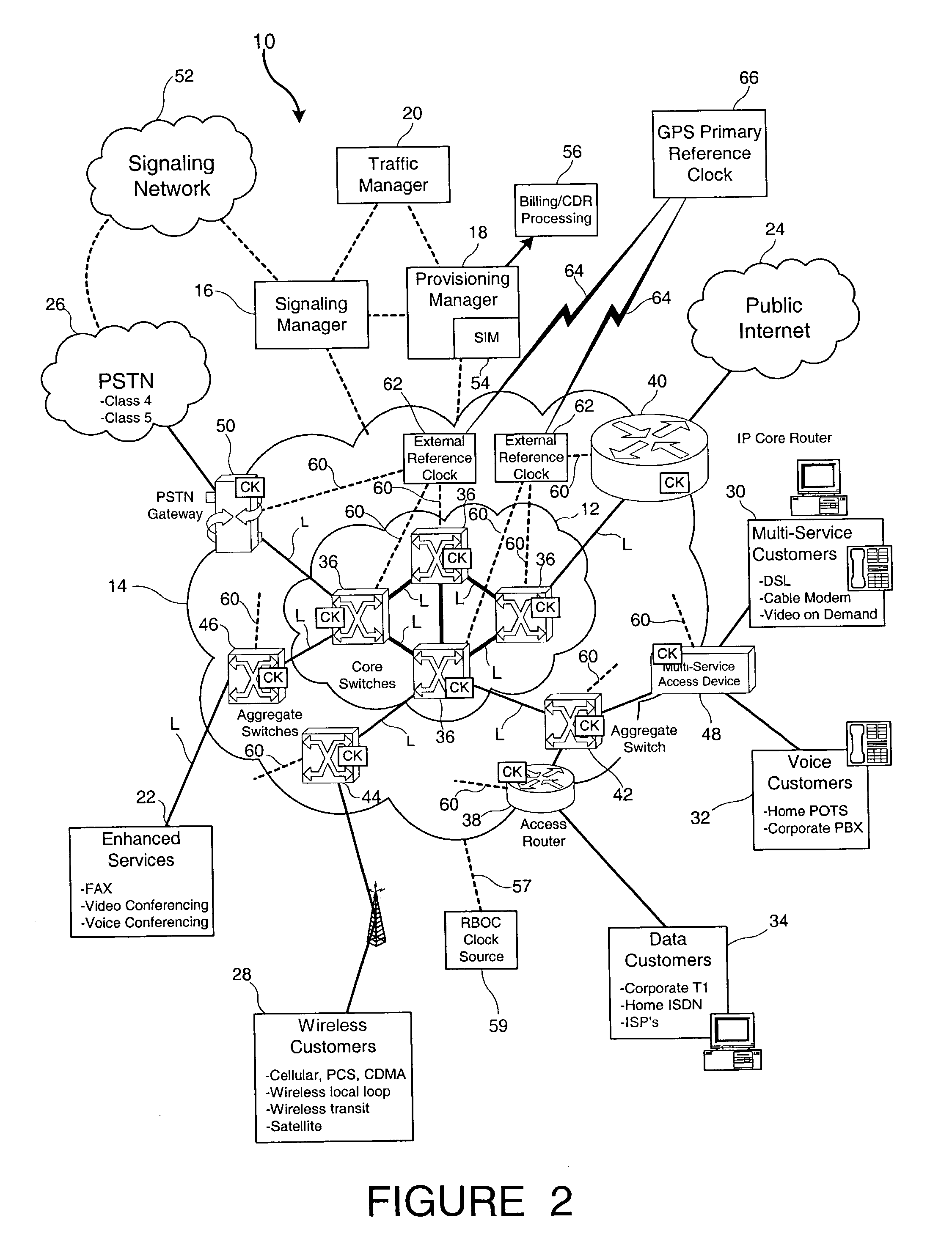
Traffic manager, gateway signaling and provisioning service for all packetized networks with total system-wide standards for broadband applications including all legacy services
InactiveUS7190676B2Improve performanceMaximum network efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLow speedNetwork management
Broadband integrated services are performed via digital, channelized or optically coded networks by a system which organizes, interfaces, provisions, loads and controls, in real time, the transport of grouped or organized information (such as packetized cell data) through interface access devices and packet switches that are compliant with domestic and international communication standards. A packet core network includes multiple packet switches and interface access devices coupled to an existing narrowband or broadband network. A signaling manager, a provisioning manager and a traffic manager perform all broadband and narrowband routing, port provisioning and connecting functions for all network devices. A set of software interface modules for each equipment vendor allows the provisioning manager, the signaling manager and the traffic manager to impose control demands and make network management decisions on a real time basis via an application protocol interface. Bit error rate caused by the disparity between low speed (such as TDM) networks and high speed (such as OCR) networks is substantially reduced by synchronizing the overall network and all switching components to a primary reference clock that has an accuracy of 1×10−11 second per month or better.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
On IP fragmentation in gtp tunnel
ActiveUS20120155460A1Reduce processing timeReduce the numberNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementComputer networkIP fragmentation
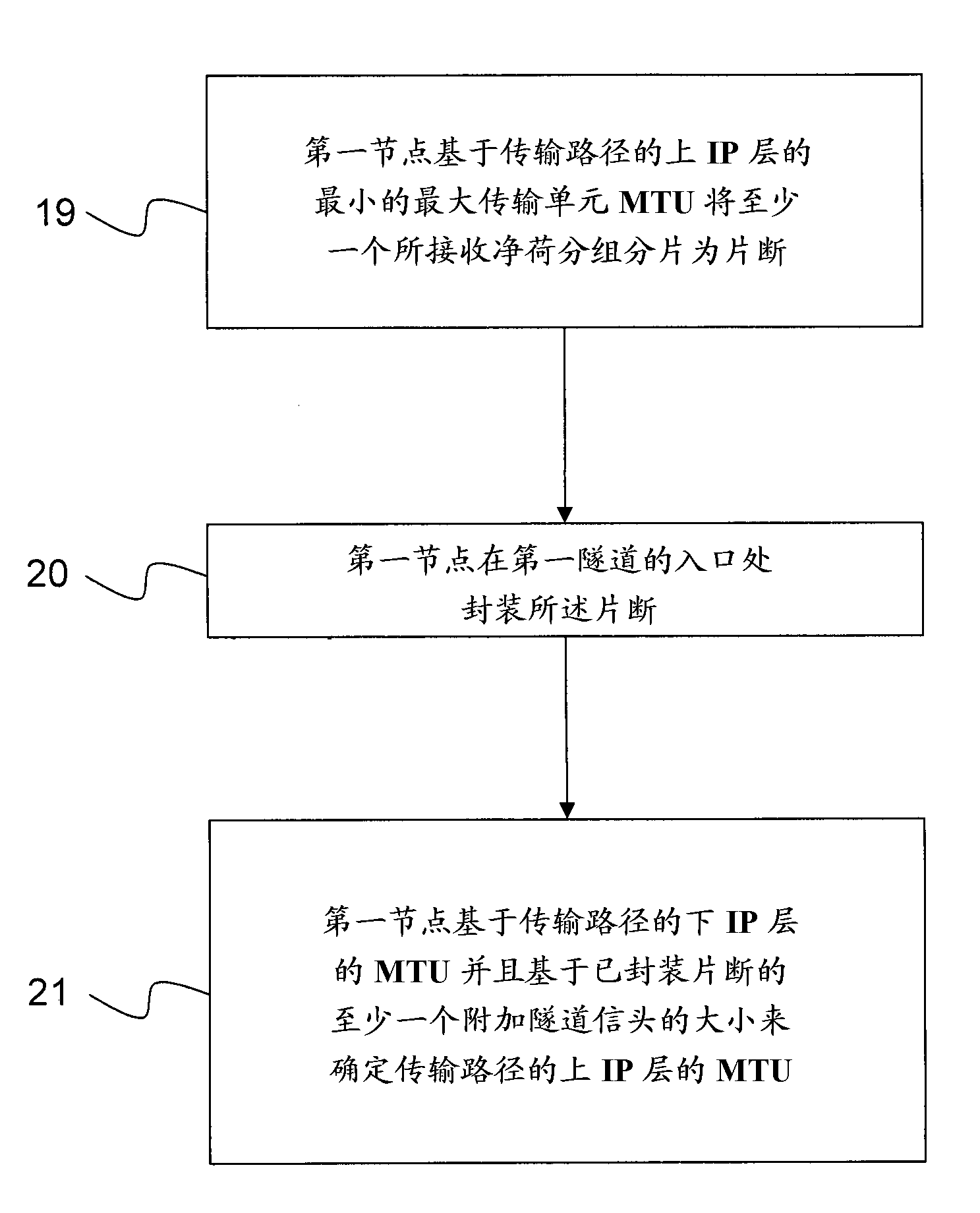
The present invention relates to a method for improving IP fragmentation and transmission of user payload between a User Equipment, UE 10, and a Peer Node, PN 14. The payload is transmitted through a transmission path enabled by at least a first 17,18 and a second 17,18 established tunnel, said tunnels connecting a first 11, 13 and a second 11,13 node in a Packet Core Network, PCN. The method comprises the steps of:The first node 11,13 fragments 19 at least one received payload packet 15 into fragments 16 on the basis of a minimum Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU, for an upper IP layer of the transmission path.The first node 11,13 encapsulates 20 said fragments at the entry of the first tunnel 17,18. What particularly characterizes the method is that it further comprises a step where the first node 11,13 determines 21 the MTU for the upper IP layer of the transmission path on the basis of an MTU of a lower IP layer of the transmission path and on the basis of the size of at least one additional tunnel header for the encapsulated fragments 16.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for bypassing 3GPP packet switched core network when accessing internet from 3GPP UES using 3GPP radio access network
Techniques for bypassing a packet core network for Internet bound traffic from user equipment (UE) via a RAN are described herein. According to one embodiment, it is determined whether a packet of data is destined for the Internet, in response to receiving the packet from a radio network controller (RNC) of a radio access network (RAN). The packet is originated from user equipment (UE) over the RAN. The packet is routed directly to the Internet without sending the packet to an SGSN (serving GPRS support node) of a packet core network, if the packet is destined to the Internet. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:MAVENIR SYST INC
Method, radio system, and base station
ActiveUS8503393B2Support mobilityNetwork topologiesConnection managementRadio networksExchange network
There is provided a method including providing a local breakout service to an Internet protocol gateway while retaining user access control and a remote Internet protocol gateway of a packet core network of a radio network for a mobile terminal; providing information on neighboring macro cells in which the local breakout service can continue, the macro cells belonging to a network using another tracking area than that of the serving cell of the mobile terminal; executing a handover process of the mobile terminal from a source base station in the serving cell of the mobile terminal to a target base station in a neighboring macro cell; and providing session continuation of the mobile terminal local breakout service traffic in the neighboring macro cell by controlling user plane tunneling between the target base station and the local packet switched network from which an Internet protocol address for the local breakout service was assigned.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method and system for bypassing 3GPP packet switched core network when accessing internet from 3GPP UEs using IP-BTS, femto cell, or LTE access network
Owner:MAVENIR SYST INC
Method and system for realizing multi-access
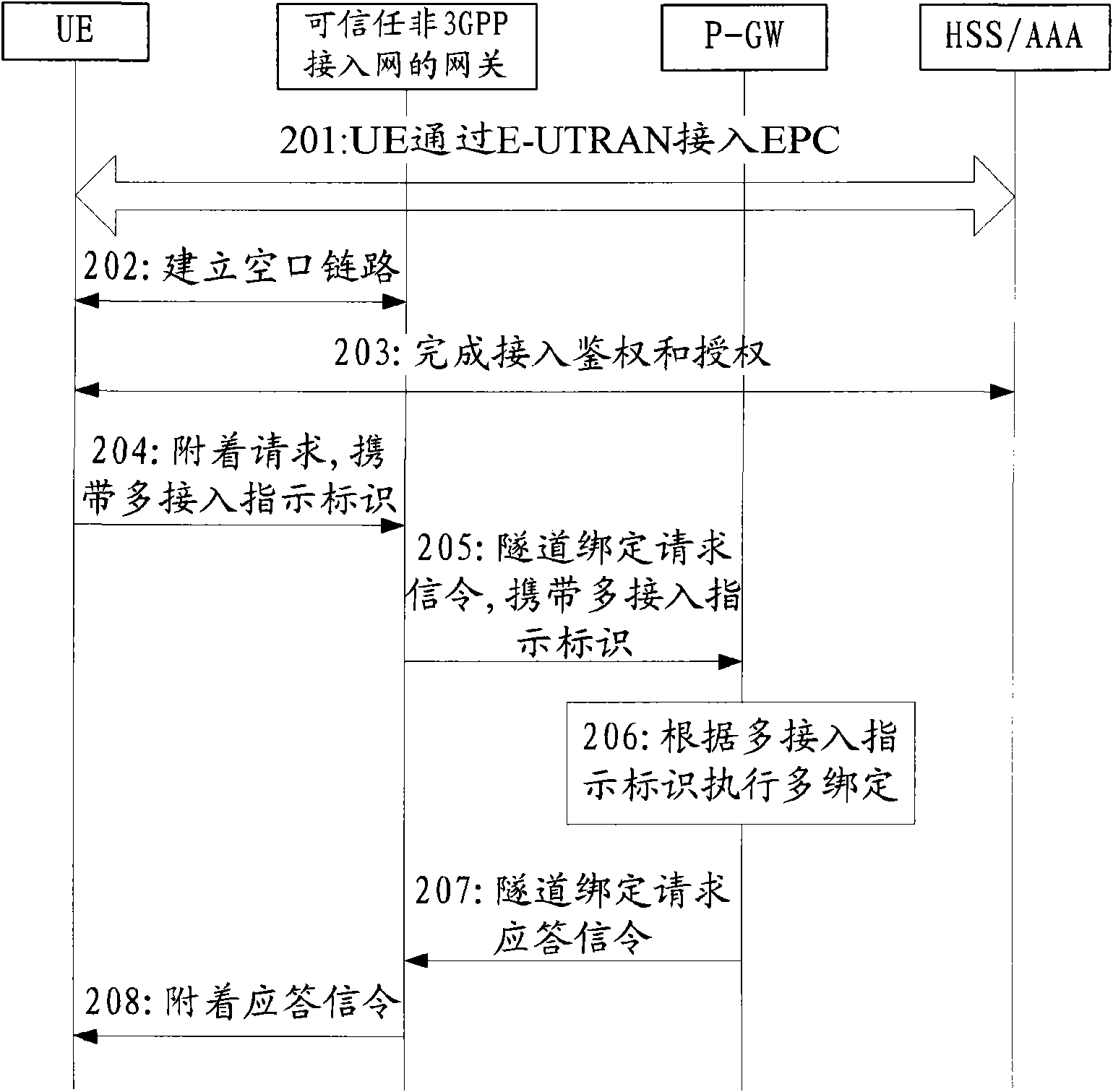
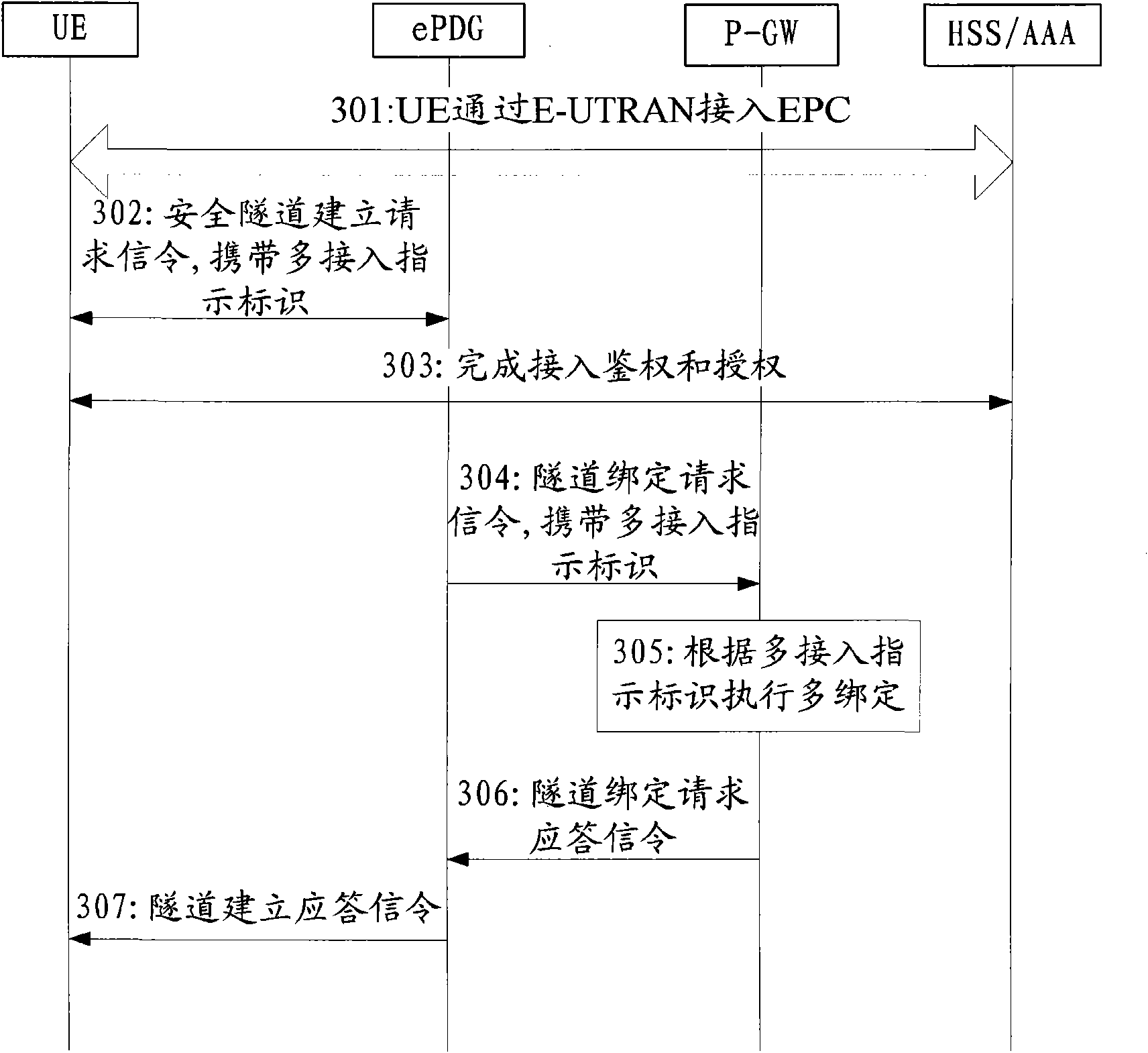
ActiveCN101577931AMultiple access implementationReduce the impactNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementAccess networkPacket data gateway
The invention discloses a method for realizing multi-access, which is applied in an evolved packet system EPS of a 3rd generation partnership project 3GPP. When user equipment UE gets access to a packet data network PDN through a first access network and then requests adhesion to an evolved packet core network EPC through a second access network, the UE tells a packet data gateway P-GW to perform the multi-binding of an access network gateway by carrying multi-access indicator identification in signaling sent for requesting adhesion; and the P-GW executes the multi-binding of a first access network gateway and a second access network gateway according to the received multi-access indicator identification. When the UE initiates adhesion to the EPC, the UE informs the P-GW about the adhesion as a multi-access scene, and the P-GW executes the multi-binding of a plurality of different access network gateways. The invention realizes the multi-access of the UE under the condition of having little influence on the access networks.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Network entity emigration method for grouping core network
ActiveCN101132612AAchieve migrationReduce the risk of dropped callsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationGPRS core networkAnchor point
This invention discloses a migration method for network entity of a packet core network including: A, T-eNodeB informs a UE to a source packet core network entity to finish switching from S-eNodeB to T-eNodeB and carries with a migration parameter in the notification, B, the source packet core network entity triggers migration according to said migration parameter and transmits context of the UE to a target packet core network entity, C, the source entity sends the address information of the target entity to the T-eNodeB and informs it to exchange service packet core network eitity, D, the T-eNodeB asks the target one to provide service, which carries out route update between anchor points with the access system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
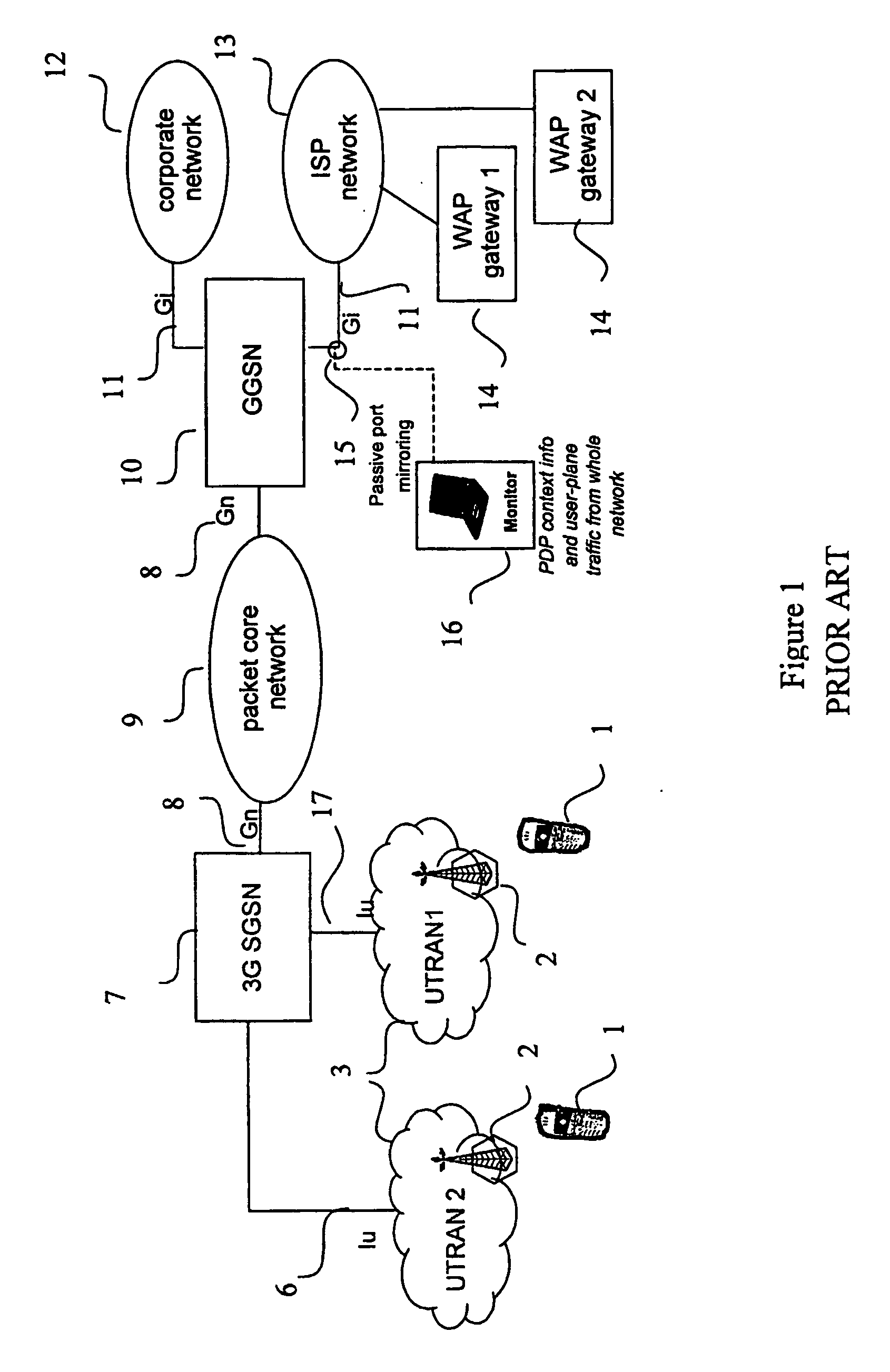
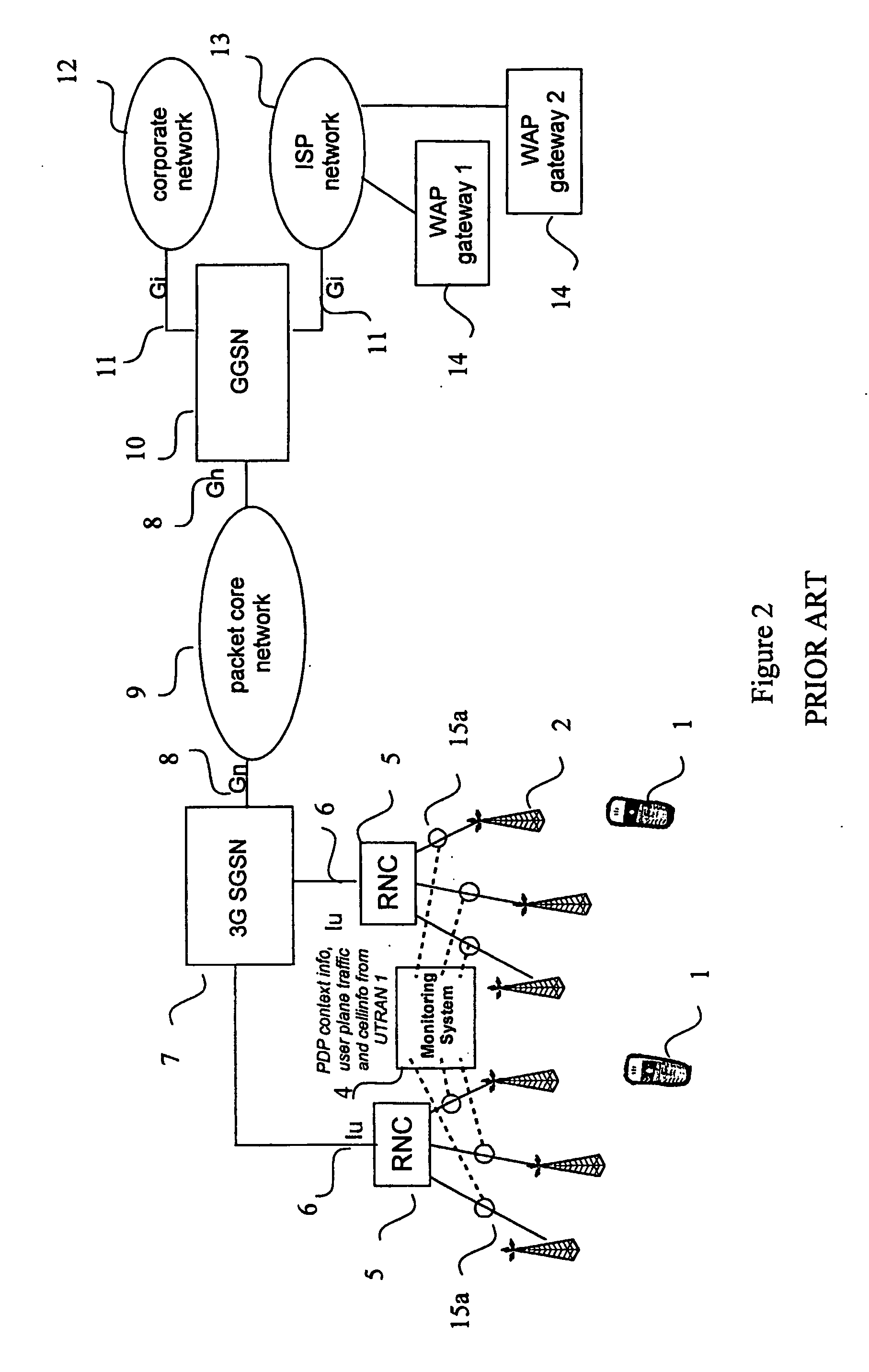
Location signaling for large-scale, end-to-end, quality-of-service monitoring of mobile telecommunication networks
ActiveUS20070082645A1Cost-efficient collectionReduce in quantityError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTelecommunications network
A method, network, and device for measuring and analyzing packet-switched traffic in a packet-switched radio telecommunication network. When cell-level location information for a mobile station (1) changes due to a handover, the location information is transmitted toward a packet core network (9) by adding the information to userplane packet headers such as a GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) header (26). The measurement device measures the cell-level location information at a level (15b) in the network where the information from a plurality of mobile stations (1) is aggregated, together with PDP context information prior to analyzing information for the entire network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
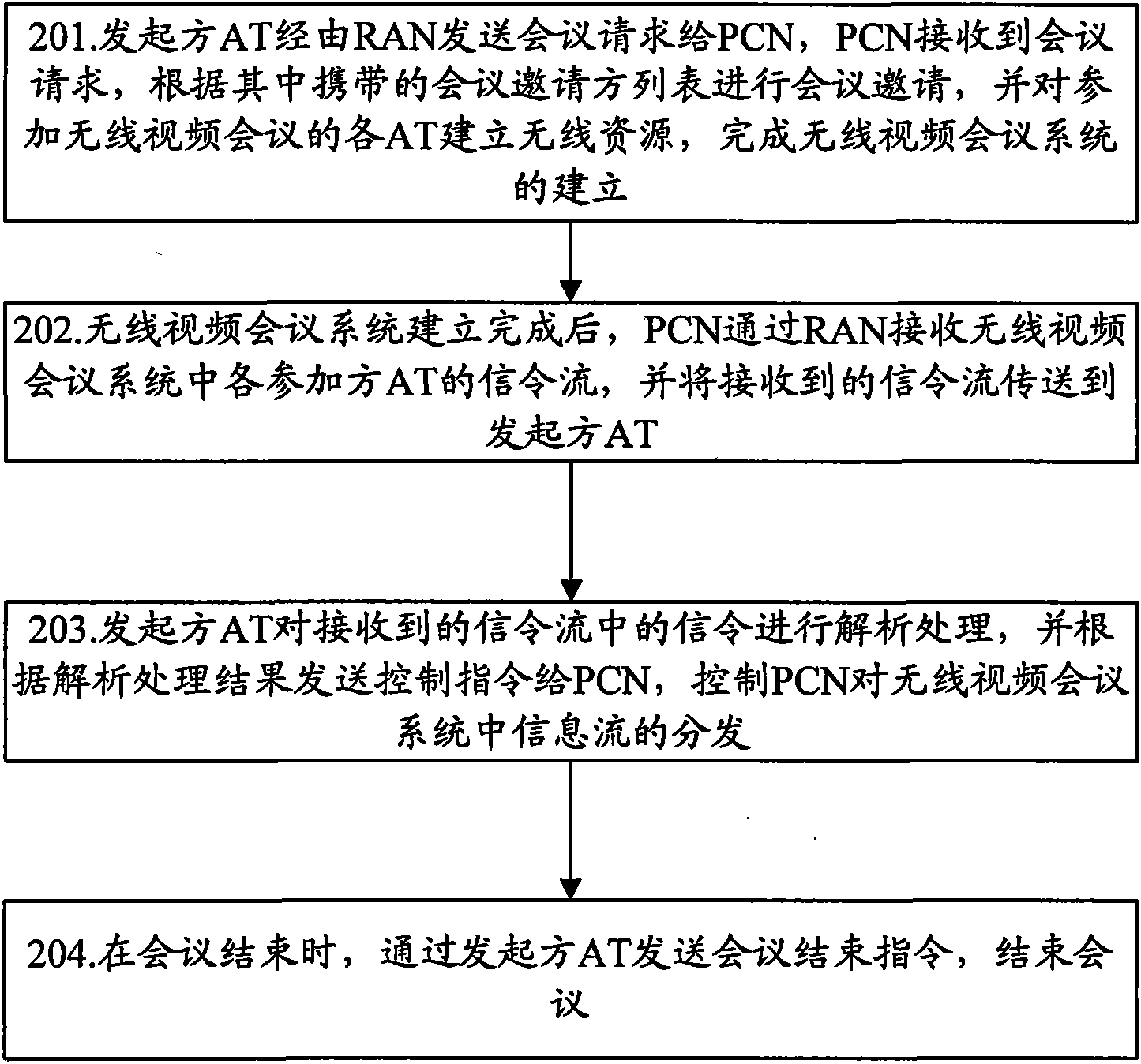
Method for realizing wireless video conference, system thereof and terminal thereof
ActiveCN101610382AAssurance controlRealize safe and reliableTelevision conference systemsConnection managementWireless videoPacket core network
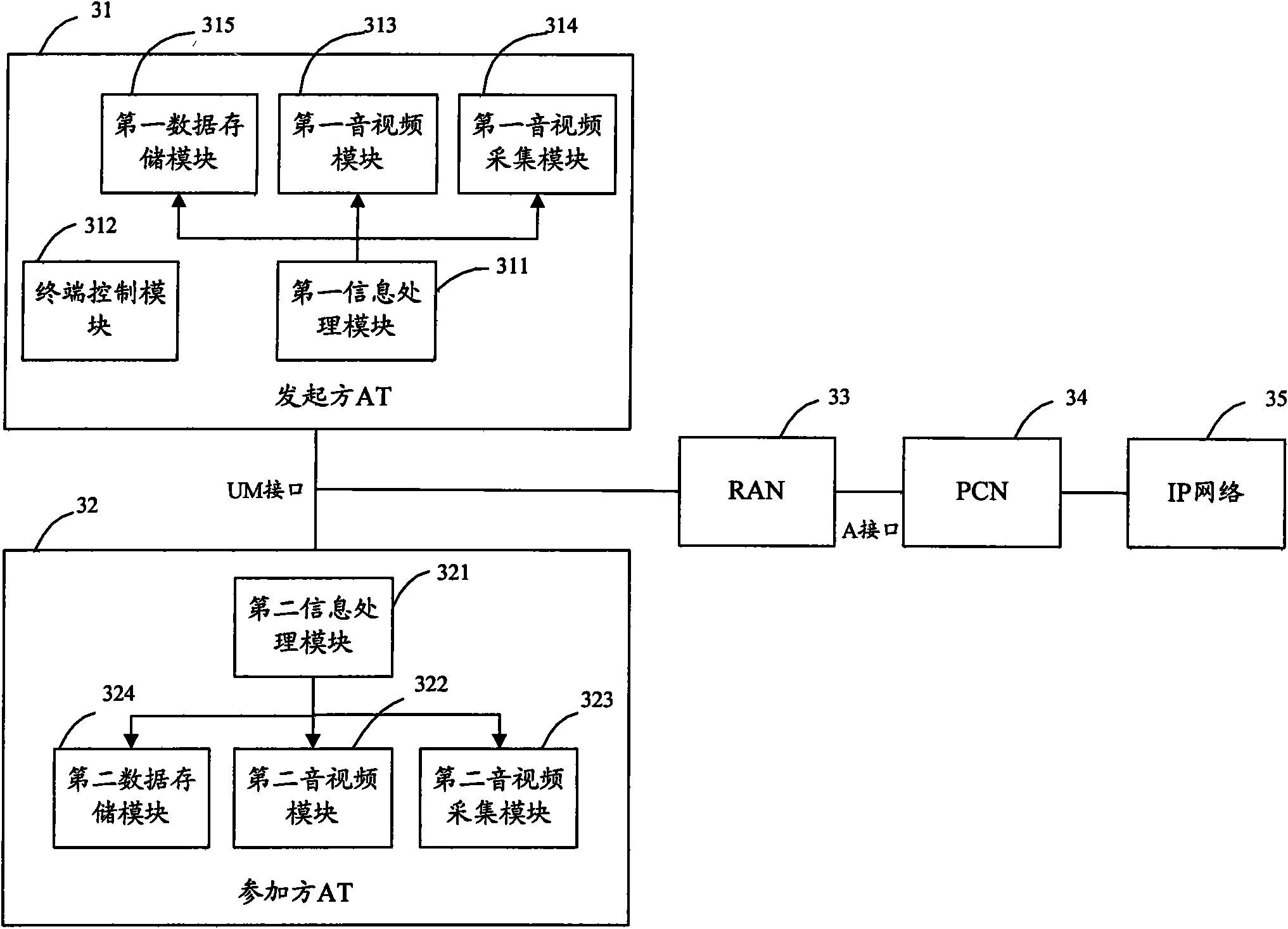
The invention discloses a method for realizing a wireless video conference, comprising the following steps: a wireless access terminal (AT) of an initiating party sends a conference request to a packet core (PCN); the PCN carries out conference invitation according to a list of a conference requesting party in the received conference request, sets up wireless resource and initiates for each AT that attends the wireless conference, and sends information of the conference member that attends the wireless conference video conference to the AT of the initiating party and to be memorized to set up a wireless video conference system; after the wireless video conference system is successfully set up, the PCN receives signaling stream of the AT in the wireless video conference system and sends the received signaling stream to the AT of the initiating party; and the AT of the initiating party sends control command to the PCN according to the signaling in the received signaling stream and controls the PCN to distribute the information stream of the wireless video conference system. The invention also discloses a system for realizing the wireless video conference and an AT, and can realize a multi-party wireless video conference.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Quick cluster business establishment method and related equipment and system
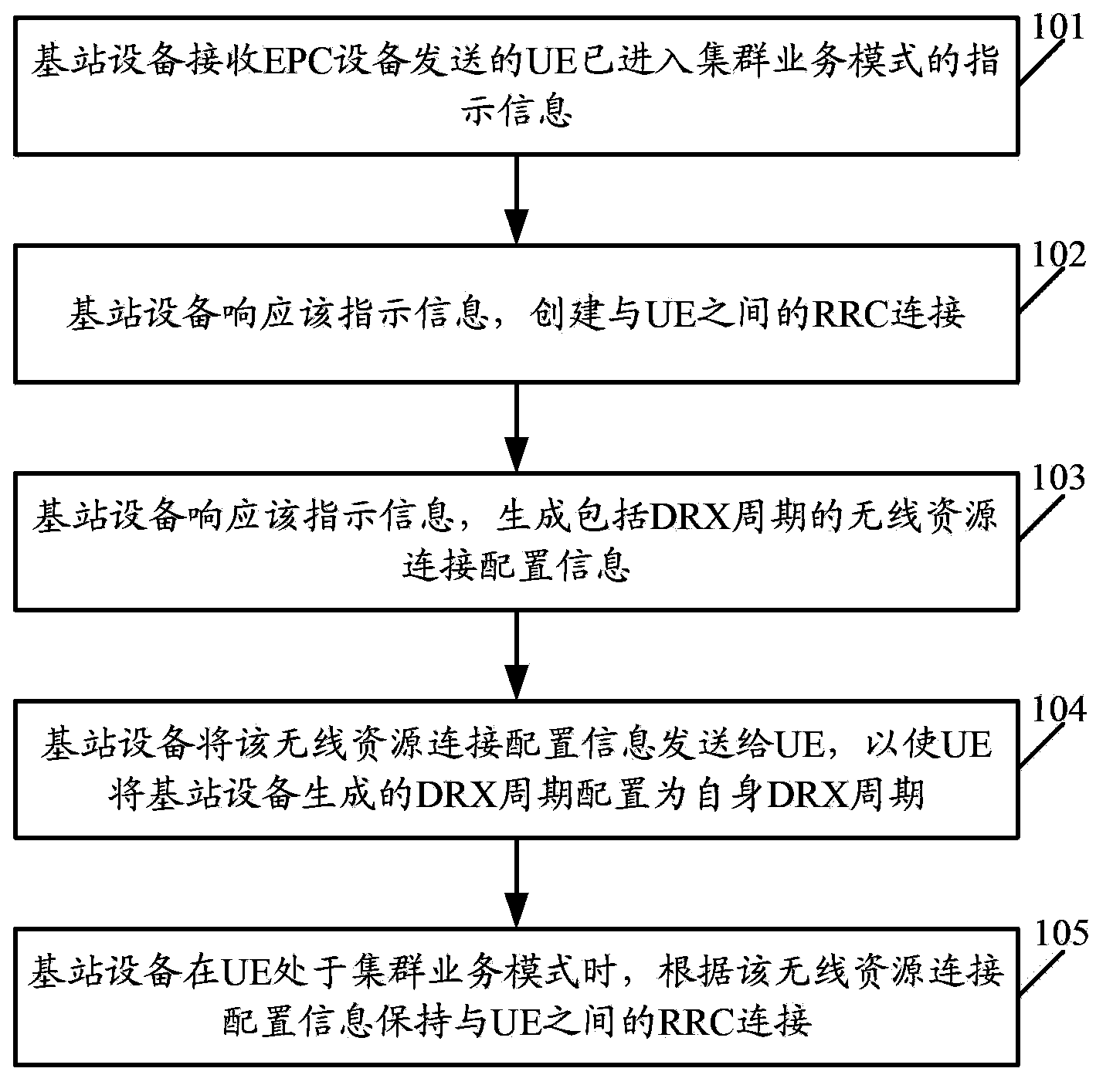
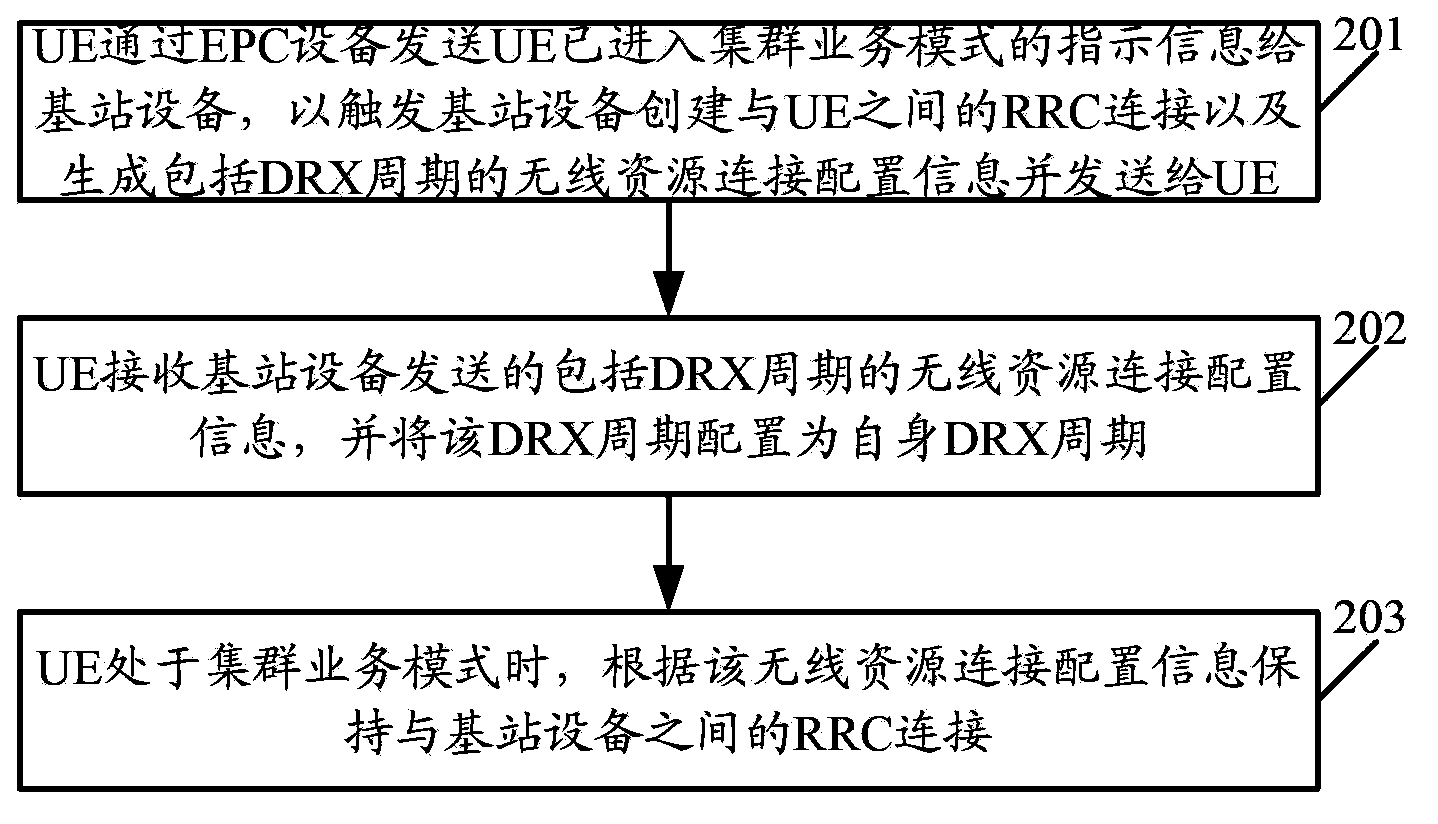
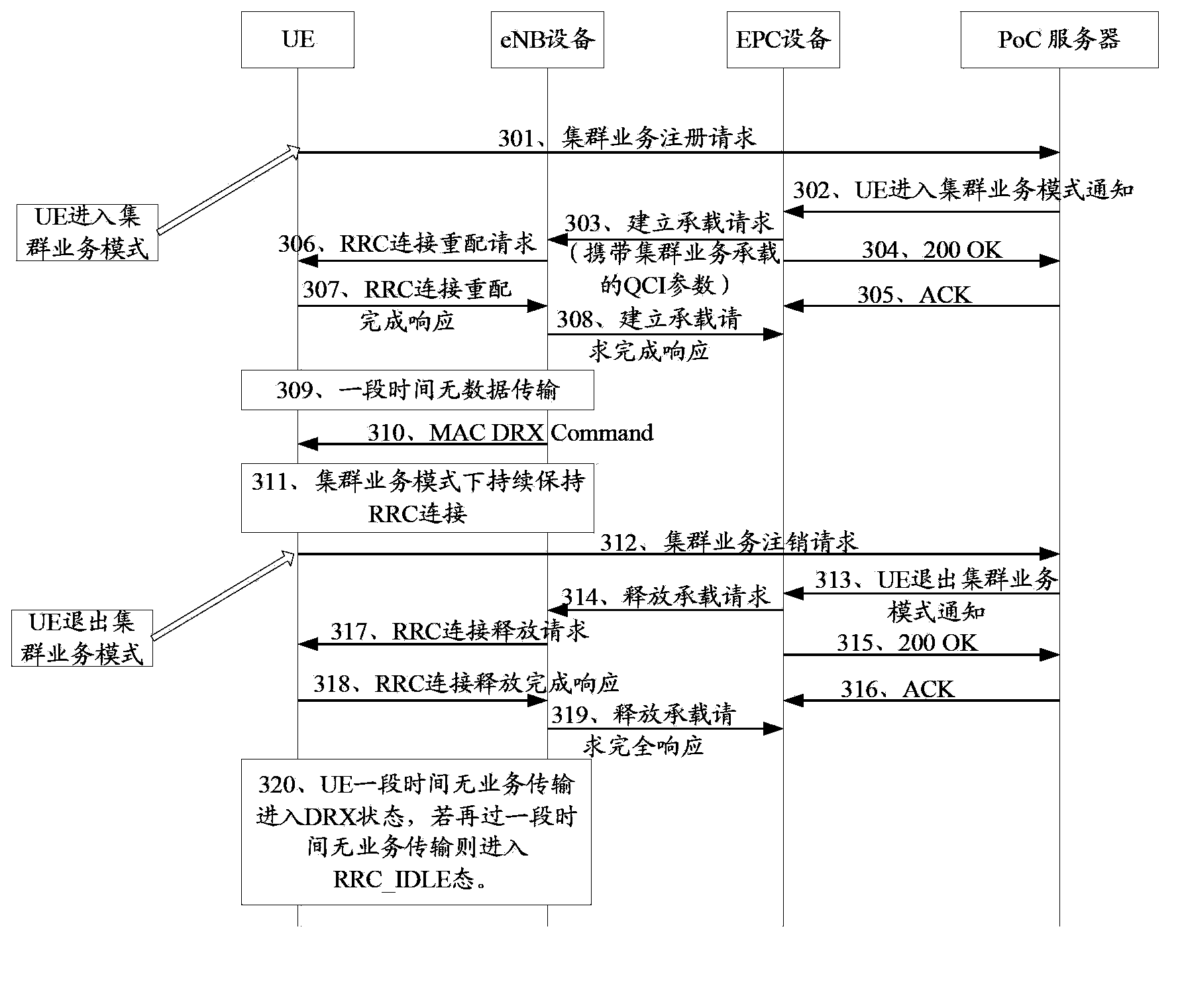
ActiveCN103686619AQuick buildReduce latencyPower managementTransmission path divisionPacket core networkWireless resources
The invention discloses a quick cluster business establishment method and related equipment and a related system. The method comprises the following steps: receiving indication information that user equipment sent by grouping core network evolution equipment has already been in a cluster business mode by base station equipment; responding the indication information by the base station equipment to establish a wireless resource control connection with the user equipment; responding the indication information by the base station equipment to generate wireless resource connection configuration information comprising non-continuous receiving cycle; sending the wireless resource connection configuration information to the user equipment by the base station equipment, so that the non-continuous receiving cycle is configured into self-non-continuous receiving cycle by the user equipment; keeping the wireless resource control connection with the user equipment according to the wireless resource connection configuration information by the base station equipment when the user equipment is in the cluster business mode. According to the quick cluster business establishment method and the related equipment and the related system, the time delay when the cluster business is established can be effectively reduced, and quick establishment of the cluster business is ensured.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
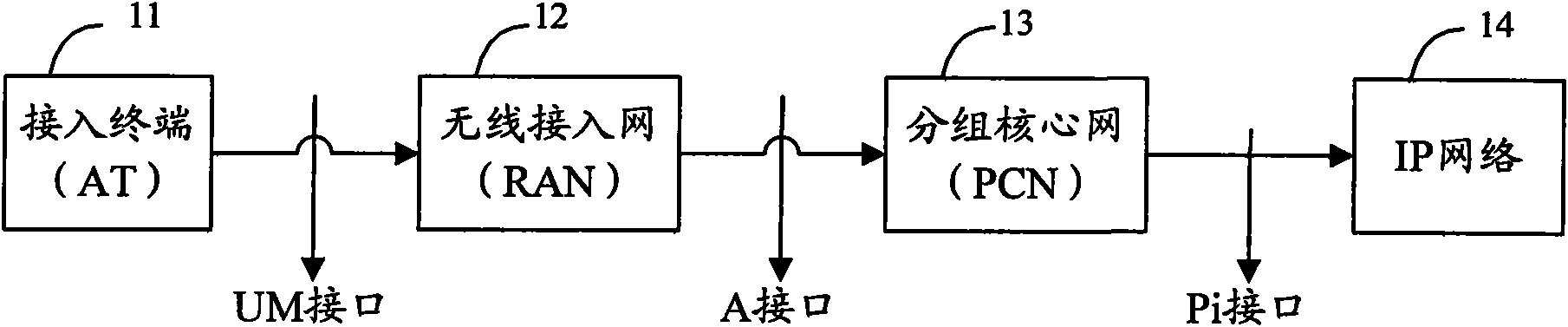
A method, apparatus and system for implementing PDN connections
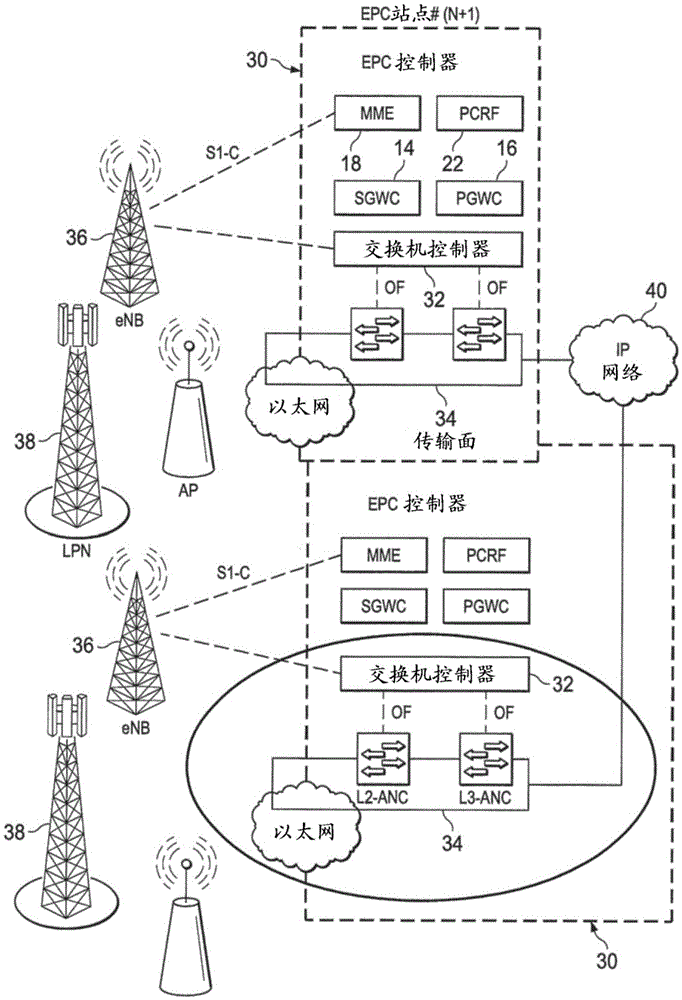
InactiveCN105637905ALarge delayWide rangeConnection managementWireless commuication servicesRadio access networkEthernet
A method, apparatus and system related to a packet data network (PDN) connection for a radio access network (RAN) (38) are provided. The PDN connections between eNB (36) of the RAN and an Evolved Packet Core (EPC) are forward though Ethernet switching network (34). A controller at Evolved Packet Core (EPC) site (30) such as EPC controller or centralized switch controller (32) is configured to configure flow table entries along the transport path from eNB to a gateway (14) of the EPC.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Lightweight data transmission mechanism
InactiveCN103155615ASecurity arrangementMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceAccess networkSecurity association
A method of sending user plane data between a user device and a network entity within a packet core network via a radio access network. The method comprises 1) authenticating the user device to the network entity and establishing a Security Association between the user device and the network entity; 2) maintaining the user device in a connectionless state, such that no Security Association is established between the user device and the radio access networkand no data bearer is set up between the user device and said packet core network; 3) with the user device in said connectionless state, sending uplink and downlink user plane data between the user device and said network entity by including the data within signalling messages on the Non Access Stratum.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
An improvement on ip fragmentation in gtp tunnel
ActiveCN103262606AImprove performanceFragmentation processing time reductionNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementComputer networkIP fragmentation
The present invention relates to a method for improving IP fragmentation and transmission of user payload between a User Equipment, UE (10), and a Peer Node, PN (14). The payload is transmitted through a transmission path enabled by at least a first (17, 18) and a second (17, 18) established tunnel, said tunnels connecting a first (11), (13) and a second (11, 13) node in a Packet Core Network, PCN. The method comprises the steps of: - The first node (11,13) fragments (19) at least one received payload packet (15) into fragments (16) on the basis of a minimum Maximum Transmission Unit, MTU, for an upper IP layer of the transmission path. The first node (11, 13) encapsulates (20) said fragments at the entry of the first tunnel (17, 18). What particularly characterizes the method is that it further comprises a step where the first node (11, 13) determines (21) the MTU for the upper IP layer of the transmission path on the basis of an MTU of a lower IP layer of the transmission path and on the basis of the size of at least one additional tunnel header for the encapsulated fragments (16).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com