Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
252 results about "Packet data serving node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
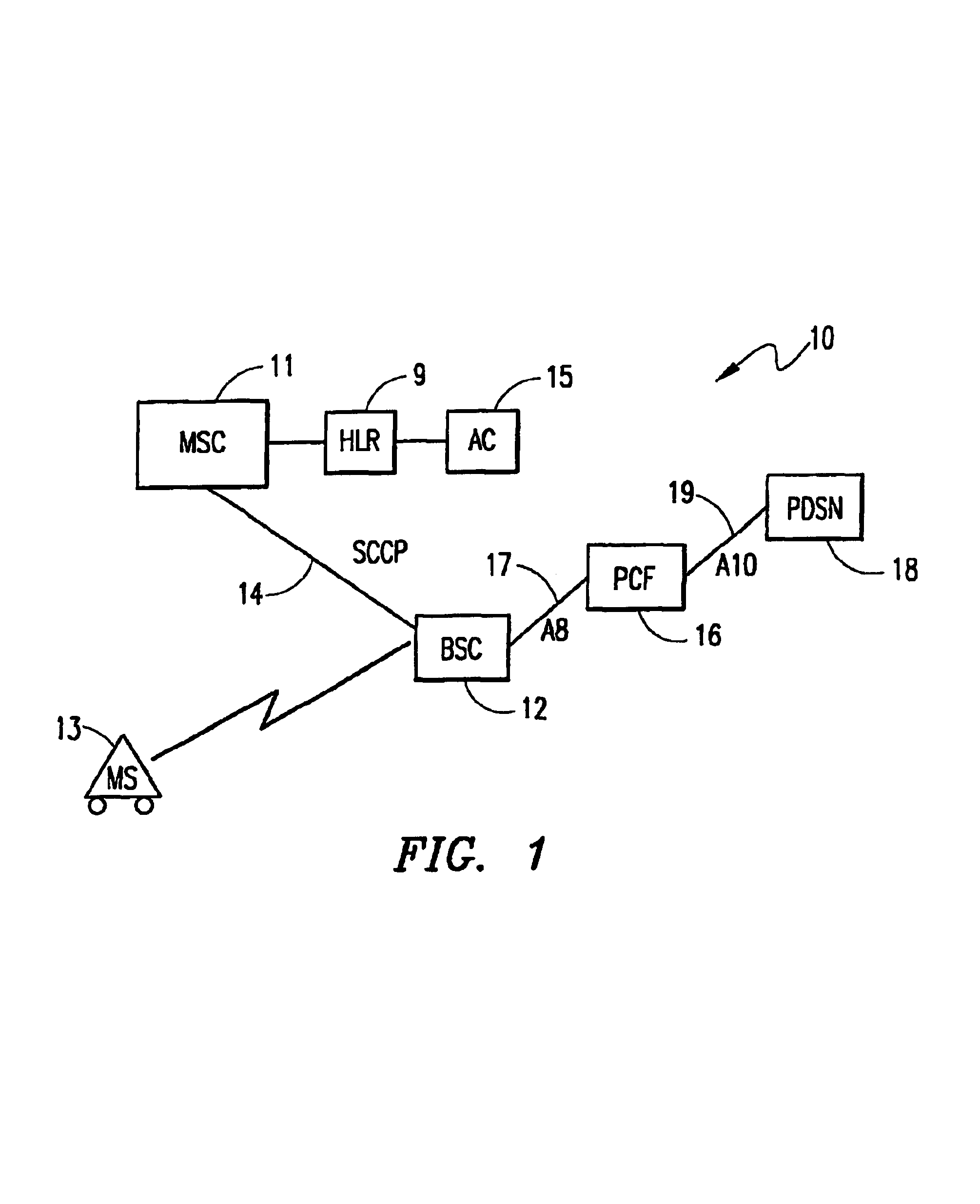
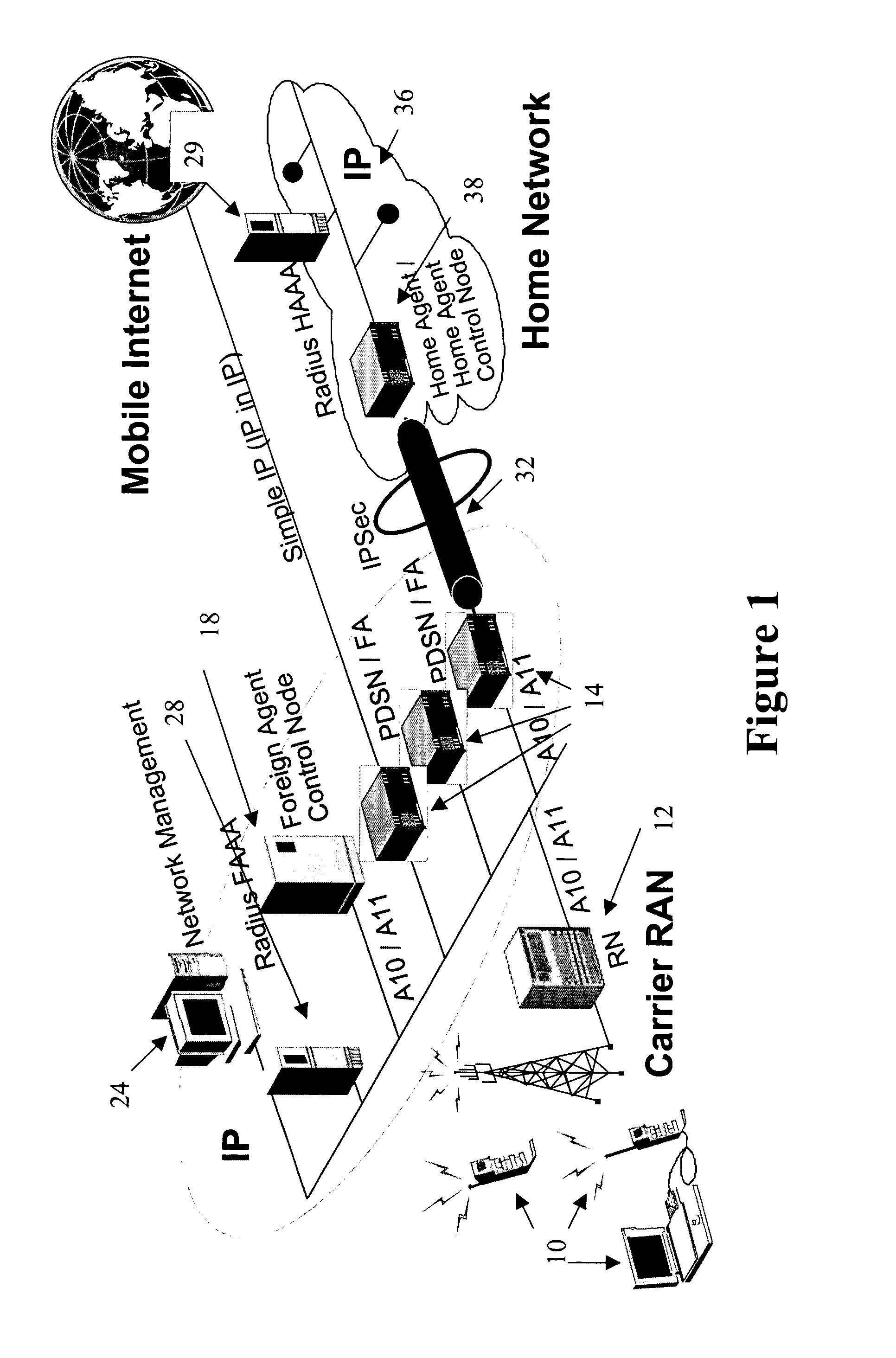
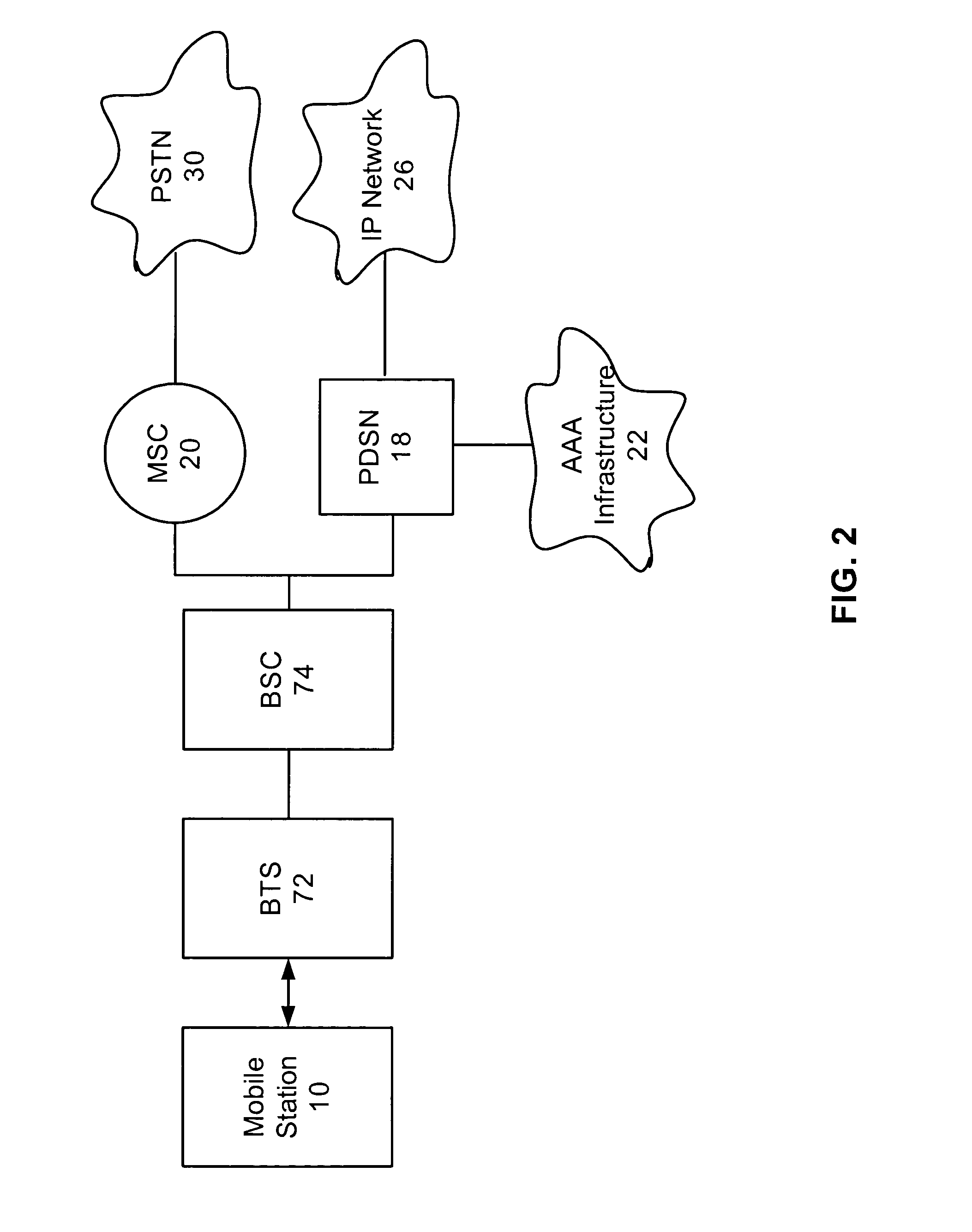
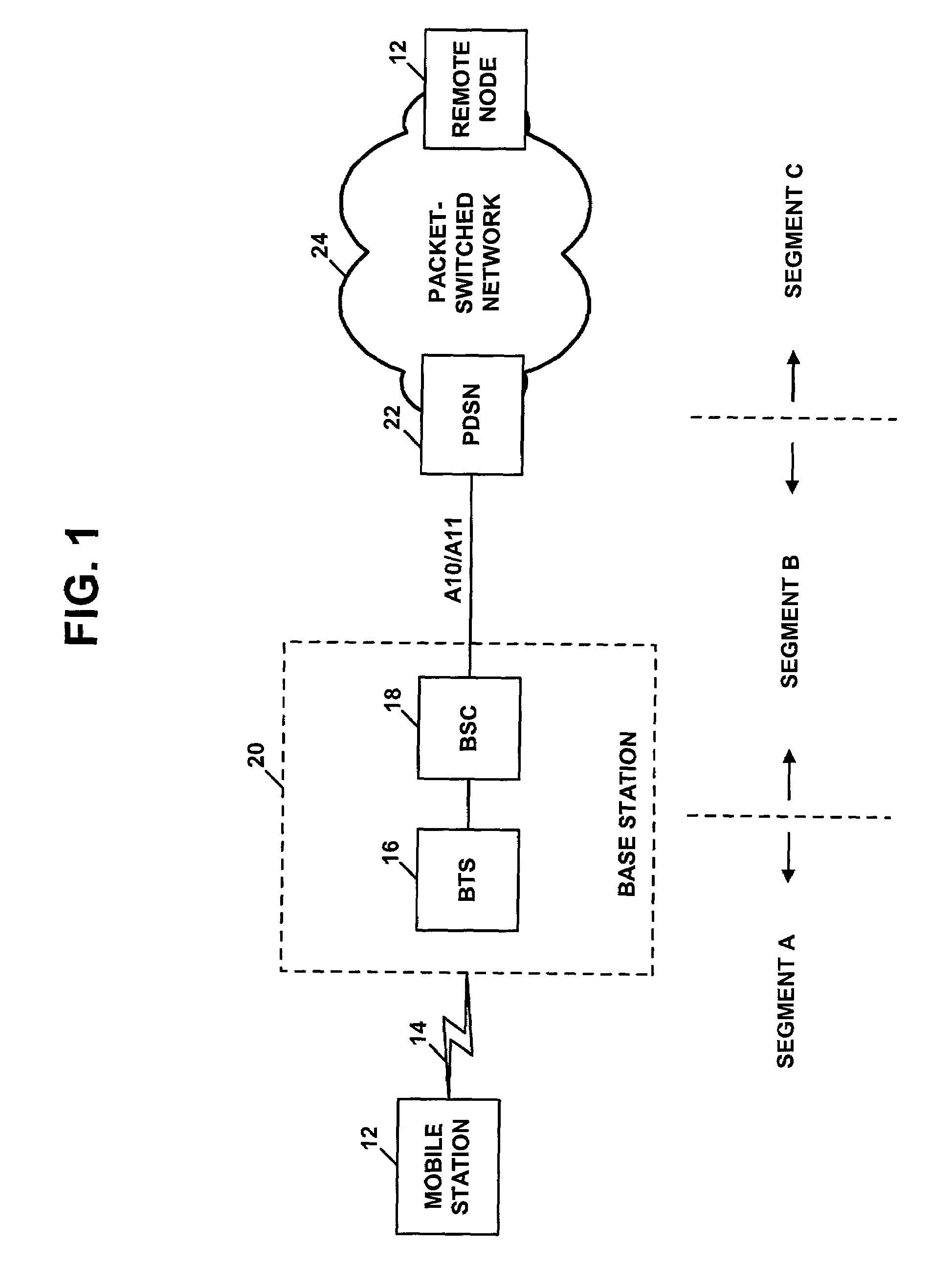
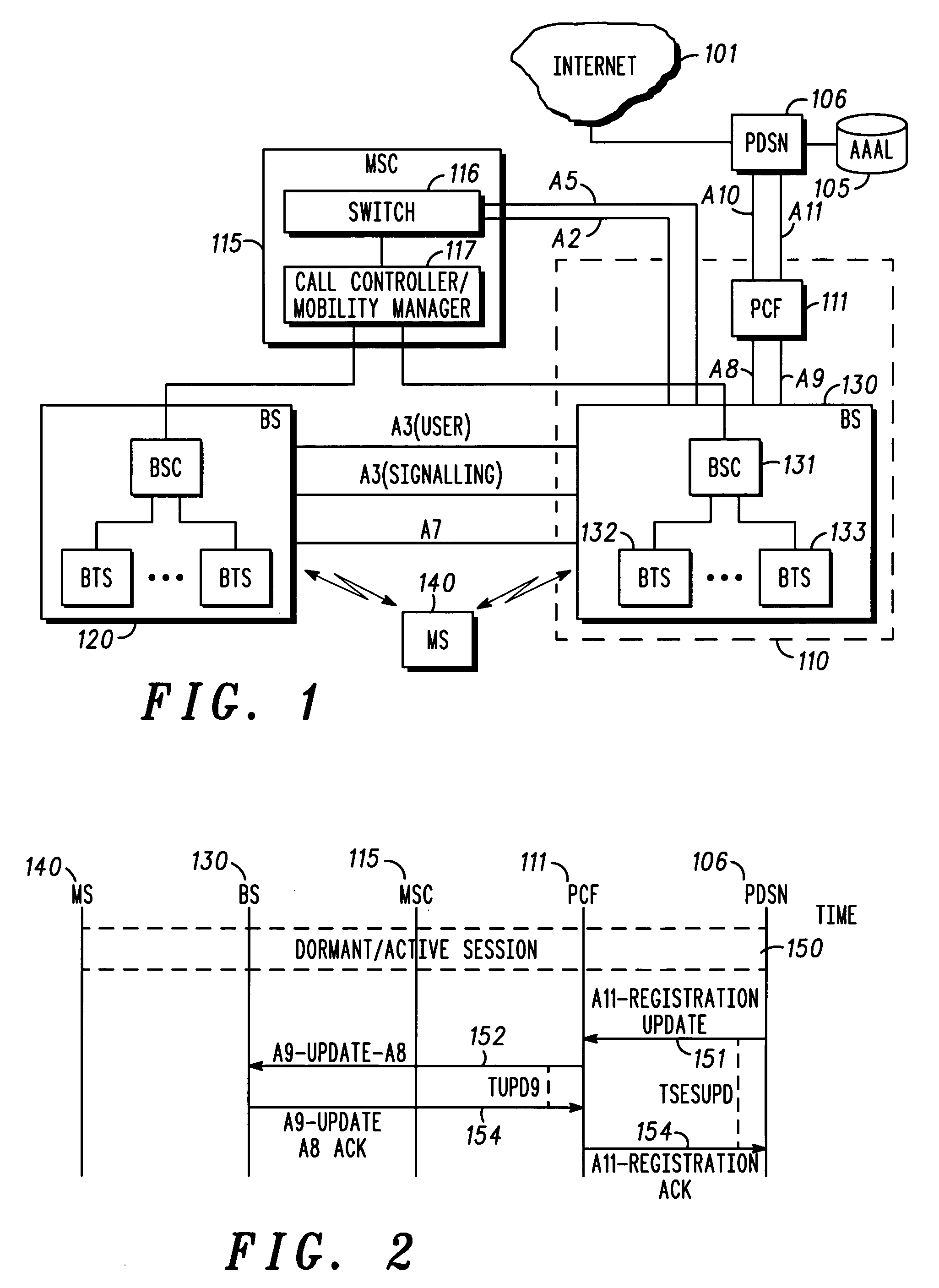
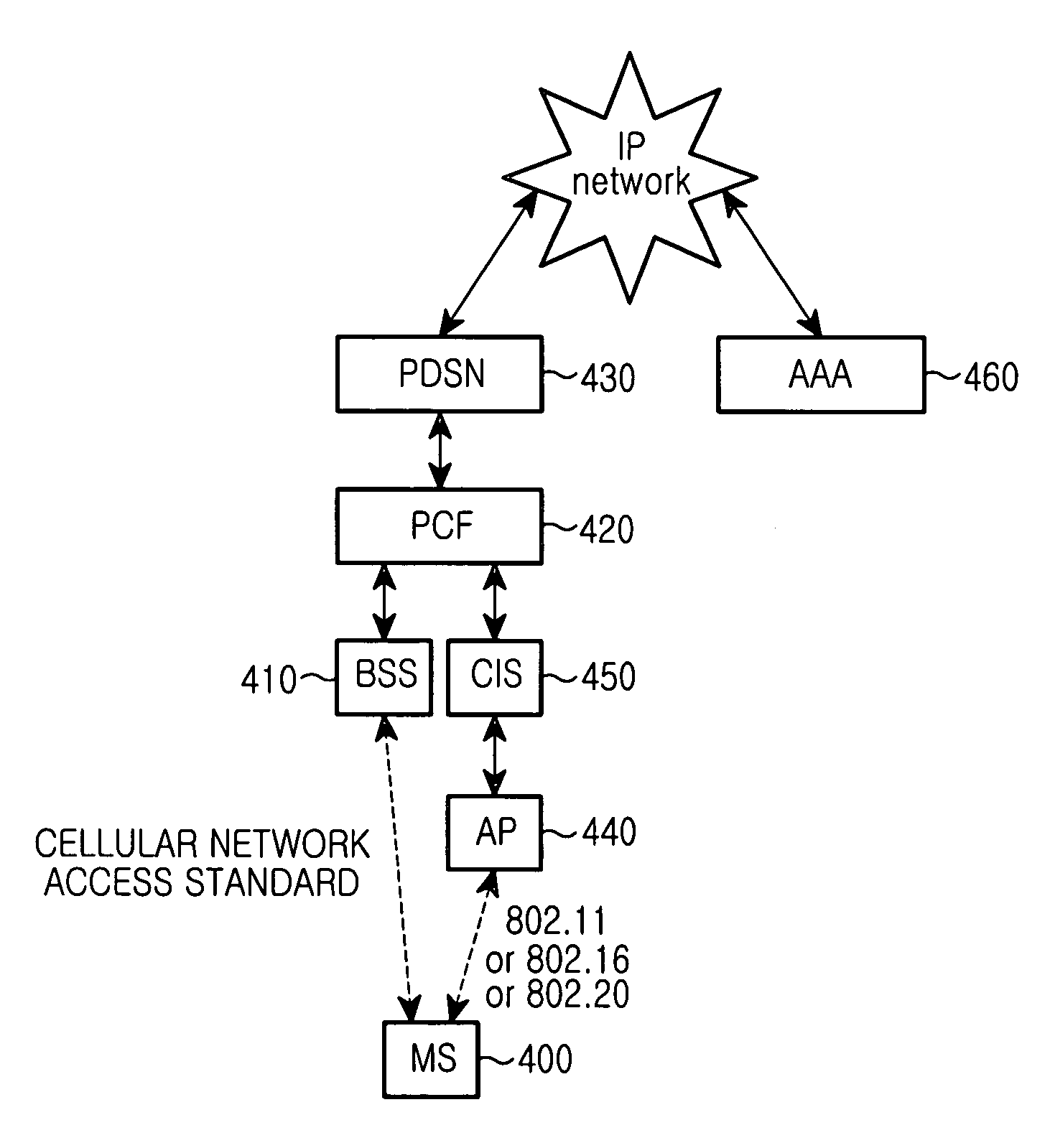
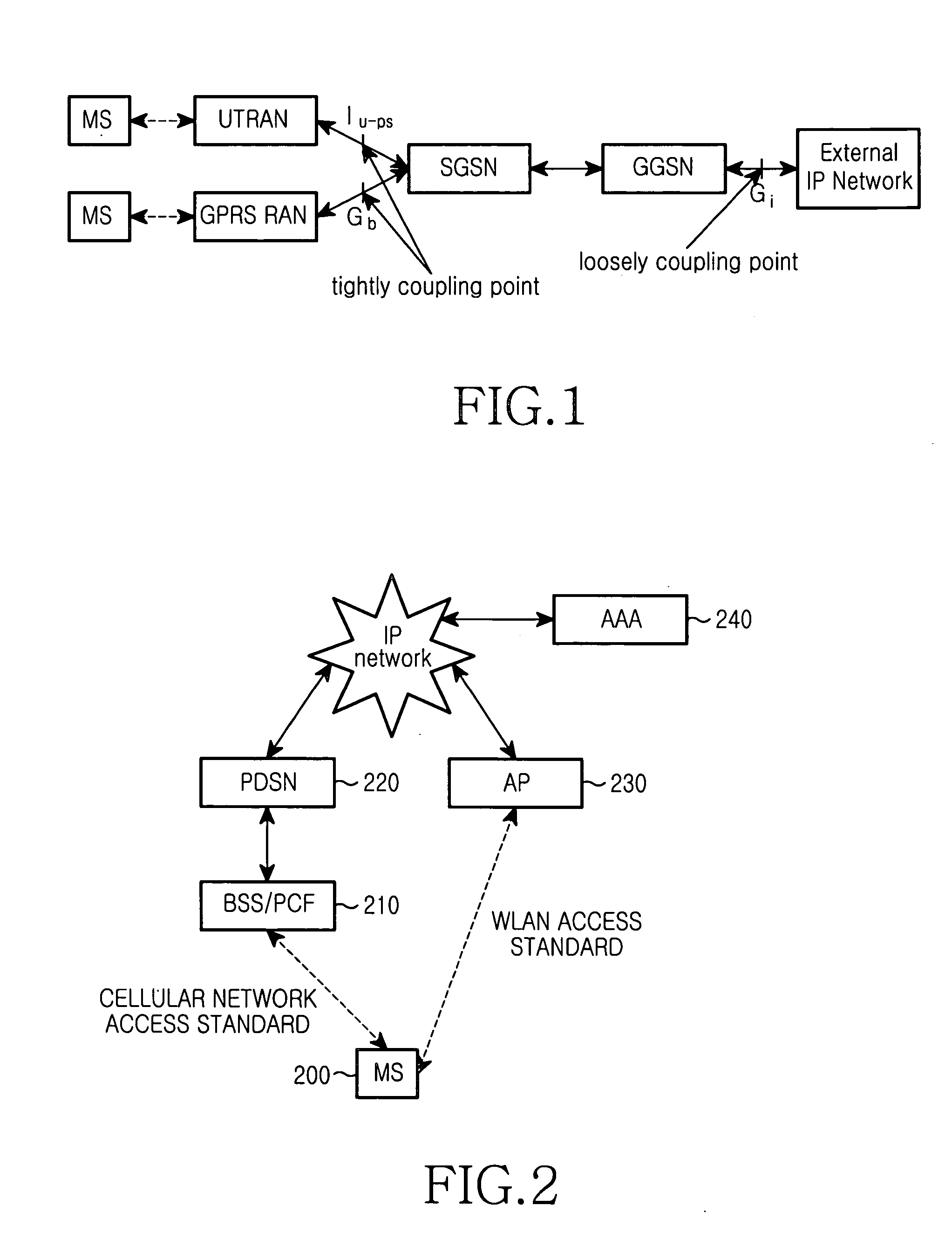
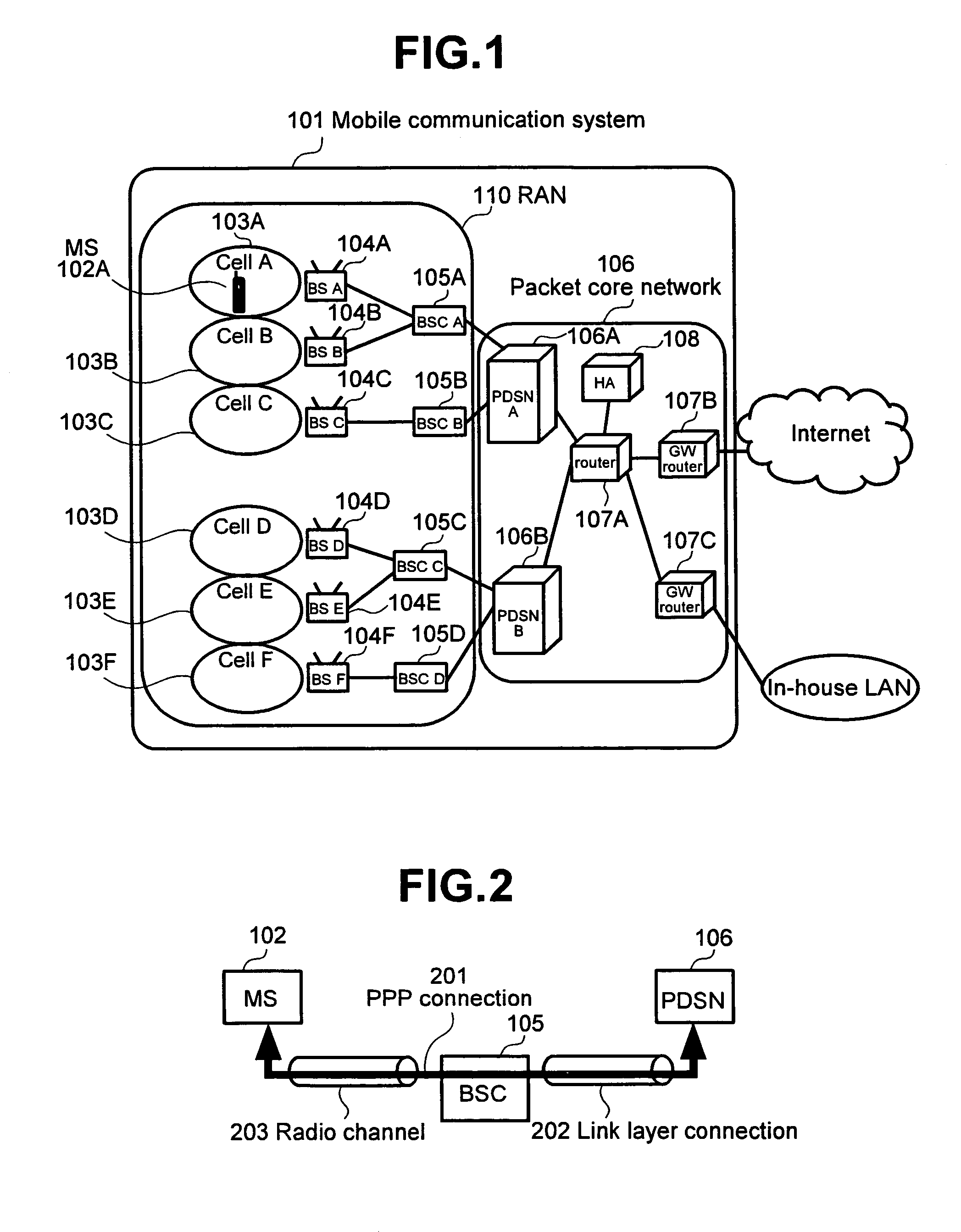
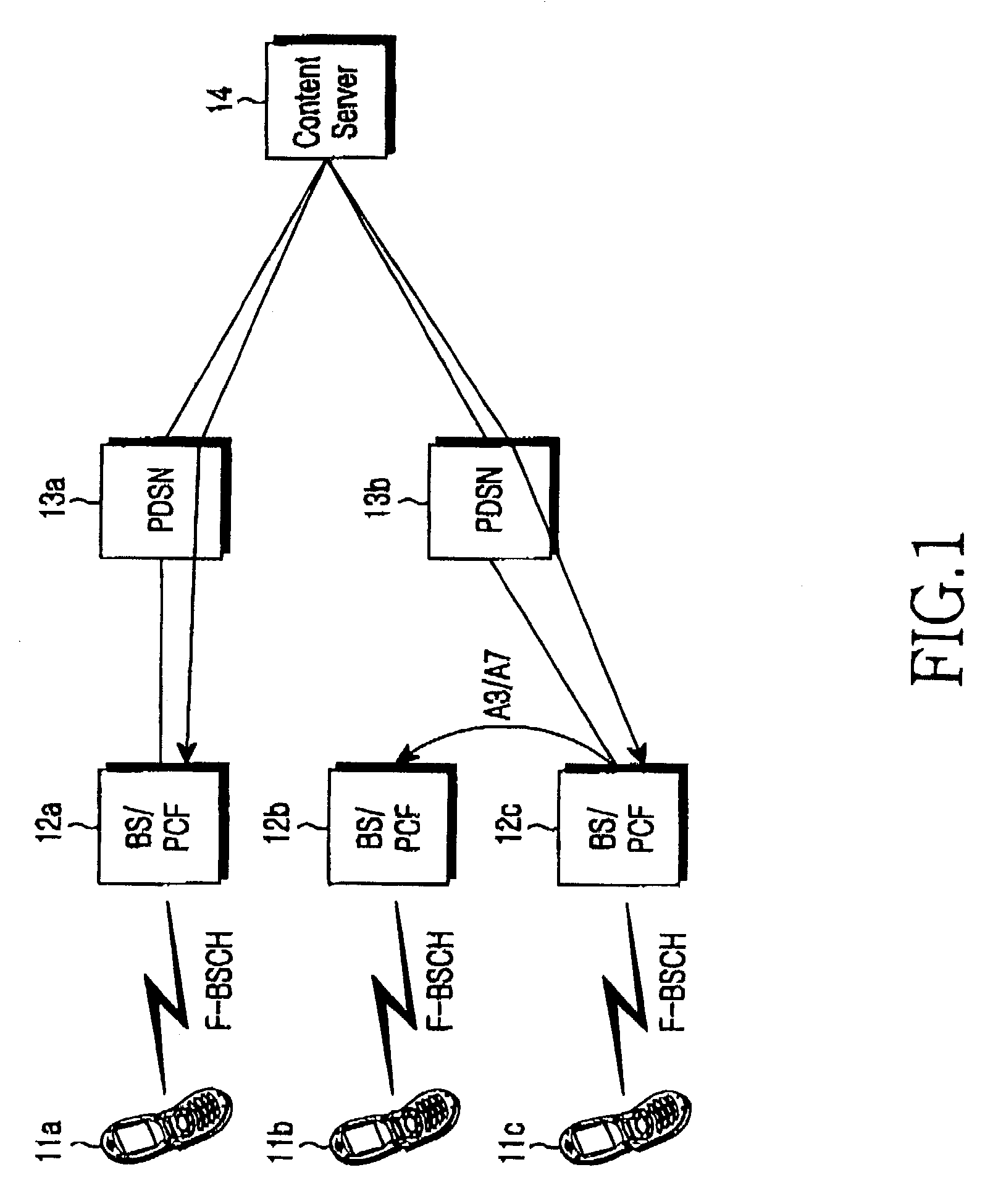
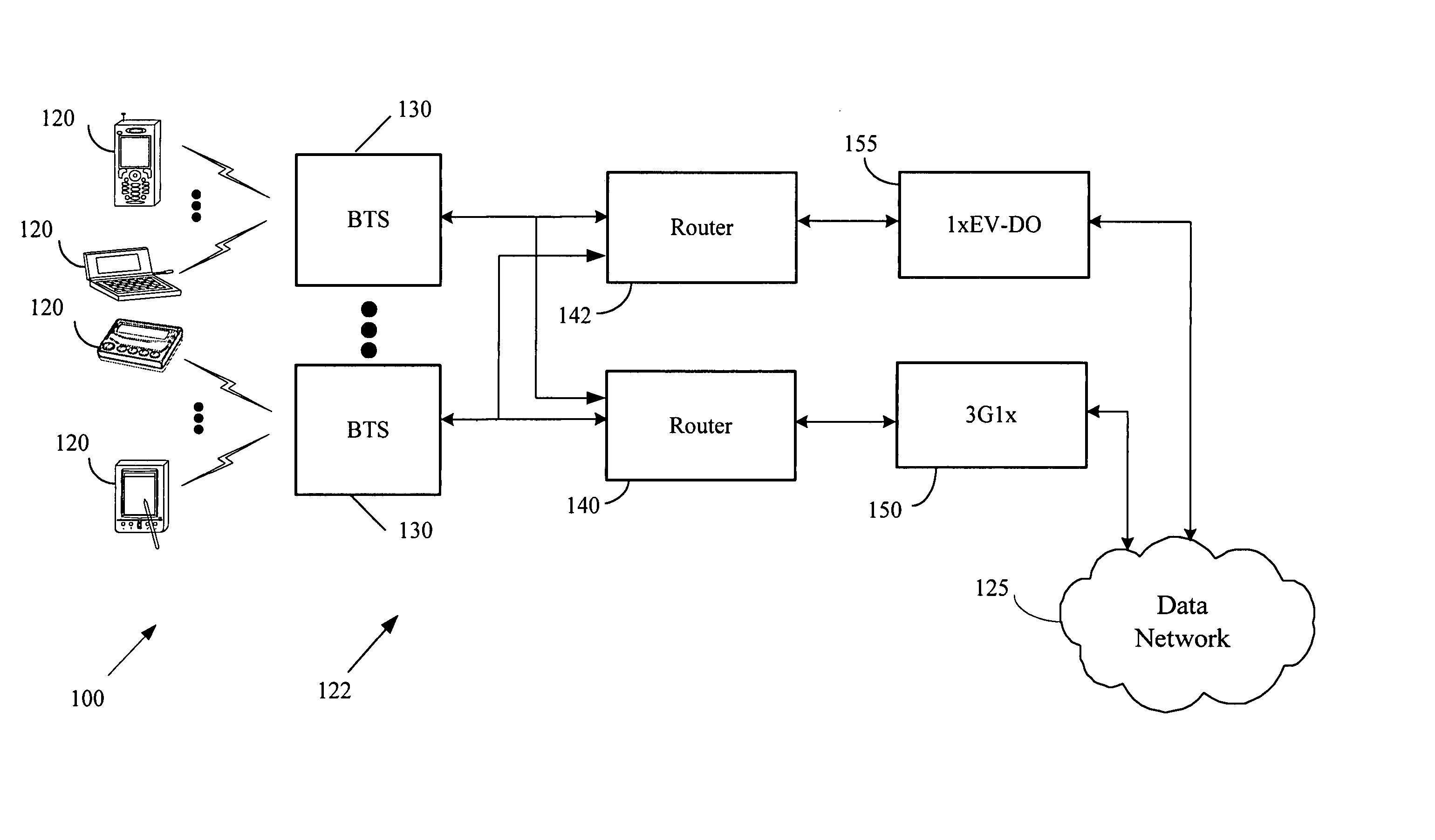
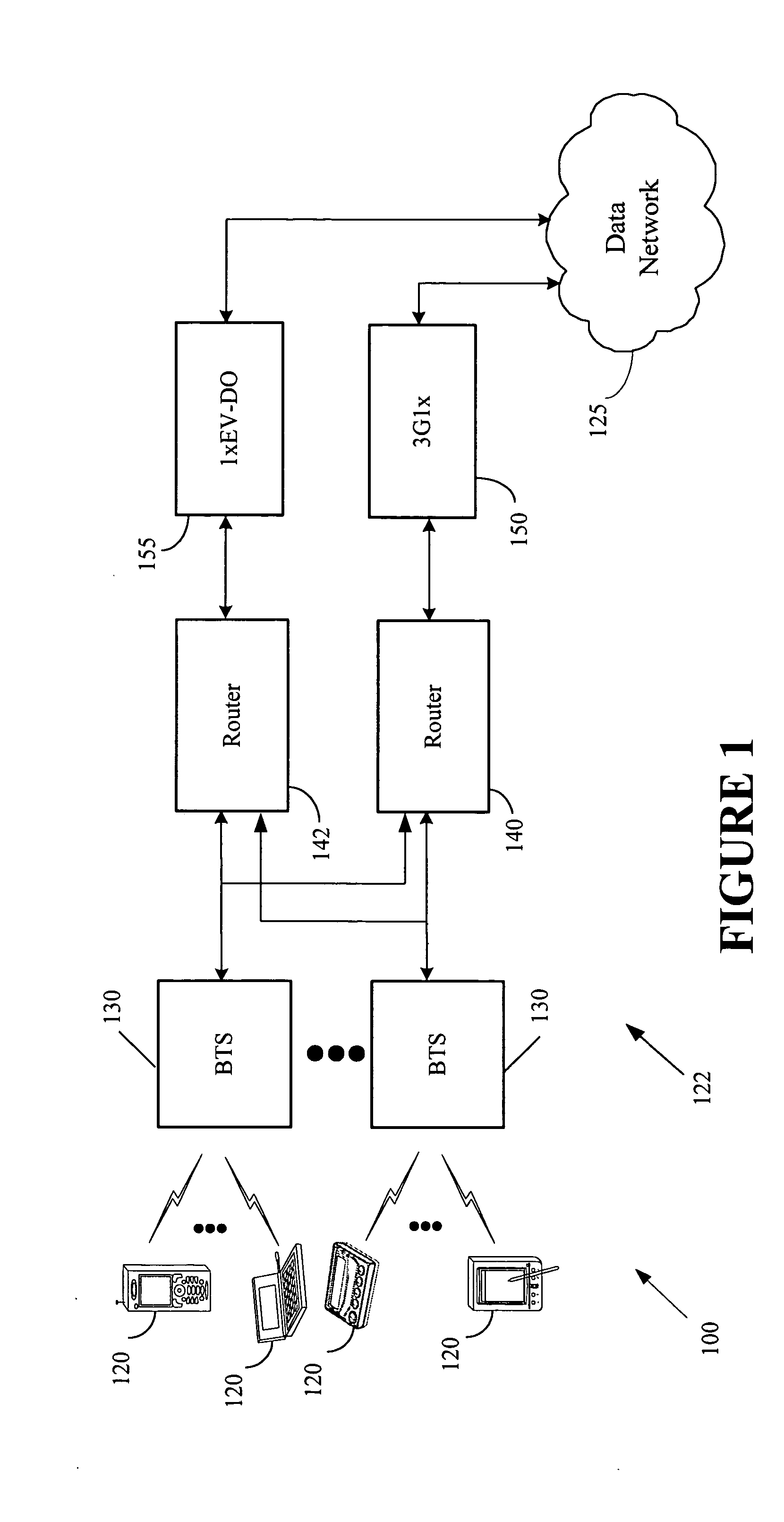
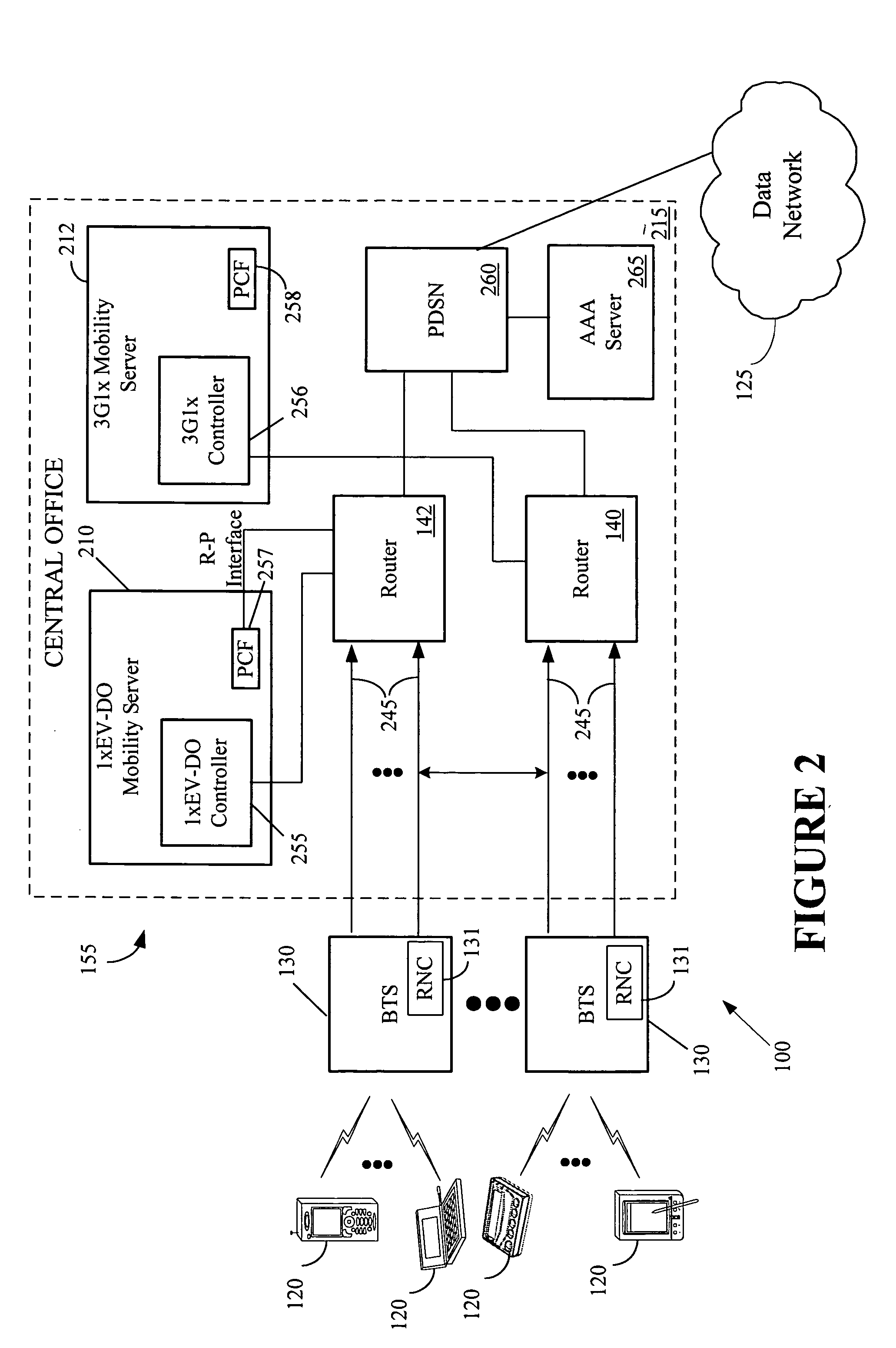
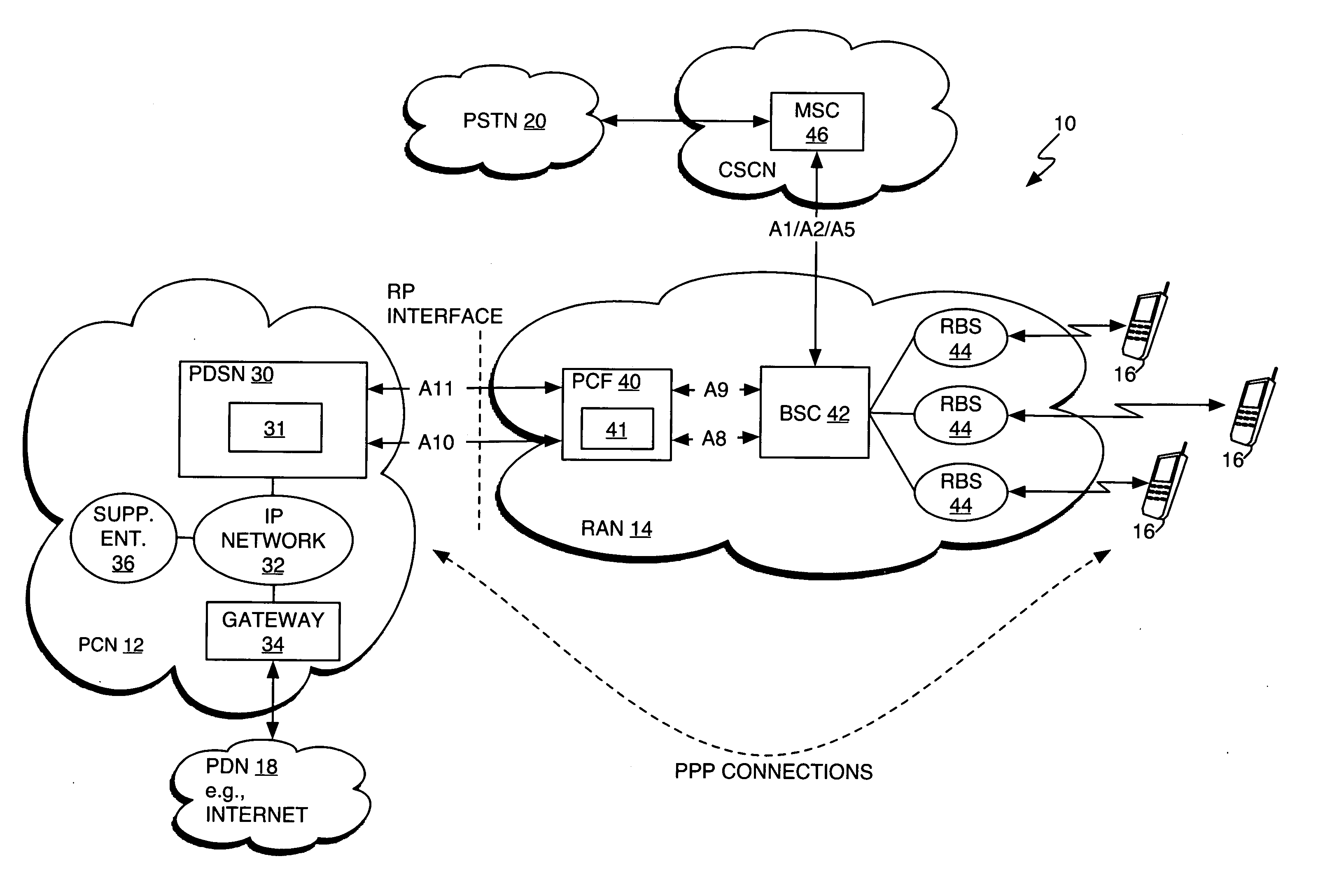
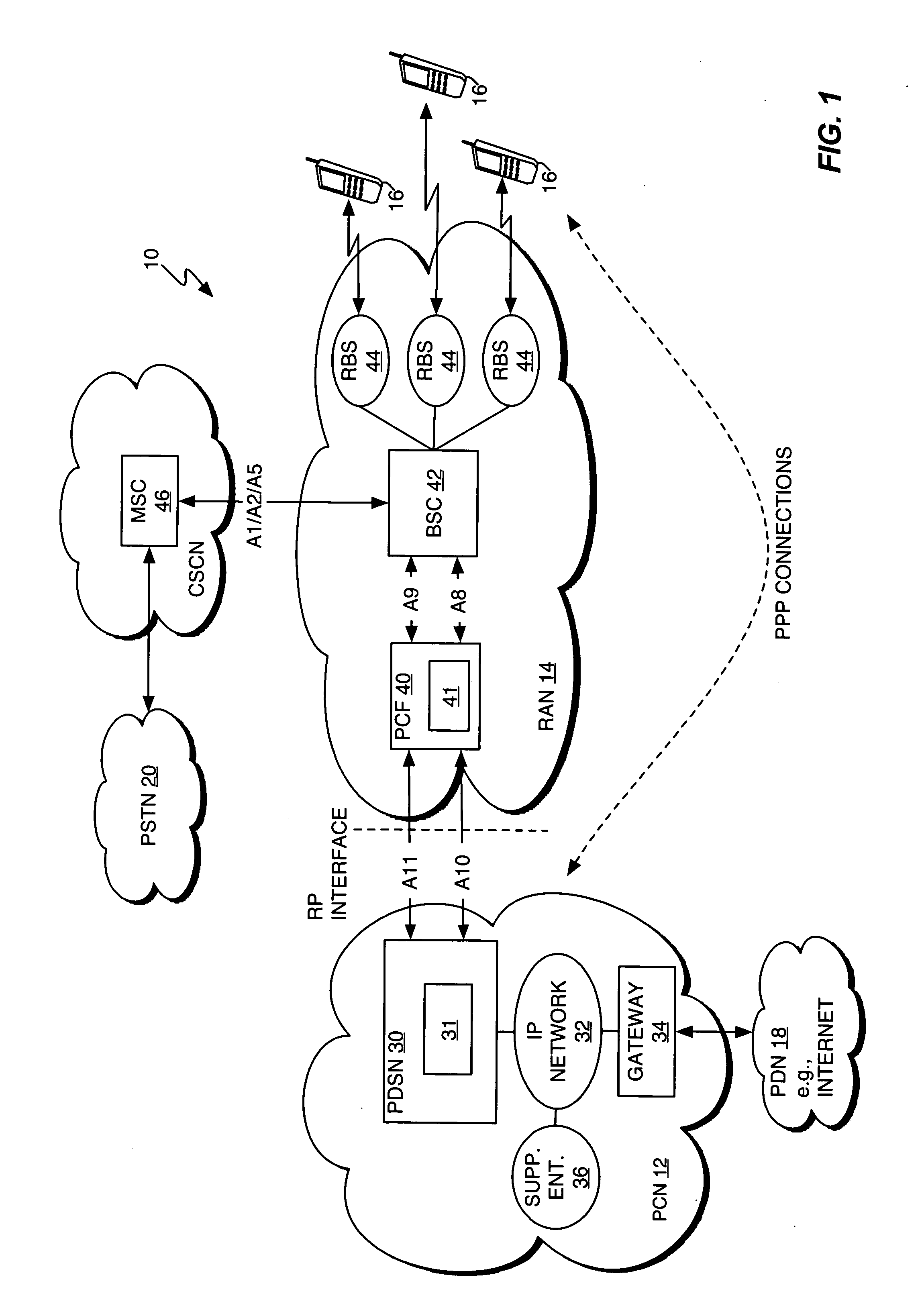
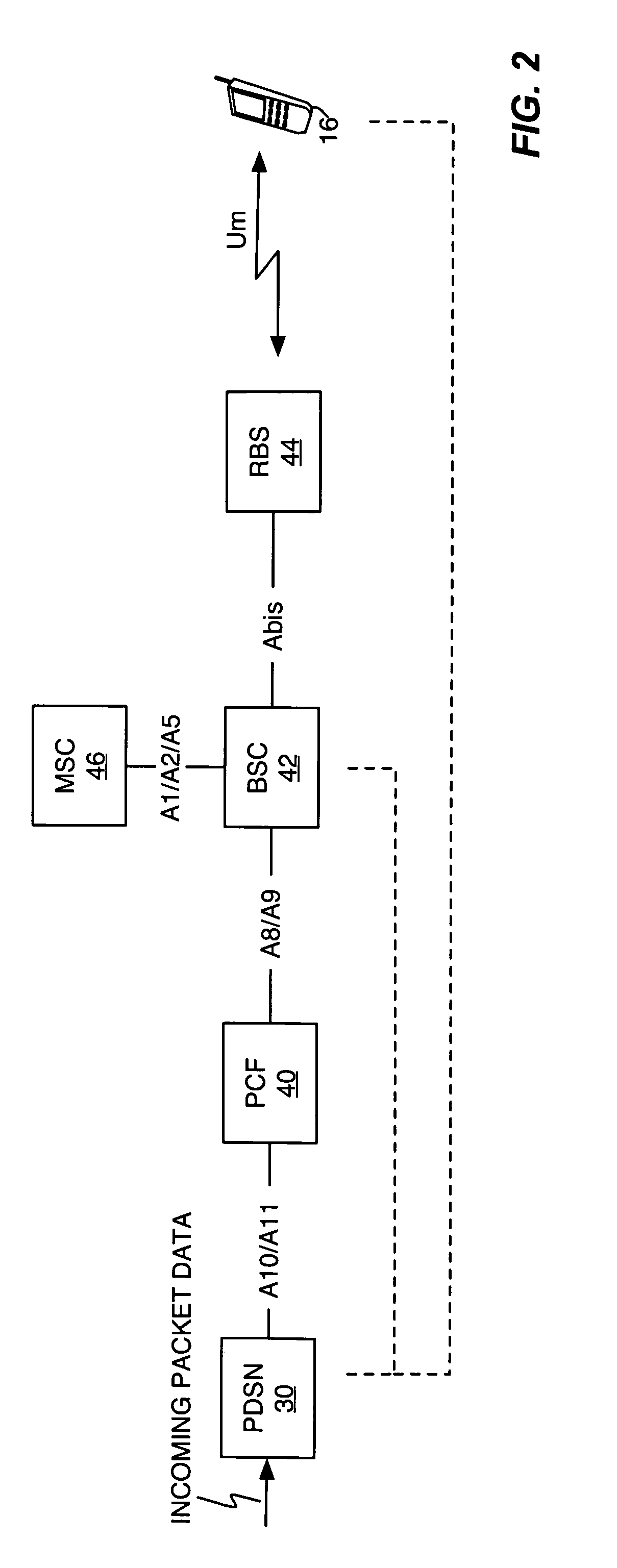
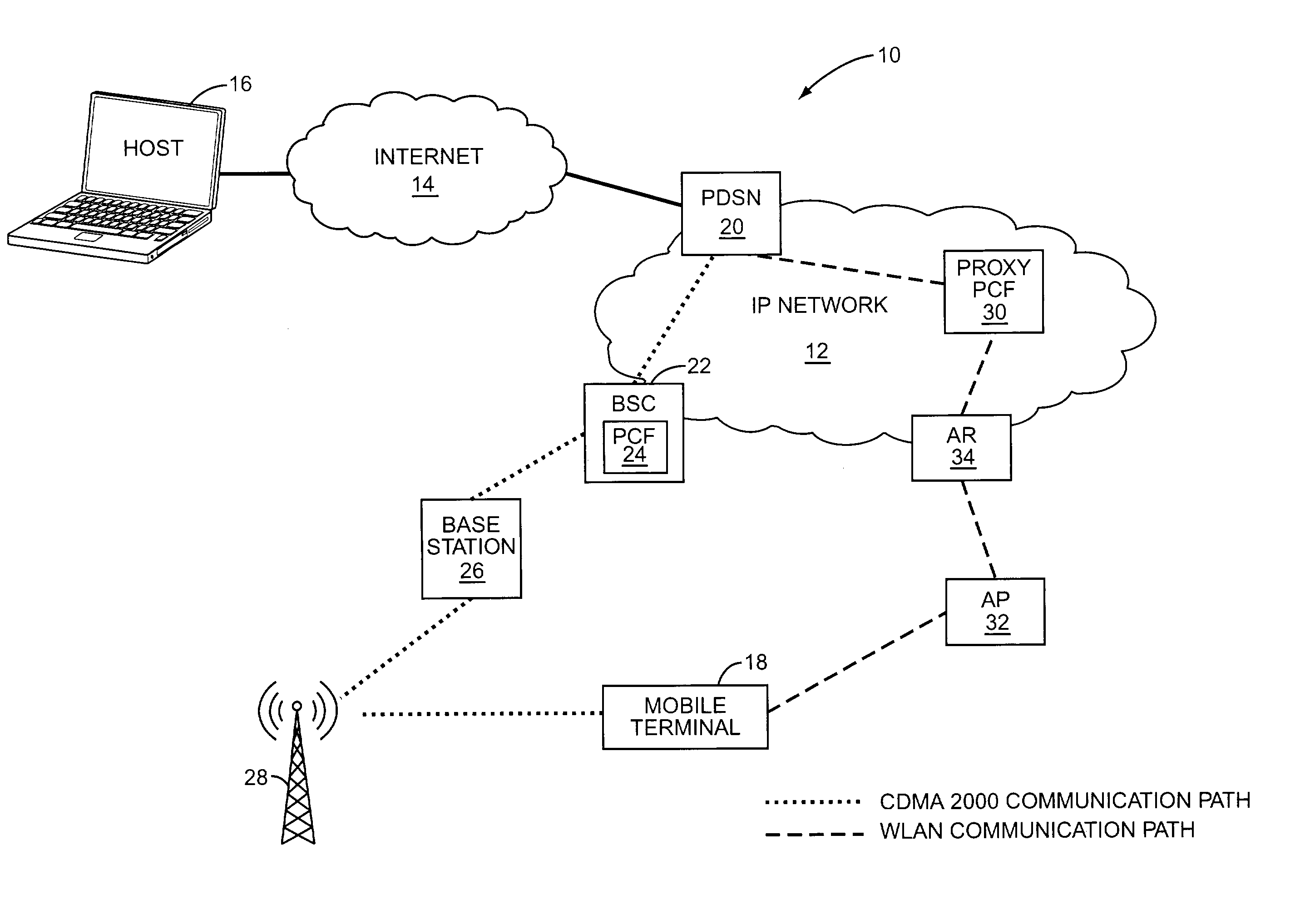
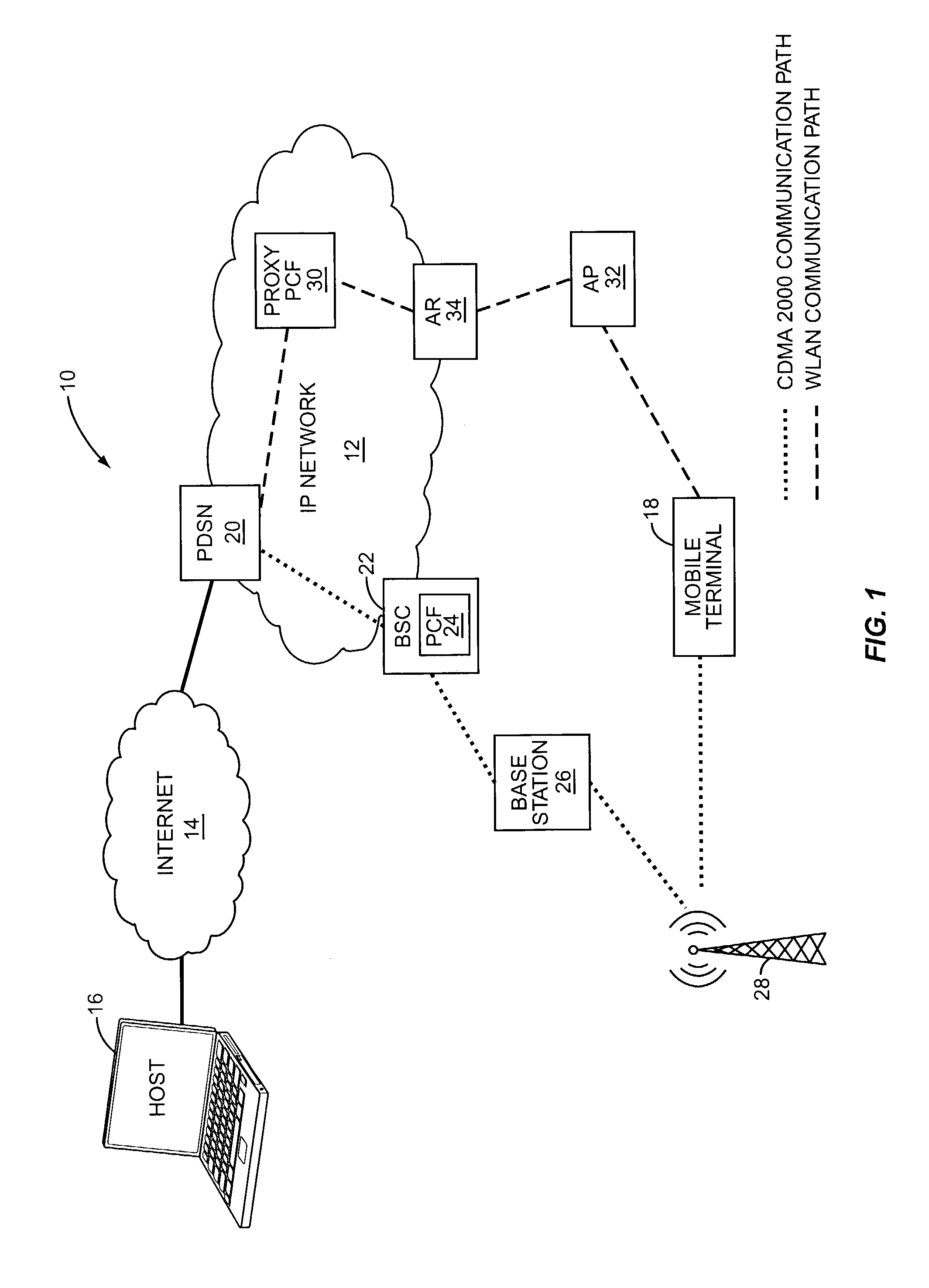
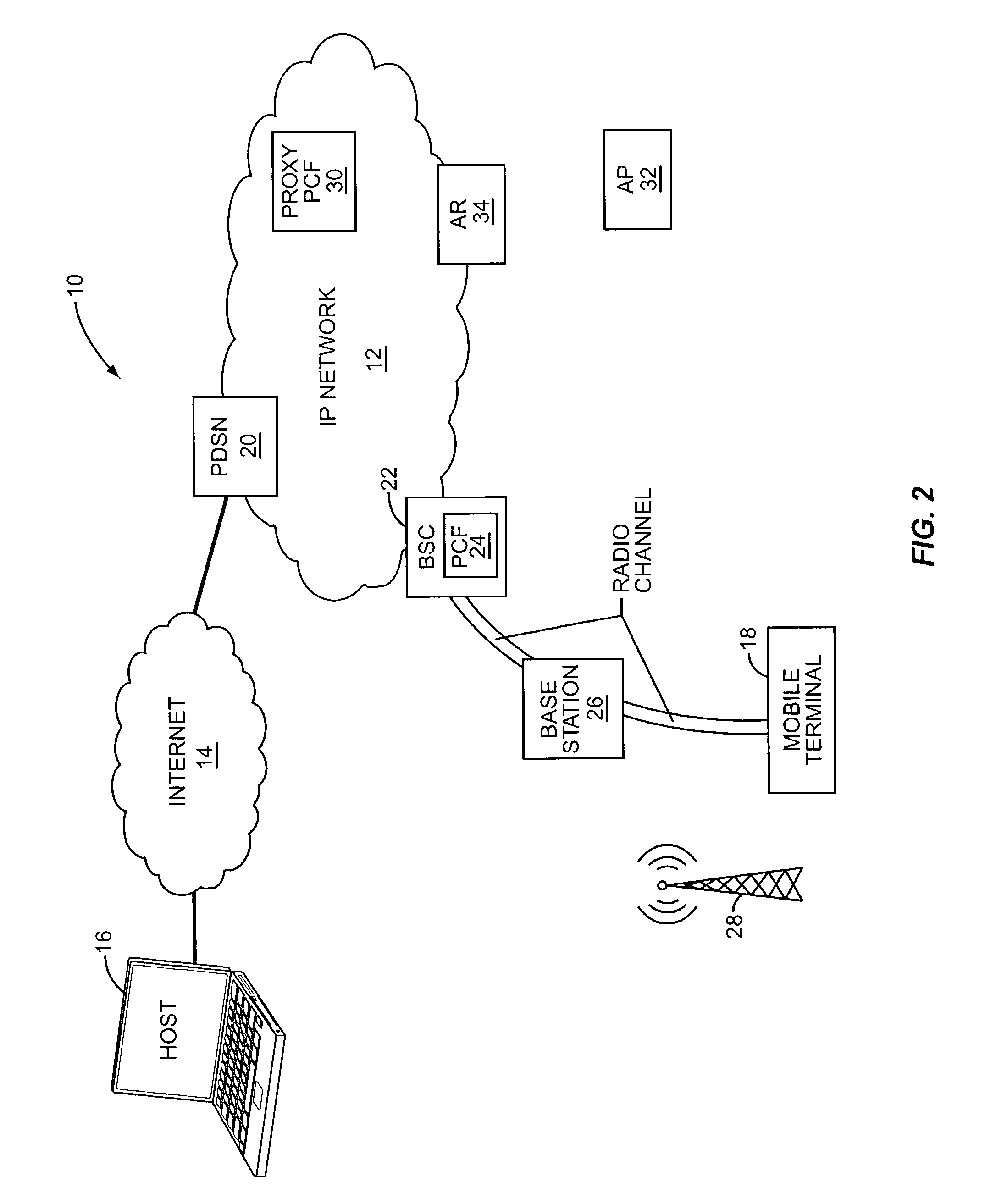
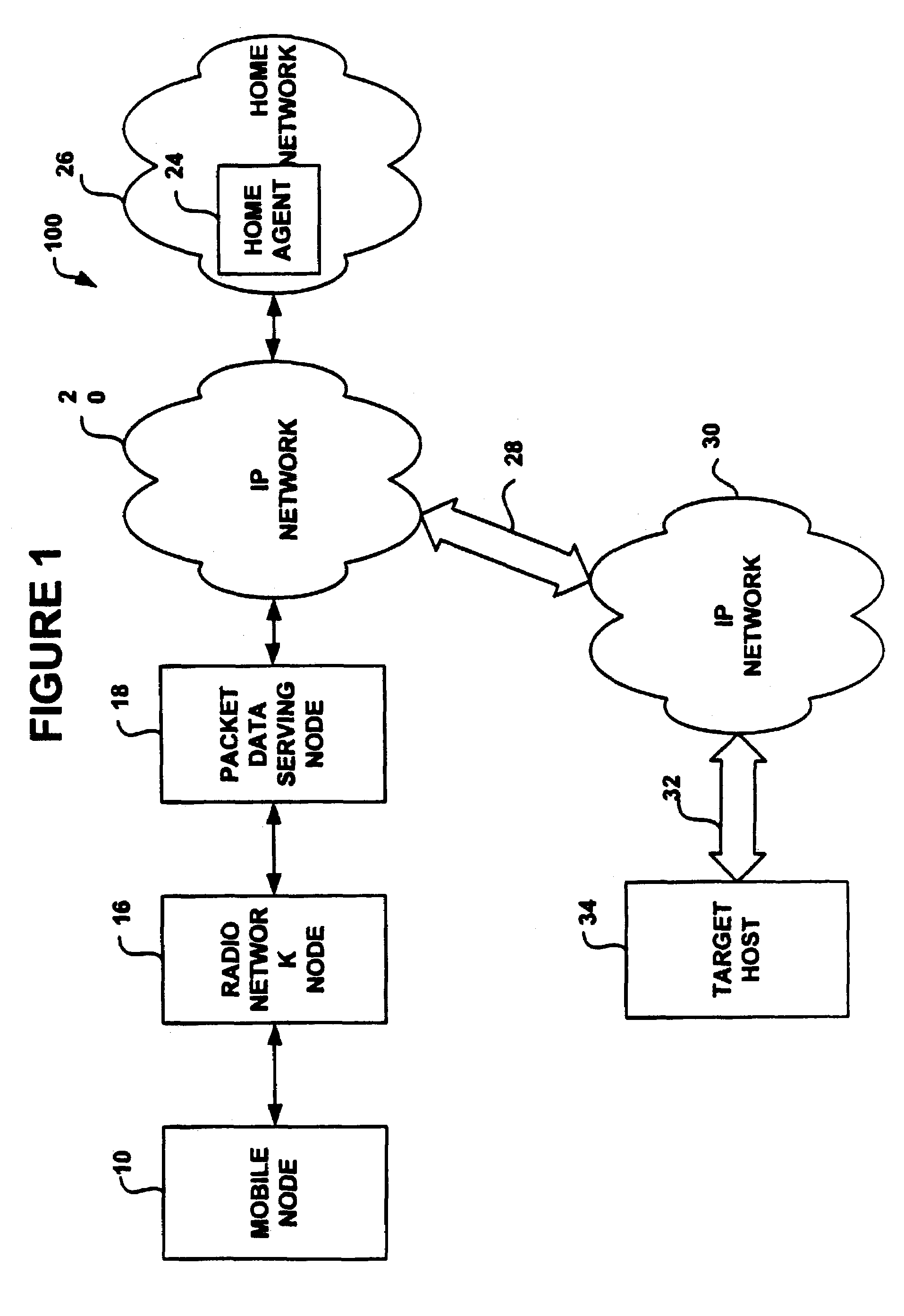
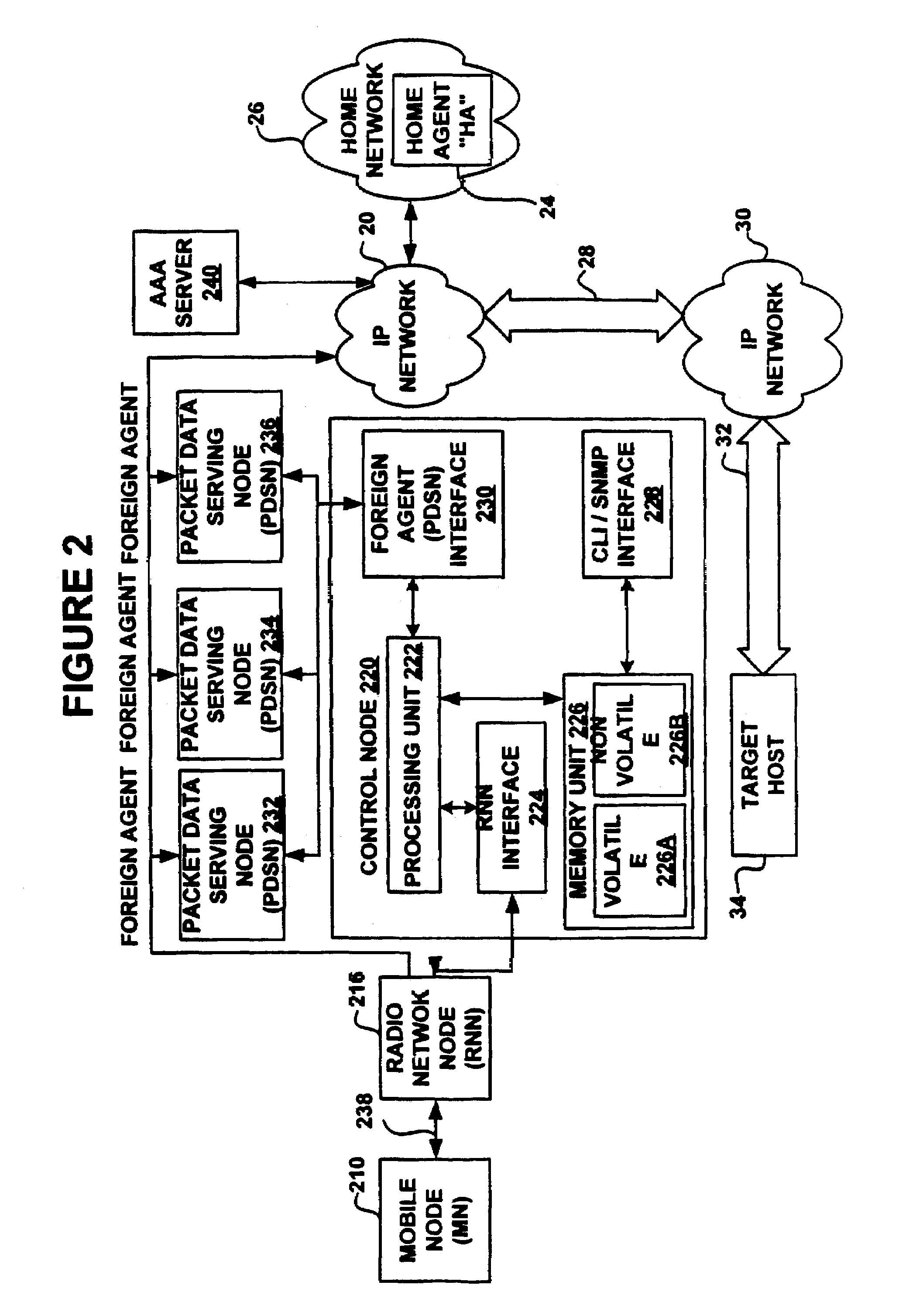
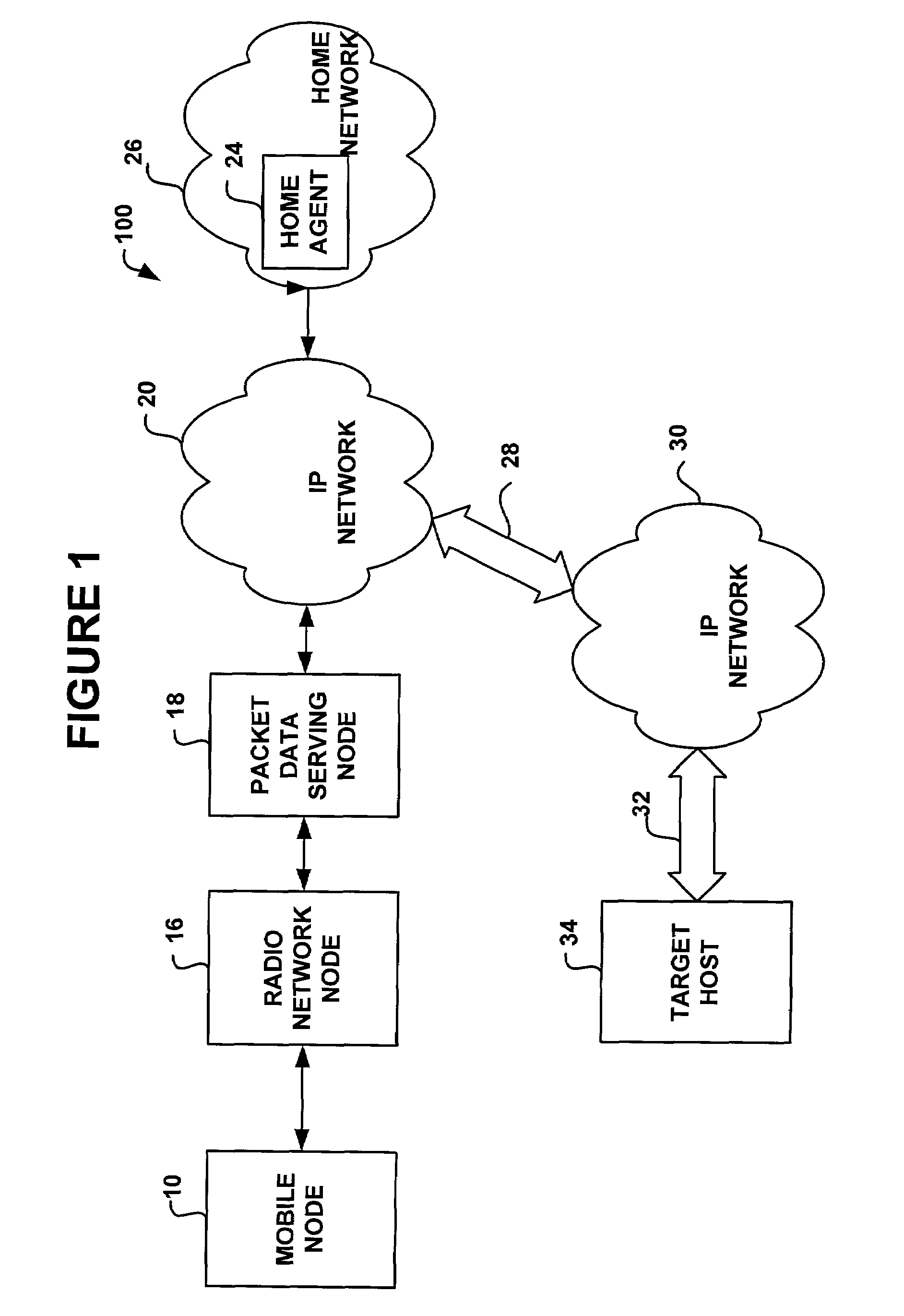
The Packet Data Serving Node, or PDSN, is a component of a CDMA2000 mobile network. It acts as the connection point between the radio access and IP networks. This component is responsible for managing PPP sessions between the mobile provider's core IP network and the mobile station (mobile phone). It is similar in function to the GGSN (GPRS Gateway Support Node) that is found in GSM and UMTS networks.
Managing backhaul connections in radio access networks
InactiveUS20070140218A1Network connectionsWireless communicationPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications
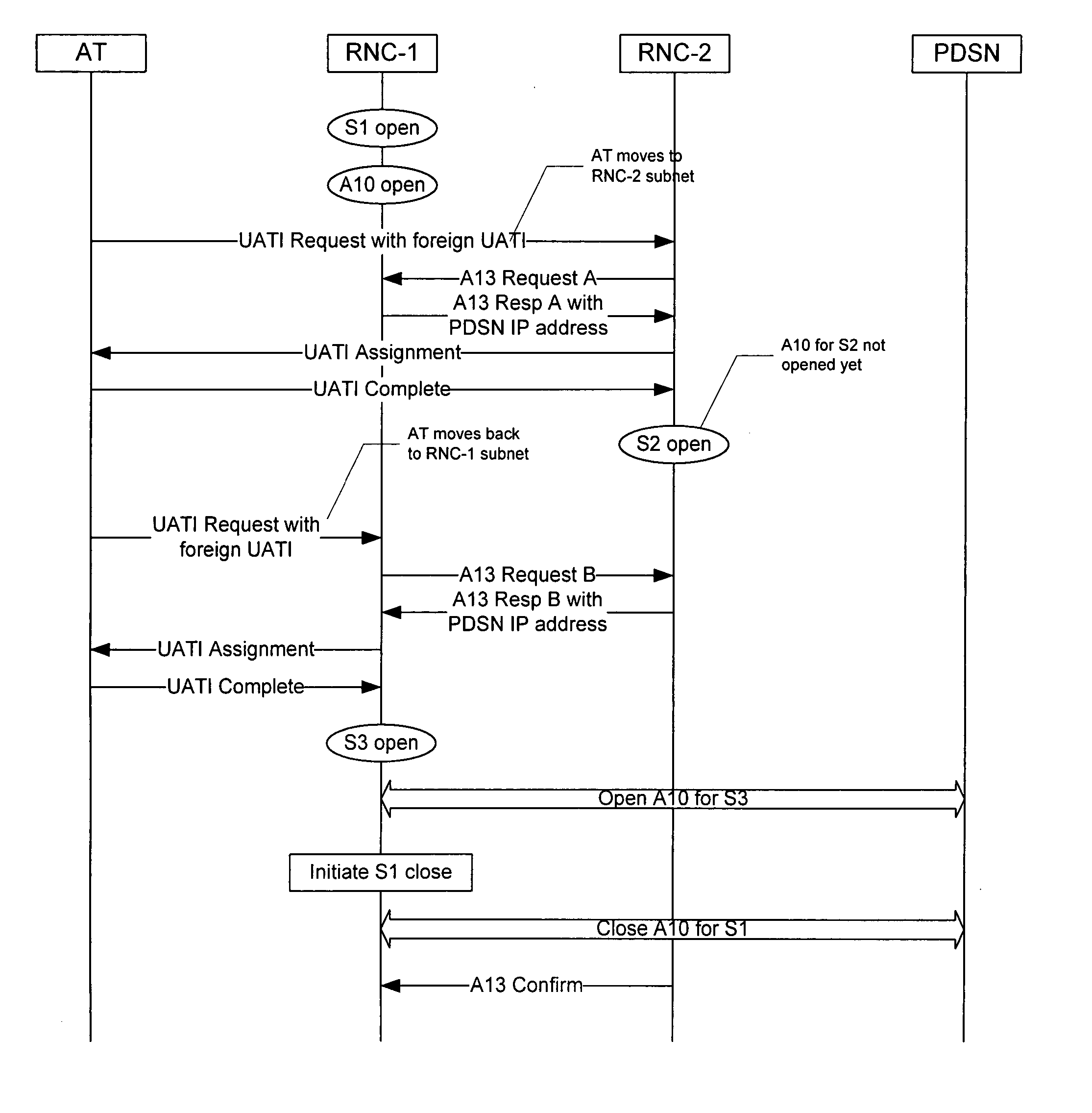
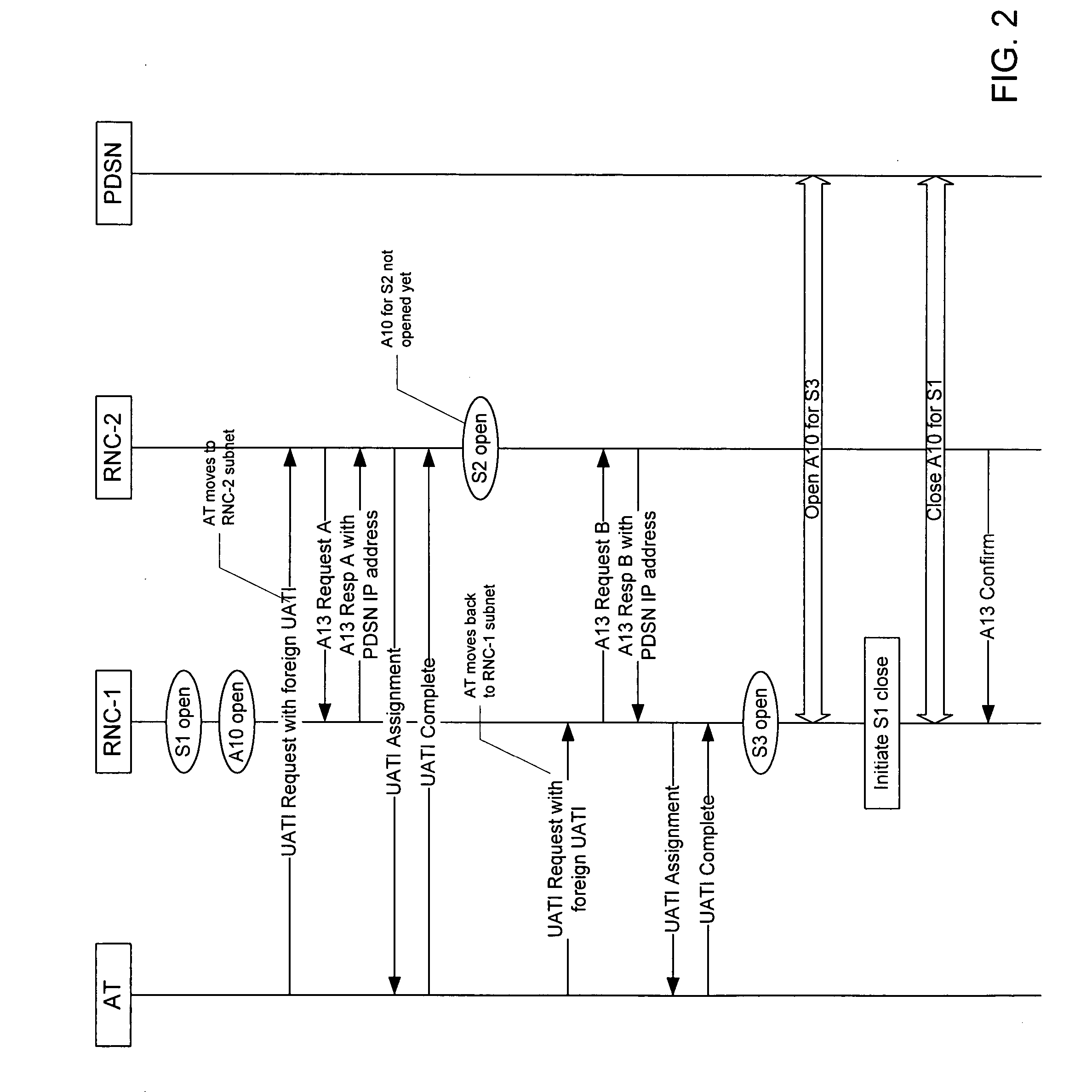
Techniques for initiating a backhaul connection between a radio node controller and a packet data serving node of a radio access network based on a determination of a presence of a packet data session on an access terminal. Techniques for enabling a dormant access terminal in communication with a radio access network to maintain a point-to-point (PPP) session with a packet data serving node as the dormant access terminal moves from a coverage area associated with a first radio node controller to a coverage area associated with a second radio node controller prior to a completion of a backhaul connection setup by the first radio node controller.
Owner:ERICSSON EVDO INC
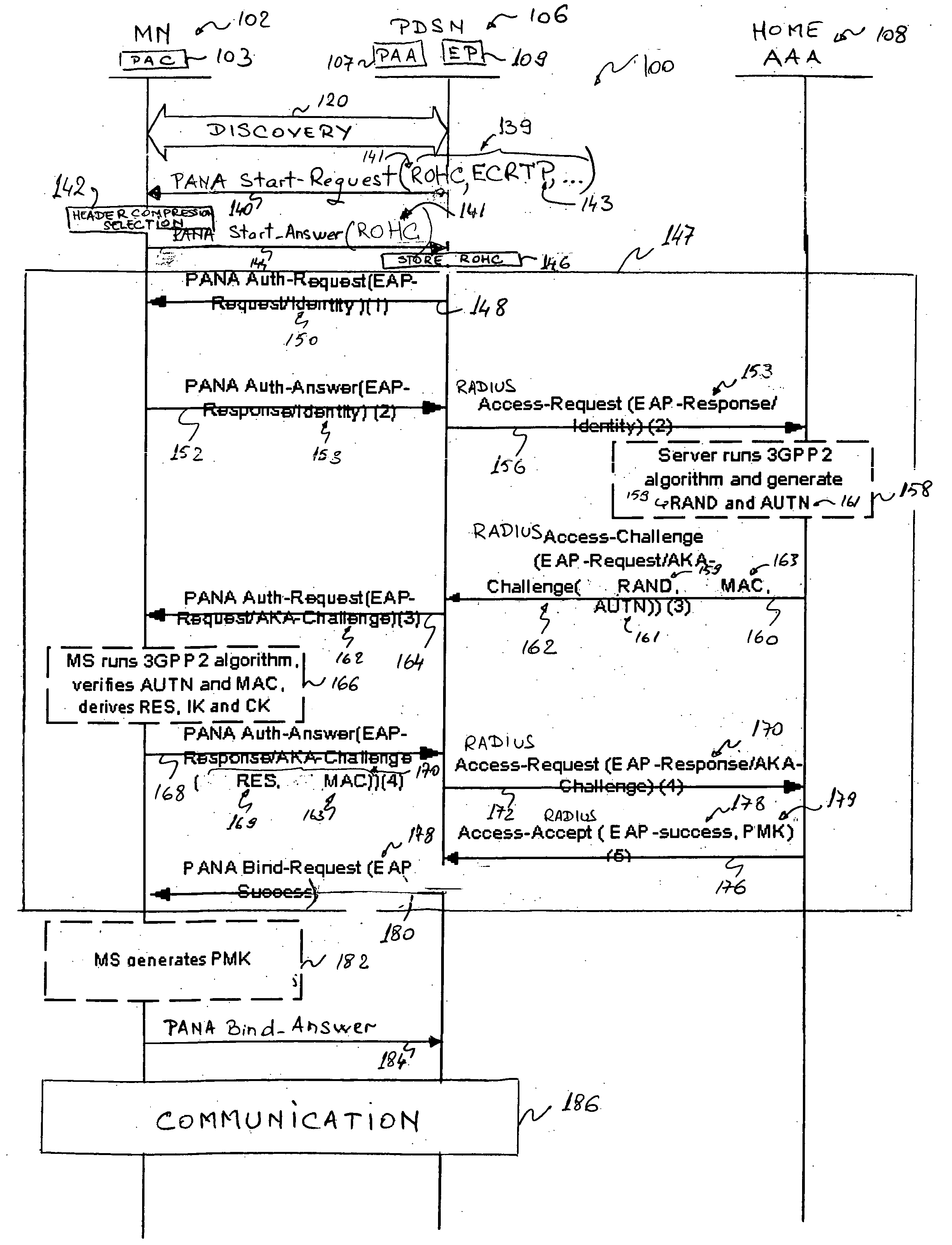
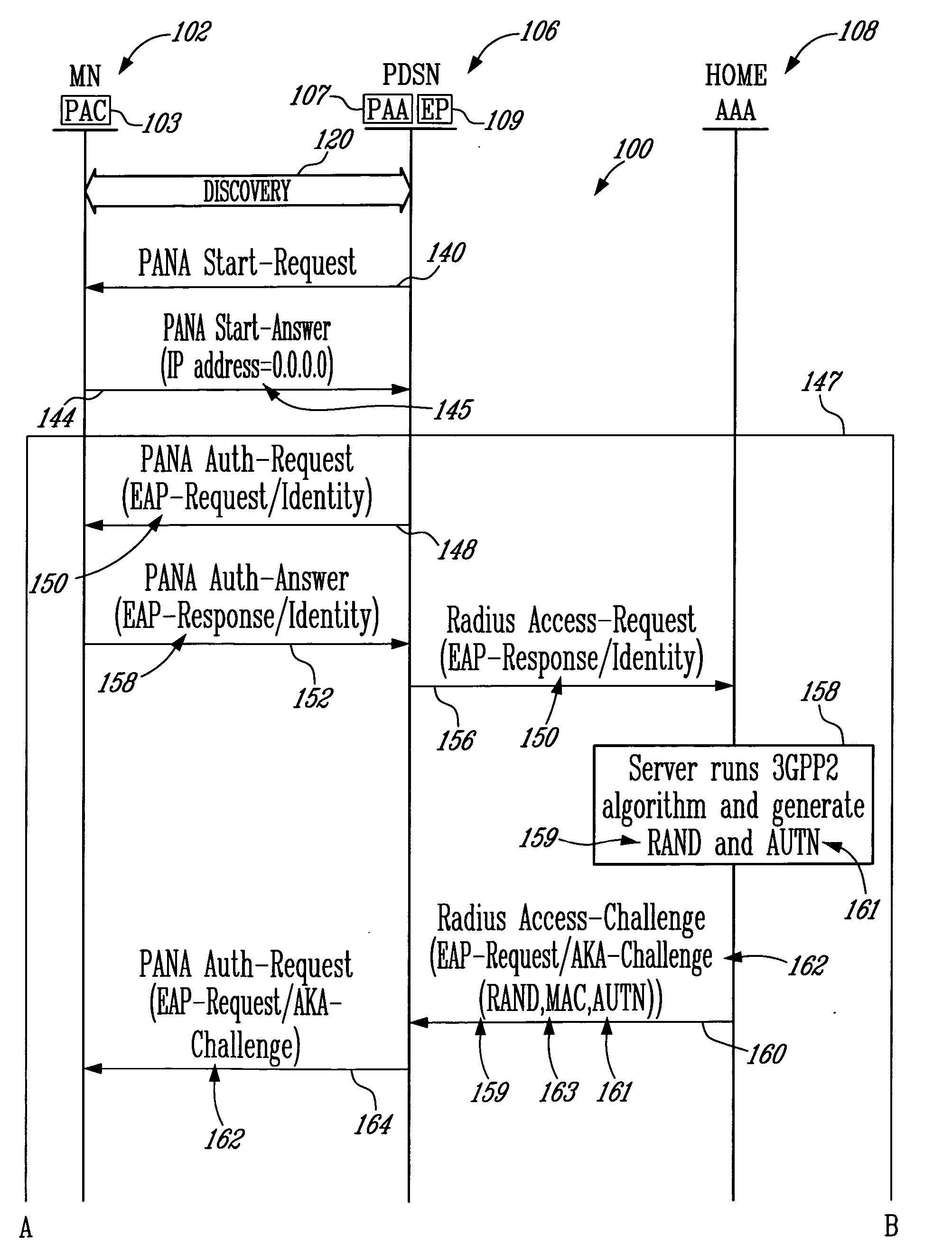
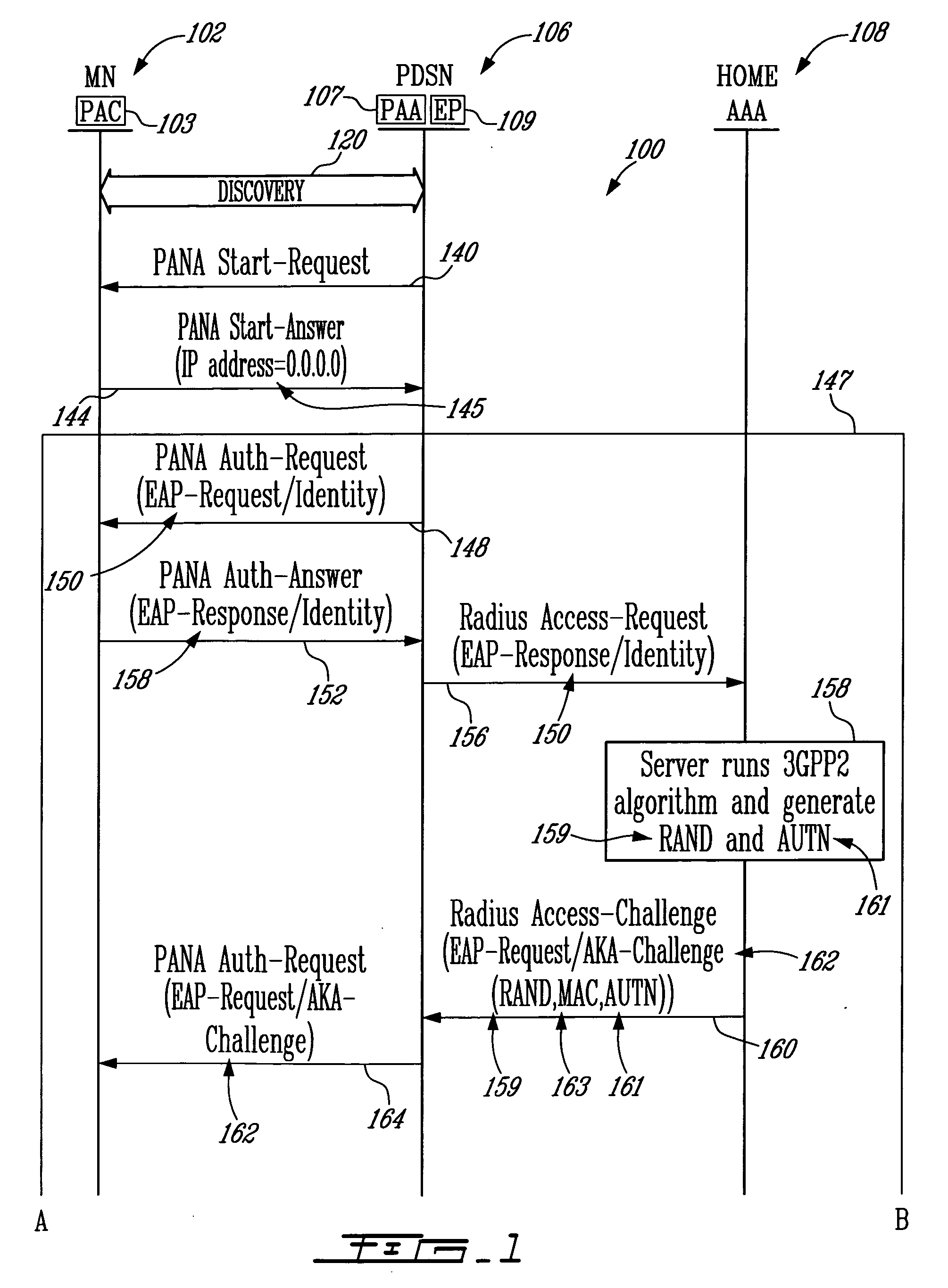
Header compression negotiation in a telecommunications network using the protocol for carrying authentication for network access (PANA)
InactiveUS20060002426A1Easy to useTime-division multiplexWireless network protocolsPacket data serving nodeCDMA2000
A method, a telecommunications node, and a Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access (PANA) Authentication Agent (PAA) of an IP-based network such as a CDMA2000 telecommunications network are provided for negotiating packet data header compression mechanisms. A first and second node, which may be, for example, a Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) and a Mobile Node (MN) are first involved in a discovery phase. Then the PDSN sends a PANA Start-Request message to the MN with a list of supported header compression mechanisms. The MN receives the PANA Start-Request message with the list, and selects one or more supported mechanism from the list. The MN then responds back to the PDSN with the selected one or more header compression mechanisms via a PANA Start-Answer message. The PDSN stores the selection of the header compression mechanisms, authenticates the MN, possibly in combination with an Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server, and if the authentication is successful, allows the start of a data session using the selected header compression mechanism(s).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
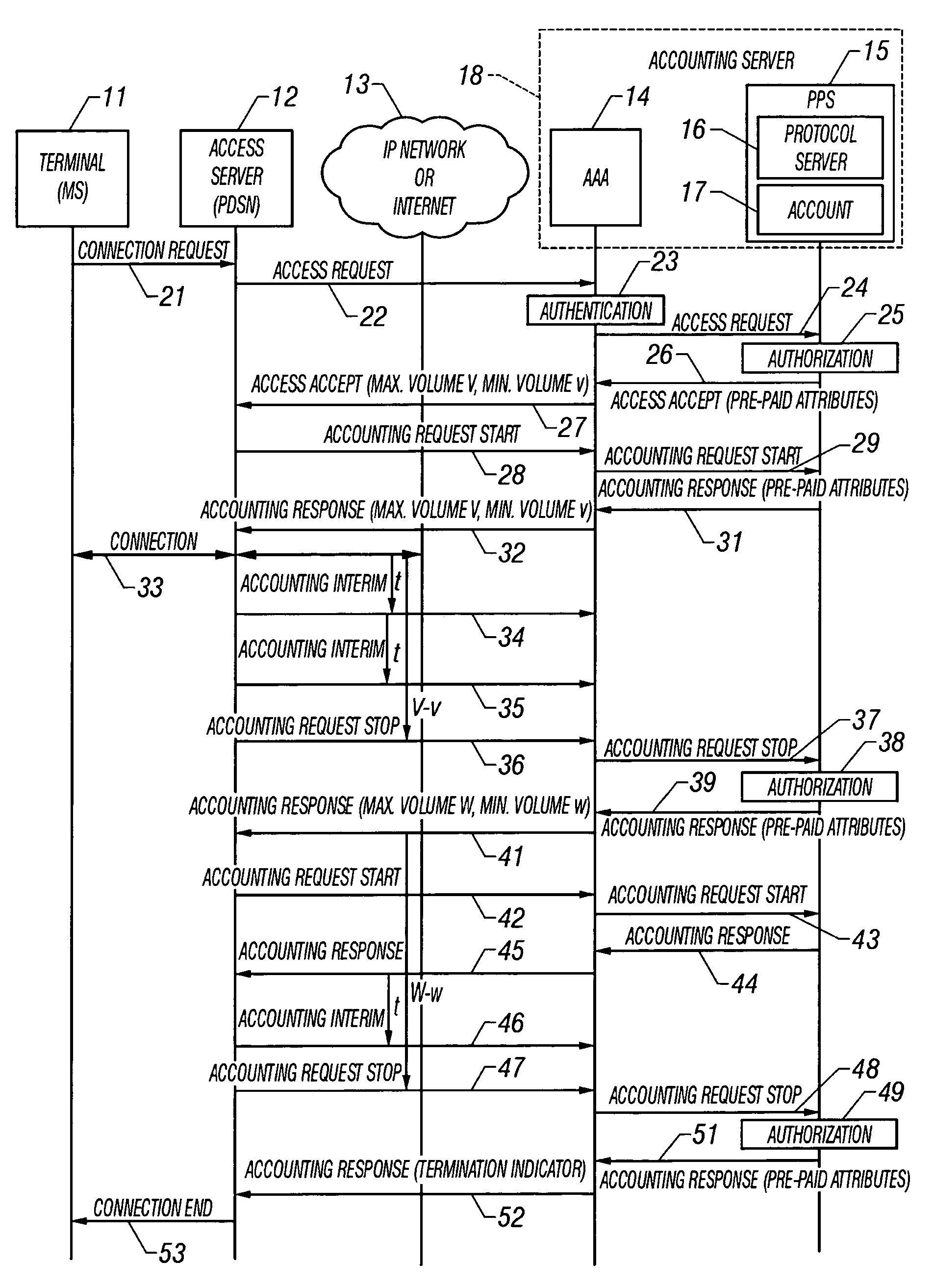
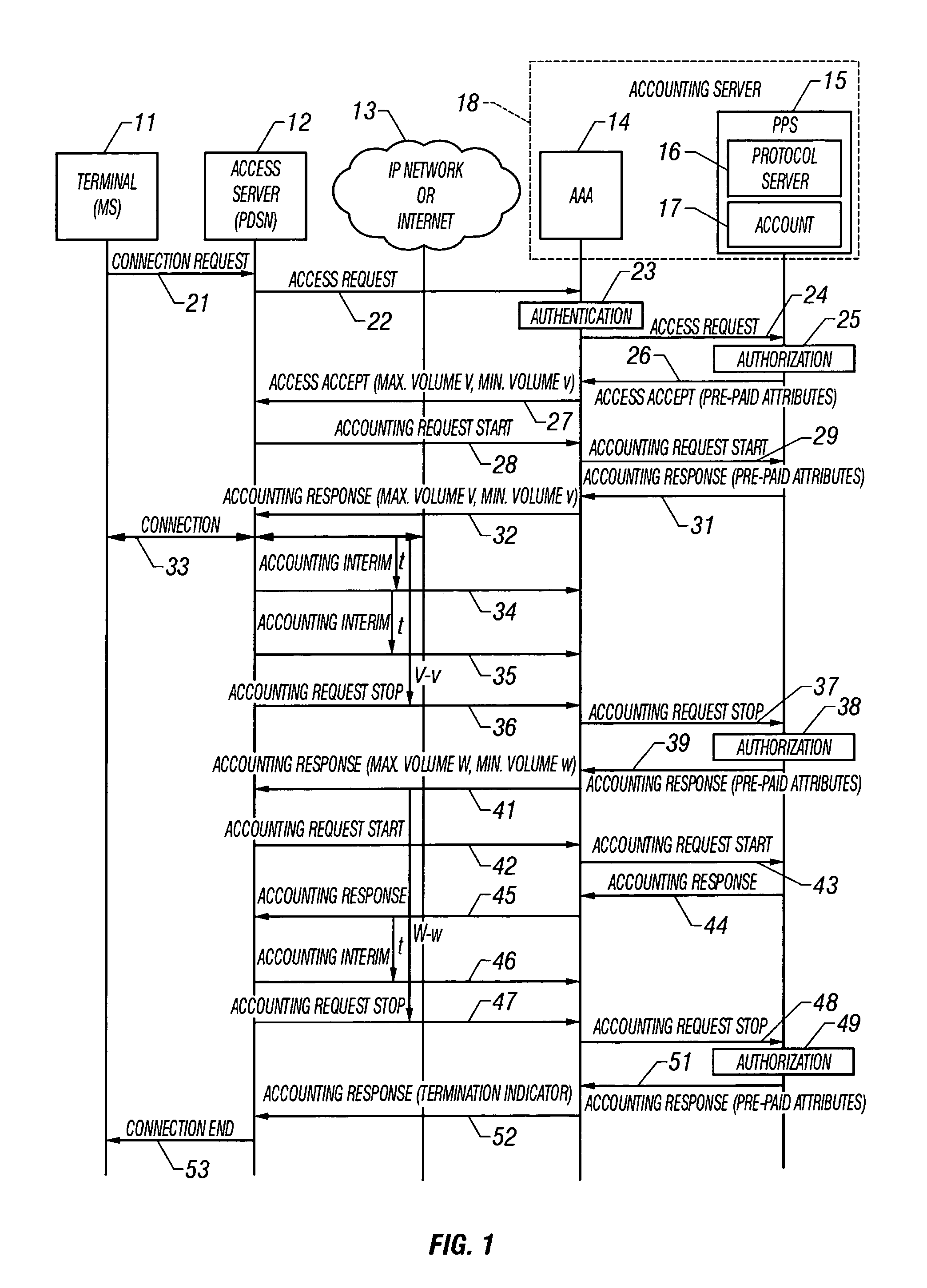
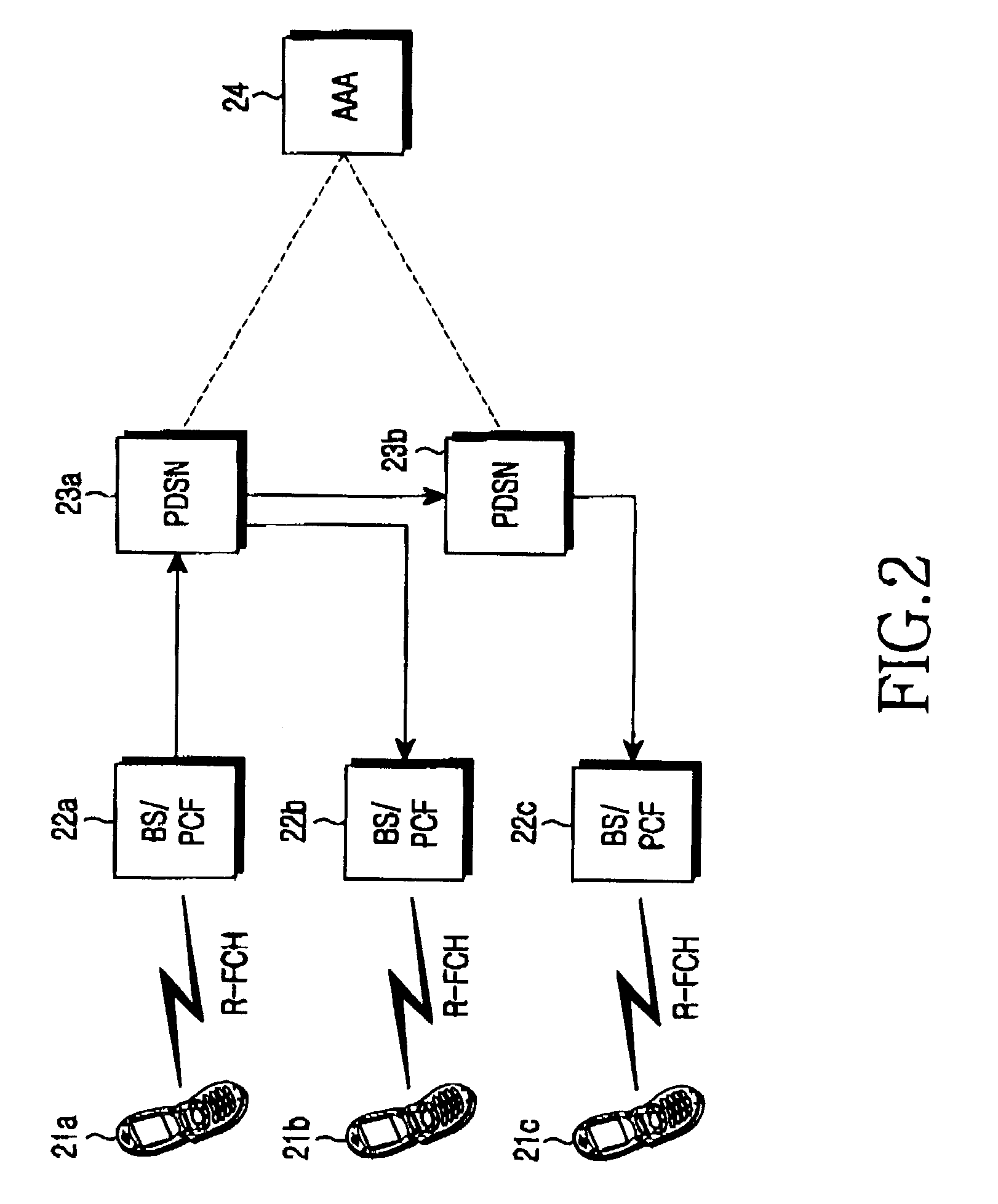
System and method of monitoring and reporting accounting data based on volume
ActiveUS20020046277A1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsDigital computer detailsPacket data serving nodeData mining
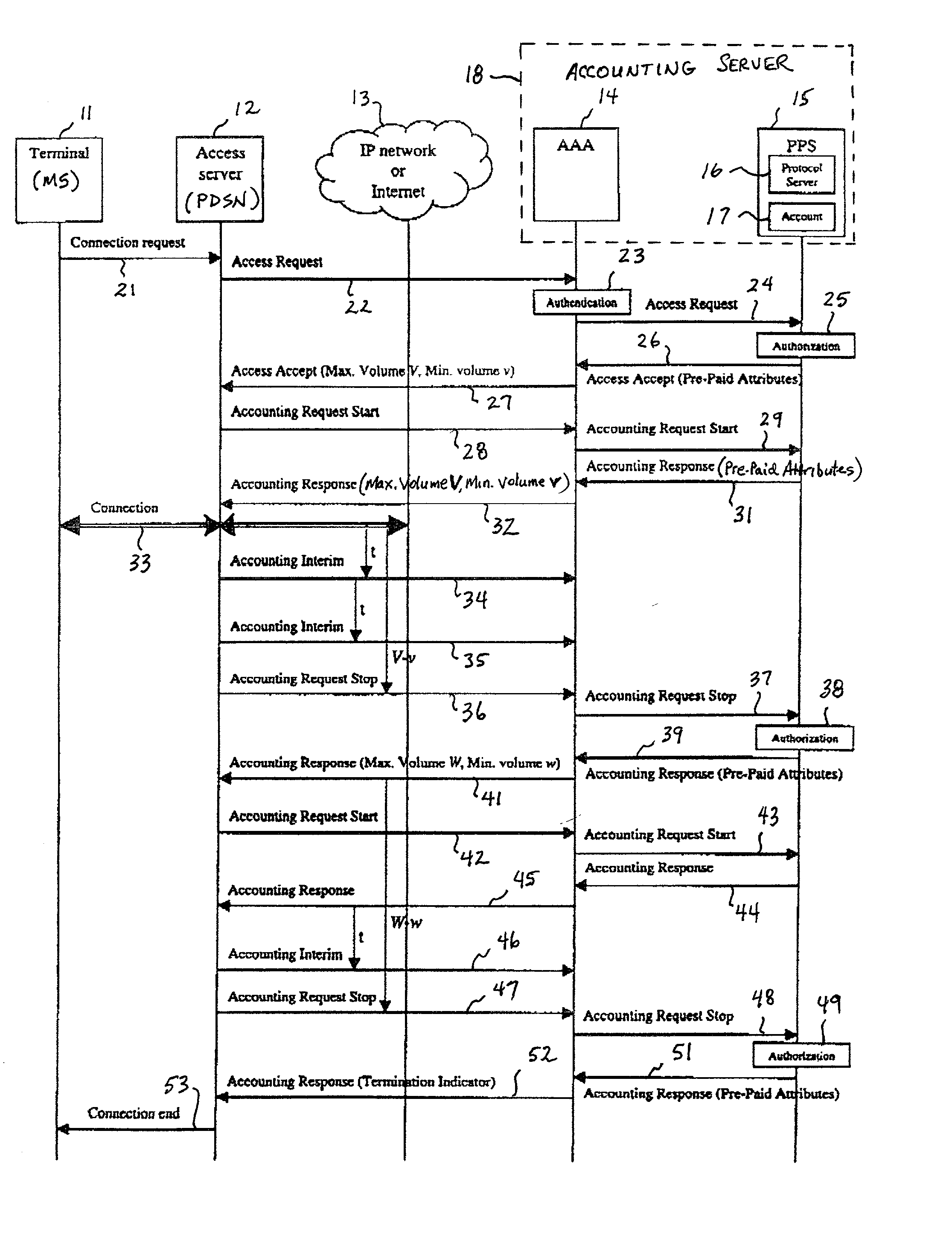
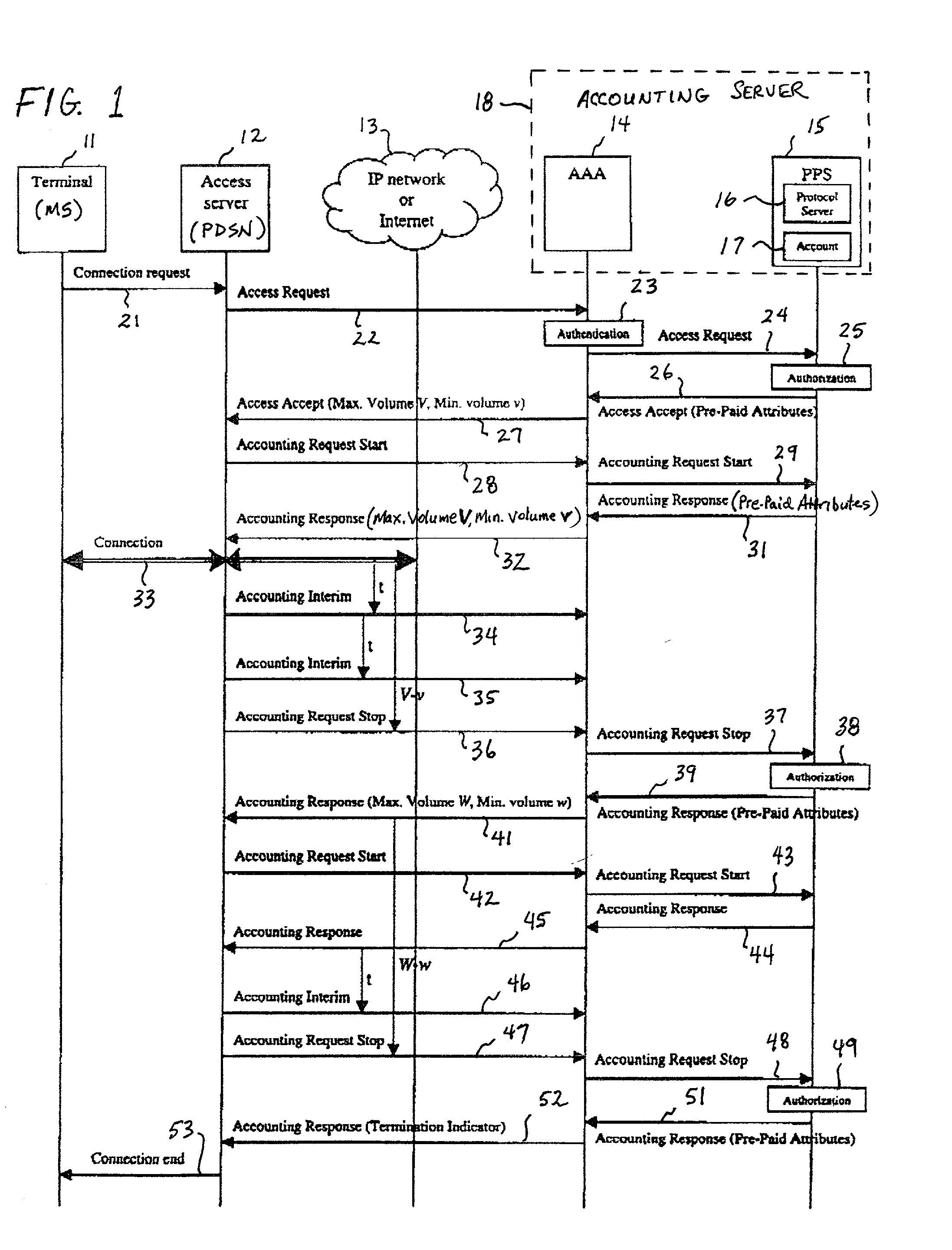
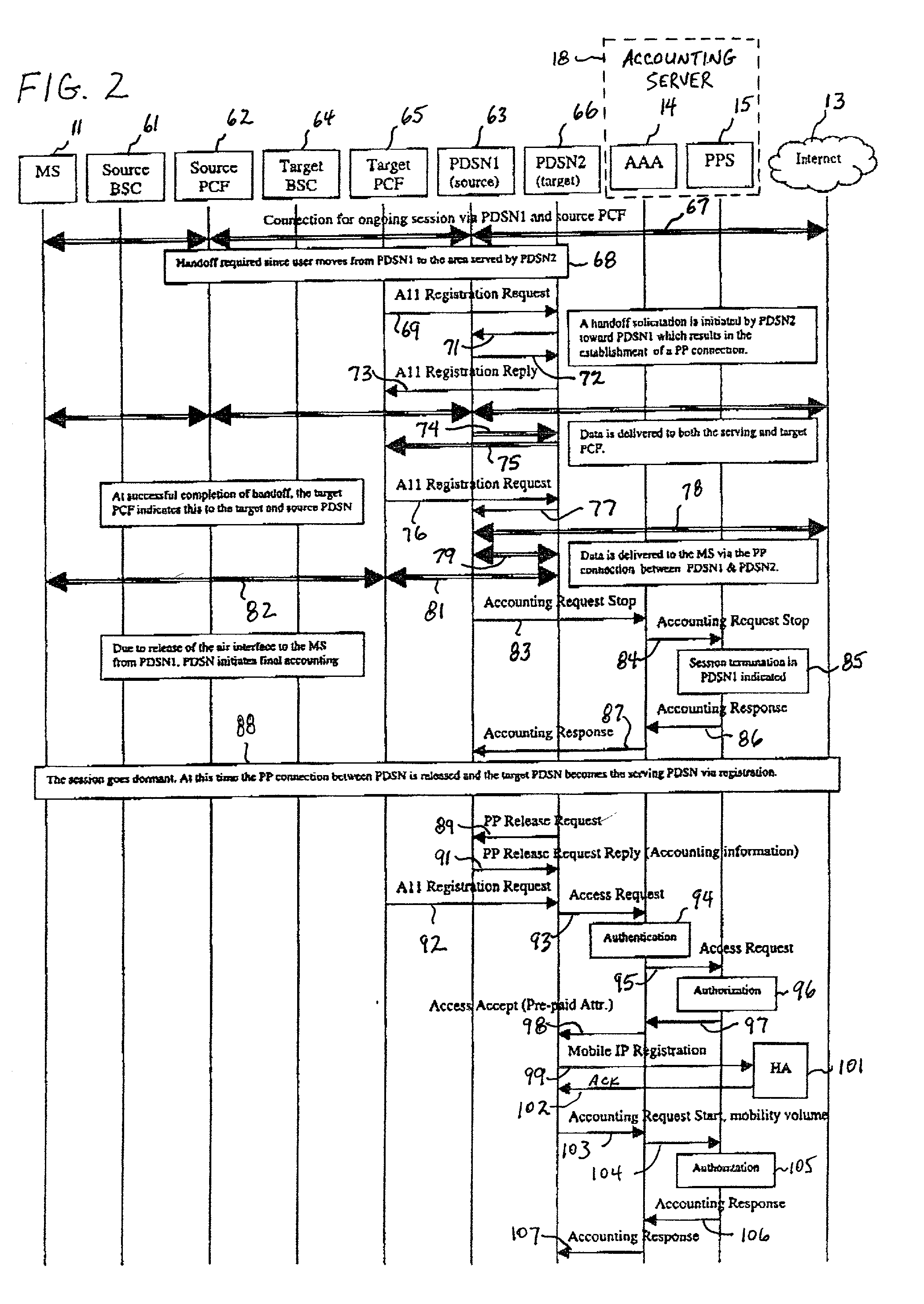
A system and method for monitoring and reporting a volume of data transferred between a Mobile Station (MS) and a data network during a data session. A Prepaid Server (PPS) maintains an MS account and informs a AAA Server of a predetermined volume of data that may be transferred during the session. A Packet Data Service Node (PDSN) sends interim accounting messages to the AAA Server which determines when the predetermined volume of data has been transferred, and notifies the PPS. When the account balance goes below a threshold volume, the data session is terminated. During handoff of the MS from a first PDSN to a second PDSN, a data tunnel is established between them. When the handoff is complete, the tunnel is torn down. The first PDSN reports the volume of data transferred through the tunnel to the second PDSN which reports the volume to the AAA Server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
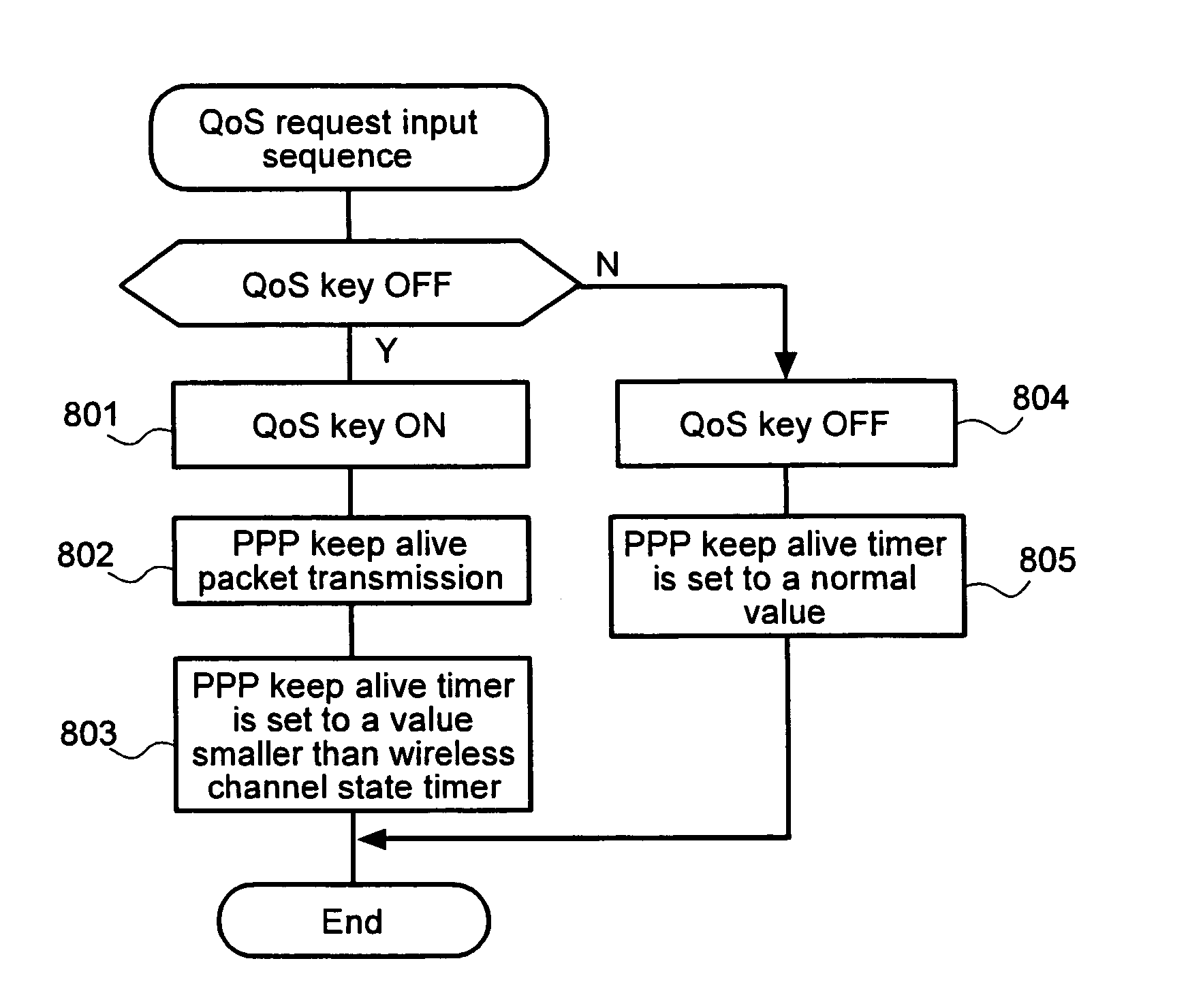
QoS support method in a high-rate packet data system
ActiveUS20050094611A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationQuality of servicePacket data serving node
Disclosed is a Quality-of-Service (QoS) Support method in a mobile communication system including an access terminal, an access network for performing packet data communication with the access terminal, a packet control function for controlling transmission and reception of packet data between the access network and the access terminal, and a packet data service node for exchanging packet data with the packet control function. The access terminal maps a requirement based on an application characteristic to an IP QoS parameter, generates a resource reservation protocol message, and transmits the resource reservation protocol message to the packet data service node. The packet data service node maps IP QoS information to be transmitted to the access terminal to QoS information needed in the access network, and transmits the mapping result to the access network via the packet control function. The access terminal receives data including QoS information from the packet data service node, and performs communication according to the QoS information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for packet data servicing node (PDSN) initial assignment and reselection
InactiveUS20050025116A1Assess restrictionNetwork topologiesPacket data serving nodeCommunications system
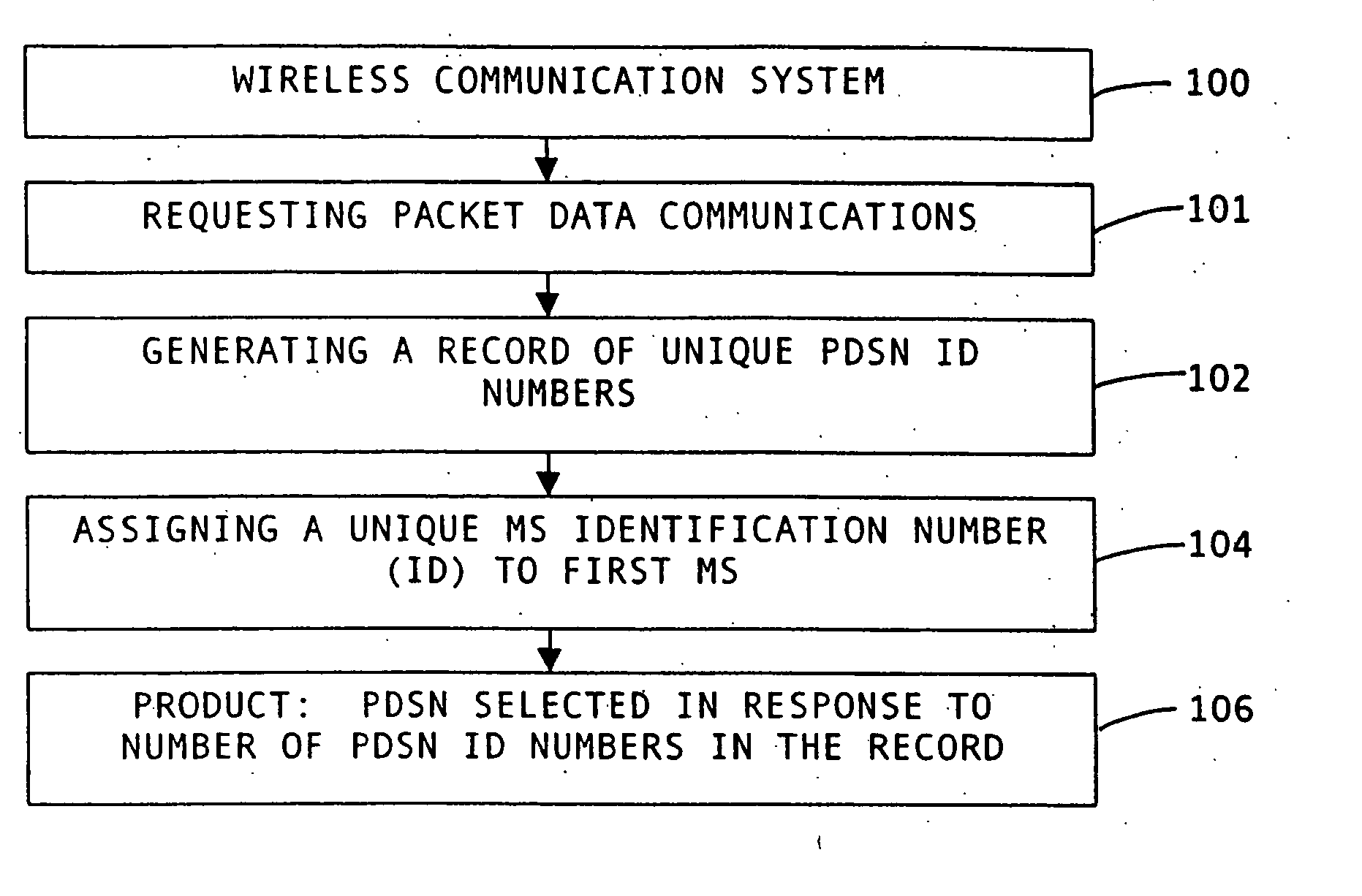
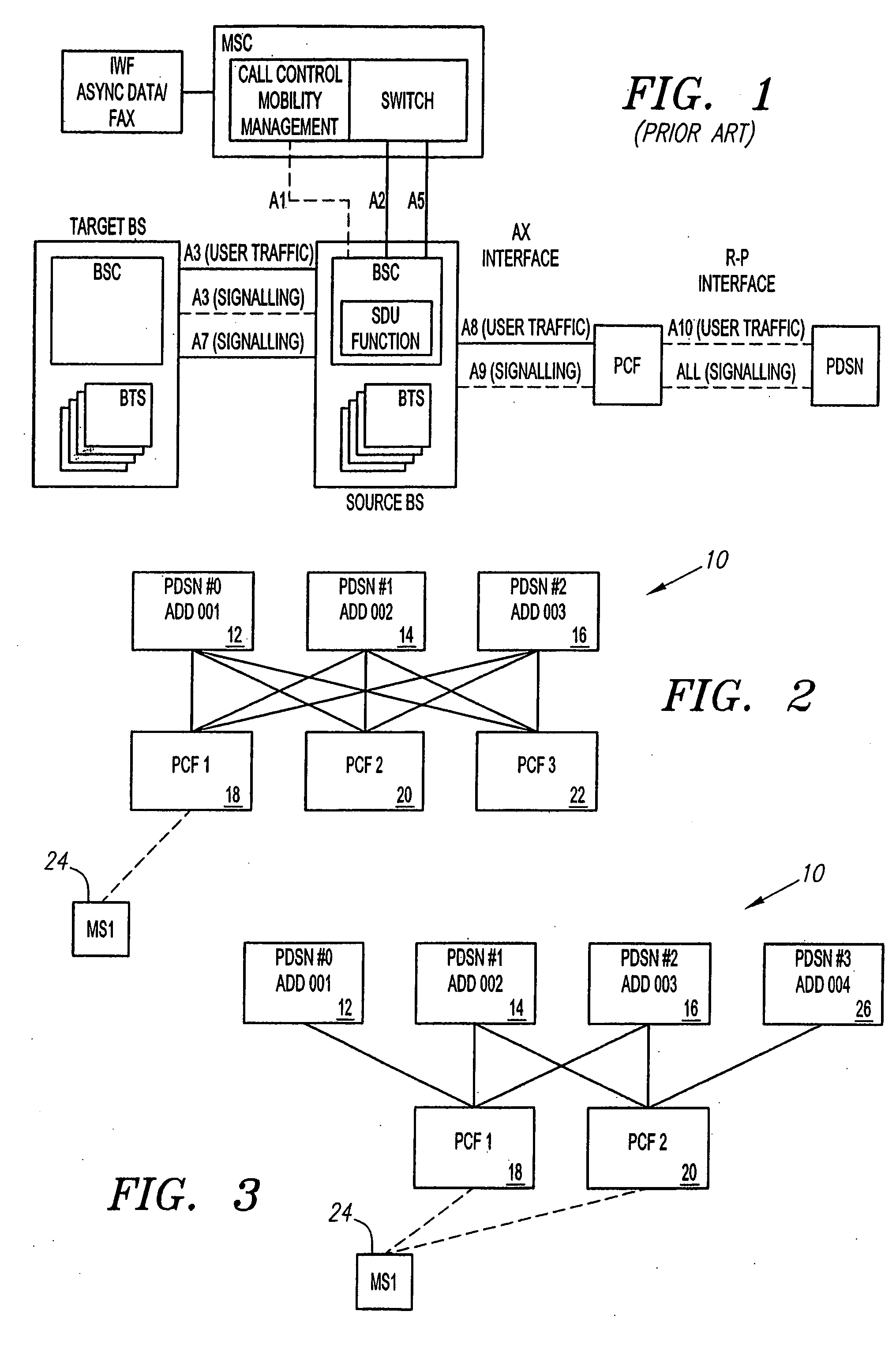
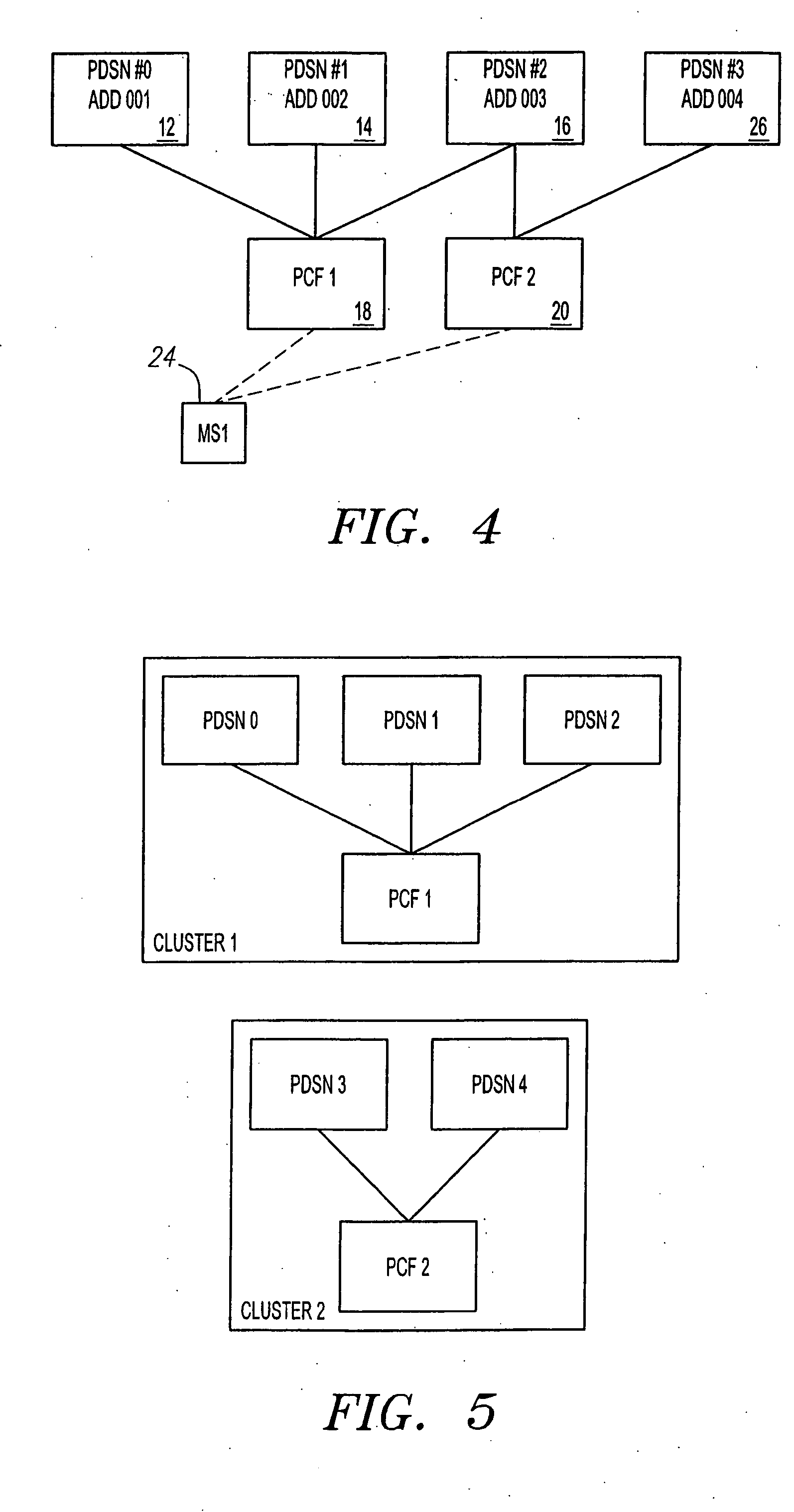
An method for PDSN (Packet Data Serving Node) initial assignment and re-selection in a wireless communication system is provided. The method is implemented in PCF (Packet Control Function) within a third-generation (3G) CDMA Radio Access Network (RAN). The methodology reduces the number of point-to-point (PPP) re-establishments, when a Mobile Station (MS) roams to a different packet zone / PCF. The method generates a table of PDSN identification numbers cross-referenced to the PDSN Internet protocol (IP) addresses, residing with each PCF. A PDSN Id number is selected from the table using the MS IMSI (International Mobile Station Identifier) as a key to perform the selection. The present invention methodology addresses the issue of forward and backward compatibility, scalability, reliability, and load sharing in the PDSN selection.
Owner:CHEN NING NICHOLAS +3
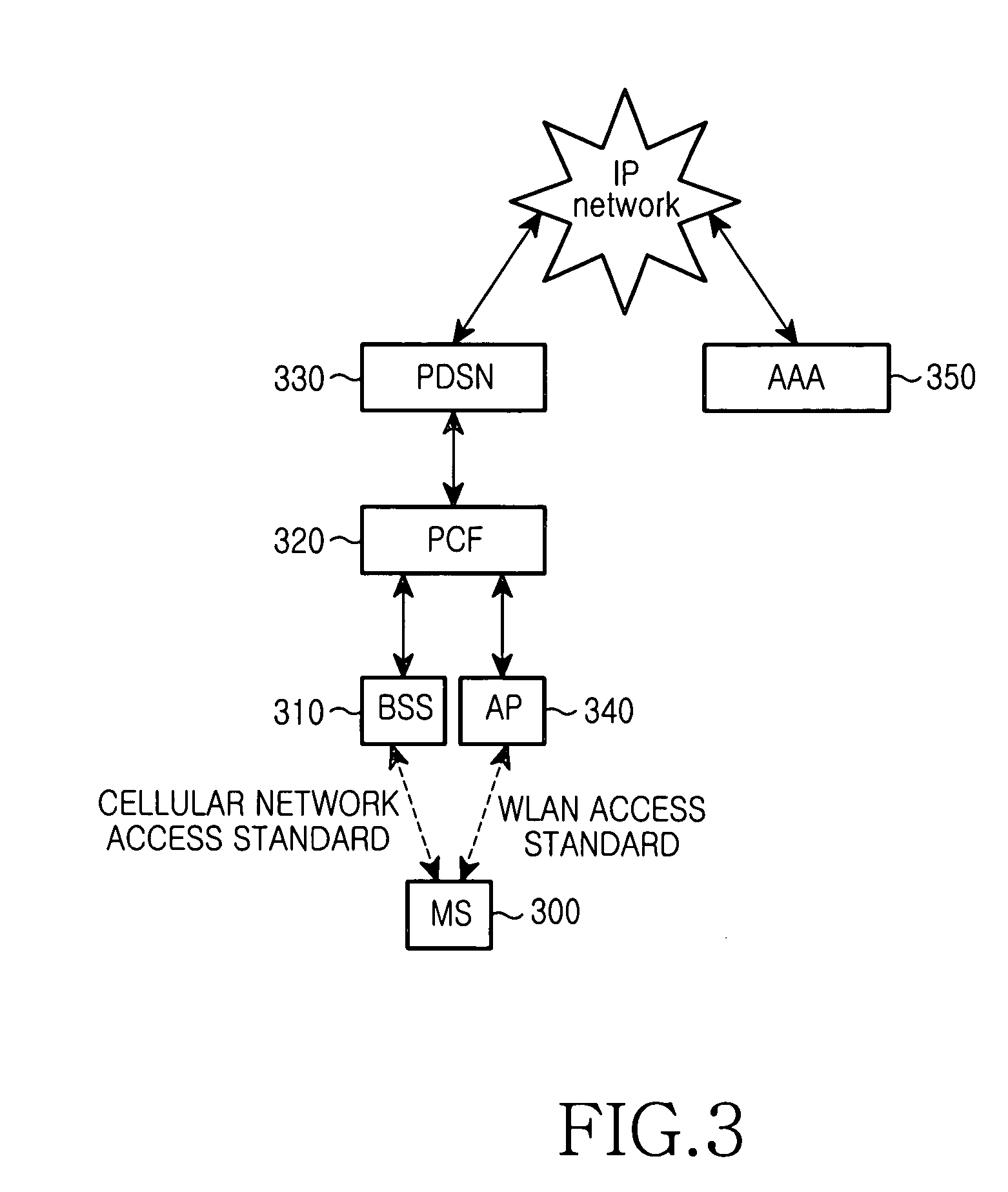
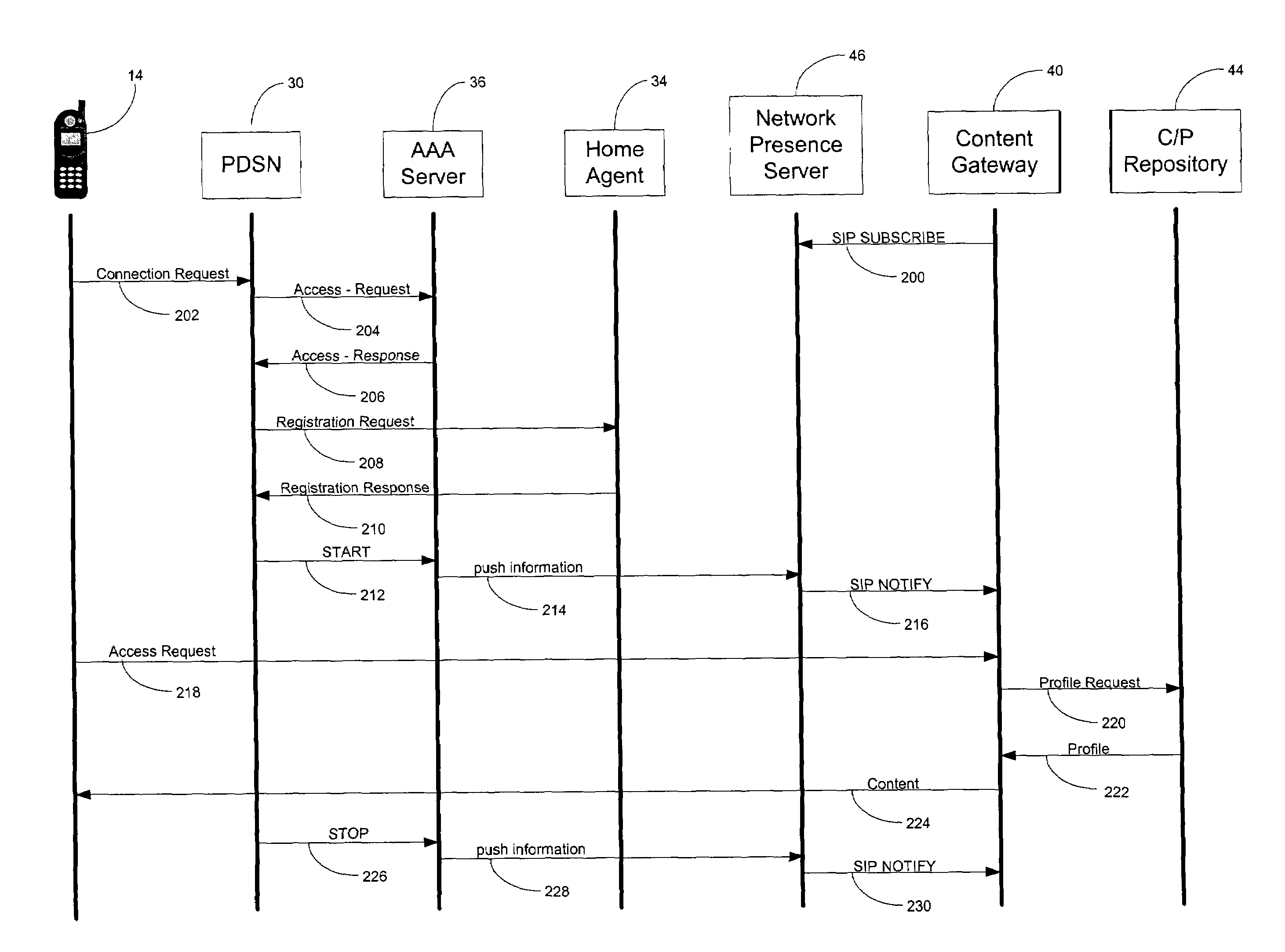
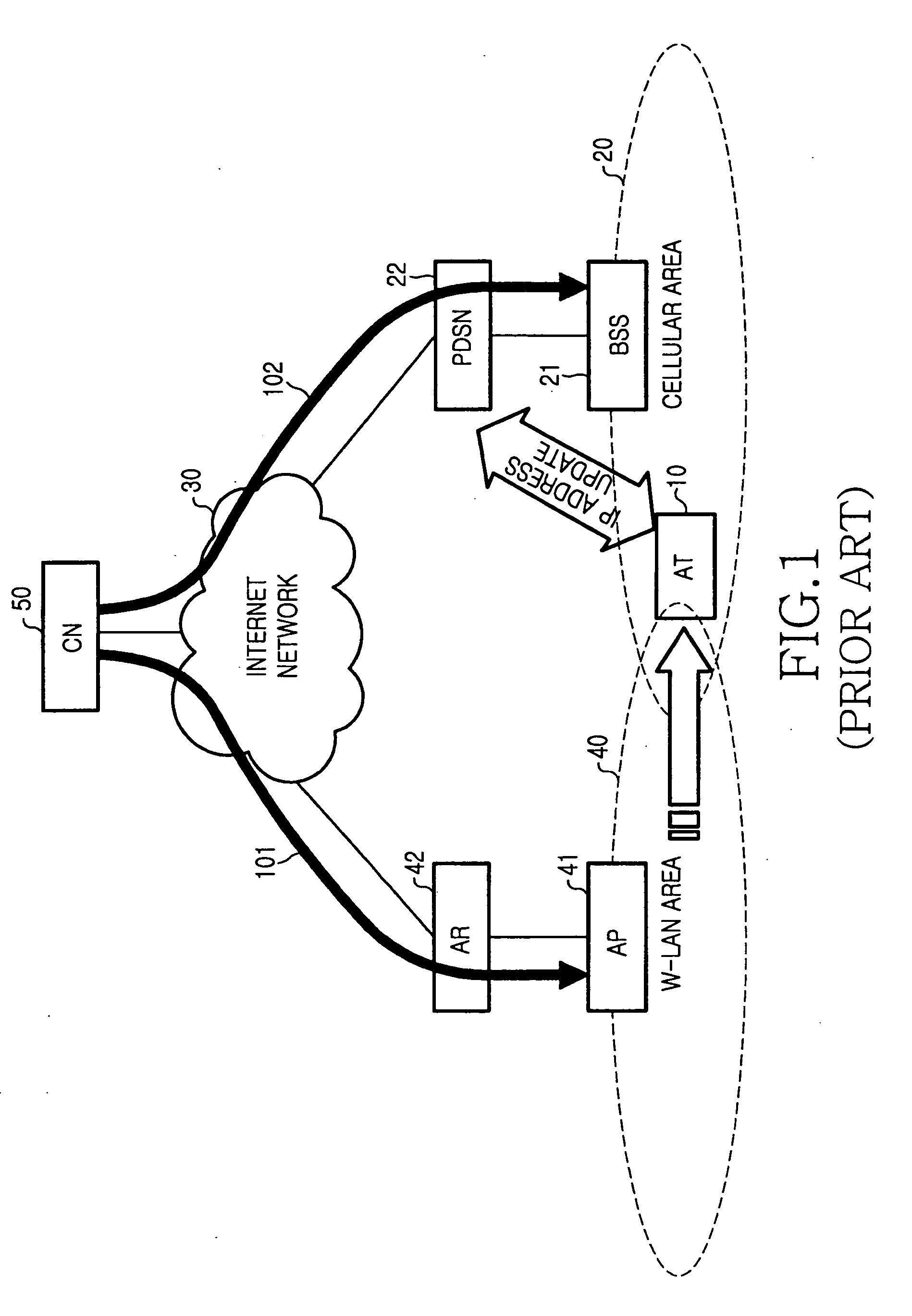
System and method for interworking between cellular network and wireless LAN
A method and system for providing a packet data service of a cellular network to an access terminal (AT) that accessed a wireless local area network (LAN) are provided. The AT accessing the wireless LAN transmits a session request message. Once the session request message is received, an interworking—entry server (IES) sends an authentication request for the AT, and after completing authentication on the AT, transmits a session response message to the AT. Once the session response message is received, the AT sets up a generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnel to an interworking—packet control function (I-PCF). The I-PCF sets up a GRE tunnel to a packet data serving node (PDSN) that provides the packet data service to the AT. The AT exchanges packet data with the PDSN.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optimized packet-resource management
InactiveUS20010050907A1Easy to useError preventionTransmission systemsPacket data serving nodeData connection
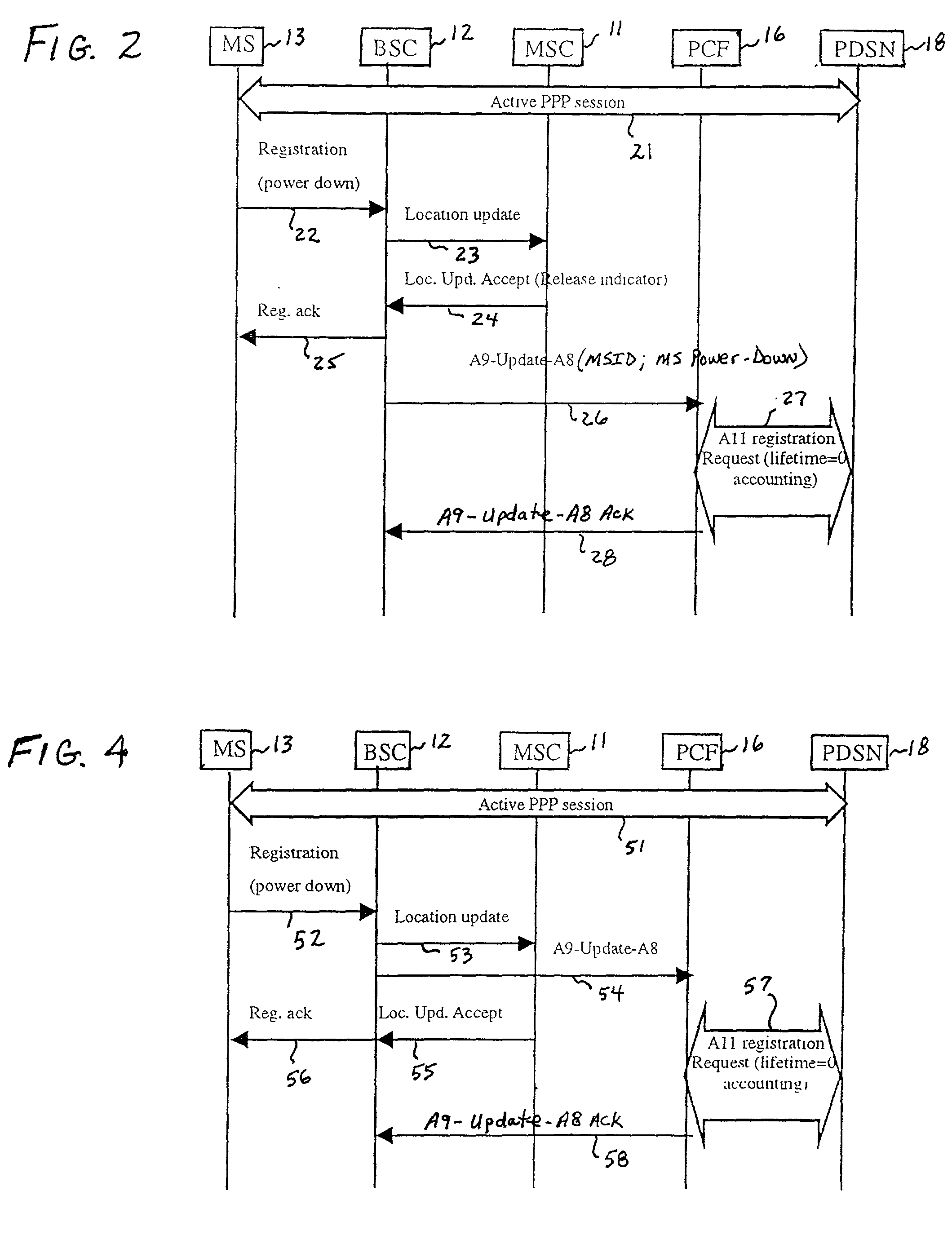
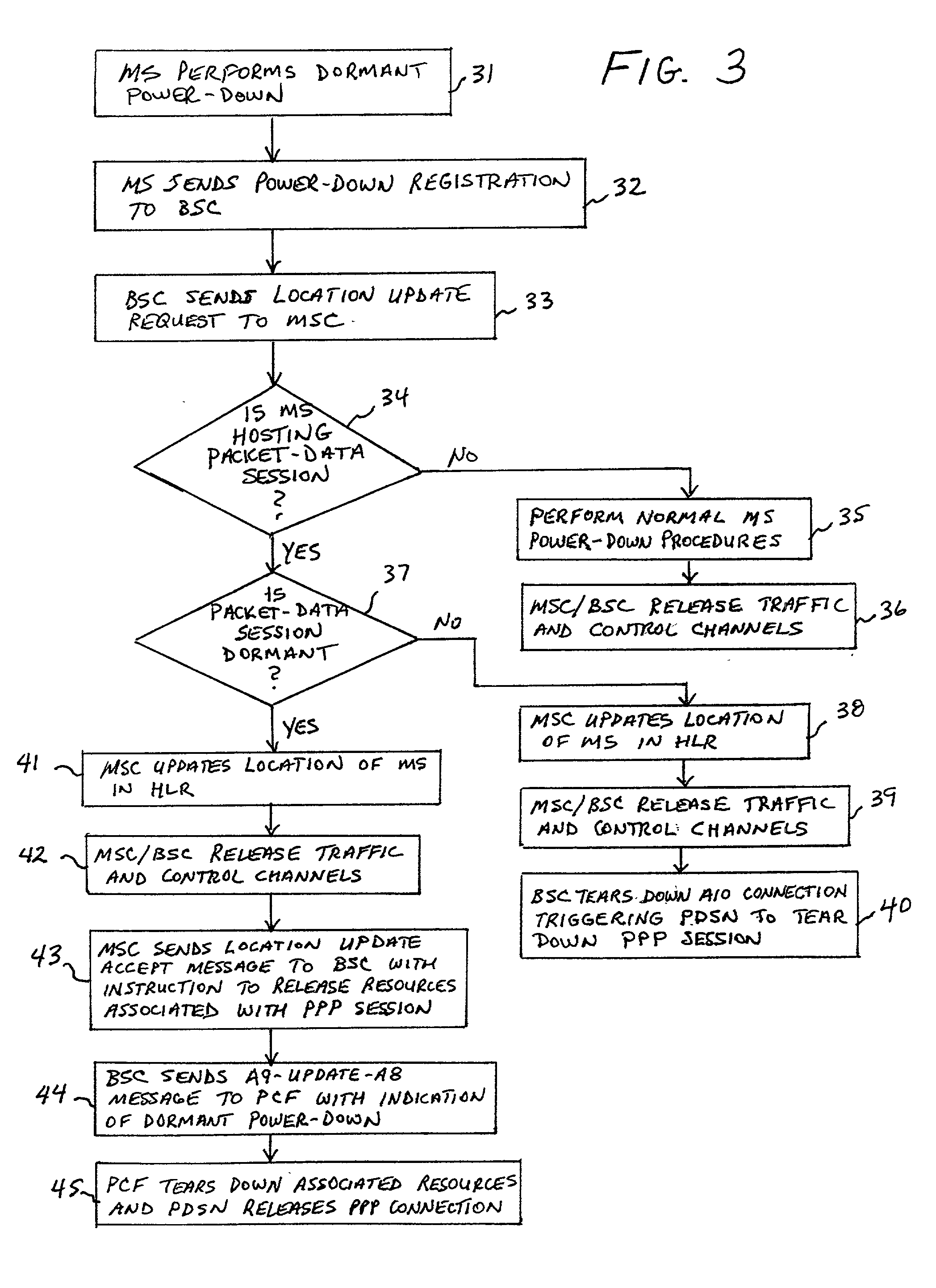
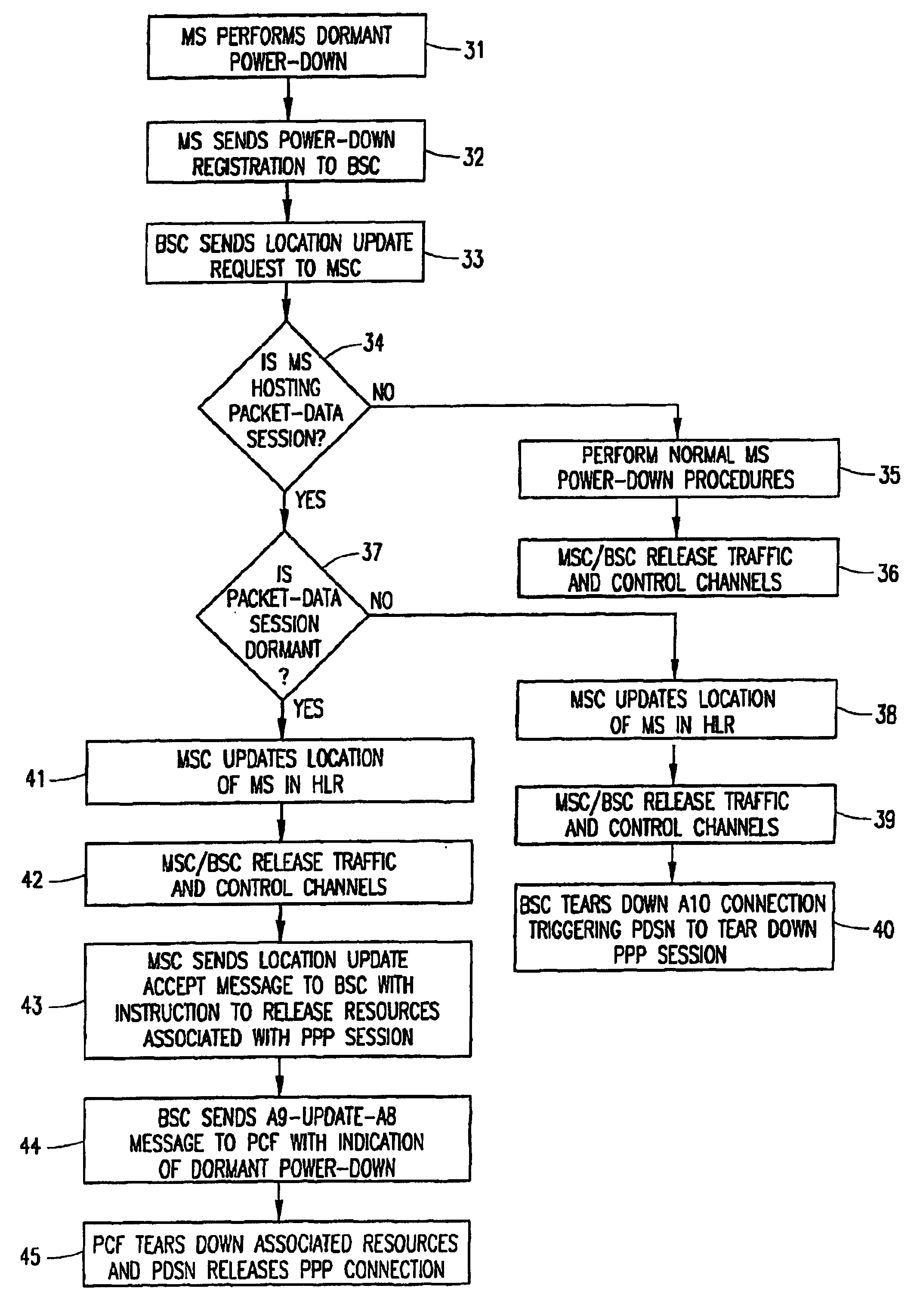
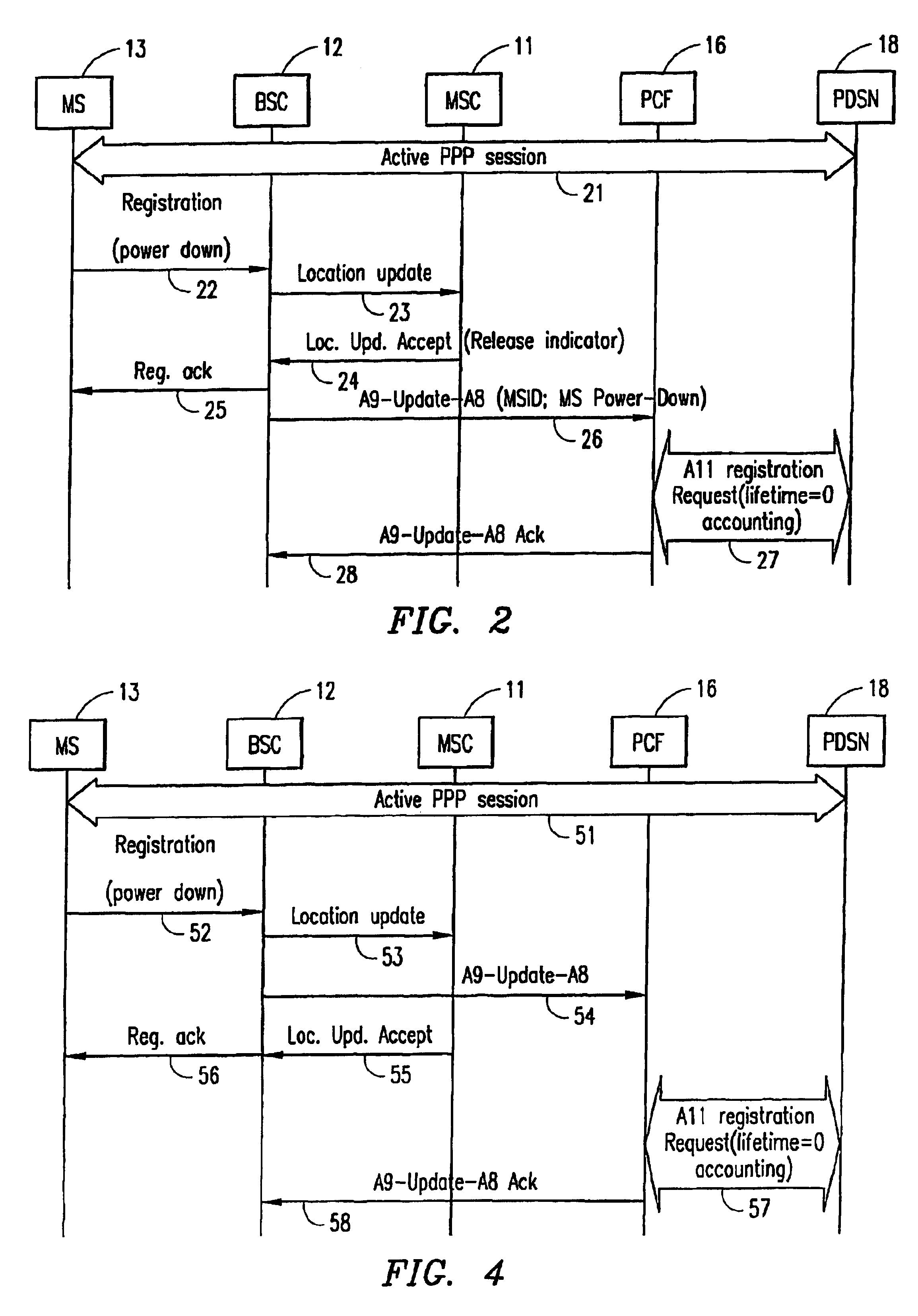
A system and method for optimizing the use of packet-resources by releasing a hanging packet-data connection when a Mobile Station (MS) performs a power-down while involved in a dormant packet-data session. A Base Station Controller (BSC) sends a message to a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) indicating that the MS has powered down. The MSC determines that the packet-data session is dormant, and sends an instruction to the BSC in a class-0 connectionless transaction to release network resources associated with the packet-data session. The BSC then sends an instruction to a Packet Control Function (PCF) to tear down the associated resources, and the packet-data connection is released by a Packet Data Service Node (PDSN) in response to the tearing down of the resources by the PCF.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of and system for processing prepaid wireless data communications
ActiveUS7239862B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsPacket data serving nodeProcessing Instruction
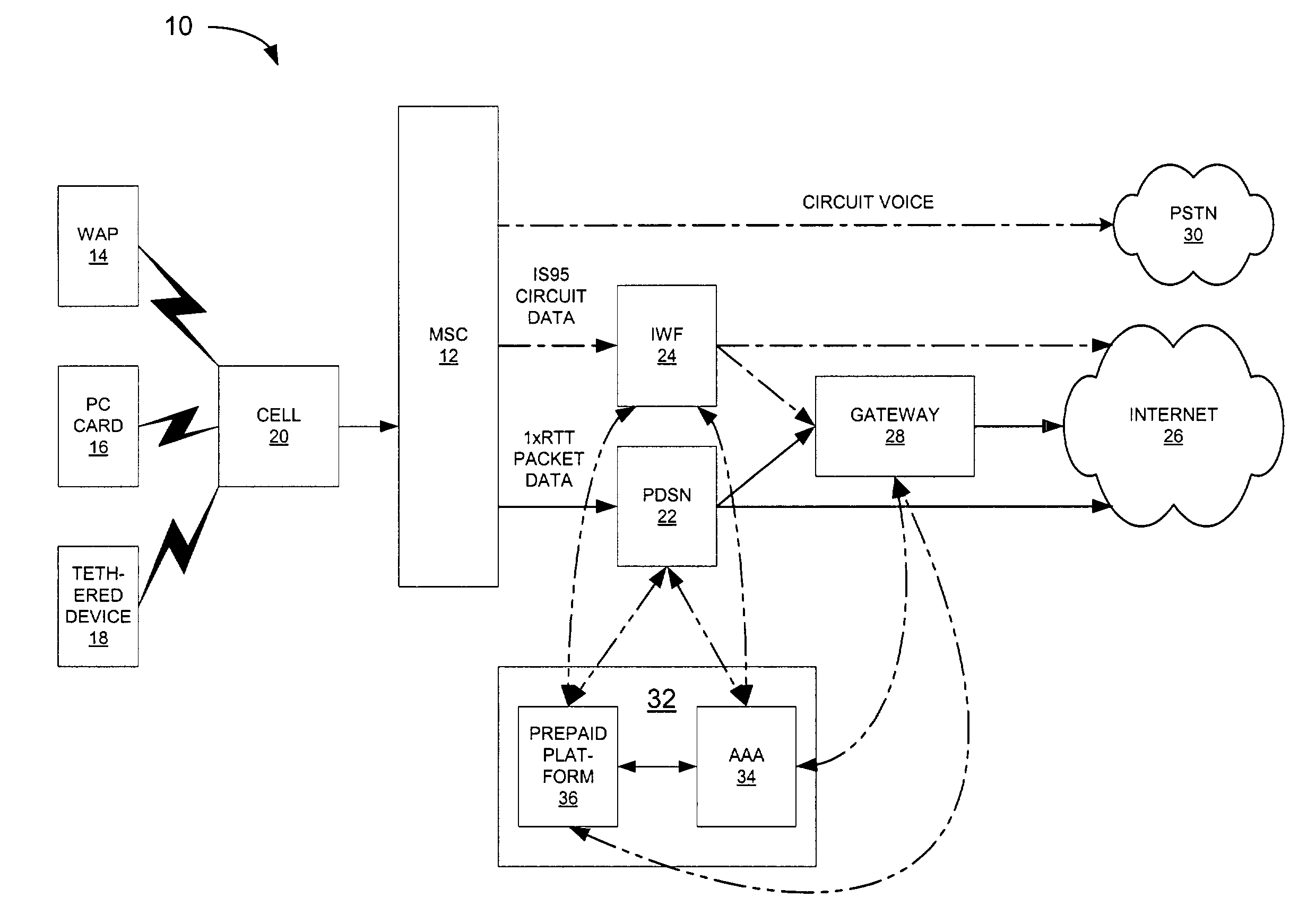
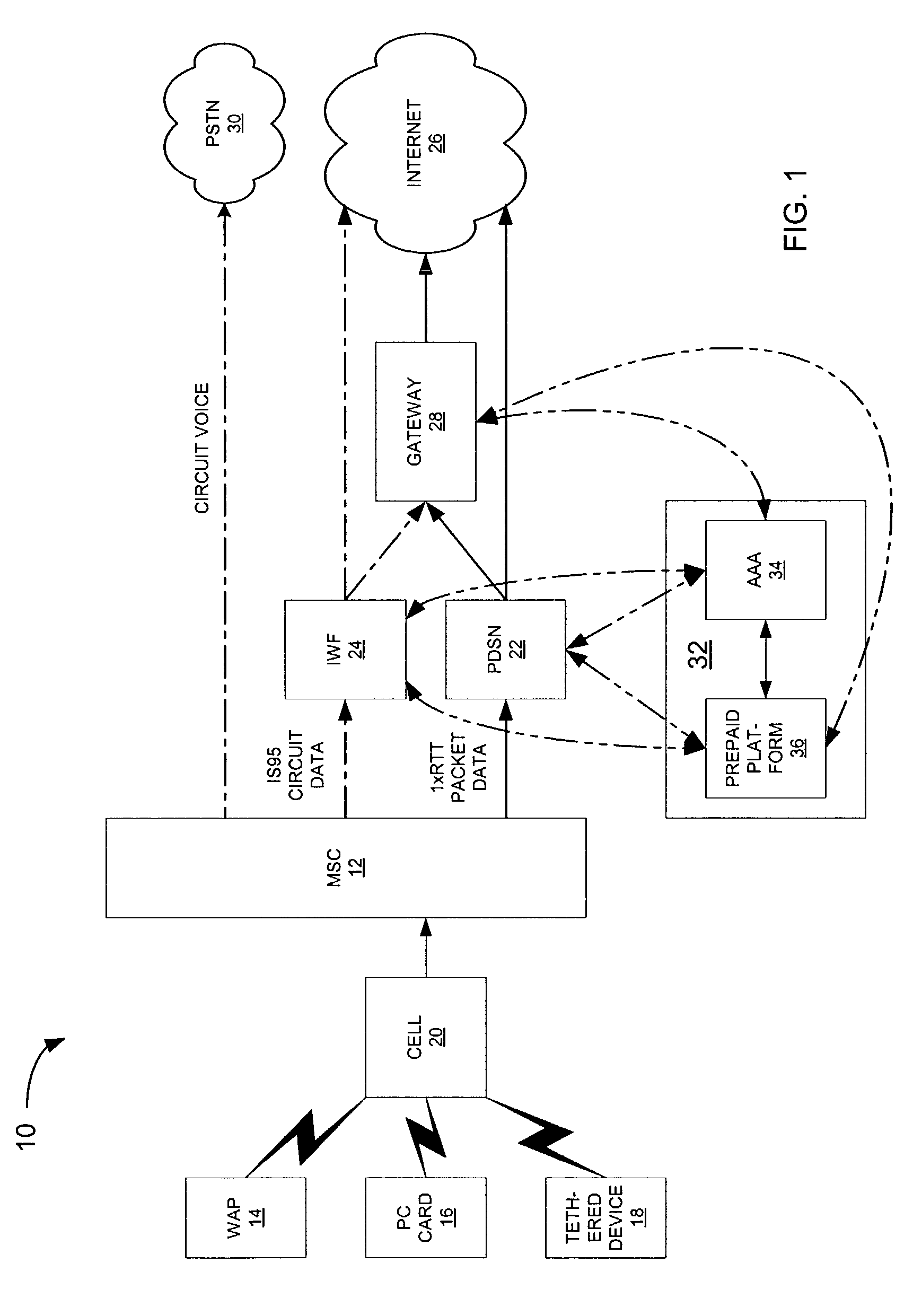
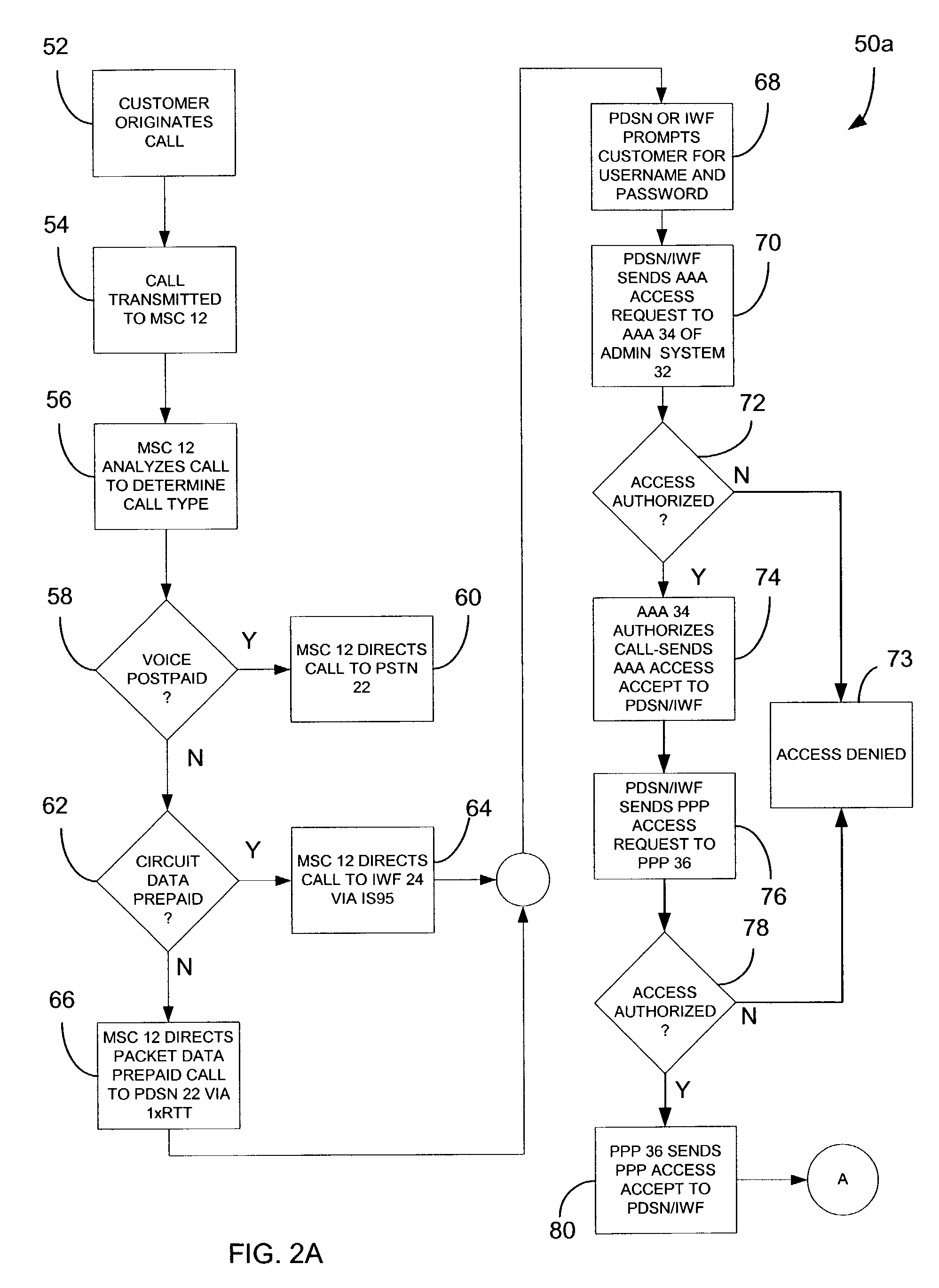
A prepaid communications system includes a wireless call handling device for receiving wireless calls from wireless customers, a packet data serving node for receiving wireless packet data calls from the wireless call handling device and transmitting the calls to a communications network and an administration system in communication with the packet data serving node. Upon a wireless customer originating a wireless call, the wireless call handling device receives the wireless call and transmits the wireless call to the packet data serving node. The packet data serving node accesses the administration system with identification information input by the customer to obtain a call access authorization for the customer. The administration system transmits the call access authorization to the packet data serving node, the call access authorization including a prepaid volume record indicating an amount of prepaid units available for use by the customer and processing instructions. The packet data serving node then enables the wireless call to proceed on the communications network while monitoring the wireless call and decrementing the available prepaid units from the prepaid volume record associated with the customer. Upon the available prepaid units reaching a predetermined level, as indicated in the processing instructions, the packet data serving node notifies the administration system that the predetermined level has been reached, and the processing instructions are executed.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Optimized packet-resource management
InactiveUS6912214B2Easy to useHybrid switching systemsConnection managementPacket data serving nodeData connection
A system and method for optimizing the use of packet-resources by releasing a hanging packet-data connection when a Mobile Station (MS) performs a power-down while involved in a dormant packet-data session. A Base Station Controller (BSC) sends a message to a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) indicating that the MS has powered down. The MSC determines that the packet-data session is dormant, and sends an instruction to the BSC in a class-0 connectionless transaction to release network resources associated with the packet-data session. The BSC then sends an instruction to a Packet Control Function (PCF) to tear down the associated resources, and the packet-data connection is released by a Packet Data Service Node (PDSN) in response to the tearing down of the resources by the PCF.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for automatic call monitoring in a wireless network
ActiveUS7324499B1Reduce difficultyTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications
A method and system for call monitoring in a wireless network by querying various network components for information about a call path through the wireless network. The network components in the wireless network may include foreign agent control nodes, home agent control nodes, packet data serving nodes, home agents, and / or authentication, authorization, and accounting servers. These network components may be queried to determine the foreign agent and the home agent to which a call is assigned. The foreign agent and the home agent may also define information about a call on the wireless network, i.e., the state of the call. Advantageously, the information provided by the foreign agent and the home agent may allow for monitoring a call path through the wireless network.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
System and method for point-to-point protocol device redundancey
InactiveUS7082130B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket data serving nodePoint-to-Point Protocol
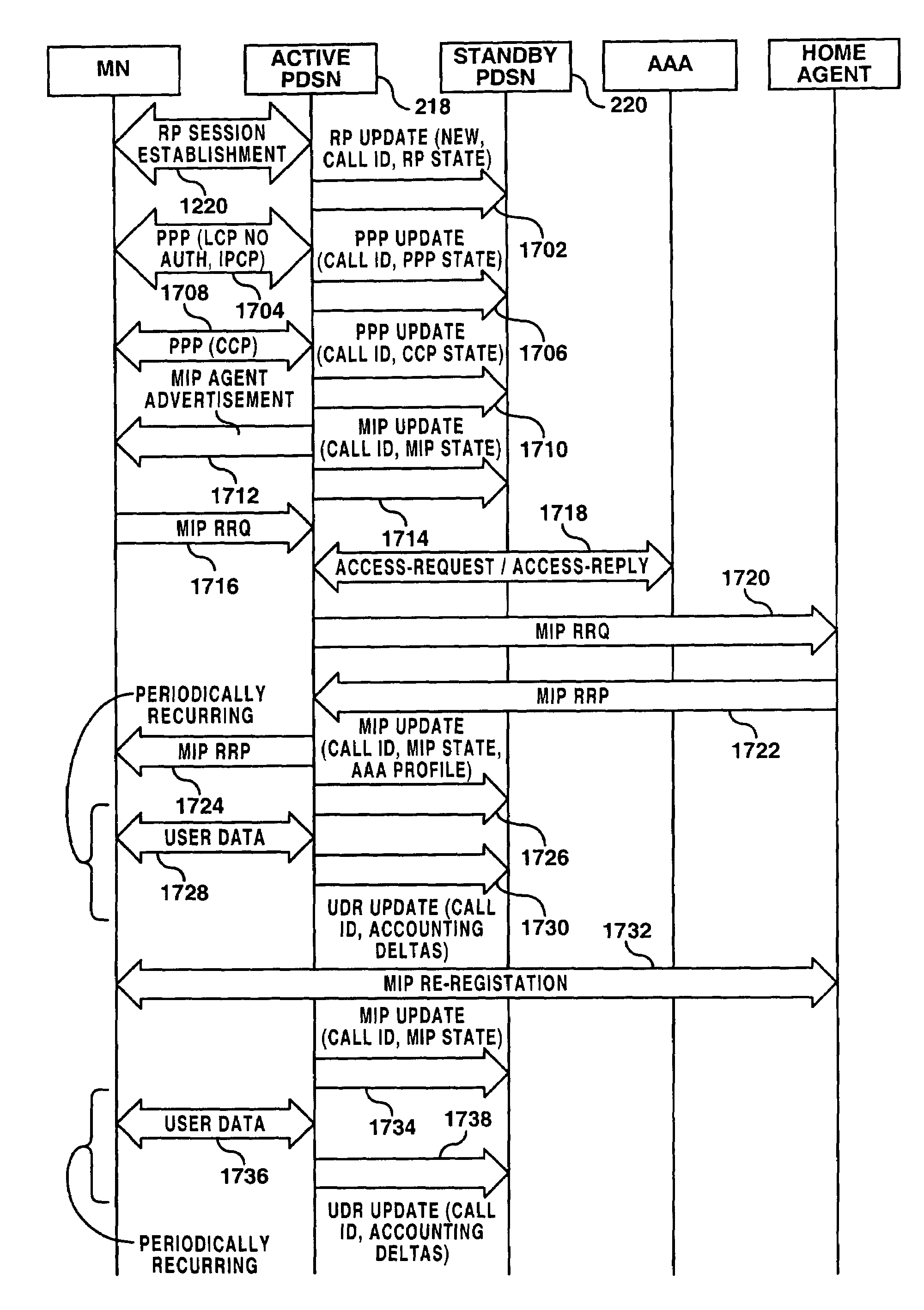
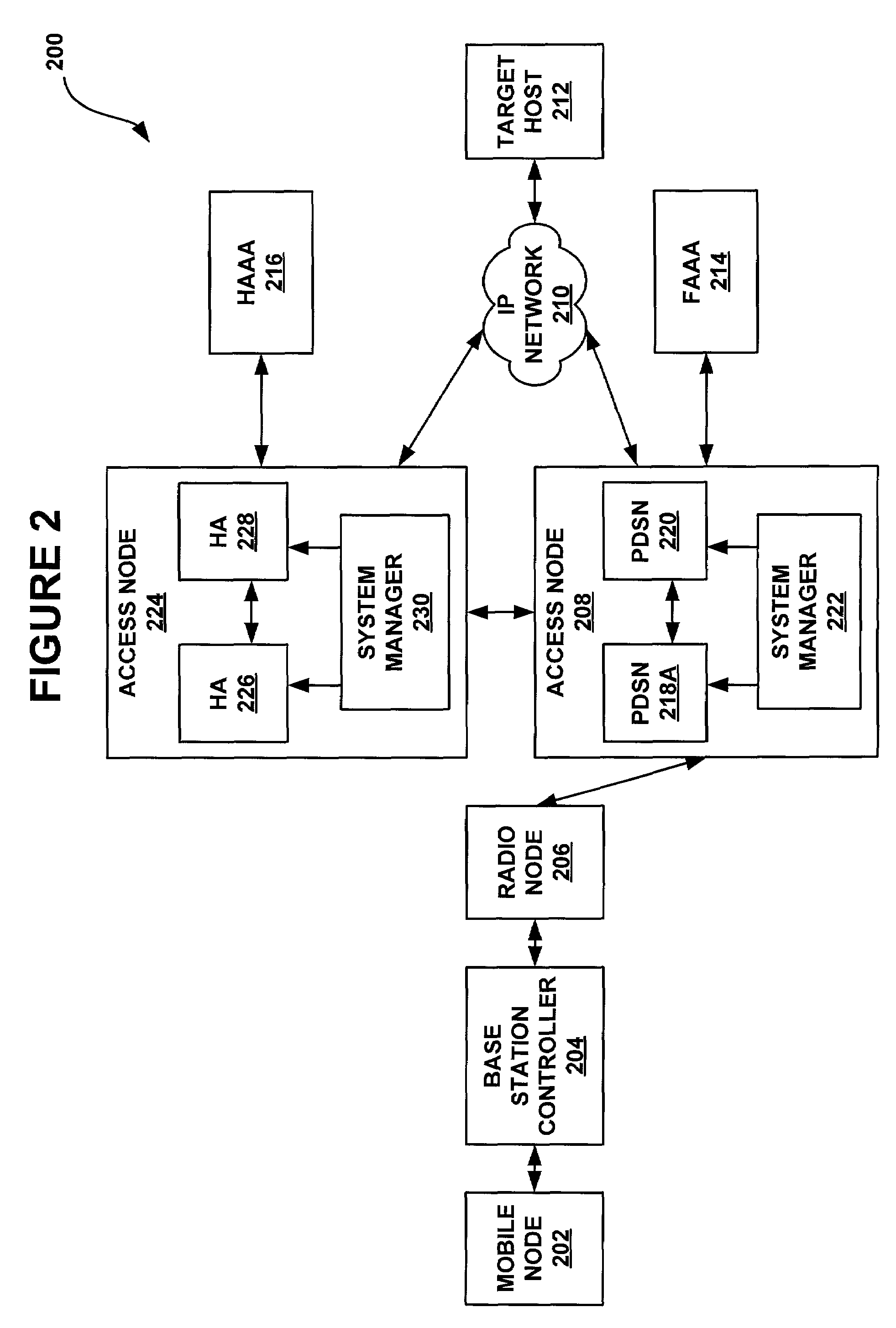
A system and methods are shown for providing packet data serving node (PDSN) redundancy. One exemplary method includes providing an access node with a plurality of packet data serving nodes and at least one system manager, establishing an N to 1 redundancy of active to standby PDSNs. Upon establishing a communications session with a mobile node, each active PDSN provides state updates to the standby PDSN including only non-recoverable data. Upon failure of any active PDSN, the standby PDSN reassigned as an active PDSN replacing the failed unit and assuming the communications session with the mobile node. The remaining active PDSNs are notified of the reassignment and transmission of updated state data is discontinued.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
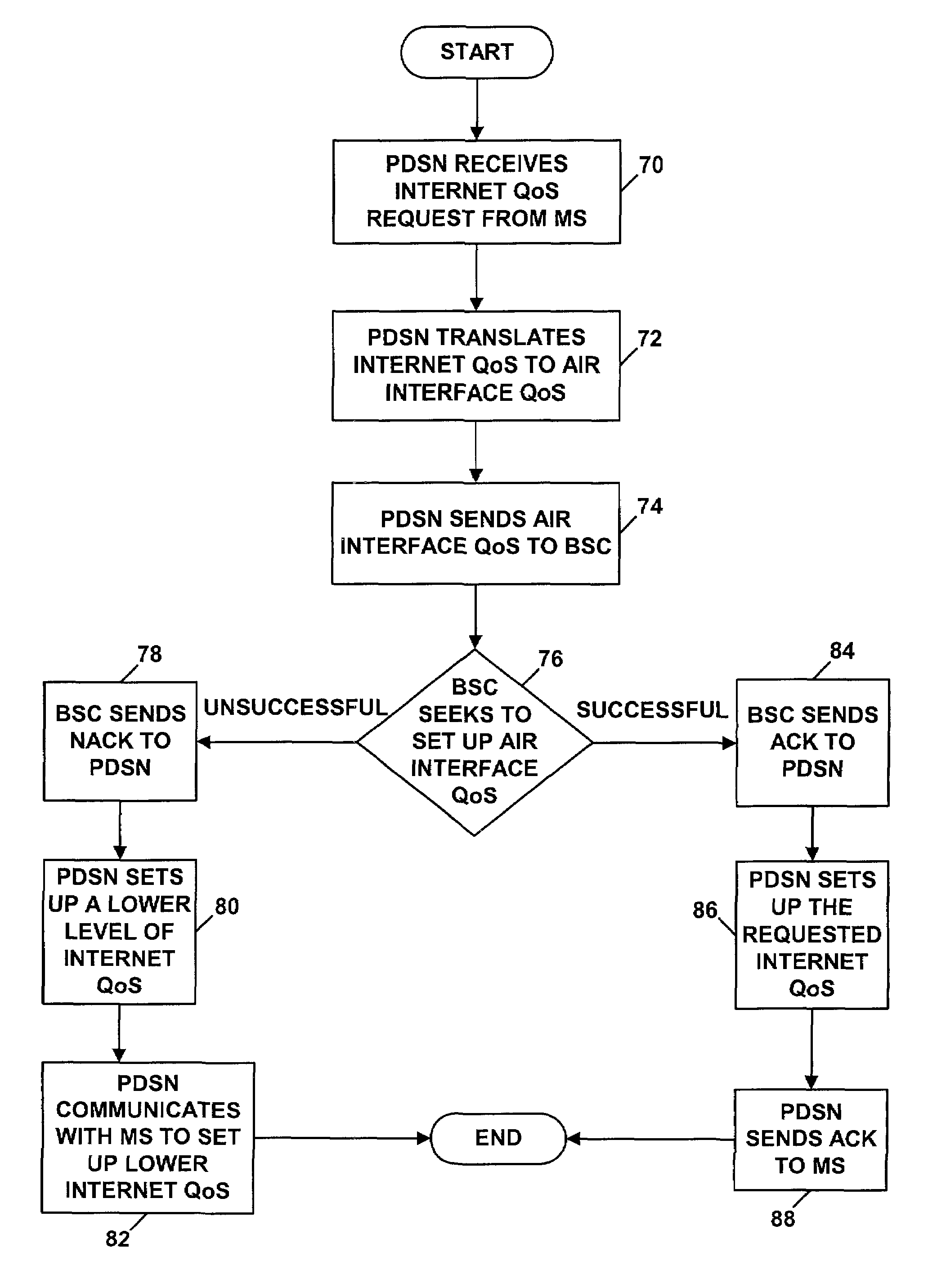
Method and system for facilitating end-to-end quality of service in a wireless packet data system
ActiveUS6980523B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket data serving nodeQuality of service
A method and system for facilitating end-to-end quality of service in a 3G packet data network. A packet-data session is set up between a mobile station and a packet-data network, via a base station and a packet data serving node (PDSN). The base station manages quality of service for the session as it passes over the air interface, and the PDSN manages quality of service for the session as it passes into the packet-data network. The PDSN translates between quality of service on the packet-data network and quality of service on the air interface, and the PDSN and base station communicate the quality of service information, so that both the base station and PDSN can work to set up consistent levels of quality of service on their respective links.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
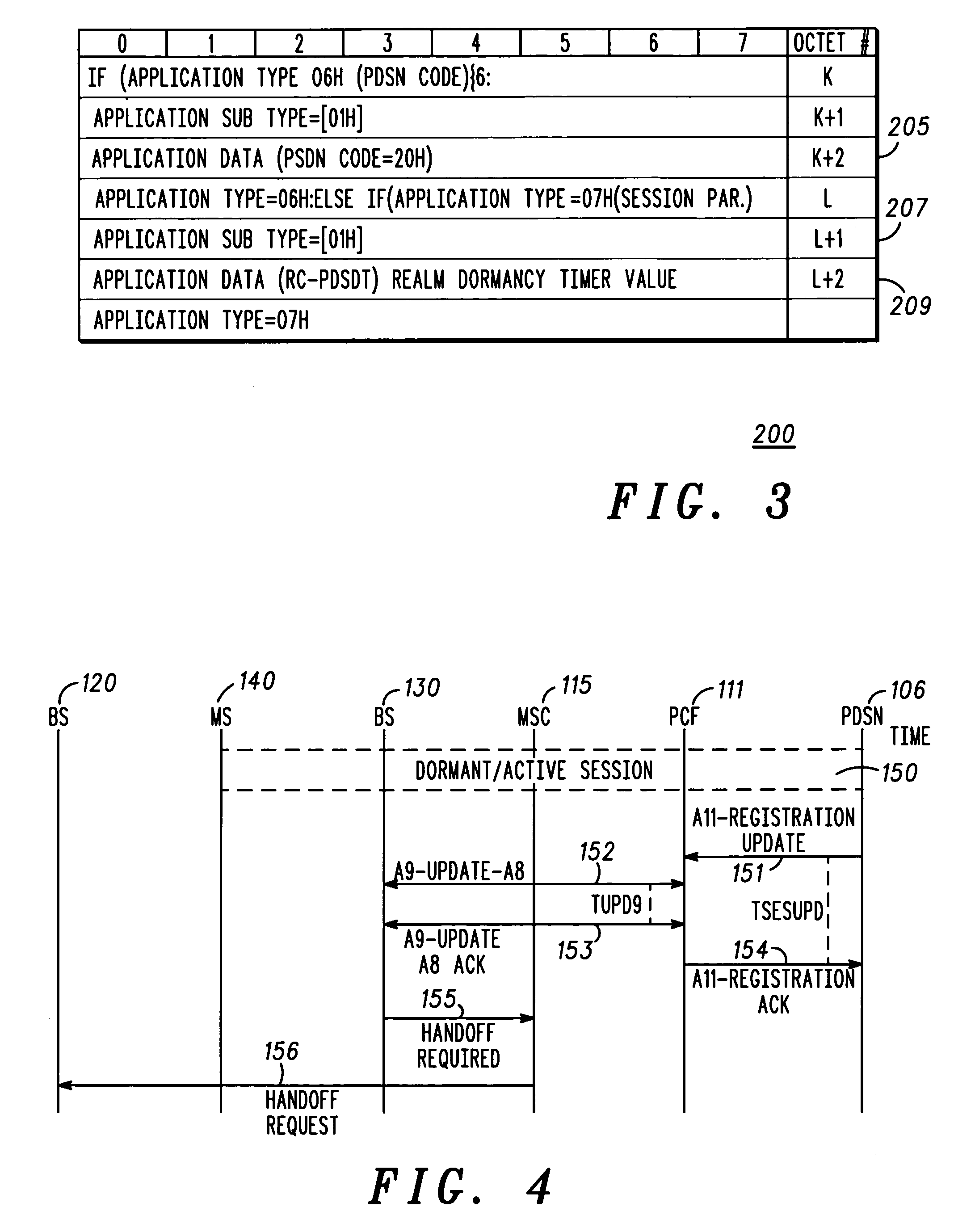
Packet data serving node initiated updates for a mobile communications system
InactiveUS7043249B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket data serving nodeCommunications system
A packet data serving node (106) initiates a packet data session update procedure with the RAN by passing a session update message containing packet data session parameters associated with at least one packet data service to a packet control function (111) which may be part of a radio access network (110). The session parameter may include a packet data service inactivity timer, QoS parameters, user information or any other session related parameters. Packet control function (111) examines the PSDN code and inhibits tearing down the link (A10 / A11) between PCF (111) and PDSN (106). Further, if a handoff occurs, the BS passes the packet data session parameters associated with each of the service instances to the MSC that in turn passes them on the target BS of the handoff.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
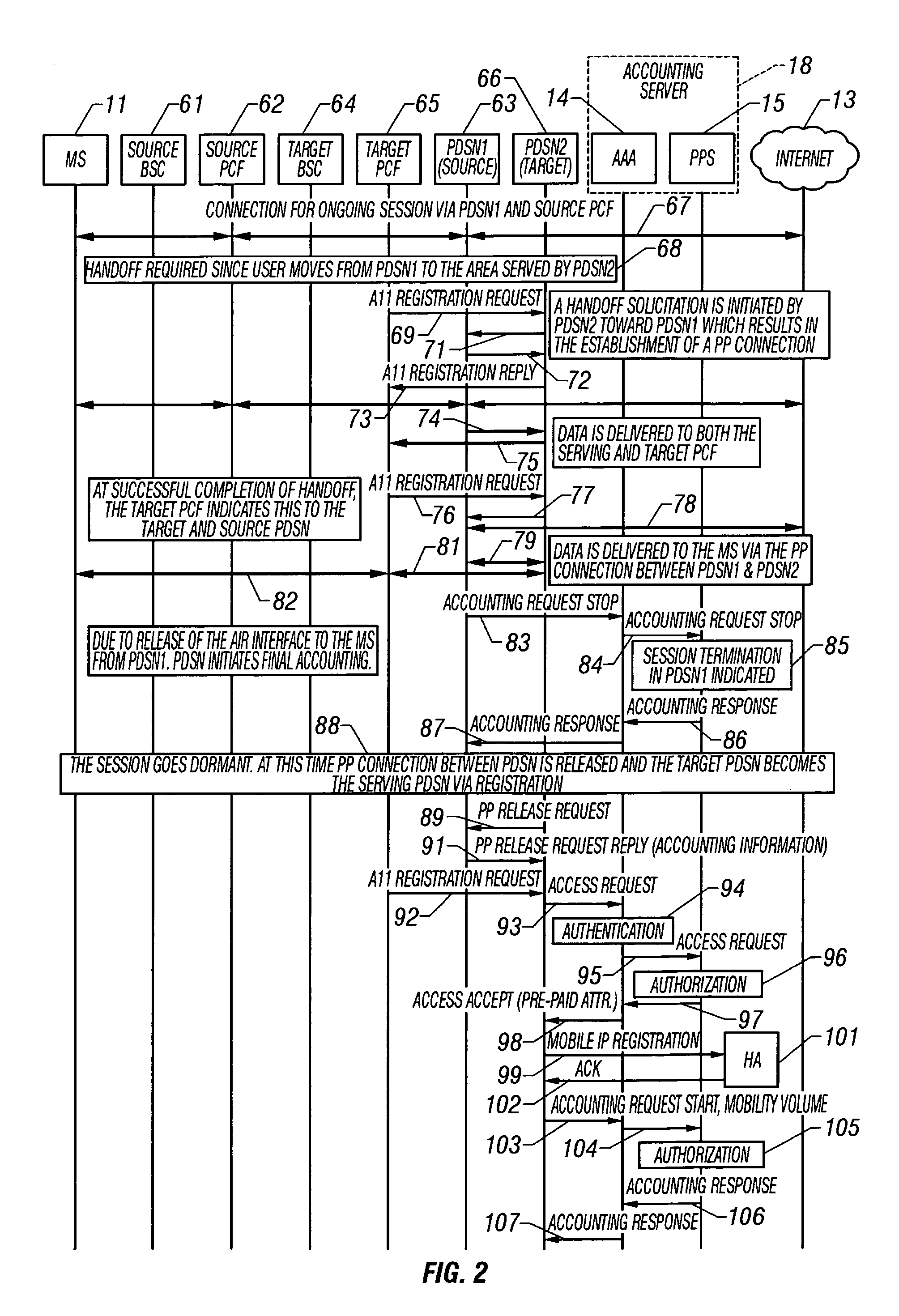
System and method of monitoring and reporting accounting data based on volume
ActiveUS6999449B2Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccount details/uasgePacket data serving nodeData mining
A system and method for monitoring and reporting a volume of data transferred between a Mobile Station (MS) and a data network during a data session. A Prepaid Server (PPS) maintains an MS account and informs a AAA Server of a predetermined volume of data that may be transferred during the session. A Packet Data Service Node (PDSN) sends interim accounting messages to the AAA Server which determines when the predetermined volume of data has been transferred, and notifies the PPS. When the account balance goes below a threshold volume, the data session is terminated. During handoff of the MS from a first PDSN to a second PDSN, a data tunnel is established between them. When the handoff is complete, the tunnel is torn down. The first PDSN reports the volume of data transferred through the tunnel to the second PDSN which reports the volume to the AAA Server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
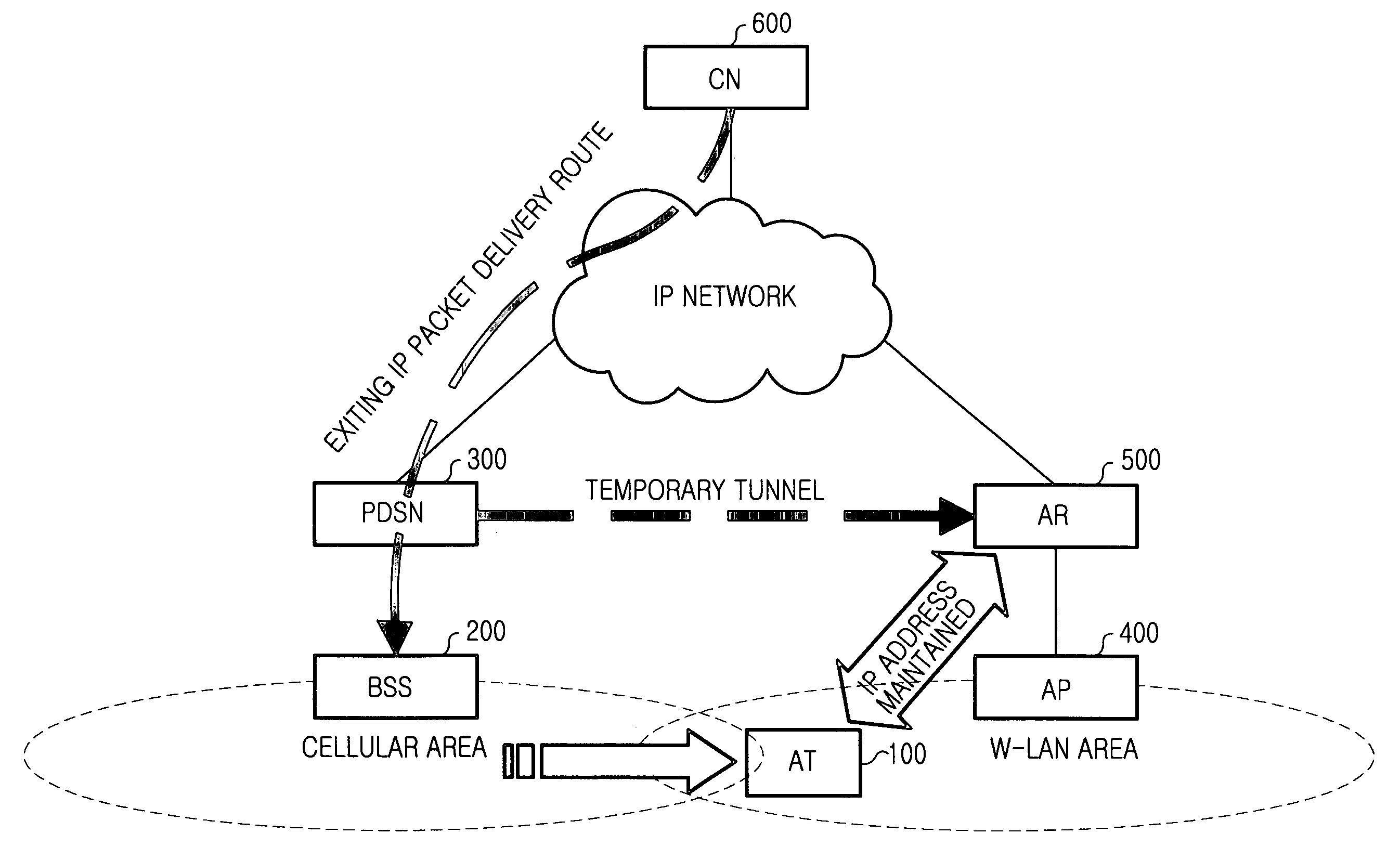
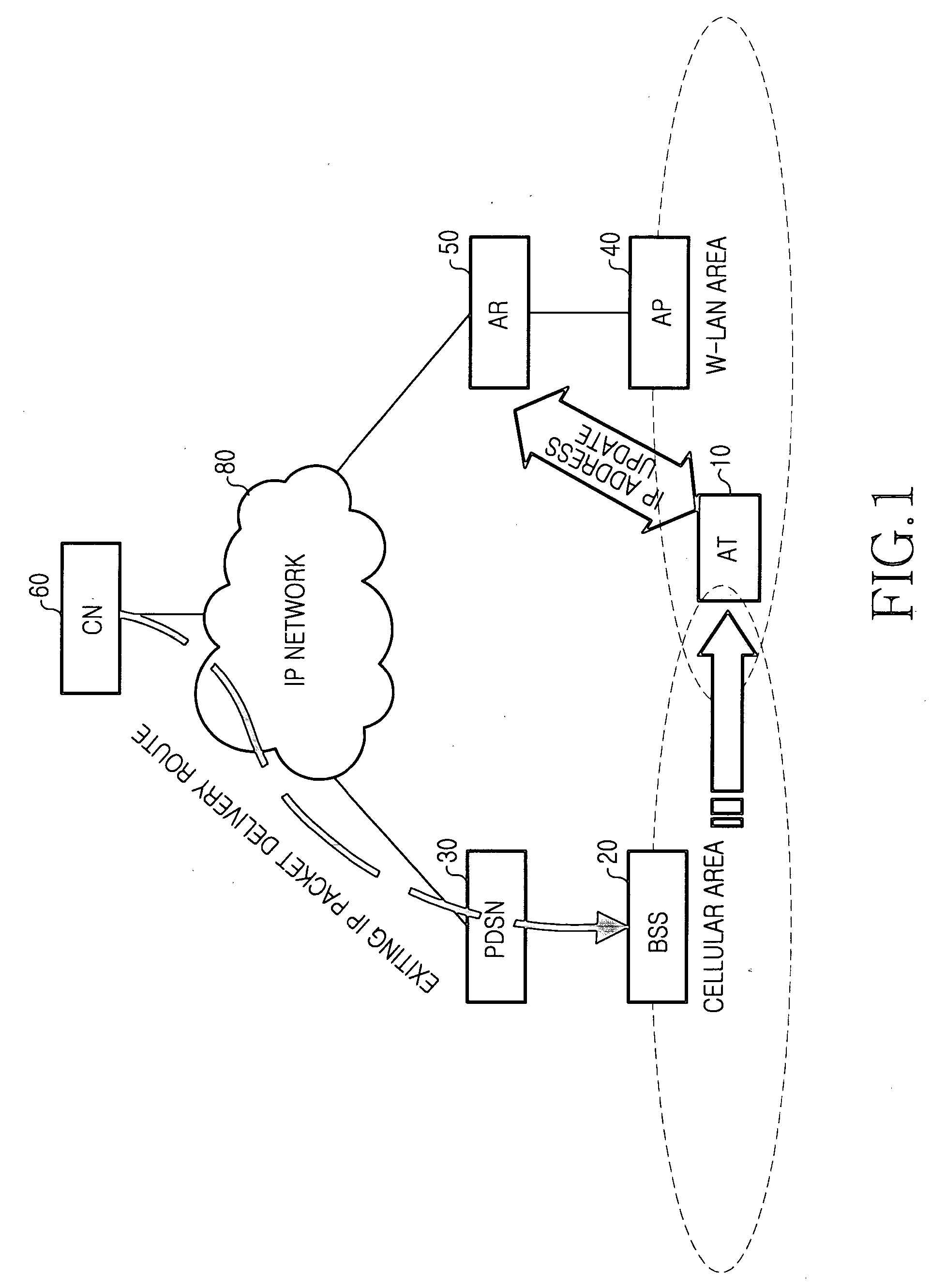
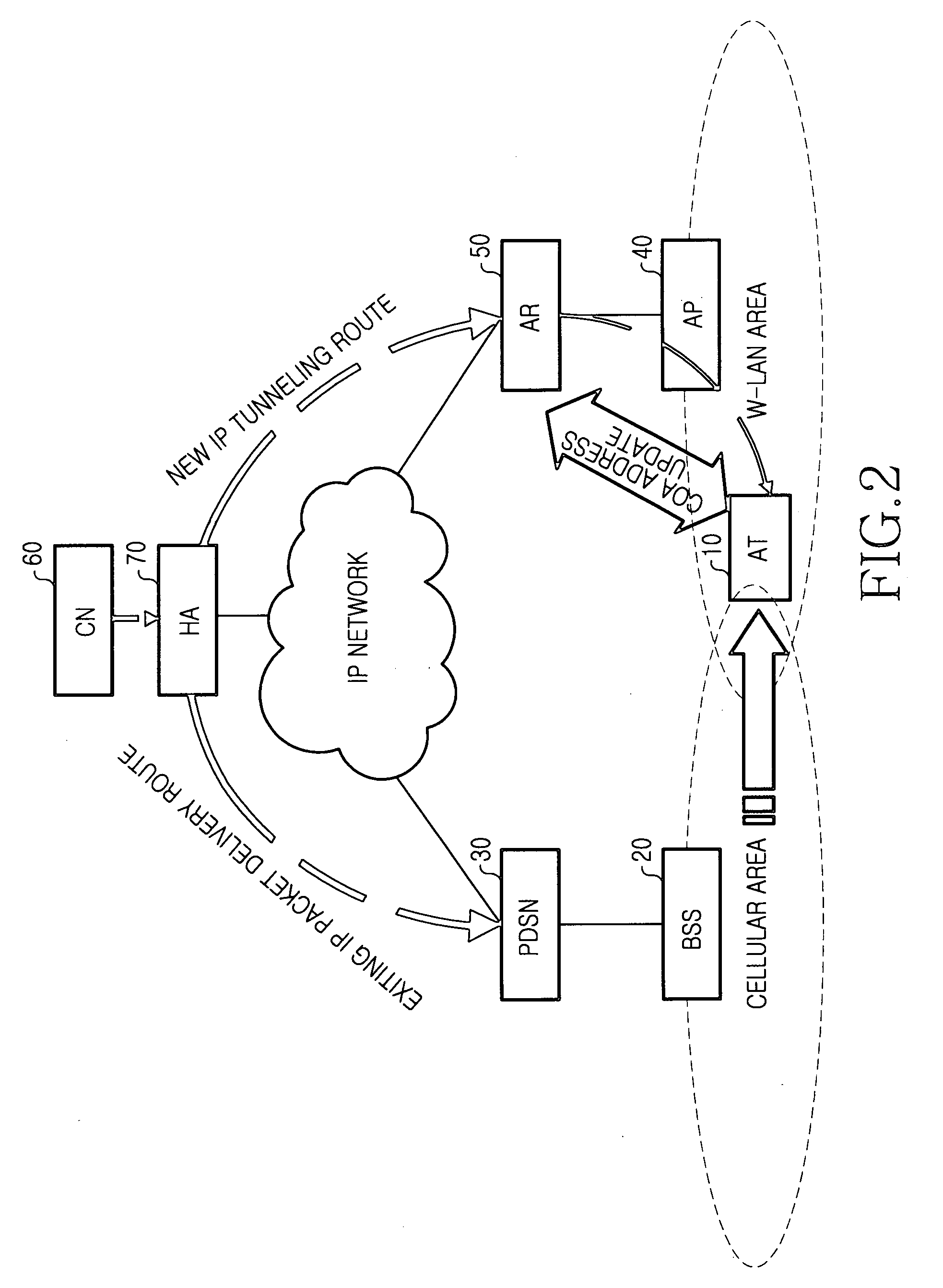
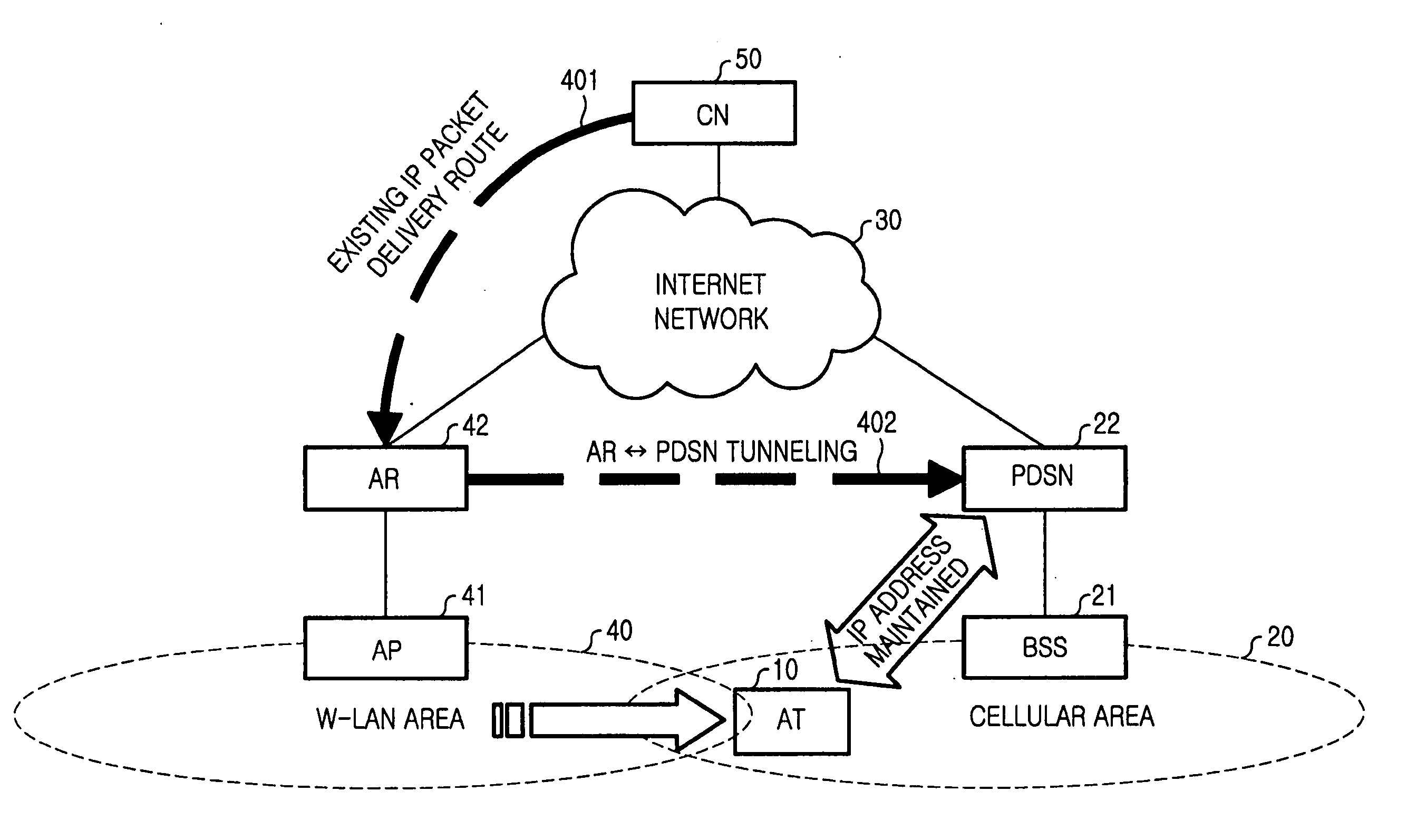
Handoff system and method between mobile communication network and wireless LAN
InactiveUS20060023683A1Avoid lostReduce processing timeNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsPacket data serving nodeWireless lan
A handoff system and method is provided for performing handoff from a mobile communication network, including a packet data service node (PDSN) connected to a base station system (BSS) for supporting an Internet protocol (IP) routing function, to a wireless local area network (LAN) including an access router (AR) supporting the IP routing function. An access terminal (AT) detects its movement to the wireless LAN and exchanges information with the AR for tunneling between the PDSN and the AR. The AR sets up a tunnel for packet delivery between the AR and the PDSN, and delivers packets delivered from a correspondent node (CN) to the AT via the set tunnel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
An integrated access method and system for mobile cellular network and WLAN
ActiveCN101150594ASimplify the certification processEasy to operateData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket data serving nodeService flow
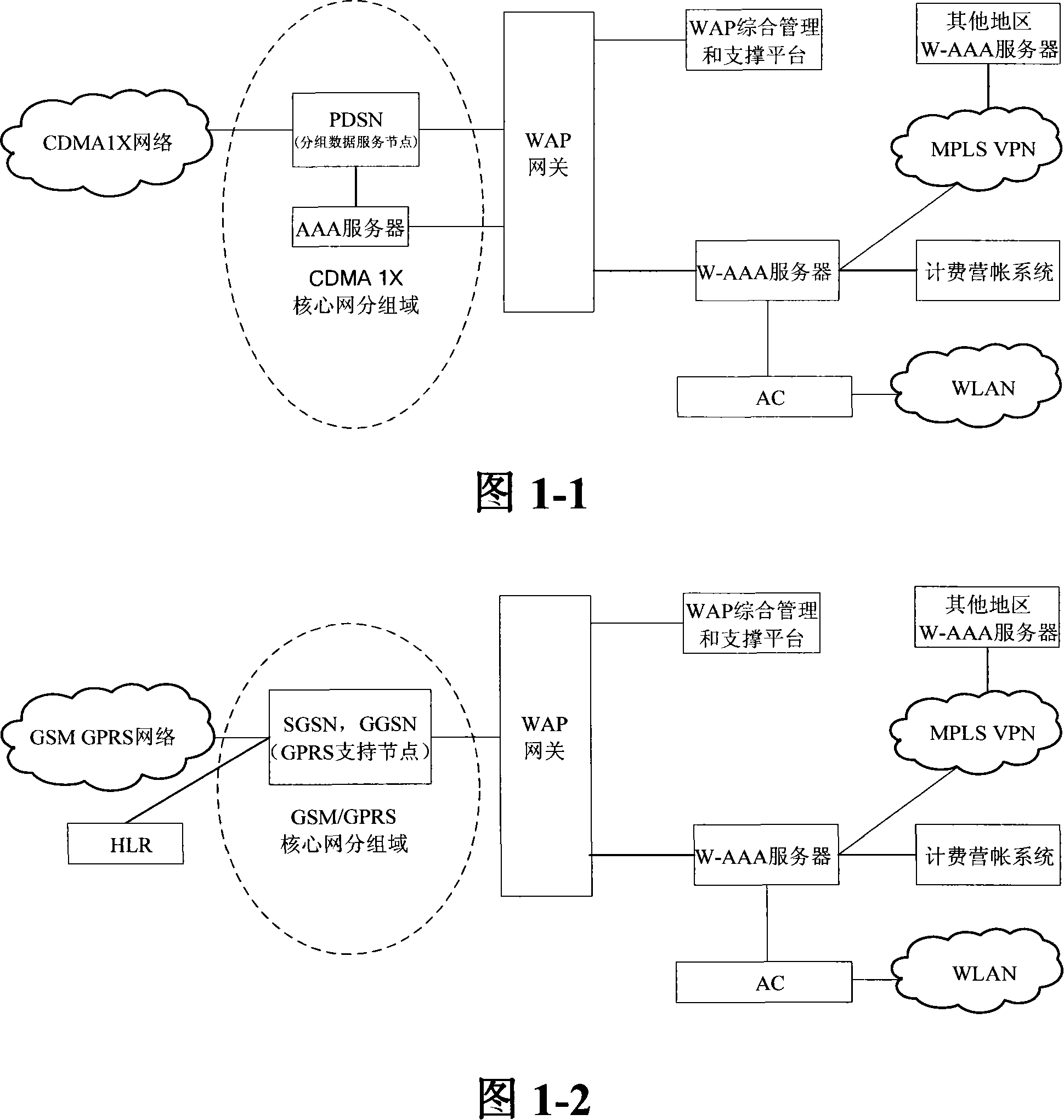
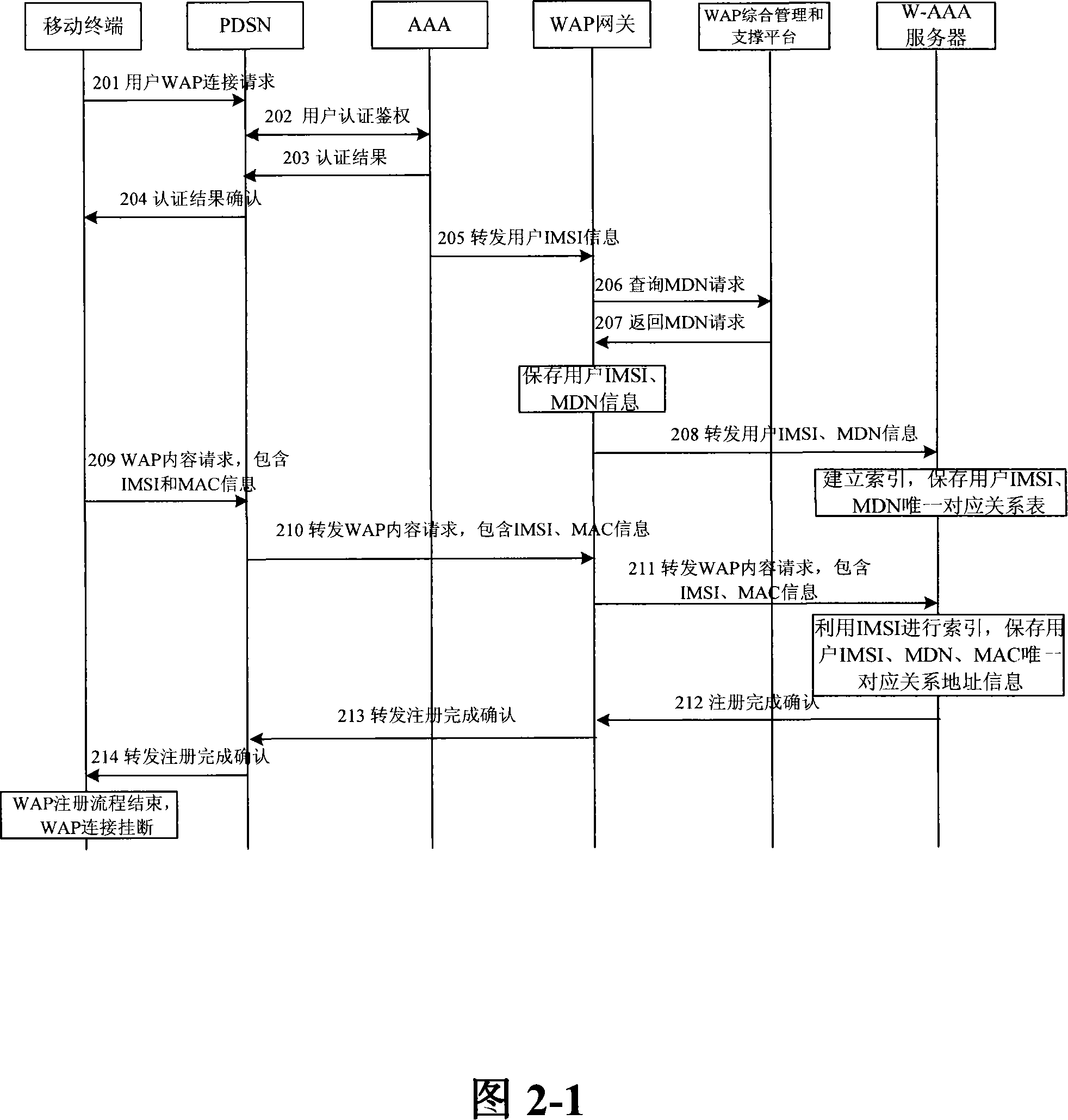
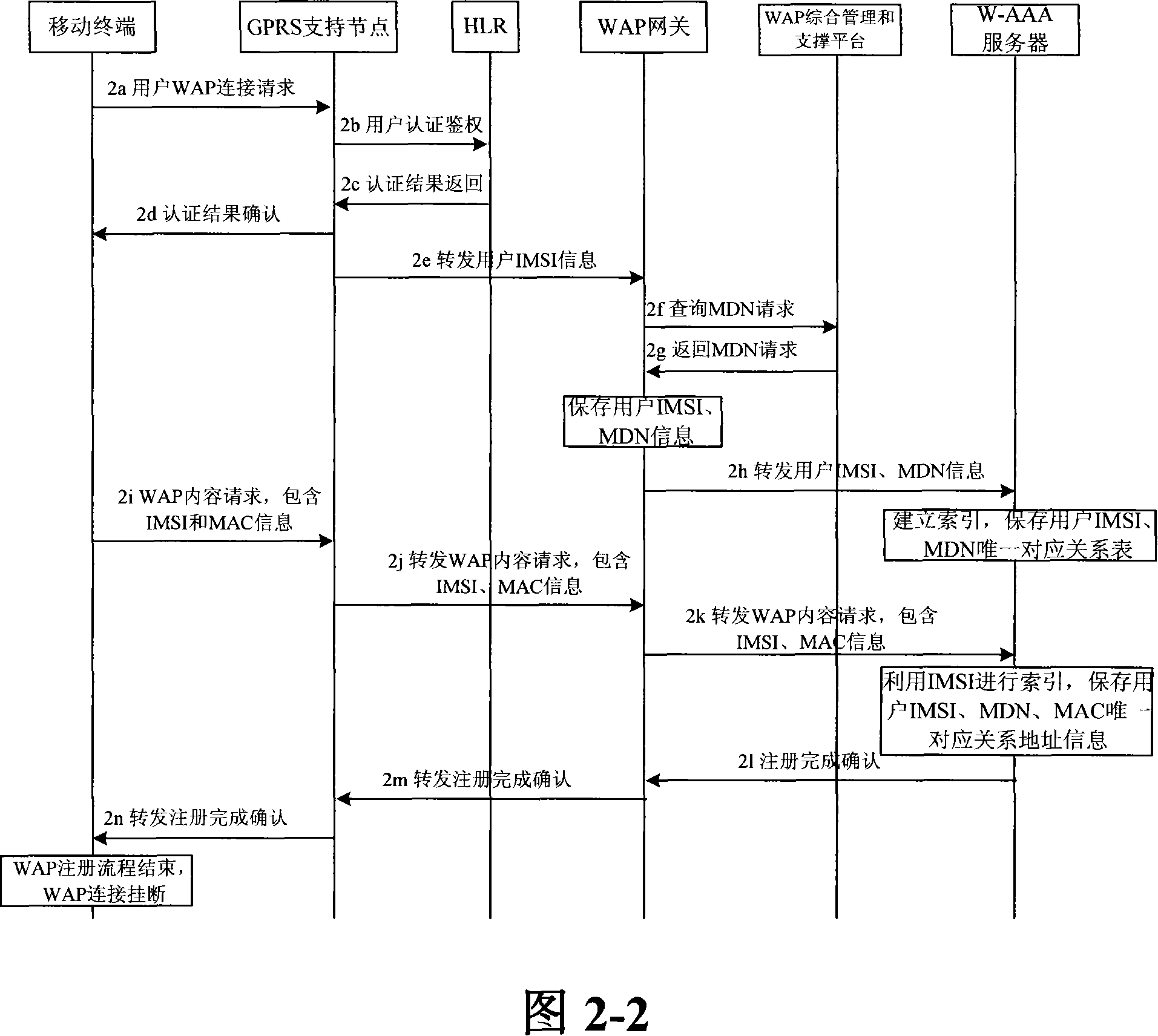
The invention relates to a unified access method for mobile cellular network and radio local area network, comprising: step 1, setting a radio local area network authentication, authorization, charging server which is connected with a WAP gateway, a wireless controller respectively; step 2, a mobile terminal does a WAP registration to the radio local area network authentication, authorization, charging server; step 3, a radio local area network authentication of the mobile terminal is authenticated by the radio local area network authentication, authorization, charging server. The invention needs not rebuild PDSN (package data service node) of the CDMA1X network or SGSN / GGSN, WAP gateways of the GSM / GPRS network, keeps the package data service flow of the original mobile cellular network basically, does not change existing CDMA1X, CDMA1X service flow and net element functions, has high safety, centralized service flow, which is convenient to manage.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
System and method for coupling between mobile communication system and wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050068929A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionPacket data serving nodeWireless lan
A system for providing communication when a mobile station moves between a wireless LAN system and a mobile communication system. A packet data service node provides a packet data service between an IP network and the mobile station when the mobile station accesses the mobile communication system. A packet control function provides the packet data service between a correspondent node connected to the IP network and the mobile station when the mobile station previously connected to the mobile communication system is connected to an access point, and provides the packet data service between the correspondent node connected to the IP network and the mobile station when the mobile station previously connected to the access point is connected to a base station system. An interworking server connected between the access point of the wireless LAN system and the packet control function of the mobile communication system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
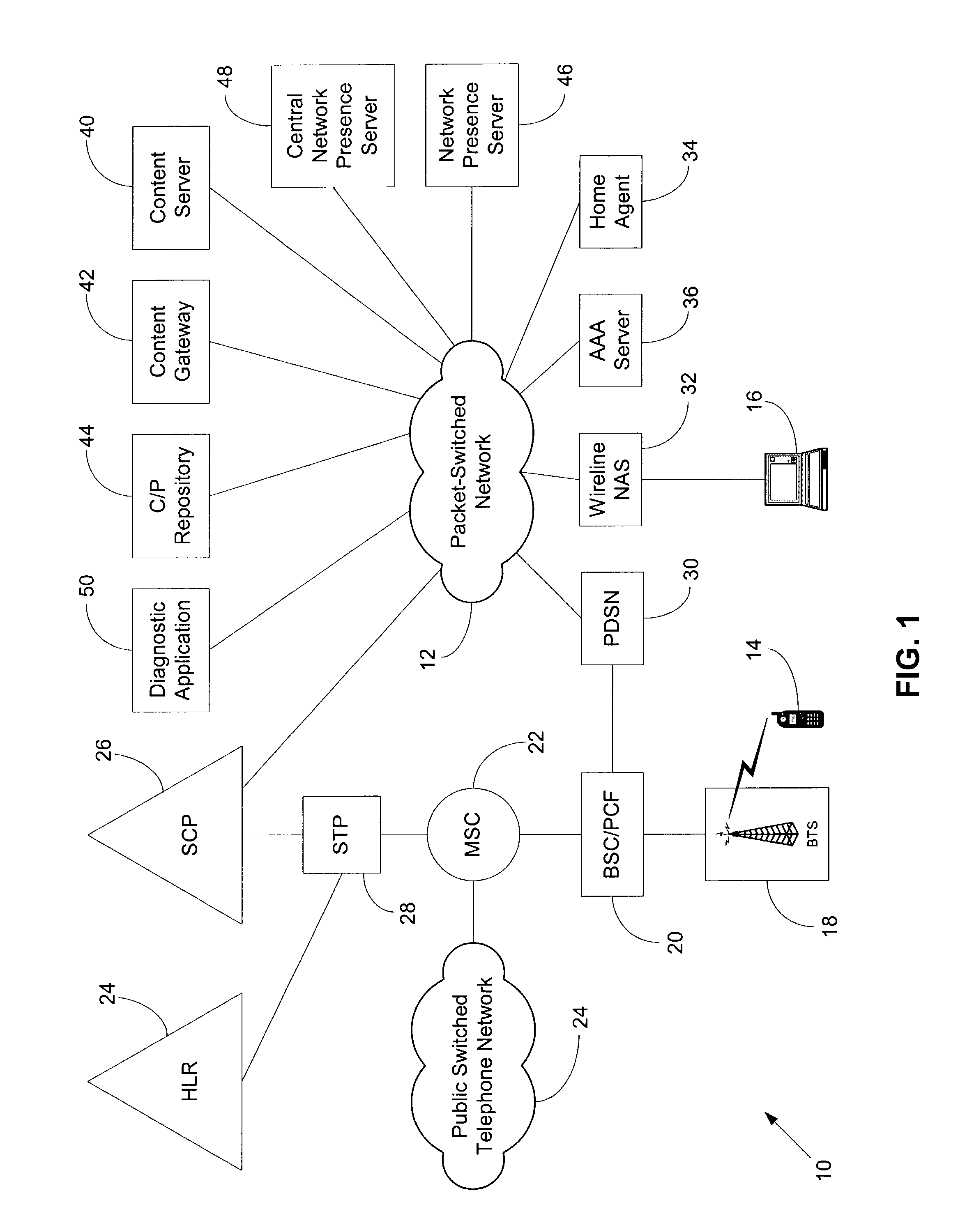
Method and system for network presence notification
ActiveUS7545762B1Assess restrictionData switching by path configurationNetwork access serverPacket data serving node
In a packet-switched network, a subscribing application subscribes to a network presence server to receive selected network presence information. The network presence server obtains the selected network presence information, at least in part, from status messages that a network access server, such as a packet data serving node (PDSN), sends, for example, to an accounting server. The network presence server then provides the selected network presence information to the subscribing application. The selected network presence information may include an identification of a particular customer that has just initiated or terminated a data session and the network address the particular customer is or was using.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
Handoff system and method between a wireless LAN and mobile communication network
InactiveUS20060045049A1Reduce lossesTime-division multiplexConnection managementPacket data serving nodeWireless lan
A method for performing a handoff between a wireless local area network (LAN) including an access router (AR) supporting an Internet protocol (IP) routing function and a mobile communication network including a packet data service node (PDSN) connected to a base station system (BSS), for supporting the IP routing function. An access terminal (AT) detects its movement from the wireless LAN to the mobile communication network, and exchanges information for tunneling between the AR and the PDSN, with the PDSN. The PDSN sets up a tunnel for packet delivery between the PDSN and the AR, and delivers packets to the AT through the set tunnel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
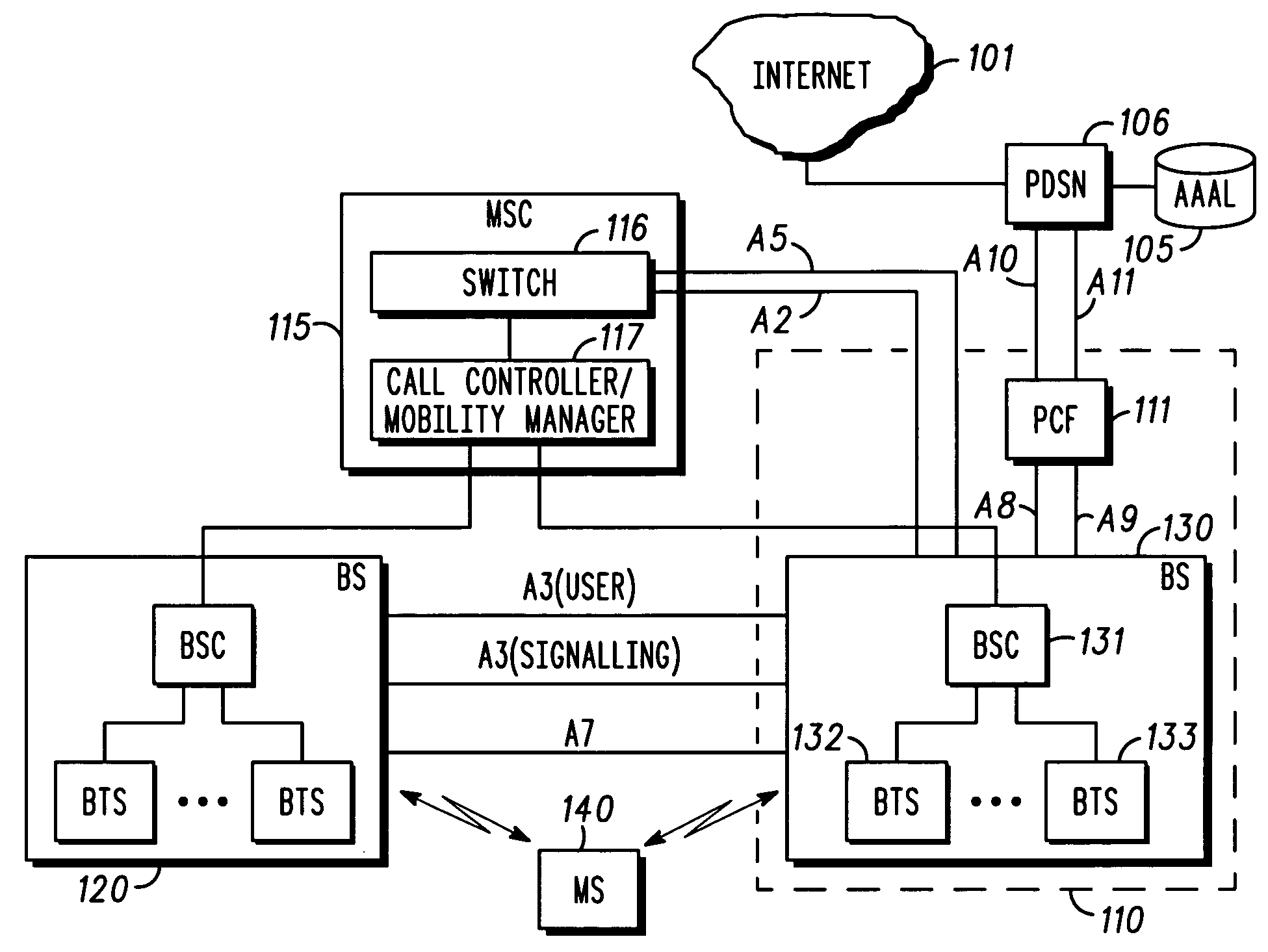
Mobile communication systems, mobile stations, base station controllers and packet data service nodes
InactiveUS7085579B2Power managementConnection managementPacket data serving nodeCommunication quality
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and system for providing roaming service in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20070025298A1Accounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications
A method and system for a roaming service in a mobile communication system are provided. The system includes an access terminal for transmitting an NAI (network access identifier) to a packet data serving node of the visited network and an AAA (authentication authorization accounting) of the home network, for transmitting subscriber profile information of the access terminal to the visited network. The packet data serving node of the visited network determines whether or not the access terminal subscribes to the roaming service on the basis of the NAI, and, when it is determined that the access terminal subscribes to the roaming service, sends a request for transmitting the subscriber profile information of the access terminal to the AAA of the home network. The packet data serving node of the visited network also provides at least one data service that the home network has provided to the subscriber, using the subscriber profile information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for providing broadcast service in a CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7099655B2Easy to useLimiting transmission timeSpecial service provision for substationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionPacket data serving nodeCode division multiple access
Disclosed is a method for providing a broadcast service in a mobile communication system using code division multiple access (CDMA) technology. The novel method controls transmission of broadcast service data according to base station areas by registering a mobile station with a broadcast service. For that purpose, the mobile station requests an authentication server to authenticate a desired broadcast service, and registers the authenticated broadcast service in a packet data serving node via a base station so that the base station and the packet data serving node can set up a transmission path for the broadcast service. The method increases the efficiency of base station resources by controlling transmission times of base stations, and the packet data serving node can perform accounting on the broadcast service of the mobile station. Further, a plurality of registered mobile stations constitute a group, and broadcast service data is transmitted from one mobile station to other mobile stations within the group.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
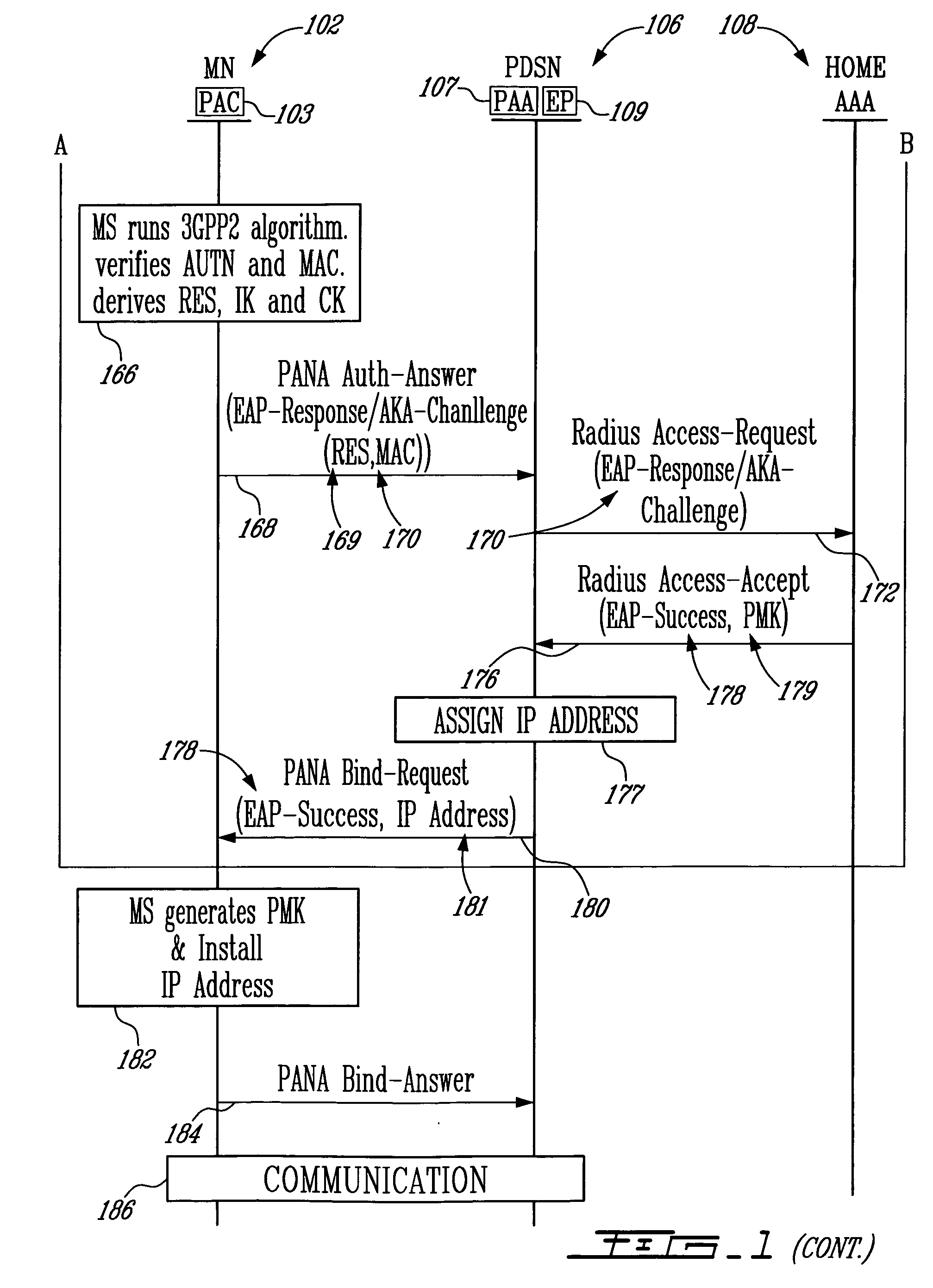
IP address assignment in a telecommunications network using the protocol for carrying authentication for network access (PANA)
InactiveUS20060002351A1Better understand the use of PANAWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications link
A method and a packet data switching node such as for example a CDMA2000 Packet data Serving Node (PDSN) for assigning an IP address to a Mobile Node (MN) in a telecommunications network. The switching node and the MN are first involved in a discovery phase, then the MN sends a Protocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access (PANA) Start-Answer message to the switching node with an indication that an IP address is requested. The indication may comprise, for example, a blank IP address. The switching node receives the PANA Start-Answer message and recognises the request for an IP address. It authenticates the MN, possibly in combination with an Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server, and if the authentication is successful, assigns a new IP address to the MN, and responds back to the MN with a PANA Bind-Request message comprising the assigned IP address.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
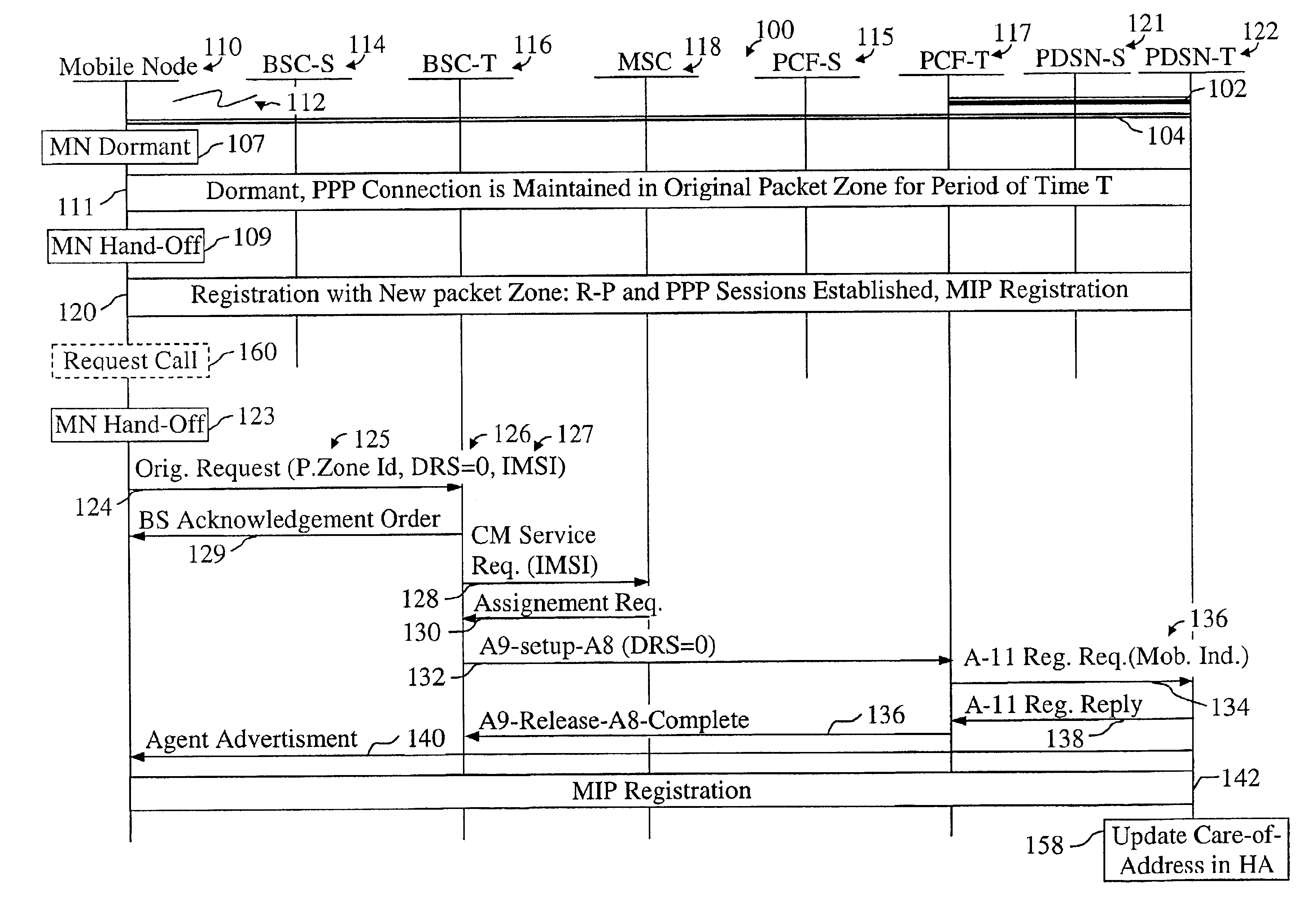
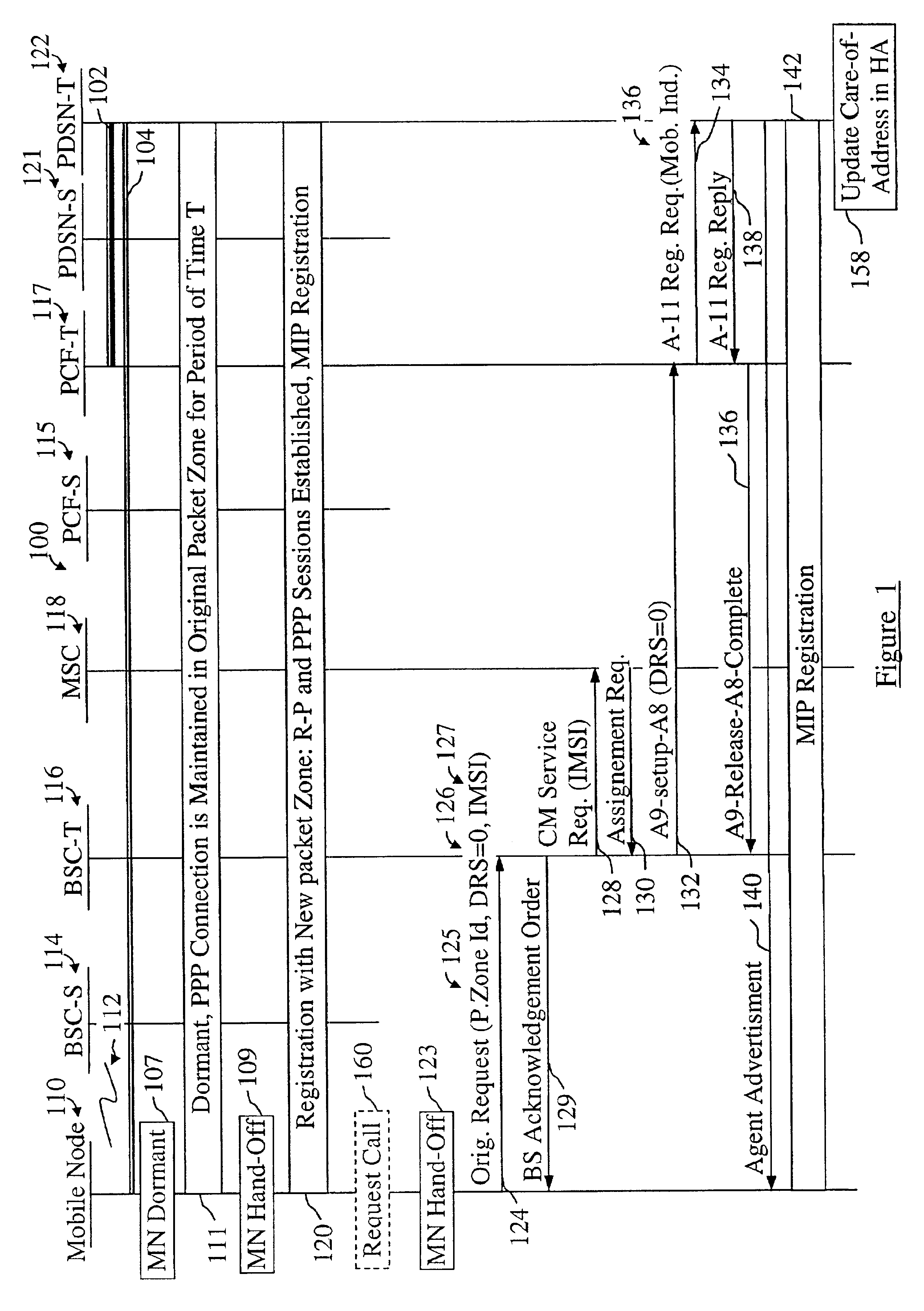
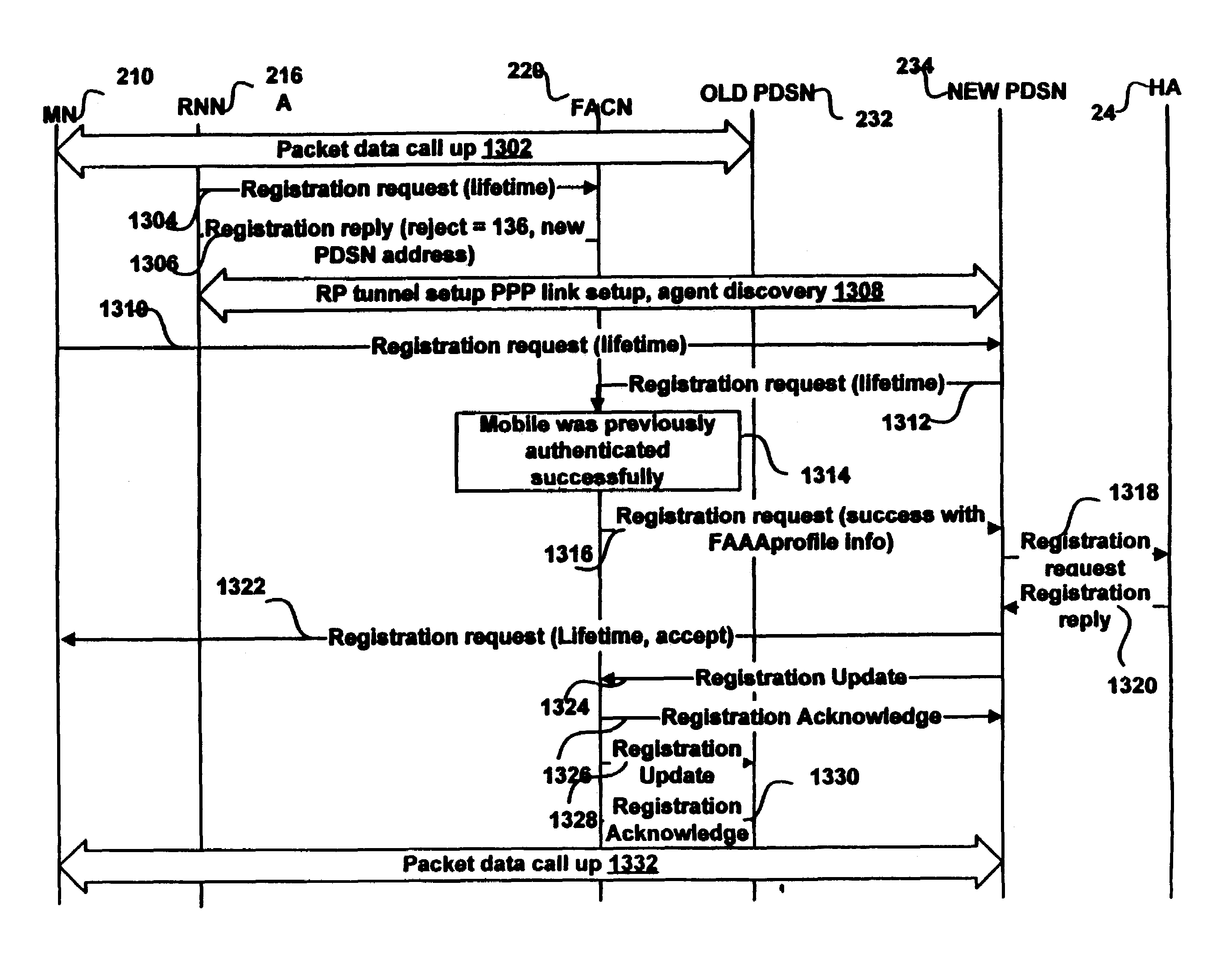
Mobile IP registration in selected inter-PDSN dormant hand-off cases in a CDMA2000-based cellular telecommunications network
InactiveUS6907016B2Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket data serving nodeTelecommunications network
In a cellular telecommunications network, a method and system for performing dormant hand-off for a dormant Mobile Node (MN) between a source packet zone an a target packet zone, when the MN still has an active A10 and Point-to Point Protocol (PPP) connection in the target packet zone. According to the method, when handed-off, the MN issues an origination request with a Data Ready to Sent (DRS) parameter set to zero for the target Base Station Controller (BSC-T) which responsive to the request further sends an A9-setup-A8 registration request to a target Packet Control Function (PCF-T). The PCF-T then sends an A-11 Registration Request message to a Packet Data Service Node (PDSN-T) of the target packet zone. Responsive to the receipt of the Registration request, the PDSN-T sends an agent advertisement message to the MN and initiates the Mobile IP (MIP) registration procedure, and the MN can register the care-of-address information relating to the new serving PDSN, the PDSN-T, with its Home Agent (HA). According to another embodiment, the same method is to be used for performing a hand-off of the dormant MN to the target packet zone, when the MN, before issuing the origination request, demands the activation of a packet data session.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus fo reducing latency during handoffs in a communications system
InactiveUS20050281227A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesPacket data serving nodeAccess network
A methodology is provided to reduce data session handoff time between 3G1x and EV-DO technologies for dual mode access terminals. Generally, a dual mode access terminal is communicating with a data network through a base station and a particular packet data service node (PDSN) using EV-DO technology. When the EV-DO technology becomes at least temporarily unavailable, a handoff process is initiated so that communications with the data network may continue using 3G1x technology. During handoff, the access terminal provides an access network identification (ANID) that contains an International Mobile Subscriber Identifier (IMSI). A radio network controller within the base station extracts the IMSI and uses it to select the same PDSN used with the EV-DO technology, which eliminates the need to access an authentication, authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server and perform a re-authentication process.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for network imposed packet data flow control
ActiveUS20050226154A1Shorten the timeError preventionTransmission systemsData connectionPacket data serving node
A method and apparatus provide network-based flow control for mobile station having data connections to the network. In an exemplary embodiment, a Packet Control Function (PCF) in a Radio Access Network (RAN) requests that a Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) in a Packet Core Network (PCN) turn flow control on and off as needed for mobile station data connections. That is, if the PCF receives data from the PDSN for delivery to a mobile station that the PCF determines to be unavailable, the PCF requests that data transfers from the PDSN be suspended for that mobile station. Such suspension avoids needless continued transfer of undeliverable data to the PCF. The PCF monitors or otherwise determines whether a flow-controlled mobile station has become available again and, if so, notifies the PDSN so that it can lift the suspension and resume data transfers as needed.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
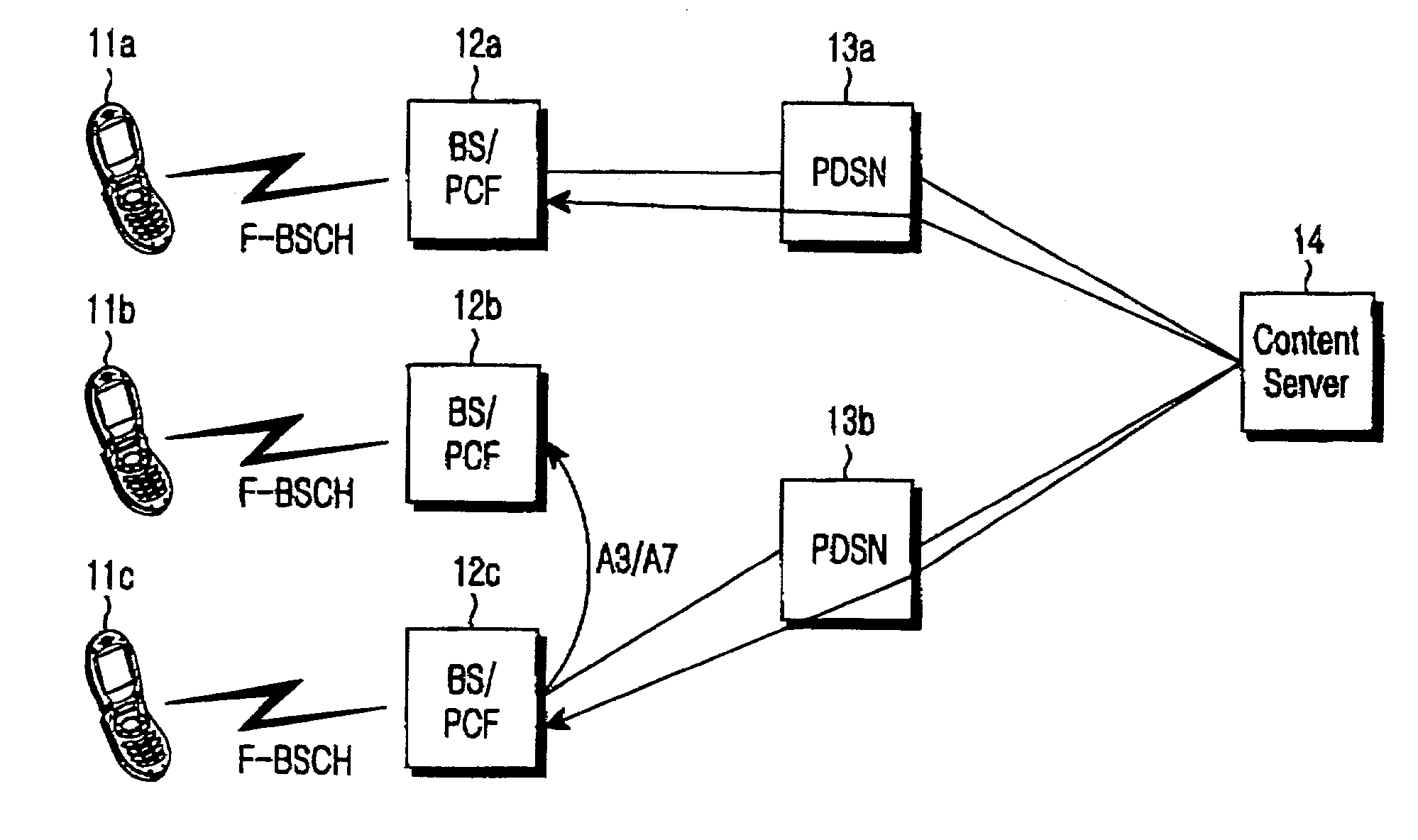
Efficient handoffs between cellular and wireless local area networks
InactiveUS7583632B2Convenient handoverOptimize networkData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesPacket data serving nodeIP tunnel
The present invention facilitates a handoff between cellular and wireless local area networks (WLANs). To facilitate a WLAN interface with the cellular network, a proxy packet control function (P-PCF) establishes a data tunnel to a packet data serving node (PDSN), as well as a WLAN association with a mobile terminal. The WLAN association is a tunnel, and is preferably implemented via an Access Router acting as a liaison between the proxy PCF and an Access Point. The Access Router and the proxy PCF establish an IP tunnel, which carries the WLAN user's PPP traffic. Handoffs between the cellular and WLAN networks are facilitated by effecting a same-PDSN, inter-PCF handoff wherein the communication session with the mobile terminal is effectively changed from between the PDSN and the proxy PCF to between the PDSN and a PCF associated with a base station controller facilitating the cellular access, and vice versa.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
System and method for control of packet data serving node selection in a mobile internet protocol network
InactiveUS7346684B2Multiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsPacket data serving nodeTTEthernet
A system and methods are shown for selecting a packet data serving node (PDSN) for a mobile node in an Internet Protocol network. A network node receives a message associated with a mobile node. The message includes a service request parameter corresponding to a requested service. The network node uses the service request parameter to select the address of a packet data serving node (PDSN) offering the service. The network node then sends a response message directing a connection with the selected PDSN. The service request parameter may be an international mobile subscriber identifier (IMSI) that identifies a subscriber requesting a static IP address, in which case the network node directs a connection with a PDSN that offers an. Internet connection with the static IP address.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
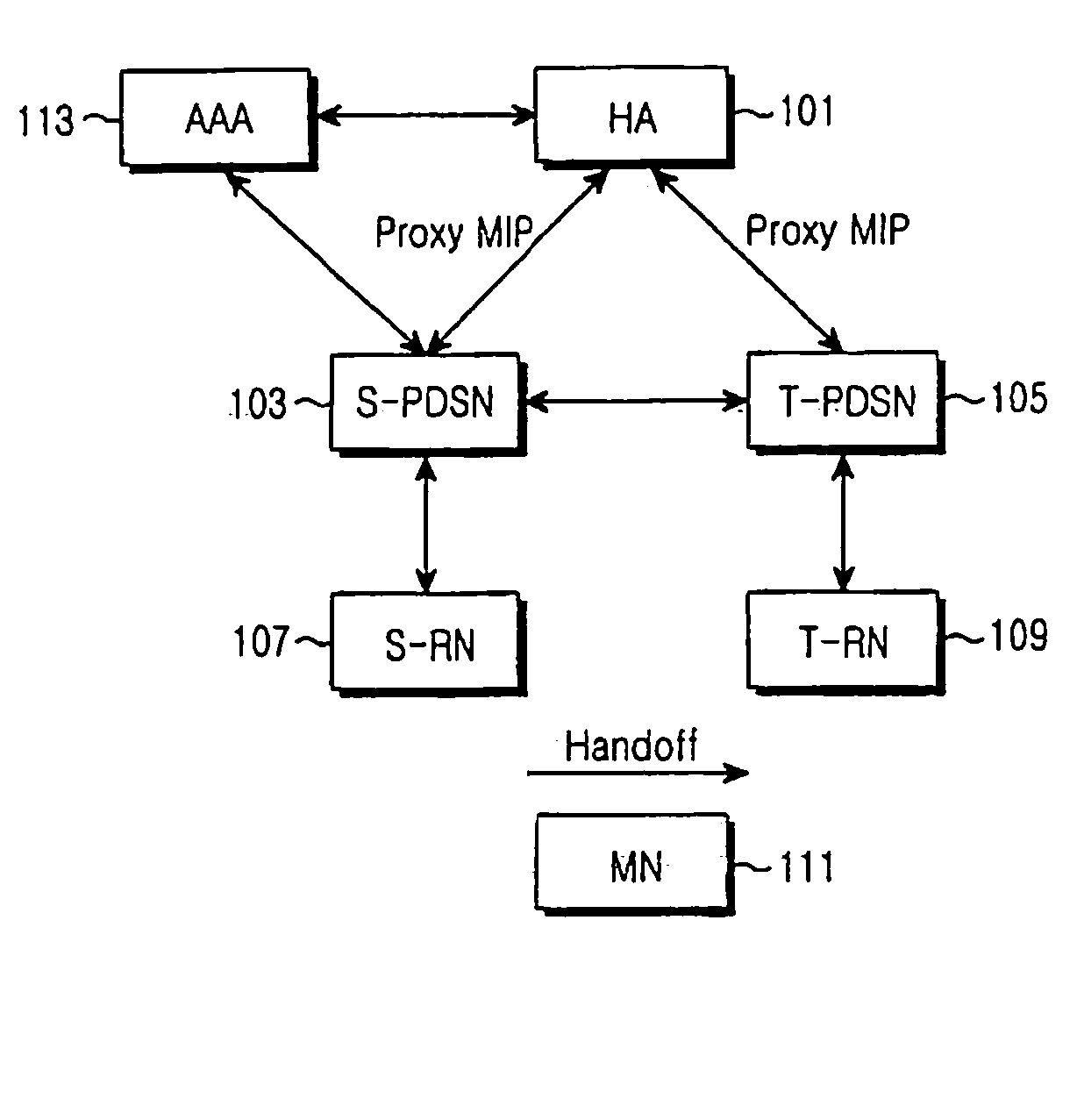
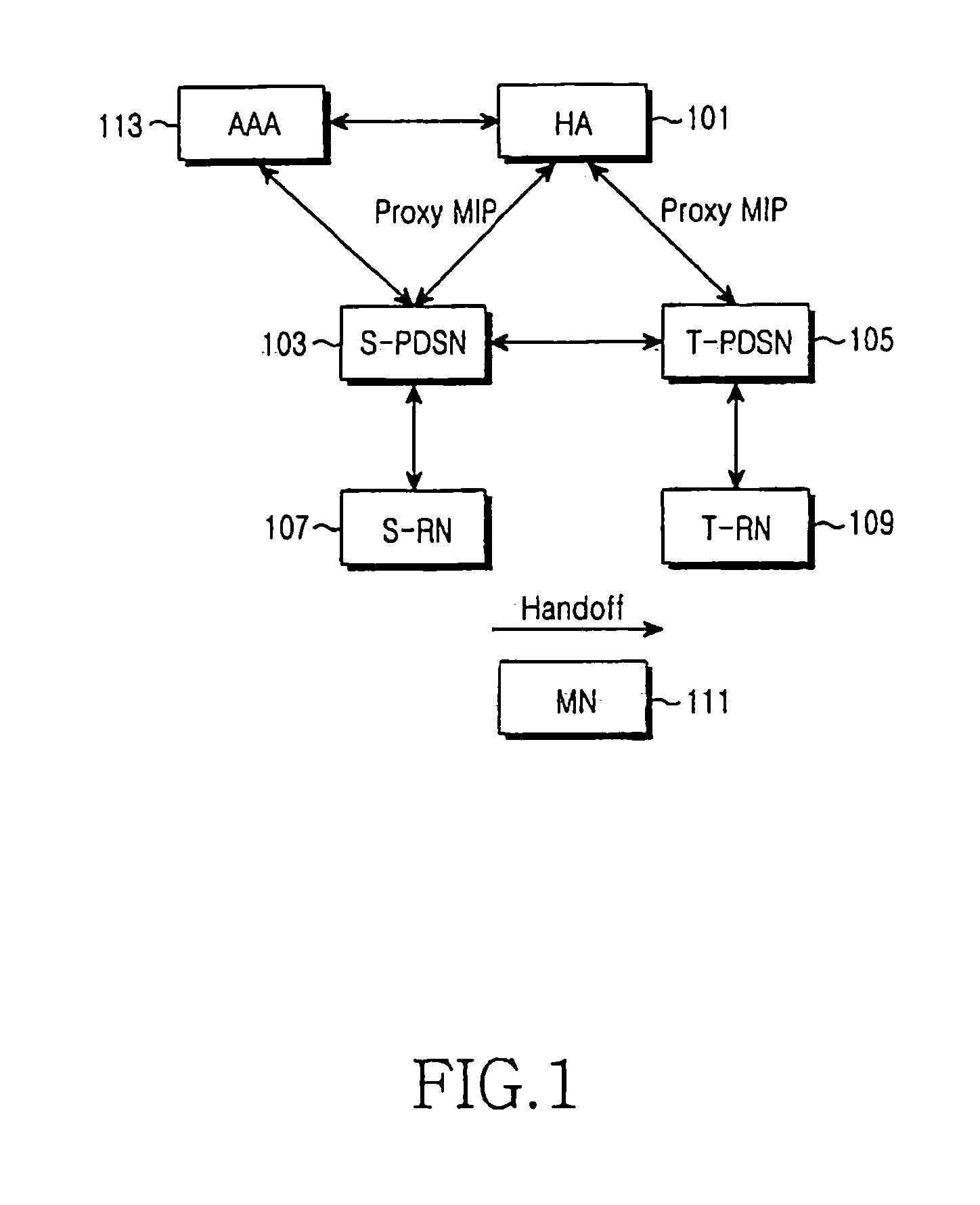
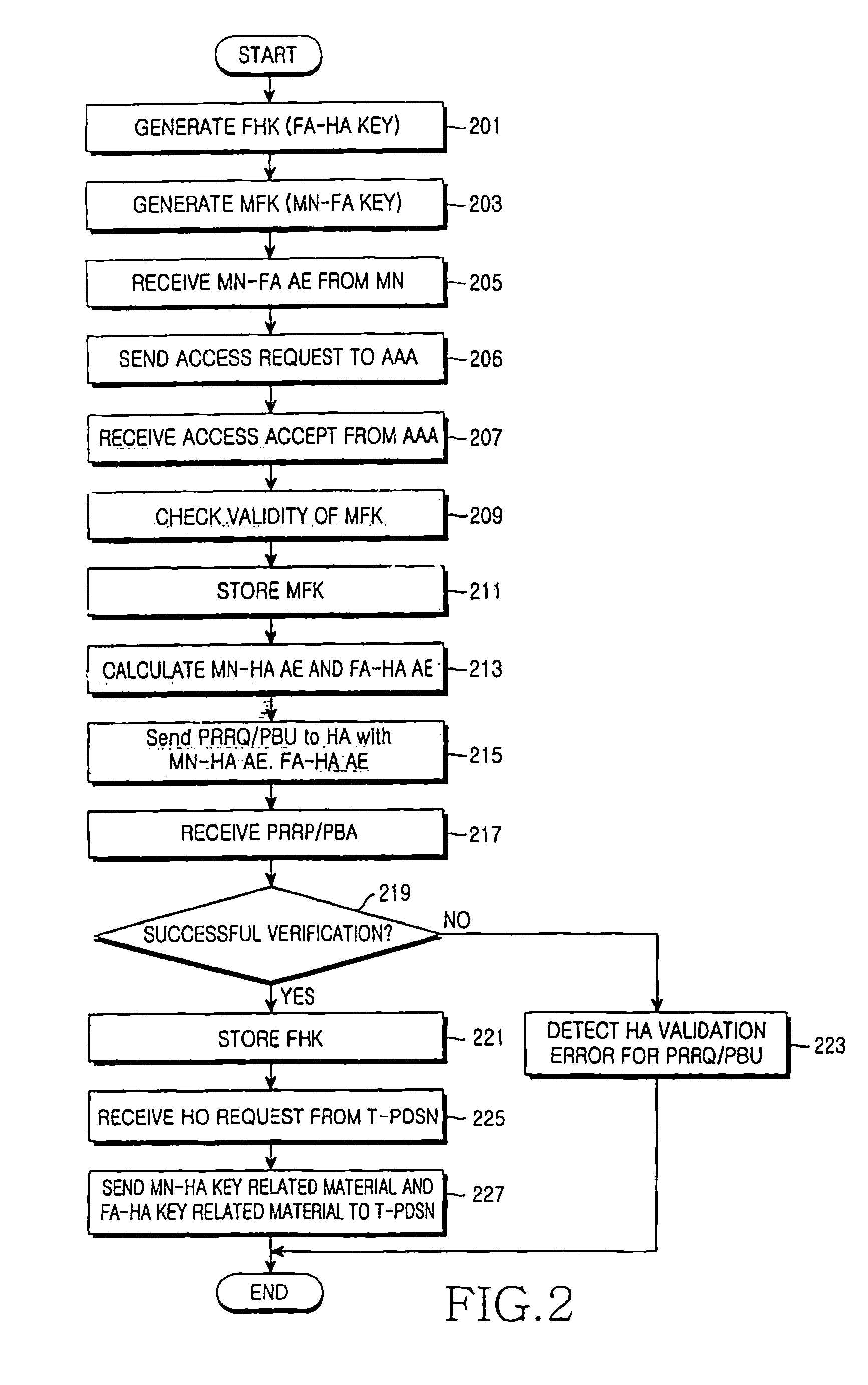
Method for managing security in a mobile communication system using proxy mobile internet protocol and system thereof
ActiveUS20080028459A1Lower latencyData taking preventionDigital data processing detailsPacket data serving nodeMobile communication systems
A security management method in a mobile communication system supporting Proxy Mobile Internet Protocol (IP). In the security management method, a Mobile Node (MN), a Serving Packet Data Service Node (S-PDSN), and an Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) server generate a security key of the Proxy Mobile IP. Upon receipt of information for authentication of a security key from the MN, the S-PDSN sends an access request message to the AAA server and receives information for verification of the security key. The S-PDSN sends a first message for requesting verification of the security-related key to a Home Agent (HA). The HA verifies the security-related key through the AAA server and sends a second message to the S-PDSN when the security-related key is verified. The S-PDSN sends a message indicating initiation of the Proxy Mobile IP, to the MN.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
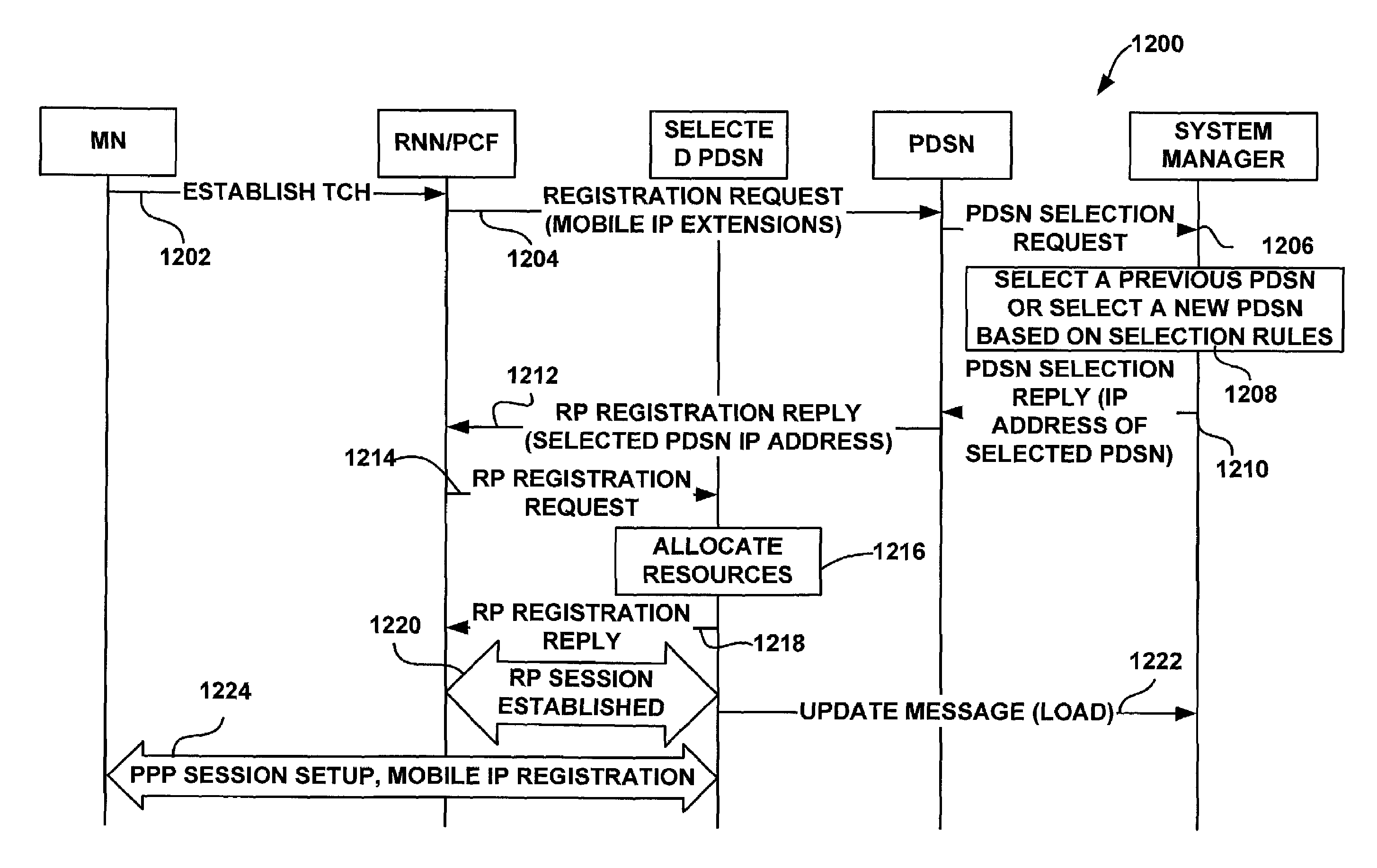
System and method for packet data serving node load balancing and fault tolerance
ActiveUS7295511B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket data serving nodeFault tolerance
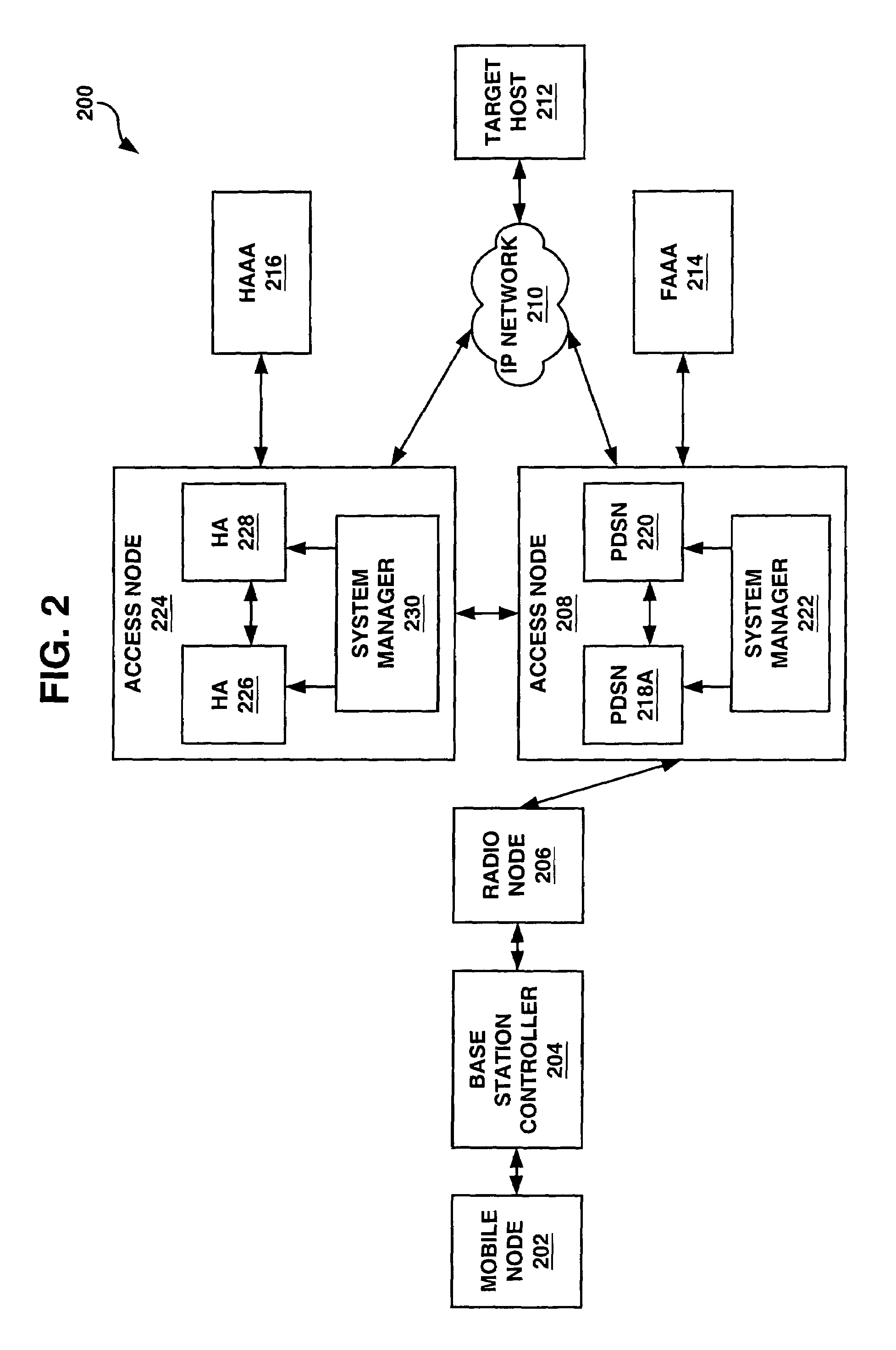
A system and methods are shown for providing packet data serving node (PDSN) load balancing and fault tolerance. One exemplary method includes providing an access node with a plurality of packet data serving nodes and at least one system manager, receiving from a radio node on a first packet data serving node a registration request, determining that the first packet data serving node is unable to serve the registration request, and sending a packet data serving node selection request from the first packet data serving node to the system manager. The method further includes determining at the system manager a second packet data serving node to serve the registration request, and providing an address of the second packet data serving node to the first packet data serving node. The method further includes sending a registration reply message from the first packet data serving node to the radio node, where the registration reply message includes the address of the second packet data serving node.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com