Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36results about How to "Improving yield and reliability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
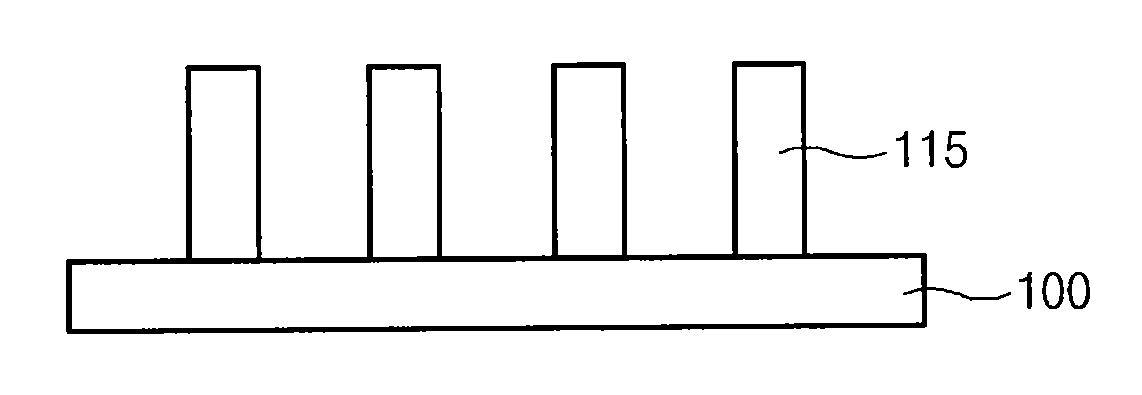
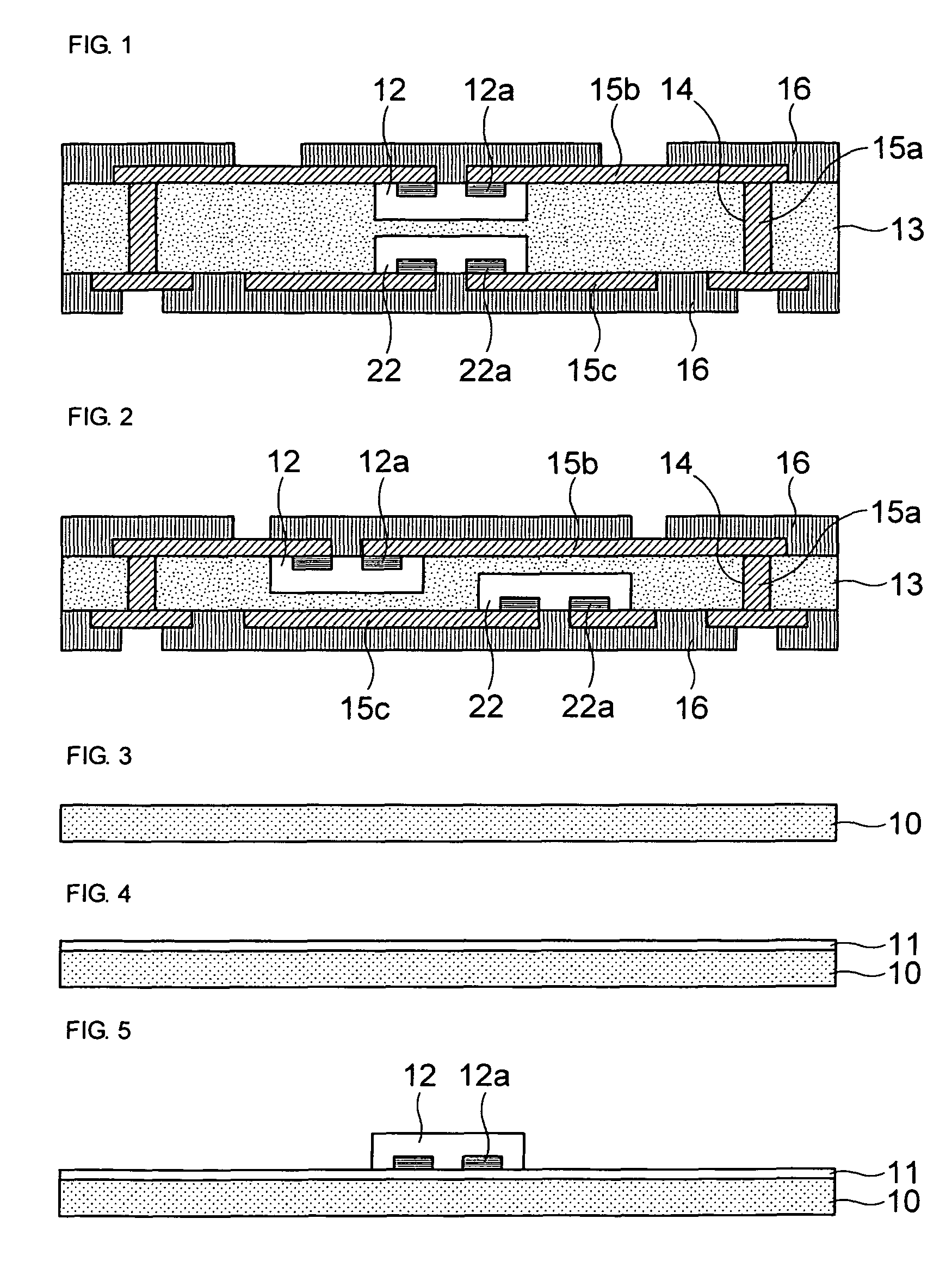
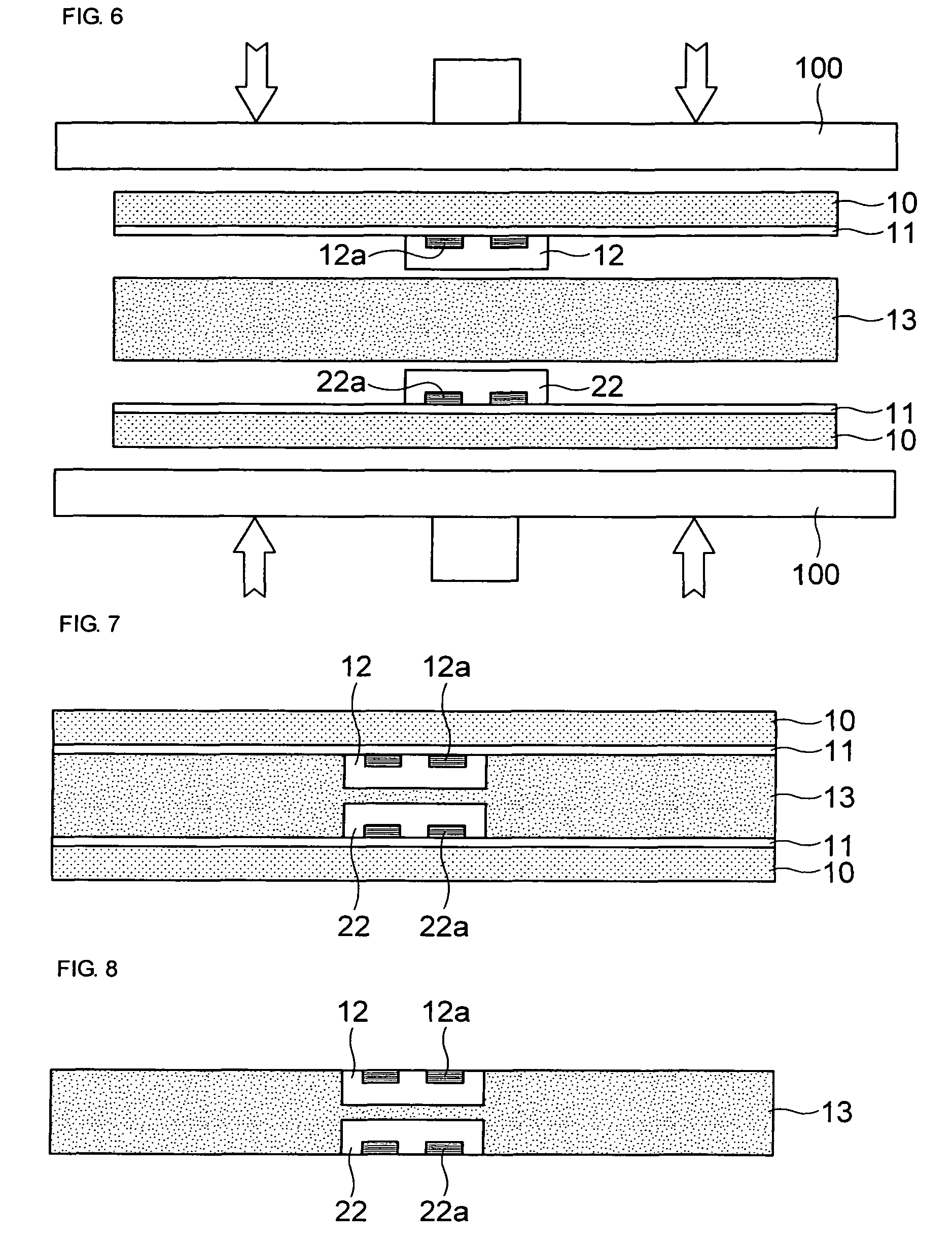
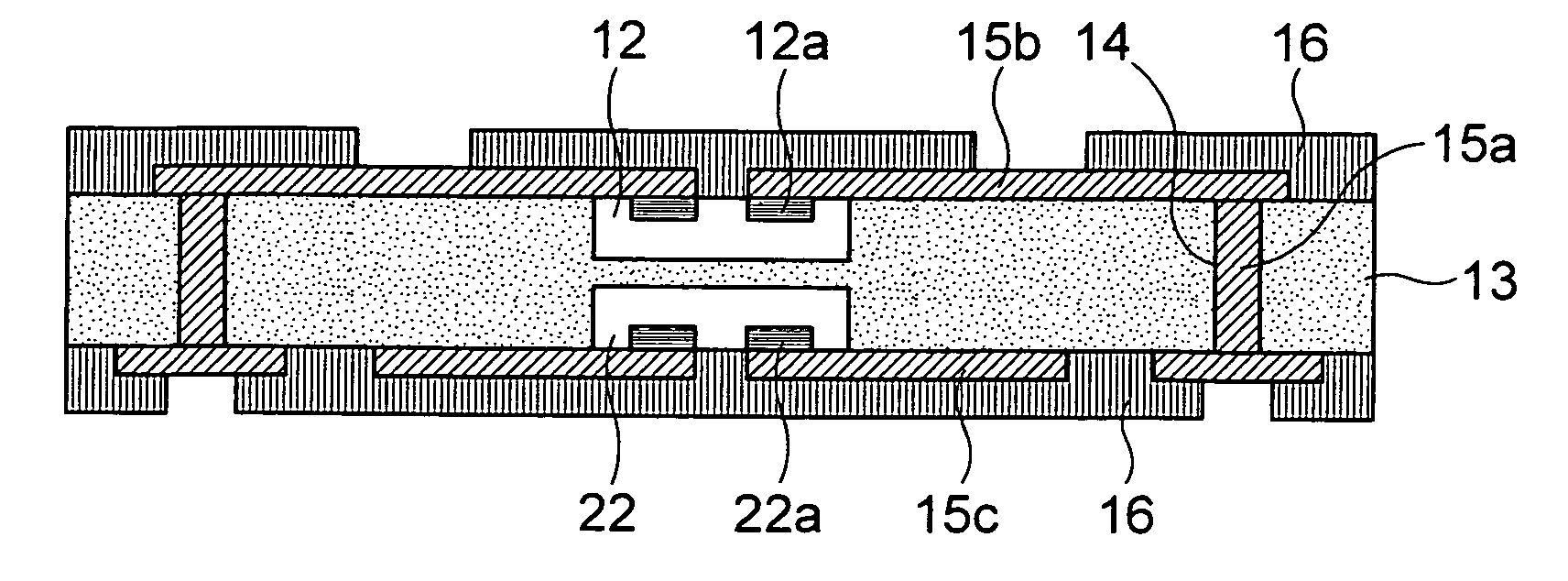
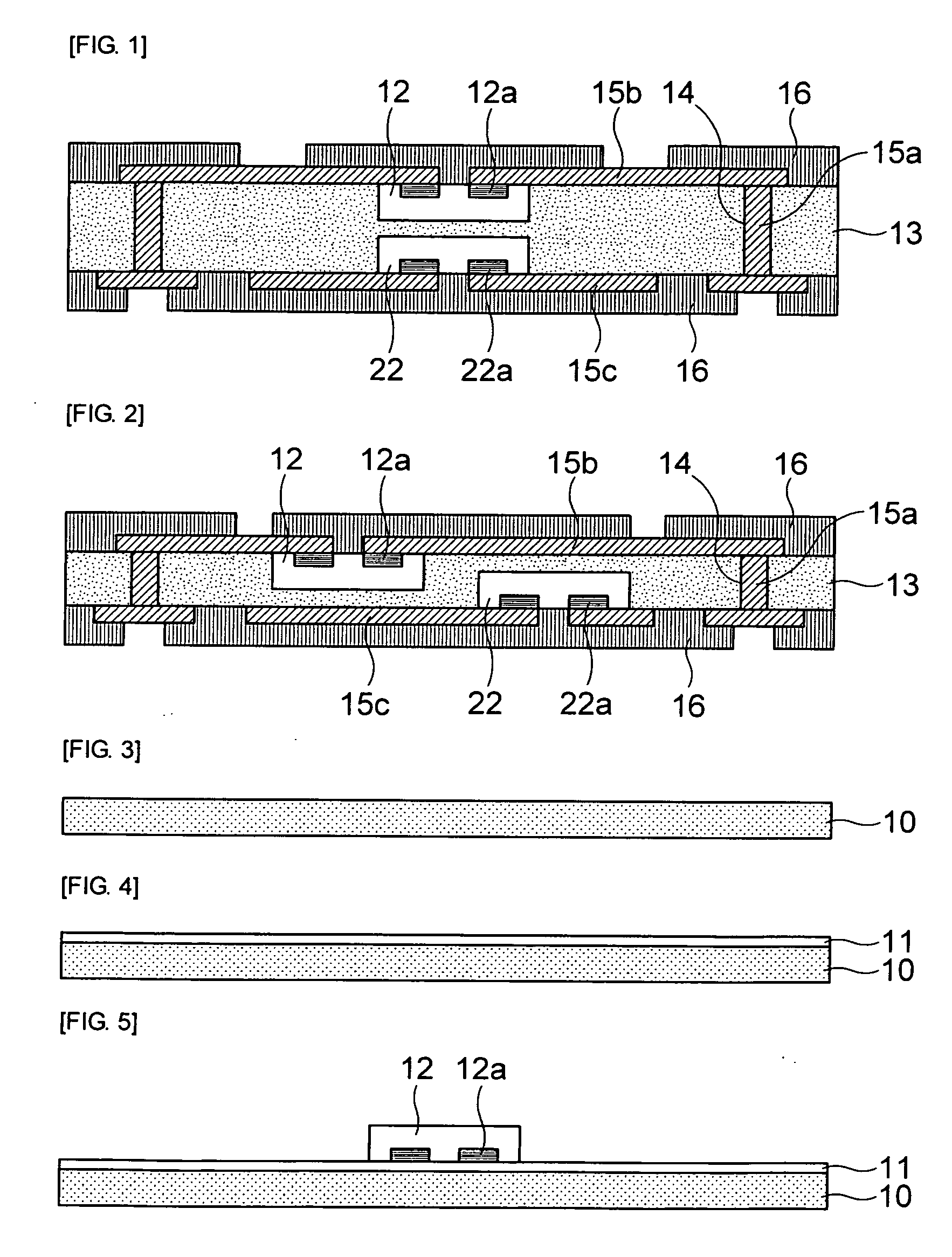
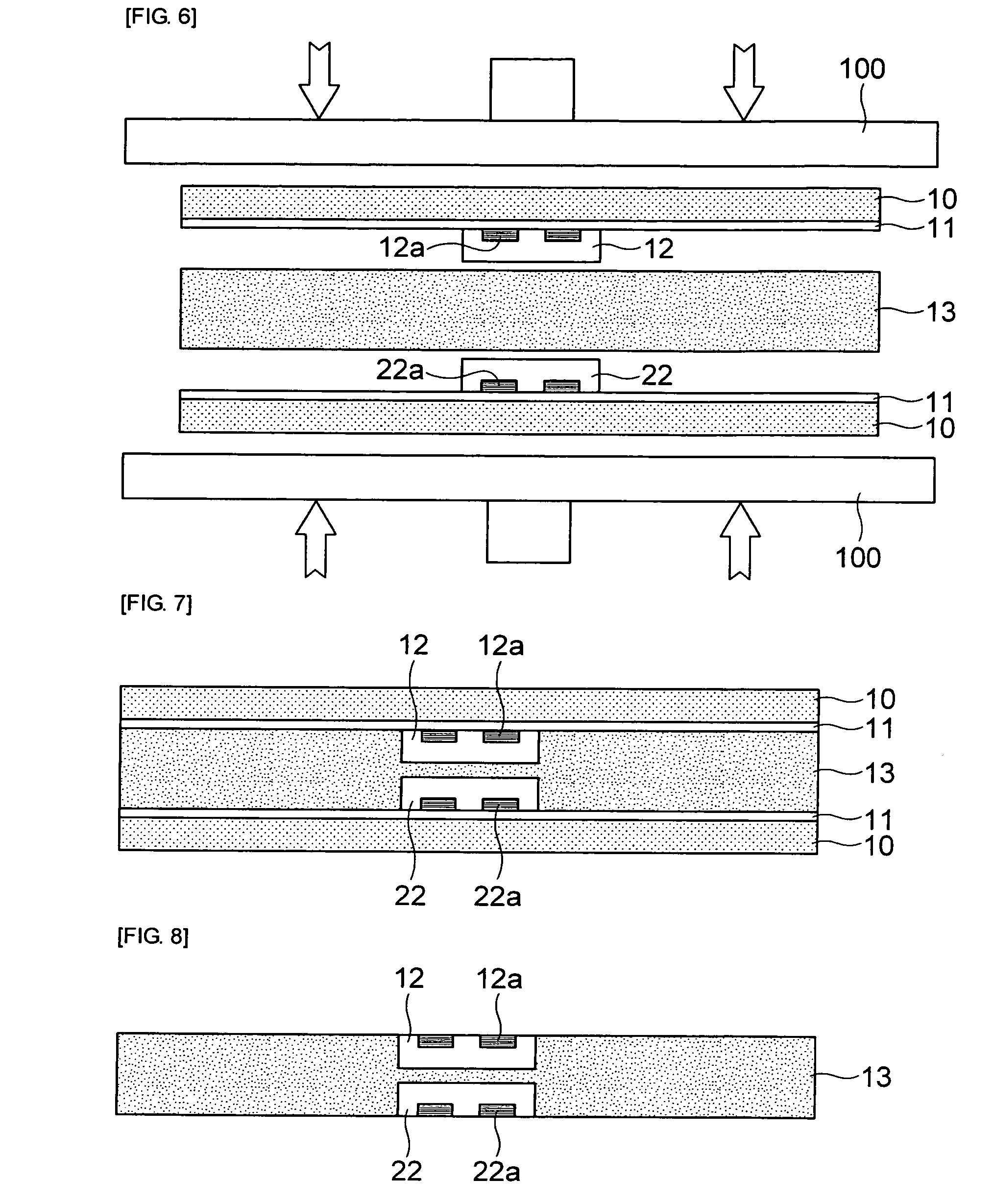
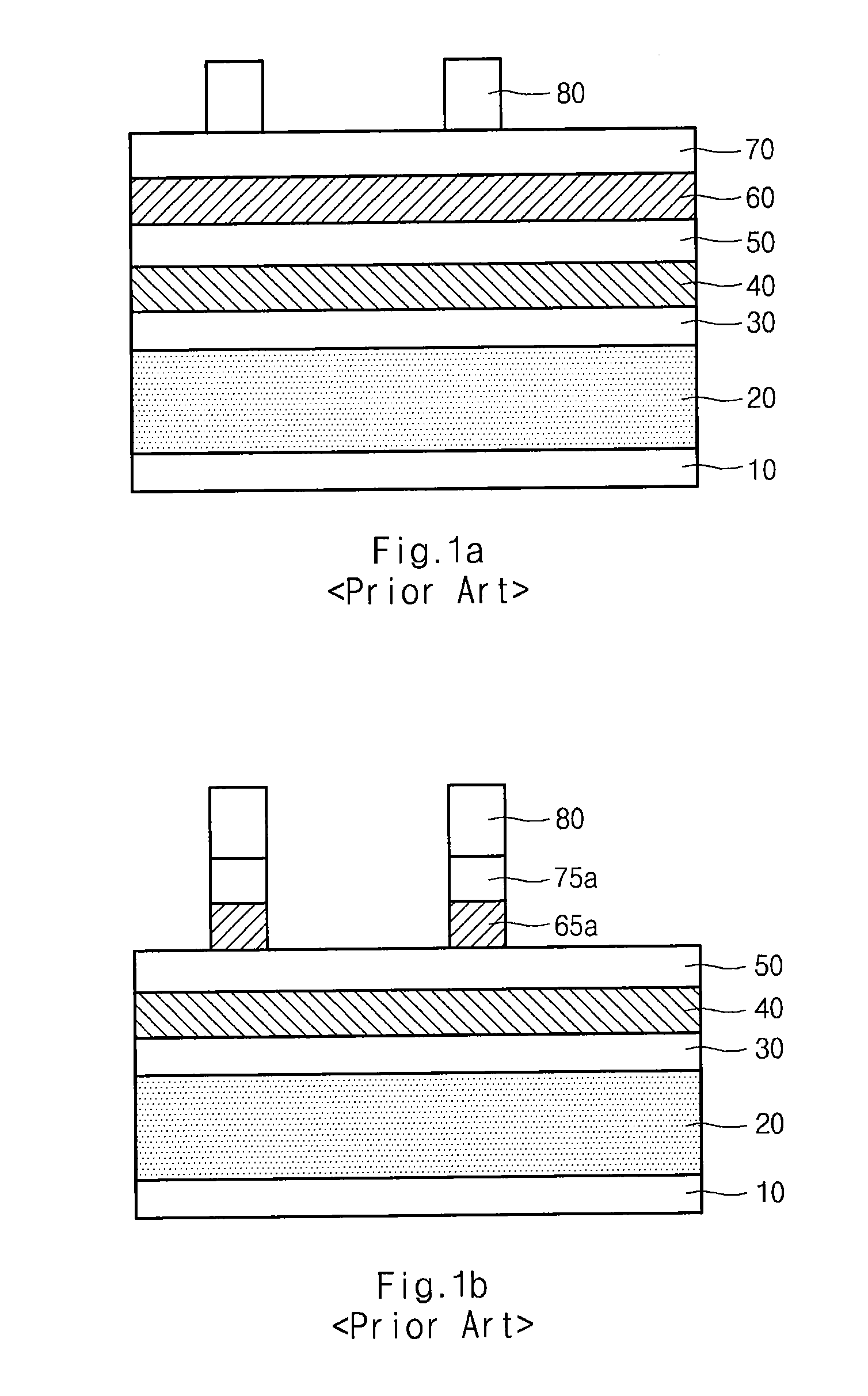
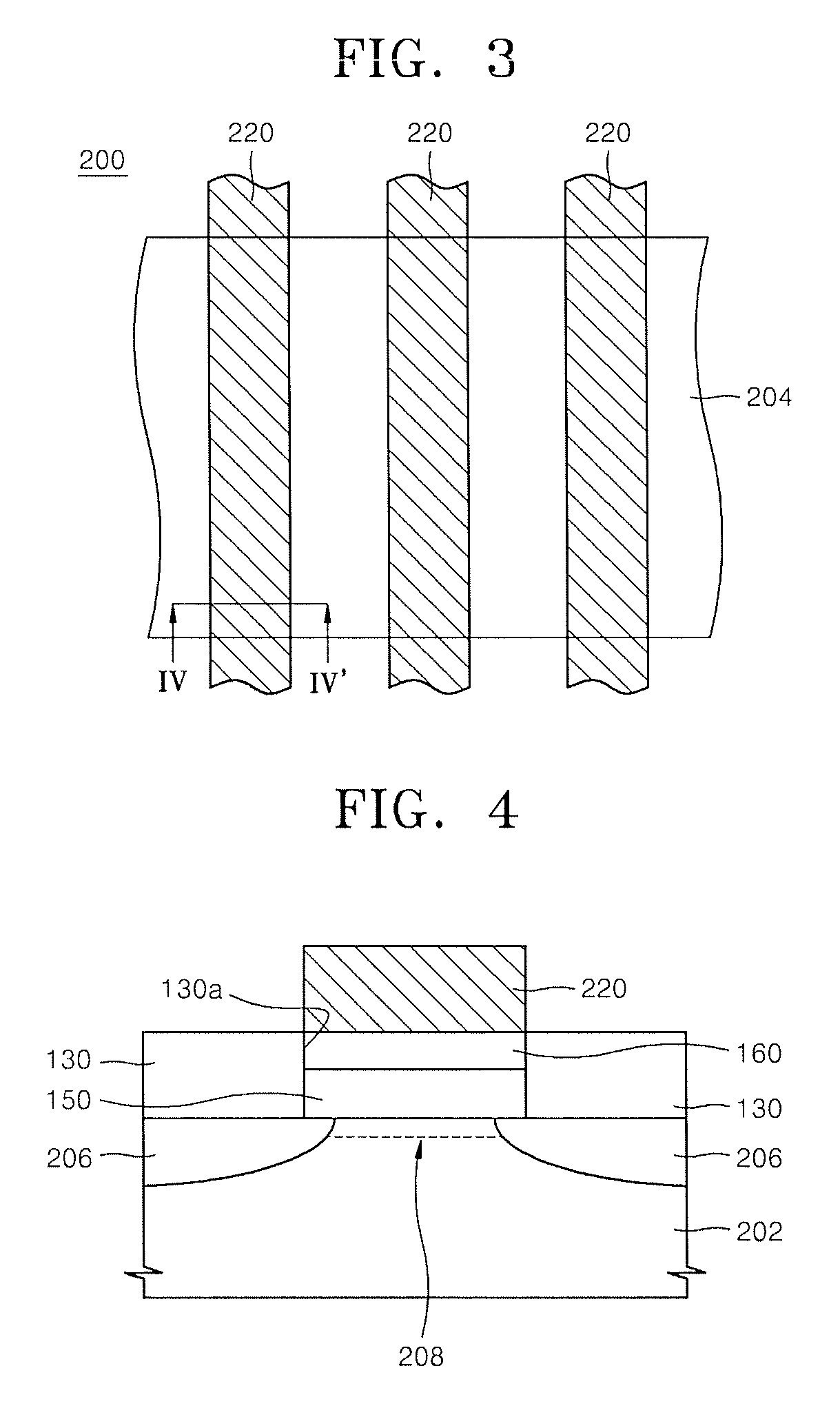
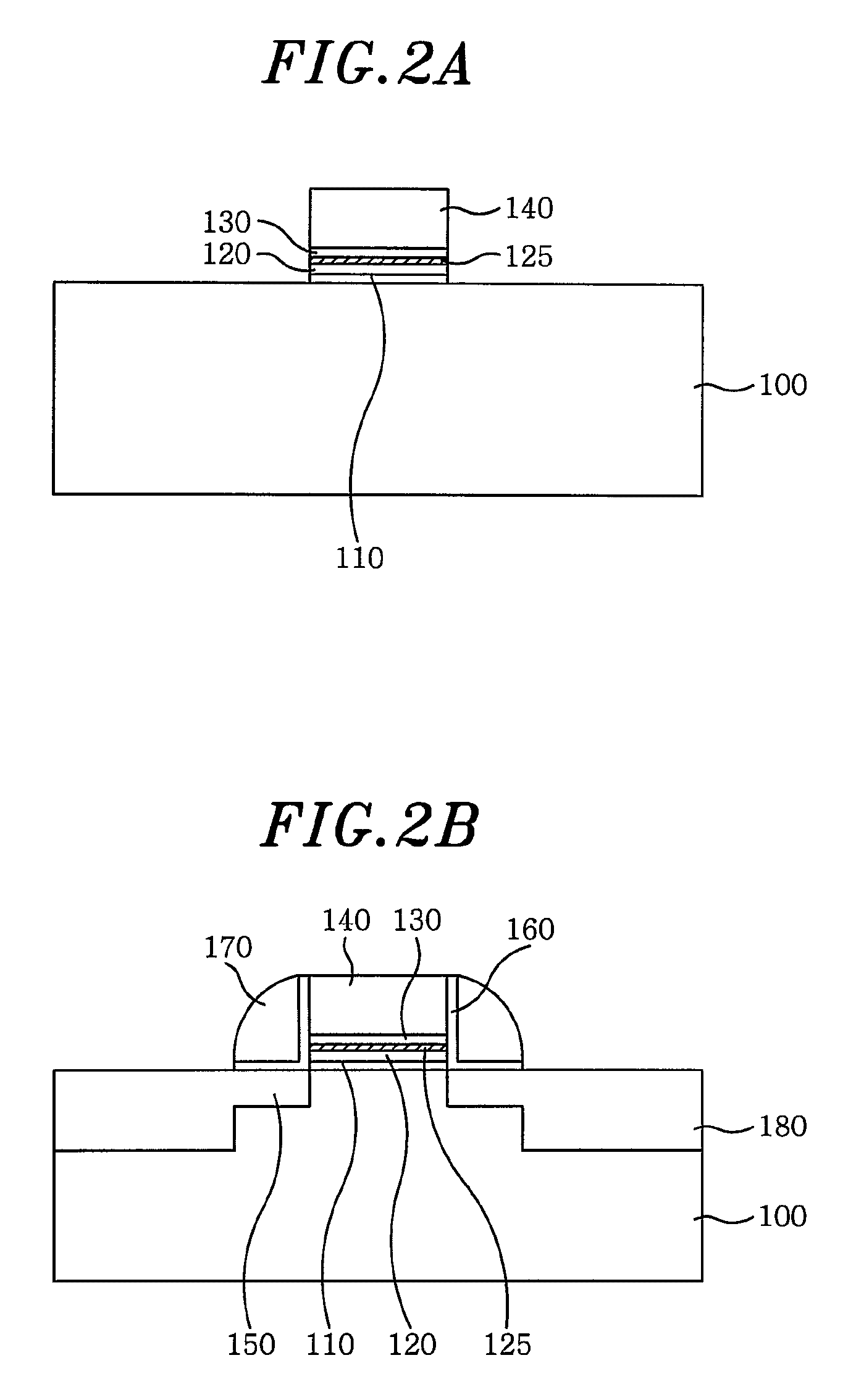
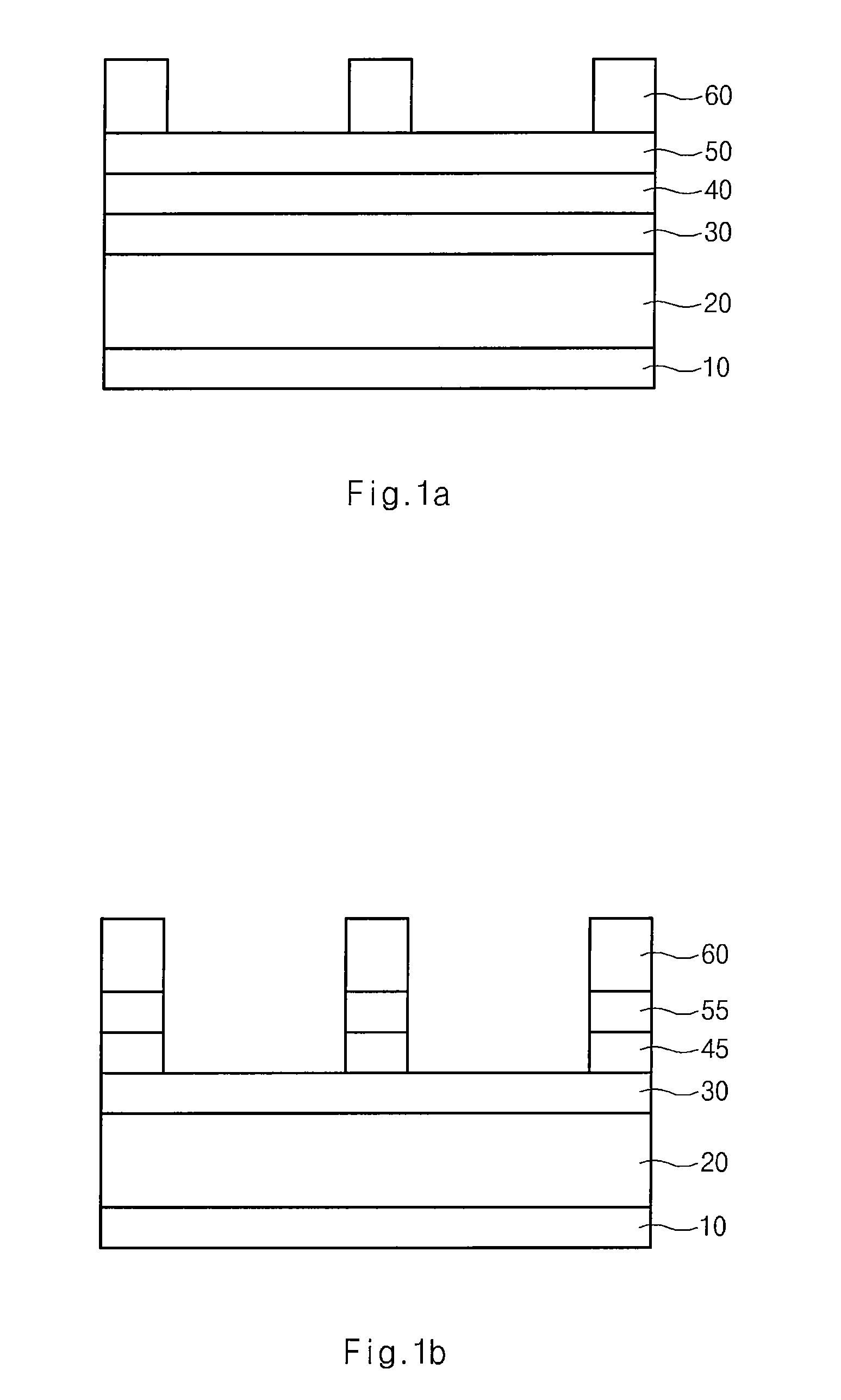
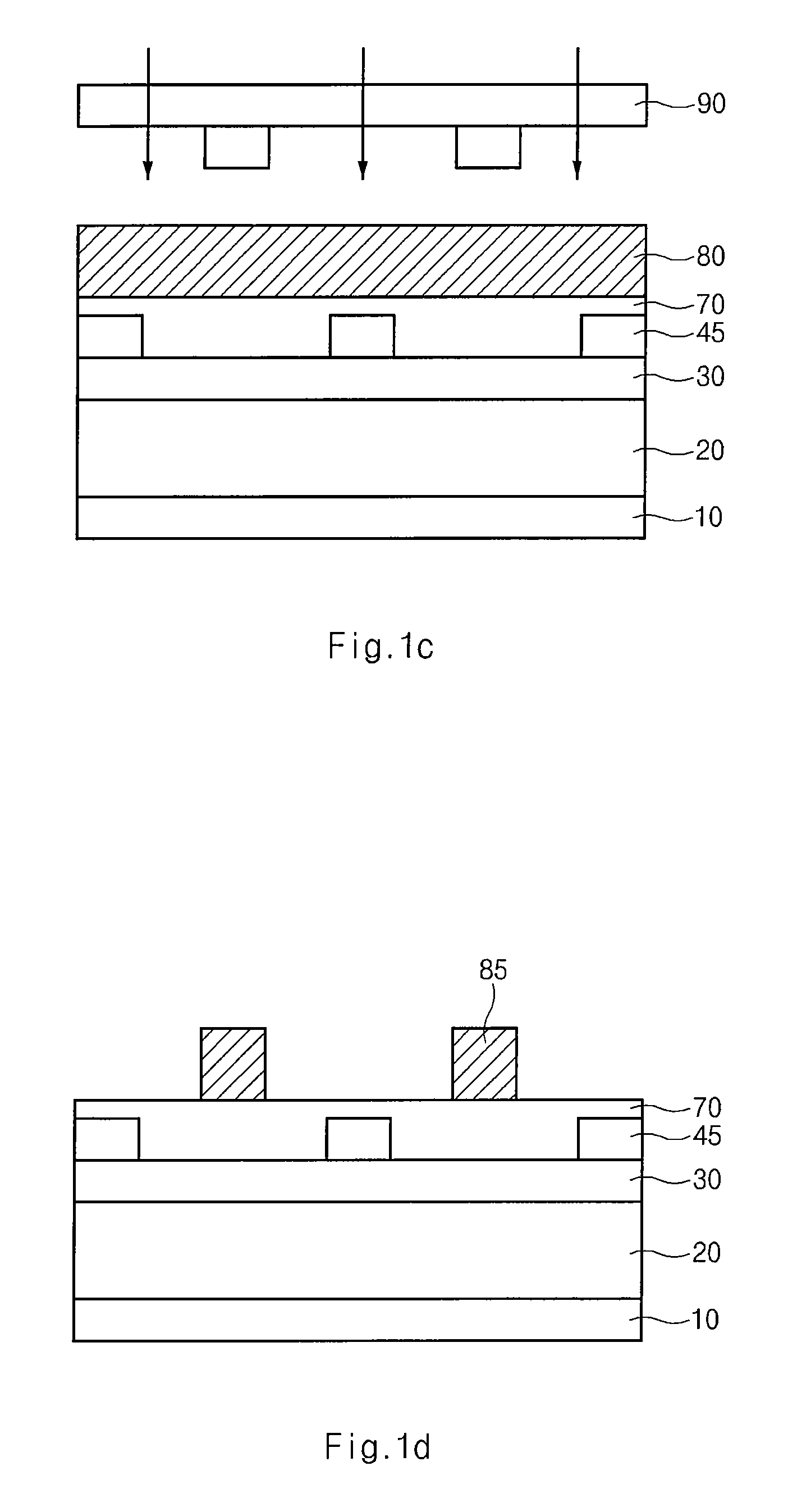
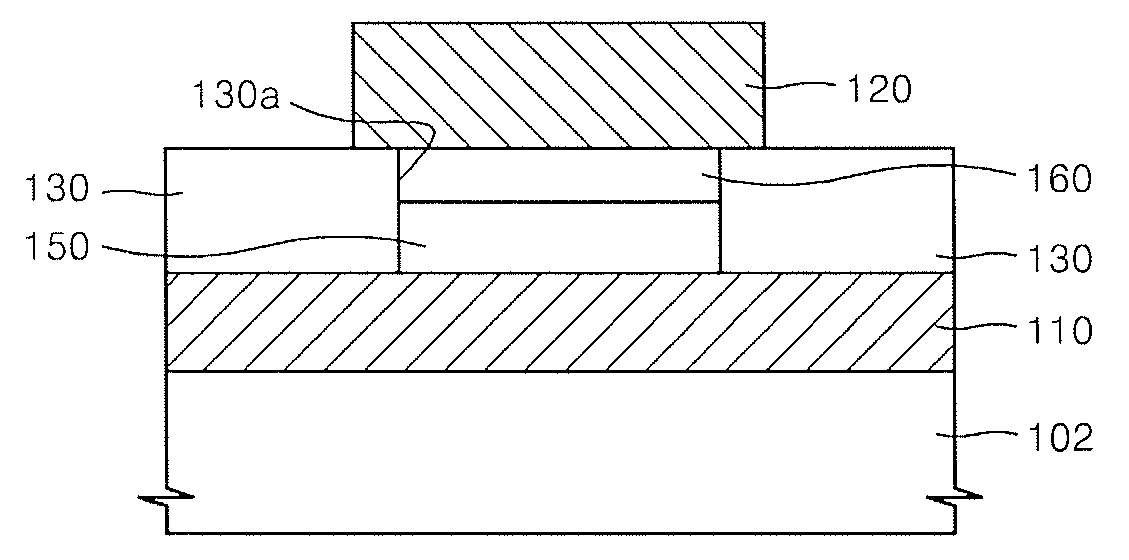
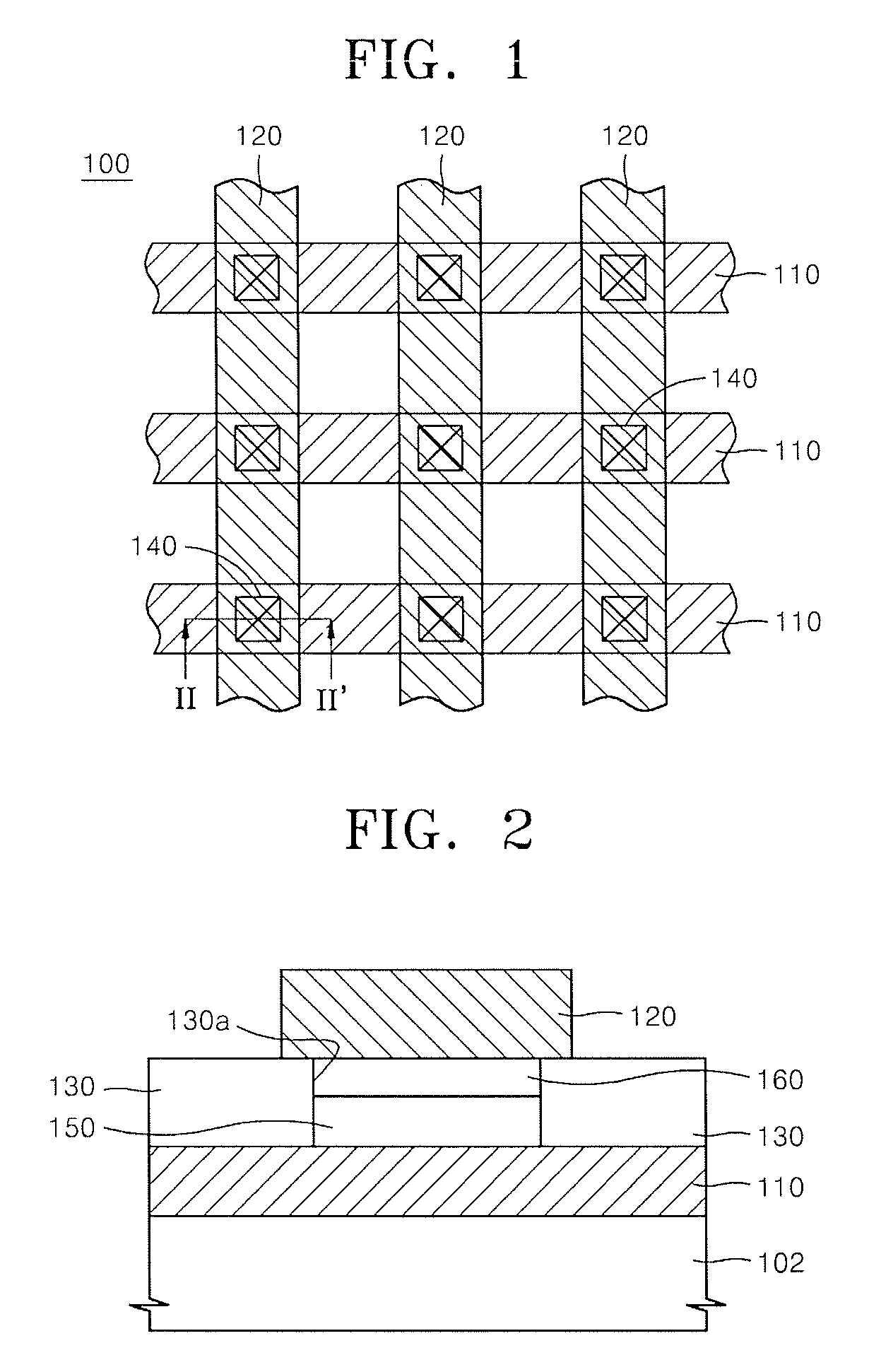
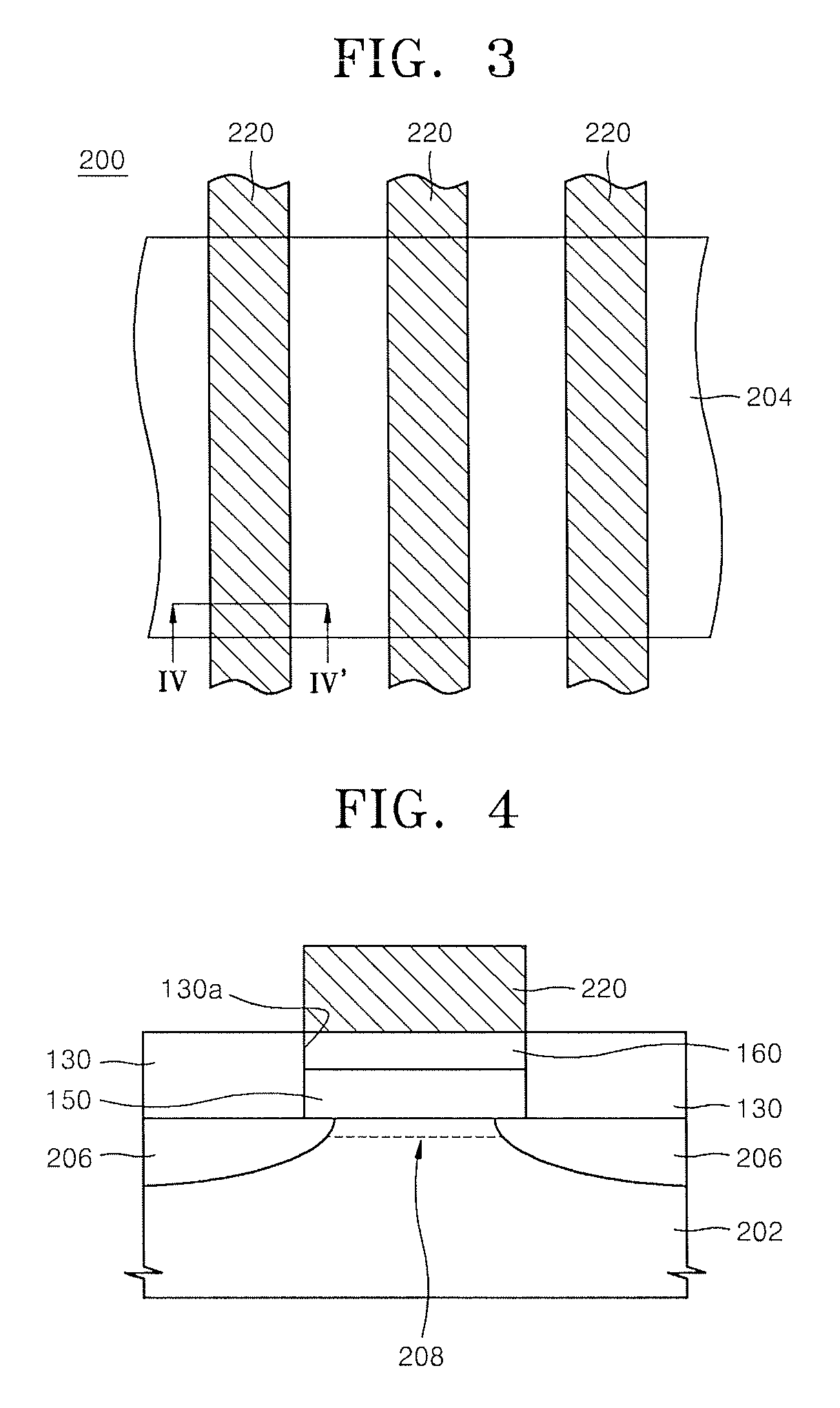
Method for forming pattern of semiconductor device
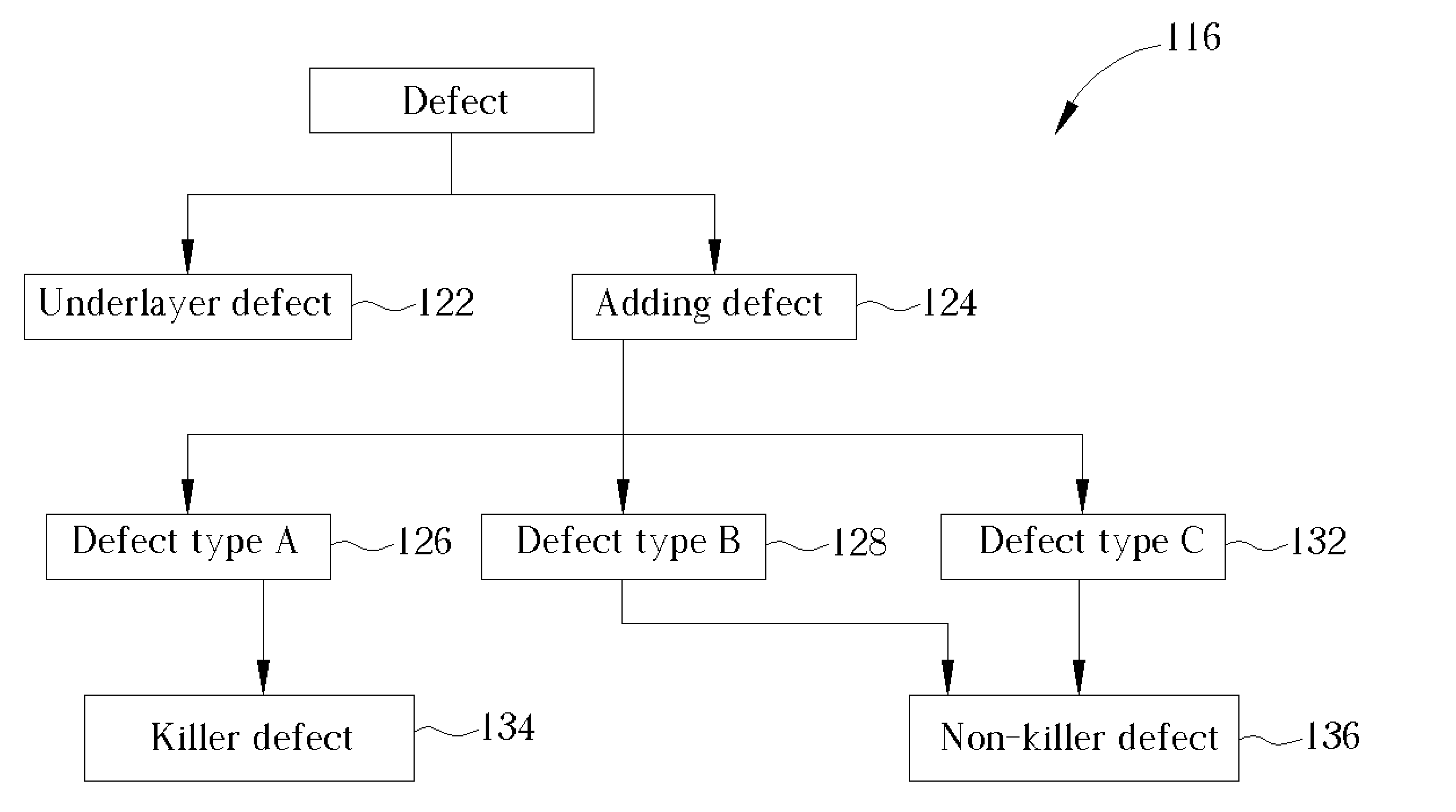
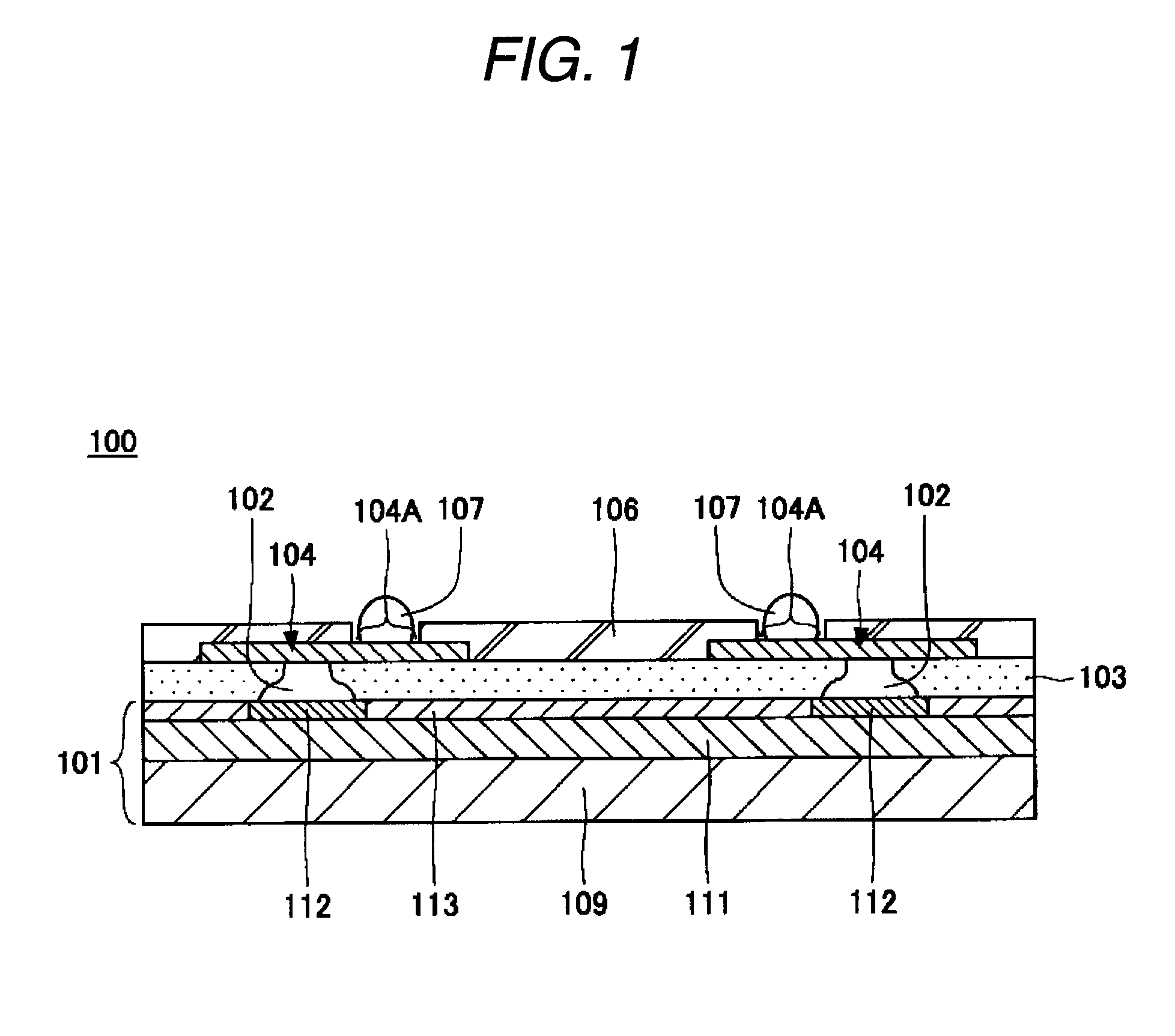
InactiveUS20090075485A1High yieldImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
A method for forming a fine pattern of a semiconductor device comprises: forming a first hard mask film and an etch barrier film over a semiconductor substrate; forming a sacrificial pattern over the etch barrier film; forming a spacer on sidewalls of the sacrificial pattern; removing the sacrificial pattern; etching the etch barrier film and the hard mask film with the spacer as an etch mask to form an etch barrier pattern and a hard mask pattern; and removing the spacer and the etch barrier pattern, thereby improving yield and reliability of the device.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of manufacturing a chip embedded printed circuit board
InactiveUS8893380B2Reduce thicknessImproving yield and reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The present invention relates to a chip embedded printed circuit board and a manufacturing method thereof and provides a chip embedded printed circuit board including: an insulating layer having vias formed therethrough; a first chip and a second chip embedded in the insulating layer and having pads, which are respectively exposed to upper and lower surfaces of the insulating layer, on one surfaces thereof; an upper pattern formed on the upper surface of the insulating layer to be connected to the pads of the first chip and the vias; and a lower pattern formed on the lower surface of the insulating layer to be connected to the pads of the second chip and the vias. Also, the present invention provides a manufacturing method of a chip embedded printed circuit board.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Chip embedded printed circuit board and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100142170A1Reduce thicknessImproving yield and reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit boardEngineering
The present invention relates to a chip embedded printed circuit board and a manufacturing method thereof and provides a chip embedded printed circuit board including: an insulating layer having vias formed therethrough; a first chip and a second chip embedded in the insulating layer and having pads, which are respectively exposed to upper and lower surfaces of the insulating layer, on one surfaces thereof; an upper pattern formed on the upper surface of the insulating layer to be connected to the pads of the first chip and the vias; and a lower pattern formed on the lower surface of the insulating layer to be connected to the pads of the second chip and the vias. Also, the present invention provides a manufacturing method of a chip embedded printed circuit board.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
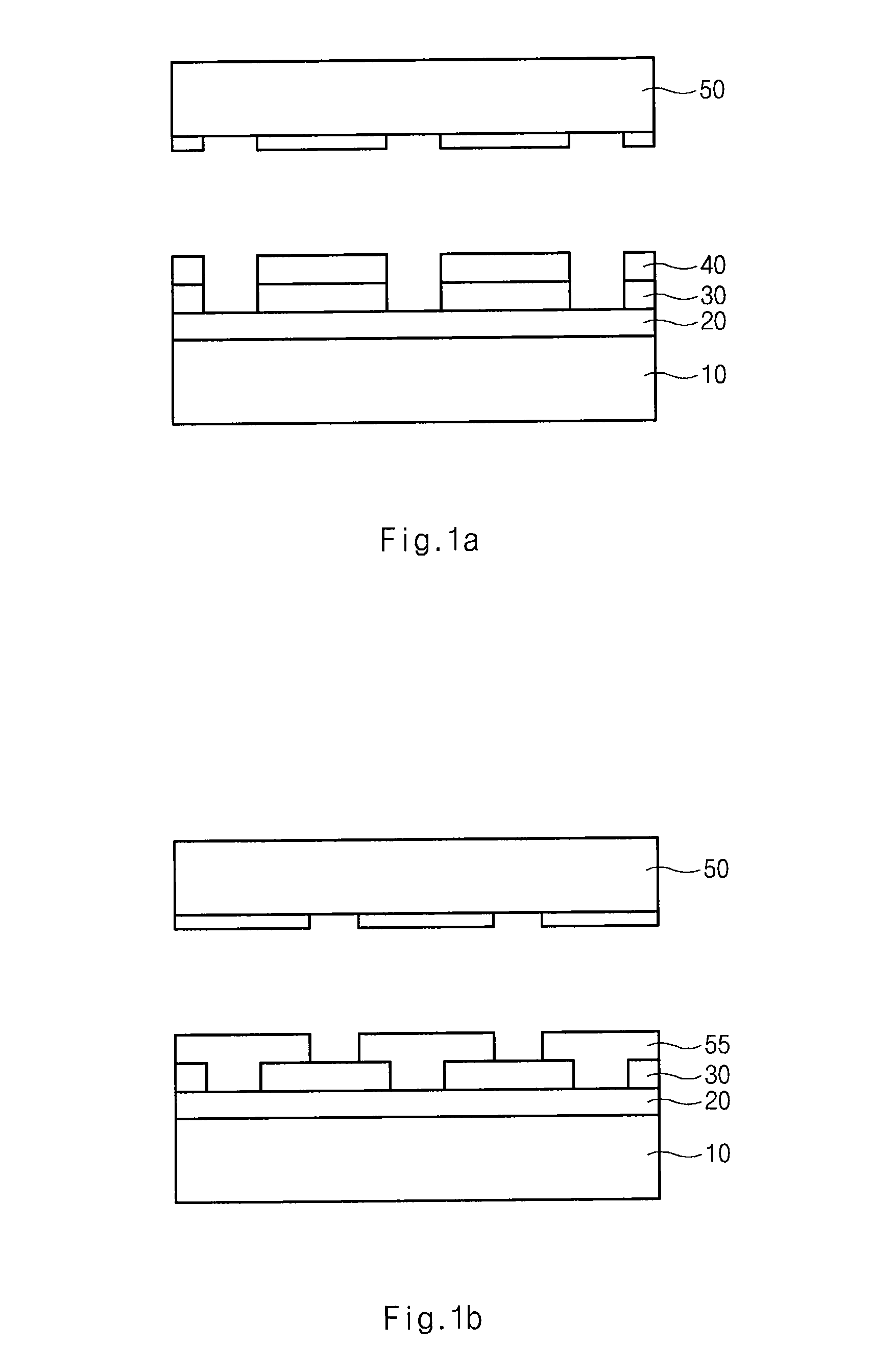
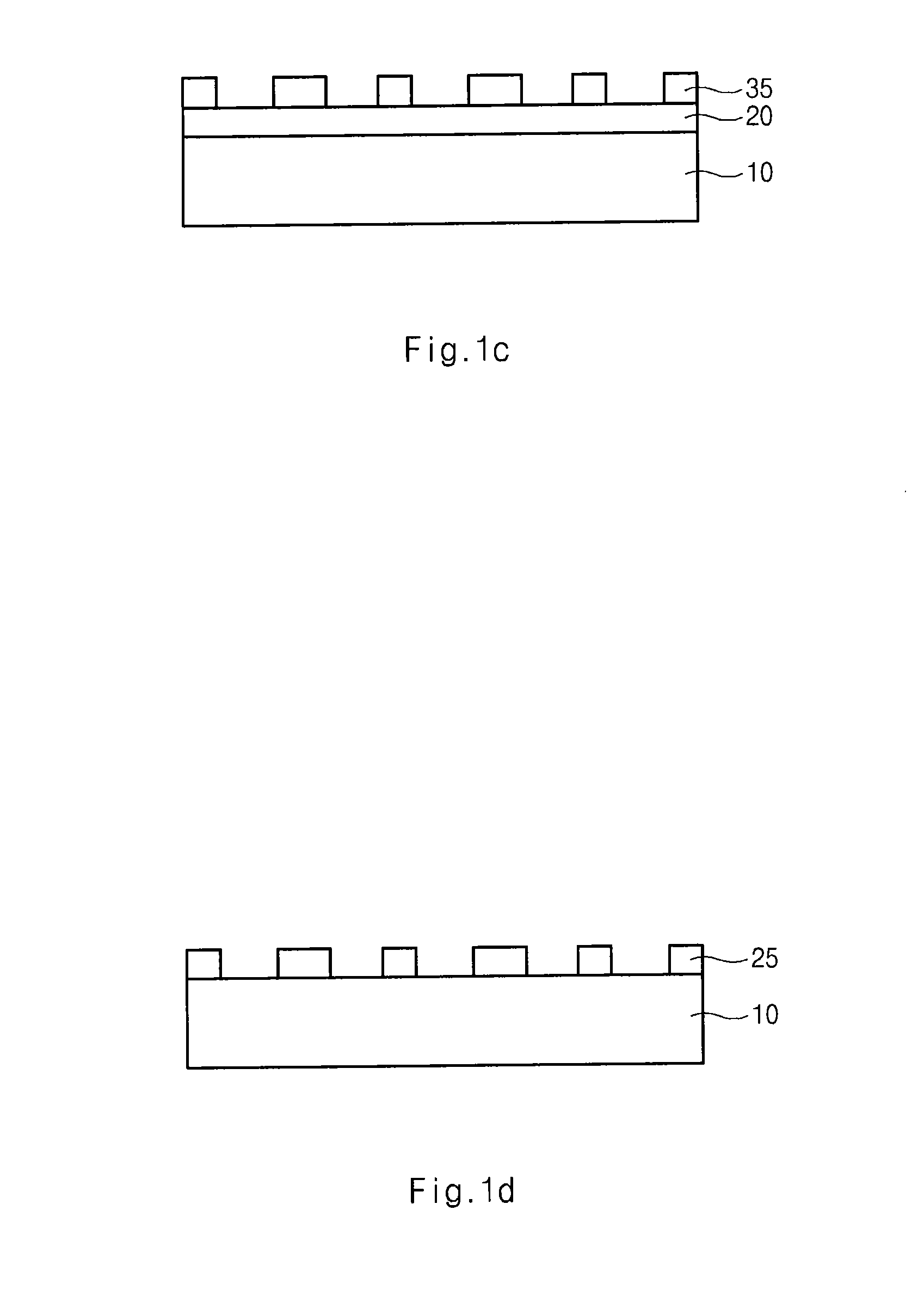
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080160770A1High yieldImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes forming an underlying layer over a semiconductor substrate; forming a hard mask layer over the underlying layer; forming first etch patterns over the hard mask layer; forming second etch patterns between the first photoresist patterns; etching the hard mask layer using the first and second etch patterns as an etch mask to form a hard mask pattern; and etching the underlying layer using at least the hard mask pattern. The first and second etch patterns are formed on the same layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
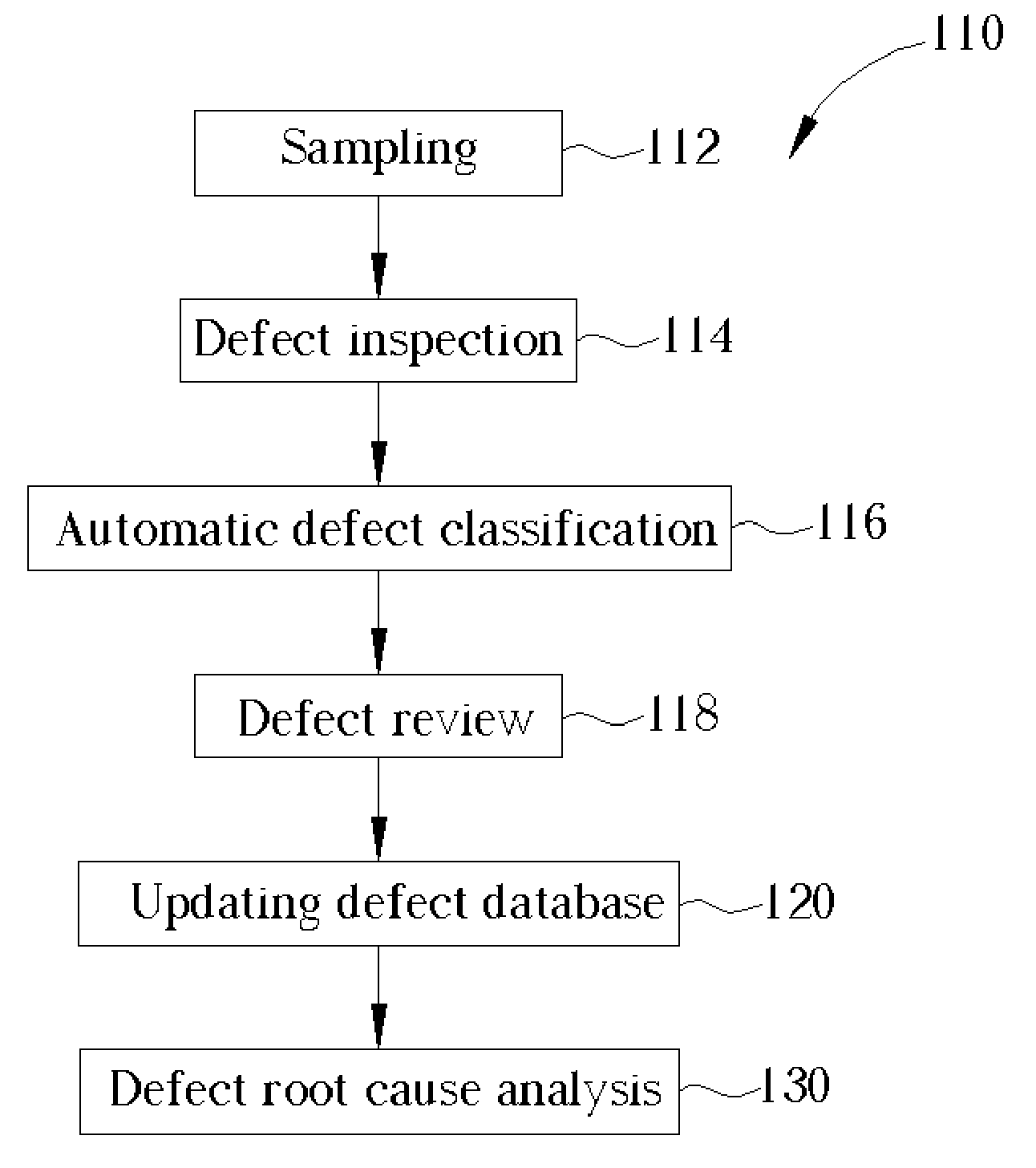
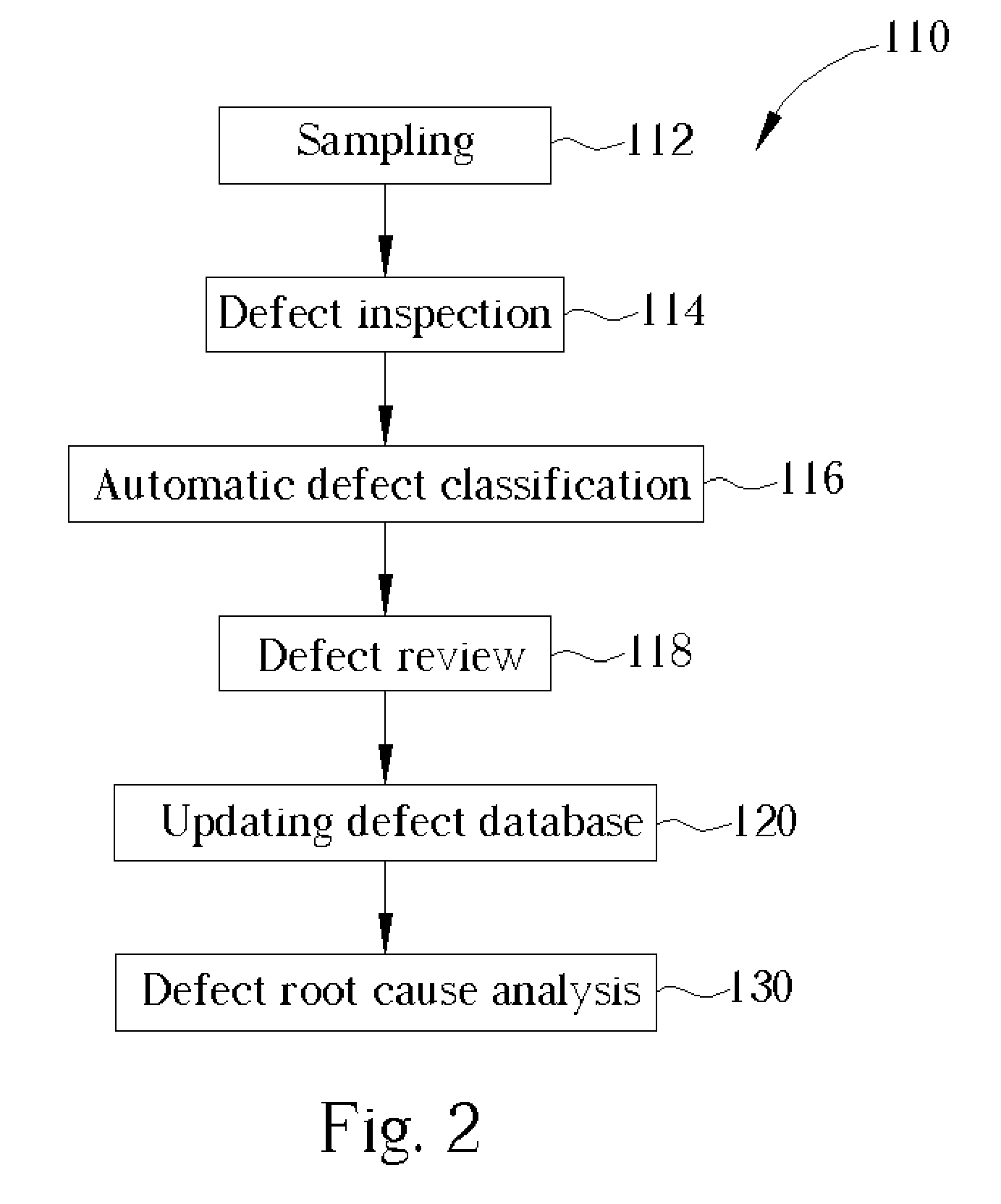
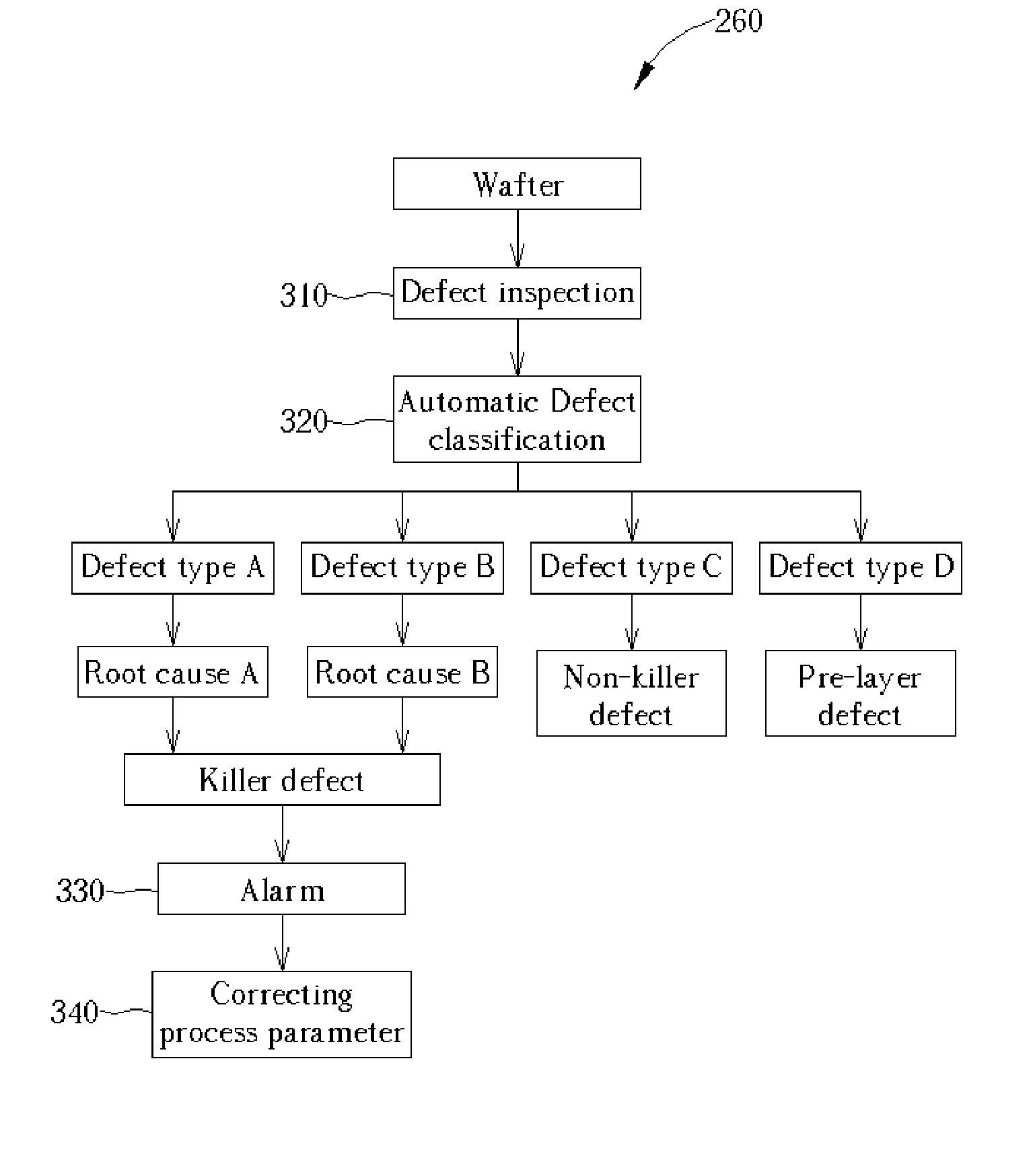
Method of defect review
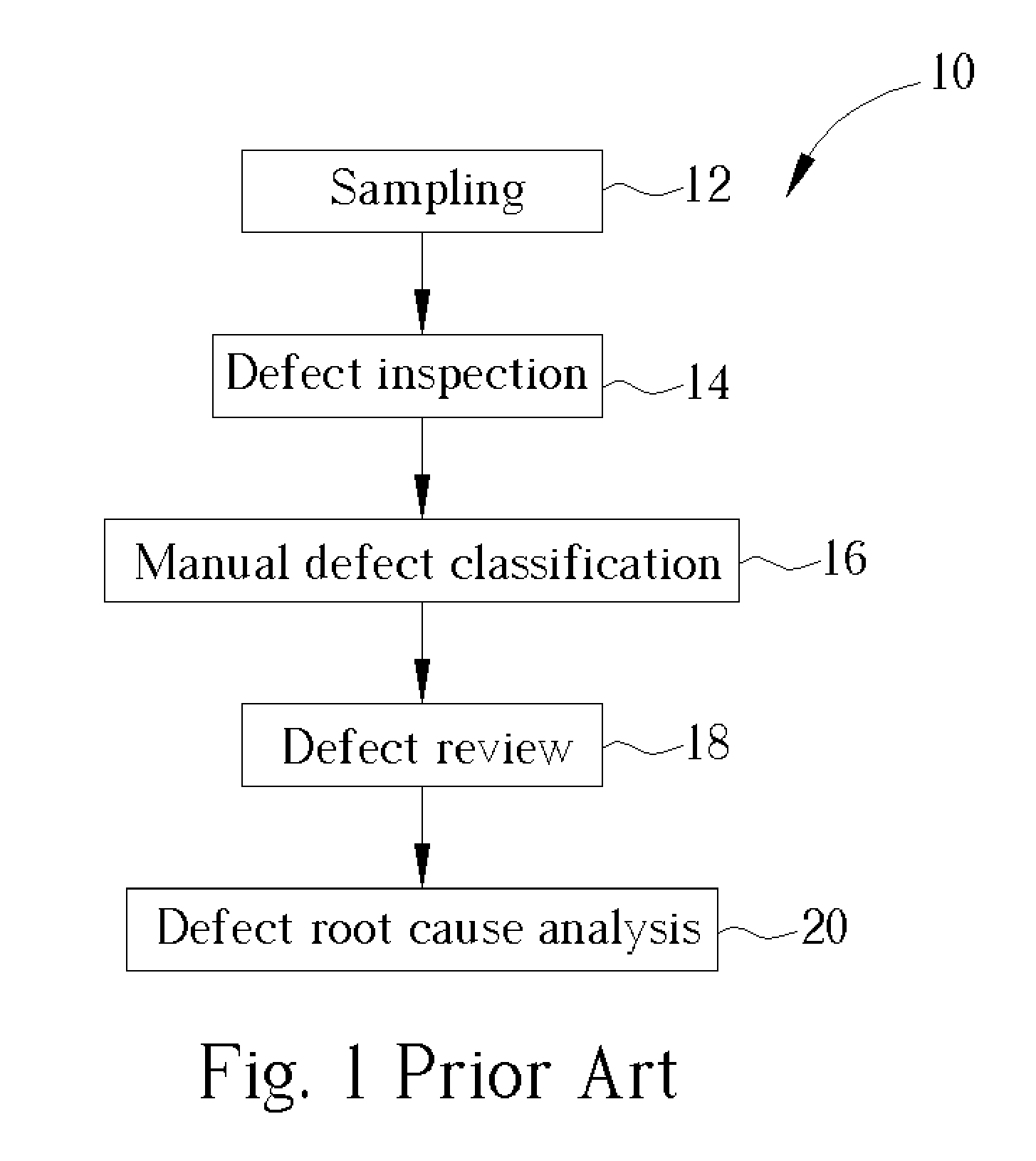
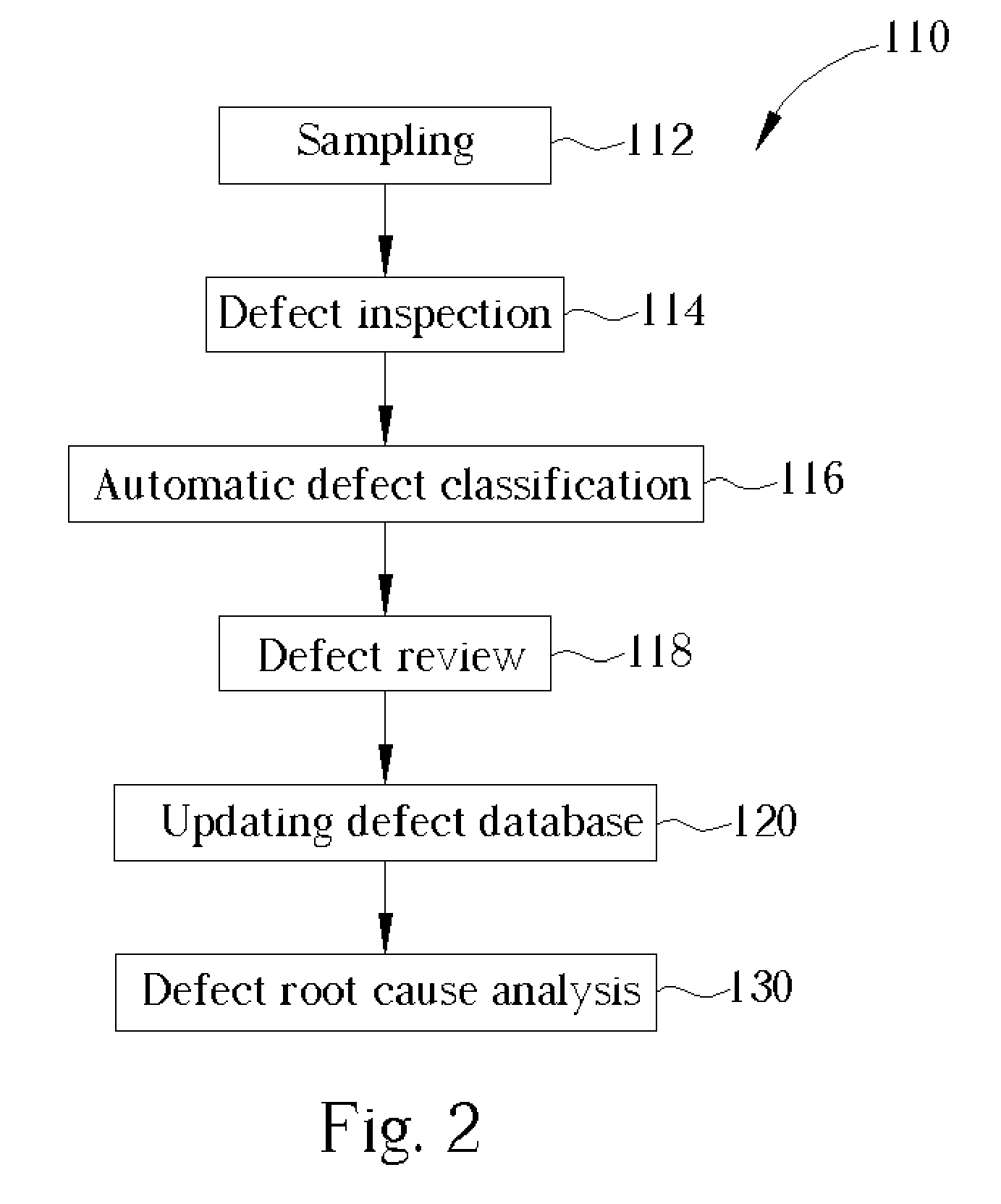
ActiveUS20050159909A1Improve efficiencyIncrease sampling rateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineering
A method of defect review. First, a wafer with a plurality of defects is provided. A defect inspection is performed to detect the defects. An automatic defect classification is then performed to divide the defects into different defect types according to a predetermined database. A defect review is performed to review different defect types of defects which are sampled in different weights according to yield killing ratios of each defect types.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090170034A1High yieldImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDevice materialImage resolution
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises: forming a first photoresist pattern in a double patterning technology (DPT) for overcoming a resolution limit of an exposer; and forming a second photoresist pattern. The method further comprises forming a hard mask film and an anti-reflective film to prevent an intermixing phenomenon generated when the second photoresist pattern is formed. As a result, yield and reliability of the process can be improved.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of defect review
ActiveUS7071011B2Improve efficiencyIncrease sampling rateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoftware engineering
A method of defect review. First, a wafer with a plurality of defects is provided. A defect inspection is performed to detect the defects. An automatic defect classification is then performed to divide the defects into different defect types according to a predetermined database. A defect review is performed to review different defect types of defects which are sampled in different weights according to yield killing ratios of each defect types.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Method of defect control
InactiveUS20050080572A1Reduce loadShort response timeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
A method of defect control by daily checking. First, a patterned wafer with a plurality of first defects is provided. After performing a semiconductor process, which generates a plurality of second defects on the wafer, a defect detecting process is performed to detect the first defects and the second defects. Then, the first defects and the second defects are divided according to a predetermined database. The second defects are classified into a plurality of defect types according to the predetermined database.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Current-leveling electroplating/electropolishing electrode
InactiveUS7803257B2Increase current densityImproving yield and reliabilityMachining electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectrochemistry
A current-leveling electrode for improving electroplating and electrochemical polishing uniformity in the electrochemical plating or electropolishing of metals on a substrate is disclosed. The current-leveling electrode includes a base electrode and at least one sub-electrode carried by the base electrode. The at least one sub-electrode has a width which is less than a width of the base electrode to impart a generally tapered, stepped or convex configuration to the current-leveling electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
High-Purity Copper Sputtering Target
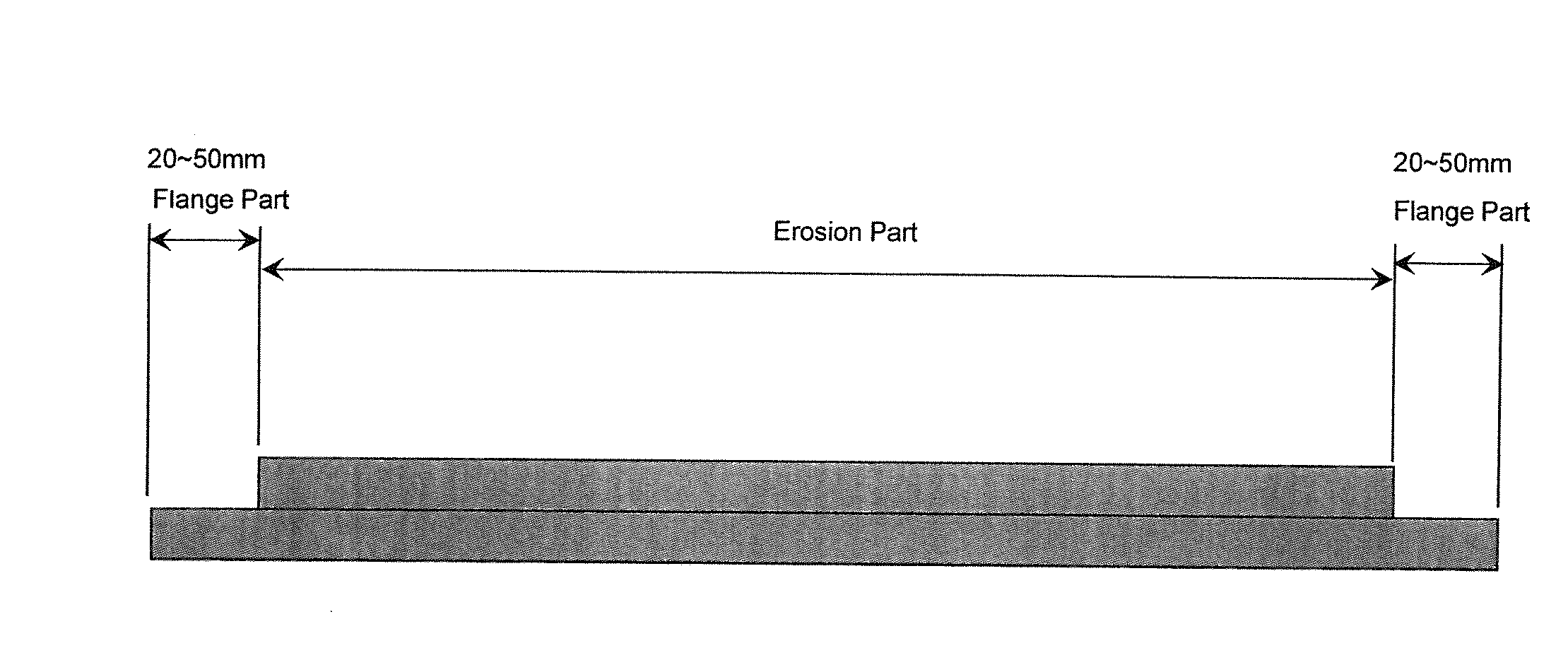
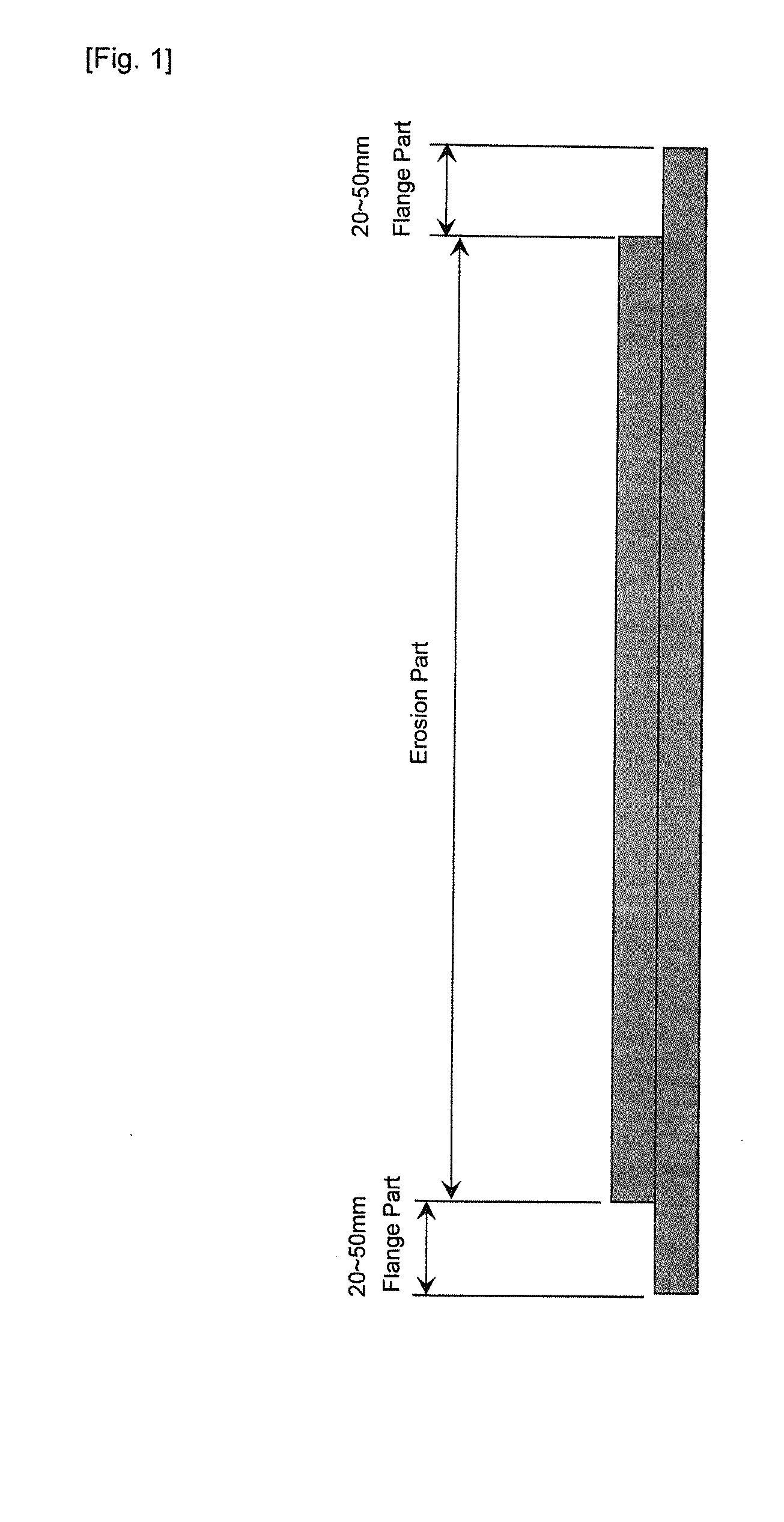
A high-purity copper sputtering target, wherein a Vickers hardness of a flange part of the target is in a range of 90 to 100 Hv, a Vickers hardness of an erosion part in the central area of the target is in a range of 55 to 70 Hv, and a crystal grain size of the erosion part is 80 μm or less. This invention relates to a high-purity copper sputtering target that does not need to be bonded to a backing plate (BP), and aims to provide a high-purity copper sputtering target capable of forming a thin film having superior uniformity by enhancing a strength (hardness) of the flange part of the target, and reducing an amount of warpage of the target. Moreover, the uniformity of the film thickness is improved by adjusting the (111) orientation ratio of the erosion part and the flange part in the target. The present invention thereby aims to provide a high-purity copper sputtering target, which is capable of improving the yield and reliability of semiconductor products that are being subject to further miniaturization and higher integration, and useful for forming a copper alloy wiring for semiconductors.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
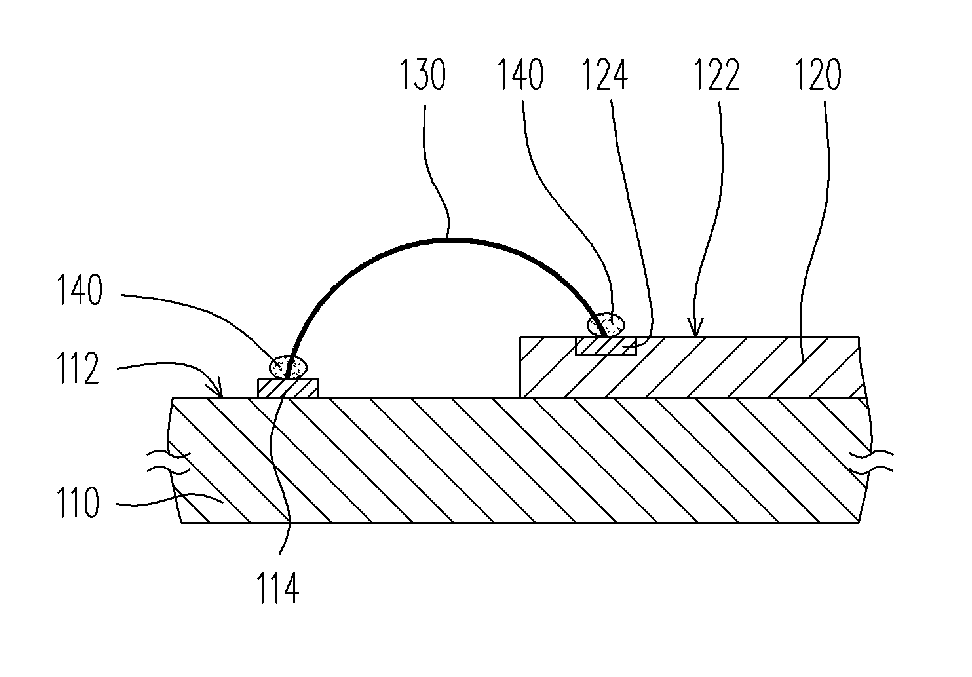
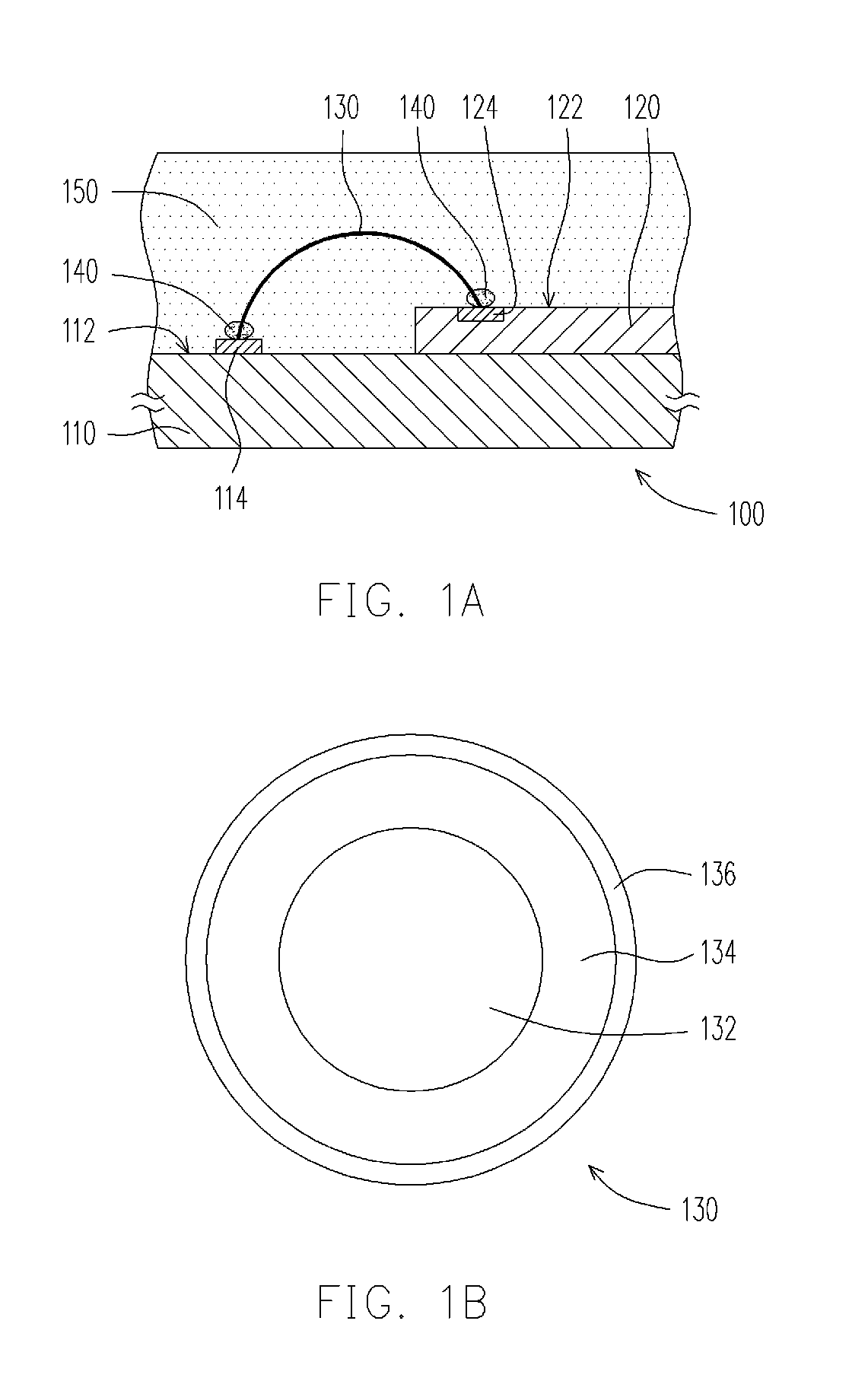
Chip package structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100264534A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padEngineering
A chip package structure includes a circuit substrate, a chip, at least one bonding wire, and an adhesive layer. The circuit substrate has a bonding surface and at least one pad disposed on the bonding surface. The chip is disposed on the bonding surface of the circuit substrate and has an active surface away from the circuit substrate and at least one contact pad disposed on the active surface. The bonding wire is connected between the contact pad and the pad, such that the chip is electrically connected to the circuit substrate through the bonding wire. The bonding wire includes a copper layer, a nickel layer covering the copper layer, and a gold layer covering the nickel layer. The adhesive layer is disposed between the pad and the bonding wire and between the contact pad and the bonding wire and respectively covers two terminals of the bonding wire.
Owner:UNIMICRON TECH CORP
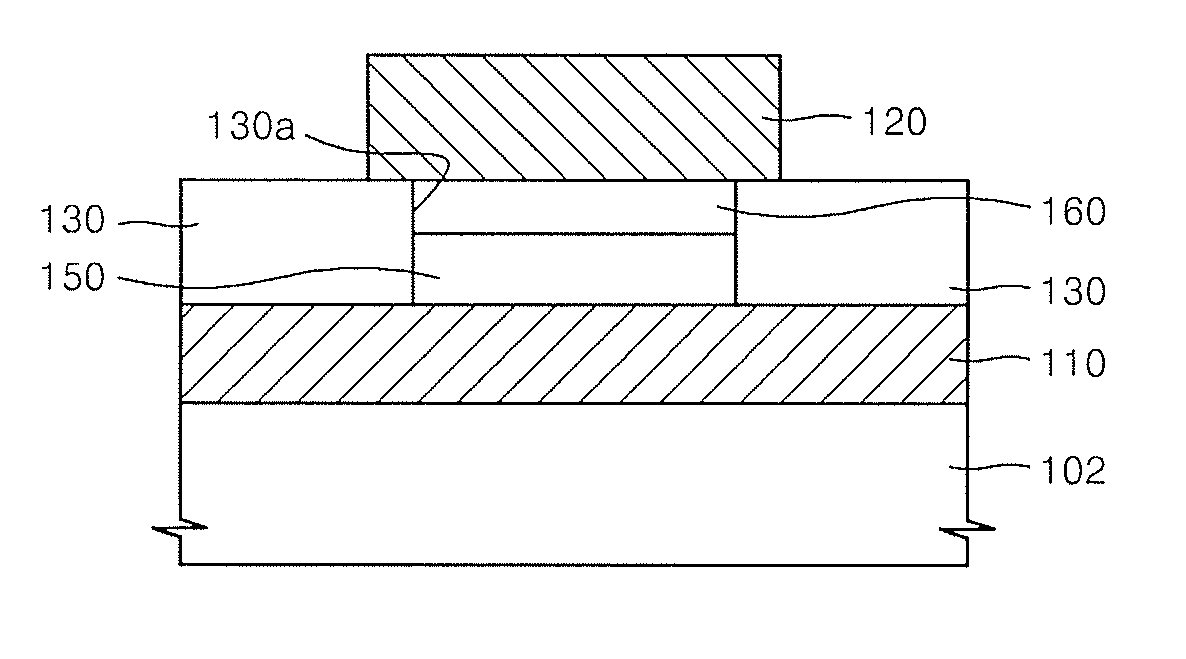
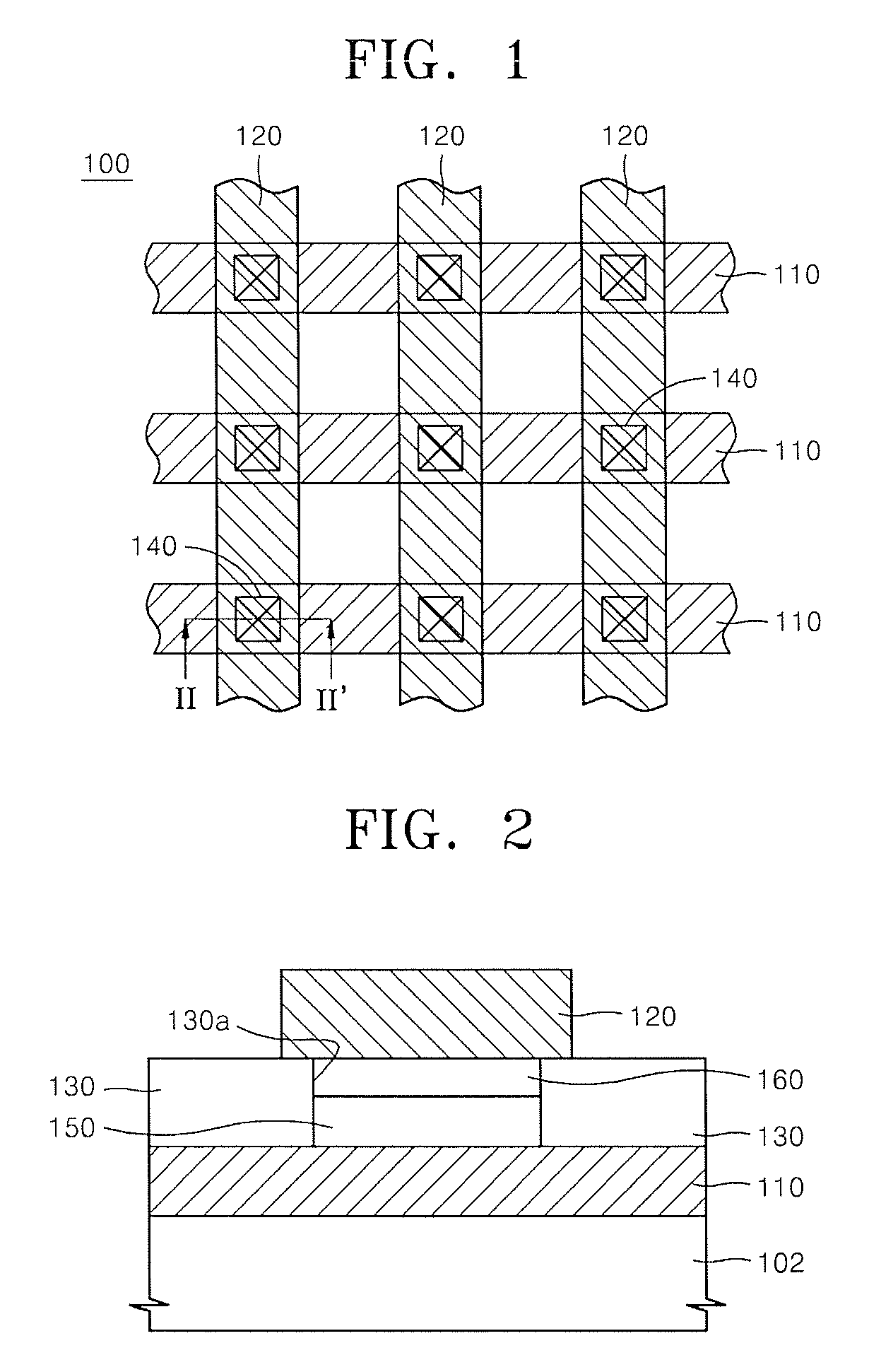
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20090127665A1Improve reliabilityReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerSemiconductor chip
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device has preparation step of preparing a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of semiconductor chip formation regions and a scribe region arranged between the plurality of the semiconductor chip formation regions and including a substrate cutting position, a semiconductor chip formation step of forming semiconductor chips having electrode pads on the plurality of semiconductor chip formation regions, a first insulation layer formation step of forming a first insulation layer on the semiconductor chips and the scribe region of the semiconductor substrate, a second insulation layer formation step of forming a second insulation layer on the first insulation layer except for a region corresponding to the substrate cutting position, and a cutting step of cutting the semiconductor substrate at the substrate cutting position.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Molecular electronic device including organic dielectric thin film and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7759677B2Preventing short circuitsImproving yield and reliabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSilanesOrganic compound
Provided are a molecular electronic device and a method of fabricating the molecular electronic device. The molecular electronic device includes a substrate, an organic dielectric thin film formed over the substrate, a molecular active layer formed on the organic dielectric thin film and having a charge trap site, and an electrode formed on the molecular active layer. The organic dielectric thin film may be immobilized on the electrode or a Si layer by a self-assembled method. The organic dielectric thin film may include first and second molecular layers bound together through hydrogen bonds. An organic compound may be self-assembled over the substrate to form the organic dielectric thin film. The organic compound may include an M′-R-T structure, where M′, R and T represent a thiol or silane derivative, a saturated or unsaturated C1 to C20 hydrocarbon group which is substituted or unsubstituted with fluorine (F), and an amino(—NH2) or carboxyl (—COOH) group, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Chip package structure and manufacturing method thereof for effectively lowering manufacturing costs and improving yield and reliability of the chip package structure
InactiveUS8242594B2Improving yield and reliabilityReduce manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing cost reductionContact pad
A chip package structure includes a circuit substrate, a chip, at least one bonding wire, and an adhesive layer. The circuit substrate has a bonding surface and at least one pad disposed on the bonding surface. The chip is disposed on the bonding surface of the circuit substrate and has an active surface away from the circuit substrate and at least one contact pad disposed on the active surface. The bonding wire is connected between the contact pad and the pad, such that the chip is electrically connected to the circuit substrate through the bonding wire. The bonding wire includes a copper layer, a nickel layer covering the copper layer, and a gold layer covering the nickel layer. The adhesive layer is disposed between the pad and the bonding wire and between the contact pad and the bonding wire and respectively covers two terminals of the bonding wire.
Owner:UNIMICRON TECH CORP
Current-leveling electroplating/electropolishing electrode
InactiveUS20060086609A1Facilitates uniform current distributionIncrease current densityMachining electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectrochemistry
A current-leveling electrode for improving electroplating and electrochemical polishing uniformity in the electrochemical plating or electropolishing of metals on a substrate is disclosed. The current-leveling electrode includes a base electrode and at least one sub-electrode carried by the base electrode. The at least one sub-electrode has a width which is less than a width of the base electrode to impart a generally tapered, stepped or convex configuration to the current-leveling electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Carrier board and power module using same
ActiveUS20210225753A1Achieve reductionLower the volumeConversion constructional detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionLoop inductanceEngineering
A carrier board and a power module using the same are disclosed. The carrier board includes a main body, two metal-wiring layers and at least one metal block. The main body includes at least two terminals and a surface. The two terminals are disposed on the surface. The two metal-wiring layers are disposed on the main body to form two parts of metal traces connected to the two terminals, respectively. The at least one metal block is embedded in the main body and connected to one of the two terminals. A thickness of the two parts of metal traces is less than that of the metal block. The two terminals connected by the two parts of metal traces have a loop inductance less than or equal to 1.4 nH calculated at a frequency greater than 1 MHz.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Method for fabricating flash memory device
InactiveUS20080153230A1Improve permeabilityElectrically stableSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricNitride
The present invention relates to a method for fabricating flash memory devices. The method may include the steps of forming an oxide / nitride / oxide (ONO) layer over a semiconductor substrate and a gate electrode on the ONO layer. Next, source / drain impurity region may be formed in a surface of the semiconductor substrate on both sides of the gate electrode and a pre-metal dielectric (PMD) layer may be formed over an entire surface of the semiconductor substrate including the gate electrode. Finally, a densification process for densifying the PMD layer may be performed under a gas atmosphere. A densification gas atmosphere used for densifying the PMD layer may include an H2 or N2 / H2 atmosphere.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Molecular electronic device including organic dielectric thin film and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100297808A1Preventing short circuitsImproving yield and reliabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSilanesOrganic compound
Provided are a molecular electronic device and a method of fabricating the molecular electronic device. The molecular electronic device includes a substrate, an organic dielectric thin film formed over the substrate, a molecular active layer formed on the organic dielectric thin film and having a charge trap site, and an electrode formed on the molecular active layer. The organic dielectric thin film may be immobilized on the electrode or a Si layer by a self-assembled method. The organic dielectric thin film may include first and second molecular layers bound together through hydrogen bonds. An organic compound may be self-assembled over the substrate to form the organic dielectric thin film. The organic compound may include an M′-R-T structure, where M′, R and T represent a thiol or silane derivative, a saturated or unsaturated C1 to C20 hydrocarbon group which is substituted or unsubstituted with fluorine (F), and an amino(—NH2) or carboxyl (—COOH) group, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Power module assembly
ActiveUS11444036B2Achieve reductionLower the volumeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical connection
A power module assembly is disclosed and includes a package body, a first wiring layer, a capacitor, and a system bus set. The package body includes a first surface, a second surface and two switches connected in series to form a bridge arm between the first surface and the second surface. The first wiring layer is disposed on the first surface. The capacitor is connected in parallel with the bridge arm to form a first high-frequency loop. The system bus set includes a positive-electrode bus and a negative-electrode bus fanned out from the first surface, respectively. The projection of the positive-electrode bus or / and the negative-electrode bus on the first surface is at least partially overlapped with the projection of the two switches on the first surface. The bridge arm is electrically connected between the positive-electrode bus and the negative-electrode bus to form a second high-frequency loop.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
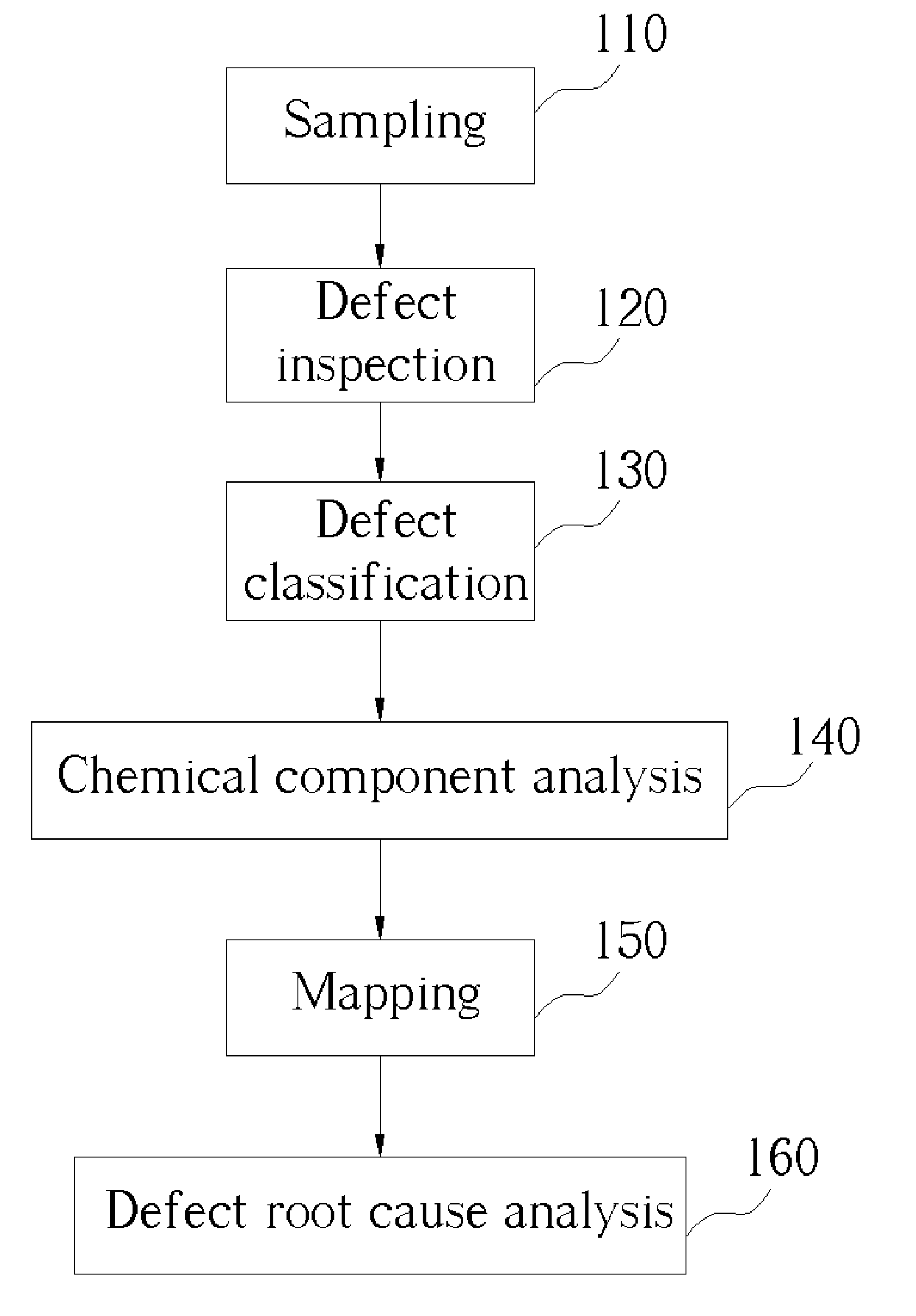
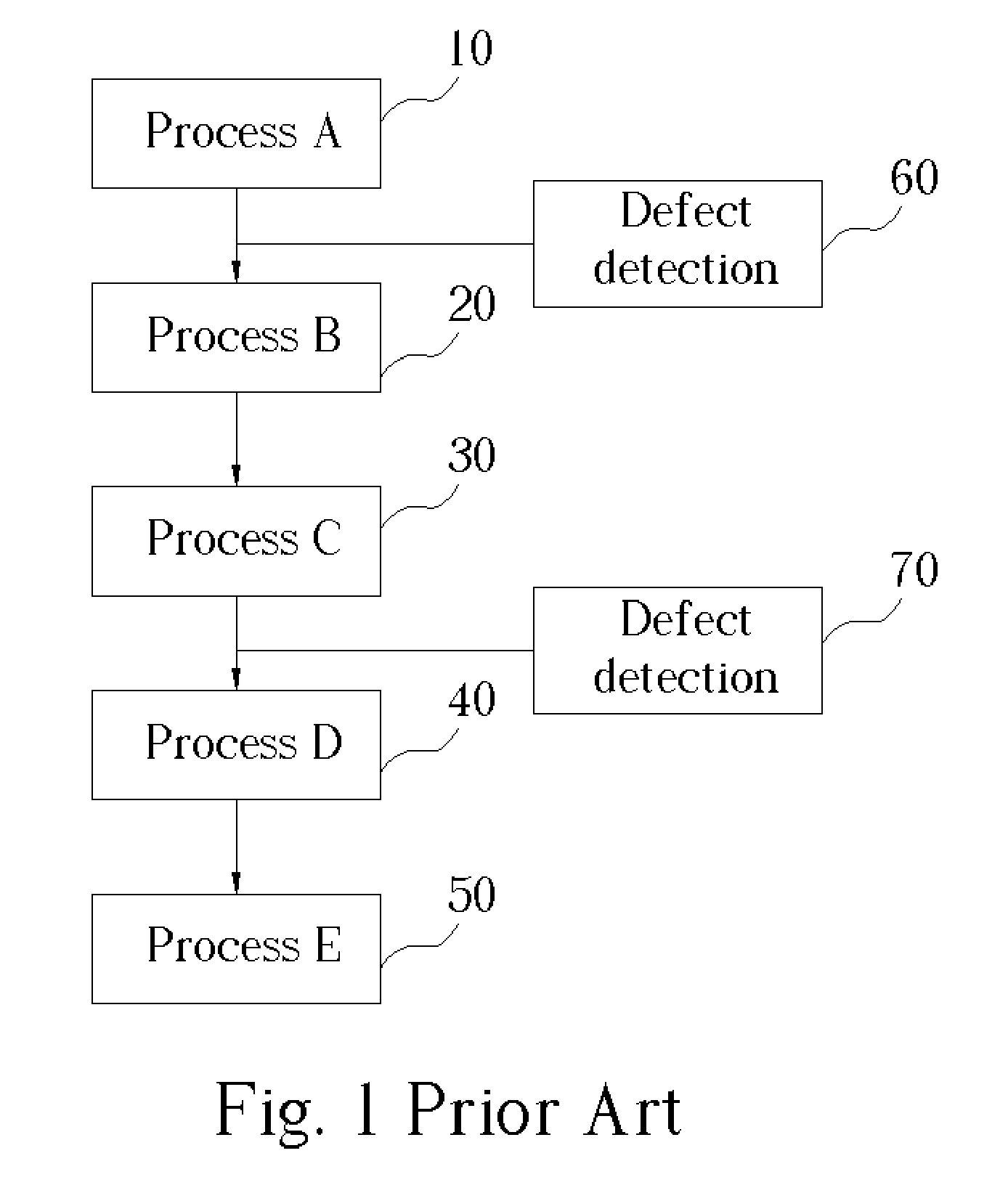
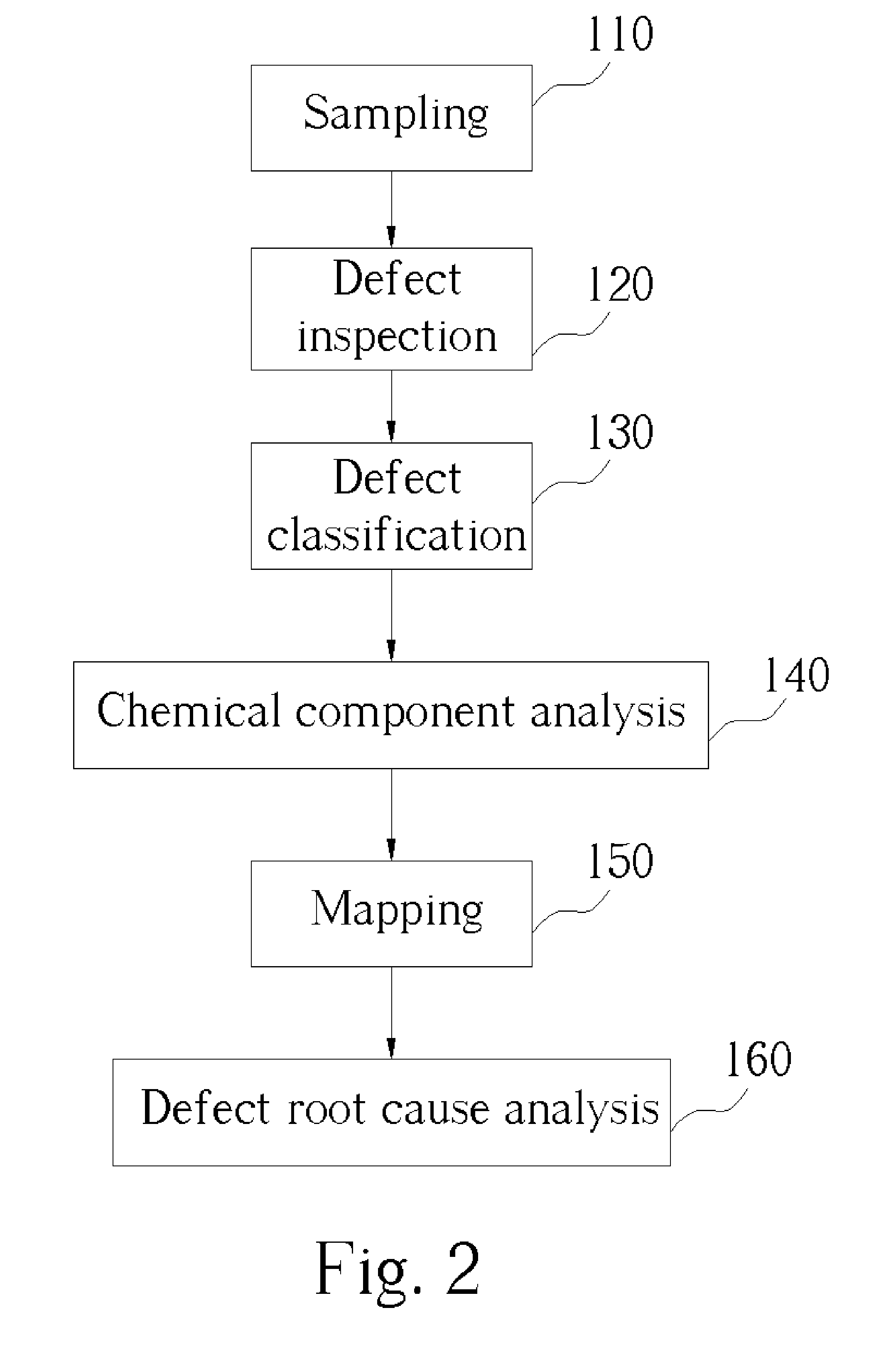
Method of defect root cause analysis
InactiveUS20050049836A1Shorten judgment timeHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesRoot causeRoot cause analysis
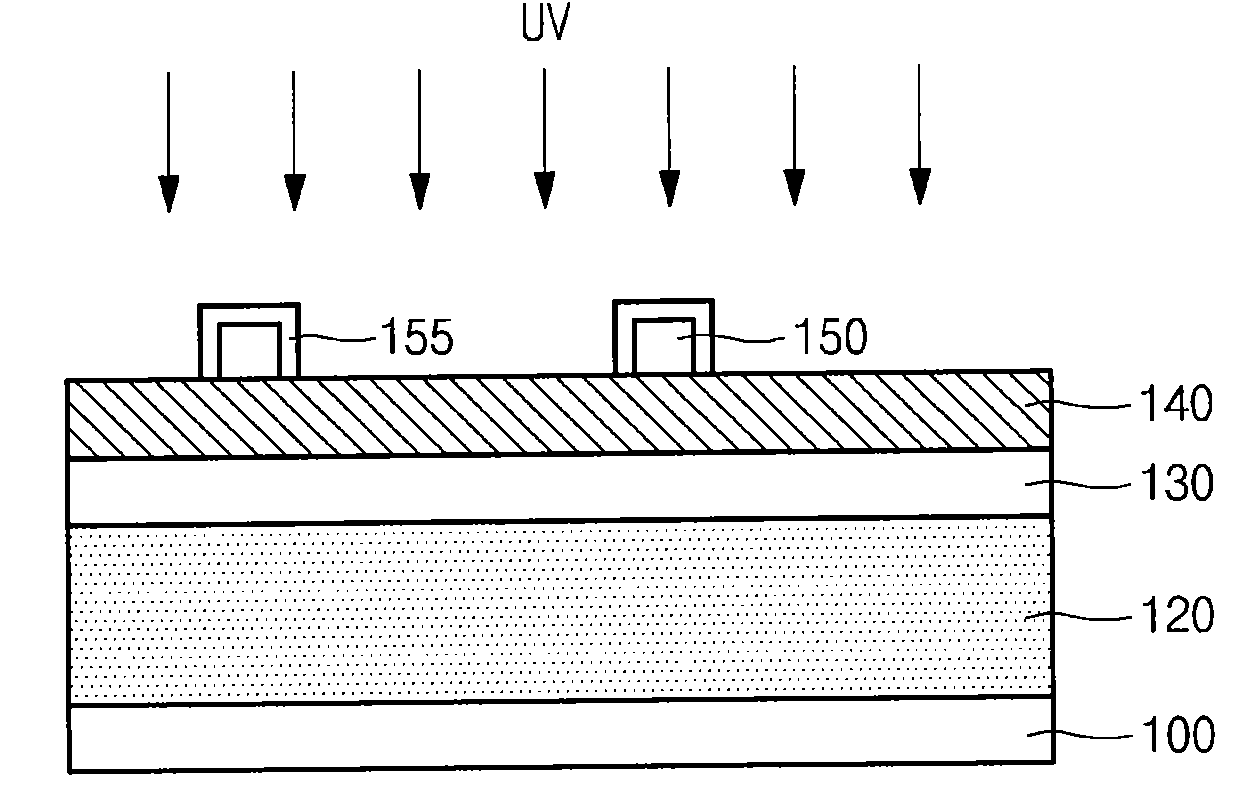
A method of defect root cause analysis. First, a sample with a plurality defects thereon is provided. Then, a defect inspection is performed to detect the sizes and positions of the defects. After that, a chemical state analysis is performed, and a mapping analysis is made according to a result of the chemical state analysis. Thus, a root cause of defects can be obtained according to a result of the mapping analysis.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Power module
ActiveUS20210227682A1Lower the volumeImprove power densityCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMechanical engineeringPhysics
A power module is disclosed. The power module includes a carrier board, two switches, at least one metal block, a clamping component and a metal conductive component. The carrier board includes an upper surface and a lower surface. The two switches are disposed on the upper surface and connected in series to form a bridge arm electrically connected between a positive terminal and a negative terminal. The metal block is electrically connected to the two switches. The clamping component is disposed on the upper surface and electrically connected in parallel with the bridge arm through the carrier board. The metal conductive component is connected from a common node of the two switches to an output terminal. The metal conductive component is located at a side of the two switches facing away from the upper surface.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
High-purity copper-cobalt alloy sputtering target
ActiveUS20150354047A1Prevent particle generationHigh yieldCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringMiniaturization
A high purity copper-cobalt alloy sputtering target containing 0.1 to 20 at % of Co, and remainder being Cu and unavoidable impurities, wherein a size (dimension) of precipitates in the target structure is 10 μm or less, and a number of precipitates is 500 precipitates / mm2 or less. It is thereby possible to provide a high purity copper-cobalt alloy sputtering target capable of inhibiting the generation of particles during sputtering, and in particular improving the yield and reliability of semiconductor products that are being subject to further miniaturization and higher integration.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS8003540B2Improving yield and reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Carrier board and power module using same
ActiveUS11342257B2Lower the volumeImprove power densityCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A carrier board and a power module using the same are disclosed. The carrier board includes a main body, two metal-wiring layers and at least one metal block. The main body includes at least two terminals and a surface. The two terminals are disposed on the surface. The two metal-wiring layers are disposed on the main body to form two parts of metal traces connected to the two terminals, respectively. The at least one metal block is embedded in the main body and connected to one of the two terminals. A thickness of the two parts of metal traces is less than that of the metal block. The two terminals connected by the two parts of metal traces have a loop inductance less than or equal to 1.4 nH calculated at a frequency greater than 1 MHz.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
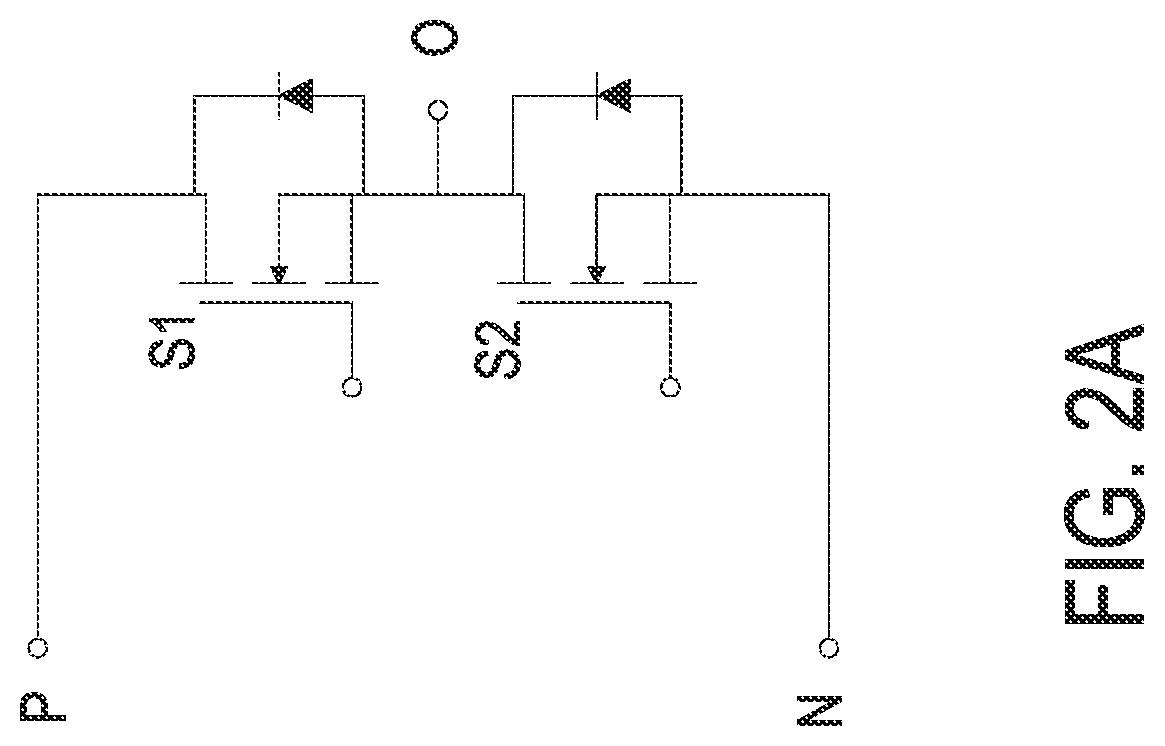
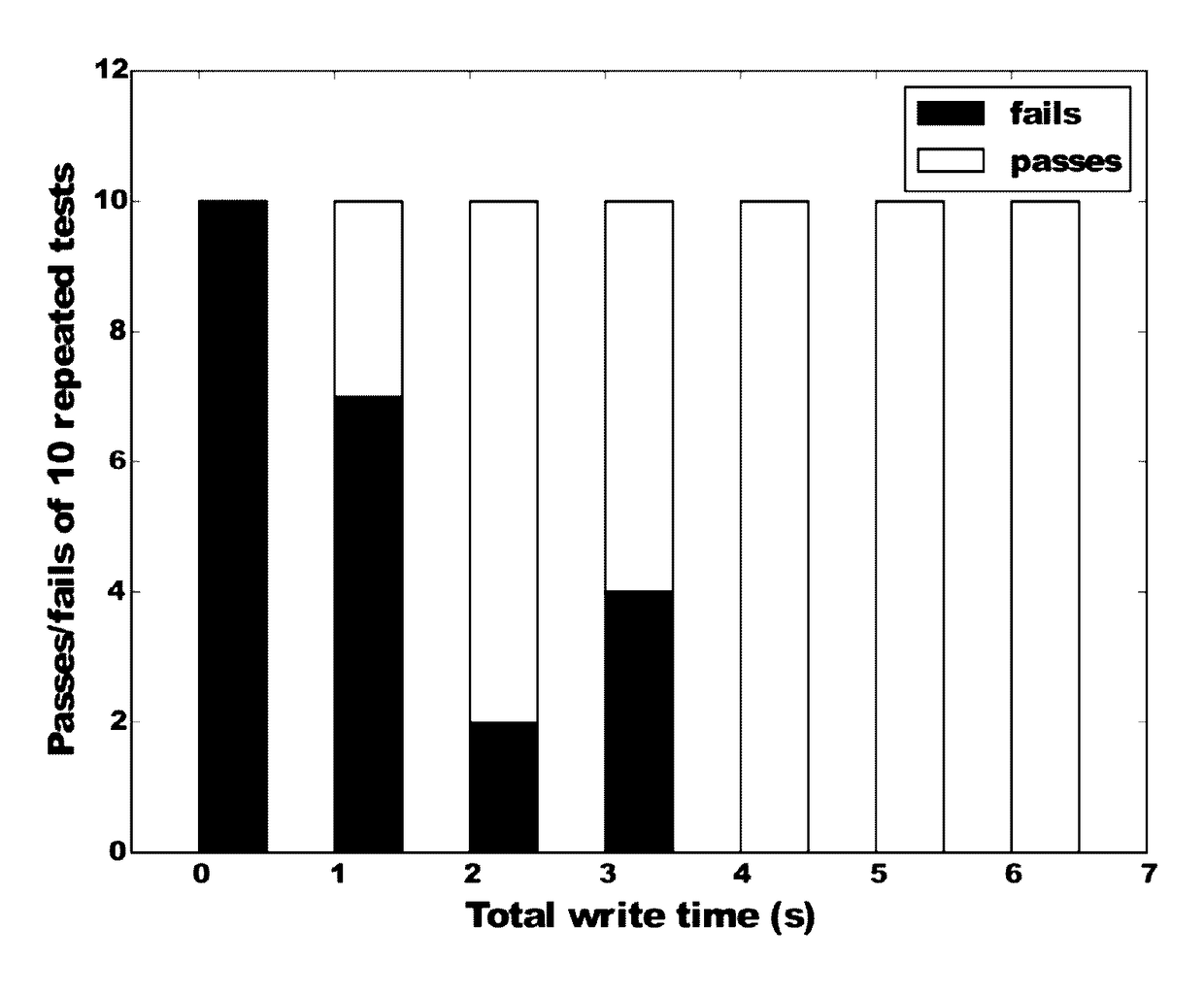
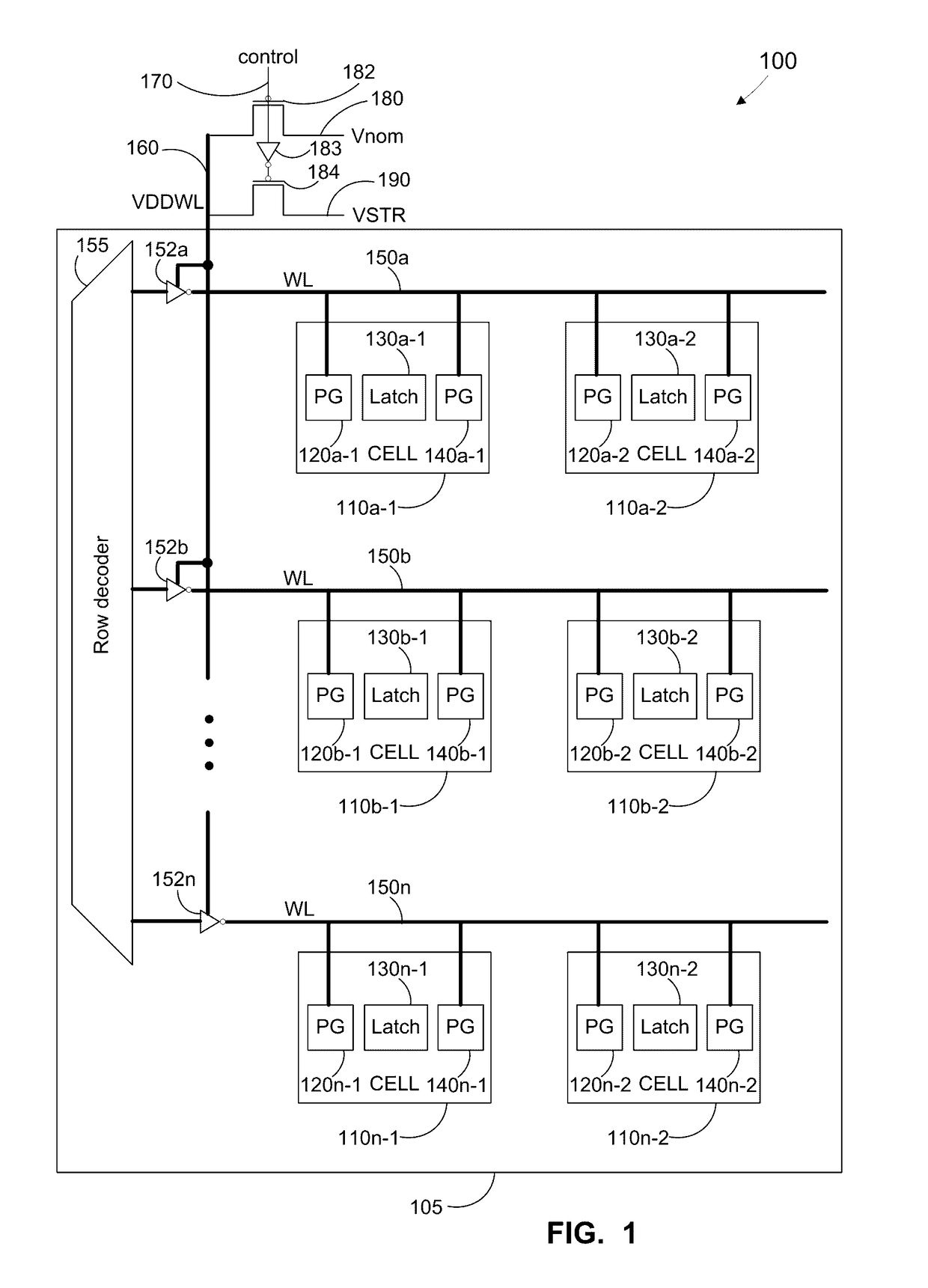
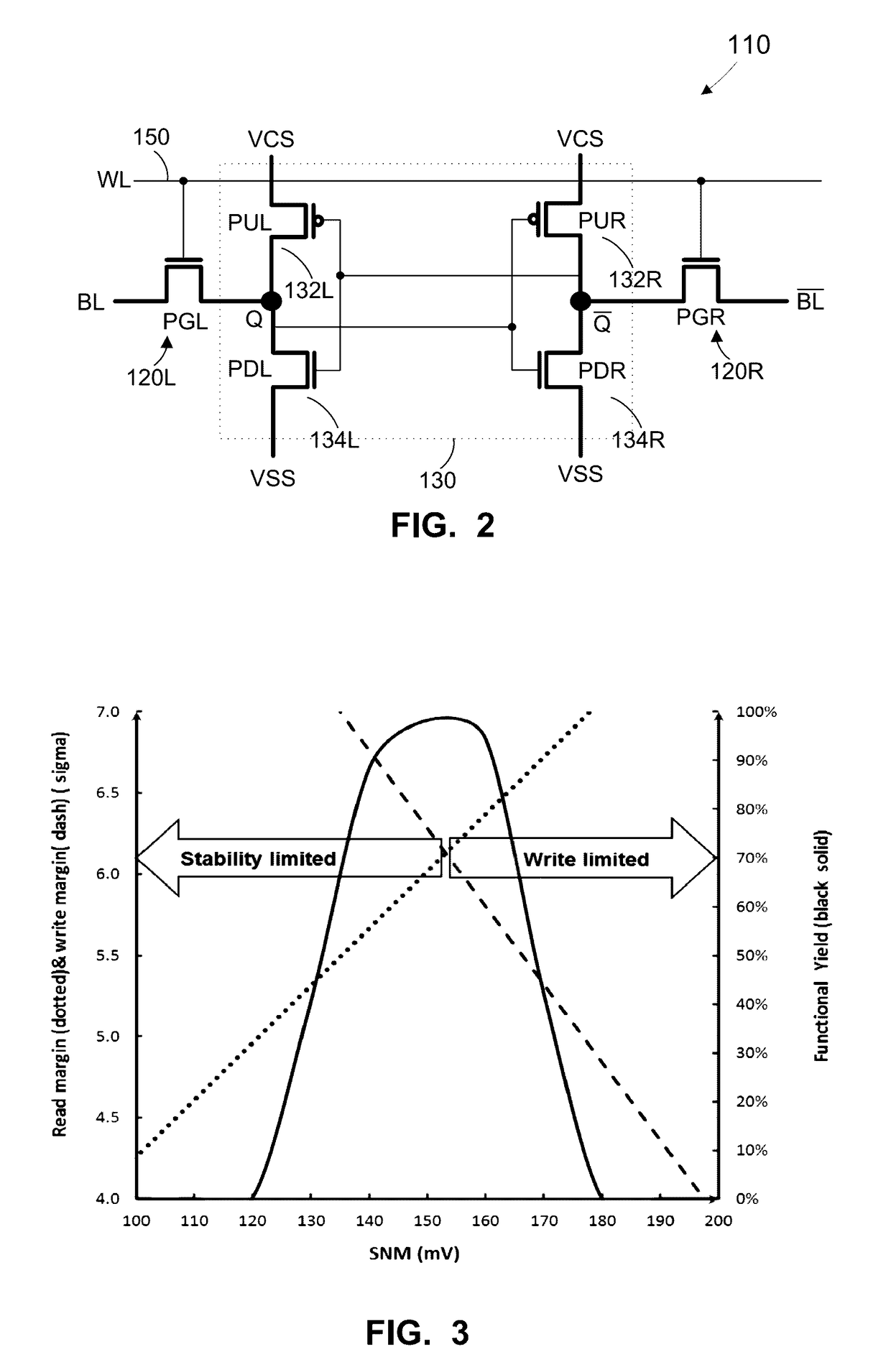
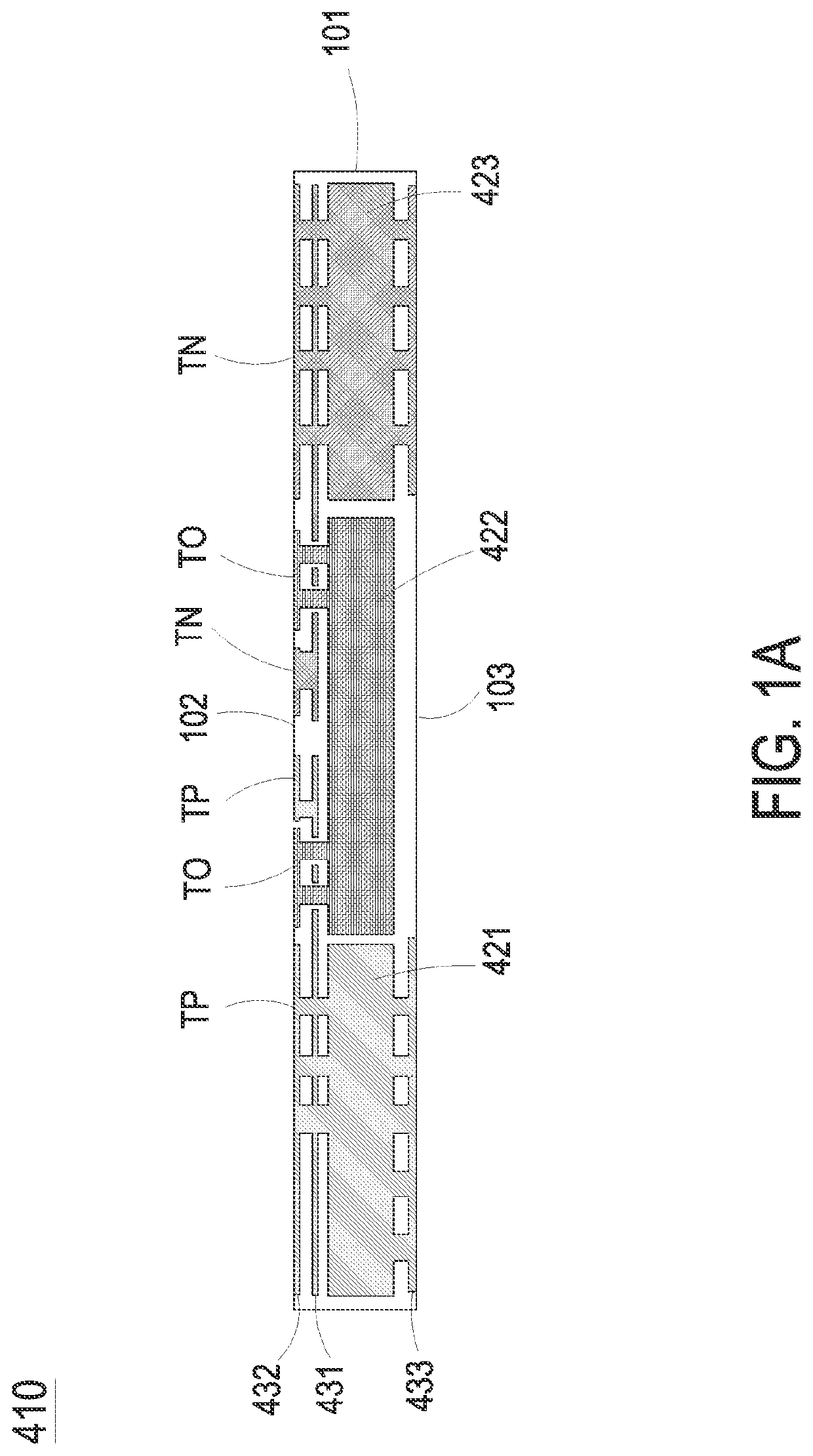
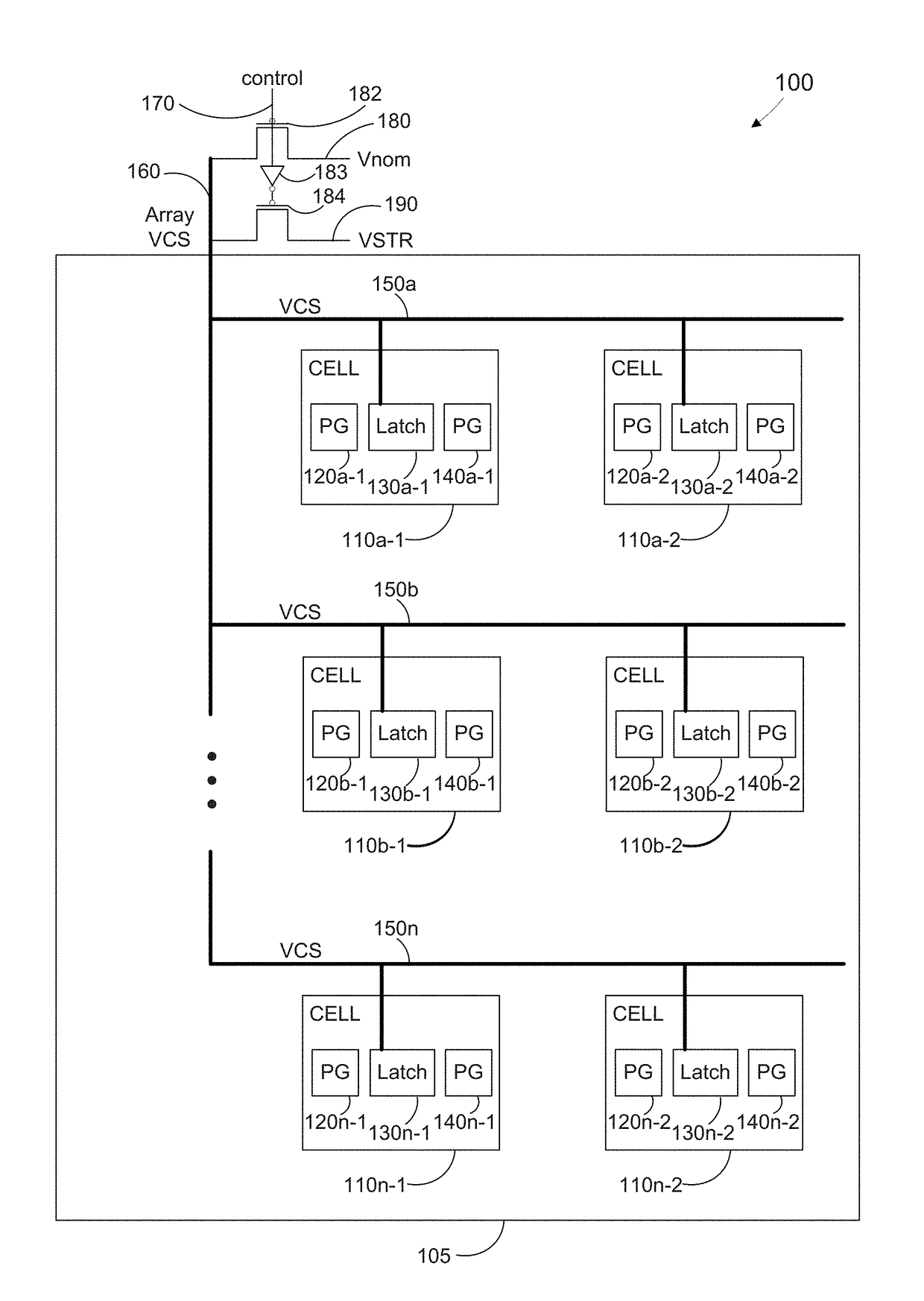
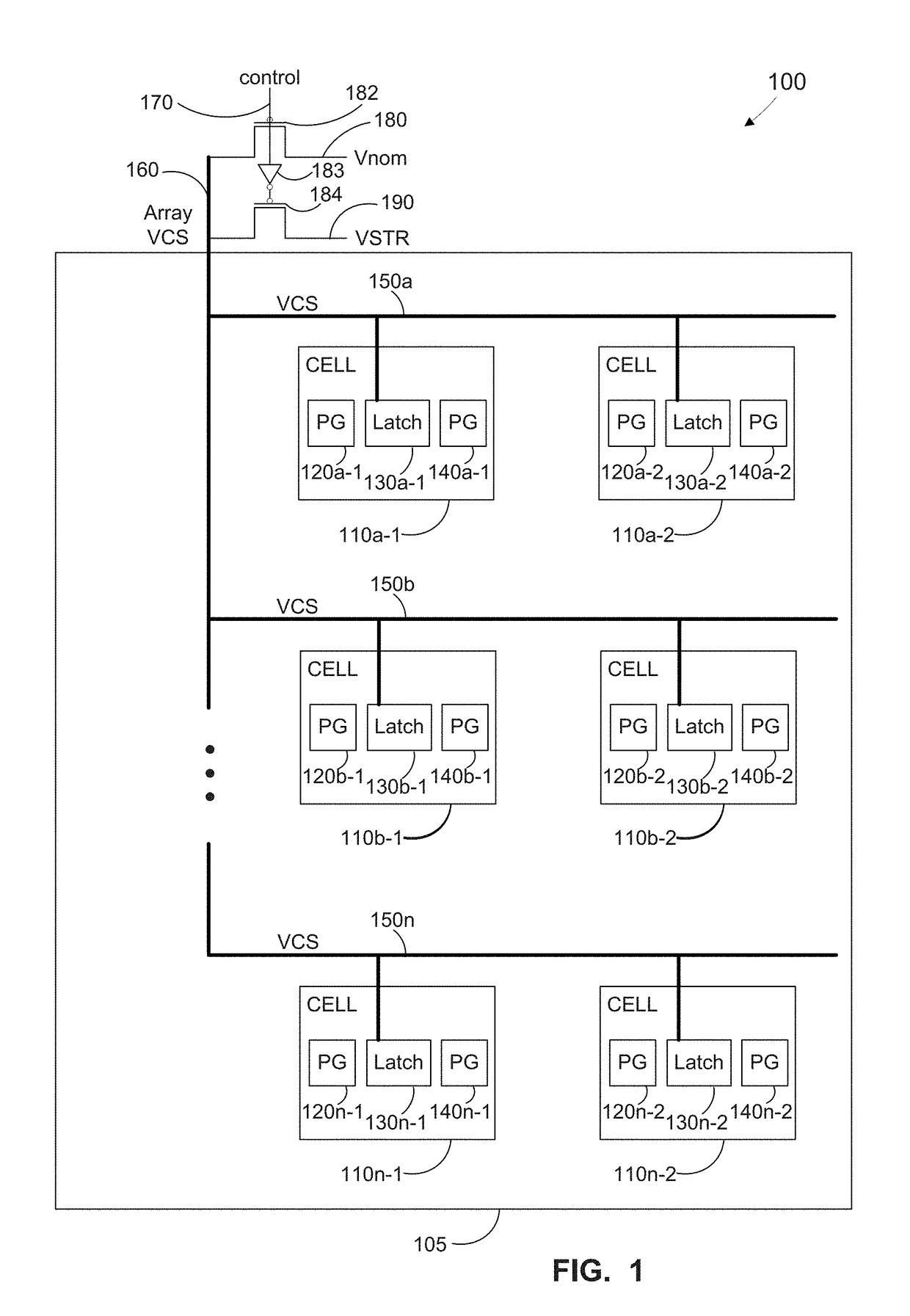
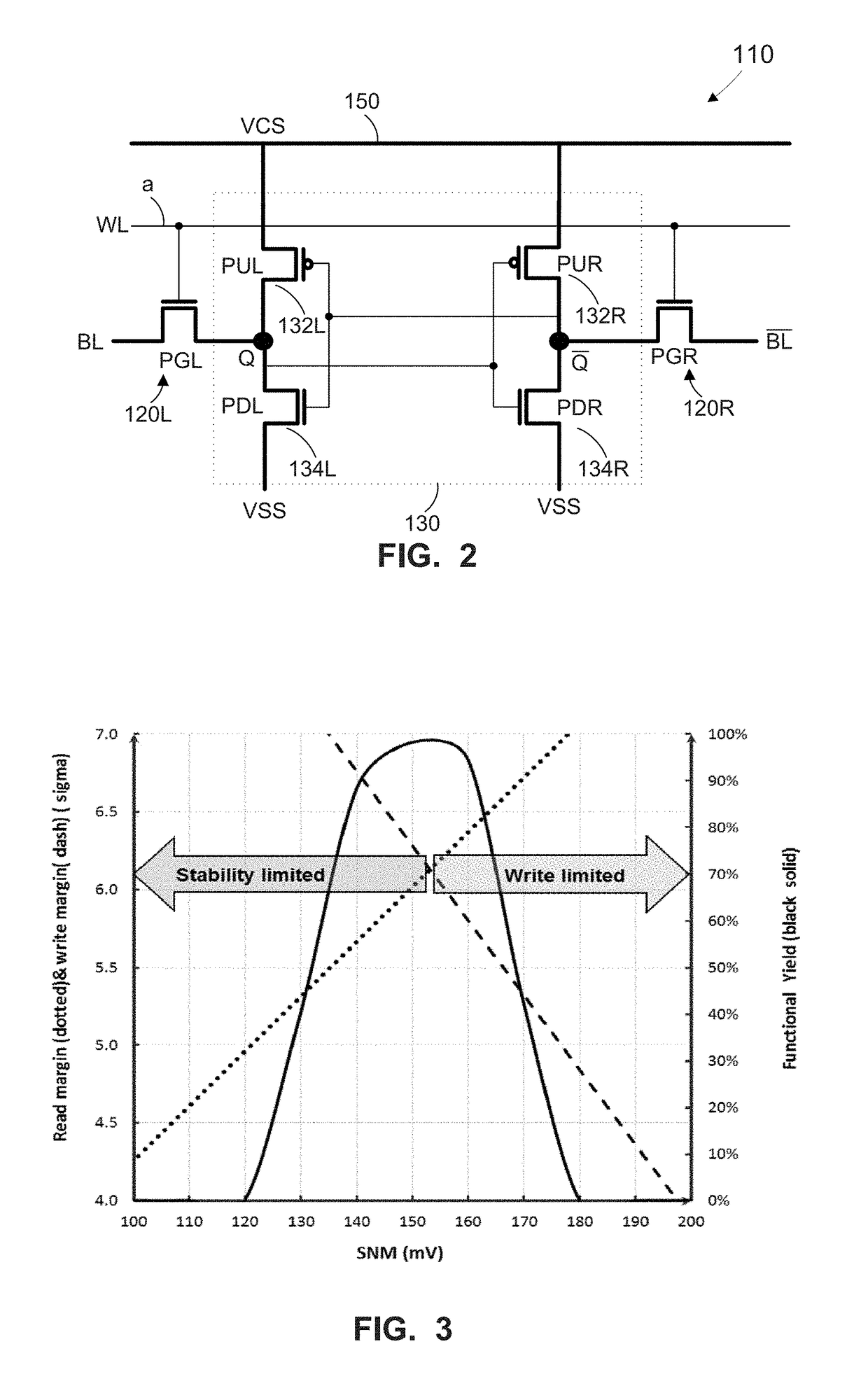
Method, apparatus, and system for global healing of stability-limited die through bias temperature instability
We disclose methods, apparatus, and systems for improving semiconductor device yield and / or reliability through bias temperature instability (BTI). One device may comprise a plurality of cells of an array, wherein each of the cells comprises a pass gate and a latch; a plurality of word lines, wherein each word line controls access to each pass gate of a first number of cells; a word line driver electrically connected to each word line; and a control line configured to provide an operational write voltage or a first write voltage to each word line through the word line driver. By virtue of BTI, application of the first write voltage may lead to improved stability of data desired to be read from one or more cells of the device.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Power module
ActiveUS11350519B2Lower the volumeImprove power densityCross-talk/noise/interference reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A power module is disclosed. The power module includes a carrier board, two switches, at least one metal block, a clamping component and a metal conductive component. The carrier board includes an upper surface and a lower surface. The two switches are disposed on the upper surface and connected in series to form a bridge arm electrically connected between a positive terminal and a negative terminal. The metal block is electrically connected to the two switches. The clamping component is disposed on the upper surface and electrically connected in parallel with the bridge arm through the carrier board. The metal conductive component is connected from a common node of the two switches to an output terminal. The metal conductive component is located at a side of the two switches facing away from the upper surface.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
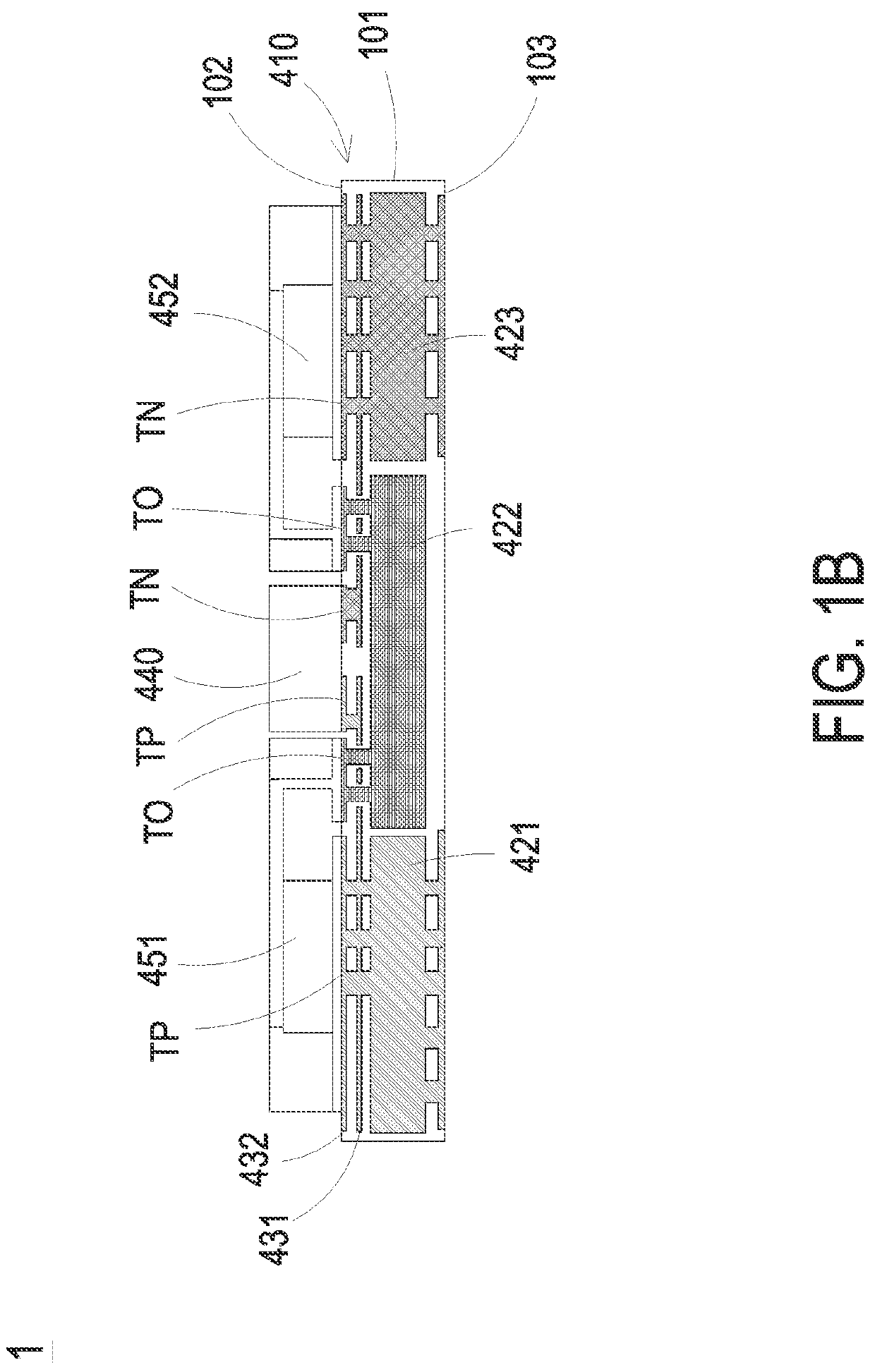
Method, apparatus, and system for targeted healing of write fails through bias temperature instability
InactiveUS20170242759A1Well formedHigh yieldDigital storageRedundant hardware error correctionElectricityInstability
Method, apparatus, and system for improving semiconductor device writeability at row / bit level through bias temperature instability. Such a device may comprise a plurality of cells of an array, wherein each of the cells comprises a pass gate and a latch; a plurality of word lines, wherein each word line comprises a supply voltage line (VCS) which supplies voltage to each latch of a first number of cells; an array VCS driver electrically connected to each VCS; and a control line configured to provide an operational array supply voltage, a first array supply voltage, or a second array supply voltage to each VCS, wherein the first array supply voltage and the second array supply voltage are greater than the operational array supply voltage. By virtue of BTI, application of the first array supply voltage may lead to improved writeability of one or more cells of the device.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
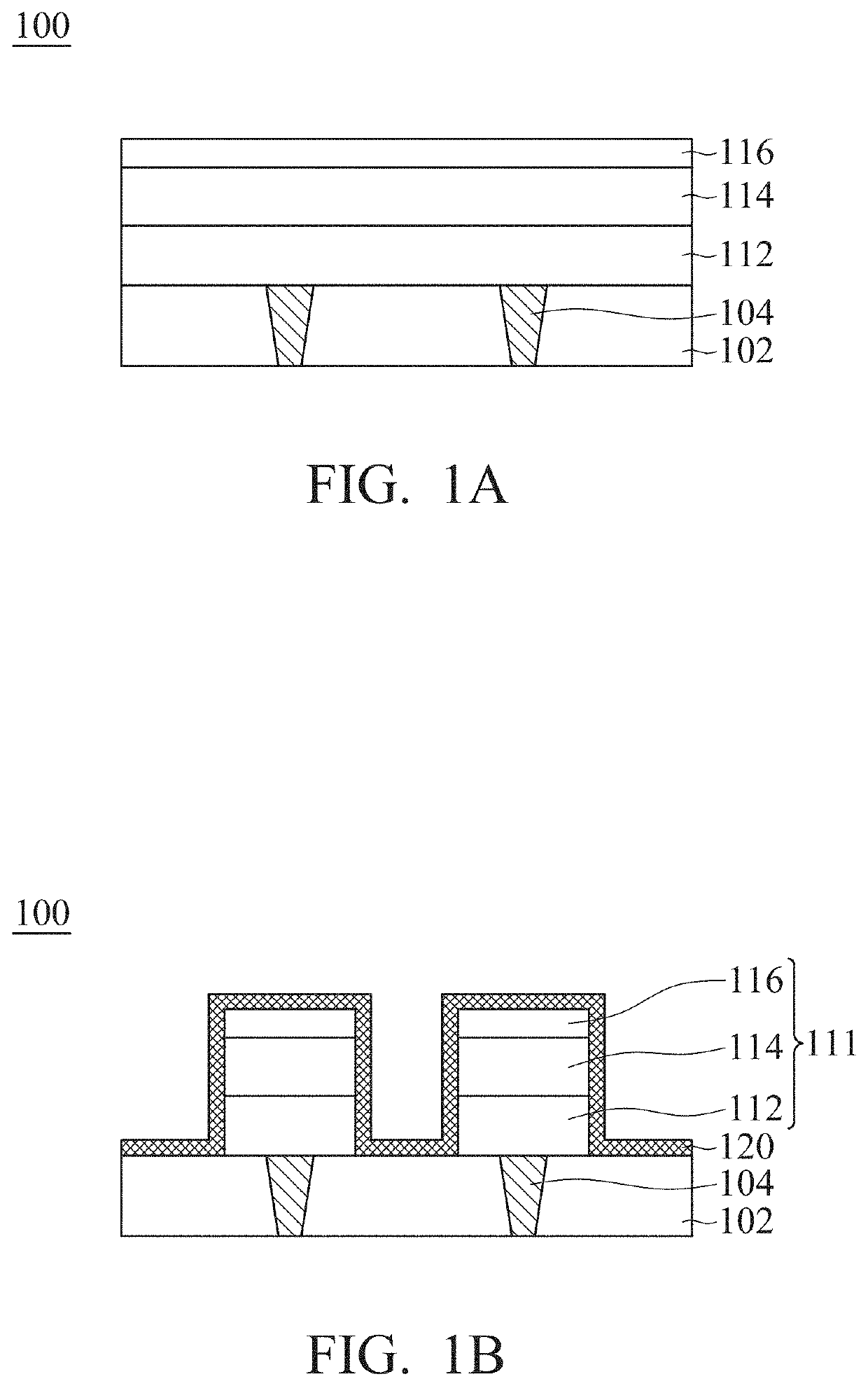
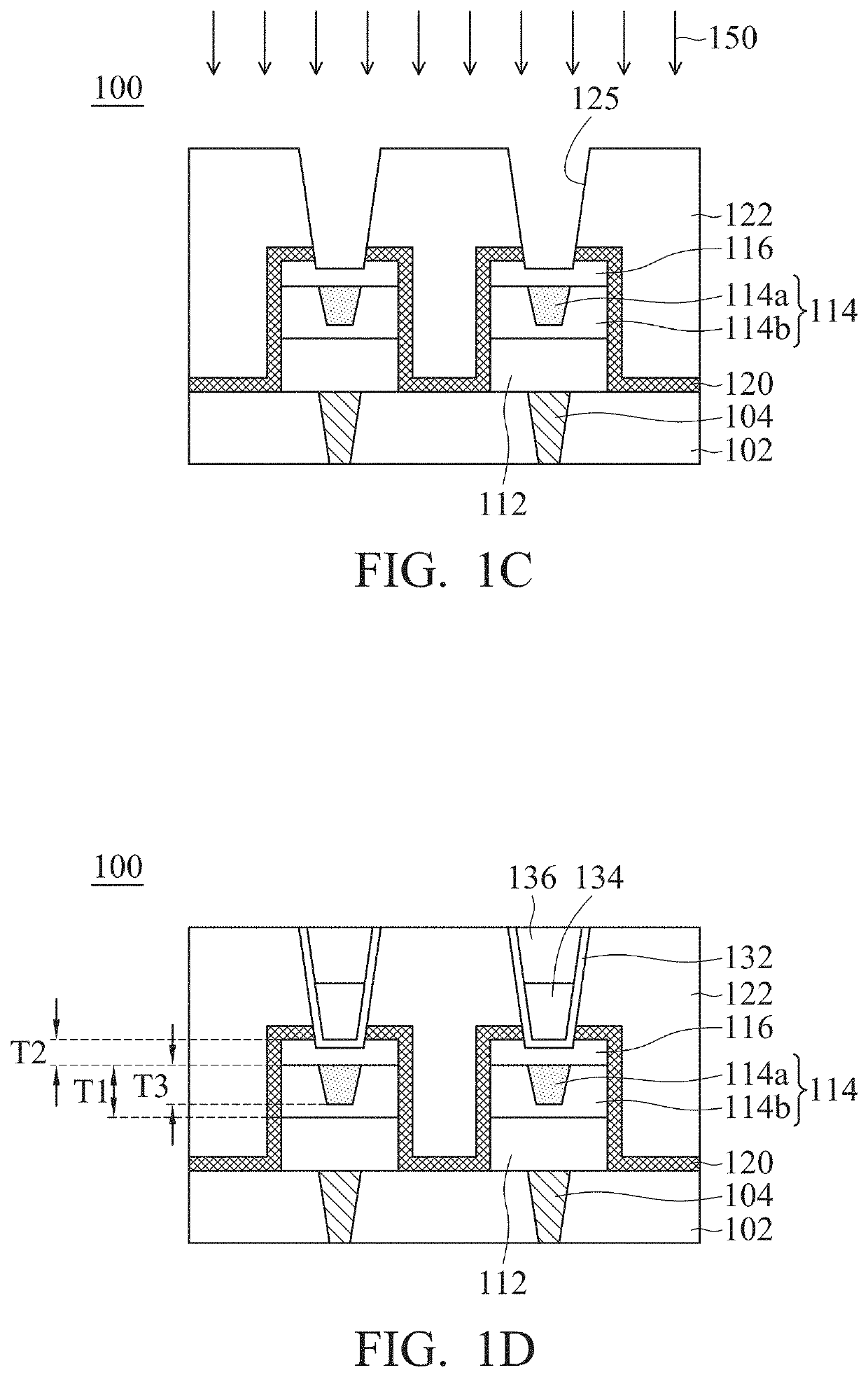
Resistive random access memory structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20210005812A1Improve reliabilityHigh yieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineering physicsMaterials science
An RRAM structure and its manufacturing method are provided. The RRAM structure includes a bottom electrode layer, a resistance switching layer, and an implantation control layer sequentially formed on a substrate. The resistance switching layer includes a conductive filament confined region and an outer region surrounding the conductive filament confined region. The RRAM structure includes a protective layer and a top electrode layer. The protective layer conformally covers the bottom electrode layer, the resistance switching layer, and the implantation control layer and has a first opening. The top electrode layer is located on the implantation control layer, and a portion of the top electrode layer is filled into the first opening. The position of the top electrode layer corresponds to that of the conductive filament confined region, and the top surface of the top electrode layer is higher than that of the protective layer.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
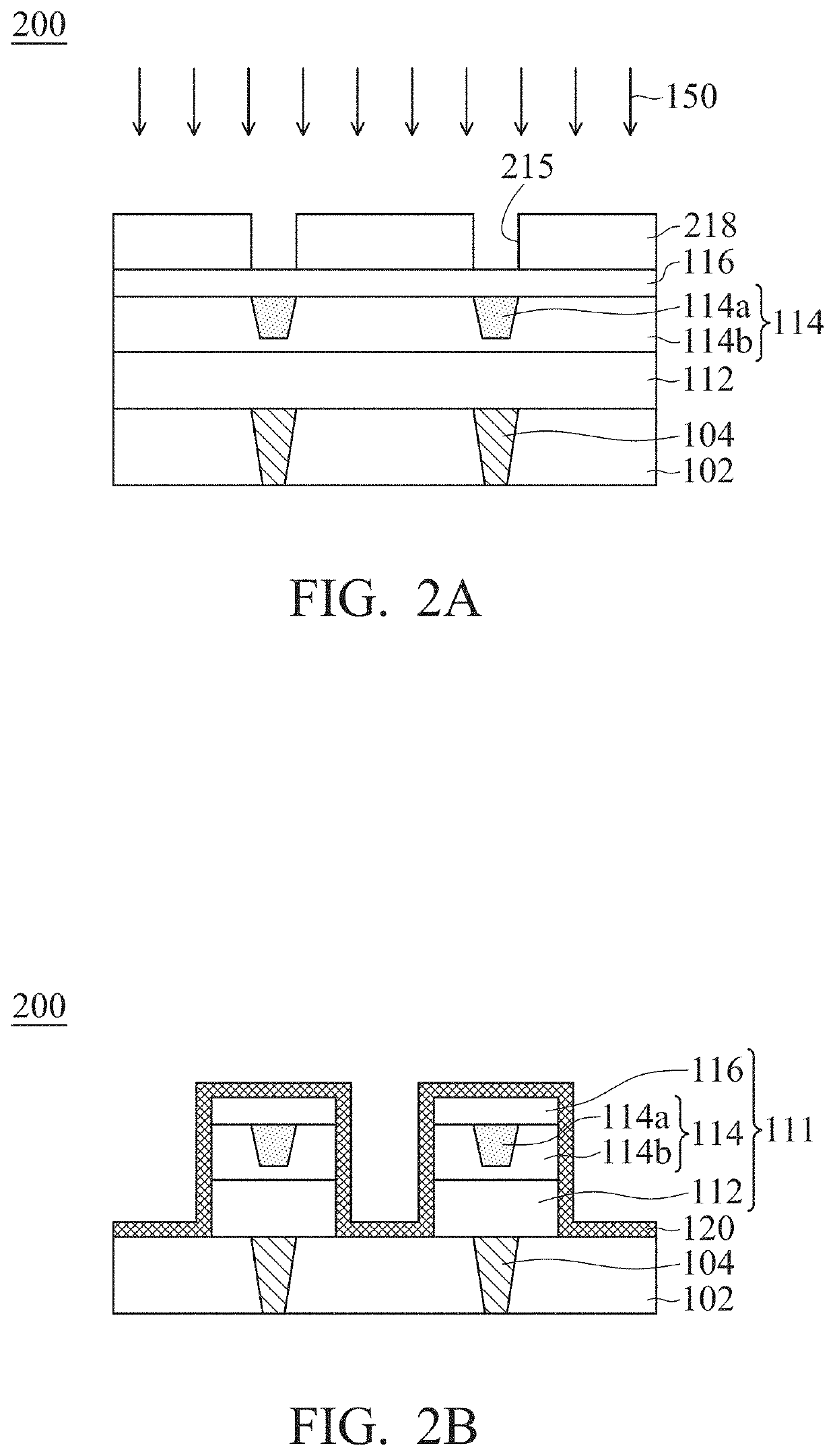
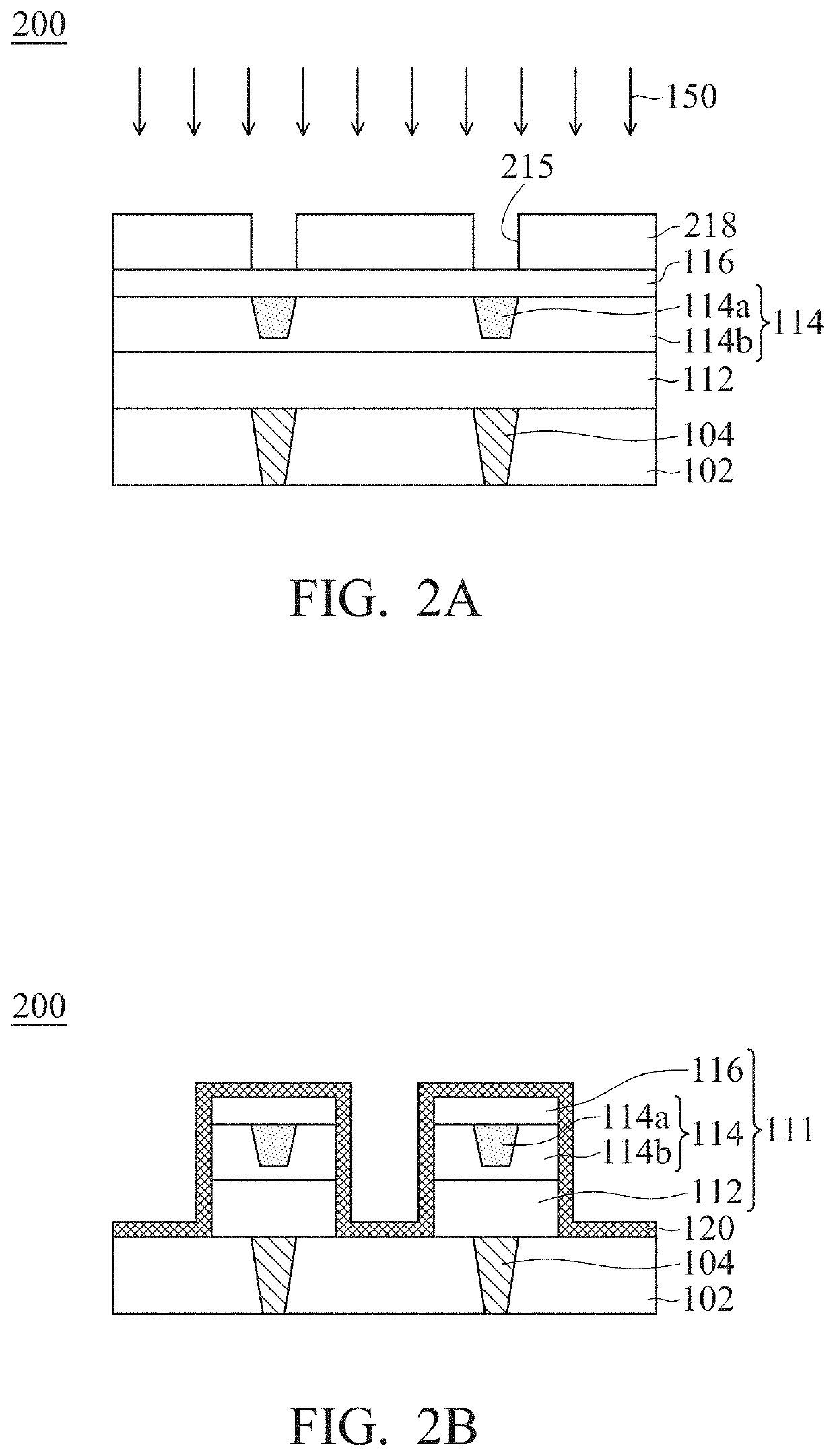
Resistive random access memory structure and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS11258011B2Improving yield and reliabilityImprove stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineering physicsMaterials science
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Molecular electronic device including organic dielectric thin film and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080054256A1High yieldImprove reliabilityNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesSilanesOrganic compound
Provided are a molecular electronic device and a method of fabricating the molecular electronic device. The molecular electronic device includes a substrate, an organic dielectric thin film formed over the substrate, a molecular active layer formed on the organic dielectric thin film and having a charge trap site, and an electrode formed on the molecular active layer. The organic dielectric thin film may be immobilized on the electrode or a Si layer by a self-assembled method. The organic dielectric thin film may include first and second molecular layers bound together through hydrogen bonds. An organic compound may be self-assembled over the substrate to form the organic dielectric thin film. The organic compound may include an M′-R-T structure, where M′, R and T represent a thiol or silane derivative, a saturated or unsaturated C1 to C20 hydrocarbon group which is substituted or unsubstituted with fluorine (F), and an amino(—NH2) or carboxyl (—COOH) group, respectively.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com