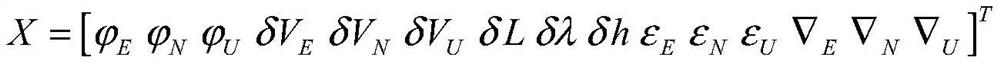Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74results about How to "Improve work adaptability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
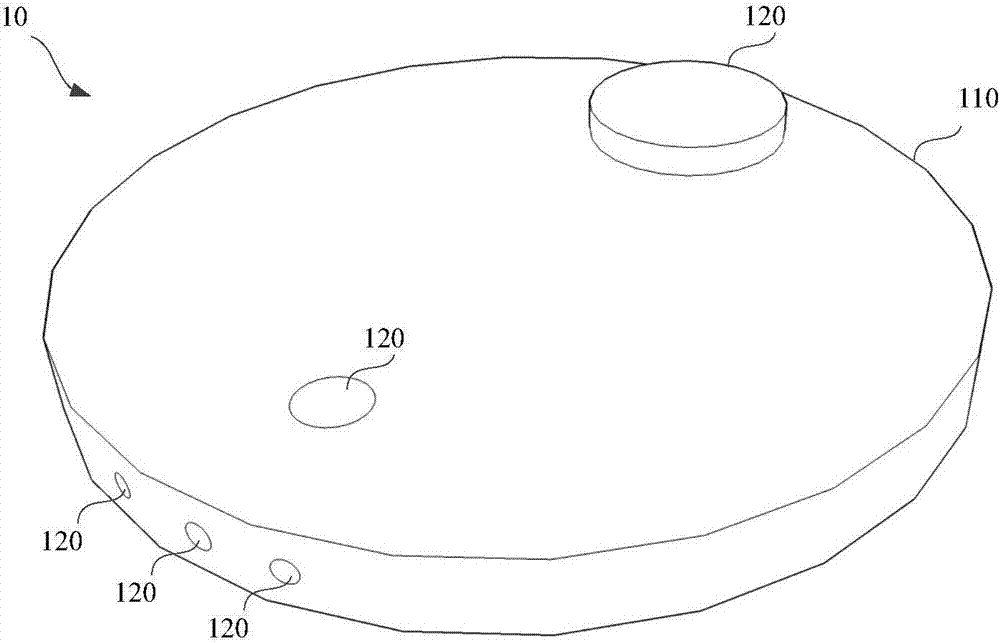
Barrier crossing method and device
ActiveCN107456173AImprove work adaptabilityImprove full automationAutomatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlControl theoryAdaptive capacity
The invention discloses a barrier crossing method and a barrier crossing device, belonging to the technical field of automatic cleaning. The method is applied to a cleaning robot with two parallel driving wheels. The method comprises the following steps: when the cleaning robot moves, detecting that whether the cleaning robot is in the barrier obstructing state or not; if the cleaning robot is in the barrier obstructing state, acquiring the inclination angle of the cleaning robot; and if the inclination angle is smaller than a preset angle, controlling the cleaning robot to cross the barrier. With the barrier crossing method and the barrier crossing device, the problem that during the moving process, the cleaning robot can not continue the cleaning task due to the obstruction of the barrier, and only can continue the cleaning task with the assistance of the outside, is solved, so that the cleaning robot can interpedently cross the barrier, and the work adaptive capacity of the cleaning robot is improved.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD +1
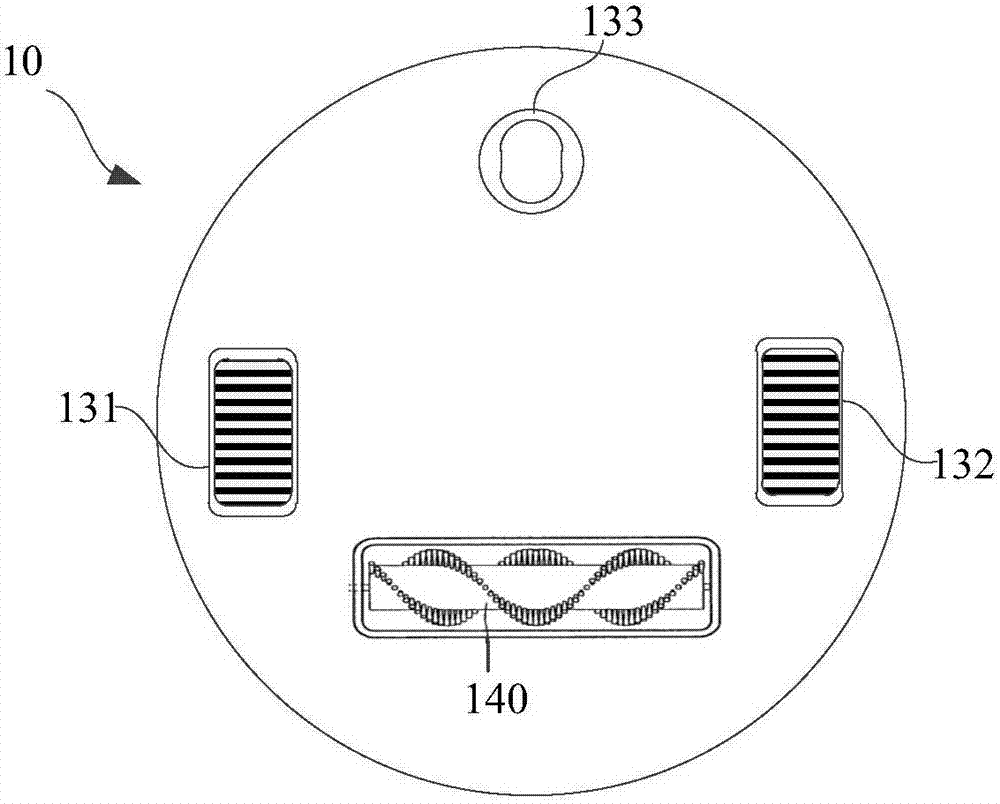
Mobile robot and method of crossing obstacle by mobile robot
ActiveCN107092260AImprove work adaptabilityAvoid issues that prevent you from continuing the corresponding missionPosition/course control in two dimensionsSensing dataControl theory
The invention provides a mobile robot and a method of crossing an obstacle by the mobile robot, which belong to the technical field of mobile robots. The method comprises steps: a sensing unit acquires sensed data and transmits the sensed data to a control unit; the control unit controls the mobile robot to rotate for a first angle in a first rotating direction according to the sensed data and controls a first driving wheel to cross a first obstacle; and the control unit controls the mobile robot to rotate for a second angle in a second rotating direction and controls a second driving wheel to cross the first obstacle. According to the sensed data transmitted by the sensing unit, the control unit controls the mobile robot to cross the obstacle, the problem that the mobile robot can not continue a corresponding task due to blocking of the obstacle during an operation process can be solved, the mobile robot can independently finish obstacle crossing, and the work adaptability of the mobile robot is improved.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD +1
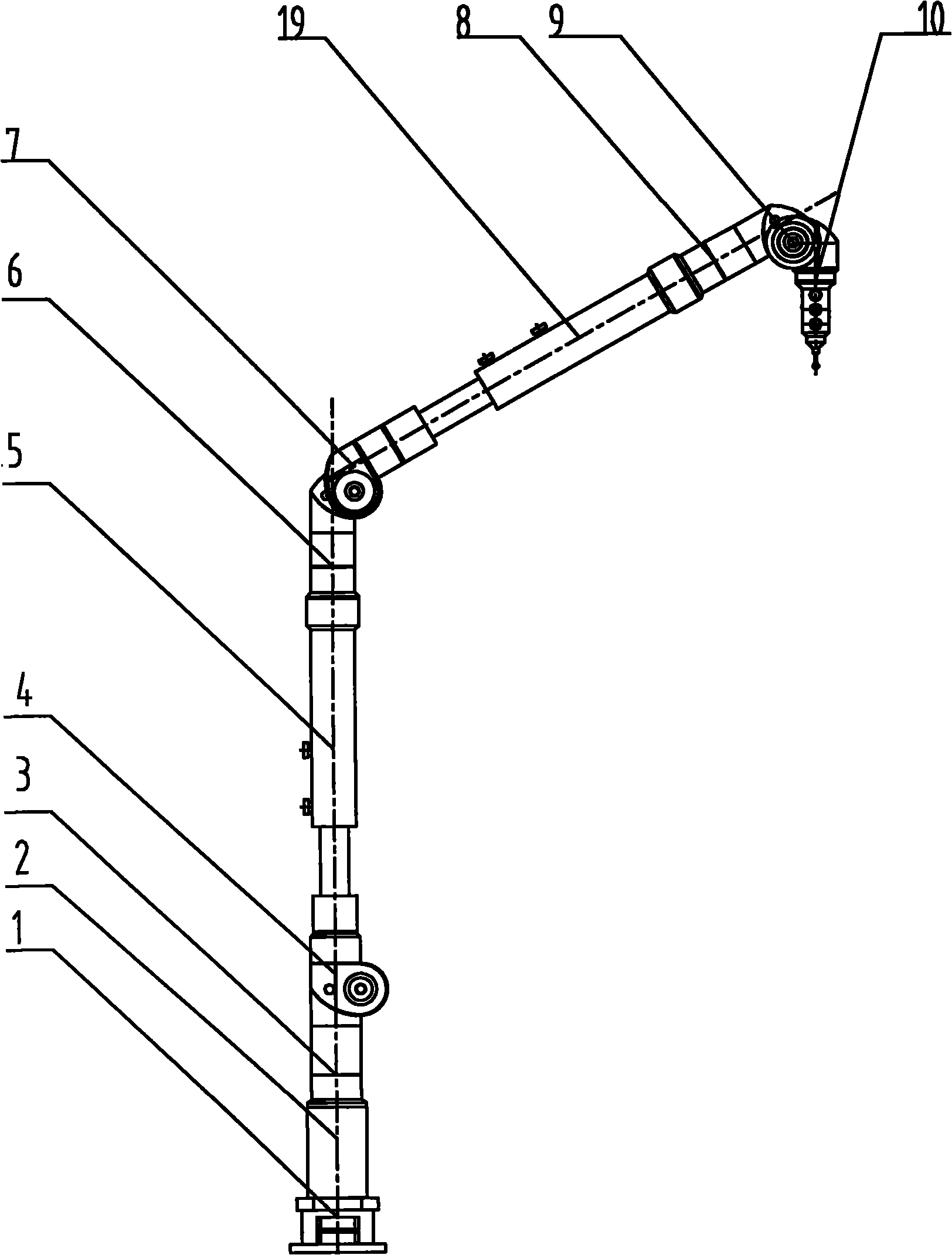
Variable rod length articulated arm type coordinate measuring machine
InactiveCN101871774AImprove work adaptabilityReduce the size of the measurement spaceMeasurement devicesObservational errorImage resolution
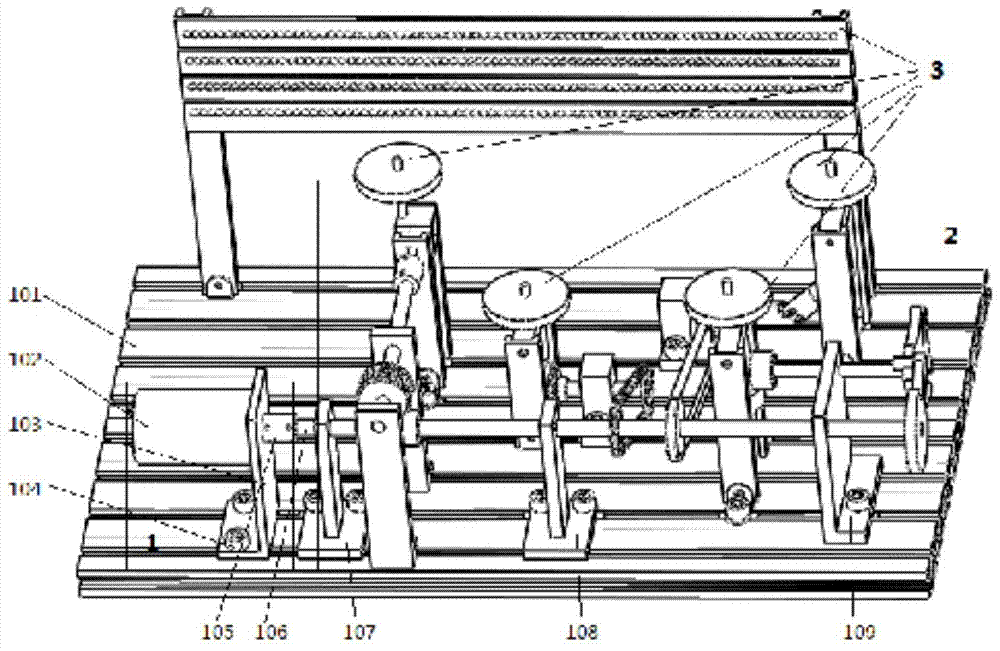
The invention discloses a variable rod length articulated arm type coordinate measuring machine which comprises a base, three rotary joints, three swing joints, a base measuring arm, two measuring arms and a measuring head, wherein the two measuring arms are telescopic measuring arms with the same structure, and each telescopic measuring arm comprises a core shaft, a fixing screw, a sleeve and a guide key; for each telescopic measuring arm, the core shaft is mounted in the sleeve, the two are in clearance fit, a section of guide slot is arranged on the inner wall of the sleeve, the guide key is arranged on the core shaft, the relative circumferential fixation of the core shaft and the sleeve can be realized through the guide key, two thread holes are arranged on the sleeve, the fixing screw is screwed in the sleeve through the thread holes, a section of V-shaped slot is arranged on the core shaft, and the fixing screw is screwed for leading an circular arc-shaped head of the fixing screw to tightly push the V-shaped slot of the core shaft, thereby realizing the relative fixation of the sleeve and the core shaft. The variable rod length articulated arm type coordinate measuring machine can reduce the size of measurement space by regulating the rod length of the measuring arms, reduce the measurement error, improve the measurement resolution, achieve the best measurement efficiency, and still have higher repeated positioning precision after the length change of the telescopic measuring arms.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cleaning robot and barrier crossing method
ActiveCN107456172AImprove work adaptabilityAutomatic obstacle detectionProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive capacityDrive wheel
The invention discloses a cleaning robot and a barrier crossing method, belonging to the technical field of automatic cleaning. The method comprises the following steps: when the cleaning robot moves, detecting that whether the cleaning robot is in the barrier obstructing state or not; if the cleaning robot is in the barrier obstructing state, controlling a first drive wheel to cross the barrier according to the detection result, and then controlling a second drive wheel to cross the barrier. With the cleaning robot and the barrier crossing method, the problem that during the moving process, the cleaning robot can not continue the cleaning task due to the obstruction of the barrier, and only can continue the cleaning task with the assistance of the outside, is solved, the cleaning robot can interpedently complete the crossing for the barrier, and thus the adaptive capacity to the environment of the cleaning robot is improved.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD +1
Substation type precision compensation for robot system with additional external shaft
ActiveCN103144109AExpand the scope of workImprove work adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsLaser tracker
The invention discloses a substation type precision compensation for a robot system with an additional external shaft, belongs to the technical field of industrial robot reverse calibration, and aims to solve the difficulty in compensating the error of the external shaft (guide rail) of the industrial robot. According to the method, based on a robot envelope line, the guide rail is divided into a plurality of substations and substation type compensation is performed. The method comprises the steps: a laser tracker is adopted to measure and recognize the error of the external shaft (guide rail) and the robot, and the compensation for the tail end error of the robot is completed through inputting corrected control commands into the robot. During measurement and recognition of the error of the external shaft, an auxiliary coordinate system is introduced so as to allow the measuring process to be simple and quick, and meanwhile to ensure the precision. Through test verification, the method can greatly improve the absolute positioning precision of the robot with the additional external shaft, so as to allow the robot to be suitable for wider applications.
Owner:江苏航鼎智能装备有限公司
Clamping type parking robot
PendingCN108166819AMeet the needs of handlingImprove work adaptabilityParkingsVehicular energy storageAutomotive engineeringWheelbase
The invention relates to a parking robot, in particular to a clamping type parking robot, and belongs to the technical field of parking robots. The clamping type parking robot comprises a front carrying trolley, a rear carrying trolley and a telescopic slide frame mechanism. The front end of the telescopic slide frame mechanism is connected with the front carrying trolley, the rear end of the telescopic slide frame mechanism is connected with the rear carrying trolley, and the bottom of the front carrying trolley and the bottom of the rear carrying trolley are each provided with a universal walking wheel group. The left corner and the right corner of the front end of the front carrying trolley are provided with a radar-carrying guide wheel assembly and a guide wheel assembly respectively,and the left corner and the right corner of the rear end of the rear carrying trolley are provided with a radar-carrying guide wheel assembly and a guide wheel assembly respectively. The left side andthe right side of the front carrying trolley and the left side and the right side of the rear carrying trolley are each provided with a clamping assembly. The requirement for carrying vehicles of different axle distances can be met, the total height of the universal walking wheel groups is lower than the distance of a vehicle chassis above the ground, 'flat-to-flat' submersible type vehicle carrying can be realized on a large plane, and the robot can be suitable for carrying various types of vehicles.
Owner:国信机器人无锡股份有限公司
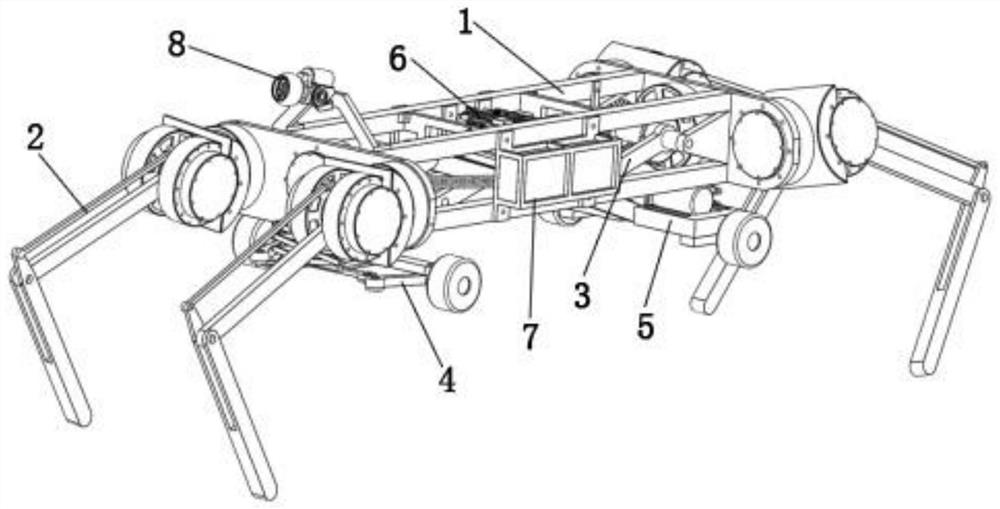
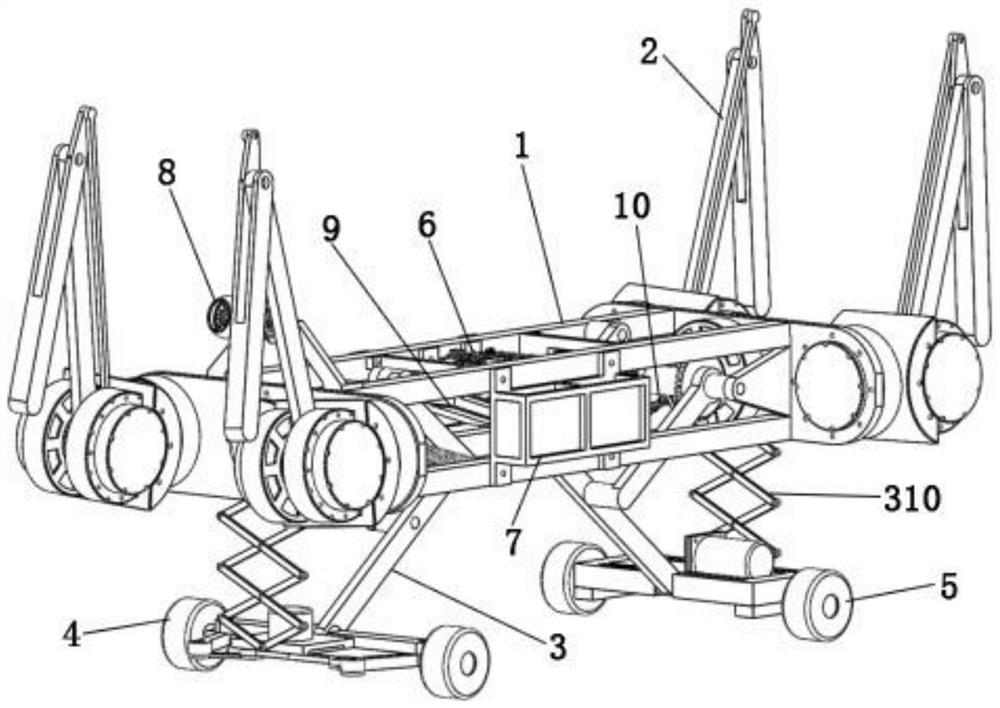
Multi-motion-mode wheel-leg separation type quadruped robot
ActiveCN113247138AEnhanced ability to cross obstaclesImprove work adaptabilityVehiclesVehicle frameControl system
The invention belongs to the field of robots, and particularly relates to a multi-motion-mode wheel-leg separation type quadruped robot which comprises a robot body, supporting legs, a wheel lifting mechanism, a front wheel module, a rear wheel module, a control system, a battery energy storage module and a visual sensor. The machine body comprises two vehicle frames, and a plurality of connecting shafts are arranged between the two vehicle frames so that the front vehicle frame and the rear vehicle frame can be connected. The four supporting legs are located on the left side and the right side of the two vehicle frames respectively. According to the robot, the wheels and the legs are independently mounted on the vehicle body, so that the robot has the speed characteristic of a wheeled robot and the stability characteristic of a legged robot, is simple in structure, easy to process and manufacture and simple in wheel-leg switching, and has relatively high bearing capacity, the obstacle crossing capacity of the robot is effectively enhanced, and the utilization rate of energy is relatively high; and the working adaptability of the robot is greatly improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Cam mechanism contour design and driven part motion characteristic mapping platform
The invention is mainly applied to science and engineering mechanical principle teaching of colleges and universities, belongs to the technical field of cam applications, teaching apparatuses and the like and mainly solves the problems of teaching planarizartion and experiment singularization. A mapping platform comprises mechanical and electrical integration power input system, a power distribution system and an output cam mapping system. The output cam mapping system can be divided into a known cam mapping driven part characteristic curve module and a known driven part curve mapping cam module. The cam mechanism driven part basic laws, the plane cam contour curve design and the cam motion characteristic curve analysis are emphasized. The power distribution system is formed by worm transmission, gear transmission, belt drive and gear and rack transmission. A work cycle of the output end cam mapping system can complete two steps of driven part characteristic curve mapping and cam mapping. By means of the mapping platform, student can master basic theories, basic knowledge and basic skills of mechanical principles and have mechanical motion scheme determination and analysis and mechanism design capacities preliminarily.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
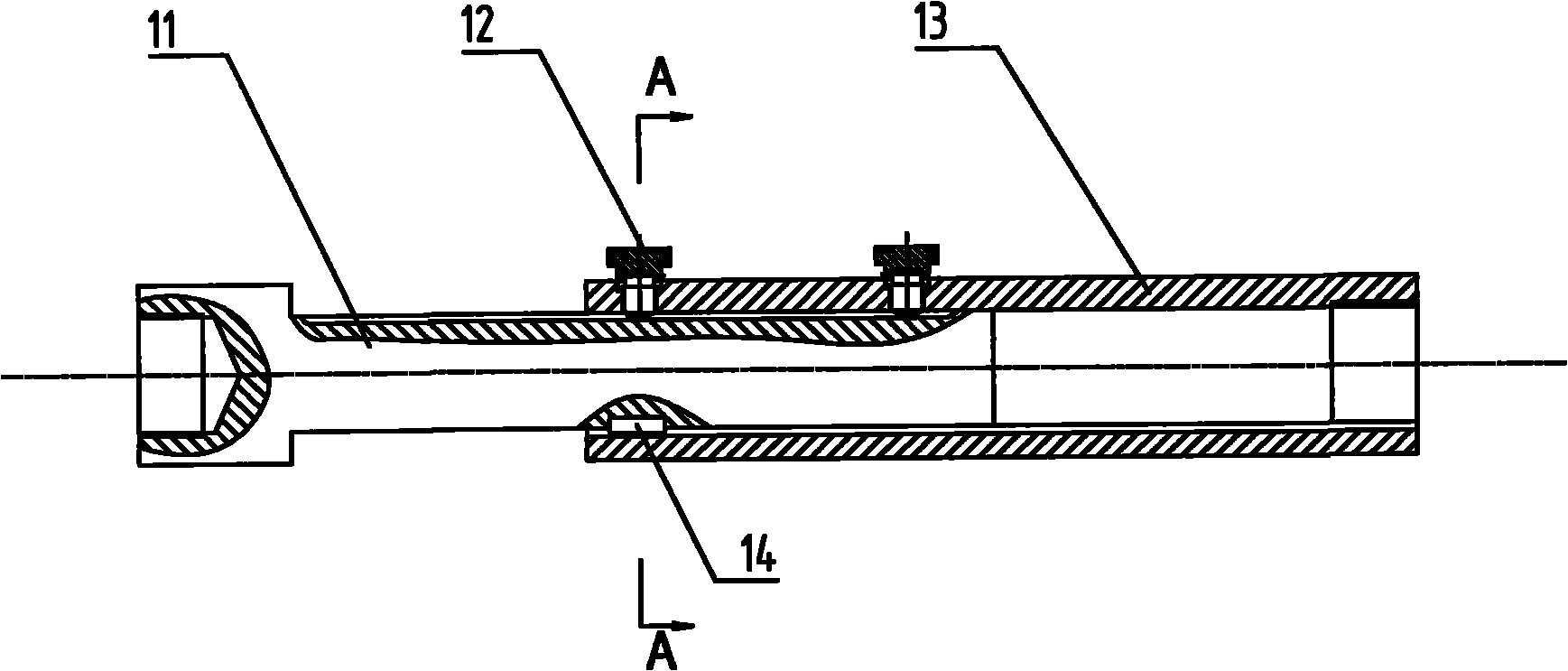
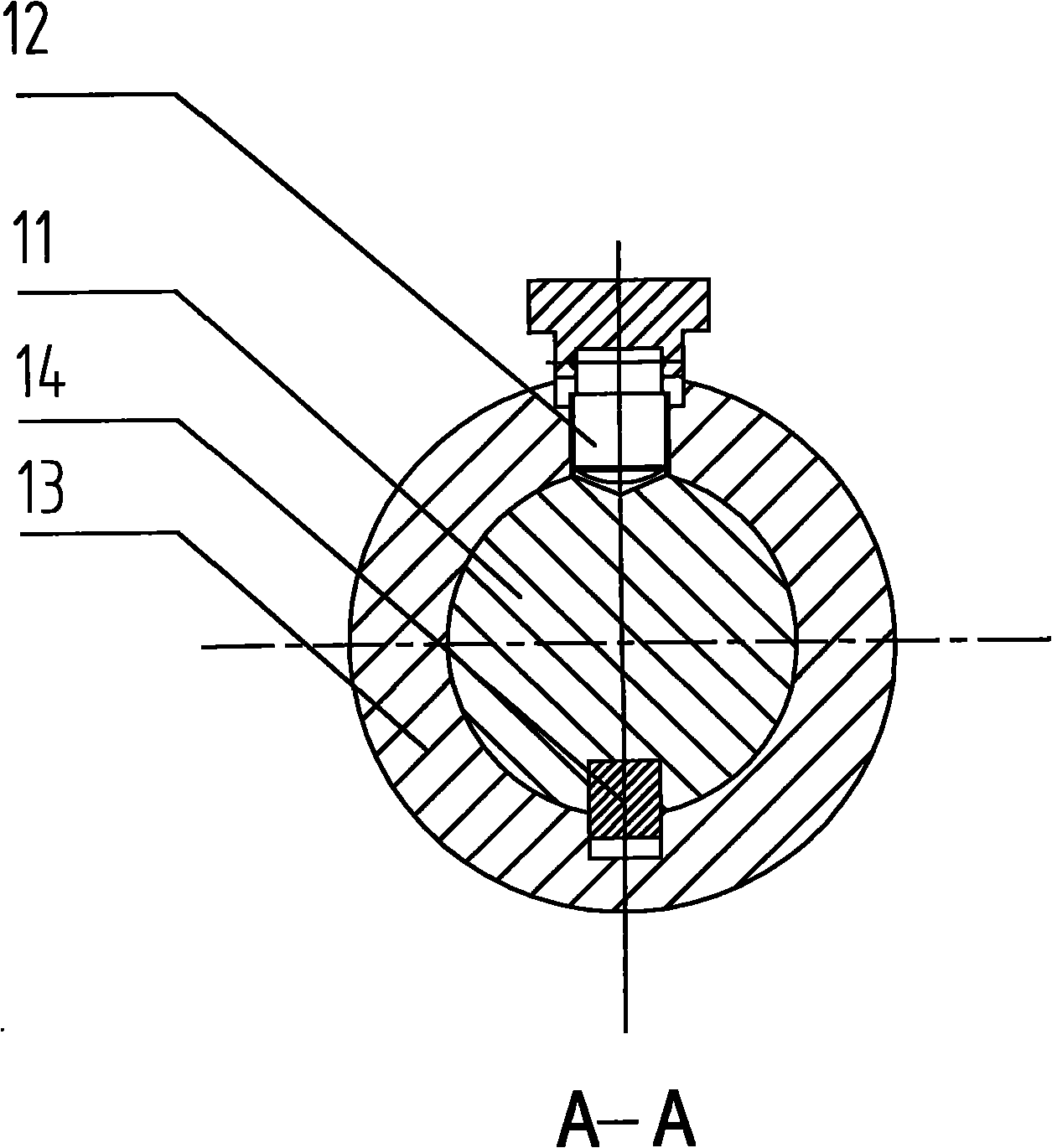
Variable-arm-length articulated-type coordinate measuring machine
InactiveCN105157638AGood measurement statusHigh repeat positioning accuracyMeasurement devicesEngineeringCoordinate-measuring machine
The invention discloses a variable-arm-length articulated-type coordinate measuring machine, and the machine comprises a substrate, three swinging joints, two variable arm length measuring arms, and a measuring head. A main shaft is disposed in an inner sleeve, and is connected through a thread of one end. A sliding table is disposed in an outer sleeve, and is connected through a thread of the other end. A guide rail is fixed on the main shaft through a screw, and a sliding block is fixed on the sliding table through a screw. The main shaft is provided with a thread hole, and the sliding table is provided with a through hole. The arm length can be locked through a screw. A limiting mechanism is fixed on the sliding table and the main shaft, and locks the length change range of the variable arm length measuring arms. Aiming at the size of a measured object, the machine is enabled to achieve the optimal measuring efficiency through the adjustment of the length of the measuring arms. After the lengths of the variable arm length measuring arms change, the machine still can achieve a very high repeated positioning precision. The distances between thread holes of the sliding table are fixed. After the adjustment of the lengths of the variable arm length measuring arms, the machine does not need to be calibrated for measurement.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Multi-transmission-element transmission form and transmission feature comparison platform
InactiveCN104637387AReduce volumeLight in massEducational modelsGear transmissionScience and engineering
The invention is mainly applied to science and engineering type mechanical principle teaching of colleges and universities, and belongs to the field in the technical fields of transmission element application and teaching instruments. By combining the characteristics of different transmission elements for serial combination and innovation, the invention designs a multi-transmission-element transmission form and transmission feature comparison platform, which comprises belt transmission, chain transmission, friction wheel transmission, gear transmission, worm rod transmission, spiral transmission, groove wheel transmission and the like. The problems of simple structure, few knowledge point design sides, huge size, heavy weight and ponderous structure the like of the existing teaching aid are solved, the analysis, the display and the explanation are carried out by aiming at main mechanical transmission elements, and the work features of various transmission elements are highlighted through comparison. The comparison platform has the advantages that students can master basic theories, basic knowledge and basic skills of the mechanical principle, and in addition, the students can primarily have the ability of determining the mechanical movement scheme and analyzing and designing the mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
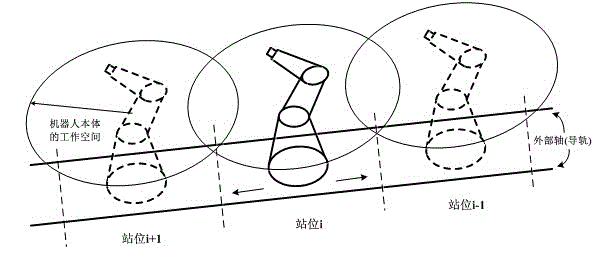
Motion planning method for additional shafts in working units of gantry hoisting robot
ActiveCN106272429AExpand the scope of workImprove work adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorProjection PrincipleWork unit
The invention relates to a motion planning method for additional shafts in working units of a gantry hoisting robot. On the basis of addition of the gantry external linear additional shafts, redundant working units linked with six joints of the industrial robot, and a fixed working platform, two of a section of machining path points monotonously changing along a motion direction of each slide table which is fixedly connected with a robot base on the corresponding additional shaft are manually selected as end points of a preferred interval. A movable initial point of each slide table is obtained through a projection principle of a straight line from a point to a space. A movable middle point and a movable termination point of each slide table are obtained through setting a step length of the slide table, that is, distances from movable positions corresponding to the machining path points in the corresponding preferred interval, of each slide table, to a zero point of the corresponding additional shaft, are obtained. Movements of the slide tables are in preference to motions of the joints of the robot when the robot machines the path points in the preferred intervals. The method is capable of reducing the change amplitudes of the joints of the robot, so that the motion of the robot is continuous and stable; and the method is suitable for machining the continuous and dense path points by the robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Clamping jaw mechanism and mechanical arm
PendingCN107398920AAchieve clampingAdapt to form factorProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a clamping jaw mechanism and a mechanical arm. The clamping jaw mechanism comprises a machine frame, a driving mechanism and clamping jaw assemblies. The machine frame is provided with arc-shaped rails. The driving mechanism and the clamping jaw assemblies are arranged on the machine frame. The driving mechanism is in driving connection with the clamping jaw assemblies. Each clamping jaw assembly comprises a matching part which is matched with the corresponding arc-shaped rails. The clamping jaw assemblies can be driven by the driving mechanism to move along the arc-shaped rails through the matching parts. The motion trails of the clamping jaw assemblies provided by the embodiment of the invention are in an arc shape, thus, articles in irregular shapes can be clamped, article clamping can be achieved in a larger dimension range, accordingly, the clamping jaw mechanism and the mechanical arm can adapt to the overall dimensions of more articles, and the work adaptation under different occasions is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG QIANSHITECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Multifunctional obstetrical and gynecological LEEP knife
PendingCN108261237AVersatileSimple and fast operationSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesLine tubingElectrocoagulation
The invention discloses a multifunctional obstetrical and gynecological LEEP knife. A multifunctional electrical cutter head is connected with an integrated host through a connecting pipeline. The multifunctional electrical cutter head is formed by an electrode, a flushing-attracting head, an electrode telescoping control switch, a LED lamp, a camera and a knife handle, which can achieve the functions such as cutting, electrocoagulation, flushing, imbibitions, smoking, illuminating and shooting. The integrated host is composed of a control system, a high frequency generation system, a negativepressure attraction system and a flushing system; the whole set of device is integrated in a movable cabinet, which can realize quick arrangement, transfer and expansion. The connecting pipeline comprises a signal control line, a vacuum suction pipe and a flushing liquid pipeline, and the three pipelines are installed in a casing pipe. The invention has the advantages of compact structure and rich functions, and mainly solves the problems of the single function of the existing LEEP knife, the difficulty of the operation in a small space, and the requirement of the surgical accessory equipment, and is particularly suitable for the emergency operation when the manpower is insufficient.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF JIANGSU UNIV
Hand-held wall grinding machine
PendingCN108942466AReduce pollutionEfficient completion of wall grinding workGrinding carriagesGrinding drivesWorking environmentHand held
The invention discloses a hand-held wall grinding machine. The hand-held wall grinding machine comprises a brushing head, a power mechanism, a dust anti-leaking mechanism, a dust storing vehicle, an air suction mechanism, a battery set and a hand-held rod. The battery set provides electric energy for the power mechanism and the air sucking mechanism; the brushing head comprises the dust anti-leaking mechanism and a grinding disc; the grinding disc is disposed in the dust anti-leaking mechanism; the power mechanism is located below the dust anti-leaking mechanism; a base is mounted below the power mechanism; the hand-held rod is mounted at the lower end of the base; the air sucking mechanism is connected with the bottom of the hand-held rod through a long telescopic hose; and the air sucking mechanism is mounted on the upper left of the dust storing vehicle. During wall grinding work, the wall grinding work can be finished efficiently, and meanwhile the dust can be reduced so as not topollute the working environment.
Owner:无为欧米伽智能科技有限公司
Swing joint for realizing force balance and mechanism limit by using internal bending springs
InactiveCN105443655AAchieve gravity balanceComfortable to useMeasurement devicesVibration suppression adjustmentsGratingJoints types
The invention discloses a swing joint for realizing force balance and mechanism limit by using internal bending springs. The swing joint comprises a left support, a right support, an embedding shaft, an embedding sleeve, two identical compression columns, two identical bending springs, two identical bearings, an inner spacing ring, an outer spacing ring, an inner nut, an outer nut, a grating bracket, a grating and a reading head; the embedding shaft and the embedding sleeve can realize relative rotation through the bearings; when the embedding shaft and the embedding sleeve relatively rotate, the two compression columns on the embedding shaft and two semicircular grooves are spaced to synchronously compress the bending springs, so that the bending springs have opposite acting force on spacing of the compression columns and the semicircular grooves, that is, the resistance is increased to realize gravity balance of a joint type coordinate measurer when the embedding shaft and the embedding sleeve relatively rotate; and when the bending springs are compressed to have no gap, the compression cannot be performed anymore to achieve a limiting effect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Near-net forming method and device for multi-axis and axis variable zero component
InactiveCN114453902AUnshackleImprove production flexibilityGrinding carriagesManufacturing driving meansGantry craneEngineering
The invention discloses a near-net forming device for a multi-axis and axis variable zero component. The near-net forming device comprises a fixed base, a first stand column, a gantry crane, a composite moving platform, a workbench, a rotating cross beam, a linkage cross beam, a laser material reducing module and the like. The rotating cross beam horizontally moves relative to the gantry crane cross beam; the linkage cross beam rotates relative to the rotating cross beam; the material adding module and the material grinding and cutting module synchronously and horizontally move relative to the linkage cross beam; the gantry crane beam moves up and down relative to the gantry crane stand columns. The composite moving platform can horizontally move relative to the fixed base, first stand columns are arranged on the outer sides of at least two end portions of the workbench, the first stand columns are fixed to the composite moving platform, and the workbench can obliquely move relative to the first stand columns. The invention has the advantages of compact structure and the like.
Owner:江西应用科技学院
Pulsed laser range finding detector APD adjustment circuit
ActiveCN105445747AImprove work adaptabilityImprove stabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationWorking temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a pulsed laser range finding detector APD adjustment circuit, which is composed of a high-voltage circuit, a detection circuit, a signal feedback circuit, a data processing circuit and a positive temperature compensation circuit, wherein the data processing circuit is connected with the high-voltage circuit, amplifying circuits are each connected with the detection circuit and the signal feedback circuit, and the signal feedback circuit is connected with the positive temperature compensation circuit. Compared with the traditional bias-voltage APD adjustment circuits, the pulsed laser range finding detector APD adjustment circuit has the advantages of wide application range of ambient working temperature, large self-voltage adjustment range, simple circuit structure, high automation degree of rapid circuit adjustment along with temperature and noise as well as accurate adjustment value, and further has the temperature consumption, noise feedback and program-controlled adjustment functions, thereby greatly improving the operating adaptability, stability and flexibility of the bias-voltage APD adjustment circuit.
Owner:河南平原光电有限公司
A motion planning method for additional axes in the work cell of a gantry-type hoisting robot
ActiveCN106272429BExpand the scope of workImprove work adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorProjection PrincipleEngineering
The invention relates to a motion planning method for additional shafts in working units of a gantry hoisting robot. On the basis of addition of the gantry external linear additional shafts, redundant working units linked with six joints of the industrial robot, and a fixed working platform, two of a section of machining path points monotonously changing along a motion direction of each slide table which is fixedly connected with a robot base on the corresponding additional shaft are manually selected as end points of a preferred interval. A movable initial point of each slide table is obtained through a projection principle of a straight line from a point to a space. A movable middle point and a movable termination point of each slide table are obtained through setting a step length of the slide table, that is, distances from movable positions corresponding to the machining path points in the corresponding preferred interval, of each slide table, to a zero point of the corresponding additional shaft, are obtained. Movements of the slide tables are in preference to motions of the joints of the robot when the robot machines the path points in the preferred intervals. The method is capable of reducing the change amplitudes of the joints of the robot, so that the motion of the robot is continuous and stable; and the method is suitable for machining the continuous and dense path points by the robot.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Portable cleaning device for substation
InactiveCN102601069AHigh working reliabilityStrong cleaning abilityCleaning using toolsEngineeringDrive shaft
The invention discloses a portable cleaning device for a substation. The device comprises a motor, a flexible shaft, a base, a driving shaft and a driven shaft, wherein the flexible shaft is driven by the motor to rotate; a flexible shaft sleeve is arranged outside the flexible shaft; the driving shaft and the driven shaft are connected on the base in a rotary manner; the driving shaft is driven by the flexible shaft; a driving gear and a driven gear, which are meshed with each other, are respectively fixedly connected on the driving shaft (5) and the driven shaft; brush holders are fixedly connected at the end of the driven shaft; and brush heads are fixedly connected on the brush holders. The device can effectively remove dirt on magnetic pillars and various loads of the substation, has high working reliability, can carry out live working, is simple and practical to assemble and can change the work modes at any time.
Owner:STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD ANQING POWER SUPPLY CO +1
Novel automatic transport device
The invention discloses a novel automatic transport device. The novel automatic transport device comprises a chassis, wherein a movement mechanism is arranged on the lower surface of the chassis; a control module and an up-down adjustment mechanism are arranged on the upper surface of the chassis; a mechanical arm gripping mechanism is arranged on the up-down adjustment mechanism; and the movementmechanism, the up-down adjustment mechanism and the mechanical arm gripping mechanism are electrically connected with the control module separately. The novel automatic transport device disclosed bythe invention is capable of automatically adjusting the height and the orientation of a gripper according to settings, and automatically controlling movement to realize automatic transport, thereby reducing human intervention, and greatly increasing the transport efficiency for articles.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Positioning mechanism for two-position north-seeker
InactiveCN100529661CImprove adaptability to vibration environmentEnsure positioning accuracyRotary gyroscopesEngineeringClockwise
The invention discloses a positioning mechanism suitable for a two-position north finder. The positioning mechanism is composed of a 180° positioning assembly, a 0° positioning assembly, a right air buffer, a left air buffer, a movable positioning assembly, and a main shaft support. 180 The °positioning assembly and the right air buffer are assembled on the right side of the upper plate of the spindle support; the 0° positioning assembly and the left air buffer are assembled on the left side of the upper plate of the spindle support; the movable positioning assembly is assembled on the two-position north finder In the A groove of the convex part of the connecting surface of the rotating body; one end of the main shaft is assembled in the E through hole of the main shaft bracket, and the other end of the main shaft extends into the D through hole of the rotating body. In the positioning mechanism of the present invention, when the rotating body drives the movable positioning assembly to rotate clockwise, the movable positioning assembly first collides with the buffer rod of the left air buffer, then decelerates, and then collides with the left contact of the 0° positioning assembly. 0° positioning point, the rotating body stops; when the rotating body drives the movable positioning assembly to rotate counterclockwise, the movable positioning assembly first hits the buffer rod of the right air buffer, decelerates, and then hits the right side of the 180° positioning assembly. After contacting the head, a 180° positioning point is generated, and the rotating body stops.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Angle and velocity increment-based vehicle-mounted posture fine alignment system
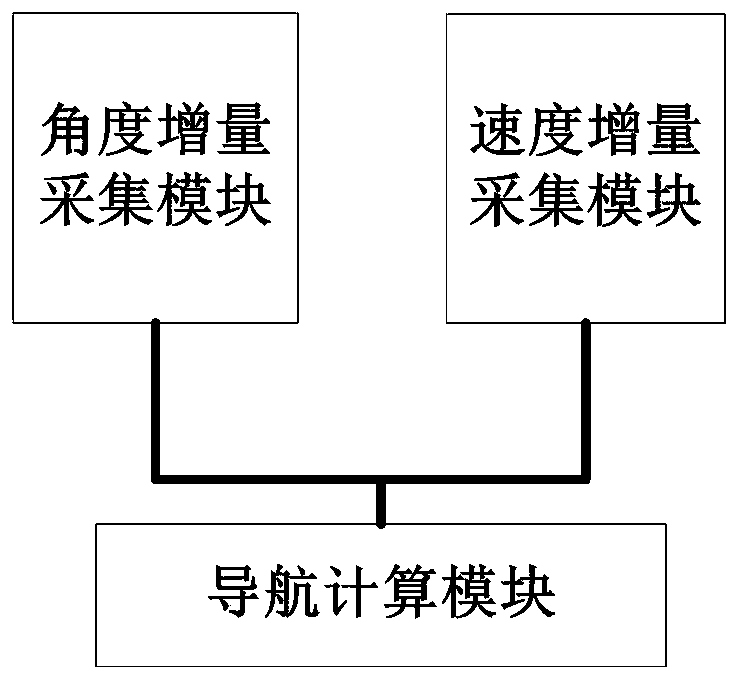
ActiveCN110388942AFast convergenceImprove alignment accuracyMeasurement devicesAdaptive filterMarine navigation
The present invention relates to an angle and velocity increment-based vehicle-mounted posture fine alignment system, belongs to the vehicle posture alignment technologies, and resolves prior-art problems of poor alignment precision and long alignment time. The system comprises: an angle increment collection module, used for collecting in real time an angle increment of deviation of a current vehicle three-axis from an original three-axis; a velocity increment collection module, used for measuring in real time a velocity increment of a vehicle along the original three-axis; and a navigation calculation module, used for error compensation separately on the angle increment and the velocity increment, performing coarse alignment according to a compensation result, then updating a real-time status of the vehicle posture alignment system, so as to modify a coarsely aligned vehicle posture and velocity, obtaining vehicle state estimation according to a filtering gain of adaptive filtering ofthe vehicle posture alignment system, determining whether the vehicle state estimation is the same as a current vehicle state; and if not, updating the real-time status of the vehicle posture alignment system again until the vehicle state estimation is the same as the current vehicle state, so as to implement vehicle posture fine alignment.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Intelligentized chain detection production line information statistics and performance monitoring system
InactiveCN104444229AEasy to set upRealize automatic controlControl devices for conveyorsProduction lineHuman–machine interface
The invention discloses an intelligentized chain detection production line information statistics and performance monitoring system. The intelligentized chain detection production line information statistics and performance monitoring system comprises a PLC, a human-computer interface, a sensor, an execution device, an extension terminal and an upper computer communication module, wherein the PLC is connected with the human-computer interface and provided with the upper computer communication module, the extension terminal is connected with the PLC, and the sensor is connected to the PLC in an execution period. In this way, the intelligentized chain detection production line information statistics and performance monitoring system has the advantages of being high in reliability, automatic to operate, simple to use, high in production efficiency, capable of conducting automatic monitoring and the like, and meanwhile has wide market prospects in the automatic chain transmission manufacturing field.
Owner:SUZHOU SHUNGE INTELLIGENT TECH
Preparation method of amphoteric polycarboxylate-type slump loss resistance agent
InactiveCN108610454ALarge steric hindranceReduce hydrolysis2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholineRelease time
The invention discloses a preparation method of an amphoteric polycarboxylate-type slump loss resistance agent. With 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine, unsaturated long-chain polyether, unsaturated carboxylic acid and hydroxyl acrylate as monomer raw materials, under the function of an initiator and a chain transfer agent, the amphoteric polycarboxylate-type slump loss resistance agent is prepared by adopting an aqueous polymerization process. Compared with conventional polycarboxylate-type slump loss resistance agents, the prepared amphoteric polycarboxylate-type slump loss resistanceagent has longer slump loss resistance release time and better slump loss resistance performance, and can well meet the requirements of newly-mixed concrete for long-time and long-distance transportation and construction.
Owner:BEIJING ACAD OF BUILDING ENG
Mechanical arm motion planning method and system for cleaning space rectangular area
ActiveCN113951761AImprove work efficiencyIncrease average speedAutomatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlPhysicsElectric machinery
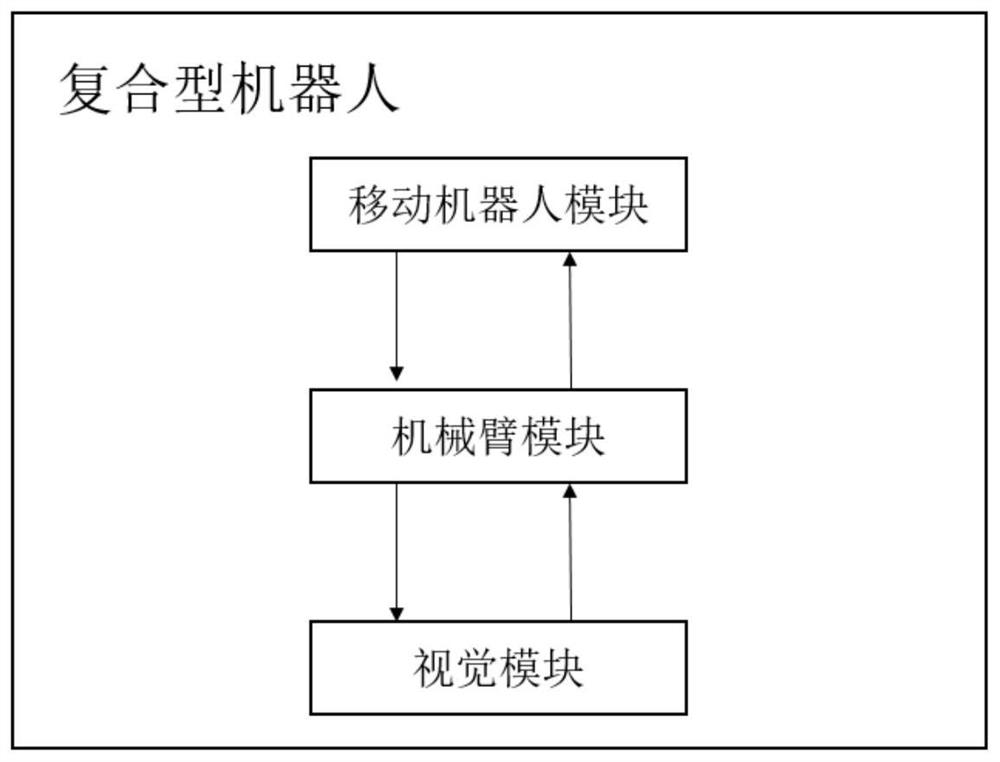
The invention provides a mechanical arm motion planning method and system for a cleaning space rectangular area, and relates to the technical field of robots. The system comprises a mobile robot module, a mechanical arm module and a visual module, each module has independent working performance, and a corresponding tool is distributed in each module; the mobile robot module is provided with universal equipment including a laser radar and a driving motor, and it is guaranteed that a mobile robot independently completes common related functions including SLAM, navigation and motion planning; the mechanical arm module comprises a mechanical arm body and a clamping jaw, and it is guaranteed that a mechanical arm can complete related operations including object grabbing and transferring; and the visual module comprises a depth camera and can provide target plane and three-dimensional point cloud data and obtain target feature points according to the data. The cleaning area can be made in a self-adaptive mode, and it is ensured that the mechanical arm does not collide with an external structure.
Owner:杭州景吾智能科技有限公司
A platform for comparing the transmission form and transmission characteristics of multiple transmission parts
InactiveCN104637387BRealize electrical integrationA lot of inventionsEducational modelsBasic knowledgeScience and engineering
The invention is mainly applied to science and engineering type mechanical principle teaching of colleges and universities, and belongs to the field in the technical fields of transmission element application and teaching instruments. By combining the characteristics of different transmission elements for serial combination and innovation, the invention designs a multi-transmission-element transmission form and transmission feature comparison platform, which comprises belt transmission, chain transmission, friction wheel transmission, gear transmission, worm rod transmission, spiral transmission, groove wheel transmission and the like. The problems of simple structure, few knowledge point design sides, huge size, heavy weight and ponderous structure the like of the existing teaching aid are solved, the analysis, the display and the explanation are carried out by aiming at main mechanical transmission elements, and the work features of various transmission elements are highlighted through comparison. The comparison platform has the advantages that students can master basic theories, basic knowledge and basic skills of the mechanical principle, and in addition, the students can primarily have the ability of determining the mechanical movement scheme and analyzing and designing the mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Adjustable SINS, DVL and USBL integrated navigation method
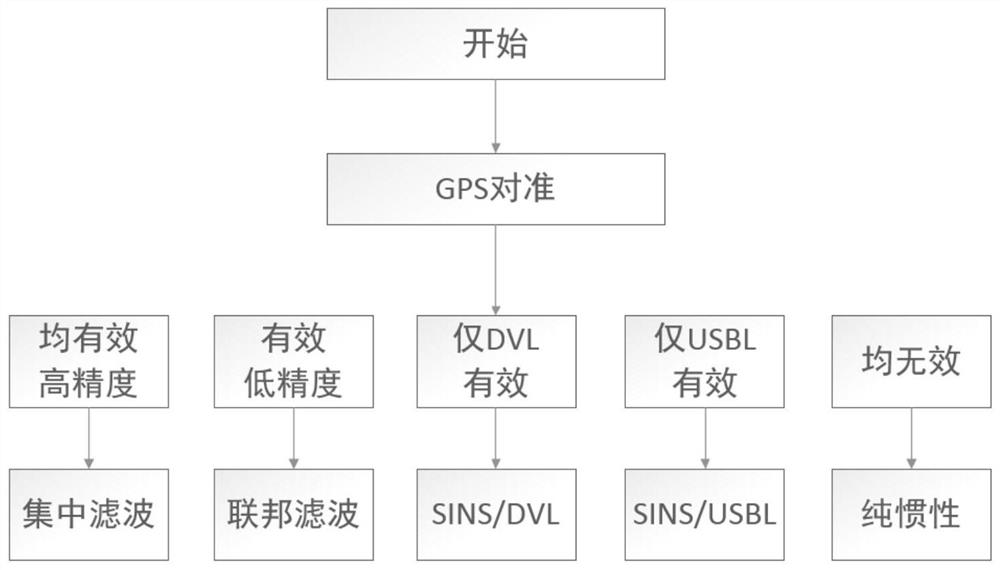
PendingCN113959434AHigh precisionImprove work adaptabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsControl engineeringAccurate estimation
According to the adjustable SINS, DVL and USBL integrated navigation method, the operation mode can be adjusted according to various actual conditions, advantage complementation is achieved, work adaptability of the whole system is improved, and integrated navigation under various conditions is completed. In the actual use of SINS, DVL and USBL integrated navigation, an adjustable flexible integrated navigation mode is adopted for different conditions, and accurate estimation of inertial navigation errors is obtained. According to the combined navigation system, complementary advantages can be realized, working adaptability of the whole system is improved, combined navigation under various conditions is completed, inertial navigation errors are effectively reduced by an adjustable flexible combined navigation mode, and precision of the combined navigation system is improved.
Owner:HEBEI HANGUANG HEAVY IND
Building assembly hoisting equipment
ActiveCN108792986AAchieve safety protectionAvoid the problem of lack of security protection capabilitiesLifting framesEngineeringCivil engineering
The invention discloses building assembly hoisting equipment, and belongs to the field of hoisting equipment. According to the technical scheme, the building assembly hoisting equipment is characterized by comprising a rigid straight barrel, a work frame and a carrying plate. According to the building assembly hoisting equipment, the problems that in existing building assembly hoisting equipment,the taking range of a sling cannot be adaptively adjusted according to the different specifications of fabricated buildings, so that the limitation of the sling during work is large, the sling cannotadapt to hoisting work of different specifications, the fabricated buildings cannot be subjected to safety protection when loaded, the device has large risk in the loading and transporting process, when the fabricated buildings or the device are collided, the influence of vibration to device transportation cannot be relieved, the device is poor in safety protection capacity, the device cannot be intelligently controlled by one person when started, the transmission mechanism of the device is too tedious in process, a tooth chain locking phenomenon is likely to be formed, and the work cooperation performance of the device is poor are solved.
Owner:SHANDONG HONGYUE STEEL SPACE FRAME STRUCTURE
Additive and subtractive double-station synchronous machining method and device for spatially asymmetric component
InactiveCN114453748AUnshackleImprove production flexibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusGrinding drivesGrindingGantry crane
The material increasing and decreasing double-station synchronous machining device comprises a fixed base, a gantry crane, a material increasing module, a grinding and cutting material module and a composite workbench, the gantry crane comprises a gantry crane cross beam and gantry crane stand columns, a rotating cross beam is arranged below the gantry crane cross beam, a first horizontal driving mechanism is arranged in the gantry crane cross beam, and a second horizontal driving mechanism is arranged in the gantry crane cross beam; the rotating cross beam is driven by the first horizontal driving mechanism to horizontally move relative to the gantry crane cross beam; a linkage cross beam is arranged below the rotating cross beam, a rotating driving mechanism is arranged in the rotating cross beam, the linkage cross beam is driven by the rotating driving mechanism to rotate, the material adding module and the grinding and cutting module are installed on the lower portion of the linkage cross beam, and a second horizontal driving mechanism is arranged in the linkage cross beam. And the second horizontal driving mechanism drives the material adding module and the grinding and cutting module to horizontally move. According to the invention, one-time additive and subtractive machining of the component with the variable cross section can be realized.
Owner:江西应用科技学院
Novel nuclear fuel assembly rod pulling production system
ActiveCN107274945AAutomatic loading and unloadingImprove efficiencyNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureWorkloadPull technology
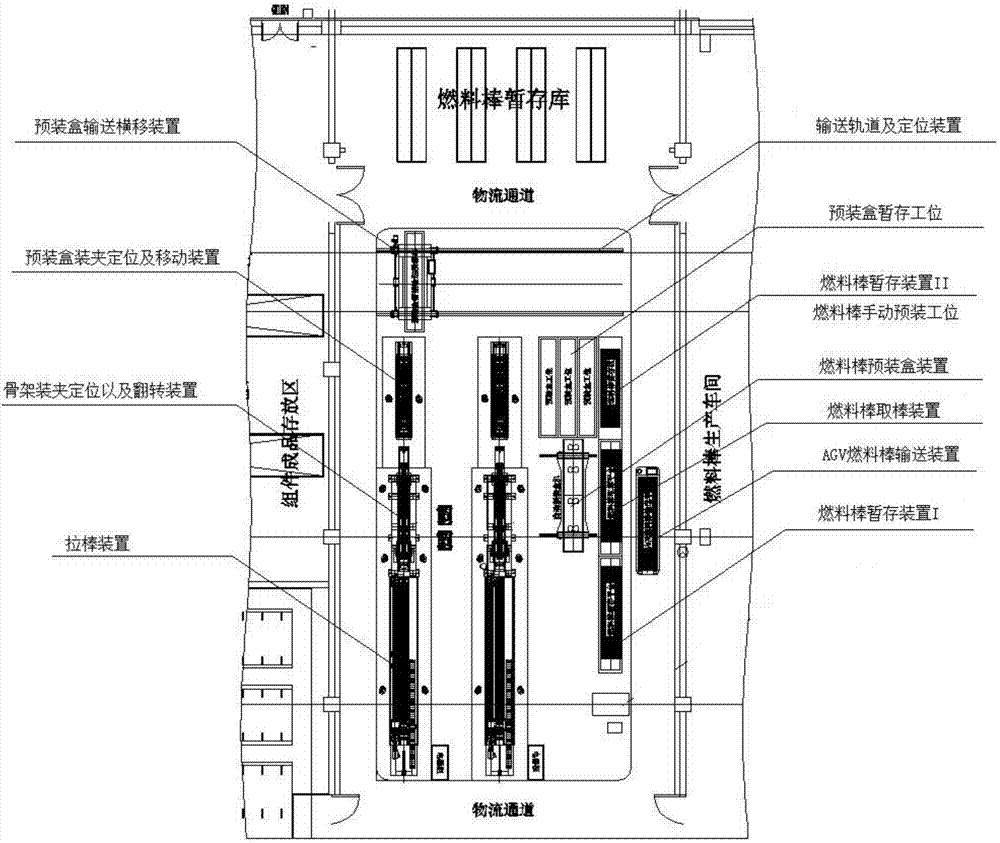
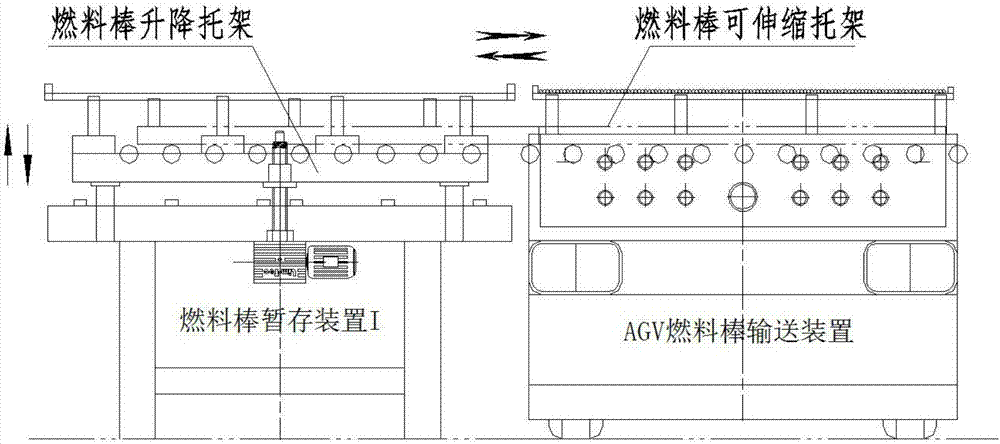
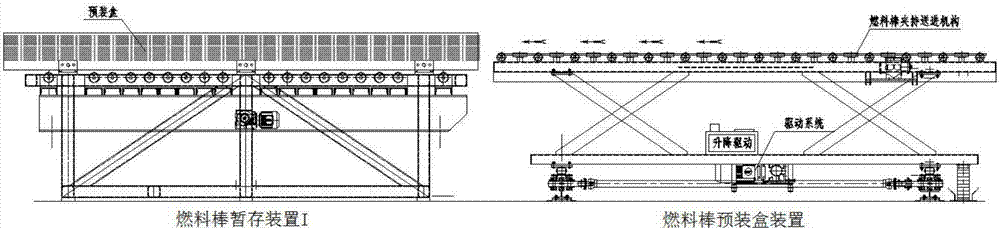
The invention relates to a novel nuclear fuel assembly rod pulling production system, and belongs to the field of nuclear fuels. The system comprises a fuel rod temporary storage device I, a fuel rod picking device, a fuel rod prepackaged box device, a fuel rod temporary storage device II, a prepackaged box conveying and traversing device, a prepackaged box clamping, positioning and moving device, a skeleton clamping, positioning and overturning device and a rod pulling device, wherein the fuel rod temporary storage device I, the fuel rod picking device, the fuel rod prepackaged box device and the fuel rod temporary storage device II are sequentially connected, the prepackaged box conveying and traversing device, the prepackaged box clamping, positioning and moving device, the skeleton clamping, positioning and overturning device and the rod pulling device are sequentially connected, and the prepackaged box conveying and traversing device moves between the fuel rod temporary storage device II and the prepackaged box clamping, positioning and moving device. The system obviously improves the mechanization degree of a nuclear fuel assembly rod pulling technology, reduces the workload, reduces the labor intensity of workers, and improves the quality of nuclear fuel assemblies.
Owner:CMCU ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com