A motion planning method for additional axes in the work cell of a gantry-type hoisting robot
A technology of work unit and motion planning, which is applied to manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of large range of robot joint changes, and achieve the effect of improving work adaptability, reducing joint changes, and continuous and stable motion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Below, take Fanuc's 1-M-20iA model robot as an example, and describe the embodiment of the present invention in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the working unit of the gantry-type hoisting robot consists of a linear guide rail 1, a slide table 2, an industrial robot 3, a workbench 4, and a processing track point 5.
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, a motion planning method for an additional axis in a gantry-type hoisting robot work cell, the additional axis includes a linear guide rail and a slide table, including the following steps:
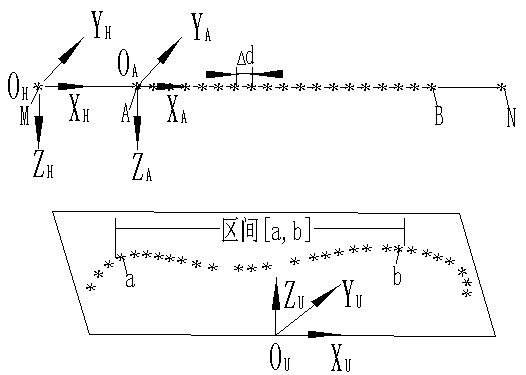
[0034] The first step: if image 3 As shown, establish the user coordinate system on the workbench {O U x U Y U Z U}; Establish the zero point coordinate system of the guide rail at the zero point M of the linear guide rail {O H x H Y H Z H}, the direction of the OX axis is the movement direction of the sliding table (ie, the axis direction of the guide rail); t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com