Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
298results about How to "Eliminate force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
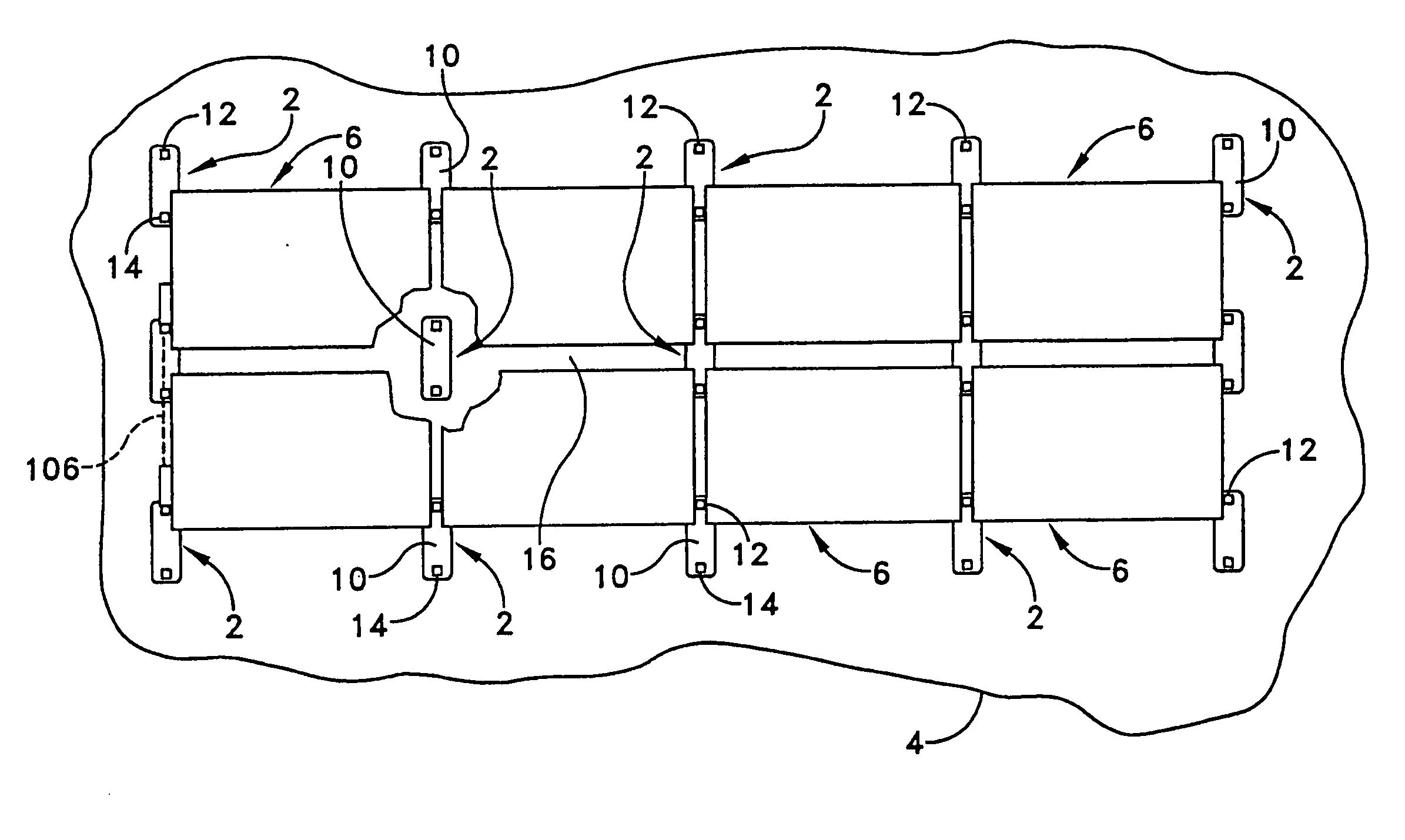
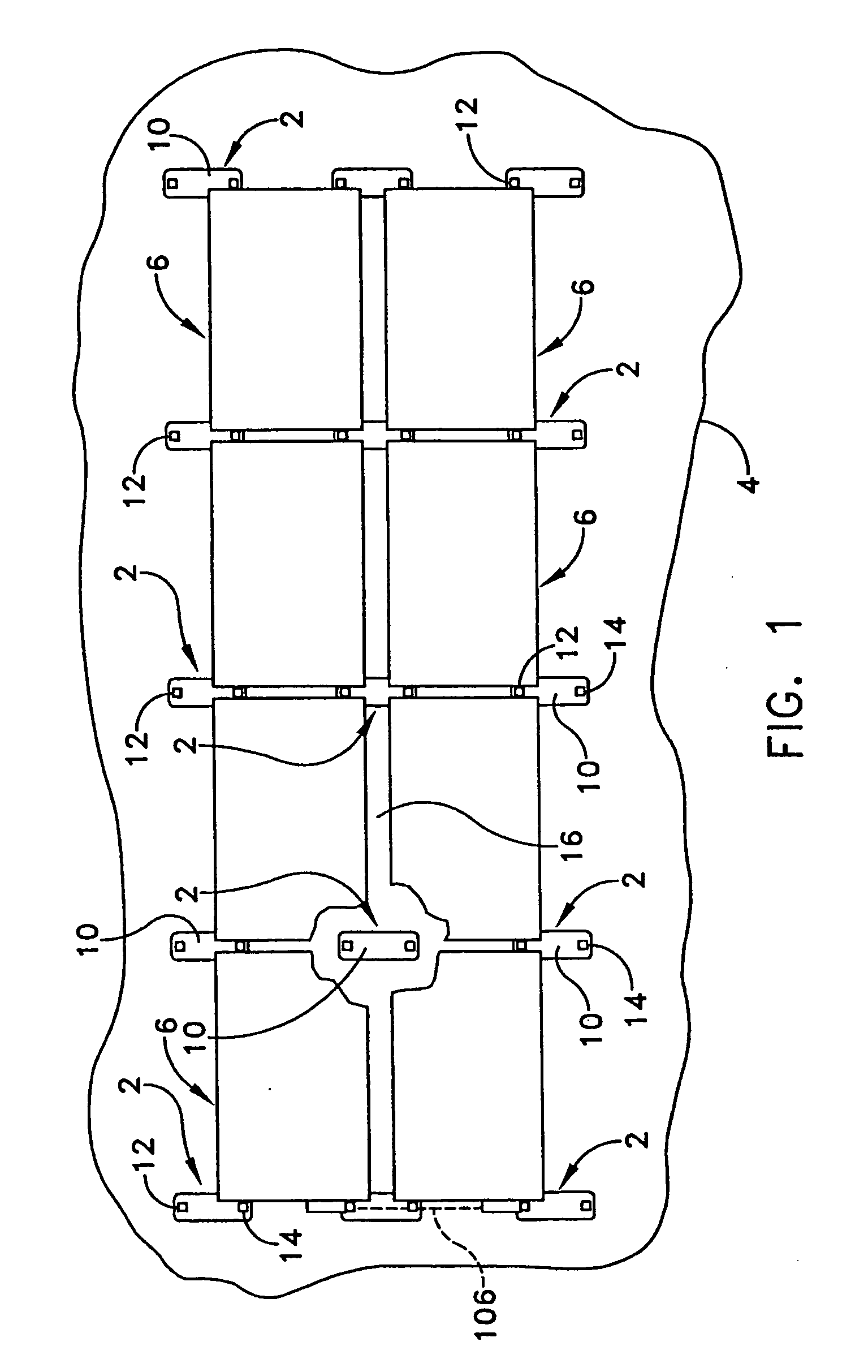
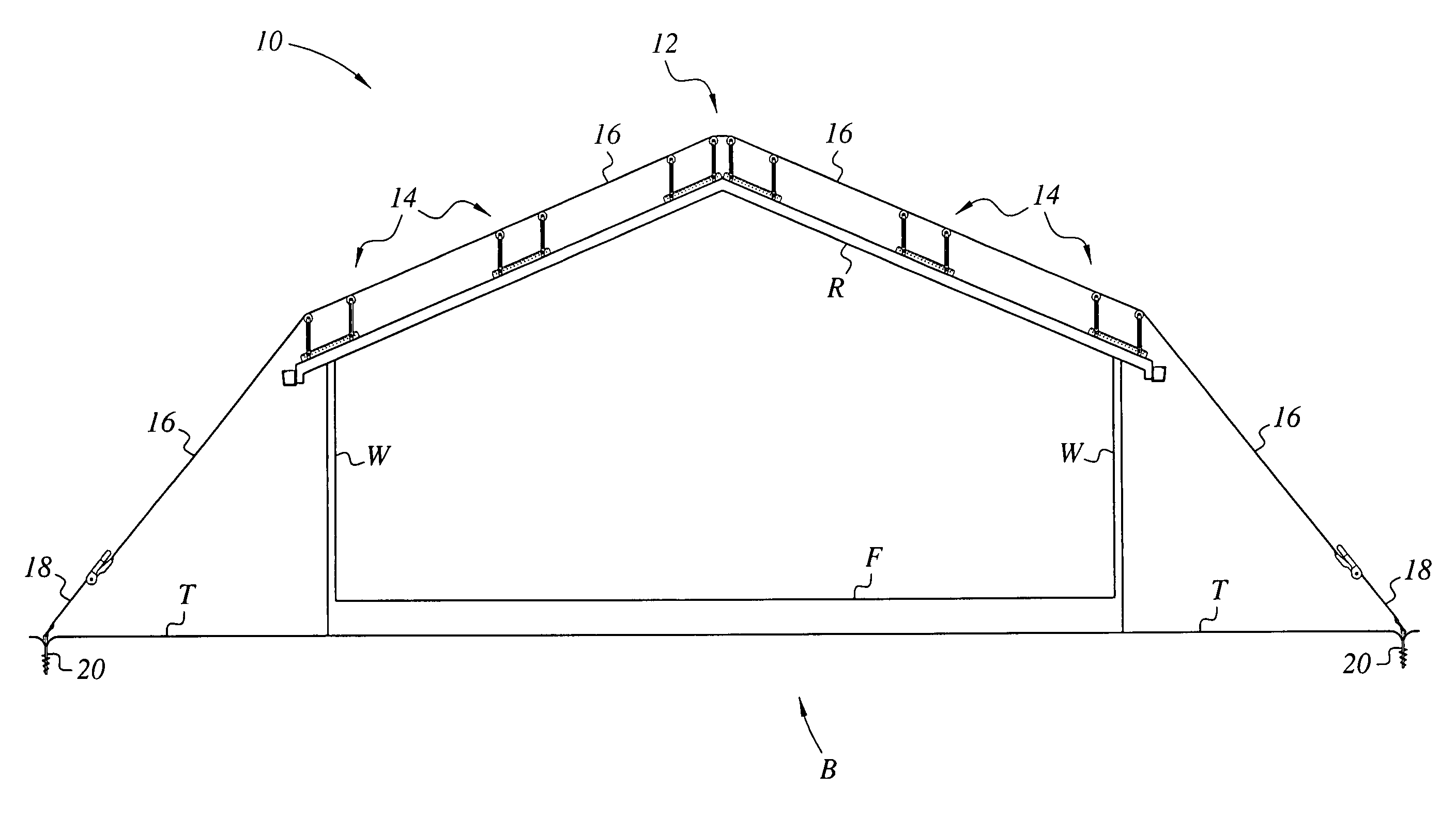
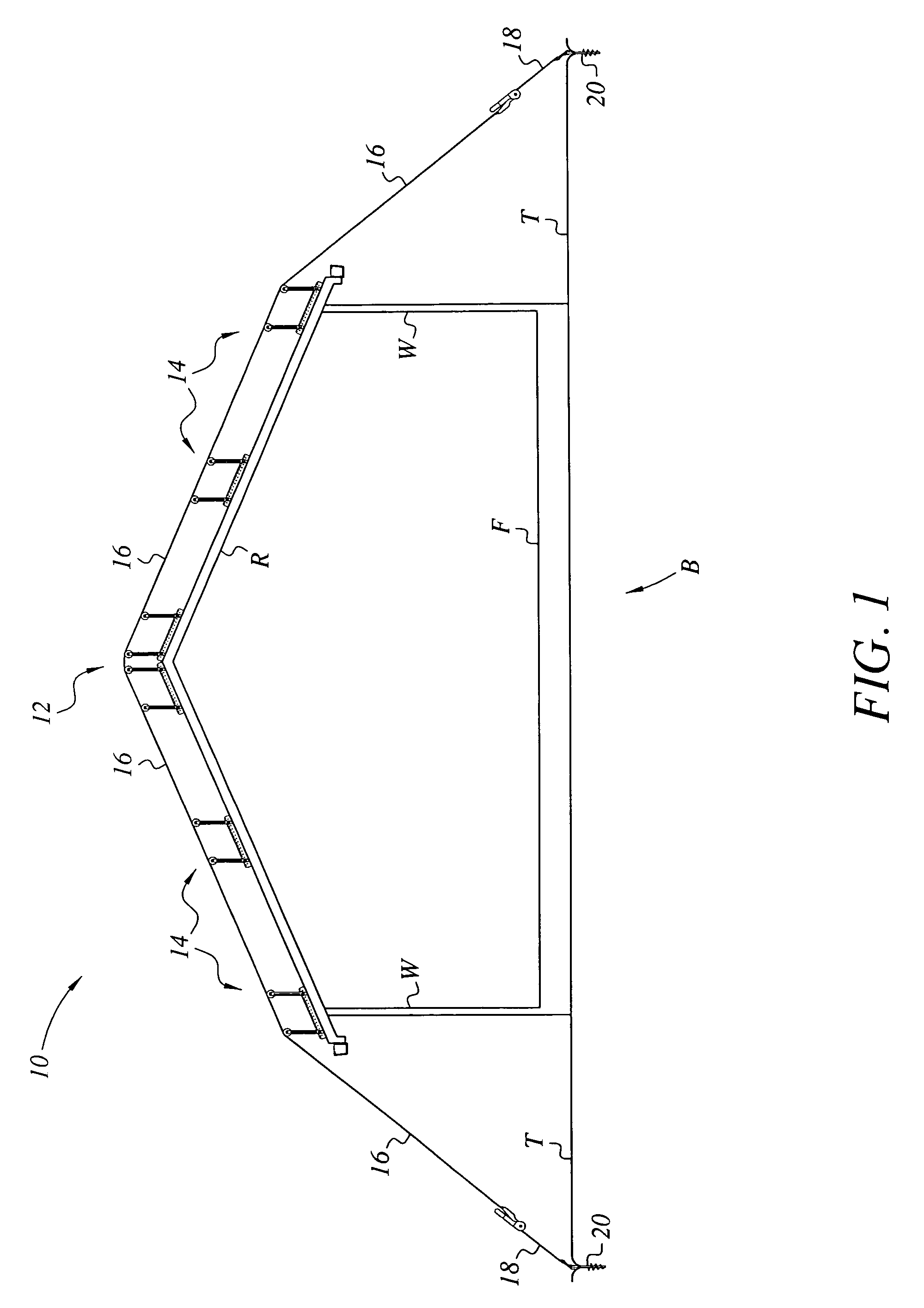
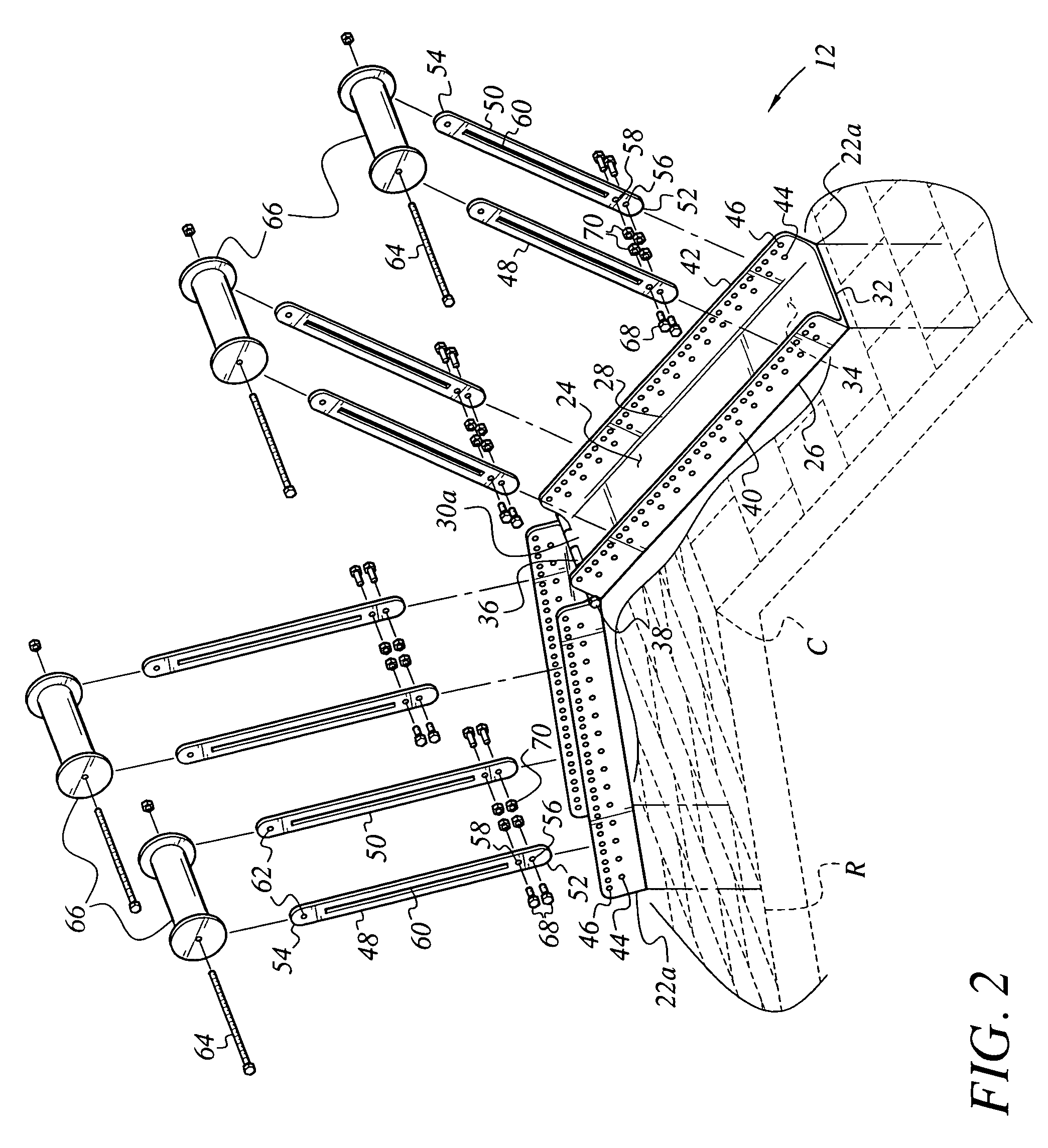
Apparatus and method for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
InactiveUS7435897B2Preserve integrity and waterproof characteristicBenefit annual energy productionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyComputer moduleEffective height
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
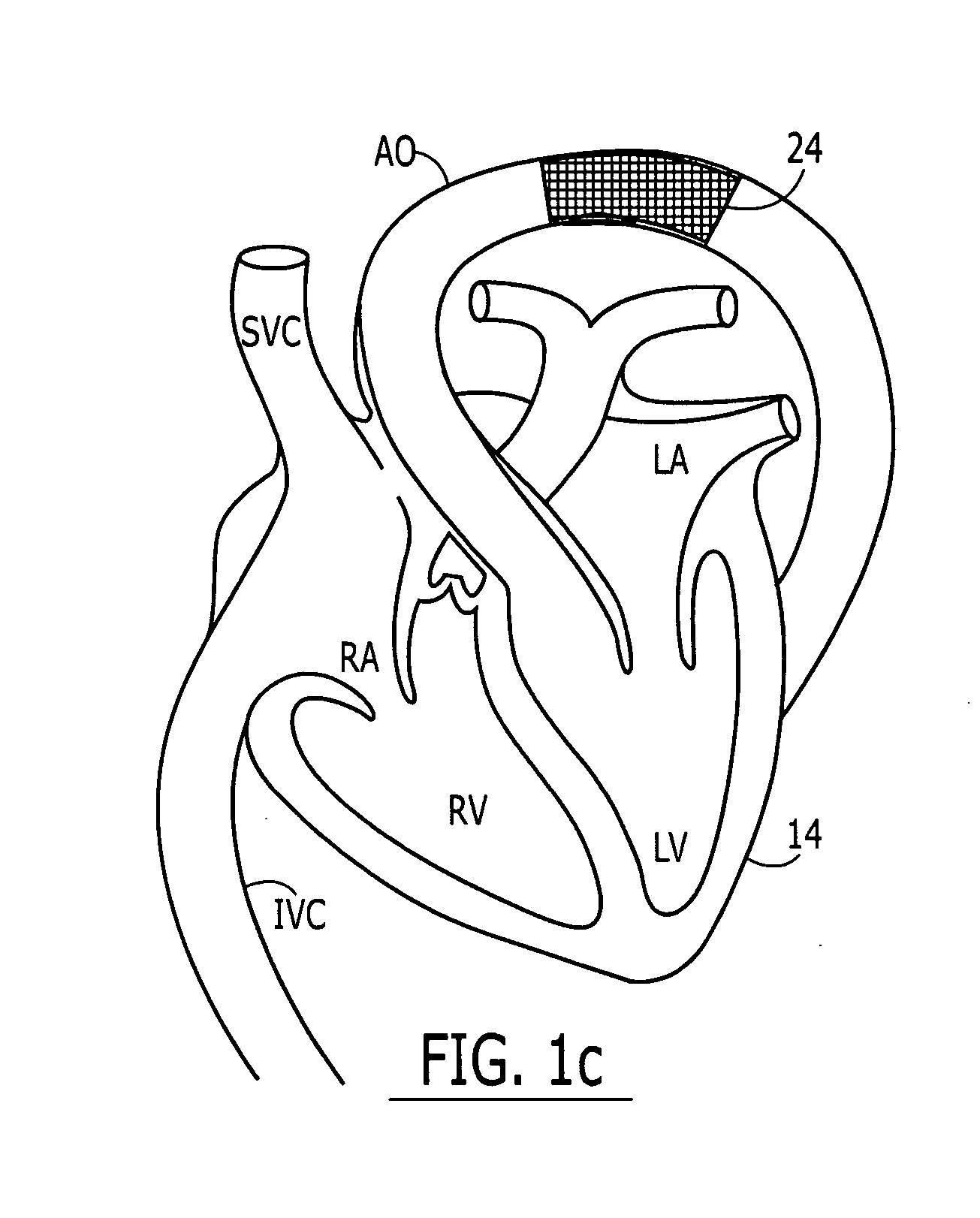
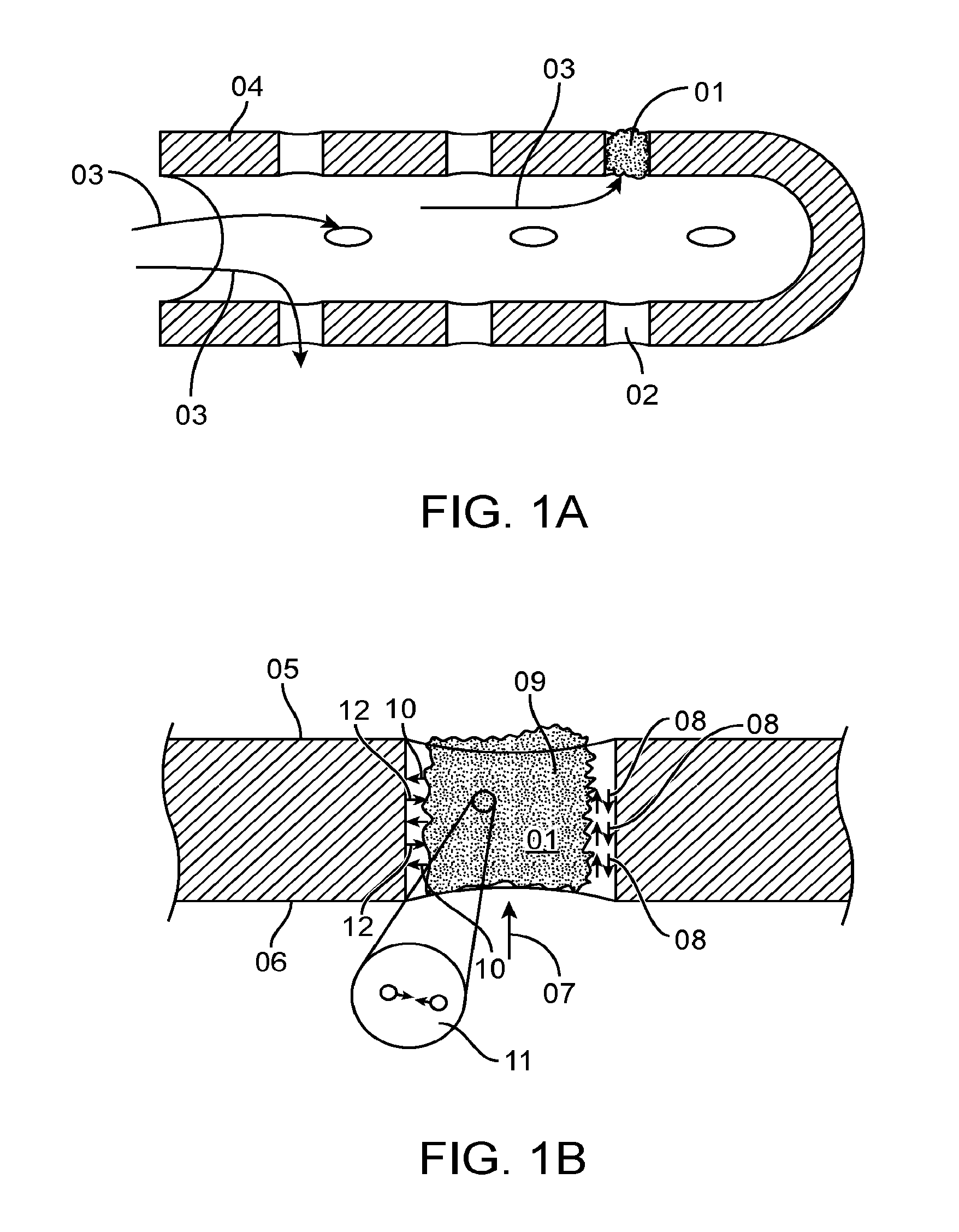
Intervertebral prosthesis
InactiveUS6165218AEvenly distributedCanting of the elastic body is preventedSurgical scissorsJoint implantsInterior spaceIntervertebral disc
An implant, in particular an intervertebral prosthesis, which consists of an elongated elastic body which is form-elastic and takes on the form of a spiral S in the force free state. The spiral can be drawn by a reverse winding up into an insertion instrument which is only insubstantially larger in the insertion region than the cross-section of the elongated elastic body in order to reach the inner space of an intervertebral disc through a small opening in the annulus fibrosus and to push in and sever off the self winding spiral when the interior is filled. This has the advantage that inner spaces of differing sizes can be filled with the same spiral.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
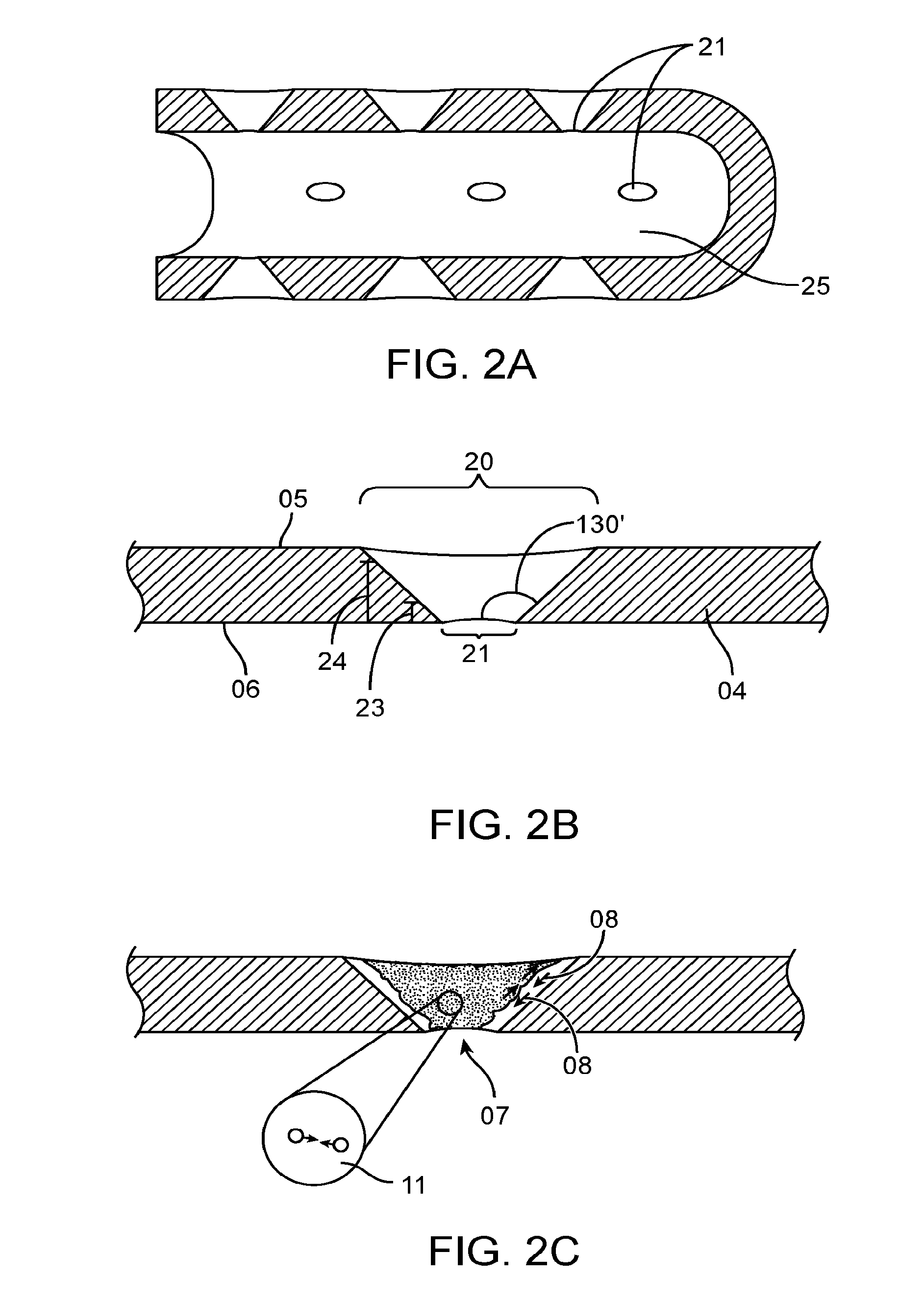
Apparatus and method for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
InactiveUS20050115176A1Preserve integrityPreserve waterproof characteristicPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEffective heightEngineering
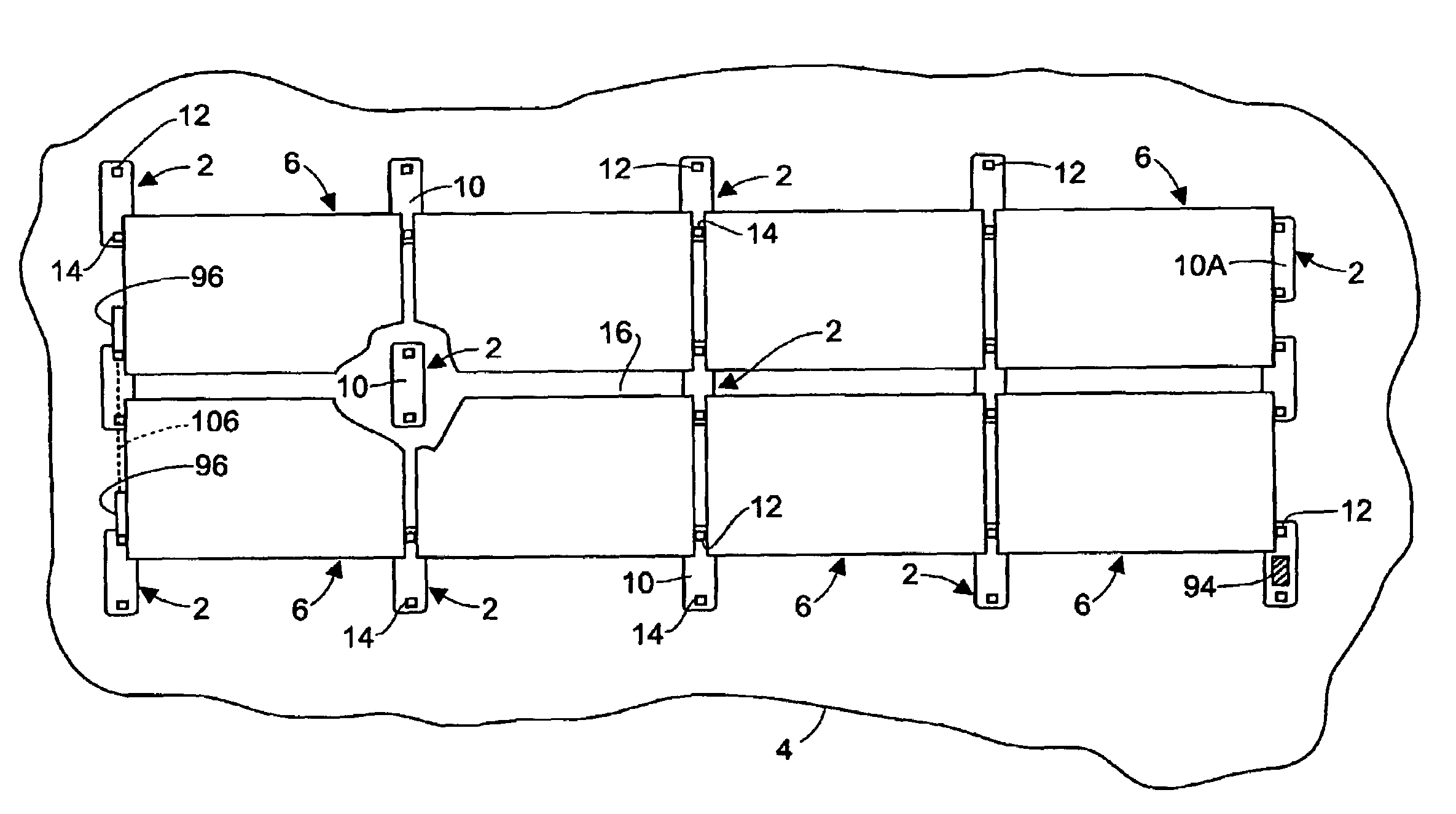
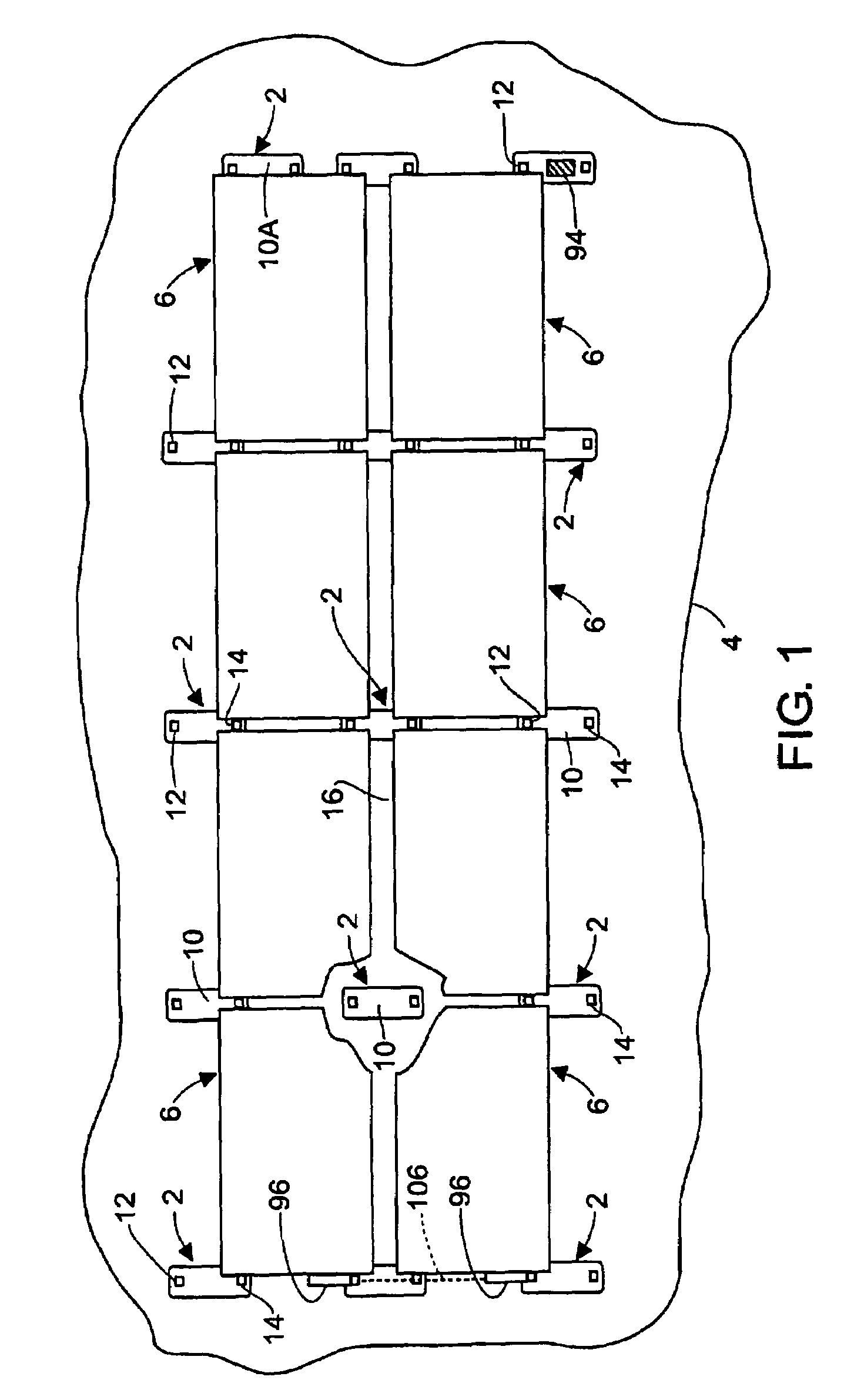
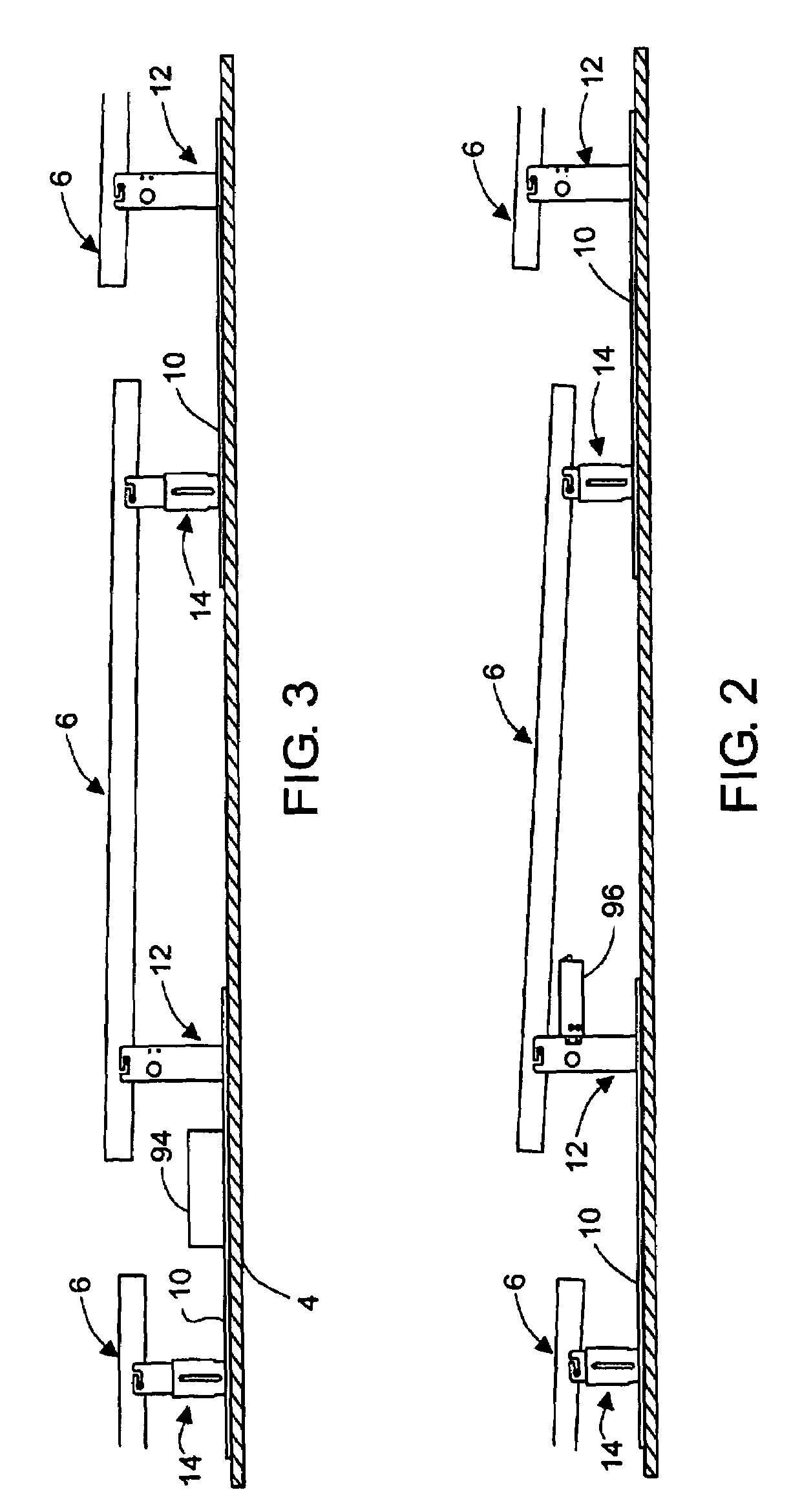
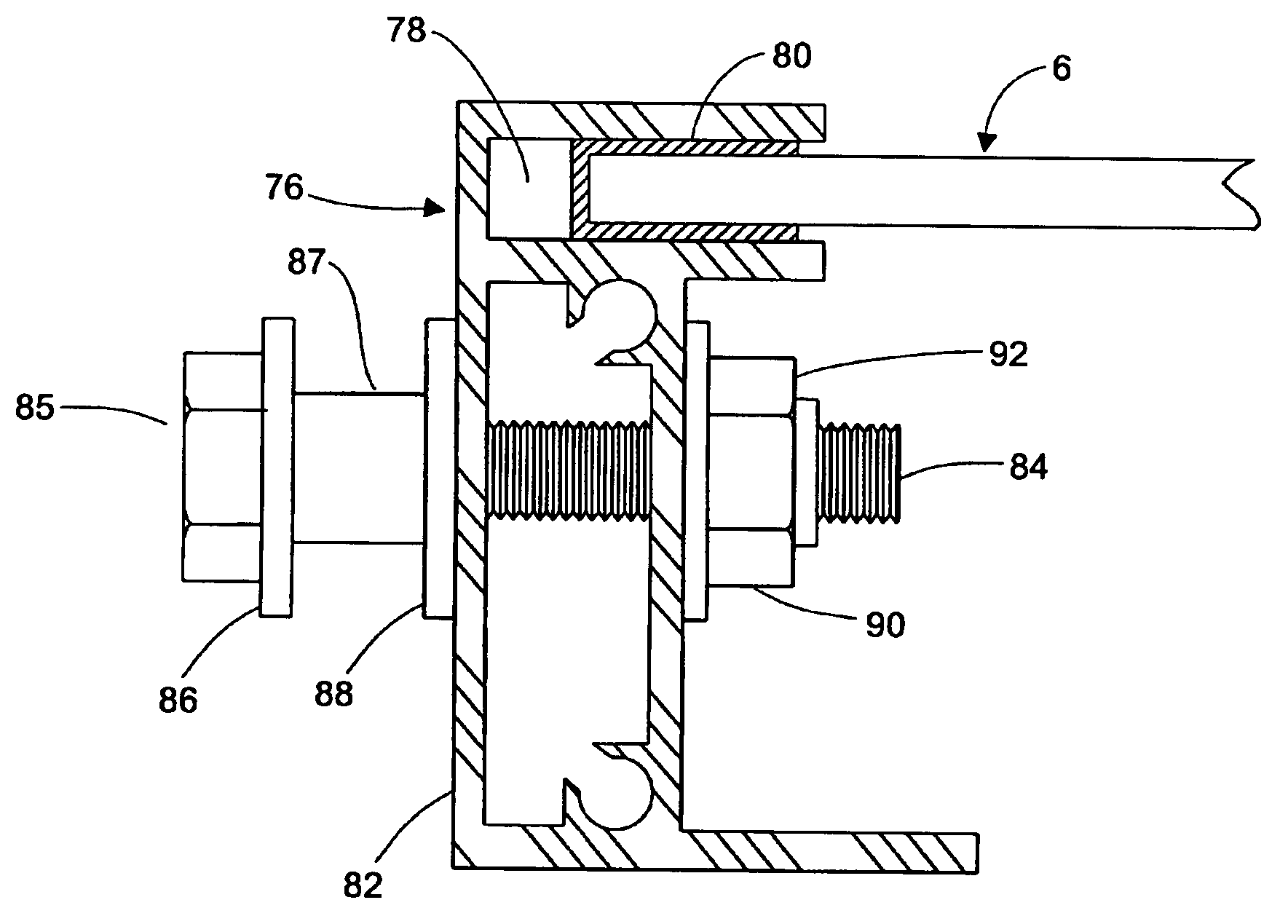
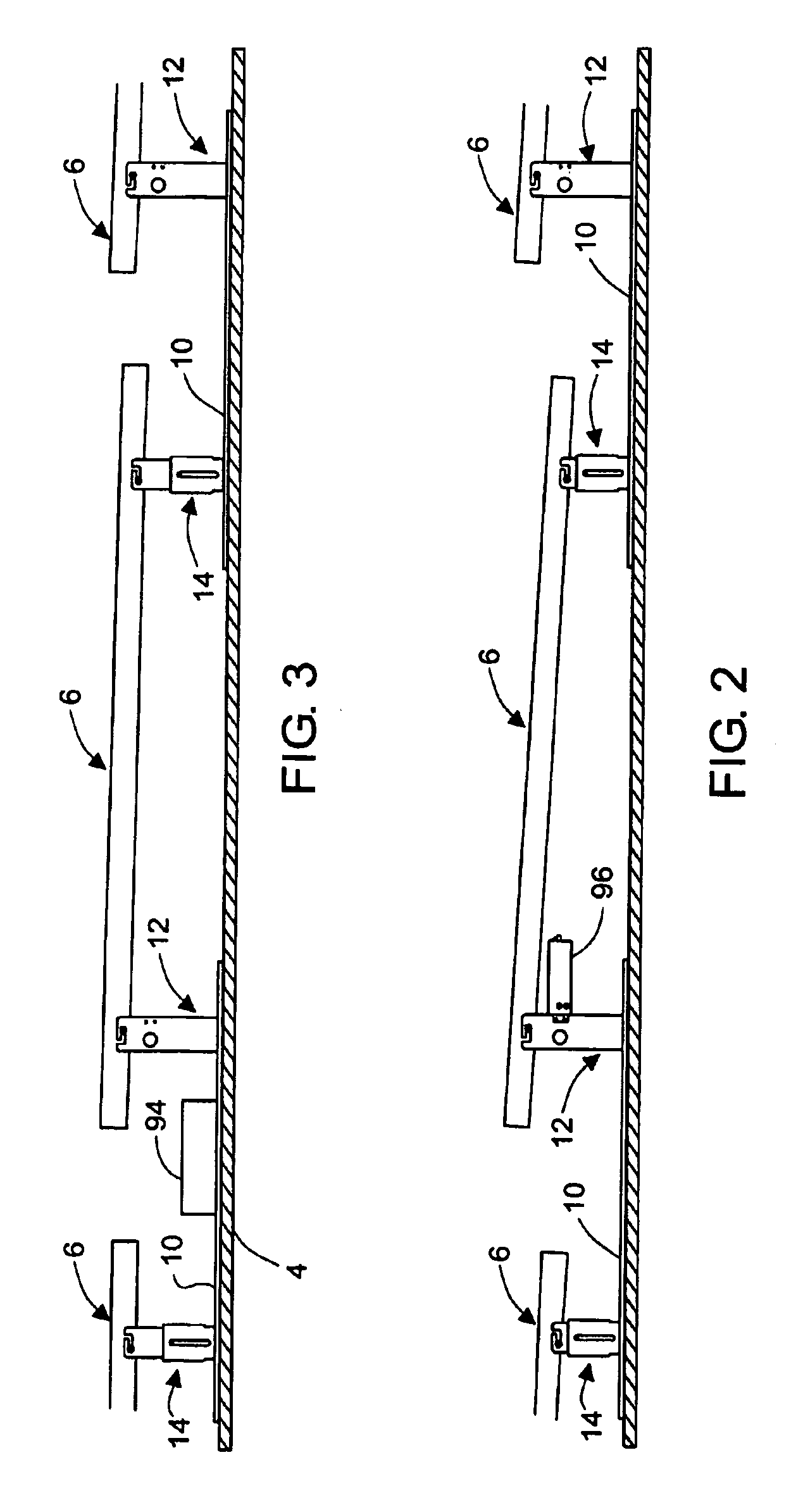
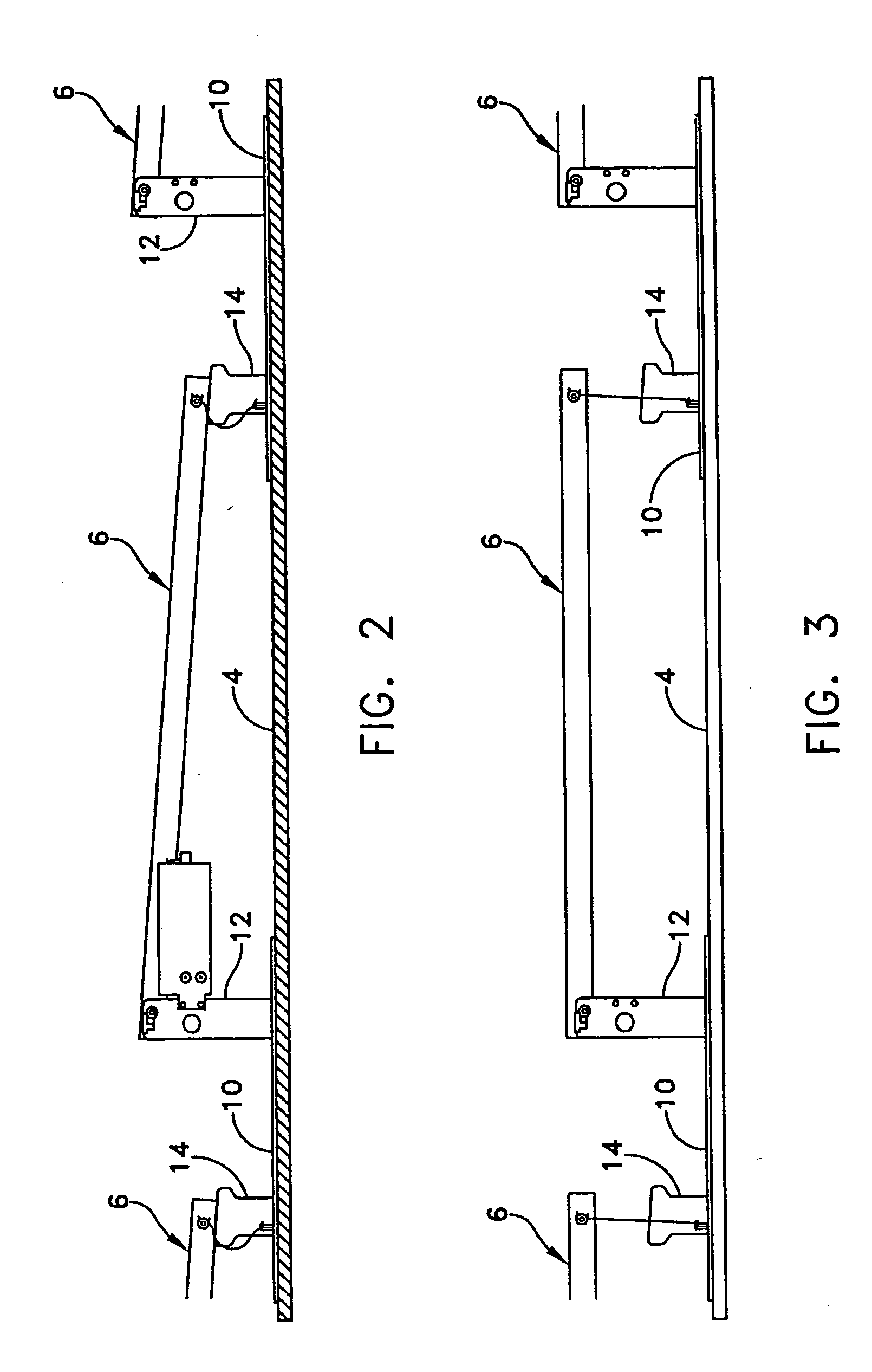
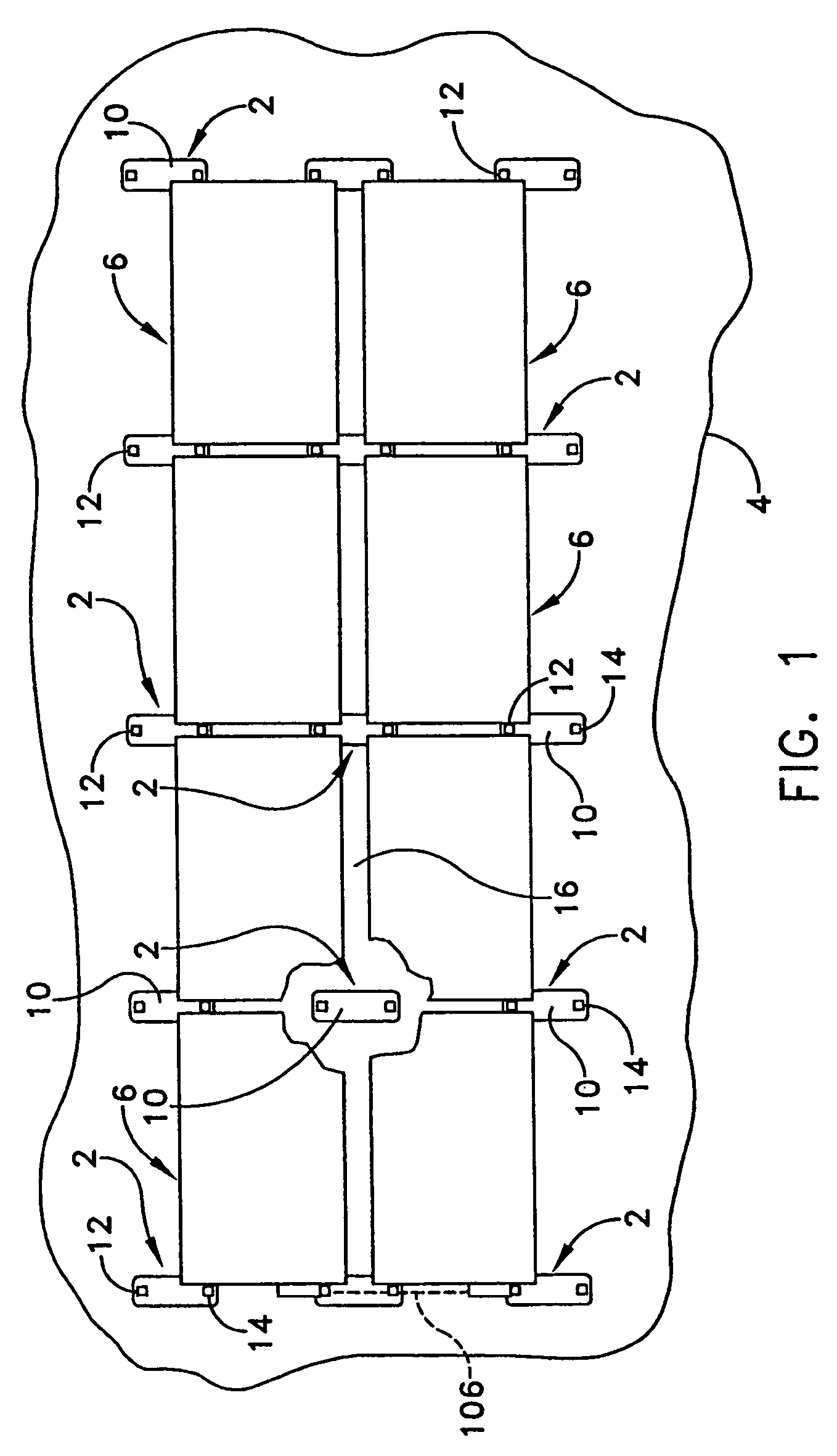
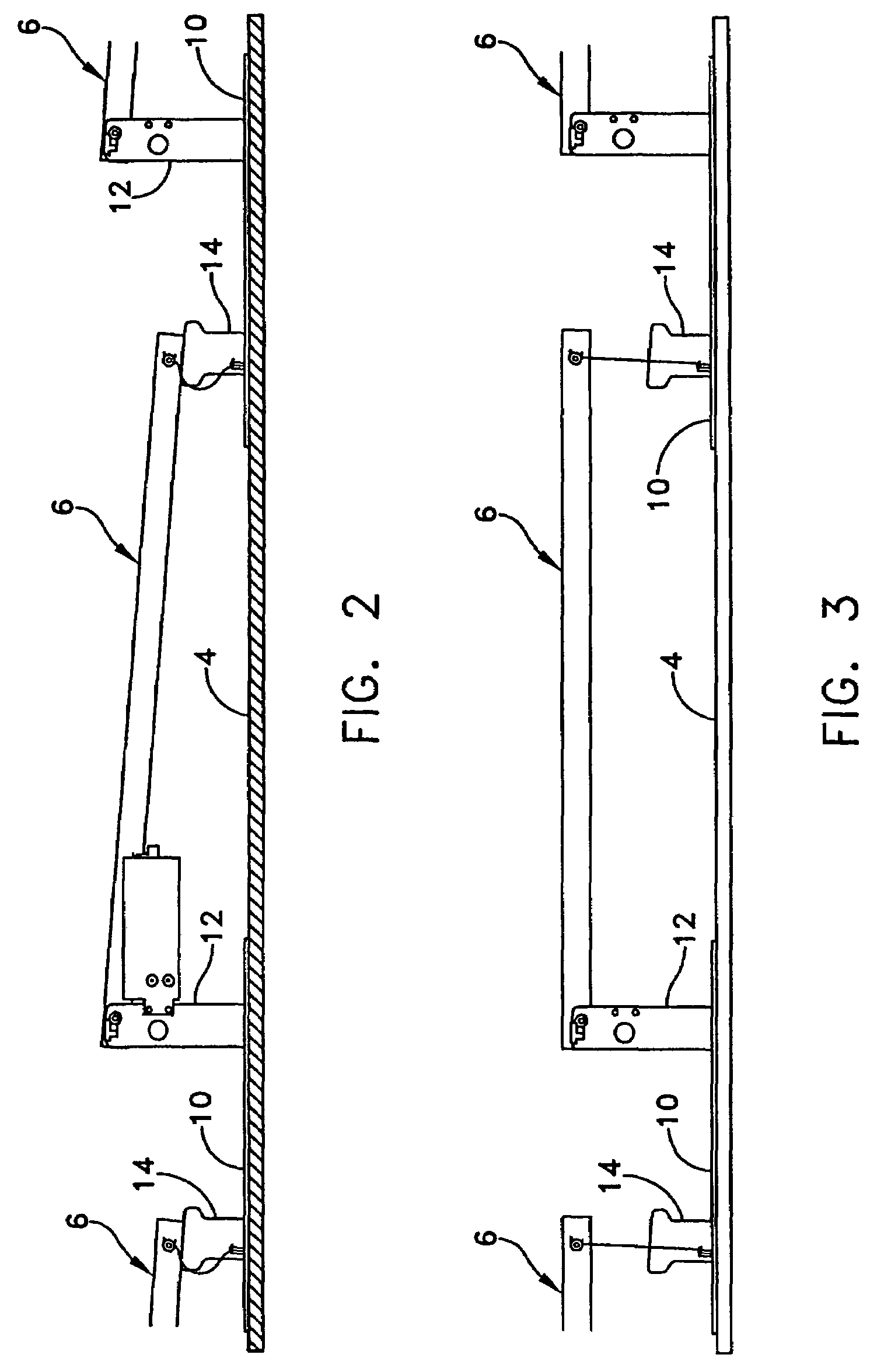
Rectangular PV modules (6) are mounted on a building roof (4) by mounting stands that are distributed in rows and columns. Each stand comprises a base plate (10) that rests on the building roof (4) and first and second brackets (12, 14) of different height attached to opposite ends of the base plate (10). Each bracket (12, 14) has dual members for supporting two different PV modules (6), and each PV module (6) has a mounting pin (84) adjacent to each of its four corners. Each module (6) is supported by attachment of two of its mounting pins (84) to different first brackets (12), whereby the modules (6) and their supporting stands are able to resist uplift forces resulting from high velocity winds without the base plates (10) being physically attached to the supporting roof structure (4). Preferably the second brackets (14) have a telescoping construction that permits their effective height to vary from less than to substantially the same as that of the first brackets (12).
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
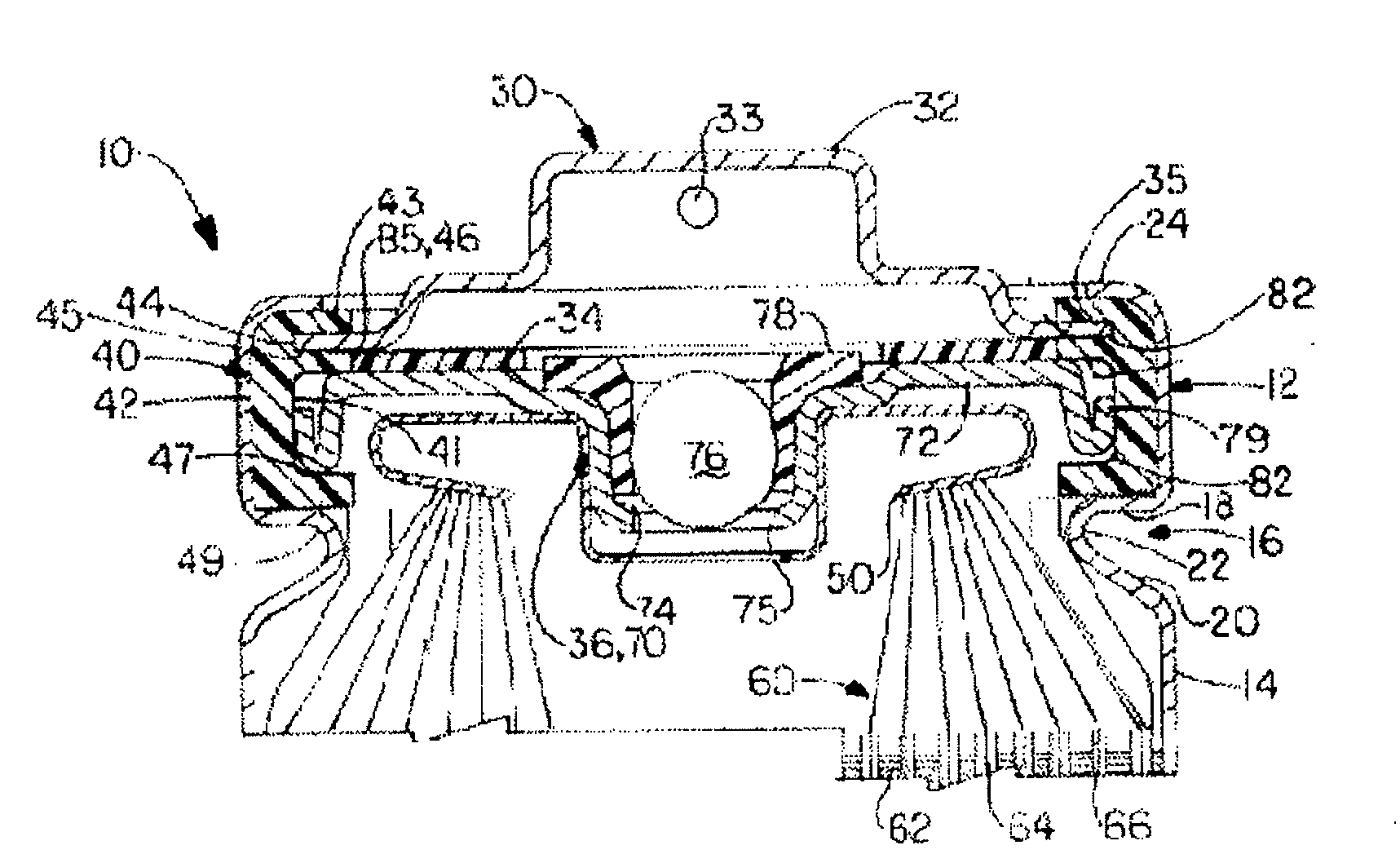
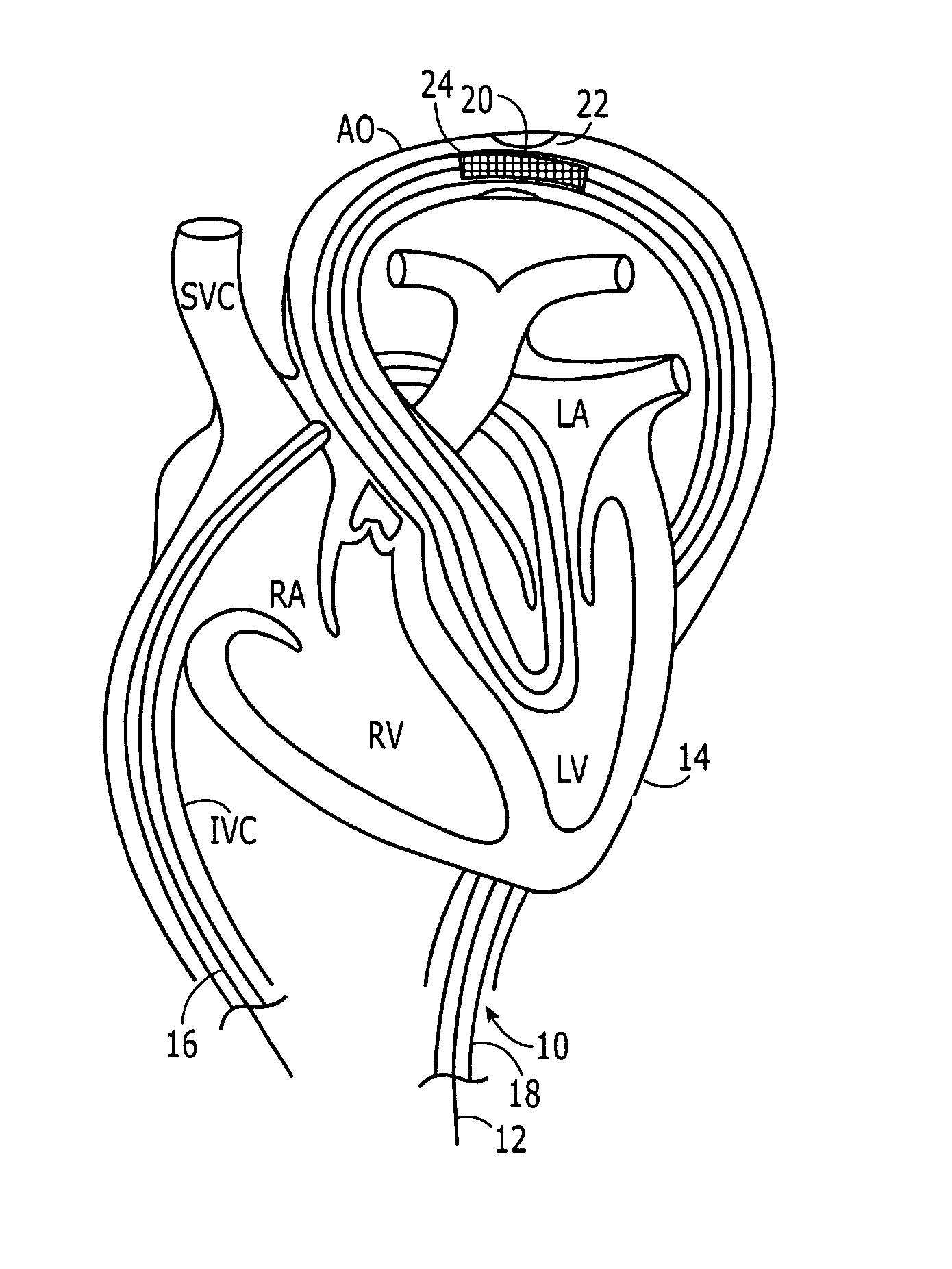
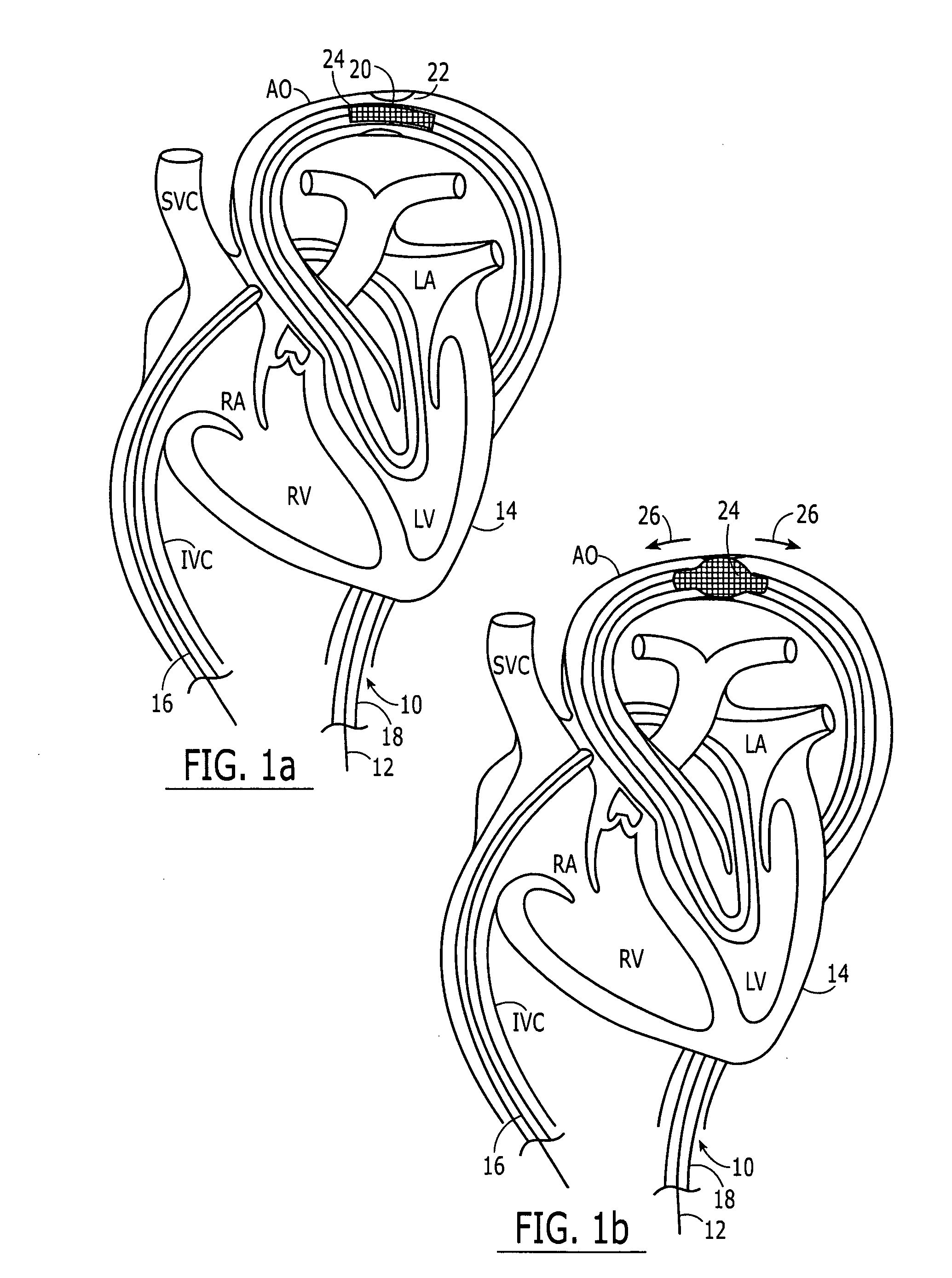
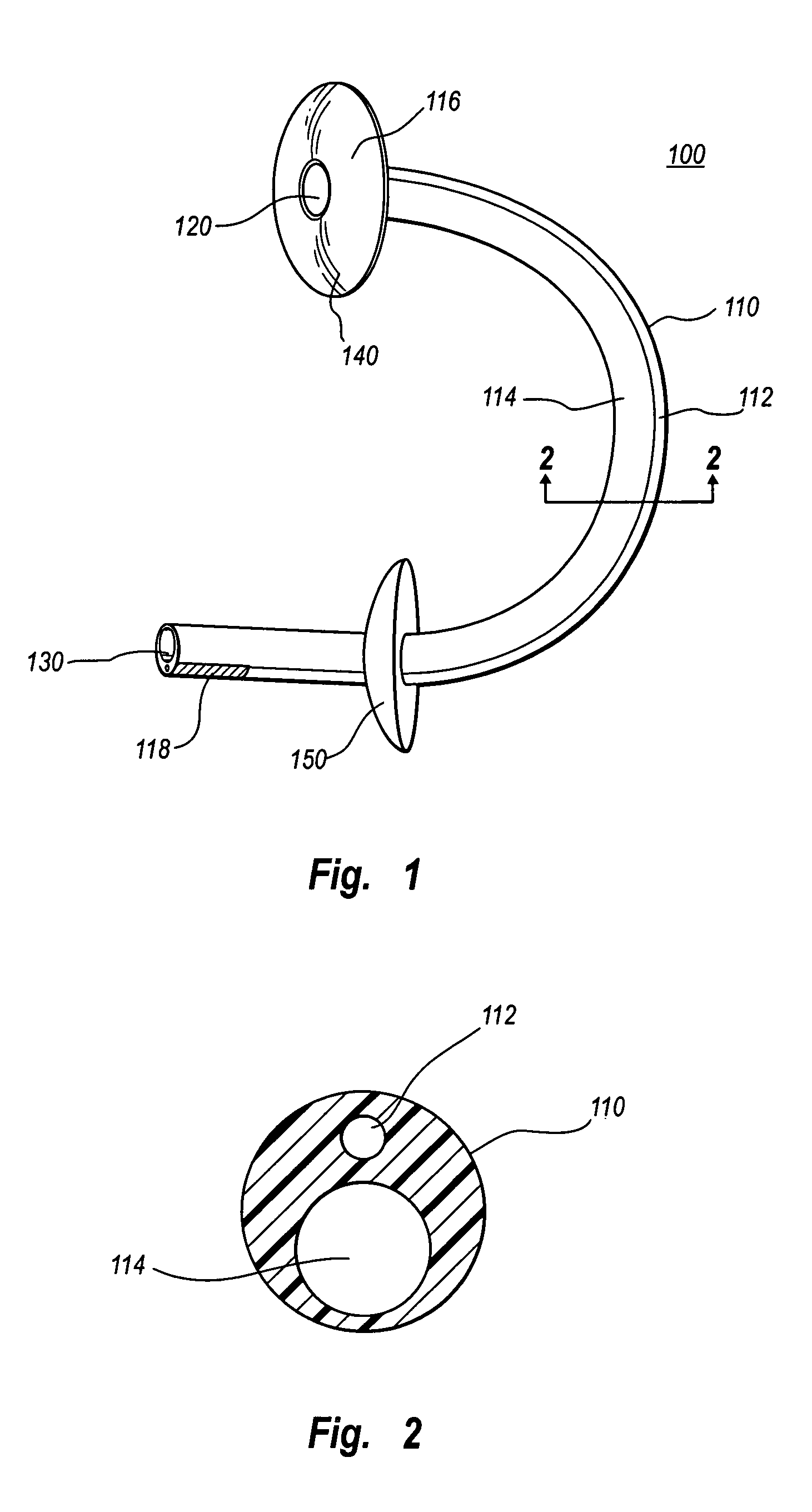
Separable sheath and method for insertion of a medical device into a bodily vessel using a separable sheath
A separable insertion sheath is for inserting a medical device into a patient. The insertion sheath includes releasably connectable ends. A medical device loaded into the insertion sheath is deployed by using an elongate member connected to the insertion sheath to shift the proximal and distal sections away from each other to expose the medical device.
Owner:RUIZ CARLOS +1
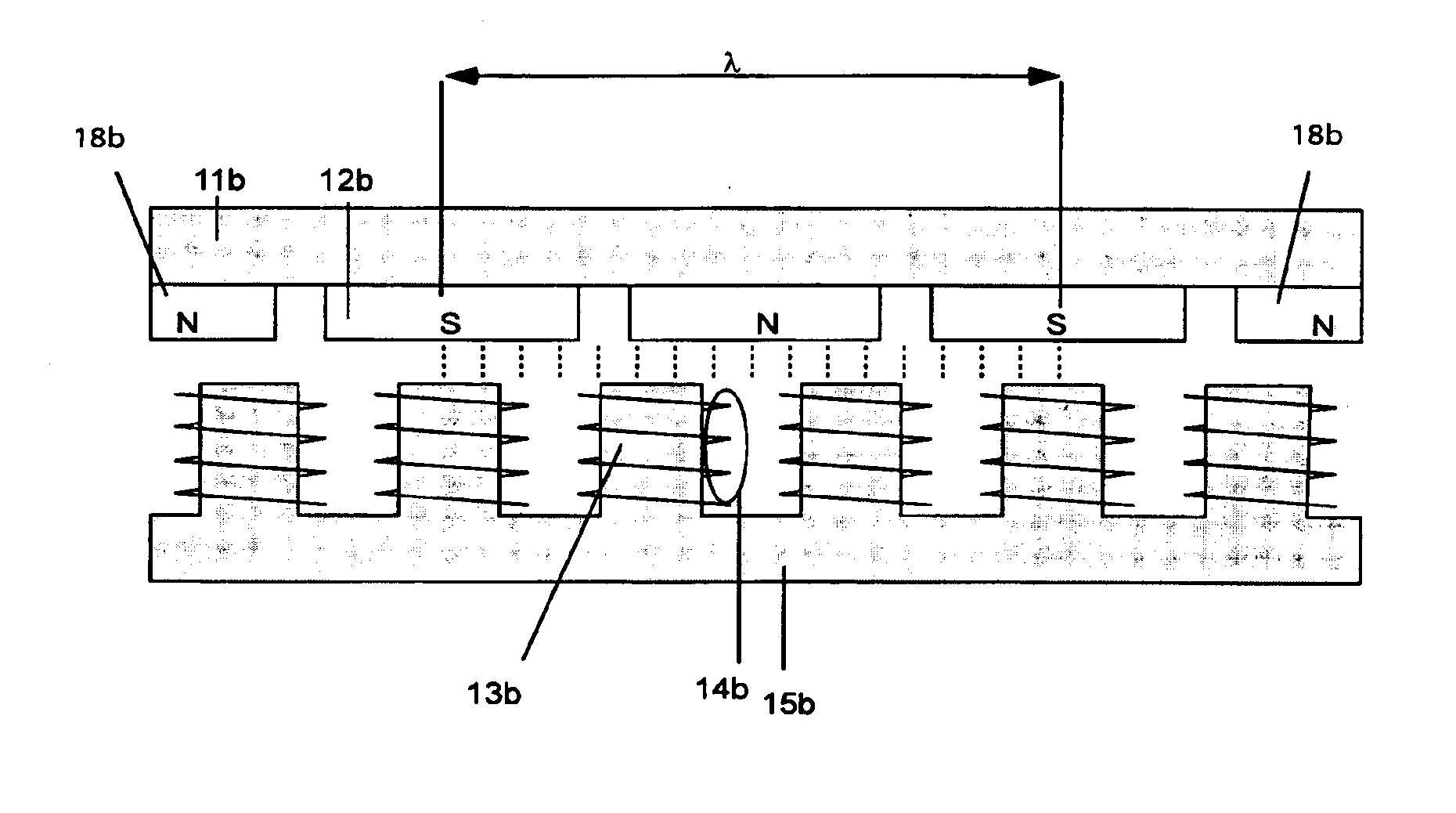
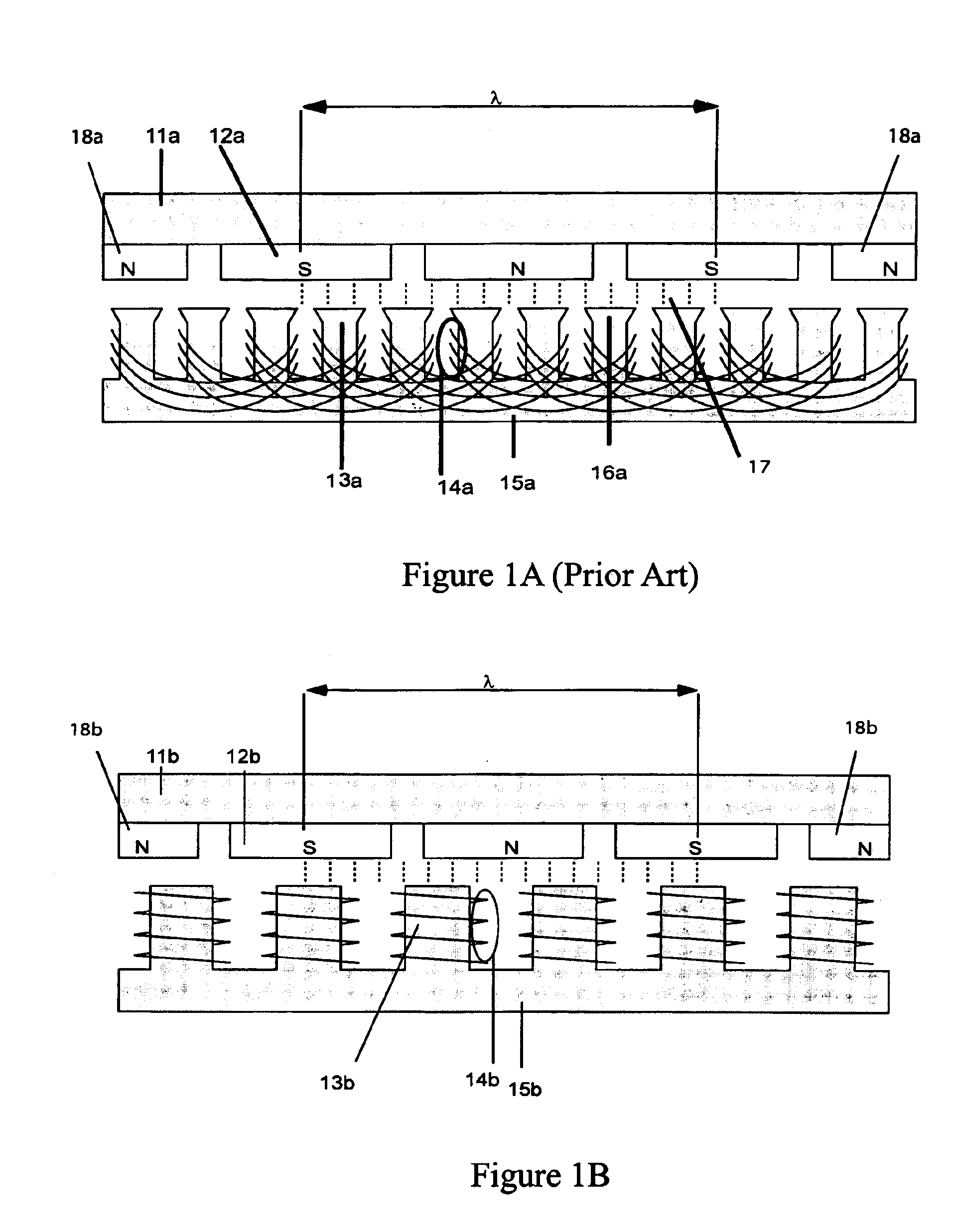
Synchronous machine design and manufacturing
InactiveUS6917136B2Increase performanceDecrease costSynchronous generatorsWindingsSynchronous motorReduced mass
Synchronous motors according to the invention operate at higher efficiency, with lower cost, reduced mass and reduced cogging. Magnet dimensions are selected that reduce cogging forces to a negligible amount even though there are fewer slots than normal. Optionally, it is possible to use non-overlapping windings with deeper and open slots. The approach is applicable to both rotary and linear motors and motors using either permanent magnets or electromagnets in the field structure. It is particularly relevant to linear or rotary motors that have a large air gap, and to small motors that must deliver a high ratio of thrust or torque to motor mass.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
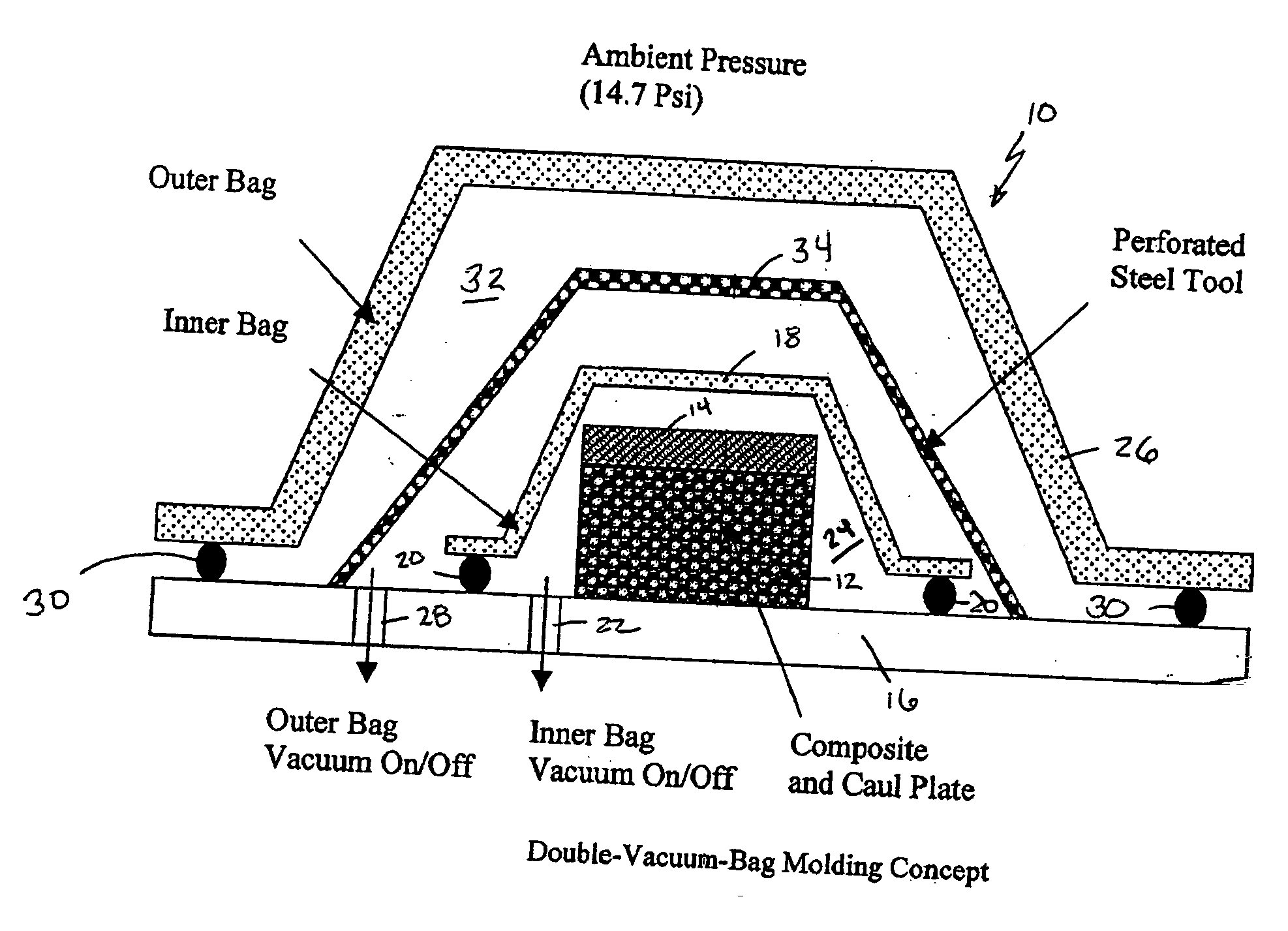
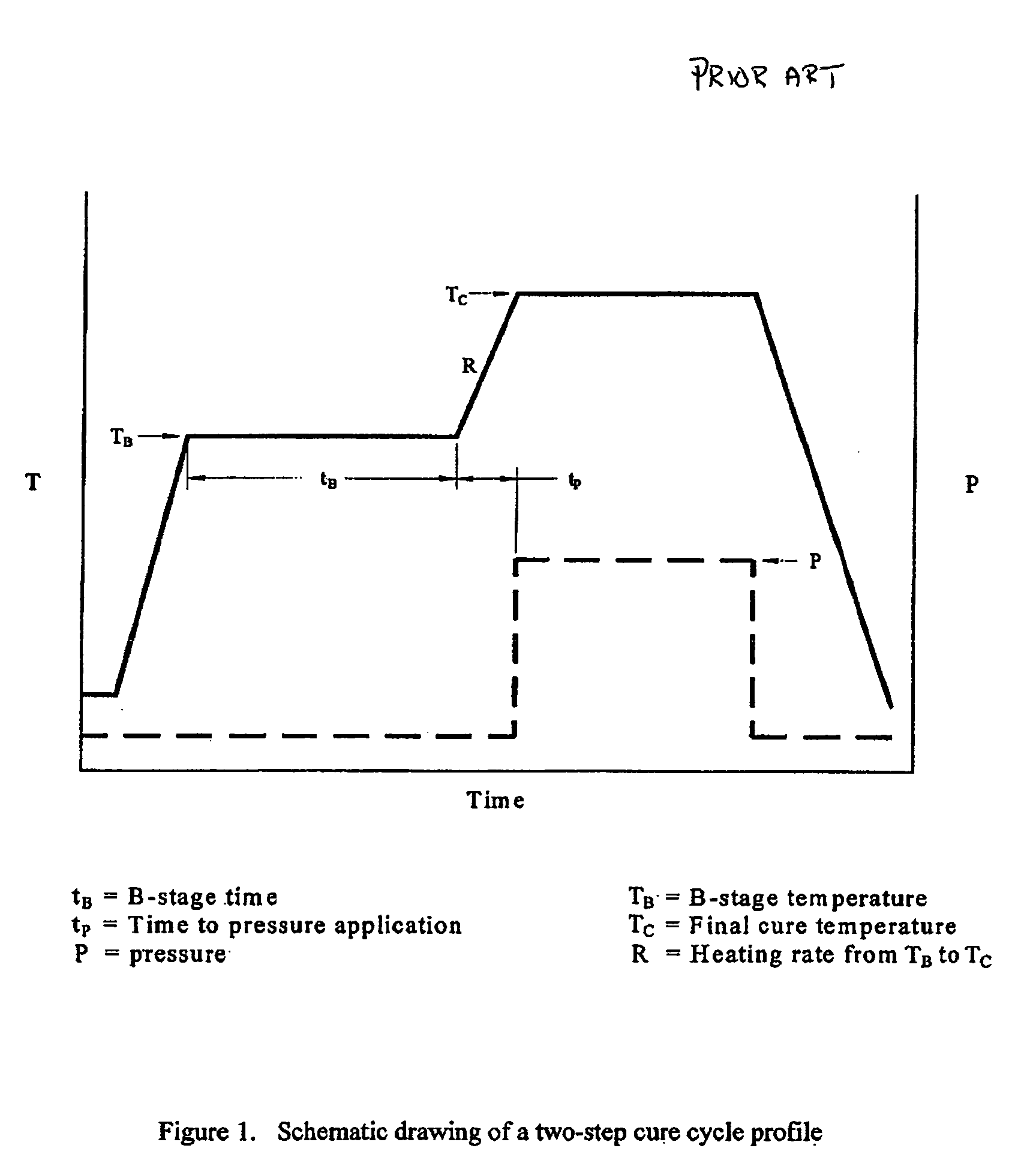
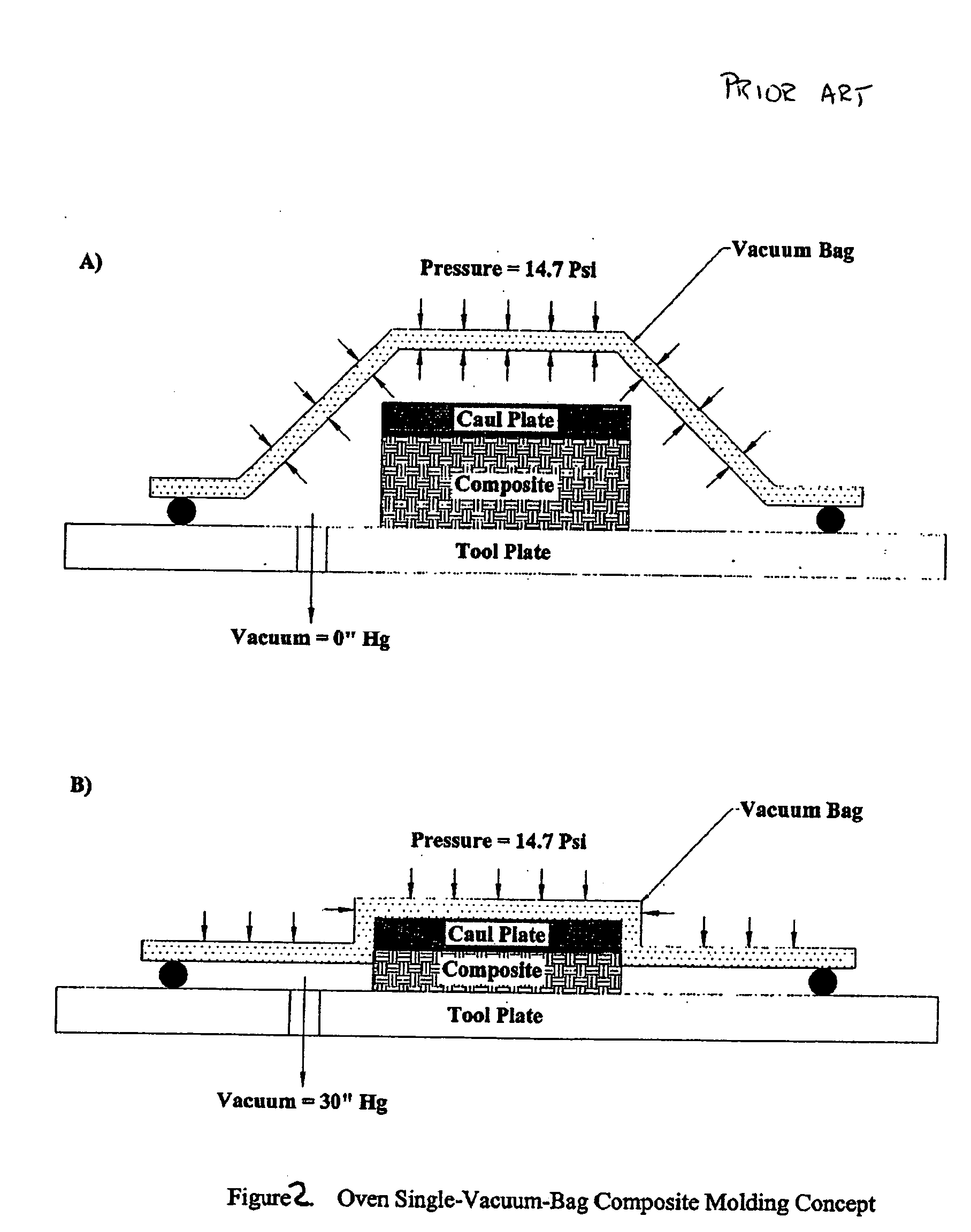
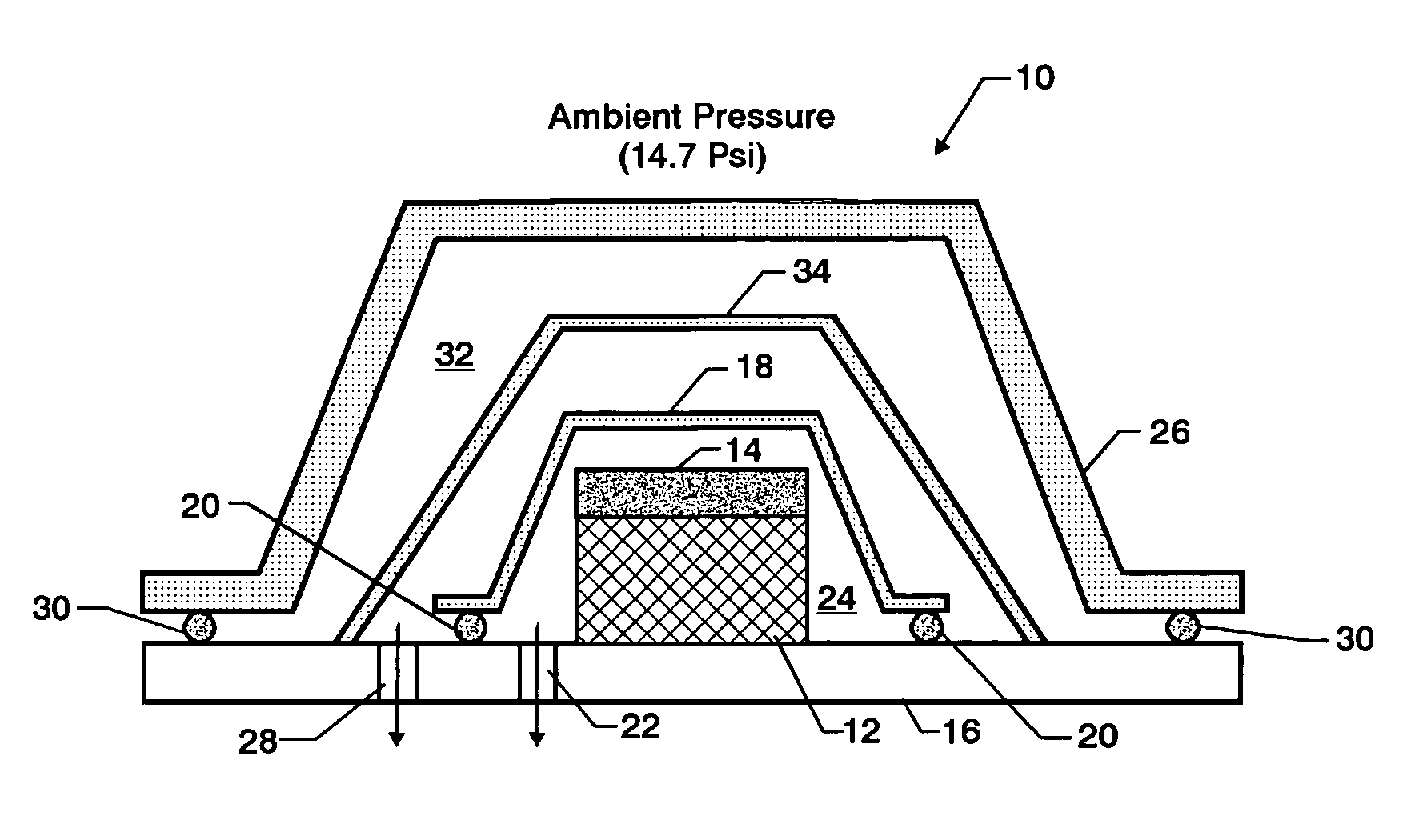
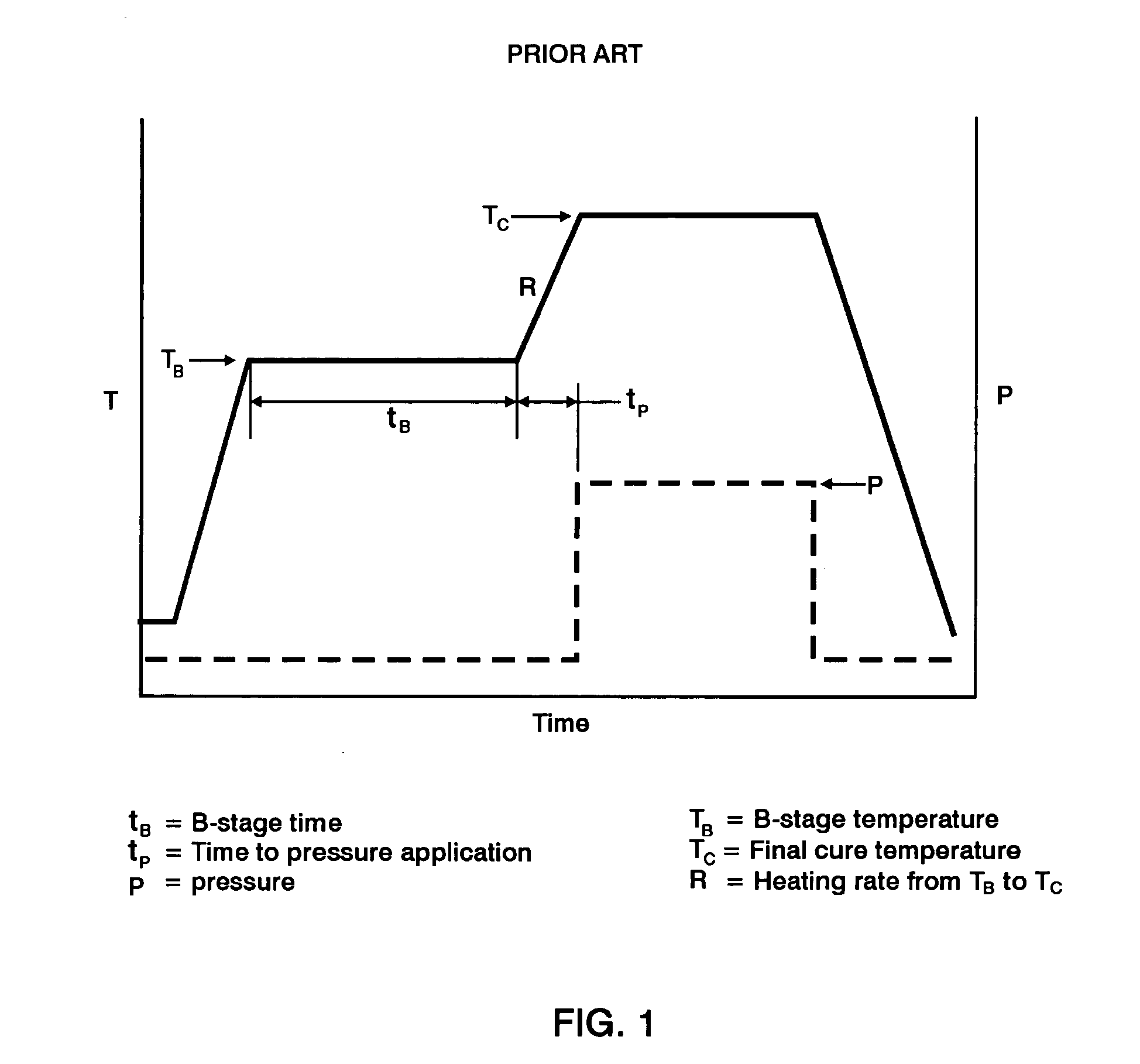
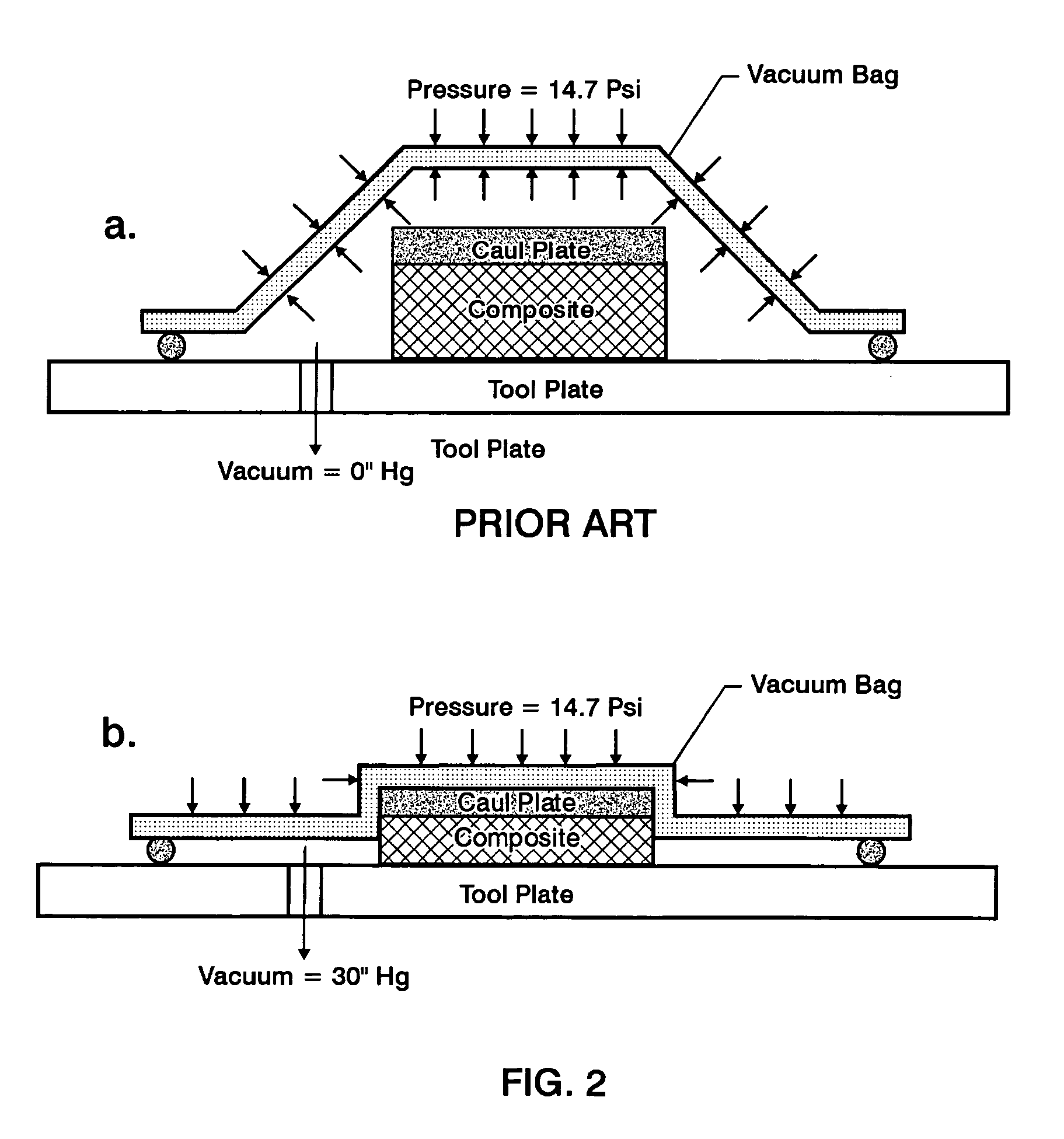
Double vacuum bag process for resin matrix composite manufacturing
InactiveUS20050253309A1Improve performanceImprove propertiesLaminationLamination apparatusRelative pressureResin matrix
A double vacuum bag molding assembly with improved void management and laminate net shape control which provides a double vacuum environment for use in fabricating composites from prepregs containing air and / or volatiles such as reactive resin matrix composites or composites from solvent containing prepregs with non-reactive resins matrices. By using two vacuum environments during the curing process, a vacuum can be drawn during a B-stage of a two-step cycle without placing the composite under significant relative pressure. During the final cure stage, a significant pressure can be applied by releasing the vacuum in one of the two environments. Inner and outer bags are useful for creating the two vacuum environments with a perforated tool intermediate the two. The composite is placed intermediate a tool plate and a caul plate in the first environment with the inner bag and tool plate defining the first environment. The second environment is characterized by the outer bag which is placed over the inner bag and the tool plate.
Owner:NASA
Apparatus for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
InactiveUS20060053706A1Reduce and eliminate module-distortingReduce and eliminate and module-destructing wind uplift forcePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Rectangular PV modules are mounted on a building roof by mounting stands that are distributed in rows and columns. Each stand comprises a base plate that rests on the building roof and first and second brackets of different height attached to opposite ends of the base plate. Each bracket comprises dual module-supporting members for supporting two different PV modules, and each PV module has a mounting stud adjacent to each of its four corners. At one end each module is supported by pivotal attachment of two of its mounting studs to module-supporting members of different first brackets. At its other end each module rests on module-supporting members of two different second brackets, whereby the modules assume a predetermined angle of tilt relative to the roof. Two tethers connect the other two mounting studs to the two different second brackets on which the module rests. The tethers allow the modules to pivot up away from the module-supporting members on which they rest to a substantially horizontal position in response to wind uplift forces, thereby enabling the PV modules and their supporting stands to withstand high velocity winds without the base plates being physically attached to the supporting roof structure.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Wellbore plug and method
InactiveUS20130008671A1Remove tensionReduce tensionFluid removalSealing/packingEngineeringMechanical engineering
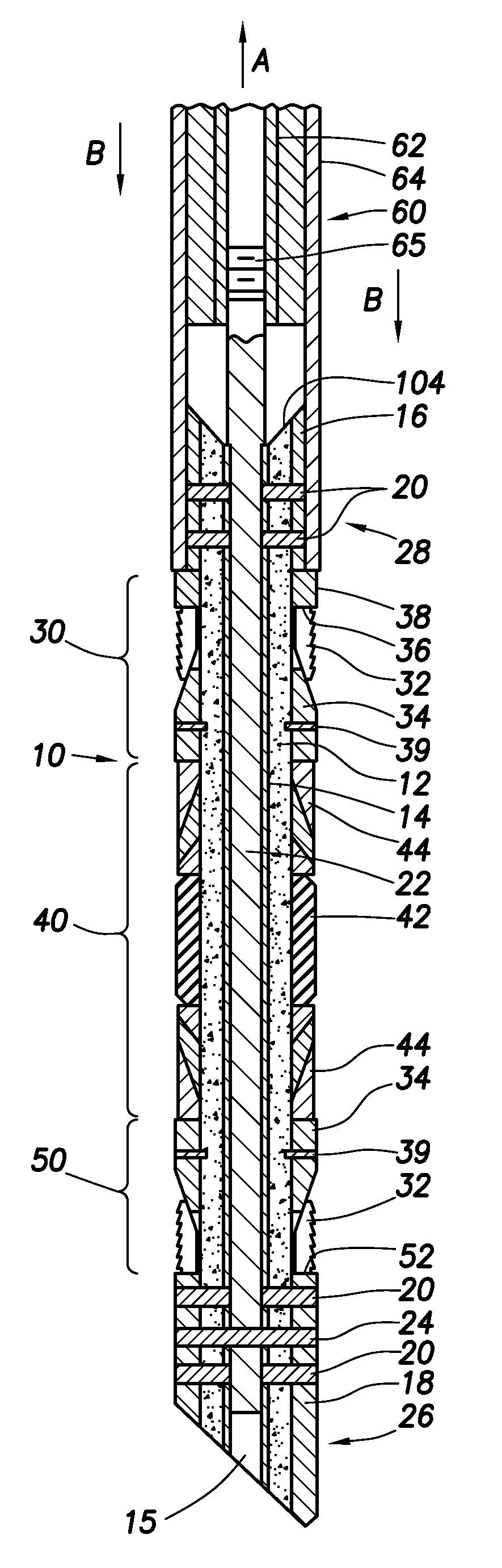
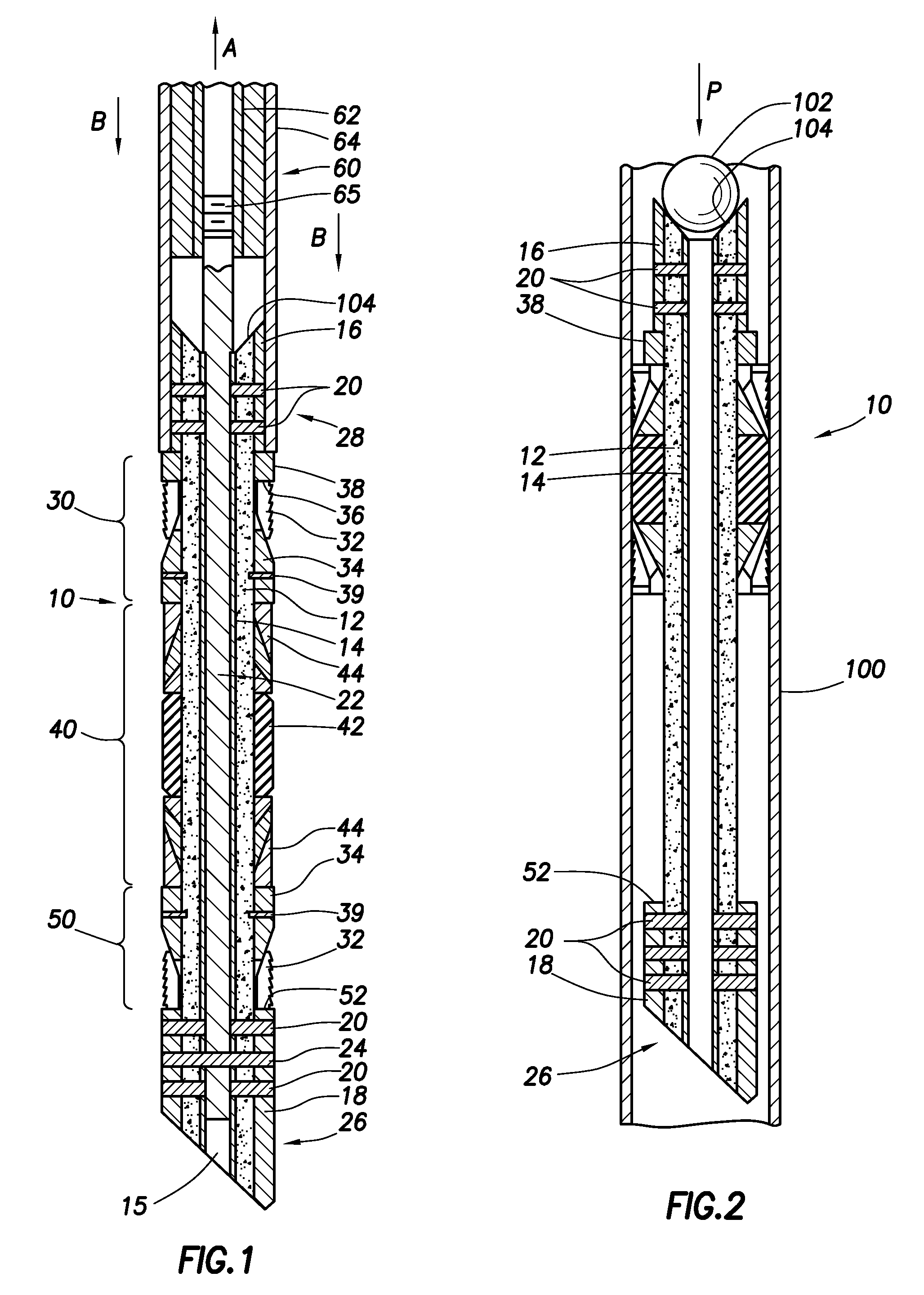
Disclosed is a wellbore plug having a design that allows the mandrel of the plug to be made of concrete or other easy-to-drill materials. Disclosed is a wellbore plug assembly with slip and packing assemblies configured to hold the plug in place during setting and use without tensioning the mandrel, thereby allowing the mandrel to be made from easily drillable material, such as concrete.
Owner:BOOTH JOHN F
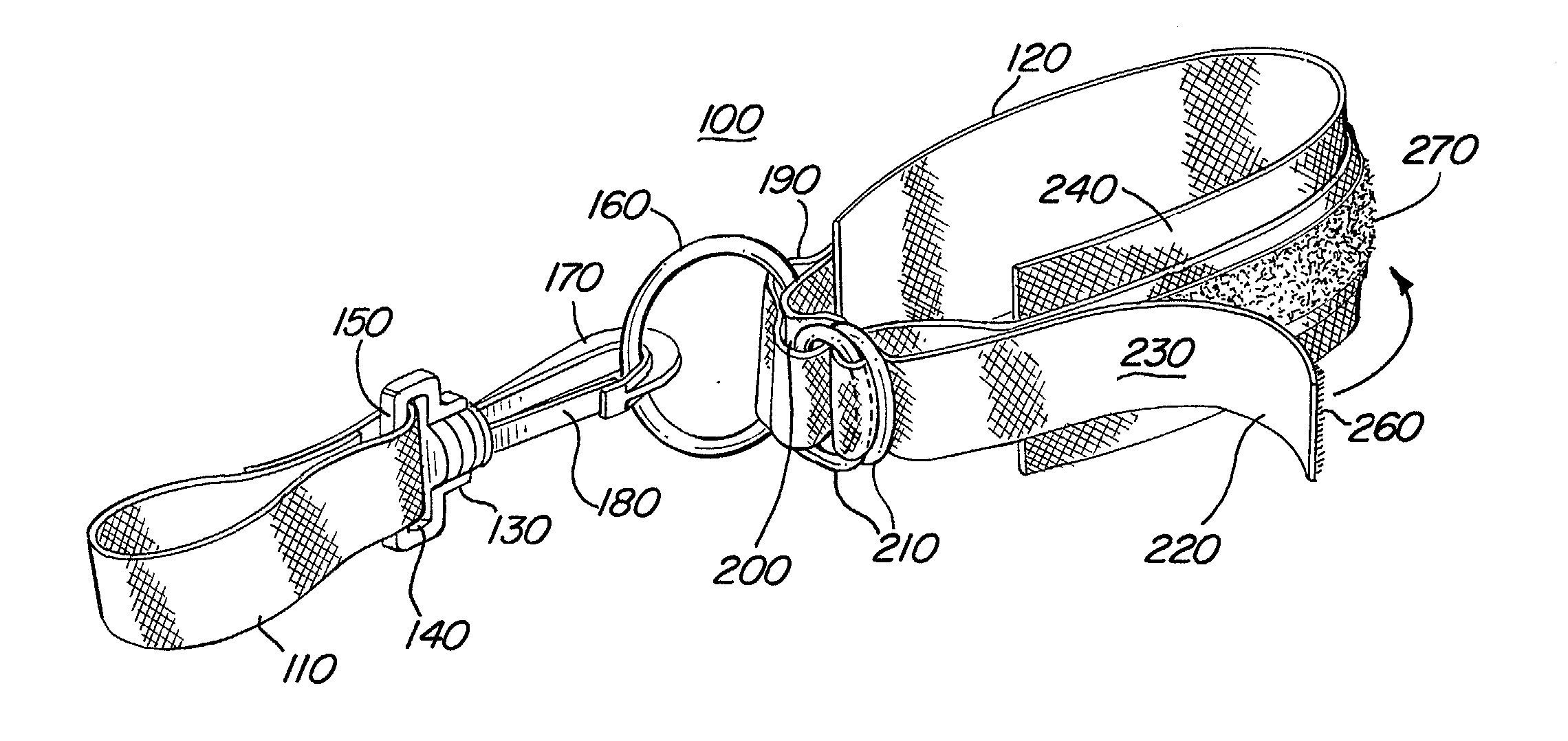
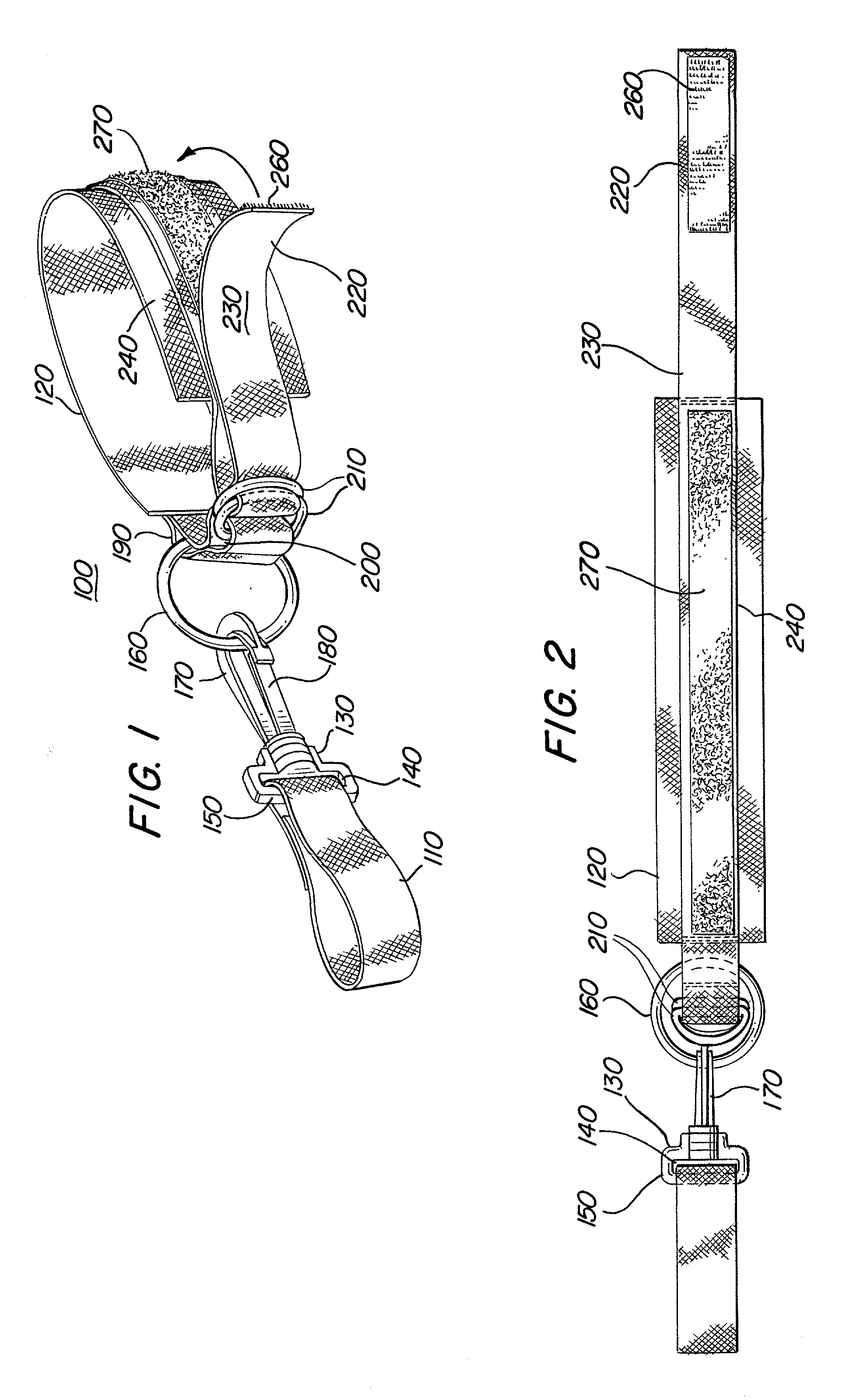
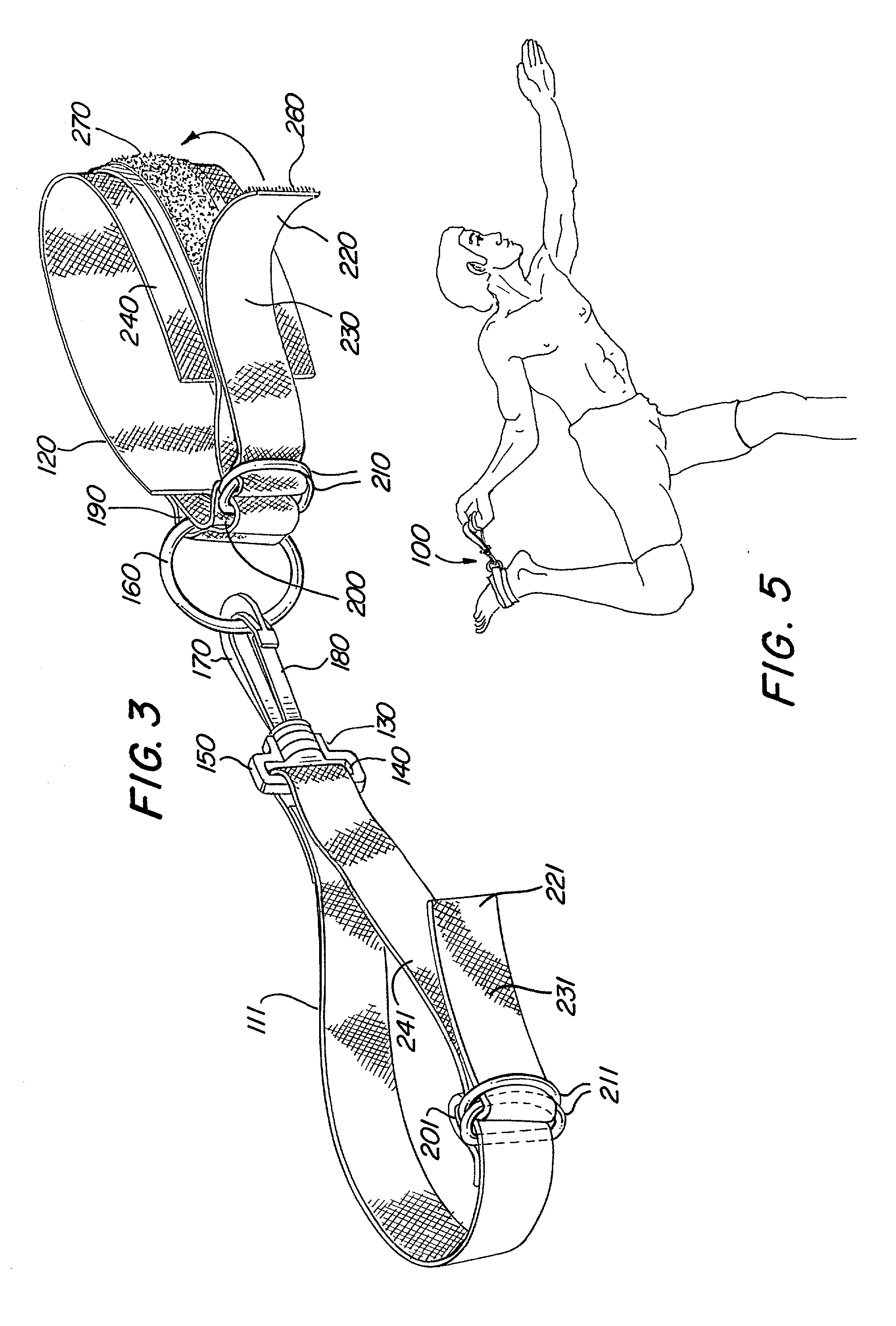
Swiveling exercise strap for stretching
An exercise device is disclosed for enabling various stretching exercises comprising an adjustable loop connected to a handle element by a swivel connector. The adjustable loop can be placed about a foot, ankle, or other body part, and the handle grasped in one hand. The swivel connector allows a user to stretch in multiple positions and postures without readjusting the exercise device. In a preferred embodiment, the handle comprises either a handle loop sized to accommodate a user's finger, fingers, or hand, or a series of loops to allow the user to gradually increase the tension in the stretch by grasping successive loops in the series. Alternatively, the handle can comprise a hand support member that allows the user to easily and firmly grasp the handle and apply a steady tension. In addition, the handle can comprise an adjustable loop to facilitate various lengths of stretching and levels of difficulty.
Owner:SHEN CHARLES
Blowout preventer and ram actuator
A blowout preventer with a main body; a base releasably connected to the main body, the base having a base space therein, the base having a ram shaft opening; a primary piston movably disposed within the base space; a ram shaft to which the primary piston is connected, the ram shaft including a ram end and a piston end; a ram connected to the ram end of the ram shaft; a housing connected to the base, the housing having a housing space therein, the housing including a middle member with a member opening; a booster piston movably disposed within the housing space and having a booster shaft projecting therefrom and a booster shaft space therein; the shaft including a push portion selectively movable to abut the ram shaft to prevent movement of the ram shaft and to transfer force of the booster piston to the primary piston; and power fluid apparatus for the primary piston and the booster piston.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Partially patterned lead frames and methods of making and using the same in semiconductor packaging
InactiveUS20050006737A1Avoid layeringEliminate forceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingBonding process
A method of making a lead frame and a partially patterned lead frame package with near-chip scale packaging (CSP) lead-counts is disclosed, wherein the method lends itself to better automation of the manufacturing line as well as to improving the quality and reliability of the packages produced therefrom. This is accomplished by performing a major portion of the manufacturing process steps with a partially patterned strip of metal formed into a web-like lead frame on one side, in contrast with the conventional fully etched stencil-like lead frames, so that the web-like lead frame, which is solid and flat on the other side is also rigid mechanically and robust thermally to perform without distortion or deformation during the chip-attach and wire bond processes. The bottom side of the metal lead frame is patterned to isolate the chip-pad and the wire bond contacts only after the front side, including the chip and wires, is hermetically sealed with an encapsulant. The resultant package being electrically isolated enables strip testing and reliable singulation without having to cut into any additional metal. The use of the instant partially patterned lead frame in making ELP, ELPF and ELGA-type CSPs is also disclosed.
Owner:UNISEM M BERHAD
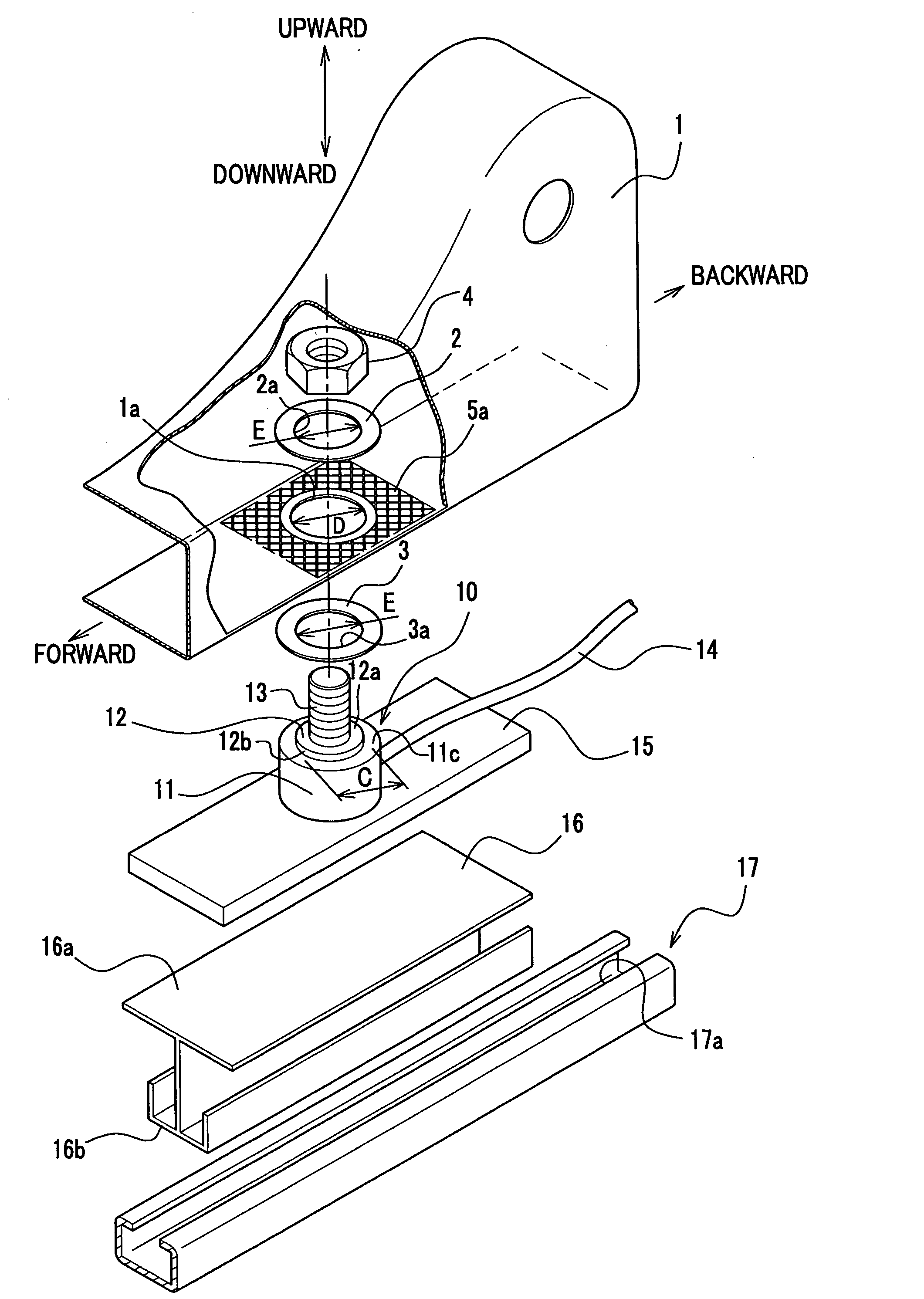
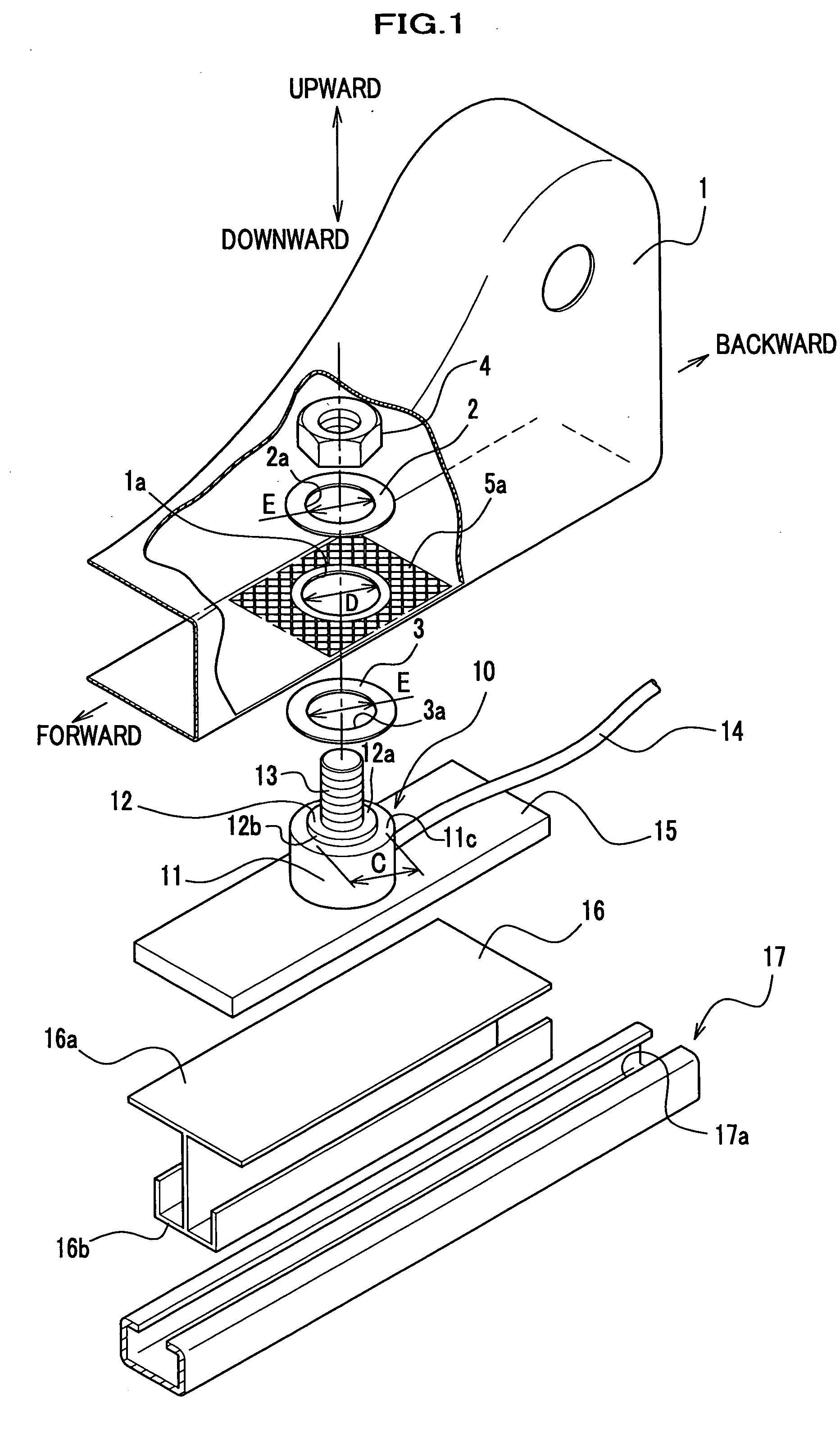
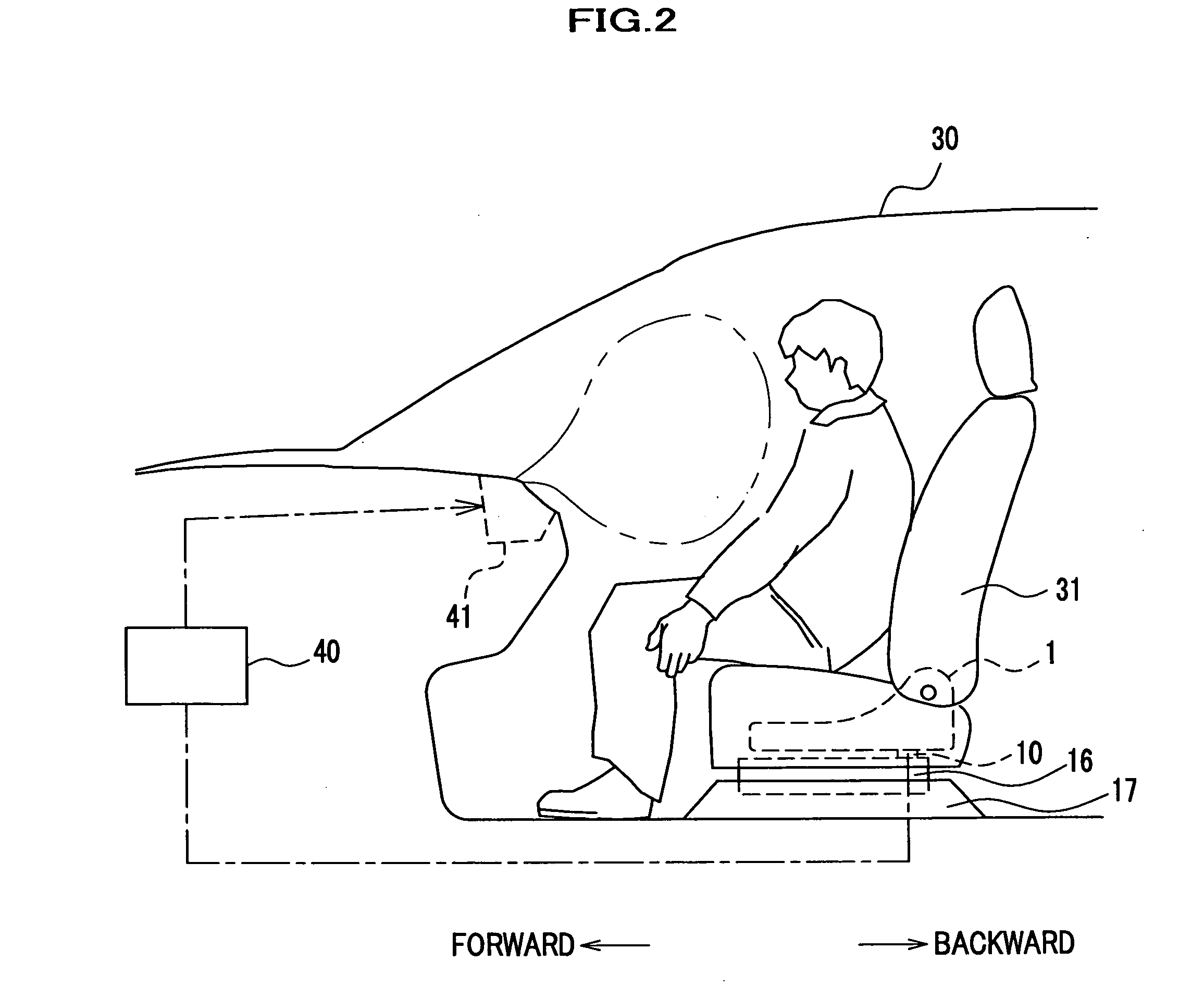
Force sensor assembly
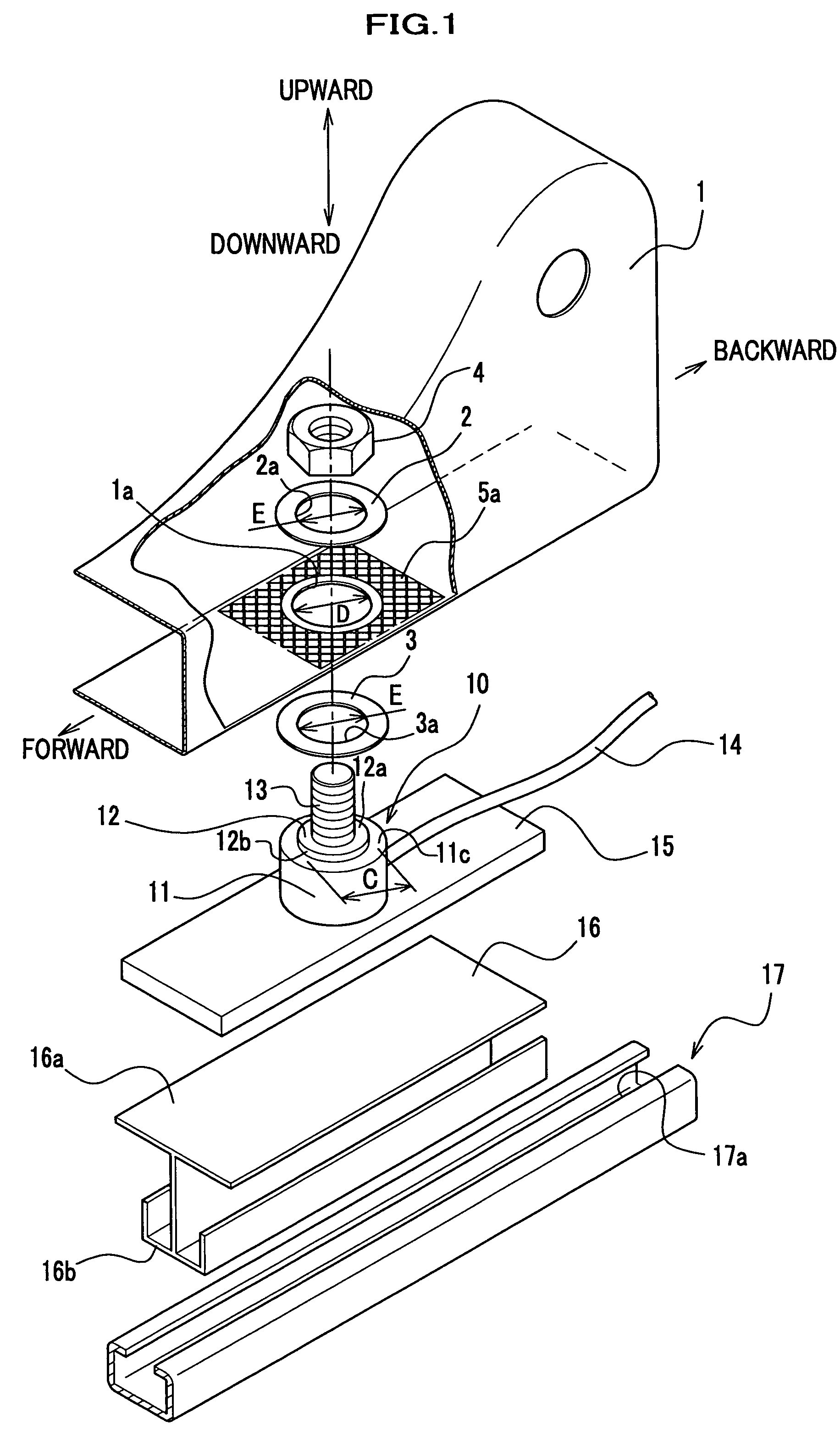
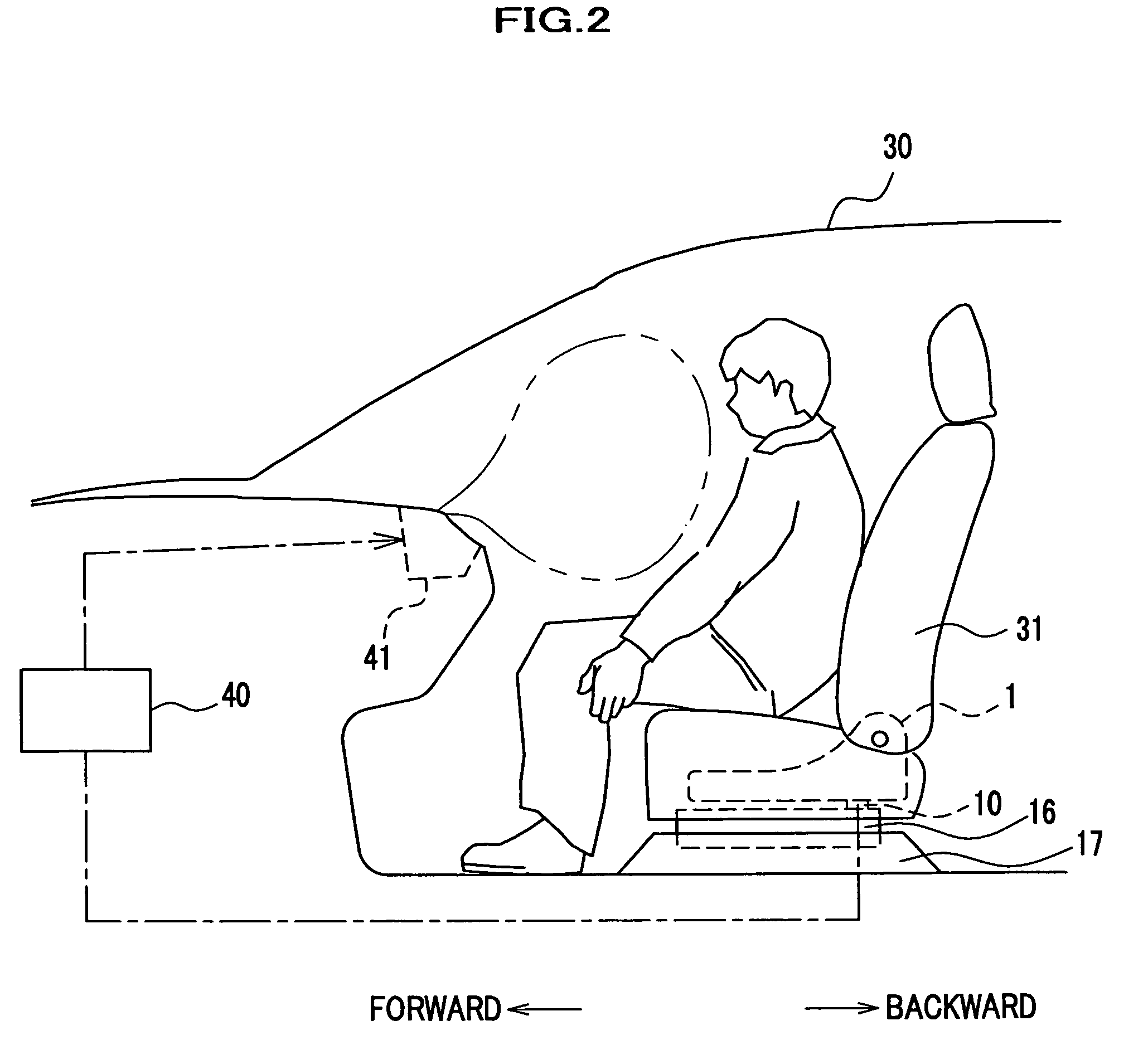
InactiveUS7210358B2Stable controlNot be excessively tightened onto the threaded portionVehicle seatsLoad modified fastenersScrew threadForce sensor
A force sensor assembly includes a force sensor, a first support member, a threaded portion, an opening made in the first support member, a nut, a restricting member and a spacer. The nut is screwed onto the threaded portion which is inserted through the opening. The restricting member is provided between the force sensor and the nut. The spacer, which is provided between the force sensor and the nut, is deformable in a direction of its thickness. The shape of the spacer is adapted to avoid interference with the restricting member. Before the nut is tightened onto the threaded portion, a summation of thickness for the first support member and the spacer is adapted to be not less than a height of the restricting member. The nut is tightened up with a predetermined fastening torque until the spacer deforms so that the nut strikes the restricting member.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
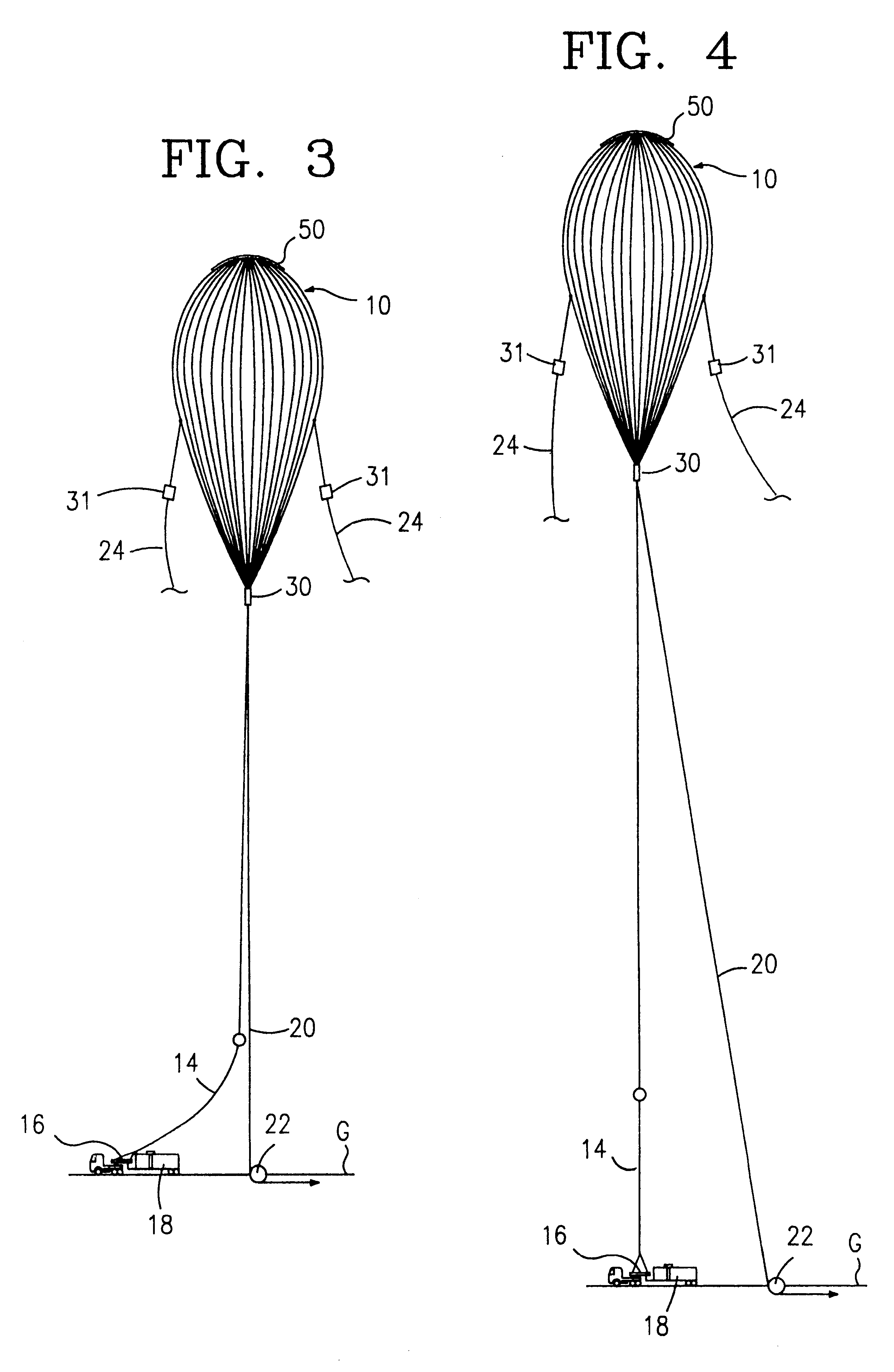
Release fitting for balloons
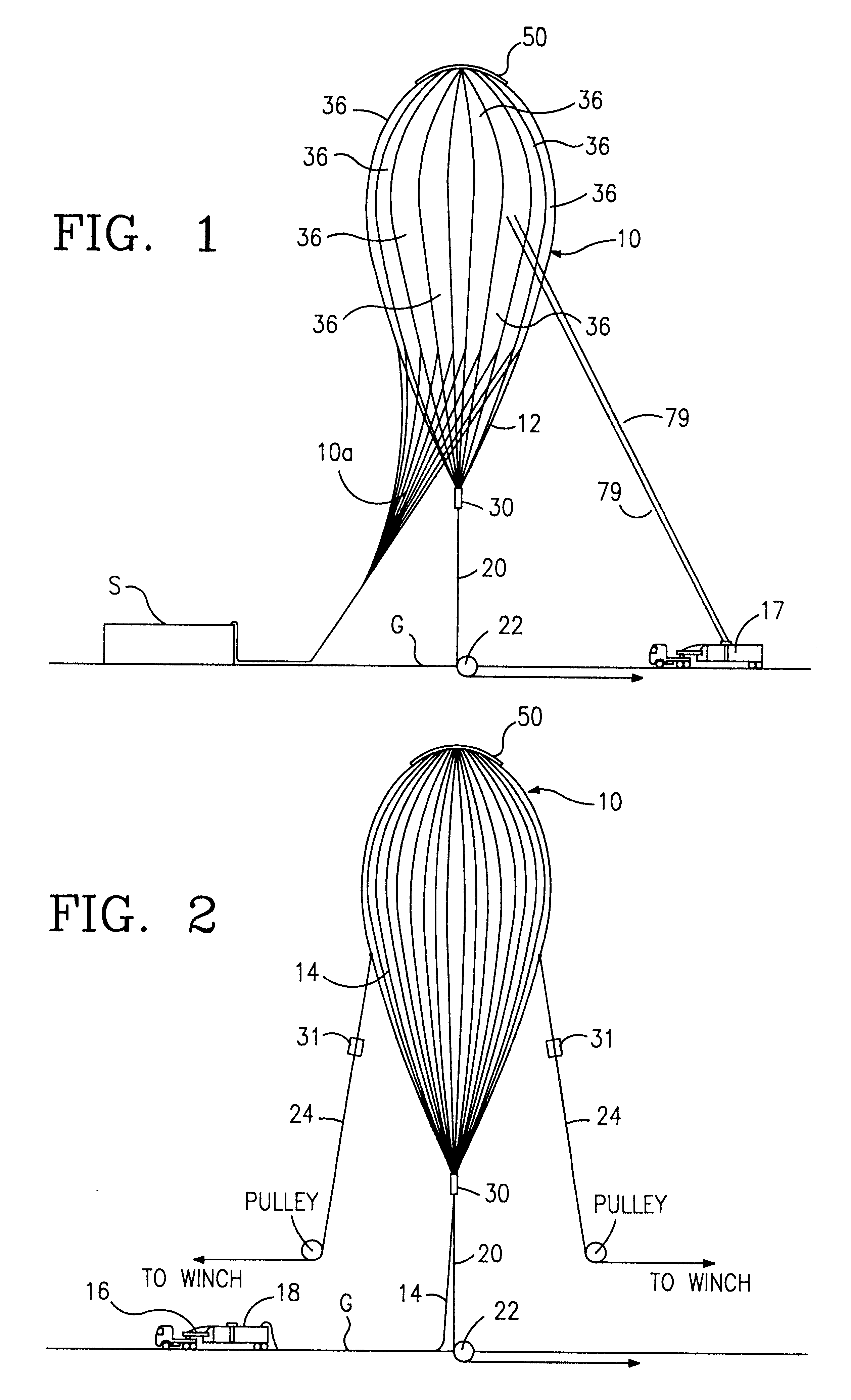
InactiveUS6234425B1SmallReduced and eliminated range safety costLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsBolt cutterEngineering
A release fitting for releasably holding at least one line to at least one item, the release fitting having a first body part, a second body part, and a third body part, the first and second body parts pivotably secured to the third body part, a bolt with a first bolt portion connected to a first portion of the first body part and a second bolt portion connected to a first portion of the second body part, at least one pin suitable for attaching thereto the at least one line, the first body part having a recess for releasably receiving an end of the pin, the bolt initially holding apart the first portion of the first body part and the first portion of the second body part to thereby maintain a second pin end in the recess, the third body part connected to the at least one item, bolt cutter apparatus for selectively cutting the bolt to release the at least one line from the pin.
Owner:WINZEN ENG
Force sensor assembly
InactiveUS20060010984A1Easily positionStable controlVehicle seatsLoad modified fastenersEngineeringClassical mechanics
A force sensor assembly includes a force sensor, a first support member, a threaded portion, an opening made in the first support member, a nut, a restricting member and a spacer. The nut is screwed onto the threaded portion which is inserted through the opening. The restricting member is provided between the force sensor and the nut. The spacer, which is provided between the force sensor and the nut, is deformable in a direction of its thickness. The shape of the spacer is adapted to avoid interference with the restricting member. Before the nut is tightened onto the threaded portion, a summation of thickness for the first support member and the spacer is adapted to be not less than a height of the restricting member. The nut is tightened up with a predetermined fastening torque until the spacer deforms so that the nut strikes the restricting member.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Double vacuum bag process for resin matrix composite manufacturing
InactiveUS7186367B2Improve performanceImprove propertiesLaminationLamination apparatusRelative pressureResin matrix
A double vacuum bag molding assembly with improved void management and laminate net shape control which provides a double vacuum environment for use in fabricating composites from prepregs containing air and / or volatiles such as reactive resin matrix composites or composites from solvent containing prepregs with non-reactive resins matrices. By using two vacuum environments during the curing process, a vacuum can be drawn during a B-stage of a two-step cycle without placing the composite under significant relative pressure. During the final cure stage, a significant pressure can be applied by releasing the vacuum in one of the two environments. Inner and outer bags are useful for creating the two vacuum environments with a perforated tool intermediate the two. The composite is placed intermediate a tool plate and a caul plate in the first environment with the inner bag and tool plate defining the first environment. The second environment is characterized by the outer bag which is placed over the inner bag and the tool plate.
Owner:NASA
Apparatus for mounting photovoltaic power generating systems on buildings
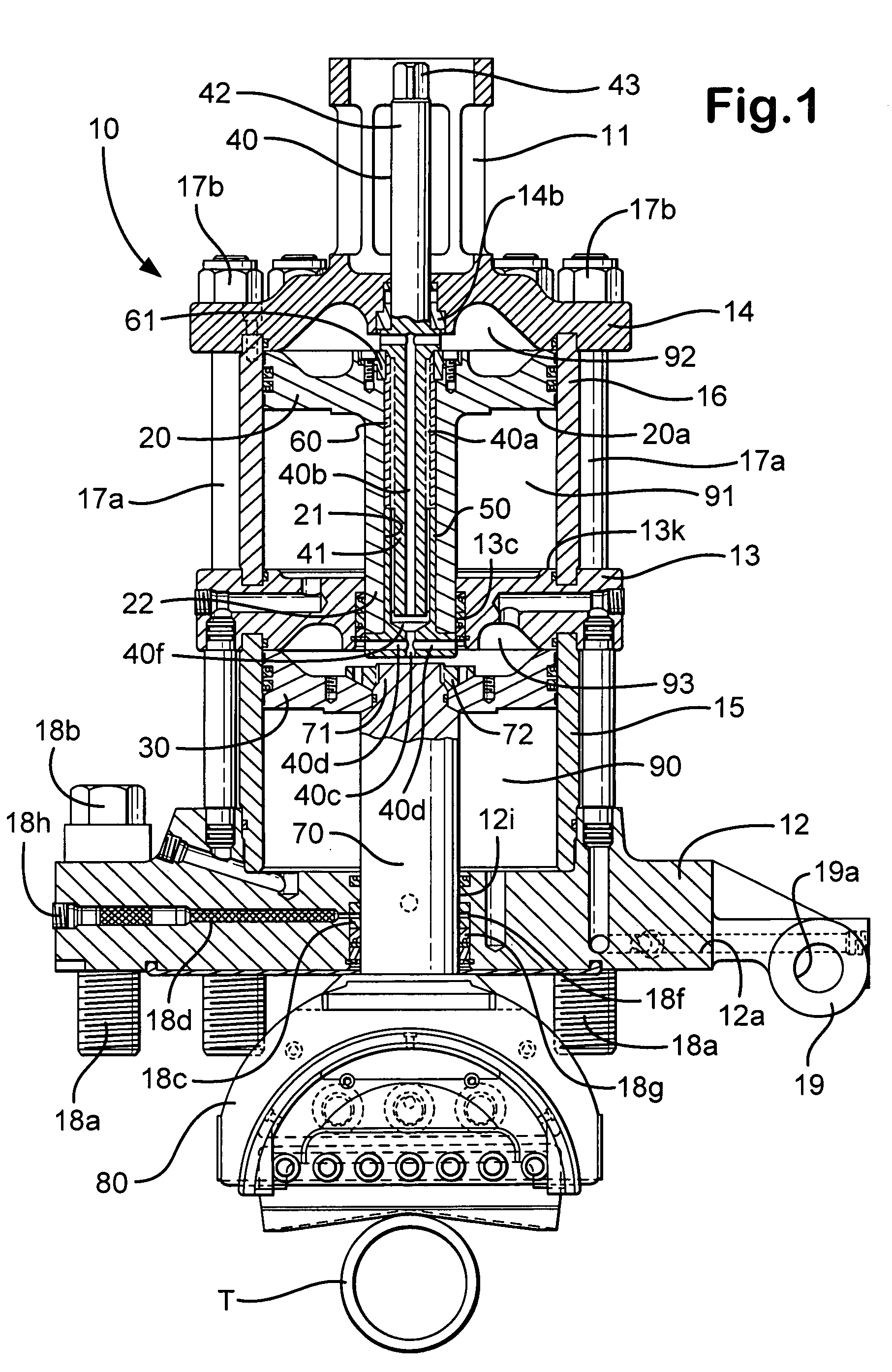
InactiveUS7574842B2Eliminate forcePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
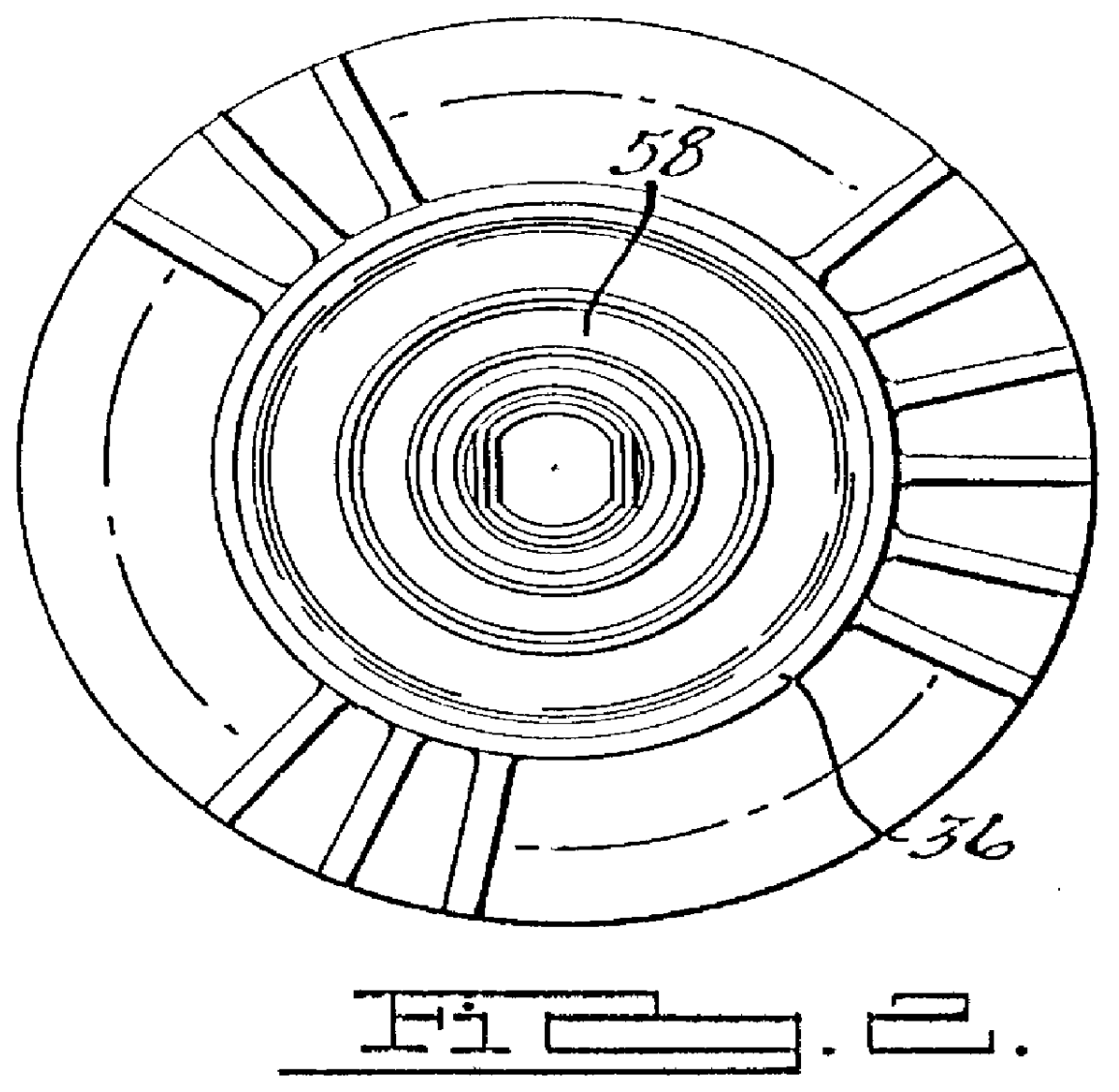
Unitized seal impeller thrust system
A unitized seal impeller thrust system includes an impeller unit which includes a tubular neck portion that has flat surfaces on opposite sides of one another. The impeller unit includes a plurality of radially extending blades and a circular trough surrounding the neck portion. The system further includes a seal head assembly which is secured within the trough, and a seal seat assembly which engages the seal head assembly. The system further includes a thrust washer which engages the seal seat assembly and the retainer ring which is secured to the tubular neck portion at an end of the neck portion. The retainer ring also engages the thrust washer in a ball and socket type arrangement. The system provides a unitized seal, impeller, thrust system that is capable of preload testing and / or leak testing before assembly of the pump unit.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
Closure Assembly for Electrochemical Cells
InactiveUS20100215996A1Not limiting abilityReduce shapingMechanical working/deformationSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAxial compressionEngineering
An end assembly seals a cylindrical electrochemical cell. The assembly includes a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) device and a gasket having a protrusion that cooperates with the end assembly isolates the PTC device from primary axial compression forces present in the closure assembly. In further embodiments of the present invention, the end assembly may be produced by insert molding a seal element about the terminal cover and the gasket itself has an E or F shaped cross section.
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Separable sheath and method for insertion of a medical device into a bodily vessel using a separable sheath
A separable or splittable insertion sheath is for inserting a medical device into a patient. The insertion sheath includes releasably connectable ends or is configured to split into proximal and distal sections upon application of a predetermined level of pulling or twisting force to opposite ends of the insertion sheath. A medical device loaded into the insertion sheath is deployed by pulling the proximal and distal sections away from each other to expose the medical device.
Owner:RUIZ CARLOS +1
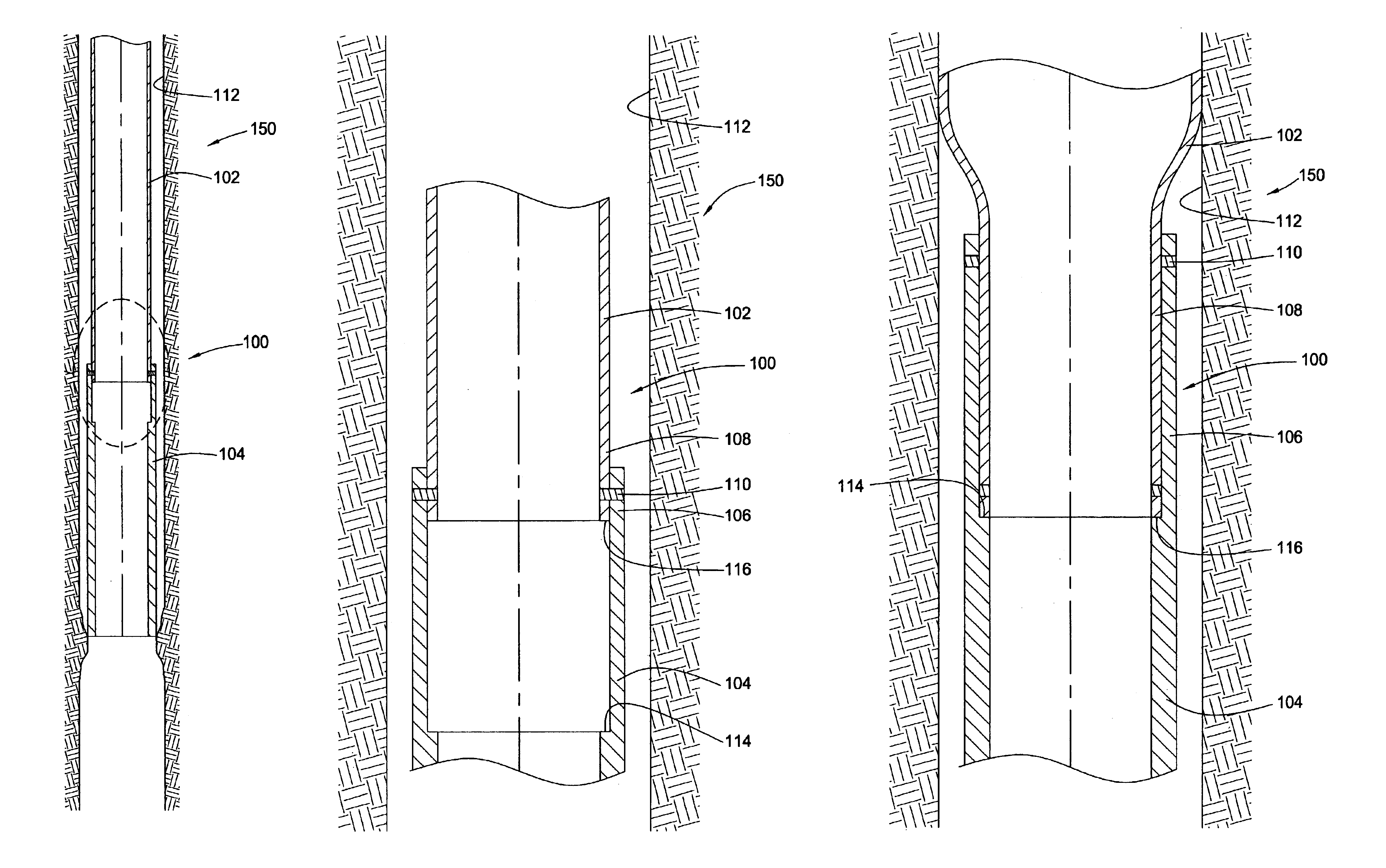
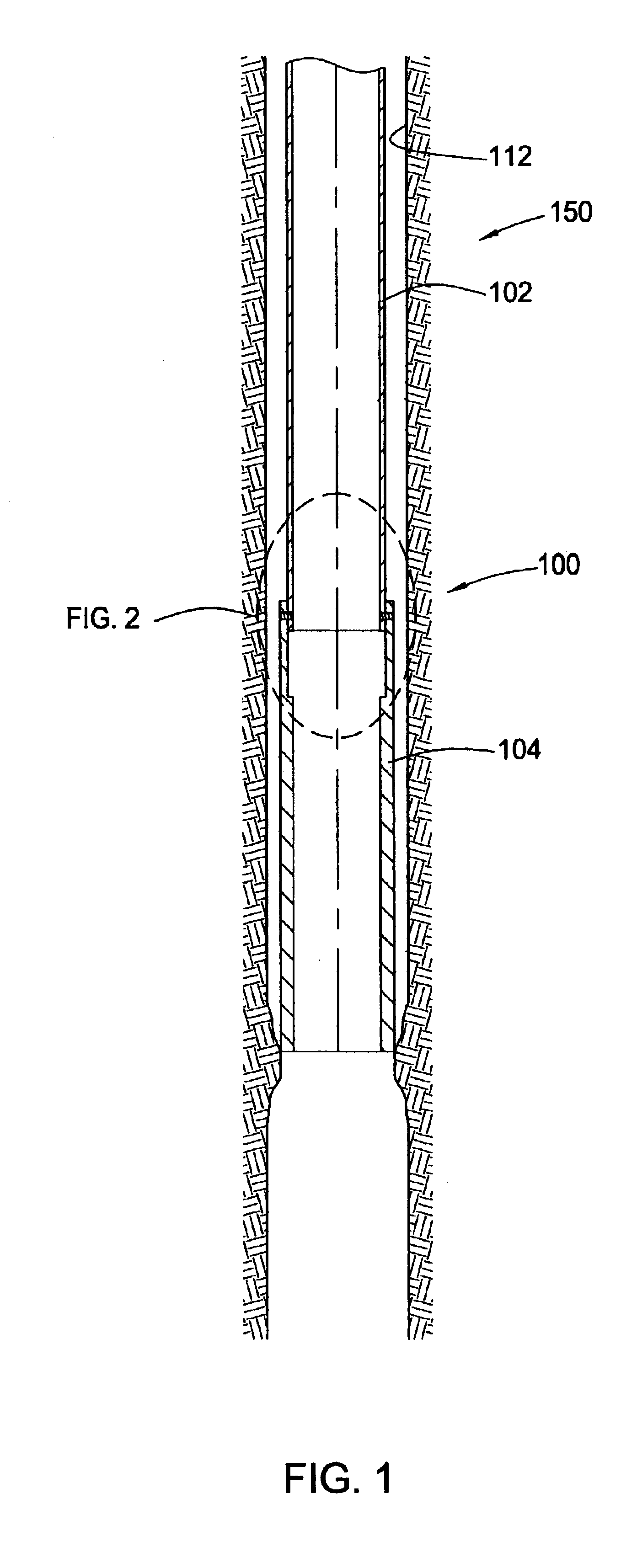
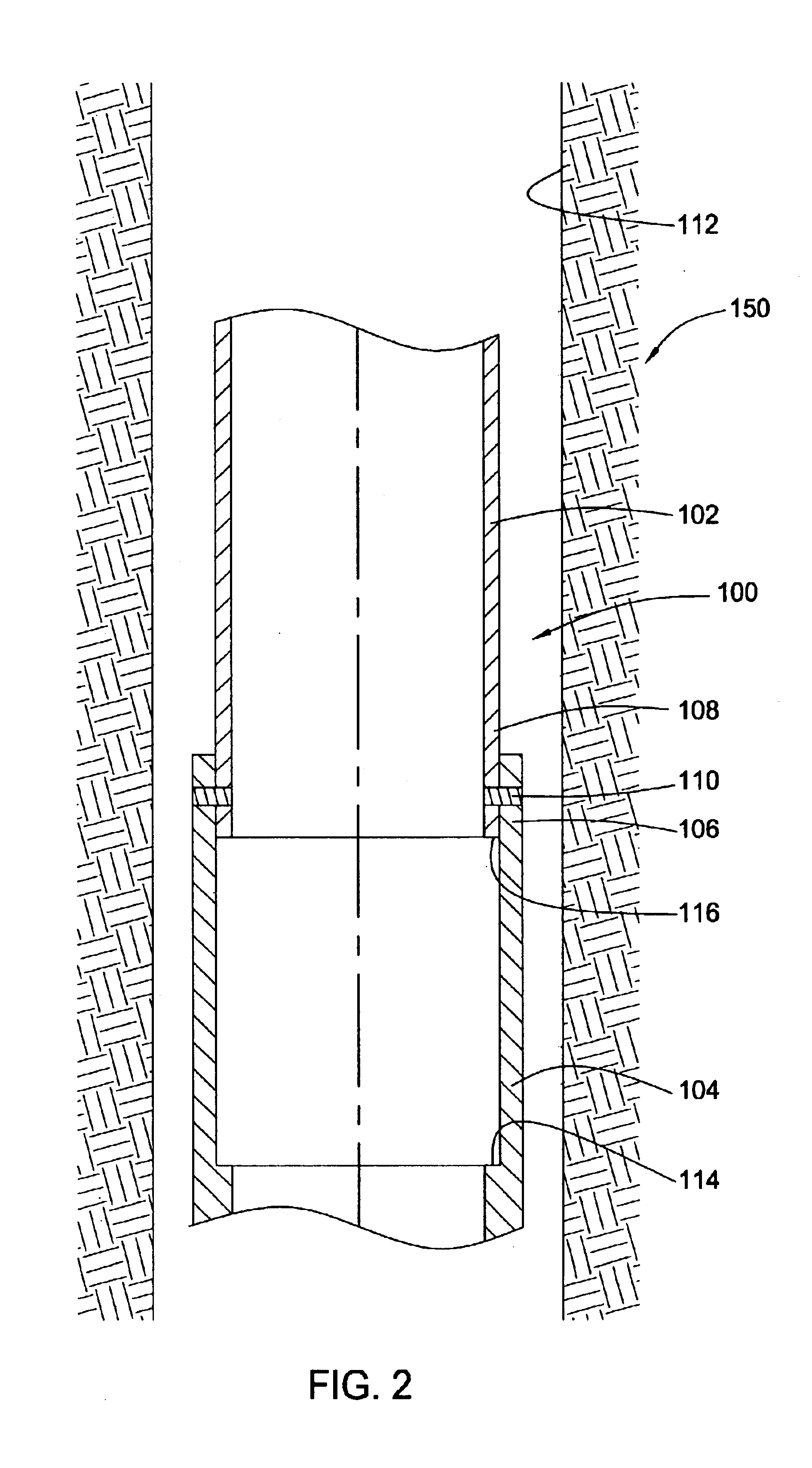
Joint for use with expandable tubulars
InactiveUS6920932B2Eliminate forceRemove tensionDrilling rodsFluid removalBiomedical engineeringWellbore
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a joint used with expandable sand screens and other expandable tubulars that permits elongation or contraction of the expandable tubulars during a tubular expansion operation within a wellbore. In one aspect, a connection assembly for use with expandable tubulars is provided. The connection assembly includes a first expandable tubular axially fixable at one end within a wellbore and a second expandable tubular axially fixable at one end within the wellbore. The second expandable tubular has an opposite end adapted to receive an opposite end of the first expandable tubular to provide a joint between the tubulars. The connection assembly further includes a releasable connection between the opposite ends of the tubulars for selectively permitting axial movement of the opposite ends relative to each other. In another aspect, a method for joining a first expandable tubular and a second expandable tubular is provided. Furthermore, a method for substantially eliminating tension or compression forces within an expandable tubular string positioned in a wellbore is provided.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
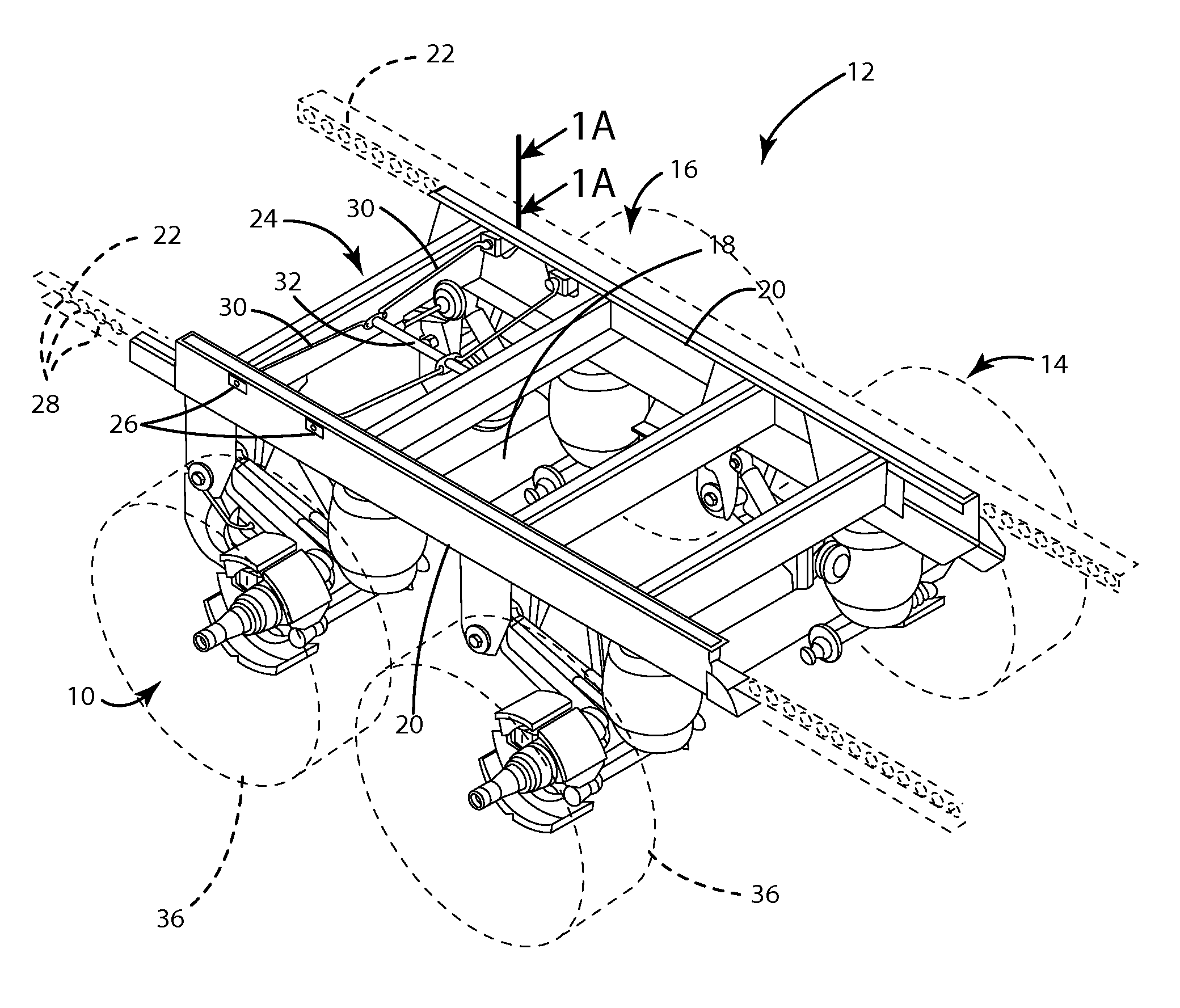
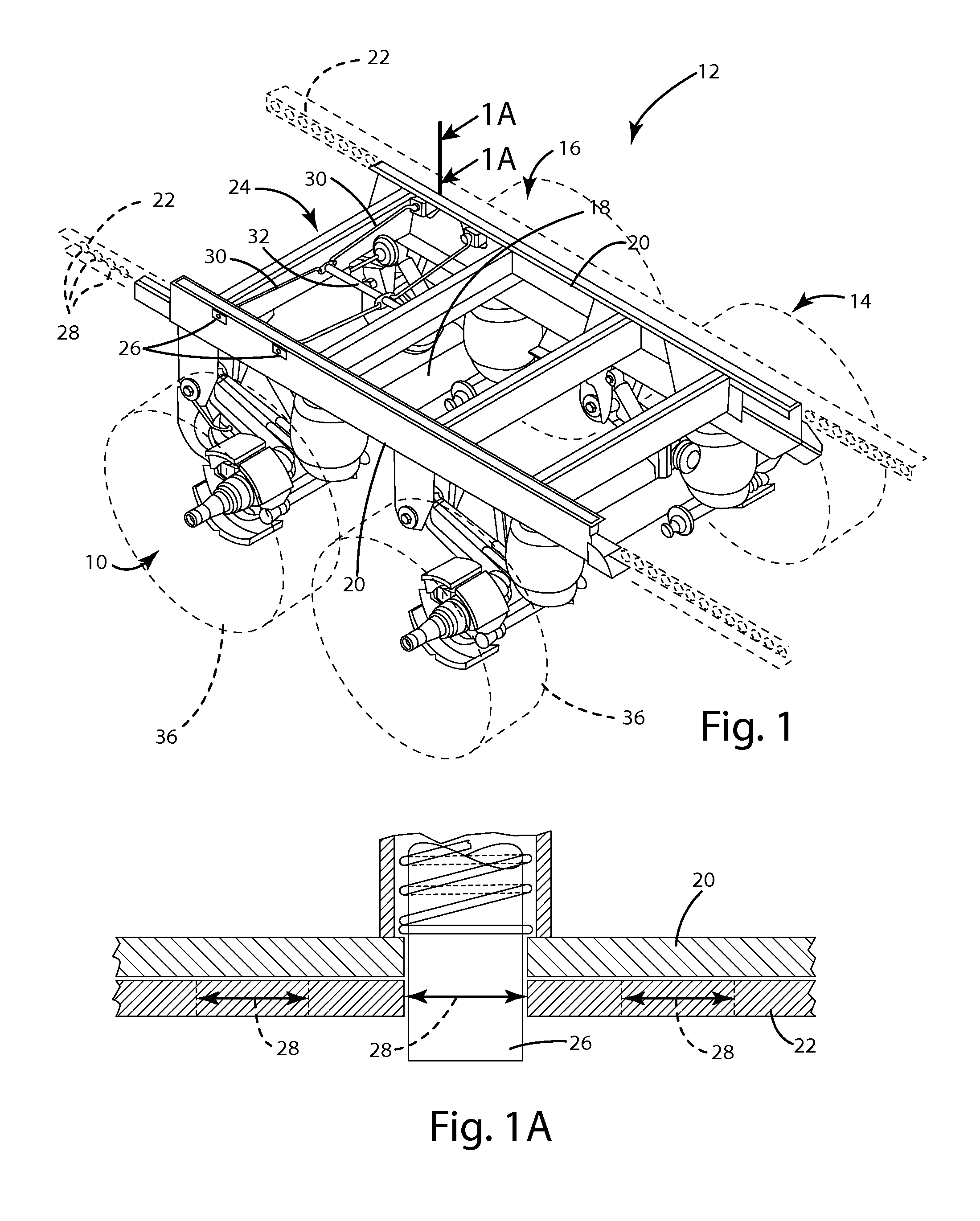
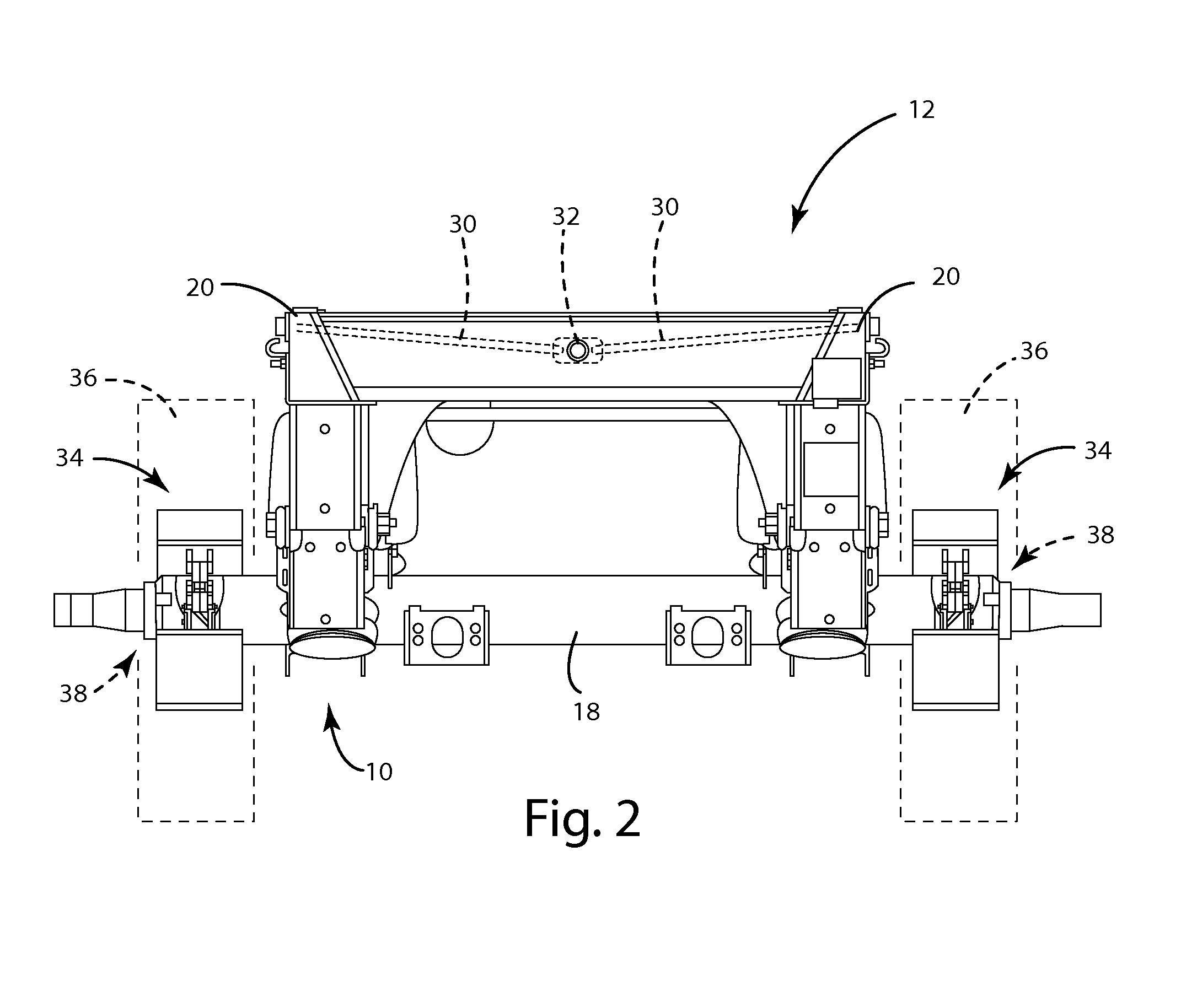
Axle lift assembly
ActiveUS8695998B1Eliminates upward forceEliminate forceResilient suspensionsPivoted suspension armsTrailing armVehicle frame
An axle lift assembly includes a beam slidably coupled with and extending on a longitudinal extent of a vehicle frame. A trailing arm has a first end pivotably coupled with the beam. An axle is rotatably coupled with an intermediate portion of the trailing arm. An air spring is disposed between a second end of the trailing arm and the beam for absorbing an upward force from the axle. A support bracket extends down from the beam proximate the first end of the trailing arm. A pneumatic actuator is disposed between the support bracket and the trailing arm for raising the axle from a deployed position to a retracted position that substantially eliminates the upward force on the air spring from the axle.
Owner:SAF HOLLAND INC (US)
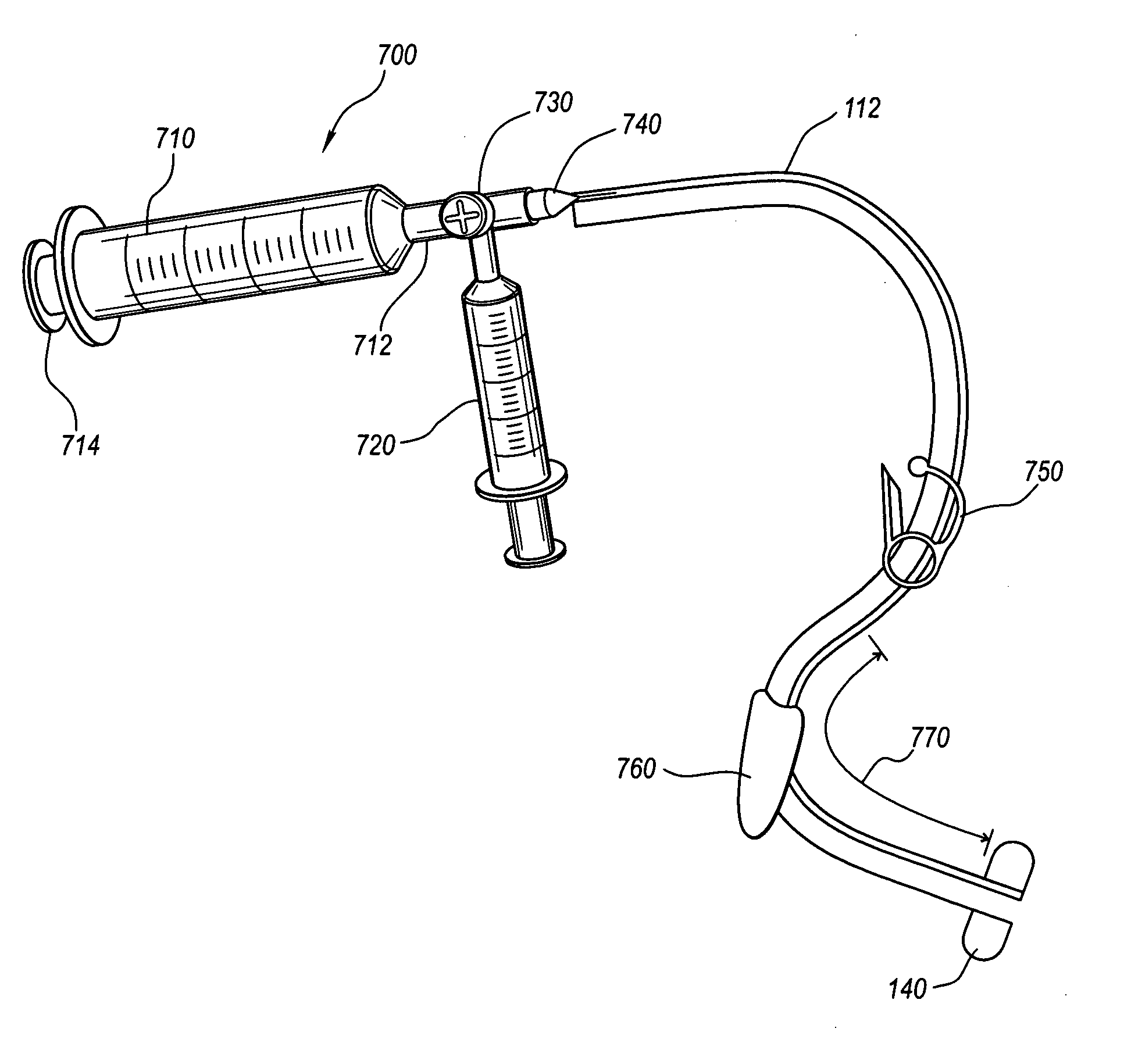
Medical devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20050267415A1Improve retentionReduce the possibilityStentsSurgical needlesBody organsFistula
A medical device for creating a fistula in a patient has a catheter including a first lumen and a second lumen for forming a fistula inside a body organ of a patient is disclosed. The second lumen may be capable of fluid communication with an internal bolster, wherein the internal bolster is attachable to the catheter near the distal end and is at least partially filled with a liquid. An external bolster may be adjustably attachable to the catheter outside the patient. Methods of use of medical devices according to the present invention are also disclosed. In one aspect of a method of use, at least a portion of the liquid within an internal bolster may be removed. Such a process may substantially collapse the internal bolster for removal of the medical device.
Owner:CR BARD INC
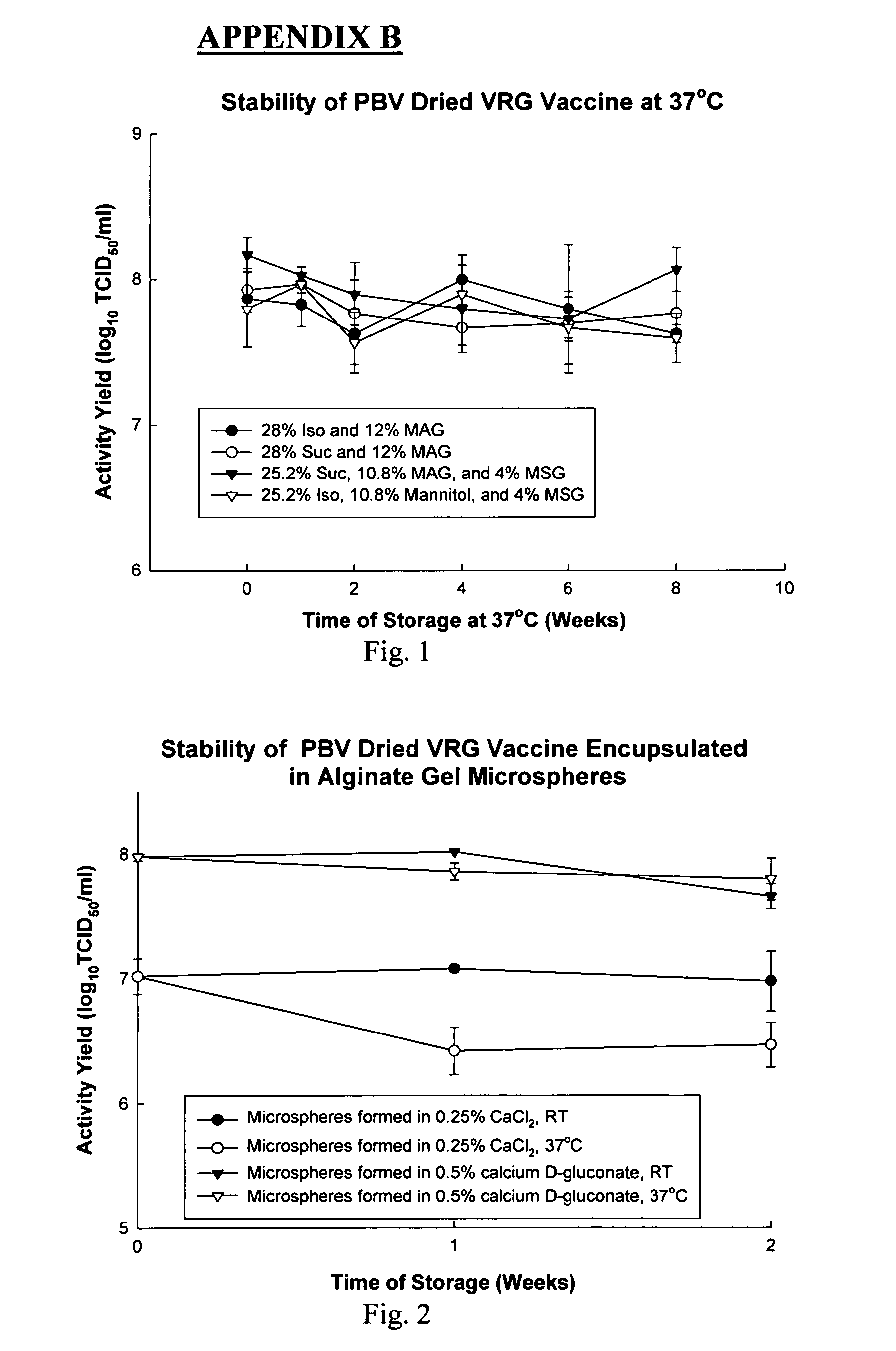
Stability Drying
InactiveUS20100120014A1Improve damage effectLong-term stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseDead animal preservationRed blood cellMicrosphere
A method of formulating high ambient temperature (room temperature and above) stable biologics (biologically active macromolecules, enzymes, serums, vaccines, viruses, pesticides, drug delivery systems, liposomes, cells suspensions, sperm, erythrocytes, other blood cells, stem cells, multicellular tissues, skin, heart valves) including secondary drying comprising at least two steps of stability drying at elevated temperature: 35° C., 40° C., 45° C., 50° C., and higher temperatures. The method could be applied to stabilize biologics encapsulated in alginate gel microspheres for better oral delivery. The method encompasses the following: microspheres are formulated using a cryo-encapsulation procedure comprised of mixing drops of frozen preservation mixture (To form the preservation mixture, biologics are mixed with preservation solutions containing sodium alginate.) with frozen drops of a calcium solution (i.e. calcium gluconate) and subsequent warming to form the gel particles.
Owner:BRONSHTEIN VICTOR
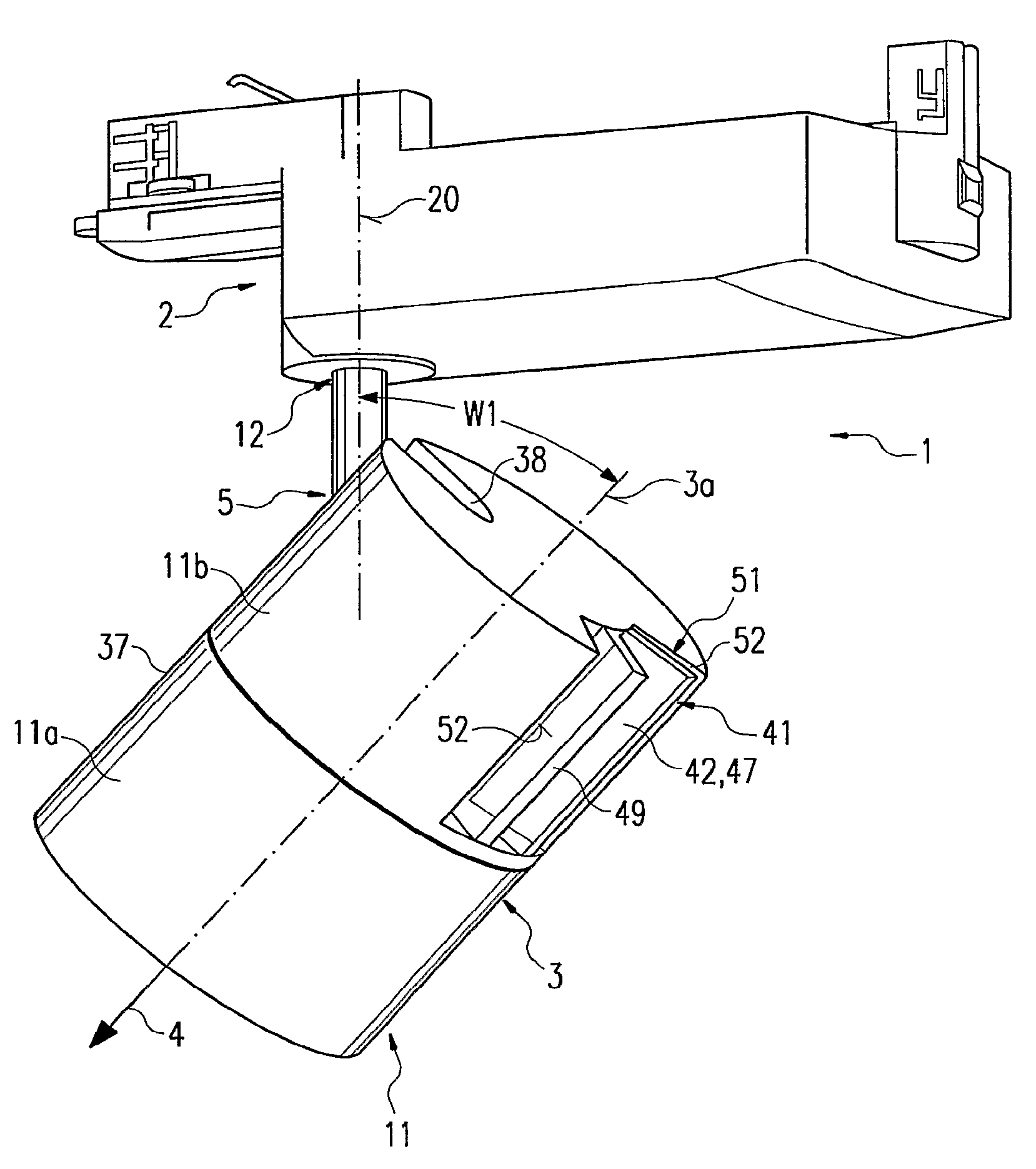
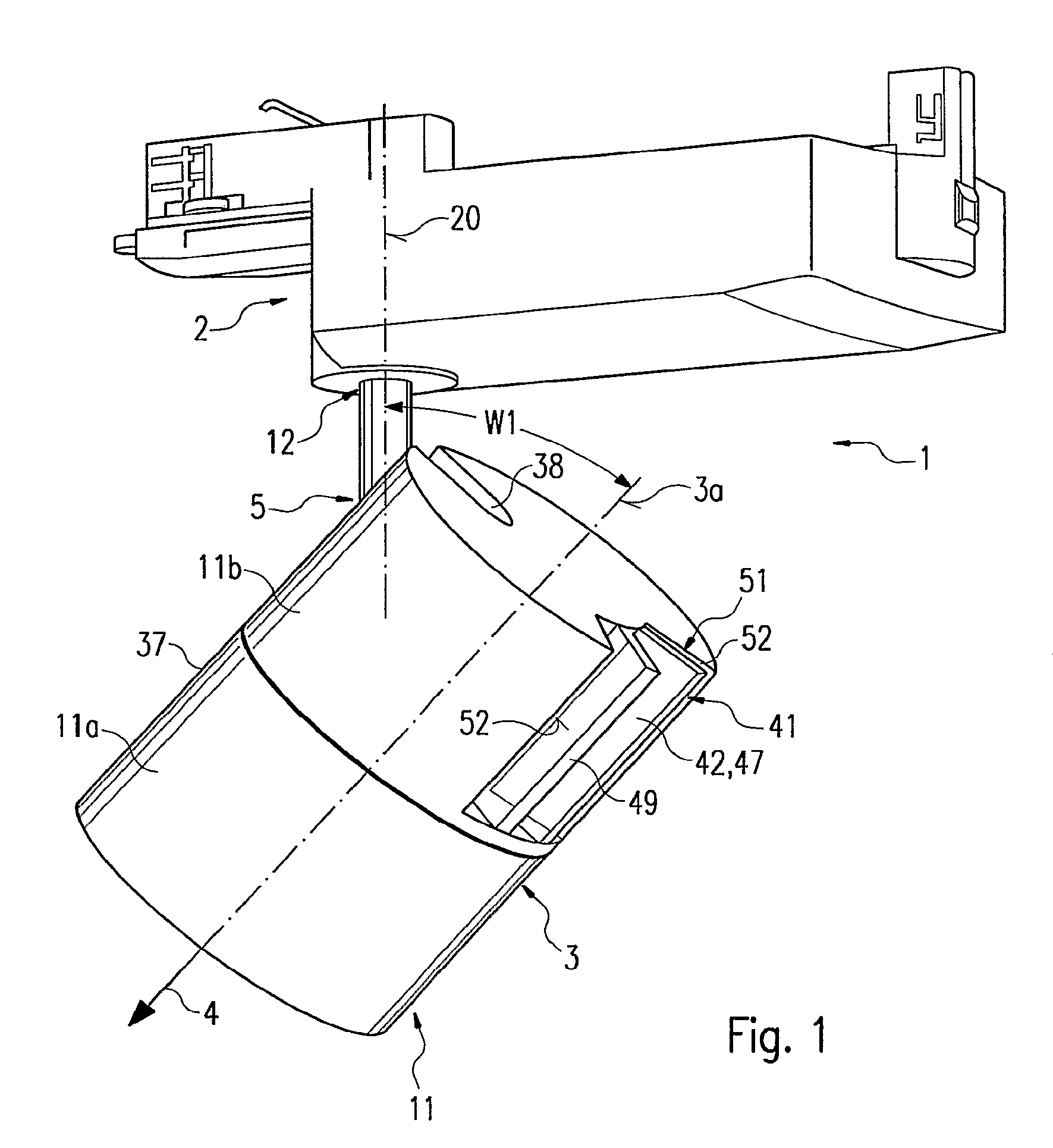
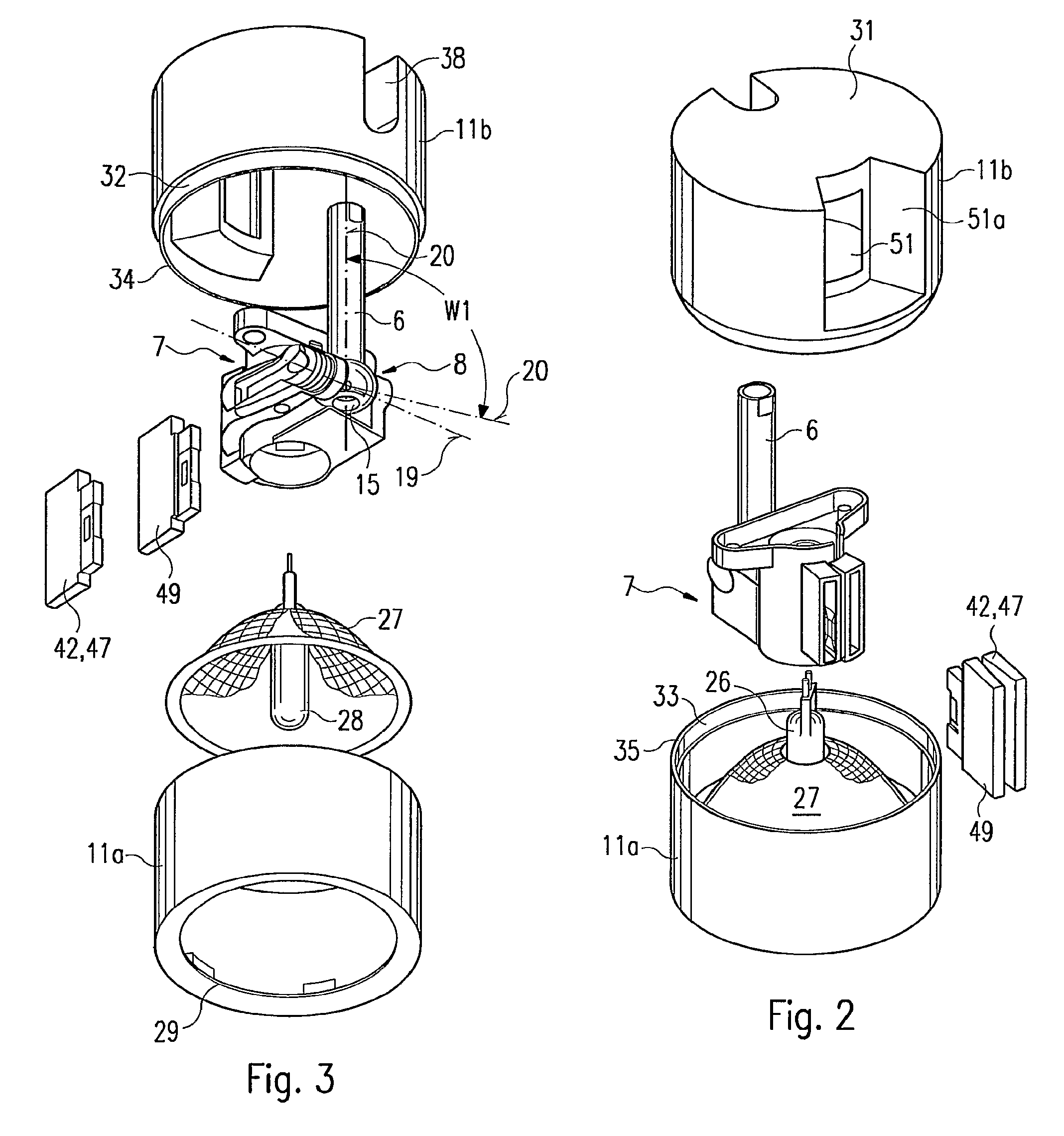
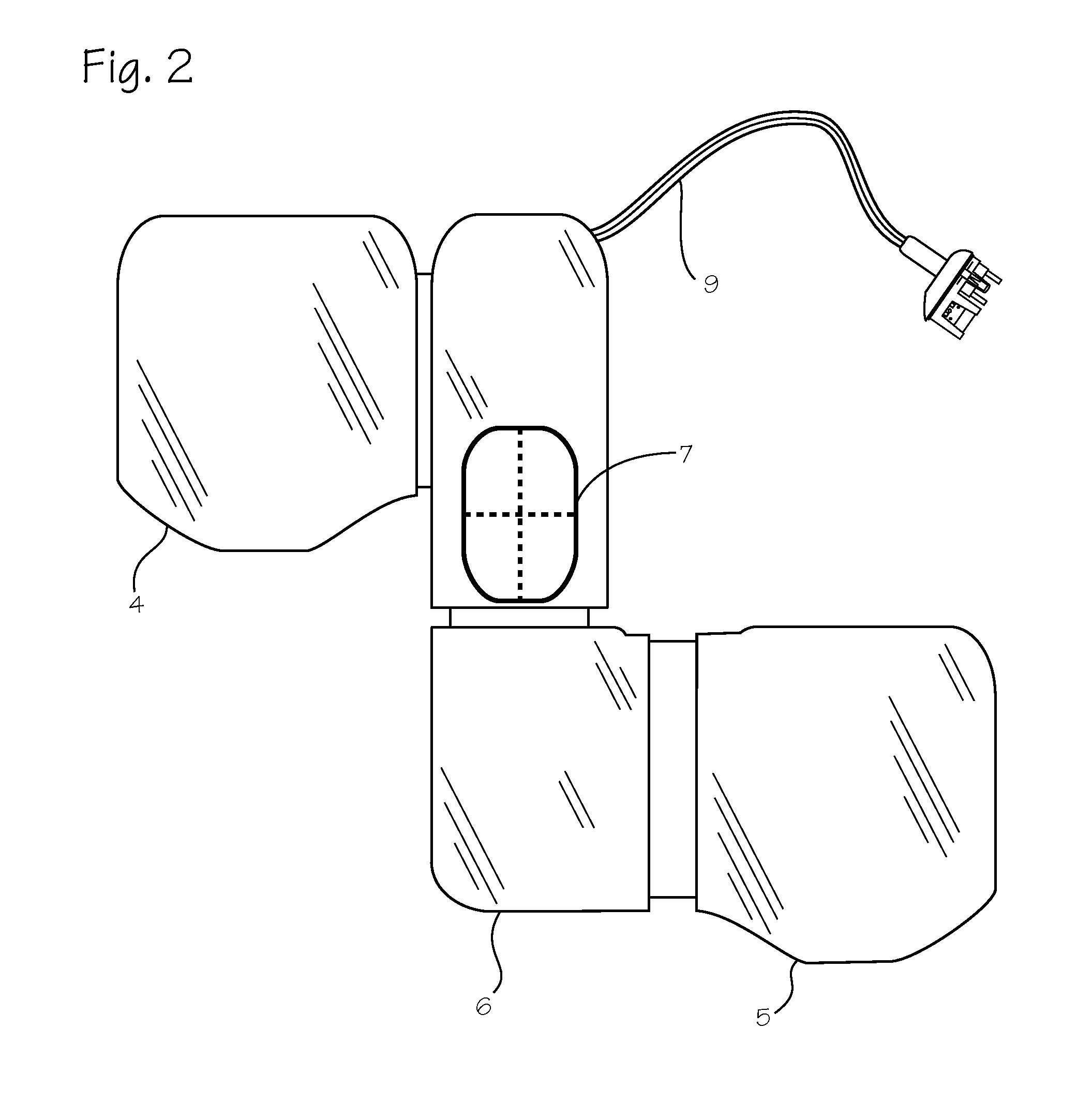
Luminaire comprising a spotlight and adjustable holding device for a spotlight
InactiveUS7762688B2Remove clamp forceLong service lifeLighting support devicesStands/trestlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
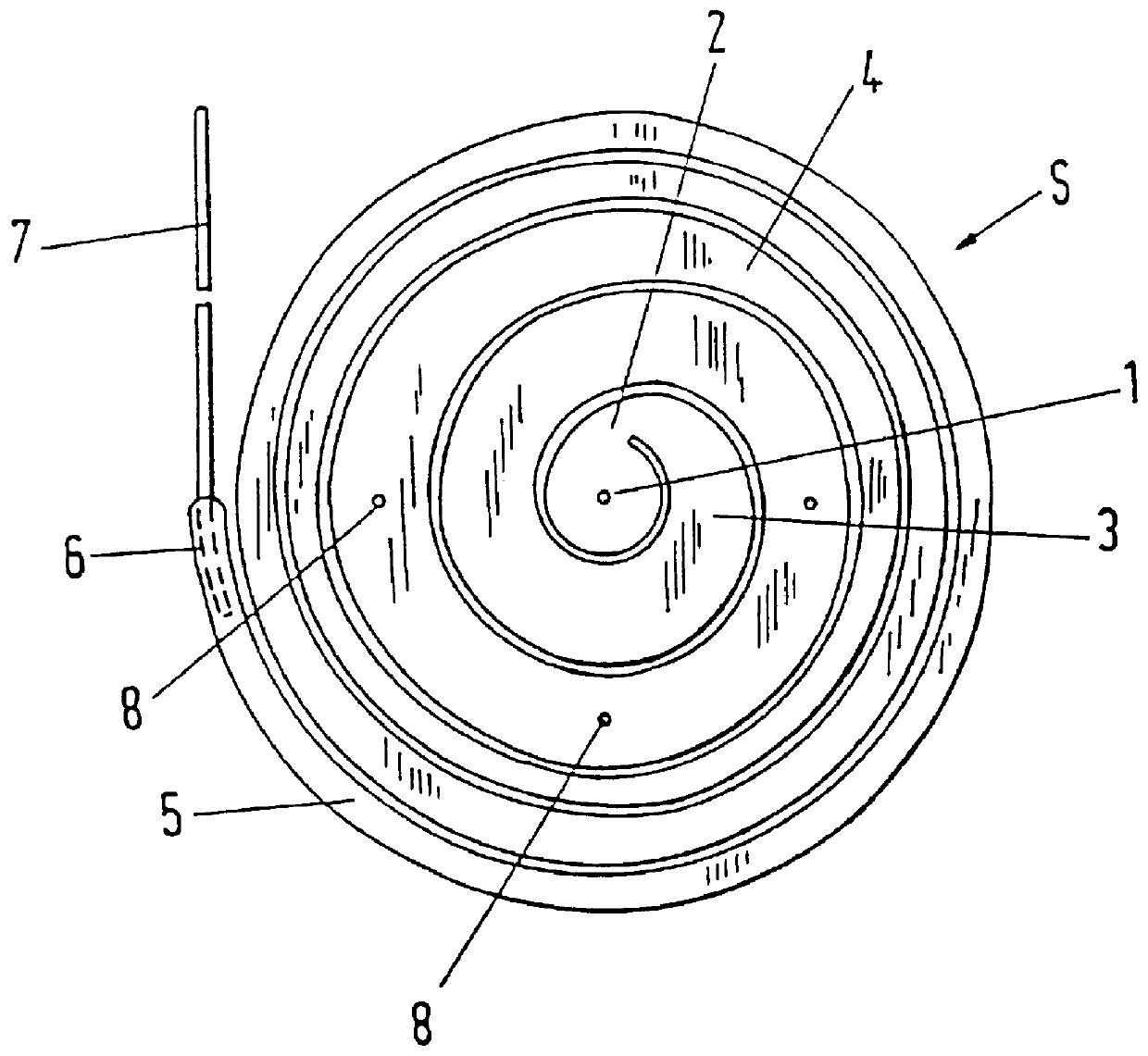
The invention relates to a lamp (1) comprising a projector (3) and an adjustable holding device (5), by means of which the projector (3) is joined to a base part (2) of the lamp (1). The holding device (5) is provided with an elongate support element (6), a holding element (7) at least for part of the projector (3), a joint (8) between the support element (6) and the holding element (7), and a clamping device (9) for locking the joint (8). The joint (8) and the clamping device (9) are disposed in a projector housing (11). In order to ensure that the projector (3) is easy to handle for adjustment purposes, a removing mechanism (41), with the aid of which the clamping force of the clamping device (9) can be reduced or canceled, is arranged in the projector housing (11). Said removing mechanism (41) is accessible from outside the projector housing (11) in order to be manually manipulated while being provided with a manually actuated actuating element (42) which is located at a distance next to a supporting element (49) that is fixed to the housing. The actuating element (42) can be moved towards the supporting element (49) by having two fingers of an operator's hand engage over both elements (42, 49).
Owner:ZUMTOBEL LIGHTING GMBH & CO KG
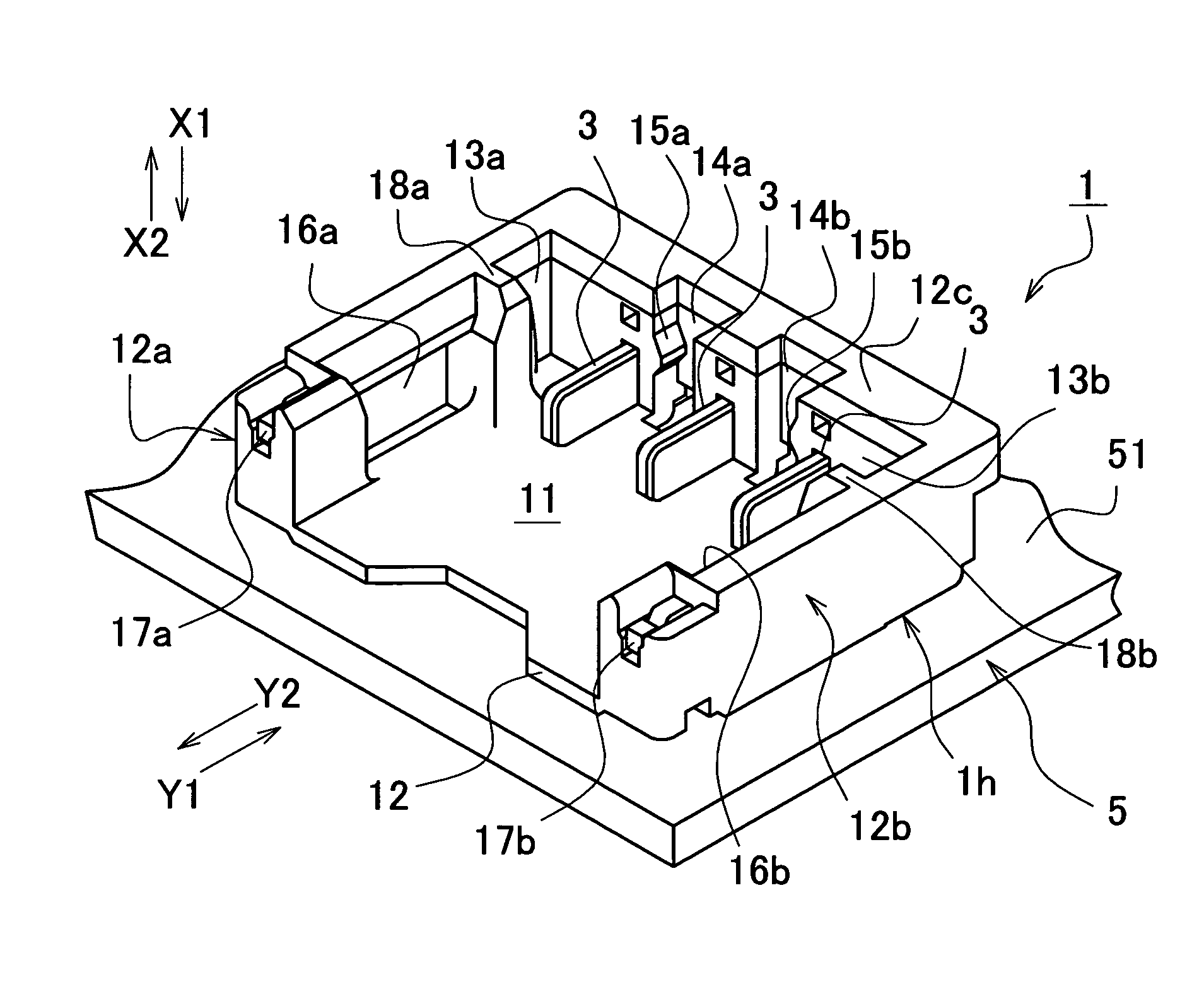
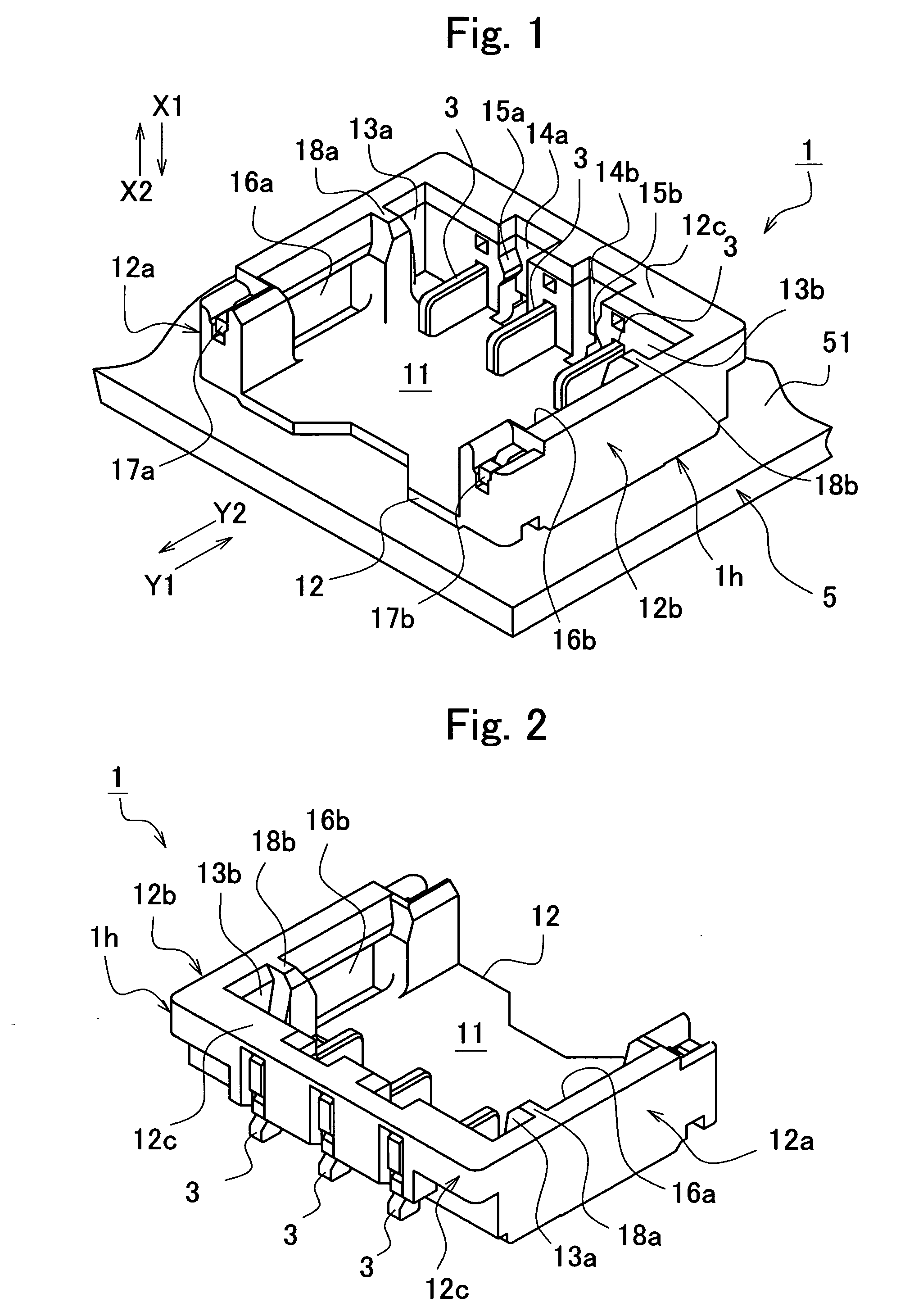
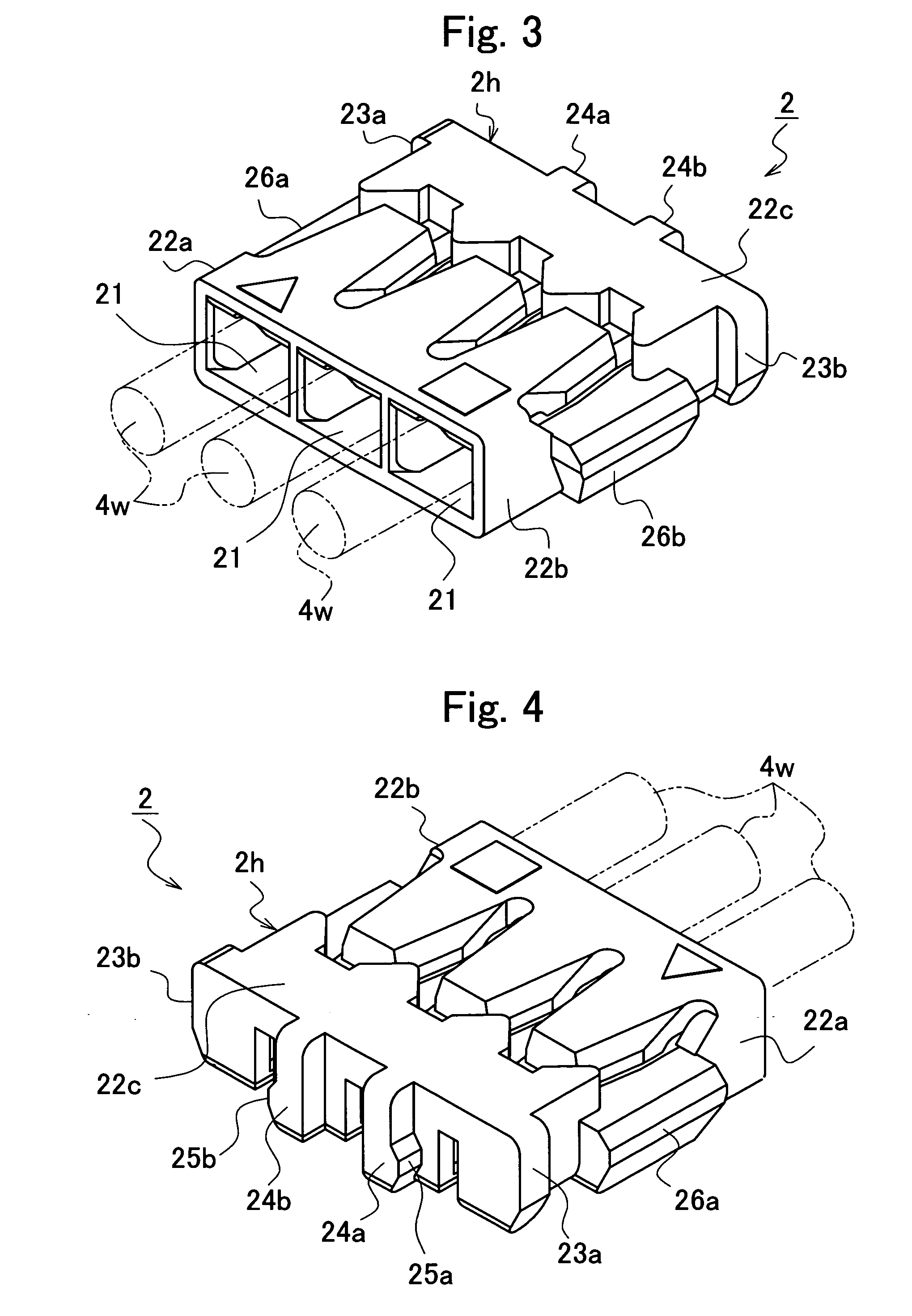
Electrical connector
ActiveUS7118424B2Increase freedomPrevent movementElectrically conductive connectionsElectric discharge tubesLocking mechanismEngineering
An electrical connector comprises: a base connector having a base housing and fixed to a print board, the base housing defining a recess having a plurality of plane opponent contacts; a socket connector having a socket housing that houses a plurality of socket contacts to be connected with the opponent contacts, the socket connector inserted into and removed from the recess; a plurality of lead wires extending in a direction substantially parallel to an attachment face of the print board; a pair of first locking mechanisms provided with the base housing and the socket housing, respectively, the first locking mechanisms engaging each other in a direction perpendicular to the direction of extension of the lead wires; and a pair of second locking mechanisms provided with the base housing and the socket housing, respectively, the second locking mechanisms engaging each other in a direction opposite the direction of extension of the lead wires.
Owner:JST MFG CO LTD
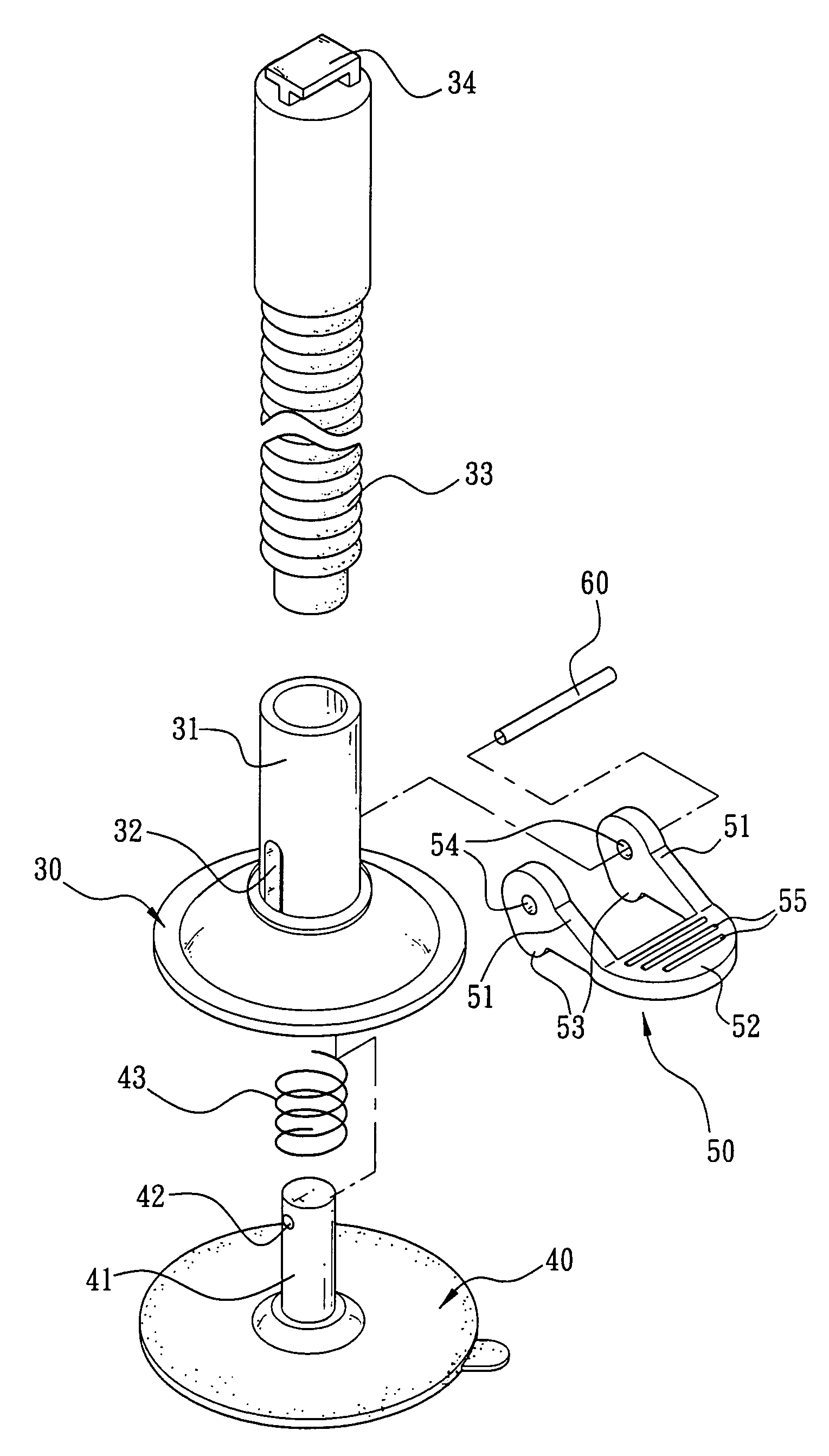
Fixed base assembly of mobile phone
InactiveUS7092521B2Complex structureEasily brokenInterconnection arrangementsVehicle componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention is to provide a fixed base assembly of mobile phone comprising a base, a cylinder extended upward from the center of the top of the base having one end coupled to a connecting rod, and the other end of the connecting rod able to clamp a mobile phone, wherein the bottom of the base is hollow and connected to the inside of the cylinder, such that the base can be slid, expanded, or contracted up and down along the cylinder. In addition, a clicking member is extended from the cylinder and the base, and the pivotal end of the clicking member symmetrically has a circular protruded head section such that when the clicking end of the clicking member is pressed, the head section of the clicking member presses against the surface of the base to lift the sucking disc of the cylinder, and make the bottom of the sucking disc vacuum and attached onto a fixed object.
Owner:WANG CHIN YANG
Wind cap for buildings
InactiveUS7310913B2Eliminate forceEliminate frictionHuman health protectionBuilding roofsTerrainEaves
A wind cap for buildings serves to anchor a building structure securely to the underlying terrain. The wind cap is a series of base plates which are temporarily and removably placed upon the roof of a structure, with a corresponding series of tiedown straps secured over the plates and attached to ground anchors on opposite sides of the structure. Two of the base plate components may be hinged together along their common edges for placement over the ridge line of the roof. Single plates are placed along the eaves and at intermediate points of the roof span. Each plate includes at least one pair of roller support arms adjustably extending upwardly therefrom, with a roller installed between each arm pair. The rollers eliminate the drag of the tiedown strap passing thereover, thereby eliminating asymmetrical loads on the underlying plates and roof as the straps are tightened.
Owner:PIERCE RILEY G
Method and apparatus for a clog resistant orifice
InactiveUS20150088090A1Minimize occurrenceReduce capacityMedical devicesCatheterEngineeringMedical device
Owner:HOSPI CORP
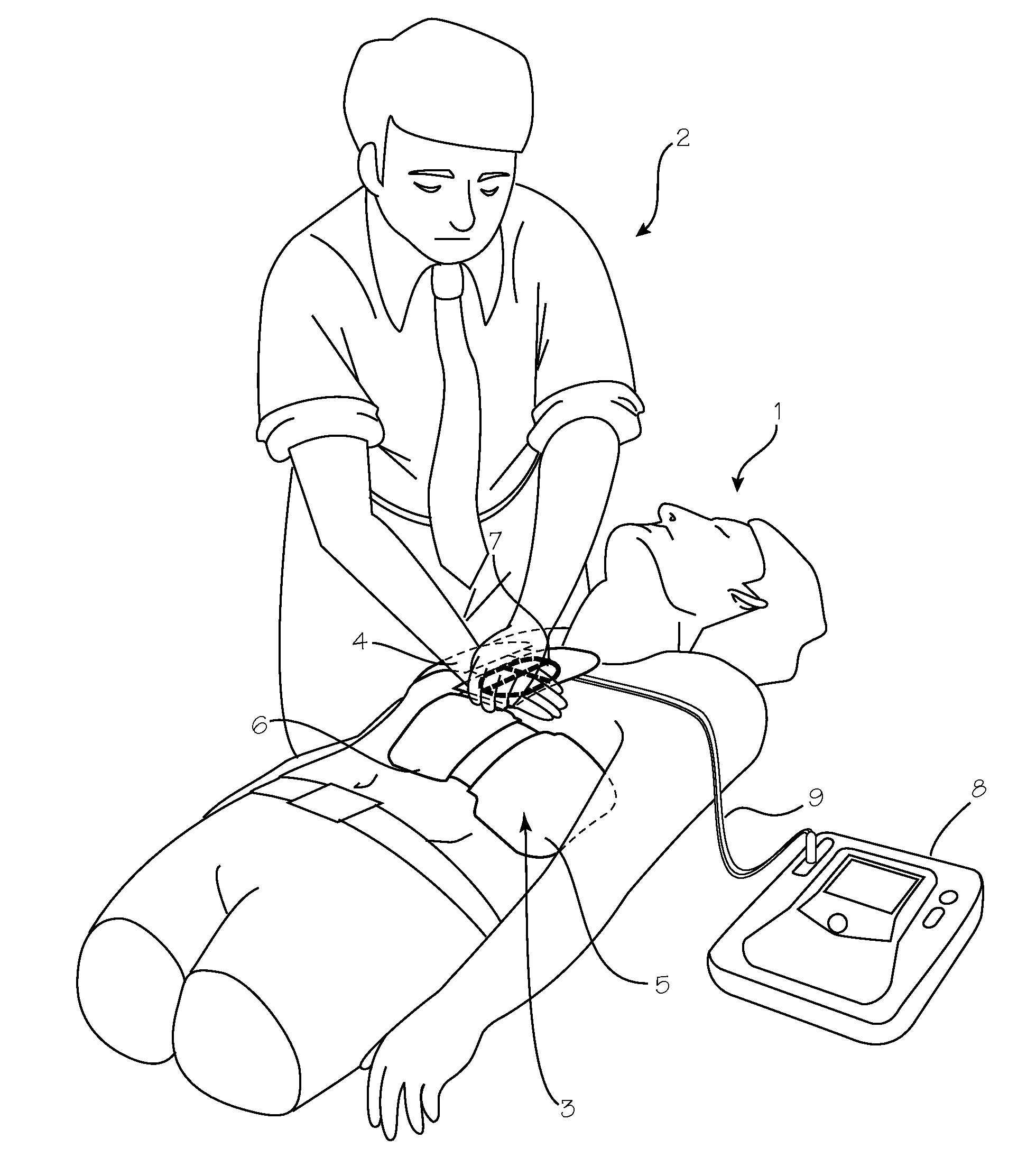
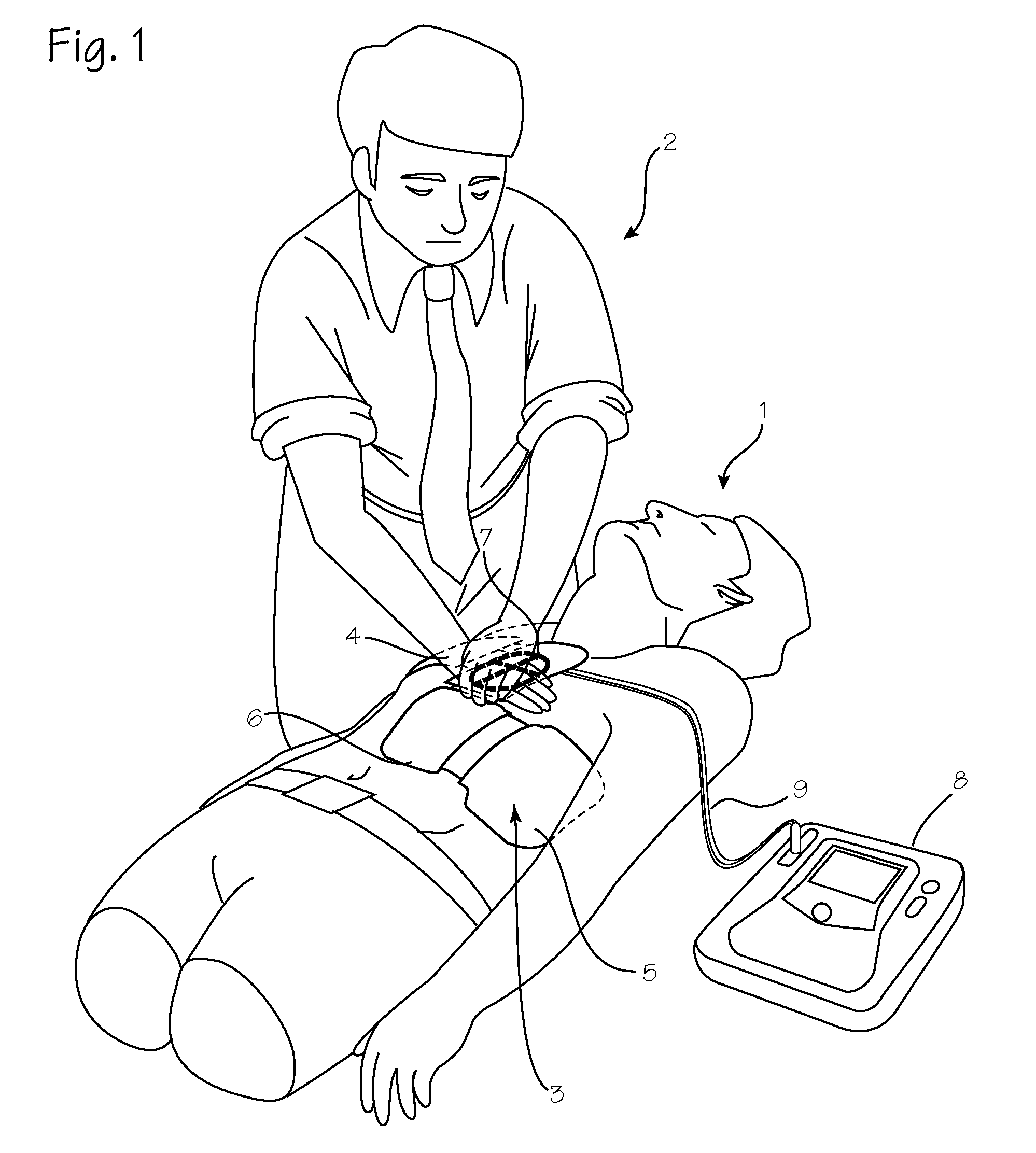
Chest Compression Monitor with Rotational Sensing of Compressions for Discrimination of CPR Movement from Non-CPR Movement
InactiveUS20140135666A1Enhance compression depth calculationRemove any compressive forceElectrotherapySurgeryControl systemChest Press
A chest compression monitor for measuring the depth of chest compressions achieved during CPR. A sensor of the chest compression monitor is disposed within its housing such that compression of the housing due to CPR compressions, and its resultant deformation, is detected by the sensor and used by the control system as the starting point for calculating chest compression depth based on an acceleration signal indicative of the downward displacement of the chest.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Pulper low in power consumption and noise
The invention provides a pulper low in power consumption and noise. The pulper mainly comprises a cylinder wall, a motor, a reducer, a seal device, a spindle, a spiral blade rotor, upper vortex board grooves, lower vortex board grooves and vortex boards. The pulper is characterized in the motor provides power, and the power is transmitted to the spiral blade rotor sequentially through the reducer and the spindle. By the inner and outer crescent arc transitions of the upper and lower vortex board grooves and the crescent cylindrical four-side arc structures at the inner edges of the vortex boards, flows can stably generate four vortexes at the four-side arcs of the vortex boards, vortex kinetic energy pulping is achieved, and low power consumption is achieved. Due to the fact that the hollow holes in two sides of the upper and lower vortex board groove retaining plates and in the middle portions of the vortex boards can be filled with damping and sound absorbing materials, fluid exciting force and solid noises can be absorbed, and low noise is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com