Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79results about How to "Data retention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
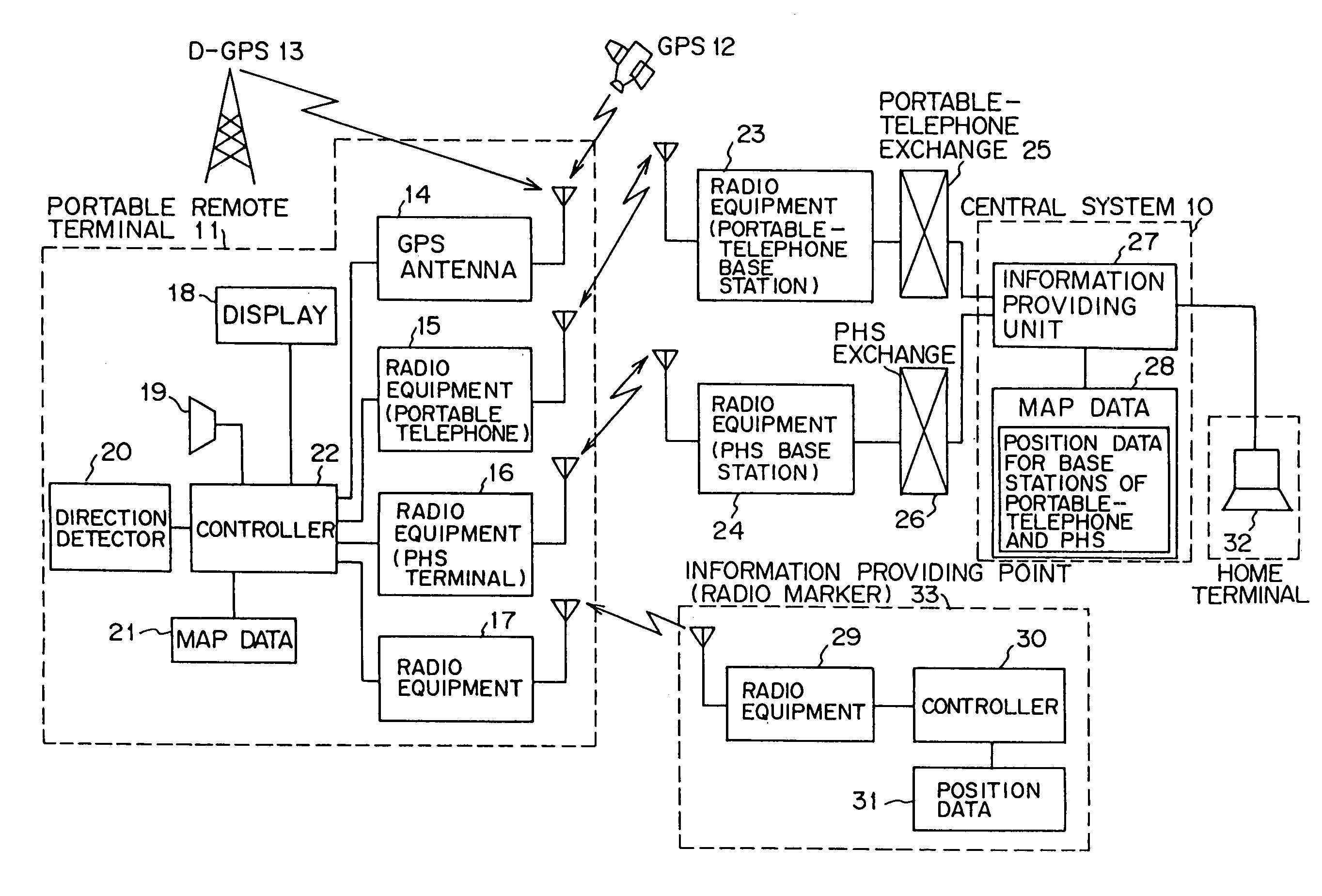
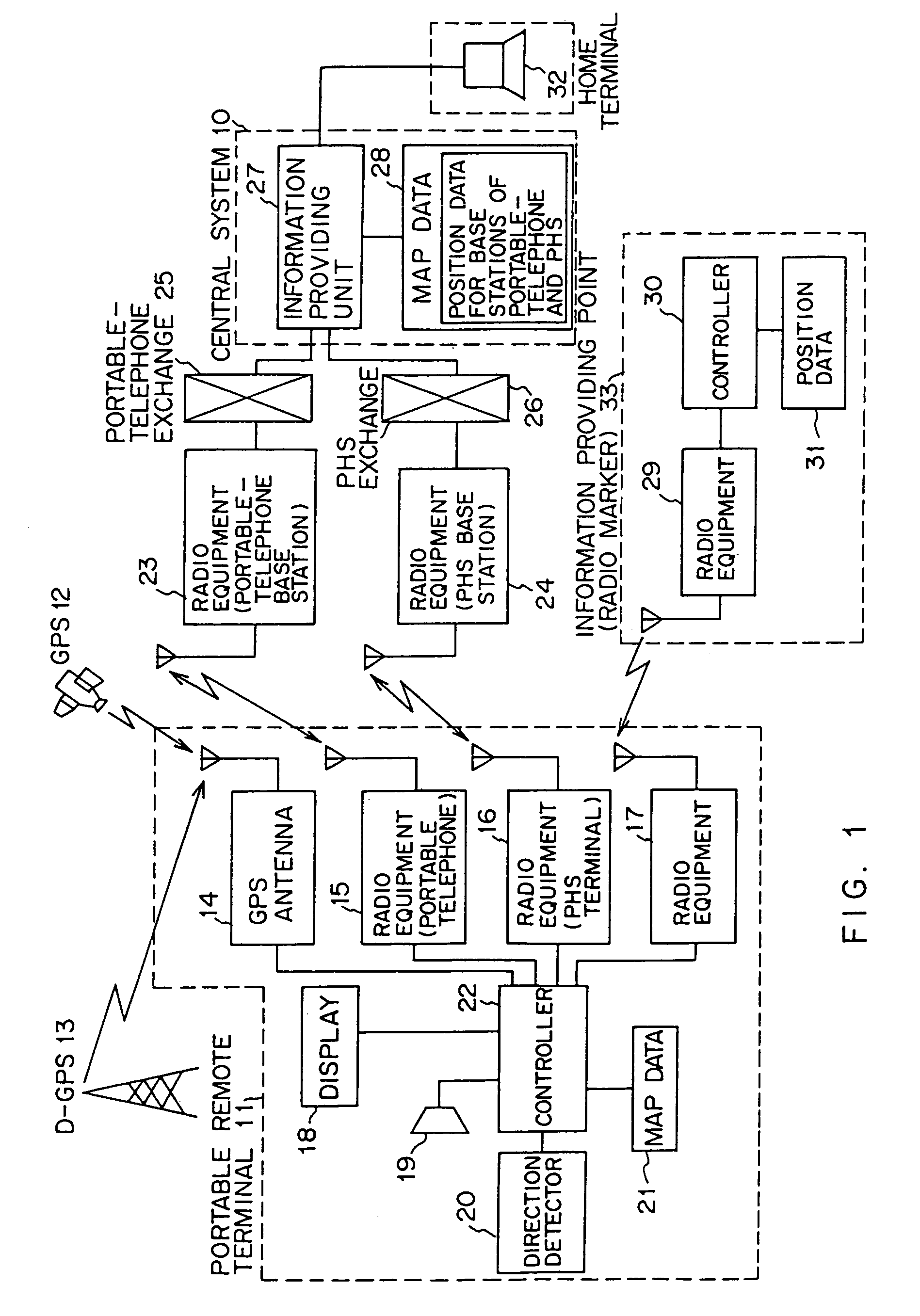
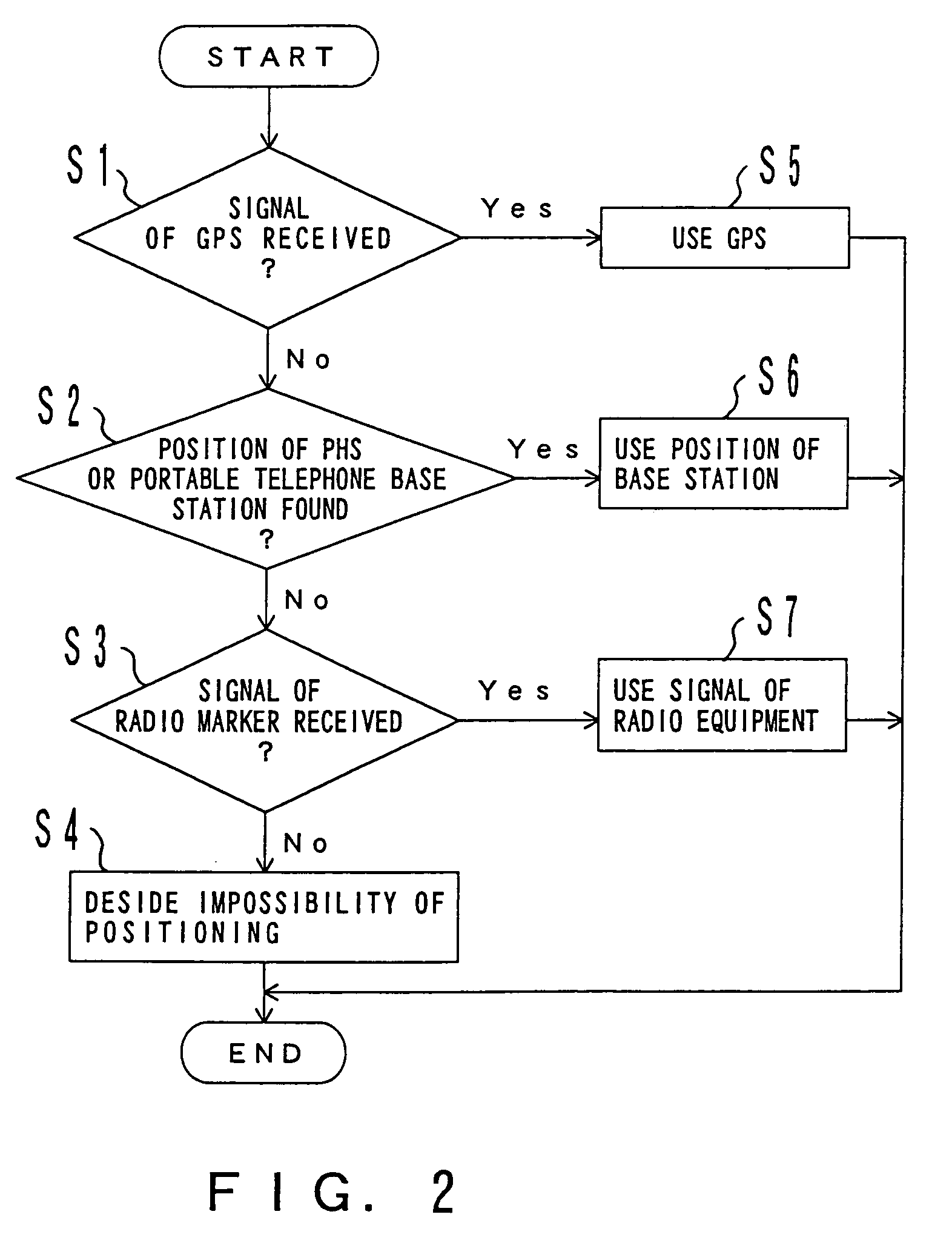
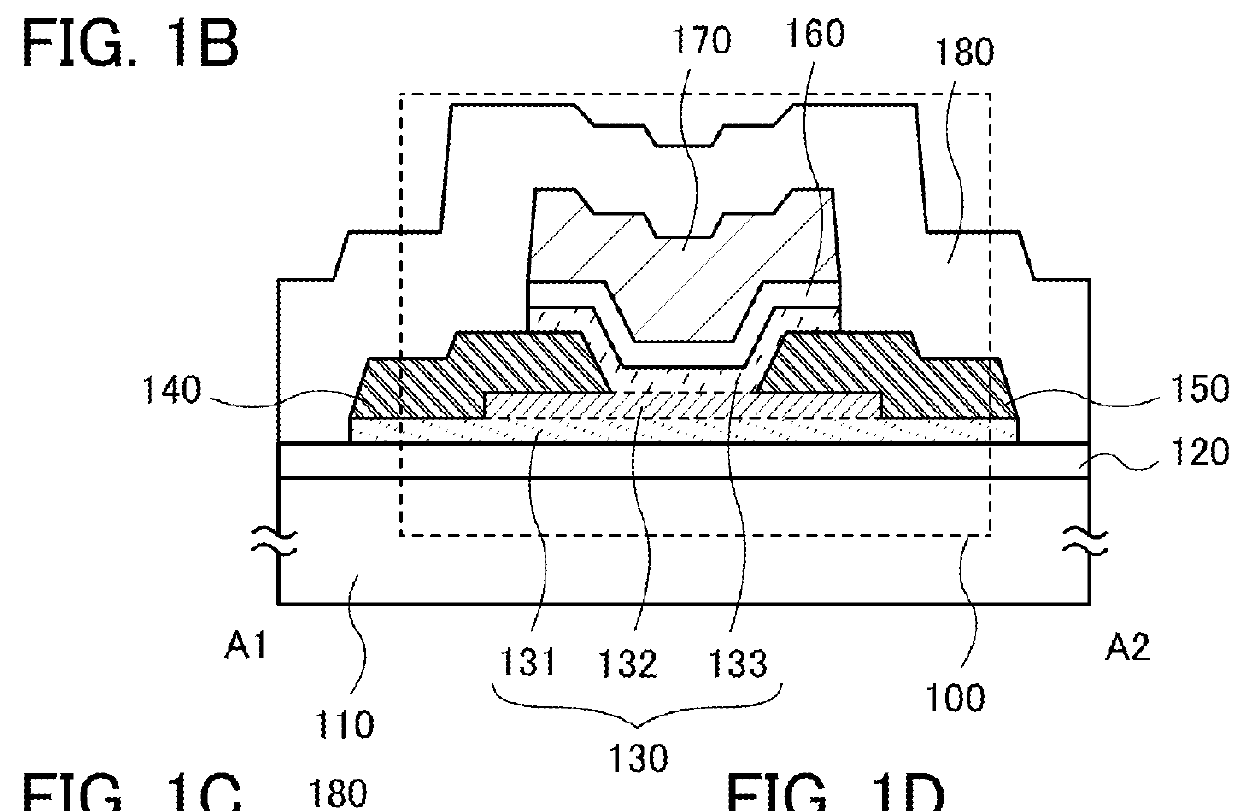
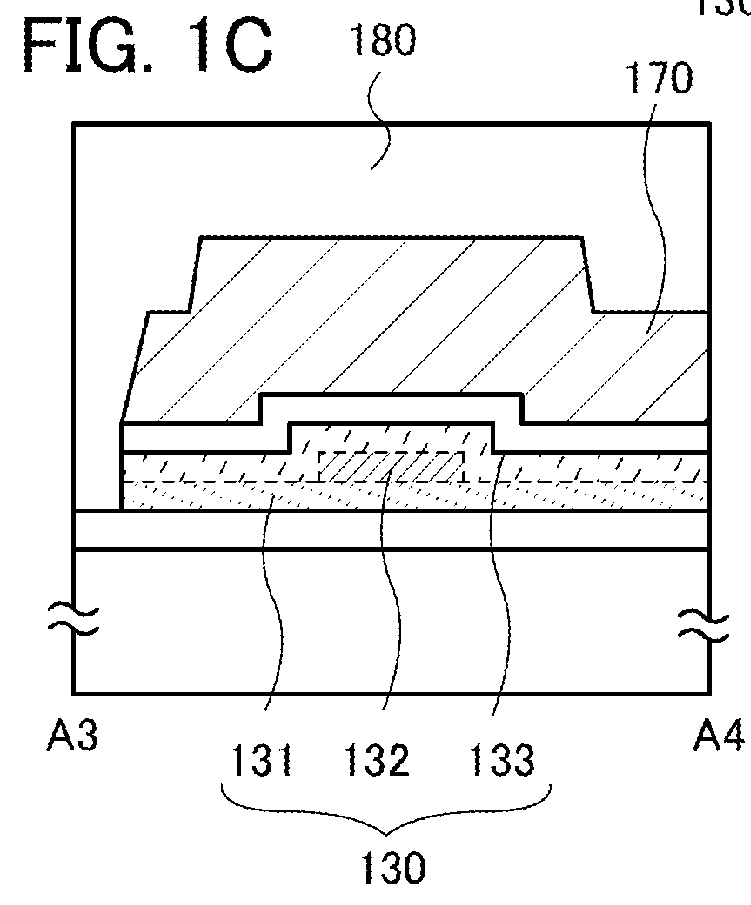
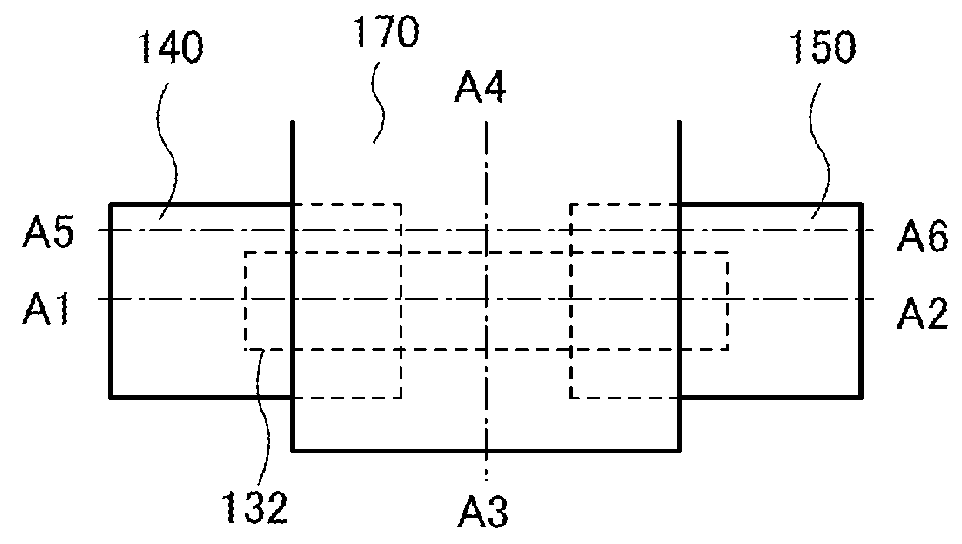
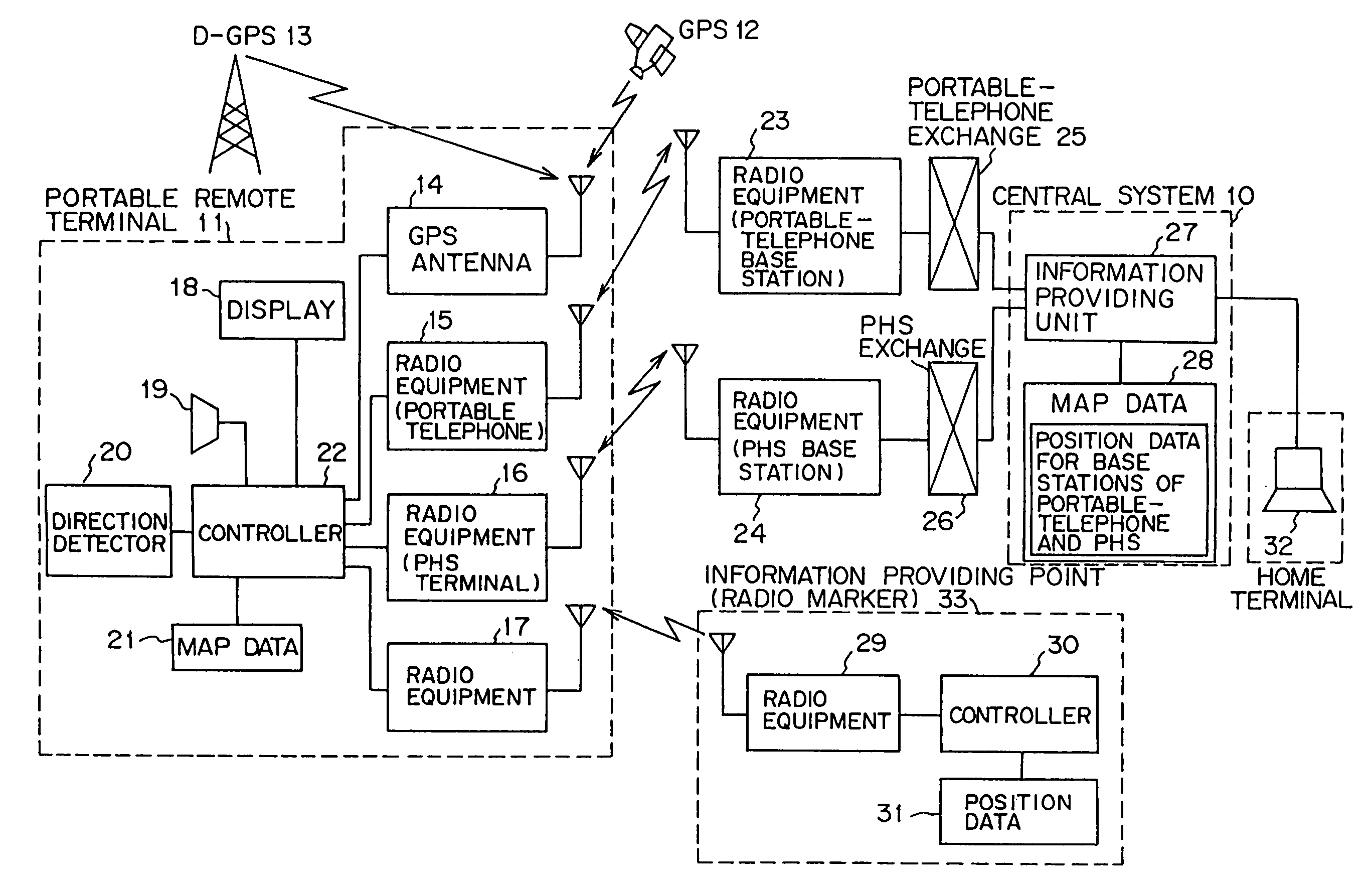
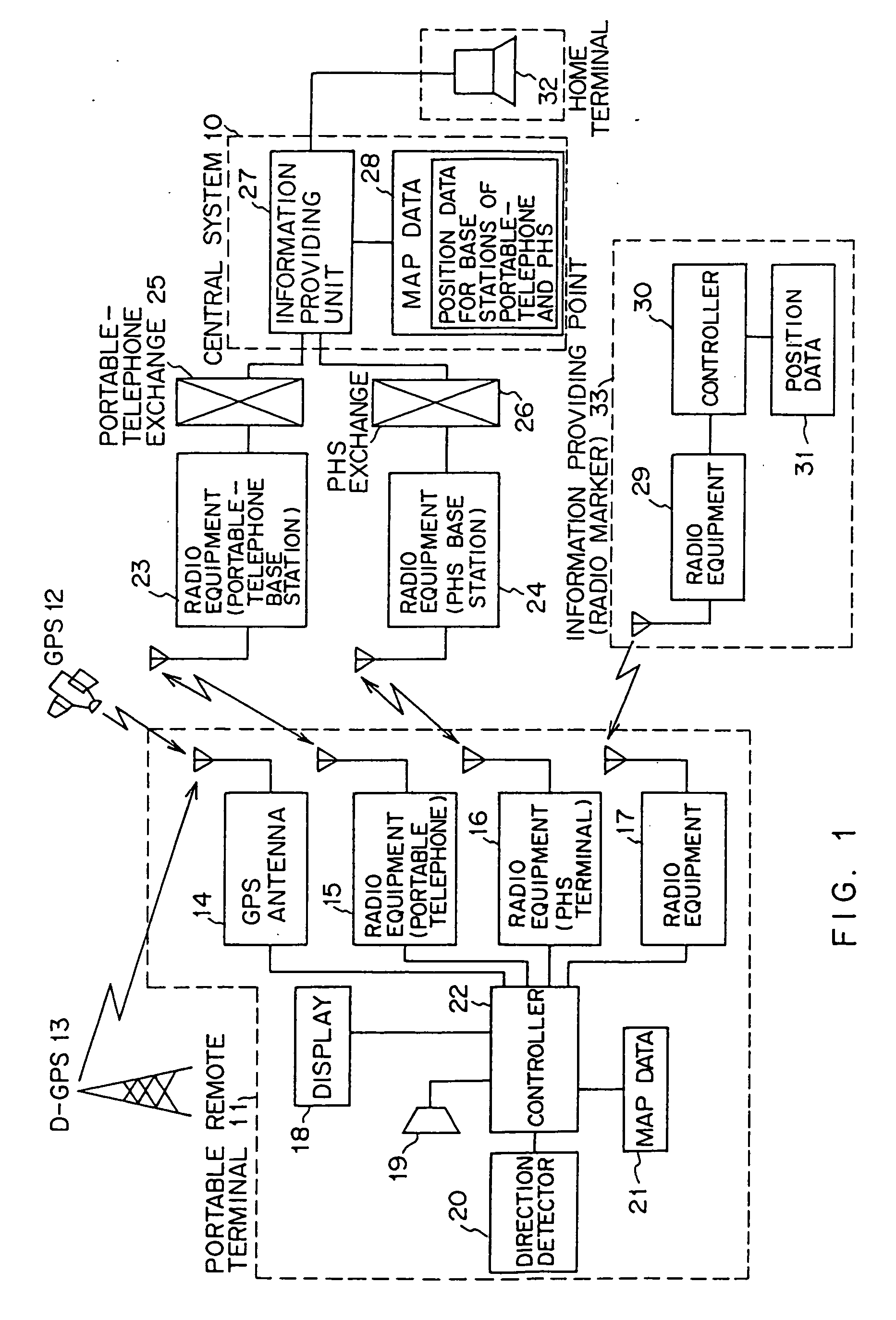
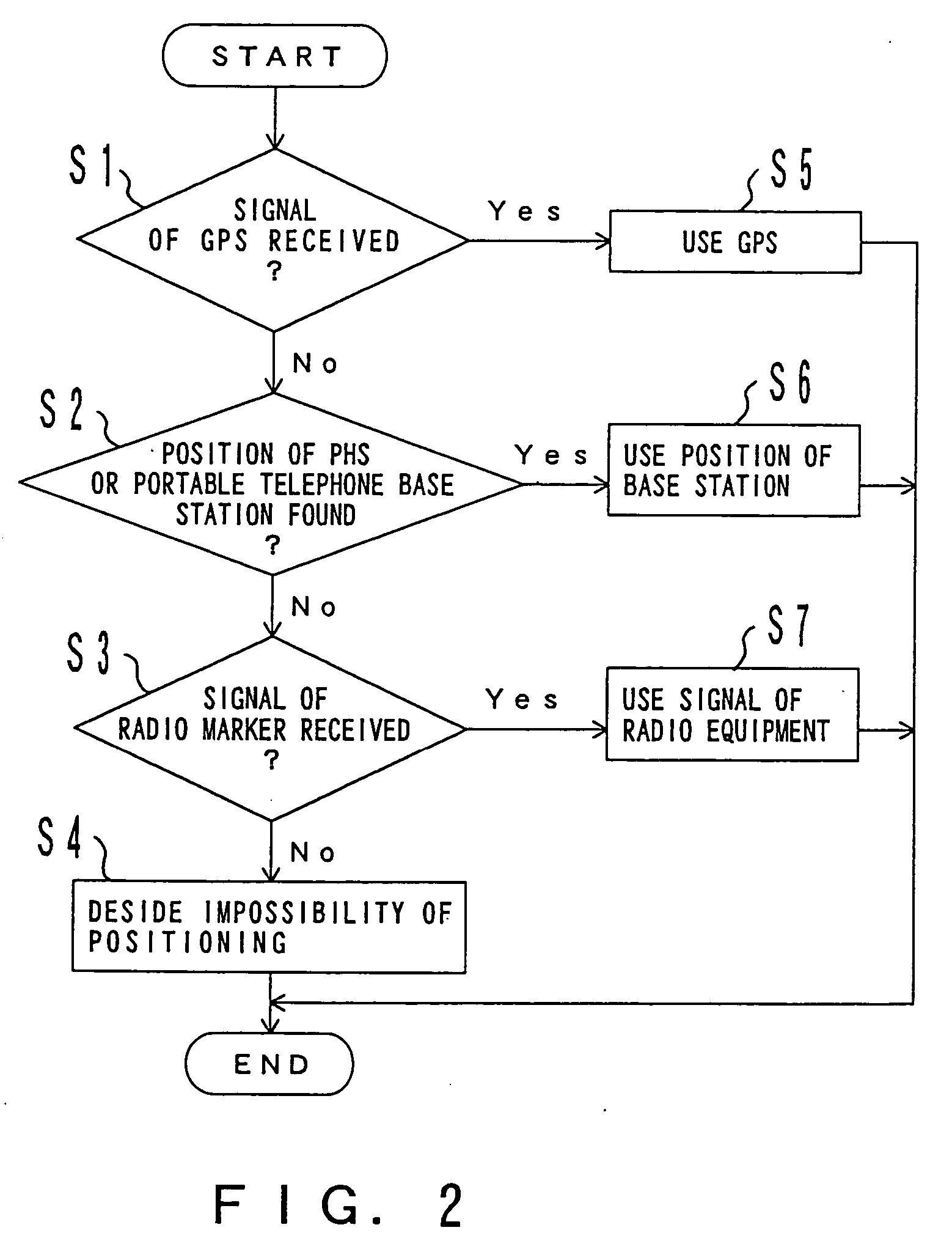
Position information management system
InactiveUS6999779B1Improve applicabilitySmall sizeTelephonic communicationPosition fixationThird partyComputer terminal
A position information management system in which a portable remote terminal includes a plurality of kinds of positioning means for positioning based on a GPS, positioning based on a portable-telephone or PHS base station, positioning based on a radio marker, and independent positioning based on a direction detector, so that the holder of the portable remote terminal can be navigated anywhere. The holder of the portable remote terminal can know the position of a third party similarly holding such a portable remote terminal, by inquiring of a central system, and he / she can supervise, for example, the action of an old person, a child, or a skier in a skiing area. Further, only the map data of a district which is often used by the holder is stored in the portable remote terminal. In this regard, when the holder is in a district not contained within the retained map data, he / she downloads corresponding map data from the central system and uses the downloaded map data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
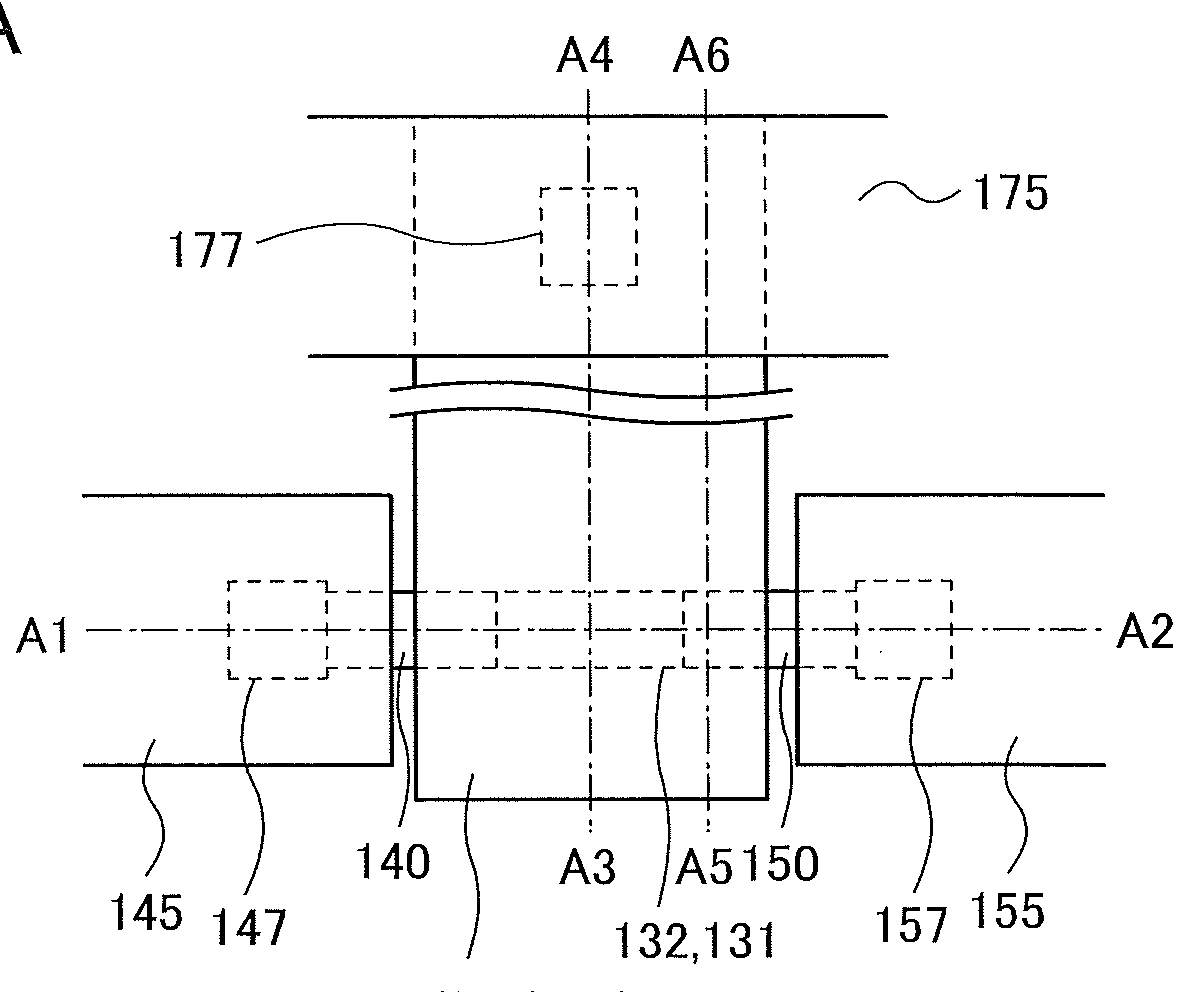
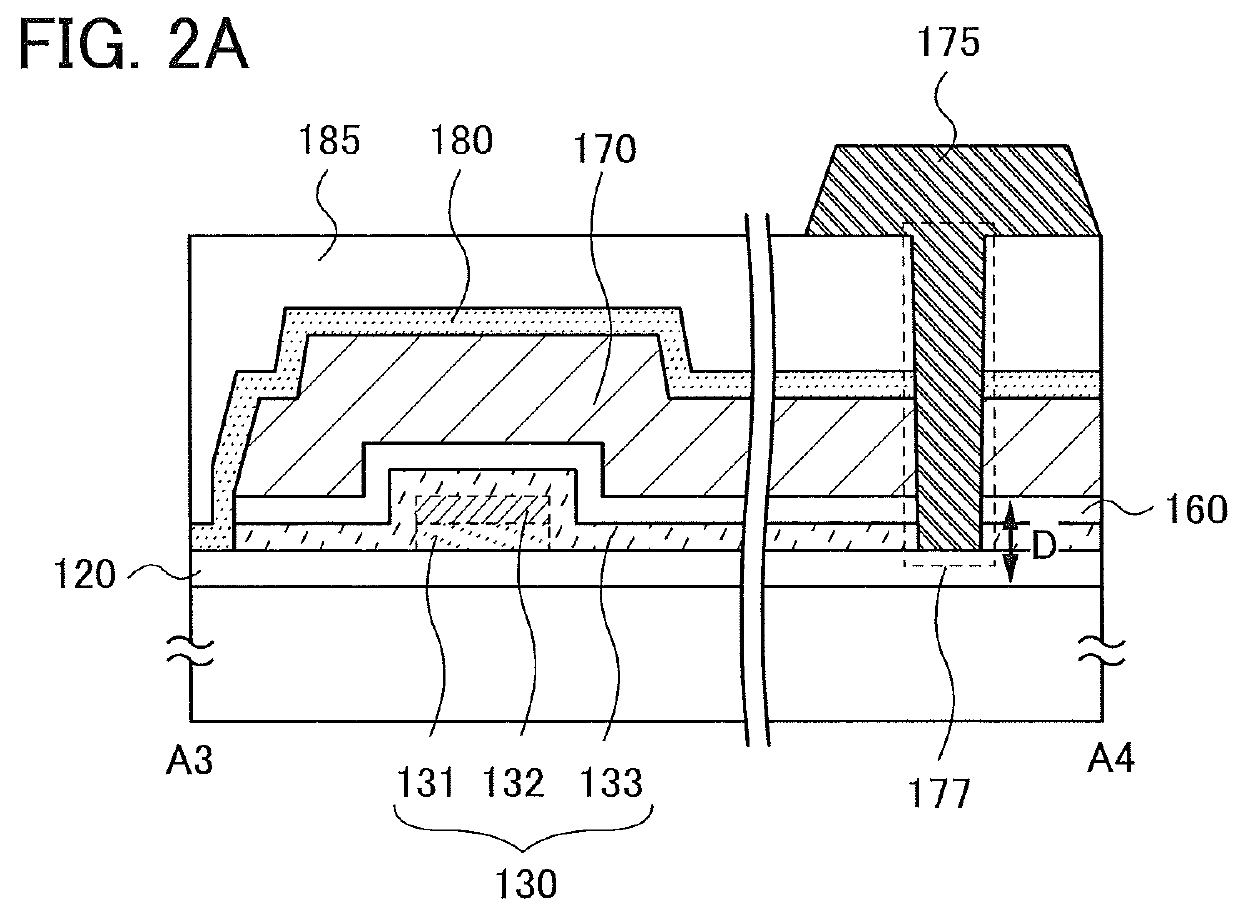
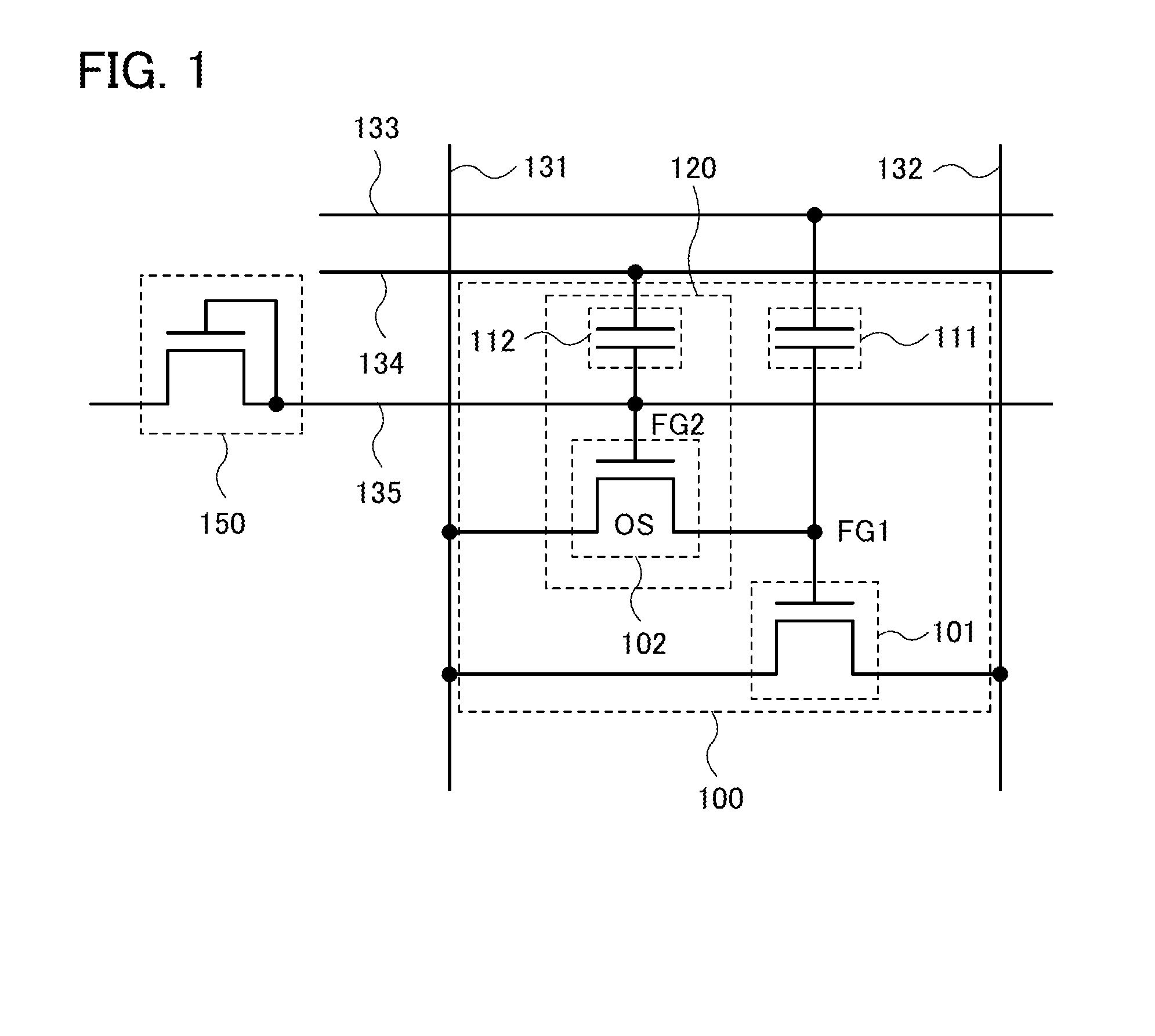
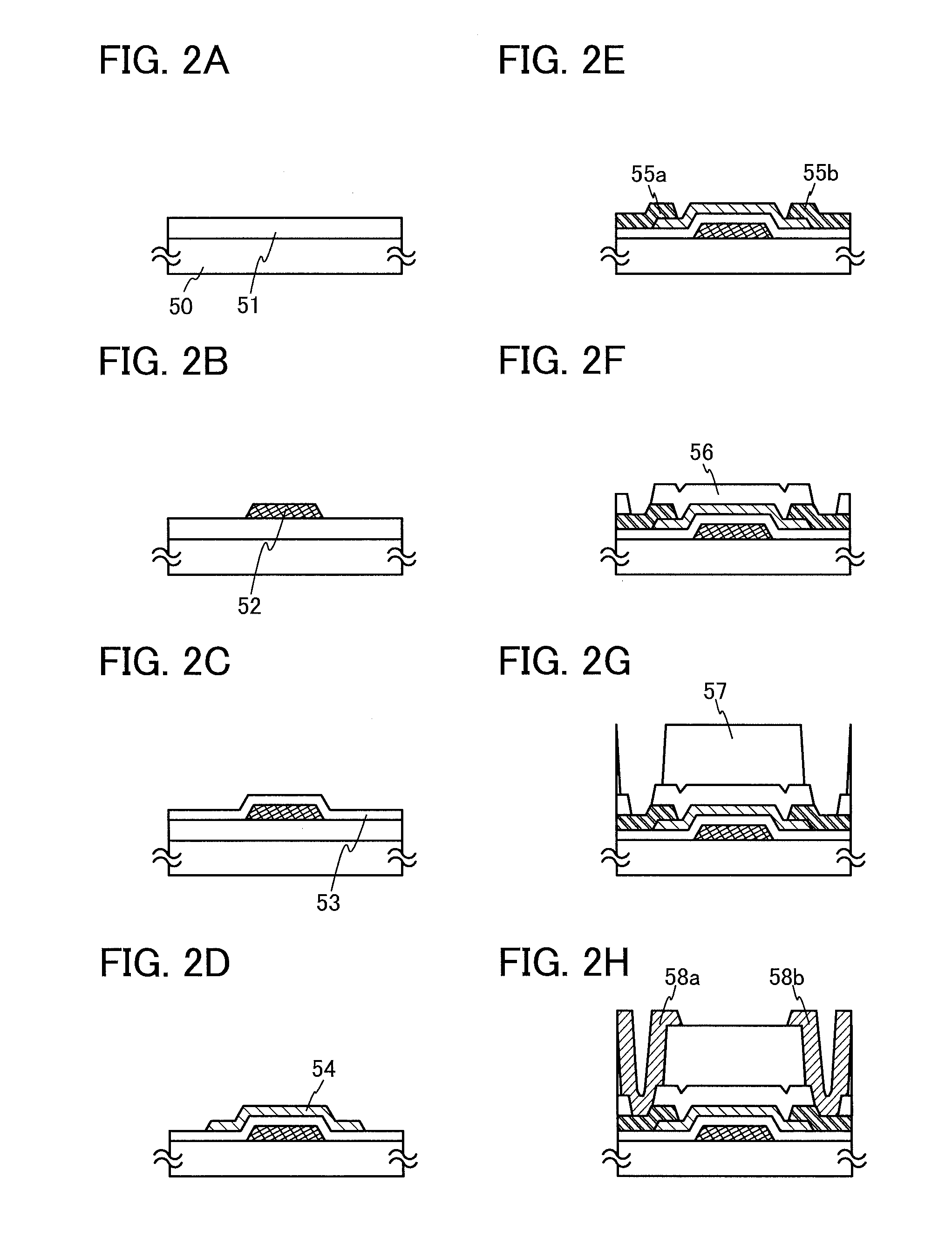
Semiconductor device
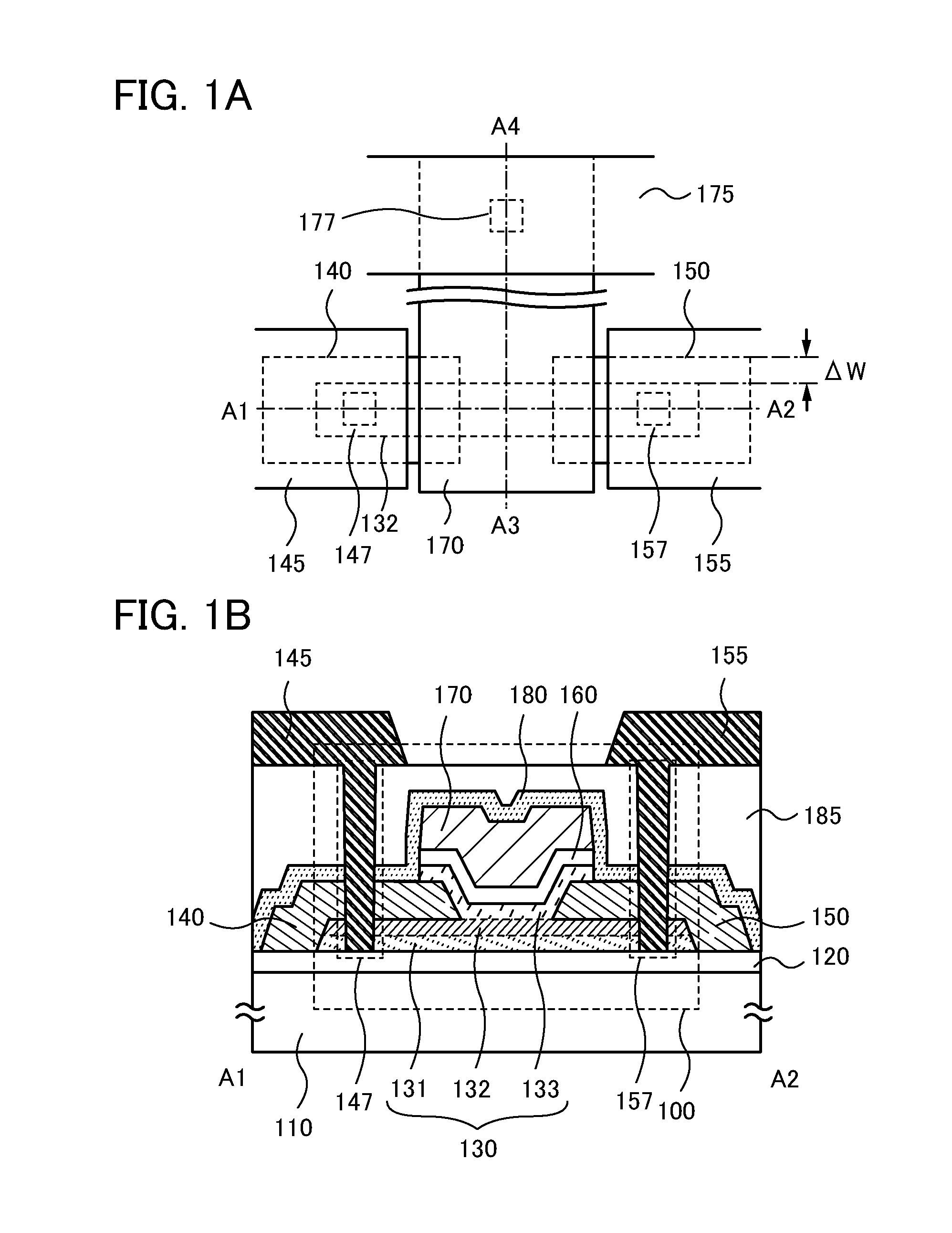
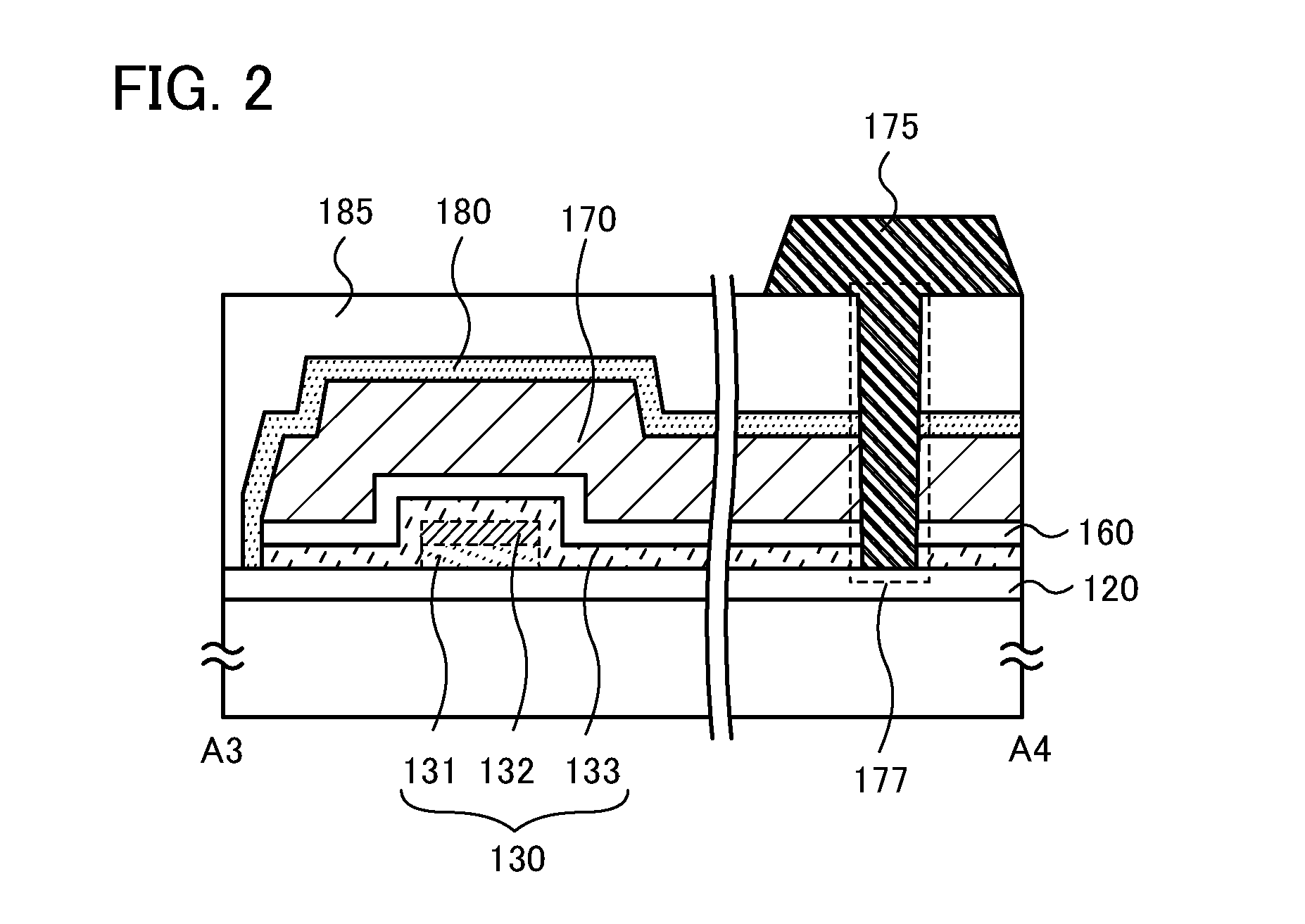
InactiveUS20140326992A1Reduce yieldEasy to integrateTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorMiniaturization
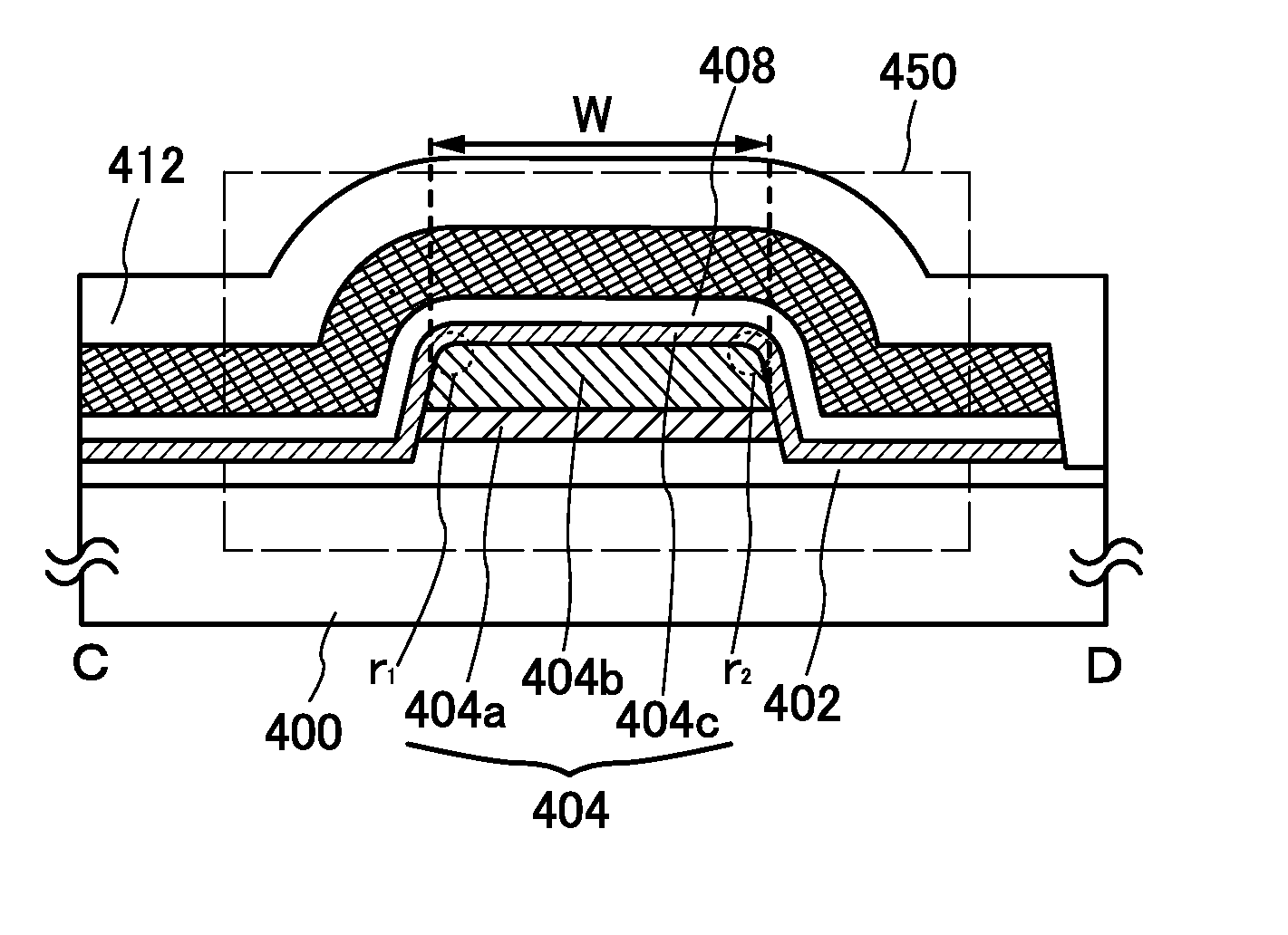
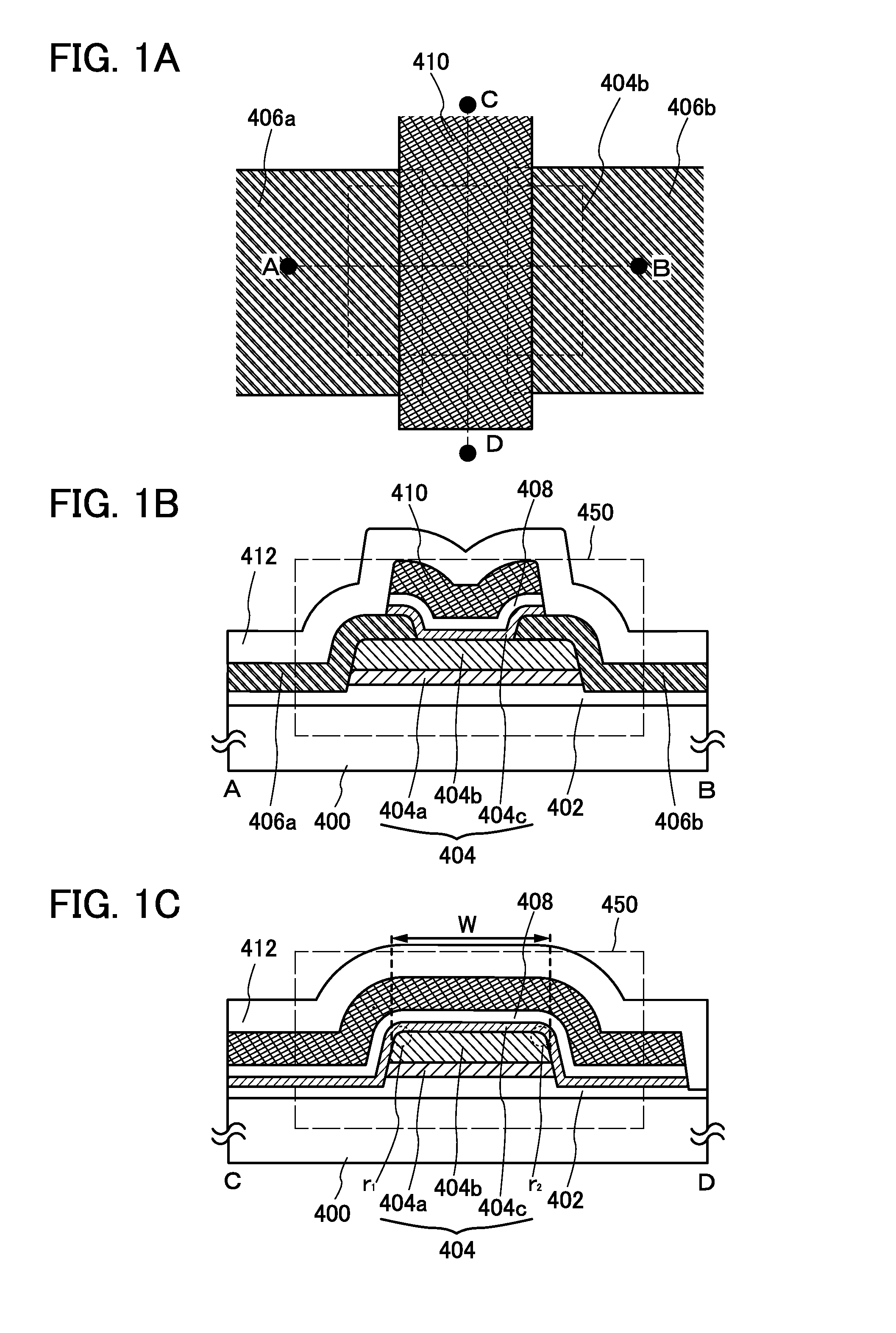
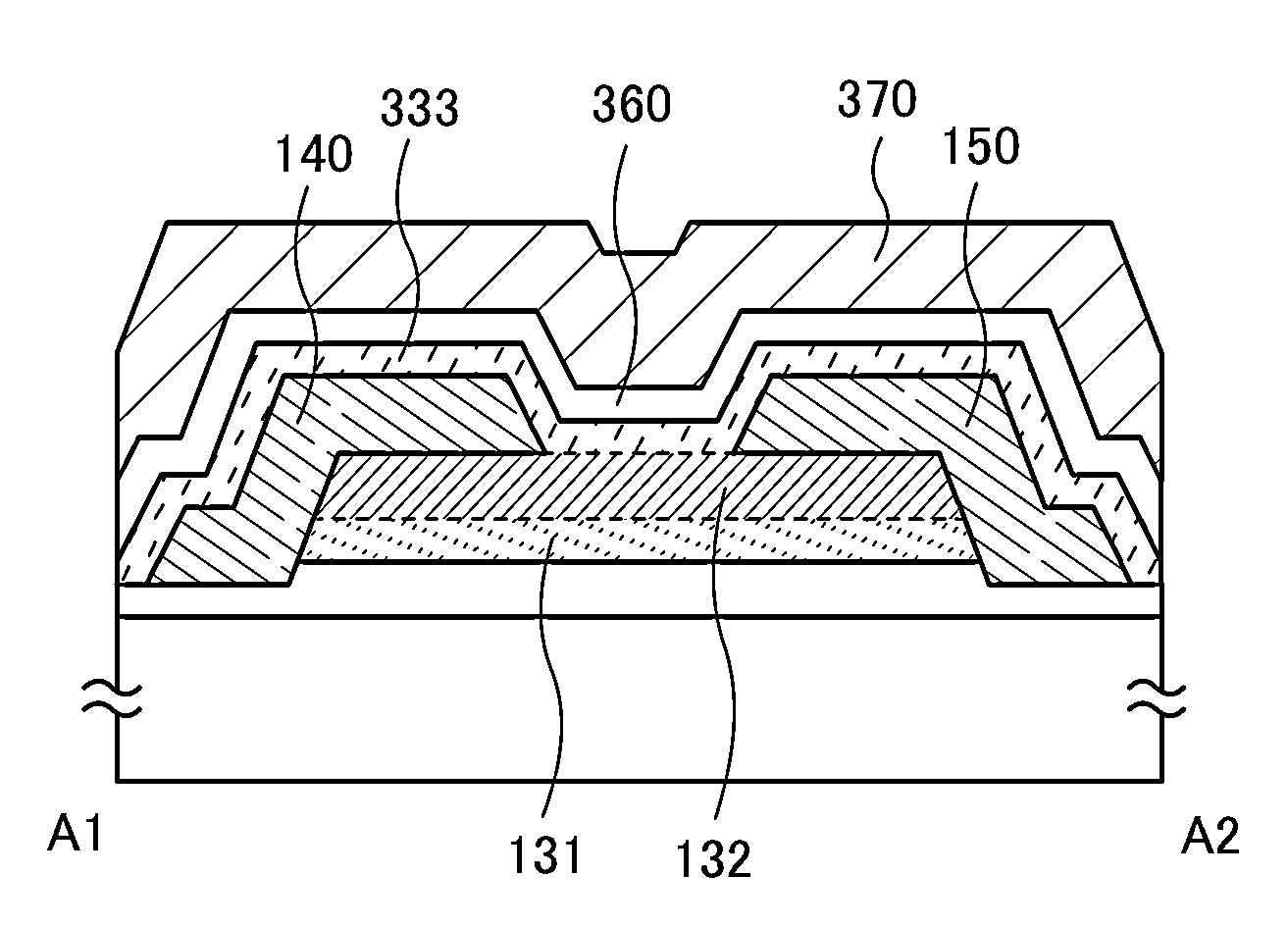
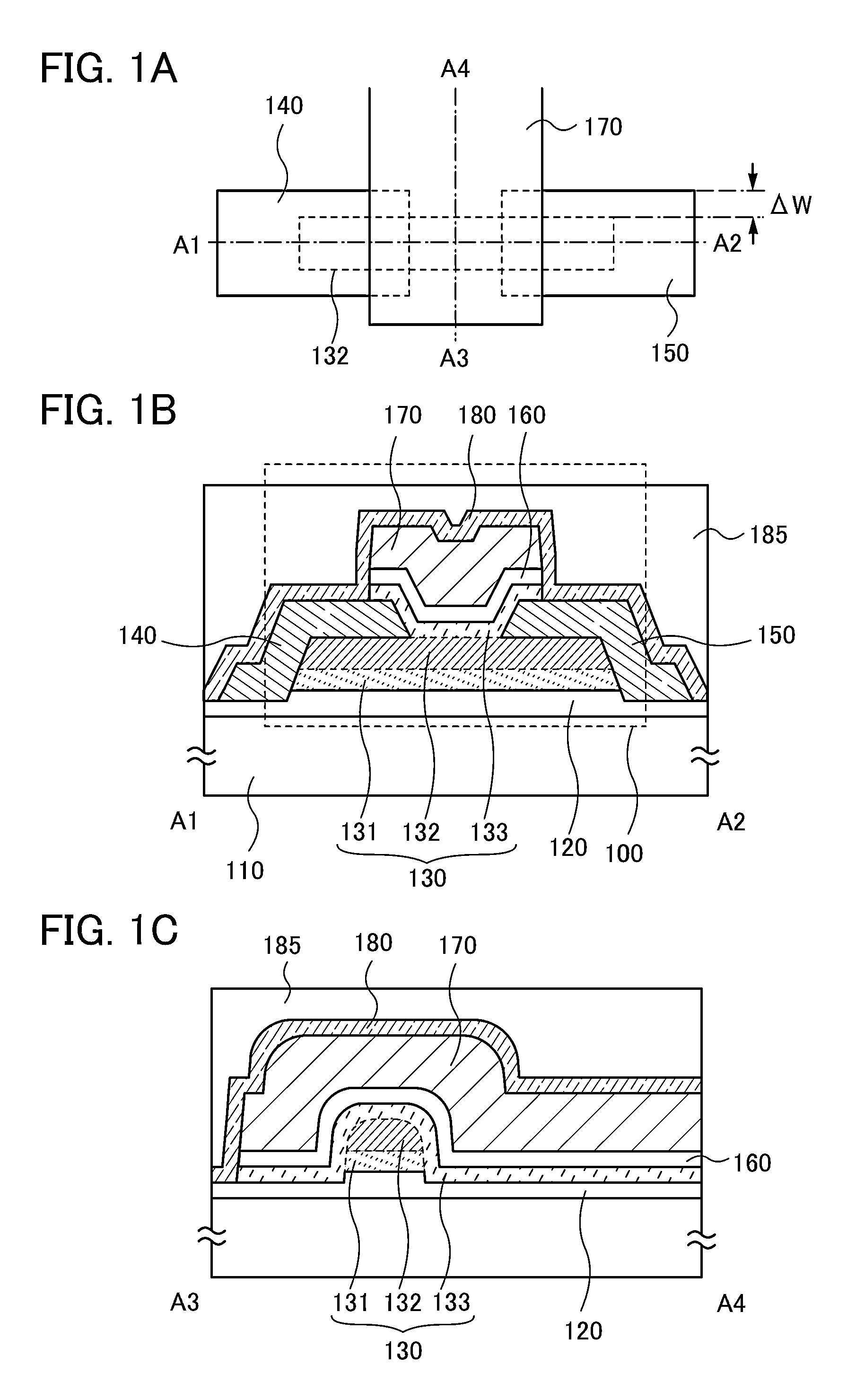
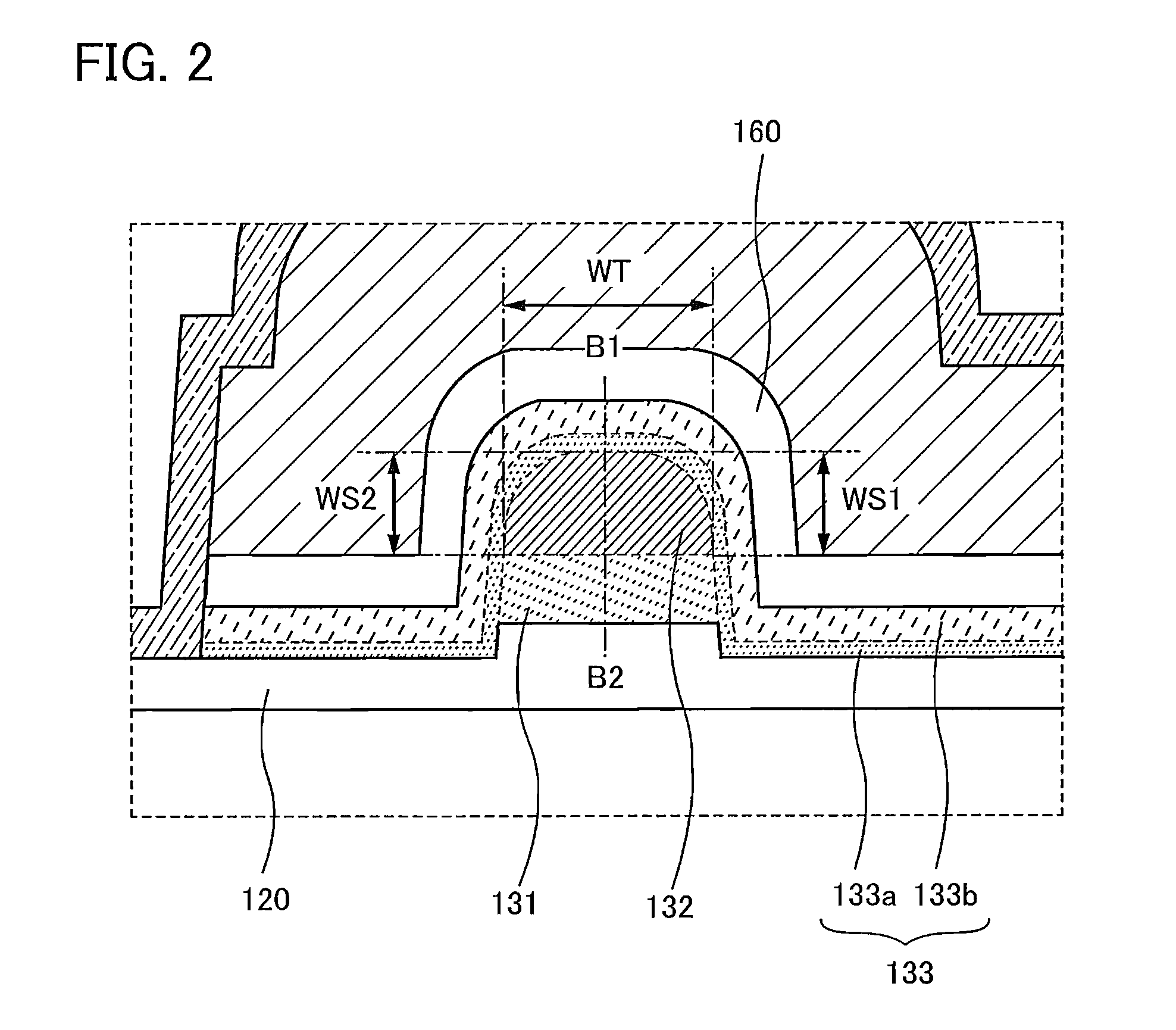
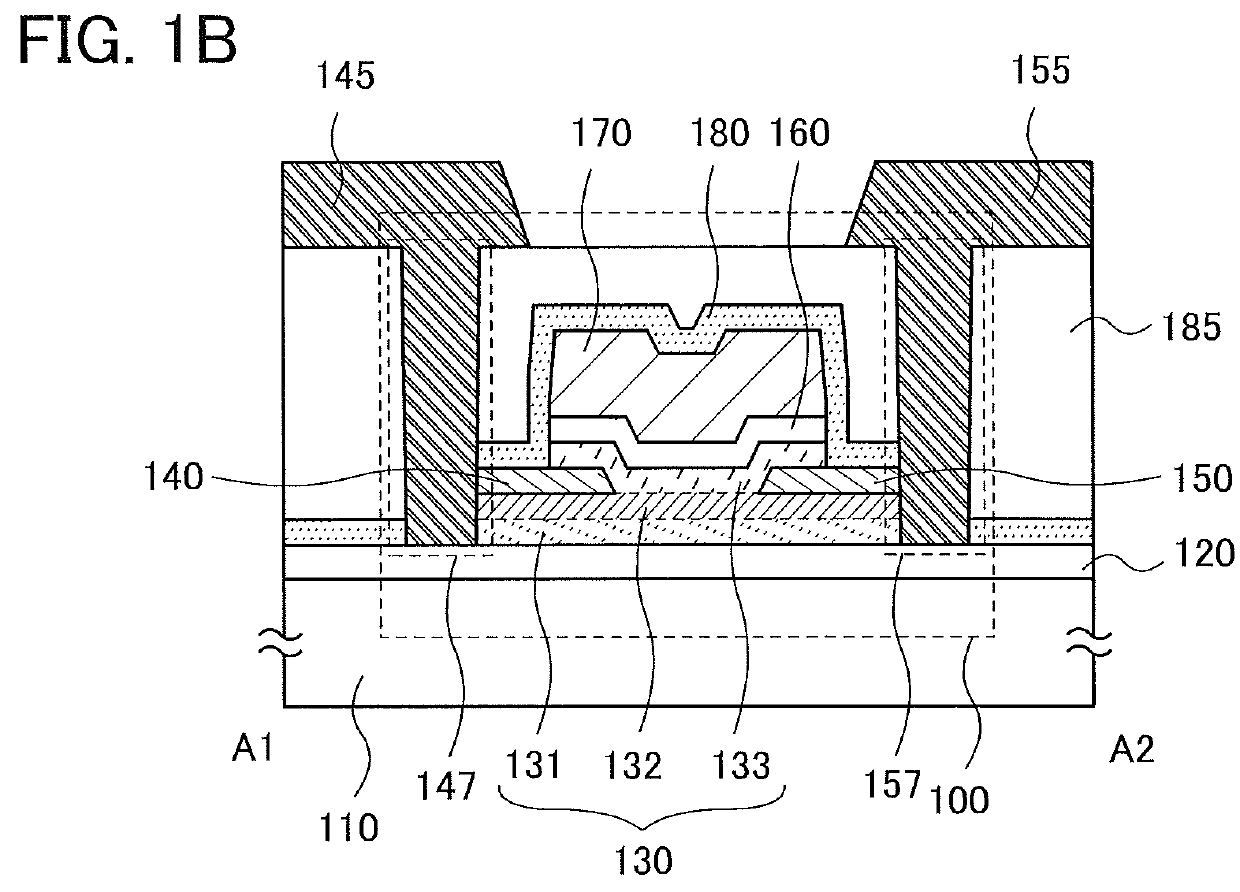
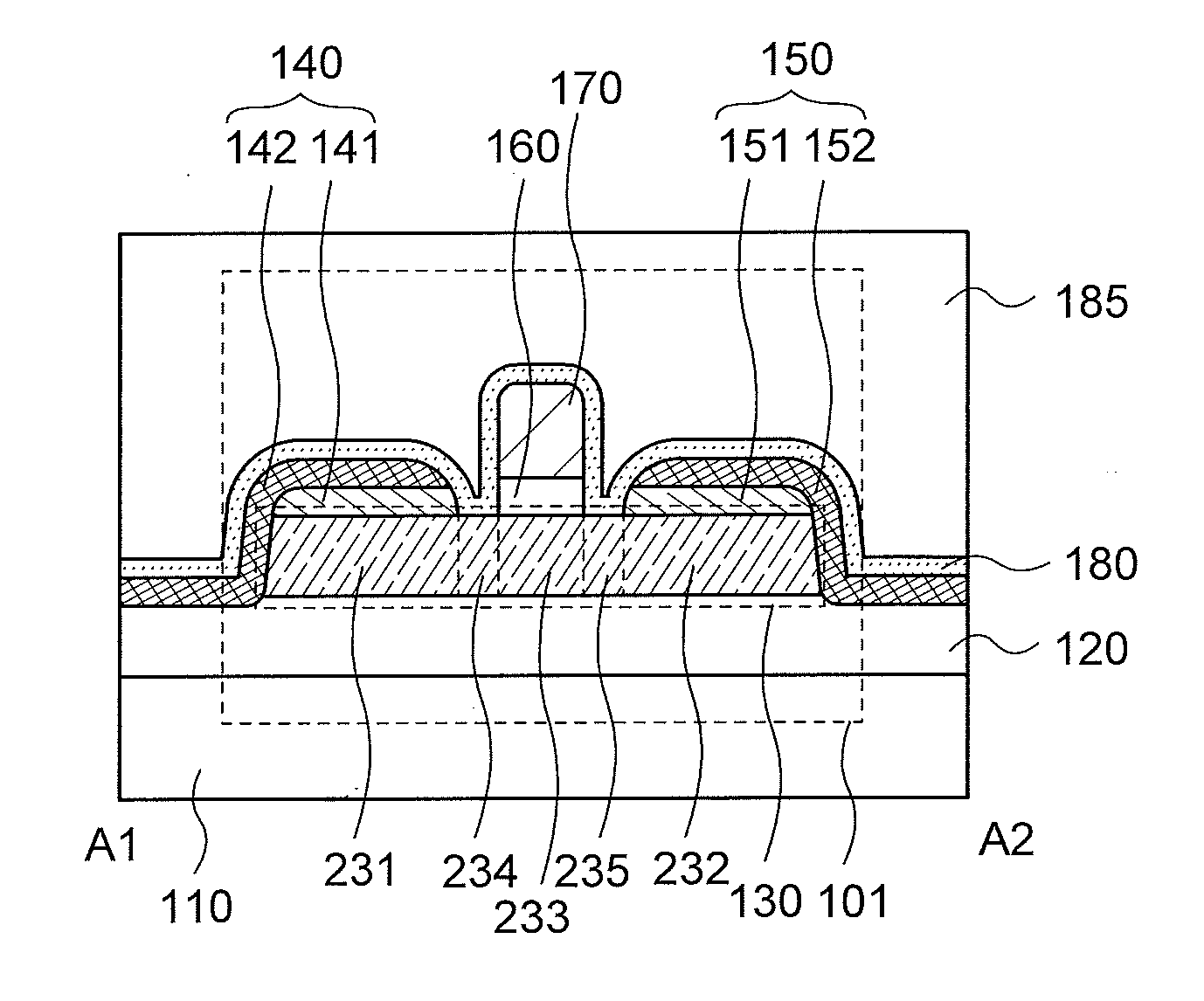
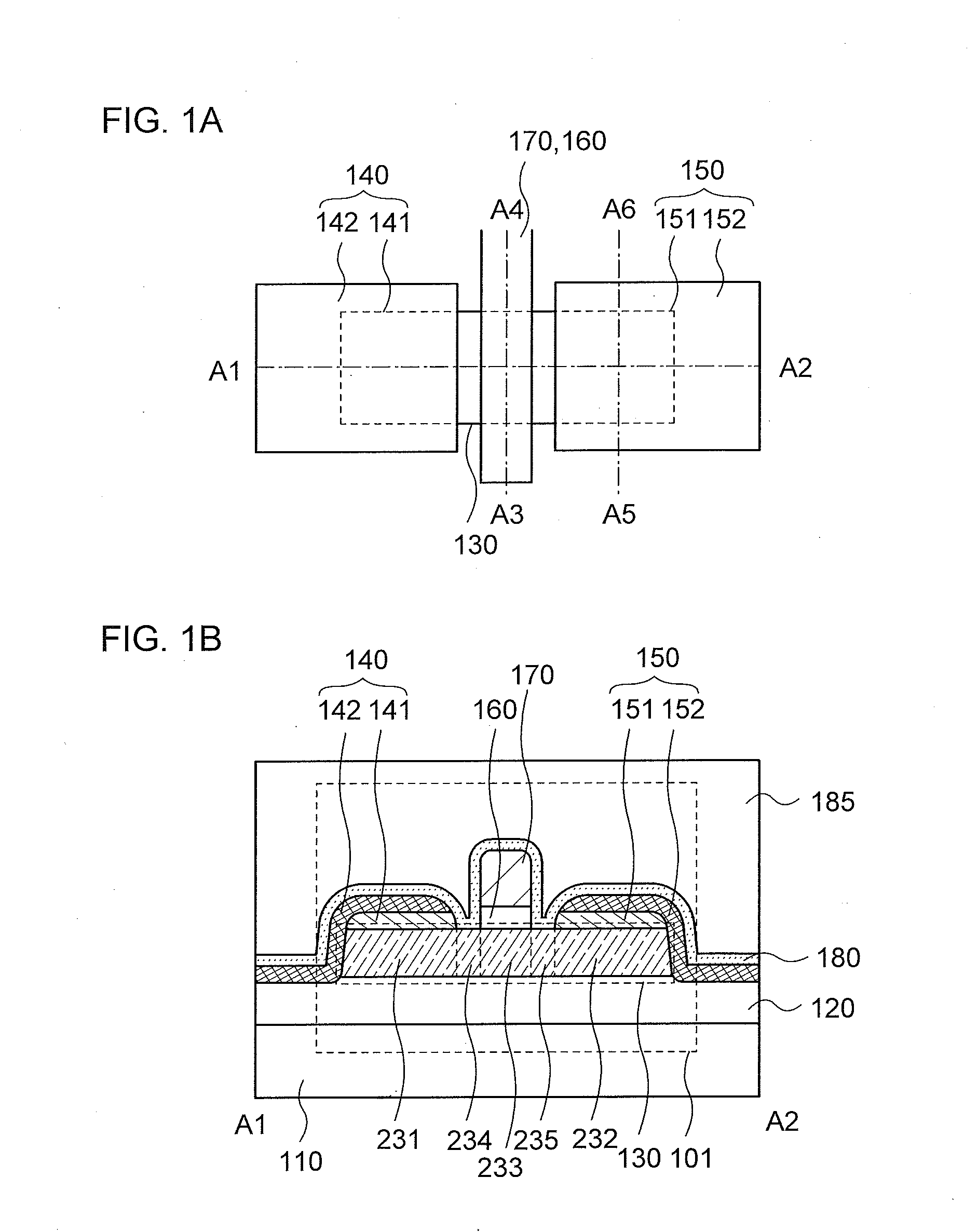
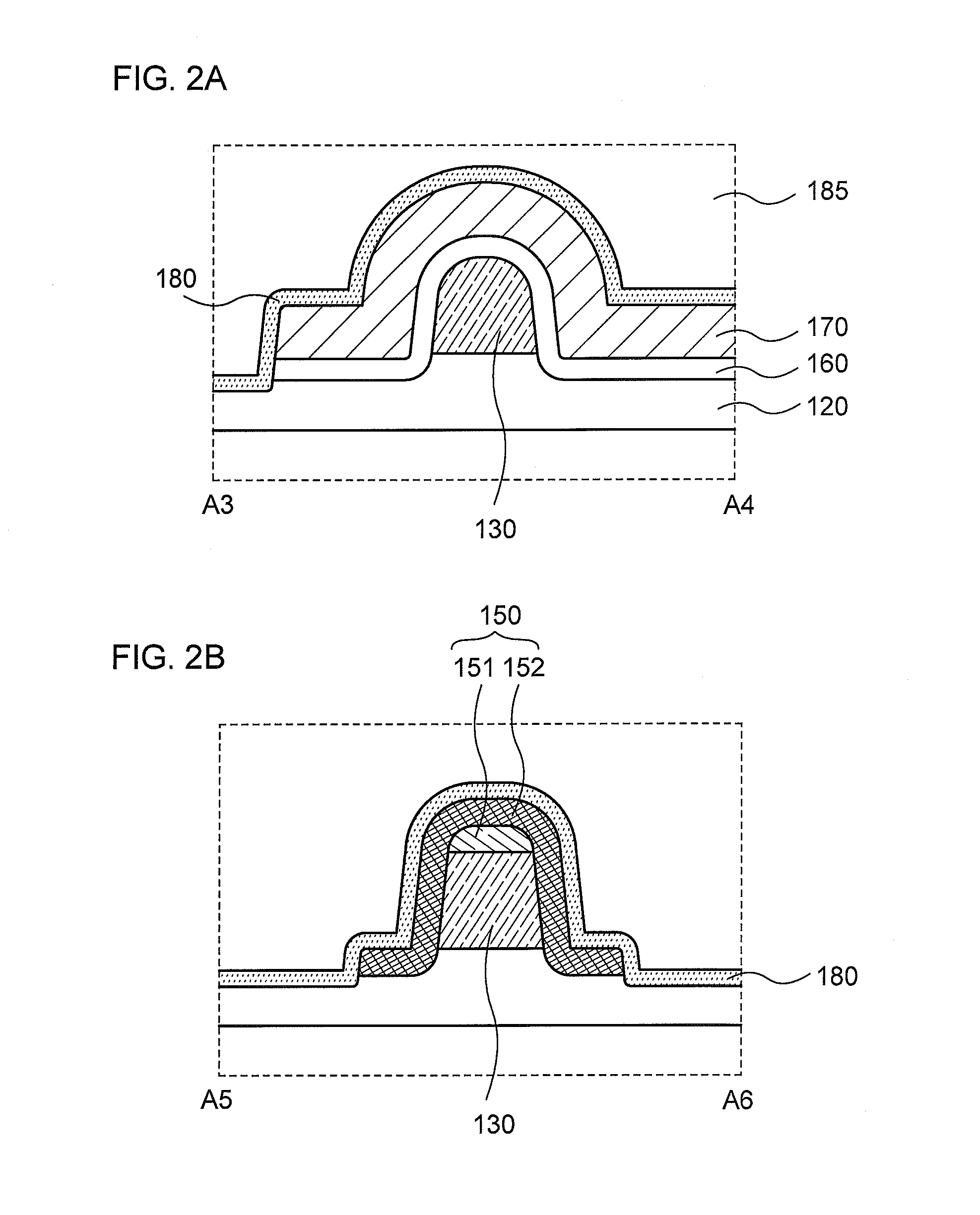
Provided is a semiconductor device that can be miniaturized in a simple process and that can prevent deterioration of electrical characteristics due to miniaturization. The semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor layer, a first conductor in contact with the oxide semiconductor layer, and an insulator in contact with the first conductor. Further, an opening portion is provided in the oxide semiconductor layer, the first conductor, and the insulator. In the opening portion, side surfaces of the oxide semiconductor layer, the first conductor, and the insulator are aligned, and the oxide semiconductor layer and the first conductor are electrically connected to a second conductor by side contact.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
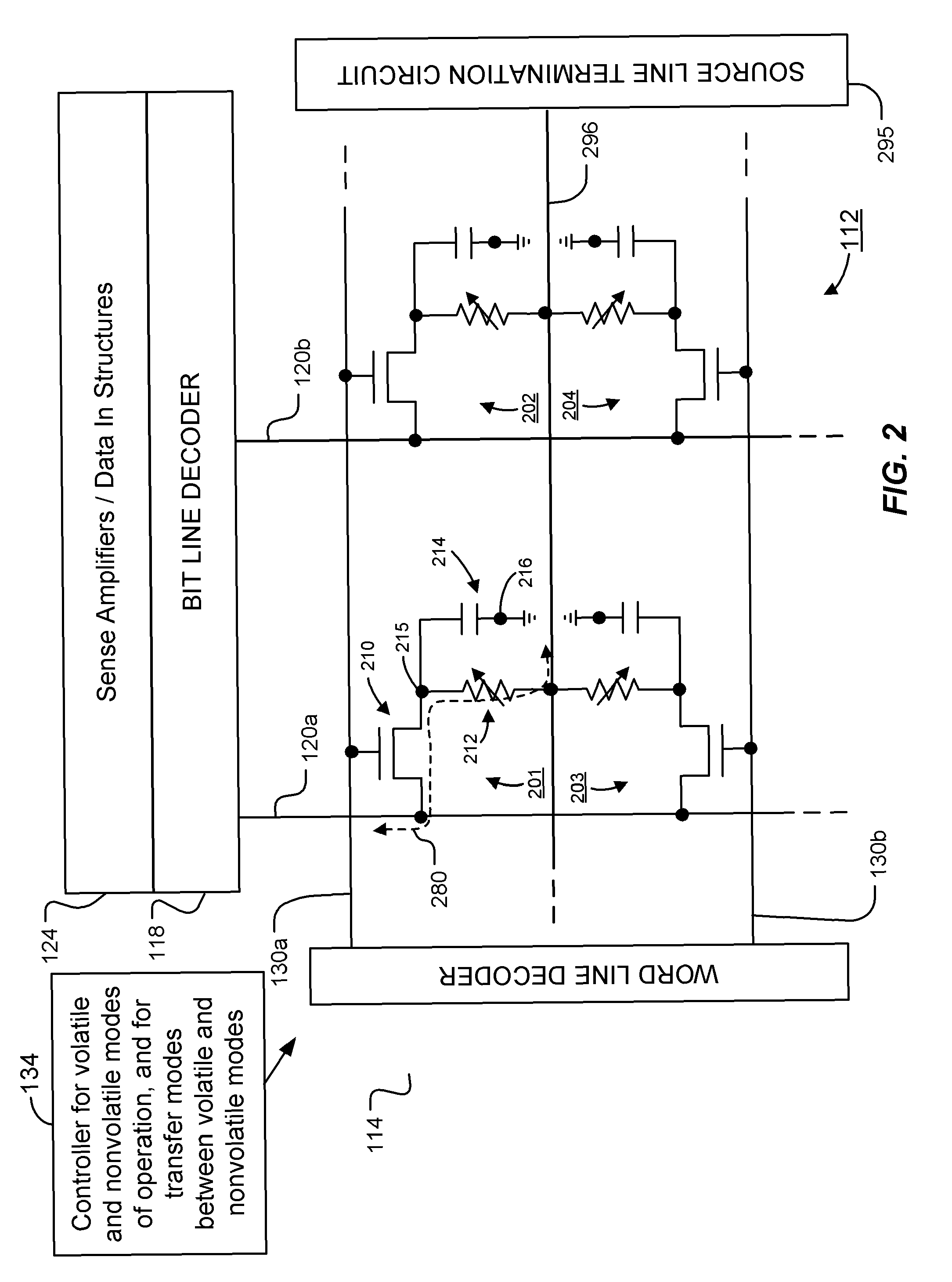
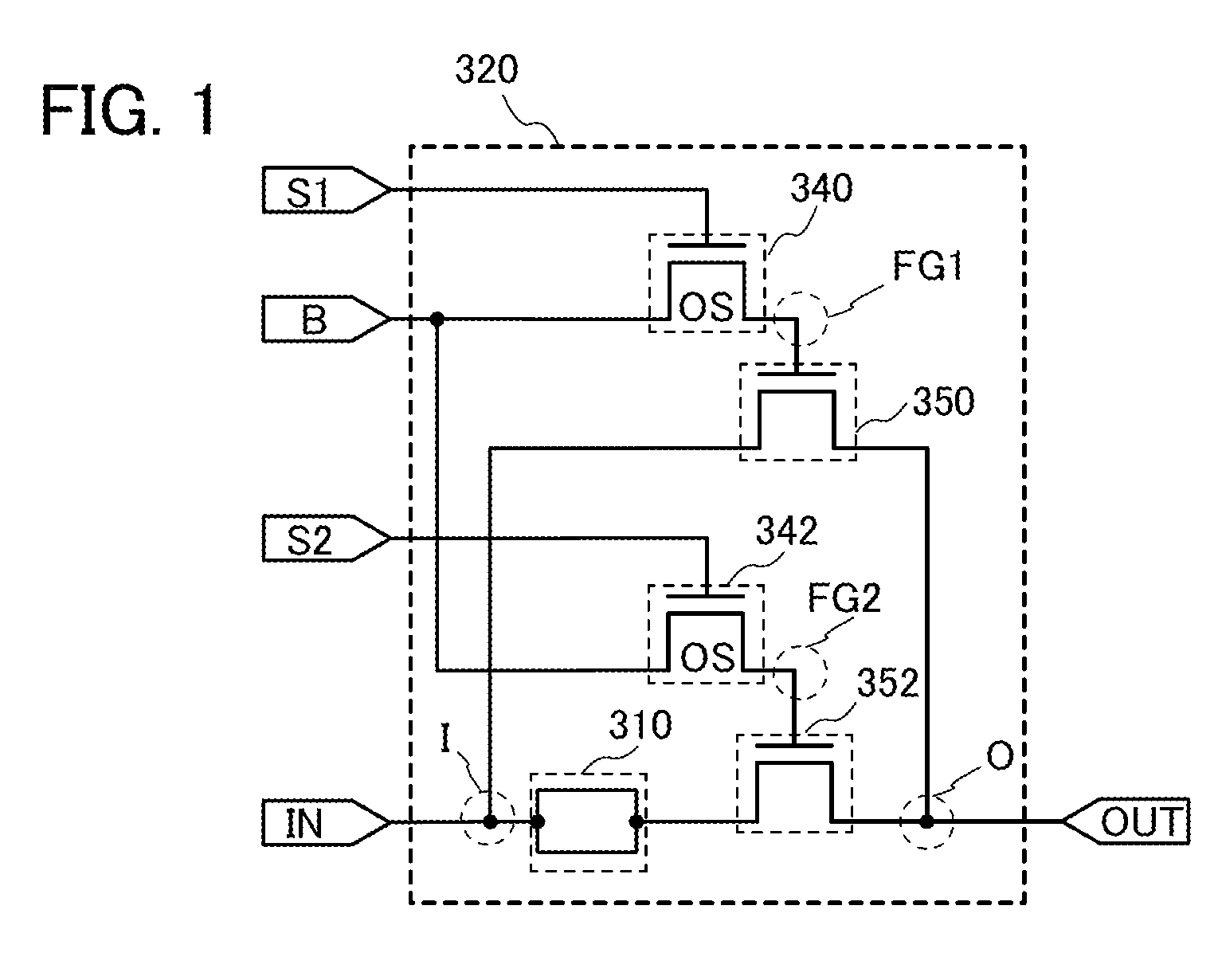
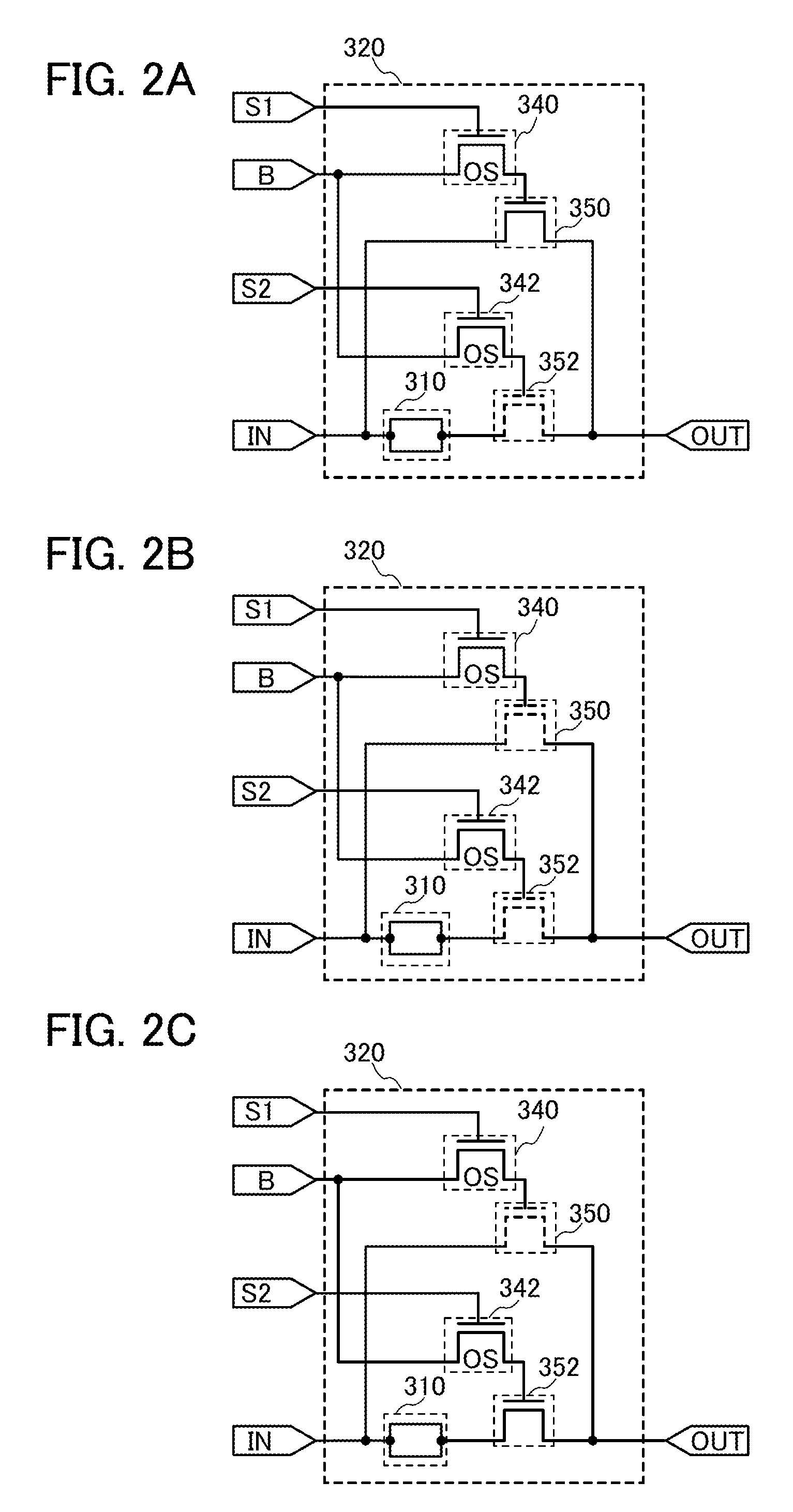
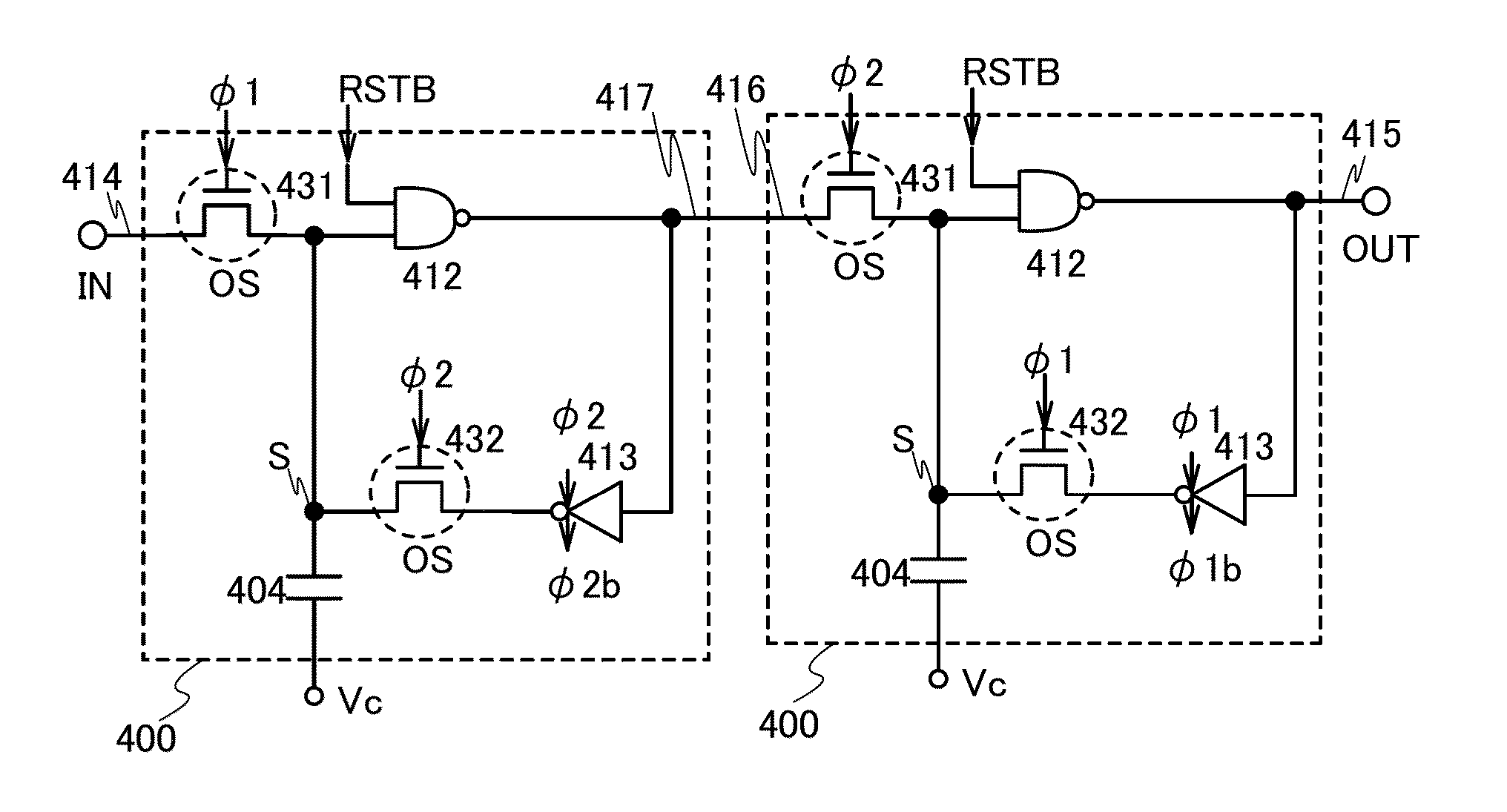
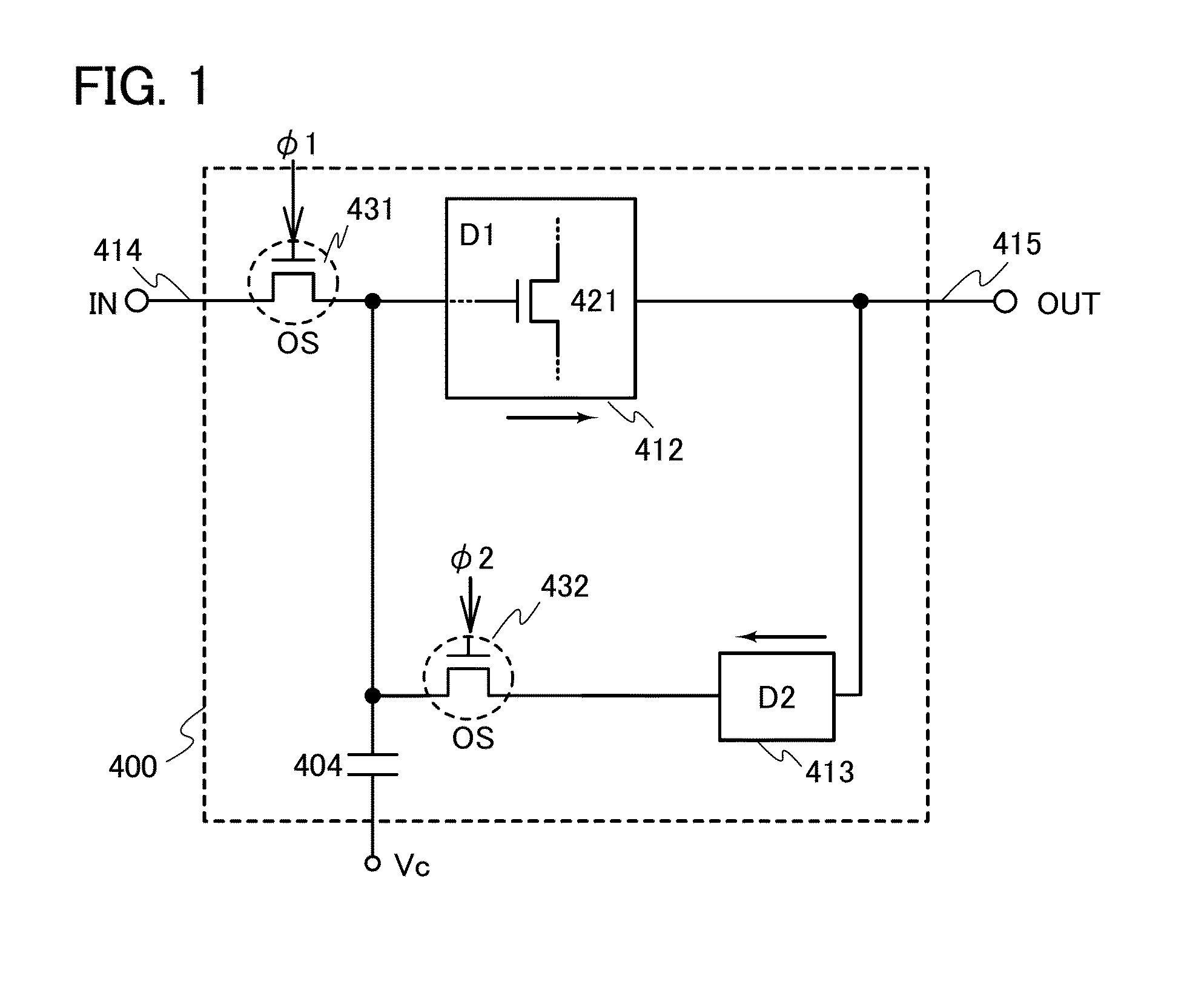
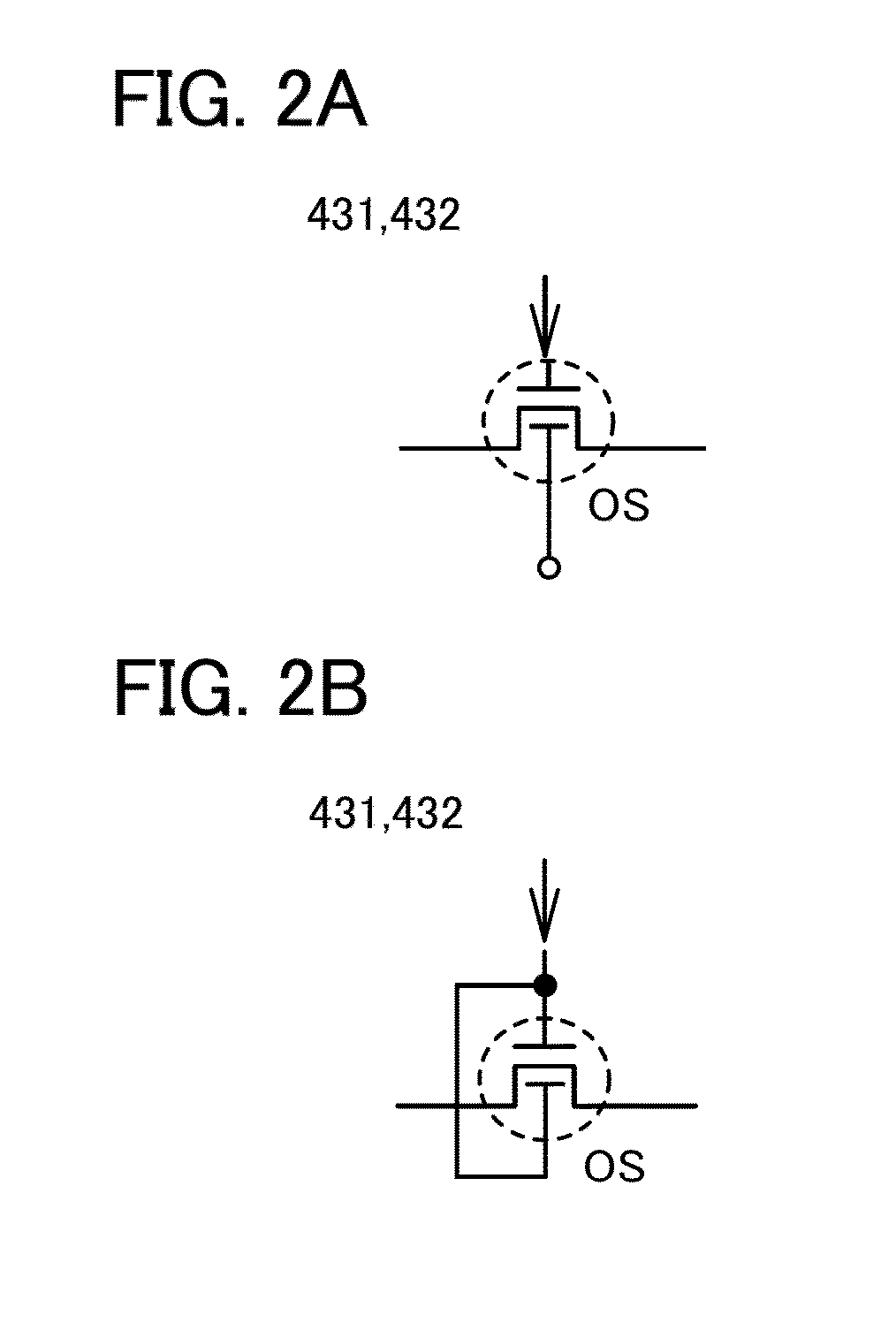
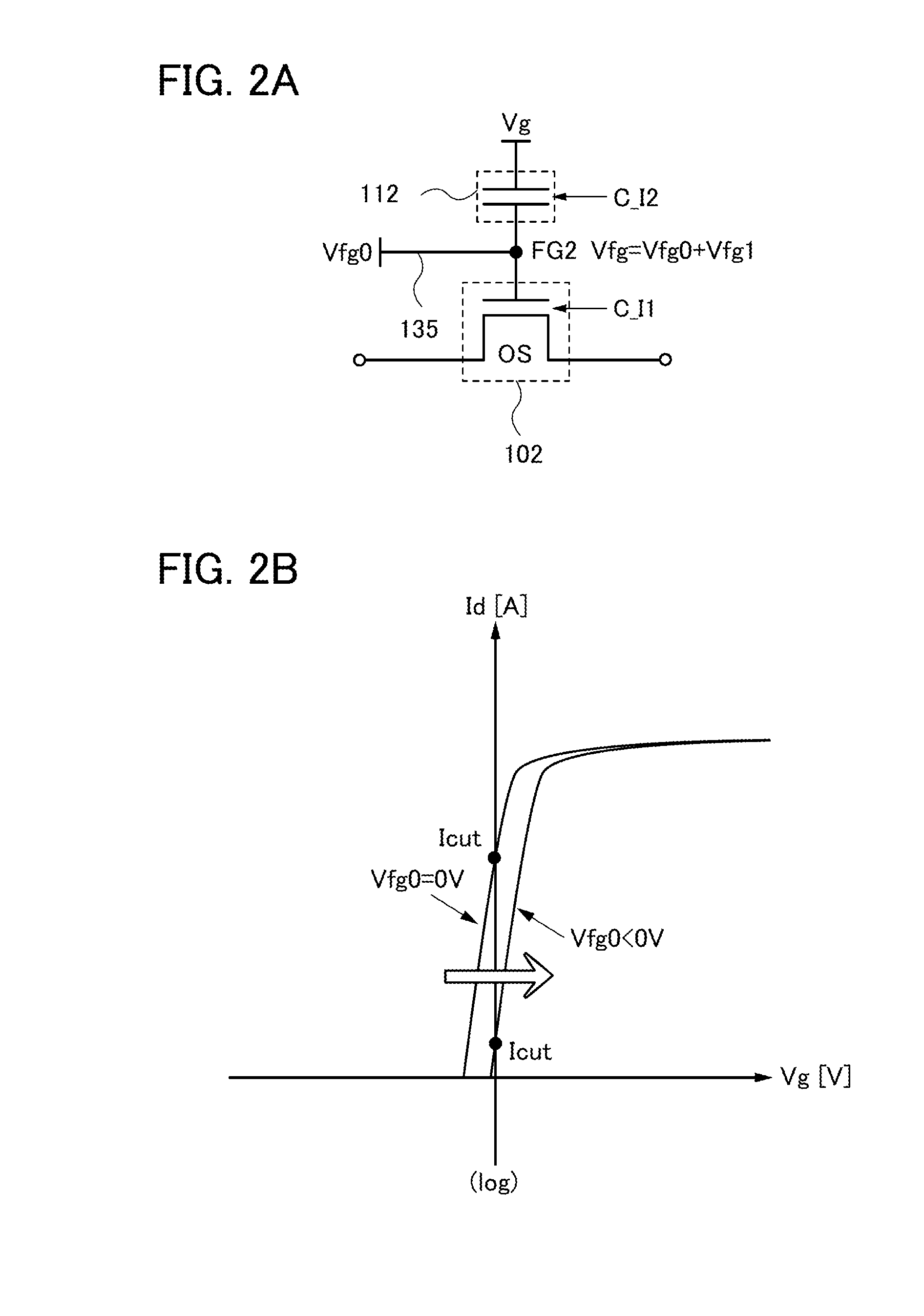
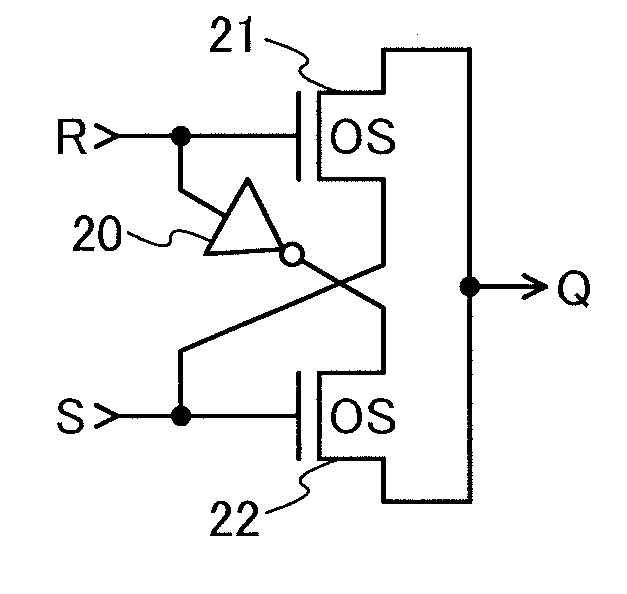
Non-volatile latch circuit and logic circuit, and semiconductor device using the same
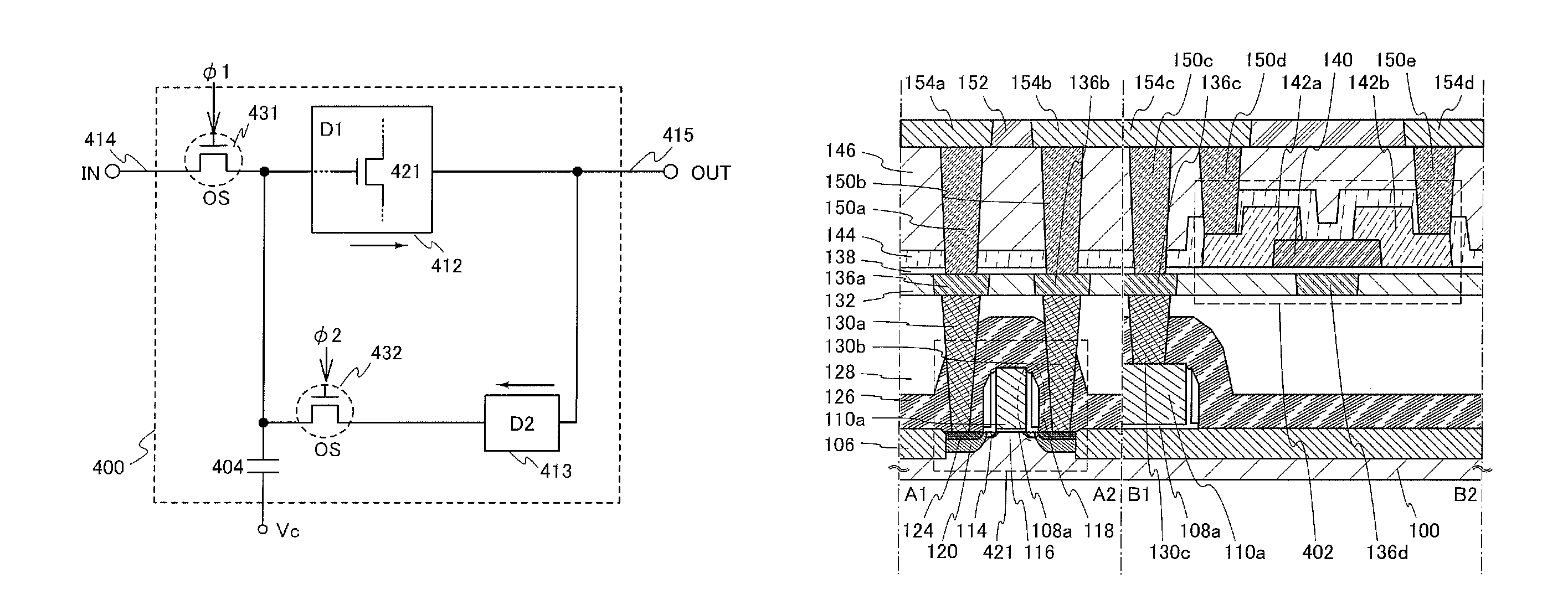
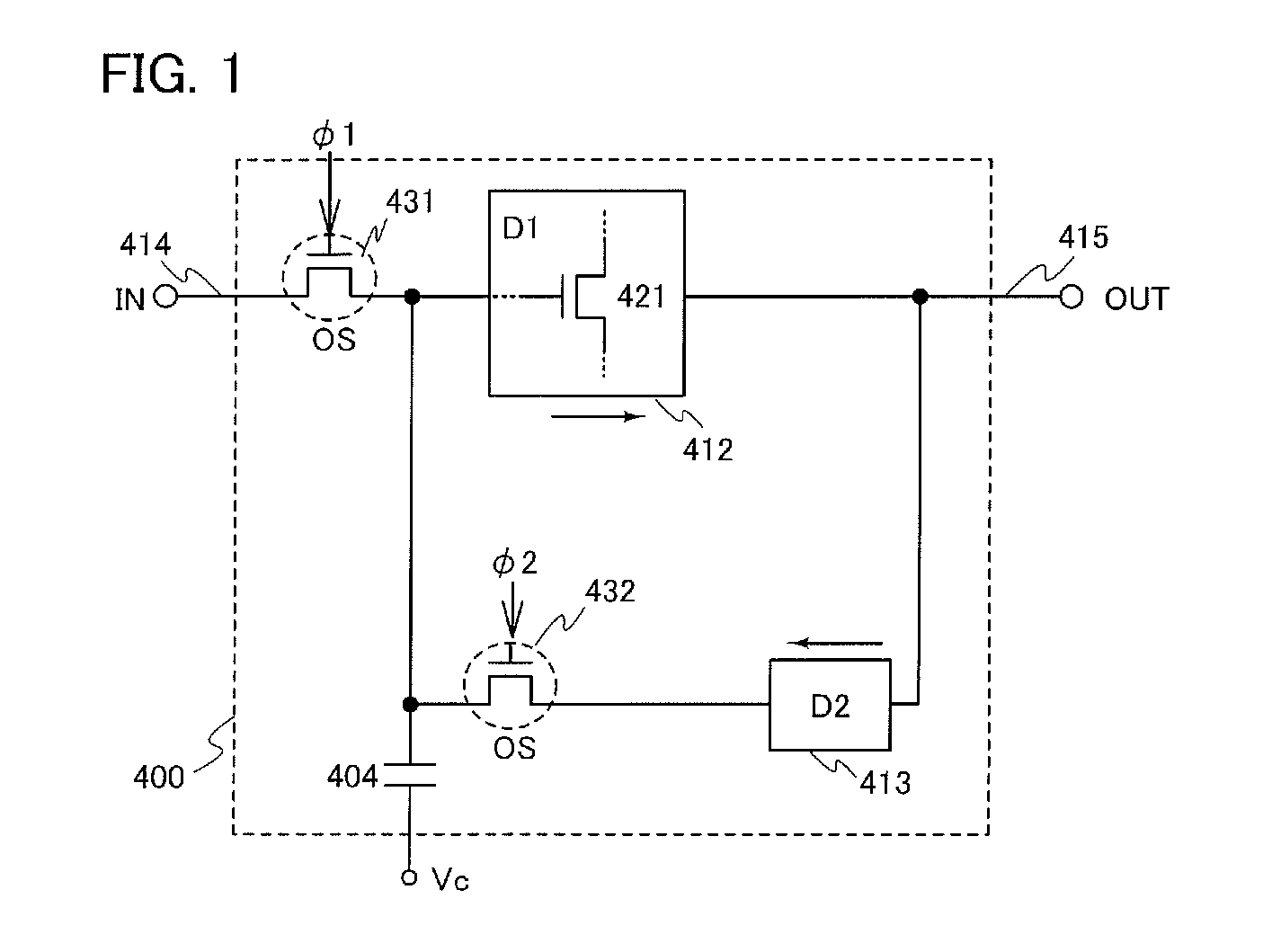
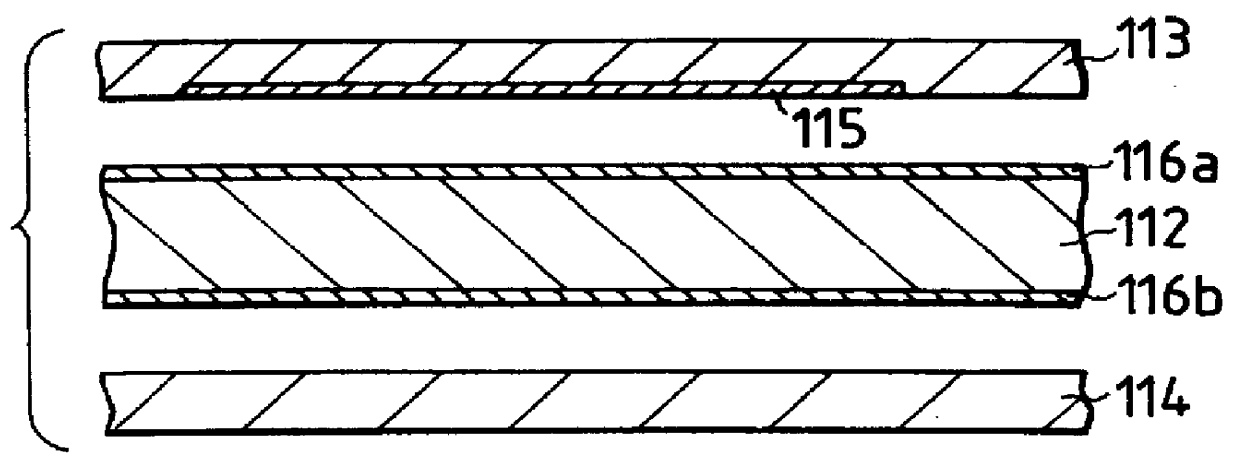
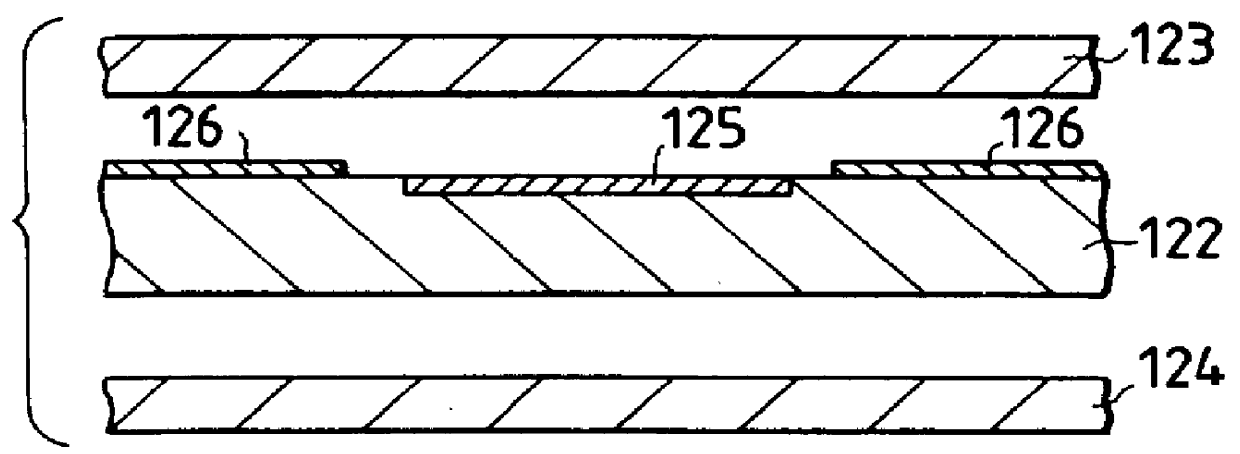
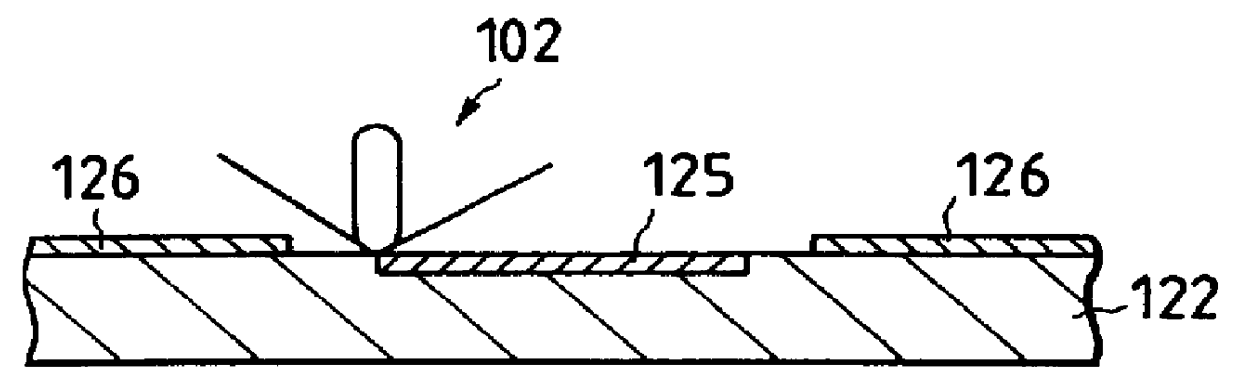
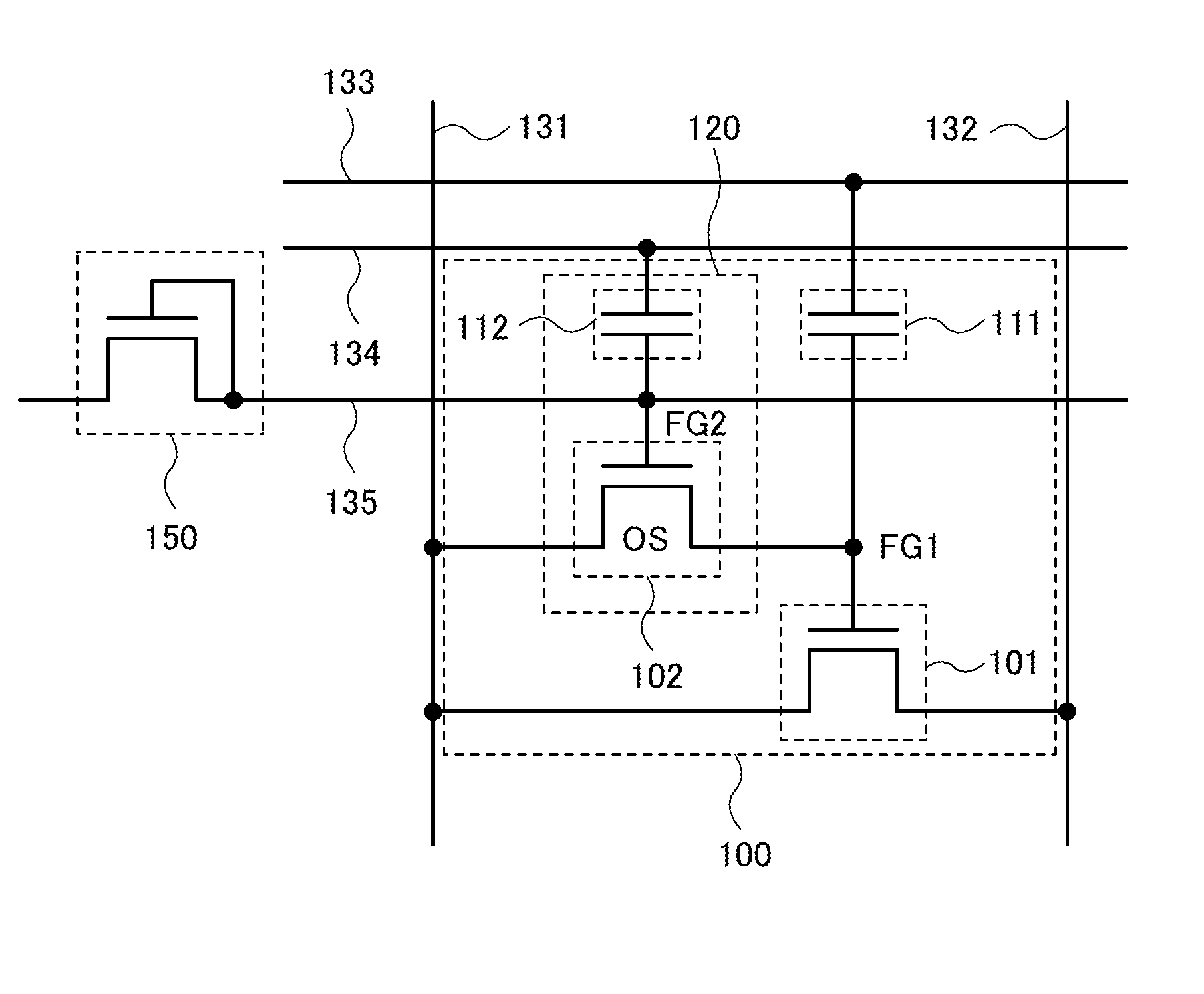
ActiveUS8314637B2Data retentionWide temperature rangeTransistorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor materialsCapacitor
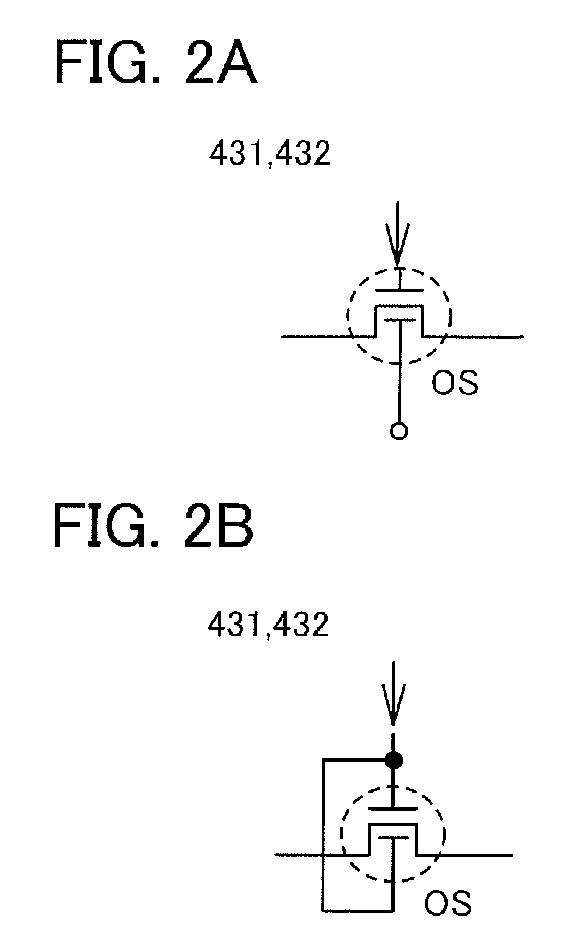
A novel non-volatile latch circuit and a semiconductor device using the non-volatile latch circuit are provided. The latch circuit has a loop structure in which an output of a first element is electrically connected to an input of a second element and an output of the second element is electrically connected to an input of the first element through a second transistor. A transistor using an oxide semiconductor as a semiconductor material of a channel formation region is used as a switching element, and a capacitor is provided to be electrically connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor, whereby data of the latch circuit can be retained, and a non-volatile latch circuit can thus be formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20140339544A1Easy to integrateReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
Provided is a semiconductor device in which deterioration of electric characteristics which becomes more noticeable as the semiconductor device is miniaturized can be suppressed. The semiconductor device includes a first oxide film, an oxide semiconductor film over the first oxide film, a source electrode and a drain electrode in contact with the oxide semiconductor film, a second oxide film over the oxide semiconductor film, the source electrode, and the drain electrode, a gate insulating film over the second oxide film, and a gate electrode in contact with the gate insulating film. A top end portion of the oxide semiconductor film is curved when seen in a channel width direction.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
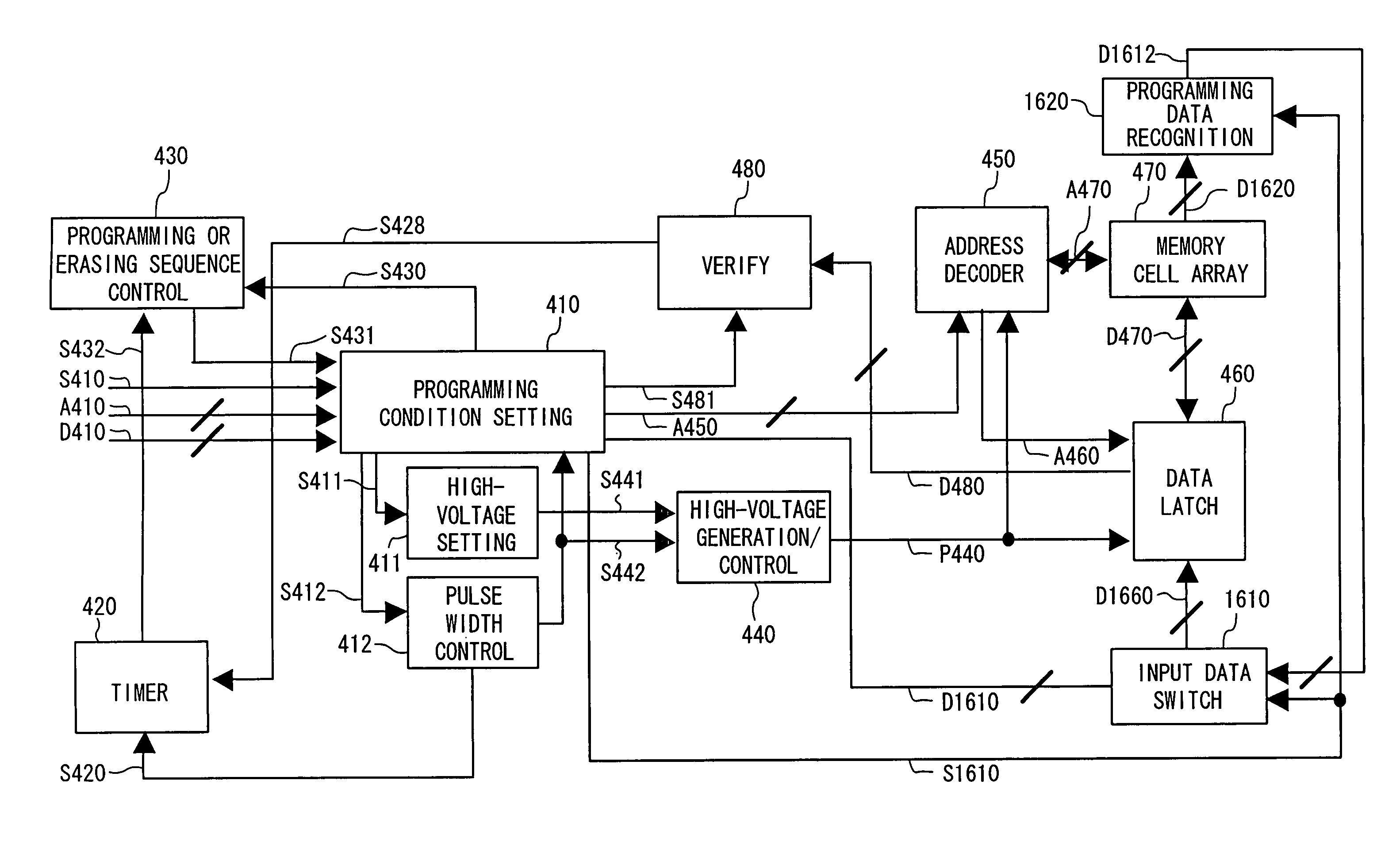
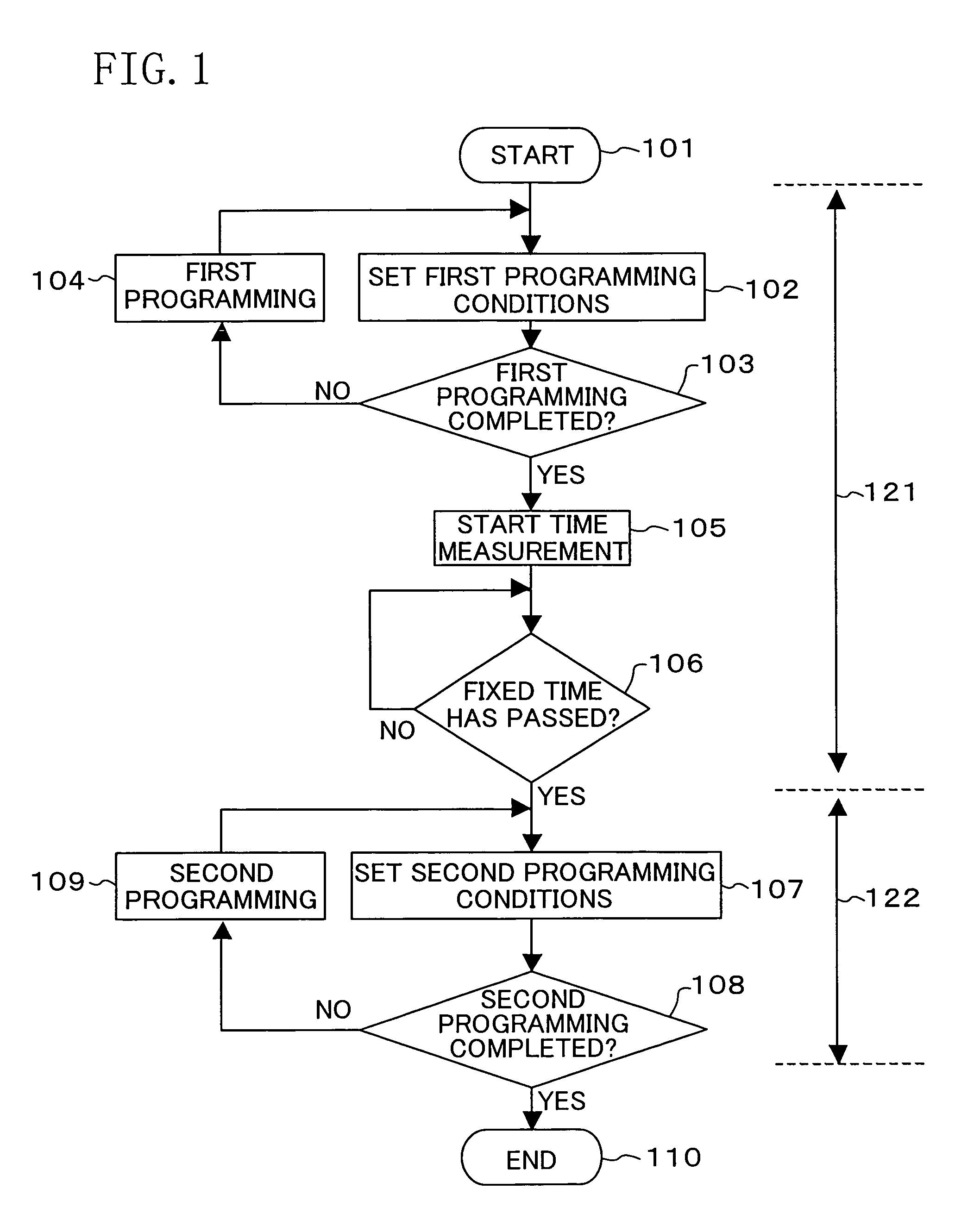
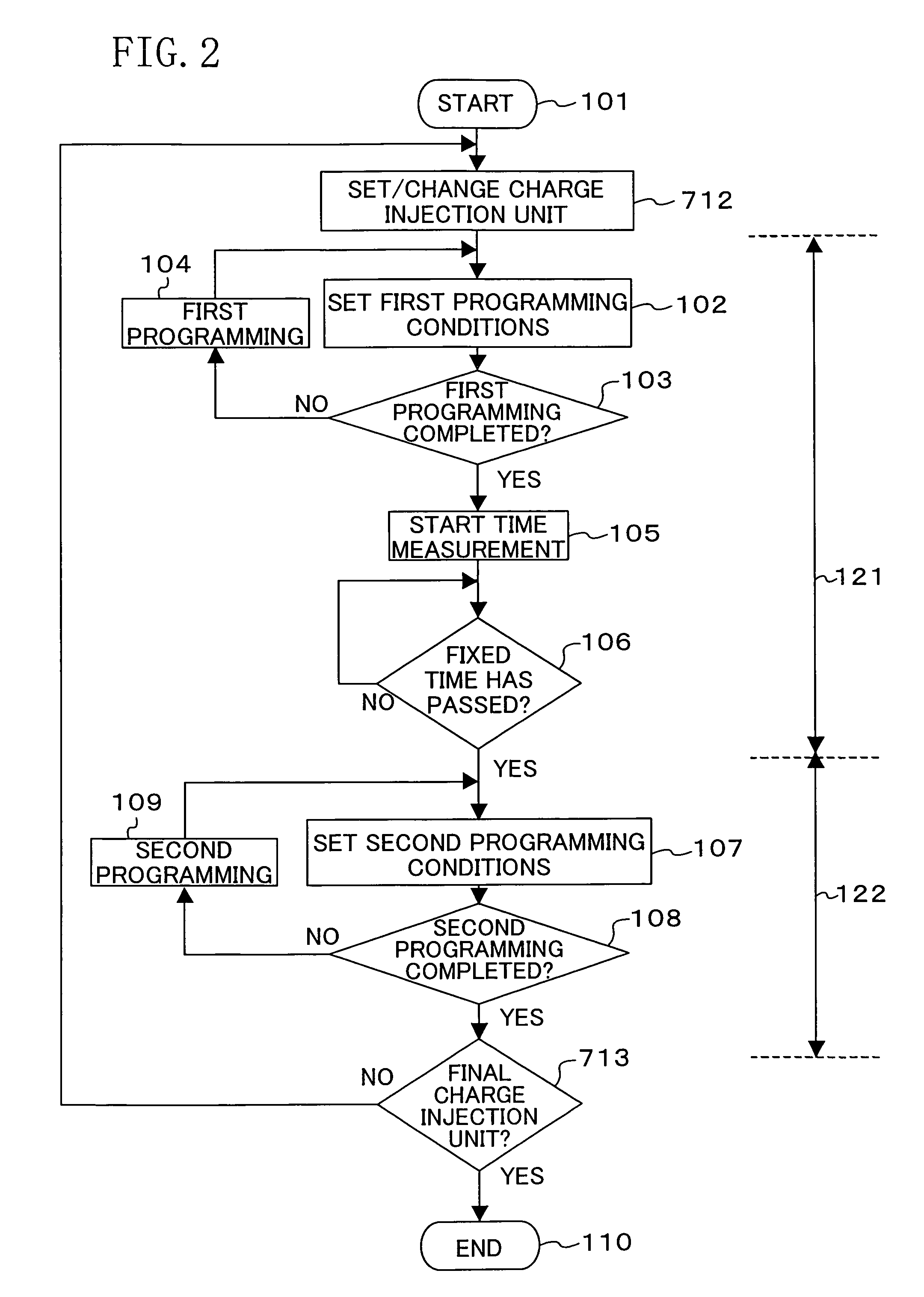
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and programming or erasing method therefor
ActiveUS7460410B2Inhibit deteriorationData retentionRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge injectionCharge loss
In a nonvolatile memory cell having a trap layer, programming or erasing is made in a sequence of first charge injection with a given wait time being secured and second charge injection executed after the first charge injection. Surrounding charge that deteriorates the data retention characteristic is reduced by use of initial variation occurring immediately after programming (charge loss phenomenon due to binding of injected charge with the surrounding charge in an extremely short time), and then the charge loss due to the initial variation is compensated, to thereby improve the data retention characteristic.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
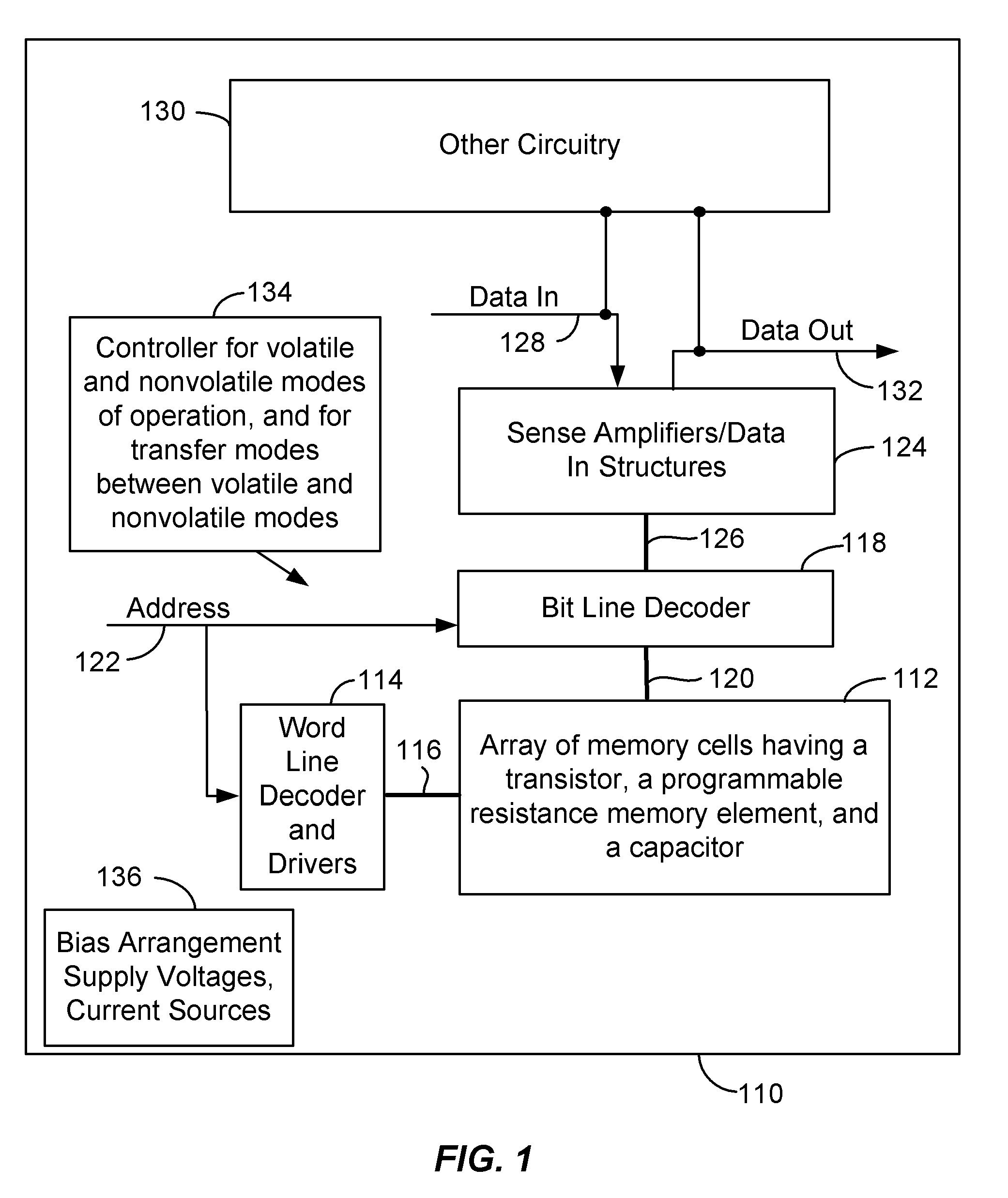
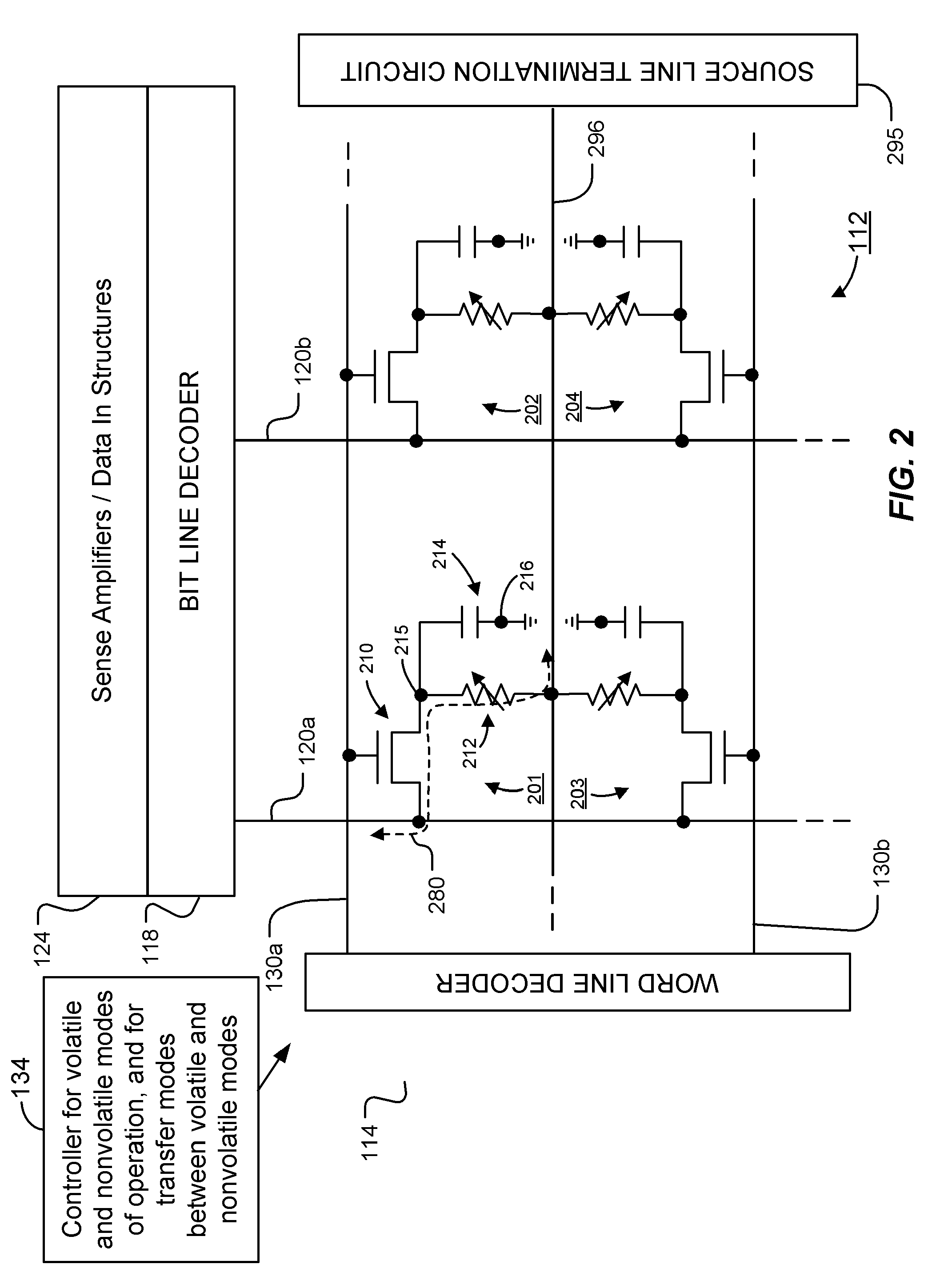
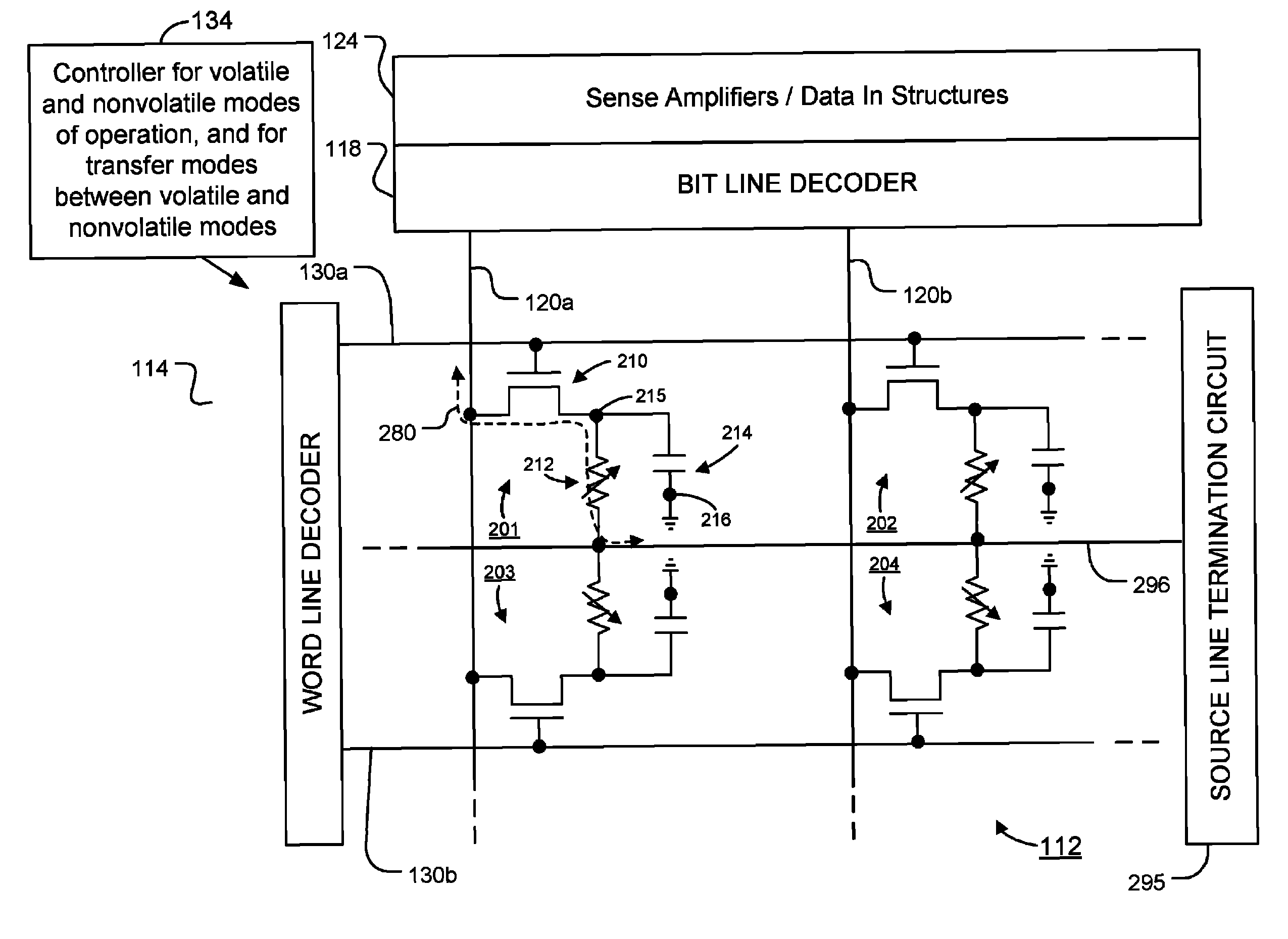
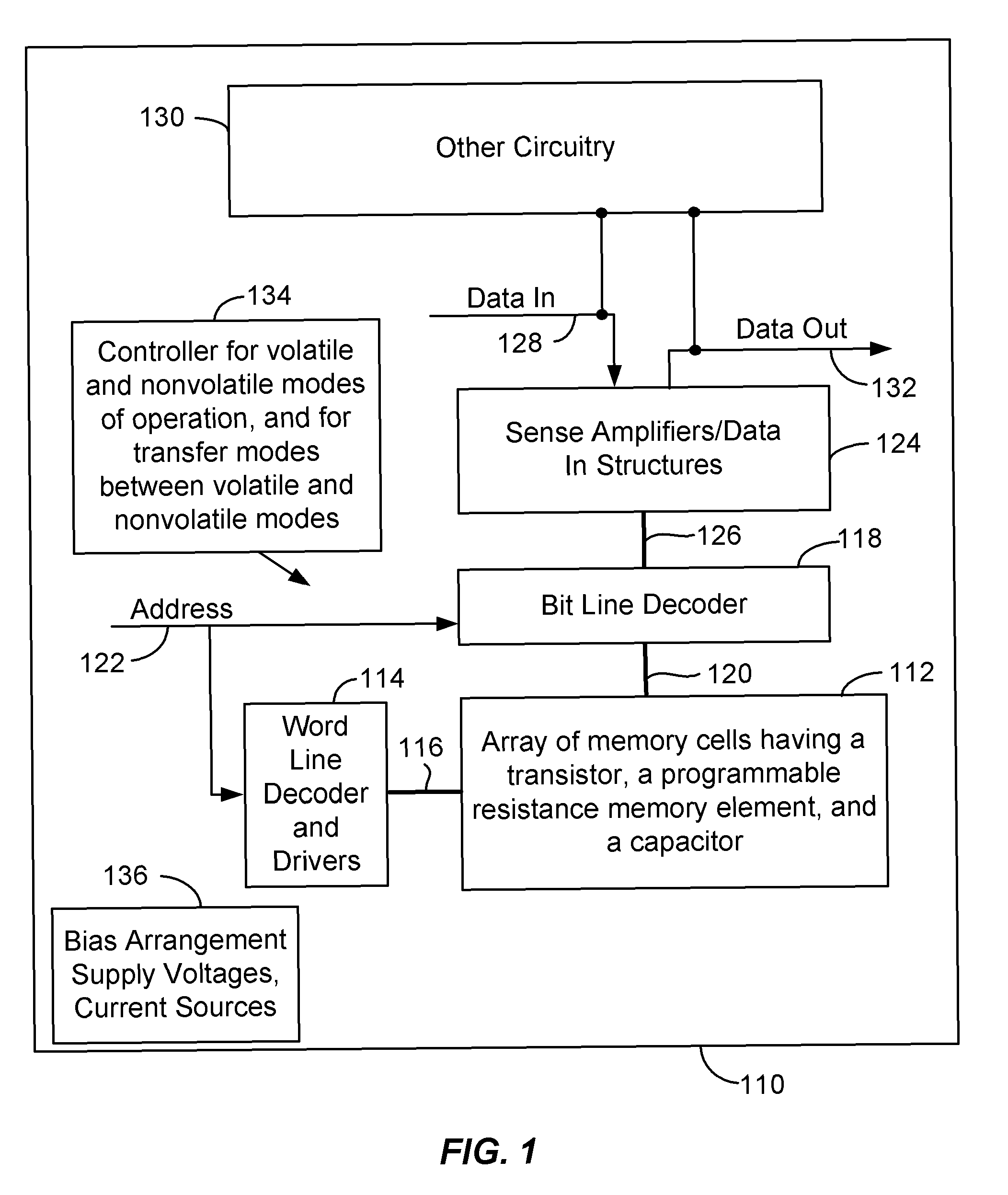
One-transistor, one-resistor, one-capacitor phase change memory
ActiveUS20100290271A1Fast program/erase speedIncrease speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesAccess lineElectrical current
Memory devices and methods for operating such devices are described herein. A memory cell as described herein comprises a transistor electrically coupled to first and second access lines. A programmable resistance memory element is arranged along a current path between the first and second access lines. A capacitor is electrically coupled to the current path between the first and second access lines.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
One-transistor, one-resistor, one-capacitor phase change memory
ActiveUS7933139B2Increase speedData retentionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceElectricity
Memory devices and methods for operating such devices are described herein. A memory cell as described herein comprises a transistor electrically coupled to first and second access lines. A programmable resistance memory element is arranged along a current path between the first and second access lines. A capacitor is electrically coupled to the current path between the first and second access lines.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
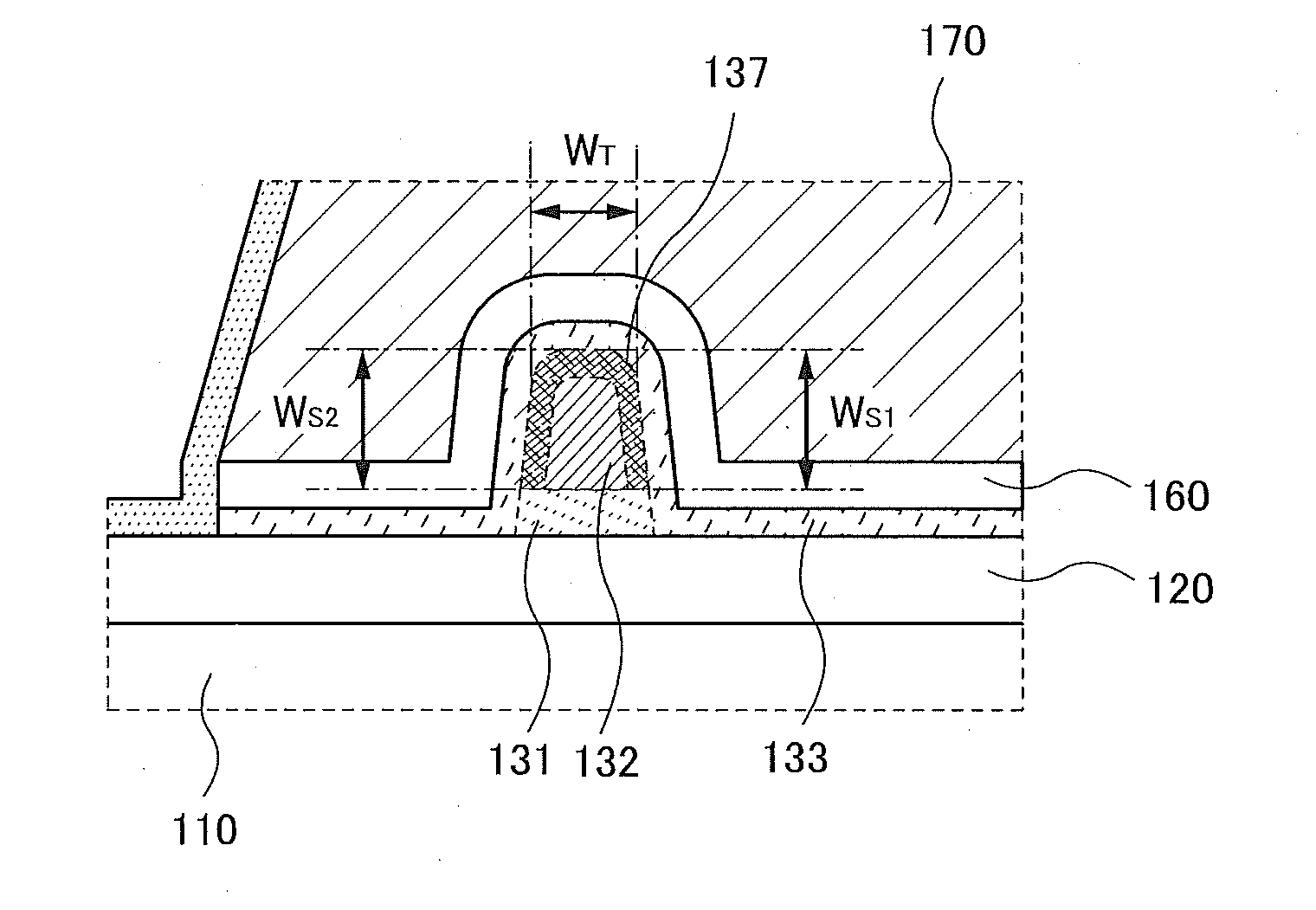
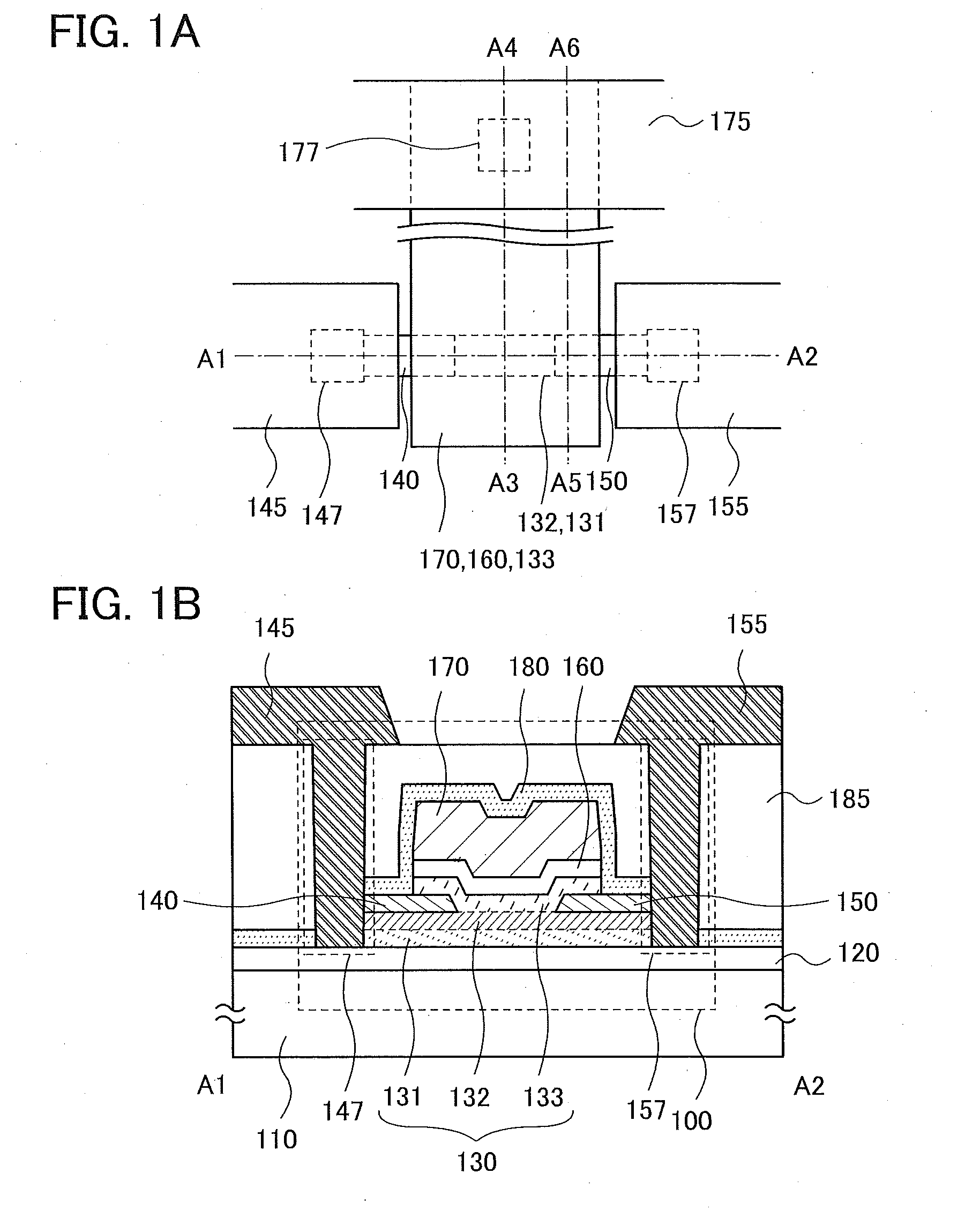
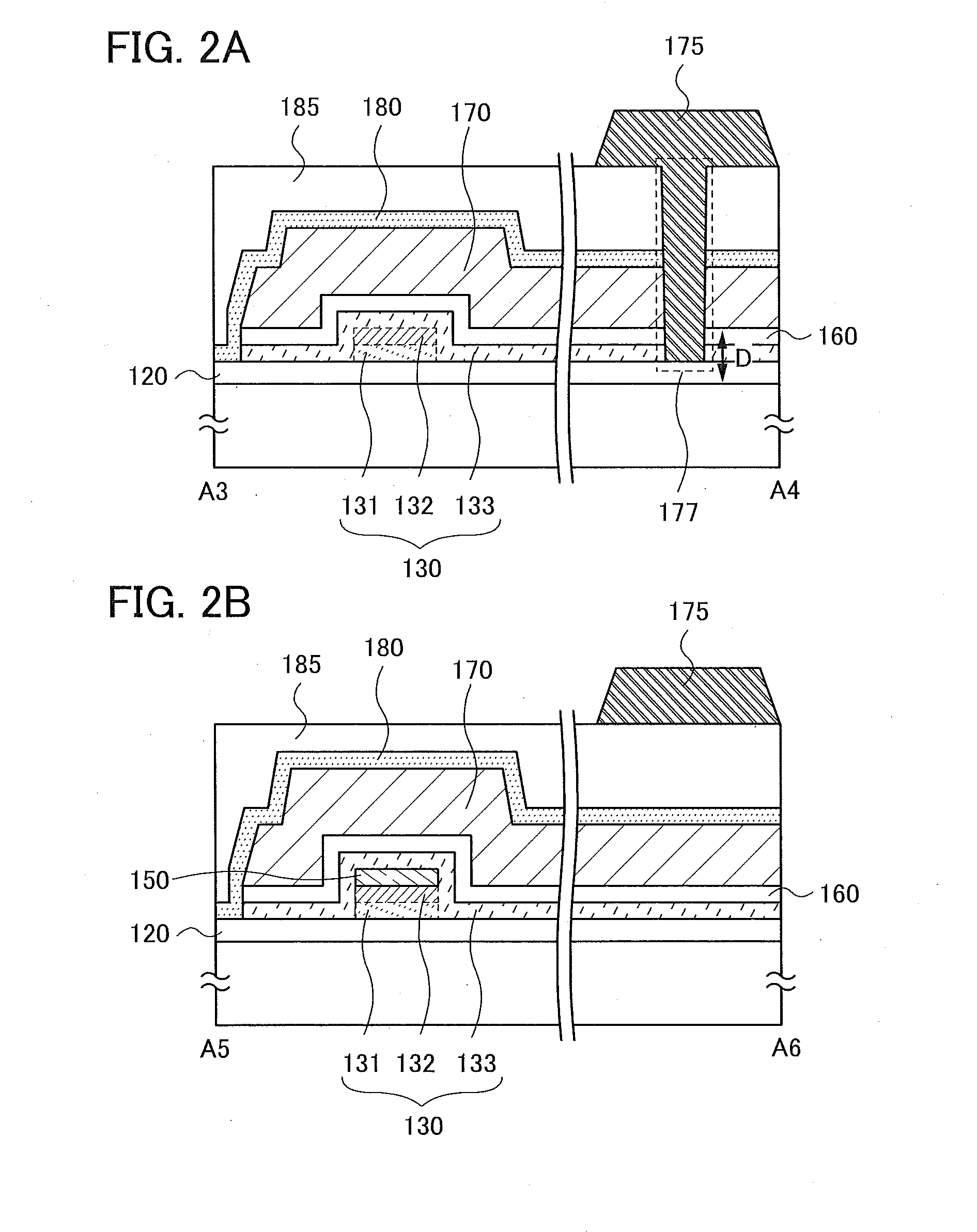
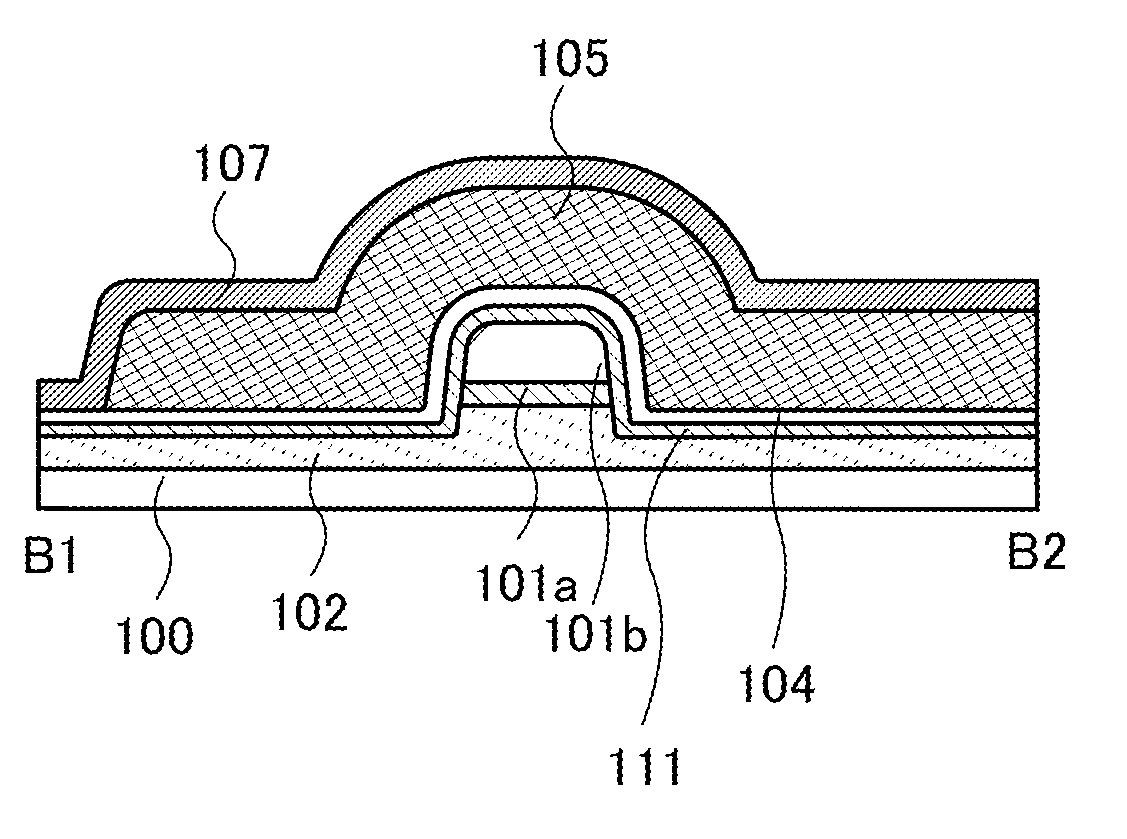
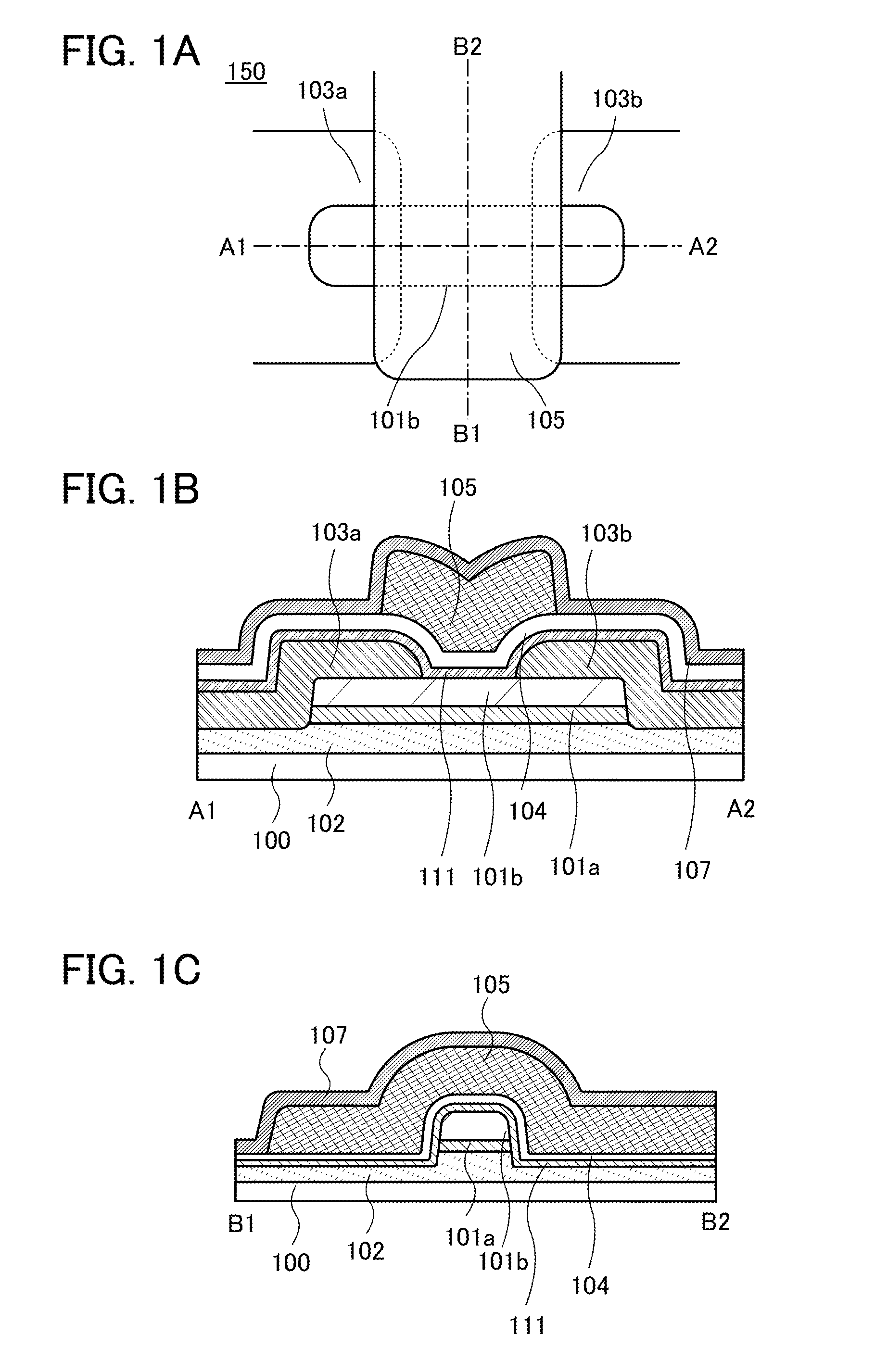
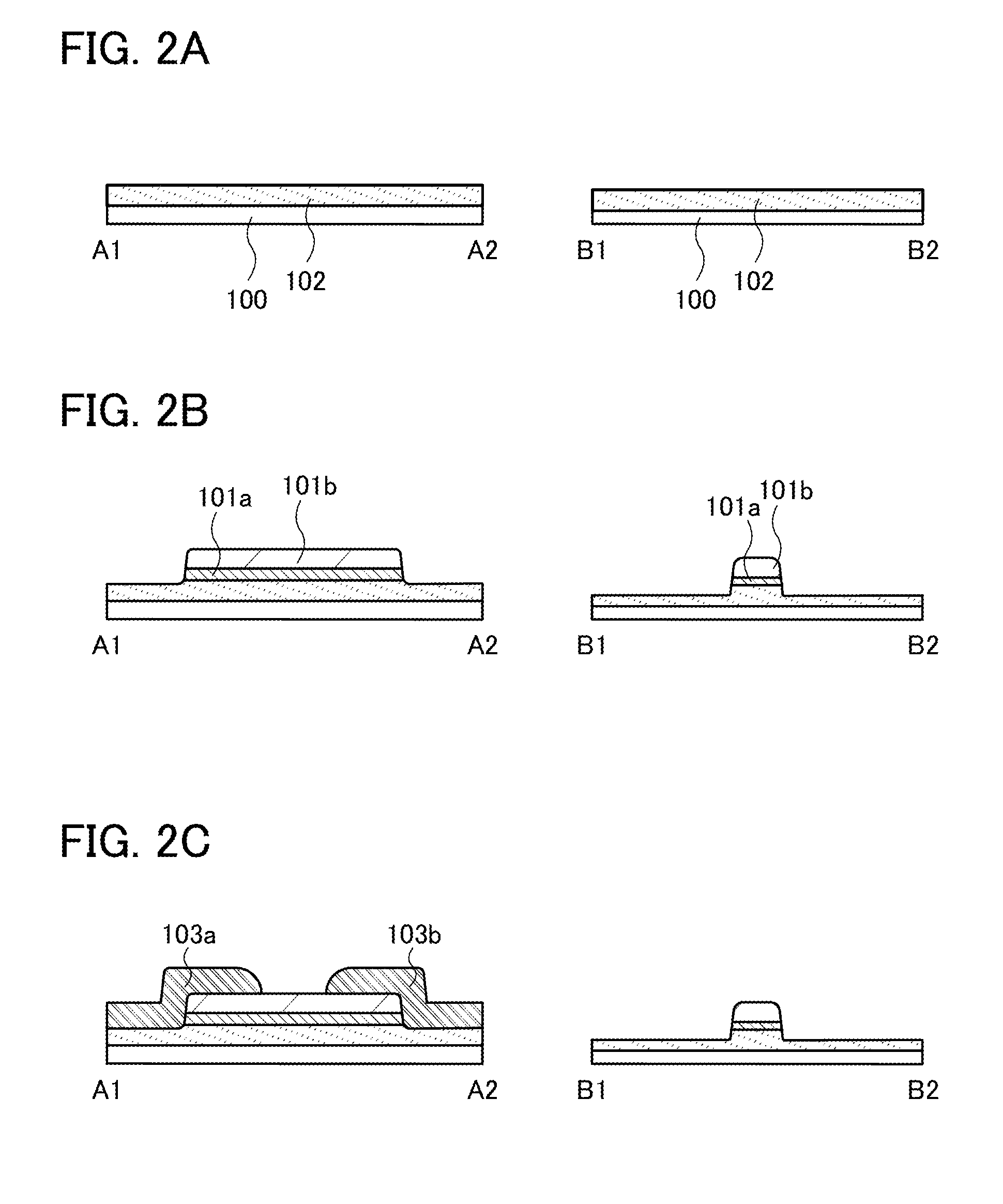
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20140332800A1High densitySimple structureTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
To provide a semiconductor device having a structure with which the device can be easily manufactured even if the size is decreased and which can suppress a decrease in electrical characteristics caused by the decrease in the size, and a manufacturing method thereof. A source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer are formed on an upper surface of an oxide semiconductor layer. A side surface of the oxide semiconductor layer and a side surface of the source electrode layer are provided on the same surface and are electrically connected to a first wiring. Further, a side surface of the oxide semiconductor layer and a side surface of the drain electrode layer are provided on the same surface and are electrically connected to a second wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140306217A1Easy to integrateDeterioration of characteristicTransistorSemiconductorSemiconductor device
Provided is a semiconductor device in which deterioration of electrical characteristics can be suppressed. The semiconductor device includes a first oxide semiconductor layer over an insulating surface, a second oxide semiconductor layer over the first oxide semiconductor layer, a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer whose one surfaces are in contact with part of the first oxide semiconductor layer and part of the second oxide semiconductor layer, a third oxide semiconductor layer over the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer, a gate insulating film over the third oxide semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode layer over the gate insulating film. The second oxide semiconductor layer wholly overlaps with the first oxide semiconductor layer. Part of the third oxide semiconductor layer is in contact with the other surfaces of the source electrode layer and the drain electrode layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
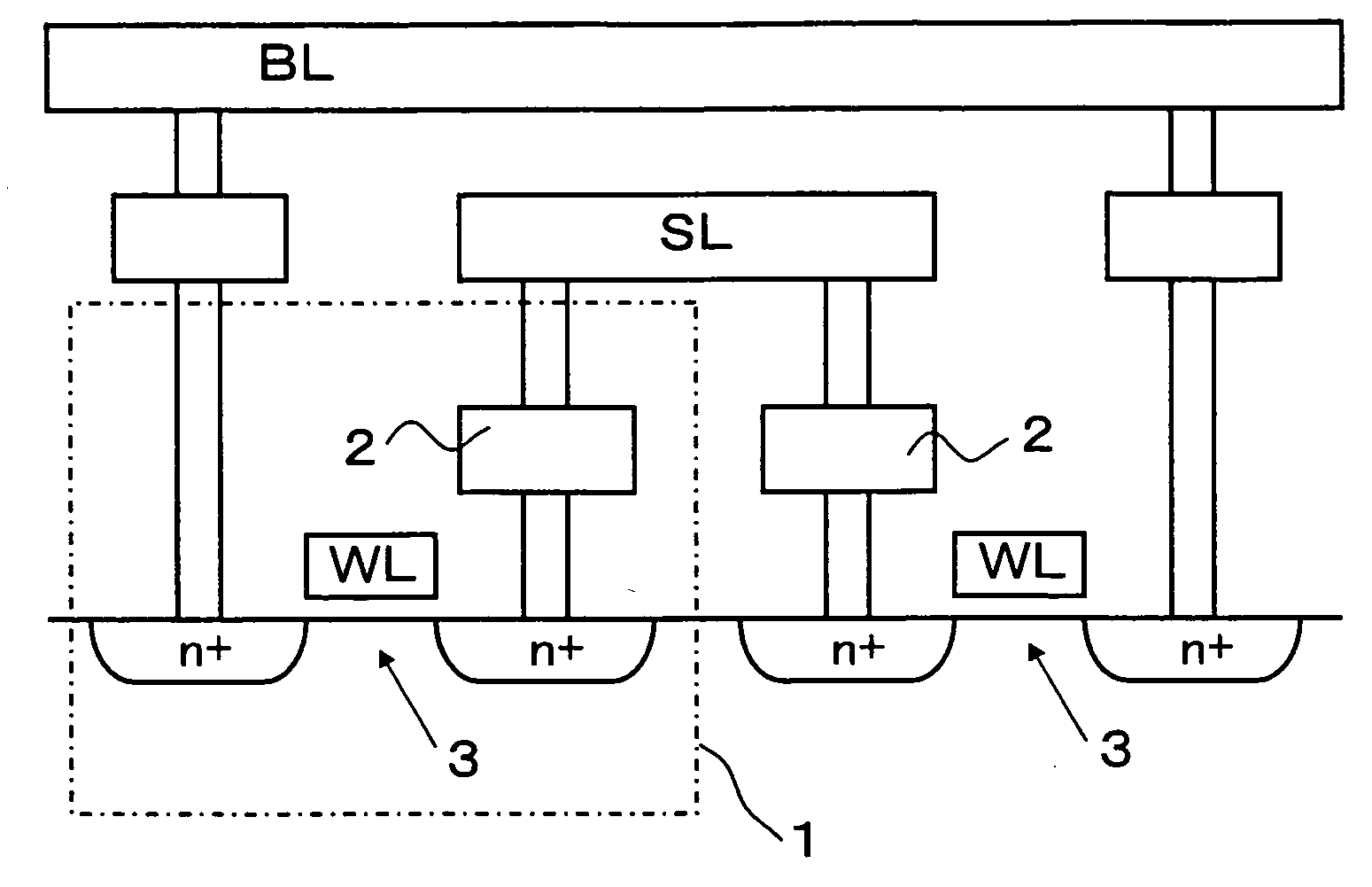
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20040130939A1Securing higher-reliability data retention characteristicReduce voltage stressSolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer architectureCommon word
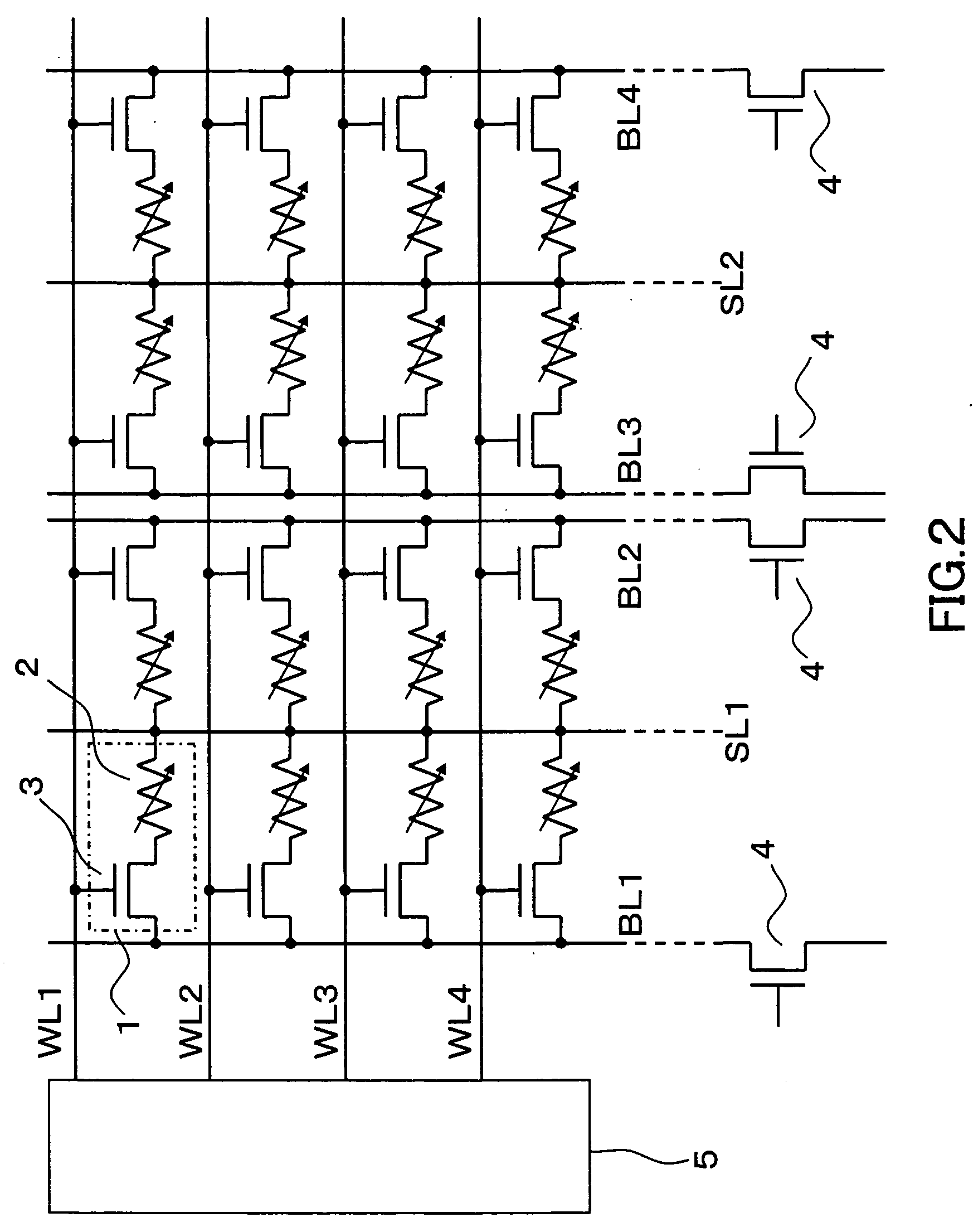
A memory cell array is included which is constituted by arranging the plurality of nonvolatile memory cells in a row direction and column direction respectively and arranging the plurality of word lines (WL) and the plurality of bit lines (BL) in the row direction and the column direction respectively in order to select a predetermined memory cell or a memory cell group out of the arranged nonvolatile memory cells, in which the memory cells are respectively constituted by connecting one end of a variable resistive element for storing information in accordance with a change of electrical resistances with the source of a selection transistor while in the memory cell array, the drain of the selection transistor is connected with a common bit line (BL) along the column direction, the other end of the variable resistive element is connected with a source line (SL), and the gate of the selection transistor is connected with the common word line (WL) along the row direction. According to the above memory cell configuration, it is possible to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing voltage stresses applied to the variable resistive element of an unselected memory cell at the time of the reading and programming operations and securing a higher-reliability data holding characteristic.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Programmable logic device
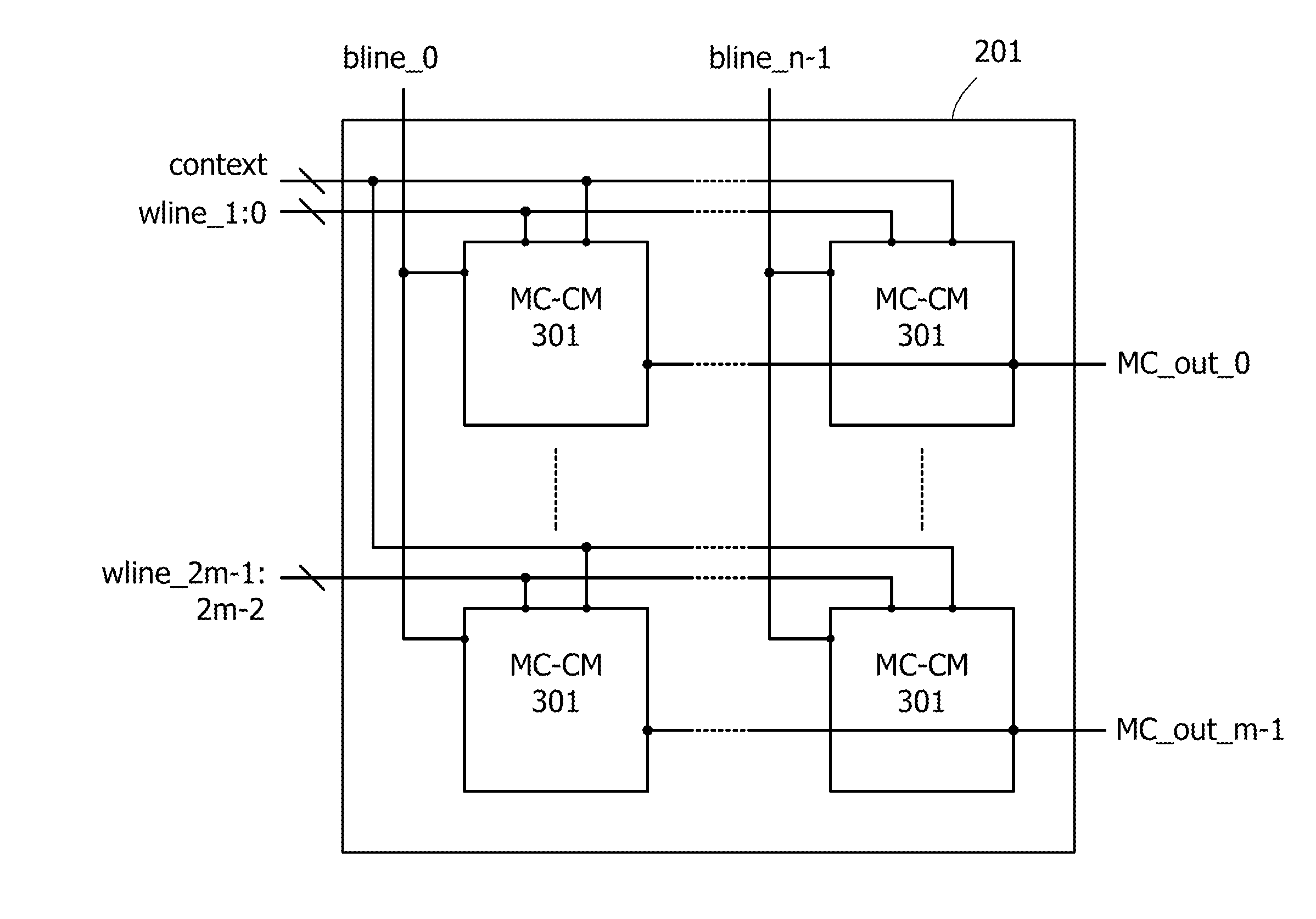
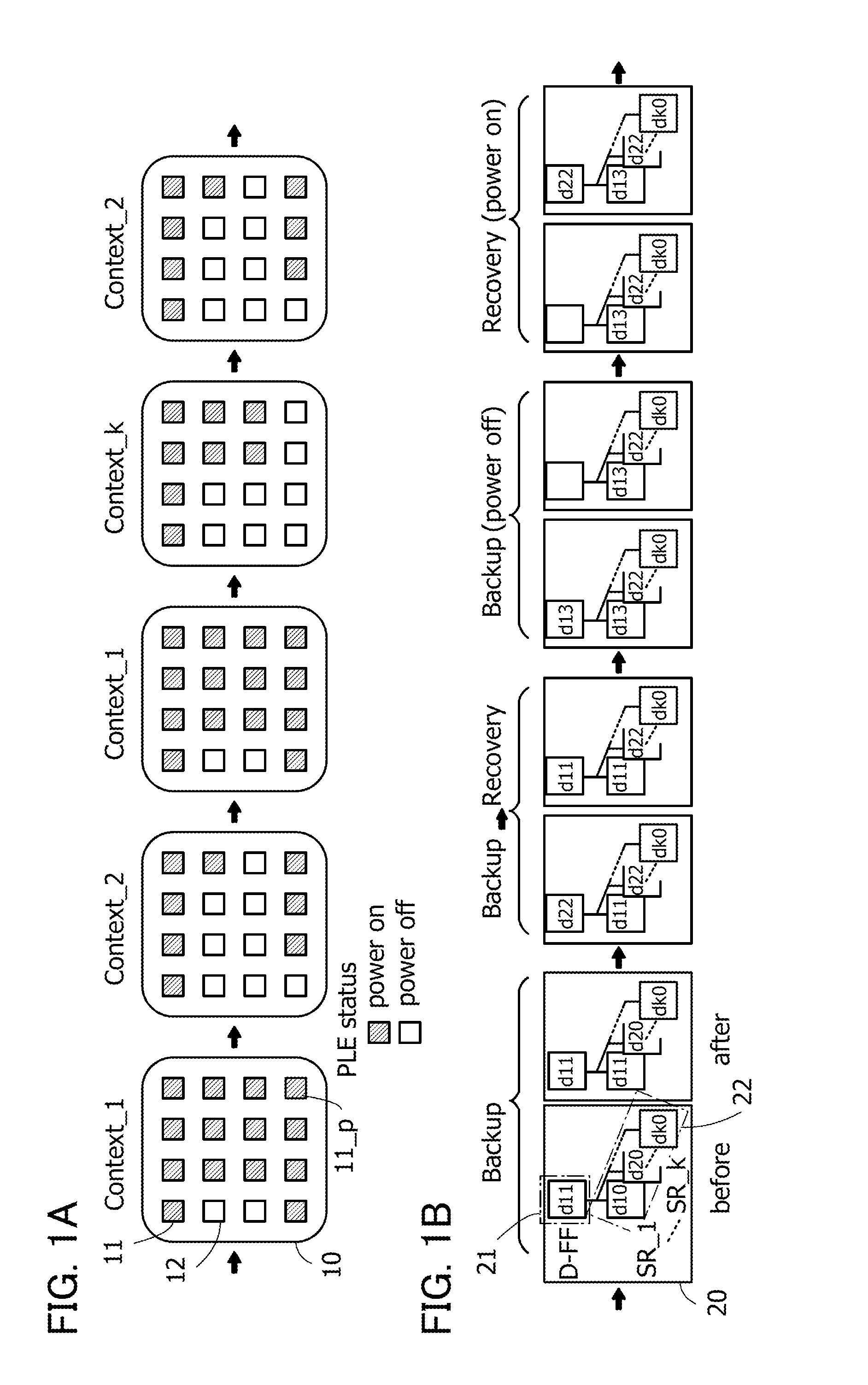
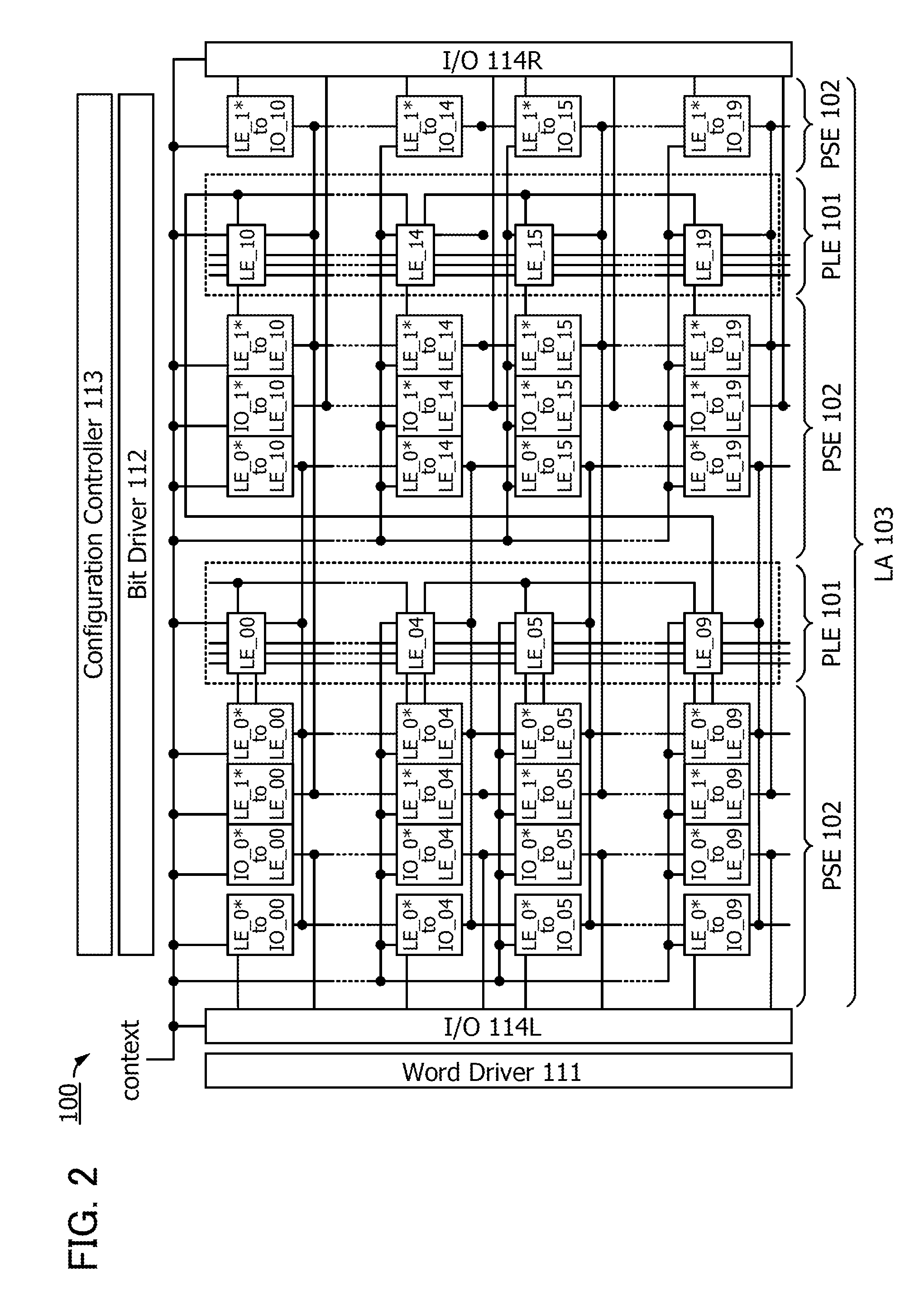
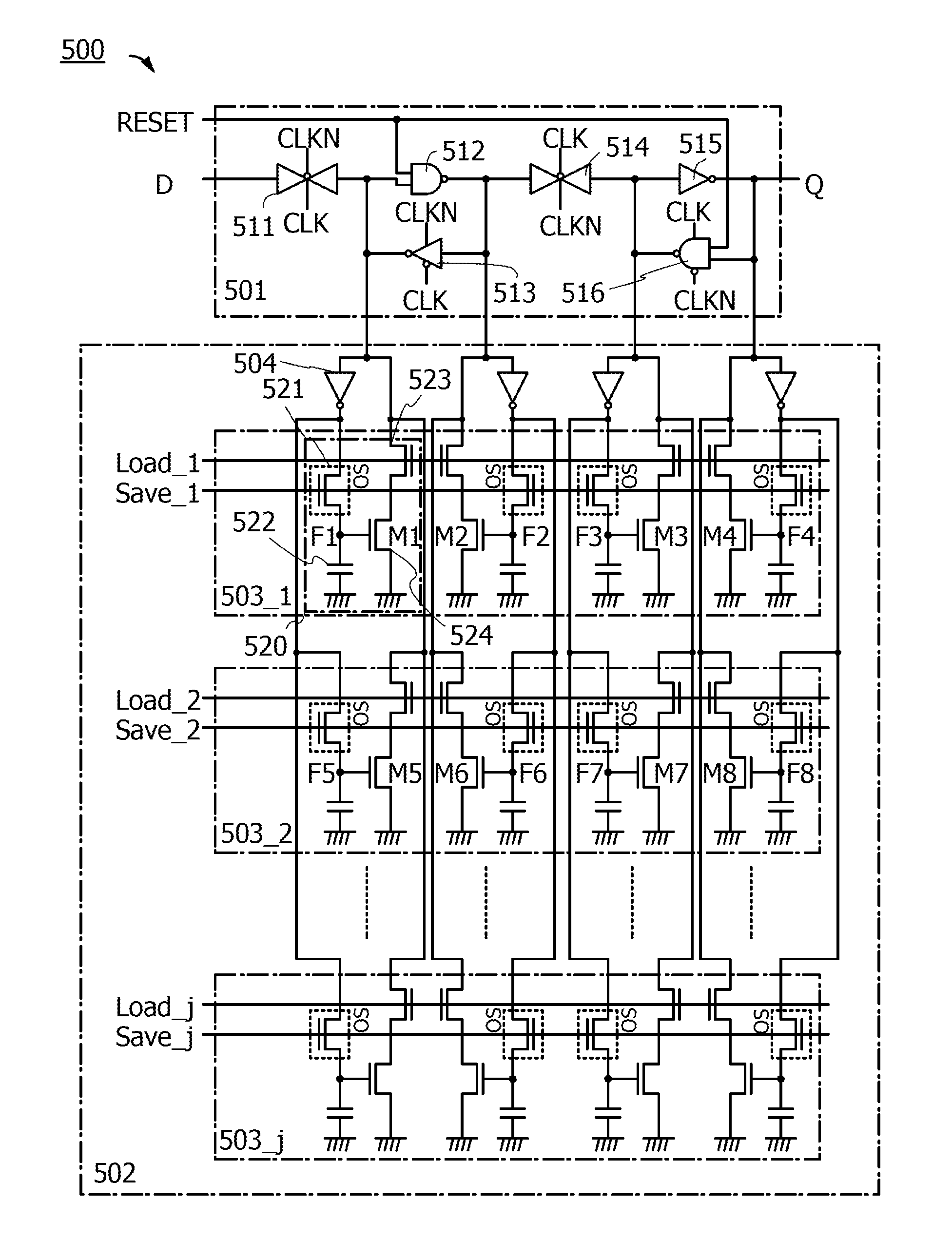
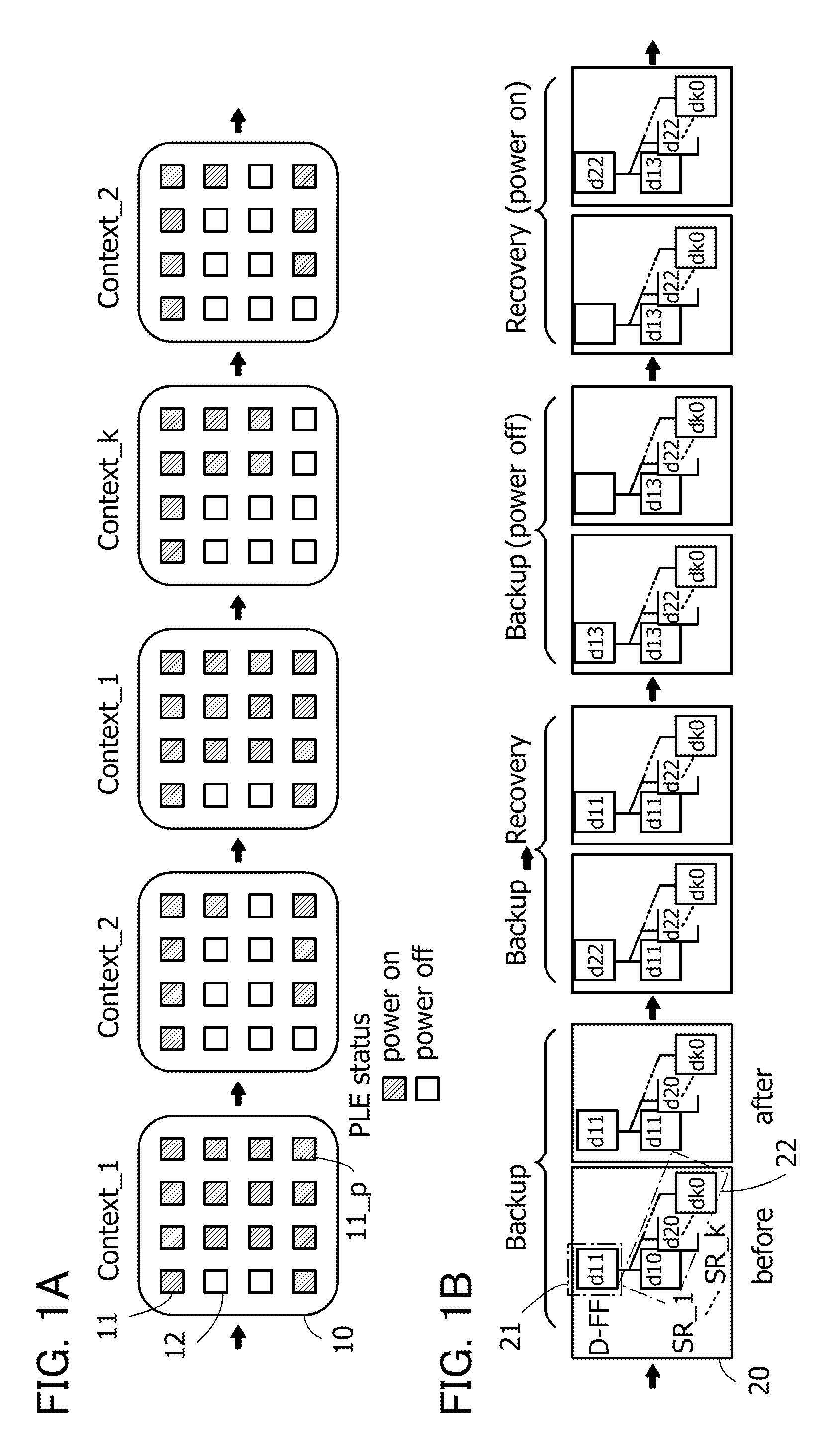
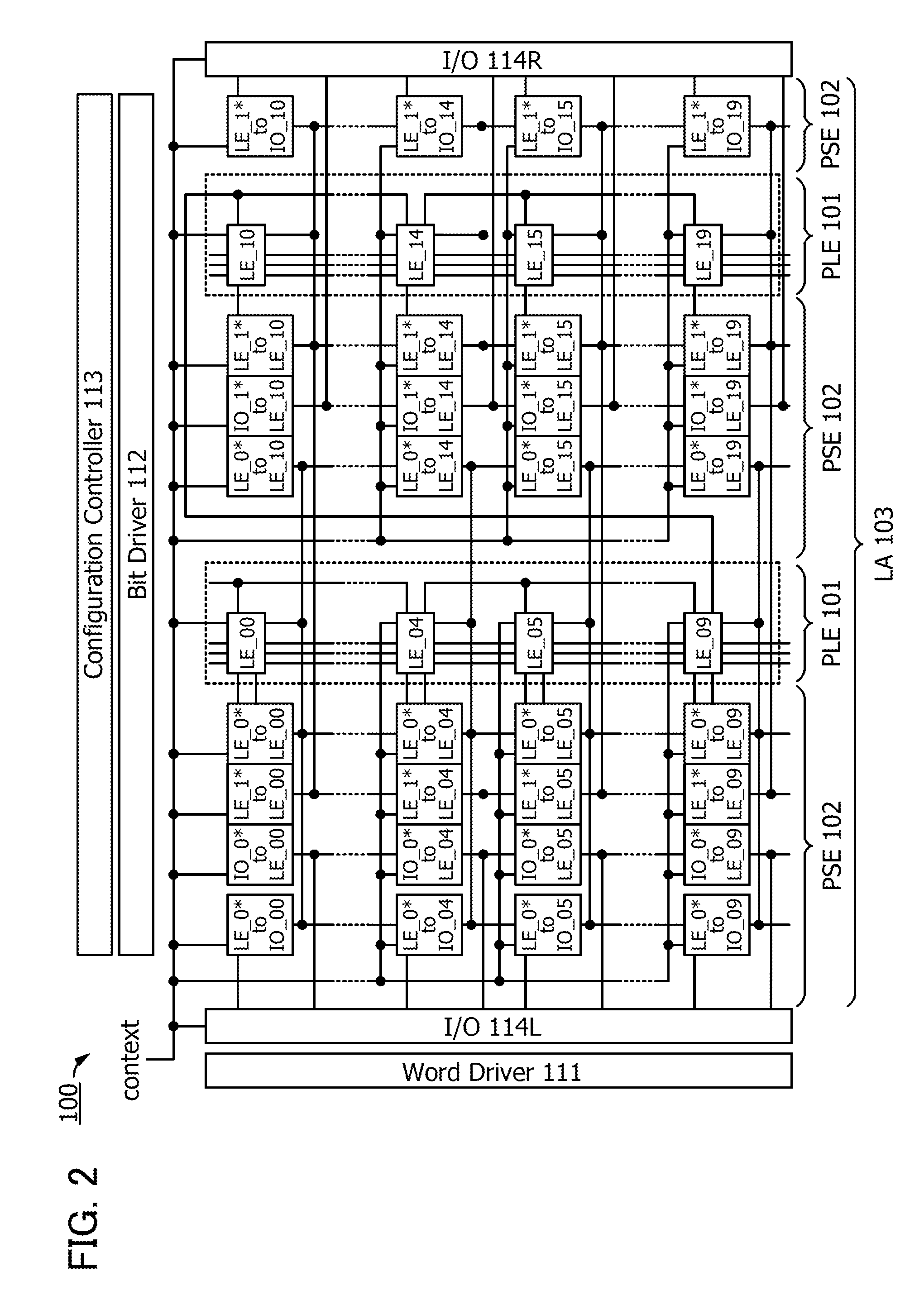
ActiveUS20140368235A1Novel structureData retentionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsMultiple contextProcessor register
Data of a register in a programmable logic element is retained. A volatile storage circuit and a nonvolatile storage circuit are provided in a register of a programmable logic element whose function can be changed in response to a plurality of context signals. The nonvolatile storage circuit includes nonvolatile storage portions for storing data in the register. The number of nonvolatile storage portions corresponds to the number of context signals. With such a structure, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and data in the register that is changed when the function is changed can be backed up to the nonvolatile storage portion in each function. In addition, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and the data in the register that is backed up when the function is changed can be recovered to the volatile storage circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Position information management system
InactiveUS20060030334A1Improve applicabilitySmall sizePosition fixationServices signallingThird partyEmbedded system
A position information management system in which a portable remote terminal includes a plurality of kinds of positioning means for positioning based on a GPS, positioning based on a portable-telephone or PHS base station, positioning based on a radio marker, and independent positioning based on a direction detector, so that the holder of the portable remote terminal can be navigated anywhere. The holder of the portable remote terminal can know the position of a third party similarly holding such a portable remote terminal, by inquiring of a central system, and he / she can supervise, for example, the action of an old person, a child, or a skier in a skiing area. Further, only the map data of a district which is often used by the holder is stored in the portable remote terminal. In this regard, when the holder is in a district not contained within the retained map data, he / she downloads corresponding map data from the central system and uses the downloaded map data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor device
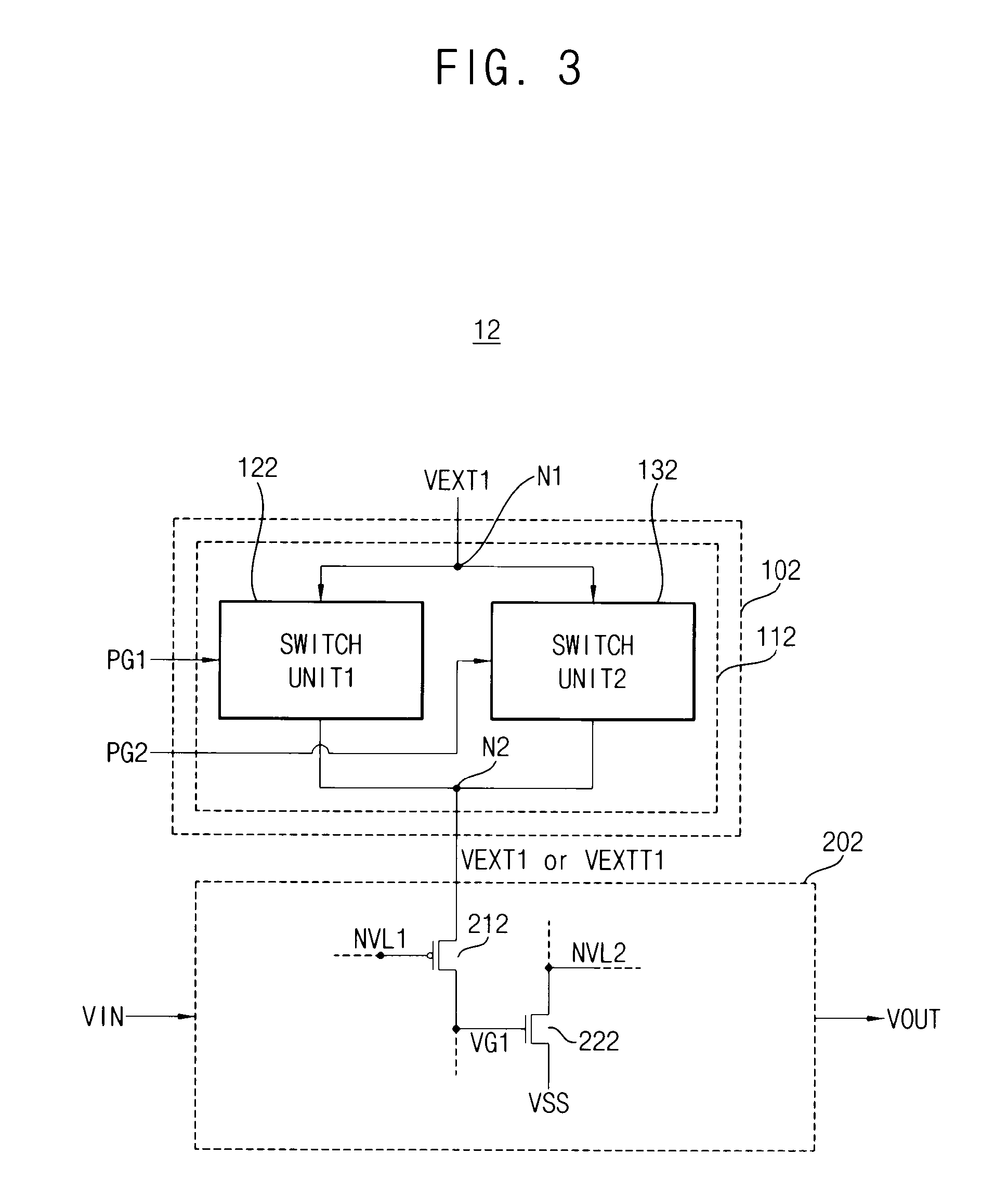
ActiveUS20120306533A1Switch accuratelyReduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceNODAL
A programmable analog device and an analog device that can retain data even when supply of a power supply potential is interrupted and consumes less power. In a semiconductor device, first to fourth transistors are used as switches in a unit cell including an analog element, and the output of the unit cell switches between a conducting state, a non-conducting state, and a conducting state through the analog element by controlling the potential of a first node where the first transistor and the second transistor are connected and the potential of a second node where the third transistor and the fourth transistor are connected.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-Volatile Latch Circuit And Logic Circuit, And Semiconductor Device Using The Same
ActiveUS20130057315A1Data retentionWide temperature rangeTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
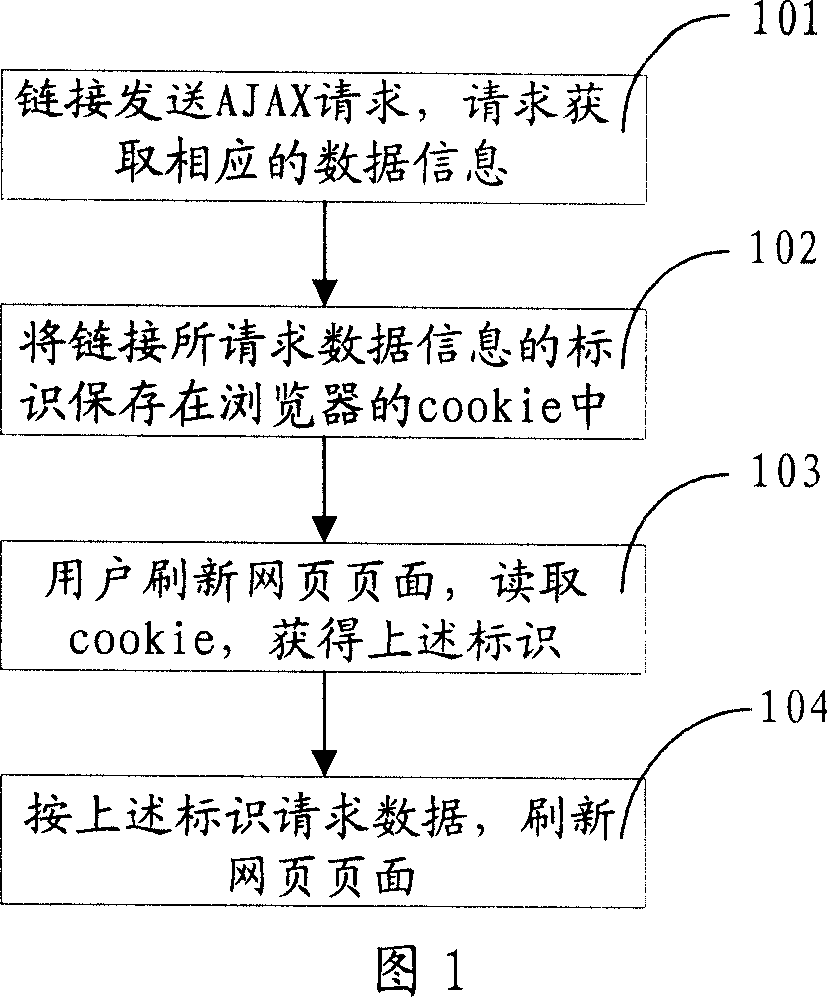
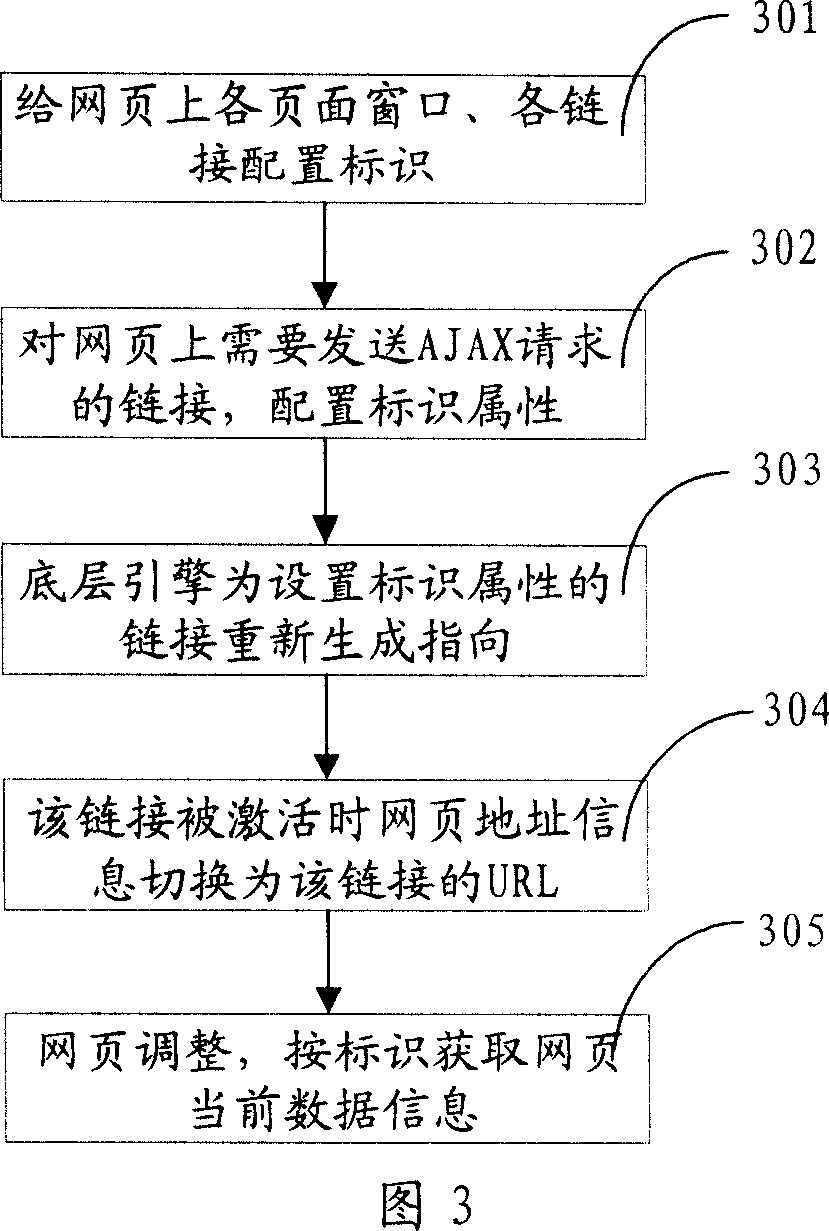
Method and system for holding page current data information
ActiveCN101067812AWill not increase the burdenDoes not affect responsivenessSpecial data processing applicationsWeb browserData information
This invention discloses a method for keeping current data information of webs including: adding an identification corresponding to an activated linkage into web address information, and picking up said identification from the address information when adjusting webs to get the current data information in terms of the identification. This invention also discloses a system for keeping current data information of webs.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9281408B2Easy to integrateReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceMiniaturization
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
To provide a semiconductor device having a structure with which the device can be easily manufactured even if the size is decreased and which can suppress a decrease in electrical characteristics caused by the decrease in the size, and a manufacturing method thereof. A source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer are formed on an upper surface of an oxide semiconductor layer. A side surface of the oxide semiconductor layer and a side surface of the source electrode layer are provided on the same surface and are electrically connected to a first wiring. Further, a side surface of the oxide semiconductor layer and a side surface of the drain electrode layer are provided on the same surface and are electrically connected to a second wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
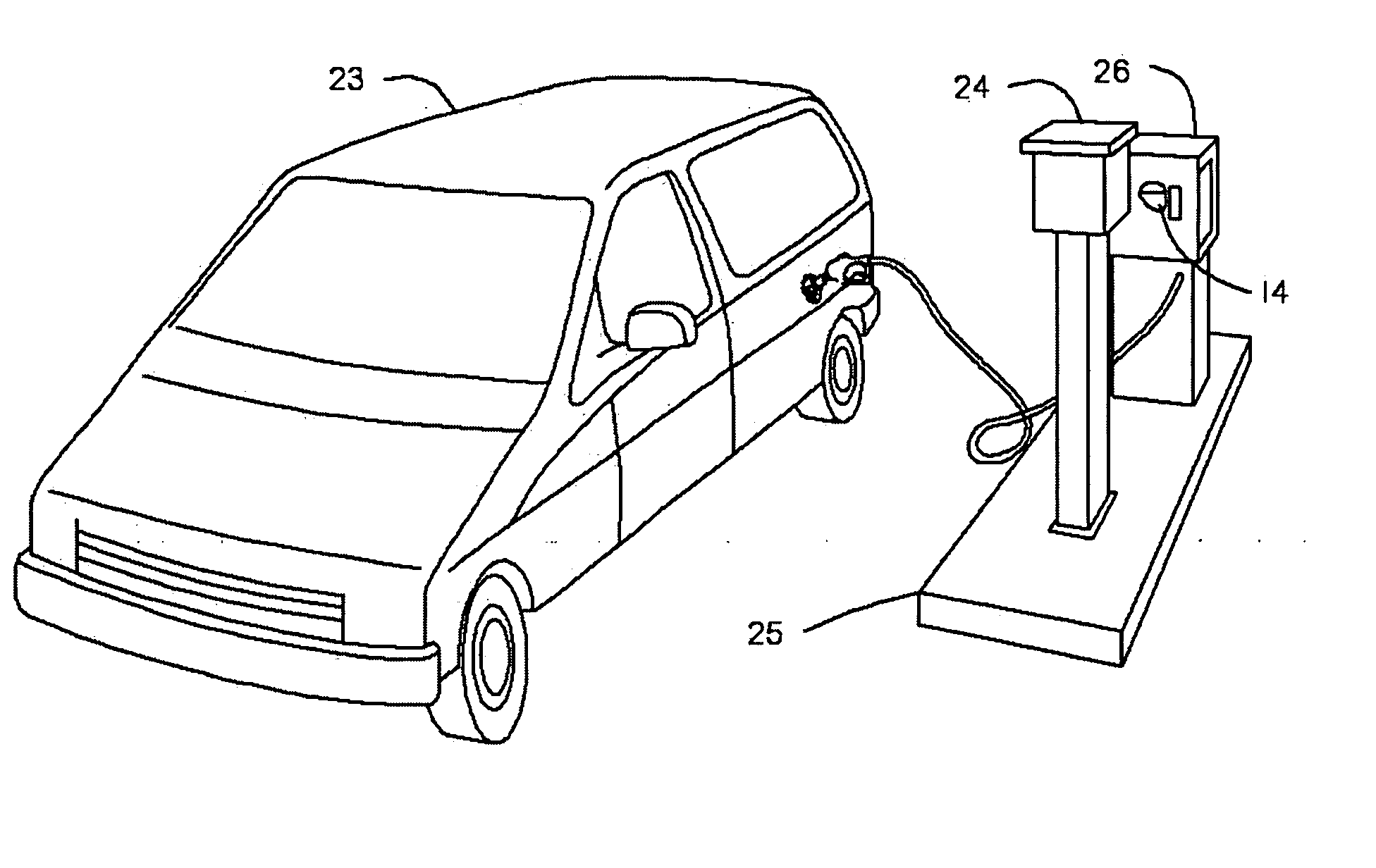
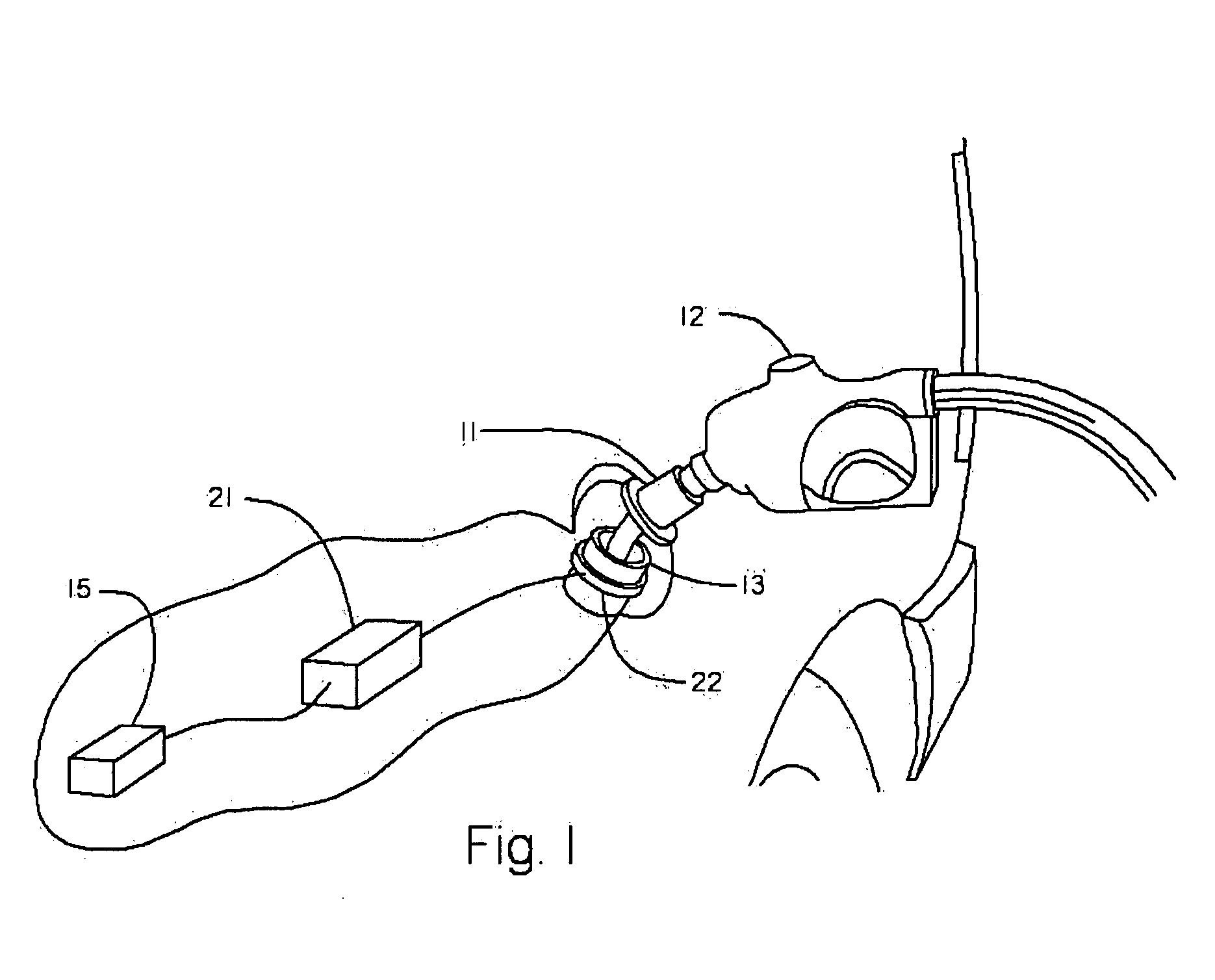
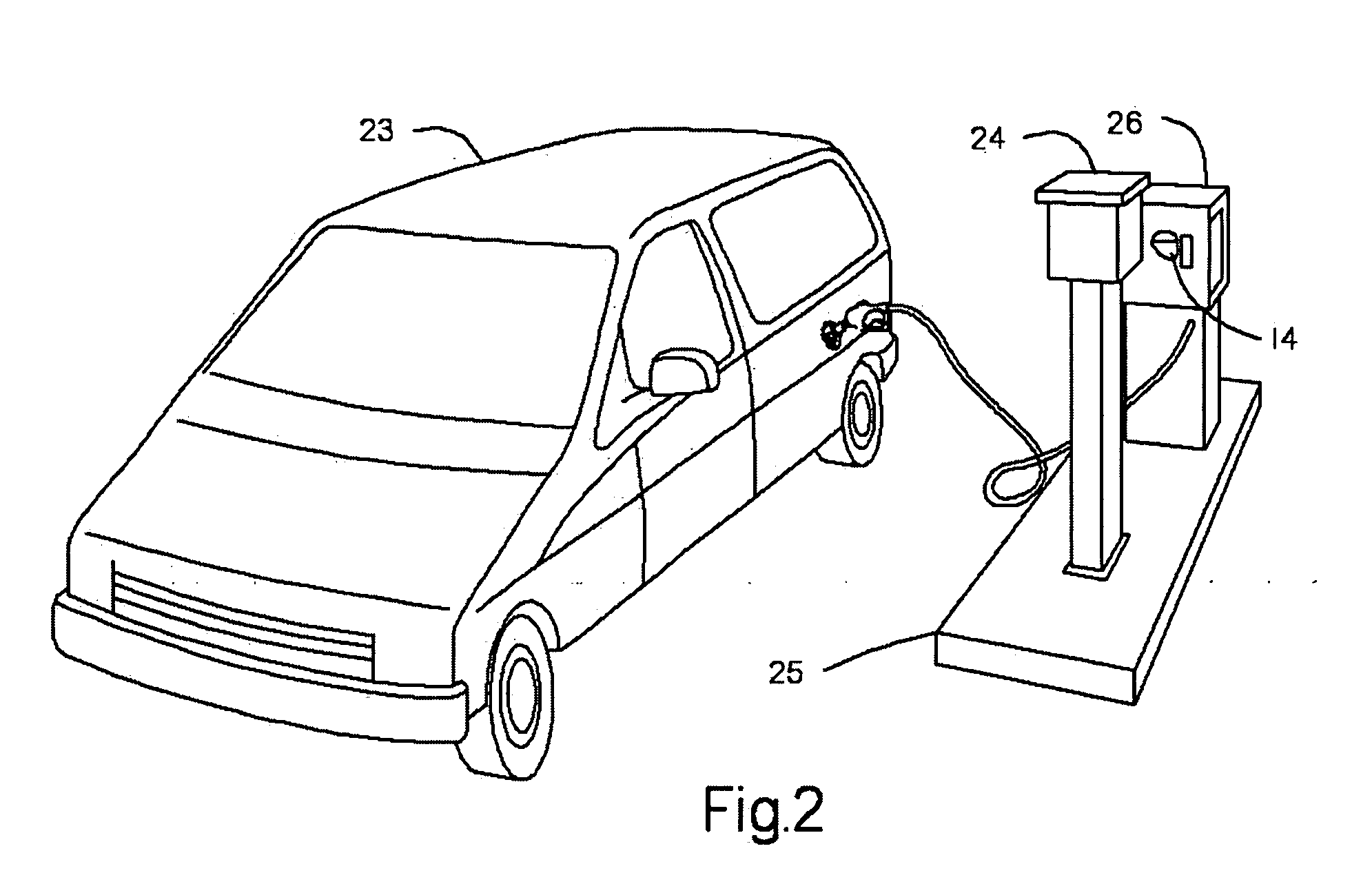
Apparatus for an automotive data control, acquisition and transfer system
InactiveUS20070250452A1Data retentionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsRadio frequencyTransfer system
A system that controls, authorizes, and accounts fuel dispensed from fuel dispensers without the need for control and authorization input from individuals performing the fueling. The system comprises a radio frequency identification tag mounted on a fuel nozzle, an automotive information module mounted in the vehicle, a fuel island-mounted fuel management unit, and on-site or remotely-located software. The automotive information module interfaces with the vehicle's on-board computer system, the radio frequency identification tag, and the fuel management unit. With these interfaces, the automotive information module allows for autonomous creation and transfer of data and operational commands with in the disclosed system. The fuel management unit interfaces with the automotive information module, the fuel dispensers, and the software. With these interfaces, the fuel island-mounted fuel management unit provides autonomous fuel data processing. The software provides system owners, operators, and users raw data, analyzed data, and reports based on accumulated data from both the automotive information module and the fuel management unit.
Owner:SYN TECH SYST
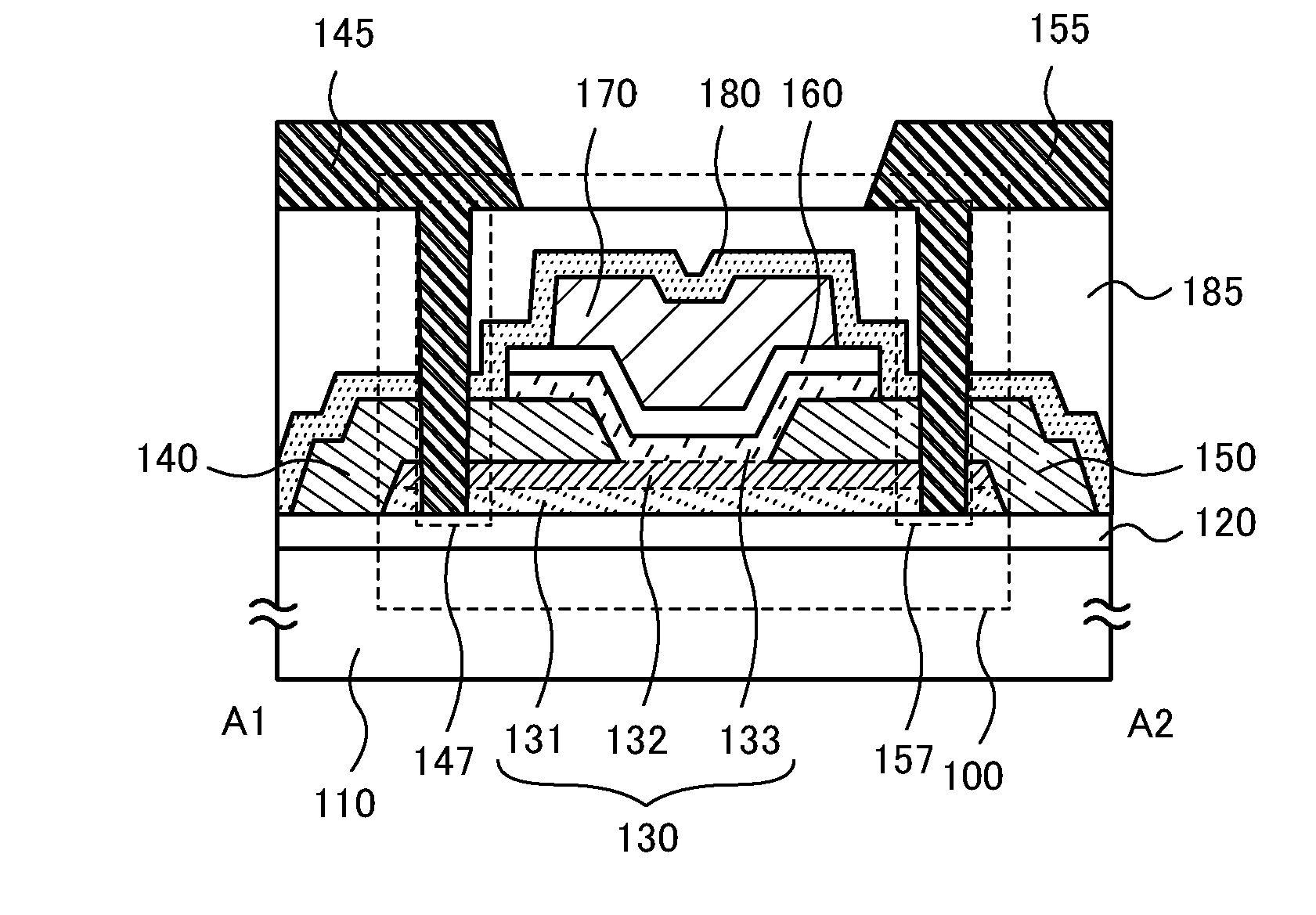
Semiconductor Device and Method for Manufacturing the Same
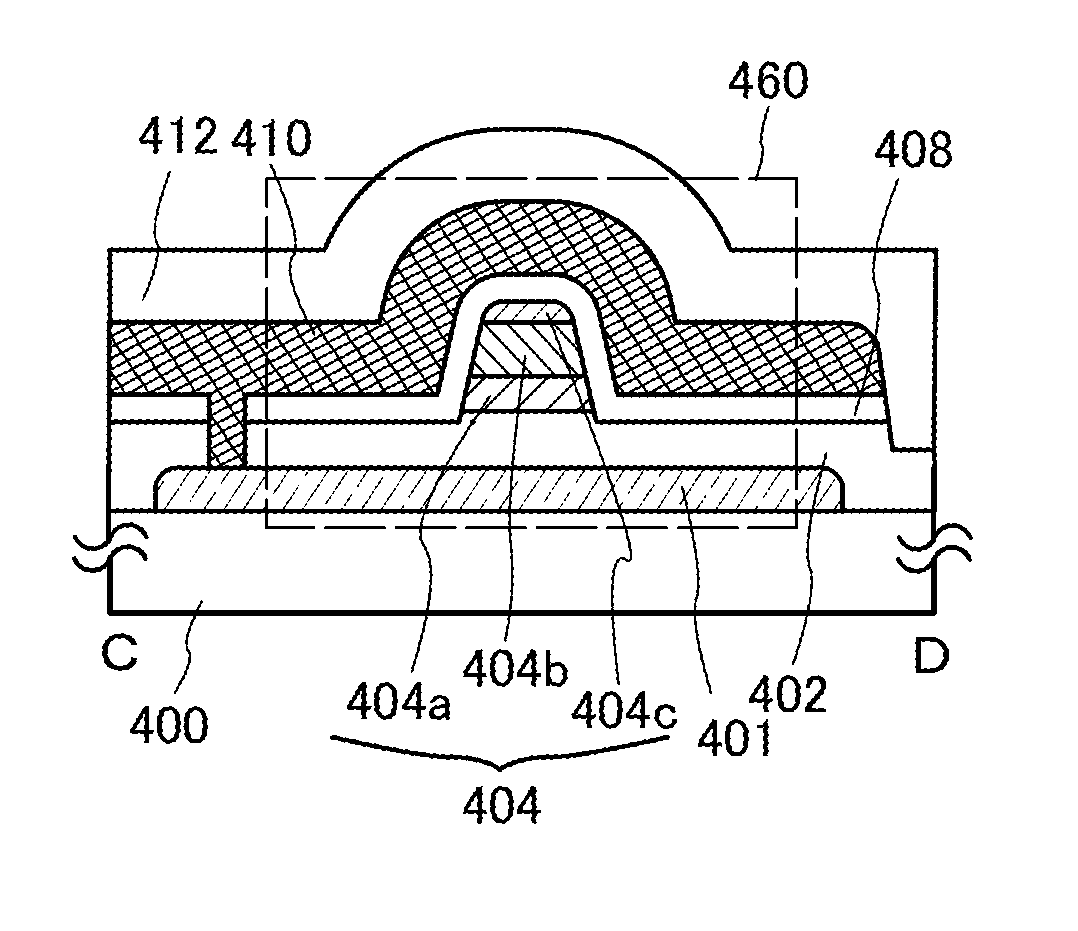
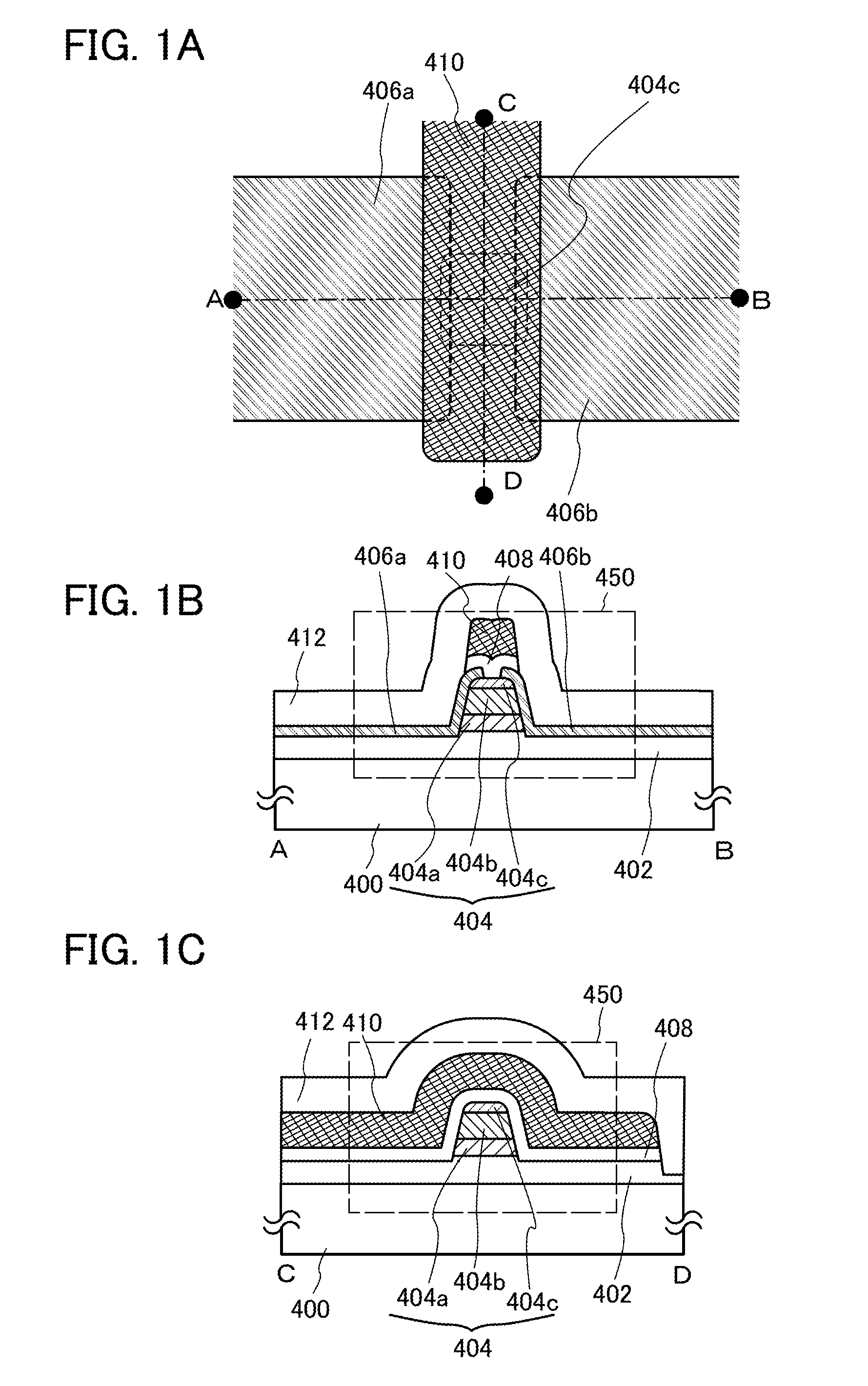
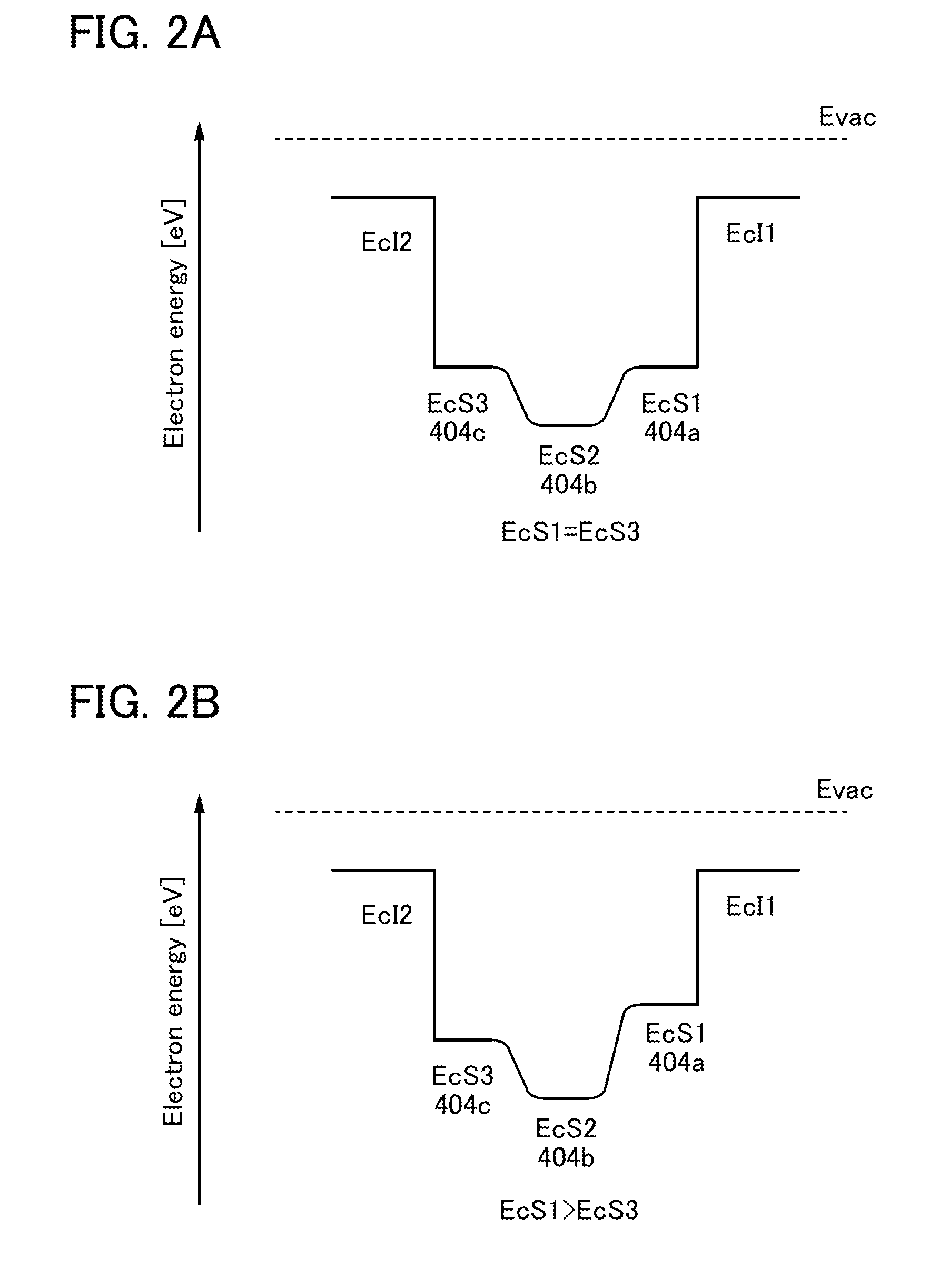
InactiveUS20140361289A1Avoid yield lossHighly-integratedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorLow resistance
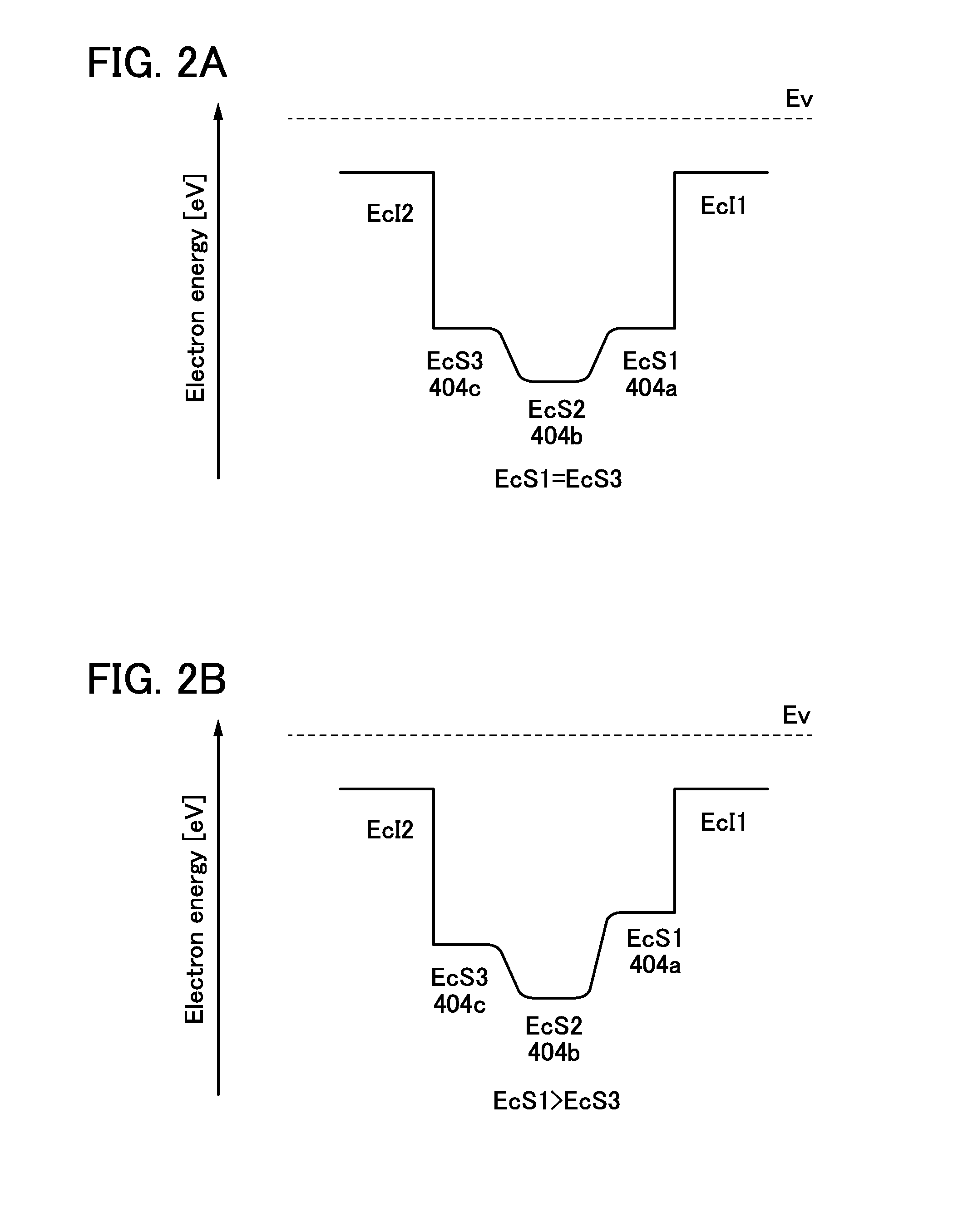
Objects are to obtain a minute transistor by reducing the channel length L of a transistor used in a semiconductor integrated circuit such as an LSI, a CPU, or a memory, increase the operation speed of the circuit, and reduce power consumption. Oxide layers having compositions different from the composition of an oxide semiconductor layer including a channel formation region are provided below and over the oxide semiconductor layer, and in the oxide semiconductor layer including the channel formation region, low-resistance regions are provided to interpose the channel formation region therebetween in the lateral direction. The low-resistance regions are formed in a region other than the channel formation region so as to be in contact with a metal film or a metal oxide film by diffusion of a metal element (e.g., aluminum) contained in the metal or metal oxide films into the parts of the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
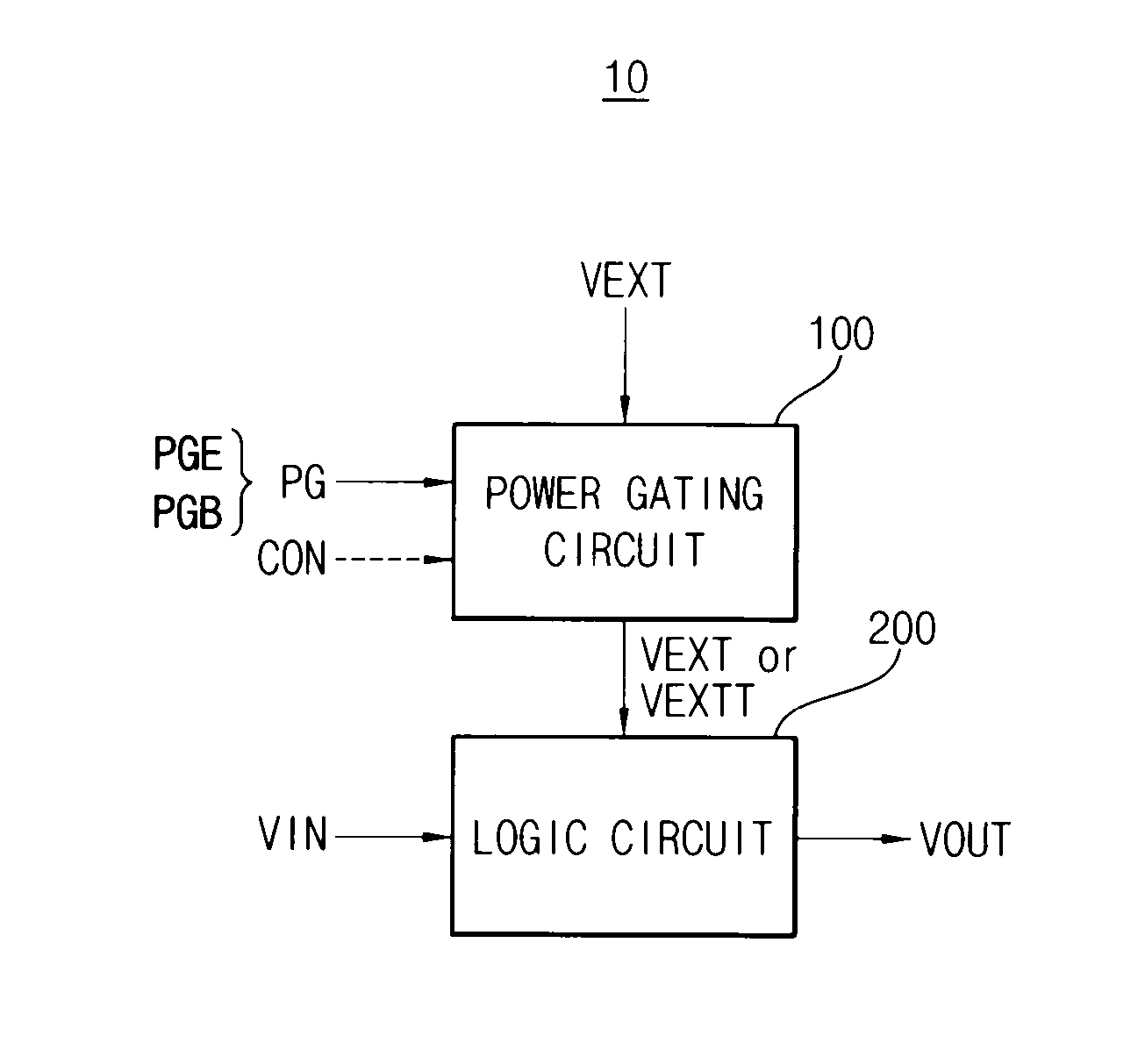
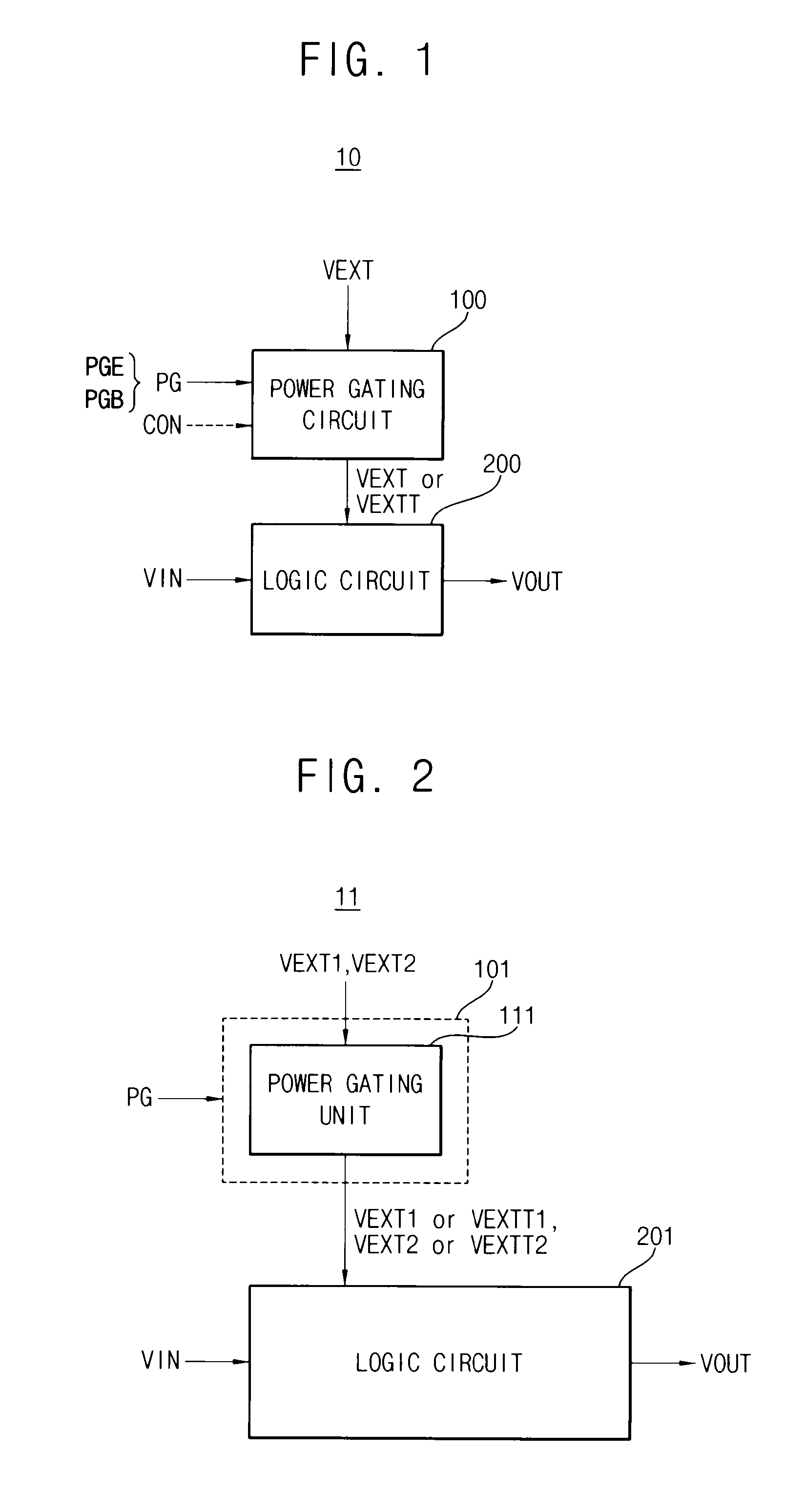
Integrated circuit having power gating function and semiconductor device including the same
InactiveUS20120200345A1Reduce power consumptionData retentionPower reduction by control/clock signalStatic storageDevice materialEngineering
An integrated circuit includes a logic circuit and a power gating circuit. The logic circuit generates an output signal based on an input signal and a first power supply voltage in a normal operation mode, and maintains a voltage level of the output signal as a stand-by logic level based on a second power supply voltage in a stand-by mode. A magnitude of the second power supply voltage is smaller than a magnitude of the first power supply voltage. The power gating circuit entirely applies the first power supply voltage to the logic circuit based on a power gating signal in the normal operation mode, and partially applies the second power supply voltage to the logic circuit based on the power gating signal in the stand-by mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20150034949A1Easy to integrateDecrease in on-state current is suppressedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceMiniaturization
Provided is a semiconductor device having a structure which can prevent deterioration of the electrical characteristics, which becomes more significant with miniaturization. The semiconductor device includes a first oxide semiconductor film over an insulating surface; a second oxide semiconductor film over the first oxide semiconductor film; a third oxide semiconductor film over the second oxide semiconductor film; a source electrode and a drain electrode each in contact with side surfaces of the first oxide semiconductor film, the second oxide semiconductor film, and the third oxide semiconductor film and a top surface of the third oxide semiconductor film; a gate insulating film over the third oxide semiconductor film, the source electrode, and the drain electrode; and a gate electrode which is on and in contact with the gate insulating film and faces a top surface and a side surface of the second oxide semiconductor film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Card and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6162160AIncreased durabilityData retentionMechanical working/deformationOther printing matterEngineeringData recording
A process for producing a card comprising: recording variable data comprising photographic data on at least one selected from a surface of a center core to be used for the card, and a back surface of an oversheet in a sheet form supplied from a roll thereof, by variable data recording means comprising a sublimation type thermal transfer device which uses a thermal transfer sheet having a dye layer imparted with a releasability, superposing the center core and the oversheet to form an integral laminate; cutting the integral laminate into a card form having a predetermined size.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140231799A1Low power consumptionThreshold voltage lowerTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
The semiconductor device of the present invention comprises first and second transistors and first and second capacitors. One of source and drain electrodes of the first transistor is electrically connected to a first wiring, the other is electrically connected to a second wiring, and a gate electrode of the first transistor is electrically connected to one of a source electrode and a drain electrode of the second transistor and one of electrodes of the first capacitor. The other of the source and drain electrodes of the second transistor is electrically connected to the first wiring, and a gate electrode of the second transistor is electrically connected to one of electrodes of a second capacitor and a fifth wiring. The other electrode of the first capacitor is electrically connected to a third wiring, and the other electrode of the second capacitor is eclectically connected to a fourth wiring.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and electronic device including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150364610A1Excellent electrical propertiesHigh on-state currentTransistorSolid-state devicesElectronSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a first oxide semiconductor film, a second oxide semiconductor film over the first oxide semiconductor film, a source electrode in contact with the second oxide semiconductor film, a drain electrode in contact with the second oxide semiconductor film, a metal oxide film over the second oxide semiconductor film, the source electrode, and the drain electrode, a gate insulating film over the metal oxide film, and a gate electrode over the gate insulating film. The metal oxide film contains M (M represents Ti, Ga, Y, Zr, La, Ce, Nd, or Hf) and Zn. The metal oxide film includes a portion where x / (x+y) is greater than 0.67 and less than or equal to 0.99 when a target has an atomic ratio of M:Zn=x:y.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device including latch circuit
InactiveUS20120049889A1Keep properlyData retentionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSilicon
The latch circuit includes a transistor whose channel region is formed with an oxide semiconductor (OS). Data is held in a node that is electrically connected to an output terminal and one of a source and a drain of the transistor and brought into a floating state when the transistor is turned off. Note that the oxide semiconductor has a band gap wider than silicon and an intrinsic carrier density lower than silicon. By using such an oxide semiconductor for the channel region of the transistor, the transistor with an extremely low off-state current (leakage current) can be realized.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20150214377A1Excellent electrical propertiesHigh on-state currentTransistorSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device having favorable electric characteristics is provided. An oxide semiconductor layer includes first and second regions apart from each other, a third region which is between the first and second regions and overlaps with a gate electrode layer with a gate insulating film provided therebetween, a fourth region between the first and third regions, and a fifth region between the second and third regions. A source electrode layer includes first and second conductive layers. A drain electrode layer includes third and fourth conductive layers. The first conductive layer is formed only over the first region. The second conductive layer is in contact with an insulating layer, the first conductive layer, and the first region. The third conductive layer is formed only over the second region. The fourth conductive layer is in contact with the insulating layer, the third conductive layer, and the second region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Programmable logic device
ActiveUS9065438B2Novel structureData retentionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsMultiple contextProcessor register
Data of a register in a programmable logic element is retained. A volatile storage circuit and a nonvolatile storage circuit are provided in a register of a programmable logic element whose function can be changed in response to a plurality of context signals. The nonvolatile storage circuit includes nonvolatile storage portions for storing data in the register. The number of nonvolatile storage portions corresponds to the number of context signals. With such a structure, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and data in the register that is changed when the function is changed can be backed up to the nonvolatile storage portion in each function. In addition, the function can be changed each time context signals are switched and the data in the register that is backed up when the function is changed can be recovered to the volatile storage circuit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
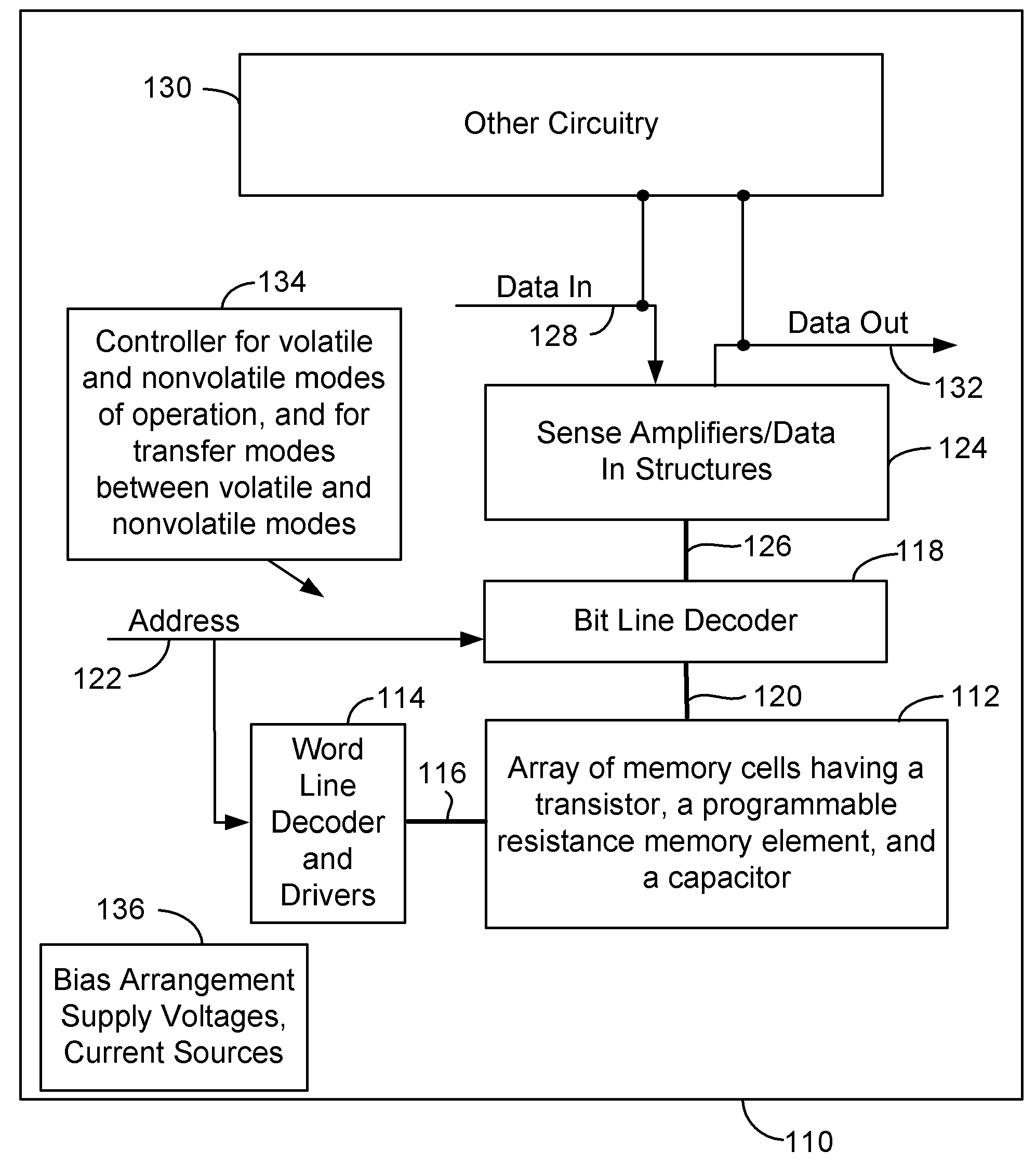
Method and apparatus of operating a non-volatile DRAM
ActiveUS8391078B2Easy accessHigh voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A non-volatile DRAM cell includes a pass-gate transistor and a cell capacitor. A read operation of the non-volatile cell begins by positively charging the cell capacitor. A cell capacitor of an associated dummy non-volatile DRAM cell is fully charged. The pass-gate transistor is activated and if the pass-gate transistor is erased it does not turn on and if it is programmed, it turns on. Charge is shared on the complementary pair of pre-charged bit lines connected to the non-volatile DRAM cell and its associated Dummy non-volatile DRAM cell. A sense amplifier detects the difference in the data state stored in the pass-gate transistor. The program and erase of the non-volatile DRAM cell is accomplished Gate-induced drain-lowering (GIDL) assisted band-to-band tunneling and Fowler-Nordheim tunneling respectively. Programming or erasing a selected row of cells does not affect the data states of the cells in the unselected rows.
Owner:CHIP MEMORY TECH
Nonvolatile magnetic memory device
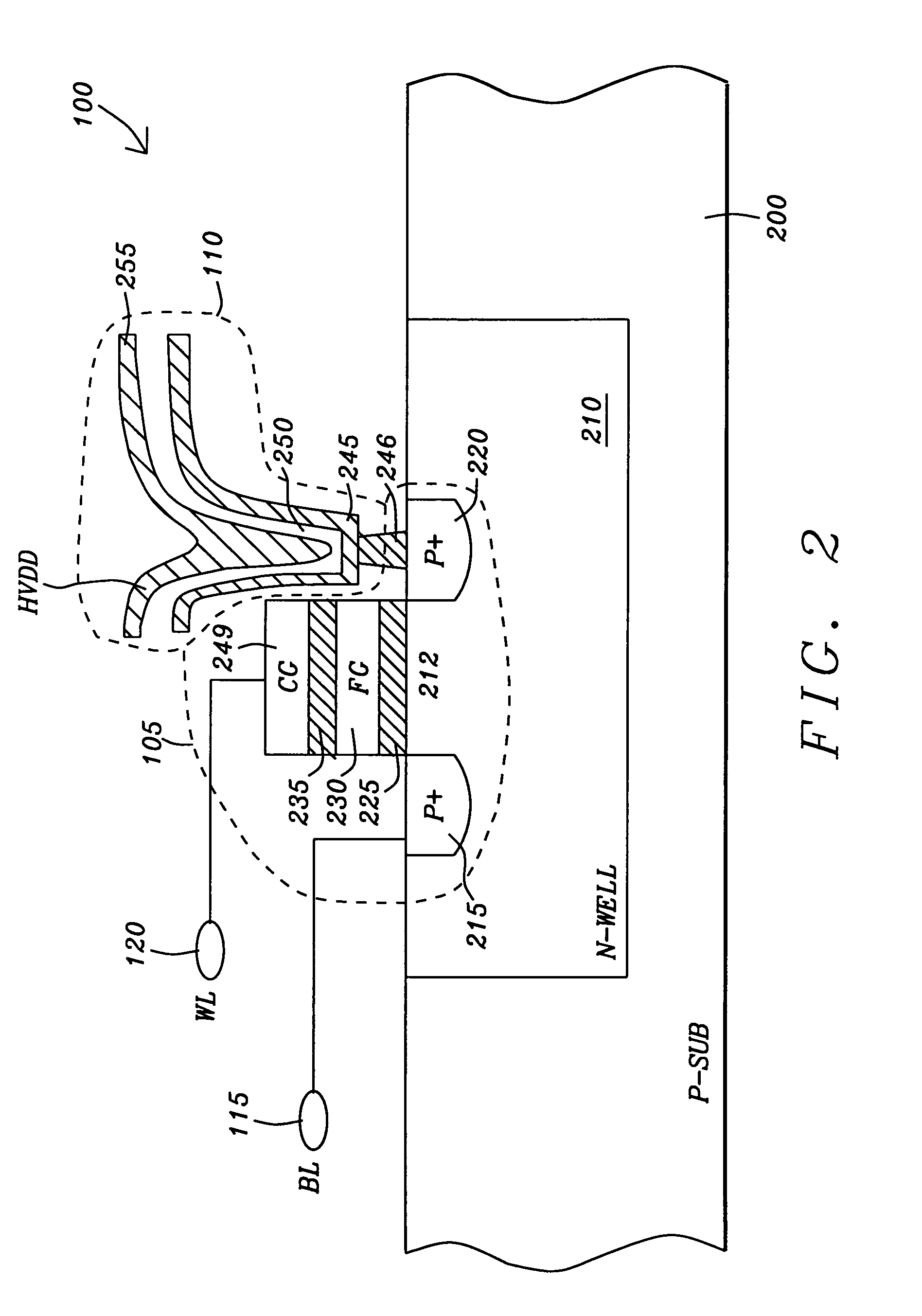
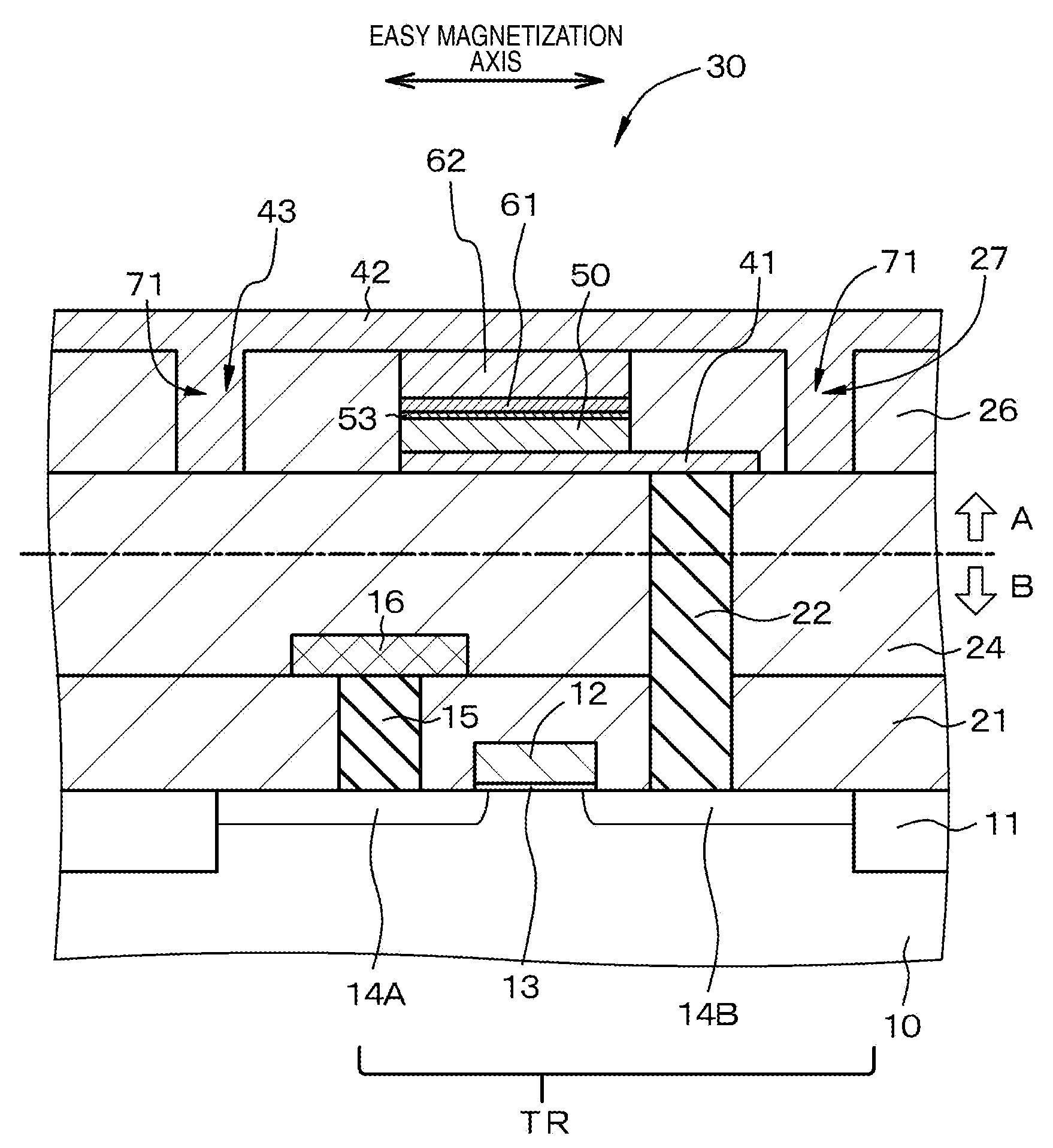
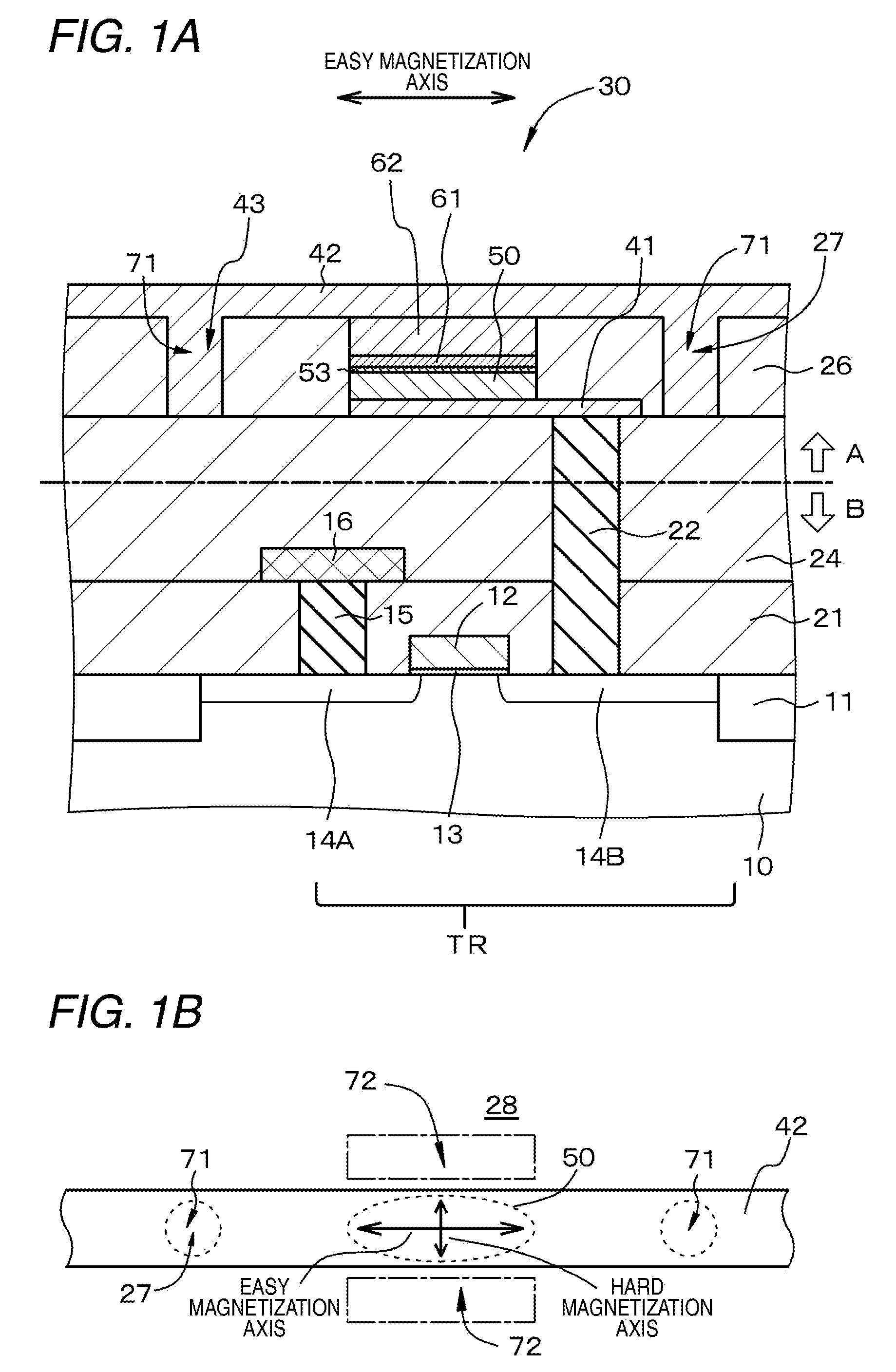
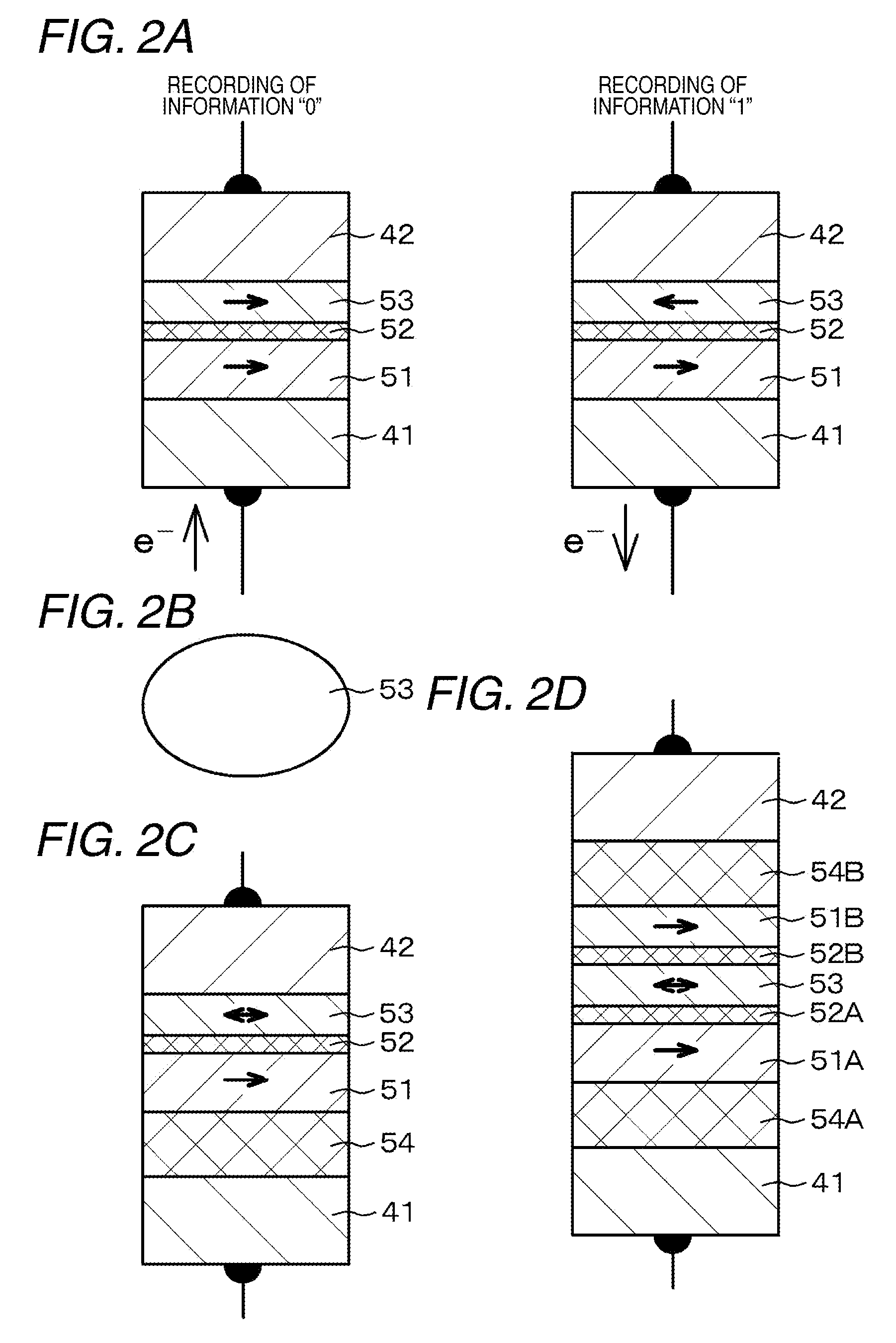
ActiveUS20090224300A1Improve thermal stabilityReduce power consumptionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerMagnetization
A nonvolatile magnetic memory device includes a magnetoresistance effect element that includes: a layered structure having a recording layer; a first wiring electrically connected to a lower part of the layered structure; a second wiring electrically connected to an upper part of the layered structure; and an interlayer insulation layer surrounding the layered structure. The magnetoresistance effect element further includes a low Young modulus region having a Young modulus lower than that of a material forming the interlayer insulation layer. The recording layer has an easy magnetization axis, and a hard magnetization axis orthogonal to the easy magnetization axis. When the magnetostriction constant λ of a material forming the recording layer is a positive value or a negative value, the low Young modulus region is disposed in an extension region of the easy magnetization axis or in an extension region of the hard magnetization axis of the recording layer, respectively.
Owner:SONY CORP
Object Identifying System for Segmenting Unreconstructed Data in Image Tomography
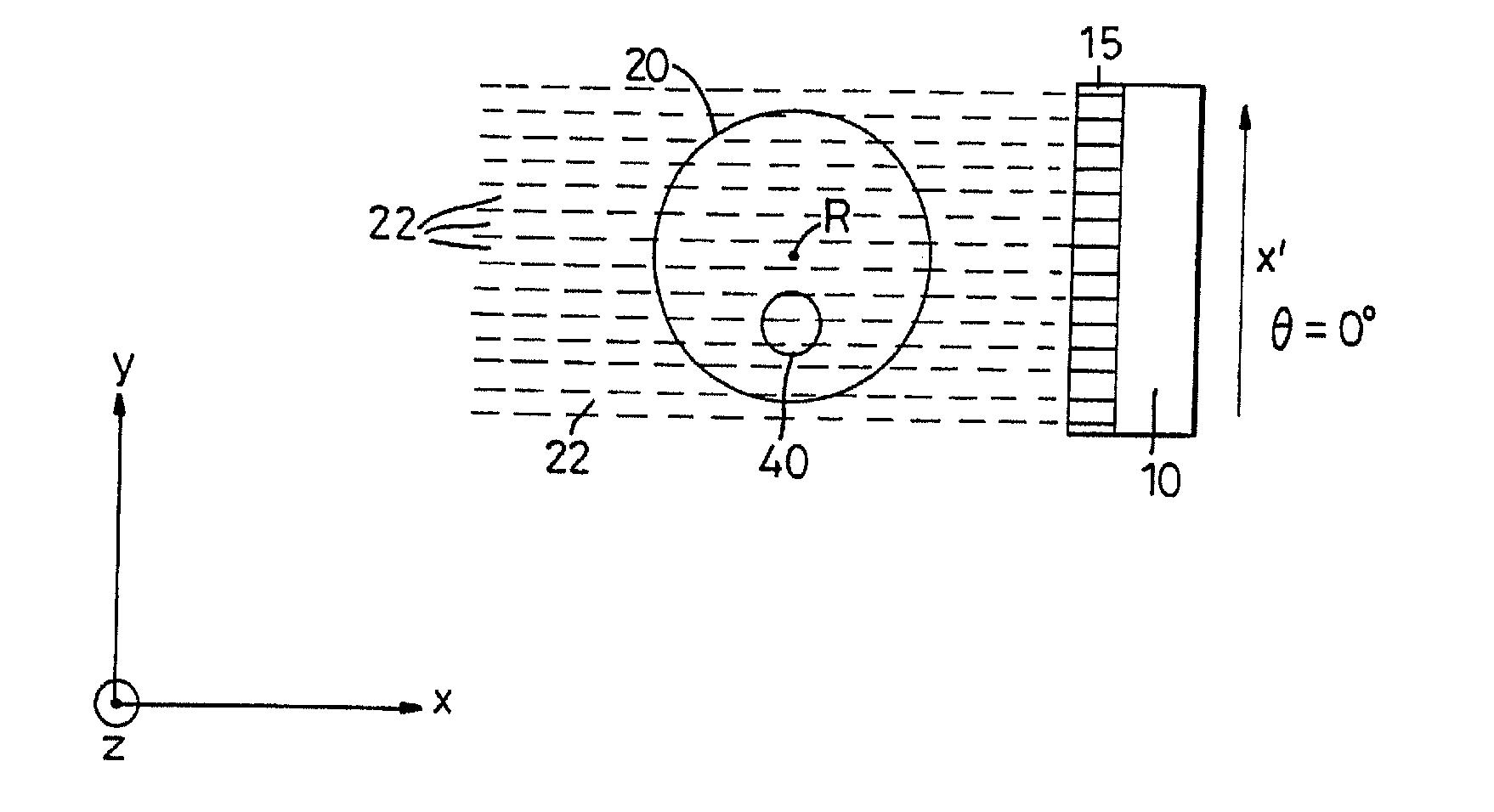
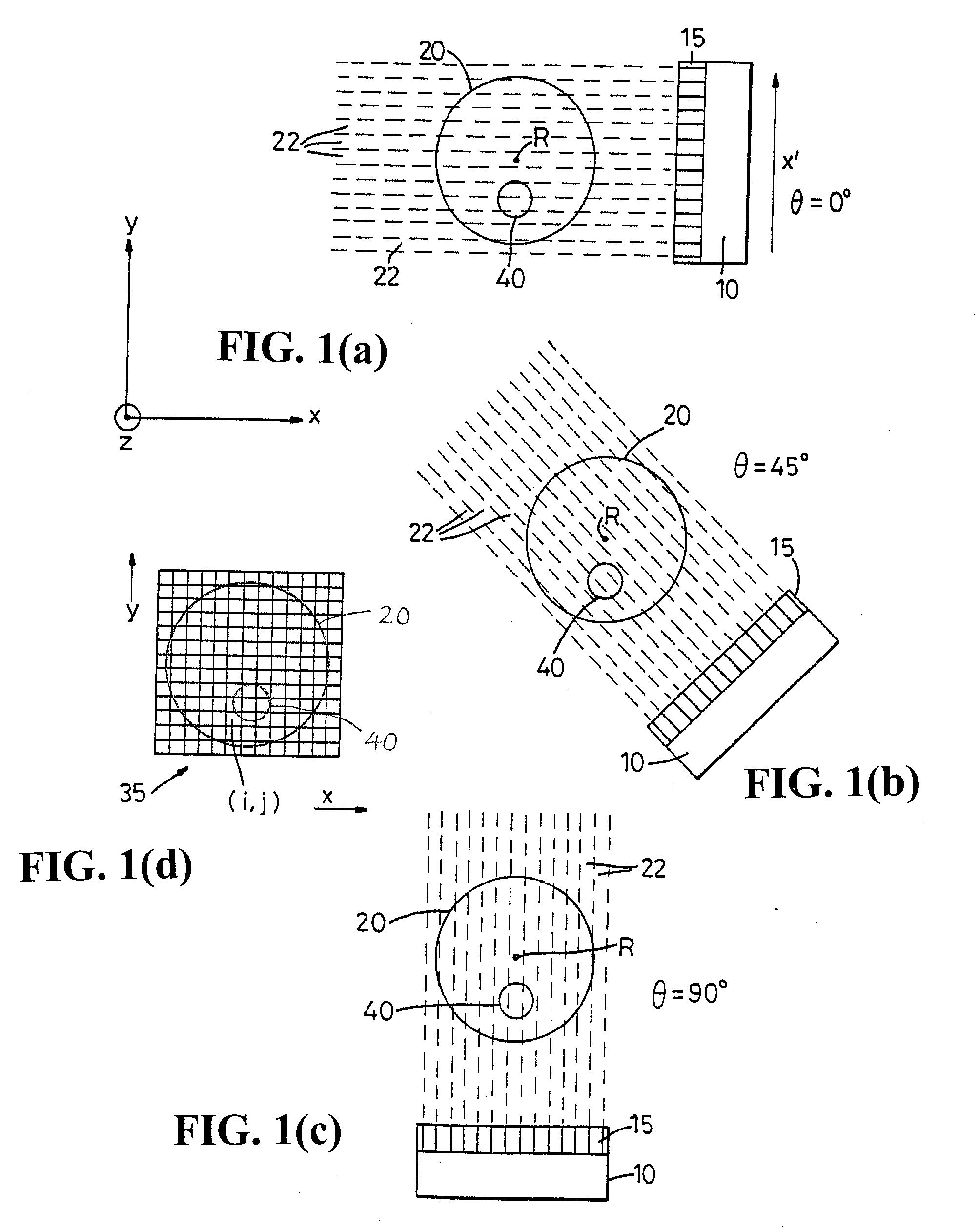
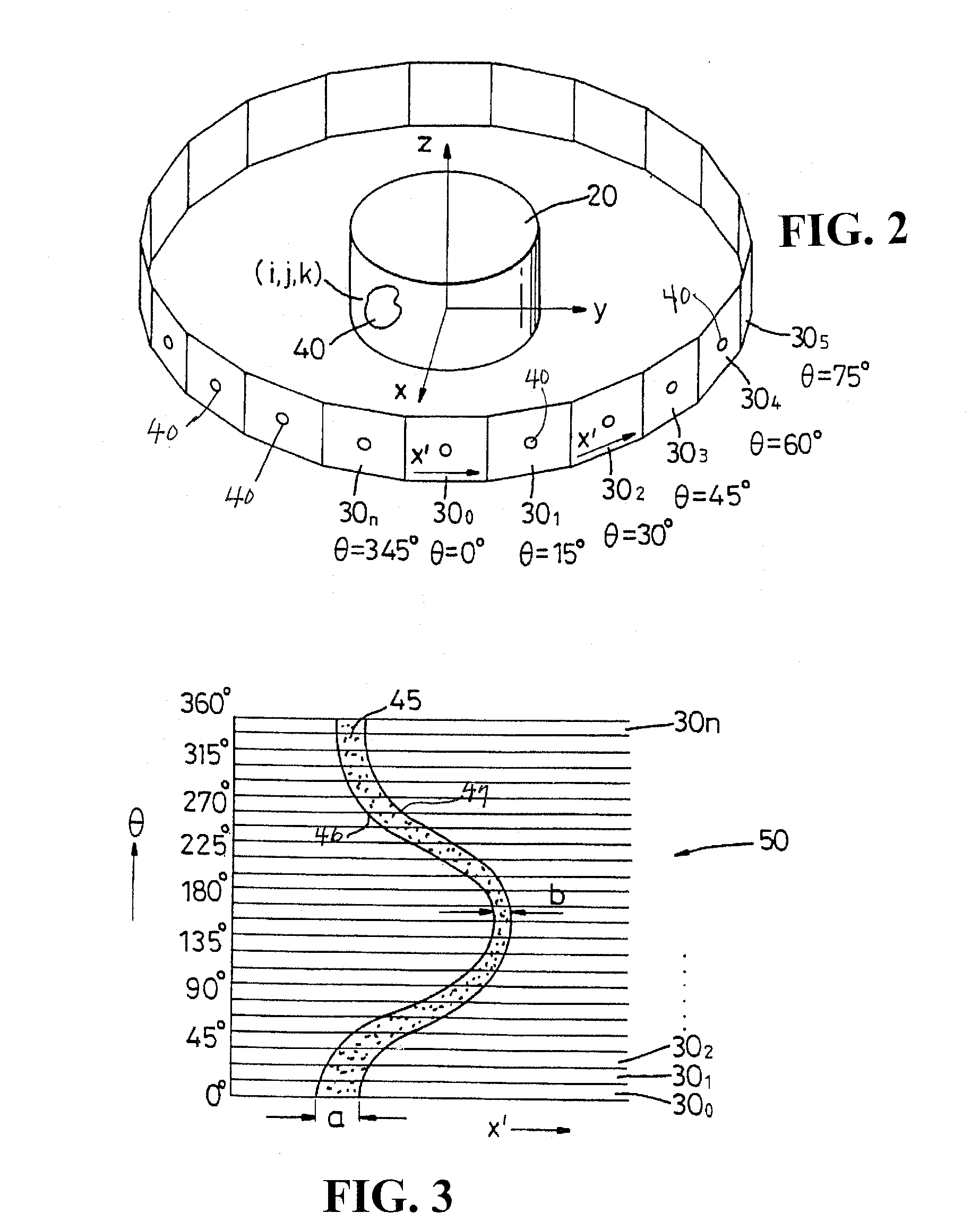
InactiveUS20060232608A1Simplifies and expeditesMaintaining the statistical independence of the object dataImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionUltrasound attenuationTomography
Tomographic projection data is segmented spatially by forming segmentation masks over the full outlines of objects appearing in isolation within selected data frame images. Further processing locates the object outlines in other data frames. Predictable effects of attenuation are used to attribute appropriate amounts of intensity to the segmented object space. Separate image reconstructions can be made of the segmented object data and the remaining projection data to independently optimize the reconstructions. Composite images can be made of the separate reconstructions.
Owner:TIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com