Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Conductivity is accurate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
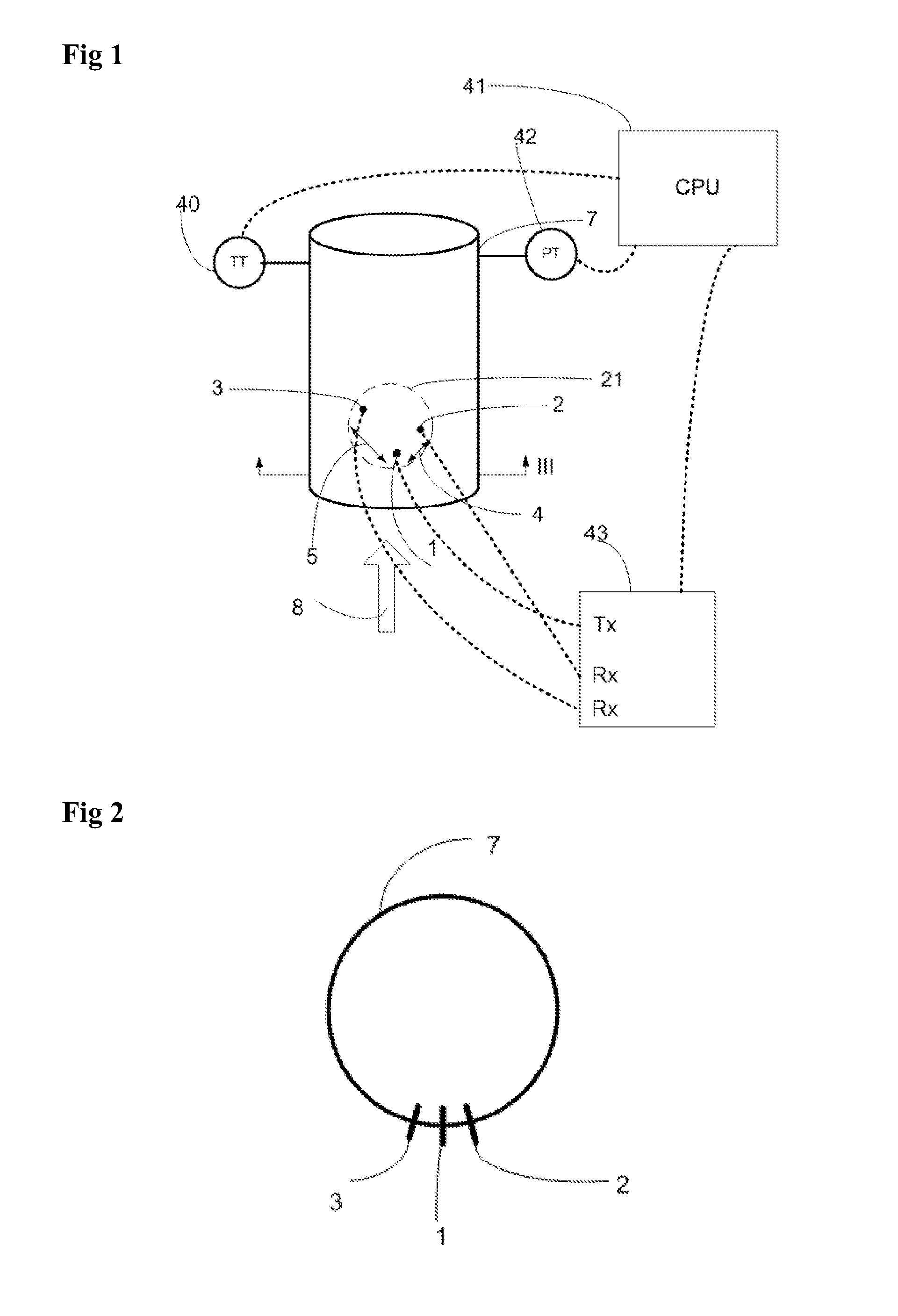
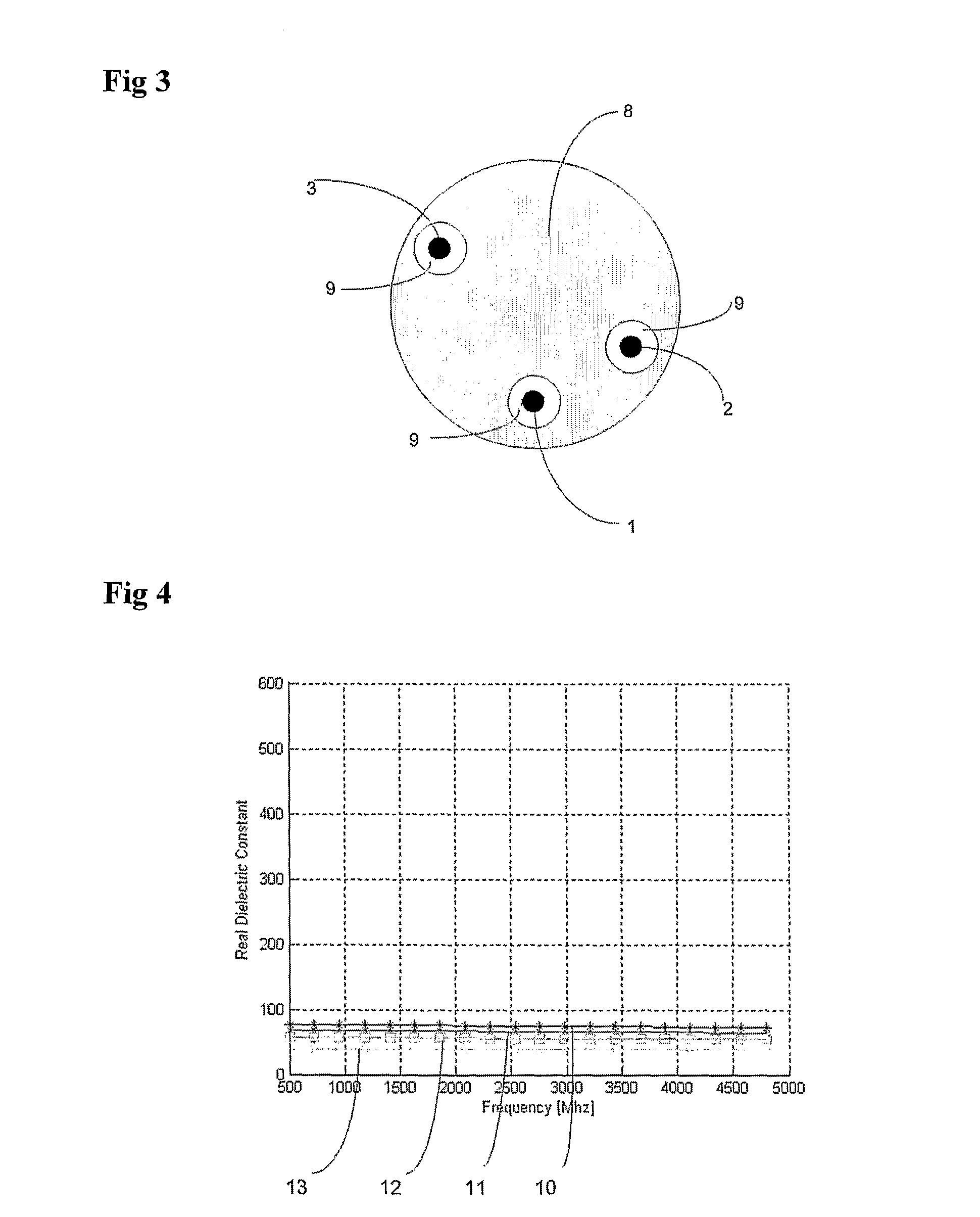
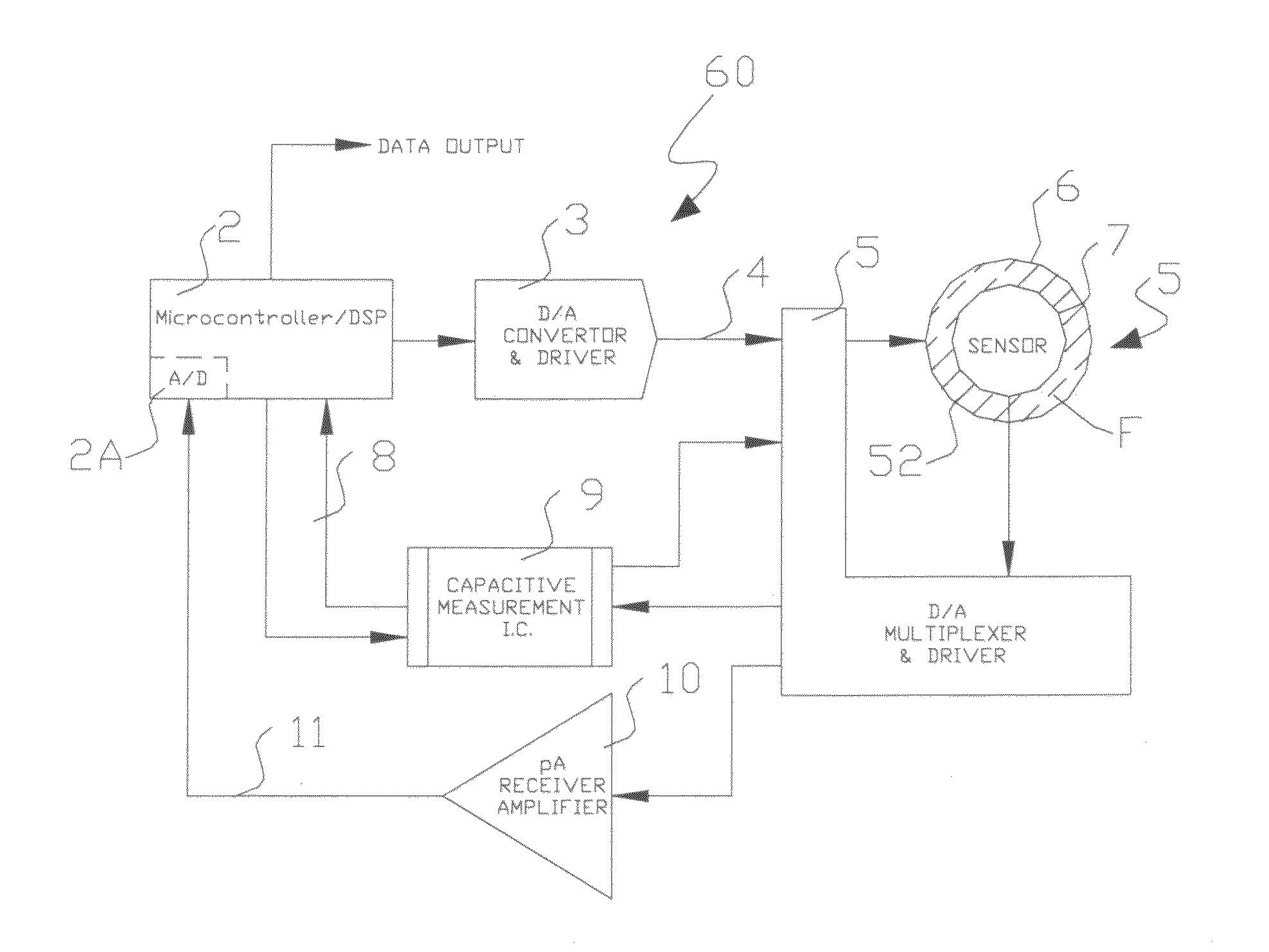
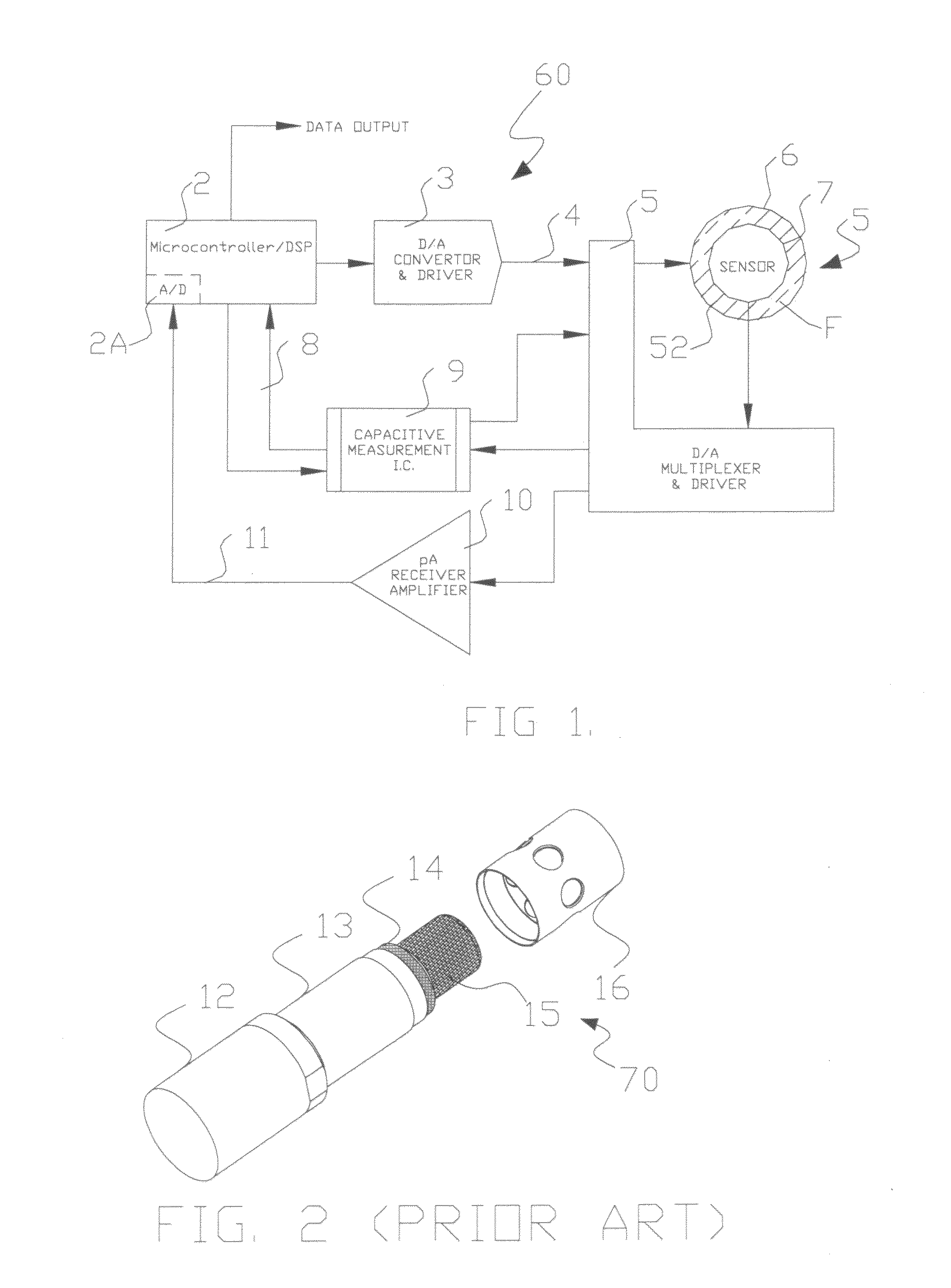
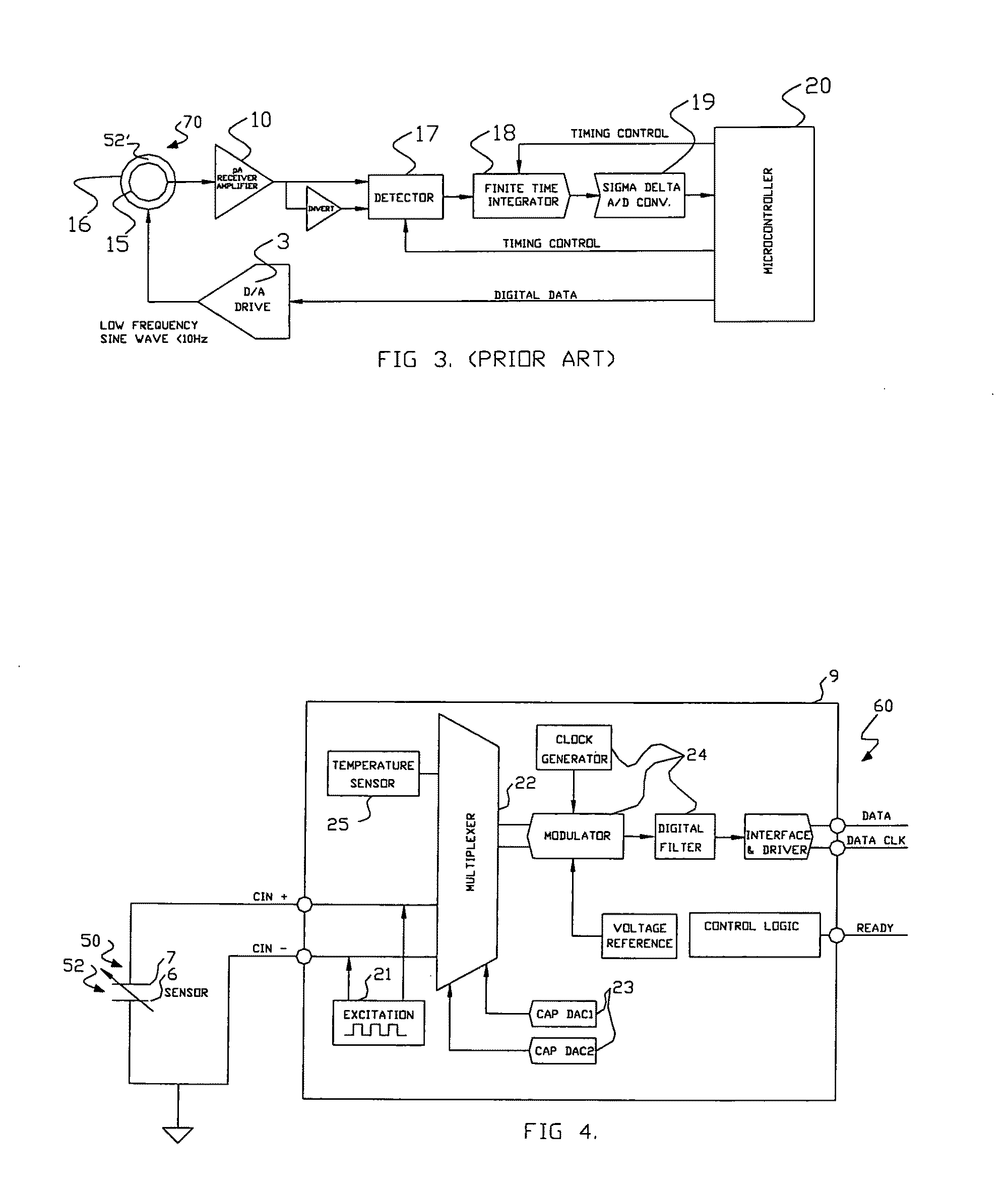
Apparatus and method for the measurement of electrical conductivity and dielectric constant of high impedance fluids
ActiveUS20100188111A1Low costLow component requirementsFluid resistance measurementsMaterial impedanceMicrocontrollerElectron
A sensor, a system of direct measurement using that sensor, and a method of direct and simultaneous measurement of conductivity and dielectric constant of a fluid, particularly high impedance, hydrocarbon-based fluids. The sensor has a cell that holds the fluids to be measured between a single pair of coaxial, bare metal electrodes connected through interface circuitry to measurement circuitry preferably implemented in one or several IC's. The sensor has a mutually compatible electrode geometry that provides both the correct cell constant for measurement of conductivity of hydrocarbons fluids (typical range 0-100,000 pS / cm), and a bulk capacitance (for use in dielectric constant measurement) in the range of measure of readily available low cost commercial IC's (having a typical capacitance measurement span of <10 pF, with a total bulk capacitance at the chip of <20 pF). The cell conductivity constant for use with hydrocarbon-based oils having a conductivity in the range of 1 to 500,000 pS / M is preferably less than or equal to about 0.1. The cell bulk capacitance with hydrocarbon fluids inside the sensor results in a bulk capacitance of at least about 4 pF. In one embodiment, the electronic circuitry is a Microcontroller / DSP that both generates synchronous drive signals at various frequencies, for both conductivity and dielectric constant measurements while directly digitizing and numerically processing the sensor output.
Owner:FALMOUTH SCI +1
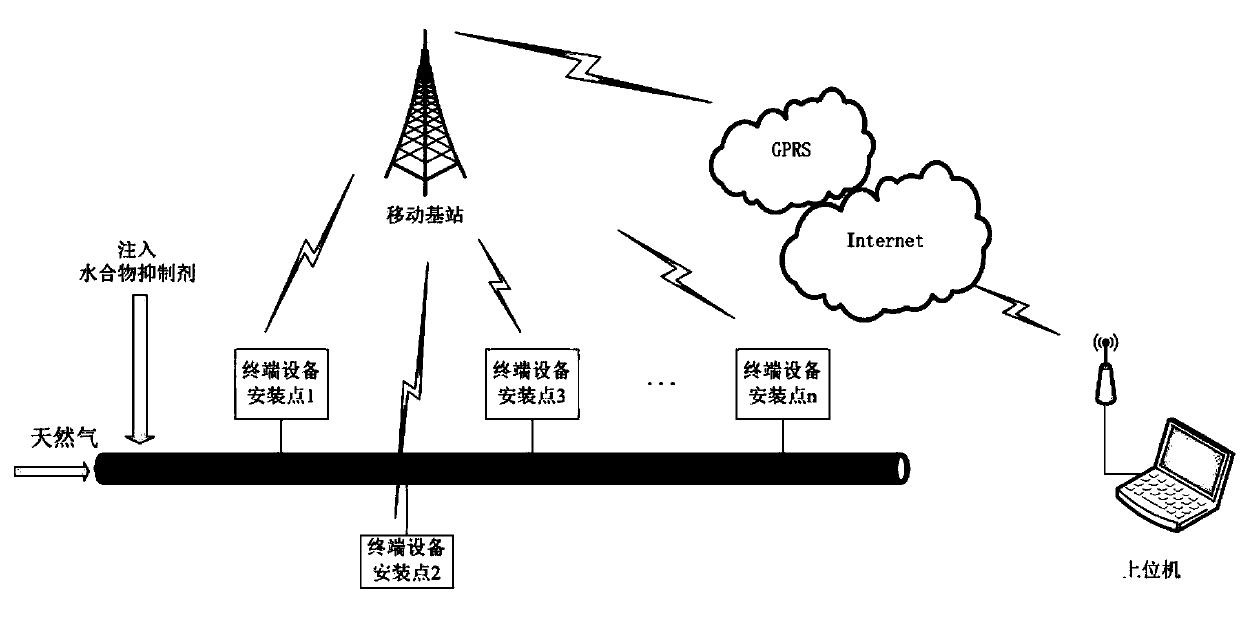
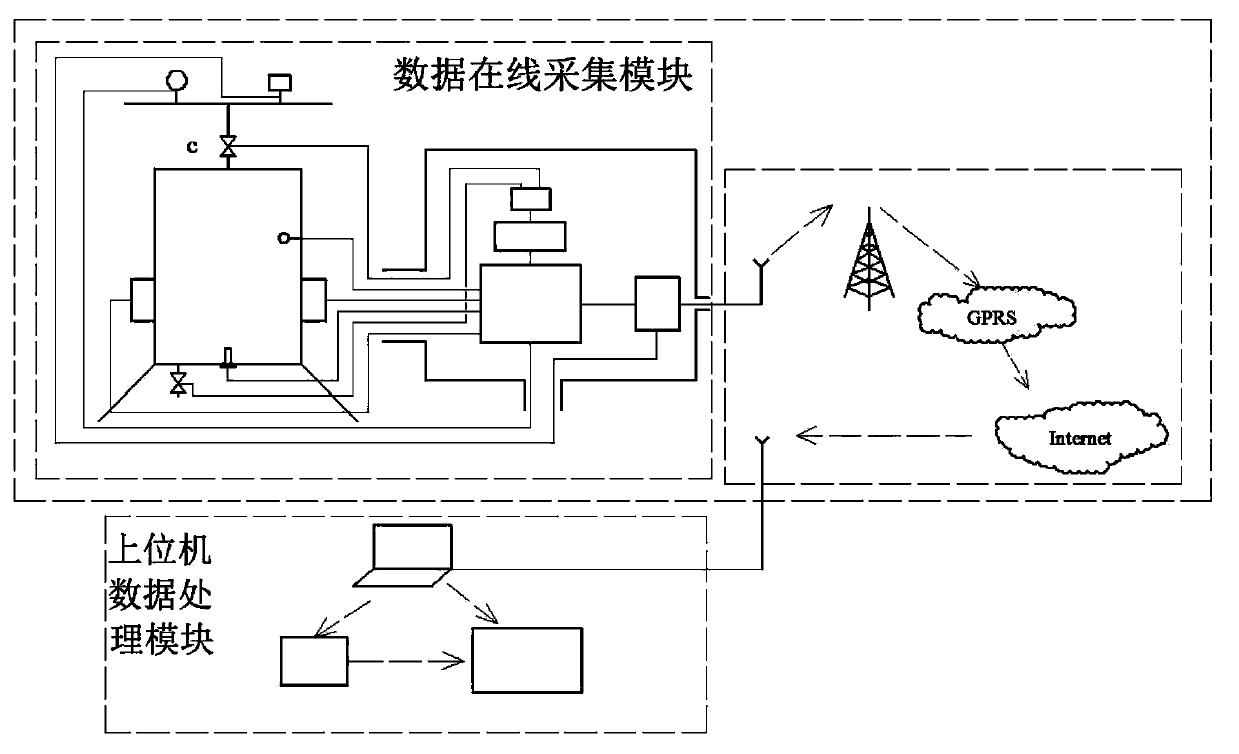
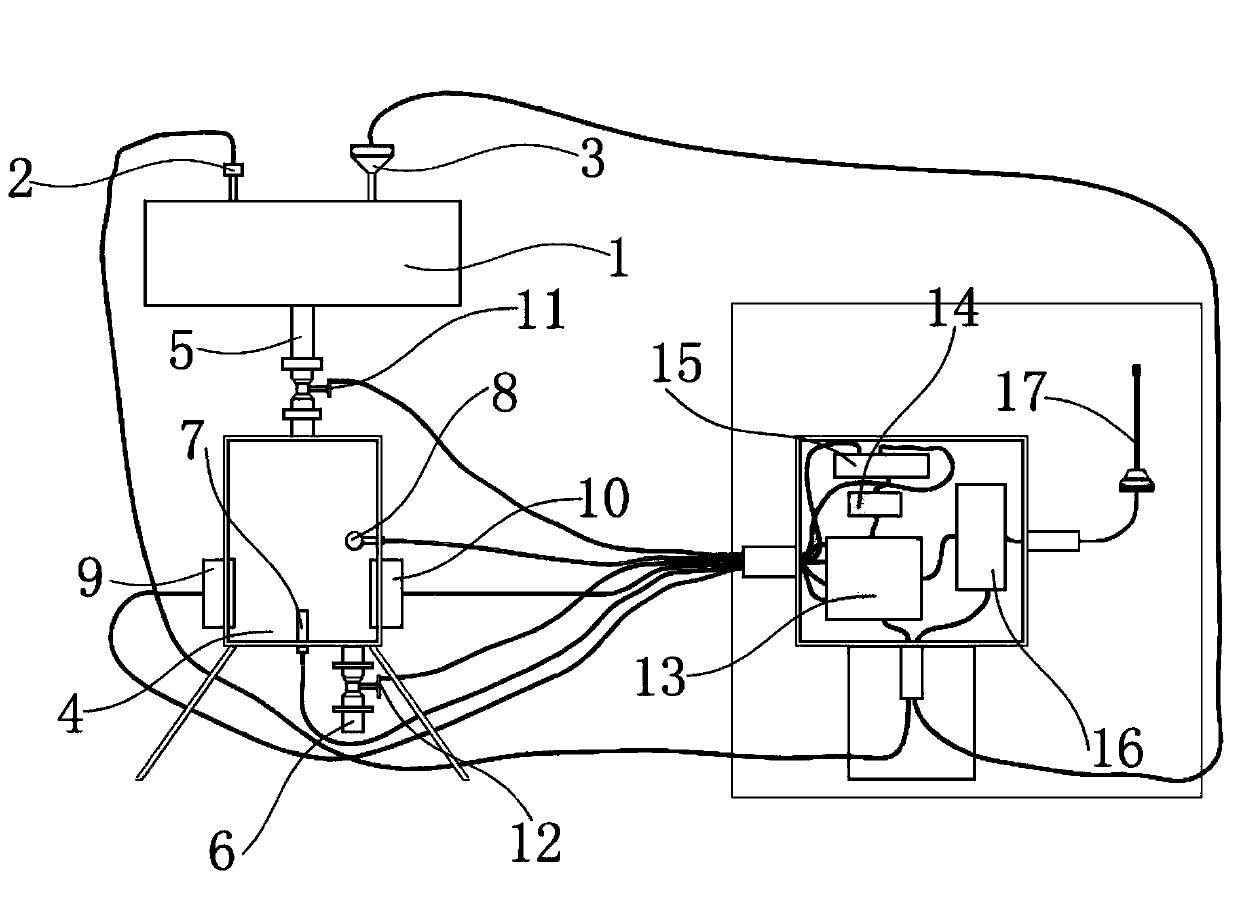
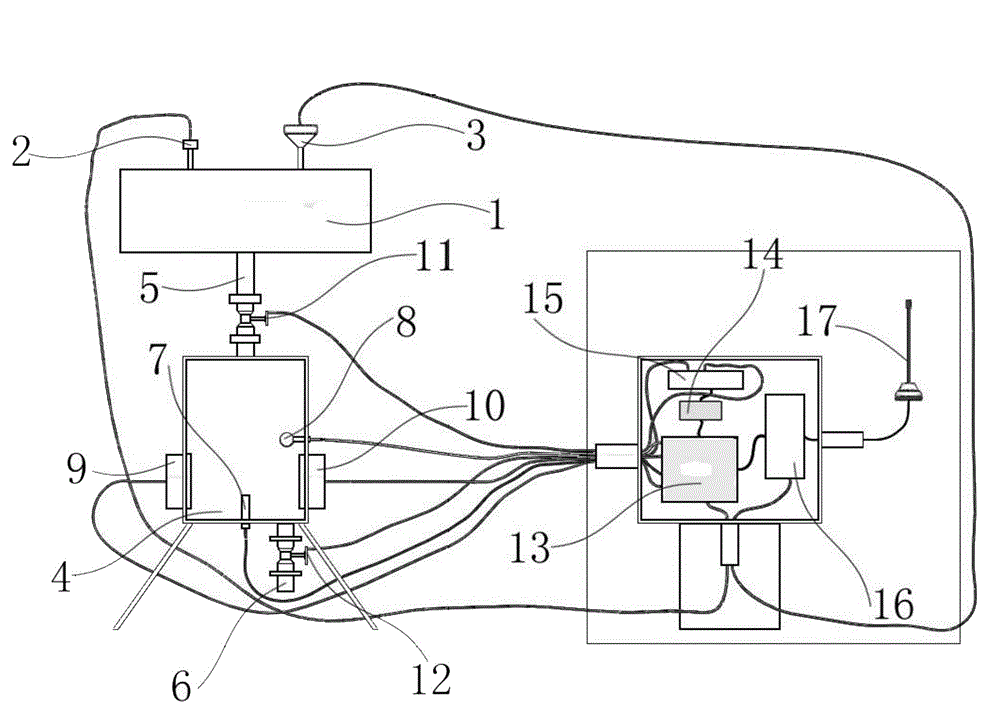
Pipeline natural gas hydrate formation online early-warning device and method
ActiveCN104198674ARealize online collectionRealize wireless transmissionTransmission systemsFuel testingInjection volumeComputer module
The invention discloses a pipeline natural gas hydrate formation online early-warning device and a method. The online early-warning device comprises an online data acquisition module which is directly arranged at a position of a gathering pipeline, required to be monitored, for tracking and monitoring parameters relevant to the hydrate formation condition on the whole pipeline and realizing online early warning for the hydrate formation and optimization of the injection volume of different types of natural gas hydrate inhibitors finally. According to an online early-warning method, the electrical conductivity and the temperature of the liquid phase as well as the propagation speed of ultrasonic waves in the water phase are monitored to calculate the concentration of the hydrate inhibitor and the saline concentration in the water phase of the monitored point, and the acquired parameters such as gaseous phase pressure, gaseous phase components and temperature are also considered to realize online early warning and the optimization of the injection volume of the inhibitor.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
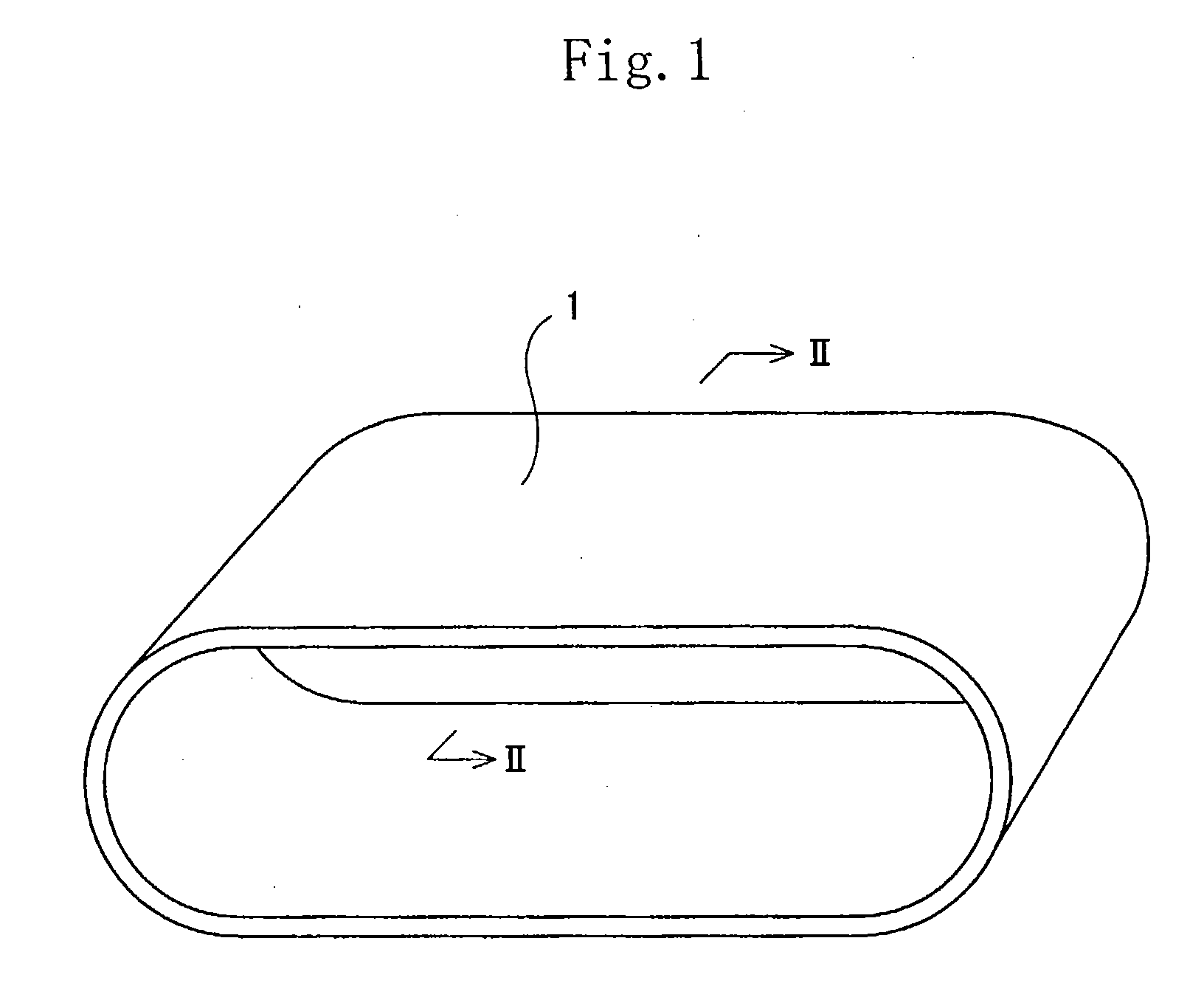
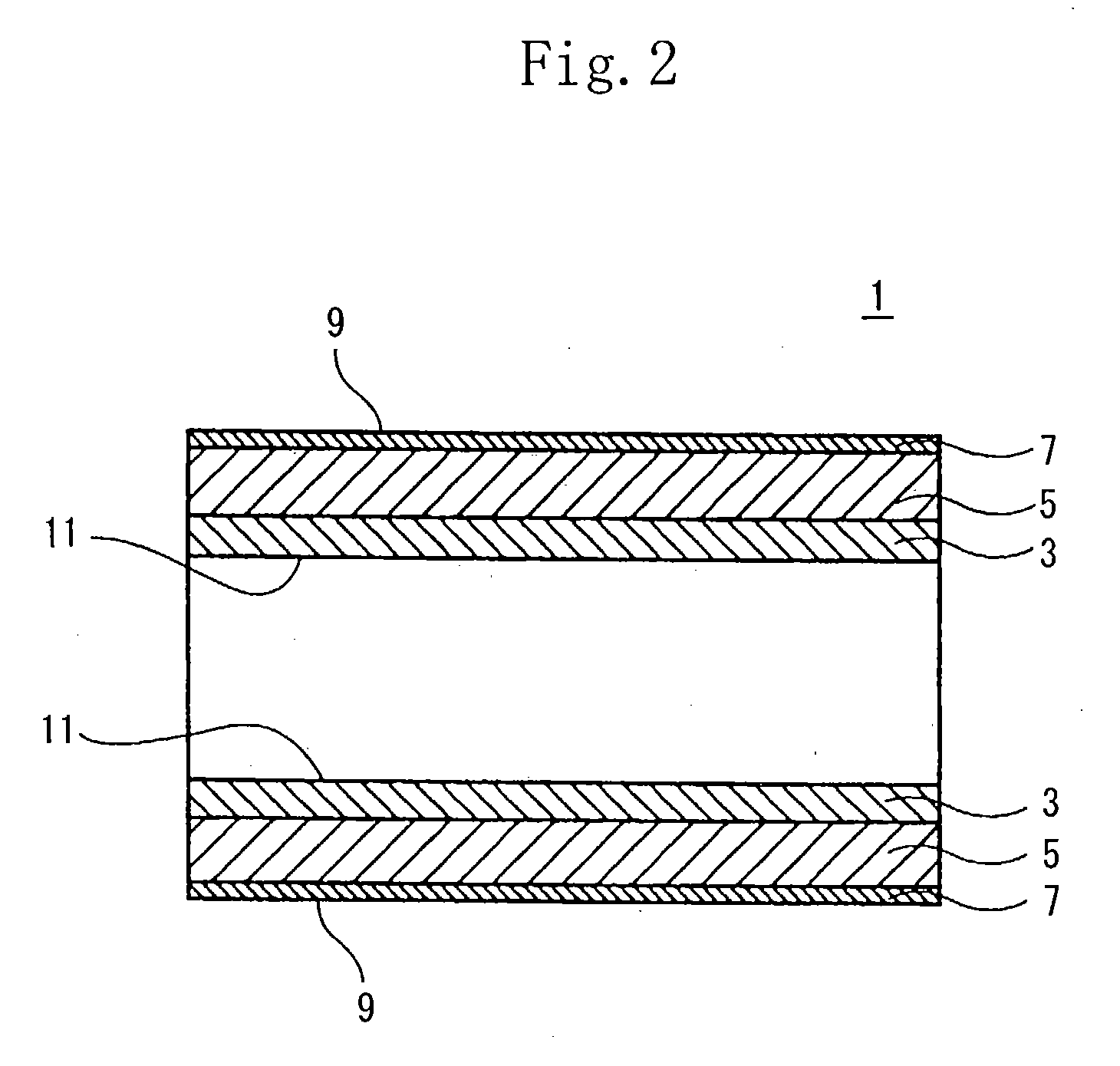
Conductive belt
InactiveUS20040013863A1Improve uniformityIncrease elasticitySynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusElastomerElectrical resistance and conductance
A conductive belt having a base layer (3) electroconductive and made of a resin, an intermediate layer (5) ionic-conductive and made of an elastomer, and a surface coating layer (7). The base layer (3) has a tensile modulus of elasticity of not less than 500 Mpa and a volume electric resistance value not less than 10<6>Omega.cm nor more than 10<11>Omega.cm. The intermediate layer (5) has a JIS A hardness less than 70, a thickness not less than 50 mum nor more than 600 mum, and a volume electric resistance value not less than 10<8>Omega.cm nor more than 10<14>Omega.cm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
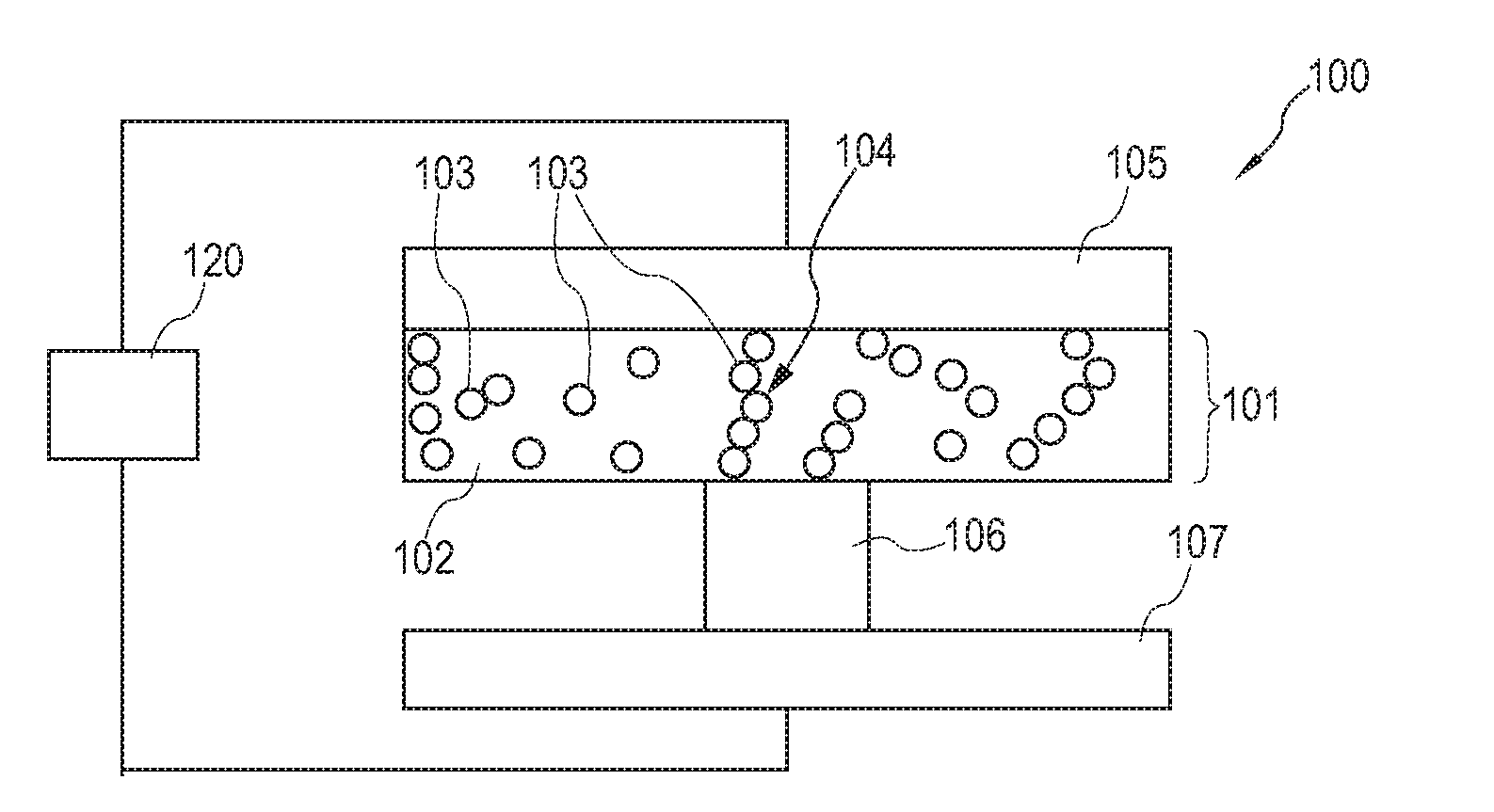
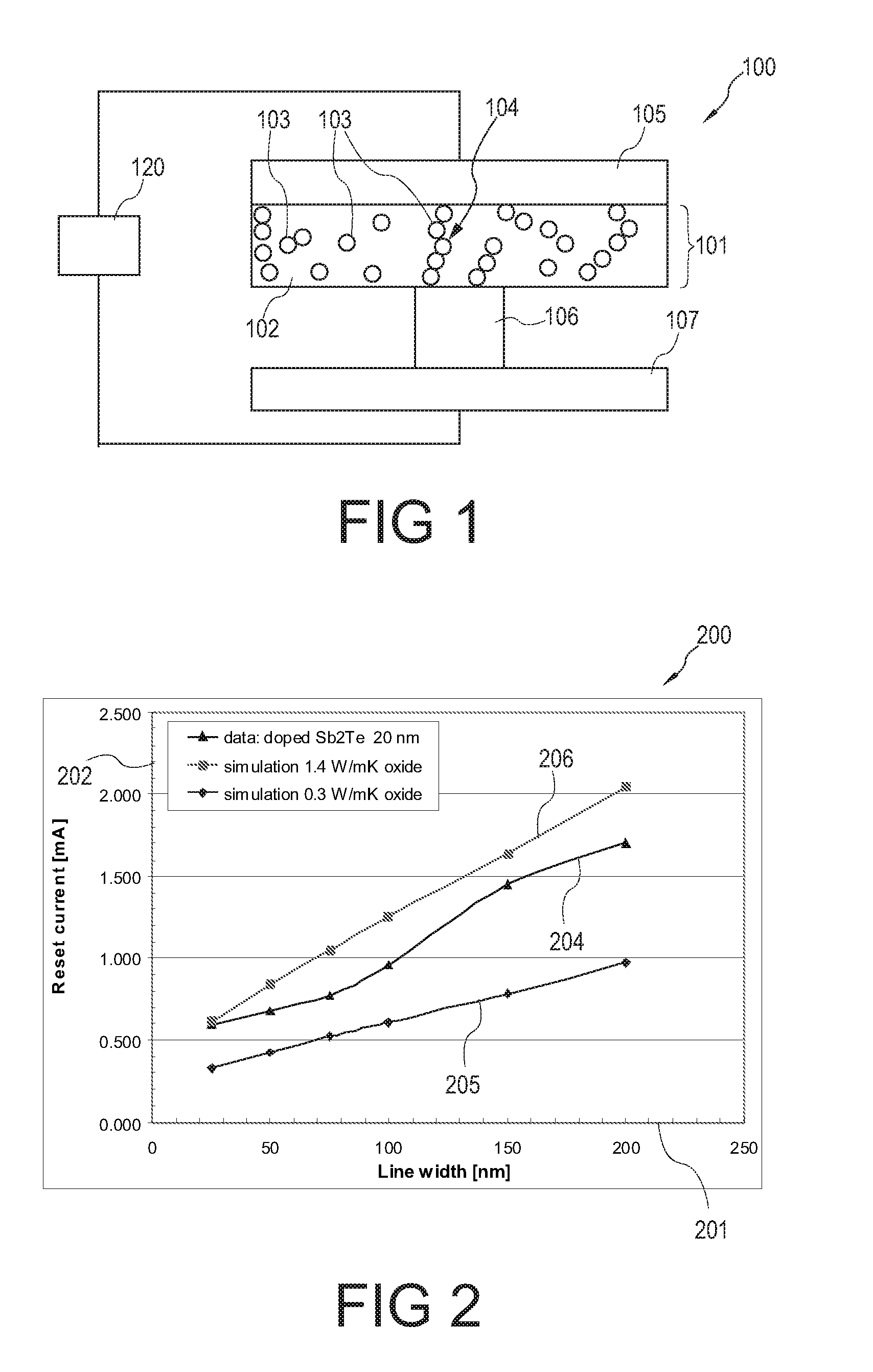
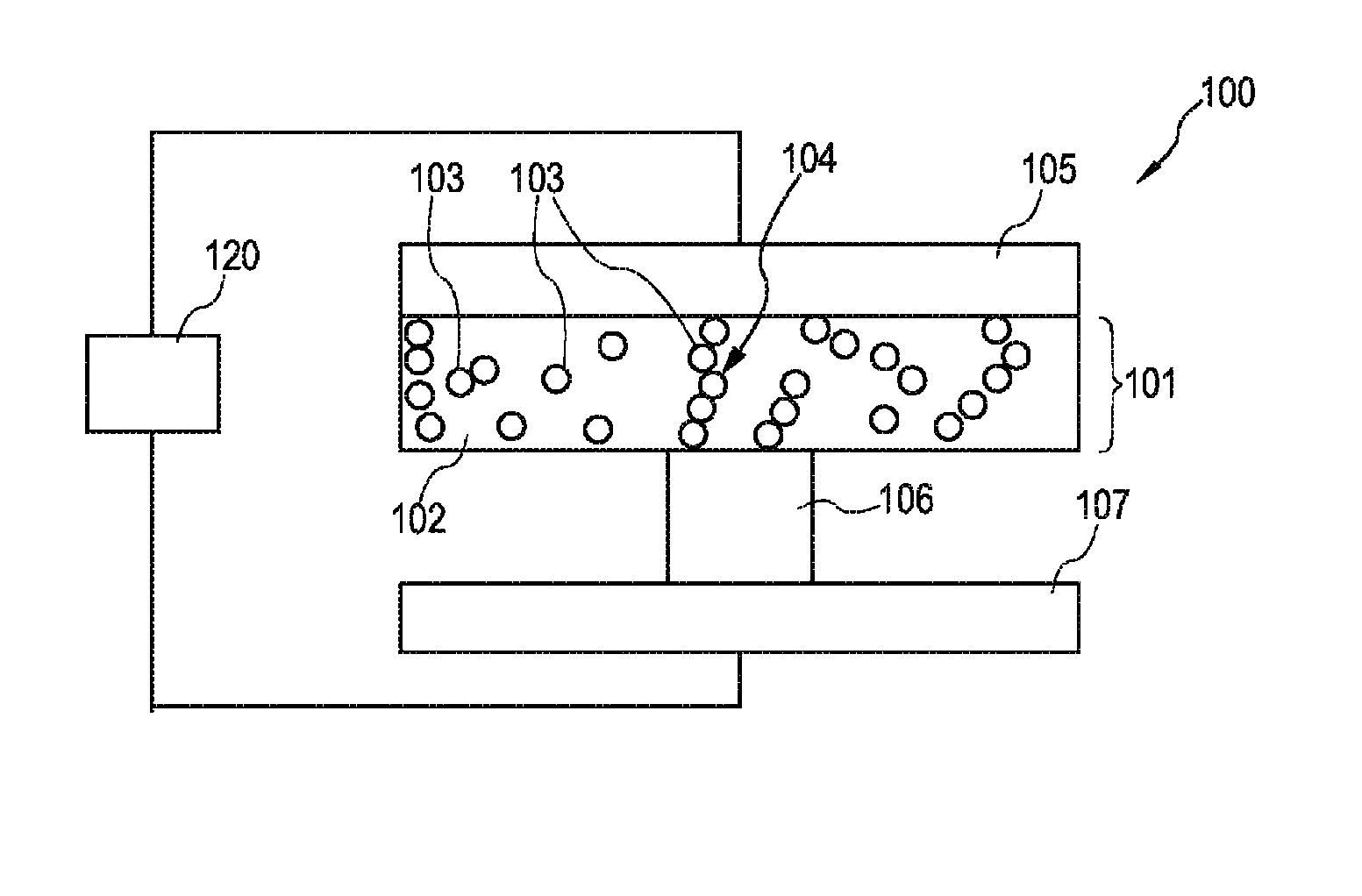
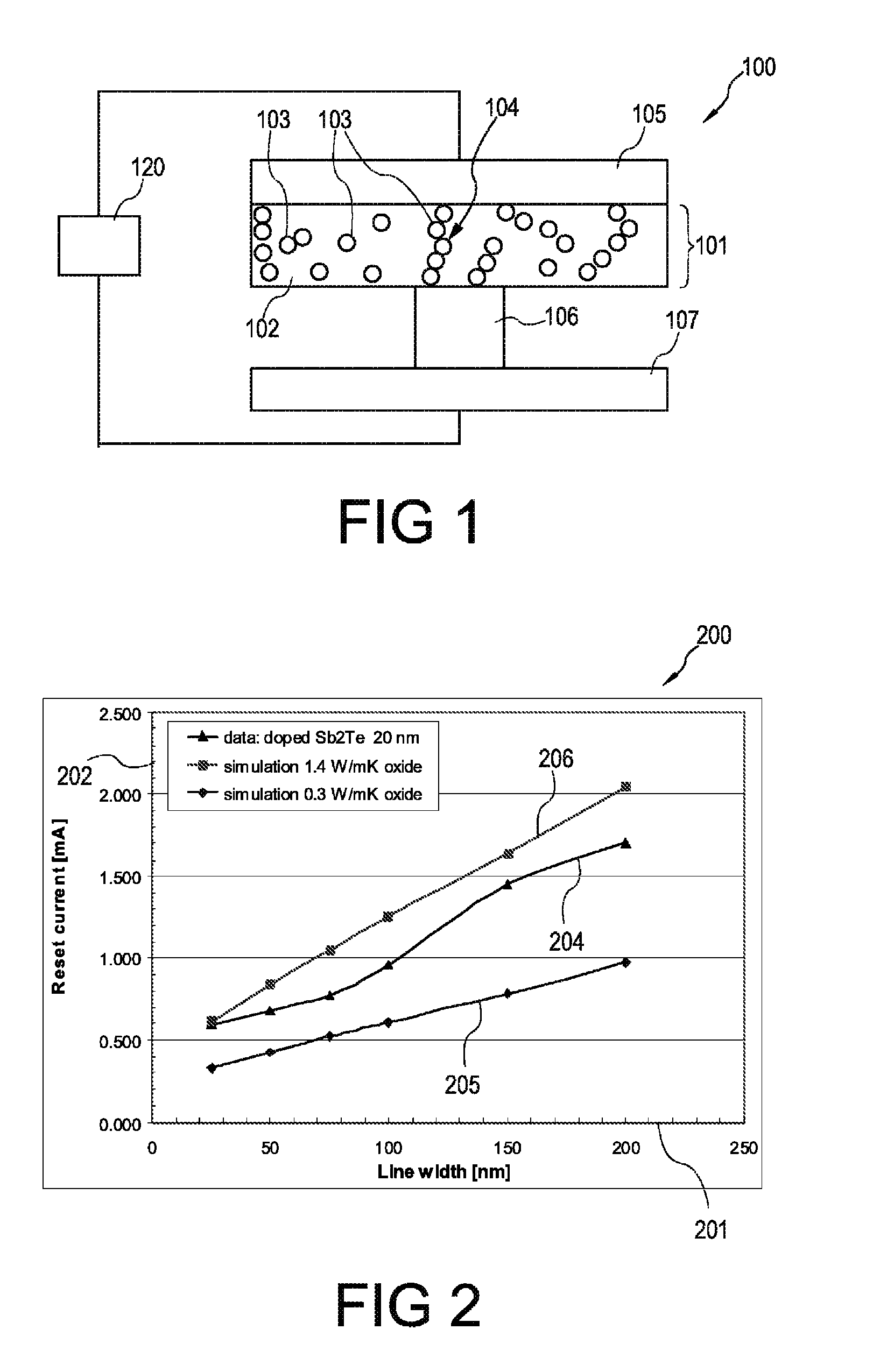
Electronic component, and a method of manufacturing an electronic component
ActiveUS20100044665A1Increase resistanceImprove integration densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesEngineeringElectronic component
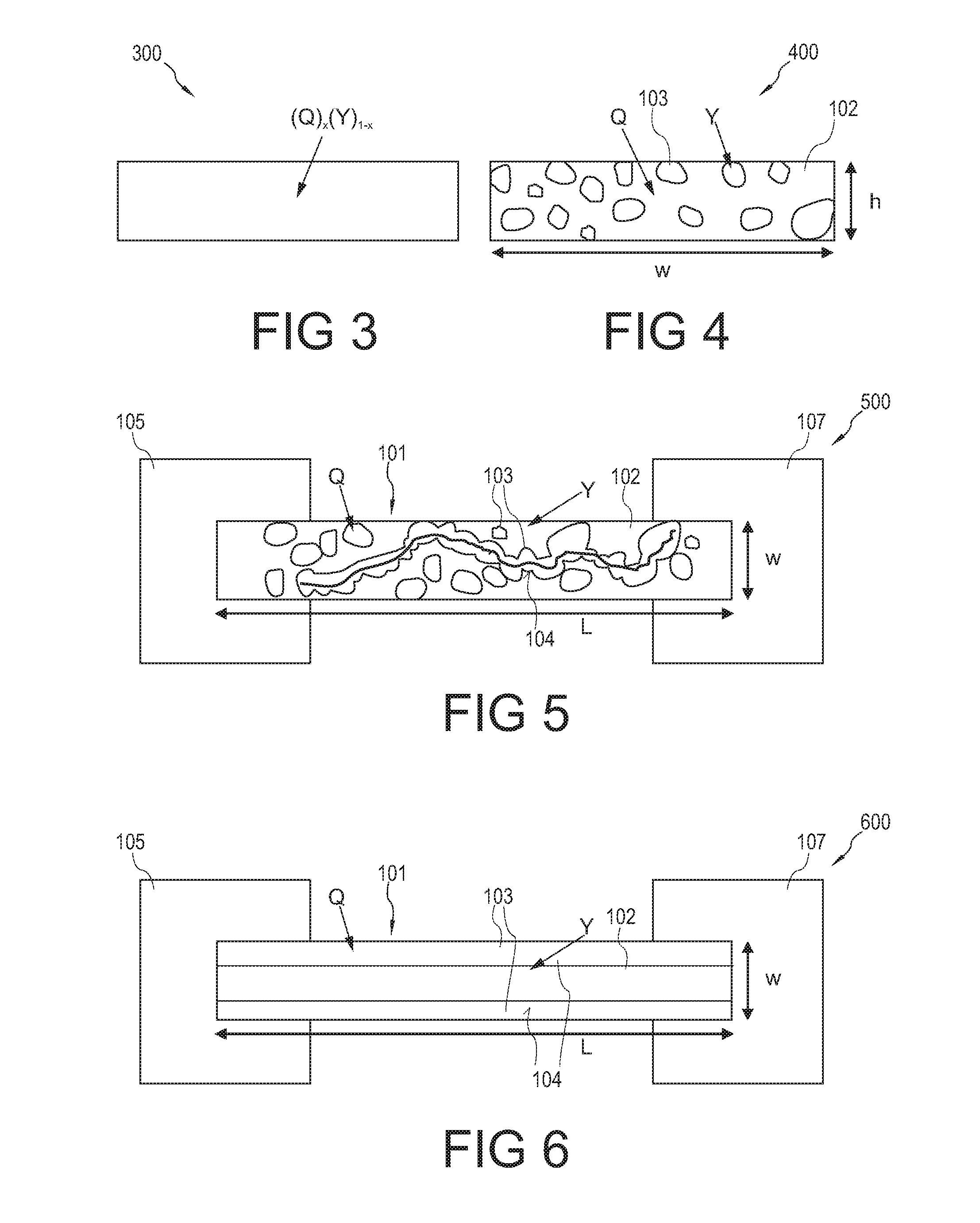
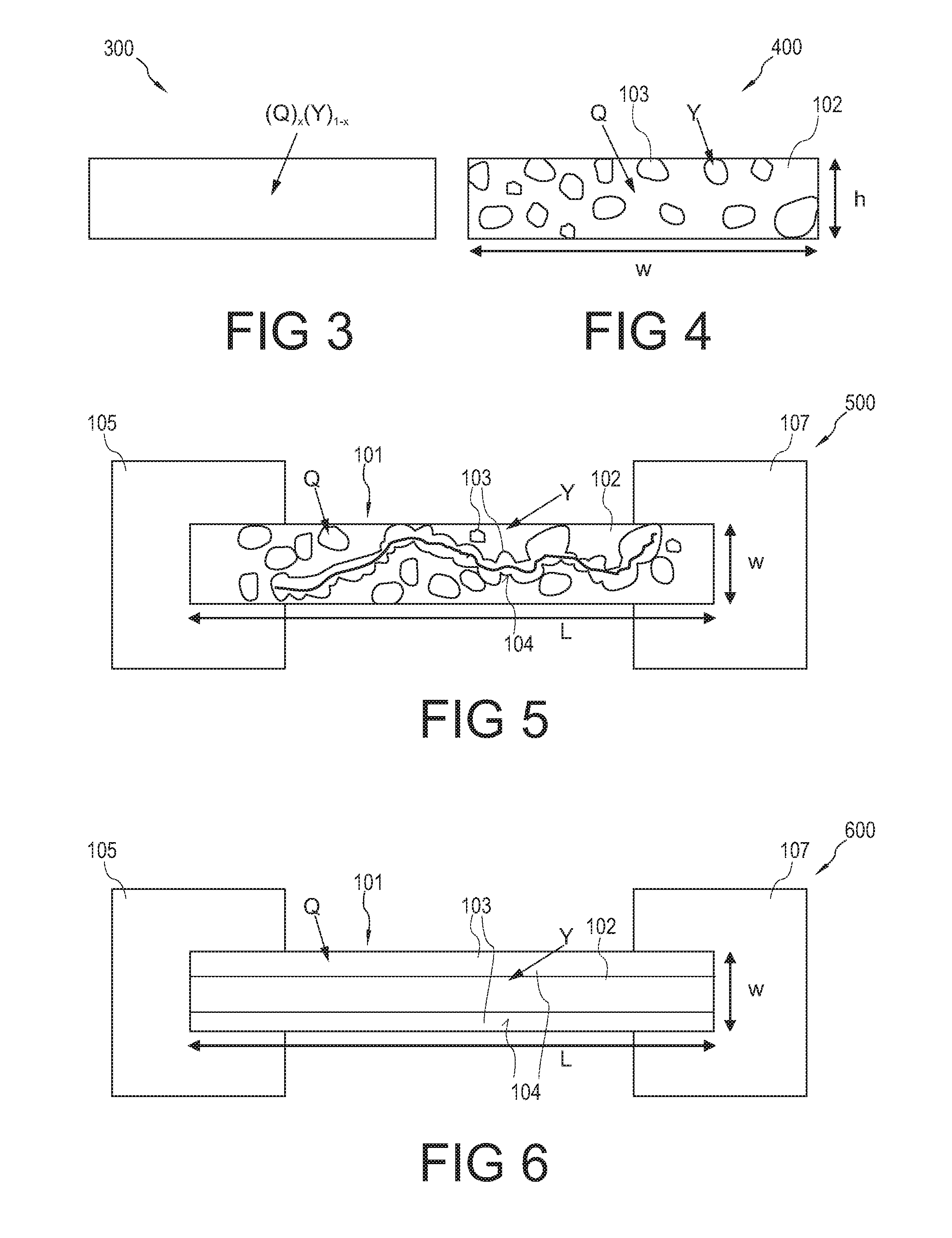
An electronic component (100) comprising a matrix (102) and a plurality of islands (103) embedded in the matrix (102) and comprising a material which is convertible between at least two states characterized by different electrical properties, wherein the plurality of islands (103) form a continuous path (104) in the matrix (102).
Owner:NXP BV
Cleanable flat-faced conductivity sensor
ActiveUS20160139070A1Conductivity is accurateEasy to shapeResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by optical meansDeployment timeEngineering
Provided is a cleanable conductivity sensor and related methods having a distal sensing end in which active sensing elements are positioned and an outer fin specially configured to minimize unwanted interference without impacting the ability for automated cleaning of the distal sensing end. A rotatable wiper or brush may be periodically rotated over the distal sensing end, thereby removing unwanted biological build-up and avoiding fouling, thereby increasing the sensor deployment time without active intervention and maintenance.
Owner:INSITU INC
Cleanable flat-faced conductivity sensor
ActiveUS9835554B2Conductivity is accurateEasy to shapeScattering properties measurementsTesting waterDeployment timeEngineering
Provided is a cleanable conductivity sensor and related methods having a distal sensing end in which active sensing elements are positioned and an outer fin specially configured to minimize unwanted interference without impacting the ability for automated cleaning of the distal sensing end. A rotatable wiper or brush may be periodically rotated over the distal sensing end, thereby removing unwanted biological build-up and avoiding fouling, thereby increasing the sensor deployment time without active intervention and maintenance.
Owner:INSITU INC
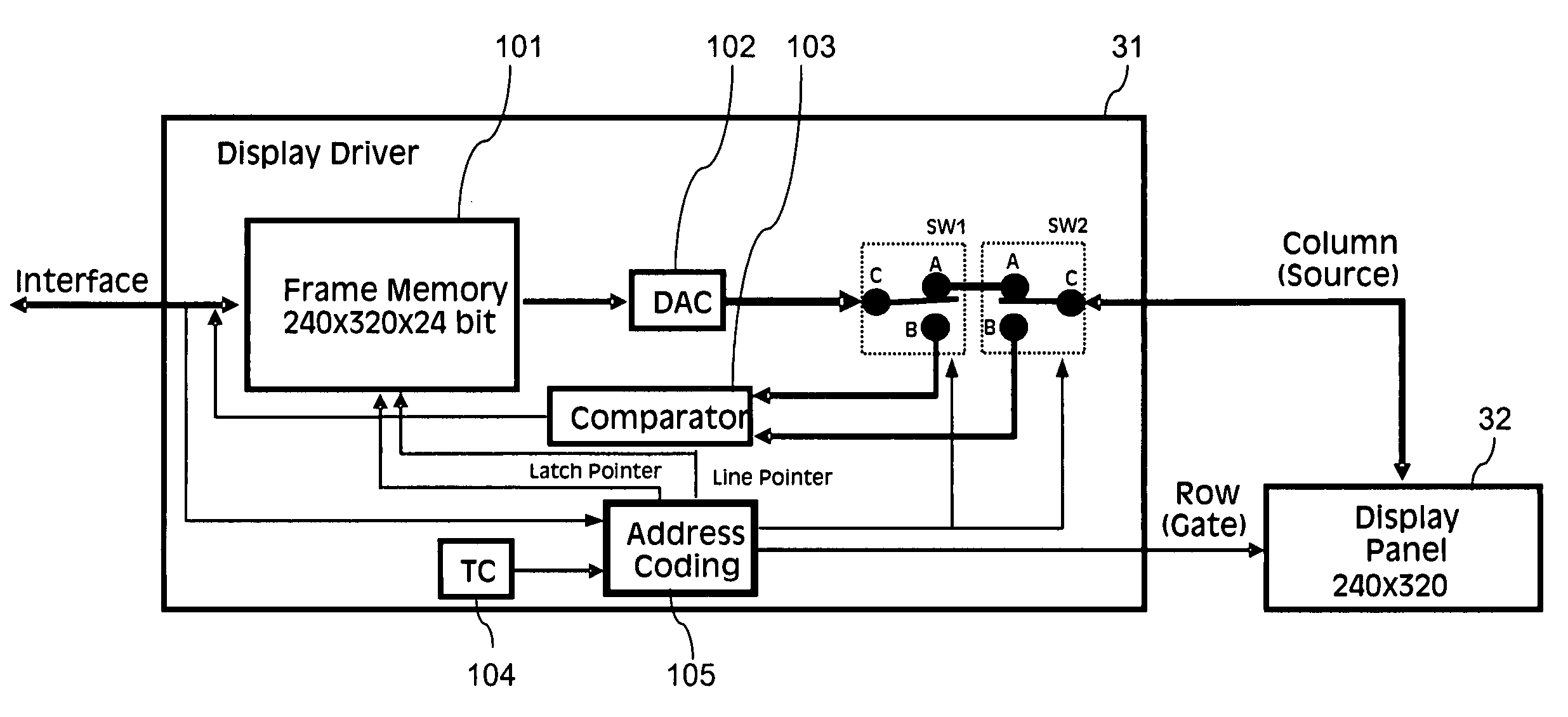
Method and apparatus for measuring the water conductivity and water volume fraction of a multiphase mixture containing water
ActiveUS8076950B2Accurate and repeatable measurementHigh precision measurementComponent separationResistance/reactance/impedenceWater volume fractionElectrical resistivity and conductivity
A method for determining the water conductivity and water volume fraction of a multi-component mixture of water and at least one additional liquid or gas in a pipe, the method comprising the following steps: a. electromagnetic phase measurements at least two measurement frequencies are performed between two receiving antennas located at different distances from a sending antenna, b. based on empirically determined constant(s) and the above measurements, the real and imaginary dielectric constants are determined, c. the temperature and pressure are determined d. based on the knowledge of the real and imaginary dielectric constants of the components of the fluid mixture and the result from the above steps a-c, the conductivity of the water and / or the volume fraction of water are determined. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:FMC KONGSBERG SUS
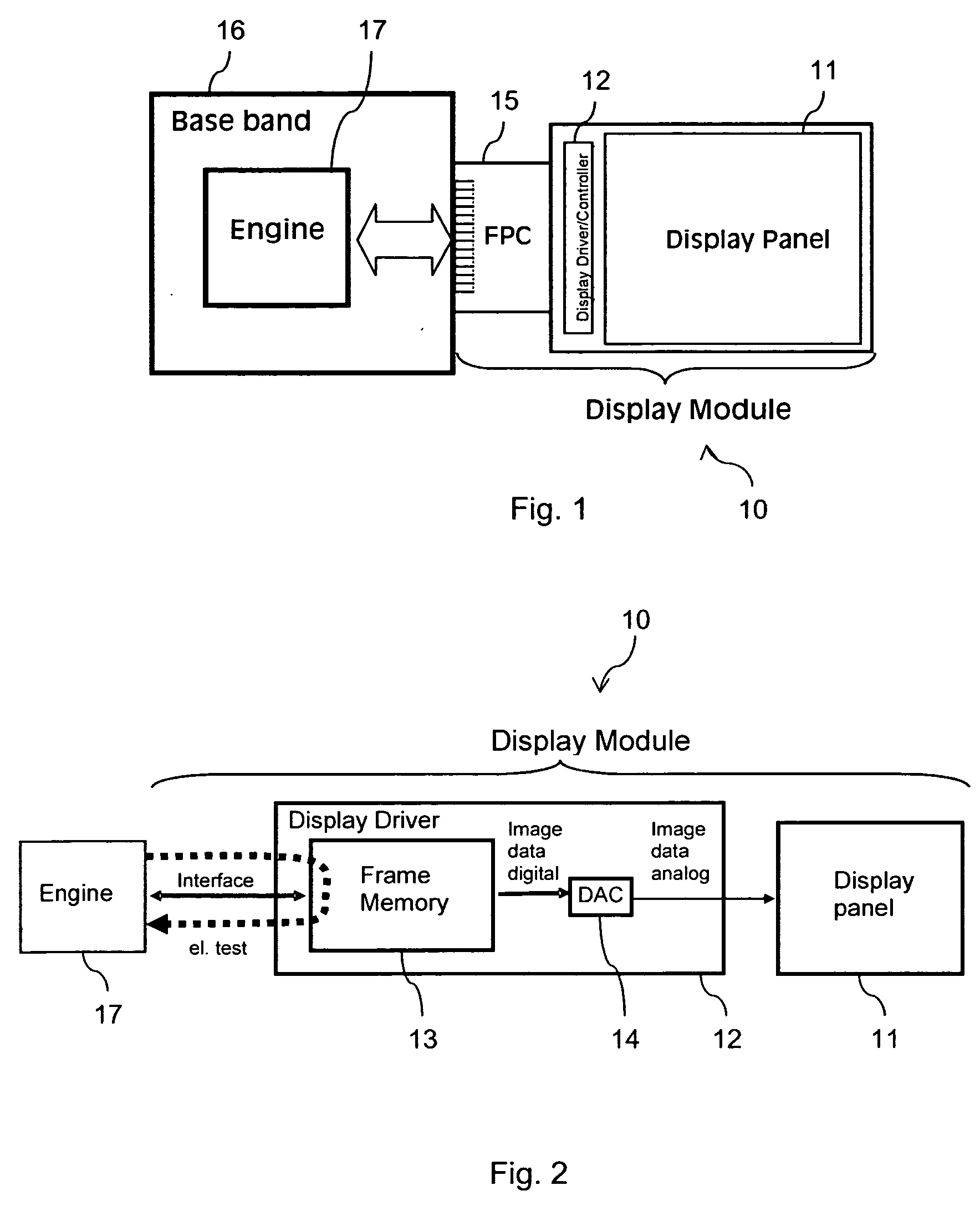
Componet supplied with an analog value
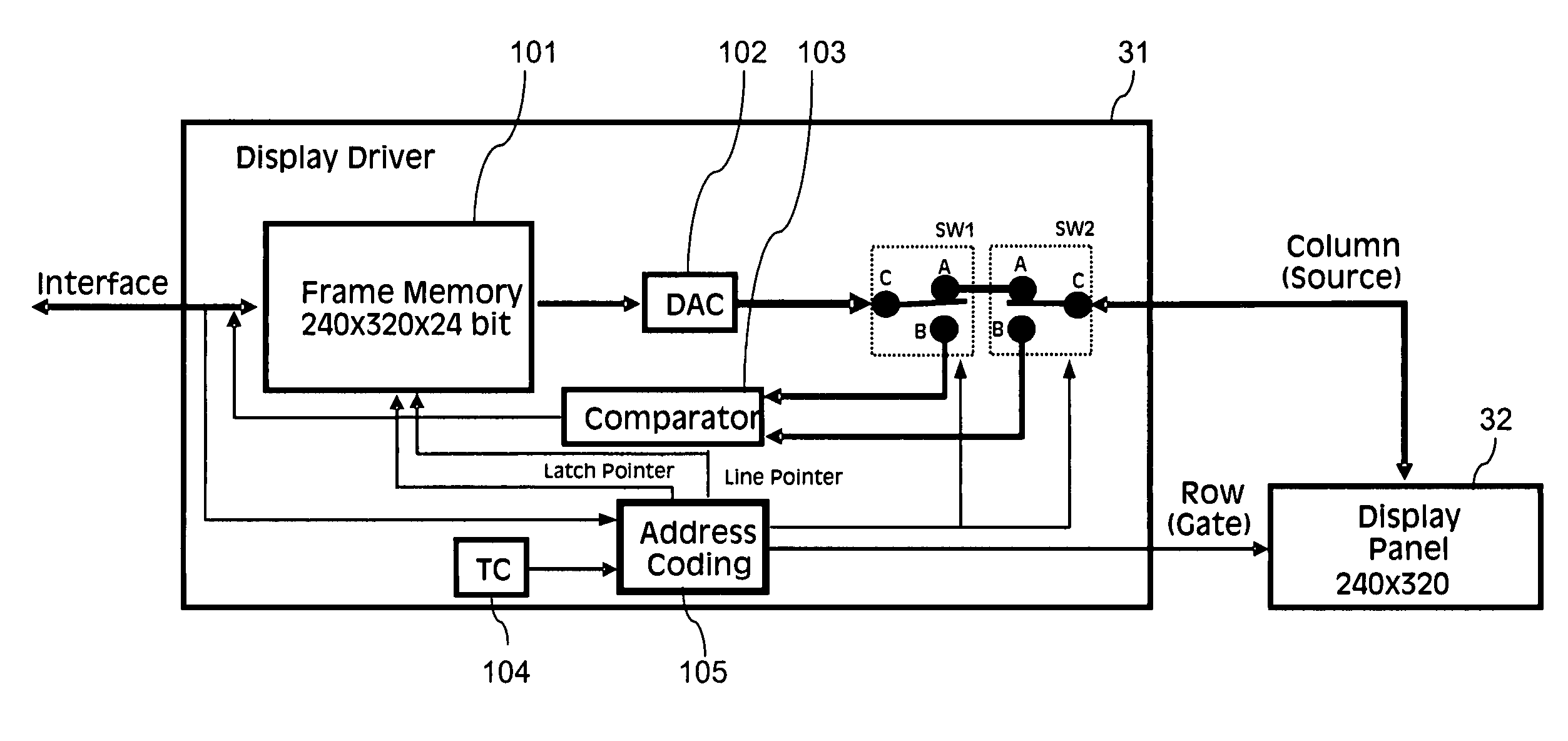
InactiveUS20080001935A1Cheap and reliable testingEasy to implementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringComparator
An apparatus comprises at least one component arranged to be supplied with at least one analog value. In order to enable a testing of the at least one component, the apparatus further comprises at least one comparator configured to compare at least one analog value, which corresponds to at least one analog value supplied to the at least one component, with at least one analog value read from the at least one component. The comparator is moreover configured to provide a result of the comparison.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
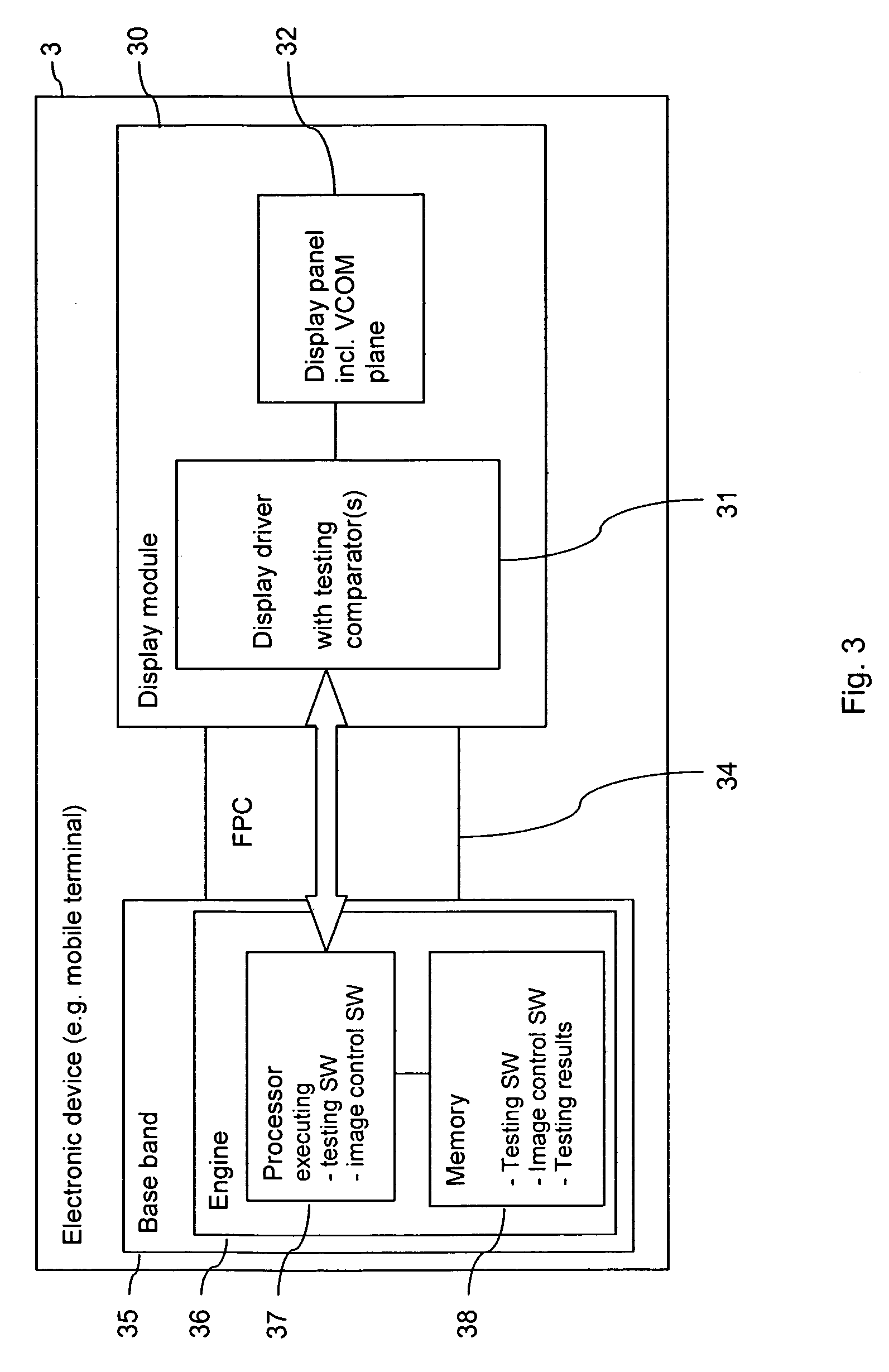
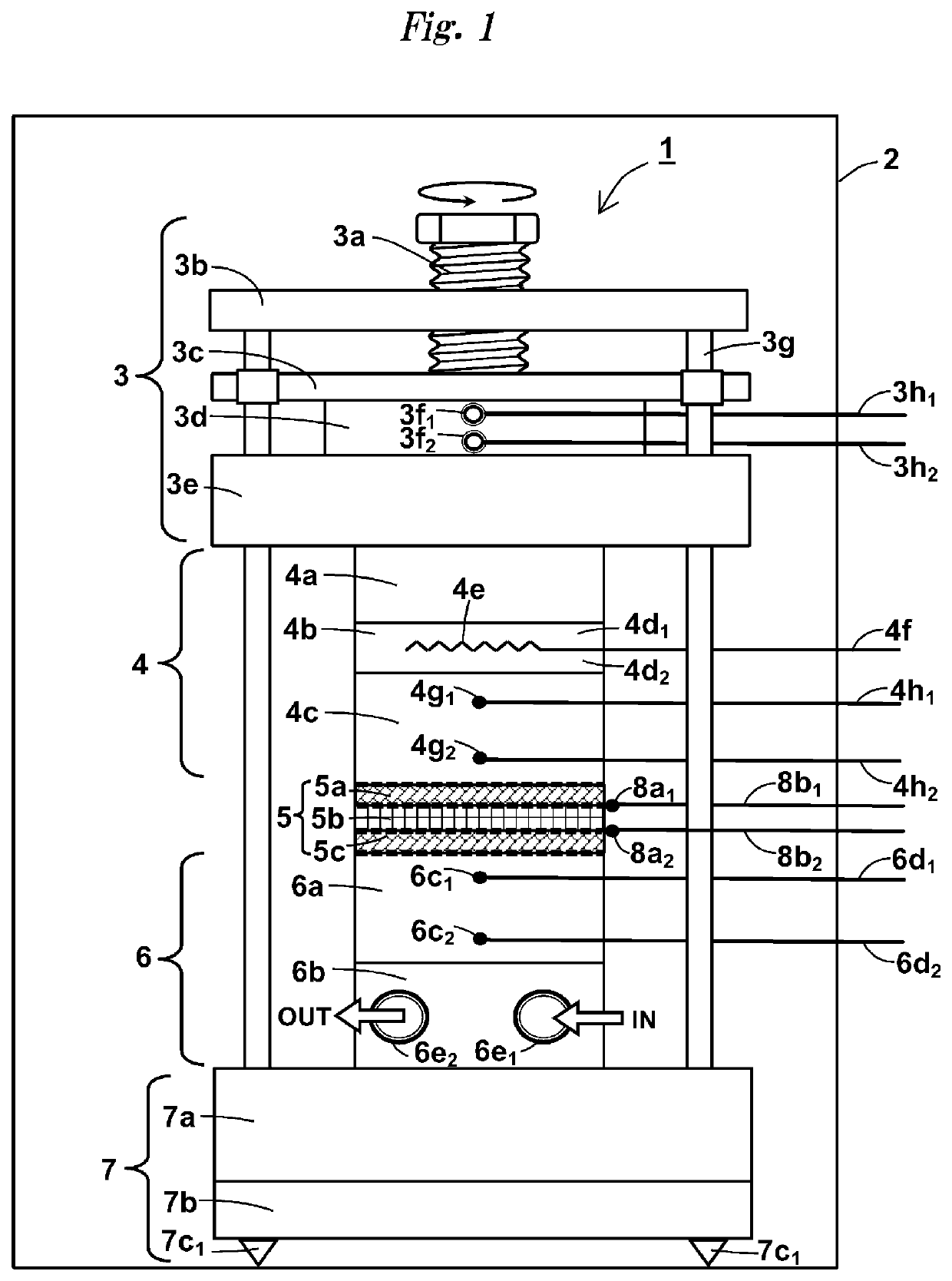
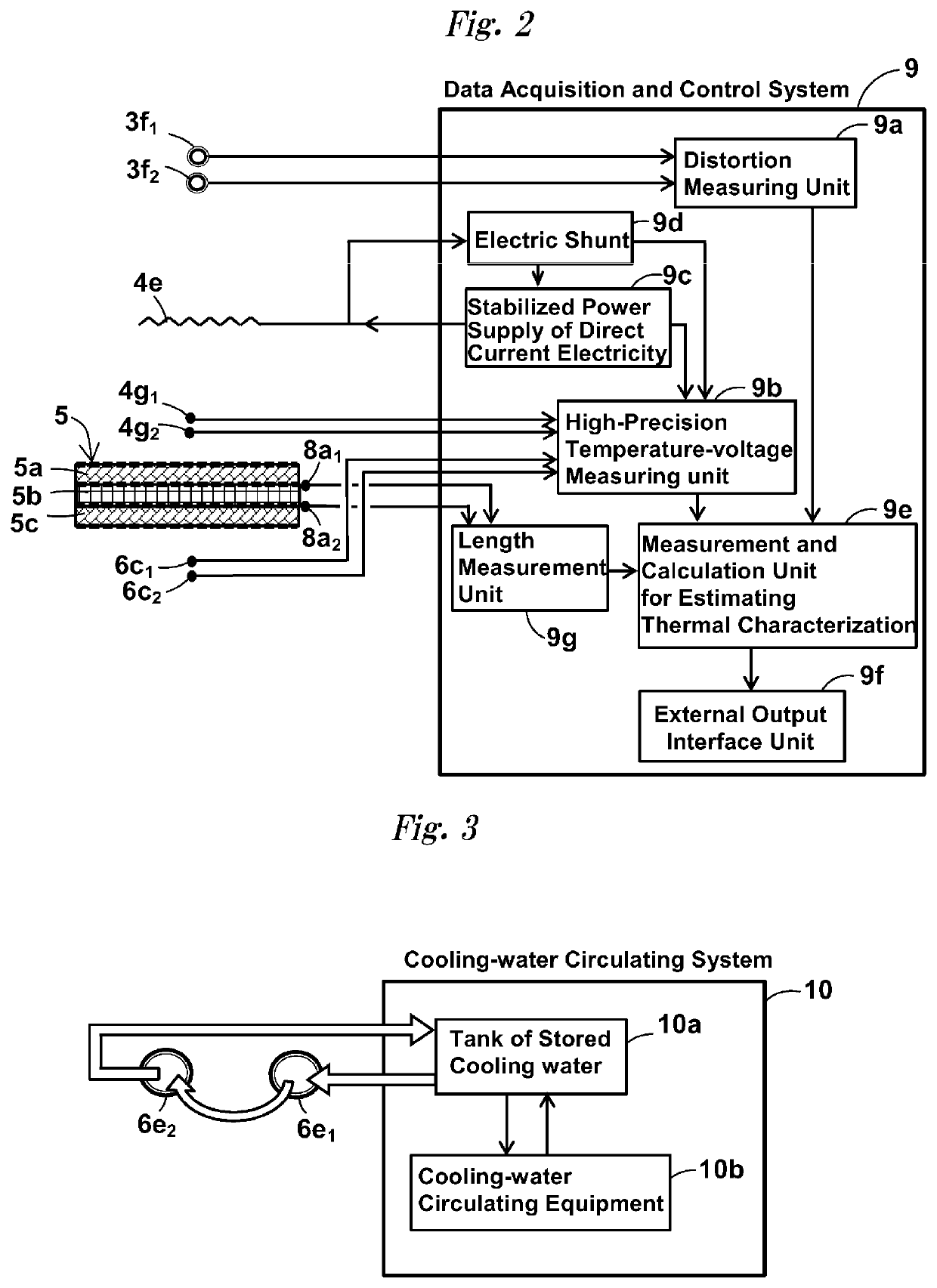
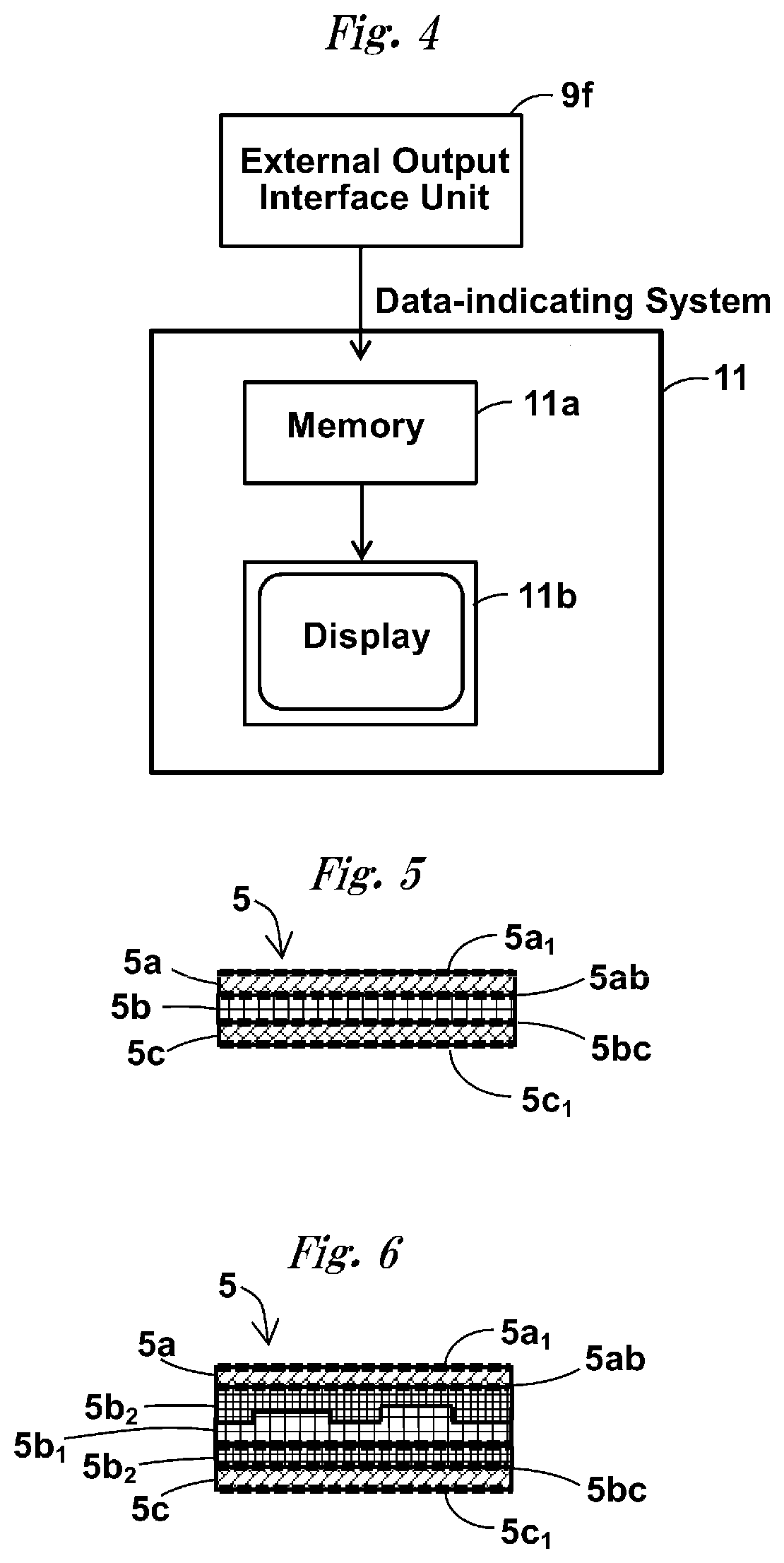
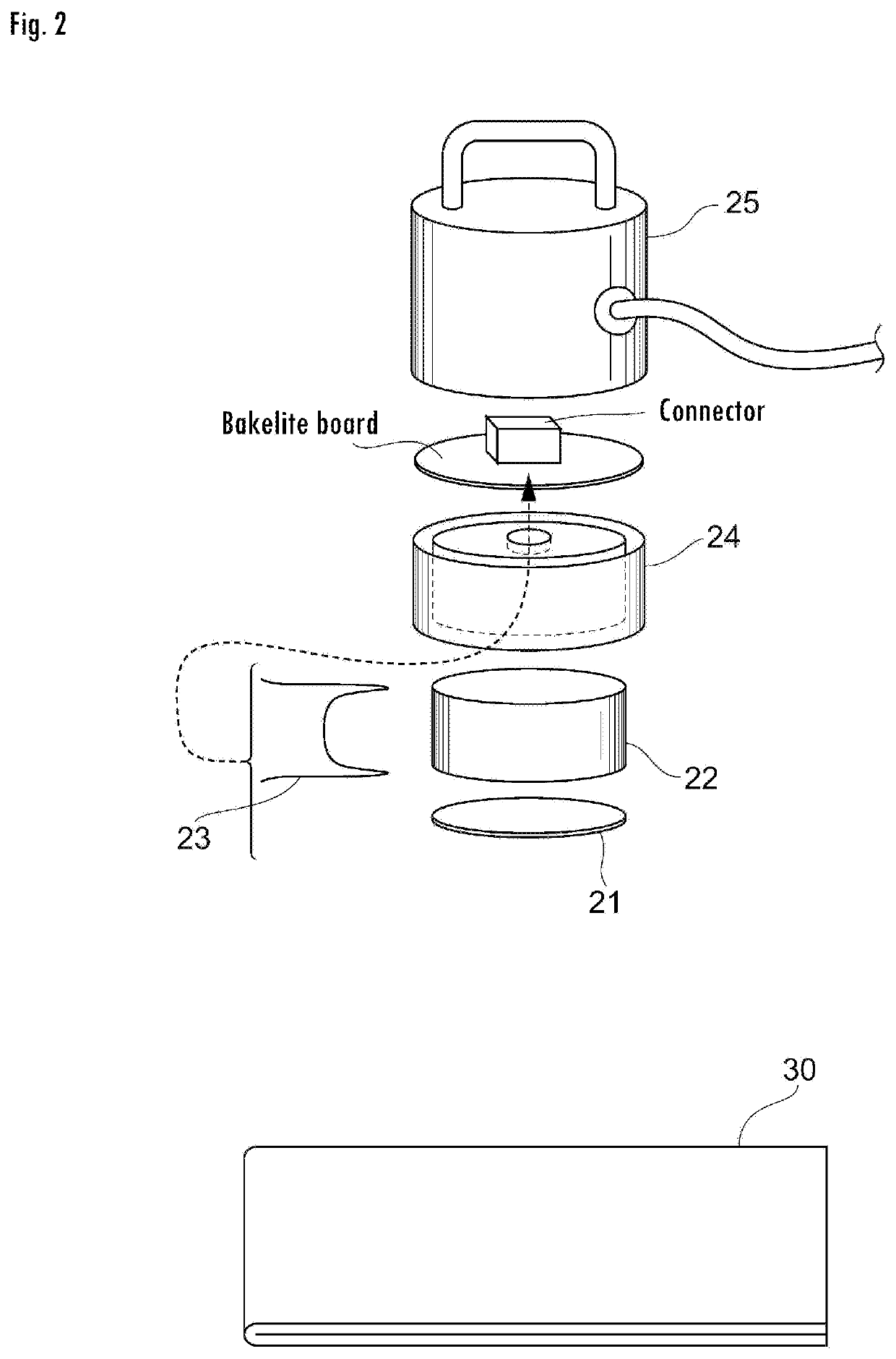
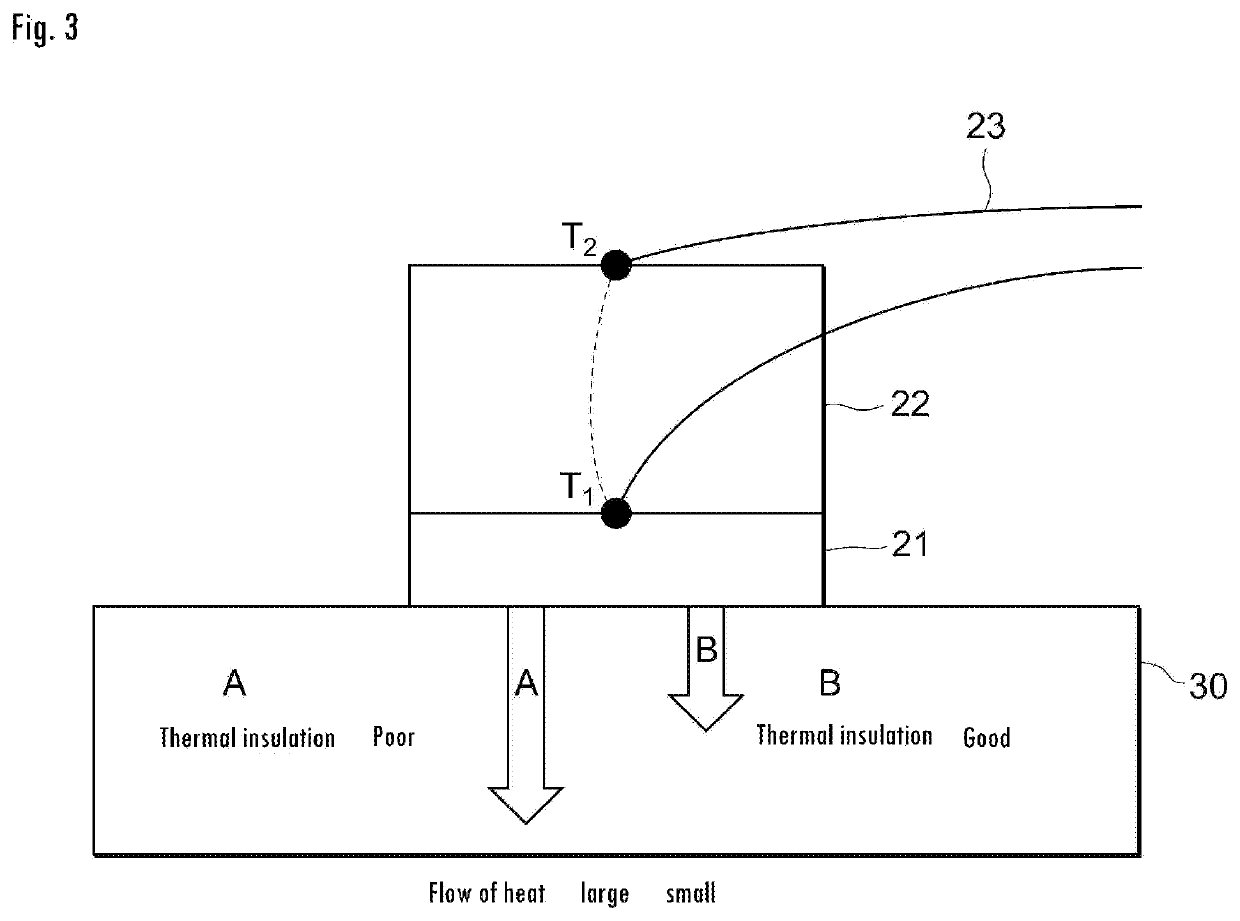
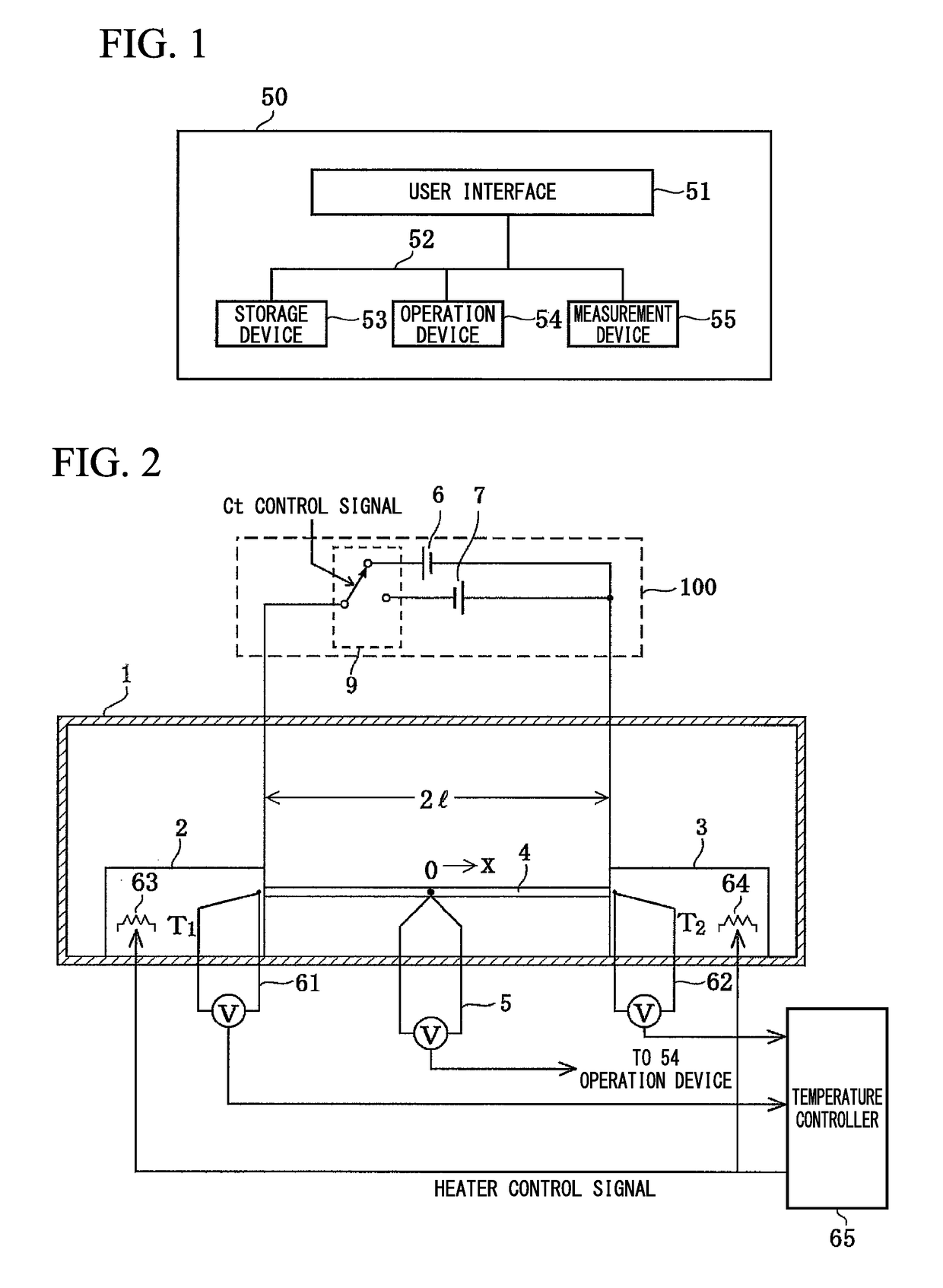
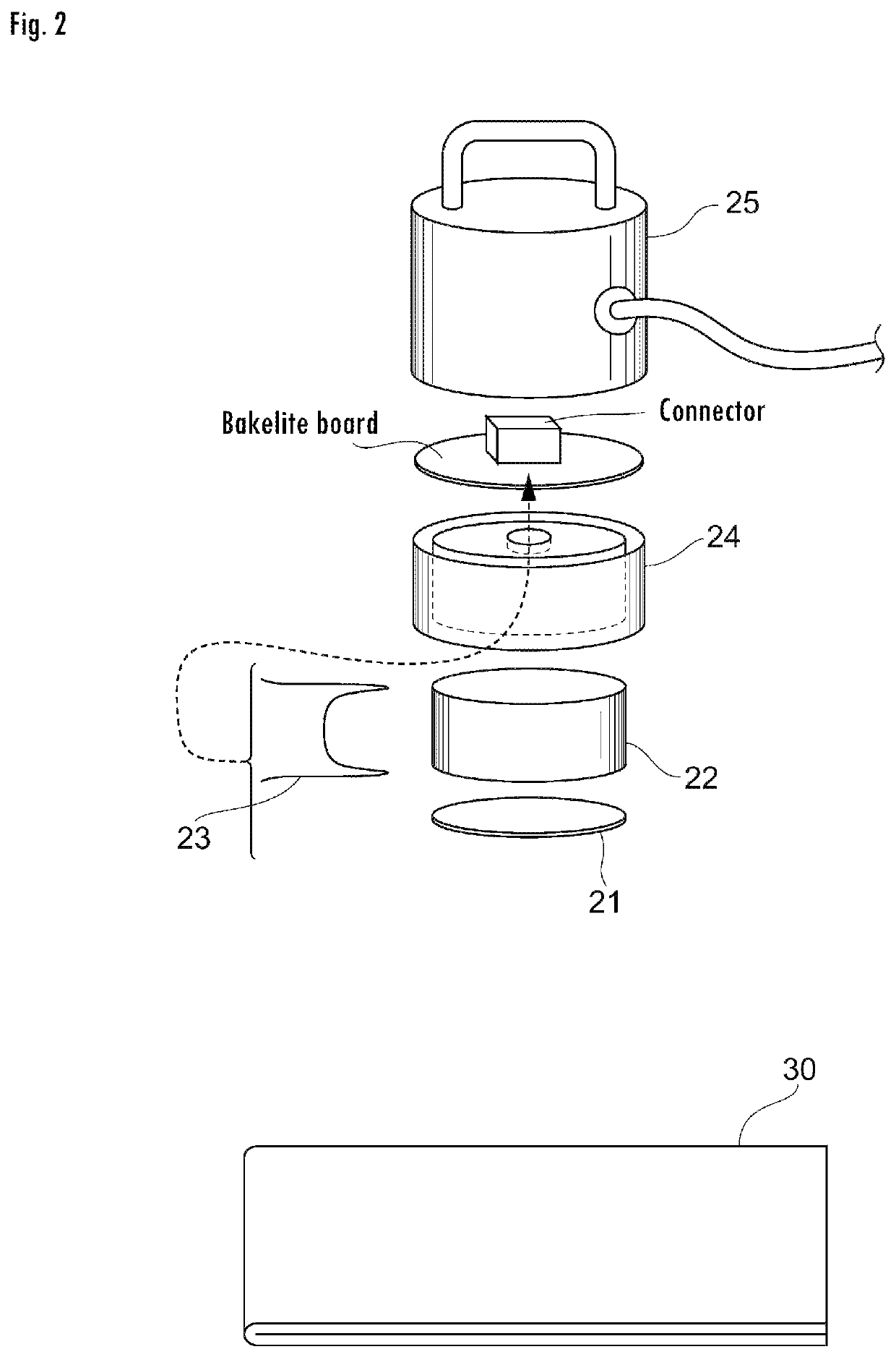
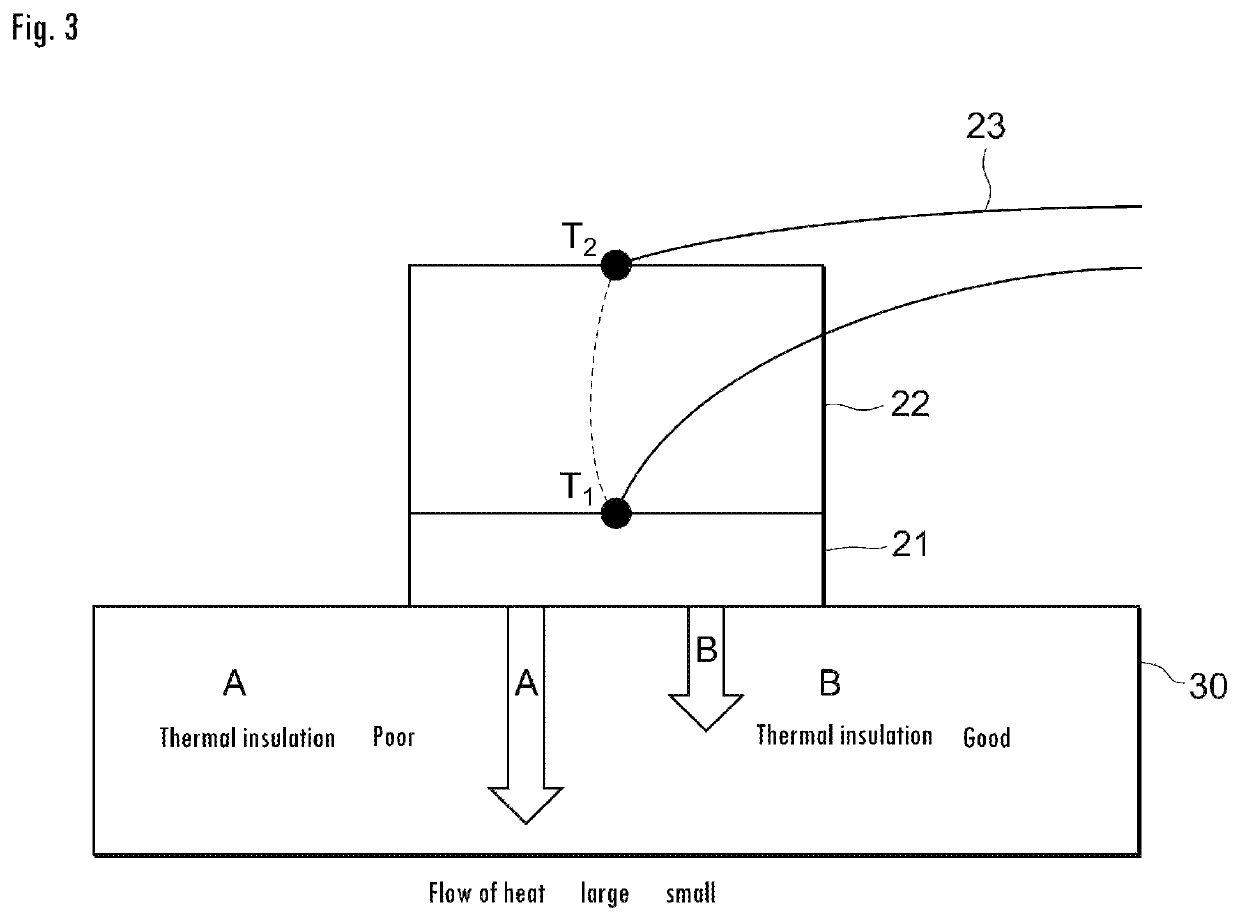
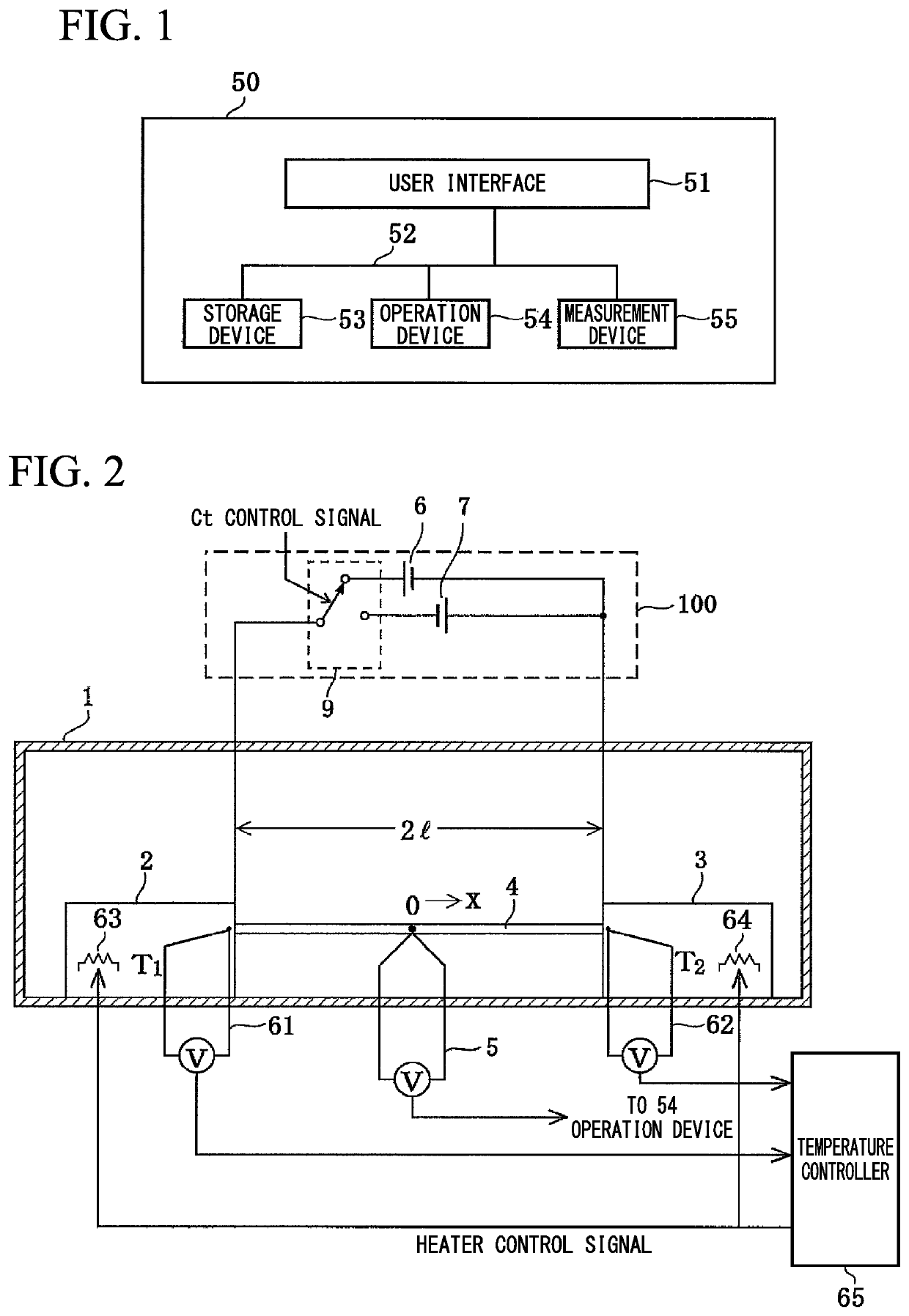
Measurement device for estimating thermal characteristics, and measurement method for estimating thermal characteristics by using same
ActiveUS20200064287A1Accurate value of thermalAccurate thermal conductivityMaterial thermal conductivityStructural/machines measurementThermodynamicsMeasurement device
A measurement device for estimating thermal characteristics includes a heat generating source unit that has heat sensors for detecting heat radiating toward a measurement sample unit, and that heats the measurement sample unit, the measurement sample unit, and a heat cooling source unit that has heat sensors for detecting heat radiating from the measurement sample unit, and that cools the measurement sample unit, wherein those units are sequentially stacked, the measurement sample unit has a three-layer structure consisting of an object to be measured for estimating thermal characteristics, and heat conducting materials that sandwich the object, the heat conducting materials are adhered to the heat generating source unit and the heat cooling source unit one another through a heat-transfer promoting agent therebetween, the object to be measured for estimating thermal characteristics and the heat conducting materials are adhered to one another through physical contact, chemical contact, and / or chemical bond contact.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
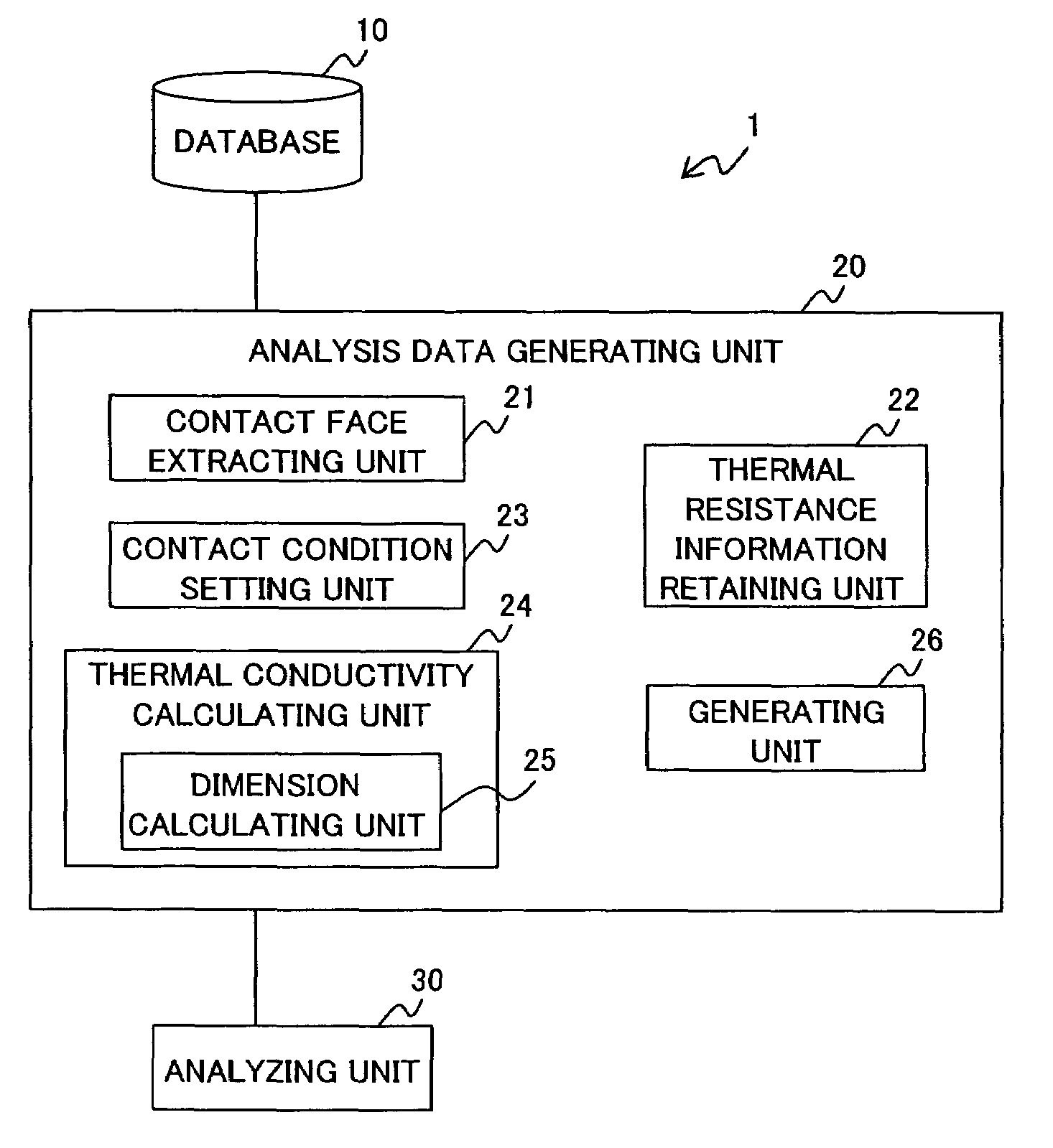
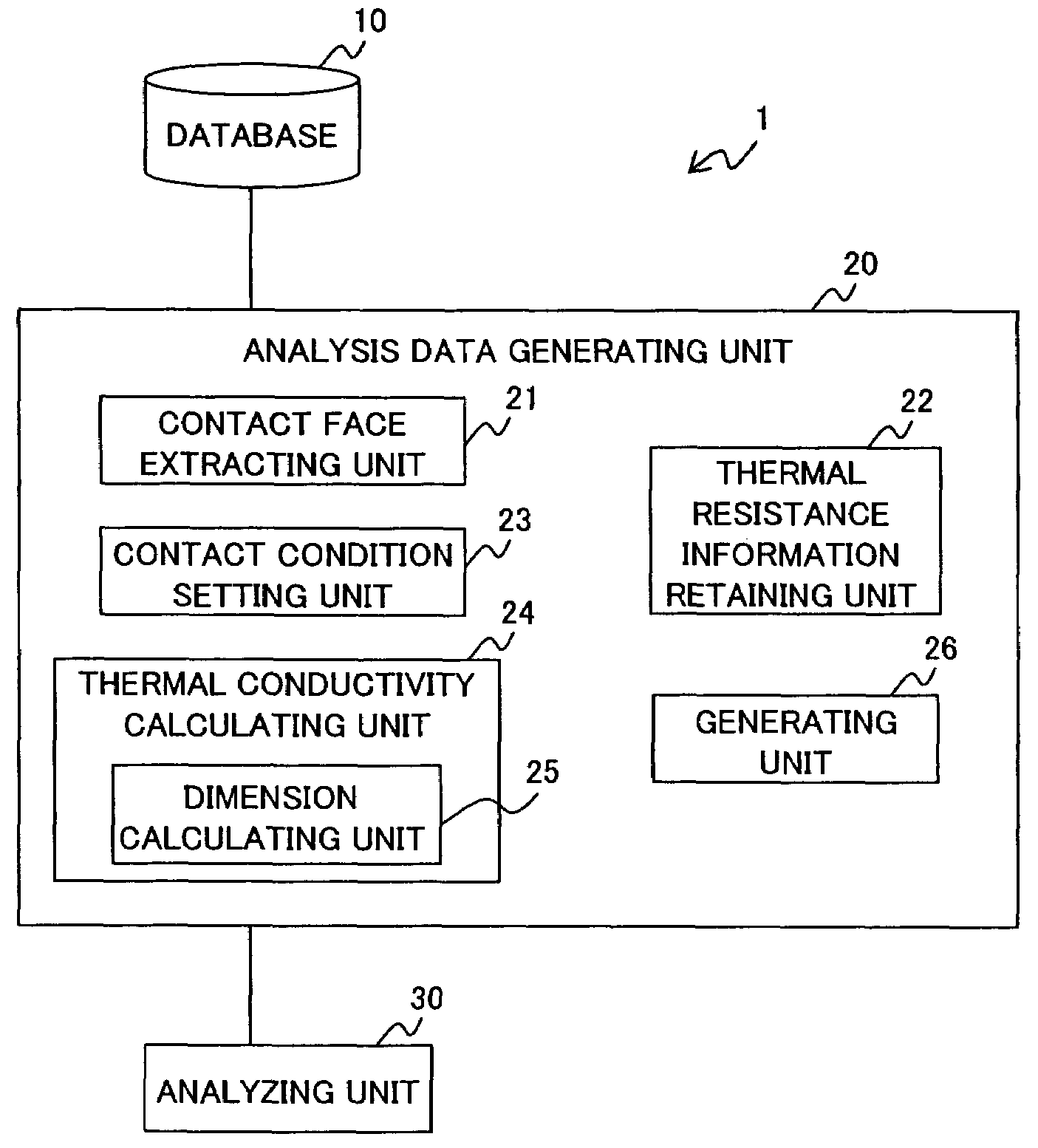
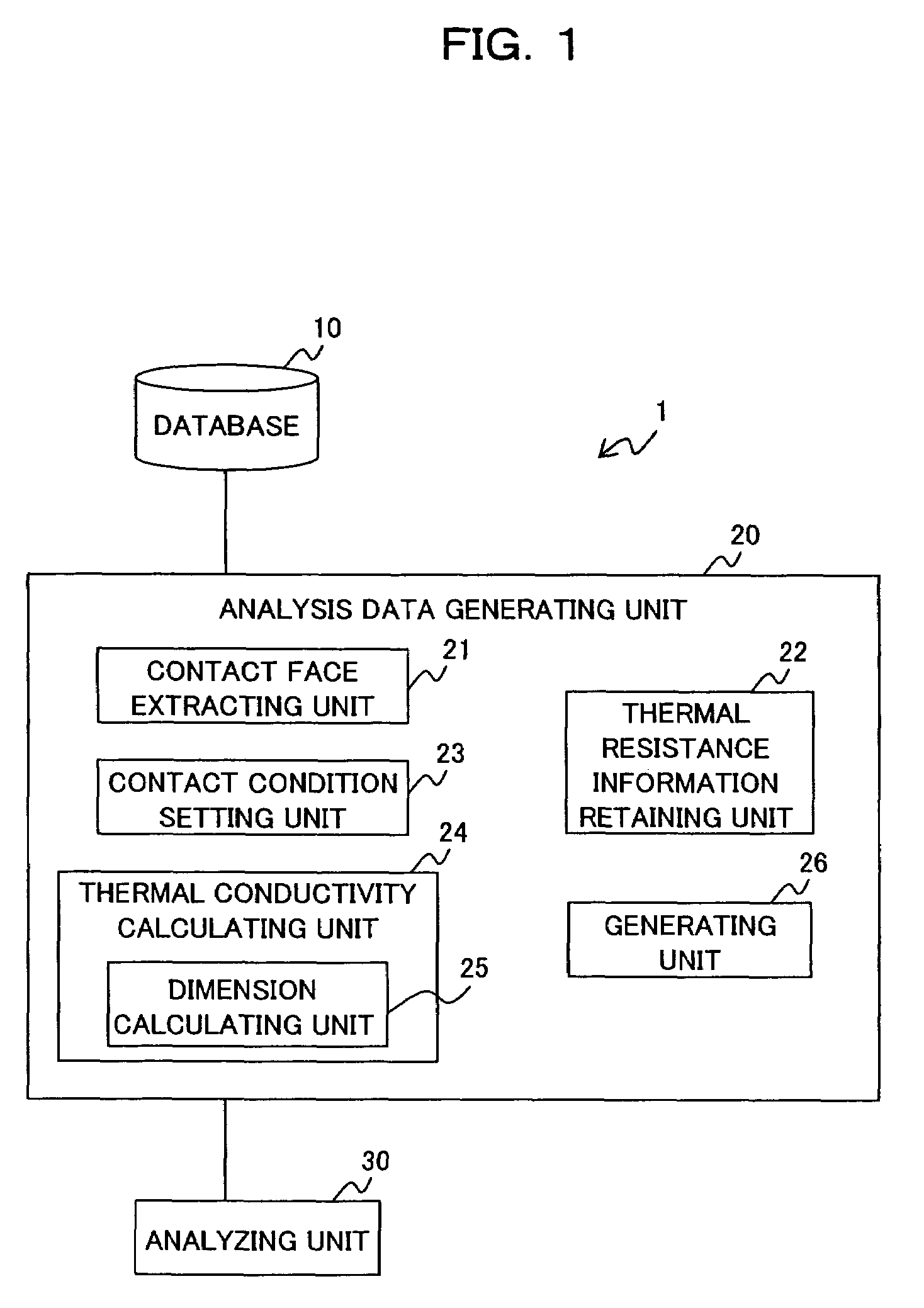
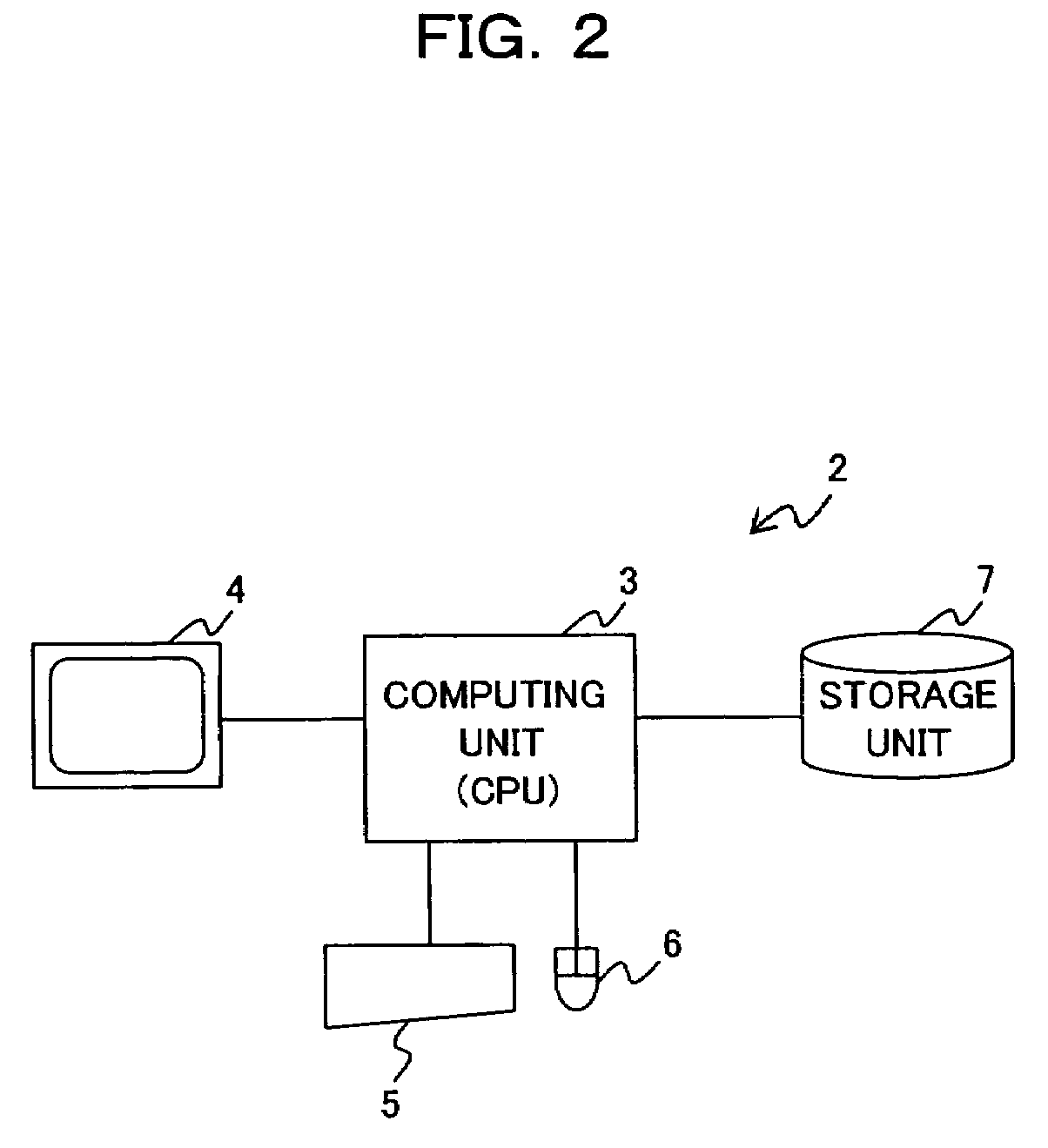
Analysis data generating apparatus, analysis data generating method and computer-readable recording medium containing analysis data generating program
InactiveUS7396156B2Conductivity is accurateGenerate accuratelyMaterial thermal conductivityDigital computer detailsAnalysis dataEngineering
The present invention has an object for setting thermal resistance corresponding to a contact condition of a contact face between two elements automatically and generating analysis data including a thermal conductivity of the contact face accurately in a short time when analysis data is generated based on three-dimensional design data of an object formed by a plurality of elements. An apparatus according to the present invention includes a retaining unit for retaining thermal resistance information for obtaining thermal resistance of the contact face in accordance with contact condition of the contact face; a thermal conductivity calculating unit for calculating a thermal conductivity of the contact face based on the thermal resistance information which is retained in the retaining unit and corresponds to the contact condition of the contact face set by a contact condition setting unit; and a generating unit for generating the analysis data including the thermal conductivity.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
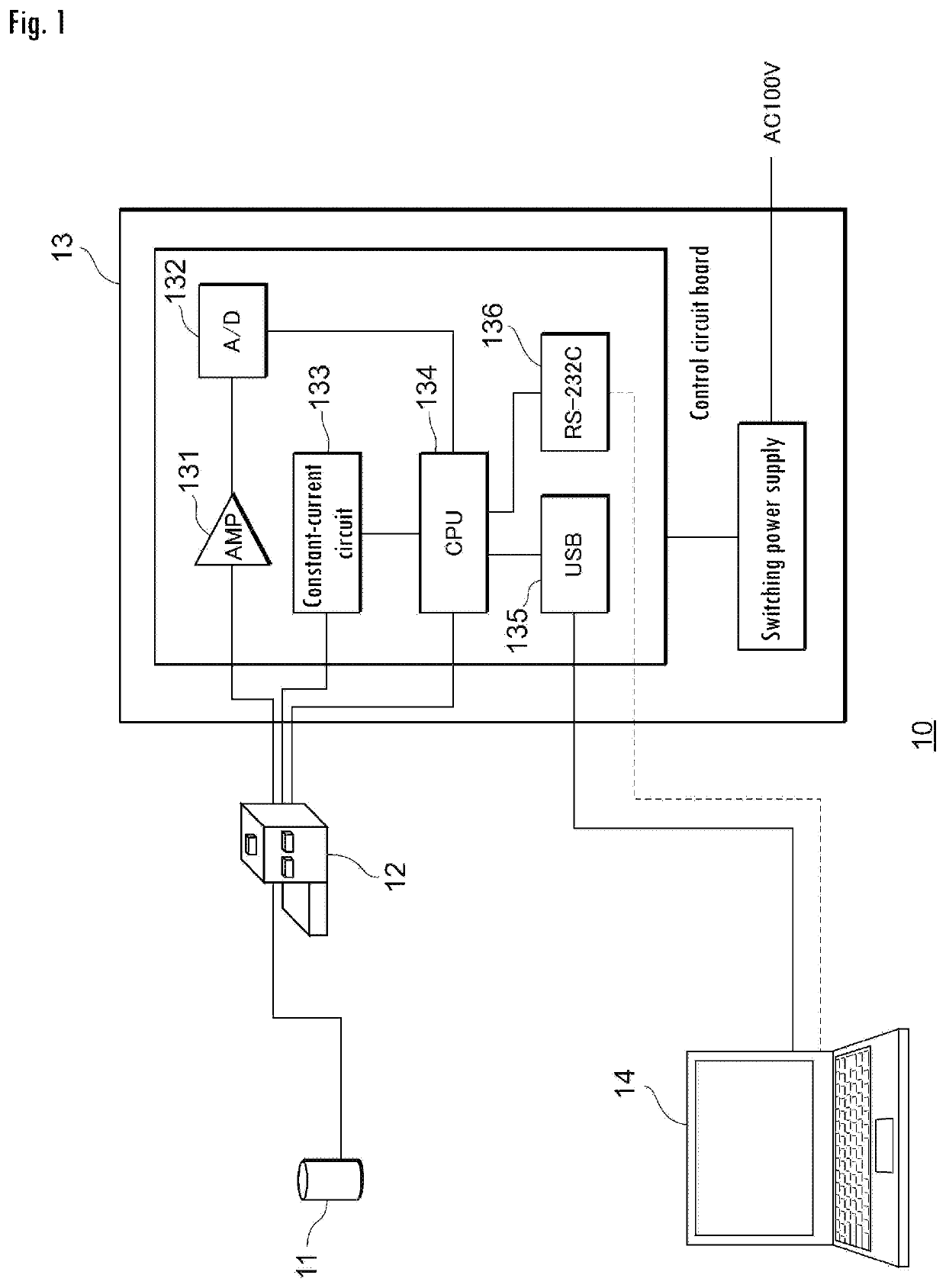
Thermal conductivity measuring device, thermal conductivity measuring method and vacuum evaluation device
ActiveUS20190360953A1Accurate thermal conductivityImprove efficiencyMaterial thermal conductivityThermal conductivity measurementEngineering
The object of the invention is to provide a thermal conductivity measuring device that comprises a heat generator arranged in such a way as to come into contact with an object to be measured for thermal conductivity, a heat resistant material arranged in such a way as to come into contact with the heat generator, at least one pair of differential thermocouples for measuring a voltage value caused by the difference in temperature of two points of the heat resistant material, the temperature being generated by allowing heat to flow from the heat generator, and a calculating device for calculating the time rate of change of output voltage of the differential thermocouples and then calculating the thermal conductivity of the object to be measured on the basis of the calculated time rate of change.
Owner:EKO INSTR
Apparatus and method for the measurement of electrical conductivity and dielectric constant of high impedance fluids
ActiveUS8552750B2Low costHigh impedanceFluid resistance measurementsMaterial impedanceMicrocontrollerHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A sensor, a system of direct measurement using that sensor, and a method of direct and simultaneous measurement of conductivity and dielectric constant of a fluid, particularly high impedance, hydrocarbon-based fluids. The sensor has a cell that holds the fluids to be measured between a single pair of coaxial, bare metal electrodes connected through interface circuitry to measurement circuitry preferably implemented in one or several IC's. The sensor has a mutually compatible electrode geometry that provides both the correct cell constant for measurement of conductivity of hydrocarbons fluids (typical range 0-100,000 pS / cm), and a bulk capacitance (for use in dielectric constant measurement) in the range of measure of readily available low cost commercial IC's (having a typical capacitance measurement span of <10 pF, with a total bulk capacitance at the chip of <20 pF). The cell conductivity constant for use with hydrocarbon-based oils having a conductivity in the range of 1 to 500,000 pS / M is preferably less than or equal to about 0.1. The cell bulk capacitance with hydrocarbon fluids inside the sensor results in a bulk capacitance of at least about 4 pF. In one embodiment, the electronic circuitry is a Microcontroller / DSP that both generates synchronous drive signals at various frequencies, for both conductivity and dielectric constant measurements while directly digitizing and numerically processing the sensor output.
Owner:FALMOUTH SCI +1
Analysis data generating apparatus, analysis data generating method and computer-readable recording medium containing analysis data generating program
InactiveUS20070274369A1Conductivity is accurateGenerate accuratelyMaterial thermal conductivityDigital computer detailsAnalysis dataEngineering
The present invention has an object for setting thermal resistance corresponding to a contact condition of a contact face between two elements automatically and generating analysis data including a thermal conductivity of the contact face accurately in a short time when analysis data is generated based on three-dimensional design data of an object formed by a plurality of elements. An apparatus according to the present invention includes a retaining unit for retaining thermal resistance information for obtaining thermal resistance of the contact face in accordance with contact condition of the contact face; a thermal conductivity calculating unit for calculating a thermal conductivity of the contact face based on the thermal resistance information which is retained in the retaining unit and corresponds to the contact condition of the contact face set by a contact condition setting unit; and a generating unit for generating the analysis data including the thermal conductivity.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
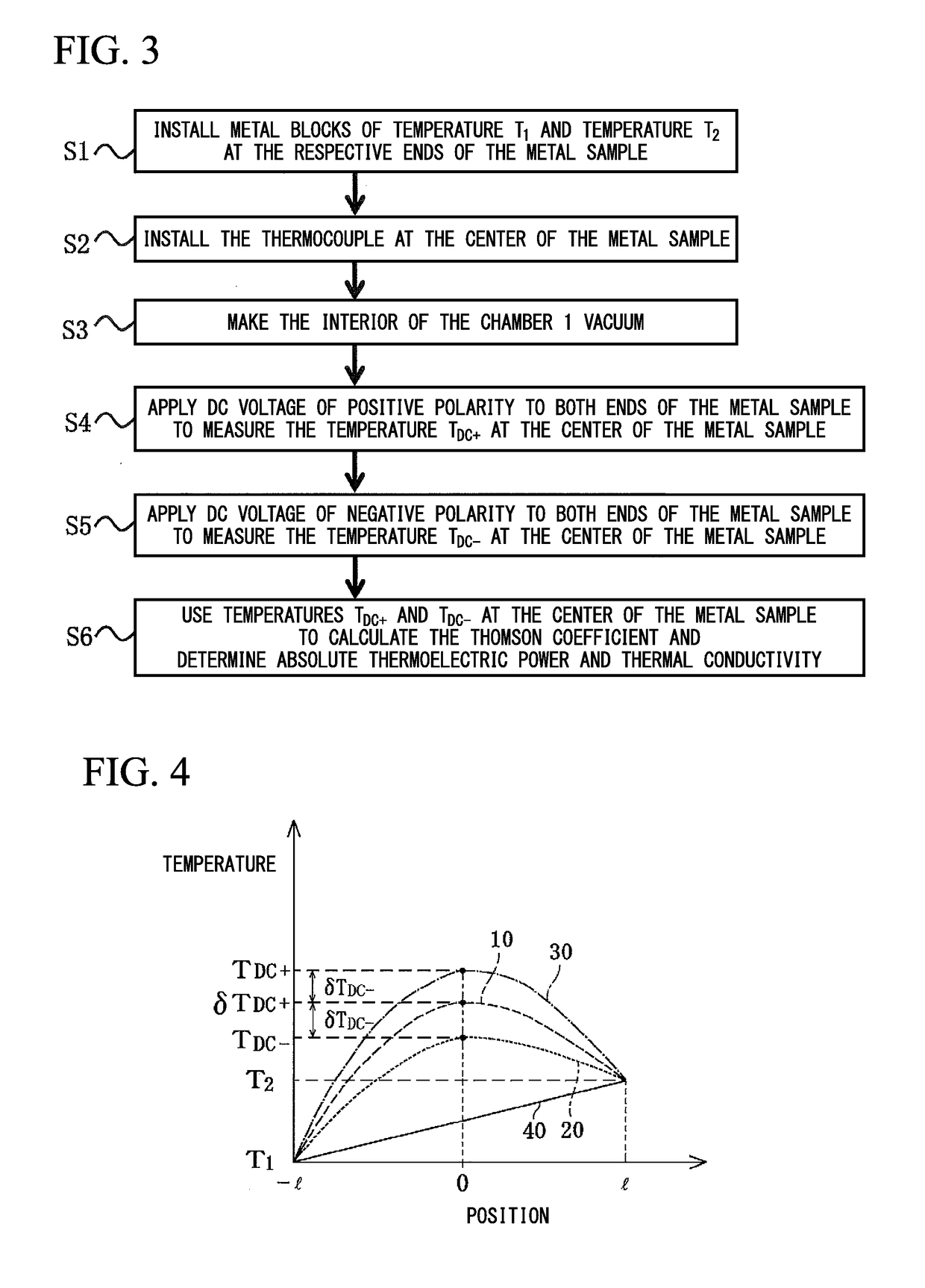
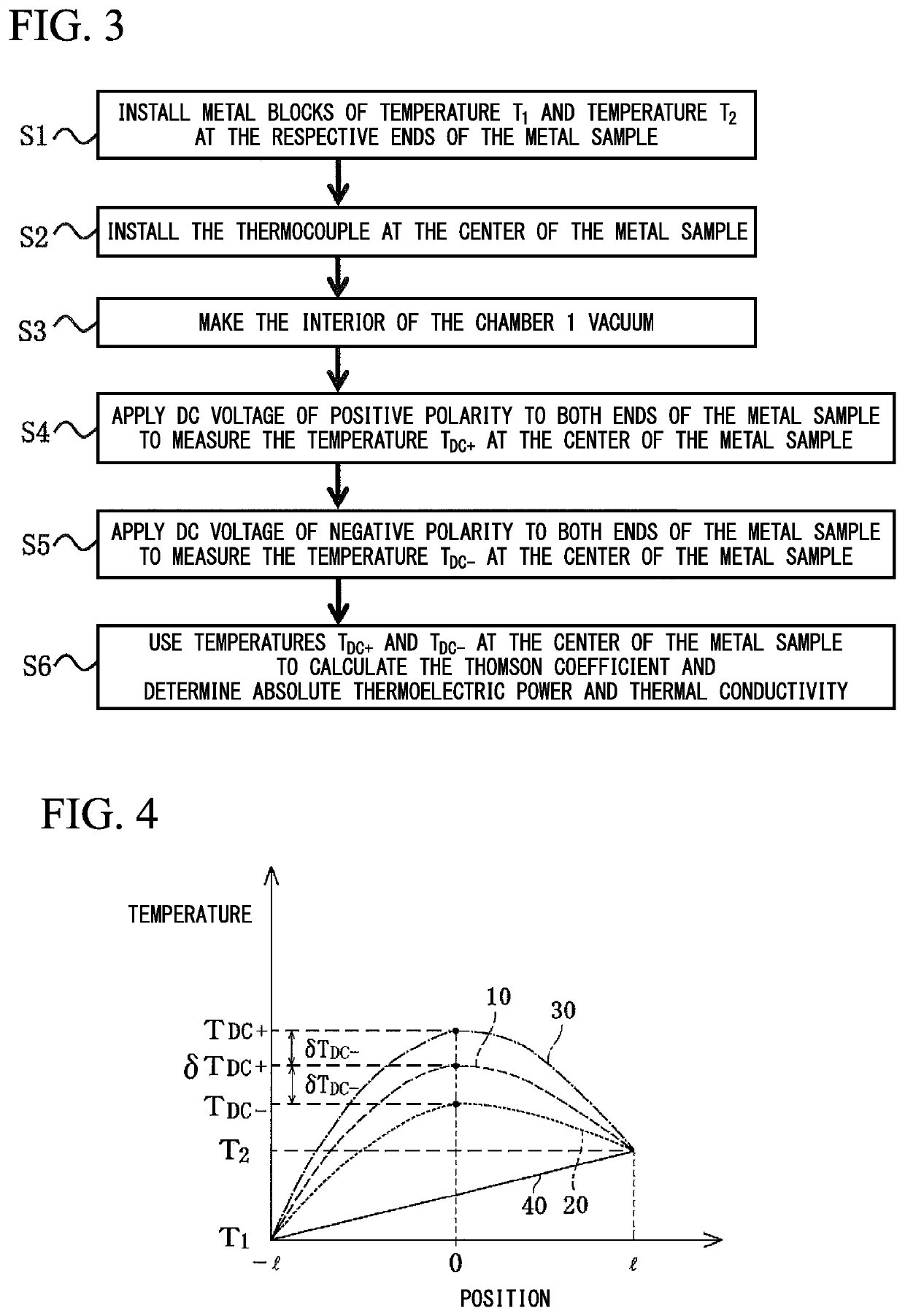
Thermophysical property measurement method and thermophysical property measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20190086346A1Conductivity is accurateAccurate powerMaterial thermal conductivityPower measurement by thermal methodsElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
Thermophysical property measurement method and apparatus are provided that make it possible to simply and conveniently obtain a highly precise absolute thermoelectric power and thermal conductivity.Embodiments of the present invention provides a thermophysical property measurement method, including a first step of applying a DC voltage or a DC current at both ends of a metal to which a temperature gradient is applied to measure a first temperature at a center of the metal; a second step of applying DC voltages or DC currents of different polarities at both ends of the metal to measure a second temperature at the center of the metal; a third step of calculating a Thomson coefficient of the metal using the first and second temperatures measured in the first and second steps; and a fourth step of calculating at least one of absolute thermoelectric power and thermal conductivity of the metal using the Thomson coefficient calculated in the third step, the third step including: calculating an average value of a difference between the first temperature and the second temperature; calculating an average value of a sum of the first temperature and the second temperature; and dividing a product of a magnitude of a current that flows through the metal, electrical resistance of the metal, and the average value of the difference by the average value of the sum and the difference between the first temperature and the second temperature.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Electronic component, and a method of manufacturing an electronic component
ActiveUS8357920B2Increase resistanceImprove integration densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesElectronic component
An electronic component (100) comprising a matrix (102) and a plurality of islands (103) embedded in the matrix (102) and comprising a material which is convertible between at least two states characterized by different electrical properties, wherein the plurality of islands (103) form a continuous path (104) in the matrix (102).
Owner:NXP BV
Method for mounting a component in or on a circuit board, and circuit board
ActiveUS20130233603A1Conductivity is accurateImprove conductivityPrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesFriction weldingUltrasonic welding
In a method for mounting an element or component having at least one metal surface in or on a circuit board containing at least one conducting layer made of metal material, a connection between the at least one metal surface of the element and the at least one conducting layer of the circuit board is formed using ultrasonic welding or high-frequency friction welding in order to create a mechanically stable and resistant connection or attachment having good conductivity. Furthermore, a circuit board is disclosed in which at least one element or component having a metal surface is or can be connected to a conducting or conductive layer of the circuit board using ultrasonic welding or high-frequency friction welding.
Owner:AT & S AUSTRIA TECH & SYSTTECHN AG
Componet supplied with an analog value
InactiveUS7825680B2Cheap and reliable testingEasy to implementElectrical testingCathode-ray tube indicatorsEngineeringComparator
An apparatus comprises at least one component arranged to be supplied with at least one analog value. In order to enable a testing of the at least one component, the apparatus further comprises at least one comparator configured to compare at least one analog value, which corresponds to at least one analog value supplied to the at least one component, with at least one analog value read from the at least one component. The comparator is moreover configured to provide a result of the comparison.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
Thermal conductivity measuring device, thermal conductivity measuring method and vacuum evaluation device
ActiveUS11193901B2Conductivity is accurateShort timeThermometers using mean/integrated valuesMaterial thermal conductivityThermal conductivity measurementThermocouple device
Owner:EKO INSTR
Cement-based material forming test die for embedding electrode
ActiveCN106706406AAvoid leaningSmooth appearancePreparing sample for investigationCeramic shaping apparatusSlurryEngineering
The invention discloses a cement-based material forming test die for embedding an electrode. The cement-based material forming test die comprises a base, a test die main body and a pressing cover. The base is composed of a large cube and four small cubes. The small cubes are arranged at four corners of the large cube, two sides of the base are provided with grooves, and two sides of the base are provided with pin holes penetrating the grooves respectively. A pressing cover main board is provided with an electrode slot, two side wings of the pressing cover are provided with a cube protrusion and a pin hole respectively, the pressing cover is buckled in the groove of the base, the pressing cover and the base are connected to be a whole through a pin, and the test die main body is placed on the base and fixed to the base through the cube protrusion positioned on the pressing cover. The die can prevent the electrode embedded in the vibrating process from being inclined, a formed cement sample is flat in surface, so test results such as electrical conductivity, pressure sensitivity and electrochemical behaviors of the sample are more accurate; during the vibration, the test die main body can be attached the base to reduce slurry leakage, and the cement-based material forming test die is simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost and high in reusing rate.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity in burns
ActiveUS20160256099A1Simply and accurately measureSimply and accurately measuring thermal conductivityMaterial thermal conductivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermal conductivityThermal transmittance
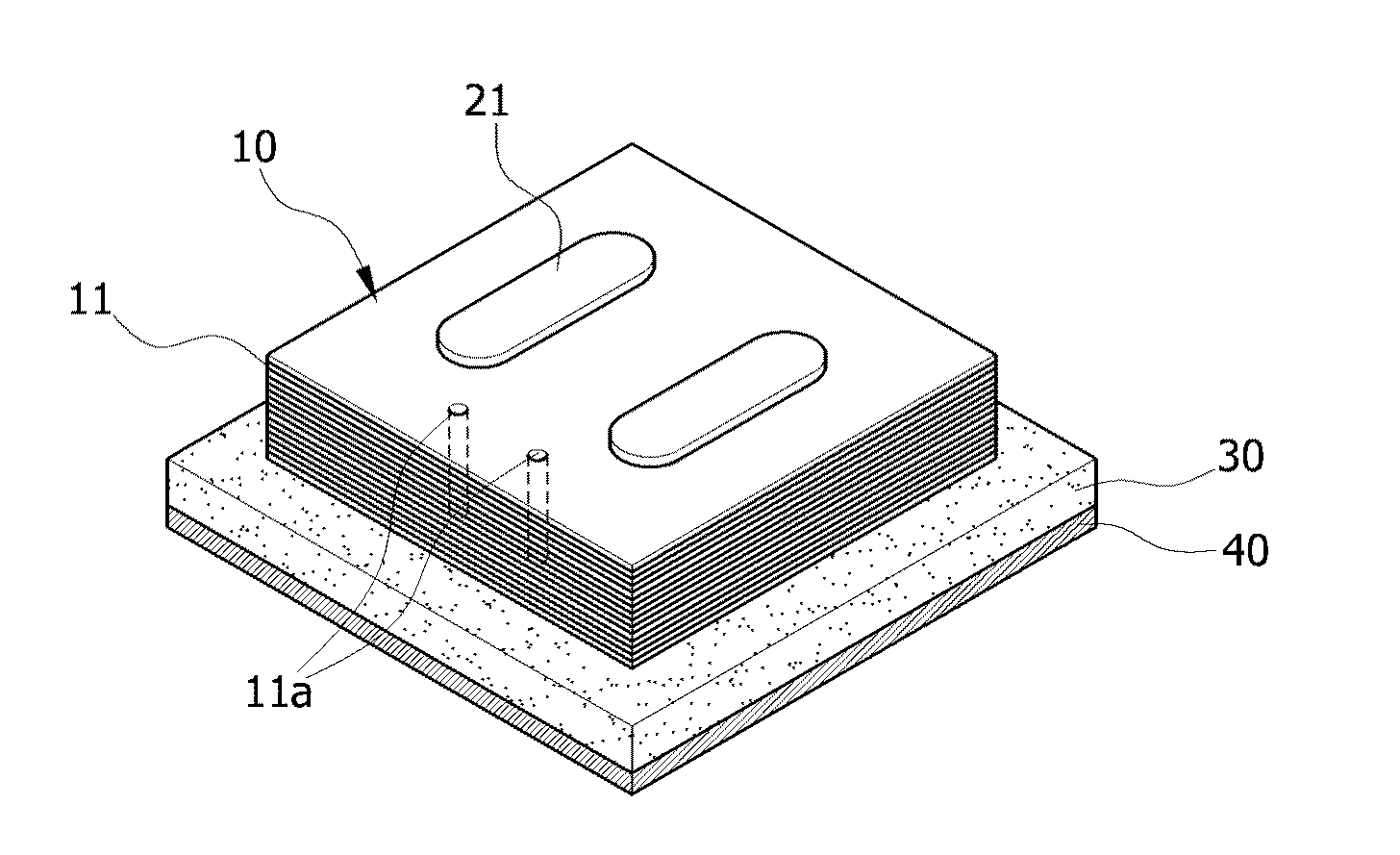
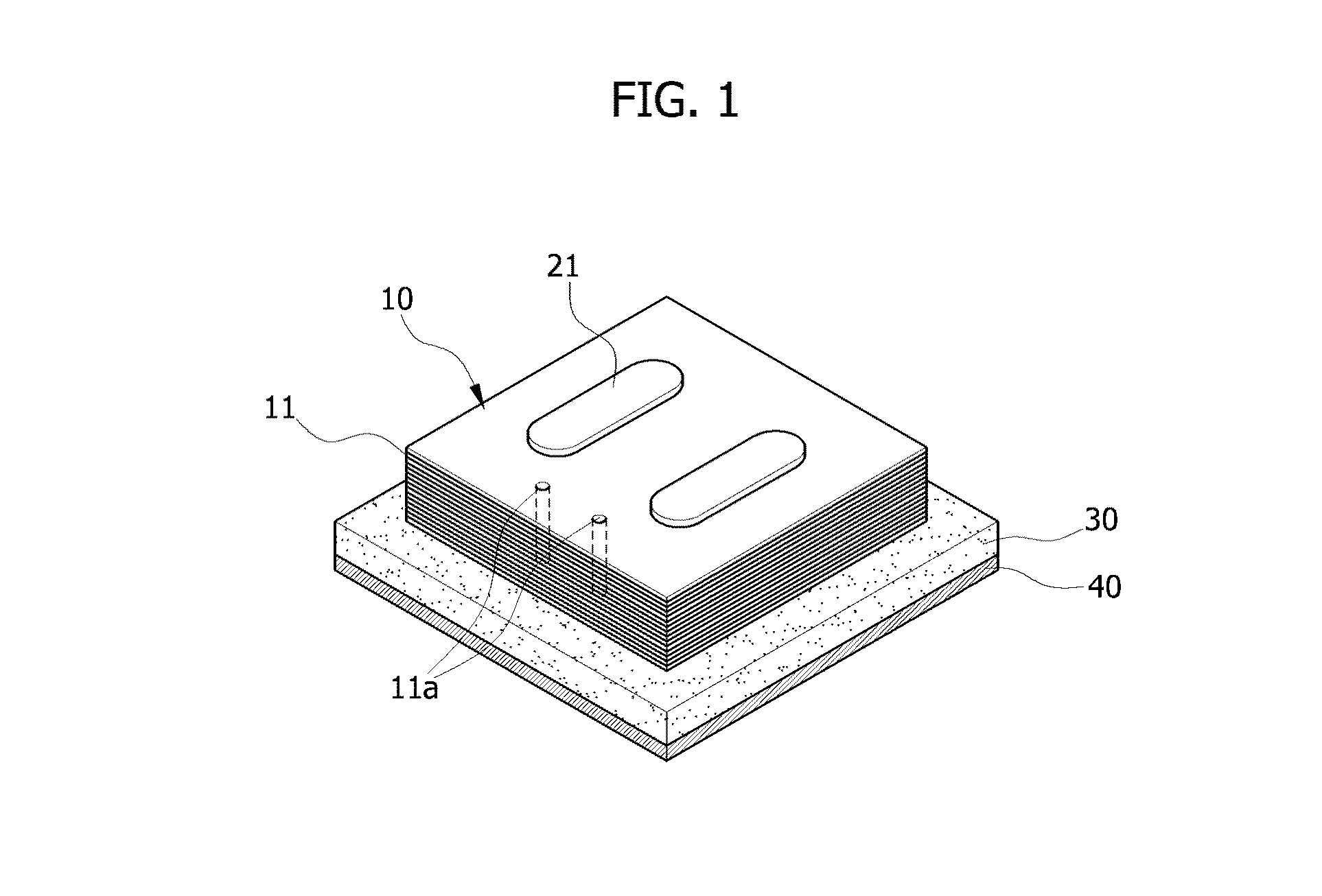
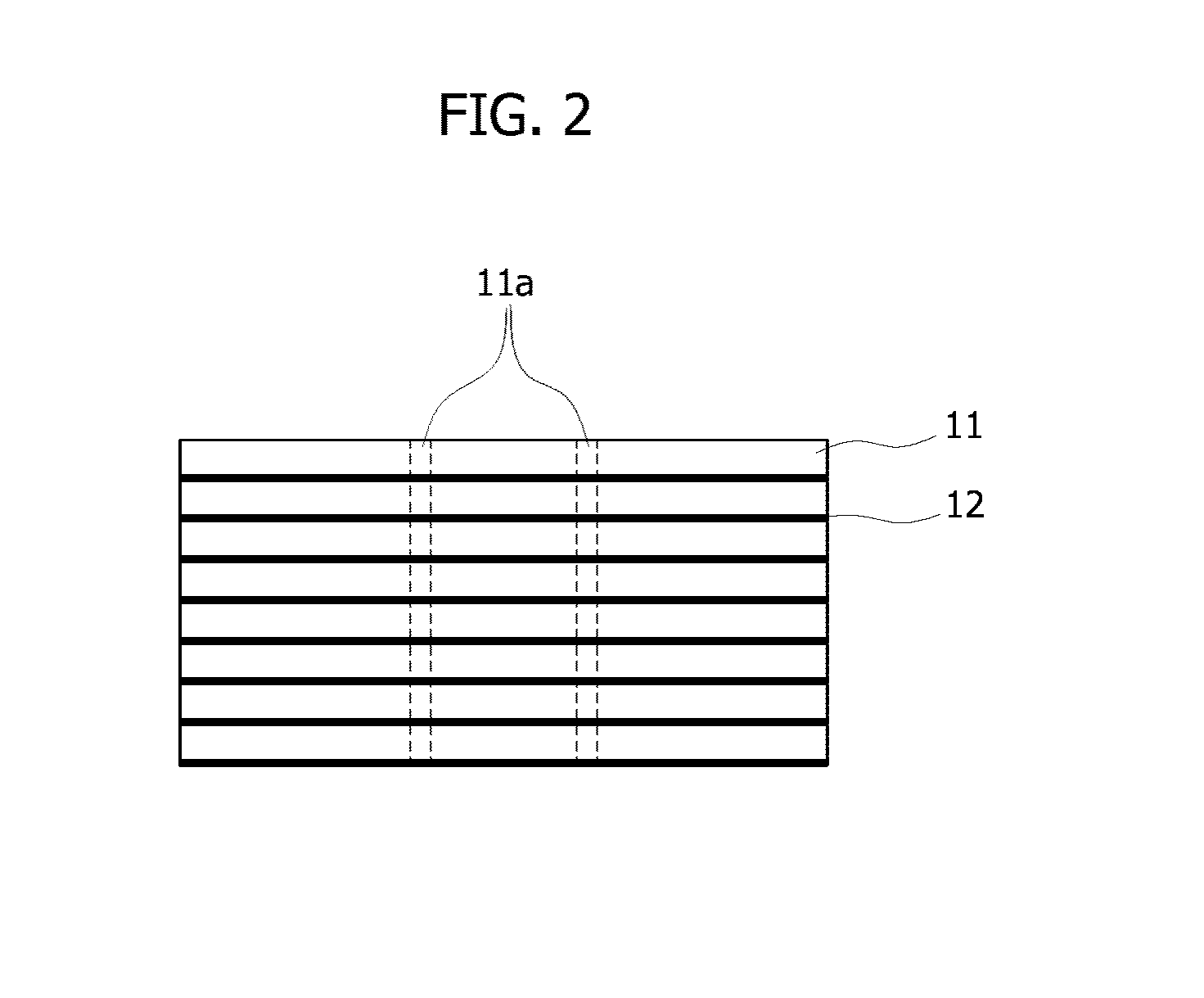
There are provided an apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity capable of easily and accurately obtaining an extent of thermal damage of a targeted tissue. The apparatus for measuring thermal conductivity in burns includes a thermal paper stacking member having a plurality of sheets of thermal paper stacked thereon to form layers, and a pressing member configured to press the stacking member so that the thermal paper is stacked and maintained in a closely adhered state. Here, an extent of thermal damage of the targeted tissue according to the depth can be calculated as an extent of thermal damage of the stacking member according to the depth.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
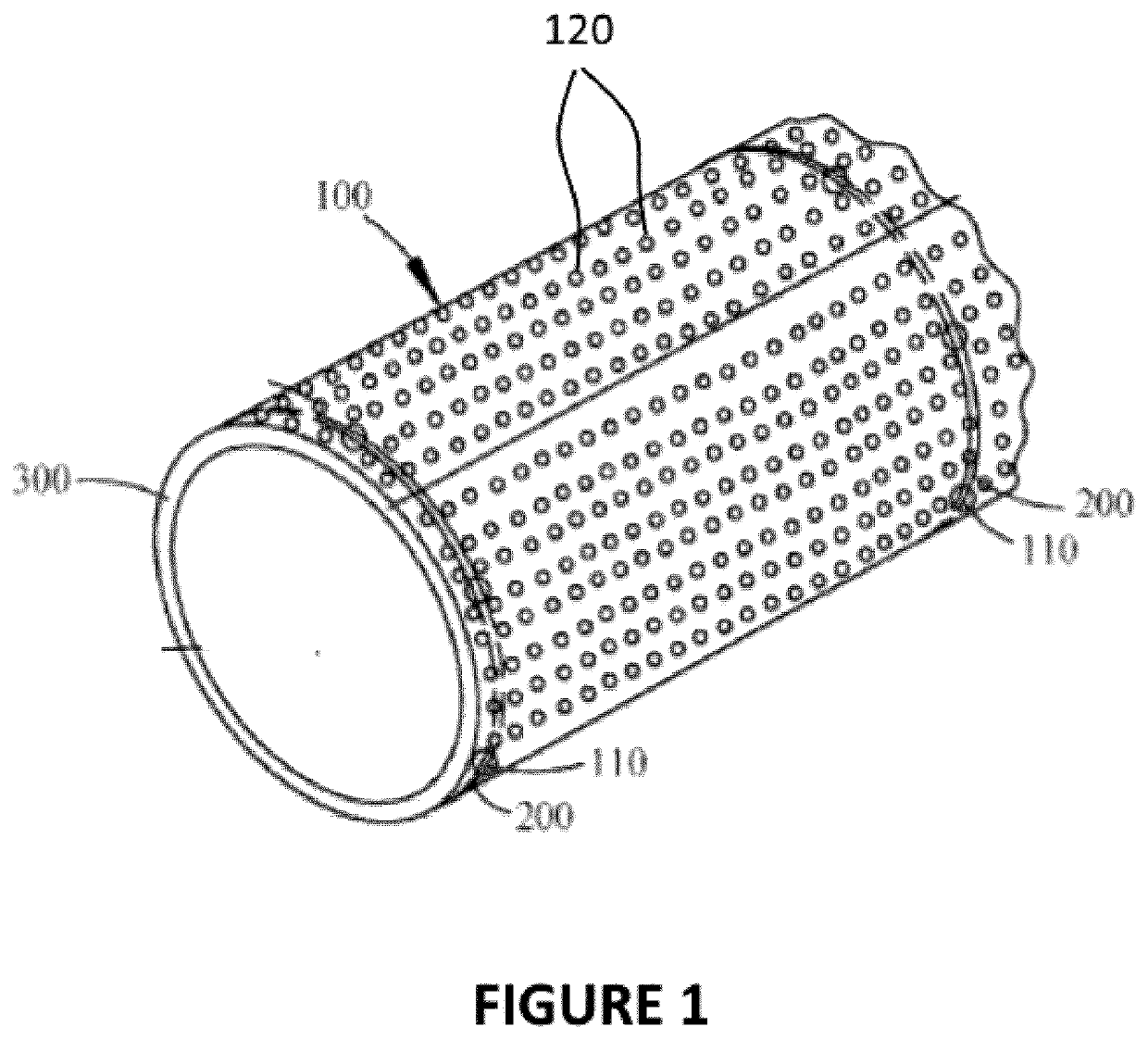
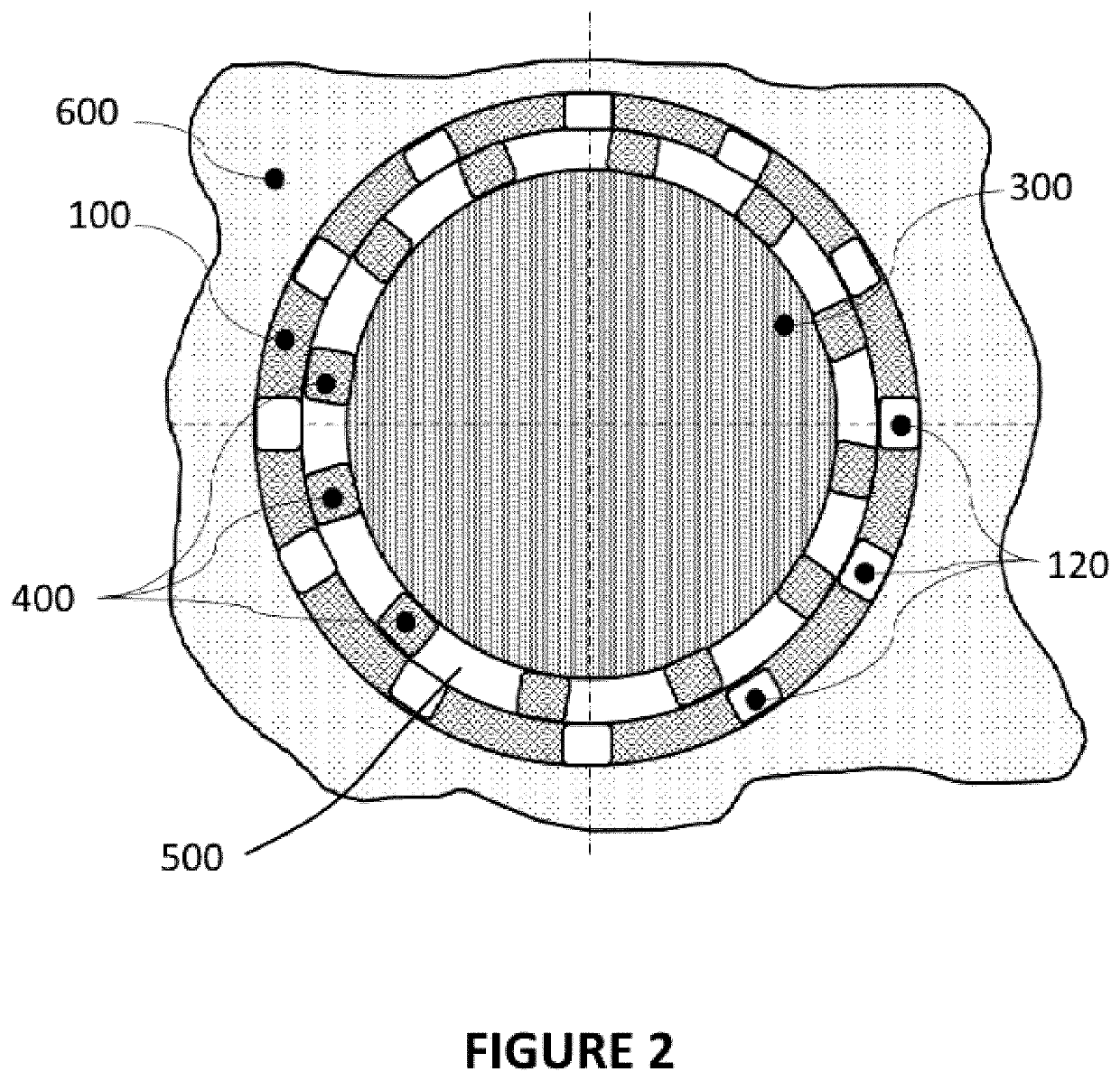
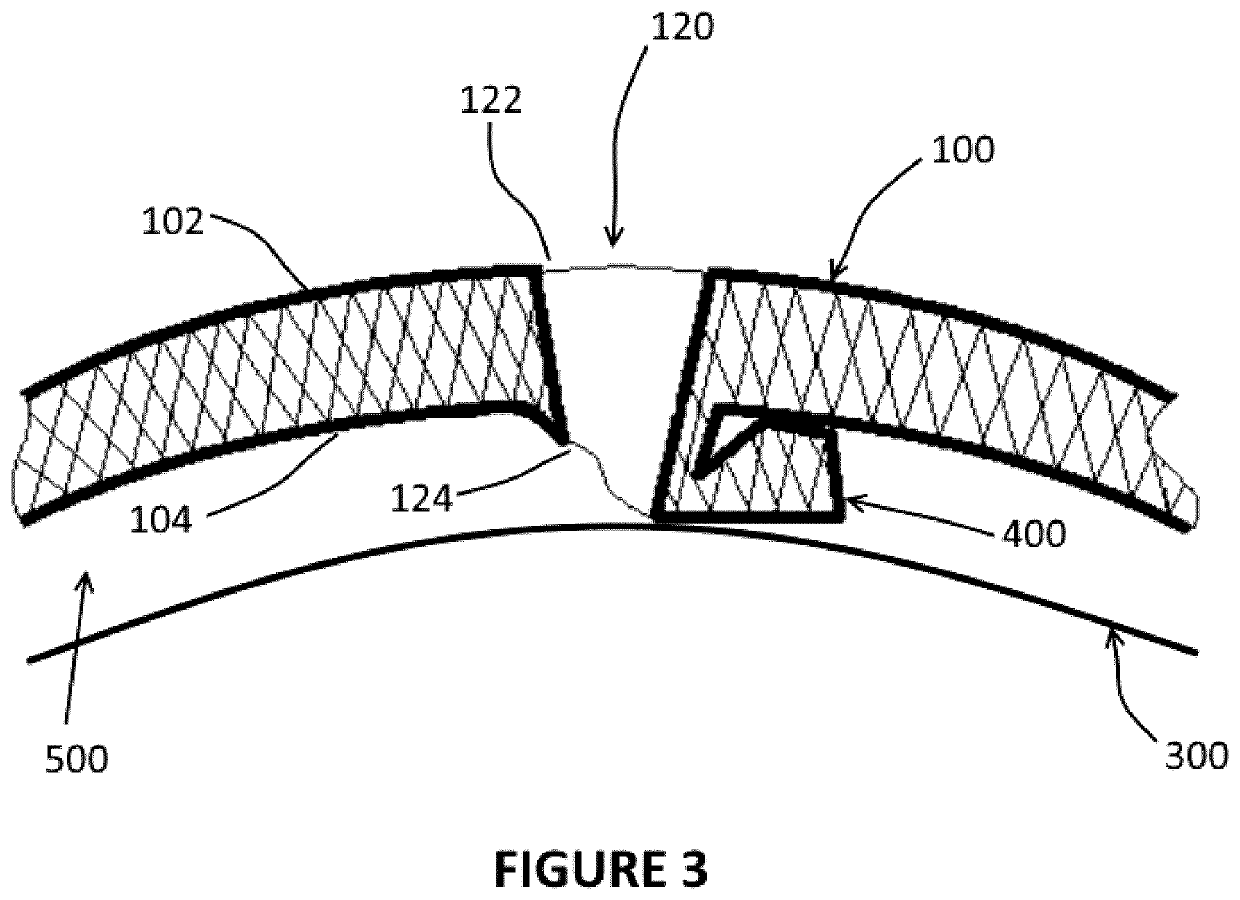
Perforated polymeric sheet with underlying spacers
ActiveUS20200238675A1Sufficient materialAvoid damageAgricultural articlesPipe protection against corrosion/incrustationStructural engineeringPolymer
A new protective polymeric sheet is described wherein said polymeric sheet includes perforations and attached spacers that allow air and water circulation when the sheet is in use. The sheet protects underlying structures from damage while ensuring moisture migration between the protective polymeric sheet and the underlying structure. The protective polymeric sheet comprises a plurality of perforations extending through the sheet and a plurality of spacers, each spacer extending from a lower surface of the sheet adjacent to one side of each perforation. The spacers are created during perforation of the polymeric sheet. The protective polymeric sheet is useful in a number of applications, including without limitation: to protect pipelines; to replace geotextiles in heap leach processes; to line sandboxes and paving stones; to cover greenhouse floors; to make industrial or residential gutter caps; and as a filter.
Owner:SOLMAX INT
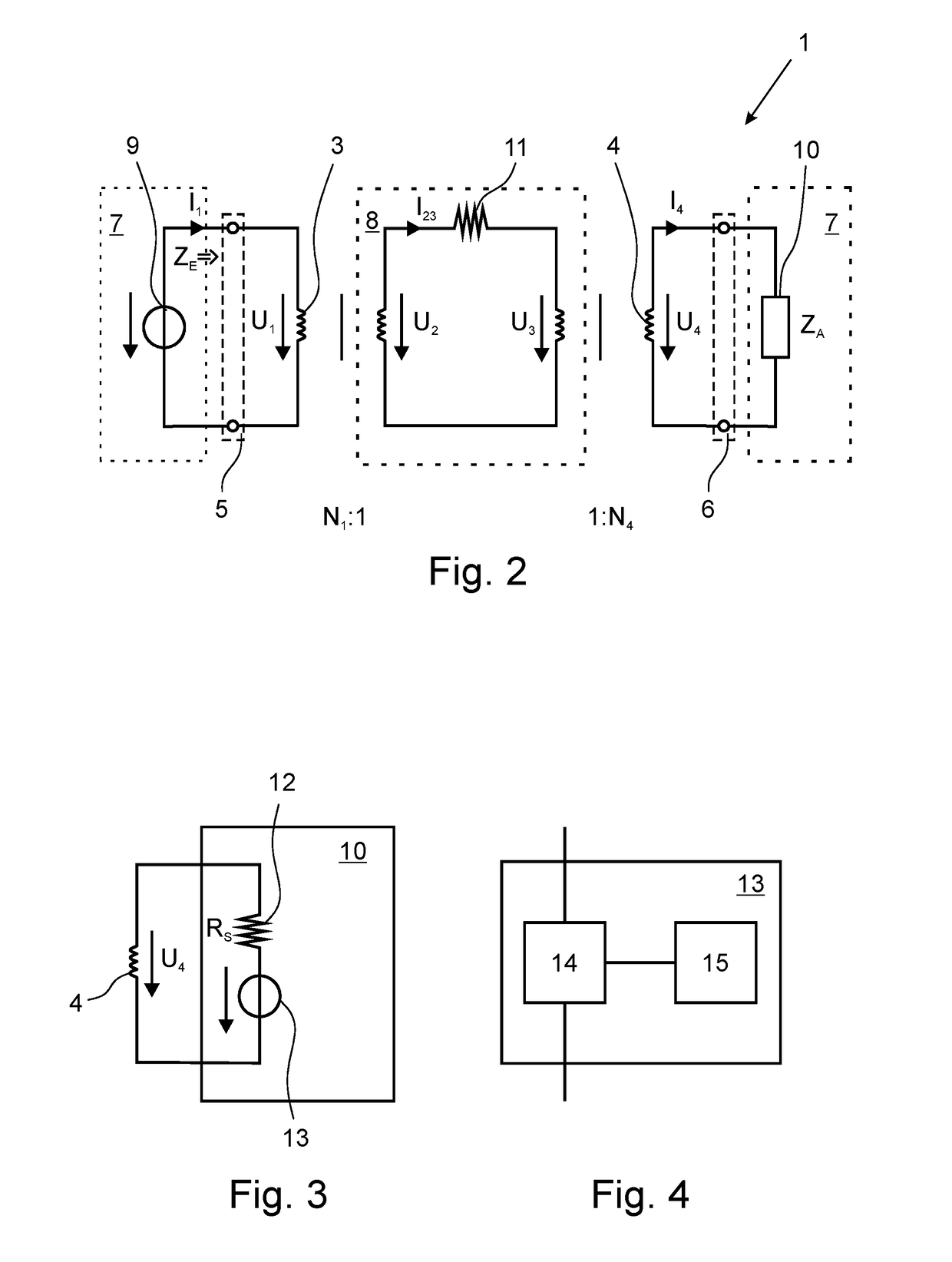
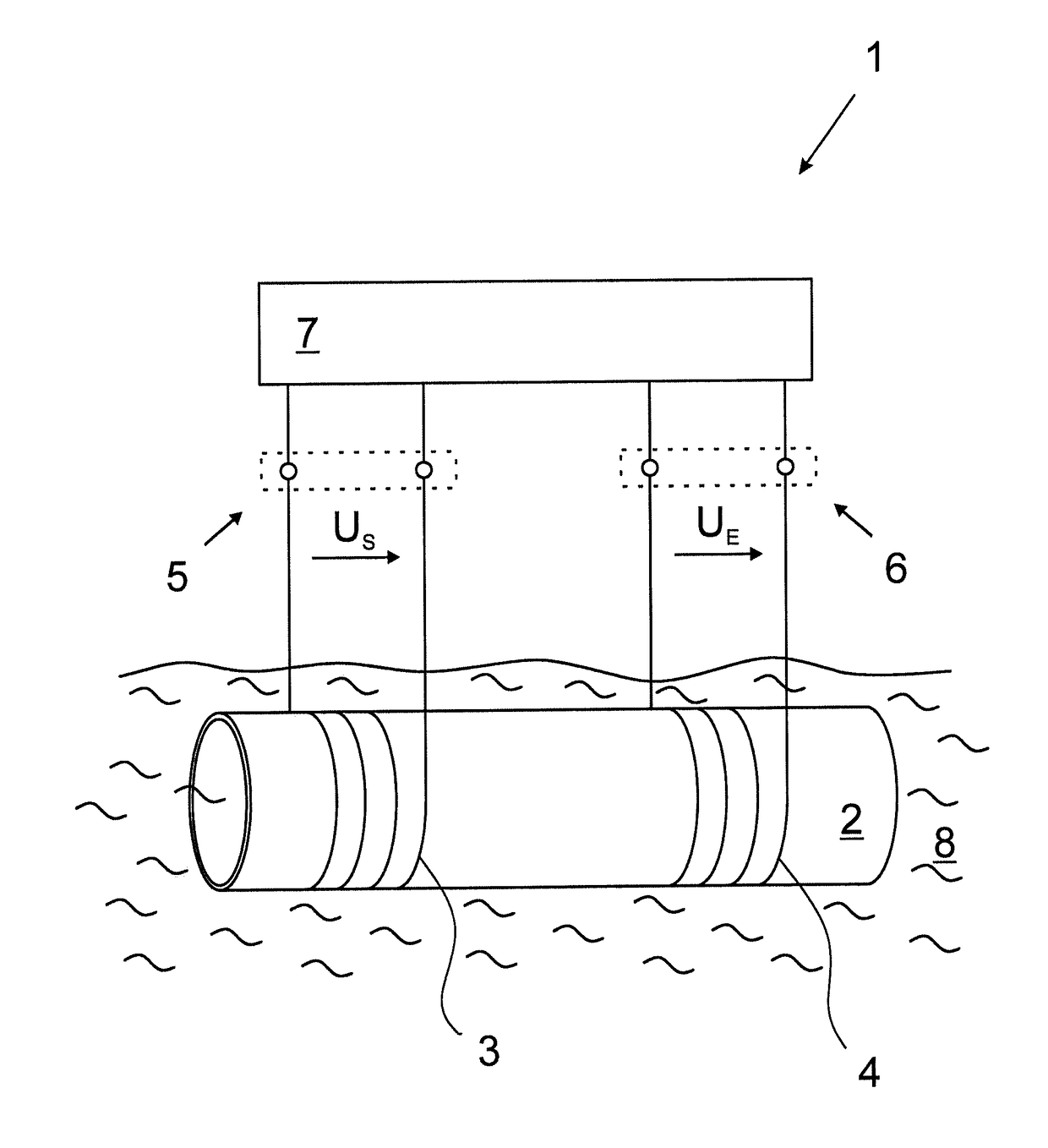
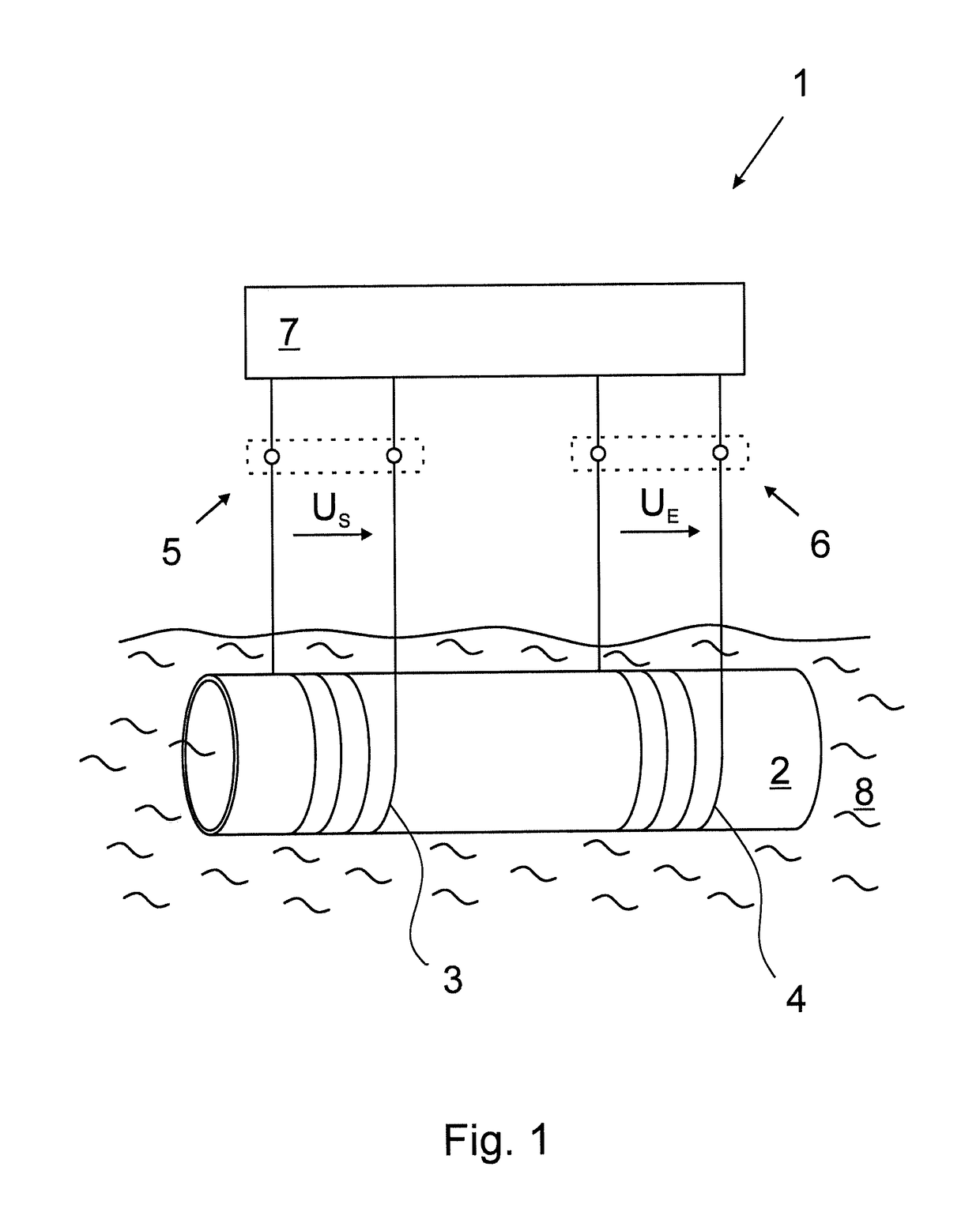
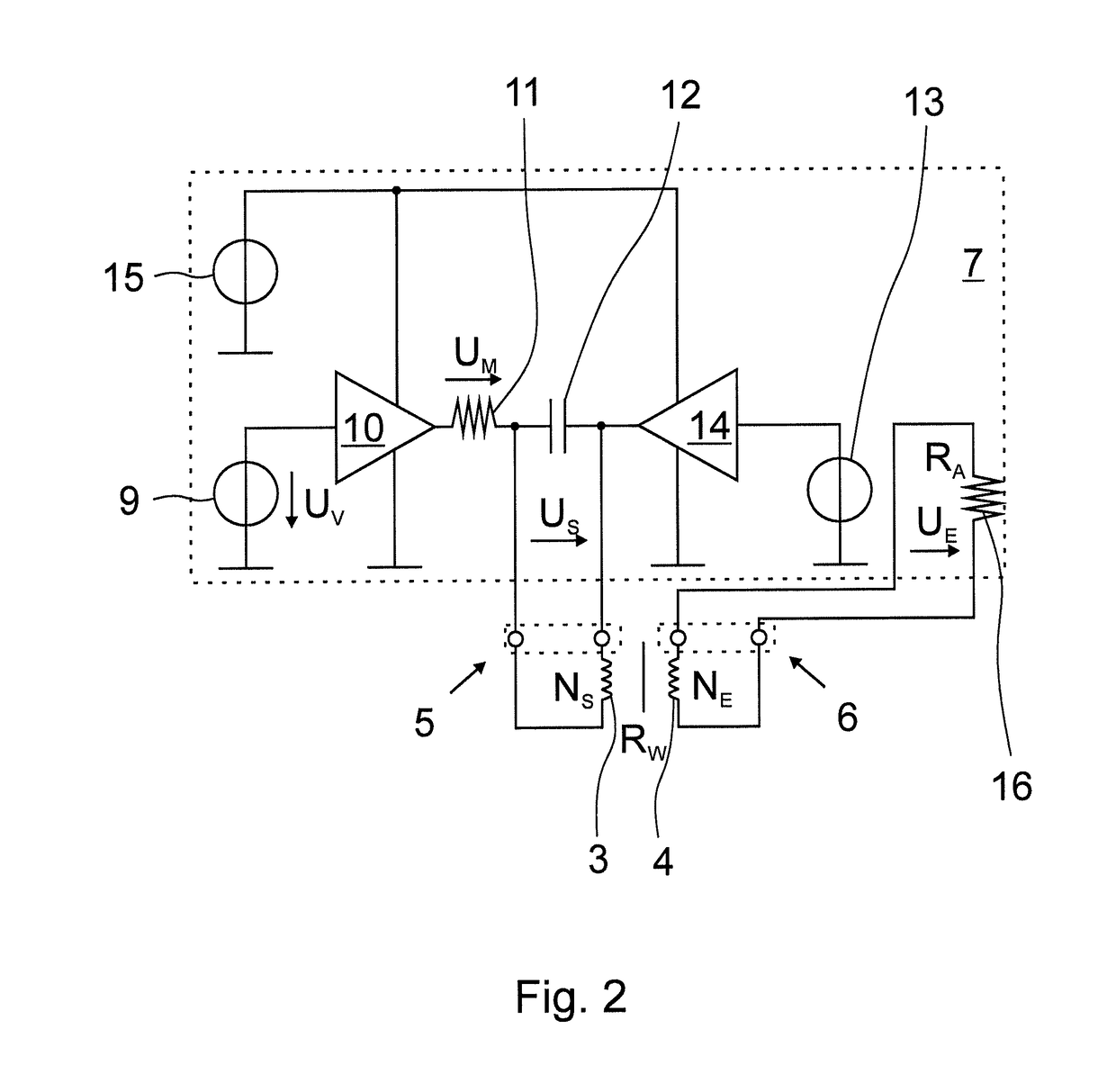
Method for operating an inductive conductivity meter and respective conductivity meter
ActiveUS10585055B2High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyInductance measurementsFluid resistance measurementsTransmitter coilInput impedance
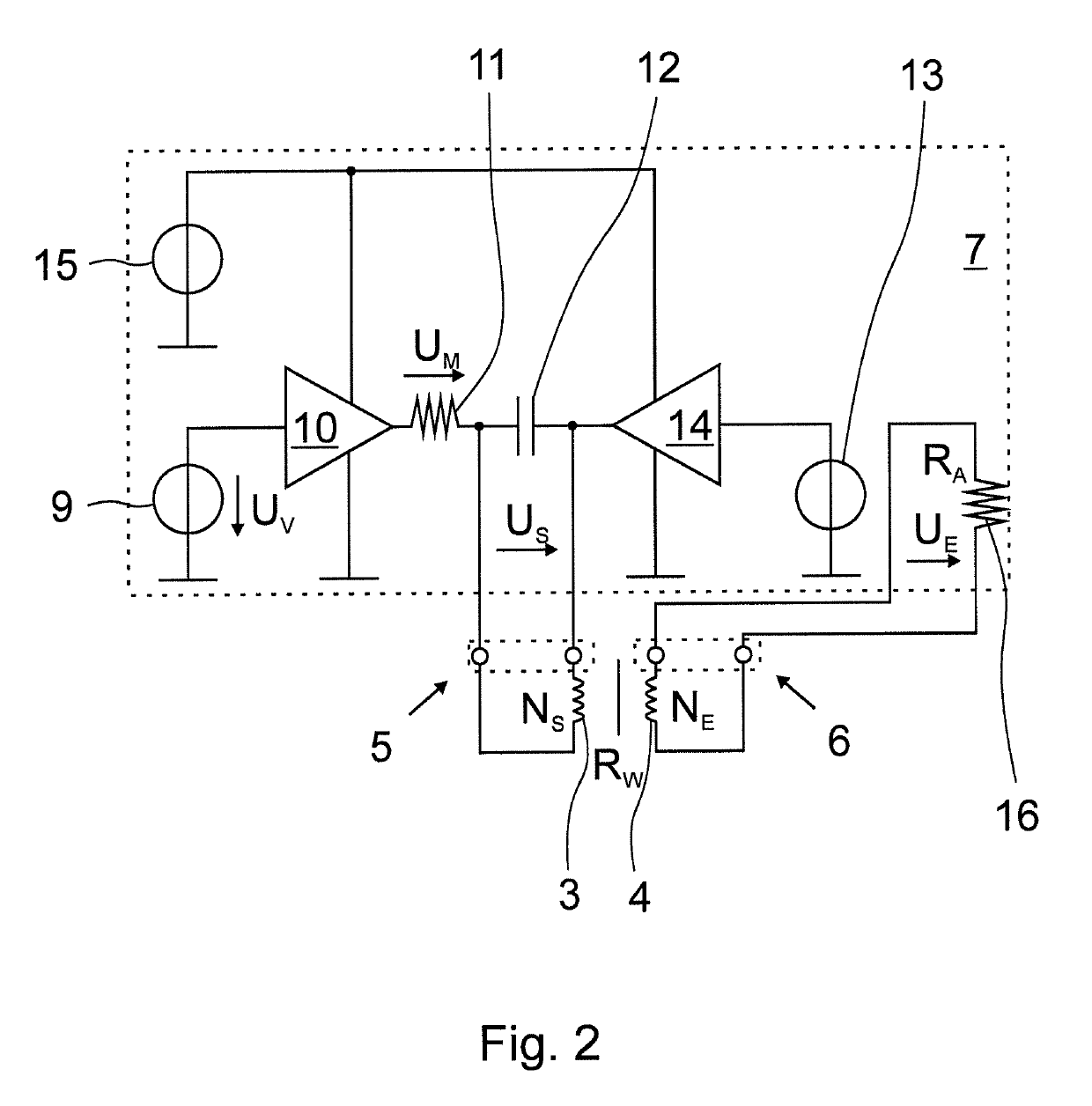
A method for operating an inductive conductivity meter having a transmitting coil, a receiving coil and a terminating impedance device, the transmitting coil having a transmitting coil terminal, the receiving coil having a receiving coil terminal and the terminating impedance device having a terminating impedance, wherein the receiving coil is terminated with the terminating impedance device and wherein the transmitting coil and the receiving coil are inductively coupled with one another by an electrically conductive medium. To provide an improved accuracy of a determination of a conductivity of a medium a setpoint input impedance is specified, an input impedance is determined at the transmitting coil terminal, the terminating impedance is set such that the input impedance is matched to the setpoint input impedance, and a conductivity of the medium is determined using the adjusted input impedance and the set termination impedance.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Method for operating an inductive conductivity meter and respective conductivity meter
ActiveUS20180259470A1High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyInductance measurementsFluid resistance measurementsInput impedanceEngineering
A method for operating an inductive conductivity meter having a transmitting coil, a receiving coil and a terminating impedance device, the transmitting coil having a transmitting coil terminal, the receiving coil having a receiving coil terminal and the terminating impedance device having a terminating impedance, wherein the receiving coil is terminated with the terminating impedance device and wherein the transmitting coil and the receiving coil are inductively coupled with one another by an electrically conductive medium. To provide an improved accuracy of a determination of a conductivity of a medium a setpoint input impedance is specified, an input impedance is determined at the transmitting coil terminal, the terminating impedance is set such that the input impedance is matched to the setpoint input impedance, and a conductivity of the medium is determined using the adjusted input impedance and the set termination impedance.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus for measuring conductivity
InactiveUS20030155937A1Conductivity is accurateAvoid stickingFluid resistance measurementsMaterial impedanceElectrical resistivity and conductivityElectrical current
An apparatus for measuring electric conductivity comprises three electrodes brought into contact with a substance to be measured. The electrodes include a detection electrode for detecting electric conductivity of the substance to be measured, and two AC current supply electrodes disposed on both sides of the detection electrode at respective distances, and an AC current of the same phase is applied to the two AC current supply electrodes. This apparatus provides stabilized measurement of the electric conductivity of a substance to be measured with a high accuracy.
Owner:ORGANO CORP
Method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device and respective inductive conductivity measuring device
ActiveUS20180149684A1Improve determination accuracyHigh measurement accuracyInductance measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrically conductiveElectricity
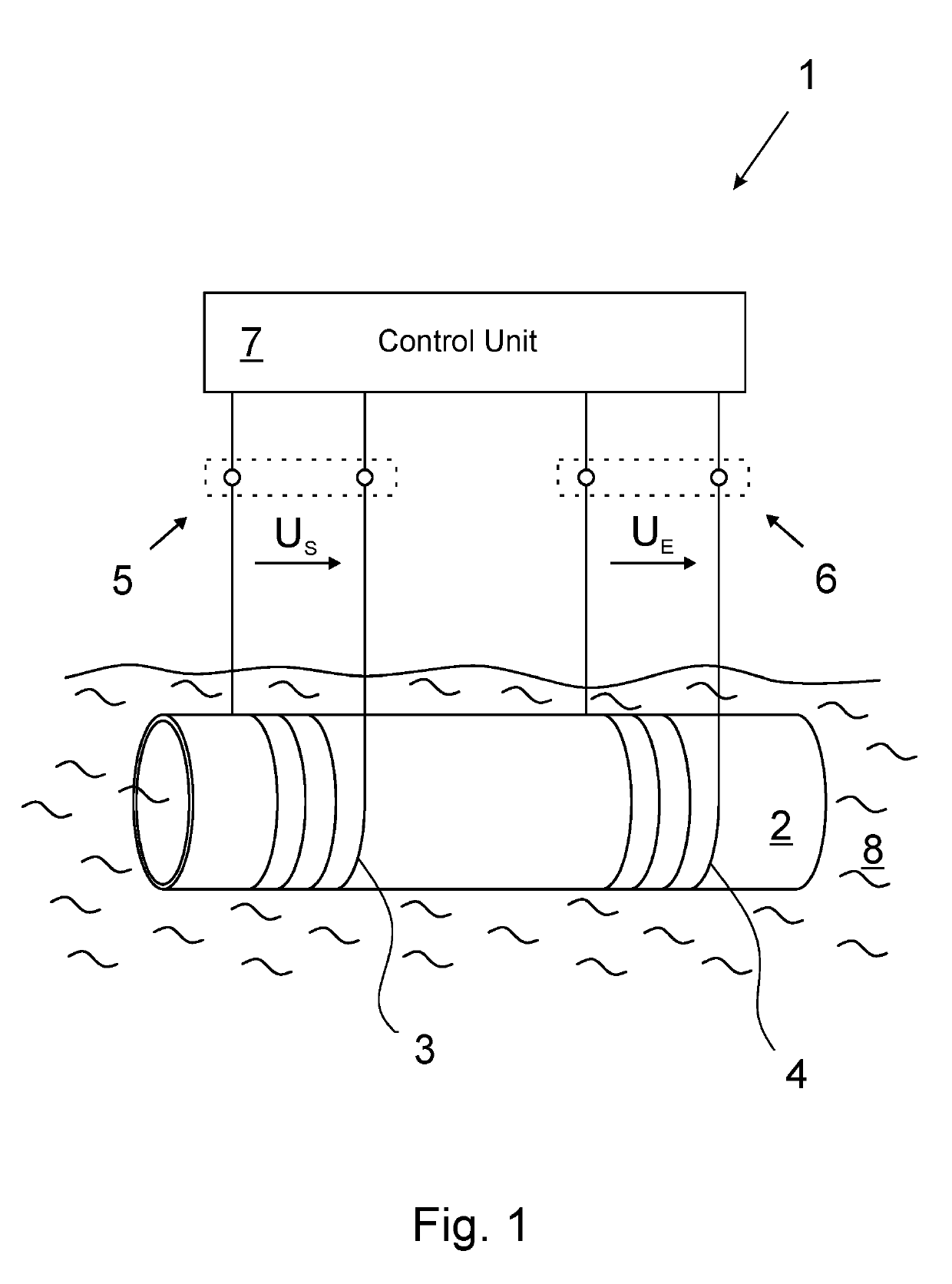
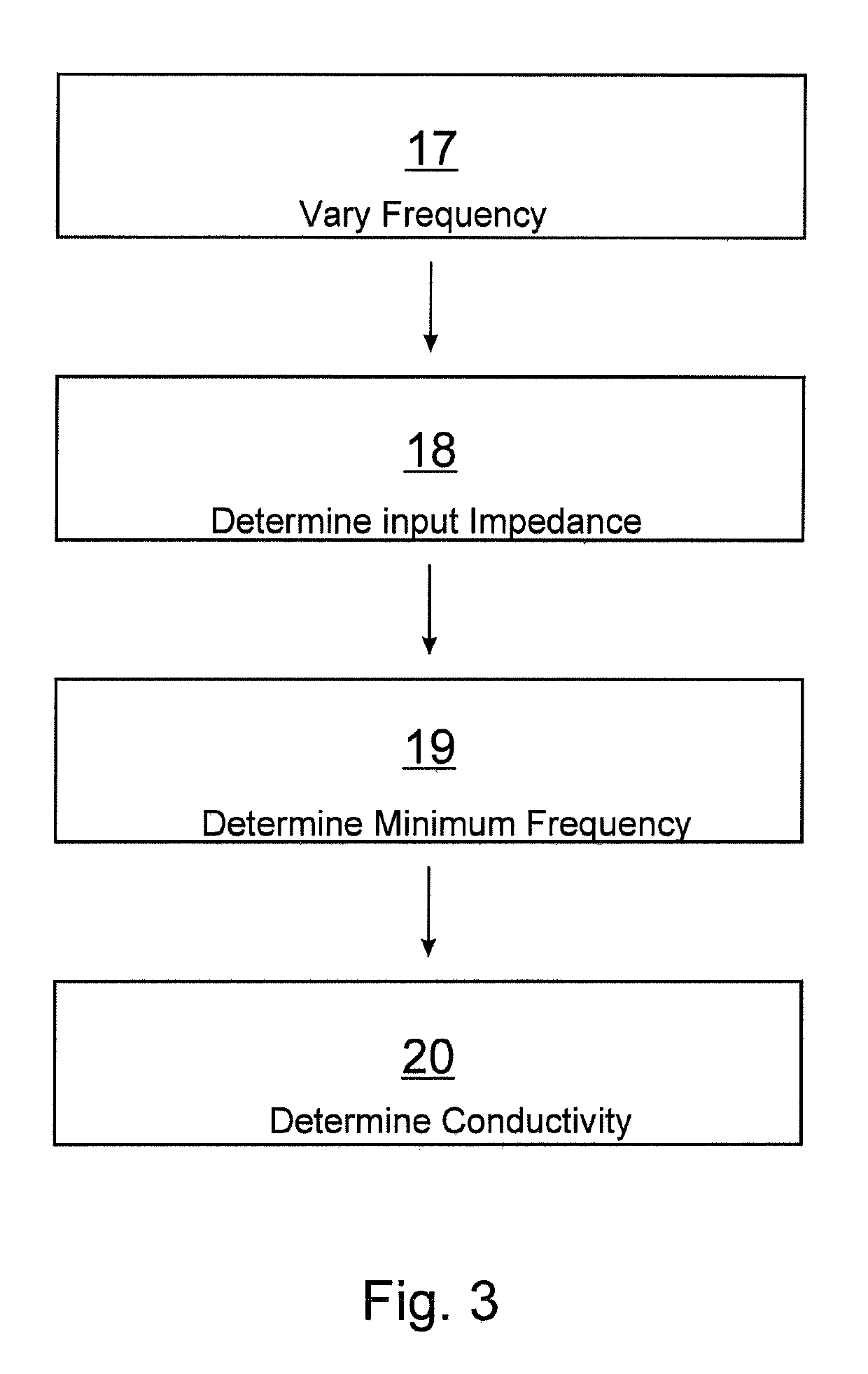
A method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device that has a transmitting coil with an input and a receiving coil, the transmitting coil and the receiving coil being inductively coupled to one another by an electrically conductive medium. An electrical preset alternating signal is generated and fed to the input of the transmitting coil. The method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device is improved in that a frequency of a preset alternating signal is varied in a frequency interval, in the frequency interval, a frequency-dependent minimum input impedance at the input of the transmitting coil is determined using a response alternating signal, a minimum frequency of the response alternating signal is determined at the minimum input impedance at the input of the transmitting coil, and a conductivity of the medium is determined using the minimum frequency of the response alternating signal.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Washing machine with water conductivity measuring electrodes
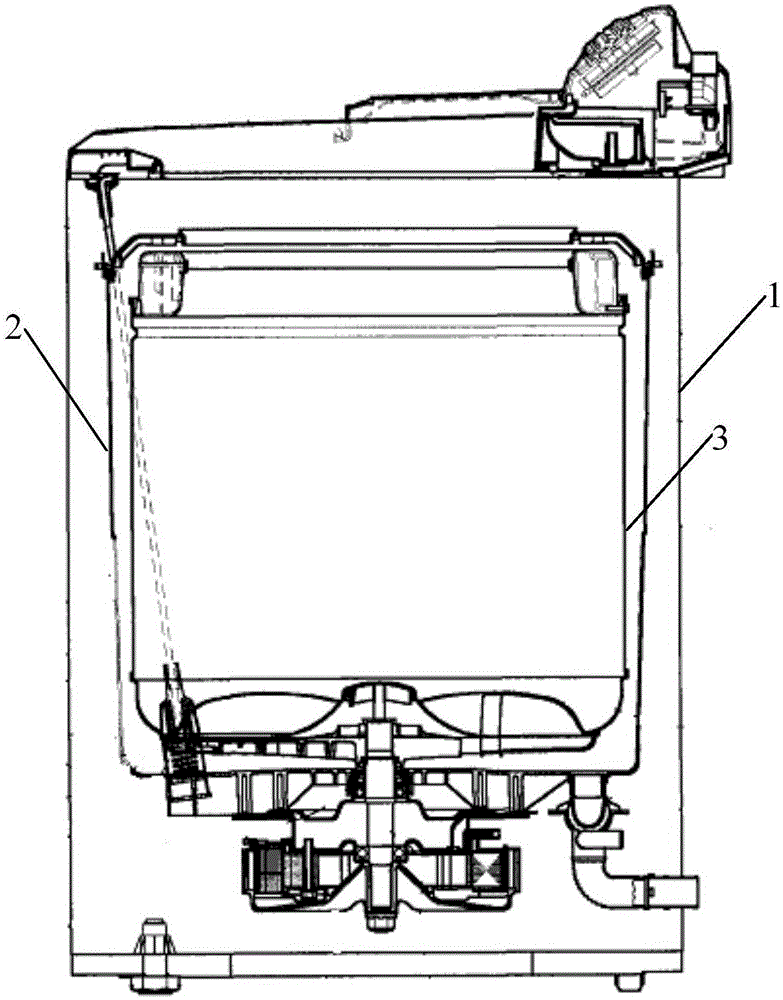
InactiveCN105002697AResolve swingConductivity is accurateControl devices for washing apparatusTextiles and paperRubber materialEngineering
The invention discloses a washing machine with water conductivity measuring electrodes. The washing machine includes a shell, an outer barrel arranged in the shell, an inner barrel rotatably arranged in the outer barrel, a plurality of electrodes nested in open holes at the bottom of the inner barrel, a waterproof layer, protective frames and a controller arranged on the cover of the washing machine; the waterproof layer coats the surfaces of the electrodes and includes an organic silicone rubber layer, a waterproof adhesive layer, a sealant layer and a polyethylene layer which are distributed from outside to inside sequentially, wherein two ends of the polyethylene layer and two ends of the organic silicone rubber layer are partially combined; the protective frames are in one-to-one correspondence with the electrodes and are nested at the upper parts of the open holes at the inner barrel; an accommodating space is formed by each protective frame and a corresponding open hole; the protective frame is made of rubber materials and includes a side wall and a top plate connected with the side wall; the electrodes are fixed in the accommodating spaces; and the detection ends of the electrodes pass through the through holes of the top plates; and the plurality of electrodes are electrically connected with the controller respectively; and the controller is used for controlling a washing program of the washing machine according to the average value of the conductivity of washing water measured by the plurality of electrodes.
Owner:万乐予
Apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity in burns
ActiveUS9826928B2Simply and accurately measuring thermal conductivityConductivity is accurateMaterial thermal conductivityThermometers using physical/chemical changesEngineeringTarget tissue
There are provided an apparatus and method for measuring thermal conductivity capable of easily and accurately obtaining an extent of thermal damage of a targeted tissue. The apparatus for measuring thermal conductivity in burns includes a thermal paper stacking member having a plurality of sheets of thermal paper stacked thereon to form layers, and a pressing member configured to press the stacking member so that the thermal paper is stacked and maintained in a closely adhered state. Here, an extent of thermal damage of the targeted tissue according to the depth can be calculated as an extent of thermal damage of the stacking member according to the depth.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device and respective inductive conductivity measuring device
ActiveUS10488451B2High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyInductance measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityInput impedance
A method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device that has a transmitting coil with an input and a receiving coil, the transmitting coil and the receiving coil being inductively coupled to one another by an electrically conductive medium. An electrical preset alternating signal is generated and fed to the input of the transmitting coil. The method for operating an inductive conductivity measuring device is improved in that a frequency of a preset alternating signal is varied in a frequency interval, in the frequency interval, a frequency-dependent minimum input impedance at the input of the transmitting coil is determined using a response alternating signal, a minimum frequency of the response alternating signal is determined at the minimum input impedance at the input of the transmitting coil, and a conductivity of the medium is determined using the minimum frequency of the response alternating signal.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Thermophysical property measurement method and thermophysical property measurement apparatus
ActiveUS10876983B2Conductivity is accurateAccurate powerThermometer detailsMaterial thermal conductivityElectrical resistance and conductanceDc current
Thermophysical property measurement method and apparatus are provided that make it possible to simply and conveniently obtain a highly precise absolute thermoelectric power and thermal conductivity.Embodiments of the present invention provides a thermophysical property measurement method, including a first step of applying a DC voltage or a DC current at both ends of a metal to which a temperature gradient is applied to measure a first temperature at a center of the metal; a second step of applying DC voltages or DC currents of different polarities at both ends of the metal to measure a second temperature at the center of the metal; a third step of calculating a Thomson coefficient of the metal using the first and second temperatures measured in the first and second steps; and a fourth step of calculating at least one of absolute thermoelectric power and thermal conductivity of the metal using the Thomson coefficient calculated in the third step, the third step including: calculating an average value of a difference between the first temperature and the second temperature; calculating an average value of a sum of the first temperature and the second temperature; and dividing a product of a magnitude of a current that flows through the metal, electrical resistance of the metal, and the average value of the difference by the average value of the sum and the difference between the first temperature and the second temperature.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com