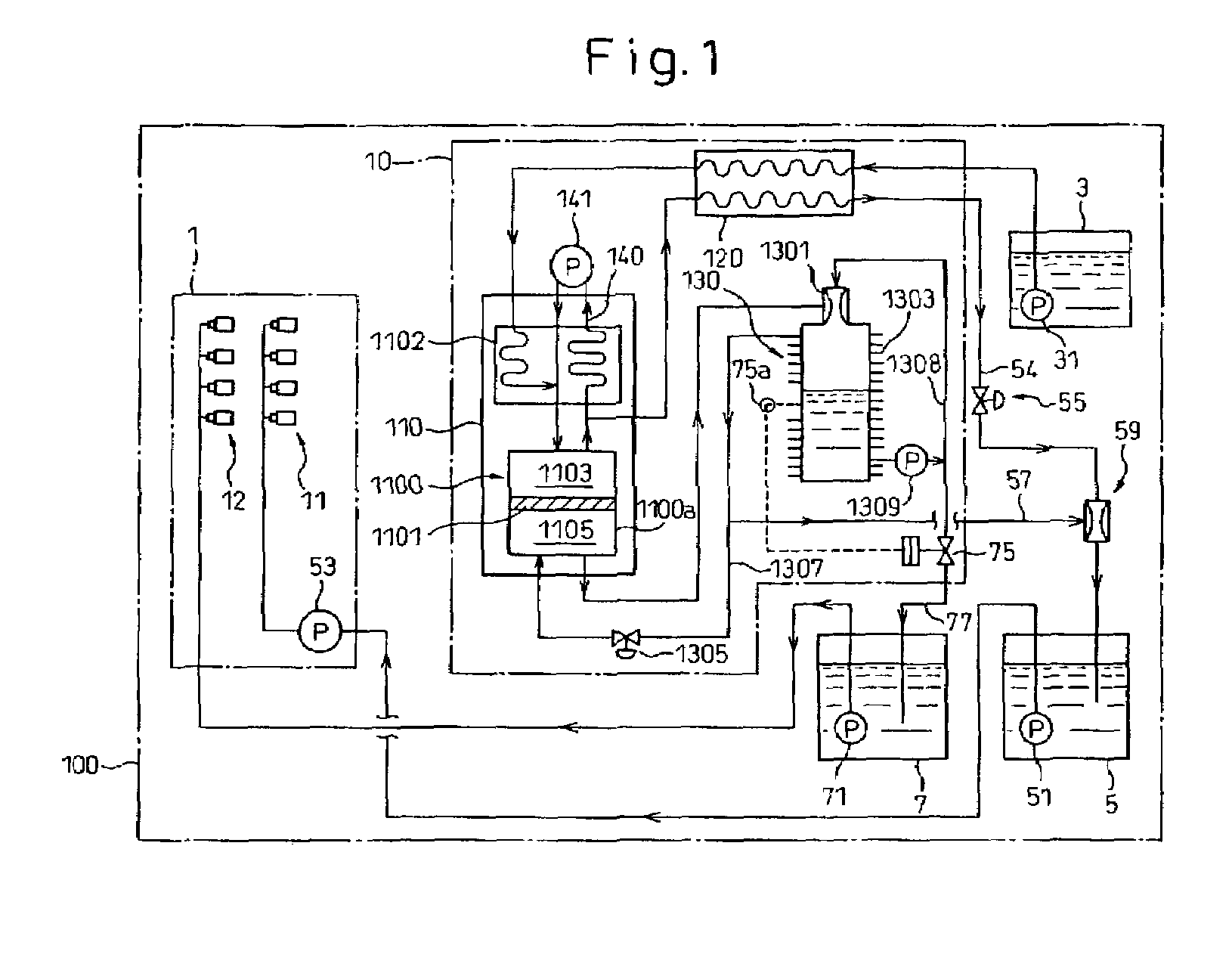
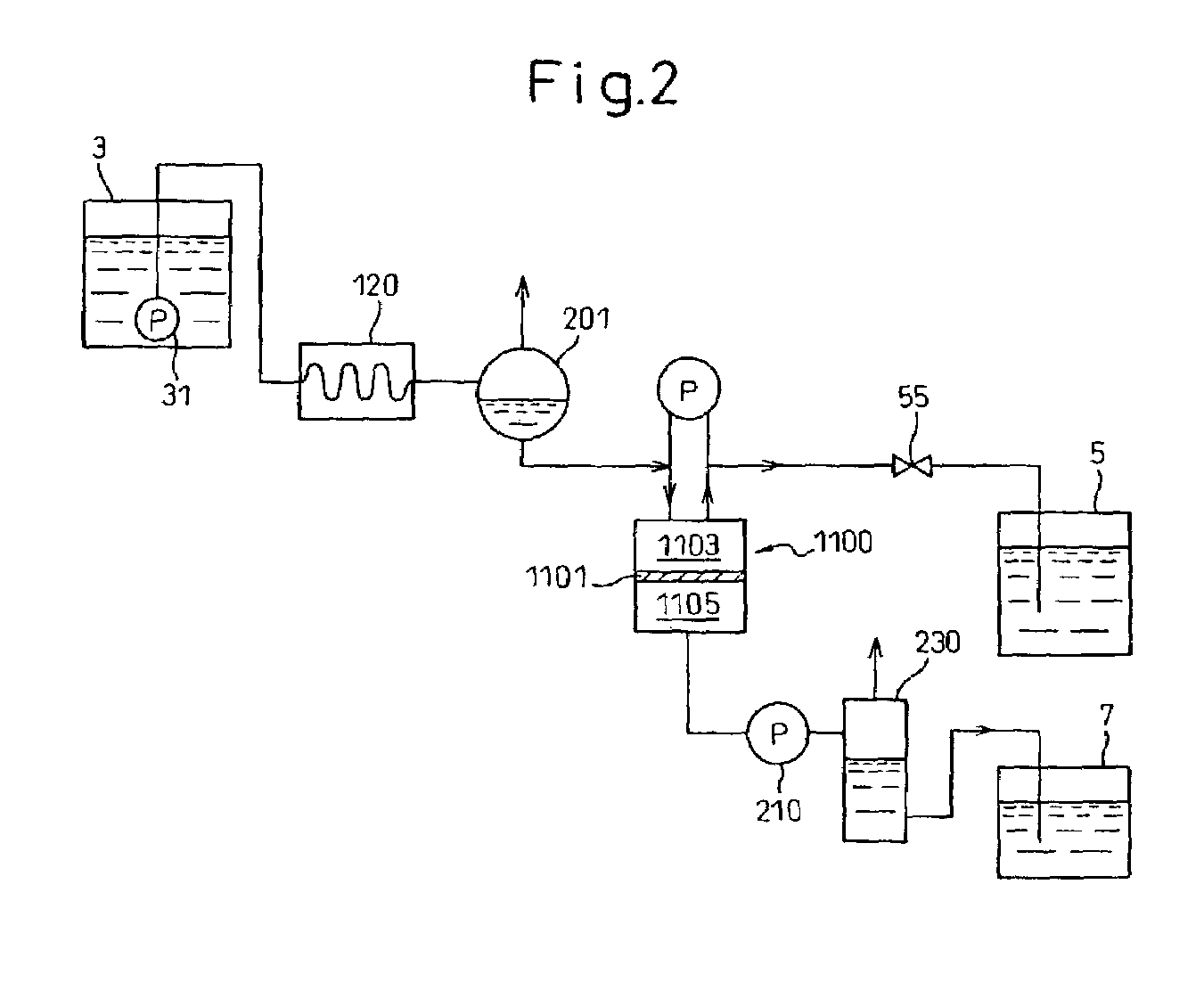
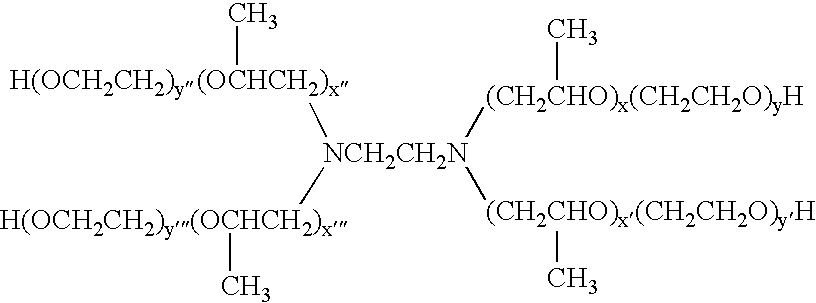
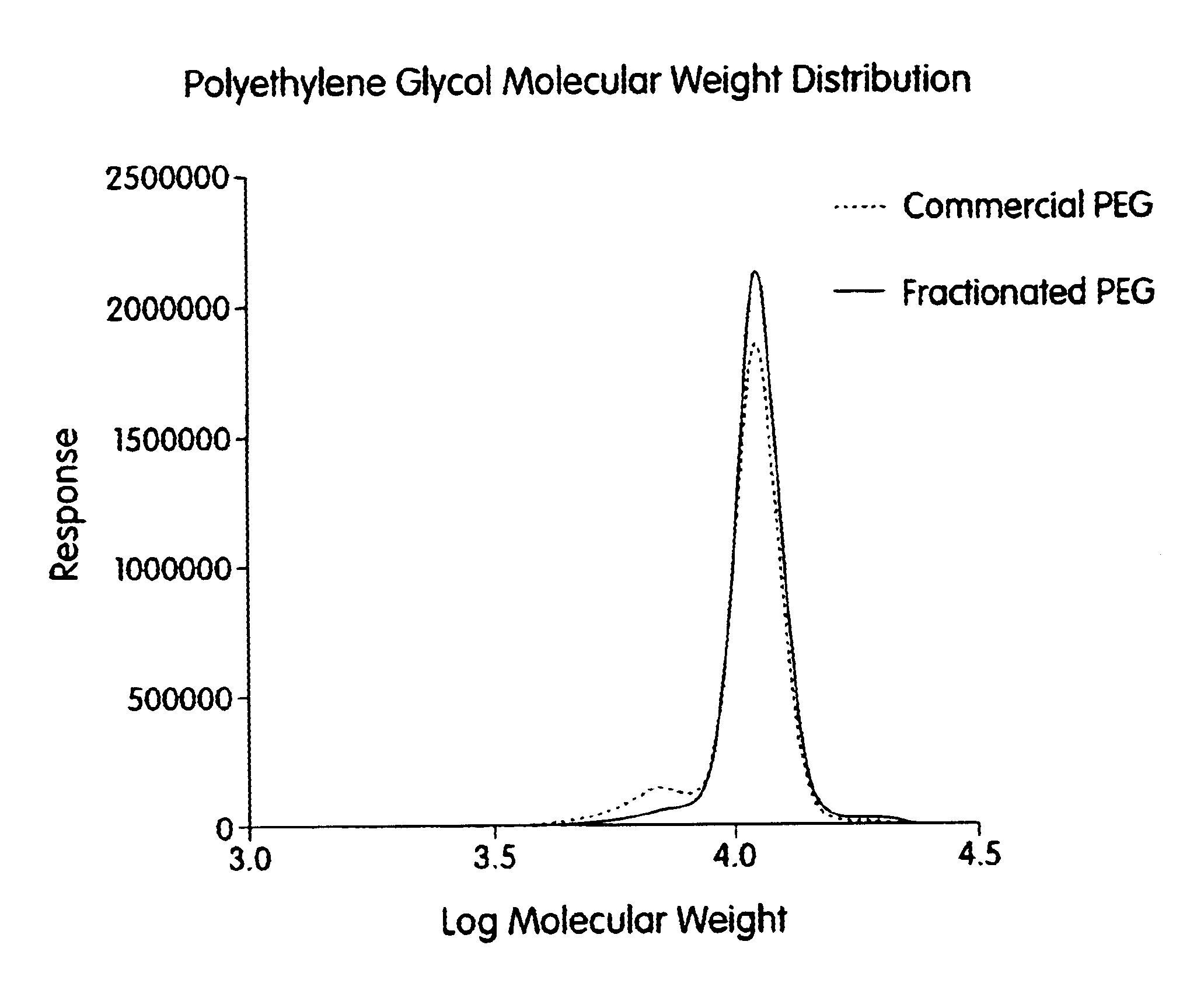
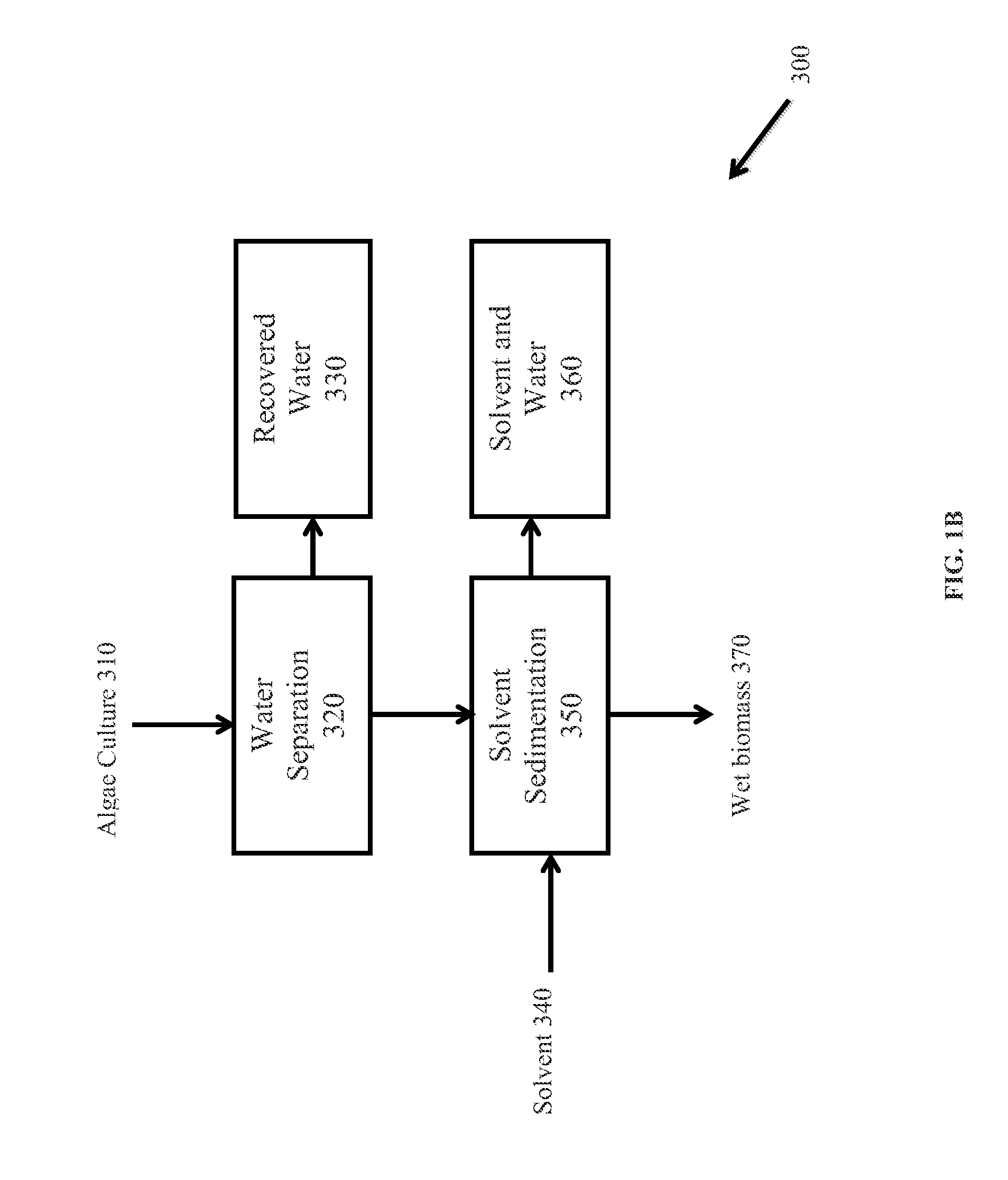
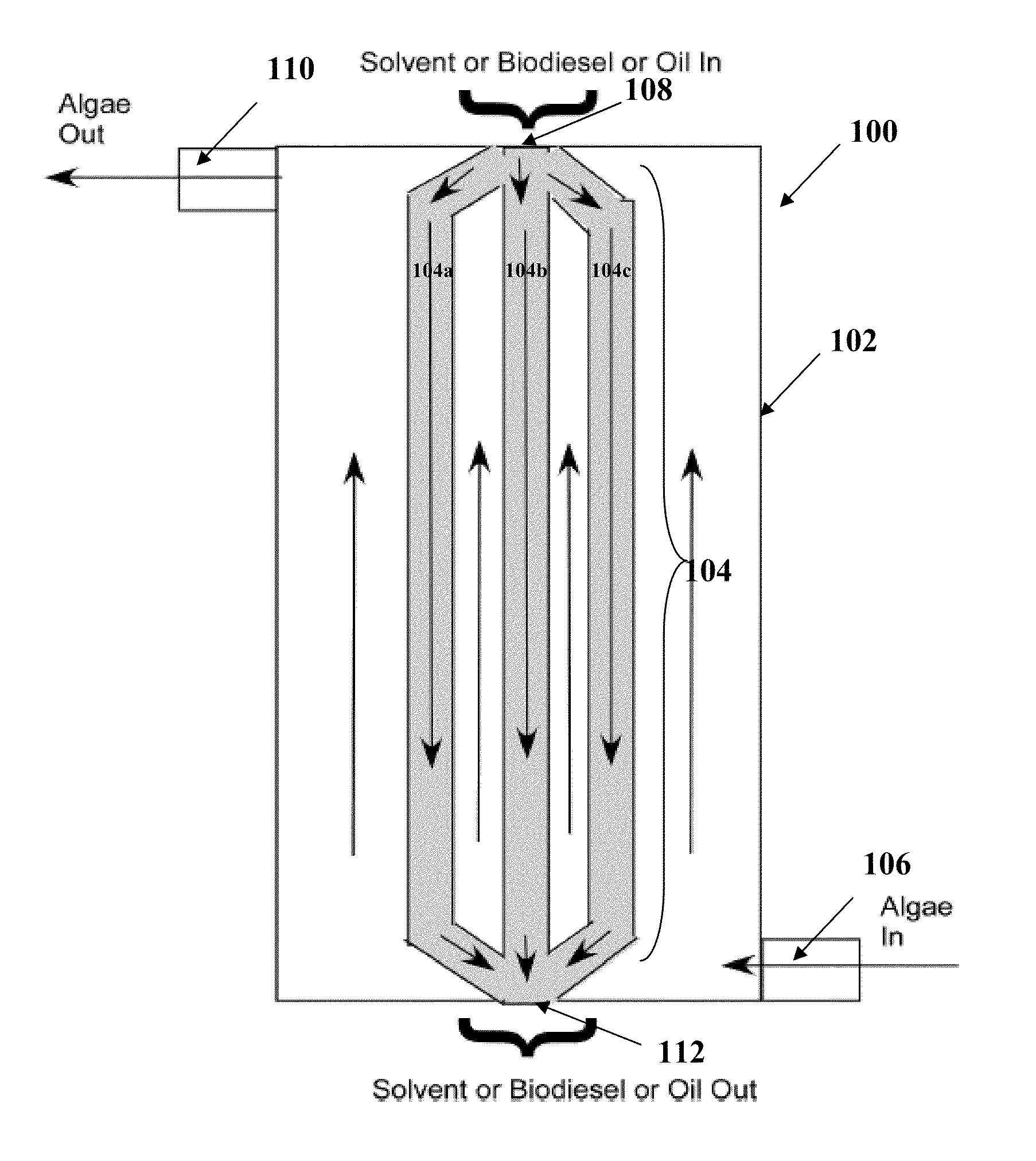
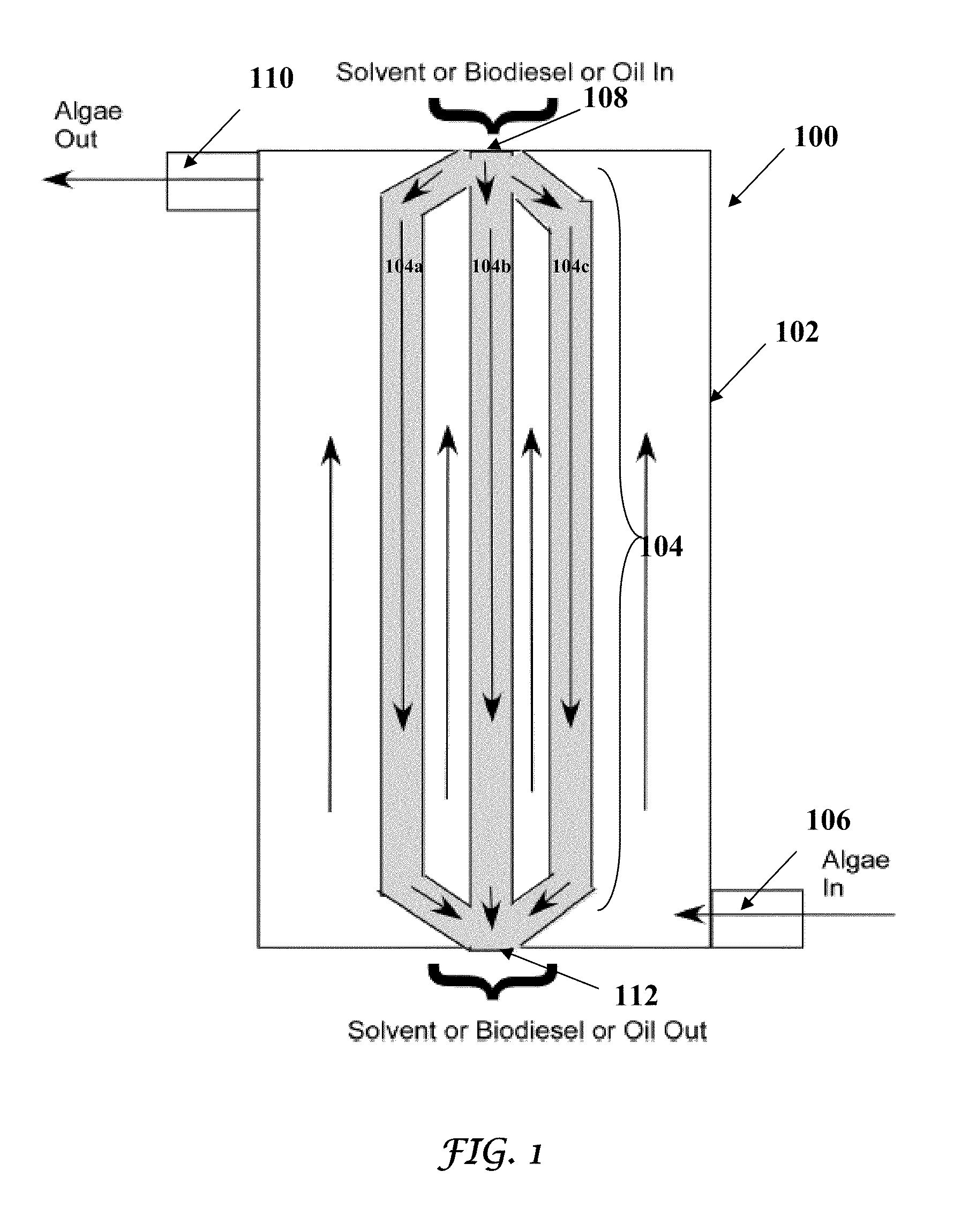
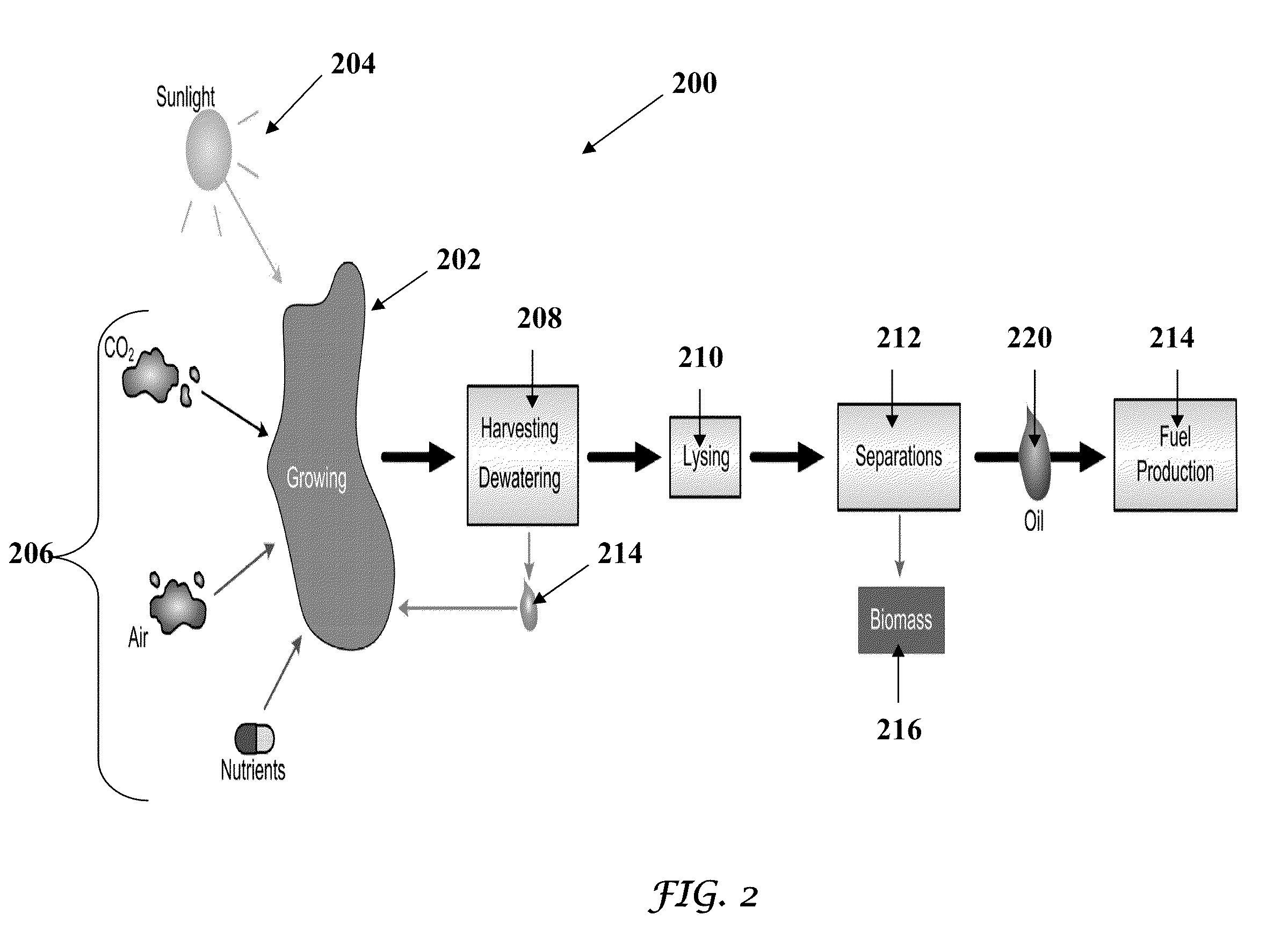
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2192results about "Water/sewage treatment by extraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfluidic Chemical Reaction Circuits
InactiveUS20080281090A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +3
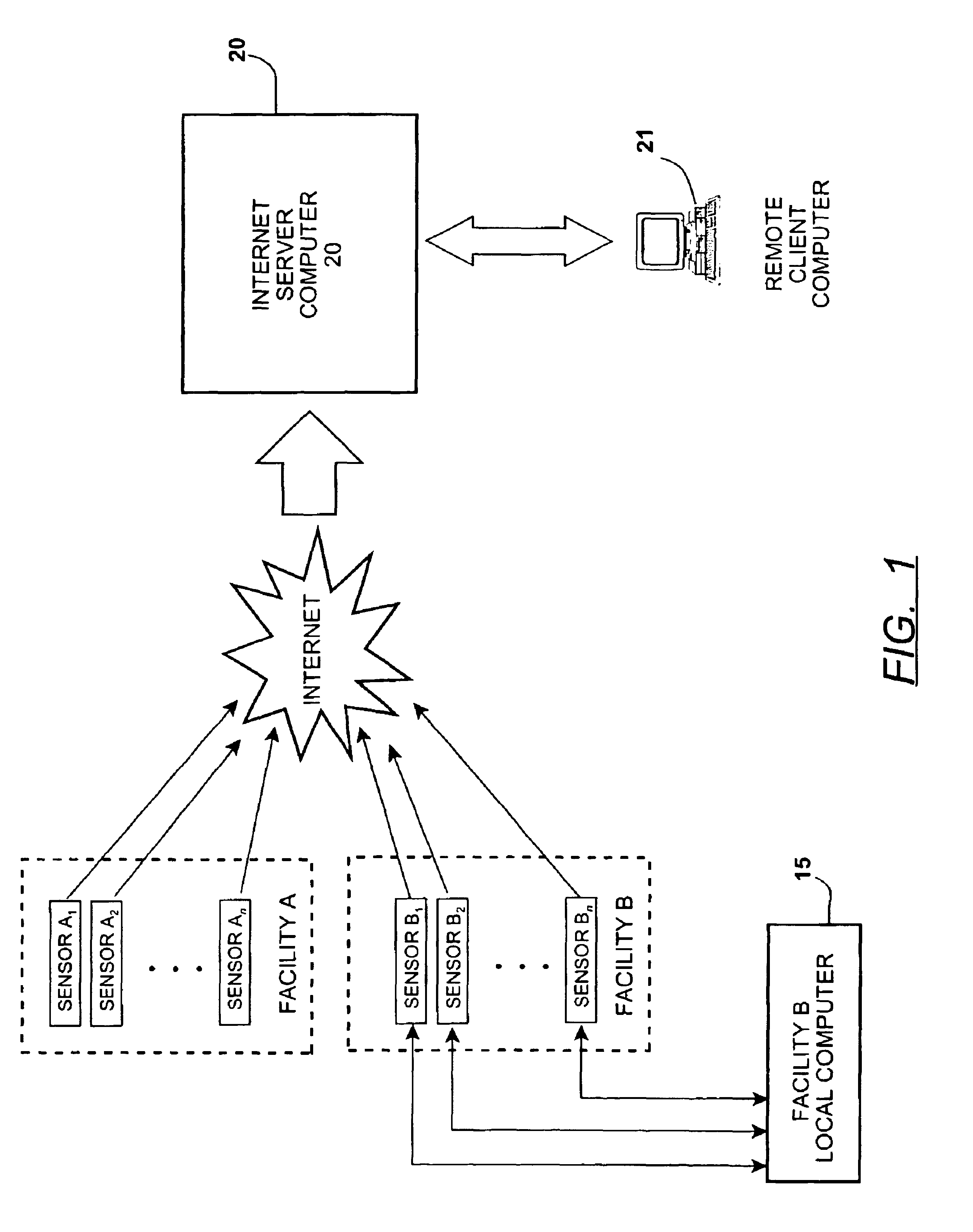
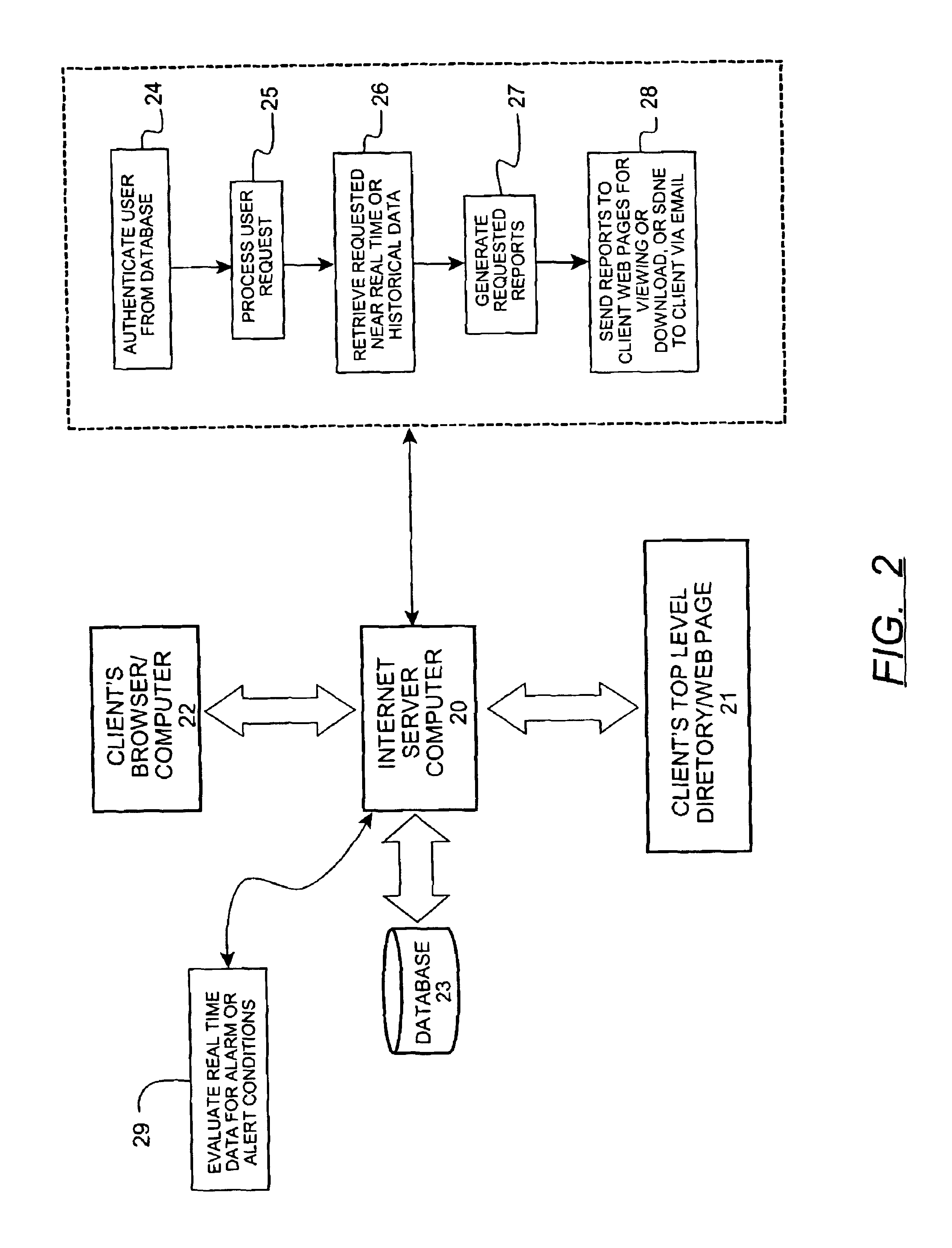
Method for remote monitoring of water treatment systems
InactiveUS6954701B2Rule out the possibilityNegating human error or tamperingUltrafiltrationSolid sorbent liquid separationWater treatment systemQuality assurance
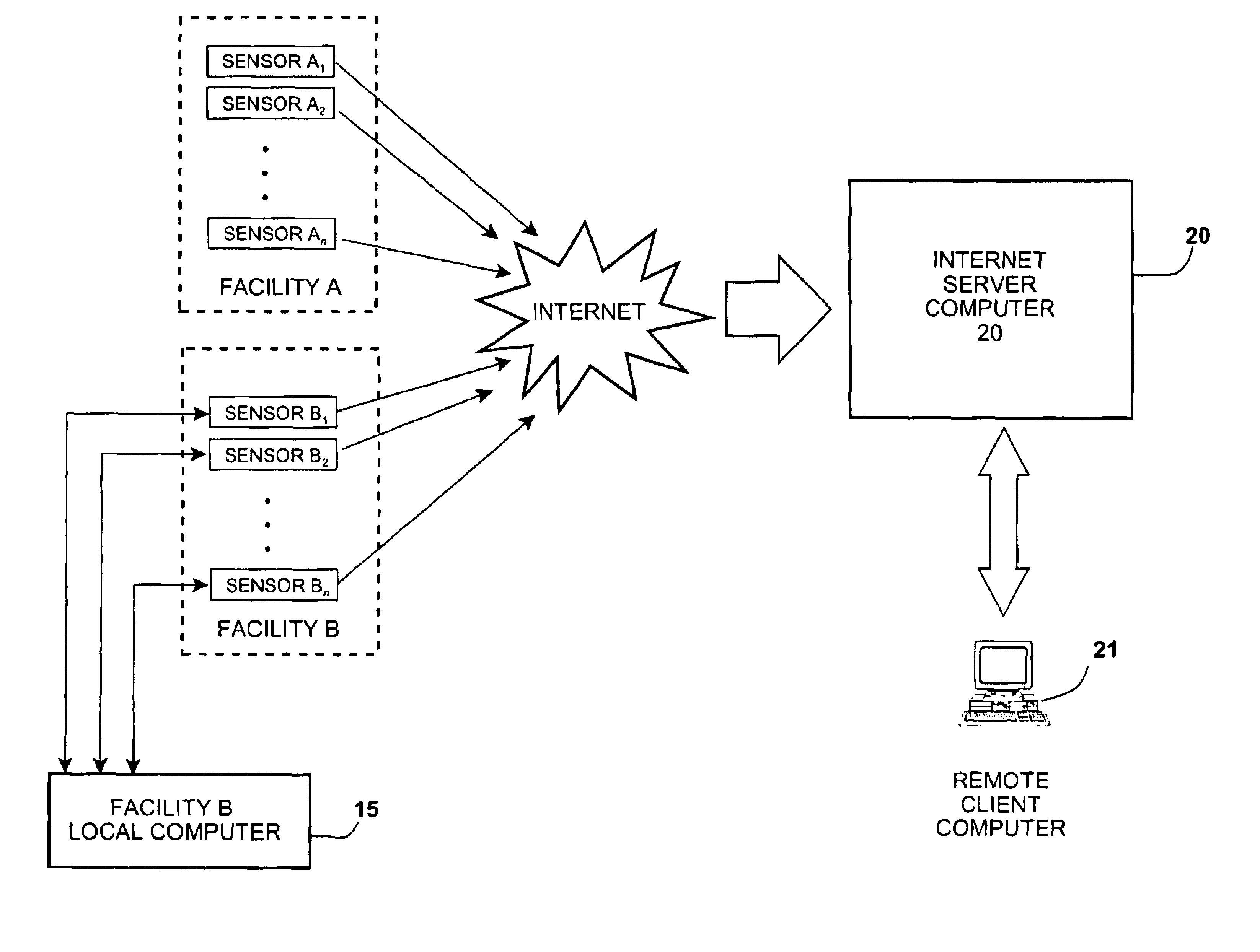
A method of monitoring the daily operating performance parameters for water treatment processes through the collection of localized data. The data is manipulated to generate preconfigured performance, maintenance, and quality assurance reports and further provide automatic submission of data as required for regulatory review of certain water treatment systems such as potable water treatment. The data is collected from sensors located at an equipment site and transferred to a remote computer located by use of the Internet, further all data received and used for generation of reports is also accessible by Internet connection and be delivered directly to the regulatory agency without additional process.
Owner:WATEREYE +1
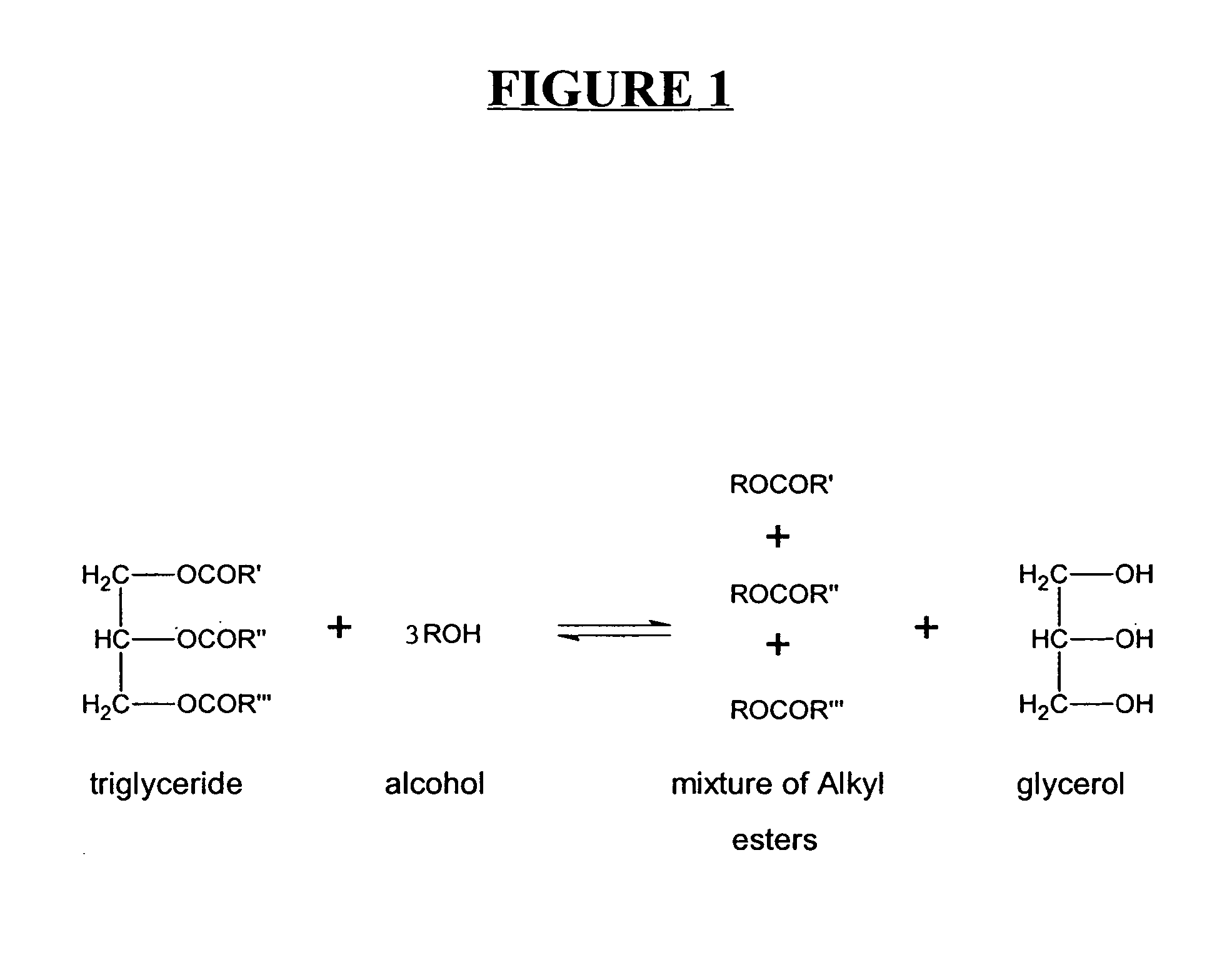
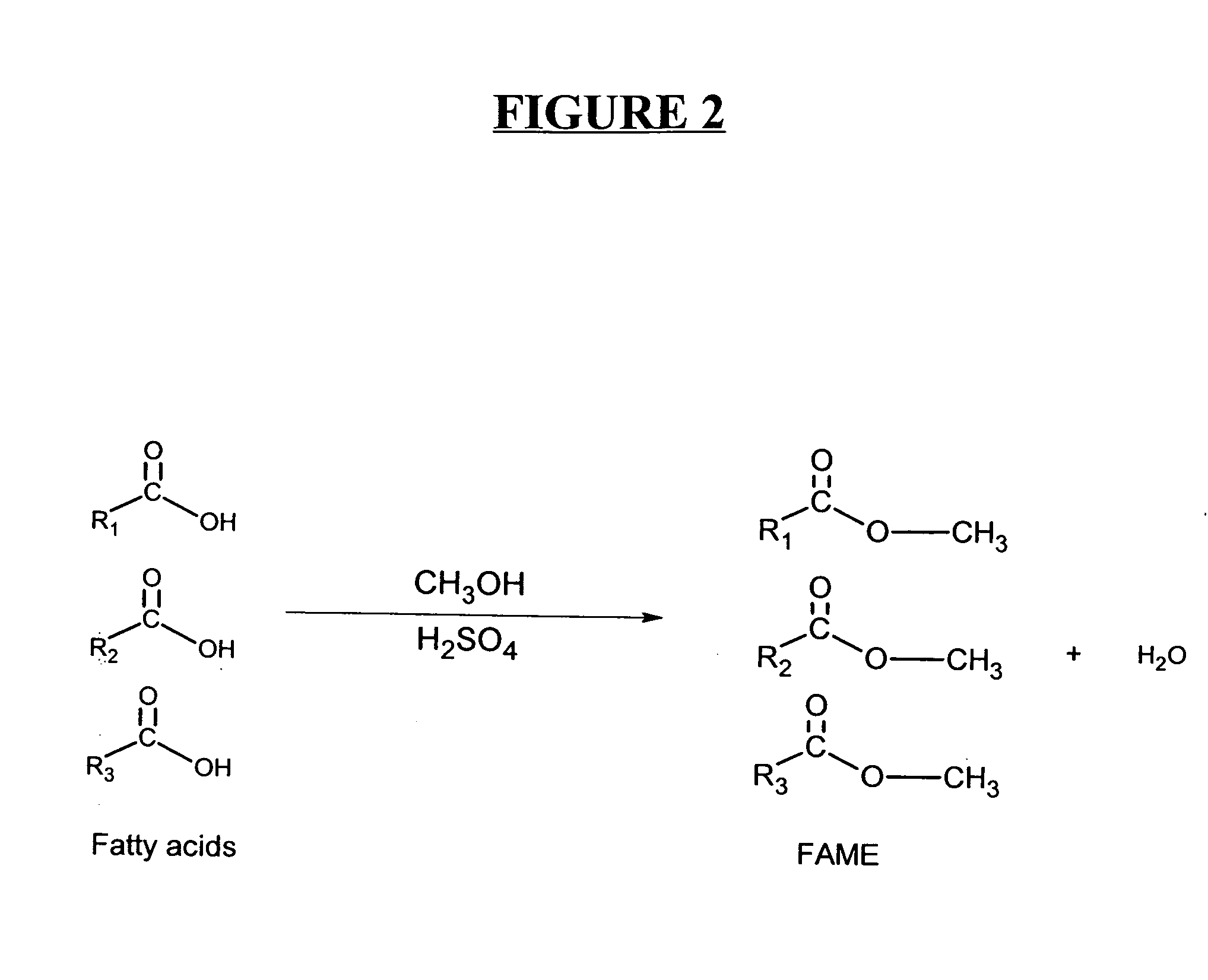
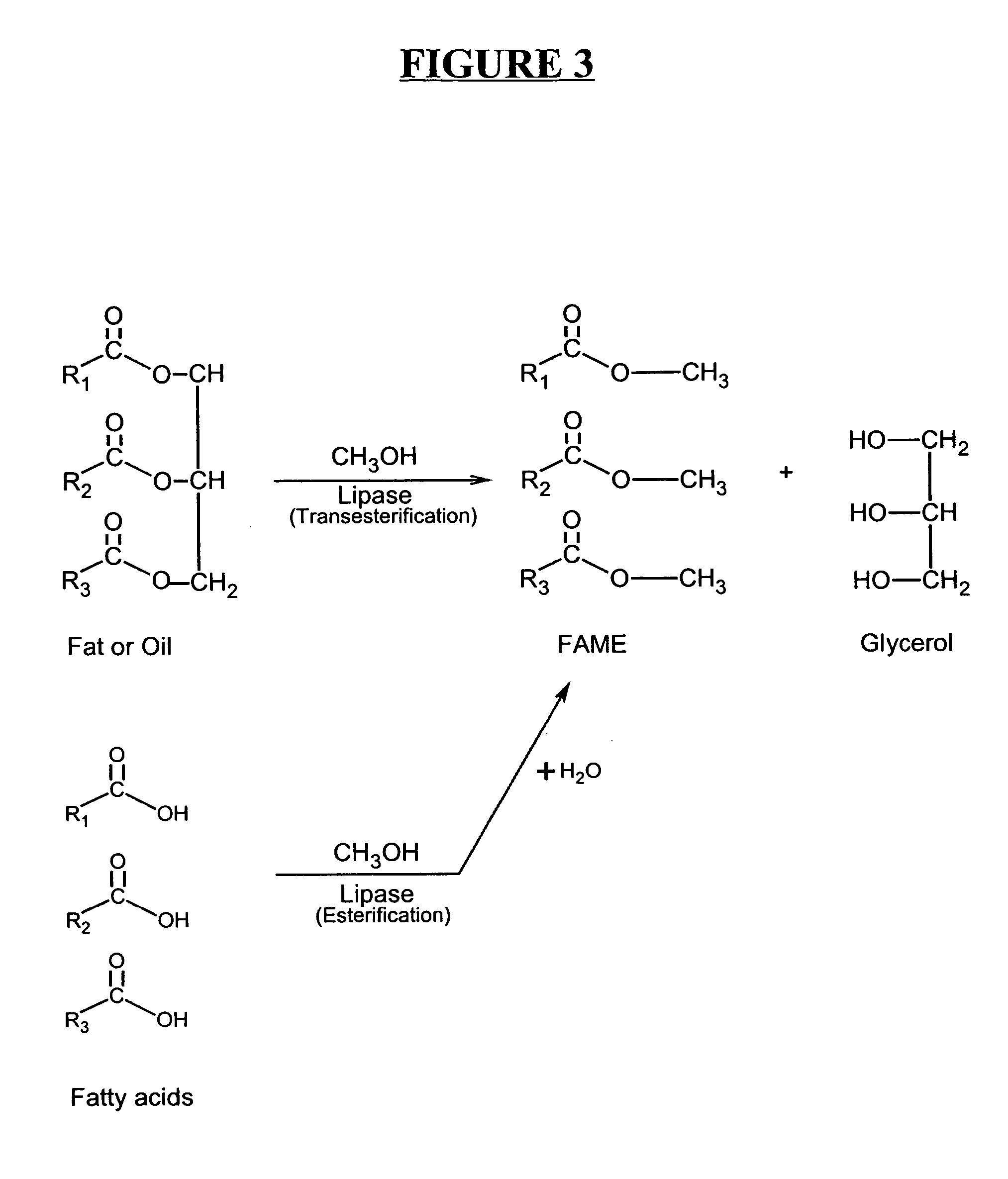
Production of biodiesel and other valuable chemicals from wastewater treatment plant sludges
ActiveUS20050112735A1Reduce the environmentPromote digestionBio-organic fraction processingByproduct vaporizationLipid formationSludge
A process for producing biodiesel has been invented by first extracting lipids from the sludges generated during primary and / or biological treatment of municipal, agricultural, and industrial wastewaters using primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments followed by the transesterification of the extracted lipids using transesterification conversion into alcohol-based esters. The resulting products from this process include biodiesel, glycerol, lipid-free proteins, various other useful chemicals and an aqueous-based substrate well suited for optimized digestion within subsequent biological digestion (either aerobic or anaerobic). The lipids extracted from the sludges containing high levels of microorganisms are phospholipids which can also be directly used as lecithin. The extraction of the lipids from the sludges will be performed using chemical extraction techniques with the transesterification of the extracted lipids accomplished using basic, acidic, and / or a combination of the two transesterification techniques.
Owner:MISSISSPPI STATE UNIV RES & TECH
Surface features in microprocess technology
ActiveUS20070017633A1Enhance unit operationEasy to useFlow mixersCircuit elementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
Additive dispensing fluid filter
InactiveUS20050194312A1Semi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A filter for filtering a liquid, such as coolant for an internal combustion engine, having a filter housing with at least one liquid inlet and at least one liquid outlet, a filter element which is arranged in a sealing manner between the inlet and outlet so that the filter element separates a filtered liquid side from an unfiltered liquid side, and having an additive or inhibitor disposed in the housing such that when contacted by liquid passing through the filter, the additive is released into the liquid, in which the additive is tightly encased in a liquid-soluble material which dissolves on coming in contact with the liquid being filtered.
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Multi-phase selective mass transfer through a membrane
Disclosed herein are embodiments relating to particular systems comprising a selective transfer membrane that can be utilized in material separation. In certain embodiments, the membrane assembly comprises part of a desalination, distillation, liquid purification, and / or heating and cooling system. Other particular embodiments allow for a high rate of thermal capture by way of the system utilizing a selective transfer membrane. Certain preferred embodiments include a selective transfer membrane comprising an ionomeric polymer that is permeable to high dipole materials.
Owner:TANGREDI PATRICIA
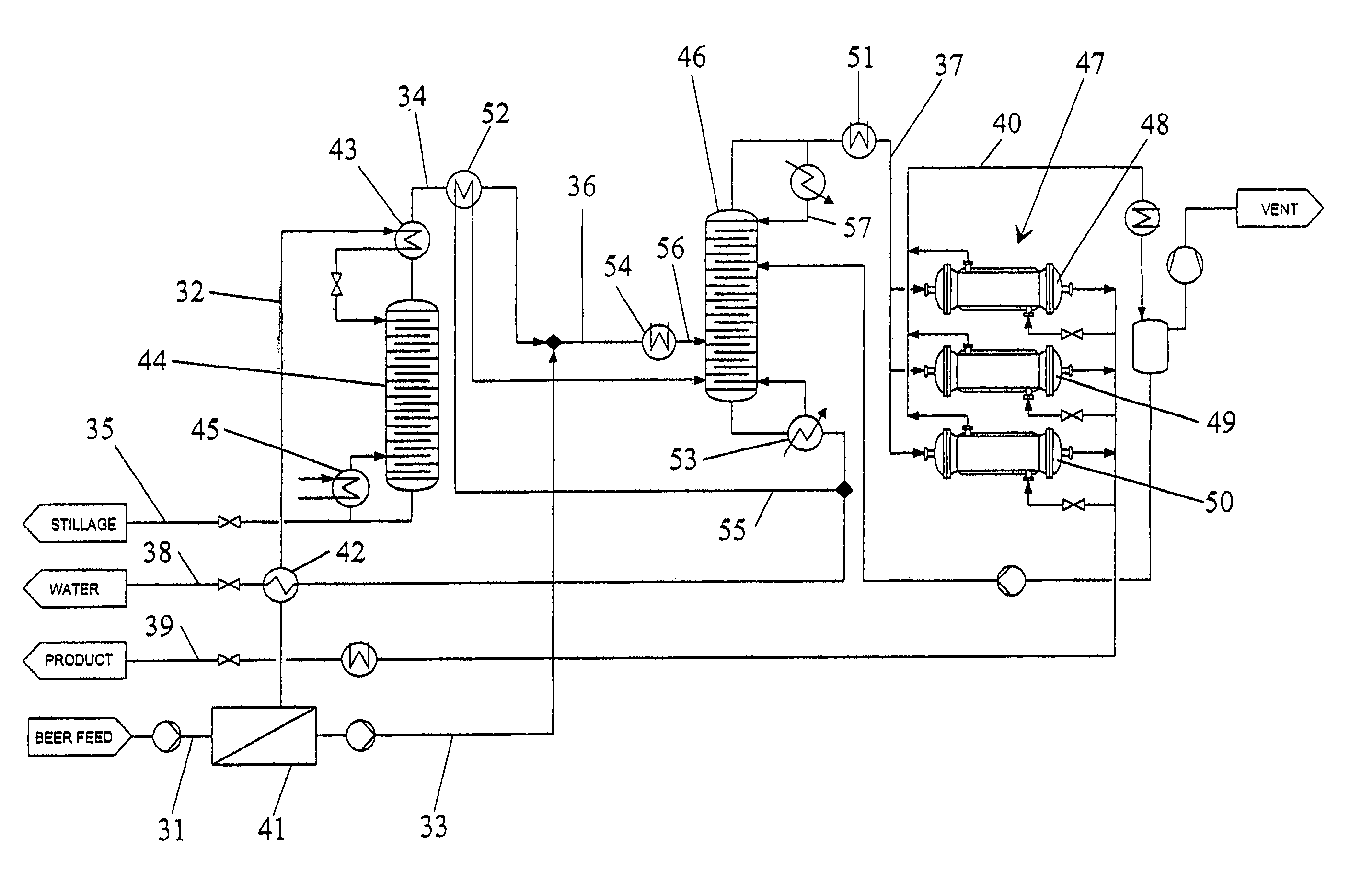
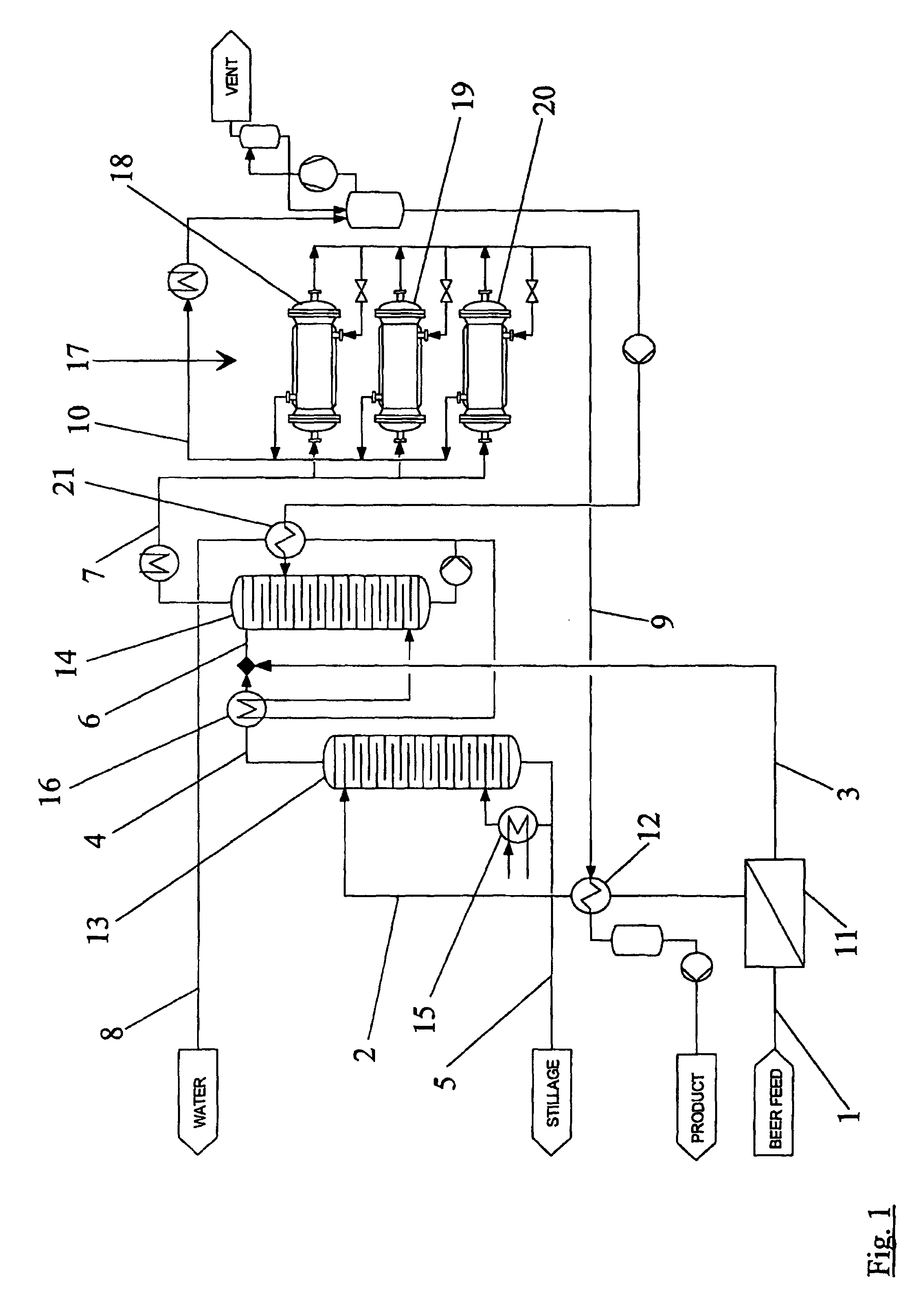
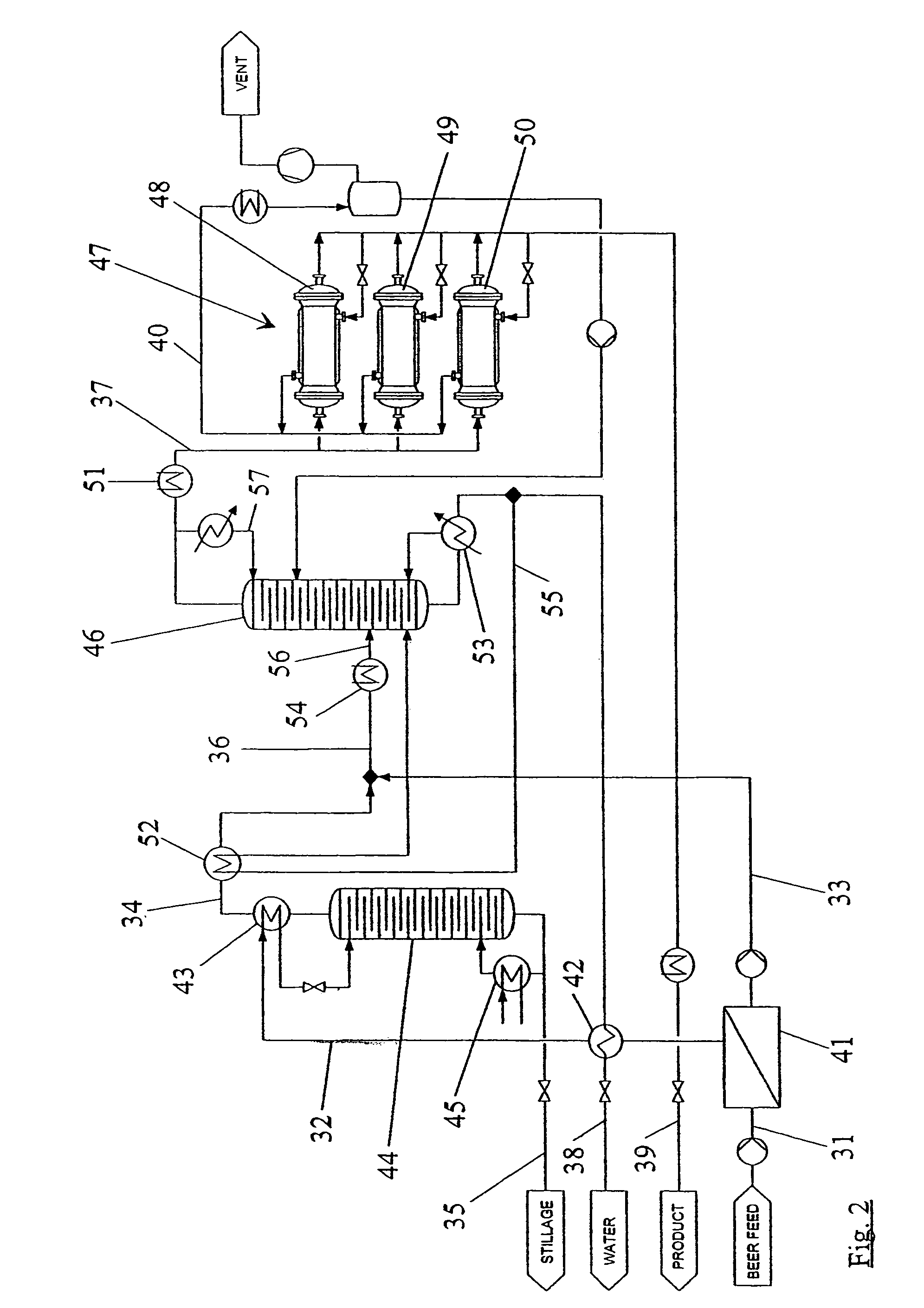
Distillation method
A method for distilling ethanol from a mash includes feeding a fluid to a first distillation column. The fluid and a distillate of the first distillation column are delivered to a second distillation column. The fed fluid and / or distillate of the second distillation column is / are purified in a first and / or last step of the method by a membrane separation process.
Owner:WHITE FOX TECH LTD
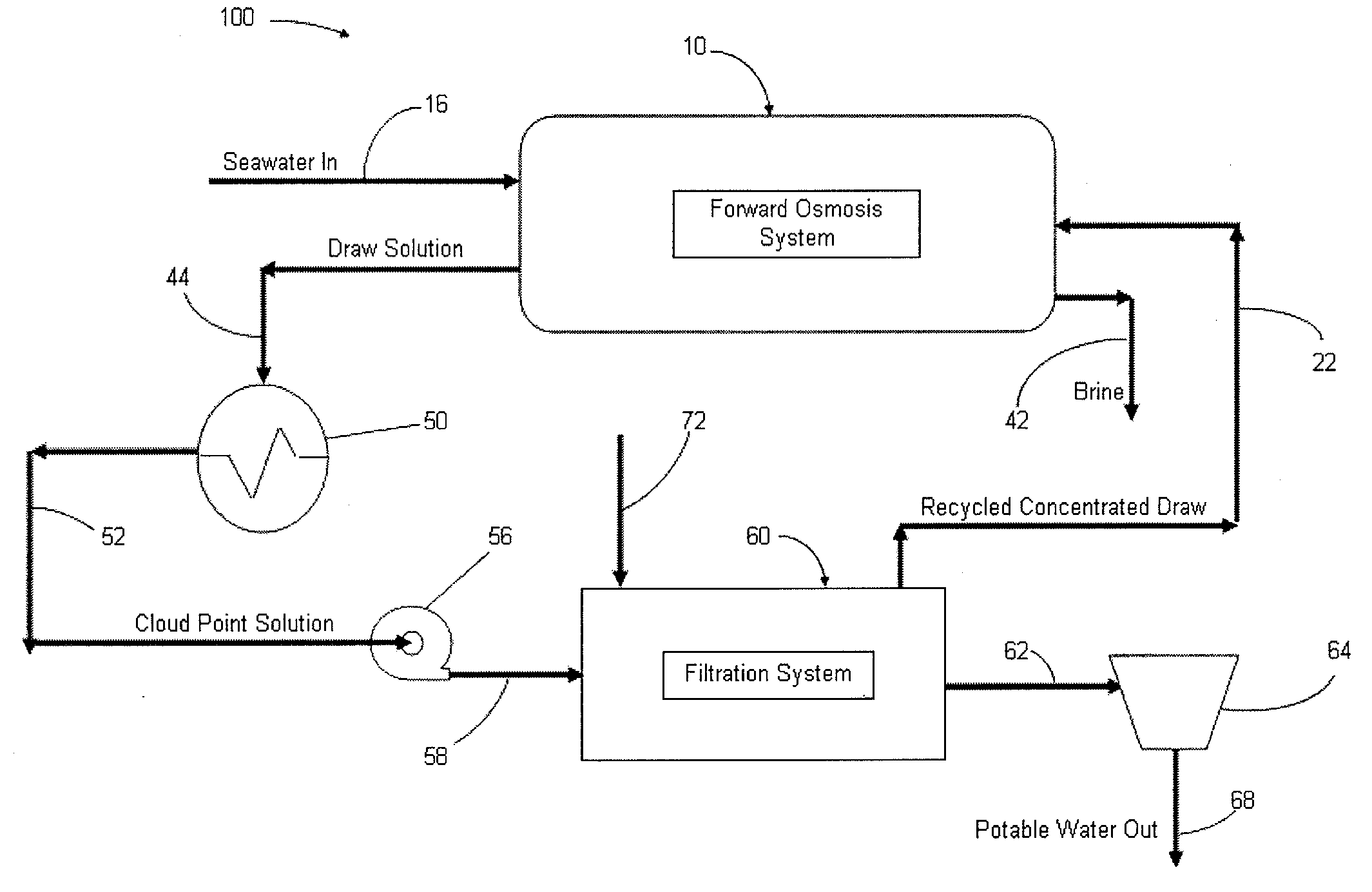
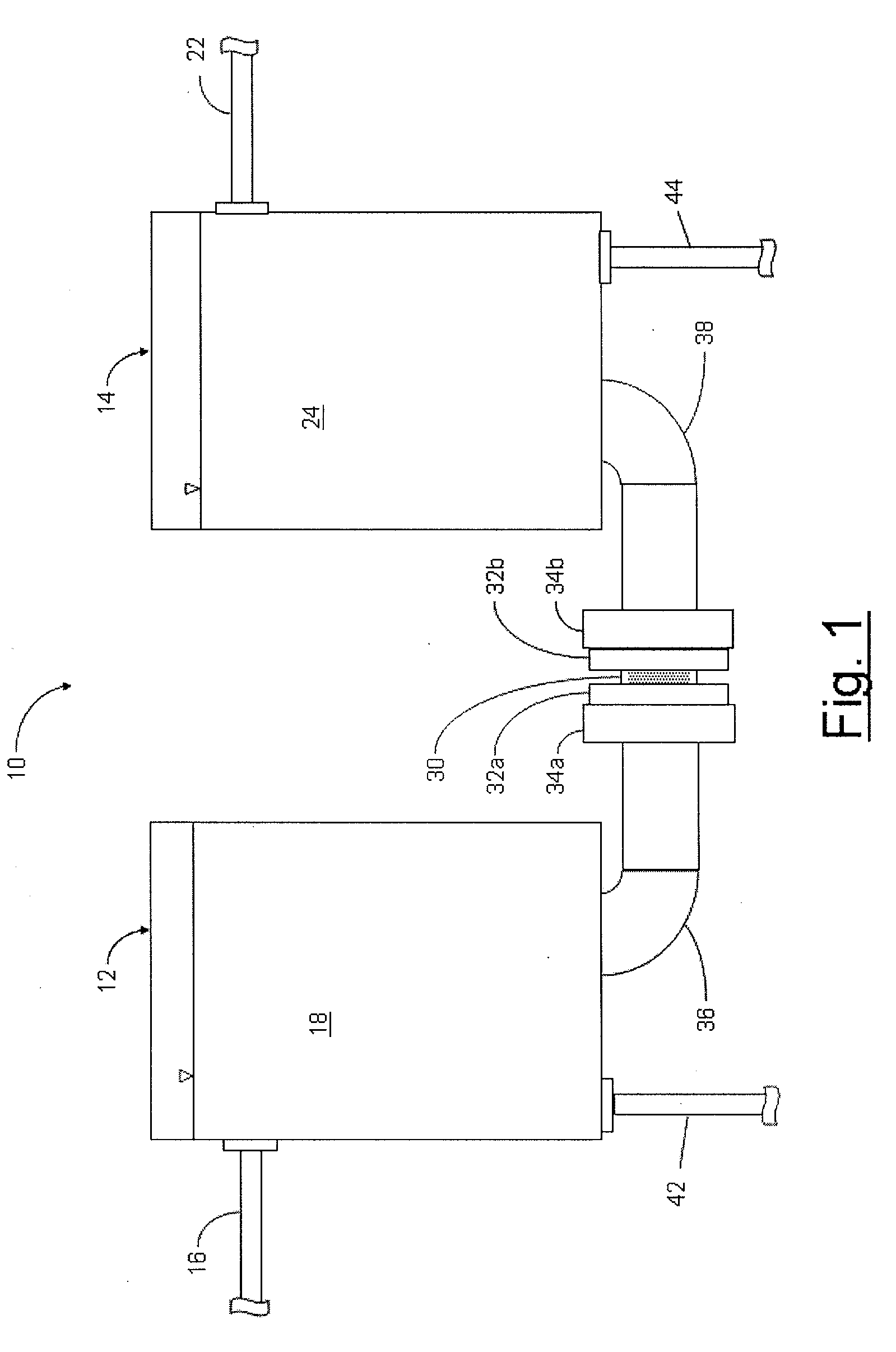
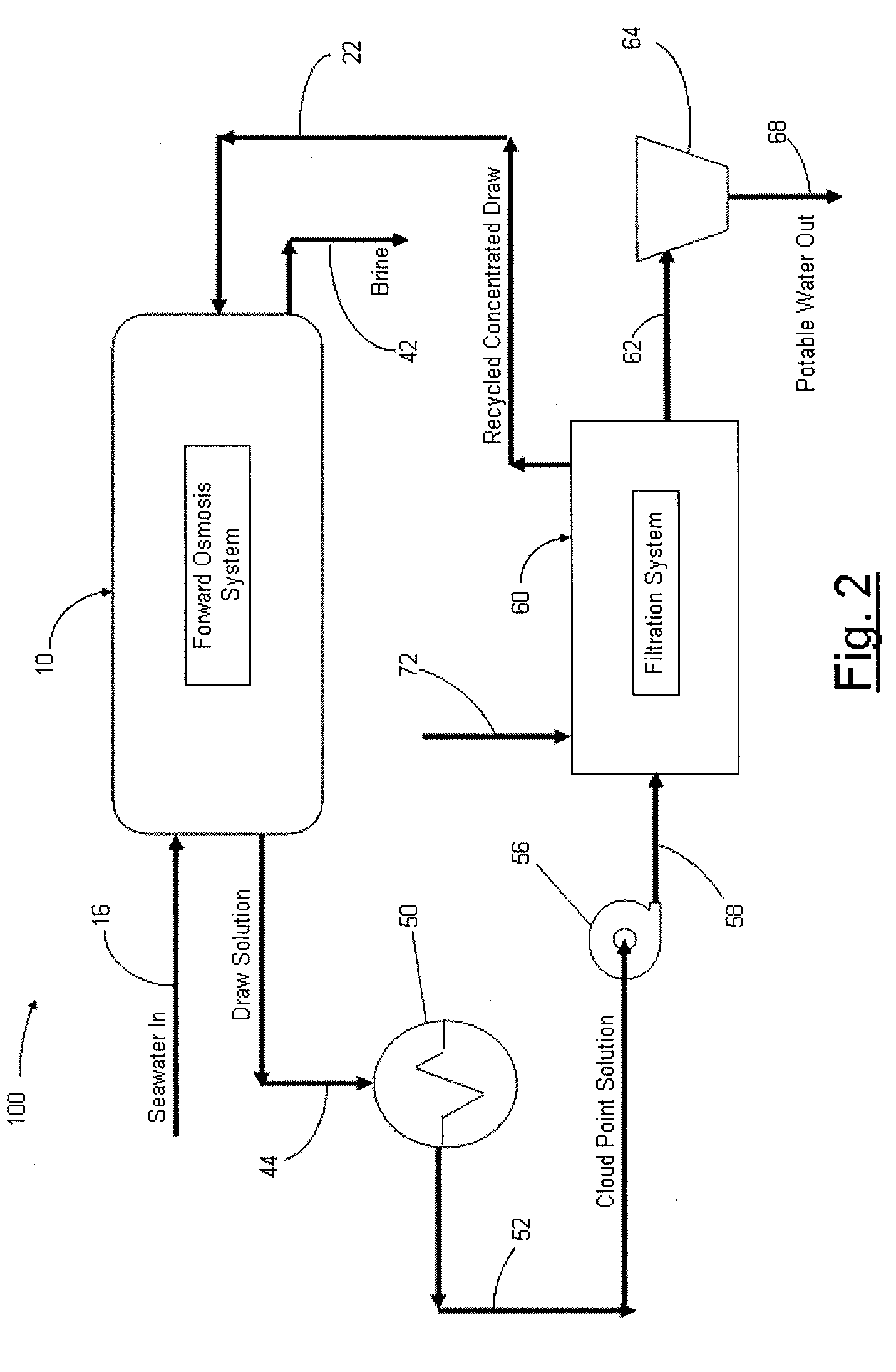
Systems and methods for forward osmosis fluid purification
ActiveUS20100155329A1Improve efficiencyFunction increaseGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentSaline waterDesalination
A process for purification of fluids, for example, desalination of seawater or brackish water, using organic solutes in a concentrated water solution for use in a forward osmosis process, to extract fresh water out of salt water through the forward osmosis membrane, and subsequently separating the organic solutes out of the diluted forward osmosis permeate by cloud point extraction, thereby regenerating a concentrated organic solution for recycling to the forward osmosis process, and fresh water for potable water use.
Owner:JFEENG CORP
Onboard fuel separation apparatus for an automobile
InactiveUS6972093B2Increase volumeBoost octaneInternal combustion piston enginesUsing liquid separation agentVolatilesEngineering
An onboard fuel separation apparatus separates a material fuel (gasoline) into a high-octane fuel having a higher octane value than the material fuel and a low-octane fuel having a lower octane value than the material fuel using a separation membrane which selectively allows high-octane value components (such as aromatic components) permeate through the membrane. The apparatus increases the ratio of the amount of the high-octane value components permeating through the membrane to the amount of the high-octane value components contained in the material fuel by, (A) Controlling the temperature of the material fuel supplied to the membrane (B) Increasing partial pressure of the low-octane value components on the high-octane fuel side of the membrane and removing volatiles from the permeate, and (C) Bypassing volatiles in the material feed around the membrane.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO +1
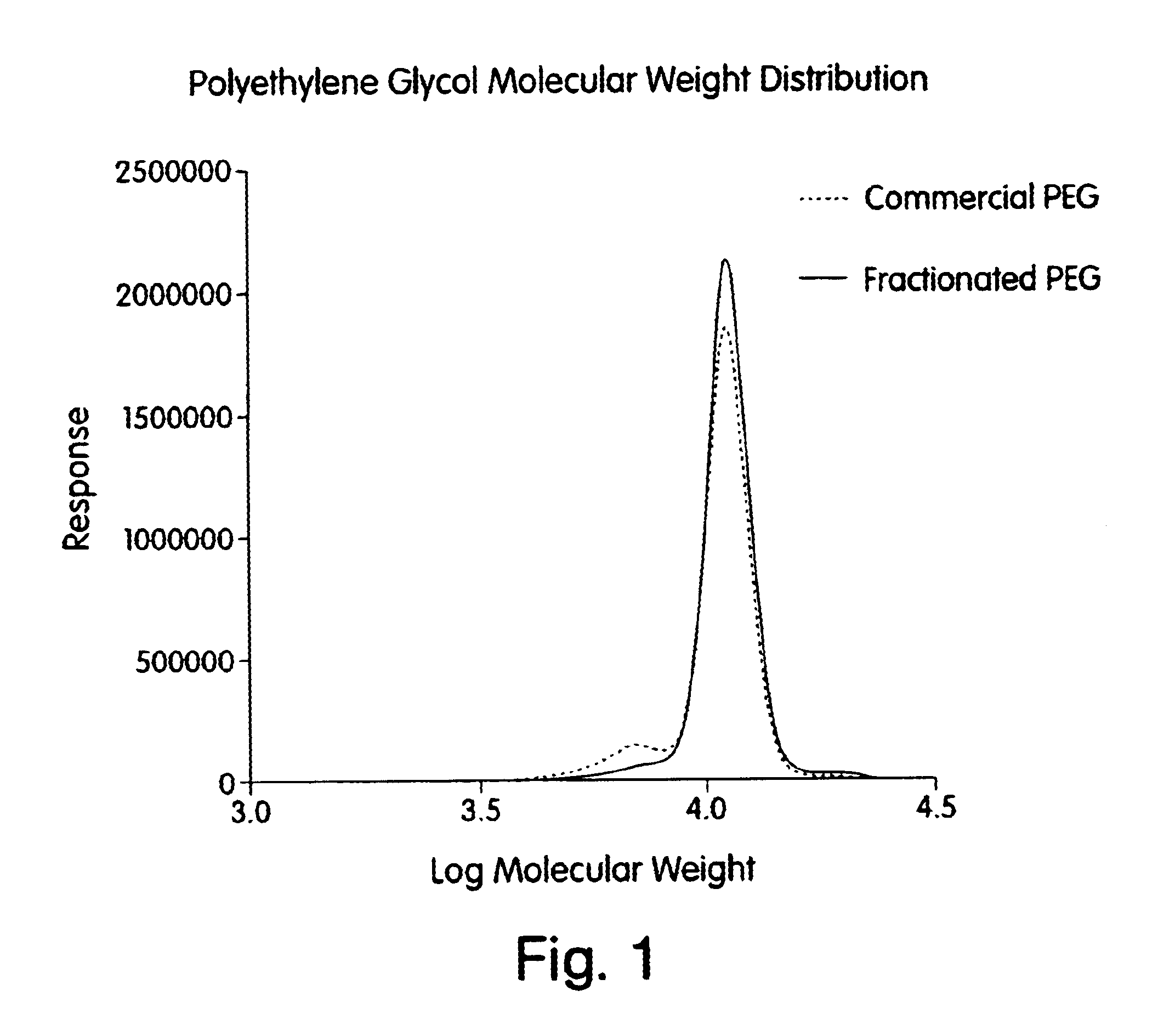
Process for the fractionation of polymers
A process for the purification or fractionation of aqueous soluble polymers using an aqueous two-phase system is described. The concentrations of the polymer to be fractionated and of an aqueous soluble salt, and the temperature of the aqueous fractionation medium are adjusted so that two phases form, the lower molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the high salt concentration phase, and the higher molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the low salt concentration phase. The resulting high molecular weight polymers are characterized by a higher average molecular weight and a narrower molecular weight distribution and decreased unsaturation than the unfractionated polymers. After being subjected to the fractionation process, polyol polymers that form hydrogels in aqueous solution exhibited higher viscosities and a liquid to gel transition over a narrower temperature range than the unfractionated polyol polymers.
Owner:HINSBERG MICHAEL G +1
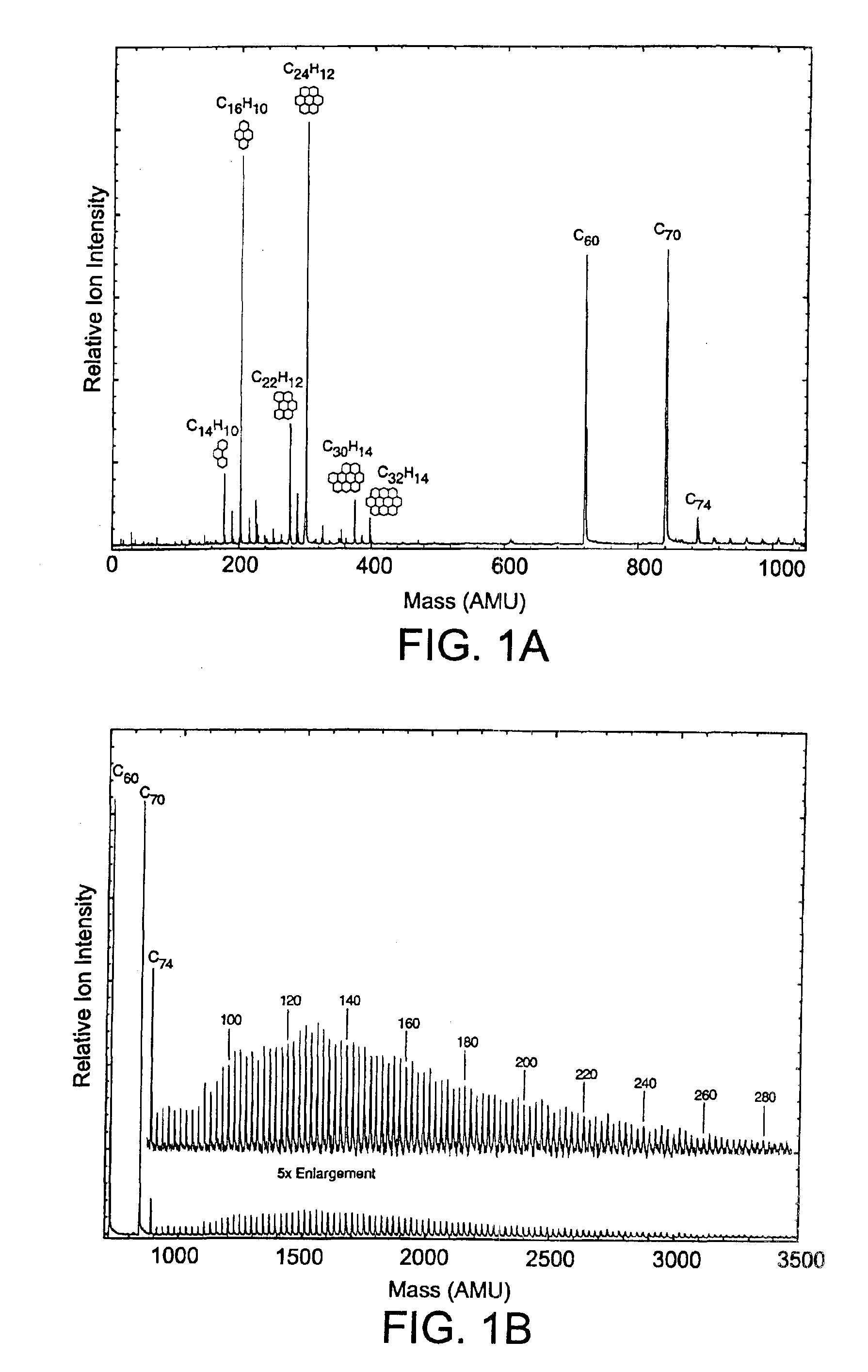
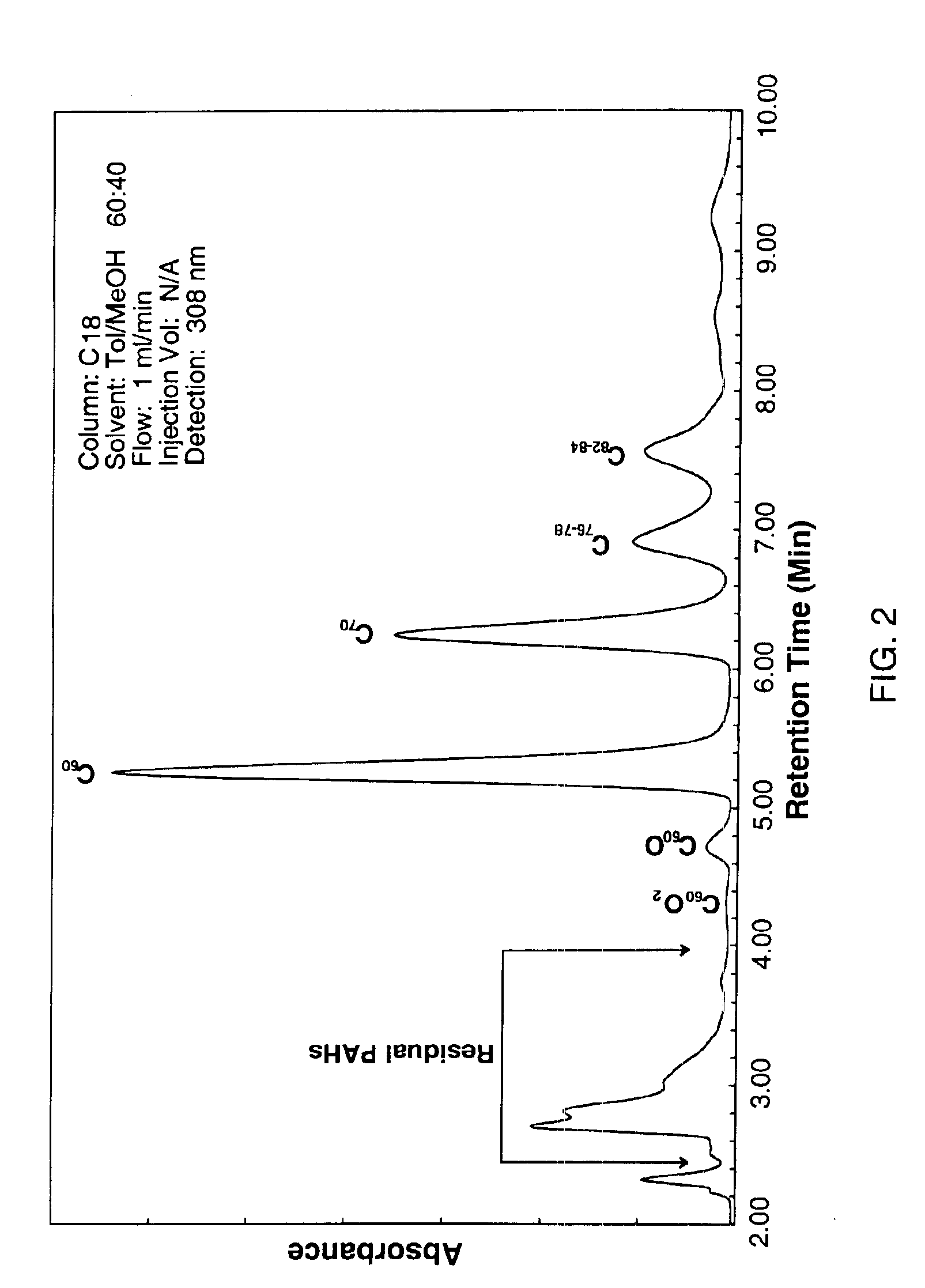
Process for the removal of impurities from combustion fullerenes
InactiveUS6923915B2Without incurring undo costEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesO-XylenePurification methods
The invention generally relates to purification of carbon nanomaterials, particularly fullerenes, by removal of PAHs and other hydrocarbon impurities. The inventive process involves extracting a sample containing carbon nanomaterials with a solvent in which the PAHs are substantially soluble but in which the carbon nanomaterials are not substantially soluble. The sample can be repeatedly or continuously extracted with one or more solvents to remove a greater amount of impurities. Preferred solvents include ethanol, diethyl ether, and acetone. The invention also provides a process for efficiently separating solvent extractable fullerenes from samples containing fullerenes and PAHs wherein the sample is extracted with a solvent in which both fullerenes and PAHs are substantially soluble and the sample extract then undergoes selective extraction to remove PAHs. Suitable solvents in which both fullerenes and PAHs are soluble include o-xylene, toluene, and o-dichlorobenzene. The purification process is capable of treating quantities of combustion soot in excess of one kilogram and can produce fullerenes or fullerenic soot of suitable purity for many applications.
Owner:FRONTIER CARBON CORP
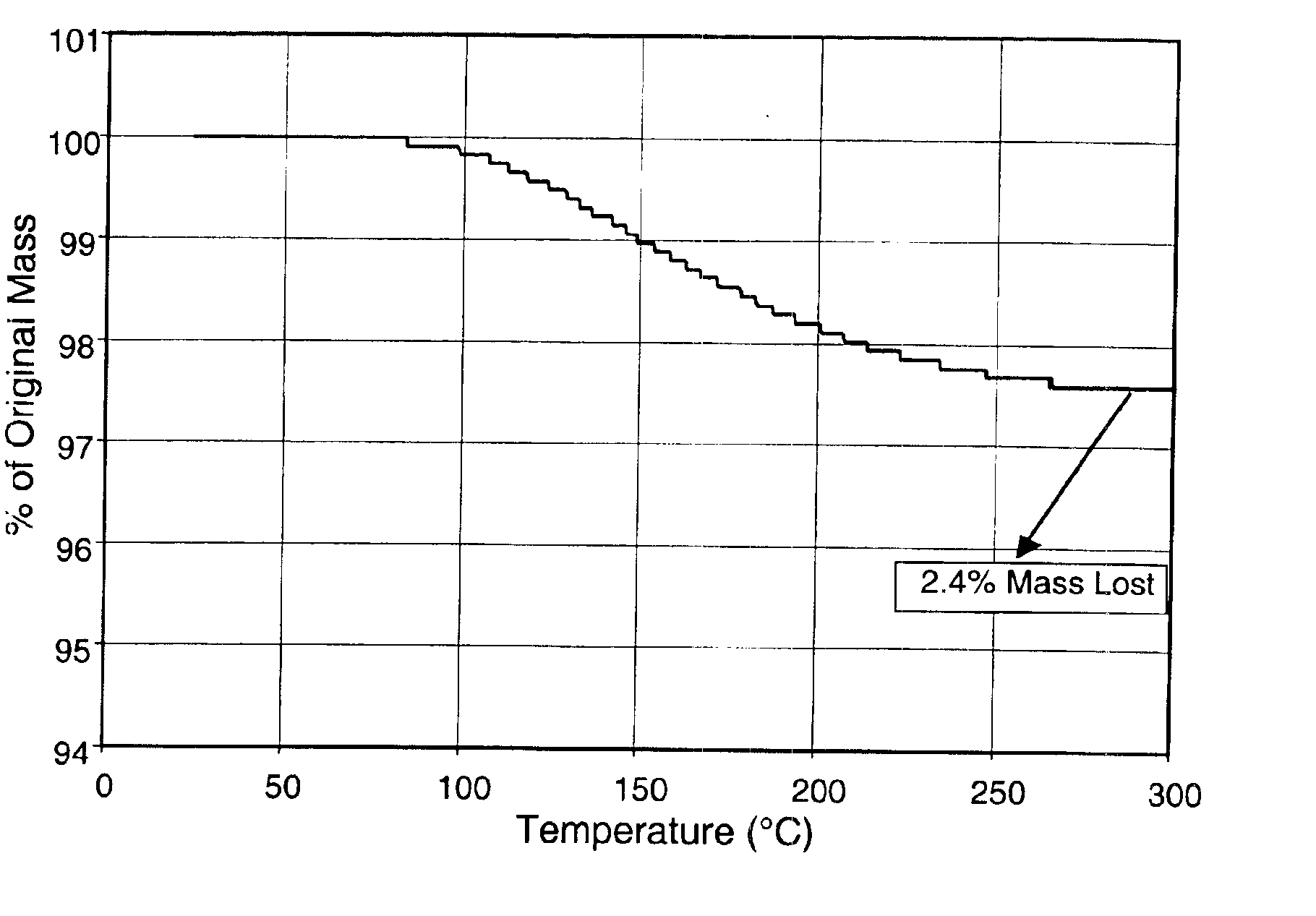
Dearomatized asphalt
InactiveUS20080006561A1Improving neat asphalt propertyHigh-temperature stiffnessWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolid sorbent liquid separationSolventAsphalt
This invention relates to a dearomatized asphalt. More particularly, an asphalt is extracted with a aromatic extraction solvent to produce an asphalt-rich phase and a solvent rich phase. The asphalt rich phase is stripped of solvent to produce dearomatized asphalt that has superior properties for paving and roofing applications.
Owner:MORAN LYLE E +1
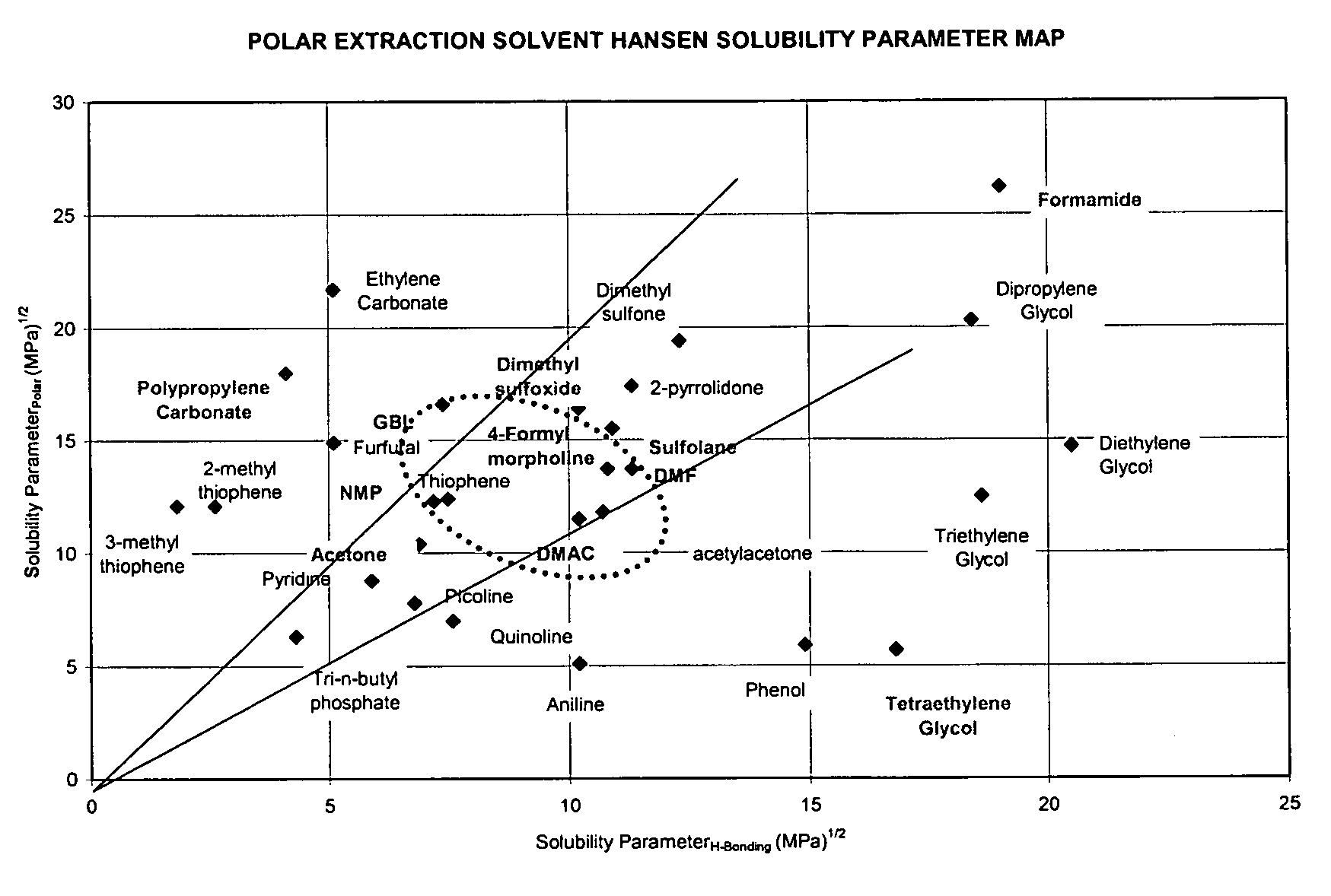
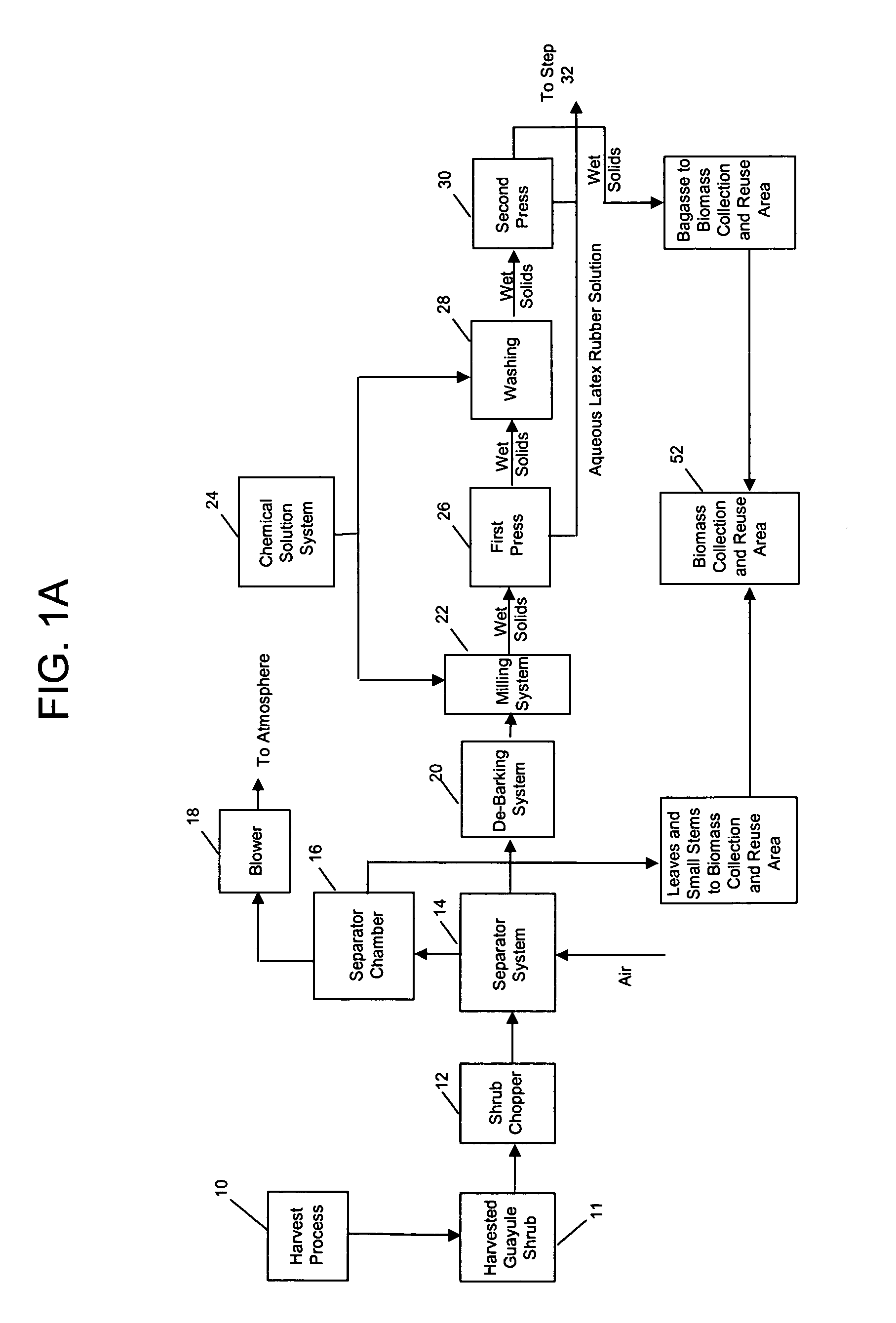
Biopolymer extraction from plant materials
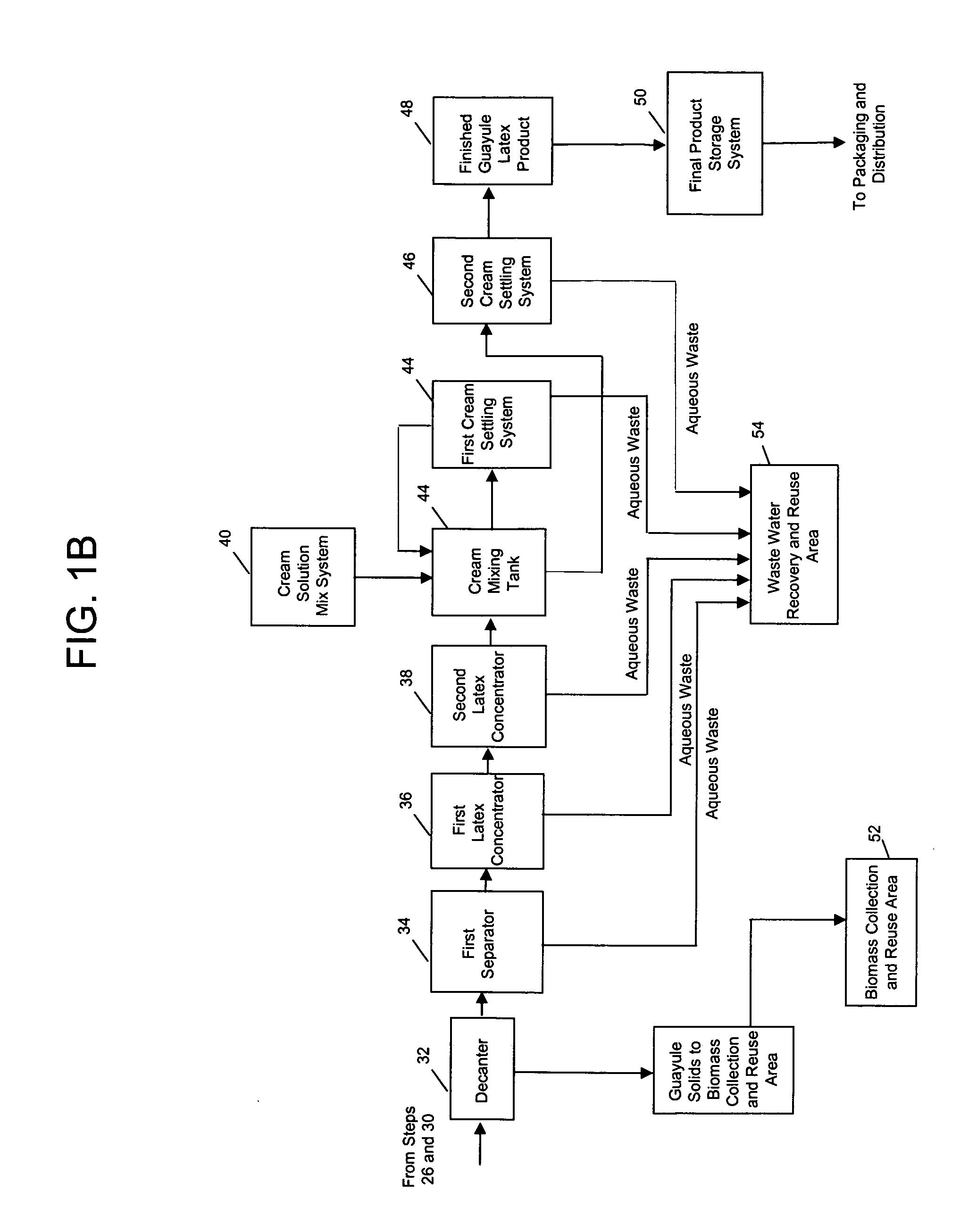
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for the extraction of high molecular weight biopolymers from plants. Specifically, invention described herein relates to the commercial processing of plant material, including that from desert plants native to the southwestern United States and Mexico, such as the guayule plant (Parthenium argentatum), for the extraction of biopolymers, including natural rubbers. More specifically, the invention relates to laboratory to commercial scale extraction of high molecular weight biopolymers from plant materials including the chemical and mechanical processing of the plants and purification of the extracted biopolymer.
Owner:YULEX LLC
Extraction with fractionation of oil and proteinaceous material from oleaginous material
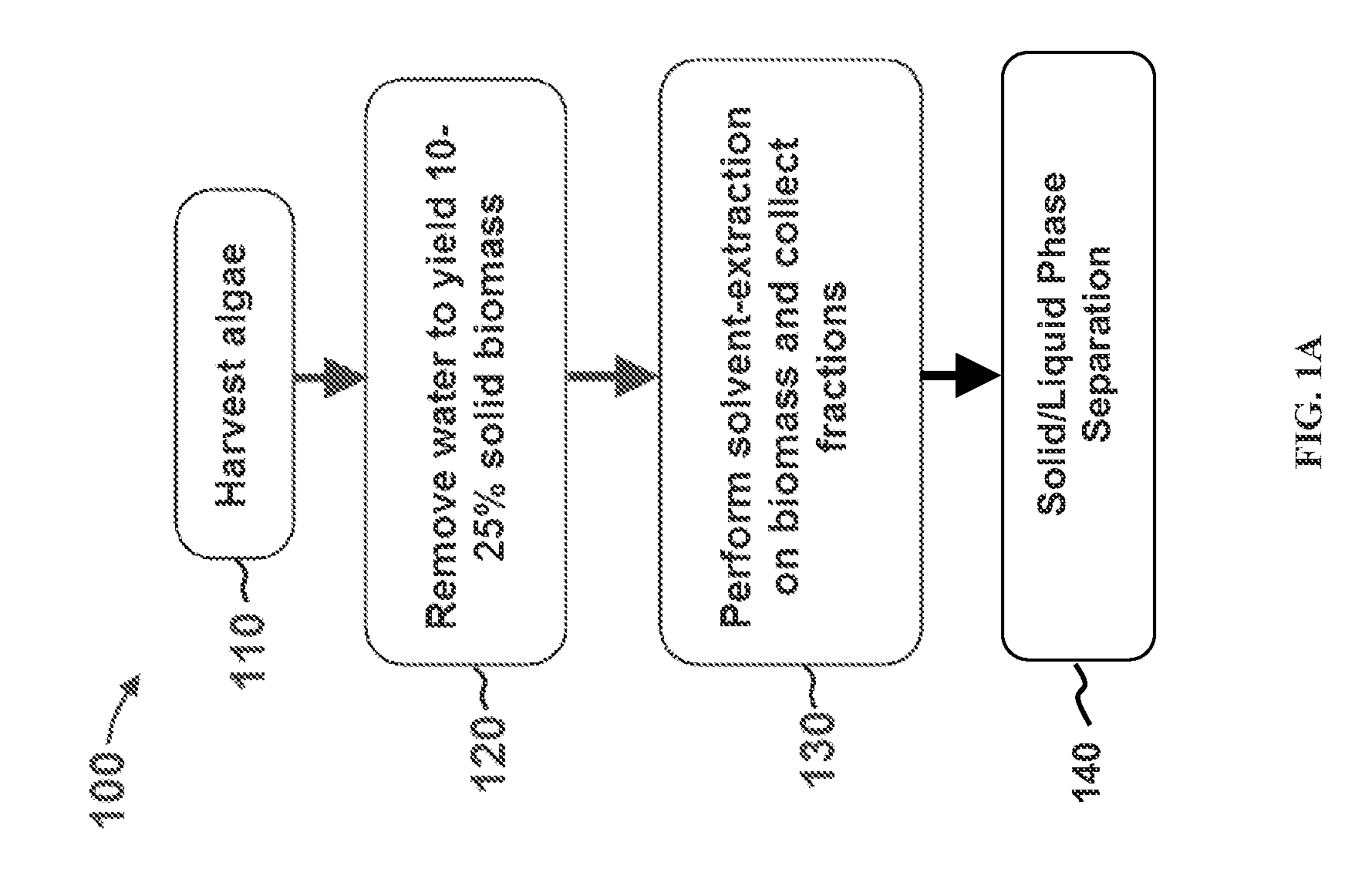
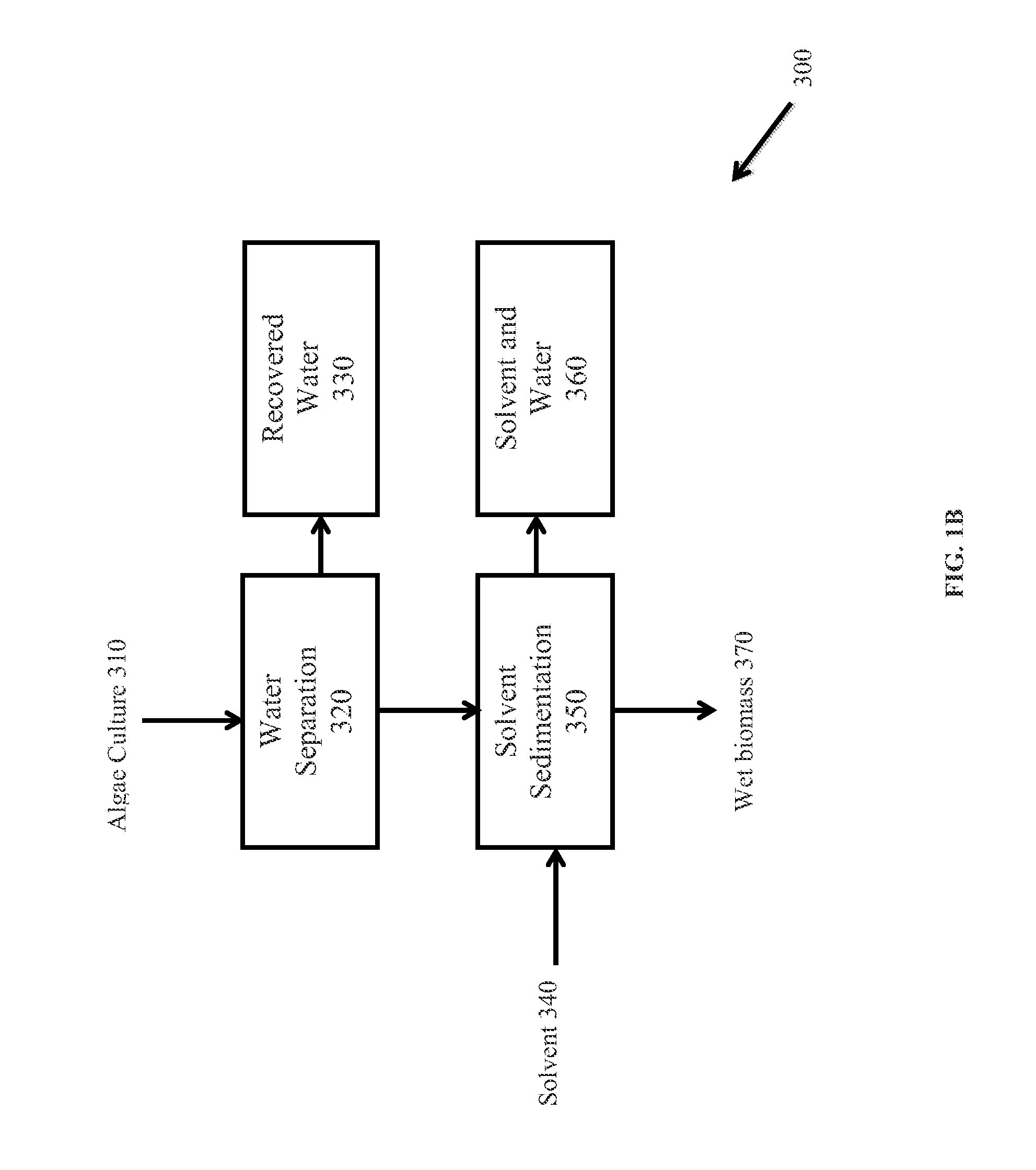
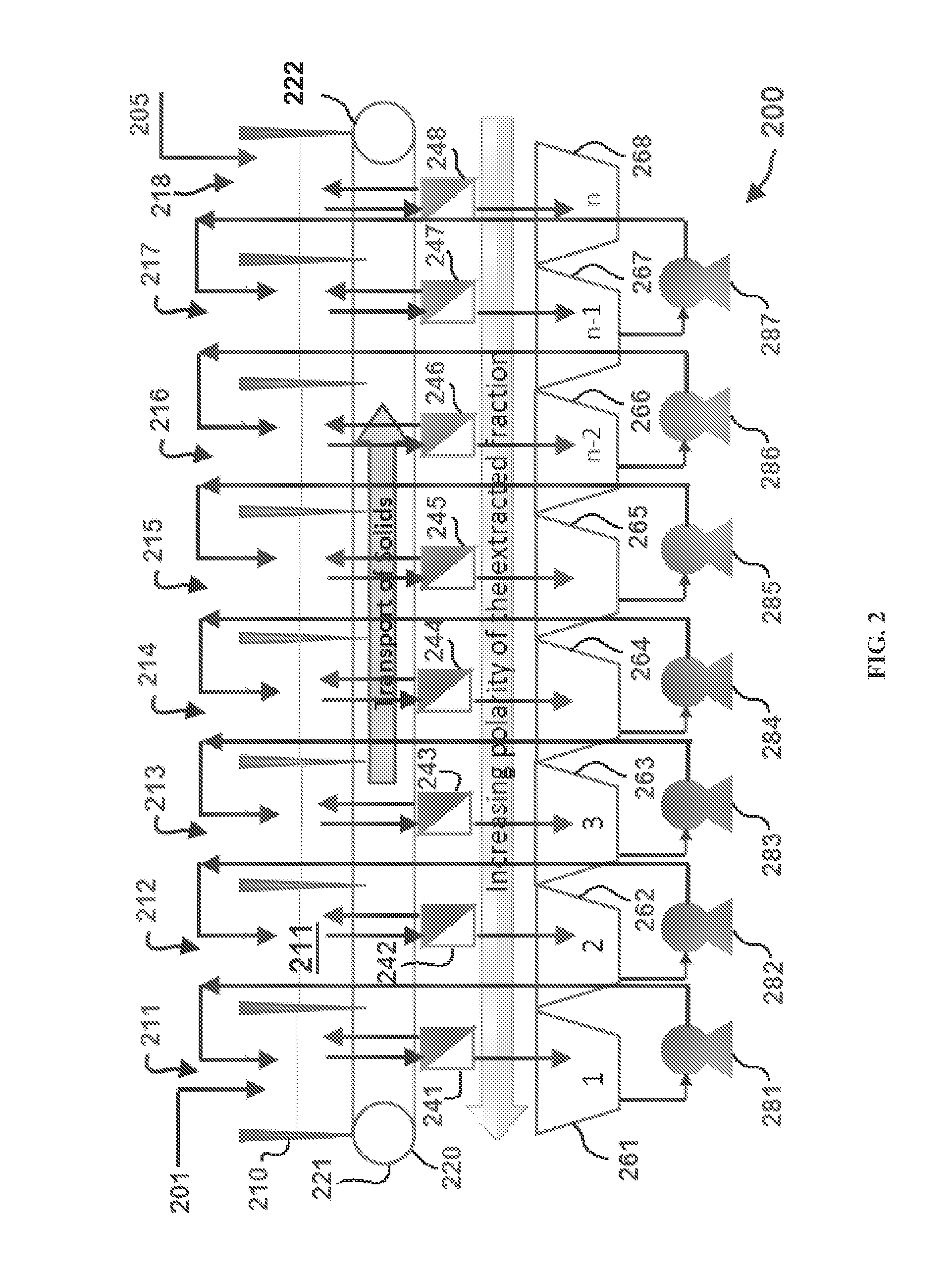
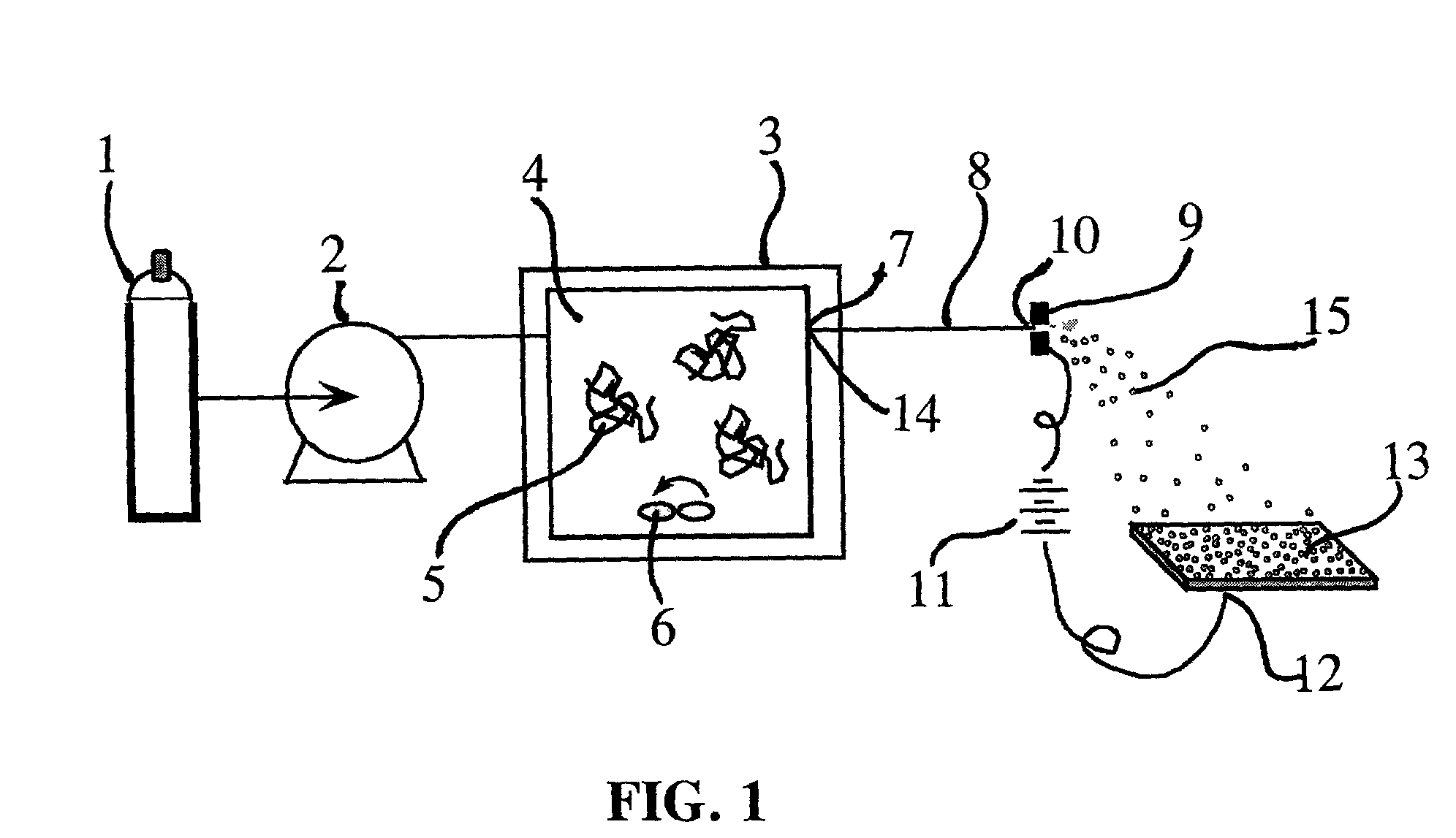
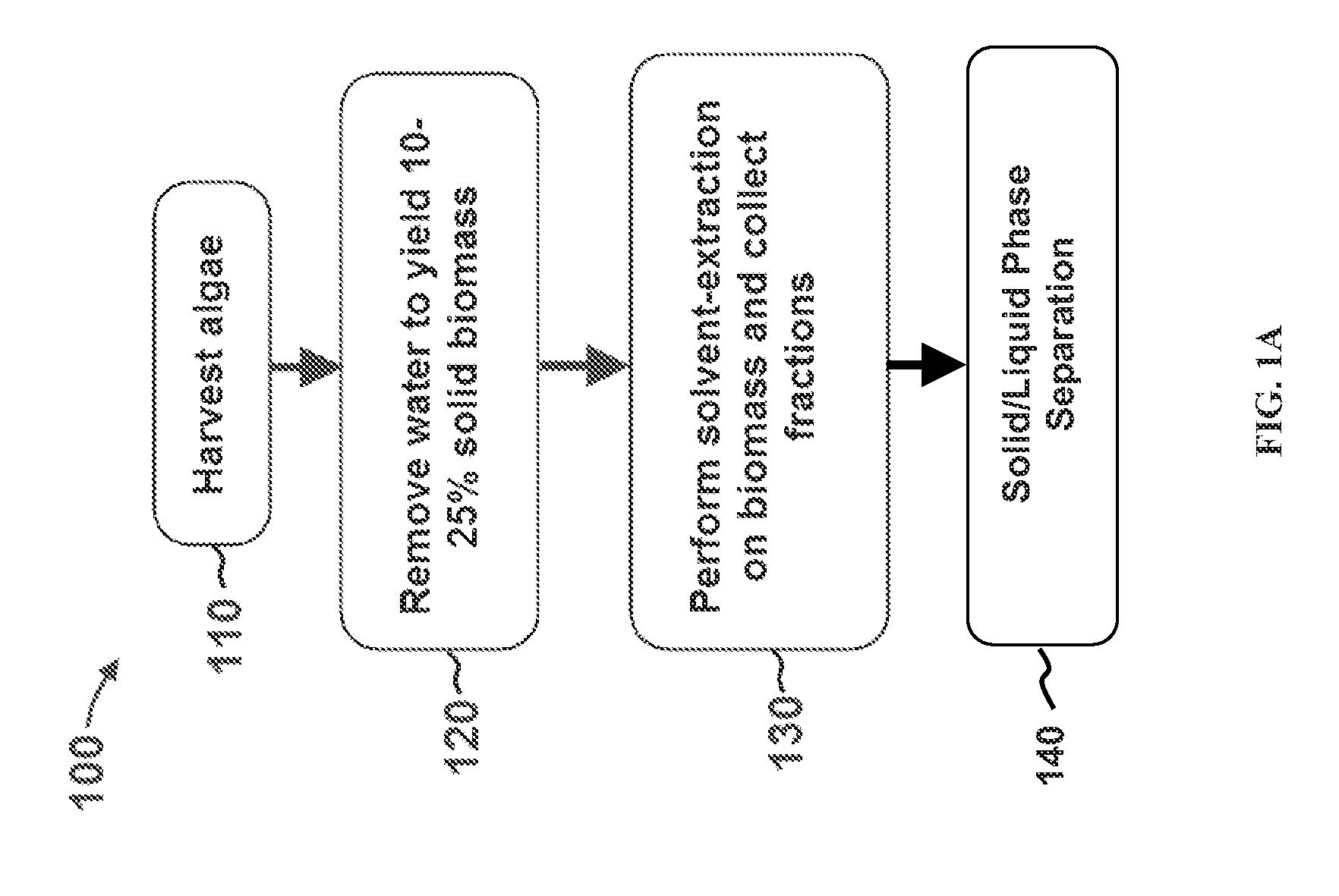
Methods for selective extraction and fractionation of algal lipids and algal products are disclosed. A method of selective removal of products from an algal biomass provides for single and multistep extraction processes which enable efficient separation of algal components. Among these components are neutral lipids synthesized by algae, which are extracted by the methods disclosed herein for the production of renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Systems and methods of blood-based therapies having a microfluidic membraneless exchange device
InactiveUS20060076295A1Reduces undesirable activationMinimizing bioincompatibilitiesComponent separationMedical devicesDiffusionThin layer
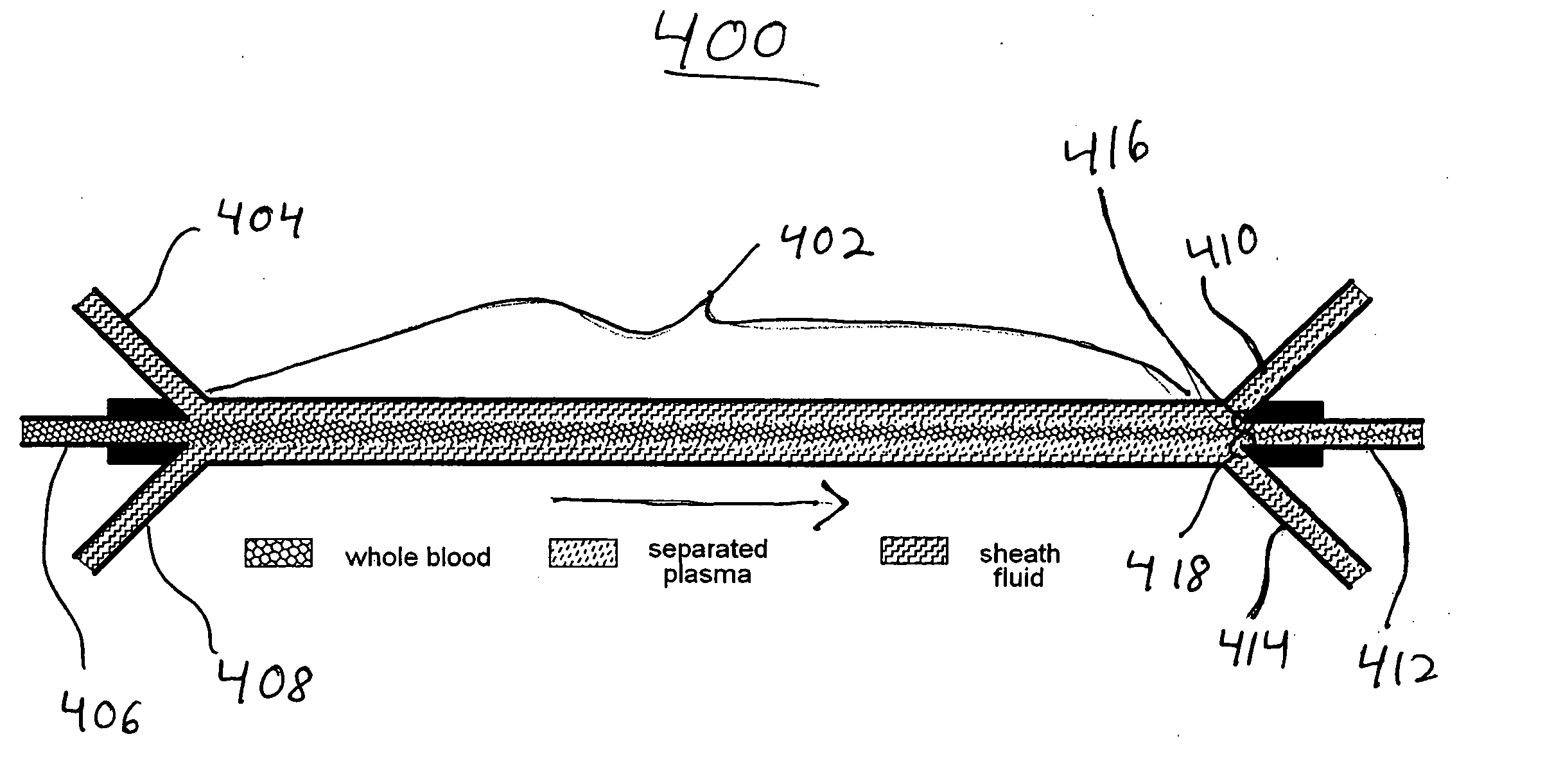
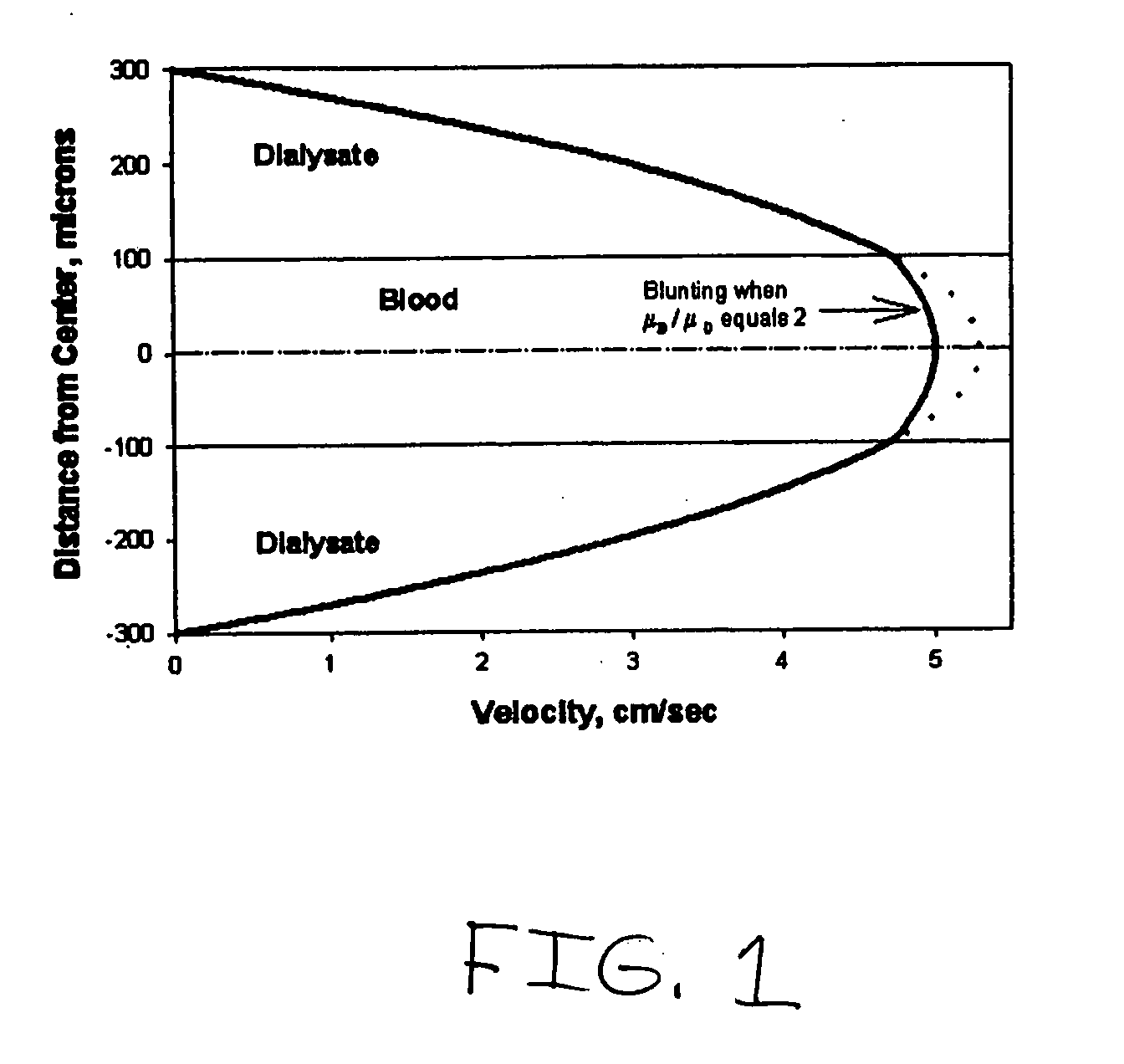
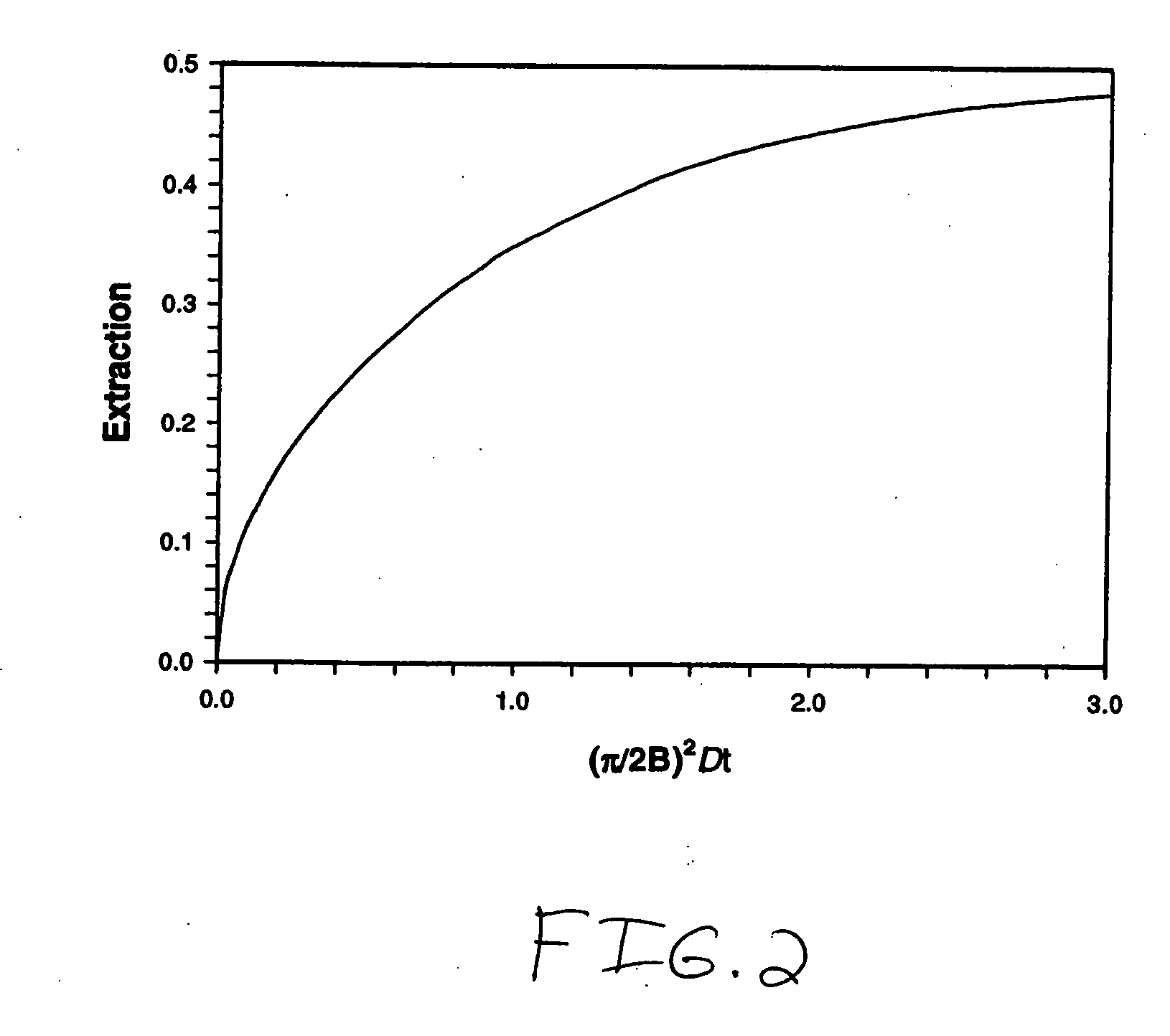
The present invention is directed to devices, systems and methods for removing undesirable materials from a sample fluid by contact with a second fluid. The sample fluid flows as a thin layer adjacent to, or between, concurrently flowing layers of the second fluid, without an intervening membrane. In various embodiments, a secondary separator is used to restrict the removal of desirable substances and effect the removal of undesirable substances from blood. The invention is useful in a variety of situations where a sample fluid is to be purified via a diffusion mechanism against an extractor fluid. Moreover, the invention may be used for the removal of components from a sample fluid that vary in size. When blood is the sample fluid, for example, this may include the removal of ‘small’ molecules, ‘middle’ molecules, macromolecules, macromolecular aggregates, and cells, from the blood sample to the extractor fluid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
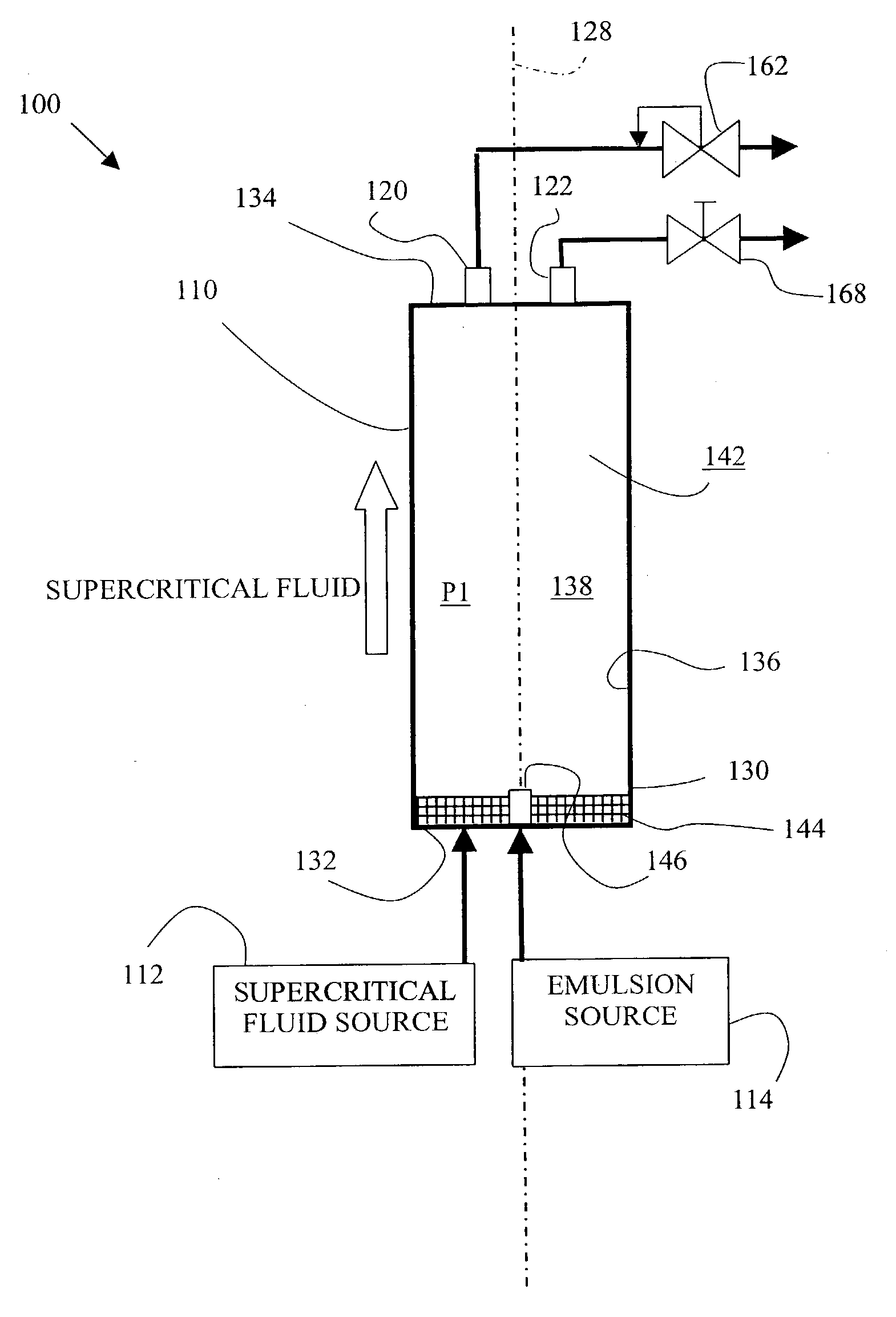
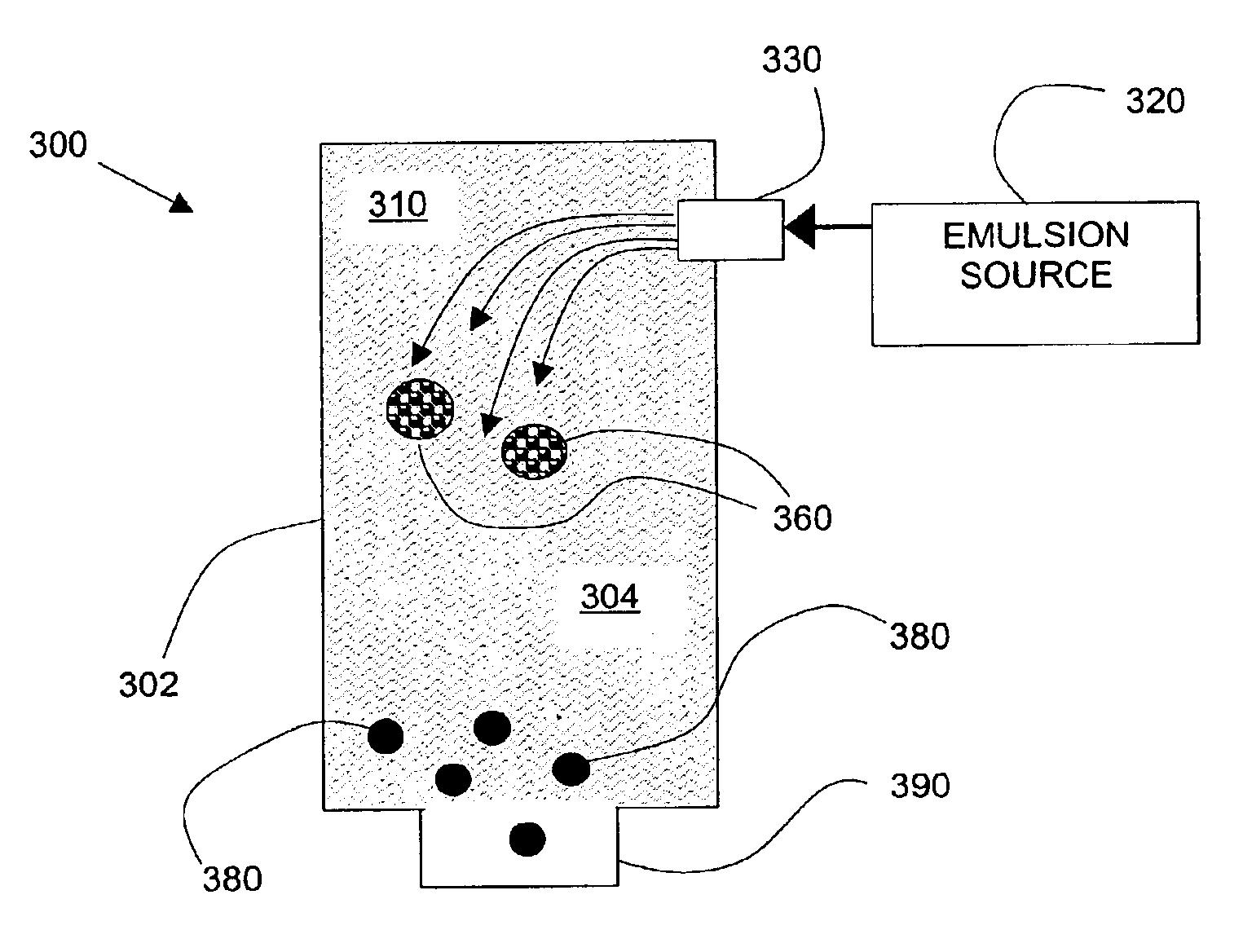
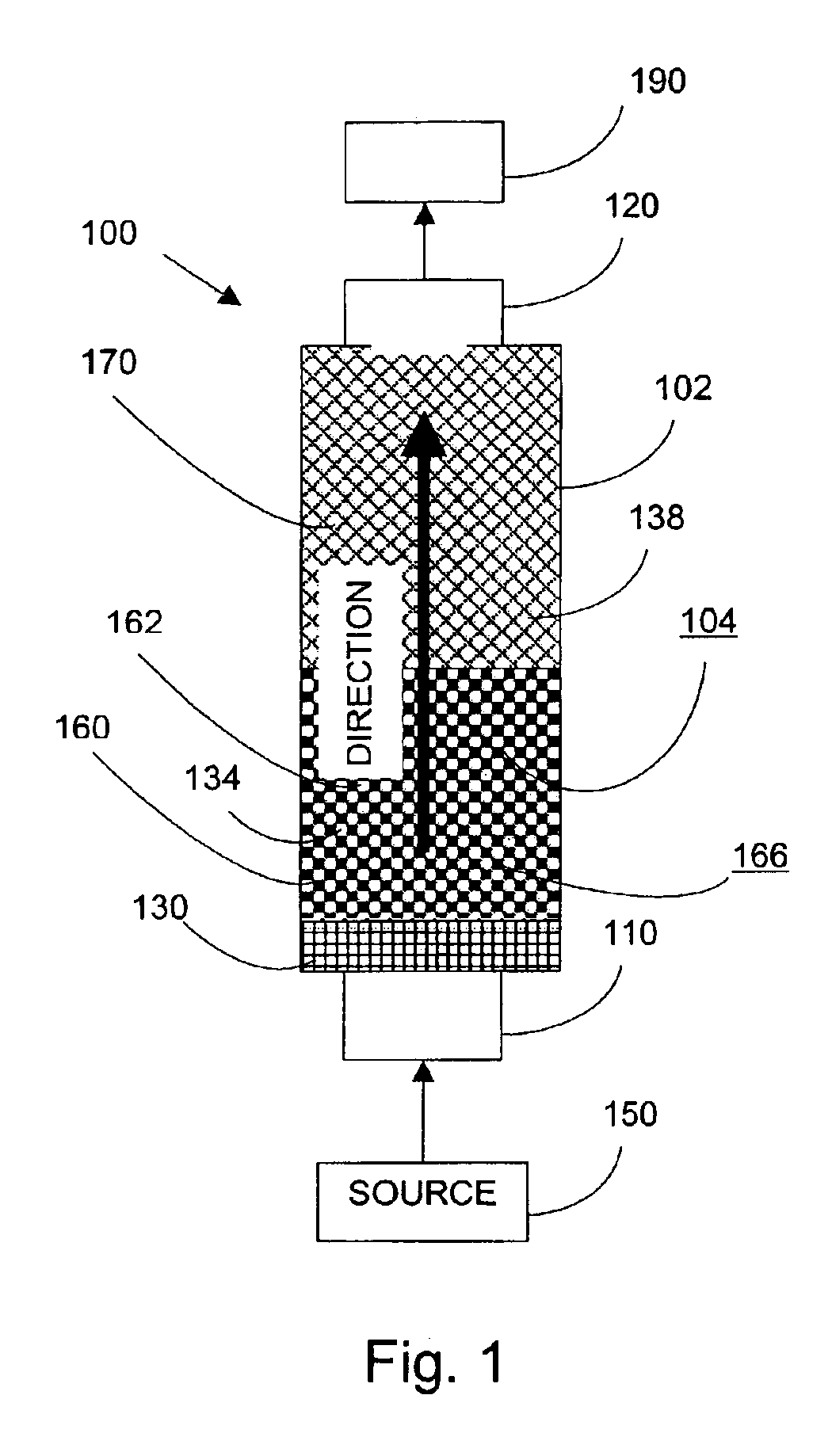
Particles from supercritical fluid extraction of emulsion
A method of producing microparticles and nanoparticles of a solute via the extraction of solvent, having the solute dissolved therein, from an emulsion using a supercritical fluid. The solute to be precipitated is dissolved in the solvent to form a solution, and the solution is dispersed in an immiscible or partially miscible liquid to form an emulsion. The particles are produced via the extraction of the solvent from the emulsion using the supercritical fluid. The process can produce an aqueous suspension of particles that are substantially insoluble in water, and the solvents used in the process to form the emulsion initially can be recovered and recycled.
Owner:FERRO CORP
Systems and methods for determining a state of fluidization and/or a state of mixing
InactiveUS20050150830A1Preserve biological activityPreserving viabilityShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringFluidization
Owner:COVARIS INC
Pathogen inactivating compositions for disinfecting biological fluids
InactiveUS6106773AAvoid bulk processingAvoid capital intensive equipmentBiocideSolvent extractionBlood componentAqueous solution
The present invention is directed to pathogen inactivating compositions that can be used to disinfect various biological fluids, such as blood, blood fractions, and the like. The compositions are suitable for disinfecting biological fluids containing valuable, but labile, components such as proteins without destroying the desired properties of such components. The pathogen inactivating compositions of the present invention are produced by contacting water or an aqueous solution with iodinated matrix material. The compositions can be pre-formulated and stored for subsequent use in disinfecting a wide range of biological fluids.
Owner:AMERICAN NAT RED CROSS
Electrostatic deposition of particles generated from rapid expansion of supercritical fluid solutions
A method for depositing a substance on a substrate that involves forming a supercritical fluid solution of at least one supercritical fluid solvent and at least one solute, discharging the supercritical fluid solution through an orifice under conditions sufficient to form solid particles of the solute that are substantially free of the supercritical fluid solvent, and electrostatically depositing the solid solute particles onto the substrate. The solid solute particles may be charged to a first electric potential and then deposited onto the substrate to form a film. The solute particles may have a mean particle size of less than 1 micron.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Field-flow fractionation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20040000519A1Simplify general constructionUse minimizedComponent separationIon-exchanger regenerationEngineeringCarrier fluid
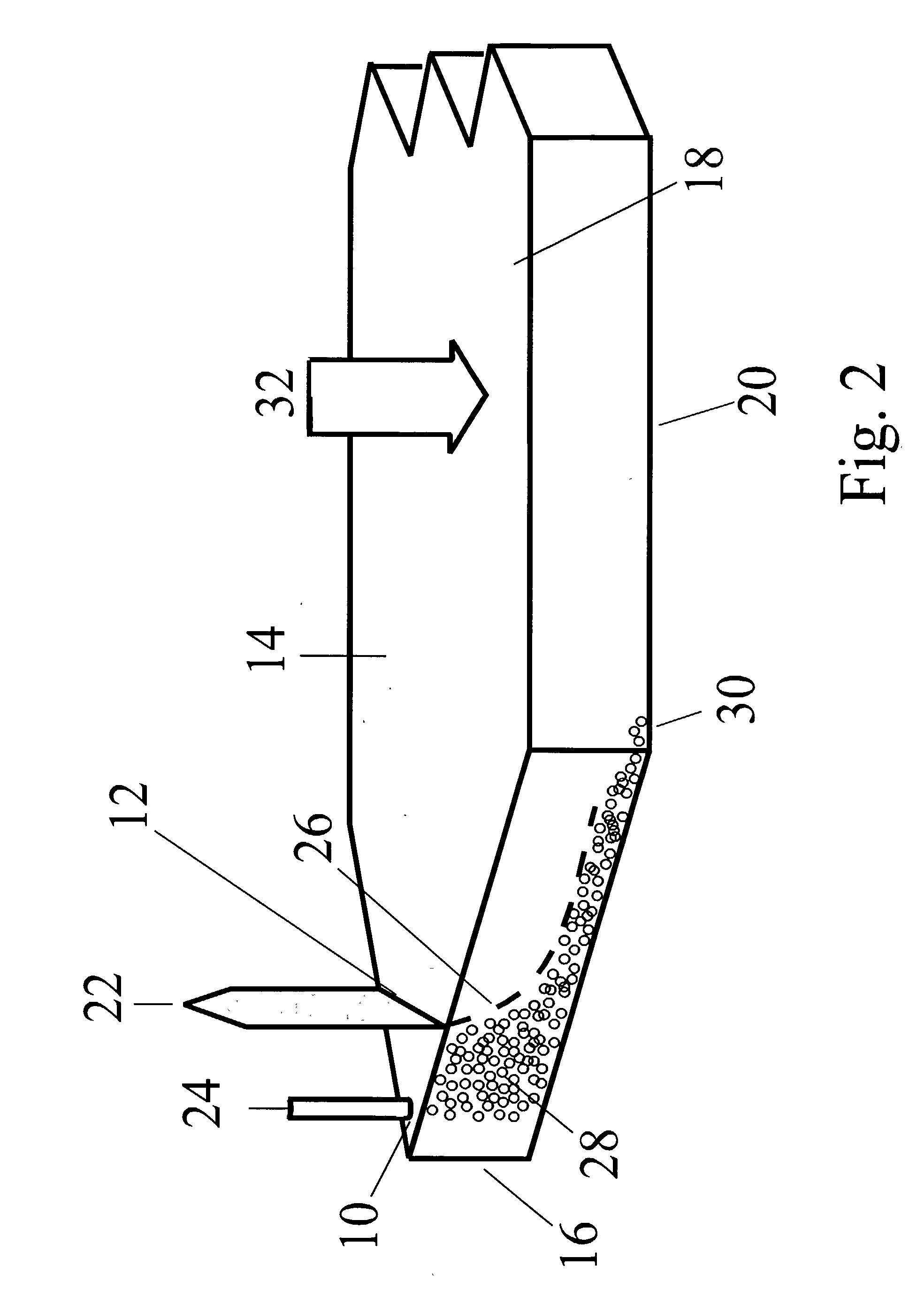
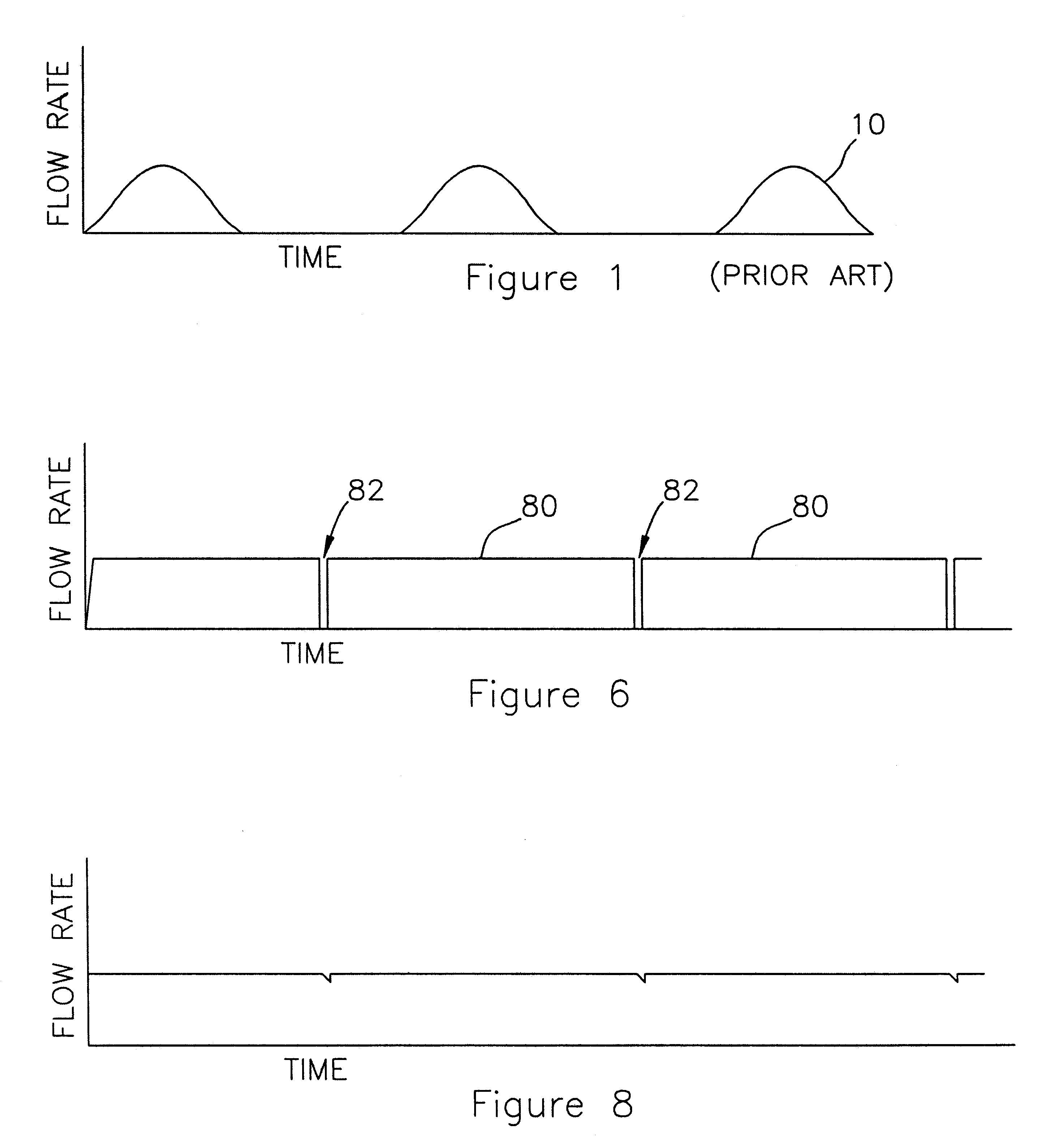
An improved field-flow fractionation method and apparatus for the separation of sample species 28 contained in a carrier fluid, wherein a stream of the sample species-containing carrier fluid is forced through a flow channel 14 having a depletion wall 18, an accumulation wall 20, side walls, a channel inlet 10, and a channel outlet 34, by introducing the sample species-containing carrier fluid into the flow channel 14 through the channel inlet 10 and withdrawing the sample species-containing carrier fluid through the channel outlet 34, a field 32 is applied to the carrier fluid in the flow channel 14 to induce a driving force on the sample species 28 acting across the flow channel 14 from the depletion wall 18 towards the accumulation wall 20 and perpendicular to the orientation of the main axis of the flow channel 14, the sample species 28 are subjected to fractionation as they flow through the flow channel 14 and emerge as sample species fractions at the channel outlet 34, wherein at least one additional stream of sample species-depleted carrier fluid is introduced into the flow channel 14 through at least one orifice 12 and the relative flow rates of the different streams are adjusted such that the stream of sample species-containing carrier fluid is positioned adjacent to the accumulation wall 20 and the sample species-depleted carrier fluid is positioned between the depletion wall 18 and the sample species-containing carrier fluid, no mechanical barrier being provided inside the flow channel 14 between the orifice 12 and the channel inlet 10 for separating the stream of sample species-depleted carrier fluid introduced through the orifice 12 and the stream of sample species-containing carrier fluid introduced through the channel inlet 10.
Owner:POSTNOVA ANALYTICS
Constant flow fluid pump
InactiveUS6227807B1Water/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisLiquid solutions solvent extractionControl theoryStreamflow
The present invention is a means and method for providing constant output flow from a fluid pump. The invention does this by controlling the radial speed of the pump motor during discreet segments of the motor's 360° angular / radial path through a revolution of the pump. The electric pump motor is controlled throughout the 360° radial path by employing a control means for controlling the speed of actuation of the radial steps of a stepper motor throughout the 360° path of rotation of the stepper motor. Control means for controlling the speed of the discreet steps of the stepper motor comprises at least a memory means, a counting means and an amplification means.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
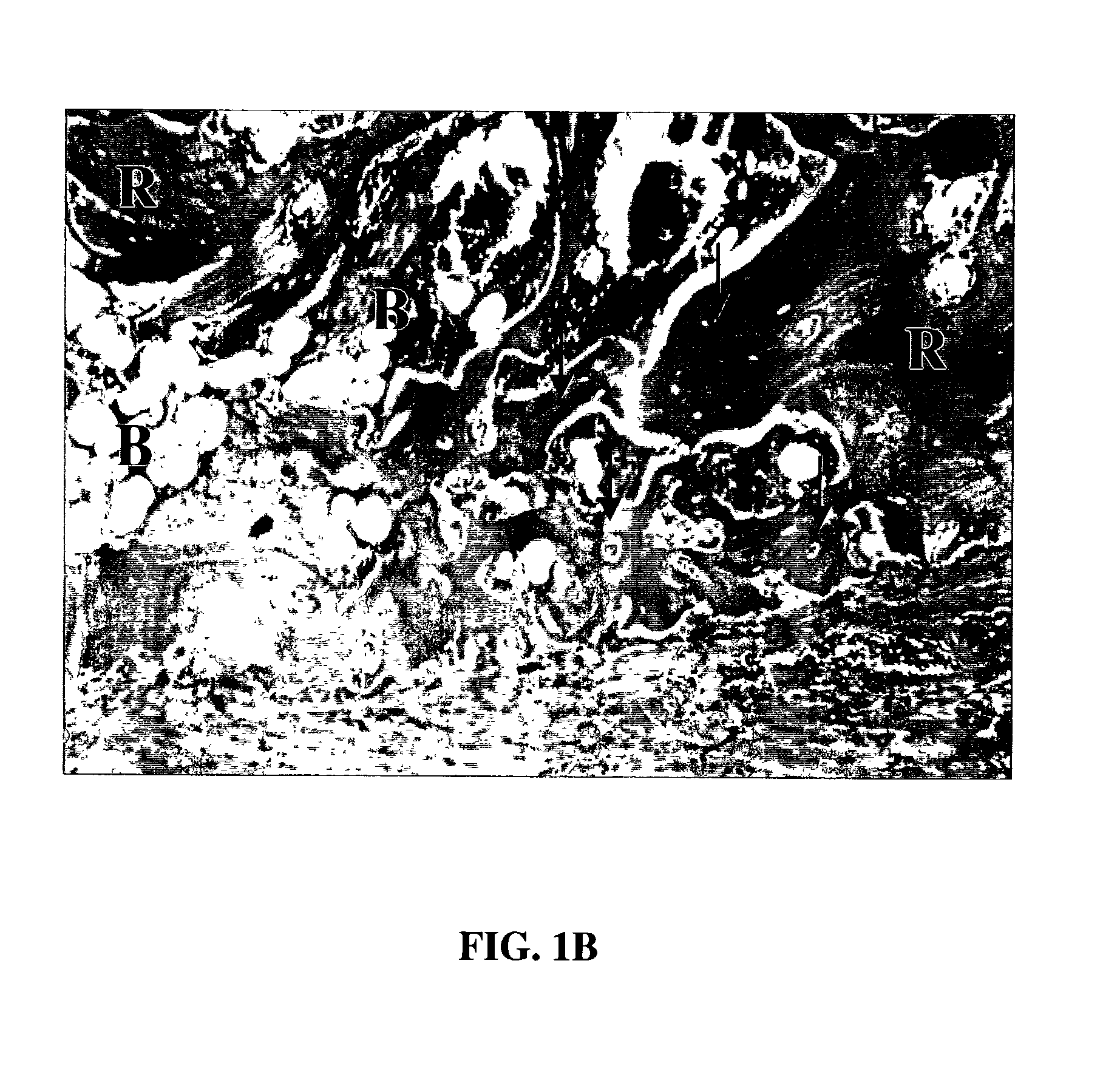
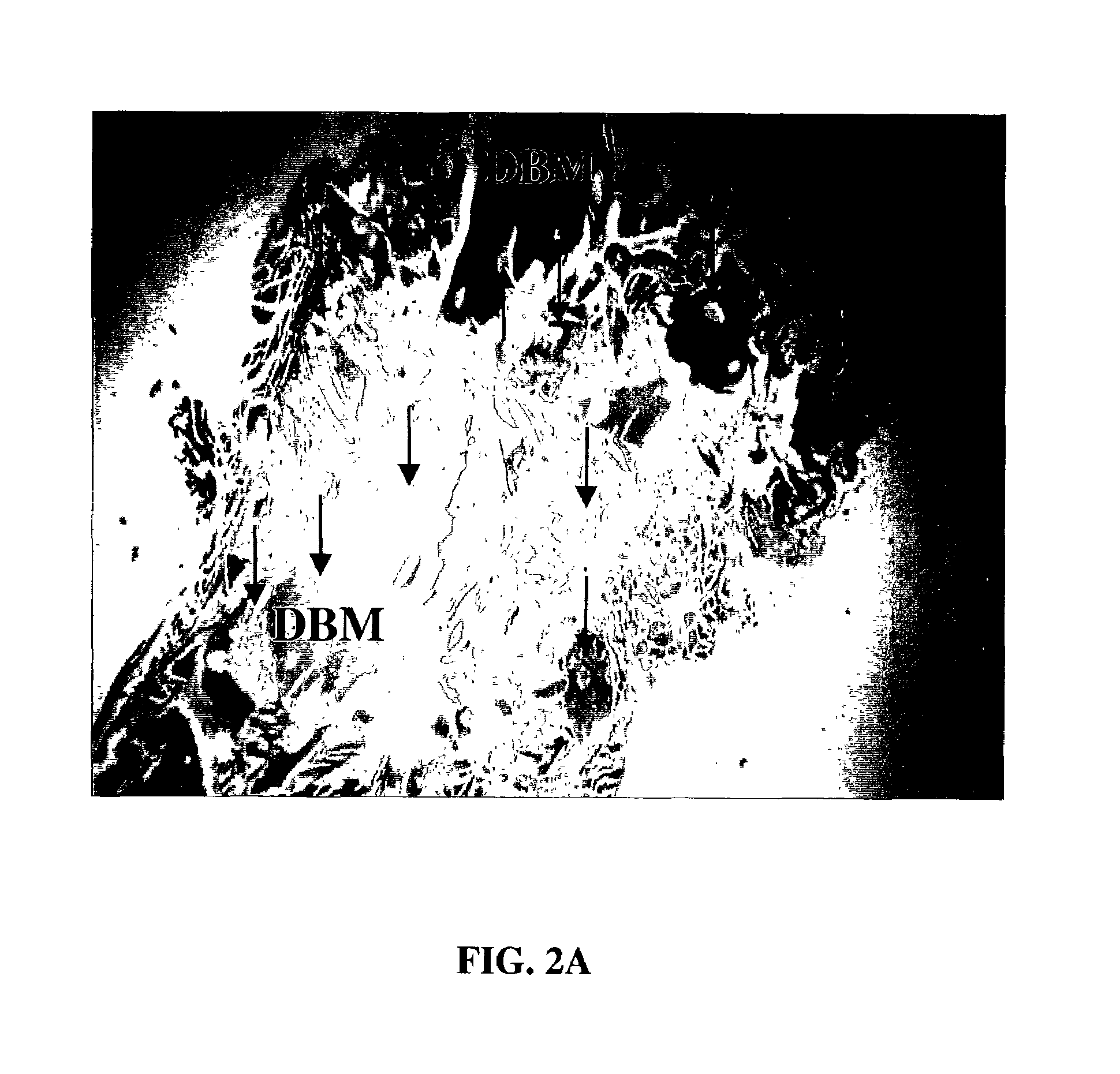
Tissue repair compositions and methods for their manufacture and use
An osteogenic composition is prepared by a process including the steps of subjecting demineralized bone to an extraction medium to produce an insoluble extraction product and a soluble extraction product, separating the insoluble extraction product and the soluble extraction product, drying the soluble extraction product to remove all or substantially all of the moisture in the soluble extraction product, and combining the dried soluble extraction product of step c) with demineralized bone particles. Preferably, the process does not involve heating.
Owner:ISOTIS ORTHOBIOLOGICS
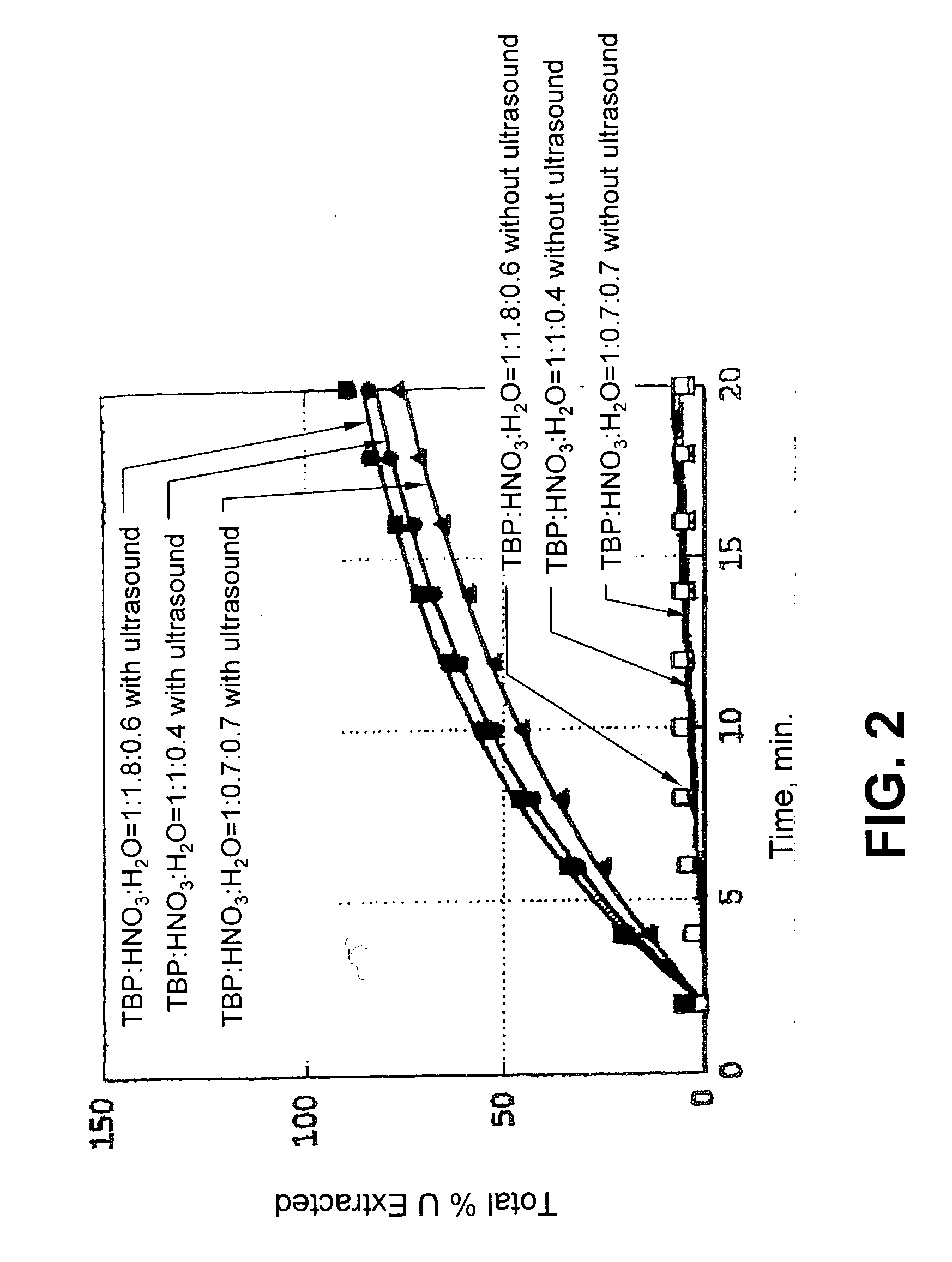
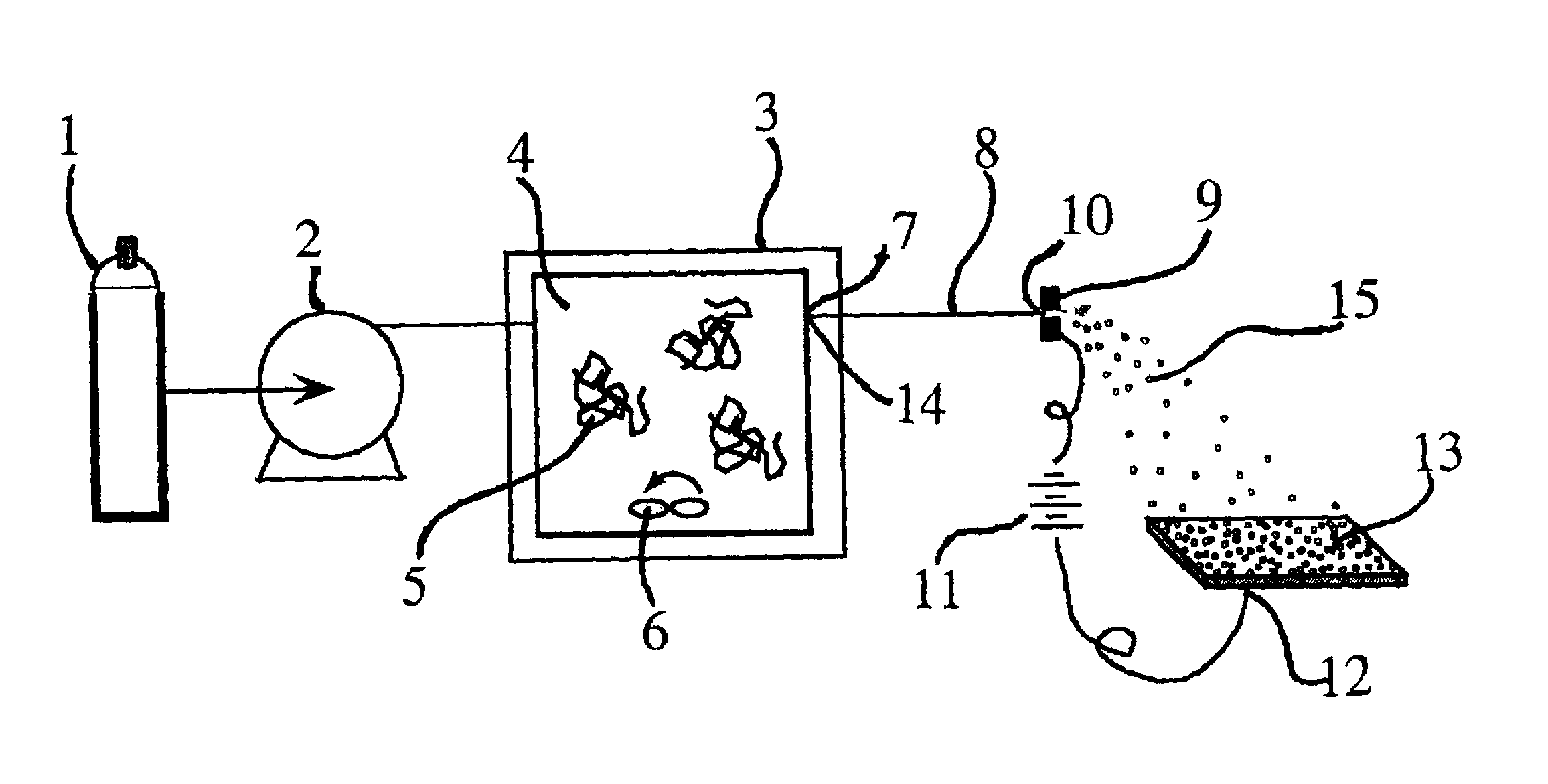
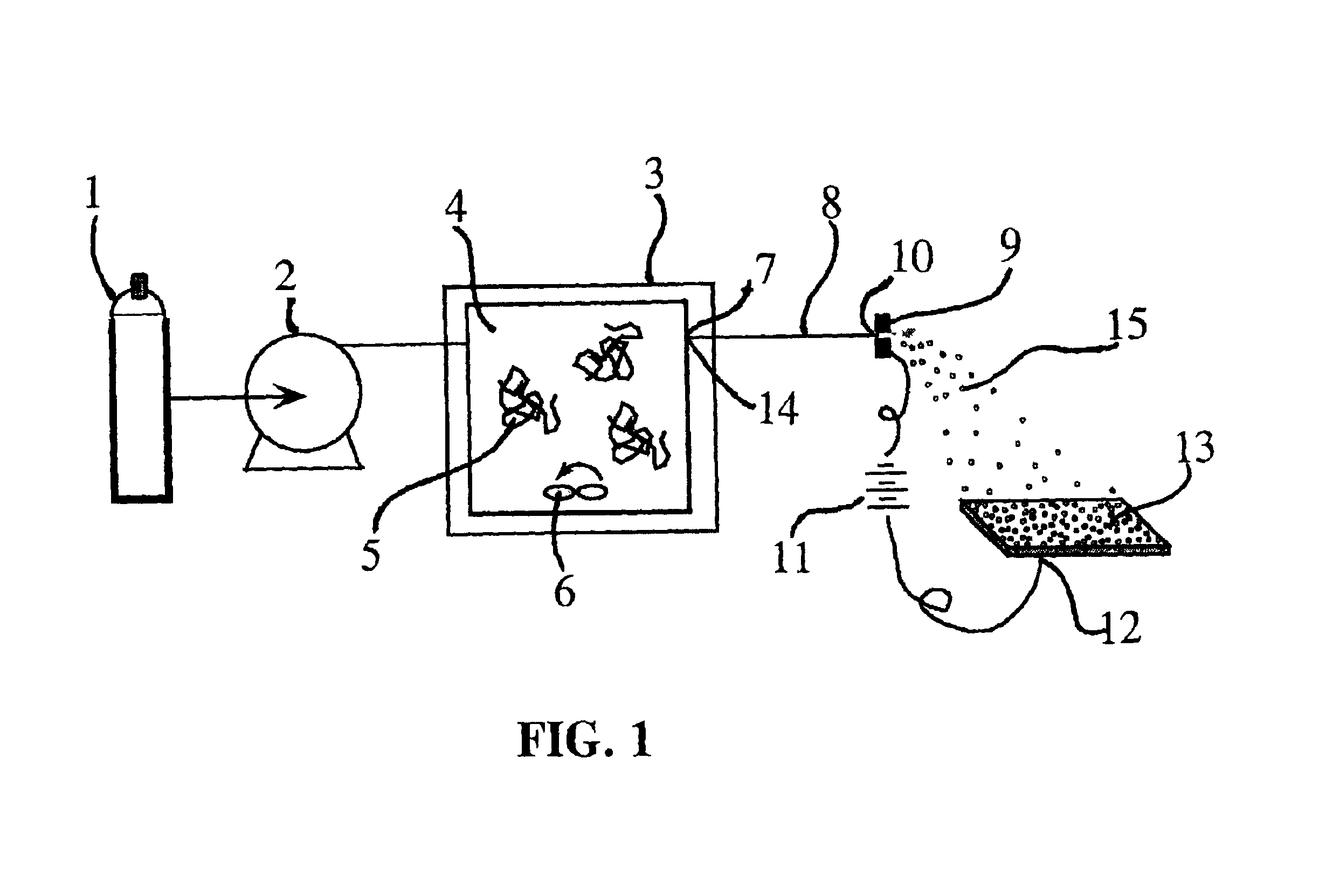
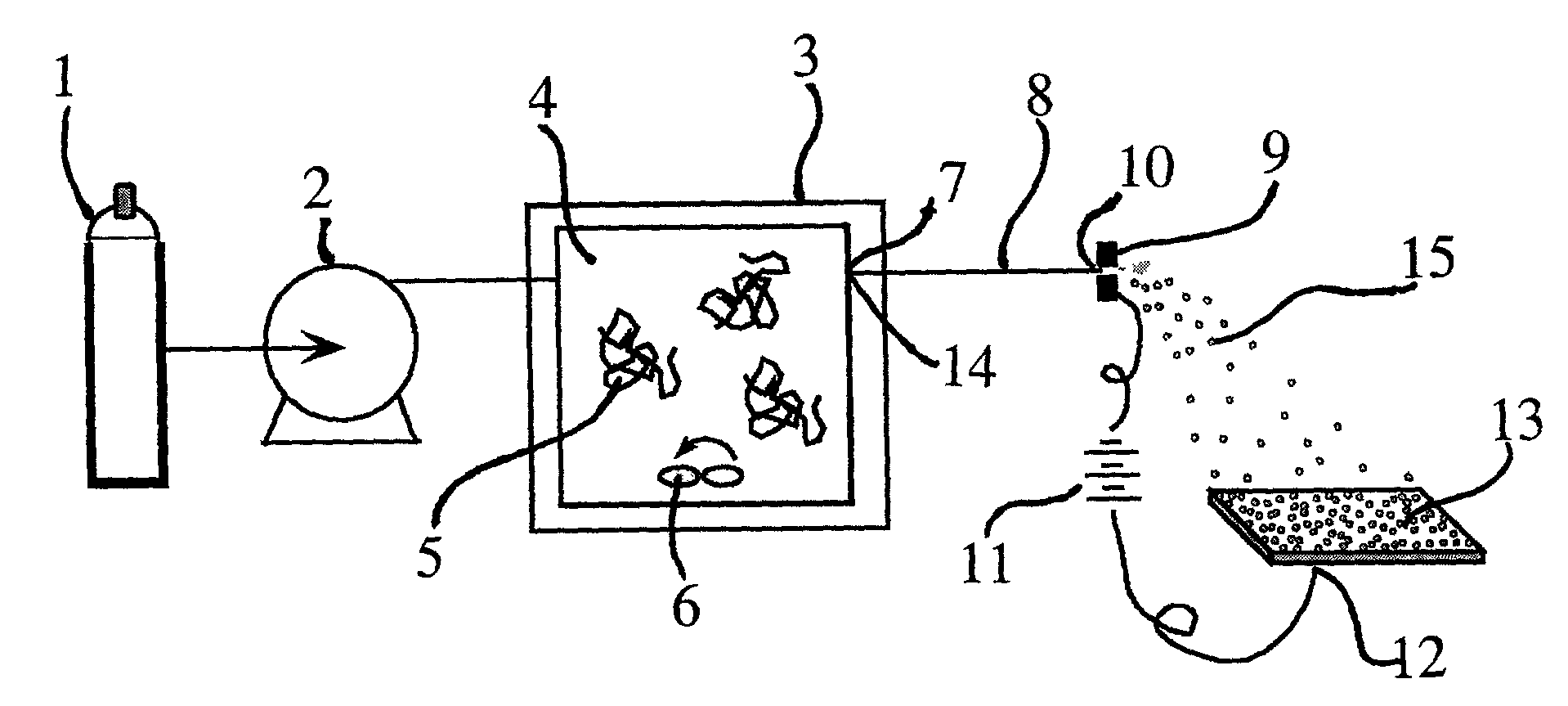
Ultrasound enhanced process for extracting metal species in supercritical fluids
InactiveUS20030183043A1Enhances rate and efficiencyReduce probabilitySolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsUranium oxidePresent method
Improved methods for the extraction or dissolution of metals, metalloids or their oxides, especially lanthanides, actinides, uranium or their oxides, into supercritical solvents containing an extractant are disclosed. The disclosed embodiments specifically include enhancing the extraction or dissolution efficiency with ultrasound. The present methods allow the direct, efficient dissolution of UO2 or other uranium oxides without generating any waste stream or by-products.
Owner:NAGOYA INDUSTRIAL SCIENCE RESEARCH INST +1
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Methods for producing films using supercritical fluid
A method for forming a continuous film on a substrate surface that involves depositing particles onto a substrate surface and contacting the particle-deposited substrate surface with a supercritical fluid under conditions sufficient for forming a continuous film from the deposited particles. The particles may have a mean particle size of less 1 micron. The method may be performed by providing a pressure vessel that can contain a compressible fluid. A particle-deposited substrate is provided in the pressure vessel and the compressible fluid is maintained at a supercritical or sub-critical state sufficient for forming a film from the deposited particles. The Tg of particles may be reduced by subjecting the particles to the methods detailed in the present disclosure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Carbon dioxide cleaning and separation systems
InactiveUS6200393B1Low costLiquid surface applicatorsSolid sorbent liquid separationCarbon dioxide cleaningSeparation system
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
Selective extraction of proteins from saltwater algae
Methods for selective extraction and fractionation of algal proteins from an algal biomass or algal culture are disclosed. A method of selective removal of products from an algal biomass provides for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal proteins. These proteins can be used as renewable sources of proteins for animal feedstocks and human food. Further, lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of proteins can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Non-Dispersive Process for Insoluble Oil Recovery From Aqueous Slurries
ActiveUS20110174734A1Efficient separationEliminate the problemFatty acid chemical modificationFatty acids production/refiningBiodieselBeta-Carotene
The development and application of a novel non-polar oil recovery process utilizing a non-dispersive solvent extraction method to coalesce and recover oil from a bio-cellular aqueous slurry is described herein. The process could apply to recovery of algal oil from a lysed algae slurry, recovery of Omega fatty acids from a bio-cellular aqueous feed, recovery of Beta-carotene from a bio-cellular aqueous feed and for the removal from produced water in oil production and similar type applications. The technique of the present invention utilizes a microporous hollow fiber (MHF) membrane contactor. The novel non-polar oil recovery process described herein can be coupled to a collecting fluid (a non-polar solvent such as heptane, a biodiesel mixture or the previously extracted oil) that is circulated through the hollow fiber membrane. In cases where the biodiesel mixture or the previously extracted oil is used the solvent recovery step (e.g. distillation) can be eliminated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Composite particles and method for preparing
A method for producing composite particles using a supercritical fluid extraction technique on an emulsion. First and second materials (for example; a polymer and a biologically active material) are dissolved or suspended in a preferably solvent to form a solution or dispersion. The solution or dispersion is emulsified in a polar solvent to form an oil-in-water or water-in-oil-in-water emulsion. The emulsion is contacted with a supercritical fluid to extract the solvent. Removal of the solvent by the supercritical fluid from the emulsion supersaturates at least the first material in the solution causing the first material to precipitate out of the solution as composite particles that include both the first and second materials.
Owner:FERRO CORP
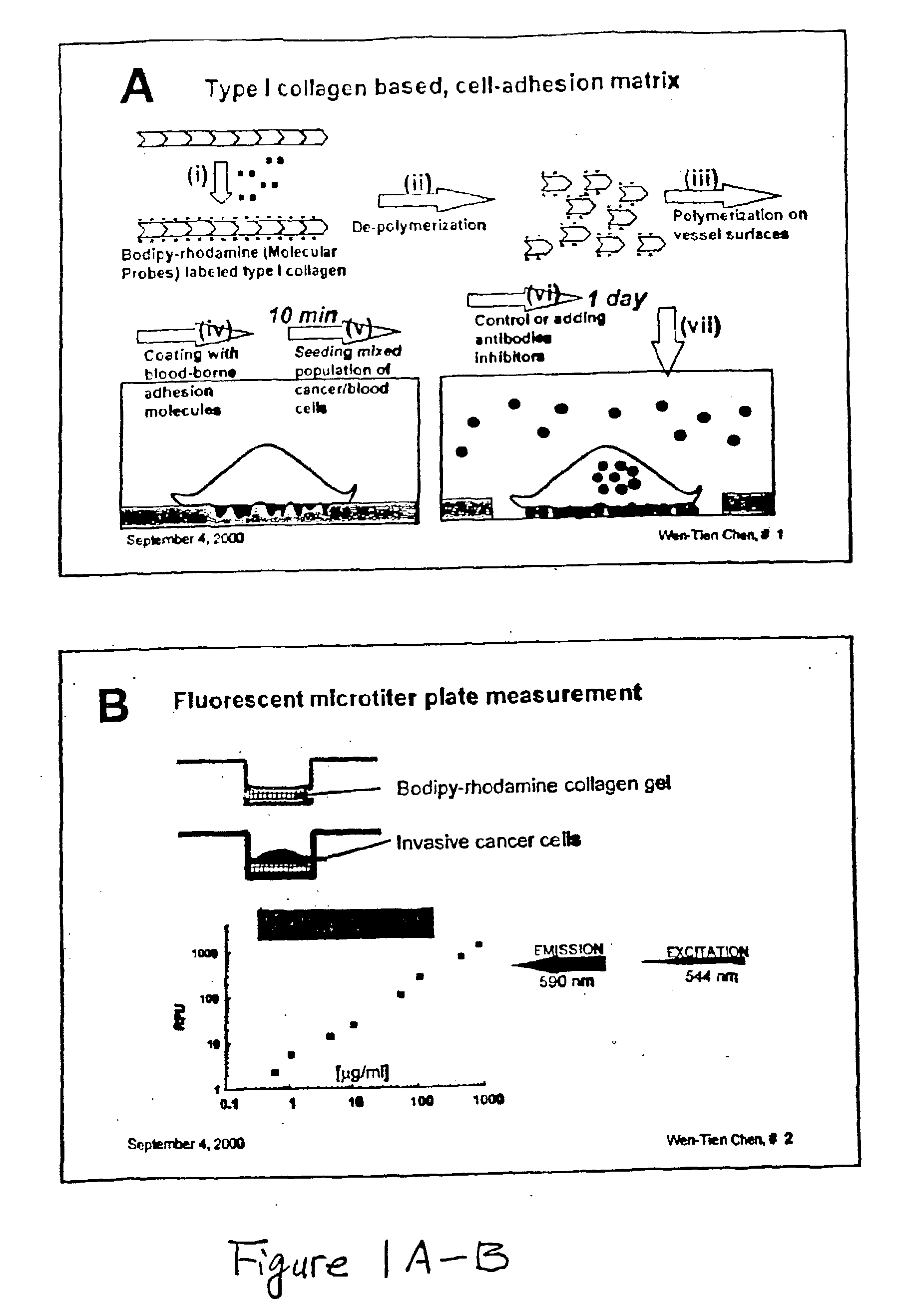
Method and compositions for isolating metastatic cancer cells, and use in measuring metastatic potentatial of a cancer thereof
InactiveUS20030206901A1Quick checkRapid isolationSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesCancer cellProteinase activity
The present invention relates to novel methods and compositions for detection and isolation of cancer cells with metastatic potential. The invention further relates to assays for measuring the metastatic potential of such cancer cells and drug screening assays for the identification of agents having anti-metastatic potential. The present invention further provides methods and compositions for inhibiting the metastatic potential of cancer cells by modulating the activity of serine integral membrane proteases [(SIMP) consisting of seprase and dipedidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV)]expressed on the surface of metastasizing cancer cells.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Popular searches
Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactors Laboratory glasswares Isotope introduction to organic compounds Liquid chemical processes Liquid-liquid reaction processes Gaseous chemical processes Additive manufacturing apparatus Sugar derivatives Other chemical processes Liquid-gas reaction of thin-film type
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com