Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1452results about "Liquid chemical processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
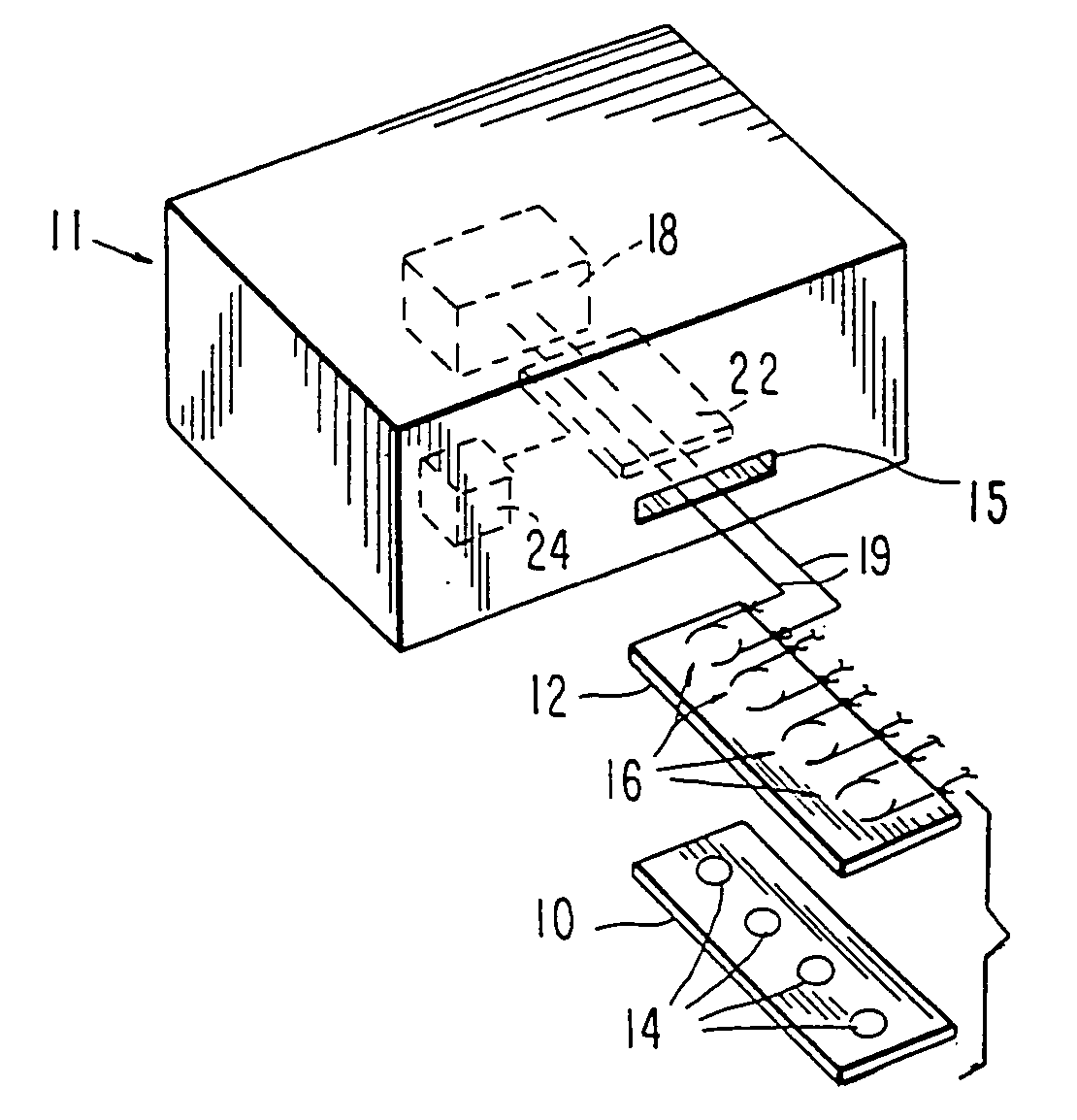
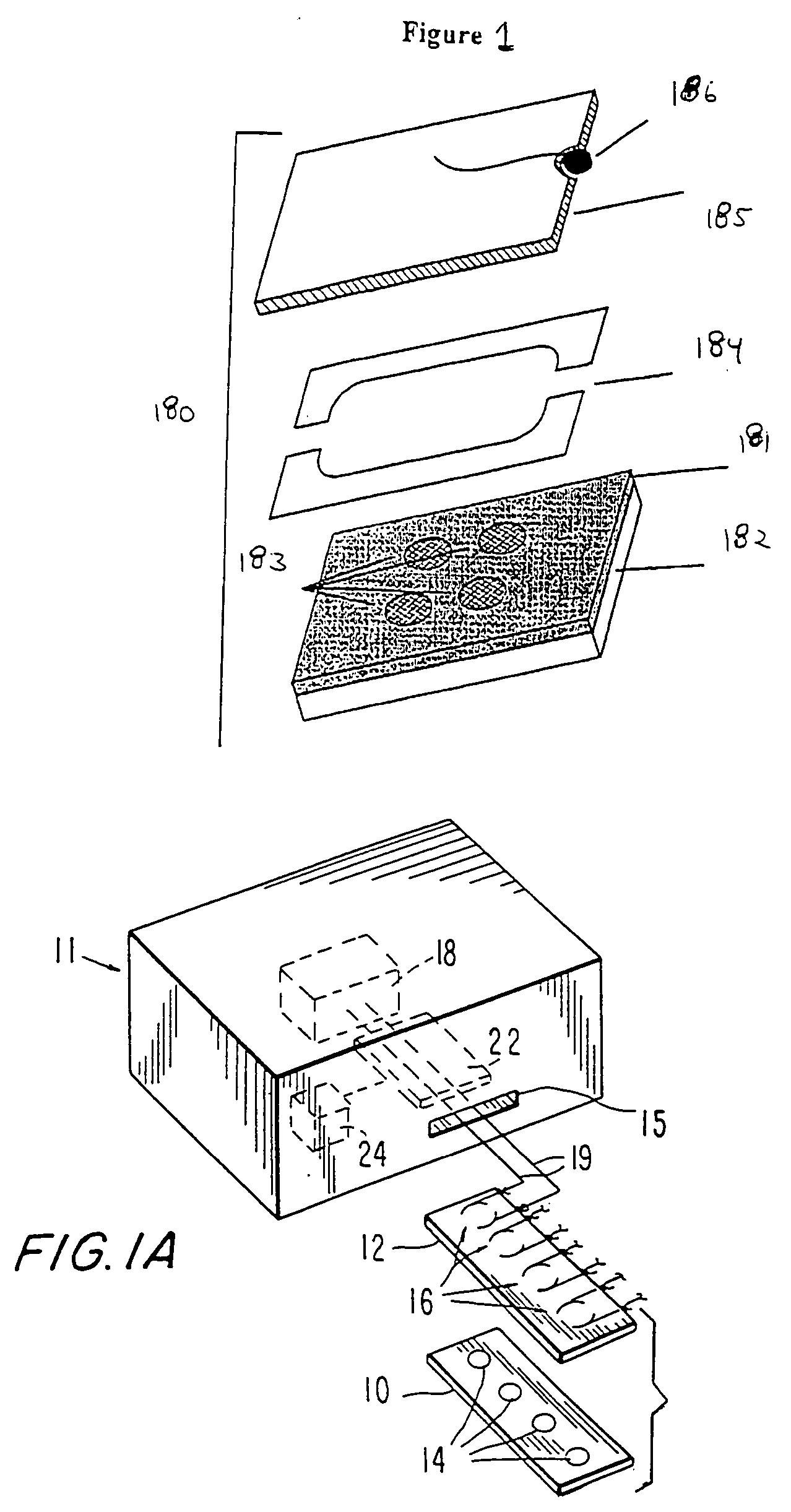
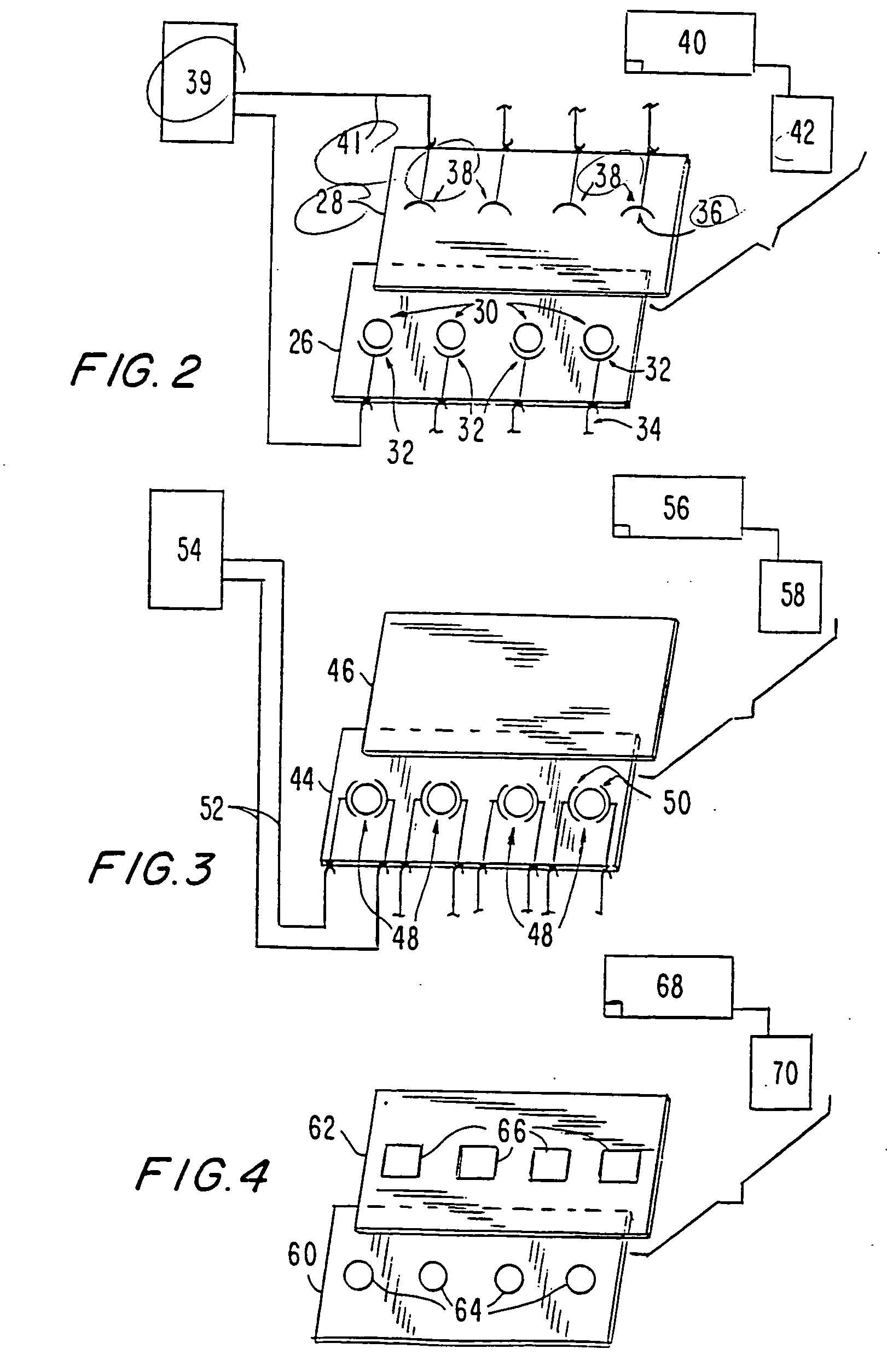
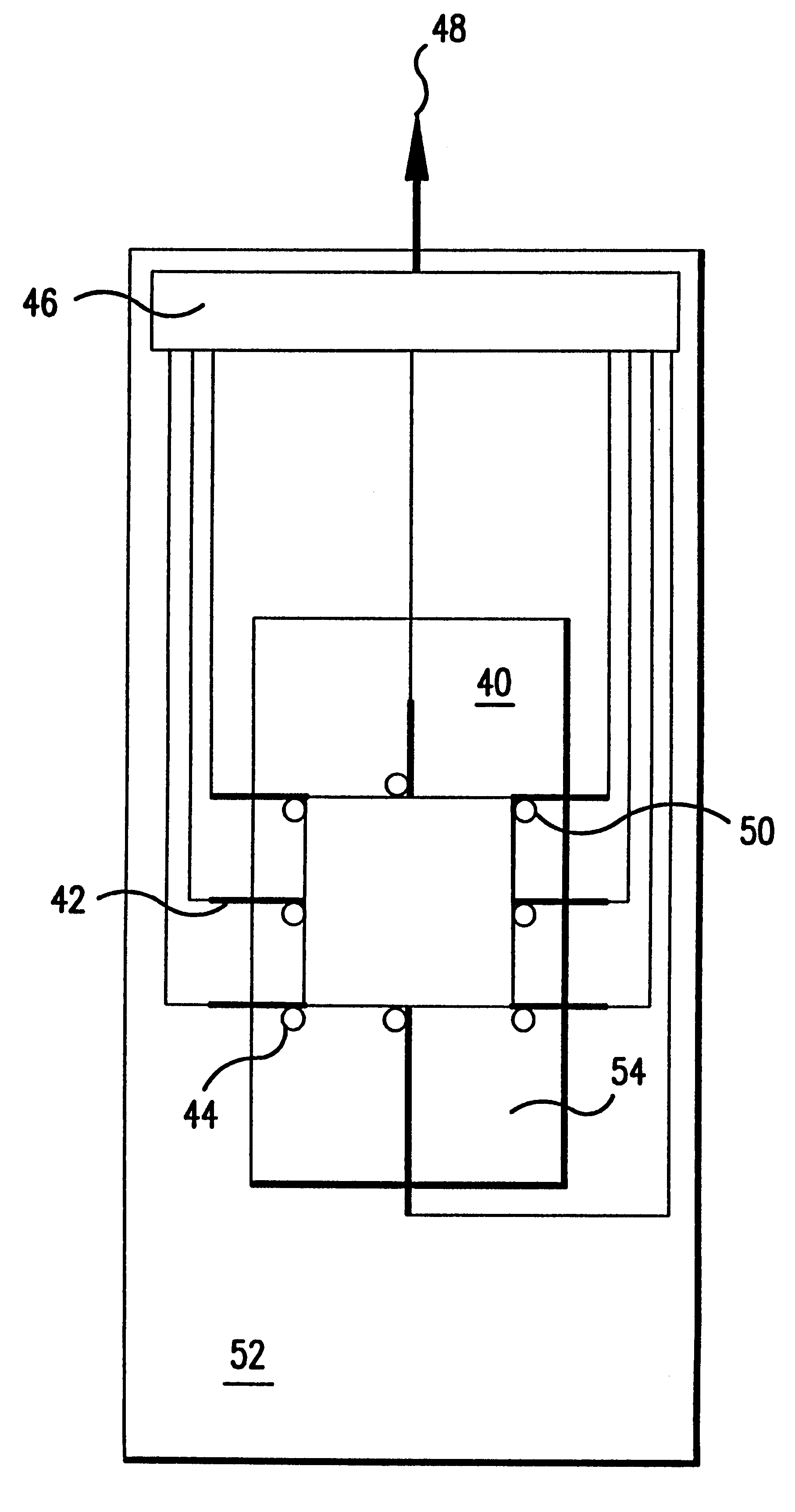
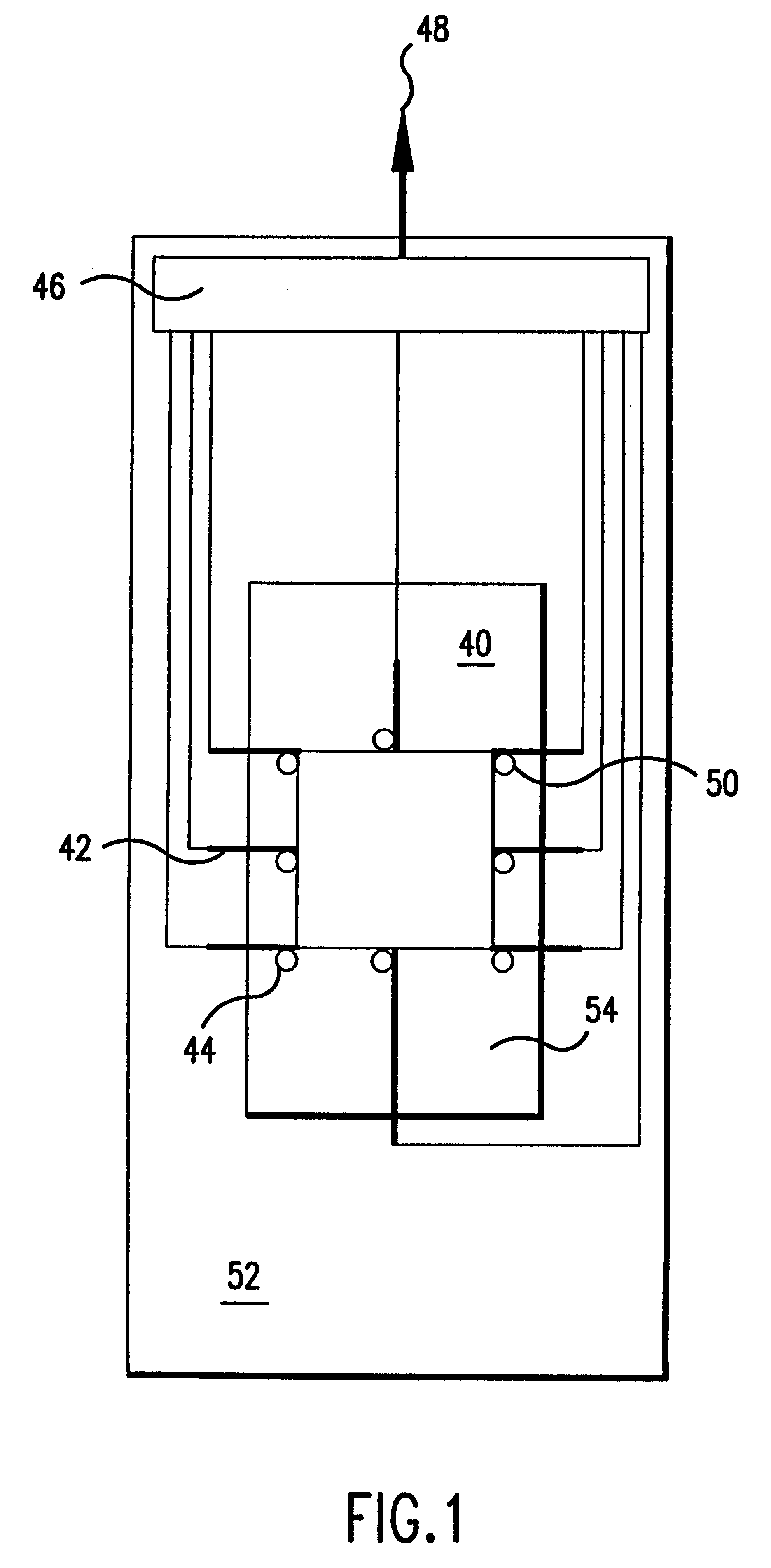
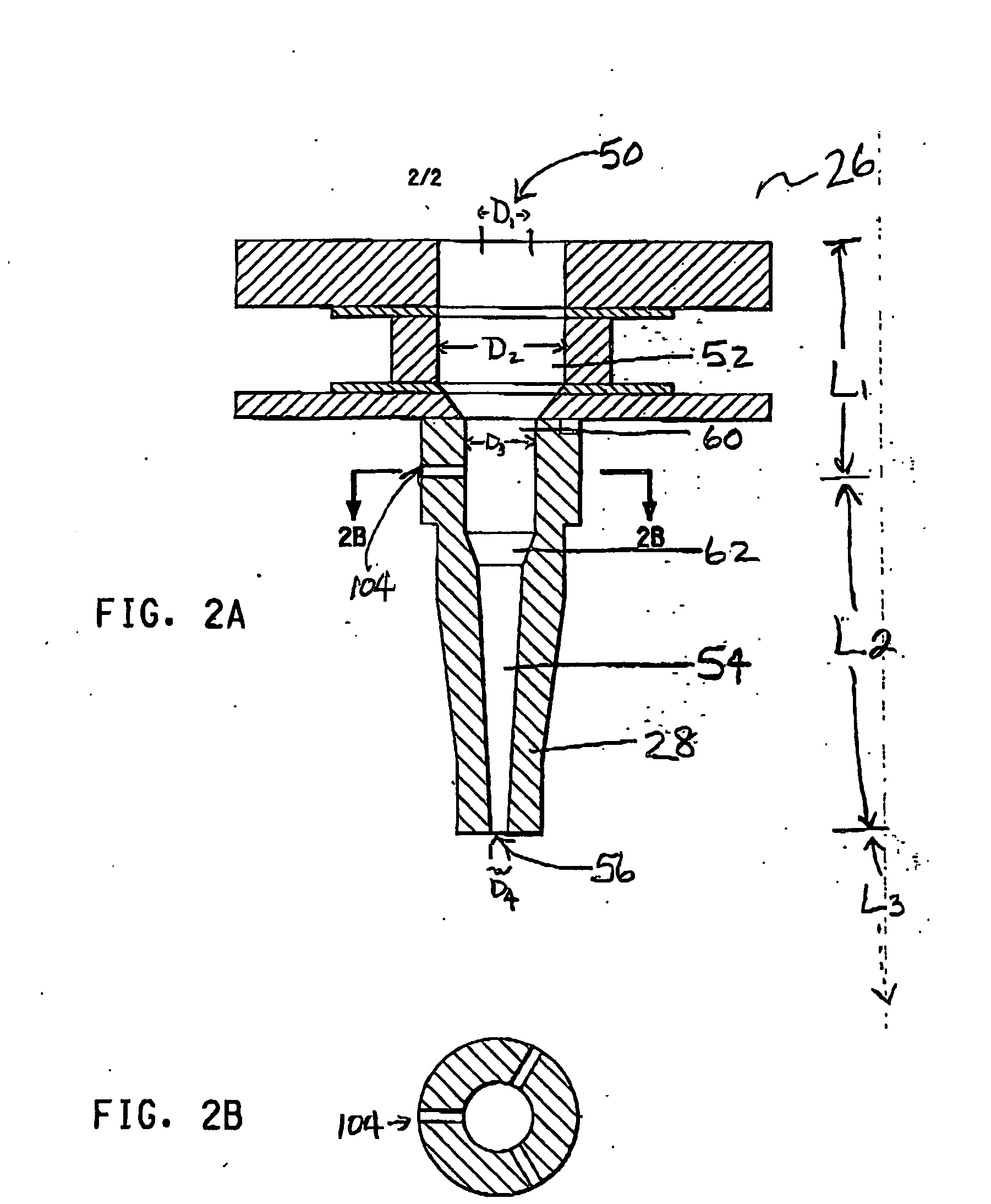
Method and system for in situ formation of gas-phase compounds
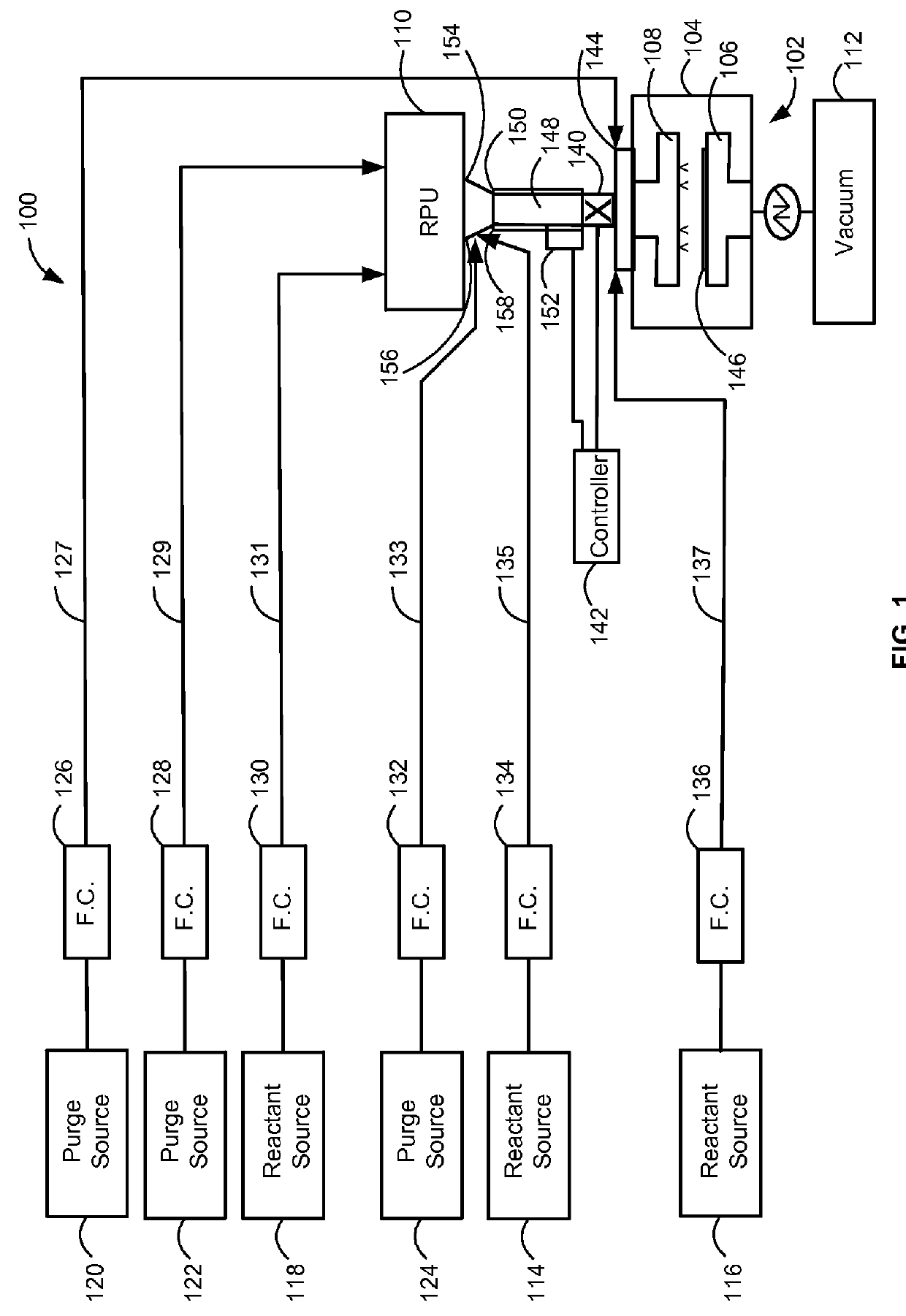
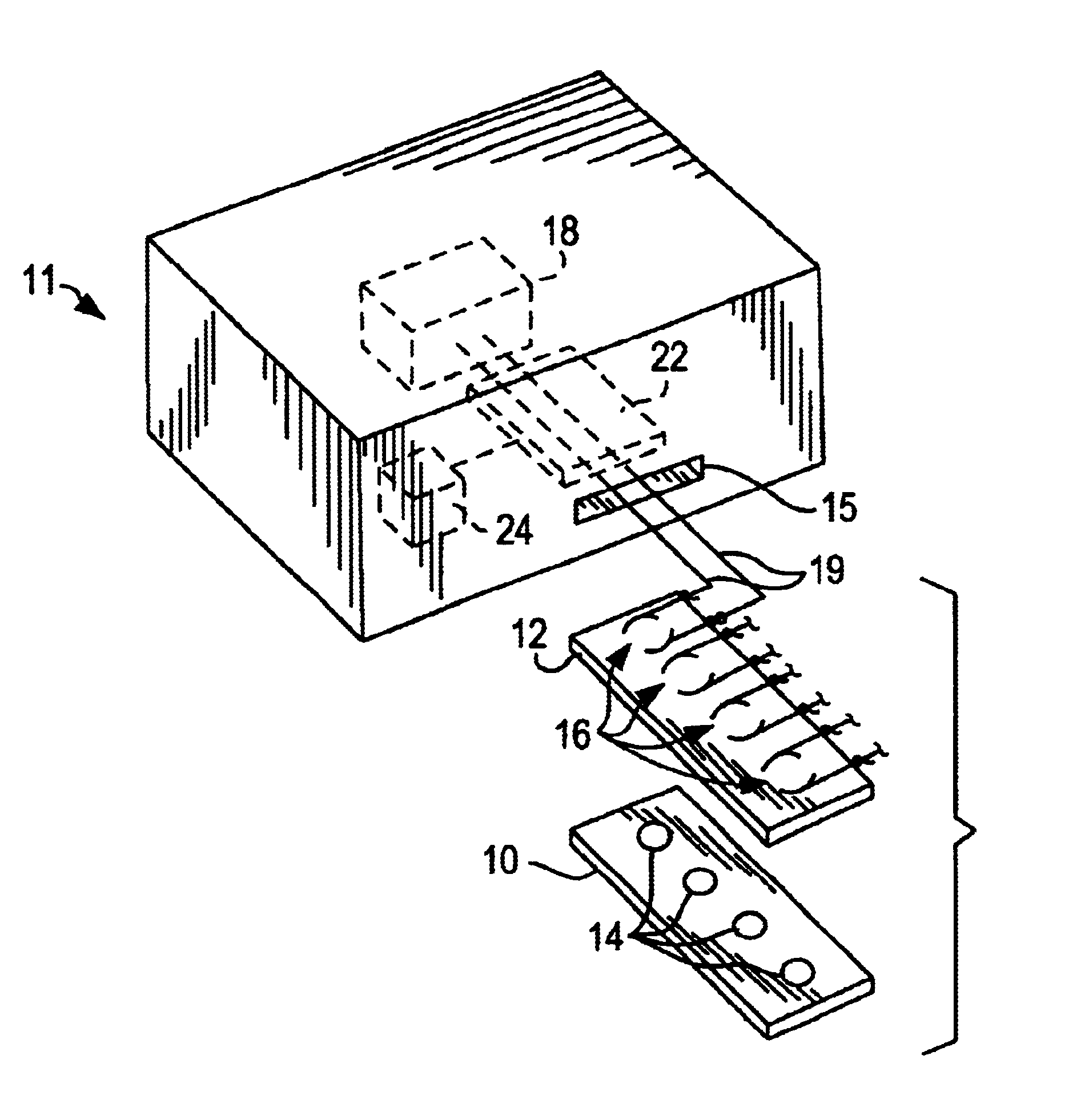
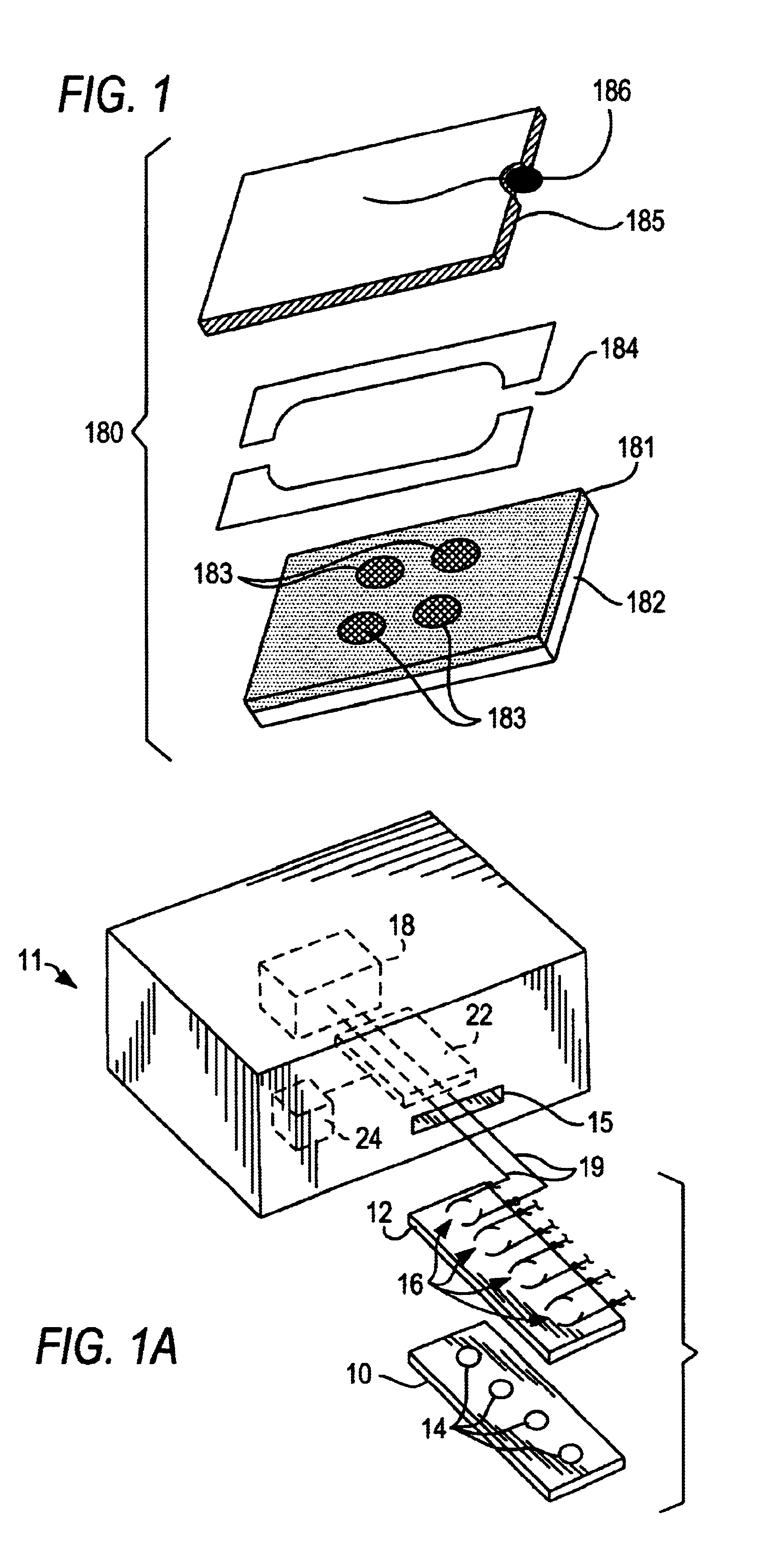
ActiveUS20160051964A1Process can be usedProcess control/regulationCell electrodesCompound aGas phase
A system and method for providing intermediate reactive species to a reaction chamber are disclosed. The system includes an intermediate reactive species formation chamber fluidly coupled to the reaction chamber to provide intermediate reactive species to the reaction chamber. A pressure control device can be used to control an operating pressure of the intermediate reactive species formation chamber, and a heater can be used to heat the intermediate reactive species formation chamber to a desired temperature.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Droplet Microreactor
InactiveUS20080124252A1Improve purification effectInexpensive to fabricateChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMicroreactorLab-on-a-chip
The present invention relates to a droplet microreactor, i.e. a microreactor consisting of a droplet of a specific liquid, the microreactor being wall-less, wherein the interface of the specific liquid with the ambient environment and with the support on which the droplet is deposited defines the limits of the microreactor. The microreactor is characterized in that it consists of a droplet comprising at least one ionic liquid. The present invention also relates to methods for carrying out chemical or biochemical reactions and / or mixes using said droplet microreactor, and also to a lab-on-chip comprising a microreactor according to the invention.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
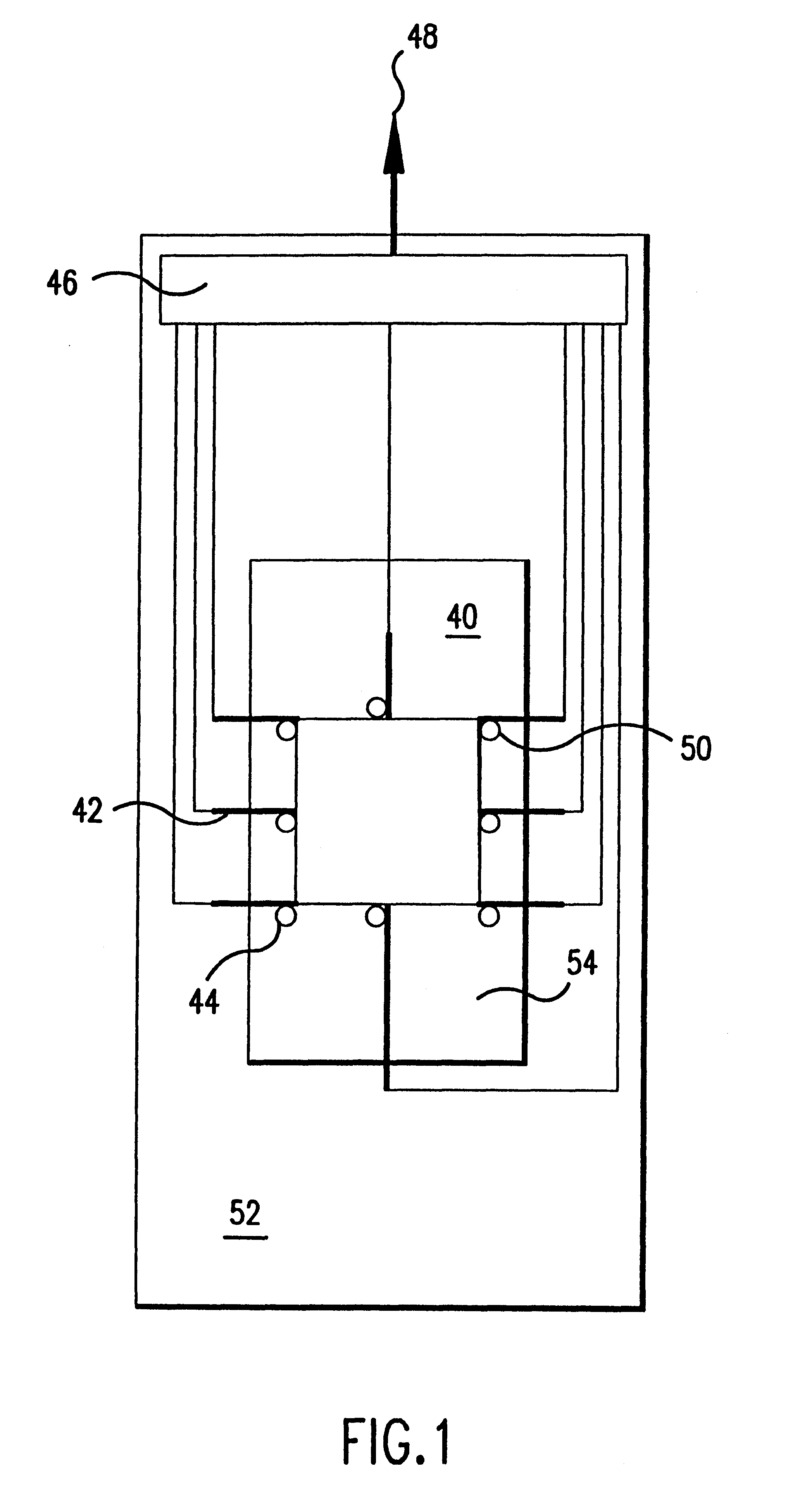
Multi-array multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6673533B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Parallel flow process optimization reactors
InactiveUS20020048536A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsProcess optimizationDistribution system
Owner:FREESLATE
Microfluidic Chemical Reaction Circuits
InactiveUS20080281090A1Shaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingChemical reactionCompound (substance)
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +3
Parallel flow reactor having variable composition
InactiveUS20020045265A1Extreme flexibilityAdvantageously and flexibly employedProcess control/regulationSequential/parallel process reactionsDistribution systemEngineering
Owner:FREESLATE
Microfluidic reaction apparatus for high throughput screening
An SBS-formatted microfluidic device where the geometry of the plate defines an array of interrogation areas, and where each interrogation area encompasses at least one reaction site.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Continuous Process for the Production of Nanostructures Including Nanotubes
The present invention provides methods for uniform growth of nanostructures such as nanotubes (e.g., carbon nanotubes) on the surface of a substrate, wherein the long axes of the nanostructures may be substantially aligned. The nanostructures may be further processed for use in various applications, such as composite materials. For example, a set of aligned nanostructures may be formed and transferred, either in bulk or to another surface, to another material to enhance the properties of the material. In some cases, the nanostructures may enhance the mechanical properties of a material, for example, providing mechanical reinforcement at an interface between two materials or plies. In some cases, the nanostructures may enhance thermal and / or electronic properties of a material. The present invention also provides systems and methods for growth of nanostructures, including batch processes and continuous processes.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Sensor having a thin-film inhibition layer, nitric oxide converter and monitor
ActiveUS20080221806A1High sensitivityLarge dynamic rangeMaterial nanotechnologyTemperatue controlDiseaseVolatiles
Sensors and detection systems suitable for measuring analytes, such as biomolecule, organic and inorganic species, including environmentally and medically relevant volatiles and gases, such as NO, NO2, CO2, NH3, H2, CO and the like, are provided. Certain embodiments of nanostructured sensor systems are configured for measurement of medically important gases in breath. Applications include the measurement of endogenous nitric oxide (NO) in breath, such as for the monitoring or diagnosis of asthma and other pulmonary conditions.
Owner:NANOMIX
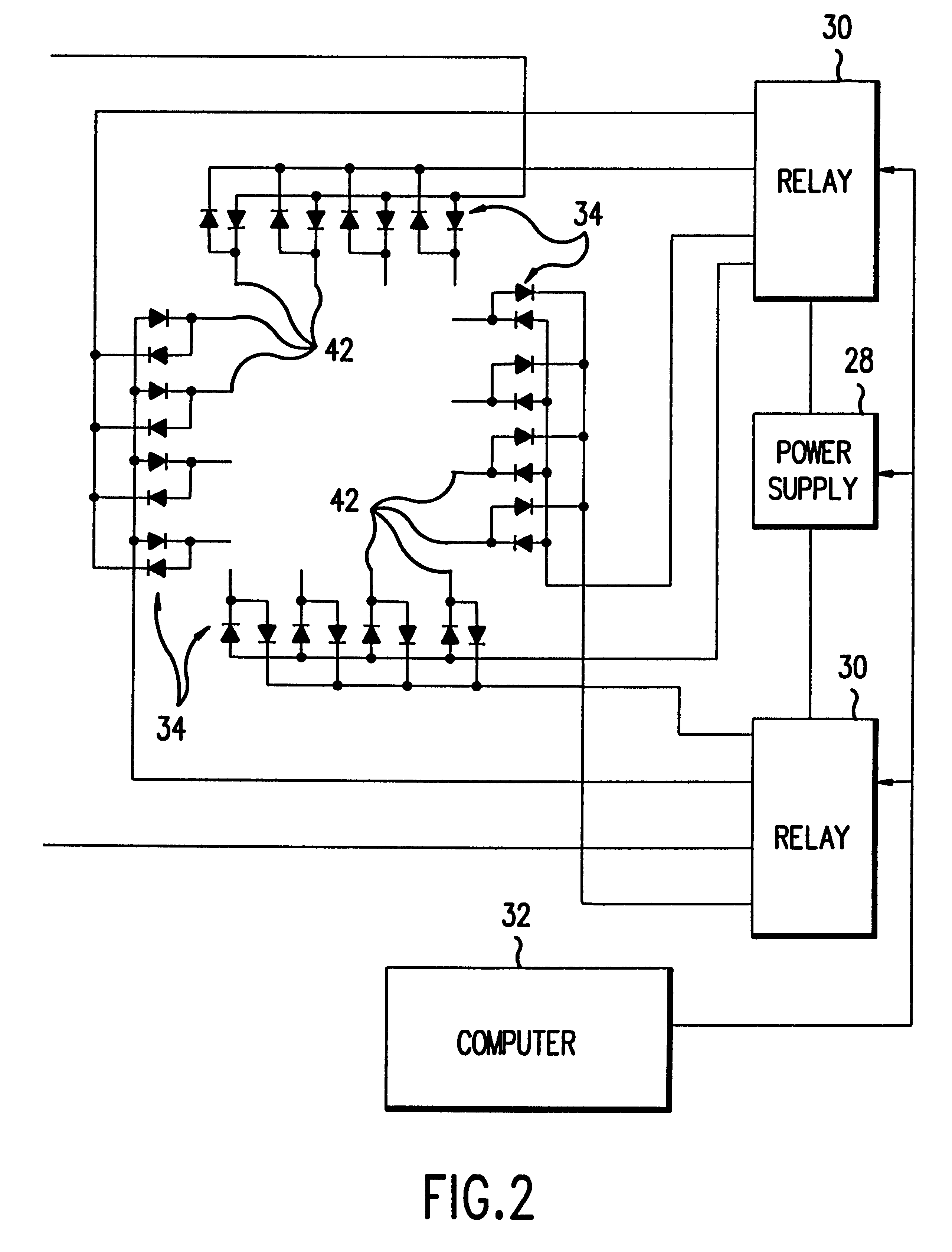
Self-regulating hydrogen generator
InactiveUS6939529B2Increase and decrease hydrogen generation rateIncrease rate of hydrogen generationPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionGeneration processGeneration rate
A hydrogen generating system regulates its rate of hydrogen generation by monitoring one or more parameters of the hydrogen generation process and then providing relative movement between the fuel tank and the catalyst chamber so as to increase or decrease the rate of hydrogen generation.In the disclosed embodiments, the catalyst chamber is disposed in a tank containing the fuel. The relative movement provided moves the catalyst chamber toward the fuel solution so as to increase the rate of hydrogen generation and moves the catalyst chamber away from the fuel solution to decrease such generation. Advantageously, such self-regulation can be provided without an external power source and can be varied to meet the requirements of different commercial applications. The overall system can be readily fabricated using commercially available parts.
Owner:PROTONEX TECH CORP
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS20040086423A1Volume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsAnalyteProviding material
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
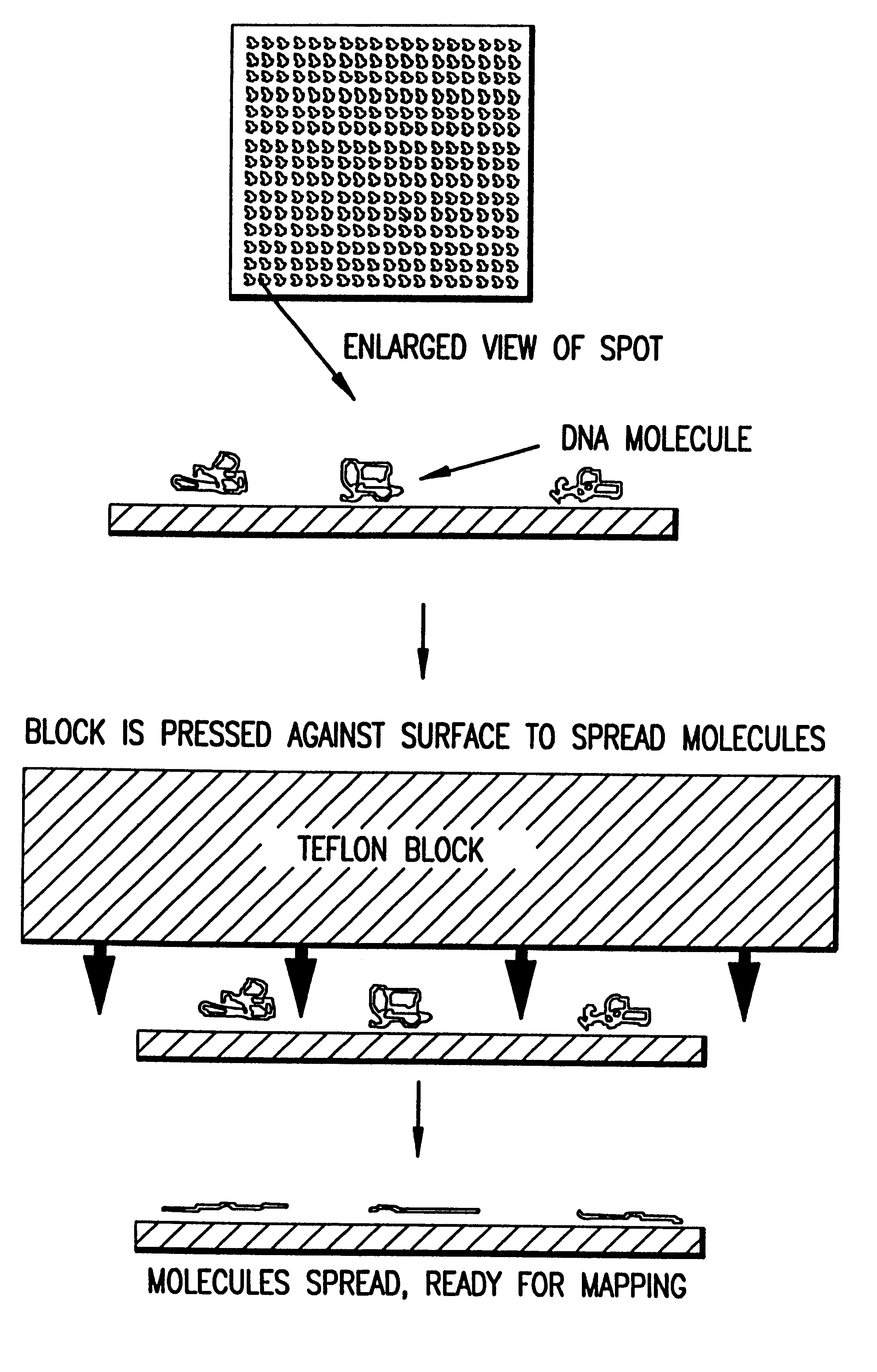
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6294136B1Improve throughputQuick buildMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresMicroscope slideMap Location
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
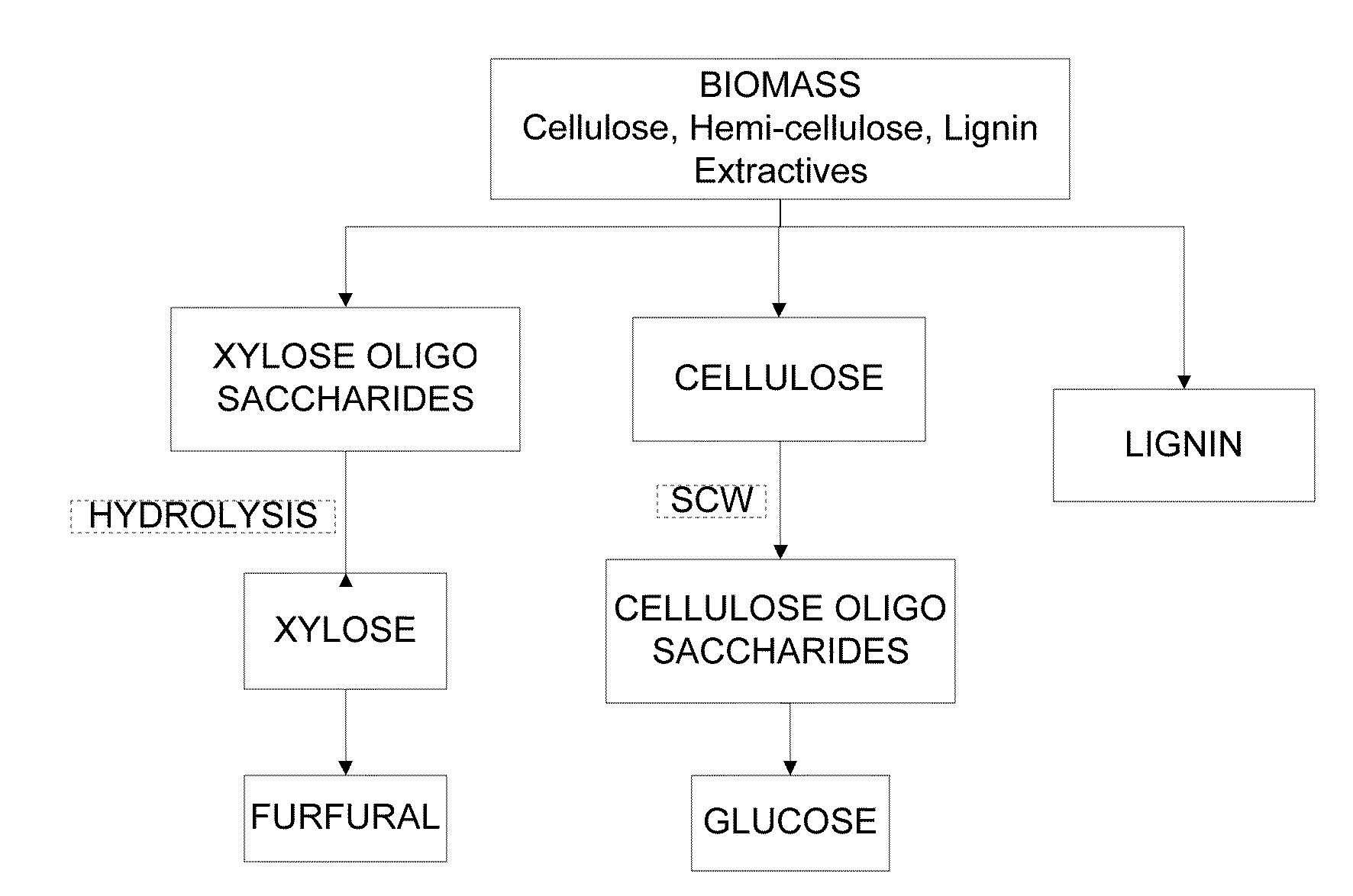
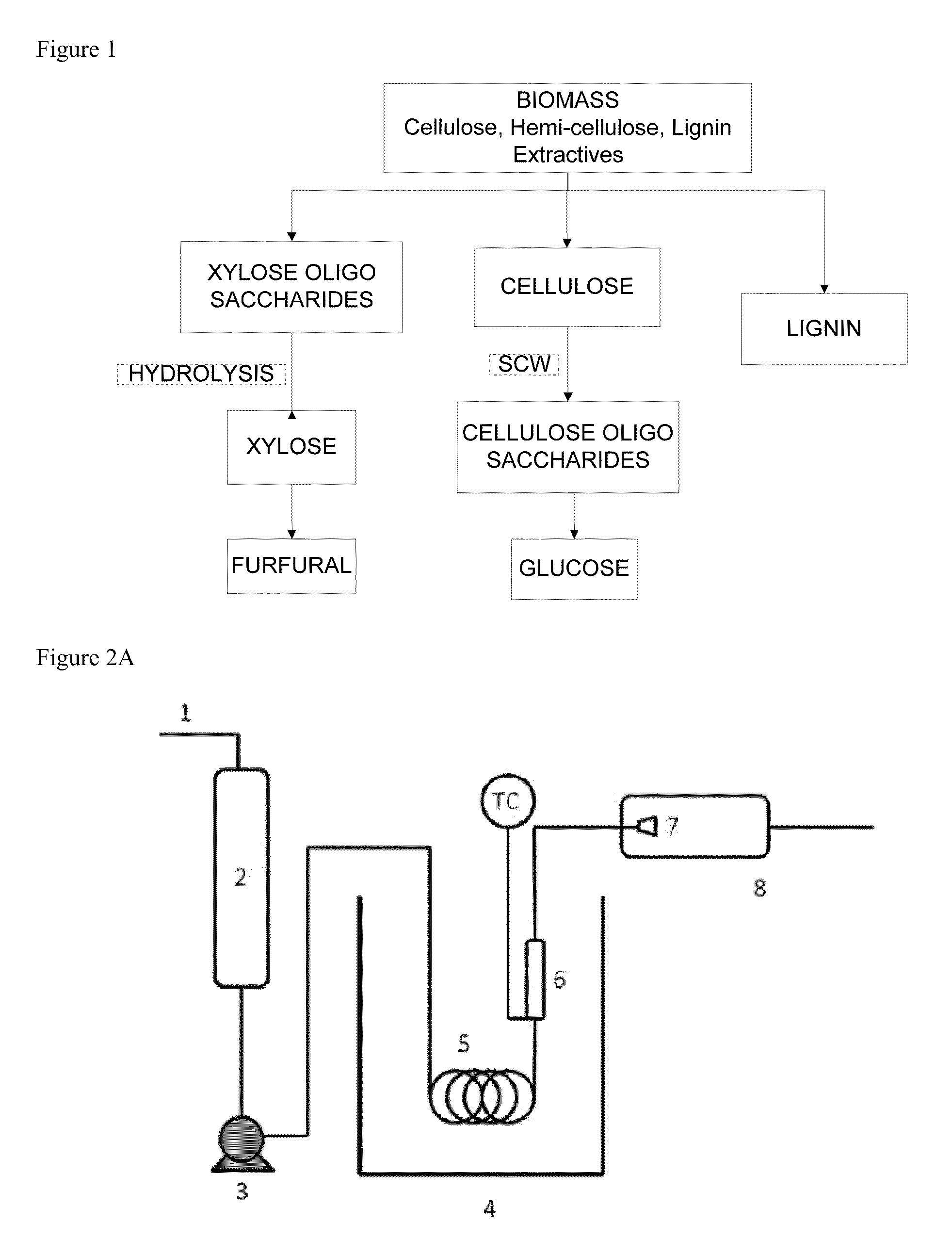
Nano-catalytic-solvo-thermal technology platform bio-refineries
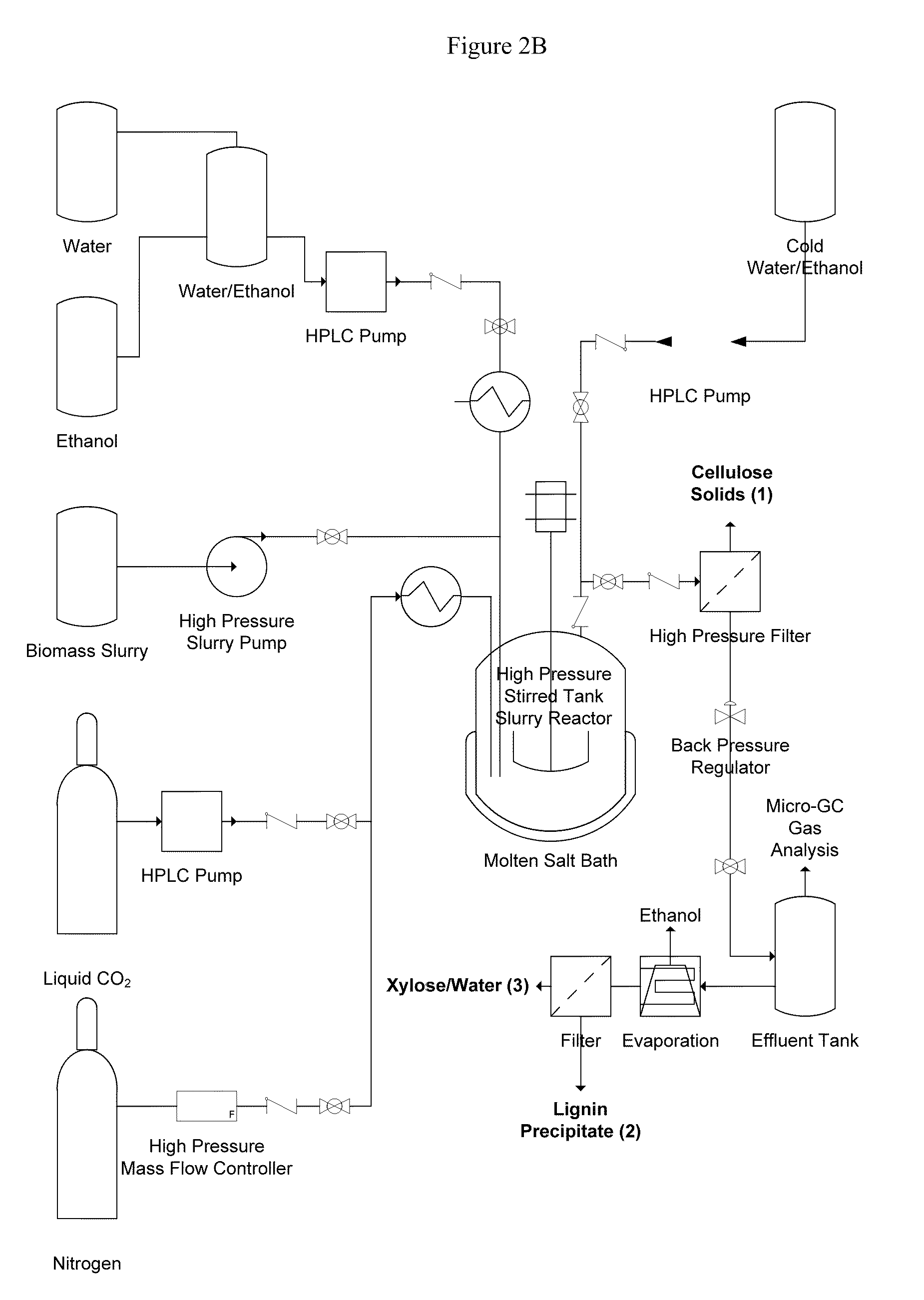
Methods of making glucose and / or furfural from biomass require one or more supercritical fluids that may be used to process biomass, cellulose from the biomass, and / or xylose from the biomass. Examples of supercritical fluids for use in processing biomass include ethanol, water, and carbon dioxide at a temperature and pressure above the critical points for ethanol and carbon dioxide but at a temperature and / or pressure below that of the critical point for water. A supercritical fluid containing carbon dioxide and water may be used to convert cellulose to glucose or convert xylose to furfural. The fluid has a temperature and pressure above the critical point of carbon dioxide, but at least one of the temperature and pressure is below the critical point for water.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Integrated sample analysis device
InactiveUS6979424B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionElectrophoresis
An analysis device comprises a body having a reaction chamber for chemically reacting a sample, a separation region for separating components of the sample, and a transition region connecting the reaction chamber to the separation region. The transition region includes at least one valve for controlling the flow of fluid between the reaction chamber and the separation region. Further, the transition region thermally isolates the reaction chamber from the separation region. In a preferred embodiment, the reaction chamber is an amplification chamber for amplifying nucleic acid in the sample, and the separation region comprises an electrophoresis channel containing a suitable matrix material, such as electrophoresis gel or buffer, for separating nucleic acid fragments. Electrodes are embedded in the body for separation of sample components. The body may also be surrounded by external, functional components such as an optical detector for detecting separated components of the sample.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
Multiple continuous microfluidic reactors for the scaled up synthesis of gel or polymer particles
ActiveUS20100184928A1Fast throughput screeningGaseous chemical processesFlow mixersStrong couplingPolymer
This present invention provides devices for the parallelization of the formation of droplets in a multiple droplet generator integrating two or more parallel flow-focusing devices (FFDs) with either identical, or different, geometries. In the parallel identical FFDs, emulsification generates droplets with a narrow (below 4%) polydispersity despite weak coupling between the identical flow-focusing devices. Formation of droplets in the integrated droplet generator comprising FFDs with different dimensions of the microchannels occurs with strong coupling between the FFDs and produces droplets with varying sizes and size distributions. For such devices the regime in which emulsification produces droplets with varying dimensions and a narrow size distribution have been identified. The results of this work can be used in scaling up the production of droplets and in the simultaneous production of droplets and particles with different dimensions.
Owner:KUMACHEVA EUGENIA
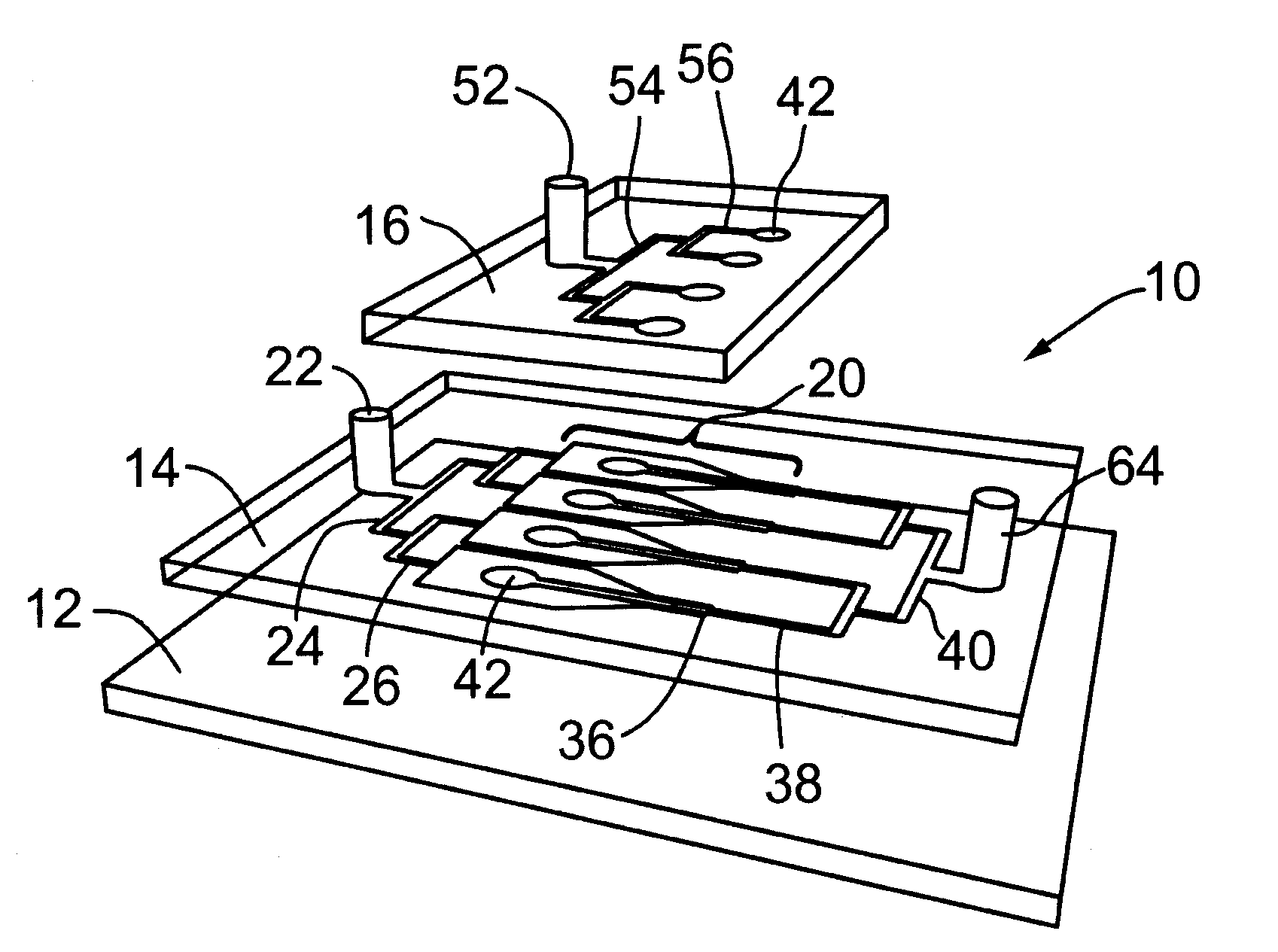
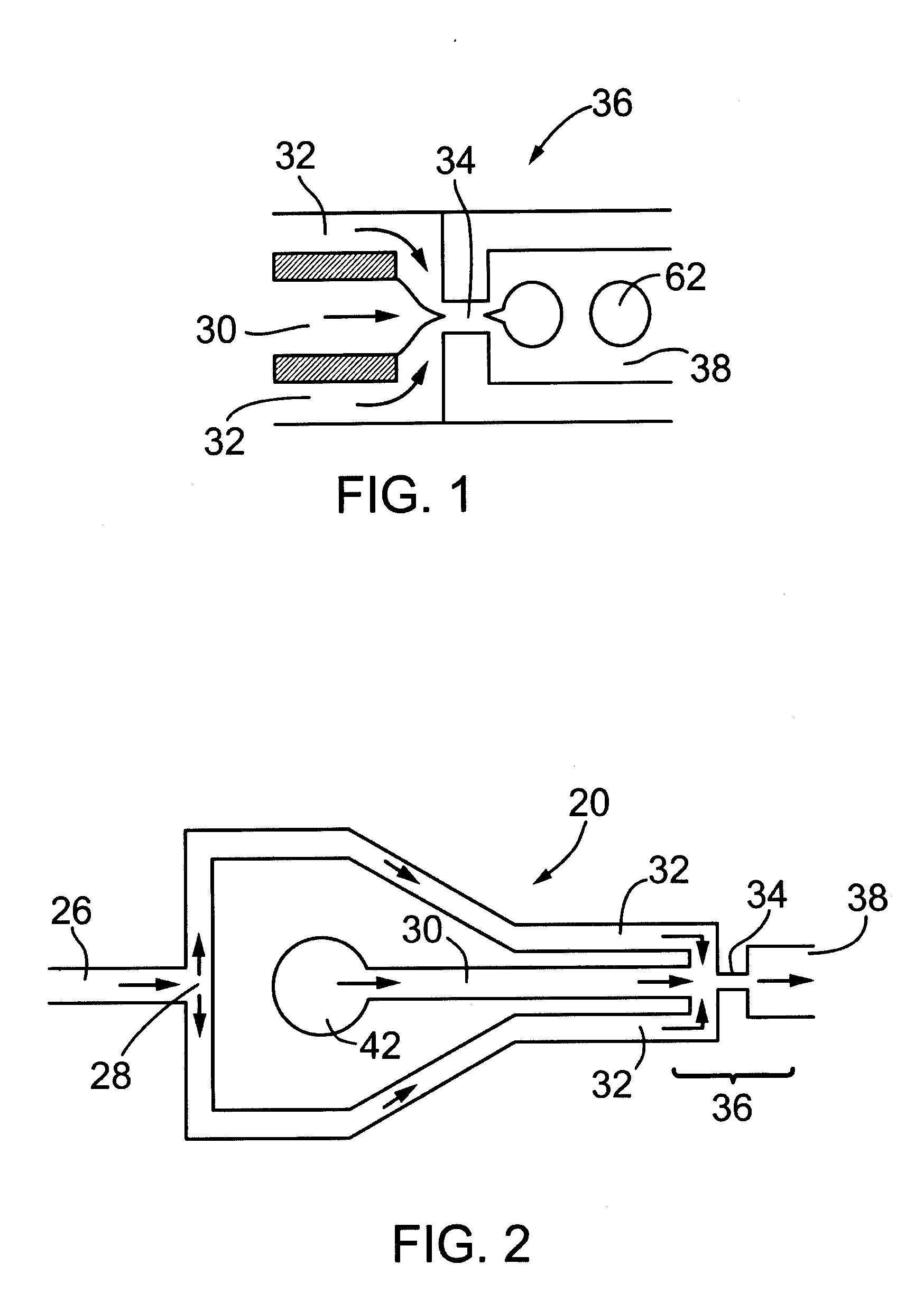
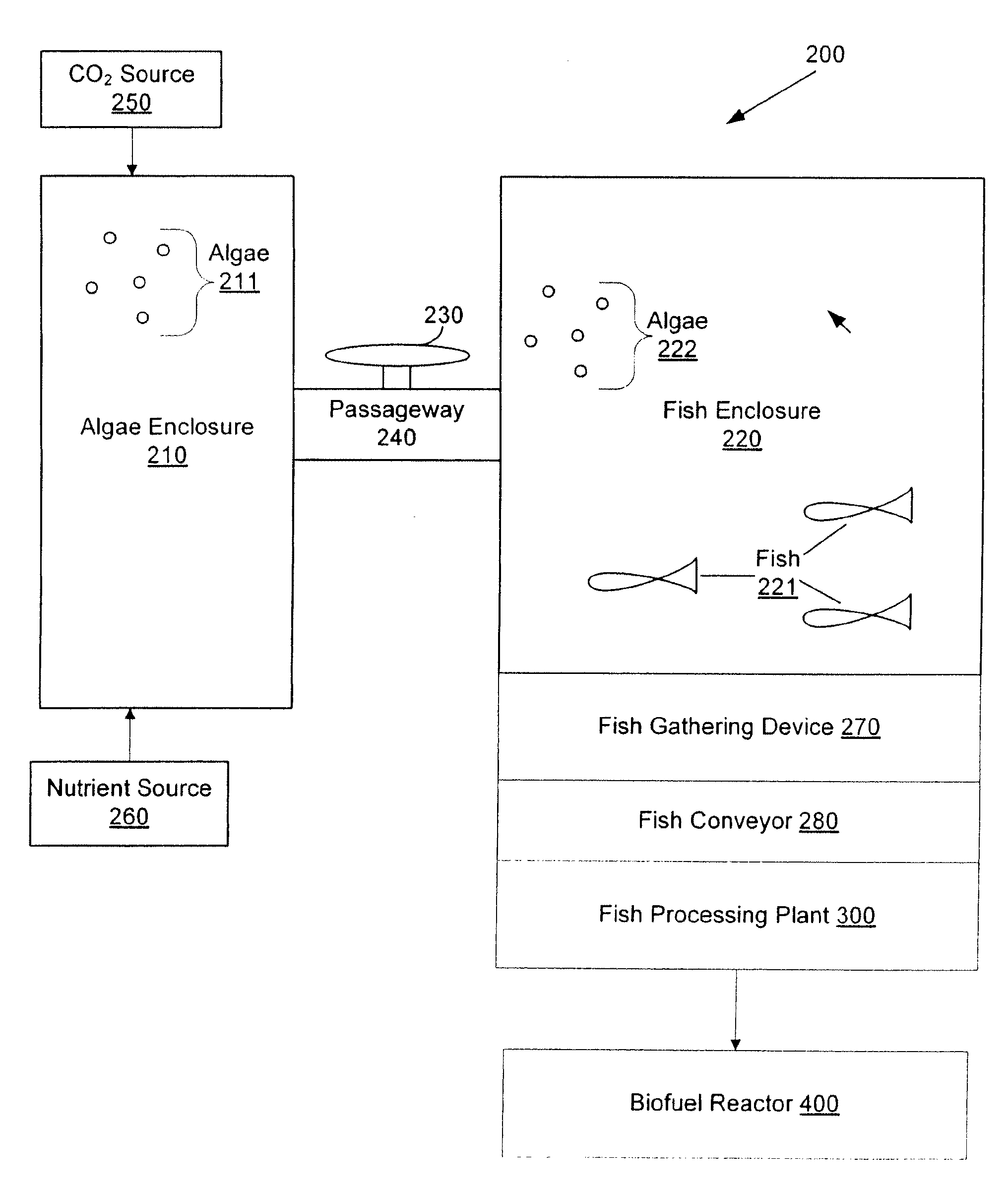
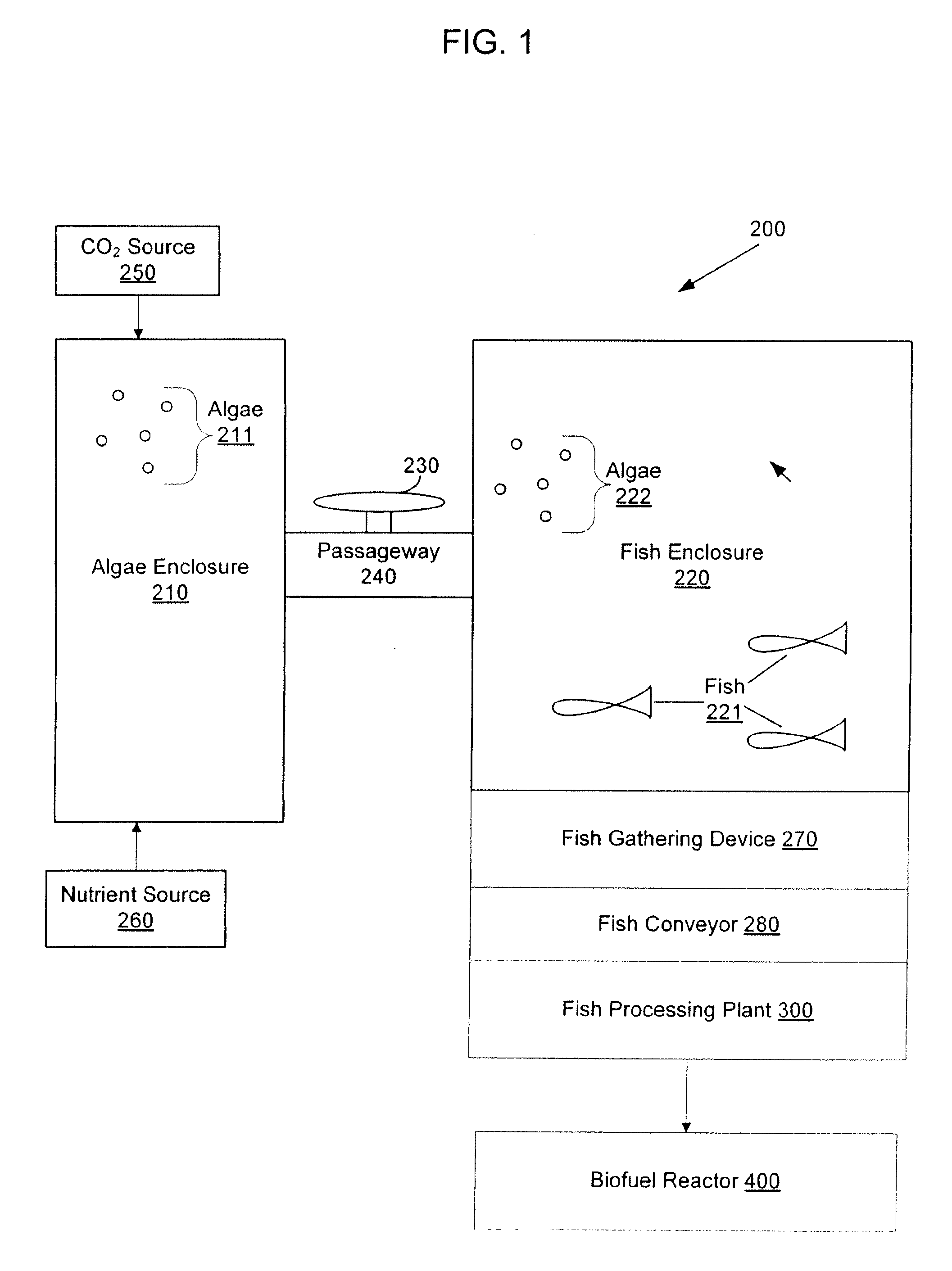
Systems and methods for producing biofuels from algae
The invention provides systems and methods for producing biofuel from algae that use cultured fish to harvest algae from an algal culture. The methods further comprise gathering the fish, extracting lipids from the fish, and processing the lipids to form biofuel. The multi-trophic systems of the invention comprises at least one enclosure that contains the algae and the fishes, and means for controllably feeding the algae to the fishes. The lipid compositions extracted from the fishes are also encompassed.
Owner:LIVEFUELS
Portable hydrogen generator
A hydrogen generation system includes a fuel container, a spent fuel container, a catalyst system and a control system for generating hydrogen in a manner which provides for a compact and efficient construction while producing hydrogen from a reaction involving a hydride solution such as sodium borohydride.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
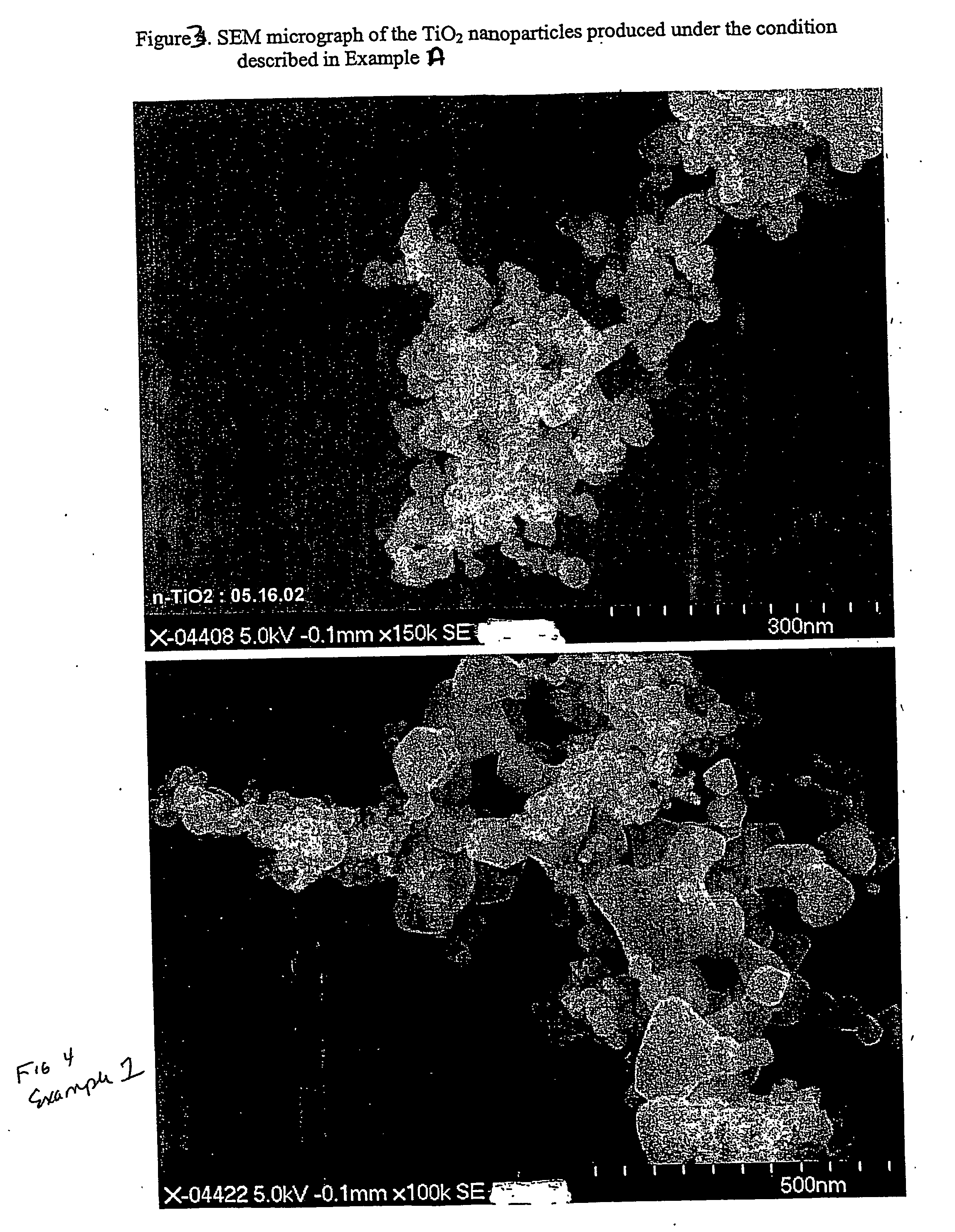
Method of producing nanoparticles using a evaporation-condensation process with a reaction chamber plasma reactor system
InactiveUS20060159596A1Reduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleReaction zone
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the controlled synthesis of nanoparticles using a high temperature process. The reactor chamber includes a high temperature gas heated by means such as a plasma torch, and a reaction chamber. The homogenizer includes a region between the reactant inlets and the plasma (the spacer zone) to ensure that feeds from the reactant inlets are downstream of the recirculation zone induced by the high temperature gas. It also includes a region downstream of the reactant inlets that provides a nearly I dimensional (varying only in the axial direction) flow and concentration profile in the reaction zone to produce nanoparticles with narrow size distribution.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS6610256B2Quick analysisQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester and equipment for realizing the same
InactiveUS7045100B2Avoid disadvantagesRational productionPressurized chemical processFatty acid esterificationAlcoholTransesterification
Method for producing fatty acid methyl ester, including compounding saturated and unsaturated higher fatty substances from at least one of vegetable and animal with an alkaline solution dissolved in alcohol to form a mixture. The method also includes emulsifying the mixture to reach a chemical balance state in a reaction section, wherein fats are transesterified into fatty acid methyl ester, wherein border surfaces of the mixture are enlarged by dynamic turbulence in the reaction section and the transesterification is performed under pressure, and wherein the pressure is reduced during transesterification. The method further includes after reaching a chemical balance state, separating residues from the fatty acid methyl ester in a phase separation section. Apparatus for producing fatty acid methyl ester.
Owner:AMERICAN RENEWABLE FUELS
Micro heat exchanger with thermally conductive porous network
ActiveUS20060245987A1Inexpensive and efficient to manufactureGaseous chemical processesAdditive manufacturing apparatusThermal energyReticulated foam
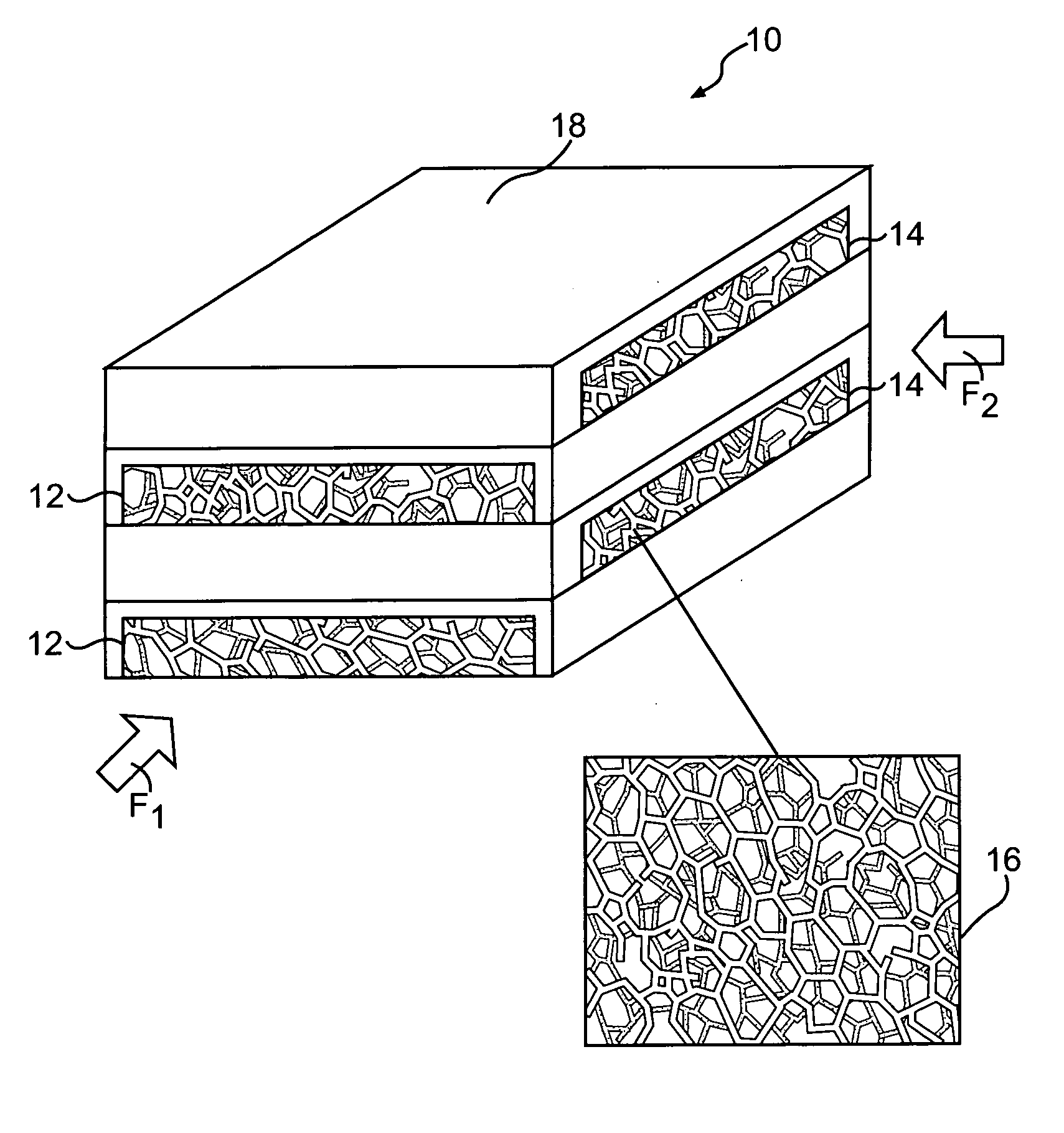
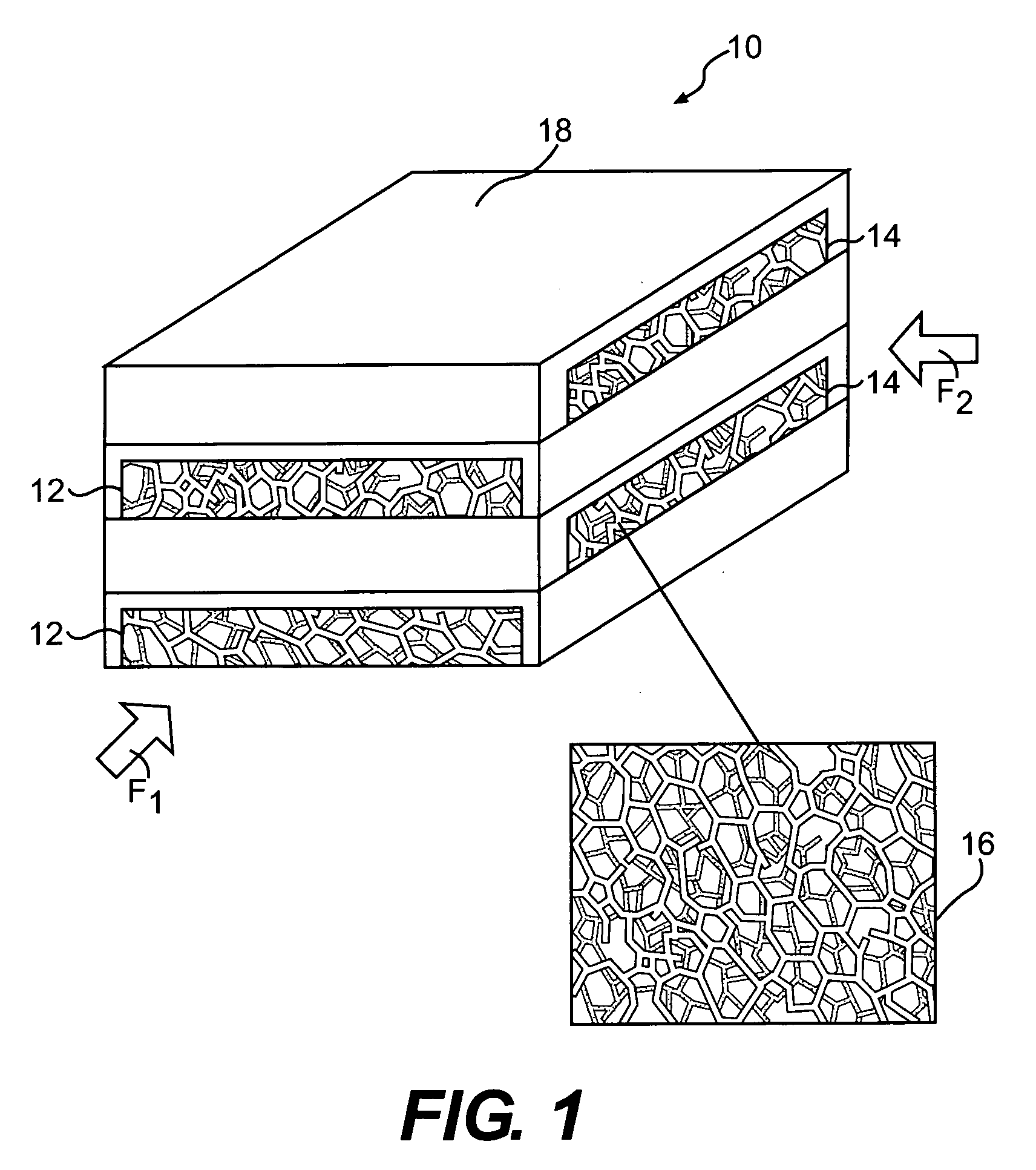
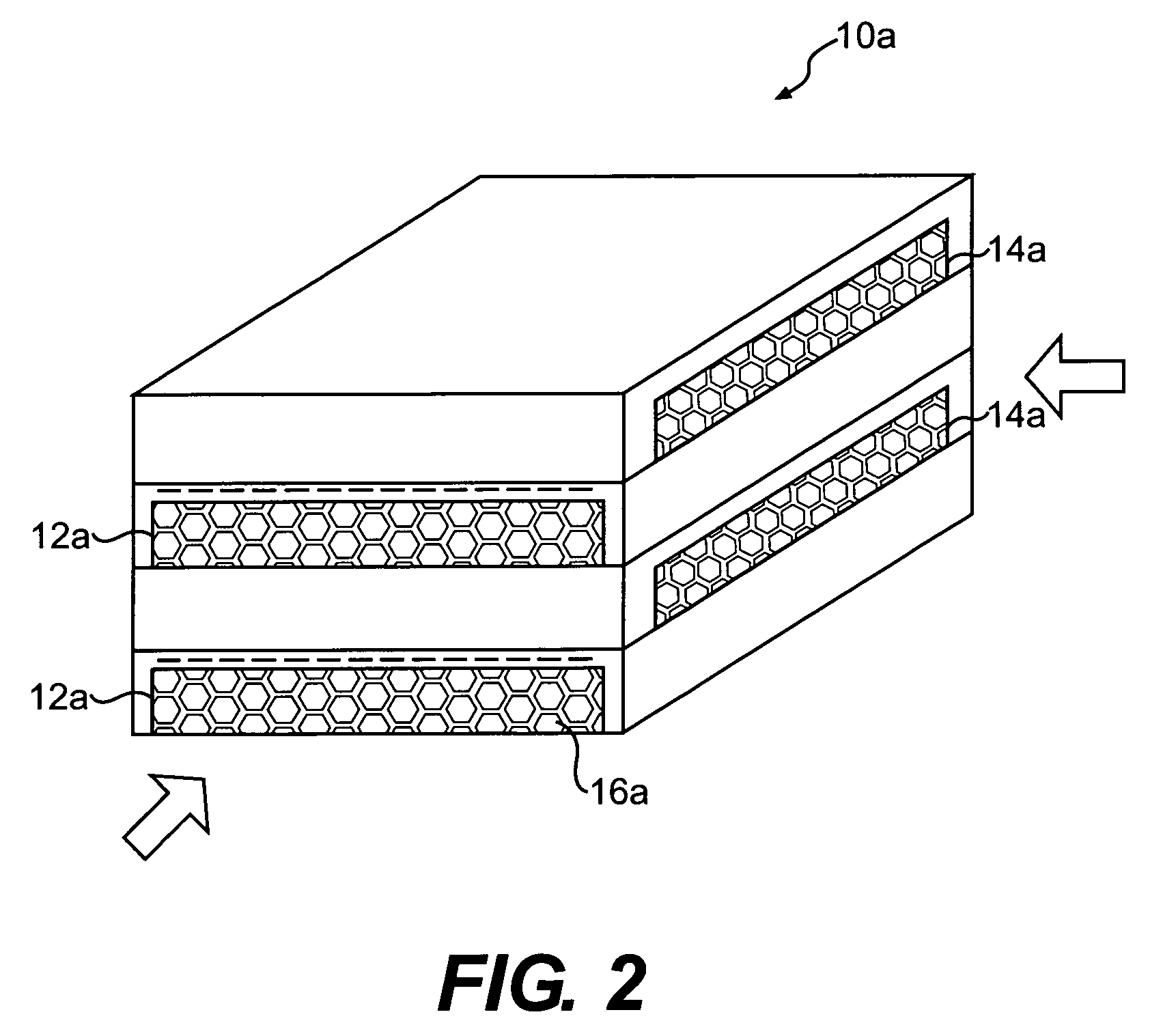
A micro heat exchanger system includes a first flow path and a second flow path transverse thereto for transferring thermal energy between a first fluid flowing through the first flow path and a second fluid flowing through the second flow path. The first flow path and the second flow path are filled with a thermally conductive porous network which incorporate unique structures, such as tubes, honeycomb, corrugated metal, reticulated foams, woven meshes or nonwoven mats or felts, engineered lattice structures, or a combination of these structures. In another embodiment, the thermally conductive porous network is coated with catalyst to provide an integrated heat exchanger and catalytic reactors.
Owner:RTX CORP
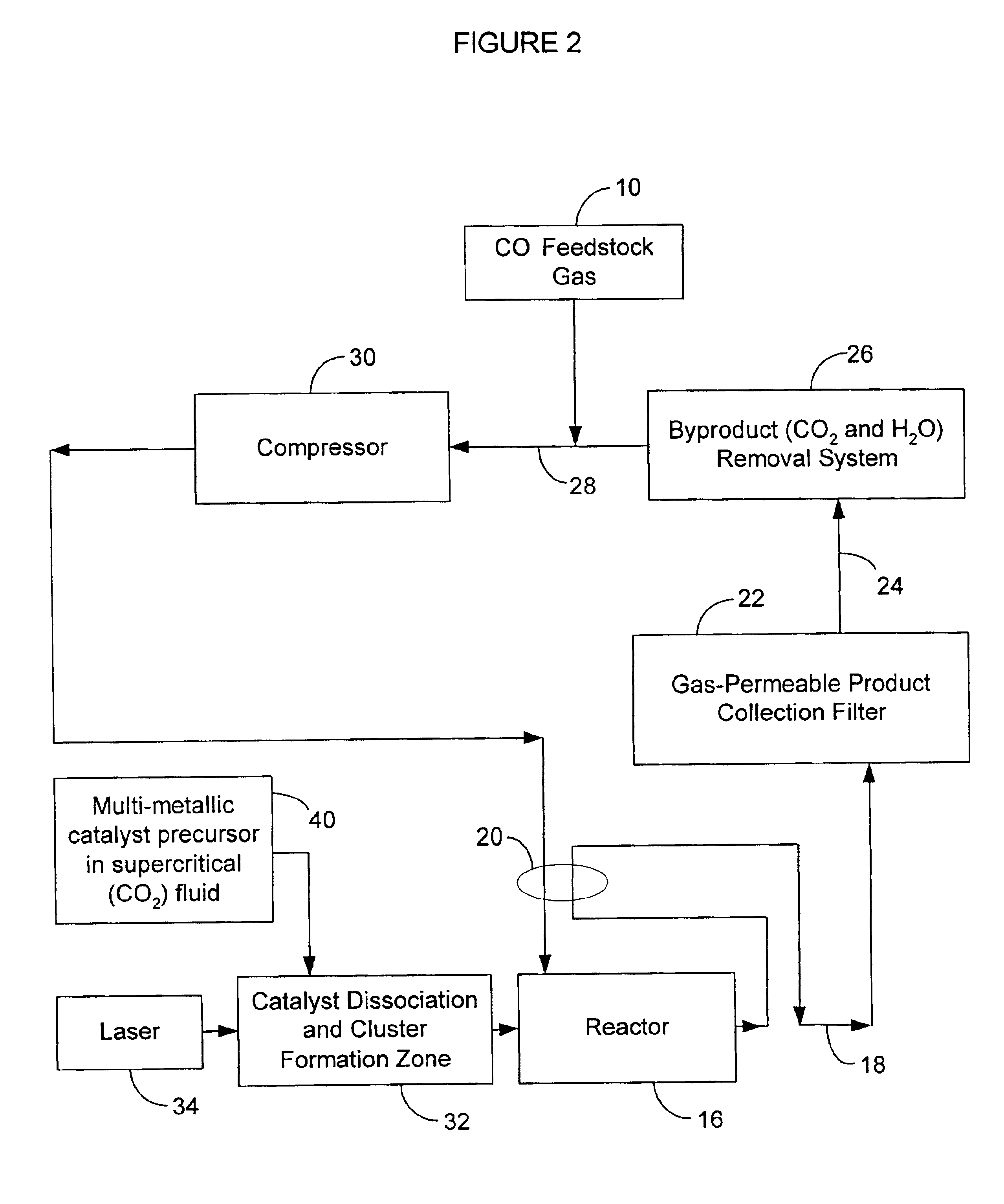
Process utilizing pre-formed cluster catalysts for making single-wall carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6913789B2Facilitates nucleation phaseFaster and more reproducible and stable clusteringMaterial nanotechnologyFibre chemical featuresGas phaseMetal catalyst
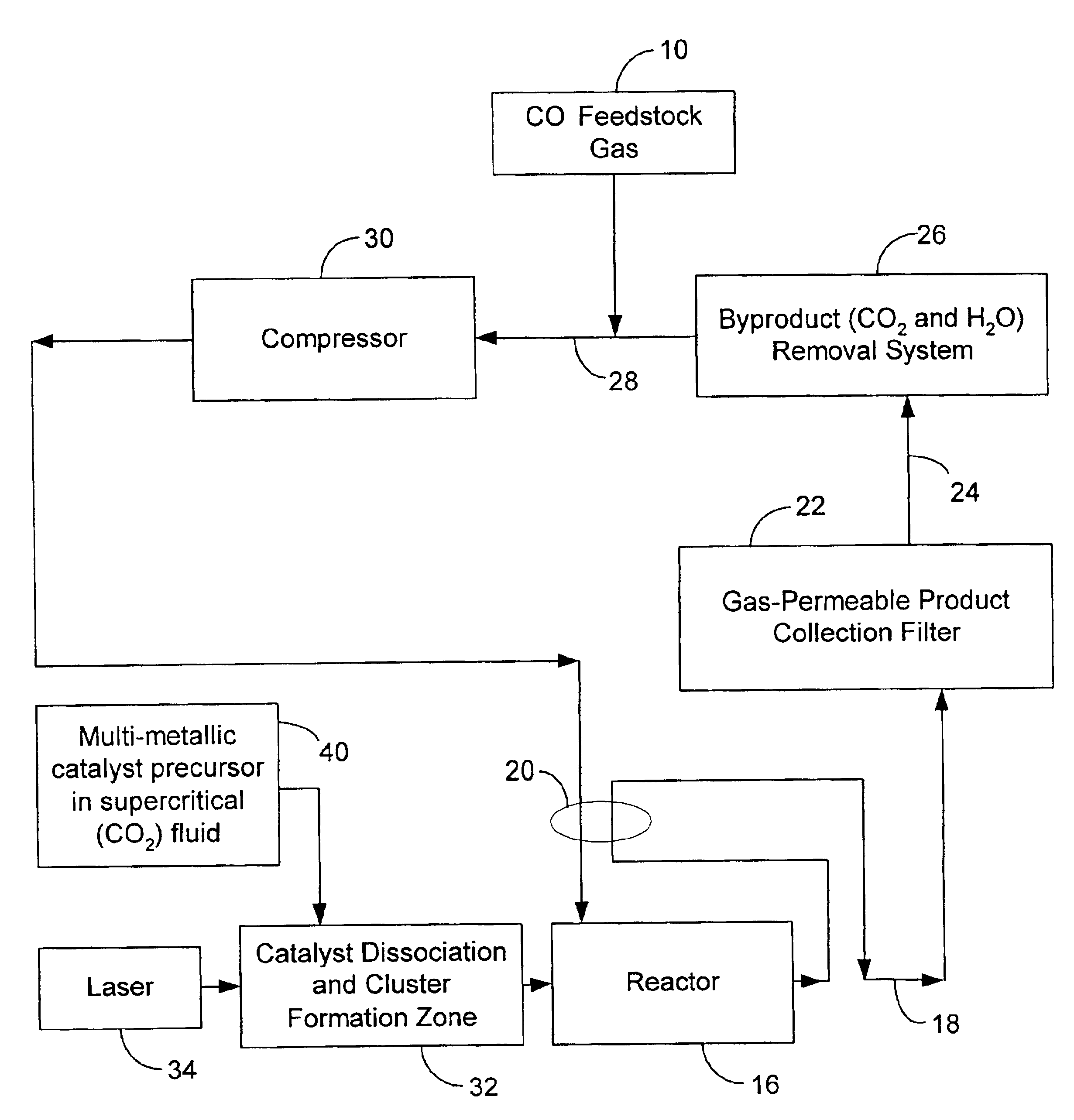
A gas-phase method for producing high yields of single-wall carbon nanotubes with high purity and homogeneity is disclosed. The method involves using preformed metal catalyst clusters to initiate and grow single-wall carbon nanotubes. In one embodiment, multi-metallic catalyst precursors are used to facilitate the metal catalyst cluster formation. The catalyst clusters are grown to the desired size before mixing with a carbon-containing feedstock at a temperature and pressure sufficient to initiate and form single-wall carbon nanotubes. The method also involves using small fullerenes and preformed sections of single-wall carbon nanotubes, either derivatized or underivatized, as seed molecules for expediting the growth and increasing the yield of single-wall carbon nanotubes. The multi-metallic catalyst precursors and the seed molecules may be introduced into the reactor by means of a supercritical fluid. In addition the seed molecules may be introduced into the reactor via an aerosol or smoke.
Owner:RICE UNIV
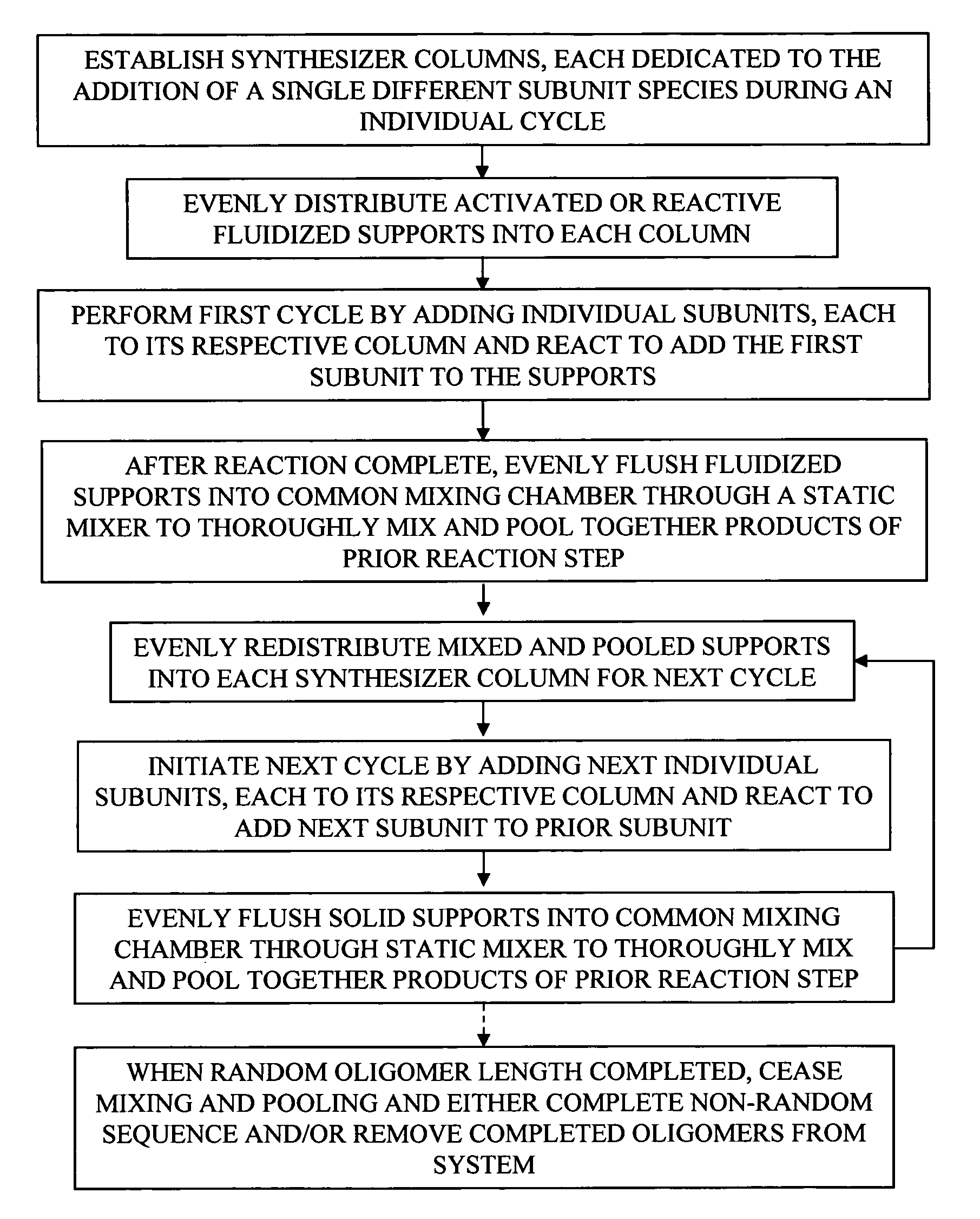
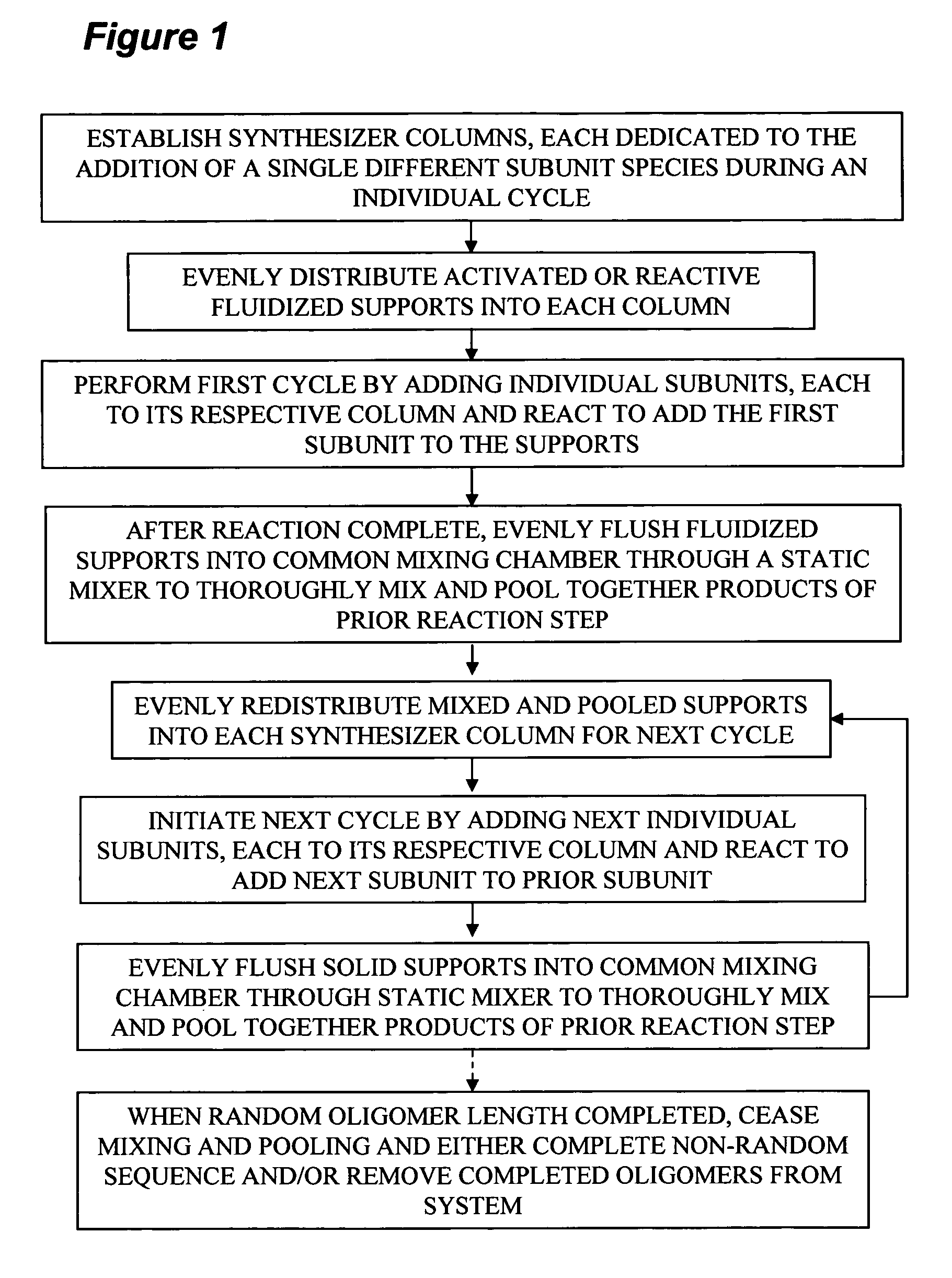
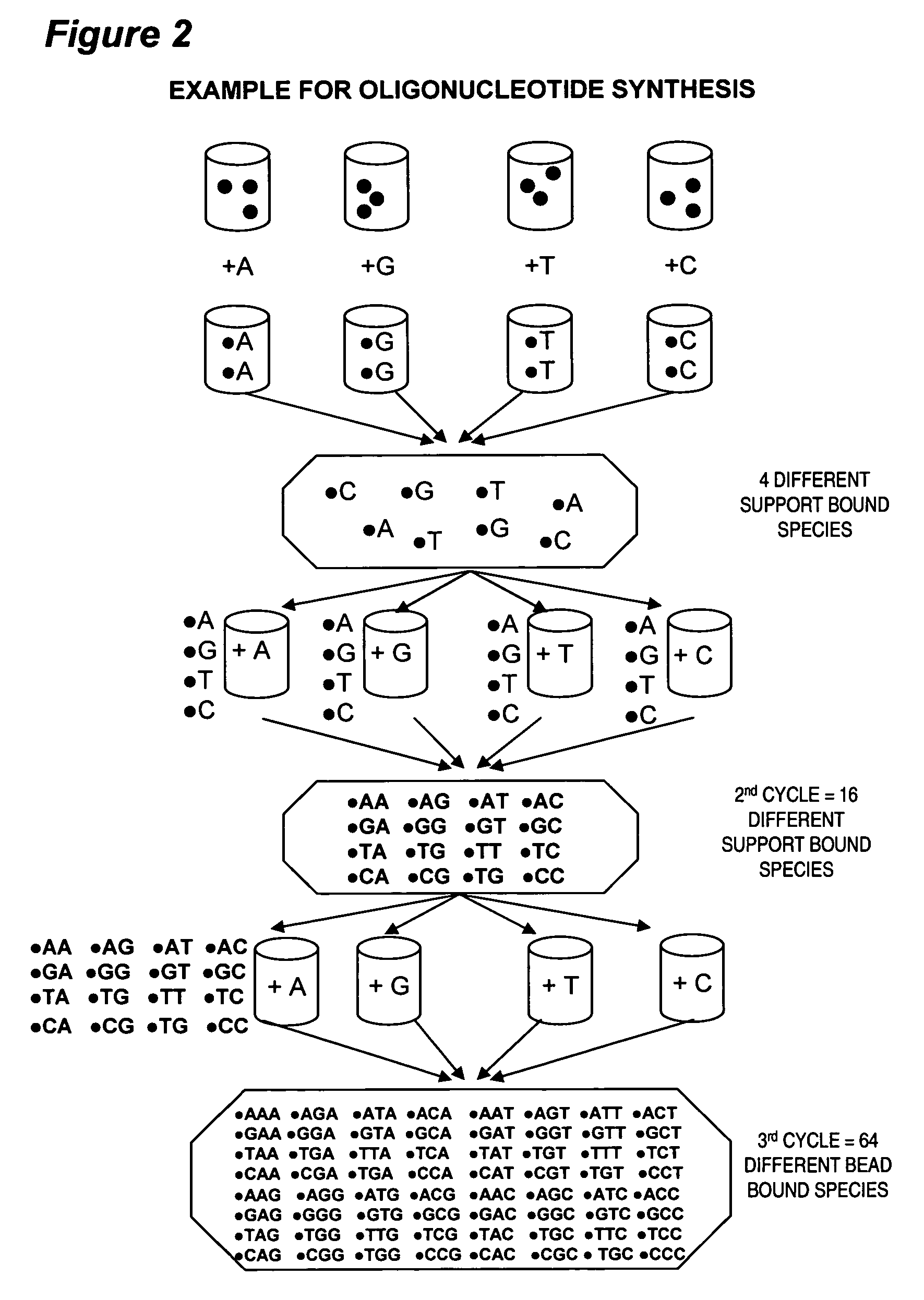
Process and apparatus for combinatorial synthesis
InactiveUS7576037B2Generate efficientlyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsCombinatorial synthesis
Apparatus and methods are described for split synthesis combinatorial chemistry that provides candidate libraries where an even distribution of theoretical products is obtainable through even mixing during the pooling step, followed by controlled redistribution of the mixed pooled products from the prior addition step into separate synthesis columns, one for each different specie of subunit to be added.
Owner:MEI TECH +1
Methods and apparatus for improved luminescence assays
InactiveUS6325973B1High sensitivityFaster assay timeImmobilised enzymesCombination devicesAnalyteElectrochemiluminescence
An apparatus for performing a binding assay for an analyte of interest in a sample based upon measurement of clectrochemiluminescence at an electrode surface comprising: (a) a cell defining a sample; (b) an electrode adjacent a portion of the sample containing volume; (c) a voltage control device for impressing electrochemical energy upon the electrode sufficient to generate luminescence; (d) means for magnetically collecting particles along the electrode surface; and (e) a light detection device for measuring the luminescence.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
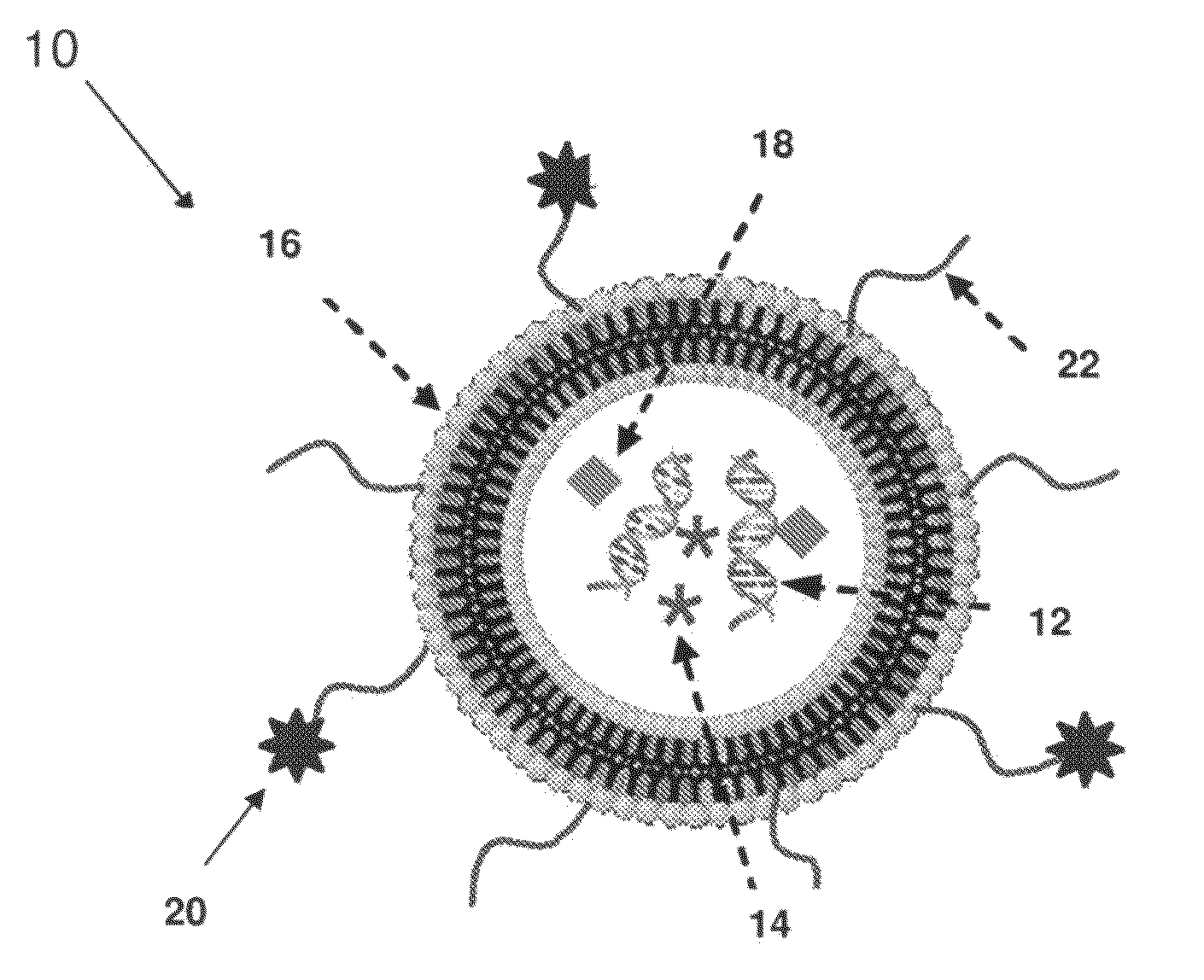
Lipid Nanoparticle Compositions and Methods of Making and Using the Same
InactiveUS20110038941A1Extend systemic circulation timeExtended circulation timeOrganic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedNanoparticleOligonucleotide
Oligonucleotide-lipid nanoparticles made of at least one oligonucleotide, at least one lipid and at least one complexation agent for the oligonucleotide, methods of making and using, and devices for making the same are disclosed.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
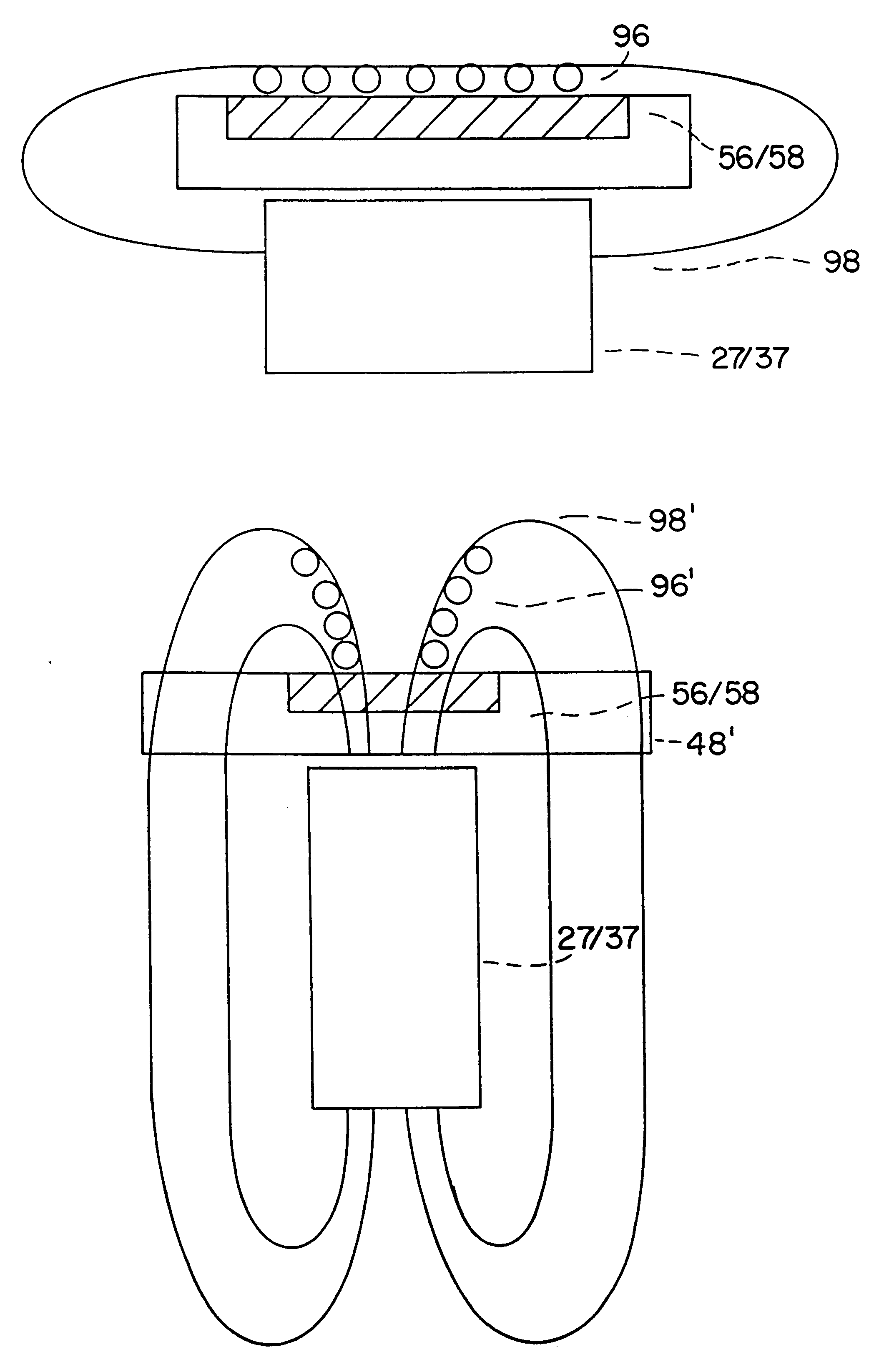
Flow control through plural, parallel connecting channels to/from a manifold
InactiveUS20060275185A1Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingControl flowStream flow
The invention provides apparatuses and techniques for controlling flow between a manifold and two or more connecting microchannels. Flow between plural connecting microchannels, that share a common manifold, can be made more uniform by the use of flow straighteners and distributors that equalize flow in connecting channels. Alternatively, flow can be made more uniform by sections of narrowed diameter within the channels. Methods of making apparatus and methods of conducting unit operations in connecting channels are also described.
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
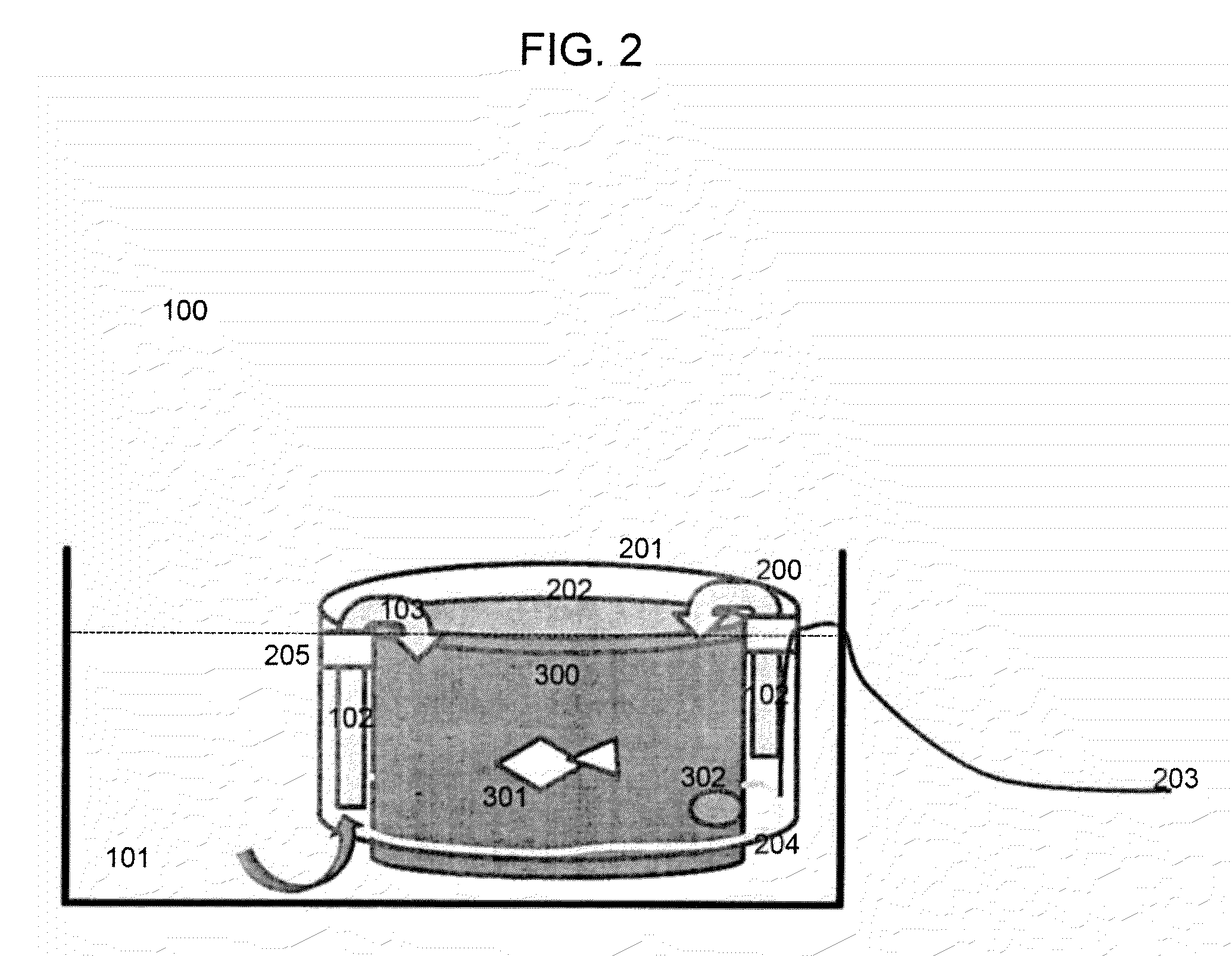
Hot solids gasifier with CO2 removal and hydrogen production
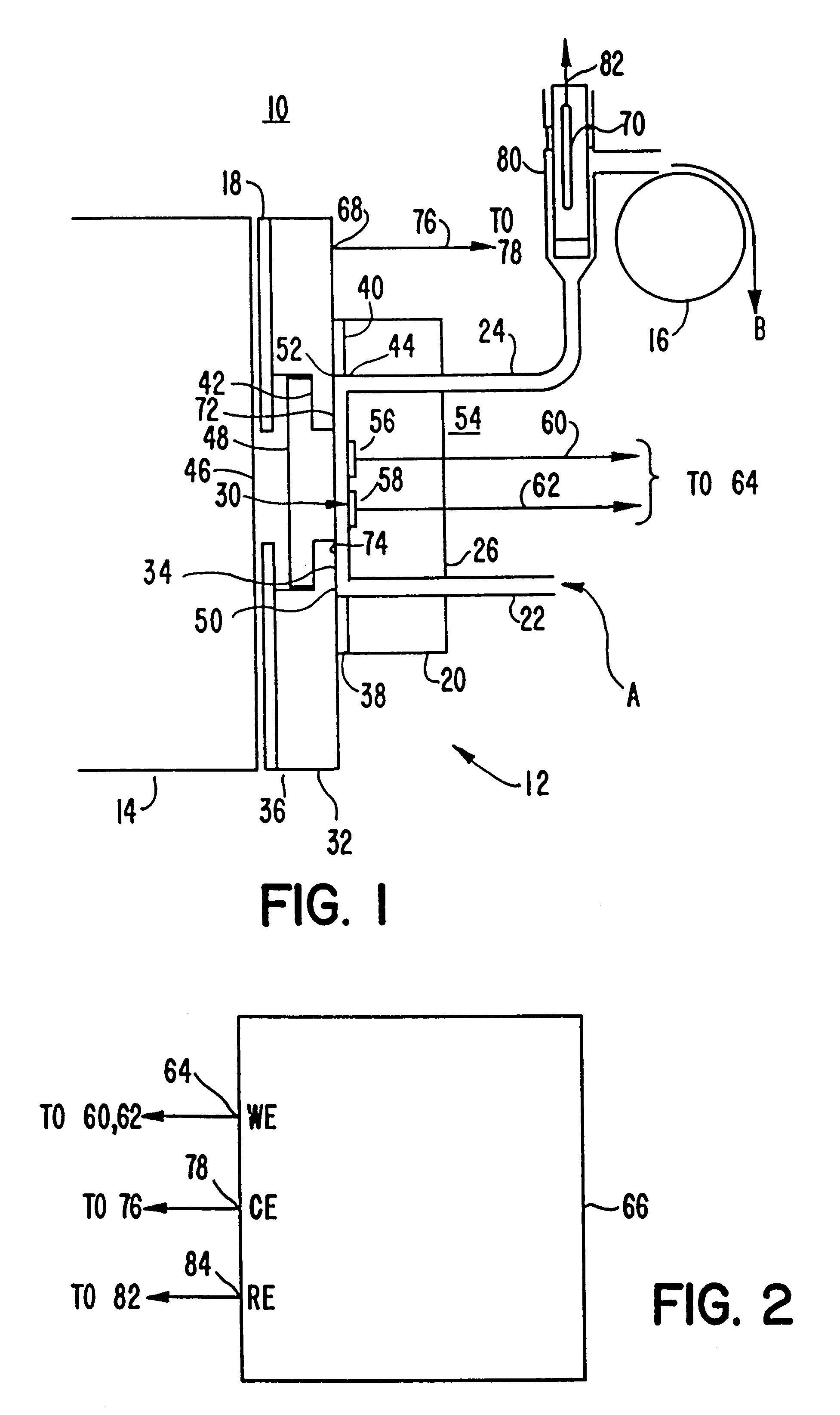
ActiveUS7083658B2Avoid entrainmentEfficient captureMuffle furnacesGas modification by gas mixingCo2 removalWater-gas shift reaction
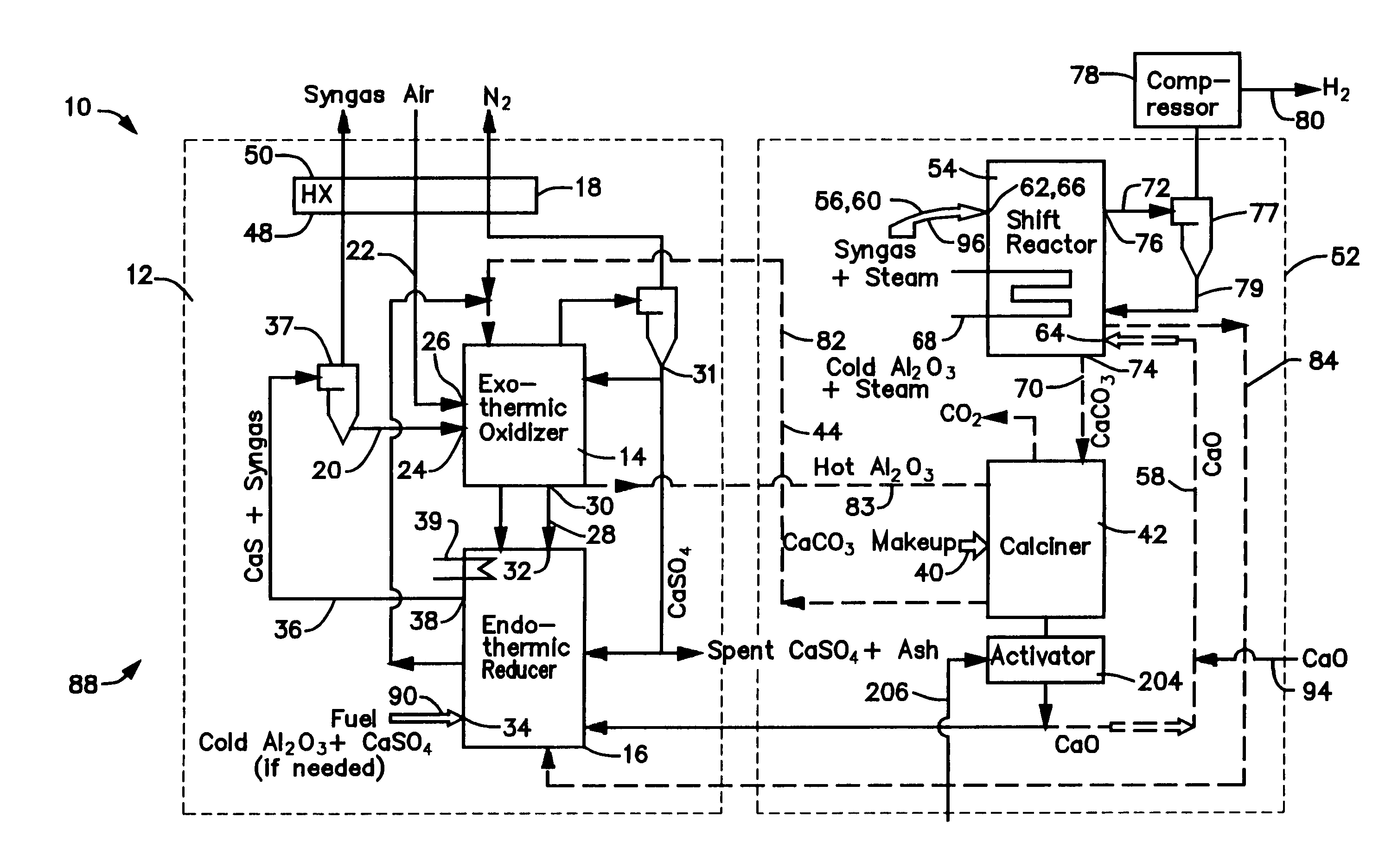
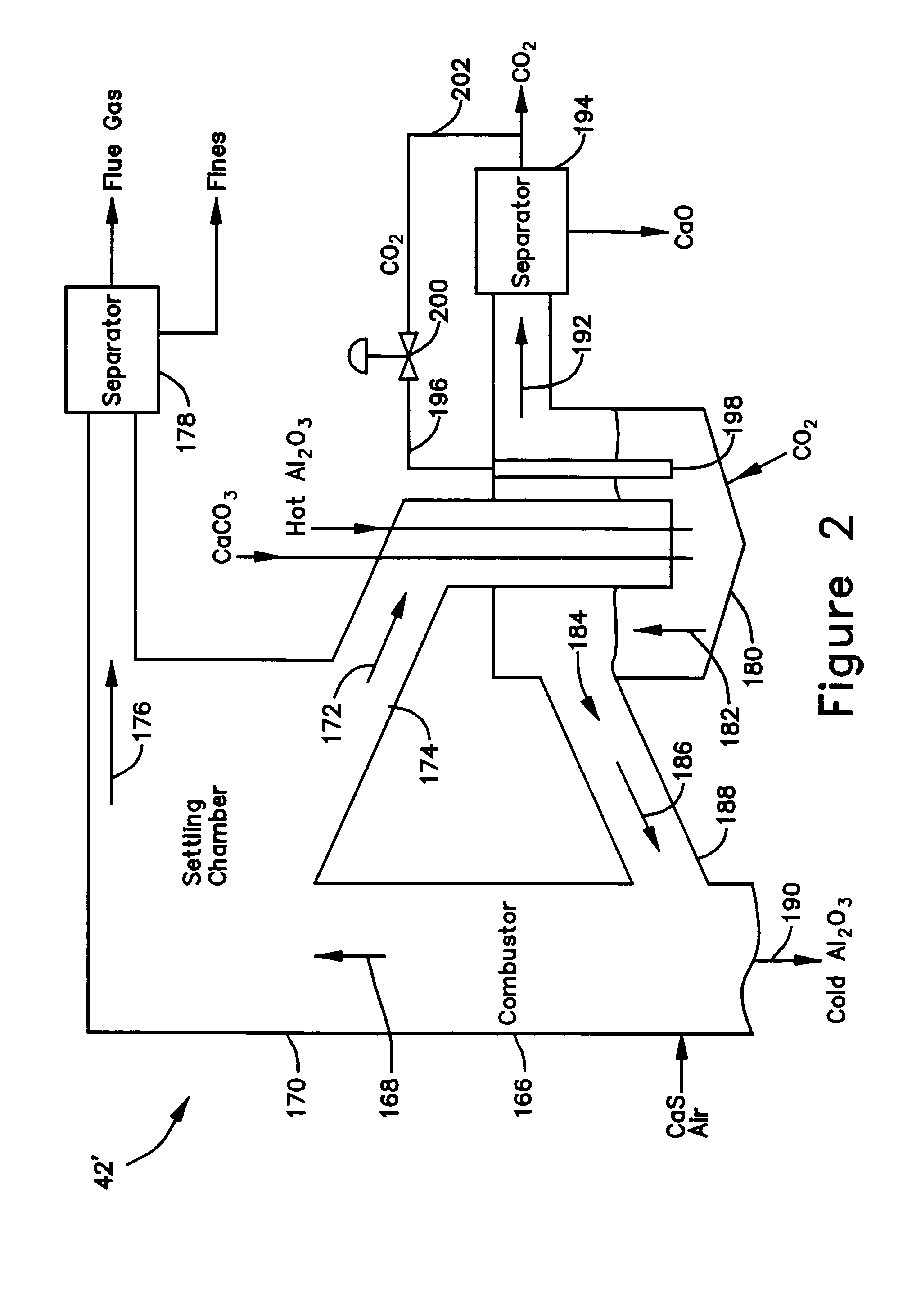
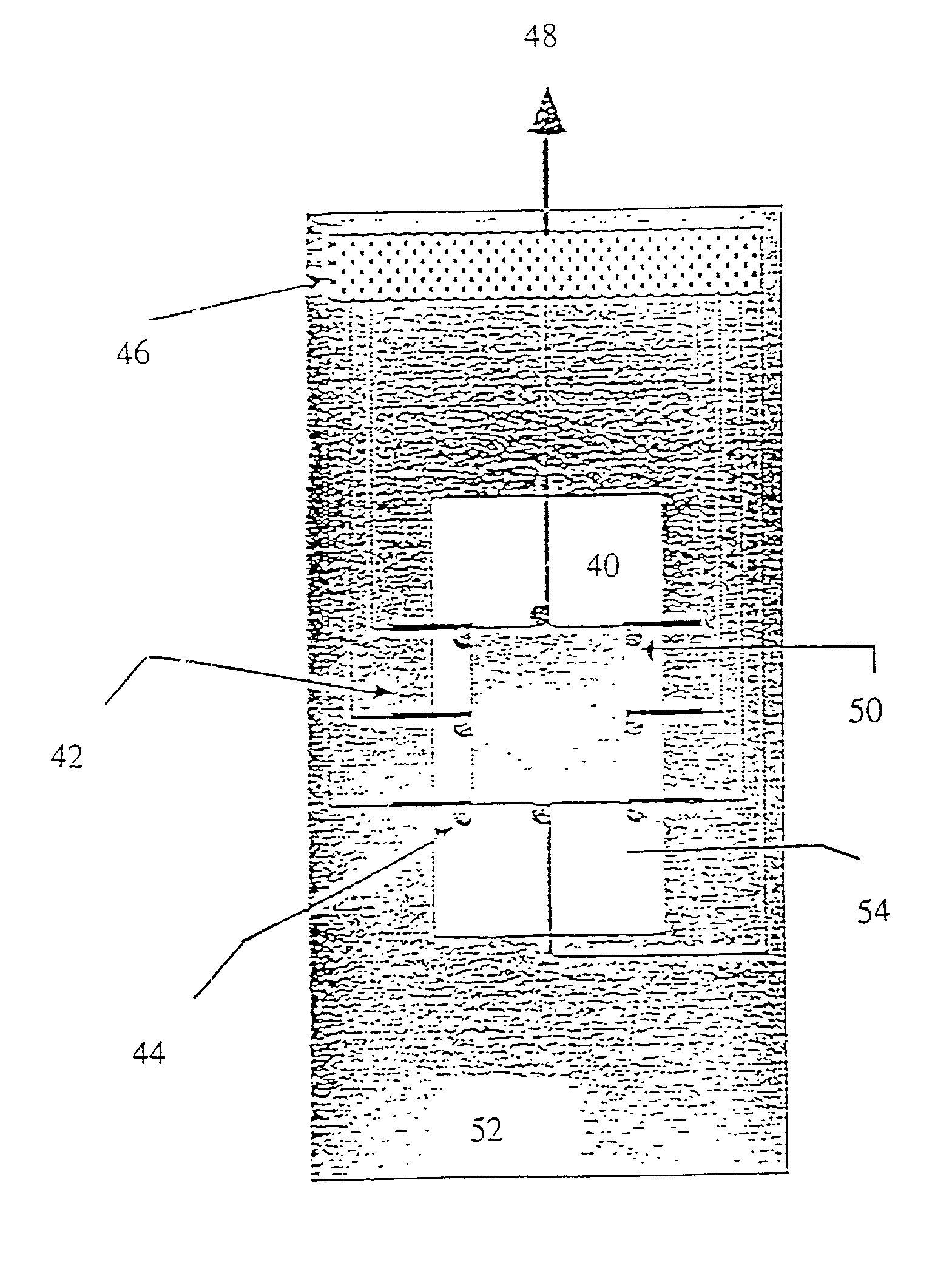
A gasifier 10 includes a first chemical process loop 12 having an exothermic oxidizer reactor 14 and an endothermic reducer reactor 16. CaS is oxidized in air in the oxidizer reactor 14 to form hot CaSO4 which is discharged to the reducer reactor 16. Hot CaSO4 and carbonaceous fuel received in the reducer reactor 16 undergo an endothermic reaction utilizing the heat content of the CaSO4, the carbonaceous fuel stripping the oxygen from the CaSO4 to form CaS and a CO rich syngas. The CaS is discharged to the oxidizer reactor 14 and the syngas is discharged to a second chemical process loop 52. The second chemical process loop 52 has a water-gas shift reactor 54 and a calciner 42. The CO of the syngas reacts with gaseous H2O in the shift reactor 54 to produce H2 and CO2. The CO2 is captured by CaO to form hot CaCO3 in an exothermic reaction. The hot CaCO3 is discharged to the calciner 42, the heat content of the CaCO3 being used to strip the CO2 from the CaO in an endothermic reaction in the calciner, with the CaO being discharged from the calciner 42 to the shift reactor 54.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC +1
Filtration and flow distribution method for chemical reactors using reticulated ceramics with uniform pore distributions
InactiveUS6291603B1Reduce turbulenceEntrance losses may be reducedCatalytic naphtha reformingMembrane filtersPore distributionFiltration
Owner:CRYSTAPHASE PRODS
Flushable hard surface cleaning wet wipe
InactiveUS7605096B2High cleaning composition loading factorBiocidePressurized chemical processLoading factorSurface cleaning
According to the present invention there is provided a wet wipe comprising a substrate that has tensile strength of at least 5 N / inch and which is biodegradable. In a further aspect, the present invention provides a flushable wet wipe comprising a substrate having a loading factor of at least 1.5 grams of cleaning composition per gram of substrate and which is biodegradable. The wet wipes is suitable for cleaning hard surfaces, especially lavatories and is flushable.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20030036067A1Improve throughputQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com