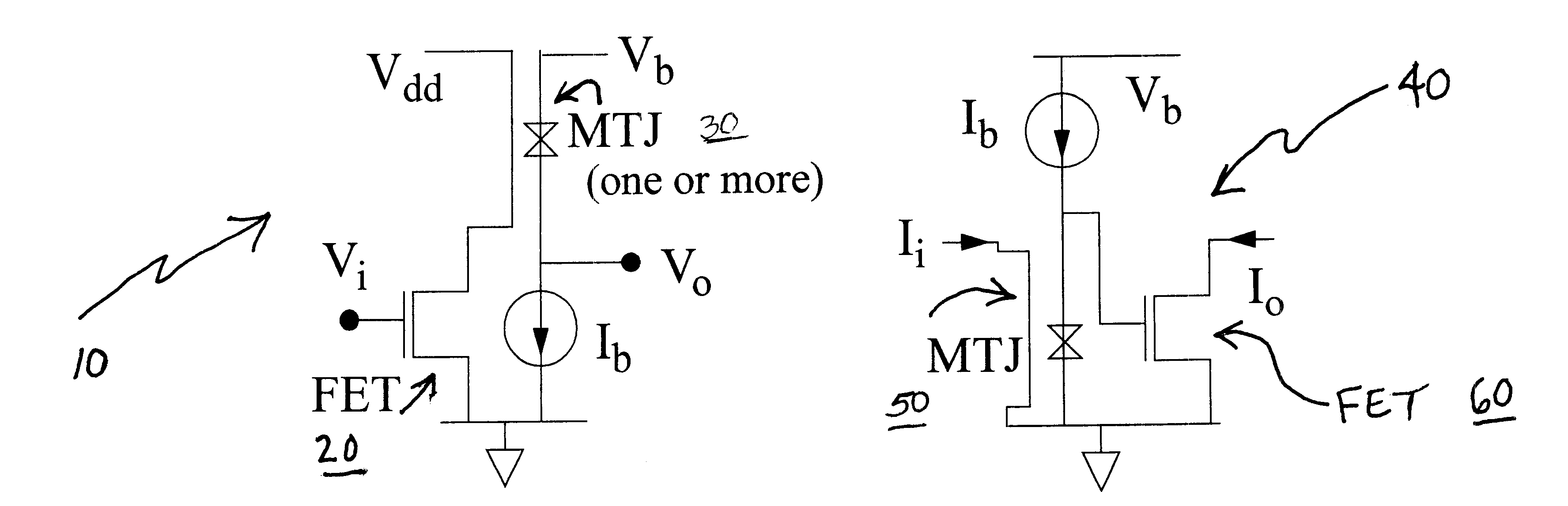Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about "Superconductive amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
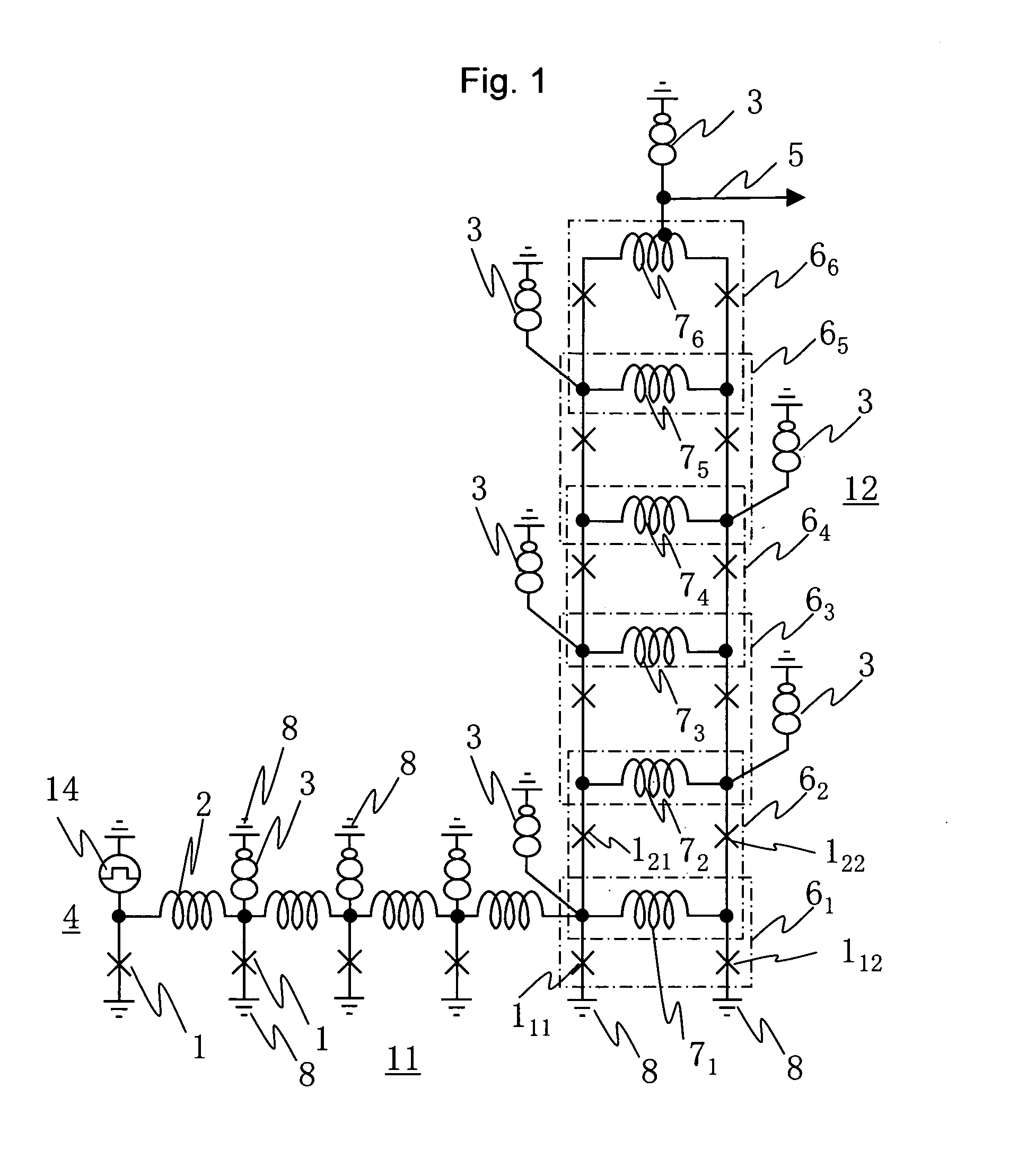
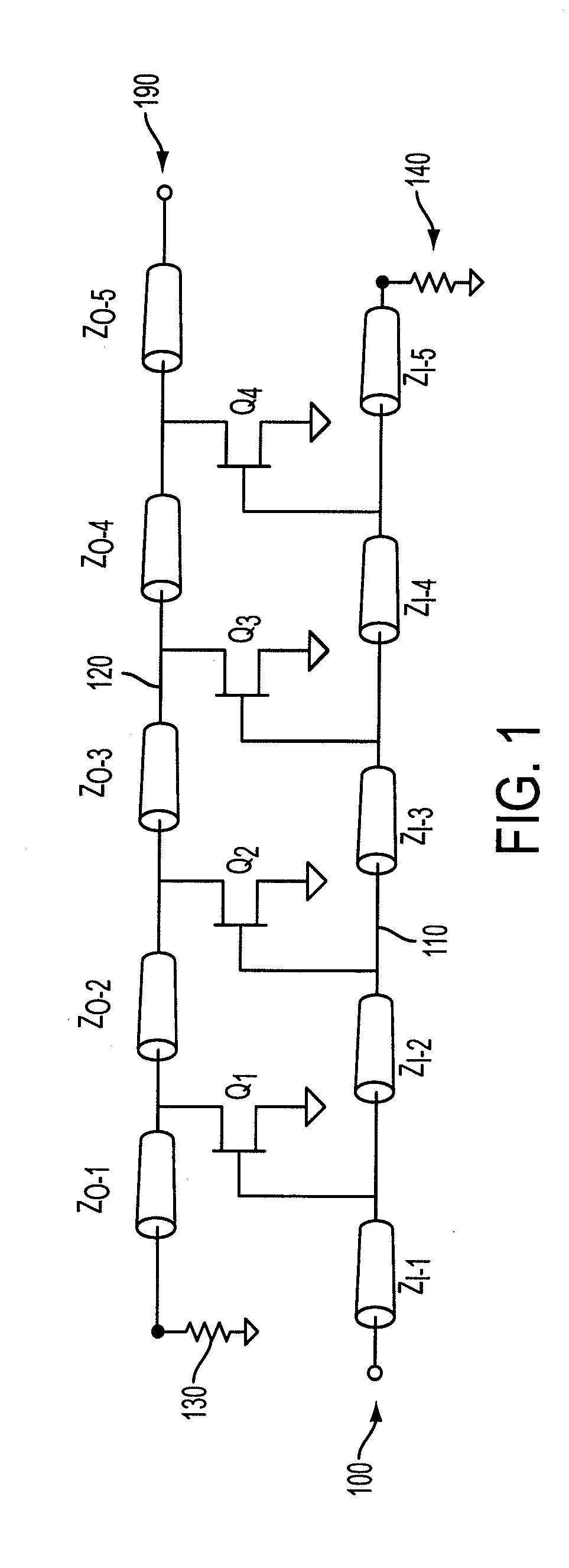
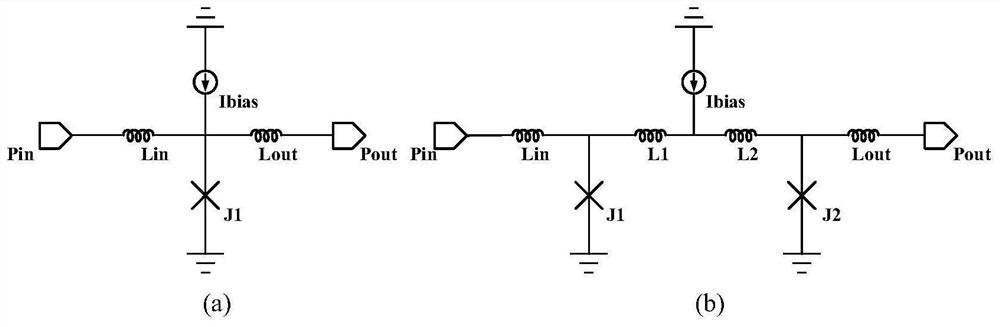
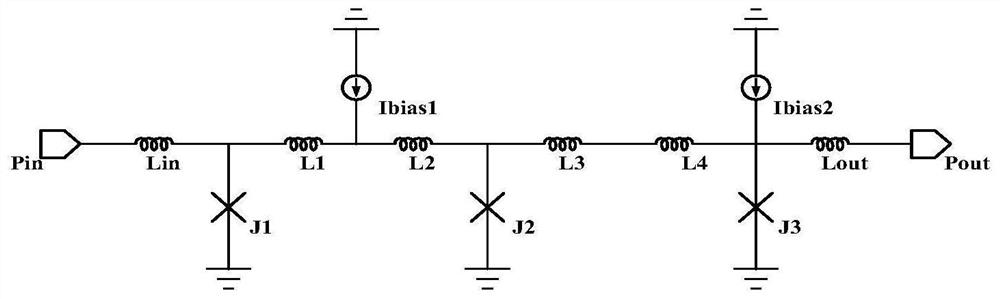
Method and apparatus for Josephson distributed output amplifier
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for providing high-speed, low signal power amplification. In an exemplary embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method for providing a wideband amplification of a signal by forming a first transmission line in parallel with a second transmission line, each of the first transmission line and the second transmission line having a plurality of superconducting transmission elements, each transmission line having a transmission line delay; interposing a plurality of amplification stages between the first transmission line and the second transmission line, each amplification stage having an resonant circuit with a resonant circuit delay; and substantially matching the resonant circuit delay for at least one of the plurality of amplification stages with the transmission line delay of at least one of the superconducting transmission lines.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
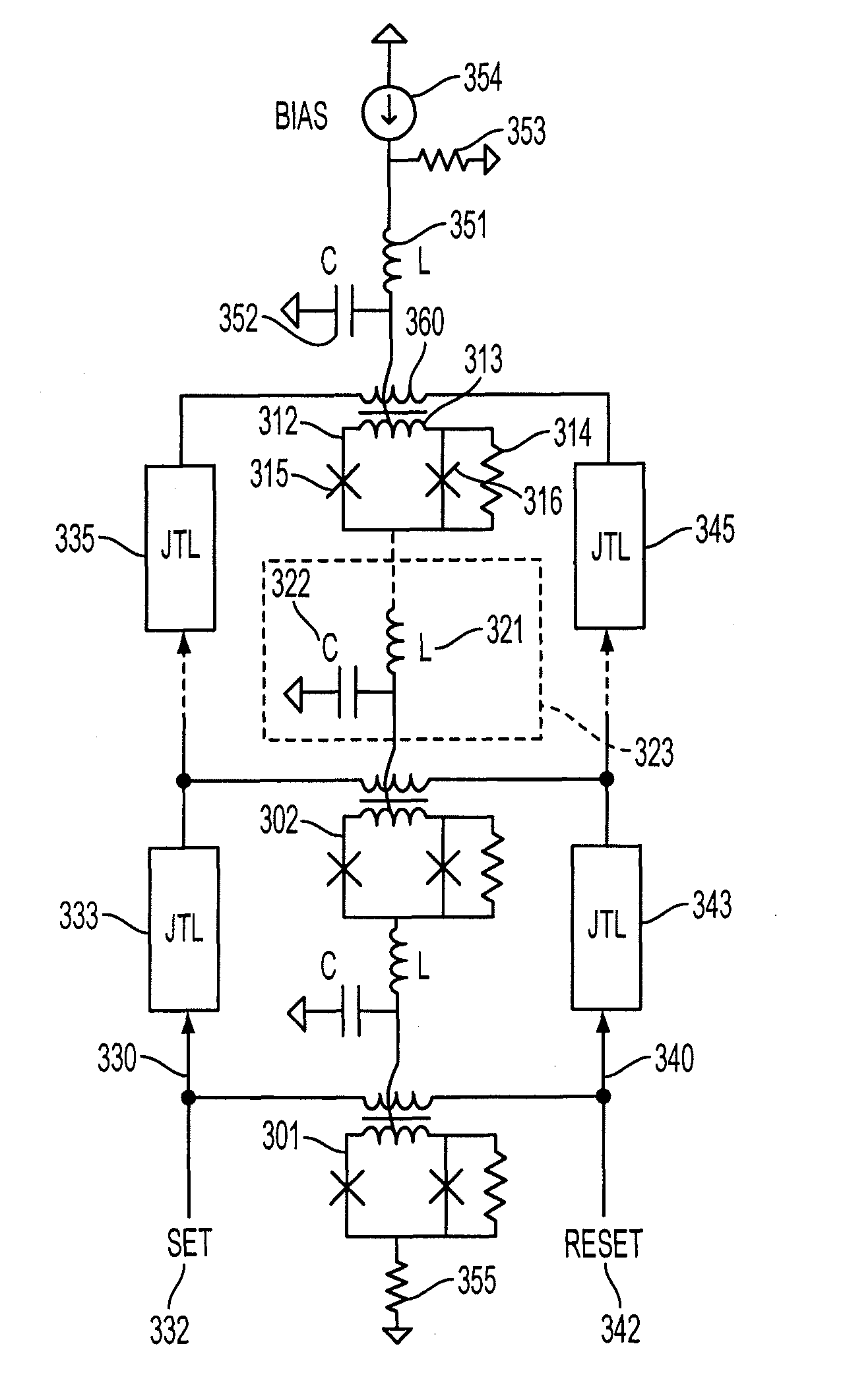
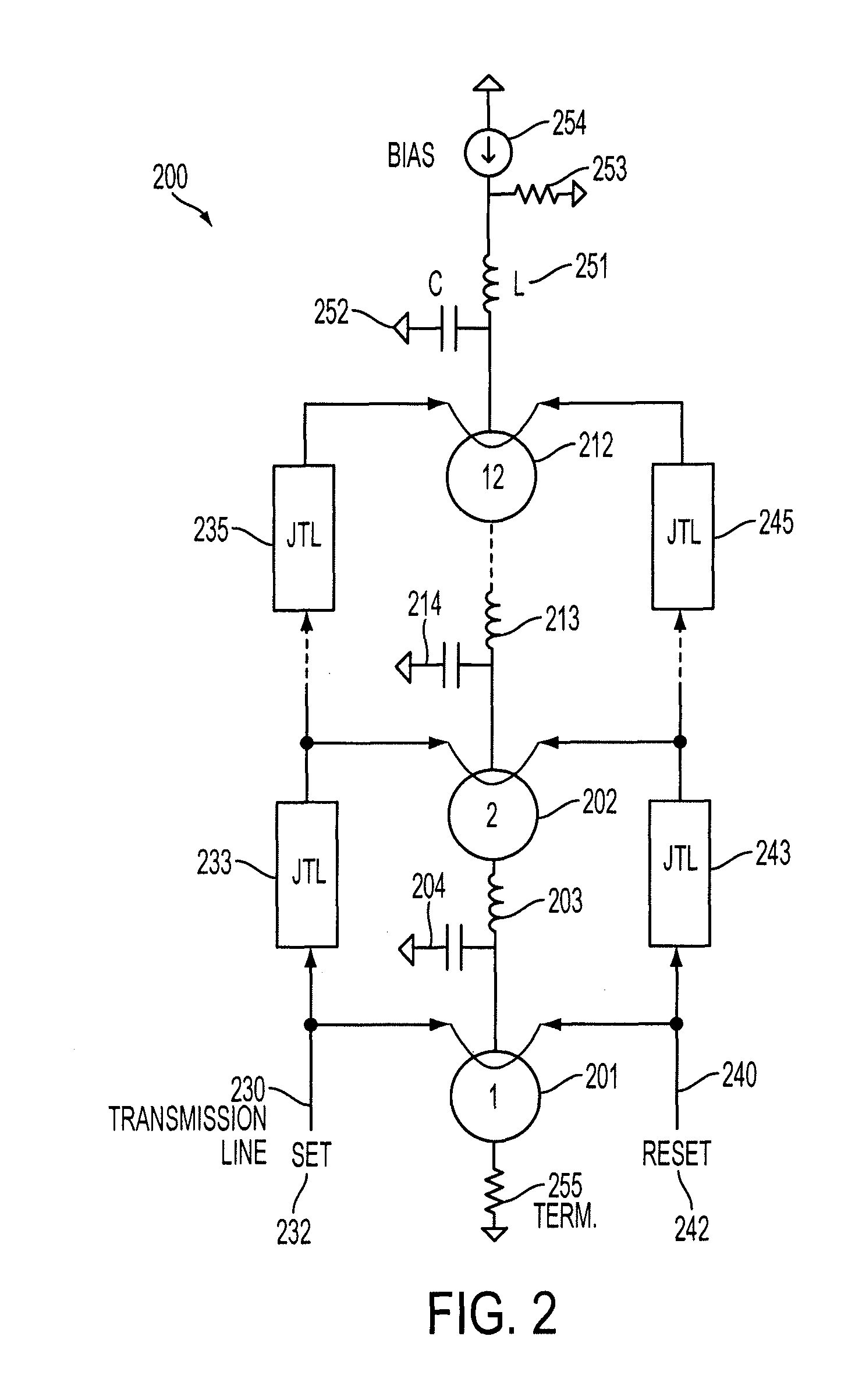
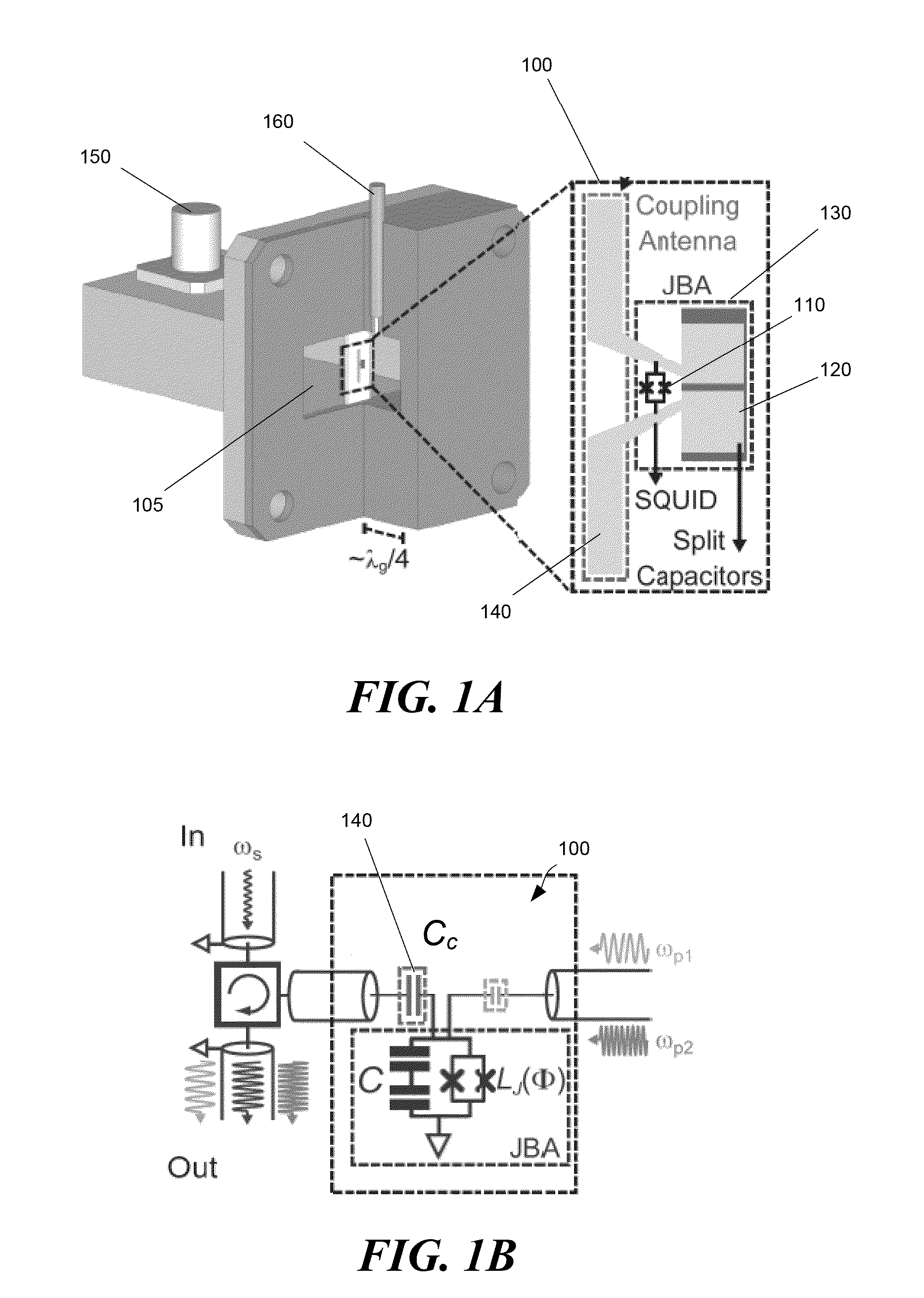
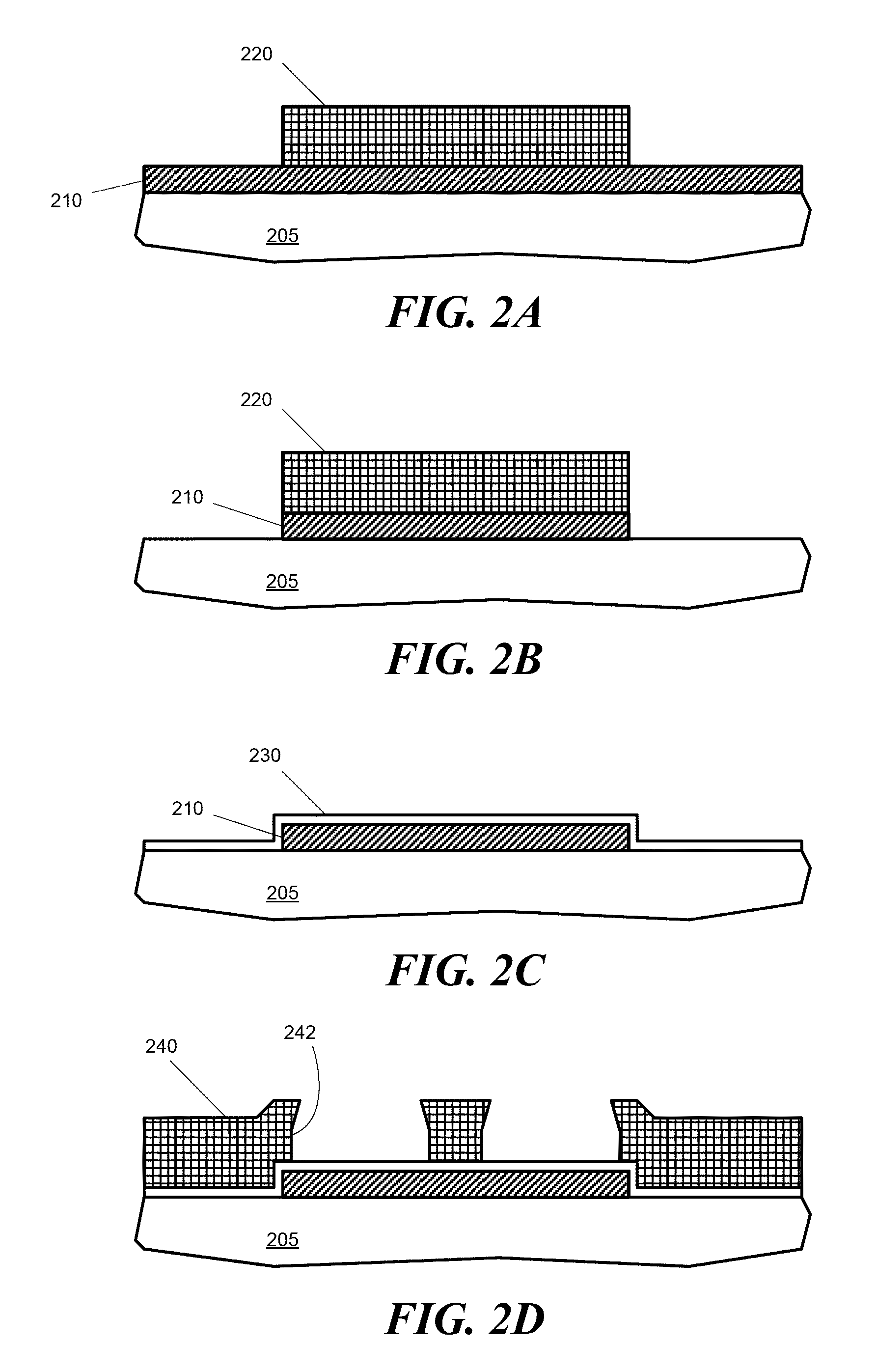
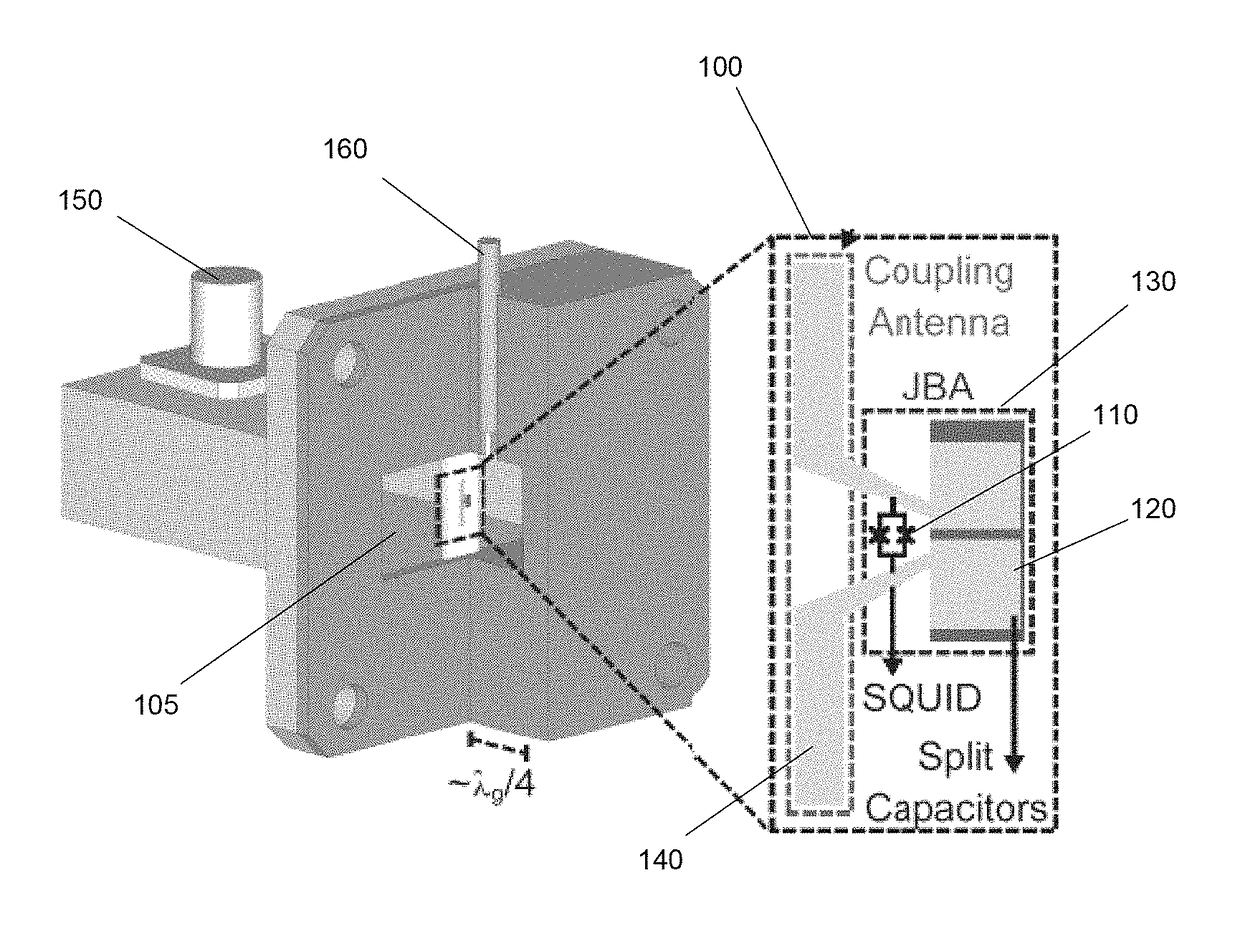
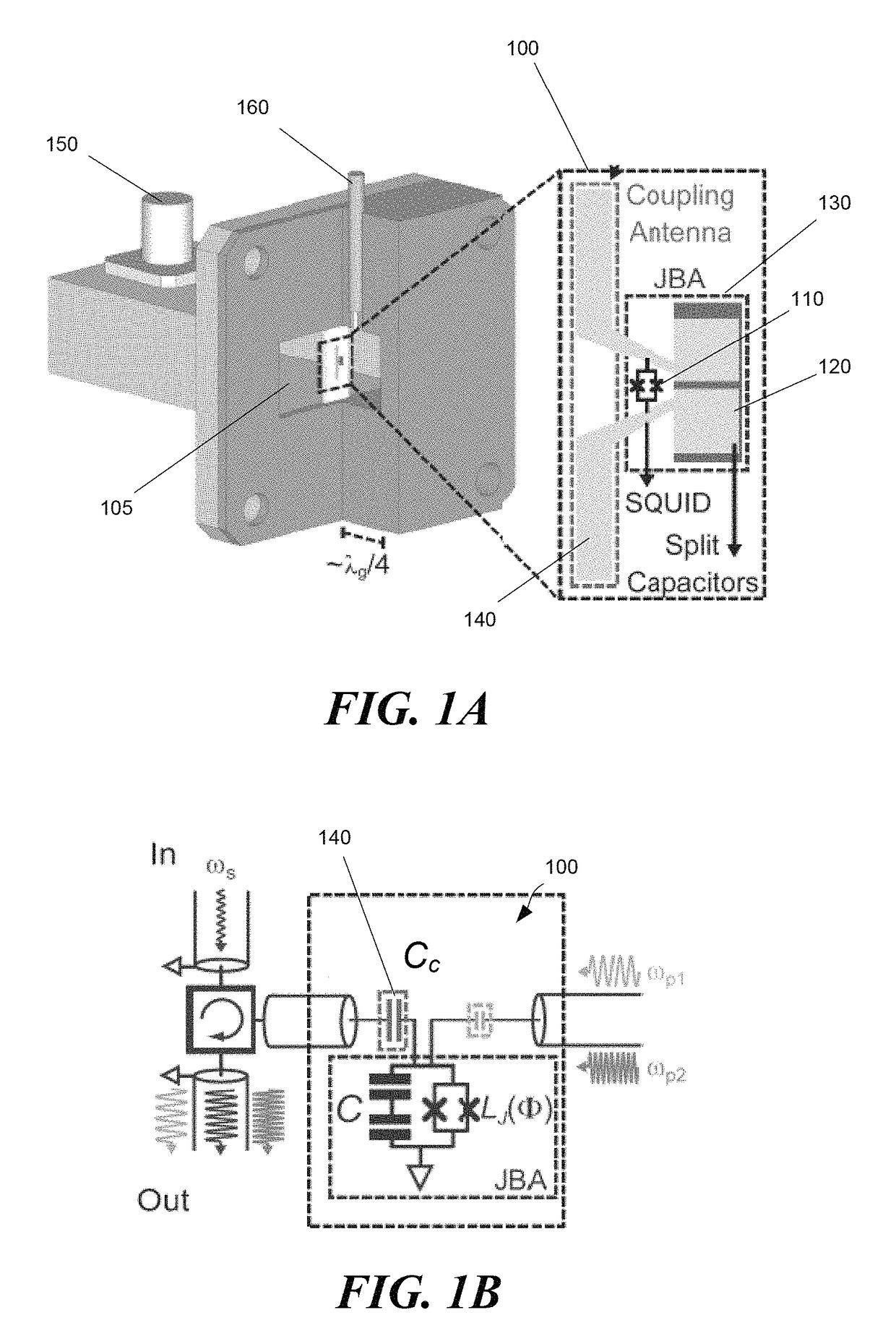
Wireless josephson bifurcation amplifier
ActiveUS20150241481A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage/current isolationCoaxial cableAudio power amplifier
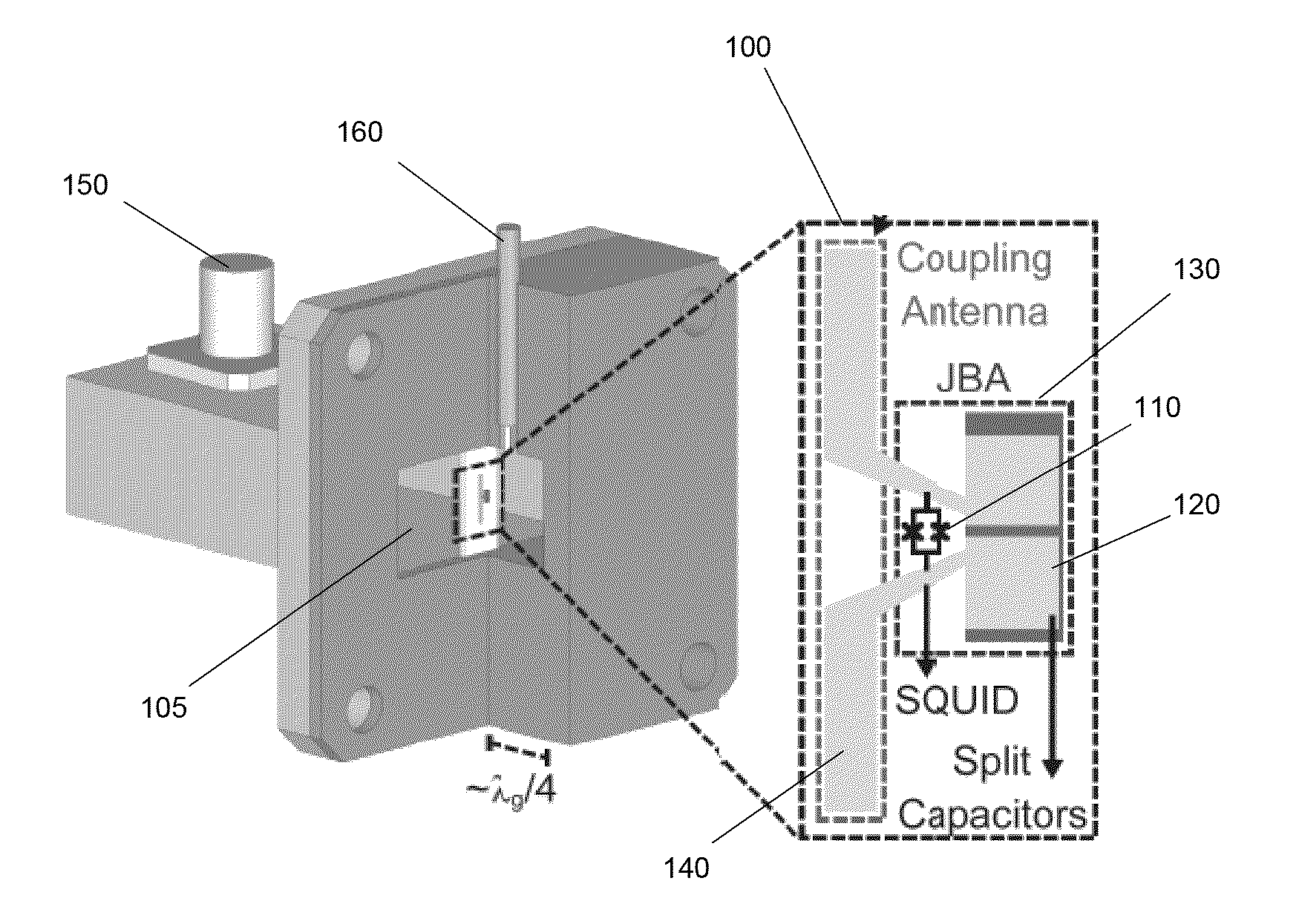
A wireless Josephson-junction-based amplifier is described that provides improved tunability and increased control over both a quality factor Q and participation ratio p of the amplifier. The device may be fabricated on a chip and mounted in a waveguide. No wire bonding between the amplifier and coaxial cables or a printed circuit board is needed. At least one antenna on the chip may be used to couple energy between the waveguide and wireless JBA. The amplifier is capable of gains greater than 25 dB.
Owner:YALE UNIV
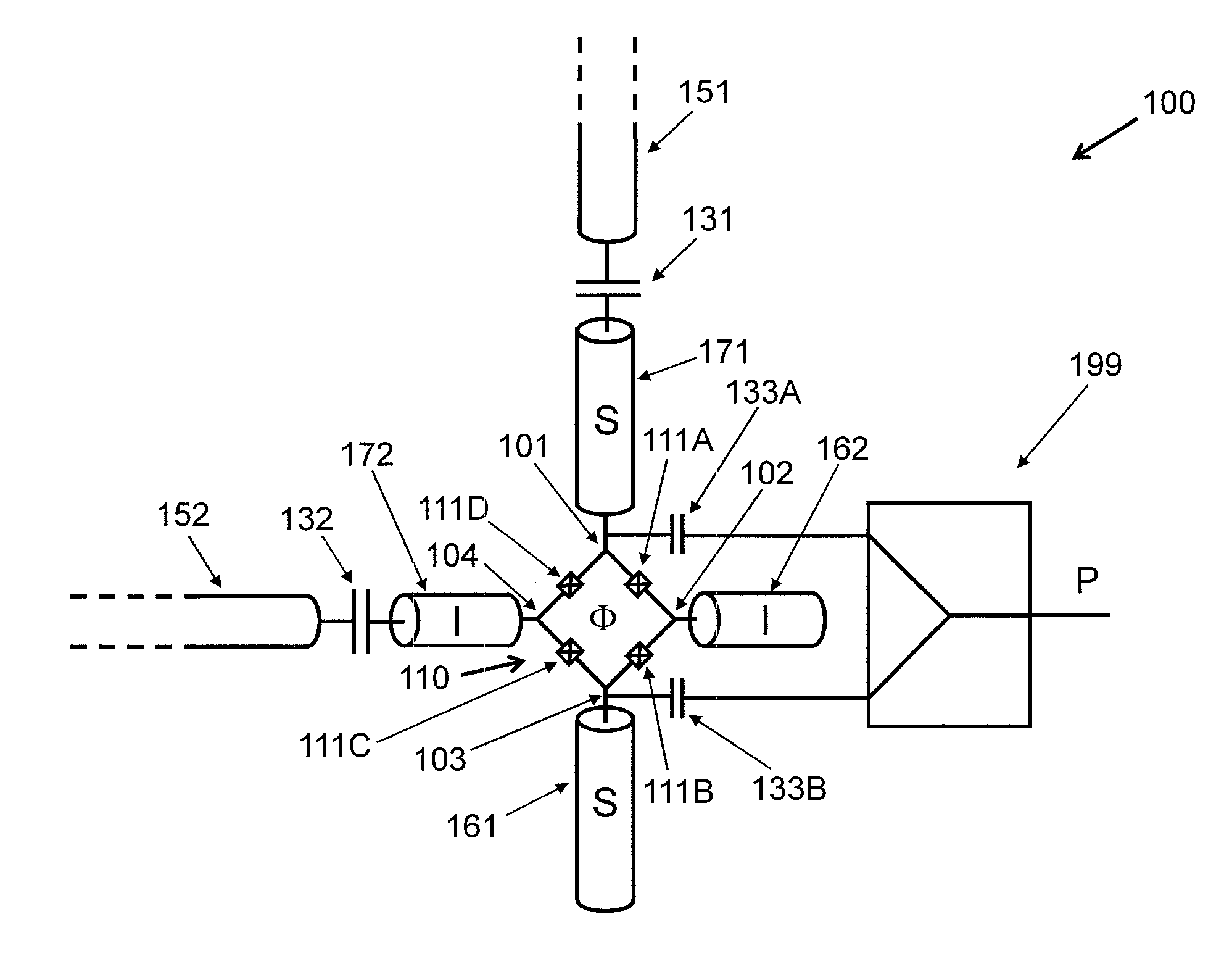
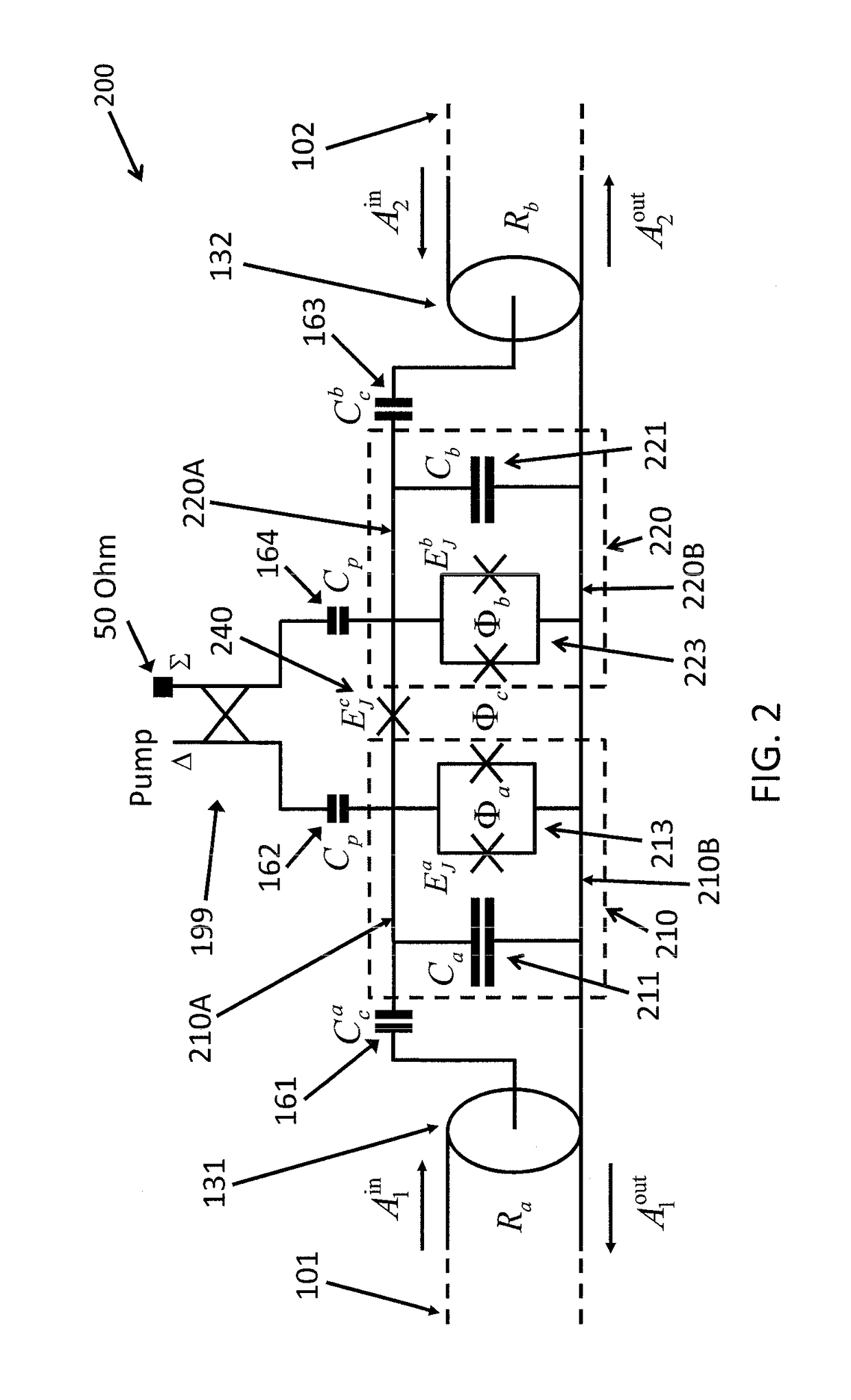
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS20160380636A1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
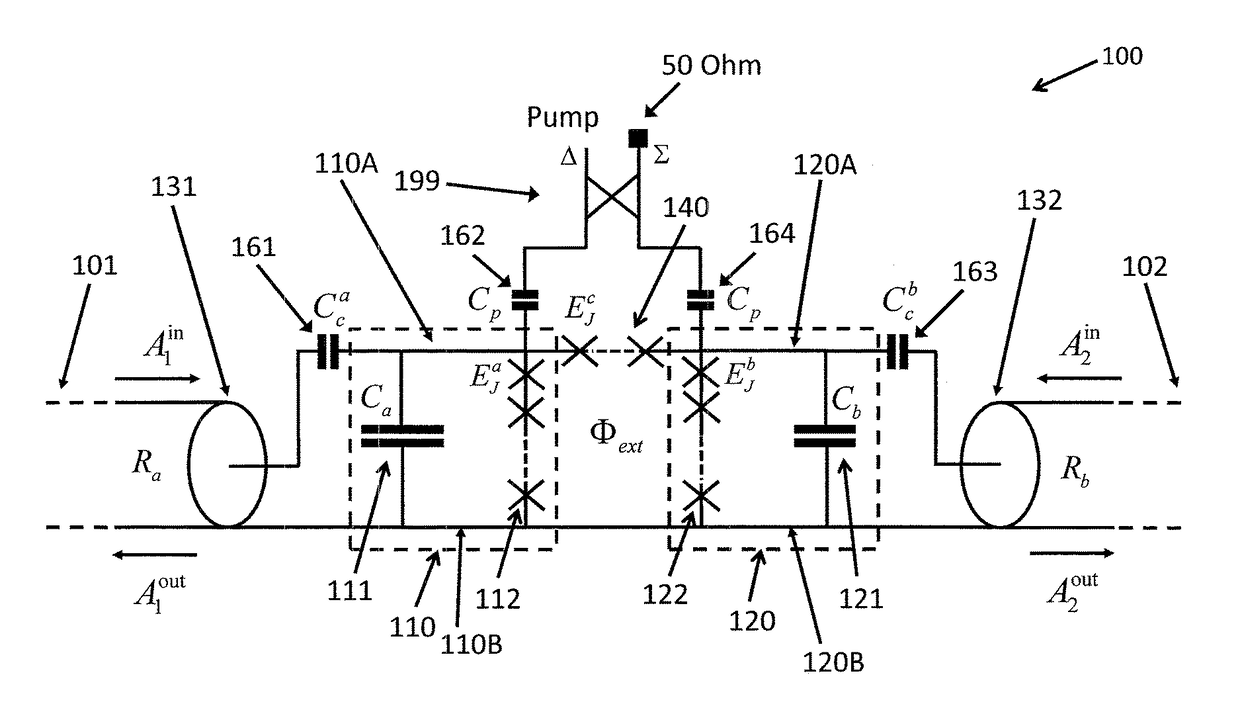
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wireless Josephson bifurcation amplifier
A wireless Josephson-junction-based amplifier is described that provides improved tunability and increased control over both a quality factor Q and participation ratio p of the amplifier. The device may be fabricated on a chip and mounted in a waveguide. No wire bonding between the amplifier and coaxial cables or a printed circuit board is needed. At least one antenna on the chip may be used to couple energy between the waveguide and wireless JBA. The amplifier is capable of gains greater than 25 dB.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS9548742B1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
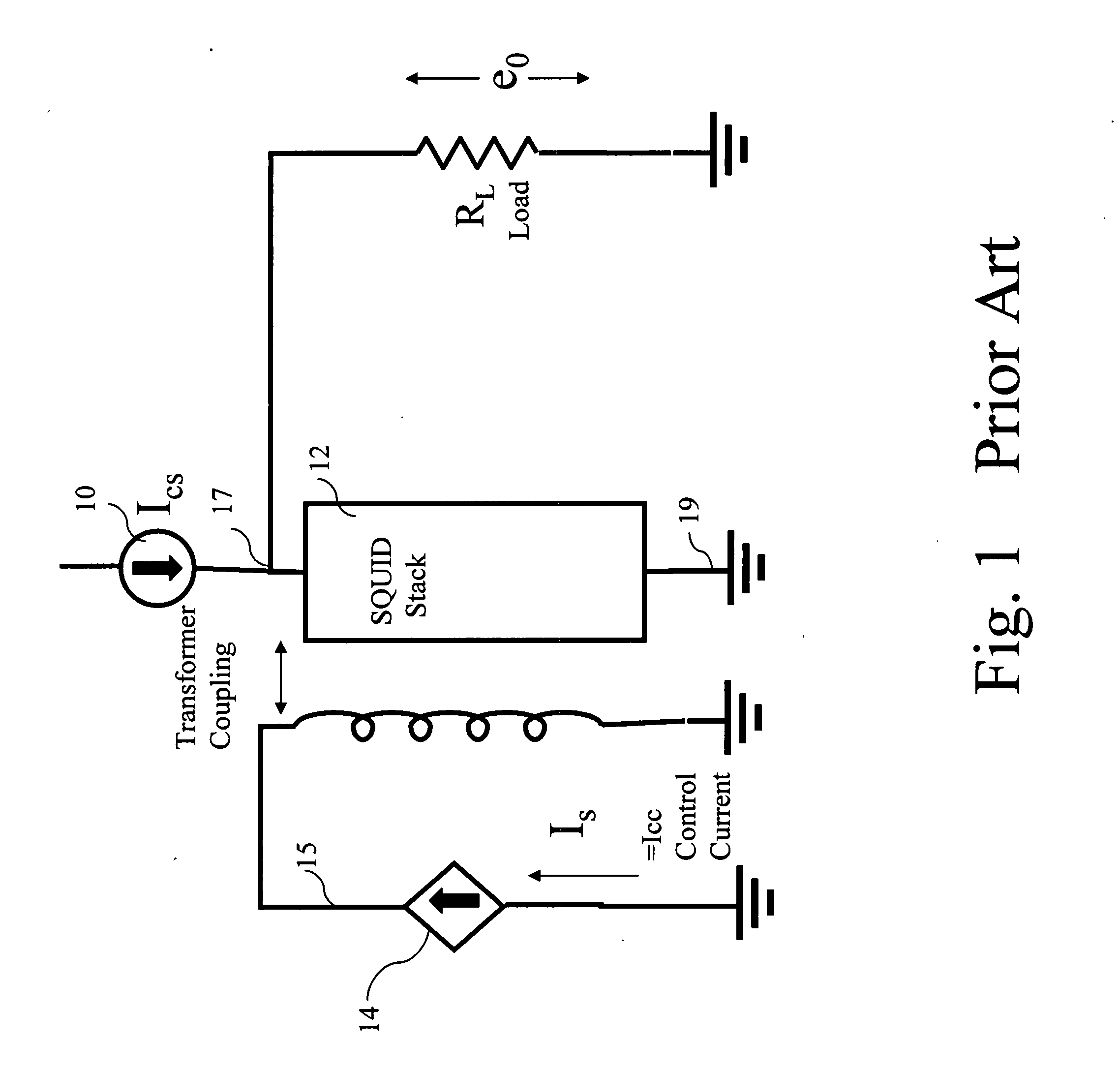
Superconducting switching amplifier
InactiveUS20080048762A1Selectively raised and loweredAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
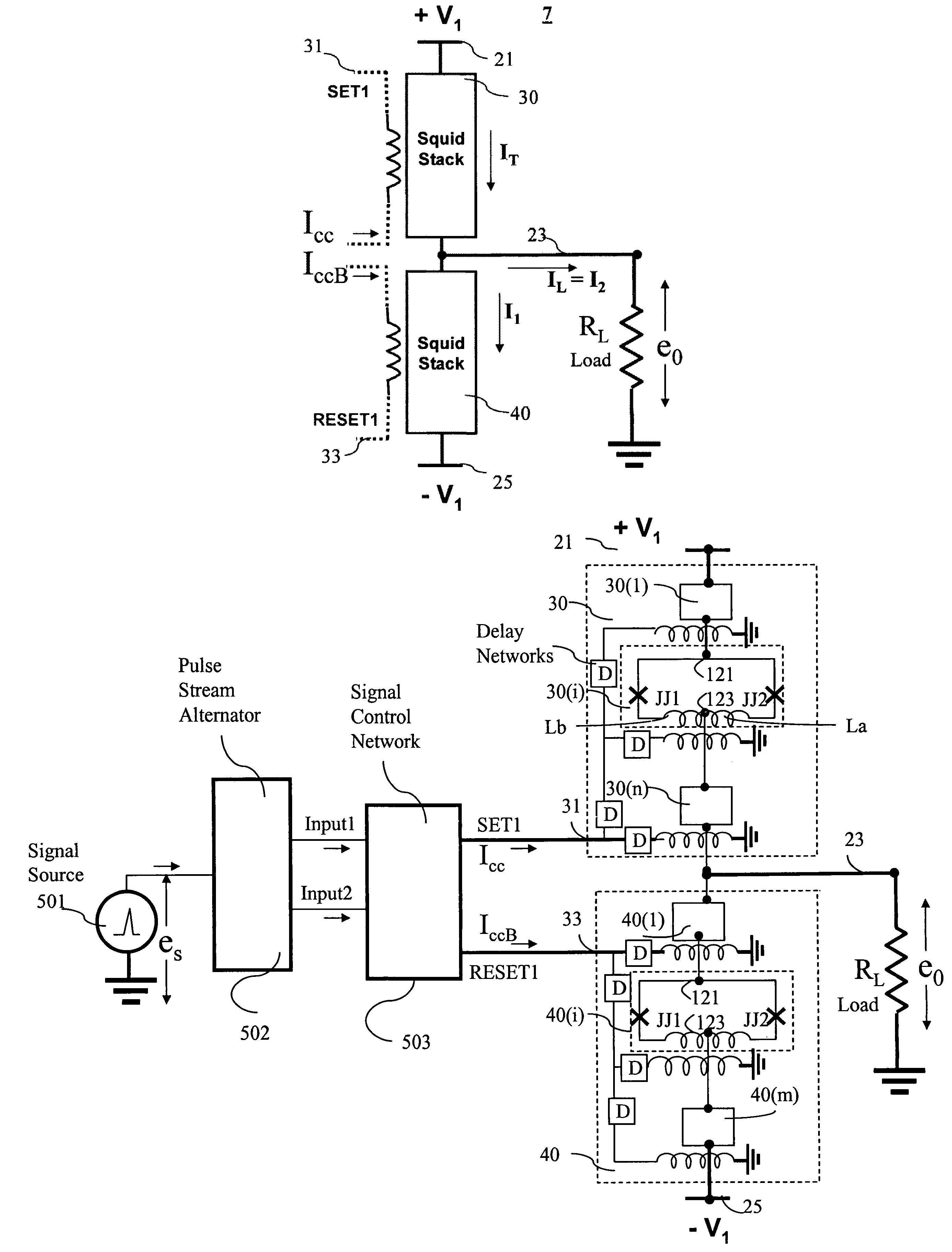
A superconducting switching amplifier embodying the invention includes superconductive devices responsive to input / control signals for clamping the output of the amplifier to a first voltage or to a second voltage. The amplifier includes a first set of superconducting devices serially connected between a first voltage line and an output terminal and a second set of superconducting devices serially connected between the output terminal and a second voltage line. The first set and the second set of devices are operated in a complementary fashion in response to control signals. When one of the first and second sets is driven to a superconducting (zero resistance) state the other set is driven to a resistive state. In accordance with the invention, the devices of each set are laid out in a pattern and driven in a manner to enable all the devices of each set to be driven to a selected state at substantially the same time. In one embodiment, the devices in each set are superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). Four sets of superconductive devices may be interconnected to function as a differential switching amplifier. The operating voltage applied to an amplifier may be varied to provide additional shaping of the output signal.
Owner:HYPRES
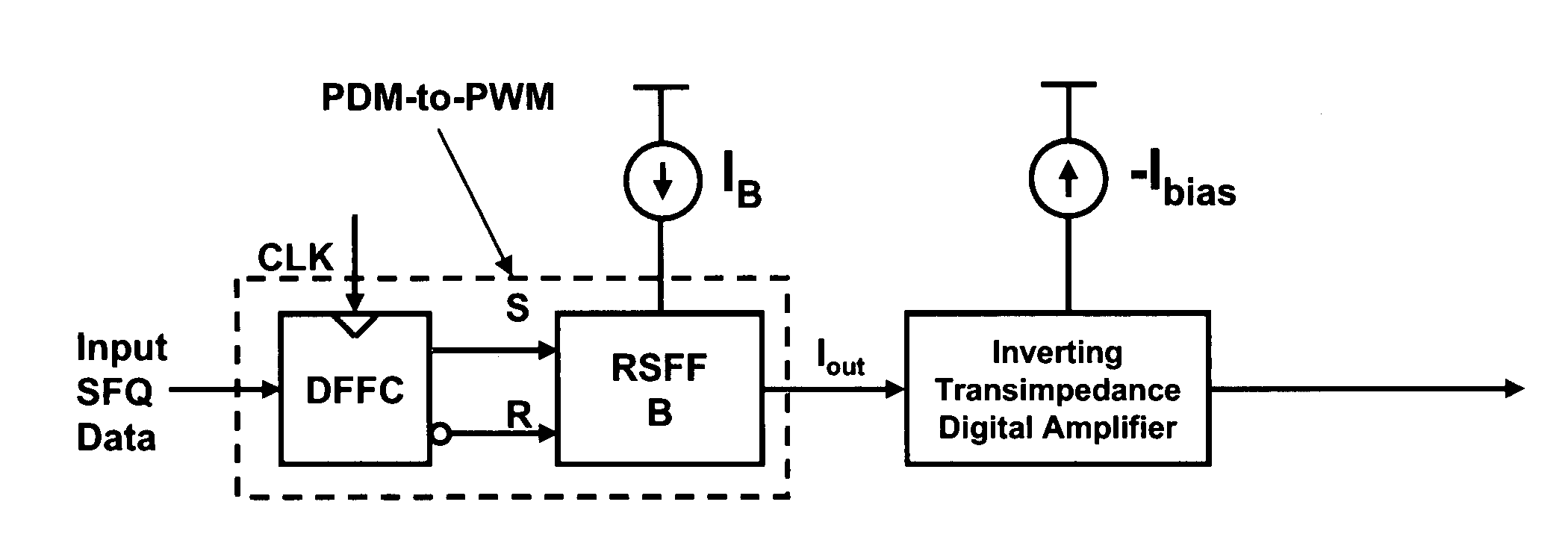
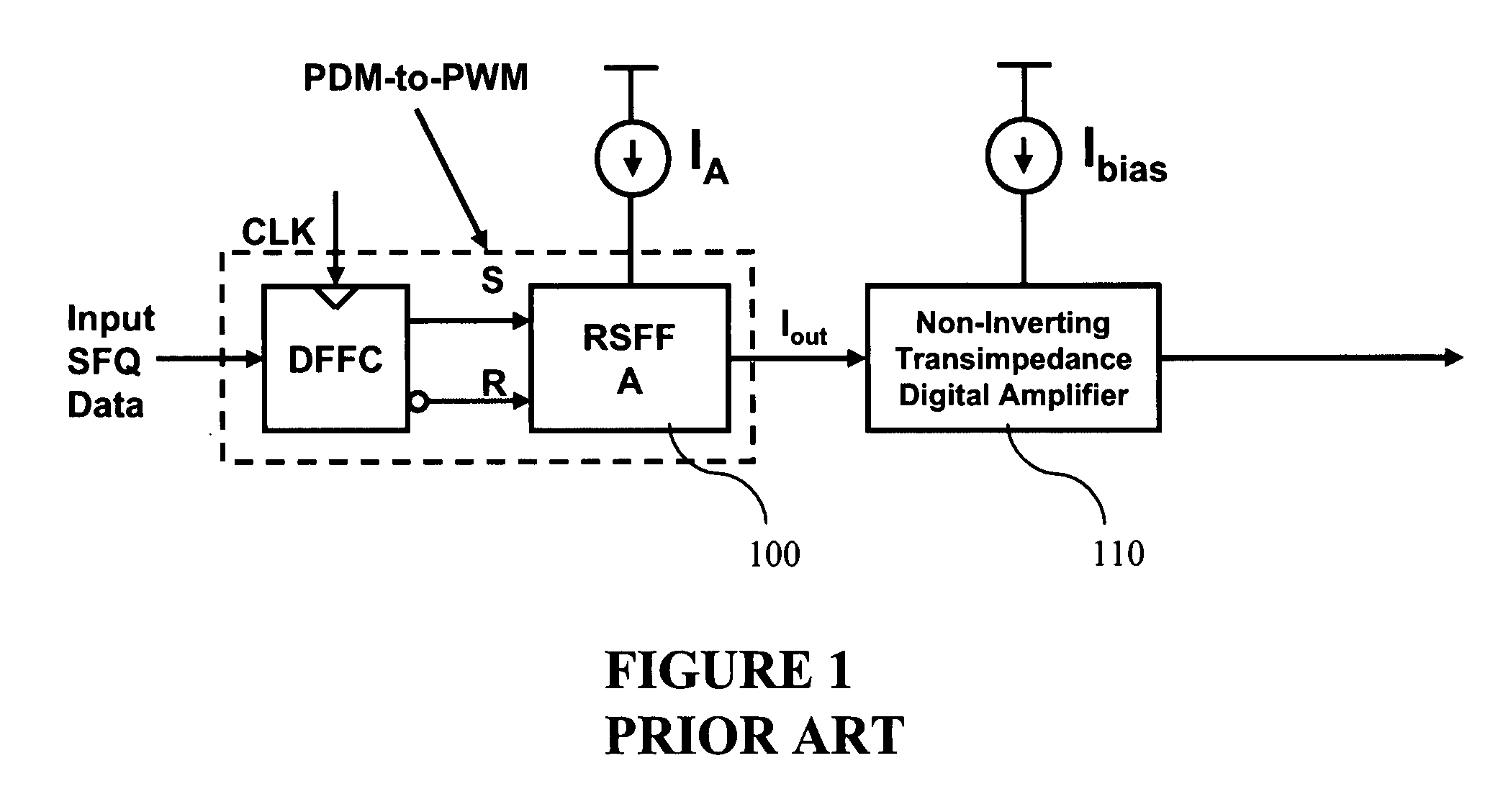
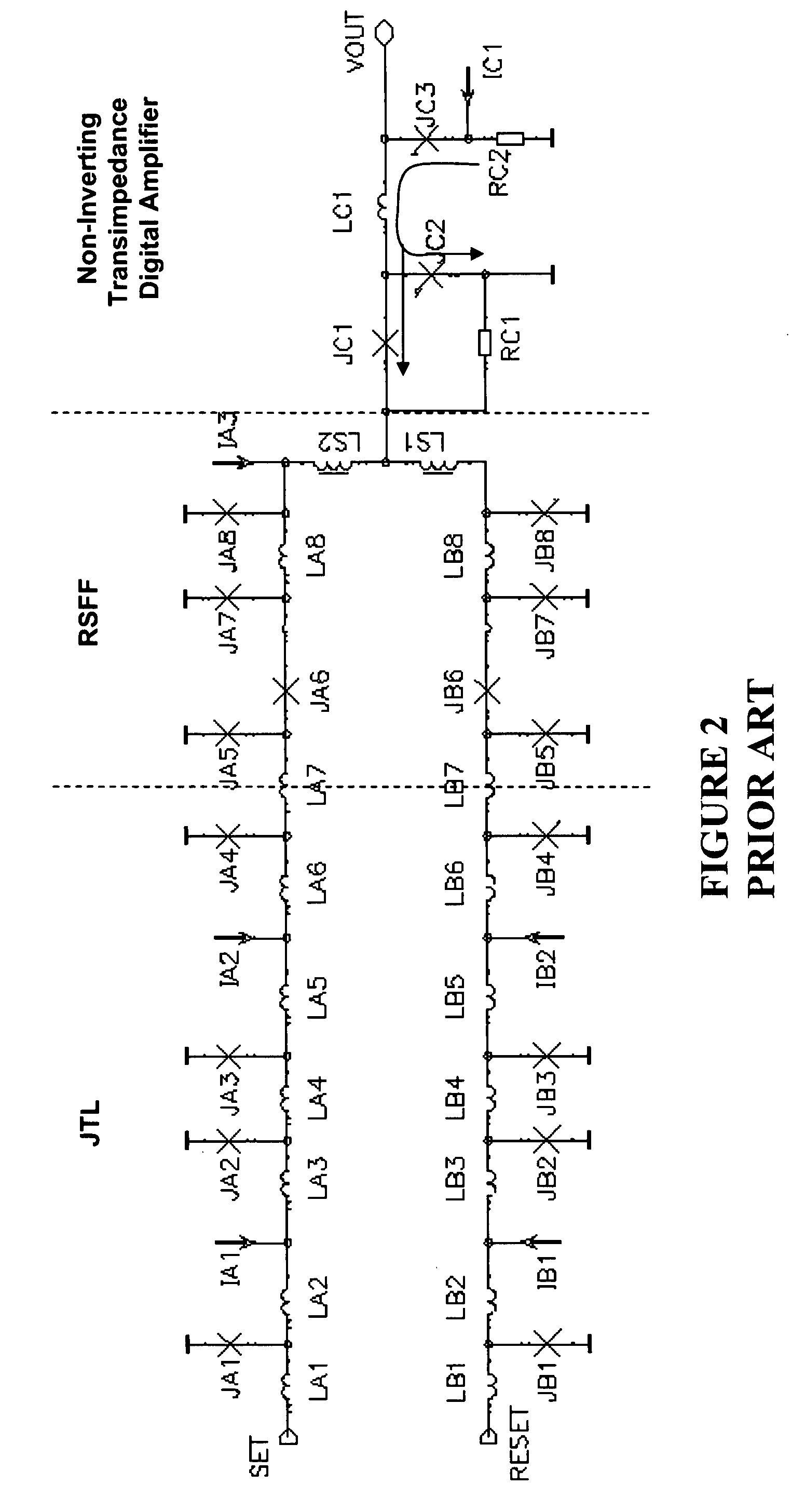
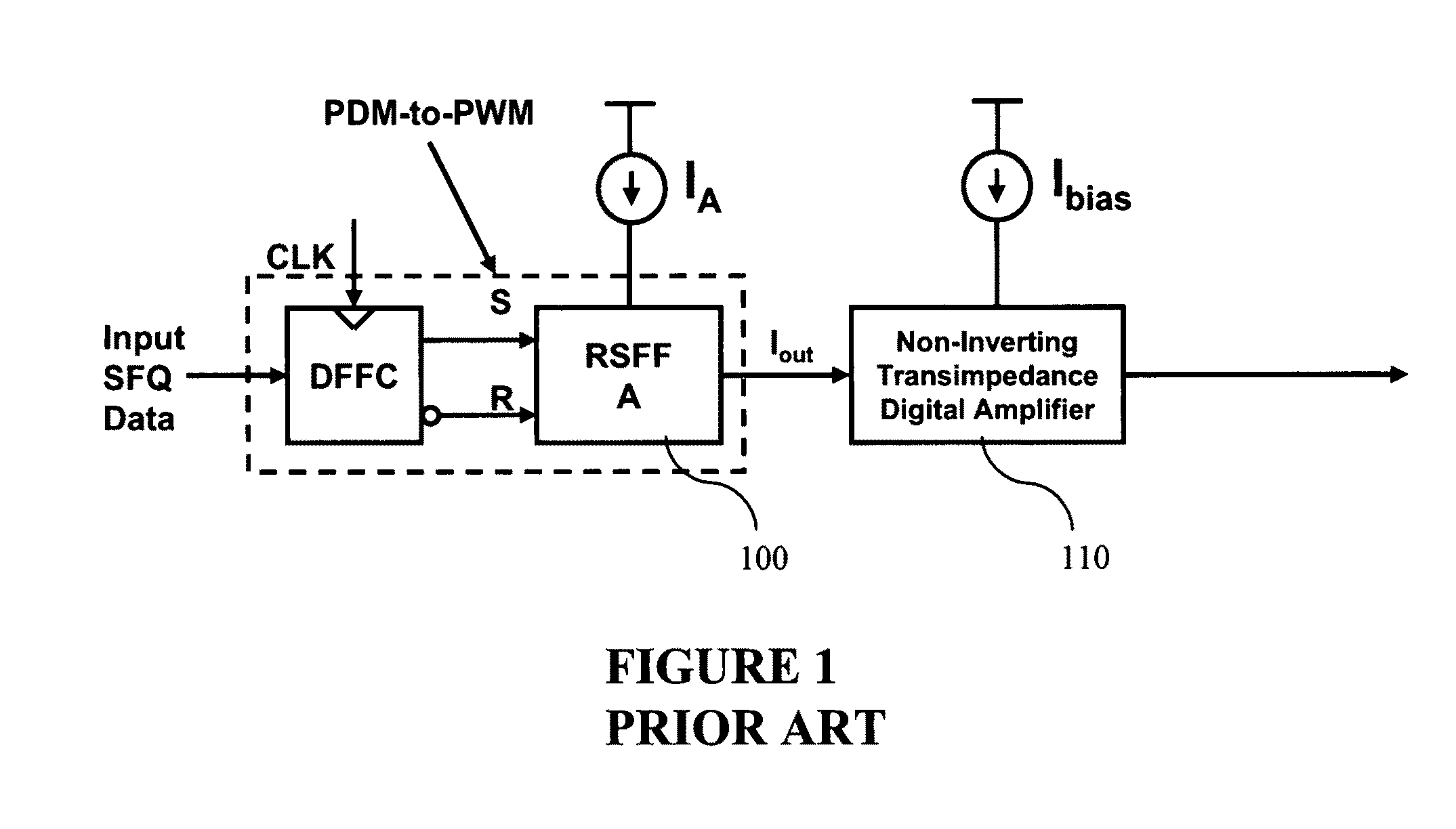
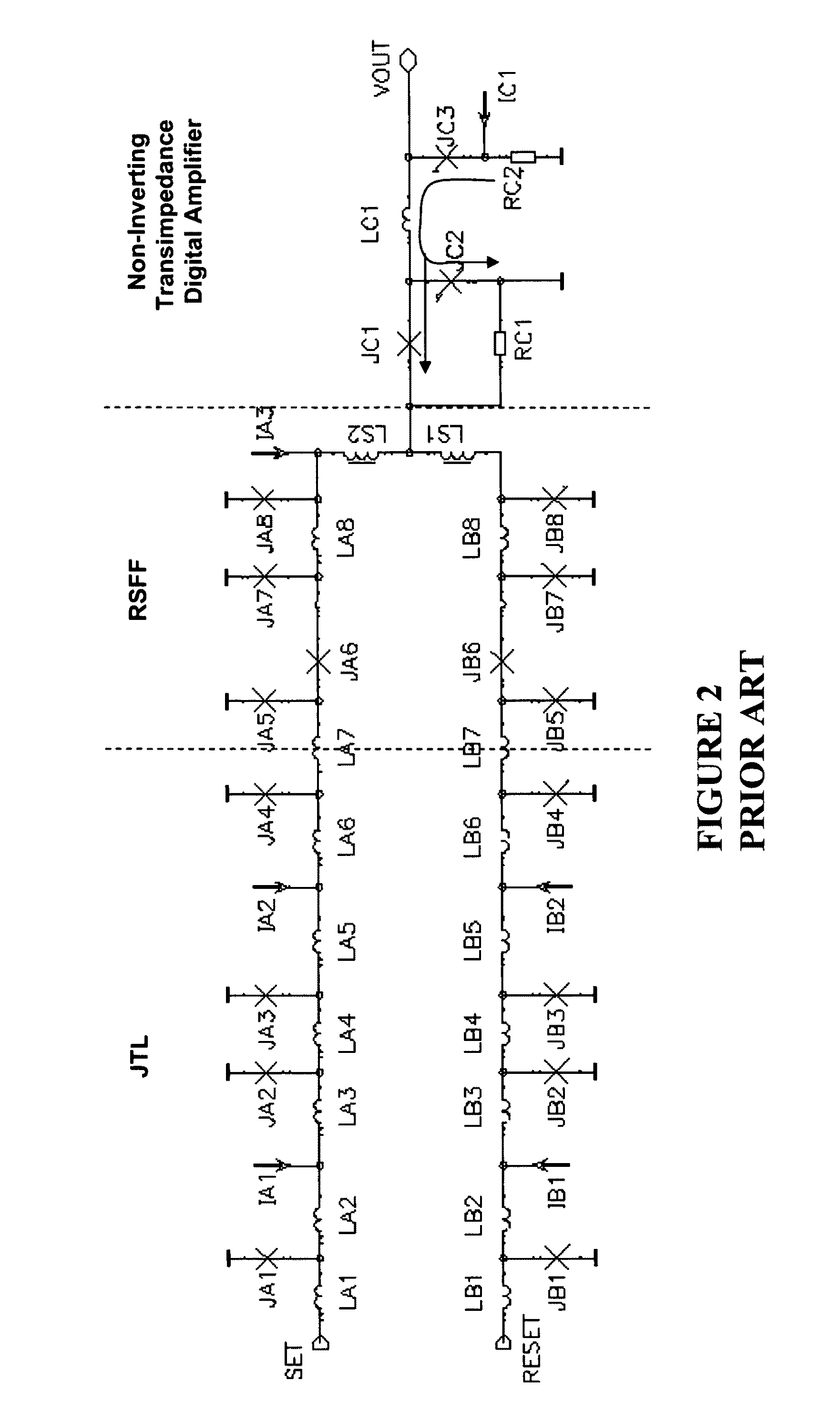
Ultra fast differential transimpedance digital amplifier for superconducting circuits
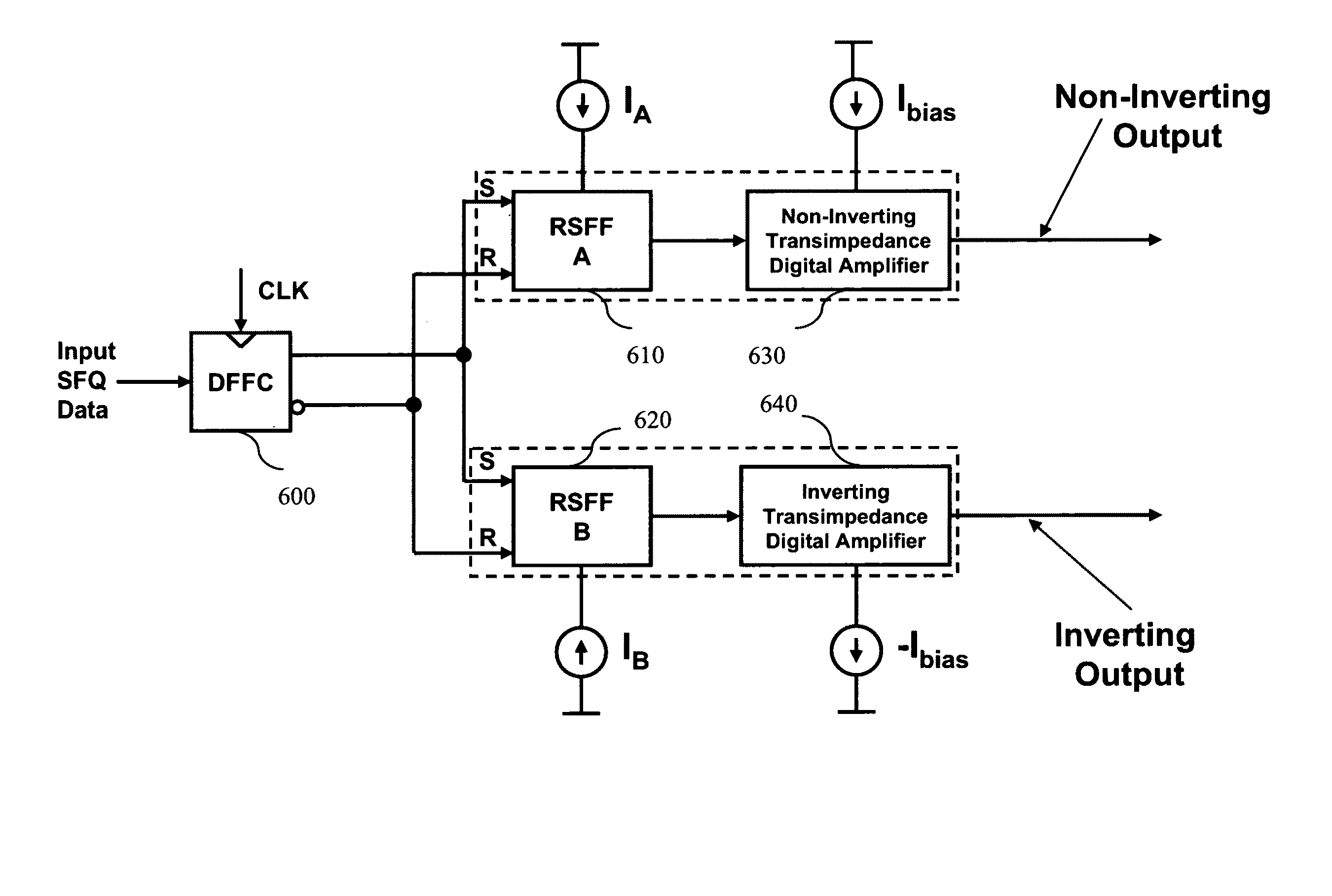
InactiveUS20090002014A1Less powerImprove yieldPulse transformerElectronic switchingRapid single flux quantumUltra fast
Supercooled electronics often use Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) digital circuits. The output voltages from RSFQ devices are too low to be directly interfaced with semiconductor electronics, even if the semiconductor electronics are cooled. Techniques for directly interfacing RSFQ digital circuits with semiconductor electronics are disclosed using a novel inverting transimpedance digital amplifier in conjunction with a non-inverting transimpedance digital amplifier to create a differential transimpedance digital amplifier that permits direct interfacing between RSFQ and semiconductor electronics.
Owner:HYPRES
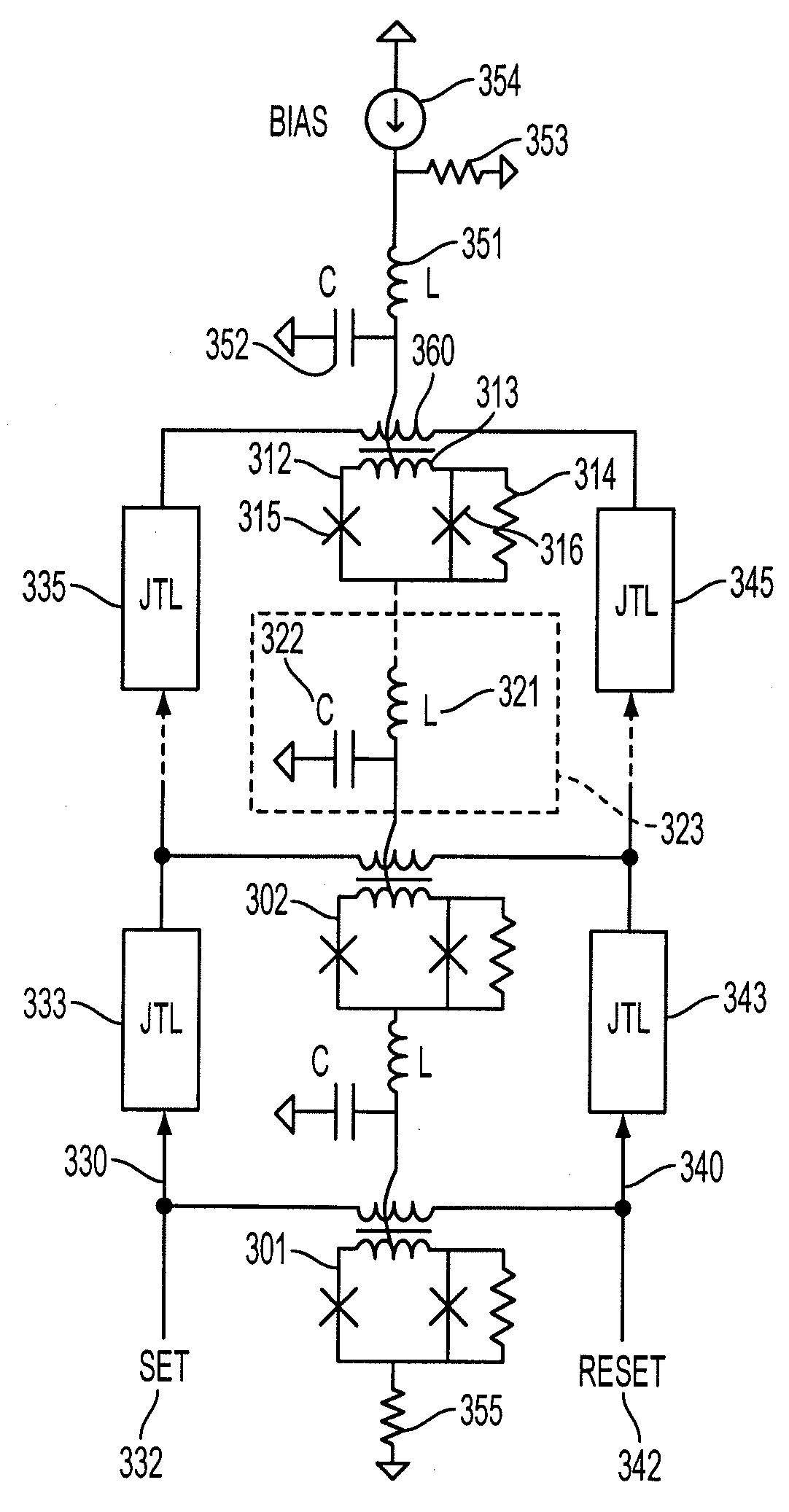
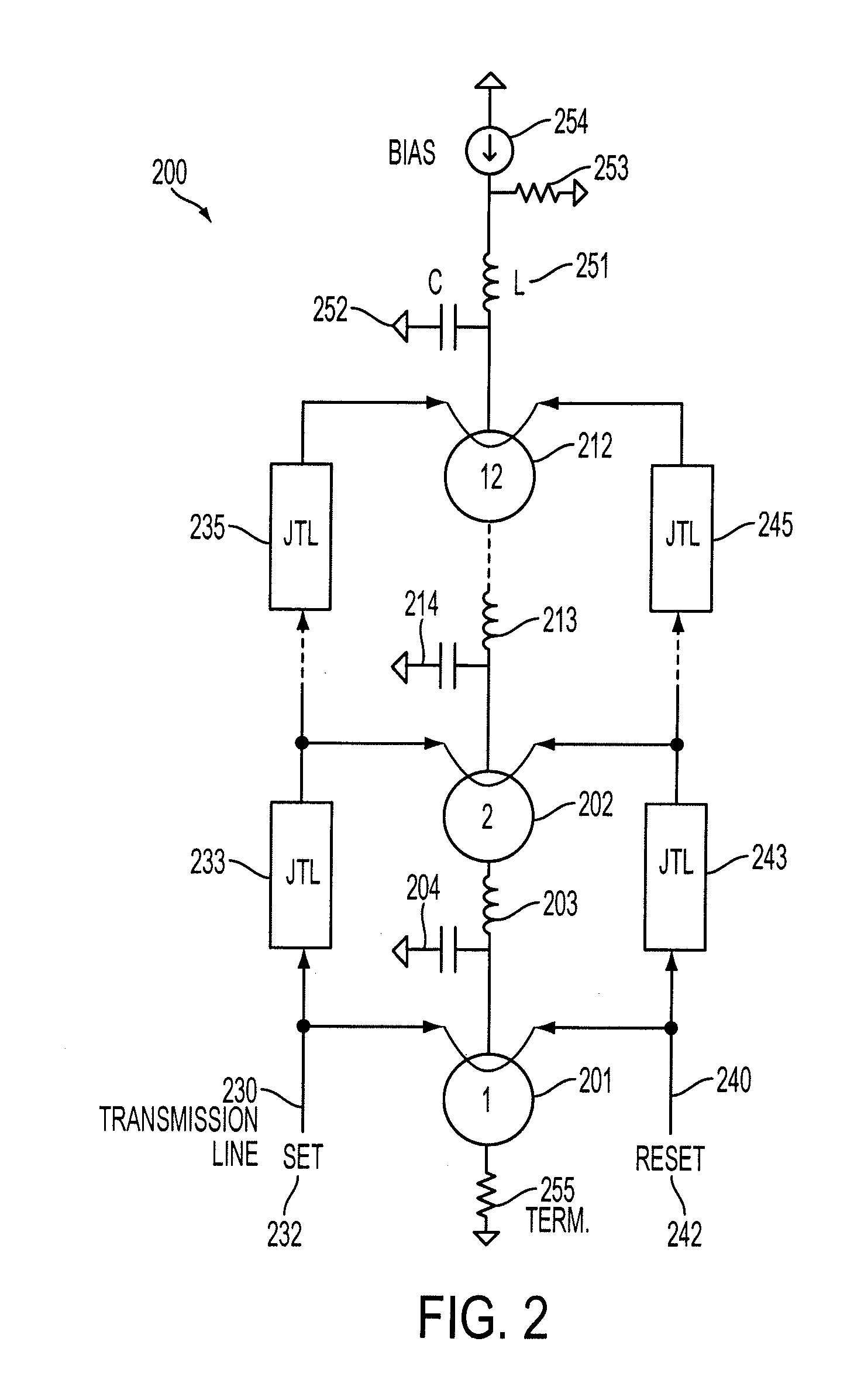
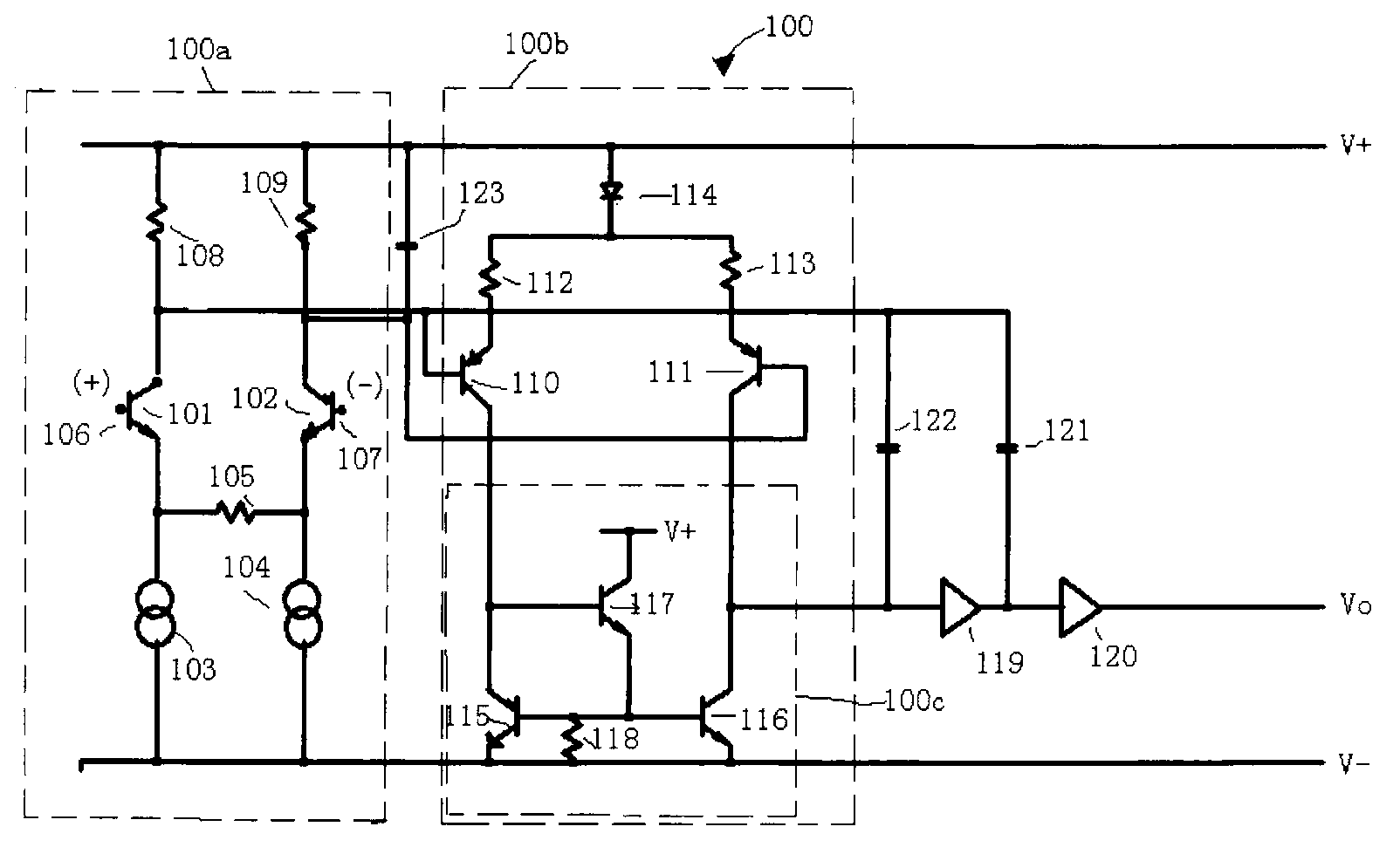
Josephson-coupled resonator amplifier (JRA)
A Josephson-coupled resonator amplifier is provided. The Josephson-coupled resonator amplifier includes a first and a second resonator, each formed from respective lumped-element capacitance and respective lumped-element inductance. The Josephson-coupled resonator amplifier further includes one or more Josephson junctions coupling the first resonator to the second resonator, whereby a superconducting loop is formed from at least the lumped-element inductance of the resonators and the one or more Josephson junctions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Superconducting driver circuit
InactiveUS7095227B2Discharge longerSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectronic switchingCapacitanceDriver circuit
To obtain a superconducting driver circuit which can obtain an output voltage of several millvolts or above, can use a DC power source as a driving power source, can form no capacitance between it and a ground plane, and has a small occupation area, the superconducting driver circuit is constructed by superconducting flux quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) each constructing a closed loop having as components two superconducting junctions and an inductor. The SQUIDs share the inductors and are connected in series in three or more stages.
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
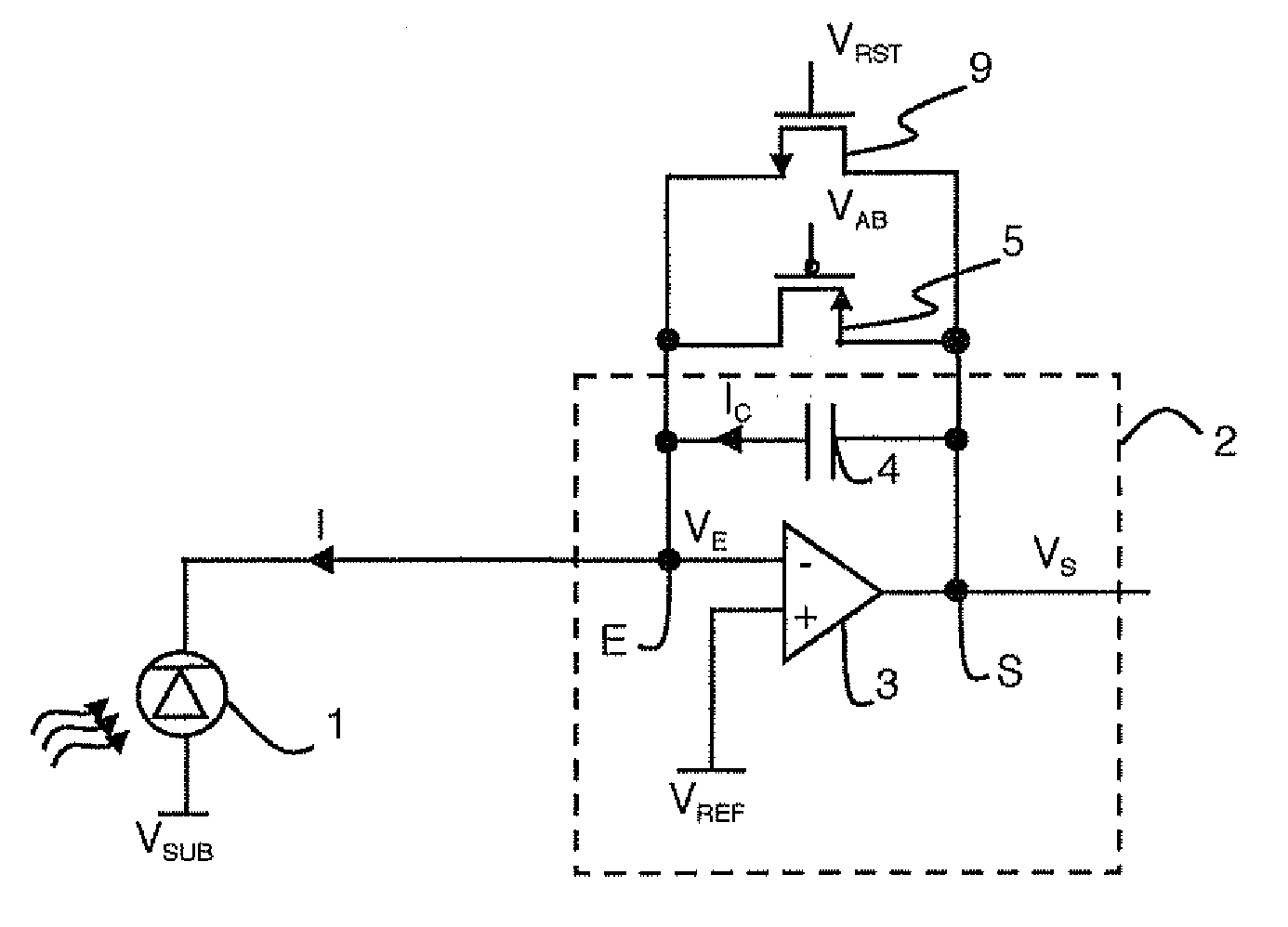
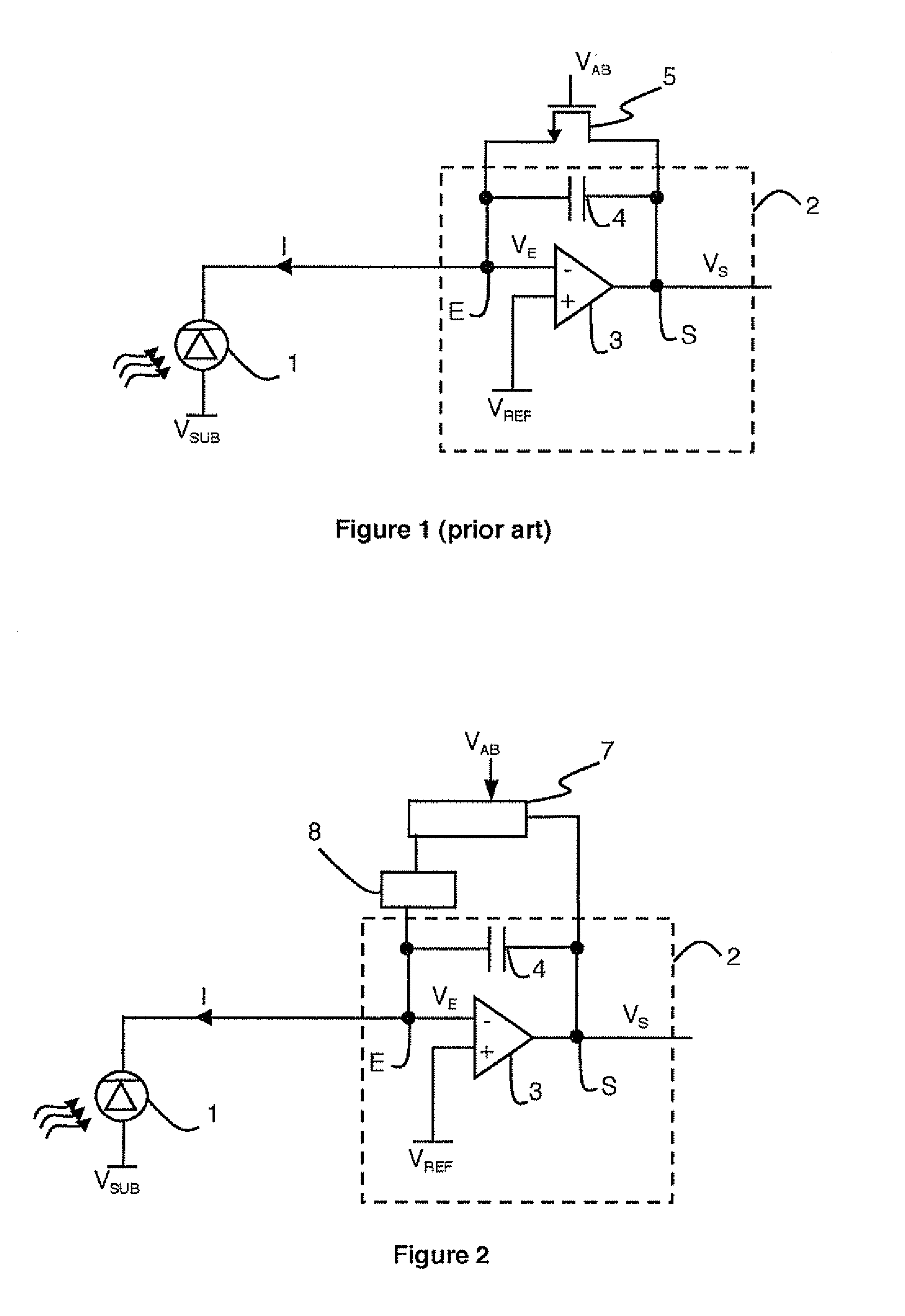
Detection circuit with improved Anti-blooming circuit
ActiveUS20110068860A1Easy to implementReliable and repeatable fabricationTelevision system detailsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
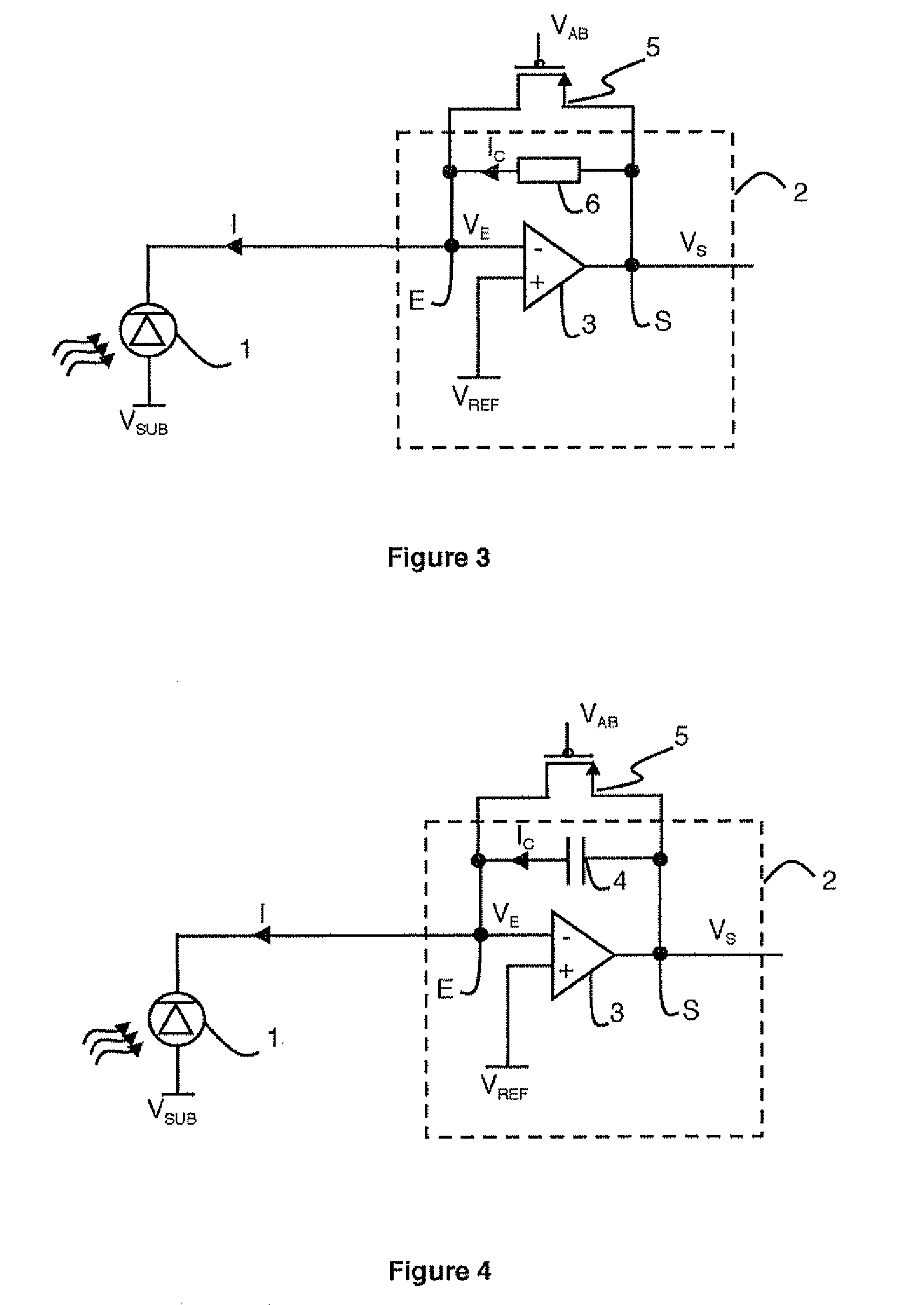
The detection circuit comprises a photodiode connected to an input of a capacitive transimpedance amplifier. The circuit comprises an anti-blooming circuit connected between the input and an output of the capacitive trans-impedance amplifier. The anti-blooming circuit comprises a field effect transistor connected between the input and output of the capacitive trans-impedance amplifier. The transistor is of pMOS type when the input of the capacitive transimpedance amplifier is connected to a cathode of the photodiode. The transistor is of nMOS type when the input of the capacitive transimpedance amplifier is connected to an anode of the photodiode.
Owner:LYNRED
Dispersion-engineered traveling wave kinetic inductance parametric amplifier
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Superconducting switching amplifier
InactiveUS7468630B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyControl signalSoftware engineering
A superconducting switching amplifier embodying the invention includes superconductive devices responsive to input / control signals for clamping the output of the amplifier to a first voltage or to a second voltage. The amplifier includes a first set of superconducting devices serially connected between a first voltage line and an output terminal and a second set of superconducting devices serially connected between the output terminal and a second voltage line. The first set and the second set of devices are operated in a complementary fashion in response to control signals. When one of the first and second sets is driven to a superconducting (zero resistance) state the other set is driven to a resistive state. In accordance with the invention, the devices of each set are laid out in a pattern and driven in a manner to enable all the devices of each set to be driven to a selected state at substantially the same time. In one embodiment, the devices in each set are superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). Four sets of superconductive devices may be interconnected to function as a differential switching amplifier. The operating voltage applied to an amplifier may be varied to provide additional shaping of the output signal.
Owner:HYPRES
Ultra fast differential transimpedance digital amplifier for superconducting circuits
InactiveUS7570075B2Improved gain-bandwidth productsIncrease speedPulse transformerElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierUltra fast
Supercooled electronics often use Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) digital circuits. The output voltages from RSFQ devices are too low to be directly interfaced with semiconductor electronics, even if the semiconductor electronics are cooled. Techniques for directly interfacing RSFQ digital circuits with semiconductor electronics are disclosed using a novel inverting transimpedance digital amplifier in conjunction with a non-inverting transimpedance digital amplifier to create a differential transimpedance digital amplifier that permits direct interfacing between RSFQ and semiconductor electronics.
Owner:HYPRES
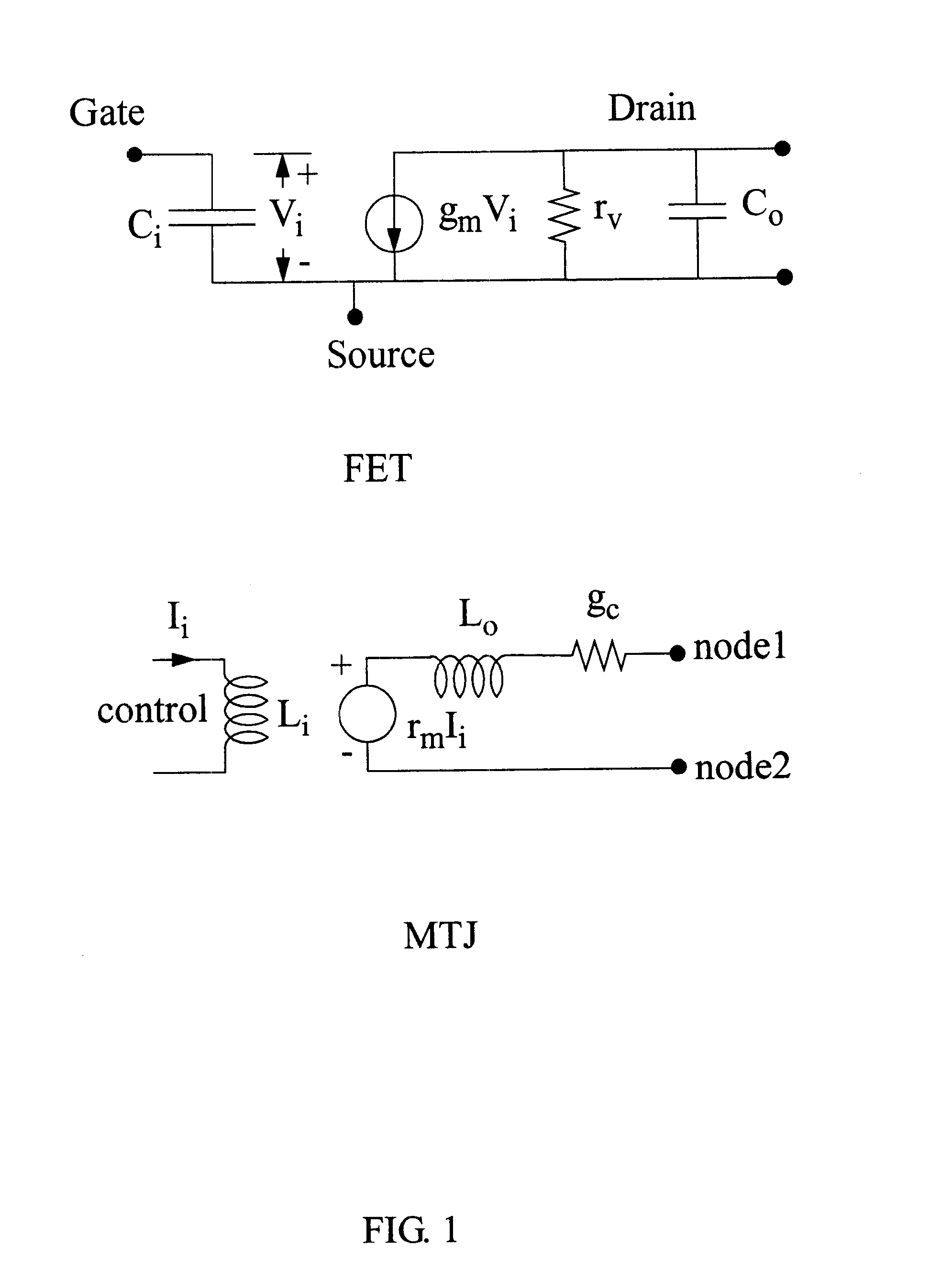
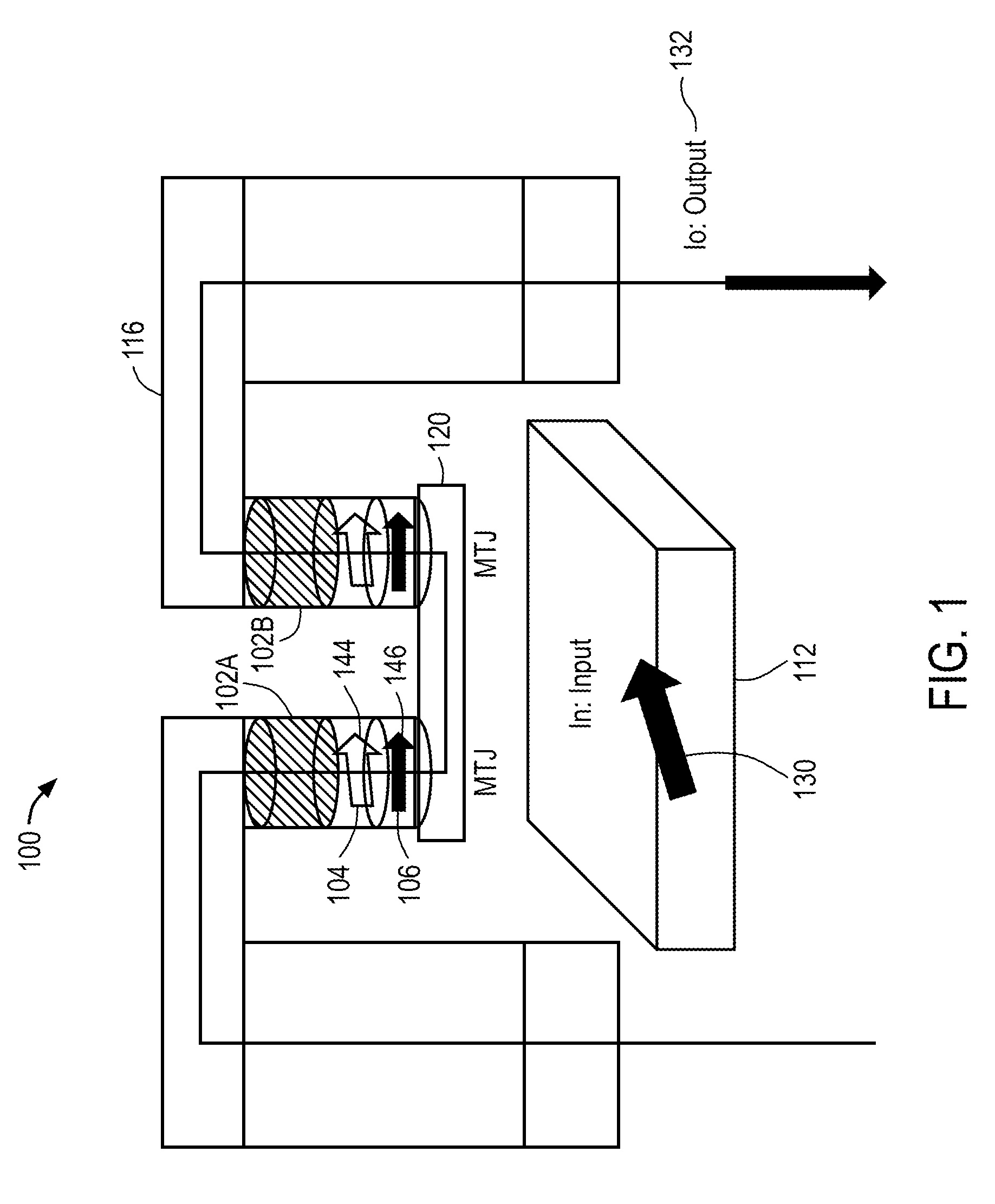
Wideband dual amplifier circuits
InactiveUS6356147B1Increased Gain BandwidthCancel noiseAmplifier combinationsAmplififers with field-effect devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
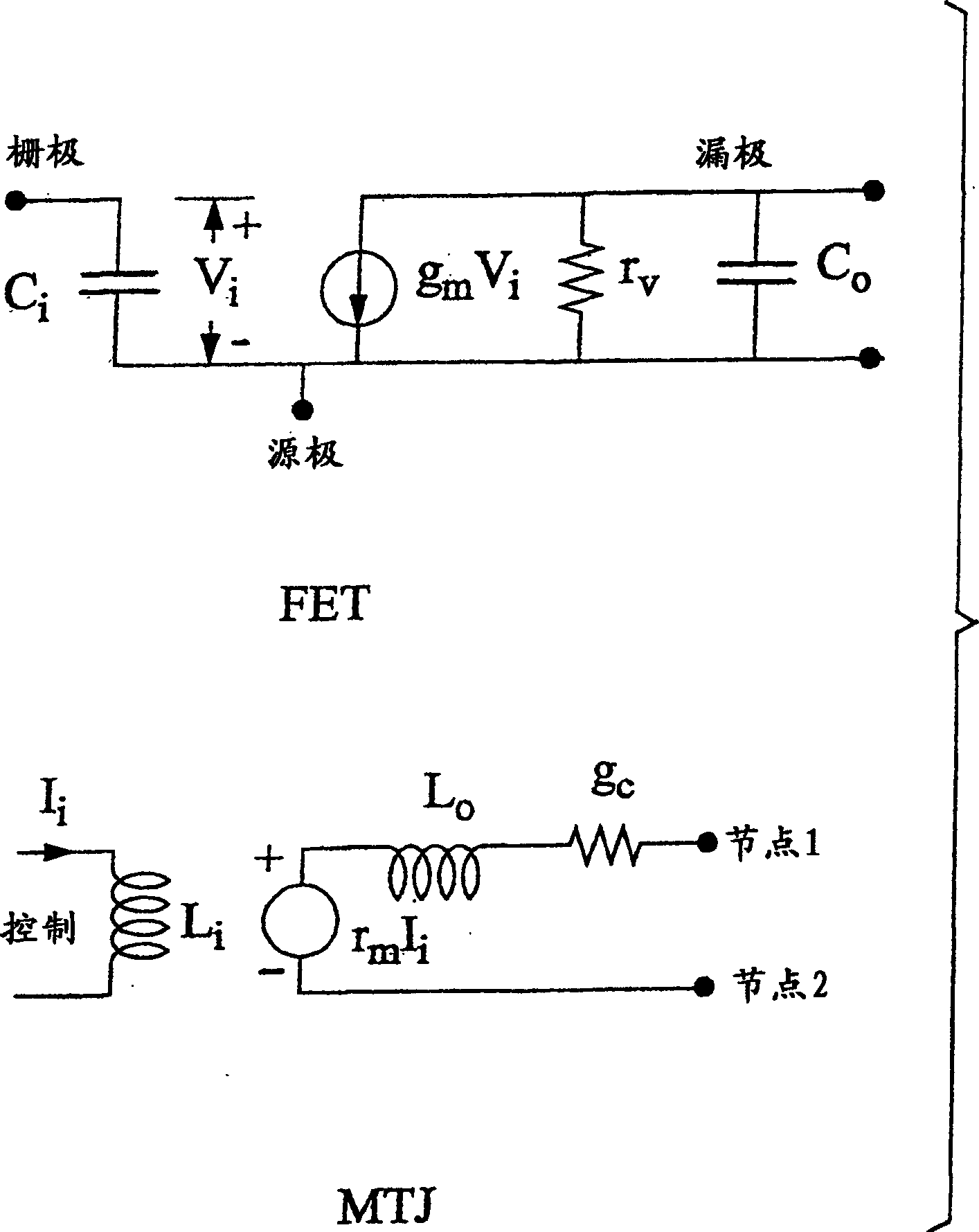
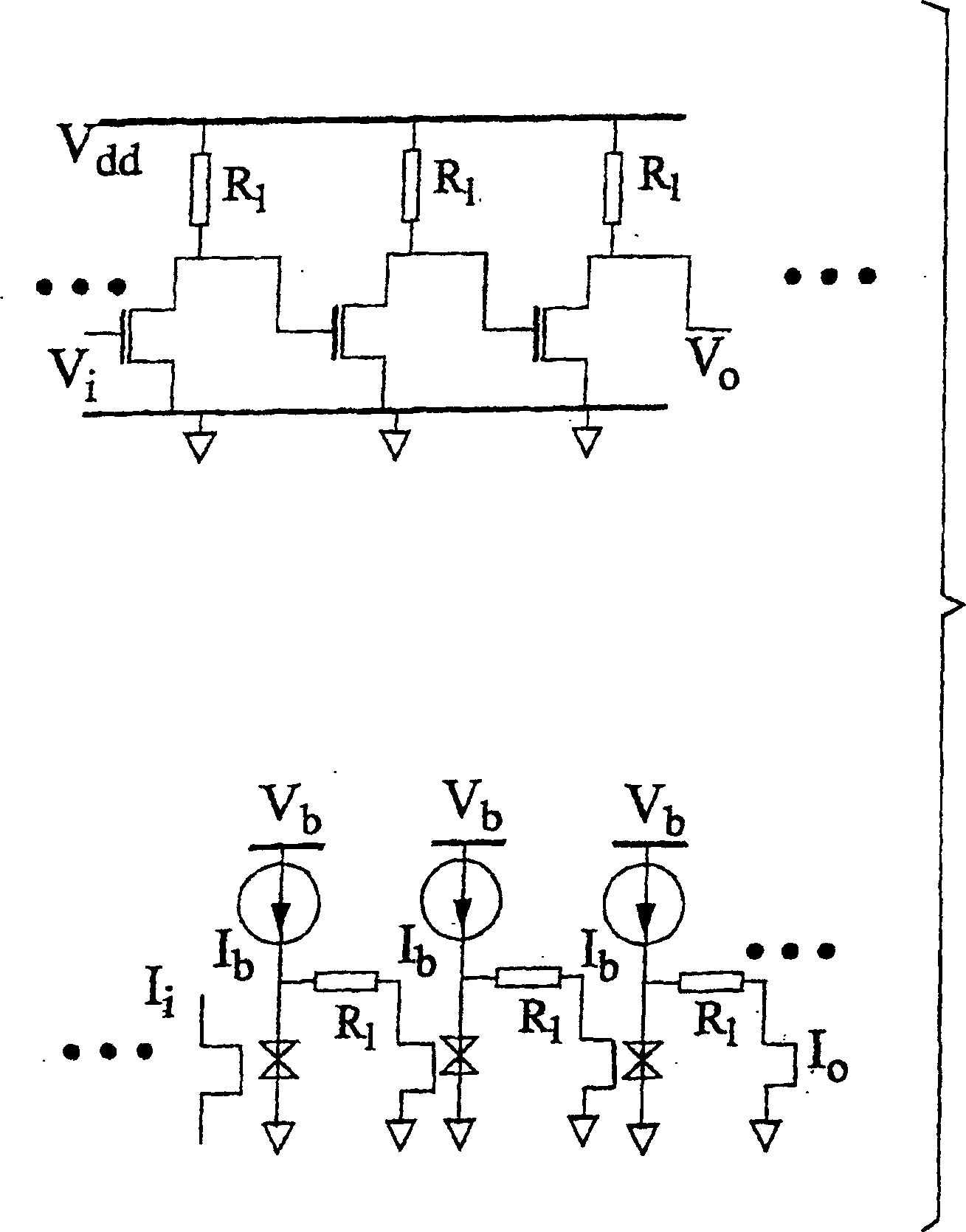
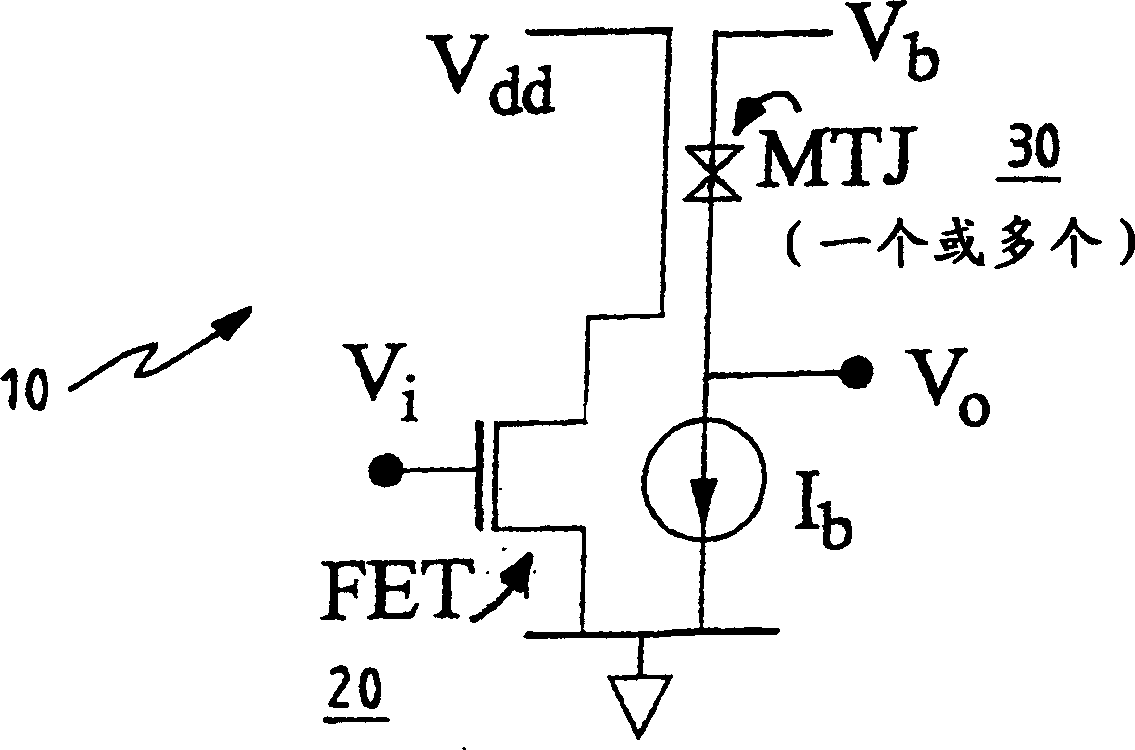
Dual amplifying circuits having a magnetic tunnel junction device and a field effect transistor configured in a complementing set are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the field effect transistor is operable to control a current level of a current operating signal flowing through the magnetic tunnel junction device. In another embodiment, the magnetic tunnel junction device is operable to control a voltage level of a voltage signal being applied to a gate terminal of the field effect transistor. The gain-bandwidth product of both embodiments is greater than the individual gain-bandwidth products of the individual devices through the elimination of noise contributing resistive type circuit elements.
Owner:IBM CORP
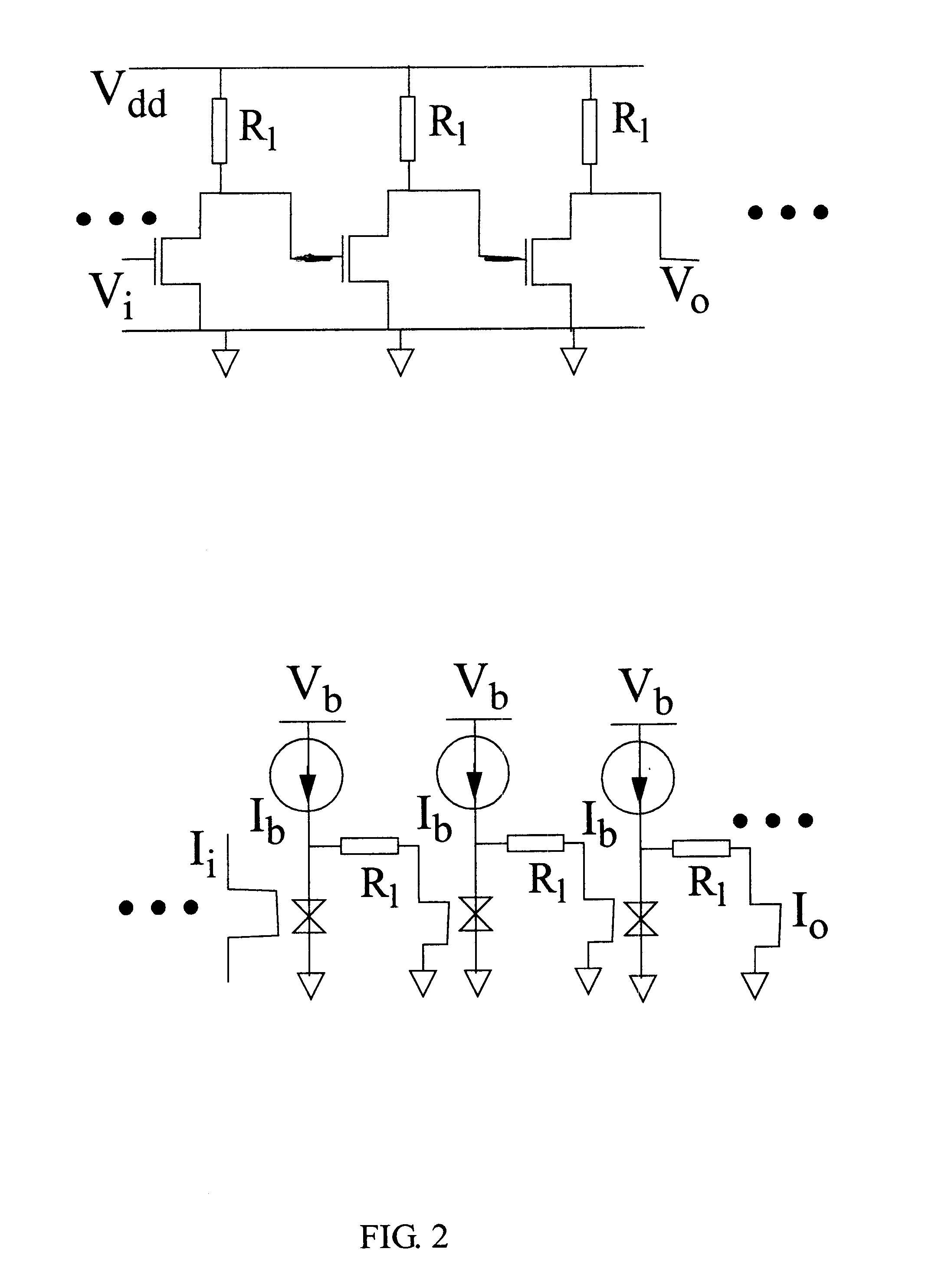
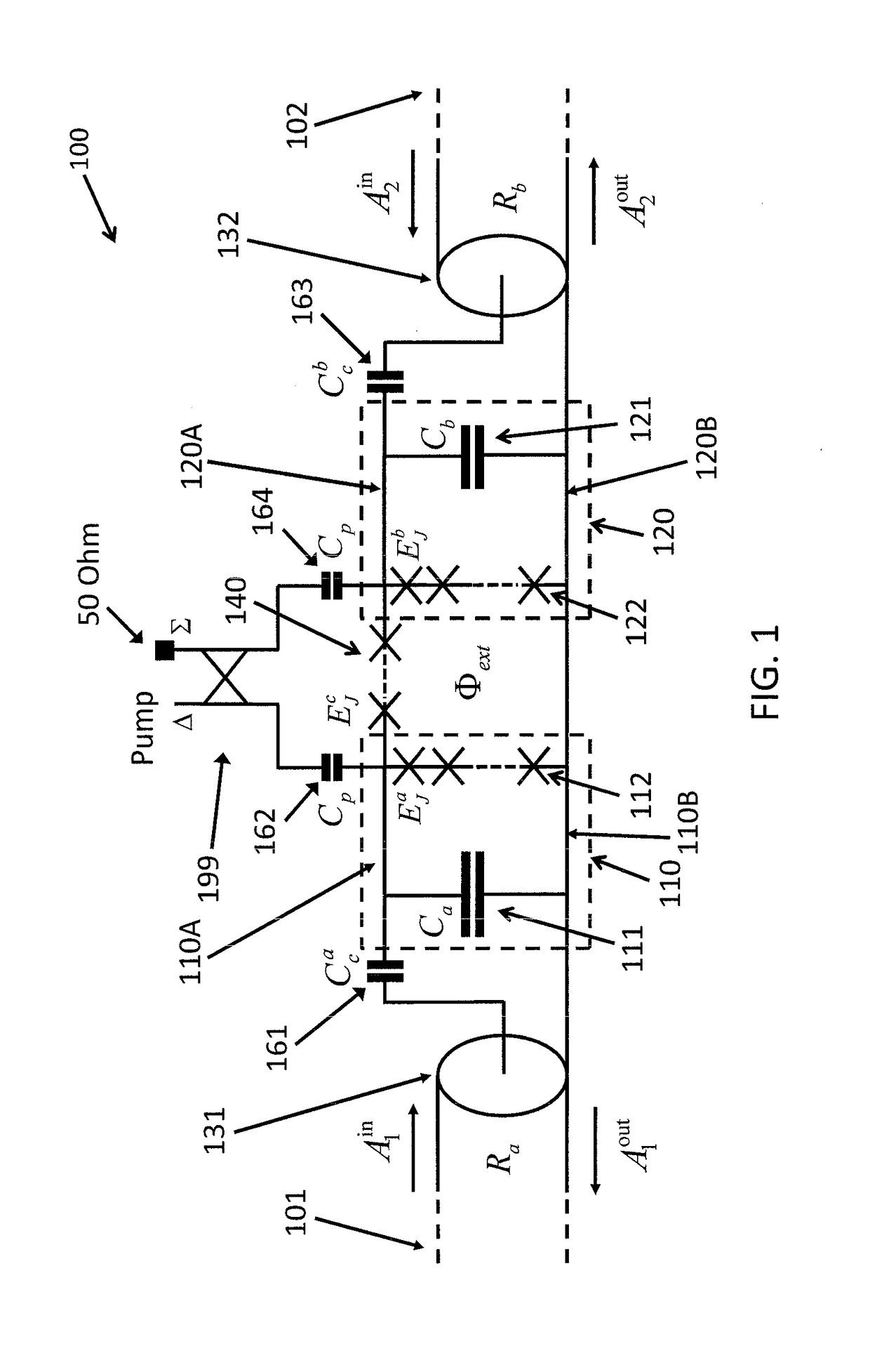
Method and apparatus for josephson distributed output amplifier
ActiveUS20100033252A1Data augmentationPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierCircuit delay
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for providing high-speed, low signal power amplification. In an exemplary embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method for providing a wideband amplification of a signal by forming a first transmission line in parallel with a second transmission line, each of the first transmission line and the second transmission line having a plurality of superconducting transmission elements, each transmission line having a transmission line delay; interposing a plurality of amplification stages between the first transmission line and the second transmission line, each amplification stage having an resonant circuit with a resonant circuit delay; and substantially matching the resonant circuit delay for at least one of the plurality of amplification stages with the transmission line delay of at least one of the superconducting transmission lines.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Superconductor output amplifier
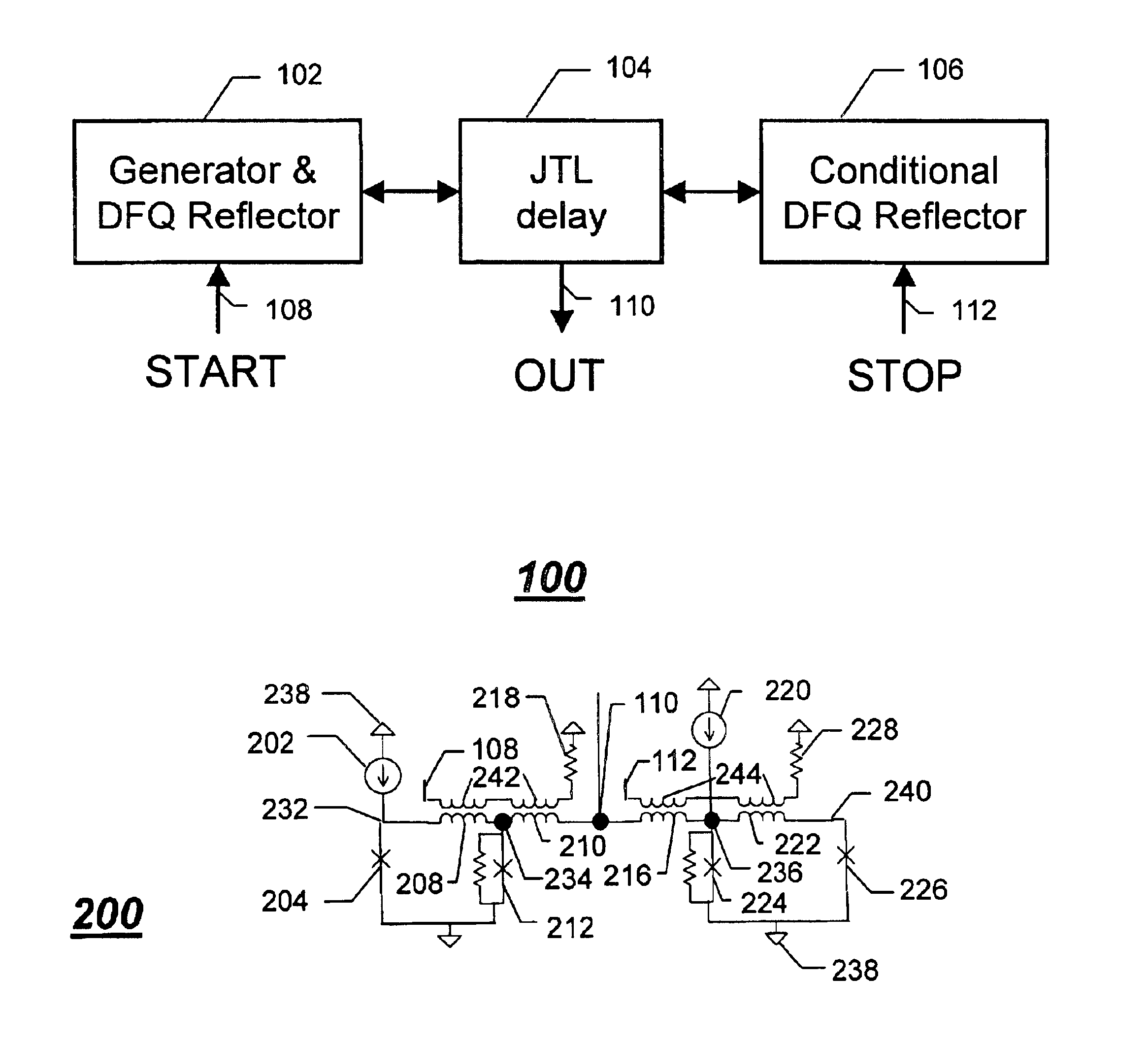
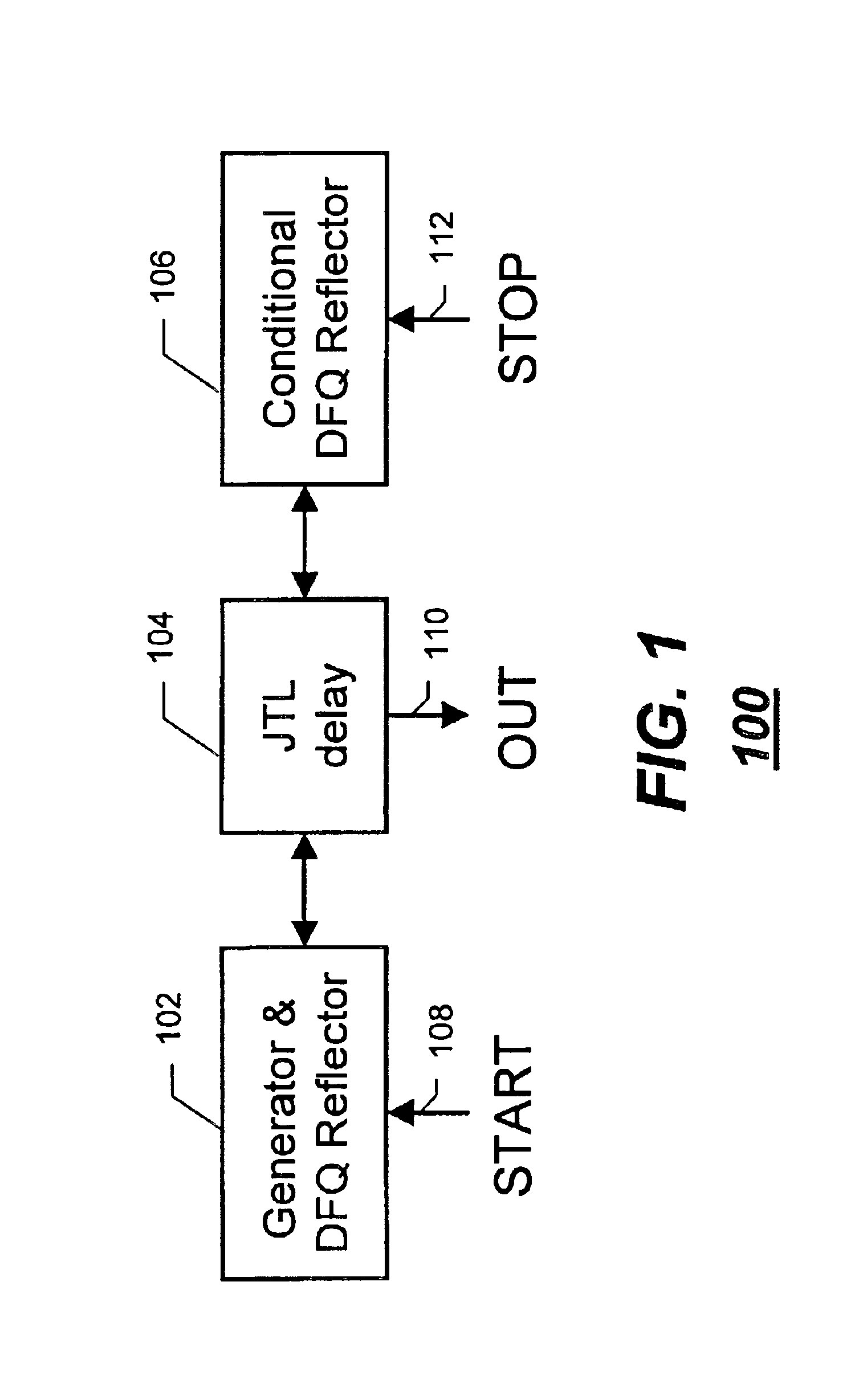
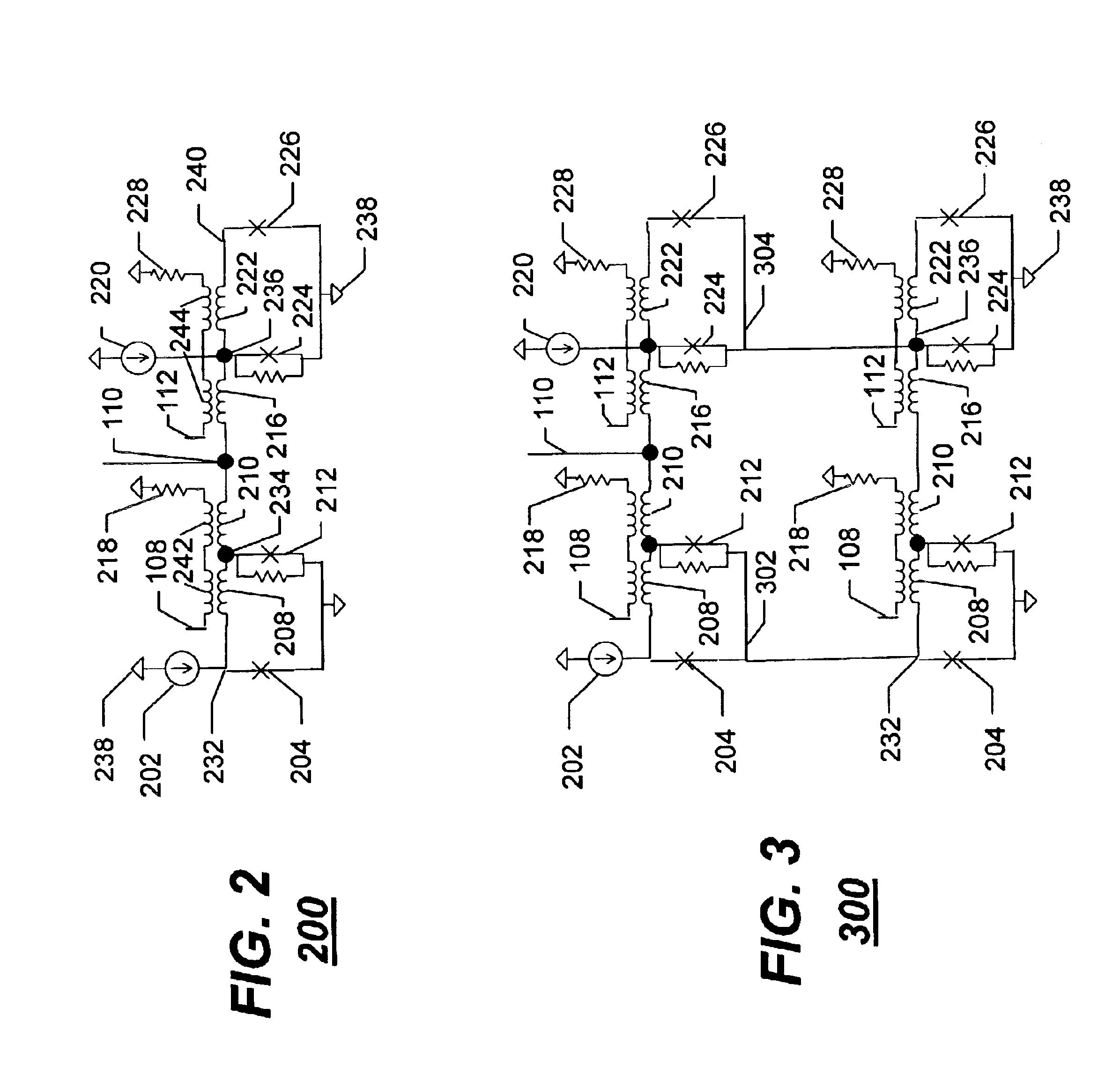
A single flux quantum (SFQ) pulse is generated (502) by injecting a superconductor output signal as a first signal at a “start” input (108) coupled to a superconductor delay element (104). The SFQ pulse is reflected (504) back and forth between first and second superconductor reflectors (102, 106) coupled to opposite ends of the superconductor delay element, thereby generating a time-disperse plurality of SFQ pulses at an output (110) coupled to the superconductor delay element. Thereafter, a second signal is input at a “stop” input (112) coupled to one of the first and second superconductor reflectors, thereby interrupting (506) the reflecting of the SFQ pulse at the one of the first and second superconductor reflectors, thus ending the generating of the time-disperse plurality of SFQ pulses at the output.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Josephson-coupled resonator amplifier (JRA)
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
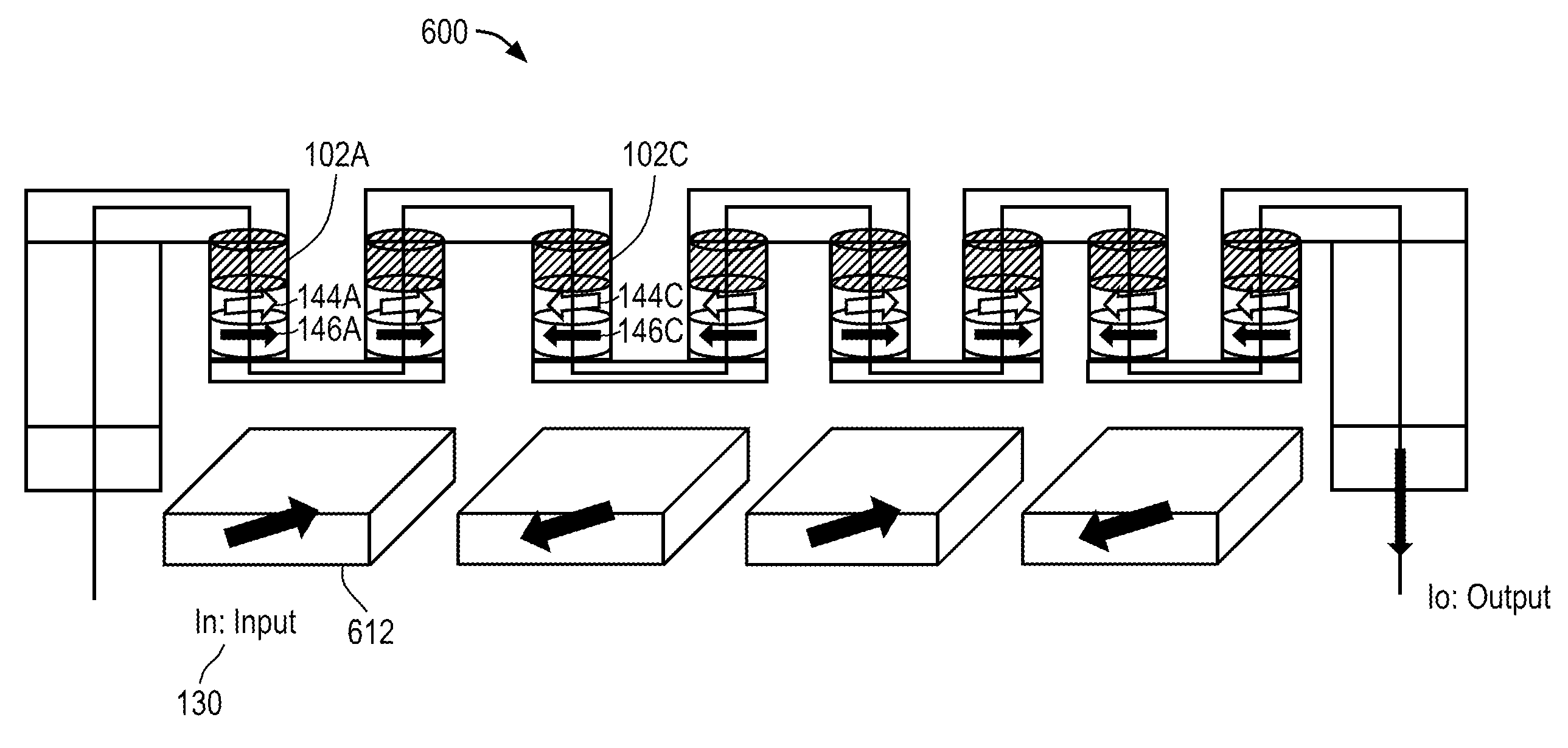
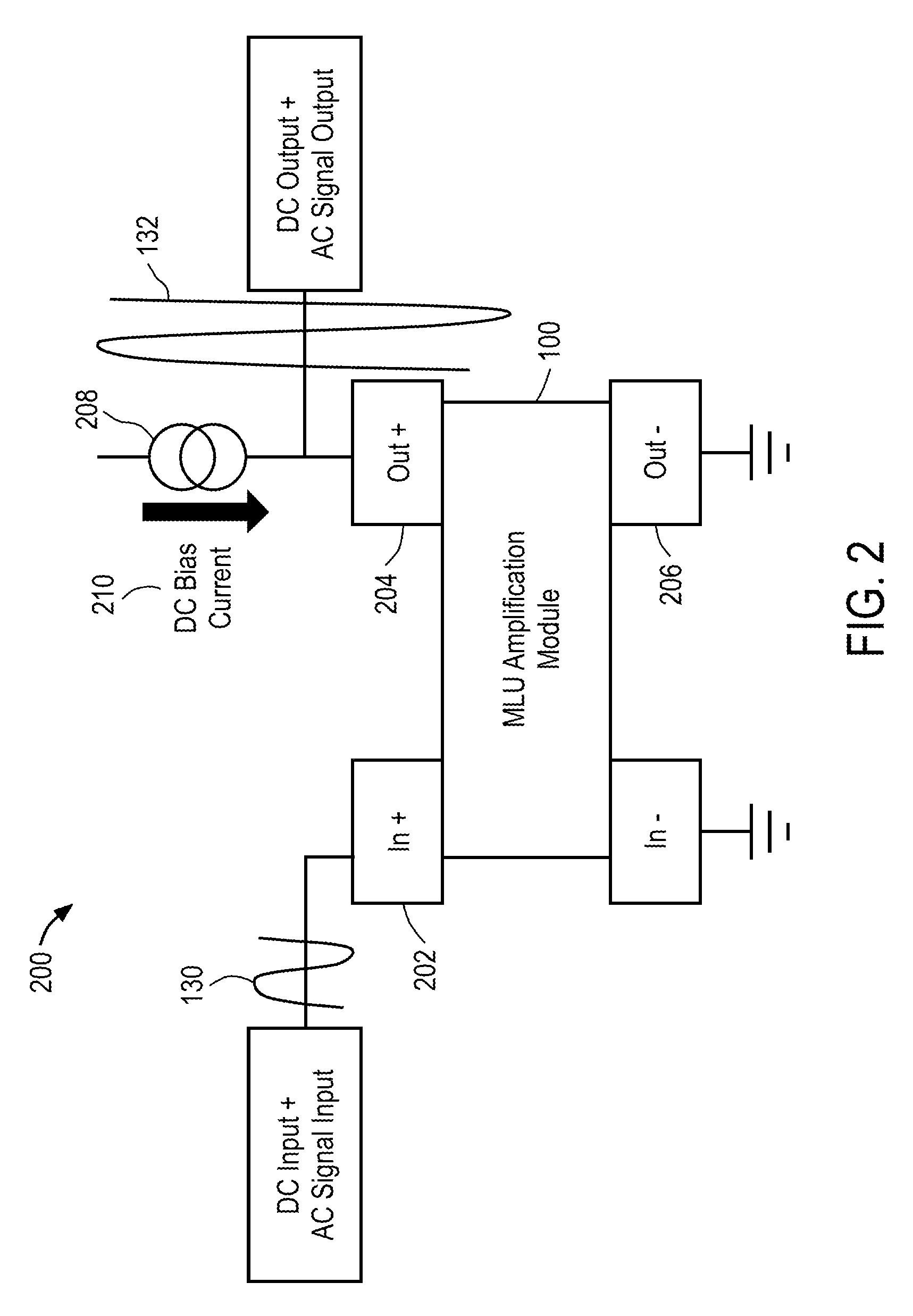
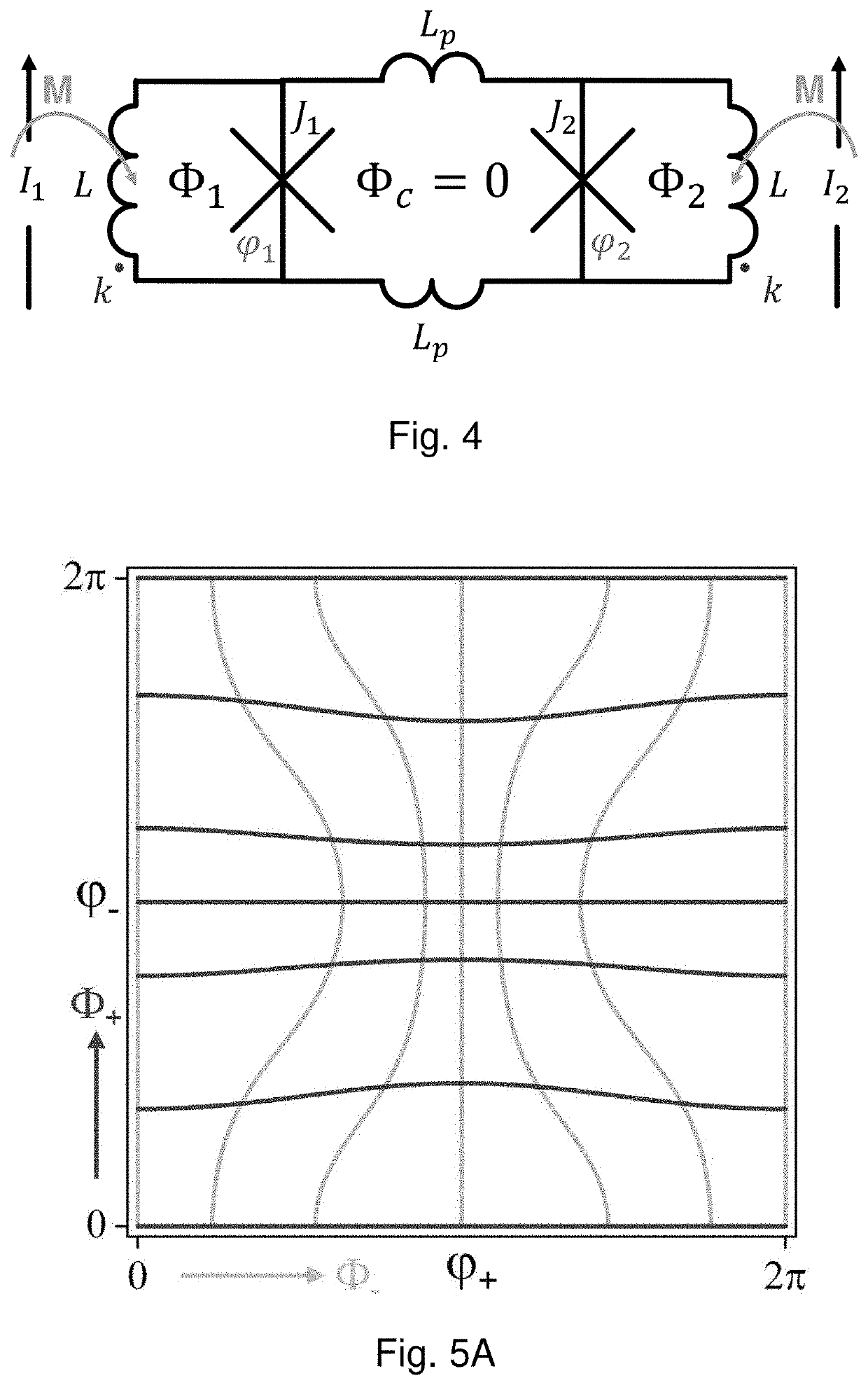
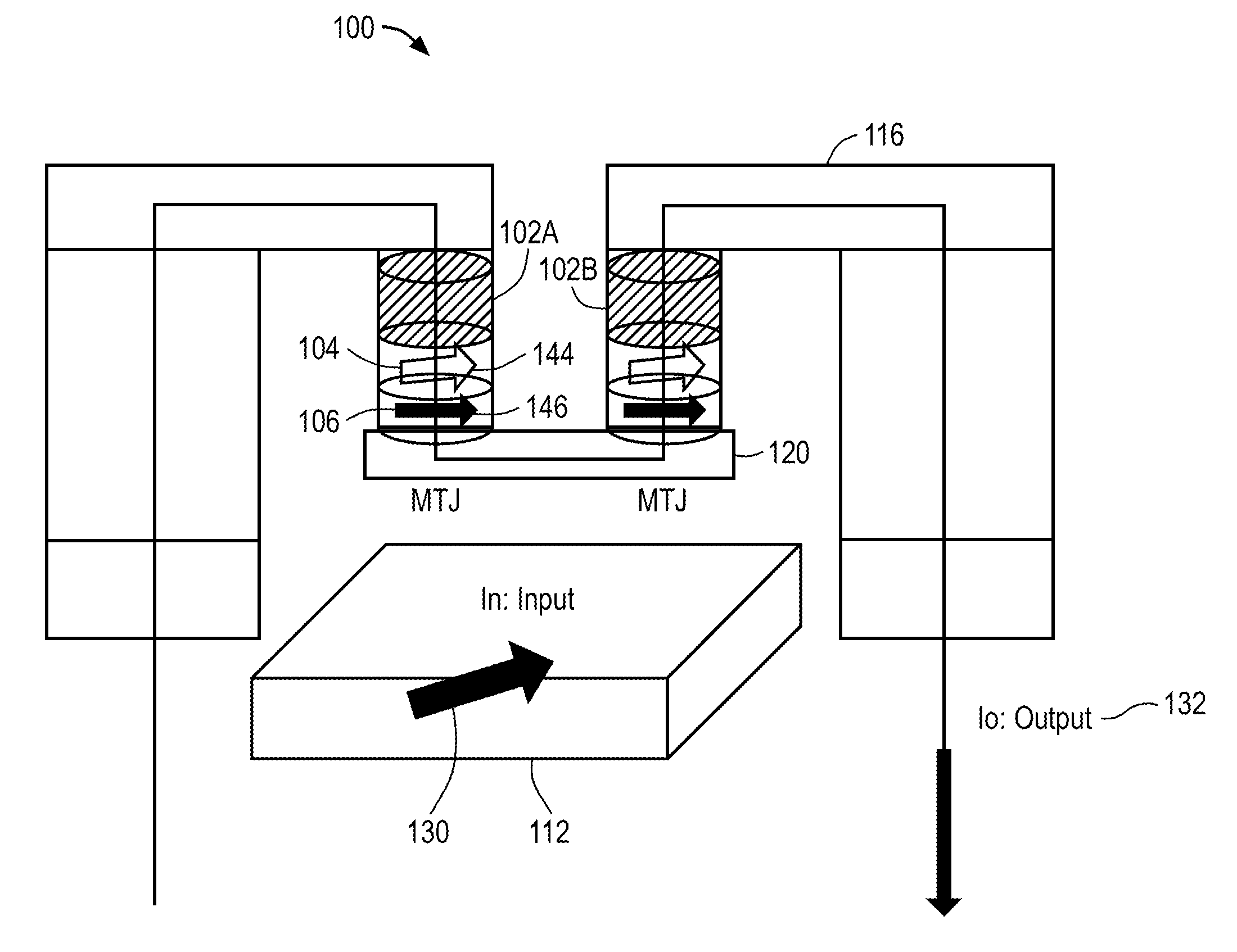
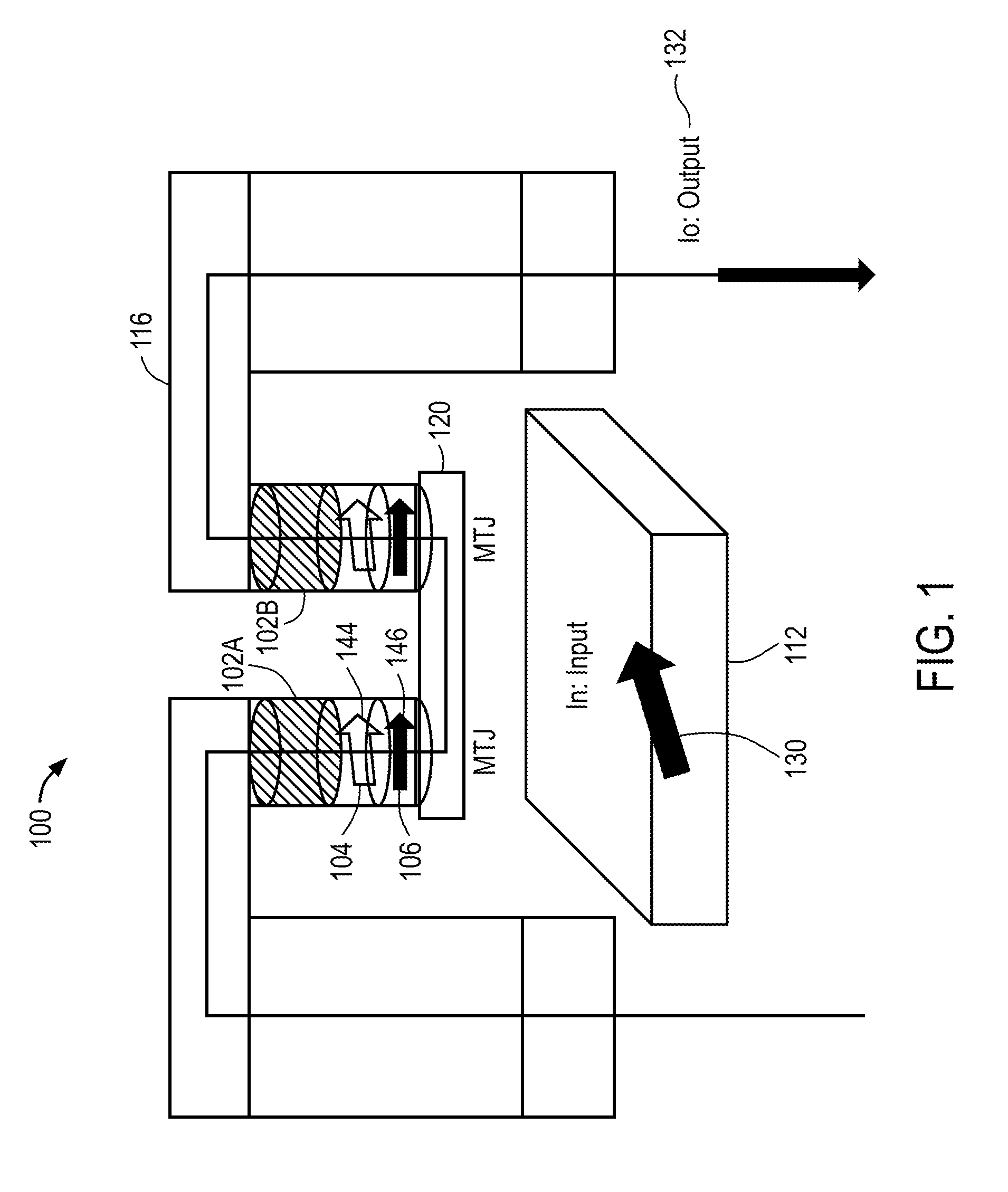
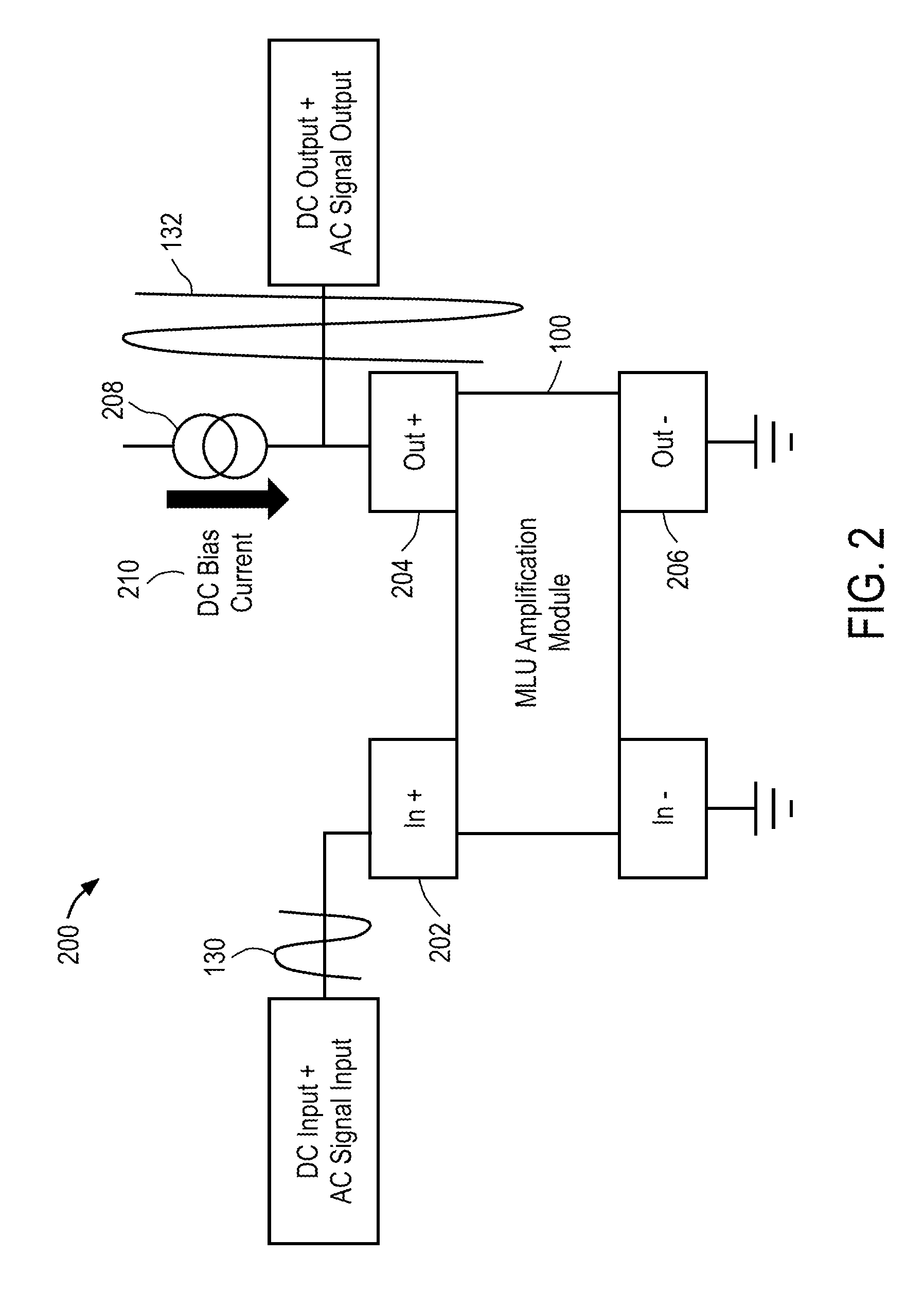
Magnetic Logic Units Configured as an Amplifier
ActiveUS20130241636A1Galvano-magnetic amplifiersMagnetic amplifiersElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
An apparatus includes a circuit and a field line. The circuit includes a magnetic tunnel junction including a storage layer and a sense layer. The field line is configured to generate a magnetic field based on an input signal, where the magnetic tunnel junction is configured such that a magnetization direction of the sense layer and a resistance of the magnetic tunnel junction vary based on the magnetic field. The circuit is configured to amplify the input signal to generate an output signal that varies in response to the resistance of the magnetic tunnel junction.
Owner:CROCUS TECHNOLOGY
High-gain level switching circuit
InactiveCN103066935ADifferential amplifiersSuperconductive amplifiersLevel shiftingAudio power amplifier
A high-gain level switching circuit does not restrain the upper limit of the common-mode input range of an operational amplifier. When the operational amplifier operates at specified low supply voltage, the upper limit of the common-mode input range is very important. Important parameters such as gain and switching speed of the operational amplifier can be controlled in the condition of no affecting the common-mode input voltage range. The high-gain level switching circuit works in a non-differential mode so that the problem of stability of a difference circuit is solved. The high-gain level switching circuit has the advantage of improving the gain through current balancing.
Owner:苏州硅智源微电子有限公司
Wideband dual amplifier circuits
InactiveCN1476666AAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCurrent-controlled magnetic amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
Dual amplifying circuits having a magnetic tunnel junction device and a field effect transistor configured in a complementing set are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the field effect transistor is operable to control a current level of a current operating signal flowing through the magnetic tunnel junction device. In another embodiment, the magnetic tunnel junction device is operable to control a voltage level of a voltage signal being applied to a gate terminal of the field effect transistor. The gain-bandwidth product of both embodiments is greater than the individual gain-bandwidth products of the individual devices through the elimination of noise contributing resistive type circuit elements.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for the definition of a library of application-domain-specific logic cells
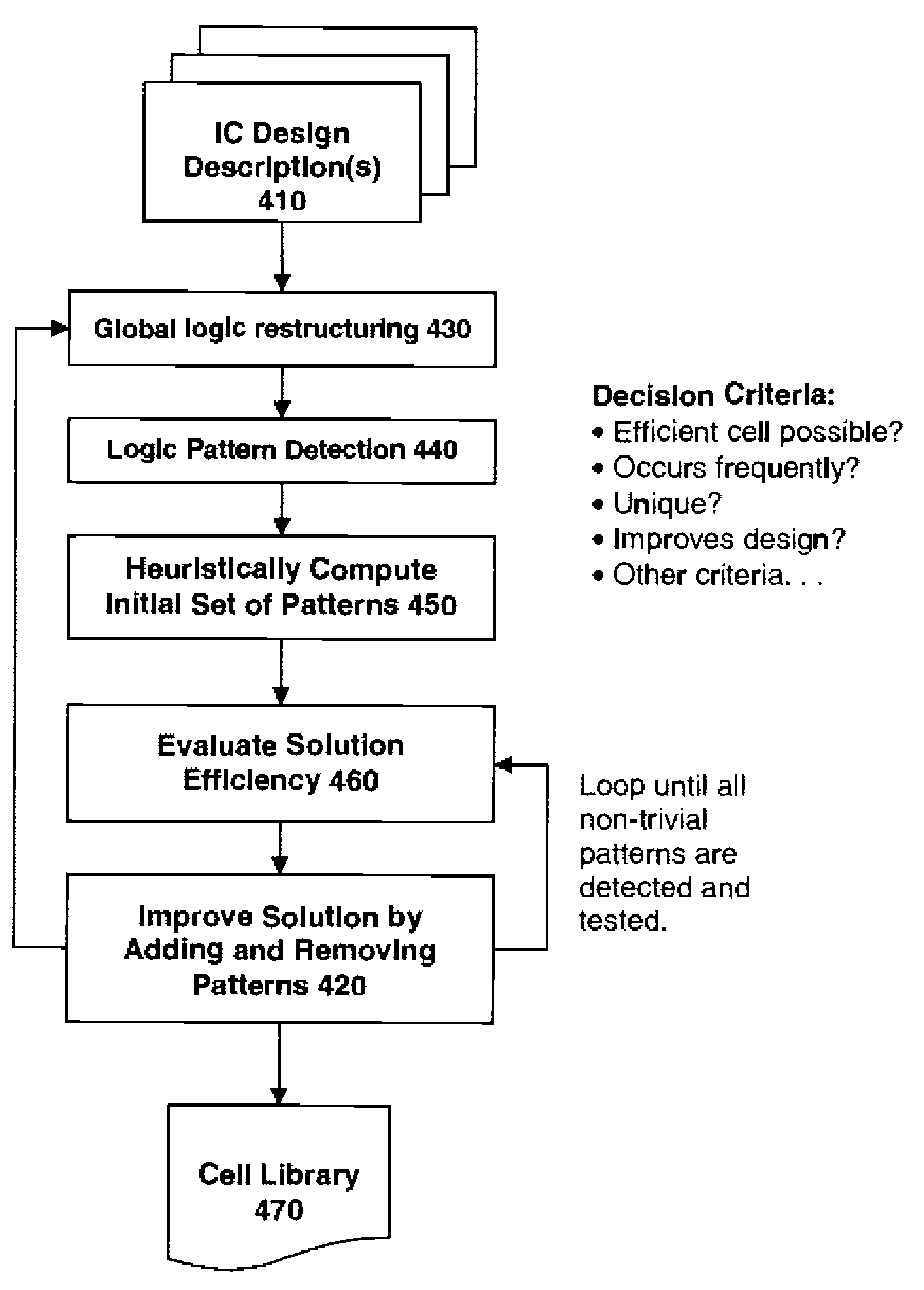
ActiveUS7784013B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic cellTheoretical computer science
The present invention provides in one aspect a method of defining a logic cell library composed of complex functions and simple functions, with some of the complex functions obtained from identifying logic function patterns. In another aspect the present invention provides a method of designing a representation of an integrated circuit that uses complex functions and simple functions, with the complex functions including a plurality of non-standard complex Boolean logic functions that are determined to collectively provide for logic pattern minimization.
Owner:PDF SOLUTIONS INC
Superconducting traveling-wave parametric amplifier
ActiveUS20200350880A1Reduce input powerEasy to controlQuantum computersSuperconductor detailsLow noiseSoftware engineering
A system and method are disclosed for a superconducting traveling-wave parametric amplifier (TWPA) with improved control and performance. In a preferred embodiment, the amplifier comprises an integrated array of symmetric rf-SQUIDs in a transmission line structure. A device was fabricated using niobium superconducting integrated circuits, and confirmed predicted performance, with a maximum gain up to 17 dB and a bandwidth of 4 GHz. A similar device can be applied as a low-noise, low-dissipation microwave amplifier for output from a superconducting quantum computer, or as a preamplifier, switch, or frequency converter for a sensitive microwave receiver, or as an output amplifier for a frequency-multiplexed superconducting detector array.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Magnetic logic units configured as an amplifier
ActiveUS8933750B2Galvano-magnetic amplifiersMagnetic amplifiersElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
An apparatus includes a circuit and a field line. The circuit includes a magnetic tunnel junction including a storage layer and a sense layer. The field line is configured to generate a magnetic field based on an input signal, where the magnetic tunnel junction is configured such that a magnetization direction of the sense layer and a resistance of the magnetic tunnel junction vary based on the magnetic field. The circuit is configured to amplify the input signal to generate an output signal that varies in response to the resistance of the magnetic tunnel junction.
Owner:CROCUS TECHNOLOGY
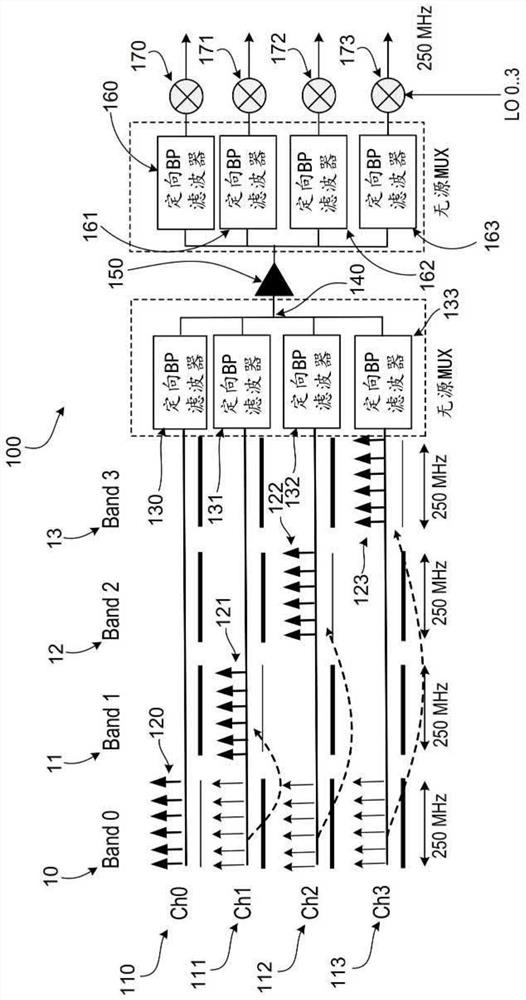
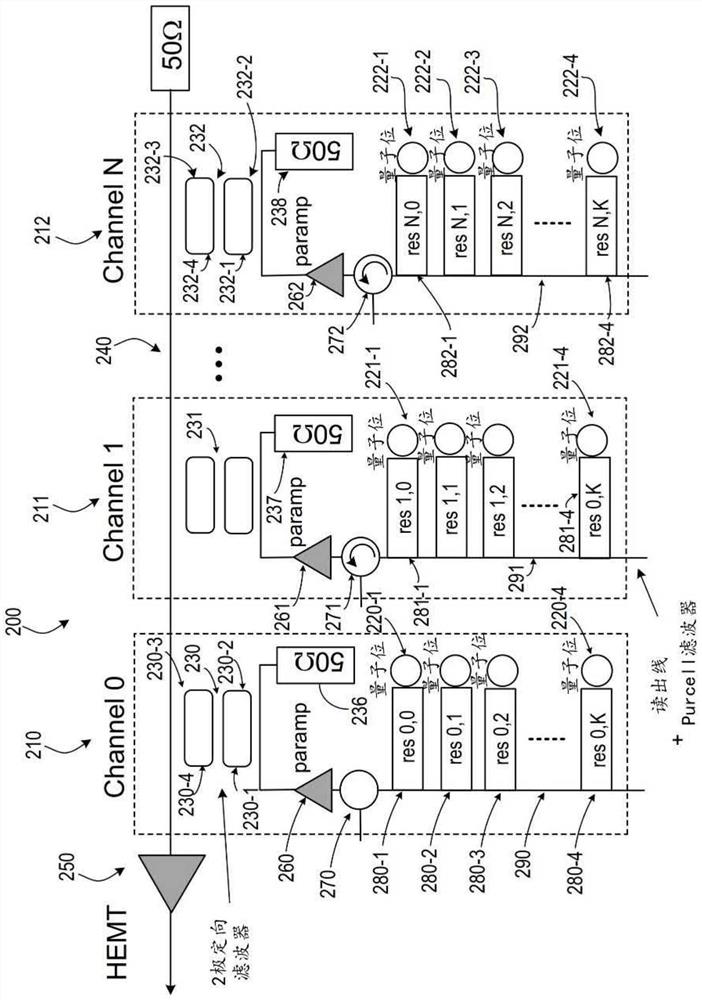
Multiplex readout system
A circuit is presented that includes a first amplifier having an input, a transmission line having a first end and a second end. A first end of the transmission line is coupled to an input of the first amplifier and the plurality of channels. Each channel includes a plurality of resonators arranged to read out a plurality of qubits, respectively, and a readout line arranged to receive readout signals from the plurality of resonators. The readout line of each channel is coupled to the transmission line, and each channel is configured to output a respective signal in a respective frequency band different from the frequency bands of other channels of the plurality of channels.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
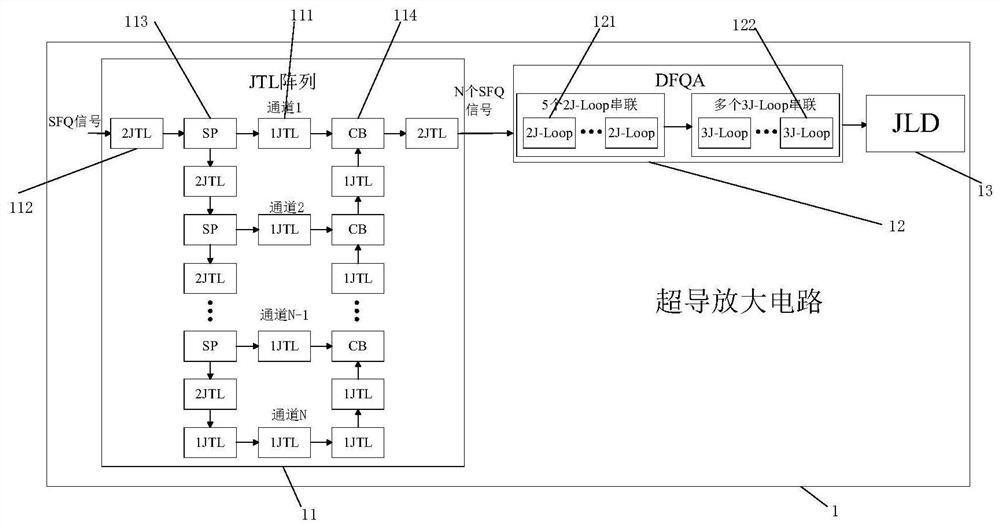
Superconducting amplifying circuit
InactiveCN112994635ATaking into account the areaConsider performanceSuperconductive amplifiersDriving currentSoftware engineering
The invention relates to a superconducting amplifying circuit, and belongs to the field of superconducting integrated circuits. The superconducting amplification circuit comprises a Josephson transmission line (JTL) array which is used as a signal multiplication circuit and is used for receiving an input single flux quantum (SFQ) signal and sending a string of SFQ signals; the double flux quantum amplifier (DFQA) is used as a first-stage amplification circuit, receives a string of SFQ signals from the JTL array to generate a level signal, and is used for providing a driving current for a subsequent circuit; and the Josephson latch driver (JLD) is used as a second-stage amplification circuit, receives the driving current provided by the DFQA, and generates an output voltage of dozens of millivolts under the condition of bias so as to drive the semiconductor integrated circuit. According to the superconducting amplifying circuit, compromise in circuit performance and area is achieved, the amplifier is divided into two stages, the two stages of amplifiers can be packaged separately, and the flexibility of circuit application is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
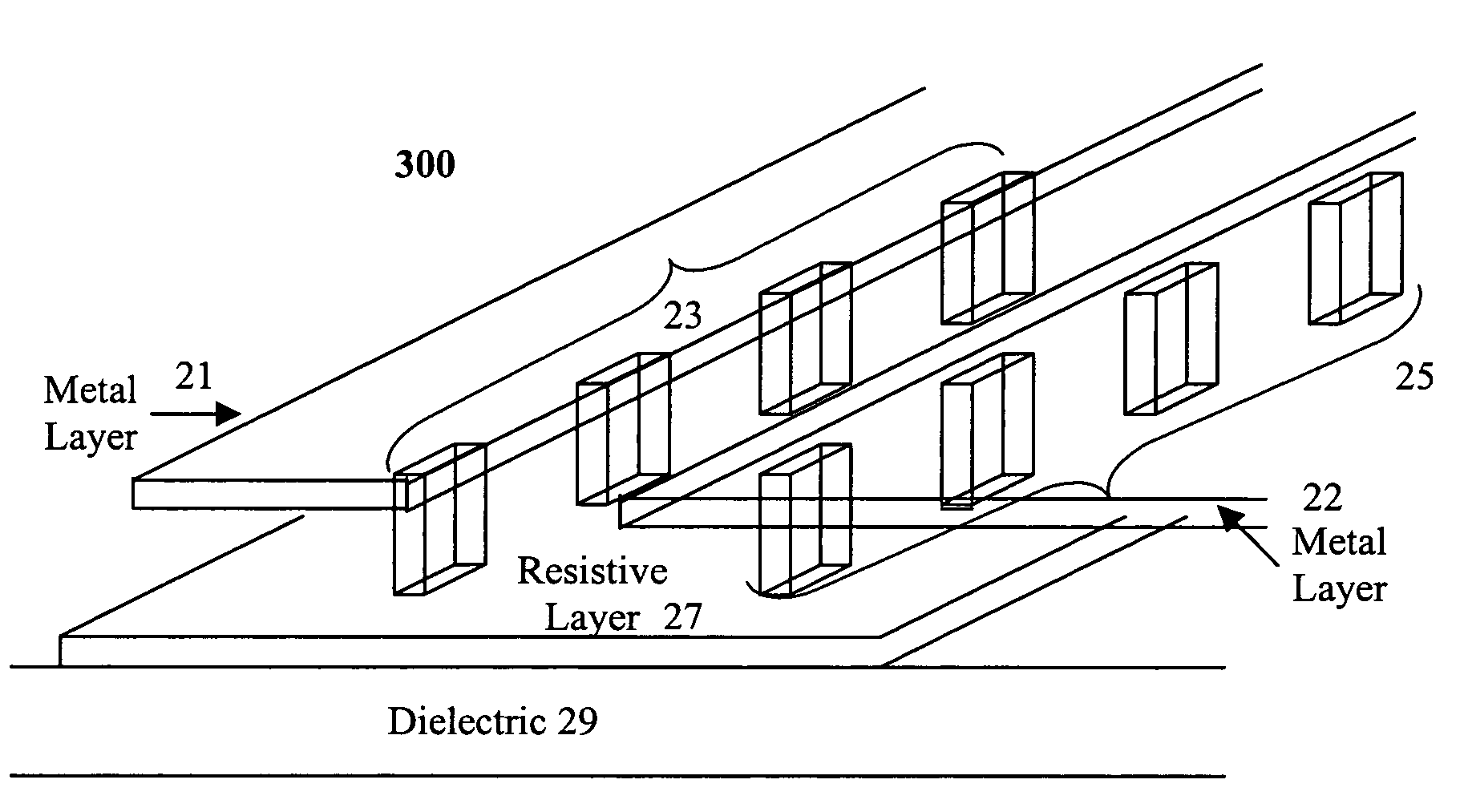
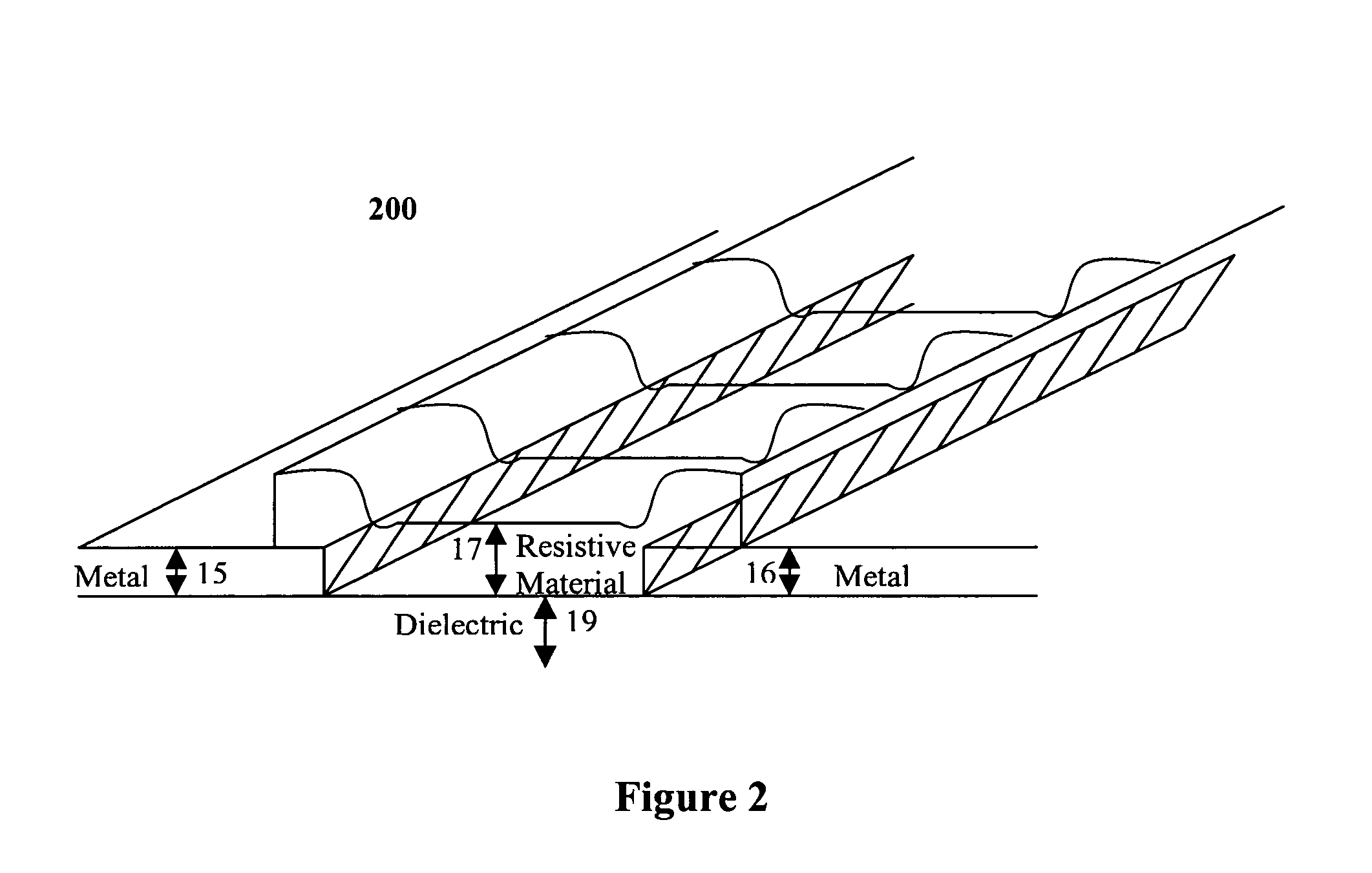
Method and system for reducing parasitic feedback and parasitic resonances in high-gain transimpedance amplifiers
InactiveUS7057453B1Reduce parasitic feedbackReduce resonanceDigital storageAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierResonance
Method and system for reducing parasitic feedback and resonances in high-gain transimpedance amplifiers. In a first embodiment of the present invention, a resistive layer is implemented in the gaps of a high-gain transimpedance amplifier's metallic planes. In a second embodiment of the present invention, a resistive layer is implemented underneath a high-gain transimpedance amplifier's ground plane, vias are implemented to create contact between the resistive layer and the ground plane.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Josephson traveling wave parametric amplifier
ActiveCN113424441AGain controlVariable-capacitor element amplifiersSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
According to an example aspect of the present invention, there is provided a traveling wave parametric amplifier comprising a waveguide transmission line comprising therein at least ten Josephson elements, wherein each of the at least ten Josephson element comprises a loop, with exactly one Josephson junction of first size on one half of the loop and at least two Josephson junctions of a second size on a second half of the loop, the second size being larger than the first size, a flux bias line configured to generate a magnetic flux threading each of the at least one loop, and a set of resistors coupled with the flux bias line.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
A parametric amplifier
ActiveUS20210135643A1Tunnelling of electrons to the quantum dot is preventedAvoid tunnelingNanoopticsVariable-capacitor element amplifiersCapacitanceQuantum dot
The present disclosure relates to parametric amplifiers that can be used in the presence of a magnetic field. In particular the present disclosure relates to an integrated signal amplifier that comprises: a quantum dot; a first conductive electrode arranged in a manner such that tunnelling of electrons to the quantum dot is prevented; and a second conductive electrode arranged in a manner such tunnelling of electrons to the quantum dot is permitted. When an oscillating signal is applied across the first and second electrodes, the equivalent capacitance across the first and the second electrodes oscillates at the frequency of the oscillating signal.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
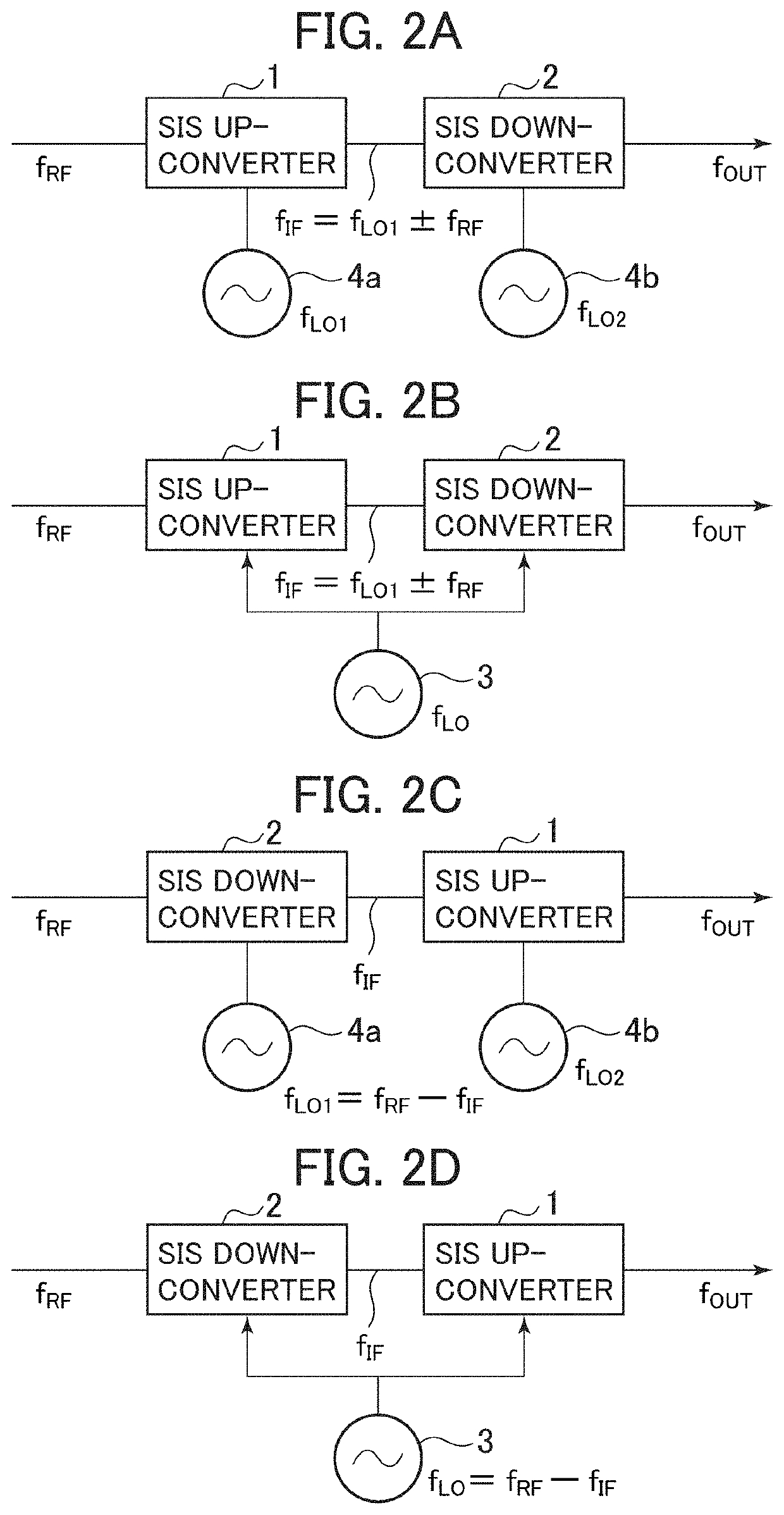
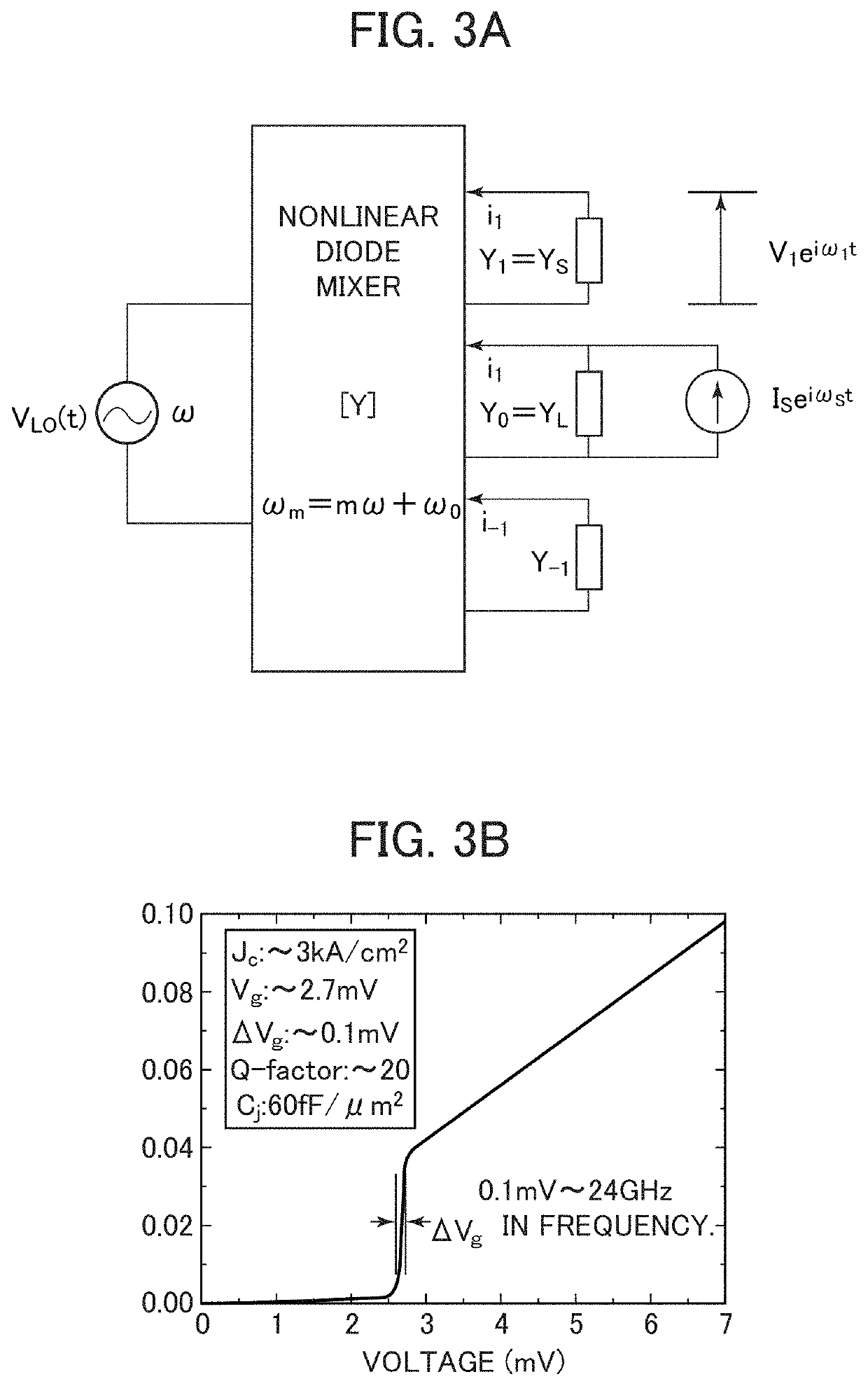
Low-noise microwave amplifier utilizing superconductor-insulator-superconductor junction
ActiveUS10680567B2Easy maintenanceEasy temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLow noiseFrequency mixer
A low-noise wide band amplifier is realized utilizing a superconductor-insulator-superconductor (SIS) junction, quasiparticle frequency mixers connected in tandem or in cascade, a first quasiparticle mixer performs first frequency mixing with use of a first local signal having a frequency not less than twice a frequency of an input signal to the first quasiparticle mixer, a second quasiparticle mixer performs second frequency mixing with use of a second local signal having a frequency not more than twice a frequency of an input signal to the second quasiparticle mixer, and signal amplification is performed through frequency conversion by extracting, from among a plurality of signals generated with the first and the second frequency mixing, a signal in a frequency band not more than a frequency band of the signal before the first frequency mixing and the second frequency mixing, using a transmission line or a filter.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST NAT INST OF NATURAL SCI
Superconducting traveling-wave parametric amplifier
ActiveUS10998869B2Easy to controlImprove performanceQuantum computersSuperconductor detailsLow noiseSoftware engineering
A system and method are disclosed for a superconducting traveling-wave parametric amplifier (TWPA) with improved control and performance. In a preferred embodiment, the amplifier comprises an integrated array of symmetric rf-SQUIDs in a transmission line structure. A device was fabricated using niobium superconducting integrated circuits, and confirmed predicted performance, with a maximum gain up to 17 dB and a bandwidth of 4 GHz. A similar device can be applied as a low-noise, low-dissipation microwave amplifier for output from a superconducting quantum computer, or as a preamplifier, switch, or frequency converter for a sensitive microwave receiver, or as an output amplifier for a frequency-multiplexed superconducting detector array.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Popular searches
Amplifiers wit coupling networks Logic circuits using superconductive devices Measurement instrument housing Pulse generation by super conductive devices Coupling devices Pulse shaping Amplifier modifications to extend bandwidth Dissimilar materials junction devices Magnitude/direction of magnetic fields Photometry electrical circuits
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com