Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3783results about "Starter details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
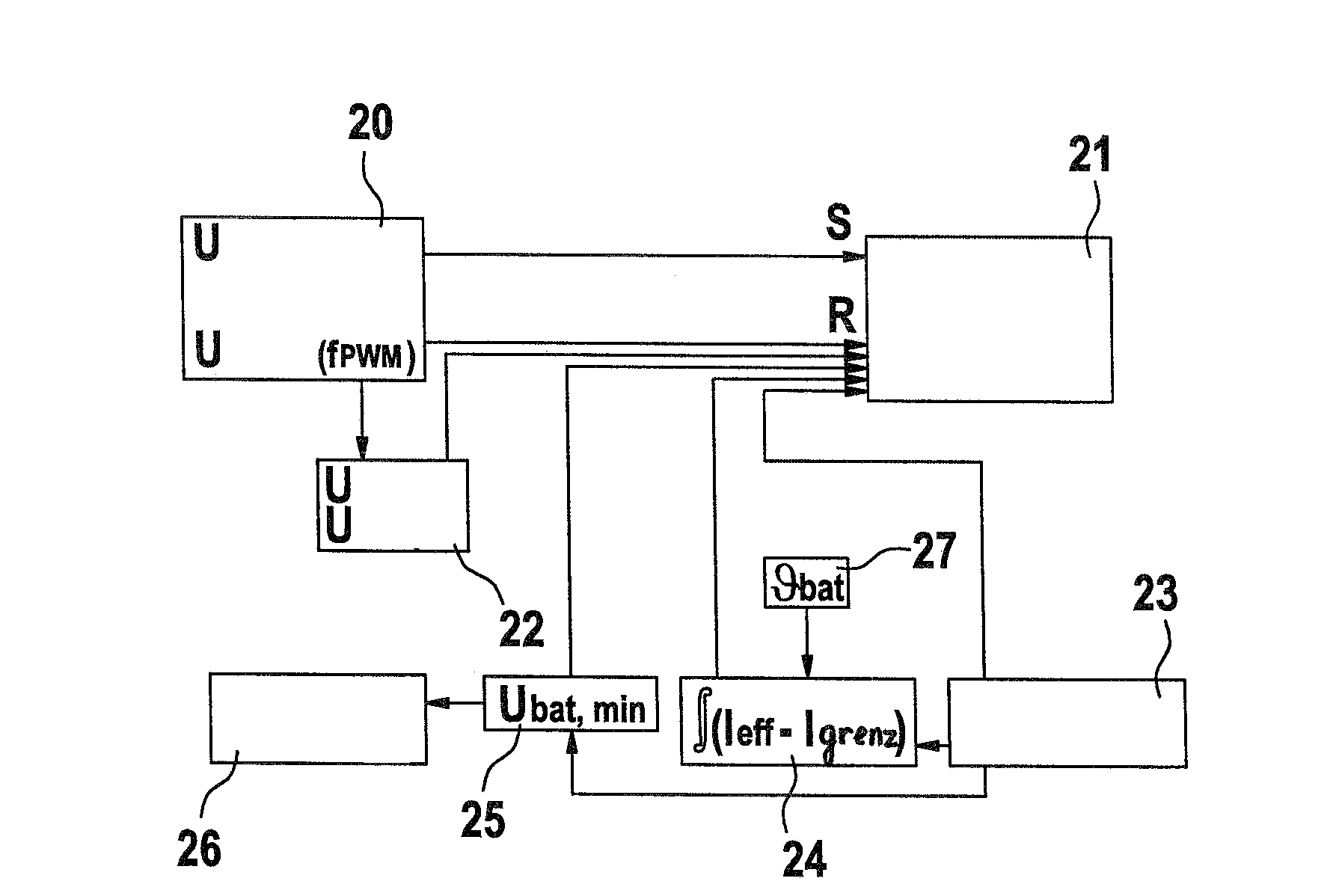
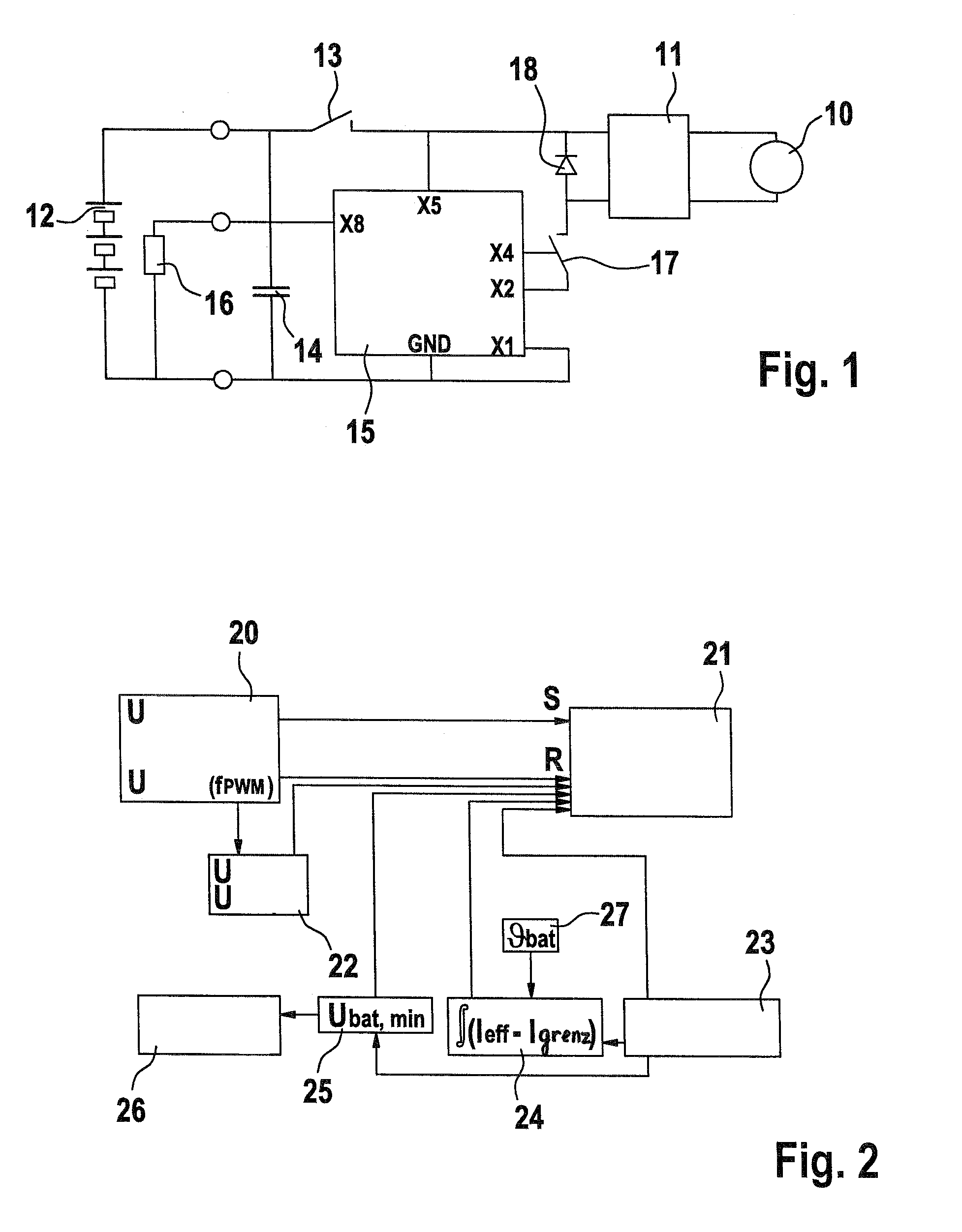
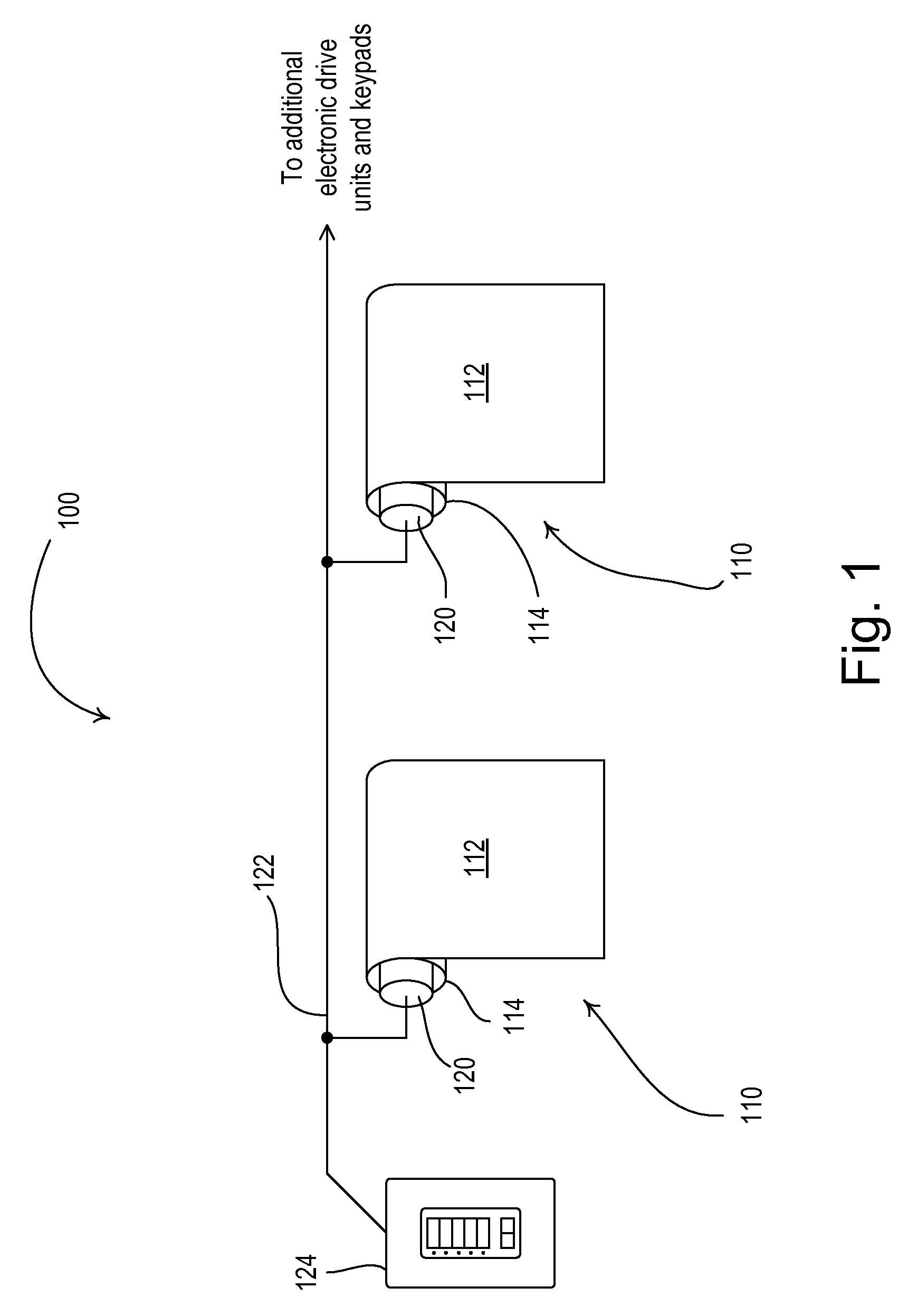
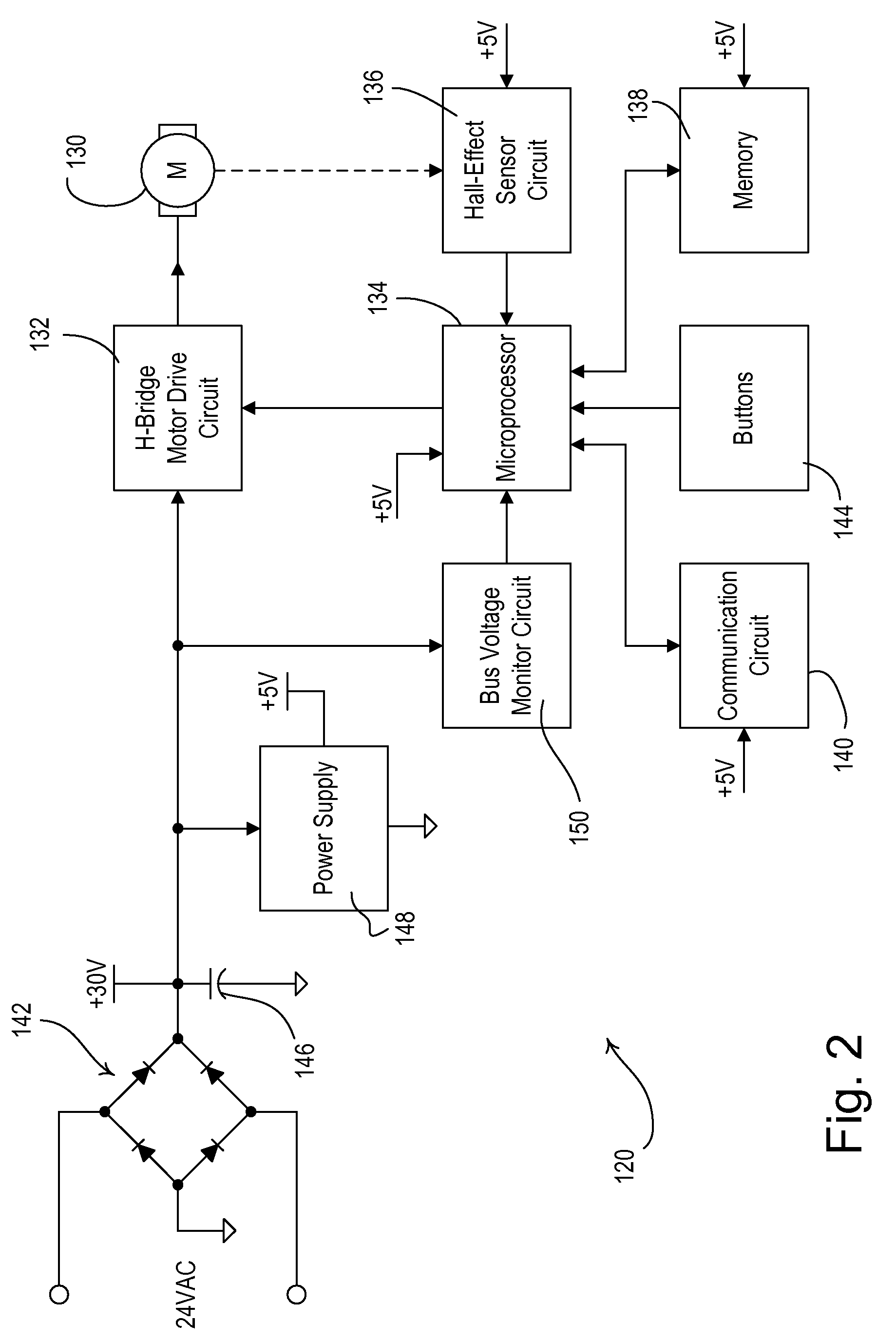
Method for operating a power tool
ActiveUS7336048B2Maintain good propertiesReduce widthTemperatue controlEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionMOSFETElectricity
In a method for operating a power tool with an energy accumulator, in particular a rechargeable energy accumulator, which supplies power to an electric drive motor, a clock frequency is generated by an electronic unit, with which a gate of a MOSFET—which supplies operating voltage to the drive motor—is switched on with each cycle, and a switching-off of the MOSFET is carried out within one cycle using different signals, as a function of operating parameters.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
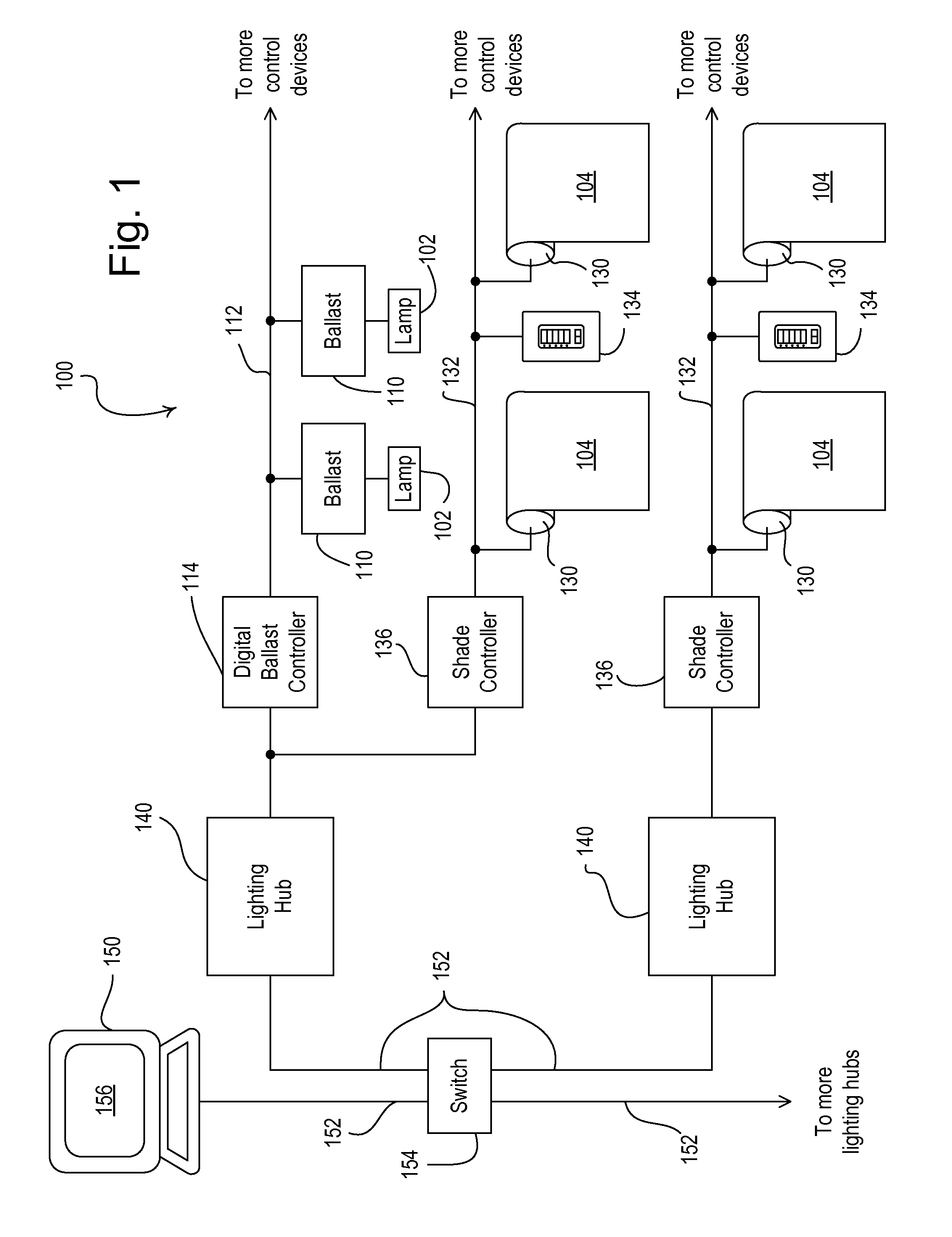
Method of controlling a motorized window treatment
ActiveUS7839109B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersDoor/window protective devicesMotor driveControl theory
A method of controlling a motorized window treatment provides for continued operation of the motorized window treatment during an overload or low-line condition. The motorized window treatment is driven by an electronic drive unit having a motor, a motor drive circuit, and a controller. The controller controls the motor drive circuit to drive the motor with a pulse-width modulated signal generated from a bus voltage. The controller is operable to monitor the magnitude of the bus voltage. If the bus voltage drops below a first voltage threshold, the controller stops the motor or reduces the duty cycle of the pulse-width modulated signal to allow the bus voltage to increase to an acceptable magnitude. When the bus voltage rises above a second voltage threshold, the controller begins driving the motor normally once again. During an overload or low-line condition, the controller is prevented from resetting, while driving the motor with minimal interruption to the movement of the motorized window treatment.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Portable drilling device
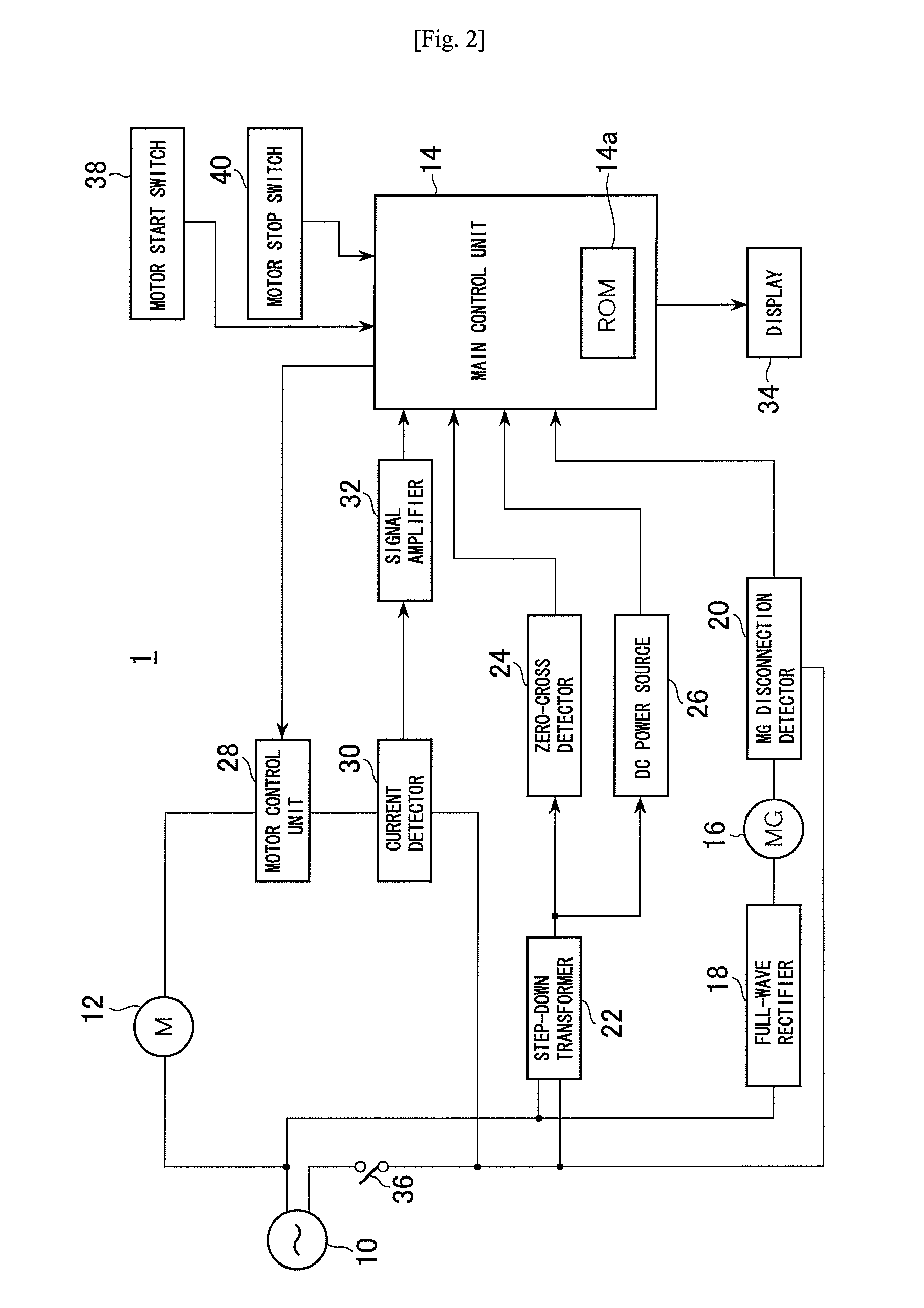
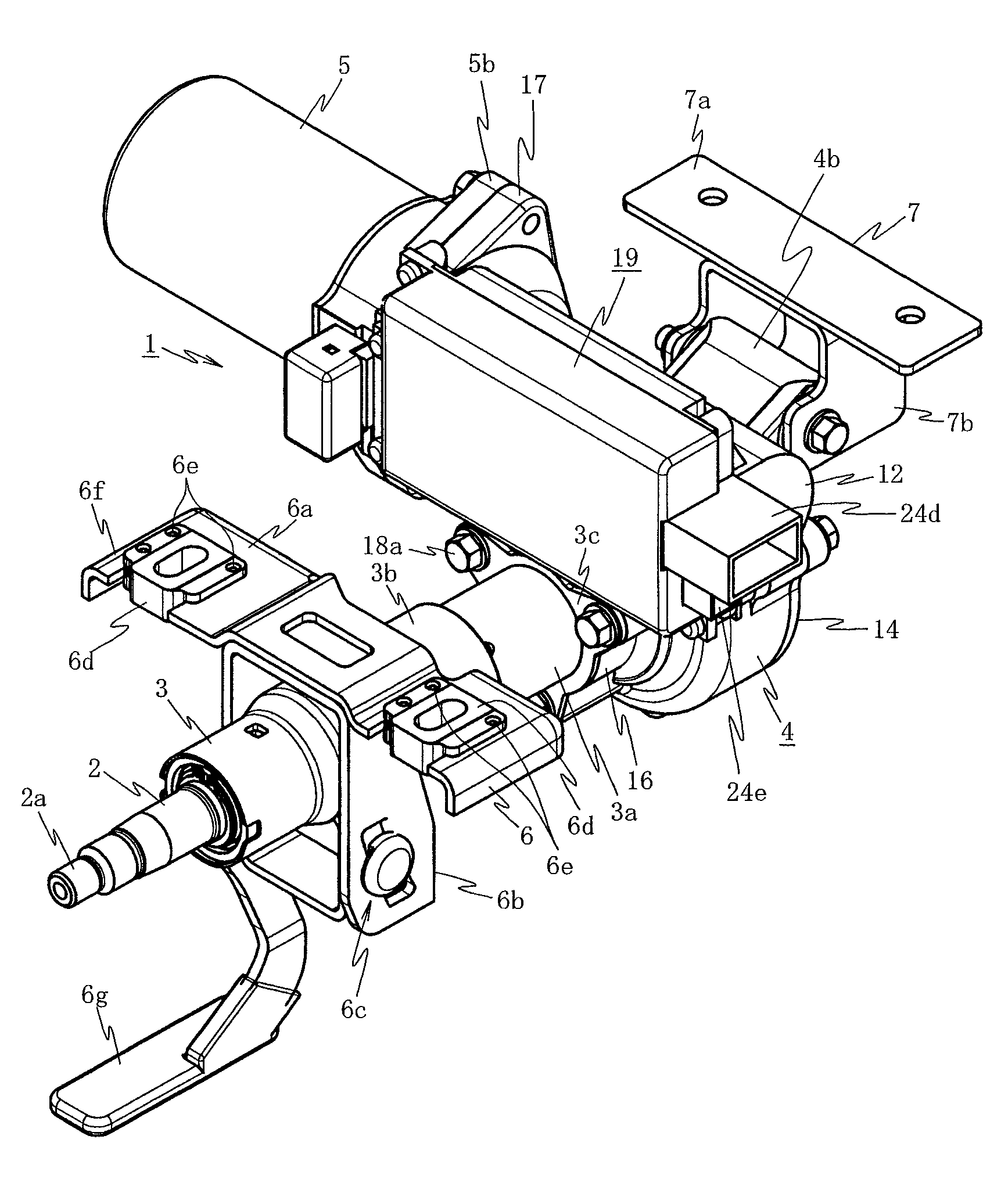
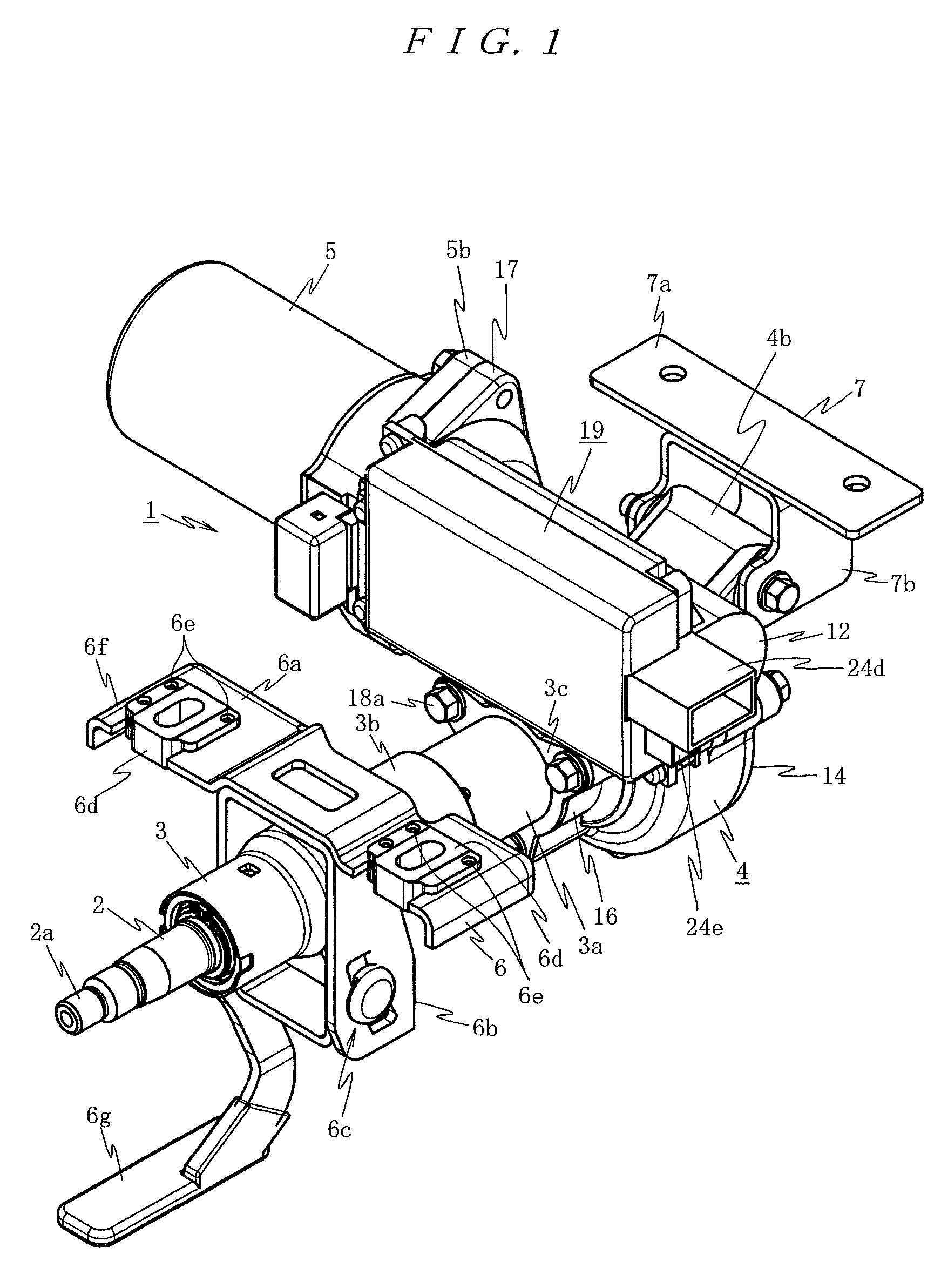
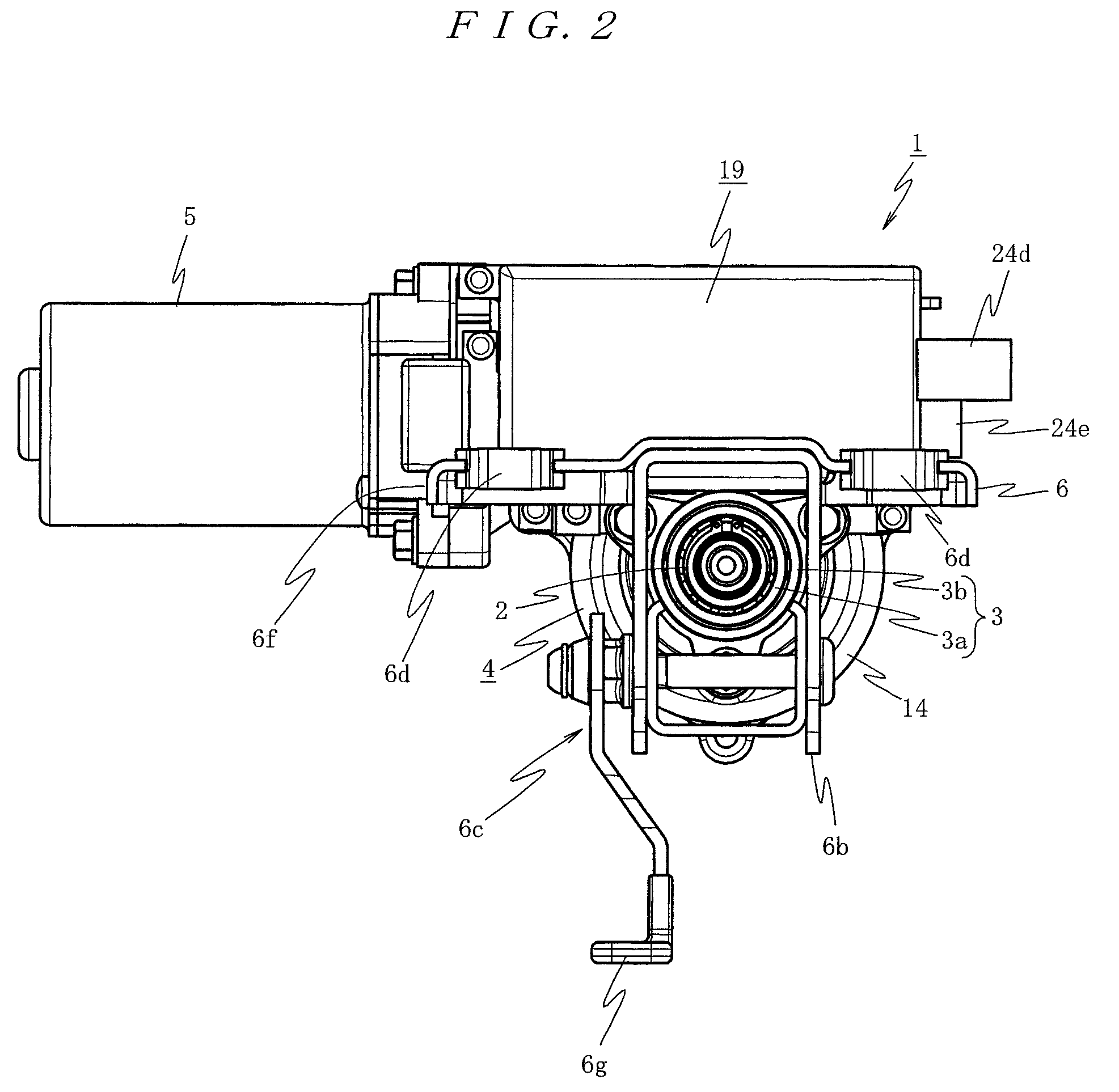
ActiveUS7936142B2Easy to operateImprove securityAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlFull waveEngineering
A drilling device prevents recurrence of an overload condition after occurrence of the overload condition, thereby improving operability and safety in the drilling device. A motor for rotating a drill is connected to an AC power source through a motor control unit, a current detector, and a power switch. A magnet is also connected to the AC power source through the power switch and a full-wave rectifier. The motor control unit rotationally drives the motor on the basis of a signal sent from a main control unit according to a state in which a motor start switch is on. The main control unit controls the motor control unit to gradually reduce a supply voltage to the motor when the motor becomes overloaded, to gradually increase the voltage to the normal power supply condition when the overload condition is vanished, and to stop power supply to the motor if the overload condition continues for a predetermined period.
Owner:NITTO KOHKI CO LTD
Electric power steering apparatus and method of assembling the same
ActiveUS8102138B2Large massDC motor speed/torque controlElement comparisonElectricityElectric power steering
A motor control apparatus includes a steering column having inserted therein a steering shaft to which steering torque is transmitted, a reduction gear box coupled to the steering shaft, and an electric motor that transmits a steering assisting force to the steering shaft via a reduction mechanism in the reduction gear box. The electric motor and its control unit including a control board mounted with a control circuit, are provided side by side in the reduction gear box. A connection terminal of the electric motor is electrically connected to the control unit directly. This minimizes a connection distance between the control unit and the electric motor.
Owner:NSK LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling electronically commutated motor operating characteristics
InactiveUS6895176B2Operation controlSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlBrushless motorsControl electronics
A permanent magnet DC brushless motor control assembly permits a user to select the permanent magnet DC brushless motor operating characteristics by selecting appropriate control circuits to interface with the motor. The assembly includes a permanent magnet DC brushless motor, a commutator electrically coupled to the motor, and at least one control module electrically coupled to the commutator, to control operating characteristics of the permanent magnet DC brushless motor.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Moisture sensor and windshield fog detector
InactiveUS6097024AAutomatic detectionLower performance requirementsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementControl signalEngineering
A control system for automatically detecting moisture on the windshield of a vehicle. The automatic moisture detecting system includes an optical system for imaging a portion of the windshield on to an image array sensor, such as a CMOS active pixel sensor. The voltages of each of the pixels which represents the illumination level is converted to a corresponding gray scale value by an analog digital converter. The gray scale values corresponding to the image are stored in memory. The spatial frequency composition of the gray scale values are analyzed to determine the amount of rain present. In order to provide a control signal to control the operation of the windshield wipers of the vehicle as a function of the amount of moisture present. The system is also adapted to detect the level of fog both on the interior of the windshield as well as the exterior of the windshield. By providing a system for automatically detecting the presence of fog on the interior and exterior of the windshield, serious performance limitations of known automatic rain sensors are eliminated.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
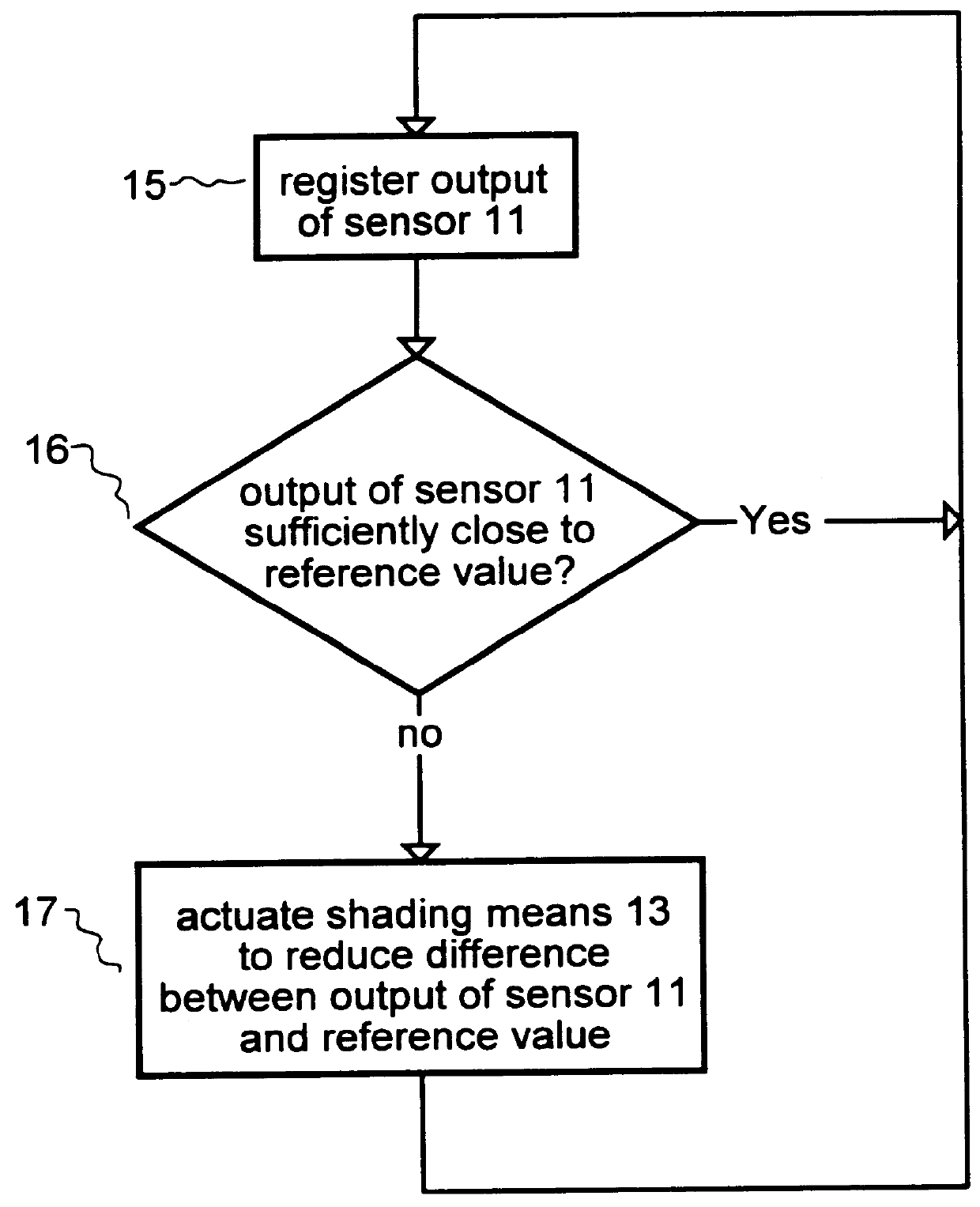
Closed-loop, daylight-sensing, automatic window-covering system insensitive to radiant spectrum produced by gaseous-discharge lamps
InactiveUS6084231AMaximized ratioOptical radiation measurementLight dependant control systemsSpectral responseLow-pass filter
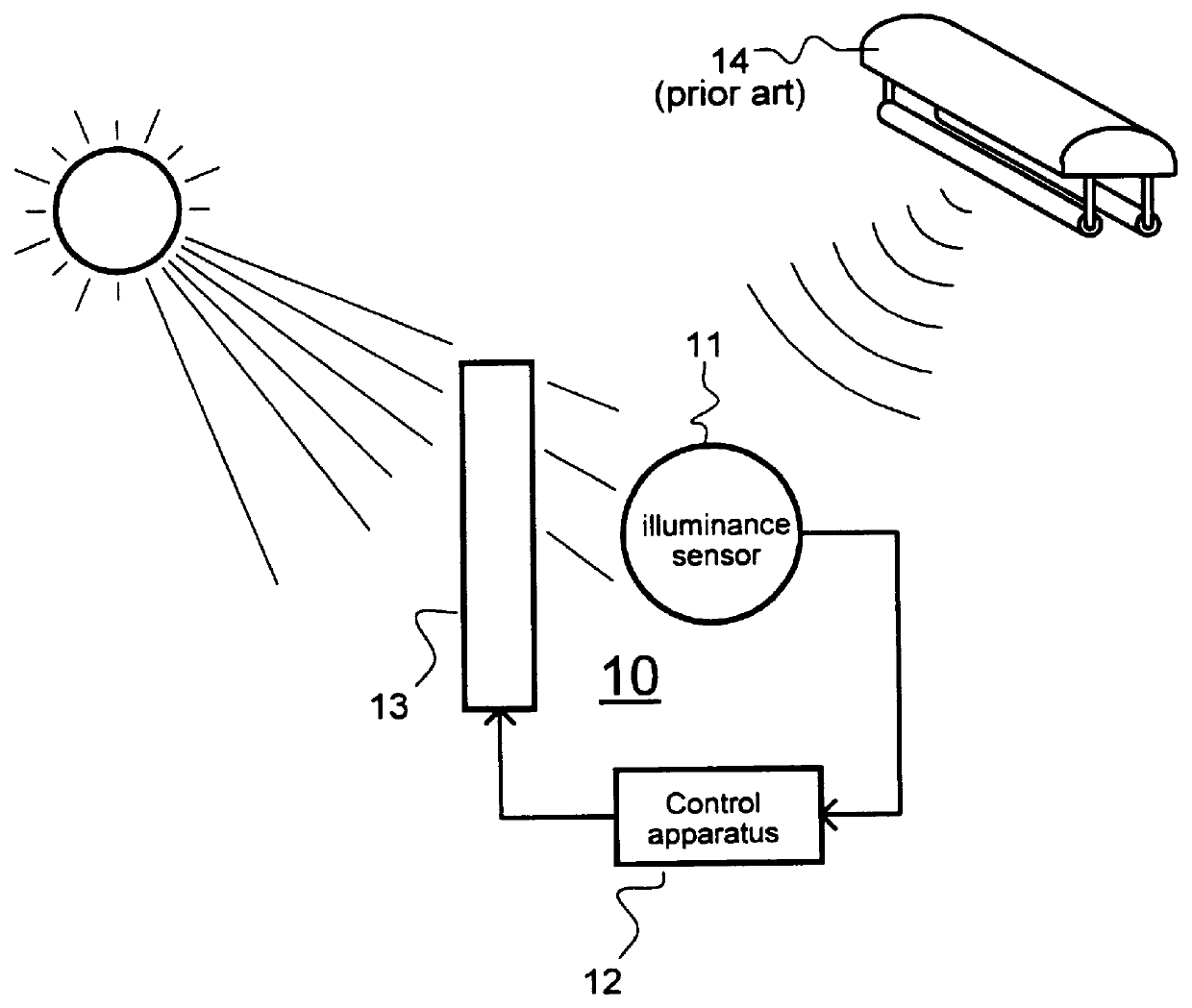
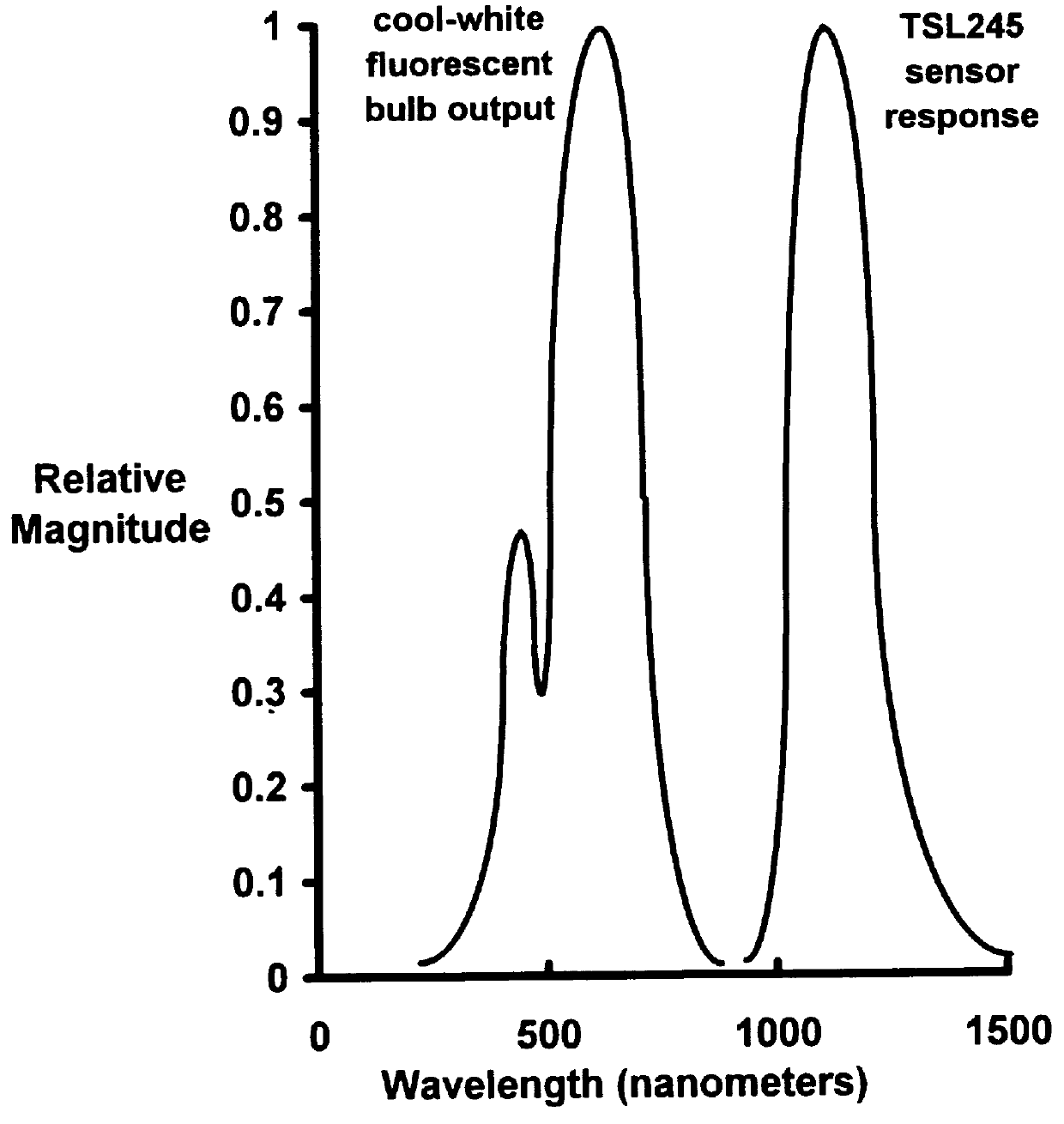
A system for automatic regulation of daylight admitted by a window in the presence of artificial illumination produced by a high-efficiency (e.g., fluorescent-type) electric lamp. A preferred embodiment, adaptive window covering system 10, consists of an illuminance sensor 11, a conventional control apparatus 12, and a conventional shading means 13. System 10 is used in conjunction with a conventional, high-efficiency, electric lamp 14 and a conventional window 18, in a room 19. Sensor 11 produces a signal dependent on power contained in a portion of the daylight spectrum, but substantially insensitive to power contained in the spectrum of artificial illumination produced by lamp 14. In a preferred embodiment, sensor 11 includes a silicon photodiode and optical low-pass filter to provide a spectral response which extends from approximately 800 to 1200 nanometers, which falls outside the spectrum produced by typical fluorescent lamps (e.g, 300 to 750 nanometers). Sensor 11 is oriented to sample the ambient illumination in room 19, which includes both daylight and artificial components. Control apparatus 12 produces an actuating signal dependent on the output of sensor 11. Shading means 13 varies the amount of daylight admitted by window 18 as a function of the actuating signal produced by control apparatus 12. Thus, system 10 varies the amount of daylight admitted by window 18 as a function of the power contained in a portion of the daylight spectrum, but independent of the power contained in the spectrum produced by lamp 14.
Owner:POPAT PRADEEP P
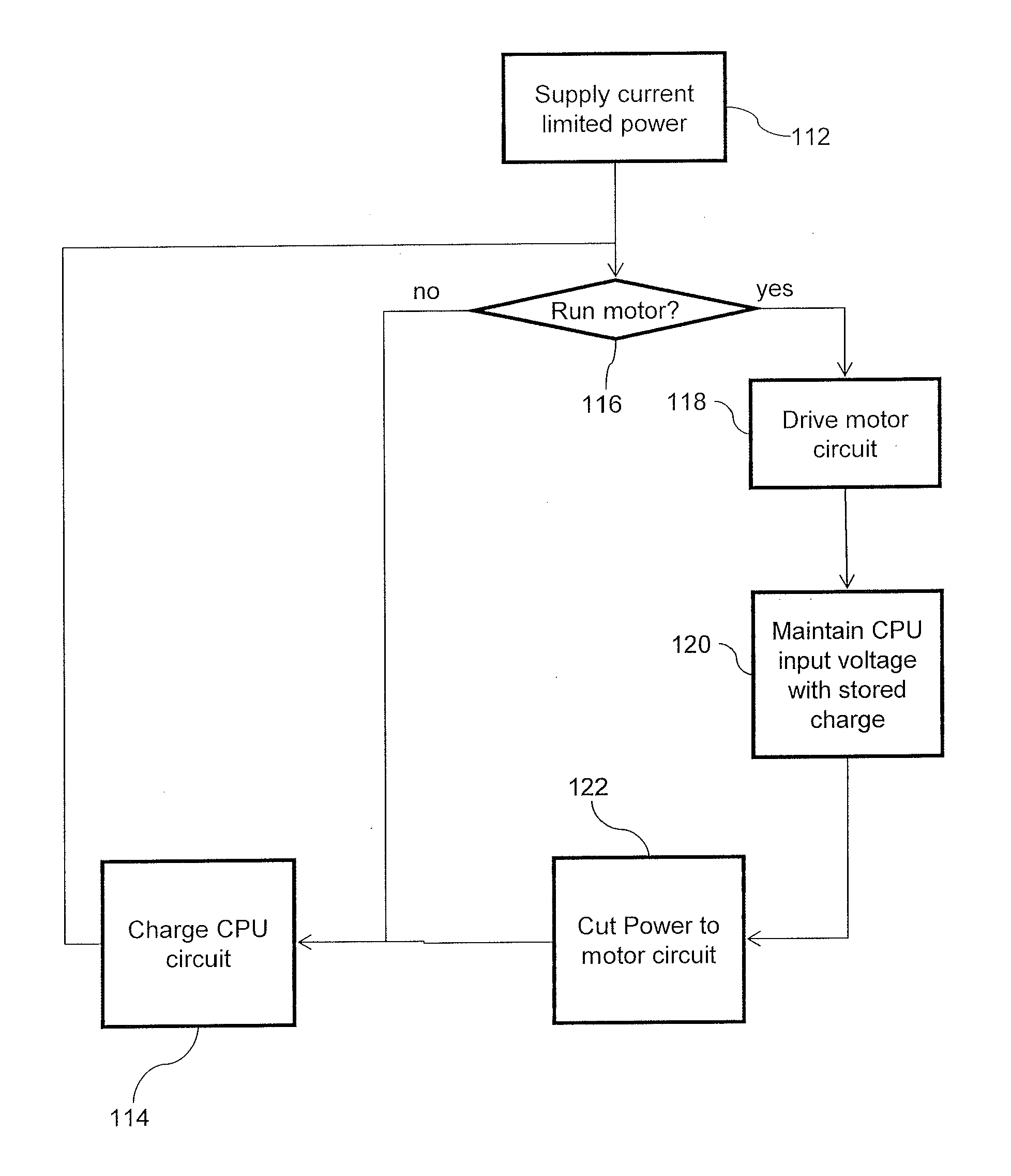
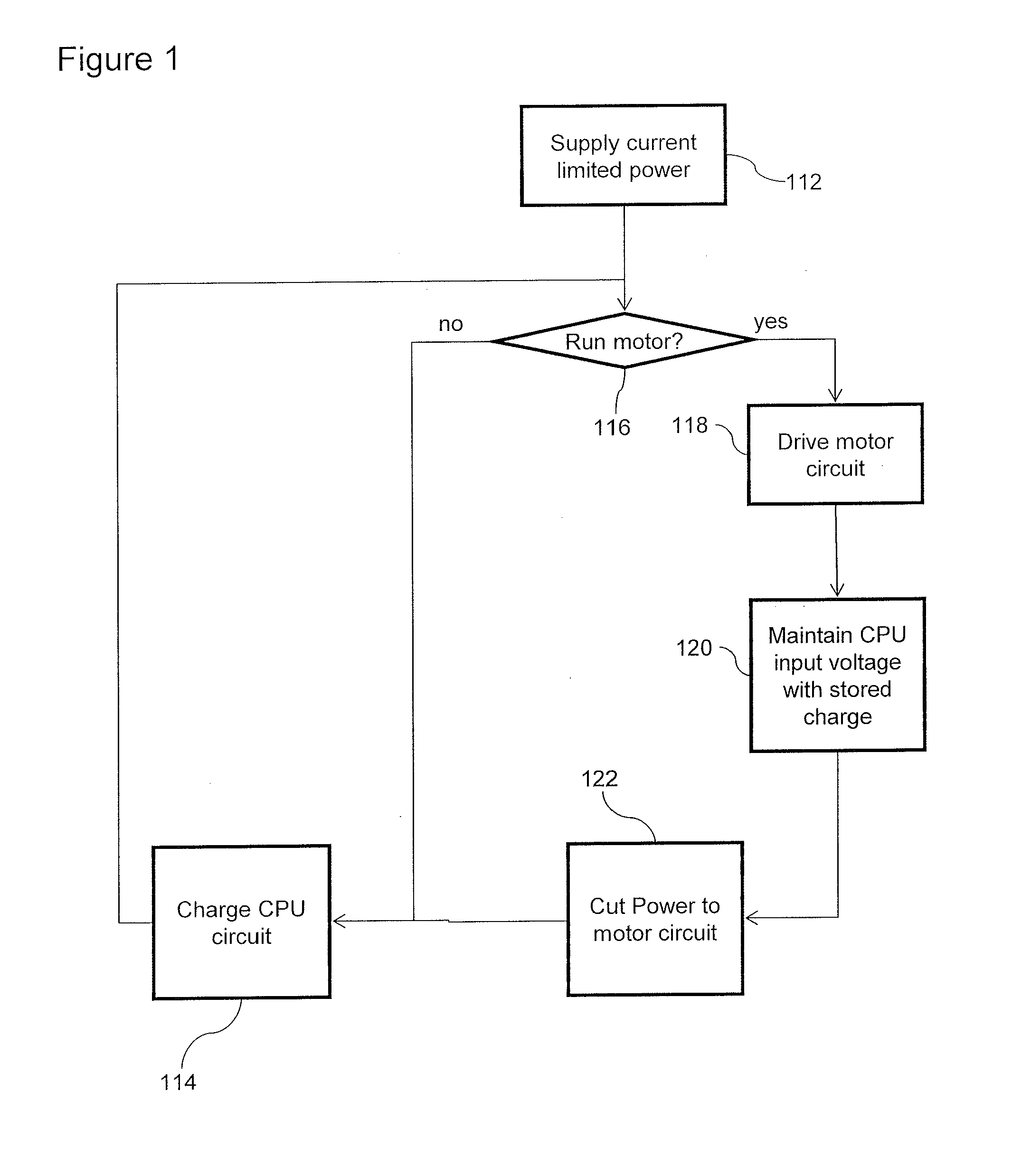
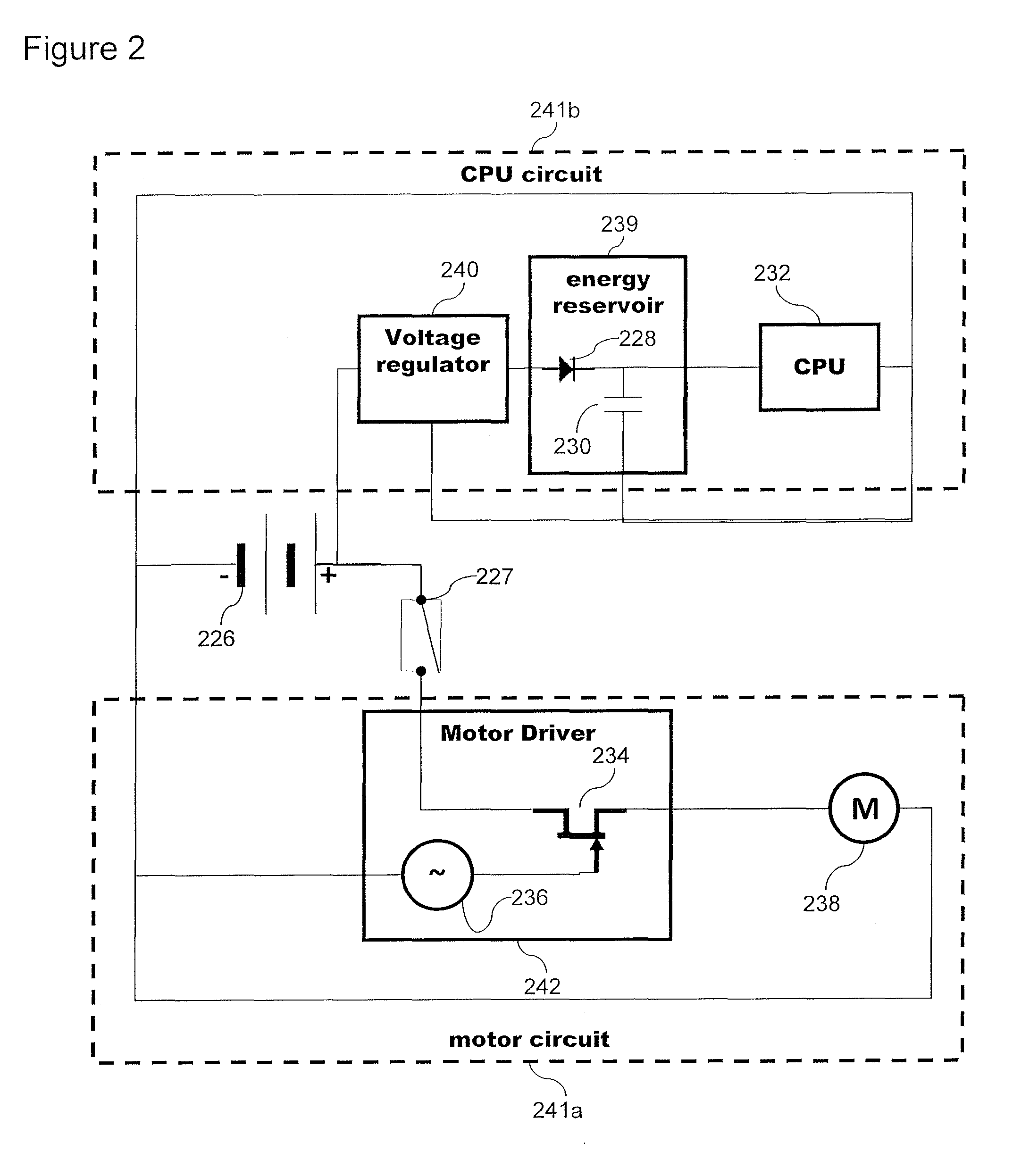
System and method to distribute power to both an inertial device and a voltage sensitive device from a single current limited power source
ActiveUS20150297824A1High voltagePrevent leakageInfusion devicesField or armature current controlCapacitanceCurrent limiting
A system may regulate voltage supplied from a power source to an integrated circuit and / or an inertial device. A minimal voltage may be maintained in the integrated circuit by temporarily cutting off current to the inertial device to supply surges of voltage to the controller. Optionally voltage may be smoothed between said surges for example by adding capacitance and / or a current restrictor.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES IL LTD
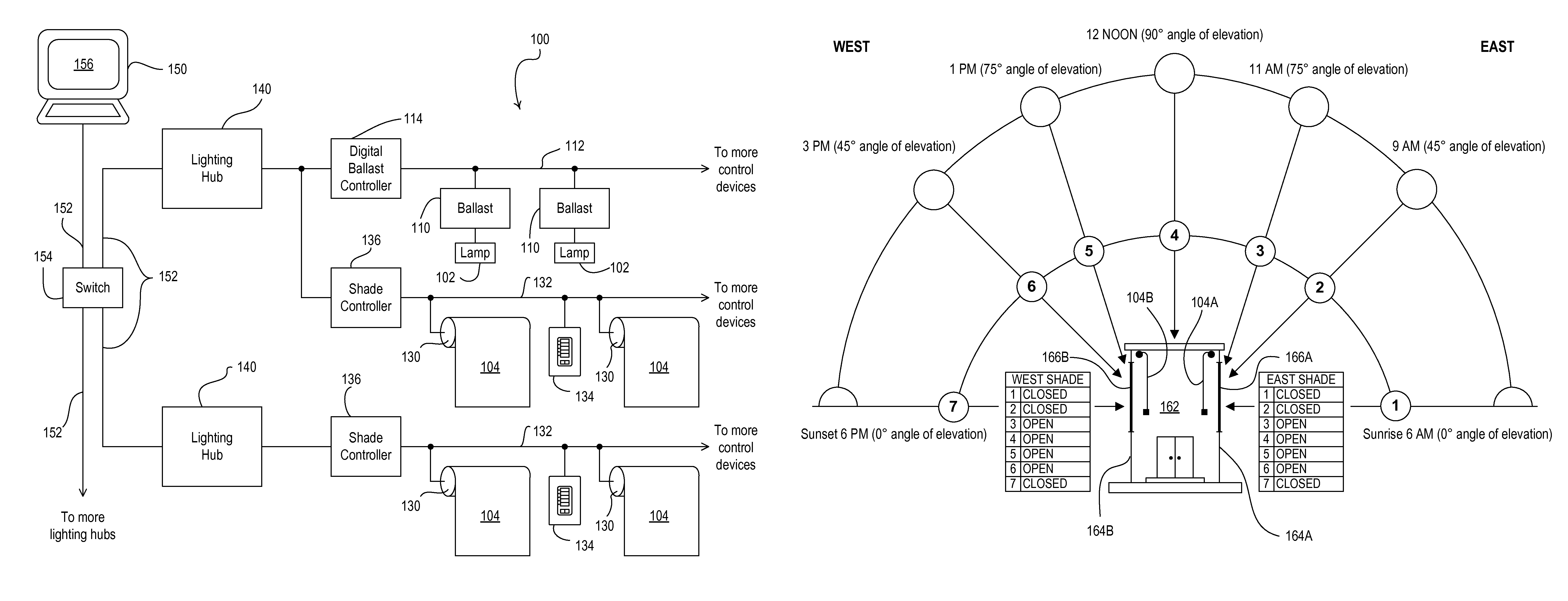
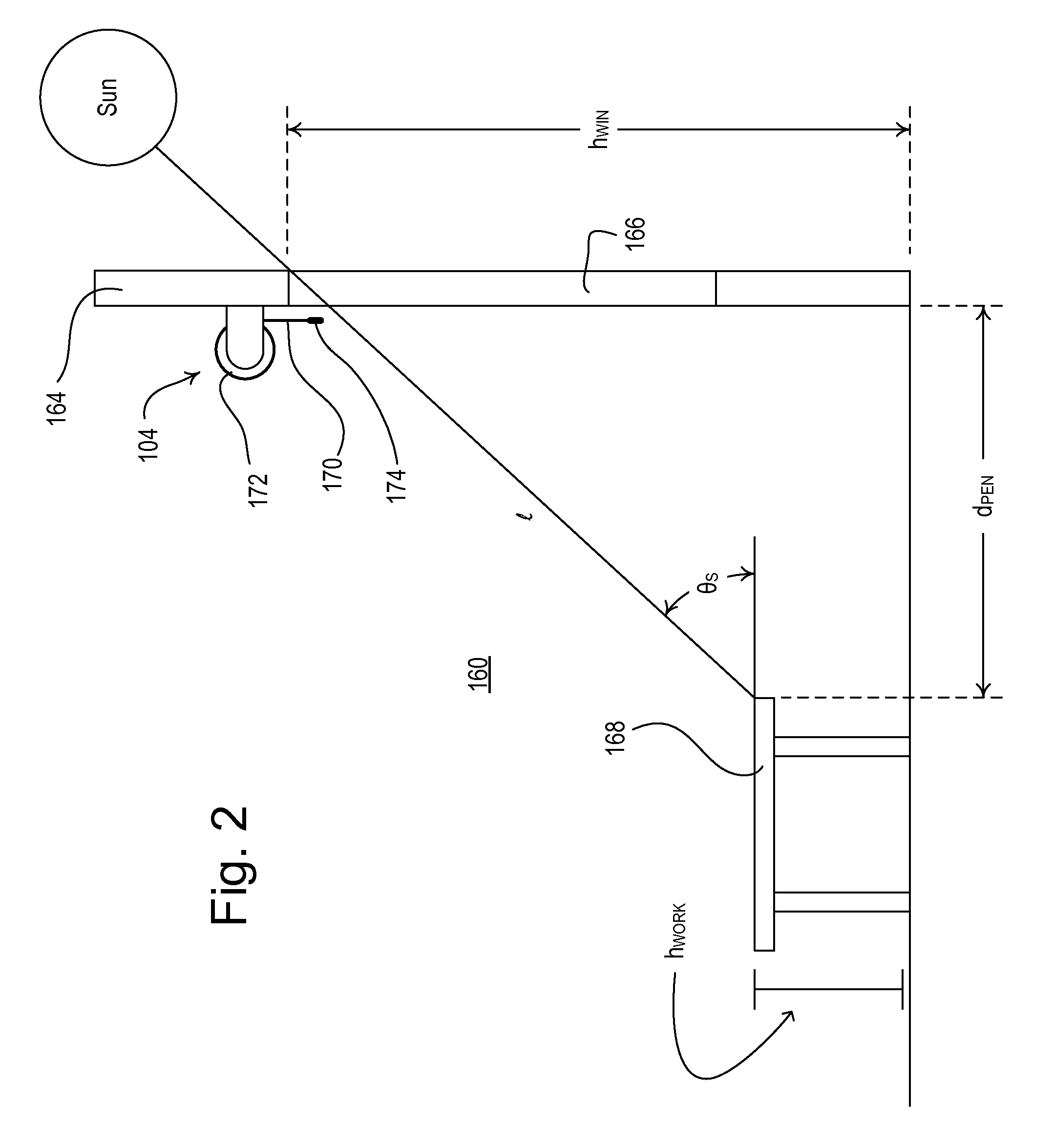
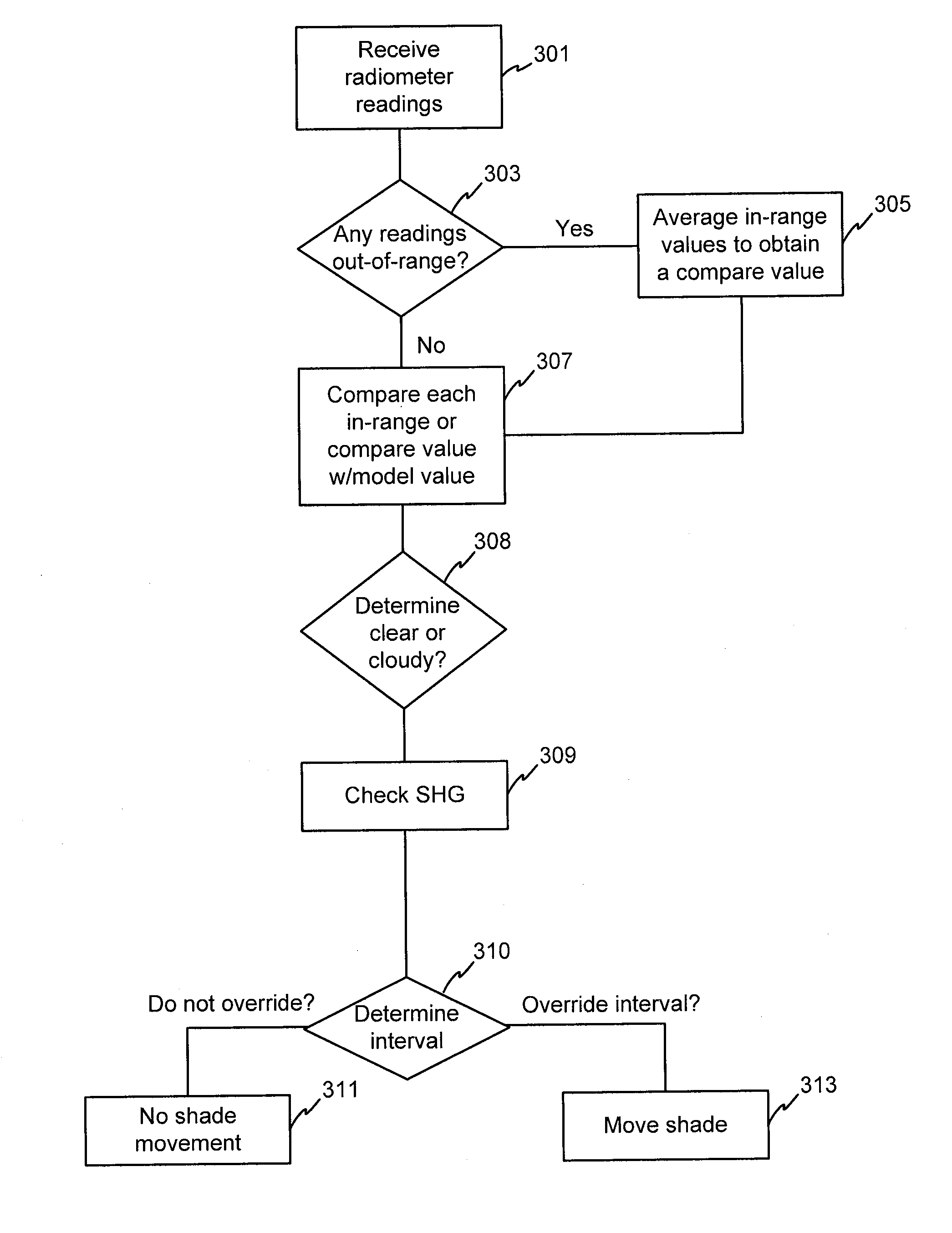
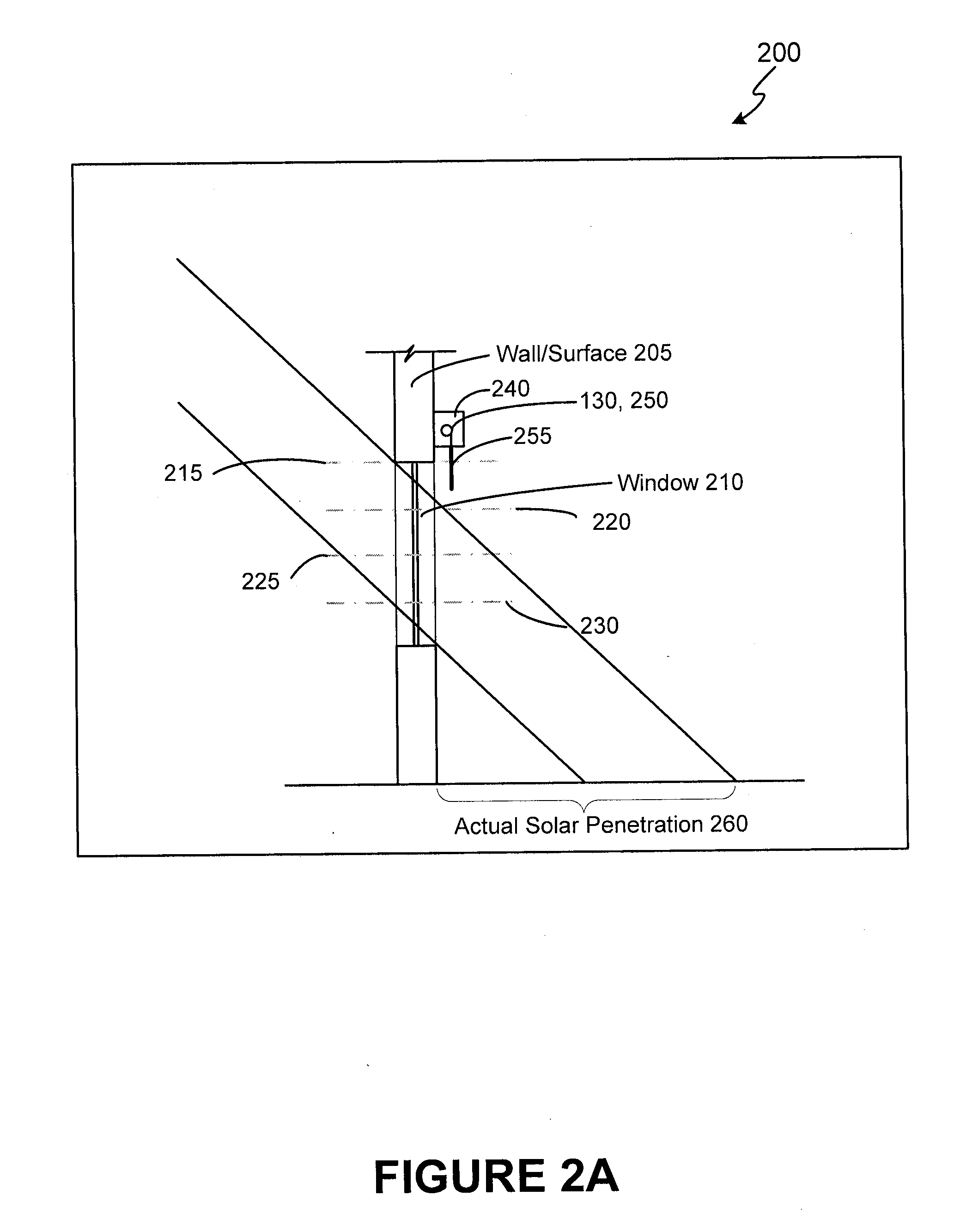
Automated shade control method and system
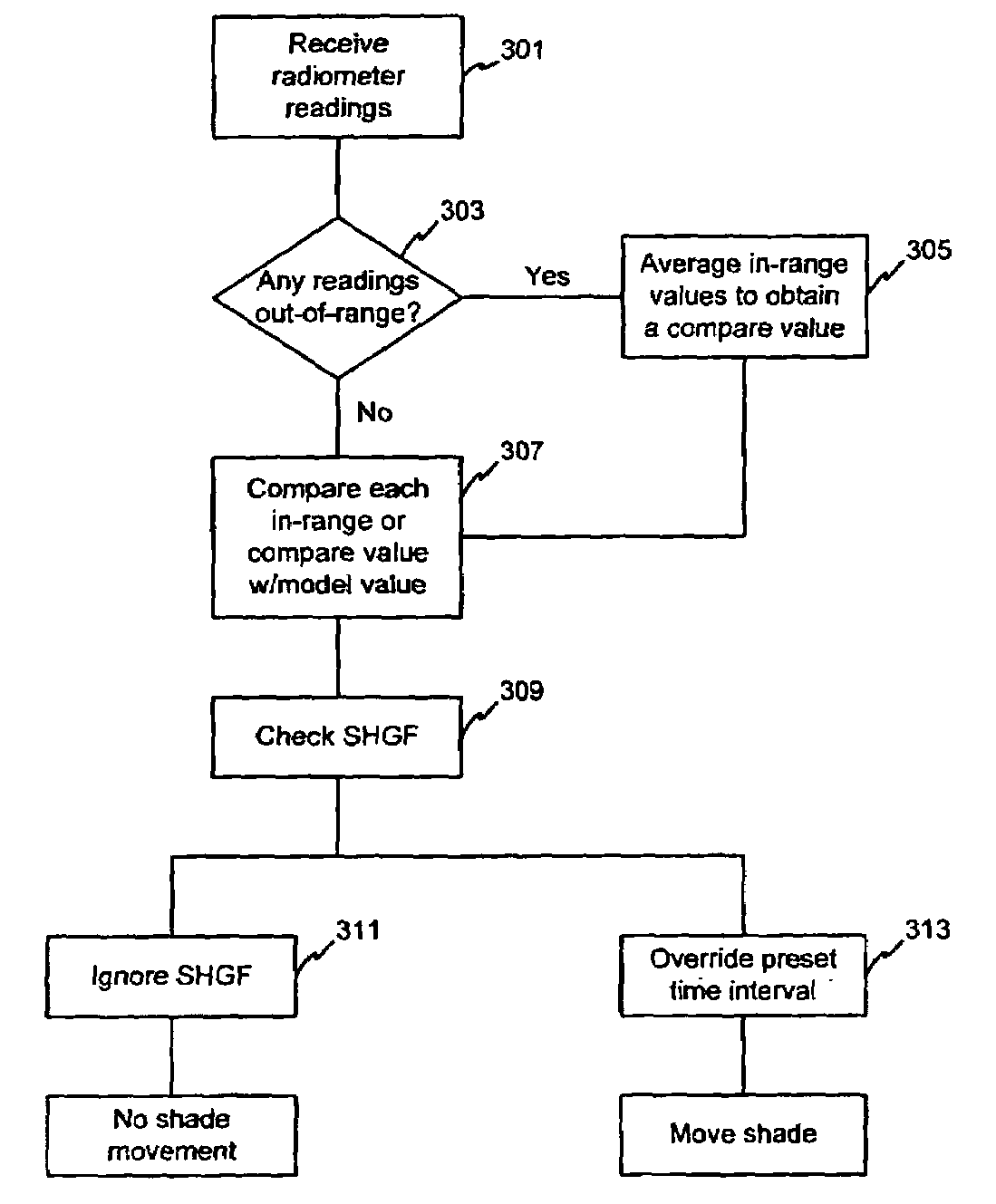
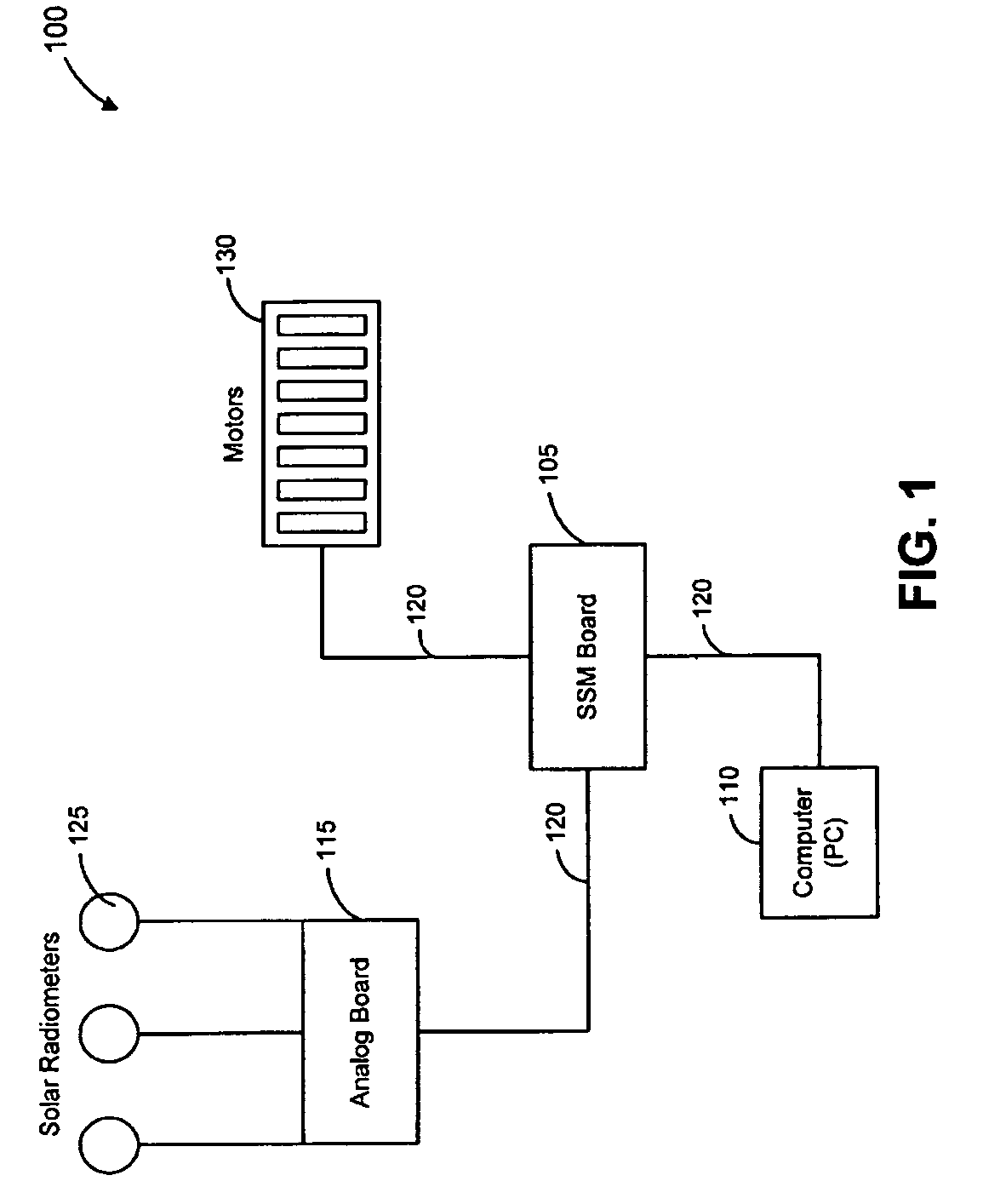
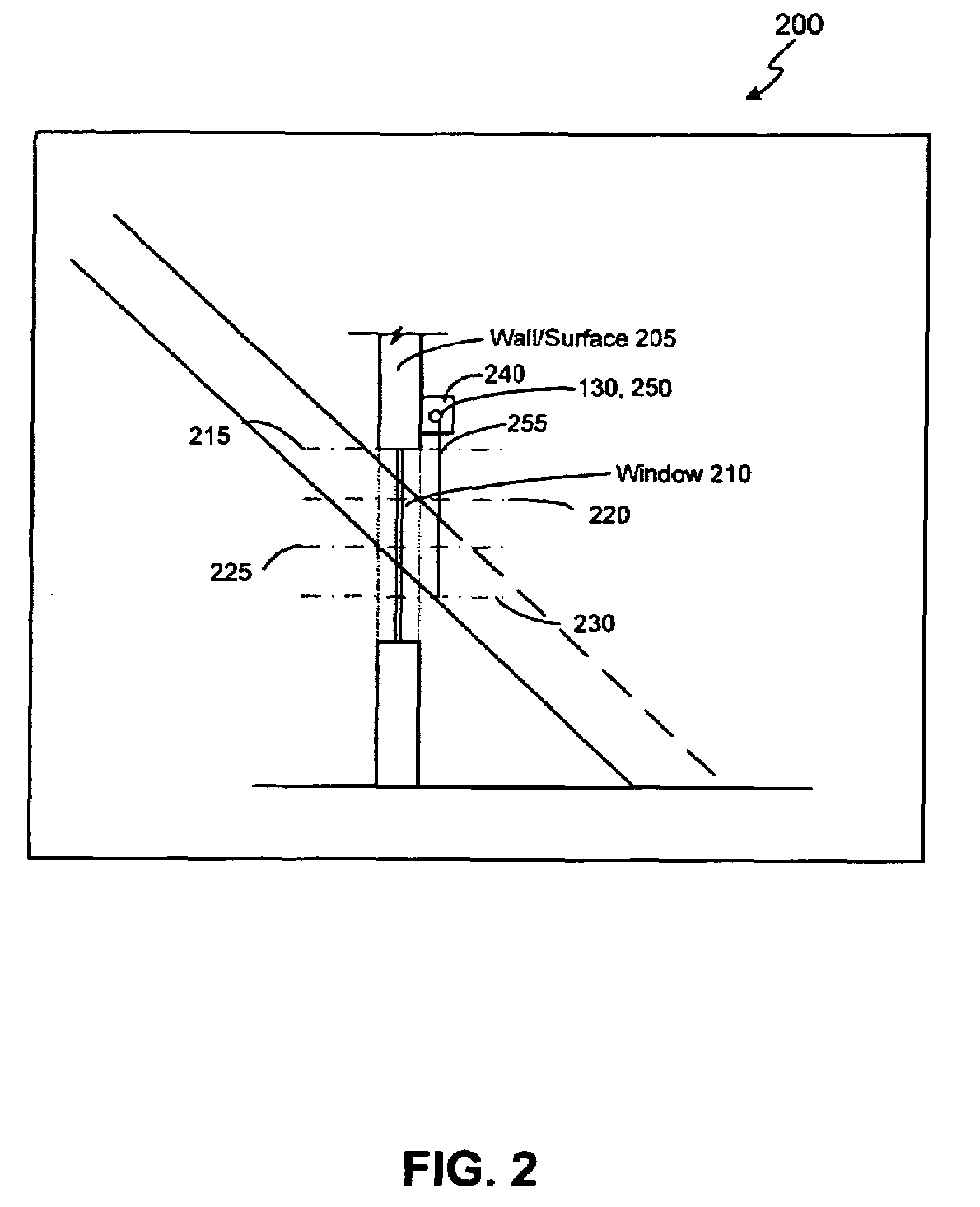
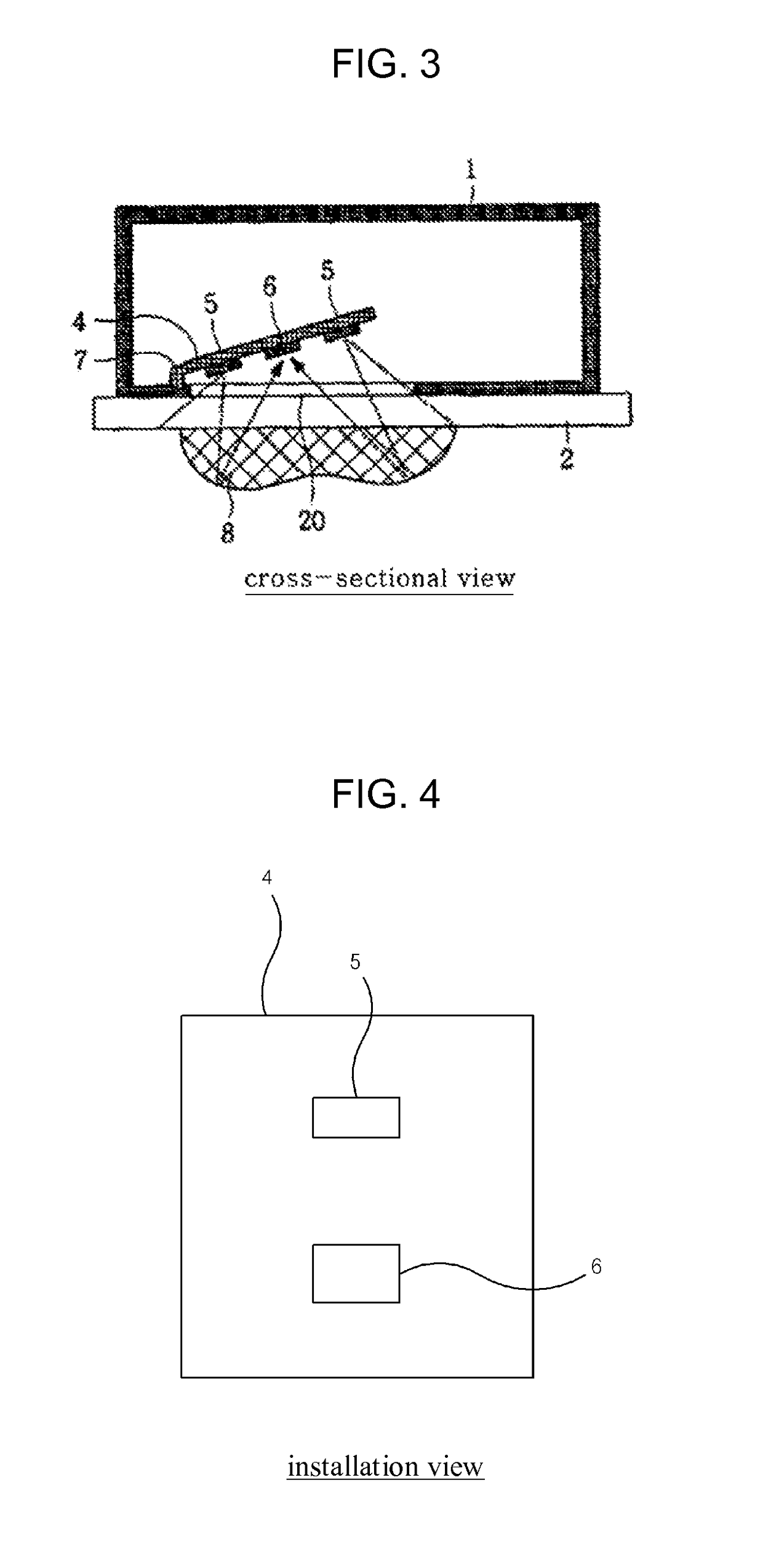
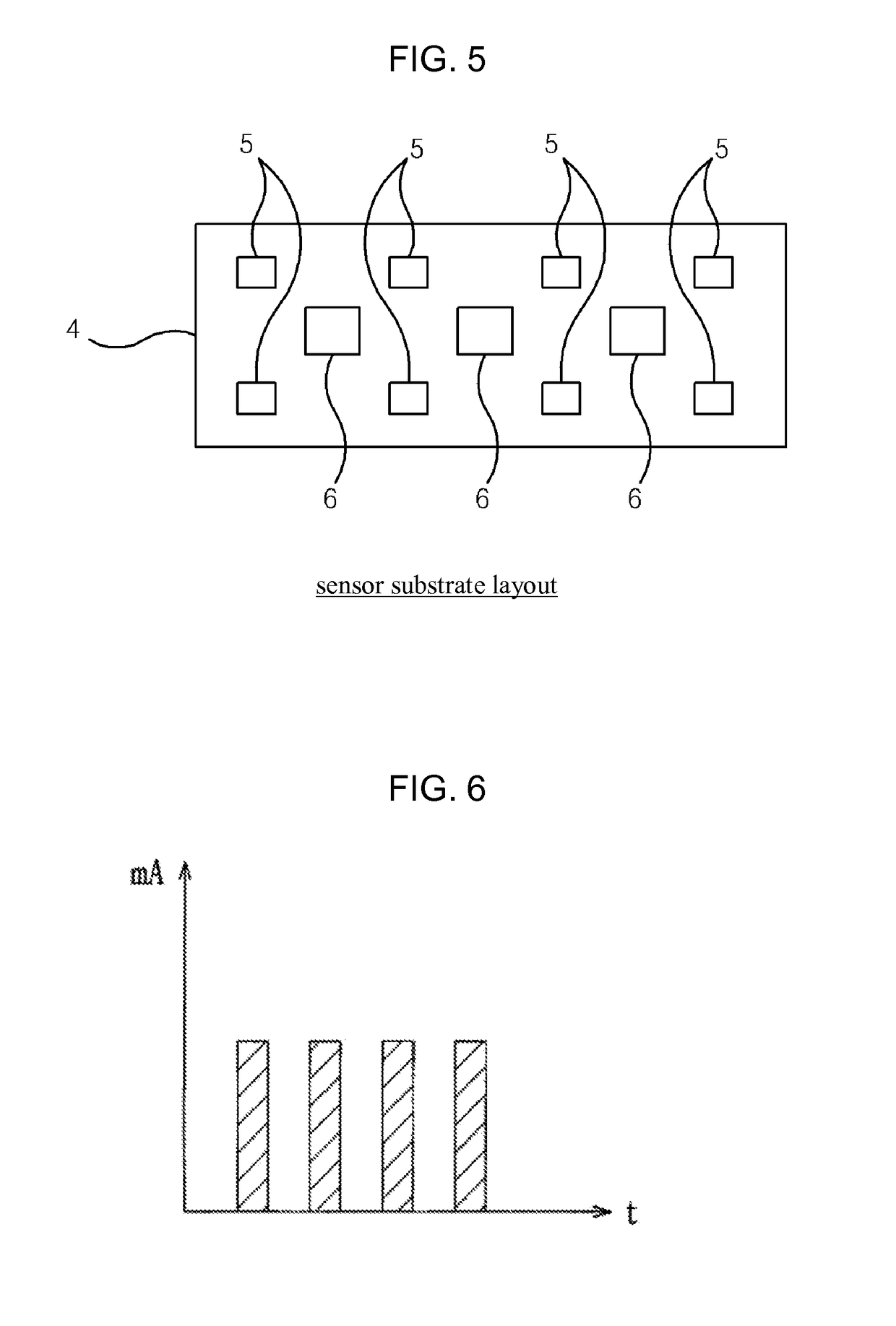
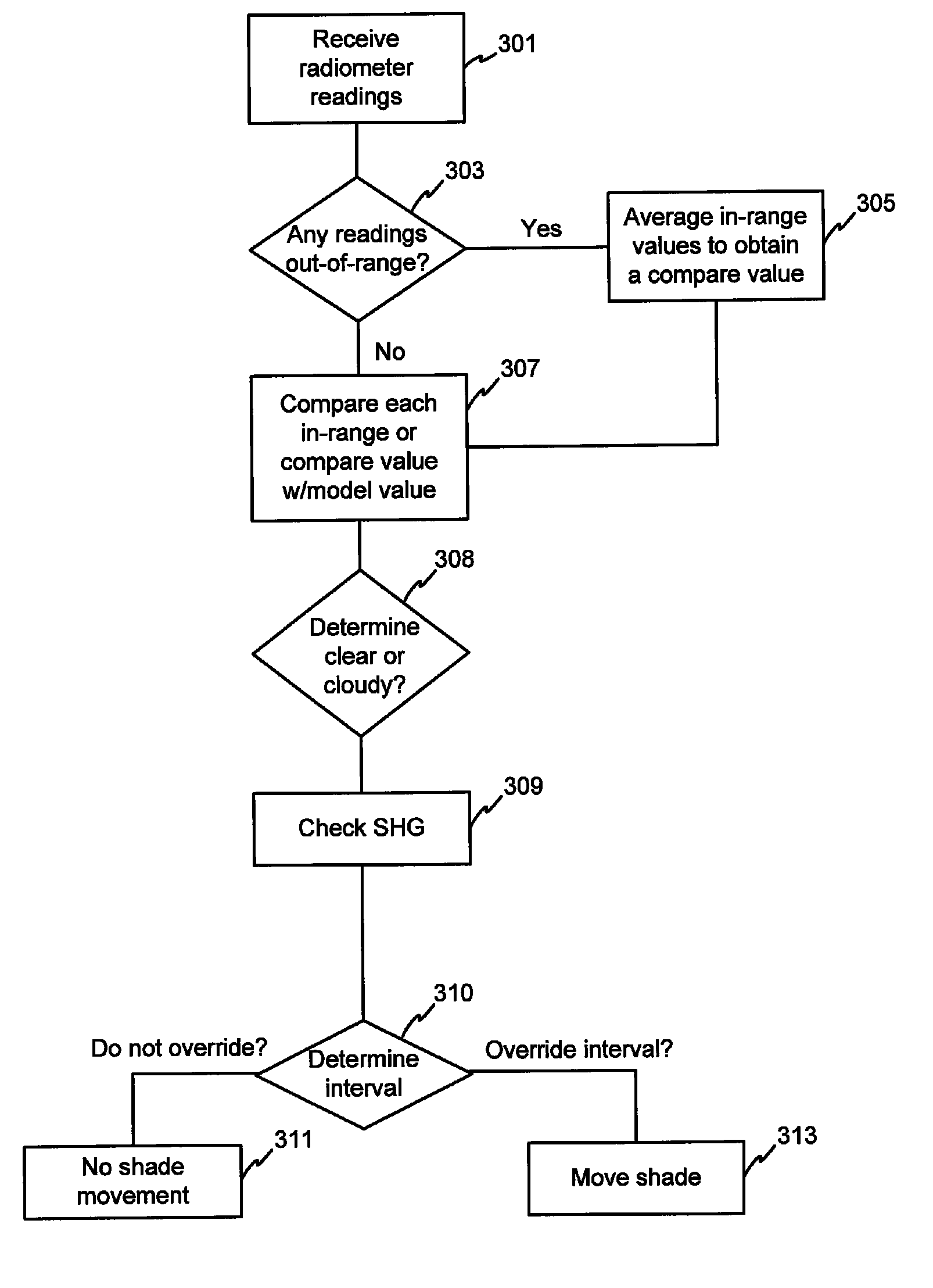
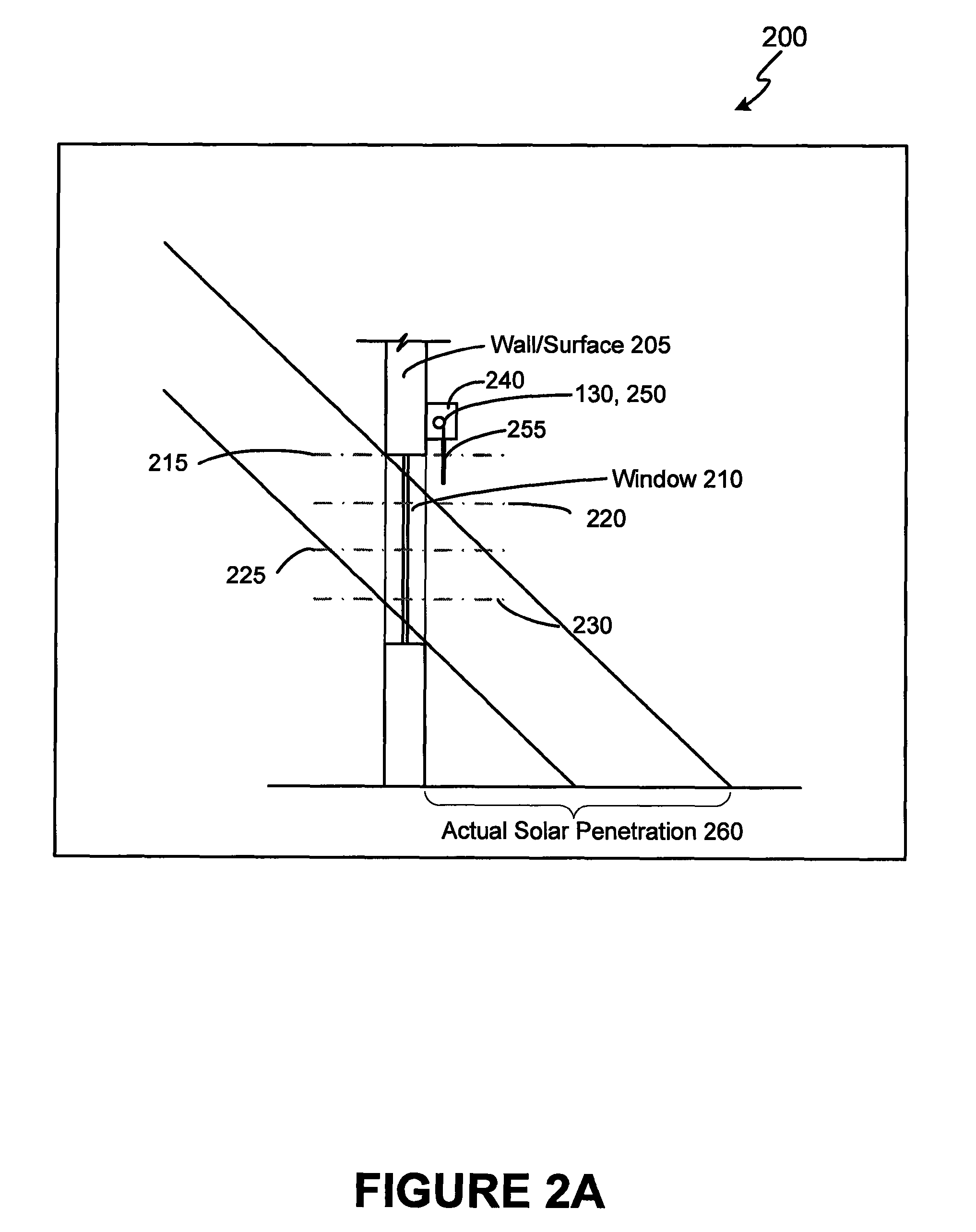
ActiveUS7417397B2Keep brightnessReduce brightnessLight dependant control systemsDC motor speed/torque controlRadiometerSolar angle
This invention generally relates to automated shade systems that employ one or more algorithms to provide appropriate solar protection from direct solar penetration; reduce solar heat gain; reduce radiant surface temperatures; control penetration of the solar ray, optimize the interior natural daylighting of a structure and optimize the efficiency of interior lighting systems. The invention additionally comprises a motorized window covering, radiometers, and a central control system that uses algorithms to optimize the interior lighting of a structure. These algorithms include information such as: geodesic coordinates of a building; solar position; solar angle solar radiation; solar penetration angles; solar intensity; the measured brightness and veiling glare across a surface; time, solar altitude, solar azimuth, detected sky conditions, ASHRAE sky models, sunrise and sunset times, surface orientations of windows, incidence angles of the sun striking windows, window covering positions, minimum BTU load and solar heat gain.
Owner:MECHOSHADE SYST LLC
Safety detection and protection system for power tools
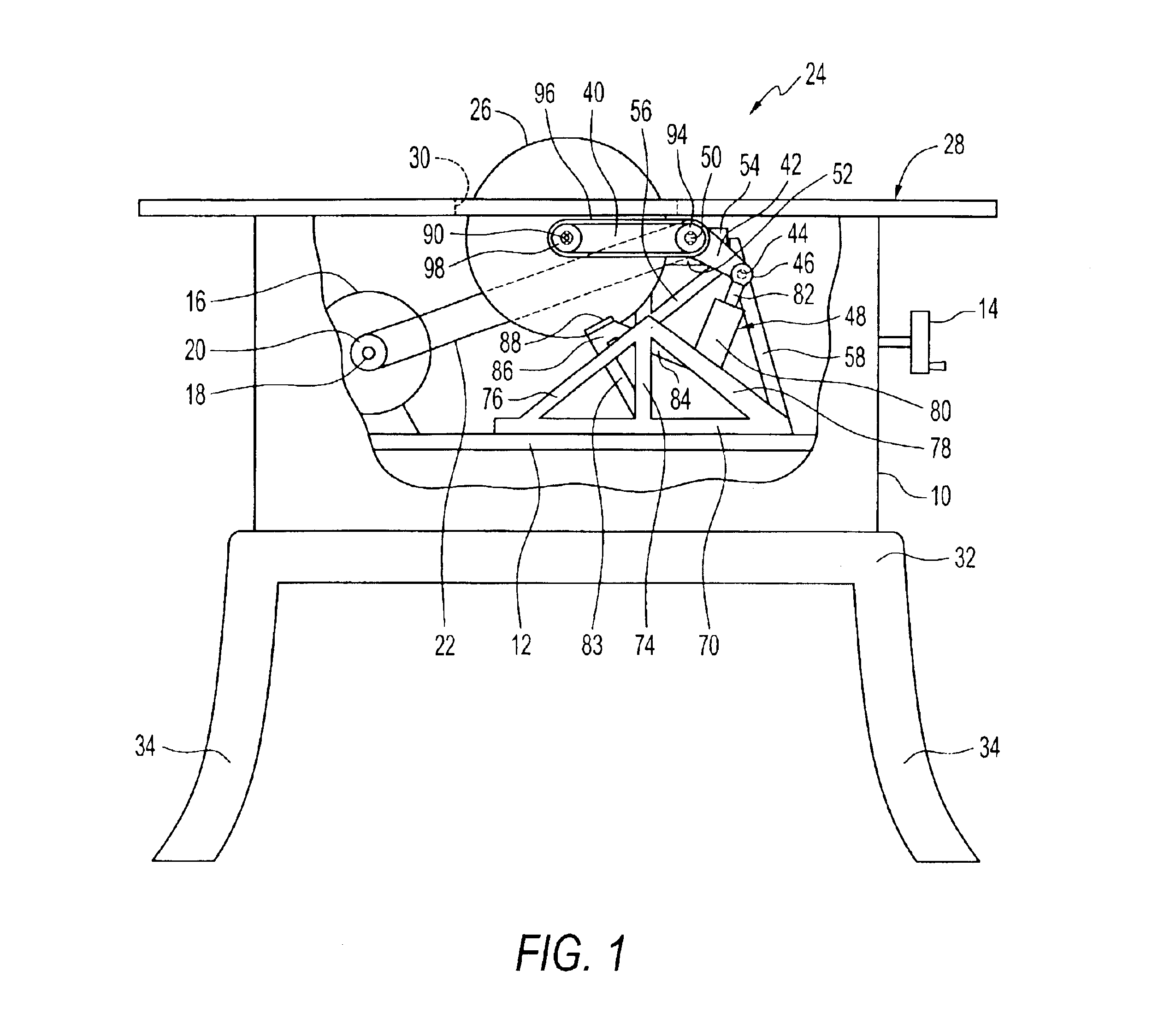
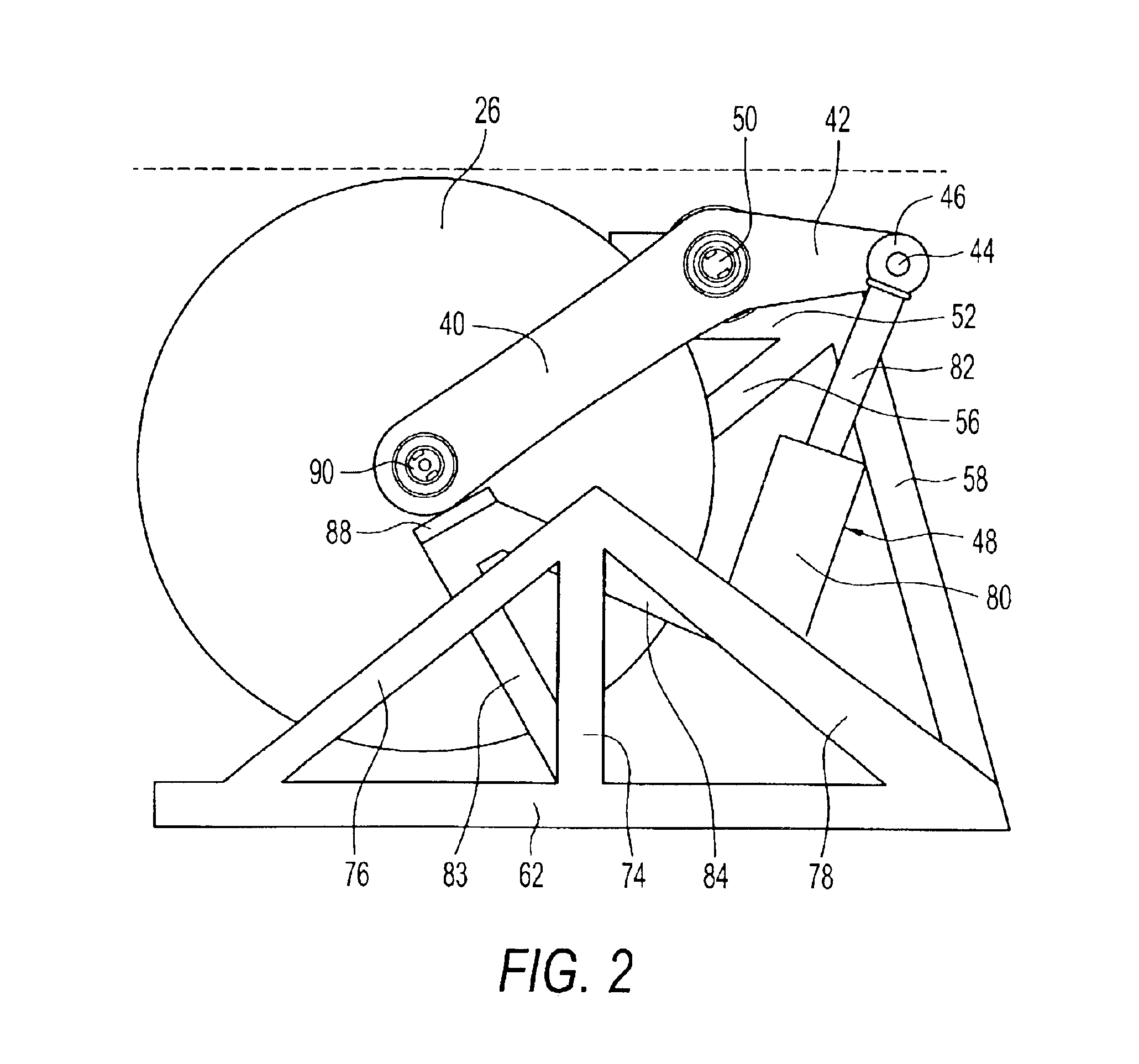
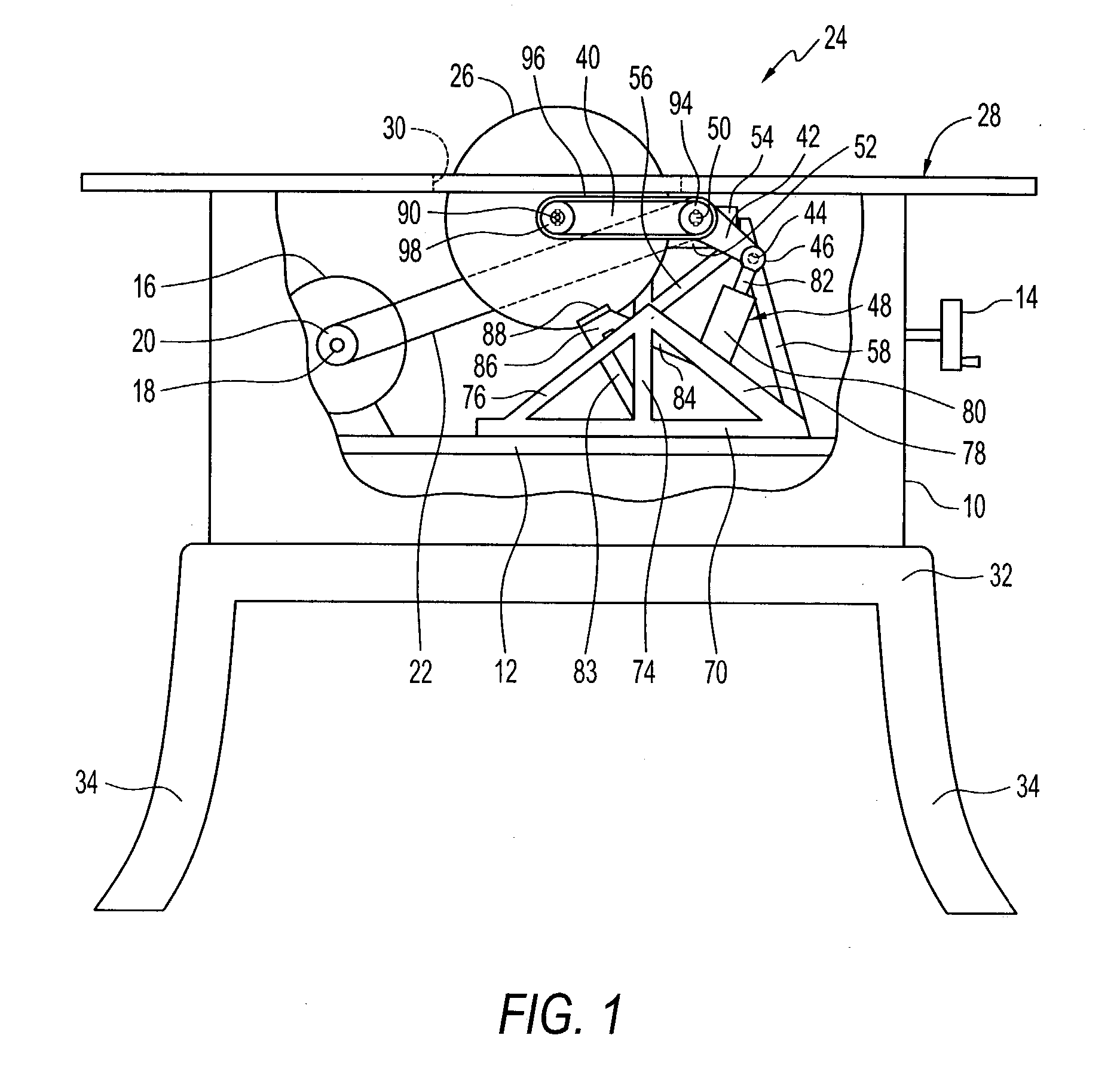
InactiveUS6922153B2Quick stopRule out the possibilityDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower toolProtection system
A detection system for detecting a dangerous condition for an operator using a power tool of the type which has an exposed blade relative to a work surface and a protection system for minimizing, if not eliminating the possibility of a user being injured by contacting the blade. In one preferred embodiment of the present invention, a proximity detection system is capable of detecting the presence of a user near the blade of a table saw and a protection system that can either retract the blade below the work surface of the table saw or terminate the drive torque to the blade which can result in rapid stopping of the saw blade by a work piece that is being cut.
Owner:CREDO TECH CORP +1
Safety detection and protection system for power tools
InactiveUS20040226800A1Quick stopQuick pullDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower toolProtection system
A detection system for detecting a dangerous condition for an operator using a power tool of the type which has an exposed blade relative to a work surface and a protection system for minimizing, if not eliminating the possibility of a user being injured by contacting the blade. In one preferred embodiment of the present invention, a proximity detection system is capable of detecting the presence of a user near the blade of a table saw and a protection system that can either retract the blade below the work surface of the table saw or terminate the drive torque to the blade which can result in rapid stopping of the saw blade by a work piece that is being cut.
Owner:CREDO TECH CORP +1
Vehicle control unit and vehicle
InactiveUS20060038520A1Simple and safe processReduce the average velocityMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlControl theoryVehicle control
A control unit controls a vehicle having a body to allow a user to step on, a power generator arranged to generate power that drives the body, and a first sensor and a second sensor. Each sensor preferably outputs a load value representing a load that has been applied to the body. The control unit preferably includes a processor arranged to output a command value associated with a bias of the load based on first and second load values that have been respectively detected by the first and second sensors, and a drive controller arranged to control the power generator in accordance with the command value.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
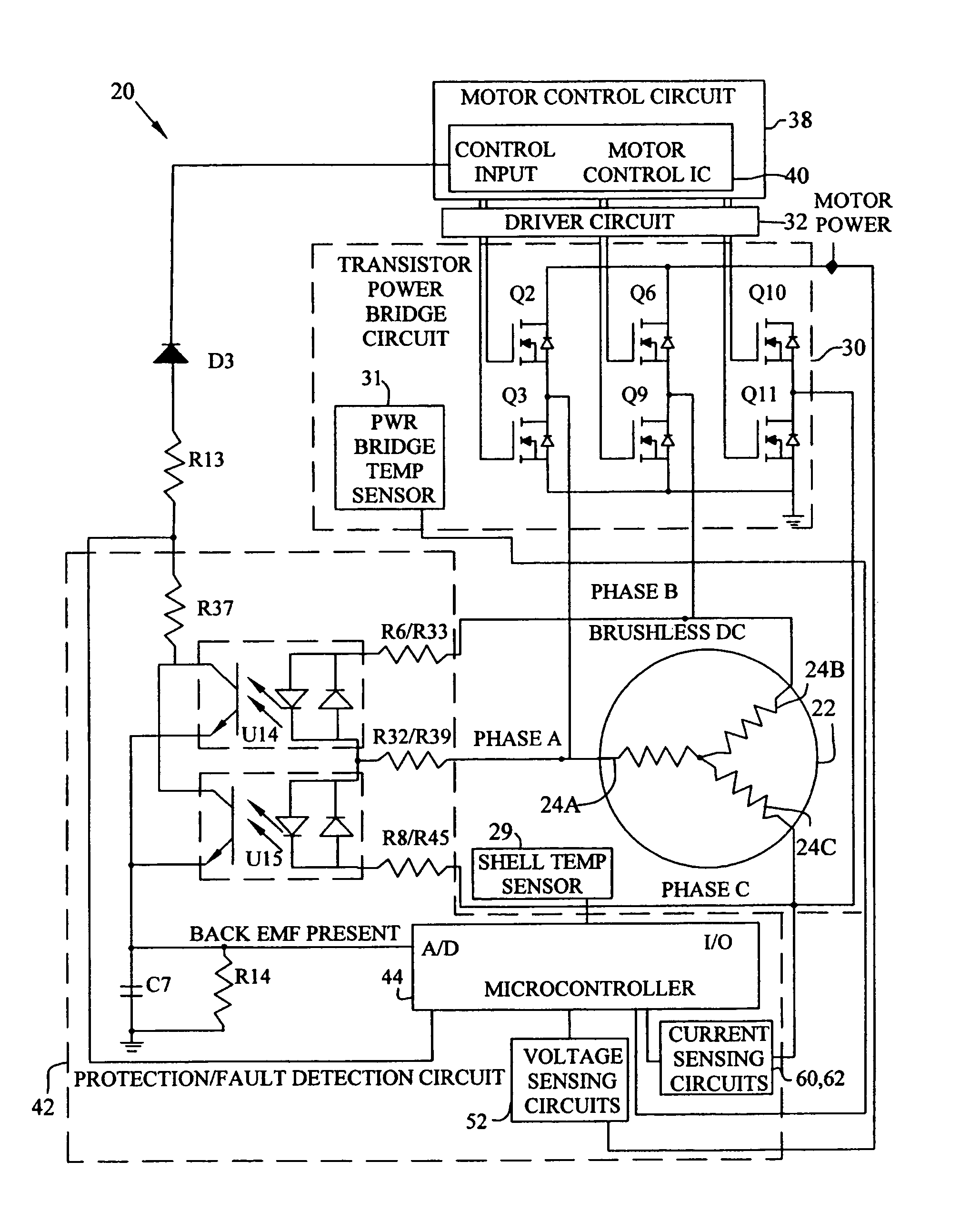
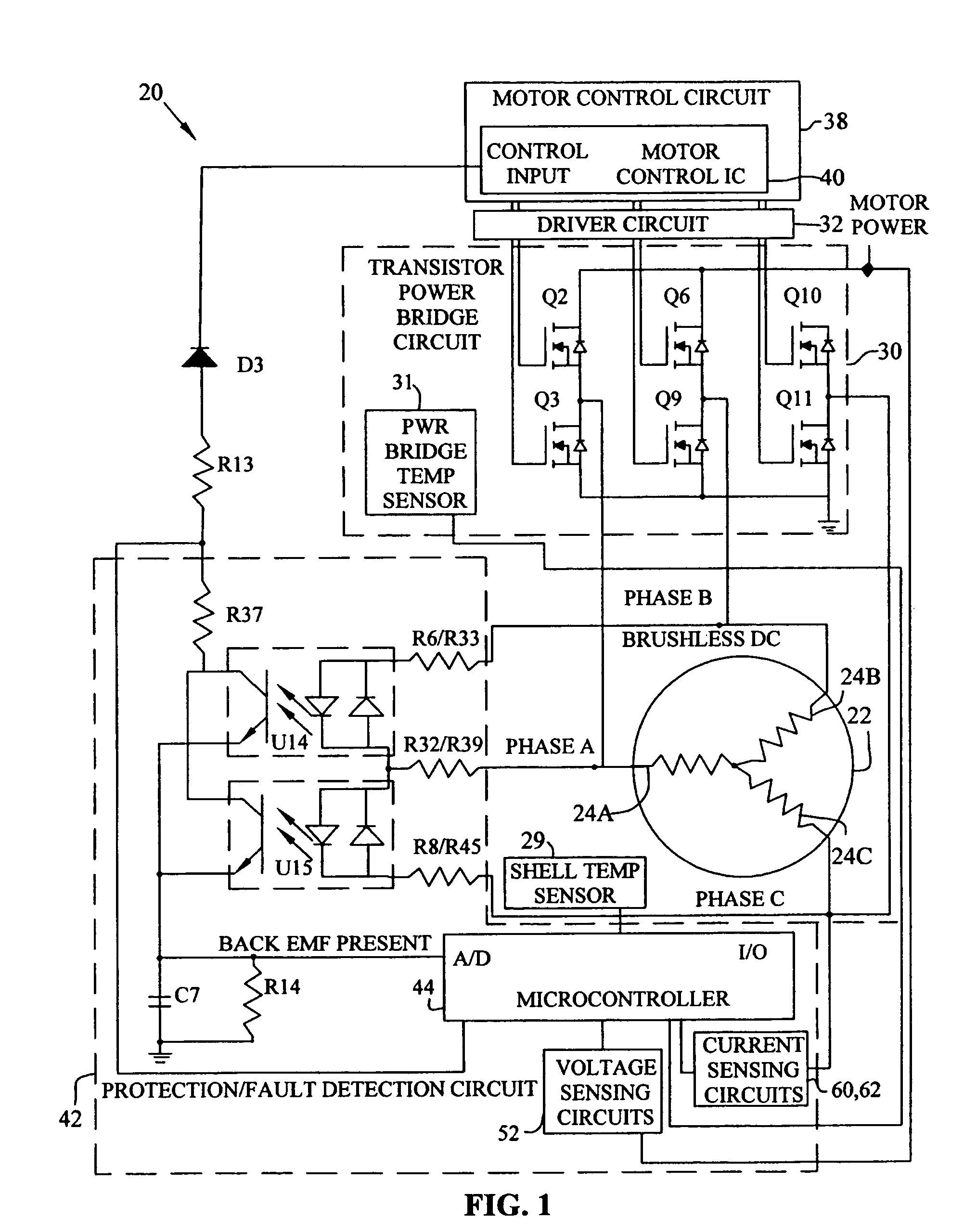
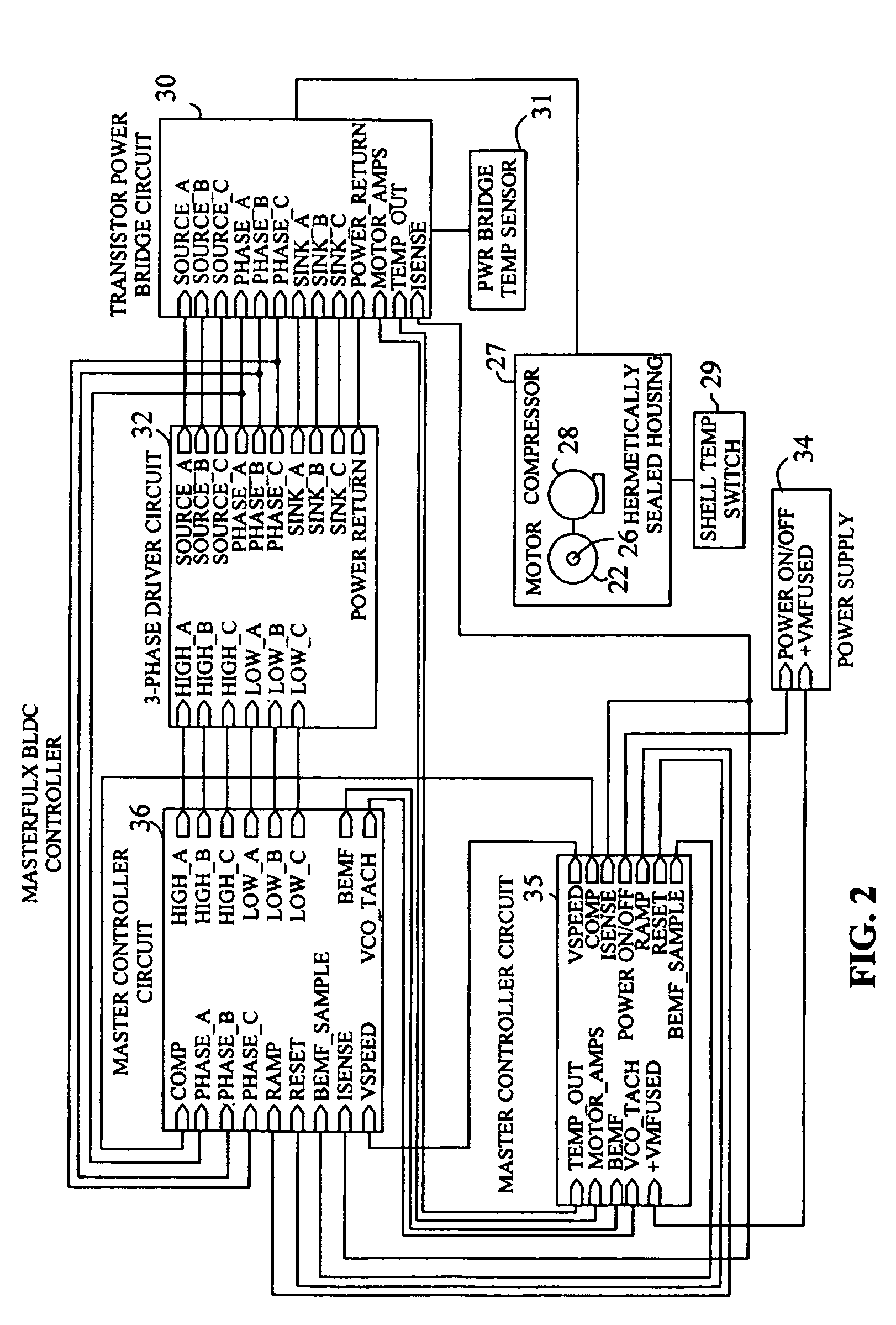
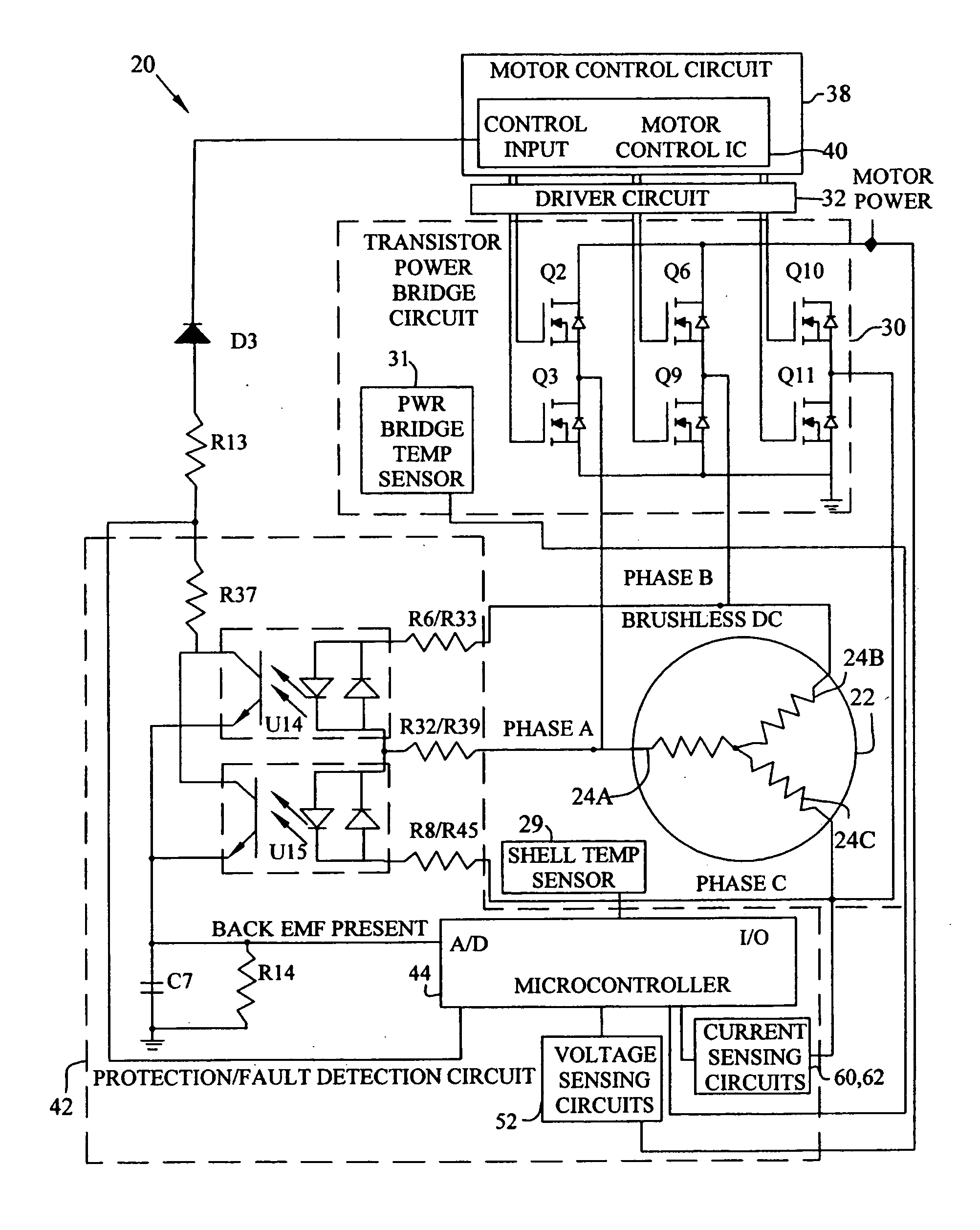
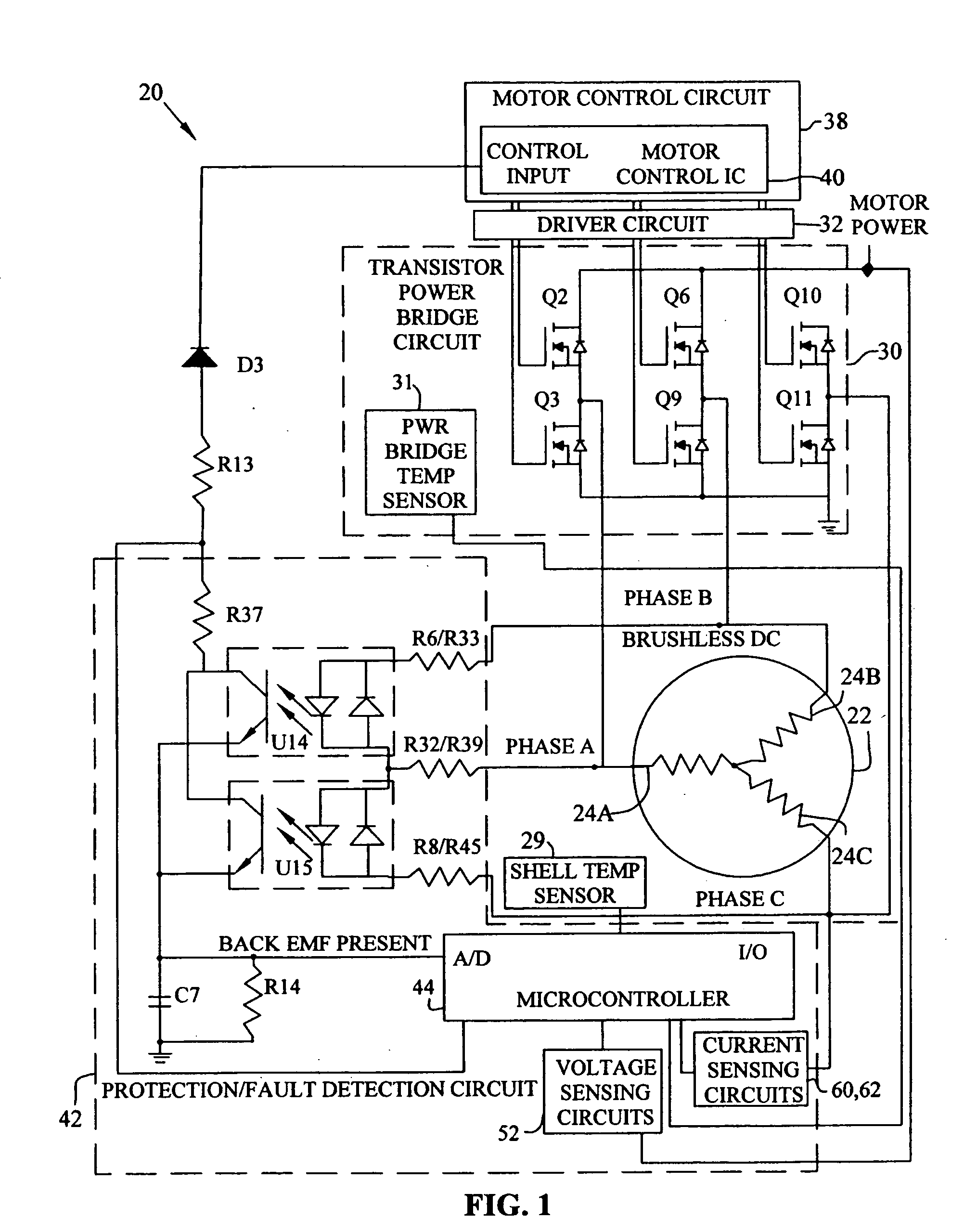
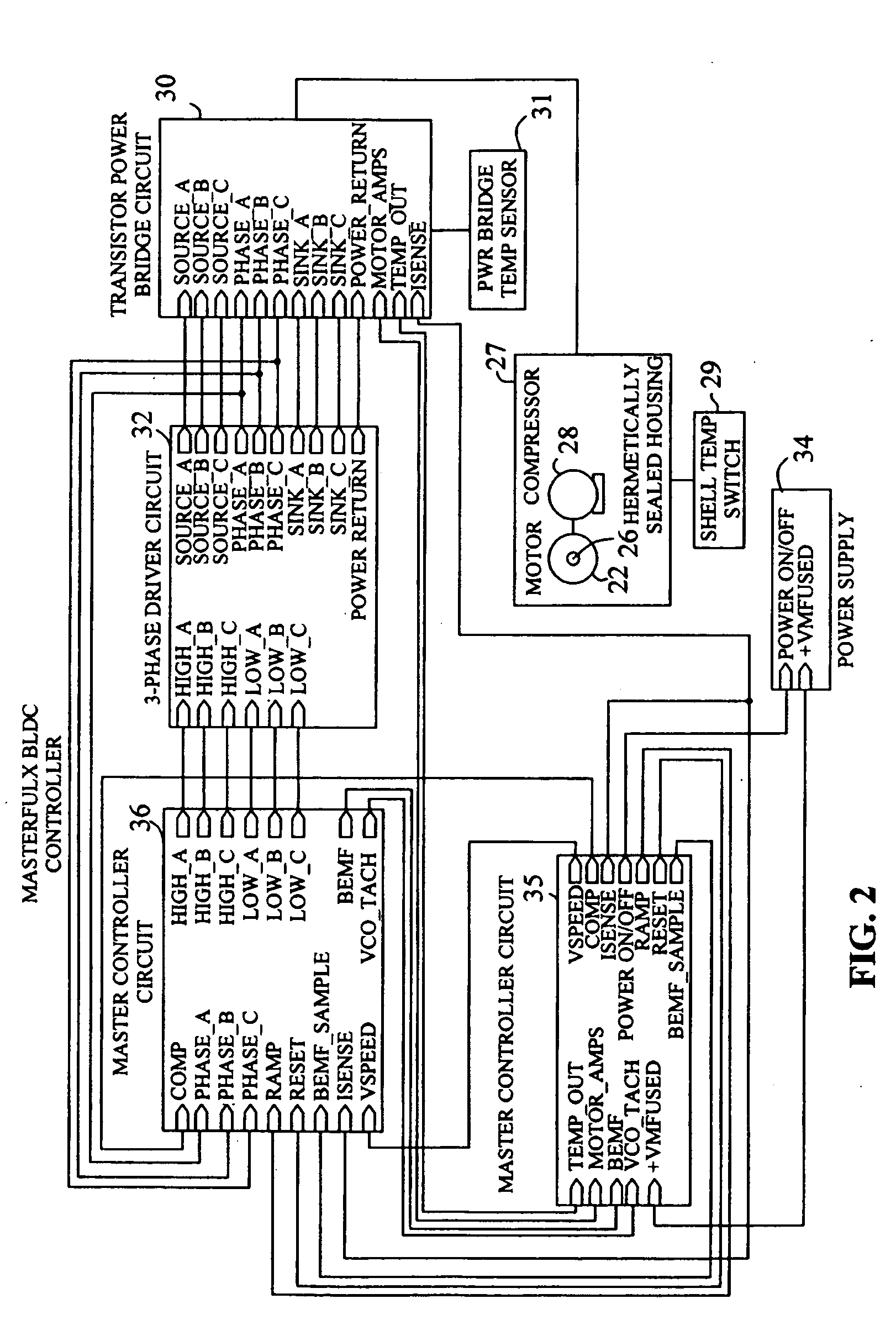
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS7042180B2Simple control methodEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringAC motor controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
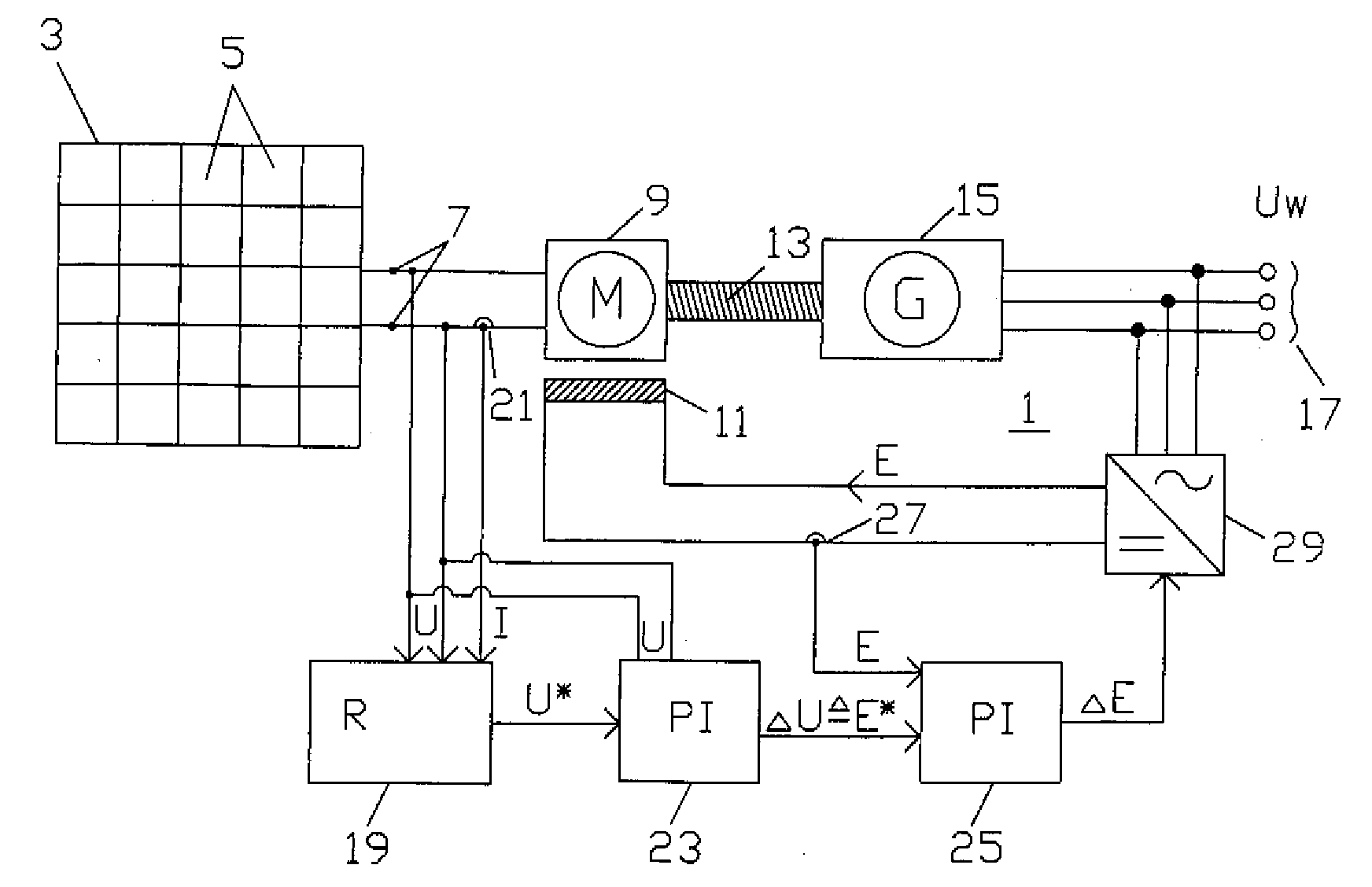
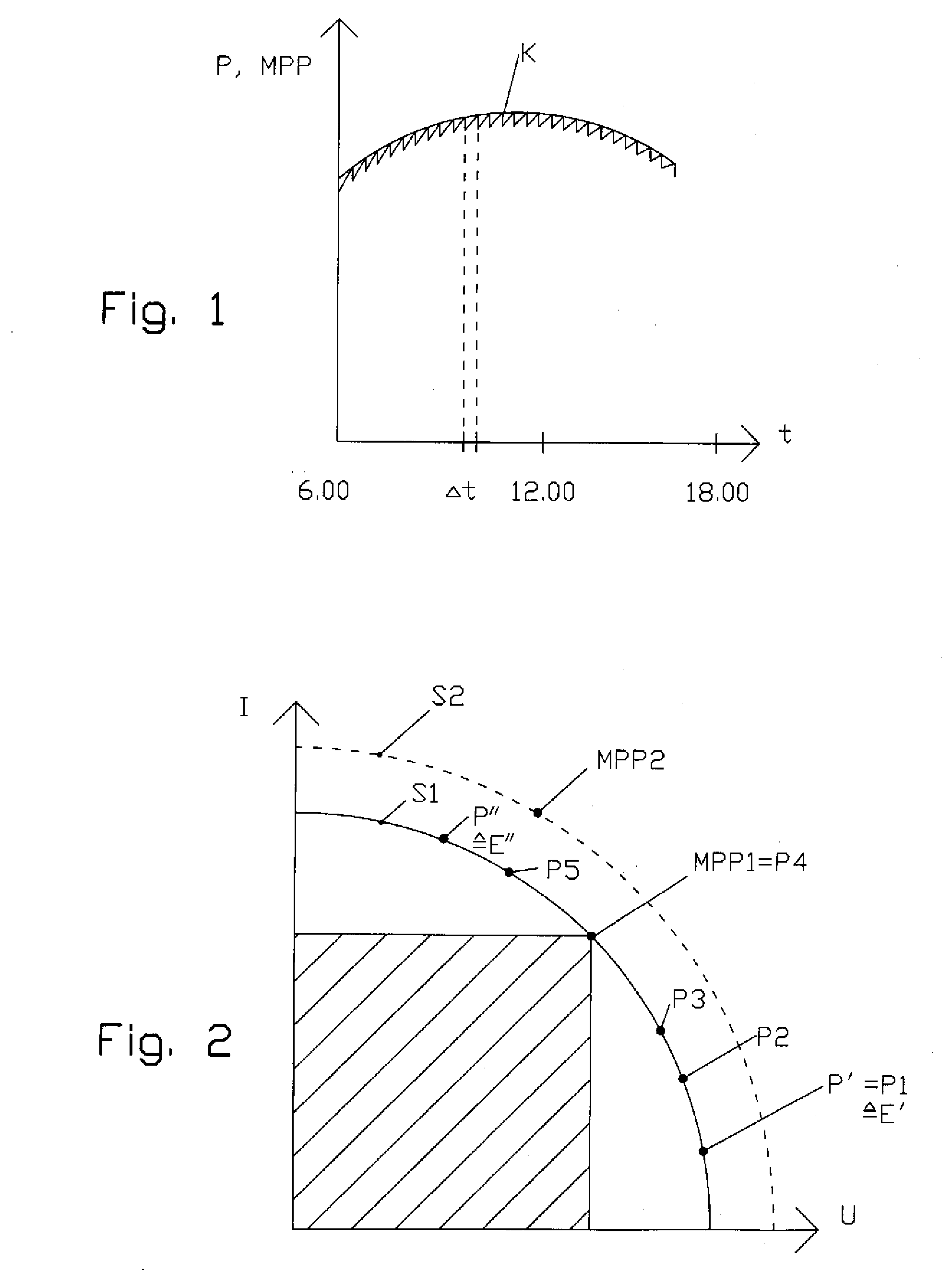
Photovoltaic system and method for operating a photovoltaic system
InactiveUS20070290636A1Easy to useReduce maintenance costsBatteries circuit arrangementsMultiple dynamo-motor startersExcitation currentEngineering
A photovoltaic system includes a plurality of photovoltaic modules and a DC motor connected to a three-phase generator driven by a shaft. The three-phase generator is connected to a power mains. The electric power supplied to the DC motor by the plurality of photovoltaic modules is repeatedly measured and adjusted, by changing an external excitation current of the DC motor, to the peak power attainable at the current ambient temperature and the current incident solar radiation intensity. The peak power is preferably determined by incrementally changing the excitation current in predetermined time intervals, until the supplied electric power produces a power level which can be regarded as the peak power.
Owner:ADENSIS
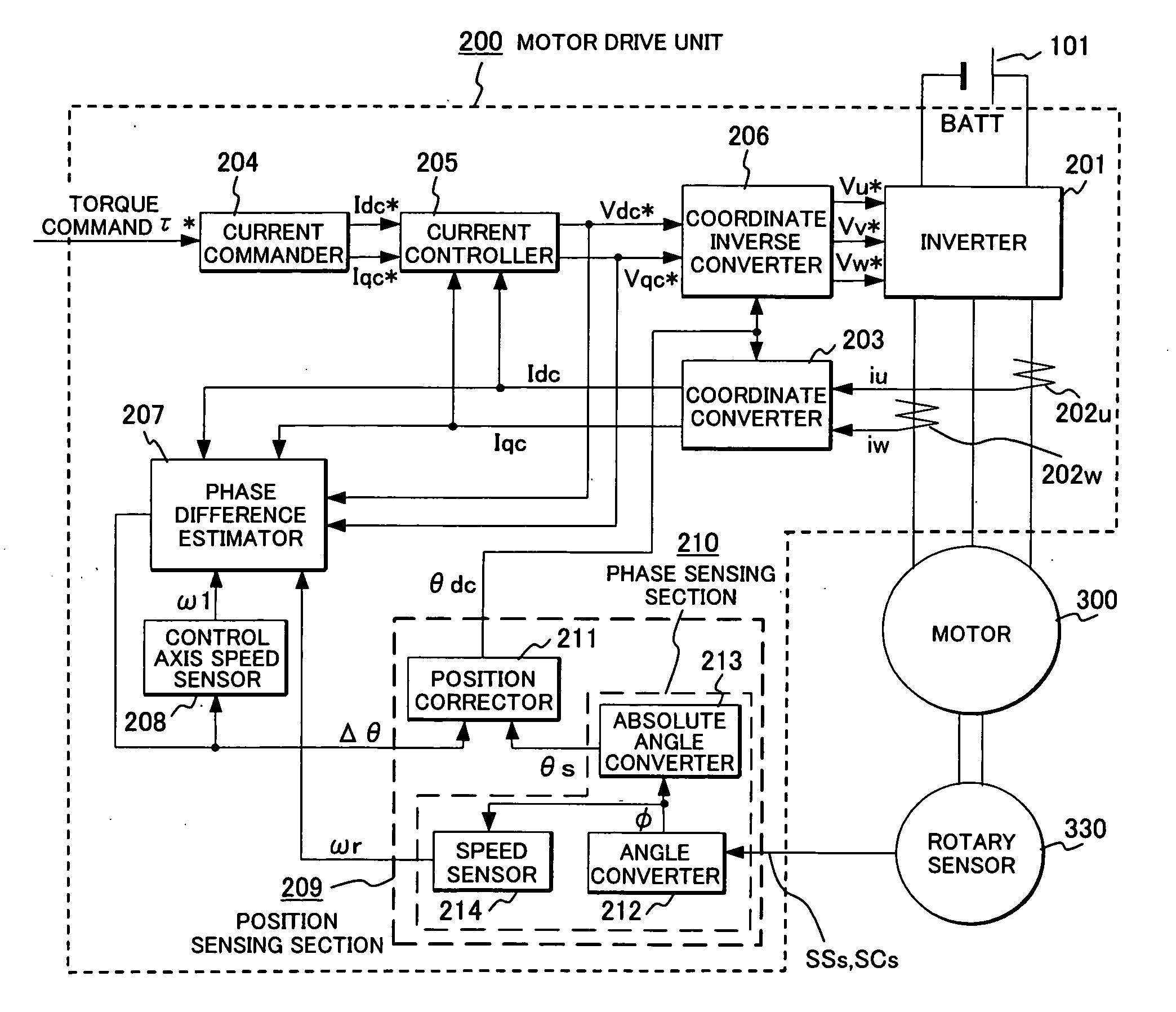
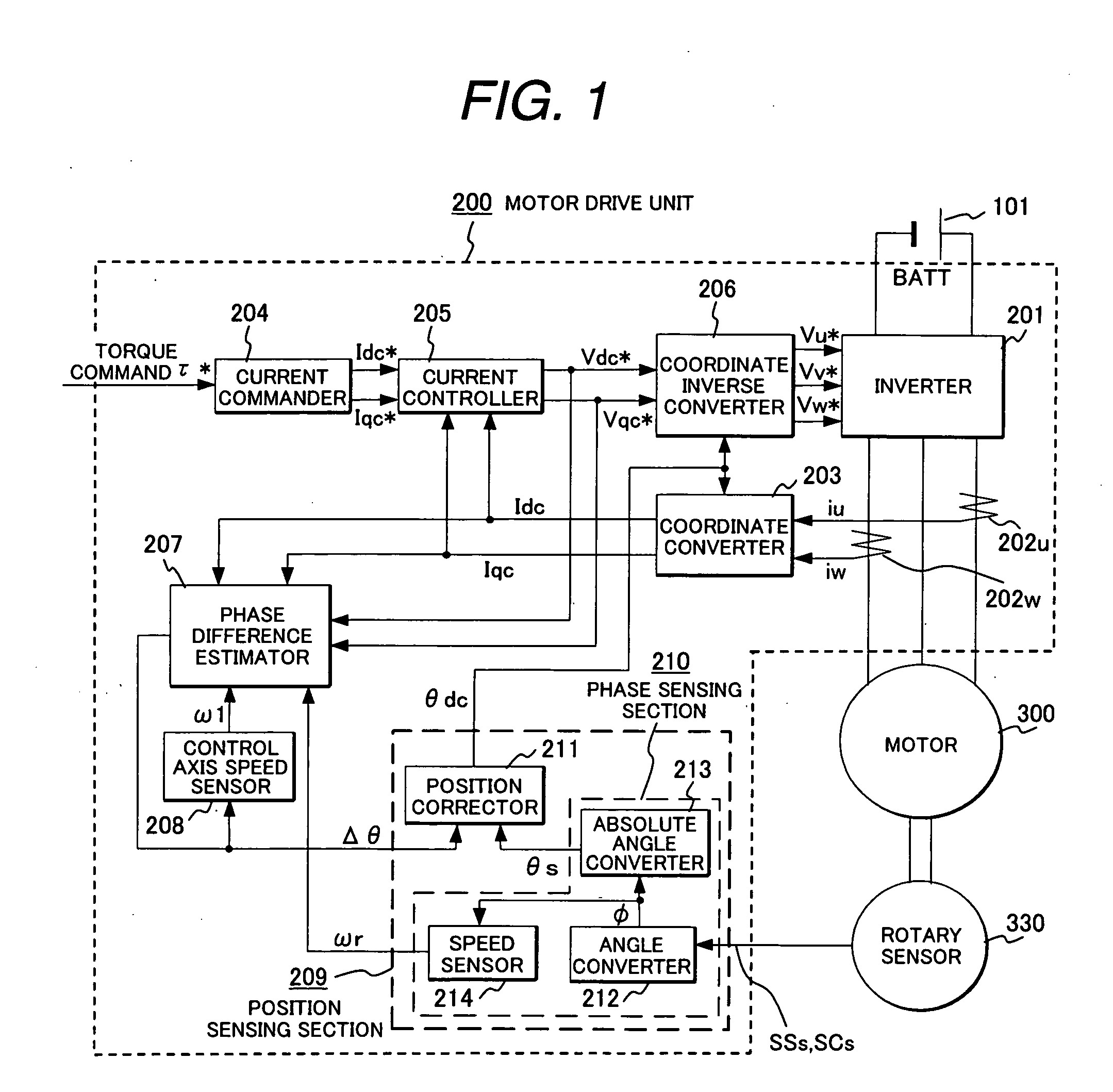
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
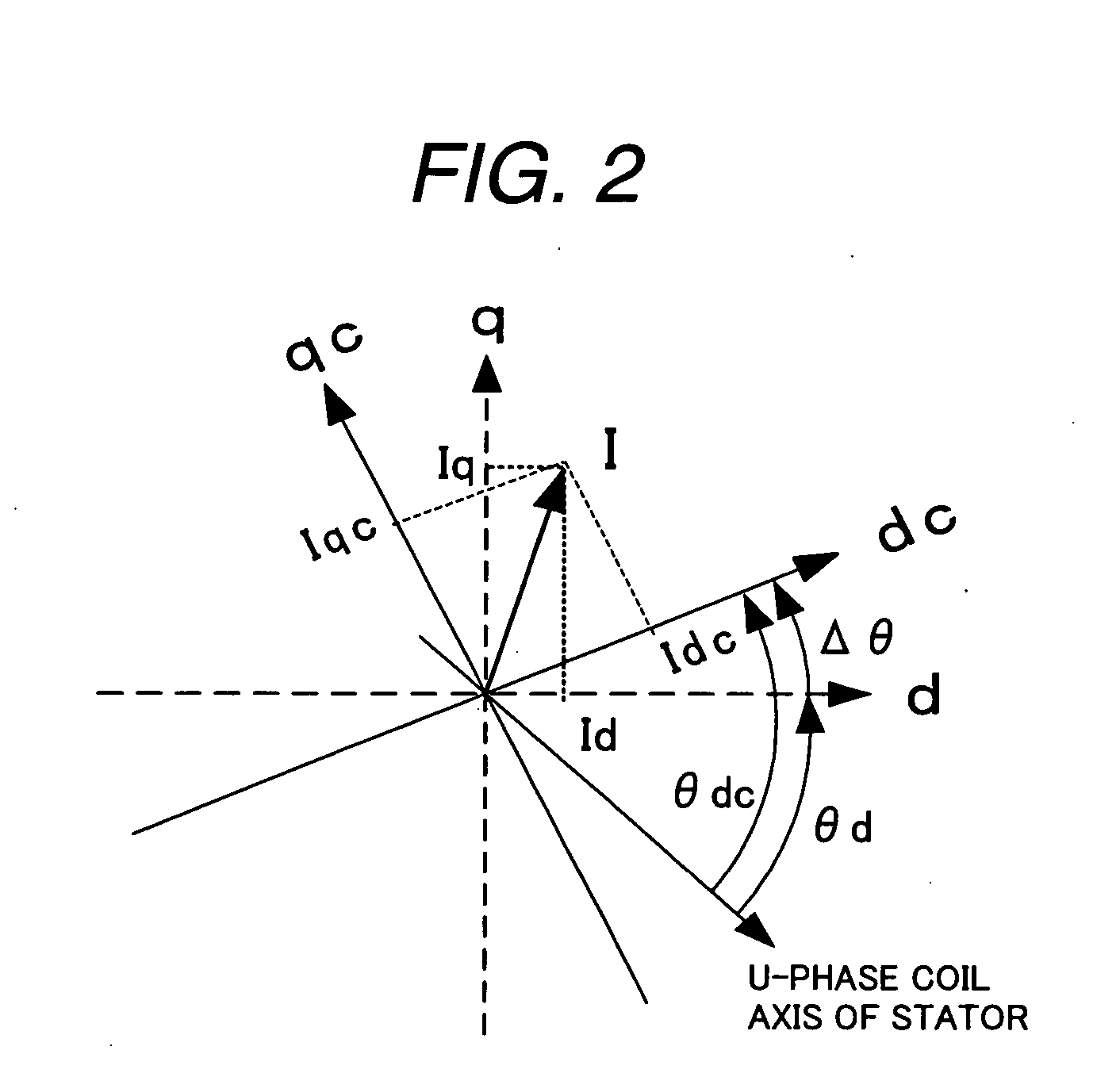
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of testing motor torque integrity in a hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20050256618A1DC motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsMotor speedEngineering
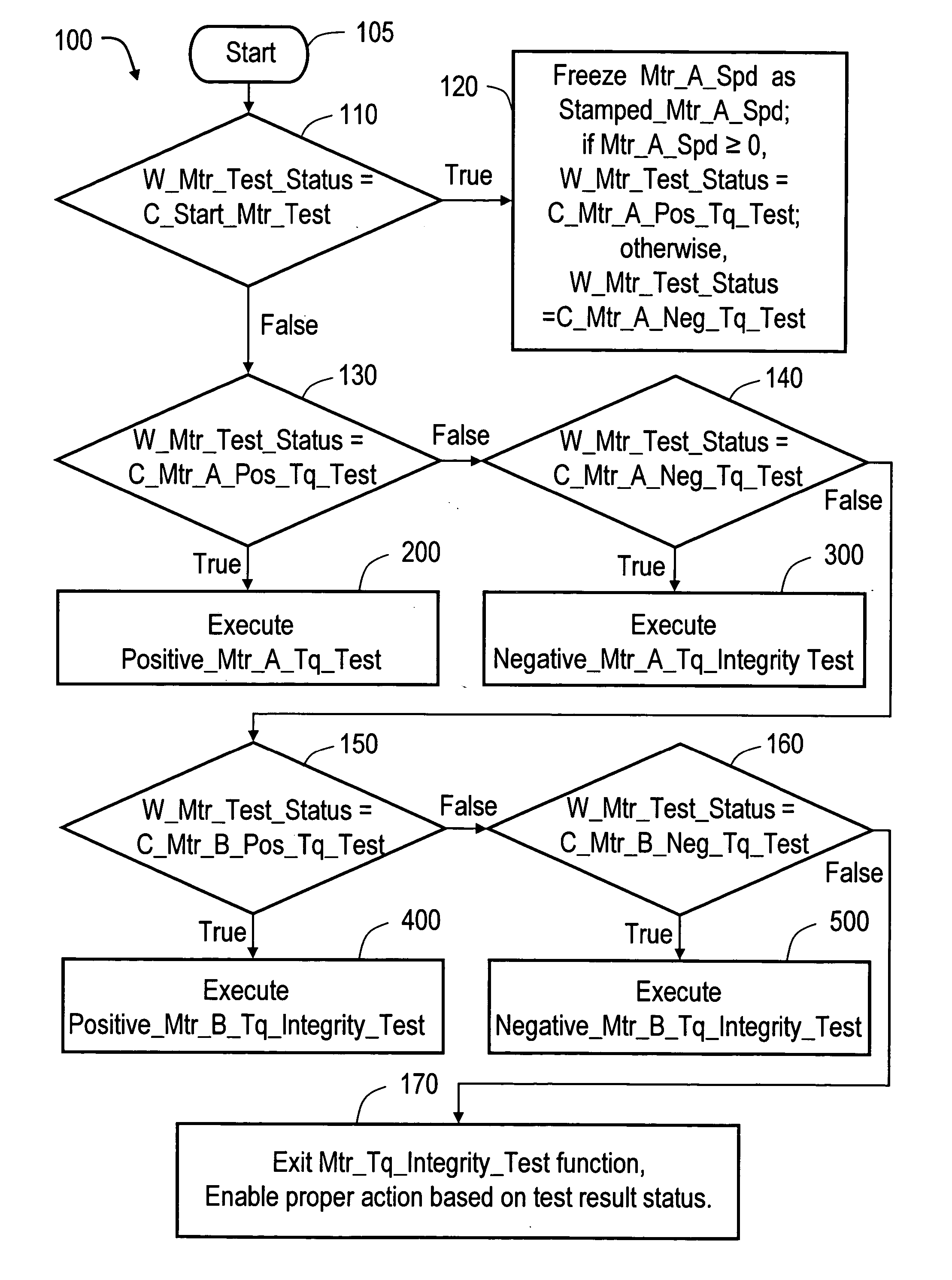
A method of testing an electric motor that is adapted to provide a desired electric motor output torque to a vehicle powertrain system comprising an engine and the electric motor which are operatively and selectively coupled to a transmission. The method includes the steps of determining an initial motor speed of the electric motor, determining a motor torque command as a function of the initial motor speed, applying the motor torque command to the electric motor to produce an output torque from the electric motor, measuring a resultant motor speed of the electric motor and establishing a motor status as a function of the resultant motor speed. The method may be implemented as a computer control and diagnostic algorithm.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Brushless and sensorless DC motor control system with locked and stopped rotor detection
ActiveUS20050029976A1Easy to modifyEasily interfaceCommutation monitoringDC motor speed/torque controlMotor speedDc motor control
A motor control system for a brushless and sensorless DC motor for driving a compressor, pump or other application, includes a protection and fault detection circuit for detecting a locked rotor and a rotor which has stopped because of lost rotor phase lock. The motor control system also includes an off-the-shelf motor control integrated circuit having an input for disabling power outputs to the motor phase coils. The protection and fault detection circuit uses a back EMF sampling circuit coupled to the motor phase coils and momentarily disables power to the motor phase coils, via the motor control integrated circuit input, to determine if the motor rotor is rotating. The system also monitors supply voltage, supply current, temperature, and motor speed limits to detect faults and protect system components.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Method of automatically controlling a motorized window treatment while minimizing occupant distractions
ActiveUS8288981B2Minimize distractionDC motor speed/torque controlDoor/window protective devicesPresent dayDistraction
A load control system provides for automatically controlling a position of a motorized window treatment to control the amount of sunlight entering a space of a building through a window located in a façade of the building in order to control a sunlight penetration distance within the space and minimize occupant distractions. The load control system automatically generates a timeclock schedule having a number of timeclock events for controlling the position of the motorized window treatment during the present day. A user is able to select a desired maximum sunlight penetration distance for the space and a minimum time period that may occur between any two consecutive timeclock events. In addition, a maximum number of movements that may occur during the timeclock schedule may also be entered. The load control system uses these inputs to determine event times and corresponding positions of the motorized window treatment for each timeclock event of the timeclock schedule.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
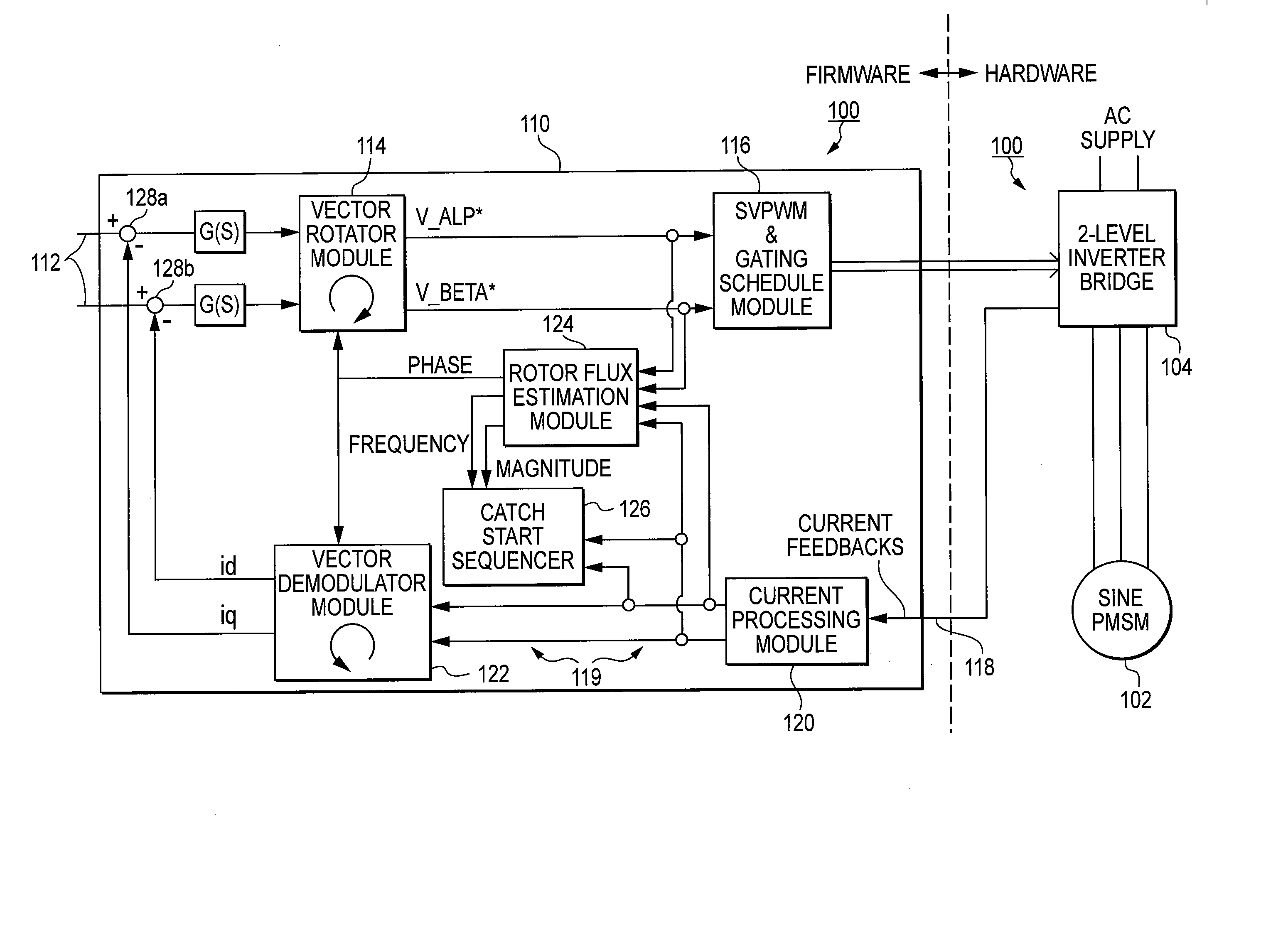
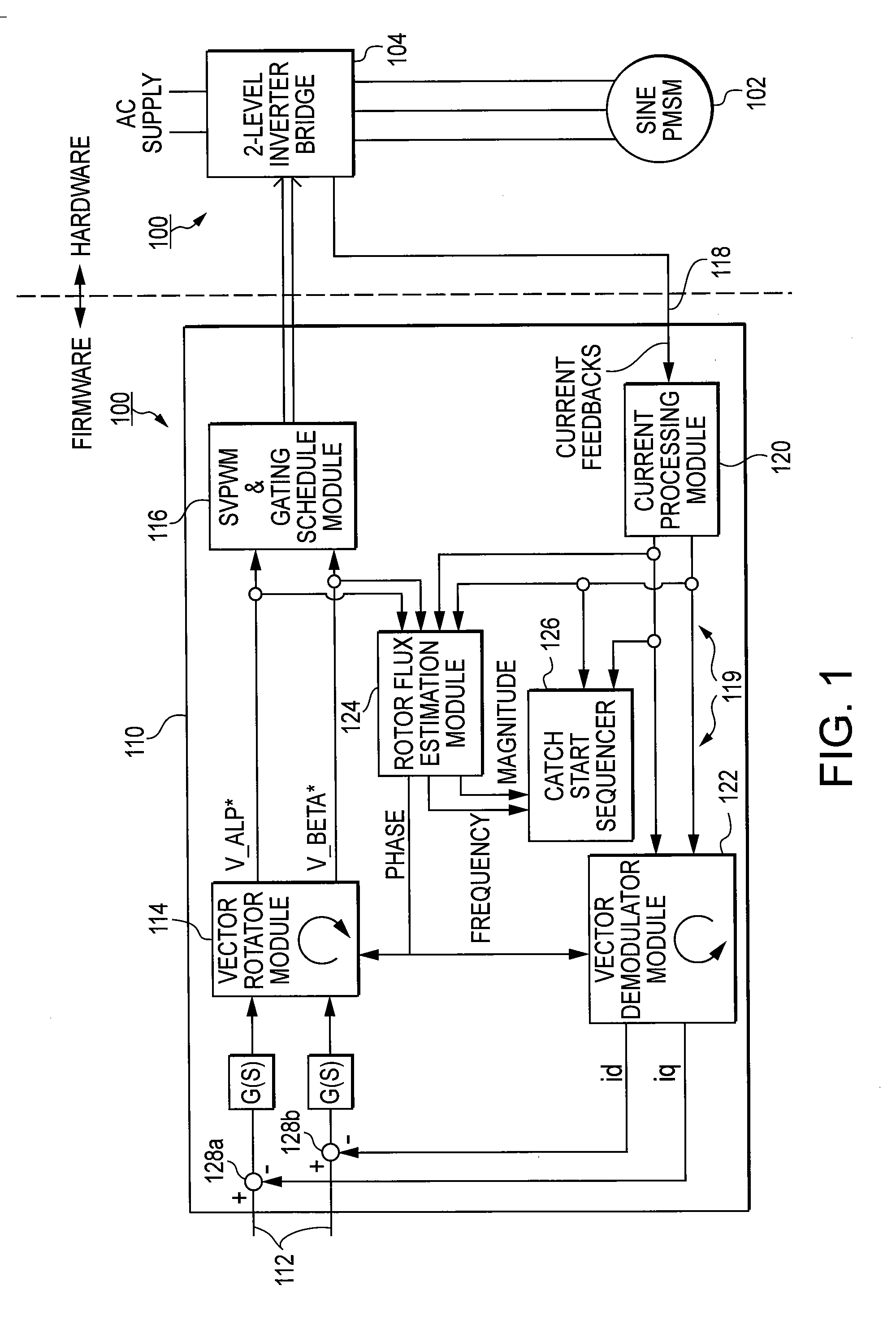
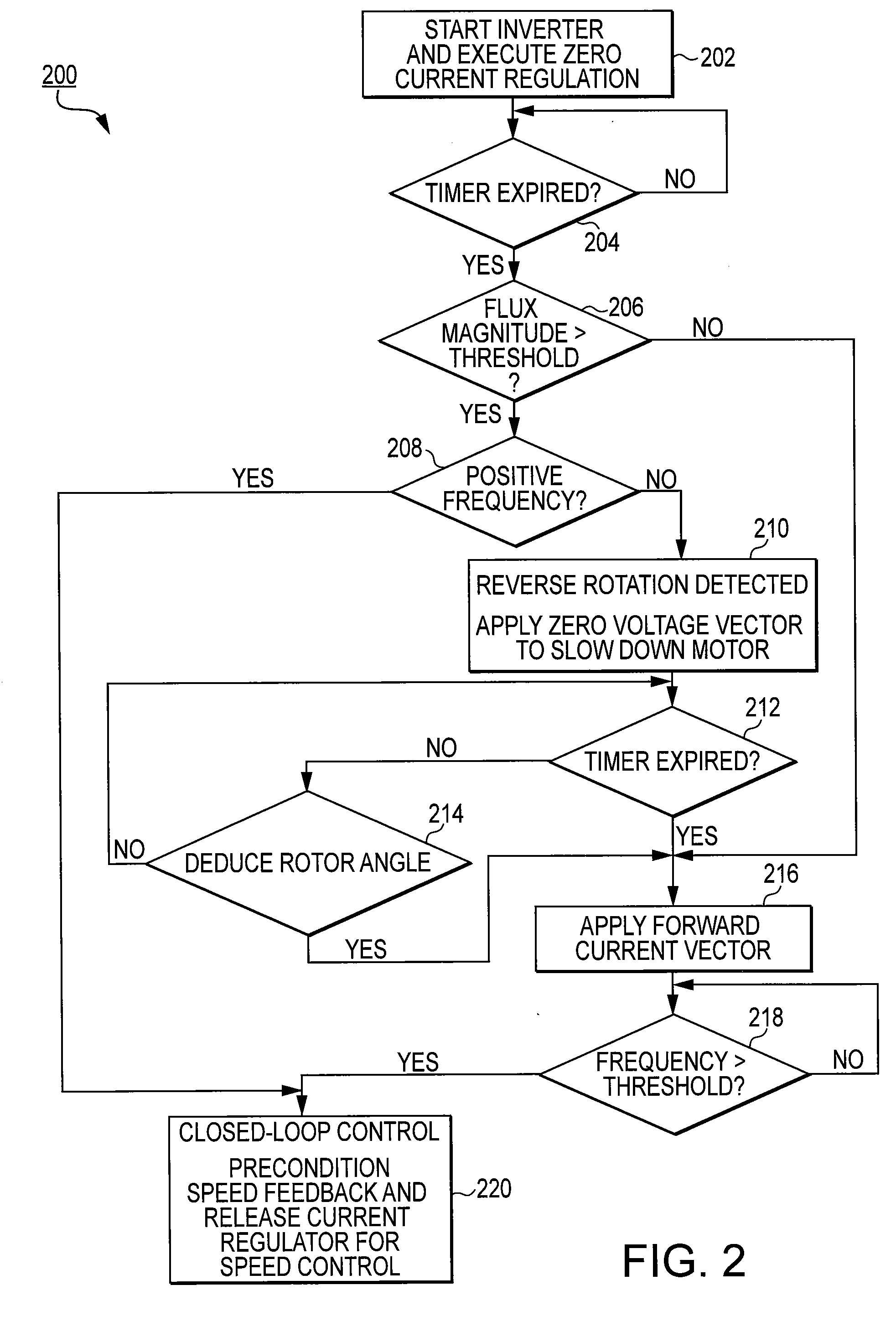
Method and system for starting a sensorless motor
ActiveUS20070001635A1Preventing over current shutdownHigh currentAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersMotor driveEngineering
A motor drive system for a sensorless motor includes a catch start sequencer that controls the motor drive system to robustly start the motor in the event the motor rotor is rotating in forward or reverse direction prior to activating the motor drive system. In particular, the catch start sequencer causes the motor drive system to initially find and track the rotor position, and then determines the speed and possibly the direction of rotation of the rotor. If the rotor is rotating in the reverse direction, the catch start sequencer controls the motor drive system to slow the speed of rotation and to then start the rotor rotating in the forward direction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Automated shade control relectance module
Automated shade systems comprise motorized window coverings, sensors, and controllers that use algorithms to control operation of the automated shade control system. These algorithms may include information such as: 3-D models of a building and surrounding structures, shadow information, reflectance information, lighting and radiation information, ASHRAE clear sky algorithms, log information related to manual overrides, occupant preference information, motion information, real-time sky conditions, solar radiation on a building, a total foot-candle load on a structure, brightness overrides, actual and / or calculated BTU load, time-of-year information, and microclimate analysis.
Owner:MECHOSHADE SYST LLC
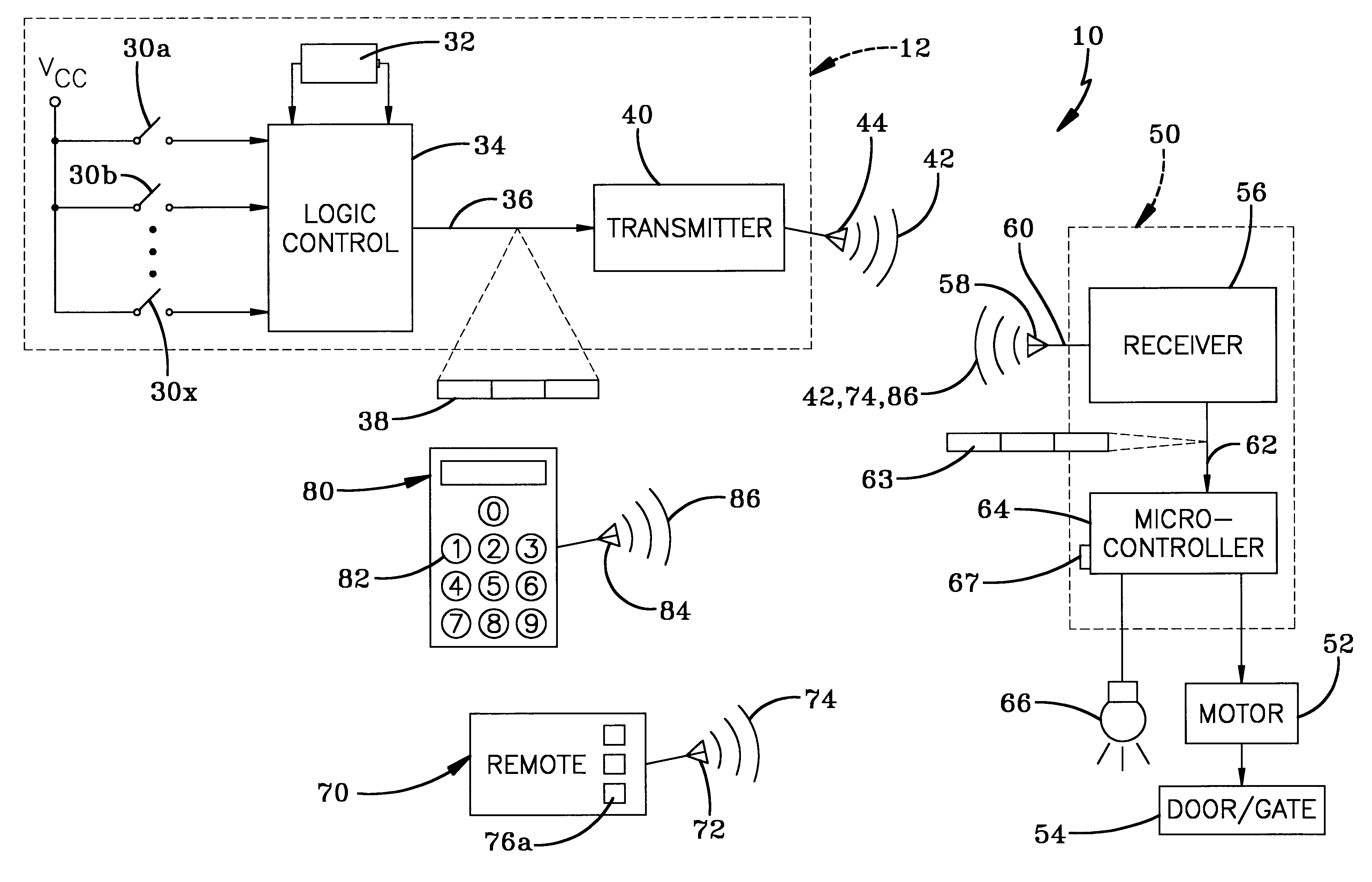
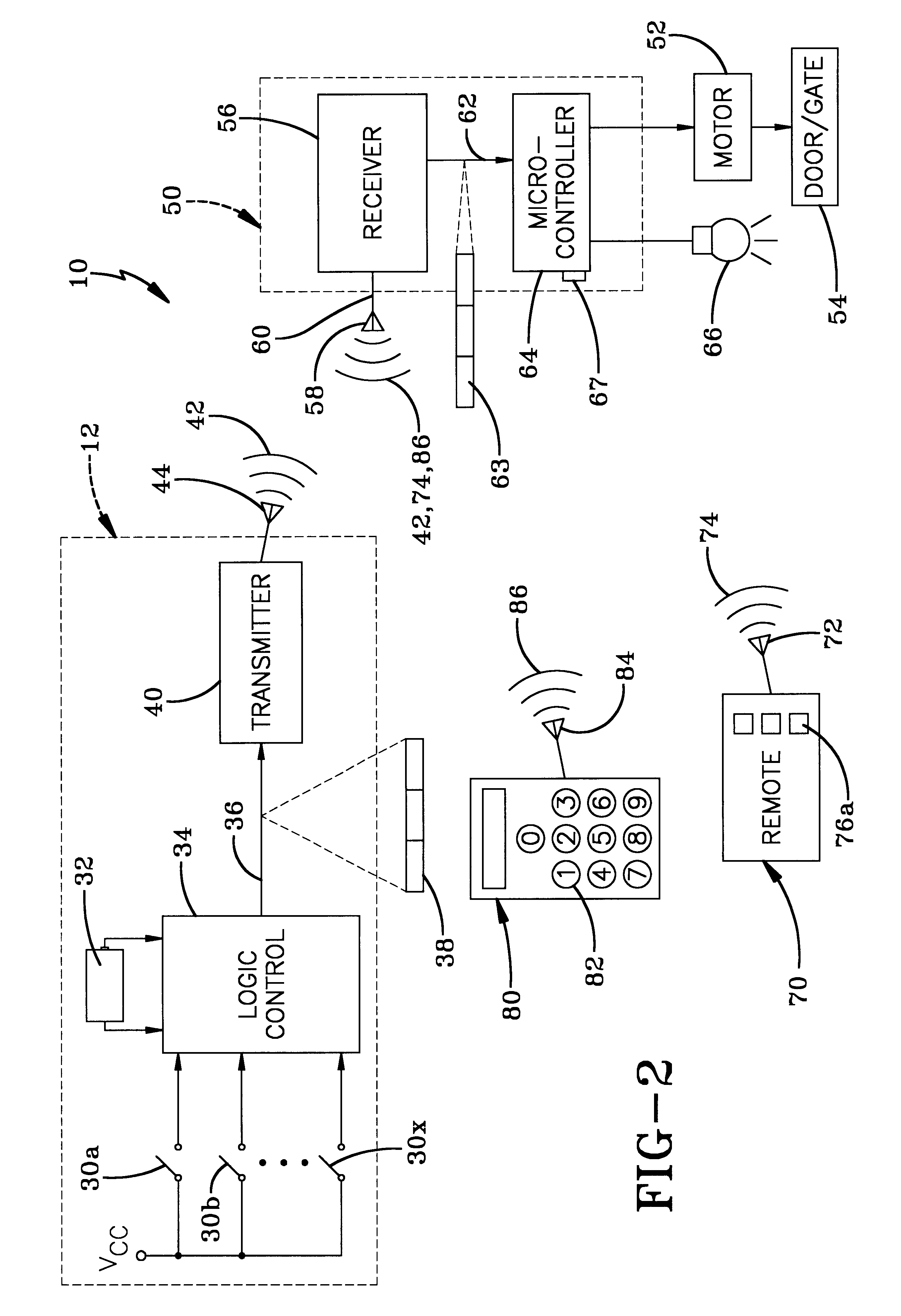
Wireless operating system utilizing a multi-functional wall station transmitter for a motorized door or gate operator
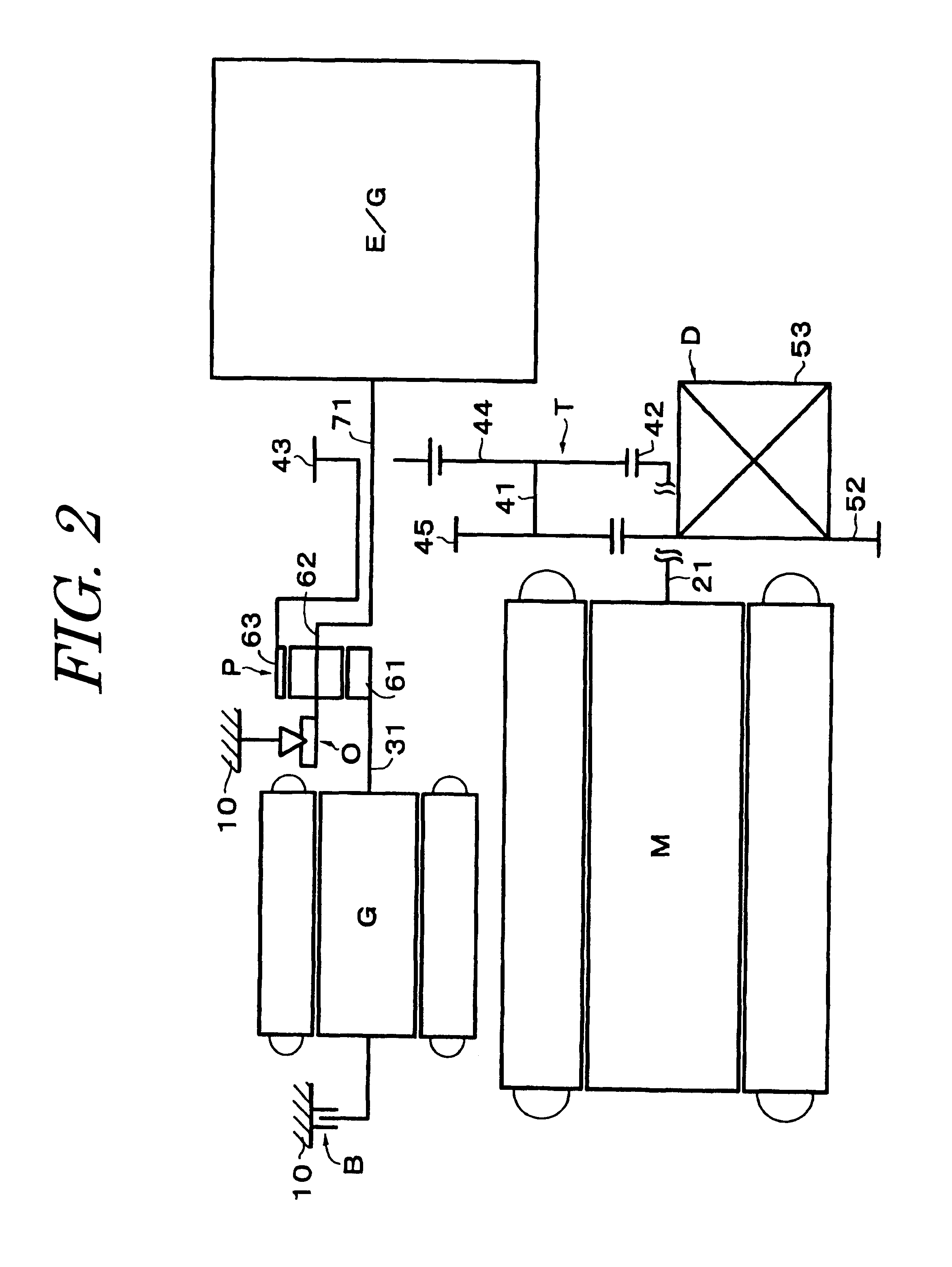
InactiveUS6326754B1Comprehensive functionsEliminate needDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOperational systemWorkstation
A wireless operating system (10) utilizing a multi-functional wall station (12) for a motorized door / gate operator includes an operator (50) for controlling the movement of a door / gate (54) between various positions. The system has an operator with a receiver (56) and a wall station transmitter (12) for transmitting a signal (42) to the receiver. The signal initiates separate operator functions in addition to opening and closing of the door / gate. A remote transmitter (70) may send a remote signal (74) received by the receiver, wherein the receiver is capable of distinguishing between the wall station signal (42) and the remote signal (74). The wall station includes a transmitter programming button (24), wherein actuation of the transmitter programming button places the wall station transmitter in a learn mode, and wherein subsequent actuation of the remote transmitter positively identifies the remote transmitter for use with the wall station. A light (66) powered by the operator and a light actuation button (18) provided by the wall station transmitter is included in the system. Actuation of the light actuation button (18) functions to switch the light on or off. A pet height button (22), provided by the wall station transmitter, selectively positions the height of the gate / door (54) from its fully closed position to allow ingress and egress of a pet. A delay-close button (20) closes the door / gate after a predetermined period of time. Actuation of a door installation button (28) sequences the door / gate and said operator through various operational parameters to establish a door operating profile. A keyless entry transmitter (80) and a second wall station may also control the operator.
Owner:WAYNE DALTON CORP
Rain sensor
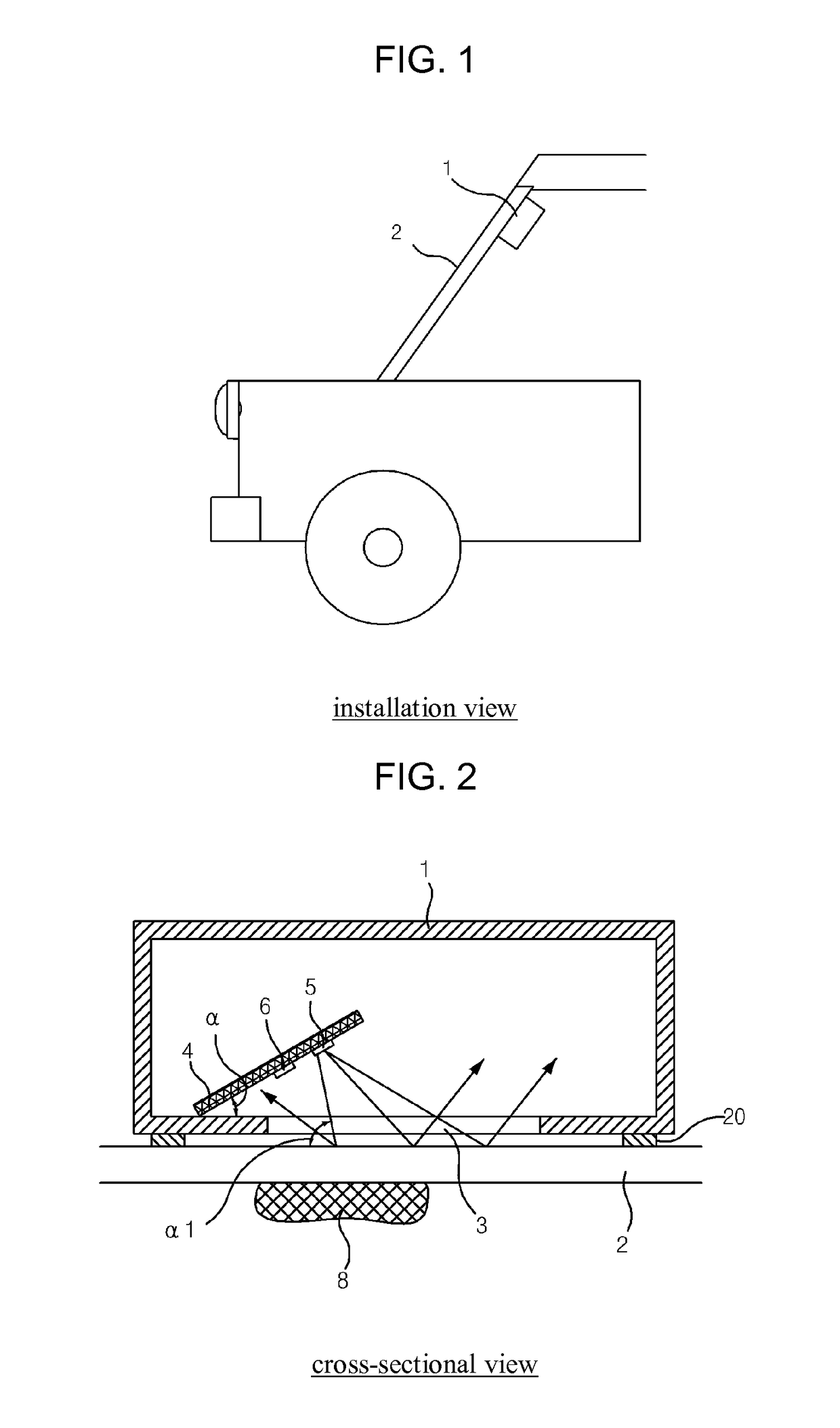
ActiveUS8471513B2Low failure ratePrevent degradationOptical radiation measurementDC motor speed/torque controlOptoelectronicsRain sensor
During rain, including a light source (5) for radiating light such that the light is transmitted through a vehicle window (2), a light receiving element (6) for sensing an optical signal when the light radiated from the light source (5) is reflected from the raindrop fallen on the vehicle window (2) and performing a photoelectric transduction, and a receiver (9) for receiving the photoelectrically transduced signal from the light receiving element (6) and judging the level of rainfall. The light source (5) and the light receiving element (6) are inclined with respect to the surface of the vehicle window (2) such that the light of the light source (5) directly reflected from the vehicle window (2) exits to the outside of the light receiving element (6) and the light reflected from a raindrop (8) on the vehicle window (2) is received by the light receiving element (6) to operate a vehicle wiper.
Owner:HAN SEA YEOUN
Automated shade control method and system
ActiveUS7977904B2Convenient lightingProtect the occupantsLight dependant control systemsDoors/windowsTemporal informationSky
This invention generally relates to automated shade systems. An automated shade system comprises one or more motorized window coverings, sensors, and controllers that use one or more algorithms to control operation of the automated shade control system. These algorithms may include information such as: 3-D models of a building and surrounding structures; shadow information; lighting and radiation information; ASHRAE clear sky algorithms; log information related to manual overrides; occupant preference information; motion information; real-time sky conditions; solar radiation on a building; a total foot-candle load on a structure; brightness overrides; actual and / or calculated BTU load; time-of-year information; and microclimate analysis.
Owner:MECHOSHADE SYST LLC
Drive unit with two coolant circuits for electric motor
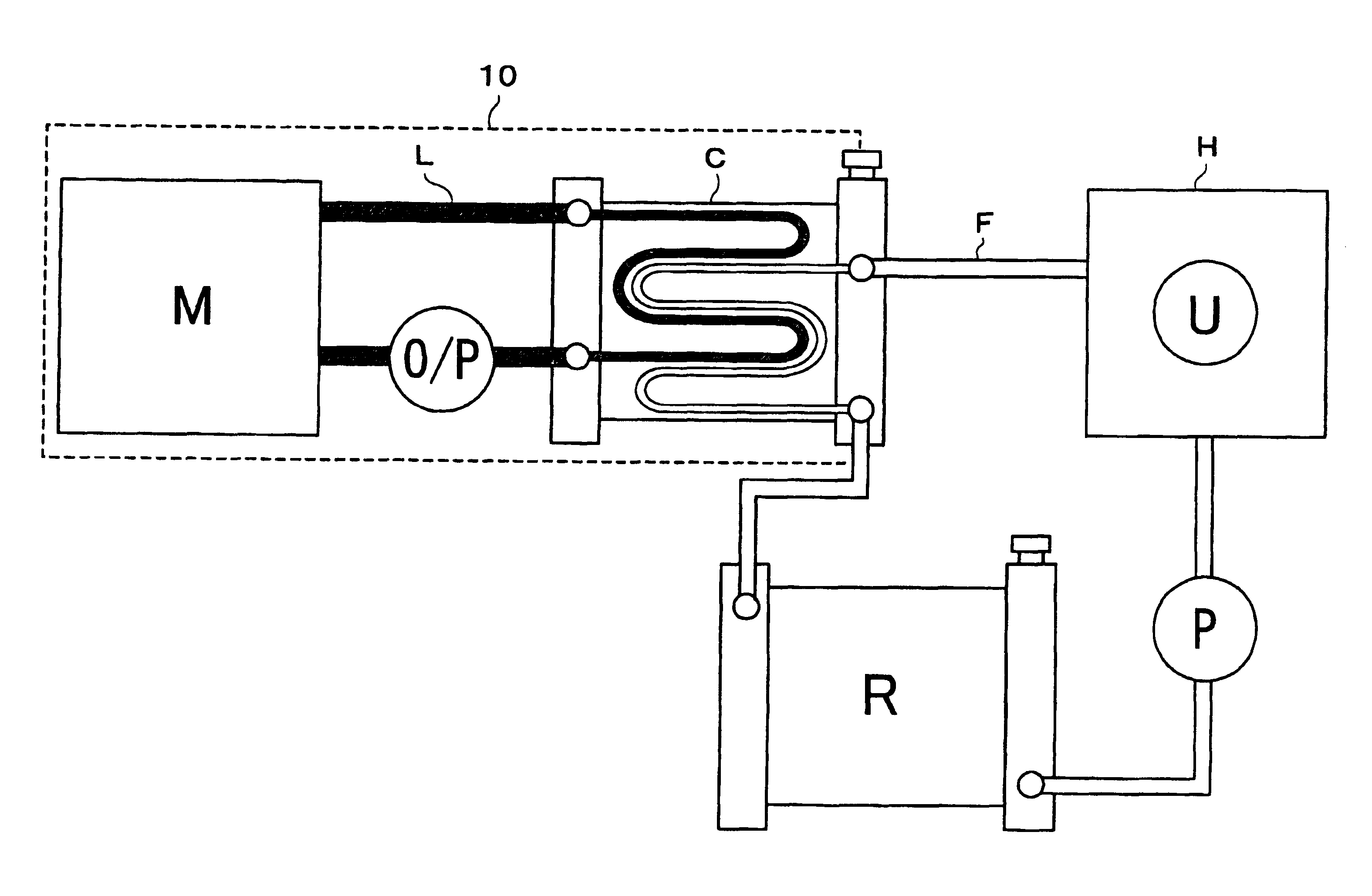
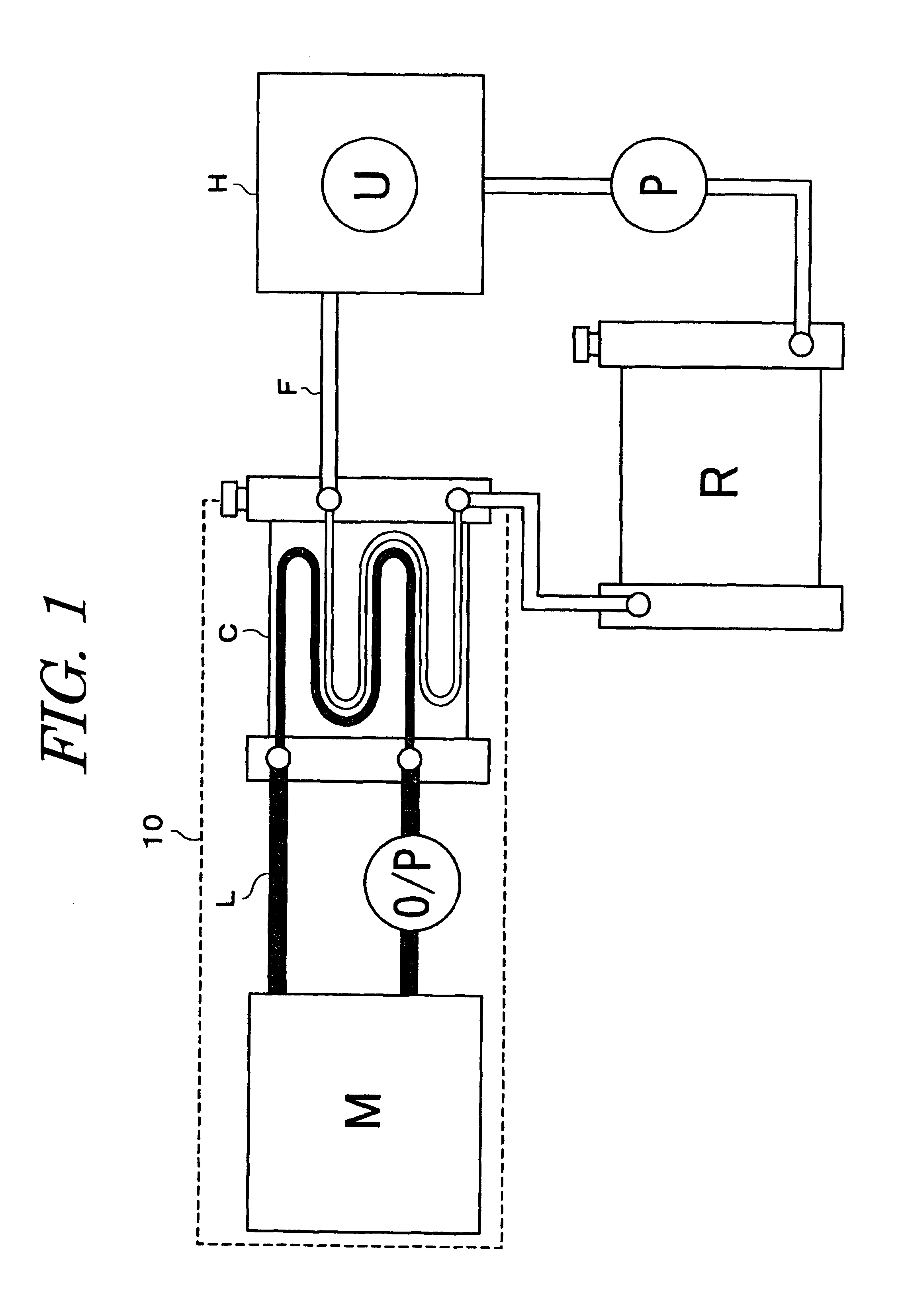
InactiveUS6323613B1Improve cooling effectHeat exchangerTemperatue controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringCooling fluid
A drive unit includes an electric motor as a power source, and a simplified coolant circuit for cooling the electric motor. The drive unit further includes, in the drive unit case, a circulation passage L for coolant for cooling the motor M. A circulation passage F for a second coolant is provided separate from the circulation passage L for coolant. A heat exchange portion C within the circulation passage L for the first coolant is provided in the drive unit case for heat exchange with the second coolant in the circulation passage F, and the first coolant for cooling the electric motor is cooled by heat transfer to the second coolant in that heat exchange portion C. Accordingly, the coolant circuit in the drive unit case is simplified.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Driving apparatus for a ceiling fan
InactiveUS7664377B2Reduce the amount presentReduce in quantityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric testing/monitoringBrushless motorsCeiling fan
A driving apparatus for a DC brushless motor of a ceiling fan is provided. By setting at least one coder and one sensor outside the DC brushless motor, the driving apparatus can sense the position of magnetic poles of the motor for driving the motor. Meanwhile, a controller set with the motor stores the rotation speed of the motor before being turned off by detecting the turn-off time of a turn-on / off signal.
Owner:RHINE ELECTRONICS
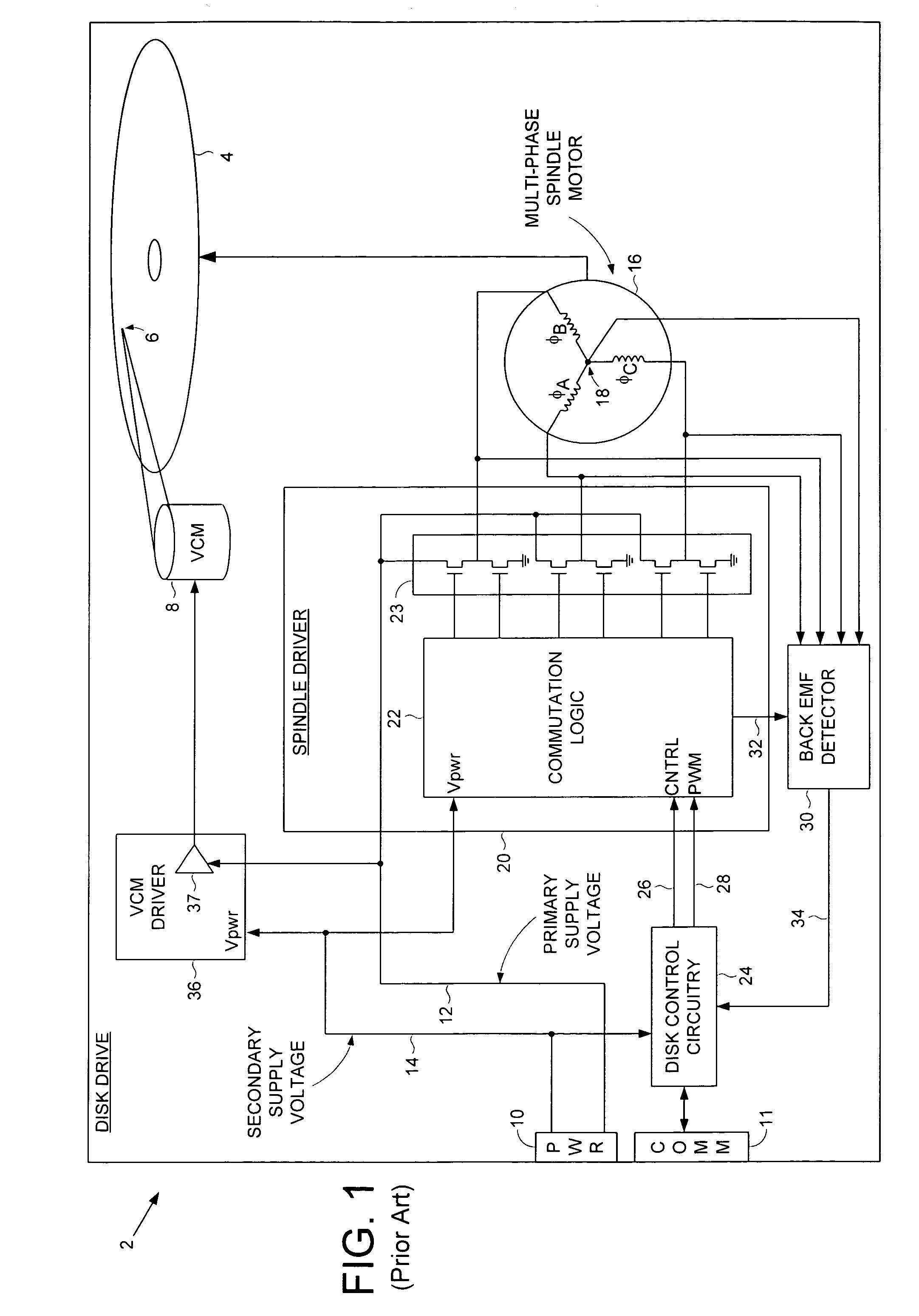
Disk drive employing active braking using inductive sense
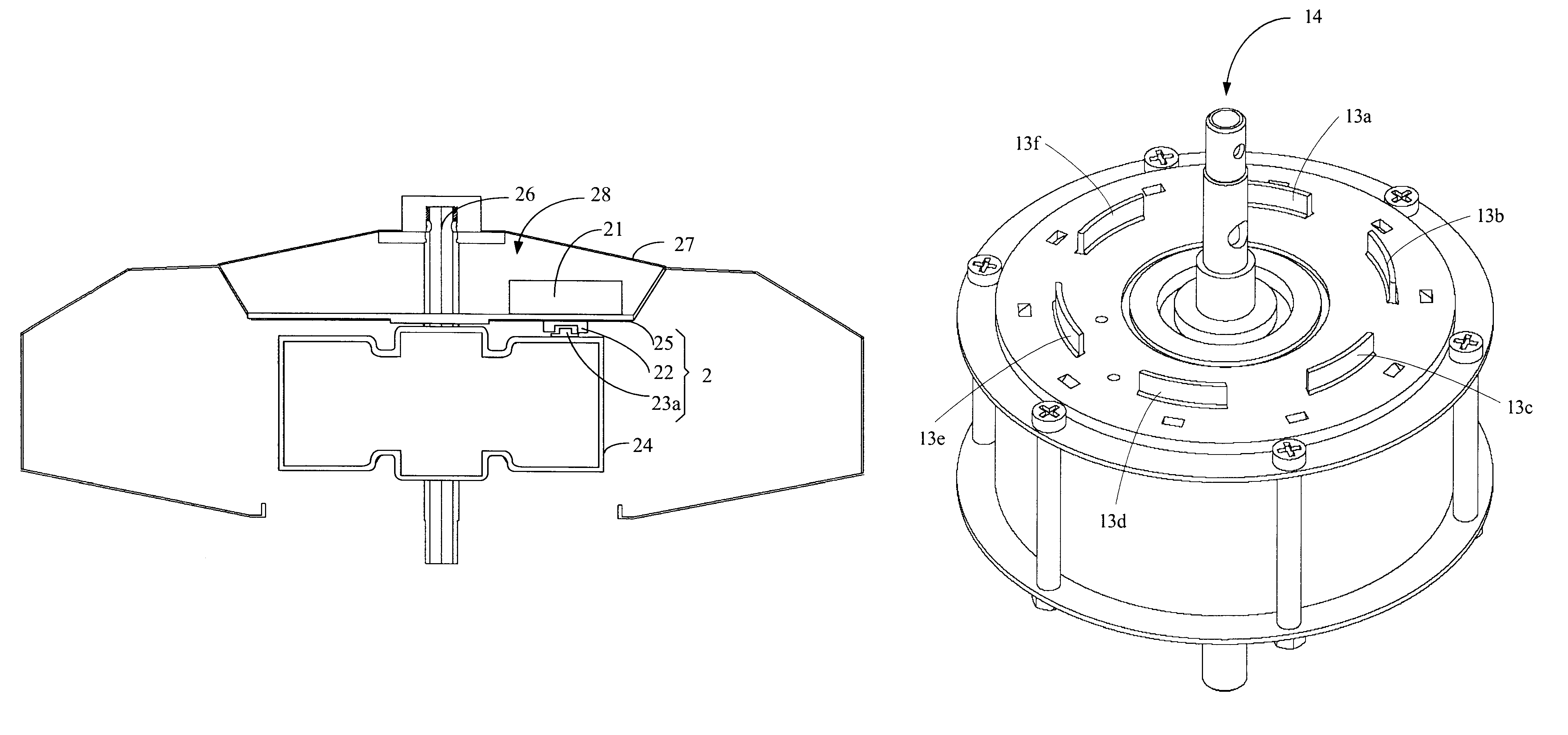
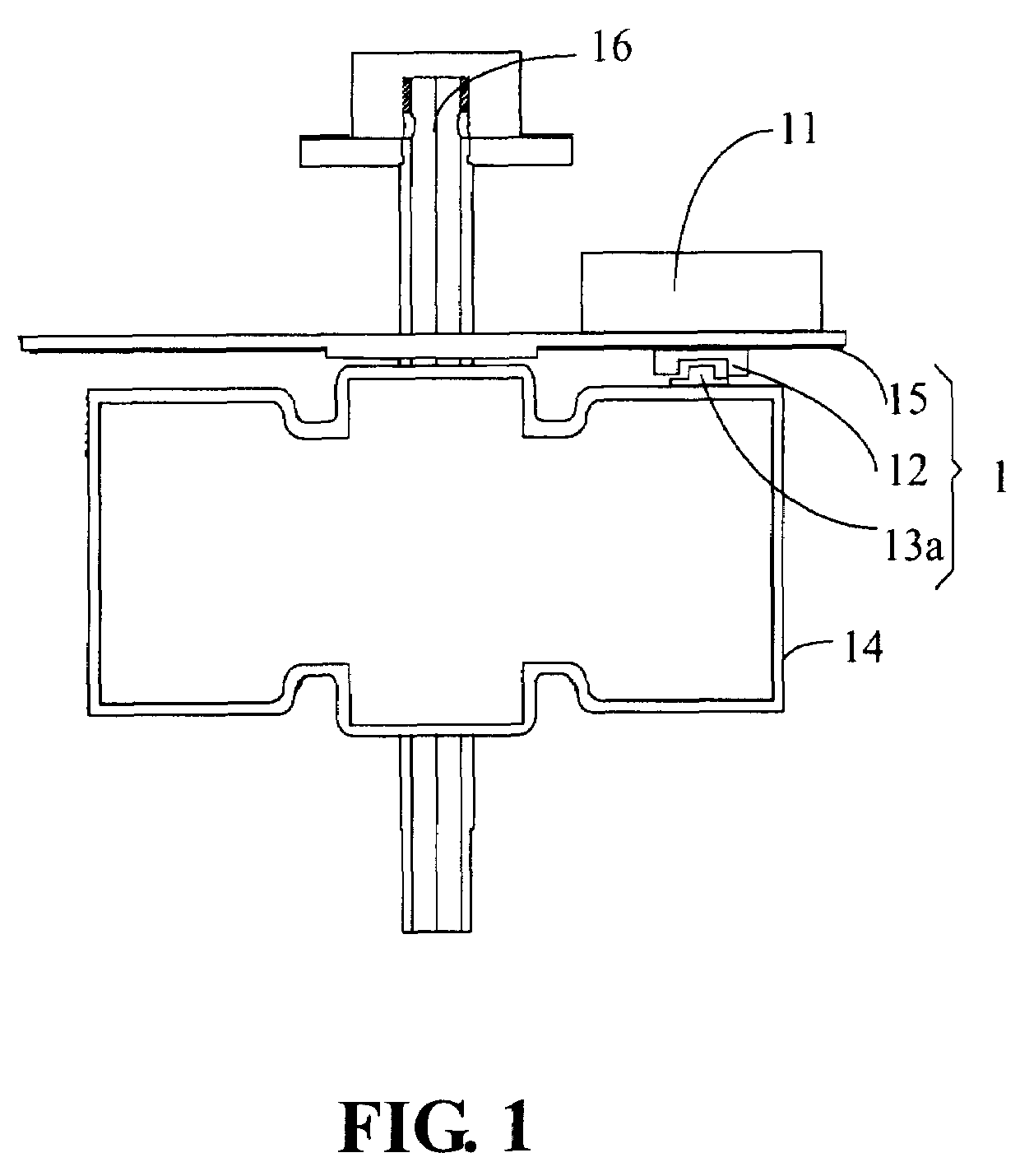
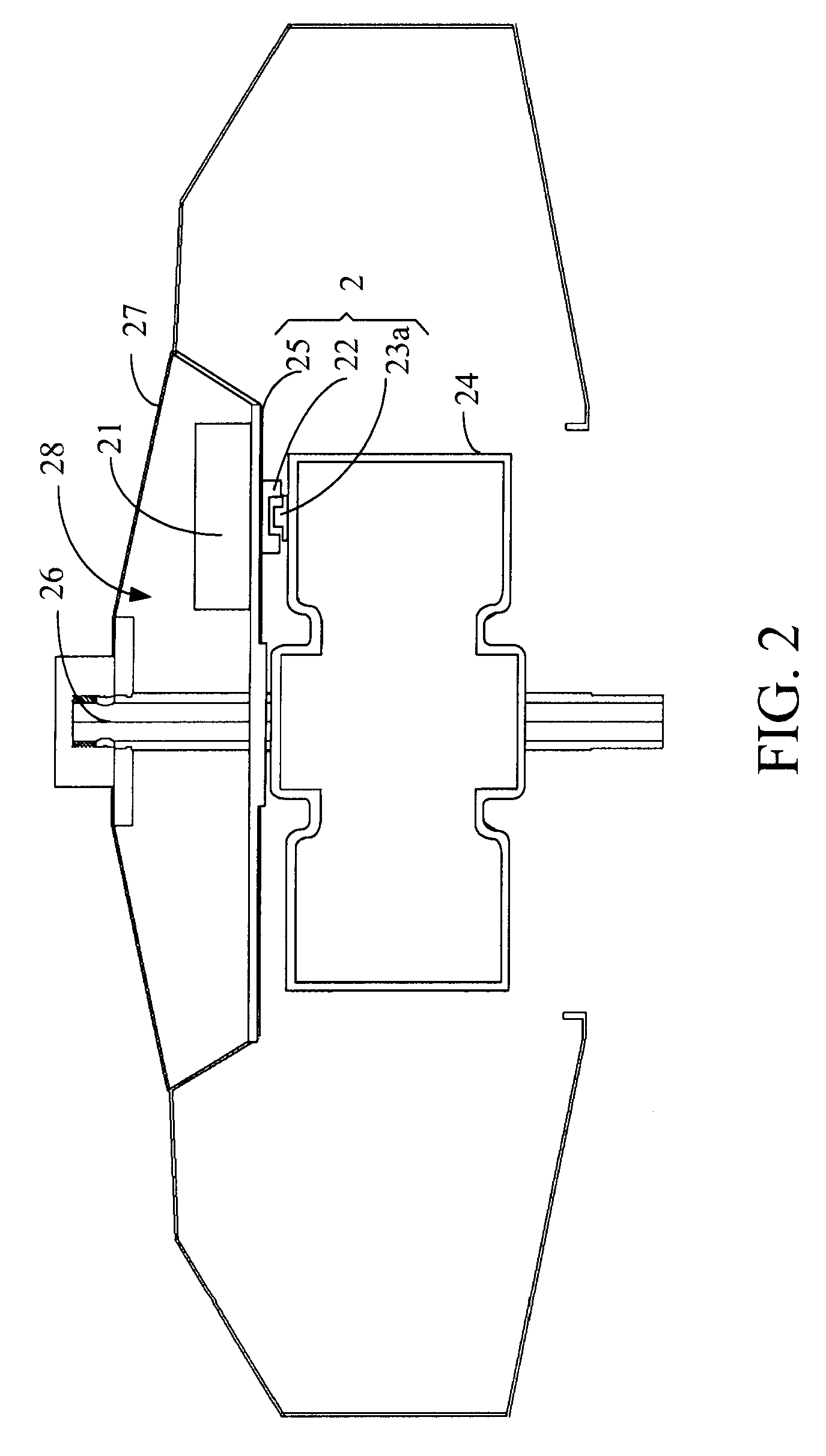
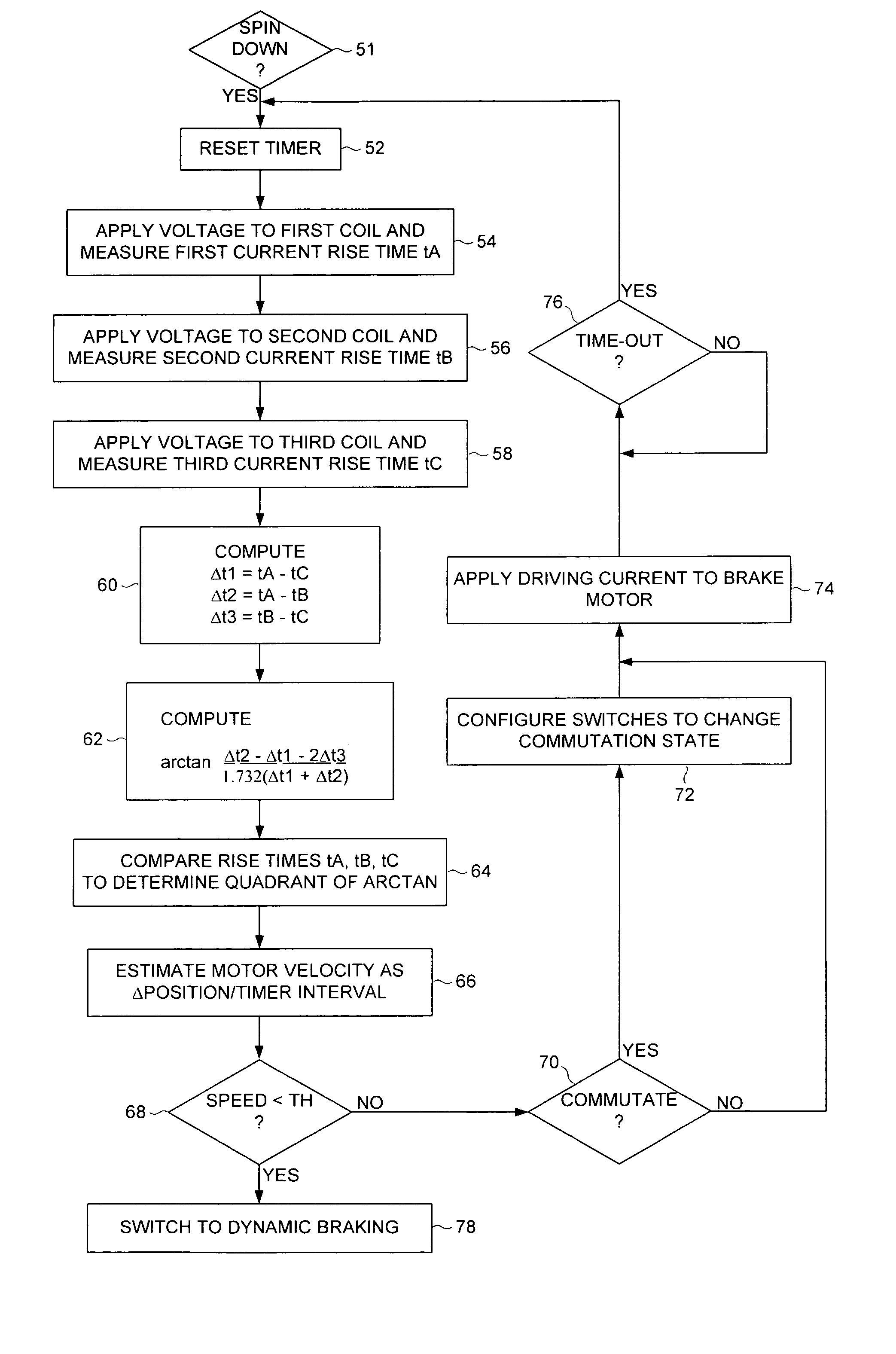
InactiveUS7158329B1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlDriving currentControl circuit
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk, a head actuated over the disk, and a spindle motor for rotating the disk, the spindle motor comprising a plurality of windings. Disk control circuitry executes a spin-down operation of the spindle motor by estimating an angular position of the spindle motor by applying a voltage to at least one of the windings and evaluating a rise time of current flowing through the winding. The windings are commutated in response to the estimated angular position, and a driving current is applied to the windings to brake the spindle motor.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
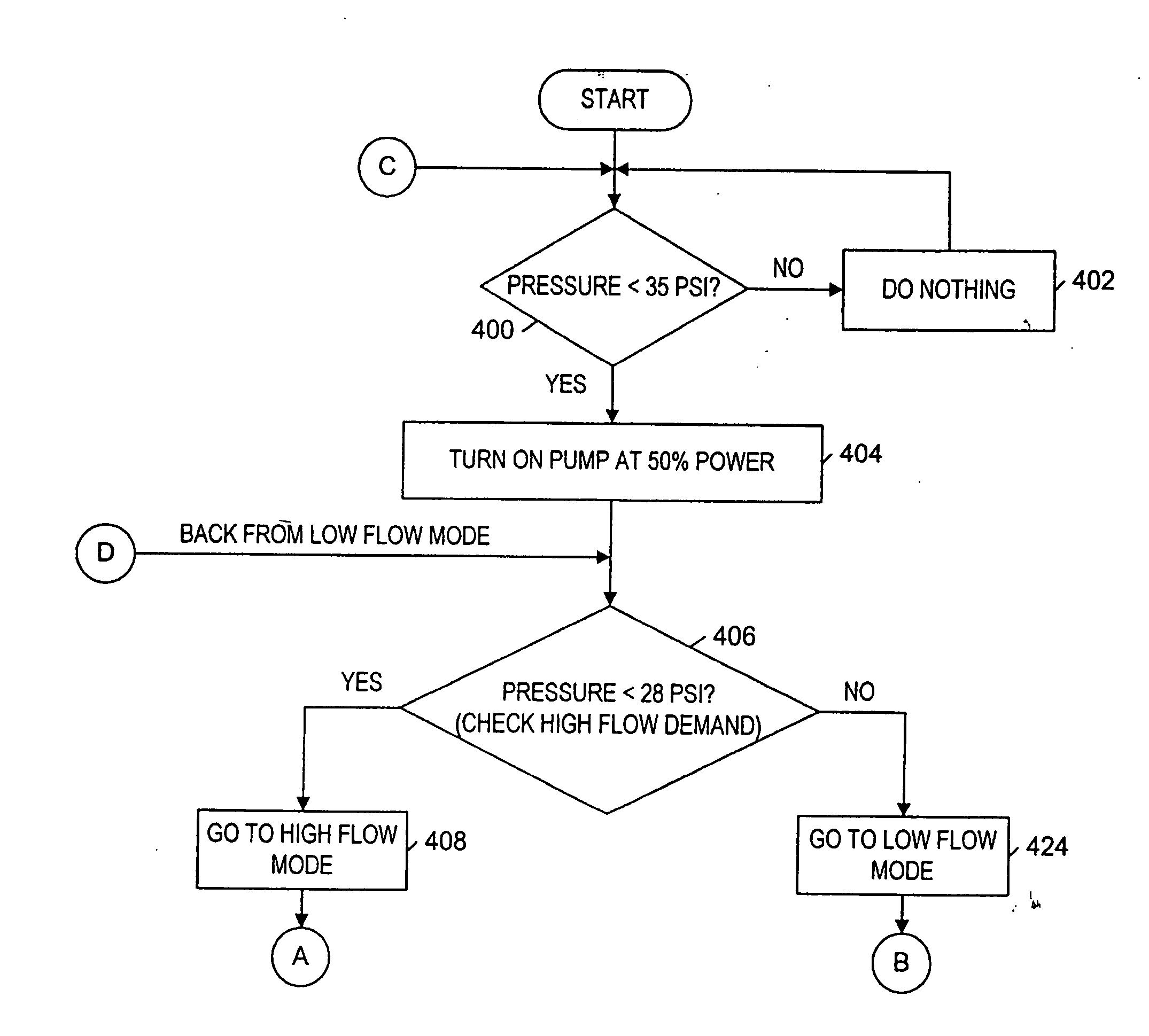
Pump and pump control circuit apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060204367A1Reduce the required powerIncrease powerMotor/generator/converter stoppersFluid parameterMicrocontrollerControl system
A method and apparatus for a pump and a pump control system. The apparatus includes a pressure sensor and a temperature sensor coupled to a pump control system. For the method of the invention, the microcontroller provides a pulse-width modulation control signal to an output power stage in order to selectively control the power provided to the pump.
Owner:SHURFLO
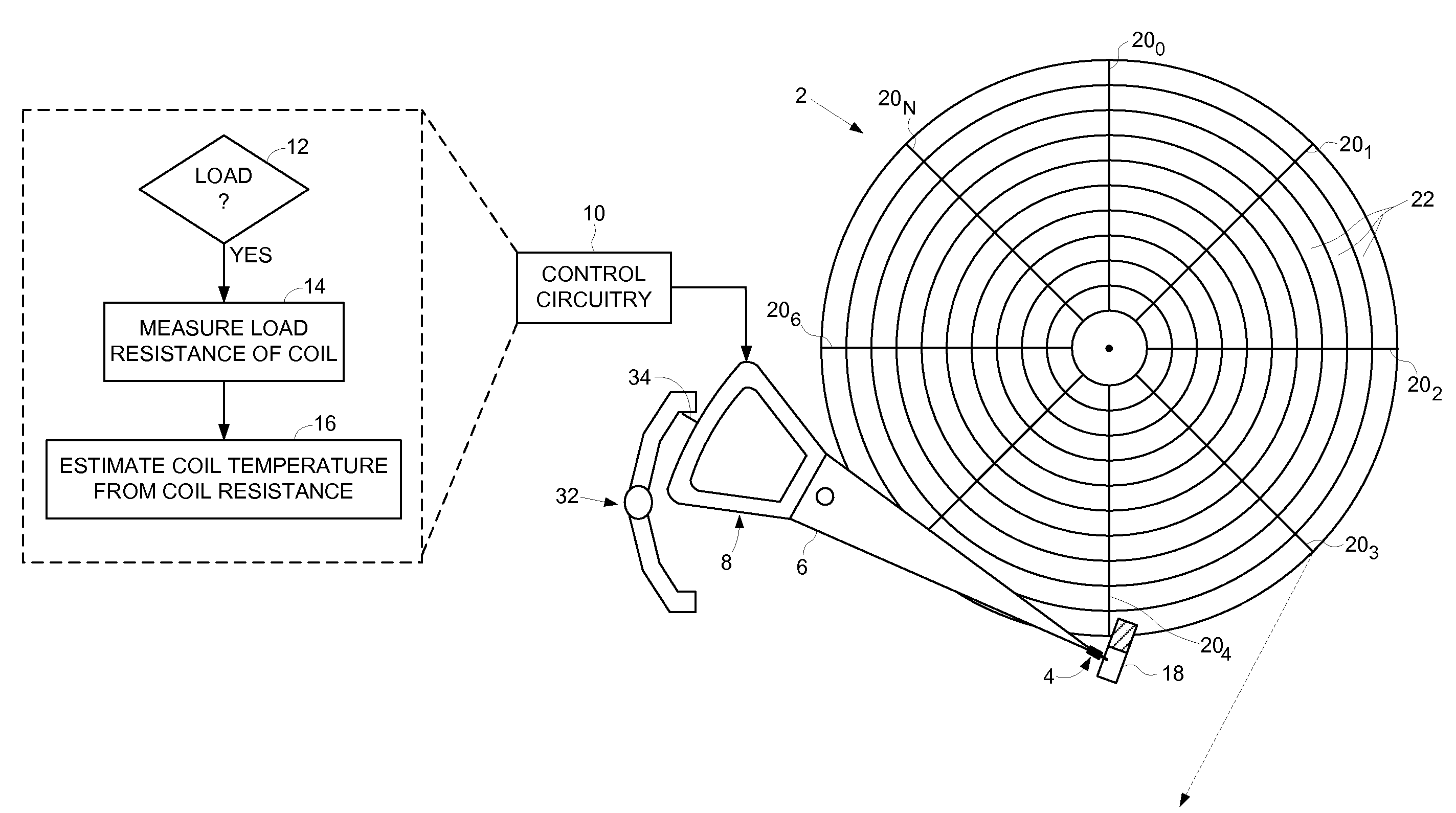
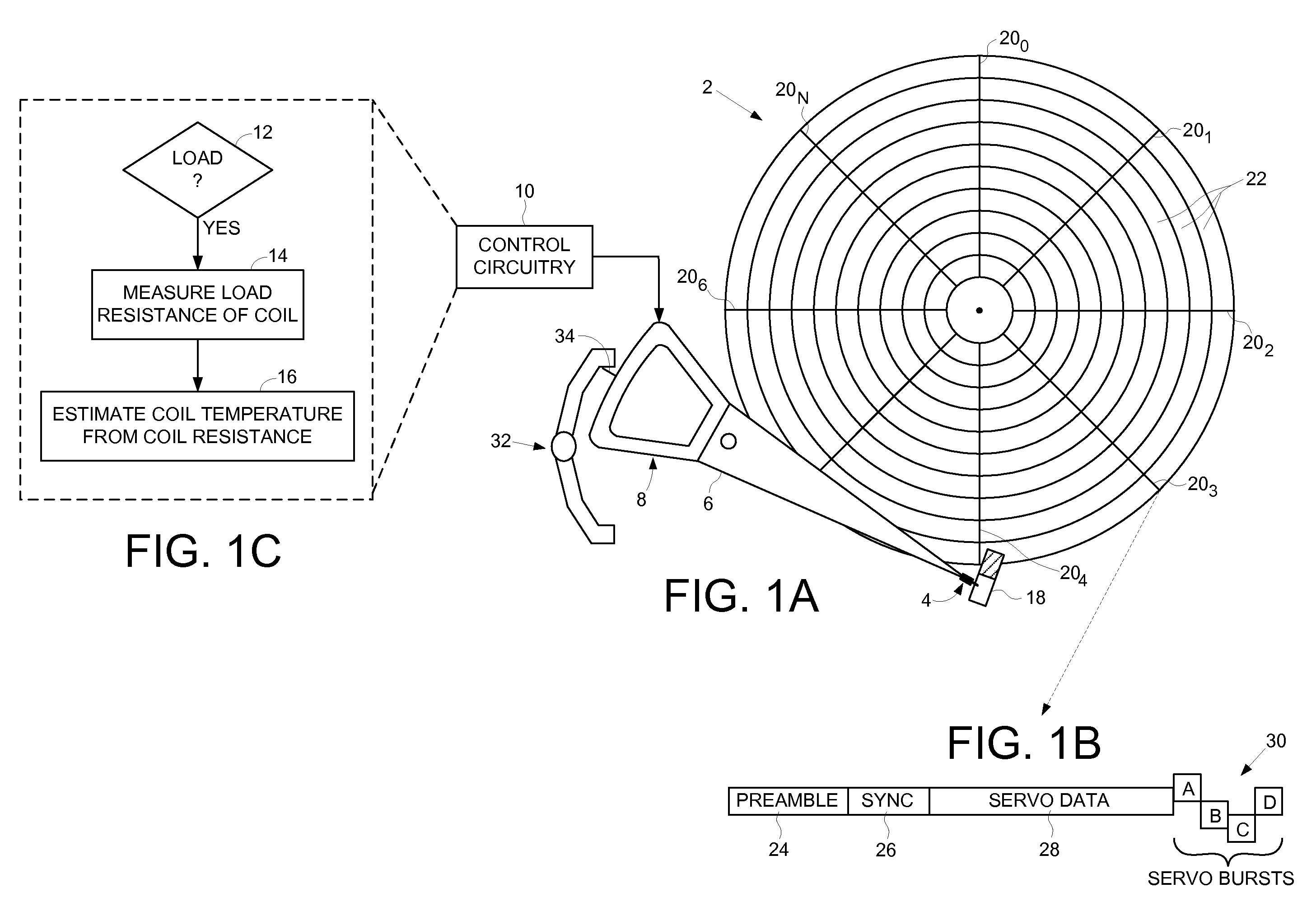
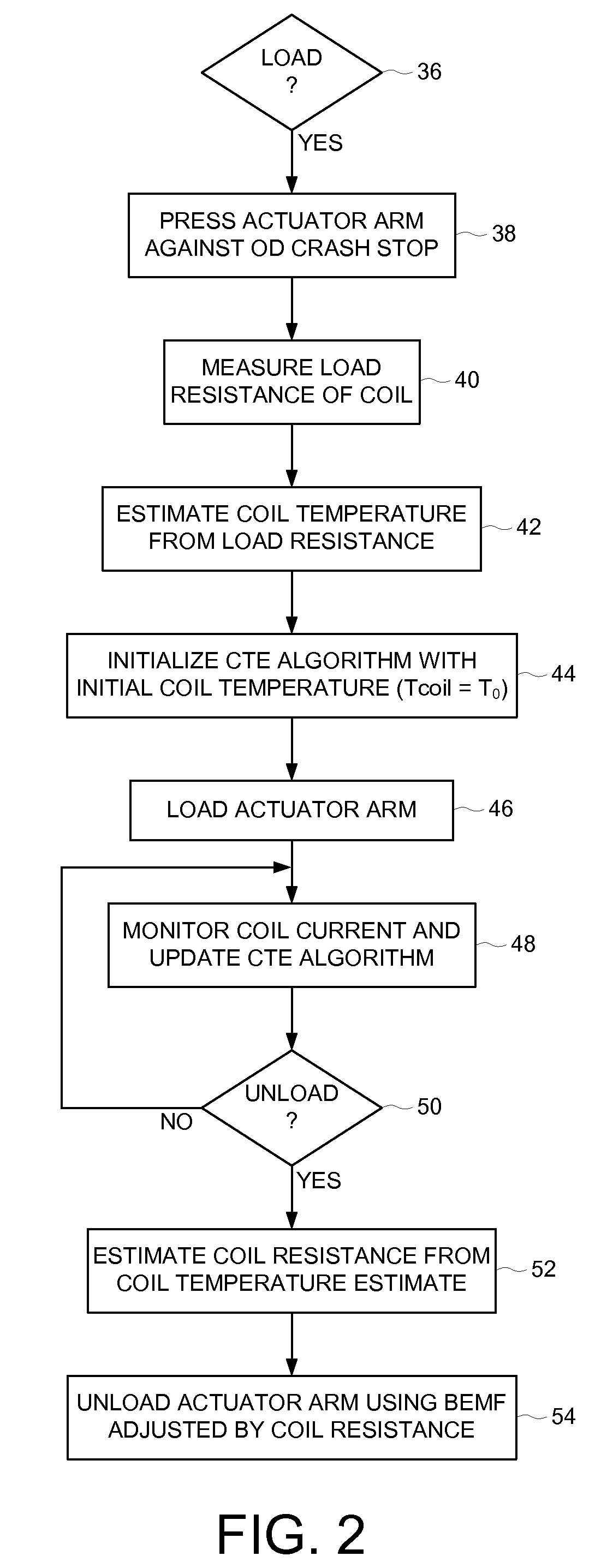
Disk drive initializing a coil temperature estimation algorithm using a resistance of the coil estimated during a load operation
InactiveUS7660067B1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLoad resistanceElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk, a head coupled to a distal end of an actuator arm, and a voice coil motor (VCM) operable to rotate the actuator arm about a pivot to actuate the head radially over the disk, wherein the VCM comprises a coil. Control circuitry within the disk drive measures a load resistance of the coil prior to executing a load operation, wherein the load operation moves the actuator arm off a ramp to load the head onto the disk. The load resistance of the coil is then converted into an initial coil temperature estimate.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
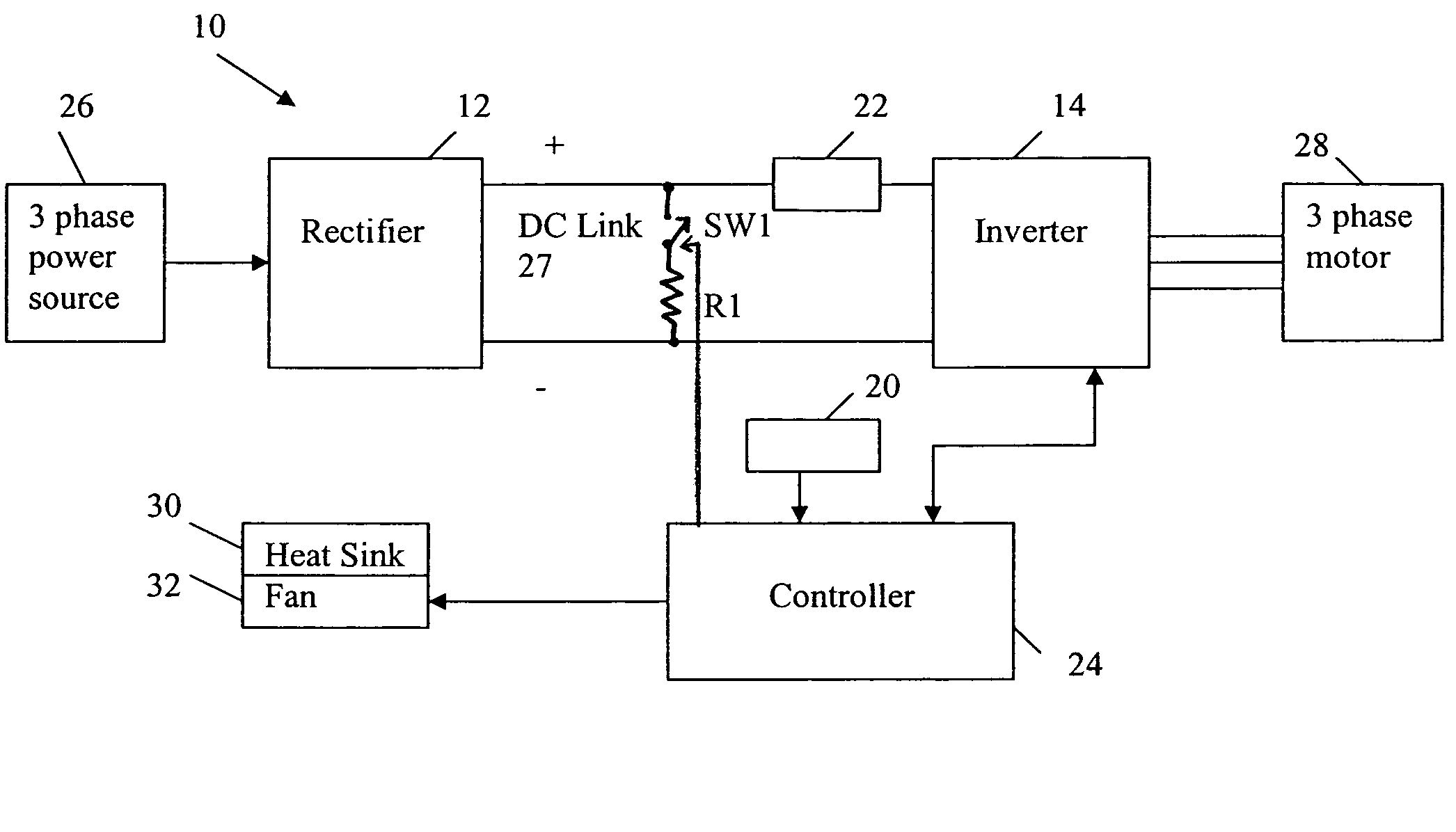
Thermal regulation of AC drive
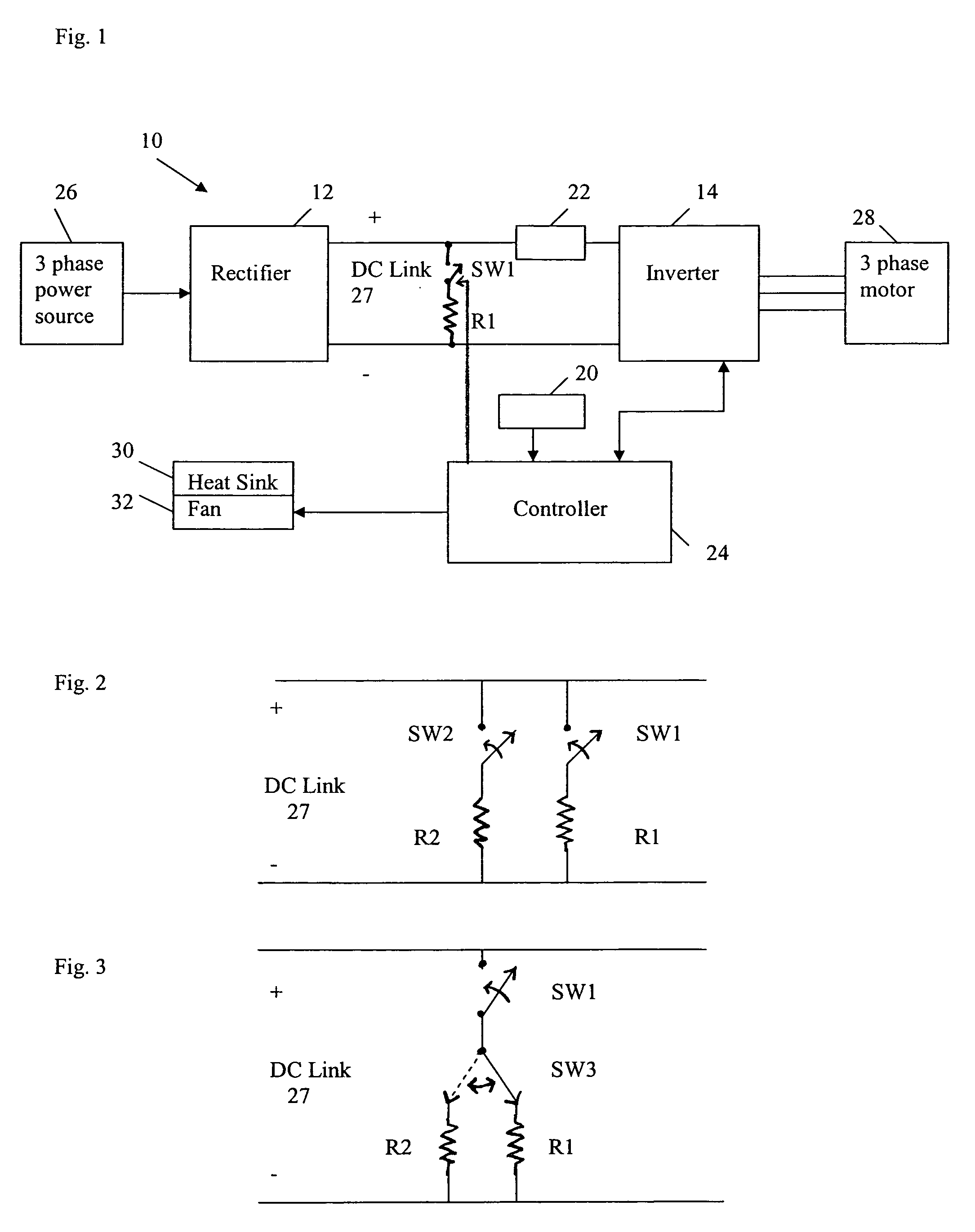
ActiveUS7312593B1Avoid condensationSimple and cost-effectiveTemperature control using analogue comparing deviceDC motor speed/torque controlEngineeringElectric power
An apparatus for the thermal regulation of an AC drive for providing power to a motor includes a temperature sensor producing a signal indicative of temperature, a heater resistor connectable across a DC link of the AC drive, and a first switch. A controller is operable to monitor the temperature signal and control the first switch to provide power via the DC link to the heater resistor if the sensed temperature is below a predetermined setpoint.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
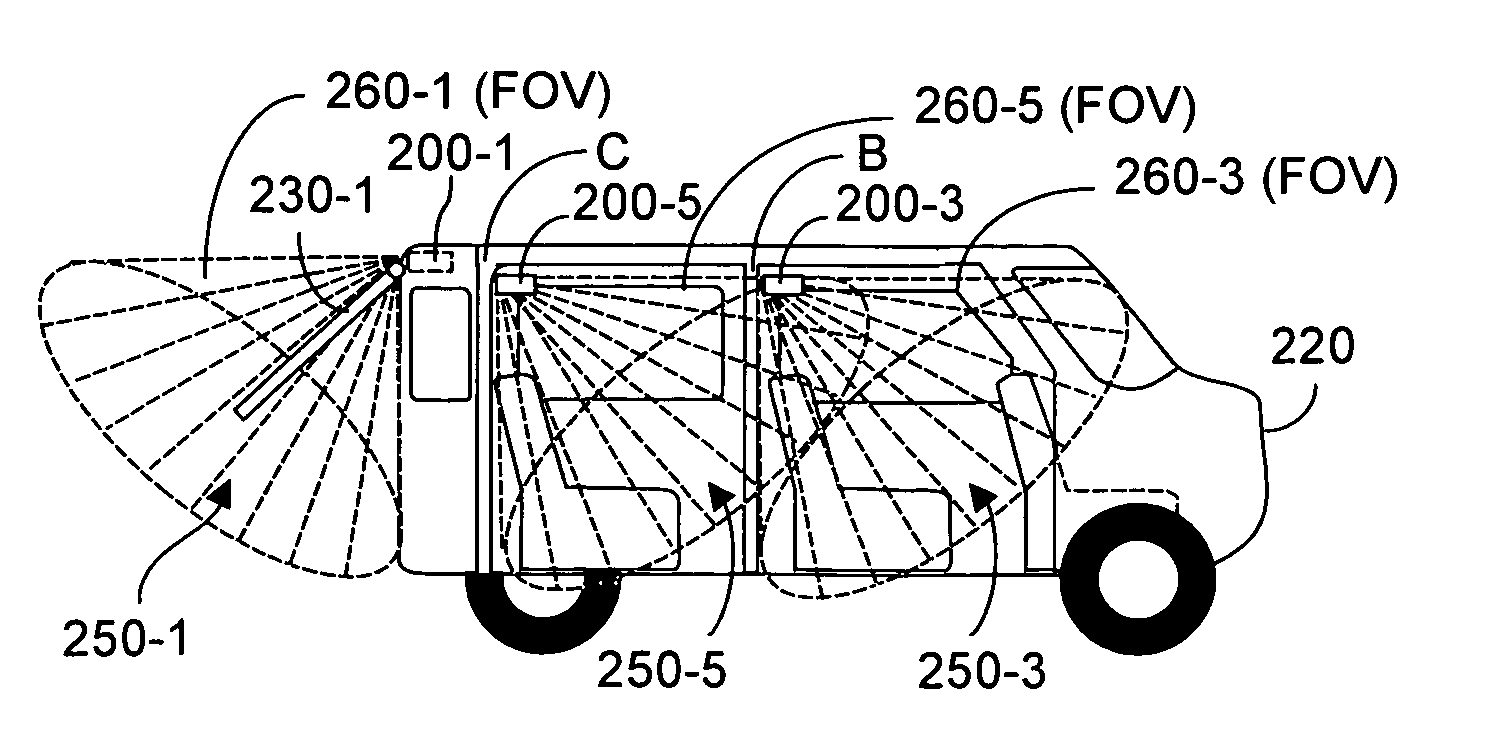
Contactless obstacle detection for power doors and the like
InactiveUS20110295469A1Quick fixImage enhancementDC motor speed/torque controlVehicle frameControl signal
Time-of-flight (TOF) three-dimensional sensing systems are deployed on or in a motor vehicle to image contact zones associated with potential contact between an avoidable object and the vehicle or vehicle frame and / or remotely controllable motorized moving door or liftgate. An algorithm processes depth data acquired by each TOF system to determine whether an avoidable object is in the associated contact zone. If present, a control signal issues to halt or reverse the mechanism moving the door. A stored database preferably includes a depth image of the contact zone absent any object, an image of the door, and volume of the door. Database images are compared to newly acquired depth images to identify pixel sensors whose depth values are statistically unlikely to represent background or the door. Pixels within the contact zone so identified are an object, and the control signal is issued.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com