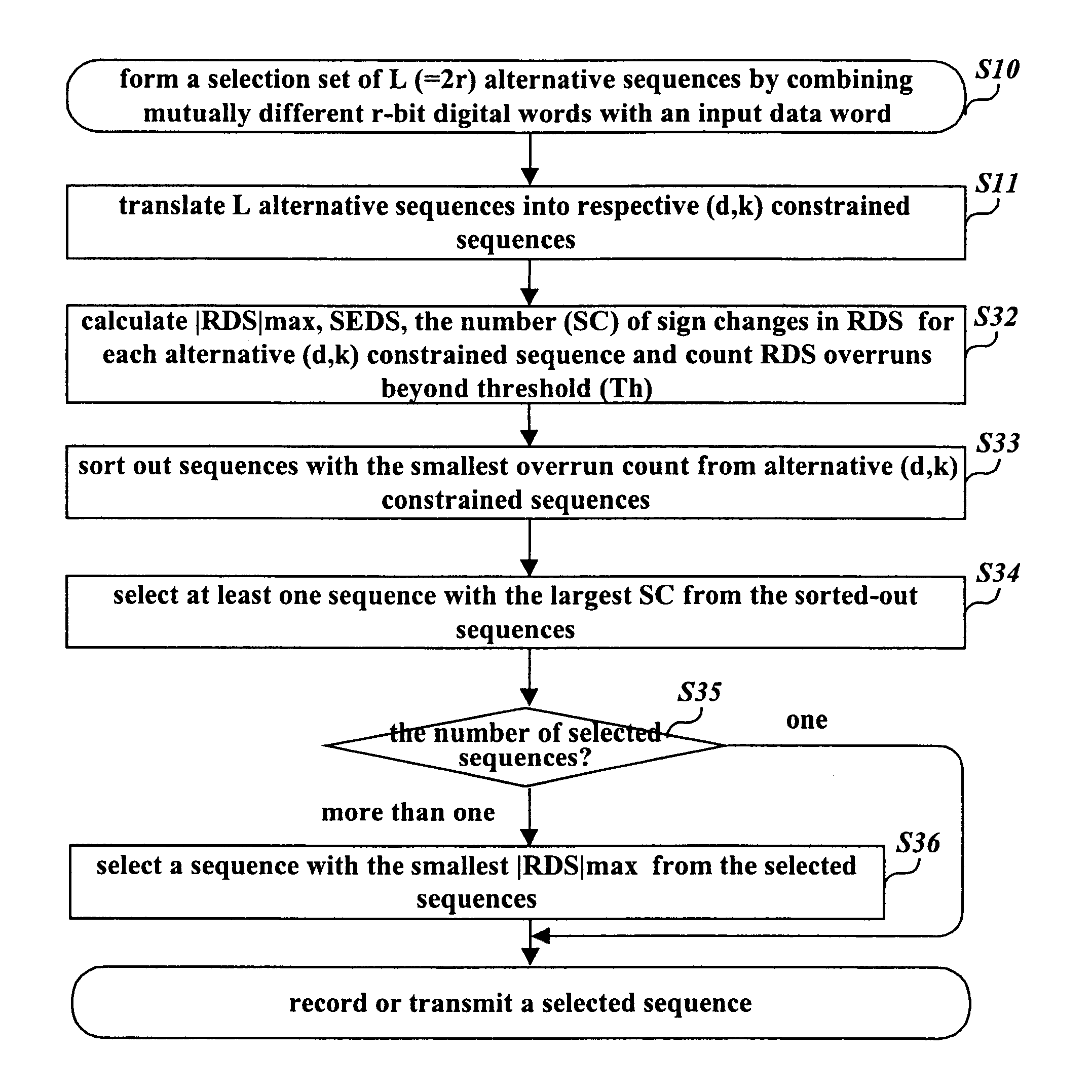
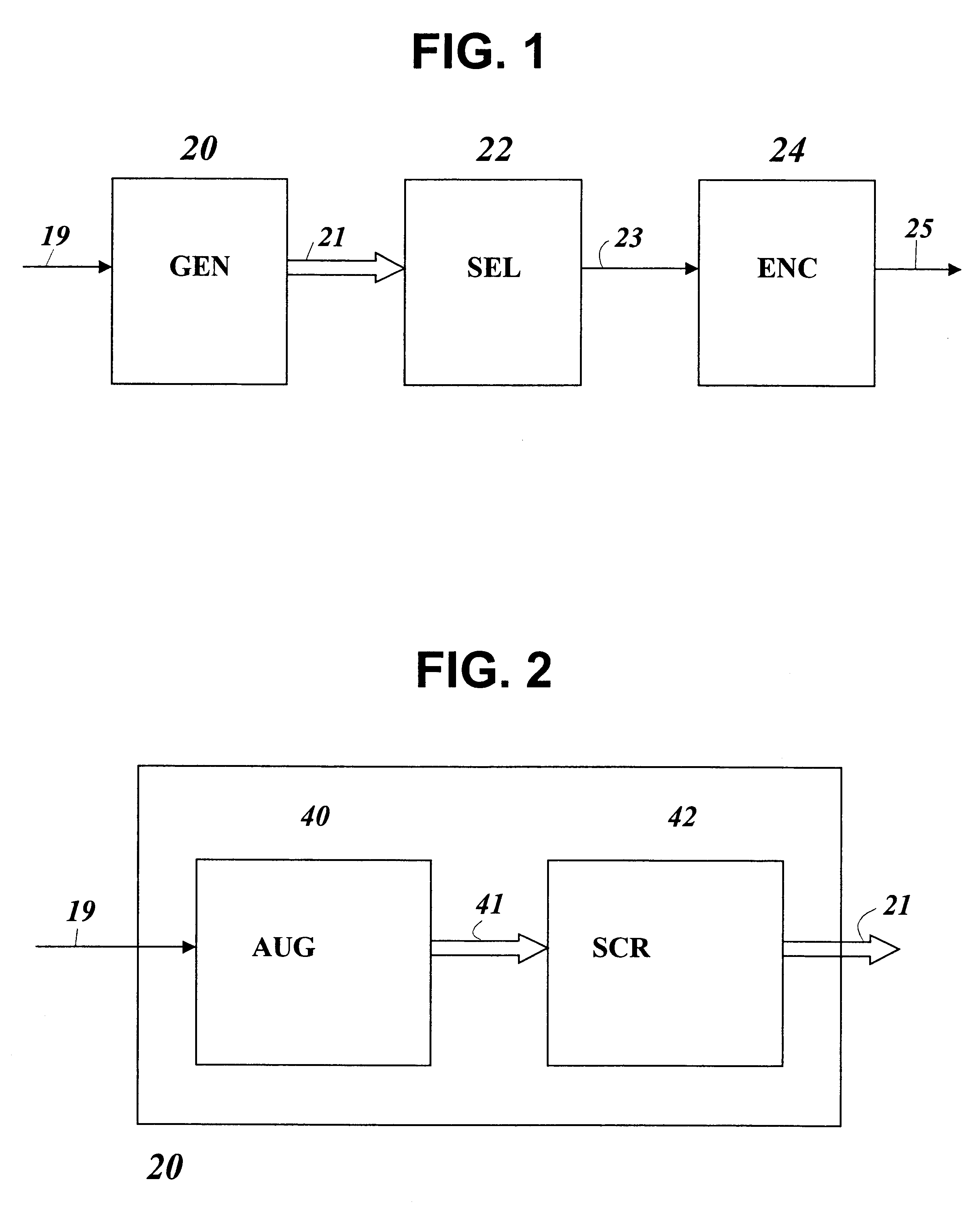
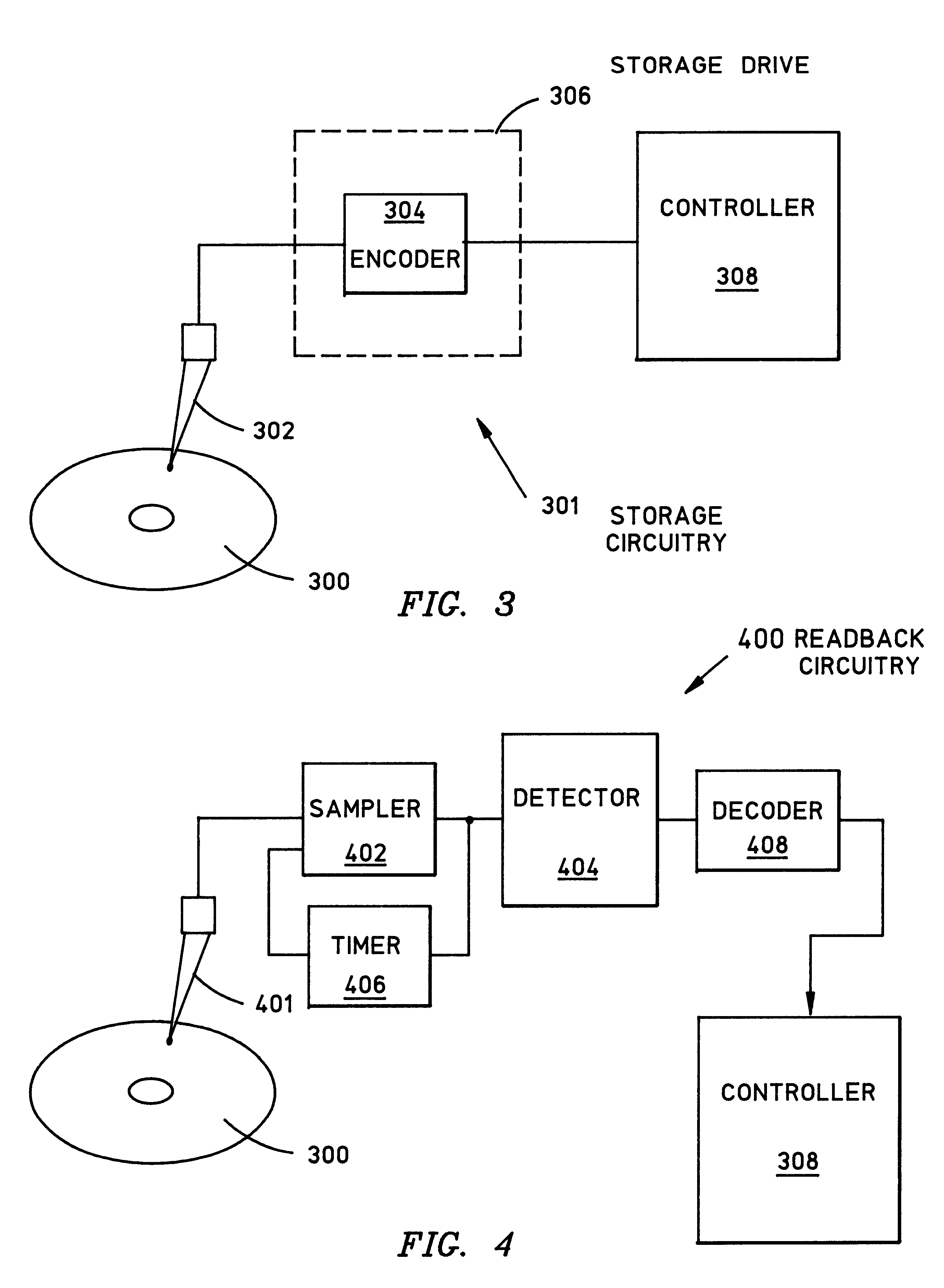
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
147results about "Signal processing using non self-clocking codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
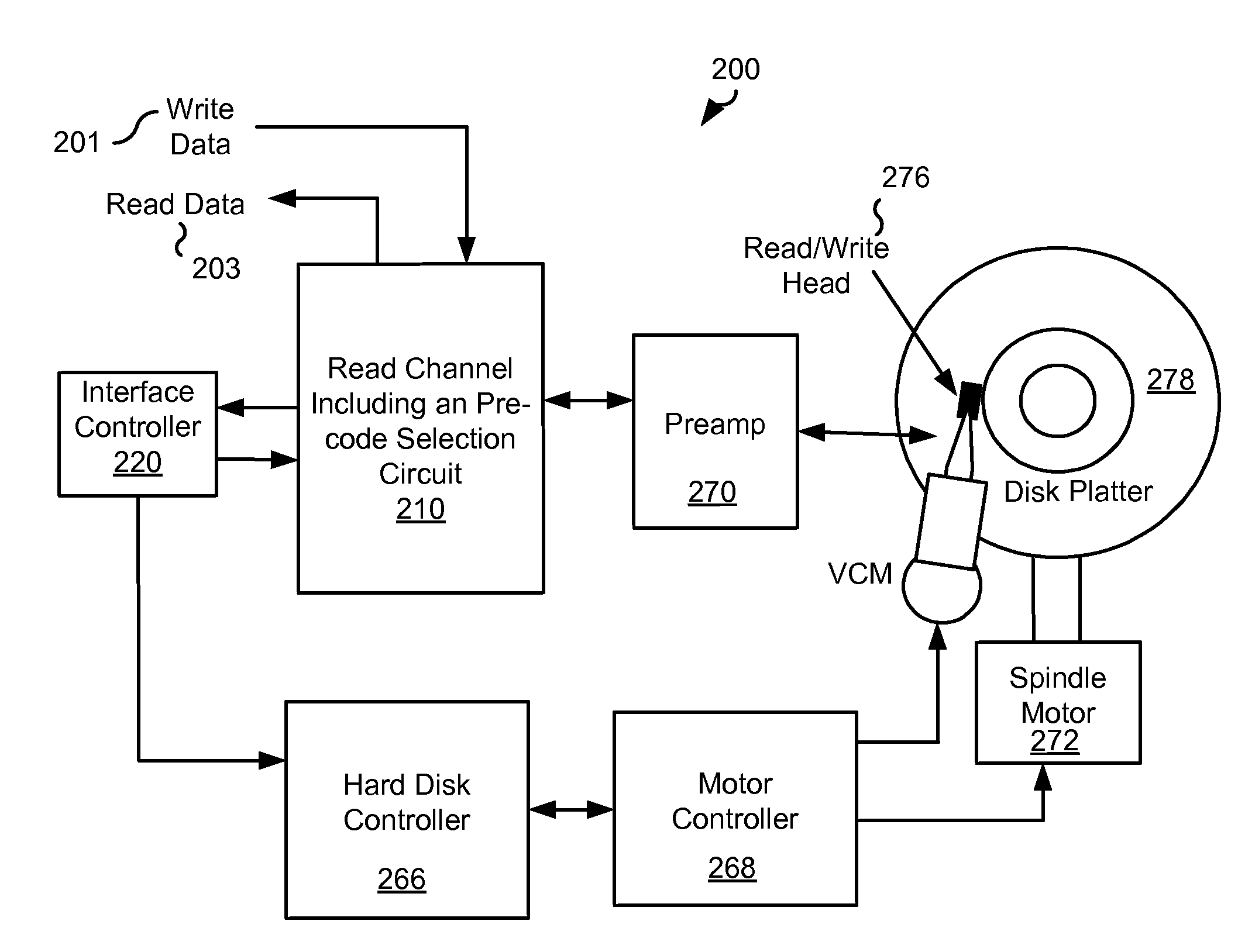
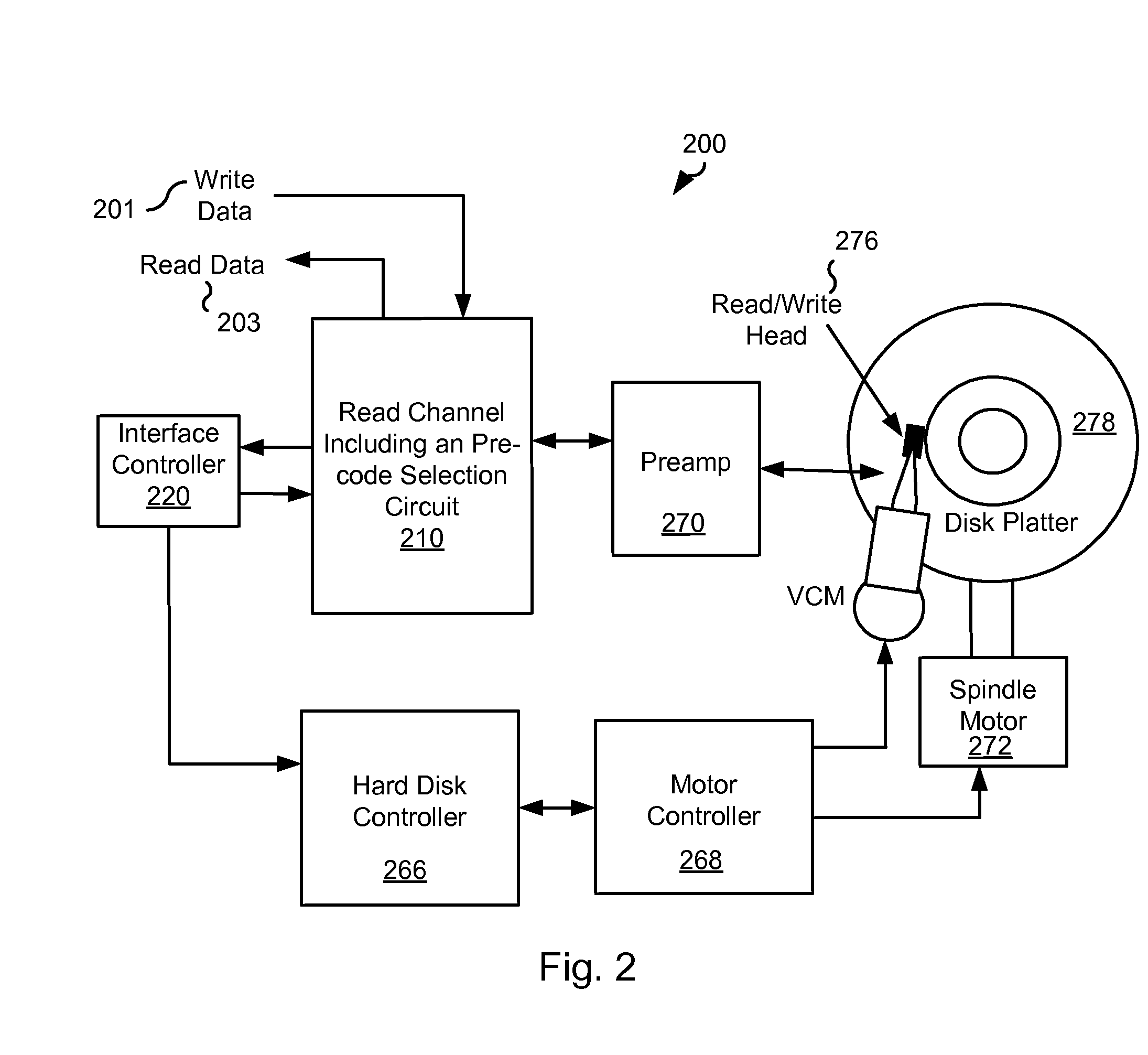
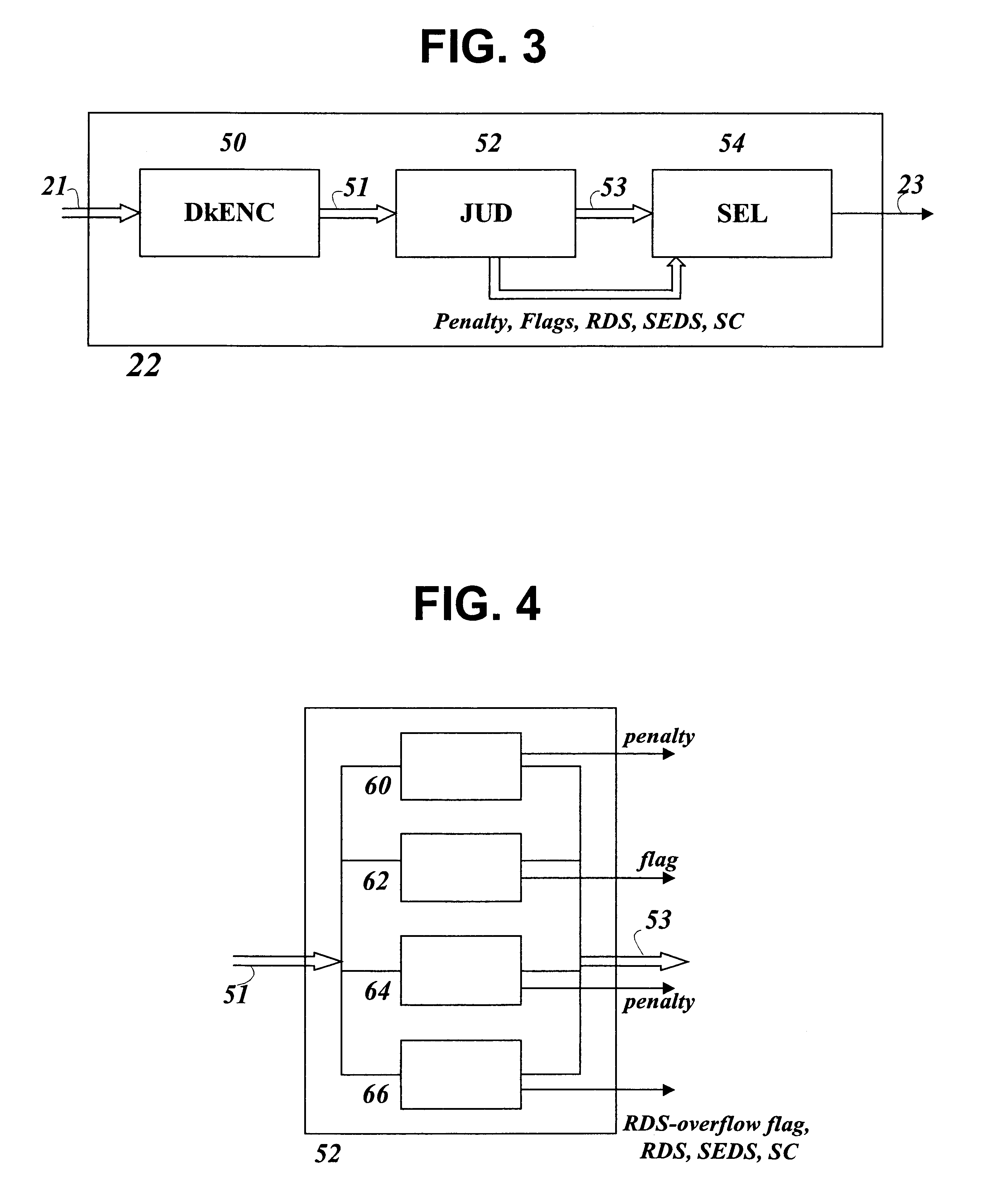
Systems and Methods for Data Pre-Coding Calibration
ActiveUS20120212849A1Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPrecodingDetector circuits
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for selecting between pre-coding and non-pre-coding. As an example, a data processing circuit is disclosed that includes: a first data detector circuit, a second data detector circuit, a first comparator circuit, a second comparator circuit, and a pre-code selection circuit. The first data detector circuit is selectably configurable to operate in a pre-coded state, and operable to apply a data detection algorithm on a data input to yield a first detected output. The second data detector circuit operable to apply the data detection algorithm to the data input to yield a second detected output without compensating for pre-coding. The first comparator circuit operable to compare the first detected output against a known input to yield a first comparison value, and the second comparator circuit operable to compare the second detected output against the known input to yield a second comparison value. The pre-code selection circuit is operable to determine a selectable configuration of the first data detector circuit based at least in part on the first comparison value and the second comparison value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
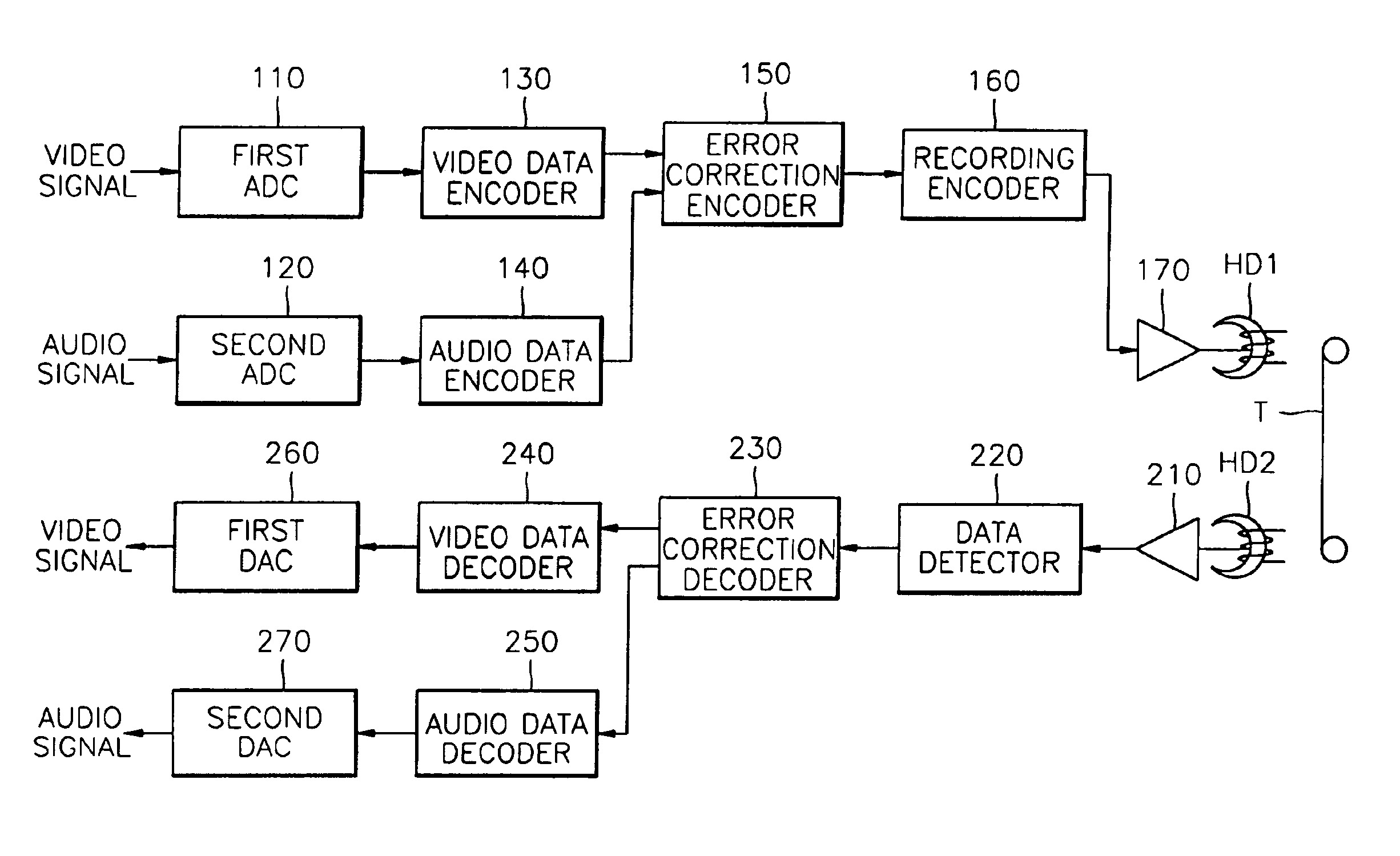
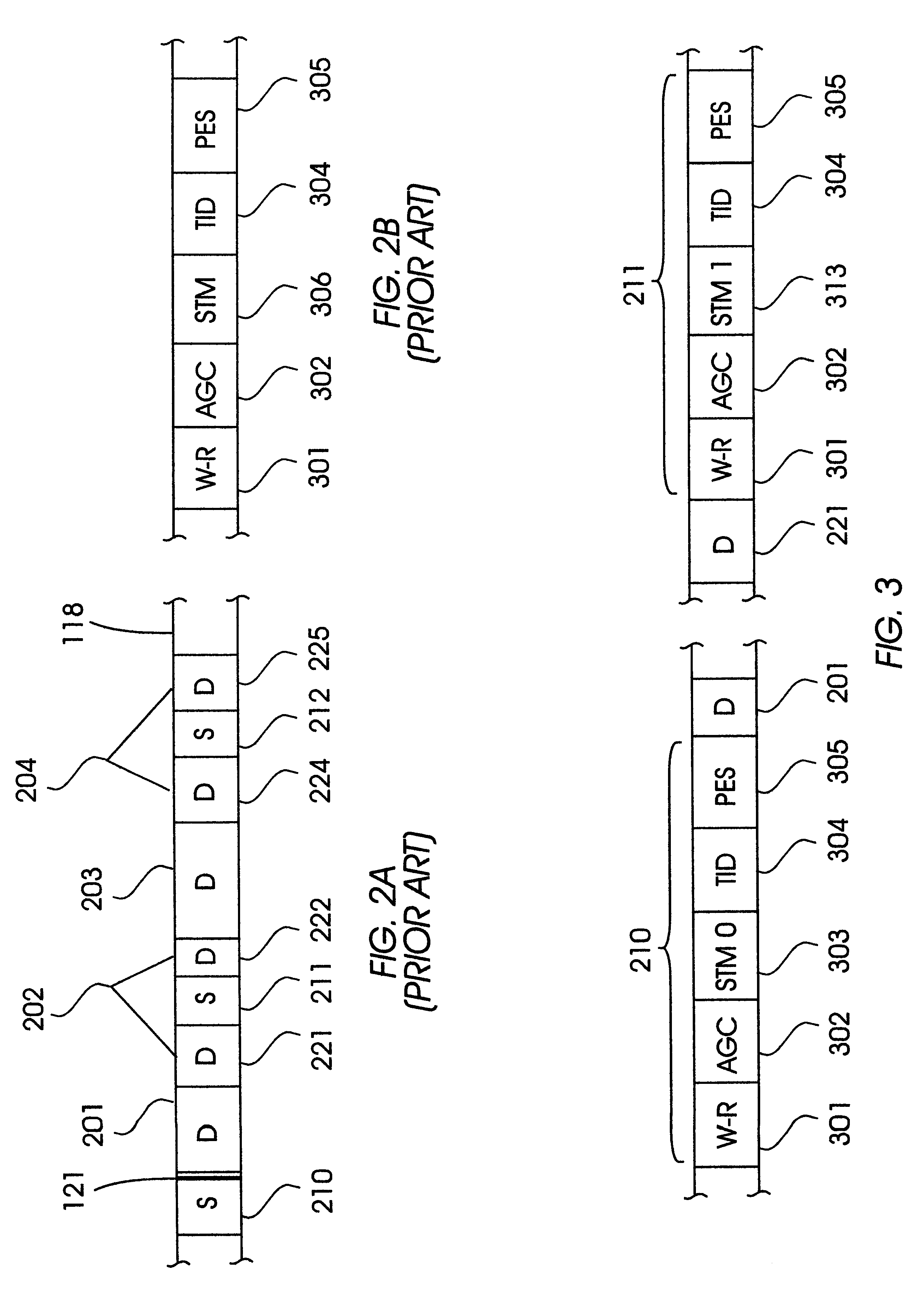
Digital recording and playback apparatus having MPEG CODEC and method therefor
InactiveUS6862402B2Increase speedTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMpeg standardsDigital recording
A digital recording and playback apparatus adopting an MPEG encoder and decoder, and a method thereof. The digital recording and playback apparatus includes: a first encoder for coding input video data in picture units, and outputting coded video data; a second encoder for coding input audio data and outputting coded audio data; a packetized elementary stream (PES) packetizer for packetizing the coded video data and audio data and user data into each PES, and outputting a video PES, audio PES and user PES; and a transport stream (TS) packetizer for multiplexing the video PES, audio PES and user PES into a TS. The digital recording and playback apparatus can be compatible with a digital television or multimedia applications adopting the MPEG standard, and can perform editing in picture units as well as high-speed search.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
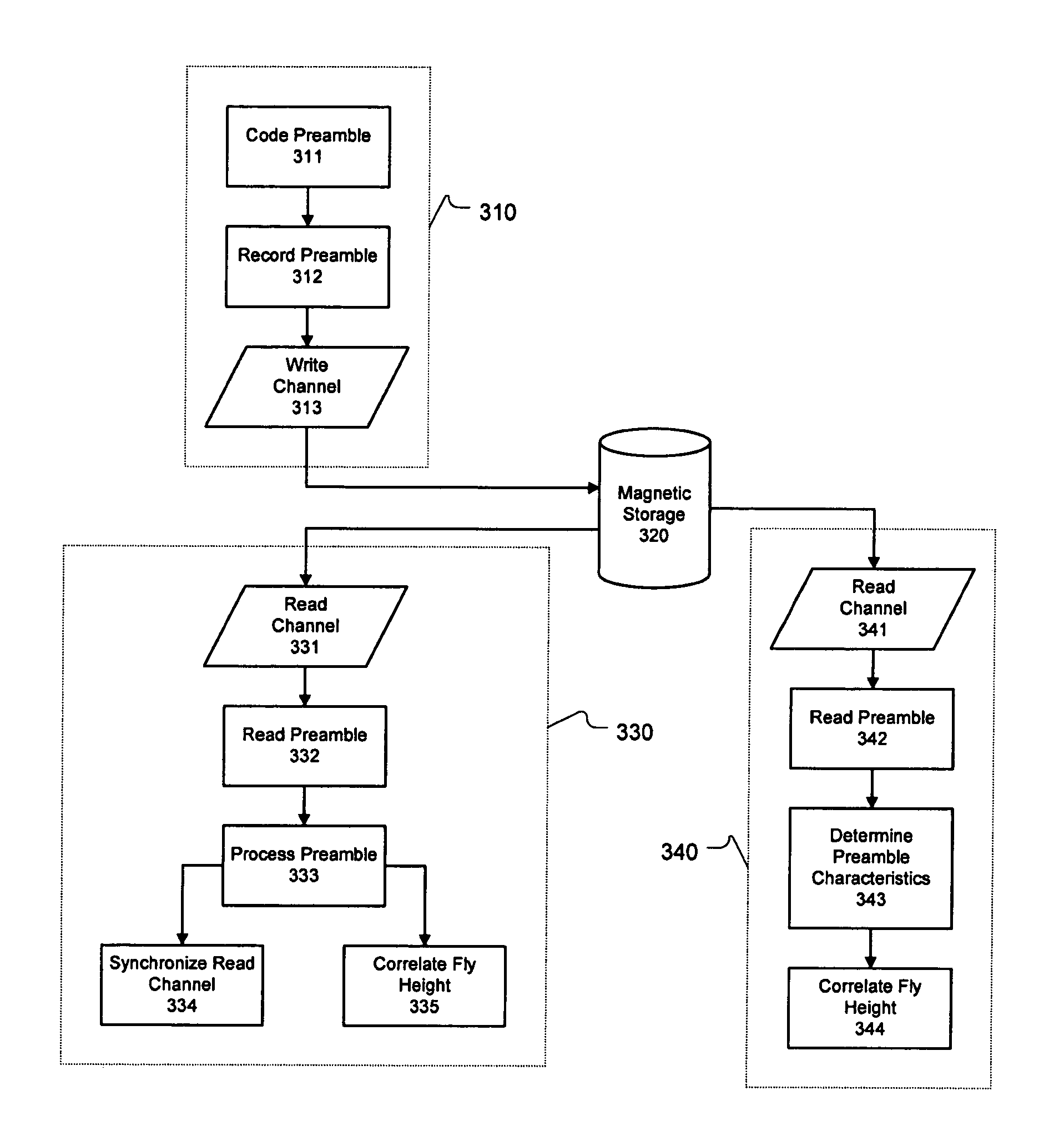
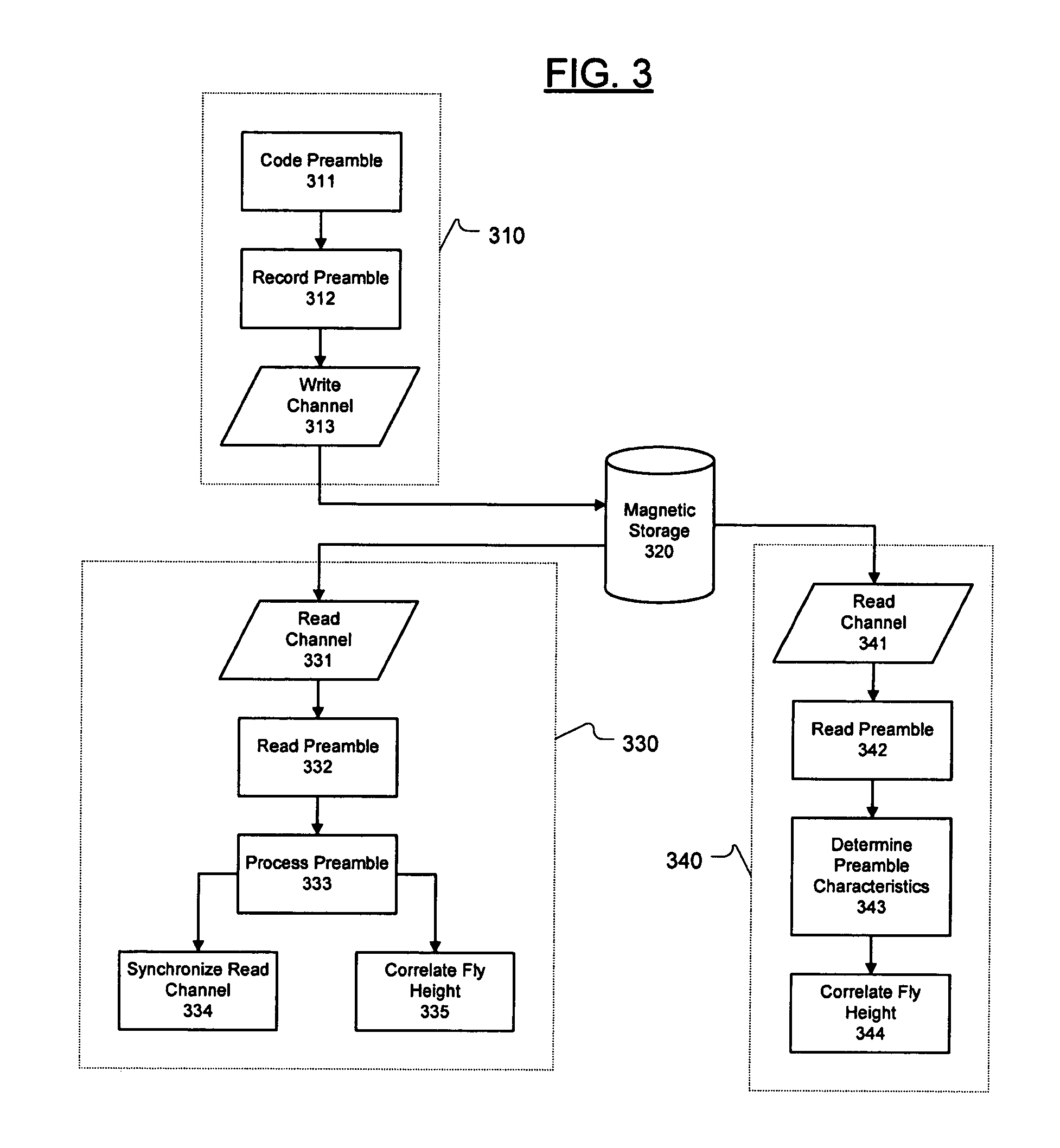
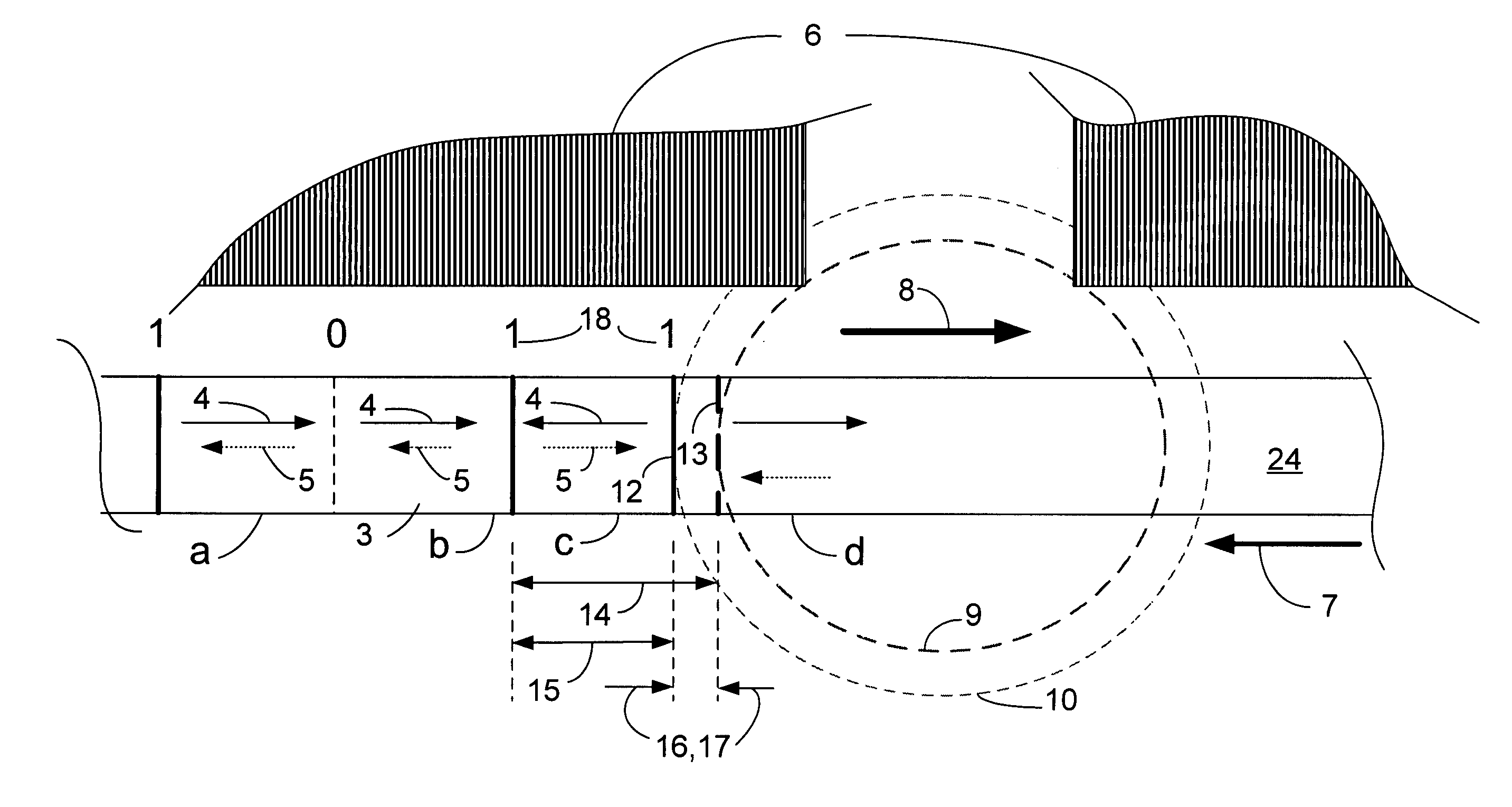
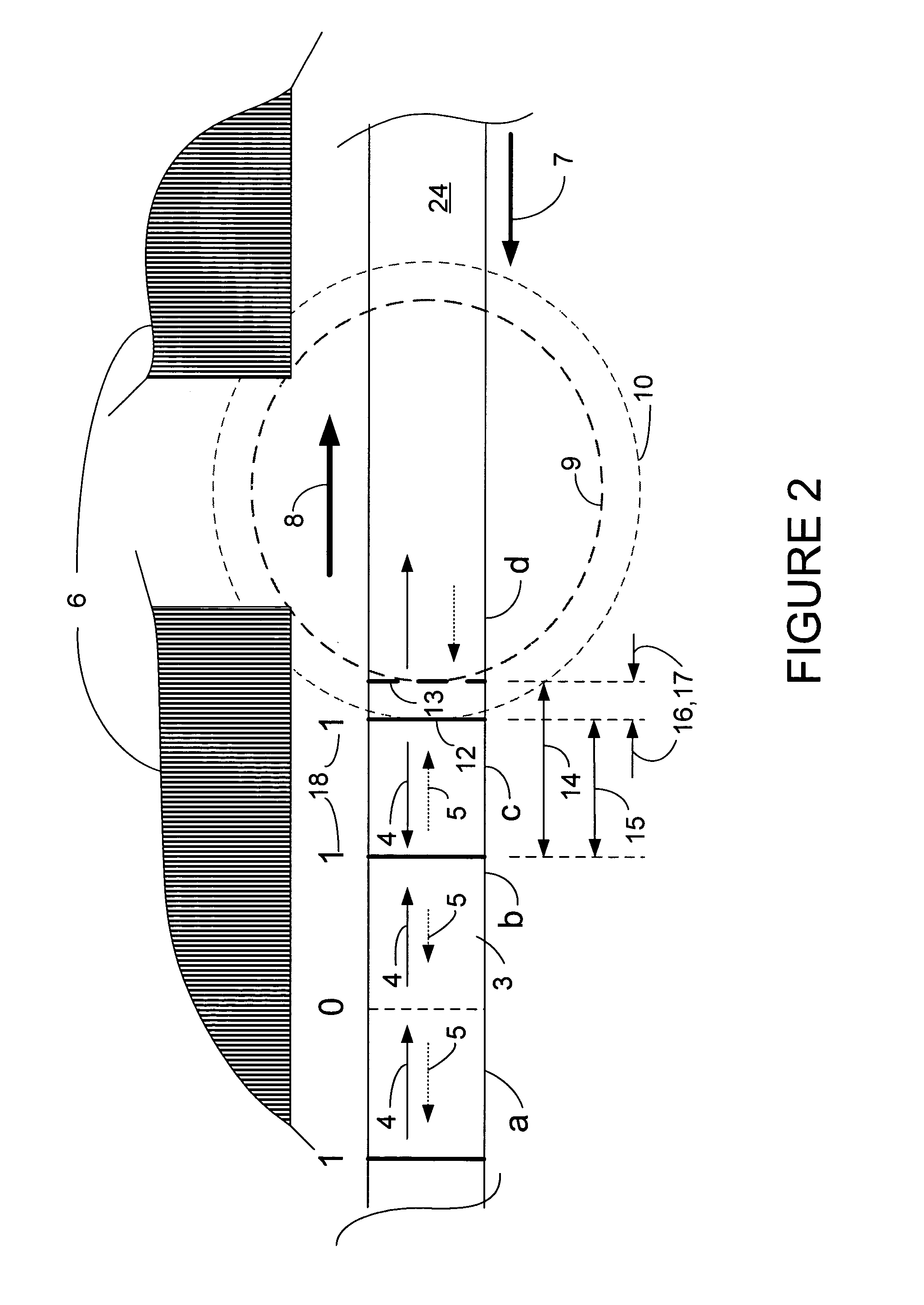
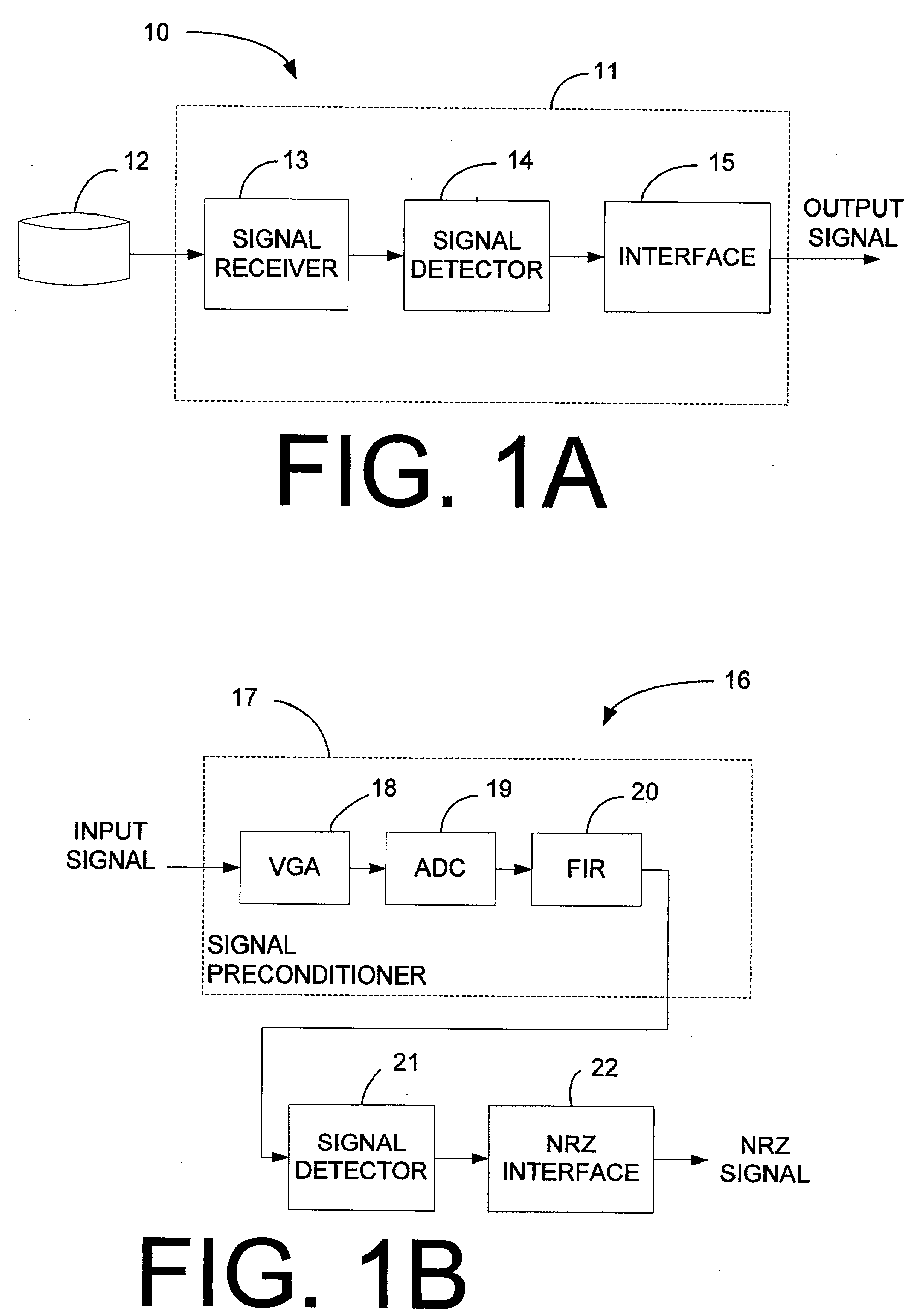
Methods, circuits, apparatus, and systems for read channel synchronization and/or fly height measurement
ActiveUS7715135B1High signal resolutionGood synchronizationDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveHarmonic
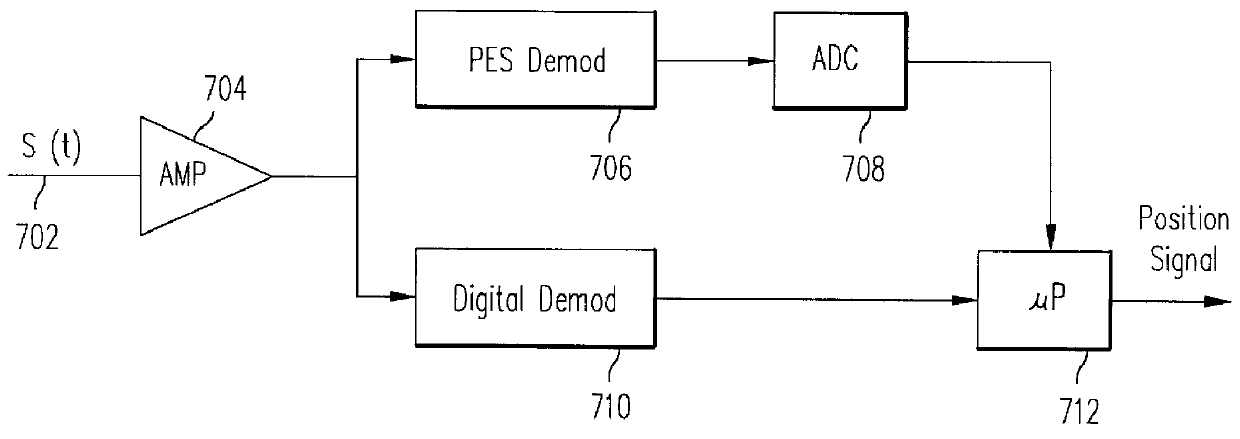
Methods, circuits, and systems for processing a preamble field in a read channel (e.g., in a magnetic storage device such as a hard disk drive). The methods generally include the steps of (a) reading the preamble field, wherein the preamble field comprises a repetitive bit pattern having a logical transition every x bit periods, where x is an integer of at least 3 when d is 0 or 1, or where x is an integer of at least d+2 when d is greater than 1, and (b) processing the repetitive bit pattern. The methods may further relate to processing the preamble for synchronization with the read channel and / or for measuring the fly height of a read / write head. The invention also relates to methods of enabling read channel synchronization and / or fly height measurement. The circuitry for fly height measurement generally includes (a) reading logic configured to read a preamble field from a read channel, wherein the preamble field comprises a repetitive bit pattern, (b) determination logic configured to determine a characteristic of the repetitive bit pattern, and (c) correlation logic configured to correlate the characteristic to the fly height. The systems generally comprise those that include a circuit embodying one or more of the inventive concepts disclosed herein. The present invention advantageously provides improved resolution of signals resulting from the preamble fields and of harmonics of said signals, and enables fly height measurement and improved channel synchronization without consuming dedicated tracks, platters, etc. on a magnetic recording medium.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Command switching for multiple initiator access to a SATA drive
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
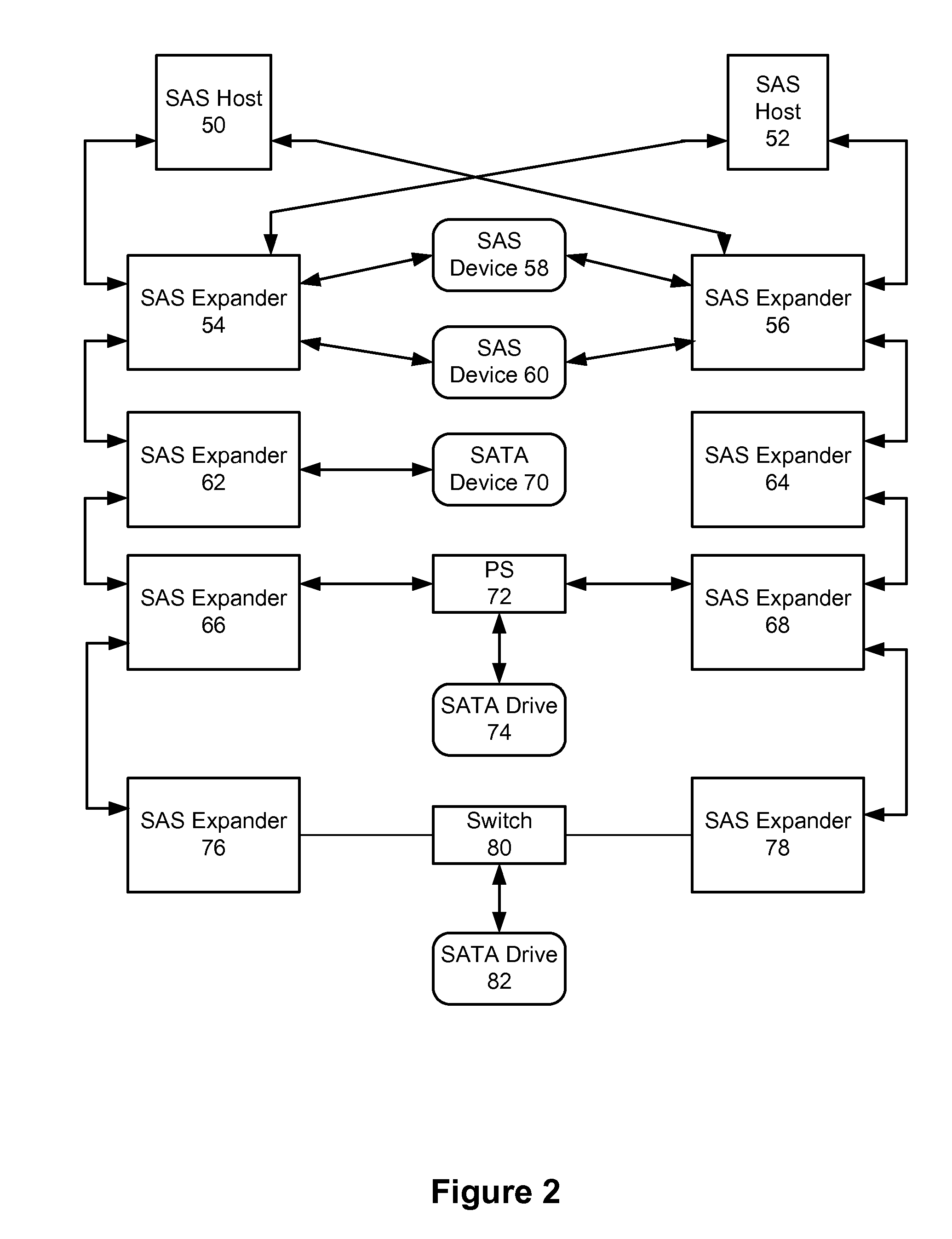
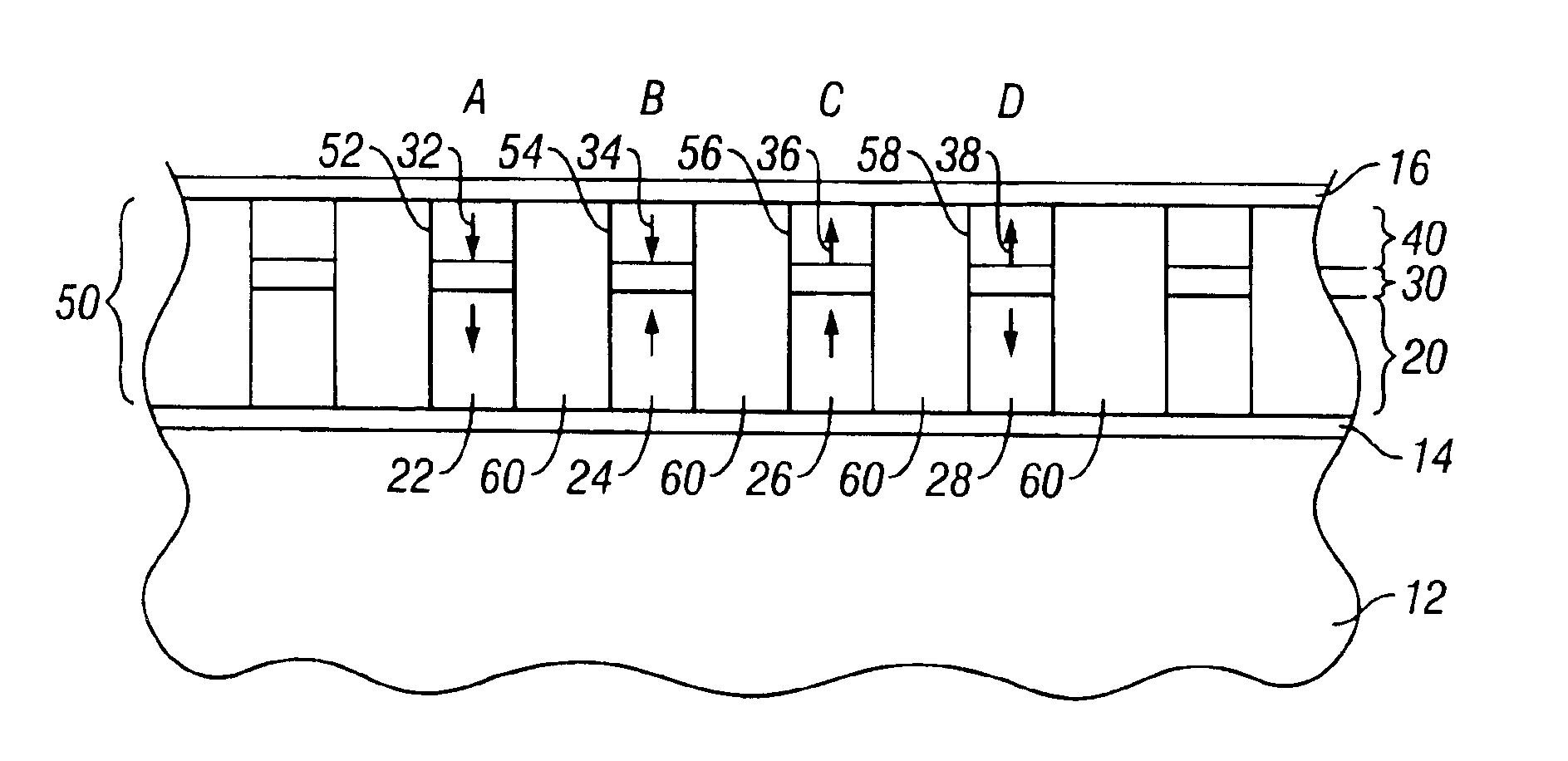
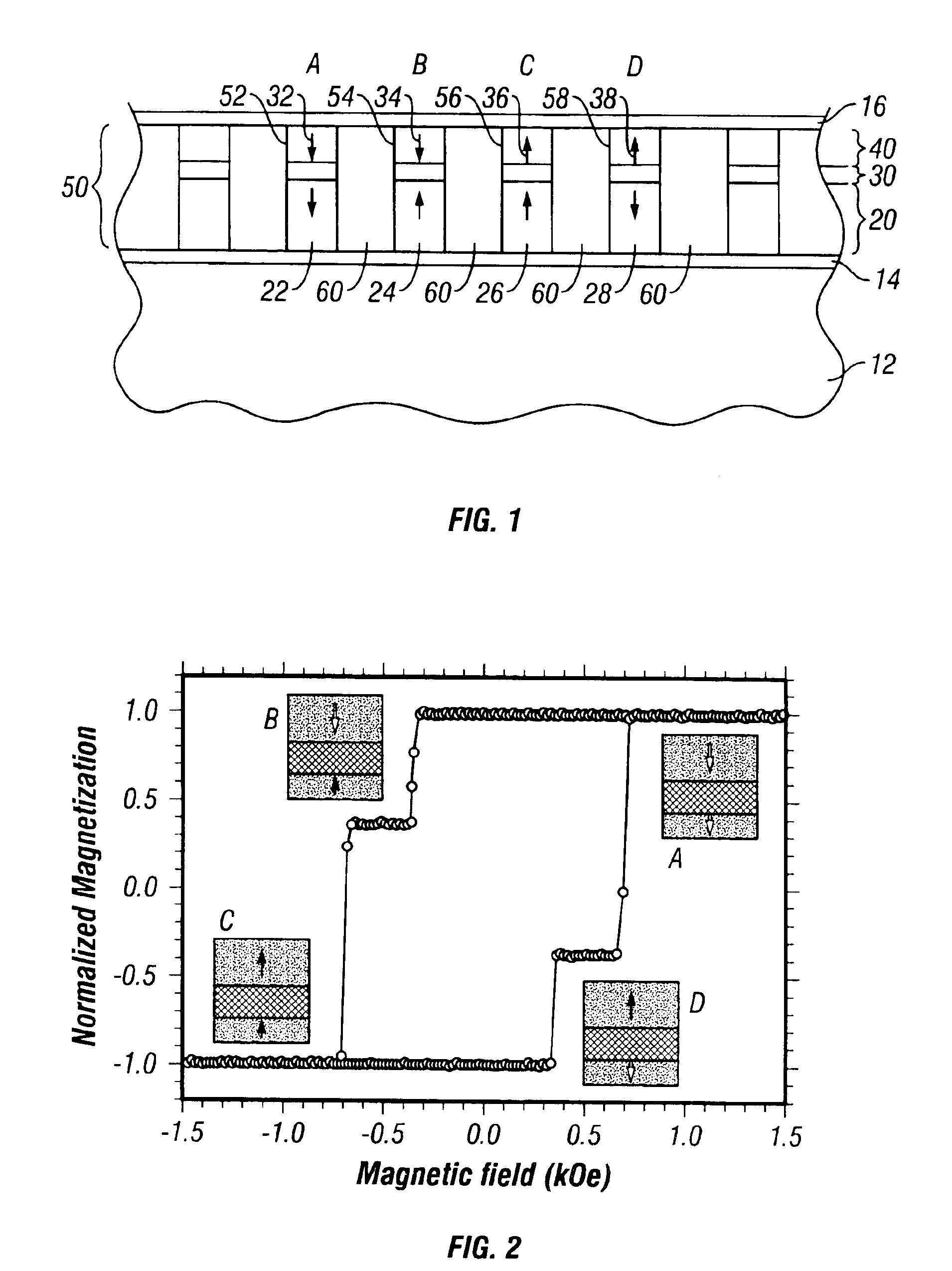
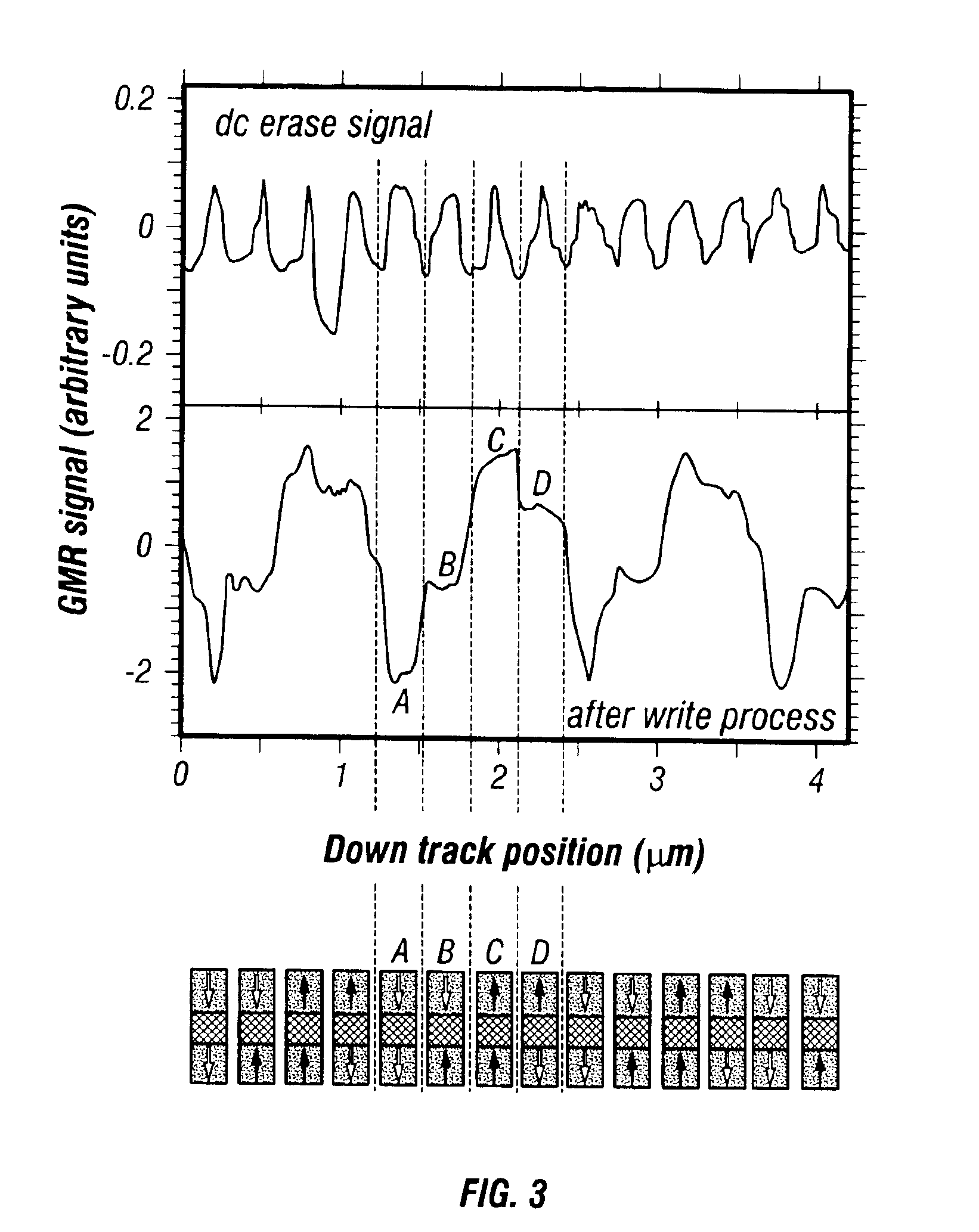
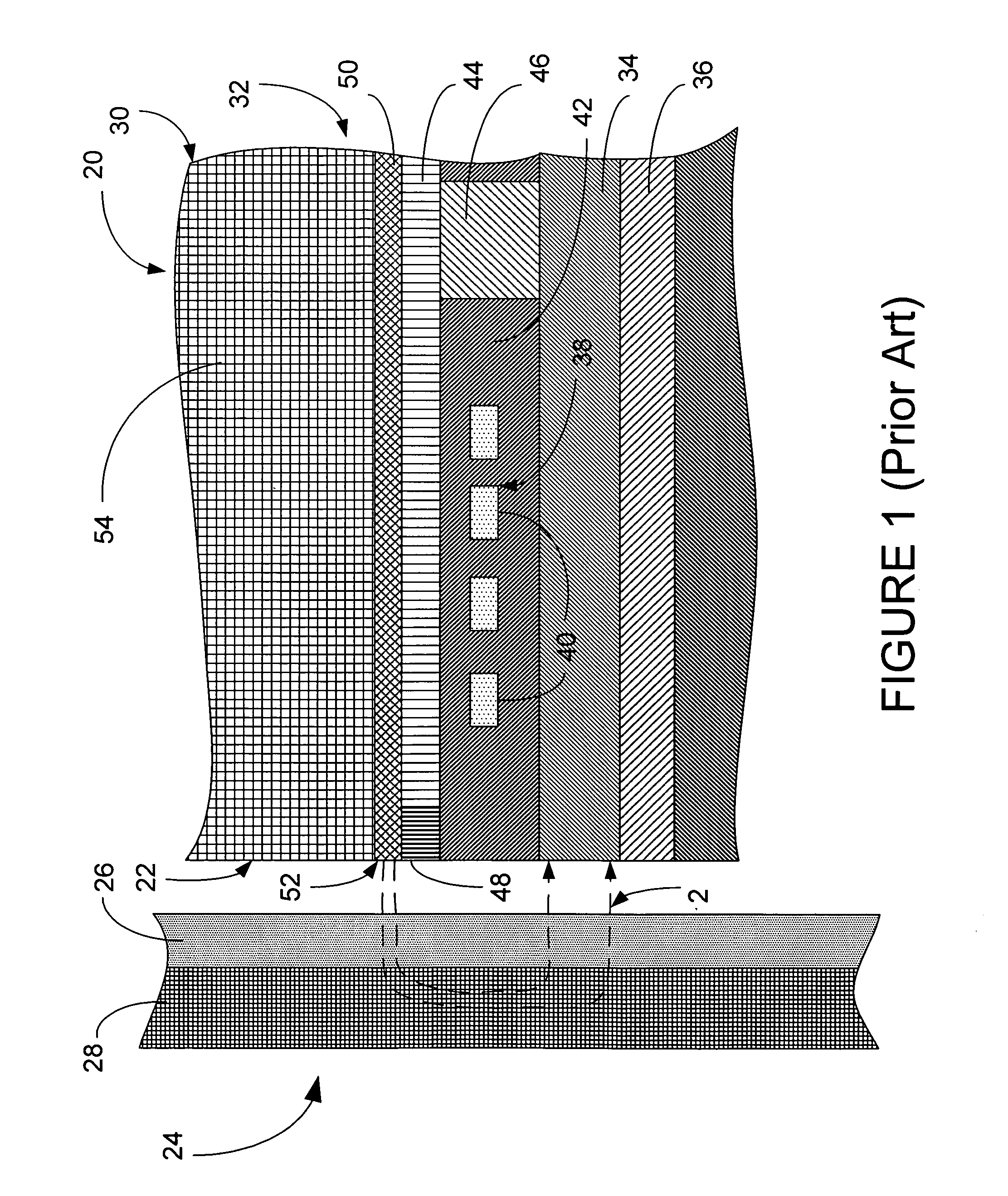
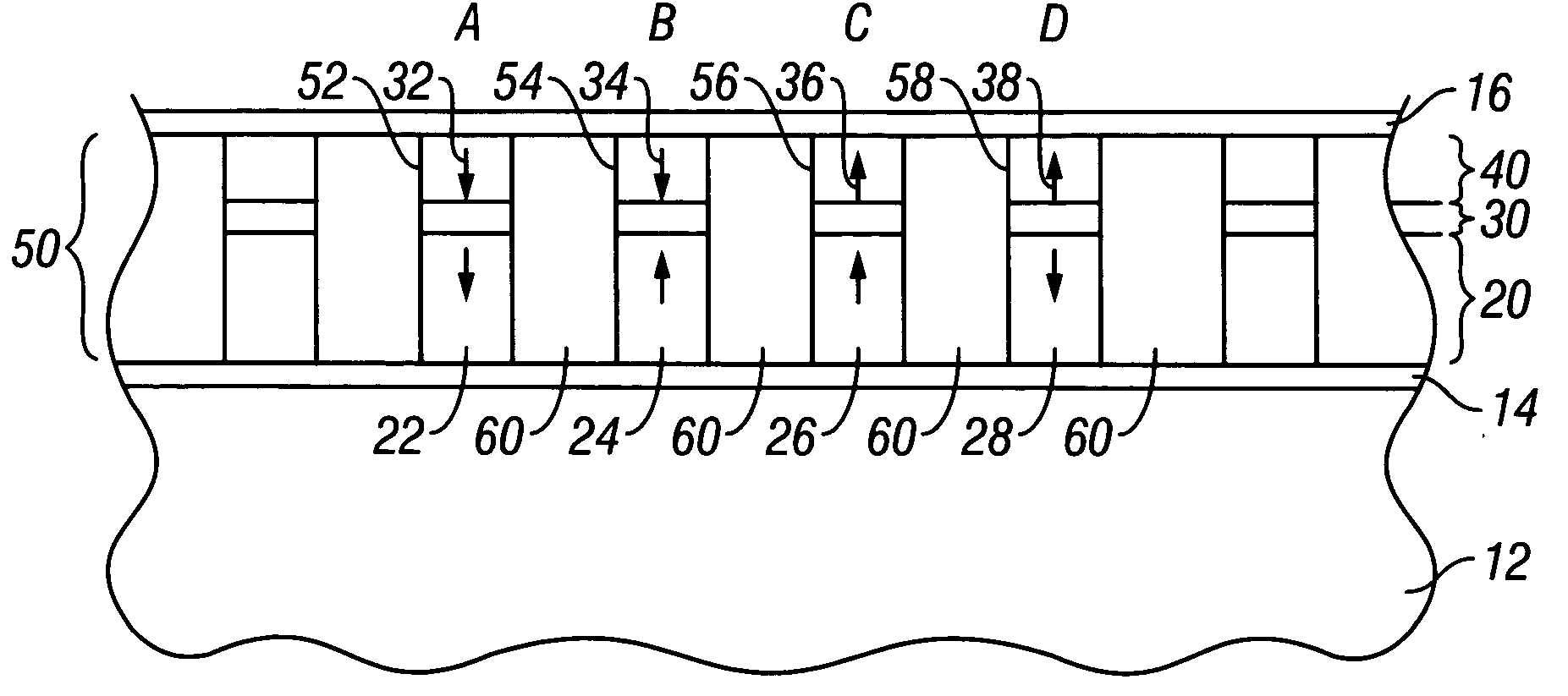
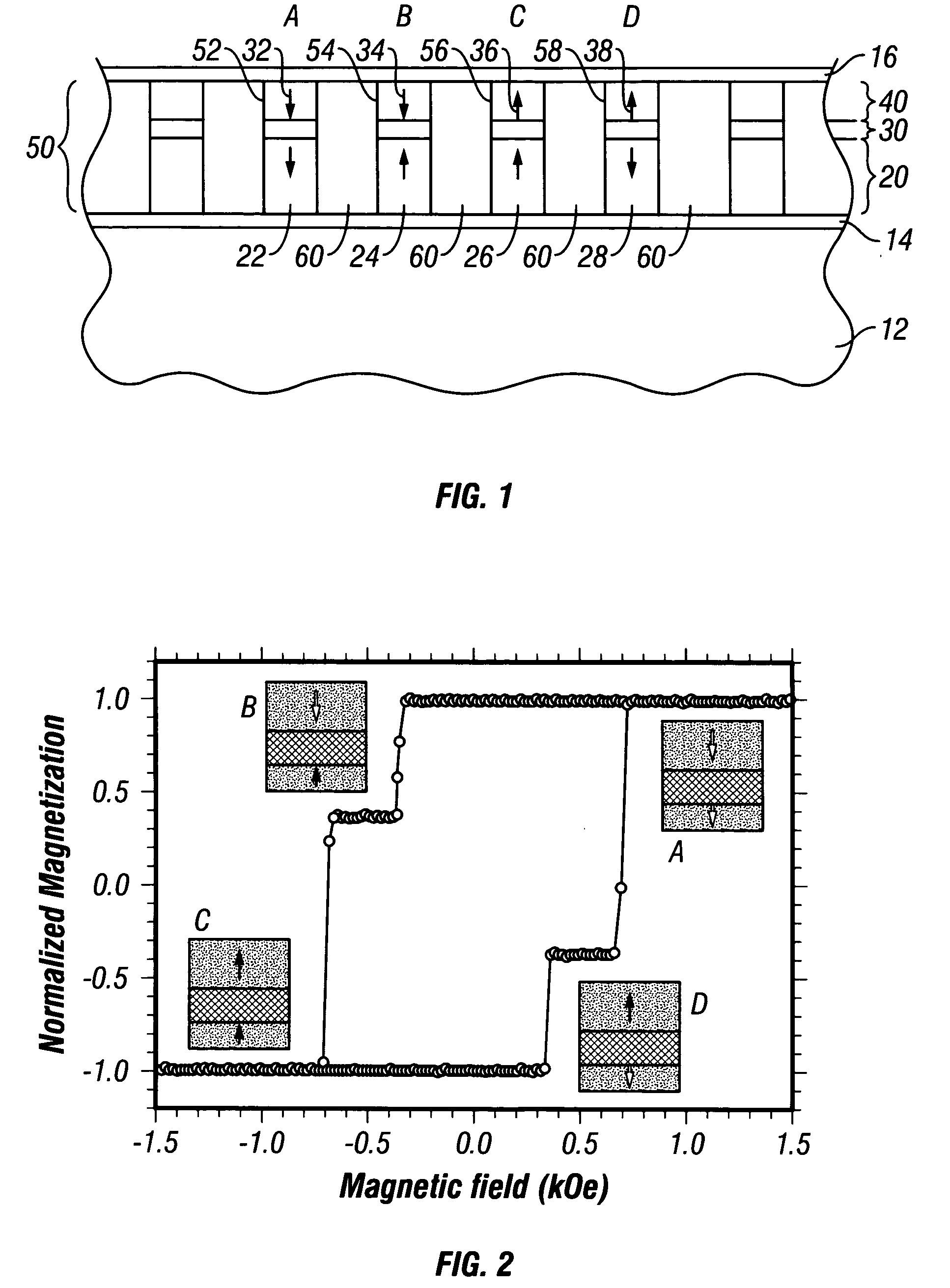
Magnetic recording system with patterned multilevel perpendicular magnetic recording
InactiveUS6906879B1Improve noiseImprove recording densityNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersMagnetic momentRecording system
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
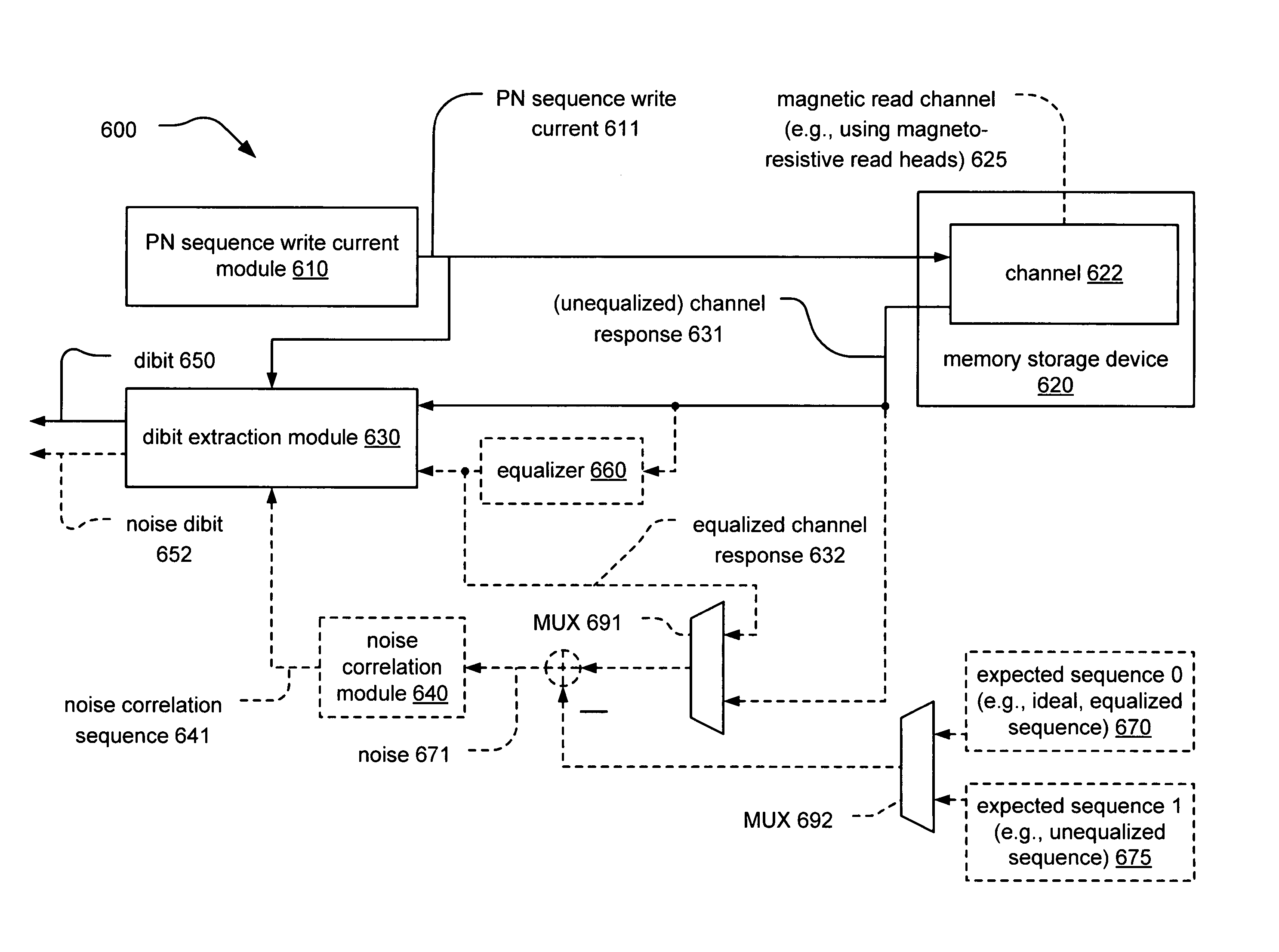
Dibit extraction
A novel means for performing dibit extraction is presented. Any one of an unequalized signal dibit, equalized signal dibit, or noise dibit can be extracted. Instead of using the correlation properties of a PN (Pseudo-Noise) sequence to approximate a PN deconvolution sequence, the use of the actual deconvolution sequence (i.e., PN sequence that includes values of +k and 0, where k is oftentimes 1) is employed so that no approximations are needed. The resulting estimate of the channel is therefore very accurate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Disk drive with sector numbers encoded by sequences of sector types
InactiveUS6288861B1Disc-shaped record carriersOther error detection/correction/protectionControl theoryHamming distance
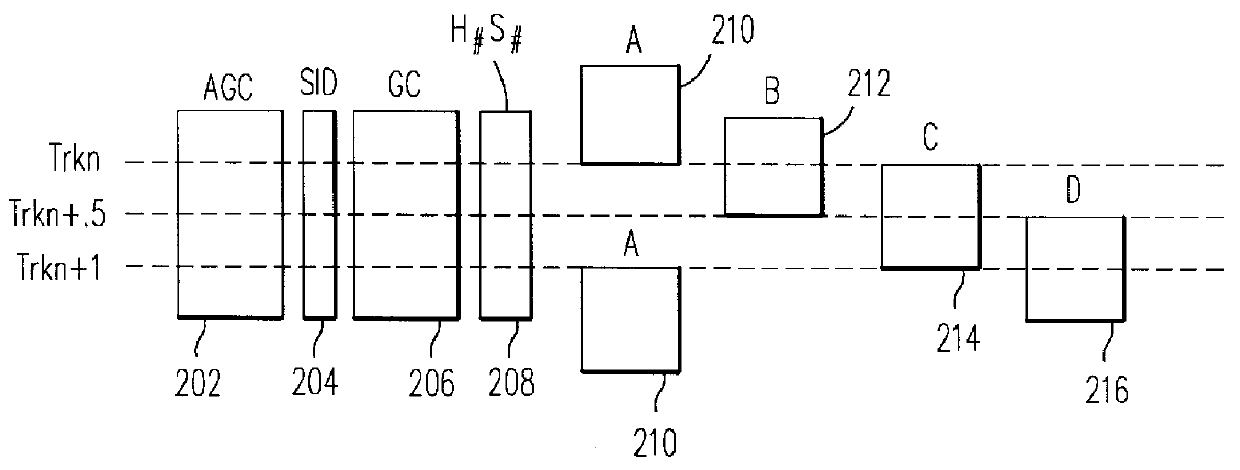
A magnetic recording disk drive has head positioning servo sectors with servo sector numbers (SSNs) that are not recorded on the disk. The SSNs are encoded through the use of multiple servo sector types that are arranged in a specific sequence around the data tracks. The different servo sector types are identified by unique types of servo timing marks (STMs), which are used to locate the servo sectors. The SSNs that are used to identify the servo sectors on the track form a set or code of m fixed n-bit patterns. A SSN is determined when the STM types read from n sequential servo sectors match one of the fixed SSN pattems. A set or code of m servo sectors, where each servo sector is identified by a unique SSN pattern having length n, is denoted as an (m,n,d) code, where d is referred to as the minimum Hamming distance of the code. The Hamming distance between two patterns refers to the number of locations that are different between the two pattems.
Owner:IBM CORP
Write precompensation method for perpendicular magnetic recording
InactiveUS7126773B1Few problemRecord information storageDigital recordingComputer scienceData conversion
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for encoding digital servo information in a servo burst
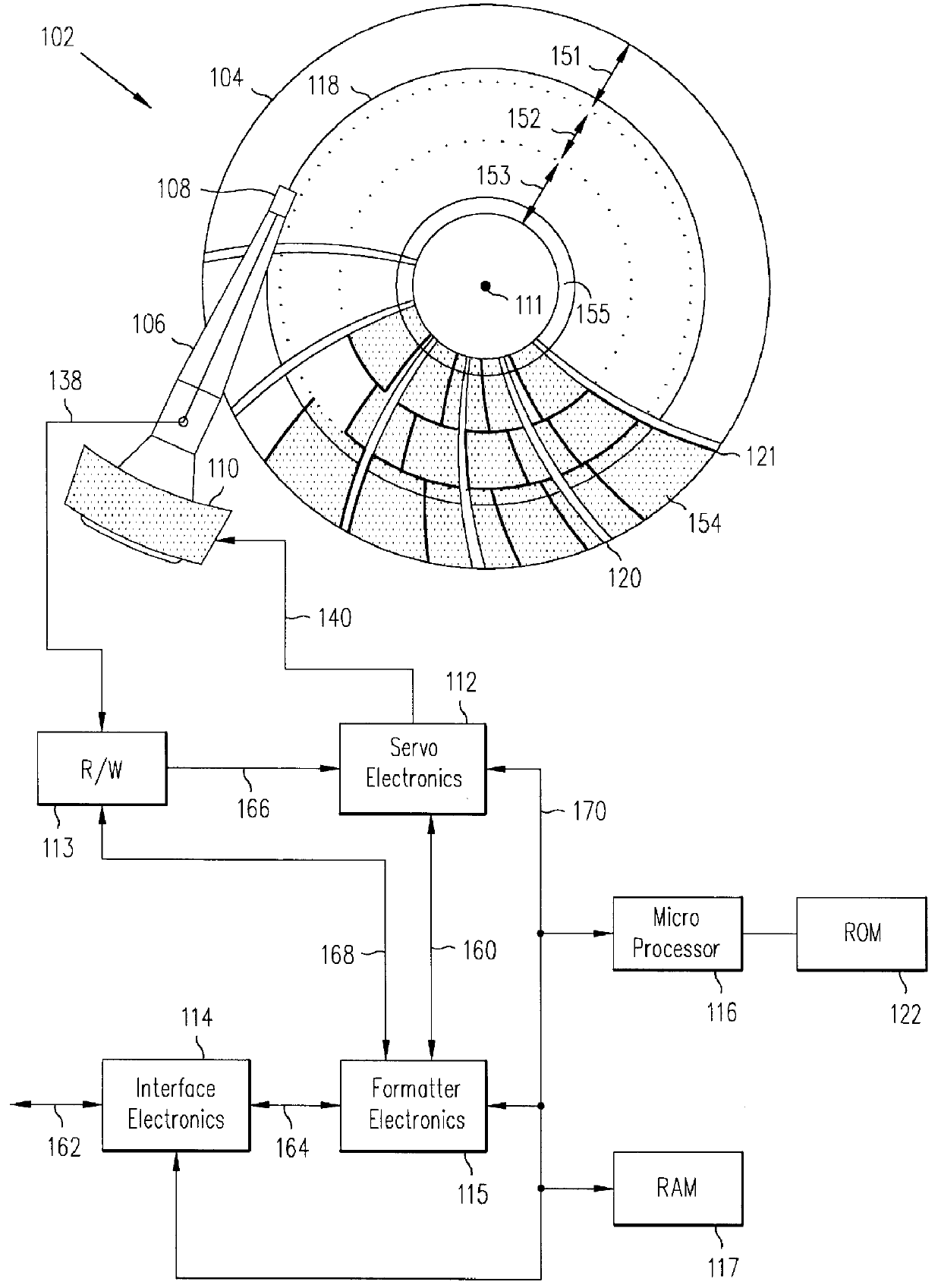
InactiveUS6049438AHigh quality PESAccurate integration detectionTrack finding/aligningMagnetic discsPeak valueBurst frequency
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Shingled magnetic recording disk drive with minimization of the effect of far track erasure on adjacent data bands
ActiveUS8537481B1Eliminate the effects ofRaise countRecord information storageCarrier monitoringShingled magnetic recordingHard disc drive
A shingled magnetic recording (SMR) hard disk drive (HDD) essentially eliminates the effect of far track erasure (FTE) in the boundary regions of annular data bands caused by writing in the boundary regions of adjacent annular data bands. The extent of the FTE effect is determined for each track within a range of tracks of the track being written. Based on the relative FTE effect for all the tracks in the range, a count increment (CI) table or a cumulative count increment (CCI) table is maintained for all the tracks in the range. For every writing to a track in a boundary region, a count for each track in an adjacent boundary region, or a cumulative count for the adjacent boundary region, is increased. When the count reaches a predetermined threshold the data is read from that band and rewritten to the same band.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
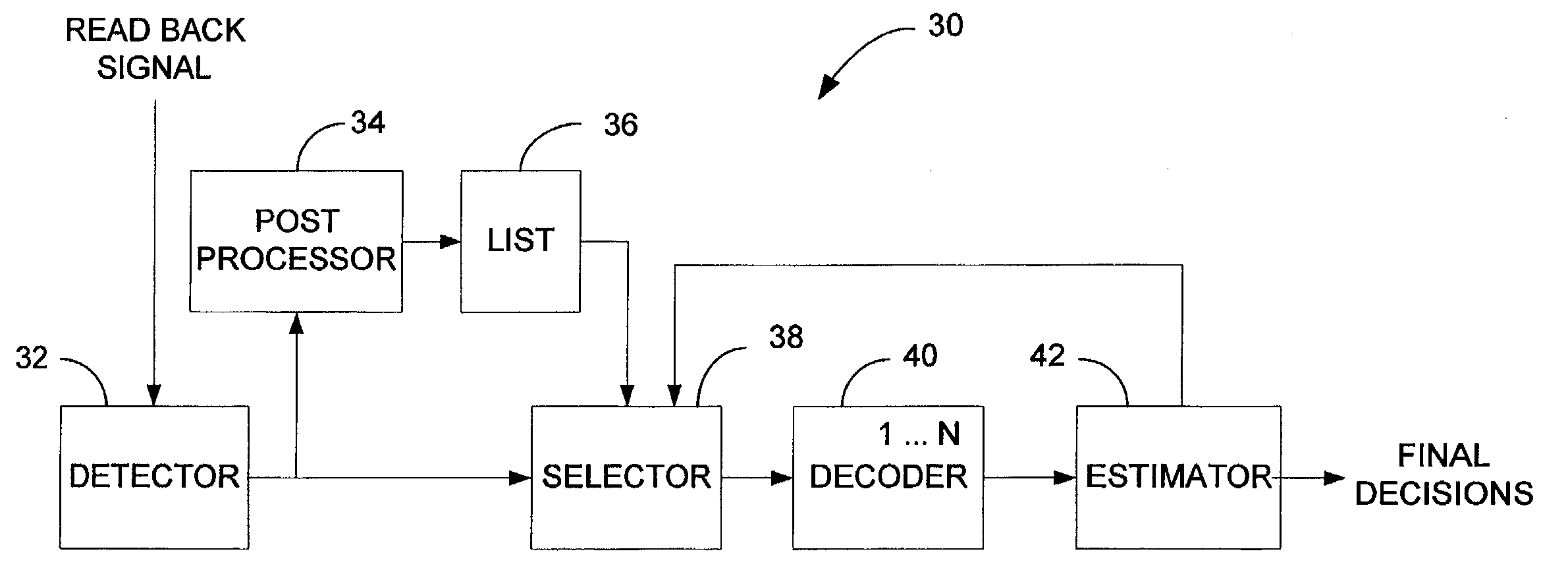
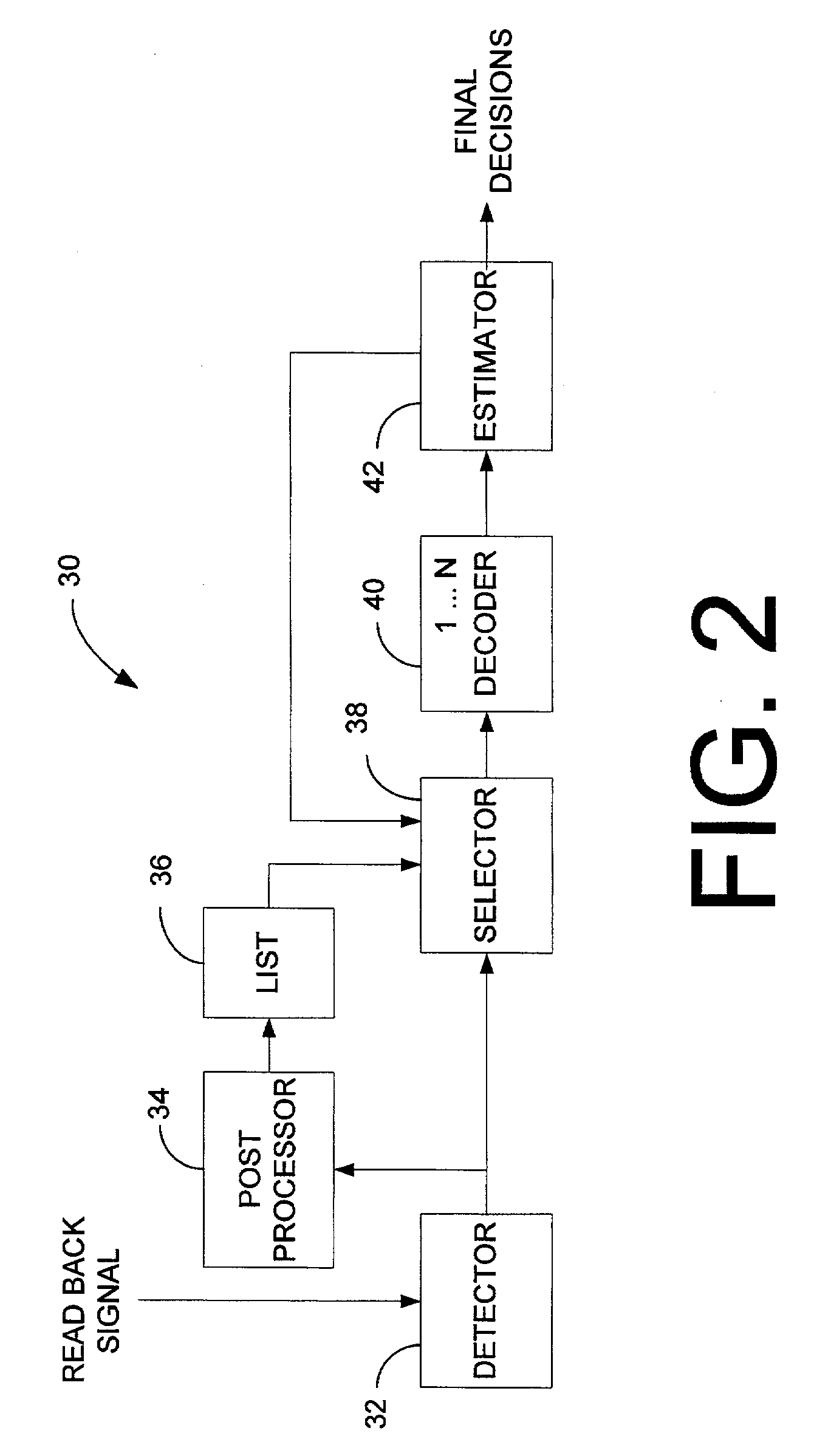
Correcting errors in disk drive read back signals by iterating with the Reed-Solomon decoder
A signal detector to detect symbols in a read back signal. The signal detector includes a first detector to generate raw decisions as a function of the read back signal. A post processor identifies possible defects in the raw decisions. A selector selects a portion of the possible defects and generates modified decisions based upon correcting the portion of the possible defects. At least one signal decoder generates final decisions as a function of the modified and raw decisions. A decision block returns control to the selector in response to detecting excess errors in the final decisions.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
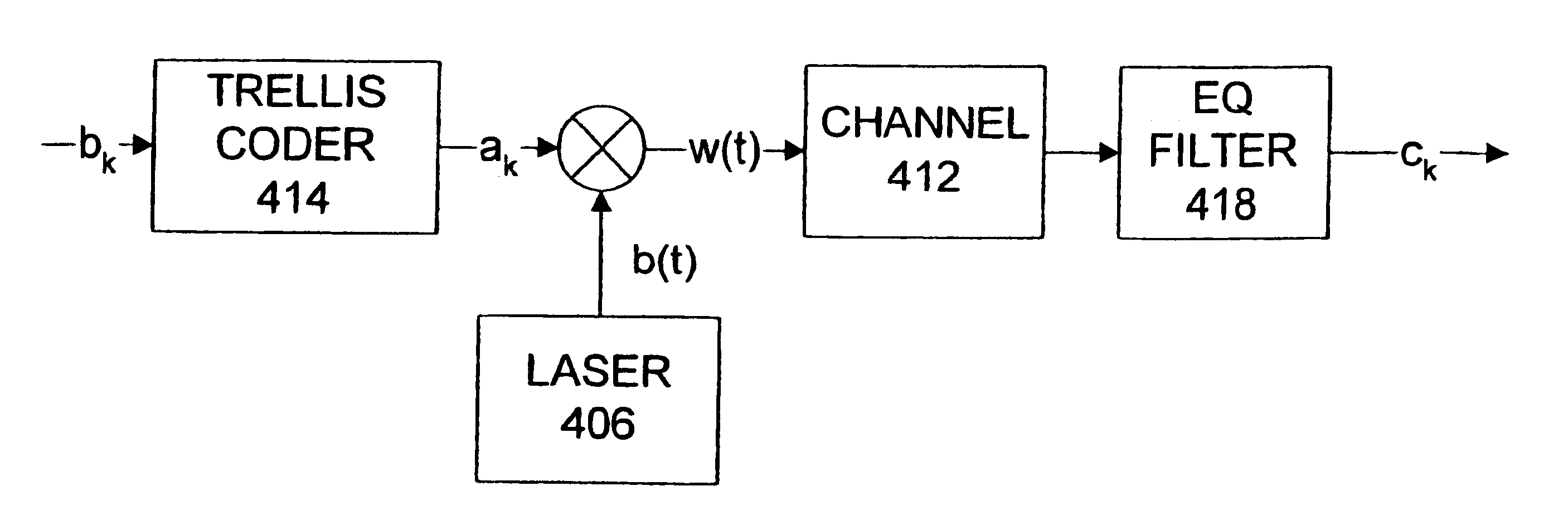
Coding system and method for partial response channels
A system and method for reading data to and writing data from multi-level (M-ary) partial response channels uses a trellis coder to encode an input bit stream sequence into a stream of multi-level data symbols. The data symbols are written to the partial response channel using any of a number of techniques. Preferably, the trellis coder anticipates the modulation transfer function of the partial response channel in encoding the data. Because the partial response channel has its own transfer function, the relationship between the data read from the channel and the actual input data bits is a function not only of the data encoder but also of the partial response channel. Therefore, a decoder specification used to implement the decoder takes into account the effect of the trellis encoder as well as the effect of the partial response channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
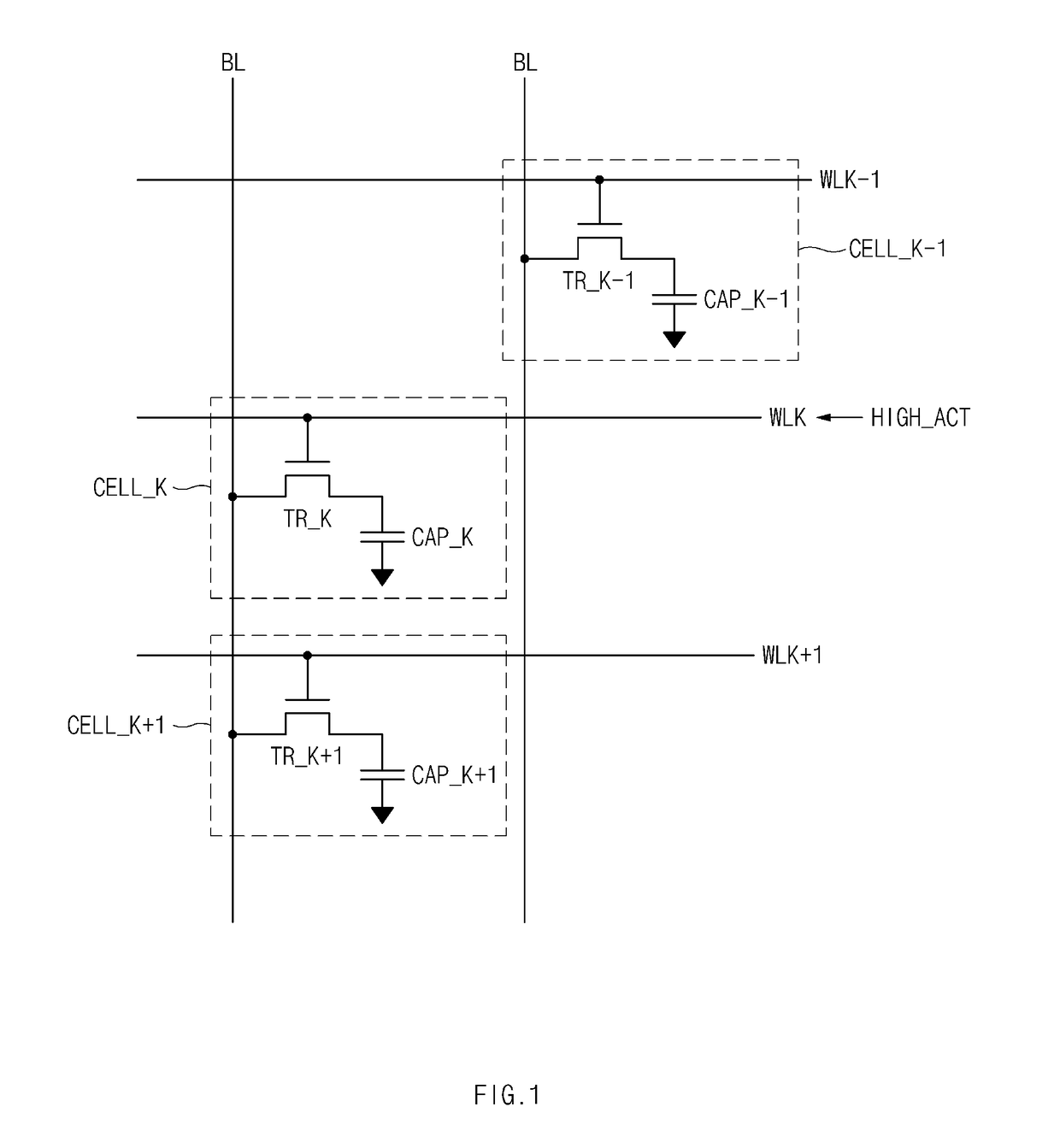
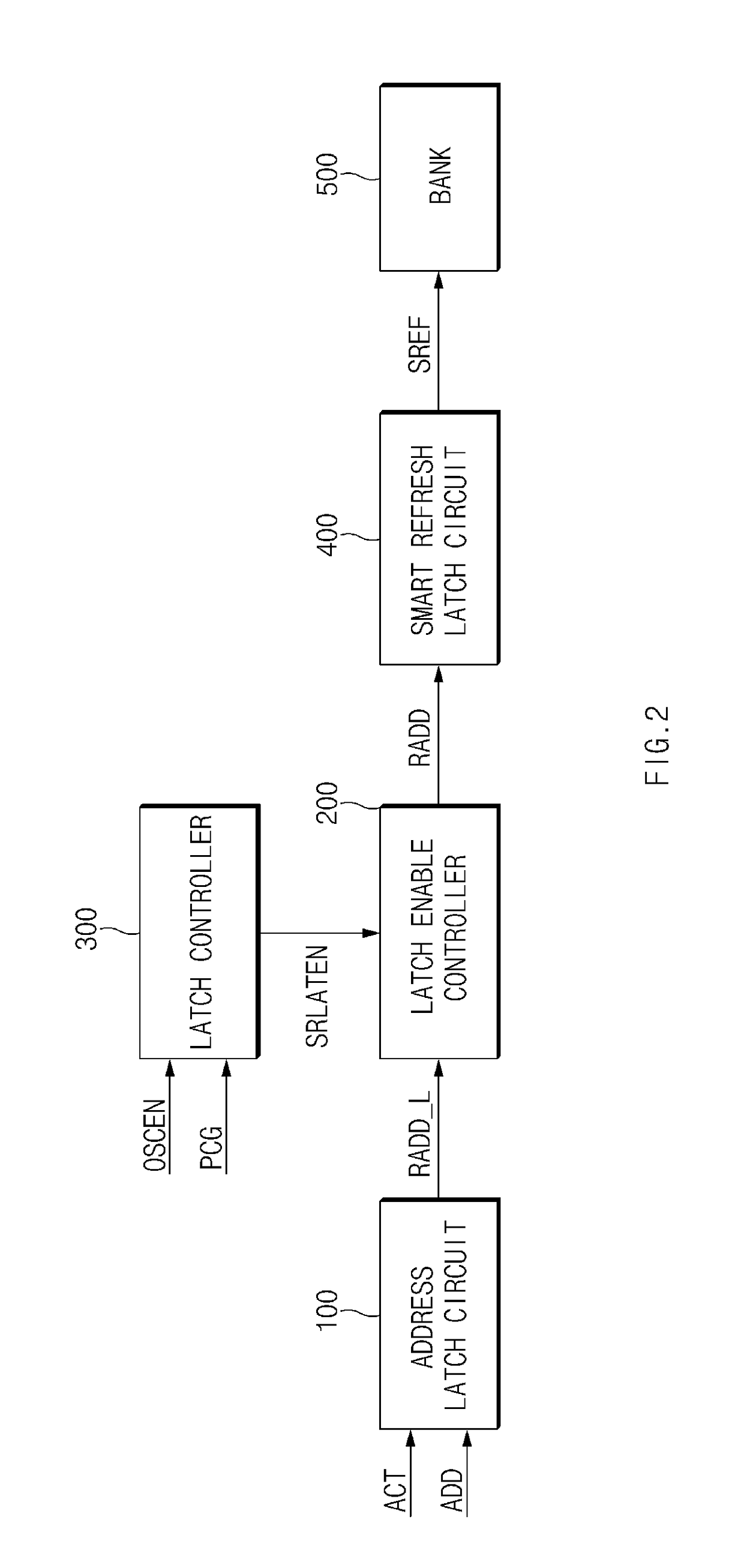
Refresh control device, and memory device including the same
ActiveUS20170352404A1Digital storageSignal processing using non self-clocking codesComputer scienceControl equipment
A refresh control device, and a memory device may be provided. The latch controller may include a first oscillator configured to generate a first oscillation signal, and a second oscillator configured to generate a second oscillation signal. The latch controller may be configured to receive a precharge signal and prevent the second oscillation signal from being synchronized with the precharge signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Magnetic recording system with patterned multilevel perpendicular magnetic recording
InactiveUS20050122612A1Improve noiseImprove recording densityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsMagnetic momentRecording system
A magnetic recording system, such as a magnetic recording disk drive, uses a patterned perpendicular magnetic recording medium where each magnetic block or island contains a stack of individual magnetic cells to provide multilevel recording. Each cell in an island is formed of a material or set of materials to provide the cell with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and is a single magnetic domain. Each cell is magnetically decoupled from the other cells in its island by nonmagnetic spacer layers. Thus each cell can have a magnetization (magnetic moment) in one of two directions (into or out of the plane of the layer making up the cell), and this magnetization is independent of the magnetization of the other cells in its island. This permits multiple magnetic levels or states to be recorded in each magnetic island.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
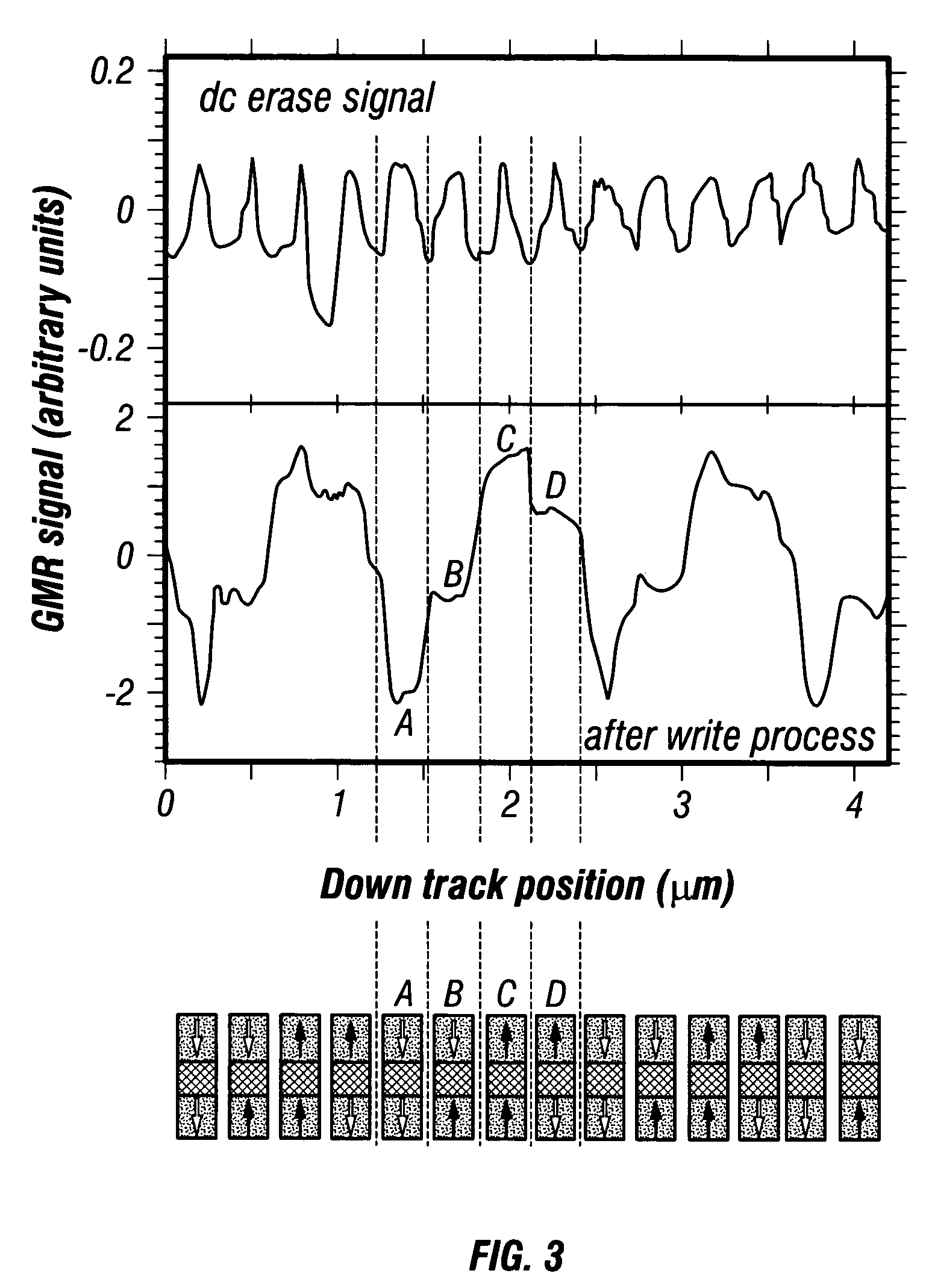
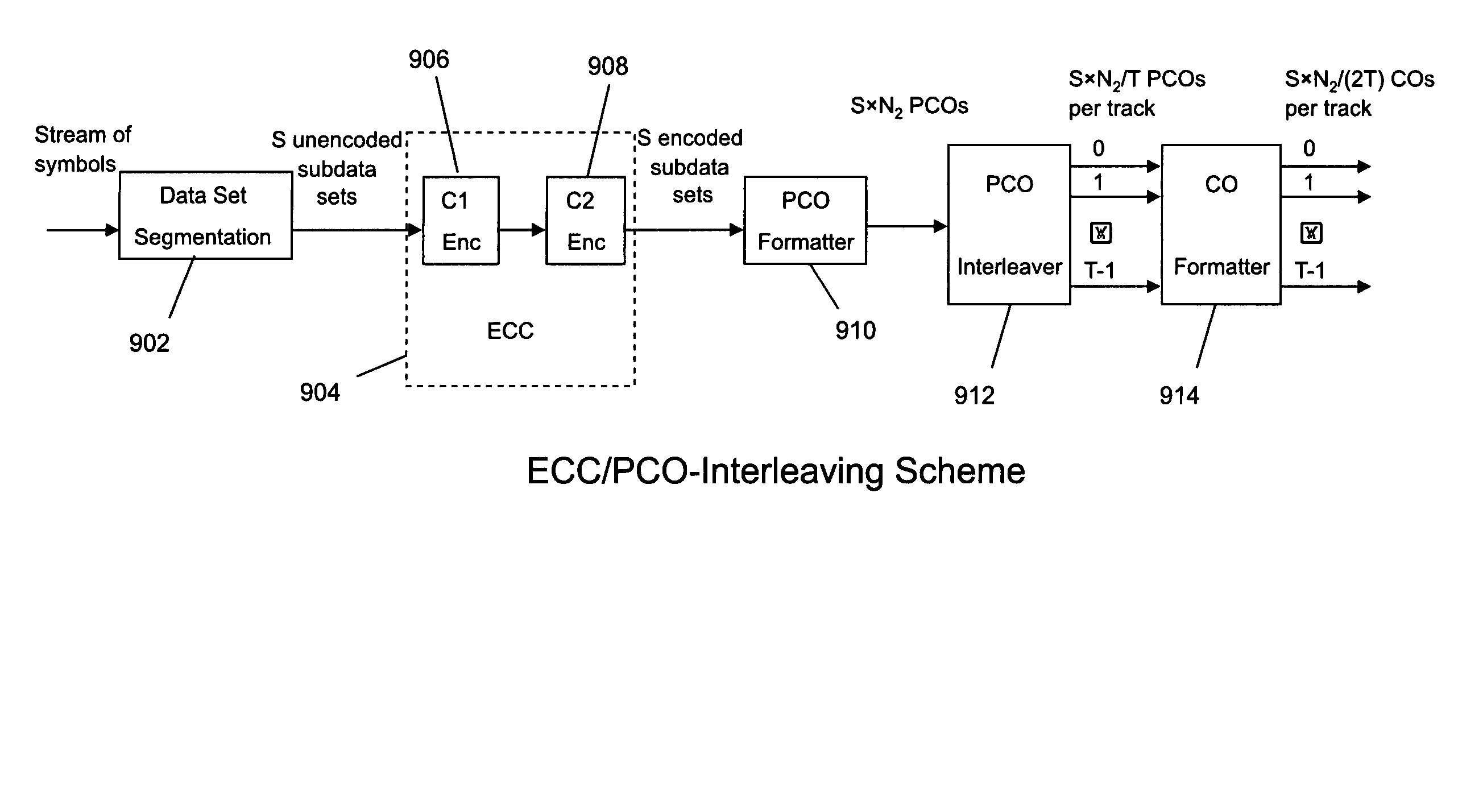
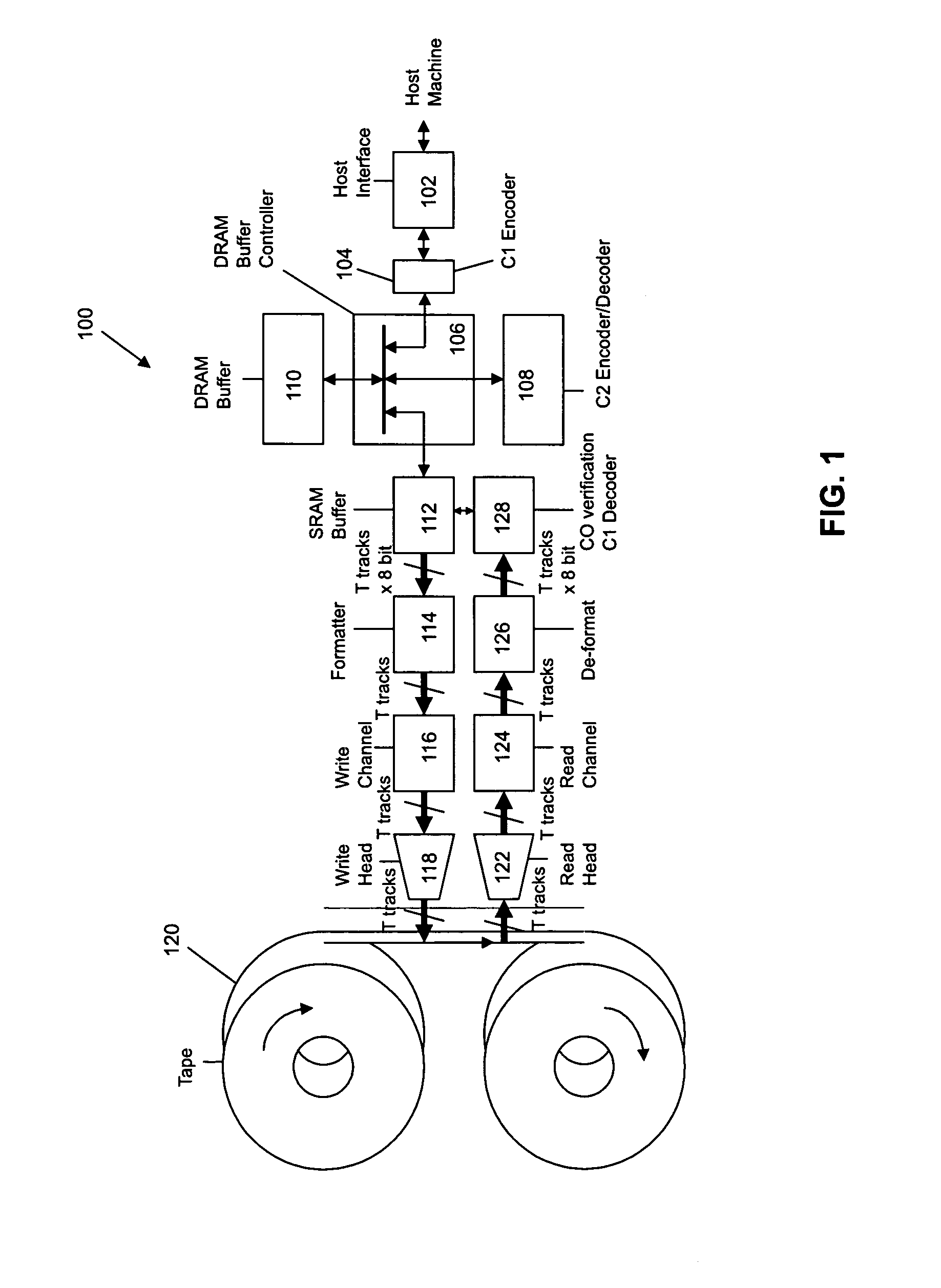
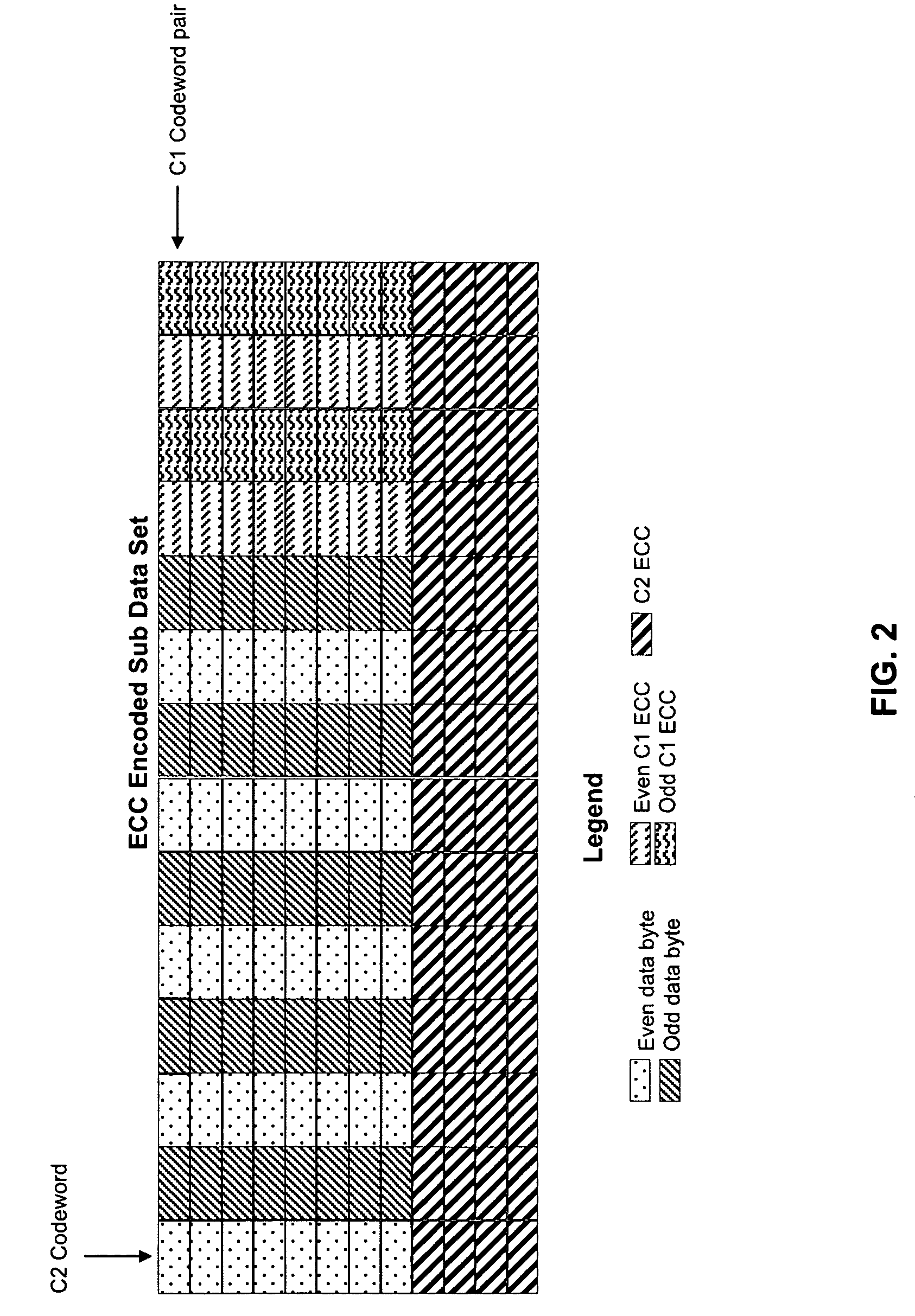
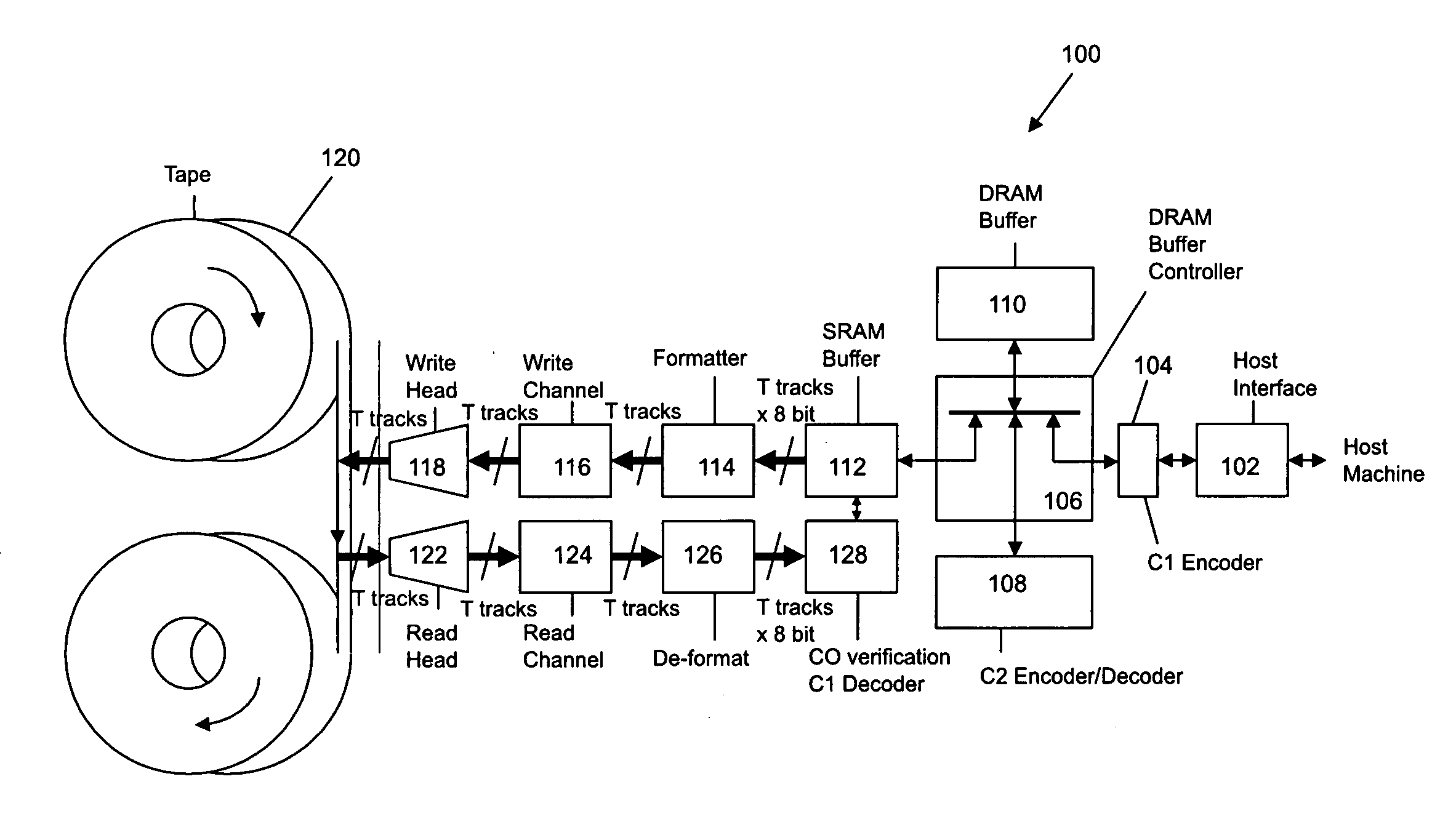
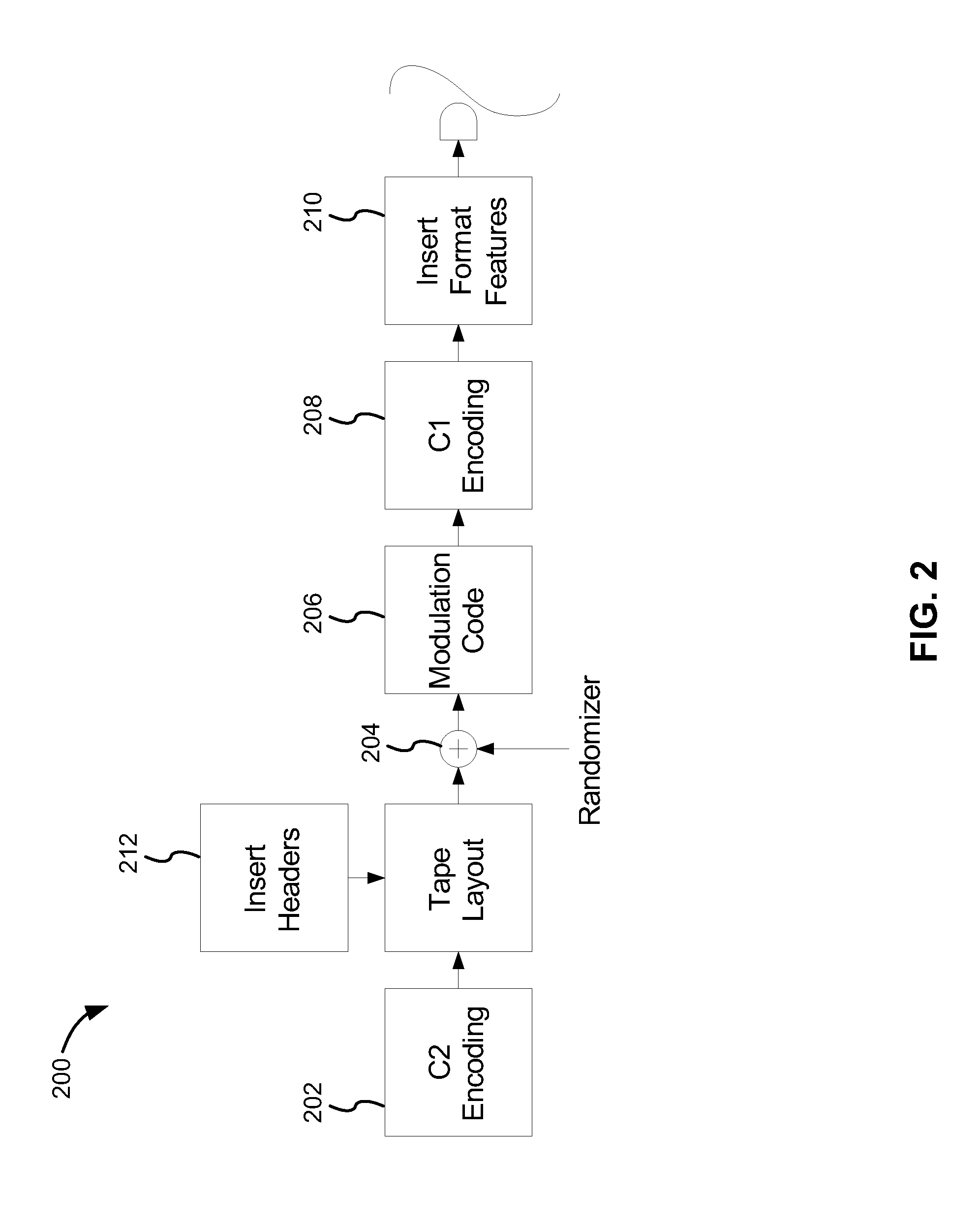
Rewrite-efficient ECC/interleaving for multi-track recording on magnetic tape
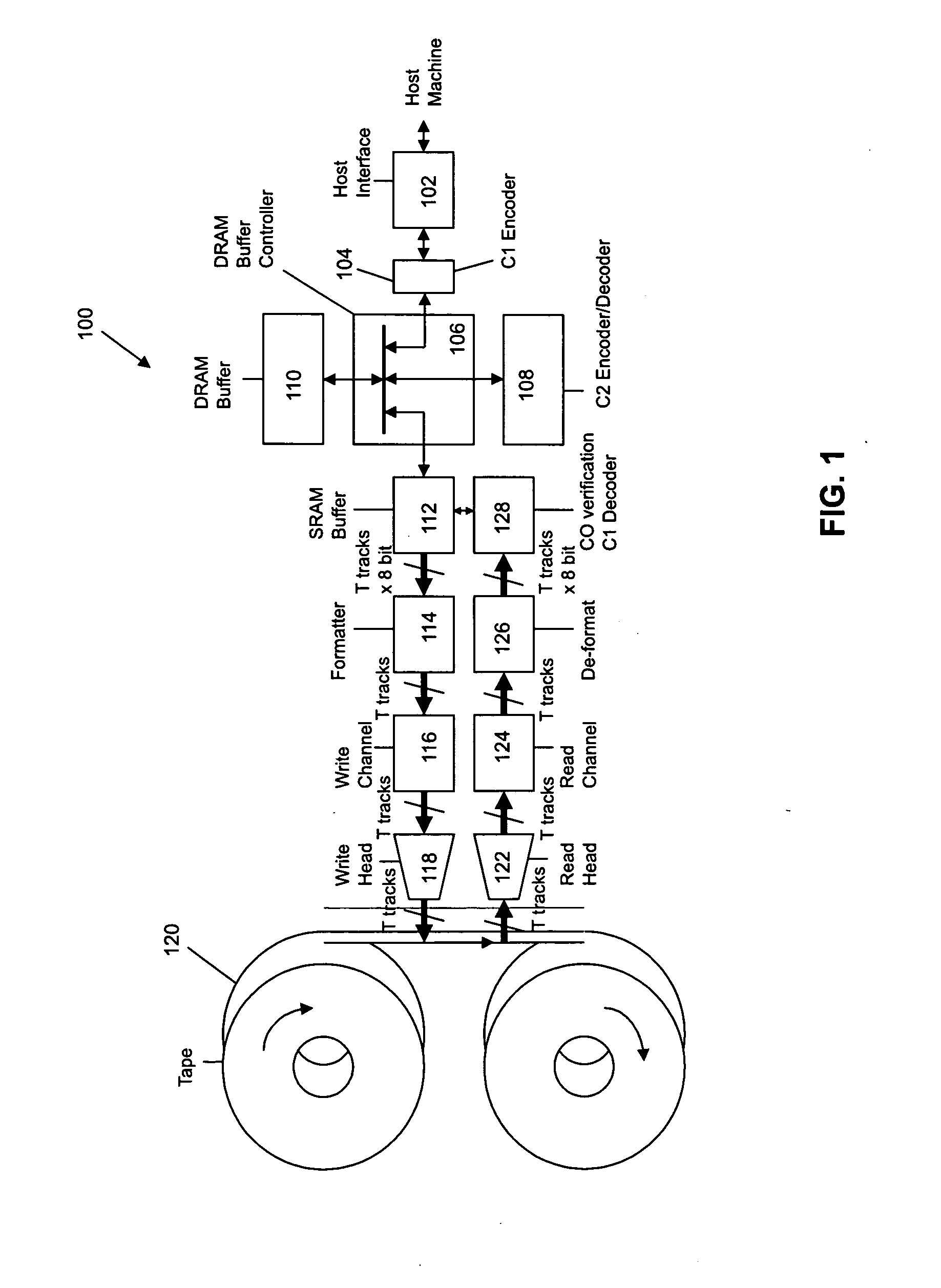
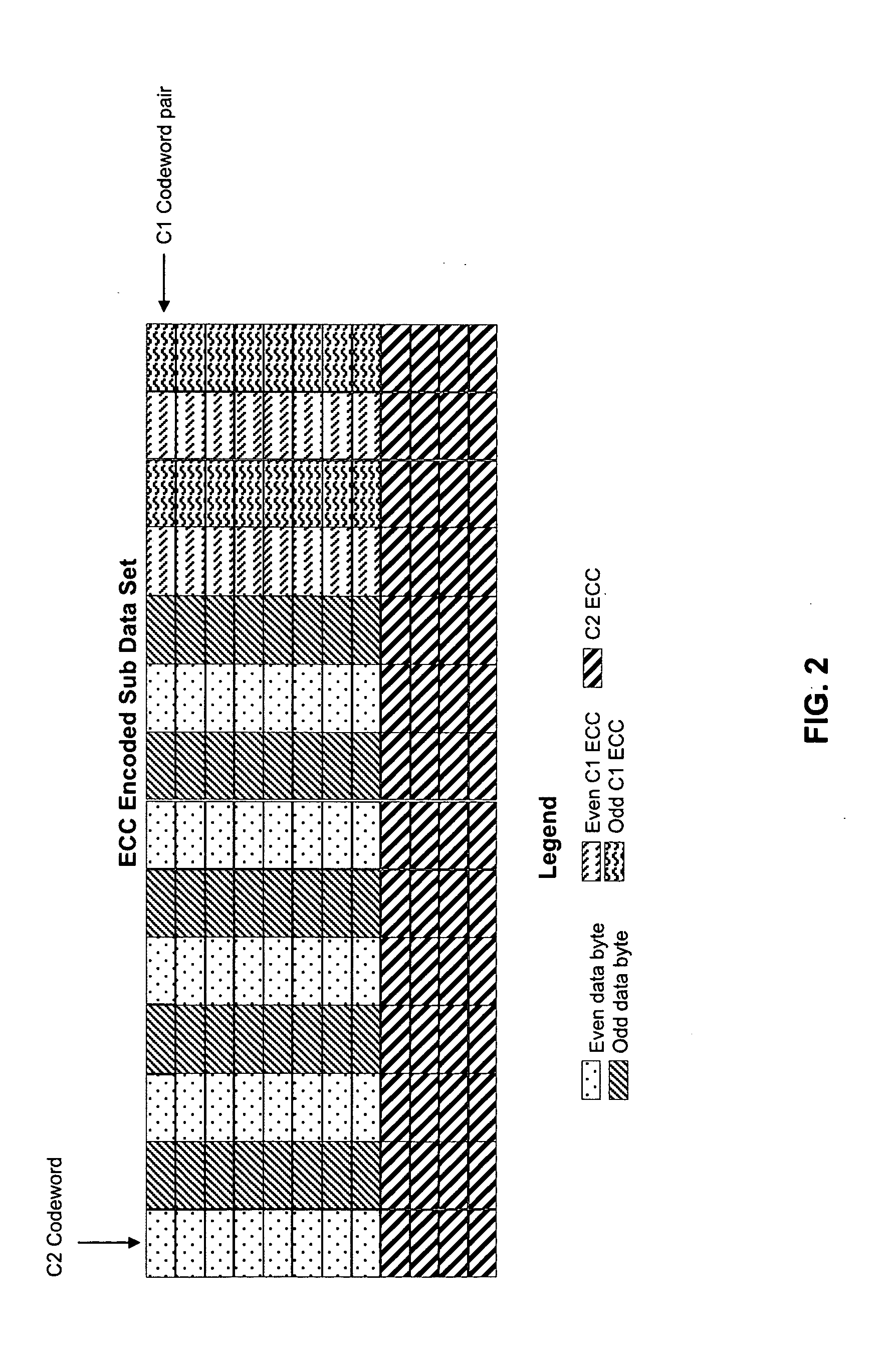
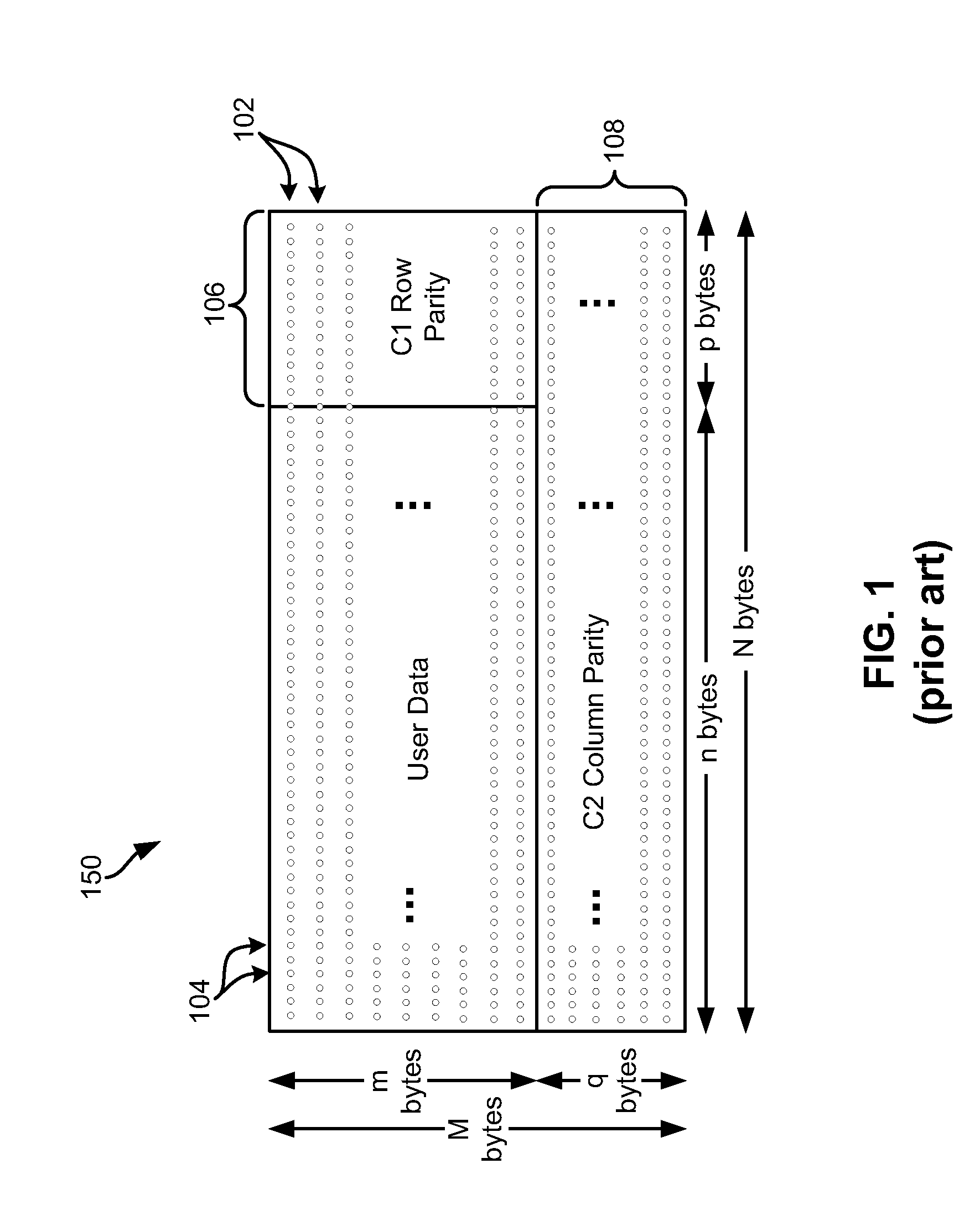
For writing data to multi-track tape, a received data set is received and segmented into unencoded subdata sets, each comprising an array having K2 rows and K1 columns. For each unencoded subdata set, N1-K1 C1-parity bytes are generated for each row and N2-K2 C2-parity bytes are generated for each column. The C1 and C2 parity bytes are appended to the ends of the row and column, respectively, to form encoded C1 and C2 codewords, respectively. All of the C1 codewords per data set are endowed with a specific codeword header to form a plurality of partial codeword objects (PCOs). Each PCO is mapped onto a logical data track according to information within the header. On each logical data track, adjacent PCOs are merged to form COs which are modulation encoded and mapped into synchronized COs. Then T synchronized COs are written simultaneously to the data tape where T is the number of concurrent active tracks on the data tape.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
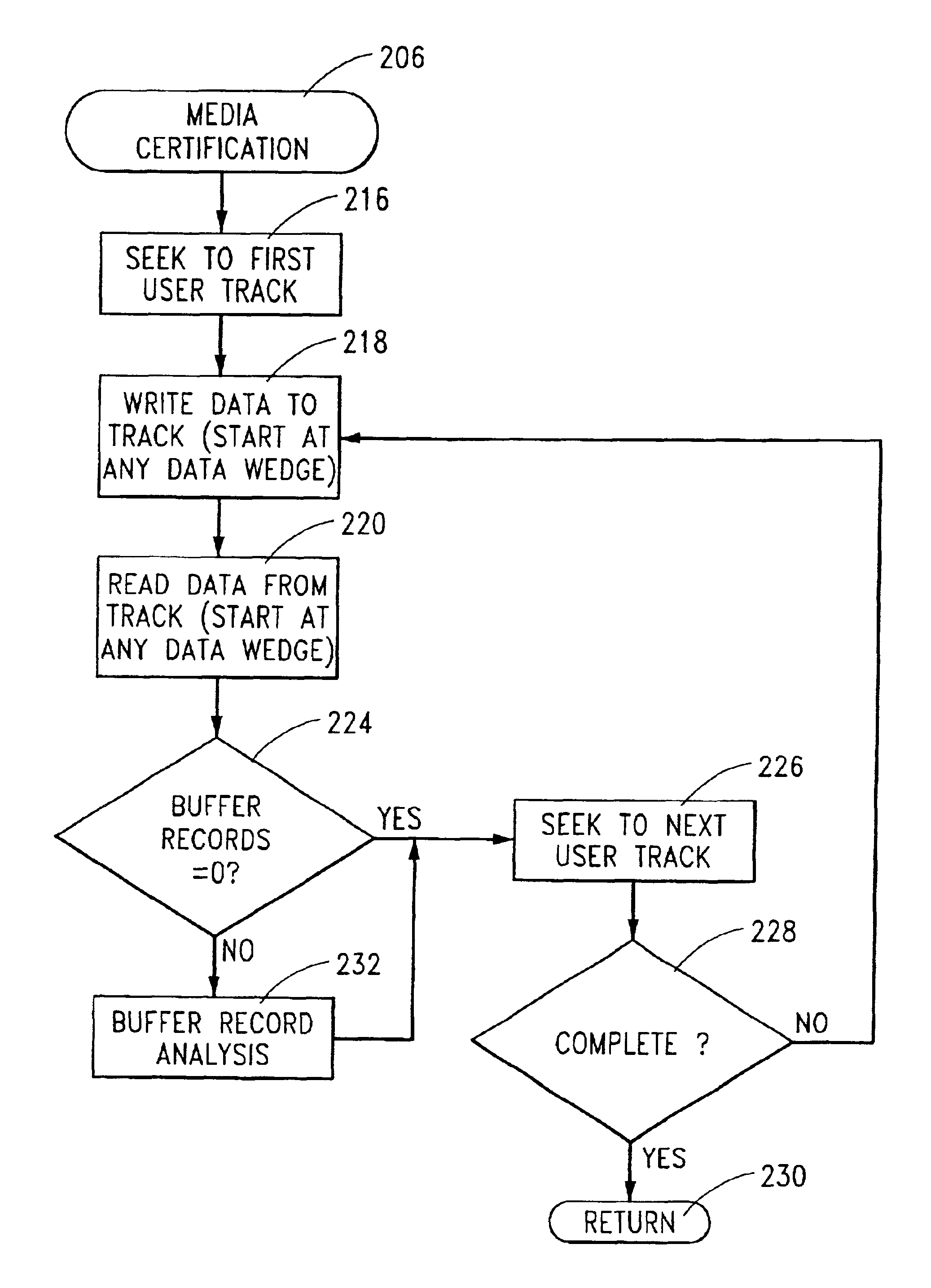
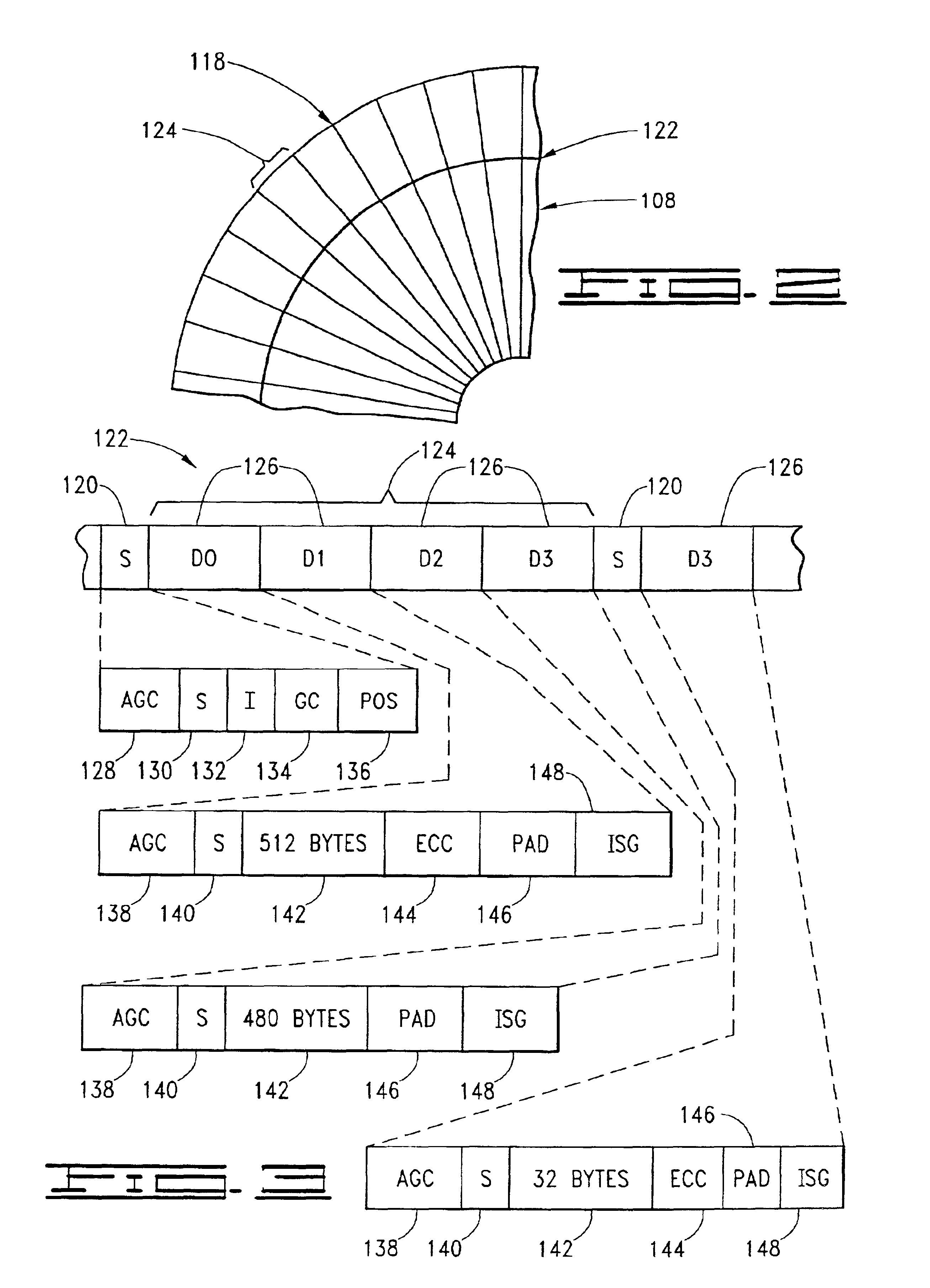
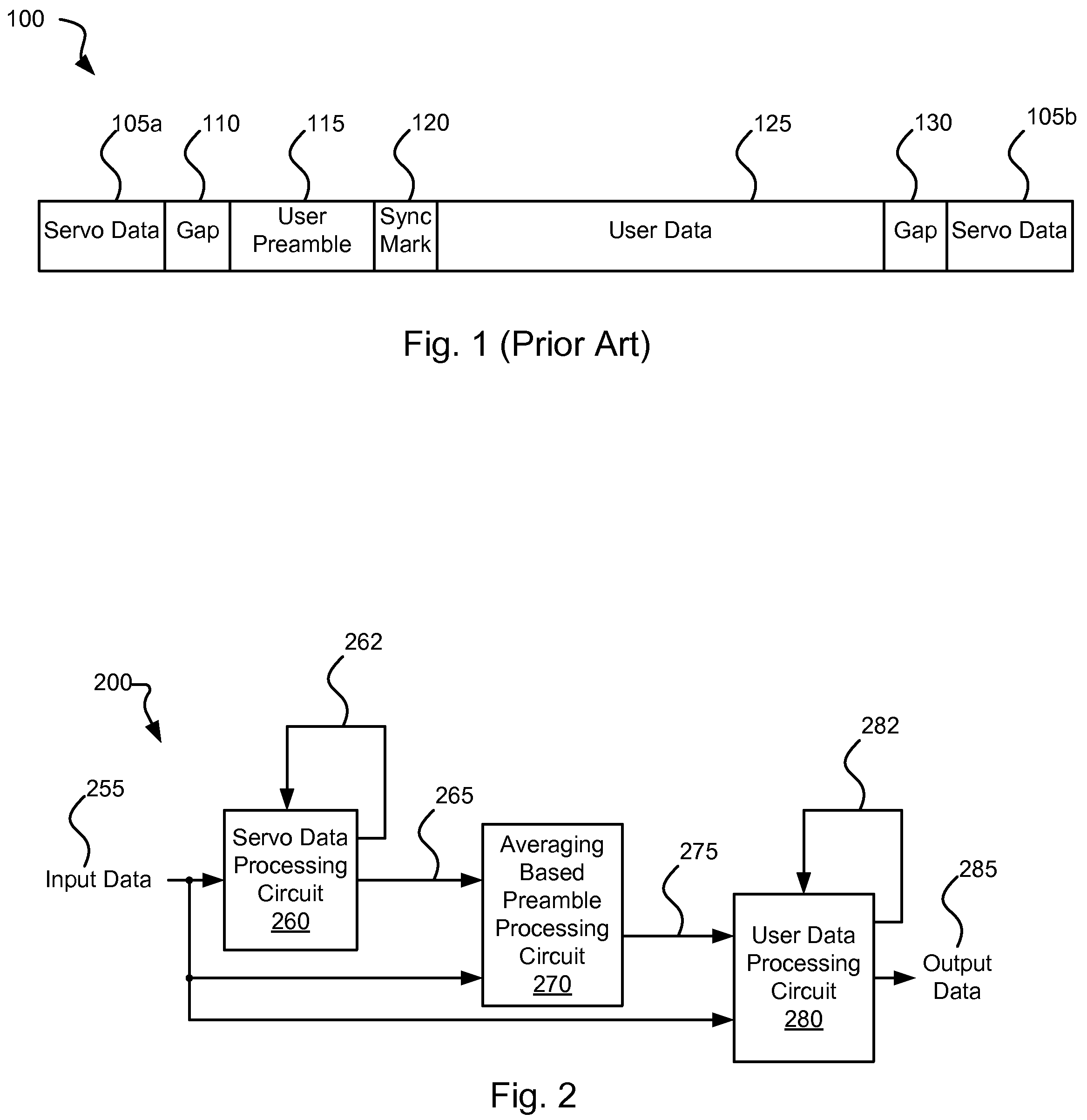
User data wedge media certification apparatus and method
InactiveUS6947232B2Save a lot of timeShorten the timeRecord information storageCarrier monitoringMagnetic mediaHandling system
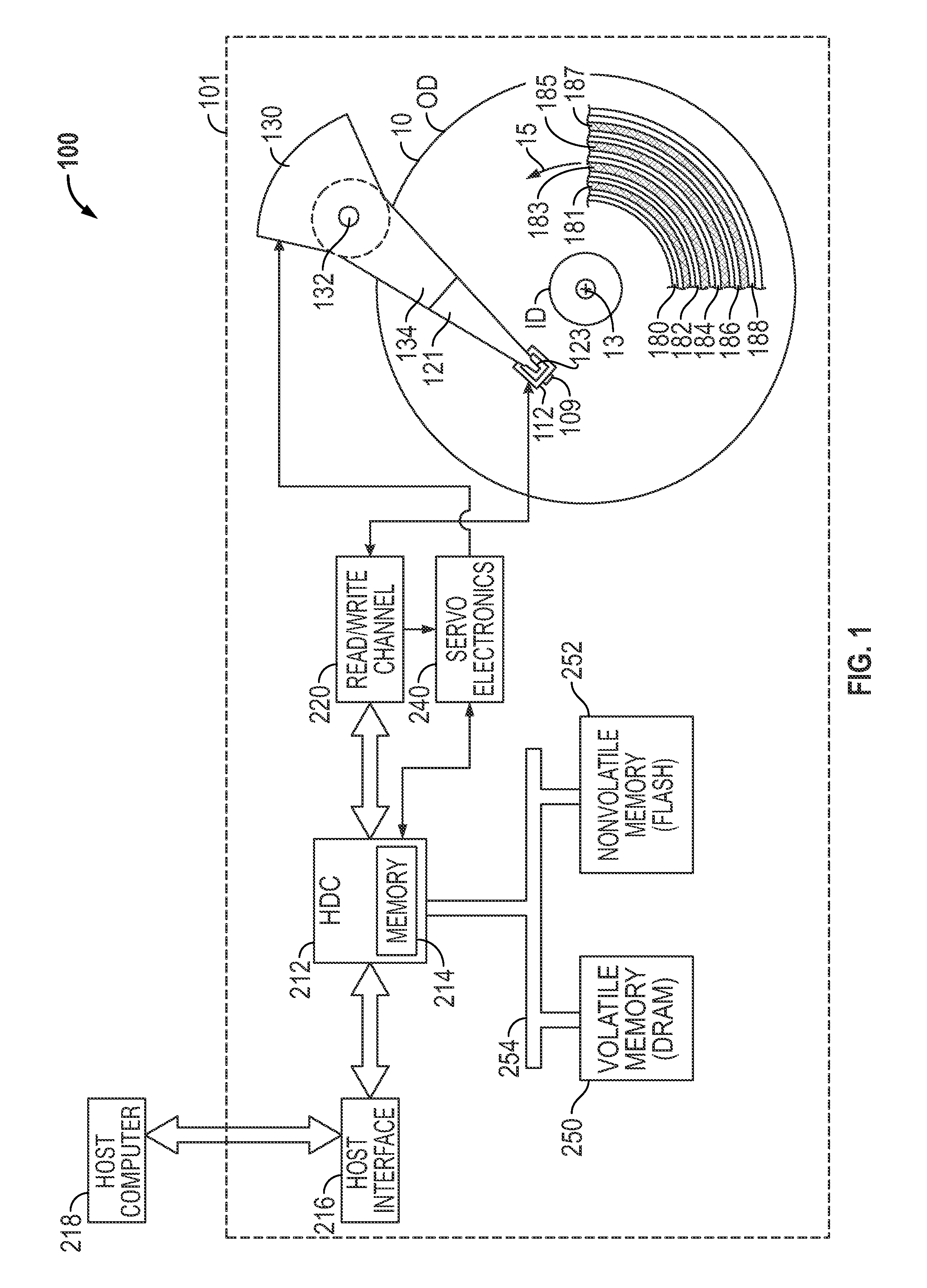
Method and apparatus for detecting defects in a magnetic medium of a data handling system. The magnetic medium includes a number of user data wedges each disposed between an adjacent pair of servo data wedges. A predetermined data sequence is written to the user data wedges, and subsequently read to generate a readback signal. A sequence of discrete time sample values are generated from the readback signal. Defects in the medium are detected in relation to the magnitudes of the discrete time samples. A media scan controller outputs a first multi-bit information record having at least one bit composing the address of the user data wedge containing a defect, and a second multi-bit information record having at least one bit composing an address of the defect within the user data wedge. No information is written to the buffer when no defects are identified.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
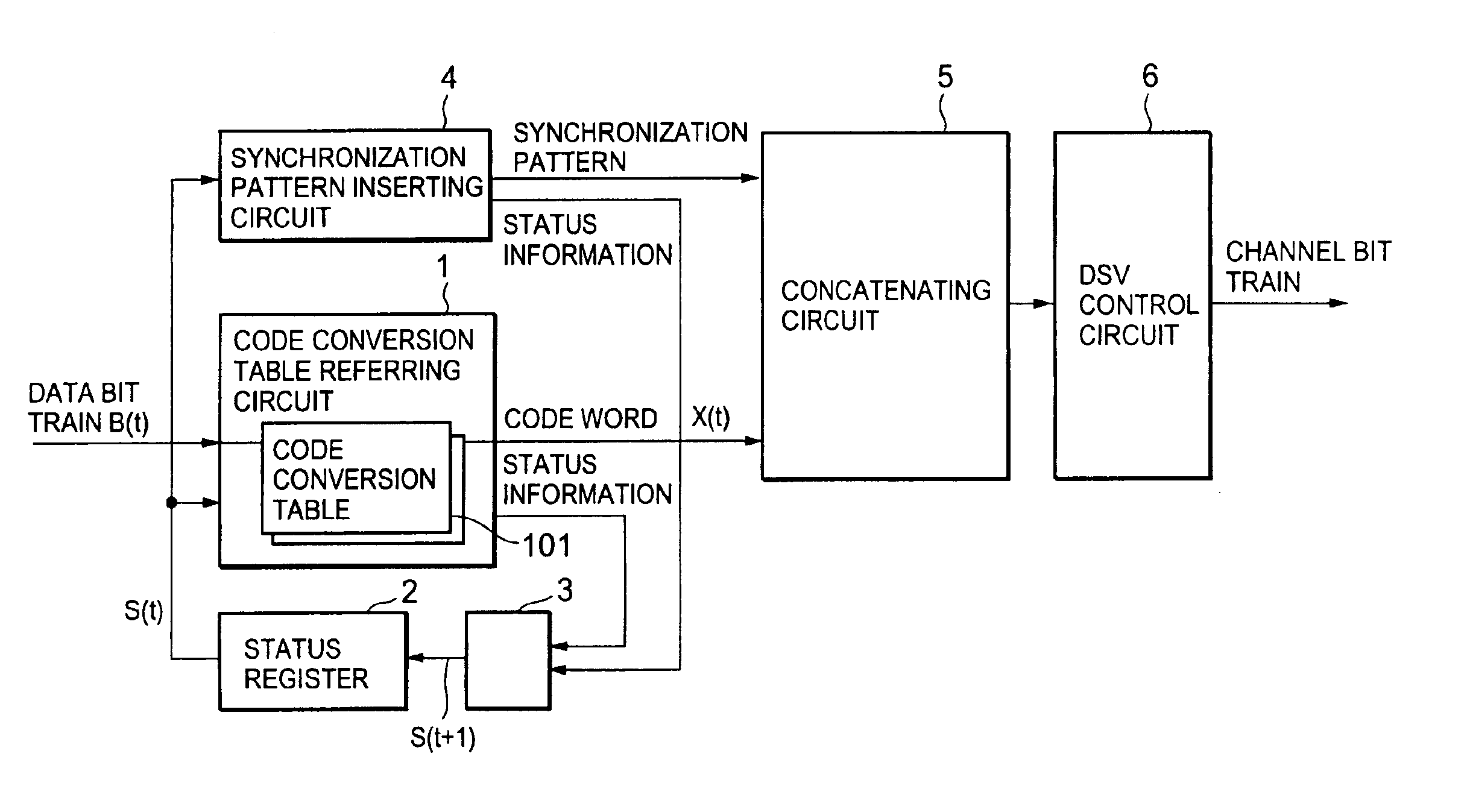
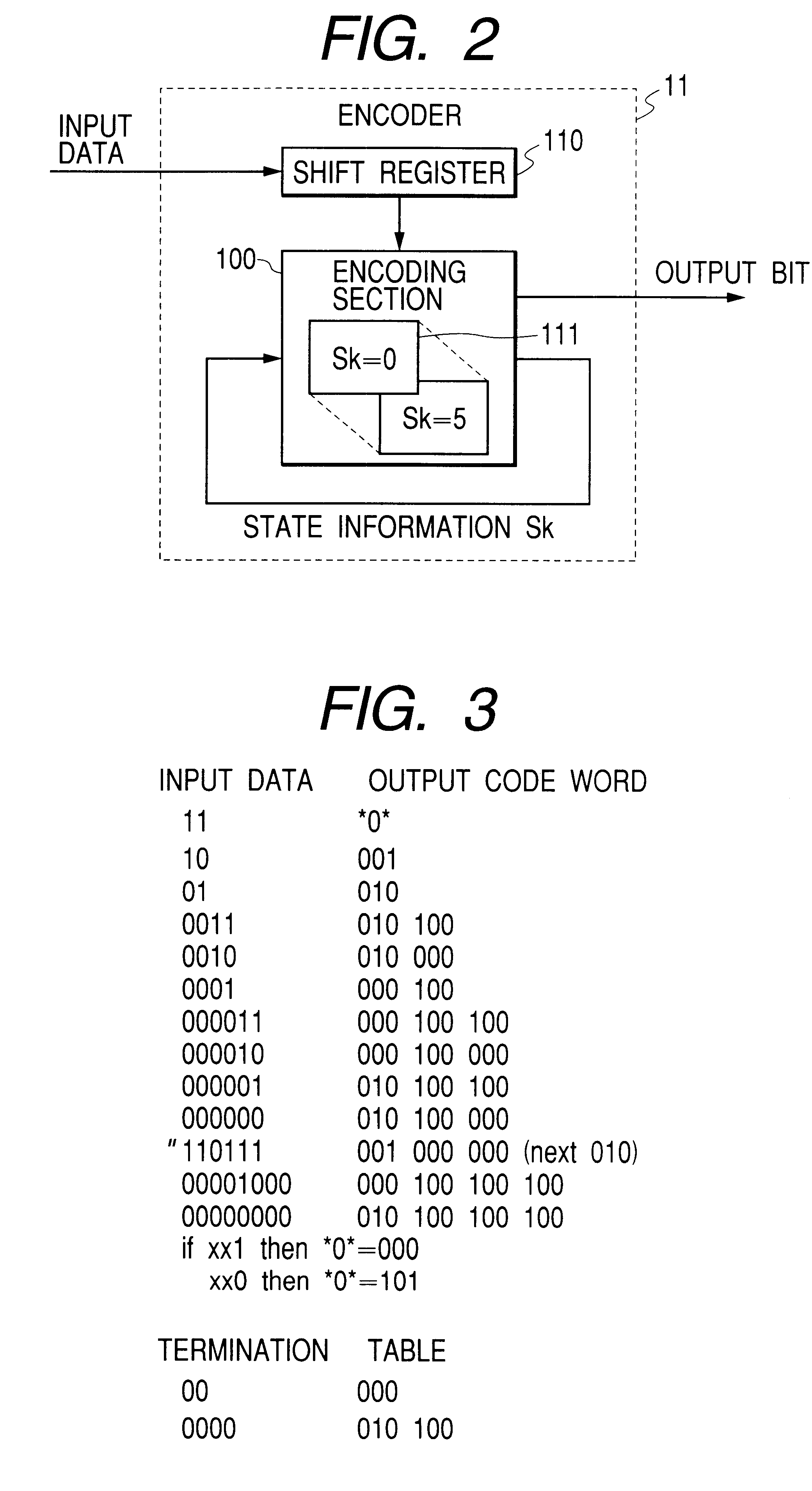
Code modulating method and code modulating apparatus, demodulating method and demodulating apparatus, and information recording medium
InactiveUS6861965B2Stable extractionAvoiding detectable occurrenceRecord information storageUsing detectable carrier informationClock rateComputer science
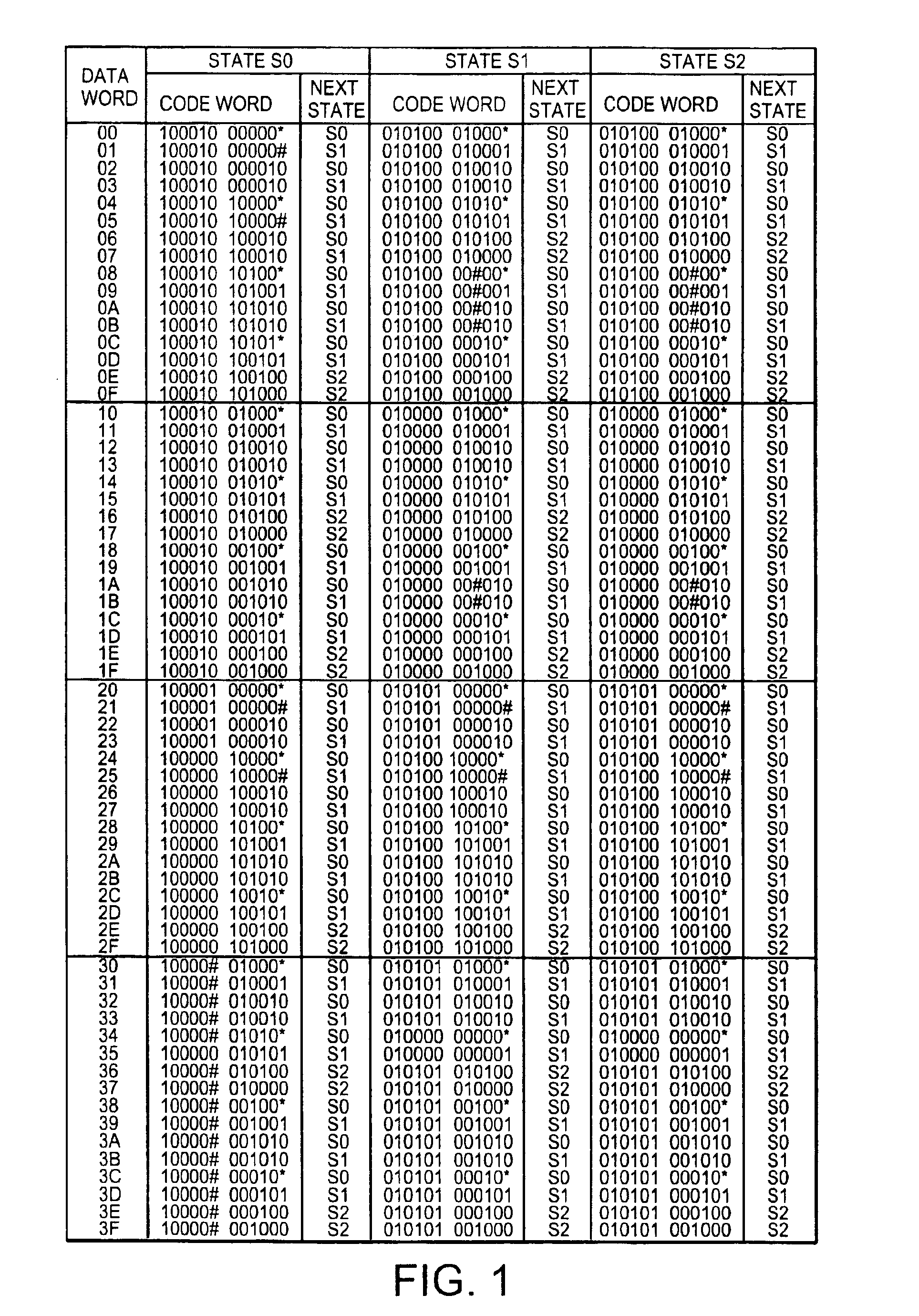
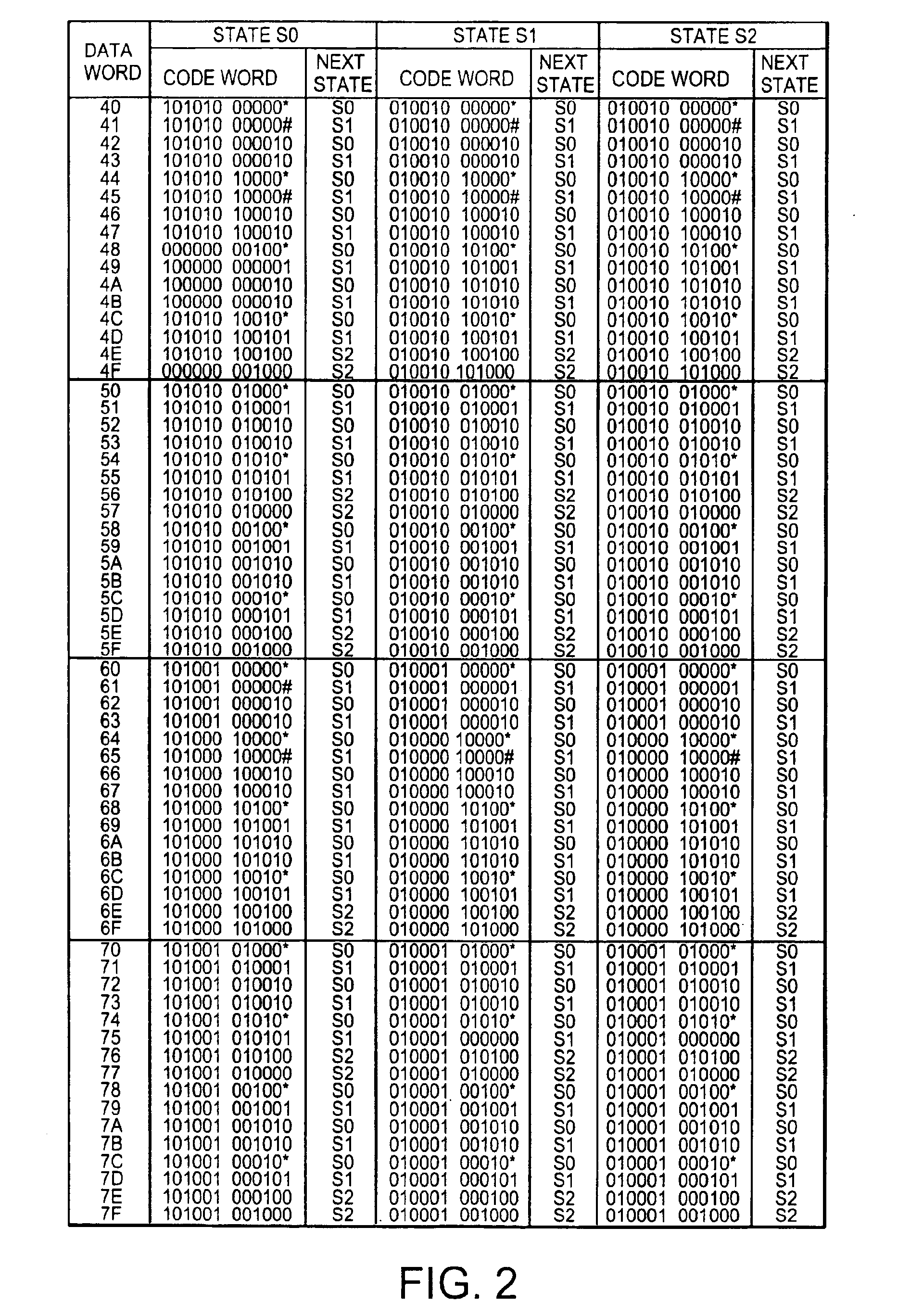
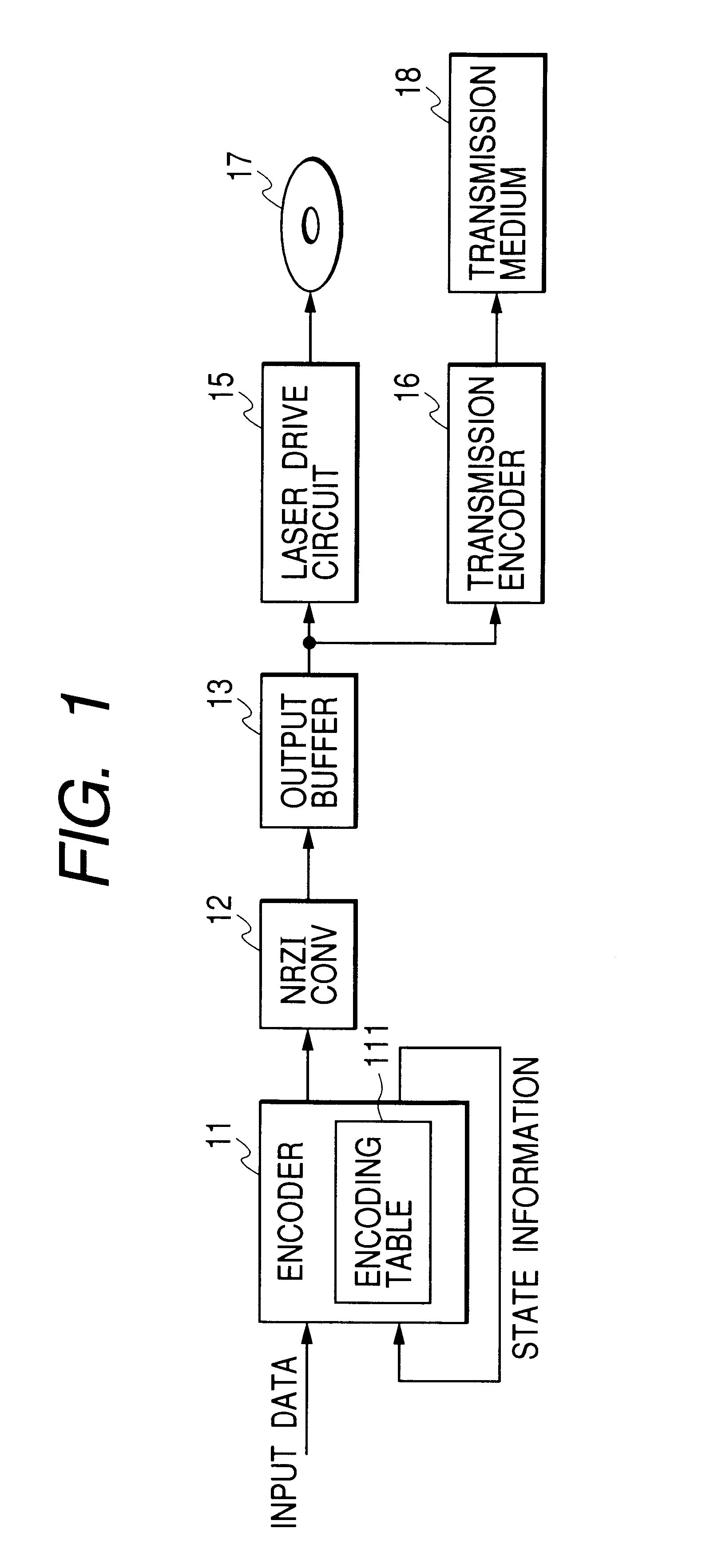
In a code modulating method and a code modulating apparatus, a run length has an encoding rate of ⅔ which is equal to that of (1, 7) modulation, and indicates the number of “0” bits between adjacent ones of “1” bits in the channel bit train. A data bit train is converted into the channel bit train so that the run length has a minimum value 1 and a maximum value 10. Further, upon converting any data bit train, the channel bit train does not include a pattern “1010101010101” in which the run length 1 is continuously repeated six times or more. The channel bit train has a DSV (Digital Sum Value) control bit which selects the “0” bit or “1” bit in accordance with a DSV. The channel bit train obtained by using random data for the data bit train is NRZI converted into a signal. A frequency component of the signal is reduced from a maximum value of the frequency component by 20 dB or less as a power density at a frequency of {fraction (1 / 10,000)} or less of a channel clock frequency.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Method and apparatus for encoding digital data
InactiveUS6577255B2Record information storageIndividual digits conversionDigital dataVariable length
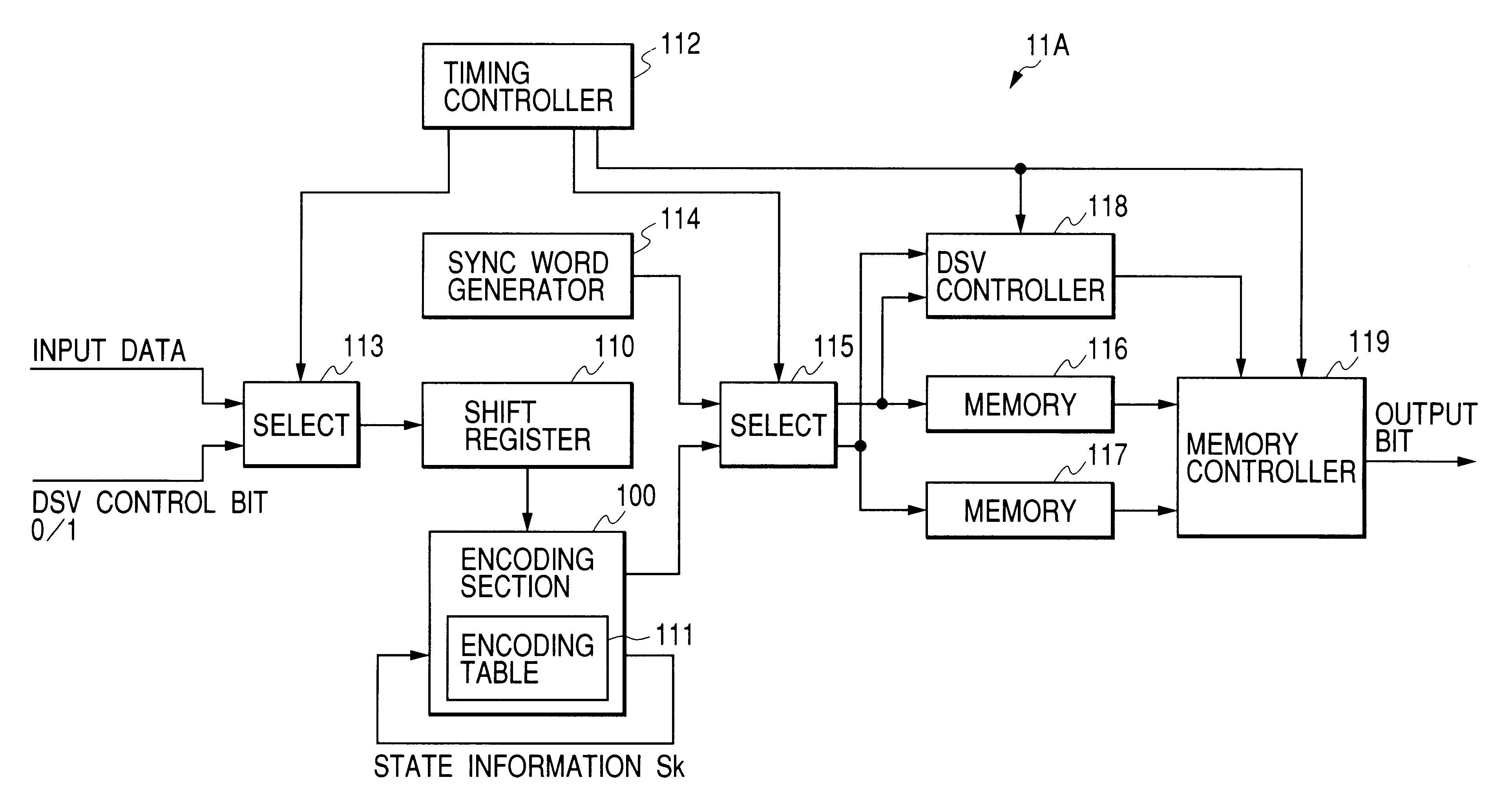
Encoding tables are accorded with variable-length encoding rules using a variable constraint length. A DSV control bit is periodically inserted into a first input bit stream to generate a second input bit stream. Every m-bit piece of the second input bit stream is encoded into an n-bit output signal forming at least a portion of an output code word by referring to the encoding tables. Thereby, the second input bit stream is converted into a first output bit stream composed of output code words and observing RLL (d, k). A sync word is inserted into the first output bit stream for every frame to generate a second output bit stream. A frame-end output code word is terminated at a position before a next-frame sync word. DSV control of the second output bit stream is implemented in response to the inserted DSV control bits.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
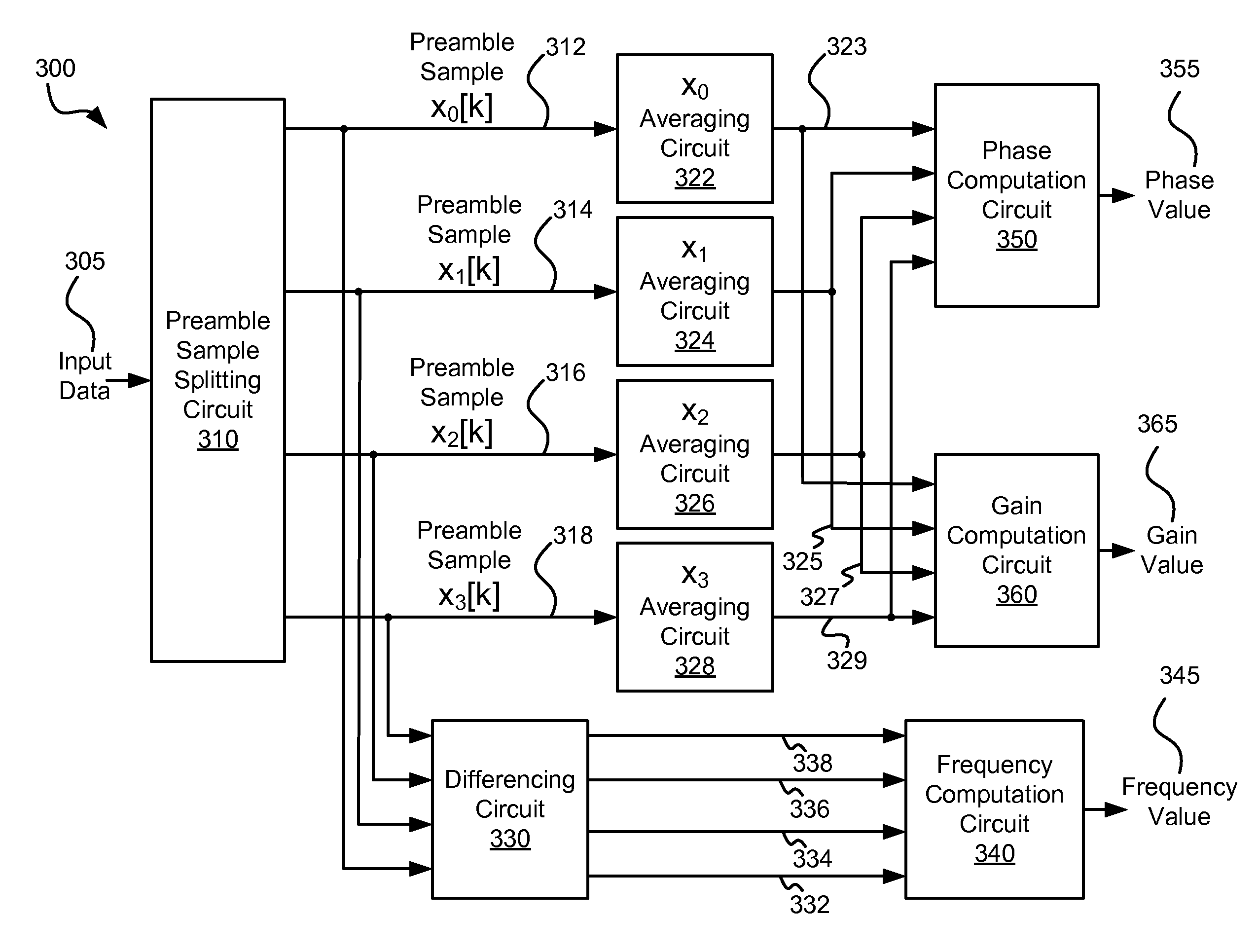
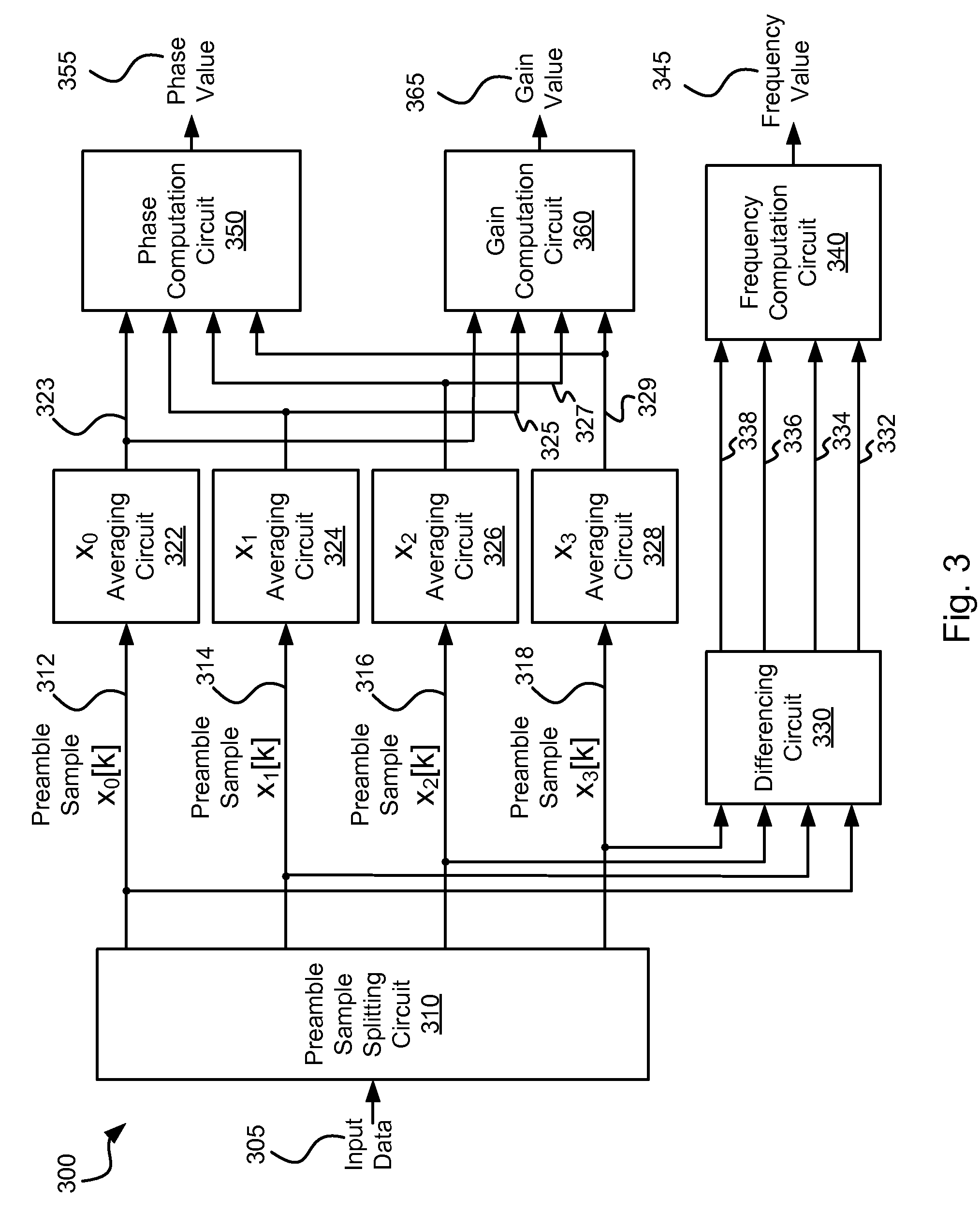
Systems and methods for timing and gain acquisition
InactiveUS8139305B2Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageComputer scienceData input
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for acquiring timing and / or gain information. For example, various embodiments of the present invention provide data processing circuits that include a sample splitting circuit, a first averaging circuit, a second averaging circuit and a parameter calculation circuit. The sample splitting circuit receives a data input that includes a series of samples that repeat periodically over at least a first phase and a second phase. The sample splitting circuit divides the series of samples into at least a first sub-stream corresponding to the first phase and a second sub-stream corresponding to the second phase. The first averaging circuit averages values from the first sub-stream to yield a first average, and the second averaging circuit averages values from the second sub-stream to yield a second average. The parameter calculation circuit calculates a parameter value based at least in part on the first average and the second average.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
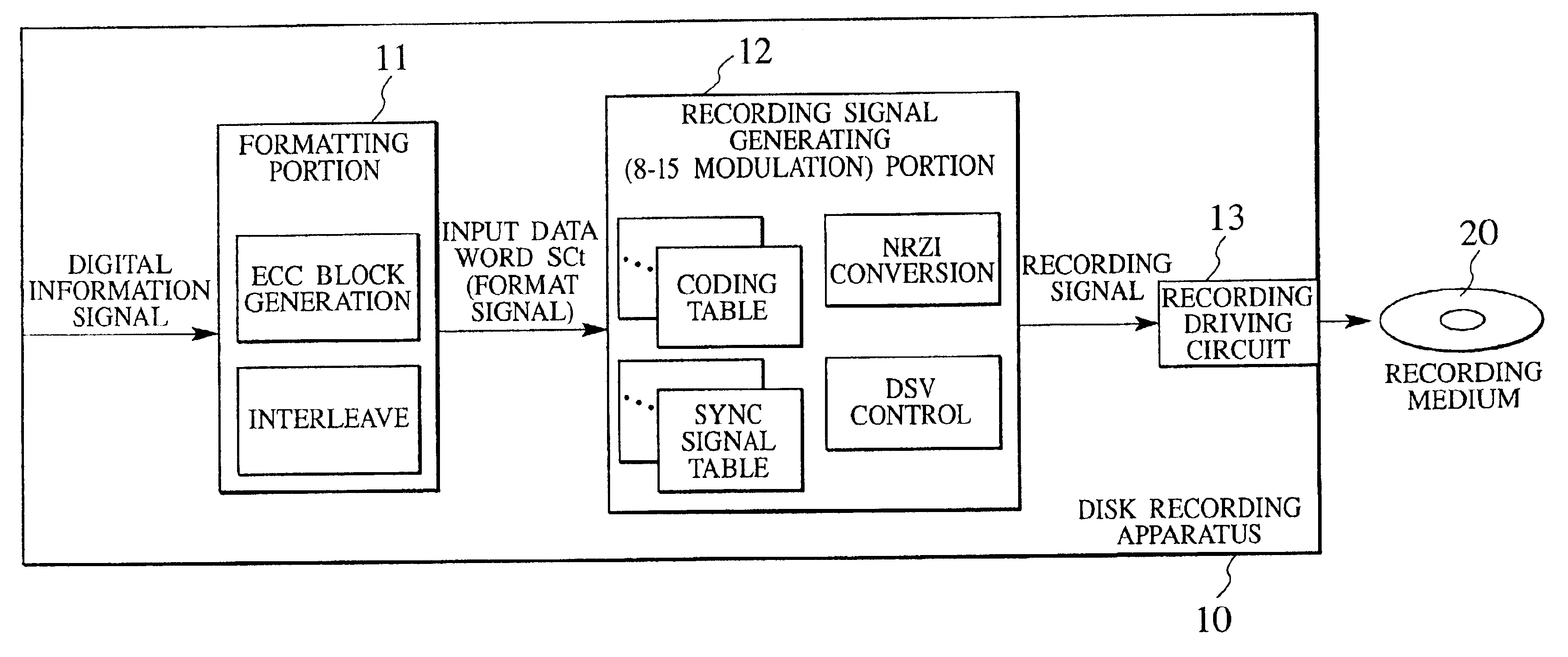
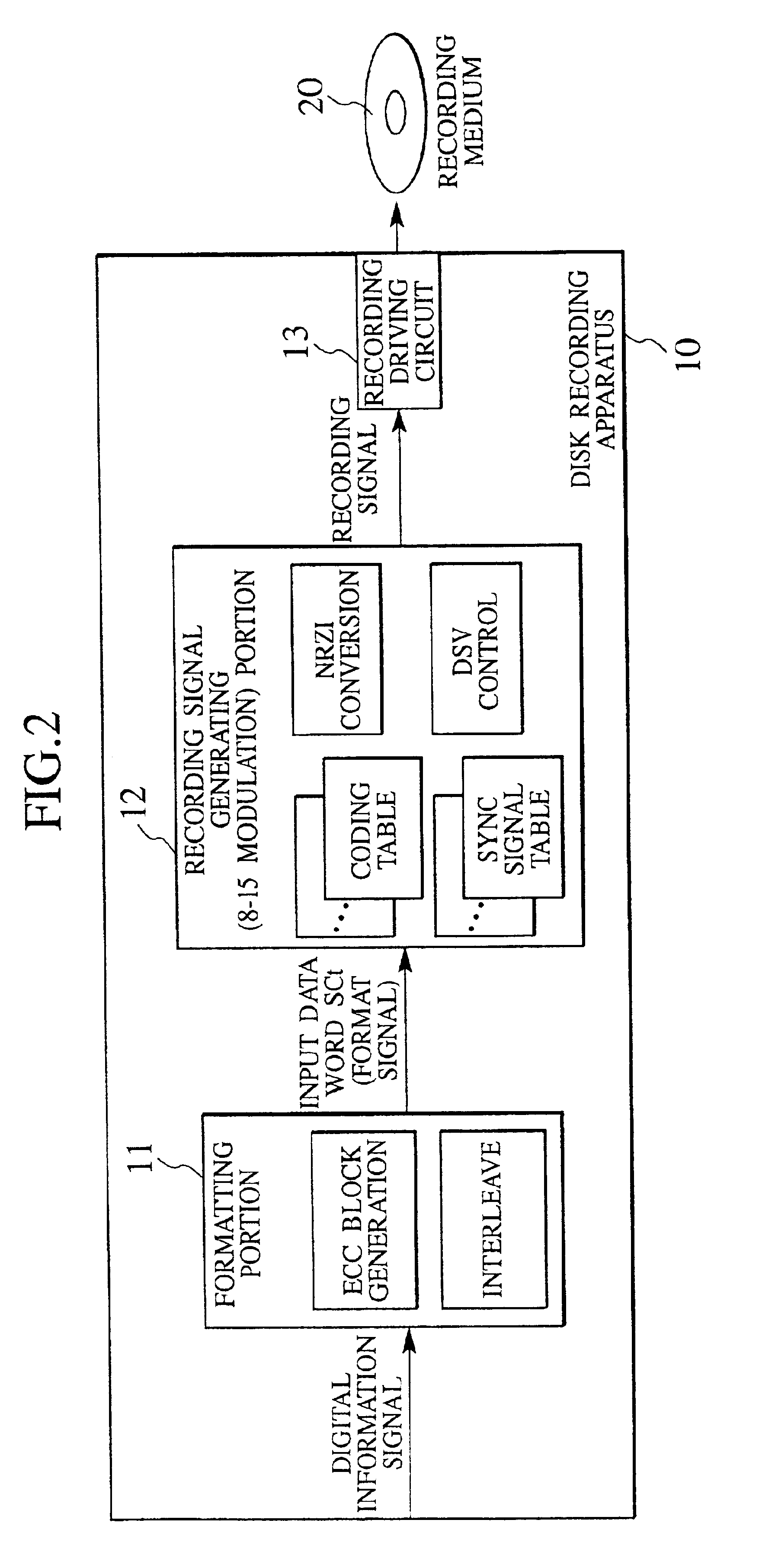
Recording method, recording apparatus, transmitting apparatus, reproducing method, reproducing apparatus, receiving apparatus, recording medium, and transmission medium
InactiveUS6963296B2High bit rateError proneTelevision system detailsRecord information storageIsochronous signal8-bit
There is disclosed a recording method for performing a DSV control while recording a recording signal generated by inserting a synchronous signal for decoding reproduction data into every predetermined number of code words in a code word string satisfying a predetermined run length restriction rule and to be outputted into a recording medium, when a plurality of coding tables are used to convert an input data word of p-bits to a code word of q-bits (q>p), and the code word string obtained by directly coupling the code words is recorded and reproduced in a recording medium such as an optical disk and magnetic disk, or transmitted via a transmitting portion, wherein the p-bits are 8 bits, the q-bits are 15 bits, and the predetermined run length restriction rule stipulates that a minimum run length of the signal obtained by NRZI-converting the code word excluding the synchronous signal is 3T, and a maximum run length is any one of 11T, 12T, 13T, and 14T.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
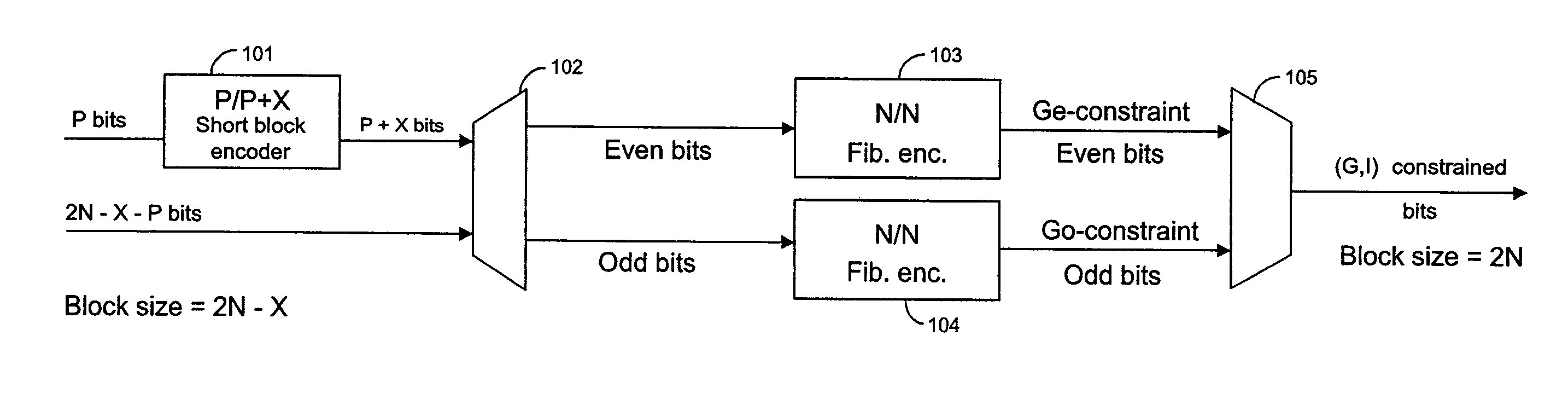
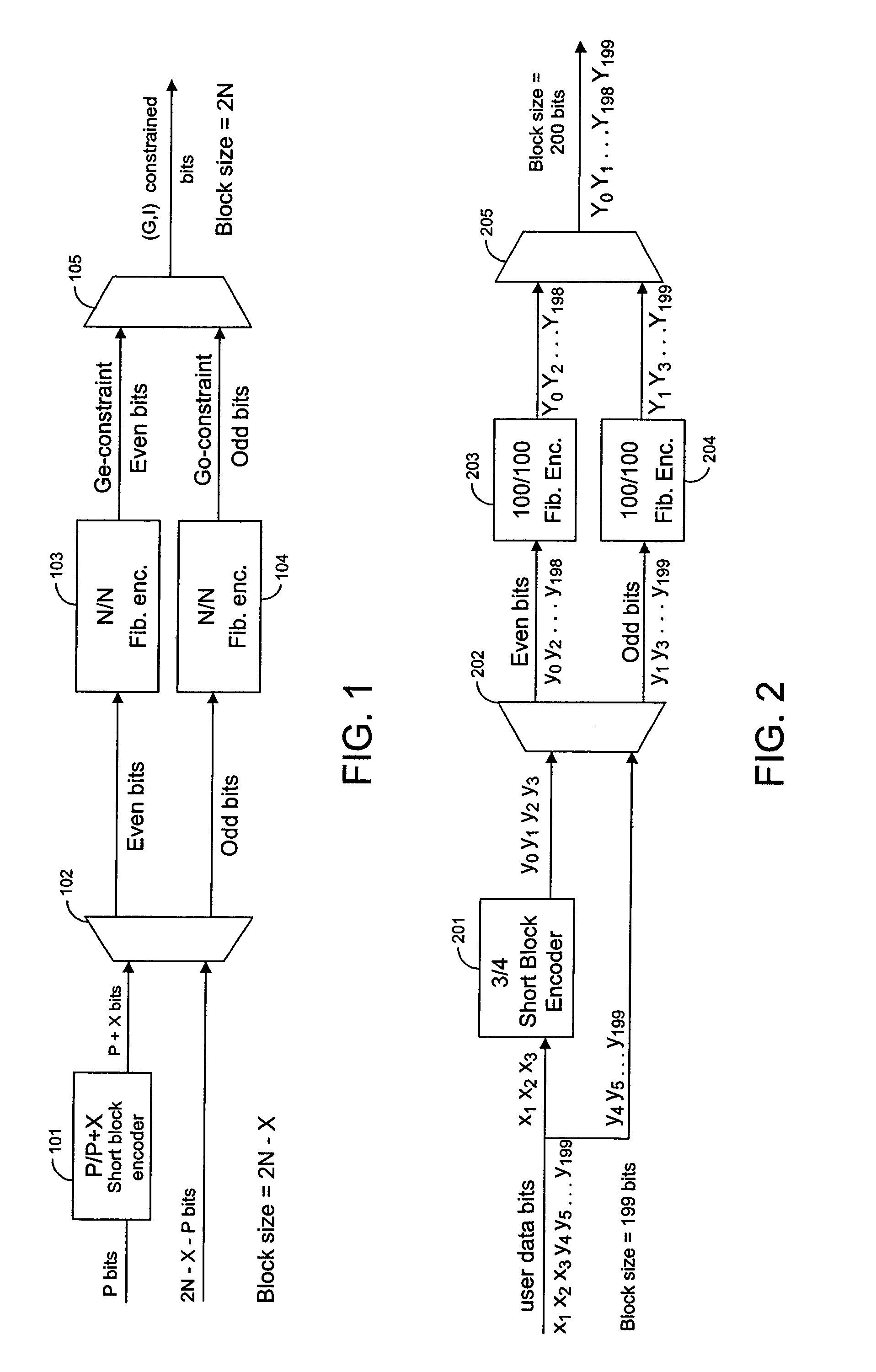
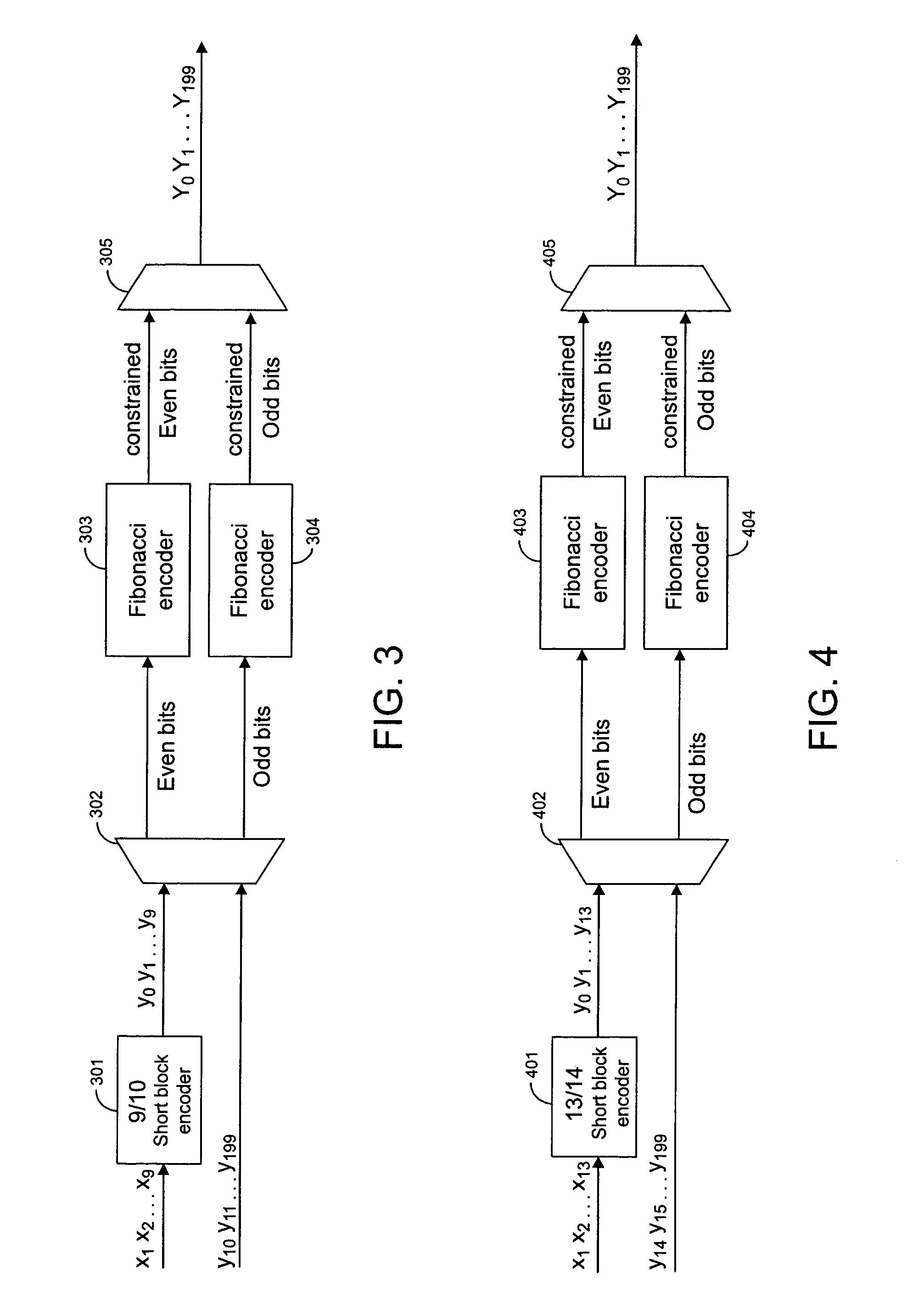
Techniques for modulating data using short block encoders
InactiveUS7064687B1Improve result rateTelevision system detailsOther error detection/correction/protectionData streamModulation coding
Techniques are provided for applying modulation constraints to data streams using a short block encoder. A short block encoder encodes a subset of the bits in a data stream. Then, the even and odd interleaves in a data stream are separated into two data paths. A first modulation encoder encodes the even interleave according to a first modulation constraint. A second modulation encoder encodes the odd interleave according to a second modulation constraint, which in general coincides with the modulation constraint for even interleave.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus of converting a series of data words into a modulated signal
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
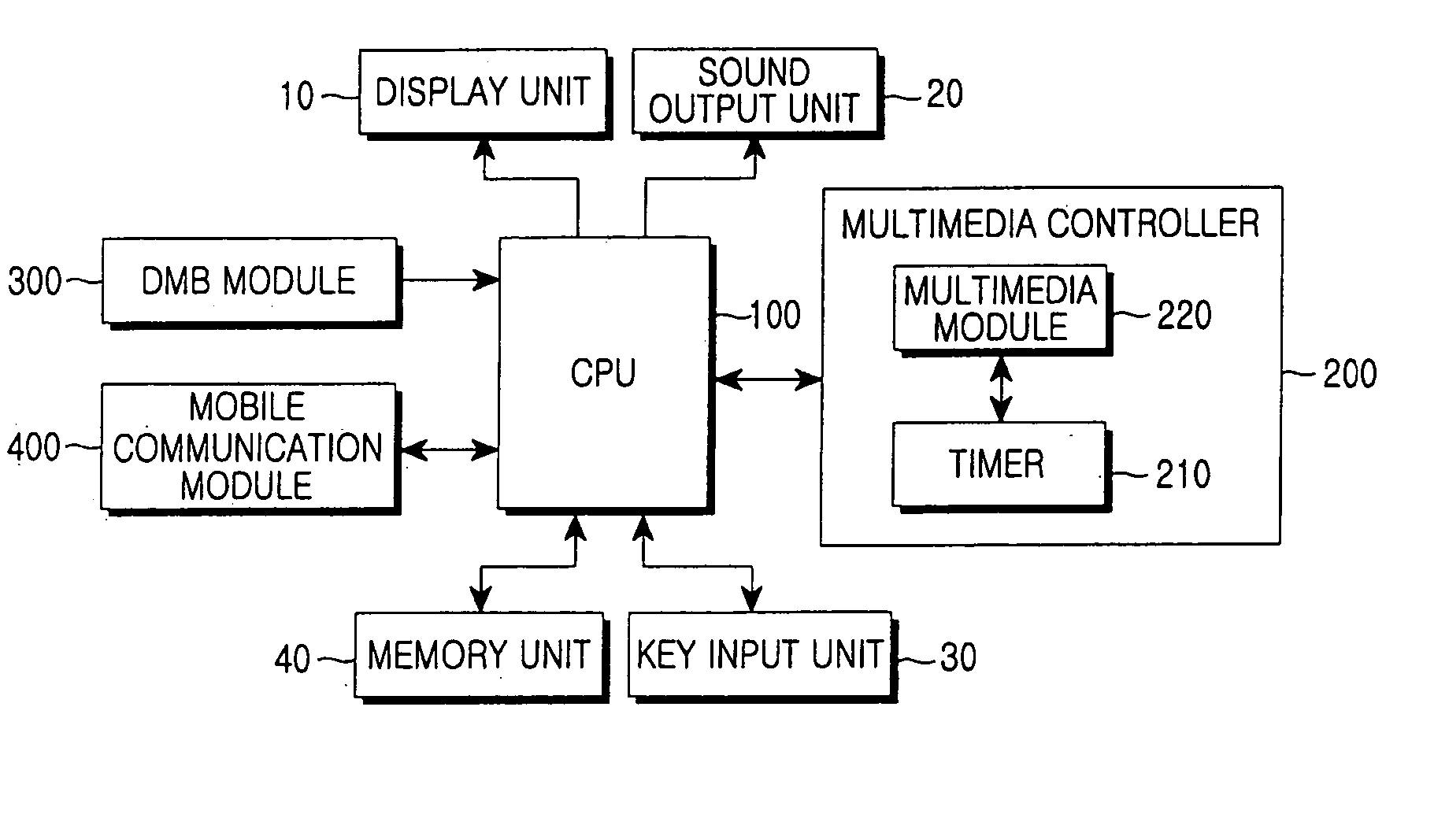
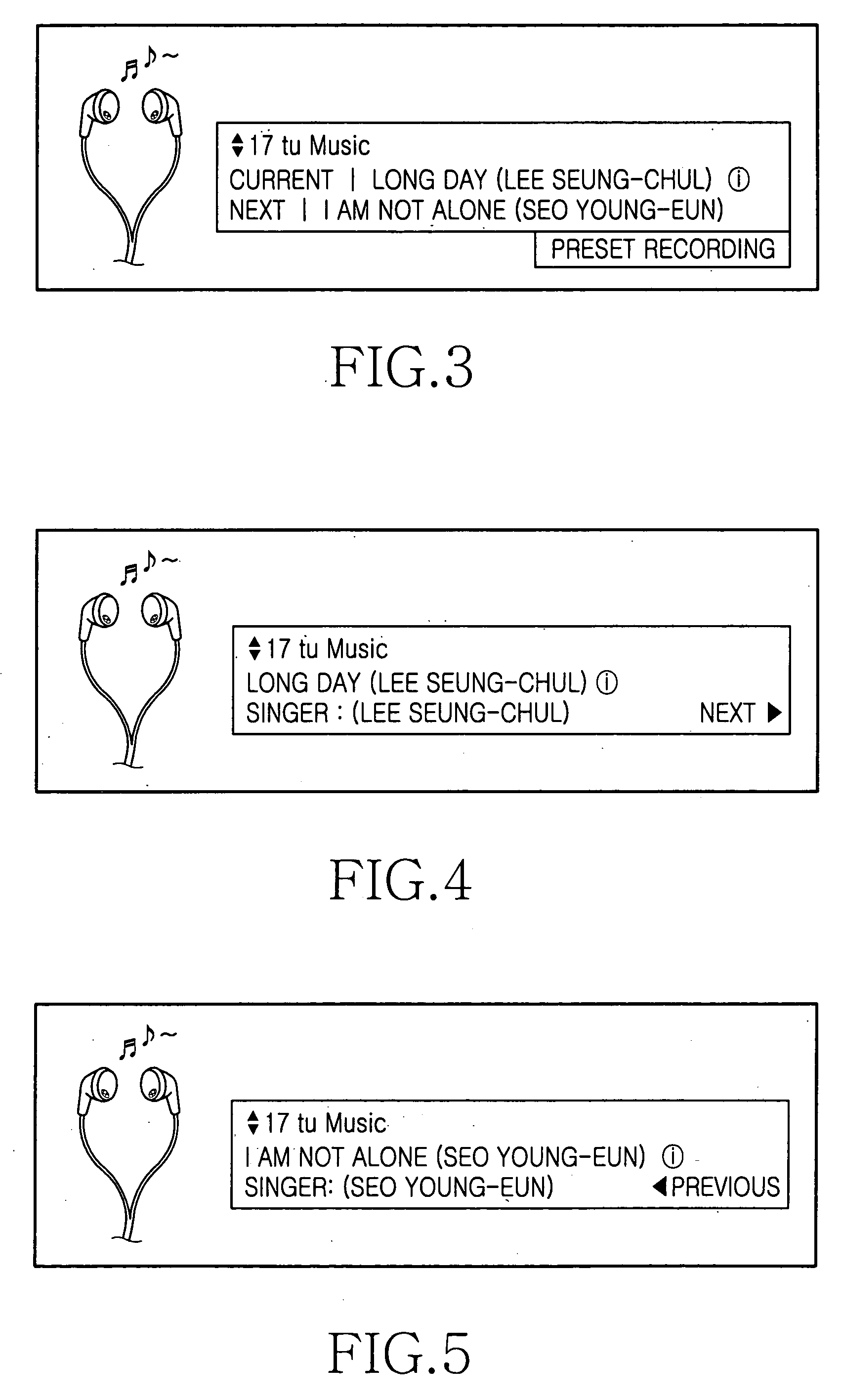
Digital multimedia broadcasting receiver for preset recording and method thereof
InactiveUS20070017347A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSpecific information broadcast systemsTime segmentDigital multimedia broadcasting
Disclosed is a digital multimedia broadcasting receiver for preset recording and a method thereof. The method for preset-recording a song provided through a music channel by using present and follow (P / F) information in a digital multimedia broadcasting receiver includes measuring a time period elapsed from a first time point at which P / F information is updated while a current song is played, when recording is preset, and calculating a first interval time by subtracting the first time point from an ending time of the currently-played song; starting recording a next-played song, when the time period measured from the first time point reaches the first calculated interval time measuring a time period elapsed from a second time point at which P / F information is updated during preset recording, and calculating a second interval time by subtracting the second time point from an ending time of the song being preset recorded; and ending recording the song being preset-recorded, when the time period measured from the second time point reaches the second calculated interval time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
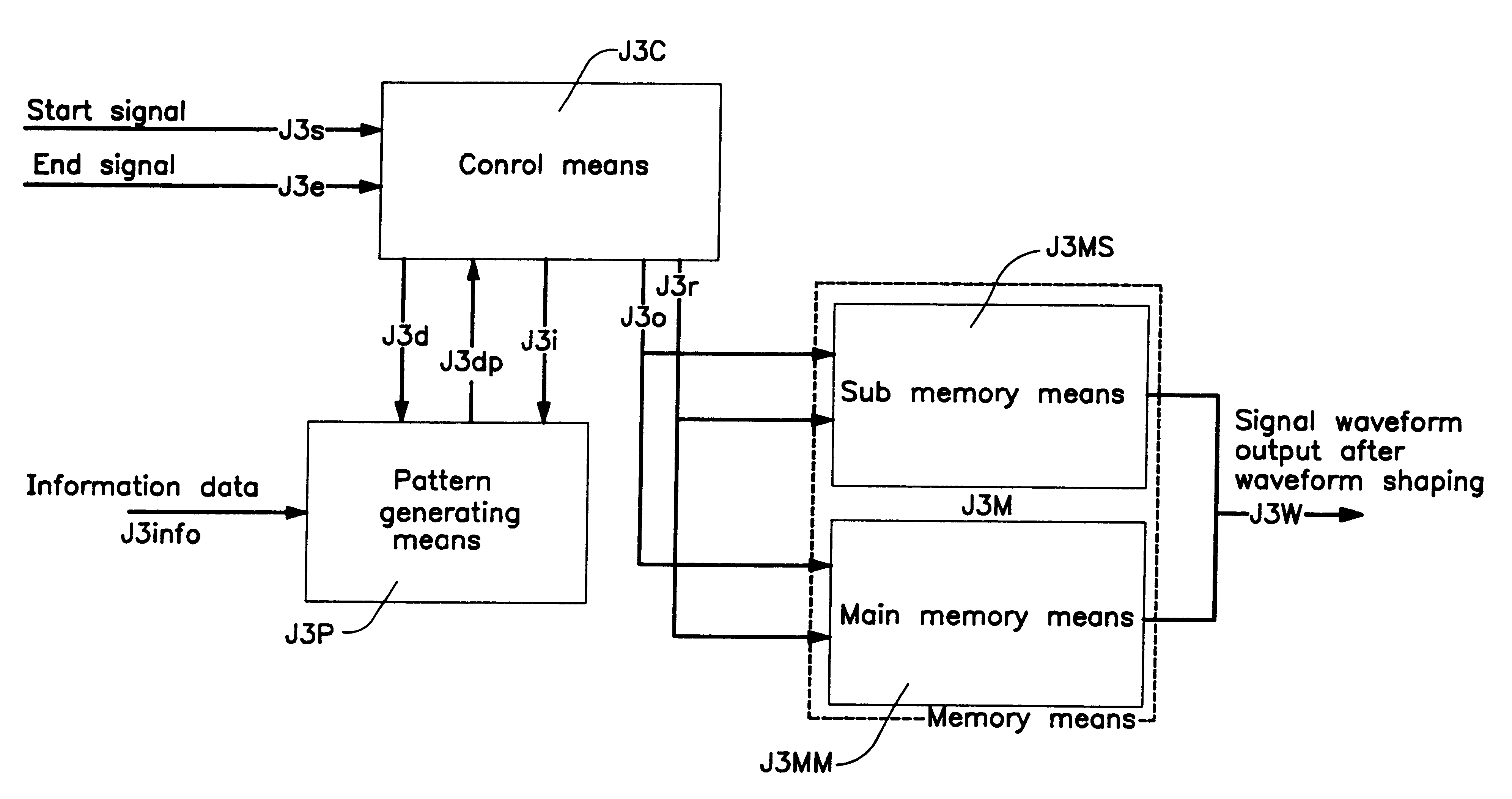
Waveform shaping method and equipment
In the transmitter which carries out burst transmission using information data as a packet, if the status is divided into four modes, namely, burst stop mode, burst rising mode, burst continuous mode, and burst falling mode, a waveform shaping equipment designed to read out shaped waveform data for each mode from outputs of either of the two memory tables, the first memory table which holds waveform data for specific data patterns used in common in burst rising mode and burst falling mode and the second memory table which holds waveform data for all data patterns used in the burst continuous mode, or a waveform shaping equipment comprising the third memory table which holds waveform data corresponding to all the data patterns used in the burst rising mode and the fourth memory table which holds waveform data corresponding to all data patterns used in the burst falling mode and generating shaped waveform data by synthesizing the two outputs of the third and the fourth memory tables at the time of burst continuous mode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Rewrite-efficient ecc/interleaving for multi-track recording on magnetic tape
For writing data to multi-track tape, a received data set is received and segmented into unencoded subdata sets, each comprising an array having K2 rows and K1 columns. For each unencoded subdata set, N1−K1 C1-parity bytes are generated for each row and N2−K2 C2-parity bytes are generated for each column. The C1 and C2 parity bytes are appended to the ends of the row and column, respectively, to form encoded C1 and C2 codewords, respectively. All of the C1 codewords per data set are endowed with a specific codeword header to form a plurality of partial codeword objects (PCOs). Each PCO is mapped onto a logical data track according to information within the header. On each logical data track, adjacent PCOs are merged to form COs which are modulation encoded and mapped into synchronized COs. Then T synchronized COs are written simultaneously to the data tape where T is the number of concurrent active tracks on the data tape.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data storage to enhance timing recovery in high density magnetic recording
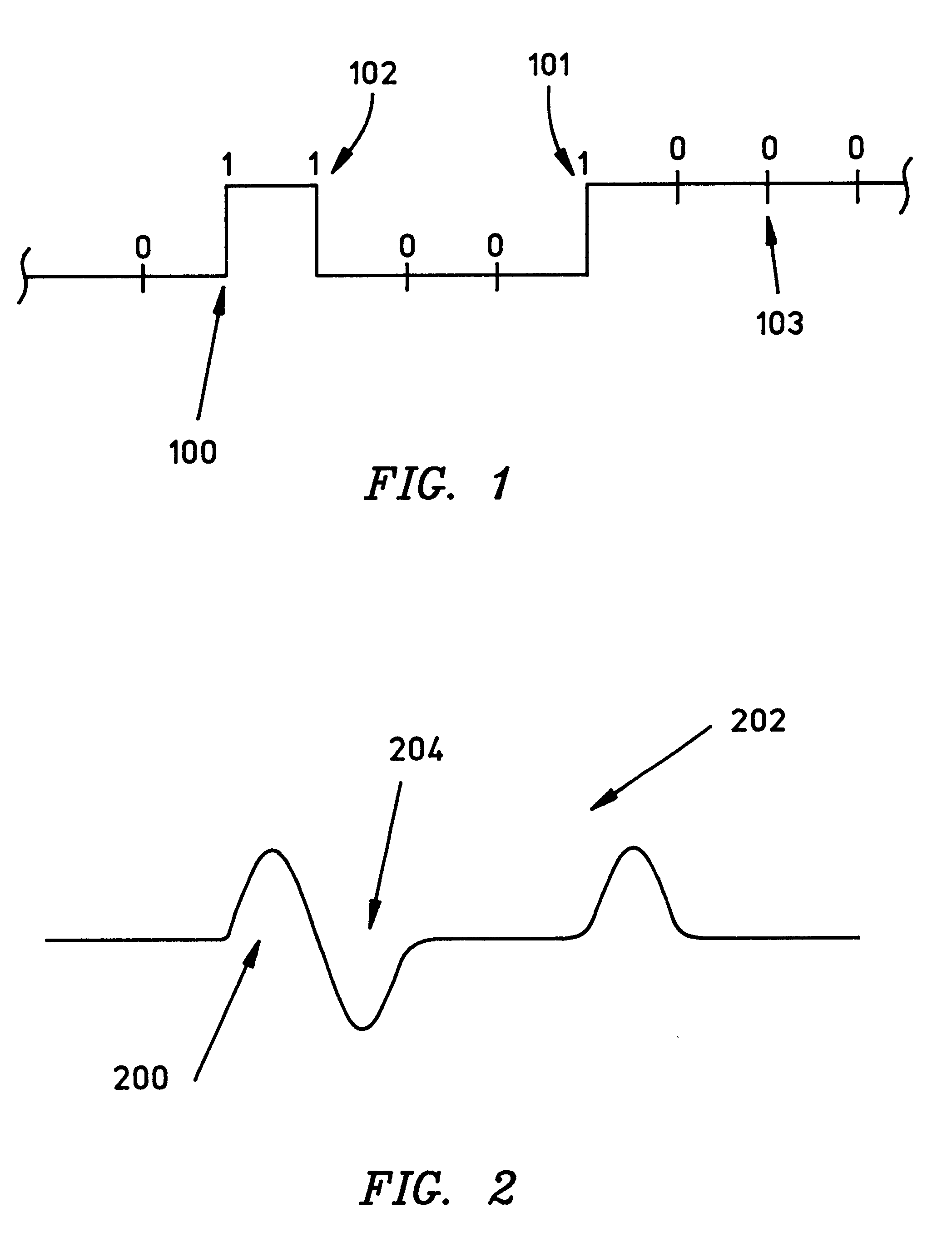
InactiveUS6429986B1Improve storage efficiencyRecord information storageDigital recordingHigh densityBlock code
A timing recovery system encodes data while impressing recognizable patterns thereon, enabling precise timing during subsequent readback operations. An uncoded binary sequence is encoded using an m / n rate block coded sequence, incorporating a unique predetermined binary bit pattern that occurs with a selected level of frequency. The encoded sequence is stored on the recording medium as a series of flux transitions. To read back the stored data, a read head measures the flux transitions stored on the medium and generates a representative analog waveform. A sampler samples the waveform in accordance with a timing scheme provided by a timing circuit. The timing circuit adjusts the timing of the samples to ensure that the analog waveform is sampled at appropriate times to yield the most accurate results. The timing circuit evaluates two consecutive samples to identify samples associated with features of the analog readback waveform that corresponds to the predetermined bit patterns. Identified samples are then compared to determine whether timing of samples should be advanced, retarded, or retained with respect to the analog waveform. After a detector translates samples into an enclosed binary bit stream, a decoder decodes the detector's binary bit stream by revising the original encoding process, recreating the original encoded binary sequence.
Owner:LINKEDIN
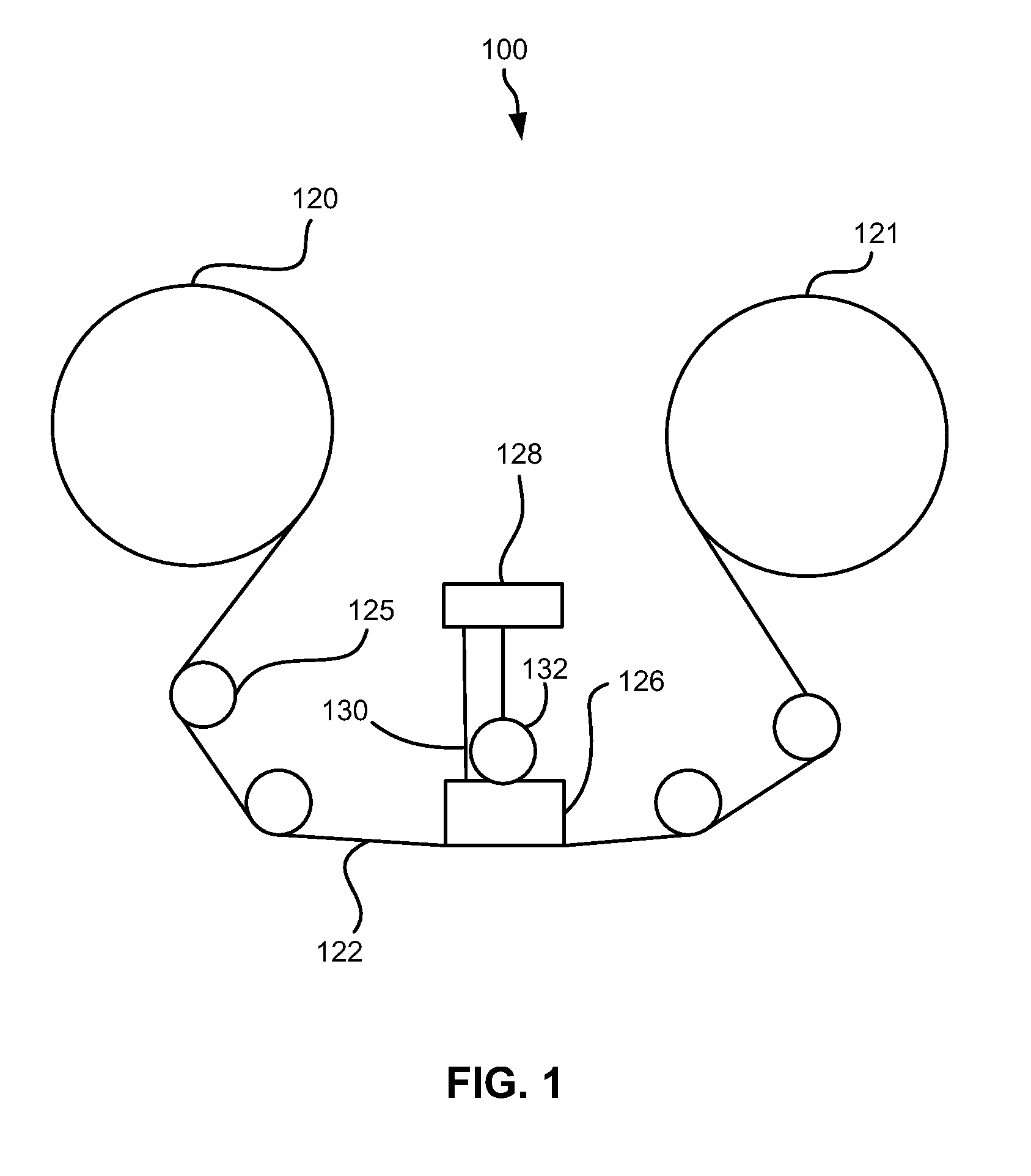
Optimum tape layout selection for improved error correction capability
According to one embodiment, a system for selecting an optimum tape layout to store data on a tape medium may include a processor and logic integrated with and / or executable by the processor, the logic being configured to: select a family of data set layouts based on parameters associated with at least a tape drive and the tape medium, compute a set of all minimum distances for the selected family of data set layouts, calculate a first performance metric associated with each possible set of parameters, select a best first performance metric from all calculated first performance metrics and store a set of parameters associated with the best first performance metric, and select a data set layout algorithm which utilizes the set of parameters associated with the best first performance metric, wherein the data set layout algorithm and a rewrite layout algorithm combine to form an optimum tape layout.
Owner:IBM CORP
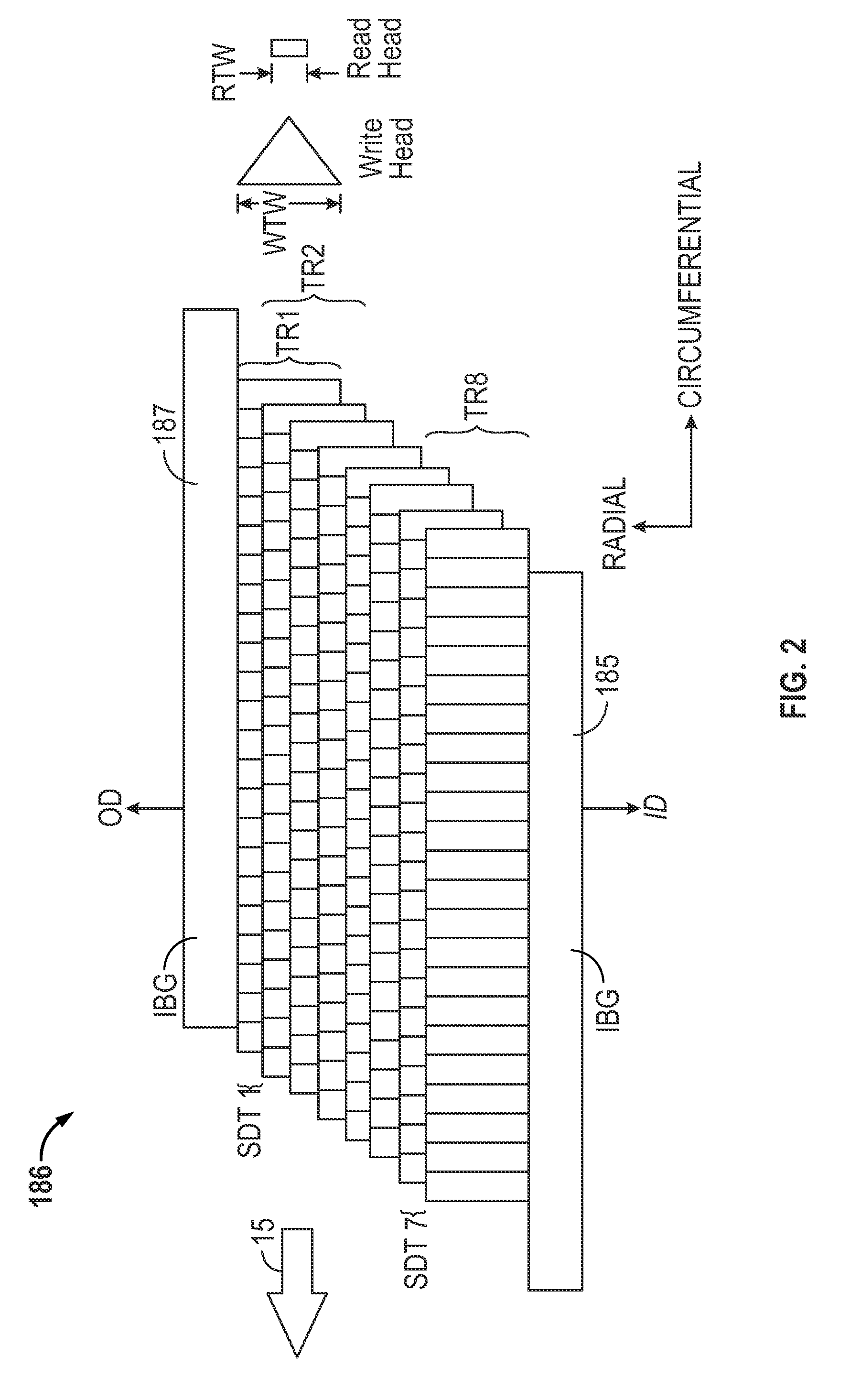
Bit patterned medium, reading head for reading data recorded on bit patterned medium, and hard disk drive for recording/reading data on/from bit patterned medium
InactiveUS20090067078A1Improve reading efficiencyPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsHard disc driveGraphics
Provided are a bit patterned medium having a super track, a reading head which reads data recorded on the bit-patterned medium, and a hard disk drive (HDD) for recording / reading data on / from the bit patterned medium. The bit patterned medium includes a substrate, and a recording layer formed with a plurality of bit cells separated from each other along a plurality of tracks forming concentric circles having different radii on the substrate, wherein each track includes a super track including a plurality of sub-tracks, and bit cells formed on one of the sub-tracks are arranged at different positions in a circumference direction of the recording layer to bit cells formed on adjacent sub-tracks. The reading head which reads data recorded on a bit patterned medium has a width in a cross-track direction sufficient for reading data of an equal number of bit cells as the plurality of sub-tracks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetic tape recording in data format using an efficient reverse concatenated modulation code
In one embodiment, a method for writing data to a magnetic tape utilizing a rate-(232 / 234) reverse concatenated modulation code includes receiving a data stream comprising one or more data sets, separating each data set into a plurality of sub data sets, encoding each sub data set with a C2 encoding, encoding each C2-encoded sub data set with the modulation code, encoding each modulated sub data set with a C1 encoding, and simultaneously writing the encoded modulated sub data sets to data tracks of the magnetic tape. Other methods for writing data to a magnetic tape utilizing a rate-(232 / 234) reverse concatenated modulation code are described according to various other embodiments.
Owner:BEIJING PIANRUOJINGHONG TECH CO LTD
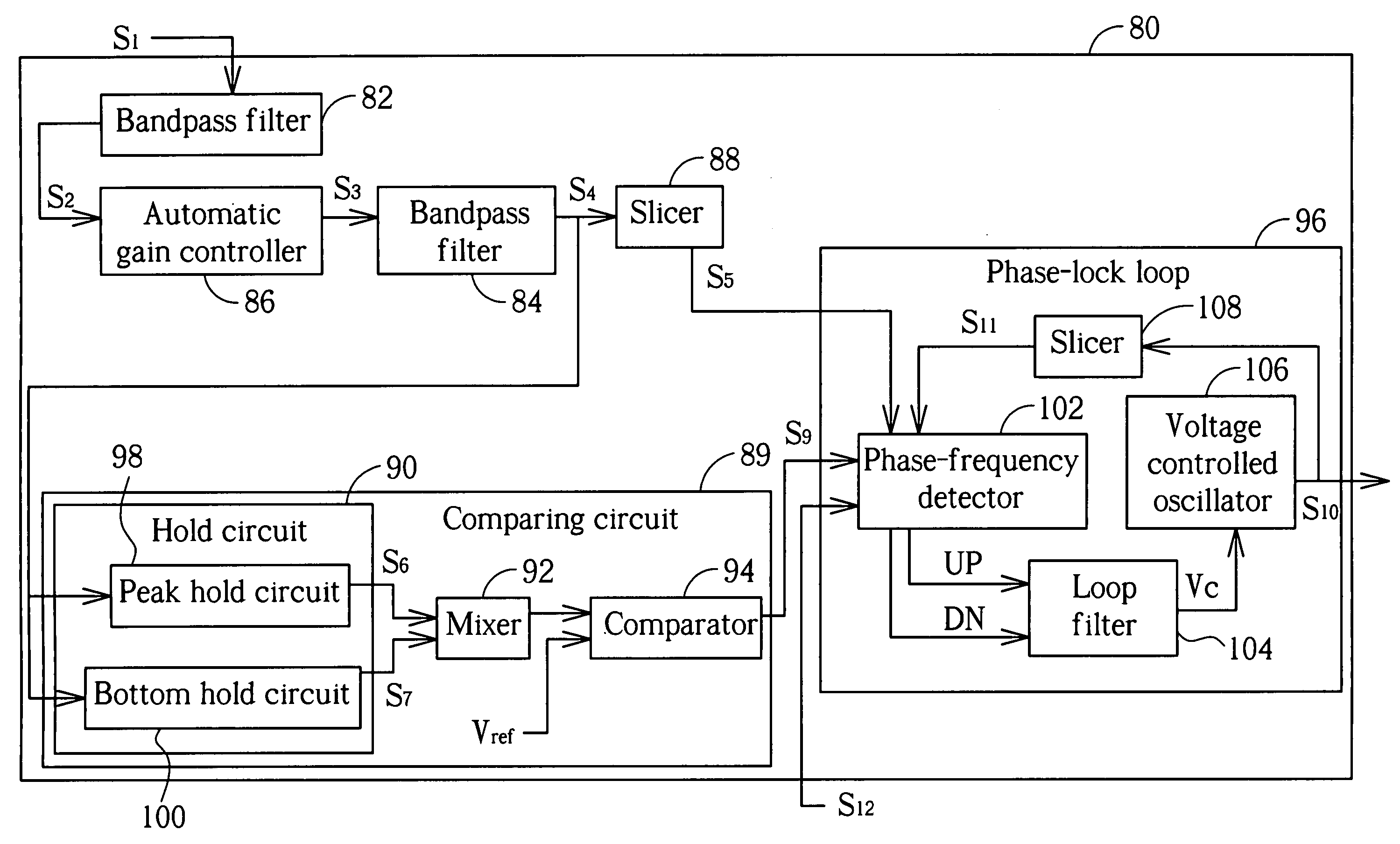
Apparatus and method for generating wobble clock
ActiveUS20050007720A1Easily embodiedRecord information storageDigital recordingControl signalEngineering
An apparatus for generating wobble clock comprises: a comparing circuit and a phase lock loop. The comparing circuit generates a combining signal according to peak values of the wobble signal and compares the output signal with a reference voltage to output a control signal. The phase lock loop drives the wobble clock to be synchronized with the wobble signal if the protection signal corresponds to a first logic level, and stops driving the wobble clock to be synchronized with the wobble signal if the protect signal corresponds to a second logic level.
Owner:TIAN HLDG
Popular searches
Angle-modulation recording Pulse-modulation recording/reproducing Delay line applications Redundant array of inexpensive disk systems Equalisers Signal processing using self-clocking codes Record carrier types Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubes Picture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanning Picture reproducers using projection devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com