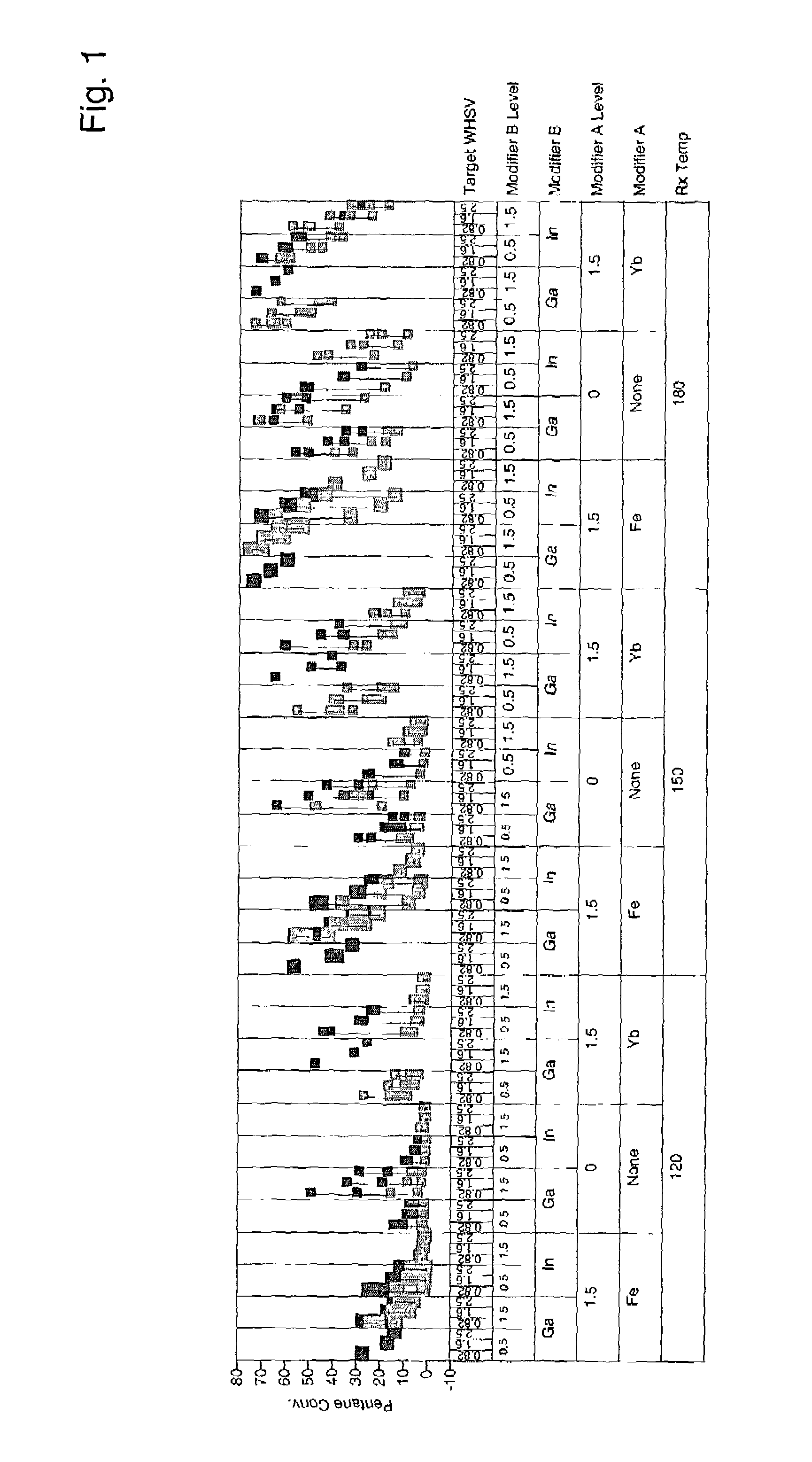
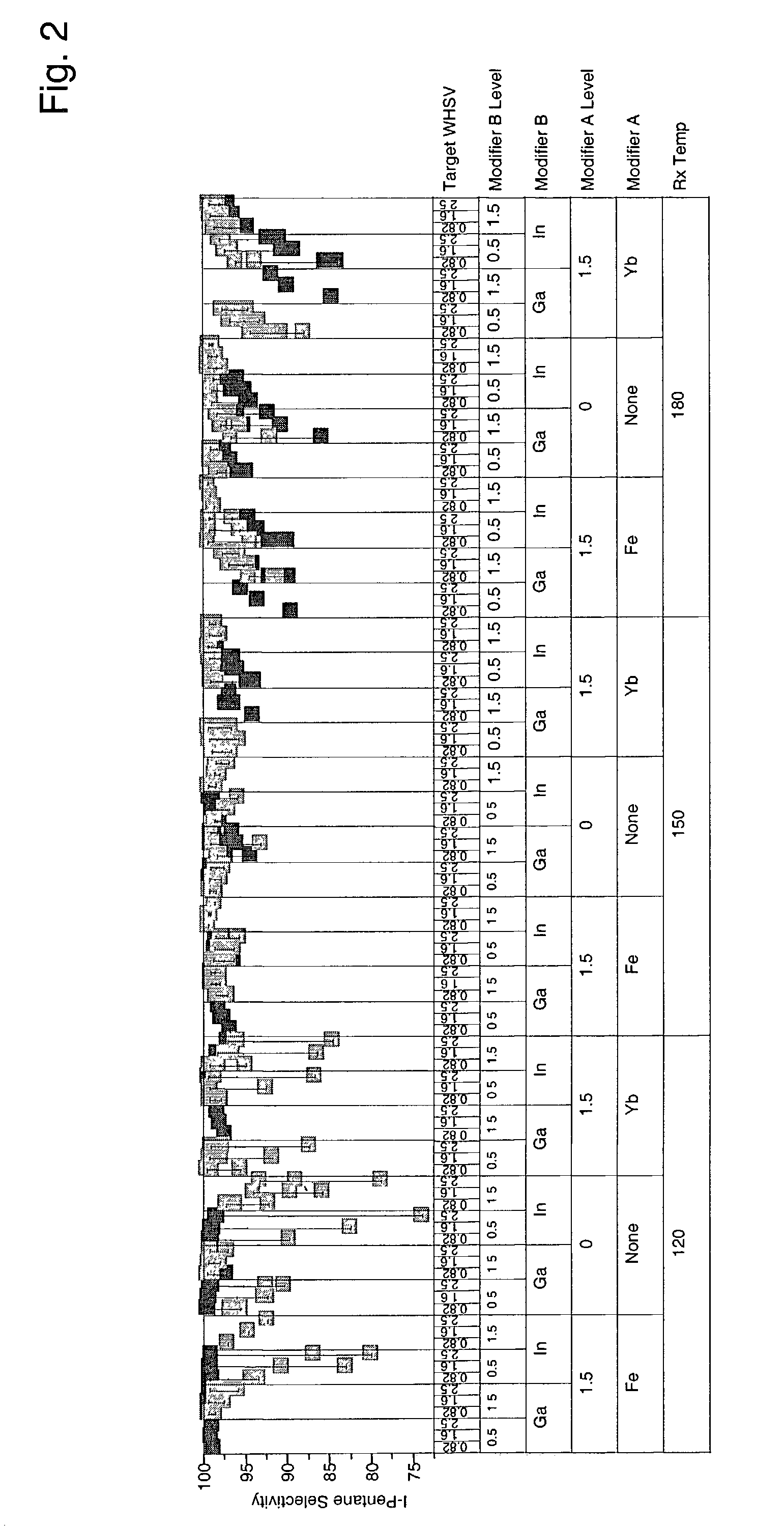
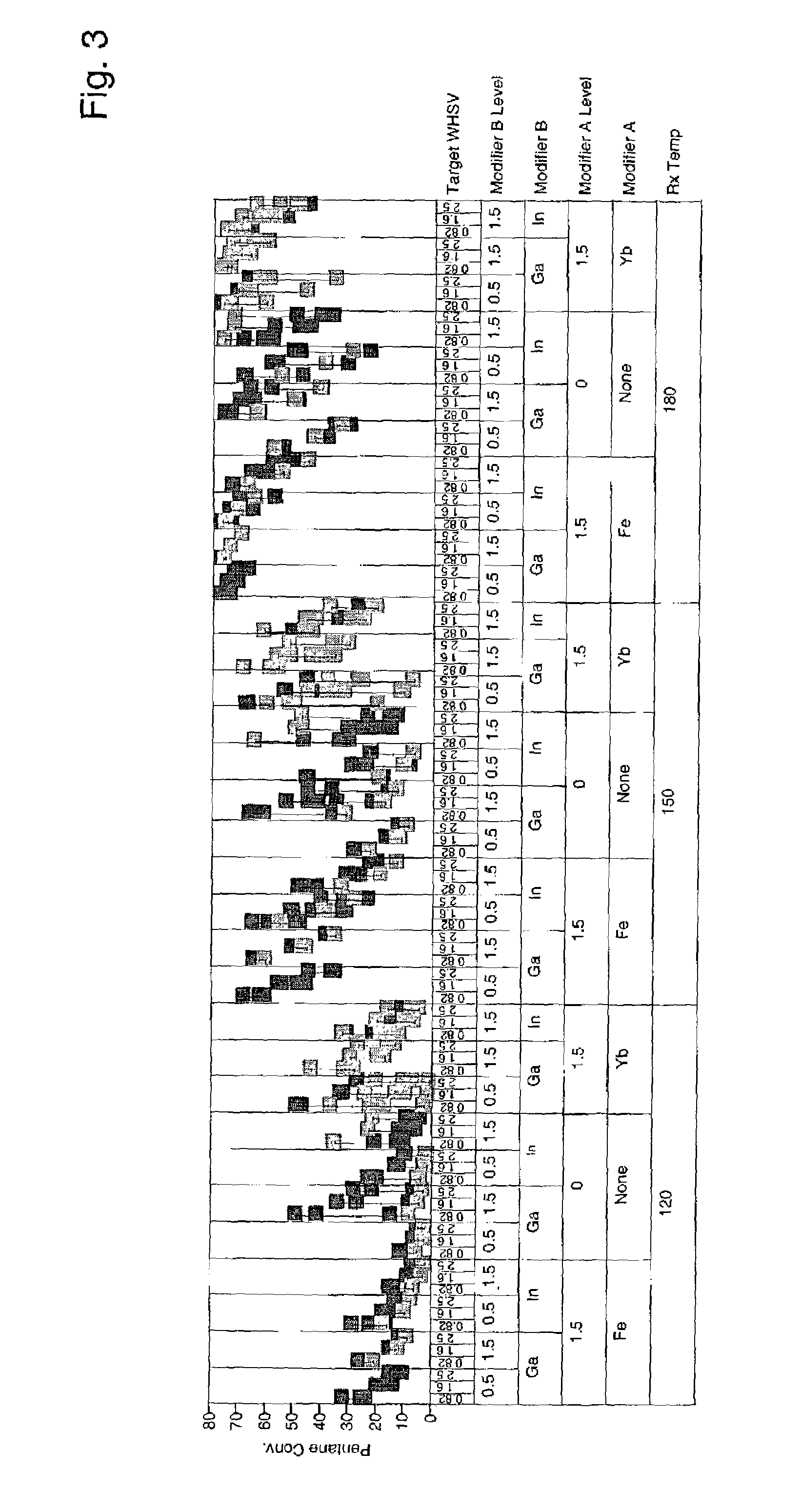
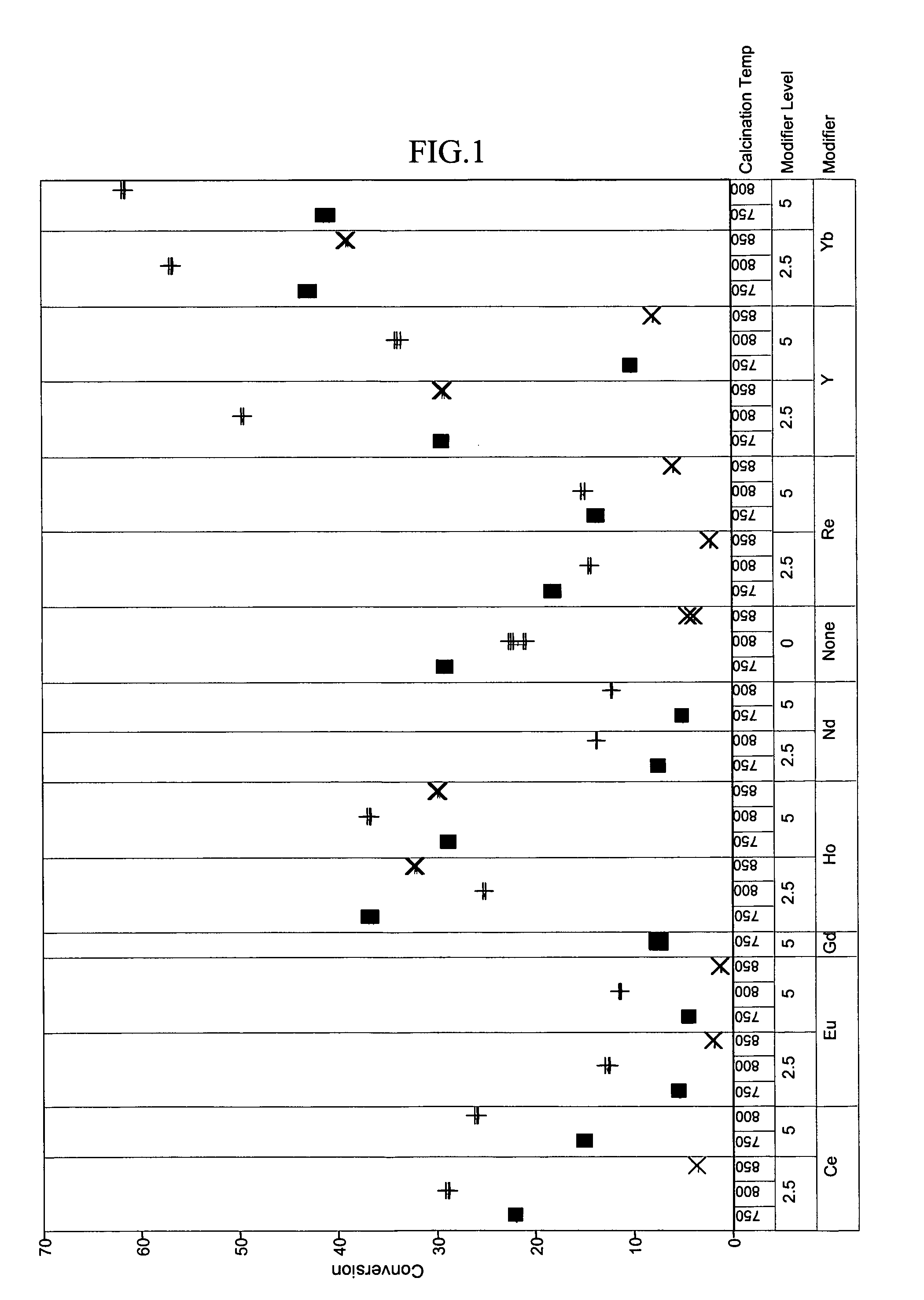
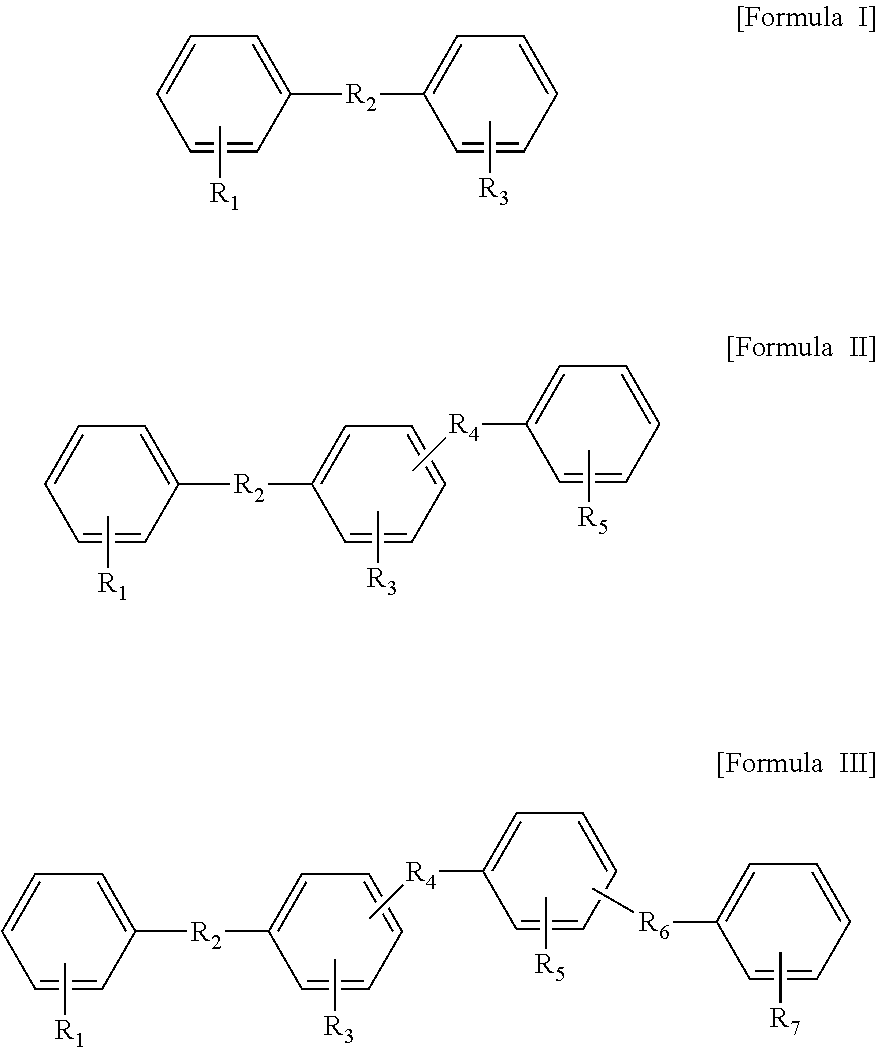
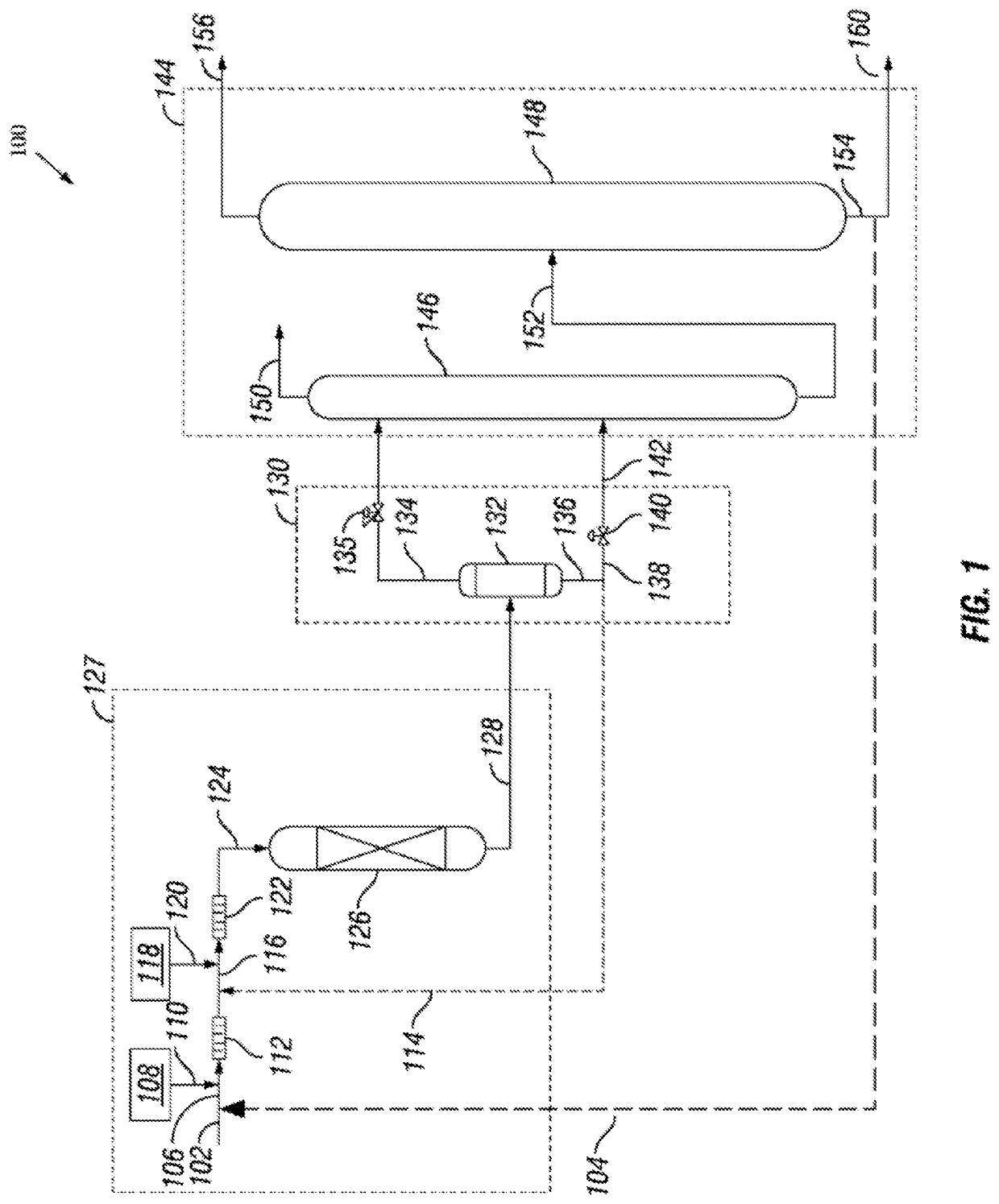
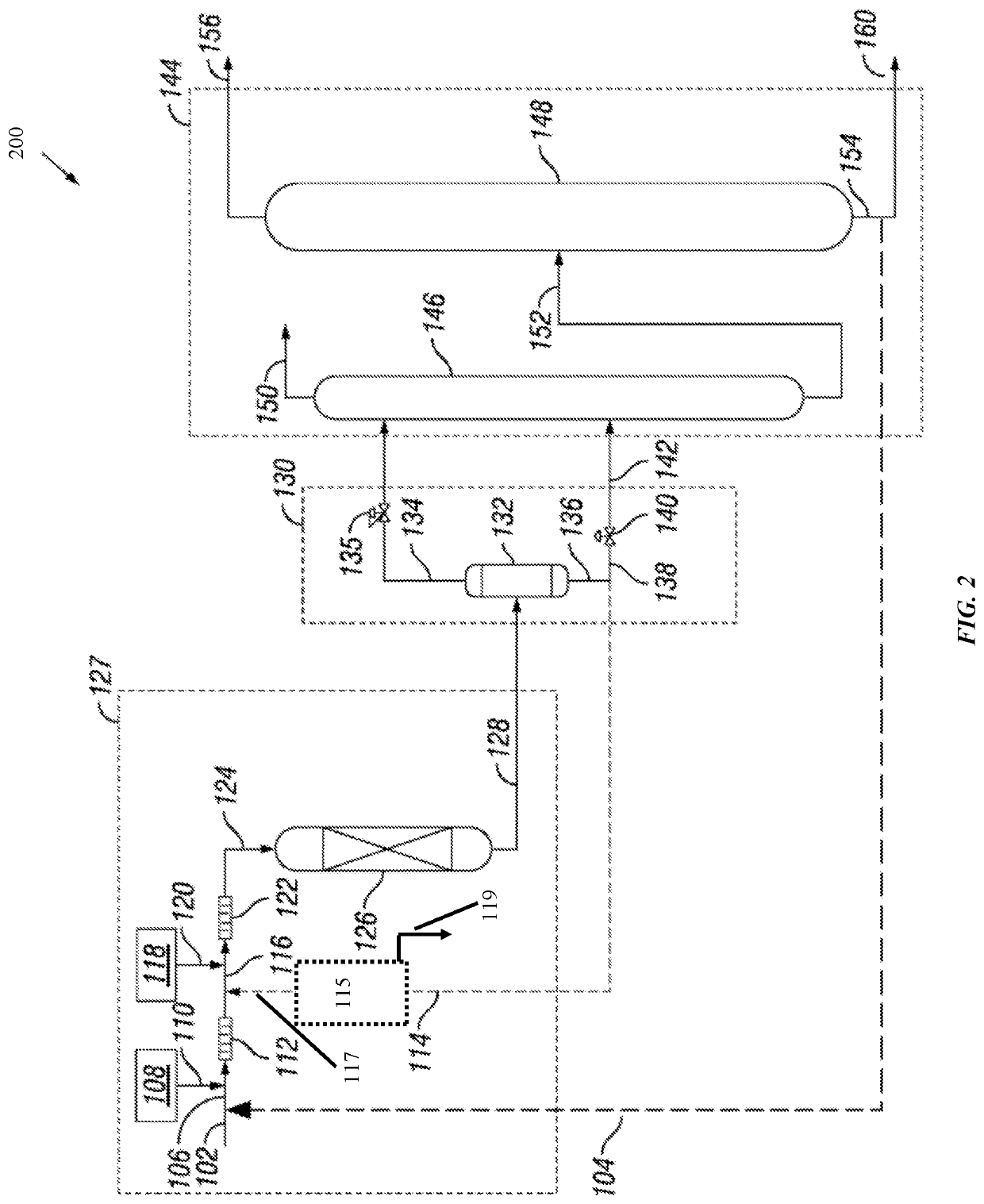
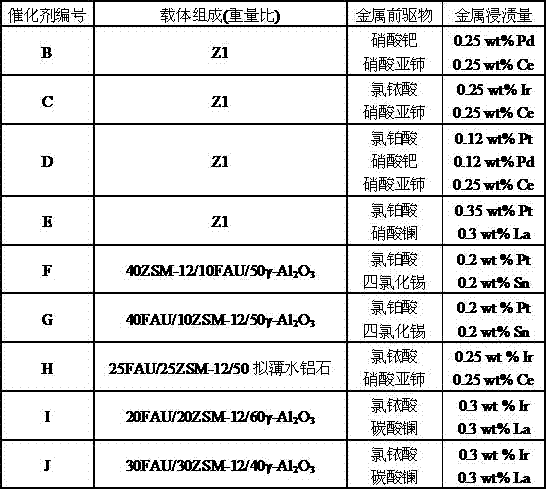
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35results about "Hydrocarbon by polyaryl split-off" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solid-acid isomerization catalyst and process
ActiveUS7041866B1Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneSulfation
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a sulfated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component comprising at least one Group III A (IUPAC 13) component, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Isomerization catalyst and processes
InactiveUS6977322B2Improve performanceImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingAlkaneIsomerization
A catalyst and process is disclosed to selectively upgrade a paraffinic feedstock to obtain an isoparaffin-rich product for blending into gasoline. The catalyst comprises a support of a tungstated oxide or hydroxide of a Group IVB (IUPAC 4) metal, a first component of at least one lanthanide element, yttrium or mixtures thereof, which is preferably ytterbium or holmium, and at least one platinum-group metal component which is preferably platinum.
Owner:UOP LLC
Hydrocarbon conversion processes using non-zeolitic molecular sieve catalysts
Hydrocarbon or oxygenate conversion process in which a feedstock is contacted with a non zeolitic molecular sieve which has been treated to remove most, if not all, of the halogen contained in the catalyst. The halogen may be removed by one of several methods. One method includes heating the catalyst in a low moisture environment, followed by contacting the heated catalyst with air and / or steam. Another method includes steam-treating the catalyst at a temperature from 400° C. to 1000° C. The hydrocarbon or oxygenate conversion processes include the conversion of oxygenates to olefins, the conversion of oxygenates and ammonia to alkylamines, the conversion of oxygenates and aromatic compounds to alkylated aromatic compounds, cracking and dewaxing.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for converting polycyclic aromatic compounds to monocyclic aromatic compounds
ActiveUS9061953B2Hydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offHydrocarbon by hydrogenationPolycyclic compoundCompound a
A process for converting polycyclic aromatic compounds to monocyclic aromatic compounds includes pyrolyzing a coal feed to produce a coke stream and a coal tar stream. The coal tar stream is cracked, and the cracked coal tar stream is fractionated to produce an aromatic fraction comprising the polycyclic aromatic compounds. The process further includes hydrocracking the aromatic fraction to partially hydrogenate at least a first portion of the aromatic fraction, and to open at least one ring of a second portion of the aromatic fraction to form the monocyclic aromatic compounds from the polycyclic compounds, and recycling the first portion of the aromatic fraction.
Owner:UOP LLC
Compound and organic el device
InactiveUS20090096368A1Improve efficiencyIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offFluorantheneOrganic compound
The present invention provides a high-performance organic EL device and a novel compound used for the device. The novel compound of the present invention is a fluoranthene compound having a specific structure. The organic EL device of the present invention is an organic EL device comprising: an anode; a cathode; and an organic compound layer interposed between the anode and the cathode, wherein the organic compound layer has the fluoranthene compound.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20140024871A1High yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingDistillationAromatic hydrocarbon
A method of producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons includes bringing a feedstock oil having a 10 vol % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 vol % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower, into contact with a catalyst for monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon production containing a crystalline aluminosilicate, in which a content ratio of monocyclic naphthenobenzenes in the feedstock oil is adjusted to 10 mass % to 90 mass %, by mixing a hydrocarbon oil A having a 10 vol % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 vol % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower with a hydrocarbon oil B containing more monocyclic naphthenobenzenes than the hydrocarbon oil A.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Aromatics hydrogenolysis using novel mesoporous catalyst system
InactiveUS20060014995A1Improve accessibilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offArylMetal
A process for the selective ring opening of ring-containing hydrocarbons in a feed stream having at least 10% ring-containing hydrocarbons includes contacting the feed stream with a ring opening catalyst containing a metal or a mixture of metals active for the selective ring opening of the ring-containing hydrocarbons on a support material, wherein the support material is a non-crystalline, porous inorganic oxide or mixture of inorganic oxides having at least 97 volume percent interconnected mesopores based on micropores and mesopores, and wherein the ring-containing hydrocarbons have at least one C6 ring and at least one substituent selected from the group consisting of fused 5- or 6-membered rings, alkyl, cycloalkyl and aryl groups.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Reproducible catalyst for converting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and preparation method of reproducible catalyst
ActiveCN104549469AGood regeneration performanceGood stability and reproducibilityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offMolecular sievePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
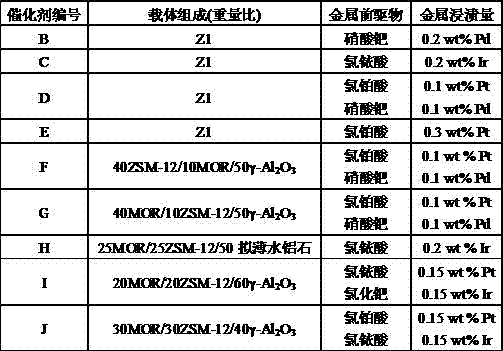
The invention relates to a reproducible catalyst for converting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and a preparation method of the reproducible catalyst, and is mainly used for solving the problems in the prior art that the conversion depth of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is low, the yield of the monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is low and the reproduction performance of the catalyst is poor. The problems are solved very well by adopting the technical scheme that the catalyst is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 30%-65% of a mixture of MOR zeolite and a ZSM-12 molecular sieve, 34.5%-69.9% of at least one adhesive selected from gamma-aluminum oxide, eta-aluminum oxide and pseudo-boehmite, and 0.1%-0.5% of at least one metal selected from Pt, Pd and Ir. The catalyst has the relatively good reproduction performance and can be used for industrial production of converting the heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon to the monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130267749A1High yieldReduction in yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonCarbon number
The catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons having 6 to 8 carbon number from oil feedstock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower. The catalyst includes crystalline aluminosilicate, phosphorus, and a binder, and the amount of phosphorus is 0.1 to 10 mass % based on the total mass of the catalyst.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
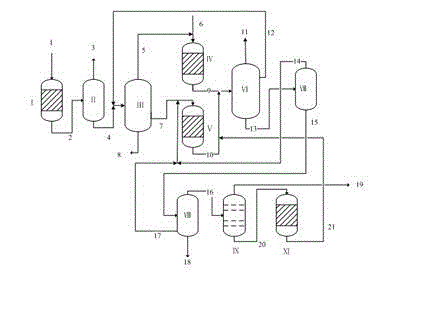
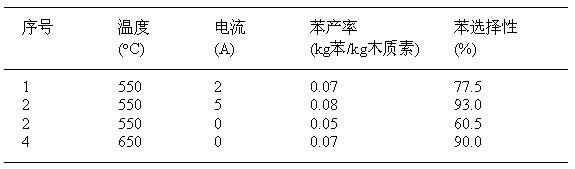
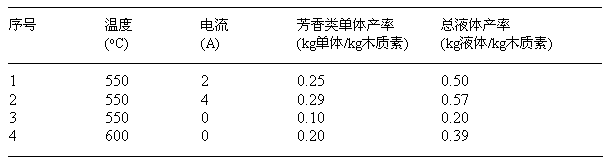
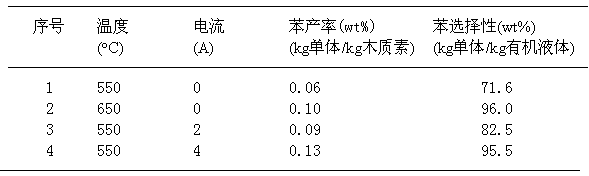
Method for directionally preparing benzene by utilizing xylogen
InactiveCN102701898AAbundant resourcesHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offBulk chemical productionBenzenePtru catalyst
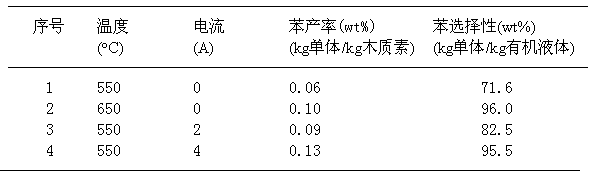
The invention relates to a method for directionally preparing benzene by utilizing xylogen. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a cylindrical fixed bed catalytic reactor with a conductive metal wire arranged in a cavity; depolymerizing to converte xylogen to an aromatic monomer, wherein a led raw material is the xylogen, a catalyst is powder zeolite catalyst or modified zeolite catalyst containing transition metal nickel element, the usage amount is characterized in that the weight ratio of the catalyst to the xylogen is 0.3-10 per hour, and a product is a liquid-state aromatic monomer mixer; and directionally converting the aromatic monomer mixer into benzene, wherein a led raw material is the aromatic monomer mixer which is preheat to be 200-250 DEG C, a catalyst is powder zeolite catalyst containing an Re element, the usage amount is characterized in that the weight ratio of the aromatic monomer mixer to the zeolite catalyst containing the Re element is 0.2-15 per hour, and a product is mixed liquid taking the benzene as the main part. According to the method, an external hydrogen source is not needed, the raw material resources are rich, and higher benzene yield and benzene selectivity can be obtained at intermediate temperature and constant pressure as well as under a green and mild reaction environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-channel pyrolysis tubes, material deposition equipment including the same and associated methods
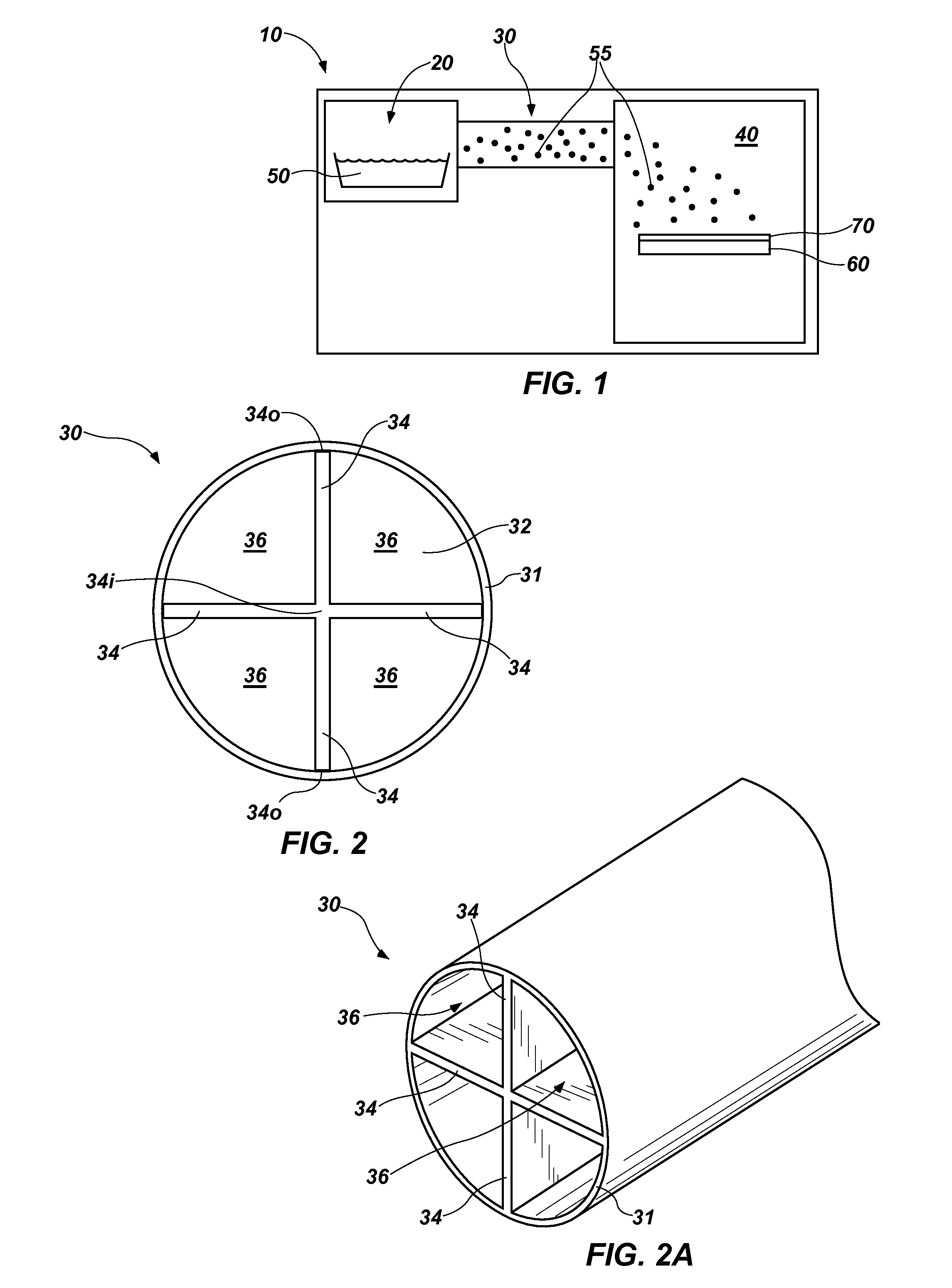
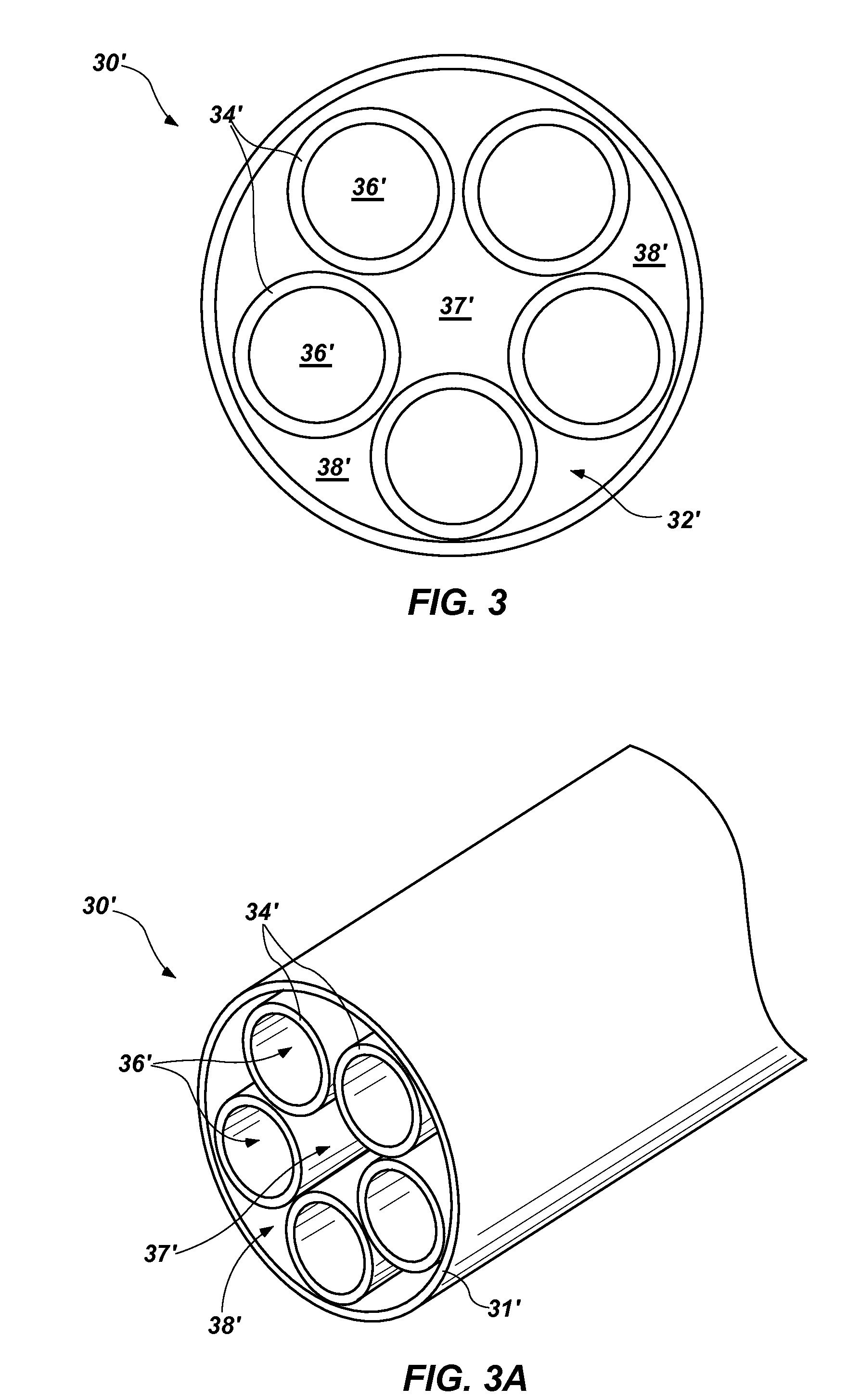
InactiveUS20150211115A1Easy to useShorten the timeHydrocarbon by isomerisationLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A pyrolysis tube for use with a material deposition system includes a plurality of channels. The channels may be defined by internal elements of the pyrolysis tube, or by internal elements that form an insert for a conventionally configured pyrolysis tube. One or more of the channels may extend straight through the pyrolysis tube, providing a direct line of sight through the pyrolysis tube. Material deposition systems that include such an insert or pyrolysis tube are also disclosed, as are methods for efficiently pyrolyzing precursor materials at temperatures that are reduced relative to conventional pyrolysis temperatures and / or at rates that are increased relative to conventional pyrolysis rates.
Owner:HZO INC
Selective ring-opening catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106582628BHigh ring-opening selectivityDelay inactivationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMolecular sieve
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20140012055A1High yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingDistillationAromatic hydrocarbon
A method of producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons includes bringing a light feedstock oil having a 10 vol % distillation temperature of 140° C. to 205° C. and a 90 vol % distillation temperature of 300° C. or lower, which has been prepared from a feedstock oil having a 10 vol % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 vol % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower, into contact with a catalyst for monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon production containing a crystalline aluminosilicate, in which a content ratio of monocyclic naphthenobenzenes in the light feedstock oil is adjusted by distillation of the feedstock oil such that the content ratio of monocyclic naphthenobenzenes in the light feedstock oil is higher than a content ratio of monocyclic naphthenobenzenes in the feedstock oil.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Process and Catalyst for the Transalkylation of Aromatics
InactiveUS20100298617A1Hydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offLiquid phasePhosphorus
Disclosed herein is a process and catalyst for producing an ethylbenzene feed from a polyethylbenzene feed, comprising the step of contacting a benzene feed with a polyethylbenzene feed under at least partial liquid phase conditions in the presence of a zeolite beta catalyst having a phosphorus content in the range of 0.01 wt. % to 0.5 wt. % of said catalyst, to provide a product which comprises ethylbenzene.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Selective ring-opening catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106582628AInhibition of agglomerationReduced inactivation rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMolecular sieve
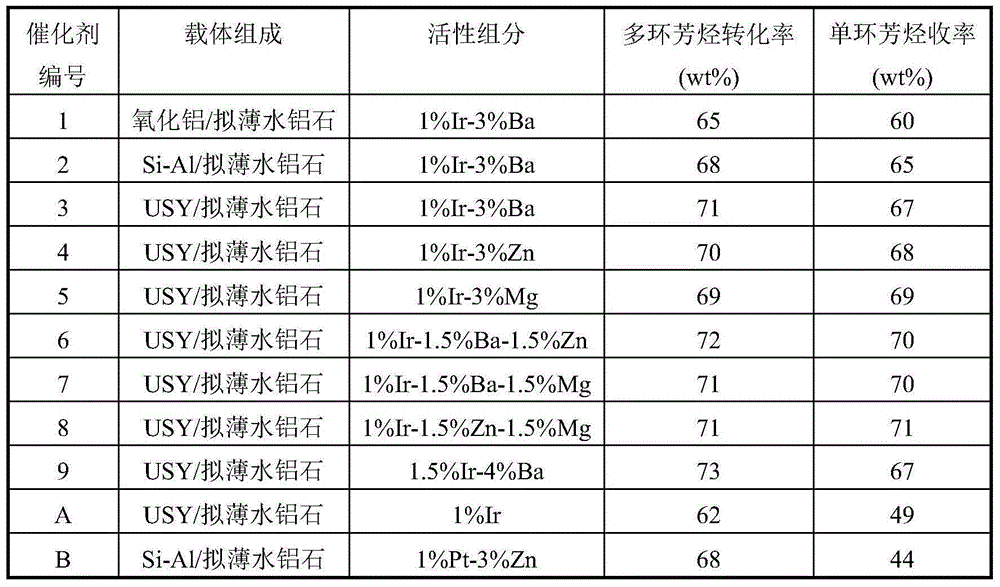
The present invention relates to a selective ring-opening catalyst and a preparation method thereof. A purpose of the present invention is to mainly solve the problems of poor polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring-opening selectivity, low monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon yield and rapid catalyst deactivation in the prior art. The technical scheme of the present invention comprises that the selective ring-opening catalyst comprises, by weight, 63.5-68.4% of at least one selected from alumina, amorphous silicon aluminum and a zeolite molecular sieve, 20-30% of pseudo boehmite, 0.1-1.5% of a noble metal Ir, and 0.1-5% of at least one selected from Ba, Zn and Mg. With the technical scheme, the problems in the prior art are well solved. The selective ring-opening catalyst of the present invention has characteristics of high polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon ring-opening selectivity, high monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon yield and slow catalyst deactivation, and can be used in the aromatic hydrocarbon refining field.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of recovering cumene
InactiveUS6900364B2Effective recoveryHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offOrganic chemistryCumene
A process for recovering cumene, characterized by subjecting 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-diphenylbutane produced in a process in which cumene is used, to hydrogenolysis in the presence of a catalyst thereby to convert it into cumene, and recovering the cumene.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
ActiveUS9815047B2High yieldReduce yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingCarbon numberPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The catalyst for producing aromatic hydrocarbon is for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon having 6 to 8 carbon number from oil feedstock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower and contains crystalline aluminosilicate and phosphorus. A molar ratio (P / Al ratio) between phosphorus contained in the crystalline aluminosilicate and aluminum of the crystalline aluminosilicate is from 0.1 to 1.0. The production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is a method of bringing oil feedstock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower into contact with the catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Method for producing p-xylene employing diverse raw materials
ActiveCN104557429ASimple processFlexible Modulation SourcesHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offCycle oilChemistry
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20130281755A1High yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingCarbon numberRare-earth element
The catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons having 6 to 8 carbon number from oil feedstock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower. The catalyst contains crystalline aluminosilicate and a rare earth element, in which the amount of the rare earth element expressed in terms of the element is 0.1 to 10 mass % based on the crystalline aluminosilicate. In the production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, oil feed stock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower is brought into contact with the catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and method for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20140364666A1High yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingCarbon numberDistillation
A catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, used for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of 6 to 8 carbon number from a feedstock oil having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of at least 140° C. and an end point temperature of not more than 400° C., wherein the catalyst contains a crystalline aluminosilicate, gallium and / or zinc, and phosphorus, the molar ratio between silicon and aluminum (Si / Al ratio) in the crystalline aluminosilicate is not more than 100, the molar ratio between the phosphorus supported on the crystalline aluminosilicate and the aluminum of the crystalline aluminosilicate (P / Al ratio) is not less than 0.01 and not more than 1.0, and the amount of gallium and / or zinc is not more than 1.2% by mass based on the mass of the crystalline aluminosilicate.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
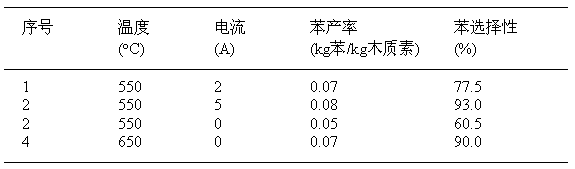
Method for directionally preparing benzene by utilizing xylogen
InactiveCN102701898BAbundant resourcesHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offBulk chemical productionBenzenePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a method for directionally preparing benzene by utilizing xylogen. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a cylindrical fixed bed catalytic reactor with a conductive metal wire arranged in a cavity; depolymerizing to converte xylogen to an aromatic monomer, wherein a led raw material is the xylogen, a catalyst is powder zeolite catalyst or modified zeolite catalyst containing transition metal nickel element, the usage amount is characterized in that the weight ratio of the catalyst to the xylogen is 0.3-10 per hour, and a product is a liquid-state aromatic monomer mixer; and directionally converting the aromatic monomer mixer into benzene, wherein a led raw material is the aromatic monomer mixer which is preheat to be 200-250 DEG C, a catalyst is powder zeolite catalyst containing an Re element, the usage amount is characterized in that the weight ratio of the aromatic monomer mixer to the zeolite catalyst containing the Re element is 0.2-15 per hour, and a product is mixed liquid taking the benzene as the main part. According to the method, an external hydrogen source is not needed, the raw material resources are rich, and higher benzene yield and benzene selectivity can be obtained at intermediate temperature and constant pressure as well as under a green and mild reaction environment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
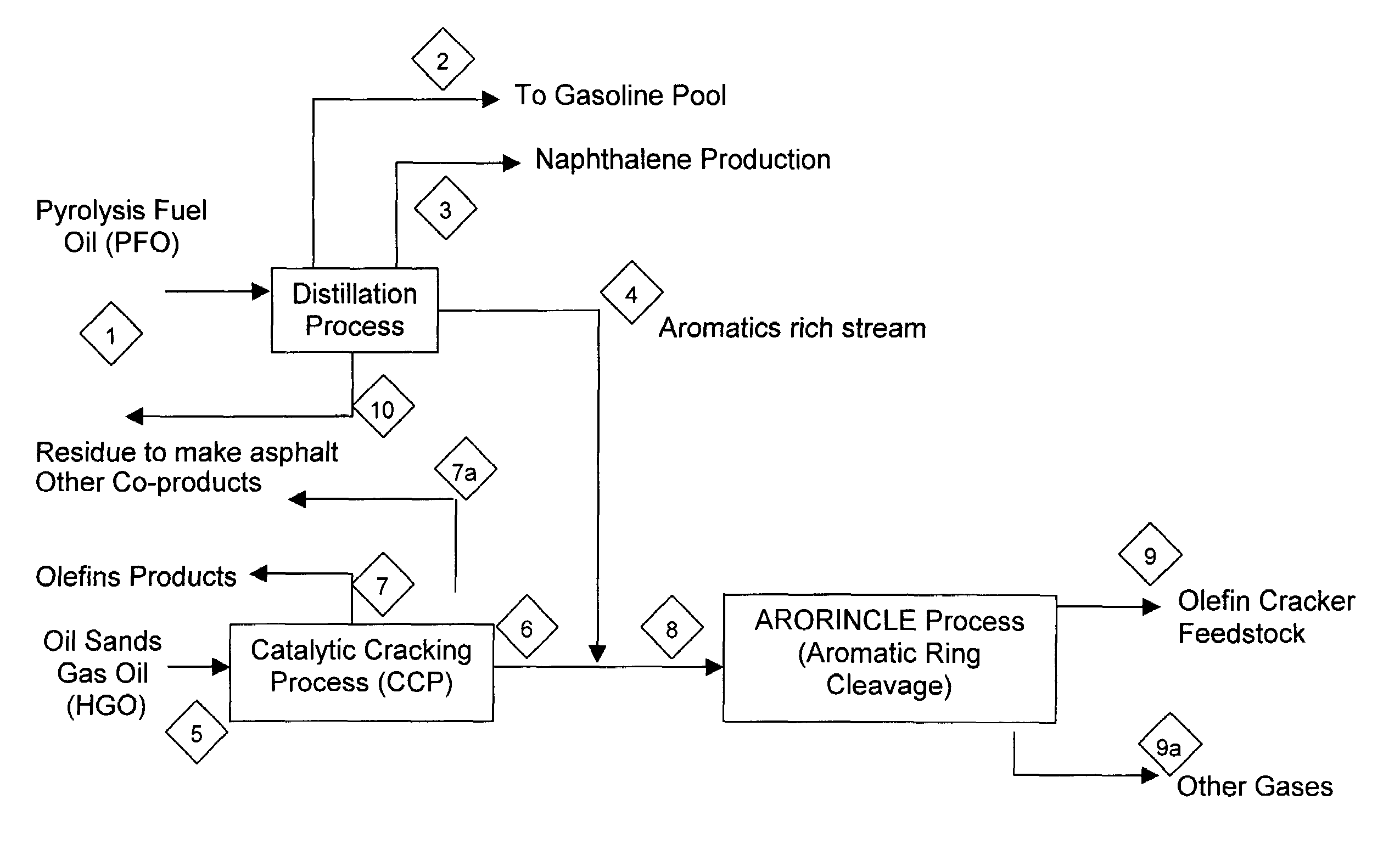
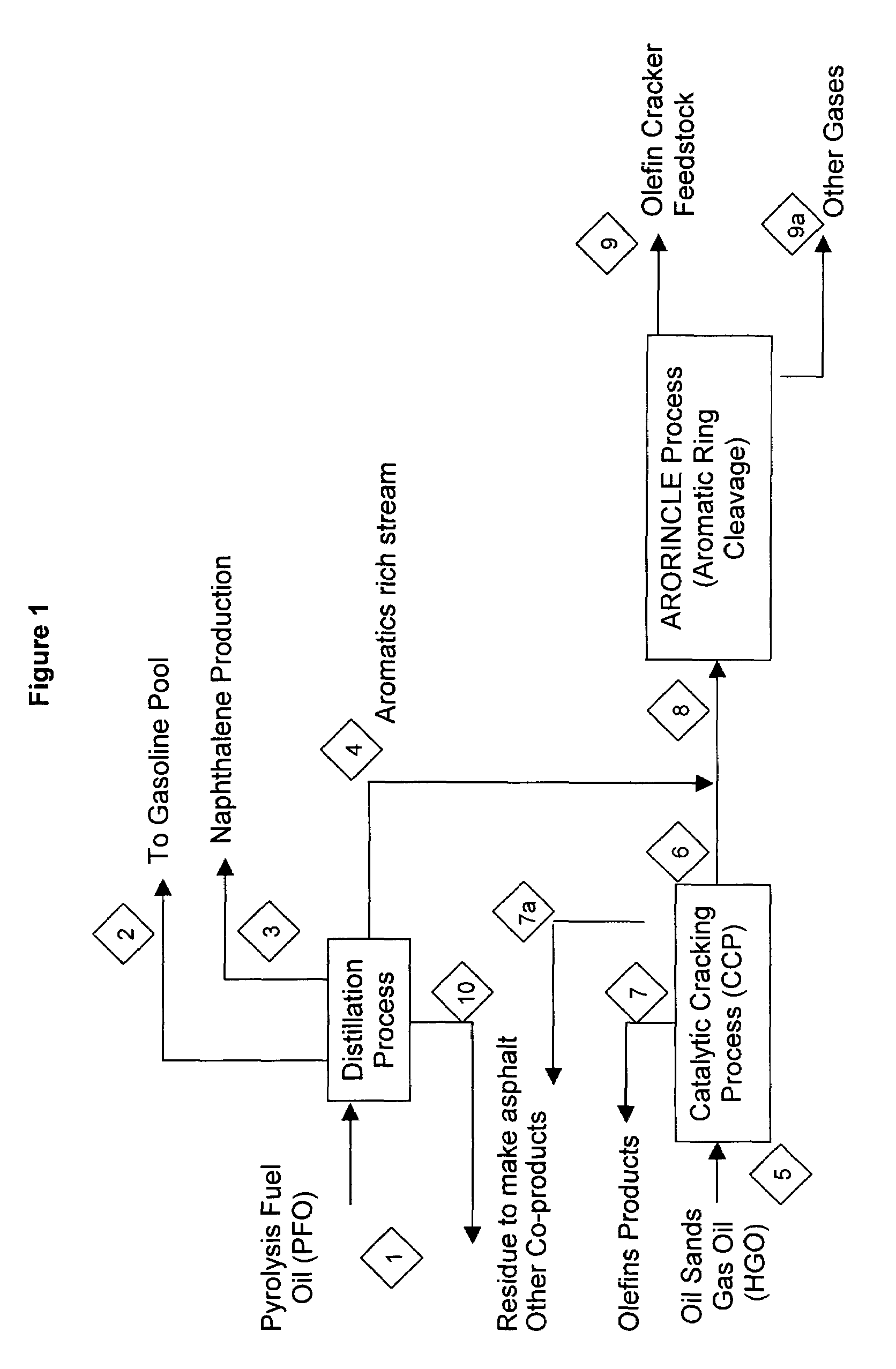
Integrated process to convert heavy oils from oil sands to petrochemical feedstock
An aromatics / naphthalene rich stream obtained by processing heavy gas oil derived from tar sands and cycle oils derived from cracking heavy gas oil may optionally be blended and subjected to a hydrogenation process and a ring opening reaction typically in the presence of a zeolite, alumina, or silica alumina based catalyst which may contain noble metals and or copper or molybdenum to produce paraffinic feedstocks for further chemical processing.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
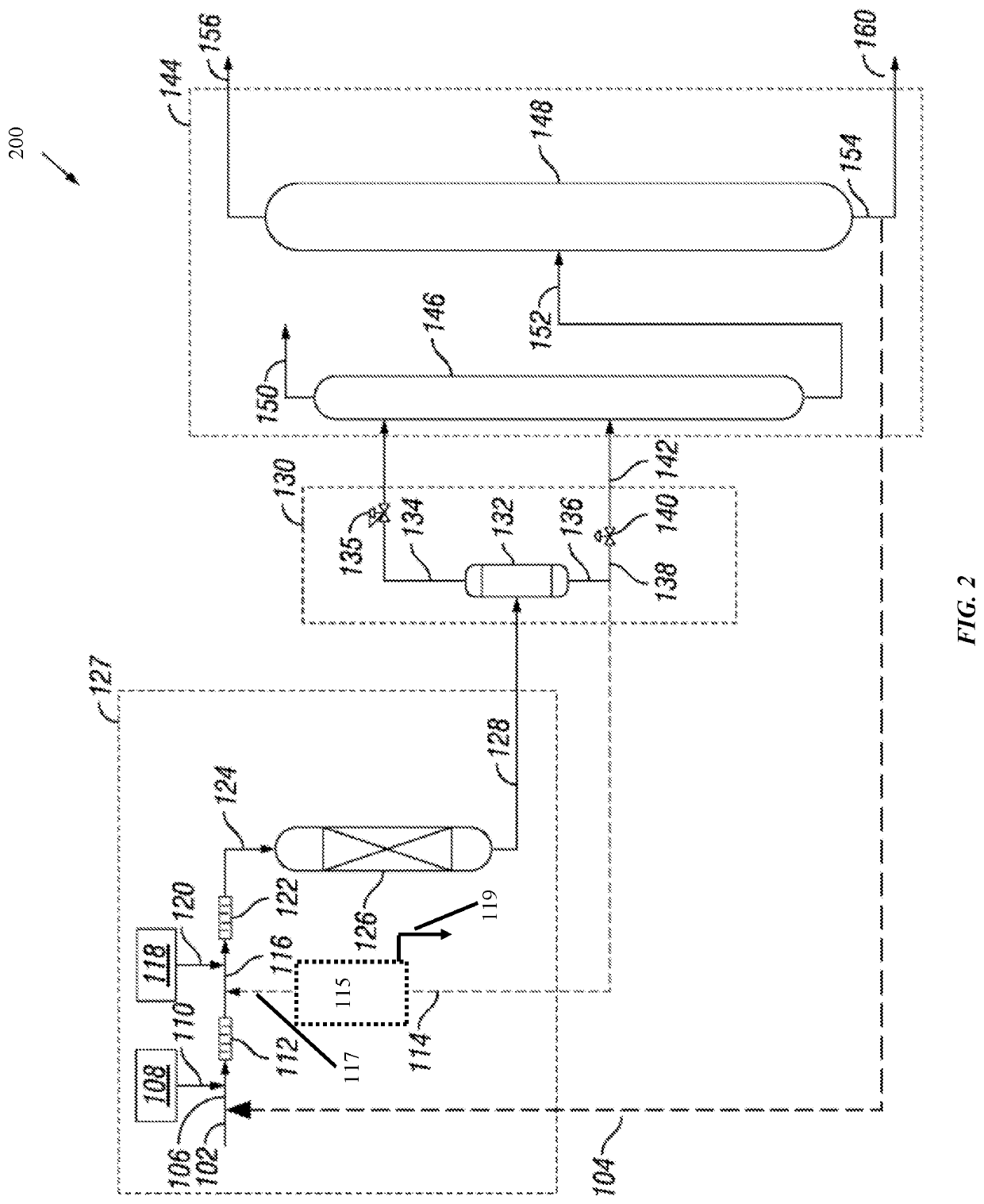
Catalytic hydrodearylation of heavy aromatic streams containing dissolved hydrogen with fractionation
ActiveUS20210139393A1Increase overall C6-C aromatics productionImprove blending suitabilityHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offFractional condensation purification/separationArylPtru catalyst
Systems and methods for hydrodearylation of a hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons, the method including supplying a hydrogen feed to the hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons; mixing the hydrogen feed with the hydrocarbon feed stream to saturate the hydrocarbon feed stream with hydrogen gas to create a hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream; passing the hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream to a hydrodearylation reactor without a separate gaseous phase of hydrogen; allowing the hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream to react in presence of a catalyst under specific reaction conditions to produce a product stream comprising a reduced concentration of di-aromatic compounds and an increased concentration of mono-aromatic compounds compared to the hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons; and recovering, from the hydrodearylation reactor, a product stream for a downstream process, wherein the non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons include at least two benzene rings connected by an alkyl bridge group having at least two carbons, wherein the benzene rings are connected to different carbons of the alkyl bridge group.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Catalytic hydrodearylation of heavy aromatic streams containing dissolved hydrogen with fractionation
ActiveUS11267769B2Improve blending suitabilityHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offFractional condensation purification/separationArylPtru catalyst
Systems and methods for hydrodearylation of a hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons, the method including supplying a hydrogen feed to the hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons; mixing the hydrogen feed with the hydrocarbon feed stream to saturate the hydrocarbon feed stream with hydrogen gas to create a hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream; passing the hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream to a hydrodearylation reactor without a separate gaseous phase of hydrogen; allowing the hydrogen-enriched liquid hydrocarbon stream to react in presence of a catalyst under specific reaction conditions to produce a product stream comprising a reduced concentration of di-aromatic compounds and an increased concentration of mono-aromatic compounds compared to the hydrocarbon feed stream comprising non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons; and recovering, from the hydrodearylation reactor, a product stream for a downstream process, wherein the non-condensed alkyl-bridged multi-aromatic hydrocarbons include at least two benzene rings connected by an alkyl bridge group having at least two carbons, wherein the benzene rings are connected to different carbons of the alkyl bridge group.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Catalyst for converting sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104549473BHigh selectivityDelay inactivationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offLoss ratePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a catalyst for converting sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and a preparation method thereof. The method mainly solves the problems of low conversion depth of sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, low yield and low selectivity of single-ring aromatic hydrocarbons, and fast catalyst deactivation rate existing in the prior art. The present invention comprises the mixture of 30~65% FAU type zeolite and ZSM-12 molecular sieve by adopting catalyst by weight percentage, 33.5~69.8% is selected from at least one in γ-alumina, η-alumina or pseudo-boehmite One is the technical scheme of binder and 0.1-0.5% of at least one metal selected from Pt, Pd or Ir and 0.1-1% of at least one metal selected from La, Ce or Sn, which better solves the problem To solve the above problems, the catalyst can be used in the industrial production of converting sulfur-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into single-ring aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Renewable catalyst for converting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104549469BMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonAromatic hydrocarbon
The invention relates to a reproducible catalyst for converting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons into monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and a preparation method thereof. The method mainly solves the problems of low conversion depth of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, low yield and selectivity of single-ring aromatic hydrocarbons, and poor catalyst regeneration performance existing in the prior art. The present invention comprises a mixture of 30-65% MOR-type zeolite and ZSM-12 molecular sieve in terms of weight percentage by using a catalyst, and 34.5-69.9% is selected from at least one of γ-alumina, η-alumina or pseudo-boehmite A kind of technical scheme that is binding agent and 0.1~0.5% at least one kind of metal selected from Pt, Pd or Ir solves the above-mentioned problems well, and the regeneration performance of the catalyst is better, and the catalyst can be used for heavy polycyclic In the industrial production of aromatics converted into single-ring aromatics.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Aromatics hydrogenolysis using novel mesoporous catalyst system
InactiveUS7608747B2Improve accessibilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by polyaryl split-offArylMetal
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Method for producing norbornene derivative
InactiveUS20100197970A1High yieldEasy to produceHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic compound preparationHydrogen atomPalladium
A method for producing a norbornene derivative wherein,in the presence of palladium and at least one selected from phosphorus compounds represented by the following General Formulae (1) and (2):[in Formula (1), R1, R2, R3 and R4 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or the like, and R5 and R6 each independently represent a branched chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms or the like], and[in Formula (2), R7 represents a branched chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 3 to 10 carbon atoms],a norbornadiene derivative represented by the following General Formula (3):[in Formula (3), R8, R9, R10, R11 and R12 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or the like, l represents an integer of 0 or 1, m represents an integer of 0 or 1, and n represents an integer of 0 or 1], and a bromine compound represented by the following General Formula (4):[Chemical Formula 4]Br—Z—R13 (4)[in Formula (4), Z represents a phenylene group or the like, and R13 represents a hydrogen atom or the like] are reacted with each other, to thereby obtain a norbornene derivative represented by the following General Formula (5):[in Formula (5), R14, R15, R16, R17 and R18 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or the like, Z represents a phenylene group or the like, R19 represents a hydrogen atom or the like, l represents an integer of 0 or 1, m represents an integer of 0 or 1, and n represents an integer of 0 or 1], the norbornene derivative having a configuration of a substituent represented by Z in General Formula (5) that is an exo configuration.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20130281756A1Reduce contentHigh yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationCatalytic crackingPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonDistillation
In the production method of monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, oil feedstock having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of 140° C. or higher and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of 380° C. or lower is brought into contact with a catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons that includes a mixture containing a first catalyst which contains crystalline aluminosilicate containing gallium and / or zinc and phosphorus and a second catalyst which contains crystalline aluminosilicate containing phosphorus.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
Catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and method for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20140364667A1High yieldPrevention of any deterioration over timeHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsCarbon numberDistillation
A catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of 6 to 8 carbon number from a feedstock oil having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of at least 140° C. and an end point temperature of not more than 400° C., or a feedstock oil having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of at least 140° C. and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of not more than 360° C., wherein the catalyst contains a crystalline aluminosilicate, gallium and / or zinc, and phosphorus, and the amount of phosphorus supported on the crystalline aluminosilicate is within a range from 0.1 to 1.9% by mass based on the mass of the crystalline aluminosilicate; and a method for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, the method involving bringing a feedstock oil having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of at least 140° C. and an end point temperature of not more than 400° C., or a feedstock oil having a 10 volume % distillation temperature of at least 140° C. and a 90 volume % distillation temperature of not more than 360° C., into contact with the above-mentioned catalyst for producing monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:JXTG NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORPORATION
Popular searches
Catalytic naphtha reforming Hydrocarbon by saturated bond conversion Treatment with hydrotreatment processes Hydrocarbon from saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon addition Hydrocarbon by polyarylsubstituted aliphatic compound split-off Refining to eliminate hetero atoms Hydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon addition Catalysts Hydrocarbon preparation catalysts Hydrocarbon oil cracking
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com