Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77results about "Engine operating parameters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oil injection lubrication system and methods for two-cycle engines
InactiveUS6422183B1Reduced deposit formationAvoid corrosionCombustion enginesEngine operating parametersSolenoid valveControl signal
The present invention provides an improved oil injection lubrication system for two-cycle engines. The system includes a variable output oil pump, the output of which can be varied in relation to the throttle level. The system also includes a solenoid valve unit containing a plurality of solenoid valves that regulate the flow of oil from the oil pump to each cylinder. The electronic control unit sends control signals to the solenoid valve unit to regulate the flow of oil based upon factors relating to the operation of the engine in accordance with a control scheme. The factors may include those that apply to all of the engine's cylinders (i.e., do not vary between the cylinders), such as intake air temperature, atmospheric pressure, battery voltage, engine break-in period, and load frequency among others.
Owner:SANSHIN KOGYO CO LTD
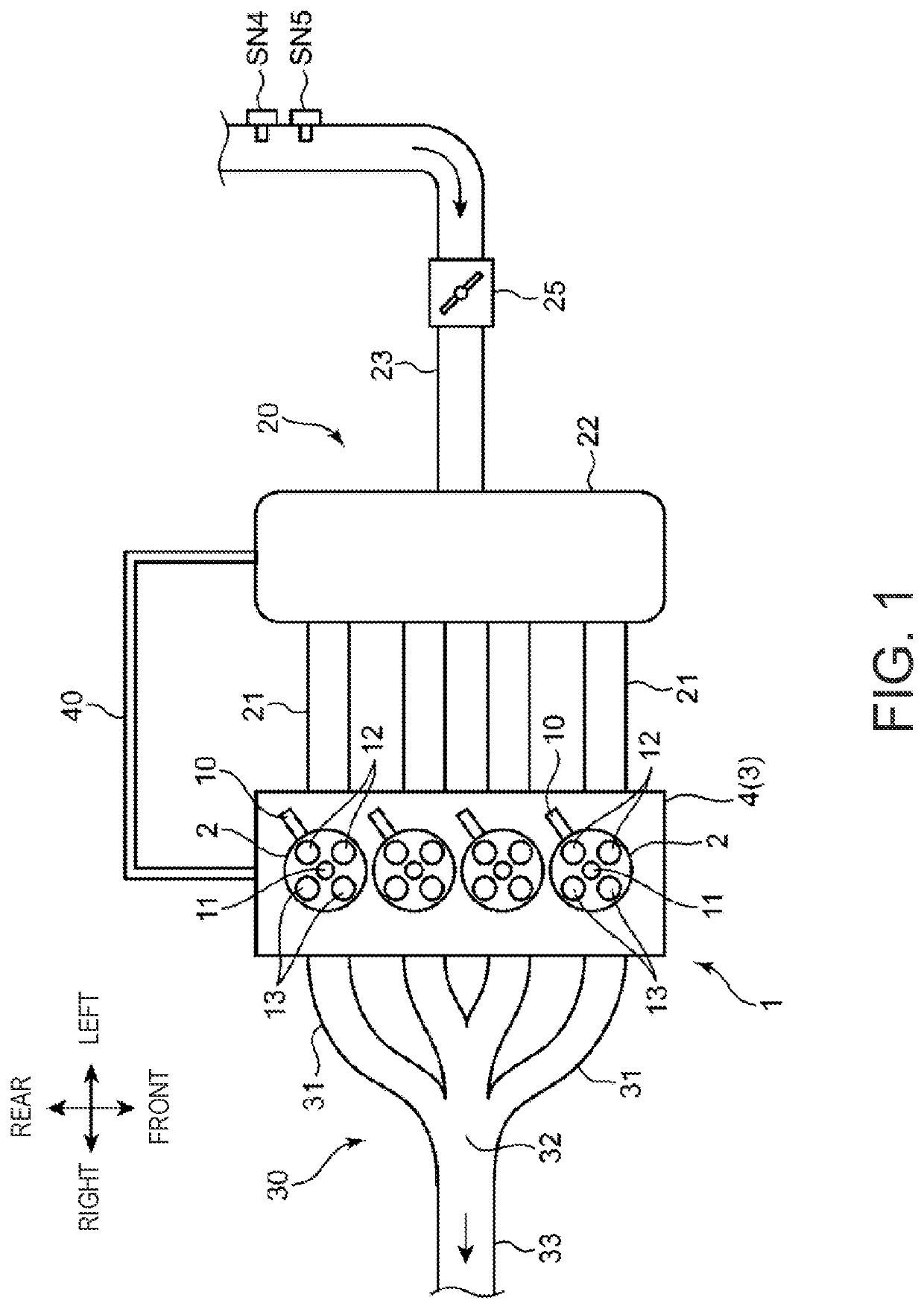
Fault detection device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20180371971A1High inner pressureImprove accuracyInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlInternal pressurePositive pressure
A fault detection unit of an internal combustion engine includes a recirculation pipe connected with an upstream-side part of an intake pipe of the internal combustion engine upstream of a supercharger, the recirculation pipe to supply an evaporated fuel that is unburned and is generated in the internal combustion engine to the intake pipe, and a fault detection unit to detect a leakage occurrence of the recirculation pipe based on a crank-case inner pressure of the internal combustion engine when the internal combustion engine is operating in a specified operation condition that the crank-case inner pressure is a positive pressure.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Oil pump system of an engine for a vehicle
InactiveUS20120118257A1Reduce engine power lossIncrease fuel consumptionLubrication of auxillariesEngine operating parametersHydraulic pumpEngineering
Reduction of engine power loss and enhancement of fuel consumption may be achieved by an oil pump system of an engine for a vehicle including an oil sump reserving engine oil used for lubrication of the engine, a hydraulic pump pumping the engine oil, a main relief valve that is disposed on an output line of the hydraulic pump and controls an output pressure of the output line depending on the output pressure and a control pressure, and an auxiliary relief valve that redirects the output pressure to the main relief valve as a control pressure depending on operating condition of the engine.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Circulating coolant fluid in hybrid electrical propulsion systems
A hybrid propulsion system includes a heat engine configured to drive a heat engine shaft. An electric motor configured to drive a motor shaft. A transmission system is connected to receive rotational input power from each of the heat engine shaft and the motor shaft and to convert the rotation input power to output power. A first lubrication / coolant system is connected for circulating a first lubricant / coolant fluid through the heat engine. A second lubricant / coolant system in fluid isolation from the first lubrication / coolant system is connected for circulating a second lubricant / coolant fluid through the electric motor.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Lubricant circuit
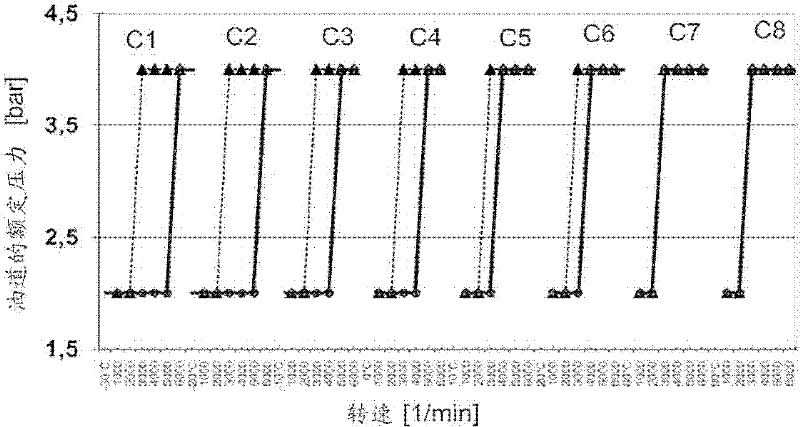
InactiveCN102235203AAvoid pressure spikesEstimated temperatureEngine operating parametersMachines/enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
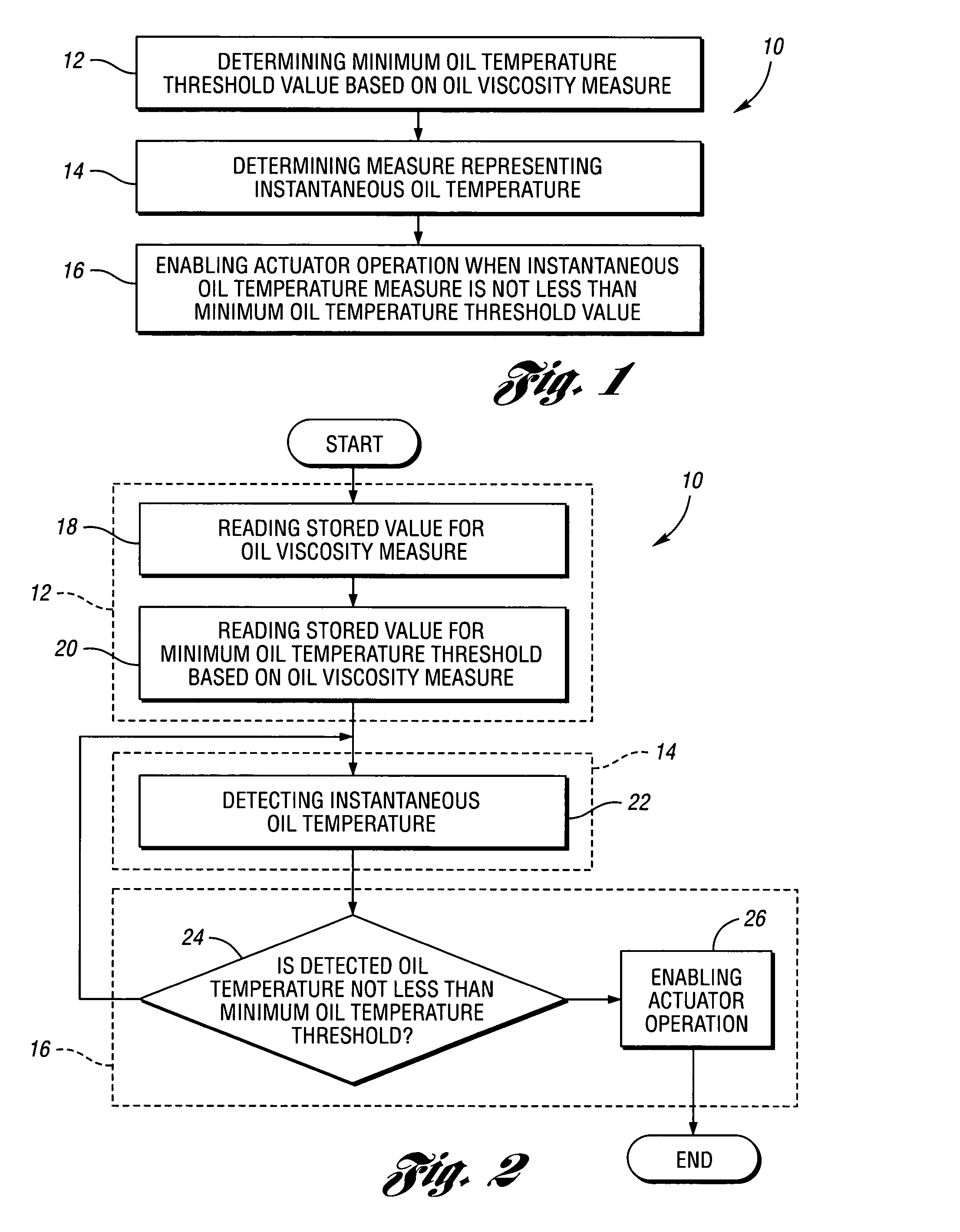
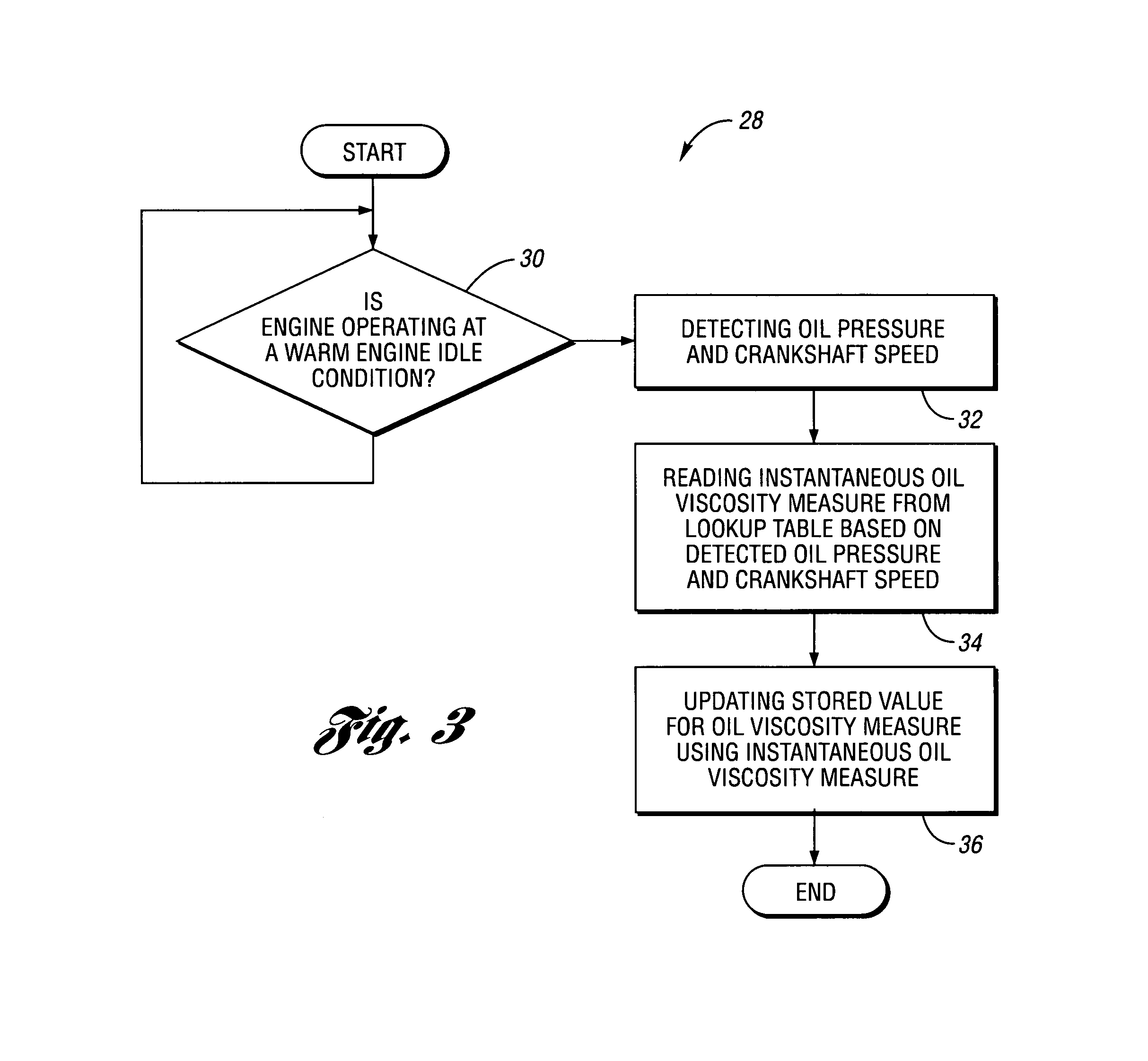
Method and code for controlling actuator responsive to oil pressure using oil viscosity measure
A method and code for controlling the operation of a deactivatable valve lifter of an internal combustion engine includes determining an oil viscosity measure based upon an engine oil pressure achieved when the engine is operating at a warm engine idle operating condition; determining a minimum oil temperature for actuator operation based on a comparison of the oil viscosity measure with a stored value representing the oil's nominal viscosity; and enabling actuator operation when an instantaneous oil temperature is not less than the minimum oil temperature.
Owner:FCA US
Method For Operating An Oil Circuit, In Particular For A Vehicle
ActiveUS20170074131A1Reduce internal consumptionThe process is simple and effectiveCoolant flow controlEngine loadEngineeringInternal combustion engine
A method for operating an oil circuit for a vehicle, the oil circuit being configured to supply oil to an internal combustion engine, wherein the oil circuit includes an oil cooler, and wherein at least one temperature sensor measures the temperature of the oil flowing through the oil circuit, downstream of the oil cooler and upstream of the internal combustion engine, the temperature sensor being connected for signaling purposes to a regulating and / or control device, includes: controlling and / or regulating, by the regulating and / or control device, the temperature of the oil flowing through the oil circuit, such that the temperature measured by the temperature sensor has a defined target temperature value; and setting and / or adjusting, by the regulating and / or control device, as a function of a drive power of the internal combustion engine, the defined target temperature value so as to reduce fuel consumption of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:MAN TRUCK & BUS AG
Oil supply apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20140190444A1Low costReliably detect lowered oil level of oilLubrication of auxillariesEngine operating parametersExternal combustion engineEngineering
Disclosed is an oil supply apparatus which can be realized at a low cost, and can reliably detect the lowered level of the oil filled in the oil reservoir unit. The oil supply apparatus is provided with an oil pump which is set to have a plurality of switching discharge pressures at which the oil discharge pressures are changed for each target rotation speeds when the rotation speed of the internal combustion engine reaches the respective target rotation speed. The ECU is adapted to determine that the level of oil stored in the oil pan is lowered under the condition that the deviation between the target rotation speed of the engine set to correspond to the switching discharge pressure and the rotation speed of the engine actually detected when the discharge pressure reaches the switching discharge pressure is not less than the determination value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
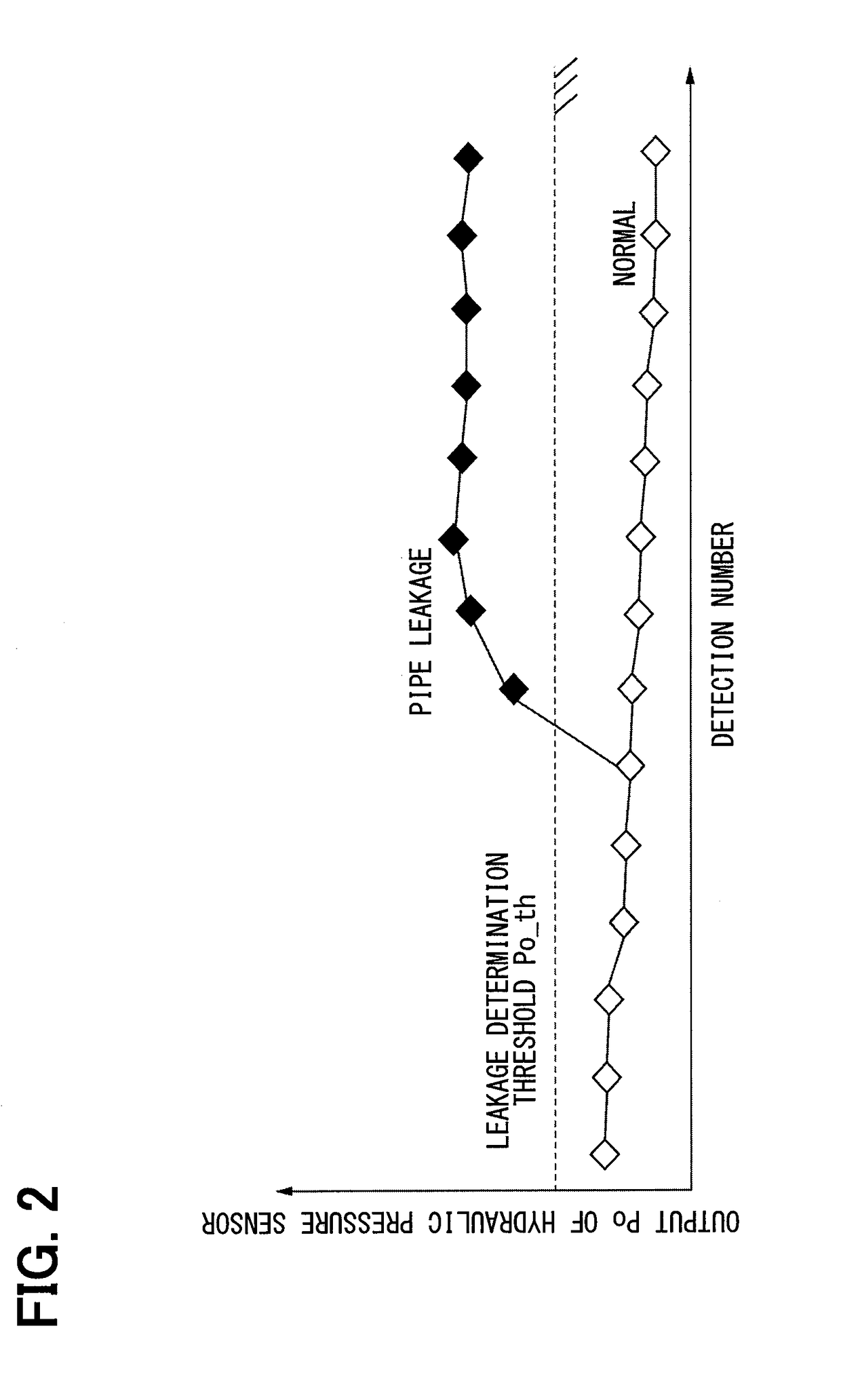
Internal combustion engine and method for detecting leak from crankcase and/or tank ventilation system
ActiveCN107532544AMeet emissionsFulfil requirementsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentCombustionExternal combustion engine
The invention relates to an internal combustion engine with a combustion air intake system in which a compressor is arranged and in which a throttle element is arranged downstream of the compressor inthe flow direction of the combustion air. The internal combustion engine also comprises a tank ventilation system and a crankcase ventilation system. The tank ventilation system can be connected to the intake system downstream of the throttle element via a first non-return valve in a first line and upstream of the compressor via a second non-return valve in a second line and a third non-return valve in a second sub-line. The crankcase ventilation system can be connected to the intake system downstream of the throttle element via a fourth non-return valve in a third line and upstream of the compressor via a fourth line and the third non-return valve. The intake system can be connected to the second line downstream of the throttle element at a transitional point between the second line andthe second sub-line via a fifth non-return valve in a fifth line. A nozzle is formed at the transitional point from the fifth line to the second line and the second sub-line, and the second line opensinto the nozzle downstream of the second non-return valve. A first pressure sensor for measuring the pressure in the second line is provided in the second line between the second non-return valve andthe nozzle. By means of the internal combustion engine design according to the invention with a crankcase and a tank ventilation system and by means of the corresponding methods, only a single pressure sensor is required to diagnose or detect a leak. A second pressure sensor can be advantageously used to locate a leak.
Owner:BAYERISCHE MOTOREN WERKE AG
Systems and methods for performing a condition-based maintenance of an engine
ActiveUS20180128134A1Electrical controlRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesThermal modelCondition-based maintenance
A method for performing condition-based maintenance of an engine is presented. The method includes obtaining one or more parameters corresponding to the engine. Also, the method includes determining a temperature profile corresponding to a portion of a fluid flow component based on a first parameter and one or more thermal models. The method further includes estimating a solid deposit in the portion of the fluid flow component corresponding to each cycle of the engine based on the temperature profile and deposition kinetics parameters. Further, the method includes predicting a total solid deposit in the portion of the fluid flow component based on the estimated solid deposit corresponding to each cycle of the engine. Moreover, the method includes performing the condition-based maintenance of the engine based on a value of the predicted total solid deposit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Lubricant circuit
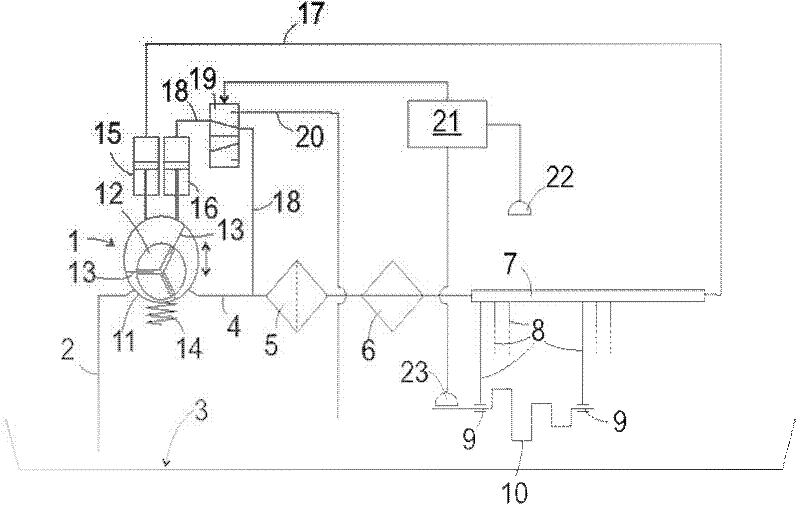
InactiveUS20110266090A1Rapid responseIncrease delayProportioning devicesEngine operating parametersDistributorLubricant
A lubricant circuit includes, but is not limited to a lubricant pump, which is connected on the suction side to a reservoir and on the pressure side to a distributor, at least one lubricating point, which is connected to the distributor and a return leading to the reservoir, and an electronic control unit, which is set up to regulate the output pressure of the lubricant pump by reference to the temperature of the lubricant.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Oil supply apparatus of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS9032929B2Low costReliably detect lowered oil level of oilLubrication of auxillariesEngine operating parametersInternal combustion engineDischarge pressure
Disclosed is an oil supply apparatus which can be realized at a low cost, and can reliably detect the lowered level of the oil filled in the oil reservoir unit. The oil supply apparatus is provided with an oil pump which is set to have a plurality of switching discharge pressures at which the oil discharge pressures are changed for each target rotation speeds when the rotation speed of the internal combustion engine reaches the respective target rotation speed. The ECU is adapted to determine that the level of oil stored in the oil pan is lowered under the condition that the deviation between the target rotation speed of the engine set to correspond to the switching discharge pressure and the rotation speed of the engine actually detected when the discharge pressure reaches the switching discharge pressure is not less than the determination value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
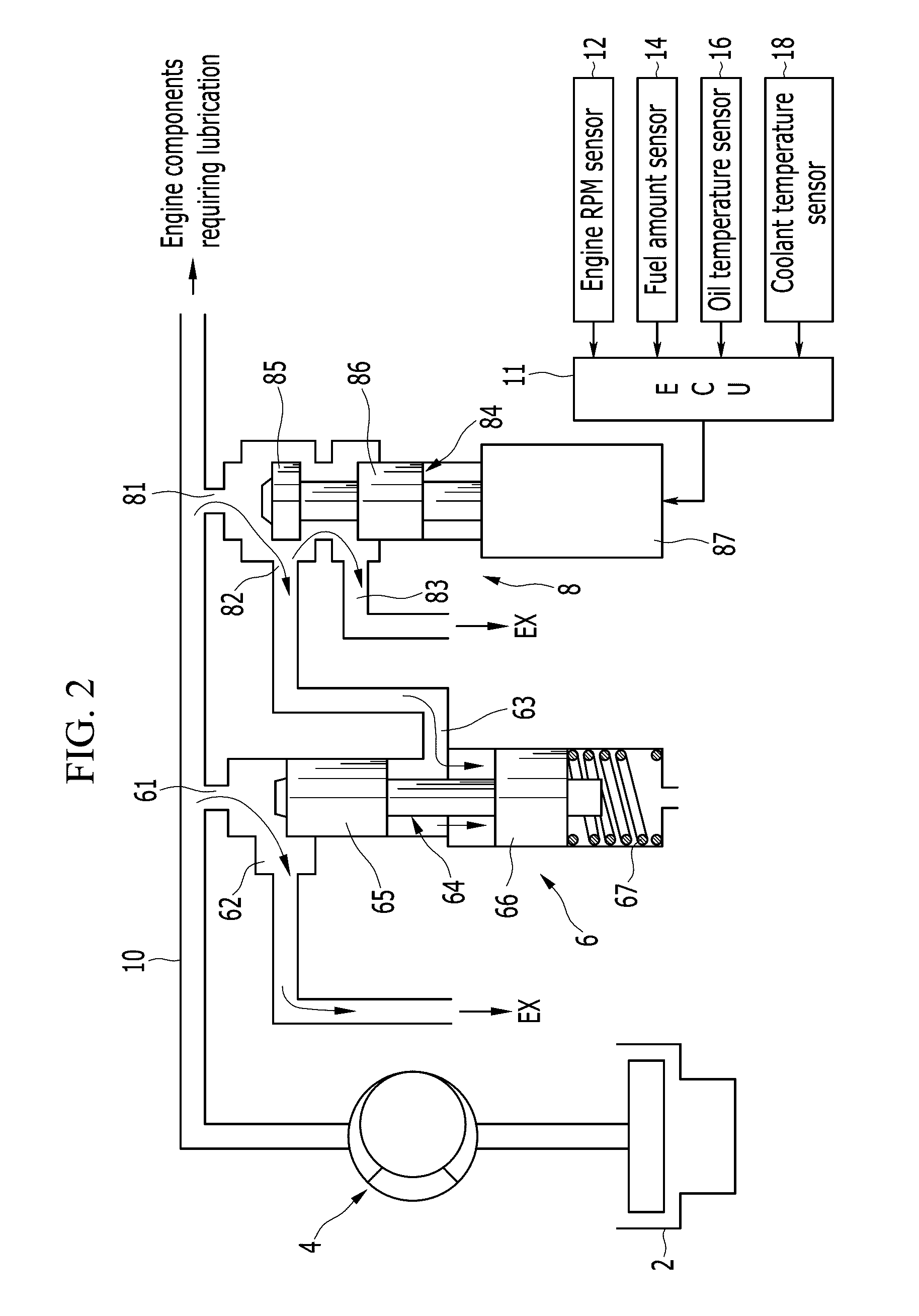
Automatic Engine Pre-Lube
InactiveUS20170122150A1Enhanced advantageAvoid disadvantagesInternal combustion piston enginesEngine operating parametersOil temperatureEnvironmental temperature
An automatic engine start / stop system and method which are compatible with recent engine requirements of a pre-lube period before engine crank, is disclosed. A temp-start controller is used to read inputs such as ambient temperature, oil temperature and engine RPMs, to determine proper conditions for engine cranking. A pre-lube pump is activated by the controller for up to 45 seconds, or a desired period of time, before engine crank. A glow plug pre-heating step may be performed as well, if necessary.
Owner:TAS DISTRIBUTING
Pressure control device, system and method
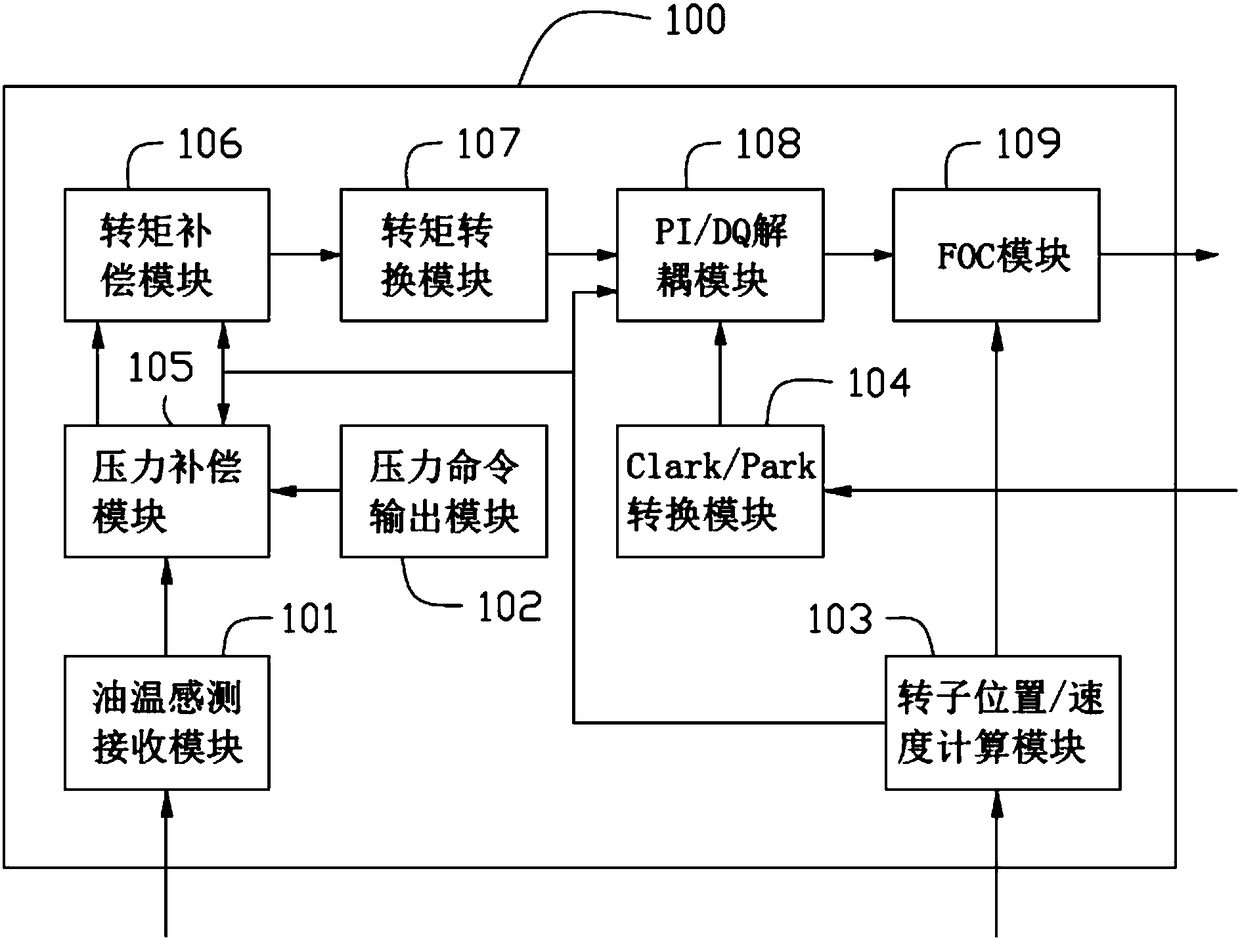
ActiveCN108336938AHigh precisionShort response timeHybrid vehiclesVector control systemsDriver circuitControl theory
The application provides a pressure control device, system and method for controlling an output oil pressure of an electric pump. The system is composed a motor, an oil pump driven by the motor, a motor driver circuit connected with the motor, and a pressure control device. The pressure control device is configured to output a target value of the oil pressure based on the oil pump, an obtained estimated motor electromagnetic torque corresponding to the target value, and an actual detection current flowing through the motor and determine an electrification voltage of the motor; and power is provided for the motor based on the electrification voltage by the motor driver circuit.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SHENZHEN
Oil Tank Filling System
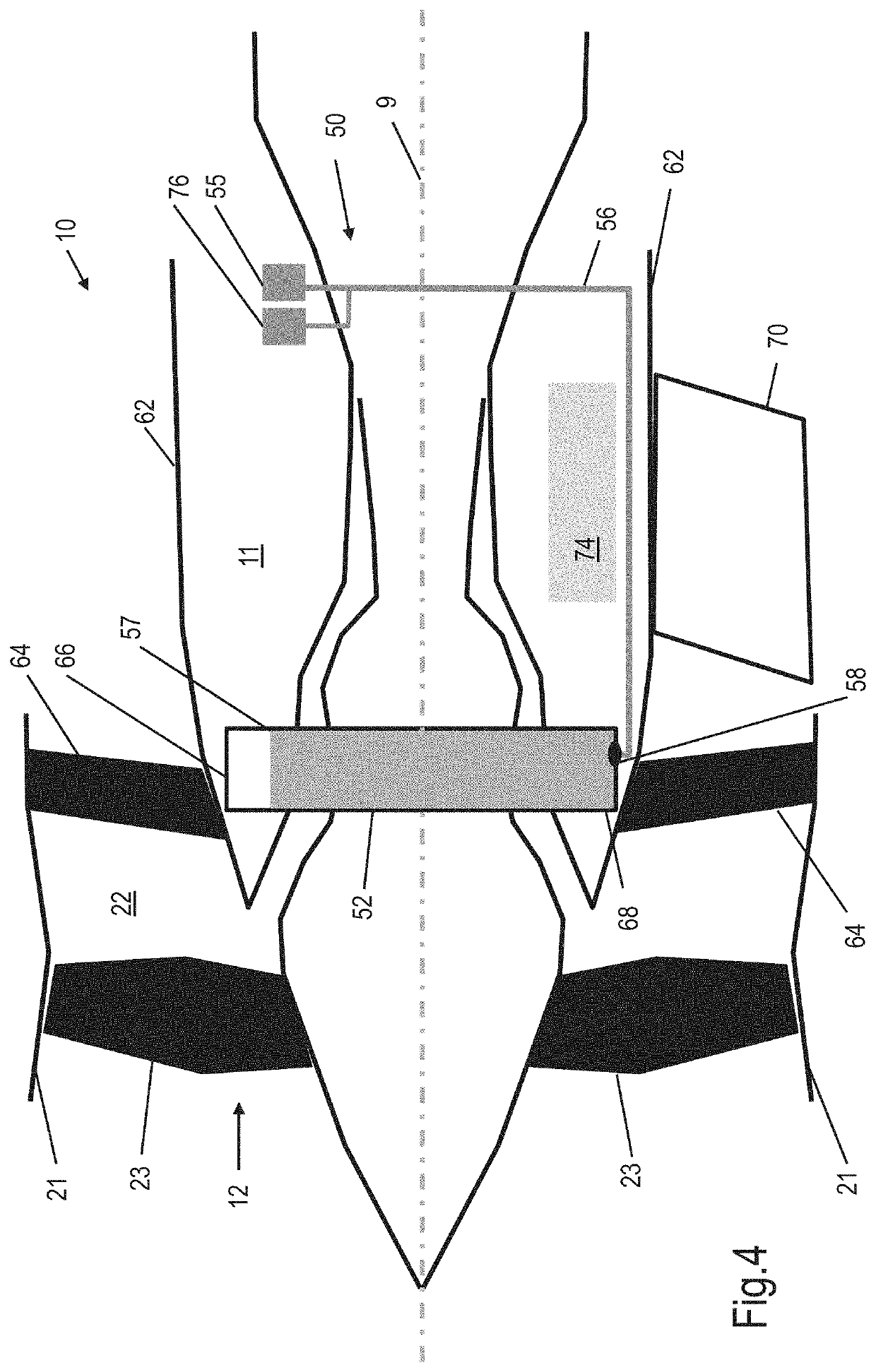
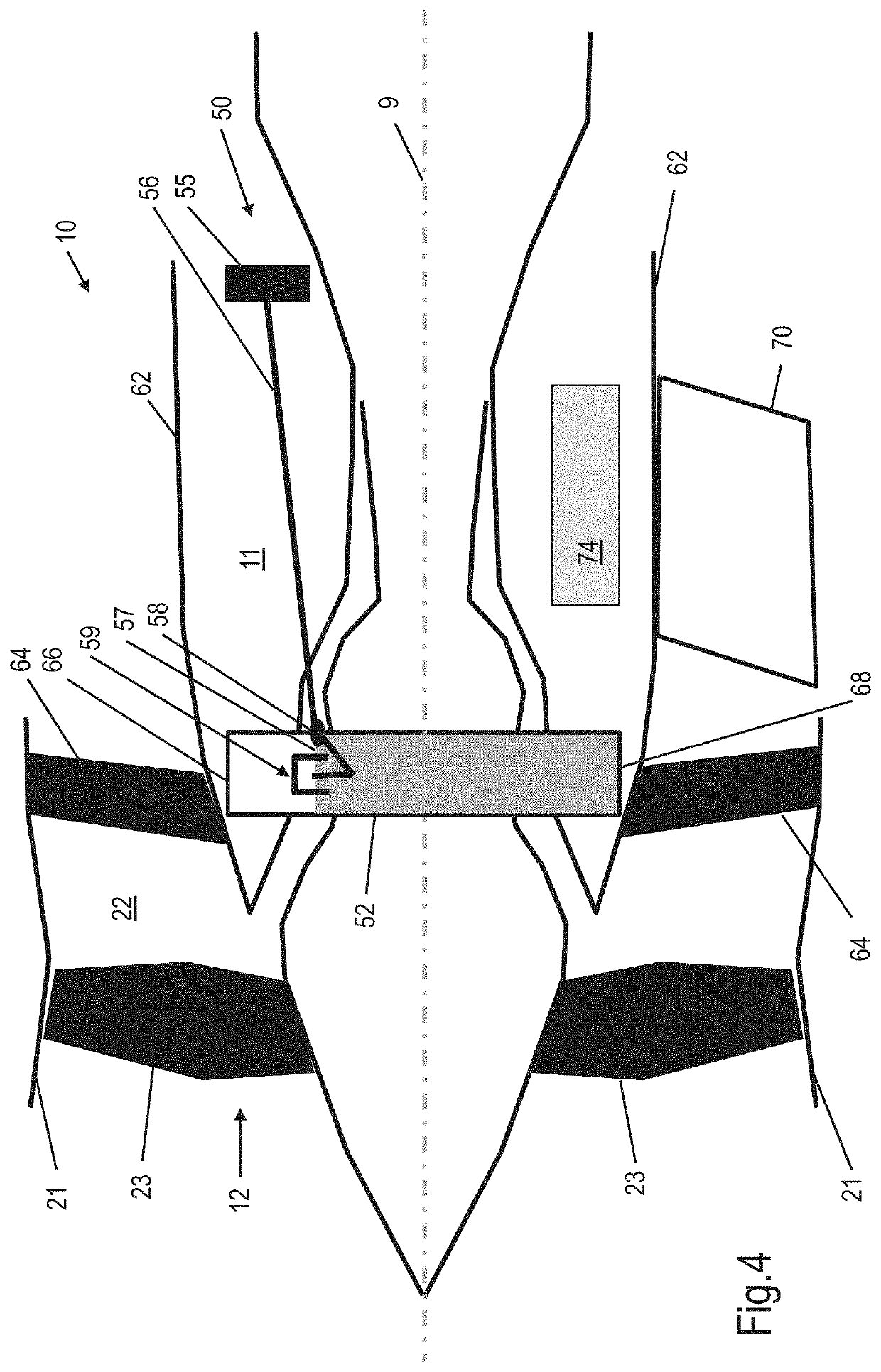
An oil tank filling system for filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine that includes an aft core cowl. The system includes an oil tank that has an oil tank top and an oil tank bottom and is located within a core of the engine, an oil access port located on the aft core cowl; and an oil tank filling pipe that leads from the oil access port to a tank filling port located at or adjacent the oil tank bottom. The system is configured so that oil that is supplied to the oil access port flows to and into the oil tank using gravitational force. A method of filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine and a gas turbine engine that includes the oil tank filling system are also disclosed.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Oil tank filling system
ActiveUS20190338674A1Avoid enteringSolve the lack of spaceTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsPower plant fuel tanksTurbineOil intake
An oil tank filling system for filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine that includes an aft core cowl. The system includes: an oil tank that is located within a core of the engine; an oil access port located on the aft core cowl; an oil tank filling pipe that connects the oil access port to a tank filling port on the oil tank; and a hydraulic lock that prevents oil entering the oil tank once the oil tank contains a predetermined volume of oil. A method of filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine and a gas turbine engine that includes the oil tank filling system are also disclosed.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
System and method for controlling operation of a vehicle based on measured fluid levels in a fluid reservoir
ActiveUS10670445B1Volume measurement apparatus/methodsTesting/calibration apparatusControl engineeringProcess engineering
System and method for controlling operation of a vehicle having a fluid reservoir. The system includes one or more fluid level indicators configured to respectively obtain a measured fluid level in the fluid reservoir. A plurality of sensors is operatively connected to the vehicle and configured to respectively obtain one or more parameters. A controller is configured to determine if a fluid level transition between the measured fluid level and a past fluid level is indicated, when there is exactly one fluid level indicator. The controller is configured to identify a reporting state from among a first state, a second state and a third state, based in part on a correlation to a dynamic event and an expected direction for the fluid level transition. A control action is executed by the controller based in part on the reporting state.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
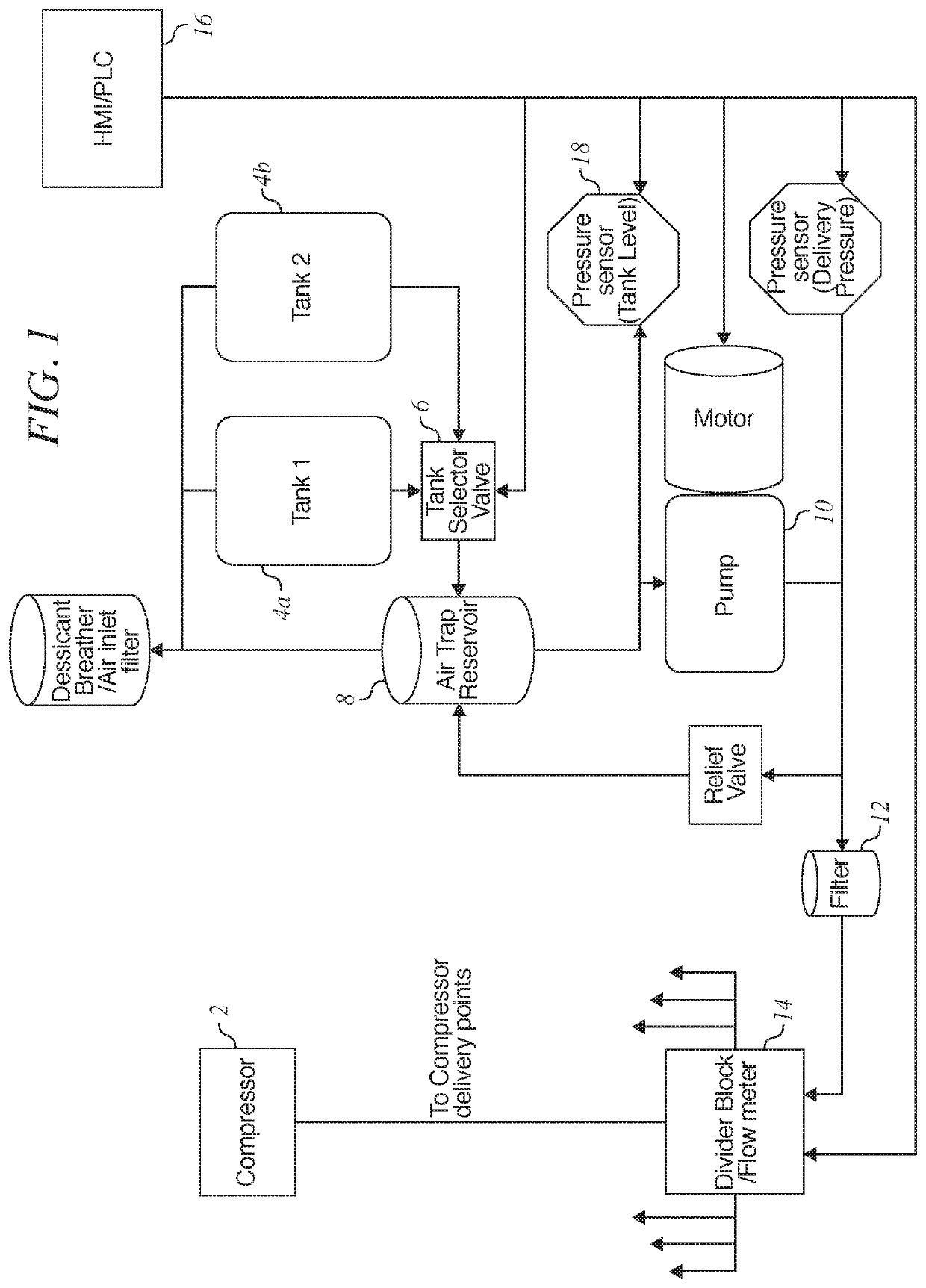
Method of controlling oil pump of vehicle
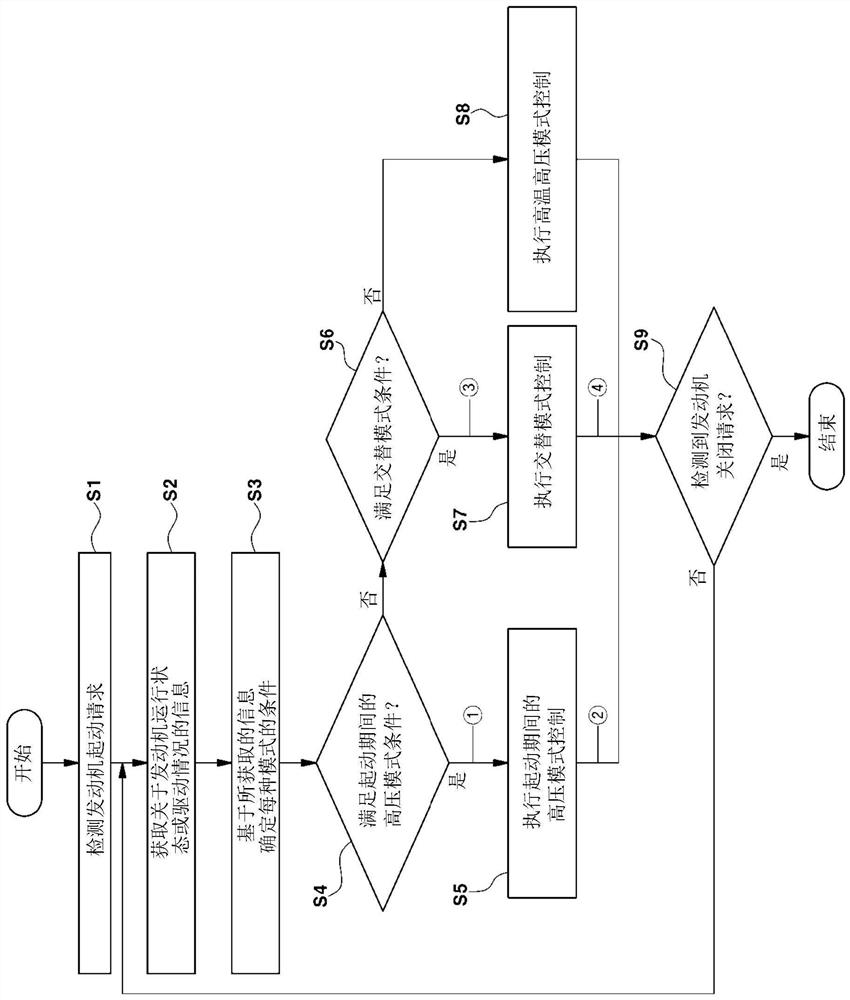
PendingCN112502808ASolve the problem of poor lubricationLiquid coolingElectrical controlControl engineeringControl theory
The invention relates to a method of controlling an oil pump of a vehicle. The method includes: acquiring, by a controller, information on an engine operating state or a driving condition detected bya driving information detection part; determining, by the controller, whether a predetermined condition of an alternate mode is satisfied on the basis of the acquired information on the engine operating state or the driving condition; and, when the condition of the alternate mode is satisfied, sequentially performing, by the controller, a high-pressure operation control that controls an operationof an oil pump system so as to an oil pressure of an engine to converge on a predetermined target high-pressure value and a low-pressure operation control that controls the oil pressure of the engineto converge on a predetermined target low-pressure value.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Engine control device
InactiveUS20220136468A1Prevent freezingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberSurge tank
A device is provided, which controls a vehicle-mounted engine provided with an engine body with a plurality of cylinders, a plurality of independent intake passages, each connected to the engine body so as to communicate with a combustion chamber of each cylinder via an intake port, and a surge tank connected to an upstream end of each independent intake passage. The device includes a phase changer, an ambient temperature sensor, and a controller configured to acquire an amount of condensate water existing in the surge tank. When the engine is stopped in a situation where the ambient temperature is lower than a given reference temperature and the condensate water amount is above a given reference amount, the controller controls the phase changer so that a lift amount of an intake valve in each cylinder of the stopped engine becomes outside a given minute lift range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Control device for vehicle oil supply device
ActiveUS20200292054A1Reduced electrical performanceLower performance requirementsGear lubrication/coolingEngine operating parametersControl theoryMotronic
There is provided a control device for a vehicle oil supply device that includes a mechanical oil pump configured to be rotatable forward and in reverse, an electric oil pump configured to suction oil stored in an oil storage portion that is common to the mechanical oil pump and the electric oil pump, a first filtering member provided to a first strainer of the mechanical oil pump, and a second filtering member provided to second strainer of the electric oil pump. The control device includes a controller configured to control the rotational speed of the electric oil pump. The controller is configured to restrict the rotational speed of the electric oil pump when the mechanical oil pump is rotated in reverse compared to when the mechanical oil pump is rotated forward.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
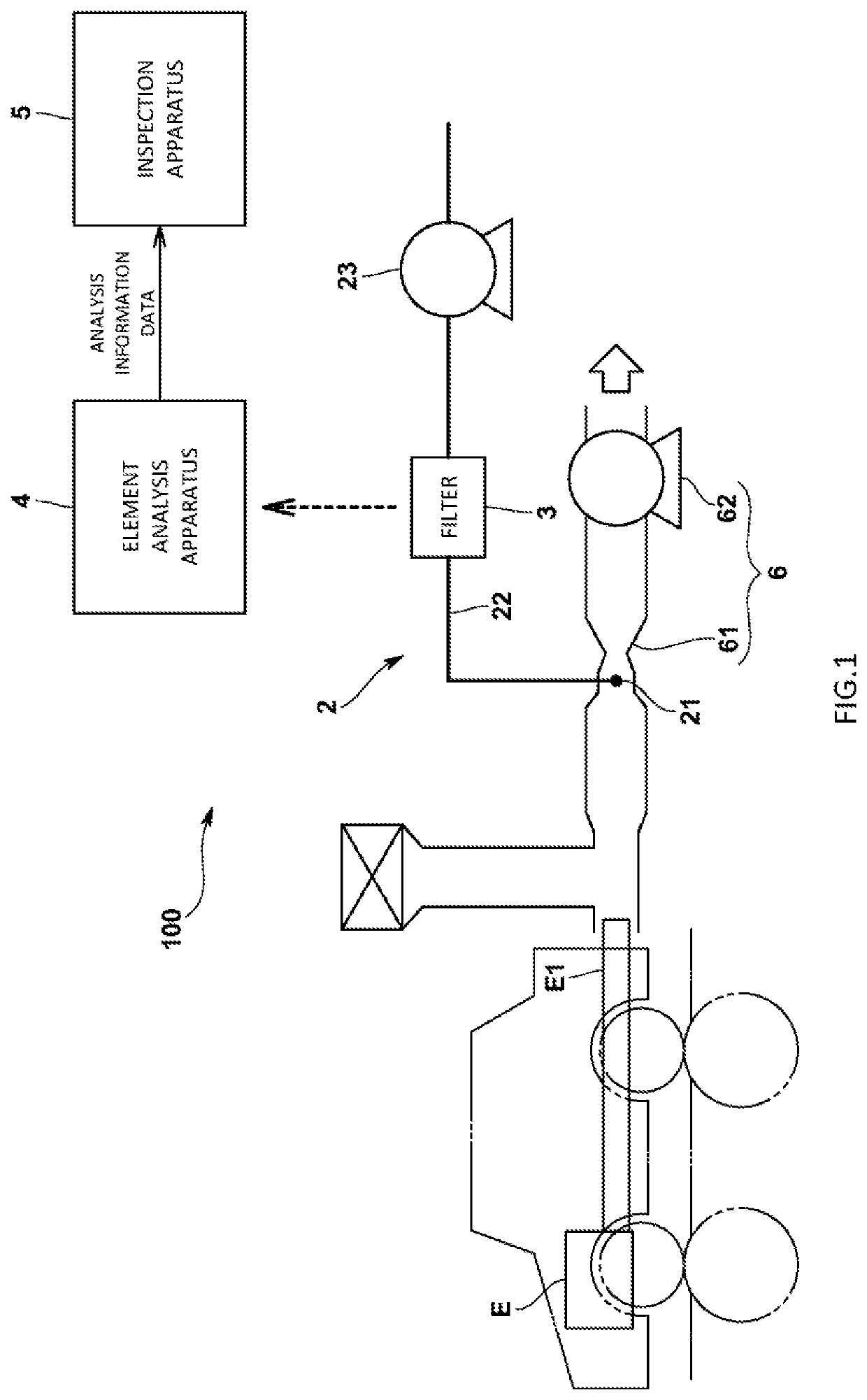
Inspection apparatus and inspection system
ActiveUS11215537B2Inspection is accurateInternal-combustion engine testingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationExhaust fumesProcess engineering
To measure an internal state of an engine, for example, the engine oil consumption conveniently and correctly, an inspection apparatus of the present invention for inspecting the internal state of the engine by using an exhaust gas of the engine including engine oil includes a data storage unit that stores content information about a plurality of elements contained in the engine oil, a data acceptance unit that accepts analysis information about a plurality of elements contained in the exhaust gas, and an inspection unit that compares the content information about the engine oil with the analysis information to inspect the internal state of the engine.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Lubrication liquid delivery methods and apparatus
ActiveUS11255233B2Simplify receipt and storage and deliveryMaintaining adjustmentEngine operating parametersPressure lubrication with lubrication pumpMonitoring systemEngineering
Disclosed is a method for delivering a lubrication liquid to a machine in a terminating liquid lubrication system. A machine and a cartridge containing a lubrication liquid are connected to each other so that the lubrication liquid is supplied to the machine. Some embodiments may include a monitoring system, a backup source of lubrication liquid, and / or a second cartridge that automatically provides lubrication liquid to the machine when the cartridge is empty.
Owner:THE SLOAN BROS CO D B A SLOAN LUBRICATION SYST
Lubricant health detection system
A system and method for activating on a user interface an indicator of a condition of a lubricant in a machine module. The system may comprise a controller and a user interface. The controller may be configured to, for each of a first time window and a second time window: receive a plurality of lubricant characteristics and measured lubricant temperatures, calculate an adjusted lubricant characteristic, and determine a slope based on the plurality of adjusted lubricant characteristics. The controller may further determine a change in slope, and generate a signal to activate the indicator on the user interface based on the change in slope, wherein, if the change in slope exceeds a threshold, the indicator is a lubricant changed indicator.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Control device for vehicle oil supply device
ActiveUS11353103B2Lower performance requirementsSuppress partial depositionGear lubrication/coolingEngine operating parametersControl theoryMotronic
There is provided a control device for a vehicle oil supply device that includes a mechanical oil pump configured to be rotatable forward and in reverse, an electric oil pump configured to suction oil stored in an oil storage portion that is common to the mechanical oil pump and the electric oil pump, a first filtering member provided to a first strainer of the mechanical oil pump, and a second filtering member provided to second strainer of the electric oil pump. The control device includes a controller configured to control the rotational speed of the electric oil pump. The controller is configured to restrict the rotational speed of the electric oil pump when the mechanical oil pump is rotated in reverse compared to when the mechanical oil pump is rotated forward.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Oil tank filling system
An oil tank filling system for filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine that includes an aft core cowl. The system includes an oil tank that has an oil tank top and an oil tank bottom and is located within a core of the engine, an oil access port located on the aft core cowl, and an oil tank filling pipe that leads from the oil access port to a tank filling port located at or adjacent the oil tank bottom. The system is configured so that oil that is supplied to the oil access port flows to and into the oil tank using gravitational force. A method of filling the oil tank of a gas turbine engine and a gas turbine engine that includes the oil tank filling system.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
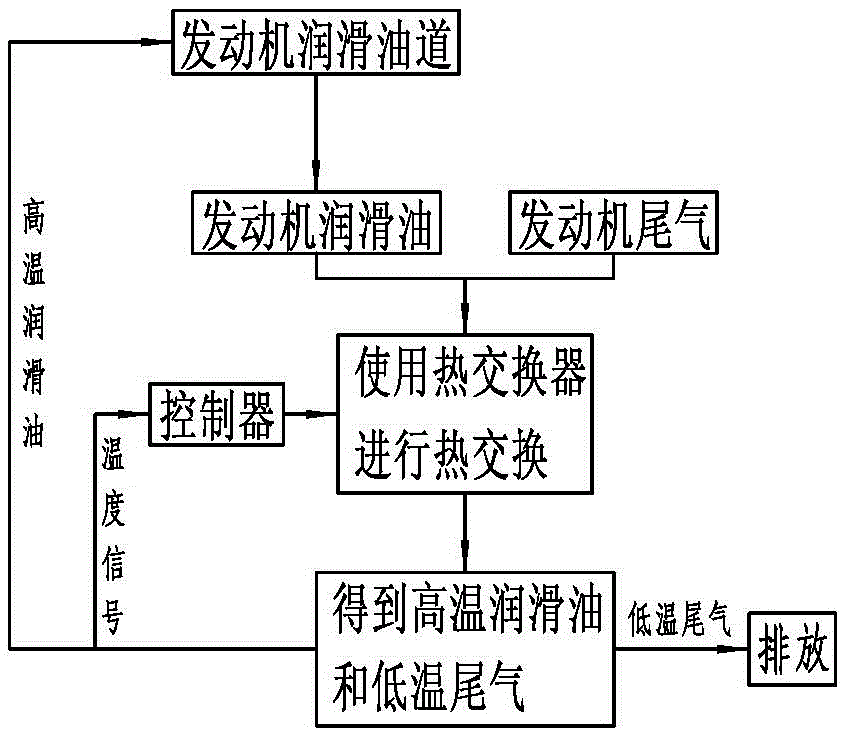
Method for reducing emission and oil consumption of engine by using tail gas waste heat
InactiveCN105569788AReduce viscosityReduce frictionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusWorking temperatureFuel oil
The invention discloses a method for reducing emission and oil consumption of an engine by using tail gas waste heat, and relates to the technical field of engines. The method comprises the following step: heating engine lubricating oil by use of tail gas exhausted by the engine, so that the engine lubricating oil reaches a set ideal lubricating working temperature as quickly as possible, and is kept at the ideal lubricating working temperature. Compared with the prior art, the method is used for reducing the emission and the fuel oil consumption of the engine by utilizing the tail gas waste heat, so that the energy waste is reduced.
Owner:黄相之
Oil tank system
ActiveUS20190338670A1Reduce swirlEnhance oil adhesionTurbinesLiquid degasificationLower faceGas turbines
An oil tank system (100) for a gas turbine engine is provided. The oil tank system (100) includes an oil tank (102) having an upper tank portion (112) and a lower tank portion (114), a waisted section (118) being provided between the upper tank portion (112) and the lower tank portion (114). Oil is received by a de-aerator (104) of the system (100) which supplies de-aerated oil to the upper tank portion (112). The waisted section (118) includes an upper face (119) configured to catch oil drips from above the waisted section (118) and to guide oil to a lower face (121) of the waisted section (118).
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Method and system for engine oil level sensing
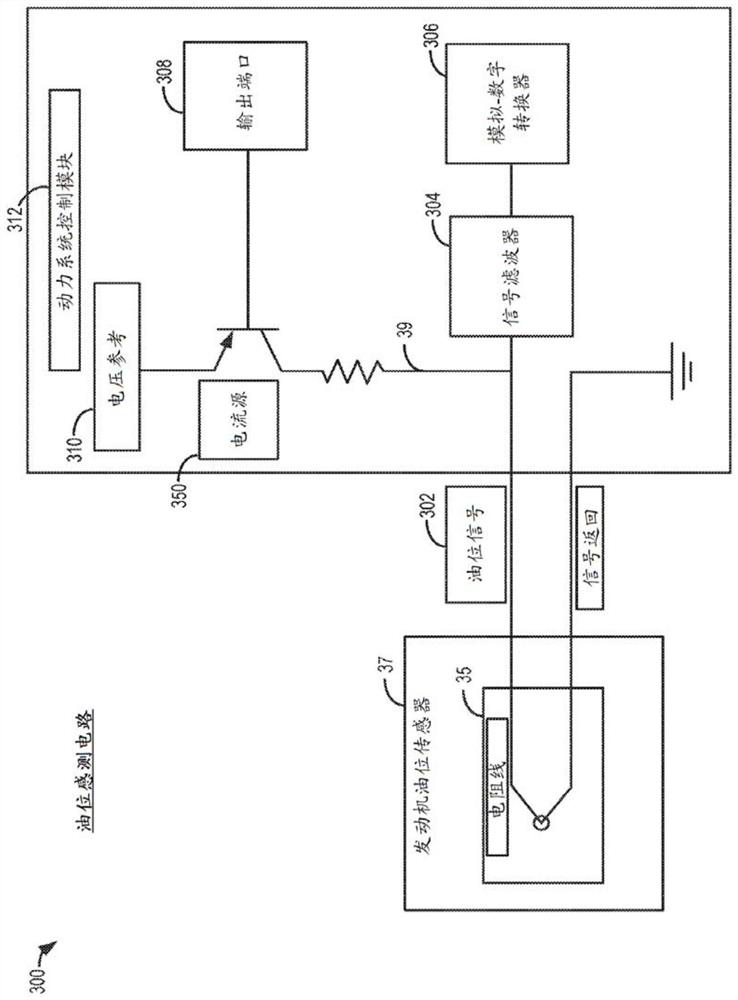
PendingCN112081640AEarly detectionReliable detectionSignal processingEngine levelsControl theoryMechanical engineering
Methods and systems are provided for improving engine oil level sensing while a vehicle is moving. The output of a hot wire sensor partially immersed in an engine oil well is sampled during selected vehicle moving conditions when lateral and longitudinal acceleration is limited and the vehicle is driving in a straight line. A transfer function is used to correlate a rate of change in sensor output, sampled during the selected vehicle operating conditions, with engine oil level.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine lubrication system
An engine lubrication system including: an oil pump configured to be driven by an engine; an oil jet mechanism configured to inject oil pressure-fed by the oil pump to a piston; and circuitry configured to set a target hydraulic pressure of the oil injected from the oil jet mechanism according to an operation state of the engine; determine a hydraulic pressure state of the oil injected from the oil jet mechanism; and change a gear stage of the automatic transmission to a lower gear stage in a case that a predetermined condition between the determined hydraulic pressure state and the target hydraulic pressure is satisfied.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com