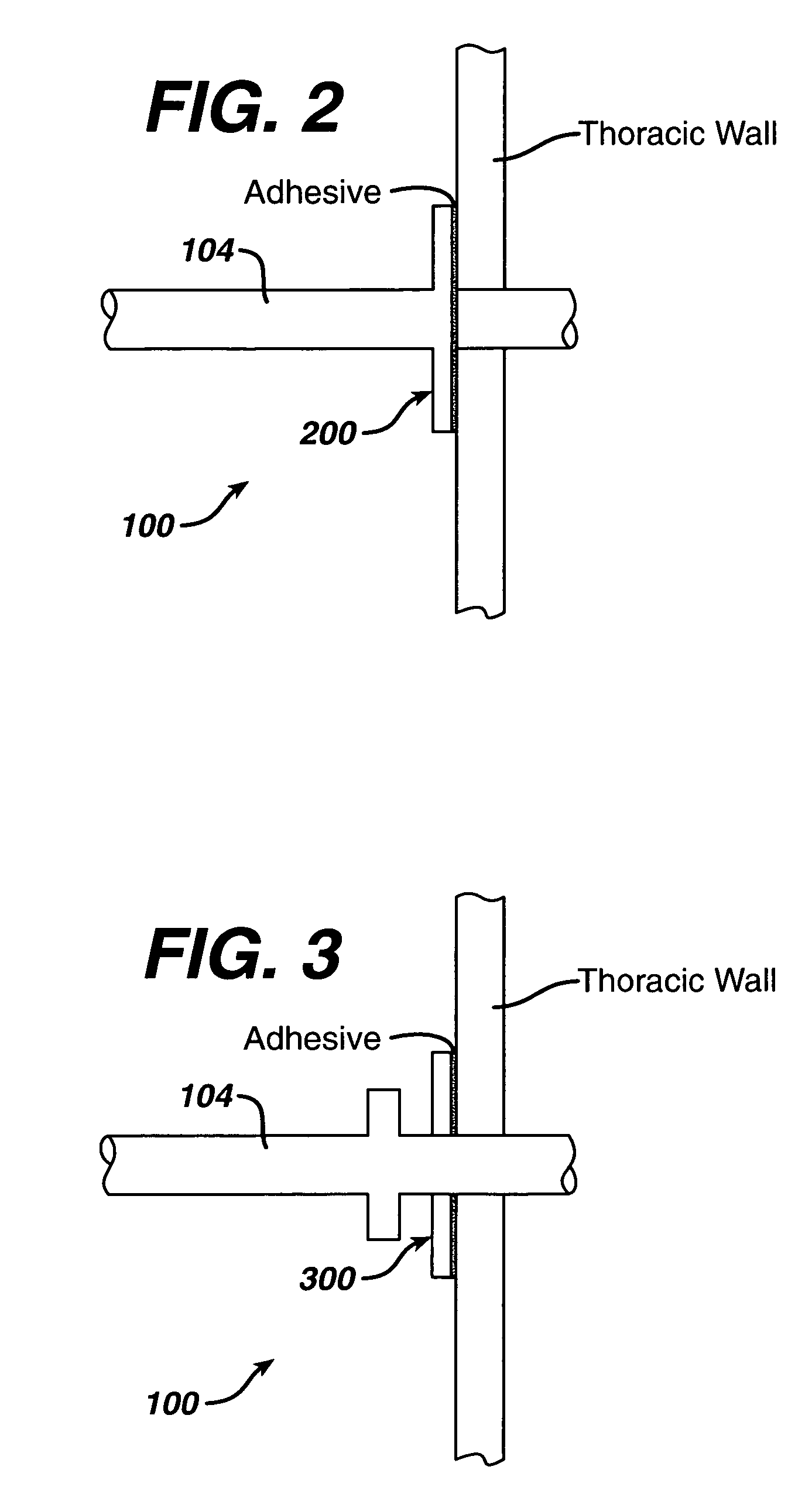
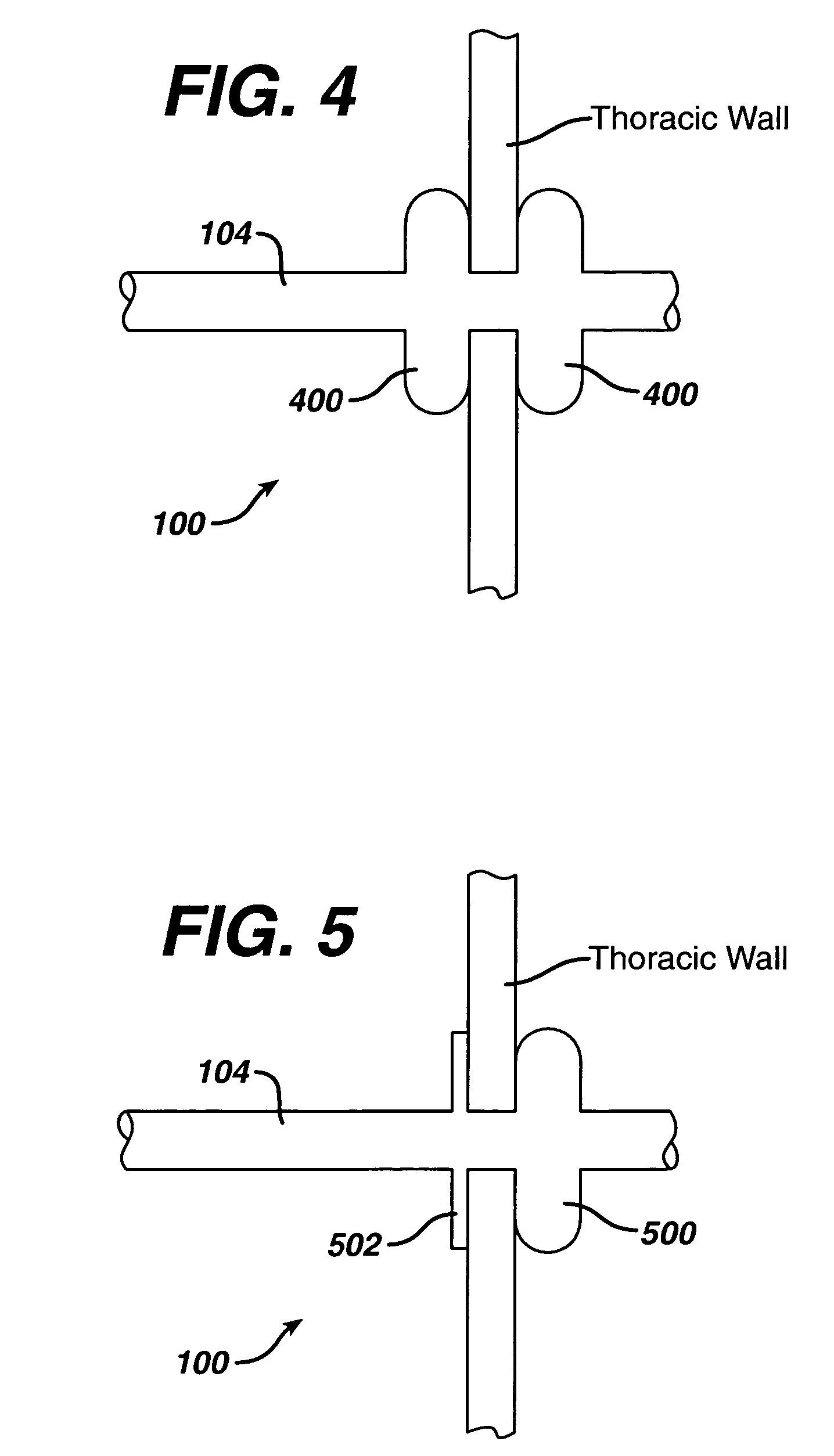
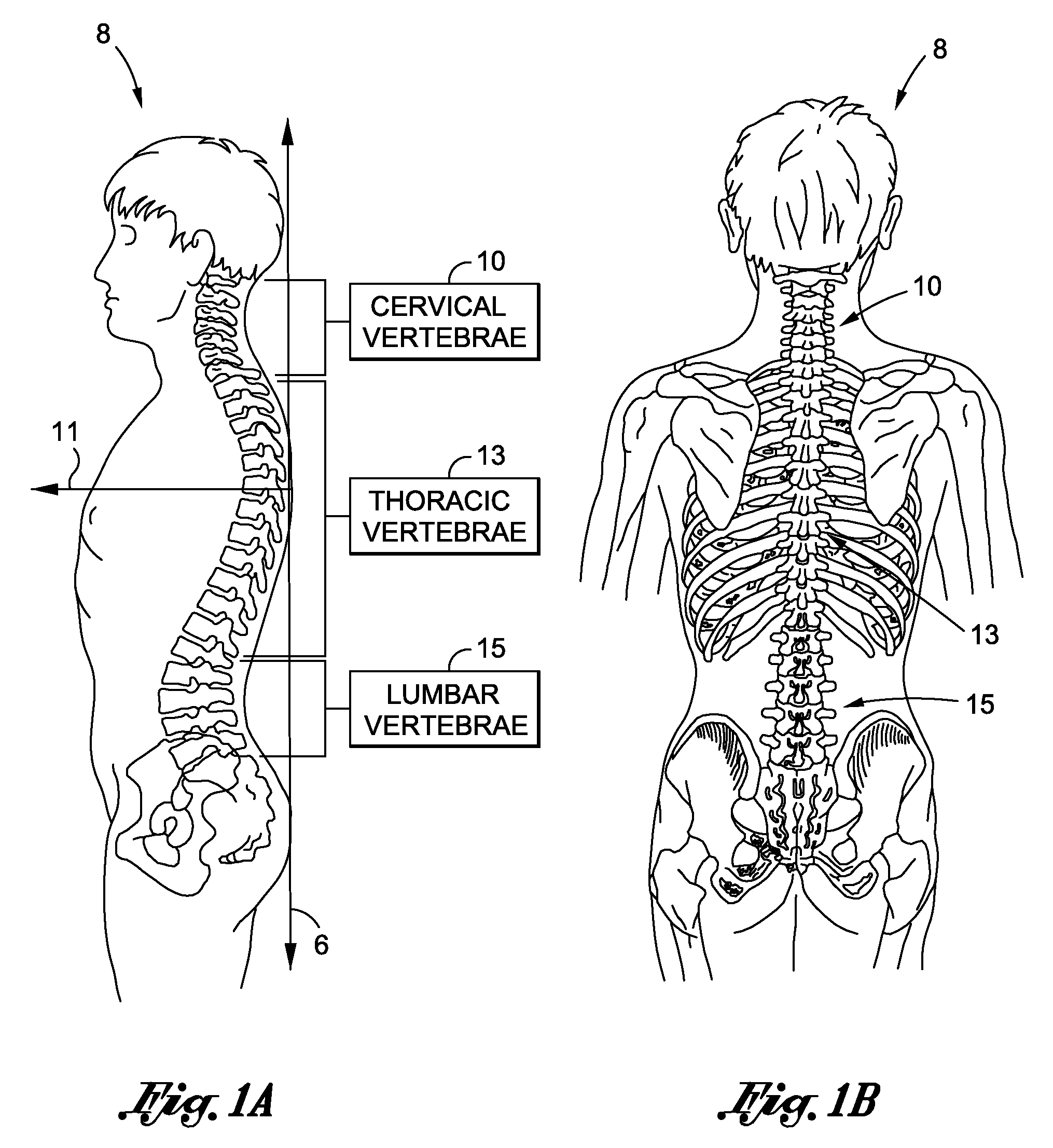
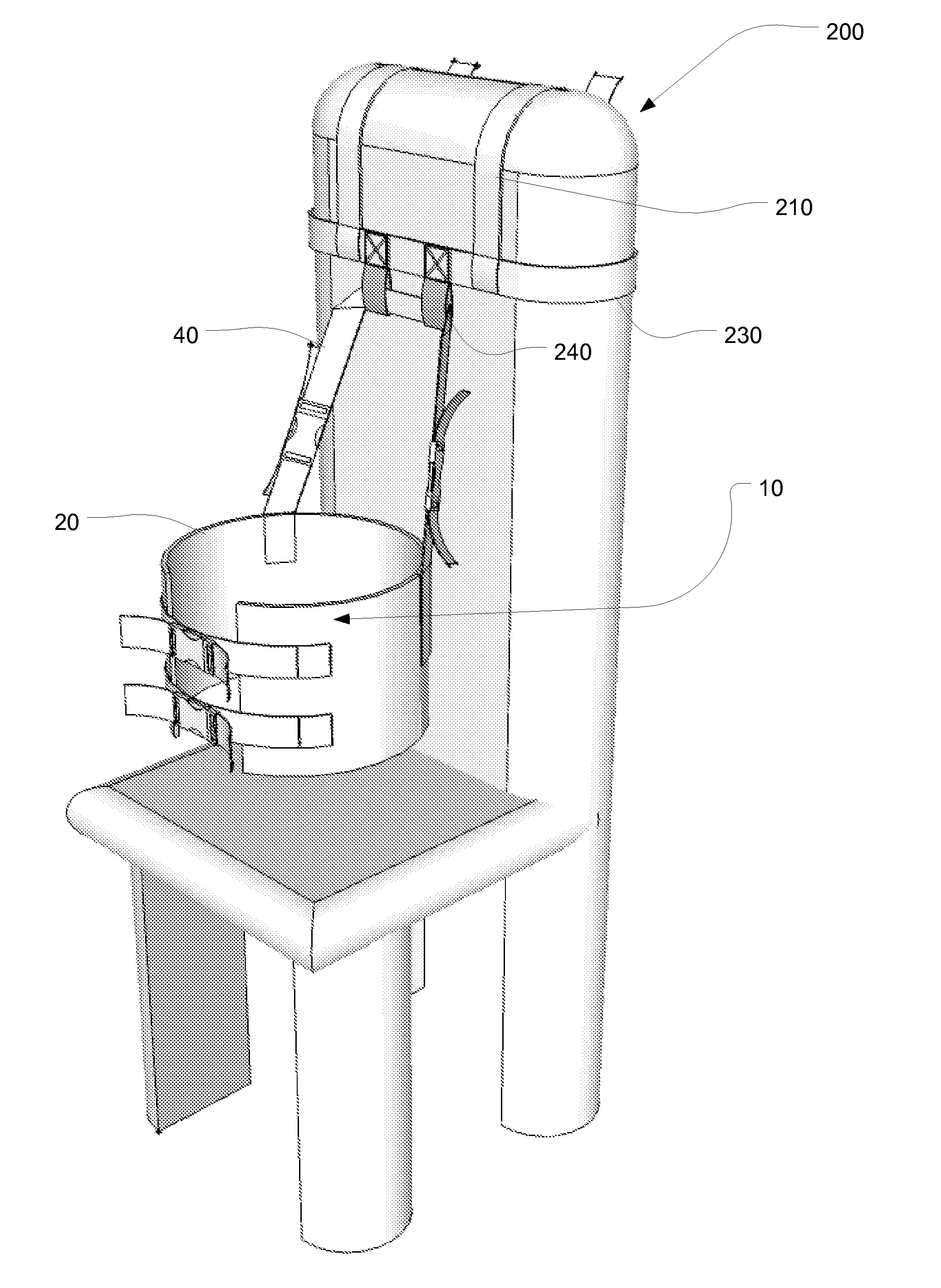
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
160 results about "Thoracic spine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
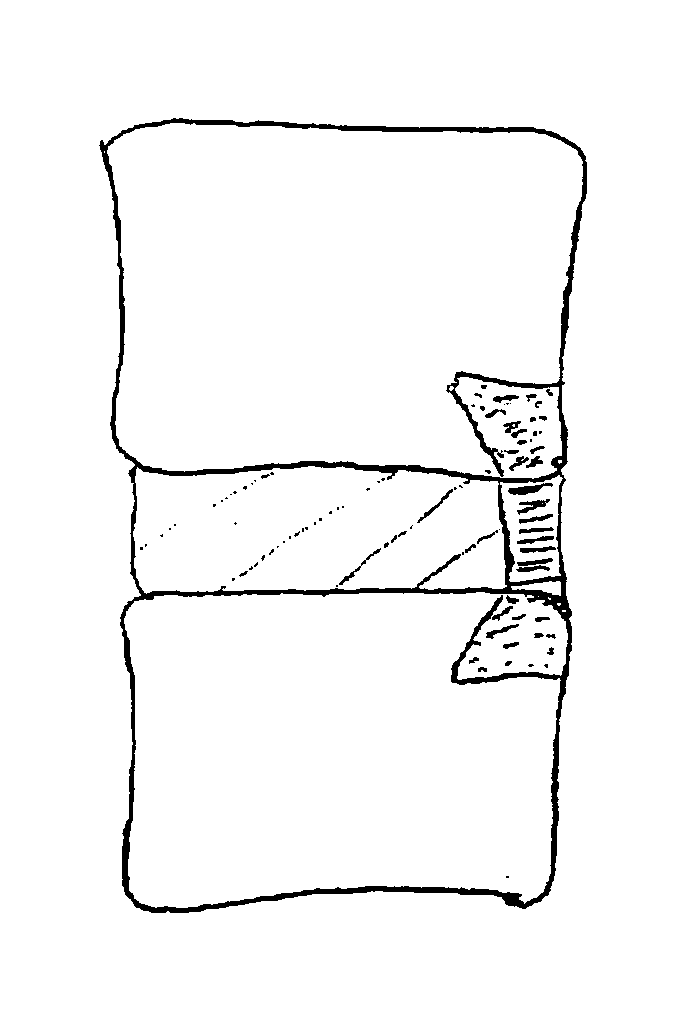
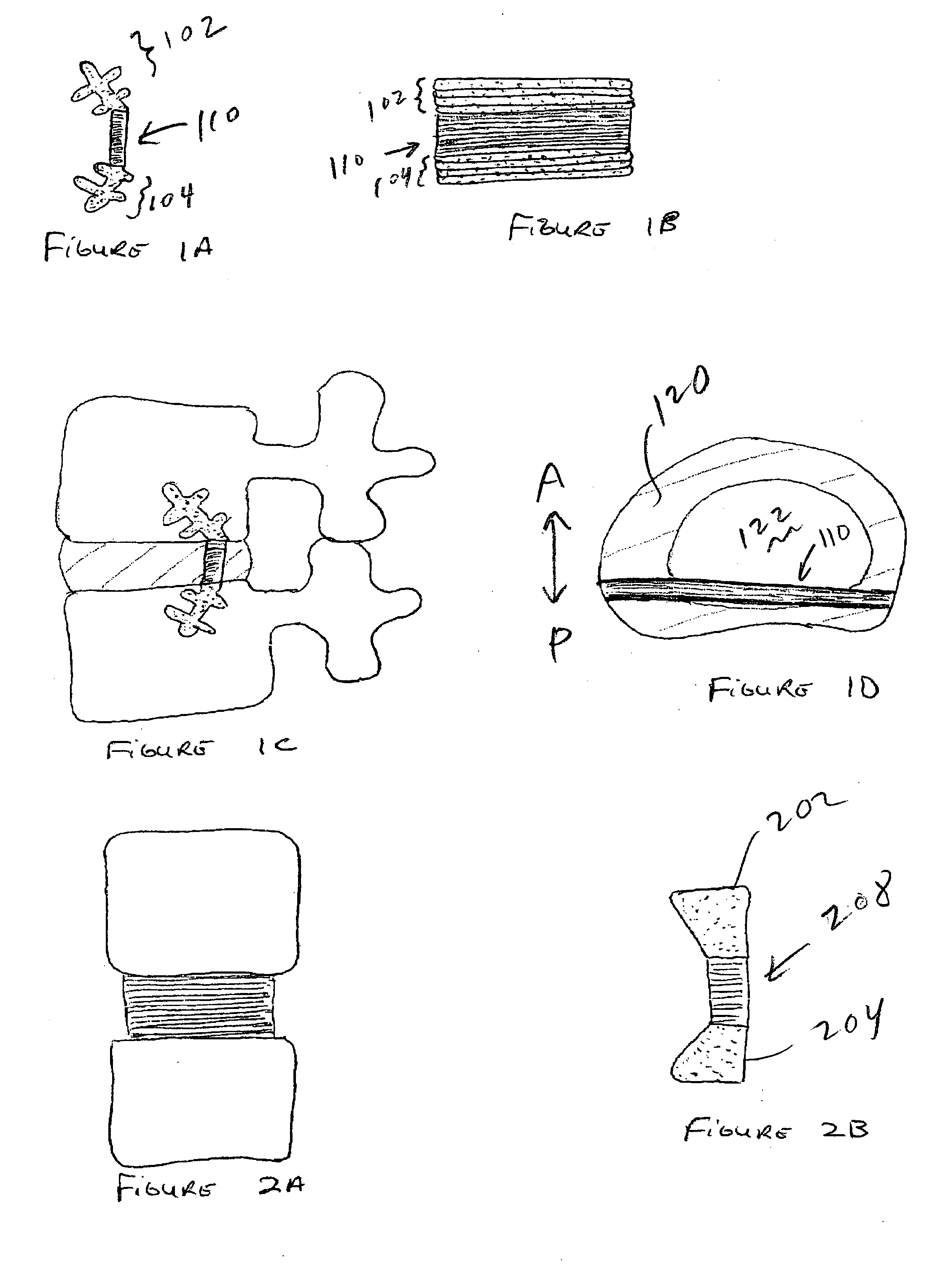
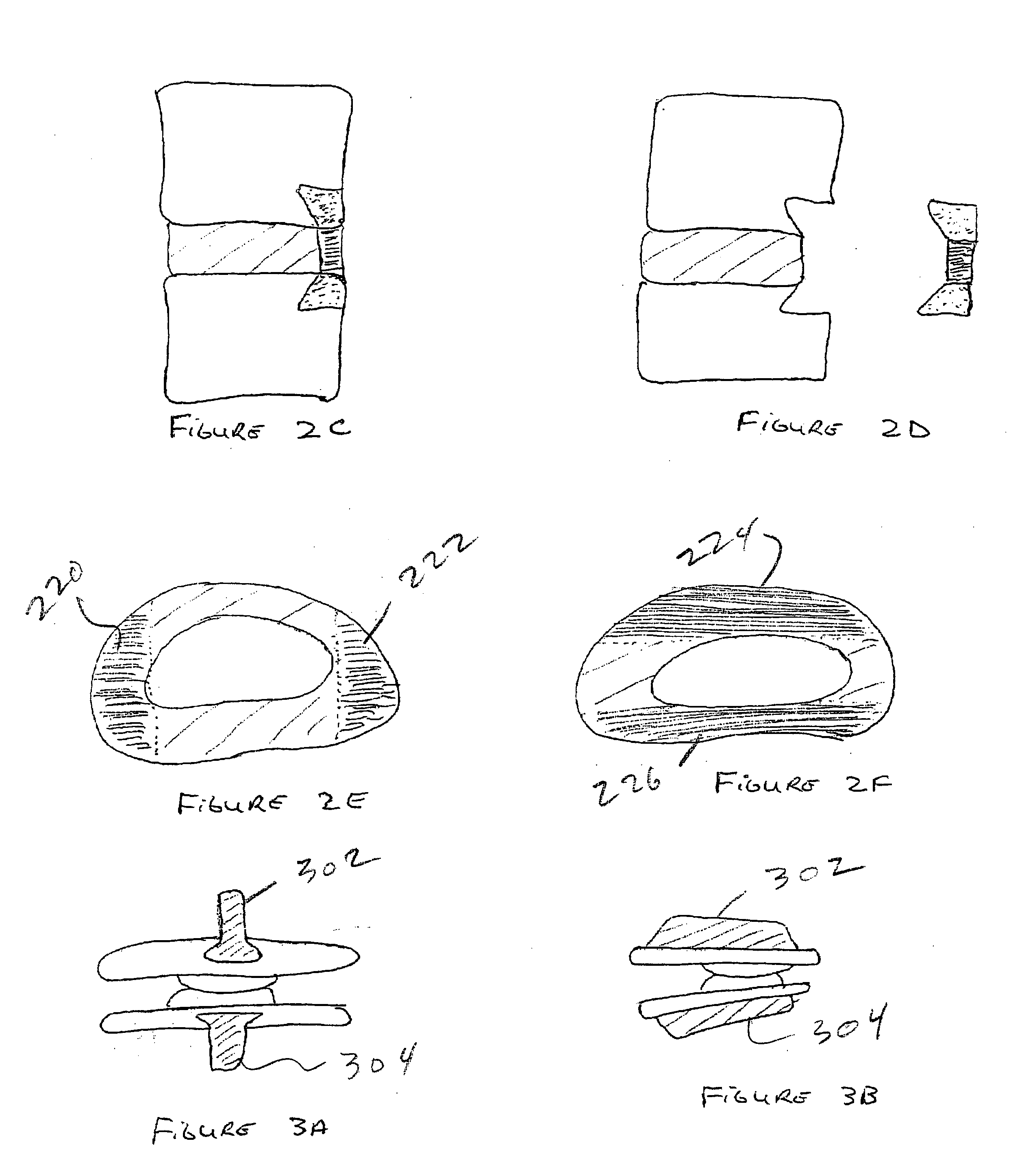
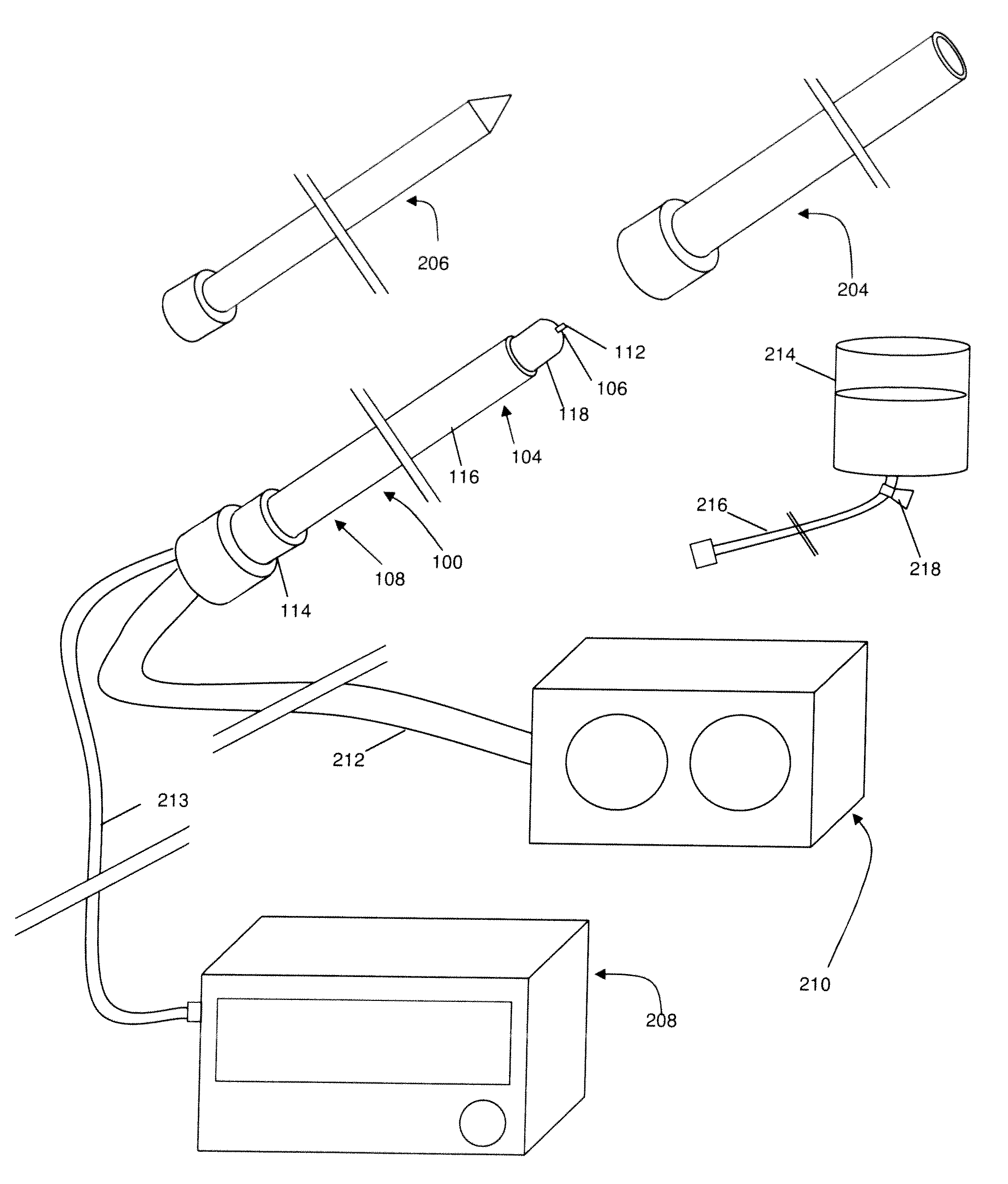
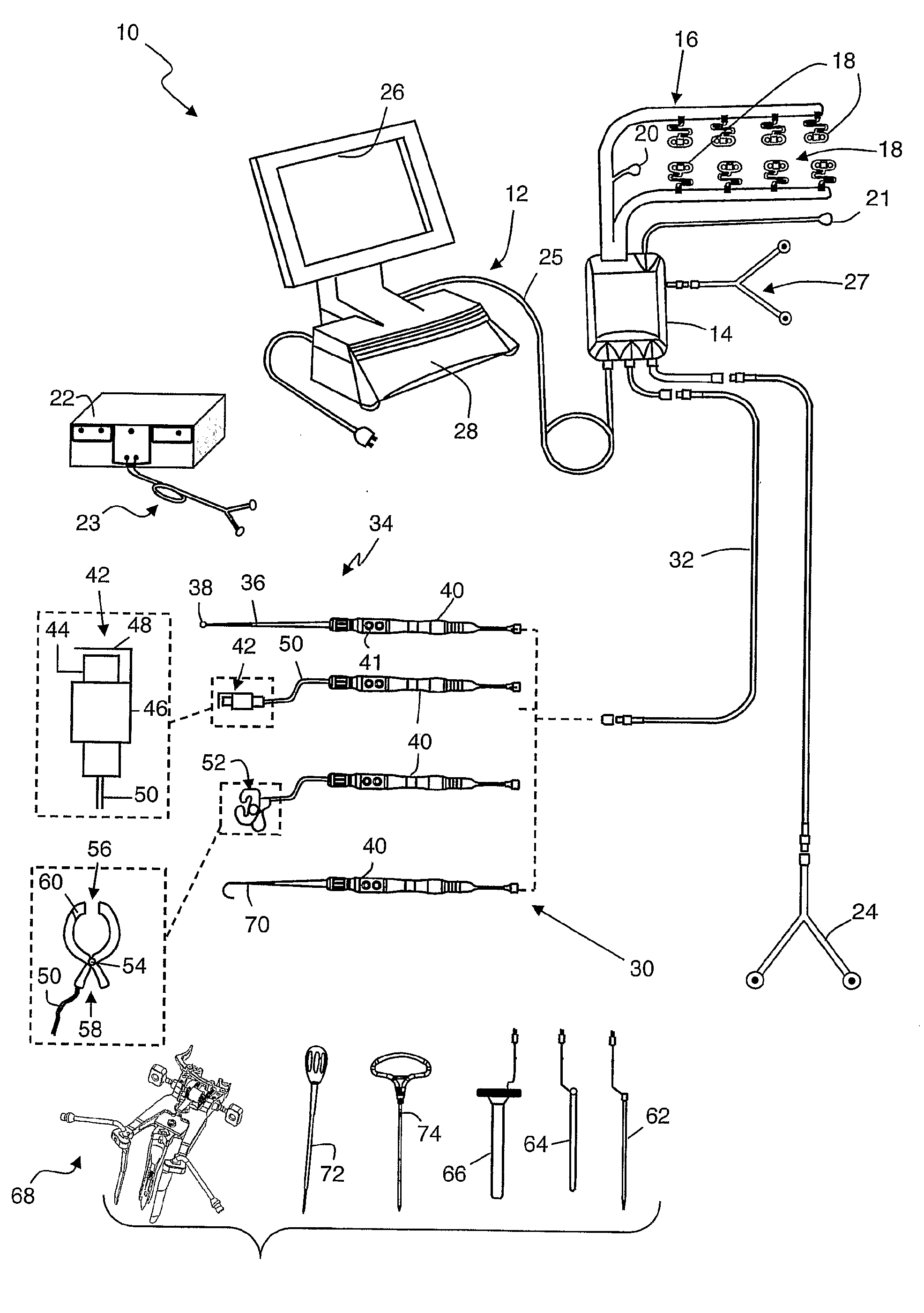
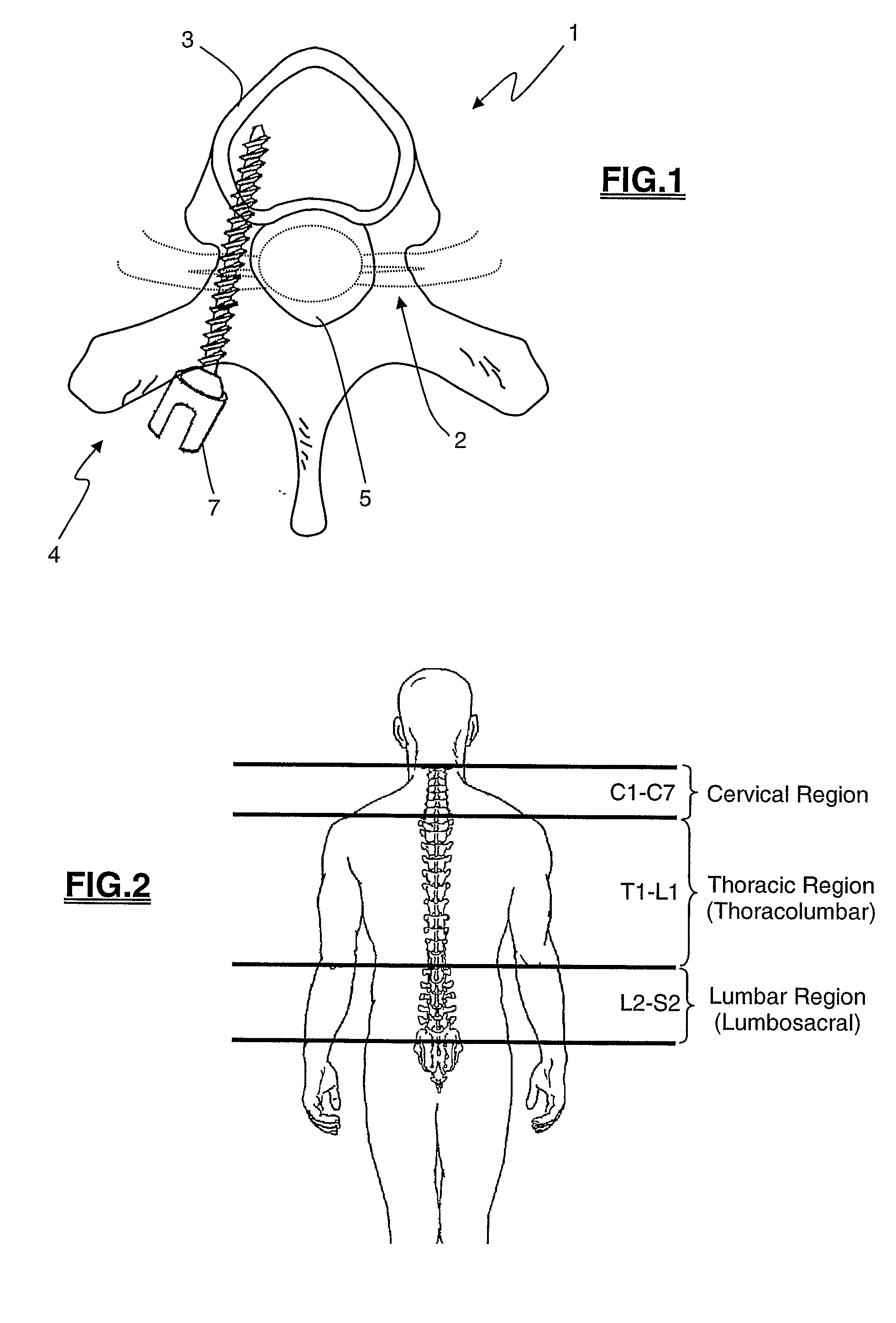
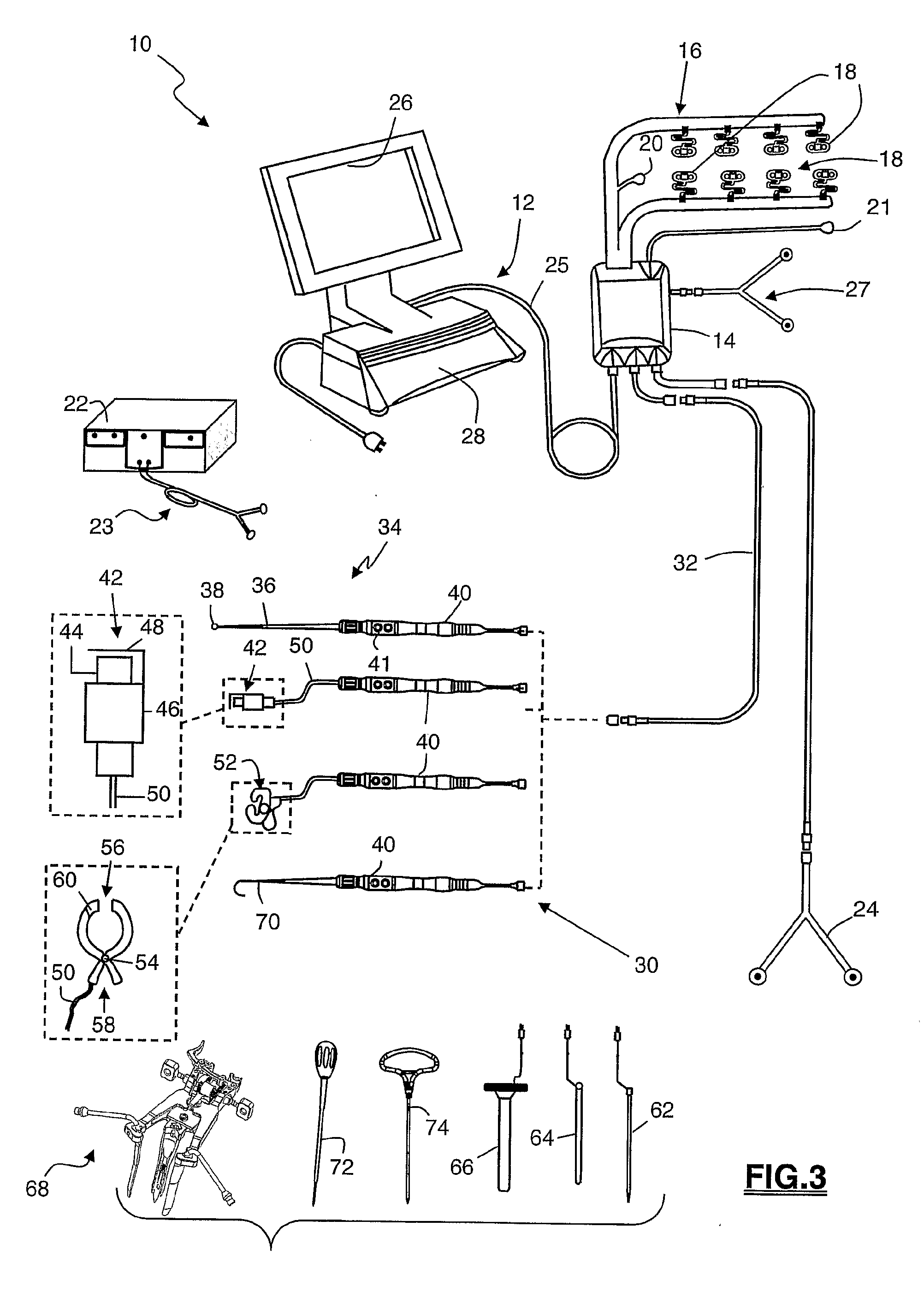
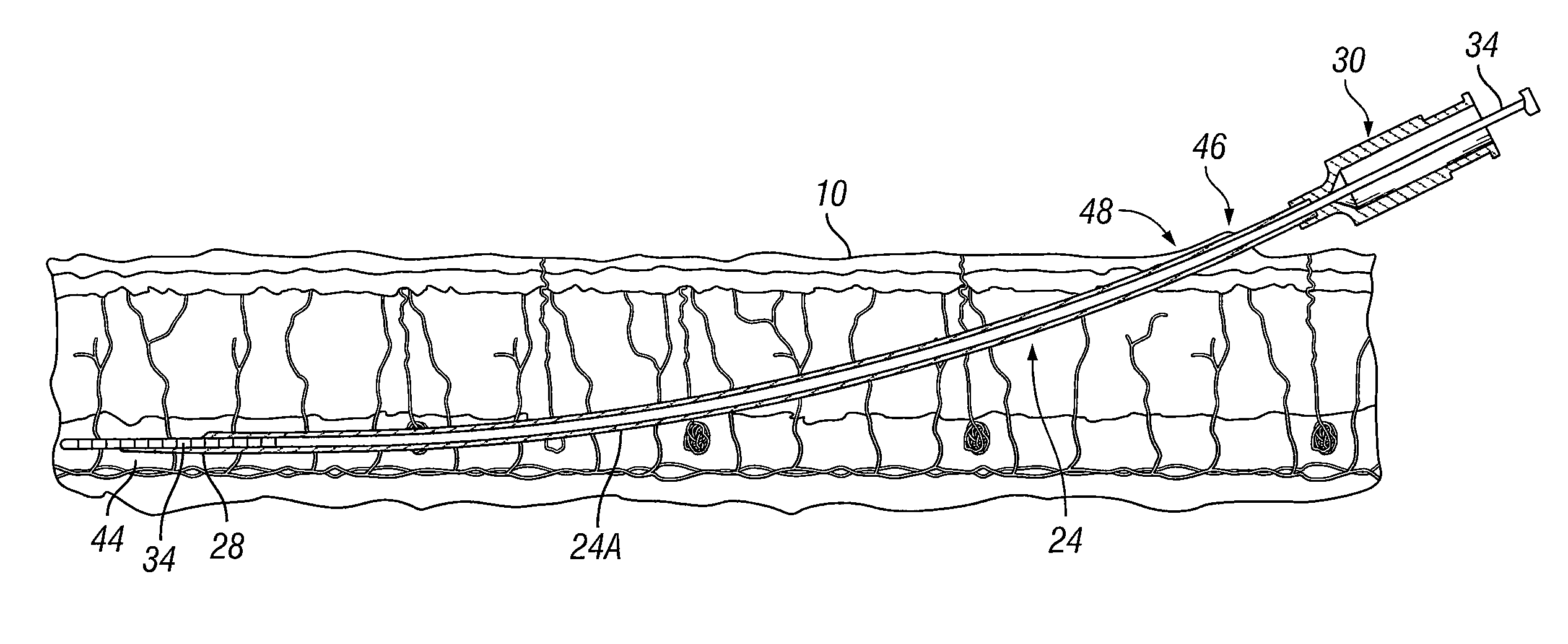
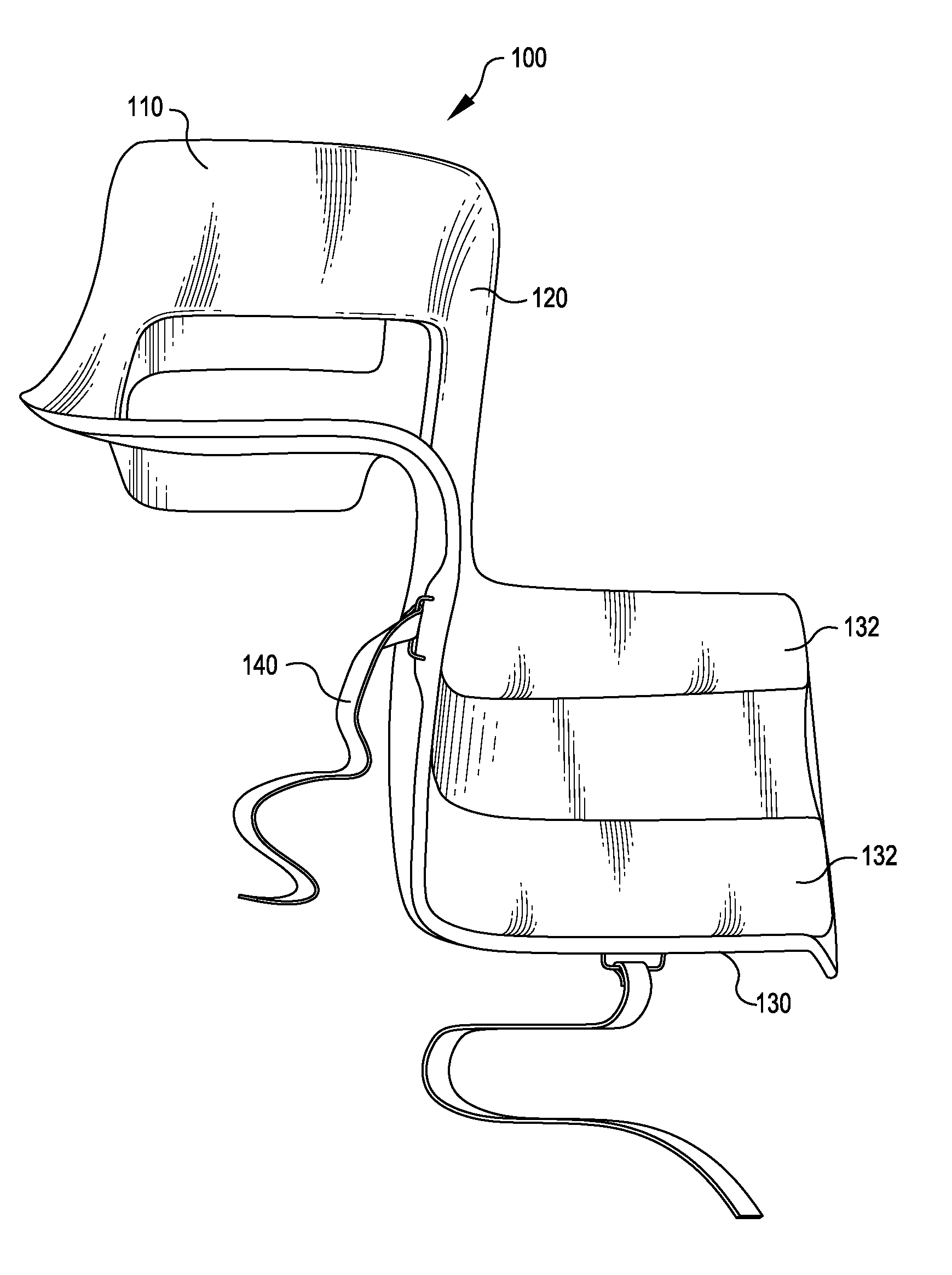
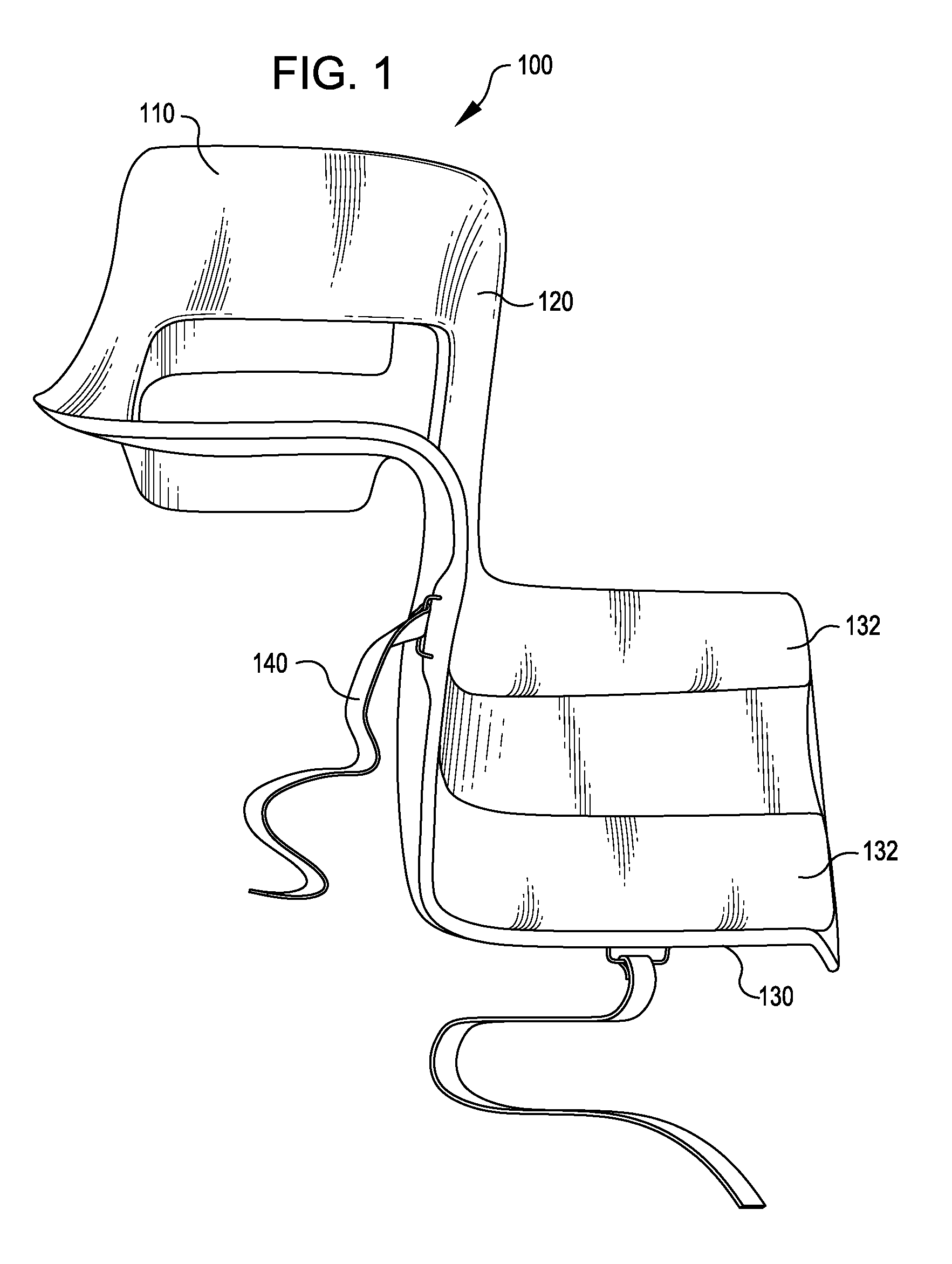
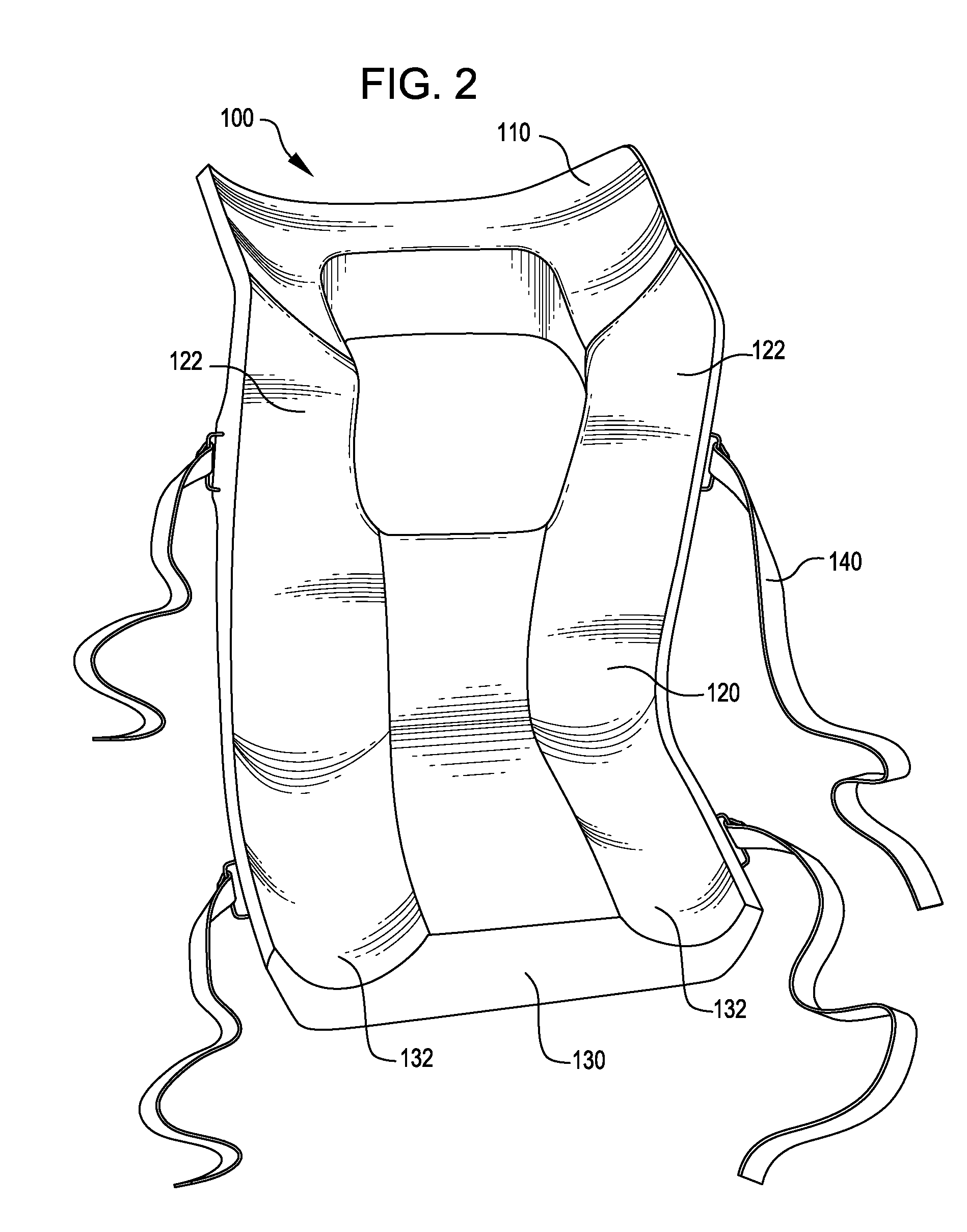
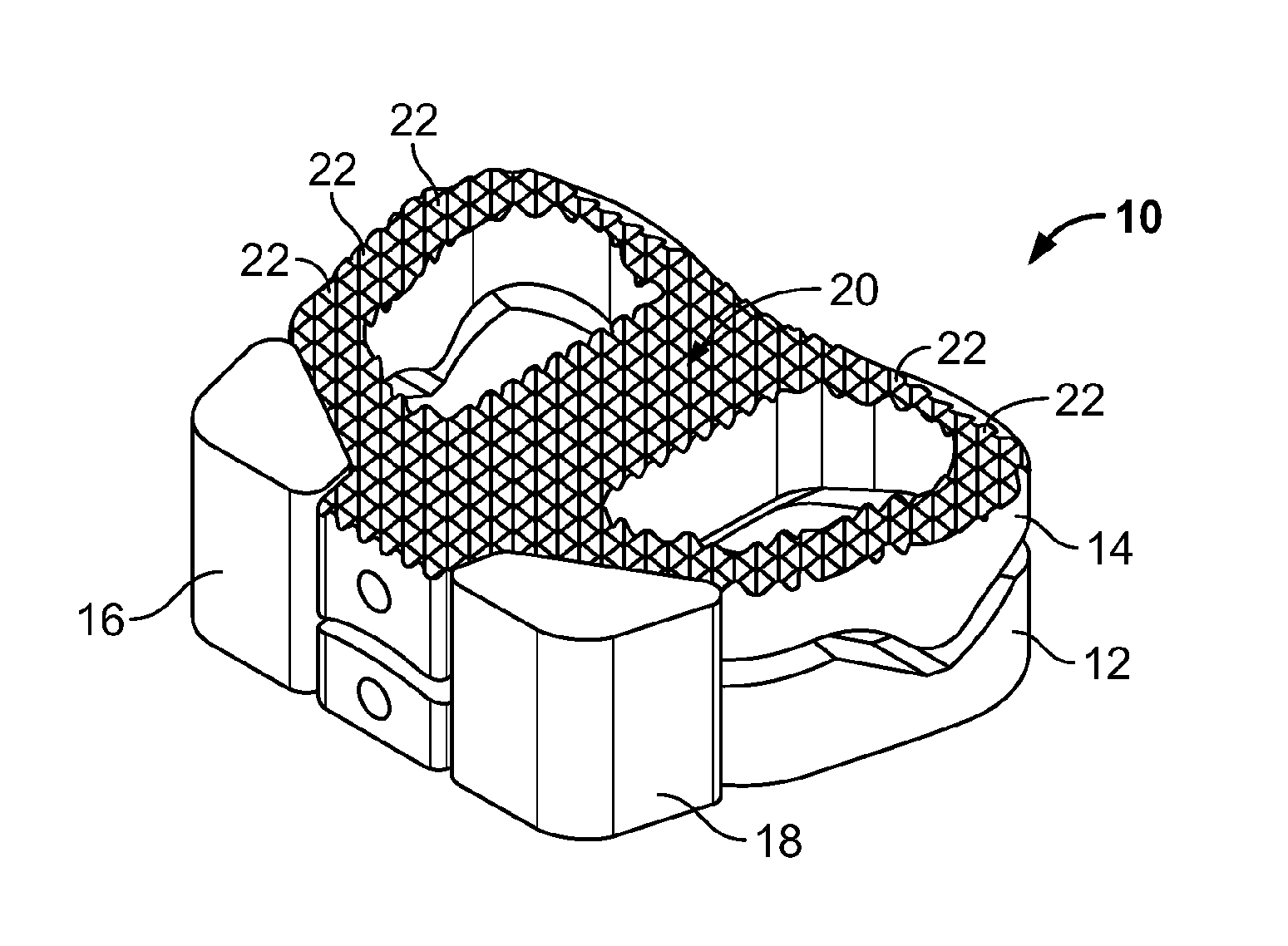
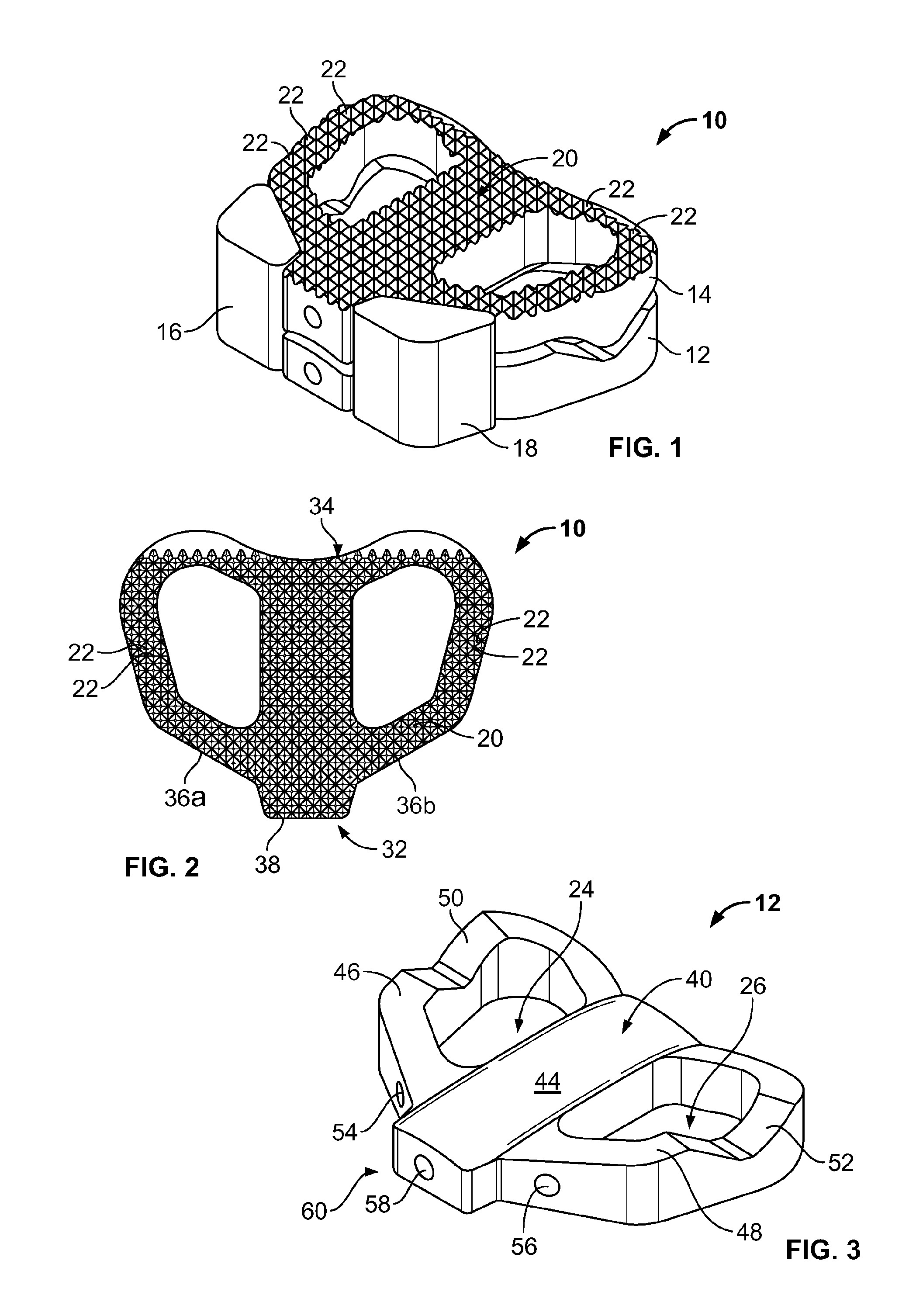
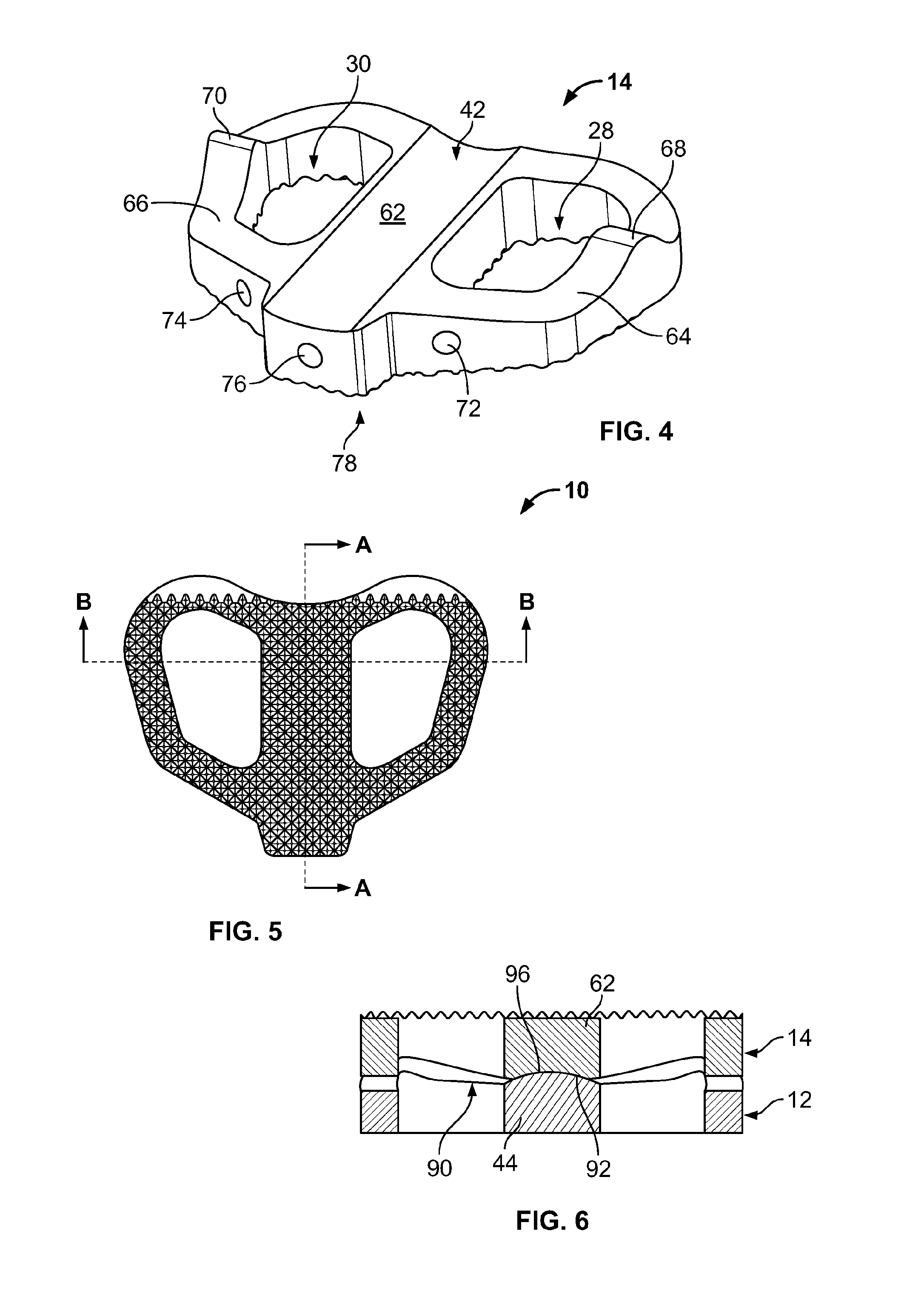
Spinal implants, including devices that reduce pressure on the annulus fibrosis
InactiveUS20050256582A1Promote reconstructionPrevents herniationInternal osteosythesisBone implantFibrosisDiscectomy
The invention broadly facilitates reconstruction of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) or the AF and the Nucleus Pulposus (NP). Such Reconstruction prevents recurrent herniation following Microlumbar Discectomy (MLD) other procedures. The invention may also be used in the treatment of herniated discs, annular tears of the disc, or disc degeneration, while enabling surgeons to preserve the contained NP. The methods and apparatus may be used to treat discs throughout the spine including the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines of humans and animals. In the preferred embodiment, a spinal repair system according to the invention comprises a first end portion adapted for placement within an intervertebral body, a second end portion adapted for placement within an adjacent intervertebral body, and a bridge portion connecting the first and second end portions, the bridge portion being adapted to span a portion of an intervertebral disc space and prevent excessive outward bulging.
Owner:ANOVA
Methods for treating the thoracic region of a patient's body
ActiveUS20090054962A1Effective treatmentEffective lesioningElectrotherapyDiagnosticsThoracic regionSurgical department
A method is disclosed for the treatment of a thoracic region of a patient's body. Embodiments of the method comprise positioning an energy delivery portion of an electrosurgical device to face a segment of a thoracic vertebra at a distance from the segment; and cooling the energy delivery portion and delivering energy through the energy delivery portion.
Owner:AVENT INC
Body rest structures
InactiveUS6154903AMaximize distanceImprove ventilationSofasBedsHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A body rest structure includes a torso support for supporting the torso of a human body in a prone, elevated position which serves to induce a mild stretch of the user's thoracic and lumbar vertebrae. The torso support includes an upper chest and shoulder support platform and a lumbar support platform. An open region extends longitudinally between the platforms to provide room for at least a portion of the weight of the chest below the shoulders to pull down on the body between the platforms. The support may include a rear supporting surface to provide lifting support from below the hips and abdomen of the body. A head support for supporting the head of the body in a downwardly facing position when the torso is supported by the torso support is also disclosed. The head support includes a front portion for providing lifting support to the forehead of the body, and parallel opposed side portions for supporting opposed sides of the face. Each side portion has an upper surface that slopes upwardly from the front portion of the head support to the associated distal end of the side portion.
Owner:WAI CHUNG PATRICK
Spinous process stabilization device and method
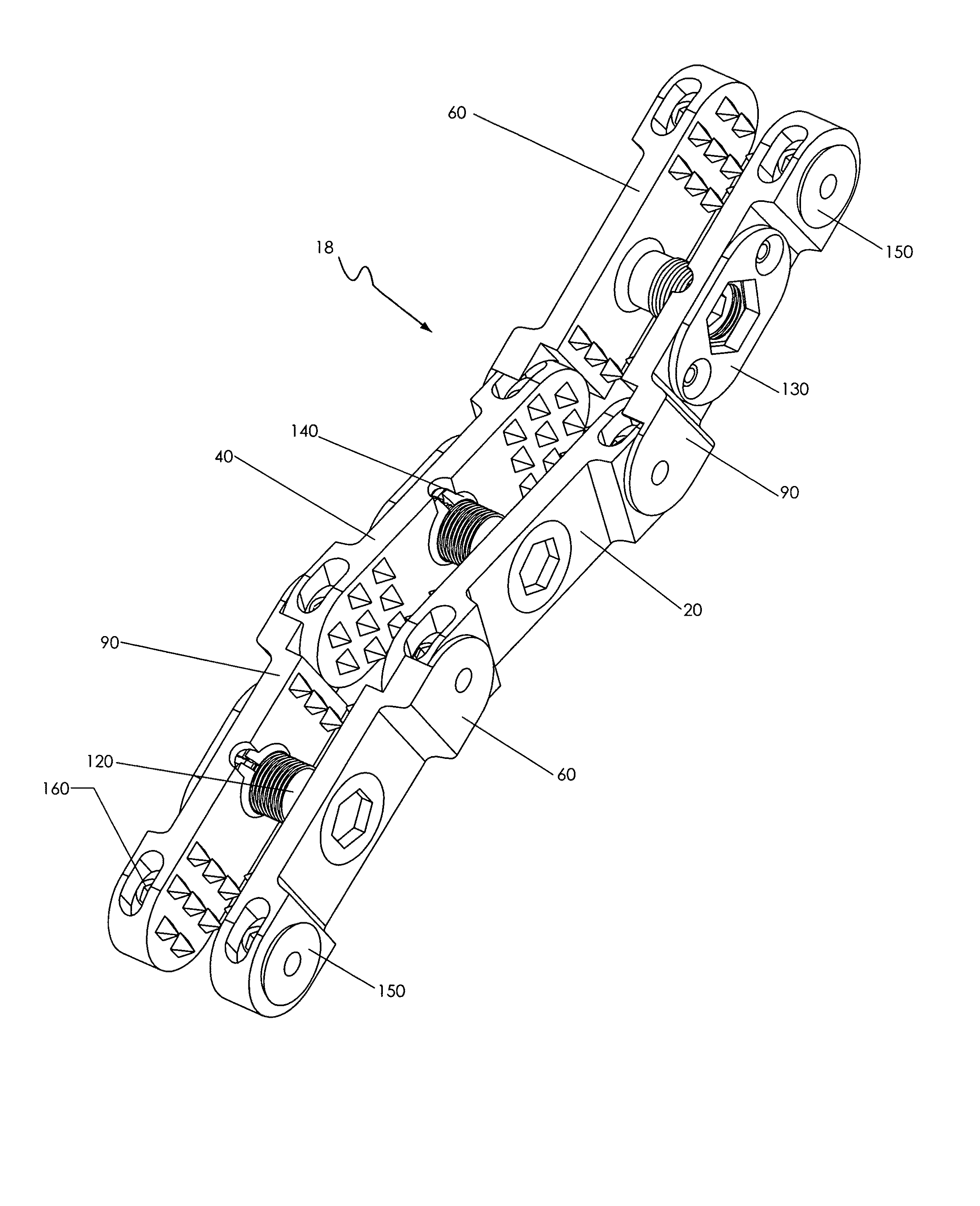
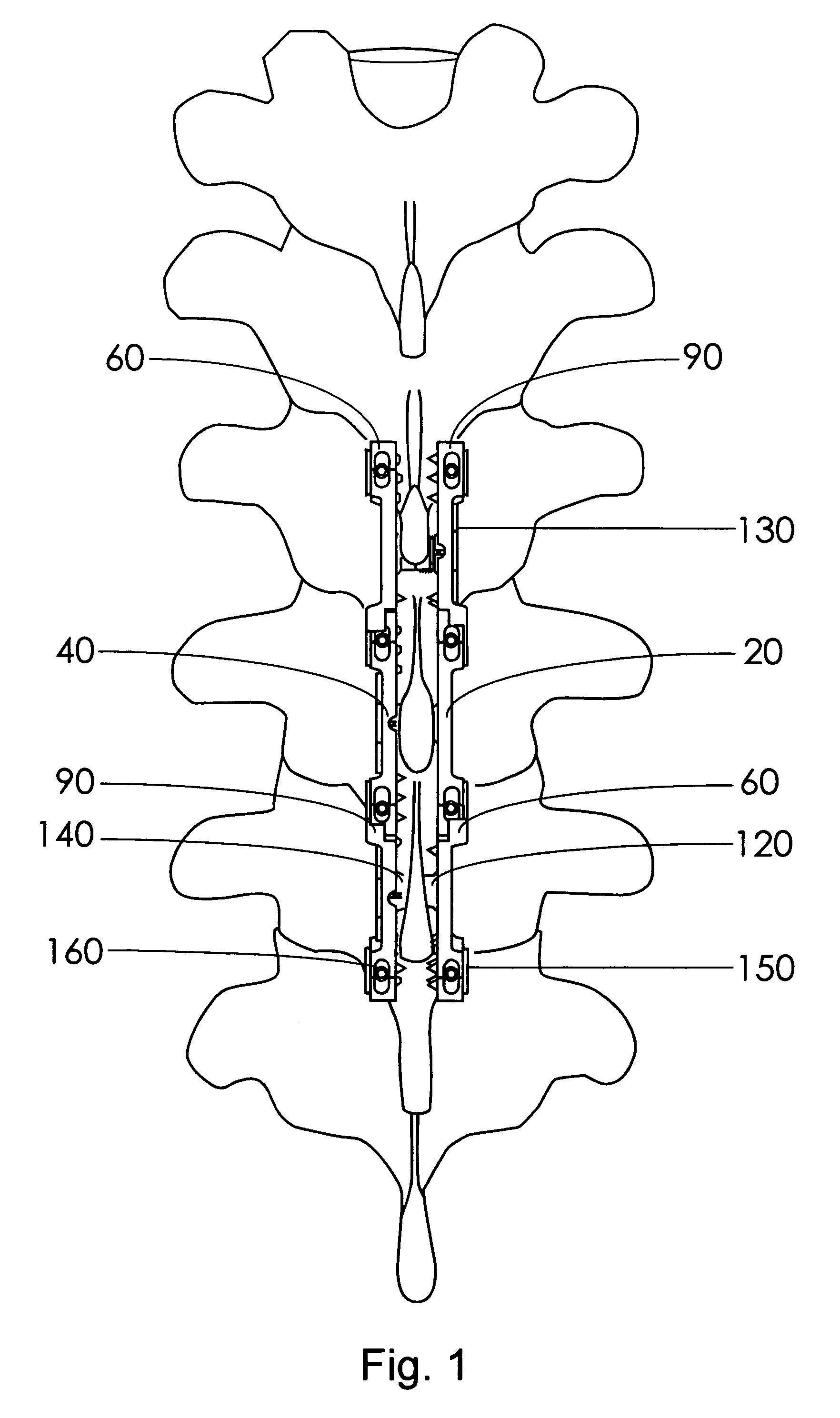
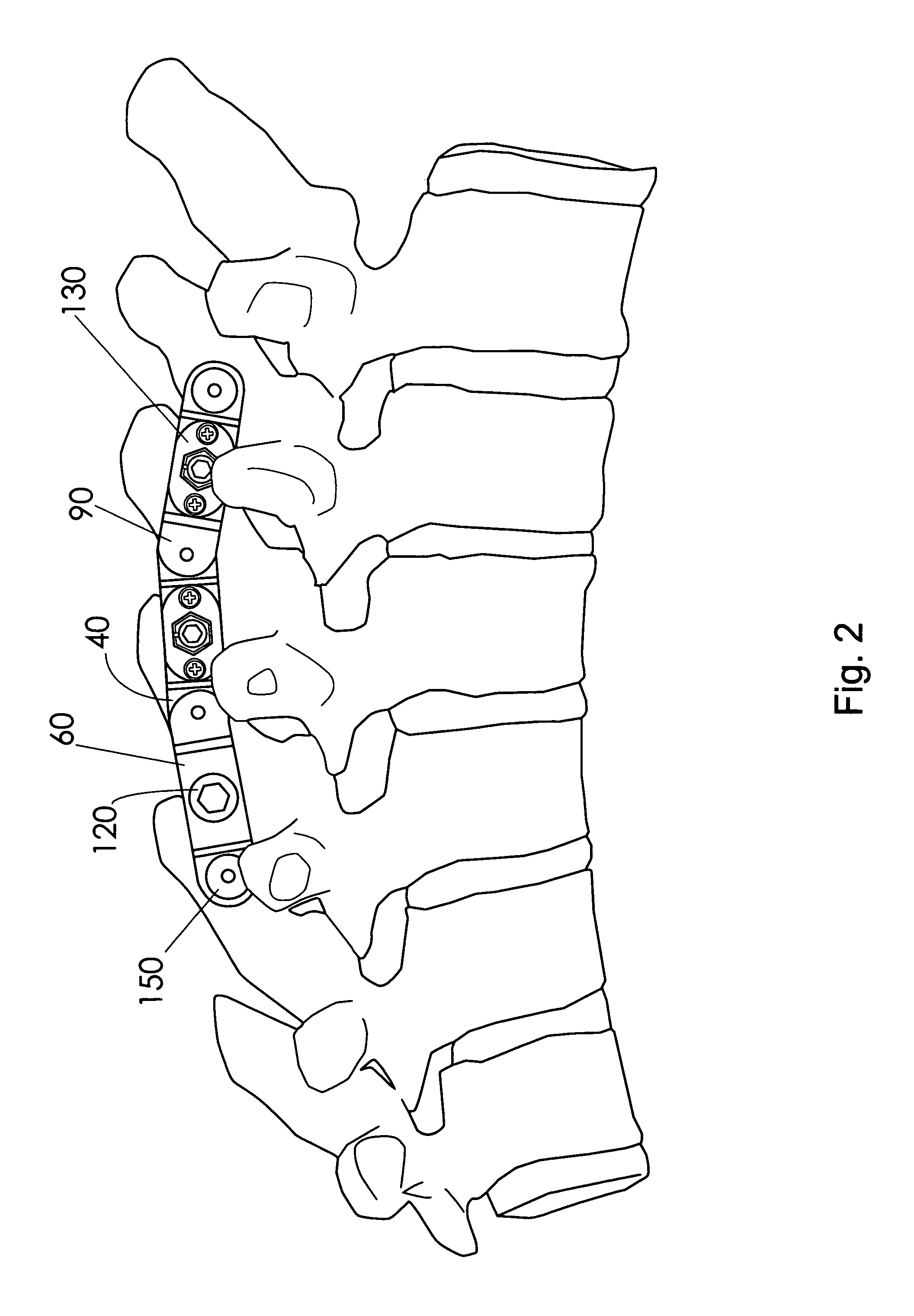
A fixation device is provided to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post passed through the interspinous process gap The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
System and Methods for Performing Pedicle Integrity Assessments of the Thoracic Spine
ActiveUS20080221473A1Good reproducibilityReliable stimulation threshold determinationElectrotherapyElectromyographyIntegrity assessmentPilot hole
The present invention includes a system and methods aimed at surgery, and more particularly to a system and methods for monitoring nervous tissue to assess the integrity of a pedicle wall during or after pilot hole formation and before, during, or after screw implantation, particularly in the thoracic spine. The system also performs other neurophysiologic assessments including, but not necessarily limited to, neuromuscular pathway status, nerve proximity detection, nerve pathology monitoring, and spinal cord health monitoring.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Peripheral nerve field stimulator curved subcutaneous introducer needle with wing attachment specification
An apparatus for use in peripheral nerve field stimulation (PNFS) whereby a plurality of curved introducer needles, of varying curvatures, are provided to permit the physician to best locate the region of oligodendrocytes that contain the A Beta fibers by matching the lumbar lordosis. A wing device is also provided that is attachable to the hub of the curved needle introducer which gives the physician better ability to maneuver the needle during insertion as well as permitting tenting of the skin. The invention benefits a large number of painful disorders arising from pathology in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. In addition, this invention can also help a large number of other conditions including but not limited to failed back surgery syndrome / post-laminectomy pain, occipital / suboccipital headaches, scar pain, post herpetic neuralgia pain, mononeuritis multiplex, and pain following joint surgery (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder).
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Methods for treating the thoracic region of a patient's body
InactiveUS20090024124A1Effective lesioningEffective treatmentDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesChest regionThoracic region
A method is disclosed for the treatment of a thoracic region of a patient's body. Embodiments of the method comprise positioning an energy delivery portion of an electrosurgical device to face a segment of a thoracic vertebra at a distance from the segment; and cooling the energy delivery portion and delivering energy through the energy delivery portion.
Owner:AVENT INC
Method and apparatus for preparing bone grafts, including grafts for lumbar/thoracic interbody fusion
A base having a substantially planar surface, an upright support member and a blade guide having a serrated surface that can be adjustably positioned along the planar surface. The blade guide is biased toward an opposing serrated plate member to securely hold a section of donor bone, and locked in place using an adjustable lever-cam linkage.
Owner:COUVILLION ROY J +1
Seat with adjustable support system
InactiveUS20060001304A1Improve comfortImprove enduranceBack restsOperating chairsAnatomical structuresStructural balance
A sacral support assembly for use with a seat is provided. The seat includes a seat frame. An adjustable sacral support assembly is connected to the seat frame. The sacral support assembly includes a sacral support member adapted to support the sacrum of a seated user even when an obstruction is located between the user and the sacral support assembly. A method is also provided for delivering primary support to a user's sacrum and sacral-pelvic anatomy and secondary support to the remaining regions of the spine and / or adjacent anatomy to reduce fatigue, increase comfort, structural balance, stability, and posture control for a user, and a system for adjusting and controlling the load distribution from the sacral anatomy to the spine and other anatomical structures adjacent to a user's sacrum, for example, the pelvis, lumbar, thoracic and cervical regions.
Owner:TRAC TEC
Advanced Combat Uniform for Medics
An advanced combat clothing system for military medics and medical professionals actively involved in the field of combat while providing acute emergency care for wounded soldiers. The Advanced Combat Uniform for Medics also referred to as the ACUM consists of a pair of trousers, a long sleeve shirt and a unique pocket receptacle invention which stabilizes the content within the pockets. The ACUM was invented to replace the use of roll-up bags and back packs used to carry the tools and supplies of the military medics during combat zone engagements.The ACUM invention was strategically designed to disburse the weight of the medical gear over the entire body, therefore, decreasing the entire weight load from exerting pressure over the lumbar and thoracic spinal locations. Additionally, by disbursing the pay-load or weight over the entire body, the military medic will be able to maneuver and combat with more accuracy and precision.The ACUM invention has a unique pull cord system in which the military medic can access lifesaving medicines and triage supplies at the pull of a cord. The ACUM can be made using any fabric including the digital camouflage material used and preferred by military personnel. The ACUM can hold over 100 required medical items while providing extremely fast easy access to the medical supplies carried by the military medics.The ACUM invention was designed to systematically place all of the medical supplies carried by the military medic in strategic areas around the wearer's body. The ACUM can be made to fit any size, male or female. This combat uniform can be produced relatively quick and easy using a line production clothing protocol. Lumbar and spinal injury affects a large population of military personnel at one time or another, by disbursing the weight or load of the military medics gear; this will significantly reduce the risk of developing lumbar spinal disease in general.
Owner:EARLEY BILLY ZACHERY
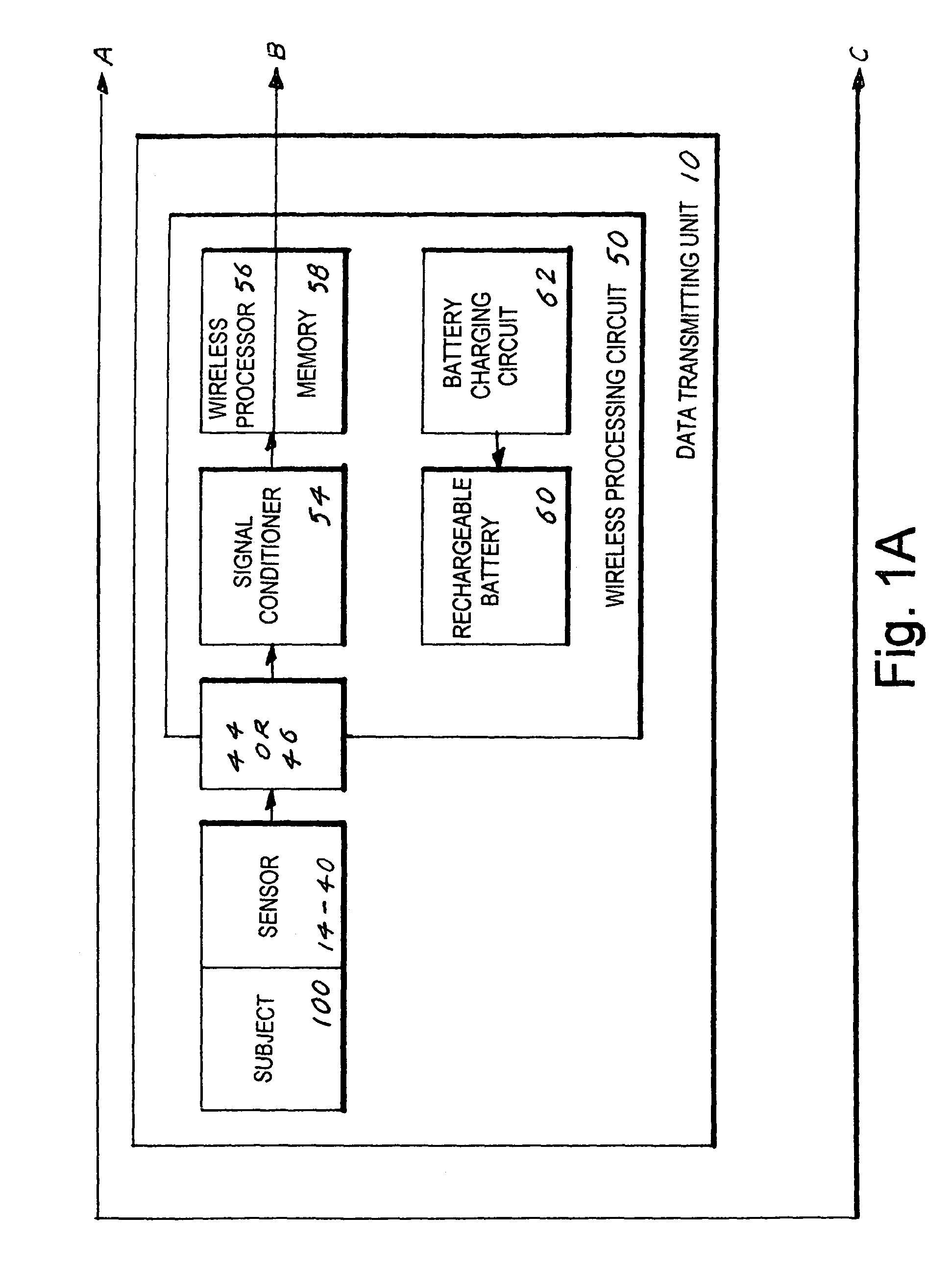
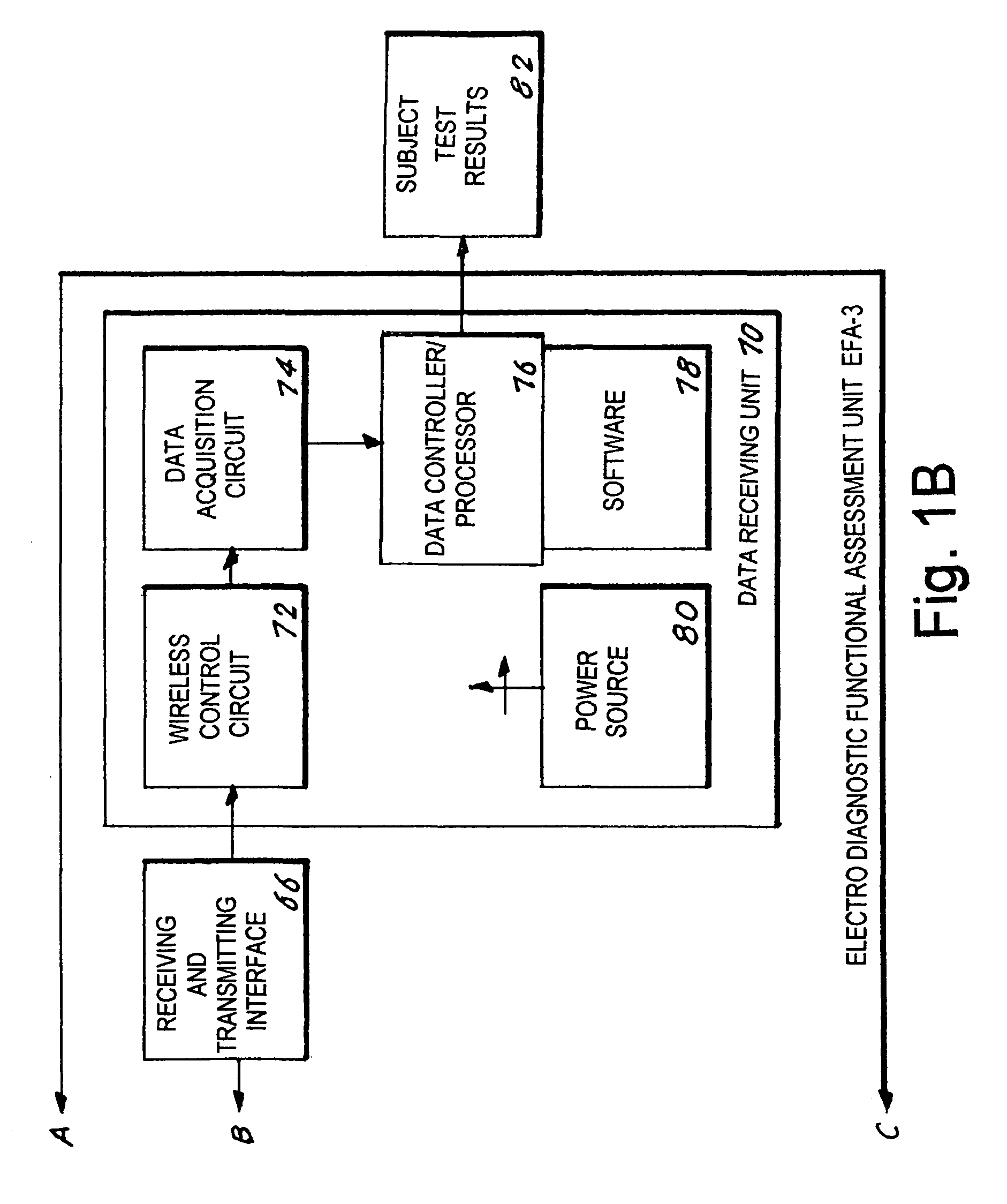
Electro diagnostic functional assessment unit (EFA-3)
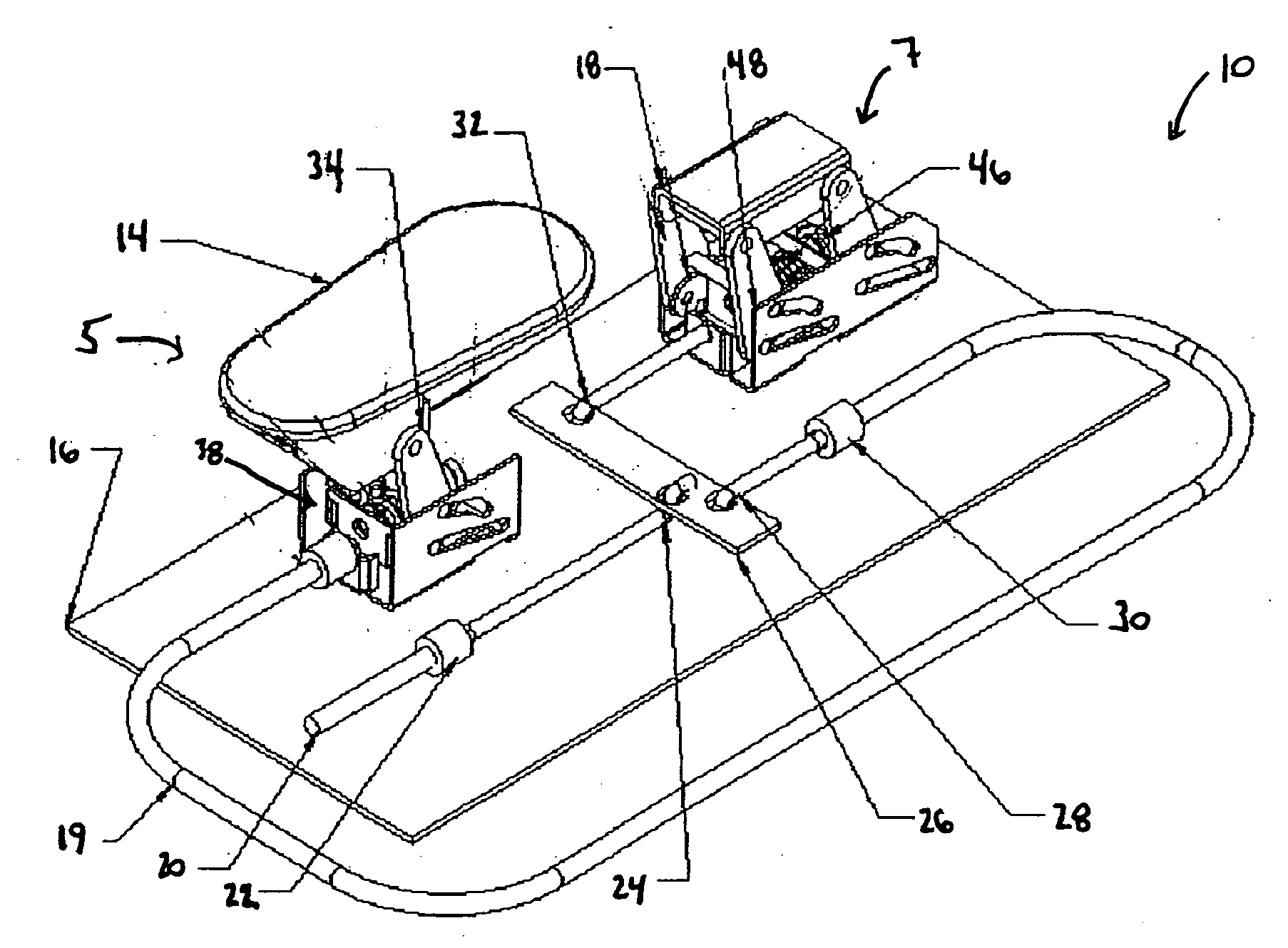
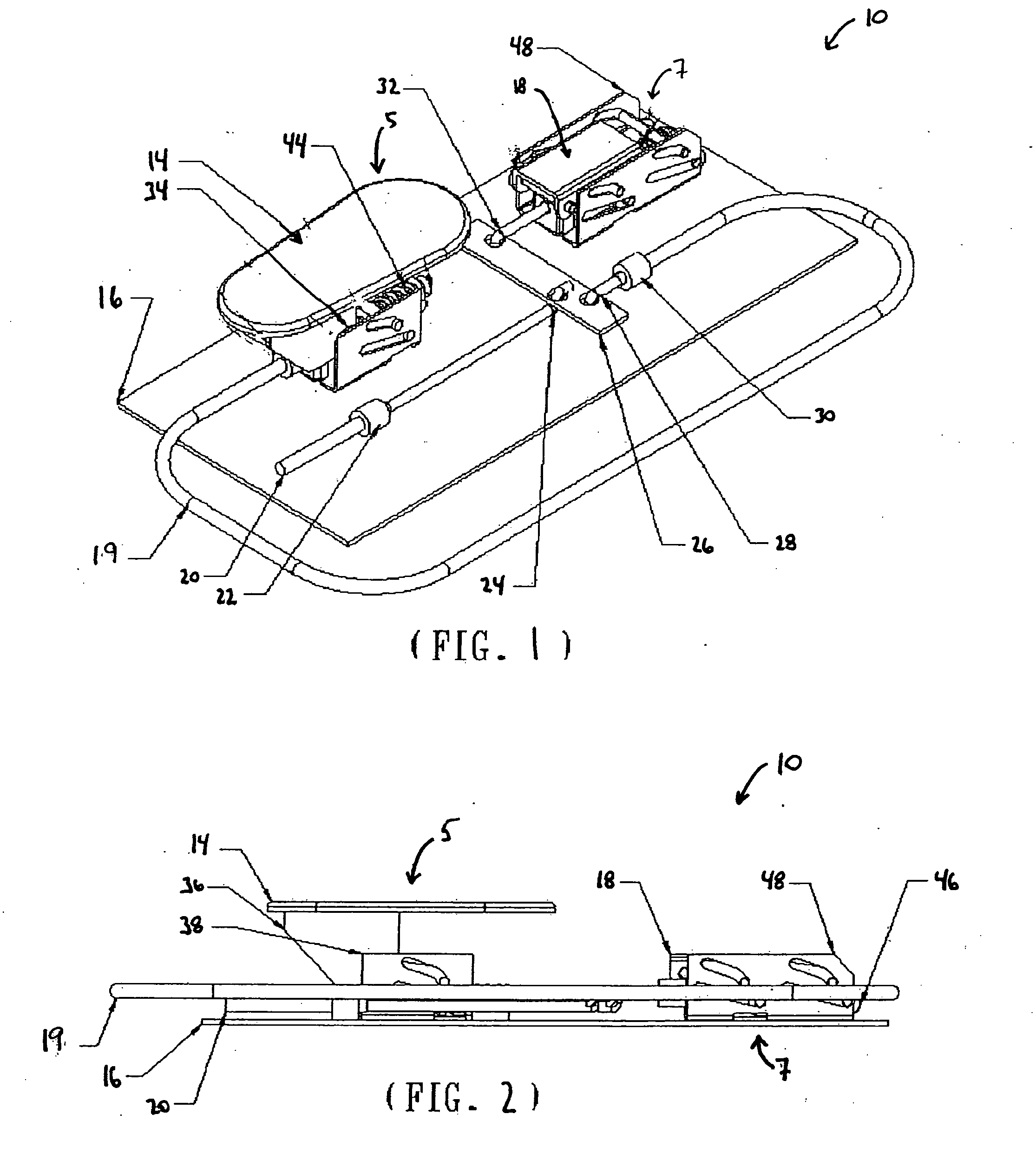
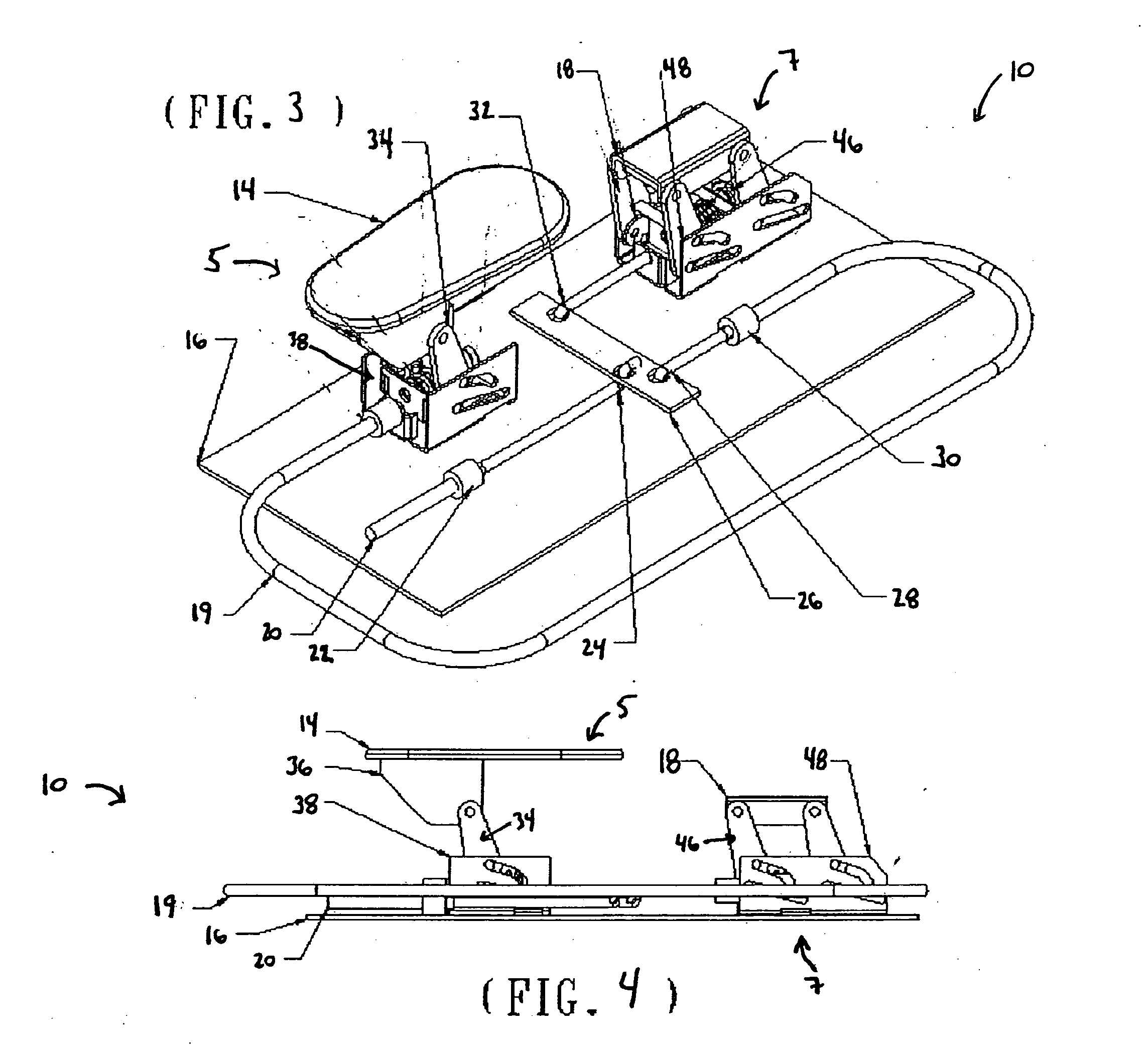
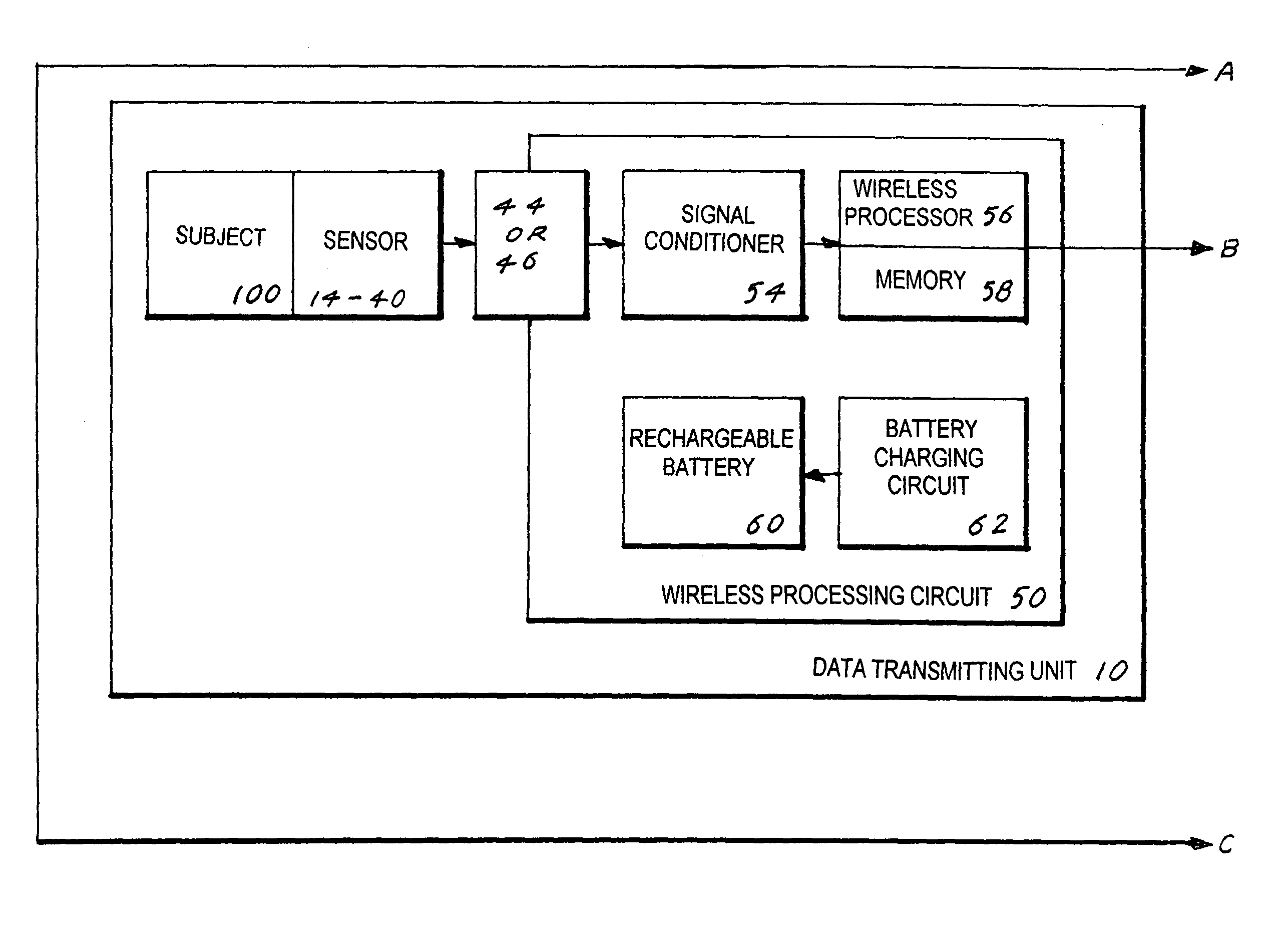
An Electro Diagnostic Functional Assessment Unit (EFA-3) that is designed to wirelessly monitor muscle group activity and to provide treatment for humans and animals. The muscle groups include the body, fascial, cervical, thoracic, upper and lower extremities, lumbosacral, bladder, cardiac, and rectal. In large animals the muscle groups include torso, legs, neck and face. The EFA-3 simultaneously correlates the muscle activity EMG with cardiac activity, nerve activity, heart rate, blood flow and brain activity with range-of-motion, grip and pinch assessment and a functional assessment in humans. The EFA-3 is operated by proprietary software (78) which provides testing protocols by utilizing a set of wireless sensor(s) (14-40) that are interchangeable and rechargeable. The treatment includes ultrasound, heat, cold, massage and electrical stimulation.
Owner:OKTX
Travel pillow for sleeping in a vertical or near-vertical reclined position
ActiveUS20130254998A1Prevents undesired slippagePrevent movementPillowsSofasEngineeringOccipital bone
The present invention is directed towards a travel pillow for sleeping in a vertical or near-vertical reclined position. When sleeping in these positions, gravity tends to pull the head forward of the shoulders causing it to droop. The current state of the art travel pillow does not provide a support means to counter this forward drooping tendency. Moreover, its rear support displaces the cervical spine forward, further increasing the tendency for the head to slump forward. The present invention holds a resting head in an upright and stable position to prevent forward head drooping and does so without forwardly displacing the cervical spine. The five novel elements of the present invention are integrally configured to maintain a healthy alignment between the occipital bone of the head, the cervical spine of the neck, and the thoracic spine of the upper back.
Owner:WALKER CEDRIC THELONIOUS MACILLIAN
System and methods for performing pedicle integrity assessments of the thoracic spine
ActiveUS8591431B2Good reproducibilityReliable stimulation threshold determinationElectrotherapyElectromyographyIntegrity assessmentPilot hole
The present invention includes a system and methods aimed at surgery, and more particularly to a system and methods for monitoring nervous tissue to assess the integrity of a pedicle wall during or after pilot hole formation and before, during, or after screw implantation, particularly in the thoracic spine. The system also performs other neurophysiologic assessments including, but not necessarily limited to, neuromuscular pathway status, nerve proximity detection, nerve pathology monitoring, and spinal cord health monitoring.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Shaped exercise cushion
There is disclosed an exercise cushion (10) for at least partially supporting an individual on a substantially level support surface (8). The cushion 10 comprises a body configured to elevate a region extending from and including the head to the thoracic spine of the individual from the substantially level support surface (8).
Owner:MAGANOV HELEN PIA
Device and method for determining image quality of a radiogram image
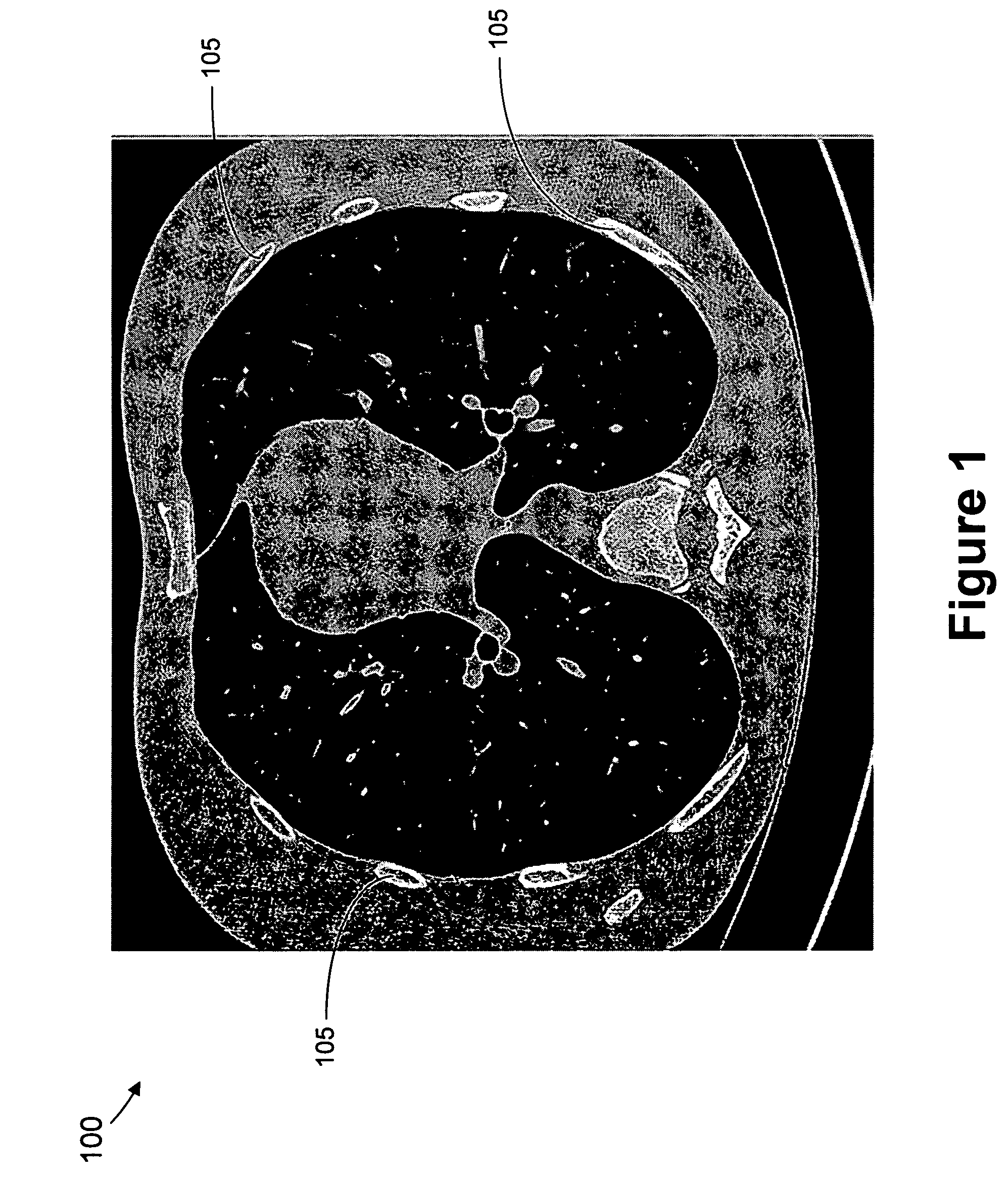
The present invention relates to a device (1) for determining image quality of a radiogram image, the device comprising: an acquiring module (10), which is configured to acquire the radiogram image; a segmentation module (20), which is configured to segment a thoracic bone structure on the acquired radiogram image into segmented thoracic bone structure contours and a tissue structure on the acquired radiogram image into segmented tissue structure contours; and a quality-determination module (30), which is configured to determine a image quality coefficient for the acquired radiogram image based on a comparison of a first position of the segmented thoracic bone structure contours with a second position of the segmented tissue structure contours.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
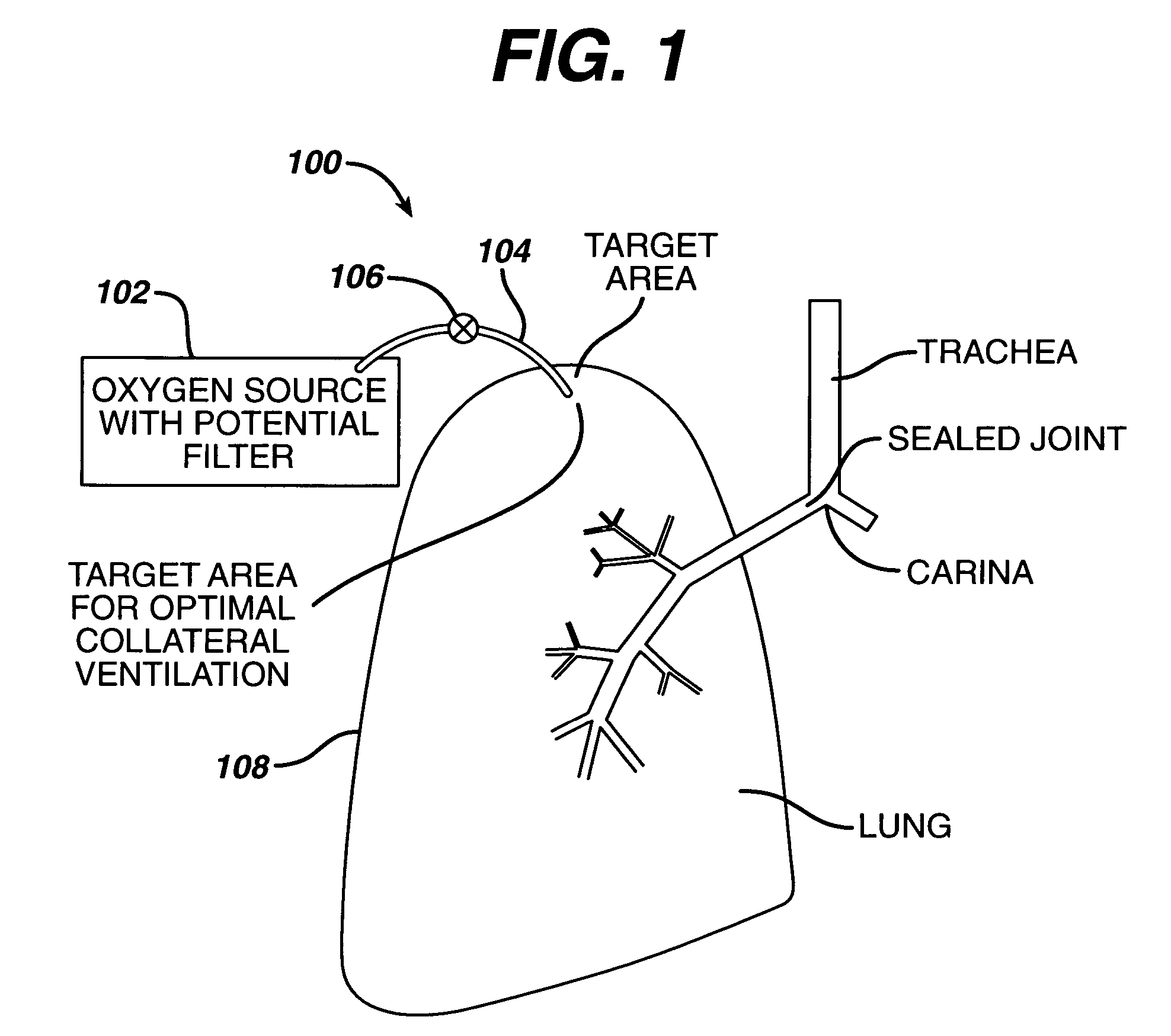
Methods to accelerate wound healing in thoracic anastomosis applications
InactiveUS7682332B2Speed up the flowOvercome disadvantagesRespiratorsElectrotherapyWound healingPleural cavity
Methods for creating an anastomosis between a channel through the chest wall and an opening in the visceral membrane of a lung using a medical device. The methods include creating the channel through the chest wall into the pleural cavity; forming an adhesion between the chest wall and the visceral membrane of the lung; creating an opening in the visceral membrane of the lung which communicates with the channel; and inserting the medical device into the channel. The medical device has a compression structure which spans the channel. The methods include configuring the compression structure to apply a compressive force to tissue surrounding the anastomosis and / or applying agents and materials to the tissue of the anastomosis thereby accelerating the formation and healing of the anastomosis.
Owner:PORTAERO
Intermittent lumbar traction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20090306568A1Extended range of motionRelieve symptomsChiropractic devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesLumbar tractionChest region
A traction method and apparatus for treating irregularities in the lateral curvature and global posture of the thoraco-lumbar, lumbar, lumbo-pelvic and / or pelvic region of the spine involving the application of an intermittent transverse traction load to a region of the patient's body. The patient is placed in a supine or semi-supine position, and a traction sling is positioned about a region of the body of the patient, where the region of the body can be the thoracic region, lumbar region and pelvic region of the body. A transverse traction load having an intermittently varying magnitude is exerted on the sling to induce an extension posture in at least a portion of the spine of the patient and / or a flexion posture of the pelvic portion of the spine of the patient. The flexion and extension postures serve to at least partially restore normal lateral curvature of the thoraco-lumbo-pelvic region of the spine, thereby reducing lower back pain, correcting abnormal posture, and easing other symptoms that are related to thoraco-lumbo-pelvic spine curvature irregularities.
Owner:MEYER DONALD W
Portable device for unloading lower back while sitting
InactiveUS20110181089A1Relieve low back painComfortable sittingOperating chairsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringThoracic cavity
A portable harness that wraps around the rib cage and thoracic spine is disclosed. Unlike other harnesses, the present invention has an extension allowing it to be suspended above the user's ribcage to apply an upward pull. This suspension strap provides a distracting / unloading force on the lower back by holding the upper torso in place while the weight of a patient's lower body creates traction on the lumbar spine. The harness can be used with any chair back, including office chairs, or vehicle seats. This allows people with lower back pain to sit more comfortably while sitting in a regular chair, driving a car, or flying in a plane. This will decrease low back pain since sitting for long periods will no longer compress the lumbar spine, it will actually be therapeutic by allowing a person to sit in an unloaded position.
Owner:LITESITTER
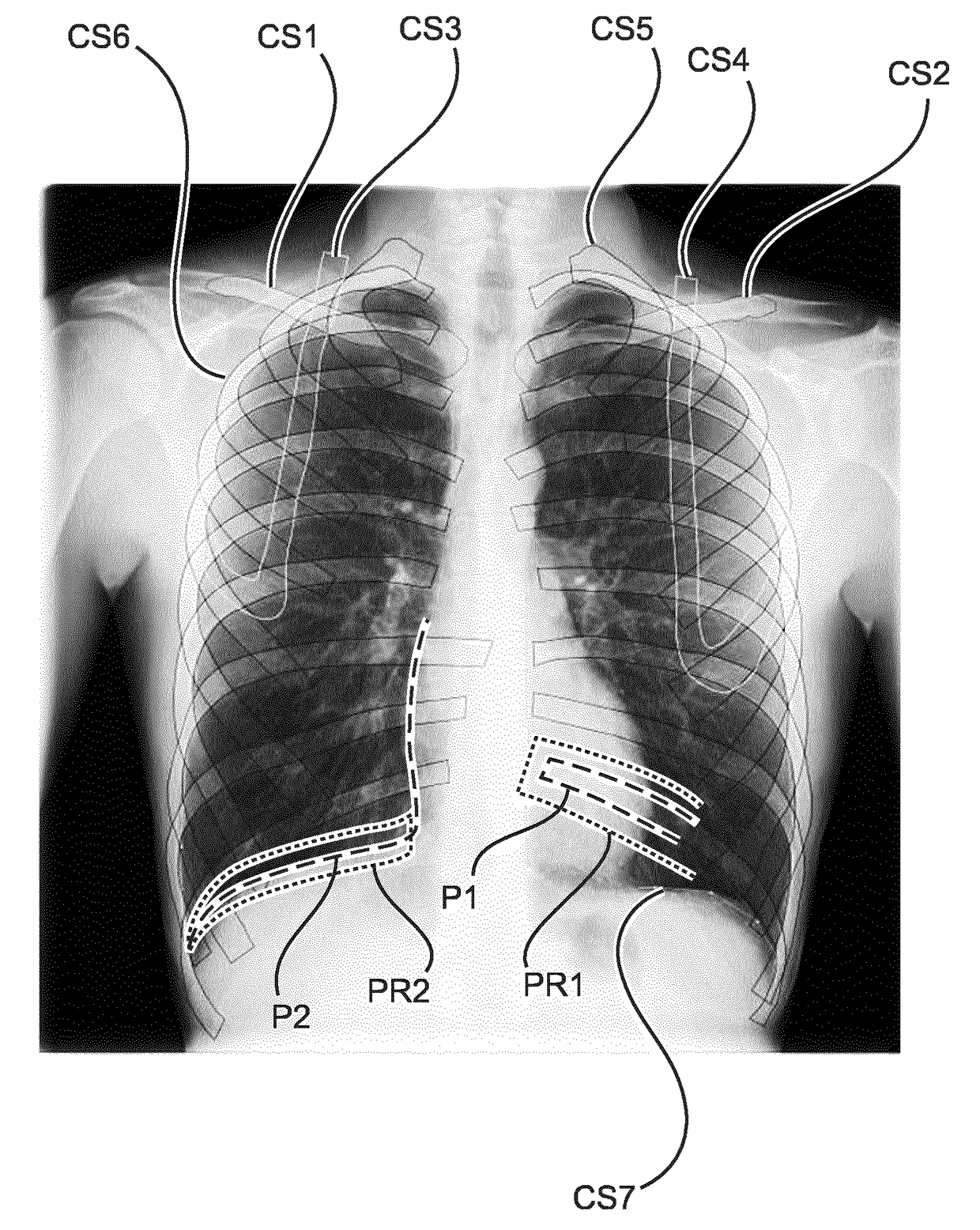
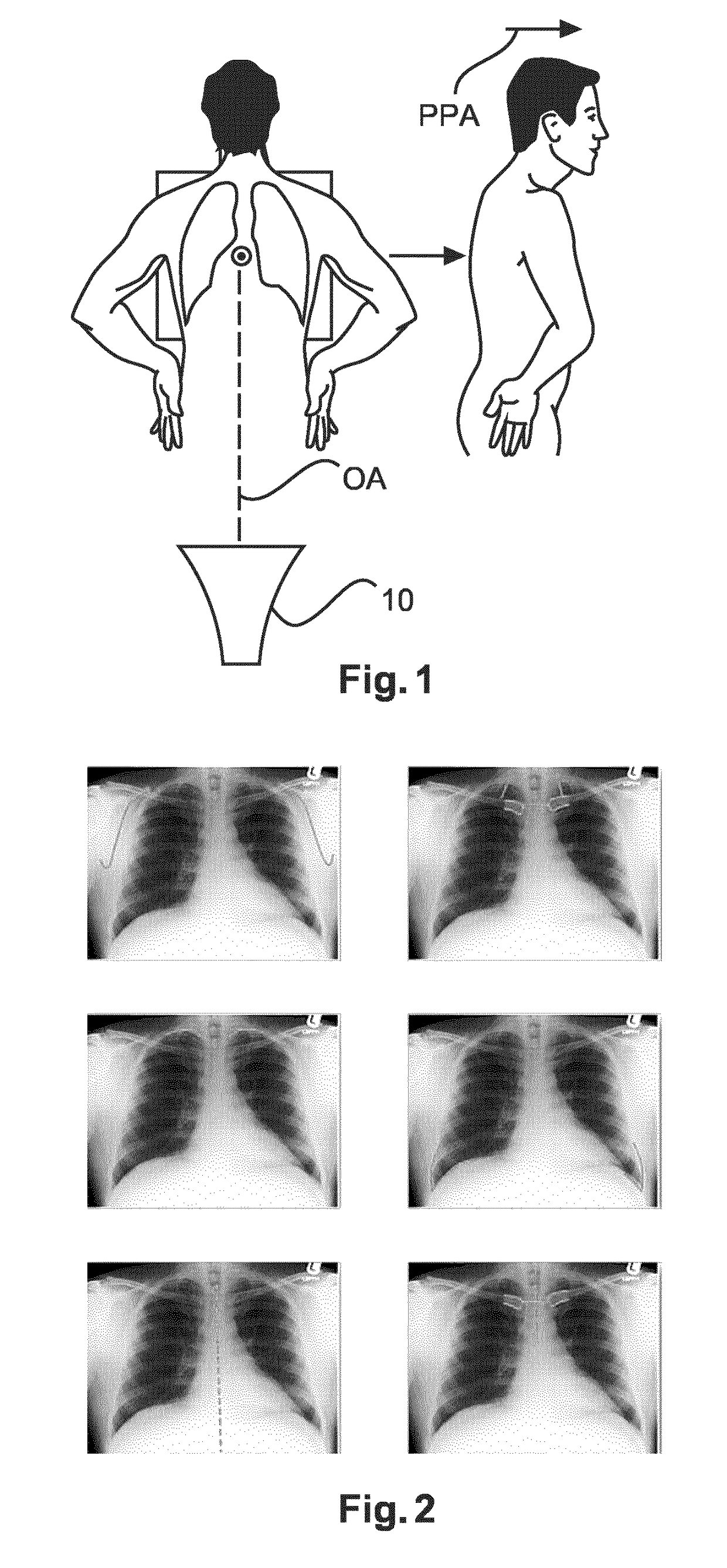
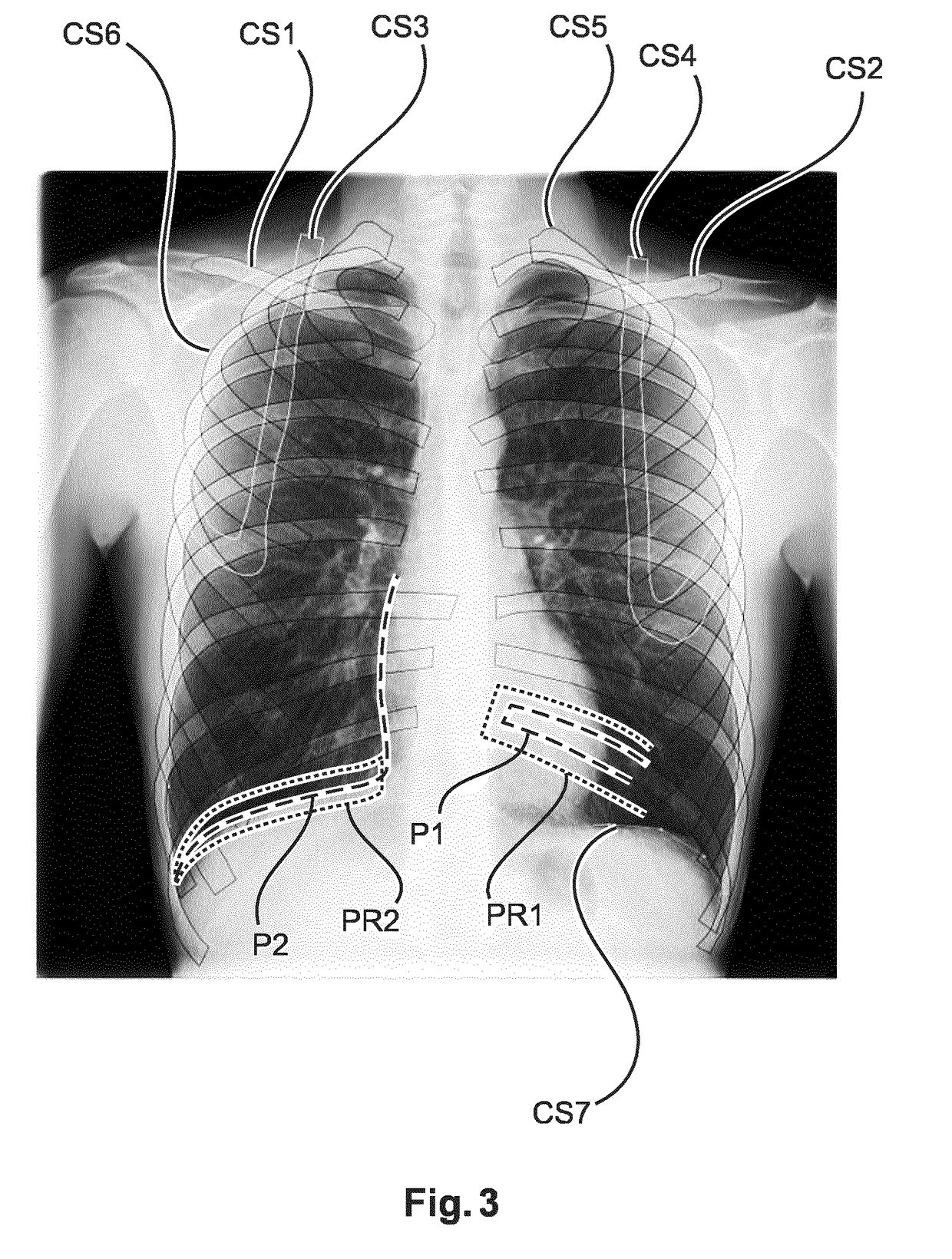
Thoracic cage coordinate system for recording pathologies in lung CT volume data
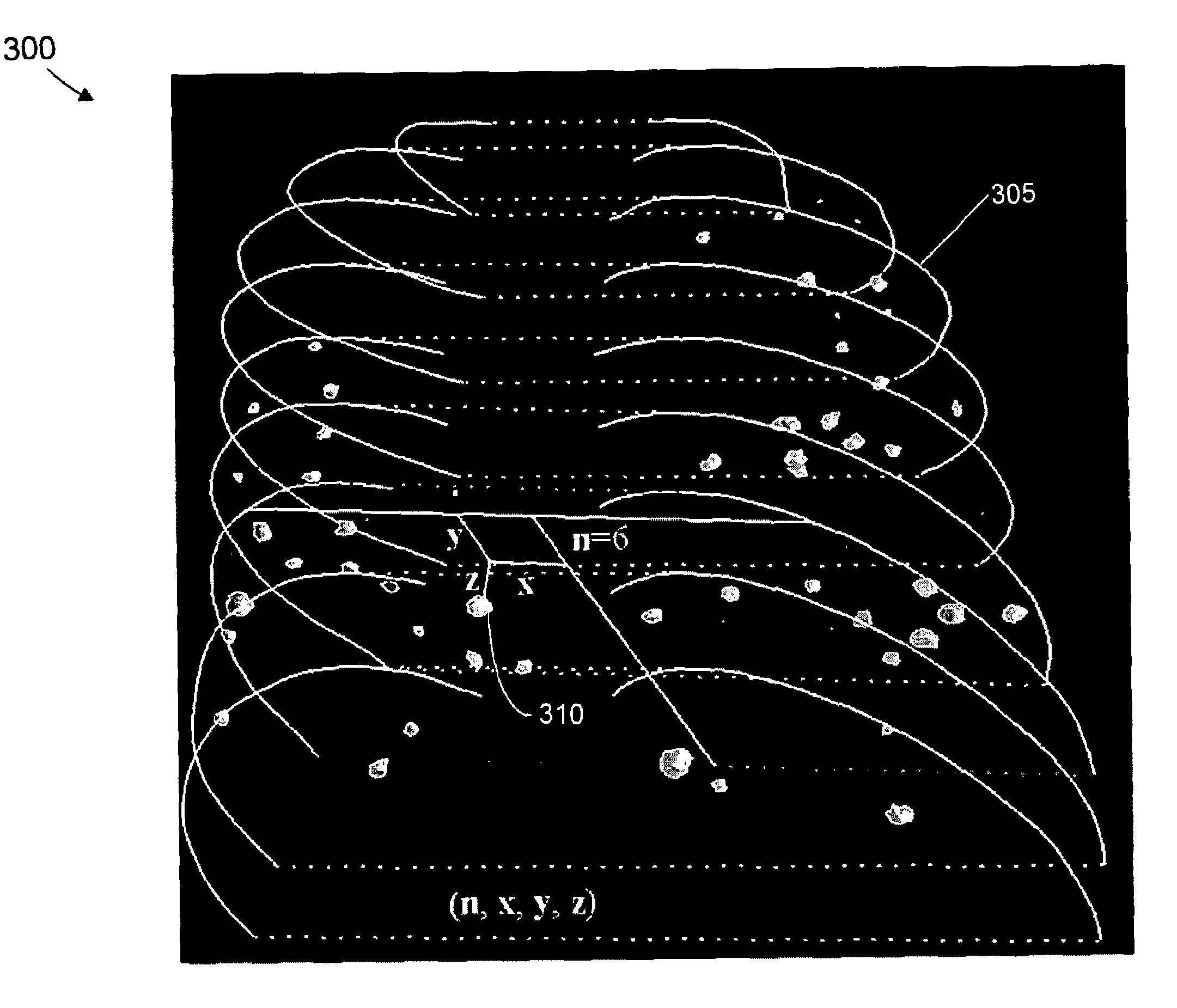
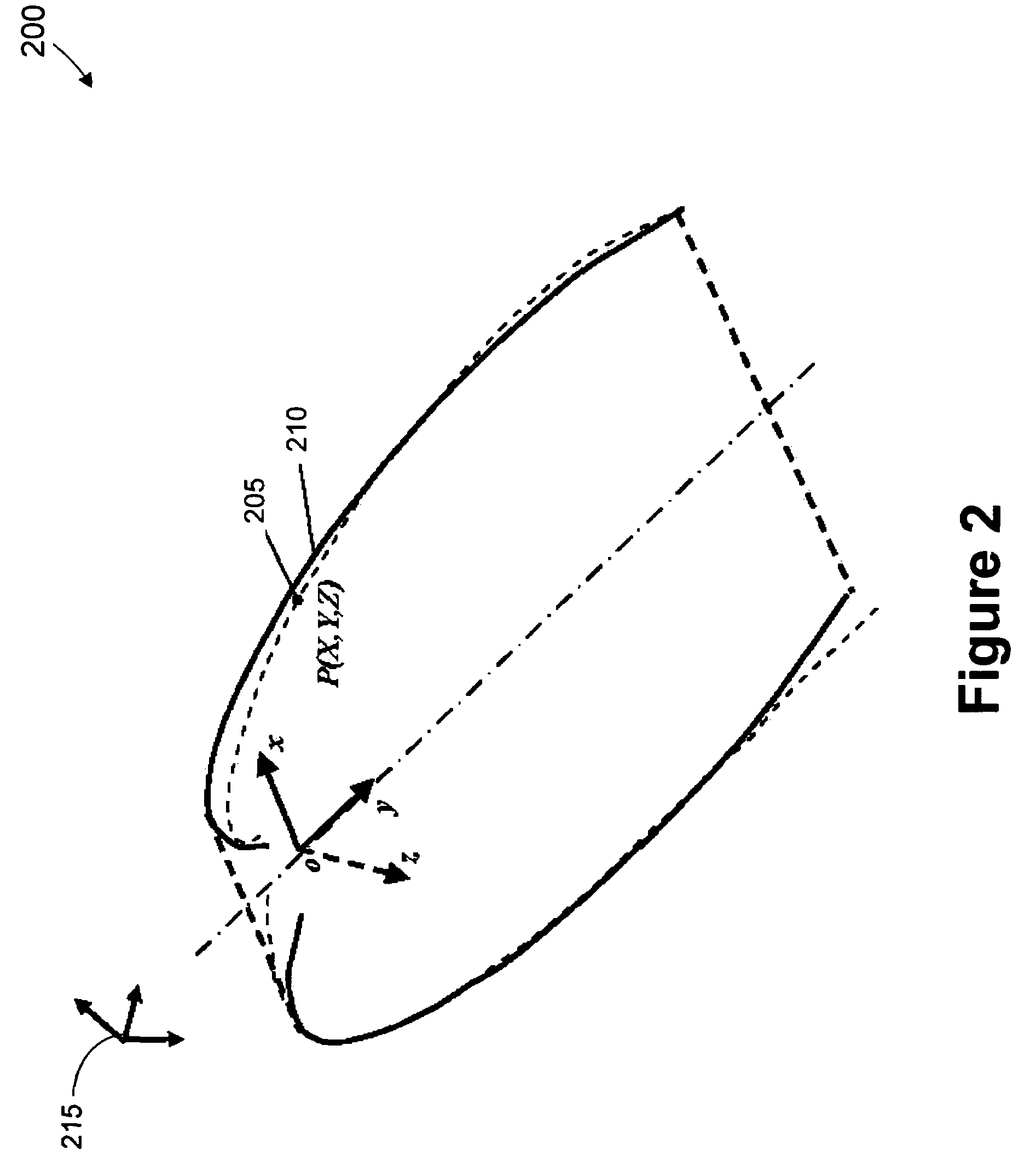
We introduce a thoracic cage coordinate system for recording pathology locations in lung CT volume data. The centerlines of each individual rib are extracted and labeled from top to bottom. For each pair of ribs, a three-dimensional (“3D”) orthogonal basis is computed by eigen-analysis of the rib centerline points, which are taken as the x, y, and z axes. The rib pairs form a set of reference planes. Therefore, there are a set of coordinate systems (x, y, z), each of which is locally valid between two adjacent planes. To define a location globally, a fourth parameter, n, is added to identify the serial number of the reference plane. The complete coordinate is recorded as (n, x, y, z). This system is robust against deformations due to bending and twisting, and is relatively stable over inhalation. Further, this system may be readily adapted in other 3D modalities, such as MRI volume data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Multi-section adjustable traction bed
The invention discloses a multi-section adjustable traction bed, and belongs to the technical field of medical equipment. The traction bed comprises two parts, namely a traction physiotherapy device and a traction table, wherein a neuromuscular feedback function is added to the traction physiotherapy device; a therapist also can remind a patient of correctly adjusting and controlling the tension degree of the body by observing the change of a surface electromyogram signal in real time besides verbal communication with the patient, and can guide the patient to fully relax skeletal muscle before traction treatment, so that separation between vertebral bodies is further increased, and the traction effect is more obvious. A pelvic tilt part is arranged, so that asymmetry of the pelvis is solved. The angle parts of the arm and the chest are respectively adjusted in the traction table, so as to maintain a spine in the neutral position. A head support pad can be lifted to 35 degrees, so that the head support pad can more easily approach to thoracic vertebra and cervical vertebra. The head is in a comfortable position all the time when the patient lies in a prostrate or supine mode by the head support pad. A plurality of support sections are arranged on the traction table, so that the angle can be adjusted, and adjuvant therapy of manipulation cheirapsis also can be carried out when the patient is pulled.
Owner:河南瑞禾医疗器械有限责任公司
Patient positioning frame device and application technique
ActiveUS20090265853A1Reducing venous blood lossMaintain positionOperating tablesSofasThighLaminectomy procedure
Devices and methods of the present invention are directed to positioning a patient in a prone position that exposes the posterior thoracic lumbar spine during a surgical procedure, such as a laminectomy procedure. The device has at least three support members, with a first support member configured and adapted to support at least a portion of a patient's torso and the patient's hips; a second support member, generally contiguous with the first, configured and adapted to contact a patient's thighs and to position the patient's thighs in a desired angular position relative to the patient's hips and torso; and a third support member, generally contiguous with the second support member, adapted to support a patient's knees and lower legs and to position the patient's lower legs in a desired angular position relative to the patient's torso and thighs. A patient is positioned in the frame device prior to being anesthetized while the patient is lying supine and, during or following administration of anesthesia, the patient (mounted in the device) is rolled onto an operating table and positioned in a prone position. Operation on the posterior thorical-lumbar spine in this position is especially advantageous, and the spinal canal remains virtually bloodless, providing excellent visualization during the surgical procedure. When the surgery is finished, the process is reversed.
Owner:MAXWELL MARGARET D
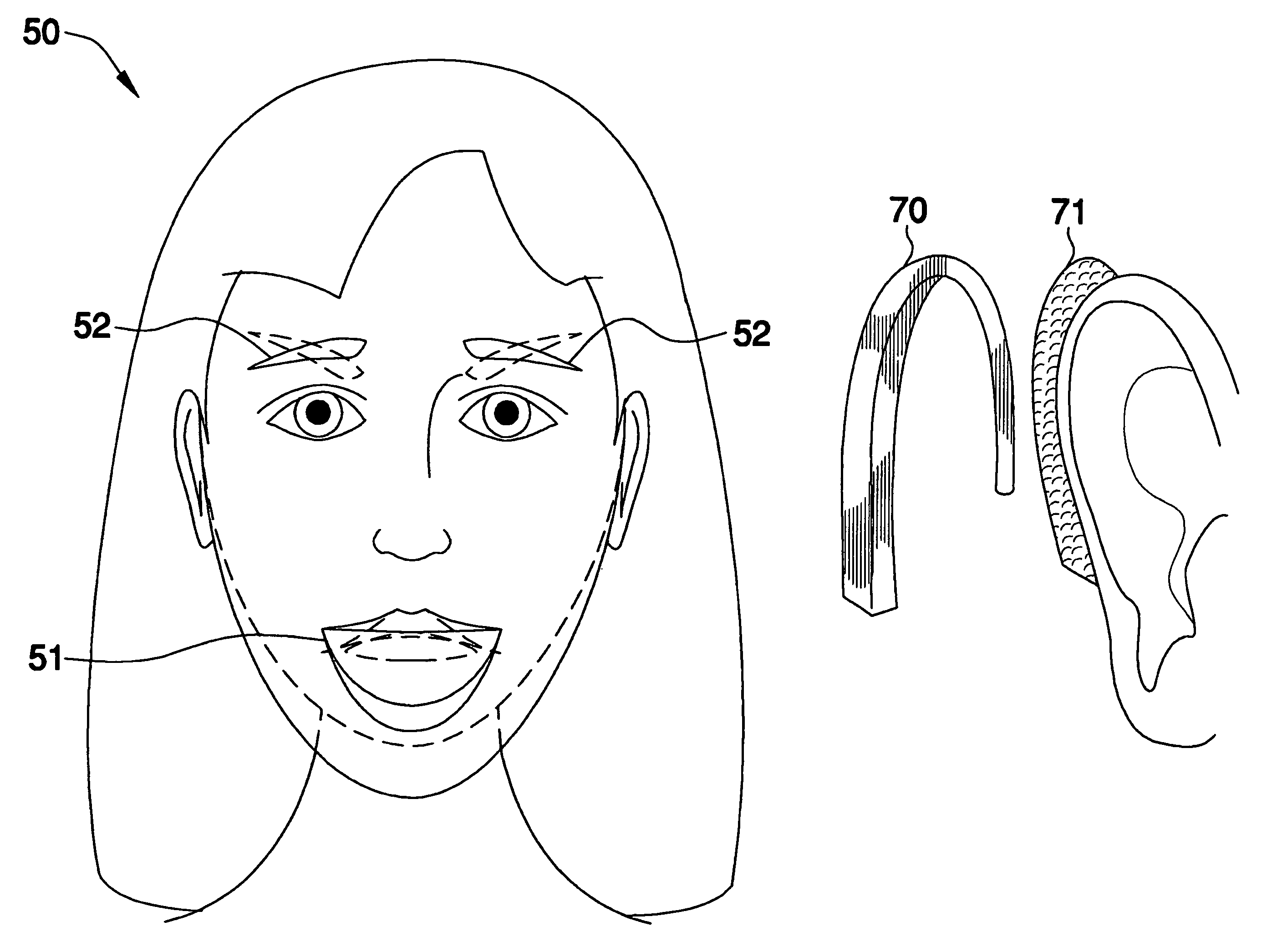
Posture correction device and posture correction method
PendingCN111158494AReduce computing costReduce economic costsInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionSpinal columnHuman body
The invention discloses a posture correction device and a posture correction method. The posture correction device comprises an adsorption part and a mobile terminal, the adsorption part comprises a first elastic film, a second elastic film and a third elastic film, strain gauge pressure sensors, processors and wireless communication modules are attached to the first elastic film, the second elastic film and the third elastic film, the strain gauge pressure sensors are connected with the processors, and the processors are connected with the wireless communication modules; the first elastic film is attached to the center of the cervical vertebra of the human skin surface, the second elastic film is attached to the center of the thoracic vertebra of the human skin surface, and the third elastic film is attached to the center of the lumbar vertebra of the human skin surface. The strain gauge pressure sensor corresponding to each elastic membrane uploads a human spinal curvature angle value acquired by the strain gauge pressure sensor to the mobile terminal through the wireless communication module; and the mobile terminal inputs the acquired human spinal curvature angle value into a pre-trained classification model, and outputs a human spinal posture correction prompt instruction.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
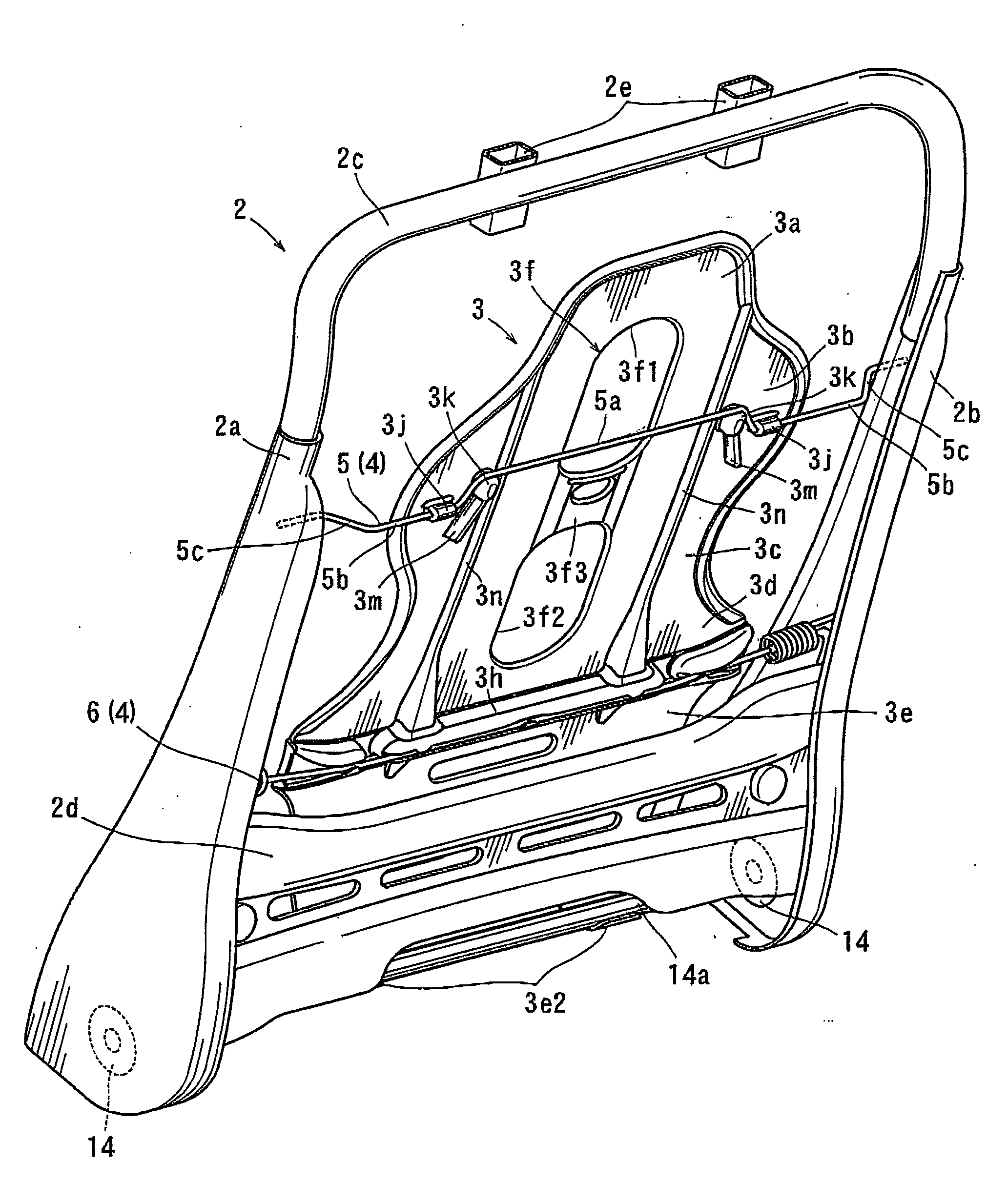
Seat backs for vehicular seats
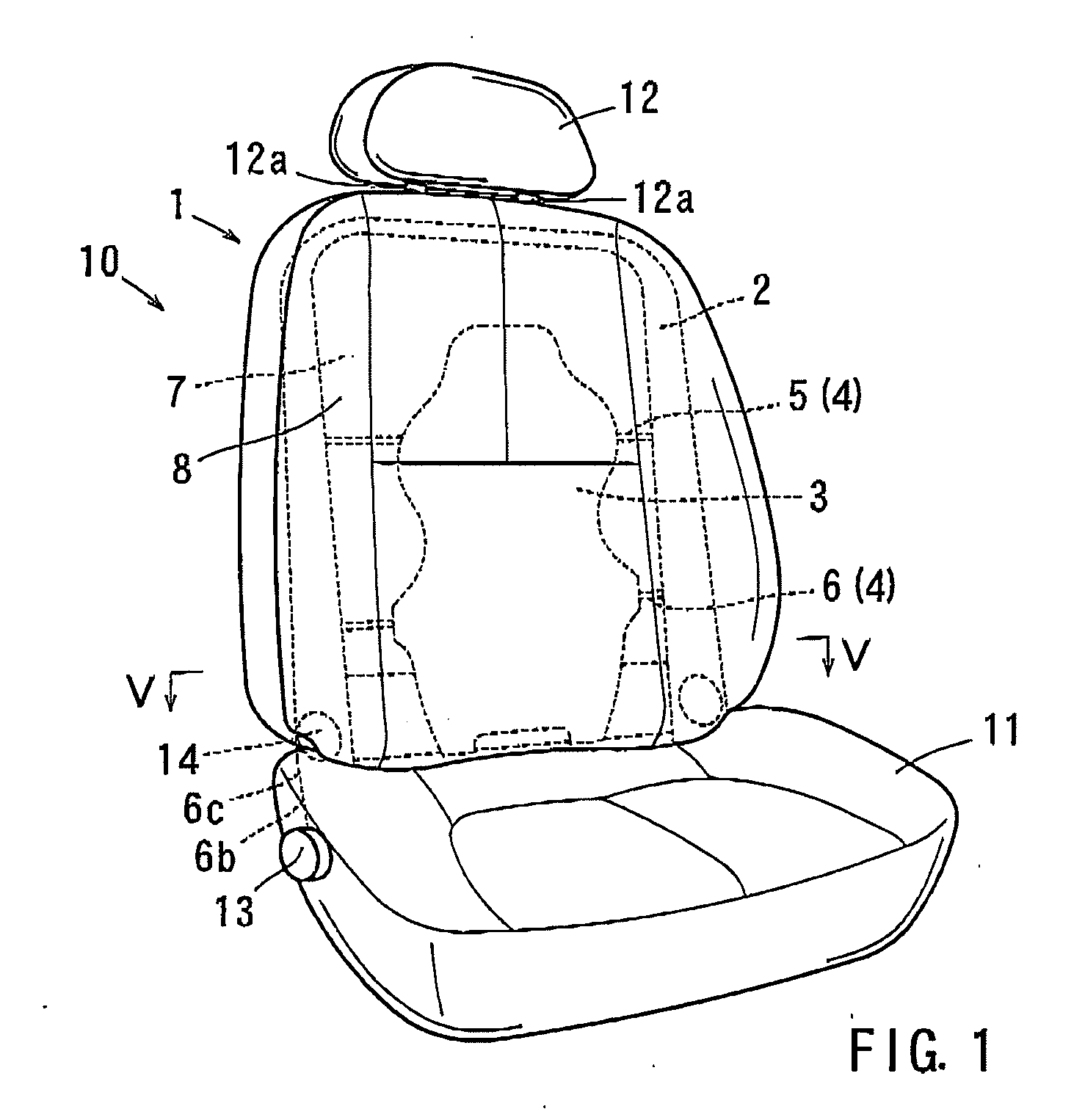
ActiveUS20090102258A1Improve rid comfortablenessImprove comfortBack restsStoolsThoracic vertebraeVertebra
A seat back for a vehicular seat has a plate member for supporting a back of a pad and an elastic support mechanism for holding the plate member for moving the plate member in a forward and backward direction. The plate member includes a thoracic vertebra avoiding portion having at least one of a hole and a recessed portion recessed in a direction away from the thoracic vertebrae of a user, so as to avoid a pushing force to the thoracic vertebrae. In addition the thoracic vertebra avoiding portion is vertically elongated at a substantially widthwise center position of the plate member and has a width of 40 to 100 mm.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK +1
Shaped exercise cushion
There is disclosed an exercise cushion (10) for at least partially supporting an individual on a substantially level support surface (8). The cushion 10 comprises a body configured to elevate a region extending from and including the head to the thoracic spine of the individual from the substantially level support surface (8).
Owner:MAGANOV HELEN PIA
Surgical Positioning Pillow with Angular Base Members
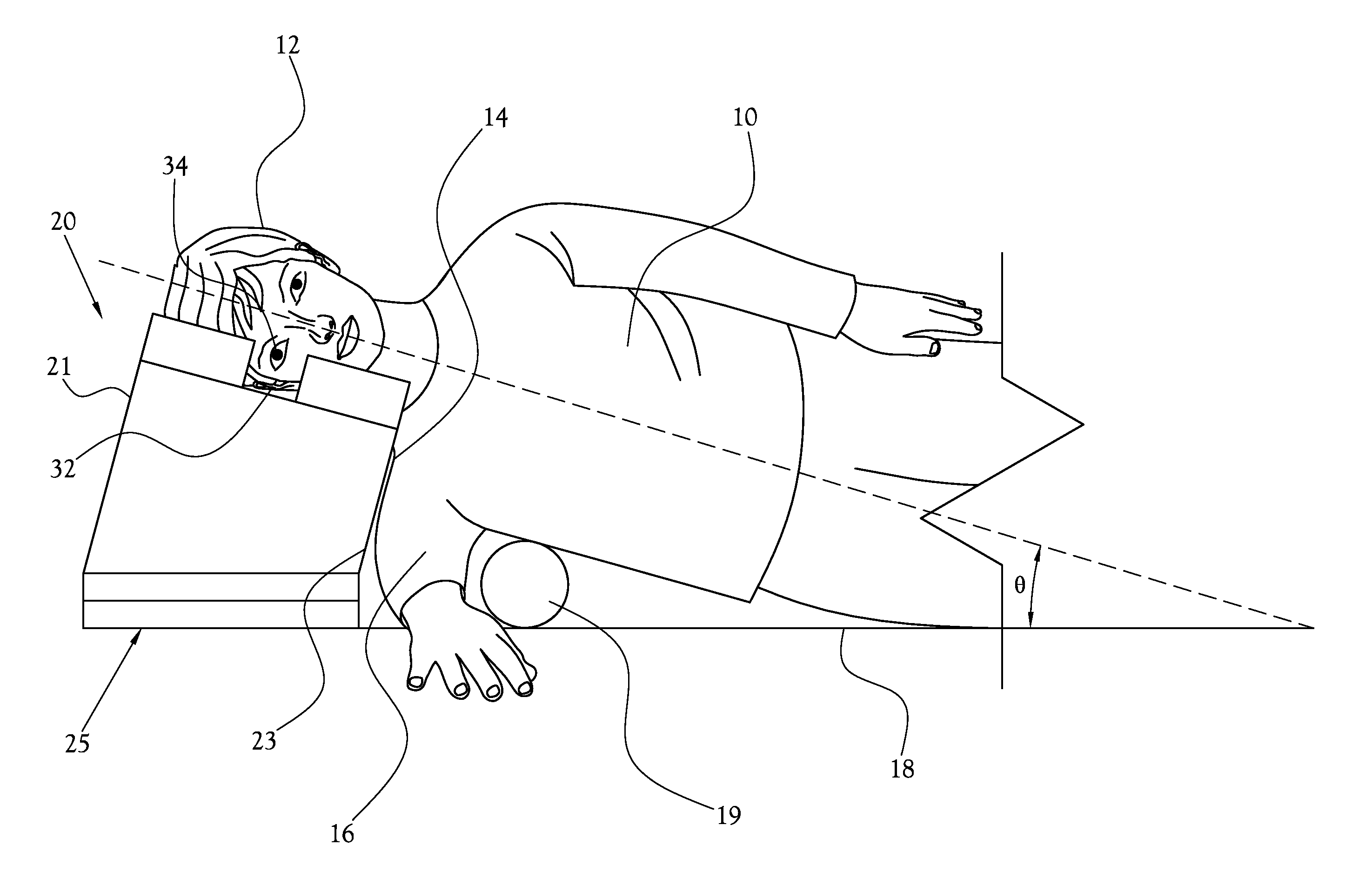
InactiveUS20130305456A1Avoiding pressure injuriesEasy to monitorOperating tablesSofasThoracic spineCervical spine
A surgical support system including a positioning pillow to support a patient on an operating table. An example embodiment of the positioning pillow includes a head supporting surface and a bottom surface disposed opposite to the head supporting surface, the head supporting surface being angled relative to the bottom surface to align the patient's thoracic and cervical spine at a predetermined angle with respect to the operating table when the patient's head is positioned on the head supporting surface, including one or more inclined removable members to adjust the height and angle of the head supporting surface relative to the bottom surface.
Owner:THOMPSON TRACY
Spinal arc adjustment
ActiveCN110200778ARelieve muscle stiffness and fatigueCorrective and preventive effect is goodChiropractic devicesRoller massagePhysical medicine and rehabilitationSpinal disease
The invention relates to a spinal arc adjustment, allowing a patient to use at home, to massage the spine and to correct the spinal arc. According to the technical scheme of solution, the spinal arc adjustment is characterized in that three carrier plates are slidably connected onto a base transversely side by side from top to bottom; the three carrier plates include a cervical carrier plate, a thoracic carrier plate and a lumbar carrier plate from right to left; the lower end of each carrier plate is provided with a left-right adjustment and a lifting device both fixedly connected to the base; each lifting device is connected with a lifting main gear rotationally connected to the base; a leg fixator is fixedly connected to the rightmost end of the base. The spinal arc adjustment is convenient and simple to operate and easy to use, can provide good corrective preventive effect for a user with early spinal diseases, and is very practical.
Owner:HENAN PROVINCE HOSPITAL OF TCM THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF TCM
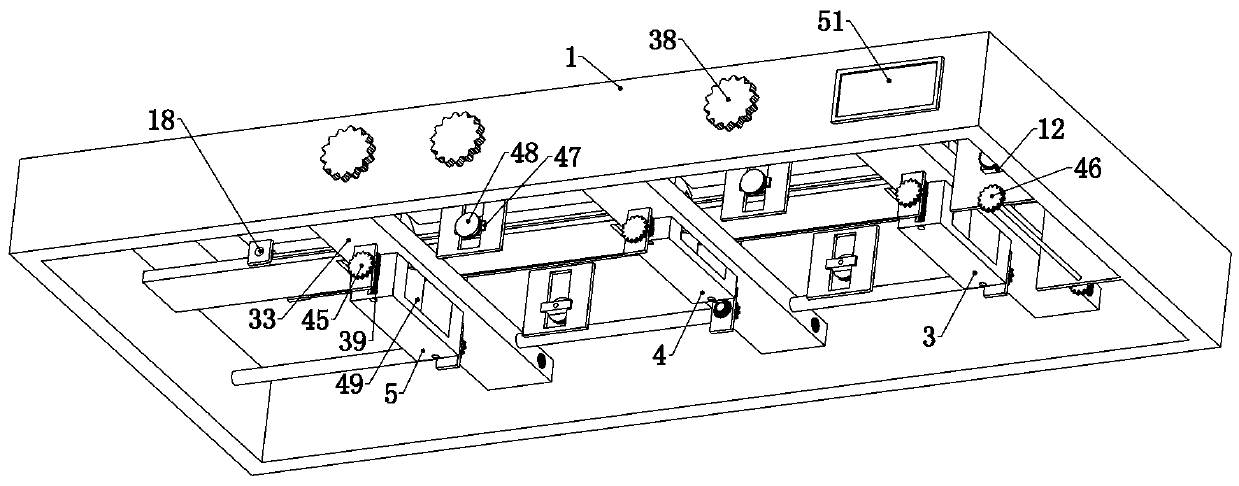
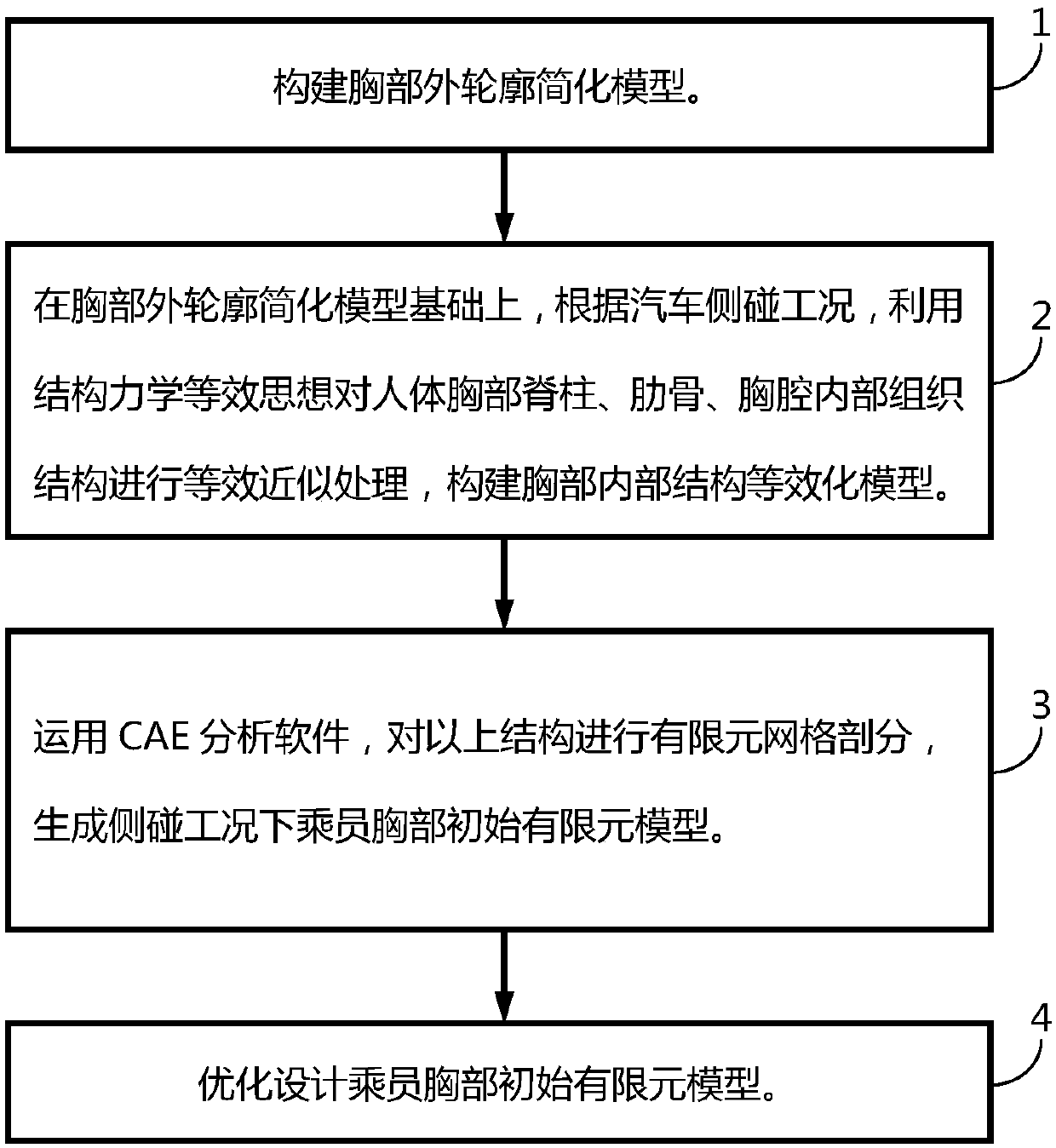
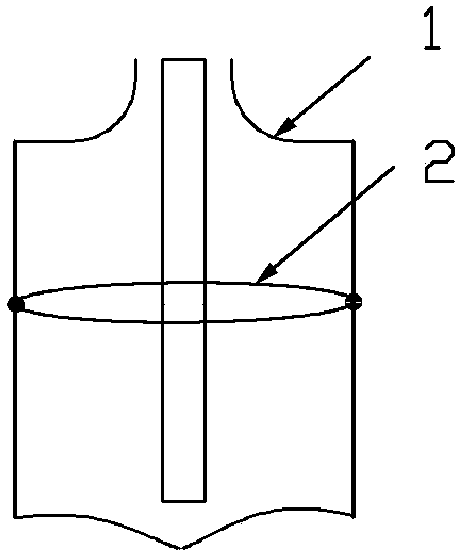
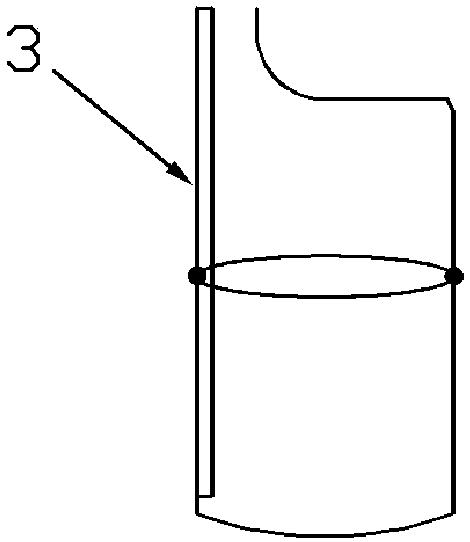
Quick modeling method for artificial human chest structure in car side collision test
InactiveCN107766665AImprove the calculation efficiency of safety simulation analysisImprove computing efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelSimulation
The invention relates to a quick modeling method for an artificial human chest structure in a car side collision test, and belongs to the field of car collision safety. The method comprises the stepsof 1, building a simplified chest outer contour model: by utilizing a medical image technology and human chest soft tissue characteristics, building a chest outer contour approximate geometric model;2, based on the geometric model, performing equivalent approximate processing on human thoracic spine, ribs and tissue structures in thoracic cavity by utilizing a mechanical equivalent thought according to a car side collision condition; 3, performing finite element grid division and material attribute assignment on the structures to generate a passenger chest initial finite element model under the side collision condition; and 4, building a passenger chest side collision structure optimization agent model, and finally building a quick modeling model of the artificial human chest structure inthe car side collision test. The quick modeling model of the artificial human chest structure, built by the method, improves the calculation efficiency by more than 3 times and provides quick and effective reference and data support for modeling in a car safety concept design stage and car passive safety performance analysis.
Owner:天津瑷睿赛福科技有限公司
Spinal Implant, Instrument for Preparation and Method of Use
ActiveUS20140336652A1The relative position is appropriateProvide goodBone implantSurgerySpinal columnSpinal Disk Implant
The present disclosure relates to the field of spine disc implants. Exemplary embodiments of the disclosed spinal disc implants advantageously and ultimately provide fusion with the body of the vertebra and stabilization of the spine in an anatomically correct position, e.g., in cervical, thoracic and / or lumbar regions. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to a disc implant that addresses and overcomes the shortcomings of the prior implants by providing first and second inter-vertebral elements that are movably coupled relative to each other and are adapted to permit bone in-growth over time. Thus, the disclosed spinal disc implants permit relative movement between the first and second inter-vertebral elements upon implantation and after the patient is mobilized—thereby permitting the implant to assume a desired position based on the specific and unique spinal balance of the patient in an initial post-implantation period—but then the first and second inter-vertebral elements become fixed relative to each other (i.e., fused). The present disclosure also provides advantageous instrumentation and associated methods for positioning a spine disc implant in a desired anatomical location.
Owner:FBCDEVICE
Educational doll
A toy for teaching sign language includes a body with a thoracic portion and a lower limb portion that are movable between rotated and stationary positions. The present invention further includes metacarpals provided with a wire frame passing therethrough, which makes them flexible for defining various sign language movements. The present invention further includes a facial section with an oral section that is adaptable to provide various expressions via a wire frame. The facial section further includes eyebrow sections that are adaptable to a corresponding position as the oral section changes shape. The present invention may further include a simulated hearing aid and fastener for removably affixing the hearing aid to the facial section.
Owner:JONES RHONDA L
Shoulder strap and neck strap comprised of an oblong shaped pad and a strap
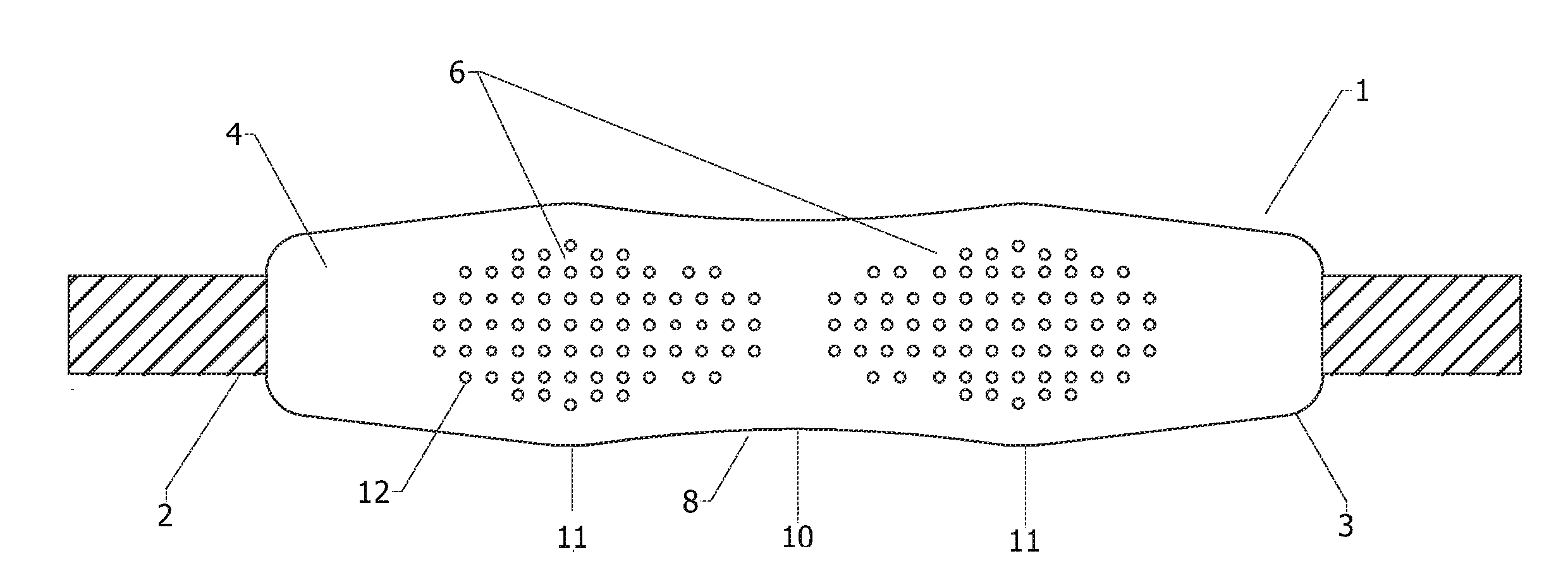
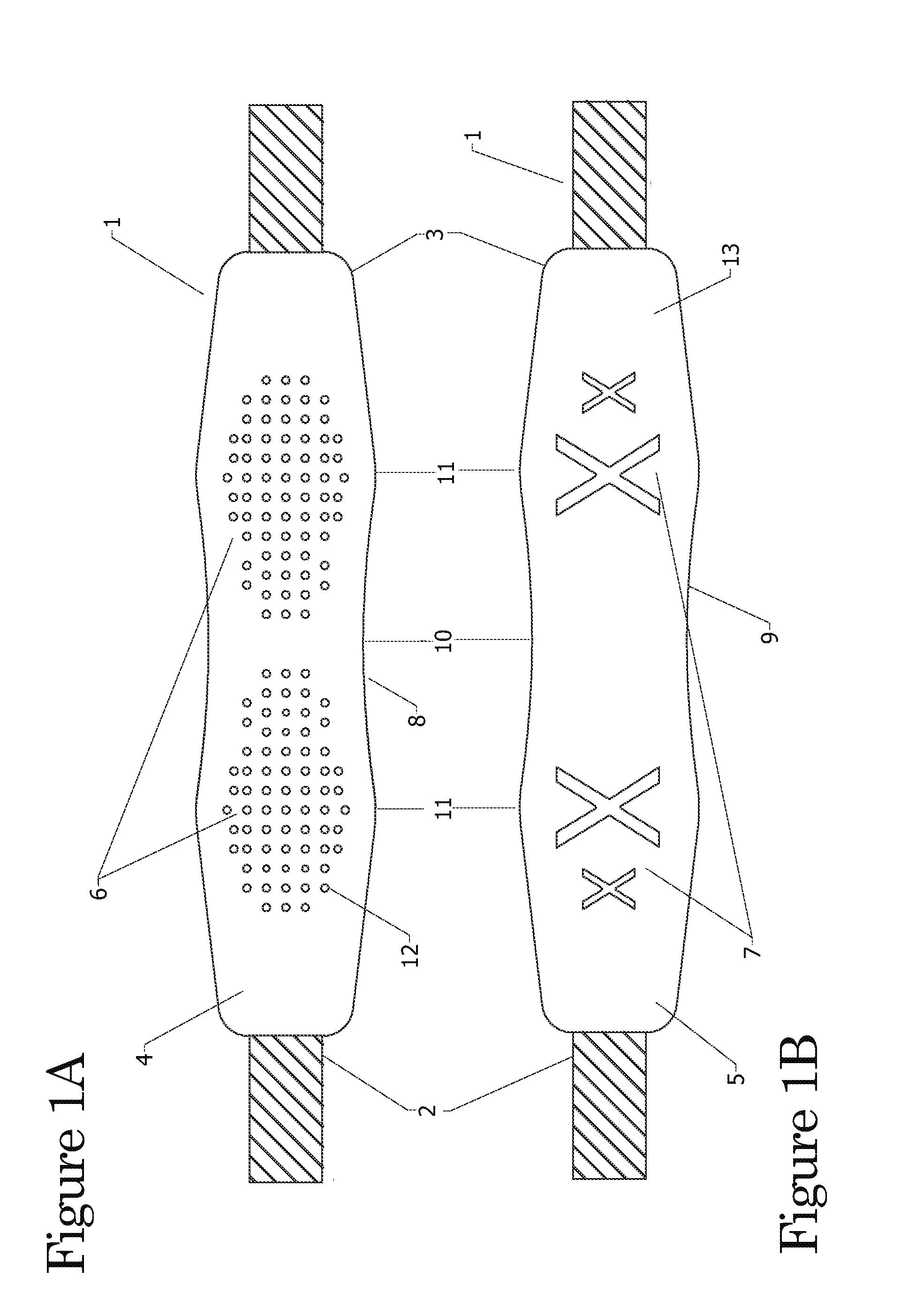
InactiveUS20120261446A1Reduce loadImprove comfortTravelling sacksShoulder strapPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPerspiration
A shoulder strap that has a strap member and a pad member and the pad member has a front side and a back side. The oblong shoulder pad shape allows for contour at the shoulder and neck putting the load to the left and right of the shoulder and reducing the pressure on the vertebra and cervical thoracic spinal nerves of the wearer's neck. The front side of the pad member has Non-Slip Traction Nibs (NSTNs) molded in a pattern so the traction nibs are facing outward from the surface at the outer shoulder. The back side of the pad member has a smooth or non-skid abrasive surface with inward X perspiration grooves (2-IPG) at a section by the side of the neck.
Owner:STEGMEYER ALFRED W
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com