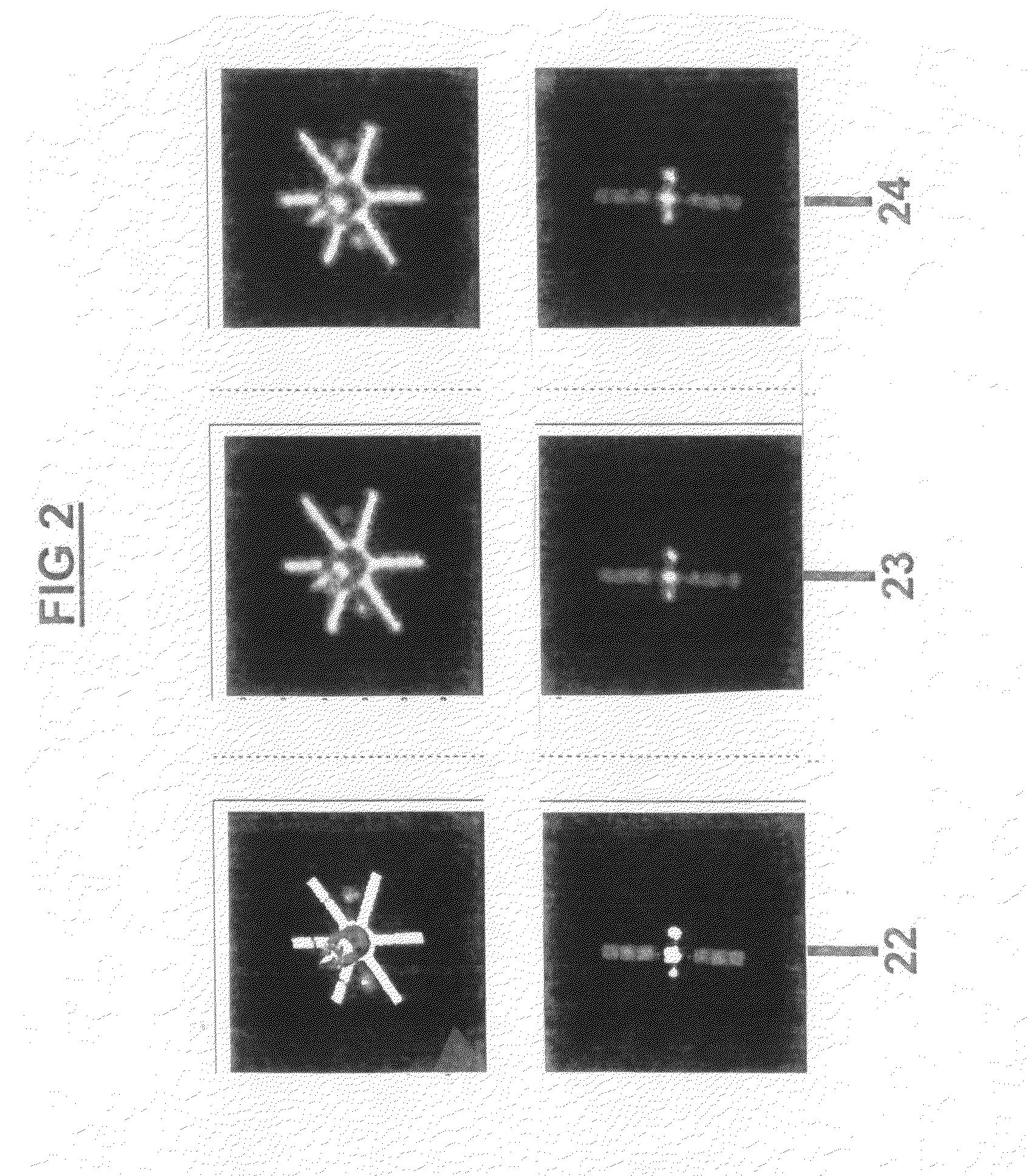
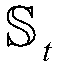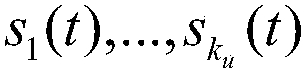Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Thinned array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
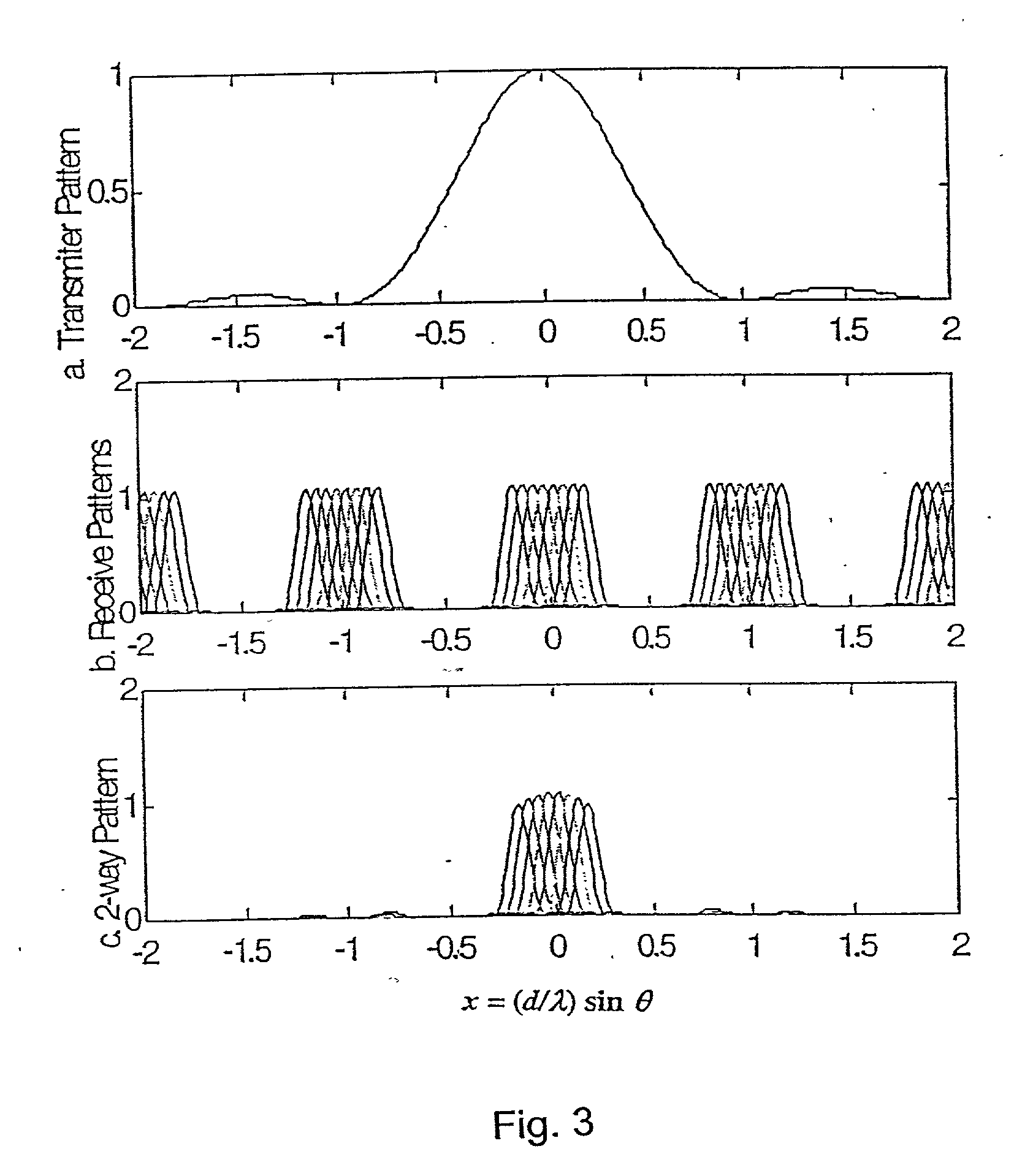
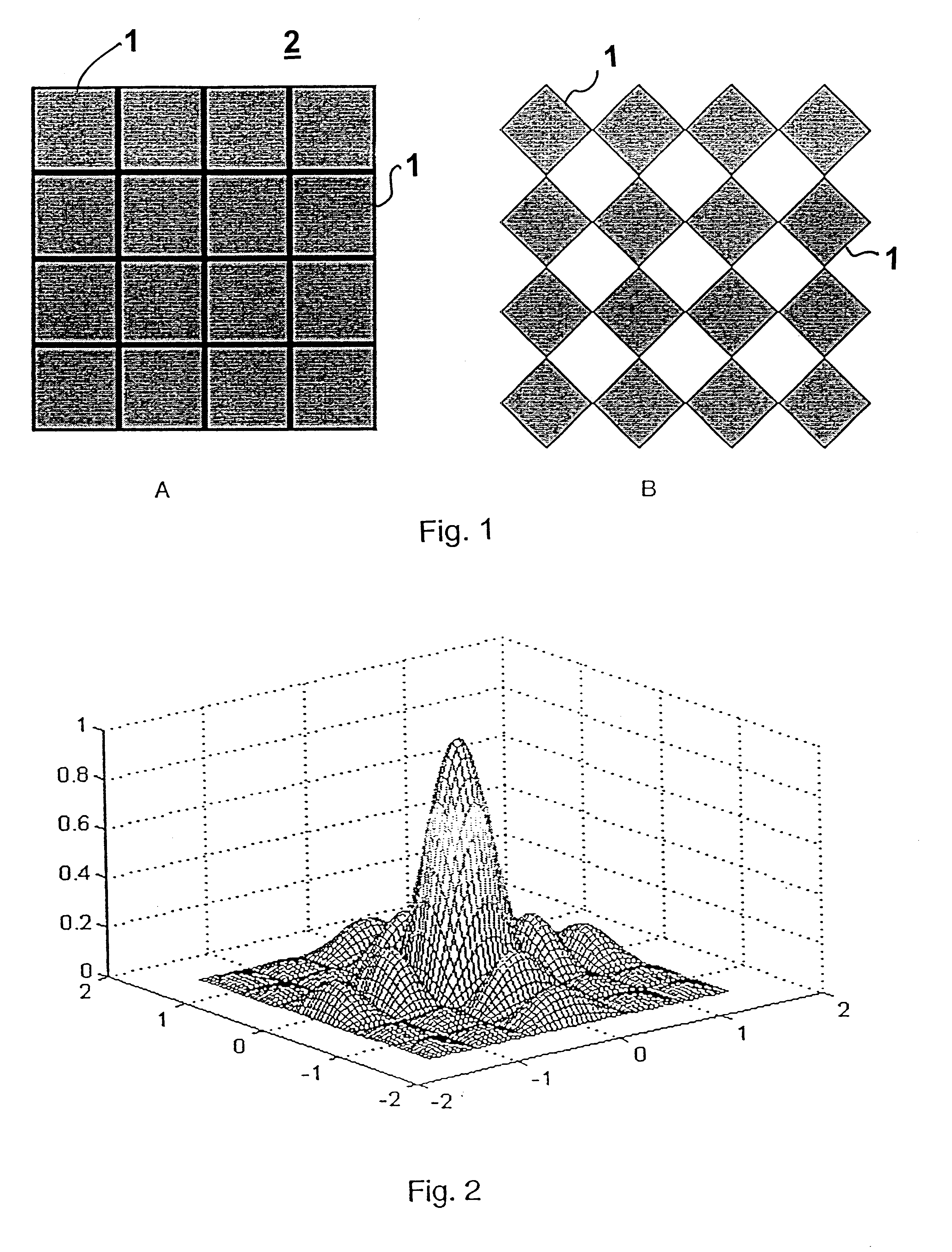
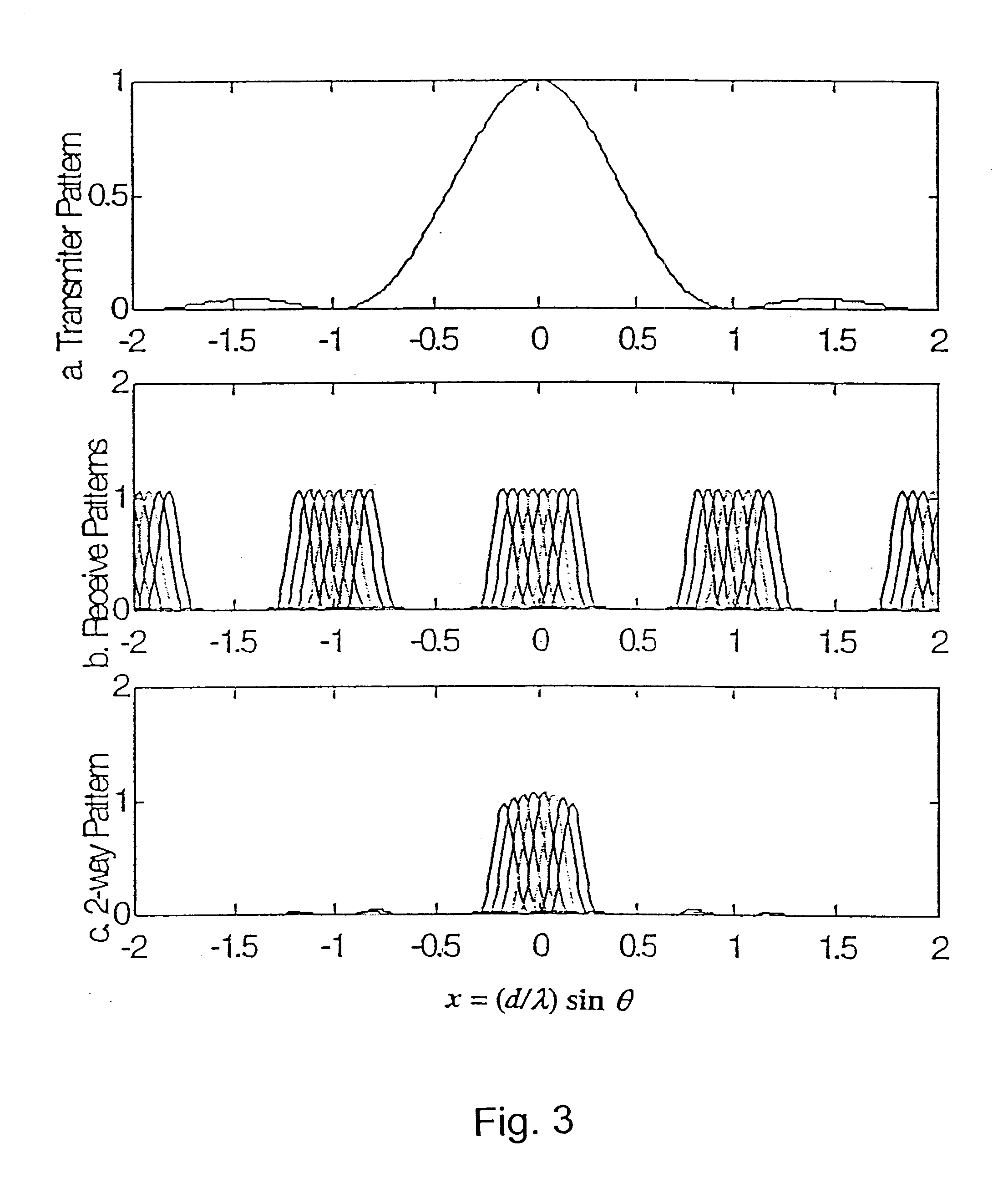
Transmitter patterns for multi beam reception
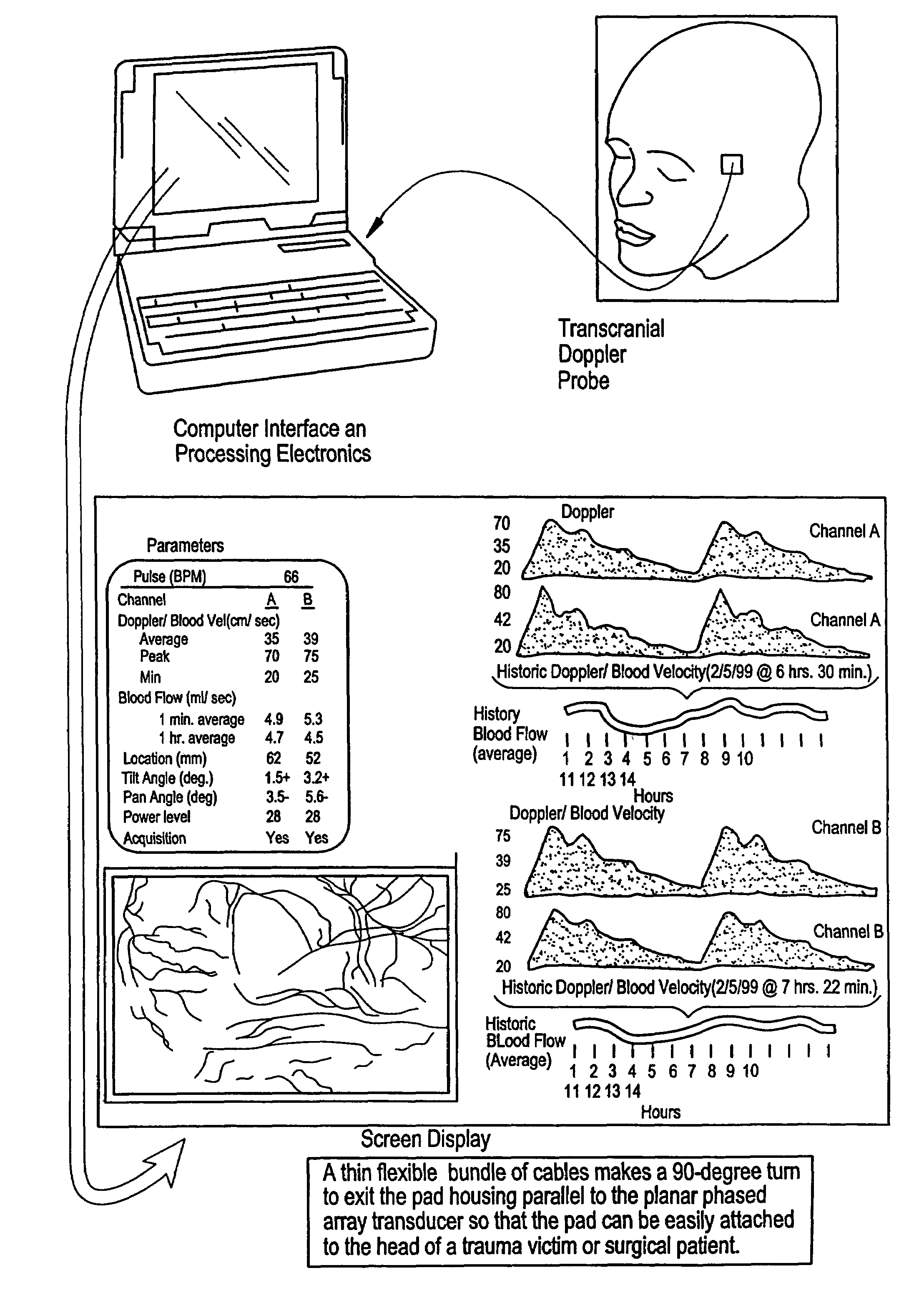
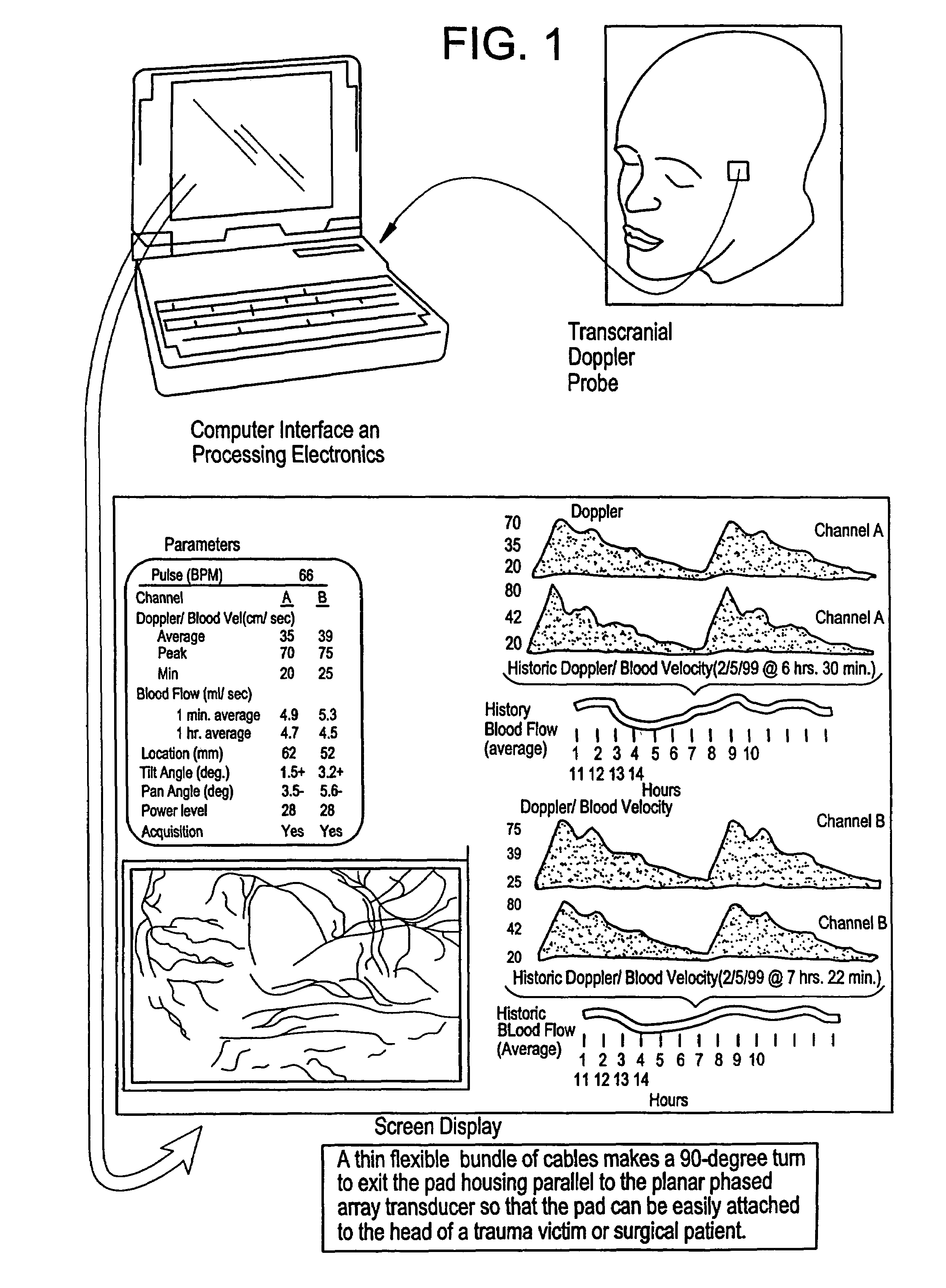
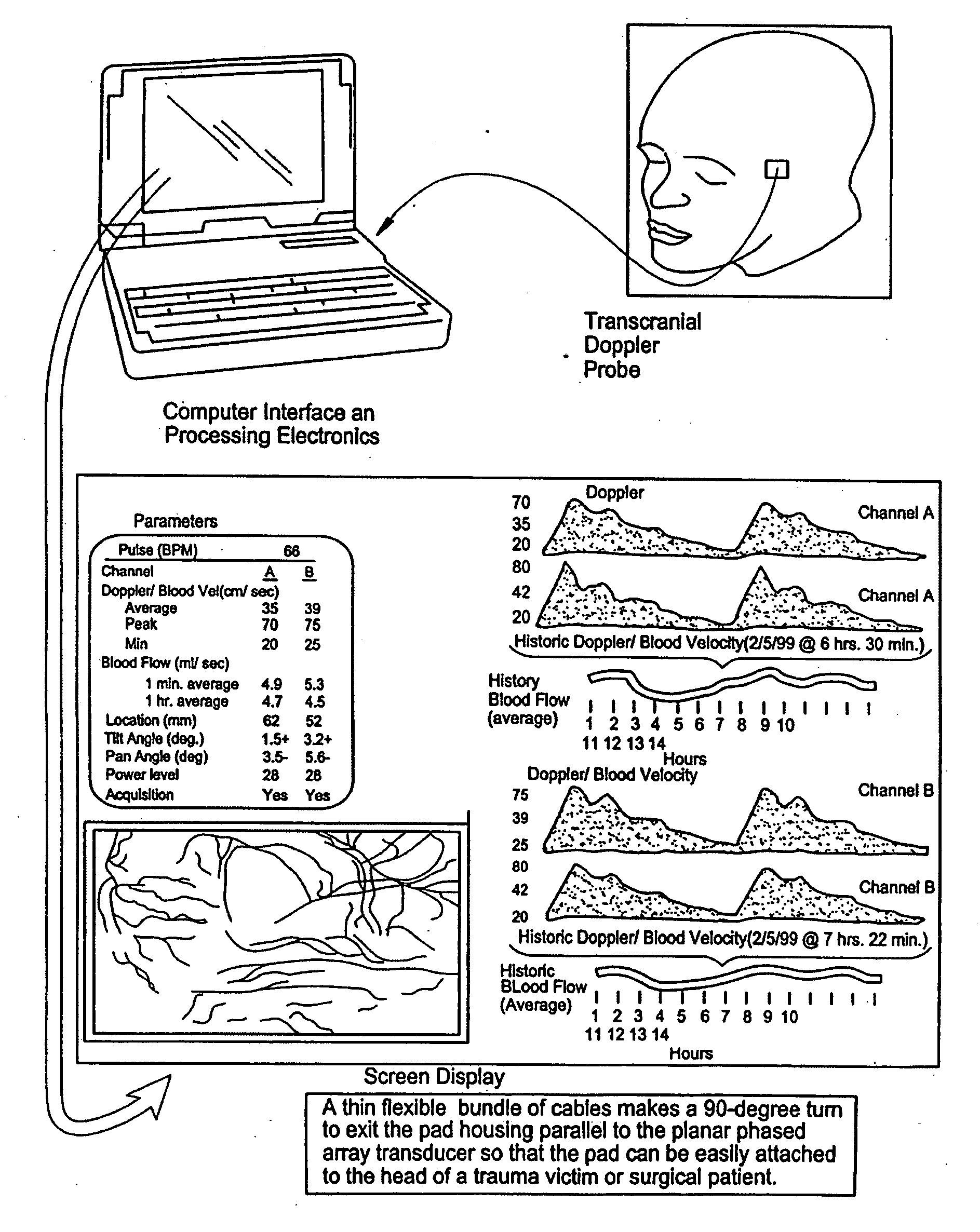
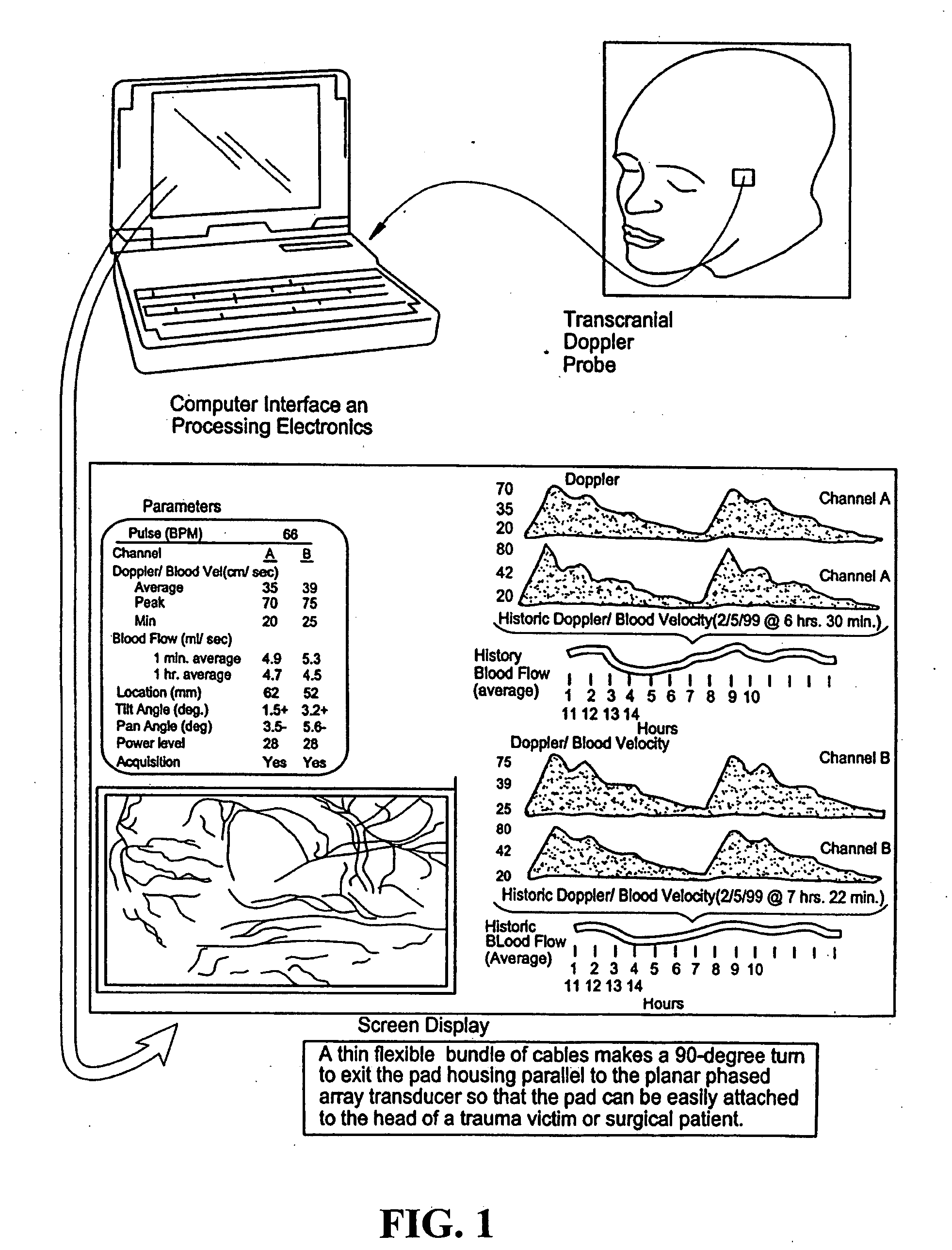
InactiveUS7399279B2High resolutionSmall sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsThinned arrayDisplay device
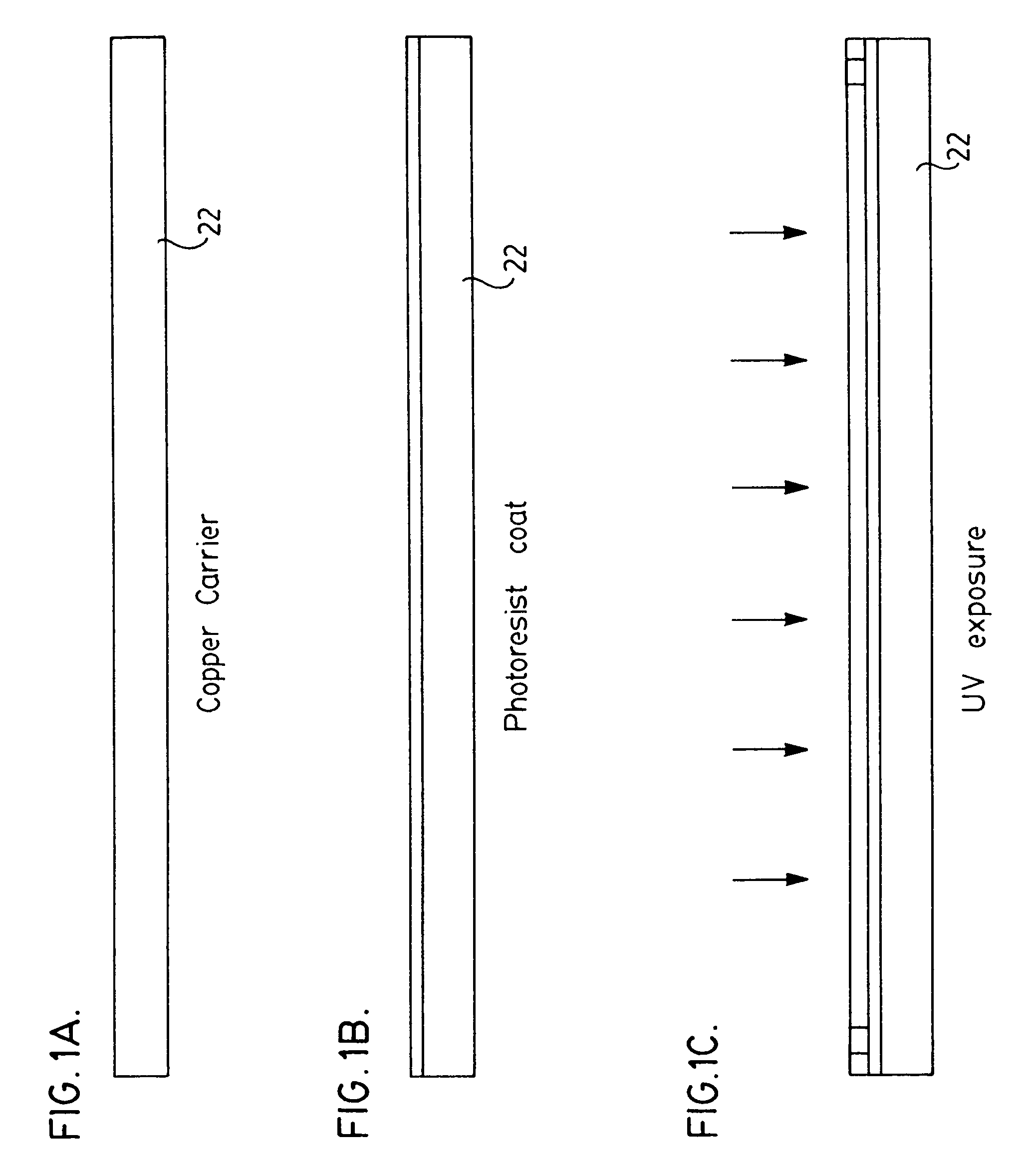
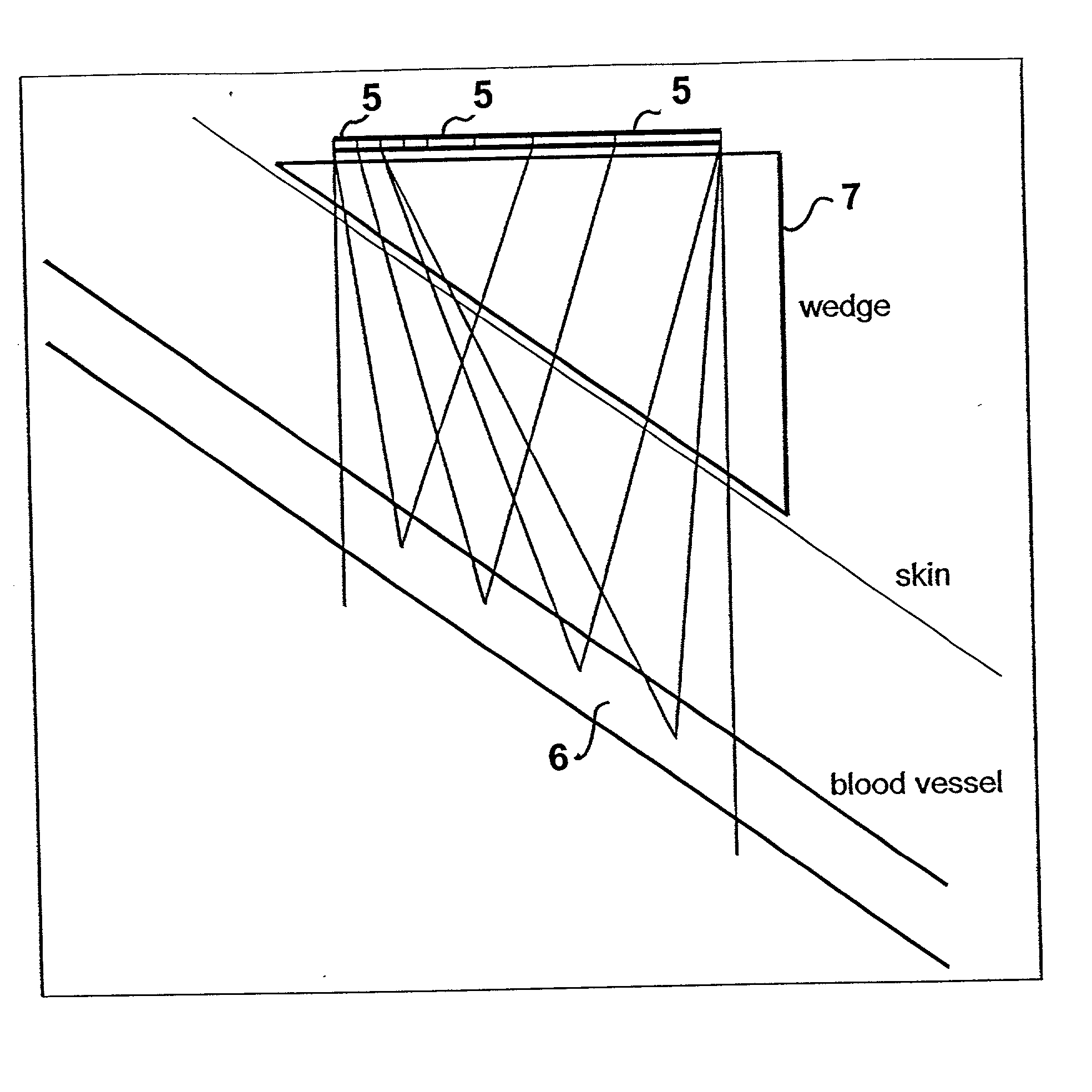
Provided herein is a method for use in medical applications that permits (1) affordable three-dimensional imaging of blood flow using a low-profile easily-attached transducer pad, (2) real-time blood-flow vector velocity, and (3) long-term unattended Doppler-ultrasound monitoring in spite of motion of the patient or pad. The pad and associated processor collects and Doppler processes ultrasound blood velocity data in a three dimensional region through the use of a planar phased array of piezoelectric elements. The invention locks onto and tracks the points in three-dimensional space that produce the locally maximum blood velocity signals. The integrated coordinates of points acquired by the accurate tracking process is used to form a three-dimensional map of blood vessels and provide a display that can be used to select multiple points of interest for expanded data collection and for long term continuous and unattended blood flow monitoring. The three dimensional map allows for the calculation of vector velocity from measured radial Doppler.A thinned array (greater than half-wavelength element spacing of the transducer array) is used to make a device of the present invention inexpensive and allow the pad to have a low profile (fewer connecting cables for a given spatial resolution). The full aperture is used for transmit and receive so that there is no loss of sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) or dynamic range. Utilizing more elements (extending the physical array) without increasing the number of active elements increases the angular field of view. A further increase is obtained by utilizing a convex non-planar surface.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Electronic components such as thin array plastic packages and process for fabricating same
InactiveUS6964918B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padThinned array
A process for fabricating an integrated circuit package includes establishing a plating mask on a first surface of a metal carrier. The plating mask defines a plurality of components including a die attach pad, at least one row of contact pads and at least one additional electronic component. A plurality of metallic layers are deposited on exposed portions of the first surface of the metal carrier. The plating mask is stripped from the metal carrier, leaving the plurality of metallic layers in the form of the plurality of components. A semiconductor die is mounted to die attach pad and pads of the semiconductor die are electrically connected to ones of the contact pads and to the additional electronic component. The first surface of the metal carrier is overmolded to encapsulate the plurality of components and the semiconductor die and the metal carrier is etched away.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Electronic components such as thin array plastic packages and process for fabricating same
InactiveUS7482690B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padThinned array
A process for fabricating an integrated circuit package includes establishing a plating mask on a first surface of a metal carrier. The plating mask defines a plurality of components including a die attach pad, at least one row of contact pads and at least one additional electronic component. A plurality of metallic layers is deposited on exposed portions of the first surface of the metal carrier. The plating mask is stripped from the metal carrier, leaving the plurality of metallic layers in the form of the plurality of components. A semiconductor die is mounted to die attach pad and pads of the semiconductor die are electrically connected to ones of the contact pads and to the additional electronic component. The first surface of the metal carrier is overmolded to encapsulate the plurality of components and the semiconductor die and the metal carrier is etched away.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Thin array plastic package without die attach pad and process for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7358119B2Low profileAssembly is smallSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padThinned array
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
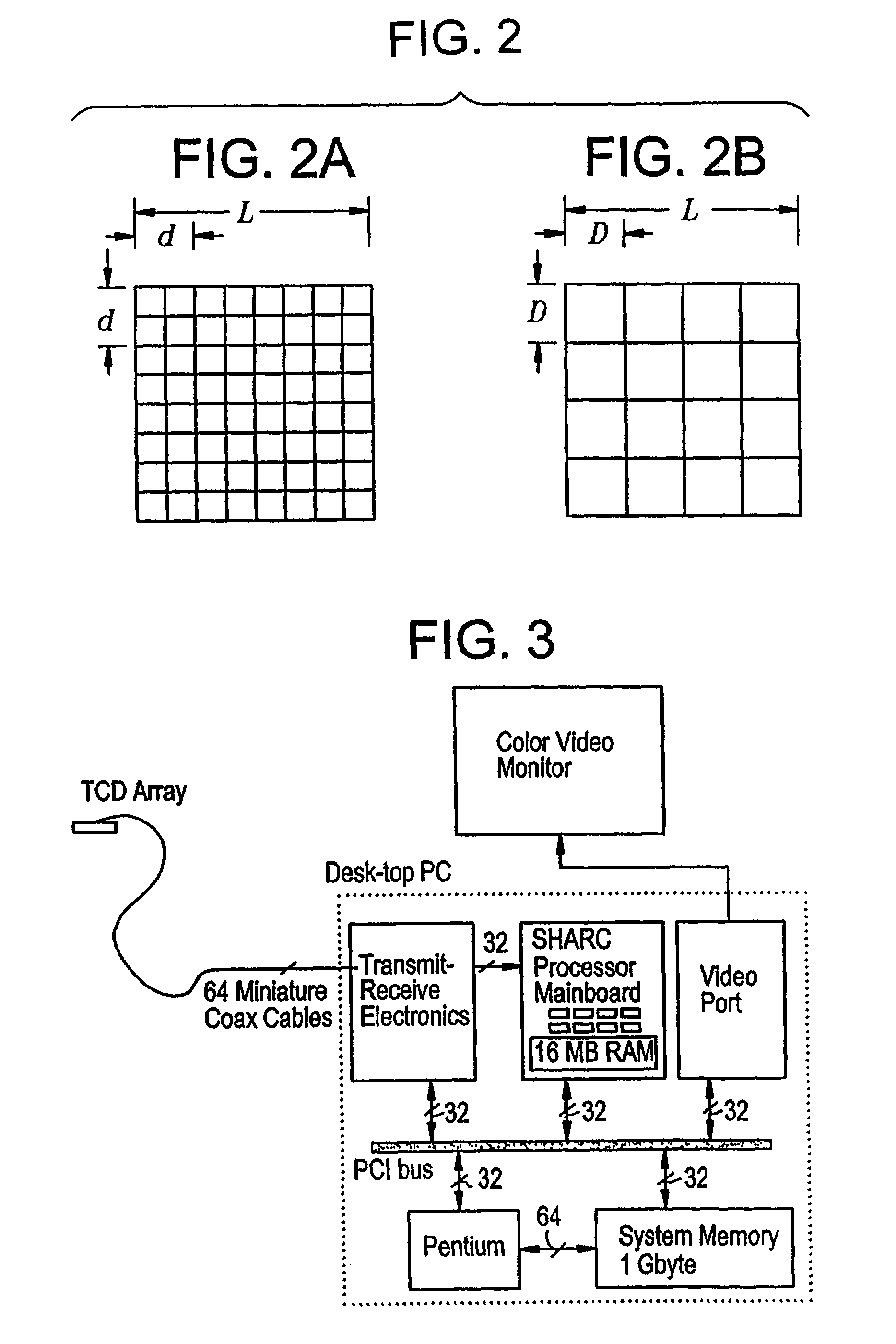
Ultrasound probe with progressive element sizing
A prior application discloses a novel probe geometry that offers a wide field of view in an ultrasonic imaging device. That geometry is referred to as a "thinned array" of transducer elements. The application discloses an improved probe geometry permitting high-resolution imaging of a large volume of the subject's body. In this improved geometry, the array elements are non-uniform in size and spacing. The probe is intended for use, for example, in a method of determining parameters of blood flow, such as vector velocity, blood flow volume, and Doppler spectral distribution, using sonic energy (ultrasound) and a novel thinned array. Also in a method of tracking blood flow and generating a three dimensional image of blood vessel of interest that has much greater resolution than images produced using heretofore known ultrasound devices and methods.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
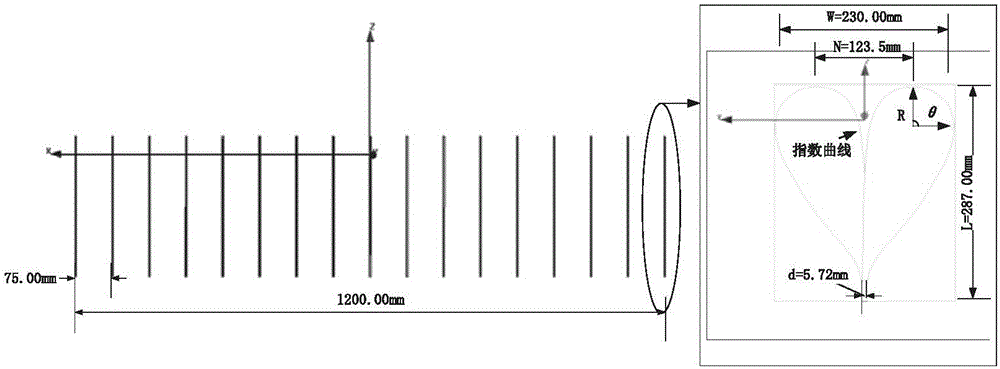
Airship radar conformal thinned array antenna and its signal processing method
ActiveCN103682677AImproving Real Aperture Imaging ResolutionEasy for large-scale sparse layoutWave based measurement systemsAntenna arraysThinned arrayActive phase
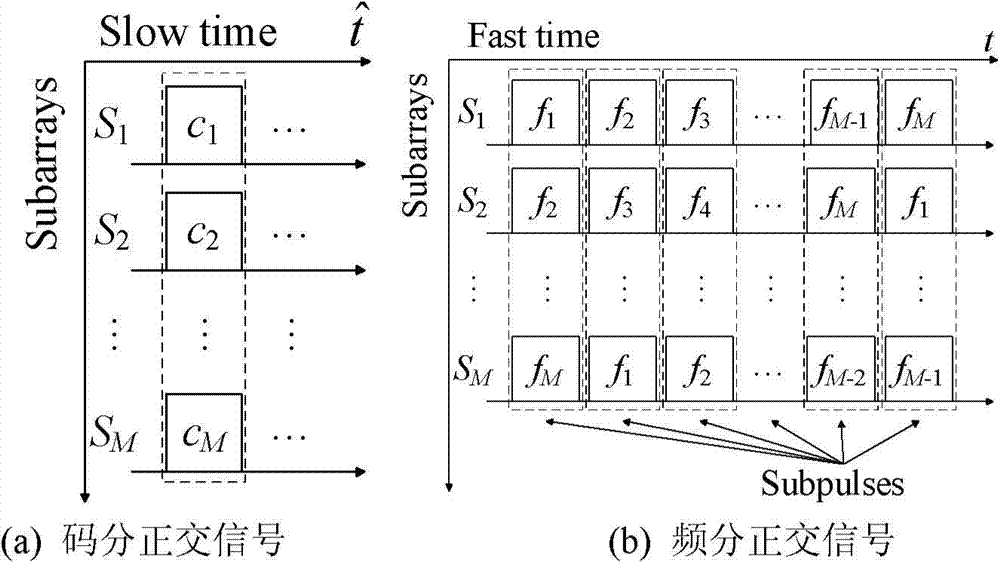
The invention discloses an airship radar conformal thinned array antenna and its signal processing method. The conformal thinned array antenna comprises a plurality of sparsely-distributed subarrays on a ship body. The subarrays adopt active phase control subarrays, and a rigid structure is adopted to guarantee subarray face control precision. A receiving / transmitting assembly of the subarrays is a stereoscopic integrated tile structure with radiation array elements. Each subarray transmits and receives frequency division or code division orthogonal signals so as to realize a full-array transmit-receive function. Observation scope of the conformal thinned array antenna is determined by subarray antenna beamwidth. High spatial resolution is realized by full-array antenna. The airship radar with the conformal thinned array antenna is used for high-resolution ground imaging and moving object detection.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave related imaging system and imaging method based on thinned array
InactiveCN103235298AReduce usageReduce complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arrayAmbiguity
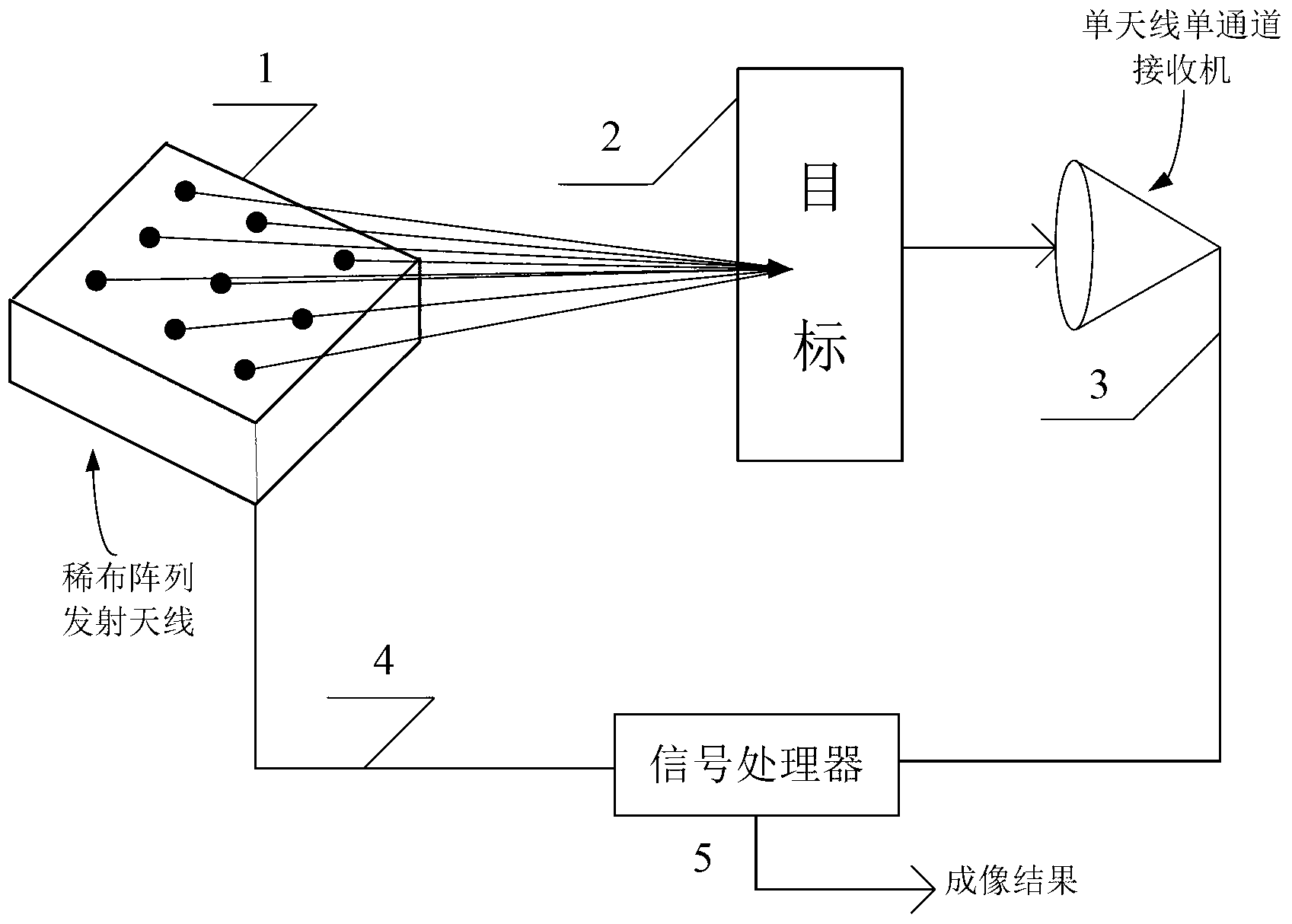
The invention discloses a microwave related imaging system and a microwave related imaging method based on a thinned array, which mainly aim to solve the problems of poor imaging effect and low resolution when non-radial relative movement does not exist between a radar antenna and a target in the prior art. The system comprises a transmitting antenna (1), a target (2), a receiver (3) and a signal processor (5), wherein the transmitting antenna (1) is formed by a thinned array antenna; different microwave coded signals are transmitted by all array elements, so as to form a microwave radiation field in space through incoherent superposition; the target (2) is irradiated through the microwave radiation field, so as to generate target scattering echoes; the microwave radiation field (4) on the surface of the target (2) is stored; the target scattering echoes are received by the receiver (3) through a single antenna and a single channel; and the target scattering echoes received by the receiver (3) and the pre-stored microwave radiation field (4) are processed by the signal processor (5), so as to obtain the imaging of the target. By using the system and the method, super-resolution imaging of the target without ambiguity can be realized when the non-radial relative movement does not exist between the radar antenna and the target, and the system and the method can be used for super-resolution imaging of the target by an airborne forward-looking radar and a ball-borne radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ultrasound probe with progressive element sizing
InactiveUS6682488B2Blood flow measurement devicesMechanical vibrations separationSonificationHigh resolution imaging
A prior application discloses a novel probe geometry that offers a wide field of view in an ultrasonic imaging device. That geometry is referred to as a "thinned array" of transducer elements. The application discloses an improved probe geometry permitting high-resolution imaging of a large volume of the subject's body. In this improved geometry, the array elements are non-uniform in size and spacing. The probe is intended for use, for example, in a method of determining parameters of blood flow, such as vector velocity, blood flow volume, and Doppler spectral distribution, using sonic energy (ultrasound) and a novel thinned array. Also in a method of tracking blood flow and generating a three dimensional image of blood vessel of interest that has much greater resolution than images produced using heretofore known ultrasound devices and methods.
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Devices and methods for tracking blood flow and determining parameters of blood flow
InactiveUS20080269609A1Small sizeBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationThinned array
Owner:PHYSIOSONICS
Sparse array millimeter wave imaging system
InactiveUS20090289833A1Reduce system costLower frame rateAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionMillimetre wave
An active millimeter-wave imaging system that can provide a means of surmounting the deficiencies of earlier millimeter-wave systems, as well as lowering the system cost substantially. Earlier systems have employed large numbers of individual millimeter-wave receivers in either focal plane arrays or frequency scanned antenna arrays, and these systems have suffered from low frame rate, poor contrast, and relatively low resolution. By employing a sparse array of millimeter-wave transmitters and receivers, covering a relatively large, flat, physical aperture, a low cost and high resolution system can be achieved. By employing active millimeter-wave illumination, contrast and frame rate issues can be mitigated, at long ranges (10's of meters). A new approach, termed Fourier Telescopy, allows the illuminating signals to interrogate the various spatial frequencies of the target, and the image to be reconstructed from these various spatial frequency components.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Thinned array near-field passive location amplitude and phase error correction method
ActiveCN105445709AAccurate estimateLow costWave based measurement systemsImage resolutionThinned array
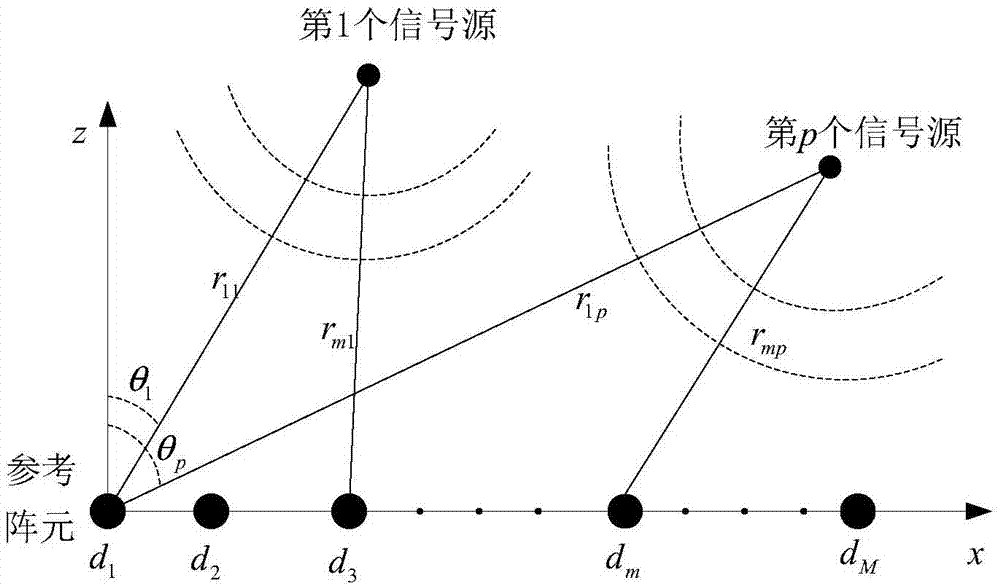
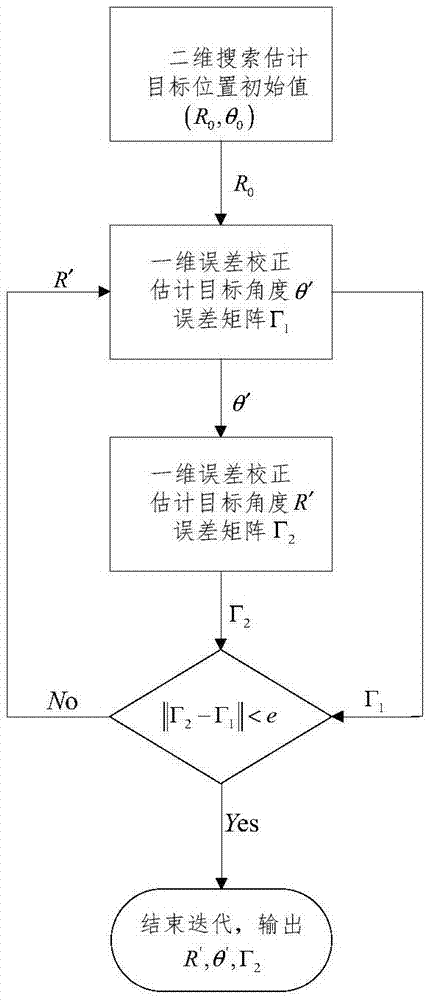
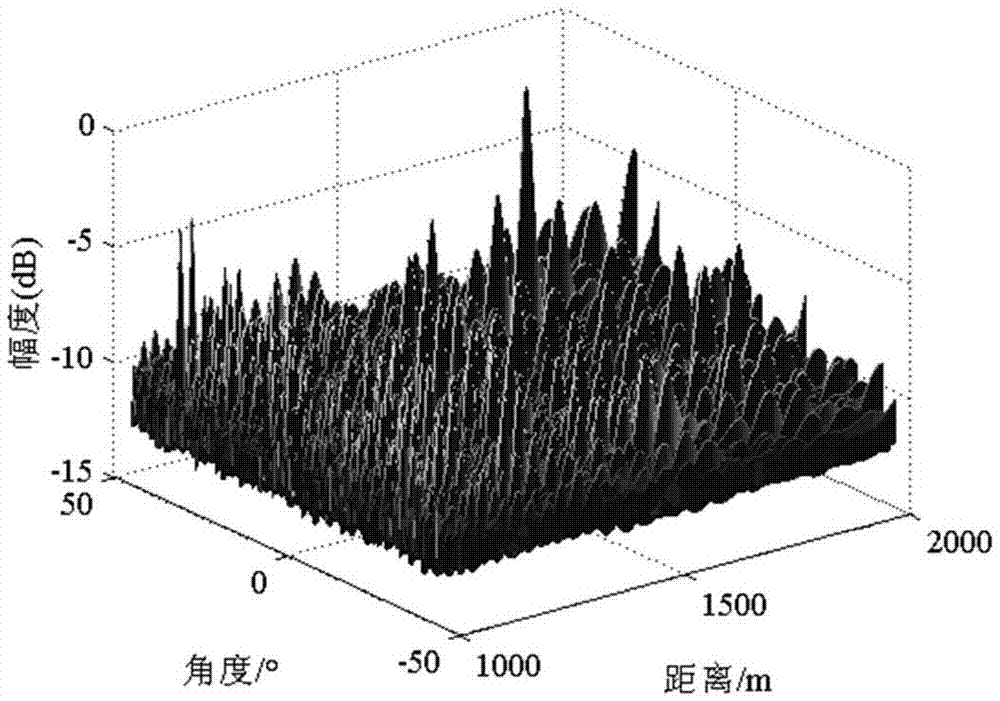
The invention discloses a thinned array near-field passive location amplitude and phase error correction method, and relates to the technical field of phased array radar. The method comprises the following steps: under the condition that a target is located in a near field, fixing the pitch angle Phi, alternately and cyclically estimating the distance and azimuth angle of the target until the two parameters converge to the real values, and taking the position as the initial position of error correction; then, carrying out one-dimensional search of the azimuth angle of the target, correcting the array amplitude and phase error using an amplitude and phase error self-correction method, and estimating an array amplitude and phase error matrix gamma(theta) and the first iteration value theta' of the azimuth angle; estimating an array amplitude and phase error matrix gamma(r) and the first iteration value of the distance of the target; and carrying out loop iteration until ||gamma(theta)-gamma(r)||<epsilon2, namely, the estimated values of the parameters converge to the real values. Array element positions are arranged randomly and sparsely within a certain arraying range, the same angle resolution can be achieved with only a small number of array elements, and the cost can be reduced in practical engineering.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Flexible MIMO (Multi-Input and Multi-Output) radar hybrid target DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on compressed sensing (CS)
ActiveCN108828551AIncrease freedomReduce mutual couplingWave based measurement systemsMulti inputThinned array
The invention discloses a flexible MIMO (Multi-Input and Multi-Output) radar hybrid target DOA (Direction of Arrival) estimation method based on compressed sensing (CS), and relates to the technical field of array signal processing technology. The present invention focuses on the following two issues for the sparse array MIMO radar structure design and hybrid target DOA estimation: (1) designing aflexible MIMO radar structure and defining it as a sparse array with a sparse array with flexible inter-element spacing (SA-FIS); (2) proposing a two-step CS algorithm with reduced complexity to makefull use of the total virtual array elements. By modifying and removing non-diagonal elements in the target covariance matrix, the improved CS algorithm can identify only the diagonal elements therein. Since the conventional CS algorithm needs to estimate all non-zero elements, the present invention can improve estimation performance and reduce complexity by estimating a smaller number of elements.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Thin array plastic package without die attach pad and process for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20060154403A1Low package profileSmall package assemblySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padManufacturing technology
A process for fabricating an integrated circuit package. Metal is plated up on a substrate to provide a plurality of contacts pads and a plurality of fiducial markings on a periphery of the contacts. A transparent mask is selectively deposited on the substrate, over the fiducial markings. A semiconductor die is mounted on the substrate such that the contact pads circumscribe the semiconductor die and the semiconductor die is wire bonded to ones of the contact pads. The wire bonds are encapsulated and the semiconductor die and contact pads are covered in a molding material. The substrate is selectively etched to thereby etch away the substrate underneath the contact pads and the semiconductor die. The integrated circuit package is singulated from other integrated circuit packages by sawing using the fiducial markings.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
Conformal retro-modulator optical devices
InactiveUS6954302B2Improve efficiencyHigh bandwidthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThinned arrayRoom temperature
Owner:HRL LAB
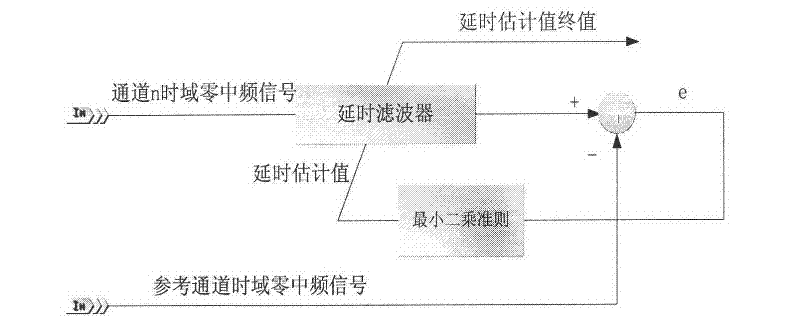
Near-field delay calibration method for channels of broadband thinned array radar
The invention relates to a near-field delay calibration method for channels of a broadband thinned array radar, which comprises the following steps of: erecting a signal source in the near-field environment to radiate frequency-modulated signals with a certain frequencies and broadbands, receiving the signals radiated by the signal source by using a large-scale thinned array antenna to be calibrated and acquiring the signals received by each channel; converting the channel signals into a frequency domain by using a dechirping technology; acquiring a high-precision estimation of a frequency difference value of the channel signals in the frequency domain by using a frequency difference value high-precision estimation method so as to obtain a delay estimation initial value of the channel signals; correcting a phase difference value of the channels by using a time domain delay high-precision estimation method to obtain a delay calibration value of the channels; and calibrating a delay filter of a signal processing unit of the thinned array radar by the calibration value.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Synthesis method of broadband frequency independent thinned array taking mutual coupling effect into account
ActiveCN106650104AReduce the numberReduce complexityAntenna arraysDesign optimisation/simulationThinned arraySynthesis methods
The discloses a synthesis method of a broadband frequency independent thinned array taking mutual coupling effect into account, and relates to array antennae. Iterative weighted first norm is adopted in a plurality of limiting conditions, and the limiting conditions comprise a spatial response change limit, a side lobe level upper boundary limit and an expected direction limit. As the limiting conditions are all convex problems, the problems are optimized through iterative second-order cone programming. In a target working frequency range, low side lobe level can be kept, the quantity of array elements can be effectively reduced under a main lobe frequency independent performance, the hardware complexity and the engineering cost are furthest reduced. In addition, electromagnetic mutual coupling effect met in the practical application is considered, and error, caused by coupling, of an antenna system is effectively avoided.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
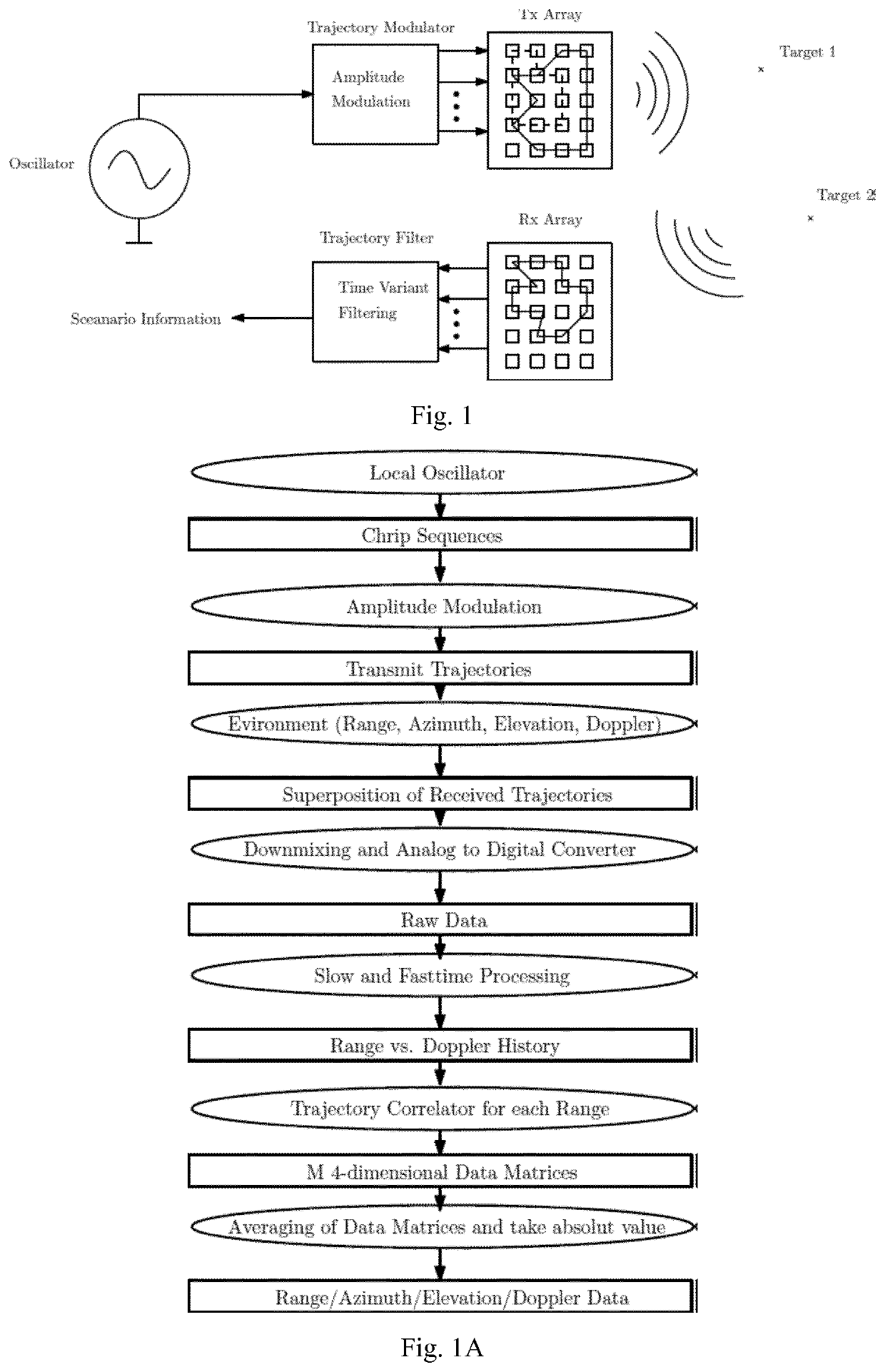
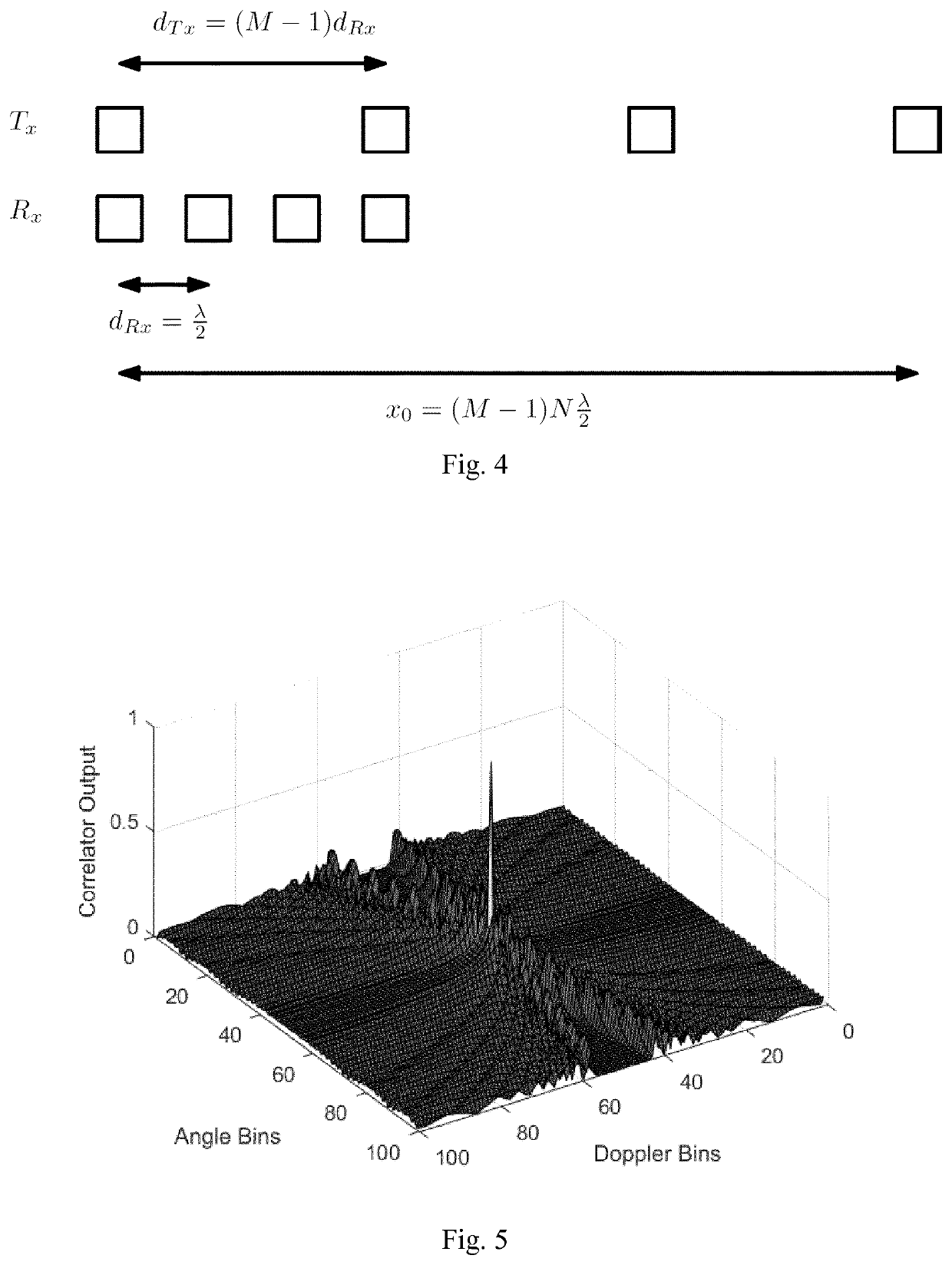
Method and system for obtaining angle-doppler signatures in MIMO radars
ActiveUS20190346544A1Reduce angle-Doppler ambiguityImprove discriminationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLinear motionArray data structure
A method for obtaining an angle-Doppler signature for a target using sparse arrays in multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar, the MIMO radar including a transmit antenna array, the transmit antenna array being at least one-dimensional (e.g. 2-D, 3-D or 4-D) and having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes generating transmit signals for transmission by the transmit antenna array, the transmit signals defining at least a first transmit trajectory (e.g. circular) of a phase center within the transmit antenna array, and transmitting the transmit signals using Amplitude Modulation on the transmit antenna array. The method further includes receiving receive signals from the target, the receive signals resulting from the incidence of the transmit signals upon the target, and determining the angle-Doppler signature from the receive signals. The first transmit trajectory is such that, in operation, the phase center undergoes non-linear motion within the transmit antenna array.
Owner:UNIV DU LUXEMBOURG +1
Conformal retro-modulator optical devices
InactiveUS20060239696A1Improve efficiencyHigh bandwidthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThinned arrayRoom temperature
A conformal retro-modulator optical apparatus. The apparatus includes an array of multiple quantum well devices disposed in a thin array. A plastic support element is bonded to the thin array, the plastic support element having a thickness greater that of the thin array. The plastic support element is preferably plastic at elevated temperatures above room temperature, thereby allowing the plastic support element and the thin array of multiple well device disposed therein to conform to a predetermined shape, yet being rigid at room temperature.
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and device for receiving communication signal of thinned array antenna system
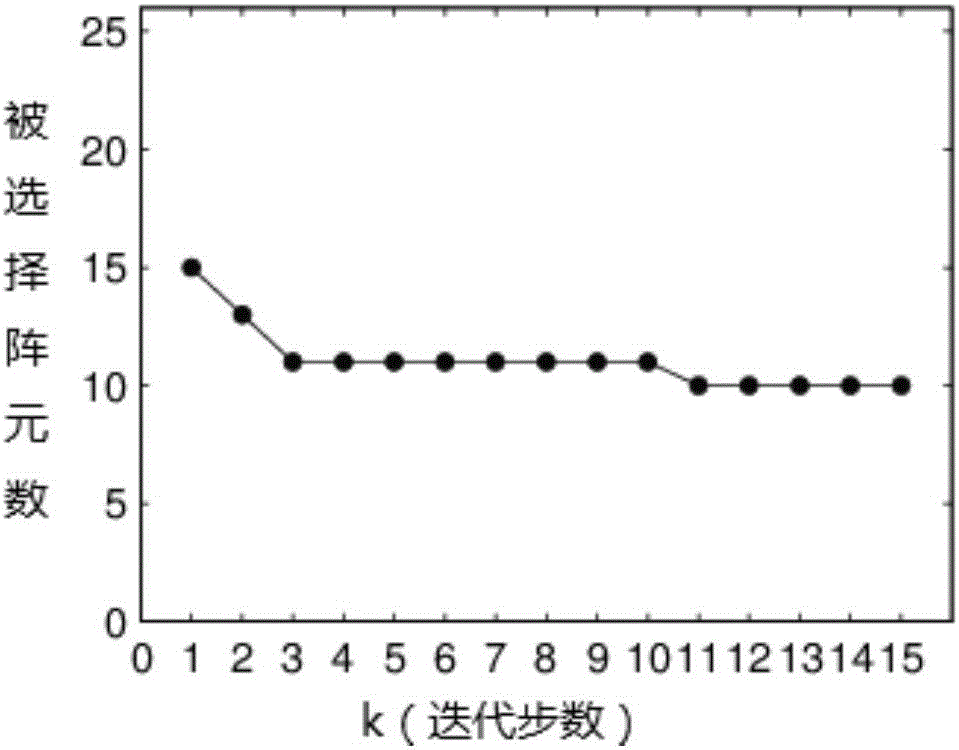
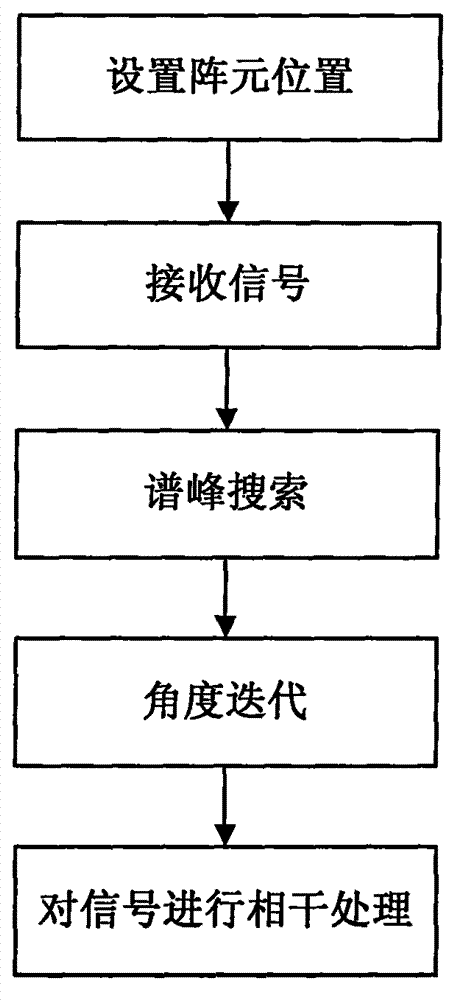
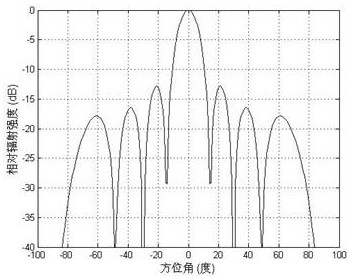
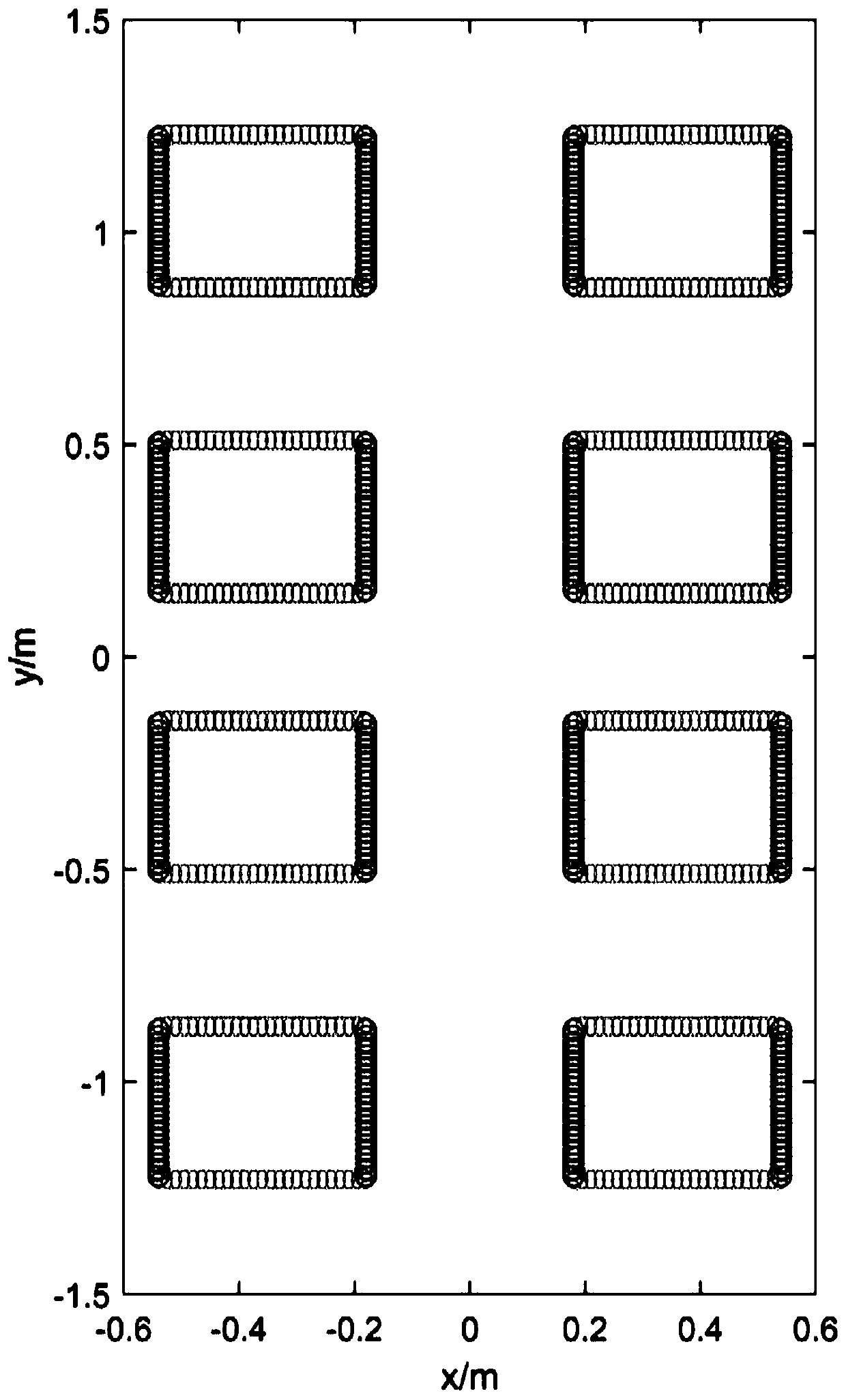
InactiveCN102957472AHigh estimated angular accuracyOvercoming the problem of receiving signal influenceSpatial transmit diversitySignal classificationTime delays
The invention discloses a method and device for receiving a communication signal of a thinned array antenna system. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting the positions of array elements; (2) receiving a signal; (3) performing spectrum peak search; (4) performing angle iteration; and (5) processing the received signal. According to the invention, the subspace power spectrum of the signal is obtained by performing spectrum peak search on the received signal according to a multiple-signal classification formula, the angles corresponding to all high spectrum peak values therein are sequentially selected and iterated, then an angle is selected according to the output power as the direction of arrival, the obtained adaptive weight vector is multiplied by the received signal, and the signals of all array elements are overlapped and output. The method and device disclosed by the invention can adapt to a thinned array receiving system in any arrangement, and can effectively offset the time delay generated by the array while avoiding influence of a pseudo peak on the received signal.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Millimeter wave sparse imaging method and system based on sparse array
ActiveCN111505721AImprove imaging resolutionReduce in quantityElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationImaging algorithmThinned array
The invention provides a millimeter wave sparse imaging method and system based on a sparse array. The method comprises the steps of enabling original electromagnetic field data collected by the sparse array to be changed into first electromagnetic field data of a dense array according to a first equivalent principle, and enabling the first equivalent principle to comprise an equivalent change ofkeeping a sparse frequency point unchanged, changing the original electromagnetic field data into second electromagnetic field data on densely distributed frequency points according to a second equivalence principle, wherein the second equivalence principle comprises changes based on the densely distributed array under different frequency points, and imaging by adopting a millimeter wave holographic imaging algorithm according to the first electromagnetic field data and the second electromagnetic field data. The imaging definition of the long-distance millimeter wave imaging system can be improved.
Owner:杭州芯影科技有限公司
Sparse array optimization configuration method for reducing distance dimension beam forming side lobes
ActiveCN114218814ATo achieve the formation effectReduce formation effectGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationThinned arraySide lobe
The invention discloses a sparse array optimization configuration method for reducing distance dimension beam forming side lobes. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, according to the aperture D and array element number N of sparse distribution antenna array distribution, taking a non-uniform array form of odd elements as a basic array form of a distributed sparse array; 2, selecting a central array element of the sparse distribution antenna array as a reference array element; step 3, calculating an array element spacing adjustment basic quantity required by the basic array; step 4, calculating an X coordinate of each array element relative to the reference array element; step 5, calculating a phase weighting matrix formed by the phase weighting vectors; step 6, calculating a distance dimension beam pattern taking the distance r as a variable; 7, random disturbance is set for the positions of the array elements; and step 8, calculating a new beam pattern. Under the condition that amplitude weighting is not needed, the distance dimension digital beam forming effect of a low side lobe is achieved only by optimally configuring the positions of the array elements, and therefore the influence of interference signals entering from the side lobe in the distance dimension is reduced.
Owner:ROCKET FORCE UNIV OF ENG
Array sparse optimization method based on adaptive genetic algorithm
ActiveCN111160556AGood direction finding performanceHigh direction finding performanceICT adaptationGenetic algorithmsThinned arrayTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a sparse array optimization method based on an adaptive genetic algorithm in the technical field of radar reconnaissance array optimization. The method comprises the following steps of optimizing a model by proposing an array, encoding arrays, then, calculating a fitness value by utilizing a Cramer-Rao bound; selecting and crossly mutating the generated individuals by utilizing the fitness value, correspondingly changing crossover probability and mutation probability along with the increase of iteration times, finally optimizing to obtain the optimal individual, and taking the sparse array placement mode corresponding to the optimal individual as the optimal placement mode of array elements in the radar array. The method is a sparse array optimization method based ona self-adaptive genetic algorithm, an array element selection mode mainly takes the maximum array aperture and the minimum array element spacing as constraint conditions, takes a Cramer-Rao bound asa fitness function, and ensures that the array has relatively high direction finding performance under the conditions of the same array element number and the same minimum array element spacing.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Millimeter wave sparse array remote monitoring imaging method and system
ActiveCN110794471ALarge imaging field of viewElectromagnetic wave flicker effect is smallOptical detectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arraySoftware engineering
The invention discloses a millimeter wave sparse array remote monitoring imaging method and system, and belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave three-dimensional holographic imaging. The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining an echo signal; S2, performing interpolation operation; S3, performing fast Fourier transform; S4, selecting a distance plane; S5, performing frequencydomain matched filtering; S6, performing fast Fourier inverse transform; S7, performing time domain matched filtering; S8, performing coherent accumulation; and S9, obtaining a three-dimensional complex image. According to the millimeter wave sparse array remote monitoring imaging method and system disclosed by the invention, a millimeter wave sparse array full-electronic scanning imaging systemis adopted, and compared with a traditional optical machine scanning far-field imaging system, the millimeter wave sparse array full-electronic scanning imaging system has the characteristics of smallelectromagnetic wave flicker effect, high image signal-to-noise ratio and large imaging field range; meanwhile, compared with a traditional time domain type imaging method, the adopted signal processing imaging method has the advantages of less hardware resources and less storage space, the algorithm process is simple and easy to understand, the algorithm main body only comprises the main body process of fast Fourier transform, matched filtering and coherent accumulation, and the calculation efficiency is higher than that of the traditional time domain type algorithm.
Owner:博微太赫兹信息科技有限公司
Method for acquiring extensible sparse array antenna layout
ActiveCN112367103ASimple design methodStrong global search capabilitySpatial transmit diversityFast Fourier transformThinned array
The invention discloses an extensible sparse array antenna layout obtaining method, and solves the problems that when a large sparse array antenna is applied to practical engineering, the array surface scale is large; the problems of complex feed network, difficult radio frequency connection design, complex beam control programming, high array directional diagram sidelobe caused by periodic sparsesubarray splicing, low antenna gain and the like caused by irregular sparse units are solved. The method comprises the steps of initializing parameters of a sparse sub-array and a rotation matrix, combining the sparse sub-array and the rotation matrix into an extended array, generating an extended array population, synthesizing extended sparse array directional diagrams through inverse fast Fourier transform, calculating the fitness of the array directional diagrams; and optimizing the extended sparse array by means of a genetic algorithm, and outputting a sparse sub-array, a rotation matrixand the extended sparse array when the target function meets the requirement or reaches the maximum number of iterations.
Owner:重庆两江卫星移动通信有限公司
Method and system for synthesizing sparse array MIMO radar joint beam directional diagram
ActiveCN113176540AEasy to solveImprove object detectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arrayRadar
The invention relates to a method and a system for synthesizing a sparse array MIMO radar joint beam directional diagram. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a uniform linear MIMO radar joint beam directional diagram transceiving array structure; constructing a sparse MIMO radar joint beam directional diagram transceiving array structure according to the uniform linear array structure; performing binary coding on array elements in the sparse array structure to obtain a transmitting-receiving position indication vector in the sparse array structure; obtaining array element positions in the sparse array structure according to the uniform linear array structure and the transceiving position indication vector; performing optimization solution on the array element position in the sparse array structure according to the obtained target function to obtain the optimal array element position in the sparse array structure; and according to the optimal array element position in the sparse array structure and the obtained uniform linear joint beam directional diagram expression of the MIMO radar, obtaining an MIMO radar joint beam directional diagram under the sparse array. According to the invention, the target detection and parameter estimation performance of the radar can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
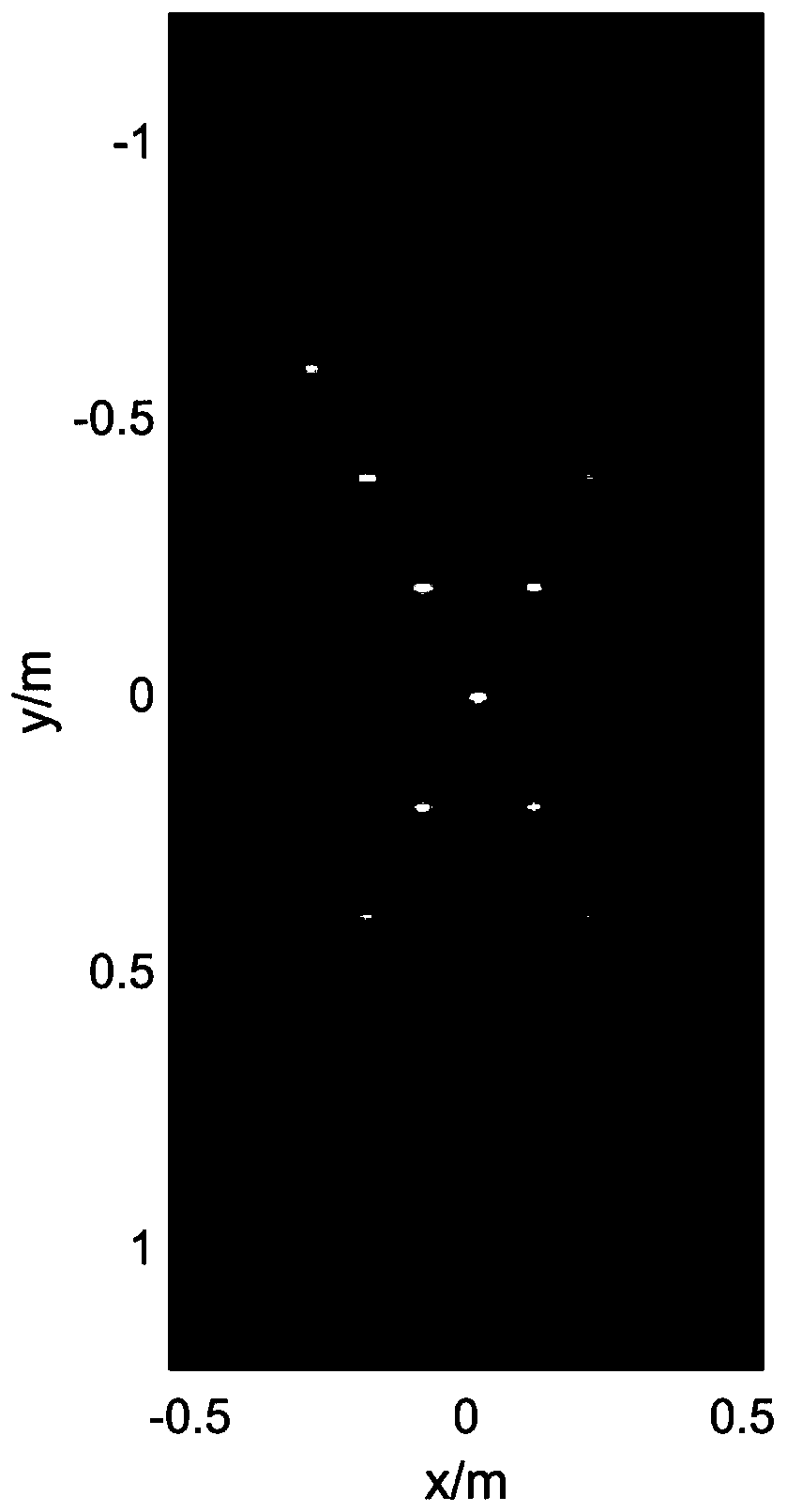
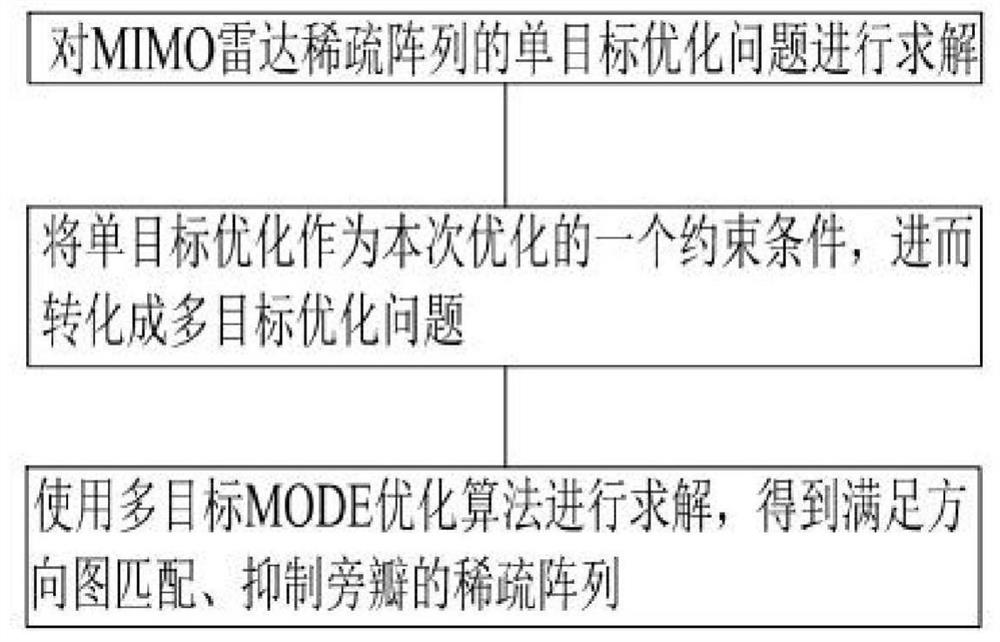
MIMO radar sparse array optimization method based on MODE algorithm
InactiveCN111665502ASimple structureEasy programmingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arrayTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an MIMO radar sparse array optimization method based on an MODE algorithm, and relates to the technical field of radar imaging systems. The method comprises two steps to complete sparse array optimization. On the basis of completing the establishment of a covariance matrix, problem modeling is carried out mainly for sparse array optimization. According to the method, a CA+CA+DE algorithm is used for solving a single-objective optimization problem, then single-objective optimization is used as a constraint condition of the optimization, then the single-objective optimization problem is converted into a multi-objective optimization problem, and finally a multi-objective MODE optimization algorithm is used for solving to obtain a sparse array which meets directional diagram matching and inhibits side lobes. The method can converge to global optimization under the condition that the directional diagram is fixed, and the convergence speed is high.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV +1
Method and system for obtaining angle-doppler signatures in MIMO radars
A method for obtaining an angle-Doppler signature for a target using sparse arrays in multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) radar, the MIMO radar including a transmit antenna array, the transmit antenna array being at least one-dimensional (e.g. 2-D, 3-D or 4-D) and having a plurality of antenna elements. The method includes generating transmit signals for transmission by the transmit antenna array, the transmit signals defining at least a first transmit trajectory (e.g. circular) of a phase center within the transmit antenna array, and transmitting the transmit signals using Amplitude Modulation on the transmit antenna array. The method further includes receiving receive signals from the target, the receive signals resulting from the incidence of the transmit signals upon the target, and determining the angle-Doppler signature from the receive signals. The first transmit trajectory is such that, in operation, the phase center undergoes non-linear motion within the transmit antenna array.
Owner:UNIV DU LUXEMBOURG +1
Automobile millimeter wave radar sparse array grating lobe false target identification method and system
ActiveCN111679266AAvoid false targetsImprove angular resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThinned arrayEngineering
The invention discloses an automobile millimeter wave radar sparse array grating lobe false target identification method and system, belongs to the technical field of automobile radar, and is used forsolving the problem of grating lobe false targets caused by the fact that an existing automobile radar adopts a sparse array. The method comprises the following steps: 1) target detection, (2) targetangle estimation, (3) target echo power sorting and normalization in different directions, (4) false interference covariance matrix construction, (5) self-adaptive weight calculation, (6) spatial spectrum recalculation based on the self-adaptive weight, and (7) false target identification after wave beam output normalization. The method and system have the advantages of grating lobe false targetavoidance, angle resolution improvement and the like.
Owner:成都纳雷科技有限公司
Target orientation and distance combined sparse reconstruction positioning method based on seabed horizontal L-shaped array
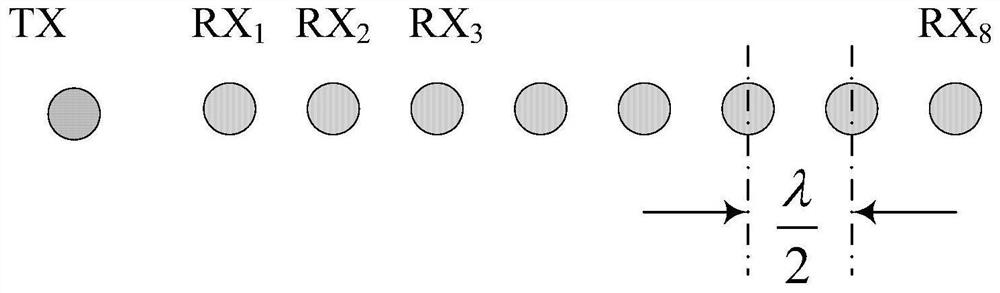
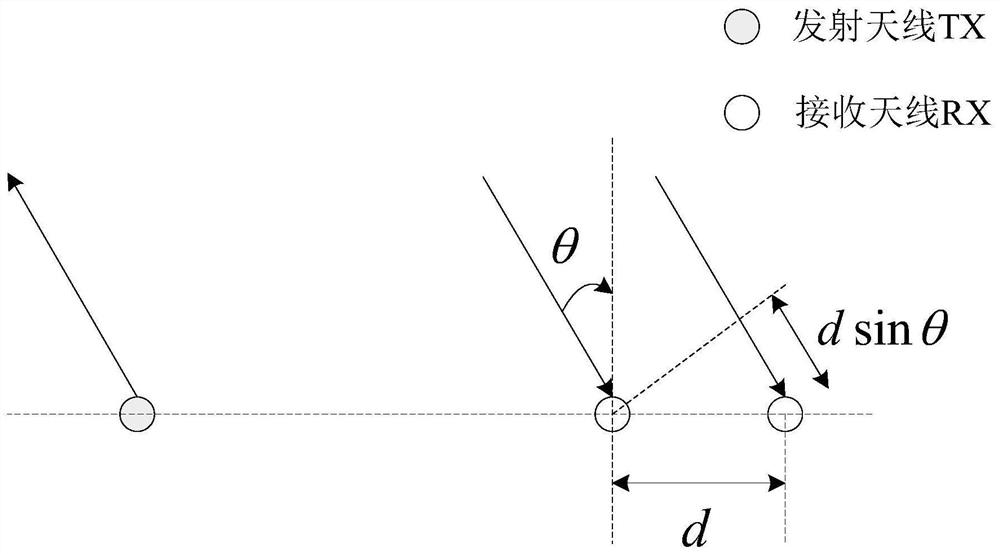
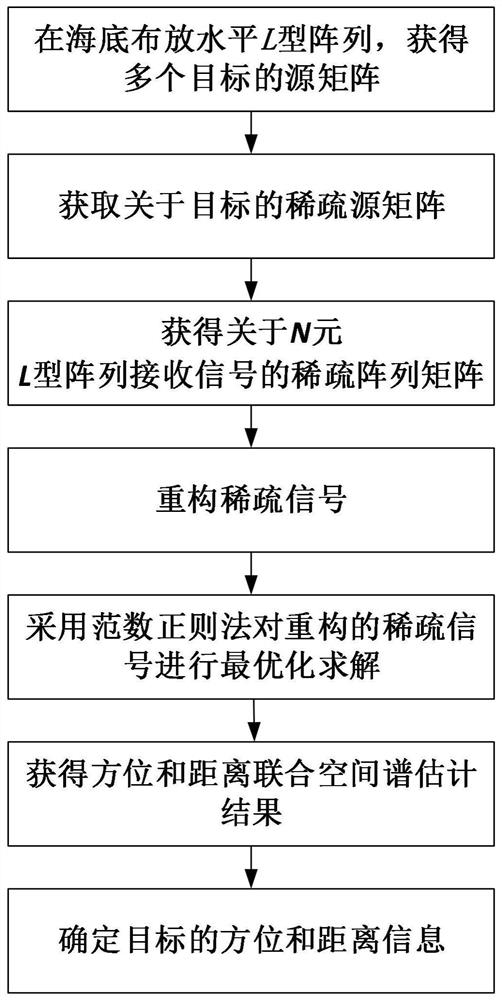
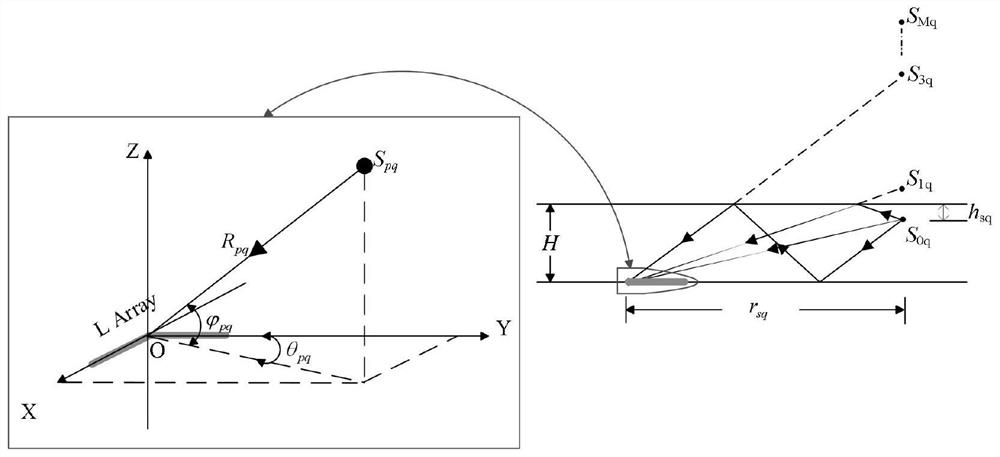
ActiveCN111679248AEfficient use ofPreserve resolutionPosition fixationMultipath interferenceThinned array
The invention relates to a target orientation and distance combined sparse reconstruction positioning method based on a seabed horizontal L-shaped array. The method comprises the following steps: laying a horizontal L-shaped array at the seabed, receiving sound signals emitted by multiple targets near the sea surface, and obtaining a source matrix of the multiple targets; in the azimuth and distance two-dimensional plane of the target, obtaining a sparse source matrix about the target; obtaining a sparse array matrix about N-element L-shaped array receiving signals; reconstructing a sparse signal by using the obtained sparse array matrix and the normalized sparse source matrix; adopting a norm regularization method to carry out optimal solution on the reconstructed sparse signals; and determining the orientation and distance information of the target according to the spectral peak position and intensity of the spatial spectrum, and judging the relative size of the target power. According to the method, the influence of multipath interference on the target azimuth-distance joint estimation precision can be effectively stripped and reduced, the target positioning result without spatial ambiguity is obtained, and the position information and the relative intensity of multiple targets can be accurately obtained at the same time.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG INST OF TECH
Motion linear sparse array optimization method based on underdetermined signal source Cramer-Rao bound
InactiveCN111812580AImprove estimation performanceDirection findersComplex mathematical operationsThinned arrayGenetics algorithms
The invention discloses a design method of an optimal motion linear sparse array under an underdetermined signal source, and solves the problem of obtaining a motion sparse array with the minimum CRB(Cramer-Rao bound) under the underdetermined signal source, wherein the motion sparse array meets the requirements of aperture and array element number. The method comprises the following implementation steps: obtaining a differential array Dc of a motion linear sparse array and an array flow pattern matrix Ac of the differential array Dc; calculating CRB of the motion linear sparse array with respect to direction of arrival estimation; and optimizing the linear sparse array by using an improved genetic algorithm to obtain an optimal array structure Sopt. The invention provides a Cramer-Rao bound expression of a motion linear sparse array relative to direction-of-arrival estimation under an underdetermined signal source. A fancy competition selection method is introduced, and a preferred strategy is adopted in the crossover mutation process so that local convergence is avoided. The CRB of the obtained optimal array relative to direction-of-arrival estimation is smaller, and DOA estimation performance is improved. The optimal array structure can be easily adjusted when the signal environment changes. The method is used for high-precision DOA estimation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com