Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
194 results about "Thermal aware" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
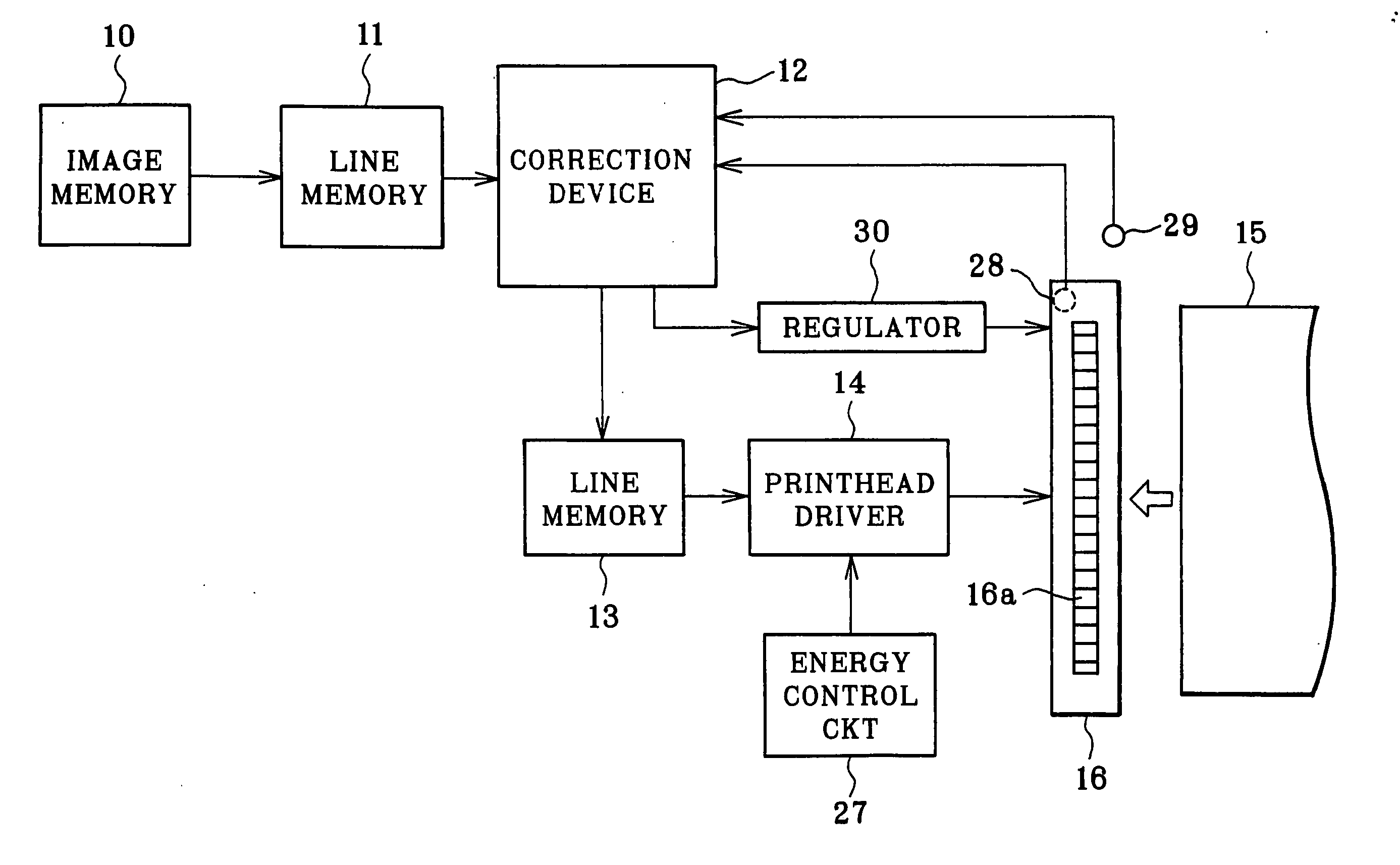
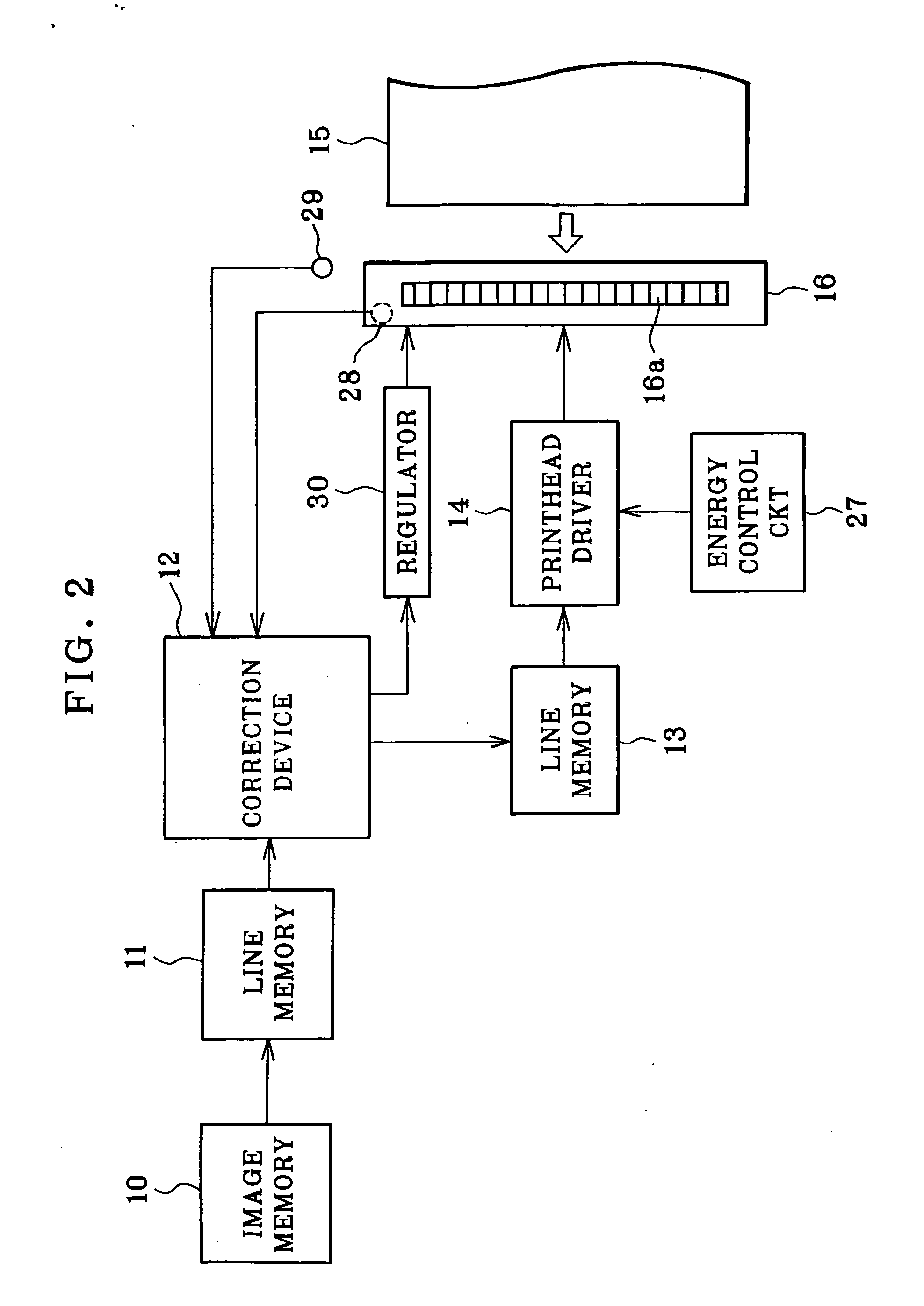
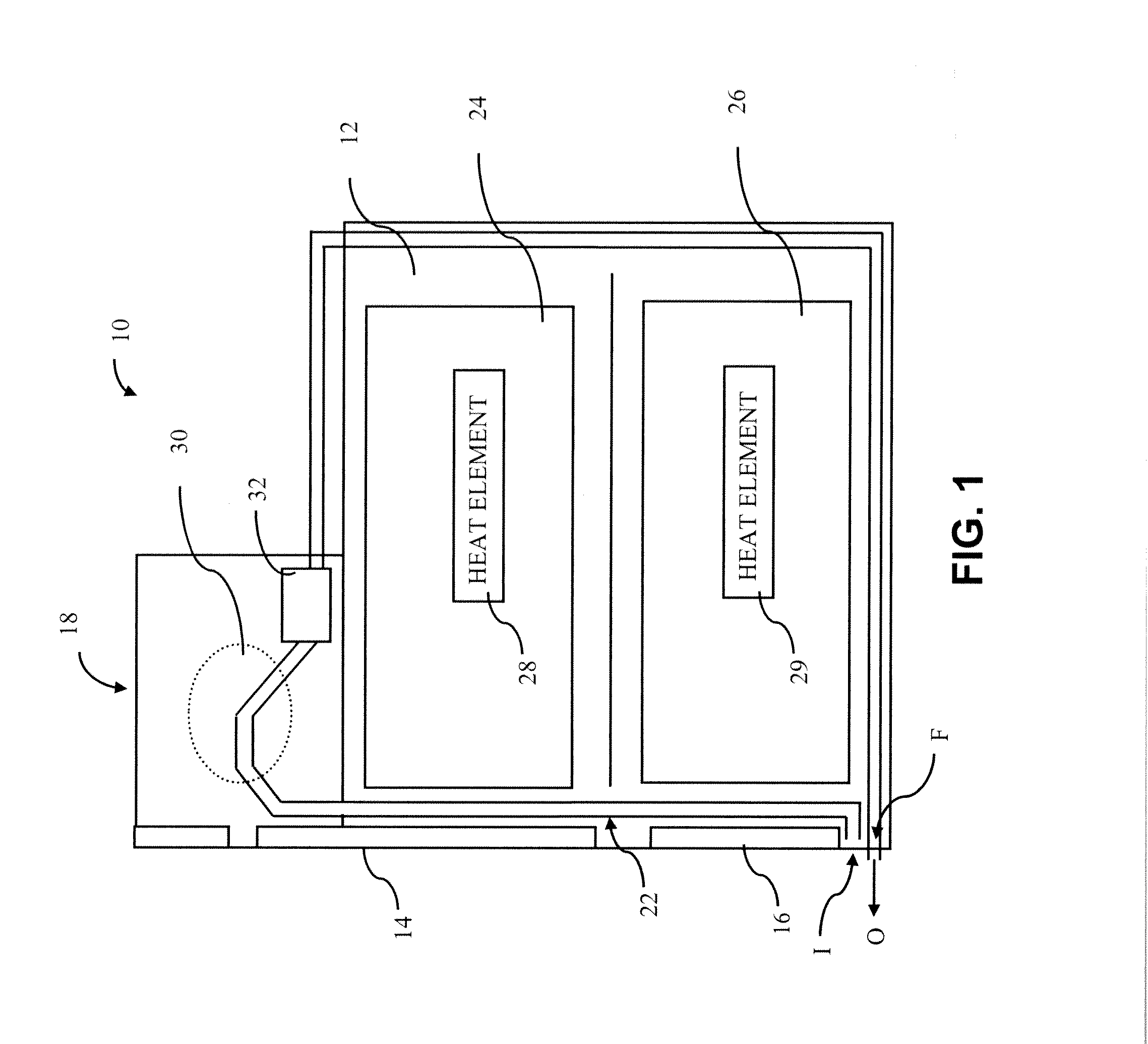
Heater control device and method to save energy
InactiveUS6293471B1Fuel supply regulationTemperature control using digital meansWater basedAutomatic control
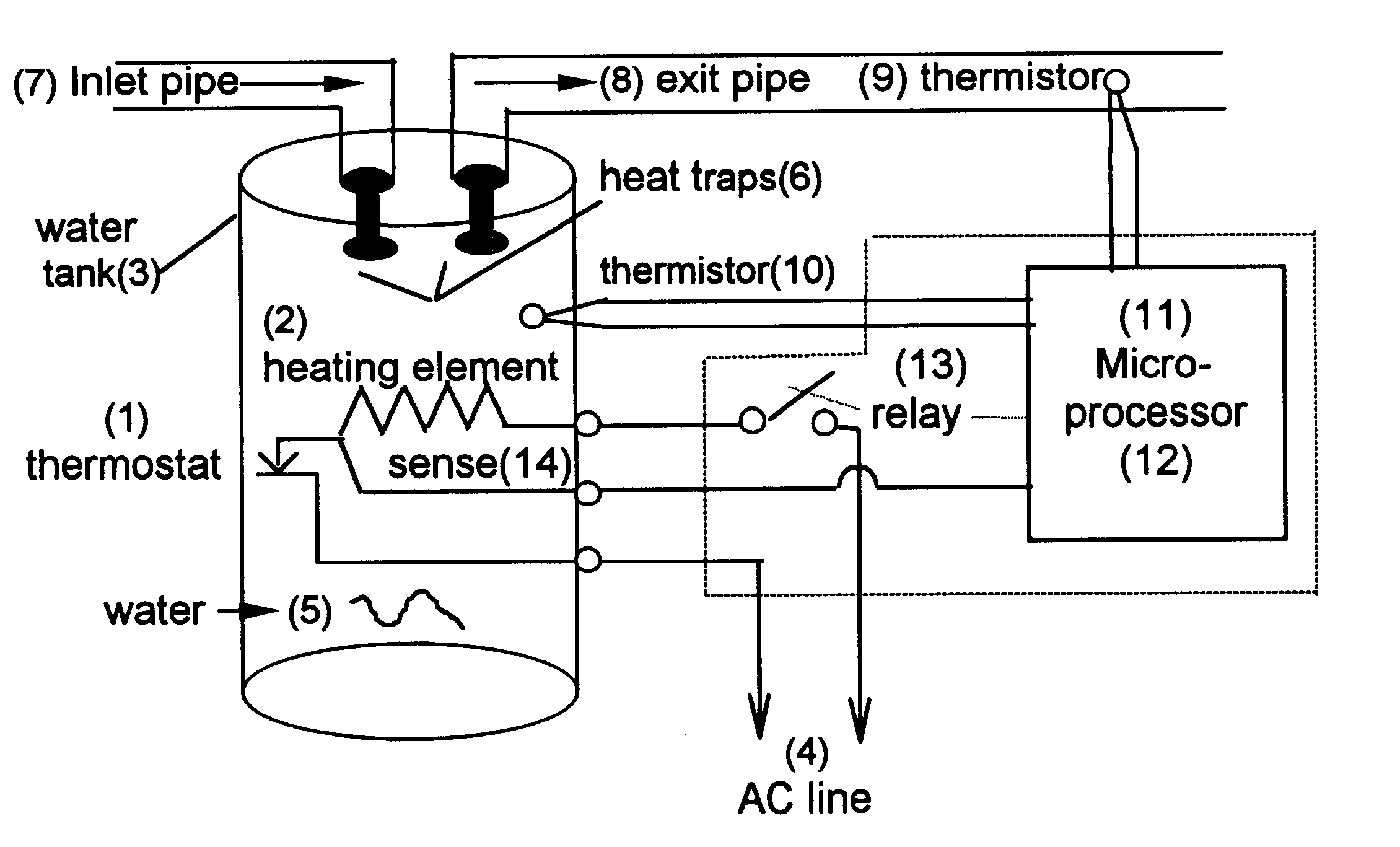
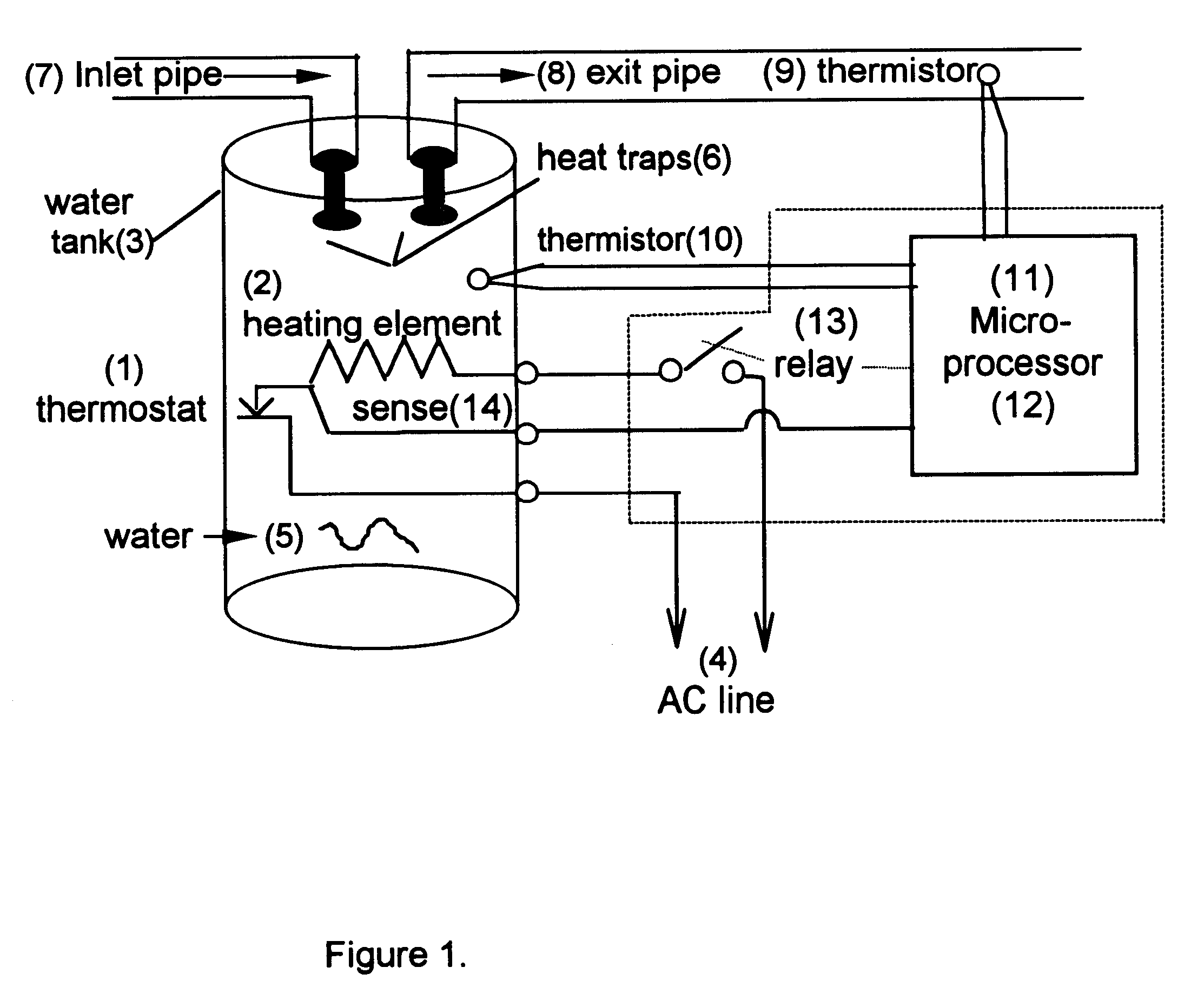
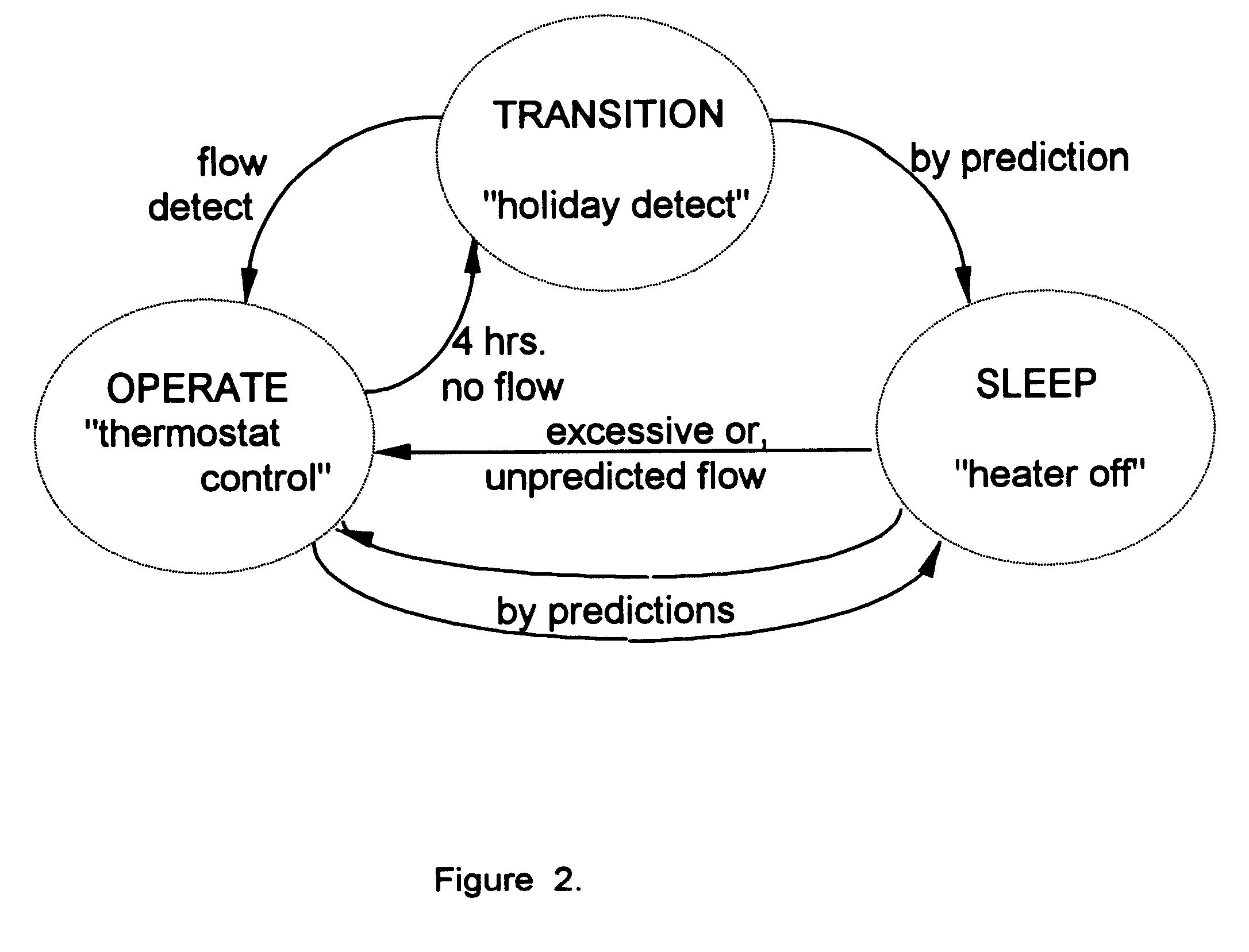
A device and method is provided for automatically controlling the heating element(s) of an electric hot water heater to minimize electric energy consumption over a prolonged time period by projecting the future need for hot water based on it's use in prior time periods as well as by monitoring the use of hot water during current periods. The device saves energy by switching the heater "off" during times when the projected and current need for hot water is low or nonexistent thereby reducing the tank temperature and therefore energy losses to the ambient, while detecting the instantaneous requirement for hot water through utilization of a flow sensor arrangement, one of which is the utilization of thermistors on the exit pipe and on the tank or body of the heater. The device leaves all existing controls intact and may be adapted by end users to existing heaters or by manufacturers of original equipment (OEMs).
Owner:STETTIN DANIEL R +1
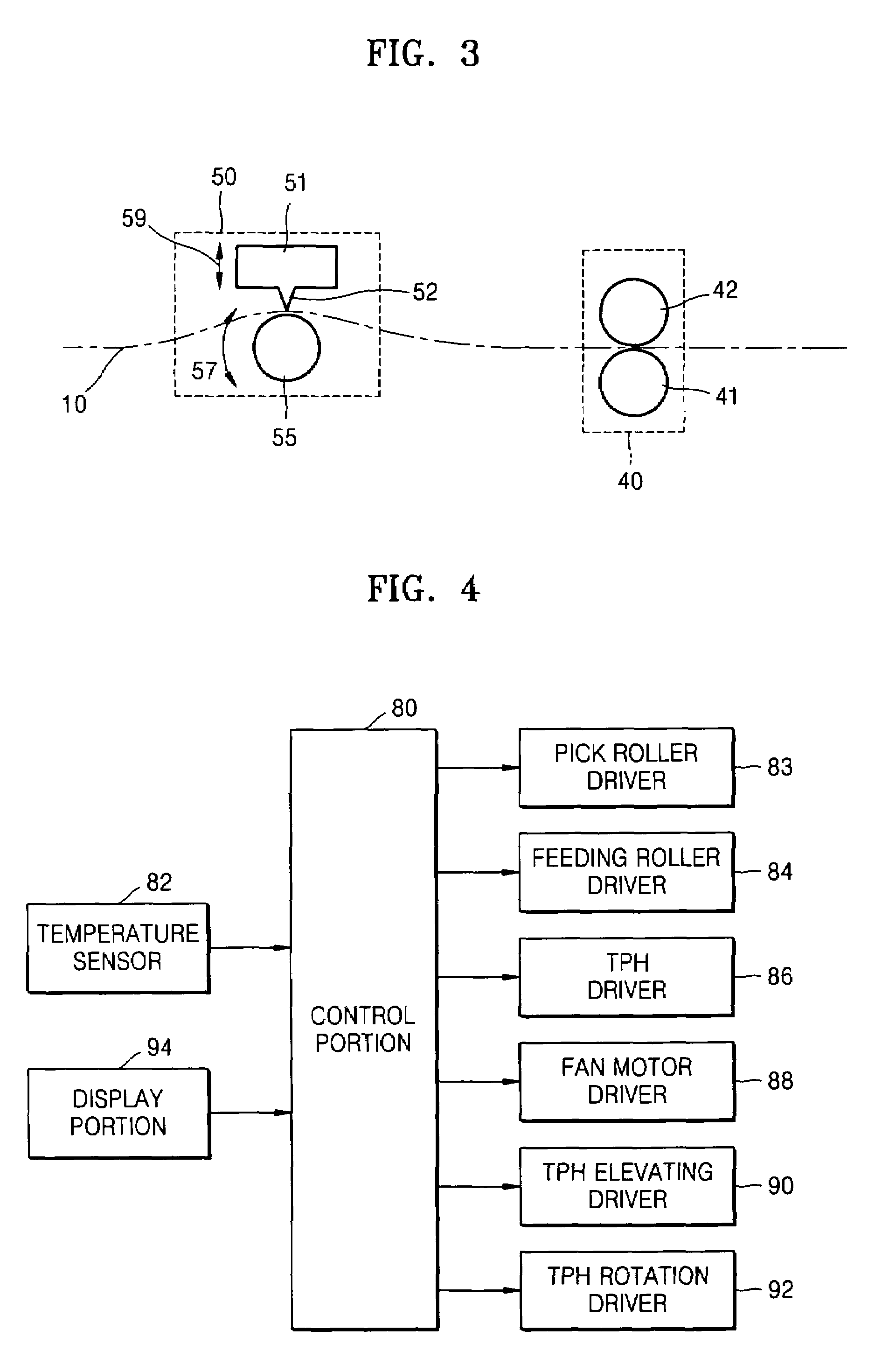
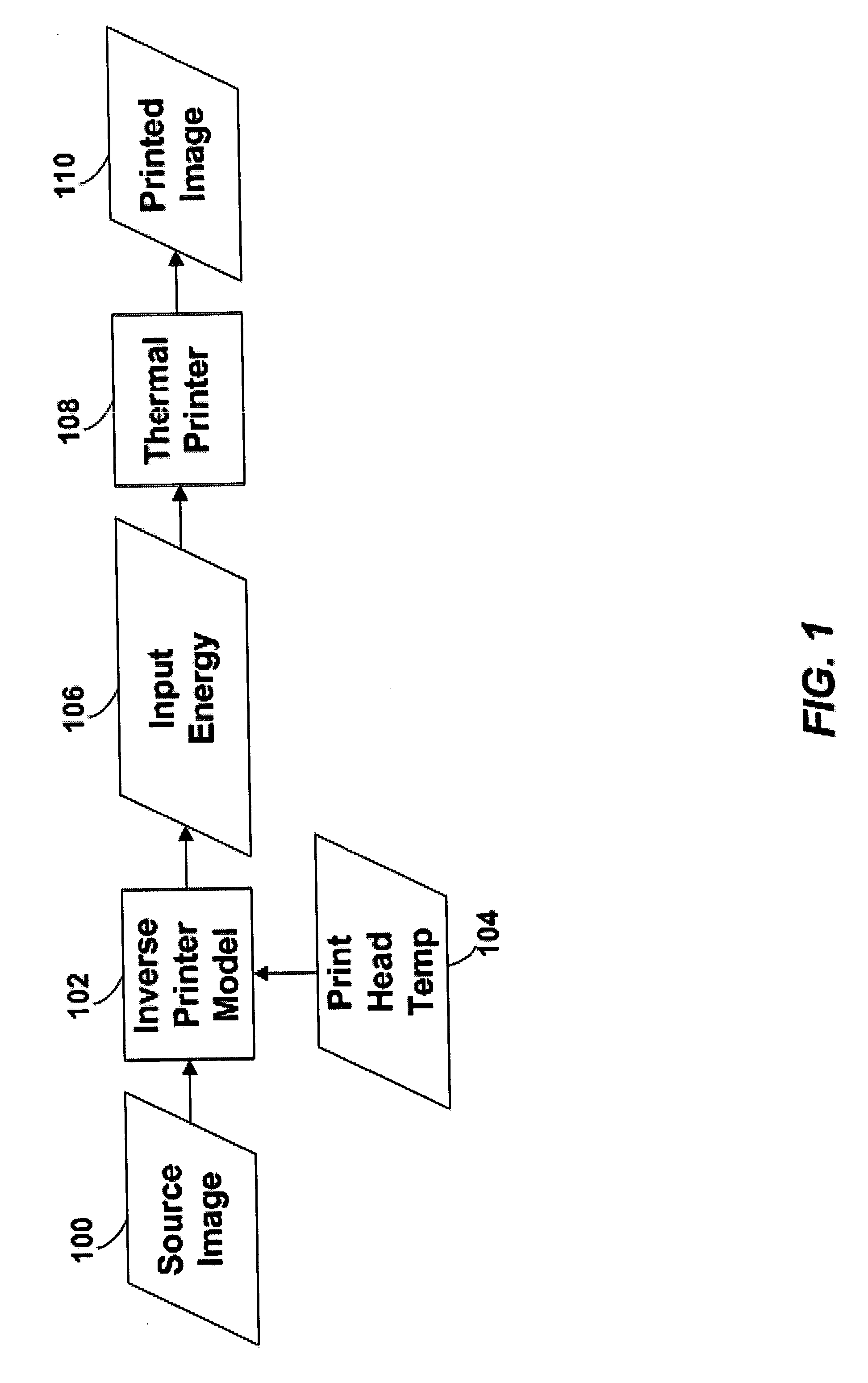
Thermal response correction system
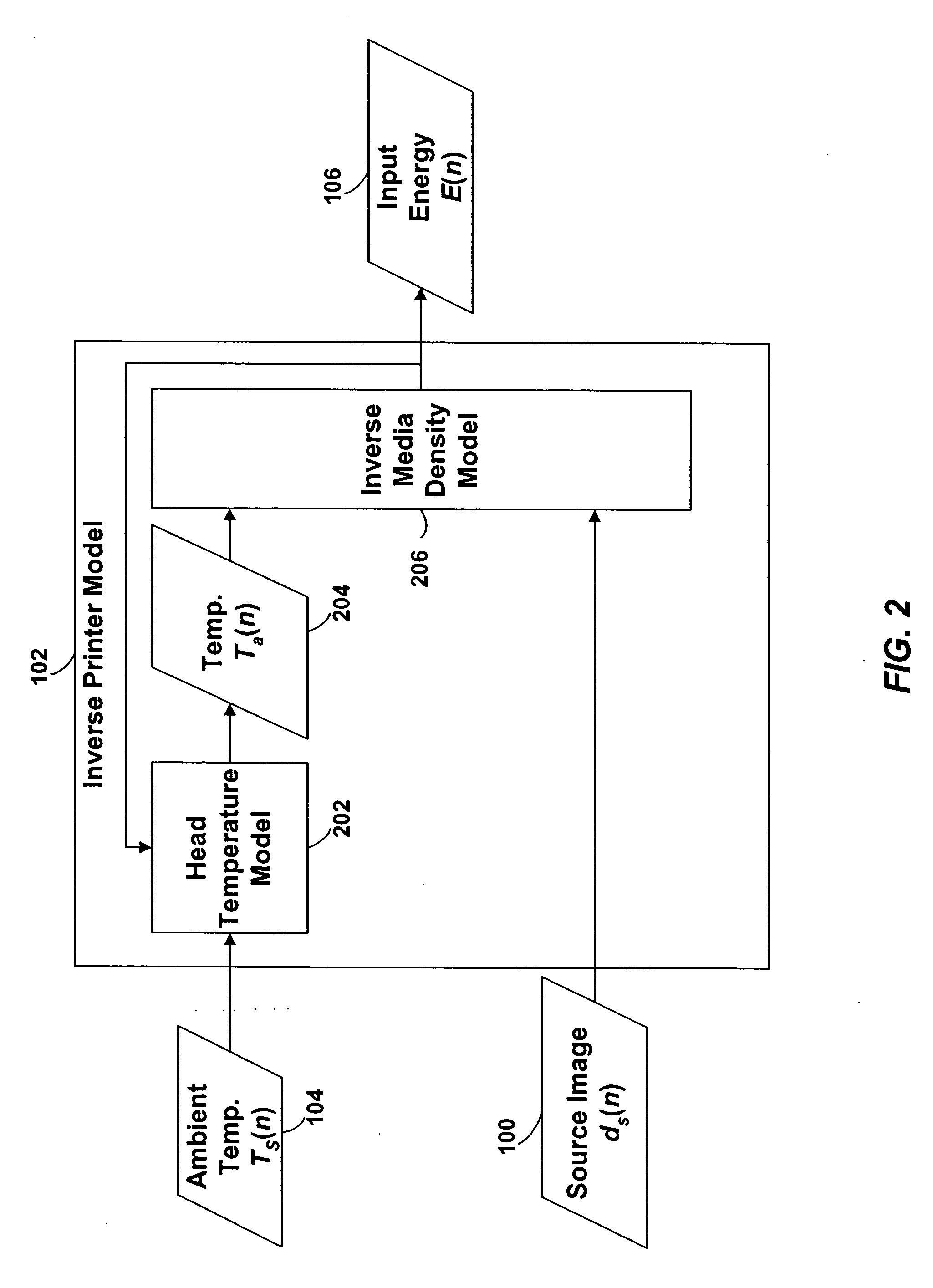
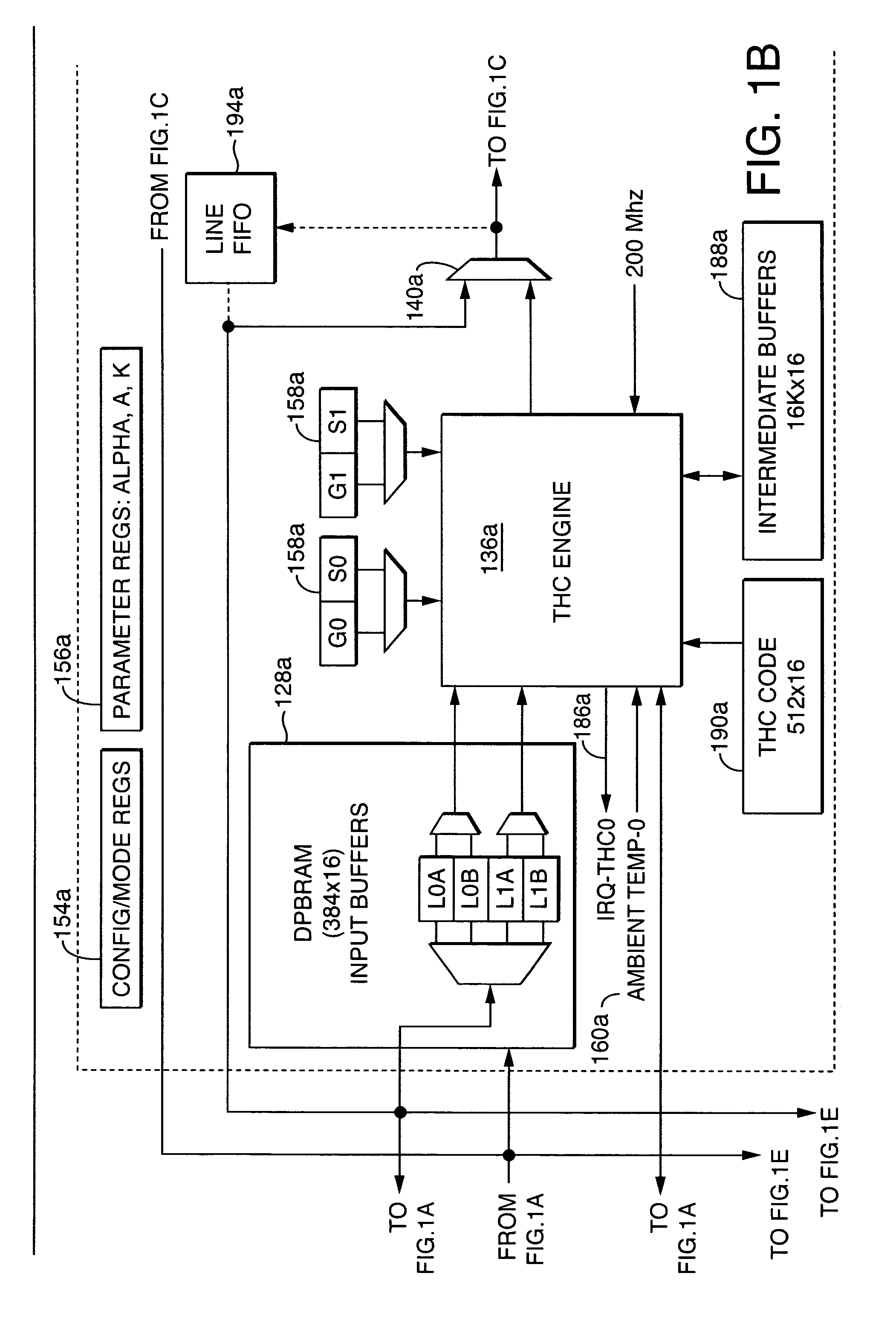
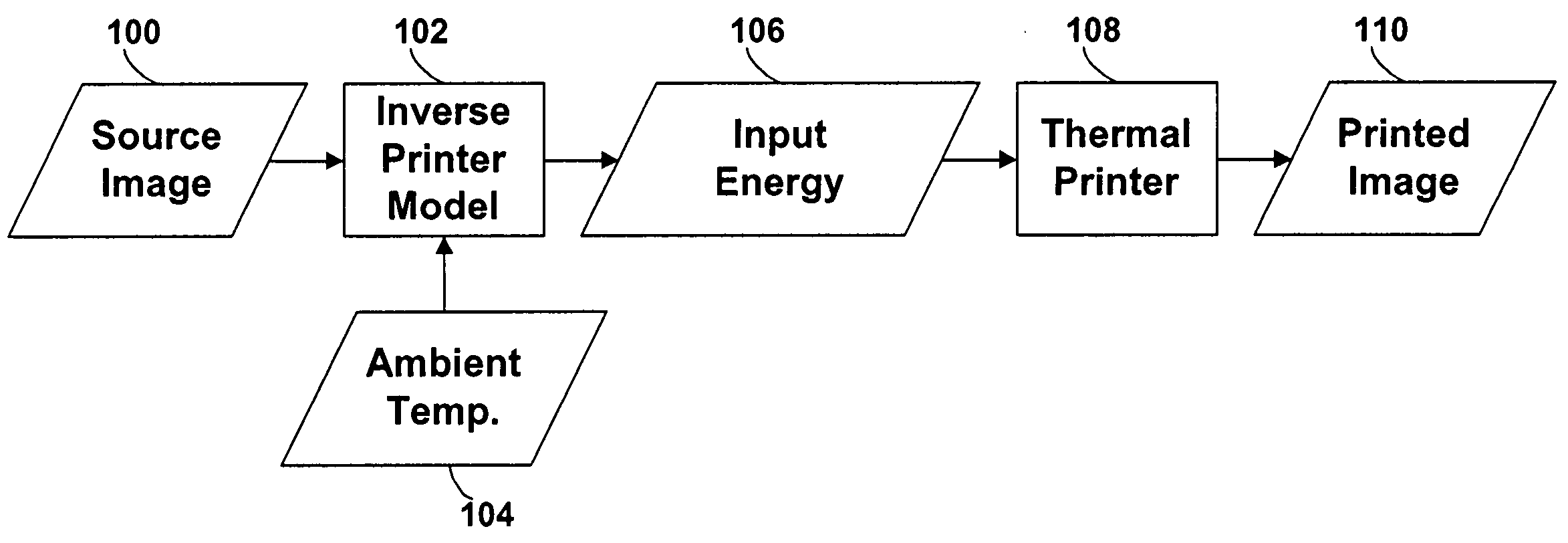
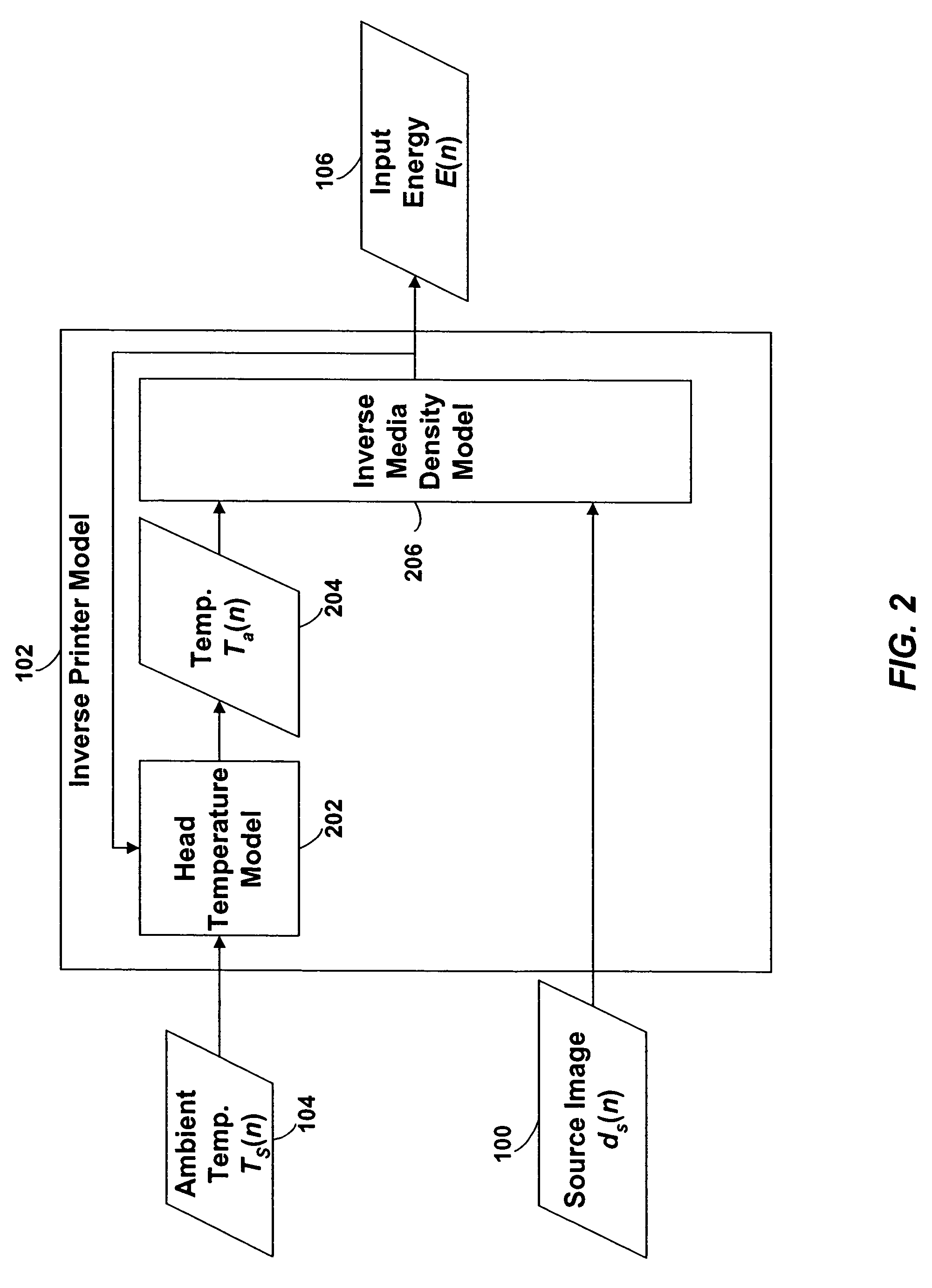
Techniques are disclosed for performing thermal history control in a thermal printer in which a single thermal print head prints sequentially on multiple color-forming layers in a single pass. Each pixel-printing interval may be divided into subintervals, which may be of unequal duration. Each sub-interval may be used to print a different color. The manner in which the input energy to be provided to each print head element is selected may be varied for each of the subintervals. For example, although a single thermal model may be used to predict the temperature of the print head elements in each of the subintervals, different parameters may be used in the different subintervals. Similarly, different energy computation functions may be used to compute the energy to be provided to the print head in each of the subintervals based on the predicted print head temperature.
Owner:TPP TECH LLC
Thermal printer and thermal printing method
The present invention relates to a thermal printer. The thermal printer comprises a stepping motor, a thermal element, a roller driven by the stepping motor to drive thermo-sensitive papers to paper skip and a control module. The control module comprises: a PWM timing controller configured to generate PWM signals to control the rotation of the stepping motor; a serial bus controller configured to control the serial bus to transmit the printing data to the thermal element through the serial bus; a first timing controller configured to generate interruption to start the serial bus to transmit the printing data; and a second timing controller configured to control the heating time of the thermal element. The present invention further relates to a thermal printing method. A PWM timing controller, a first timing controller and a second timing controller are configured to control the printing process, and a thermal printing mode with adjustable printing speed and printing concentration is realized through comparing the counter values of the first timing controller and the second timing controller with the relation of the printing speed and the printing concentration.
Owner:SHENZHEN COMEN MEDICAL INSTR
Method and apparatus for controlling in thermal printer
InactiveUS7379082B2Increase temperatureOther printing apparatusThermal awareElectrical and Electronics engineering
A system and method is provided for controlling printing in a thermal printer which includes measuring a temperature of a thermal printhead (TPH), heating the TPH by applying a TPH driving strobe pulse when the temperature of the TPH is lower than a first set temperature, and printing on a thermal reactive paper when the temperature of the TPH is equal to or greater than the first set temperature.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
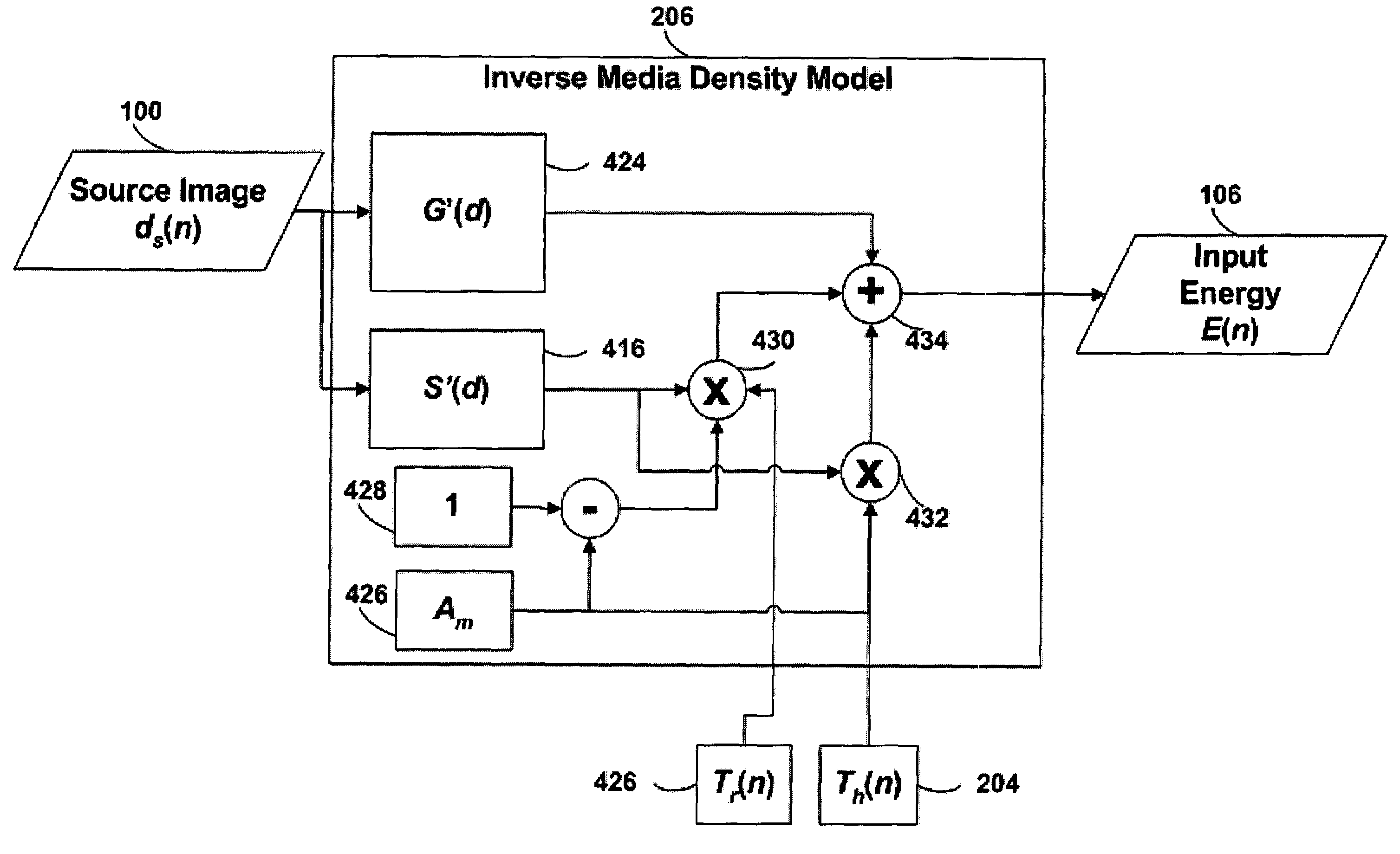
Thermal response correction system
A model of a thermal print head is provided that models the thermal response of thermal print head elements to the provision of energy to the print head elements over time. The amount of energy to provide to each of the print head elements during a print head cycle to produce a spot having the desired density is calculated based on: (1) the desired density to be produced by the print head element during the print head cycle, (2) the predicted temperature of the print head element at the beginning of the print head cycle, (3) the ambient printer temperature at the beginning of the print head cycle, and (4) the ambient relative humidity.
Owner:TPP TECH LLC
System and method for thermal transfer print head profiling
InactiveUS7372475B2Improve output qualityDisclose useRecording apparatusPrintingThermal contactThermal aware
A thermal transfer print head is disclosed. The print head includes a housing configured and dimensioned to be installable within the printer, a plurality of resistive heating elements positioned on an external surface of the housing and in thermal contact with a printable media, the resistive heating elements receive electrical energy from the printer and have adjustable thermal output, and a print head memory positioned within the housing and accessible by the thermal printer, the print head memory including a first and second memory regions, the first memory region configured to store a printing profile pertaining to operating parameters of the resistive heating elements and the second memory configured to store usage data pertaining to operation of the print head.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
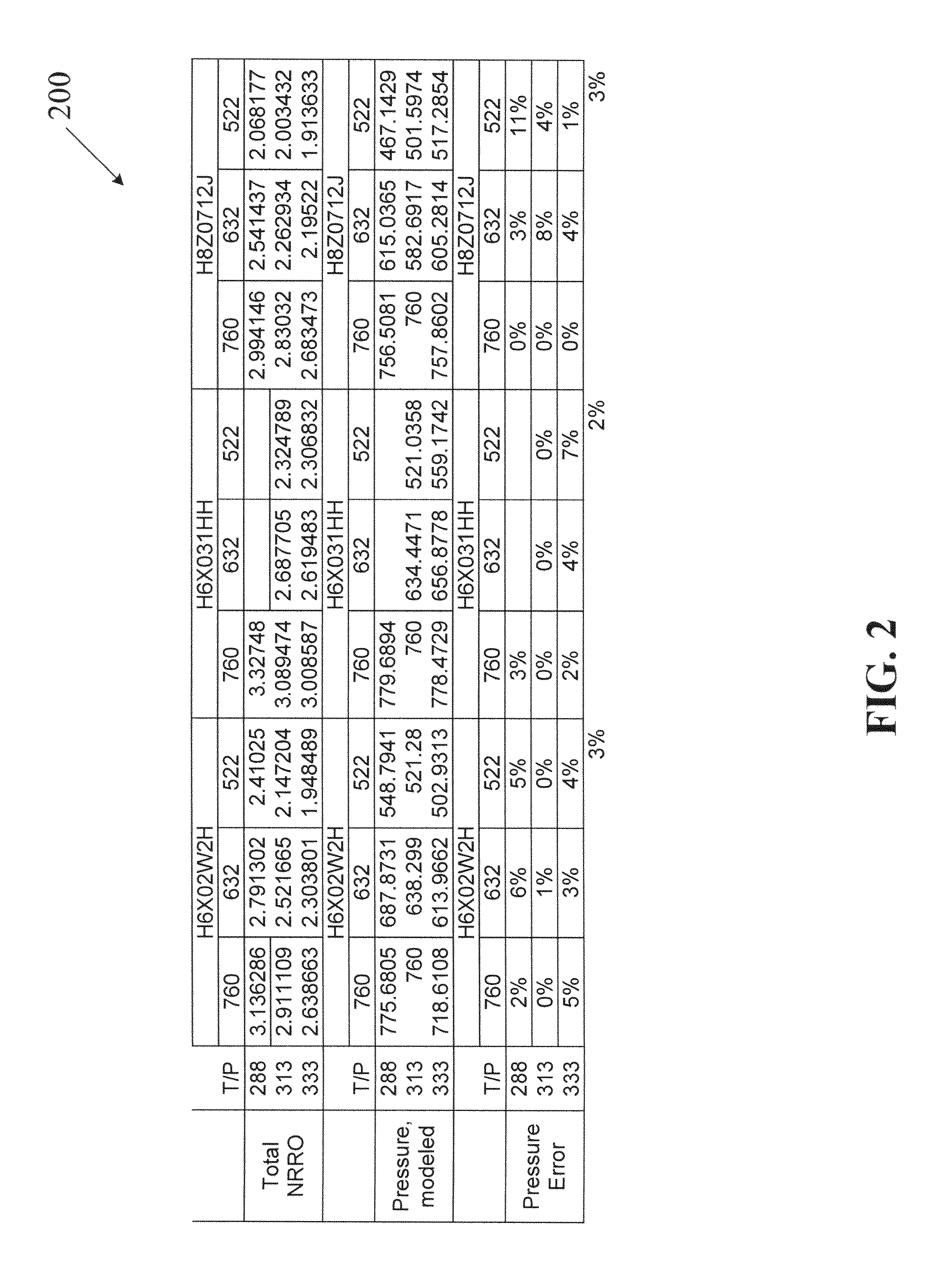
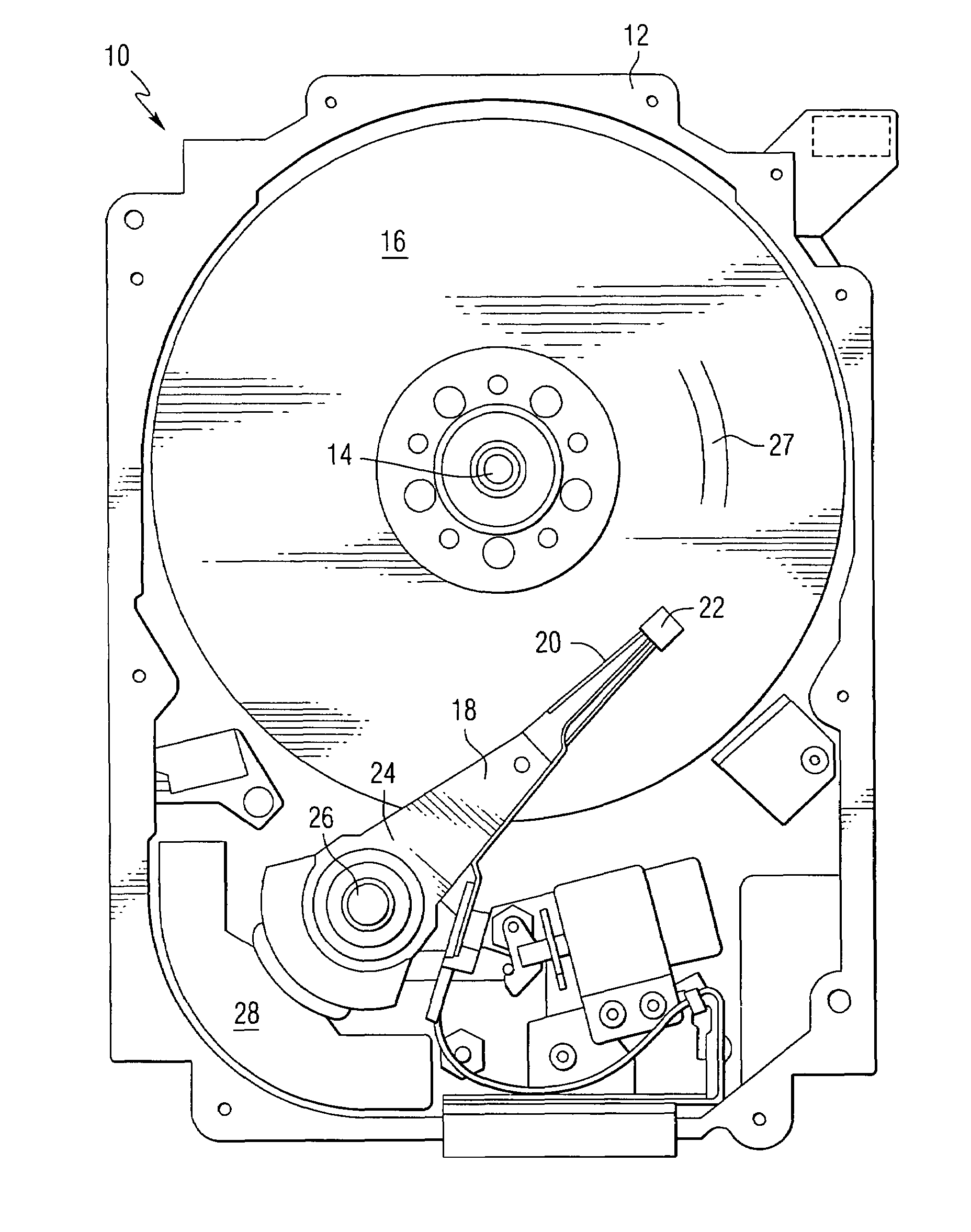
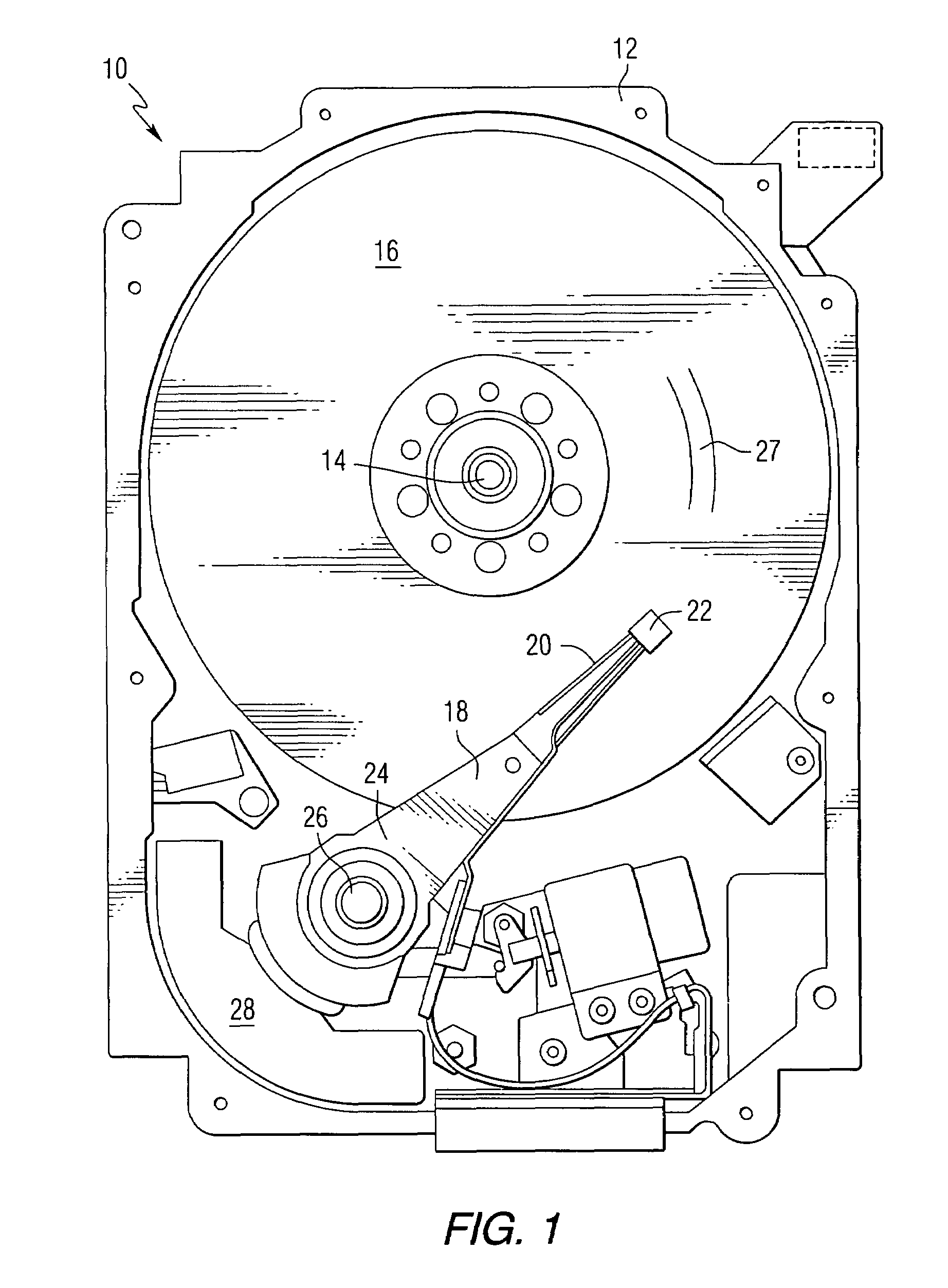
Fly height compensation using temperature and non-repeatable runouts
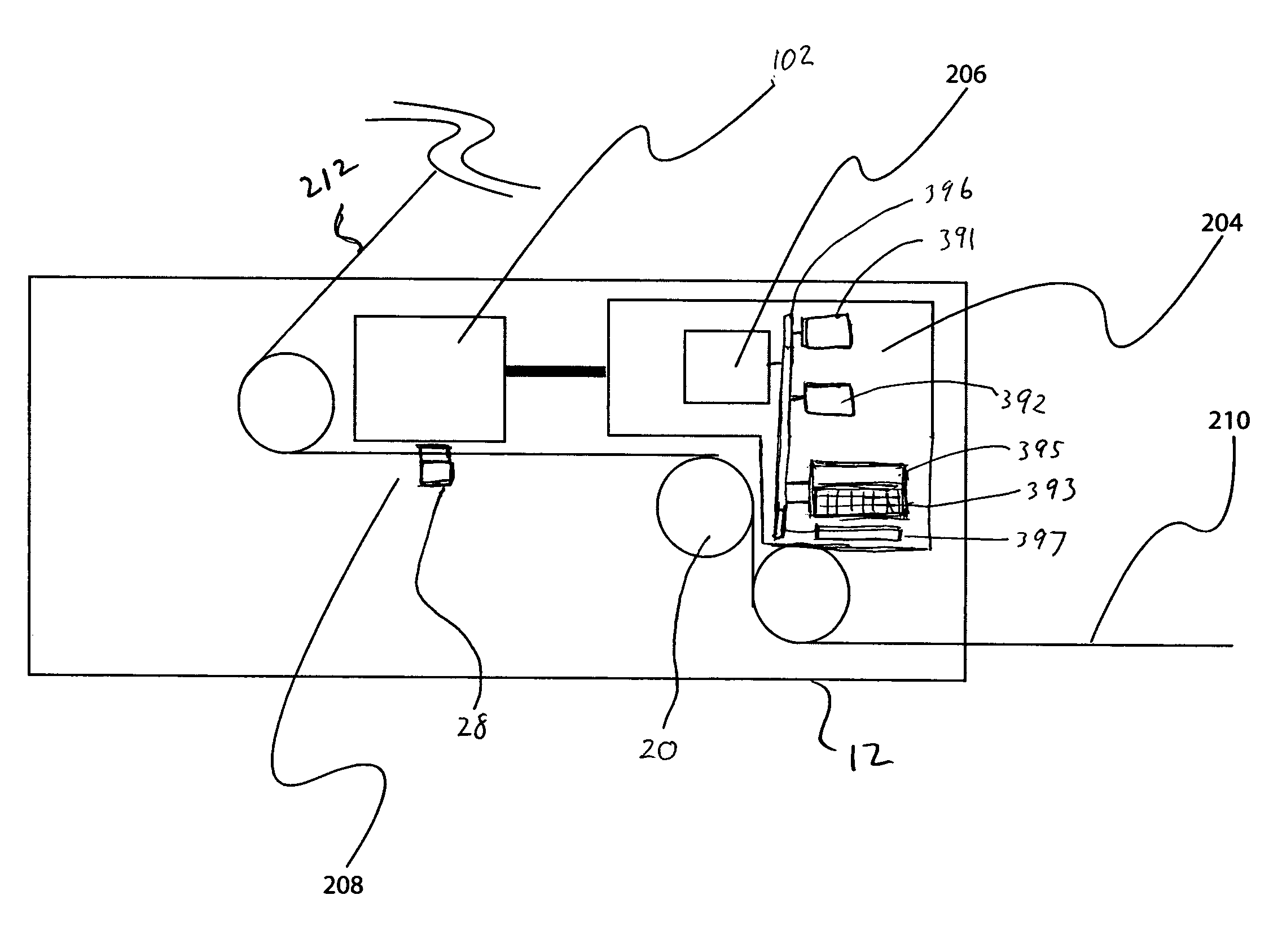
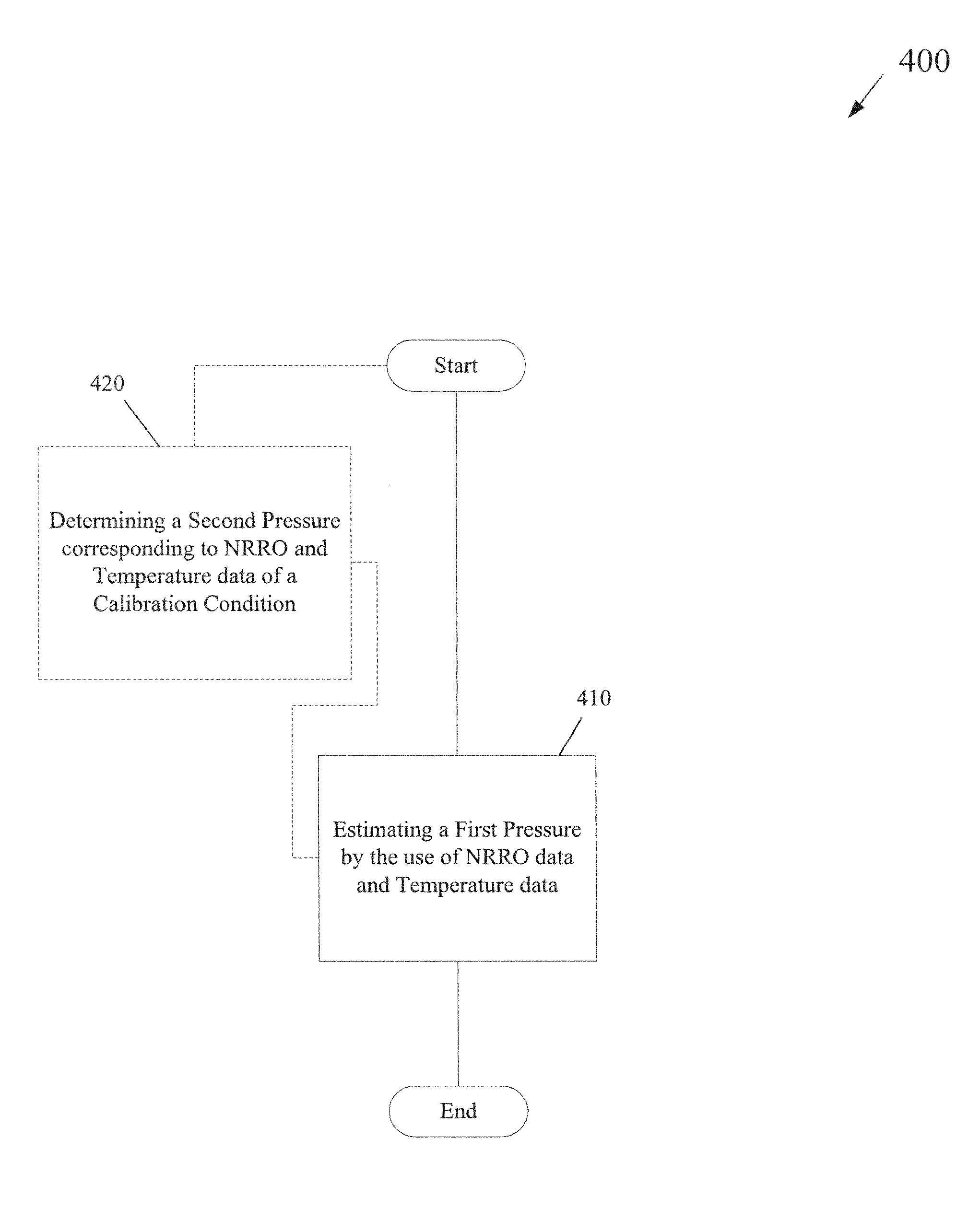
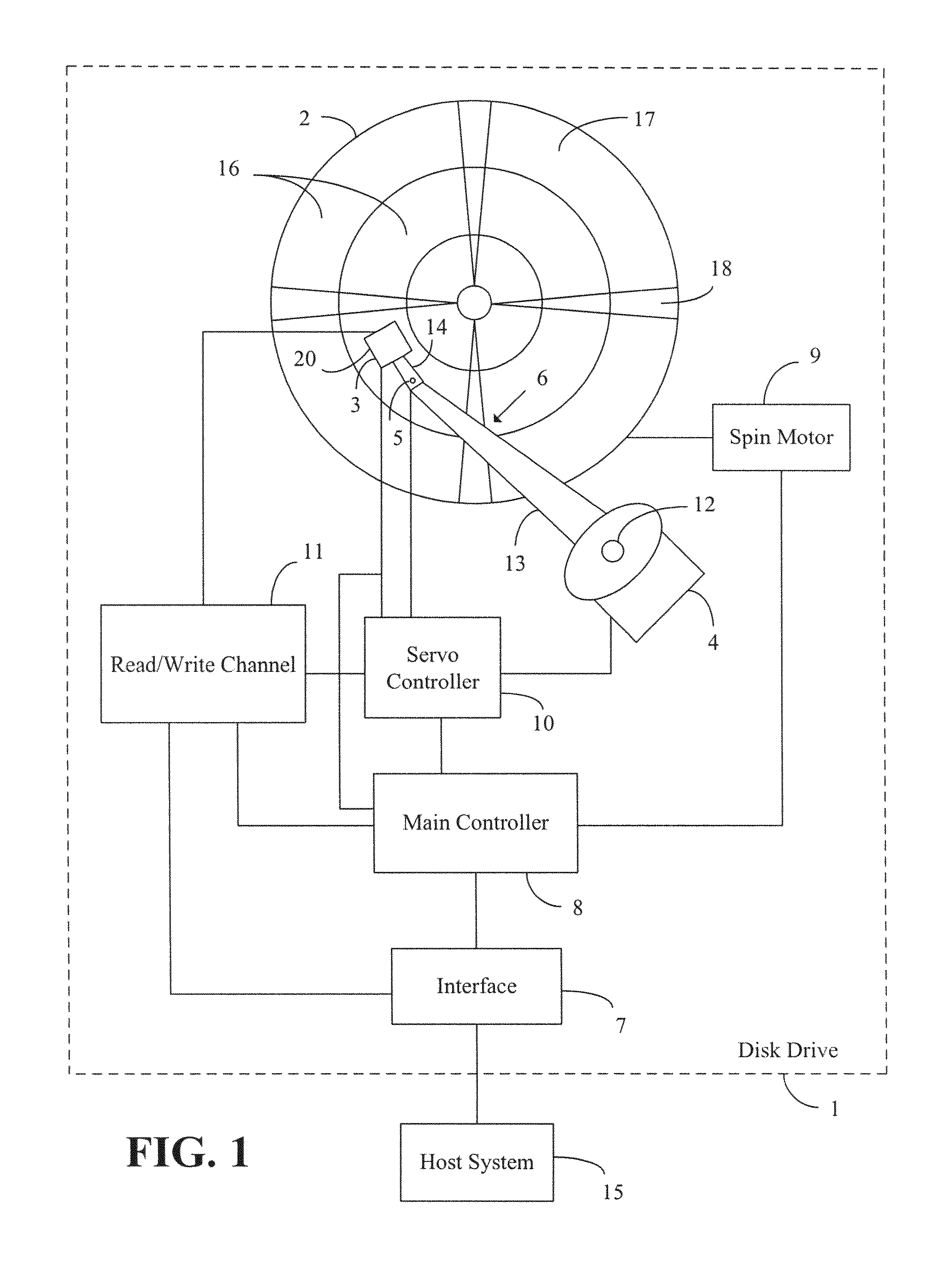
InactiveUS7511914B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageData controlFlying height
A controller is provided having a circuit that uses non-repeatable run-out data and temperature data to provide a compensation for a fly height of a head. A disk drive may also be provided having a head for reading data from a disk, a thermistor, and a controller for controlling a fly height of the head based on temperature data obtained from the thermistor to refine a pressure determination. A method can include estimating a first pressure by the use of non-repeatable run-out data and temperature data corresponding to a disk drive.
Owner:MAXTOR
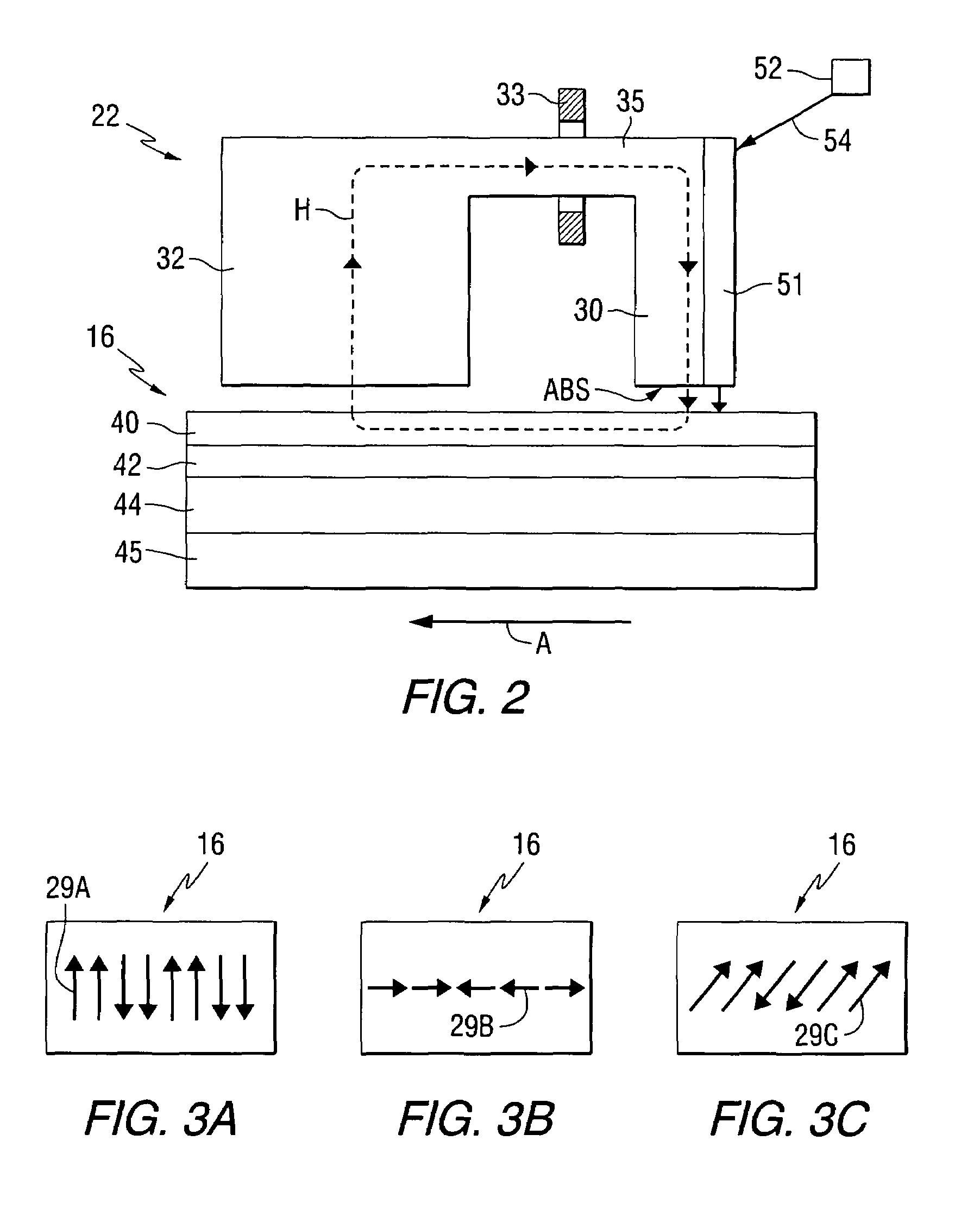
Thin film structure with controlled lateral thermal spreading in the thin film
An apparatus includes a magnetic layer, a heat sink layer, and a thermal resistor layer between the magnetic layer and the heat sink layer. The apparatus may be configured as a thin film structure arranged for data storage. The apparatus may also include an interlayer positioned between the magnetic layer and the thermal resistor layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Cascade long-period pohotonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor
InactiveCN102980685AHigh measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityCladded optical fibreThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingThermal aware
The invention relates to a cascade long-period pohotonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor. A photonic crystal fiber is provided with a cladding consisting of periodically arrayed air holes; the cladding and a fiber core of the fiber are made of SiO2; a long-period grating with a certain period is written onto the fiber; the air holes of the cladding are filled with thermosensitive substances sensitive to temperature; the refractive indexes of the thermosensitive substances are less than the refractive index of the fiber core; and the total internal reflection photonic crystal fiber is formed. The effective refractive index of a coupled mode of the grating can be changed by controlling the temperatures of the thermosensitive substances, so that the resonant wavelength of a transmission spectrum of the grating is changed, the temperature variation is shown as spectral shift, and the wavelength-tunable temperature sensor is realized. As the bandwidth of the transmission spectrum of the single long-period grating is greater, the temperature sensitivity and the measurement precision of the transmission spectrum of the long-period grating are limited, and the sensor is transformed into a cascade long-period grating structure. The sensor achieves the tunable wavelength, the sensitivity is improved, and the sensor has a very large application prospect in the transduction field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
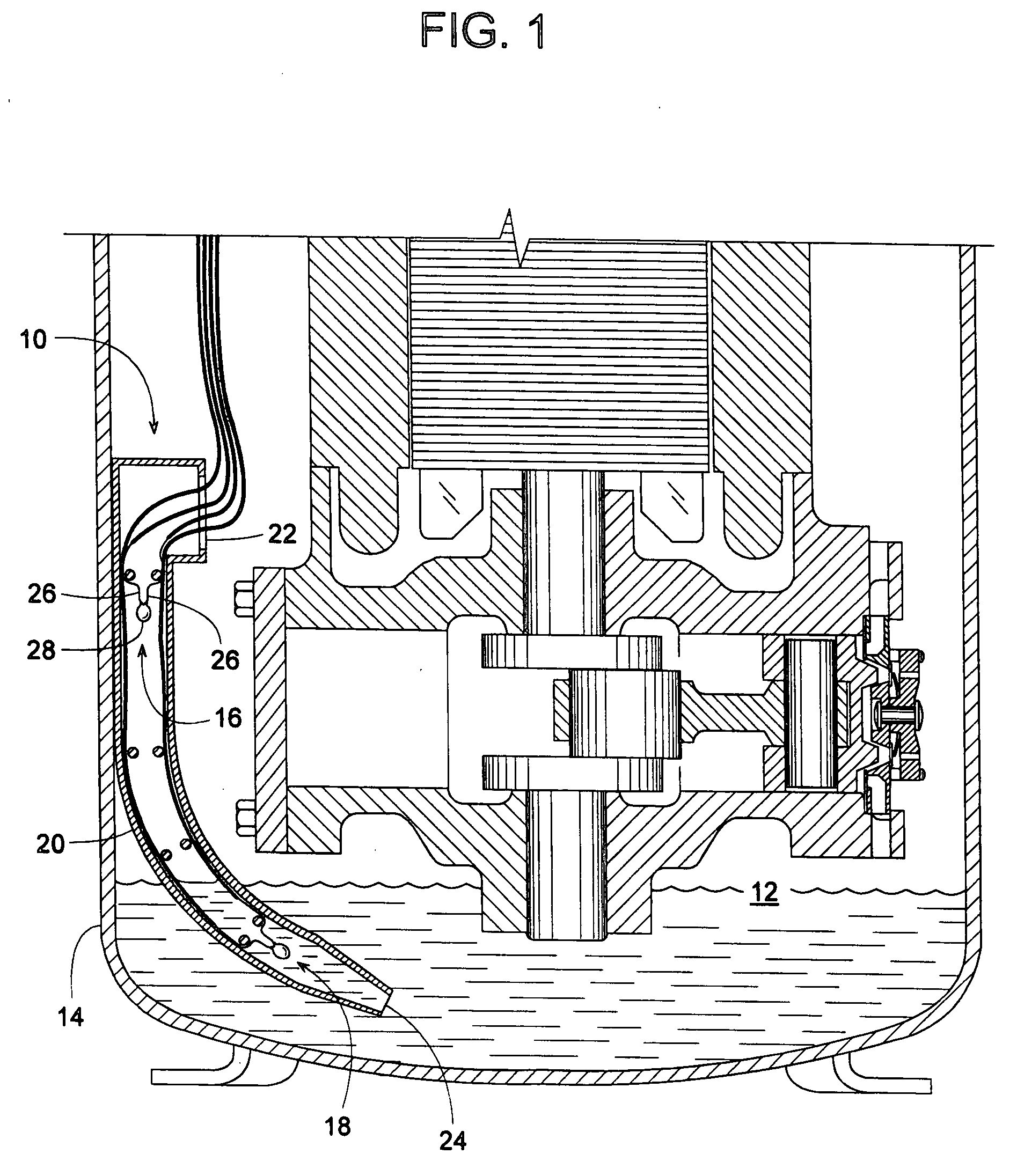
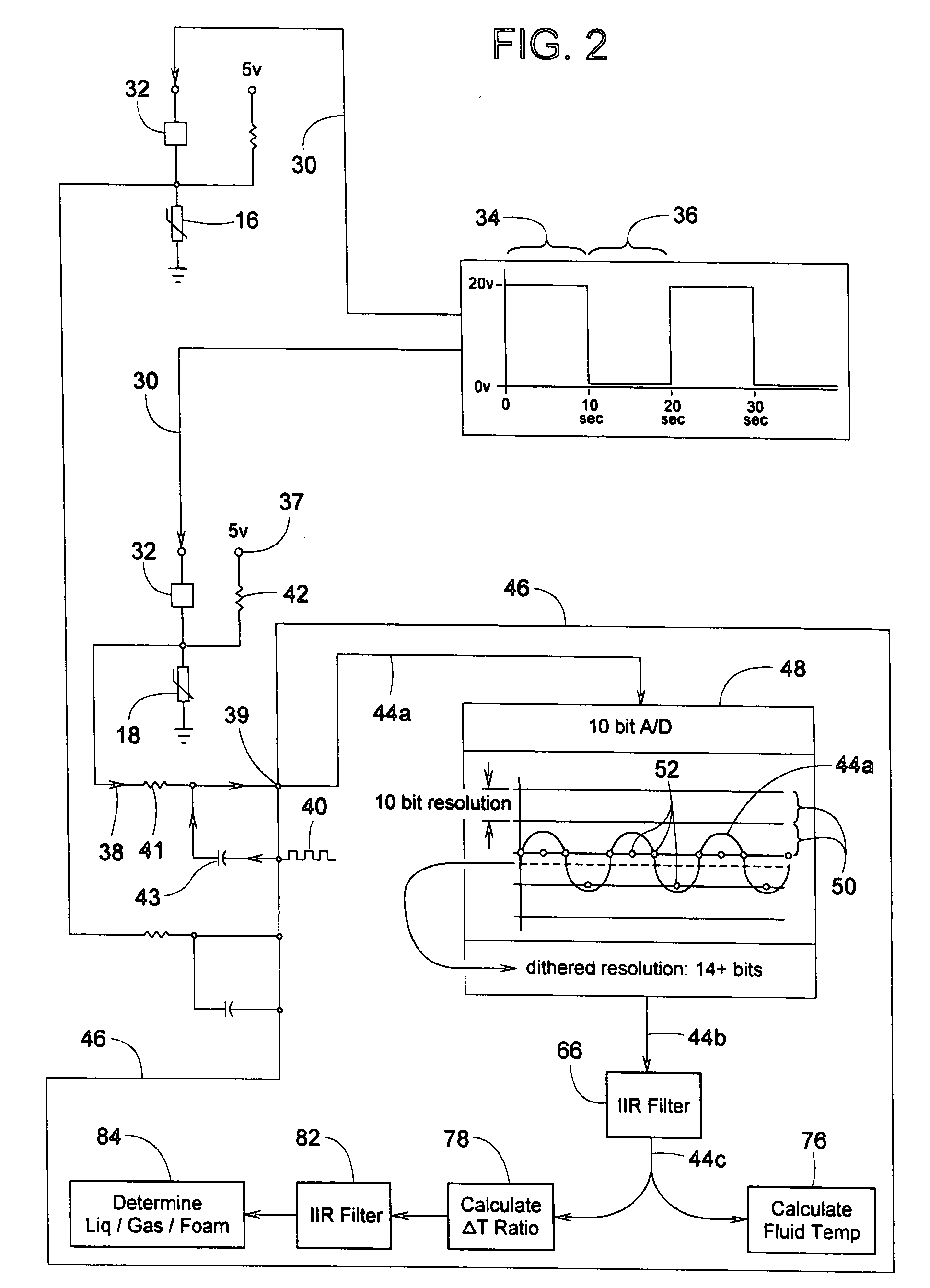
Method for sensing the liquid level in a compressor
ActiveUS20080250798A1Correction factorQuickly and accurately determineThermometer detailsTesting/calibration apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Two vertically offset thermistors for sensing a fluid such as oil and refrigerant in a compressor shell are monitored by a method that takes into account rapidly changing conditions within the shell. The system can determine the fluid's sump temperature, high / low liquid levels, and can determine whether the thermistors are sensing the fluid as a liquid, gas, or a mixture of the two, such as a foam or mist of liquid and gas. For greater accuracy, thermistor readings can be dithered and filtered to provide temperature or voltage values having more significant digits than the readings originally processed through a limited-bit A / D converter. For faster response, limited microprocessor time is conserved by sampling thermistor readings at strategic periods that enable the microprocessor to identify certain conditions and temperatures via simple delta-temperature ratios and undemanding equations rather than resorting to exponential functions or lookup tables to determine time constants.
Owner:TRANE INT INC
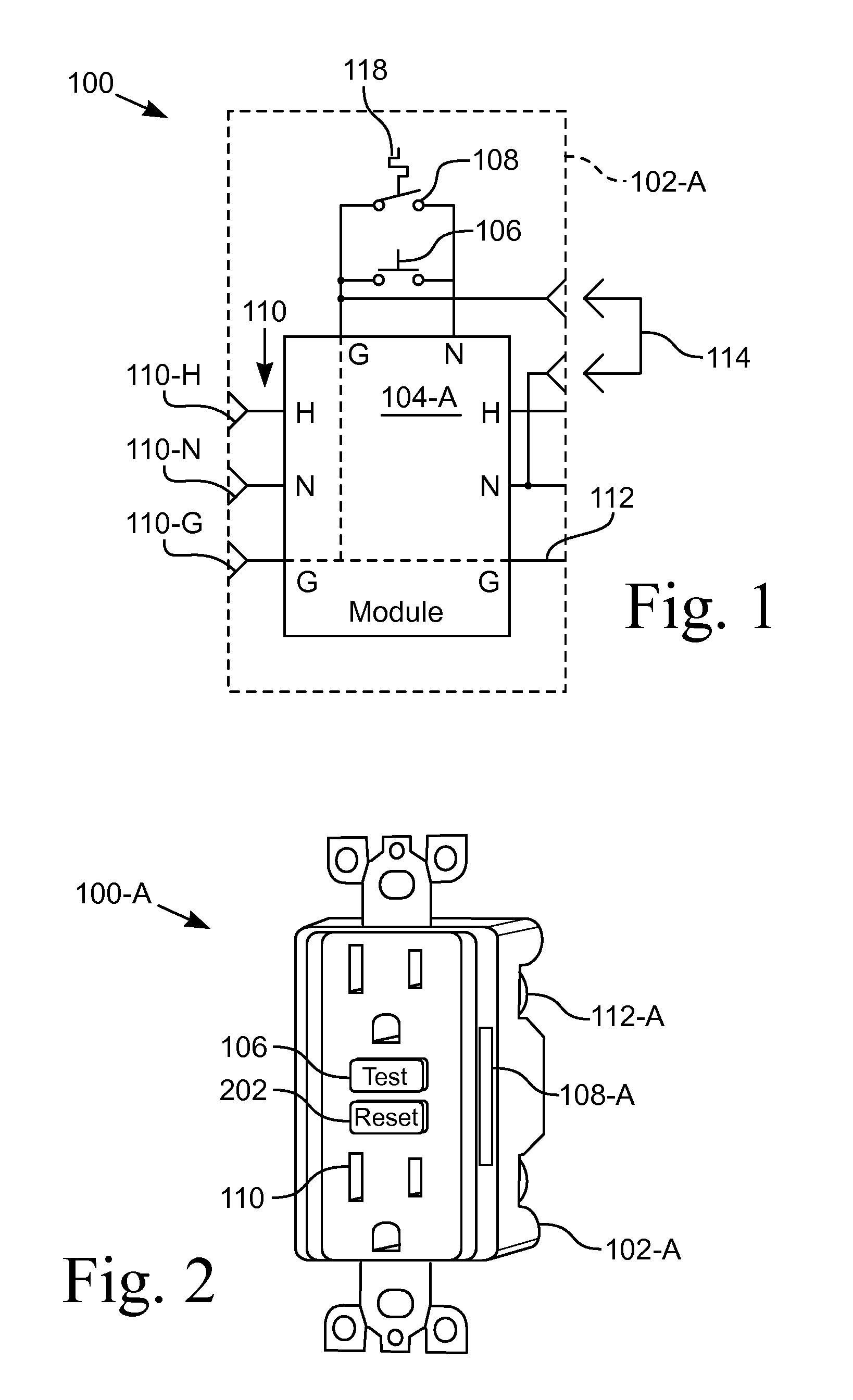
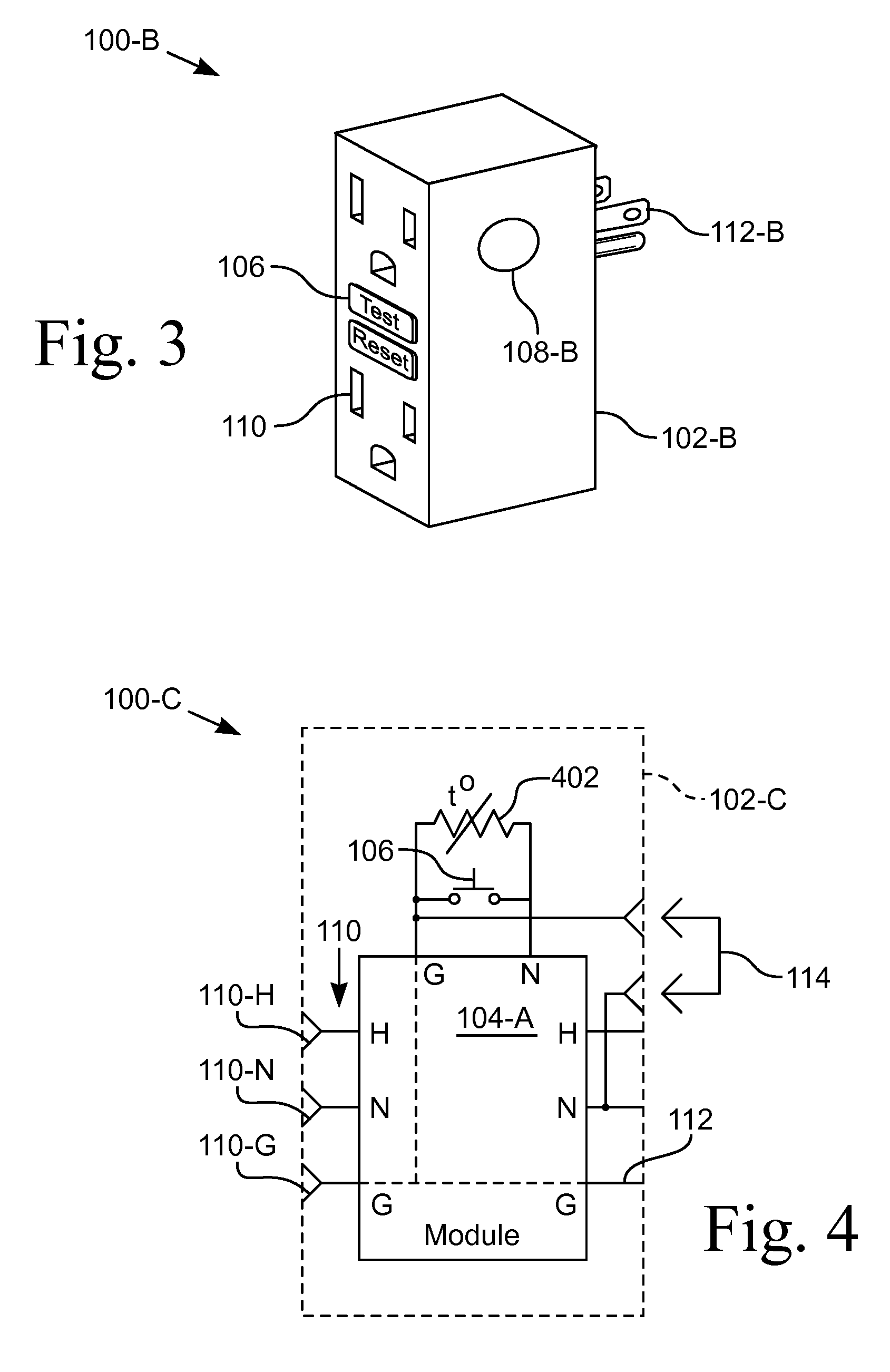
Heat sensor responsive to electrical overloads
ActiveUS20110134575A1Avoid developmentThermometer detailsThermometer applicationsElectric forceElectrical resistance and conductance
Apparatus for detecting an overheating condition at an electrical power device and automatically breaking the circuit when the temperature exceeds a setpoint value. In various configurations the device is a receptacle adapted to be used in a wall mounted box or a receptacle unit that is plugged into an existing receptacle. A temperature sensor is wired parallel to a normally open test switch on a ground fault circuit interrupter or other circuit interrupting device. The temperature switch is responsive to the temperature local to the receptacle, such as is caused by poor connections to or in the receptacle or a near-overload condition. The temperature setpoint is less than the melting temperature of the insulation of the electrical wiring. The temperature sensor is a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient that allows current to flow thereby latching the interrupting device in a tripped position until the device is reset for reuse.
Owner:WARD MICHAEL
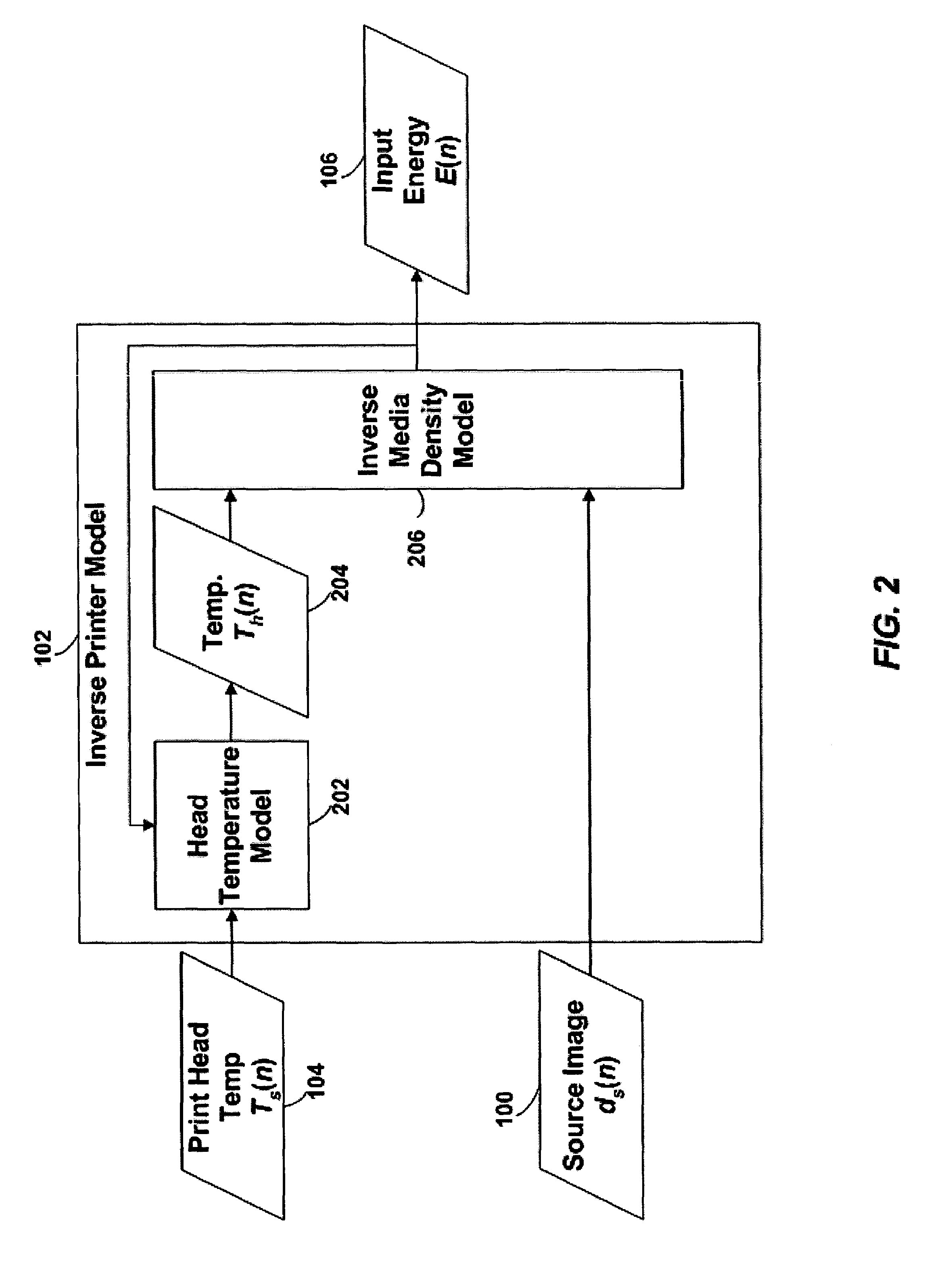
Thermal response correction system
A model of a thermal print head is provided that models the thermal response of thermal print head elements to the provision of energy to the print head elements over time. The thermal print head model generates predictions of the temperature of each of the thermal print head elements at the beginning of each print head cycle based on: (1) the current ambient temperature of the thermal print head, (2) the thermal history of the print head, (3) the energy history of the print head, and (optionally) (4) the current temperature of the print medium. The amount of energy to provide to each of the print head elements during a print head cycle to produce a spot having the desired density is calculated based on: (1) the desired density to be produced by the print head element during the print head cycle, and (2) the predicted temperature of the print head element at the beginning of the print head cycle.
Owner:TPP TECH LLC
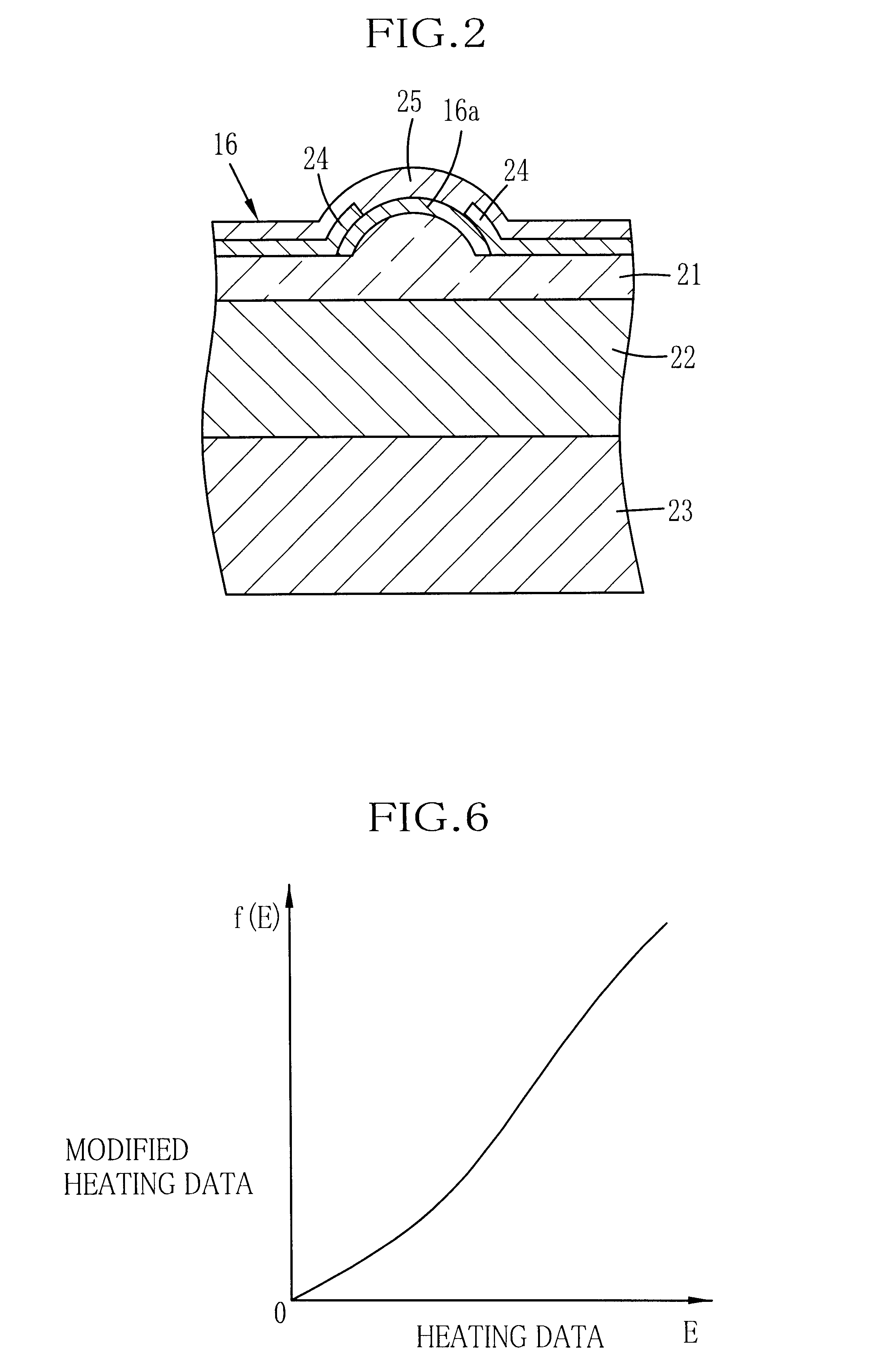
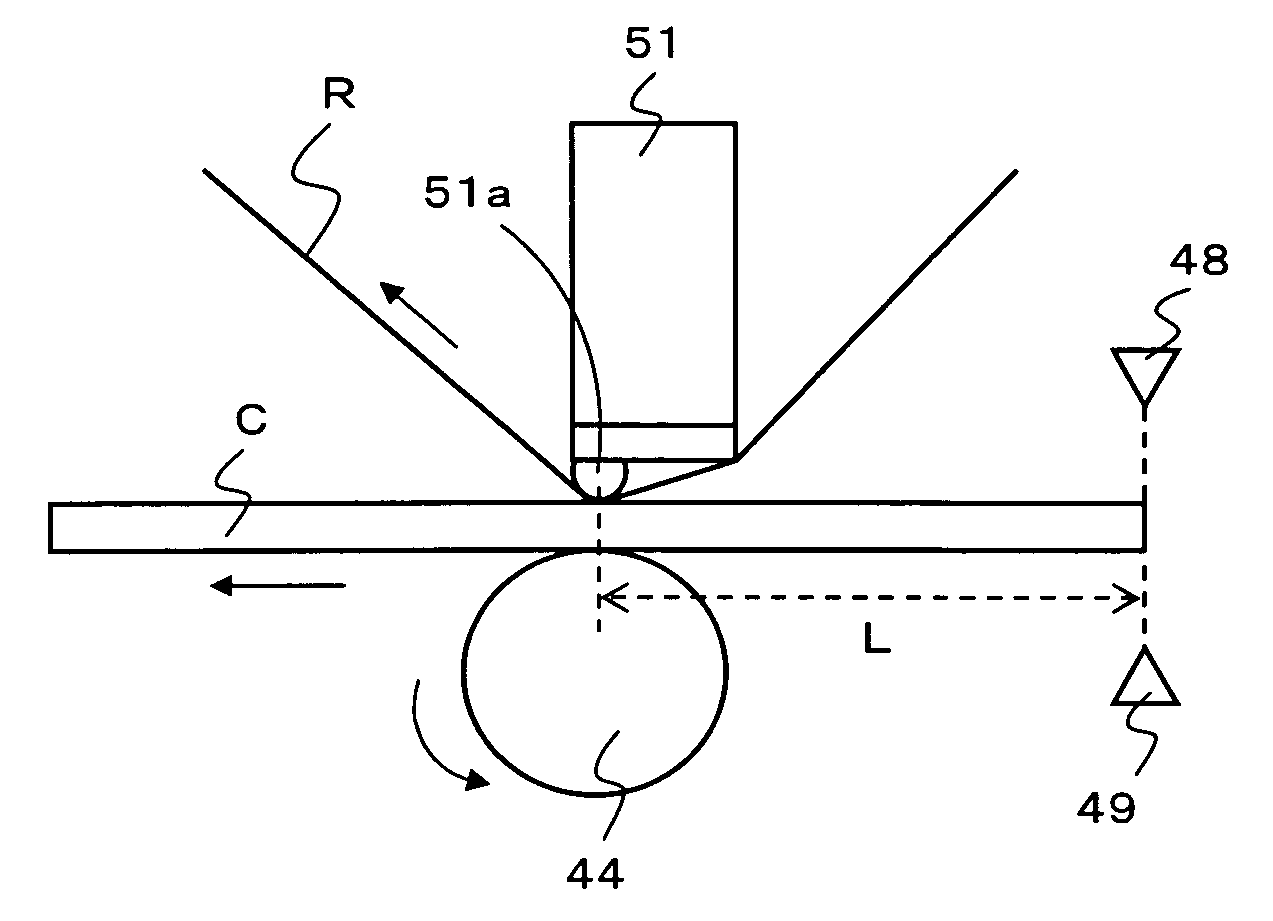
Accumulated-heat correction apparatus and accumulated-heat correction method for thermal head
InactiveCN101037051AImprove picture qualityPrintingDigital output to print unitsEngineeringThermal aware
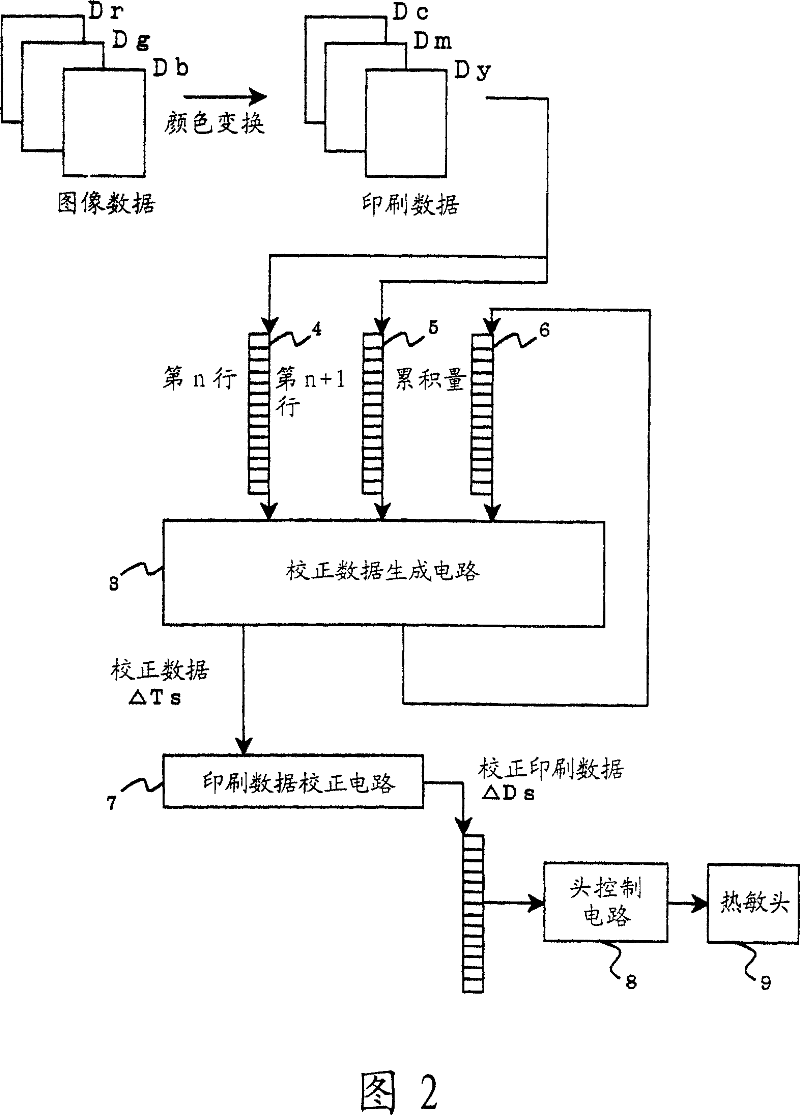
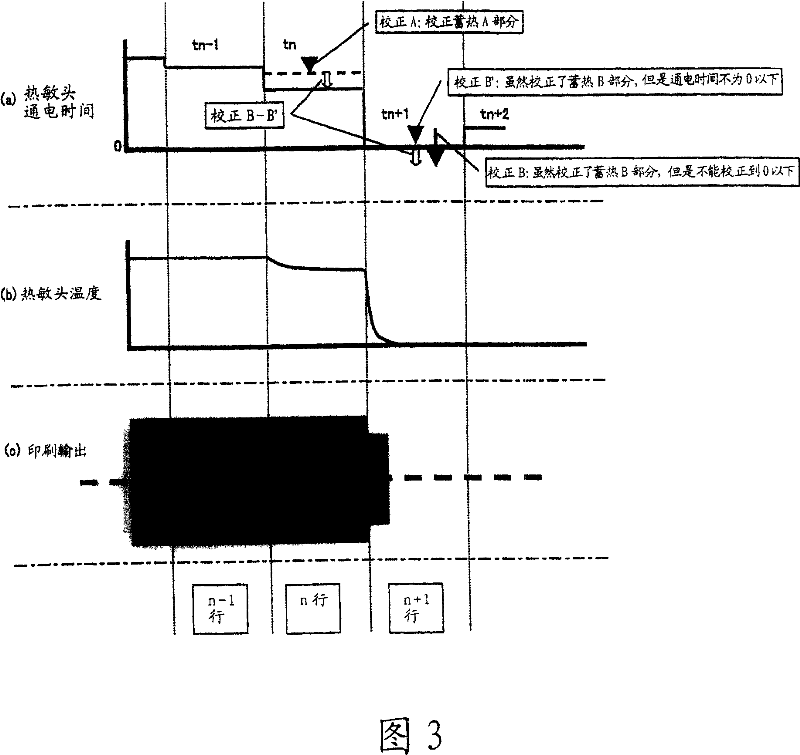
The device for correcting thermal storage of the thermal head 5 which outputs printing data for every line to the thermal head 5 and controls an electrification time of the thermal head 5 on the basis of the printing data, is equipped with an accumulated data operating means which operates accumulated data caused by the thermal storage of the thermal head 5 up to the previous line n-1, a next line data operating means which operates the printing data of the next line n+1, a correction data generating means which operates correction data [Delta]Ts to correct the printing data of the present line n by using the accumulated data and the next line data, and a head controlling means which controls the electrification time of the thermal head 5 on the basis of the correction data [Delta]Ts generated by the correction data generating means.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
High efficiency printing system for improved image quality
ActiveCN105431298AExtend working lifeSave energyInk ribbonsColor measuring devicesImaging qualityThermal printing
A high efficiency thermal printing system, comprising: a donor ribbon having donor material; a receiver medium; a test pattern to be printed on the receiver medium using the donor ribbon; a print head, a sensor, and a processor is disclosed. The present invention is adapted to print the test pattern on the receiver medium by heating the donor ribbon to cause the donor material to transfer from the donor ribbon onto the receiver medium, thereby depleting donor material on the donor ribbon. Moreover, the sensor is adapted to measure a depletion amount of the donor material on the donor ribbon after printing the test pattern, and the processor is adapted to calibrate the thermal printing system by adjusting a lookup table in response to the measured depletion amount of donor material.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
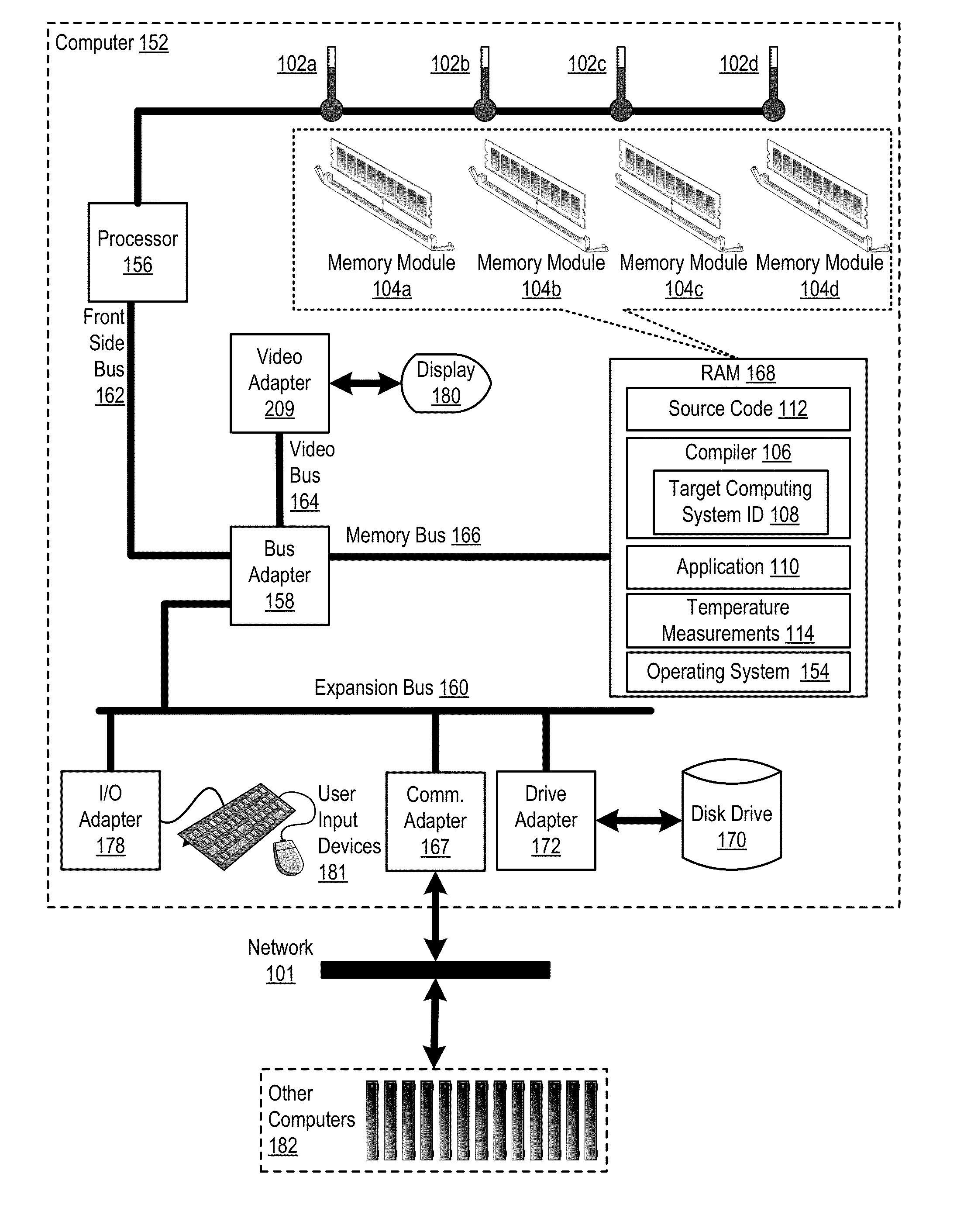
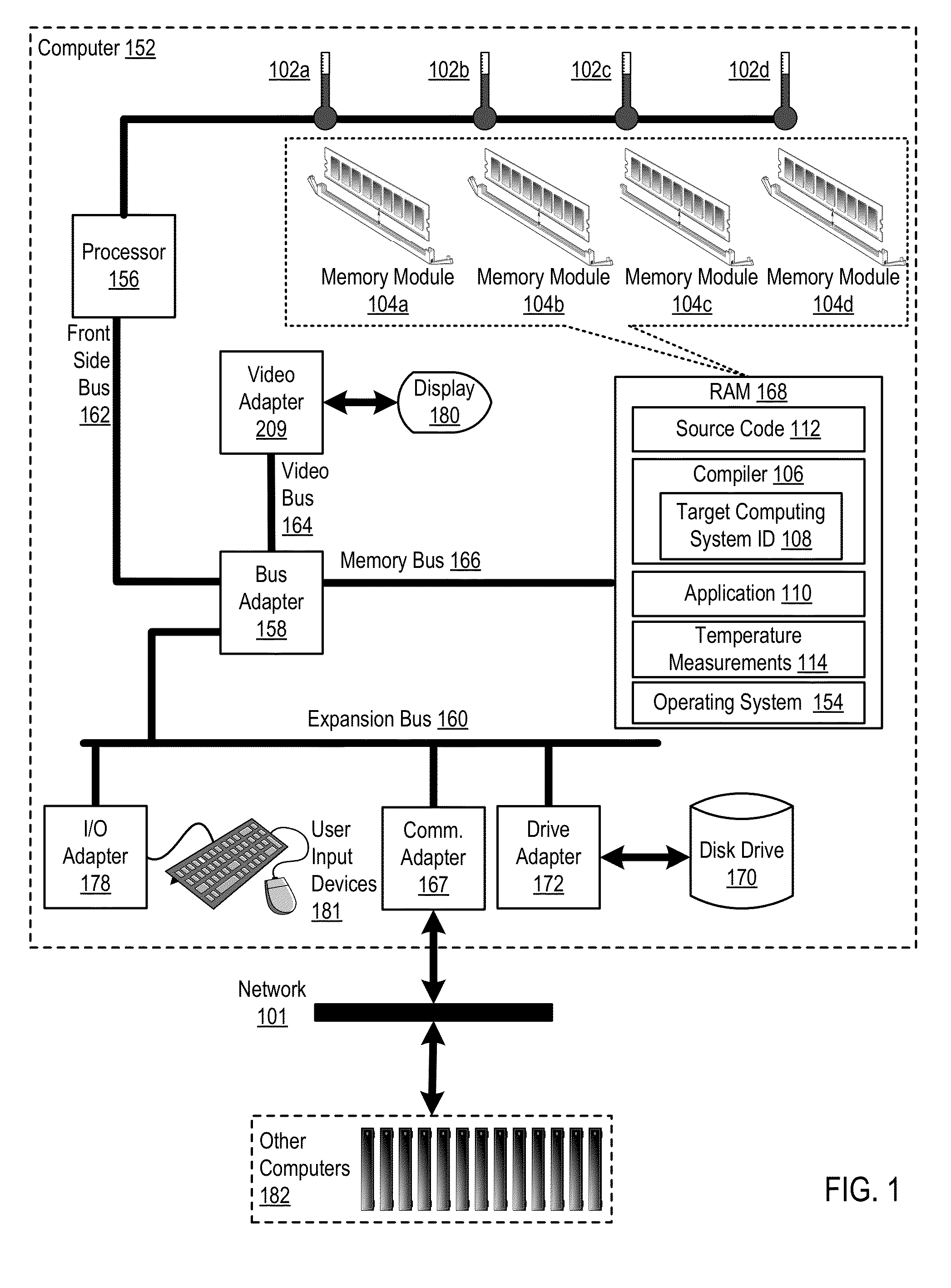
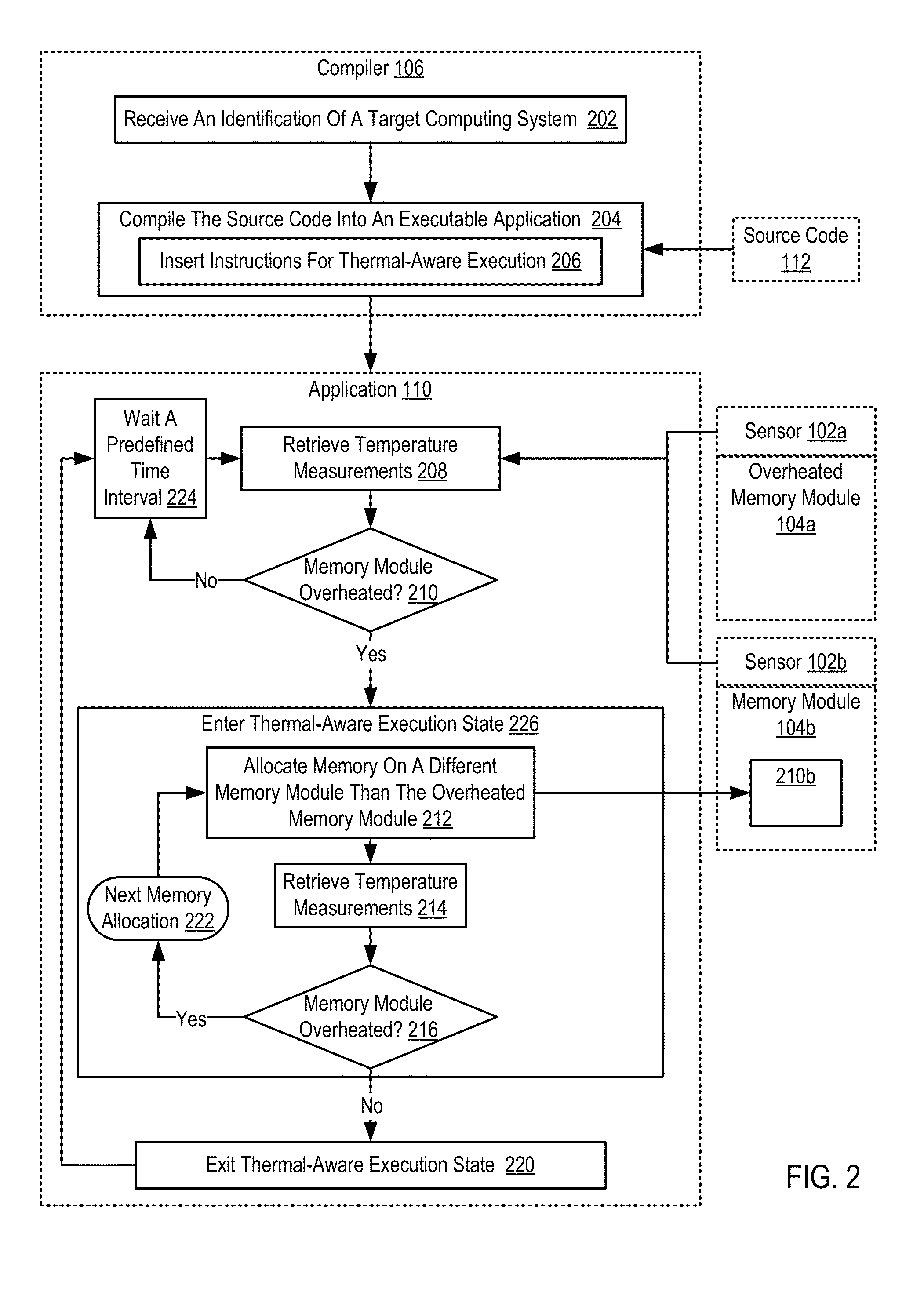
Thermal-Aware Source Code Compilation
ActiveUS20130047142A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingThermal aware
Thermal-aware source code compilation including: receiving, by a compiler, an identification of a target computing system, the identification of the target computing system specifying temperature sensors that measure temperature of a memory module; compiling the source code into an executable application including inserting in the executable application computer program instructions for thermal-aware execution, the computer program instructions, when executed on the target computing system, carry out the steps of: retrieving temperature measurements of one or more of the target computing system's temperature sensors; determining, in real-time in dependence upon the temperature measurements, whether a memory module is overheated; if a memory module is overheated, entering a thermal-aware execution state including, for each memory allocation in the executable application, allocating memory on a different memory module than the overheated memory module; and upon the temperature sensors indicating the memory module is no longer overheated, exiting the thermal-aware execution state.
Owner:IBM CORP
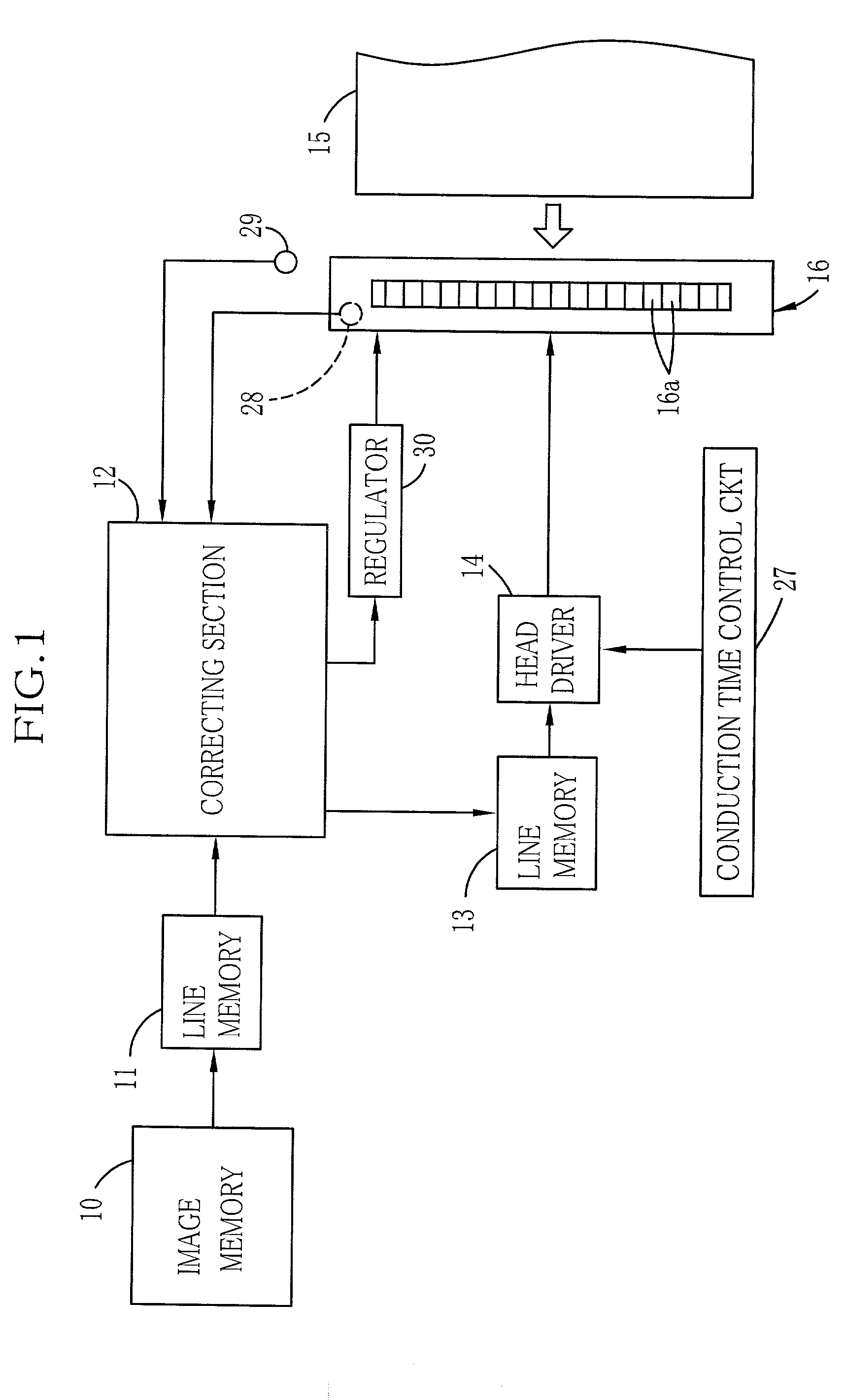
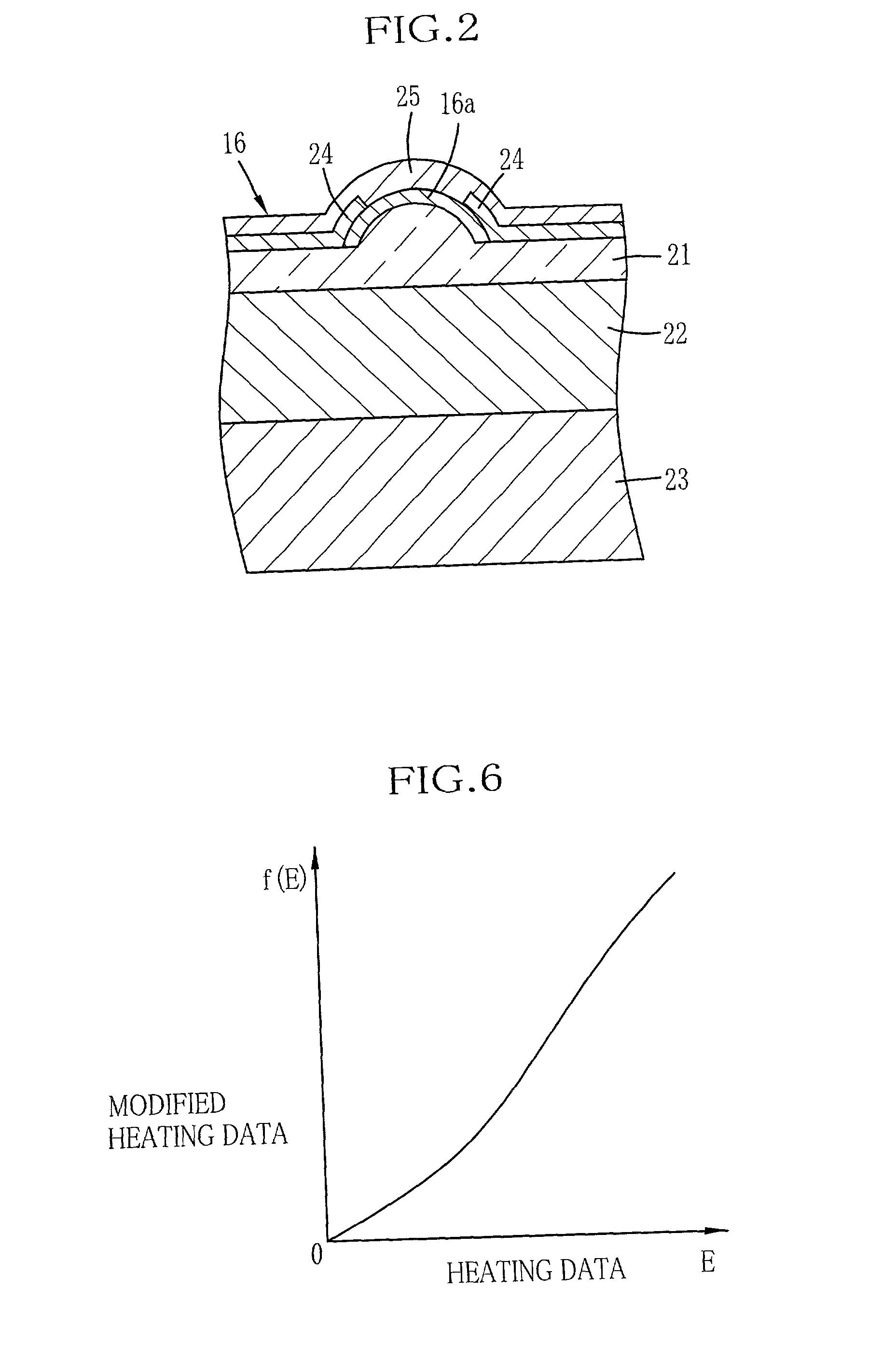
Data processing method for eliminating influence of heat accumulation in thermal head of thermal printer
InactiveUS6494629B2Improve accuracyEfficient printingPrintingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
There is disclosed a data processing method for correcting heating data for a thermal head of a thermal printer, to eliminate influence of heat energy accumulated in first to Nth heat accumulating layers of the thermal head. Basic heating data of a subject line is corrected with first to Nth correction data obtained by multiplying first to Nth heat accumulation data by predetermined coefficients respectively. The heating elements are driven in accordance with the corrected heating data, to print the subject line. A drive voltage to be applied across heating elements of the thermal head is determined at the start of printing a frame of image, according to an environmental temperature around the thermal head and a head temperature measured through a thermistor mounted in the Nth heat accumulating layer of the thermal head. The Nth coefficient is calculated according to a formula that includes the head drive voltage as a parameter.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
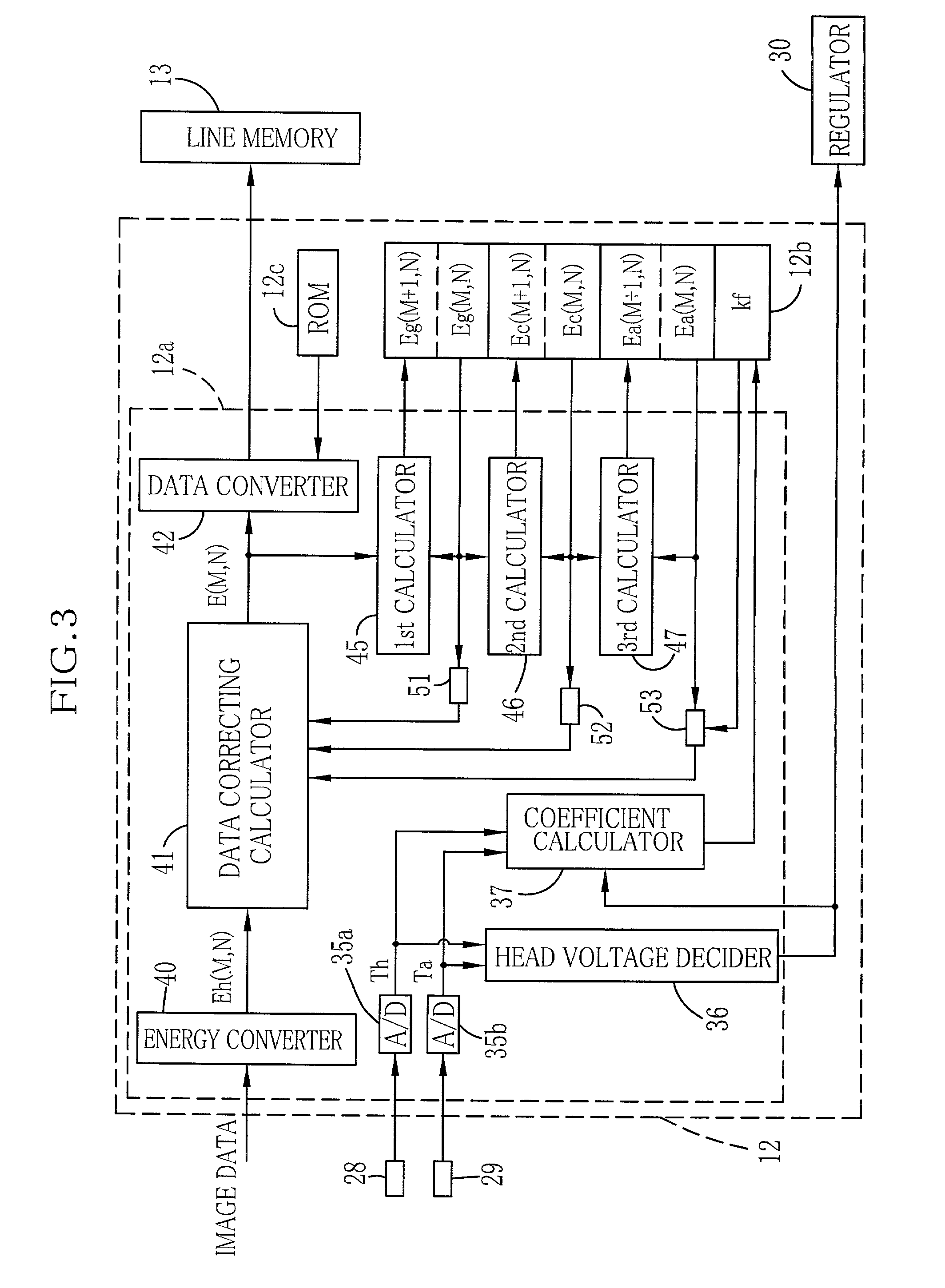
Heat accumulation correcting method, thermal printer, and computer-executable program
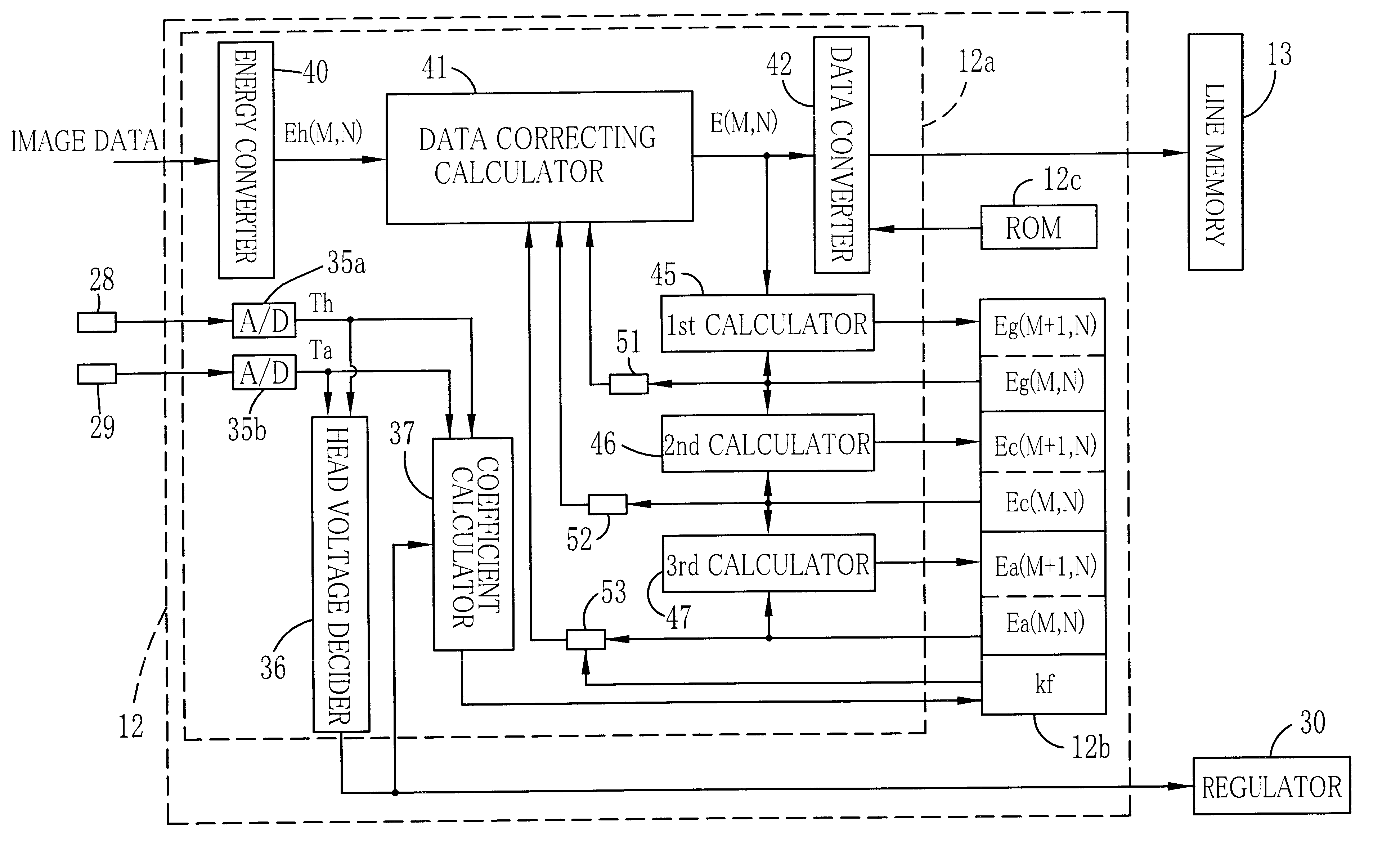
A thermal head in a thermal printer has heating elements, a glaze layer and a ceramic board. Equations are used for correcting heat accumulation. Eg1(M+1,N)=(1−k1).E(M,N)+(1−k2).Eg1(M,N) Eg2(M+1,N)=k2(1−k3)(1−k4).Eg1(M,N) Ec1(M+1,N)=k2(1−k3).k4.Eg1(M,N)+(1−k5).Ec1(M,N) E(M,N): heat data of an Nth pixel of an Mth line after heat accumulation correction; Eg1(M,N): accumulated heat data of the glaze layer at point Pg1 and obtained in the correction of an (M−1)th line; Eg2(M,N): accumulated heat data of the glaze layer at point Pg2 and obtained in the correction of the (M−1)th line; Ec1(M,N): accumulated heat data of the ceramic board at point Pc1 and obtained in the correction of the (M−1)th line.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Thermal Response Correction System for Multicolor Printing
Thermal history control is performed in a thermal printer in which a single thermal print head prints sequentially on multiple color-forming layers in a single pass. Each pixel-printing interval may be divided into segments, each of which may be used to print a different color. The manner in which the input energy to be provided to each print head element is selected may be varied for each of the segments. Different energy computation functions may be used to compute the energy to be provided to the print head in each of the segments based on the predicted print head element temperature at the beginning of the segment, the color to be printed, and the energy that was supplied when printing other colors during the time period between the beginning of the segment of the current pixel-printing interval and the end of the equivalent segment of the previous pixel-printing interval.
Owner:ZINK IMAGING
On-site certificate card manufacturing equipment and method
ActiveCN102173214AConvenient on-site evidence collectionImprove work efficiencyPattern printingTypewritersPersonalizationService efficiency
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUABIAO SCIENCEAND TECH DEV CO LTD
Parametric programmable thermal printer
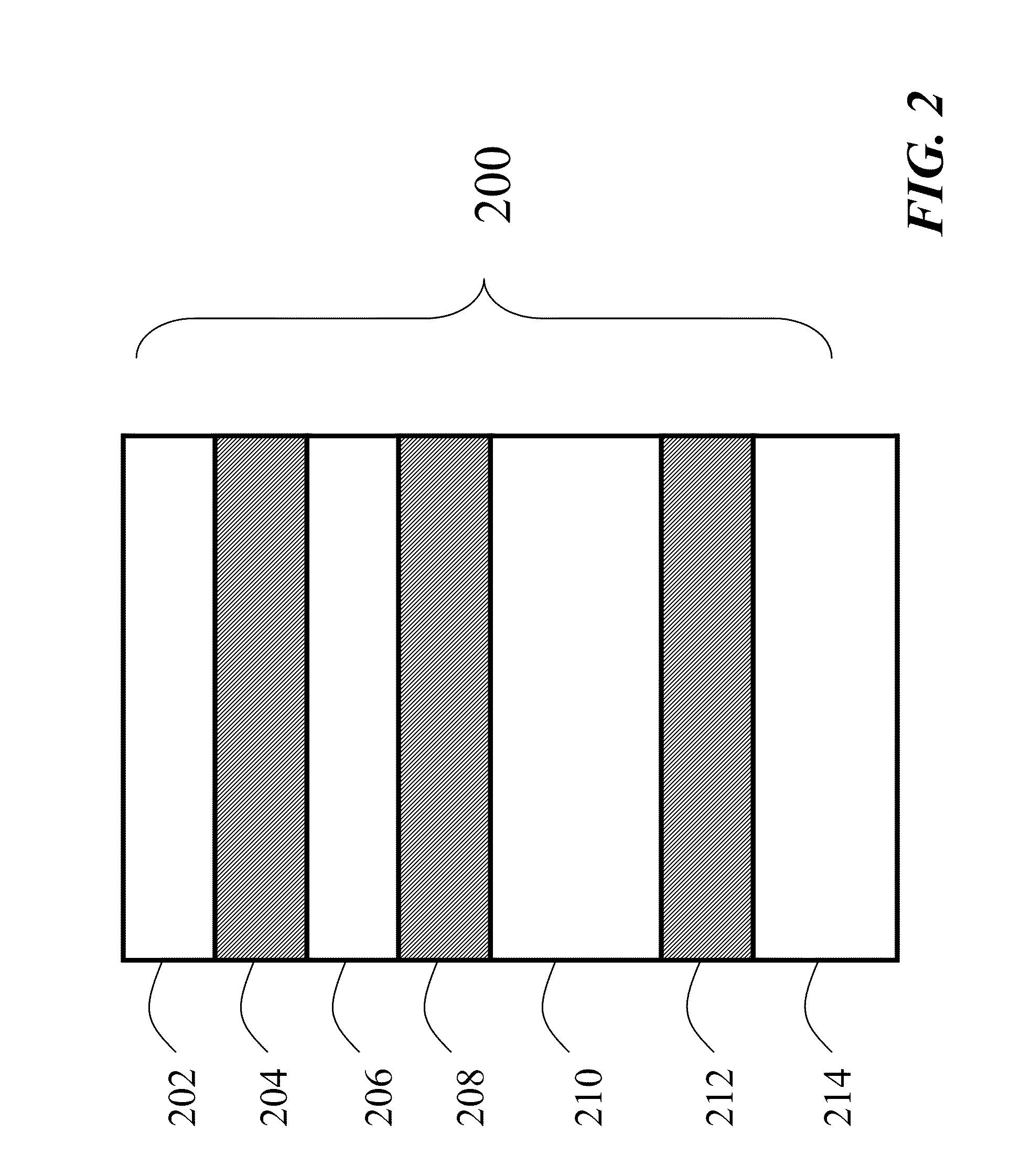
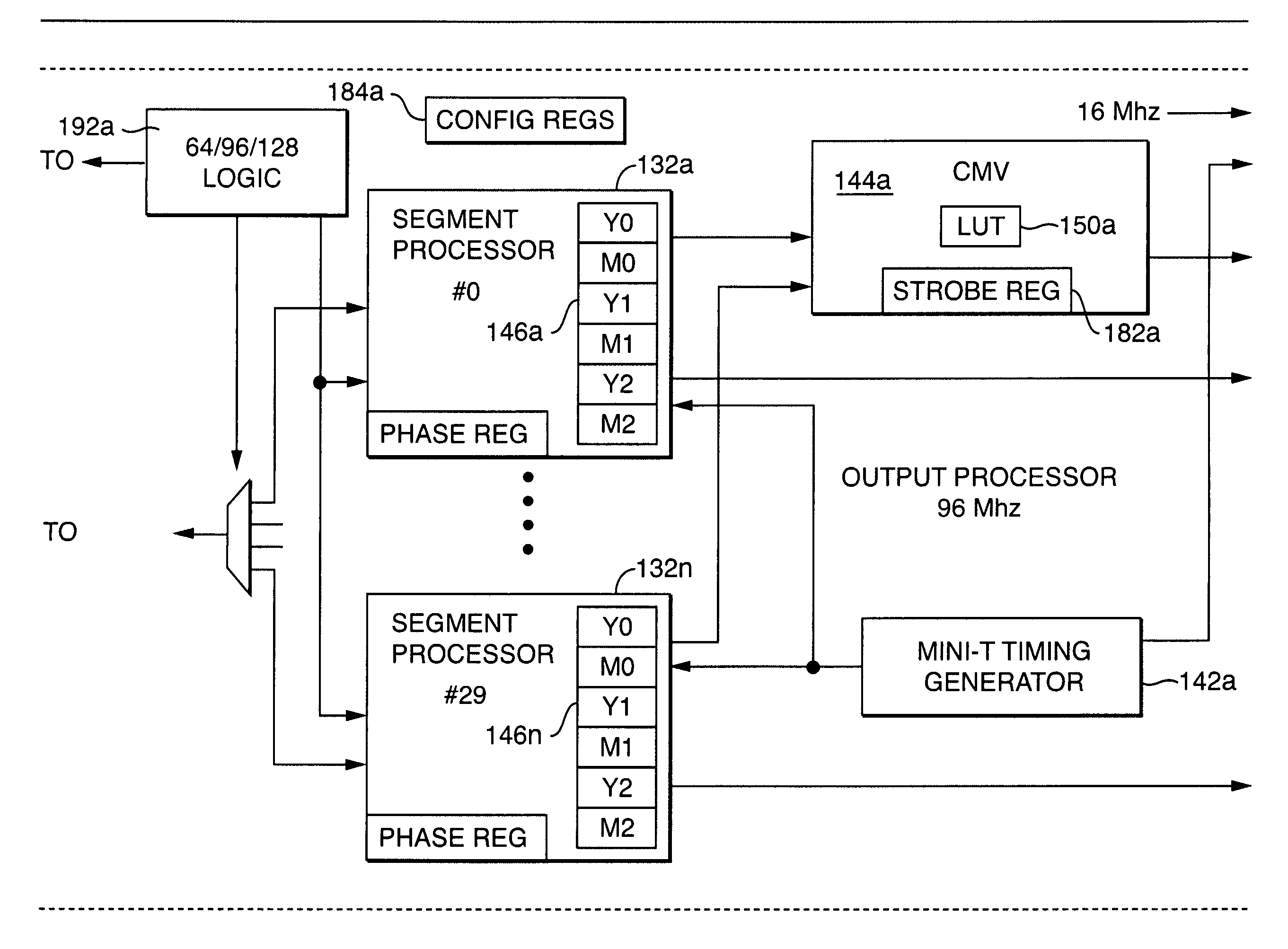
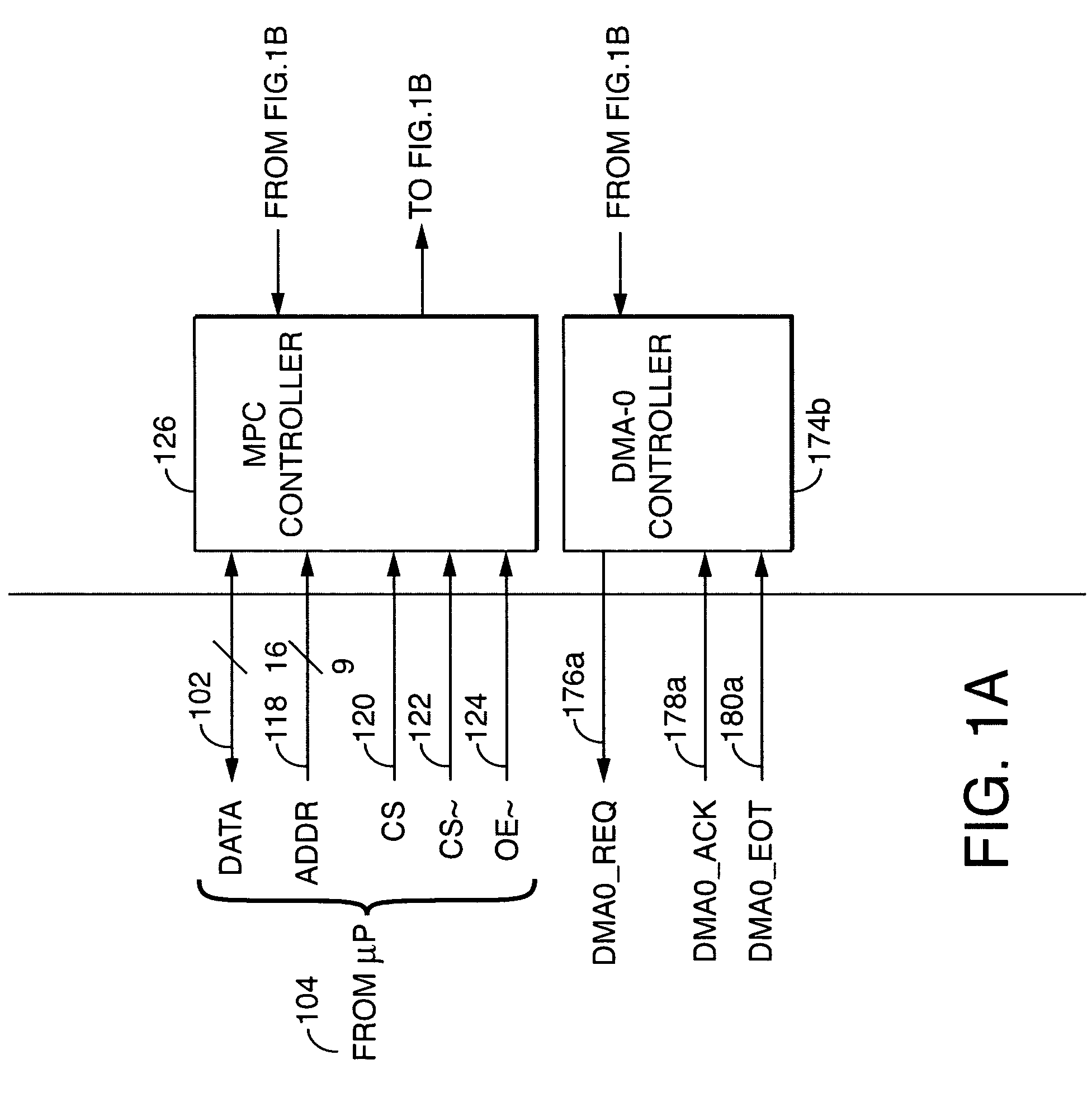
A parametric programmable thermal printer is disclosed. The printer may include a controller that performs functions such as thermal history control and common mode voltage correction. The controller may be implemented in an integrated programmable medium such as a Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). Functions performed by the controller may be parameterized, and parameter values may be stored in registers. The controller may be used with a different thermal printer by changing the parameter values and / or reprogramming the programmable medium, and without otherwise redesigning or remanufacturing the controller.
Owner:ZINK IMAGING
Appliance airflow detection using differential heating of electronic devices
ActiveUS20130025364A1Power dissipationContinuous operationTobacco treatmentVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringThermistor
Apparatus and methods are disclosed to measure airflow within a chassis-cooling pathway of an appliance. The rate of airflow is determined based on the differential heating among a pair of sensor devices, such as thermistors, transistors, diodes or resistive thermal devices operating at distinctly different power levels. The appliance utilizes the calculated airflow rate to perform safety-related tasks, such as de-energizing heating elements when low or no airflow is detected.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Data processing method for eliminating influence of heat accumulation in thermal head of thermal printer
InactiveUS20010031165A1Improve accuracyEfficient printingPrintingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
There is disclosed a data processing method for correcting heating data for a thermal head of a thermal printer, to eliminate influence of heat energy accumulated in first to Nth heat accumulating layers of the thermal head. Basic heating data of a subject line is corrected with first to Nth correction data obtained by multiplying first to Nth heat accumulation data by predetermined coefficients respectively. The heating elements are driven in accordance with the corrected heating data, to print the subject line. A drive voltage to be applied across heating elements of the thermal head is determined at the start of printing a frame of image, according to an environmental temperature around the thermal head and a head temperature measured through a thermistor mounted in the Nth heat accumulating layer of the thermal head. The Nth coefficient is calculated according to a formula that includes the head drive voltage as a parameter.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Device and method for printing information on glass surfaces
InactiveUS8013884B2Exact matchPrecise positioningRecording apparatusTypewritersEngineeringThermal aware
A printing device transfers slide dependent information onto glass surfaces such as a glass slide for holding a medical specimen. A single slide is transferred from a storage section, passing under a thermal print head. The thermal print head defines and transfers an image from an ink media onto the slide as the slide passes across the print head. The print head utilizes pixel like heating elements to apply the desired image. The ink media moves in tandem with the motion of the slide, presenting a continuously fresh section of ink between the print head and the slide throughout the printing process. The information on the slide should be both human and machine readable to reduce any chances of misidentification of the specimen as to the patient. The ink media is endures any chemical processes and handling encountered throughout the expected life of the slide.
Owner:AUTOMATIC MFG SYST
Heating element incorporating an array of transistor micro-heaters for digital image marking
The exemplary embodiments disclosed herein incorporate transistor heating technology to create micro-heater arrays as the digital heating element for various marking applications. The transistor heaters are typically fabricated either on a thin flexible substrate or on an amorphous silicon drum and embedded below the working surface. Matrix drive methods may be used to address each individual micro-heater and deliver heat to selected surface areas. Depending on different marking applications, the digital heating element may be used to selectively tune the wettability of thermo-sensitive coating, selectively change ink rheology, selectively remove liquid from the surface, selectively fuse / fix toner / ink on the paper.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method of controlling electric conduction through thermal heat and thermal printer
ActiveUS20090115831A1Increasing and reducing numberReduce in quantityInk ribbon cartridgesRecording apparatusThermal energyEngineering
A thermal printer detects an environmental temperature, and directly or indirectly detects a change in tension of an ink ribbon R. A correction value is read or calculated according to at least one of the detected environmental temperature and the detected change in the tension of the ink ribbon R. Thermal energy of each heating element in the thermal head is controlled based on the correction value so as to adjustably increase or reduce number of print lines on a print medium in a sub-scanning direction.
Owner:NISCA KK
Chromogenic Media Responsive to Environmental Conditions
The present invention relates to chromogenic material that may respond and shift in color due to environmental conditions such as heat, light or humidity. The light may include both visible and non-visible light, such as ultraviolet light. The chromogenic material may therefore provide a method to independently develop a latent image on a given substrate, and in particular, to a substrate that includes conventional thermosensitive image forming media.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
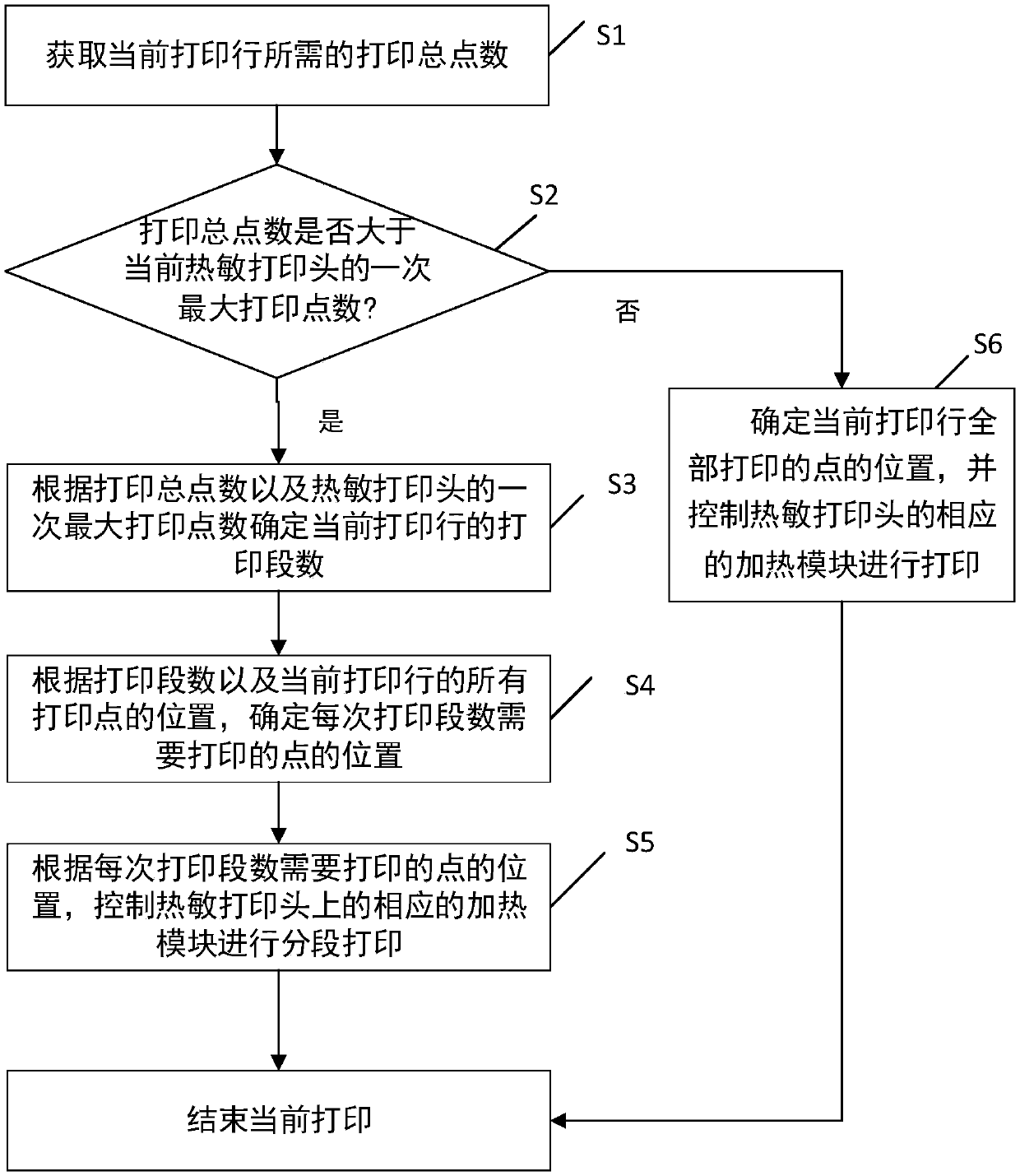
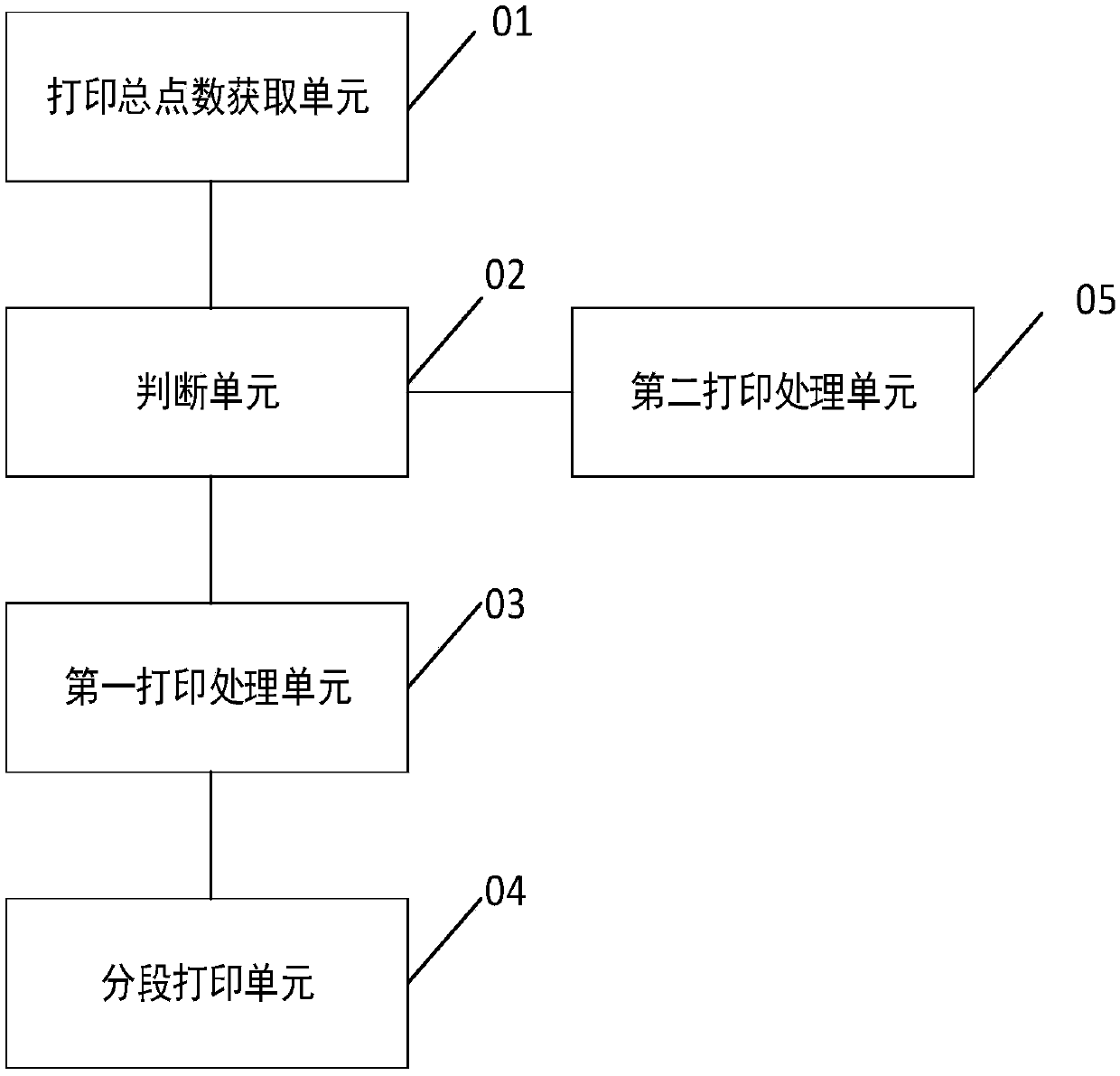
Segmented printing method and device for printer and thermal printer
The embodiment of the invention provides a segmented printing method and device for a printer and a thermal printer. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the total printing point numberneeded by current printing; judging whether the total printing point number is greater than a primary maximum printing point number of a current thermal printing head or not; if so, determining the printing segment number of current printing according to the total printing point number and the primary maximum printing point number of the current thermal printing head and determining the positionsof points needed to be printed in each printing segment number, wherein the positions of points needed to be printed in each printing segment number are discontinuous; and controlling corresponding heating module on the thermal printing head to print segmentally according to the positions of points needed to be printed in each printing segment number so as to achieve printing of a current printedline after printing all printing segment numbers. Based on the invention, the problem that the writing printed by the printer is unclear as a result of overheating can be solved, and the printing efficiency and practicality of the printer are improved.
Owner:XIAMEN HANIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Thermal response correction system
A model of a thermal print head is provided that models the thermal response of thermal print head elements to the provision of energy to the print head elements over time. The thermal print head model generates predictions of the temperature of each of the thermal print head elements at the beginning of each print head cycle based on: (1) the current ambient temperature of the thermal print head, (2) the thermal history of the print head, (3) the energy history of the print head, and (optionally) (4) the current temperature of the print medium. The amount of energy to provide to each of the print head elements during a print head cycle to produce a spot having the desired density is calculated based on: (1) the desired density to be produced by the print head element during the print head cycle, and (2) the predicted temperature of the print head element at the beginning of the print head cycle.
Owner:TPP TECH LLC
Pressure controlled constant tempeature crystal oscillator
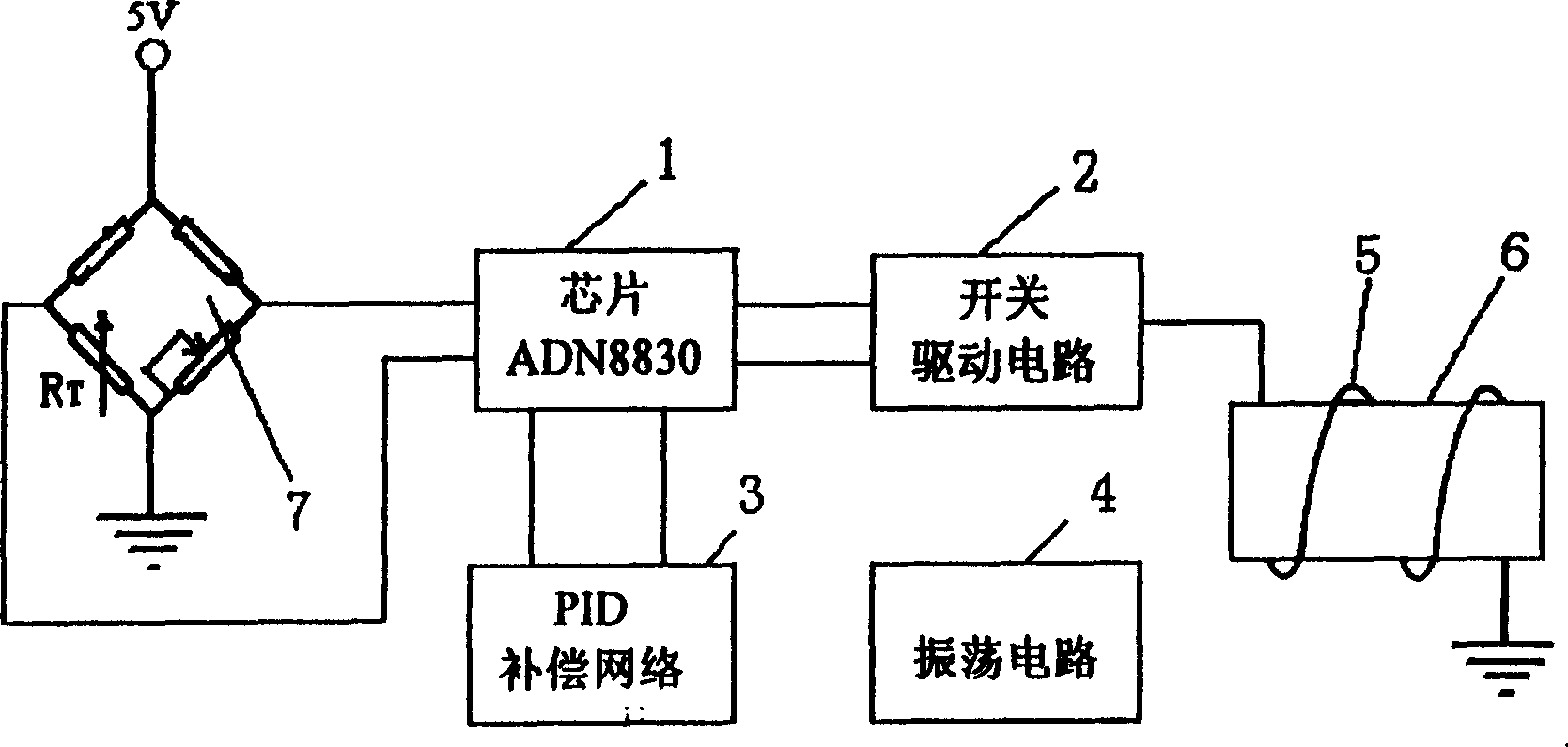
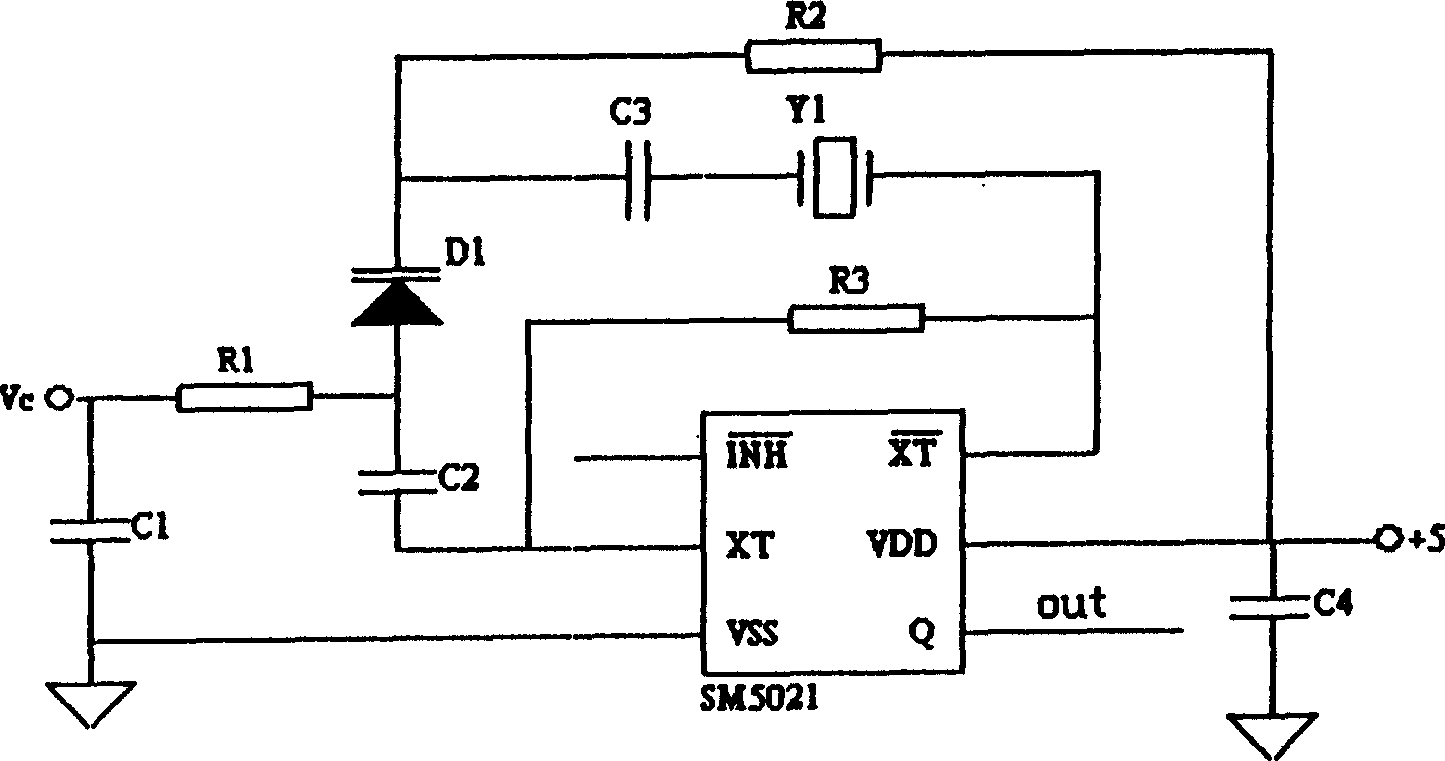
InactiveCN1538614AHigh temperature control accuracyReduce volumeTemperature control using electric meansOscillations generatorsThermistorThermal aware
New mode for controlling temperature and new structure of thermostated trough are adopted in the invention. For control temp, IC chip ADN8830 in PWM mode outputs square wave in certain duty ratio to switch drive circuit. The duty ratio is controlled by PID compensation circuit to control heating power of resistive heater to reach target for controlling temp. Thermostated trough includes trough body, and trough cover. Resistance wire is enwound on thermostated trough. Resonator Y1 is put in cavity inside trough body. Thermistor RT is in trough at side of the trough body. Cover seals oscillating circuit board on trough body. Advantages of the invention are small size and high frequency stability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
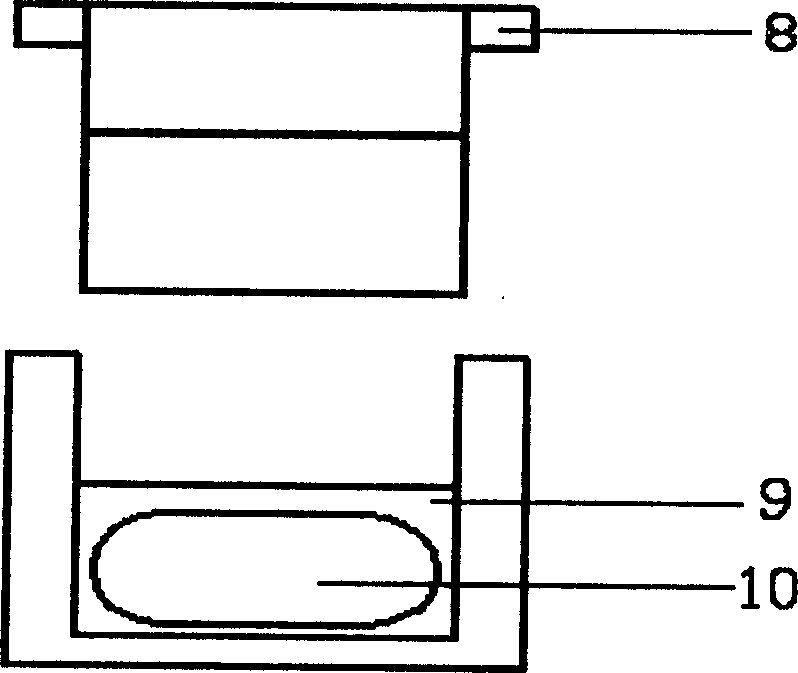
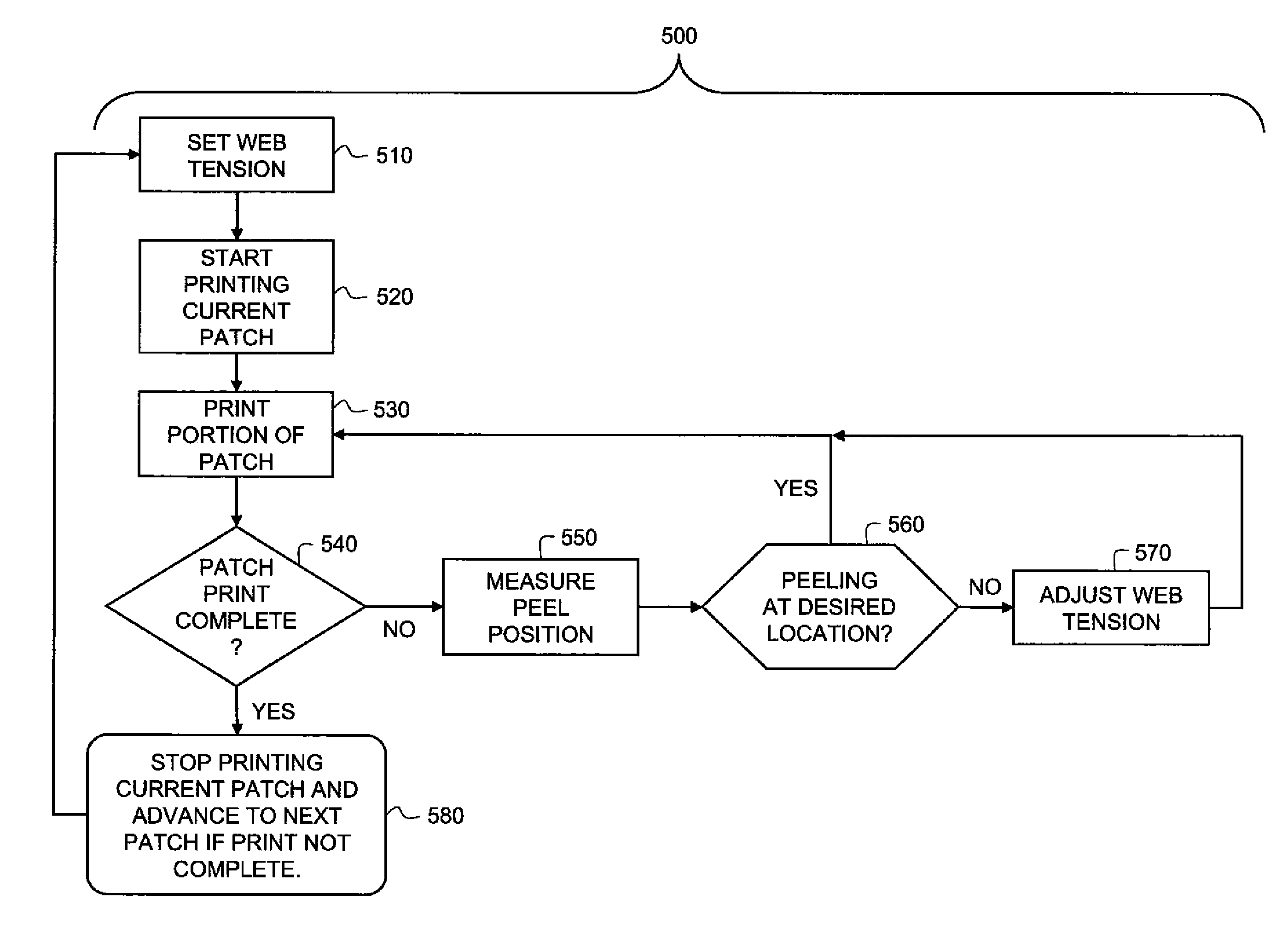
Method for controlling peel position in a printer
InactiveUS20110074904A1Less printer defectReduce morbidityRecording apparatusPrinting mechanismsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A method for maintaining a peel location and for peeling a layer of media from a surface in a thermal printer. An optical probe, that includes a light source and a photodetector, transmits light from the optical probe toward a first web. The web reflects a portion of the transmitted light onto the photodetector, which then outputs an electrical signal which is compared with a preselected signal level and the difference between them provides an indication as to how much adjustment the peel location requires. Adjusting the peel location may comprise changing environmental characteristics of the first web or the second web (surface) or adjusting a tension of the first or second web. The difference between the measured electrical signal levels is related to a physical distance of the first web from the desired peel location.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com