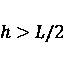Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
167 results about "Terrain mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
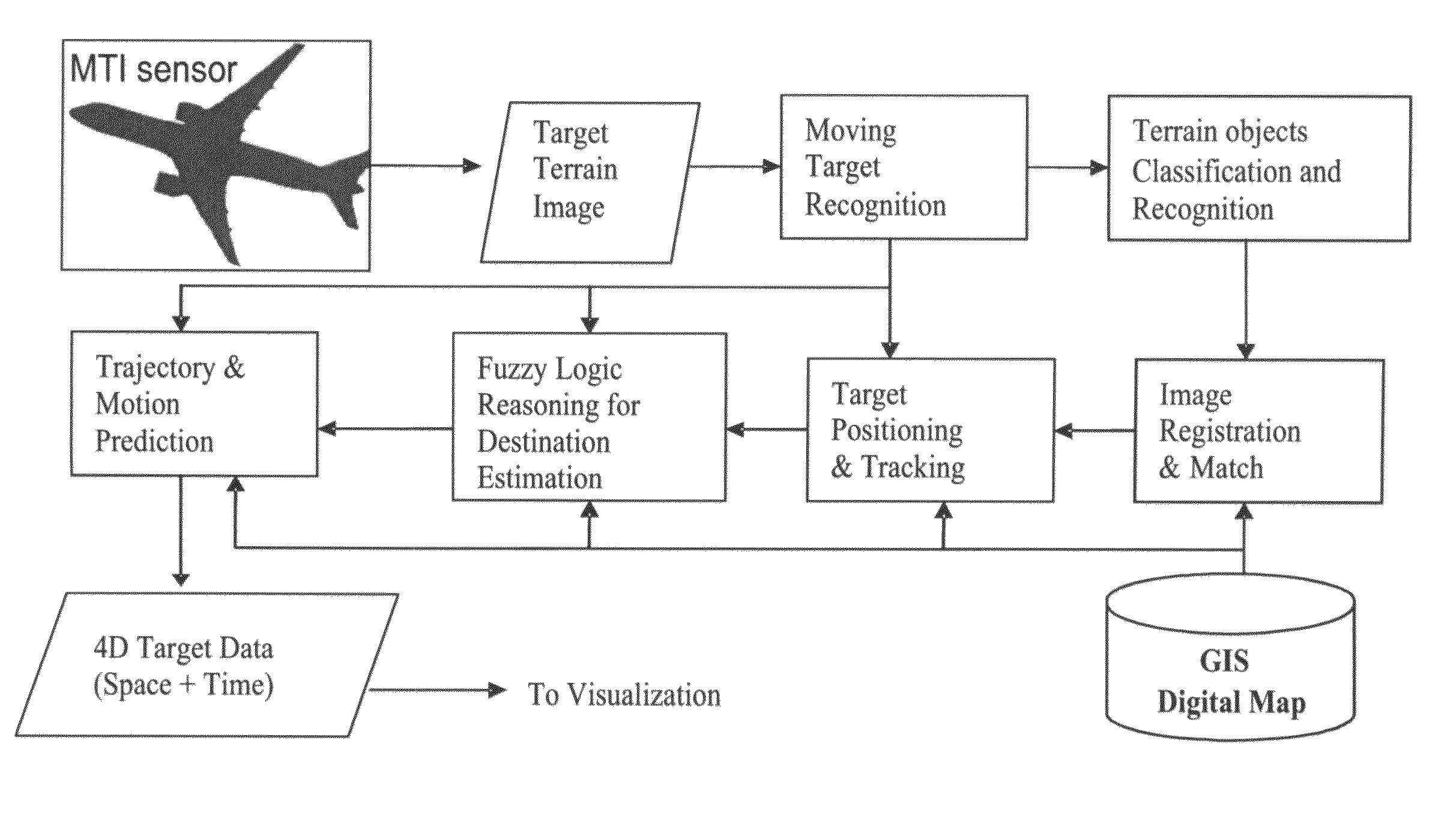
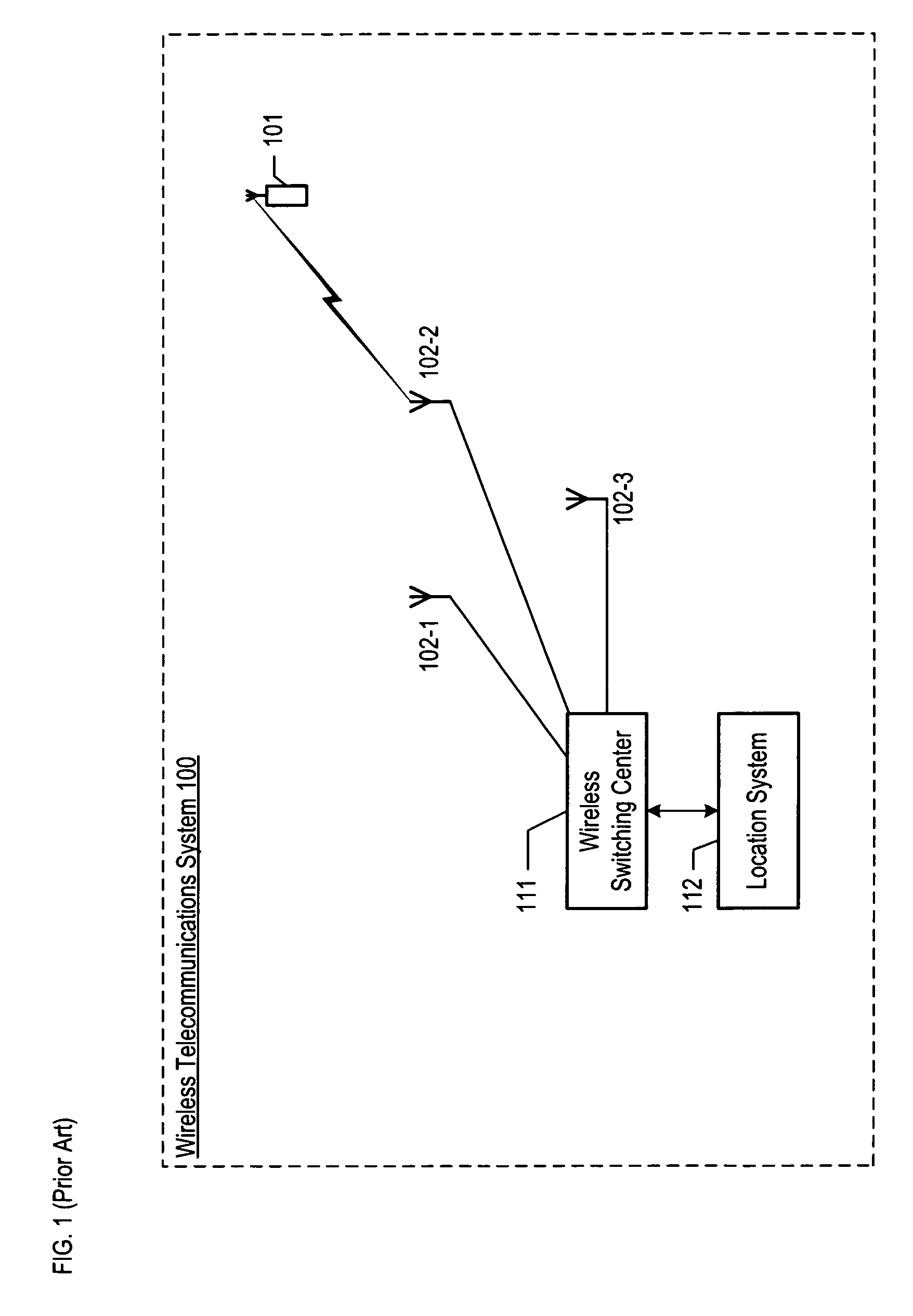
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS8229163B2Precise processConfidenceImage enhancementImage analysisFuzzy logic inferenceLandform
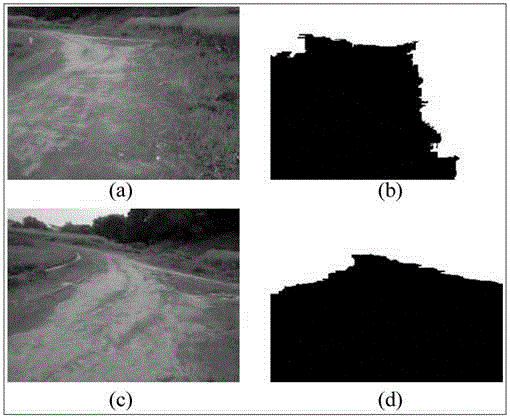
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
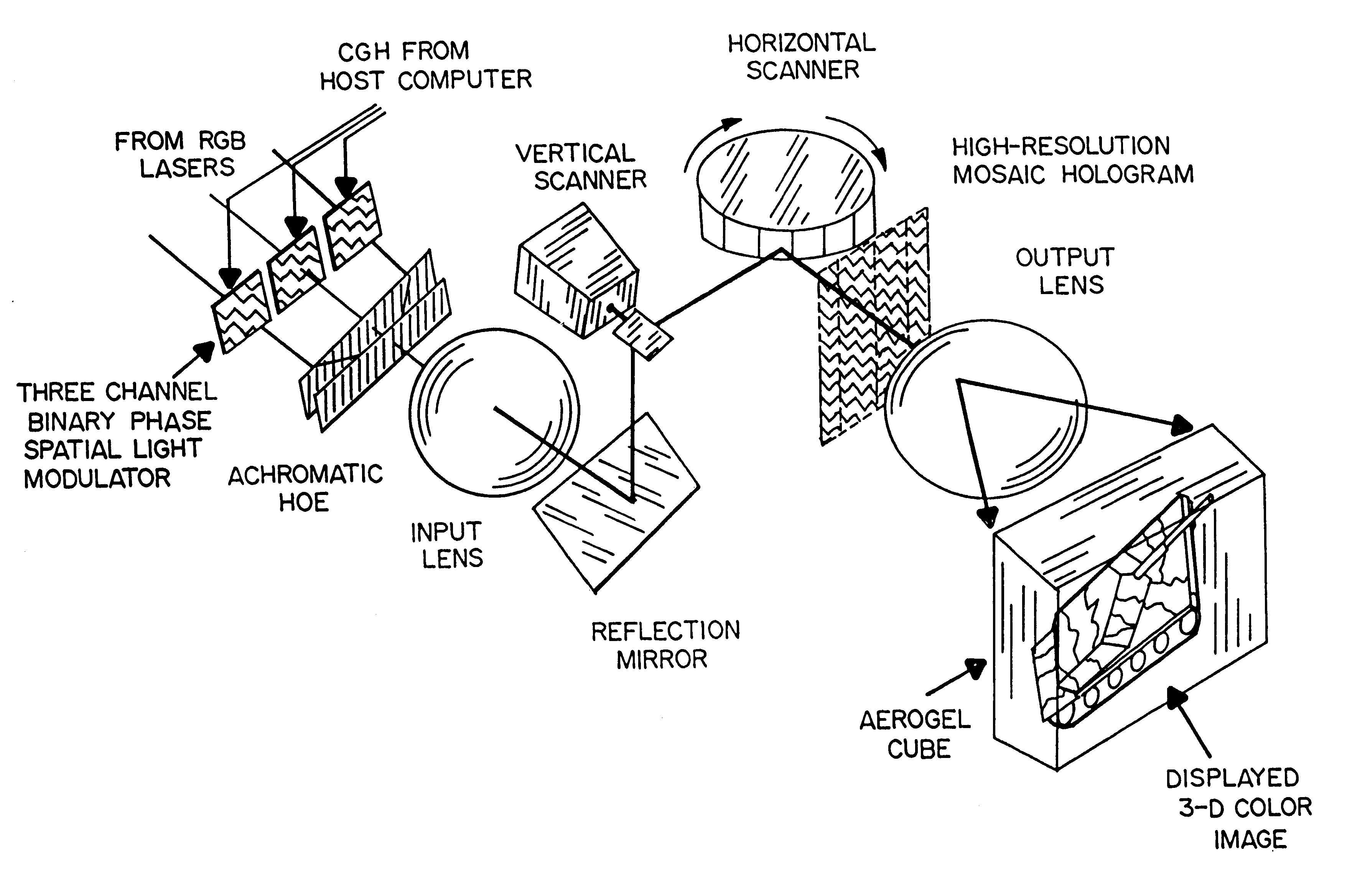
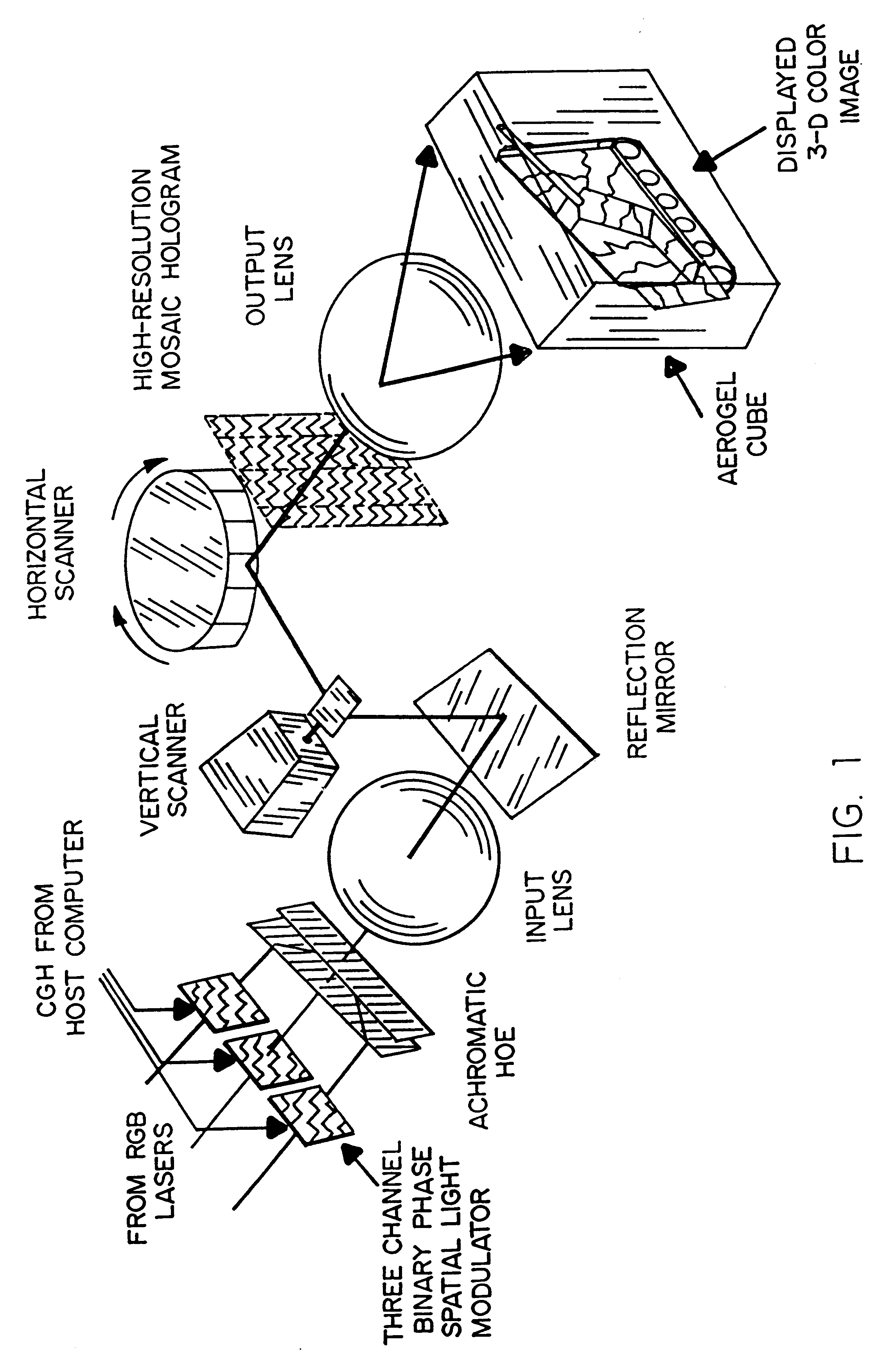
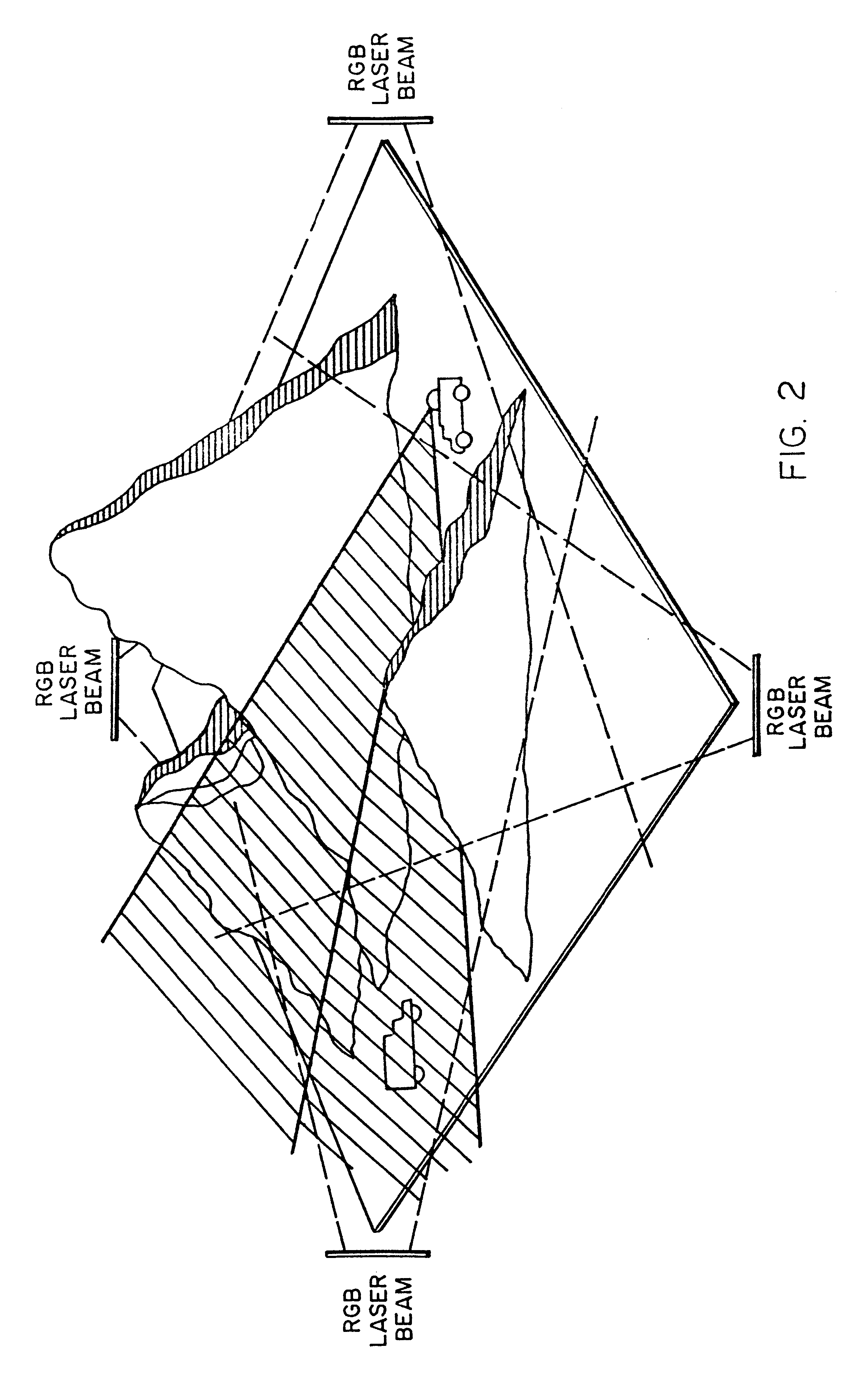
High-resolution large-field-of-view three-dimensional hologram display system and method thereof
InactiveUS6195184B1High efficiencyLimit in sizeHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic object characteristicsTerrainImage sensor
A real-time, dynamic, free space-virtual reality, 3-D image display system which is enabled by using a unique form of Aerogel as the primary display media. A preferred embodiment of this system comprises a 3-D mosaic topographic map which is displayed by fusing four projected hologram images. In this embodiment, 4 holographic images are projected from 4 separate holograms. Each holographic image subtends a quadrant of the 4pi solid angle. By fusing these four holographic images, a static 3-D image such as a featured terrain map would be visible for 360 degrees in the horizontal plane and 180 degrees in the vertical plane. An input, either acquired by 3-D image sensor or generated by computer animation, is first converted into a 2-D computer generated hologram (CGH). This CGH is then downloaded into large liquid crystal (LC) panel. A laser projector illuminates the CGH-filled LC panel and generates and displays a real 3-D image in the Aerogel matrix.
Owner:NASA
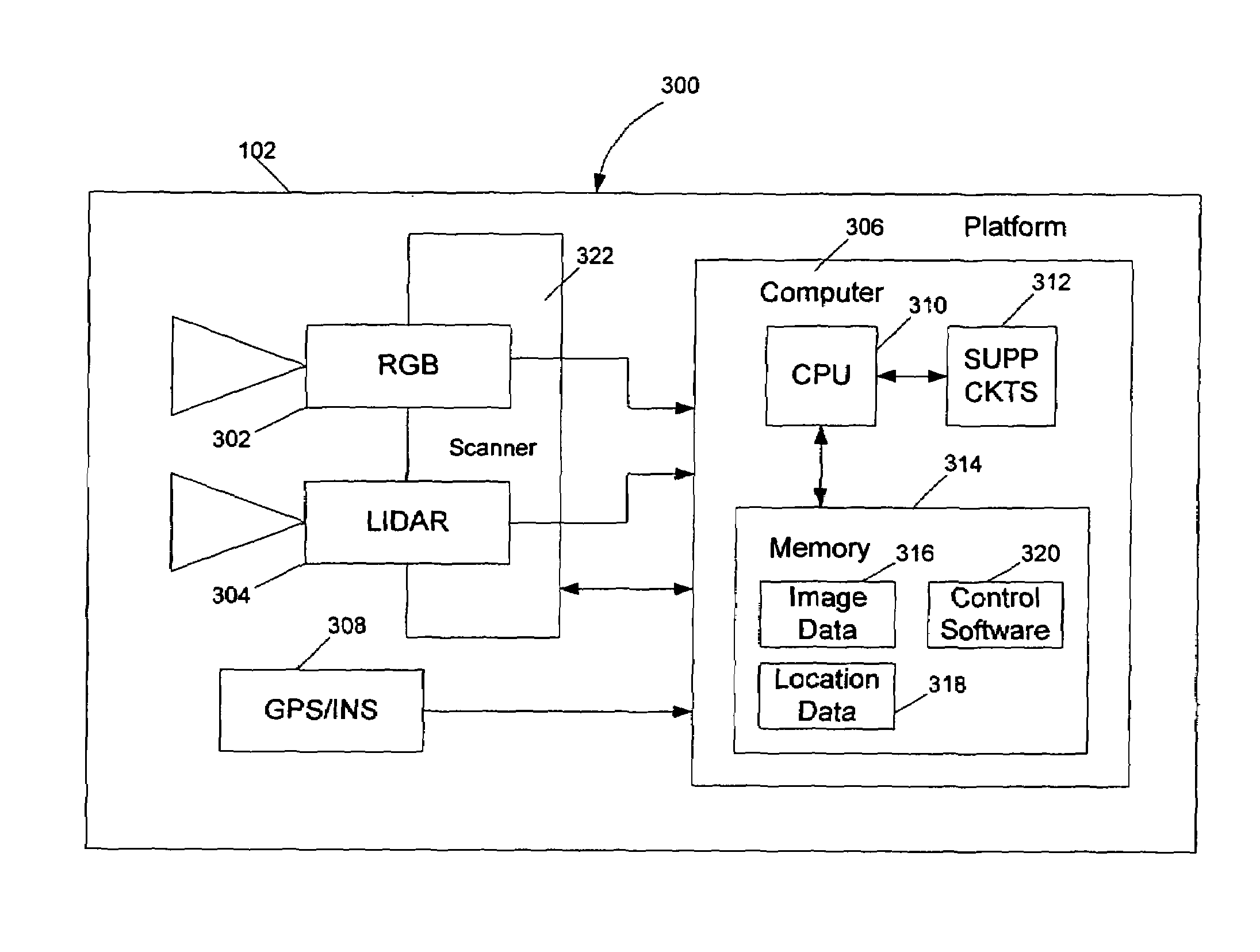
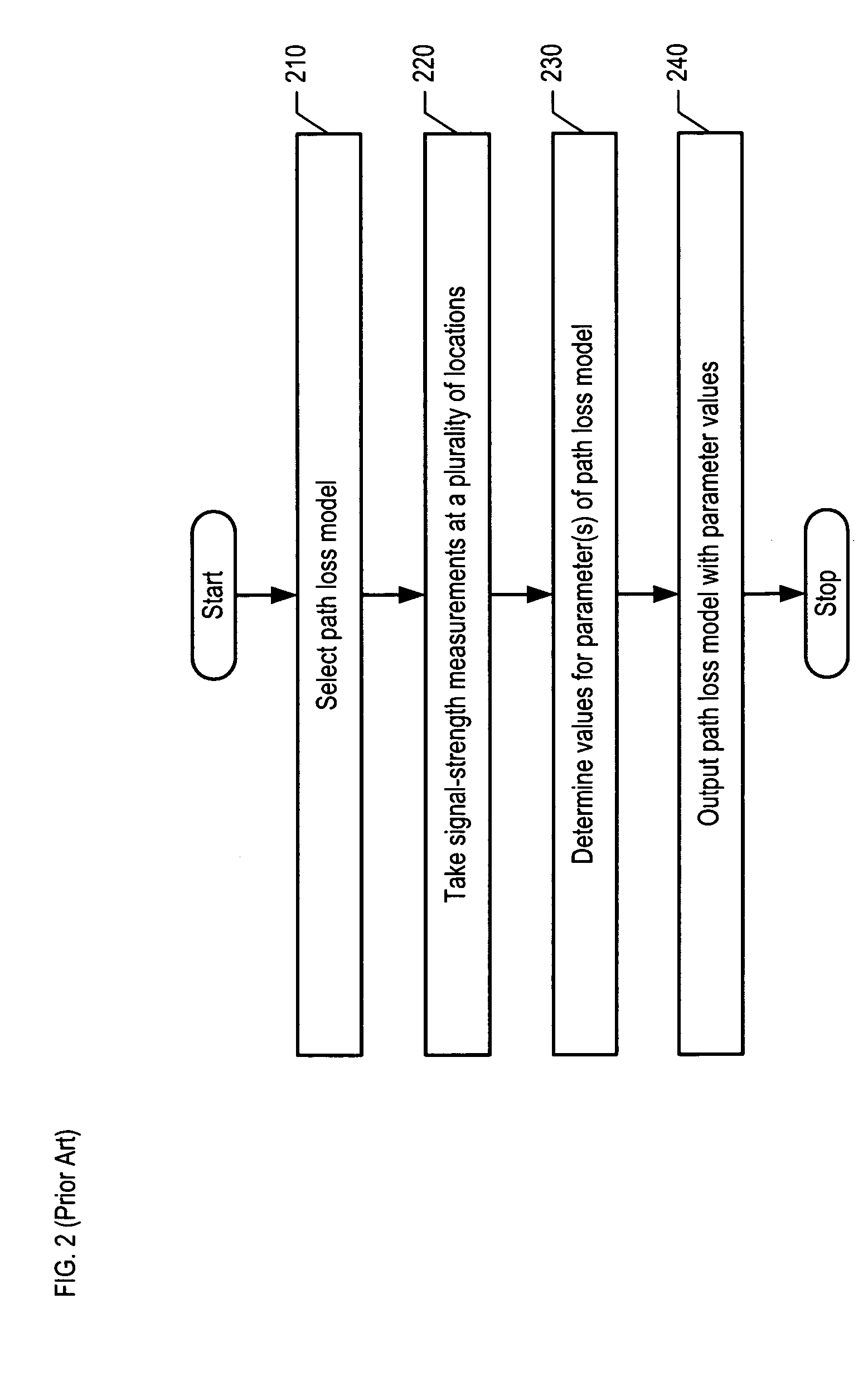
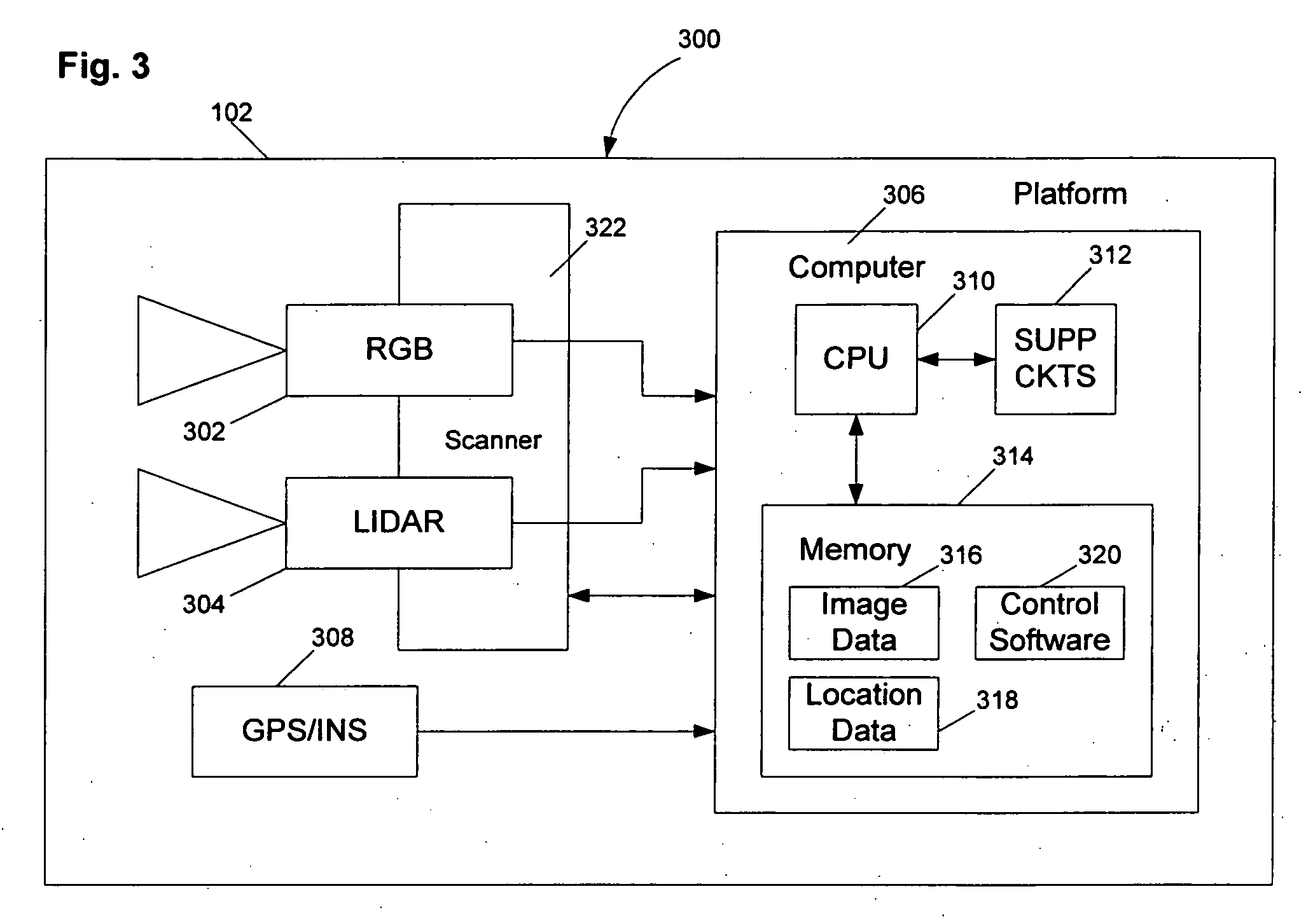
Method and apparatus for performing wide area terrain mapping
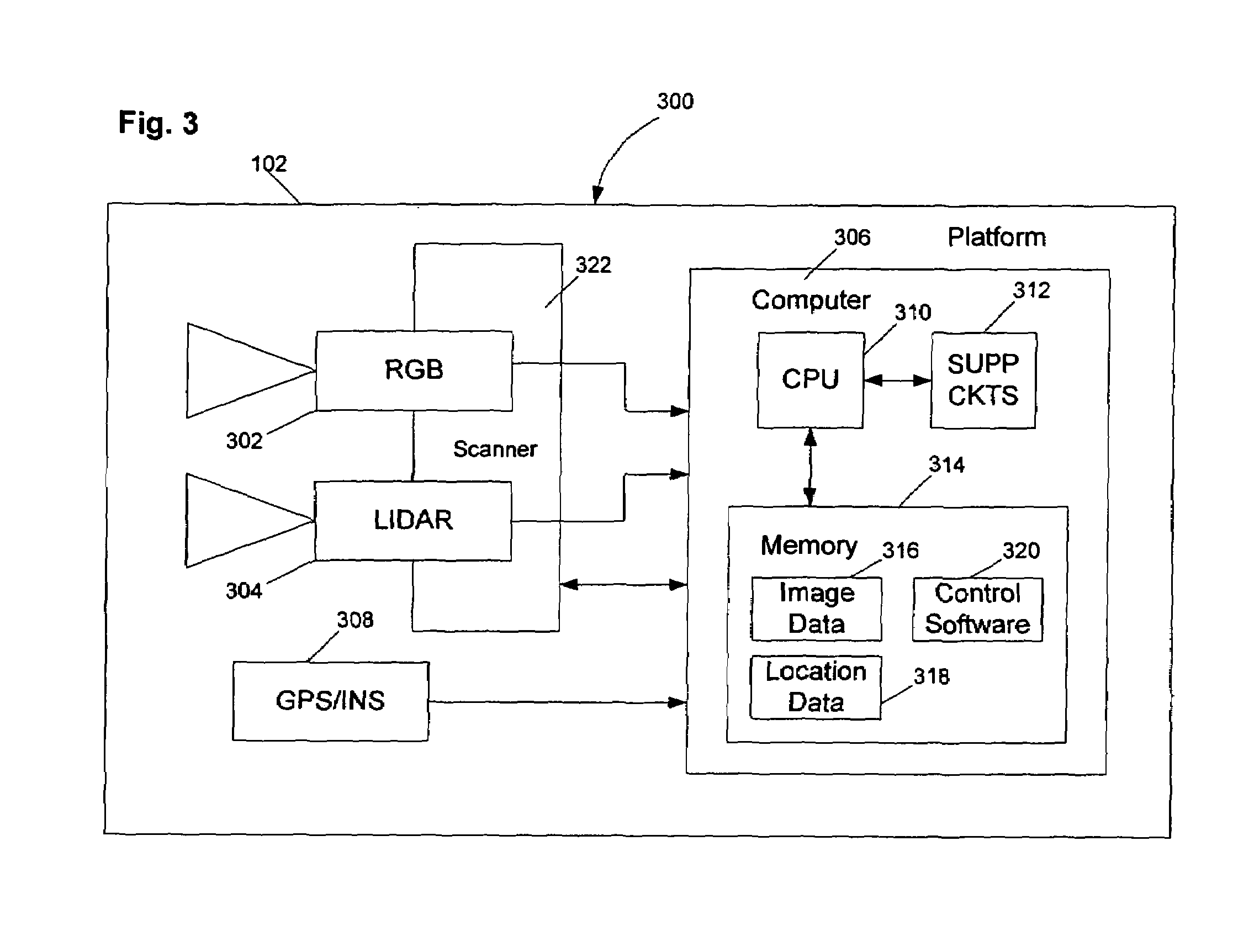
ActiveUS7363157B1View accuratelyDigital data processing detailsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryLandformDigital elevation map
A method and apparatus for performing wide area terrain mapping. The system comprises a digital elevation map (DEM) and mosaic generation engine that processes images that are simultaneously captured by an electro-optical camera (RGB camera) and a LIDAR sensor. The image data collected by both the camera and the LIDAR sensor are processed to create a geometrically accurate three-dimensional view of objects viewed from an aerial platform.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Obstacle and terrain avoidance sensor
InactiveUS20040178943A1Improve elevation accuracyHigh resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClassical mechanicsLight beam
A method of terrain mapping and / or obstacle detection for aircraft, comprising: (a) transmitting a non-scanning beam that illuminates the terrain and / or obstacles; (b) receiving a Doppler shifted signal that is Doppler frequency shifted by an amount dependent on an angle between a line of flight of the aircraft and scatterers that reflect the transmitted beam; (c) determining the angle from the Doppler frequency; (d) determining the range of at least some of said scatterers; and (e) determining the azimuth and elevation of the scatterers.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
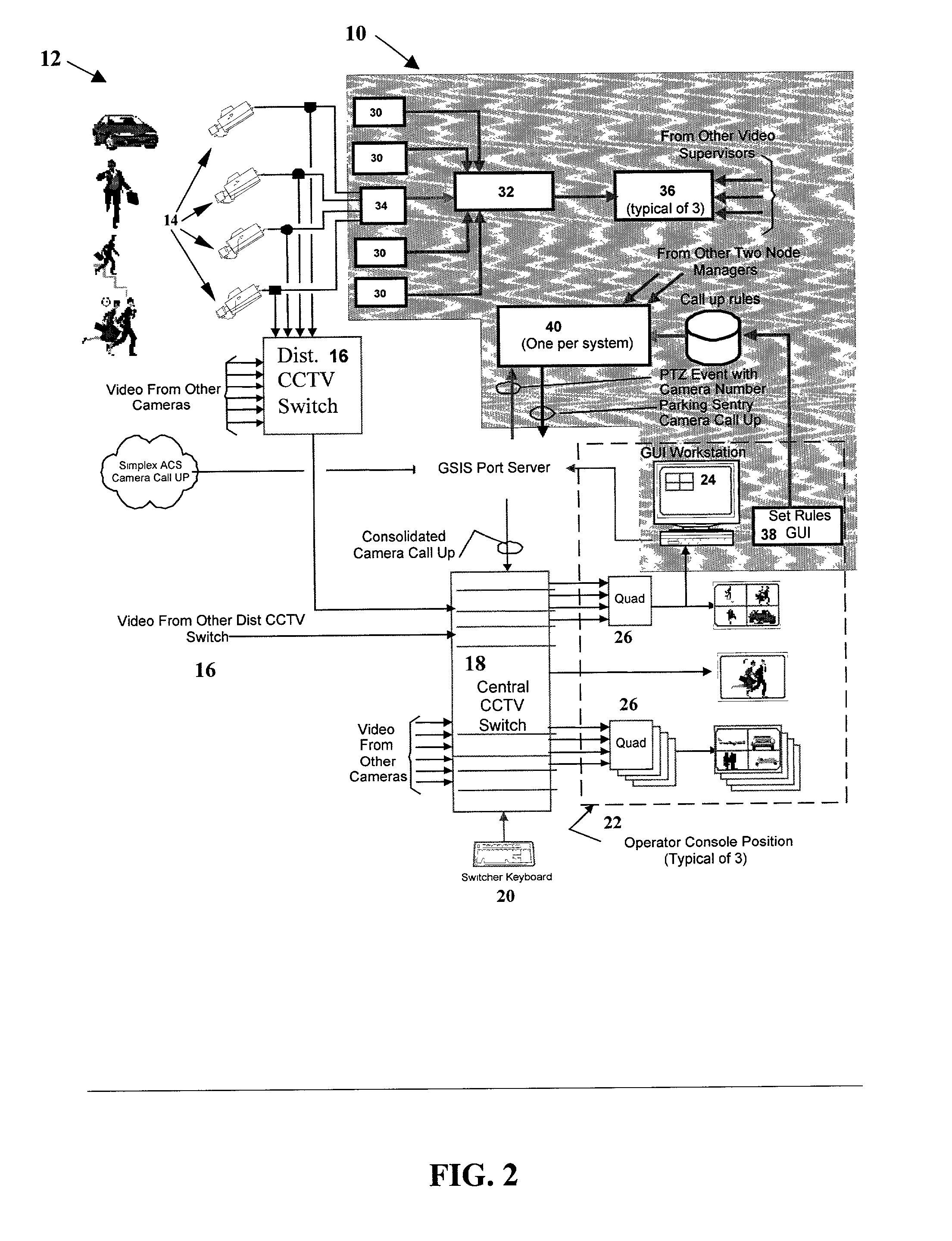
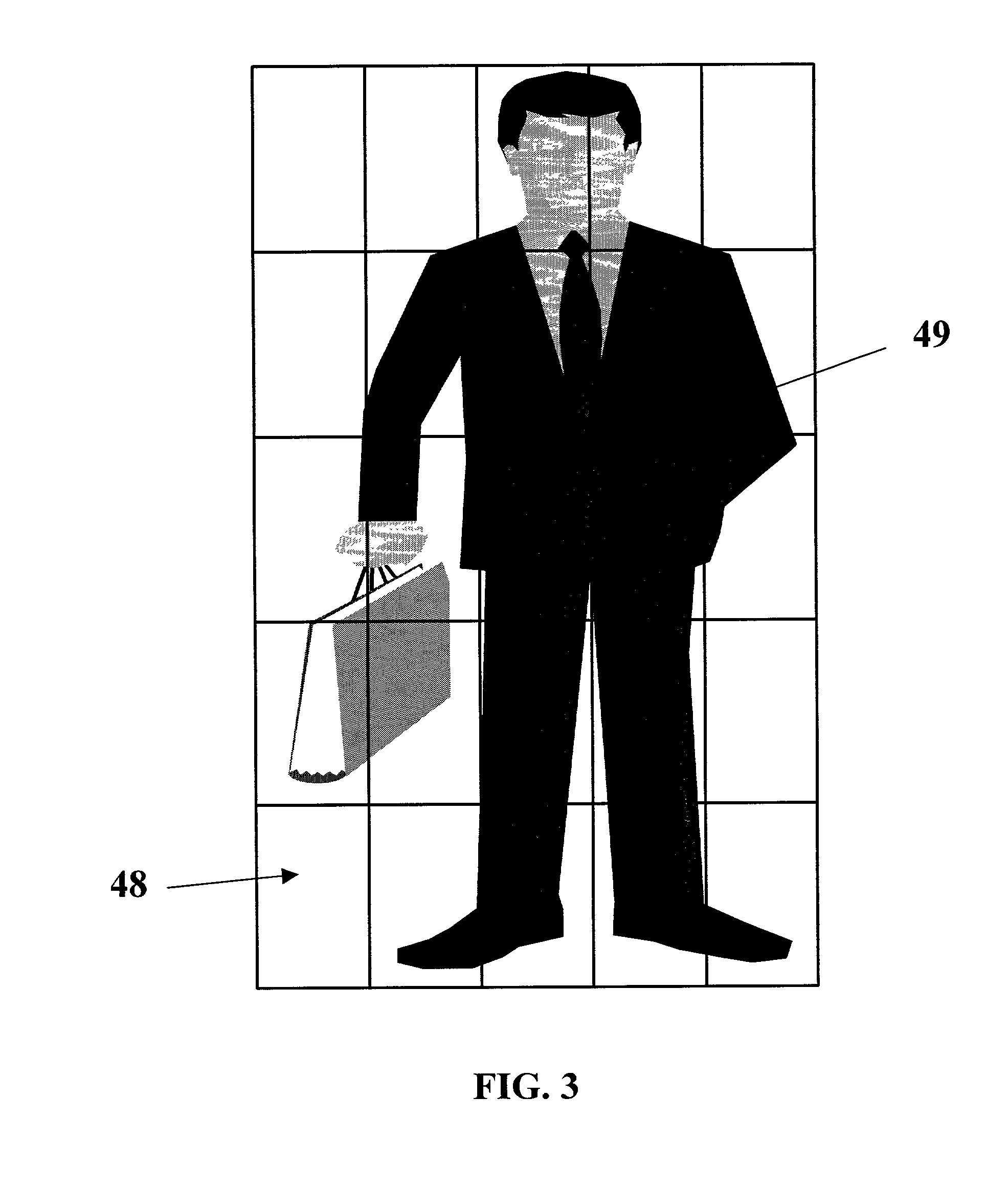
System for automated screening of security cameras
InactiveUS20010033330A1Reduce numberReduce operator fatigueTelevision system detailsImage analysisTerrainImage analysis
The present invention involves a system for automatically screening closed circuit television (CCTV) cameras for large and small scale security systems, as used for example in parking garages. The system includes six primary software elements, each of which performs a unique function within the operation of the security system to provide intelligent camera selection for operators, resulting in a marked decrease of operator fatigue in a CCTV system. Real-time image analysis of video data is performed wherein a single pass of a video frame produces a terrain map which contains parameters indicating the content of the video. Based on the parameters of the terrain map, the system is able to make decisions about which camera an operator should view based on the presence and activity of vehicles and pedestrians, furthermore, discriminating vehicle traffic from pedestrian traffic. The system is compatible with existing CCTV (closed circuit television) systems and is comprised of modular elements to facilitate integration and upgrades.
Owner:CHECKVIDEO
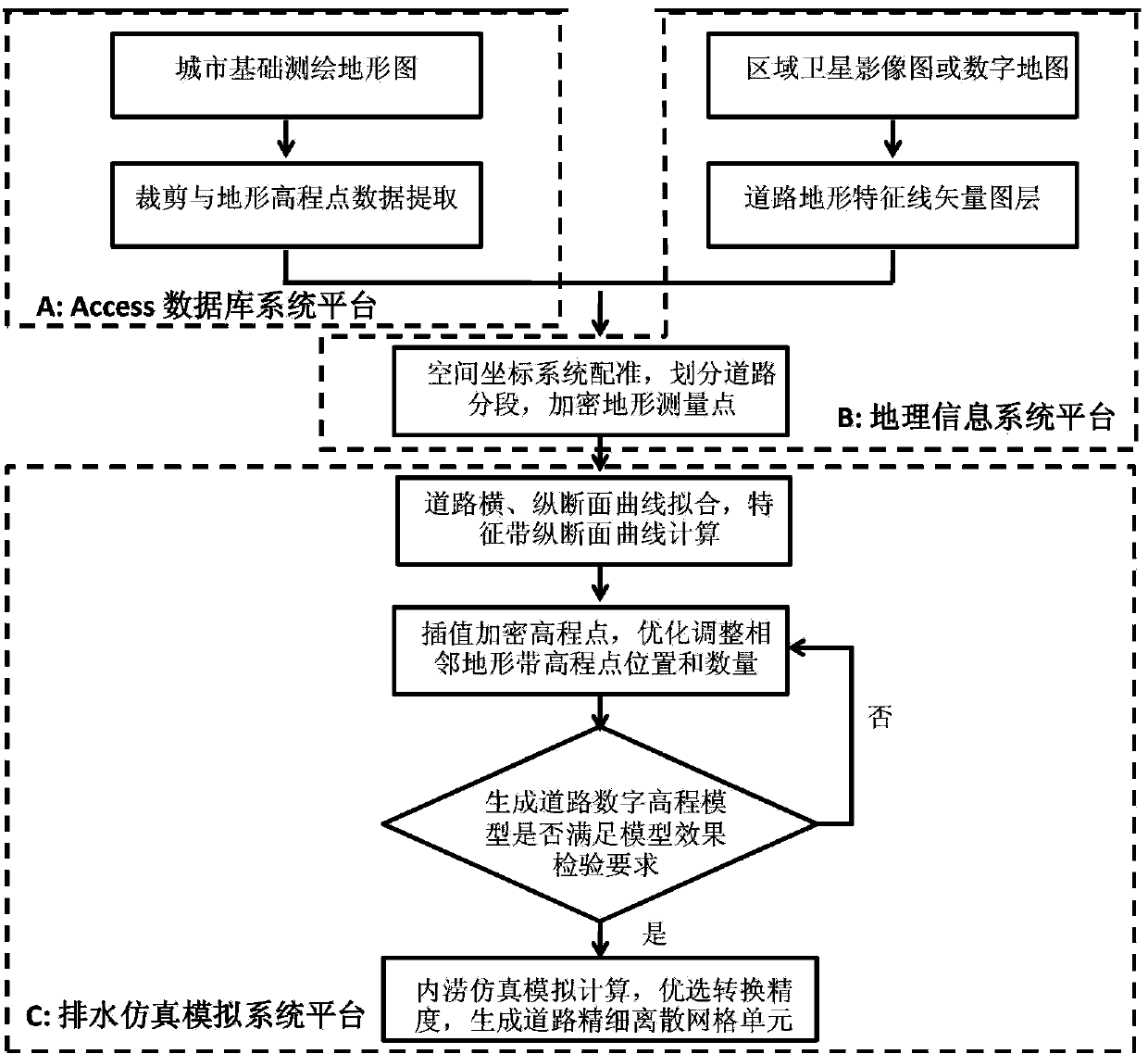
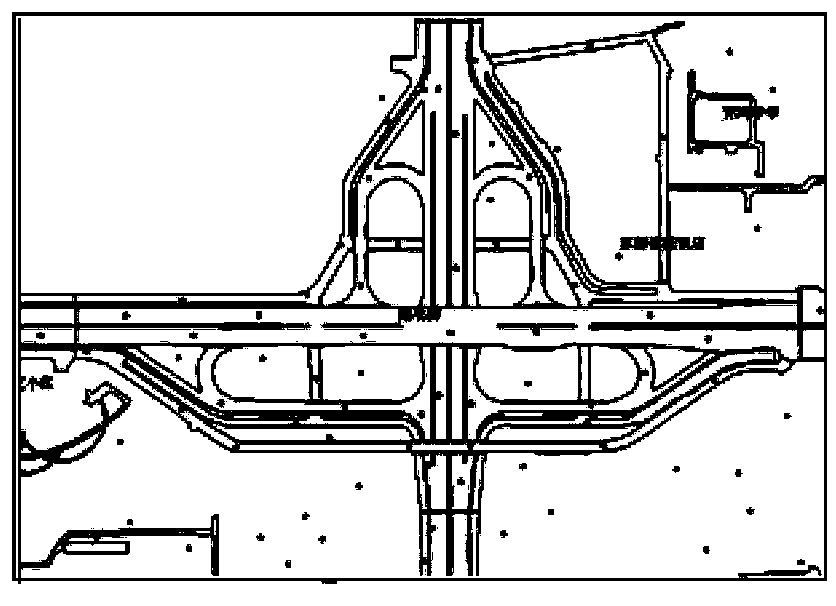
Method of constructing fine discrete road grid in urban drainage simulation system
InactiveCN103399990ARealize the expression of micro-topographic featuresBuild accuratelySpecial data processing applicationsTerrainMathematical model
The invention relates to a method of constructing a fine discrete road grid in an urban drainage simulation system and belongs to the cross field of municipal engineering information technology, database technology and geologic information system technology. From the demand on construction of a waterlogging simulation model, under the restraint conditions in road design specifications and on the basis of conventional map measured elevation points, the number and positions of interpolation points are optimized under the drainage simulation system platform by the fitting method of local elevation change curves of cross-longitudinal road section and by road characteristic terrain vector layers according to mathematical model interpolation encryption plane and elevation information of physical road tomography; accordingly, a fine discrete road elevation grid unit is constructed, true tomographic road features are expressed quickly and economically, the demand on precise simulation of waterlogging models is met, especially the dredging and resisting actions of road micro-tomographic features upon waterflow can be correctly expressed, and the method is significant to promotion and application of the drainage simulation technology.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Airborne, tethered, remotely stabilized surveillance platform
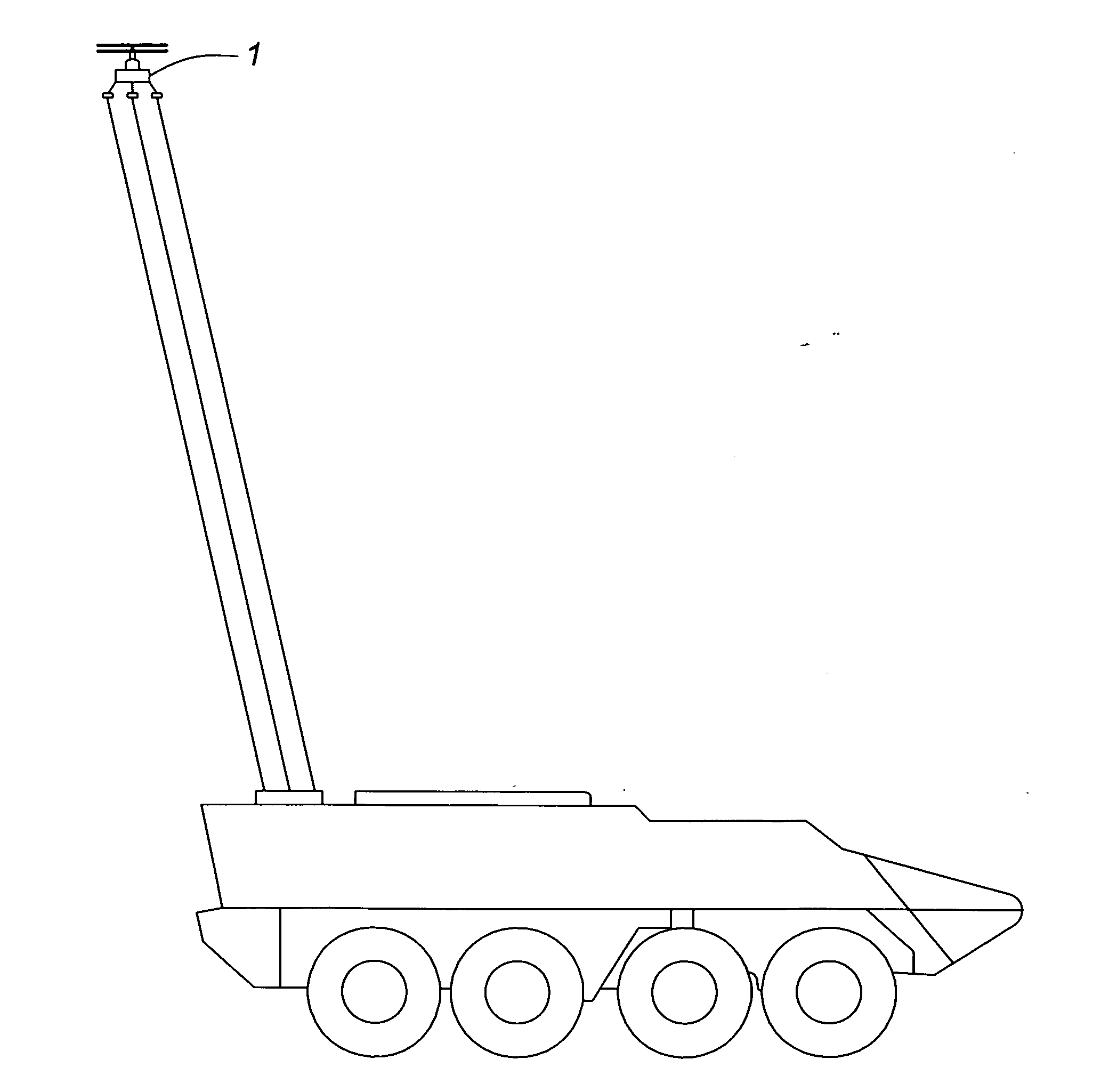
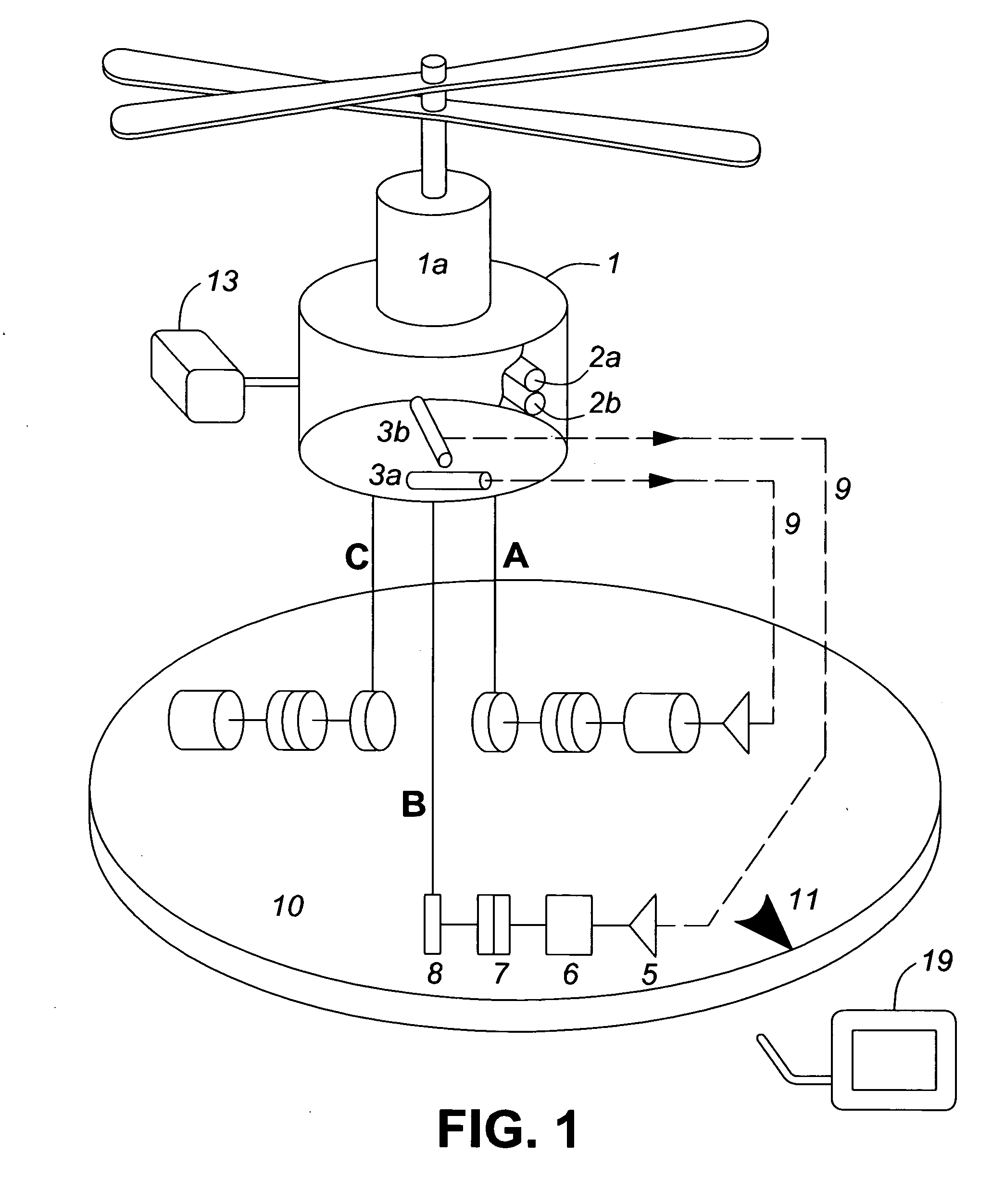
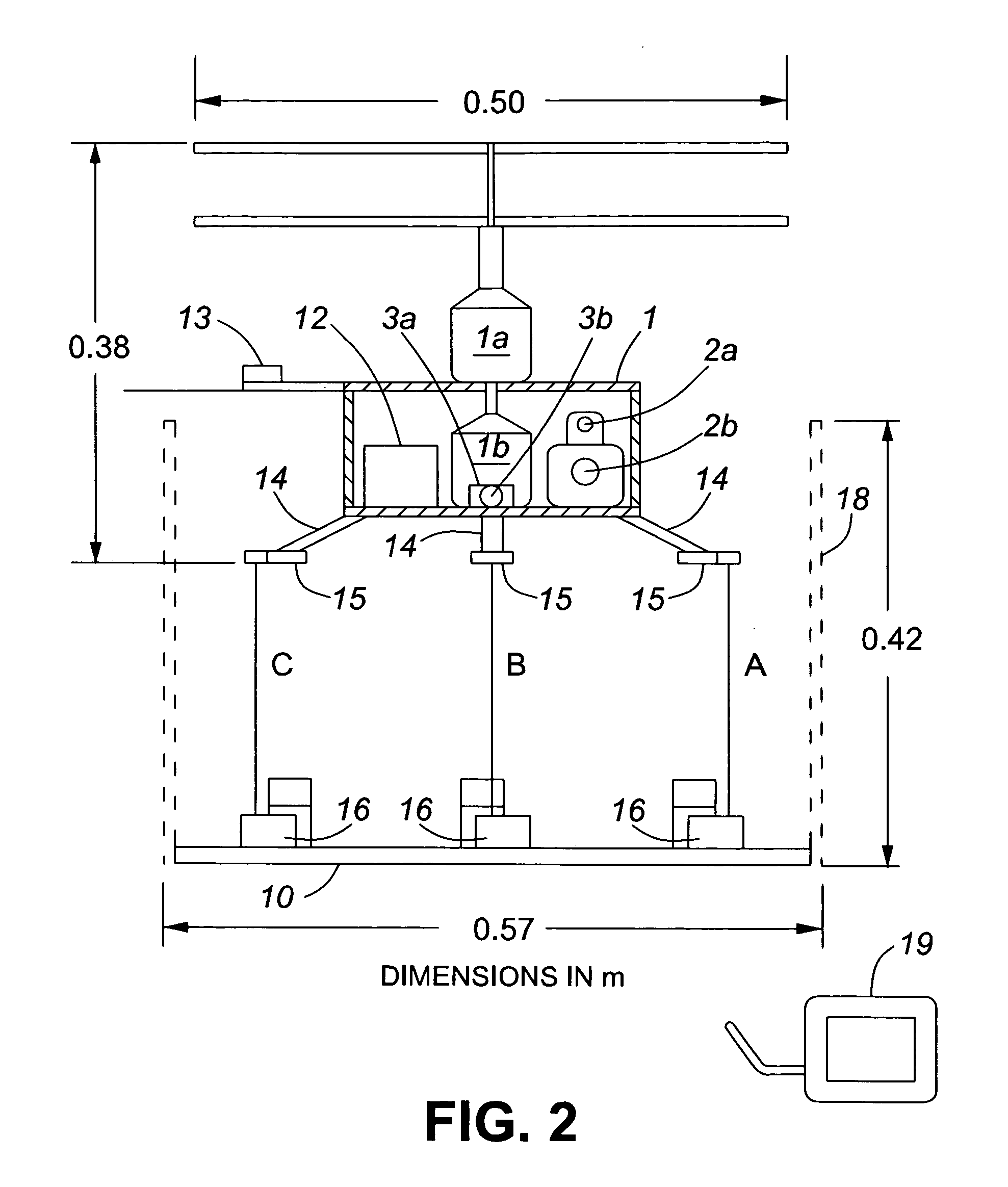
An airborne surveillance platform supporting optoelectronic and electronic sensors, including level sensors, is automatically stabilized in a horizontal plane by varying the length of two tethers out of three. Error signals from the level sensors are transmitted over a wireless link to control components on a rotating platform on the host vehicle, which automatically vary the length of tethers. Applications include images of the surrounding terrain generated by a video camera and a thermal imager in military, police and civil emergency operations.
Owner:PETROV DIMITRI
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) adopted plant protection system, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for plant protection and its control method
PendingCN106020233AGuarantee the quality of plant protection workImprove work efficiencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsUncrewed vehicleTerrain mapping
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) adopted plant protection system, an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for plant protection and its control method. The control method comprises the following steps: obtaining the terrain image of a working area; acquiring the GIS information based on the terrain image calculation so as to automatically plan the working path of one unmanned aerial vehicle or more and controlling the unmanned aerial vehicle(s) in operation according to the working path for plant protection. Therefore, on the one hand, it is possible to make an unmanned aerial vehicle(s) carry out plant protection autonomously according to the planned working path and ensure the quality of plant protection. On the other hand, operators do not need to control the UAV(s) manually, and multiple unmanned aerial vehicles can work simultaneously, meaning that working efficiency can be increased substantially.
Owner:聂浩然
Scanning Non-Scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS20130044309A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptoelectronicsVisual perception
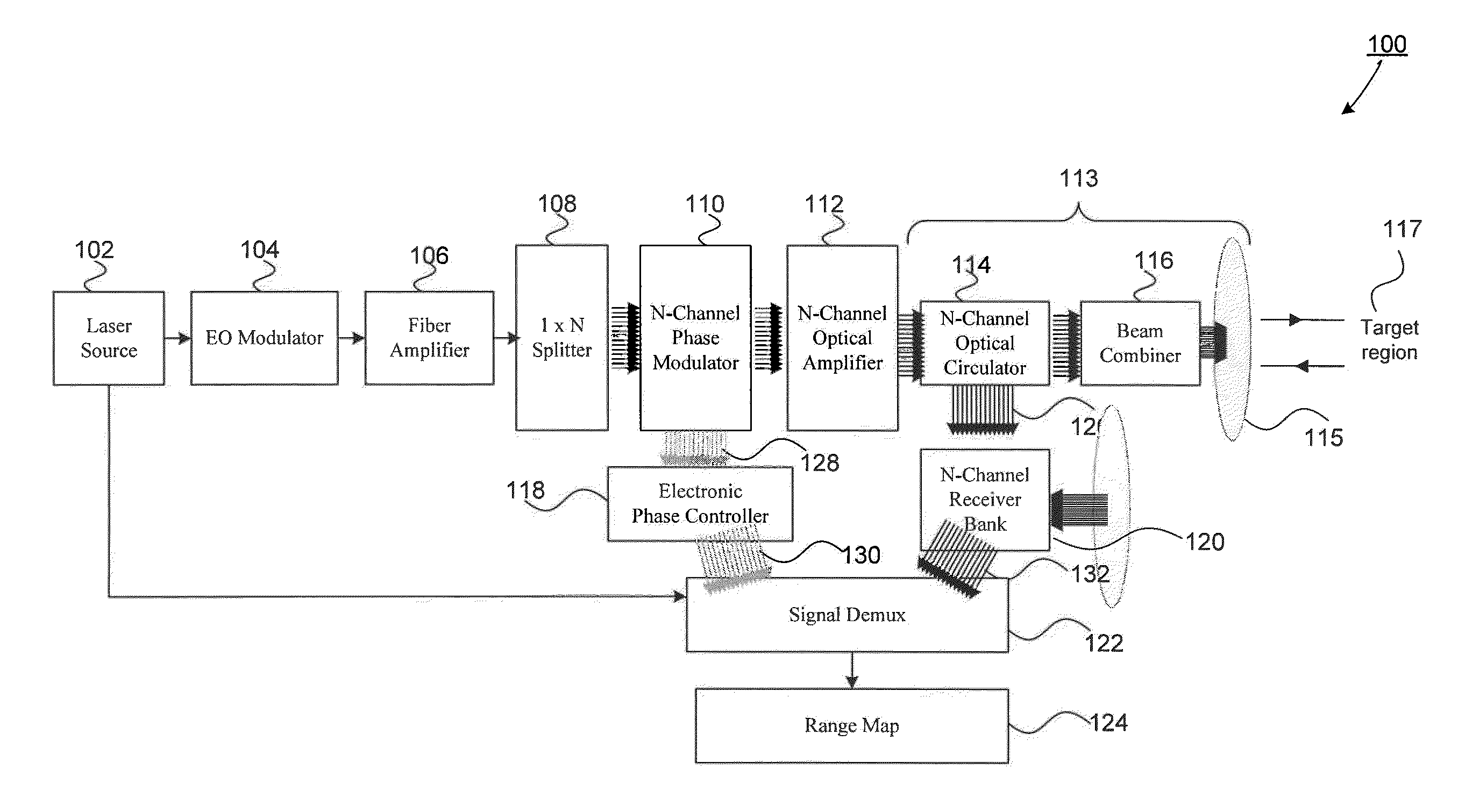
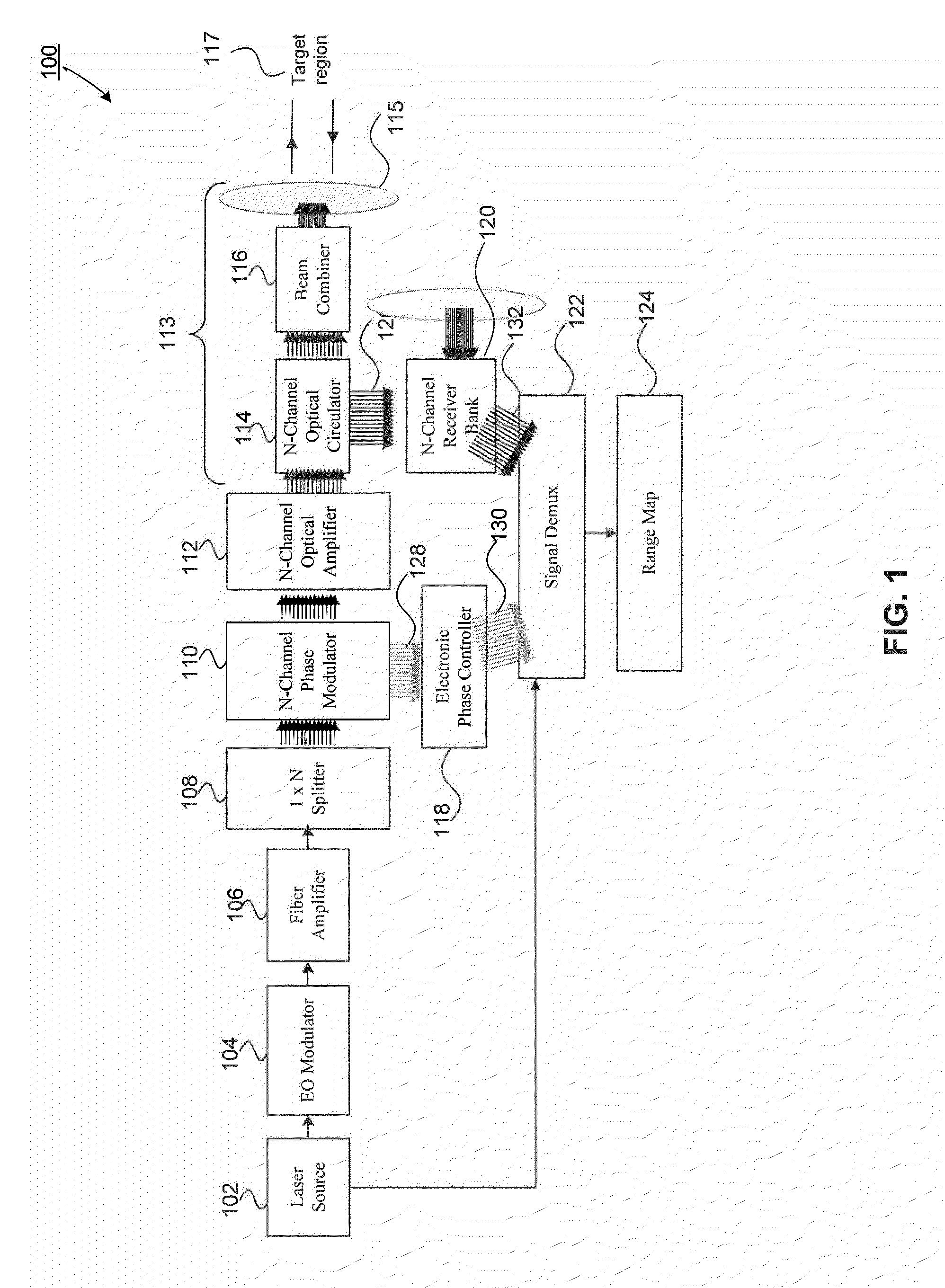
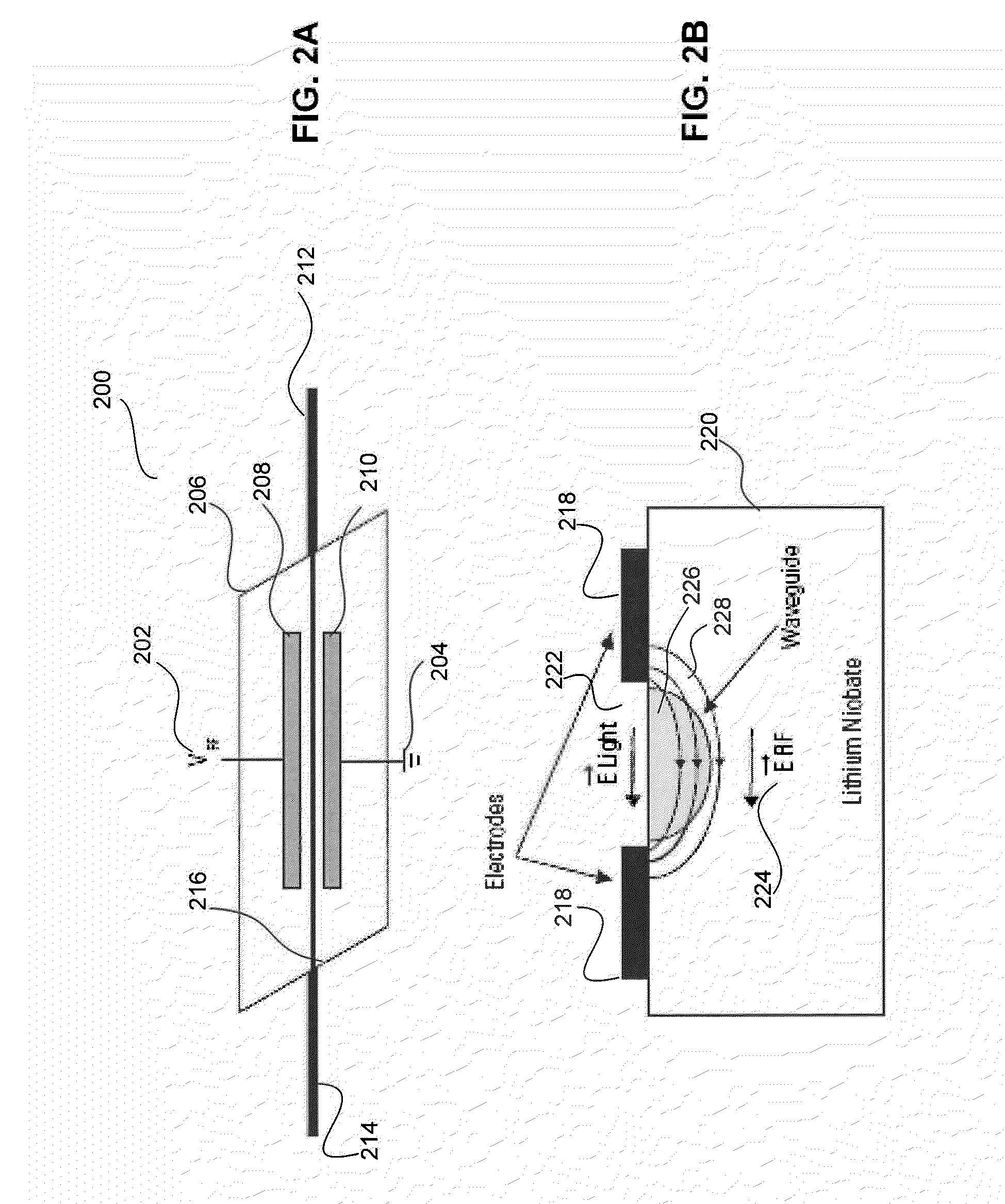
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
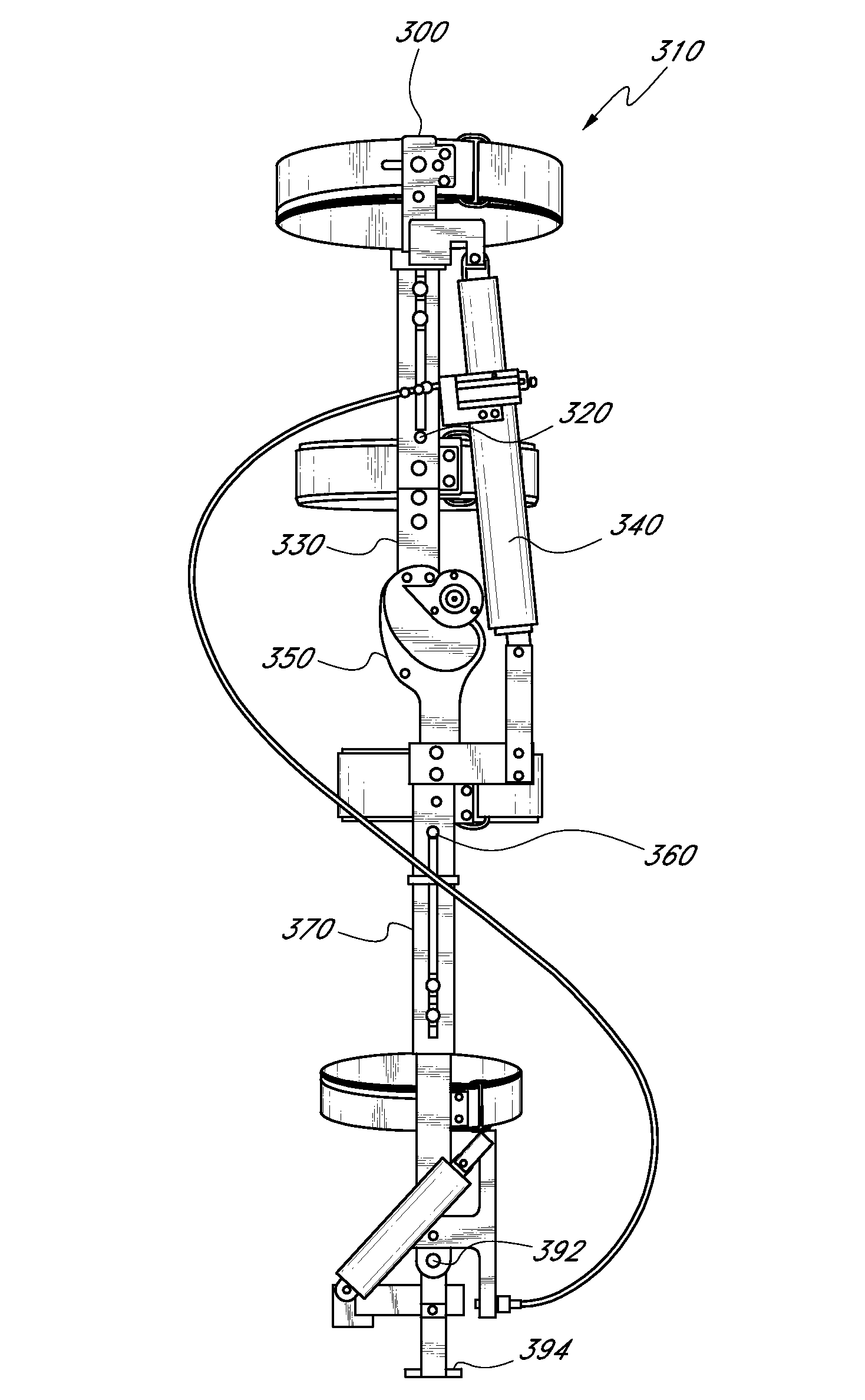
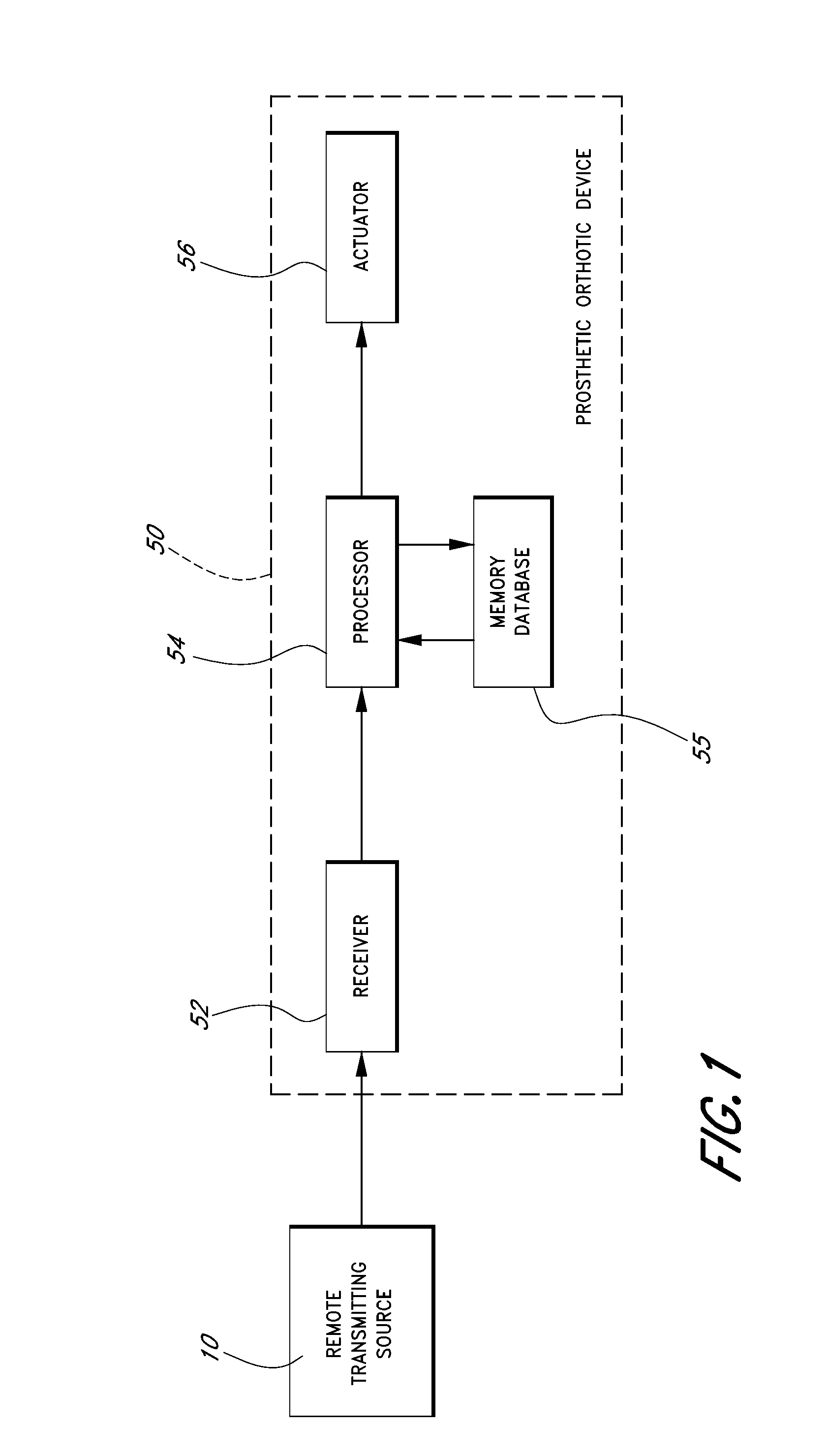
Feedback control systems and methods for prosthetic or orthotic devices
Methods and systems are used for monitoring a global position or location of a prosthetic or orthotic device and to provide feedback control of the device. Certain methods may employ remote transmitting devices and receivers to recognize when a prosthetic or orthotic device user is in a moving vehicle and, therefore, initiate automatic shut-off, driving mode, or relaxed mode. Other methods may employ remote transmitting devices and receivers to identify the global position of the prosthetic or orthotic device, compare the global position to a stored terrain mapped database and output feedback control instructions and / or alerts to the prosthetic or orthotic device based at least in part on the stored terrain mapping information.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Obstacle and terrain avoidance sensor
A method and apparatus for terrain mapping and / or obstacle detection for aircraft, including (a) transmitting a non-scanning beam that illuminates the terrain and / or obstacles; (b) receiving a Doppler shifted signal that is Doppler frequency shifted by an amount dependent on an angle between a line of flight of the aircraft and scatterers that reflect the transmitted beam; (c) determining the angle from the Doppler frequency; (d) determining the range of at least some of said scatterers; and (e) determining the azimuth and elevation of the scatterers.
Owner:RODRADAR LTD
Increasing measurement rate in time of flight measurement apparatuses
An apparatus for measuring distance to a surface is disclosed. The apparatus transmits at least one subsequent pulse of light prior to receiving a reflection of a previously sent pulse of light. Thus, multiple pulses of light are in-flight at a given time. The embodiments are applicable to terrain mapping, bathymetry, seismology, detecting faults, biomass measurement, wind speed measurement, temperature calculation, traffic speed measurement, military target identification, surface to air rangefinding, high definition survey, close range photogrammetry, atmospheric composition, meteorology, distance measurement, as well as many other applications. Examples of such apparatuses include laser ranging systems, such as light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, and laser scanners. Data received from the apparatus by a data processing unit can be used to create a data model, such as a point cloud, digital surface model or digital terrain model describing the surface, terrain, and / or objects.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Scanning non-scanning LIDAR
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
Spectral mixture process conditioned by spatially-smooth partitioning
InactiveUS20050047663A1Accurate global labelingImprove global labelingScene recognitionClassification methodsEnergy functional
A method that facilitates identification of features in a scene enables enhanced detail to be displayed. One embodiment incorporates a multi-grid Gibbs-based algorithm to partition sets of endmembers of an image into smaller sets upon which spatial consistency is imposed. At each site within an imaged scene, not necessarily a site entirely within one of the small sets, the parameters of a linear mixture model are estimated based on the small set of endmembers in the partition associated with that site. An, enhanced spectral mixing process (SMP) is then computed. One embodiment employs a simulated annealing method of partitioning hyperspectral imagery, initialized by a supervised classification method to provide spatially smooth class labeling for terrain mapping applications. One estimate of the model is a Gibbs distribution defined over a symmetric spatial neighborhood system that is based on an energy function characterizing spectral disparities in both Euclidean distance and spectral angle.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Bump detection and effect reduction in autonomous systems
In one embodiment, a control system for a base station includes a first transceiver configured to receive a first signal and send a second signal to an agricultural vehicle. The first signal indicates at least an acceleration of the vehicle, a current velocity of the vehicle, and a location relative to a terrain where the vehicle experienced the acceleration, and the second signal indicates a vehicle target velocity. The control system includes a controller configured to determine a bump severity value based on the acceleration and the current velocity of the vehicle, mark an area indicative of the bump on a map of the terrain when the bump severity value exceeds a threshold, and automatically generate the second signal when the vehicle enters the area. The target velocity is based on a proximity of the vehicle to the bump, the bump severity value, or some combination thereof.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS +1
Electro-magnetic propagation modeling
ActiveUS7433652B2Efficient of admissibilityEffective calculationDirection finders using radio wavesTransmission monitoringCommon frameworkData acquisition
A generalized framework is disclosed in which a wide variety of propagation models can be cast in a matrix-based format using arbitrary matrix coefficients. Casting propagation models in the matrix-based framework enables efficient computer implementation and calculation, ease of tuning, admissibility, and aggregating multiple propagation models into a single matrix-based model. Matrix-based propagation models based on transmitter-receiver azimuth orientation, transmitter antenna height, terrain elevation, and clutter are also disclosed. The propagation models can be used in conjunction with automated data acquisition from information sources such as topographic maps, clutter maps, etc.
Owner:POLARIS WIRELESS
System and method for combining independent scene layers to form computer generated environments
A system and method is provided for combining independent scene layers to form computer generated environments. The method includes the operation of constructing a terrain layer using stored terrain data. Another operation is generating a feature layer using feature layer data that is stored separately from the stored terrain data. The feature layer and the terrain layer can then be combined to form a composite scene.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS SIMULATION & TRAINING SOLUTIONS
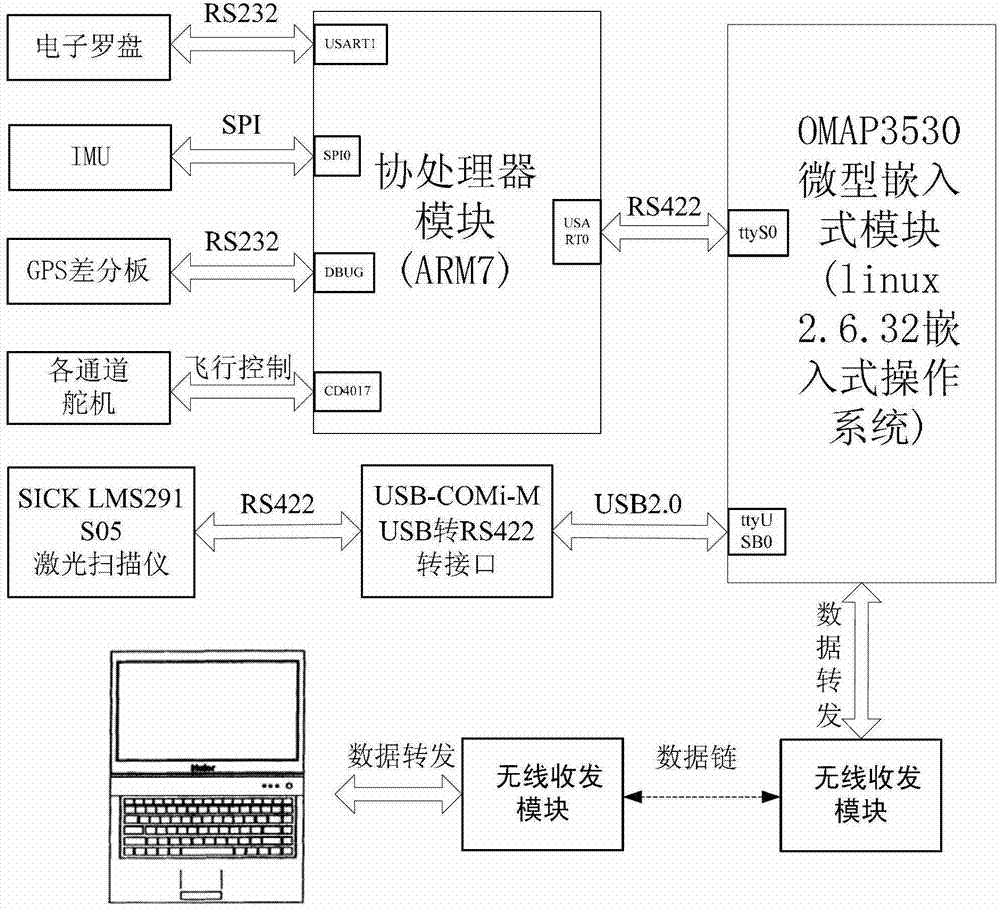
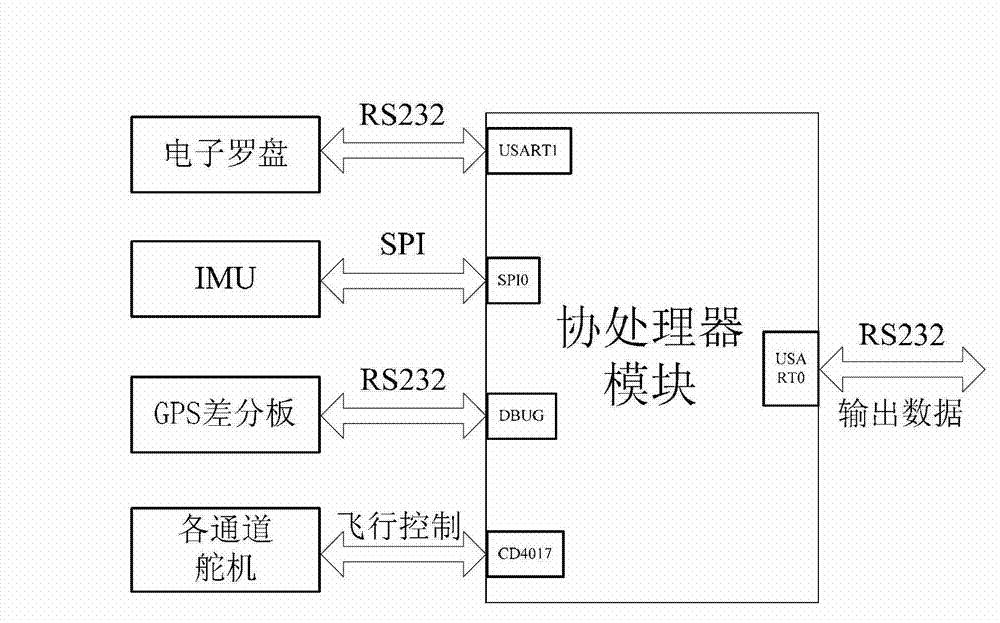
Extreme-low-altitude laser radar digital terrain mapping system and extreme-low-altitude laser radar digital terrain mapping method of small-sized unmanned helicopter
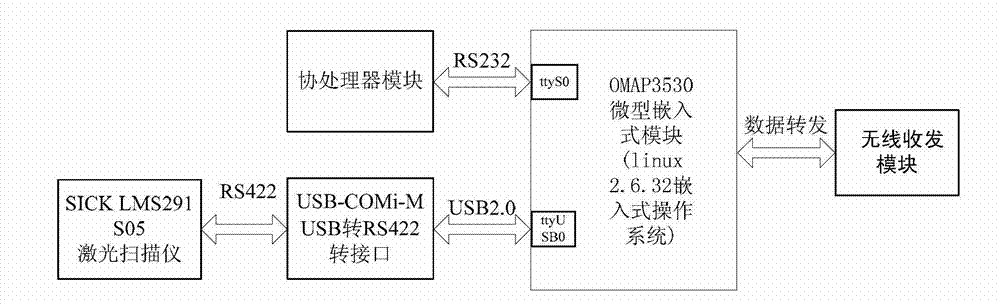
ActiveCN102928846AGuaranteed synchronicityReal-time acquisitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationCoprocessorRadar
The invention discloses an extreme-low-altitude laser radar digital terrain mapping system and an extreme-low-altitude laser radar digital terrain mapping method of a small-sized unmanned helicopter. The system is formed by an airborne system and a ground station system, wherein the airborne system is used for accurately collecting data of each sensor, carrying out synchronization processing on the data of the sensors and navigation control of the unmanned helicopter, and can realize data interaction with data of the ground station system through wireless receiving and dispatching equipment; the ground station system is used for receiving and processing data from an airborne laser radar hardware system or checking and processing a data file in an offline manner; the airborne system is formed by a coprocessor and a main processor; and the coprocessor is used for collecting gesture data and position data of the system or realizing the navigation control of the airborne system. According to the extreme-low-altitude laser radar digital terrain mapping system, a mode of matching the coprocessor with the main processor is utilized so that the requirements of the instantaneity and the stability of the navigation control of the small-sized unmanned helicopter are guaranteed, the system is flexible and the function of the airborne system is conveniently expanded; and the system has the advantages of low power consumption, low cost, high integration, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
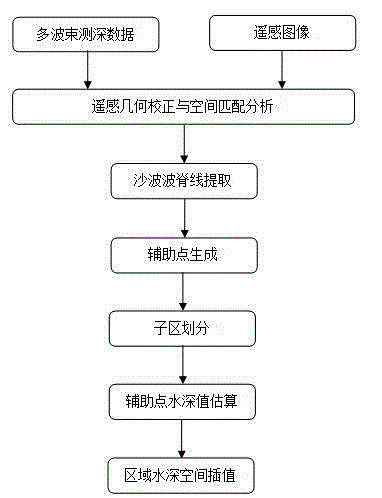
Shallow sea sand wave area multi-beam sounding terrain reconstruction method based on remote sensing image features
The invention provides a novel shallow sea sand wave area multi-beam sounding terrain reconstruction method based on remote sensing image features. Terrain reconstruction is conducted to multi-beam sounding data which are obtained in an interval type measuring line mode by that feature information (sand wave ripples and wave crests) and a sand wave terrain distribution law are utilized, wherein the feature information (sand wave ripples and wave crests) and the sand wave terrain distribution law of the shallow sea sand wave terrain are presented in a remote sensing image. Therefore, integrated sand wave terrain information is obtained. The shallow sea sand wave area multi-beam sounding terrain reconstruction method based on the remote sensing image features aims at terrain mapping requirements of wide distributed shallow sea sand wave terrain areas. Sand wave textures and sand wave crest lines in the remote sensing image are served as reference control information to lead into the multi-beam sounding data terrain reconstruction. High-accuracy shallow sea sand wave area terrain can be reconstructed through the multi-beam sounding data, wherein the multi-beam sounding data are obtained in an interval type measuring line mode. The shallow sea sand wave area multi-beam sounding terrain reconstruction method based on the remote sensing image features is an innovation of a cross application aspect of remote sensing information technology and multi-beam sounding technology. The shallow sea sand wave area multi-beam sounding terrain reconstruction method based on the remote sensing image features has great practical values.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Visual segmentation of lawn grass
ActiveUS20120212638A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Thresholding
This invention provides a method for identifying lawn grass comprising capturing an image of the terrain in front of a mower, segmenting the image into neighborhoods, calculating at least two image statistics for each of the neighborhoods, generating a binary representation of each image statistic. The binary representation of each image statistic is generated by comparing the calculated image statistic values to predetermined image statistic values for grass. The method further comprises weighting each of the binary representations of each image statistic, and summing corresponding neighborhoods for all image statistics. A binary threshold is applied to each of the summed neighborhoods to generate a binary map representing grass containing areas and non-grass containing areas.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV +1
Terrain data collection device and data collection method based on river work dynamic bed model
InactiveCN102538760AEasy to storeEasy to updateHydrodynamic testingPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryTopographic profileSynchronous motor
The invention discloses a terrain data collection device and a data collection method based on a river work dynamic bed model. The device comprises a support, a data acquisition system, a computer and a power supply, wherein the support comprises two panels and two mutually parallel rail beams; the data acquisition system comprises a translation device, a terrain profile acquisition device and an image collection and correction device; the translation device comprises a bearing platform, a lifting motor, a traction motor and a counter weight; the terrain profile acquisition device comprises an upper stable plate, a lower stable plate, a synchronous motor, an electronic cloud platform and a line laser; and the image collection and correction device comprises a framework, a camera, a universal rod and a point laser. The terrain data collection device based on the river work dynamic bed model has the beneficial effects that the collected terrain image information is rich and intuitive, and is easy to store and update; point-group-type collection is carried out on the terrain surface information, thus the measuring efficiency is improved greatly; the measuring belongs to non-contact-type measuring which can avoid the damage of the measuring terrain form and is suitable for measurement of terrains under various conditions; and the device provided by the invention is simple in structure, low in cost and easy to popularize.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
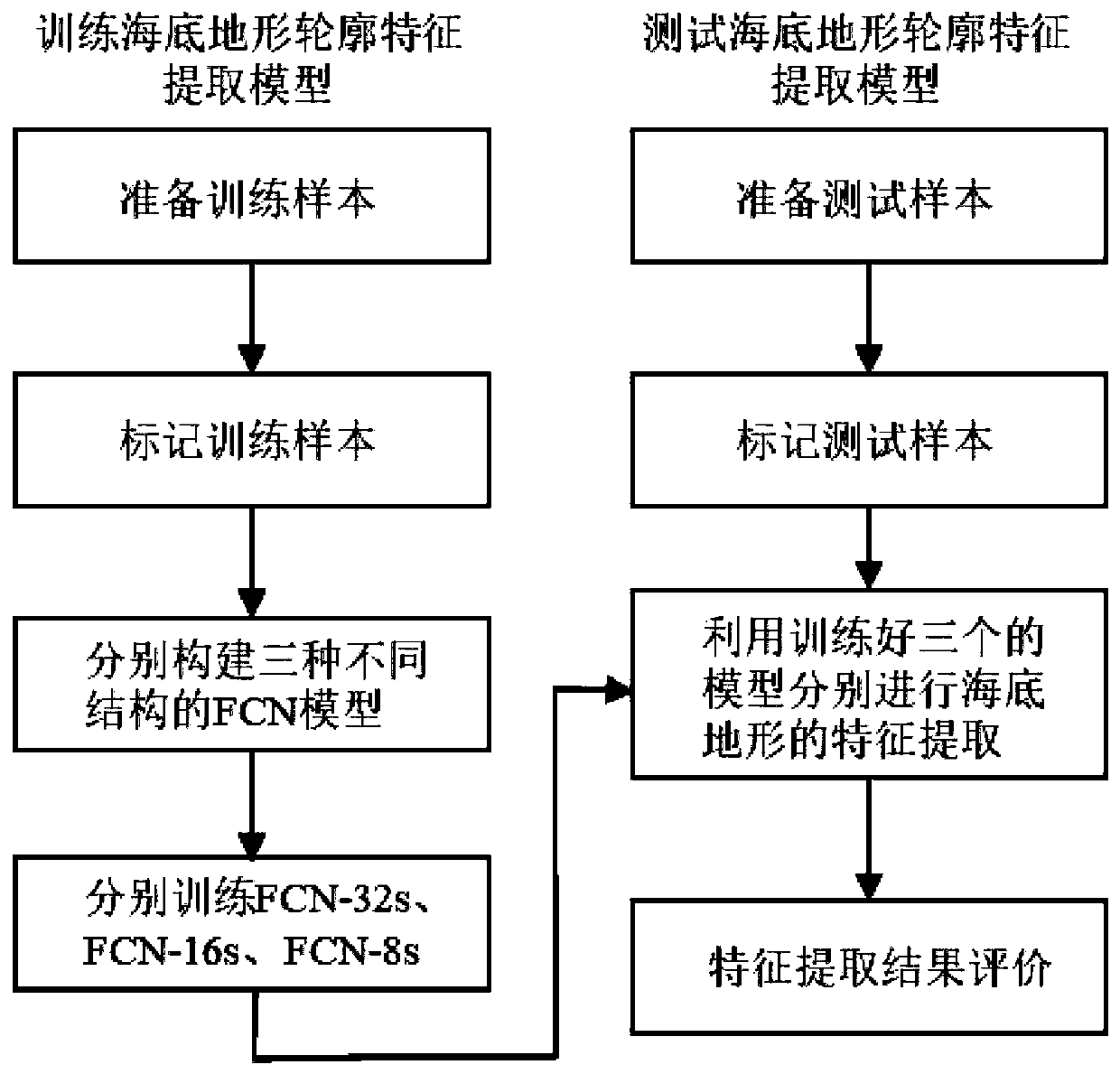
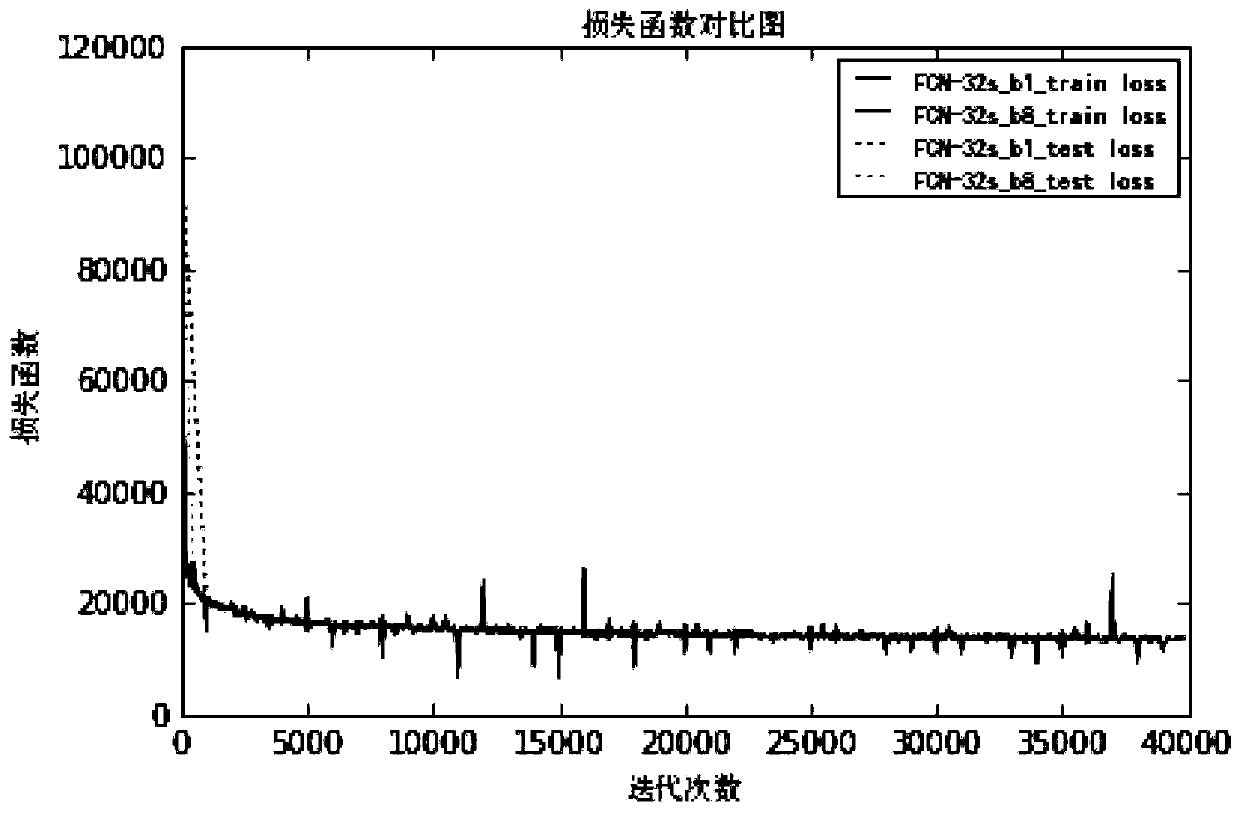
Side-scan sonar image feature extraction method based on full convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110781924AOvercome speedOvercome efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesEngineeringNetwork model
The invention provides a side-scan sonar image feature extraction method based on a full convolutional neural network. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out the data augmentation through an original sonar image, and set needed by model training and testing; manually labeling the edge area of the submarine topography of each image in the sample set, distinguishing a target and a background, and obtaining a model training and testing label graph; an FCNs model is constructed; inputting the submarine topographic map and the corresponding label map into a network, training the network by adopting a small-batch gradient descent method of a driving quantity item, and storing an optimal network model; comparing convergence and stability of the network under a random gradient descent method and a small-batch gradient descent method; and extracting terrain edge contour features, outputting a feature extraction result, and carrying out qualitative evaluation on the result. According to the method, complex preprocessing is not needed, and the sonar feature extraction method is high in speed, high in efficiency and high in speckle noise resistance; the performance of the network is improved, and the convergence and stability of each network model of the FCNs are ensured.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing wide area terrain mapping
ActiveUS20080103699A1Photogrammetry/videogrammetryLevel indicatorsWide areaComputer graphics (images)
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Airborne Reconnaissance System
The present invention relates to an airborne reconnaissance system for capturing images in a wide field of regard which comprises: (a) An array of a plurality of n prisms being one next to the other, each prism having an essentially flat and rectangular front surface, and at least an output surface wherein: (a1) a front surface of each of the plurality of prism is being directed toward a different section of a strip of terrain transversal to the flight direction of the aircraft, thereby collecting light rays coming mostly from that terrain strip section; (a2) each output surface of each of the prisms directs light rays which are received through said front prism surface toward a front lens of an optical unit; (b) A focal plane array; (c) Optical unit comprising a front lens, the front lens receiving light separately but simultaneously through the output surfaces of all the prisms, said optical unit comprises addition optics for directing the light received from said lens thereby to produce separate corresponding prism images on said focal plane array; (d) Control unit for periodically capturing all the images that are produced on the focal plane array at each instant, and transferring them into an electronic storage; and (e) Processing and combining unit for processing and combining all the separate stored prism images into a full image of the terrain relating to said wide field of regard.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT
Feedback control systems and methods for prosthetic or orthotic devices
Methods and systems are used for monitoring a global position or location of a prosthetic or orthotic device and to provide feedback control of the device. Certain methods may employ remote transmitting devices and receivers to recognize when a prosthetic or orthotic device user is in a moving vehicle and, therefore, initiate automatic shut-off, driving mode, or relaxed mode. Other methods may employ remote transmitting devices and receivers to identify the global position of the prosthetic or orthotic device, compare the global position to a stored terrain mapped database and output feedback control instructions and / or alerts to the prosthetic or orthotic device based at least in part on the stored terrain mapping information.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Method for extracting shallow sea terrain by single-shot high-resolution optical remote sensing image
InactiveCN104197902AReduce extraction costsReduce dependenceMeasuring open water depthPicture interpretationSea wavesShallow sea
The invention provides a method for extracting a shallow sea terrain by a single-shot high-resolution optical remote sensing image. The method comprises the following steps: performing information extraction and conversion treatment according to related theories by sea wave characteristic information (waves and change information thereof) presented in the optical remote sensing image to obtain near-shore shallow sea terrain information. Aiming at the terrain mapping requirements of a shallow sea region, the method for extracting the shallow sea terrain based on the single-shot high-resolution optical remote sensing image is built by the wave characteristic information on the high-resolution optical remote sensing image according to the shallow-water wave theory and the linear wave theory; the terrain information of the shallow sea region can be extracted by the single-shot high-resolution optical remote sensing image under the circumstance that any external initial parameter and control parameter are not input; the method is an innovation on the aspect of remote sensing information technology application, is a beneficial complement of near-shore shallow sea terrain measurement, and has a very high practical value.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Star Tracker-Aided Airborne or Spacecraft Terrestrial Landmark Navigation System
ActiveUS20180080787A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data information retrievalTerrainStar tracker
Methods and apparatus automatically determine a location, such as of an aircraft or spacecraft, by matching images of terrain below the craft, as captured by a camera, radar, etc. in the craft, with known or predicted terrain landmark data stored in an electronic data store. A star tracker measures attitude of the camera. Optionally, a rangefinder measures altitude of the camera above the terrain. A navigation filter uses the attitude, and optionally the altitude, to resolve attitude, and optionally altitude, ambiguities and thereby avoid location solution errors common in prior art terrain matching navigation systems.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Single-channel HRWS-SAR imaging method based on pulse phase encoding
InactiveCN107942327AEliminate Image Quality ImpactsSolve the distance blur problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDisaster monitoringAmbiguity
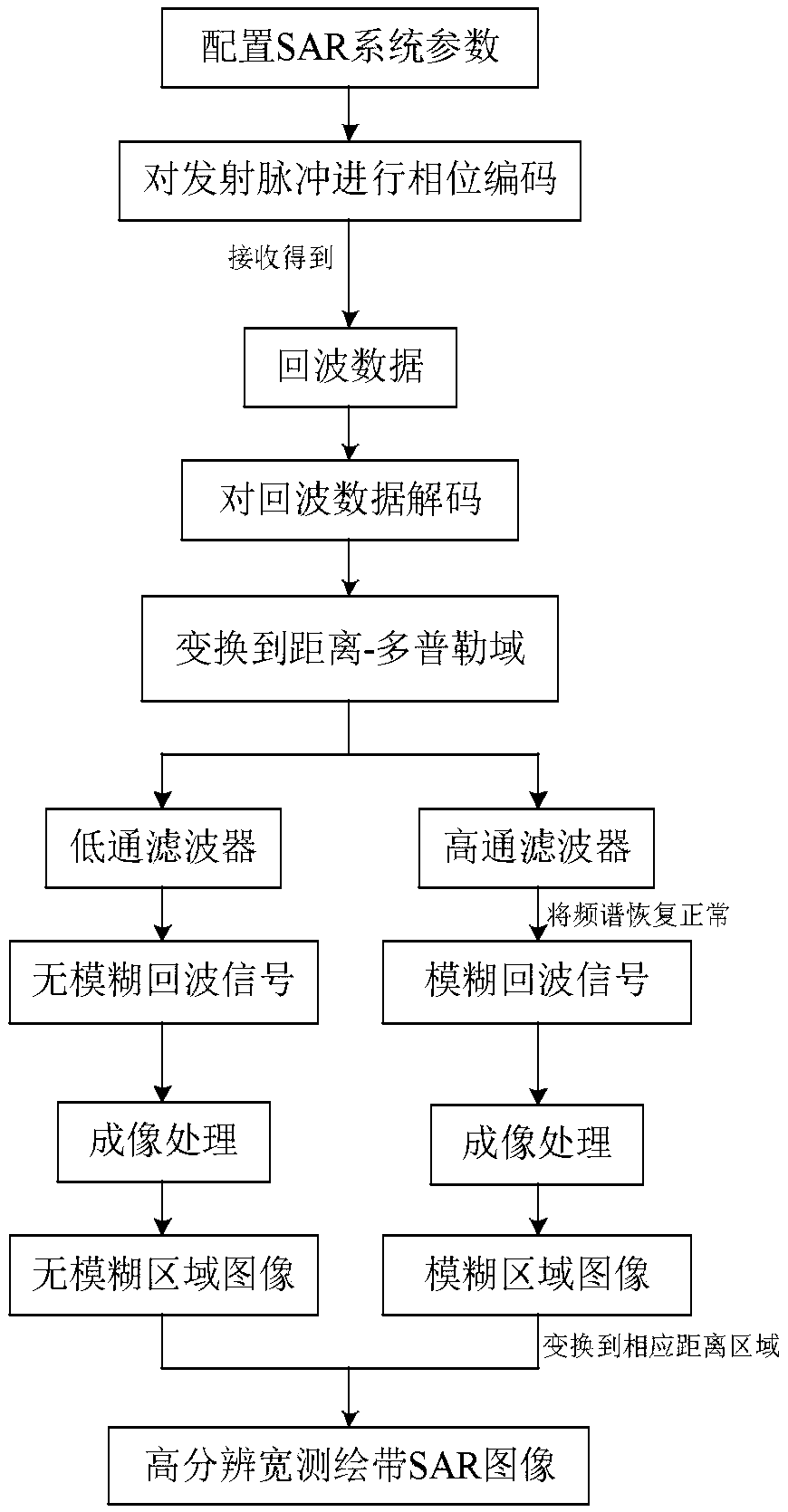
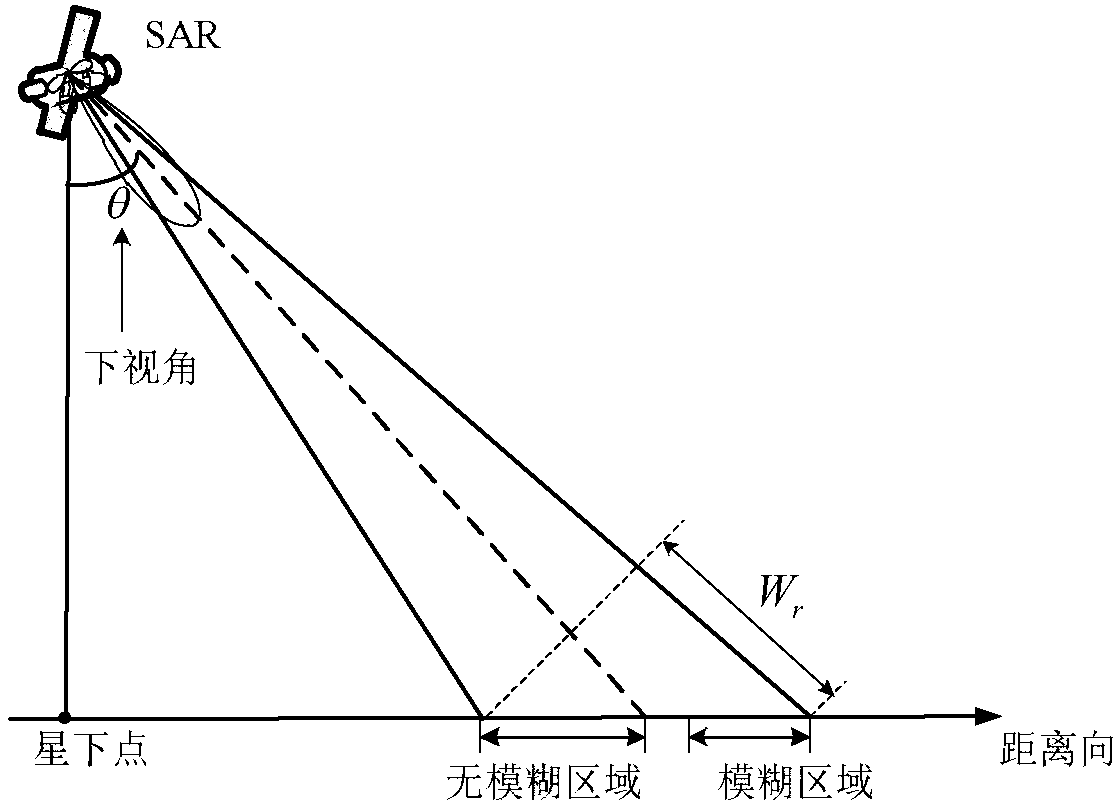
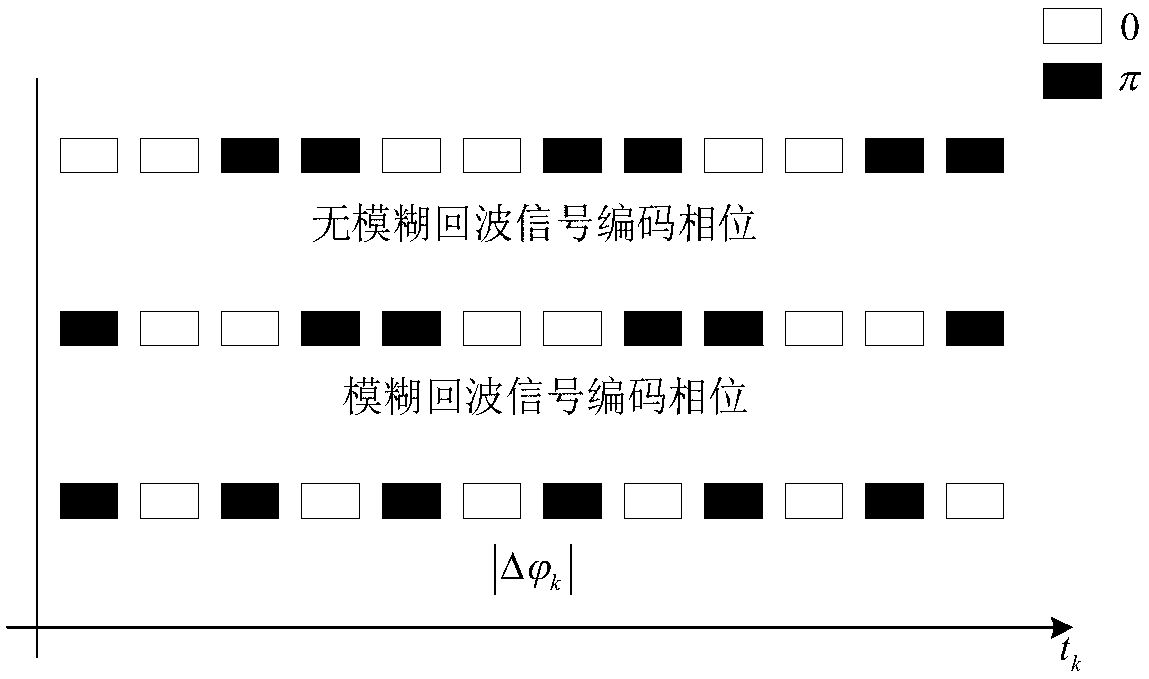
The invention discloses a single-channel HRWS-SAR imaging method based on pulse phase encoding, which mainly solves the contradiction between high resolution and wide swath in the existing single-channel SAR system. The single-channel HRWS-SAR imaging method comprises the steps of: configuring parameters of an SAR system, and ensuring that range ambiguity only appears once within a main beam illumination range; performing phase encoding on a transmitted pulse signal; decoding an entire echo signal; transforming the entire echo signal after decoding into a range-Doppler domain, and extracting an unambiguous echo signal and an ambiguous echo signal in the range-Doppler domain; and forming an image of an unambiguous region by utilizing the extracted unambiguous echo signal, and forming an image of an ambiguous region by utilizing the extracted ambiguous echo signal. The single-channel HRWS-SAR imaging method based on pulse phase encoding breaks through the constraints of the minimum antenna area on the single-channel SAR system, has low system complexity, requires few space resources, is easy in real-time processing, and can be applied to terrain mapping, environment and disaster monitoring, geological exploration, marine monitoring and investigation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Global detection method of unstructured outdoor terrains
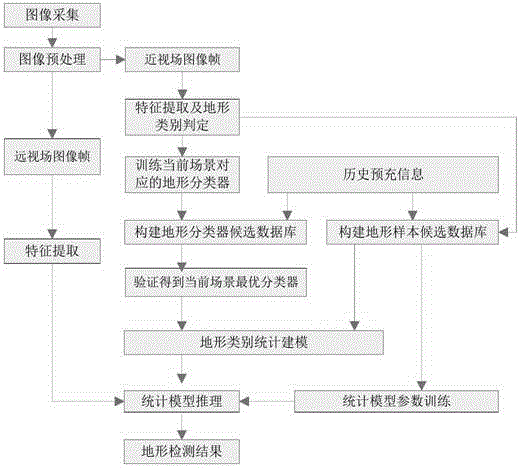
ActiveCN104700105AImprove stabilityHigh intelligenceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage segmentationModel parameters
The invention provides a global detection method of unstructured outdoor terrains in the technical field of robots. The method comprises the specific steps of image acquisition, image preprocessing, scene image segmentation, appearance characteristic extraction, terrain type judgment, terrain classifier candidate database establishment, current scene optimal classifier verification, terrain type statistical modeling, statistical model parameter training and statistical model reasoning. According to the global detection method, the navigation experience of different time points is integrated in principle, and the stability and the intelligence degree of terrain detection under the condition of uneven and even deficient view field samples are improved; a combined multi-layer sensor classifier adopted for the global detection method takes the uncertainty and the nonlinearity of the appearance-terrain mapping relation of the scenes into consideration, so that the accuracy of terrain detection can be improved; in addition, the space relations at variable scales in the current scene and the compatibility of types are modeled in principle, and the global detection of the unstructured outdoor terrains is realized.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
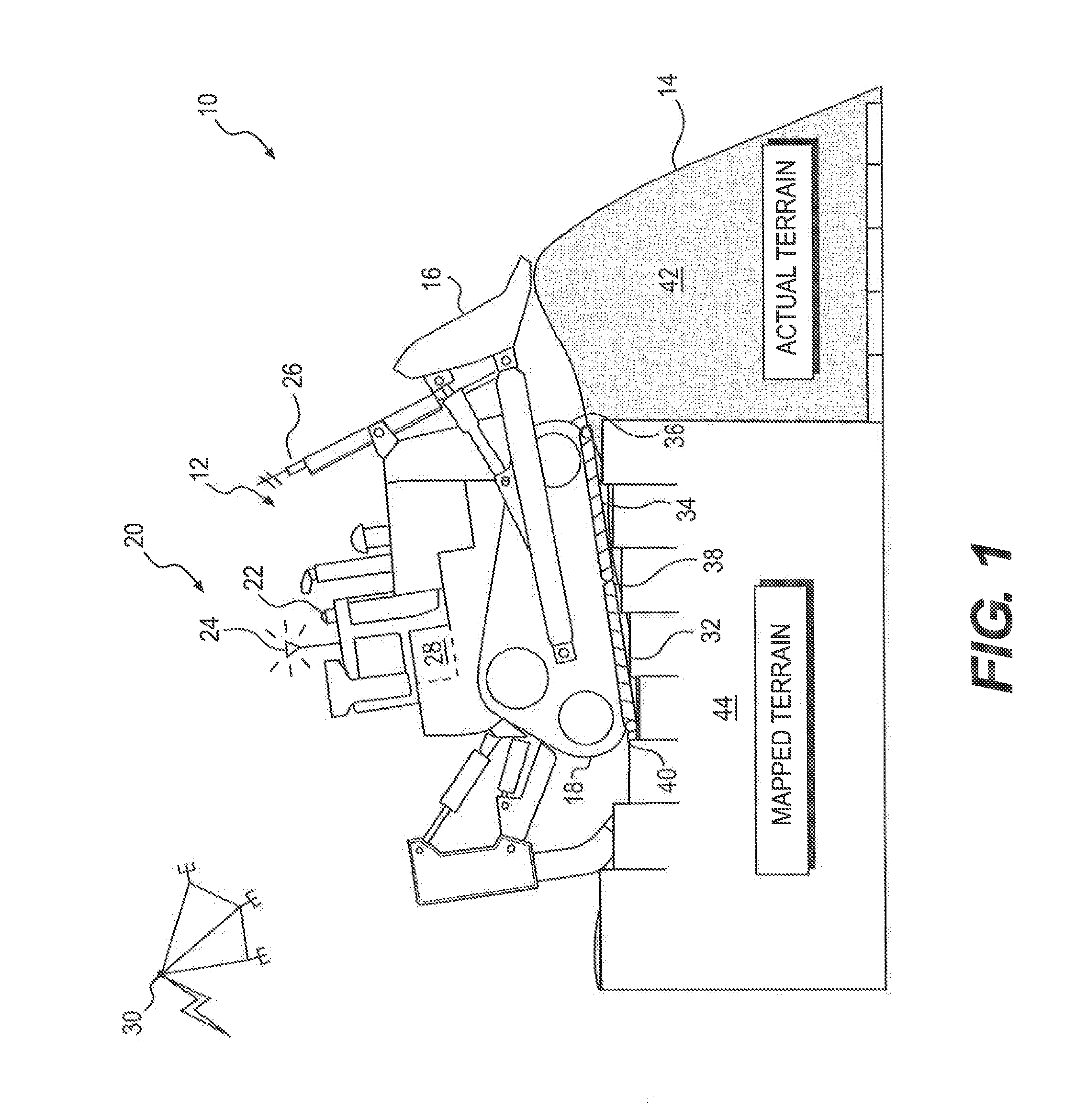
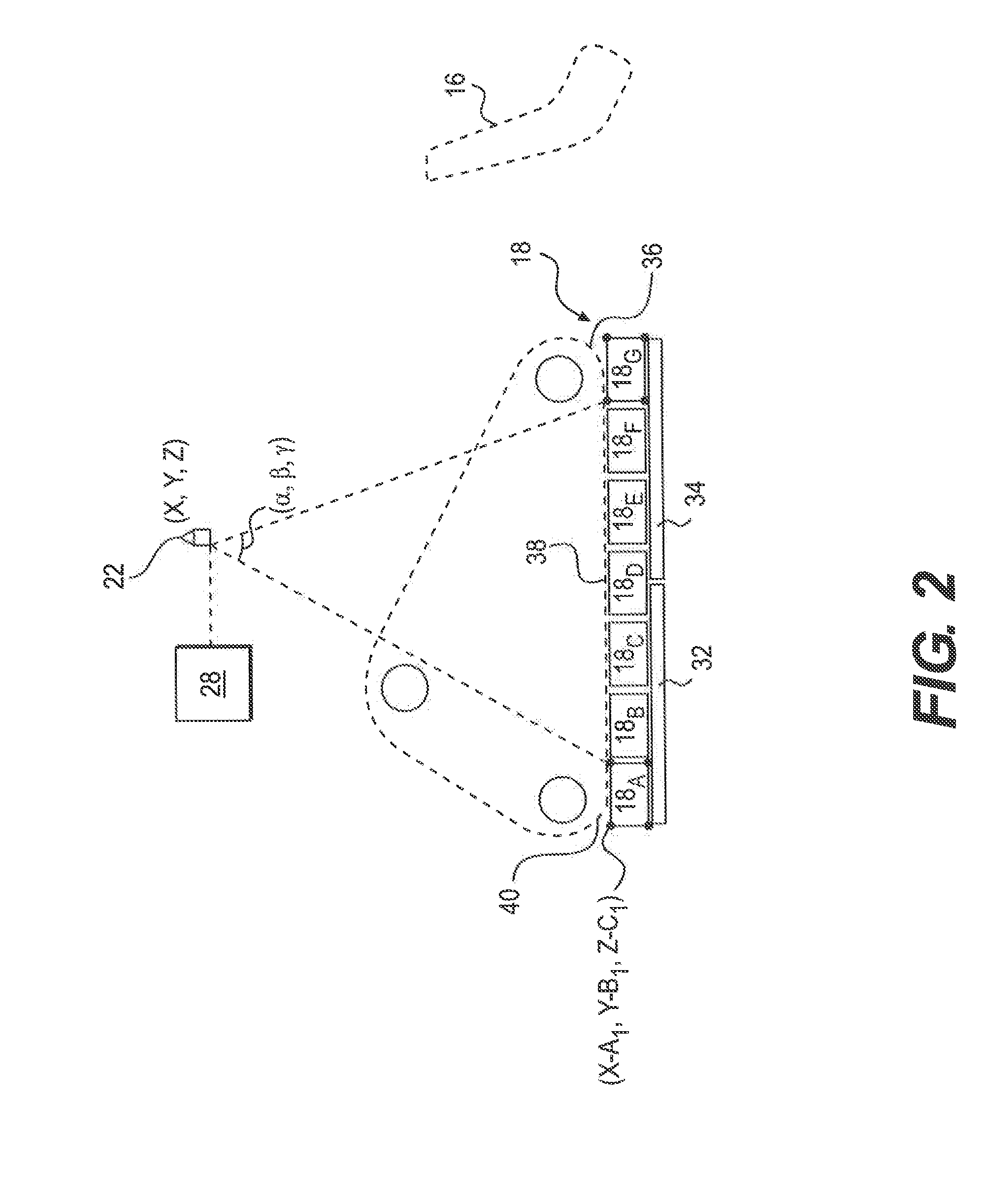
Terrain mapping system using virtual tracking features
ActiveUS20150198736A1Navigational calculation instrumentsProcess and machine controlComputer graphics (images)Engineering
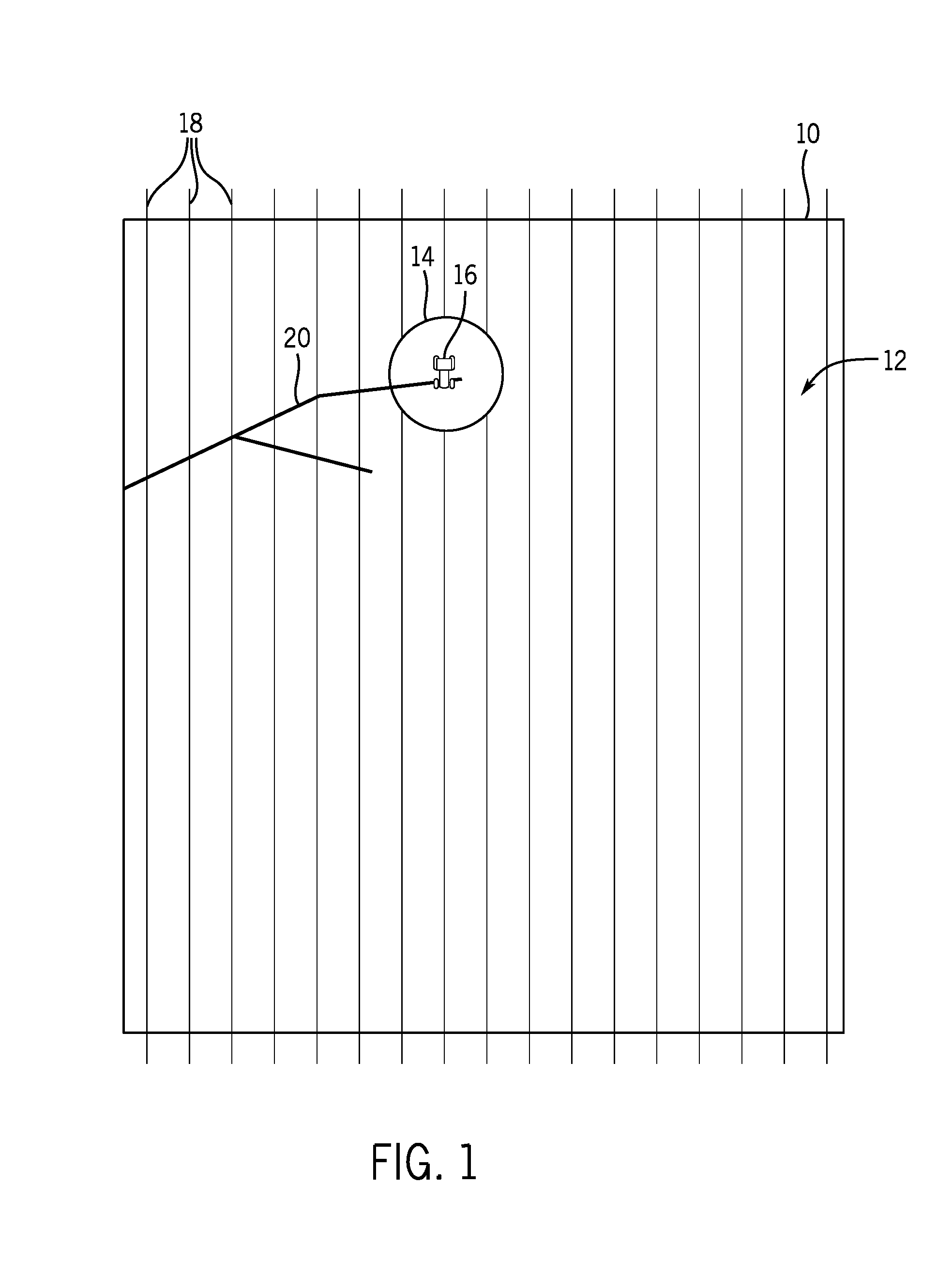
A terrain mapping system is disclosed for a machine having at least one traction device. The system may have a sensor associated with the machine and configured to generate a signal indicative of a position of the machine. The system may also have at least one controller in communication with the sensor. The at least one controller may be configured to receive the signal from the sensor, and divide an area between the at least one traction device and a work surface into a plurality of virtual tracking features based on the signal and known geometry of the machine. The at least one controller may also be configured to track movement of the plurality of virtual tracking features, and update an electronic terrain map of a worksite based on the movement of the plurality of virtual tracking features.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com