Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
190 results about "Tangential point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
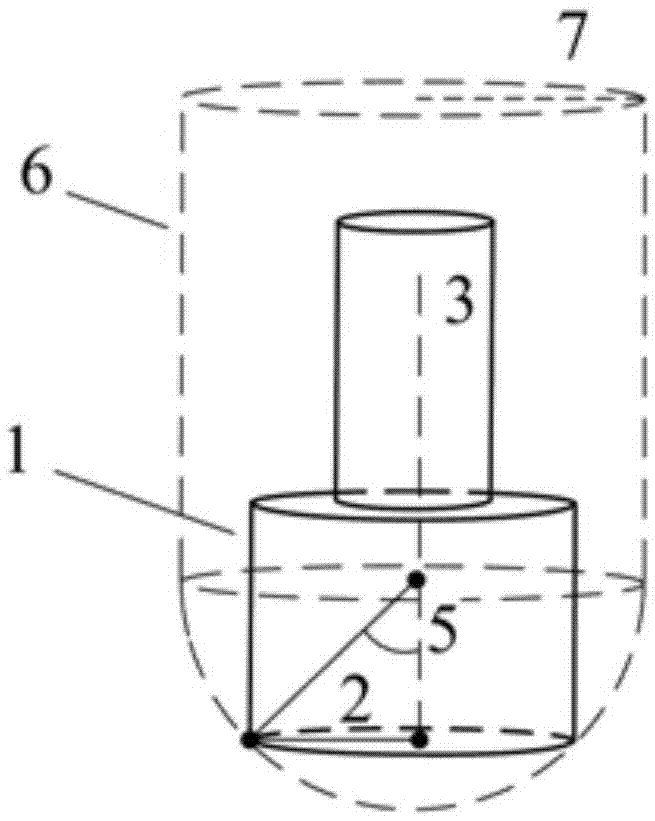
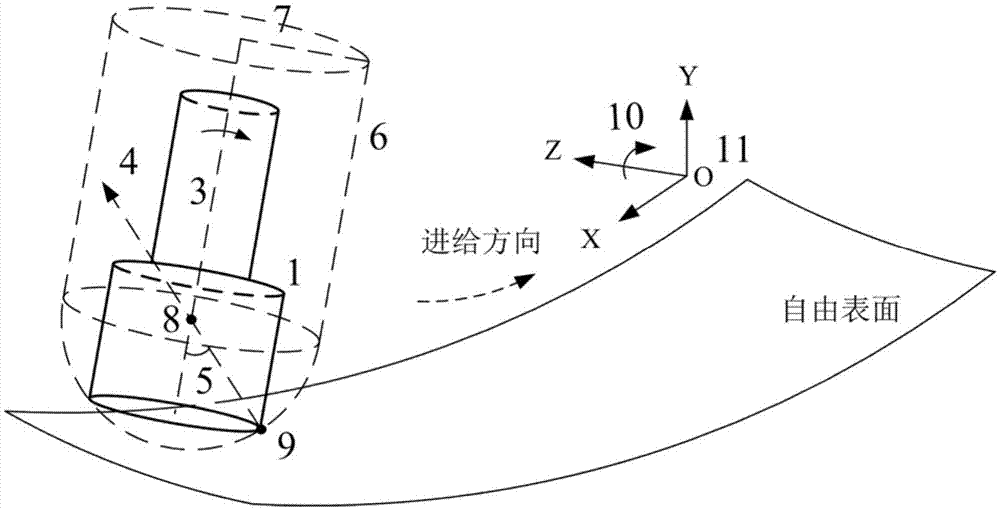
Point of tangency is the point where the tangent touches the circle. At the point of tangency, a tangent is perpendicular to the radius. Several theorems are related to this because it plays a significant role in geometrical constructions and proofs.
Function approximation processing method and image processing method
InactiveUS20050238244A1Reduce in quantityImprove image qualityDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsImaging processing
A function approximation processing method comprises inputting and binarizing image data, extracting contour from the binarized image data, estimating tangent points in horizontal and vertical directions from the contour, and approximating contour between adjacent tangent points among the estimated tangent points with a predetermined function, thereby an input object such as a character or a figure can be processed at high speed, and outline data with high image quality can be generated with a reduced number of points.
Owner:CANON KK
Absorbent article having complementary edges for an umbilical notch cut
A disposable absorbent article having a non-linear notch cut without the presence of a significantly laterally extending resulting piece. The resulting absorbent article having a front end edge and a back end edge which are complementary. The front end edge having at least three tangential points (a1, a2, b). Tangential point b is longitudinally inboard of a1 and a2. The back end edge having at least three tangential points (x1, x2, y), wherein y is longitudinally outboard of x1 and x2. The absorbent article being longitudinally folded about a first fold line. The first fold line may be drawn between points a2 and x2. The absorbent article being longitudinally folded about a second fold line, said second fold line may be drawn between points a1 and x1.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Vehicle tread measurement method based on stereo vision and laser
InactiveCN101059340AHigh precisionExpand field of viewUsing optical meansPicture interpretationVisual perceptionTangential point
The invention provides a wheel distance measuring method based on stereo vision and laser, which uses a stereo vision laser measuring system to obtain relative measuring parameters. The method uses a digit camera to shoot laser pattern projected on the tyre crown, uses image processing method to extract laser pattern target, uses stereo match algorism and three-dimension rebuild algorism to obtain laser pattern stereo point. And the invention projects the laser pattern stereo point on a simulated plane of the laser pattern, uses the projected point to generate a two-dimension curvature, to calculate out an extreme point of the two-dimension curvature, while the extreme point is relative to the tangential point of the tyre crown. And the invention uses one tangential point at inner tyre crown and at least three tangential points at outer tyre crown to simulate a tangential plane to calculate out the central plane of tyre. And the invention calculates out the distance between the cross lines of the central planes of left and right tyres on one shaft and the wheel support plane to obtain the vehicle wheel distance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for precisely measuring and processing profile of disc cam
ActiveCN102049731AHigh measurement accuracyEliminate the effects of precisionMeasurement devicesGrinding feed controlNumerical controlEngineering
The invention discloses a method for precisely measuring and processing the profile of a disc cam. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the primary data of discrete points of a primary wheel profile through a delicate cam measurement instrument; determining the tangent point deviation angle of each discrete point of the primary wheel profile and a measuring head through a tangent point deviation angle determination method; obtaining the real approximate data of the primary wheel profile through a lift compensation method as per the tangent point deviation angle of the primary wheel profile and the measuring head; determining the tangent point deviation angle of each discrete point of the cam profile and a grinding wheel through the tangent point deviation angle determination method as per the real approximate data of the primary wheel profile; calculating to obtain the data of each discrete point of the cam profile for processing through the lift compensation method as per the tangent point deviation angle of the cam profile and the grinding wheel; and inputting the data of the discrete points of the cam profile for processing into a numerical control grinding machine to process a cam blank to obtain a cam finished product. The precise cam profile data can be obtained through the method, and the cam with good synchronicity same as the primary wheel can be processed.
Owner:盐城市纺织染整产业园实业开发有限公司
Particle matter sampling method and sampler with a virtual impactor particle concentrator
InactiveUS7325465B2Minimizes air turbulenceEasy to cutWithdrawing sample devicesParticulatesMedicine
An apparatus for sampling ambient air to obtain coarse and fine fractions of particulate matter includes a single acceleration tube and a collection tube coaxially arranged along a central axis with a gap between facing distal ends thereof within a range of d / D1 of 1 to 2, wherein d is the distance or gap between the distal ends and D1 is the inside diameter of the outlet at the distal end of the acceleration tube. A housing surrounding the acceleration and concentration tubes is provided with a side-wall nozzle connected to a suction device for drawing a major portion of the sampled ambient air therethrough and for separation of particulate matter, as a fine fraction, from that major portion. A second suction device draws a minor portion of the sampled ambient air, containing the coarse fraction of the particulate matter, in a straight path approximating the central axis, through the acceleration tube and through the collection tube for passage through a filter for separation of the coarse fraction of particulate matter. The ratio of the flow rates of the major and minor portions of the sampled ambient air is adjusted to provide a cutpoint within the range of 2-3 microns. The apparatus is preferably operated with a flow rate for the sampled ambient air within the range of 900-1200 liters per minute.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
Processing method and device for forming aspheric surface part by numerical control tangent line turning method
InactiveCN101376229ARequirements to ensure surface accuracyEasy to ensure surface accuracy requirementsLensNumerical controlSurface roughness
The invention provides a non-spherical surface element shaping and processing method by using a numerical control tangent revolution method and a device thereof, and relates to an optical element processing technique. The processing method and the device can always conduct the tangent point processing for the meridional profile curve of any designed and given axisymmetrical non-spherical surface (including higher order and quadric spherical surface) and spherical surface element, so as to obtain a theoretical continuous smooth high precision surface without corrugation. The tangent point processing of the non-spherical surface is realized through the rotation of a workpiece and an abrasive wheel, and the numerical control linkage of an oscillating shaft, a workpiece shat and an abrasive axle. The tangent point processing of the spherical surface is realized through the rotation of the workpiece and the abrasive wheel, the oscillation of the oscillating shaft and the fixation of the abrasive axle at a certain distance. The processing technique has the advantages of good commonality, high precision and processing efficiency, easily ensured surface roughness and surface texture, low processing cost and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Method and system for performing static timing analysis on digital electronic circuits
InactiveUS20050246673A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSnipsStatic timing analysis
A method for performing static timing analysis on digital electronic circuits is disclosed. A snip (or DC adjust) file is initially generated. Static timing analysis is then performed on the final circuit netlist using the snip file. If the final circuit netlist meets all the timing constraints, the snip file is converted to a group of cutpoints, and formal verification is performed on the cutpoints. A determination is made as to whether or not the cutpoints pass formal verification. If the cutpoints pass formal verification, the user analysis on the final circuit netlist is completed, and the final circuit netlist can proceed to manufacturing. Otherwise, if the cutpoints do not pass formal verification, a flag is issued to alert a user. The user then has to either modify certain snip point(s) within the snip file or modify the circuit netlist, and perform the user analysis again.
Owner:IBM CORP
Golf ball dimple profile
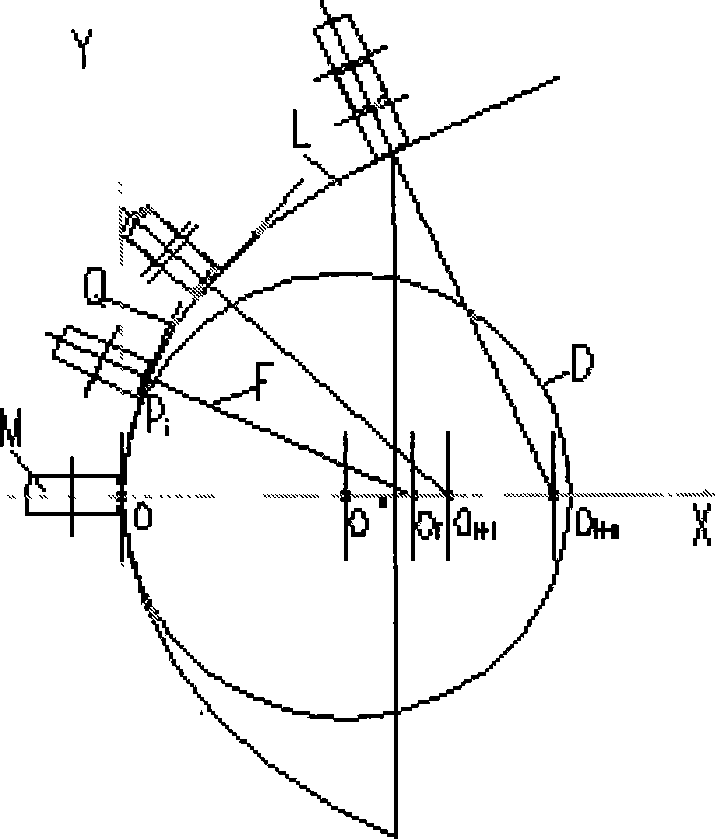
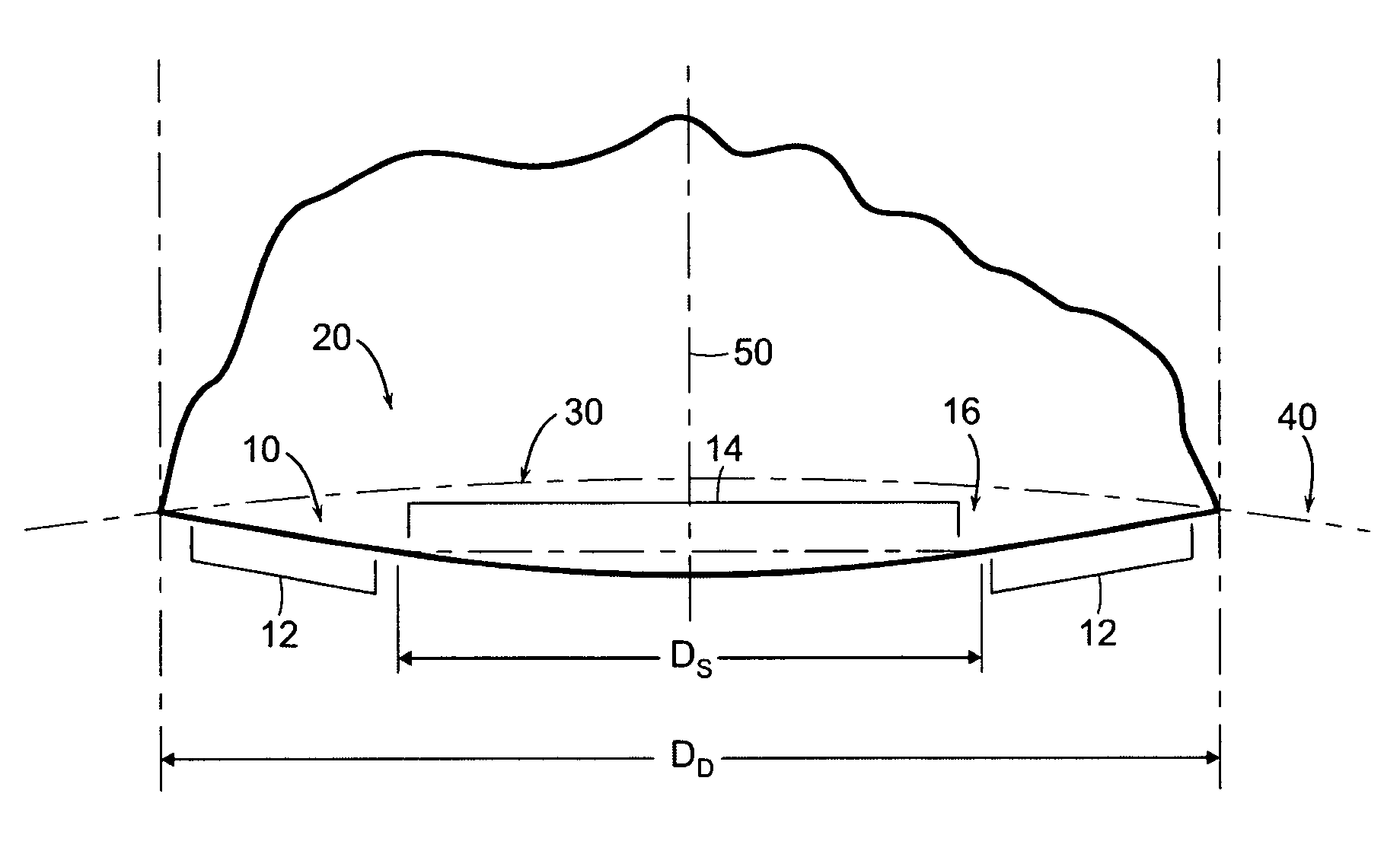
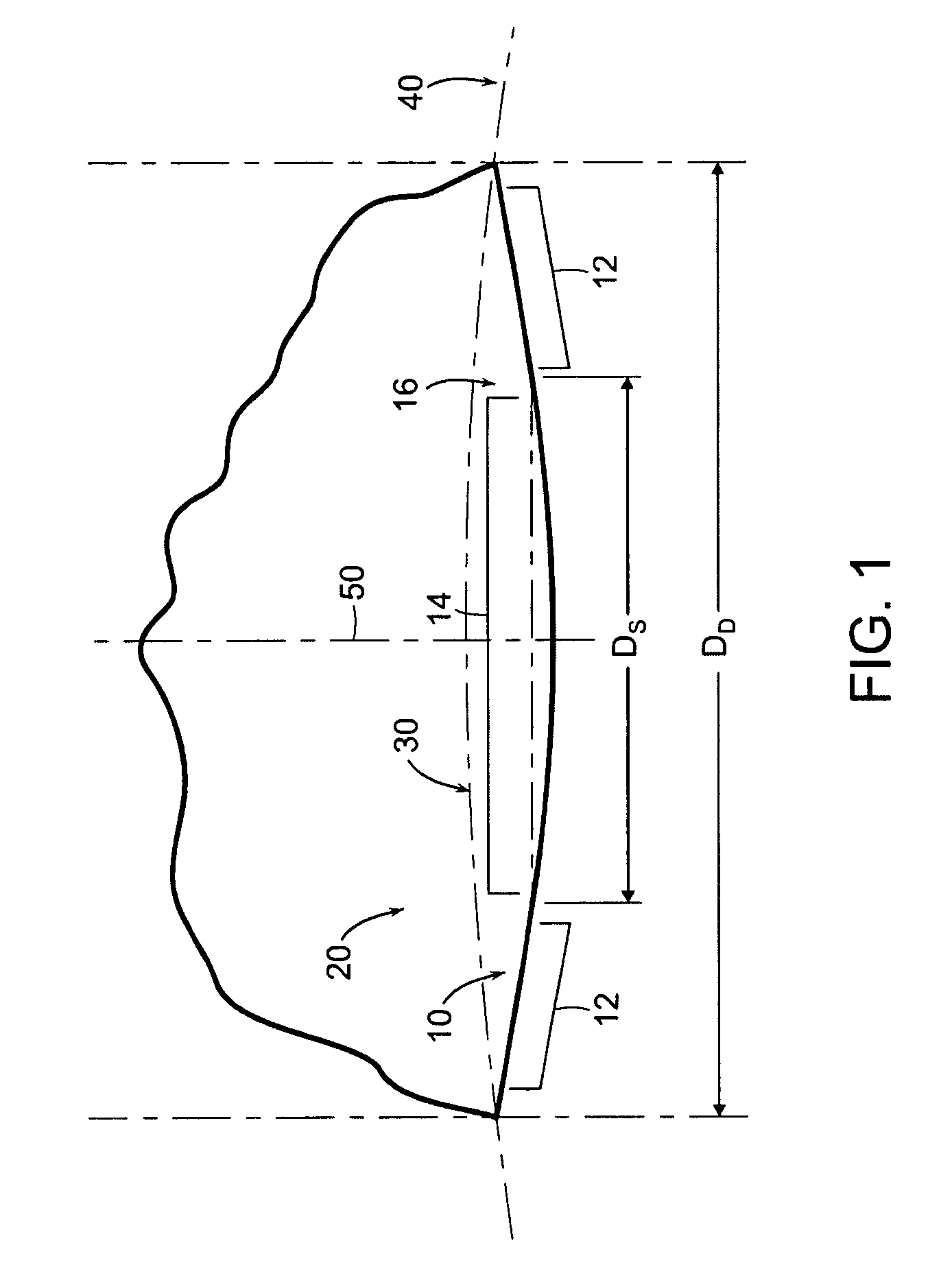
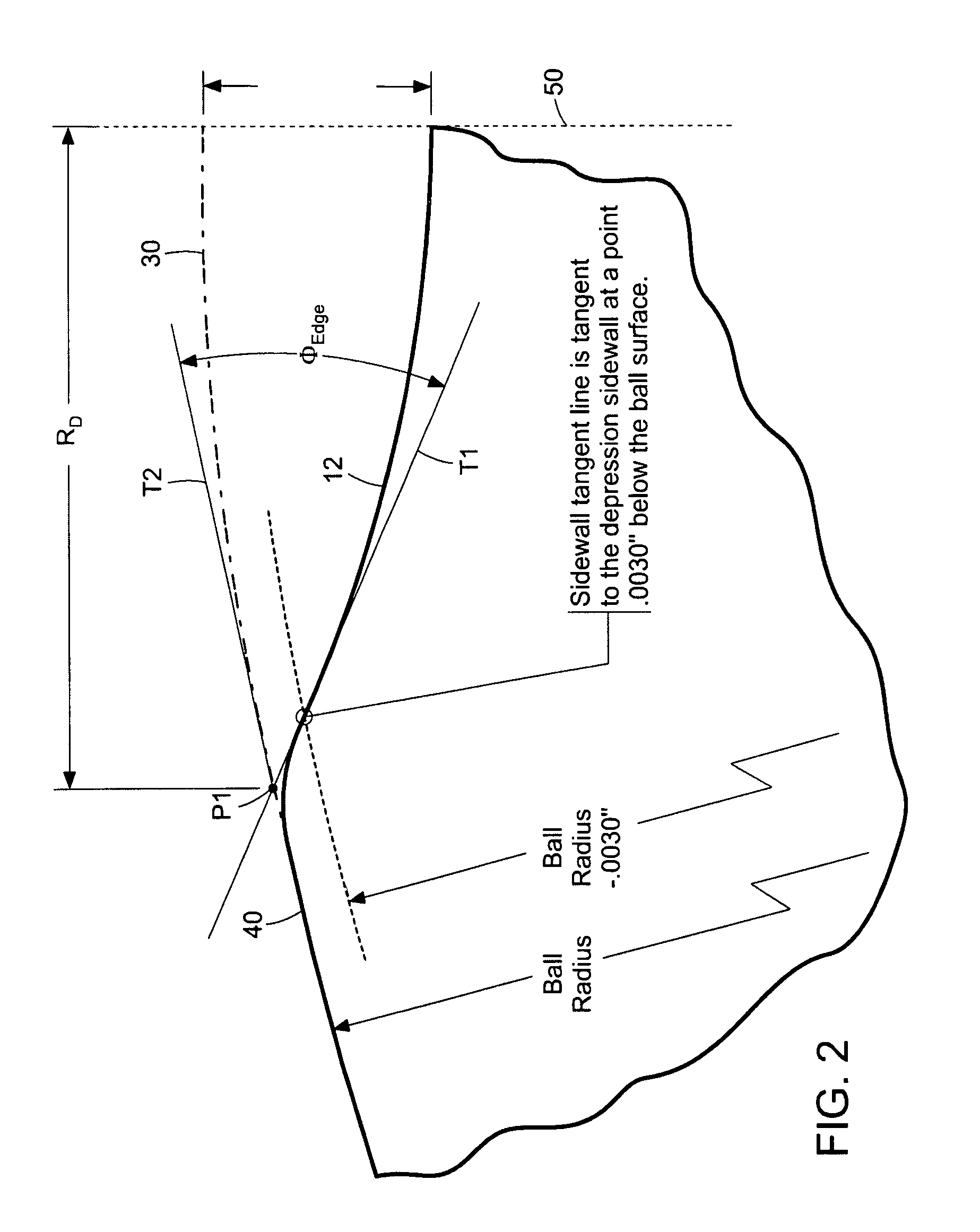
The present invention concerns a golf ball with dimples having a cross-sectional profile comprising a conical base shape and a spherical cap with a prescribed point of tangency to the cone sidewall. More particularly, the conical profiles of the present invention are defined by three independent parameters: dimple diameter (DD), edge angle (ΦEDGE), and saucer ratio (Sr) which is a measure of the relative curvature of the dimple bottom. These parameters fully define the dimple shape and allow for greater flexibility in constructing a dimple profile versus conventional spherical dimples. Further, conical dimples provide a unique dimple cross-section which is visually distinct.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Method for measuring and compensating surface profile error of large rotary body part in real time
ActiveCN102890475AImprove machining accuracySolve the problem that the jump cannot be compensatedProgramme controlComputer controlEngineeringContour error
The invention discloses a method for measuring and compensating a surface profile error of a rotary body part in real time. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a common tangent of each carrier roller and a profile surface tangency point of the rotary body part, and thus obtaining an included angle which is formed by intersecting two tangents; (2) uniformly sampling the profile surface of the rotary body part to obtain a plurality of sampling points which are uniformly distributed on the circumferential direction, measuring a total error at each sampling point, and thus obtaining a profile error of two carrier rollers, which corresponds to each sampling point; (3) computing the surface profile error of the rotary body part at each sampling point; and (4) measuring a carrier roller radius error in real time, computing an error compensation value of each sampling point according to a real-time measurement value of a carrier roller profile error and a surface profile error value of the rotary body part, and compensating the error in real time. By adoption of the method, the surface profile error of a large rotary body can be measured and compensated in real time. The method has the advantages of convenience for measurement and accuracy in computation. The processing accuracy of a rotary body workpiece can be greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU GAOJING MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT CO LTD
Indoor unit of air conditioner
InactiveCN105042698ALarge air volumeLow costLighting and heating apparatusSpace heating and ventilation detailsImpellerAir volume
The invention discloses an indoor unit of an air conditioner. The indoor unit comprises an air outlet air flue of a through-flow impeller, and an air outlet air flue wall of the through-flow impeller, wherein an air opening is formed in the air outlet air flue wall of the through-flow impeller; the upper side end and the lower side end of the air opening are perpendicular to a shaft axis of the through-flow impeller of the indoor unit; an air outlet of the indoor unit is positioned in a projection plane at the left lower side; and a clockwise included angle between a connecting line from the upper side end to the lower side end and a tangent line positive direction section of the air outlet air flue wall which takes the upper side end as a point of tangency is greater than or equal to 10 degrees but smaller than or equal to 200 degrees. The indoor unit has the advantages that air quantity of outlet air is great and outlet air is mixed air, which is cool but not cold, formed by exchange air and indoor air.
Owner:孙海潮
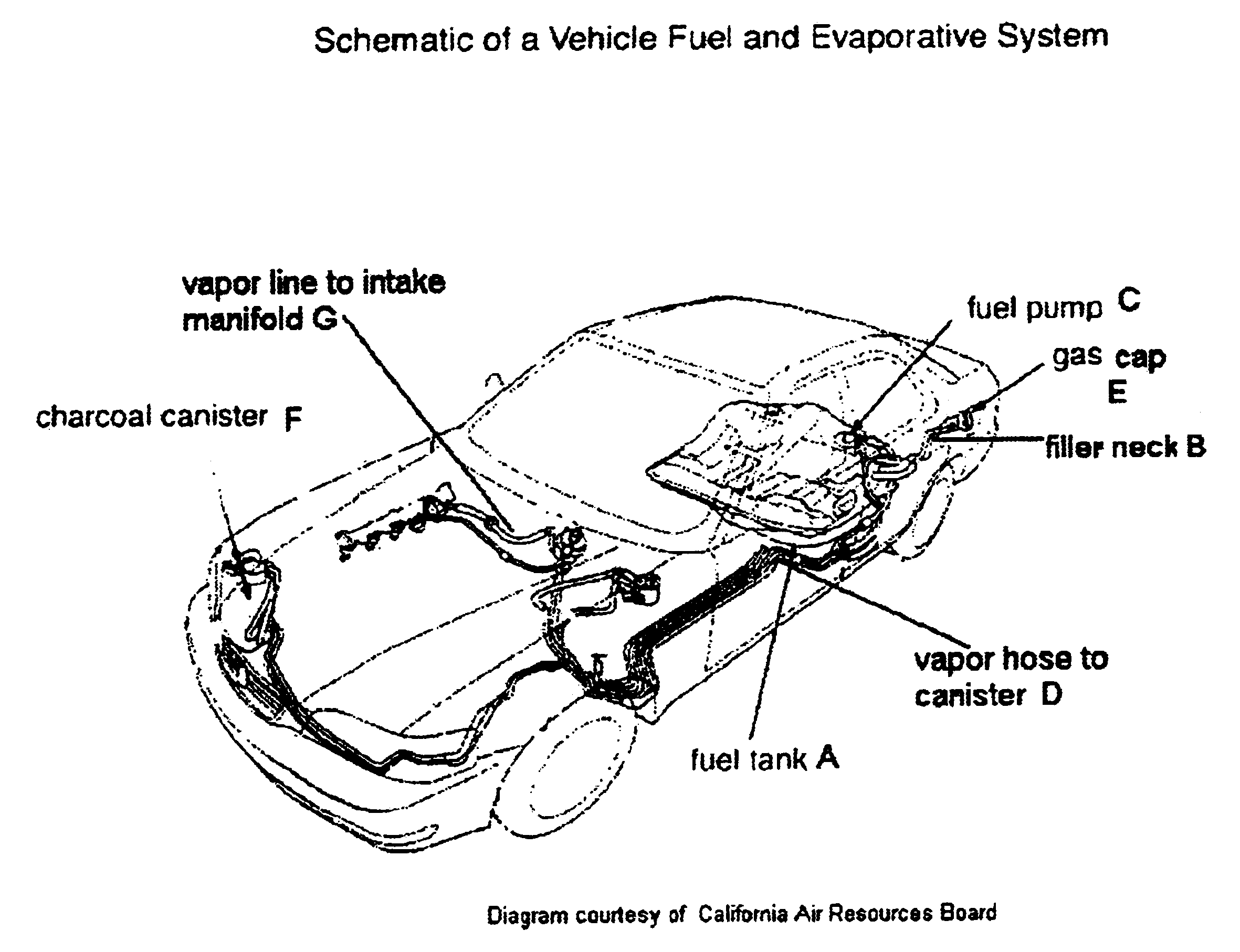
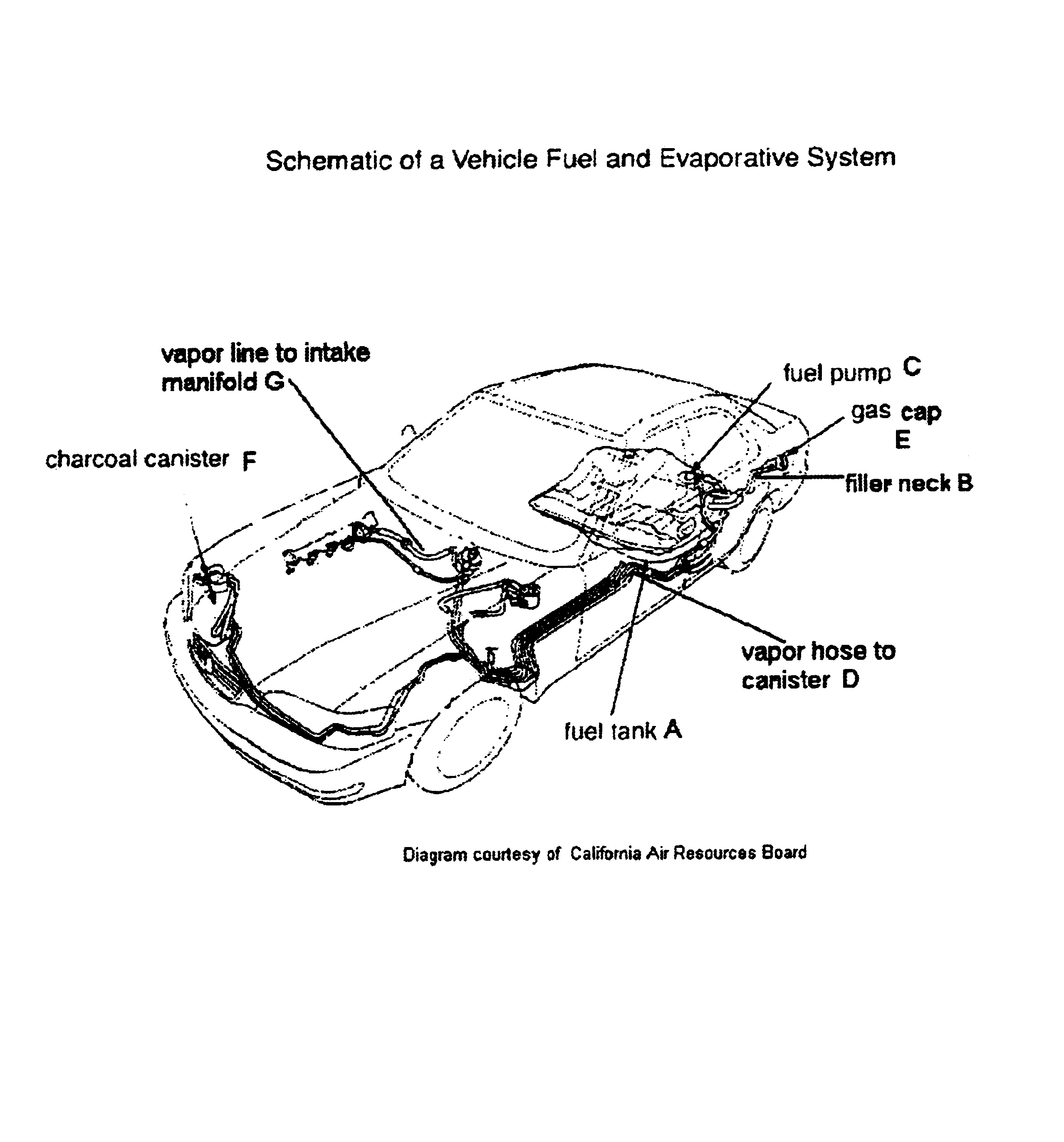
Temperature, vapor space and fuel volatility-compensated evaporative emissions system leak test method
A method for the leak testing of a motor vehicle fuel tank and associated evaporative emissions control system is provided. Nitrogen, compressed air or other gases are used to pressurize the system. The time required for pressurization is used to determine the tank headspace volume. The system pressure is then monitored for 120 seconds. The pressure drop in this period is then compared with a pass-fail value cutpoint from a look-up table stored in a computer attached to the testing apparatus. A pass-fail determination is then made. The pass-fail value cutpoint is pre-determined for a specified vapor volume and estimated liquid fuel temperature, as well as time of year, so that systems with leaks larger than a specified diameter consistently fail the test, while systems with leaks smaller than this value consistently pass the test. The test pass-fail criterion is thus compensated for the conditions (tank fill level and fuel temperature, and seasonal variations in fuel volatility) experienced the actual test.
Owner:STATE OF CALIFORNIA BUREAU OF AUTOMOTIVE REPAIR
Mixed air outflow air conditioning indoor unit
InactiveCN105674399APromote circulationImprove physical comfortLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsImpellerAir volume
The invention discloses a hybrid air conditioner indoor unit, which comprises an indoor unit casing, a cross-flow impeller air outlet duct, and a cross-flow impeller air outlet duct wall, and is characterized in that: the cross-flow impeller air outlet duct wall is set There is an air inlet, the air inlet is perpendicular to the axis line of the cross-flow impeller of the indoor unit, and the projection line on the projection plane where the air outlet of the indoor unit is located on the lower left side, the point where it intersects with the wall of the air outlet duct is the upper tangent point of the outlet air The clockwise included angle of the positive direction section of the tangent line of the channel wall is greater than or equal to 12° to less than or equal to 198°, and an induction fan is installed on the outside of the air outlet wall of the cross-flow impeller, and the air outlet of the induction fan is connected to the induction air duct. The air outlet communicates with the air induction opening provided on the wall of the air outlet duct of the cross-flow impeller. The invention has the advantages of large air volume and speed, long shooting range, and the heat exchange air and indoor air form cool but not cold mixed air.
Owner:孙海潮
Judging method of suspension curve model for power line sag calculation
ActiveCN102646163AHigh precisionSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsPower equipmentEngineering
The invention discloses a judging method of a suspension curve model for power line sag calculation, belonging to the technical field of installation and maintenance of power equipment. The judgment method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a power line image; extracting power line image characteristics; selecting a characteristic point set of single power line for sag calculation from power line image characteristic point sets; determining two end points of the single power line in the characteristic point set of the single power line and calculating a gradient k of a straight line for connecting the two end points; calculating tangency point coordinates of the straight line which takes the k as the gradient and the single power line; calculating parameters of the suspension curve model according to the tangency point coordinates; respectively determining a catenary curve, an inclined parabola curve and a horizontal parabola curve; respectively calculating Hausdorff distances between the single power line and the catenary curve, and between the inclined parabola curve and the horizontal parabola curve; and taking a model corresponding to the curve with the minimum Hausdorff distance as the suspension curve model for meeting the requirement of the power line. The judging method disclosed by the invention improves the precision of the power line sag calculation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Staged wheel type robot moving path planning method
ActiveCN108594815AAddress situations where it won't fit into a smaller spaceUniversalPosition/course control in two dimensionsThree stageEngineering
The invention discloses a staged wheel type robot moving path planning method. The process that a wheel type robot is converted from a known initial full state to a known target full state is dividedinto three stages, and planning control is carried out. In the speed suppressing state, when the current speed direction of the wheel type robot is inconsistent with the current target position direction, the speed is suppressed, and the direction is adjusted, so that the wheel type robot moves in the target direction as soon as possible. In the straight line section stage, the straight line pathis tangent to a small arc path so that the wheel type robot can get close to a target tangent point as straight as possible, and meanwhile the reaching speed and the reaching posture are controlled. In the small arc section state, the radius of an arc path is limited by using the maximum centrifugal acceleration, so that the wheel type robot gets close to a target along the arc path cuts into thetarget at a desired angle. According to the method, the full-state change of the wheel type robot can be achieved, the requirement of the surrounding environment for space size is avoided, and the universality and stability are high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV +1
Method for curve surface grinding with cylindrical grinding wheel at virtual ball cutter radius
ActiveCN106853598AInterference handling is simpleImprove processing precisionGeometric CADOther manufacturing equipments/toolsRotational axisSurface roughness
The invention discloses a method for curve surface grinding with a cylindrical grinding wheel at a virtual ball cutter radius. The method includes the steps that 1, the attitude angle of the cylindrical grinding wheel is designed, and the inclination angle of the axis of the cylindrical grinding wheel on a curve surface tangency point normal vector is designed through a virtual ball cutter model; 2, a cutter path is planned and determined according to the curved surface tangency point normal vector and the virtual ball cutter model, and the set inclination angle in the step 1 is guaranteed through a rotating shaft of a machine tool; 3, by the adoption of an axial feeding mode, a workpiece is subjected to grinding machining according to the cutter path. The cylindrical or quasi-cylindrical grinding wheel can be used for four-axis machining of a free curved surface, and the method has the advantages that planning of the cutter path is simple and flexible, the precision of a machining shape is high, and surface roughness is low, and is suitable for machining free curve surfaces of optical glass and other hard brittle materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Unmanned aerial vehicle route planning algorithm based on polygonal obstacle detection
InactiveCN107478231APromote resultsNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in three dimensionsUncrewed vehicleTwo step
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle route planning algorithm based on polygonal obstacle detection. The unmanned aerial vehicle route planning algorithm mainly comprises two steps of connected graph establishment and route generation. The algorithm is based on the operation taking a point as a tangent point relative to an original polygon of an obstacle, recursion obstacle detection is performed from an original point to the tangent point, so that an initial detouring route is obtained, and convex hull operation is performed on part of the polygon to optimize a route result. An accurate global optimal route is produced. In the current unmanned aerial vehicle map testing containing carious polygonal obstacle regions, an accurate global optimal route can be produced, and a problem of route depression is solved. The algorithm is not limited to unmanned aerial vehicle route planning. Tangent point operation corresponding to specific shapes can further be arbitrarily selected according to scenes.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
Screw Joint for Oil Well Tubing
InactiveUS20080191479A1Improve maintainabilityExcellent in seal performanceDrilling rodsHose connectionsInternal pressureSurface roughness
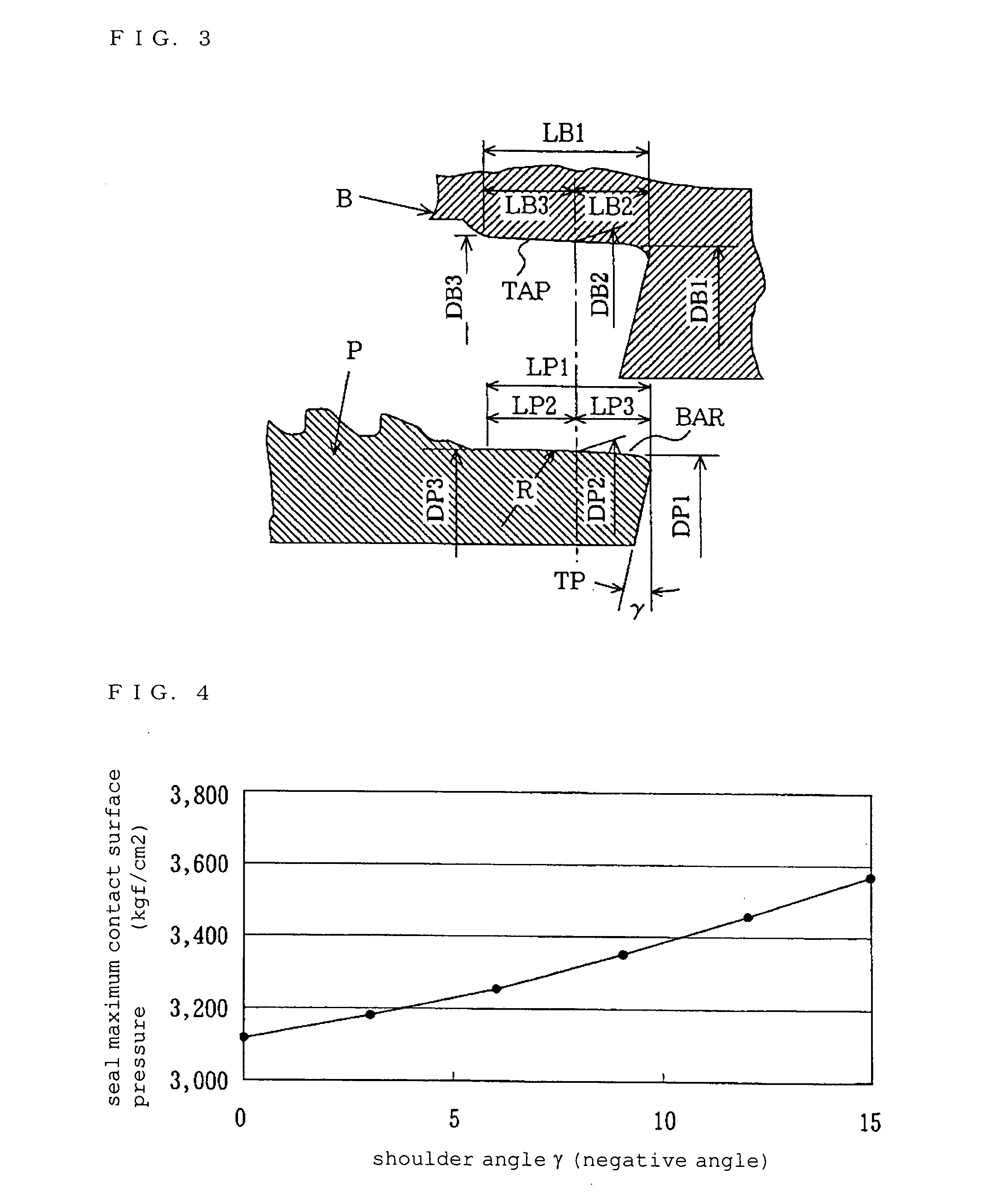
There is provided a screw joint for oil well tubing, excellent in seal performance and having a high maintainability.A screw joint for oil well tubing comprising a male screw tube equipped with a seal forming portion having a convex curved surface shape on a tip end portion of the tube and a female screw tube equipped with a tapered seal portion, wherein when the convex curved surface shape comes into contact with the tapered seal portion, a contact surface pressure Pc60 equivalent to 60% of a maximum contact surface pressure Pcmax applied to a contact surface is larger than an inner pressure Pi applied to the screw joint and is smaller than a proportional limit or of a screw joint material, wherein a taper angle θs of the tapered seal portion and an angle θt of a tapered screw satisfy a formula θs≧θt, and curvature radius R of the convex curved surface shape is not smaller than 90 mm and not larger than 170 mm, wherein the angle θs is from 1.4 degree to 9.5 degree at an apex angle, wherein a length of the convex curved surface shape in an axial direction is at least not smaller than 1.5 mm backward and forward from a tangent point, and wherein a surface roughness H of the convex curved surface and the tapered seal portion is not larger than 12s.
Owner:METAL ONE CORP
Fishing line guide device
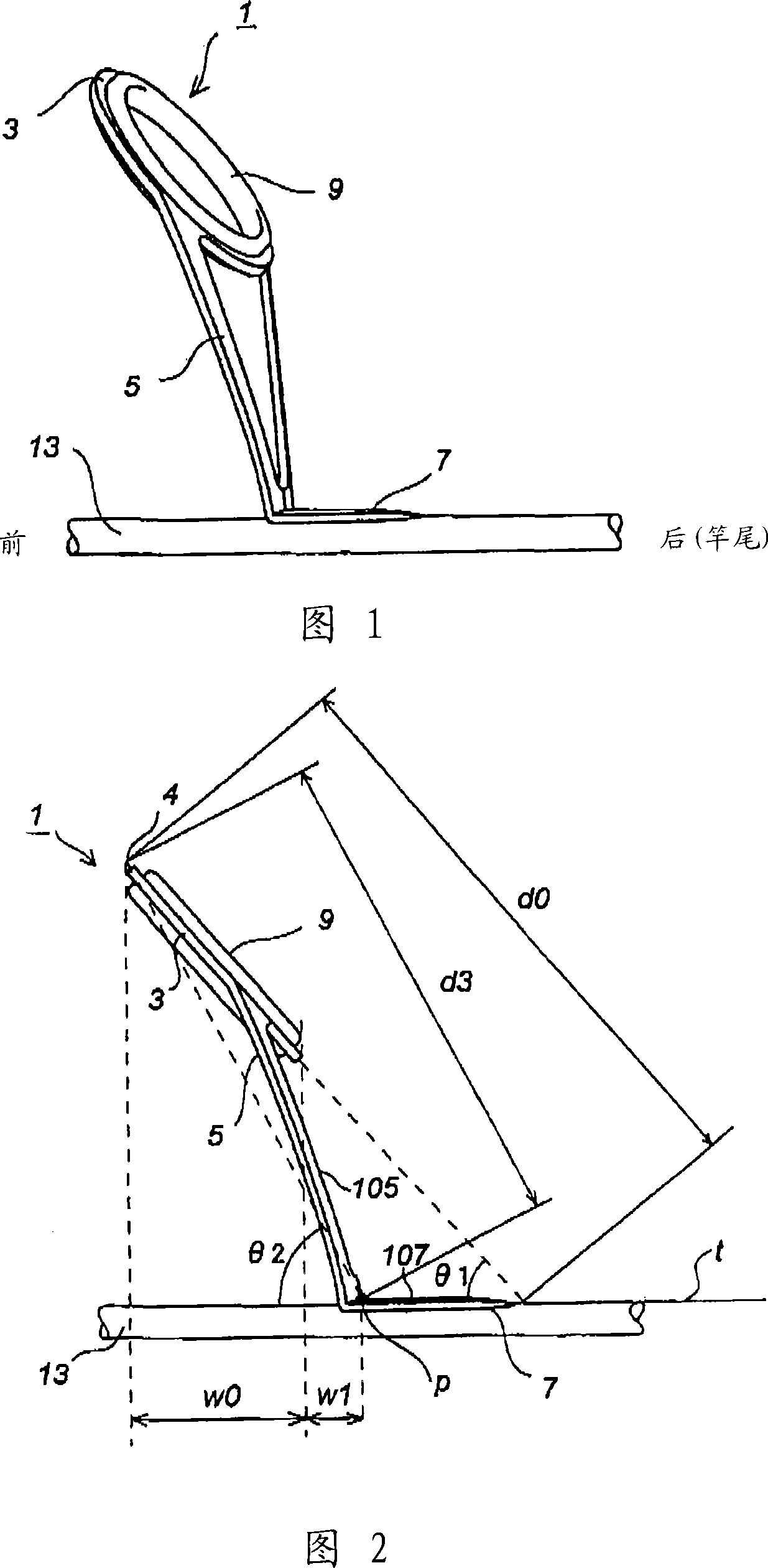
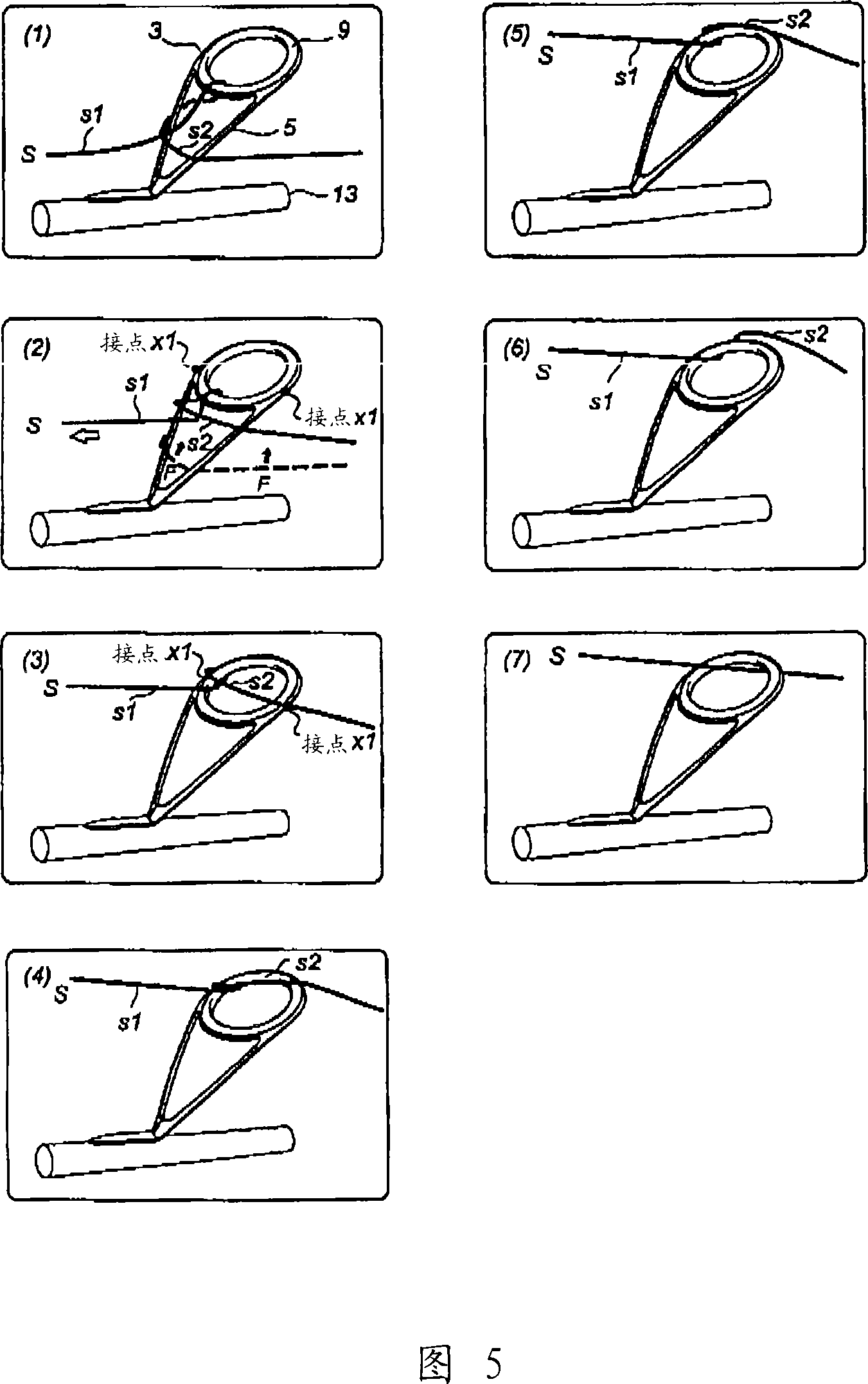
The invention relates to a hook-thread guiding device. The high guiding device which utilizes the priority of flying distance is unable to applicable to the prior proposal of preventing the thread which is used in a low guiding device from winding together without any change. The guiding device is characterized in that a holding ring is inclined towards to the front side relative to the lateral supporting foot and the lateral supporting foot beginning from the horizontal projection width range of the holding ring has an extension length which is larger than 0 and smaller than 1.0 when viewed from the side; and when viewed from the front side, the point of contact between the outer contour line of the lateral supporting foot and the outer peripheral contour line of the holding ring is positioned at or above the position which is 80% of the maximum horizontal width range of the lower peripheral contour line of the holding ring, the point of intersection between a horizontal line passing through the lowest point of the inner peripheral contour line of the holding ring and the outer peripheral contour line of the lateral supporting foot is positioned at or at the outer side of the position which is 80% of the maximum horizontal width range of the outer peripheral contour line of the holding ring, and the outer peripheral contour line of the lateral supporting foot is positioned between the point of intersection and the point of contact or the point of intersection and the horizontal center line of the holding ring, wherein, the shorter part is positioned on or at the outer side of a vertical line passing through the point of intersection.
Owner:FUJI IND
Speed control method of cam tangential point tracking grinding
ActiveCN102198632AEasy to rotate speedRealize Tracking GrindingGrinding feed controlCamControl theory
The invention relates to a speed control method of cam tangential point tracking grinding. The method is used for locally correcting the speed change movement of a head frame in the cam tangential point tracking grinding; a triangle function approximation method is used for replacing a curve representing the excessive change of the rotating speed of the head frame; a polynomial parameter is rationally rotated according to the maximum of the cam lift change; and a polynomial is used for interpolating and defining the rotating speed curve of the head frame. The method solves the problem of excessive rotating acceleration of the head frame in the constant line speed grinding; the rotating speed of the head frame in the excessive acceleration section is only modified; and the integer is substantially kept in the head frame speed change revolving control model based on the constant grinding point line speed; the polynomial parameter calculated by interpolating and defining the rotating speed of the head frame through the polynomial, synthetically considering the parameter obtaining accuracy and the calculating convenience and selecting the proper parameter range PL and the coefficient matrix is more rational, thus the defect of vibration corrugations on the surface of the head frame is made up; the rotating speed of the head frame is increased; and the processing efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Screw coupling for oil well pipe
ActiveCN1977124AImprove sealingImprove maintenance effectDrilling rodsDrilling casingsInternal pressureCoupling
A screw coupling for an oil well pipe, comprising a male screw pipe having a seal forming portion in a projectedly curved shape at the tip part of the pipe and a female screw pipe having a tapered seal part. The screw coupling is characterized in that, when the projectedly curved shape is brought into contact with the tapered seal part, a contact surface pressure Pc60 equivalent to 60% of the maximum contact surface pressure Pcmax applied to the contact surface is larger than an inner pressure Pi applied to the screw coupling and smaller than the proportional limit sigmar of the material of the screw coupling. The taper angle thetas of the tapered seal part is thetas >= thetat where the angle of a tapered screw is thetat, and the radius R of the curved surface of the projectedly curved shape is 90 to 170 mm or shorter. The angle thetas is 1.4 to 9.5 DEG at an apex angle, the axial length of the projectedly curved shape is at least 1.5 mm or longer on the front and rear sides of a tangent point, and the surface roughnesses H of the projectedly curved shape and the tapered seal part are 12 s or less.
Owner:株式会社美达王
Pulling-rope positioning and control method, device and system
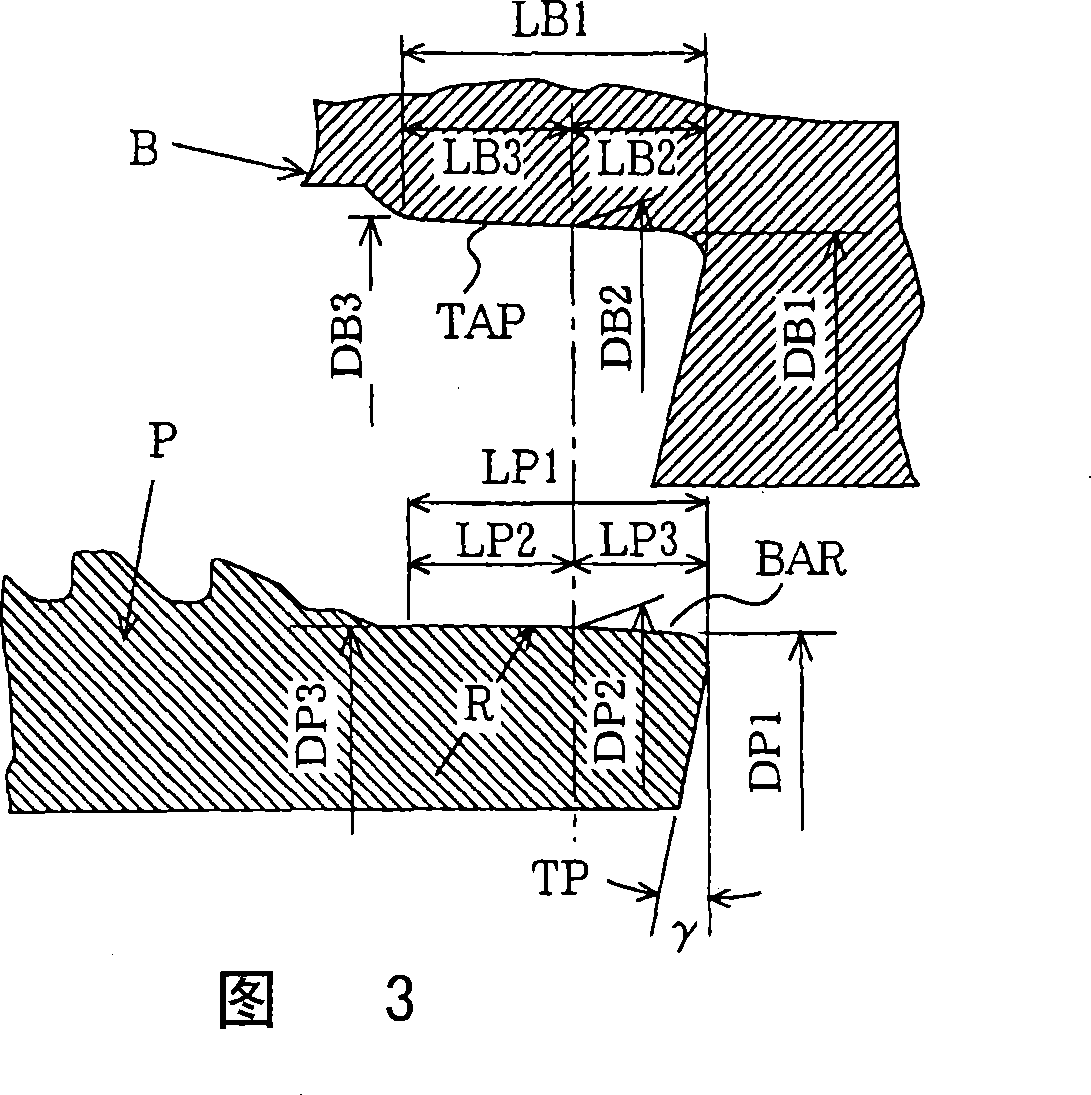
ActiveCN102995673AImprove test accuracyReduce mistakesMechanical machines/dredgersTangential pointExcavator
The invention relates to the technical field of earthmoving machines and discloses a pulling-rope positioning and control method, device and system applied to excavating-force test of an excavator. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining position information of a movable arm, a bucket rod and a shoveling bucket according to a detected result of a sensor; and determining the excavating track according to the position information; determining that a tooth root of the shoveling bucket is used as a tangential point according to the excavating track and a pulling rope arranged along the tangential direction of the excavating track is fixed on the anchoring position on an anchor frame. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme of the invention has the advantages that the errors caused by artificial visual inspection or manual measurement are greatly reduced, the anchoring position of the pulling rope on the anchor frame is more accurate and the testing accuracy of the excavating force test is greatly increased.
Owner:ZOOMLION HEAVY IND CO LTD
Flexible pipe connected to an end fitting
A pipe structure comprising a length of a flexible pipe connected to an end fitting, the flexible pipe comprising an armour layer and an underlying pipe layer the armour layer, the underlying pipe layer having an outer surface around which armouring wires of an armouring layer are helically wound. The pipe structure provides a coupling between a flexible pipe comprising armouring wires and an end fitting, the coupling exerting a relatively low bending or flexure strain on the wires during normal operation of the flexible pipe. The transition path of an armouring wire between the flexible pipe and the end fitting comprises a straight-line-section between a wire-pipe-exit-point where the wire extends away from its underlying pipe layer and a straight-line-end-point on a support unit of the end fitting where the armouring wire in question has its first tangential point of contact. This has the advantage that in a loaded situation where the armouring wires will elongate elastically leading to a change in the helical angle of the armouring wires, the pipe structure will experience a slight twist and a controlled bending of the armouring wires on the surface of the support unit (due to a possible change in the base point of contact of the armouring wire with the support unit induced by the change of helical angle), thereby avoiding substantial bending of the individual armouring wires, which is of particular importance when the armouring wires are formed of a composite material. The pipe structure may be used in flexible pipes for the off shore transport of fluids (e.g. oil).
Owner:NKT FLEXIBLES IS
Grooved fastener
ActiveUS7845889B2Reduce the amount requiredMinimally affecting the bending yield strength of the nailPinsStaplesEngineeringTangential point
A nail having a plurality of grooves configured to reduce the amount of material needed to create the nail and increase the holding power of the nail, while only minimally affecting the bending yield strength of the nail and other important properties. The nail includes a relatively high number of grooves having a relatively shallow depth to retain a cross-sectional geometry of the shank that permits the formation of a full round head of sufficiently large diameter such that pull through resistance of the nail is not significantly affected. Various embodiments of such a nail are disclosed. In a first embodiment, the grooves are semi-circular and are disposed evenly and symmetrically about the circumference of the shank. In a second embodiment, a protrusion is formed at one tangent point (corner) of each of the plurality of grooves. In a third embodiment, a protrusion is formed at each tangent point of each of the plurality of grooves. In other embodiments the grooves may be unevenly and asymmetrically disposed about the circumference of the shank, the grooves may comprise non-semi-circular geometries and the grooves may comprise deformations.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Method for demarcating small-scale vision measuring video camera based on composite planar target drone
InactiveCN101425185AEasy to processLow costImage analysisUsing optical meansVisual perceptionTangential point
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
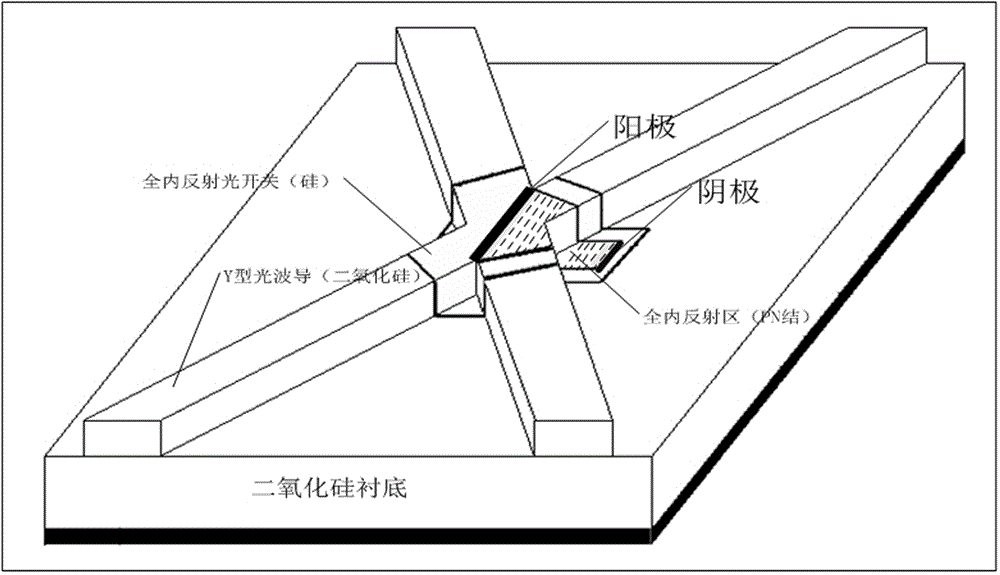
Micro annular resonant cavity based vortex-controllable light transmitter
ActiveCN105891950AReduce crosstalkReduce leakageCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsResonant cavityCommunications system
The invention relates to a micro annular resonant cavity based vortex-controllable light transmitter. The micro annular resonant cavity based vortex-controllable light transmitter comprises a Y type light waveguide, an arc-shaped light waveguide coupler and an annular resonant cavity, wherein an Si-based junction type optical switch for controlling reflection and transmission of incident light is arranged on a branching node of the Y type light waveguide; the Y type light waveguide is connected to the arc-shaped light waveguide coupler through a first S type bent waveguide attenuator and a second S type bent waveguide attenuator; the first S type bent waveguide attenuator and the second S type bent waveguide attenuator are used for reducing the crosstalk of the Si based junction type optical switch; the arc-shaped light waveguide coupler is internally tangential to the annular resonant cavity, and a silicon-based total reflector for coupling an incident light beam from the arc-shaped light waveguide coupler into the annular resonant cavity is arranged at a tangential point. The micro annular resonant cavity based vortex-controllable light transmitter can be realized through a mature semiconductor Si process, can be used as an encoding and decoding device of a vortex light communication system, and is high in economic value.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Whirlpool compressor
InactiveCN1570390ASmall volumeIncrease the compression ratioRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesEngineeringAir conditioning
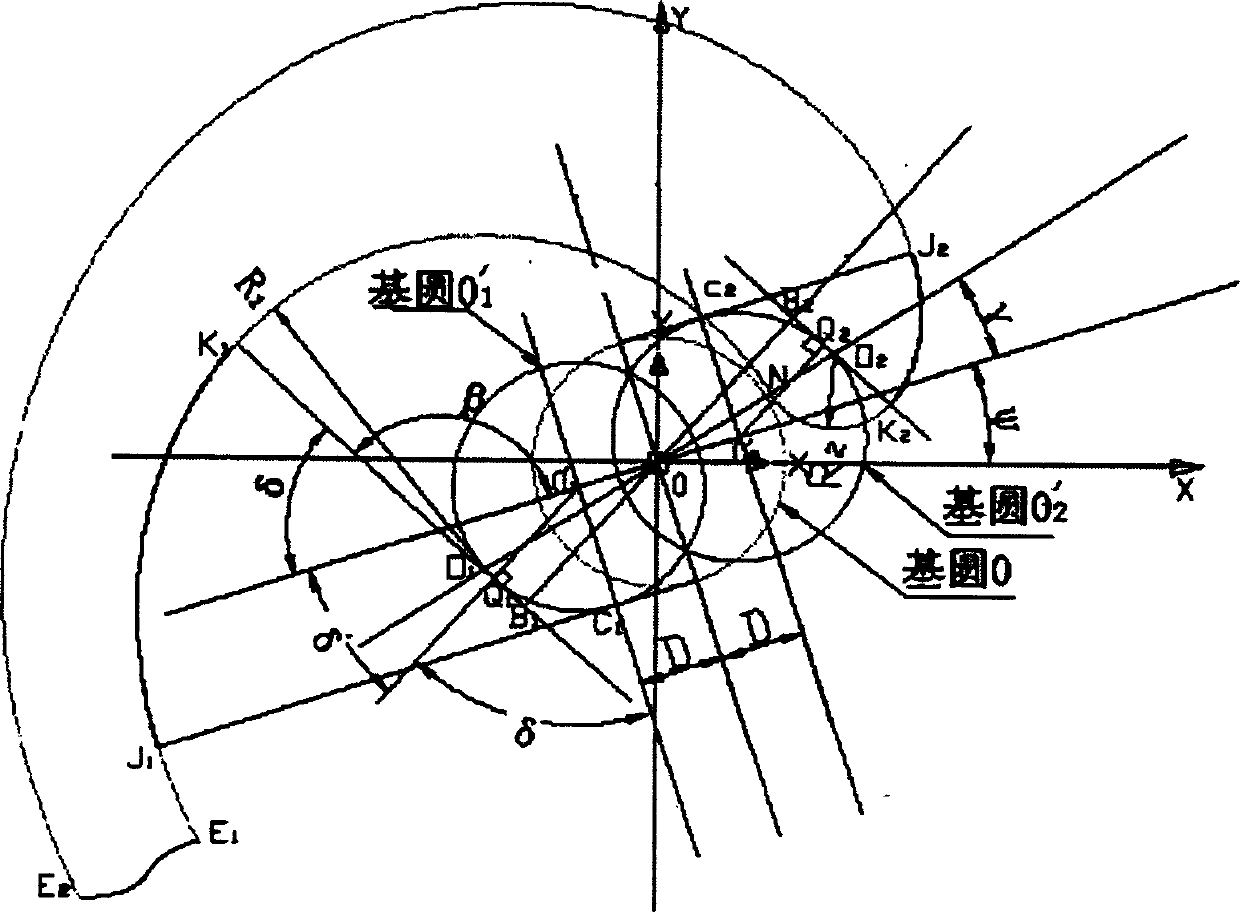
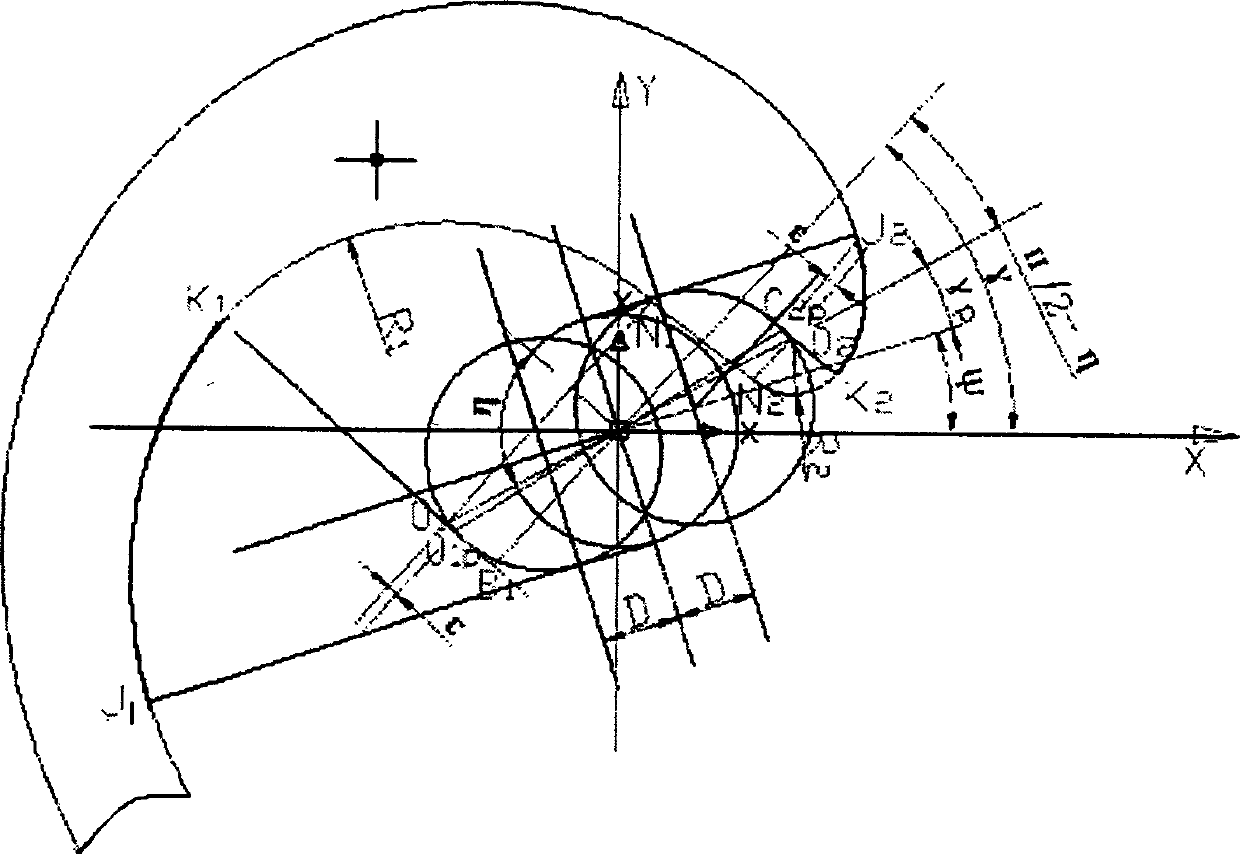
One kind of new vortex compressor, its vortex root line based on three base circle (Three Basic Cricle, is called TBC) the theory to extend the revision line. This line inside revises involute the section E1J1, inside by flank host involute section J2E2, the connection tangential path E2E1, to revise involute section J1k1, revision great-circle segmental arc K1N1, the revision small circle segmental arc NK2, flank to revise involute section K2J2 to be composed. Revision circular arc center of a circle O1 and O2 in do not bind me first base circle tangent on. This invention has solved the PMP line turbulence root section (namely high pressure region spot) the intensity and the compression ratio mutually limits, the vortex compressor compression ratio cannot largely enhance tangential point, thus while enhances the vortex compressor compression ratio, the vortex root intensity also has the enhancement.This invention involves the vortex compressor is suitable for the air conditioning, the refrigeration, aspect and so on vacuum pump and gas loading.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Sheet type medium thickness identifying device and identifying method thereof
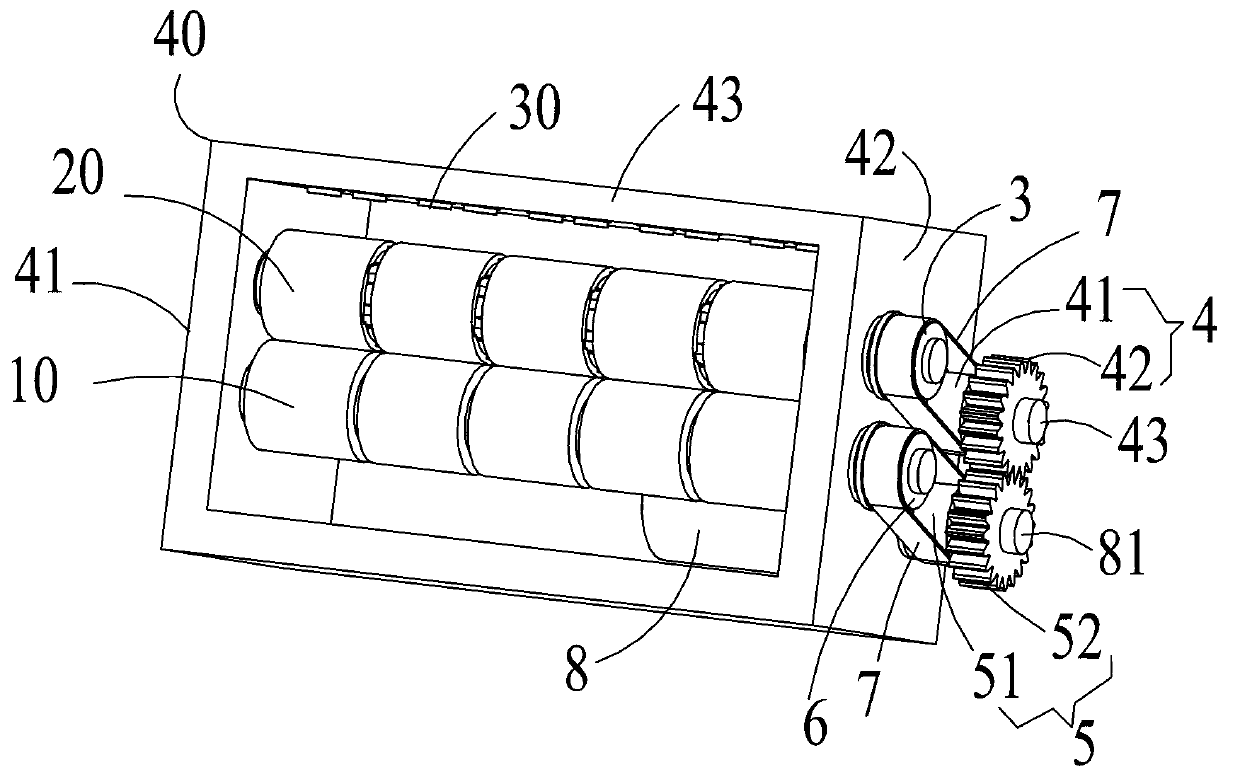
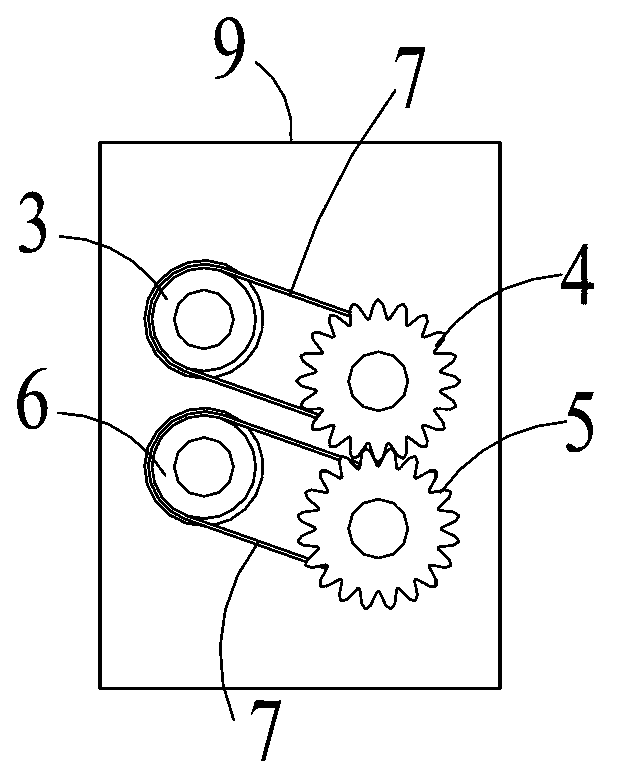
ActiveCN103106729AReduce mistakesPrevent slippingPaper-money testing devicesDrive motorTangential point
The invention relates to a sheet type medium thickness identifying device which comprises a thickness shaft, a floating shaft and a sensor, wherein two ends of the thickness shaft are installed on two side boards of a frame through bearings; two ends of the floating shaft are installed on the two side boards of the frame through bearings, and the outer surface of the floating shaft contacts the outer surface of the thickness shaft in a tangential mode; and the sensor is installed on the front face of the frame and used for detecting the amplitude of the tangential point of the floating shaft and the thickness shaft. The sheet type medium thickness identifying device is characterized in that one end of the thickness shaft is fixedly connected with a first synchronous belt wheel, and the first synchronous belt wheel is connected with a first synchronous belt gear wheel through a first synchronous belt; one end of the floating shaft is fixedly connected with a second synchronous belt wheel, and the second synchronous belt wheel is connected with a second synchronous belt gear wheel through a second synchronous belt; and the first synchronous belt gear wheel is meshed with the second synchronous belt gear wheel, and the first synchronous belt gear wheel is assembled on a shaft of a driving motor. The sheet type medium thickness identifying device avoids the slipping phenomenon between the thickness shaft and the floating shaft.
Owner:GRG BAKING EQUIP CO LTD
Centreless type inner circle grinding force online measuring device and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN102430978ASimple structureEasy to install and maintainGrinding feed controlMeasurement deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a centreless type inner circle grinding force online measuring device. The technical scheme includes that the centreless type inner circle grinding force online measuring device comprises a magnetic disc, an end surface support, a front support and a rear support, the front support consists of a support connector successively arranged axially, a sensor base, a one-way force transducer, a positioning part, a ball and a limiting cap are sequentially connected at the front end of the support connector along the axial direction of the support connector, the structure of the rear support is identical to that of the front support, the ball is tangent to a workpiece required to be ground and processed, the direction of a line between a tangent point and the center of the ball is consistent to a force measuring direction of the one-way force transducer, mechanics characteristics during processing are converted into electric signals by the one-way force transducer, the electric signals are outputted after being filtered, and amplified electric signals are converted into digital signals to be inputted into a computer via an amplification processor and an A / D (analog / digital) converter). The centreless type inner circle grinding force online measuring device has the advantages of ingenious, simple and reasonable structure, high sensibility, fine linearity, high repeatability and measurement precision and the like, and can be mounted in a centreless type internal circular grinding machine conveniently.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
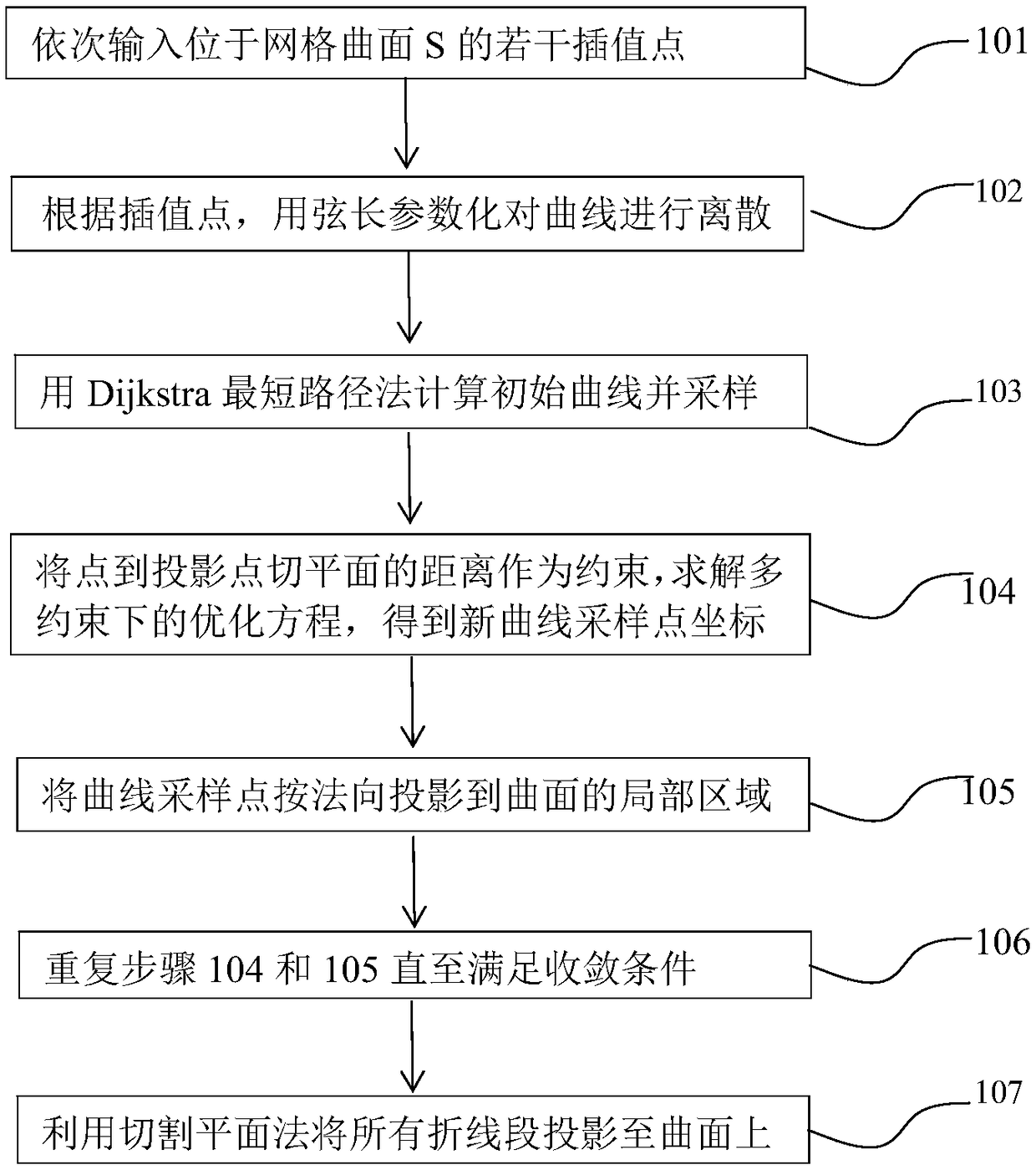
A mesh surface curve design method based on distance constraint
ActiveCN109360272AImprove efficiencyImprove robustness3D modellingDistance constraintsCutting-plane method
The invention discloses a mesh surface curve design method based on distance constraint. The designed curve passes through a given interpolation point and is smooth (in the sense of discreteness) andstrictly located on the mesh surface. The method transforms the complex manifold constraints into distance constraints and describes them as optimization problems together with smooth constraints andinterpolation constraints. The local surface is approximated by the tangent plane, and the distance constraint is relaxed to the distance from the point to the tangent plane. Because the points on thecurve used to calculate the distance are interdependent with their corresponding tangent points, a global-local iterative strategy is adopted and Gauss- Newton idea method is used to control its convergence behavior: in the whole stage, it is relaxed into a convex optimization problem by distance approximation to solve the iterative step size; In the local phase, a robust and efficient projectionmethod is used to map the optimized curves to the surface to update the tangent points. Finally, all the relaxed polygons are mapped to the mesh surface by using the cutting plane method. Compared with the existing methods, this method has many advantages in efficiency, robustness and application range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for designing a blower wheel scroll cage
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com