Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Stromal cell-derived factor 1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1), also known as C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12), is a chemokine protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL12 gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. Stromal cell-derived factors 1-alpha and 1-beta are small cytokines that belong to the chemokine family, members of which activate leukocytes and are often induced by proinflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide, TNF, or IL1. The chemokines are characterized by the presence of 4 conserved cysteines that form 2 disulfide bonds. They can be classified into 2 subfamilies. In the CC subfamily, the cysteine residues are adjacent to each other. In the CXC subfamily, they are separated by an intervening amino acid. The SDF1 proteins belong to the latter group. CXCL12 signaling has been observed in several cancers. The CXCL12 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.
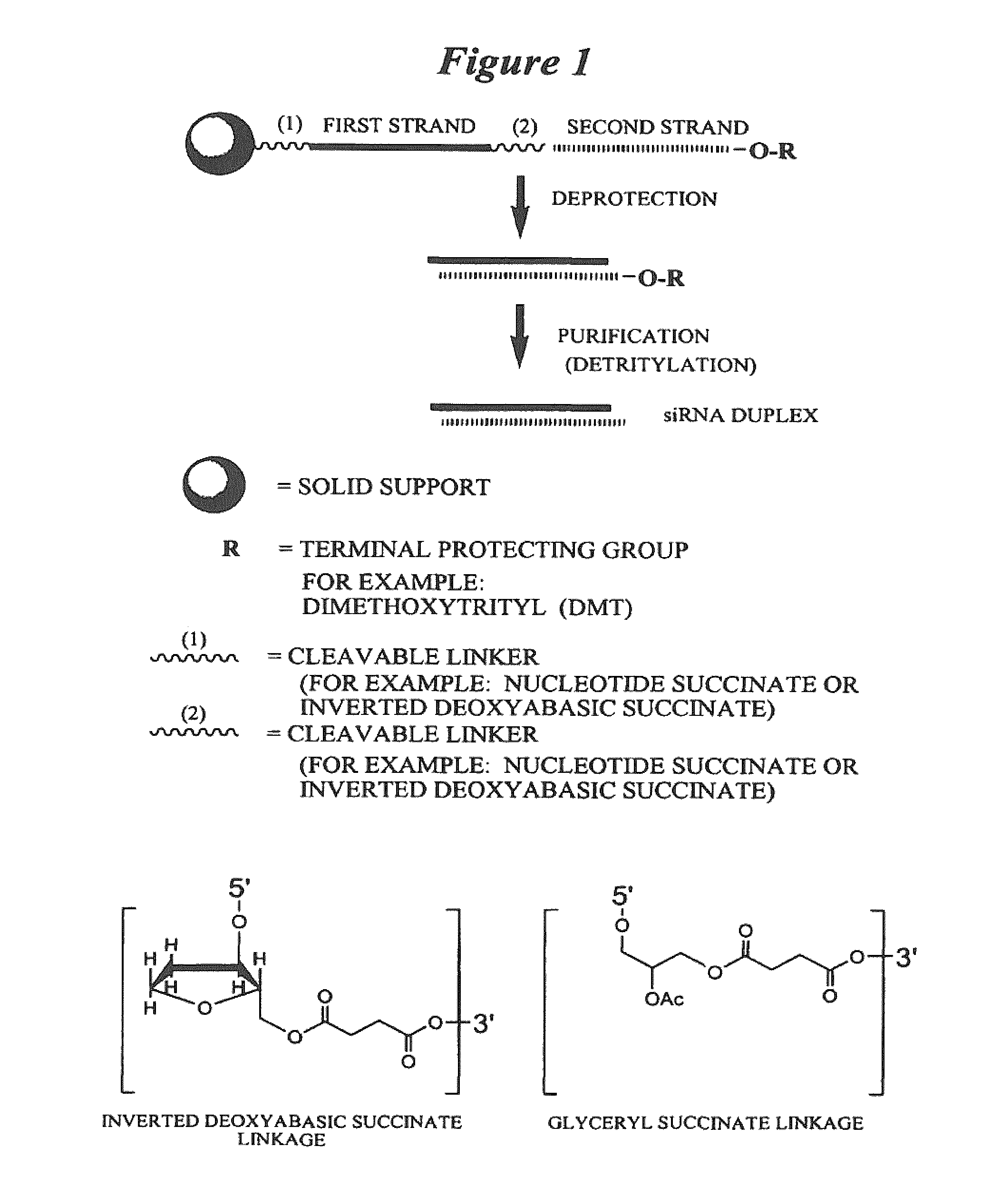
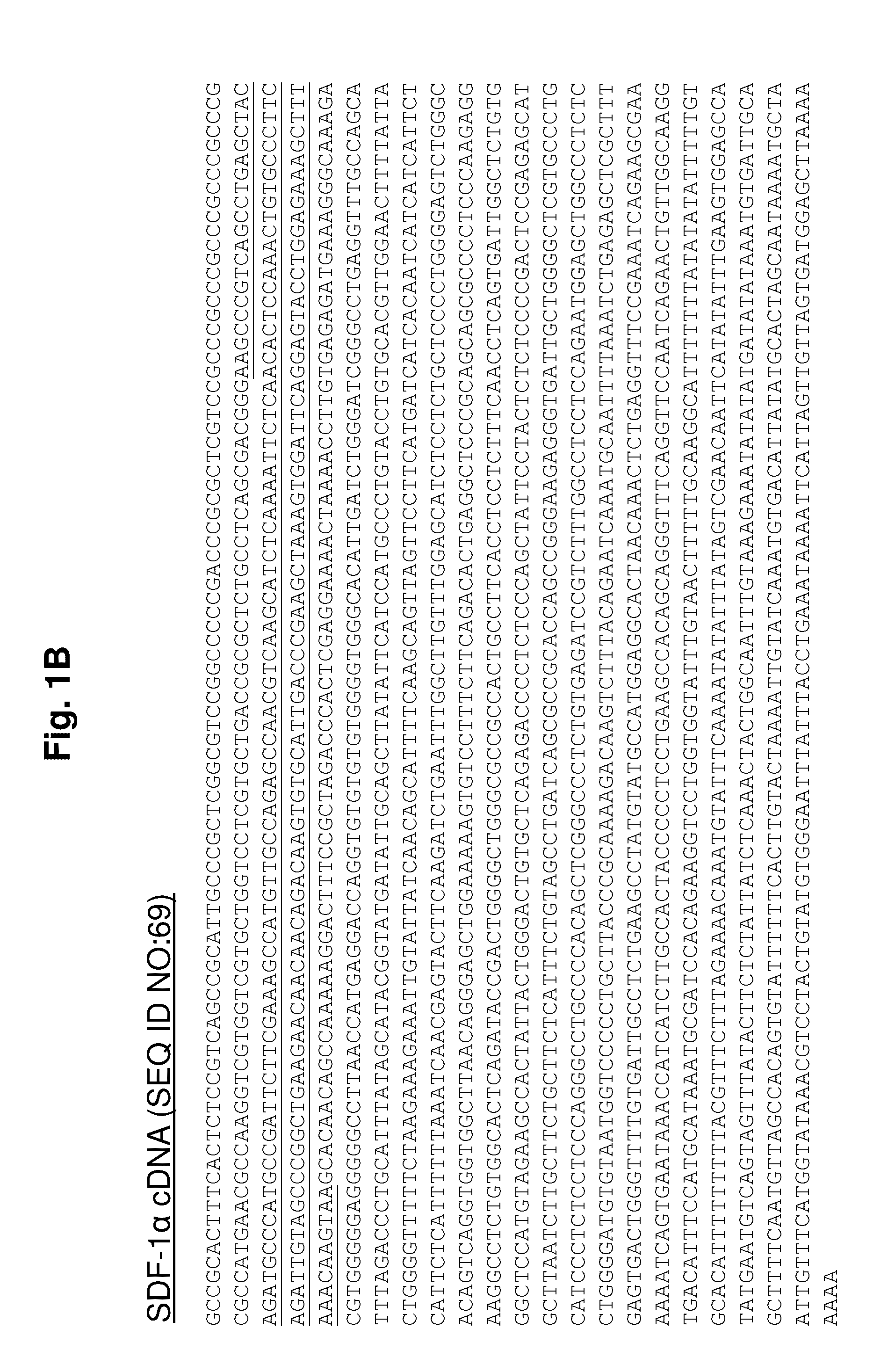
RNA interference mediated inhibition of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20060019917A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsCellular processDouble strand
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in SDF-1 gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating or that mediate RNA interference (RNAi) against SDF-1 gene expression. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions for treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that can respond to modulation of SDF-1 expression in a subject, such as ocular disease, cancer and proliferative diseases and any other disease, condition, trait or indication that can respond to the level of SDF-1 in a cell or tissue.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Protease resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1 in the repair of tissue damage
ActiveUS20080095758A1Increase concentrationObviates abilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseMutant
The present invention is directed stromal cell derived factor-1 peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to digestion by the proteases dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) but which maintain the ability of native SDF-1 to attract T cells. The mutants may be attached to membranes formed by self-assembling peptides and then implanted at sites of tissue damage to help promote repair.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Method to accelerate stem cell recruitment and homing
InactiveUS20060110374A1Facilitate patient treatmentConvenient treatmentBiocideElectrotherapyProgenitorStromal cell
A method is provided for facilitating treatment of a patient, including stressing a portion of the patient to an extent sufficient to induce homing of progenitor cells to the portion of the patient. A method is additionally provided for use with tissue of a patient, including evaluating an indication of a level of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) in the tissue, and determining an indication of a number of stem cells in the tissue responsive to the indication of the level of SDF-1. A method is yet additionally provided for use with tissue of a patient, including evaluating an indication of a level of SDF-1 in the tissue, and determining an indication of a level of stress of a portion of the patient, responsive to the indication of the level of SDF-1. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:KWALATA TRADING
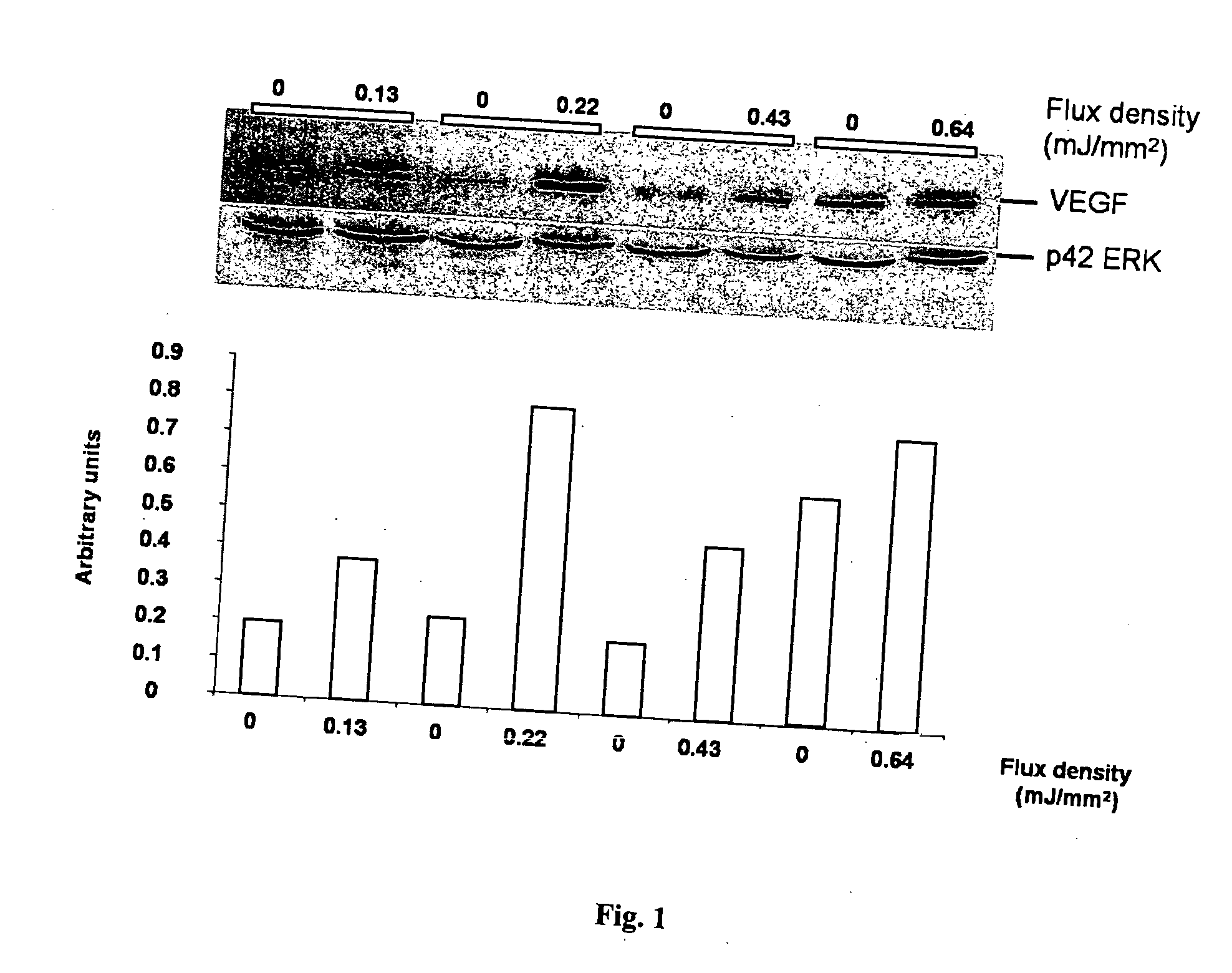
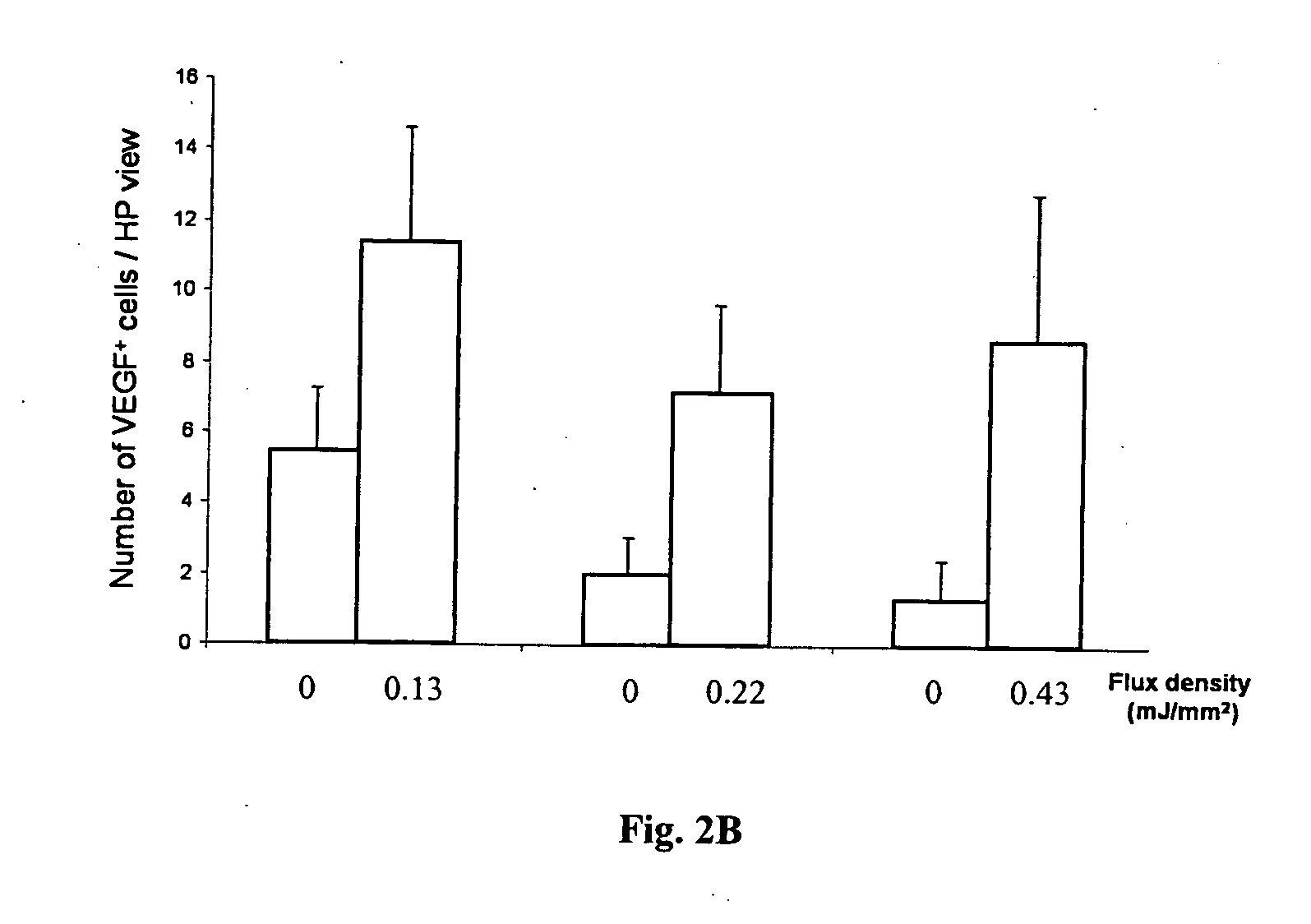
Methods for improving cell therapy and tissue regeneration in patients with cardiovascular and neurological diseases by means of shockwaves
InactiveUS20060246044A1Improving targeted recruitmentReduced ability to homeBiocideNervous disorderShock waveEtiology
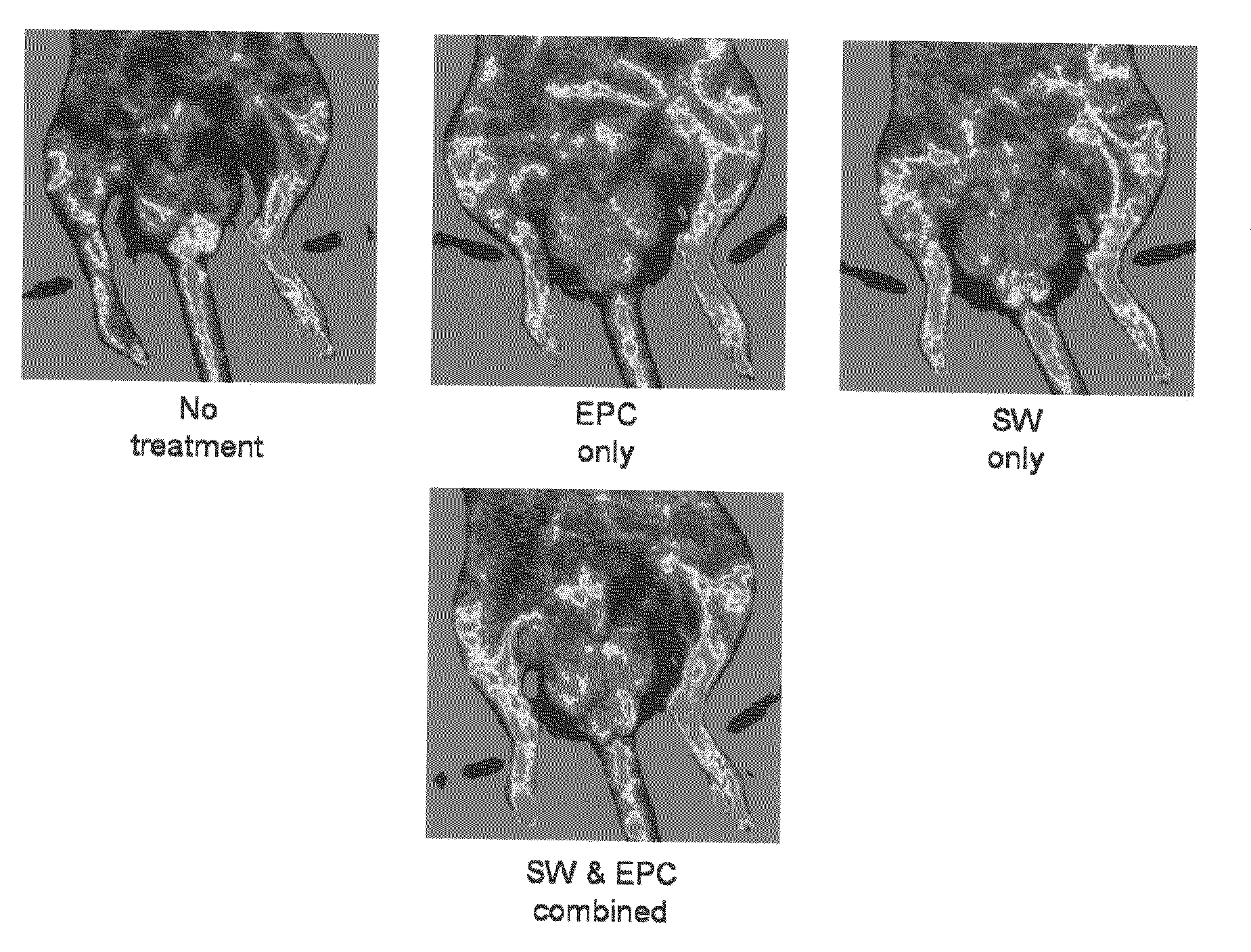
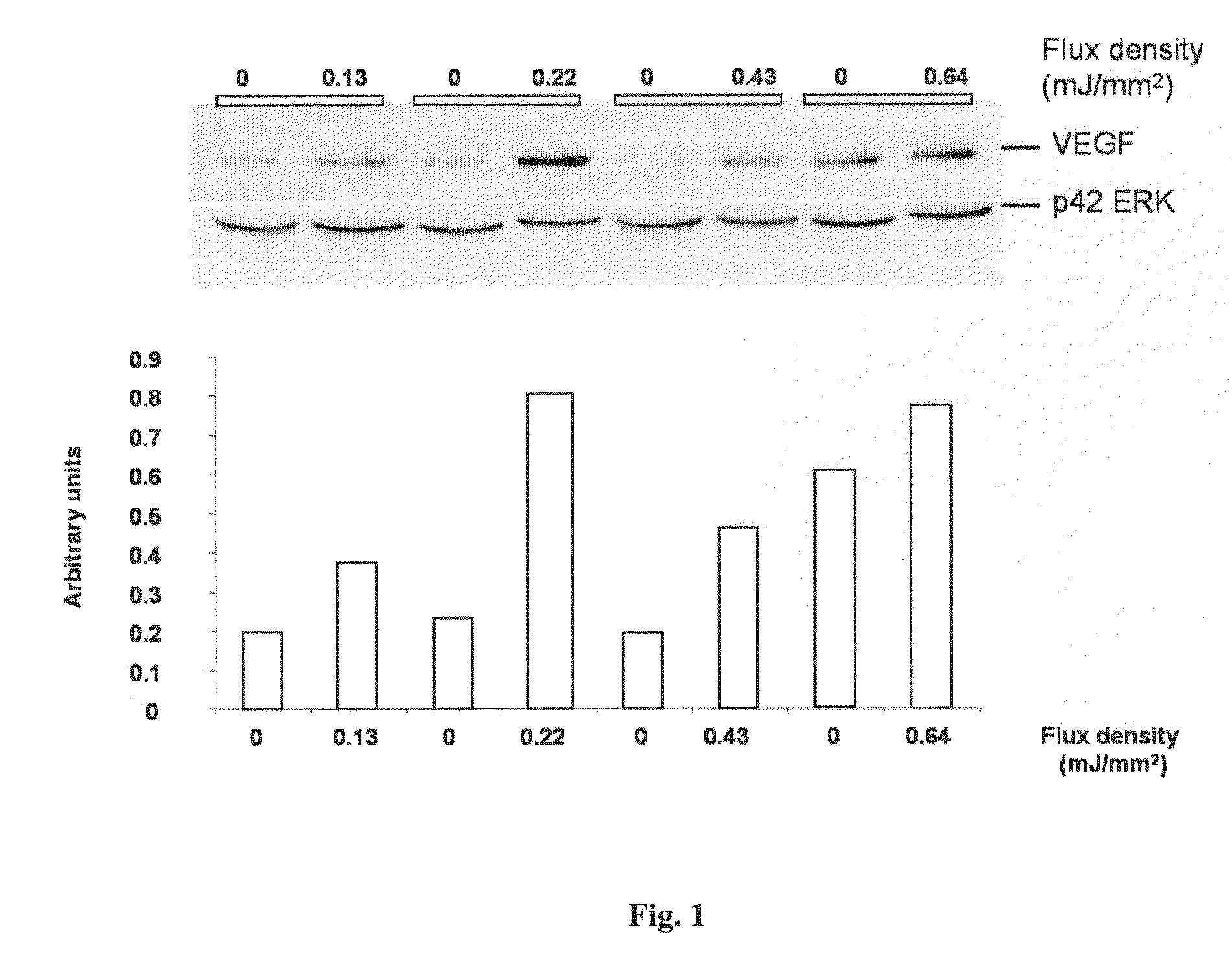
Improving cell therapy and tissue regeneration in a patient suffering from a cardiovascular or a neurological disease by treating a tissue of the patient with shock waves and / or applying to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of stem cells and / or progenitor cells. Such treatment increases expression of chemoattractants, pro-angiogenic factors, and pro-survival factors. The chemoattractants can be, for example, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or stromal cell derived factor 1 (SDF-1). For example, the treated tissue can be located in the patient's heart or in a skeletal muscle of the patient, and the shock waves can be extracorporeal shock waves (ESW) or intracorporeal shock waves. The cardiovascular disease can have an ischemic or non-ischemic etiology. For example, the cardiovascular disease can be a myocardial infarction, ischemic cardiomyopathy, or a dilatative cardiomyopathy. For example, the neurological disease can be a peripheral neuropathy or neuropathic pain.
Owner:DORNIER MEDTECH SYST GMBH
External Agent for Treatment of Skin Ulcer
InactiveUS20090285785A1Good curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStromal cellG-csf therapy
[Problems] To provide a novel external agent for treatment of skin ulcer which has an excellent healing effect on intractable skin ulcer such as bedsore, diabetic skin ulcer and ischemic skin ulcer.[Means for Solving Problems] The agent is characterized in that it comprises a composition containing at least one selected from the group consisting of granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF), stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and CD41-positive cells, and a hydrophilic high molecular substance.
Owner:CELLGENTECH
3D print scaffold material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107115561AImprove physical and chemical propertiesPromotes Adhesive GrowthAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationStromal cellPeriodontal tissue
The invention relates to a 3D print scaffold material and a preparation method and application thereof and particularly relates to a 3D print scaffold material for periodontal tissue reconstruction and a preparation method and thereof. The material comprises the following components: a stromal cell-derived factor-1 (stromal cell-derived factor-1, SDF-1) and a bone morphogenetic protein 2 (Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, BMPs). By adopting two functional molecules of SDF-1 and BMP2, endogenous stem cells are collected into a periodontal defect area, osteogenic differentiation is accelerated, periodontal tissue regeneration is accelerated, meanwhile, an individual bionic degradable polymer scaffold is designed on the basis of 3D printing, and the external form and the internal microstructure of the material is precisely controlled through a computer.
Owner:HOSPITAL OF STOMATOLOGY SUN YAT SEN UNIV
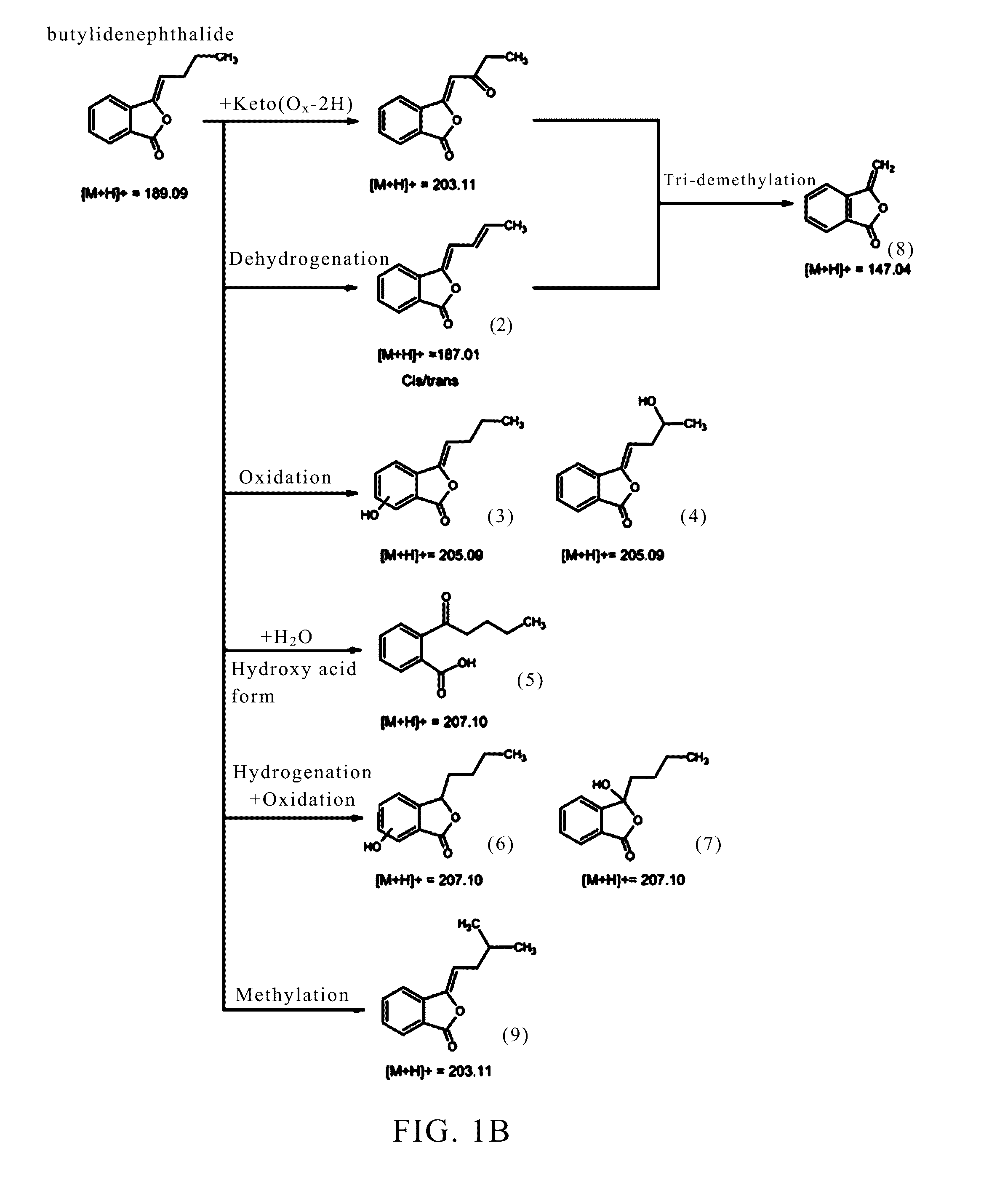
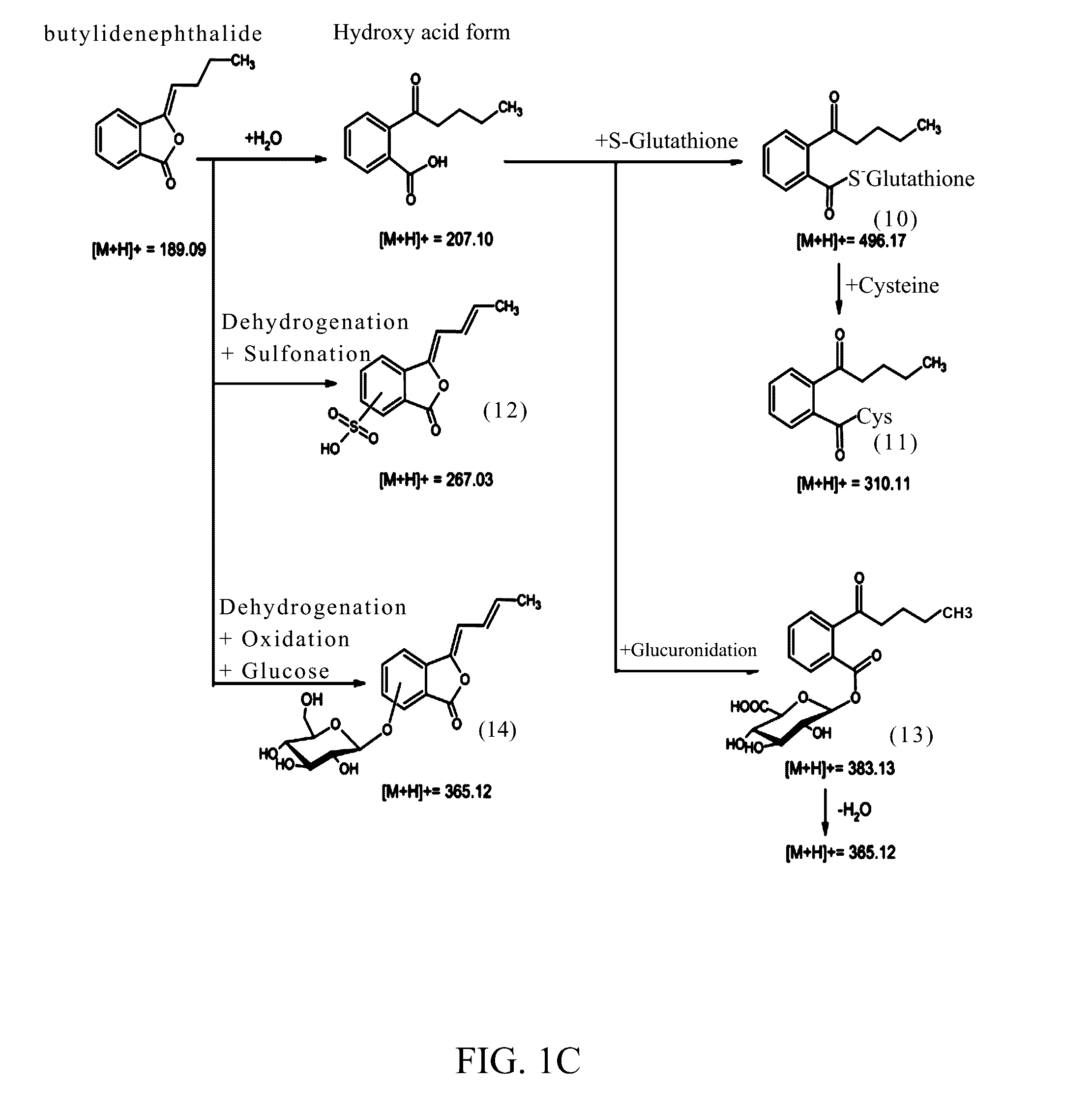
Application of phthalide compound
ActiveCN104042606AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderTelomeraseBrain-derived neurotrophic factor
An application of a phthalide compound in preparing a medicament. The medicament is specially used for promoting a stem cell to secrete one of the following items: telomerase, a neurotrophic factor (brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF), a stem cell chemotactic factor (stromal cell-derived factor-1, SDF1), a stem cell chemotactic factor receptor (CXC chemokine receptor 4, CXCR4), and an immunoregulatory factor; a kit comprising a phthalide compound and a stem cell is also provided.
Owner:HAWKING BIOLOGICAL TECH
Methods for improving cell therapy and tissue regeneration in patients with cardiovascular diseases by means of shockwaves
InactiveUS20080267927A1Improving targeted recruitmentReduced ability to homeBiocideNervous disorderProgenitorEtiology
Improving cell therapy and tissue regeneration in a patient suffering from a cardiovascular or a neurological disease by treating a tissue of the patient with shock waves and / or applying to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of stem cells and / or progenitor cells. Such treatment increases expression of chemoattractants, pro-angiogenic factors, and pro-survival factors. The chemoattractants can be, for example, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or stromal cell derived factor 1 (SDF-1). For example, the treated tissue can be located in the patient's heart or in a skeletal muscle of the patient, and the shock waves can be extracorporeal shock waves (ESW) or intracorporeal shock waves. The cardiovascular disease can have an ischemic or non-ischemic etiology. For example, the cardiovascular disease can be a myocardial infarction, ischemic cardiomyopathy, or a dilatative cardiomyopathy. For example, the neurological disease can be a peripheral neuropathy or neuropathic pain.
Owner:DORNIER MEDTECH SYST GMBH
Method of treating ischemic disorders
InactiveUS20100166717A1Increase the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsStromal cellApoptosis
A method of treating an ischemic disorders in a subject includes administering stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) to ischemic tissue of the subject in an amount effective to inhibit apoptosis of cells of the tissue.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Protease resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1 in the repair of tissue damage
ActiveUS7696309B2Obviates abilityRecovery is limitedNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseT cell
The present invention is directed stromal cell derived factor-1 peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to digestion by the proteases dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) but which maintain the ability of native SDF-1 to attract T cells. The mutants may be attached to membranes formed by self-assembling peptides and then implanted at sites of tissue damage to help promote repair.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Reactive-oxygen-species sensitive nanoparticle capable of promoting vascularization of surface of wound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104587449ARelease stabilityTo achieve the effect of slow-release encapsulation proteinPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineActive component
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and discloses a reactive-oxygen-species sensitive nanoparticle capable of promoting the vascularization of the surface of a wound and a preparation method thereof. The active component of the nanoparticle is a stromal cell derived factor 1 alpha (SDF-1alpha), and the medicine carrying nanomaterial is poly(1,4-phenyleneacetone dimethylenethioketal) (PPADT). The nanoparticle has a size of 70-130nm. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the nanoparticle. The medicine carrying nanoparticle is prepared by adopting a multiple emulsion-solvent evaporation method. The product has a good slow-releasing effect, is reduced in protein denaturation and improved in encapsulation rate and has good stability and low biotoxicity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Protease-resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1 in the repair of tissue damage
ActiveUS9308277B2Treating and reducing likelihoodPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDipeptidyl peptidaseCathepsin G
The present invention features mutant stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to digestion by, for example, the proteases dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), leukocyte elastase, cathepsin G, carboxypeptidase M, and carboxypeptidase N, but which retain chemoattractant activity.
Owner:MESOBLAST INTERNATIONAL SARL
Skin ulcer healing combination and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106074605AGood restorativeConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsAerosol deliveryFreeze-dryingStem cell culture
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, and particularly relates to a skin ulcer healing combination and a preparation method thereof. The combination comprises an intravenous drip component and an outward spray component, wherein the intravenous drip component is normal saline containing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, and the outward spray component comprises umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell supernate freeze-dried powder, platelet rich plasma, a stromal cell-derived factor-1 and normal saline. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are intravenously re-infused, various factors in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell culture solution are mixed with the platelet rich plasma and the stromal cell-derived factor-1 and locally sprayed outwards, and rapider and better skin ulcer healing effects are achieved. Experiments indicate that the skin ulcer healing effect of the combination is obviously superior to that of the prior art.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Methods of treating incontinence and other sphincter deficiency disorders
A method of treating a sphincter deficiency disorder (e.g., incontinence; gastrointestinal disorders) is carried out by administering stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) to a sphincter or sphincter complex, such as a urethral or gastrointestinal sphincter (e.g., a rectal sphincter) of the subject in a treatment-effective amount.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
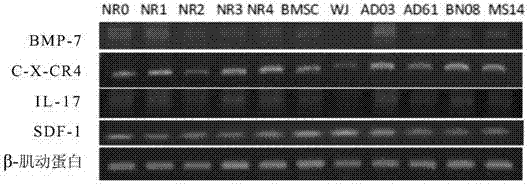
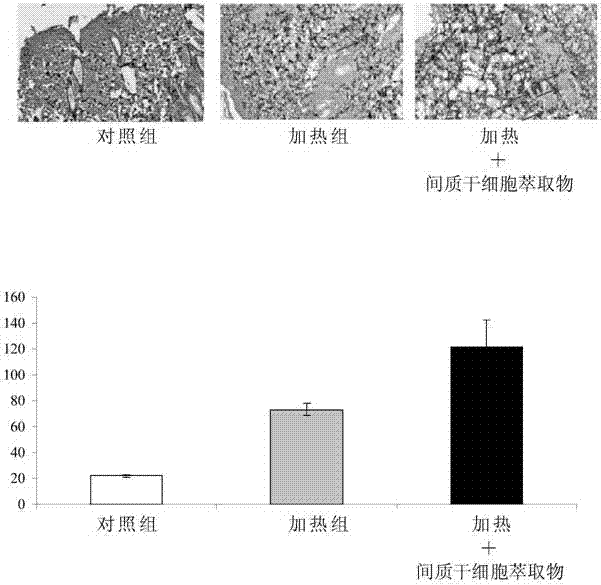
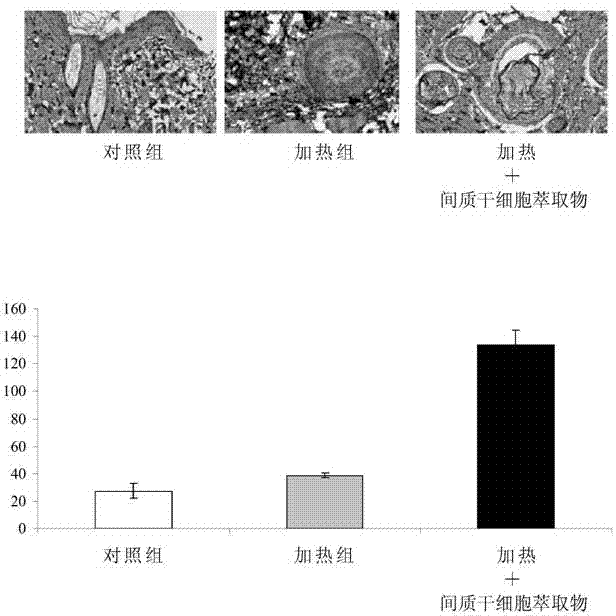
Mesenchymal stem cell extract and its use
A mesenchymal stem cell extract and its use are provided, wherein the mesenchymal stem cell extract comprises a trophic factor(s), such as bone morphogenetic protein-7 (BMP-7), stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), C-X-C chemokine receptor type-4 (CXCR4), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and / or interleukin-17 (IL-17), and wherein the extract is especially suitable for repairing skin aging.
Owner:GWOXI STEM CELL APPL TECH CO LTD
Methods for repairing tissue damage using protease-resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1
InactiveUS20160303197A1Treating and reducing likelihoodGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderRepair tissueProteinase activity
The present invention features methods for treating or ameliorating tissue damage using intravenous administration of compositions (for example, isolated peptide compositions or stem cells expressing such peptides) that include stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) peptides or mutant SDF-1 peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to protease digestion, but which retain chemoattractant activity.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
Protease-resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1 in the repair of tissue damage
ActiveUS20160375100A1Treating and reducing likelihoodChemokinesPeptide/protein ingredientsCarboxypeptidase MCell biology
The present invention features mutant stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to digestion by, for example, the proteases dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), leukocyte elastase, cathepsin G, carboxypeptidase M, and carboxypeptidase N, but which retain chemoattractant activity.
Owner:MESOBLAST INTERNATIONAL SARL
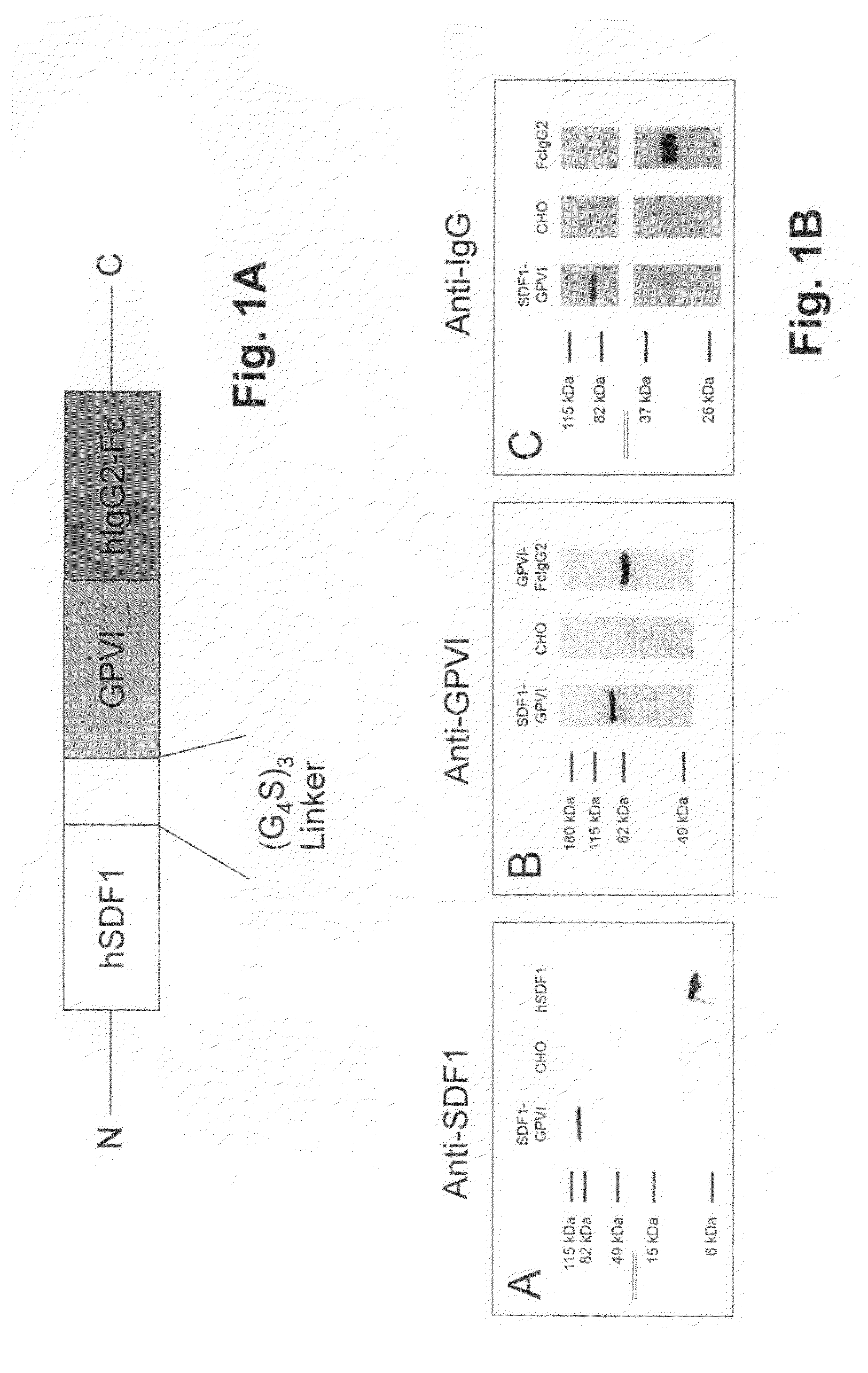
Fusion protein and its uses
InactiveUS20130108580A1Promote chemotaxisEffective toolSaccharide peptide ingredientsFusions for specific cell targetingDiseaseStromal cell
The present invention relates to a fusion protein comprising a) a first polypeptide selected from among SDF-1 (stromal cell derived factor-1) or peptidase / protease-resistant variants or fragments thereof which have the CXCR4- / CXCR7- binding function of SDF-1; and b) a second polypeptide which is selected from among GPVI (glycoprotein VI), or the extracellular domain of GPVI, or fragments or variants of the extracellular domain of GPVI which contain the collagen binding function of GPVI, wherein the first polypeptide and the second peptide are linked to one another directly or via a linker molecule. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the fusion protein for treating diseases.
Owner:UNIV TUBINGEN
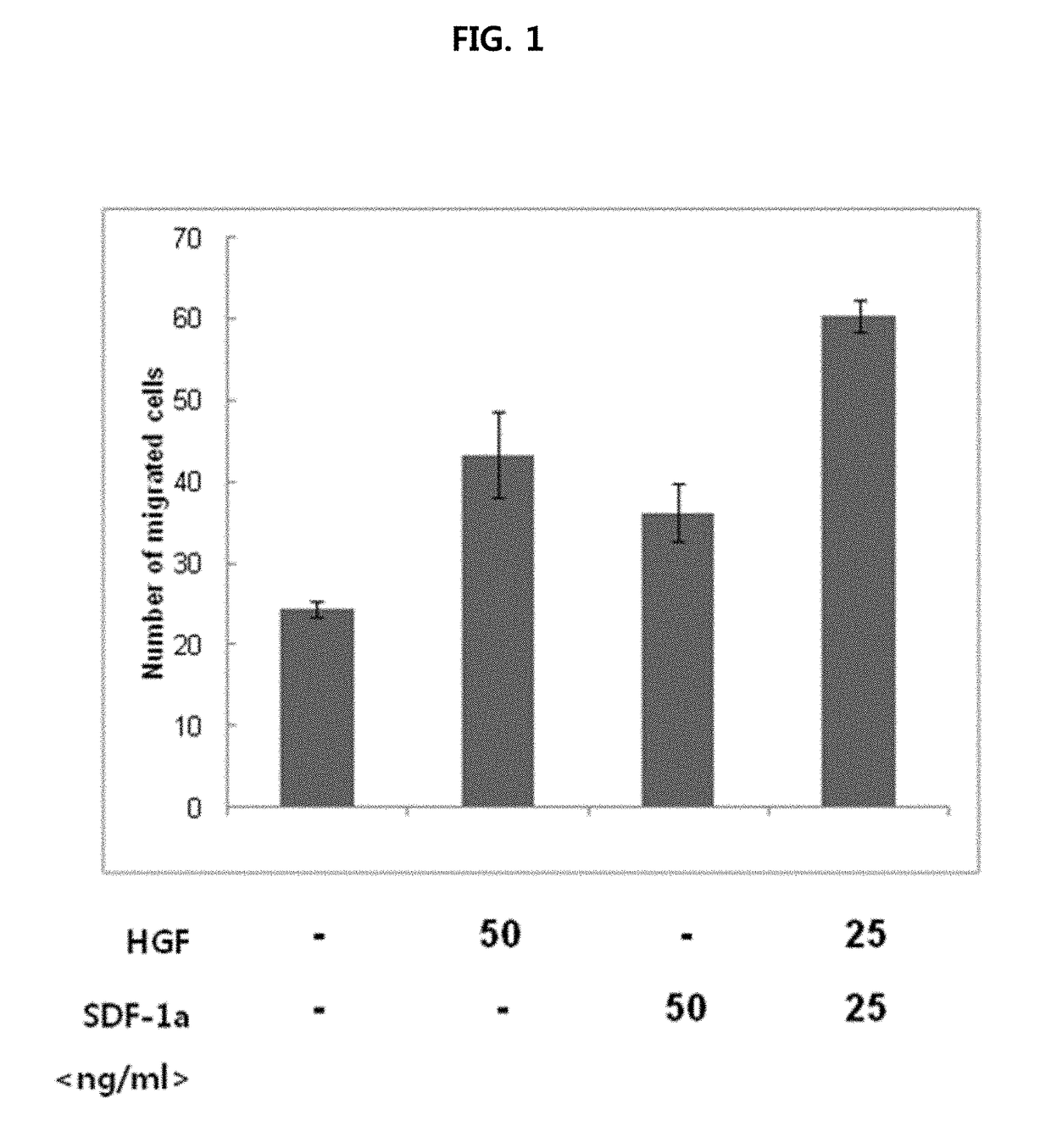
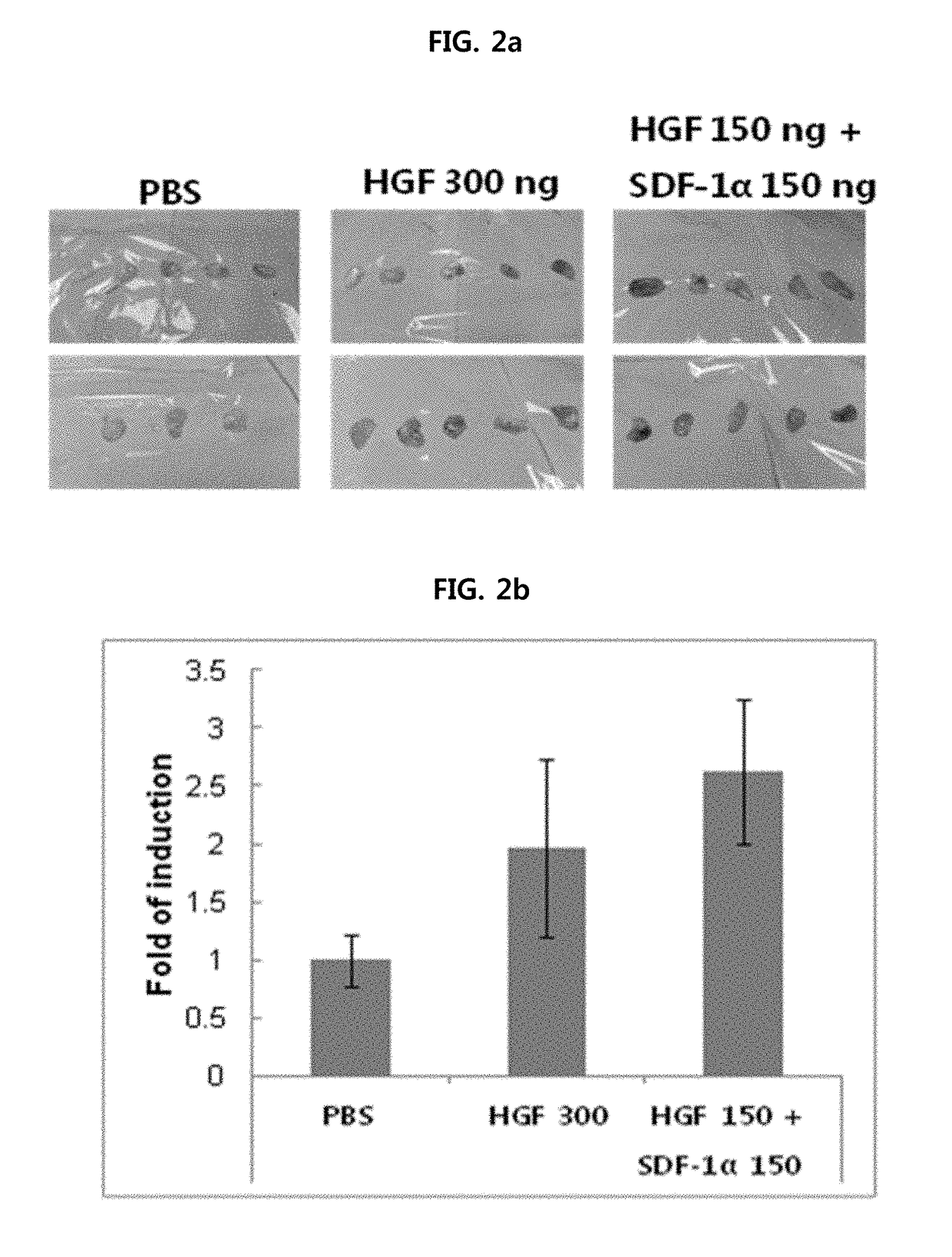
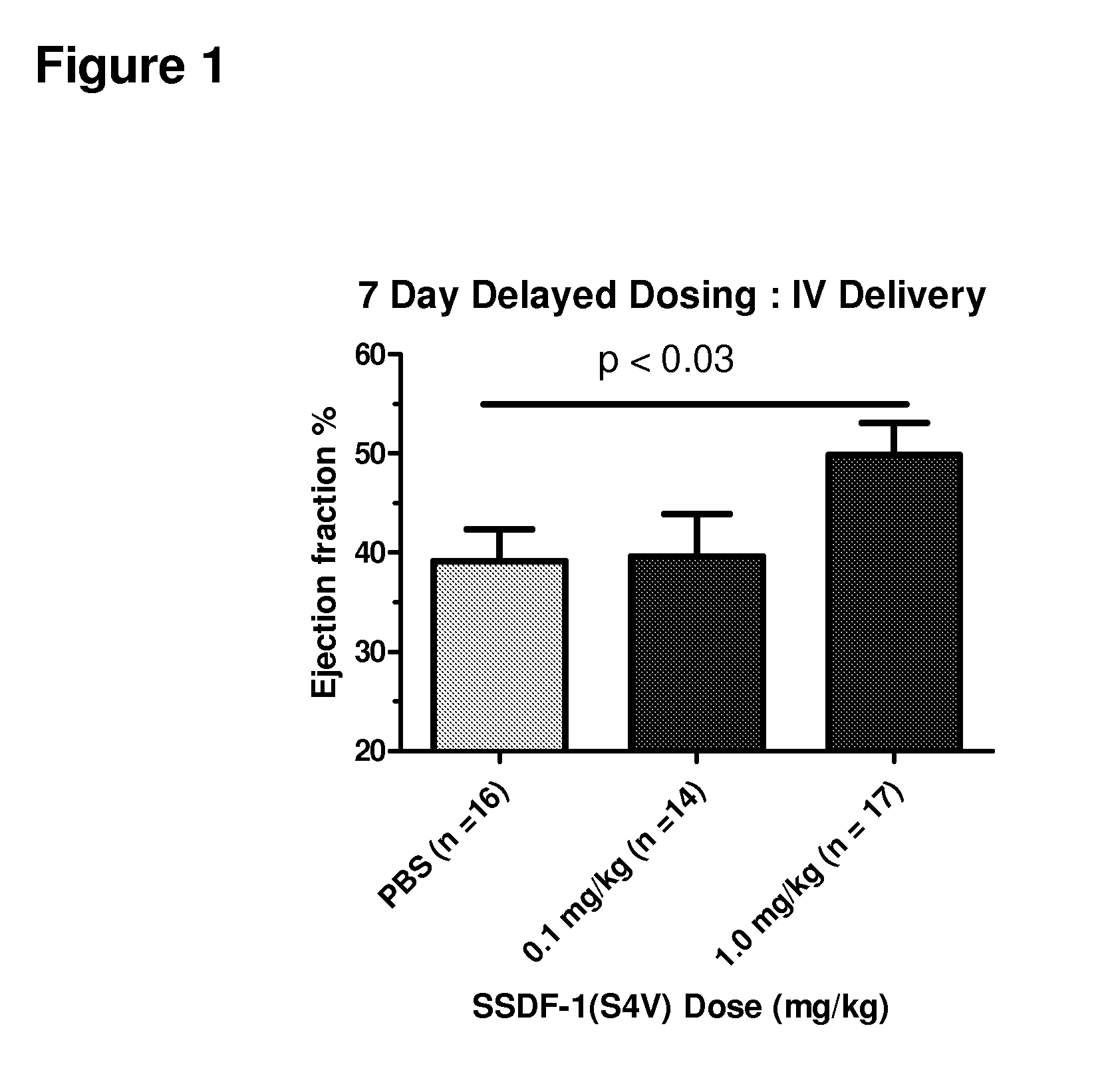
Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha]
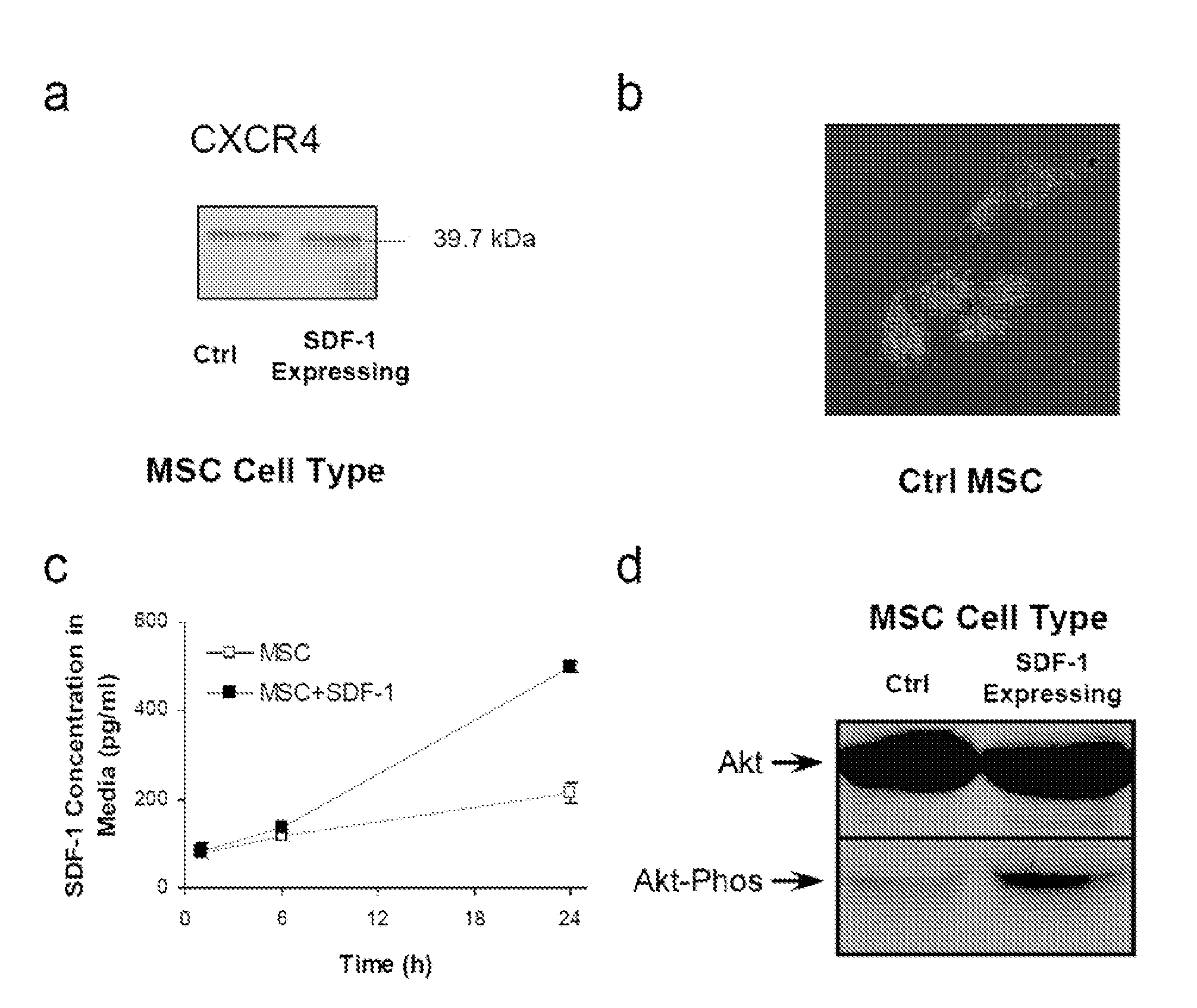
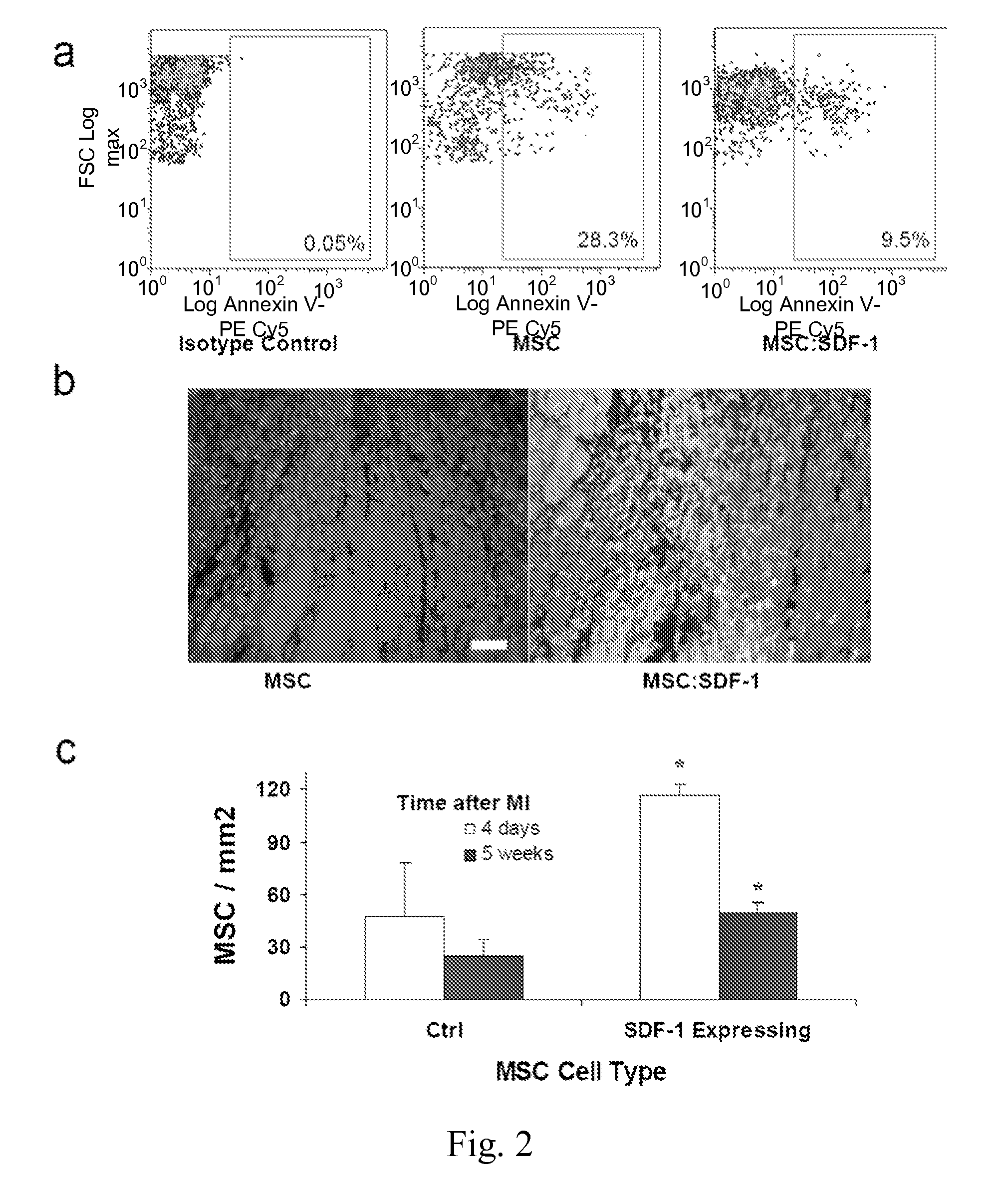
ActiveCN107073078APromote generationPeptide/protein ingredientsGene therapyBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTCell migration
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease, the composition comprising, as an active ingredient: (a) hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or an isoform thereof, and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha] (SDF-1[alpha]); or (b) a polynucleotide encoding the HGF and a polynucleotide encoding the SDF-1[alpha]. The peripheral vascular disease (for example, ischemic limb disease) can be more effectively prevented or treated through the significant promotion of vascular endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis in the case of singly using the composition of the present invention than in the case of using HGF, an isoform thereof, SDF-1[alpha] or a polynucleotide codes a protein thereof.
Owner:HELIXMITH CO LTD
RNA interference mediated inhibition of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS7928220B2Improves various propertyImprove the immunitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsFhit geneCellular process
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in SDF-1 gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating or that mediate RNA interference (RNAi) against SDF-1 gene expression. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions for treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that can respond to modulation of SDF-1 expression in a subject, such as ocular disease, cancer and proliferative diseases and any other disease, condition, trait or indication that can respond to the level of SDF-1 in a cell or tissue.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Method for providing an increased expression of telomerase, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, stromal cell-derived factor-1, cxc chemokine receptor 4, and/or immune regulatory factor of stem cell
ActiveUS20160324826A1High expressionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTelomeraseFactor ii
A method for providing an increased expression of at least one of telomerase, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF1), CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), and an immune regulatory factor of a stem cell in a subject is provided. The method comprises simultaneously or separately administering to the subject an effective amount of (a) a phthalide and (b) a stem cell.
Owner:HAWKING BIOLOGICAL TECH
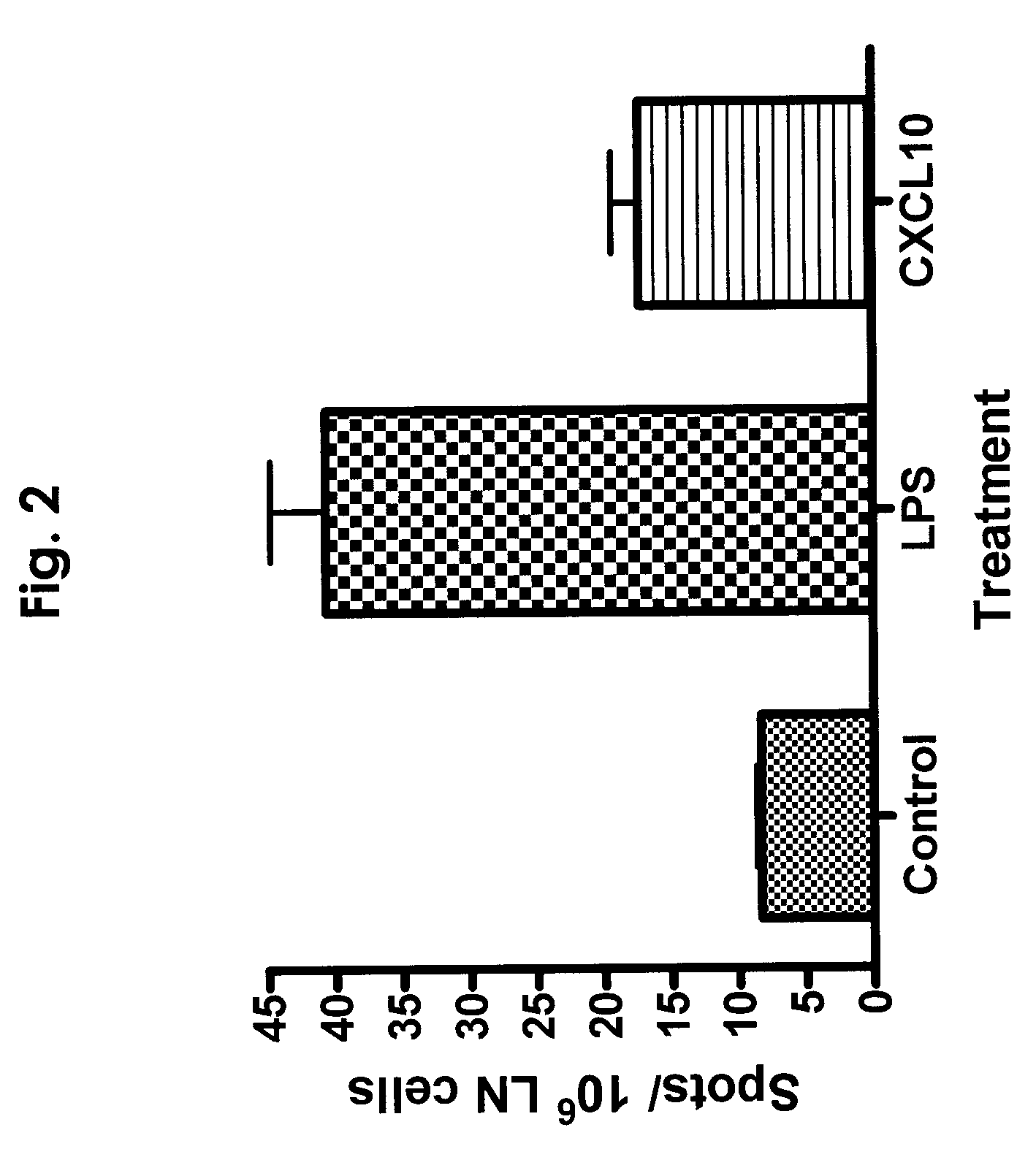
Composition and Method for Inducing Protective Vaccine Response Using SDF-1
InactiveUS20080014214A1Stimulate immune responseReduce degradationViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesRegulatory T cellStromal cell
A method for inducing a protective immune response is disclosed, the method utilizing a composition comprising a CXCR3-binding chemokine and stromal cell-derived factor 1 which may be administered in conjunction with a protein, peptide, polynucleotide, or other target antigen to promote the development of regulatory T cells and boost the immune response to an infectious agent from which the protein, peptide, polynucleotide, or other target antigen is derived.
Owner:KRATHWOHL MITCHELL
Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1a
ActiveUS20170281729A1Prevent or treatPromotion of the migration and angiogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsGene therapyDiseaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease, the composition comprising, as an active ingredient: (a) hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) or an isoform thereof, and stromal cell derived factor 1α (SDF-1α); or (b) a polynucleotide encoding the HGF and a polynucleotide encoding the SDF-1α. The peripheral vascular disease (for example, ischemic limb disease) can be more effectively prevented or treated through the significant promotion of vascular endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis in the case of singly using the composition of the present invention than in the case of using HGF, an isoform thereof, SDF-1α or a polynucleotide codes a protein thereof.
Owner:HELIXMITH CO LTD
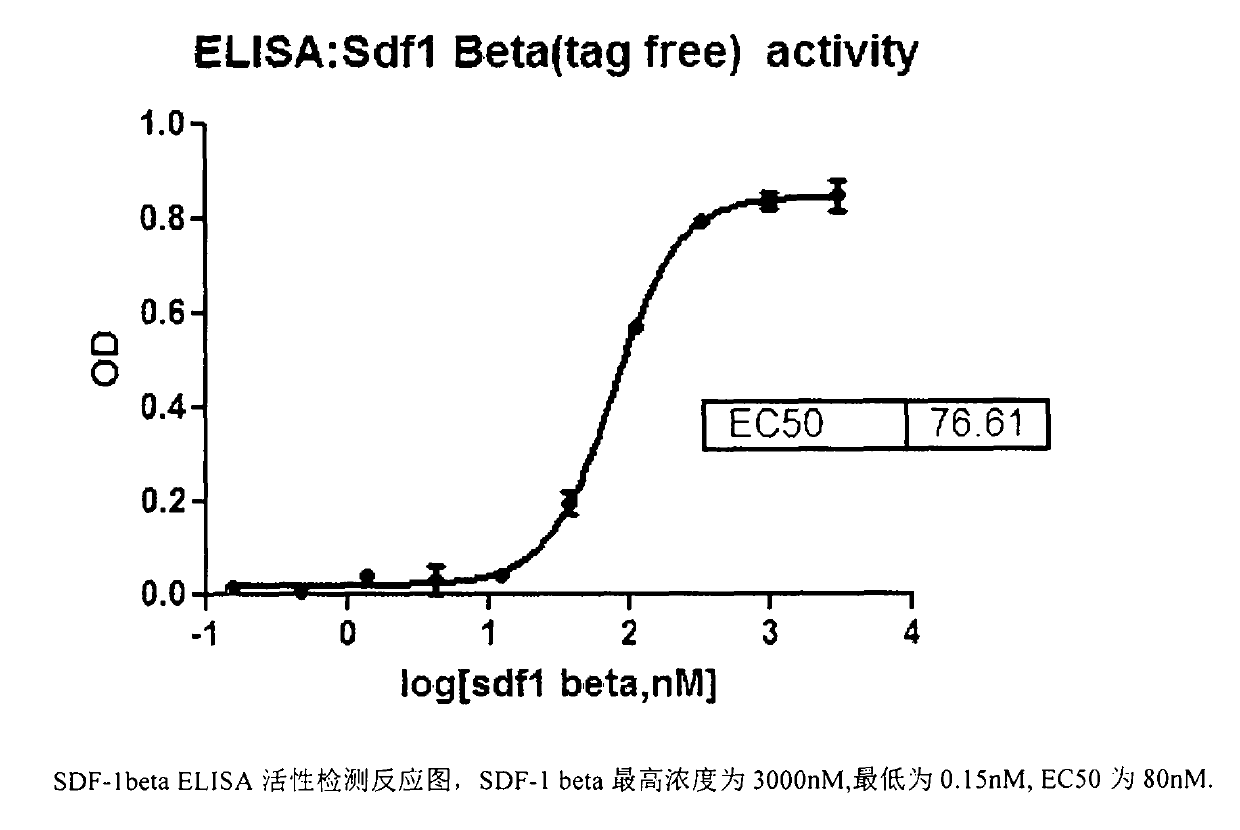
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit for direct detection of activity of human stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)
The invention relates to an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) kit for direct detection of activity of a human stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1). A method for detecting the activity of the SDF-1 by using the ELISA kit comprises the steps of: coating SDF-1 on an ELISA plate, treating by using a sealing solution in a sealing manner, adding a proper amount of anti-SDF-1 antibodies and a corresponding second antibody, and adding a corresponding developing solution; when the color changes obviously, adding a stopping solution for stopping; measuring an OD (Outside Diameter) value on a microplate reader, and judging the activity of the SDF-1 according to the magnitude of the OD value. The ELISA kit can be used for rapidly and conveniently detecting the activity of the SDF-1 directly, and detecting a plurality of SDF-1 samples in one step in an actual utilization process. The chart in the specification is an SDF-1beta ELISA activity detection reaction chart, the highest concentration of the SDF-1beta is 3,000nM, the lowest concentration of the SDF-1beta is 0.15nM, and EC50 (Encephalitozoon Cuniculi 50) is 80nM.
Owner:ABZYME BIOTECH
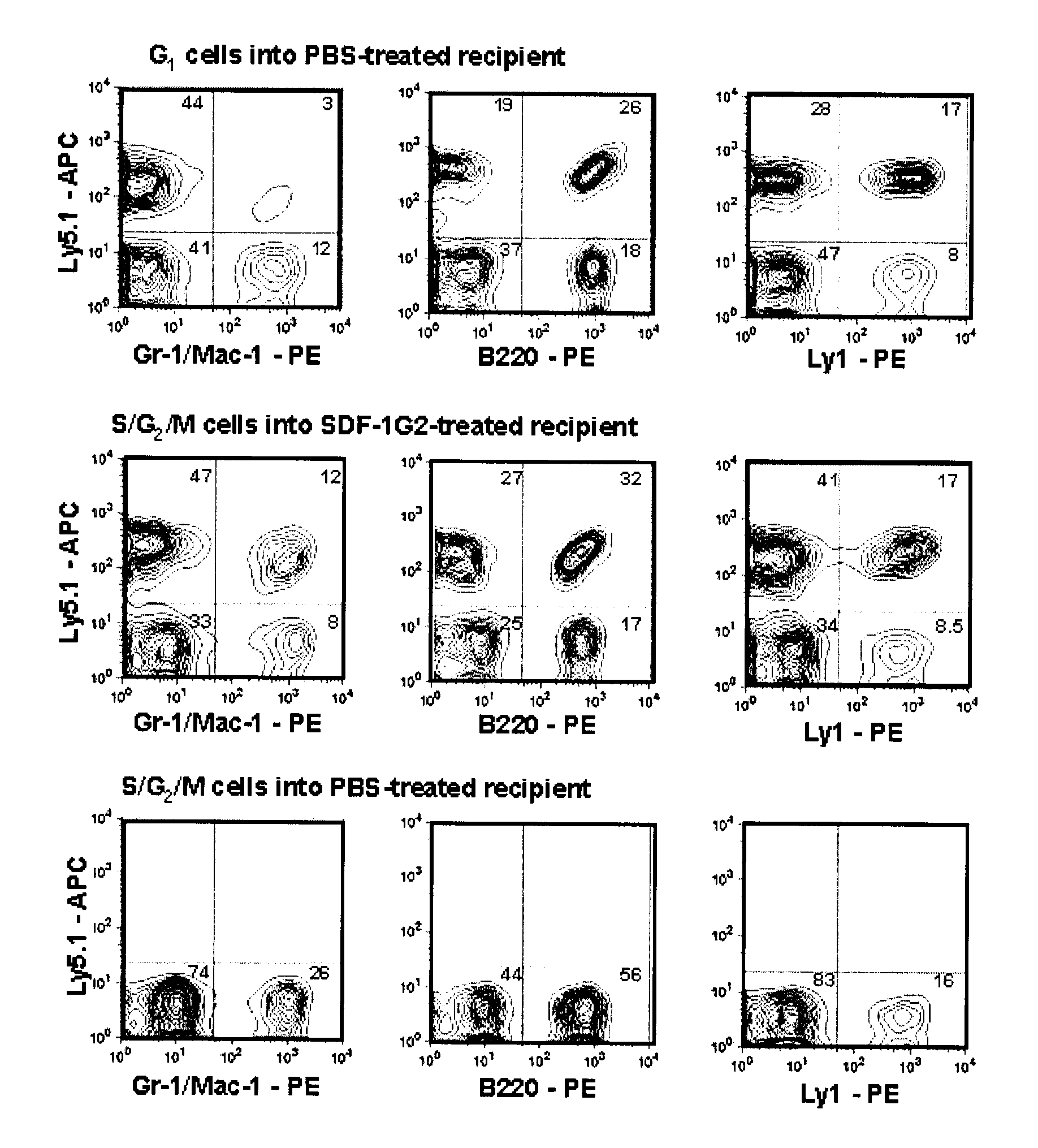
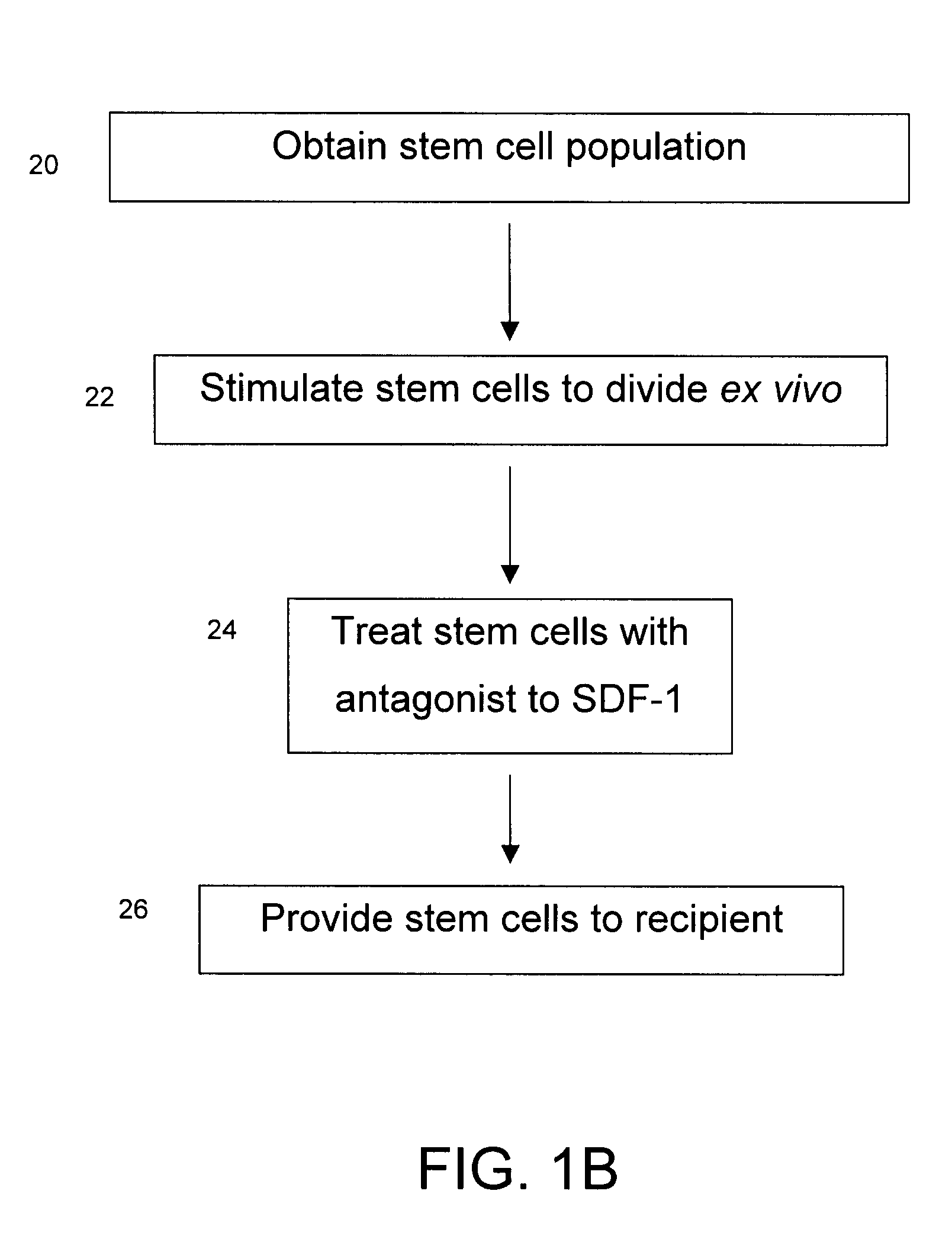
Method and composition for increasing the engraftment efficiency of stem cells
InactiveUS20090035318A1Organic active ingredientsBiocideStromal cellReceptor for activated C kinase 1
A method is described for increasing the engraftment efficiency of S / G2 / M phase stem cells, which involves treating a recipient with the stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) antagonist SDF-1G2 prior to delivery of the cells to said recipient. Further, a method of transplanting proliferating or S / G2 / M phase stem cells is described, comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining stem cells; (b) inducing stem cells ex vivo to proliferate or enter S / G2 / M phase; (c) treating the recipient with the SDF-1 antagonist SDF-1G2; and (d) providing the stem cells to the recipient.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
SDF-1-based glycosaminoglycan antagonists and methods of using same
The present invention relates to novel mutants of human stromal cell-derived factor-1 which exhibit increased glycosaminoglycan (GAG) binding affinity and inhibited or down-regulated GPCR activity compared to wild type SDF-1, methods for producing these mutants and to their use for preparing medicaments for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:PROTAFFIN BIOTECHNOLOGIE AG
Construction method of lactococcus lactis MG1363 and application of lactococcus lactis MG1363 in treating bacterial vaginitis
InactiveCN109112155AImprove acid resistanceImprove featuresAntibacterial agentsChemokinesChemical synthesisElectricity
The invention discloses construction method of lactococcus lactis MG1363 and application of the lactococcus lactis MG1363 in treating bacterial vaginitis. The construction method comprises the following steps of firstly, chemically synthesizing human and mouse chemokine CXCL12, also called stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and belonging to small molecular proteins of a CXC chemokine family; and then adding specific secretory expression cell-penetrating peptide SPusp45 of the lactococcus lactis, constructing pMG36e-CXCL12 recombinant plasmids, and then enabling the pMG36e-CXCL12 recombinantplasmids to enter the lactococcus lactis MG1363 with electricity facing to realize secretory expression of chemokine CXCL12. The chemokine CXCL12 is continuously expressed with a manner of vagina embolization administration, so that the effects of remission and treatment to the bacterial vaginitis are realized.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Methods of treating incontinence and other sphincter deficiency disorders
A method of treating a sphincter deficiency disorder (e.g., incontinence; gastrointestinal disorders) is carried out by administering stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) to a sphincter or sphincter complex, such as a urethral or gastrointestinal sphincter (e.g., a rectal sphincter) of the subject in a treatment-effective amount.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Methods for repairing tissue damage using protease-resistant mutants of stromal cell derived factor-1
ActiveUS20140199304A1Treating and reducing likelihoodGood effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWhole bodyStromal cell
The present invention features methods for treating or ameliorating tissue damage using intravenous administration of compositions that include stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) peptides or mutant SDF-1 peptides that have been mutated to make them resistant to protease digestion, but which retain chemoattractant activity. Systemic delivery, and specifically intravenous (“IV”) delivery, of SDF-1 and protease resistant SDF-1 mutants is very effective for the treatment of tissue damage.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
Construction of Lactobacillus crispatus BT1386 and application in treatment of bacterial vaginosis
InactiveCN109022475AImprove acid resistanceImprove featuresAntibacterial agentsUnknown materialsChemical synthesisBacterial vaginosis
The invention discloses construction of Lactobacillus crispii BT1386 and application in treatment of bacterial vaginosis. First, human and mouse chemokine CXCL12 also known as stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) is chemically synthesized, and the human and mouse chemokine CXCL12 belongs to is a small molecule protein in a CXC chemokine family. Secretory expression transmembrane peptide SPusp45 which is unique to Lactococcus lactis is added to construct a recombinant plasmid pMG36e-CXCL12, and the recombinant plasmid is then electrotransformed into the Lactobacillus crispii BT1386 to achievesecretory expression of the chemokine CXCL12. The chemokine CXCL12 is continuously expressed by vaginal embolization to achieve the remission and treatment of the bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

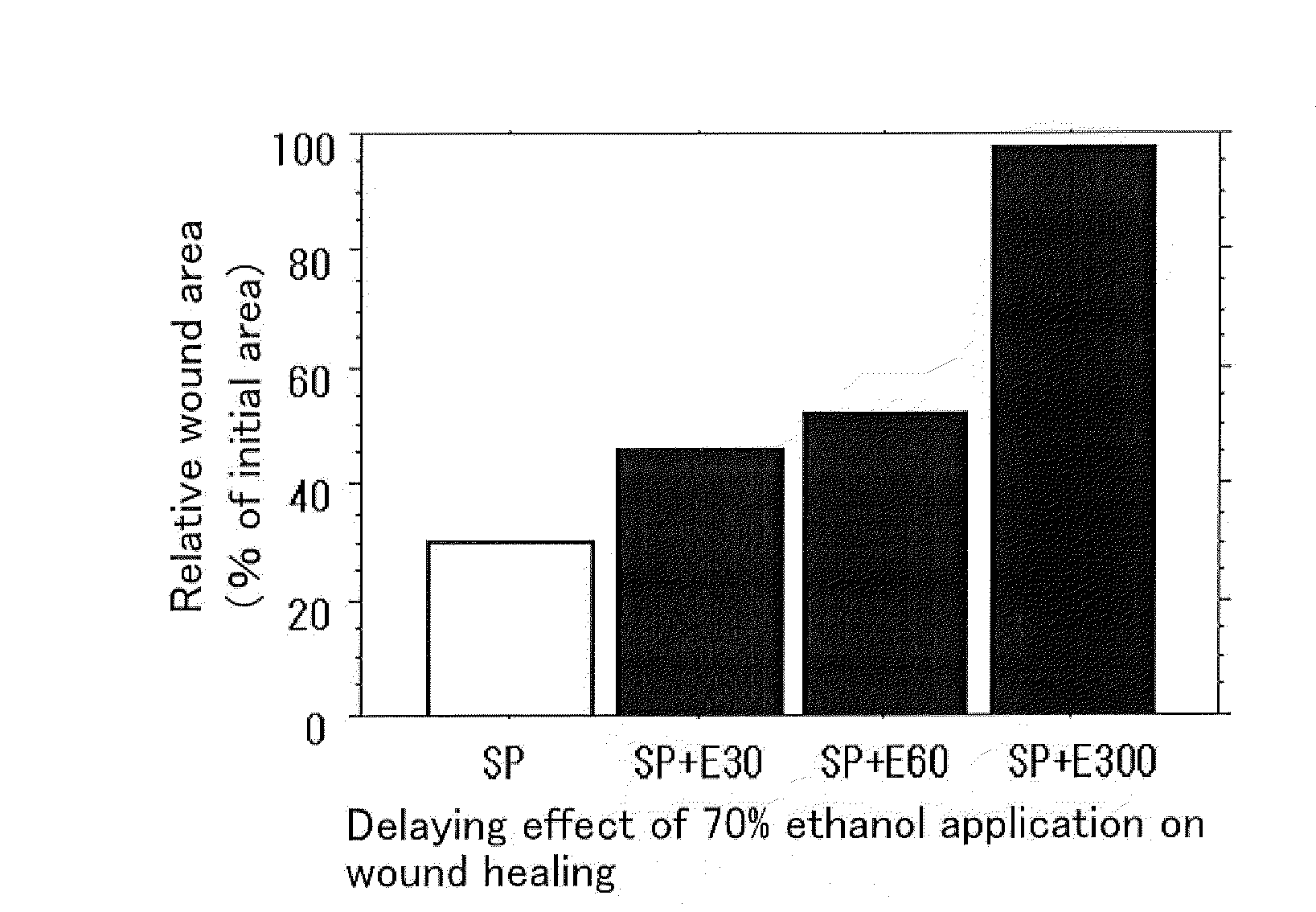
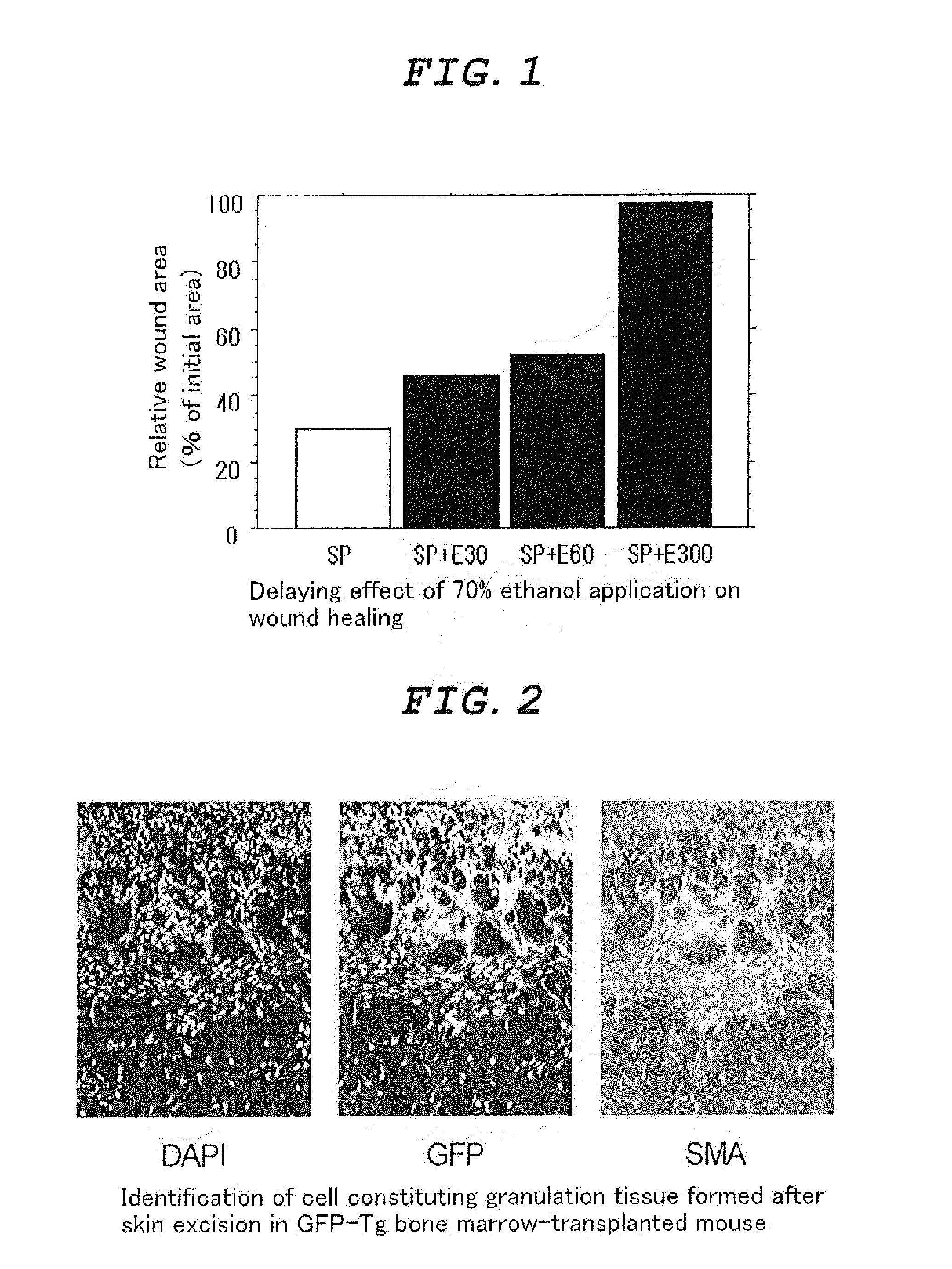















![Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha] Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/0b85a5d9-930e-4e10-9287-e420bb3d42bc/HDA0001254208790000011.png)
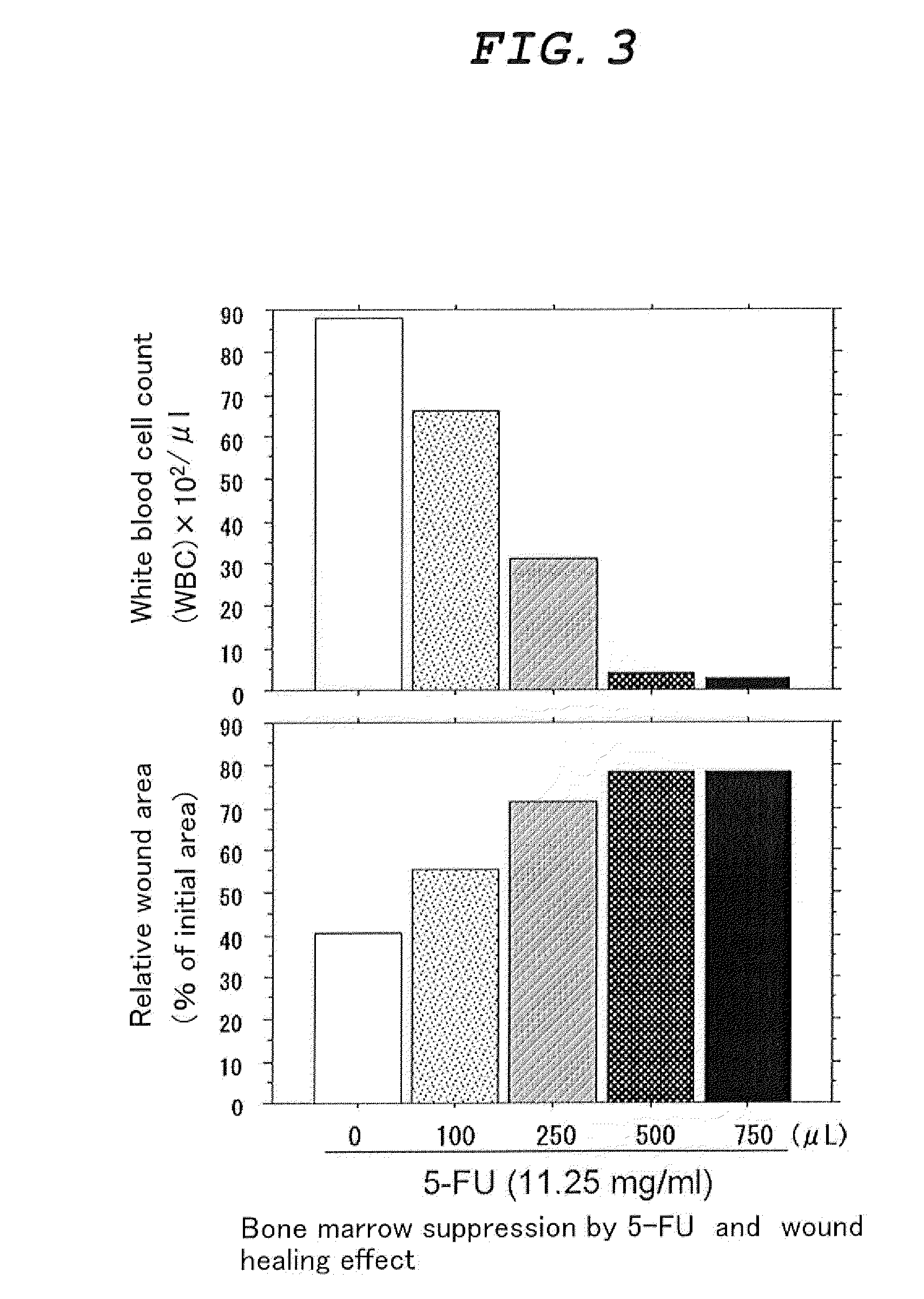
![Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha] Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/0b85a5d9-930e-4e10-9287-e420bb3d42bc/HDA0001254208790000021.png)
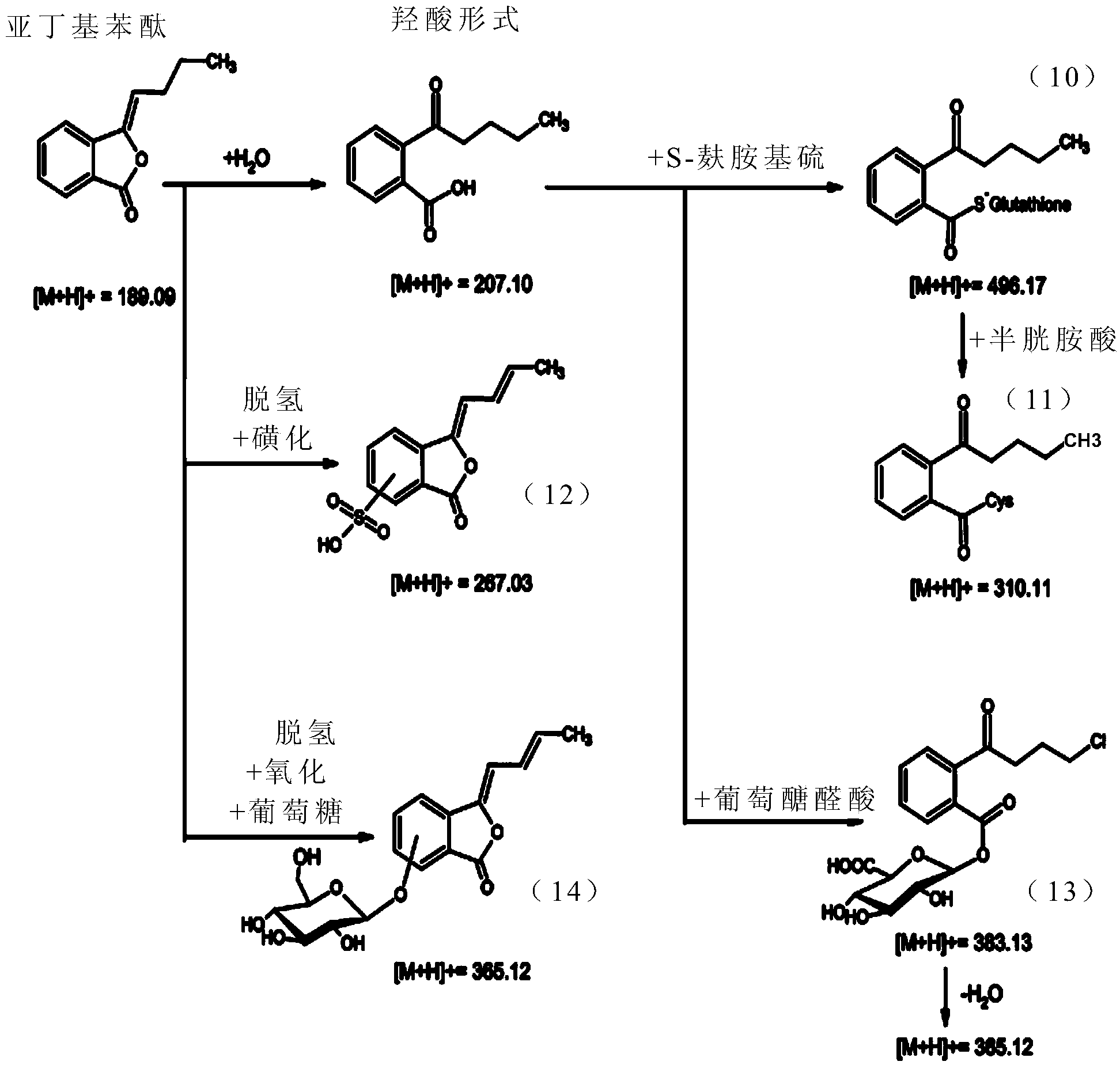
![Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha] Composition for preventing or treating peripheral vascular disease using hepatocyte growth factor and stromal cell derived factor 1[alpha]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/0b85a5d9-930e-4e10-9287-e420bb3d42bc/HDA0001254208790000022.png)