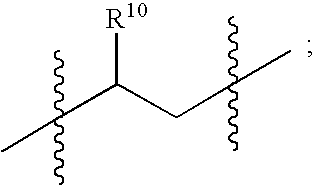
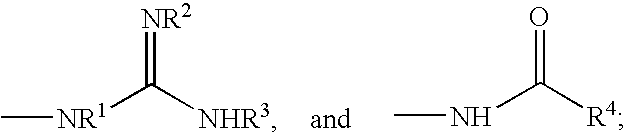Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Streptomyces thioluteus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
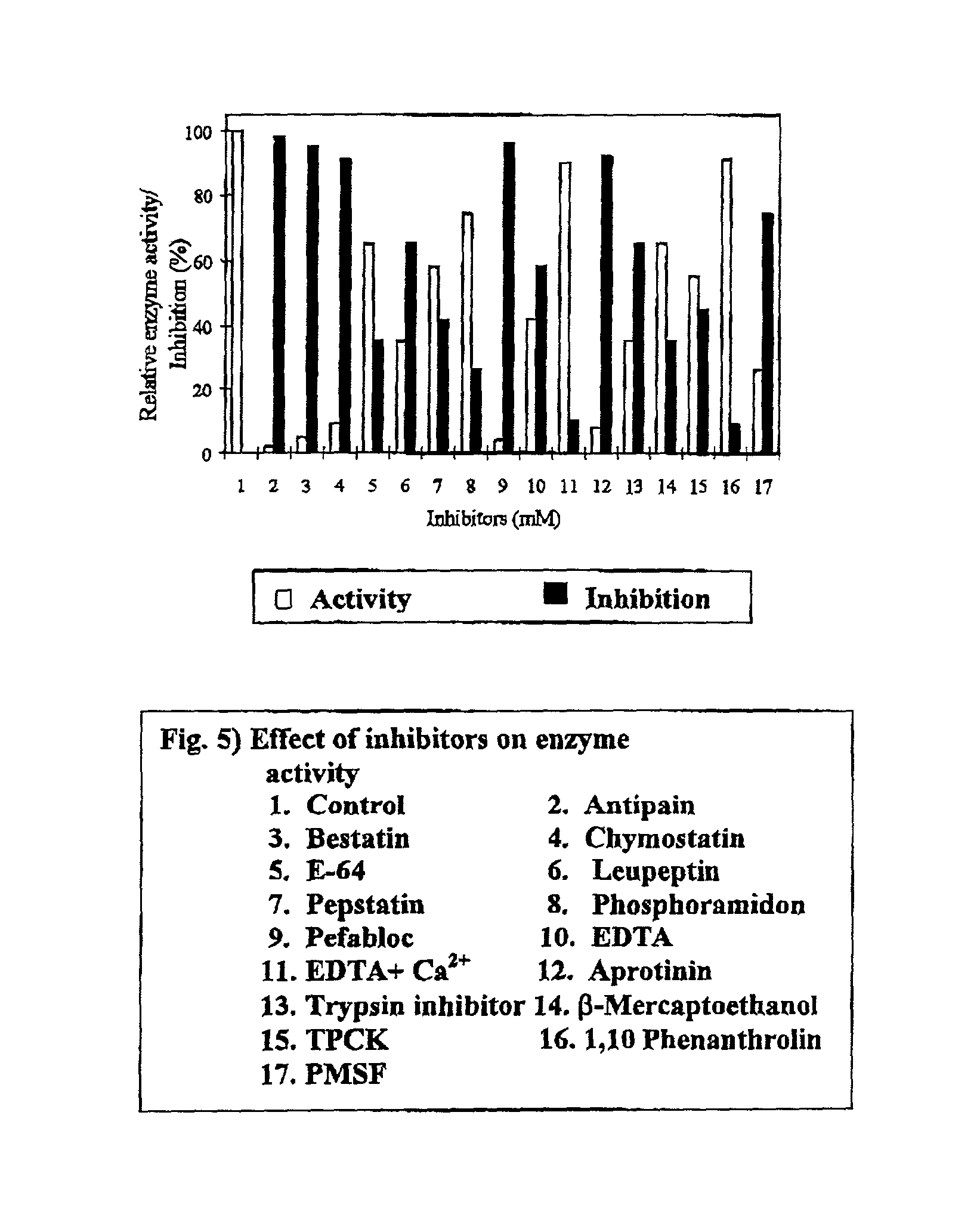
Streptomyces thioluteus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces thioluteus produces leupeptins, phenazines, phenoxazinones, dioxopiperazines, questiomycin A, aureothricin and aureothin.
Streptomyces parvus and application thereof for preparing daptomycin
The invention discloses a streptomyces parvus and application thereof for preparing daptomycin. The strain is reserved in the CCTCC and has the reservation number of CCTCC NO: M2010136, and the reservation data is June 4, 2010. The method for preparing the daptomycin is as follows: a, taking streptomyces parvus CCTCC NO: M2010136 as a fermentation strain; b, strain cultivation: inoculating slope lawn into a shake flask seeding tank to cultivate to obtain shake flask seeding liquid; inoculating the shake flask seeding liquid into the seeding tank to be cultivated; inoculating the seeding tank culture solution into fermentation tank culture medium to be cultivated, and collecting fermentation liquor; carrying out feed supplement in the fermentation and cultivation process; and c, extracting a fermentation product. The fermentation technology provided by the invention has stable production capability, high fermentation unit and few fermentation byproducts by the pilot plant test and the experiment in a 10-ton fermentation tank, greatly lowers post-extracting difficulty and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUADONG MEDICINE GRP PHARMA RES INST +1
Novel aromatic prenyltransferases, nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
ActiveUS20060183211A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenyltransferase activityIsoprene
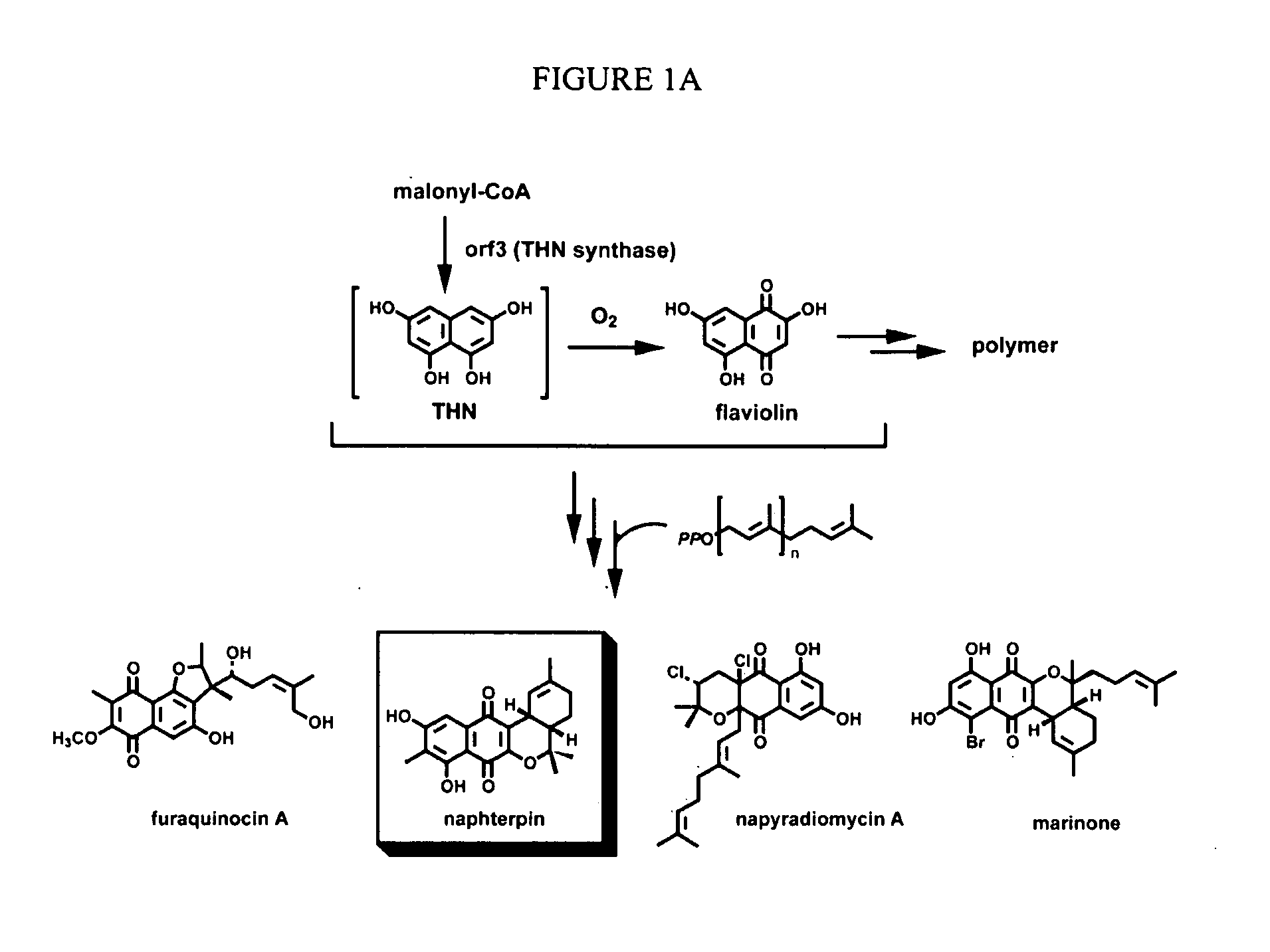
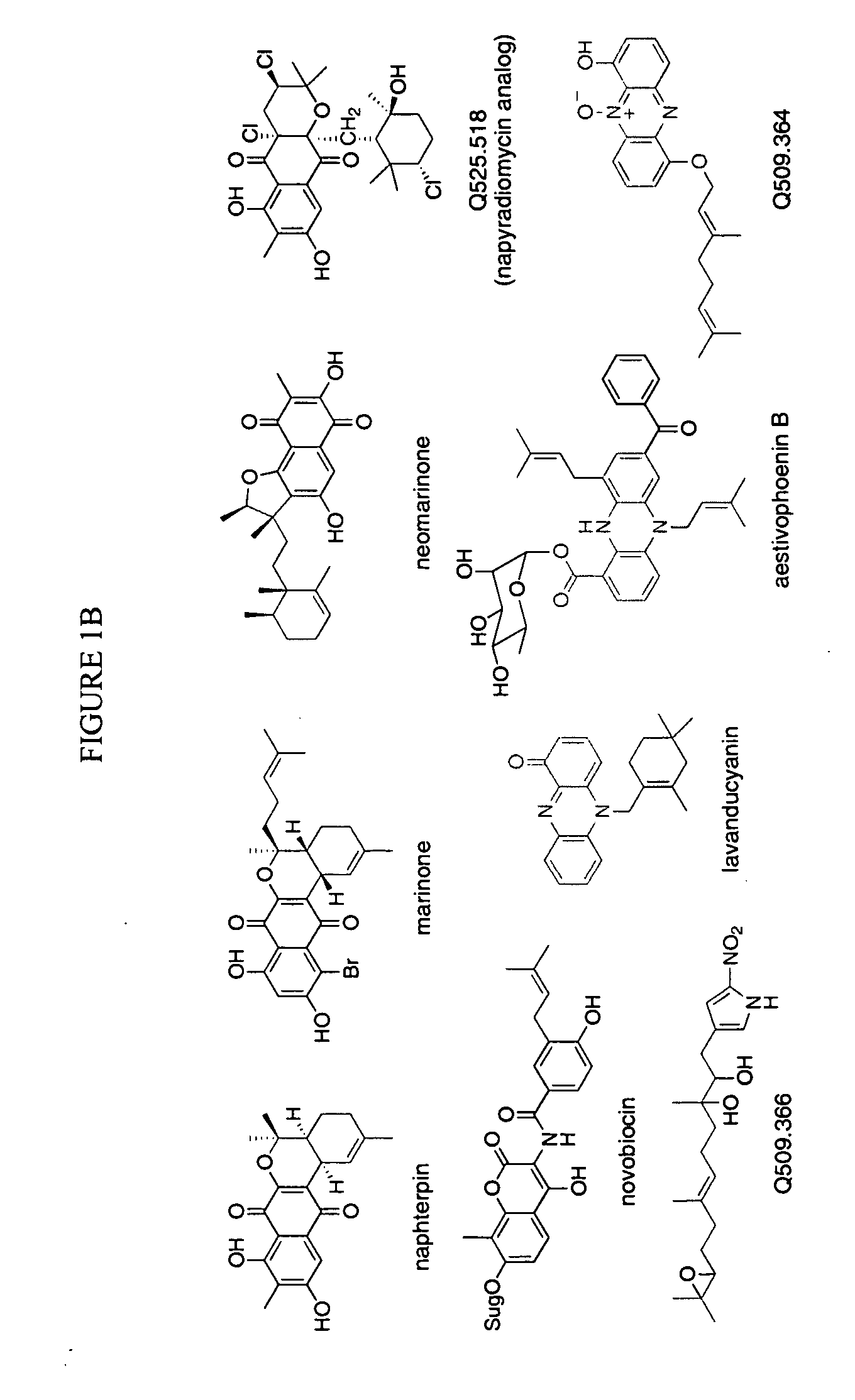
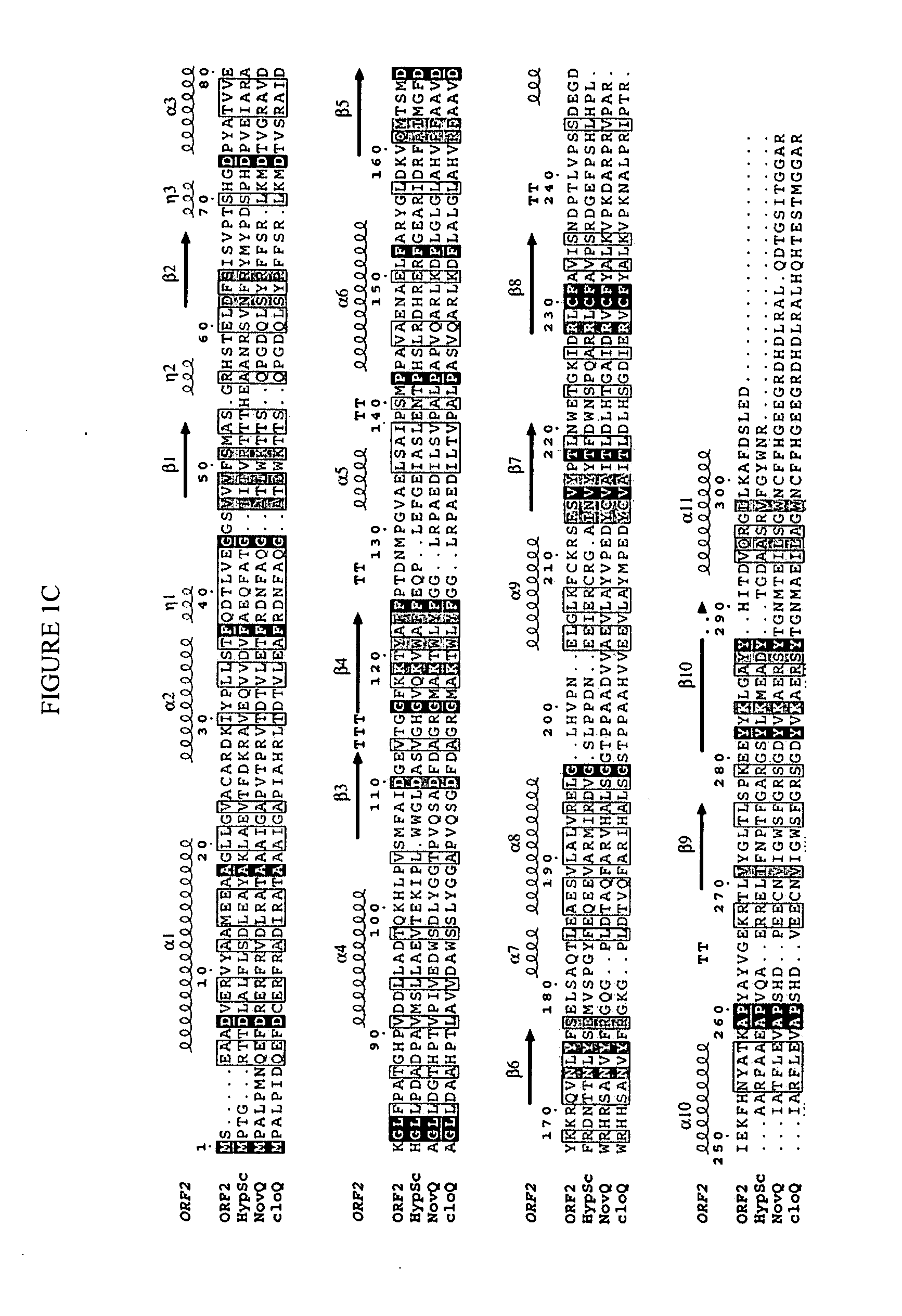
In accordance with the present invention, a novel aromatic prenyltransferase, Orf2 from Streptomyces sp. strain CL190, involved in naphterpin biosynthesis has been identified and the structure thereof elucidated. This prenyltransferase catalyzes the formation of a C—C bond between a prenyl group and a compound containing an aromatic nucleus, and also displays C—O bond formation activity. Numerous crystallographic structures of the prenyltransferase have been solved and refined, e.g., (1) prenyltransferase complexed with a buffer molecule (TAPS), (2) prenyltransferase as a binary complex with geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and Mg2+, and prenyltransferase as ternary complexes with a non-hydrolyzable substrate analogue, geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate (GSPP) and either (3) 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,6-DHN), or (4) flaviolin (i.e., 2,5,7-trihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, which is the oxidized product of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN)). These structures have been solved and refined to 1.5 Å, 2.25 Å, 1.95 Å and 2.02 Å, respectively. This first structure of an aromatic prenyltransferase displays an unexpected and non-canonical (β / α)-barrel architecture. The complexes with both aromatic substrates and prenyl containing substrates and analogs delineate the active site and are consistent with a proposed electrophilic mechanism of prenyl group transfer. These structures also provide a mechanistic basis for understanding prenyl chain length determination and aromatic co-substrate recognition in this structurally unique family of aromatic prenyltransferases. This structural information is useful for predicting the aromatic prenyltransferase activity of proteins.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
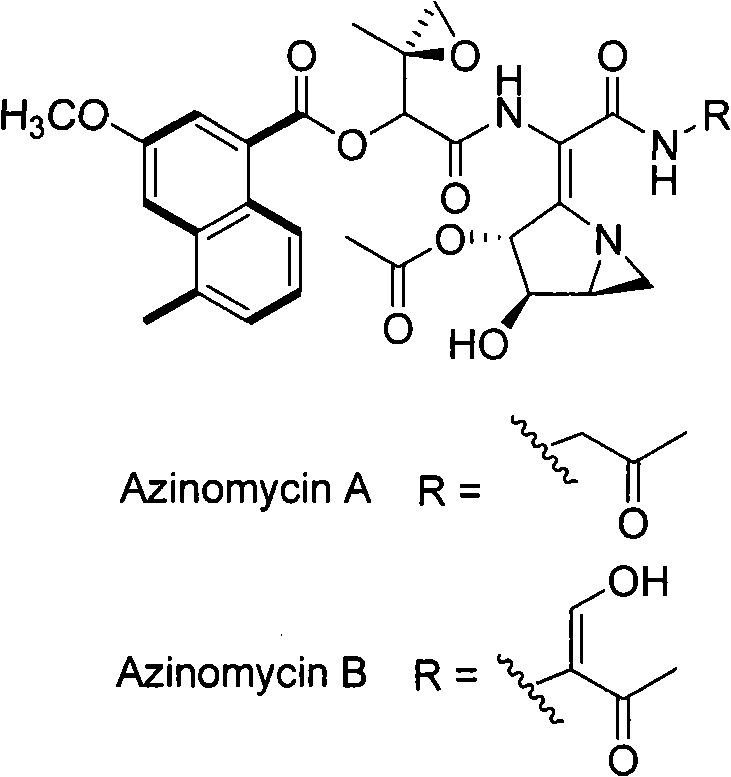
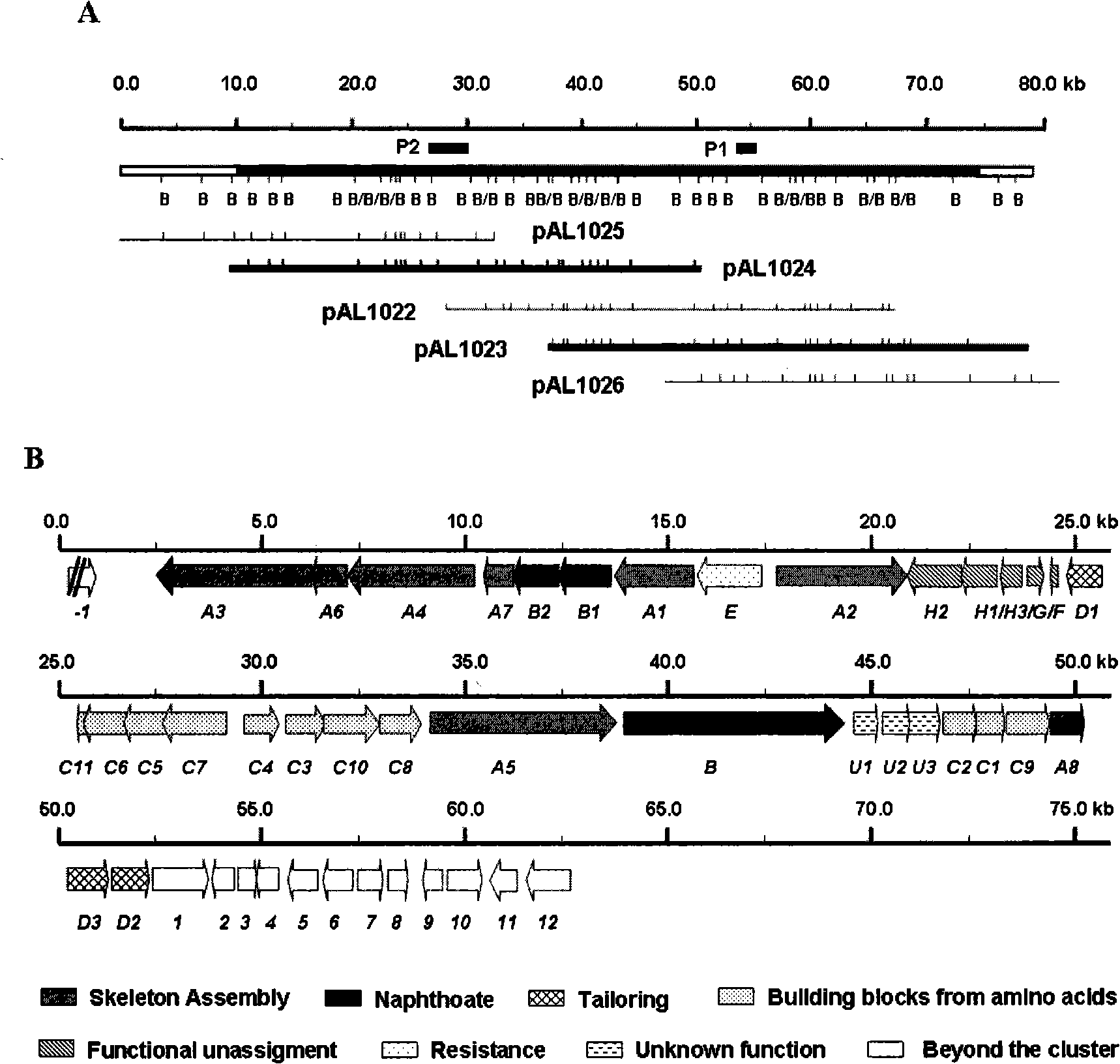
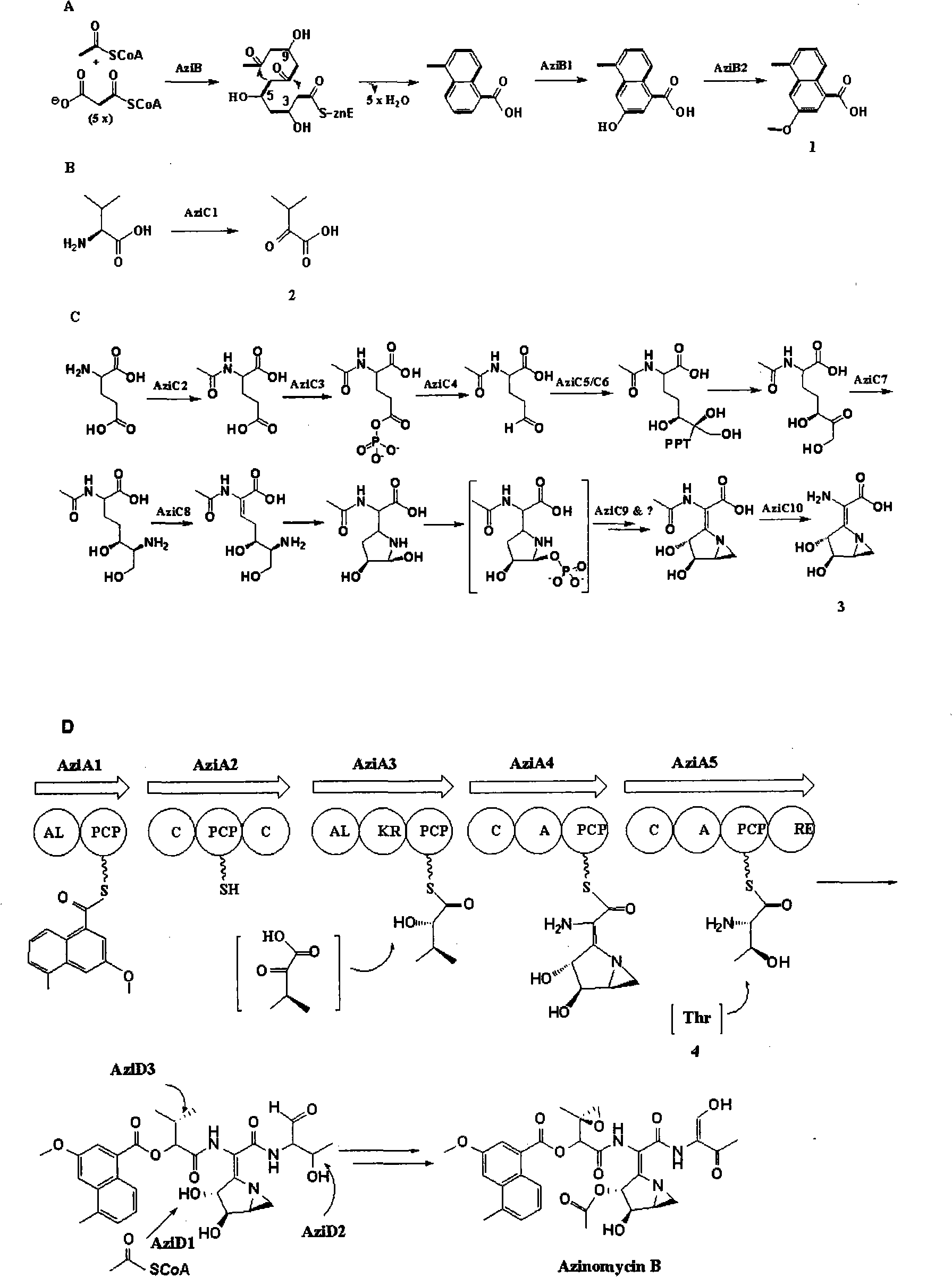
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Kit for detecting equine piroplasmosis and preparation method and using method thereof
ActiveCN102181556AExpand the scope of detectionImprove sensitivity and specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePolymerase chain reaction
The invention discloses a detection kit for identifying and diagnosing whether an equine animal is infected with piroplasmosis or not, and a preparation method and a using method thereof. A detection film for detecting equine piroplasmosis and a piroplasmosis universal primer are arranged in the kit for detecting the equine piroplasmosis. The using method of the kit comprises the following steps:extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from blood of a horse to be detected, further using the piroplasmosis universal primer to perform amplification, combining an amplification product with the detection film, enabling biotin at the terminal of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) product to be in action with streptavidin-peroxidase, and then playing a catalysis role in enabling a substrate of peroxidase, namely an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent (ECL-detection) to emit fluorescence, thereby exposing an X-photosensitive film; and performing development and fixing treatment on the film so asto emerge a shadow in a region corresponding to specificity hybridization of a probe on the detection film and the PCR product, and further judging whether the detected animal is infected with the piroplasmosis or not according to whether the shade is left on the film or not.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Polyene polyketides, processes for their production and their use as a pharmaceutical
This invention relates to a new class of polyene polyketides, their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives, and to methods for obtaining the compounds. One method of obtaining these compounds is by cultivation of novel strains of Streptomyces aizunensis; another method involves expression of biosynthetic pathway genes in transformed host cells. The present invention further relates to the novel strains of Streptomyces aizunensis used to produce these compounds, to the use of these compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives as pharmaceuticals, in particular to their use as inhibitors of fungal cell growth and cancer cell growth. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these novel polyketides or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts or derivatives thereof. Finally, the invention relates to novel polynucleotide sequences and their encoded proteins, which are involved in the biosynthesis of these novel polyketides.
Owner:THALLION PHARMA
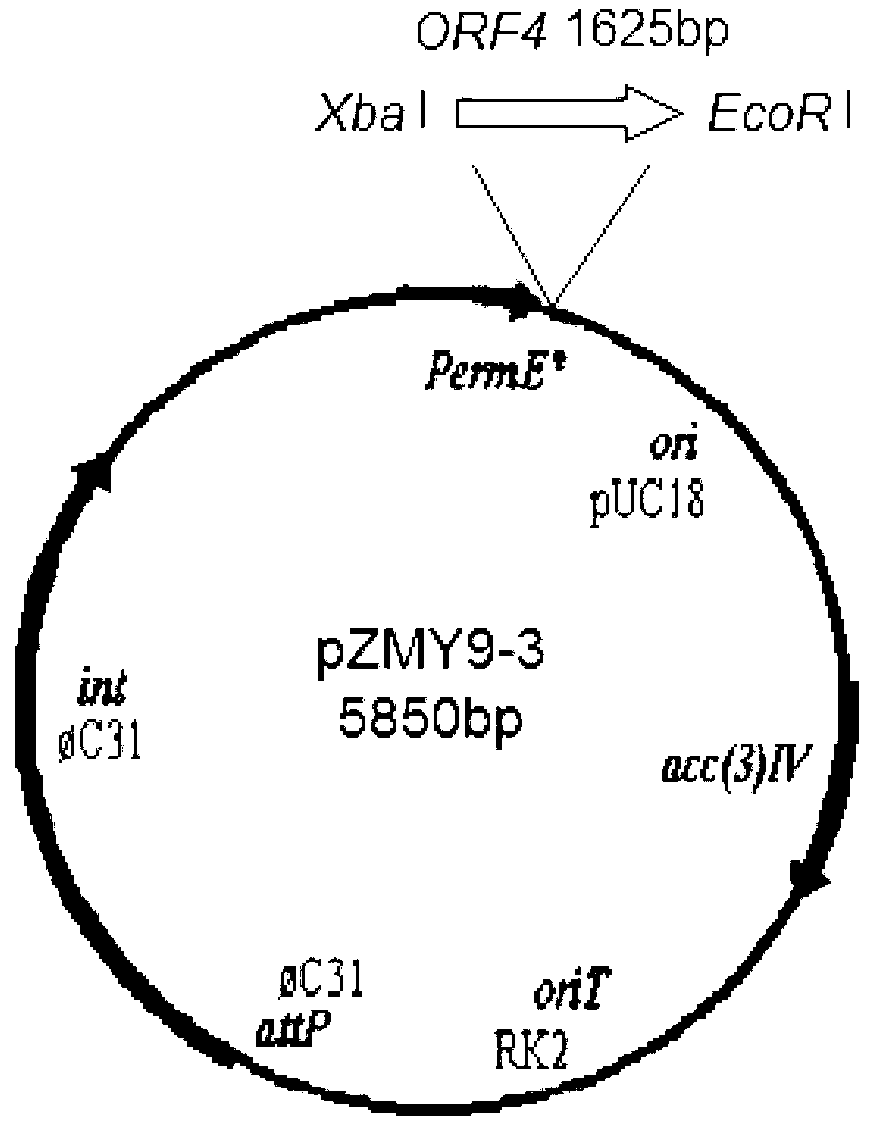
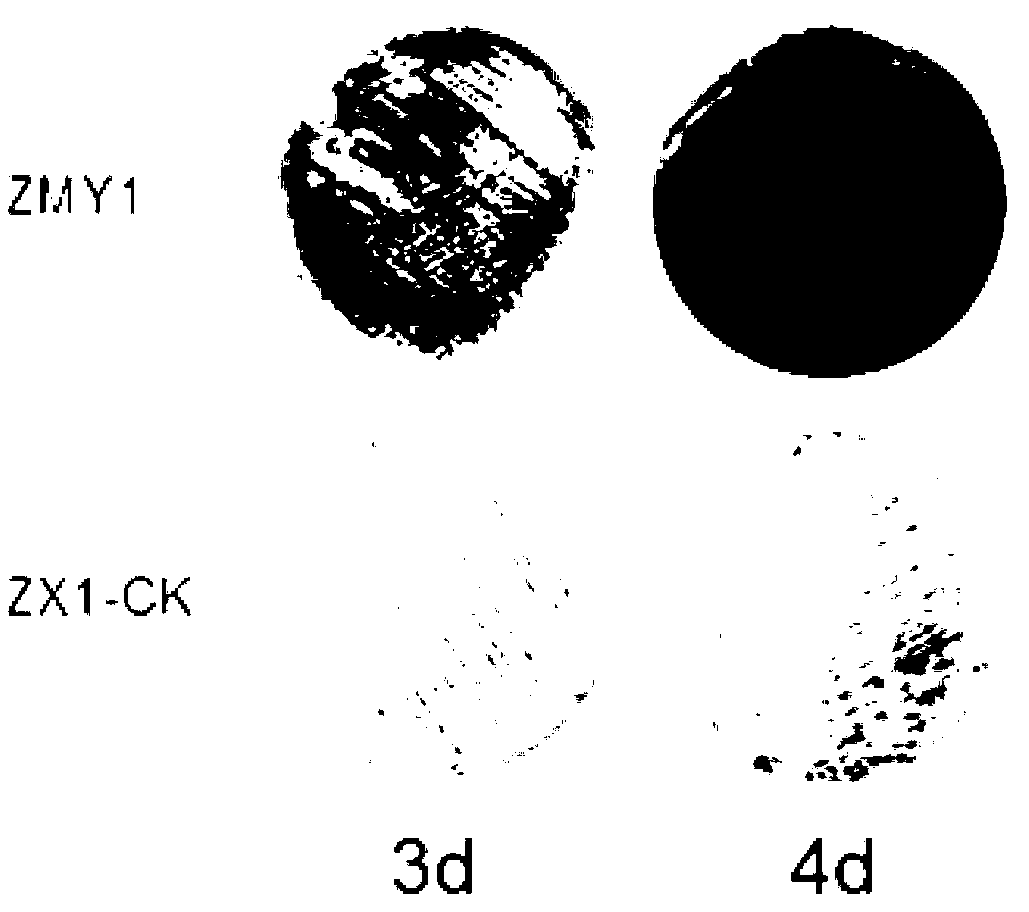
Streptomyces thioluteus antibiotic regulation gene and method for increasing yield of streptomyces antibiotic
InactiveCN103290032ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotide sequencingStreptomyces flavoviridis
The invention discloses a streptomyces thioluteus antibiotic regulation gene ORF4, wherein the nucleotide sequence is shown by SEQ ID No:1, or the nucleotide sequence codes the same protein with the nucleotide shown by the SEQ ID No:1. The invention also discloses an application of the gene in preparing an antibiotic high-yield streptomyces gene mutant strain and a method for increasing the yield of the streptomyces antibiotic. According to the gene and method disclosed by the invention, by adopting the streptomyces thioluteus antibiotic regulation gene ORF4, the problems of high workload and high blindness of traditional streptomyces breeding are solved, the function is realized in multiple antibiotic producing bacteria, the antibiotic high-yield strain bred by genetic engineering is obtained, and the application prospect is broad.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Streptomyces violaceorubidus and application thereof
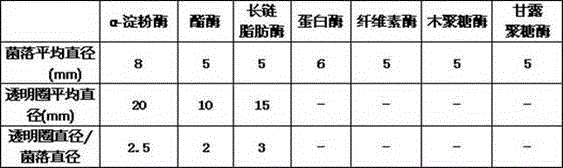
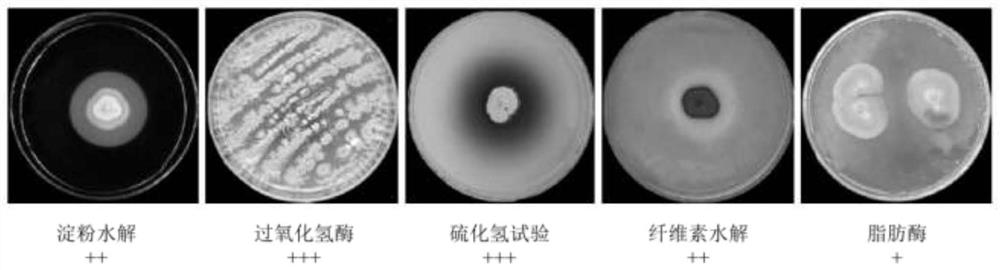
The invention discloses a Streptomyces violaceorubidus JG-1CGMCCNo.7921 and an application thereof. The condition that the Streptomyces violaceorubidus JG-1CGMCCNo.7921 disclosed by the invention contains negative protease, cellulase, xylanase and mannose, and positive alpha-amylase, esterase and lipase is determined by sampling from a wild walnut grove in Jalalabad State of Kyrgyzstan Kyzyl-Suu (N41.3069778 degrees and E72.9628194 degrees), separating, screening, and carrying out physiological and biochemical identification, and the Streptomyces violaceorubidus can be widely applied to the field of production of the alpha-amylase, the esterase and the lipase.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
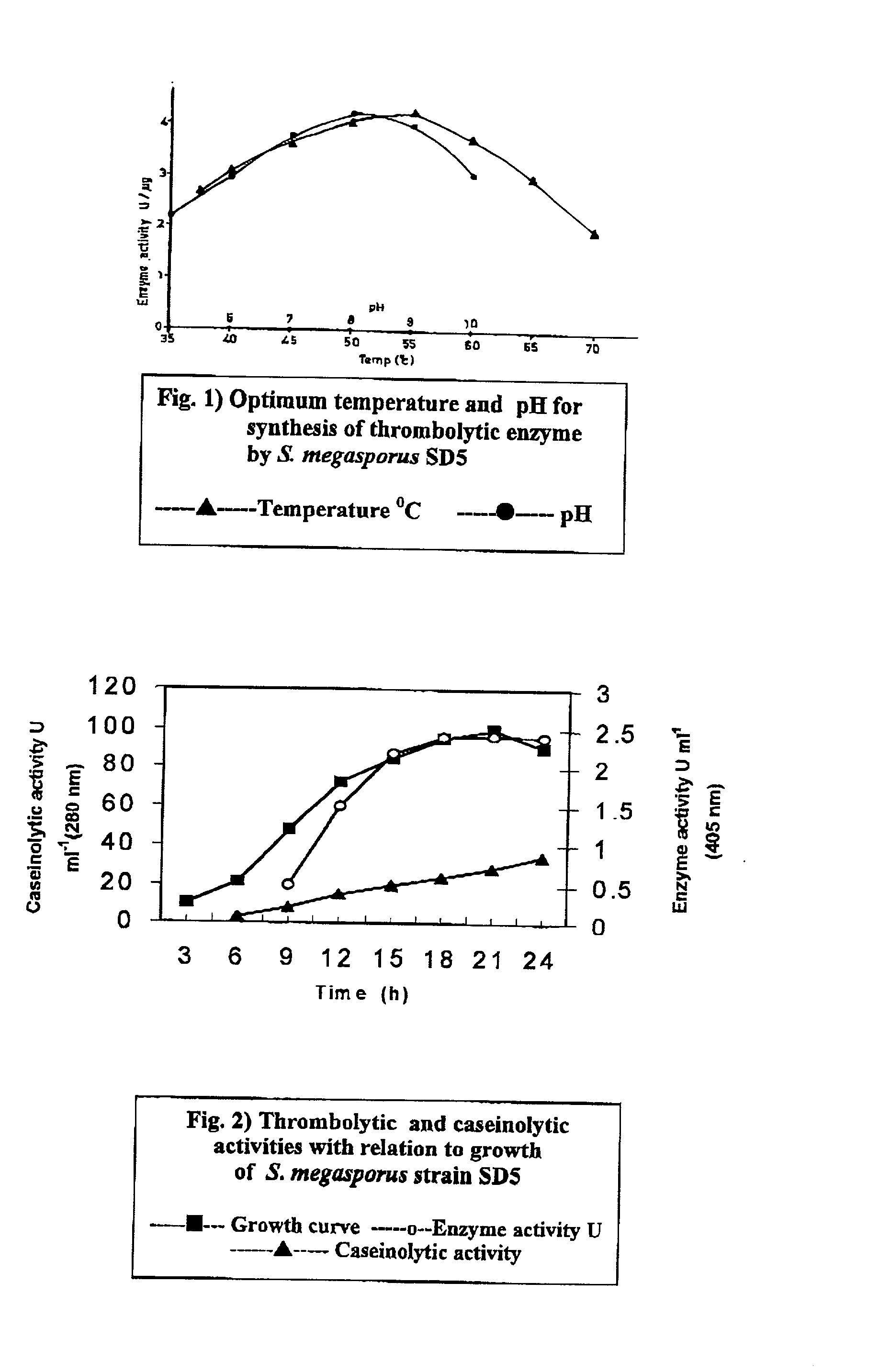
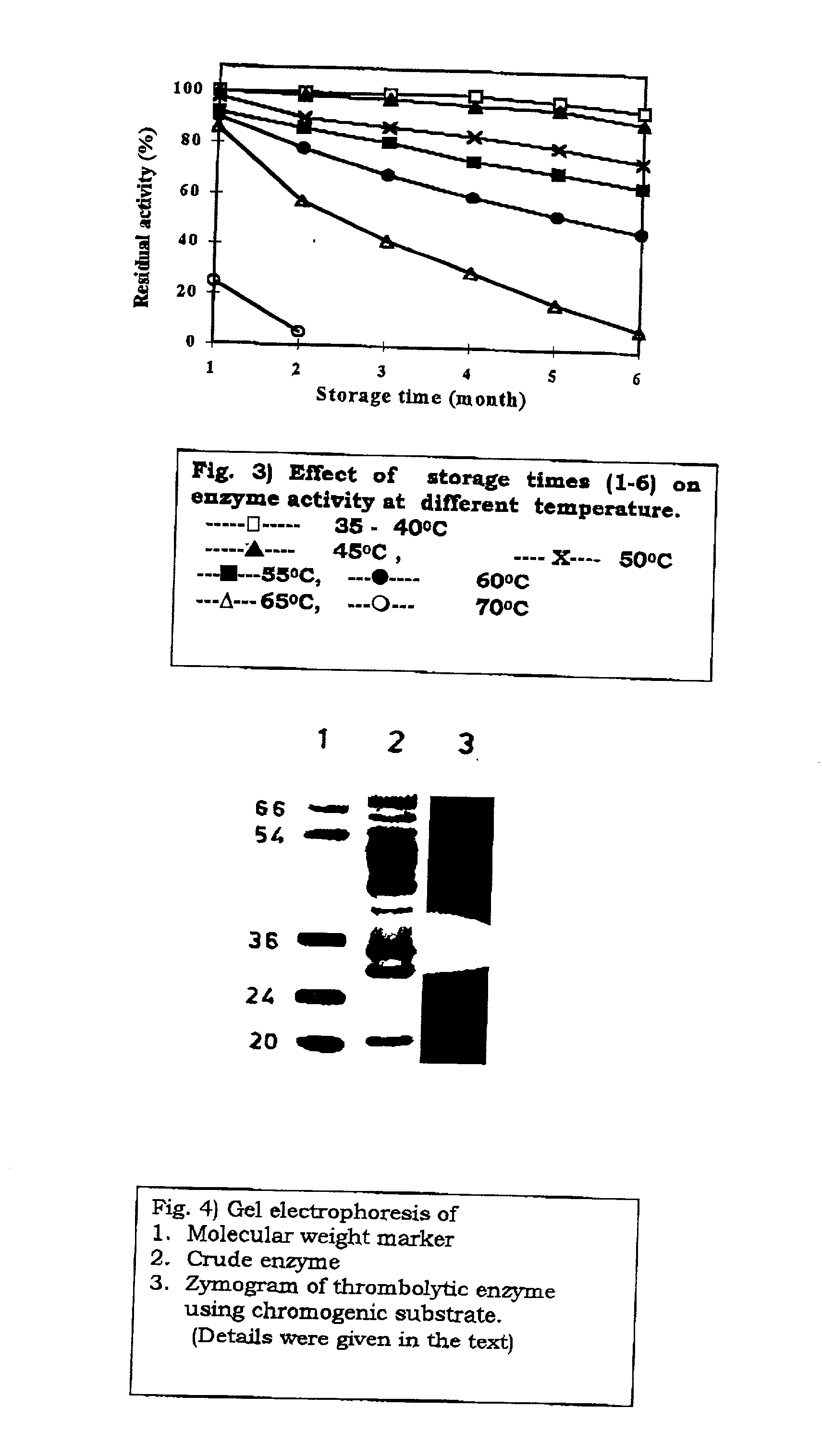
Streptomyces megasporus sd5, process for the isolation thereof, novel fibrinolytic enzyme prepared therefrom, process for the production of said enzyme and method of treatment of thrombolytic disorders using said enzyme
The present invention relates to a novel microorganism Streptomyces megasporus SD5. The present invention also relates to a process for the isolation of said Streptomyces megasporus SD5. The invention also relates to a novel fibrinolytic enzyme actinokinase extracted from said microorganism and to a process for the extraction of said enzyme. In another aspect, the invention also pertains to a method for the treatment of thrombolytic disorders using said enzyme.
Owner:MAHARASHTRA ASSOC FOR THE CULTIVATION OF SCI
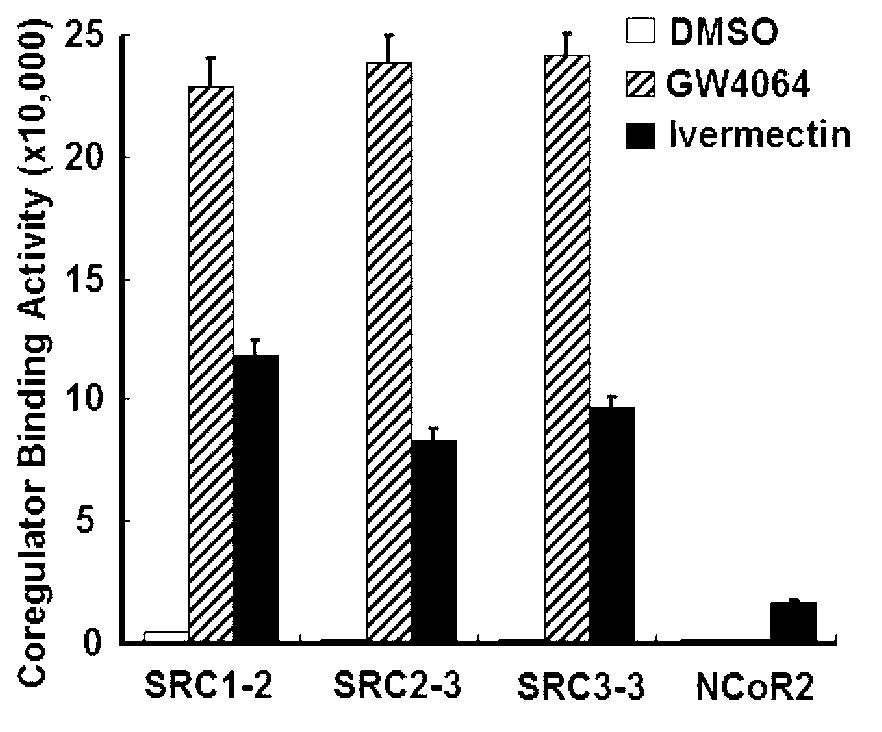
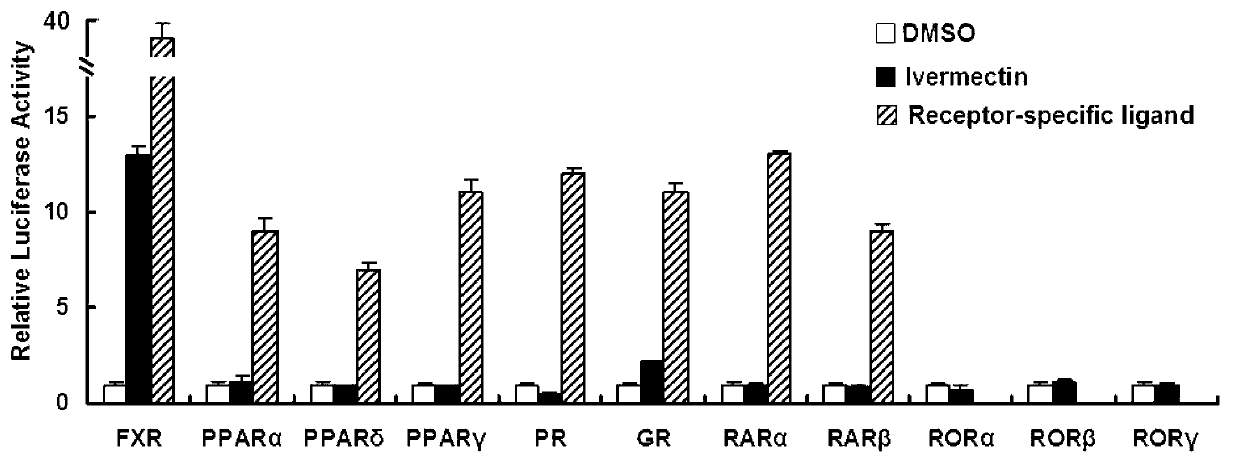
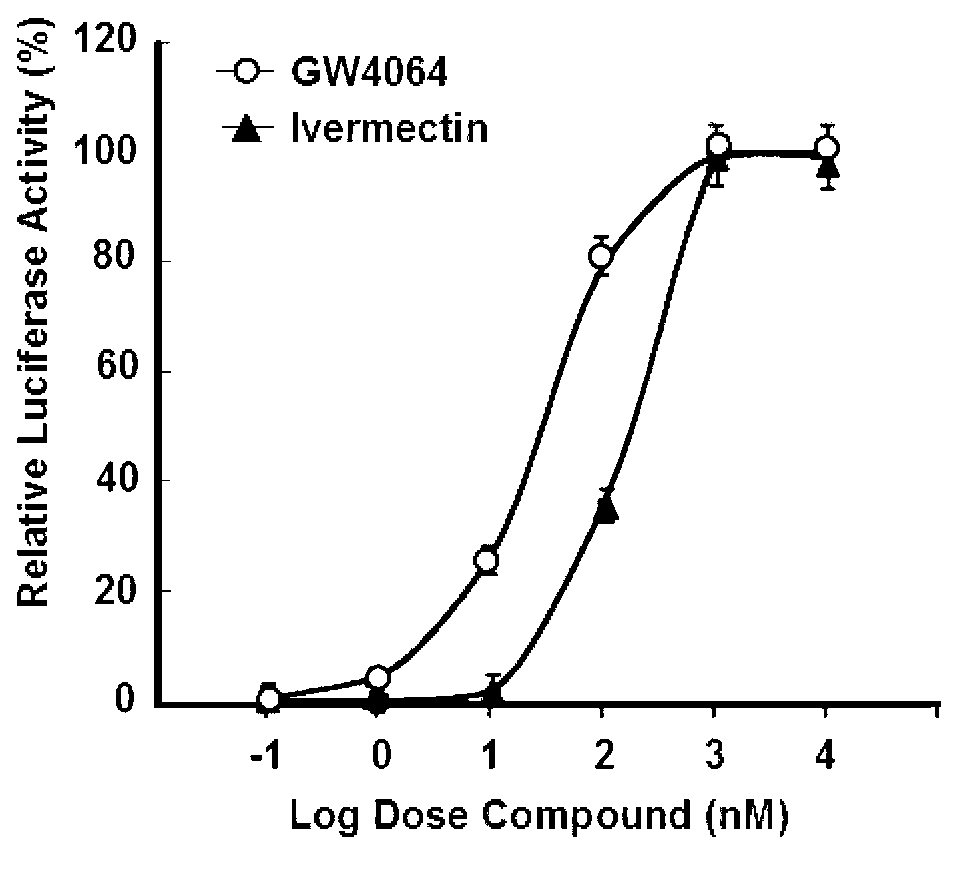
Ivermectin and application of derivative thereof
ActiveCN102872066AOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcute hyperglycaemiaInsulin resistance
The invention discloses ivermectin and application of a derivative thereof, and relates to ivermectin. The ivermectin is a derivative of macrolide abamectin generated by streptomyces, and the ivermectin and the derivative thereof are used for preparing medicines for treating metabolism-related diseases such as mammalian hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes and obesity, and can be applied to medicines for treating diseases such as farnesol receptor-mediated bile obstruction, gallstone, non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, atherosclerosis, inflammation and cancer.
Owner:丁佳隆
Negative regulator gene of streptomyces roseofulvus as well as preparation method and application thereof
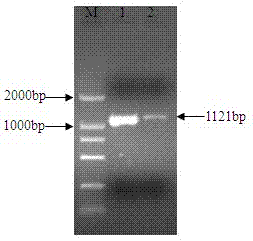
The invention relates to an nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, primers Ns8F and Ns8R are designed by utilizing an important negative regulator gene nsdB sequence in a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) antibiotic metabolic pathway, and genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 is amplified to obtain a 1121bp segment; and two ends of a target sequence are extended by utilizing a primer anchoring polymerase chain reaction) (NPA-PCR ) method by a non-specific primer, thus obtaining the nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63. The preparation of the nsdBmgh gene provides an important basis for further researching and verifying the Streptomyces roseoflavus antibiotic metabolic pathway and regulatory mechanism, and establishes an important base for obtaining high-yield antibiotic gene engineering strains.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Recombined streptomycete, construction method thereof and method for increasing antibiotic yield
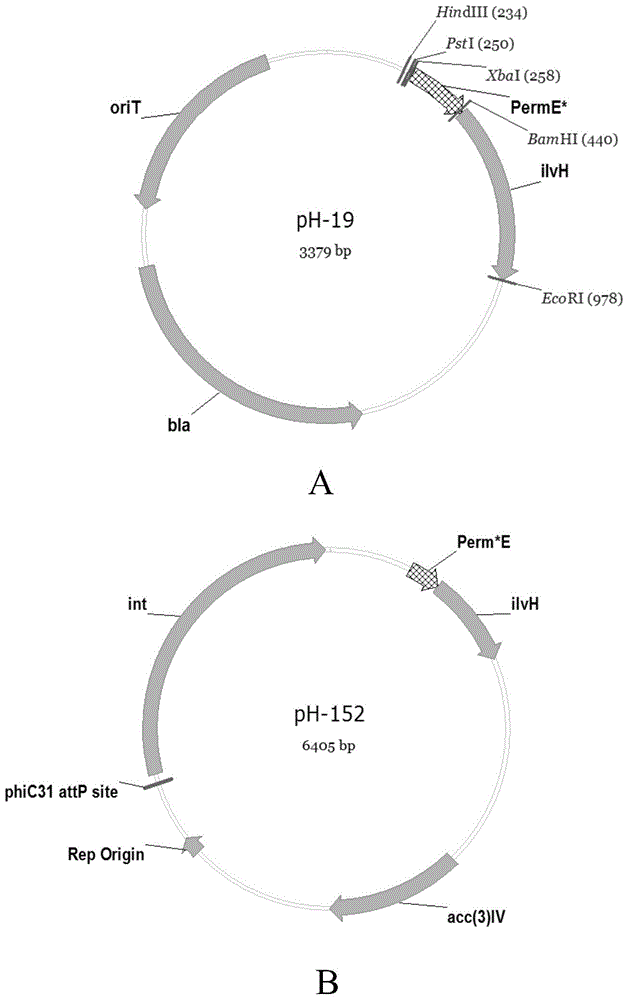
ActiveCN104531598AIncrease productionIncrease the amount of enzymeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetolactic acidAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a recombined streptomycete, a construction method of the recombined streptomycete and a method for increasing the antibiotic yield. The recombined streptomycete over-expresses acetolactic acid synthase small subunit ilvH. The recombined streptomycete over-expresses acetolactic acid synthase to adjust subunit genes, and the yield of products such as antibiotics for conducting secondary metabolism with L-isoleucine and / or L-valine and / or L-leucine as precursors / a precursor can be remarkably increased.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
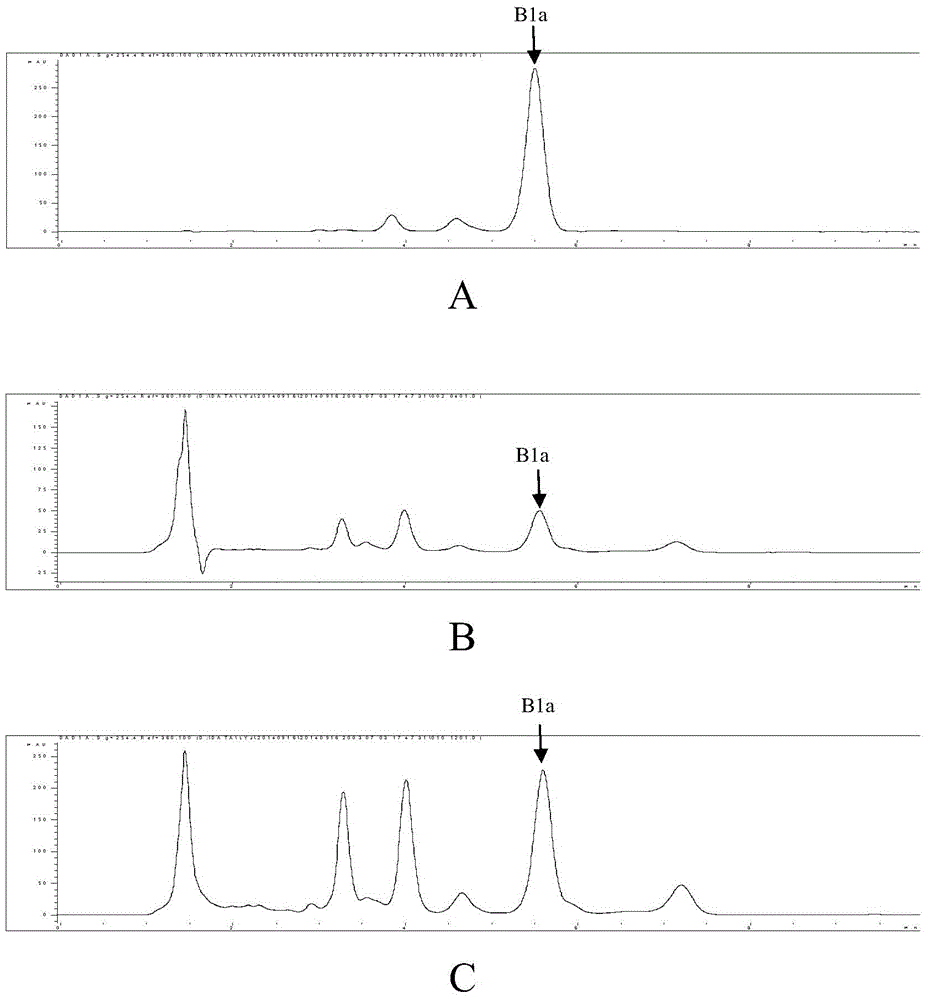
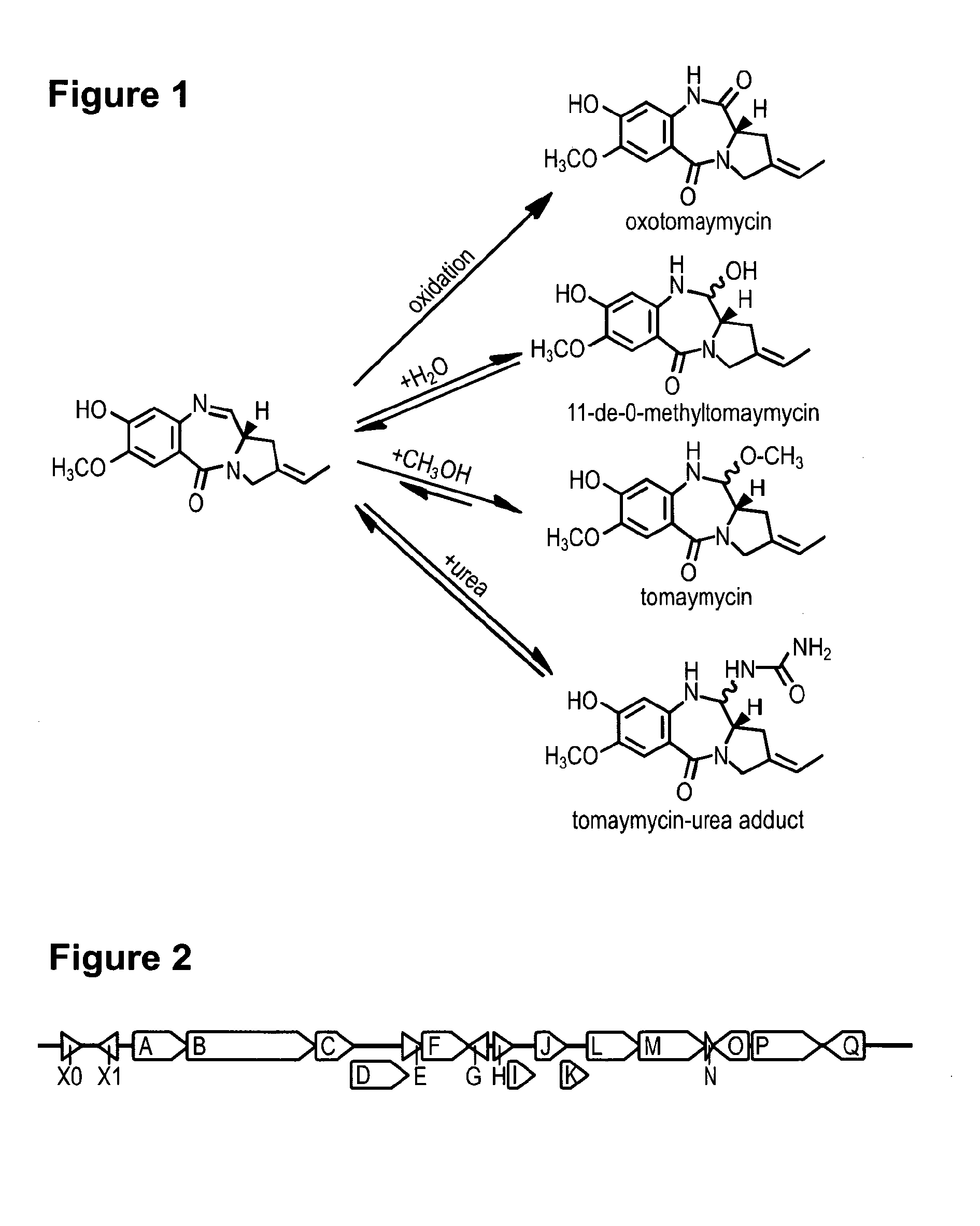
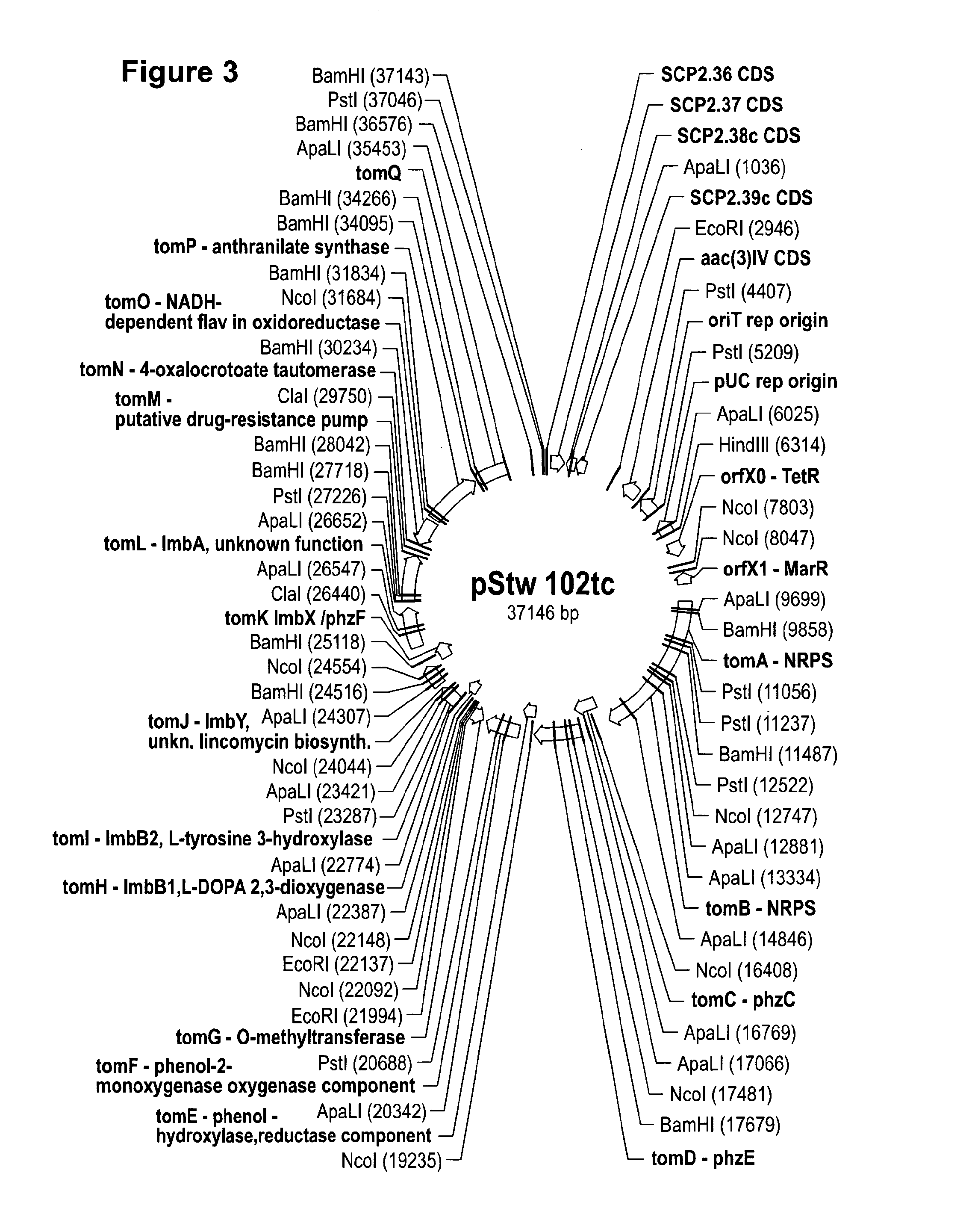
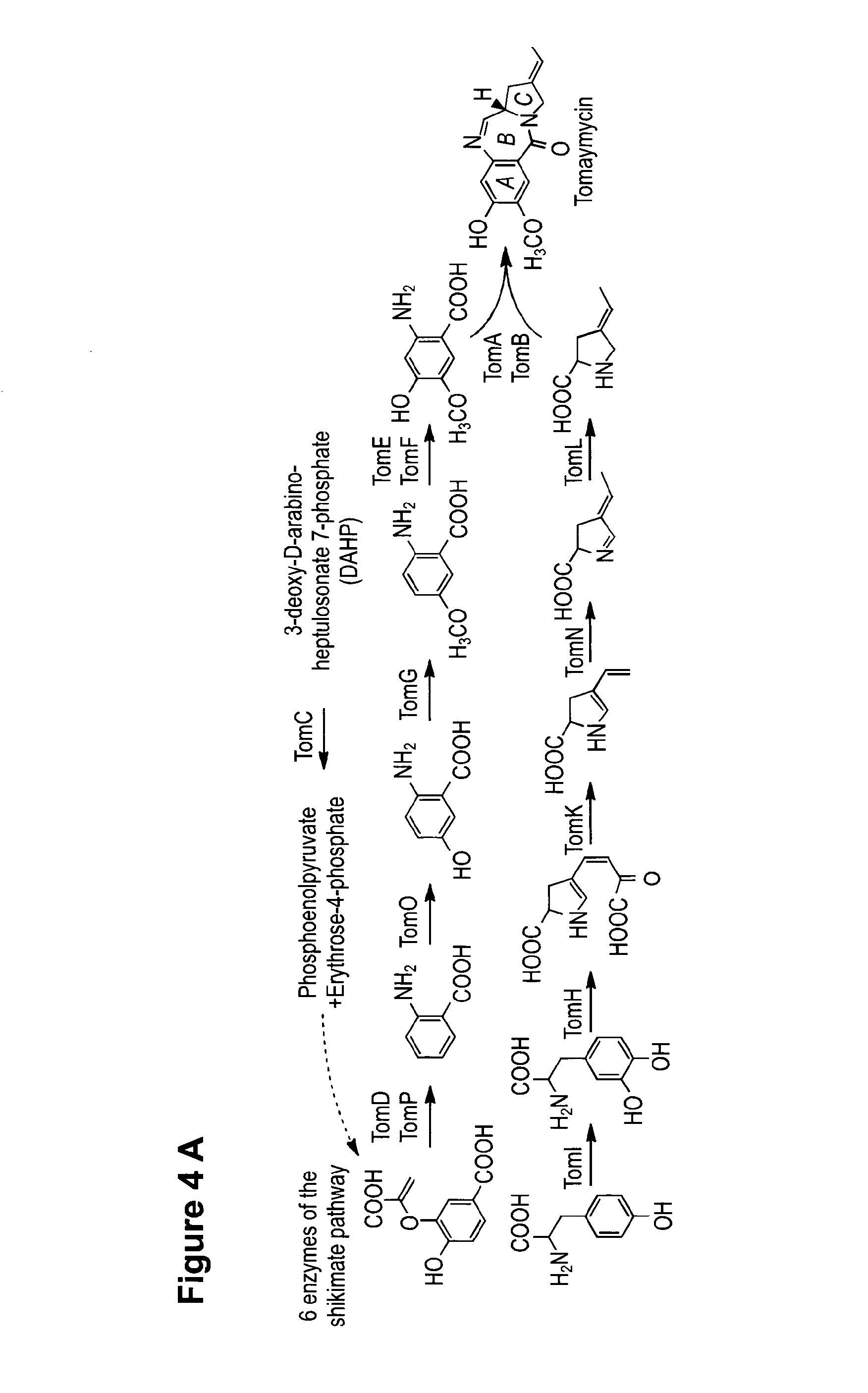
Method for Producing Recombinant 11-De-O-Methyltomaymycin
The present invention provides a tomaymycin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces species FH6421, and its use for producing 11-de-O-methyltomaymycin.
Owner:SANOFI SA
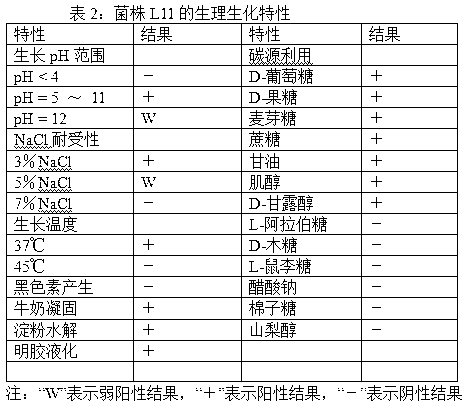
Gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L11 construction and culture method
InactiveCN103131662ARaise the fermentation unitStable genetic traitsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStreptomyces chattanoogensis
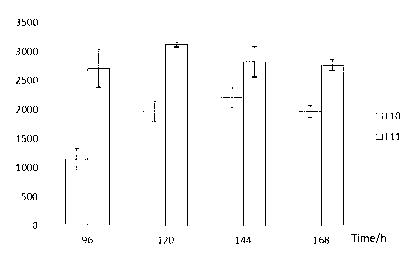
The invention provides a gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis. The preservation registration number of the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is CGMCC No.7182, the nucleotide sequence of the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is obtained through the genetic construction of a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthetic way of natamycin. Compared with gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10, the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L11 has the advantages of more stable hereditary characters, improvement of the natamycin fermentation unit to 3.12g / L from 2.21g / L, shortening of the natamycin fermentation period to 120h from 144h, improvement of the natamycin output by 40%, shortening the fermentation period by 24h, and reduction of the industrialized production process, and can be applied to the generation of natamycin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Actinomycetes strain and application thereof in preparation of aromatic hydroxylamine
InactiveCN101735961AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydroxylamineD-Glucose
The invention relates to an actinomycetes (Streptomyces thioluteus) strain CGMCC No. 2725 and application thereof in the preparation of aromatic hydroxylamine. The strain CGMCC No. 2725 is easy to obtain and culture, and has a complete coenzyme regeneration system exists in a cell body of the strain, the spontaneous cyclic regeneration of coenzyme can be performed only by adding an appropriate quantity of auxiliary substrates (such as glucose or ethanol and the like) without additionally adding expensive reduced coenzyme. In addition, the use of intact cells can leave out the process of extracting and purifying enzyme, so the strain is more suitable for large-scale commercial application.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
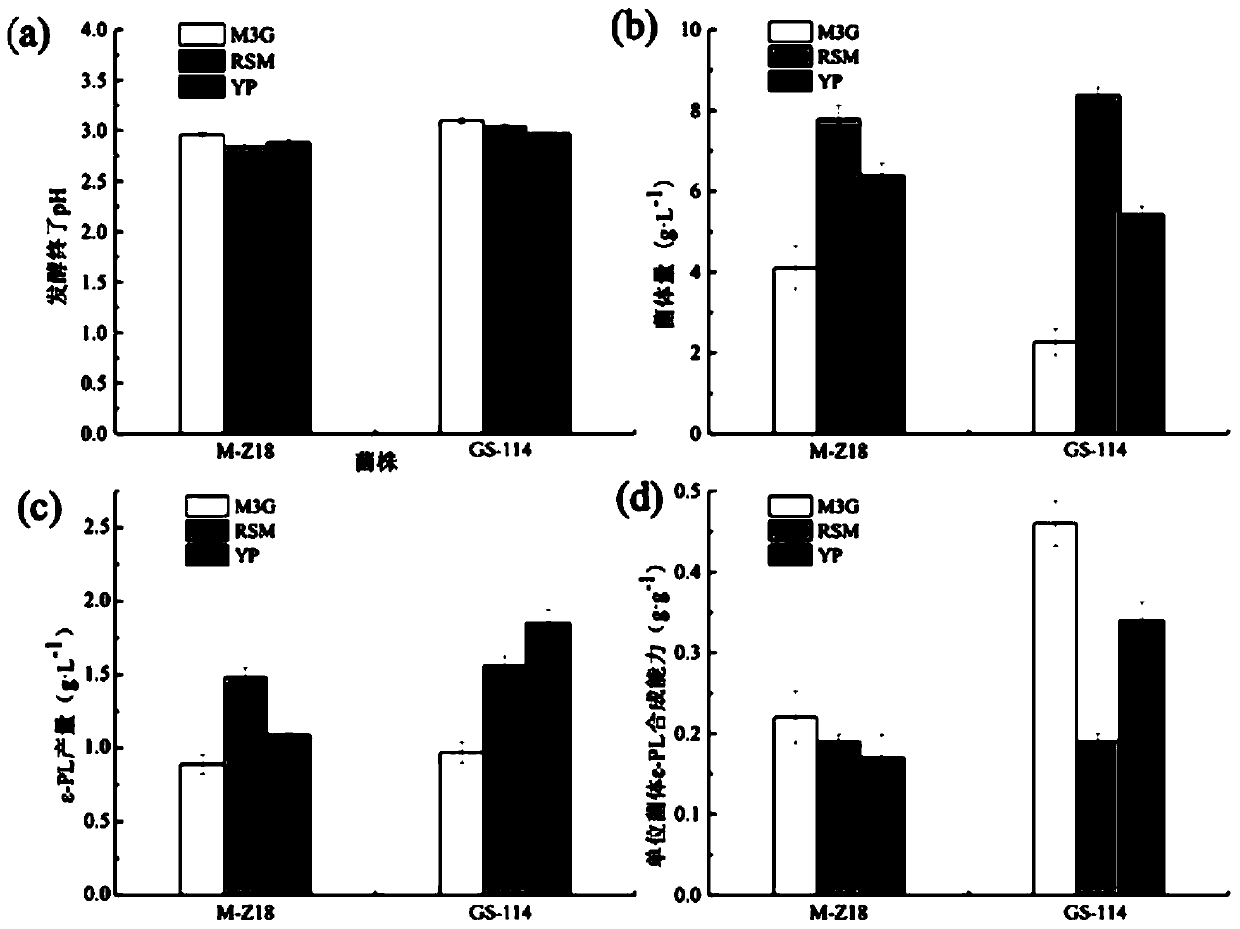
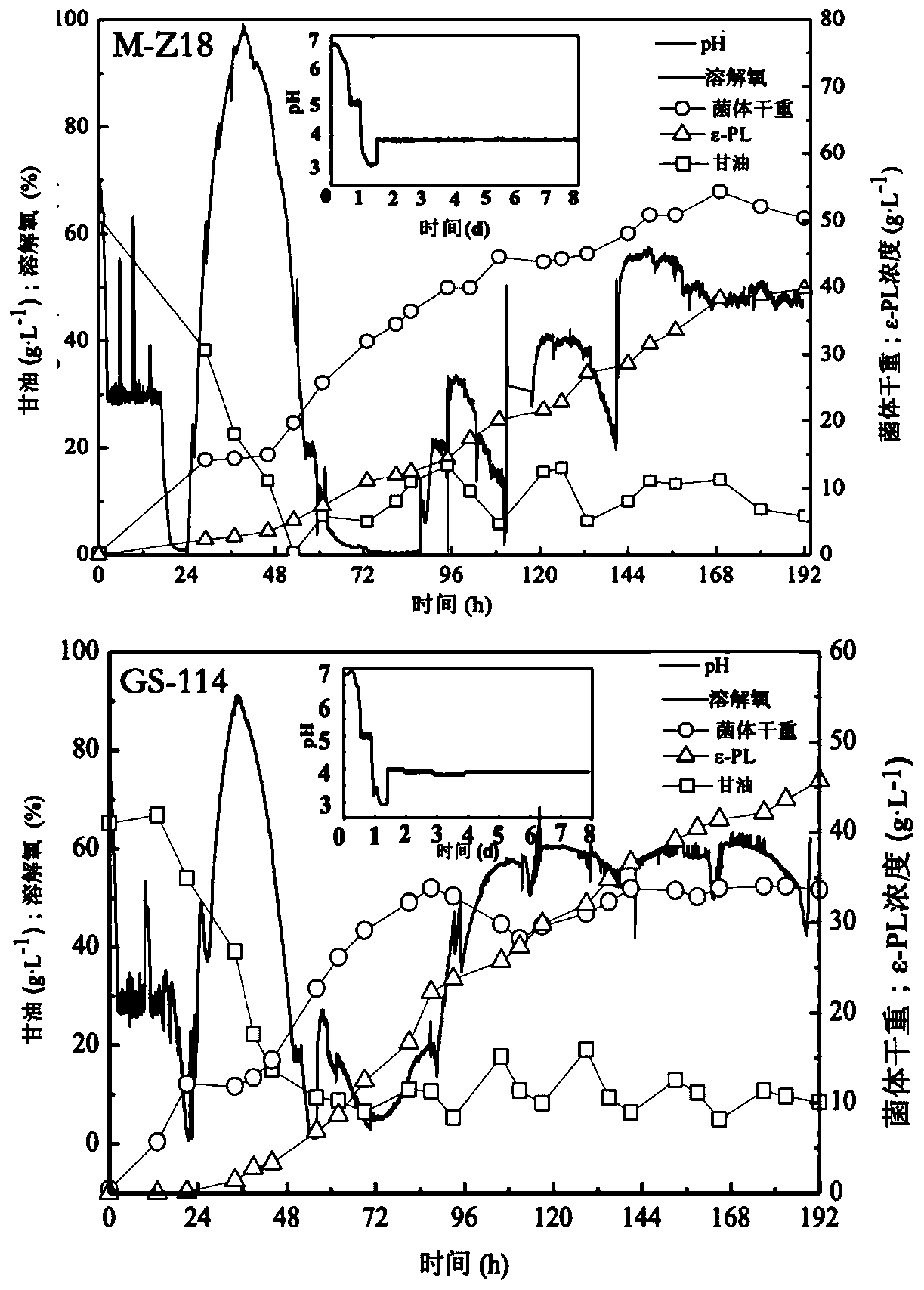
Streptomyces albulus (GS-114) and method of the same to prepare epsilon-polylysine
InactiveCN110804572AStrong synthetic abilityIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStreptomyces albulus
The invention discloses streptomyces albulus (GS-114) and a method of the same to prepare epsilon-polylysine, and belongs to the field of microbial fermentation engineering. The provided streptomycesalbulus (GS-114) has resistance to streptomycin, gentamicin and rifamycin with 3 [mu]g / mL, 1 [mu]g / mL and 0.1 [mu]g / mL or higher concentrations, and can efficiently synthesize epsilon-PL in quantity,the yield with 192 h of fermentation can reach 56.3 g / L, and production efficiency can reach up to 7.03 g / L / d. The streptomyces albulus (GS-114) also has good passage stability and has strong potential for the industrial production of the epsilon-PL.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Macrolide antibiotics sodium hyaluronate eye transfer system
InactiveCN1814299AInvestigate the stay situationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsRoxithromycinClarithromycin
This invention relates to an eye use transmission system of macrolide type antibiotic hyaluronic acid natrium. The goal of this invention is to provide a macrolide type antibiotic eye use medicine preparation with carrier is hyaluronic acid or its salt. It is used to cure germ eye region infection. The macrolide type antibiotic in this invention includes antibiotic that has 14 yuan,15yuan, 16yuan large ring construction features , for example, natural antibiotic bring by streptomycete erythromycin, josamycin, spiramycin, medemycin etc. and semisynthesis derivant from by structure modification of natural antibiotic, such as roxithromycin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, rokitamycin, telithromycin.
Owner:无锡康福特药物科技有限公司
Streptomyces thiogamboges St-79 and application thereof
ActiveCN113234642AEnhanced inhibitory effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyConiella castaneicola
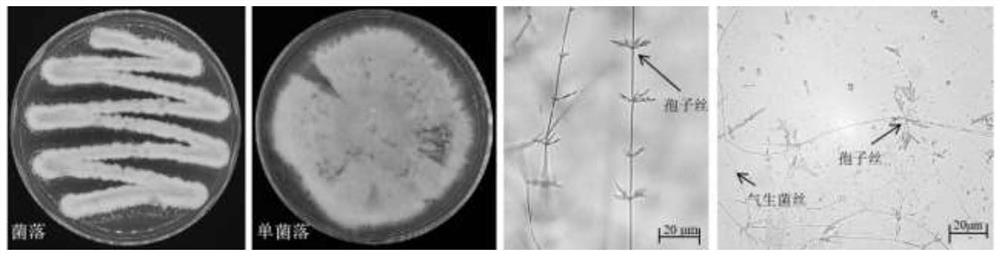
The invention discloses streptomyces thioluteus St-79, and the preservation number of the streptomyces thioluteus St-79 is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2020962. The application of the streptomyces thioluteus St-79 strain is as follows: the germination of rice seeds is promoted, the bacterial blight of rice is prevented and treated, and the pathogenic bacteria of plants are inhibited.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Vector for knocking out streptomycete gene as well as constructing method and application of same
ActiveCN103074356AFacile gene knockoutMake up for false positivesFungiBacteriaMultiple cloning siteMolecular biology
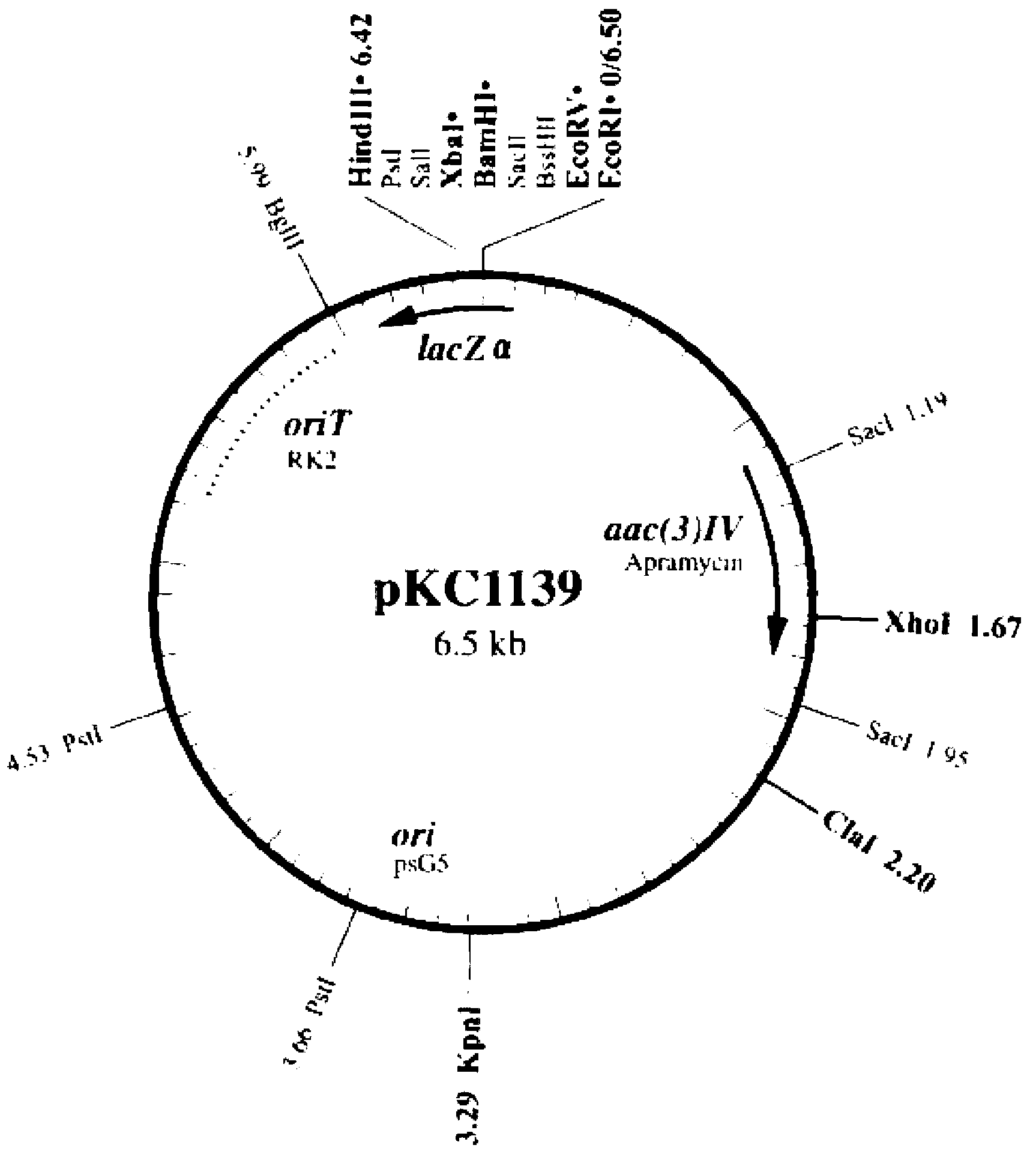
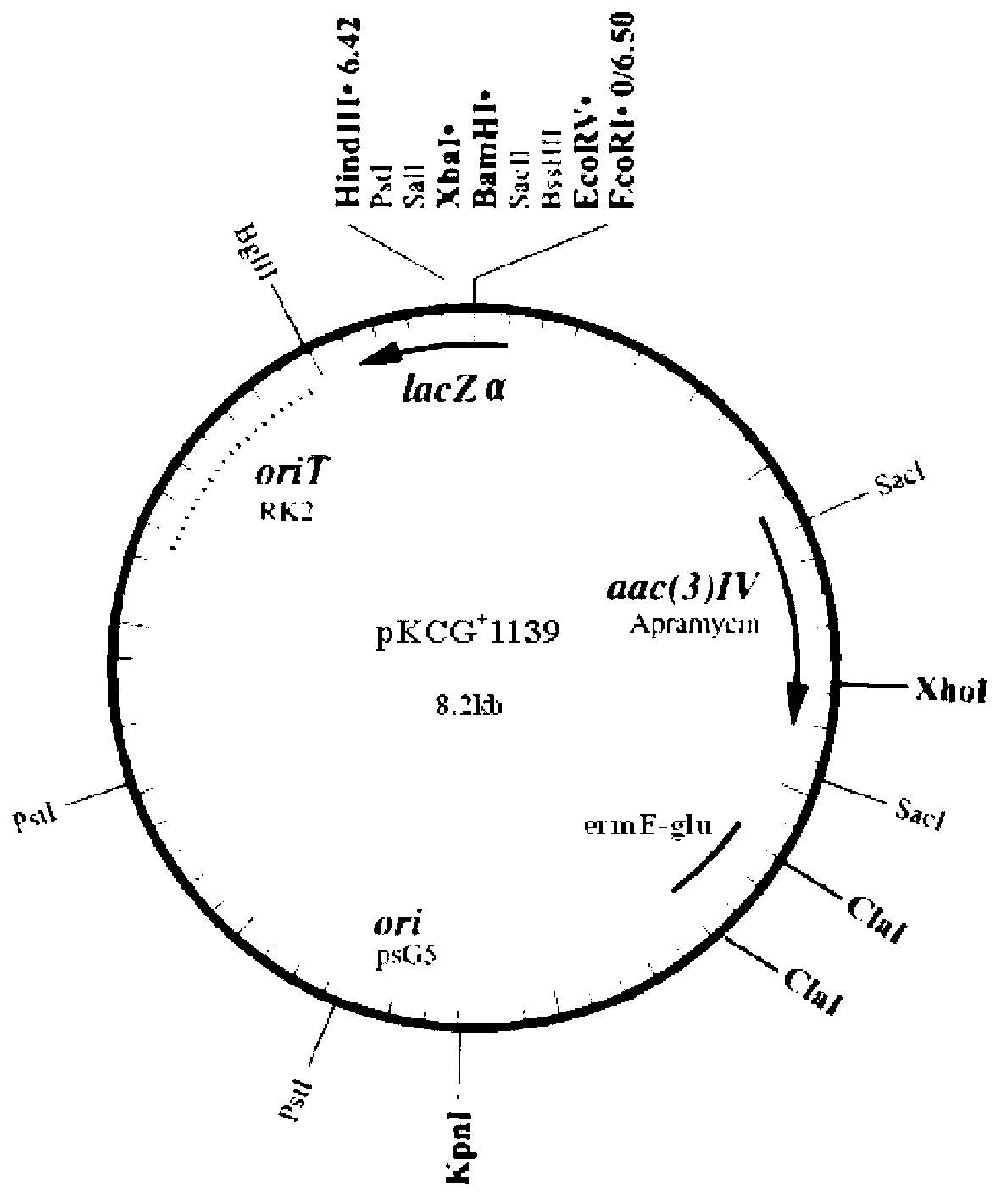
The invention discloses a vector for knocking out a streptomycete gene as well as a constructing method and an application of the vector. A recombinant vector is a recombinant DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) obtained by inserting a locus ClaI of pKC1139 into a glucanase gene. In actual application, a streptomycete target gene knockout vector can be obtained after a DNA fragment for knocking out a streptomycete target gene is inserted in a multiple clone site of the recombinant vector; after the streptomycete target gene knockout vector is introduced into streptomycete with the target gene to be knocked out, transformants with thiostrepton resistances are screened; cellulose degradation and screening are carried out on the transformants with the thiostrepton resistances; and specifically, a homologous double-exchange transformant can be obtained through inserting the transformants with the thiostrepton resistances into a cellulose screening flat plate and then carrying out Congo red staining on the transformants with the thiostrepton resistances so as to directly observe degradation situation of the cellulose. Therefore, the phenomenon of incomplete knockout of the gene due to false positive antibiotics resistance can be avoided. Meanwhile, PCR verifications of a large amount of transformants can be avoided. The vector for knocking out the streptomycete gene, disclosed by the invention, can be used for screening any gene knockout double-exchange transformant of strains with no glucanase yield.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Mutants of fatty acid adenosine monophosphate (AMP) ligase with improved substrate affinities and application thereof
The invention relates to mutants of a fatty acid adenosine monophosphate (AMP) ligase and application of the mutants, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The fatty acid AMP ligase comes from streptomyces roseosporus. The 296th glycine of the fatty acid AMP ligase is changed into alanine, and the 302th isoleucine of the fatty acid AMP ligase is changed into valine to respectively obtain the mutants pAL296 and pAL302. The mutants of the fatty acid AMP ligase can improve the binding level with exogenous precursor decanoic acid to enhance the yield of daptomycin. According to the invention, an encoding gene dptE of the fatty acid AMP ligase is subjected to site-directed mutagenesis in vitro by using computer simulation, overlap extension PCR and site-directed mutagenesis technologies to screen out the mutants pAL296 and pAL302 of which the affinities are obviously improved, recombinant shuttle plasmids pAK296 and pAK302 are constructed and sequentially led to the streptomyces roseosporus, and zygotes are screened to obtain streptomyces roseosporus DCE296 and DCE302 of the fatty acid AMP ligase with improved substrate affinities to lay a foundation for improving the production level of daptomycin.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
New streptomyces secretion expression plasmid and application thereof
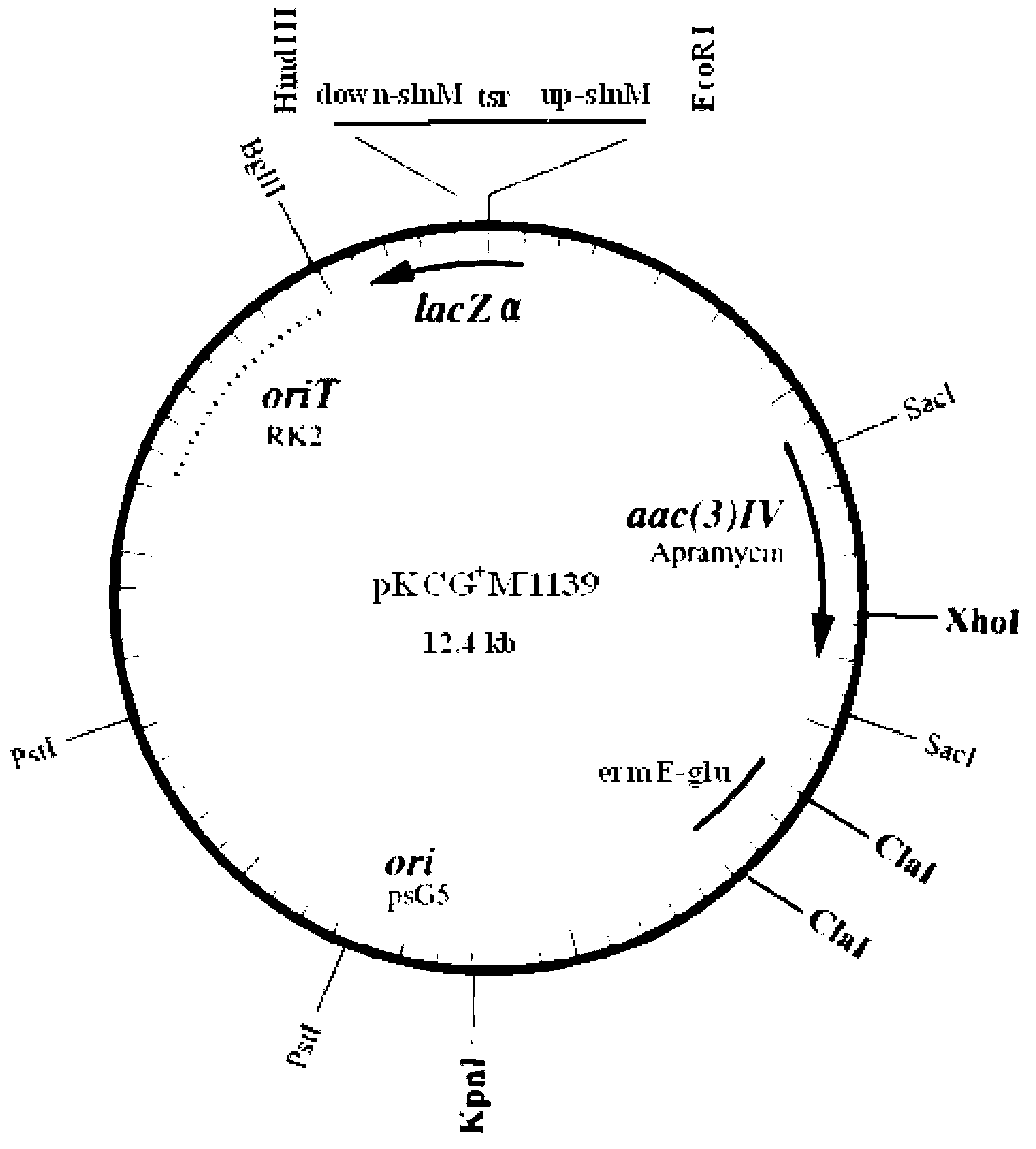
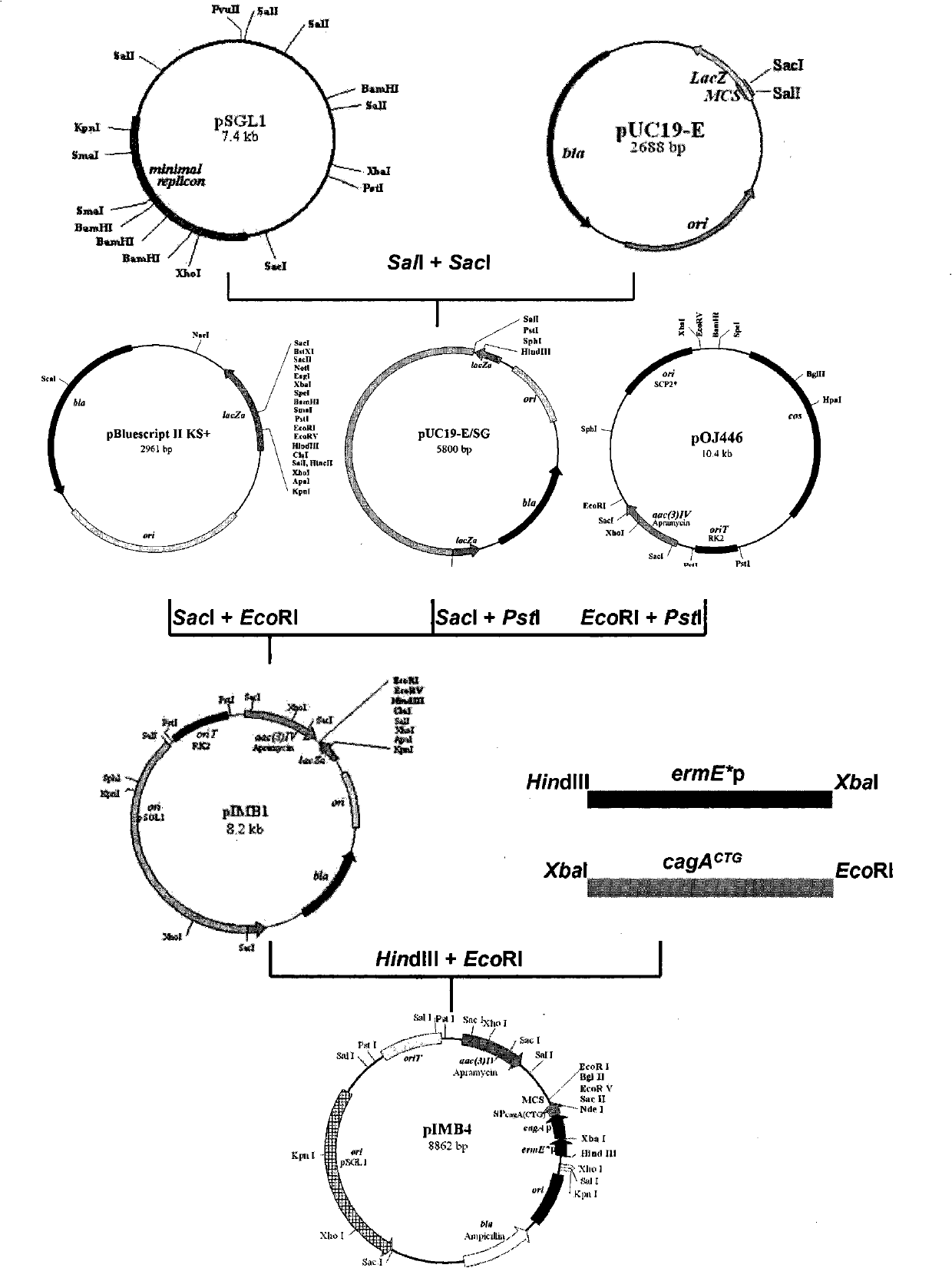
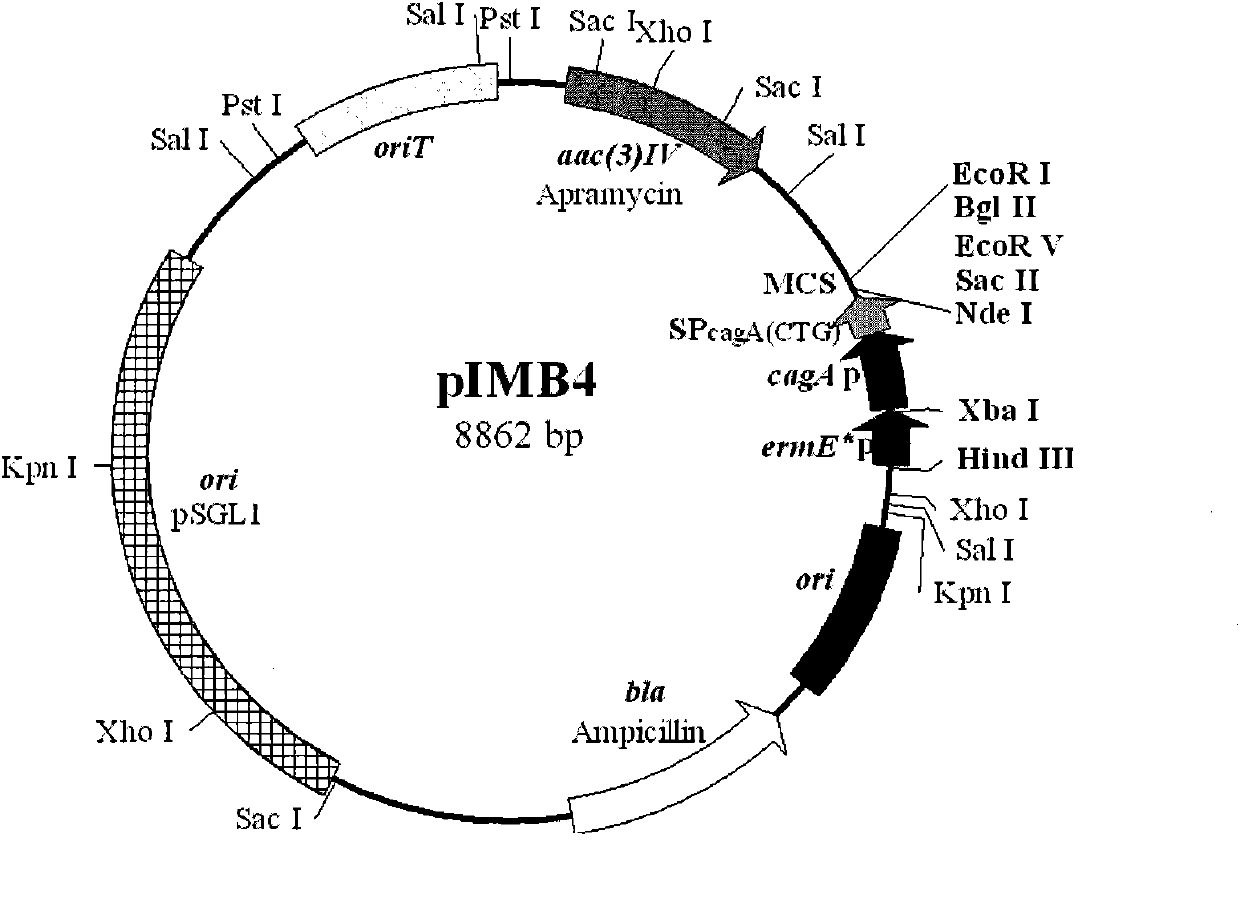
InactiveCN102002510AHigh copy numberEasy genetic manipulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSecretion expression
The invention relates to a new streptomyces secretion expression plasmid and application thereof. The new streptomyces secretionexpression plasmid is particularly characterized by being cloned with a colon bacillus replication original region ori, a streptomyces conjugational-transfer essential region oriT, a penbritin resistance gene bla, an apramycin resistance gene aac (3) IV, a promoter ermE*p, a lidamycin prosthetic-group protein gene promoter cagAp, a lidamycin prosthetic-group protein gene mutation type signal peptide SPcagA (CTG) and multiple cloning sites by taking a minimum replicon of a pSGL1 plasmid naturally existing in streptomyces globisporus C-1027 as a framework. The new streptomyces secretory expression plasmid can be used for efficiently secreting and expressing various heterologous proteins in streptomyces.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Construction method for efficient biosynthesis of streptomycete drugs
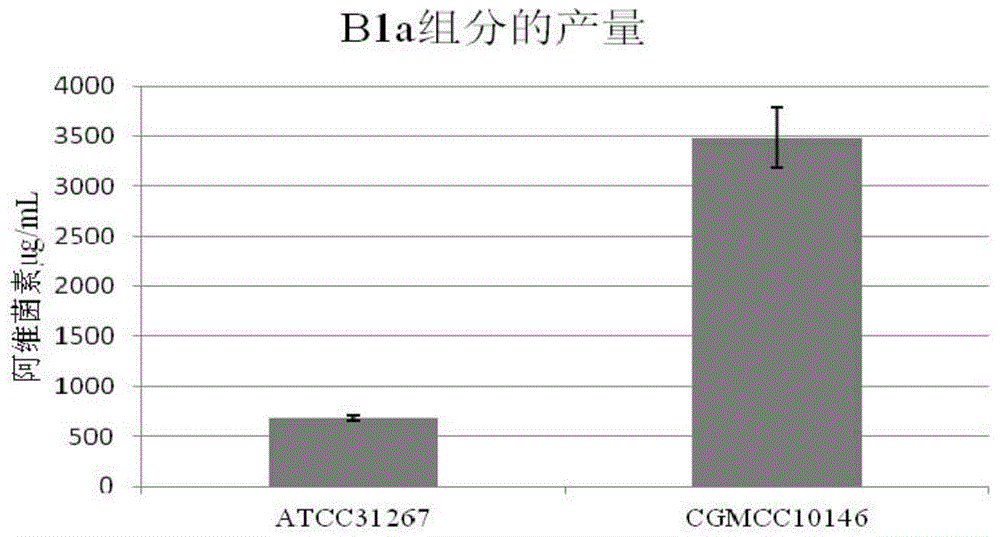
ActiveCN105018514AOvercoming difficult preparationOvercoming purchasing problemsMicroorganism based processesFermentationPharmaceutical SubstancesRate limiting enzyme
The present invention provides a construction method for efficient biosynthesis of streptomycete drugs. The construction method comprises: based on an inducible promoter O[R]O[lac] and a strong promoter ermEp<*>, firstly constructing a gradient induction expression system in streptomycete; controlling the expression level of target gene through the gradient induction, and carrying out coupled analysis on the relationship between the expression level of the target gene and the yield of the target drug so as to reveal the rate-limiting reaction in the drug biosynthesis path and the suitability of the rate-limiting enzyme; and through a constitutive promoter ermEp<*>, rationally carrying out series coupling on the encoding genes highly expressing the relevant rate-limiting enzyme so as to obtain a strain of the high-yield S Chattanoogensis producing strain L12, and transporting the strain to the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center to preserve, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No.10157. According to the present invention, the shake flask fermentation results show that the Natamycin yield in the S Chattanoogensis L12 is 3.3 times the yield in the S Chattanoogensis L10, and the 50 L fermentation tank small test results show that the highest yield achieves 15.7 g / L; and the method of the present invention has characteristics of efficiency, accuracy and simple operation, and is generally suitable for other streptomycetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
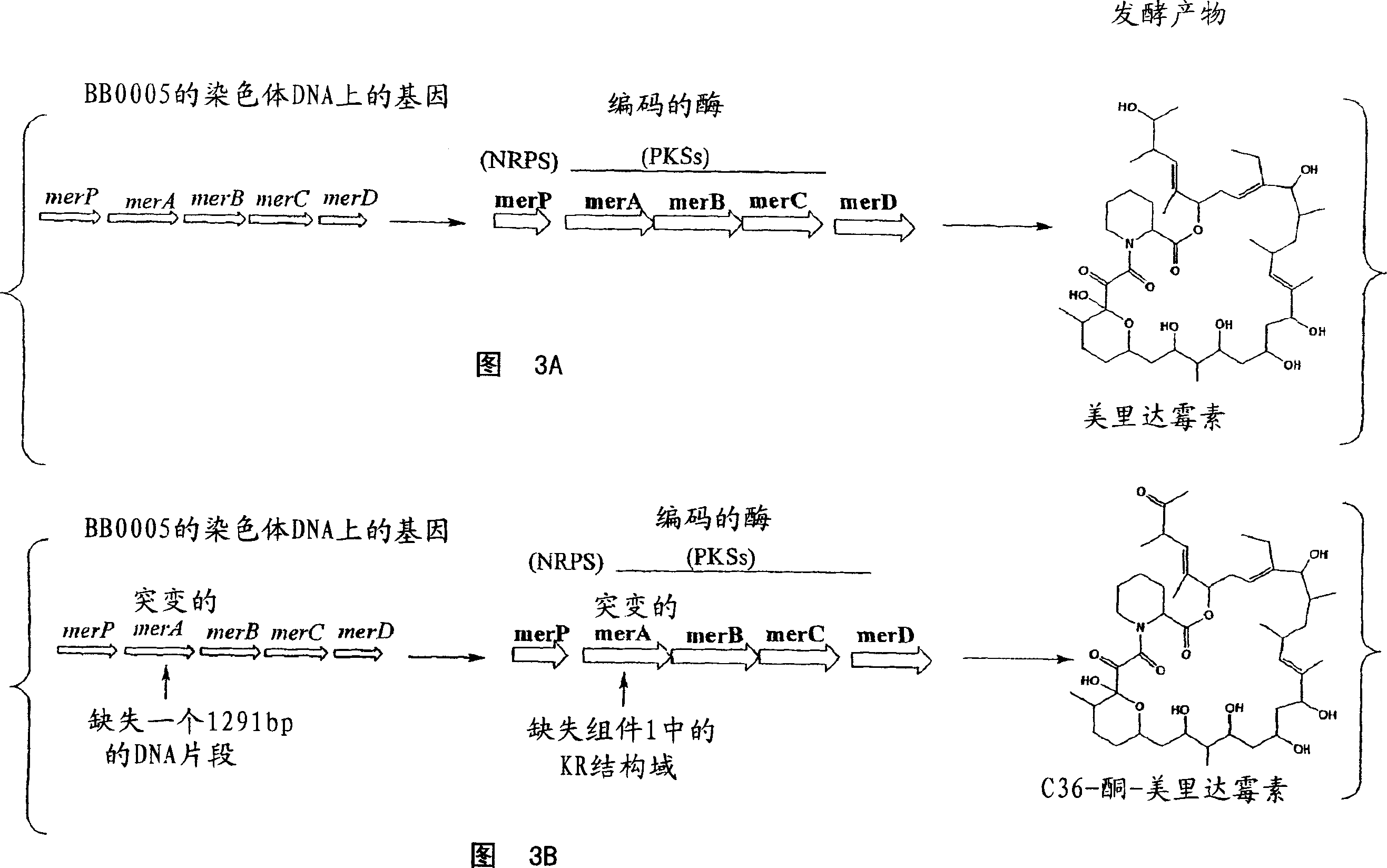
Biosynthetic gene cluster for the production of a complex polyketide
A polyketide synthase complex composed of polyketide synthase with 15 total modules, a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase with I module, and a cytochrome P450 hydroxylase is described. Also provided are novel Streptomyces species and methods of modified Streptomyces species. Further described are novel compounds, 36-ketomeridamycin, C9-deoxomeridamycin, and C9-deoxoprolylmeridamcyin and uses thereof.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Straw fiber seedling-raising substrate for colonizing biocontrol bacteria, production method of straw fiber seedling-raising substrate, and two-step biocontrol bacteria colonizing method of straw fiber seedling-raising substrate
ActiveCN111727847AVigorousConvenient sourceGrowth substratesSewage/sludge fertilisersBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses a straw fiber seedling-raising substrate for colonizing biocontrol bacteria, a production method of the straw fiber seedling-raising substrate, and a two-step biocontrol bacteria colonizing method of the straw fiber seedling-raising substrate, and belongs to the technical field of crop colonization biocontrol bacteria. Specifically the two-step biocontrol bacteria colonizing method comprises the following steps: the first step is the colonization of a biocontrol bacteria powder mixed with the substrate, the spray colonization of a biocontrol bacteria water agent, or thespray colonization of a biocontrol bacteria liquid; and the second step is that 10-15 days after the straw fiber substrate colonization biocontrol bacteria, the straw fiber substrate colonized with biocontrol bacteria, and crop seedlings are transplanted into a field simultaneously, and the substrate and crop seedling biocontrol bacteria are colonized in the field, wherein the used biocontrol bacteria are one or a mixture of more than one of Trichoderma aureoviride, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Streptomyces parvus, Talaromyces flavus, and Chaetomium aureum. According to the straw fiber seedling-raising substrate for colonizing biocontrol bacteria, the production method of the straw fiber seedling-raising substrate, and the two-step biocontrol bacteria colonizing method of the straw fiber seedling-raising substrate, the biocontrol bacteria can be effectively colonized, thereby the disease resistance of the seedlings is improved, and the stress resistance of seedling transplanting is significantly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES +1
High-efficiency low-toxicity low-residue cucumber root knot nematode disease prevention and treatment agent
InactiveCN113973855AHelps control root-knot nematode diseaseConducive to the prevention and treatment of nematode diseasePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyAbamectin
The invention discloses a high-efficiency low-toxicity low-residue cucumber root knot nematode disease prevention and treatment agent, and relates to the technical field of cucumber planting, and used raw materials comprise fluopyram, abamectin, beauveria bassiana, streptomyces microflavus, phosphate solubilizing bacteria, potassium solubilizing bacteria, a marigold extract, a maidenhair extract, an asparagus extract and a macleaya cordata extract. The cucumber root knot nematode disease prevention and treatment agent is beneficial to prevention and treatment of cucumber root knot nematode disease, has little damage to beneficial insects, can provide comprehensive and lasting protection for new leaves, stems, tubers and young fruits of cucumbers, provides reliable guarantee for cucumber disease prevention, has the capabilities of converting nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in soil and improving soil fertility, reduces the use amount of chemical fertilizers, stimulates cell division, promotes rooting, germination and maturation of cucumber crops, increases the yield of cucumbers, remarkably improves the quality of cucumbers, is low in toxicity and residue, is safe to crops and environment, and has a wide development prospect.
Owner:济宁市农业科学研究院
Formula for preparing high-efficiency bio-organic fertilizer from organic materials and preparation method of high-efficiency bio-organic fertilizer
PendingCN113511943AImprove water retentionImprove fat retentionBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersBacillus megateriumLivestock manure
The invention relates to a formula for preparing a high-efficiency bio-organic fertilizer from organic materials and a preparation method of the high-efficiency bio-organic fertilizer. The preparation method comprises the steps: firstly, fully mixing livestock manure with auxiliary materials including peanut meal, humic acid, enzyme microorganisms, fishbone dust, soybean leaf powder and amino acid; adding bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus megaterium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus laterosporus, bacillus mucilaginosus, streptomyces jingyangensis, azotobacter chroococcum, actinomycetes, photosynthetic bacteria flora, lactic acid bacteria flora, saccharomycetes, bacillus coagulans, aspergillus oryzae, aspergillus niger and trichoderma viride, coarsely adjusting the moisture content and carbon nitrogen ratio of the materials according to the raw material components, mixing and fermenting; and thus obtaining the bio-organic fertilizer which does not have pesticide residues and naturally improves the crop yield.
Owner:中烜生物科技(湖北)有限公司
Valinomycin B, preparation method and medical purpose thereof
ActiveCN105968067APrevent proliferationReduce protein expressionOrganic chemistryBacteriaPharmaceutical SubstancesCell cycle
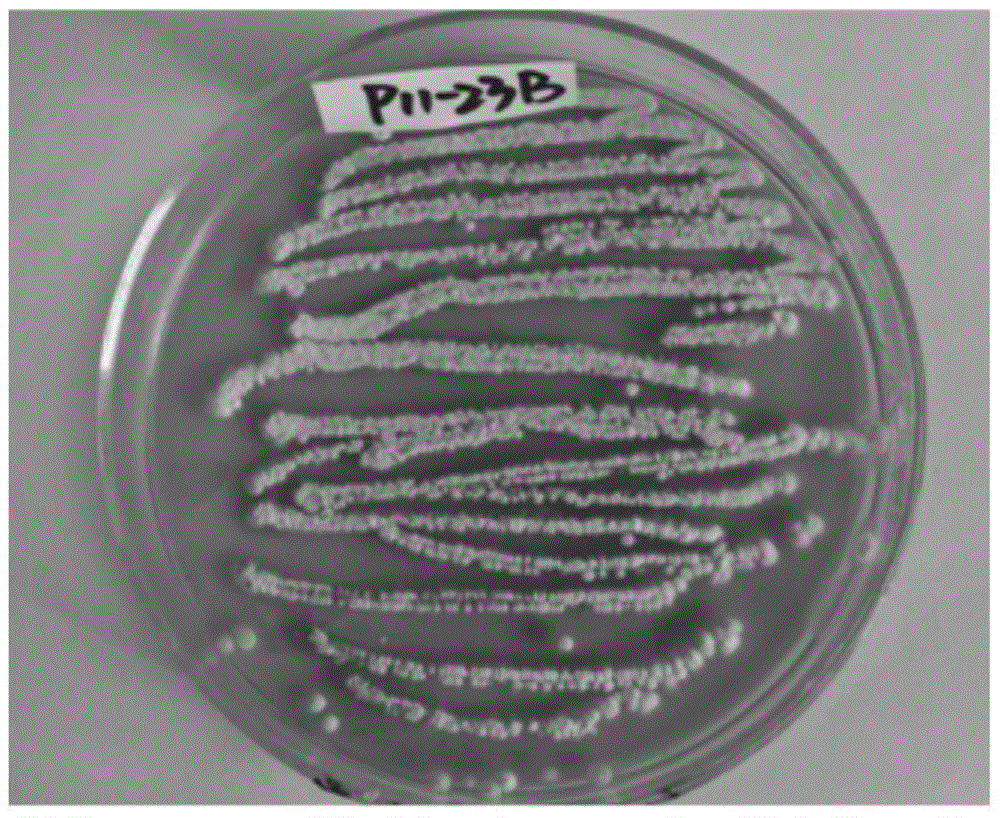
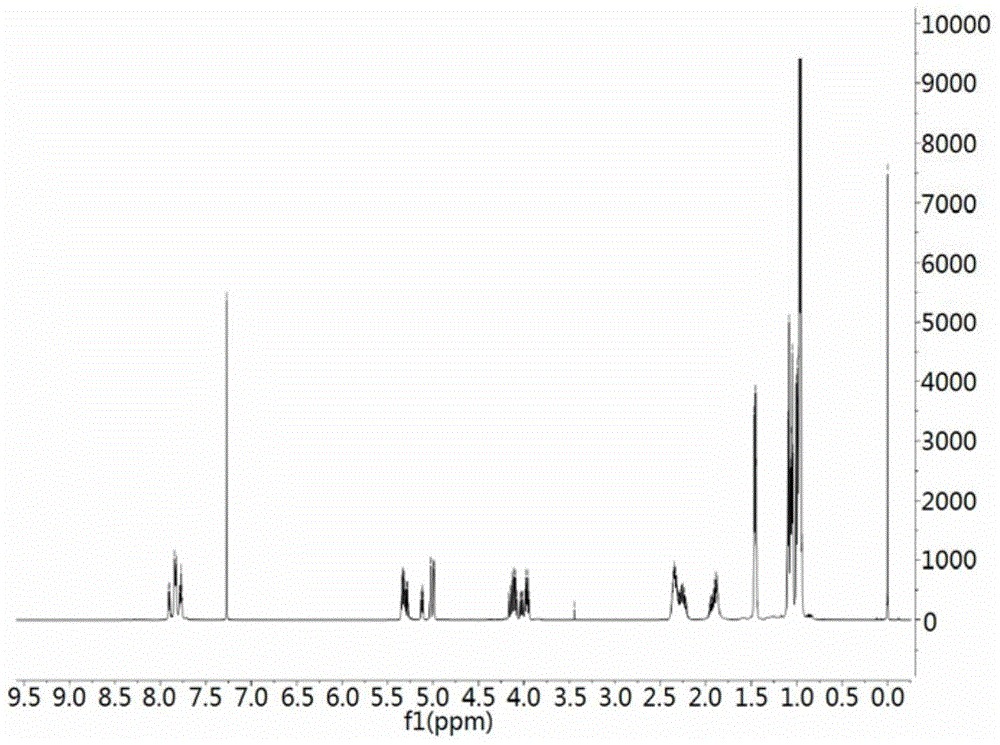
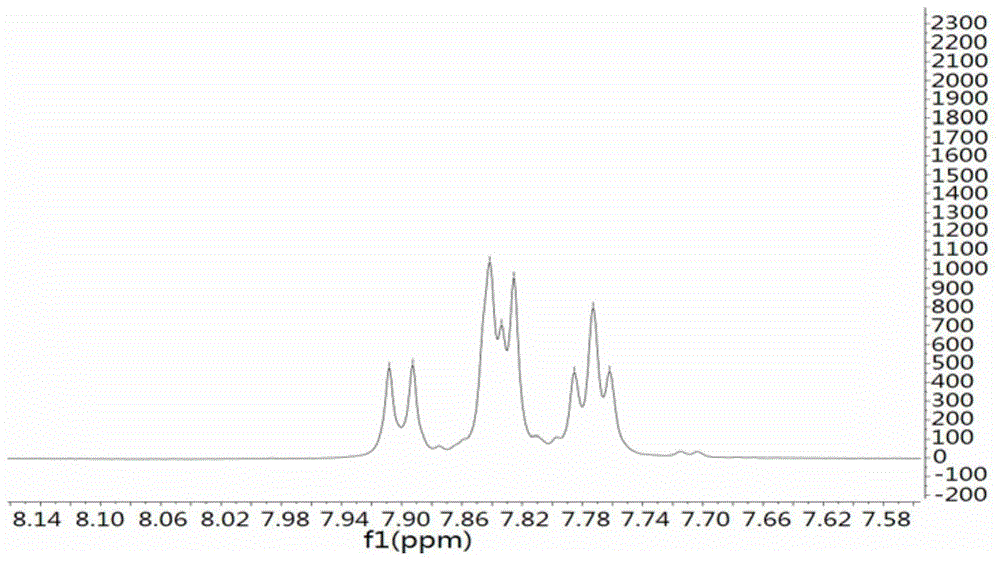
The invention provides a compound valinomycin B having glioma activity resistance, provides an active substance producing strain streptomyces parvus separated and cultured from sea mud, and the active substance valinomycin B can be prepared. The streptomyces parvus is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection and named as P11-23B (Streptomyces parvus P11-23B) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2015675 on Nov, 12th, 2015. The valinomycin B has features of obviously inhibiting multiplication of various kinds of glioma cells, obviously inhibiting glioma cell cycle at G0 / G1 phase, and reducing the protein level expression of several key enzymes with different metabolism approaches of glioma cells, and has unique anti-tumor effect. The valinomycin B can be used for preparing medicines for treating glioma. The chemical structural formula of the valinomycin B is as shown in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Streptomycete 2-nitropropane dioxyenase gene and its application
The present invention relates to the application of environmental microbe. Especially, by means of molecular technology, one new gene is cloned from Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 and the gene encodes one kind of 2-streptomycete dioxyenase. The encoded product has great value in biologically degrading industrial pollutant nitroalkane and in improving environment.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Salinomycin strain
InactiveCN104017756AIncrease productionCoincident mutagenesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
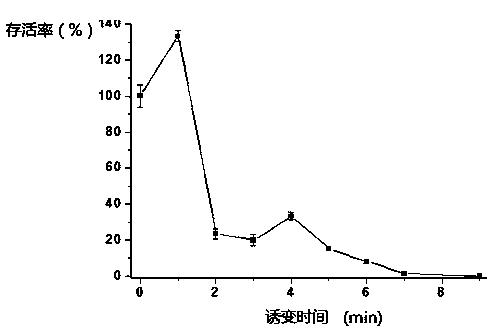
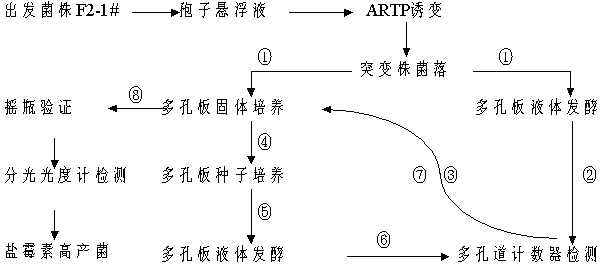
The invention discloses a salinomycin strain with the class name of streptomycesalbums S-610-11, and the preservation number is CCTCCM2012492. The salinomycin high-yielding strain streptomycesalbums S-610-11 is obtained by combination of plasma mutagenesis at normal temperature under normal pressure with high-throughput synergy screening method, the content of salinomycin can be greatly improved, and the stability is good, after 5 times of continuous passages of the strain, and the salinomycin titer has no obvious change. By use of shake flask fermentation, the yield of salinomycin reaches 56000u / ml, and is improved by 70% compared with that of original strain F2-1#. The salinomycin strain is fully consistent with mutagenesis and screening requirements of industrialization salinomycin production strains, and can be applied in industrial fermentation production, and has great economic value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGHUA BIOK BIOLOGY
Cloning method of antibiotics biosynthetic gene cluster based on site-specific recombination
InactiveCN103060362AExtensive cloningCloning operation implementationMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiosynthetic genesSite-specific recombination
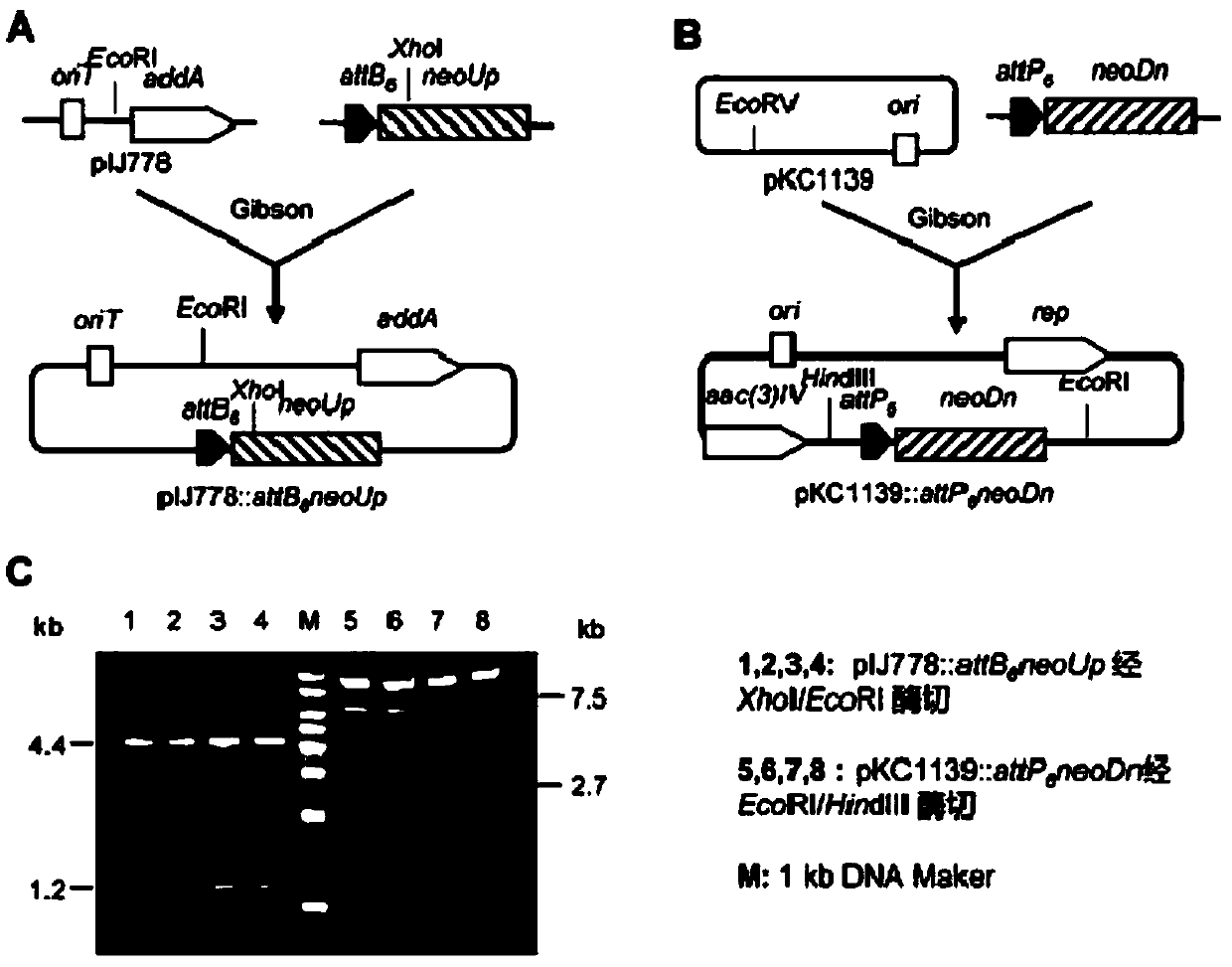
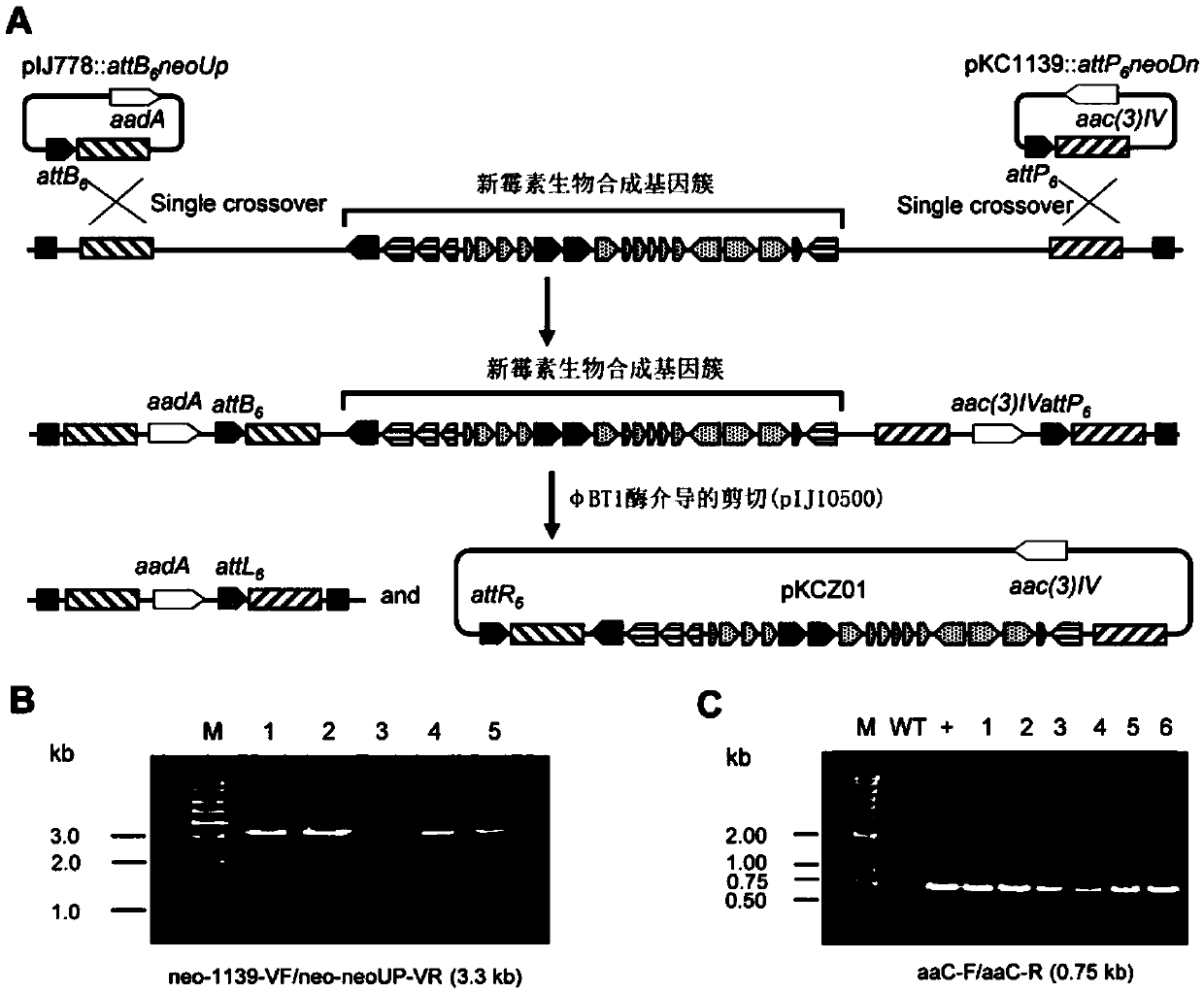
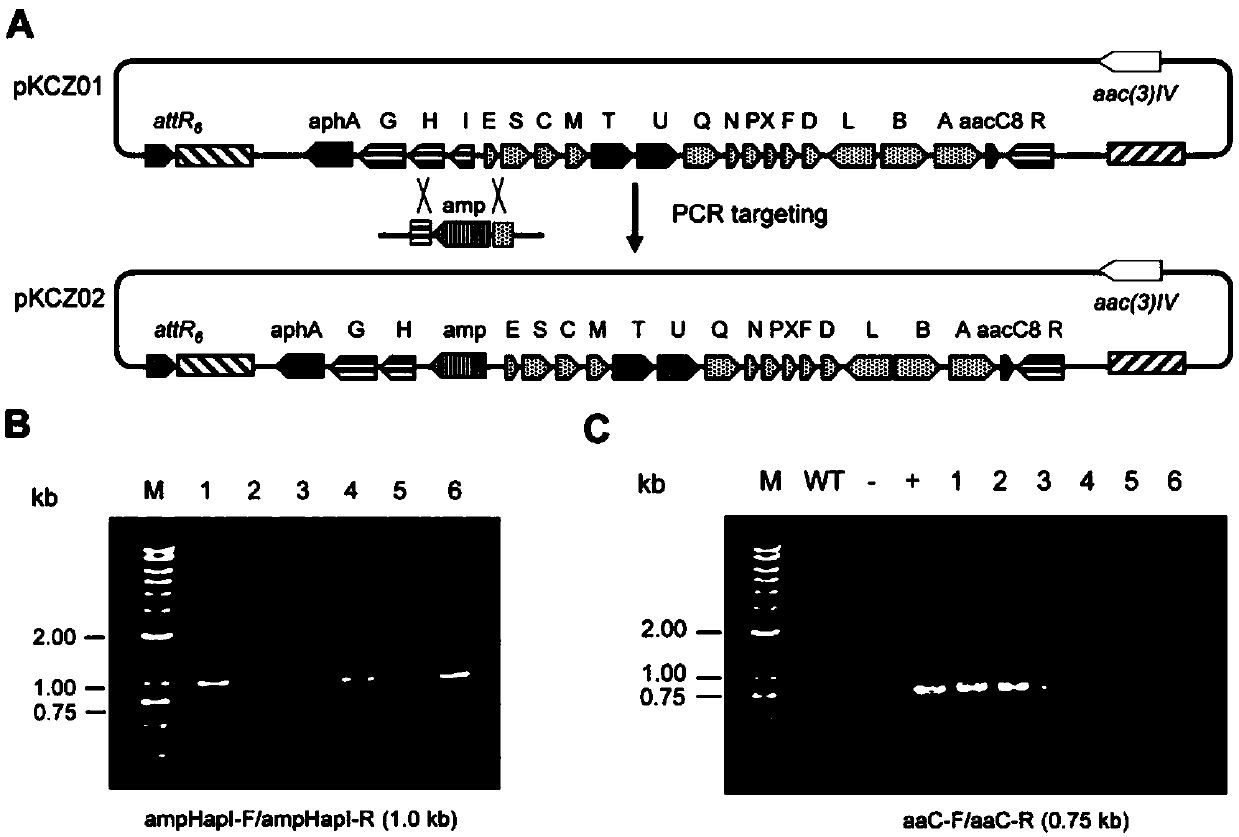
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, and specifically discloses a cloning method of antibiotics biosynthetic gene cluster based on site-specific recombination. The method comprises the following steps of: based on the site-specific recombination reaction mediated by the integrase encoded by the streptomycete bacteriophage Phi BT1, firstly, executing genetic modification on the strains, which hare generated by the antibiotics, by means of homologous recombination mode; respectively inserting the BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) vector, the resistant gene and the site-specific recombination sites attB and attP identified by the Phi T1 integrase at two ends of the targeted gene cluster, and extracting chromosome genome segments; under the action of the Phi T1 integrase, causing site-specific recombination reaction between the sites attB and attP in vitro; enabling the target gene cluster to cyclize itself, thereby realizing clone of dozens or even hundreds of kb of large-segment antibiotics biosynthetic gene clusters. The cloning method of antibiotics biosynthetic gene cluster based on site-specific recombination lays good foundation for further genetic modification of the biosynthetic gene clusters, and has better application foreground.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Engineering bacteria genetically modified by neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster, and applications thereof
ActiveCN111019965AIncrease total outputHigh compositionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNeomycinBiosynthetic genes
The invention provides a method for constructing a high-yield neomycin engineering strain streptomyces fradiae. The method comprises: introducing a neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of streptomyces fradiae into wild streptomyces fradiae. The method can also comprise: carrying out genetic engineering modification on the neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of streptomyces fradiae to be introduced into wild streptomyces fradiae, wherein genetic engineering modification can comprise: blocking the negative regulatory gene neoI in the neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster or blocking the negative regulatory gene neoI in the neomycin biosynthetic gene cluster while driving the transcription of a key enzyme encoding gene neoE-neoD co-transcription unit by using a strong promoter. The invention also provides high-yield neomycin streptomyces fradiae obtained by the method.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com