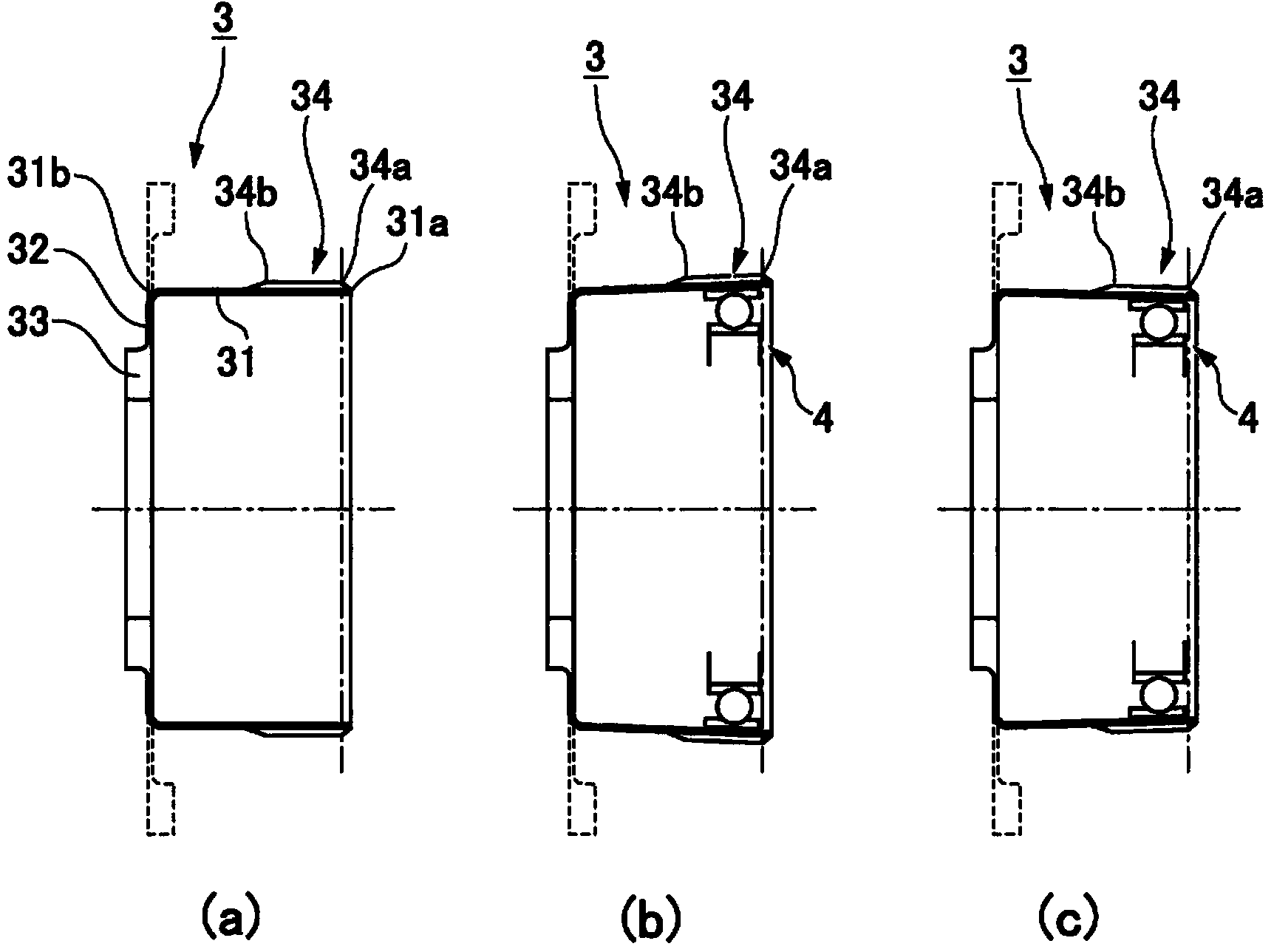
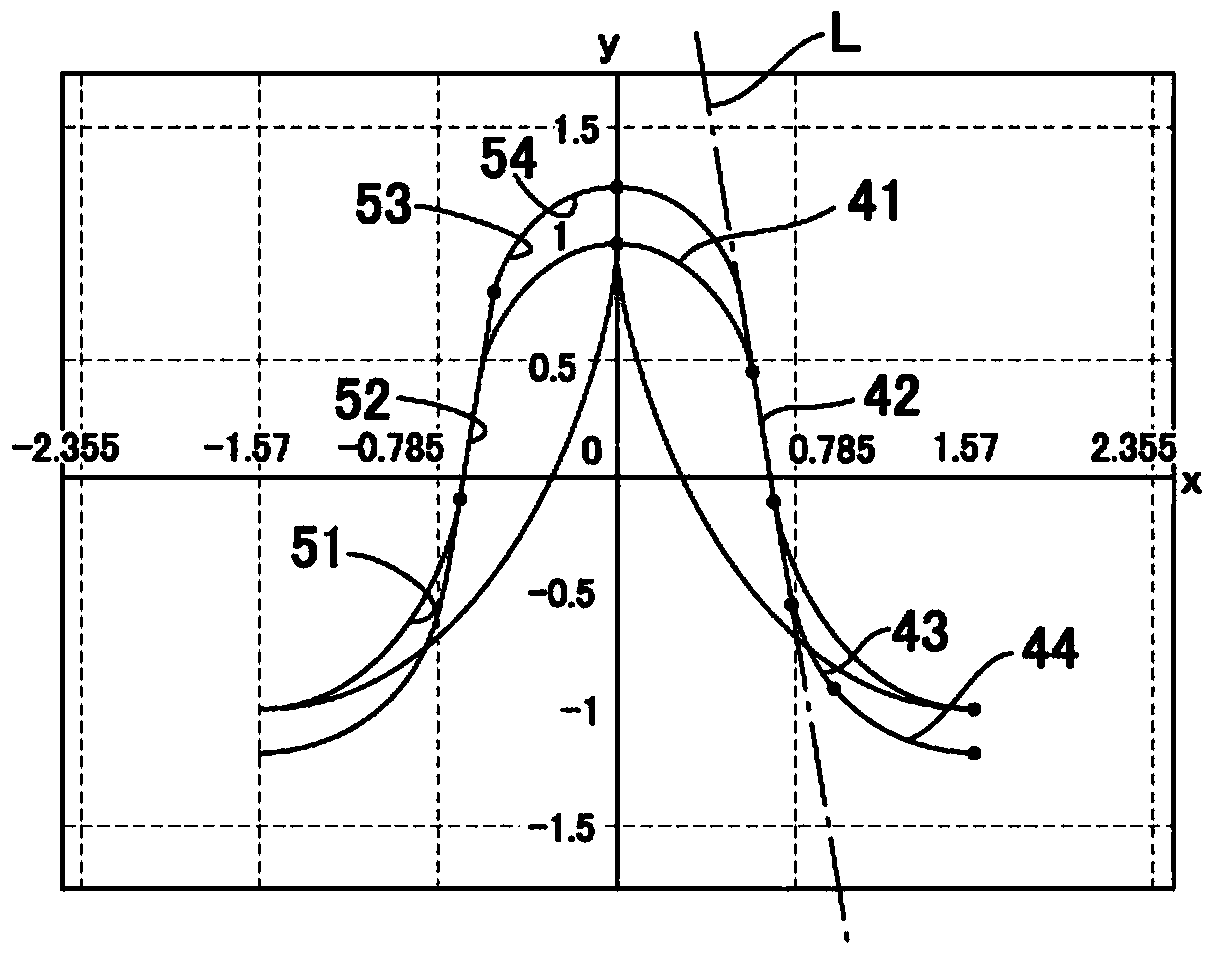
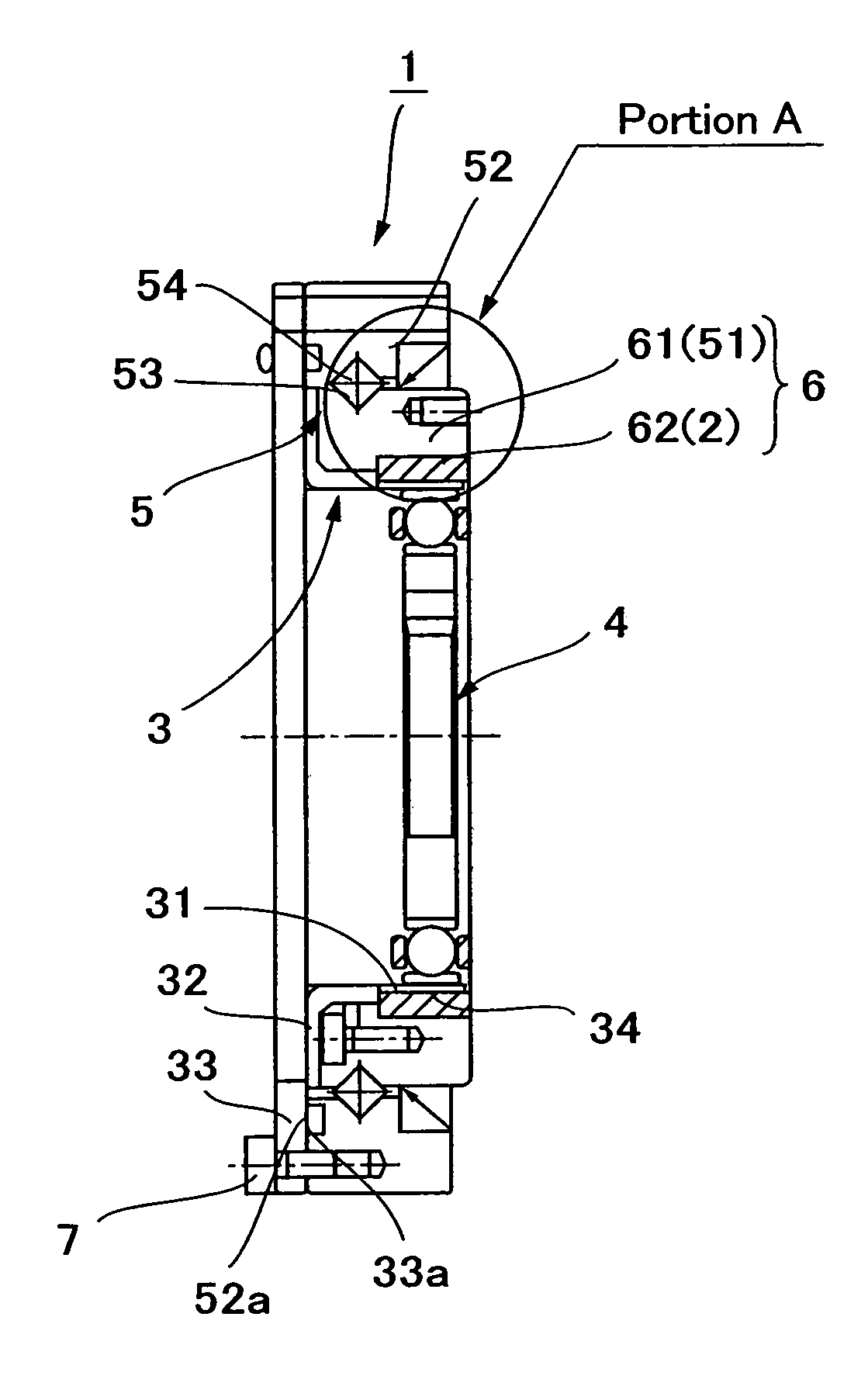
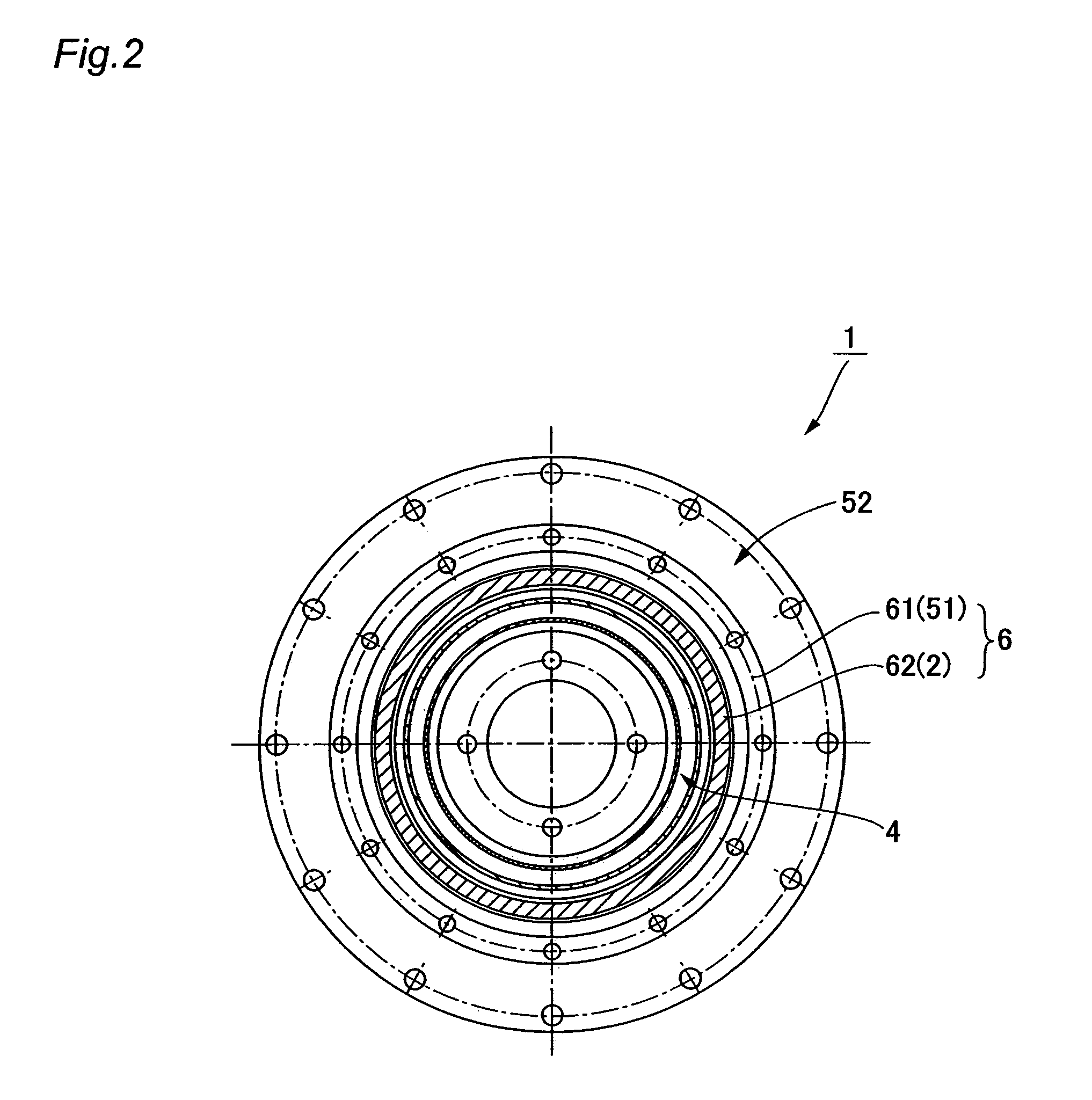
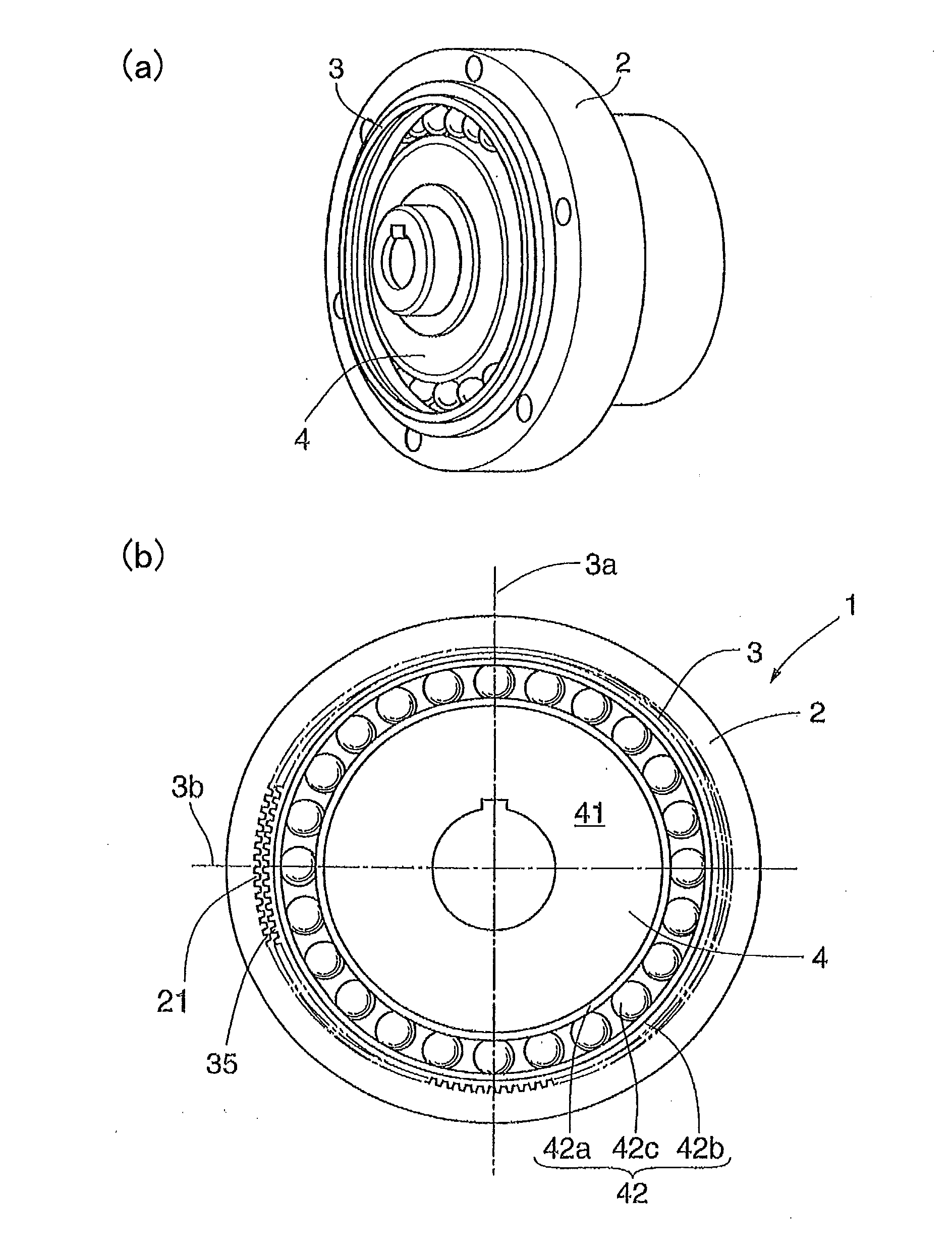
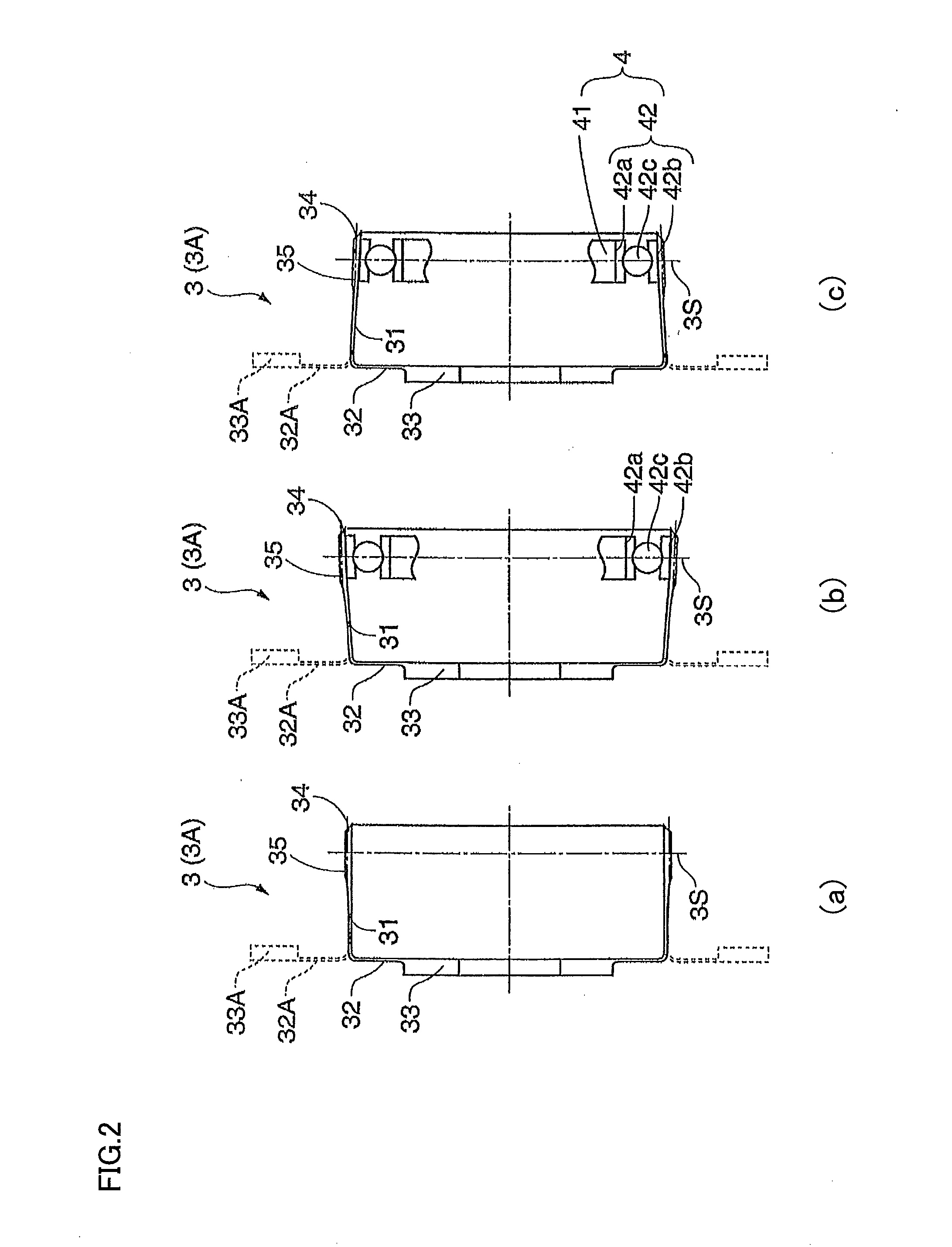
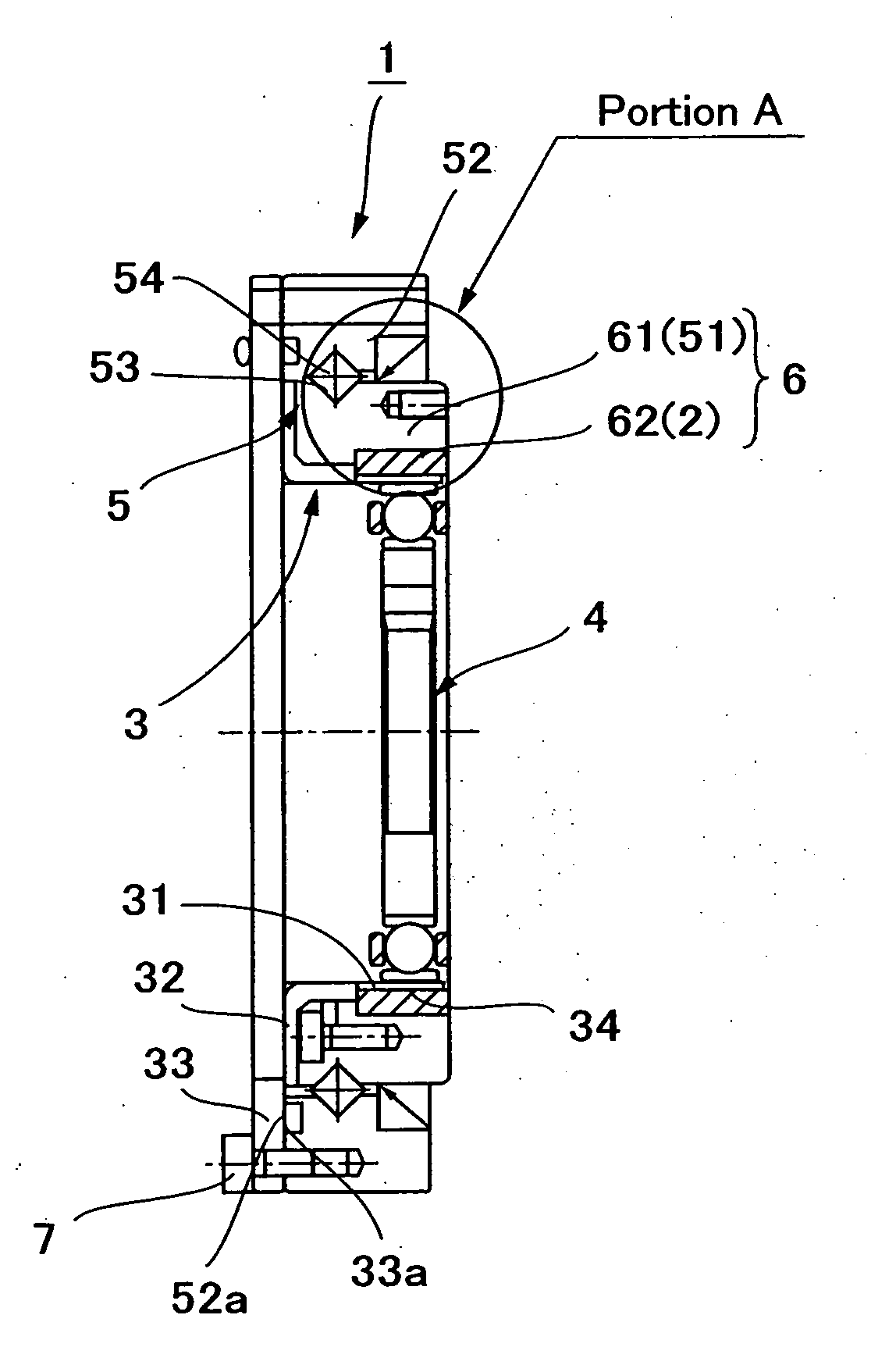
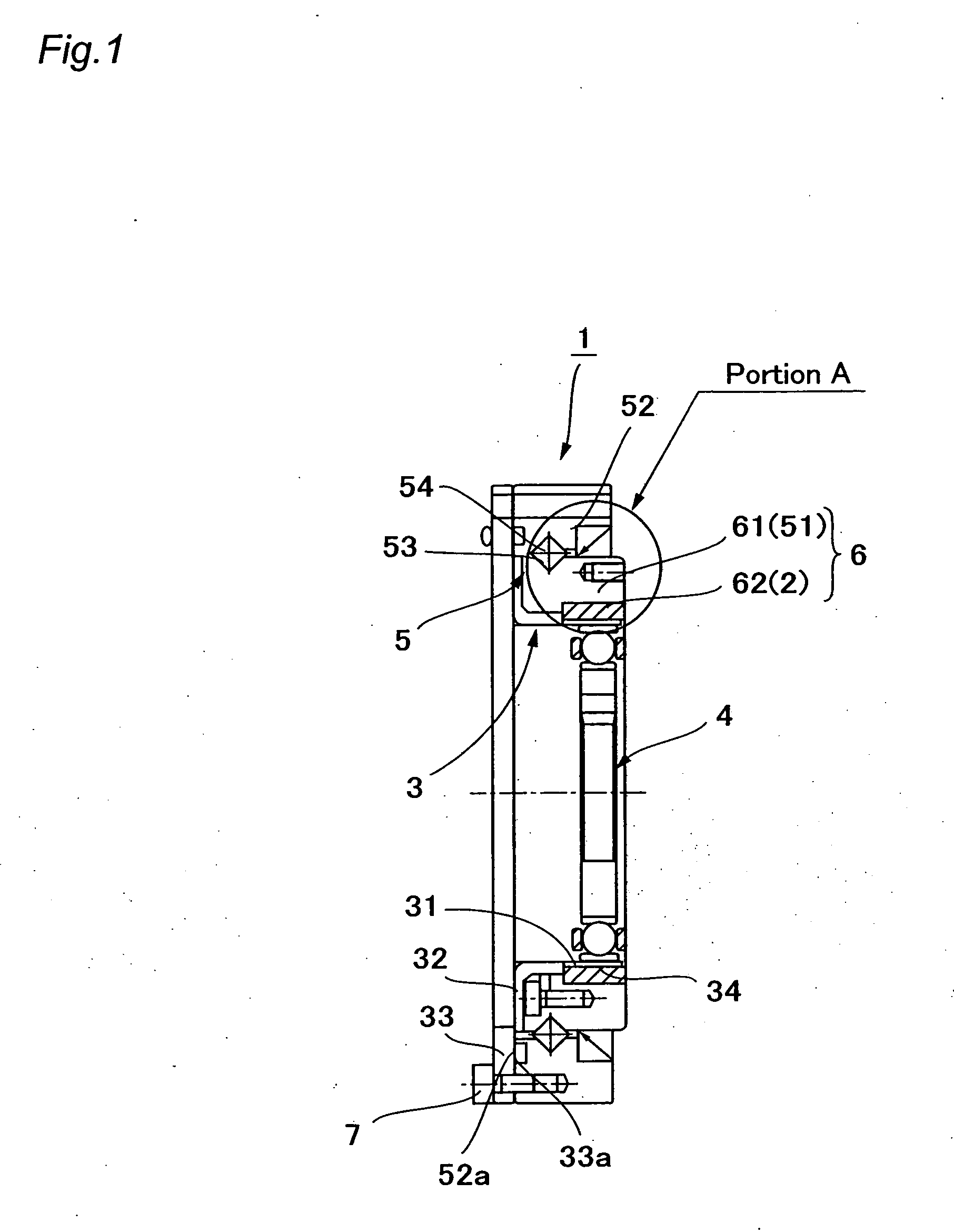
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
129 results about "Strain wave gearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
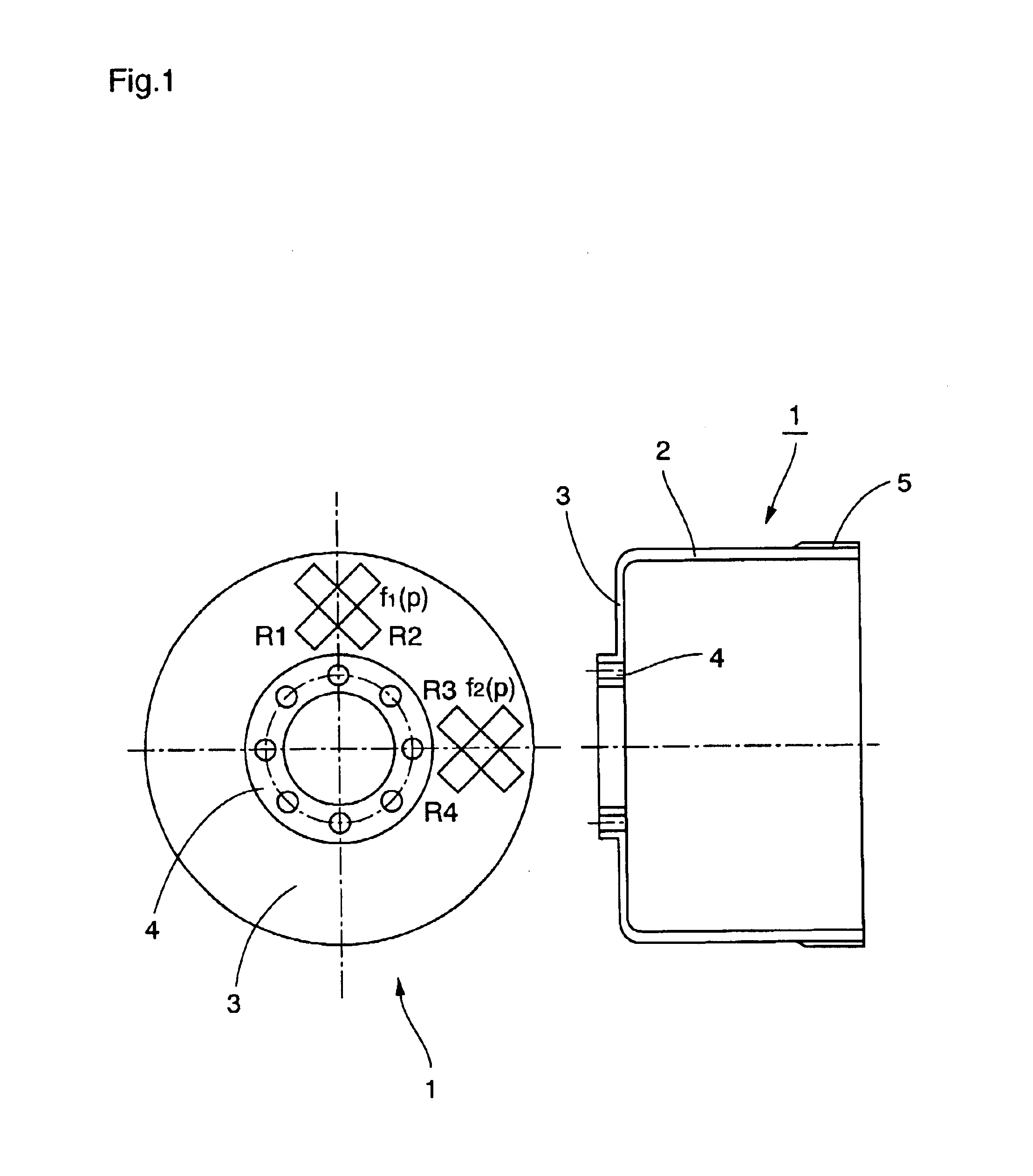
Strain wave gearing also known as harmonic gearing is a special type of mechanical gear system that can improve certain characteristics compared to traditional gearing systems such as helical gears or planetary gears. It was invented in 1957 by C.W. Musser while he was a research advisor at United Shoe Machinery (USM). The advantages include: no backlash, compactness and light weight, high gear ratios, reconfigurable ratios within a standard housing, good resolution and excellent repeatability when repositioning inertial loads, high torque capability, and coaxial input and output shafts. High gear reduction ratios are possible in a small volume (a ratio from 30:1 up to 320:1 is possible in the same space in which planetary gears typically only produce a 10:1 ratio). Disadvantages include a tendency for 'wind-up' (a torsional spring rate) in the low torque region. Strain wave gears are typically used in industrial motion control, machine tool, printing machine, robotics and aerospace, for gear reduction but may also be used to increase rotational speed, or for differential gearing.
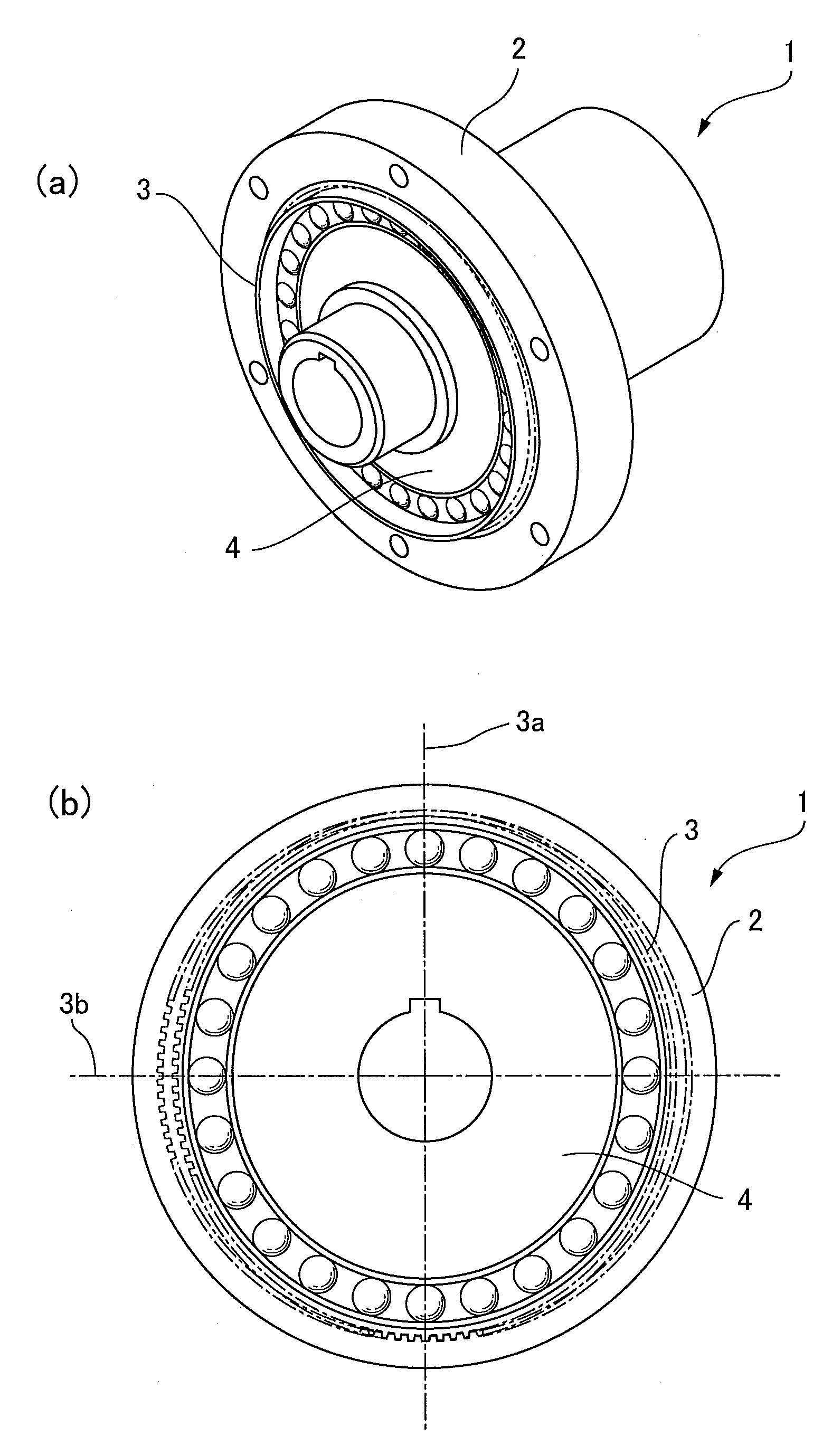
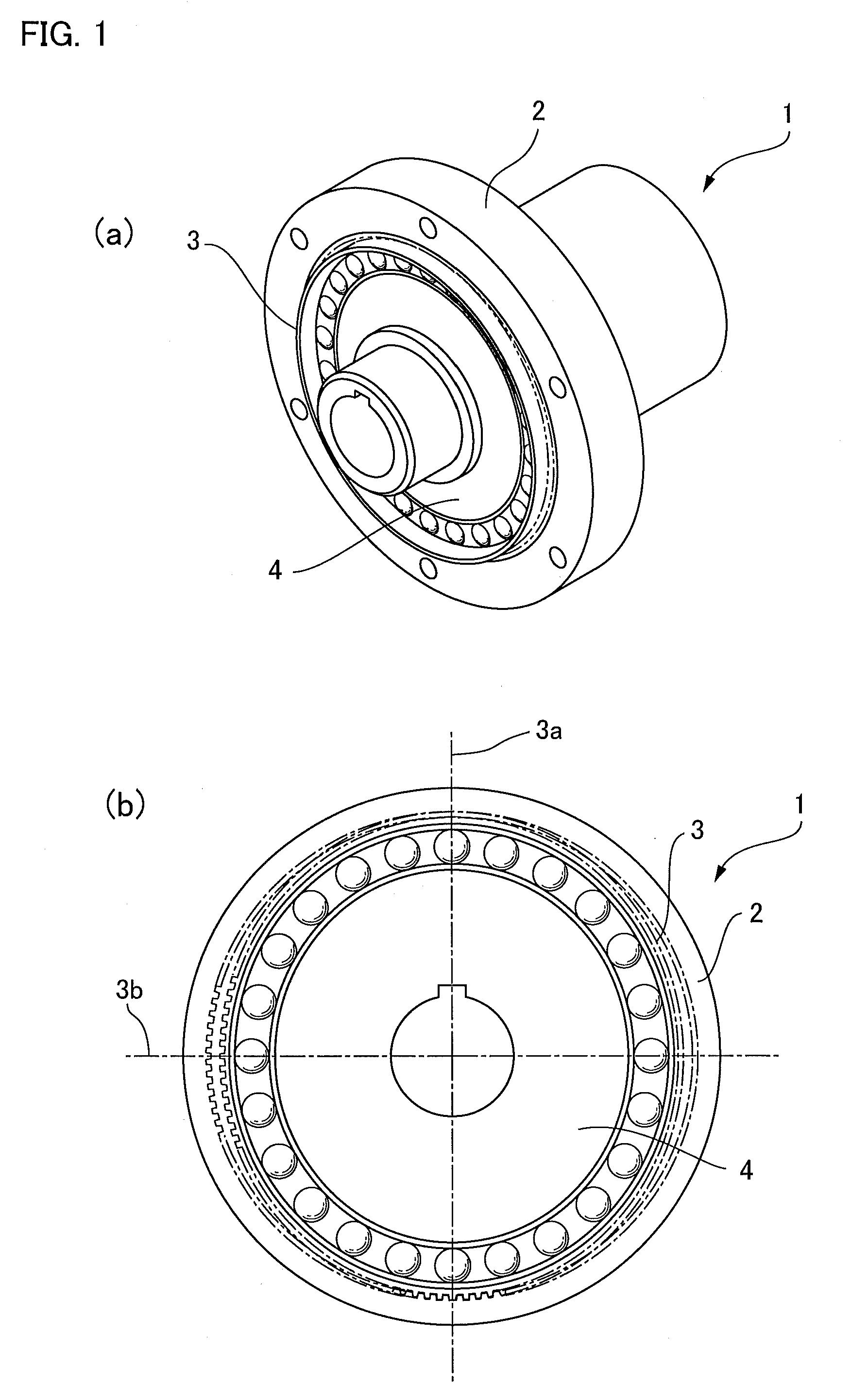
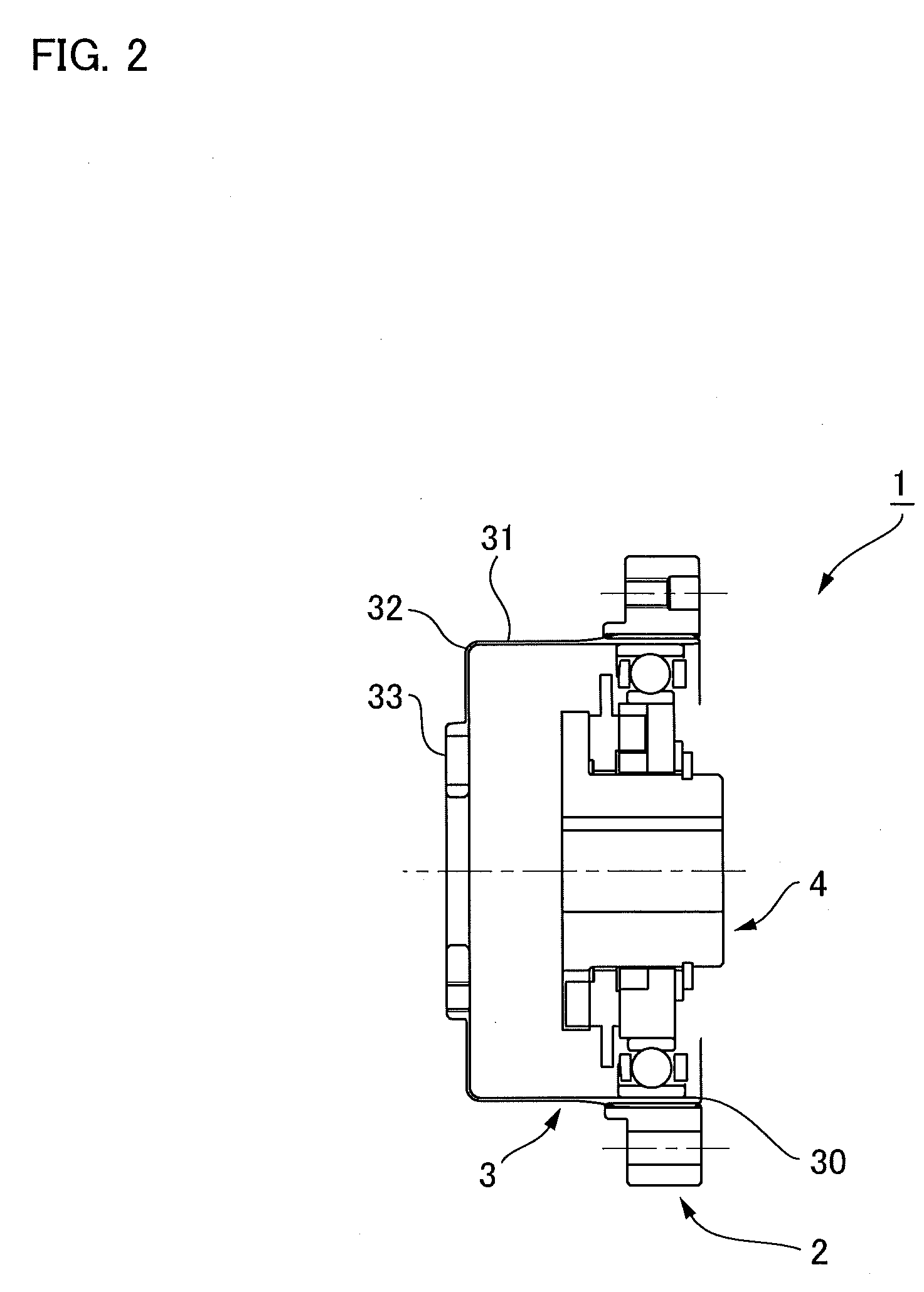
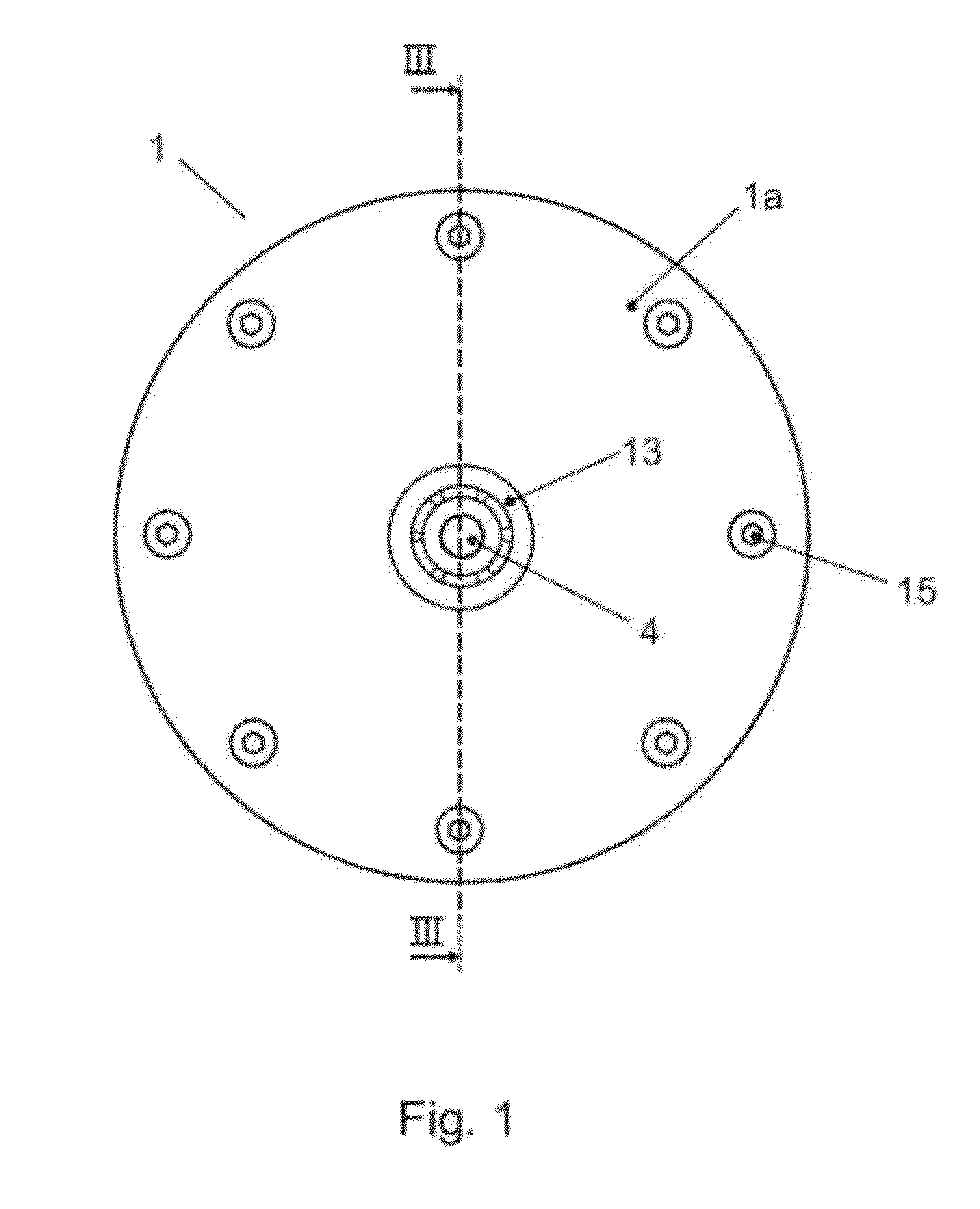
Strain wave gearing and robotic arm
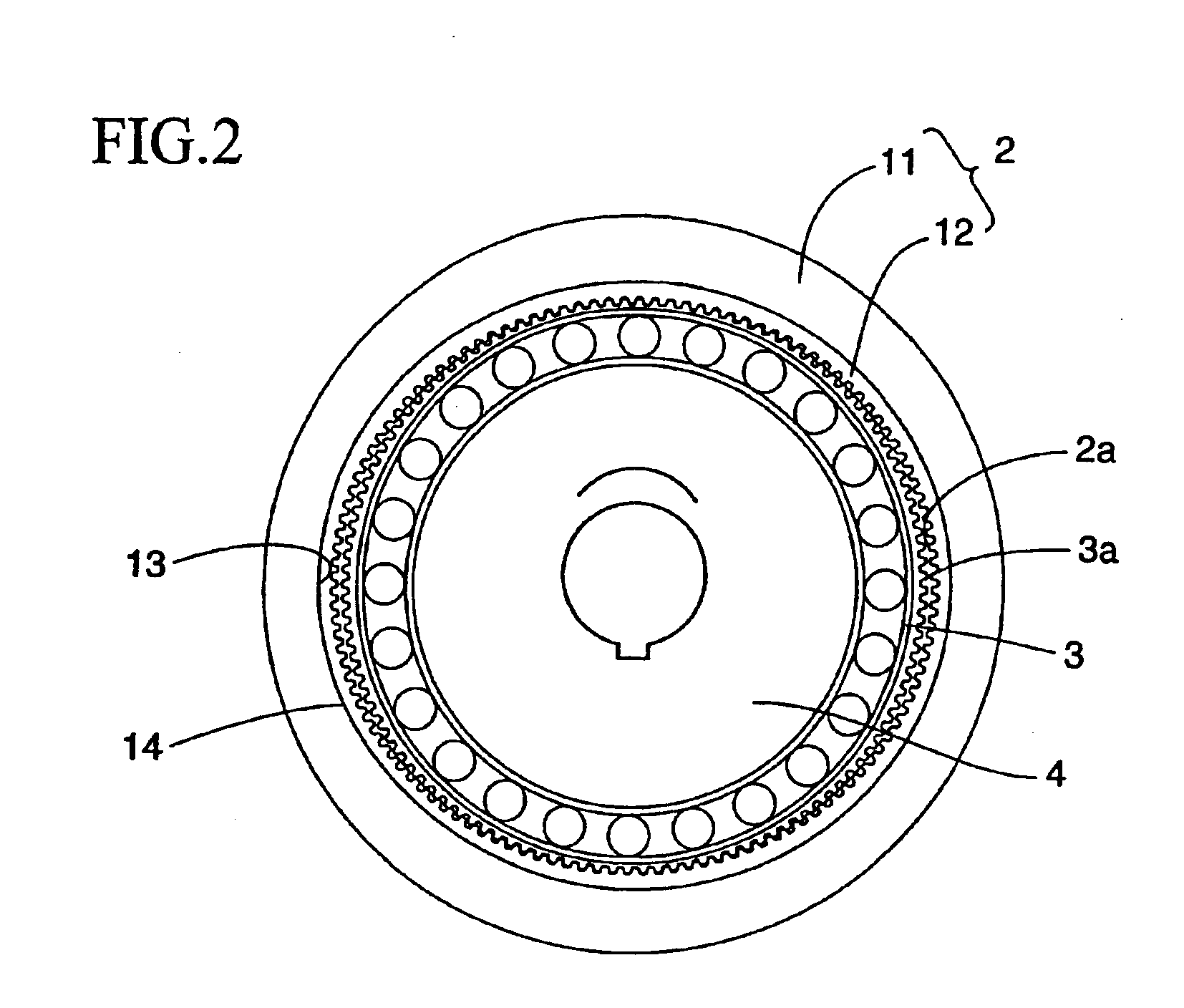
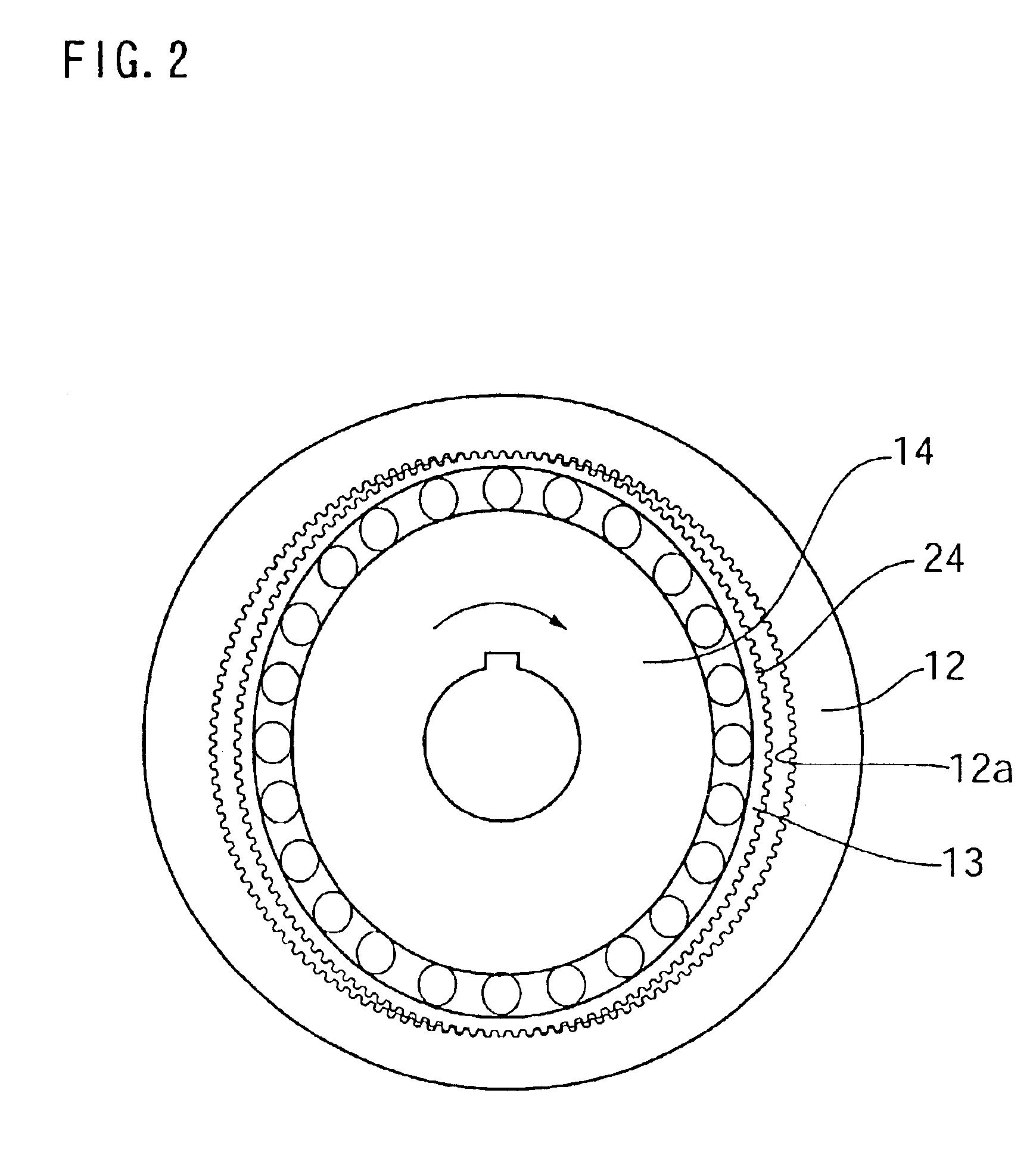
InactiveUS20110245006A1Increase stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorToothed gearingsHigh stiffnessGear wheel
Provided is a strain wave gearing having a high stiffness and no limitation imposed on rotation, and a robotic arm including the strain wave gearing. A strain wave gearing includes an electric motor and a strain wave gearing reducer. The strain wave gearing reducer includes: an outer ring member including a first internal gear; a pair of second internal gears each having internal teeth formed along an inner periphery thereof, and the pair of second internal gears differing from the first internal gear in number of teeth; a flexible gear; and a cam member, which distorts the flexible gear in a radial direction to cause the flexible gear to engage with the first internal gear and the pair of second internal gears. The pair of second internal gears is fixed to a pair of fixing plates coupled to each other by a shaft penetrating the cam member.
Owner:CANON KK
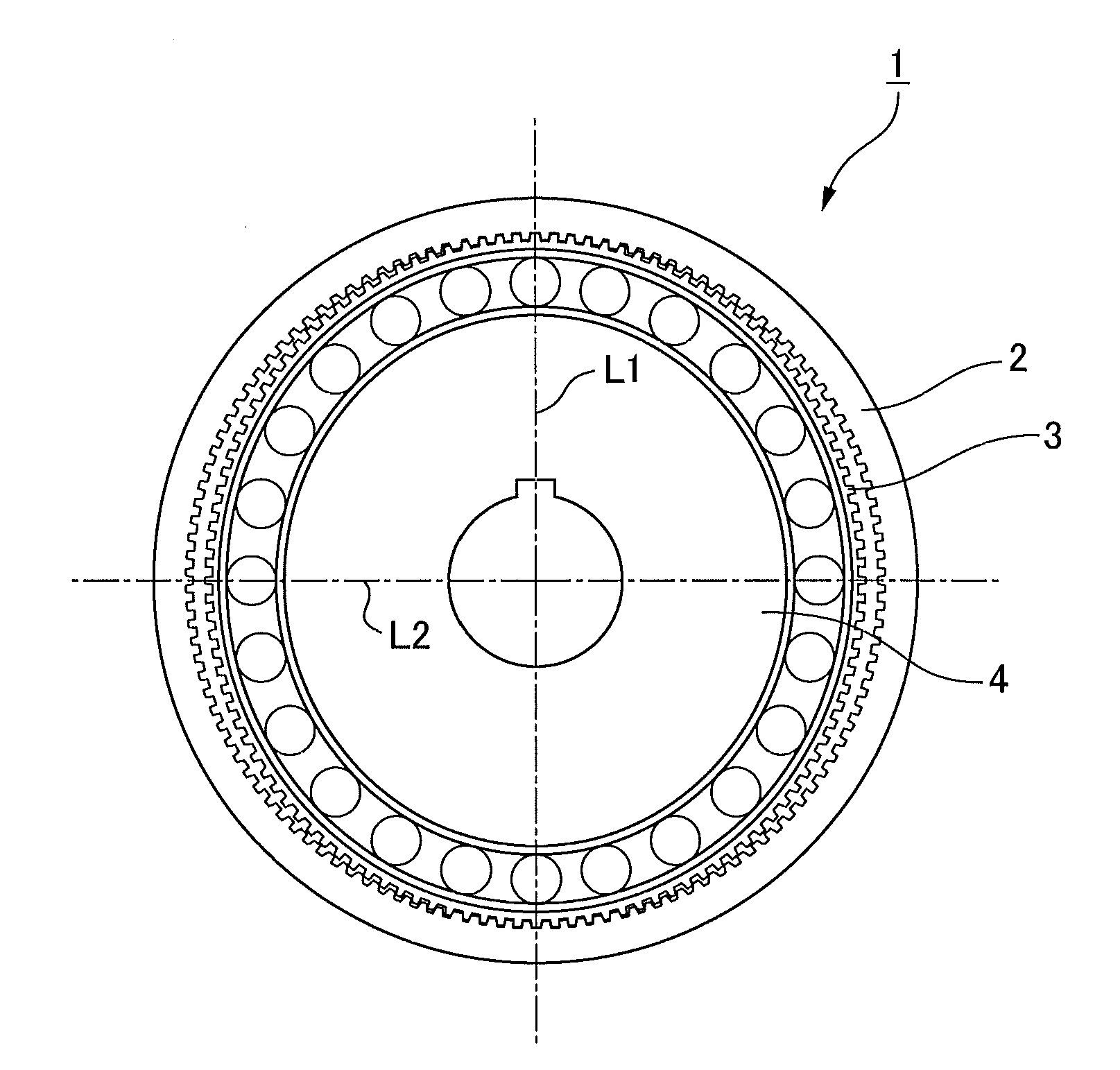
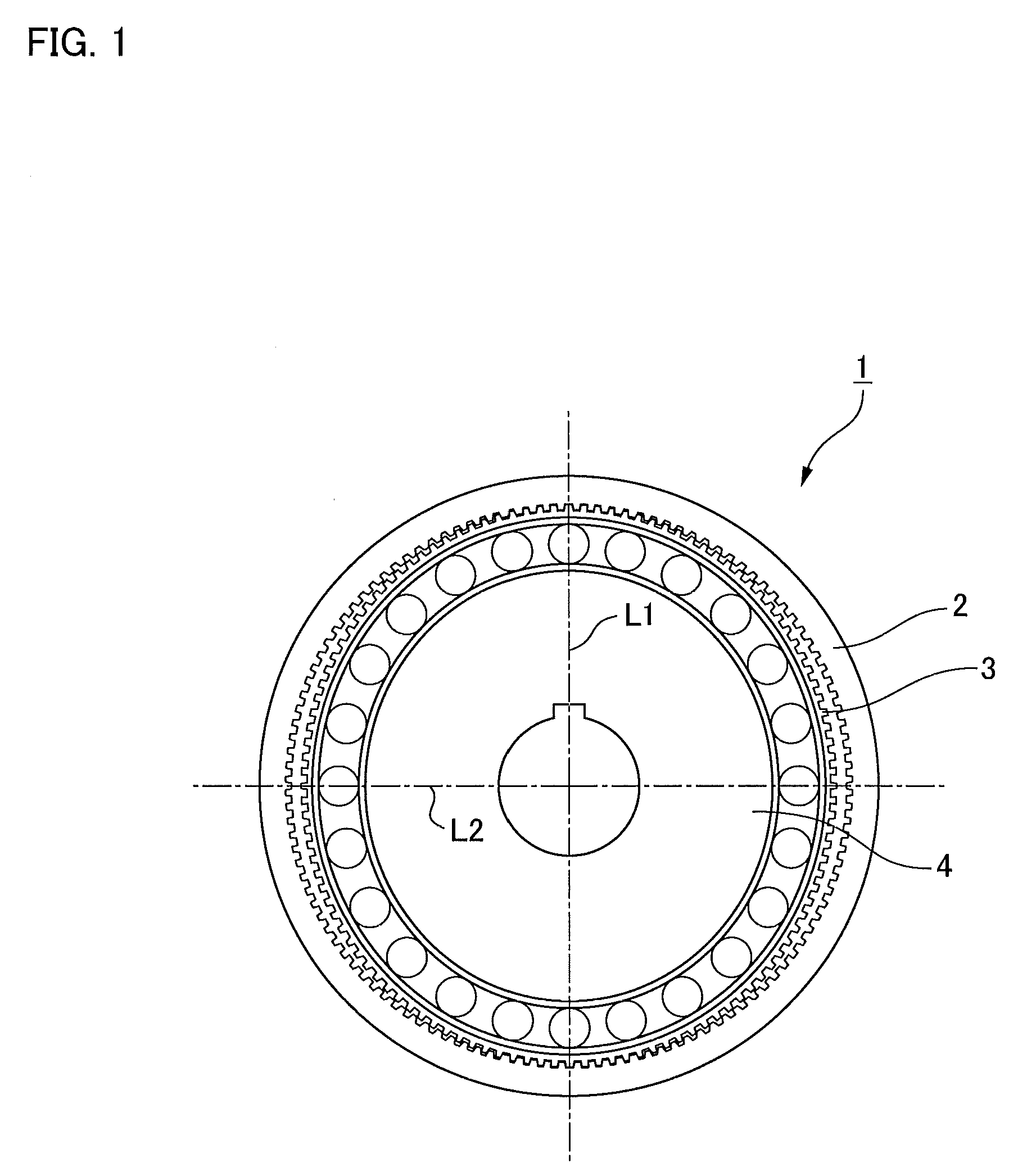
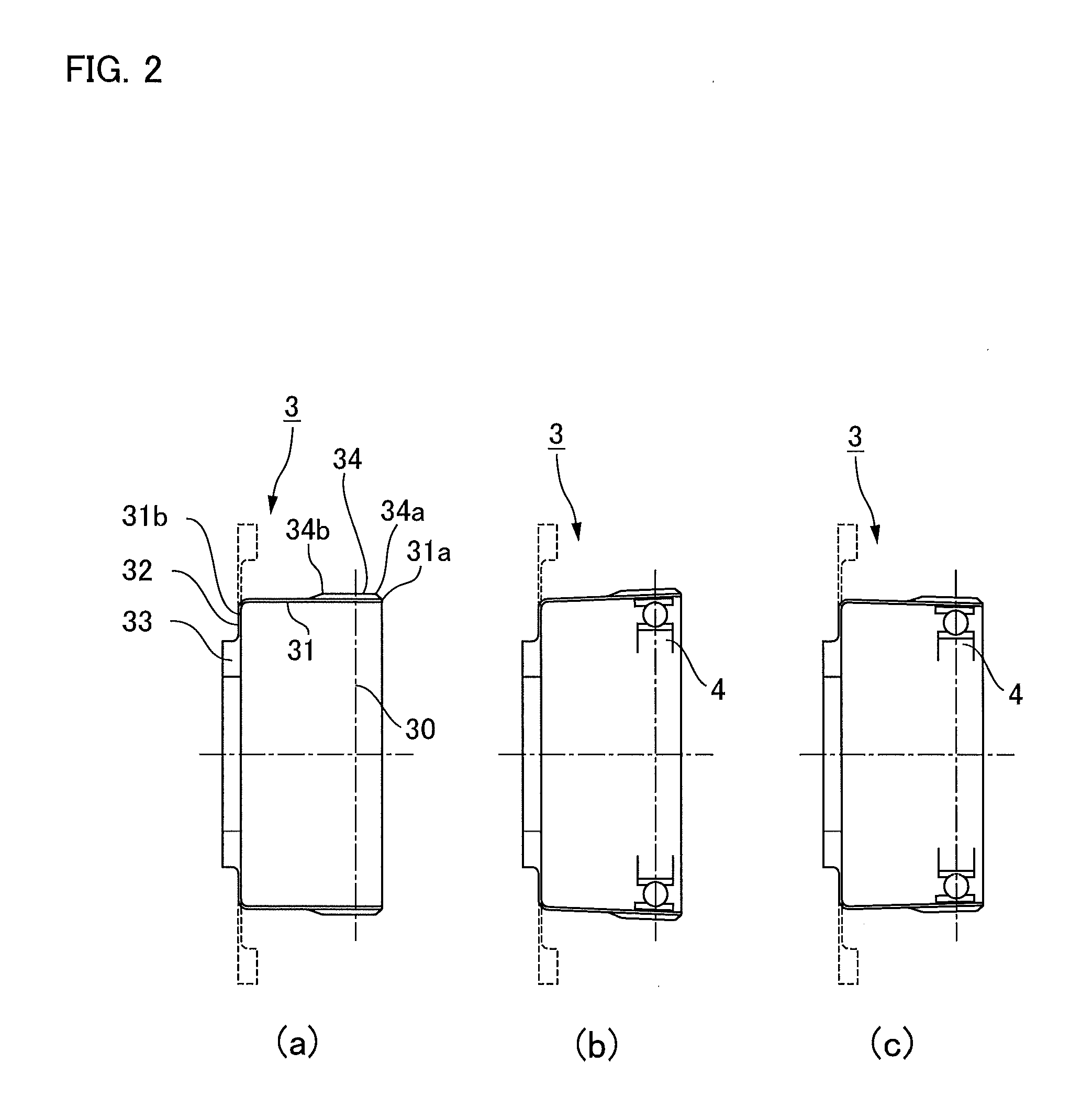
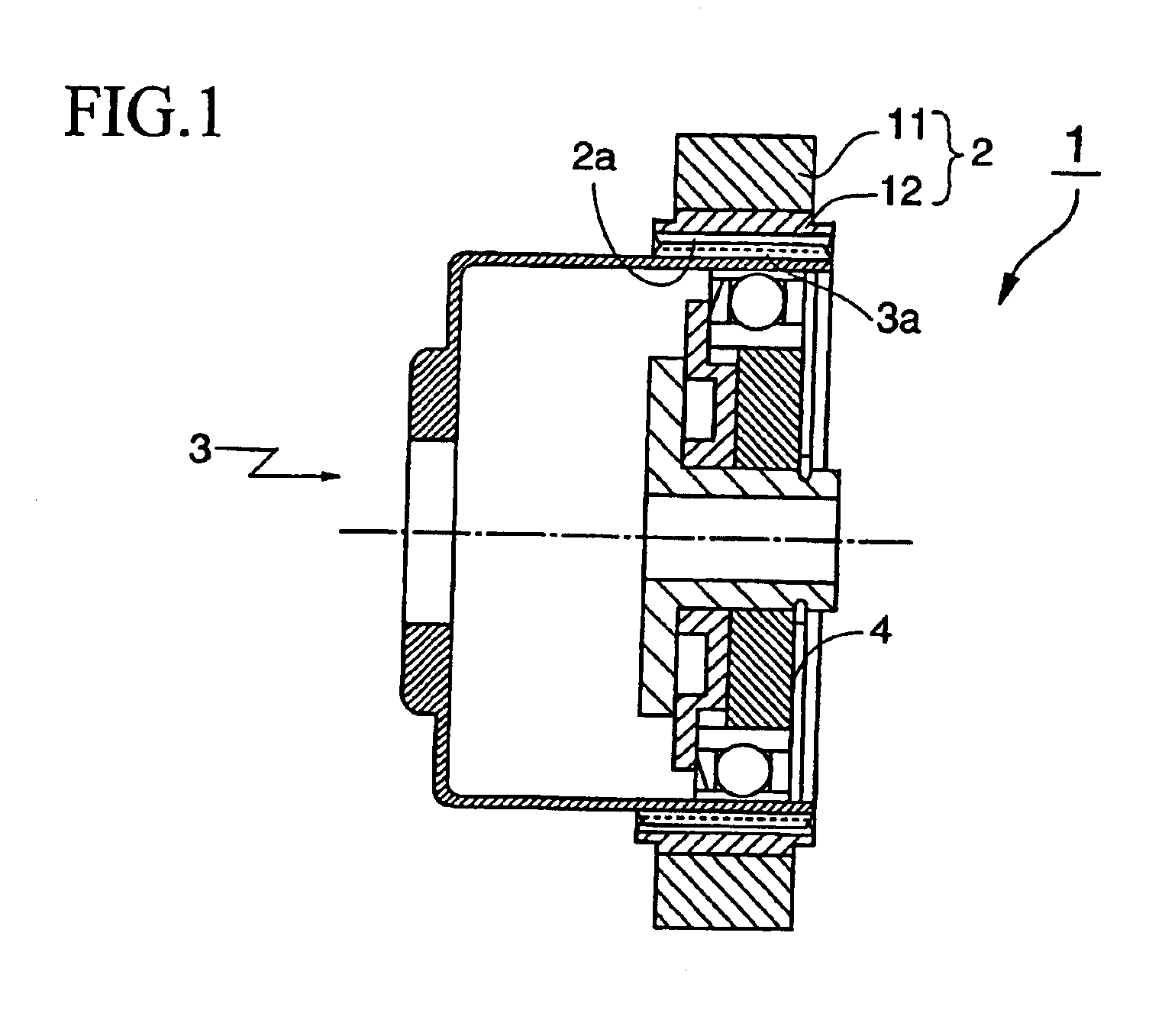
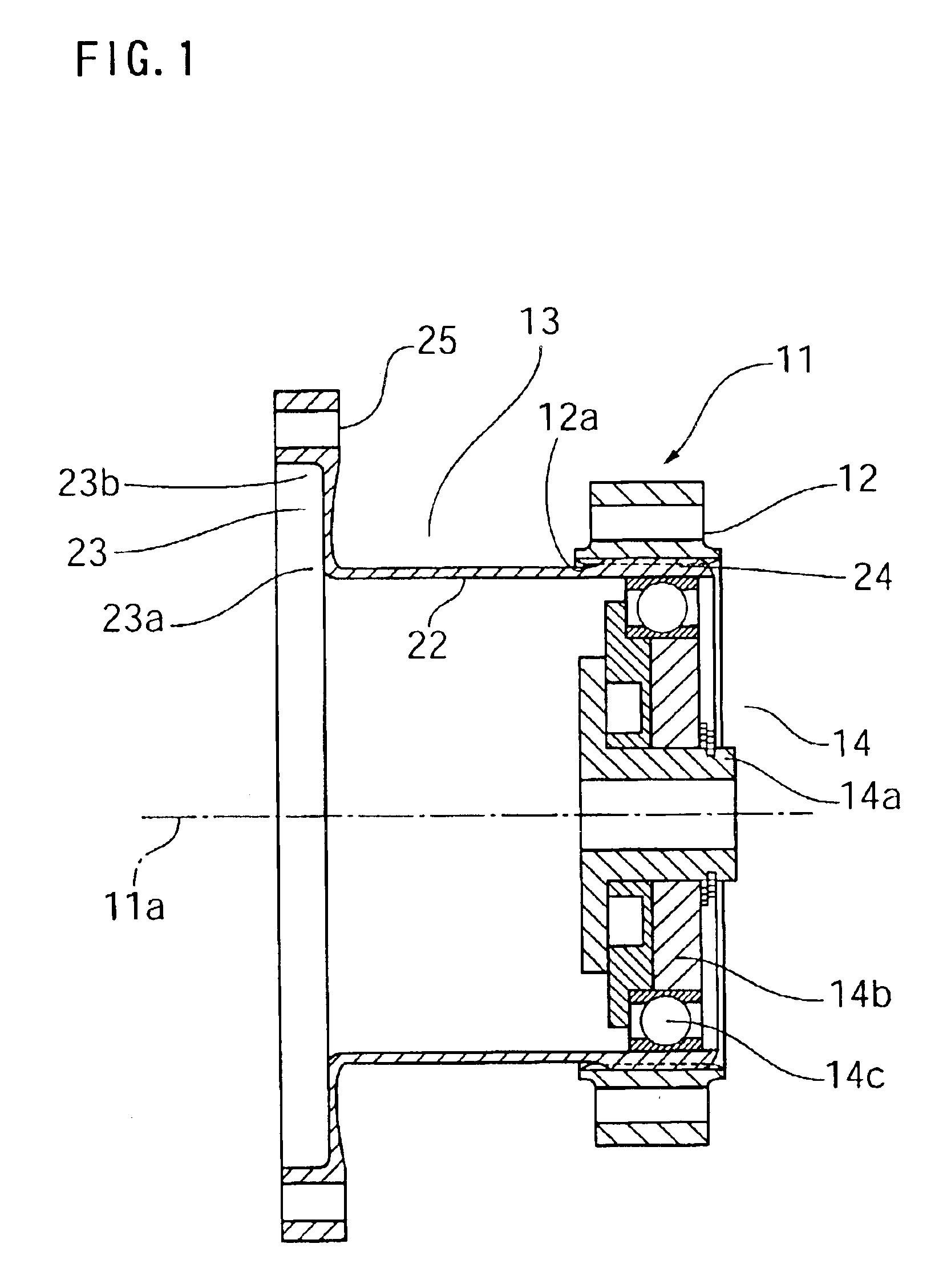
Method of manufacturing a rigid internal gear of a wave gear device
InactiveUS20020184766A1Increase pressureForming accuratelyToothed gearingsGear wheelsCopperAluminum coating
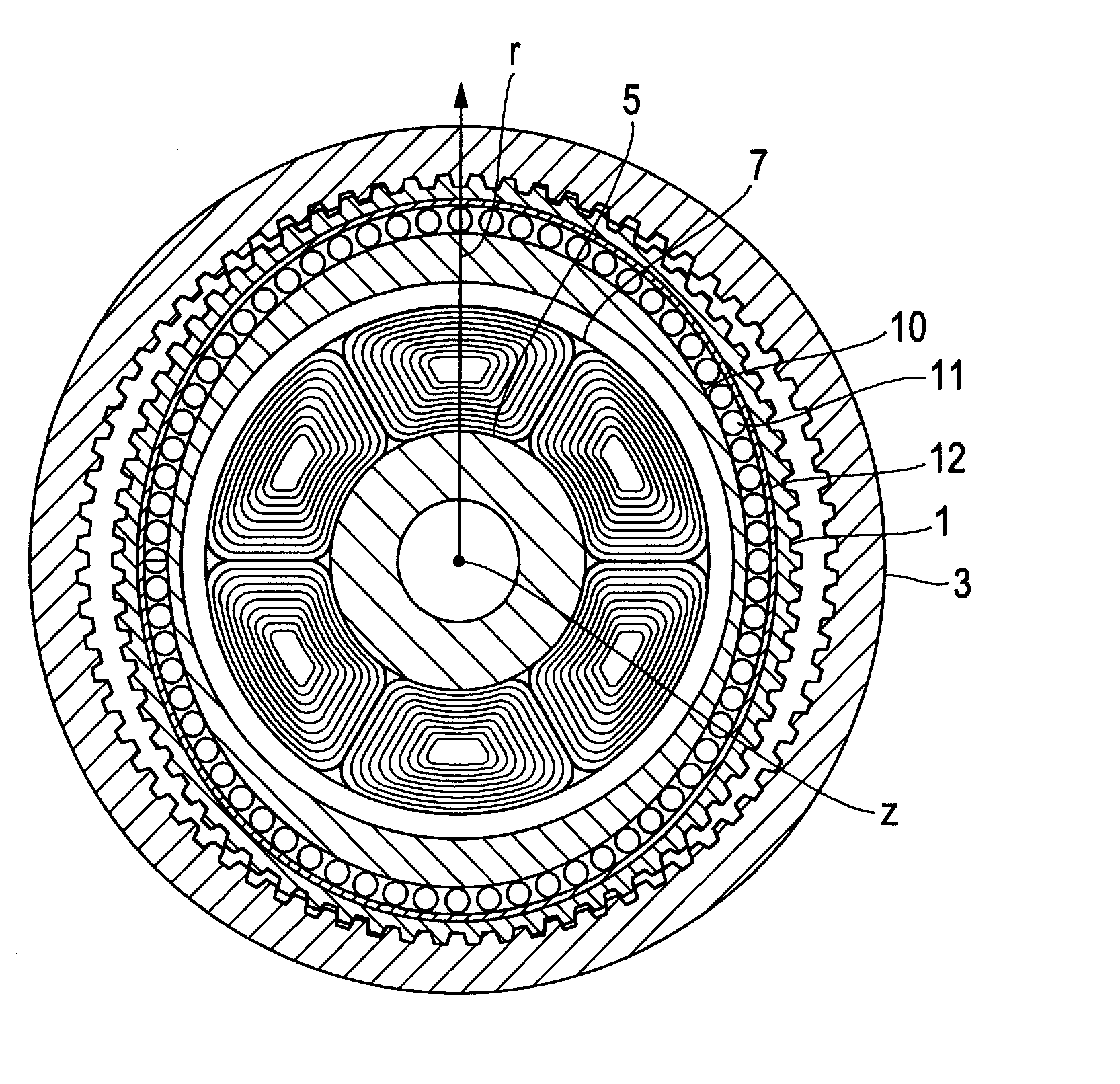
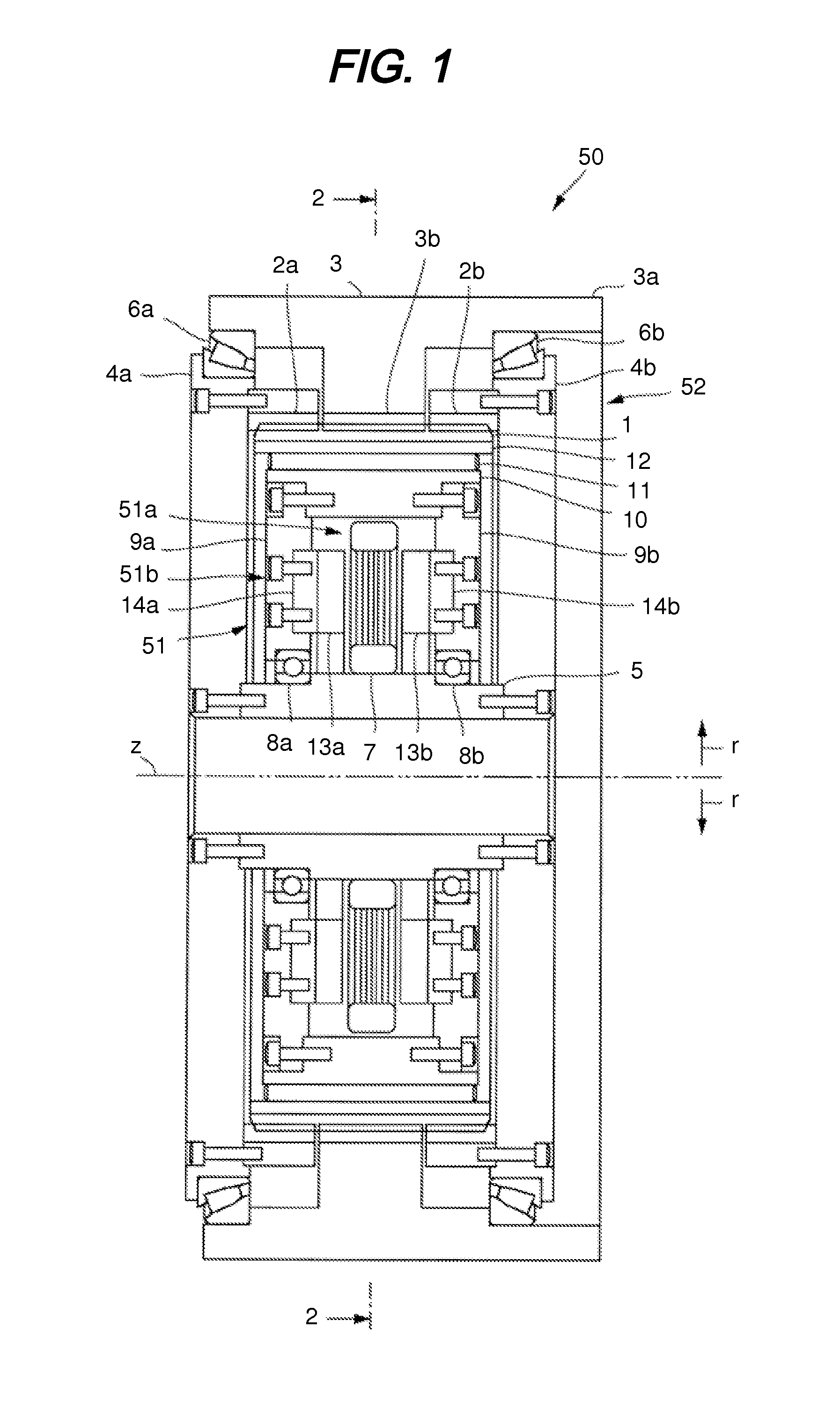
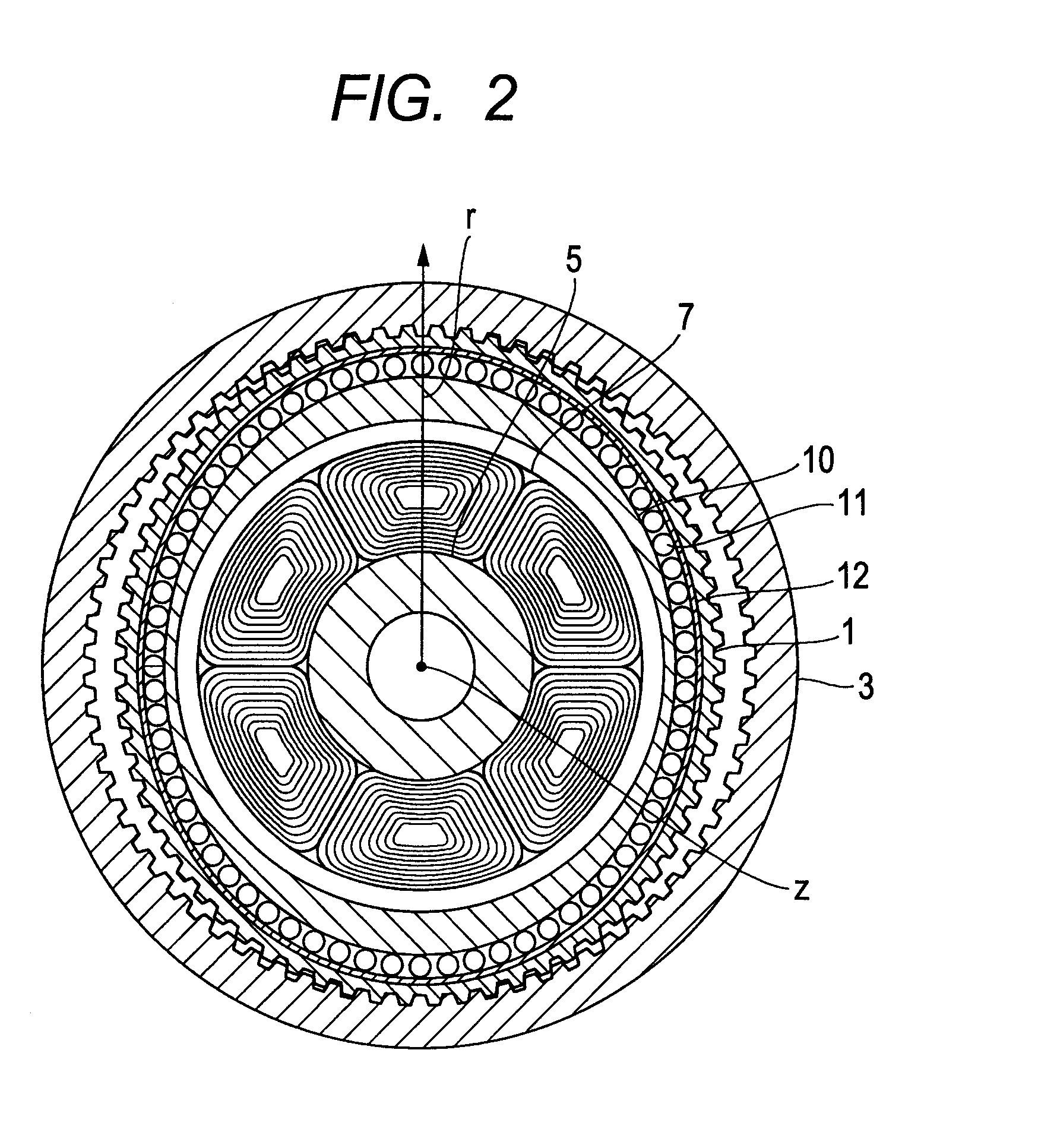
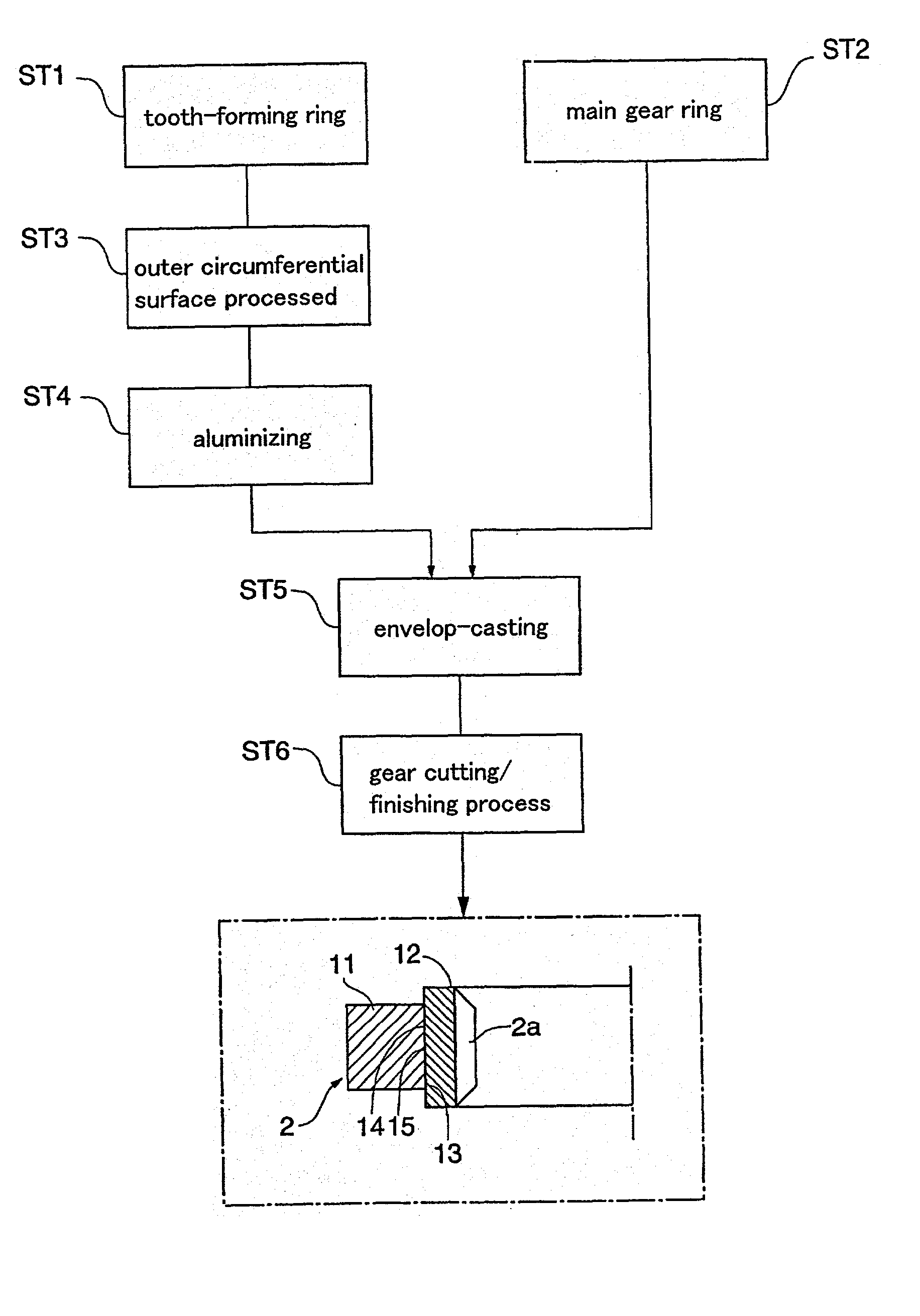
A rigid internal gear 2 of the wave gear device is composed by integrating a tooth-forming ring 12 formed with internal teeth, and a main gear ring 11 into a single body. The tooth-forming ring 12 is manufactured from a ferrous or copper material that has superior strength and abrasion resistance, while the main gear ring 11 is manufactured from a lightweight material, such as an aluminum alloy. The outer circumferential surface of the tooth-forming ring 12 is aluminized to form a dispersed aluminum coating 15, before the tooth-forming ring 12 is cast within the main gear ring 11 so as to integrate the main gear ring 11 and the tooth-forming ring 12. Both parts are reliably integrated so that a large amount of torque can be transmitted, whereby realizing a rigid internal gear that is lighter than conventional models.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device
InactiveUS20050066769A1Increasing the thicknessPrevent degradationPortable liftingToothed gearingsGear wheelEngineering
A wave gear device has a rigid internal gear, a flexible external gear, and a wave generator. The tooth profiles of both gears are initially defined by a basic rack tooth profile shape. The lower parts of the dedendum portions of these tooth profiles are modified by curves C2 and C3 having pressure angles α2 and α3 that are less than the standard pressure angle α1 of the basic rack tooth profile shape C1. An increase in thickness of the tooth bottom side can be minimized even if the tooth depth is increased and the tooth thickness / tooth space ratio changed to increase the tooth thickness. Hence, the ratcheting torque of a wave gear device having a high reduction gear ratio can be increased without reducing the service life and strength of a pinion cutter for the rigid internal gear, or the fatigue strength of the flexible external gear.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
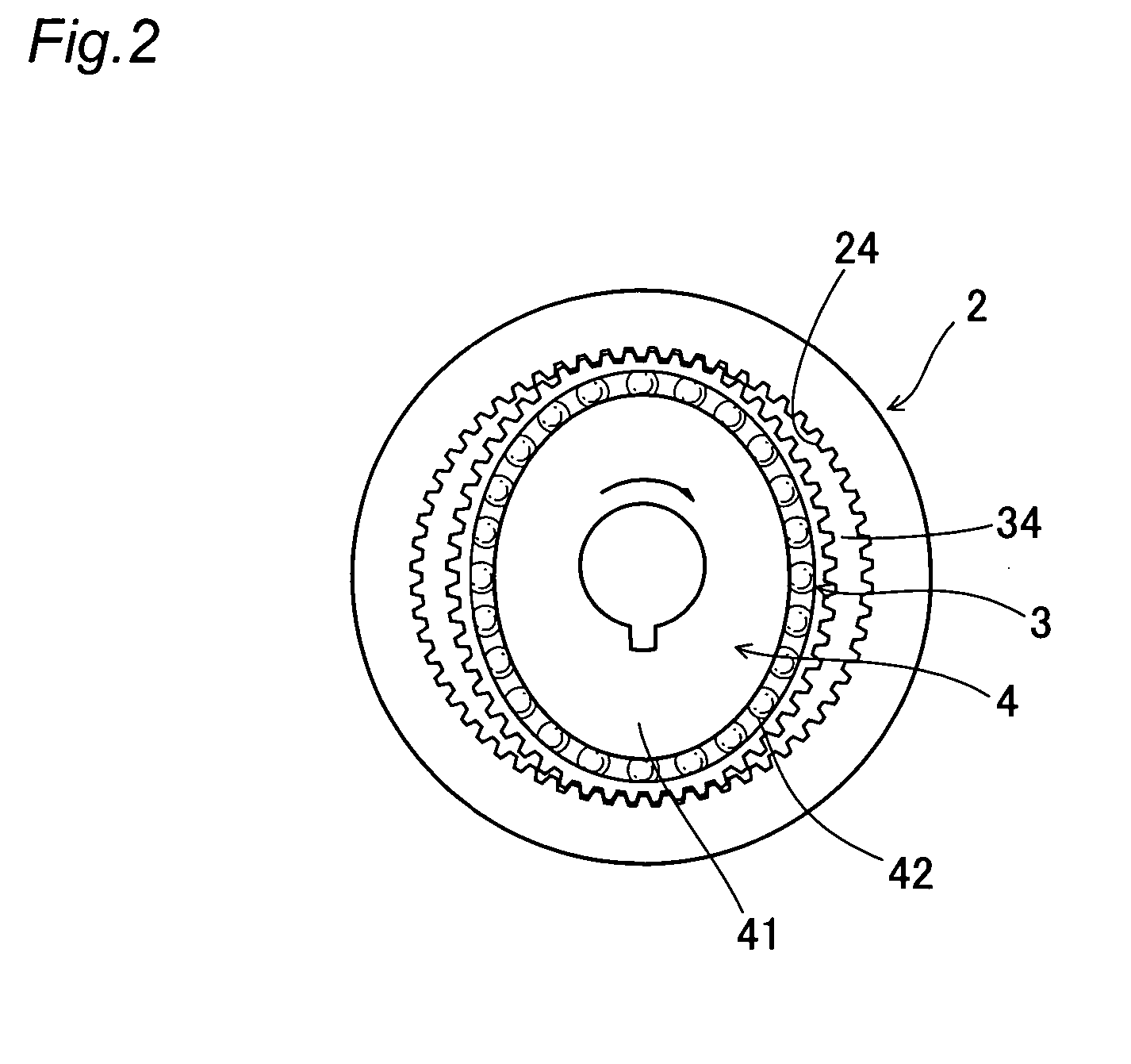
Method for compensating for angular transmission error of wave gear device
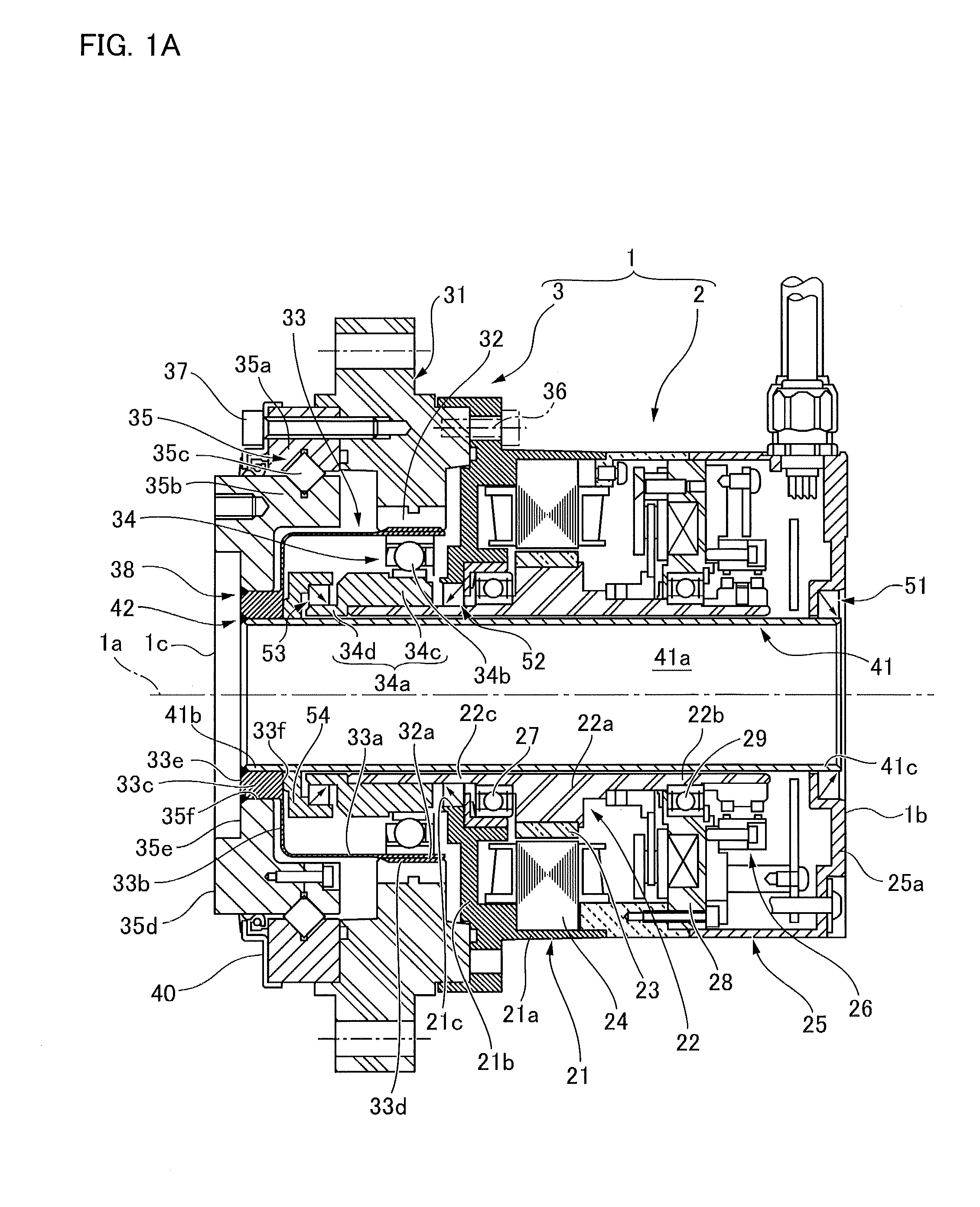
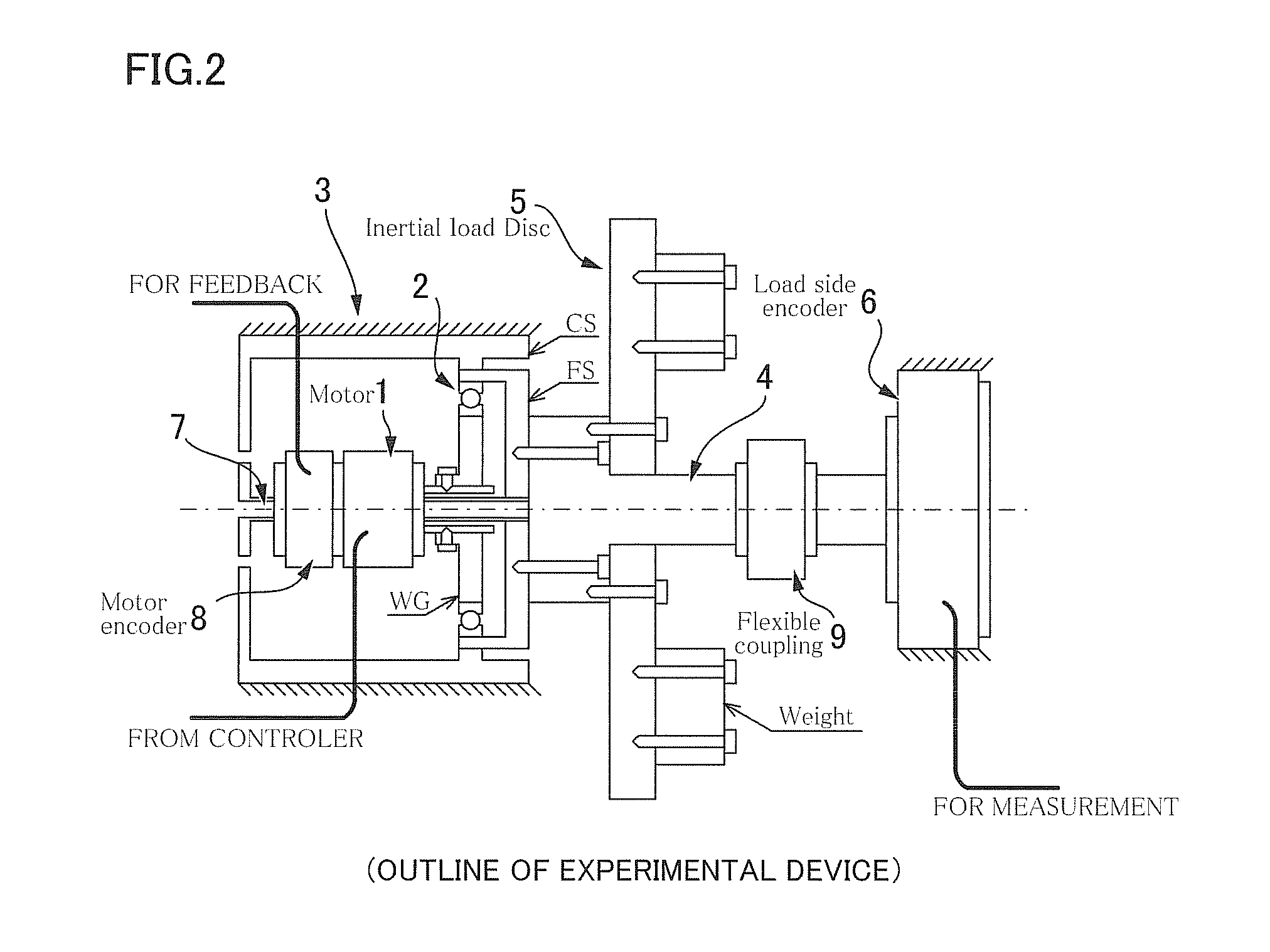
ActiveUS20110054820A1Precise positioningReduction of the positioning precision by the motor shaft synchronous component can be inhibited or preventedDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlPower flowElectric machine
A positioning system (1) provided with an actuator (2) having a wave gear device (4) is driven and controlled by a semi-closed loop control for controlling the load position of a load device (5) based on the motor position of a motor shaft (31) of a motor (3). In a method for compensating for an angular transmission error by compensating for a motor shaft synchronous component θSync that occurs in synchrony with the motor position and is a relative rotation-synchronous component that includes an angular transmission error component of the wave gear device (4), the positioning system (1) is represented as a two-inertia model, and the motor shaft synchronous component θSync is represented as an oscillation source for producing a twisting action between the two inertia bodies in the two-inertia model. A motor current command iref is corrected by a compensation current command icomp calculated so as to allow the effect of the motor shaft synchronous component θSync on the load position to be compensated in this case, and a motor position command r is corrected by a motor position correction signal θcomp calculated in order to compensate for the effect of the motor shaft synchronous component θSync.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
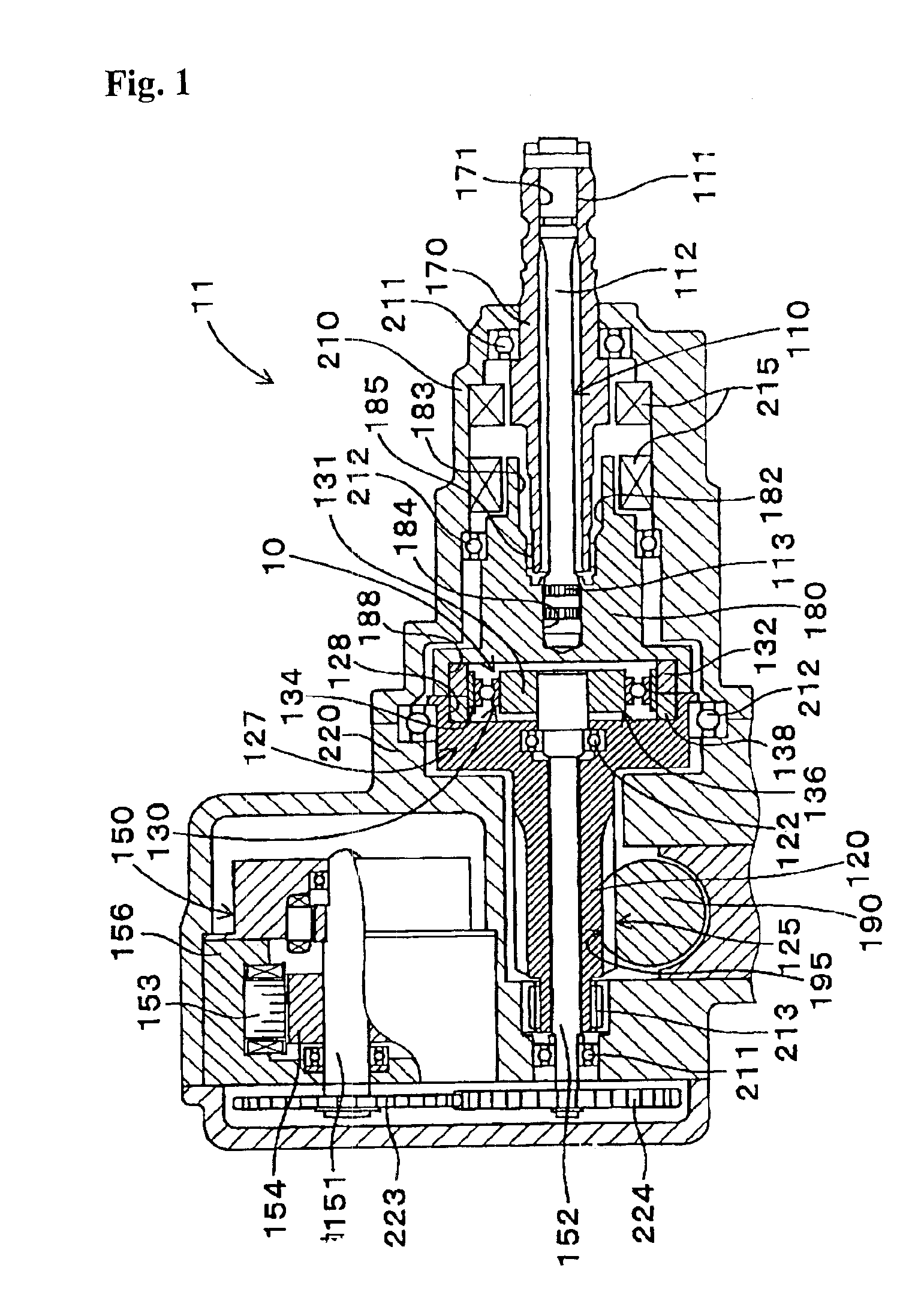
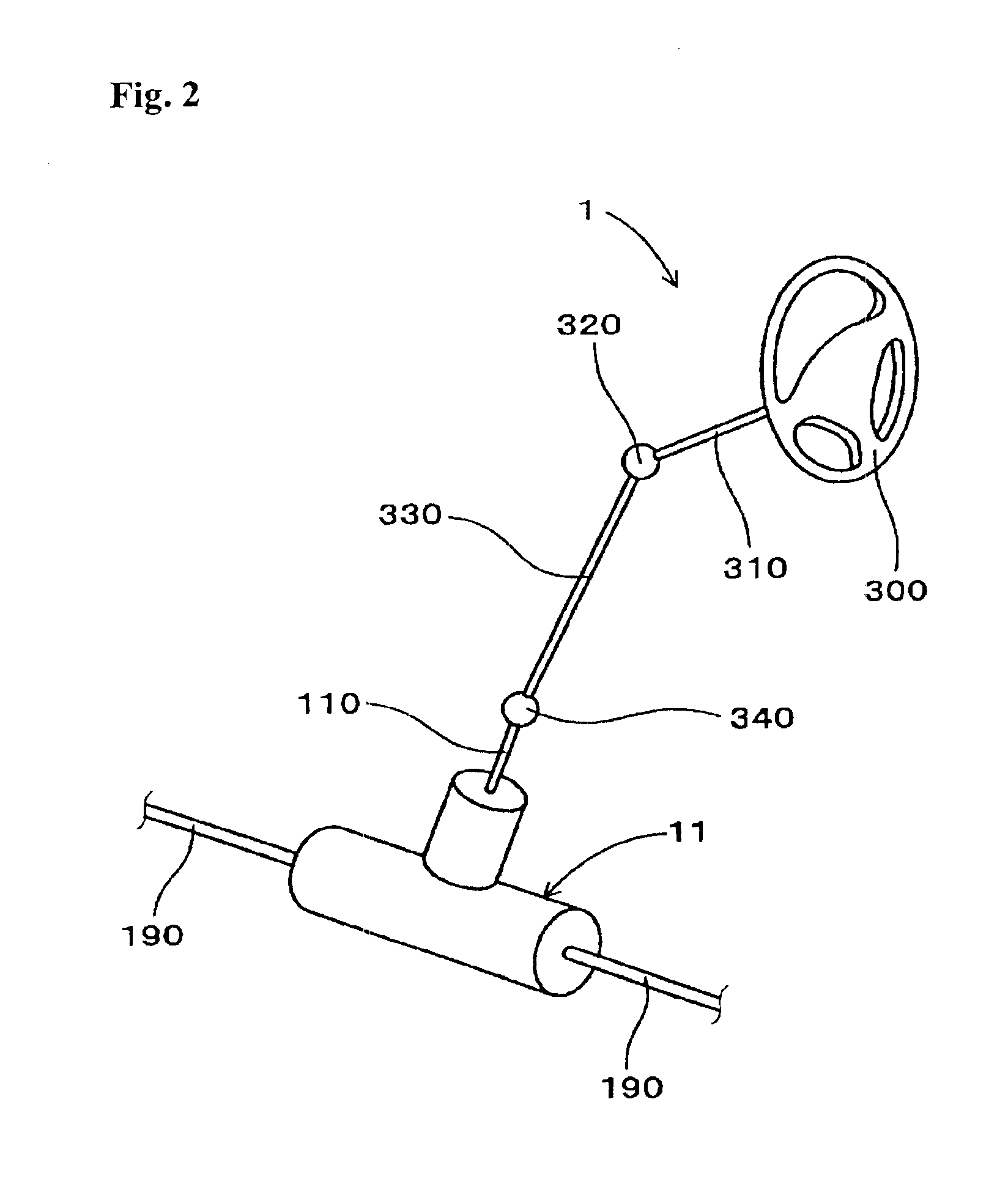
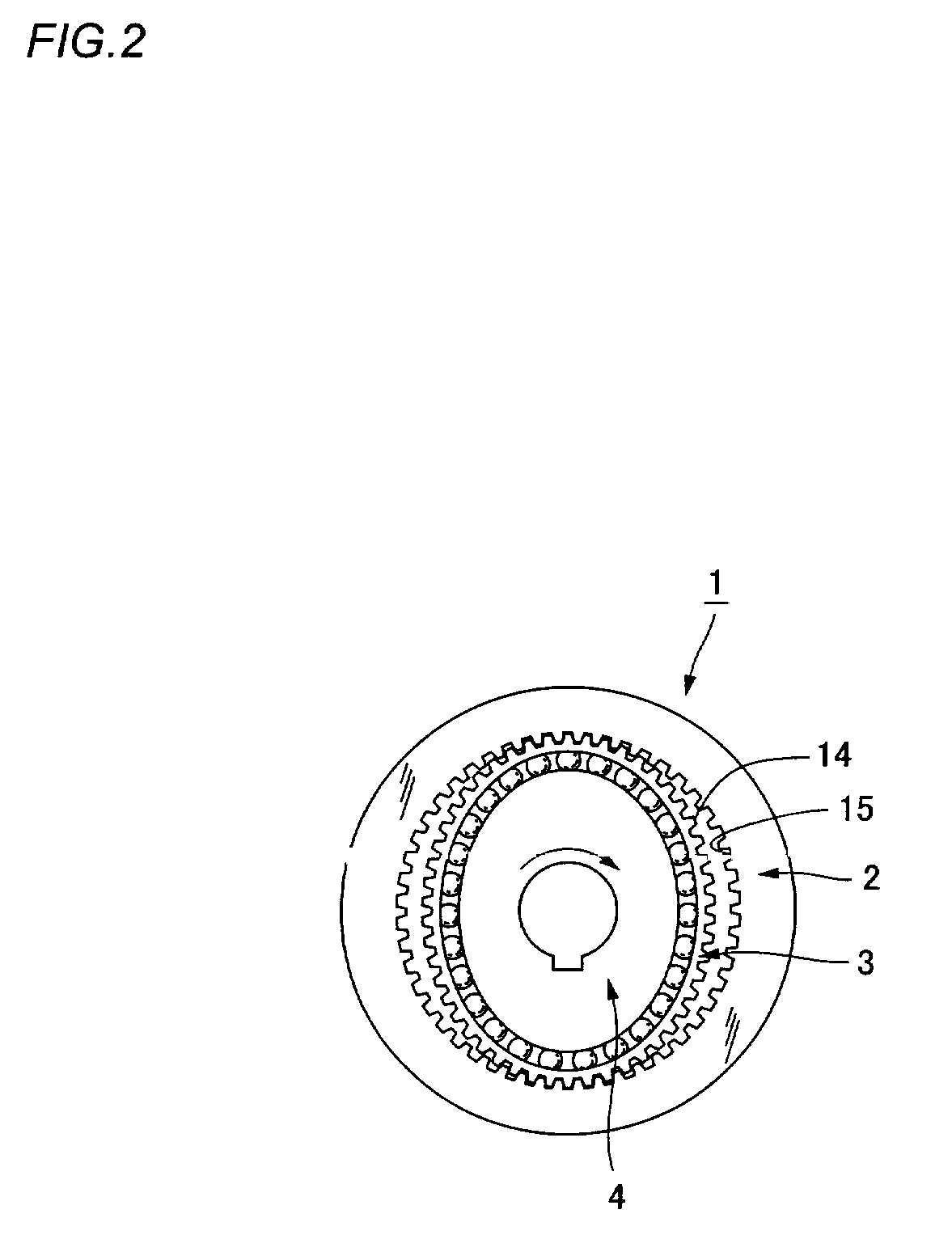
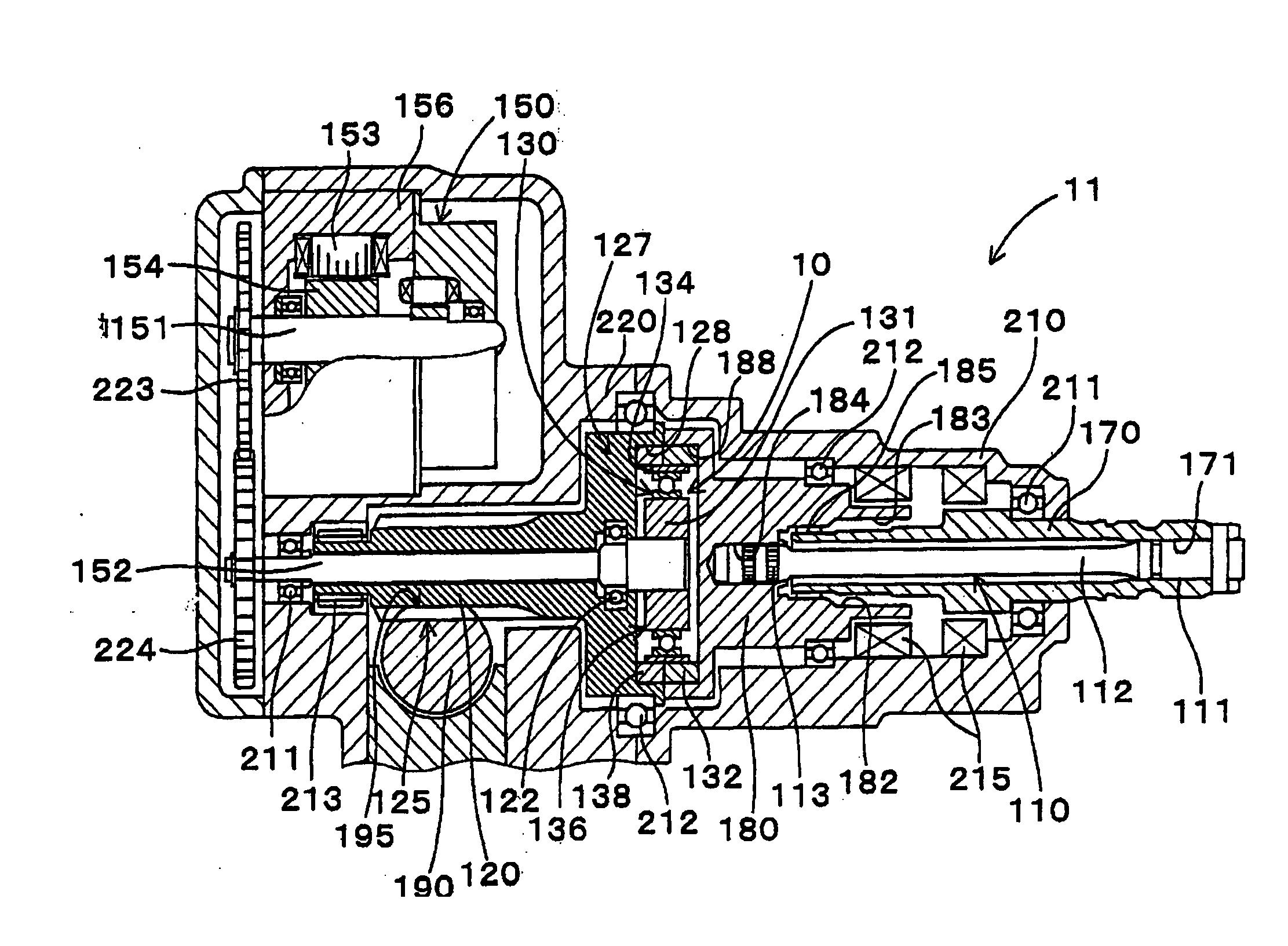
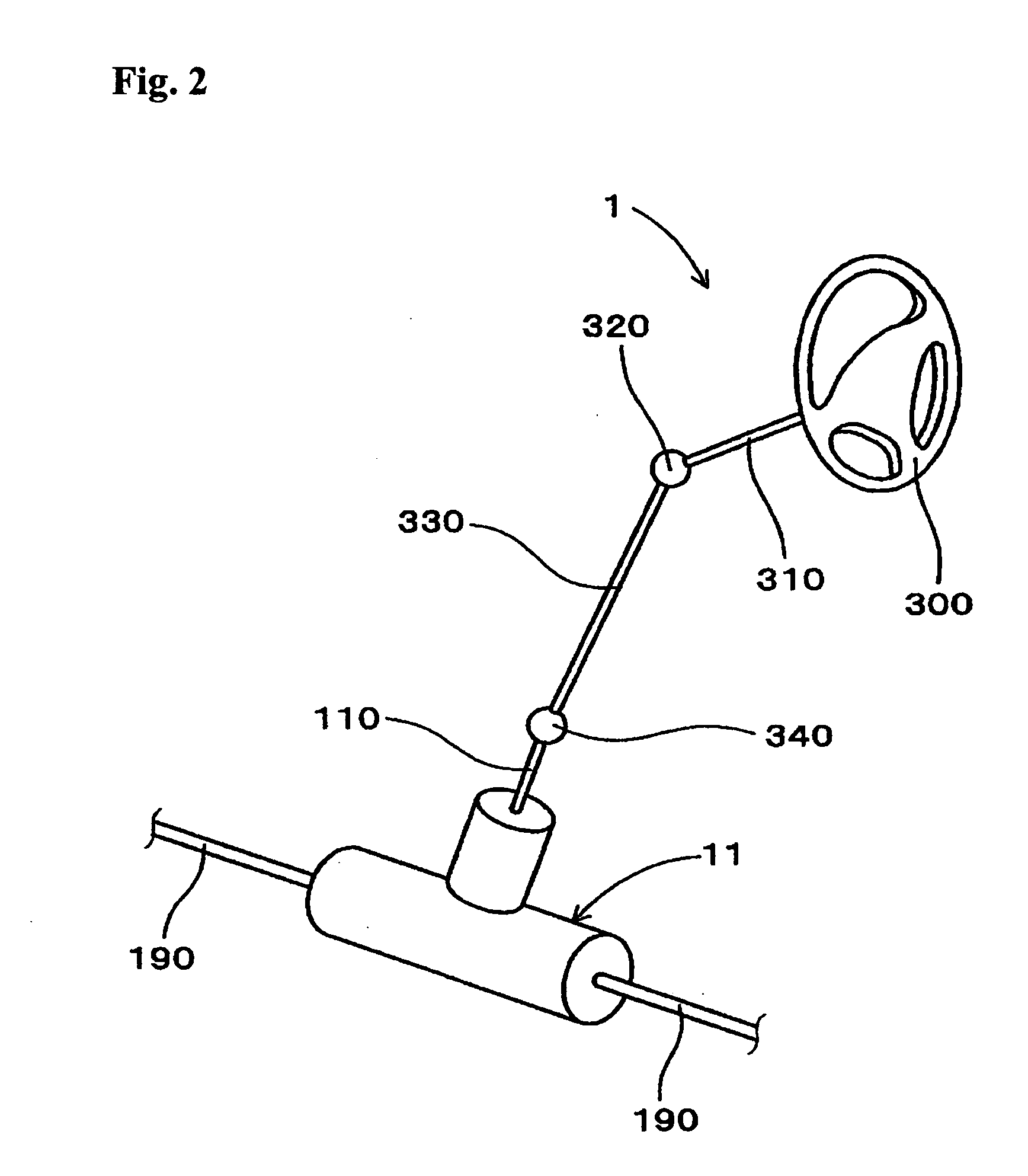
Motor vehicle steering device
The invention provides a compact and highly reliable motor vehicle steering device that does not require a spiral flat cable. The motor vehicle steering device includes variable gear ratio system that modifies the transmission ratio of the rotary motions between first steering shaft and second steering shaft. Variable gear ratio system comprises Strain Wave Gearing Speed Reducer that modifies the transmission ratio between first steering shaft and second steering shaft in response to the rotating speed of motor shaft. Motor shaft and second steering shaft forms a substantially concentric dual structure, drive motor is affixed, and output shaft is connected to motor shaft.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
Wave Gear Device
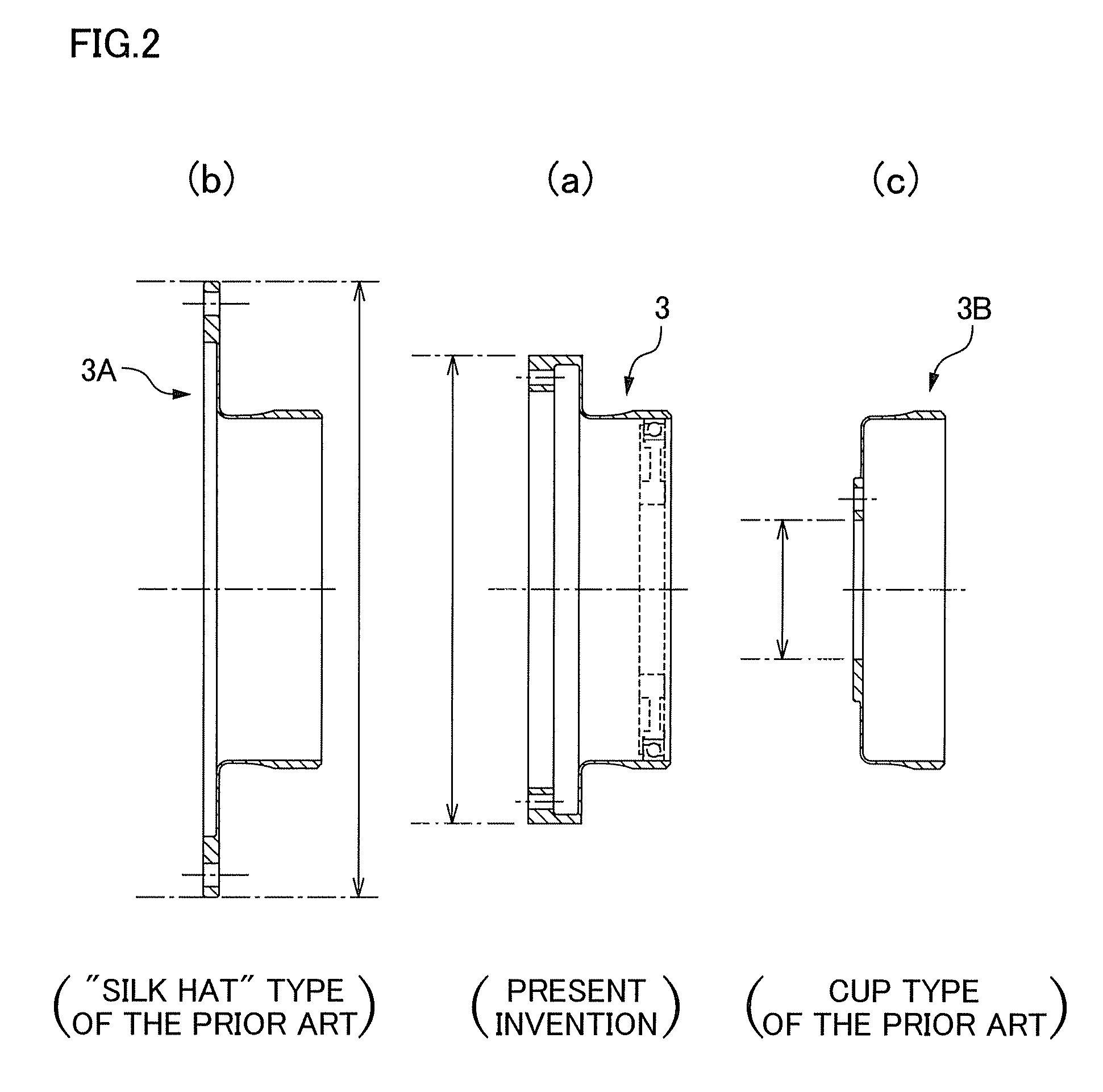
A bending state known as “coning,” in which the amount of bending of the flexspline gradually decreases in accordance with the distance from the open end of the spline, occurs in cup-type or “silk hat”-type wave gear devices. A tooth profile in which the tooth depth is kept constant and in which the bottom lands and top lands are parallel to each other along the tooth trace direction is used as the basic tooth profile for the circular spline and the flexspline of the wave gear device. A taper surface is formed on a part of the top land near the open end of the flexspline in the basic tooth profile, whereby a modified tooth profile is obtained. The modified tooth profile is employed as the tooth profile for both of the splines. Both of the splines can be caused to mesh together without generating coning-induced interference. Both of the splines can also be subjected to gear cutting by a simple process using a typical machining mechanism.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
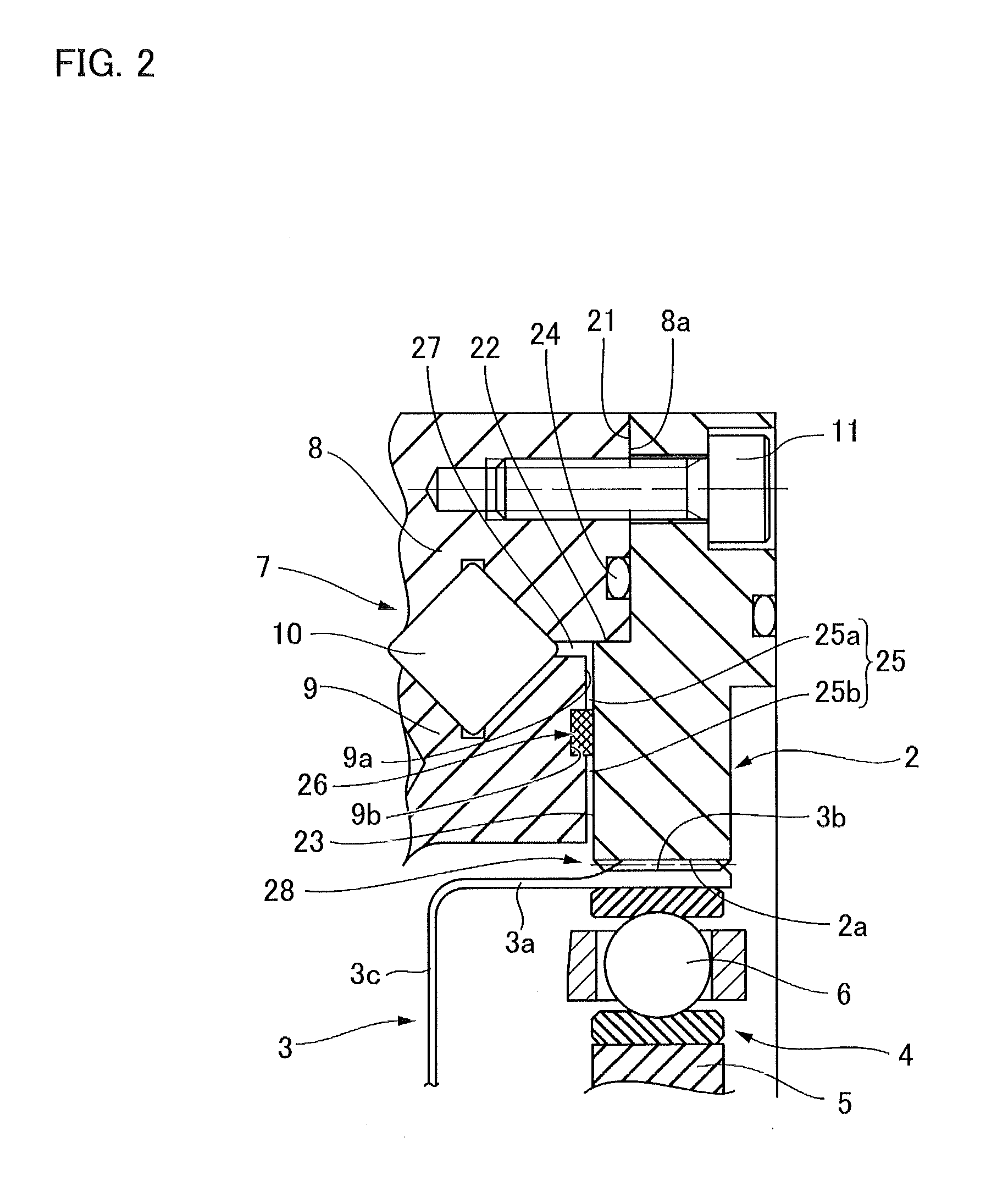
Harmonic motor, drive assembly, industrial robot, robot boom and robot joint
InactiveUS20120204674A1Guaranteed uptimeShorten the lengthPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGearingHarmonicEngineering
A harmonic motor with a circular and internally geared stator, a flex spline coaxially arranged within the stator which comprises both external and internal gears, and a geared output shaft coaxially arranged within the flex spline. A drive assembly that includes a motor with a motor housing, a rotor, a rotor shaft, and a rear bearing for supporting the rotor shaft in the motor housing at a rear side of the rotor; and a strain wave gearing including a circular spline secured to the motor housing, a flex spline engaging the circular spline, a wave generator engaging the flex spline and secured to a drive end of the rotor shaft, and a wave generator bearing between the circular spline and the wave generator. The wave generator bearing serves as an exclusive drive end bearing for supporting the rotor shaft in the motor housing at a front side of the rotor.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Joint assembly
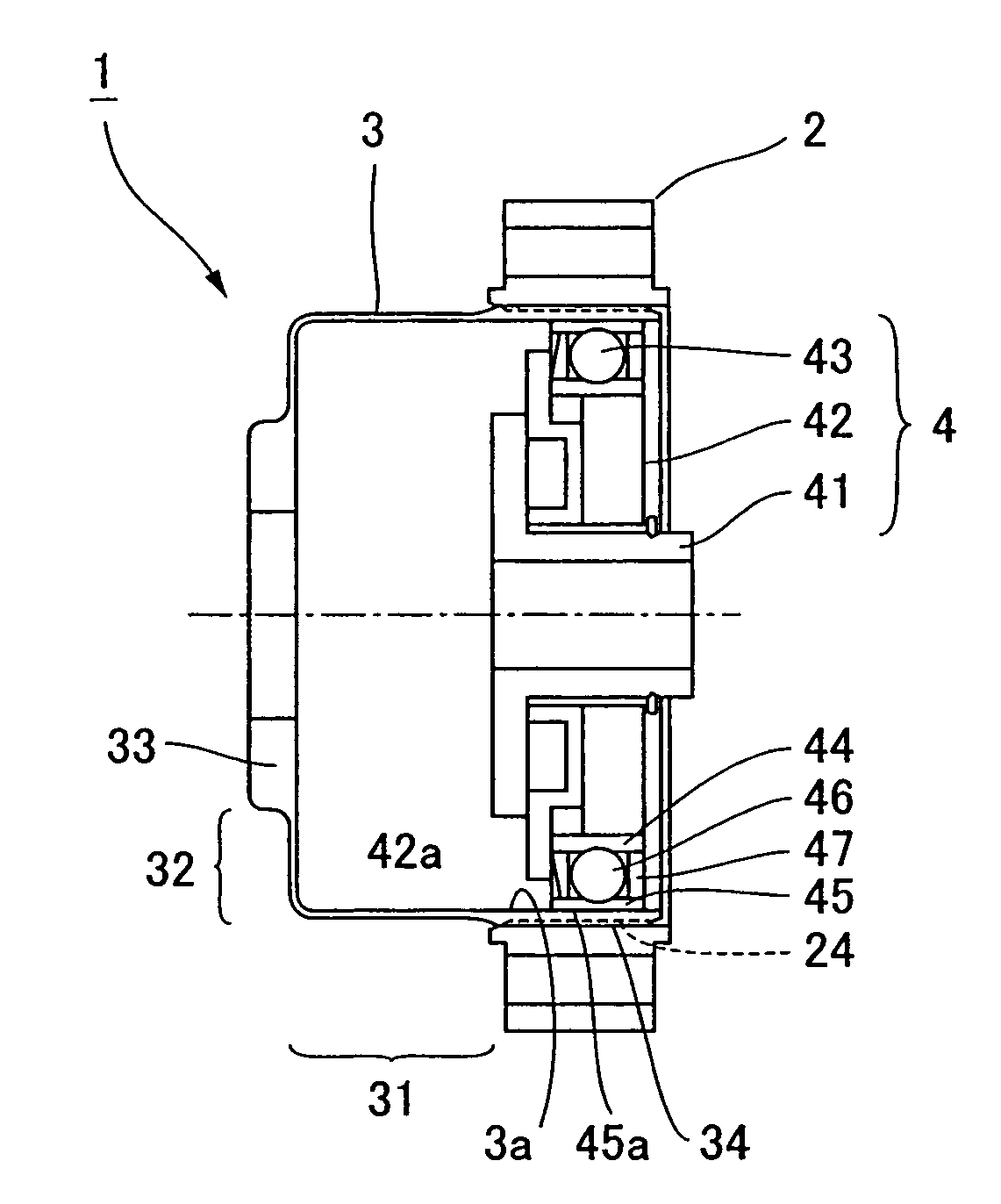
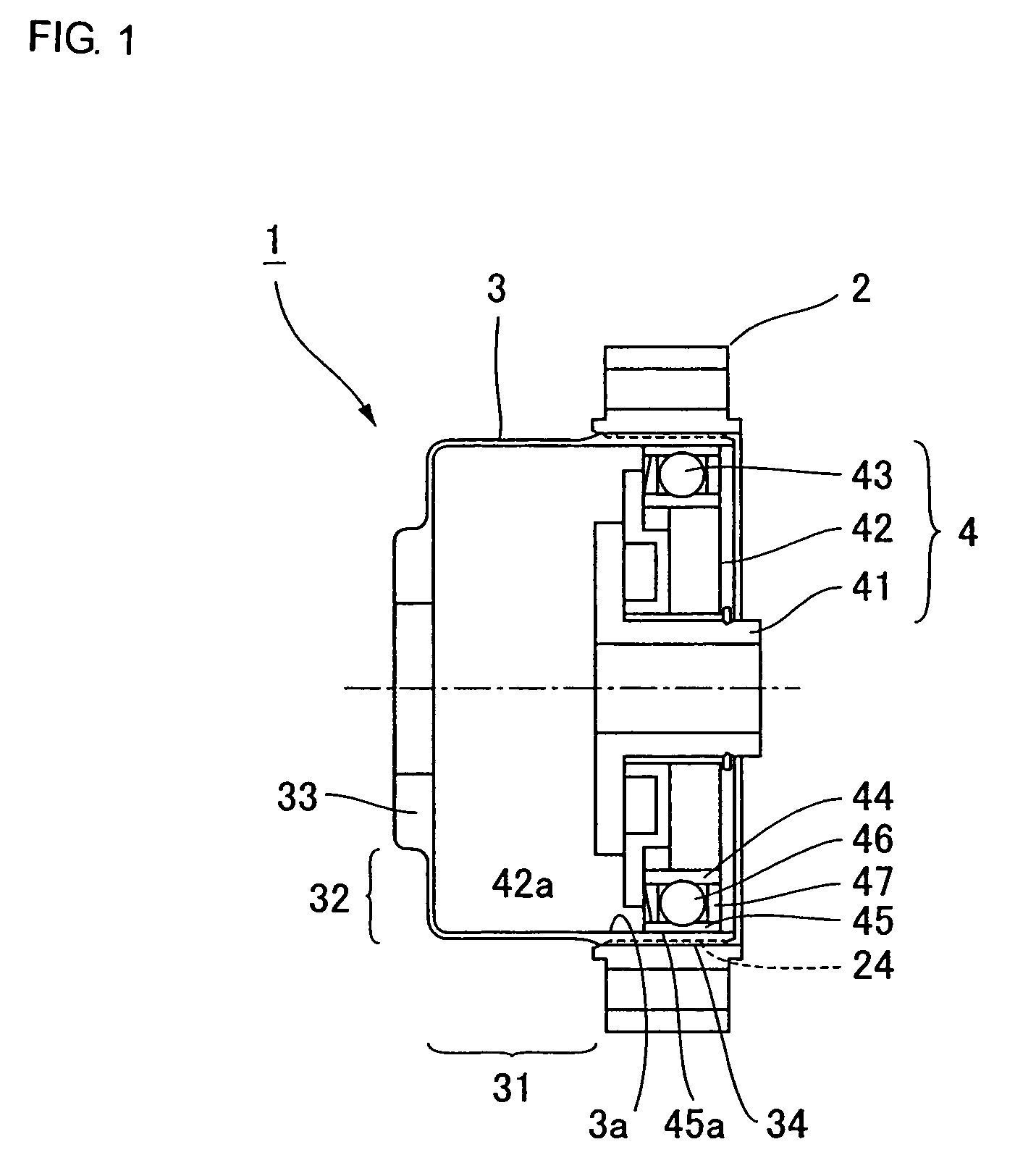
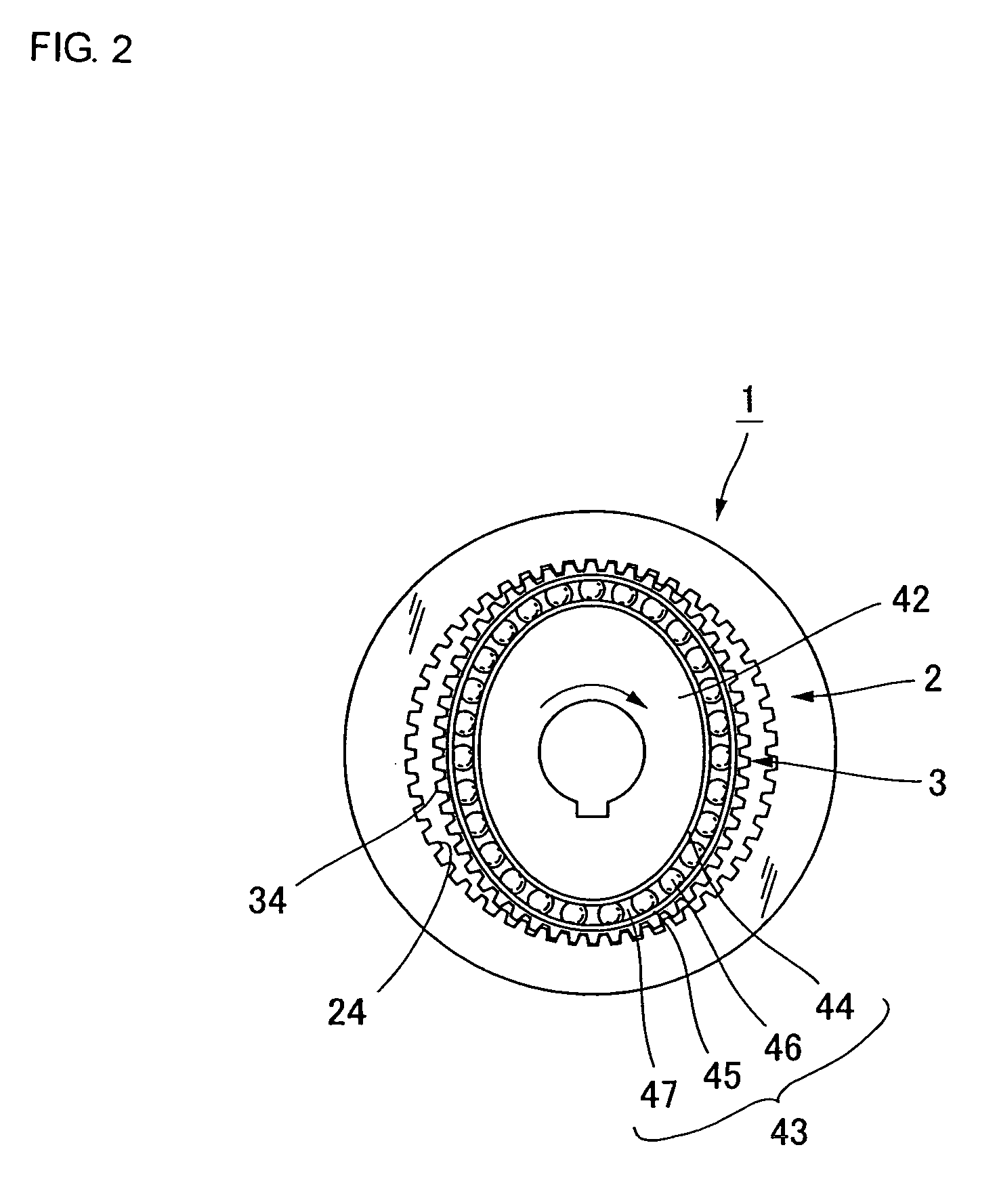
ActiveUS20180215050A1Easy to assembleRisk minimizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsRotor magnetsRobotic arm
The present invention relates to a joint assembly (1) for a robot (100), comprising a housing (26) connected with an output part (8), the housing comprising a housing wall (26A), a strain wave gearing system (90) comprising a wave generator (7), a flexspline (13), and a circular spline (36) connected to the output part (8), wherein the wave generator (7) is rotated by a rotor shaft (3), the rotor shaft being driven by an electric motor (140) comprising a stator (15) and a rotor magnet (16), the rotor magnet (16) being affixed to the rotor shaft (3), and wherein the joint assembly (1) further comprises a rotor brake (30) configured to stop / prevent relative movement between the rotor shaft (3) and the flexspline (13), and sensors arranged to measure the position of the housing (26) in relation to the output part (8). Furthermore, the present invention also relates to a robotic arm (100) comprising a joint assembly according to the present invention and to the use of the joint assembly according to the present invention.
Owner:KASSOW ROBOTS APS
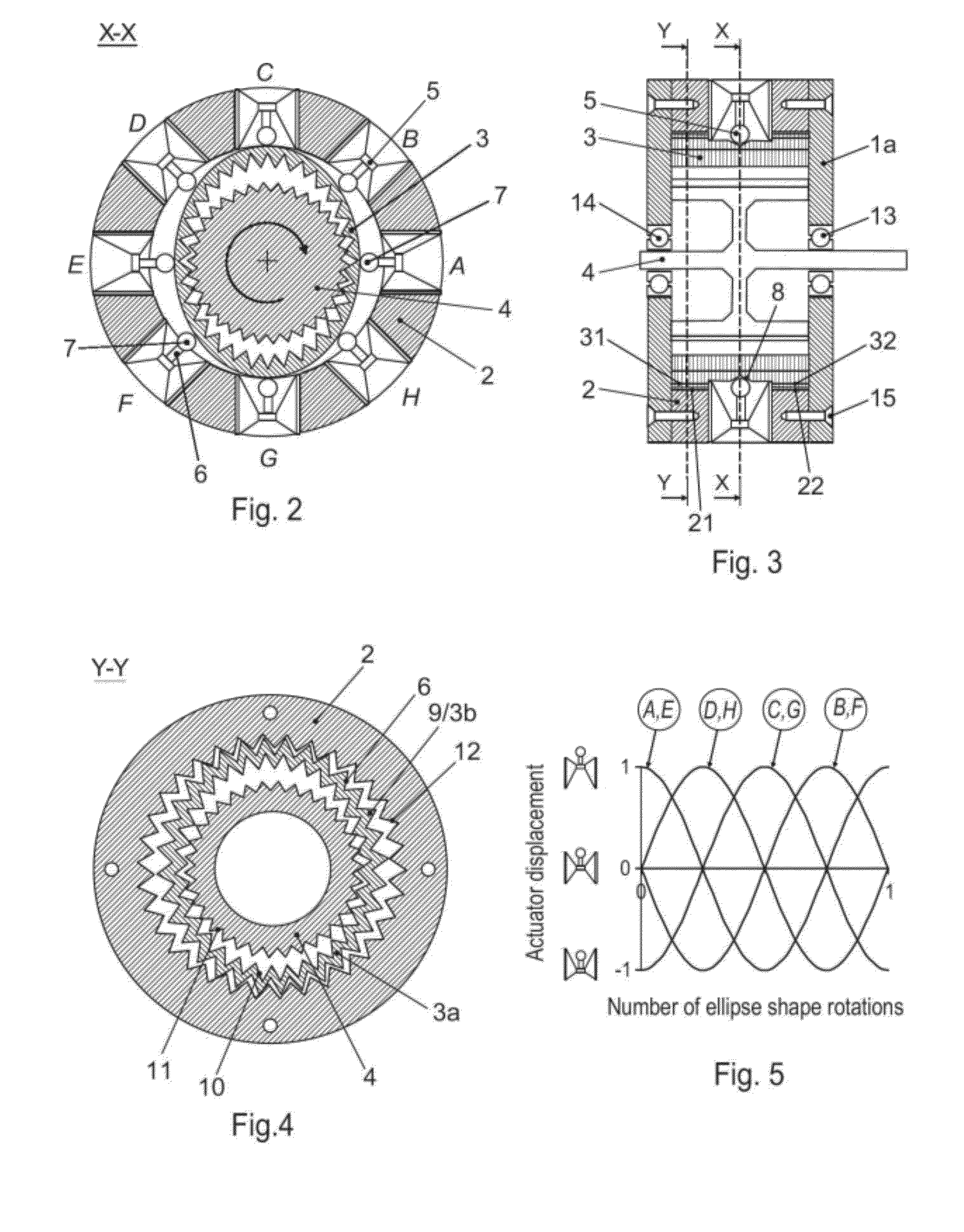
Wave gear device having three-dimensionally contactable shifted tooth profile
ActiveUS20110237382A1Reasonable meshing engagementEffective engagementToothed gearingsGearing elementsStrain wave gearingRack and pinion
Disclosed is a wave gear device (1) for setting the flexible state of the principal section (30) of a flexible external gear in a normal-deflection state (at a deflection coefficient κ=1). The moving locus of a tooth profile in the principal section (30) is determined by a rack approximation, and a similar curve (BC), which is obtained by similarly transforming a curve (AB) cut from that moving locus, is used to define the fundamental addendum shape of the tooth profile in the principal section. The portion of the tooth profile of the flexible external gear other than the principal section is shifted so that both each negative-deflection side moving locus (M3), which is obtained in each plane of rotation to deflect in a negative deflection state (at the deflection coefficient κ<1) closer to the diaphragm side than the principal section and each positive-deflection side moving locus (M2), which is obtained in each plane of rotation to deflect in a positive deflection state (at the deflection coefficient κ>1) closer to the front end opening side than the principal section, may become curves (M3a and M2a) to contact at the bottom (a point (P)) of a normal-deflection moving locus (M1). The partial meshing engagement can also be held at the section other than the principal section in the tooth trace direction, so that the load torque performance of the wave gear device can be advantageously improved.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave Gear Device
ActiveUS20060037430A1Increase the reduction ratioSpeed up the restore processGearingStress concentrationGear wheel
A diaphragm of a cup-shaped flexible external gear of a cup-shaped wave gear device having a high reduction ratio of 100 or higher is given a thickness t in a position of a radius r of the diaphragm whereby the thickness t is a value that satisfies the expression A / r2 when A is a constant. The constant A is preferably a value that satisfies the expression 0.0014D3<A<0.0026D3, where D is a pitch diameter of the flexible external gear, and the range of the radius r whereby the thickness t is defined as described above in the diaphragm is preferably set to satisfy the expression 0.6d<r<0.4D, where d is a diameter of a discoid rigid boss made continuous with an internal peripheral end of the diaphragm. Stress concentration can be alleviated, and it is possible for the allowable transmission torque to be increased compared to the prior art.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
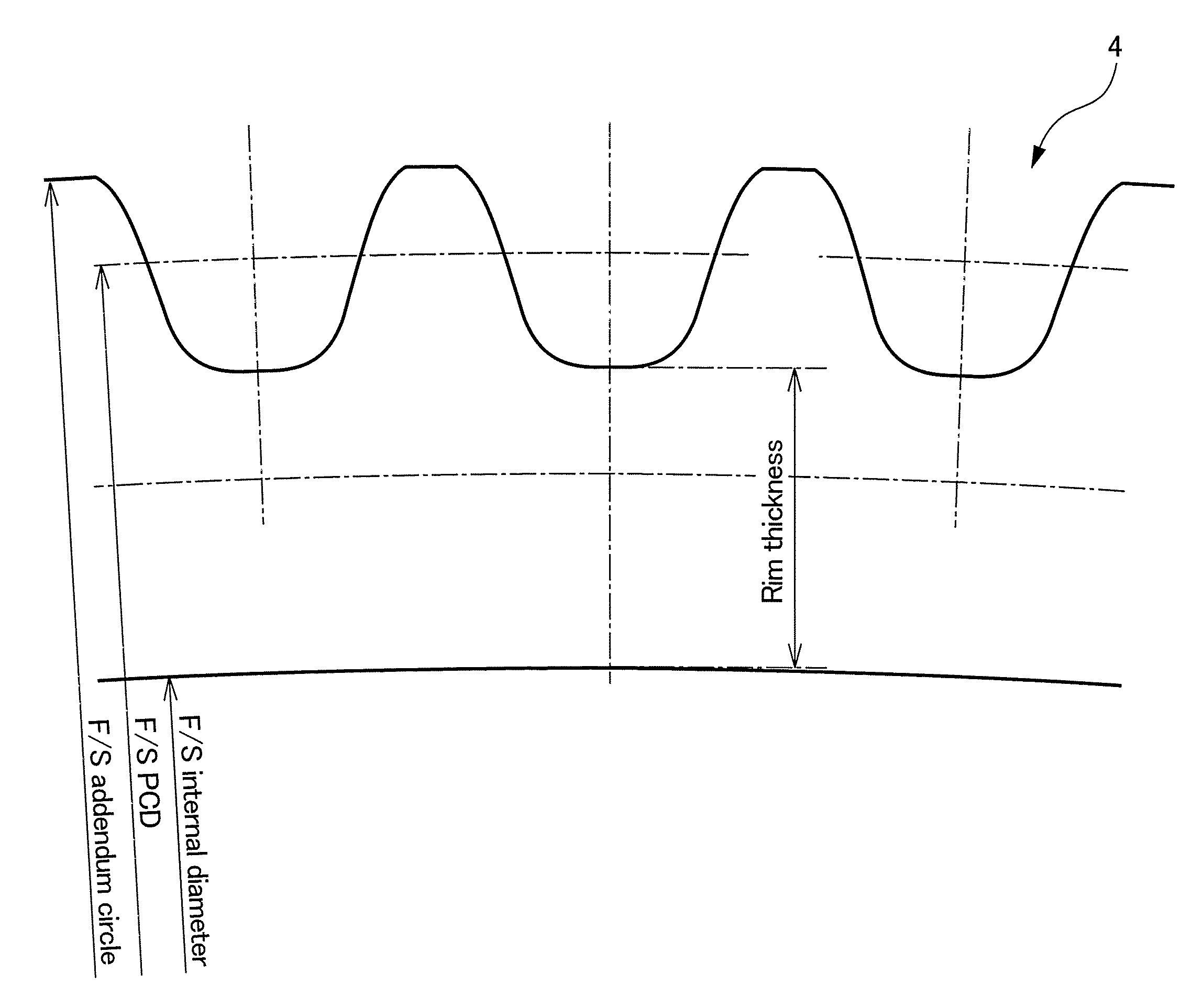
Flat type wave gear device
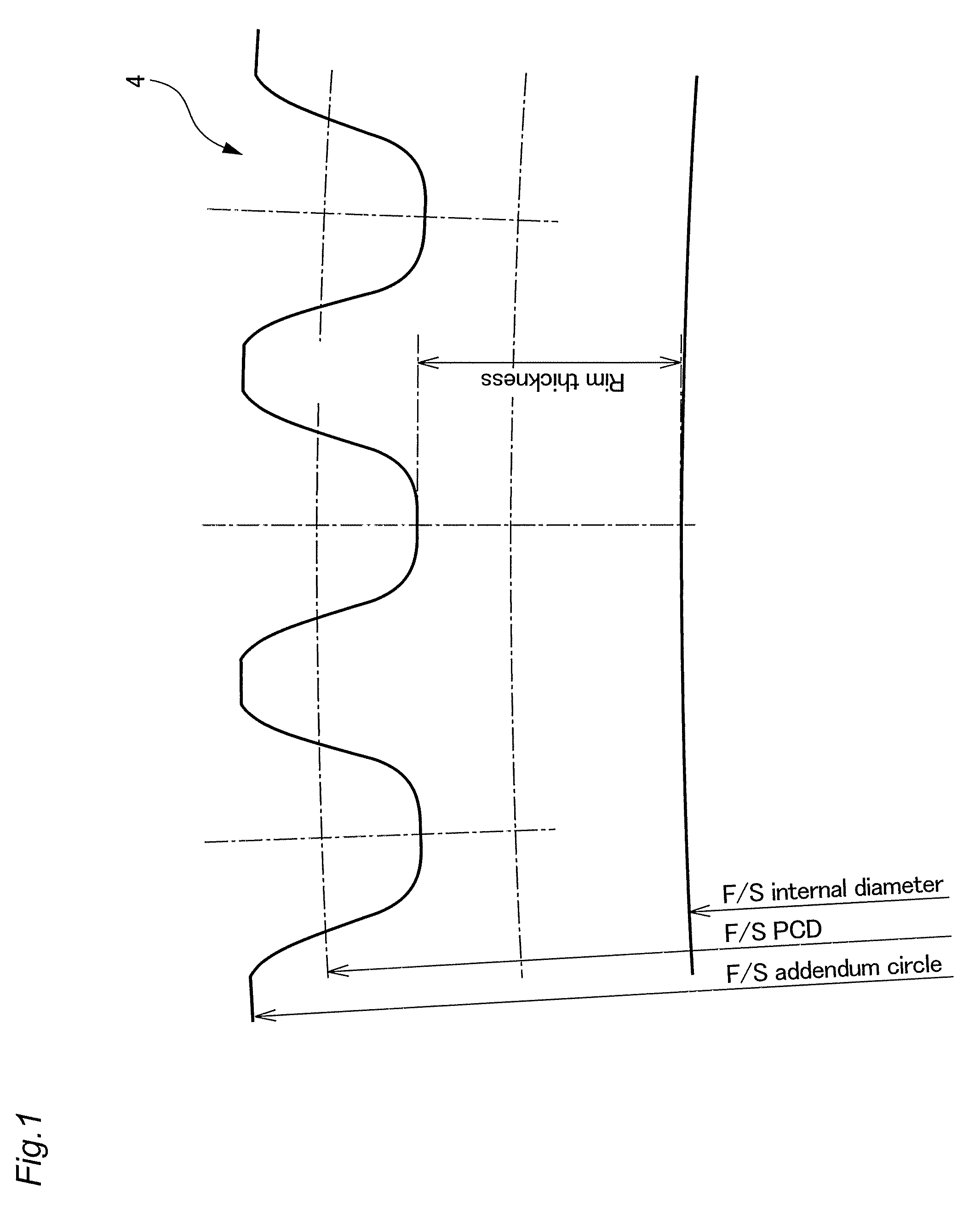
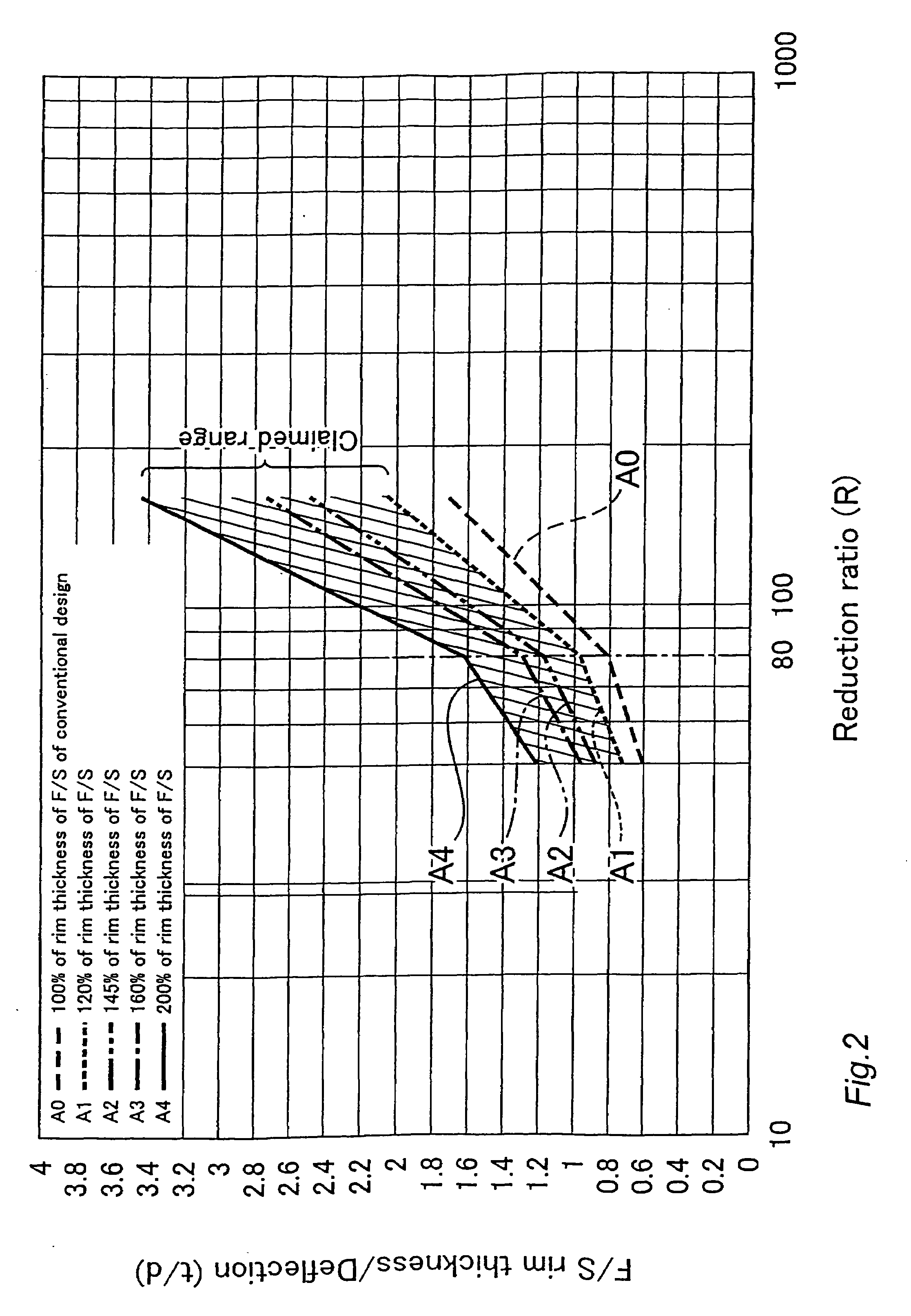
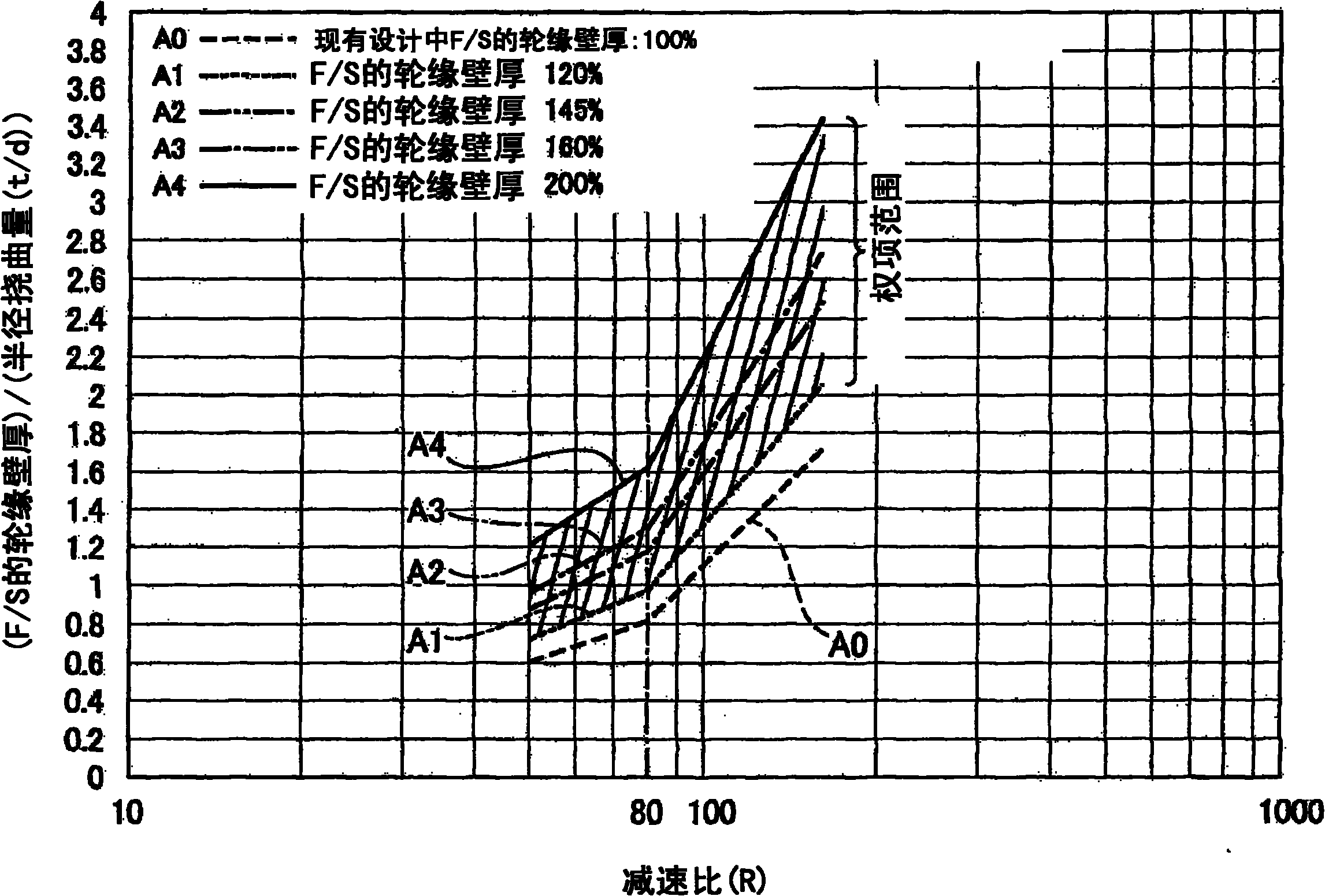
ActiveUS20080173130A1Improve root strengthIncrease load capacityGearingPortable liftingGear wheelReduction ratio
A flat type wave gear device is realized having a much improved load capacity. When d is an amount of radial flexing at a major axis location of a rim neutral circle of the flexible external gear of a flat type wave gear device flexed into an elliptical shape and t is the rim thickness of the flexible external gear, then(0.5237 Ln(R)−1.32)d≦t≦(0.8728 Ln(R)−2.2)d when the reduction ratio R of the wave gear device is less than 80, and(1.5499 Ln(R)−5.8099)d≦t≦(2.5832 Ln(R)−9.6832)d when the reduction ratio R of the wave gear device is 80 or more. Using this setting makes it possible to increase the tooth root fatigue limit strength of the flexible external gear, thereby making it possible to improve the load capacity of the flexible external gear.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device having three-dimensional continuous contact tooth profile
ActiveUS20120285283A1Effective engagementHigh torquePortable liftingGearing elementsEngineeringEntire tooth
In a wave gear device, similarity curve tooth profiles for defining the tooth-face tooth profile of each of a flexible externally toothed gear and a rigid internally toothed gear is determined from the movement trajectory, relative to a tooth of the rigid internally toothed gear, of a tooth of the flexible externally toothed gear at a main cross-section at which the deflection factor is κ=1. Tooth profile curves, which have been subjected to profile shifting corresponding to the difference between the deflection factor κo (>1) of the opening-end cross-section of the flexible externally toothed gear and the deflection factor κ of the main cross-section, are determined from the similarity curves; and the tooth profile curves are used to form the tooth-face tooth profile portions of the two gears. High-gear-tooth compound tooth profiles, defined from the tooth-face tooth profile portions, straight-line tooth profile portions continuing from the tooth-face tooth profile portions, and appropriate tooth-flank tooth profile portions for avoiding interference are used as tooth profiles of the internal teeth and the external teeth. Also, taking coning of the flexible externally toothed gear into account, negative profile shifting is applied from an opening-end cross-section to an inner-end cross-section of the flexible externally toothed gear, and rational meshing between the two gears is obtained along the entire tooth trace.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
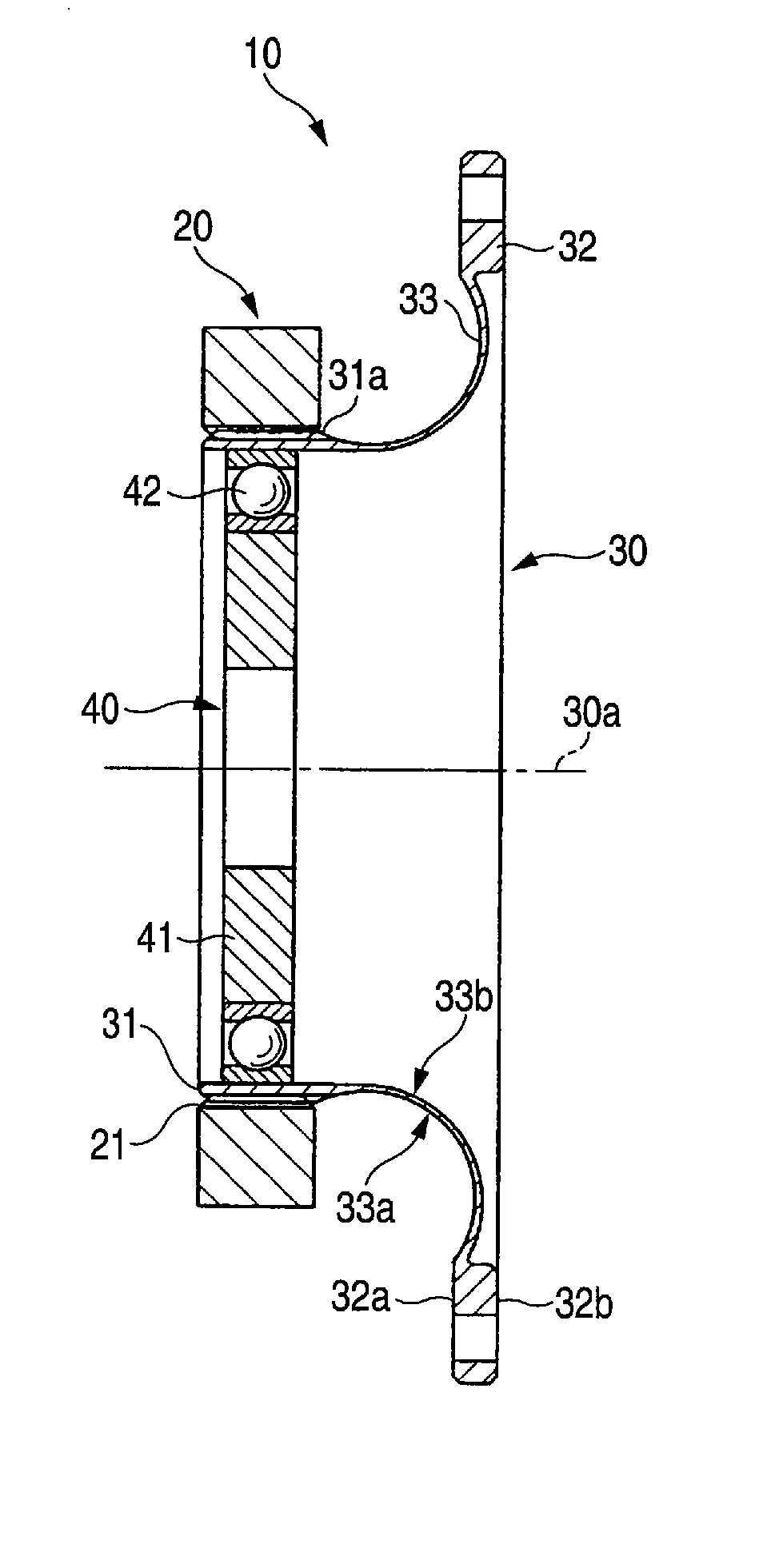
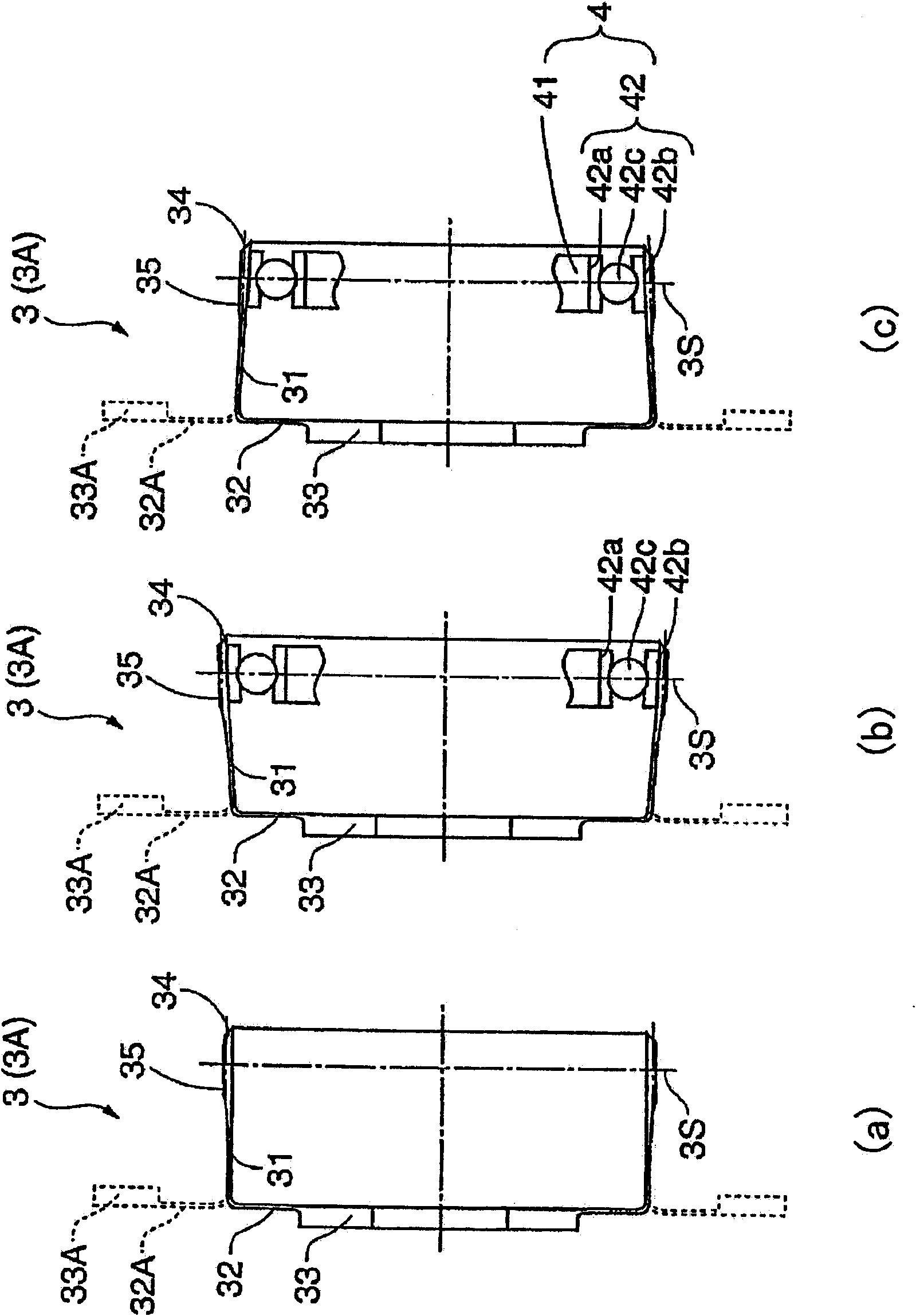
Flexspline and wave gear device
ActiveUS8646360B2Reduce overall outer diameterHollow diameter can be more readily increasedPortable liftingToothed gearingsEngineeringFlange
In a flexspline of a wave gear device, an annular flange thereof is constructed from a first annular part bent at a right angle from an outer peripheral edge of a diaphragm, and a second annular part caused to inwardly protrude at a uniform width from a leading end of the first annular part. It is possible for the annular flange to be disposed within the region where the diaphragm is formed, as viewed in the direction of an axis of the device. An outer diameter can be reduced to a greater extent than with a “silk hat”-shaped flexspline; and when a hollow wave gear device is manufactured, a hollow diameter can be more readily increased than in a case where a cup-shaped flexspline is used.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
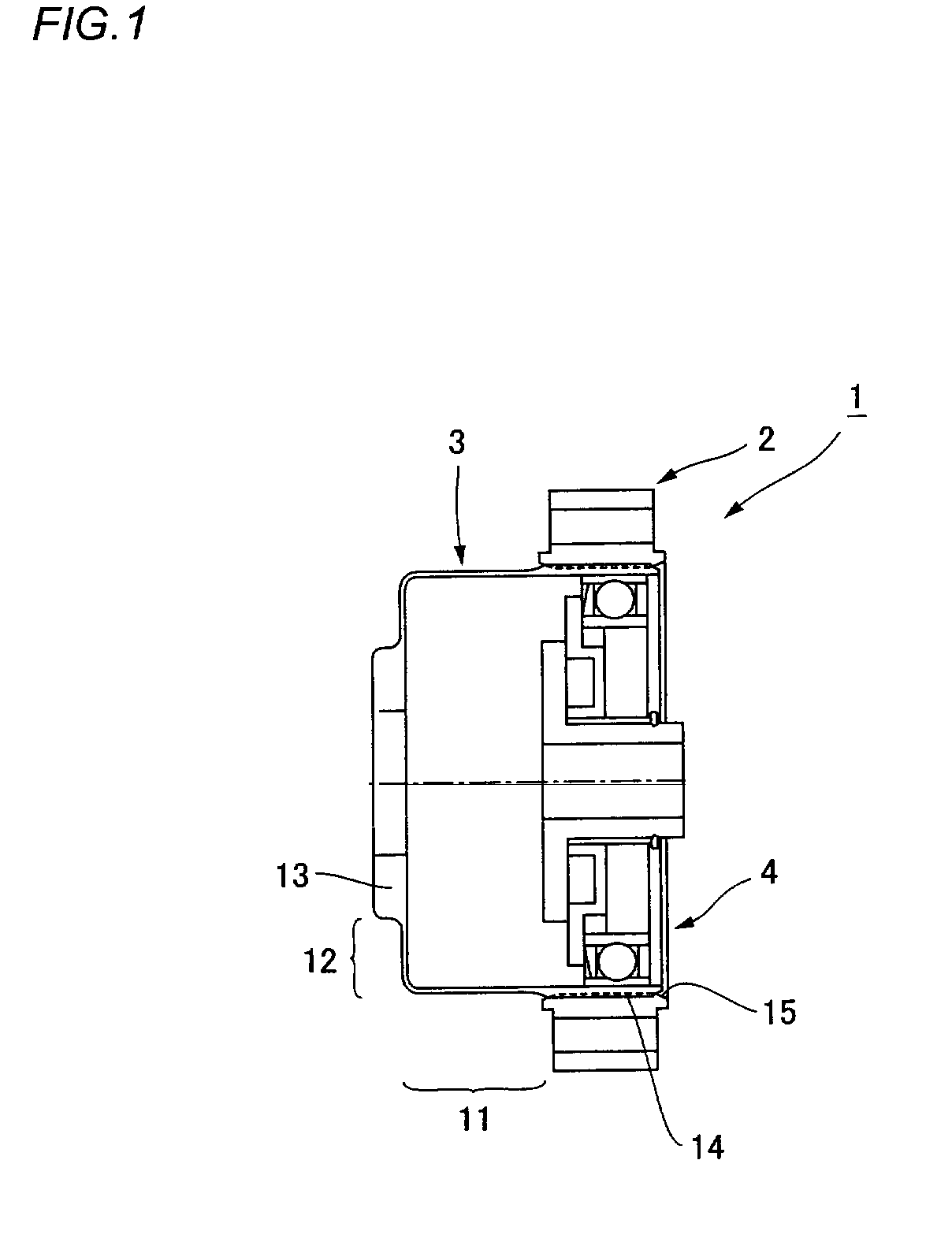
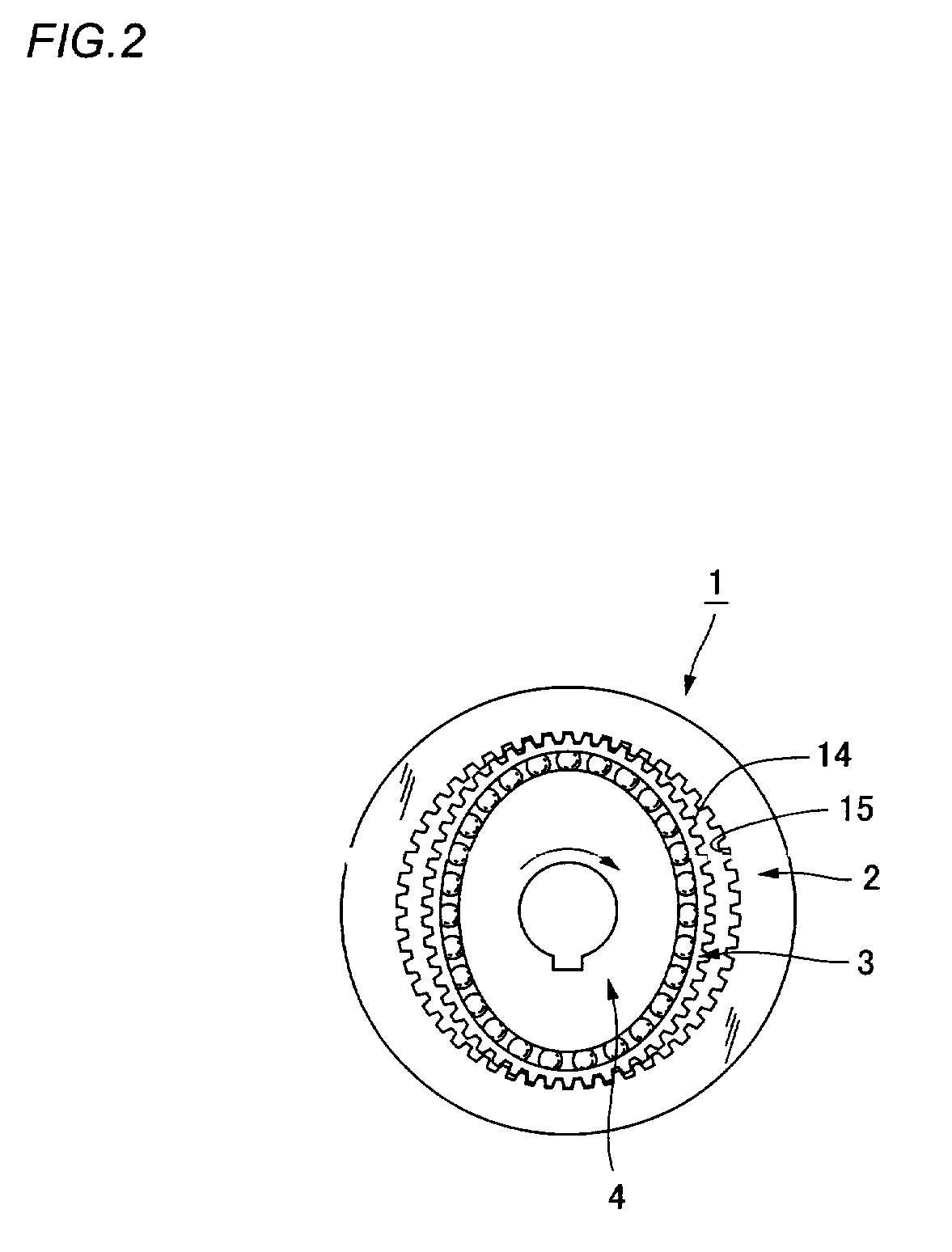
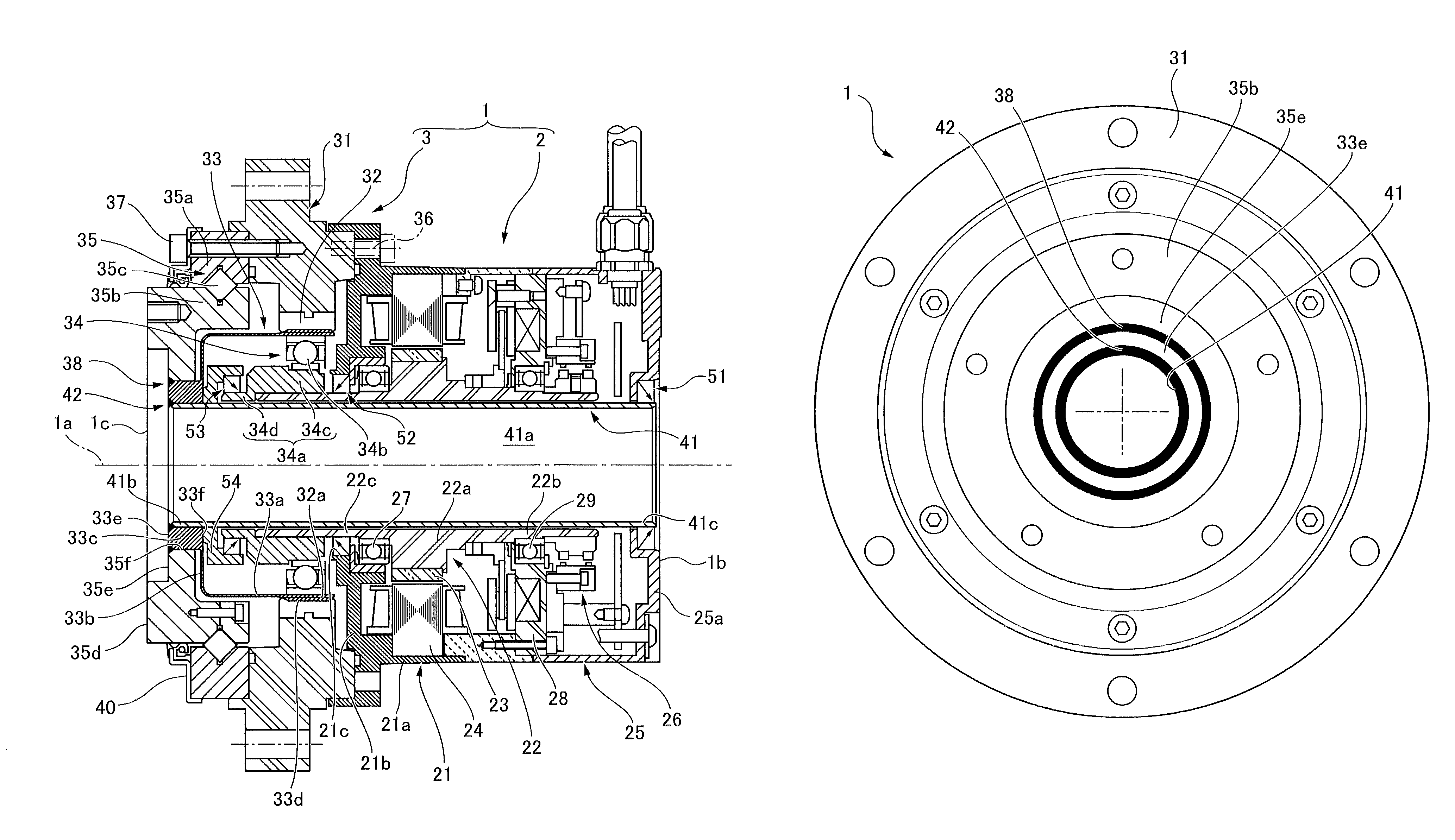
Wave gear device
ActiveUS7484436B2Avoid lubricationRotary combination bearingsRolling contact bearingsLow speedGear wheel
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device torque detection method
A wave gear device torque detection method in which the gain of the output of each of a plurality of strain gauge sets affixed to the diaphragm of a flexible external gear is amplified and the outputs are then combined to form a detection signal. Adjusting the gain of each of the strain gauge outputs makes it possible to compensate for rotational ripple included in the output. Compensation of up to n order ripple components is possible by using at least (2n+1) strain gauges.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Method for manufacturing rigid internal gear of wave gear device
ActiveUS7748118B2Increase resistanceIncreased durabilityMetal-working apparatusToothed gearingsStrain wave gearingPost treatment
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a rigid internal gear for a wave gear device comprising an internally toothed portion and a gear main body portion comprised of different materials. In this method, a gear main body ring for forming a gear main body portion is preformed using a first aluminum alloy powder; an internal teeth-forming ring is preformed using a second aluminum alloy powder that has lower processability, is less durable, has higher abrasion resistance, and is harder than the first aluminum alloy powder; the internal teeth-forming ring is fitted inside the gear main body ring and the assembly is integrated by powder forging; and the resulting ring-shaped forging is subjected to post-processing, including cutting teeth. The gear main body portion and internally toothed portion are securely integrated by powder forging, and a lightweight rigid internal gear with high durability can therefore be obtained.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
Wave Gear Device
Provided is a wave gear device capable of transmitting a high torque. The silk hat type wave gear device comprises an annular circular spline having internal teeth formed thereon; a flexible flex spline having external teeth formed to mesh partially with the internal teeth and arranged on the inner side of the circular spline; and a wave generator arranged on the inner side of the flex spline. The flex spline includes a boss portion adapted to be fixed on an external member, and a connecting portion for connecting the external tooth portion and the boss portion. The connecting portion is so shaped that a sectional shape when cut in a plane extending through an axis of rotation of the flex spline is gradually reduced in thickness toward the substantial center from the side of the external tooth portion and the side of the boss portion.
Owner:NABLESCO CORP
Wave gear device
The invention provides a cup-type or ''silk hat''-type wave gear device capable of largely increasing load capacity. In the cup-type or ''silk hat''-type wave gear device (1), the rim thickness t of the flexible externally toothed gear (3) thereof satisfies the relations: (0.5237Ln(R)-1.32)d<=t<=(0.8728Ln(R)-2.2)d, if the reduction ratio R of the wave gear device is less than 80, and (1.5499Ln(R)-5.8099)d<=t<=(2.5832Ln(R)-9.6832)d, if the reduction ratio R is equal to or greater than 80, where d is the radial deflection, measured at the position of the major axis of the neutral circle of the rim, in a state in which the flexible externally toothed gear is bent into an elliptical shape. The effective face width L of the external teeth (35) is a value within the range of 21% to 30% of the pitch circle diameter. Such settings make it possible to increase the bottom fatigue strength of the flexible externally toothed gear and improve the load capacity of the wave gear device (1).
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device having tapered flexible external gear
ActiveCN103827542AMesh wide rangeIncreased transfer load torqueToothed gearingsGearing elementsLoad torqueEngineering
With a wave gear device (1), the gears (2, 3) employ homothetic curve tooth profiles AD, BE, which are derived from the movement locus M1 at the aperture end (34a) of the external teeth (34) of the non-deflecting (kappa = 1) flexible external gear (3) with respect to inner teeth (24). Furthermore, a transposition is applied to the external teeth (34) along the tooth trace such that the movement loci M2, M3 of the external teeth (34) in a section perpendicular to the axis, from the aperture end (34a) to the inner end (34b), share the movement locus M1 of the aperture end (34a) and bottom portion thereof, and a continuous meshing of the teeth in the tooth trace direction is achieved. Furthermore, the tooth bottom rim thickness of the aperture end (34a) of the external teeth (34) is optimized using a modified Goodman diagram, and a tooth bottom rim thickness which takes into account the relationship between the tooth profile and the transmitted torque from the aperture end (34a) to the inner end (34b) is employed for the flexible external gear (3). Thus, the transmission load torque of the flexible external gear (3) can be increased.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device having internal gear integrally formed with inner ring of bearing
A wave gear device has a rigid internal gear, a flexible external gear, a wave generator, and a cross roller bearing for supporting the gears in a relatively rotatable manner. A toroidal composite member that functions as the rigid internal gear and an inner ring of the cross roller bearing has an inner ring-forming member that functions as the inner ring, and an internal teeth-forming member that functions as the rigid internal gear, and the internal teeth-forming member composed of a ductile casting is integrated by diffusion bonding with the inner ring-forming member composed of bearing steel.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device
ActiveUS7249536B2Speed up the restore processMaximum allowable transmission torqueGearingStress concentrationGear wheel
A diaphragm of a cup-shaped flexible external gear of a cup-shaped wave gear device having a high reduction ratio of 100 or higher is given a thickness t in a position of a radius r of the diaphragm whereby the thickness t is a value that satisfies the expression A / r2 when A is a constant. The constant A is preferably a value that satisfies the expression 0.0014 D3<A<0.0026 D3, where D is a pitch diameter of the flexible external gear, and the range of the radius r whereby the thickness t is defined as described above in the diaphragm is preferably set to satisfy the expression 0.6 d<r<0.4 D, where d is a diameter of a discoid rigid boss made continuous with an internal peripheral end of the diaphragm. Stress concentration can be alleviated, and it is possible for the allowable transmission torque to be increased compared to the prior art.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Motor vehicle steering device
InactiveUS20050155812A1More compact structureMore reliable structureGearingElectrical steeringReduction driveDrive motor
The invention provides a compact and highly reliable motor vehicle steering device that does not require a spiral flat cable. The motor vehicle steering device includes variable gear ratio system that modifies the transmission ratio of the rotary motions between first steering shaft and second steering shaft. Variable gear ratio system comprises Strain Wave Gearing Speed Reducer that modifies the transmission ratio between first steering shaft and second steering shaft in response to the rotating speed of motor shaft. Motor shaft and second steering shaft forms a substantially concentric dual structure, drive motor is affixed, and output shaft is connected to motor shaft.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Positioning control system for actuator provided with wave gear device
ActiveUS20140203752A1Precise positioningShorten positioning timeProgramme controlAC motor controlLinear elementFeedback controller
A positioning control system for an actuator provided with a strain wave gearing is provided with: a semi-closed feedback controller FB(s) that controls a load shaft position θl on the basis of a feedback motor shaft position θm; and a feedforward linearization compensator configured by incorporating a nonlinear plant model for an object to be controlled into a feedback linearization compensator using an exact linearization technique. The feedforward linearization compensator uses a forward-calculated state quantity estimated value x* to calculate a feedforward current instruction i*ref and a feedforward motor position instruction θ*m to be input into the feedback controller FB(s). A positioning error caused by a non-linear element (non-linear spring property, relative rotational synchronization component, and non-linear friction) of the strain wave gearing is compensated for by the feedforward linearization compensator.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
Wave gear device and hollow rotating actuator
In a wave gear device, the inner race and the boss are fixed together by a laser welded part formed along the entire periphery thereof. The laser welded part also functions as an oil seal for sealing the inner race and the boss. The boss and the inner race are fixed together in a manner that a required axial length is short, and that machining and assembling steps are reduced. Oil seal members are not required to seal the boss and the inner race.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Positioning apparatus for actuator with wave gear device
ActiveUS20120271459A1Extended stabilization timeSmooth load shaft responseSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlControl systemState variable
In a positioning apparatus for an actuator, a sliding mode controller for compensating for nonlinear characteristics of a wave gear device of the actuator generates a control input u to a controlled object, based on a position command θ1* and a state variable x for expressing the controlled object. The controlled object is defined in the following formula.{dot over (x)}=Ax+Bu+Eθl*y=Cx The switching surfaces of the sliding mode control system are defined by a variable S expressed in the following formula.S=BTP The control input u is the sum of the linear-state feedback control term ul and the nonlinear control input unlu=ul+unl=-(SB)-1(SAx+SEθl*)-k(SB)-1σσσ=Sx,where σ is the switching function, and k is the switching gain.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
Method of manufacturing a rigid internal gear of a wave gear device
A rigid internal gear 2 of the wave gear device is composed by integrating a tooth-forming ring 12 formed with internal teeth, and a main gear ring 11 into a single body. The tooth-forming ring 12 is manufactured from a ferrous or copper material that has superior strength and abrasion resistance, while the main gear ring 11 is manufactured from a lightweight material, such as an aluminum alloy. The outer circumferential surface of the tooth-forming ring 12 is aluminized to form a dispersed aluminum coating 15, before the tooth-forming ring 12 is cast within the main gear ring 11 so as to integrate the main gear ring 11 and the tooth-forming ring 12. Both parts are reliably integrated so that a large amount of torque can be transmitted, whereby realizing a rigid internal gear that is lighter than conventional models.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD +1
Silk hat shaped wave gear device
A flexible external gear of a silk hat shaped wave gear device has an annular body, external teeth formed on an outer circumferential portion of a first opening of the body, a circular diaphragm connected to a second opening portion of the body, and a circular boss connected to an outer circumferential end of the diaphragm. The shape of a connected portion of the diaphragm and the body is defined by a curved portion whose diameter decreases gradually from the diaphragm toward the body when viewed along a device axis. Since the body is wider on the diaphragm side, the wave generator 7 can be easily fitted into the flexible external gear from the diaphragm side.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Strain wave gearing unit
ActiveUS20150285357A1Solution to short lifeAvoid negative effectsGear lubrication/coolingToothed gearingsForeign matterEngineering
A strain wave gearing unit is provided with an internal gear, which surrounds the periphery of a cup-shaped external gear, and a bearing. An annular gap is formed between the inner ring of the bearing and the internal gear. The gap communicates with the sliding portions of the bearing and the section where the two gears mesh. An annular filter member made of non-woven fabric is fitted in the gap. Foreign matter such as abrasion powder, which is contained in lubricant that flows in the gap, is trapped by the filter member. The present invention can prevent penetration of abrasion powder generated in the sliding portions into the meshing section via the gap.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device
ActiveUS20100212446A1Increase bottom fatigue strengthImprove fatigue strengthPortable liftingToothed gearingsGear wheelEllipse
In a cup-type or “silk hat”-type wave gear device (1), the rim thickness t of the flexible externally toothed gear (3) thereof satisfies the relations (0.5237Ln(R)−1.32)d≦t≦(0.8728Ln(R)−2.2)d if the reduction ratio R of the wave gear device is less than 80, and (1.5499Ln(R)−5.8099)d≦t≦(2.5832Ln(R)−9.6832)d if the reduction ratio R is equal to or greater than 80, where d is the radial deflection, measured at the position of the major axis of the neutral circle of the rim, in a state in which the flexible externally toothed gear is bent into an elliptical shape. The effective face width L of the external teeth (35) is a value within the range of 21 to 30% of the pitch circle diameter. Such settings make it possible to increase the bottom fatigue strength of the flexible externally toothed gear and improve the load capacity of the wave gear device (1).
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Wave gear device having internal gear integrally formed with inner ring of bearing
ActiveUS20050217420A1High abrasionHigh precisionRoller bearingsEngine of arcuate-engagement typeGear wheelEngineering
A wave gear device has a rigid internal gear, a flexible external gear, a wave generator, and a cross roller bearing for supporting the gears in a relatively rotatable manner. A toroidal composite member that functions as the rigid internal gear and an inner ring of the cross roller bearing has an inner ring-forming member that functions as the inner ring, and an internal teeth-forming member that functions as the rigid internal gear, and the internal teeth-forming member composed of a ductile casting is integrated by diffusion bonding with the inner ring-forming member composed of bearing steel.
Owner:HARMONIC DRIVE SYST IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com