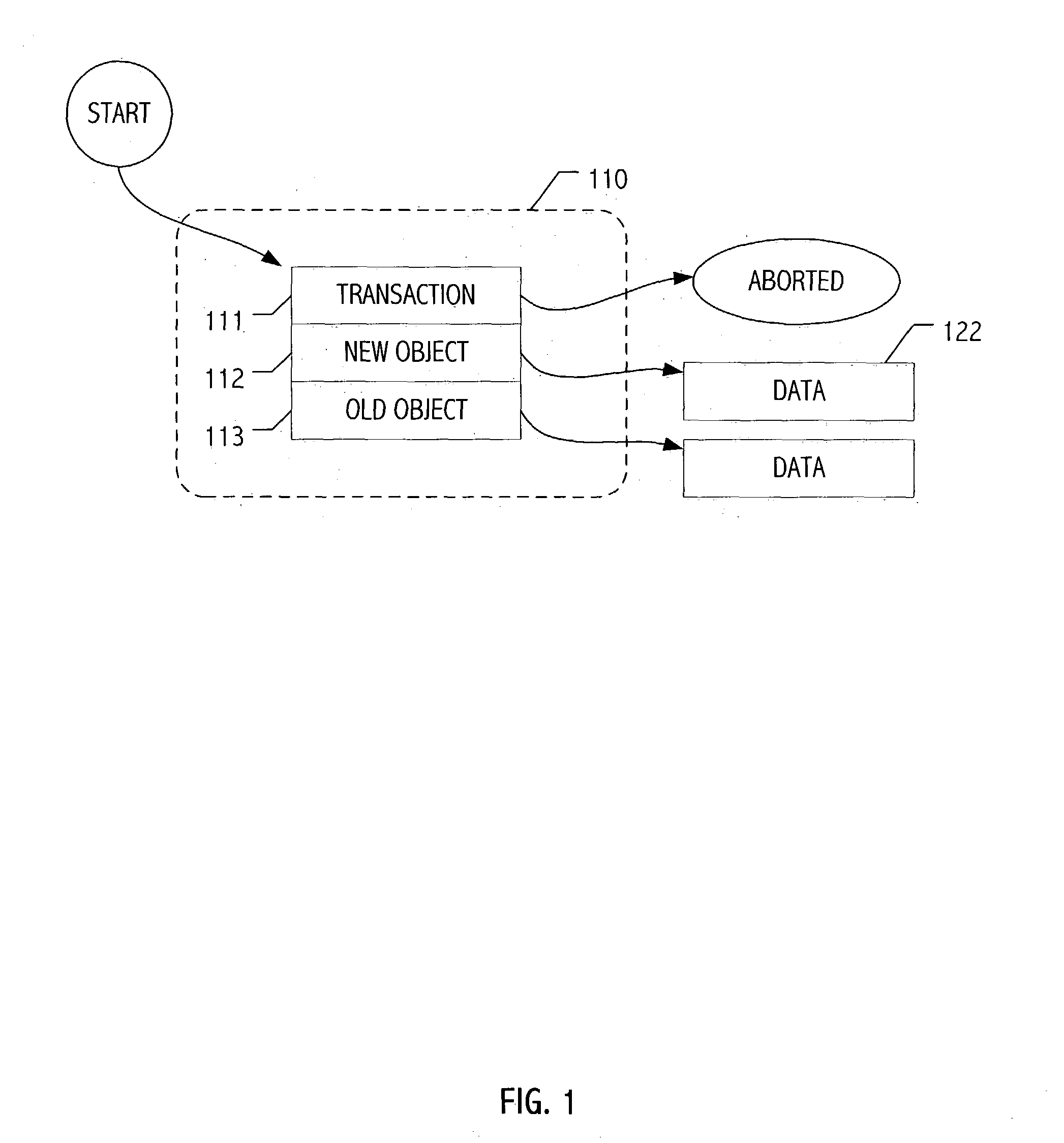
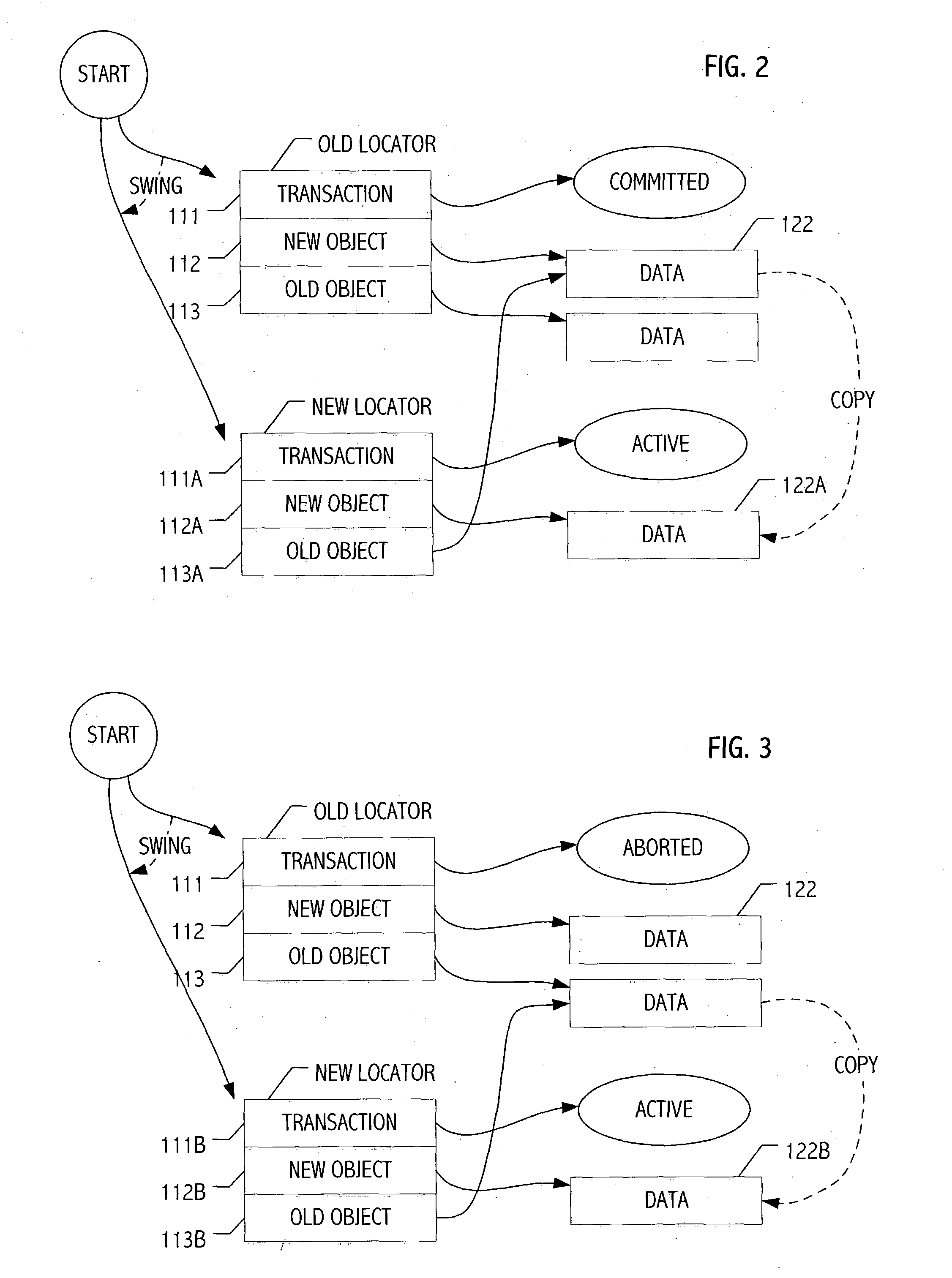
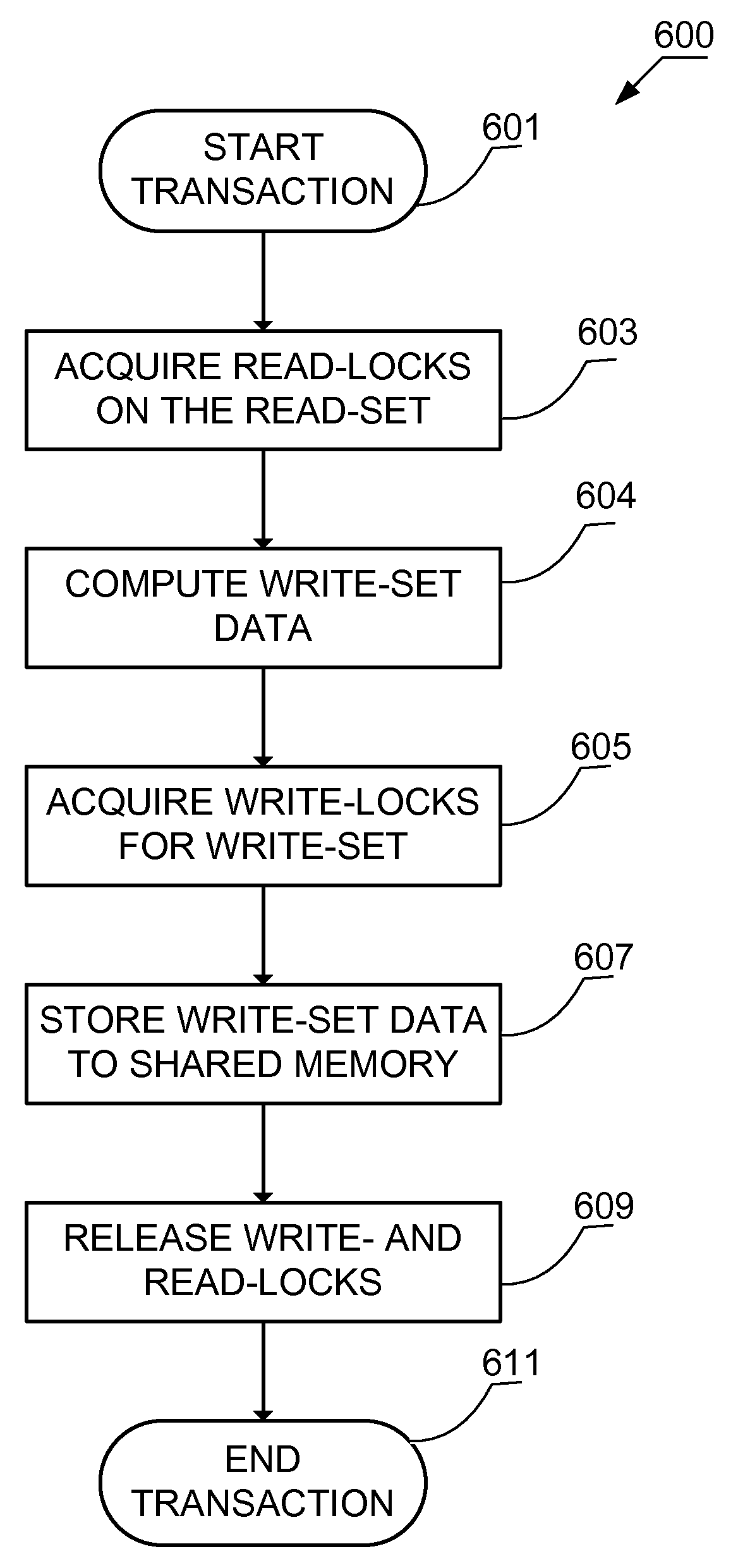
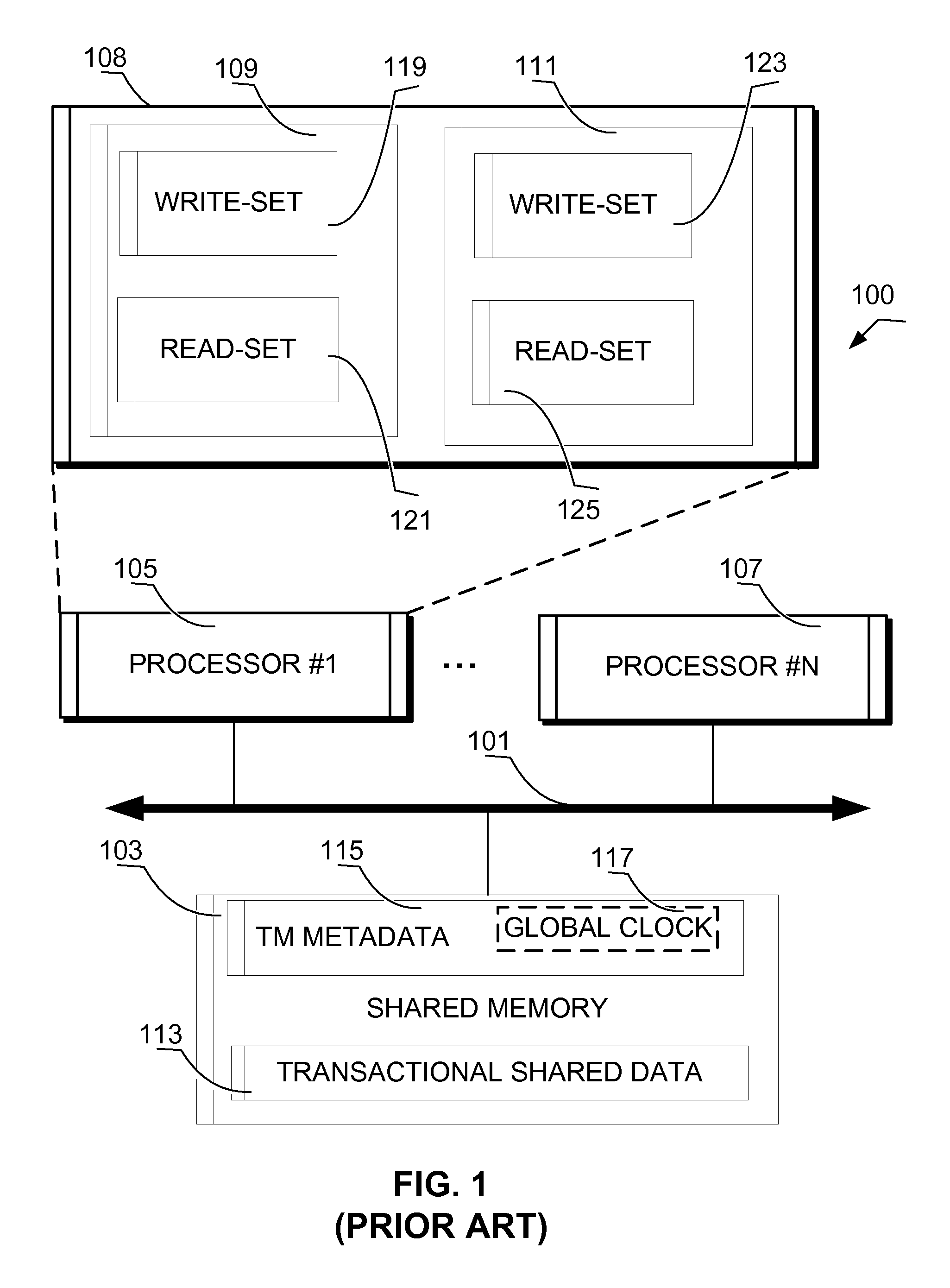
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170 results about "Software transactional memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
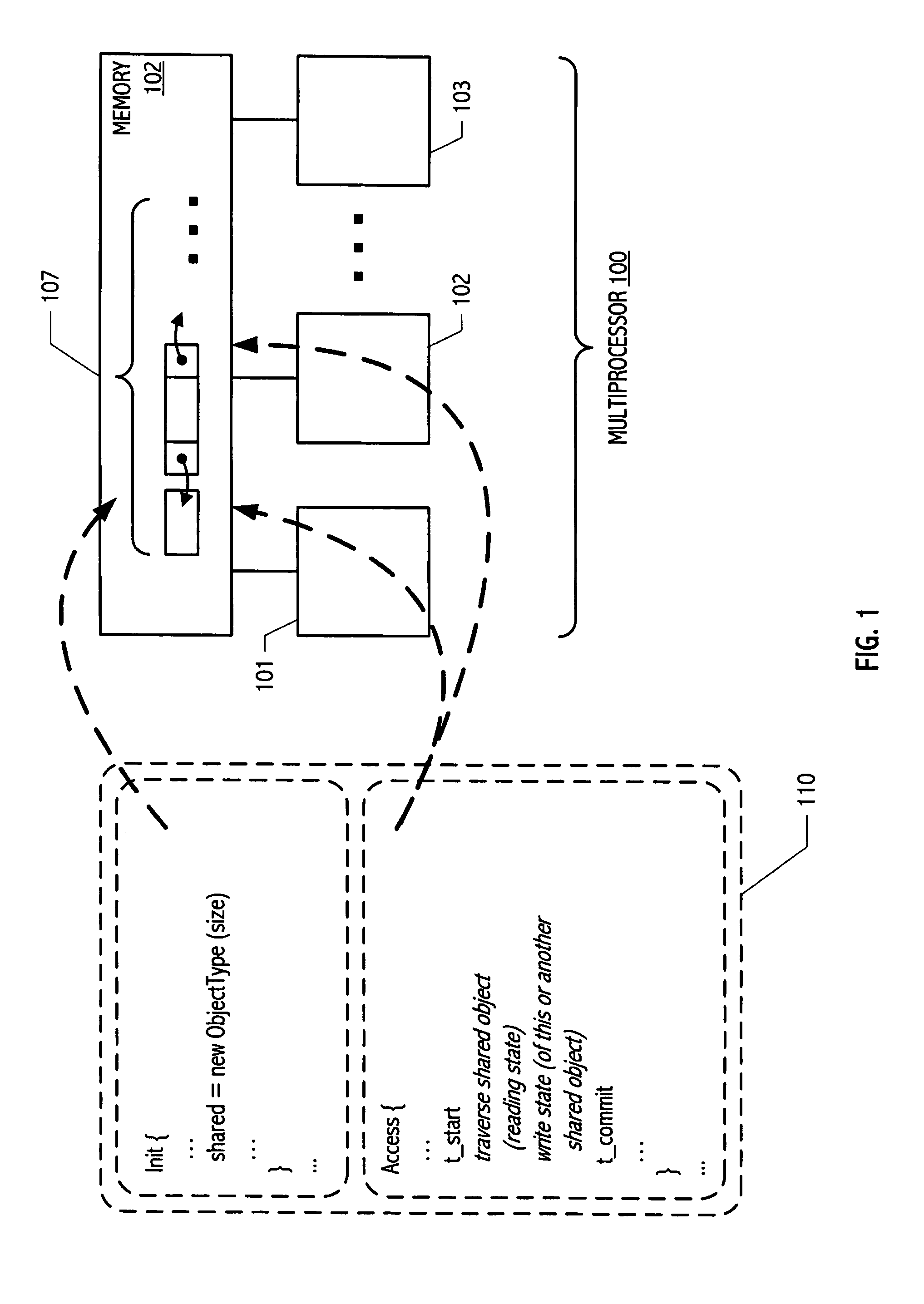
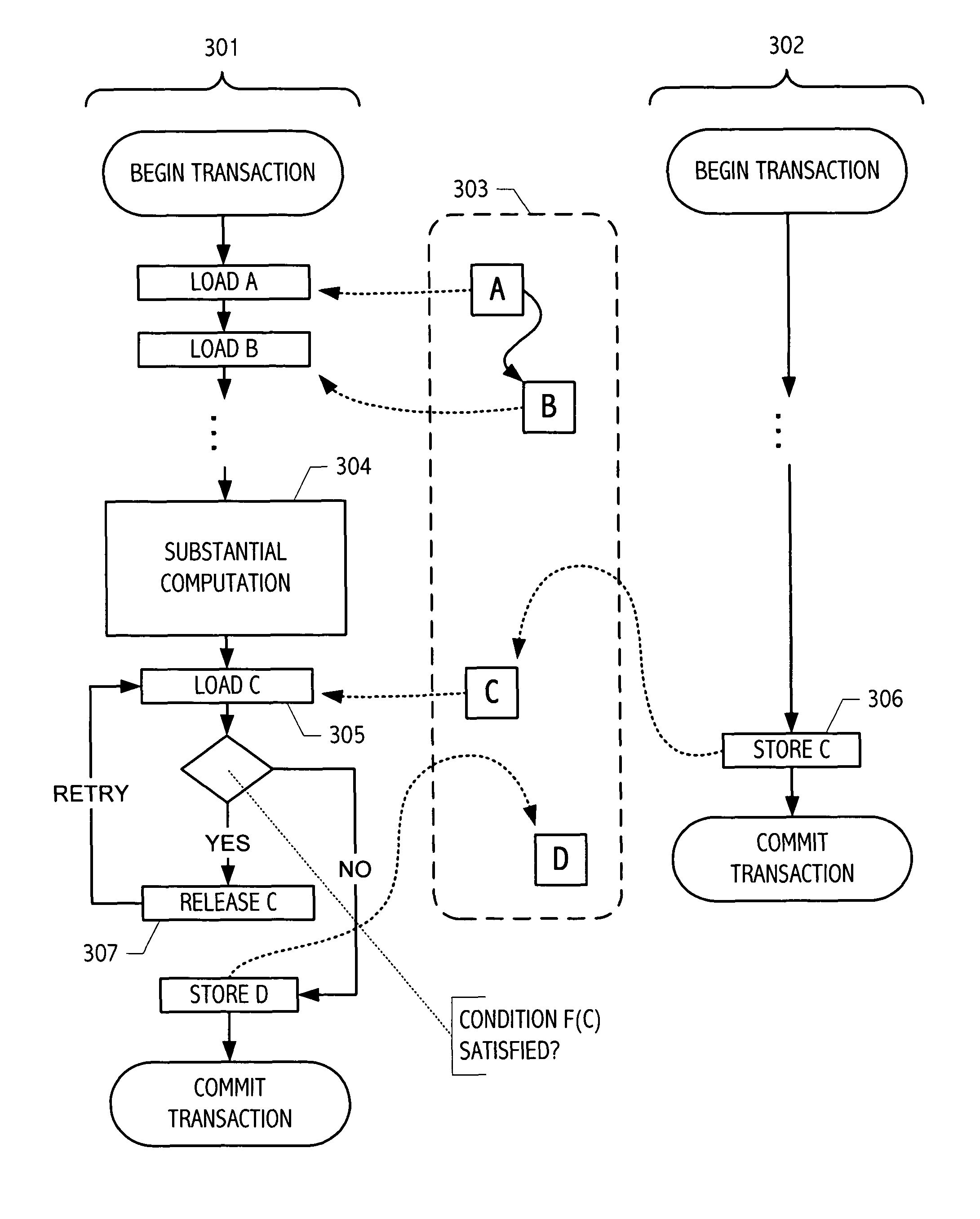
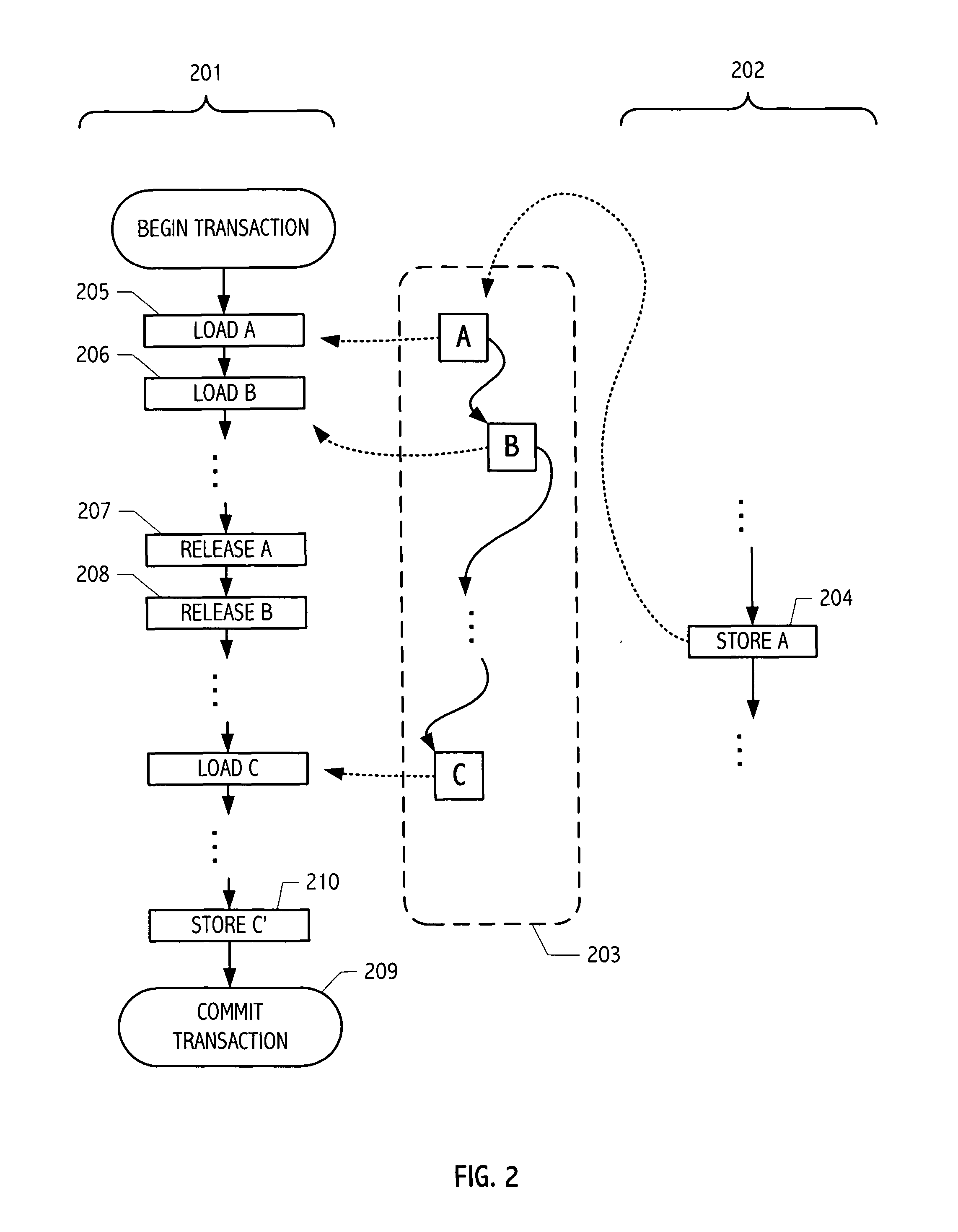
In computer science, software transactional memory (STM) is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. It is an alternative to lock-based synchronization. STM is a strategy implemented in software, rather than as a hardware component. A transaction in this context occurs when a piece of code executes a series of reads and writes to shared memory. These reads and writes logically occur at a single instant in time; intermediate states are not visible to other (successful) transactions. The idea of providing hardware support for transactions originated in a 1986 paper by Tom Knight. The idea was popularized by Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss. In 1995 Nir Shavit and Dan Touitou extended this idea to software-only transactional memory (STM). Since 2005, STM has been the focus of intense research and support for practical implementations is growing.
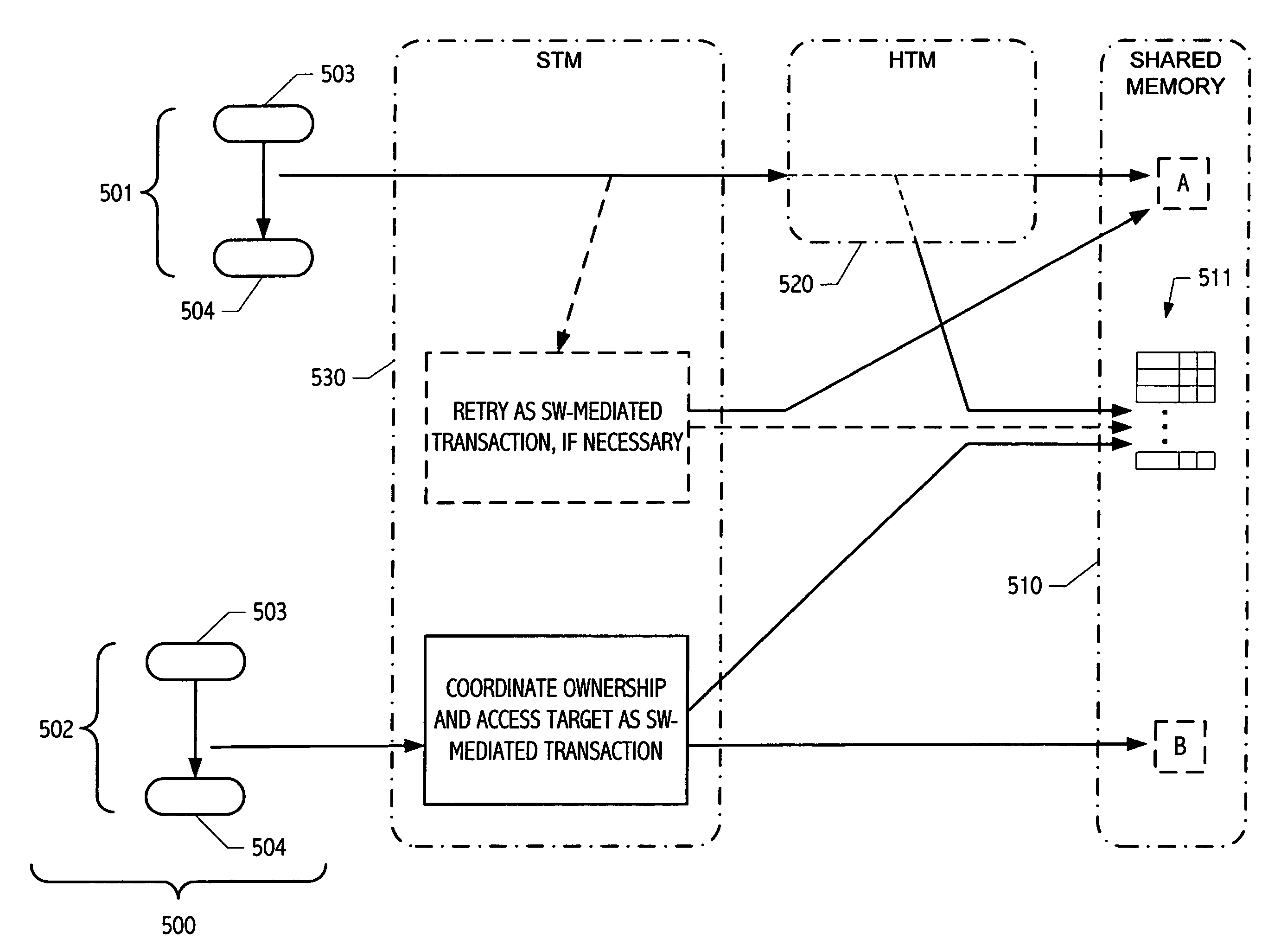
Hybrid software/hardware transactional memory
ActiveUS7395382B1Improve performanceImprove coordinationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareSoftware
A transactional memory implementation has been developed that is capable of coordinating concurrent hardware transactional memory (HTM) and software transactional memory (STM) transactions over a unified transactional memory space. Some implementations employ hardware transactional memory, if available or suitable, to improve performance. Some exploitations include a hardware transactional memory in which, or for which, hardware-mediated transactions are augmented to include within their transactional scope (or mechanism) one or more additional transactional locations that facilitate coordination with concurrently executing software-mediated transactions (if any).
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Software transactional memory for dynamically sizable shared data structures
ActiveUS20040015642A1Data processing applicationsError preventionArray data structureComputer science
We propose a new form of software transactional memory (STM) designed to support dynamic-sized data structures, and we describe a novel non-blocking implementation. The non-blocking property we consider is obstruction-freedom. Obstruction-freedom is weaker than lock-freedom; as a result, it admits substantially simpler and more efficient implementations. An interesting feature of our obstruction-free STM implementation is its ability to use of modular contention managers to ensure progress in practice.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Efficient implicit privatization of transactional memory
ActiveUS20080256074A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingSoftware transactional memory
Apparatus, methods, and program products are disclosed that provide a technology that implicitly isolates a portion of a transactional memory that is shared between multiple threads for exclusive use by an isolating thread without the possibility of other transactions modifying the isolated portion of the transactional memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Hardware accelerated transactional memory system with open nested transactions
ActiveUS8229907B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareHardware acceleration
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Mechanism to support flexible decoupled transactional memory
ActiveUS20120179877A1Maximize concurrencyEncourages forward progressMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram controlVirtual memoryVirtualization
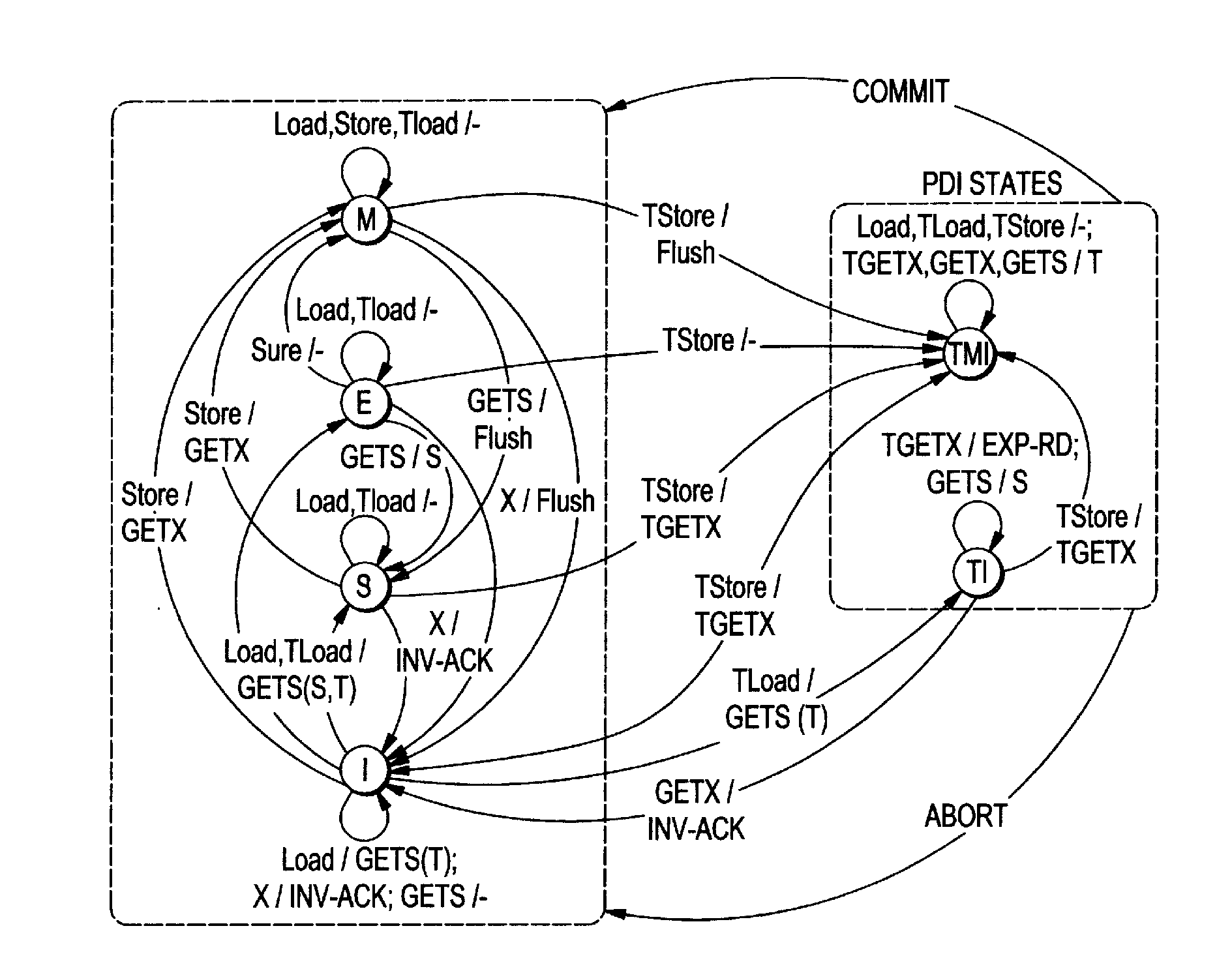
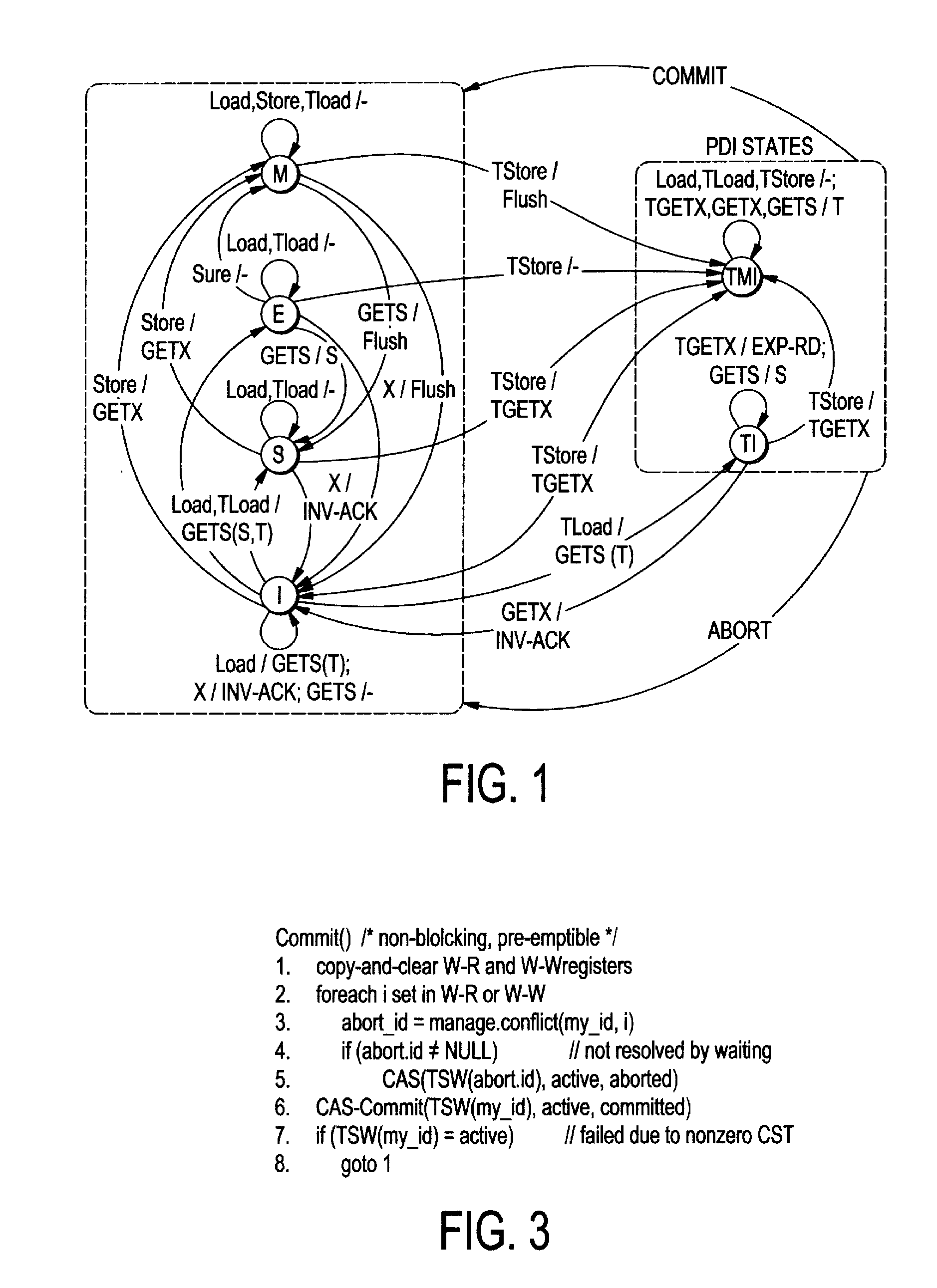
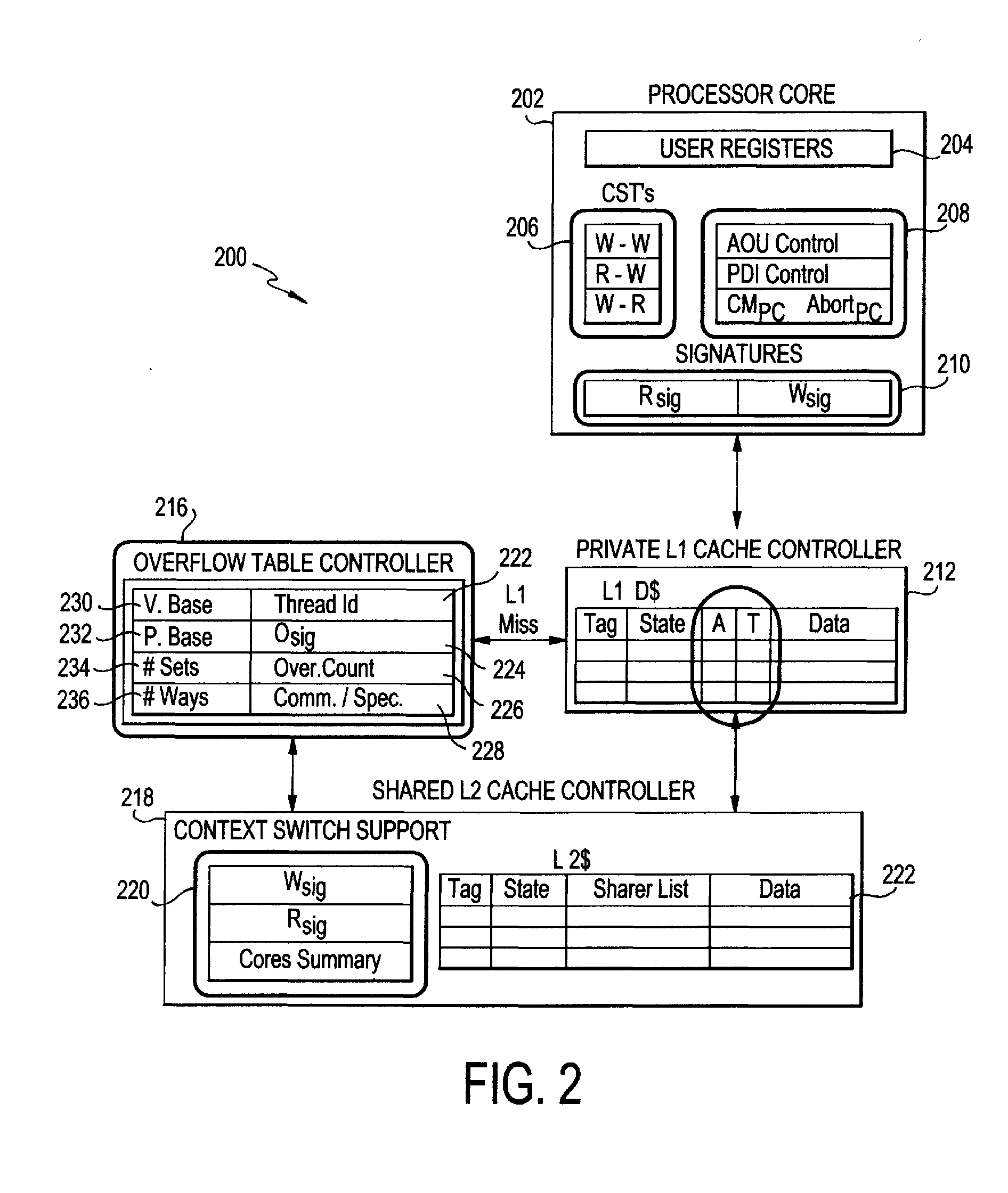
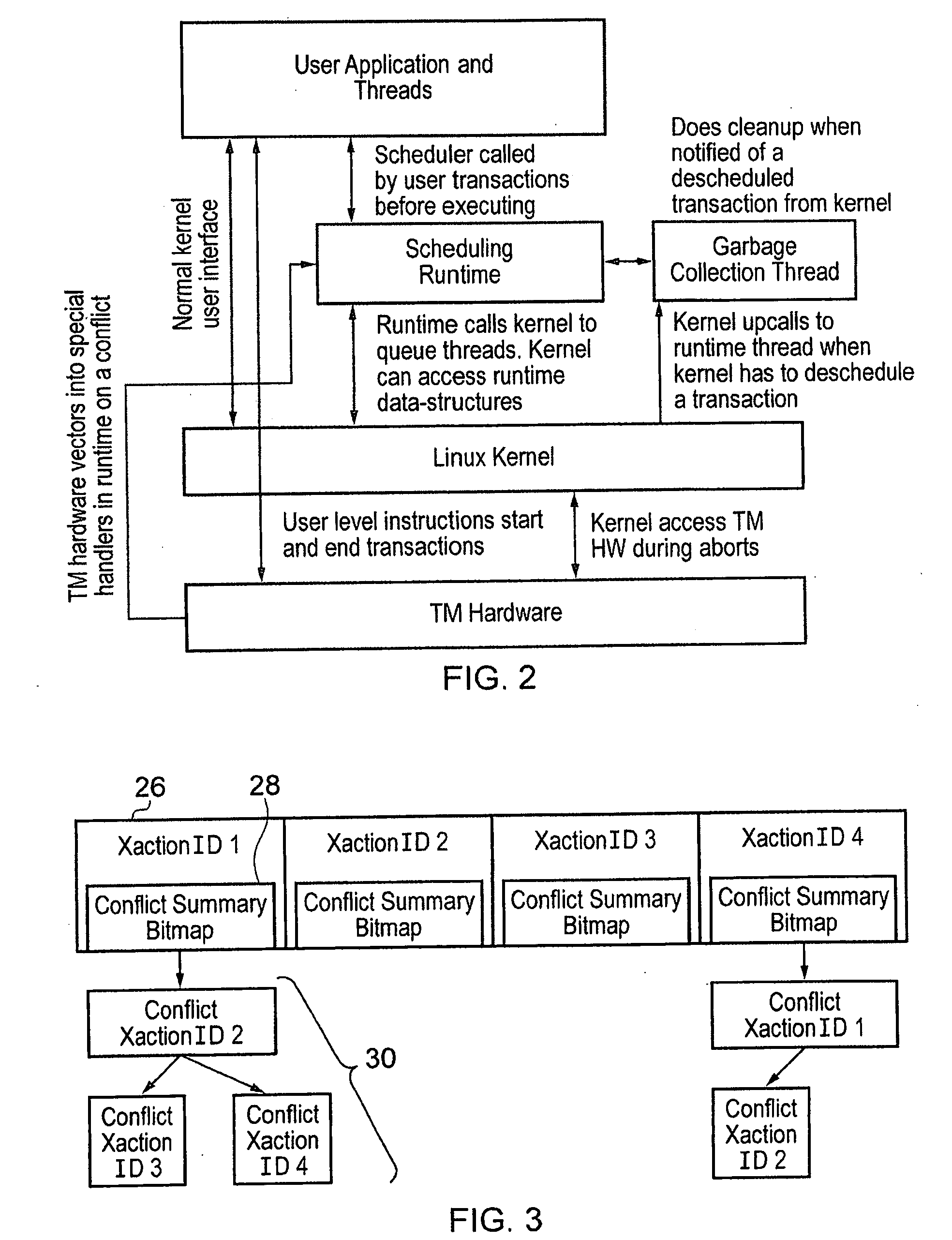
The present invention employs three decoupled hardware mechanisms: read and write signatures, which summarize per-thread access sets; per-thread conflict summary tables, which identify the threads with which conflicts have occurred; and a lazy versioning mechanism, which maintains the speculative updates in the local cache and employs a thread-private buffer (in virtual memory) only in the rare event of an overflow. The conflict summary tables allow lazy conflict management to occur locally, with no global arbitration (they also support eager management). All three mechanisms are kept software-accessible, to enable virtualization and to support transactions of arbitrary length.
Owner:UNIV OF ROCHESTER OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
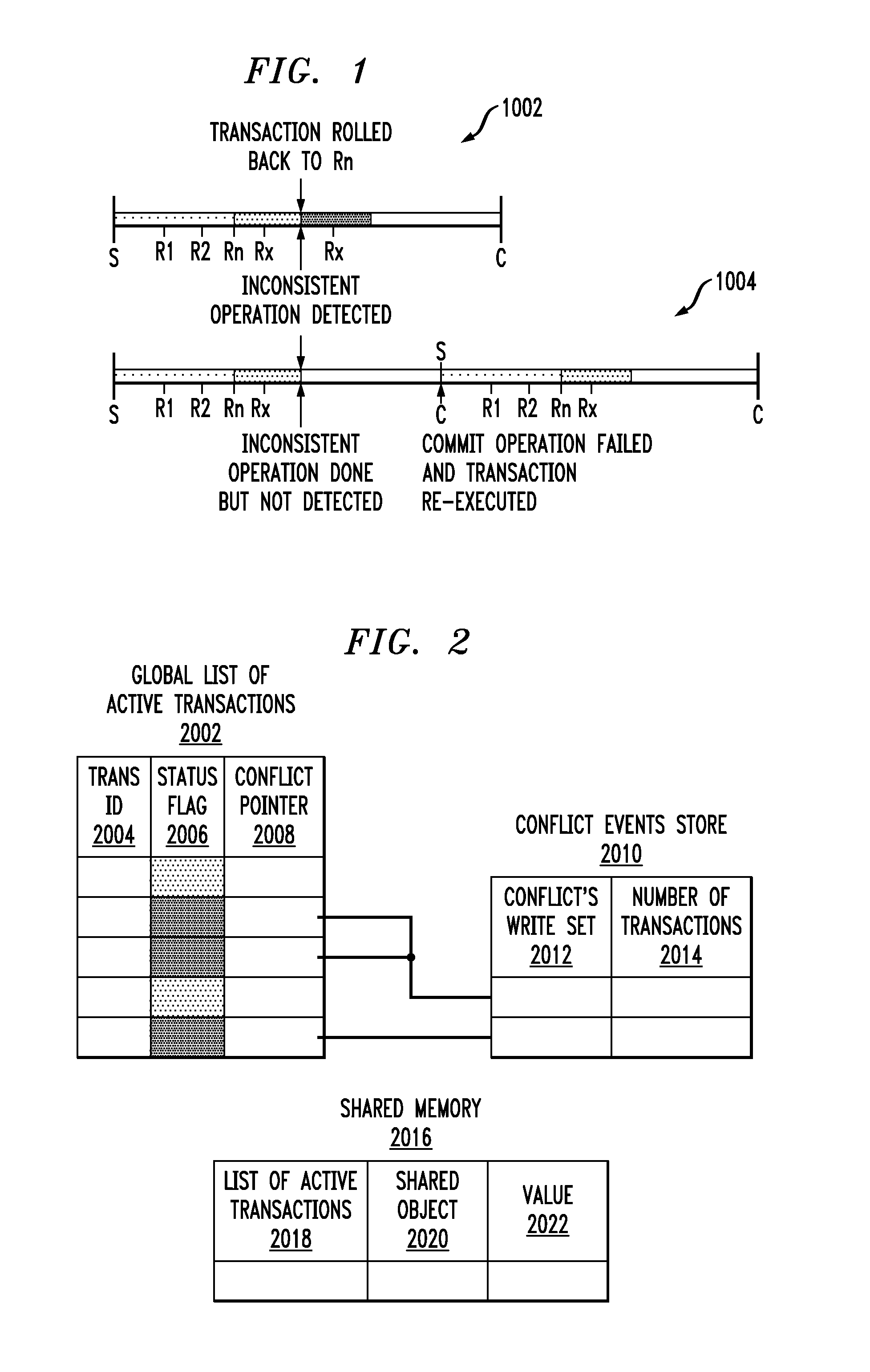
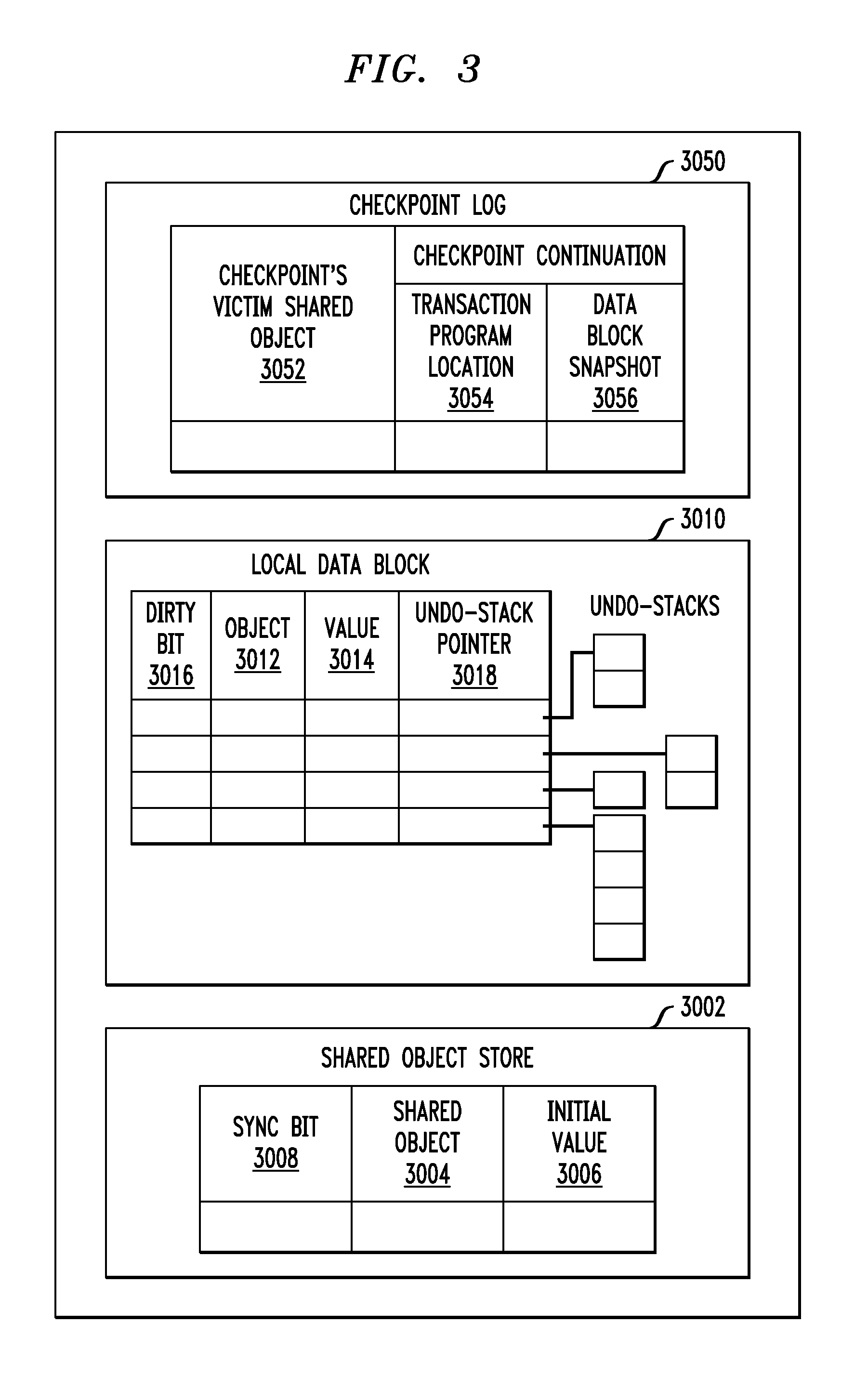
Automatic Checkpointing and Partial Rollback in Software Transaction Memory
ActiveUS20110029490A1Improve performanceDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer scienceShared memory
While speculatively executing a given one of a plurality of transactions concurrently executing on a computer, carry out write operations in a local data block, and automatically create an entry in a checkpoint log when reading from a shared memory. Continuously conflict check during read and tentative commit operations, and carry out a partial rollback upon detection of a conflict. The partial rollback is based upon the checkpoint log.
Owner:MAPLEBEAR INC
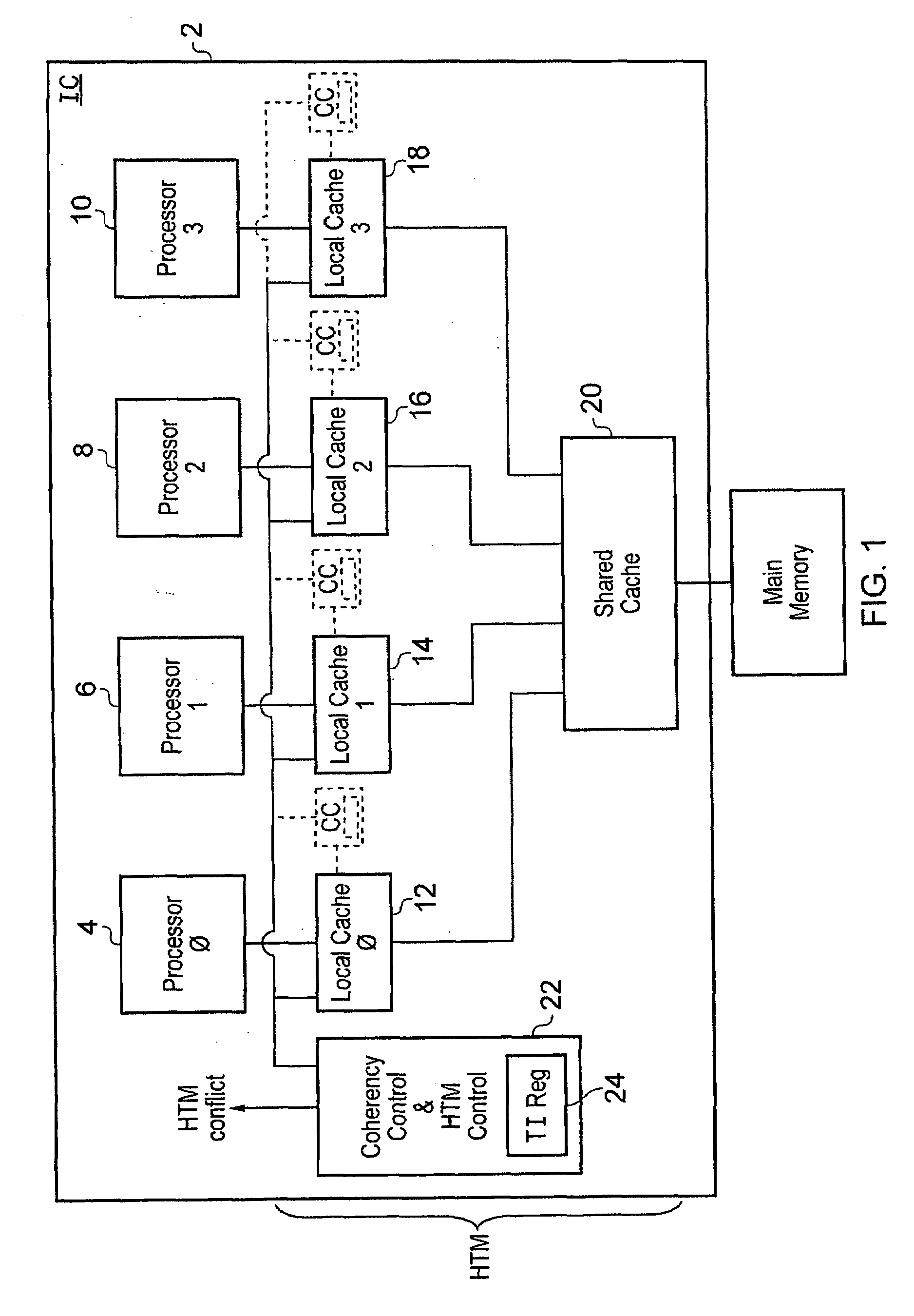
Contention management for a hardware transactional memory
InactiveUS20090138890A1Reduce storage overheadImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsConsistency controlComputer science
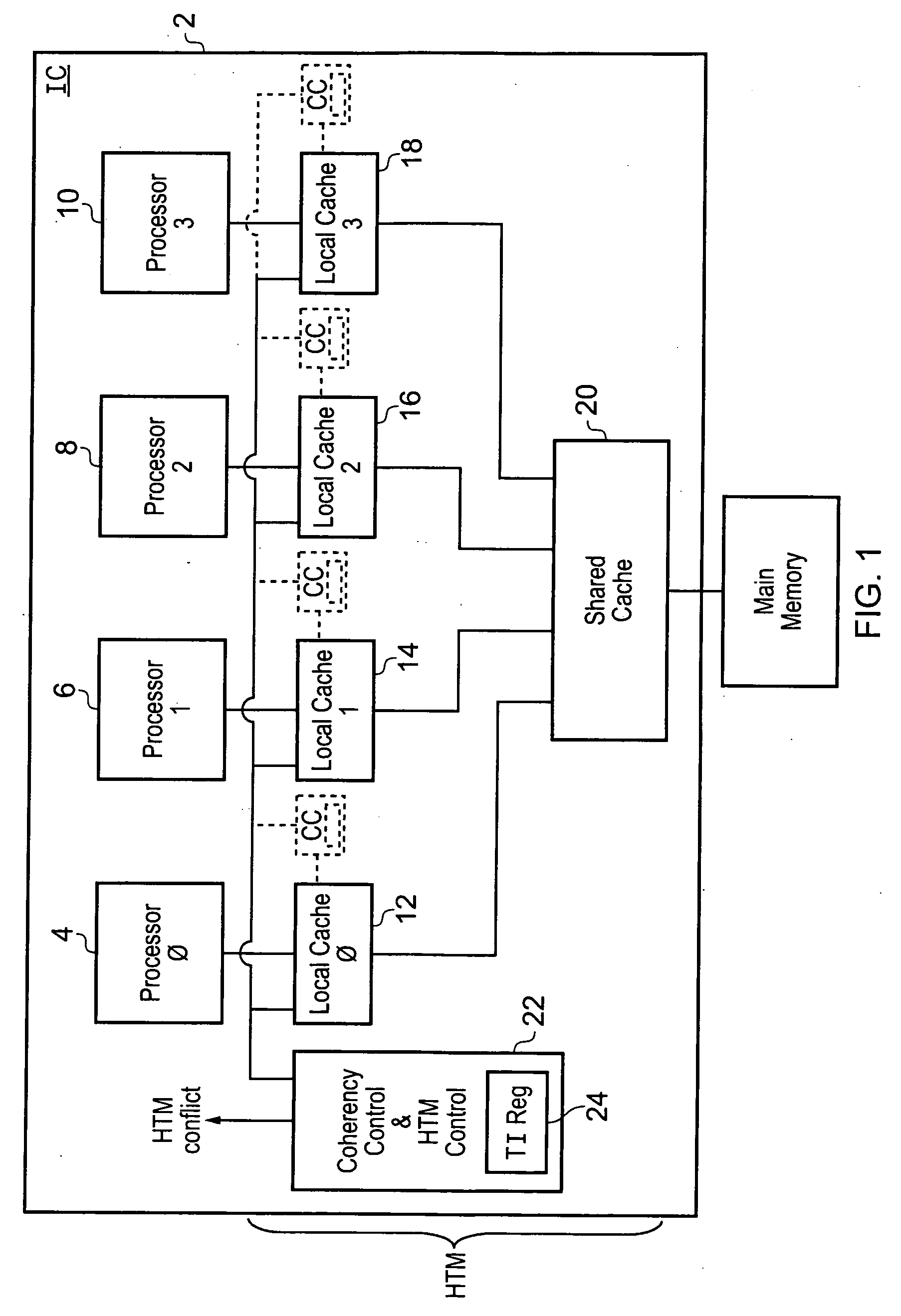
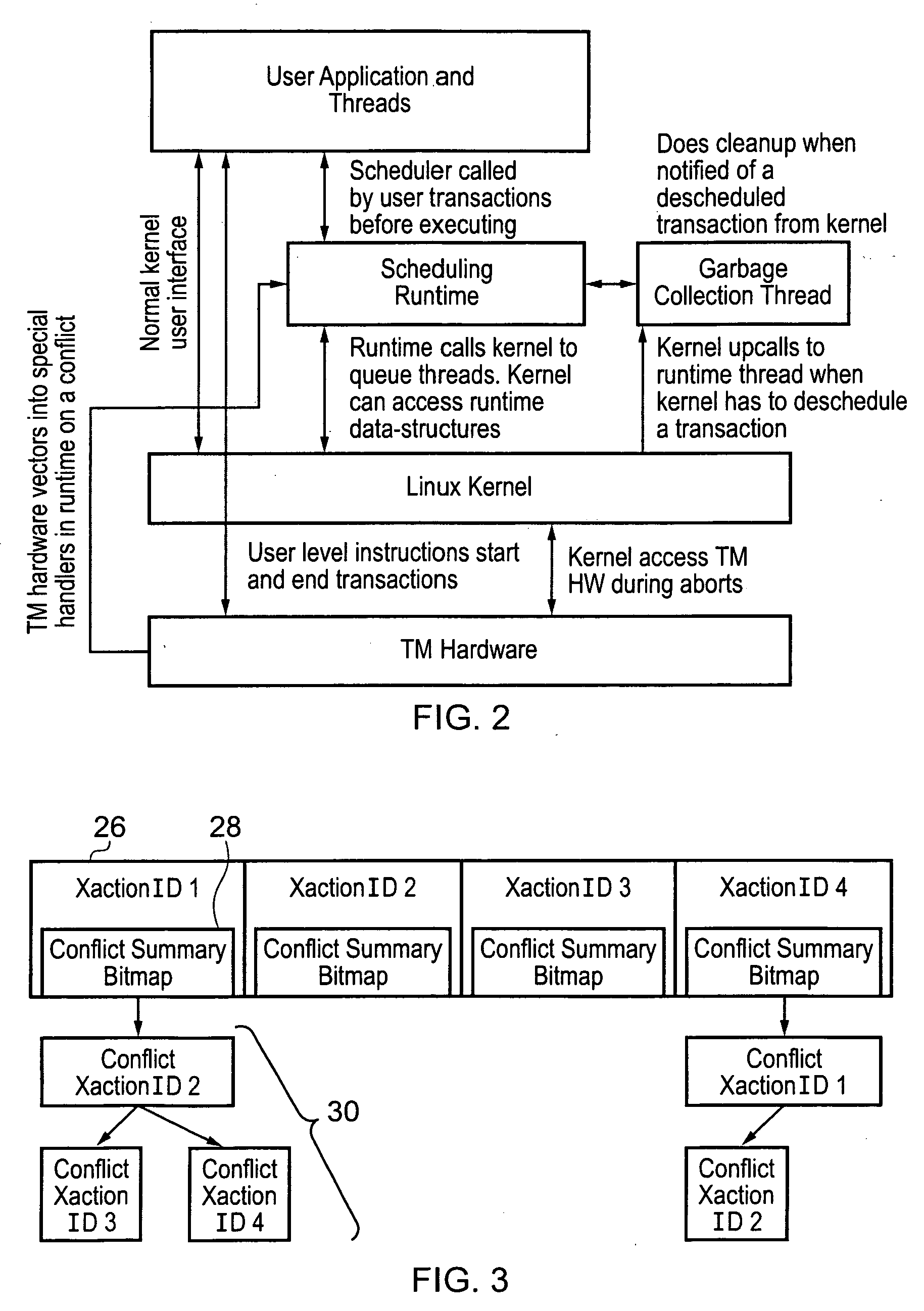
A hardware transactional memory 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 is provided within a multiprocessor 4, 6, 8, 10 system with coherency control and hardware transaction memory control circuitry 22 that serves to at least partially manage the scheduling of processing transactions in dependence upon conflict data 26, 28, 30. The conflict data characterises previously encountered conflicts between processing transactions. The scheduling is performed such that a candidate processing transaction will not be scheduled if the conflict data indicates that one of the already running processing transactions has previously conflicted with the candidate processing transaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Fine-locked transactional memory
ActiveUS20070282838A1Avoid overheadDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsDatabaseData objects
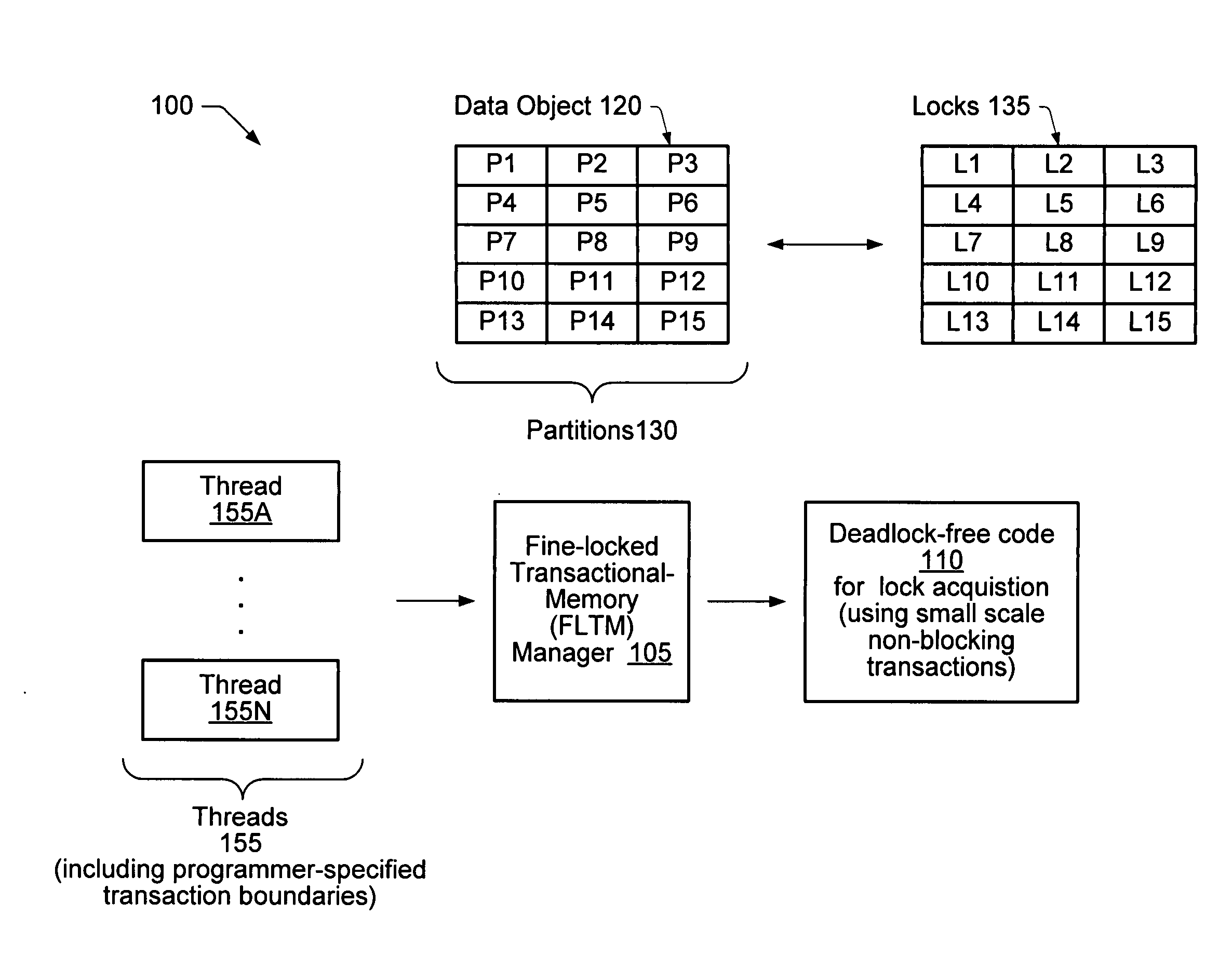
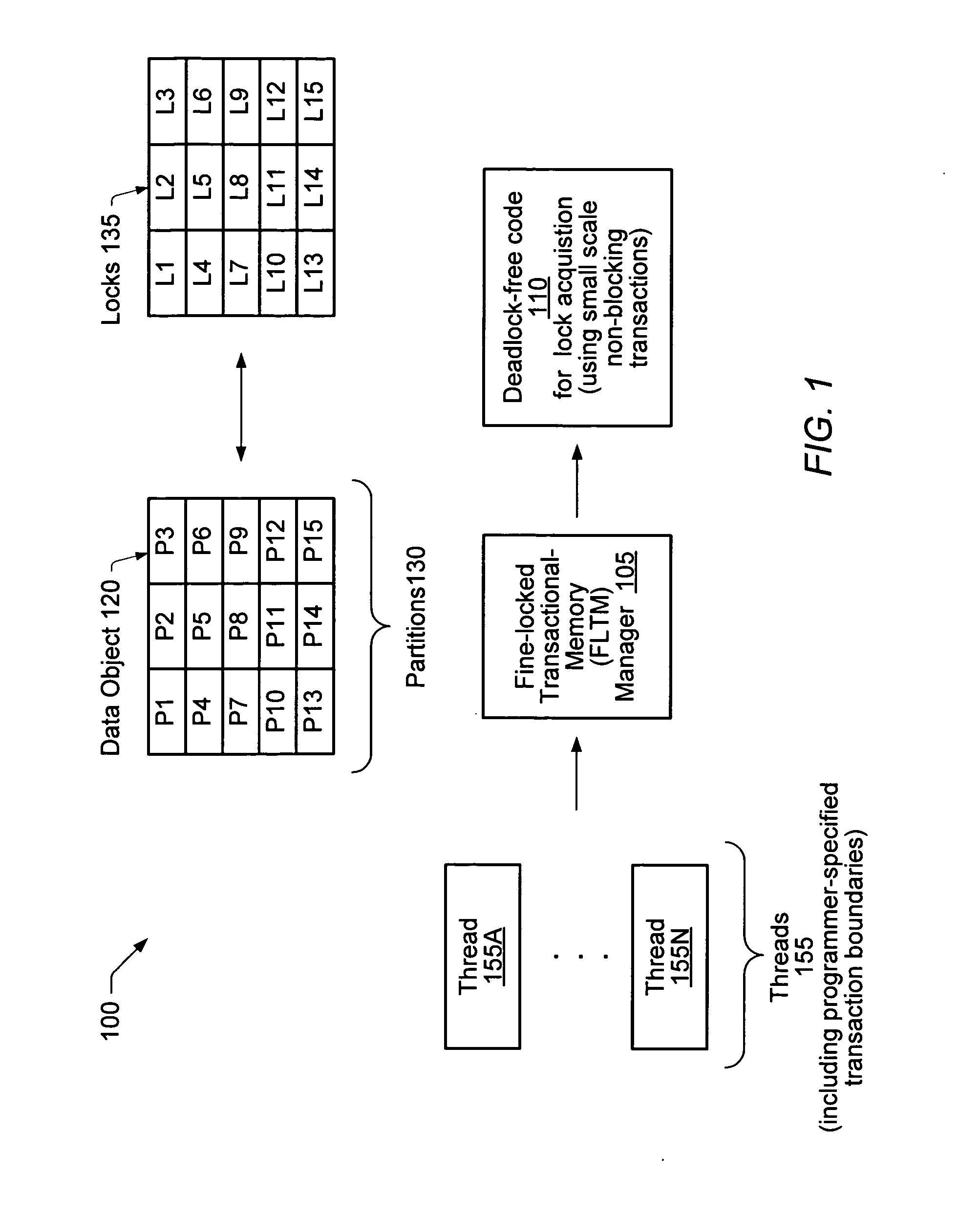
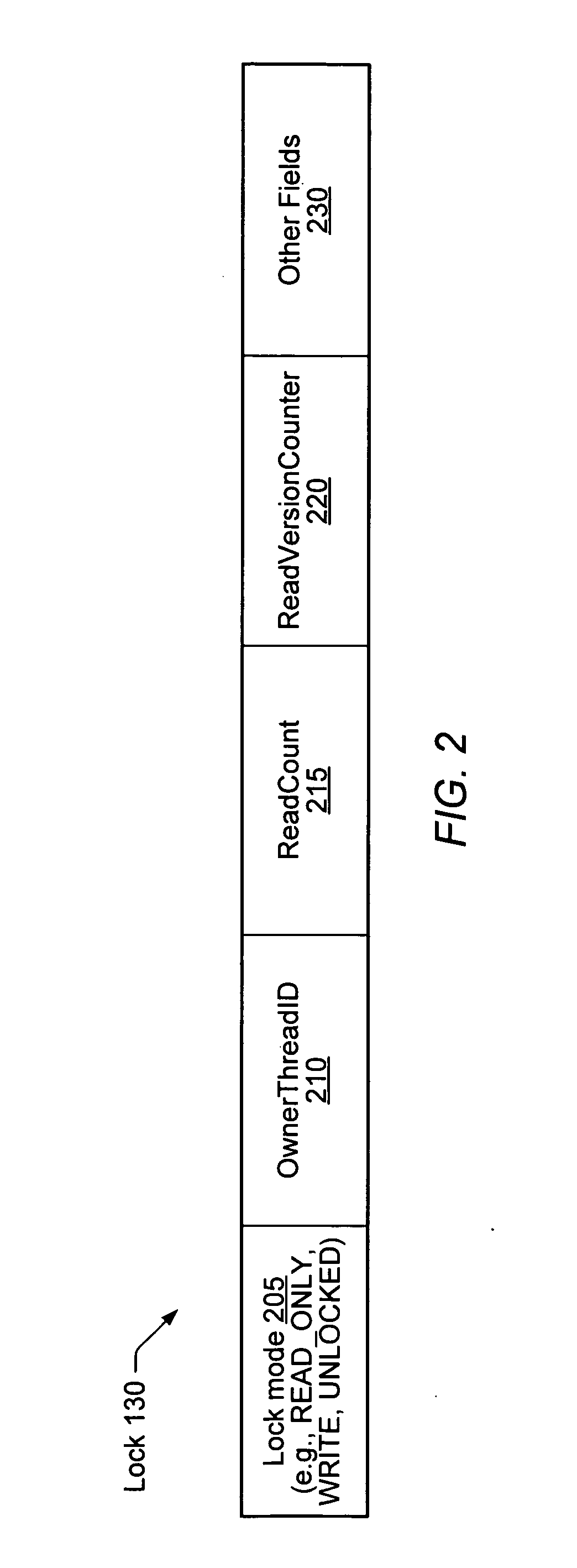
A method comprises associating a plurality of locks with a data object accessed concurrently by a plurality of threads, where each lock corresponds to a respective partition of the object. The method includes using a first non-blocking transaction (such as a Hardware Transactional-Memory (HTM) transaction) to attempt to complete a programmer-specified transaction. The first non-blocking transaction may access one or more of the locks but may not actually acquire any of the locks. In response to an indication that the first non-blocking transaction failed to complete, the method may include acquiring a set of locks in another non-blocking transaction, where the set of locks corresponds to a set of partitions expected to be accessed in the programmer-specified transaction. If the set of locks is acquired, the method may include performing the memory access operations of the programmer-specified transaction, and releasing the set of locks.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
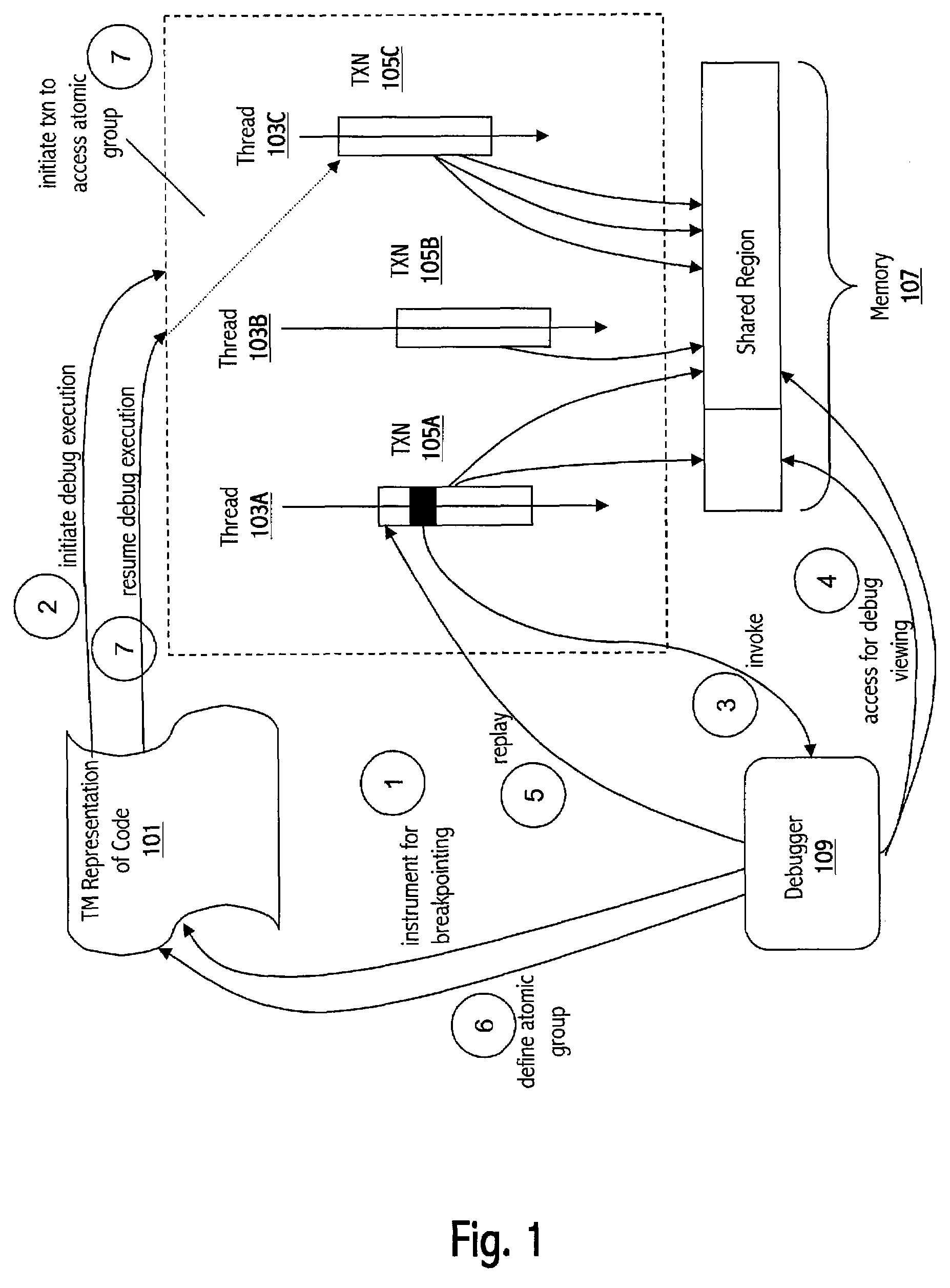
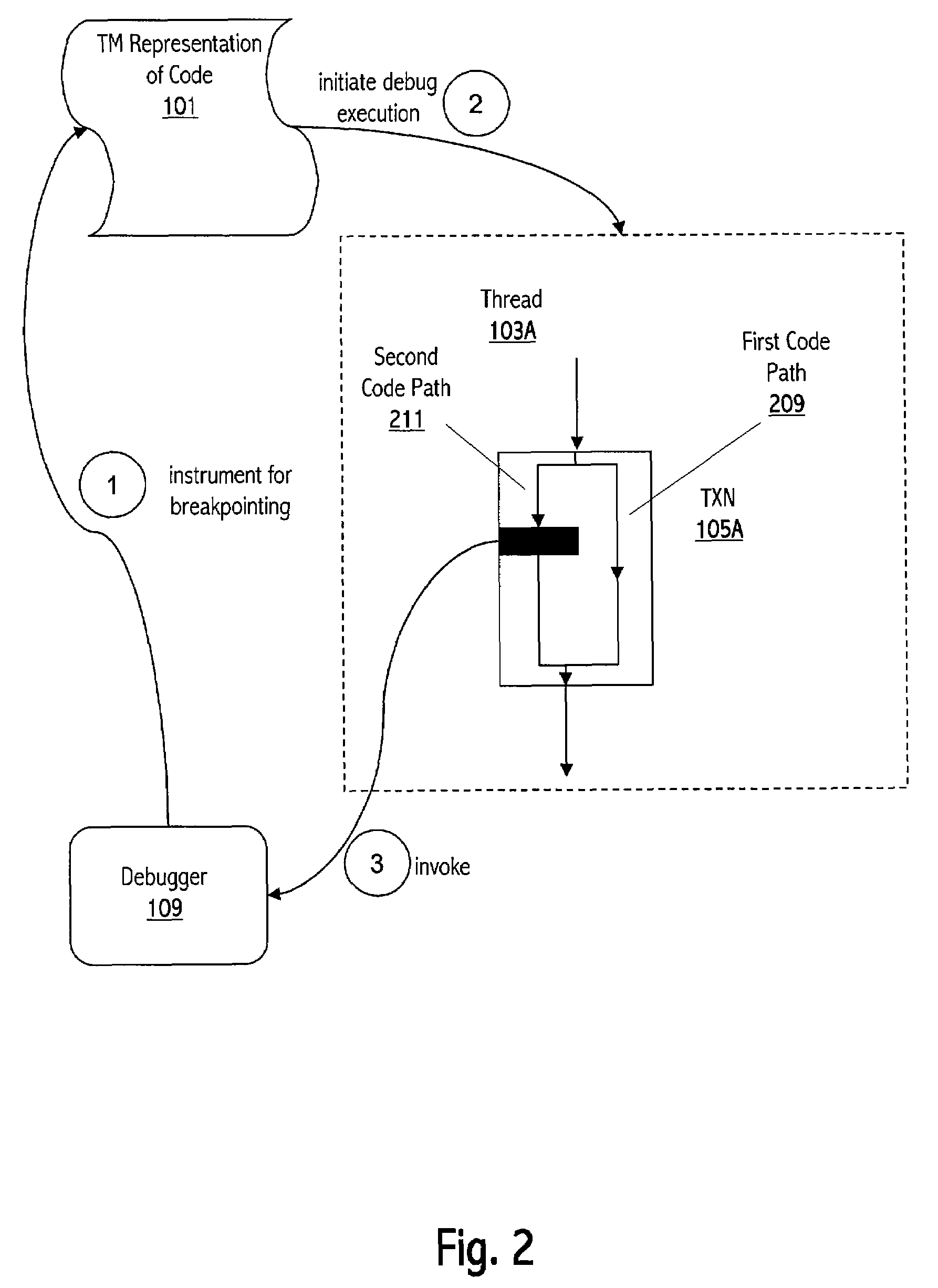
Replay debugging
ActiveUS20070288902A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingModified technique
Transactional programming promises to substantially simplify the development and maintenance of correct, scalable, and efficient concurrent programs. Designs for supporting transactional programming using transactional memory implemented in hardware, software, and a mixture of the two have emerged recently. Unfortunately, conventional debugging programs are often inadequate when employed in relation to code that employs transactional memory and new or modified techniques are needed. We describe techniques whereby certain facilities of a transactional memory implementation can be leveraged to provide replay debugging. With replay debugging, the user can examine a partial or complete execution of an atomic block after it has happened—for example, right before the execution commits. Moreover, in some cases the user can modify the replayed execution, and decide to commit the new modified execution instead of the original replayed one.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
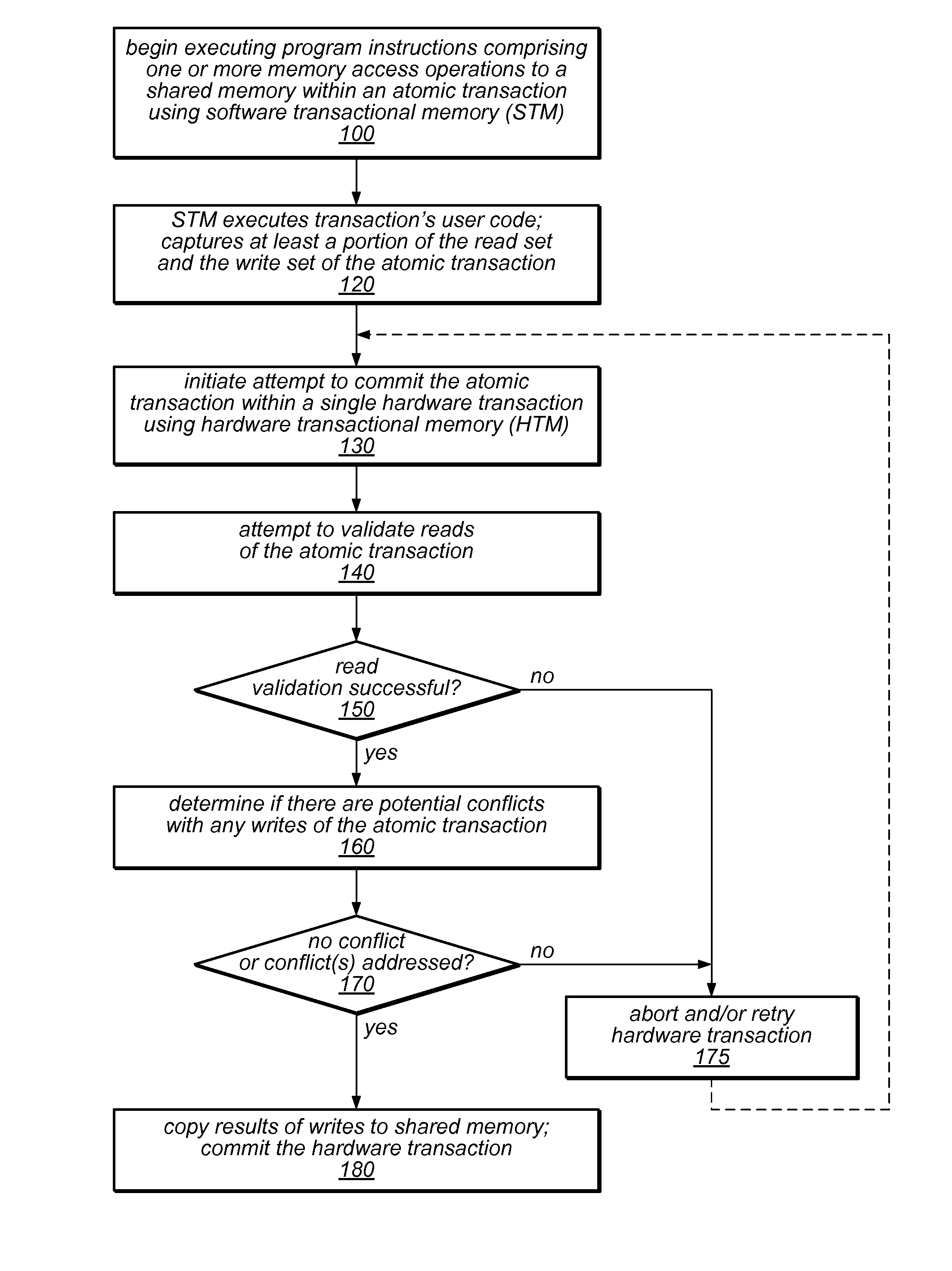
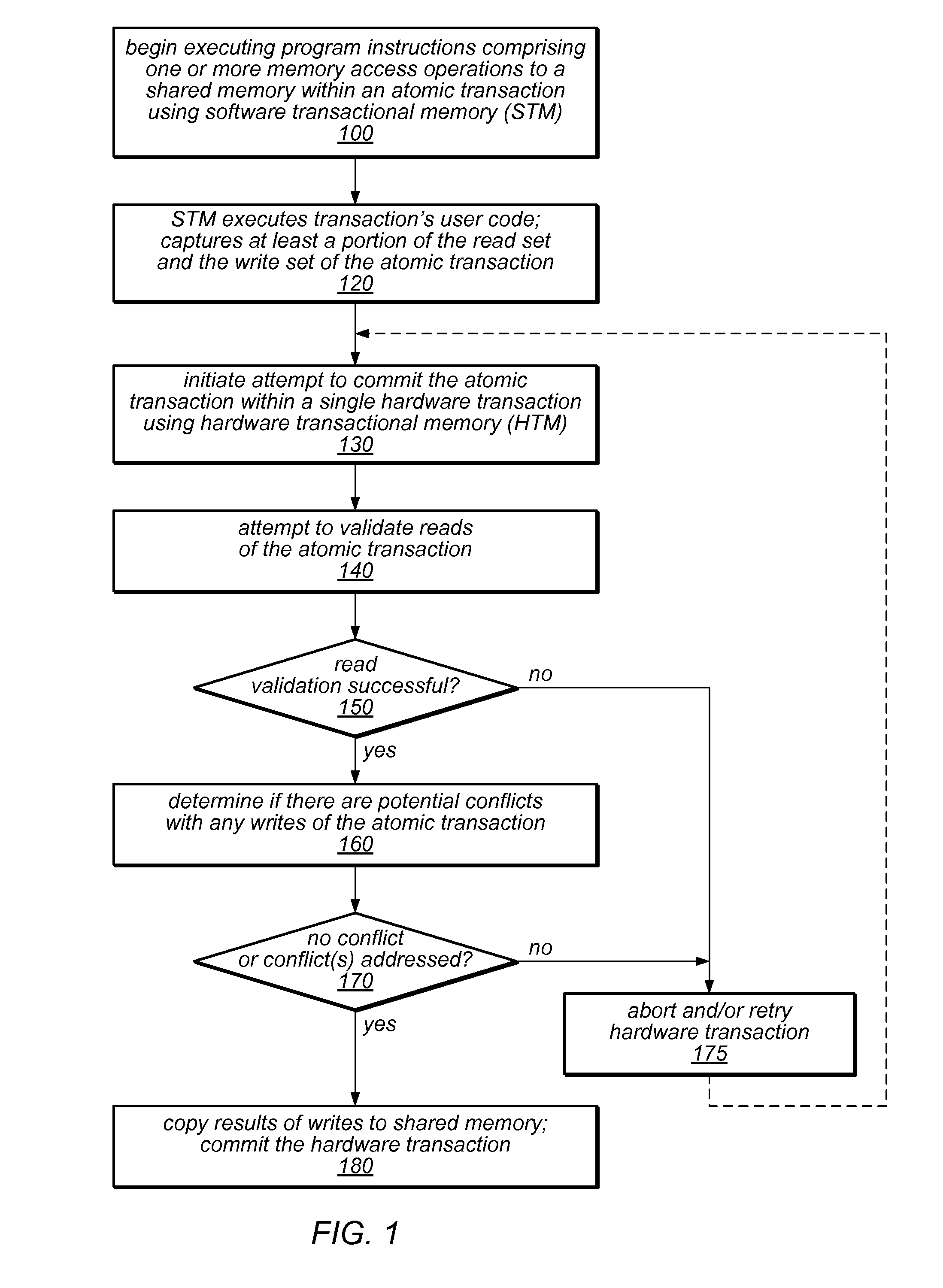
System and Method for Committing Results of a Software Transaction Using a Hardware Transaction
ActiveUS20110246725A1Improve software performanceReduce overheadMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRemedial actionUser code
The system and methods described herein may exploit hardware transactional memory to improve the performance of a software or hybrid transactional memory implementation, even when an entire user transaction cannot be executed within a hardware transaction. The user code of an atomic transaction may be executed within a software transaction, which may collect read and write sets and / or other information about the atomic transaction. A single hardware transaction may be used to commit the atomic transaction by validating the transaction's read set and applying the effects of the user code to memory, reducing the overhead associated with commitment of software transactions. Because the hardware transaction code is carefully controlled, it may be less likely to fail to commit. Various remedial actions may be taken before retrying hardware transactions following some failures. If a transaction exceeds the constraints of the hardware, it may be committed by the software transactional memory alone.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
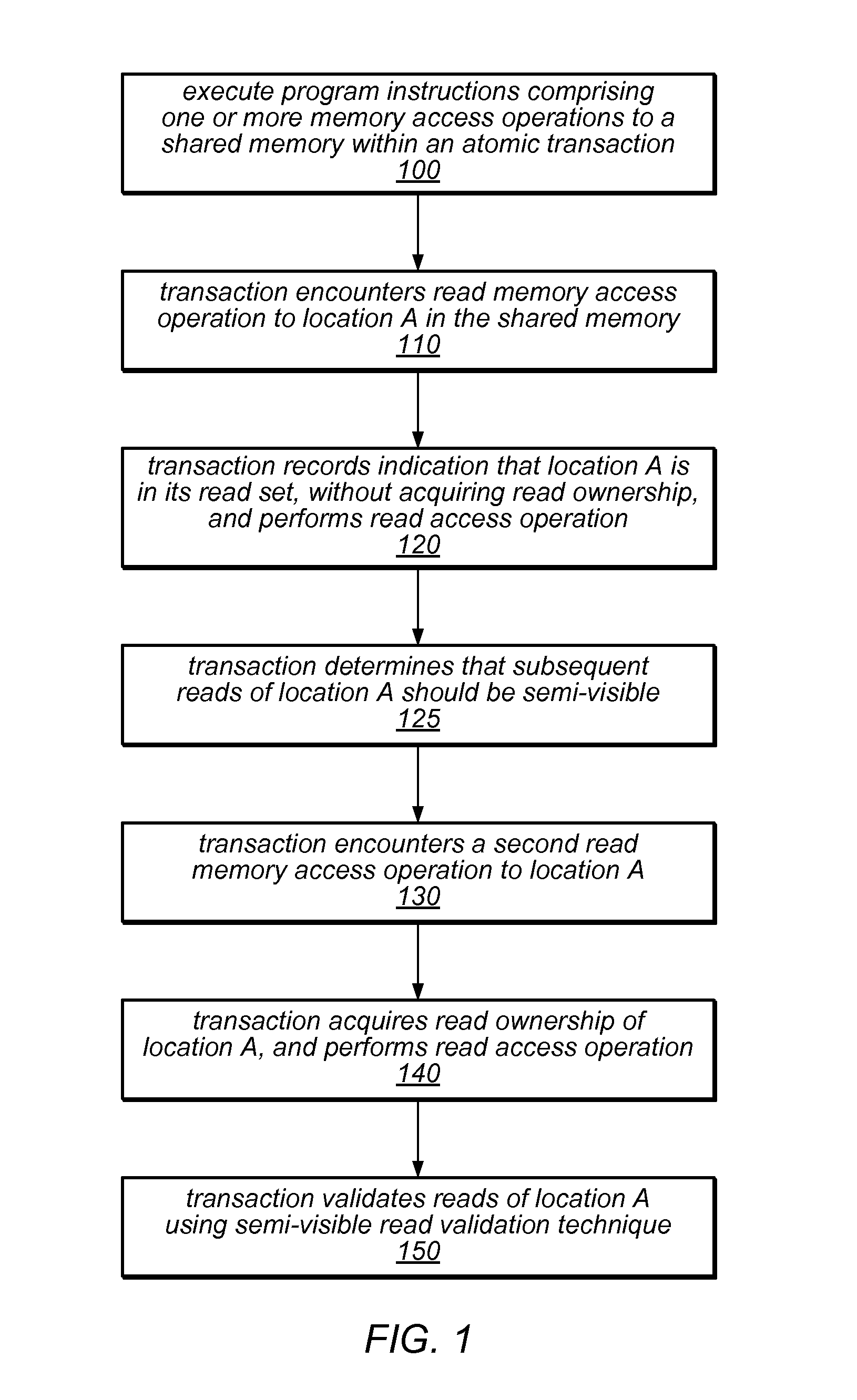
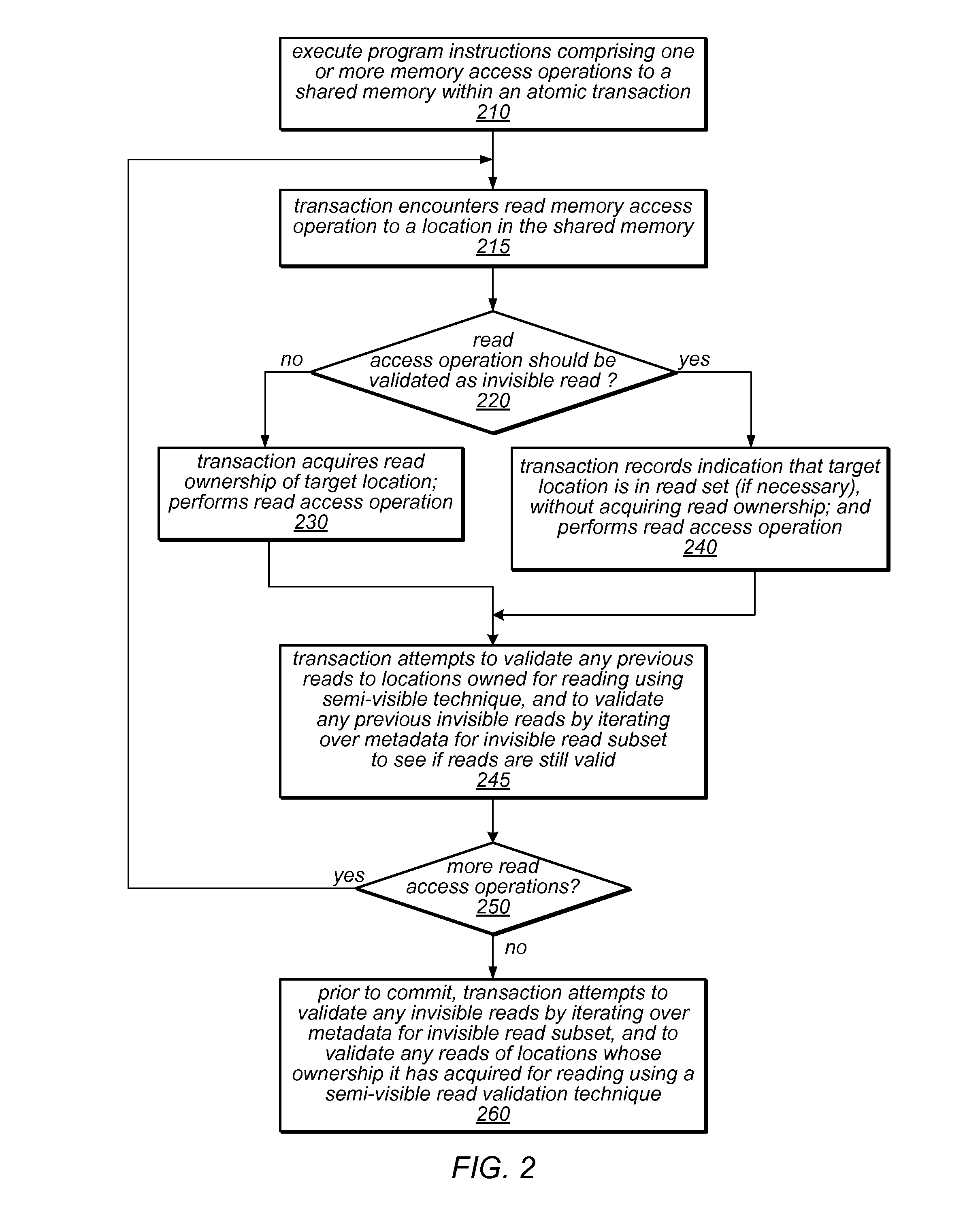
System and Method for Performing Dynamic Mixed Mode Read Validation In a Software Transactional Memory
ActiveUS20110125973A1Management costMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionMixed modeUser code
The transactional memory system described herein may apply a mix of read validation techniques to validate read operations (e.g., invisible reads and / or semi-visible reads) in different transactions, or to validate different read operations within a single transaction (including reads of the same location). The system may include mechanisms to dynamically determine that a read validation technique should be replaced by a different technique for reads of particular locations or for all subsequent reads, and / or to dynamically adjust the balance between different read validation techniques to manage costs. Some of the read validation techniques may be supported by hardware transactional memory (HTM). The system may delay acquisition of ownership records for reading, and may acquire two or more ownership records back-to-back (e.g., within a single hardware transaction). The user code of a software transaction may be divided into multiple segments, some of which may be executed within a hardware transaction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Facilitating concurrent non-transactional execution in a transactional memory system
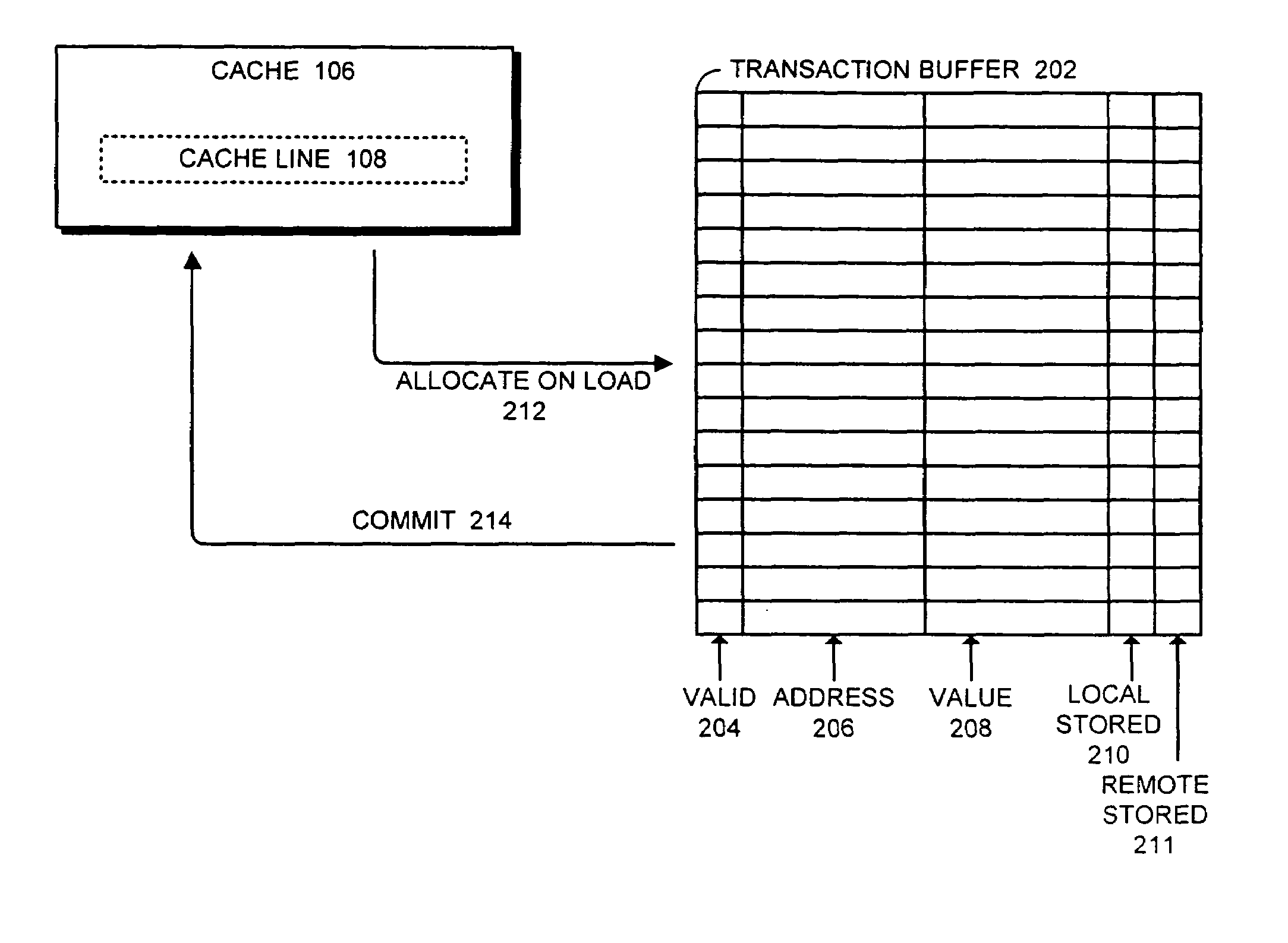
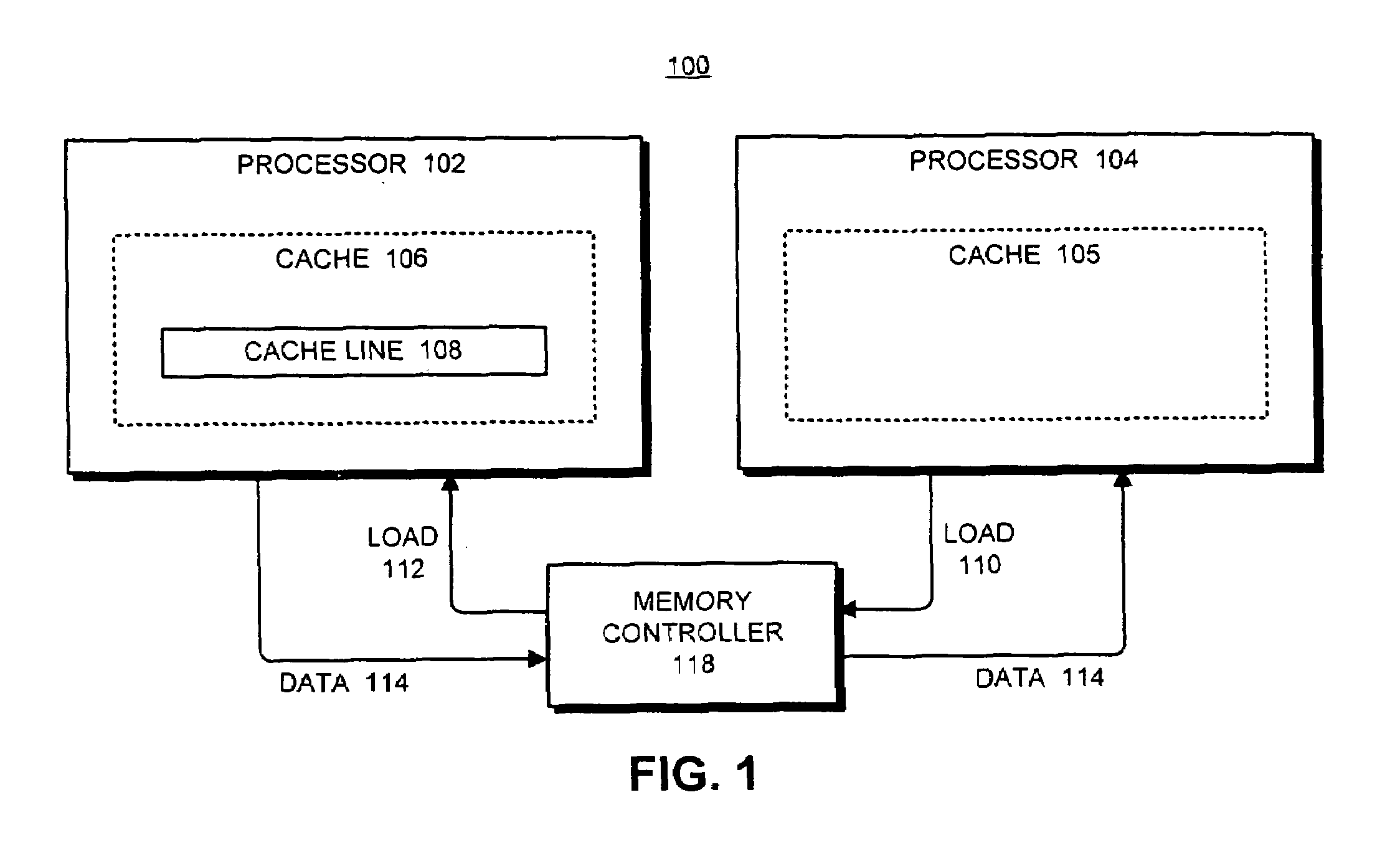
ActiveUS7421544B1Facilitates concurrent non-transactional operationMemory loss protectionTransaction processingLoad instructionParallel computing
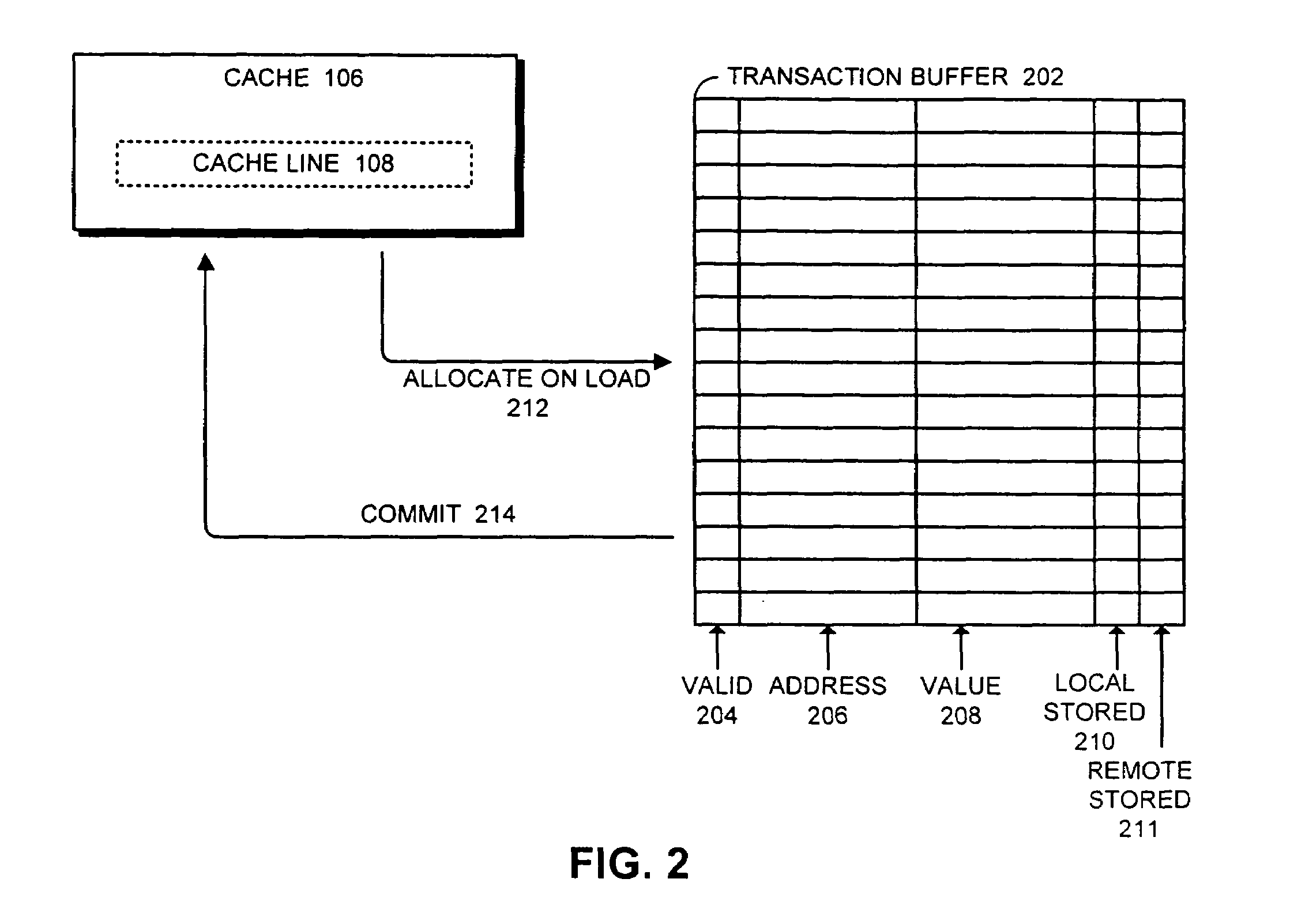
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates concurrent non-transactional operations in a transactional memory system. During operation, the system receives a load instruction related to a local transaction. Next, the system determines if an entry for the memory location requested by the load instruction already exists in the transaction buffer. If not, the system allocates an entry for the memory location in the transaction buffer, reads data for the load instruction from the cache, and stores the data in the transaction buffer. Finally, the system returns the data to the processor to complete the load instruction. In this way, if a remote non-transactional store instruction is received during the transaction, the remote non-transactional store proceeds and does not cause the local transaction to abort.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Contention management for a hardware transactional memory
ActiveUS20090133032A1Easy to shapeSimple taskMemory systemsTransaction processingConsistency controlOperating system
A hardware transactional memory 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 is provided within a multiprocessor 4, 6, 8, 10 system with coherency control and hardware transaction memory control circuitry 22 that serves to at least partially manage the scheduling of processing transactions in dependence upon conflict data 26, 28, 30. The conflict data characterises previously encountered conflicts between processing transactions. The scheduling is performed such that a candidate processing transaction will not be scheduled if the conflict data indicates that one of the already running processing transactions has previously conflicted with the candidate processing transaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Using transactional memory with early release to implement non-blocking dynamic-sized data structure
ActiveUS8074030B1Easy to optimizeSimple and convenient coordination facilityMemory systemsTransaction processingEarly releaseData dependent
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
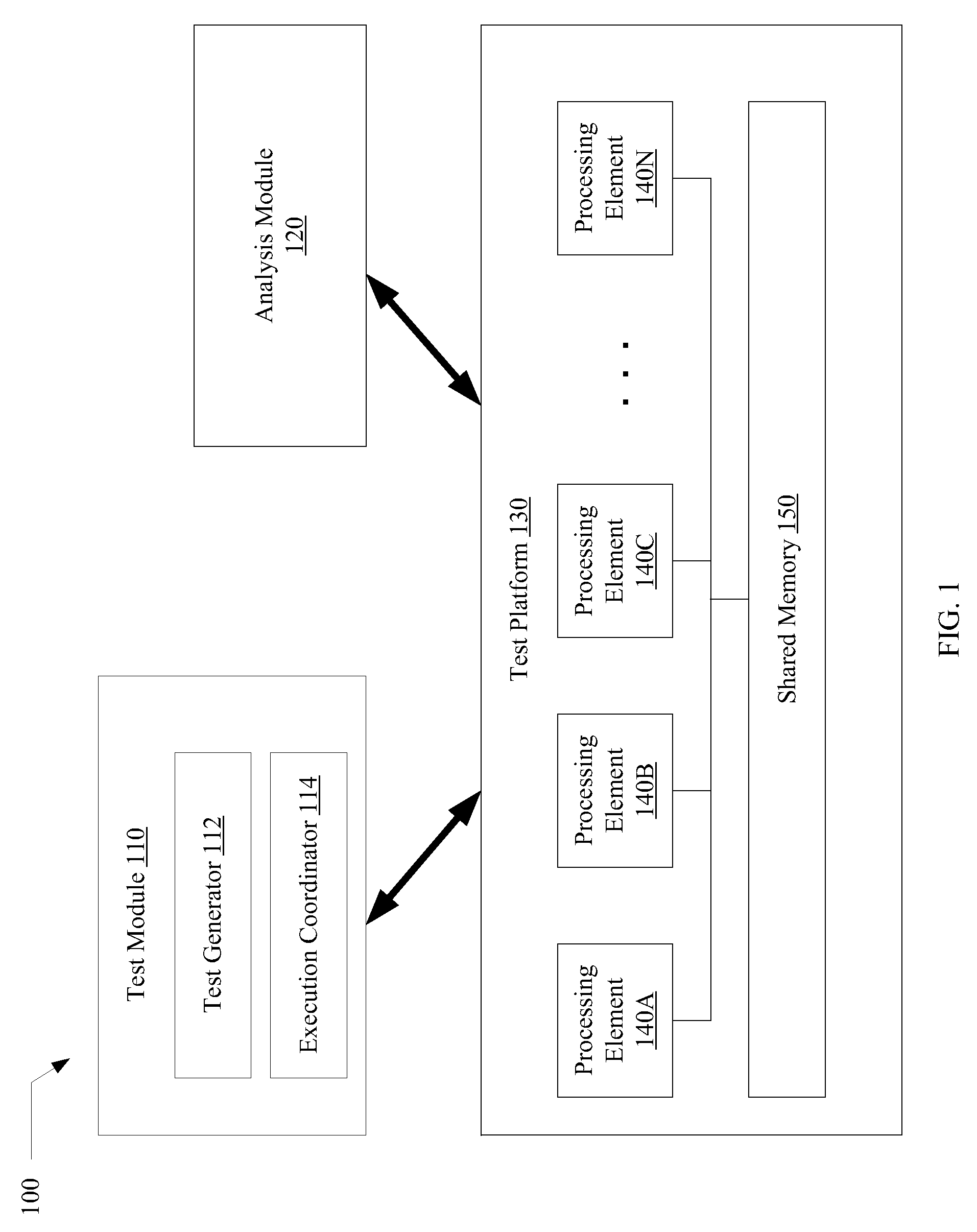
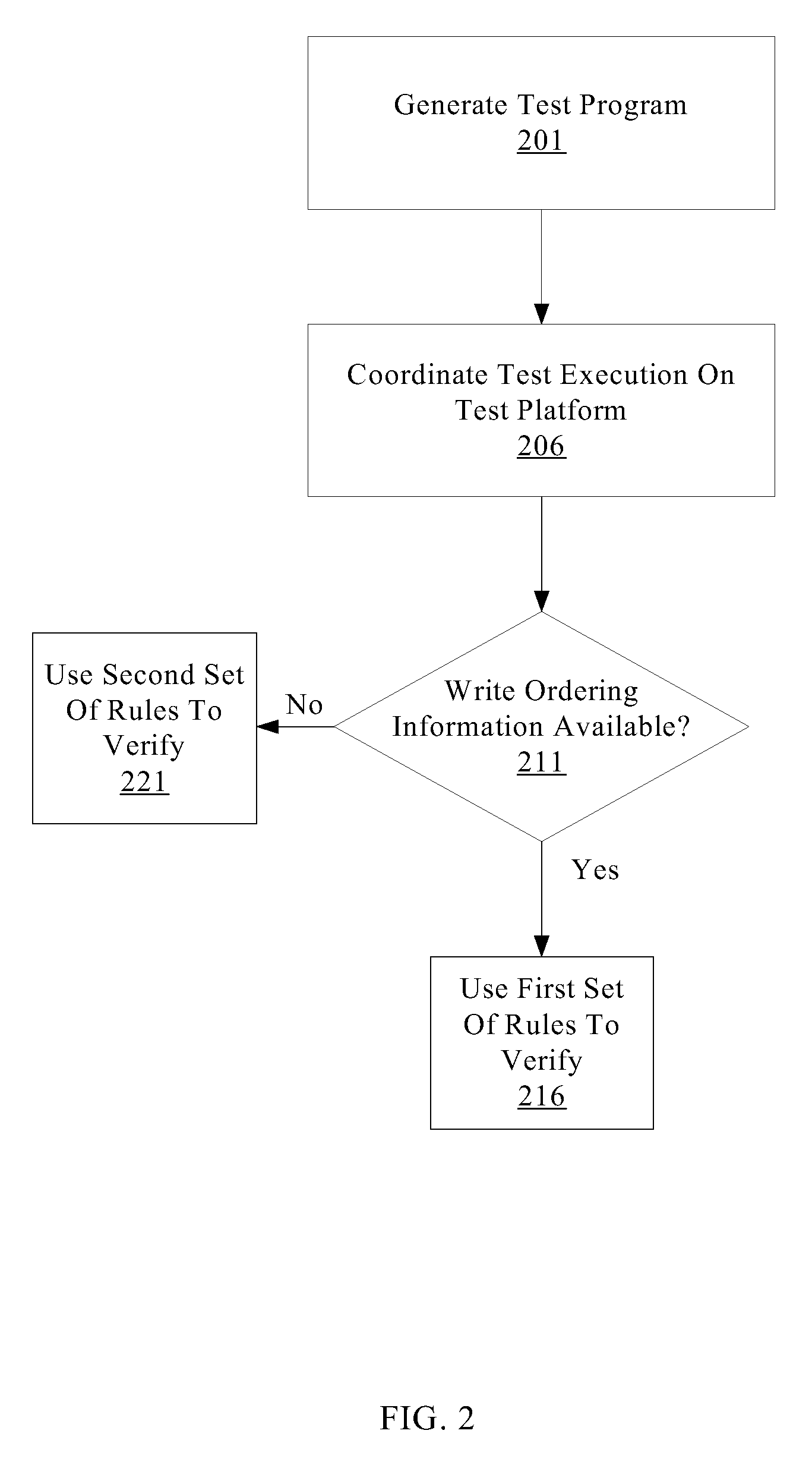
Verification of memory consistency and transactional memory
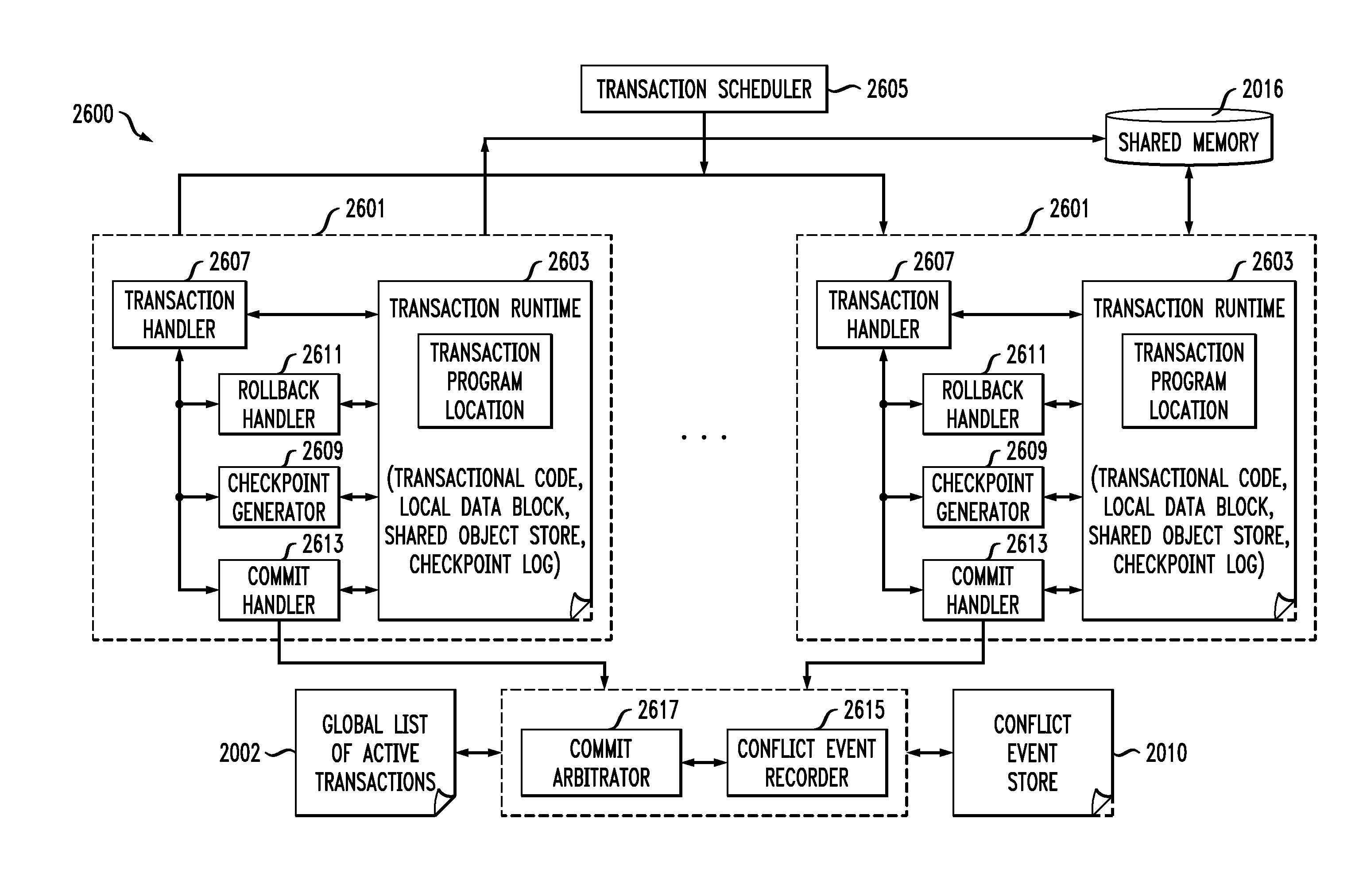
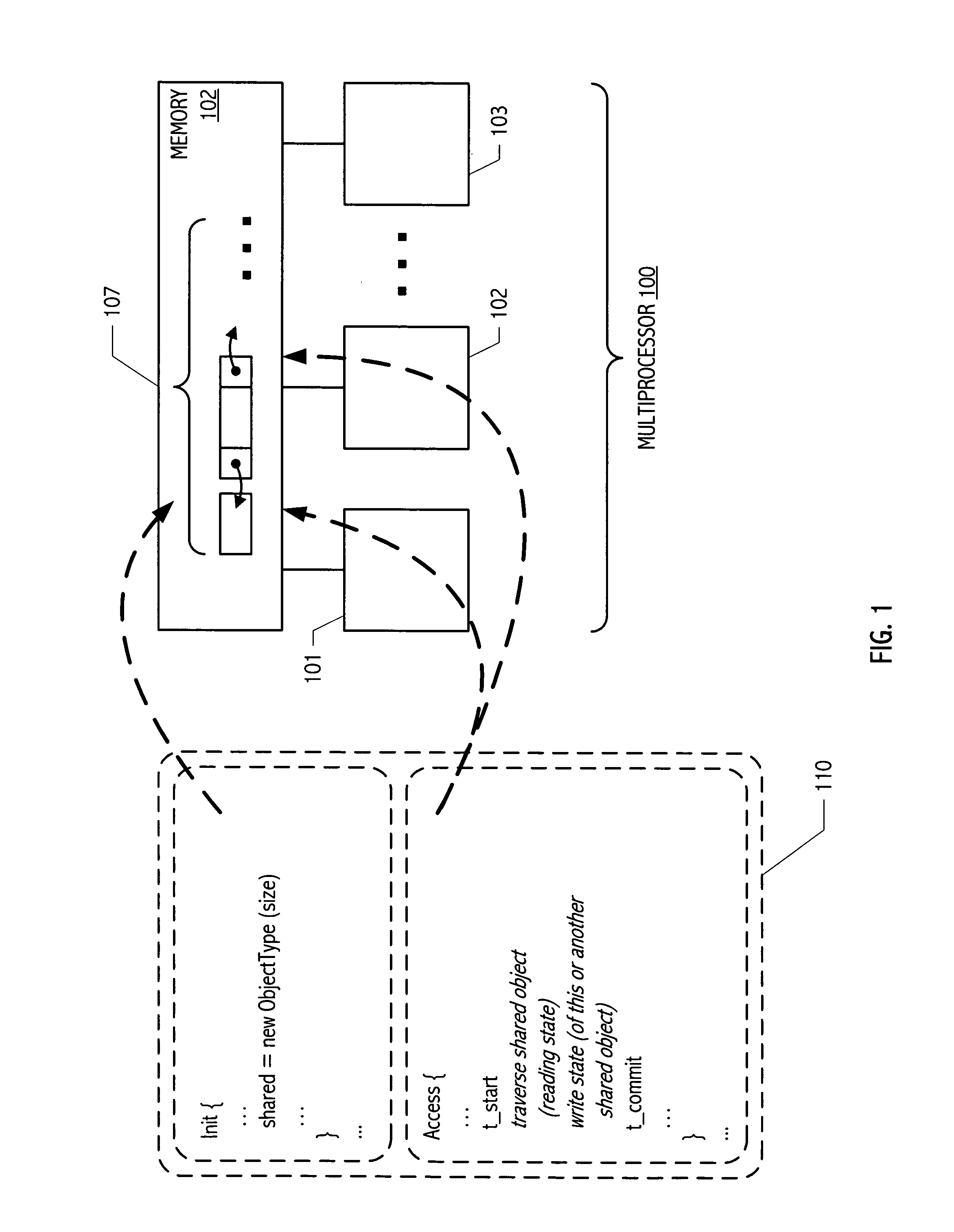
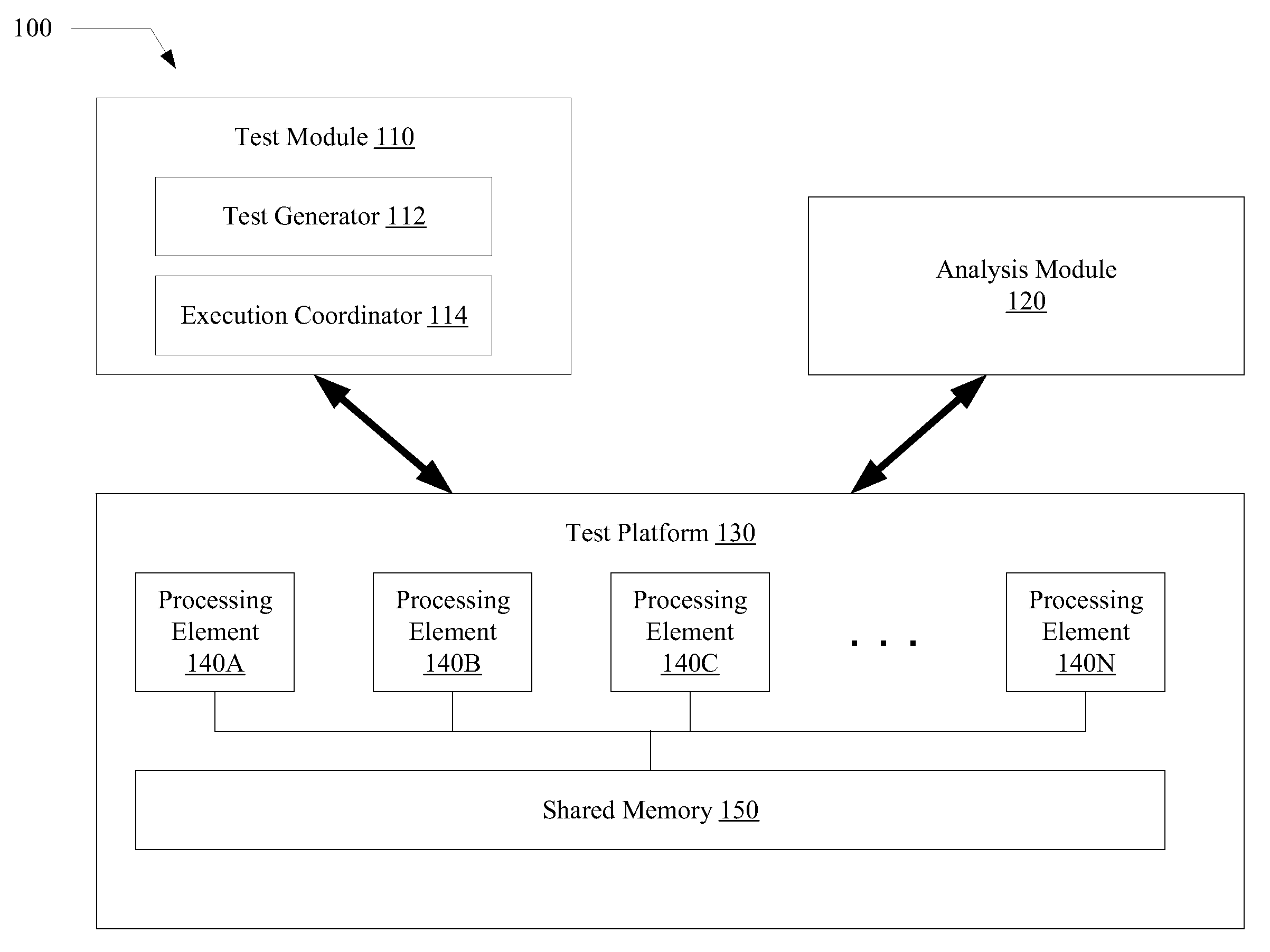
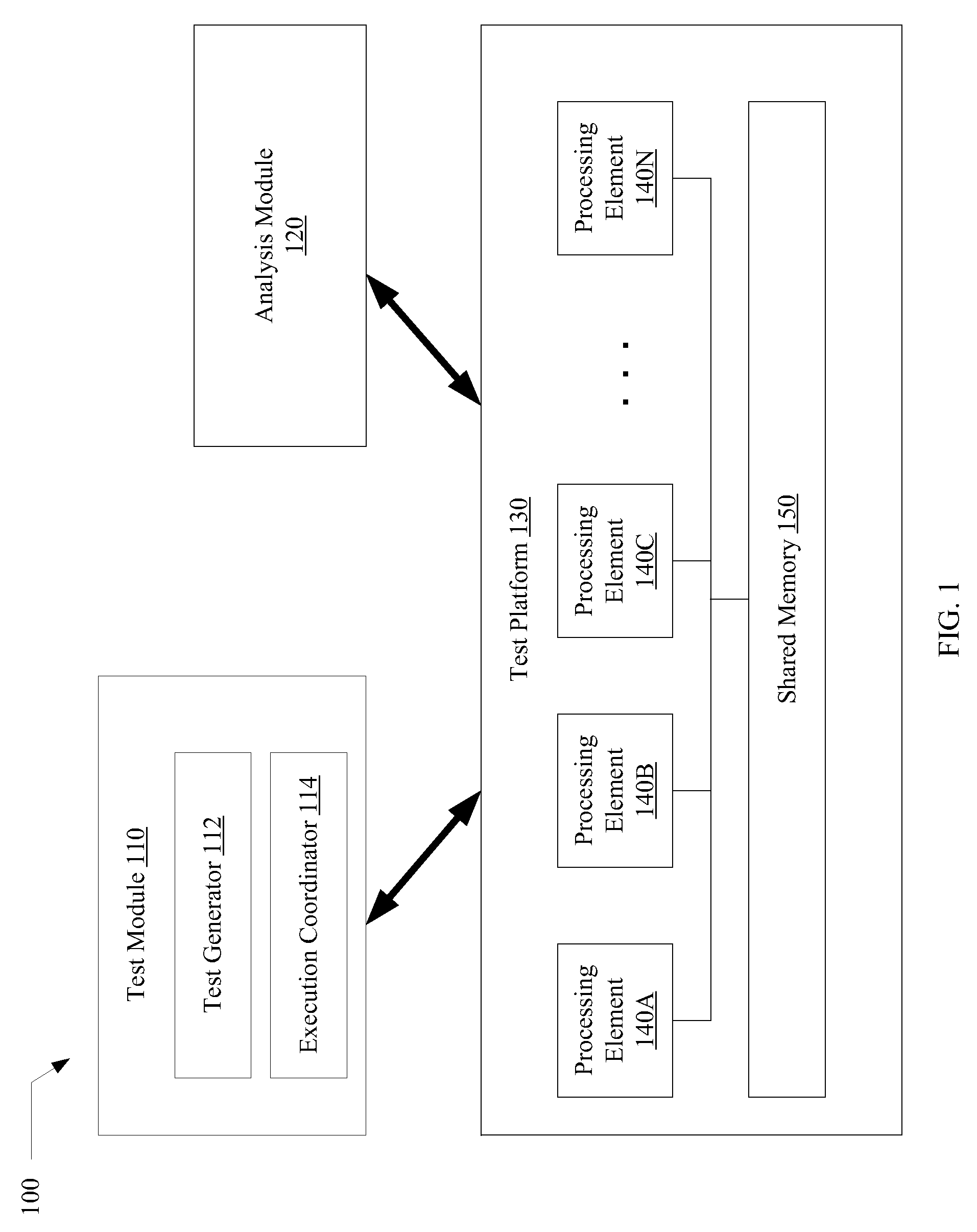
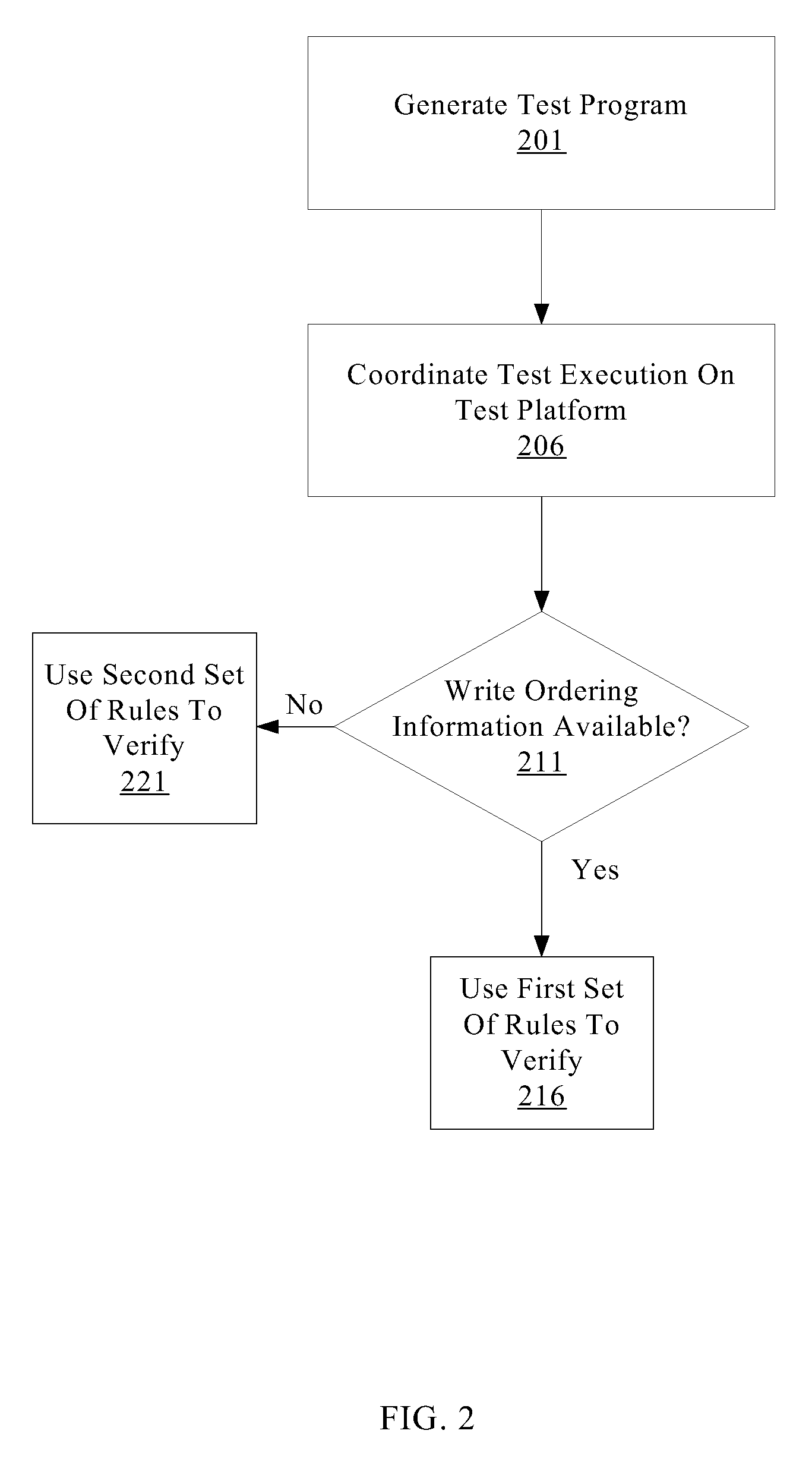
A system for efficiently verifying compliance with a memory consistency model includes a test module and an analysis module. The test module may coordinate an execution of a multithreaded test program on a test platform. If the test platform provides an indication of the order in which writes from multiple processing elements are performed at shared memory locations, the analysis module may use a first set of rules to verify that the results of the execution correspond to a valid ordering of events according to a memory consistency model. If the test platform does not provide an indication of write ordering, the analysis module may use a second set of rules to verify compliance with the memory consistency model. Further, a backtracking search may be performed to find a valid ordering if such ordering exists or show that none exists and, hence, confirm whether or not the results comply with the given memory consistency model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
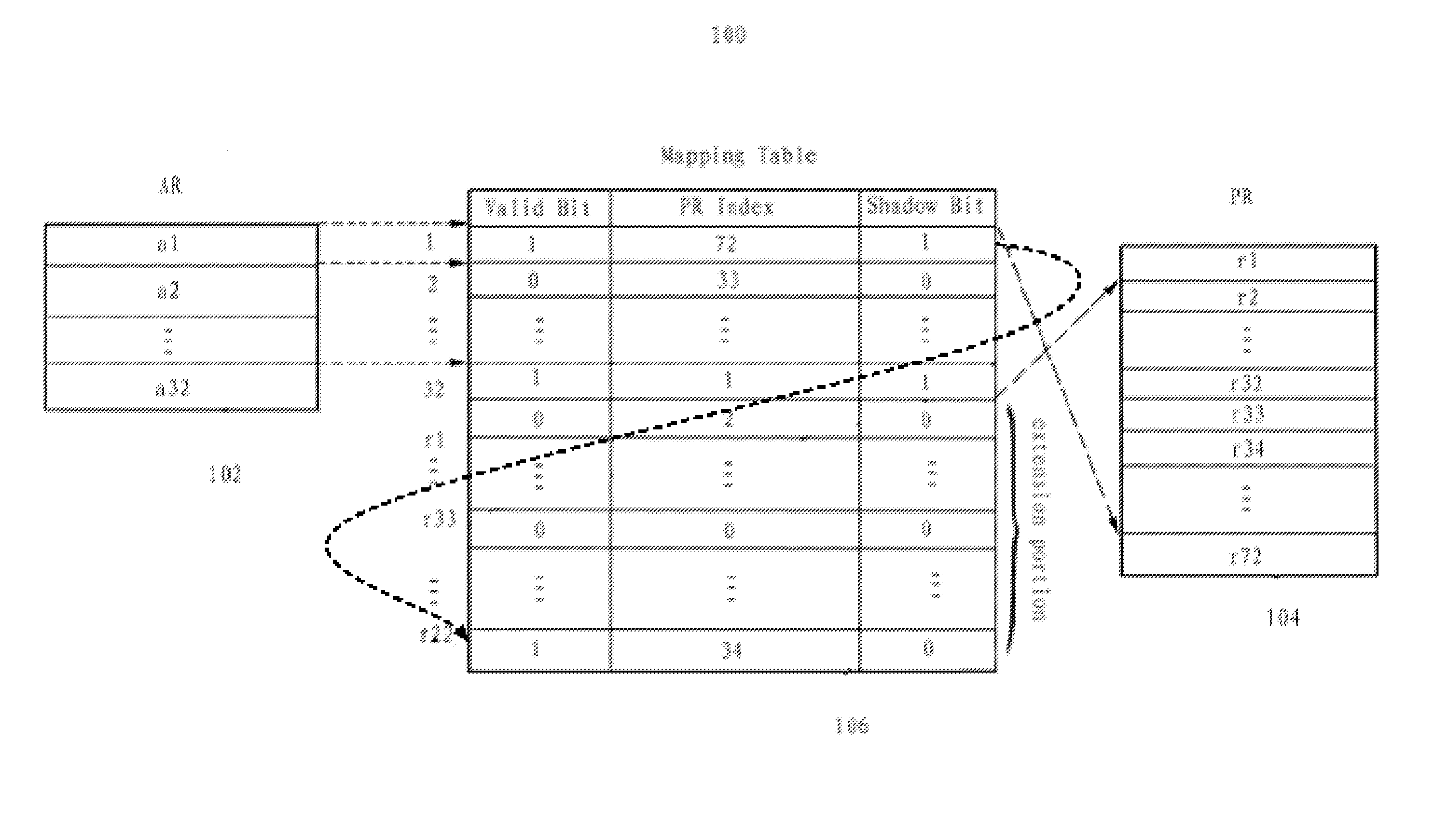
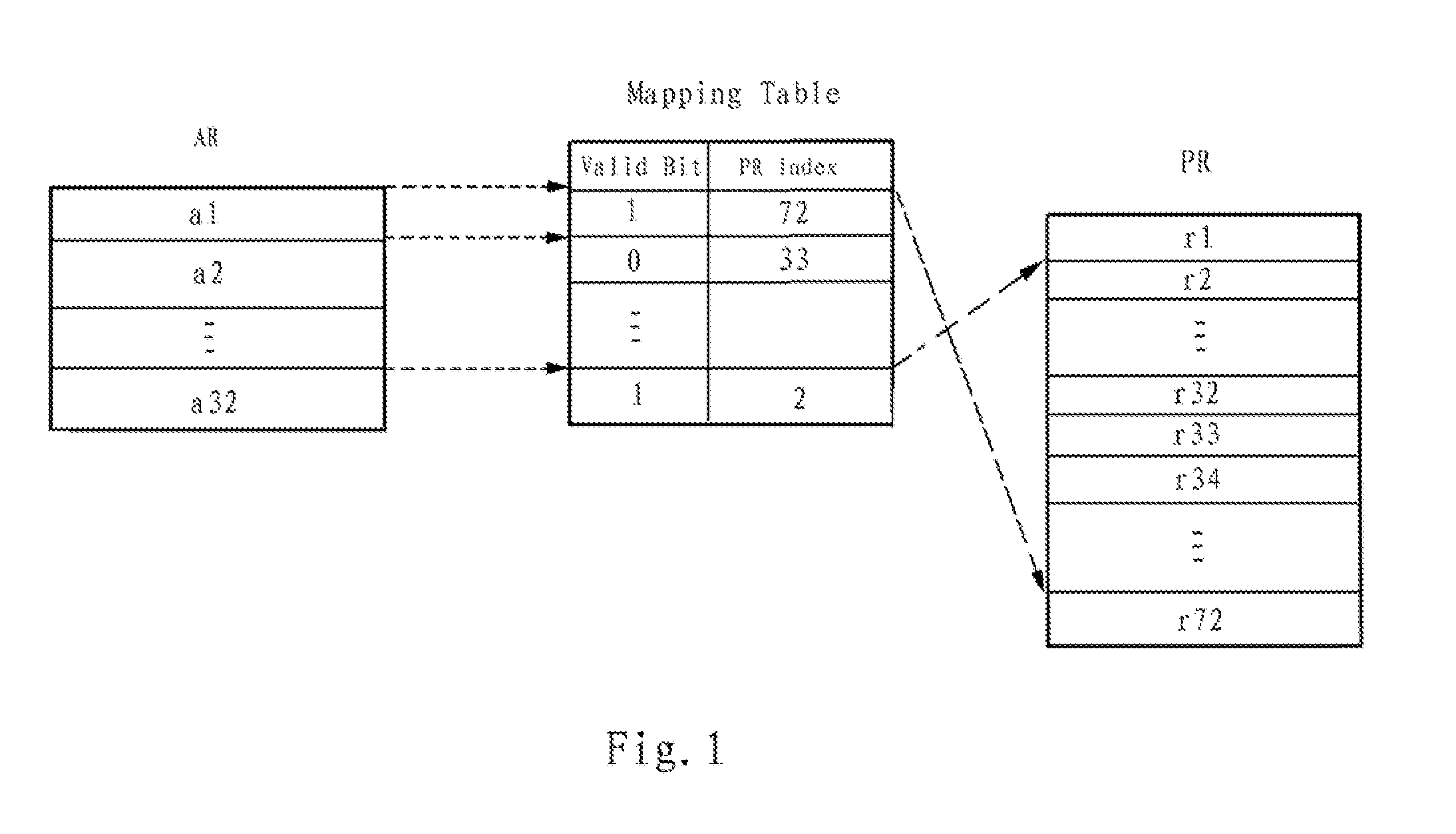
Fast context save in transactional memory
InactiveUS20100217945A1Reduce buffer requirementReduce overheadMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationComputer architectureProcessor register
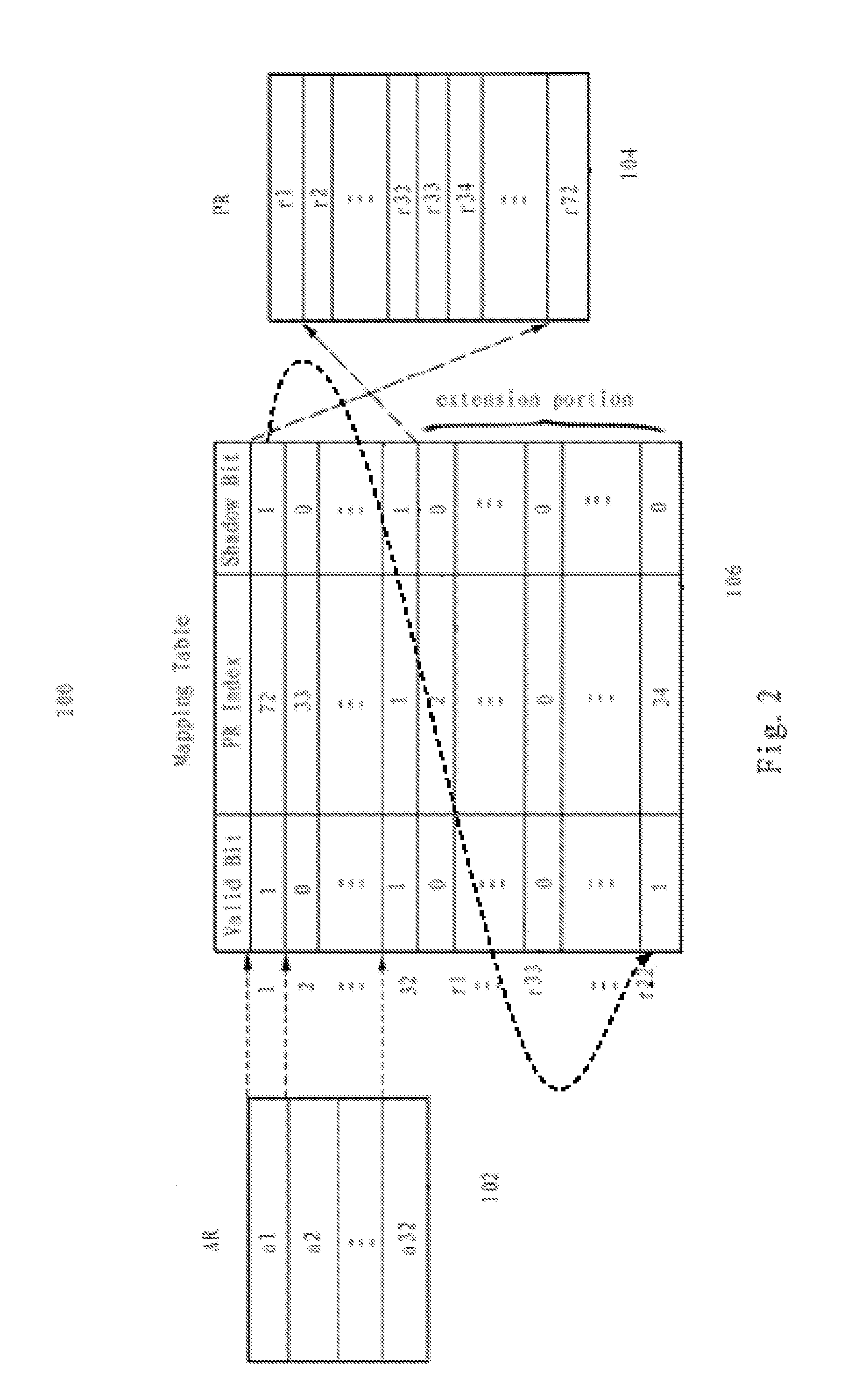
The present invention provides a method, apparatus and article of manufacture, for fast context saving in transactional memory. The method creates a mapping table that includes entries corresponding to architectural registers. Each entry includes a physical register index and shadow bit of a first physical register mapped to an architectural register. In response to a detection that an update occurs to an architectural register in a transaction and its shadow bit being an invalid value, the method sets the shadow bit to be a valid value and sets a shadow register for the architectural register using the physical register index of the first physical register. The method maps a second physical register to the shadow register in order to save a modified value generated by an update process and saves the original value before the update process by use of the first physical register corresponding to the architecture register.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and Method for Implementing Hybrid Single-Compare-Single-Store Operations
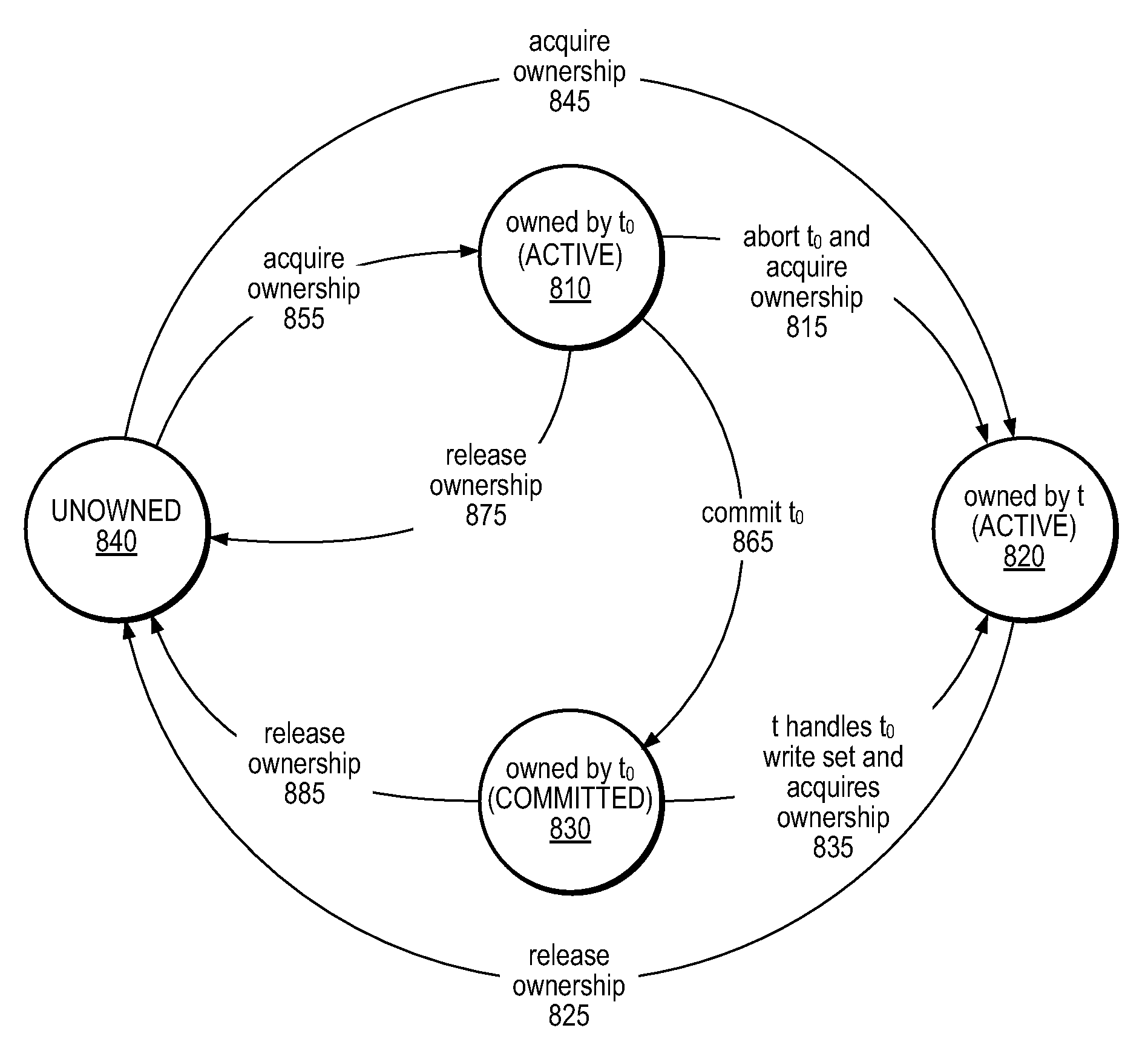
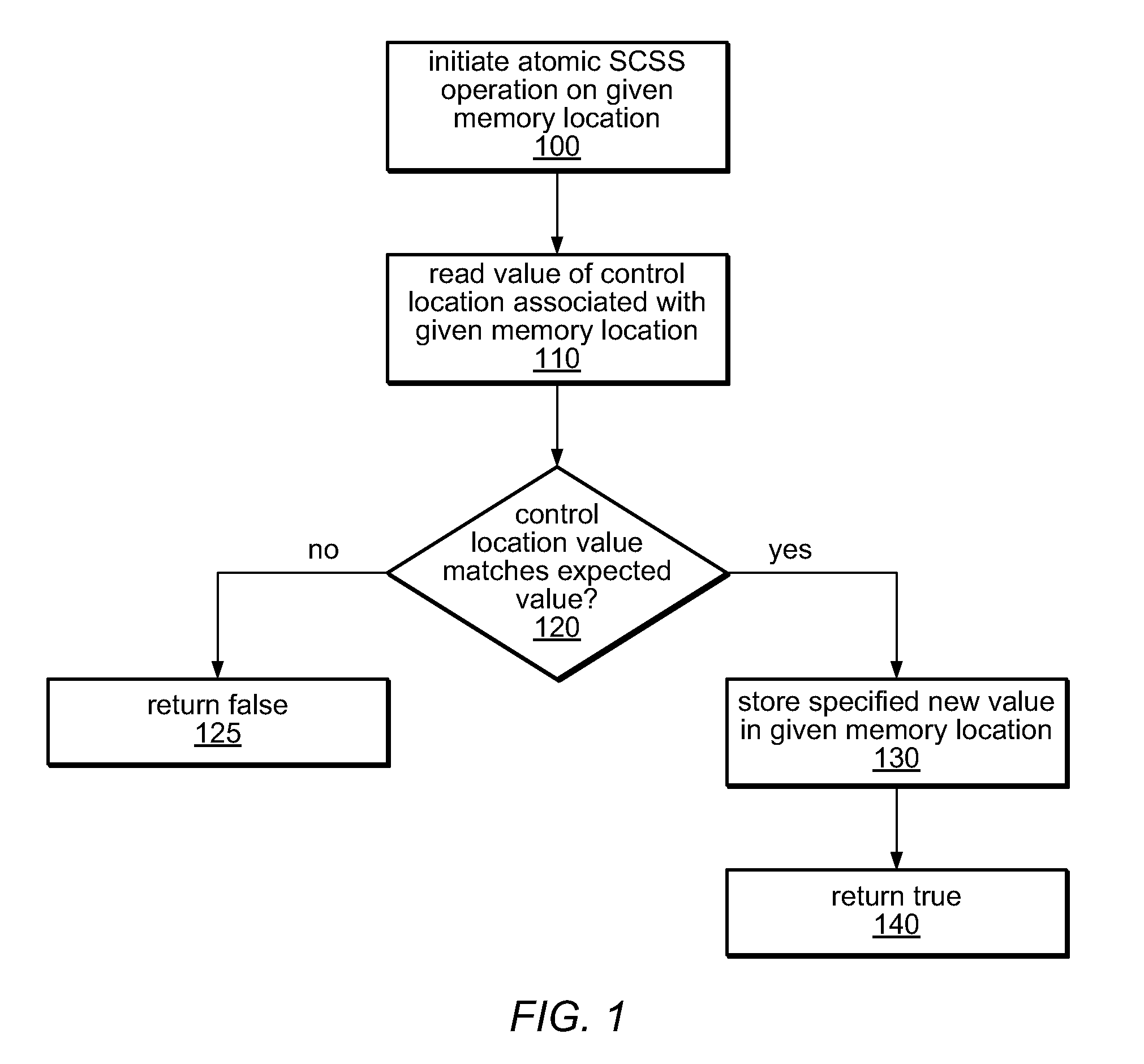
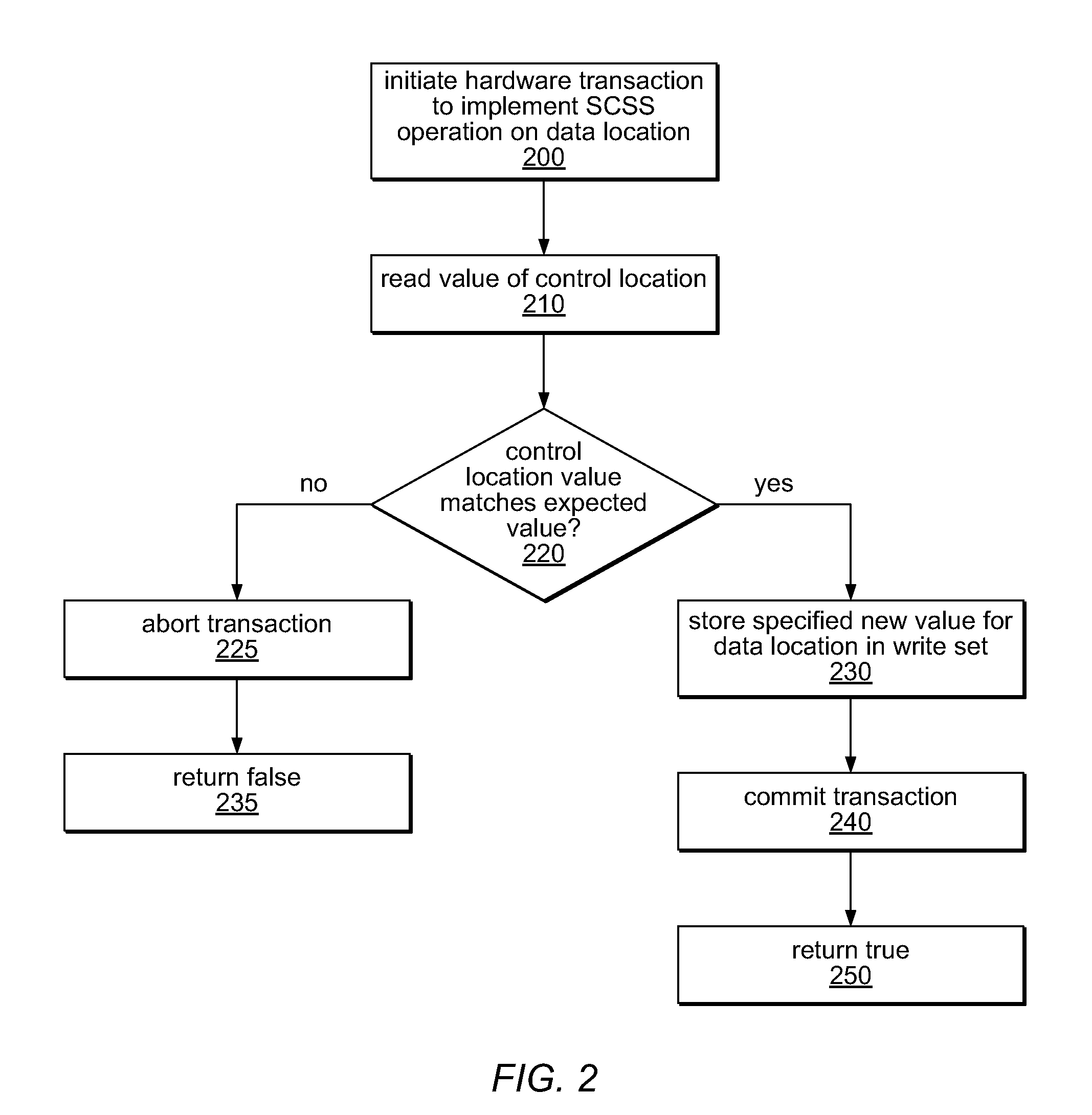
A hybrid Single-Compare-Single-Store (SCSS) operation may exploit best-effort hardware transactional memory (HTM) for good performance in the case that it succeeds, and may transparently resort to software-mediated transactions if the hardware transactional mechanisms fail. The SCSS operation may compare a value in a control location to a specified expected value, and if they match, may store a new value in a separate data location. The control value may include a global lock, a transaction status indicator, and / or a portion of an ownership record, in different embodiments. If another transaction in progress owns the data location, the SCSS operation may abort the other transaction or may help it complete by copying the other transactions' write set into its own right set before acquiring ownership. A hybrid SCSS operation, which is usually nonblocking, may be applied to building software transactional memories (STMs) and / or hybrid transactional memories (HyTMs), in some embodiments.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and Method for Implementing Nonblocking Zero-Indirection Transactional Memory
ActiveUS20090171962A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsObject basedSoftware
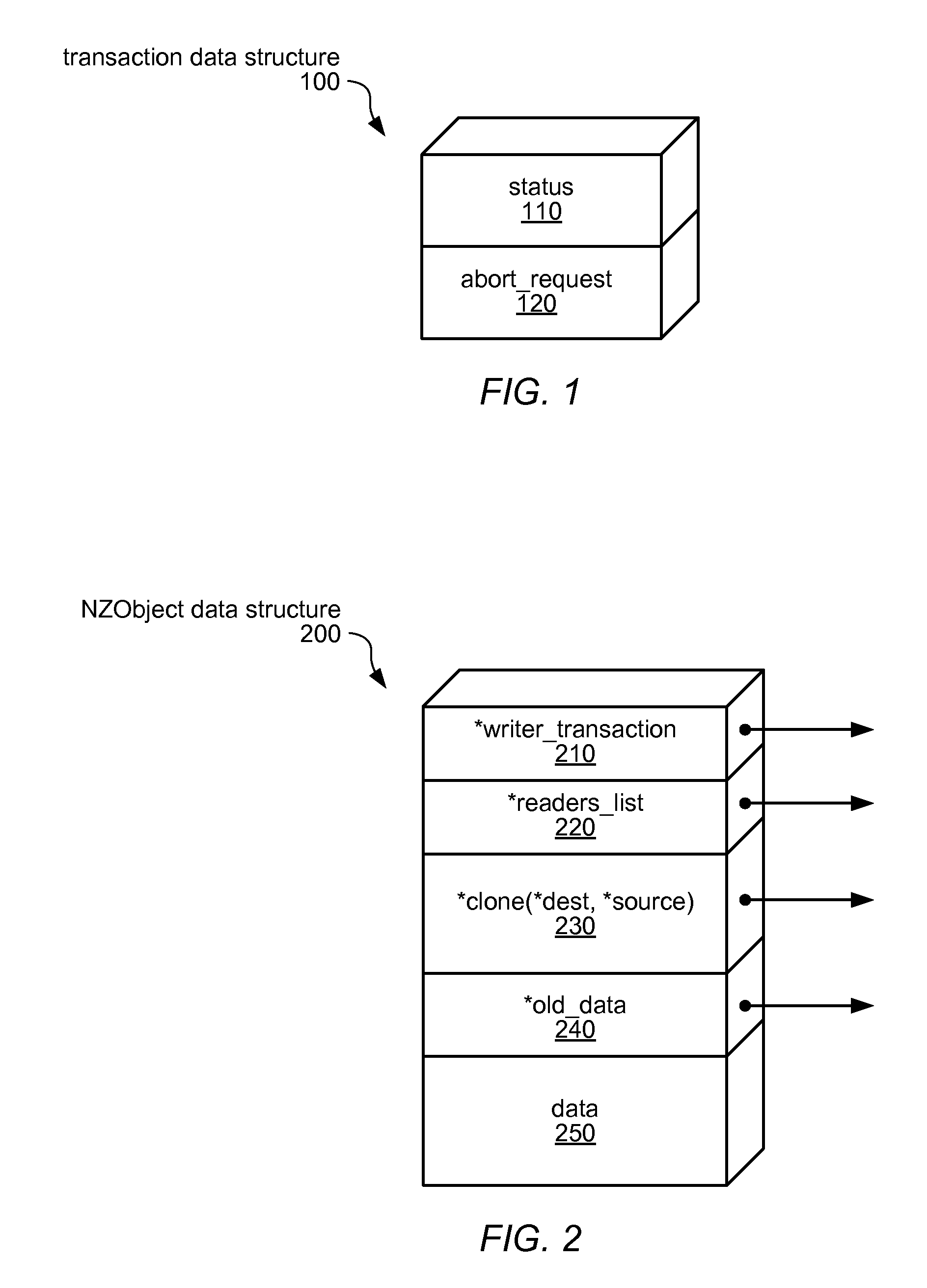
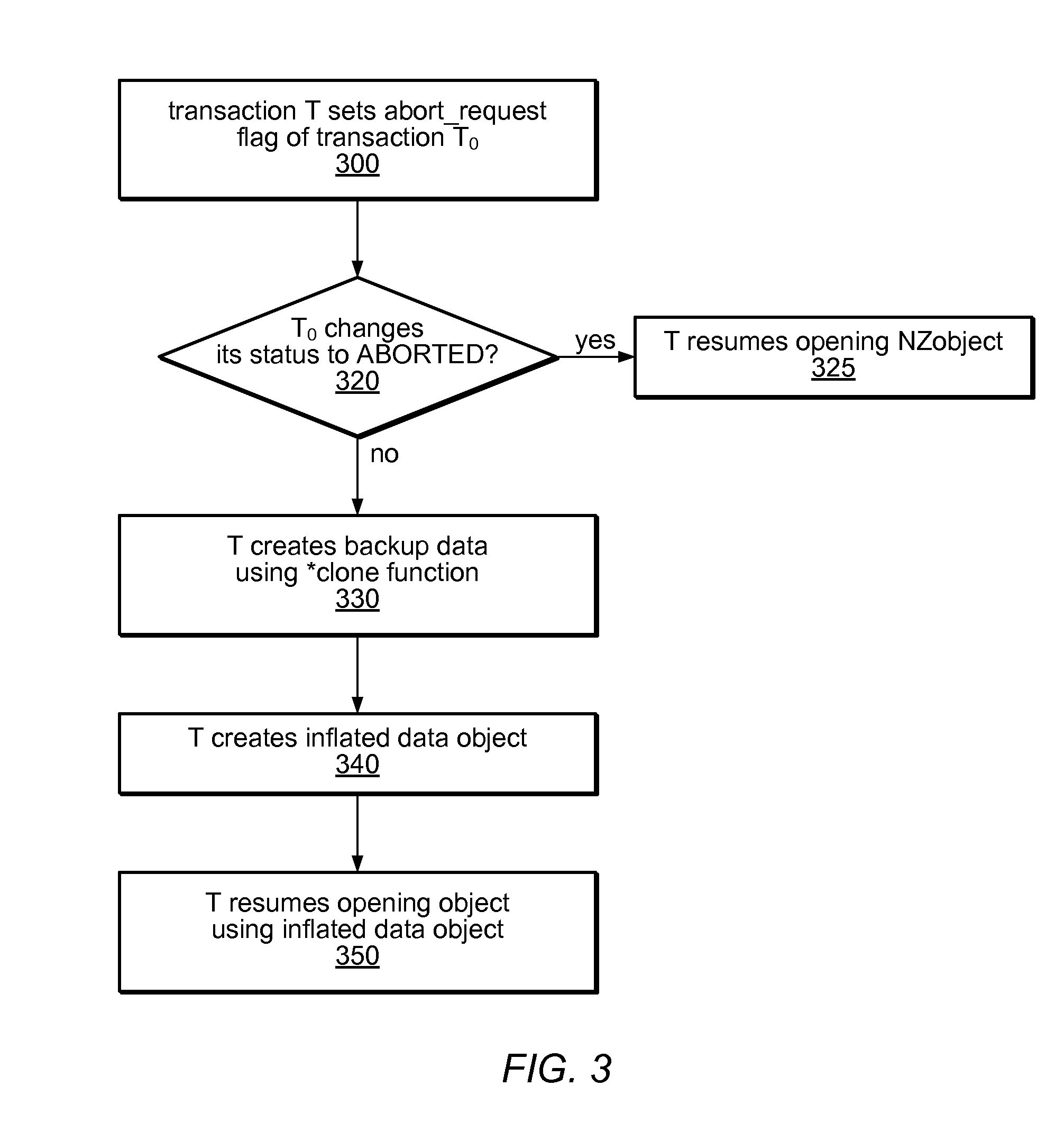
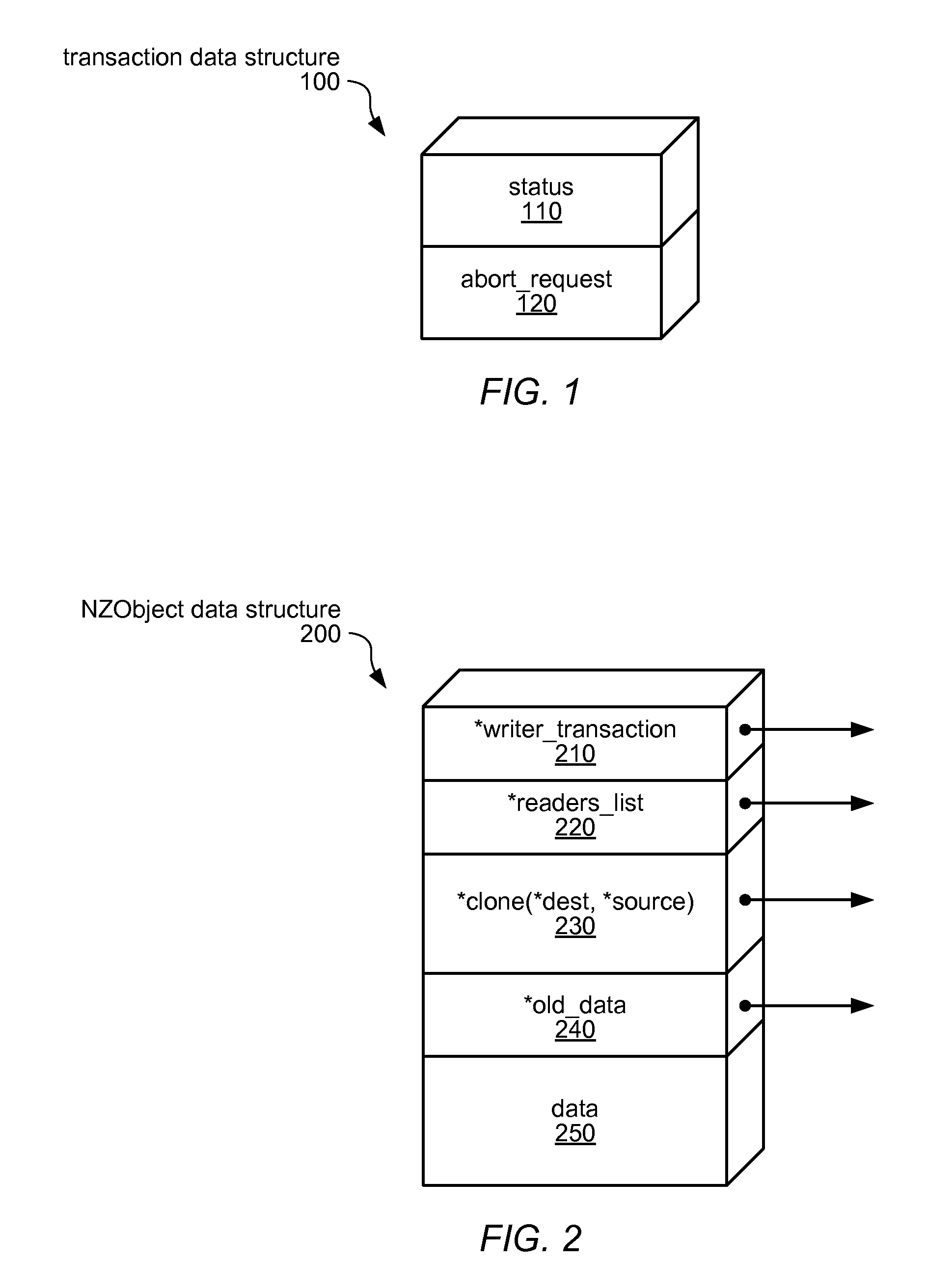
Systems and methods for implementing and using nonblocking zero-indirection software transactional memory (NZSTM) are disclosed. NZSTM systems implement object-based software transactional memory that eliminates all levels of indirection except in the uncommon case of a conflict with an unresponsive thread. Shared data is co-located with a header in an NZObject, and is addressable at a fixed offset from the header. Conflicting transactions are requested to abort themselves without being forced to abort. NZObjects are modified in place when there are no conflicts, and when a conflicting transaction acknowledges the abort request. In the uncommon case, NZObjects are inflated to introduce a locator and some levels of indirection, and are restored to their un-inflated form following resolution of the conflict. In some embodiments, transactions are executed using best effort hardware transactional memory if it is available and effective, and software transactional memory if not, yielding a hybrid transactional memory system, NZTM.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
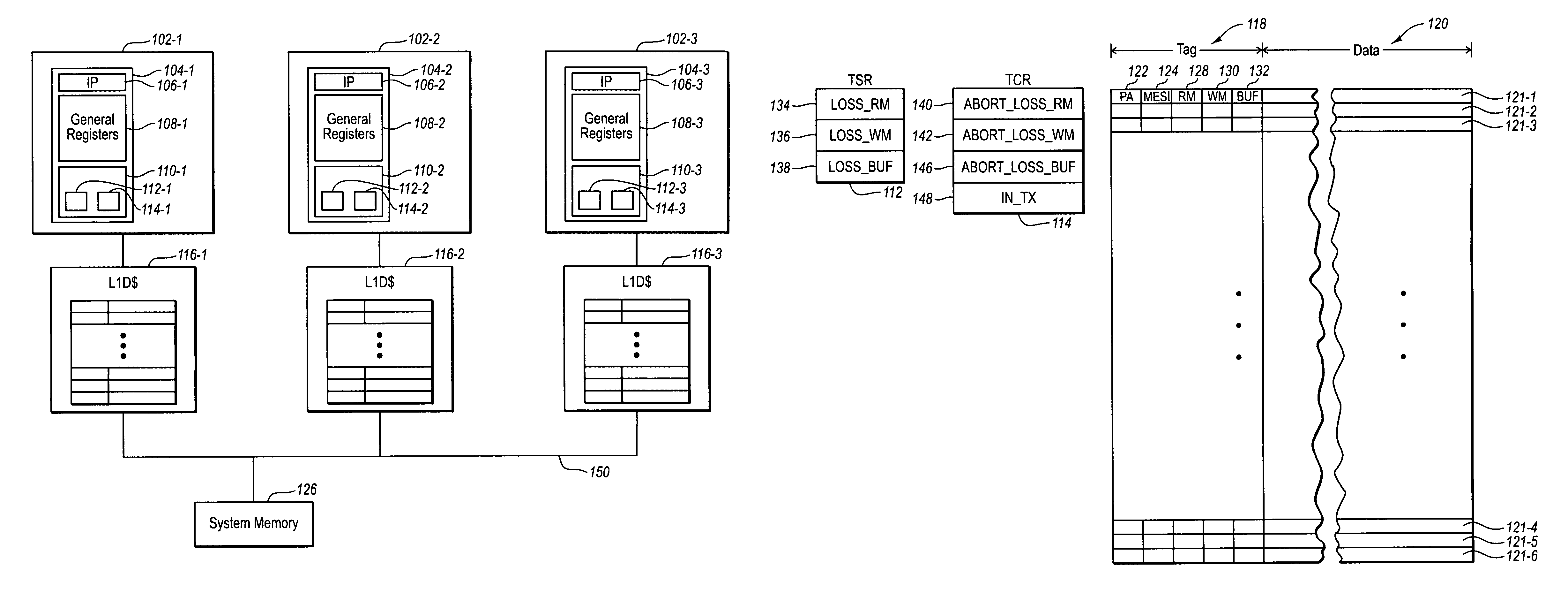
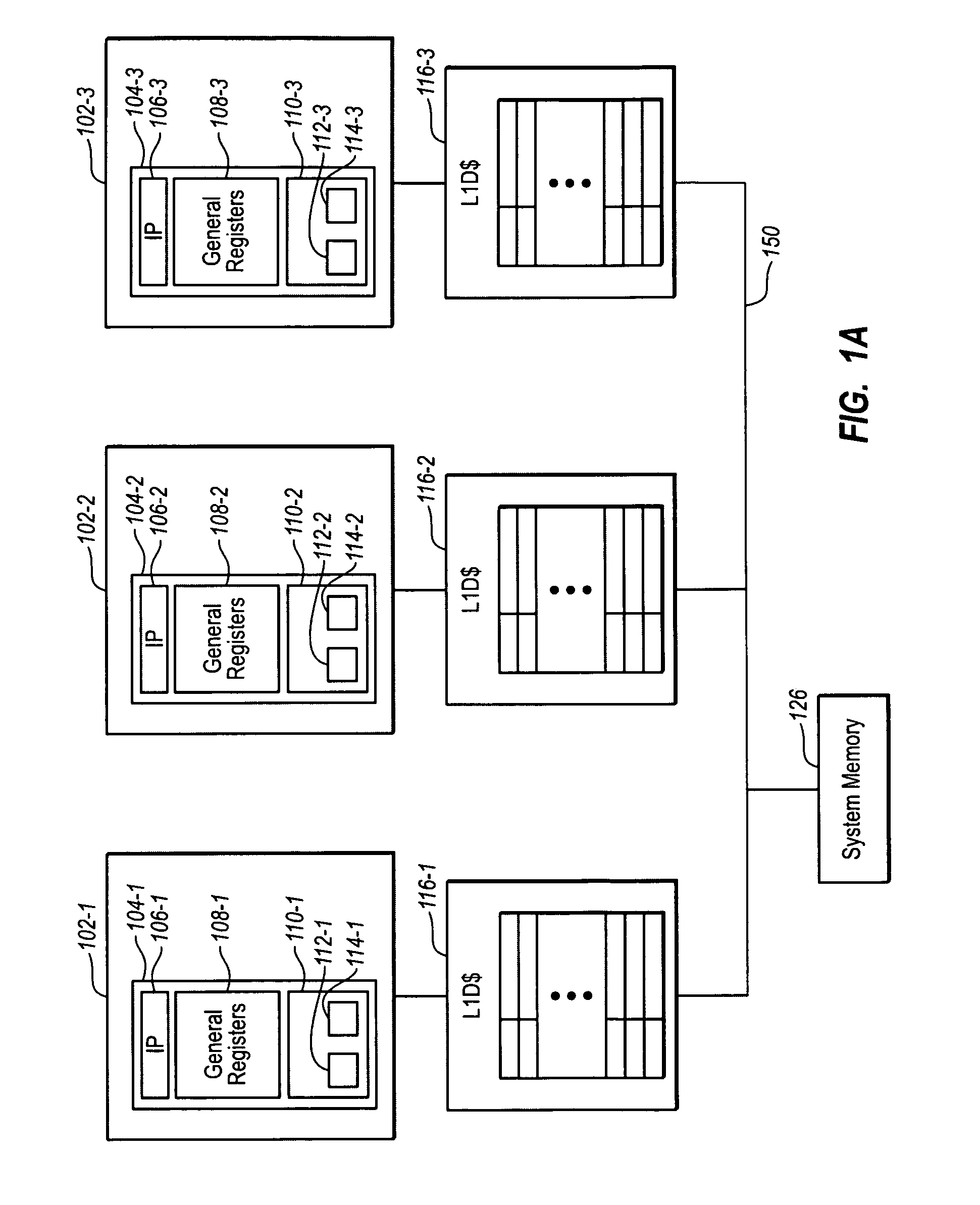
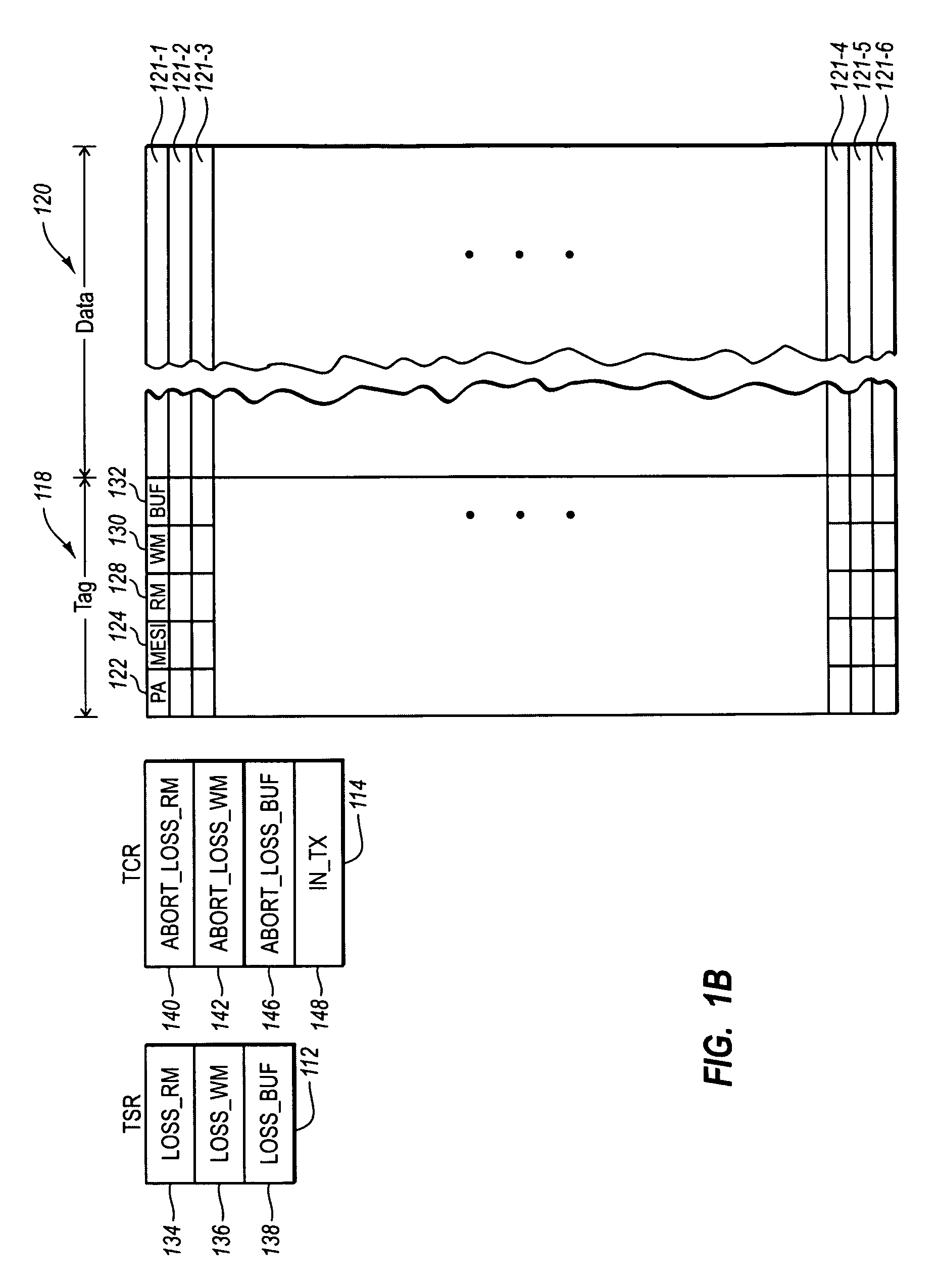
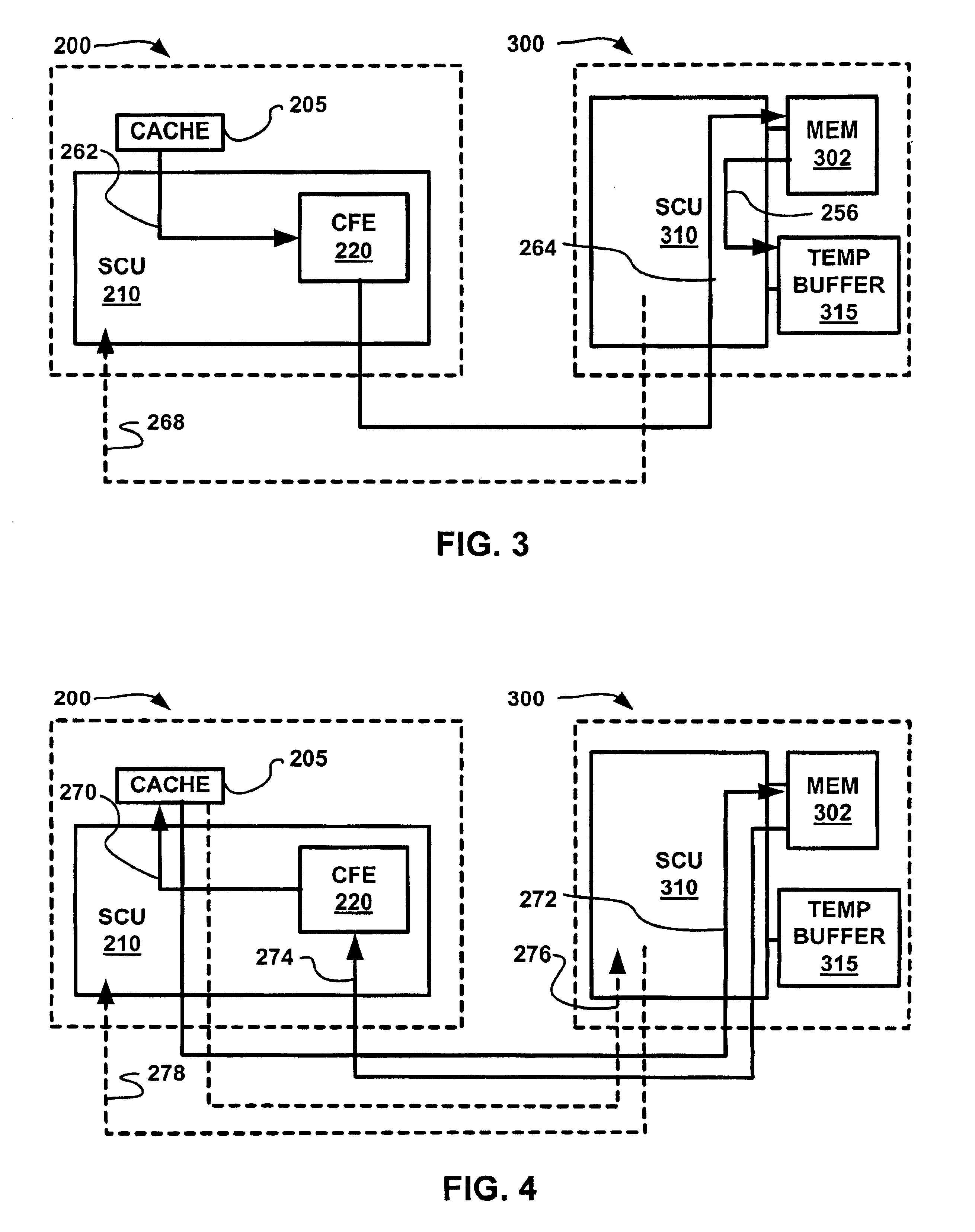
Multi-processor computer system with transactional memory
InactiveUS6880045B2Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorSemantics
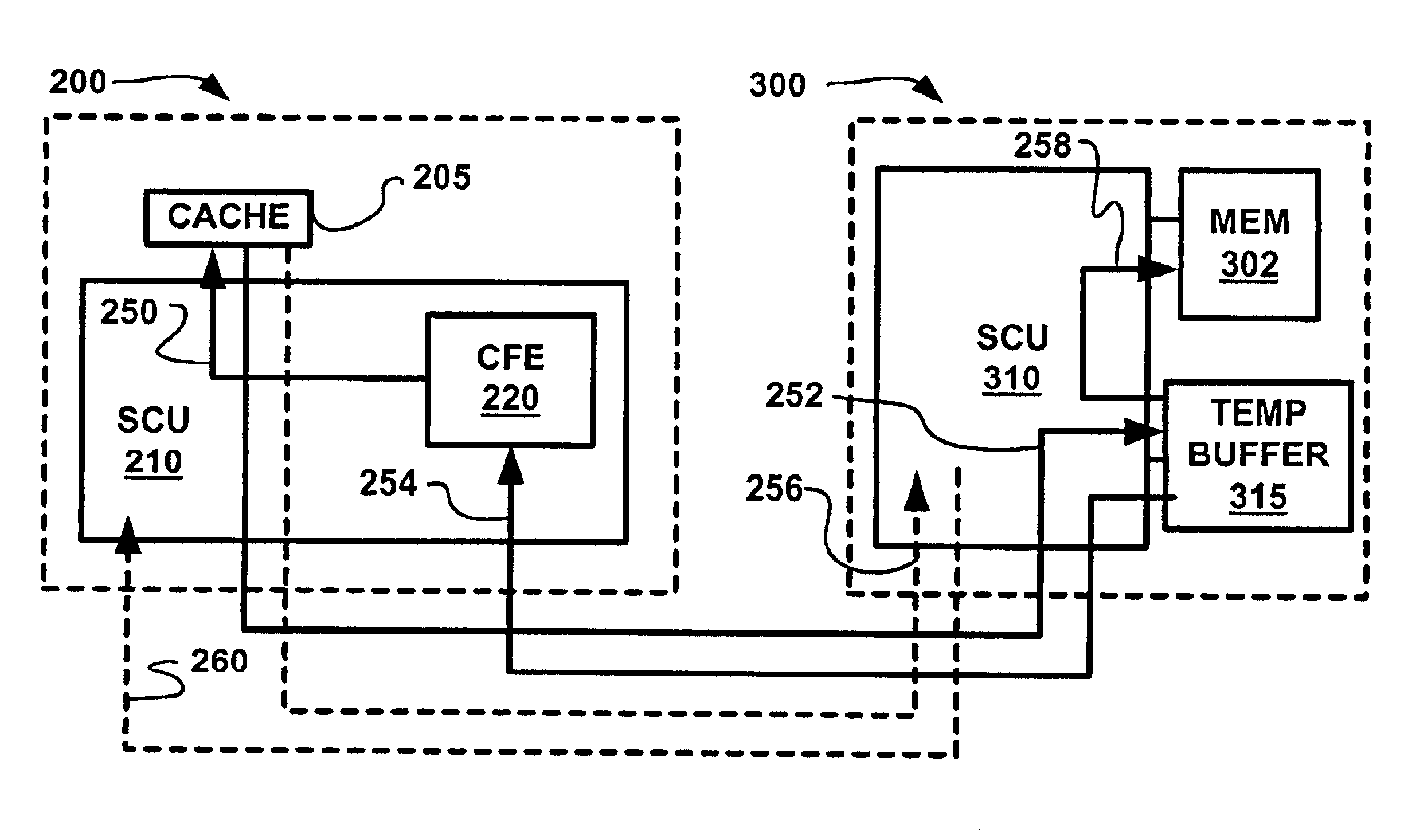
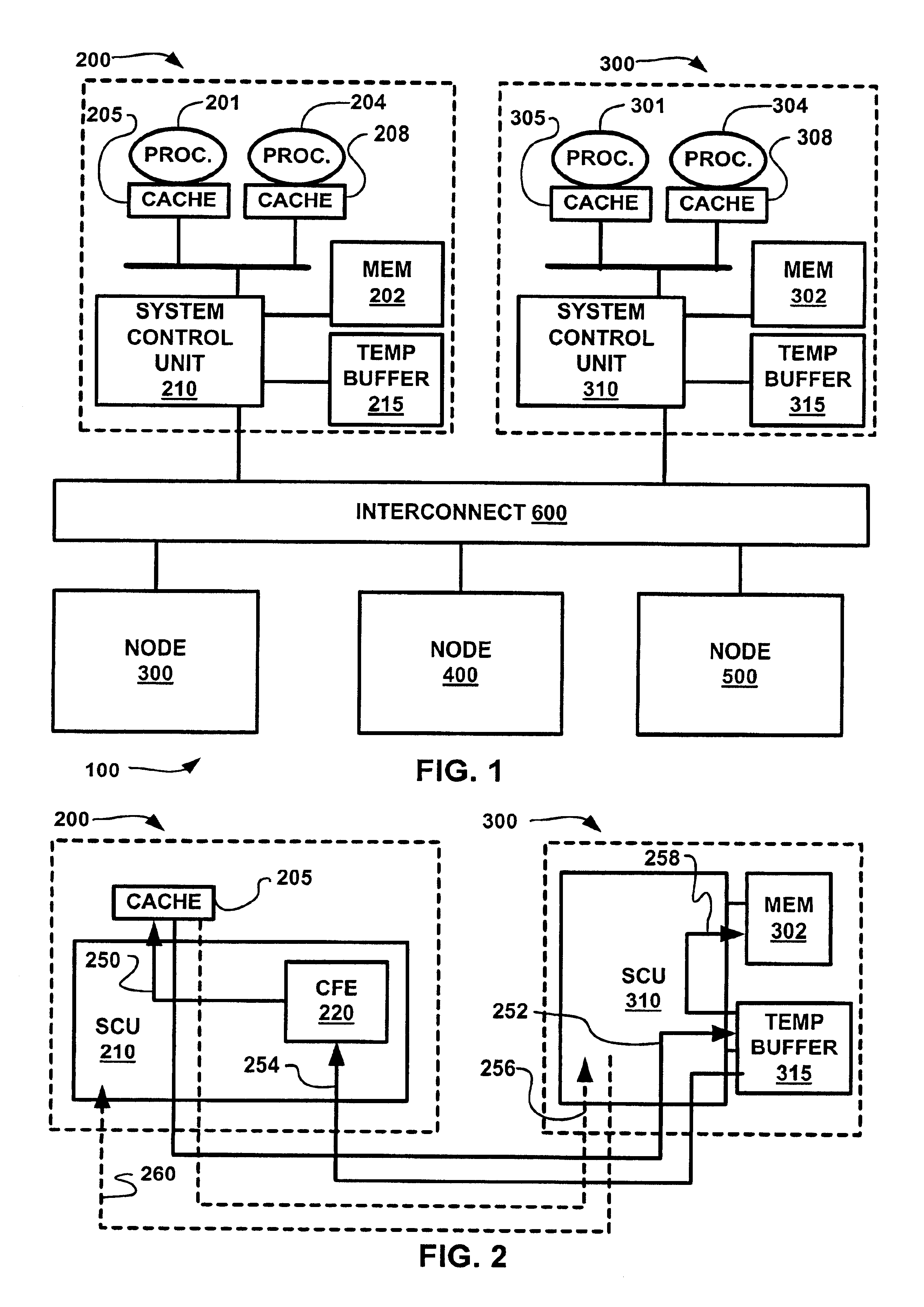
A cache coherent distributed shared memory multi-processor computer system is provided which supports transactional memory semantics. A cache flushing engine and temporary buffer allow selective forced write-backs of dirty cache lines to the home memory. A flush can be performed from the updated cache to the temporary buffer and then to the home memory after confirmation of receipt or from the updated cache to the home memory directly with the temporary buffer holding the old data until confirmation that the home memory contains the update.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
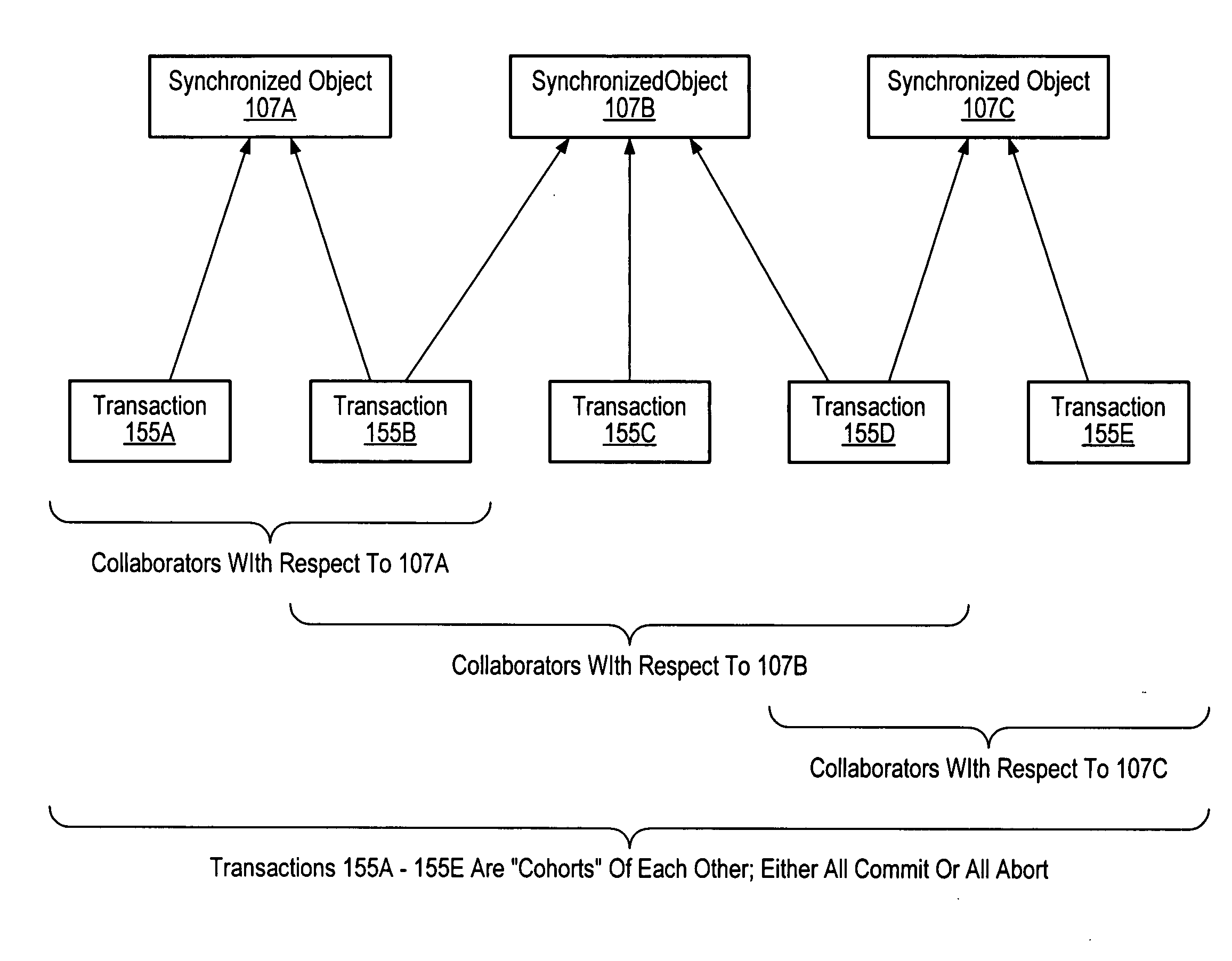
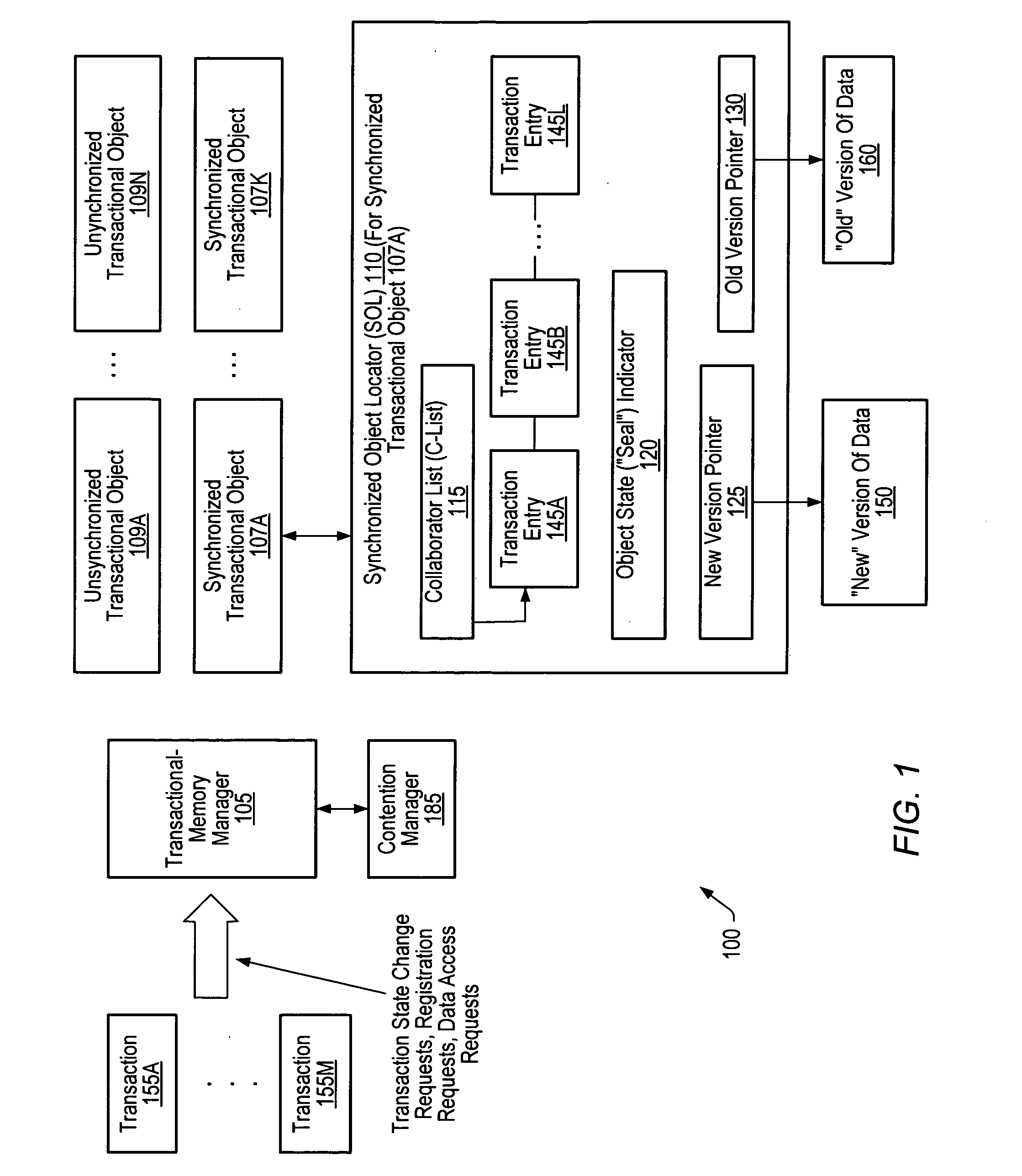
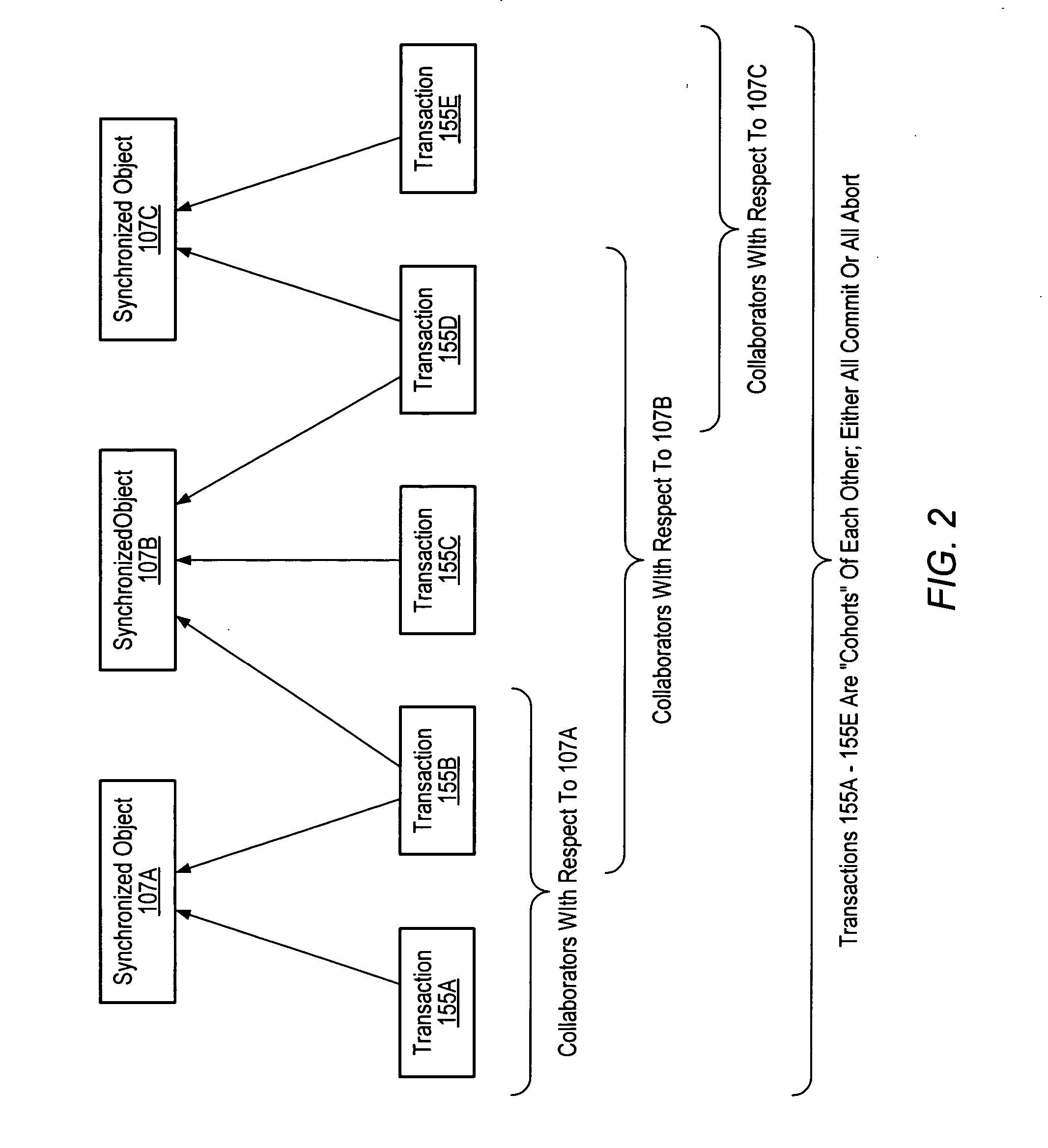
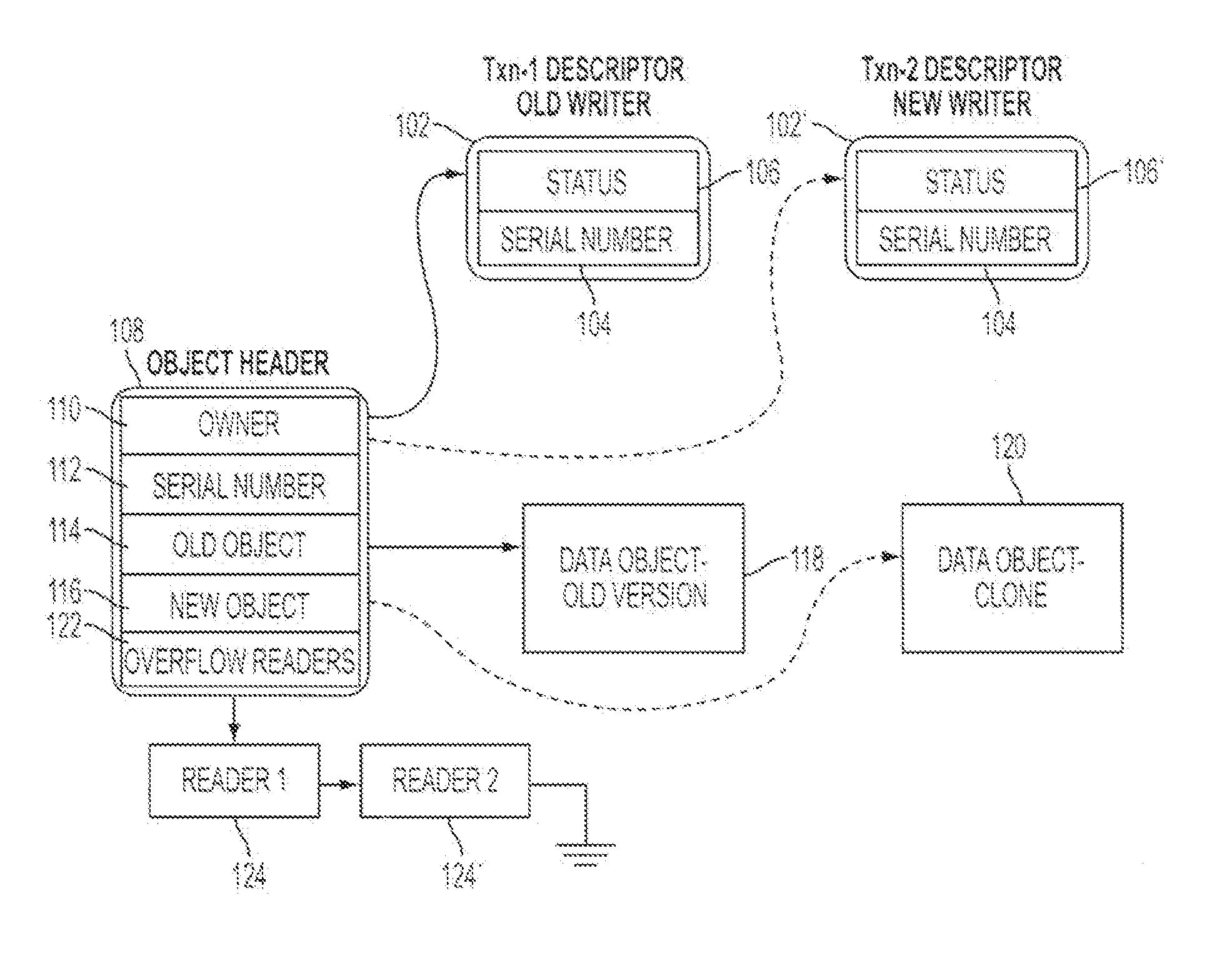
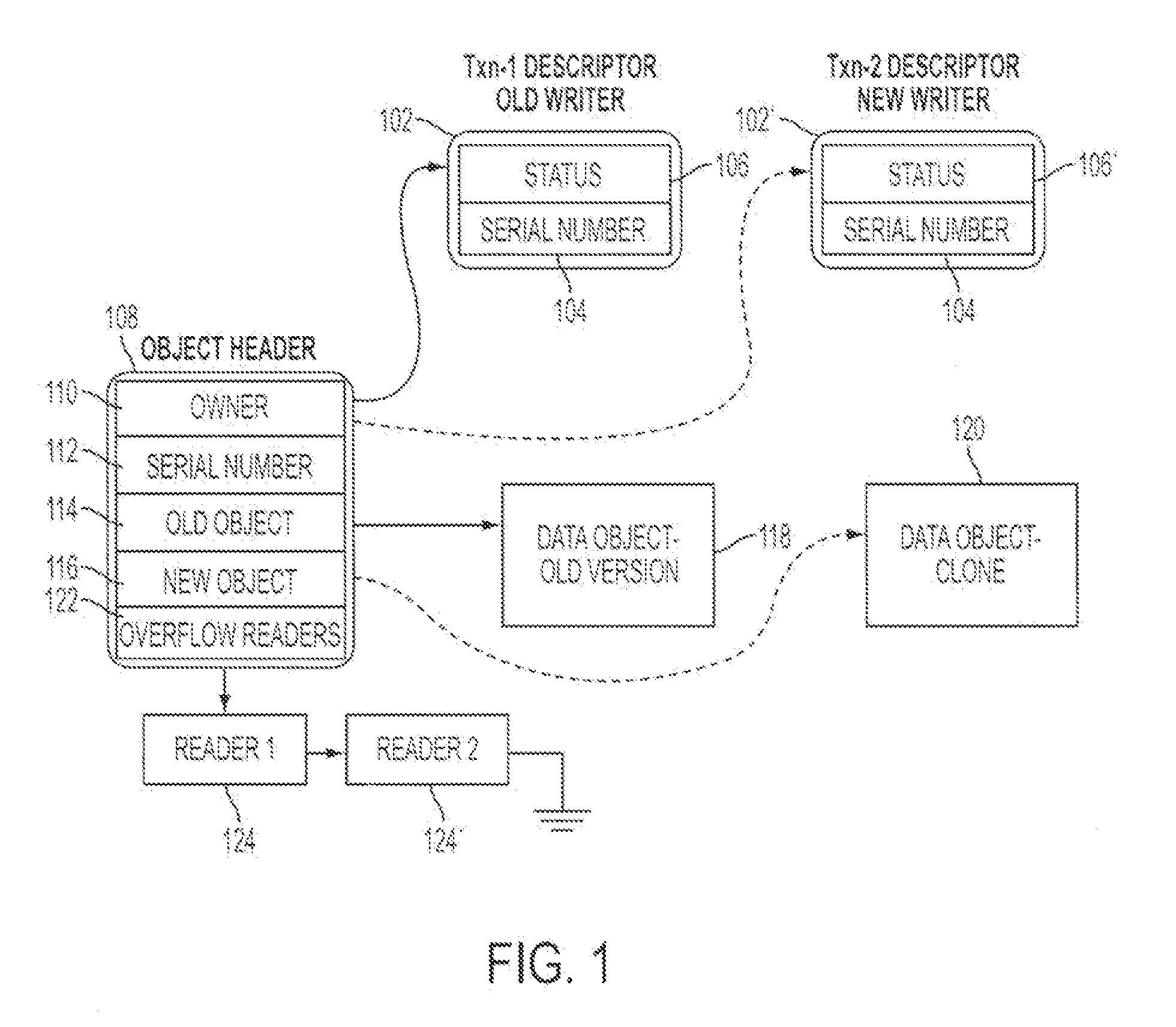
Synchronized objects for software transactional memory
ActiveUS20070198518A1Improve concurrencyAvoid changeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageProgram instruction
A system for implementing synchronized objects for software transactional memory comprises one or more processors and a memory comprising program instructions executable by the processor to implement a transactional-memory manager configured to coordinate memory access requests directed at the memory from a plurality of transactions. The transactional-memory manager records, within a collaborator record for a shared data object in the memory, identifications of a set of two or more transactions that have requested synchronization on the object. In response to a commit request from a given transaction of the set, the transactional-memory manager determines whether to commit or abort the given transaction based at least in part on the transactional states of other transactions in the set, examining the collaborator record to identify the other transactions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for implementing nonblocking zero-indirection transactional memory
ActiveUS8140497B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsObject basedIndirection
Systems and methods for implementing and using nonblocking zero-indirection software transactional memory (NZSTM) are disclosed. NZSTM systems implement object-based software transactional memory that eliminates all levels of indirection except in the uncommon case of a conflict with an unresponsive thread. Shared data is co-located with a header in an NZObject, and is addressable at a fixed offset from the header. Conflicting transactions are requested to abort themselves without being forced to abort. NZObjects are modified in place when there are no conflicts, and when a conflicting transaction acknowledges the abort request. In the uncommon case, NZObjects are inflated to introduce a locator and some levels of indirection, and are restored to their un-inflated form following resolution of the conflict. In some embodiments, transactions are executed using best effort hardware transactional memory if it is available and effective, and software transactional memory if not, yielding a hybrid transactional memory system, NZTM.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Verification of memory consistency and transactional memory
ActiveUS20080288834A1Efficiently verifying complianceError detection/correctionStatic storageProcessing elementTest platform
A system for efficiently verifying compliance with a memory consistency model includes a test module and an analysis module. The test module may coordinate an execution of a multithreaded test program on a test platform. If the test platform provides an indication of the order in which writes from multiple processing elements are performed at shared memory locations, the analysis module may use a first set of rules to verify that the results of the execution correspond to a valid ordering of events according to a memory consistency model. If the test platform does not provide an indication of write ordering, the analysis module may use a second set of rules to verify compliance with the memory consistency model. Further, a backtracking search may be performed to find a valid ordering if such ordering exists or show that none exists and, hence, confirm whether or not the results comply with the given memory consistency model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
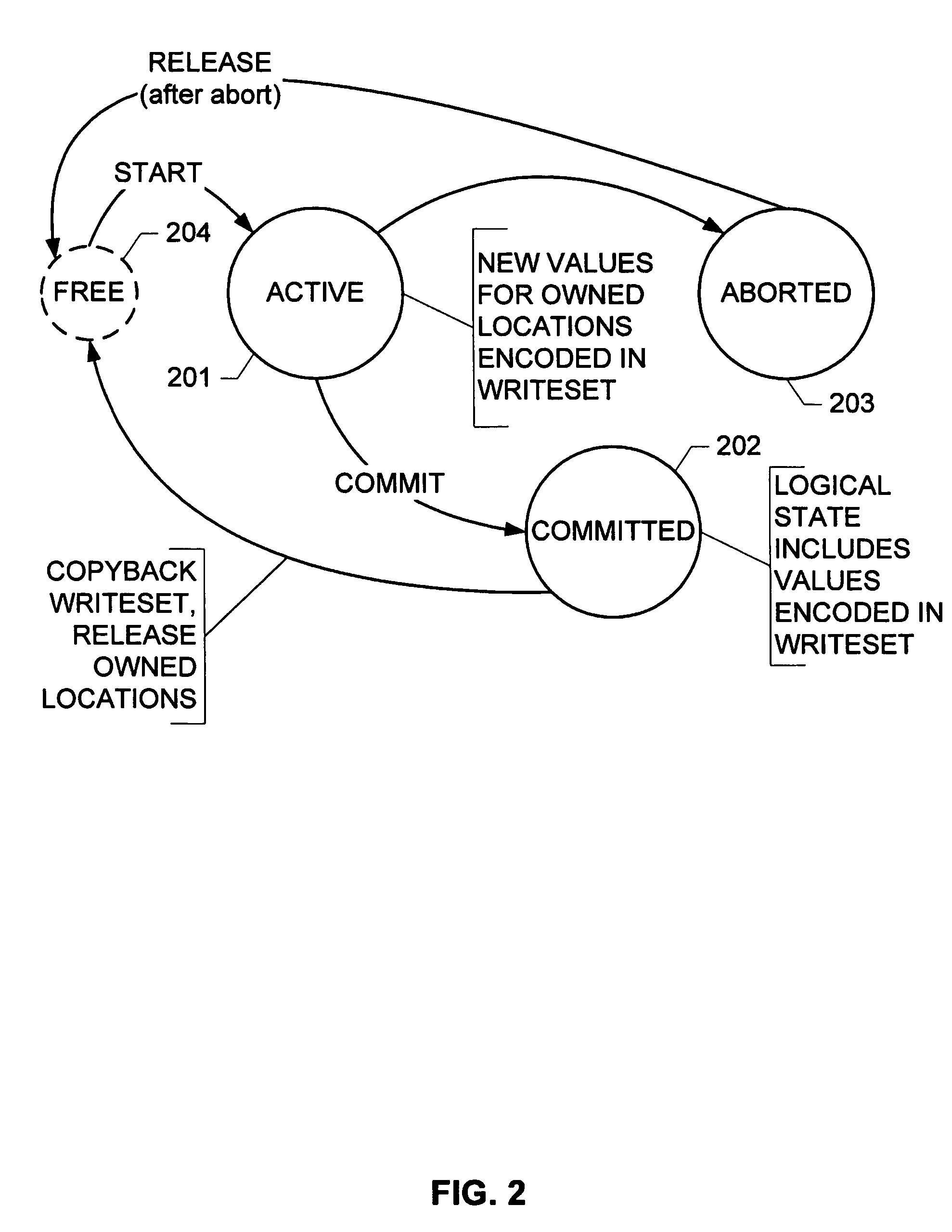
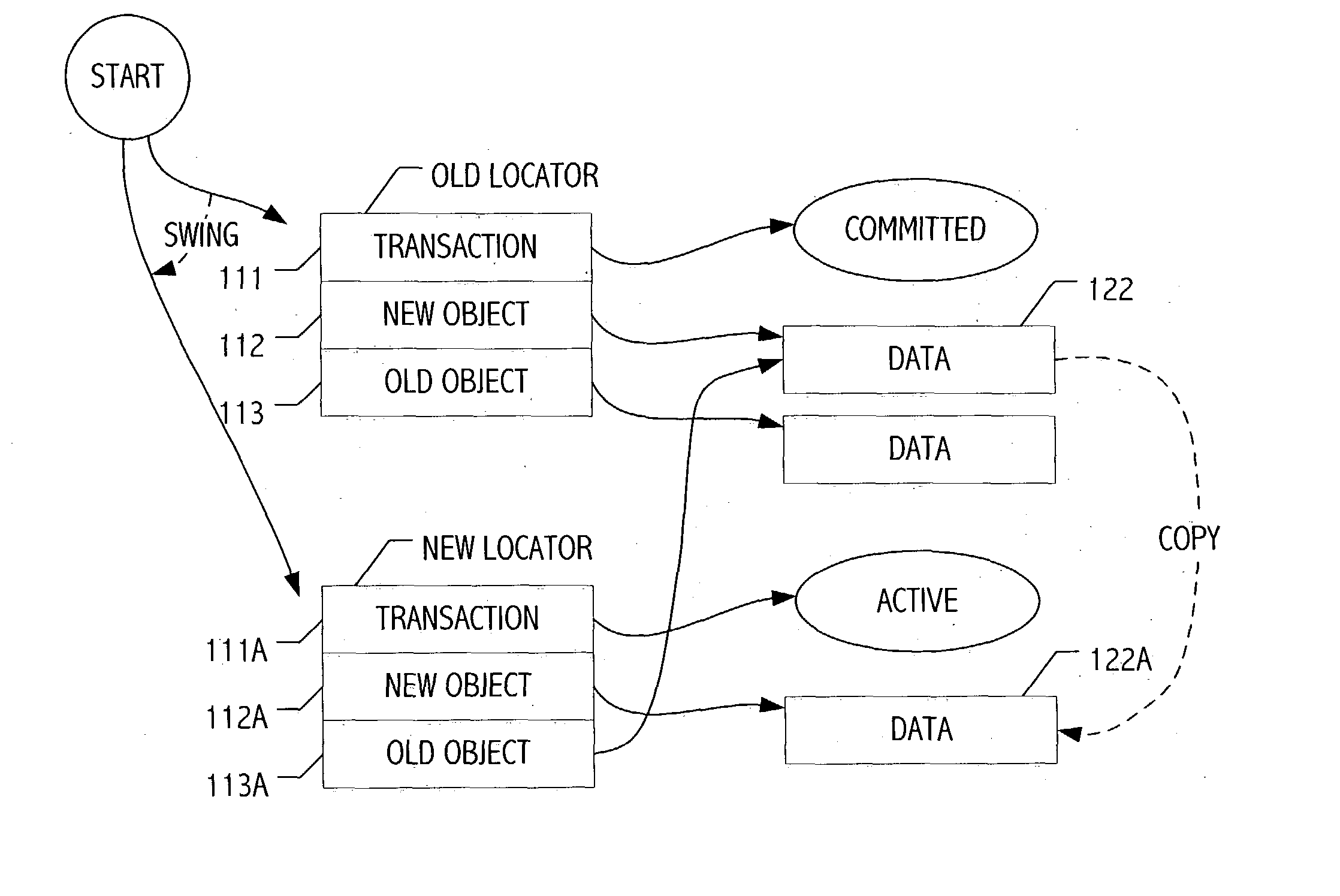
Transactional memory with automatic object versioning
InactiveUS20080021934A1Computer security arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsApplication softwareDatabase
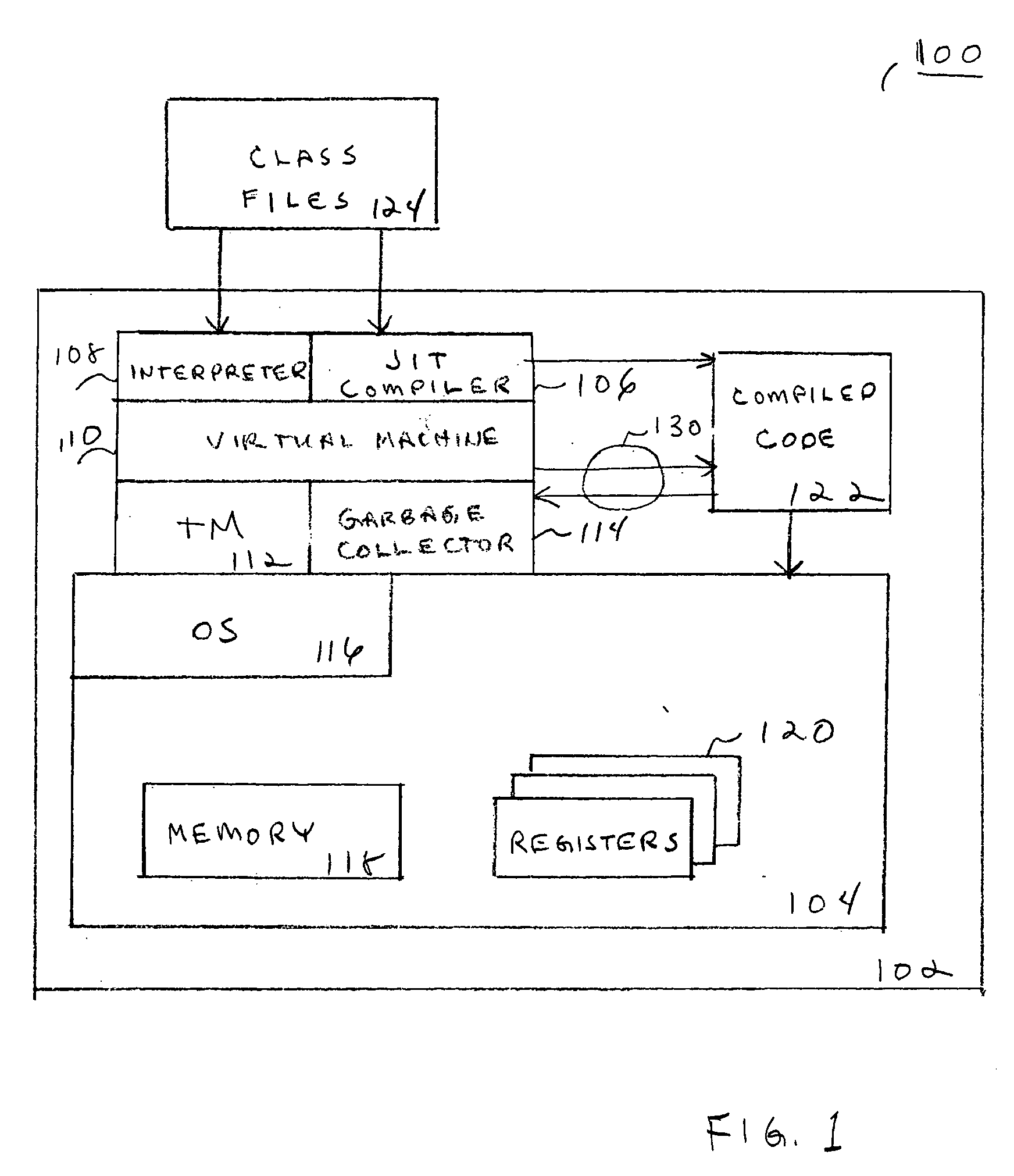
Embodiments of a system and method for transactional memory (TM) with automatic object versioning are described. Embodiments described herein include a TM system and method that facilitates the execution of object-oriented application programs in a transactional environment, including automatically versioning objects to enhance efficiency. Embodiments of the TM automatically designate versions of objects using pointers, accurately identifying usable and unusable versions. Object versioning as described herein allows the garbage collector to easily and efficiently determine which objects may be moved, freeing memory space and reducing the number of objects traversed by a transaction before finding a useable version of an object. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for hardware acceleration of a software transactional memory
InactiveUS20110099335A1Difficult to implementGuaranteed uptimeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareHardware acceleration
In a transactional memory technique, hardware serves simply to optimize the performance of transactions that are controlled fundamentally by software. The hardware support reduces the overhead of common TM tasks—conflict detection, validation, and data isolation—for common-case bounded transactions. Software control preserves policy flexibility and supports transactions unbounded in space and in time. The hardware includes 1) an alert-on-update mechanism for fast software-controlled conflict detection; and 2) programmable data isolation, allowing potentially conflicting readers and writers to proceed concurrently under software control.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
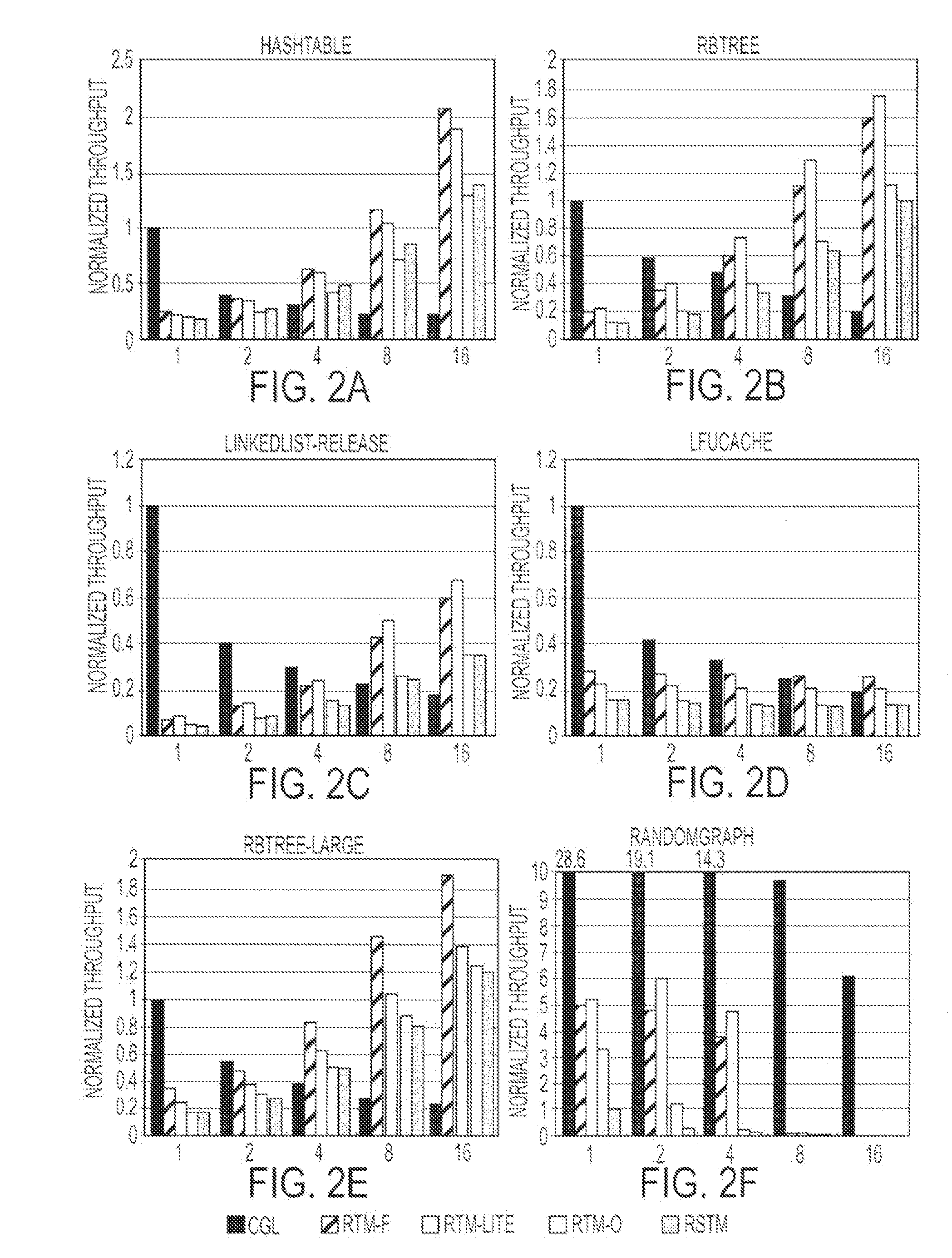
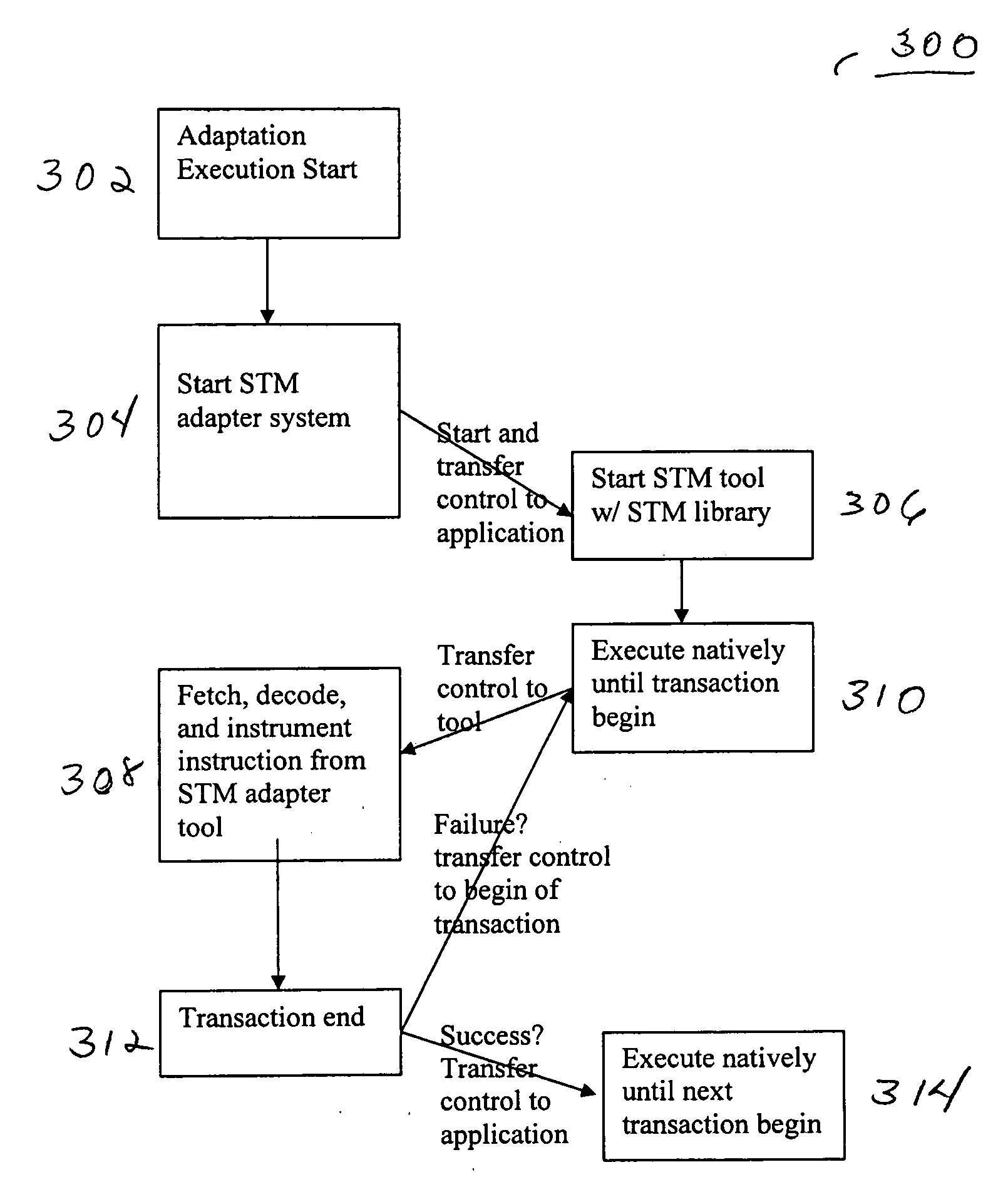
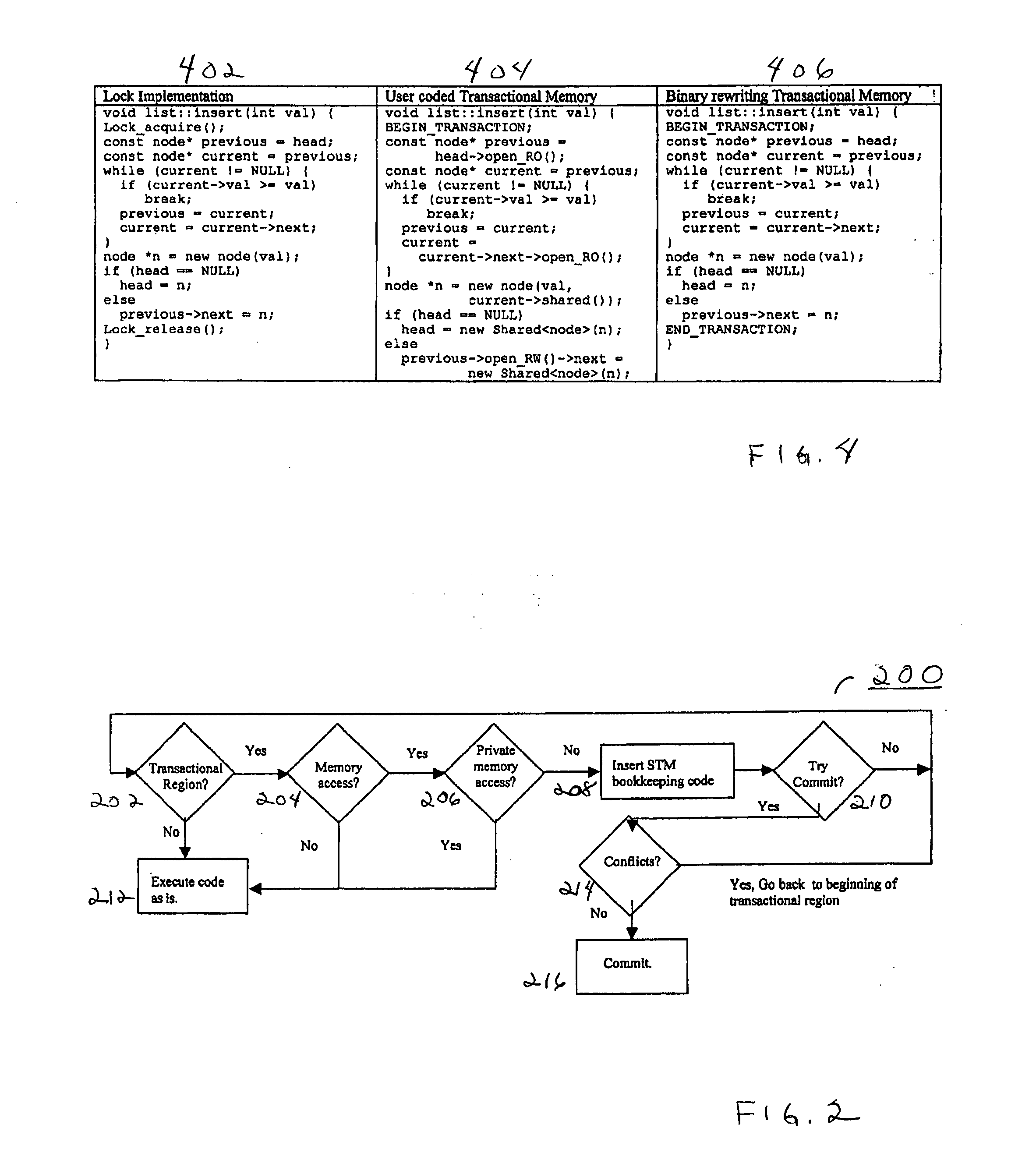
Adapting software programs to operate in software transactional memory environments
InactiveUS20070300238A1Software maintainance/managementSpecific program execution arrangementsApplication programming interfaceParallel computing
Embodiments of a system and method for adapting software programs to operate in software transactional memory (STM) environments are described. Embodiments include a software transactional memory (STM) adapter system including, in one embodiment, a version of a binary rewriting tool. The STM adapter system provides a simple-to-use application programming interface (API) for legacy languages (e.g., C and C++) that allows the programmer to simply mark the block of code to be executed atomically; the STM adapter system automatically transforms all the binary code executed within that block (including pre-compiled libraries) to execute atomically (that is, to execute as a transaction). In an embodiment, the STM adapter system automatically transforms lock-based critical sections in existing binary code to atomic blocks, for example by replacing locks with begin and end markers that mark the beginning and end of transactions. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Value predictable variable scoping for speculative automatic parallelization with transactional memory
ActiveUS20090235237A1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsCoding blockInner loop
Parallelize a computer program by scoping program variables at compile time and inserting code into the program. Identify as value predictable variables, variables that are: defined only once in a loop of the program; not defined in any inner loop of the loop; and used in the loop. Optionally also: identify a code block in the program that contains a variable assignment, and then traverse a path backwards from the block through a control flow graph of the program. Name in a set all blocks along the path until a loop header block. For each block in the set, determine program blocks that logically succeed the block and are not in the first set. Identify all paths between the block and the determined blocks as failure paths, and insert code into the failure paths. When executed at run time of the program, the inserted code fails the corresponding path.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Compiler support technique for hardware transactional memory systems
A method and apparatus for compiling software written to be executed on a microprocessor that supports at least one hardware transactional memory function is provided. A compiler that supports at least one software transactional memory function is adapted to include a runtime system that maps between the at least one software transactional memory function and the at least one hardware transactional memory instruction.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
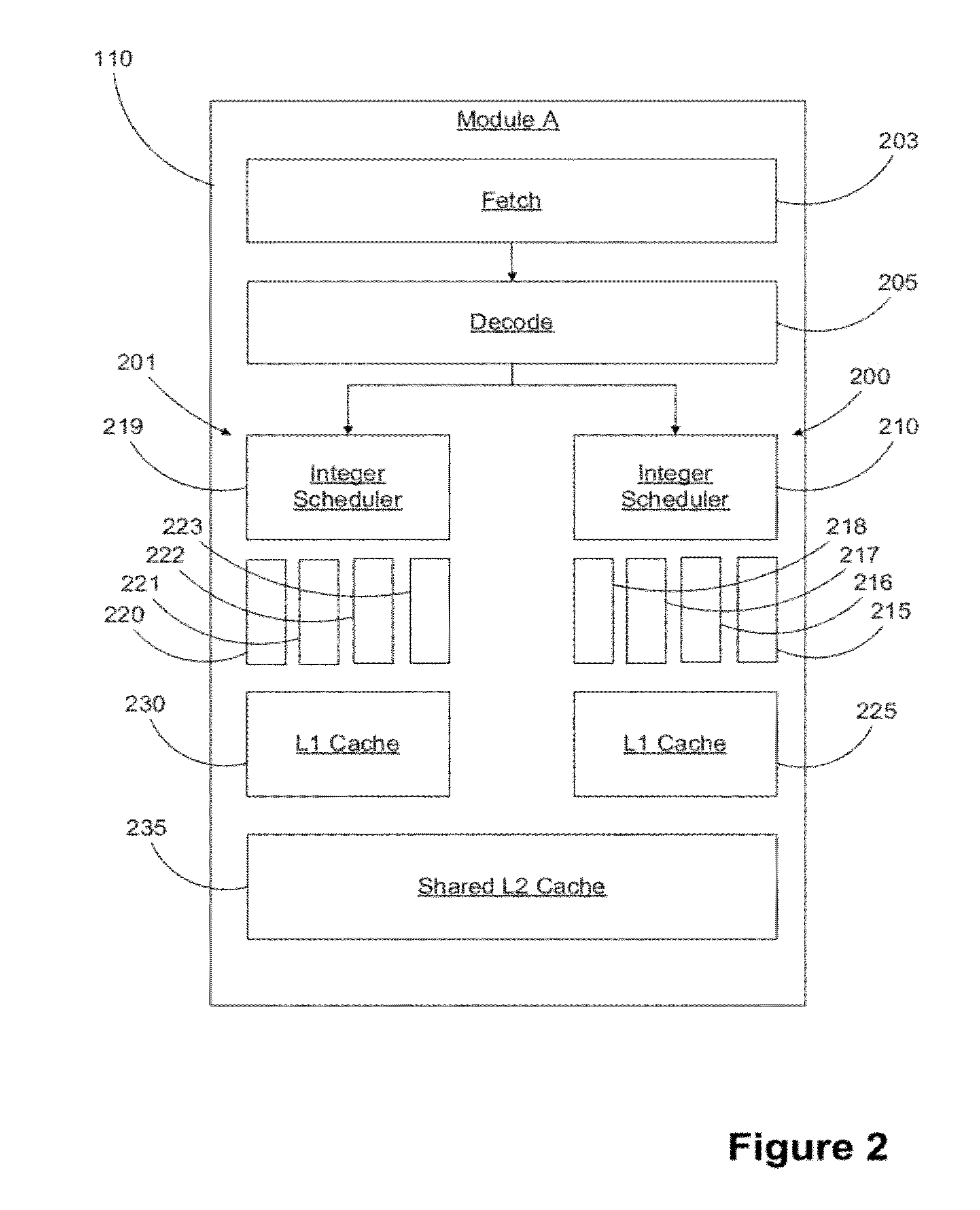
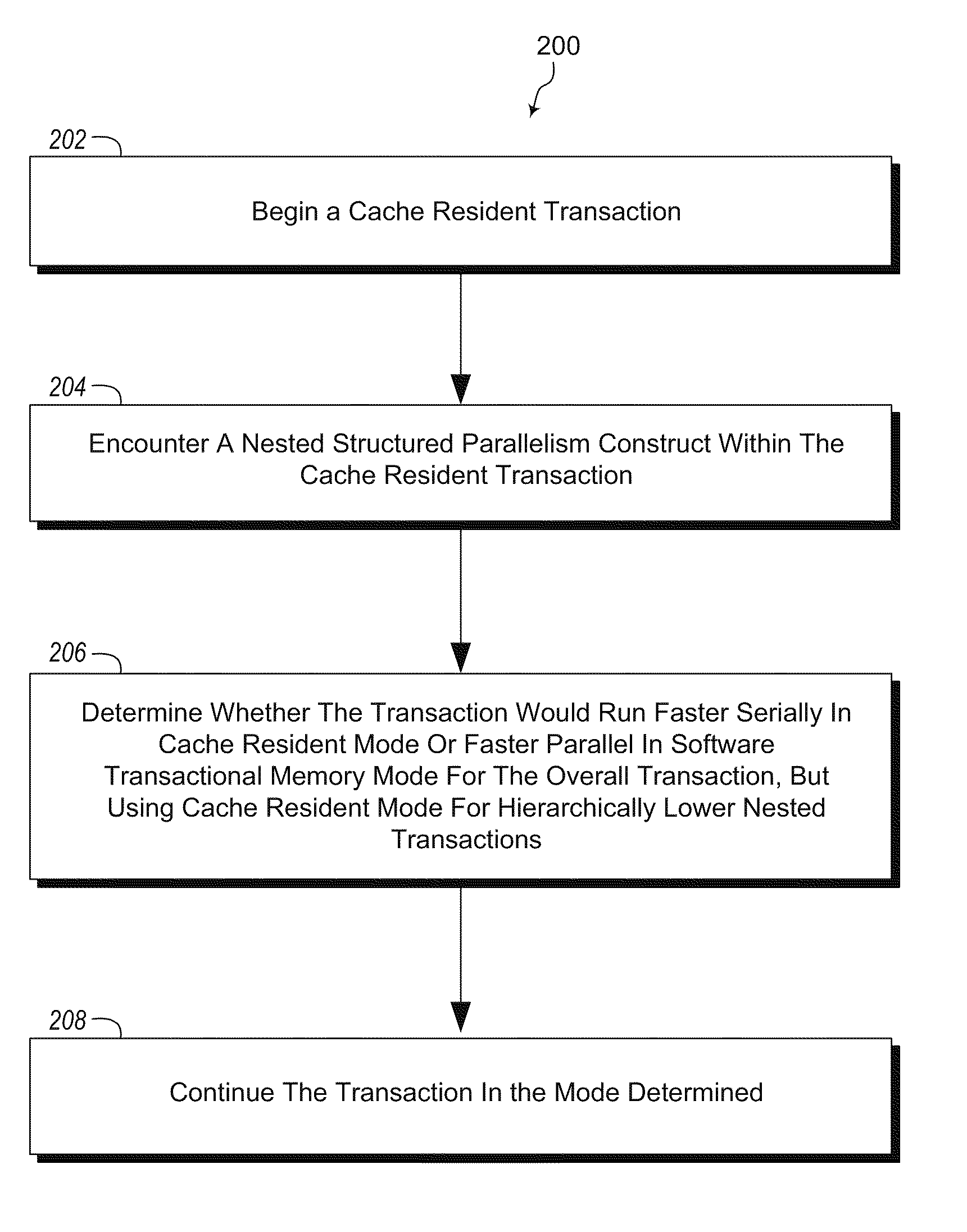
Accelerating parallel transactions using cache resident transactions
ActiveUS20110145553A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsParallel computingSoftware
Handling parallelism in transactions. One embodiment includes a method that includes beginning a cache resident transaction. The method further includes encountering a nested structured parallelism construct within the cache resident transaction. A determination is made as to whether the transaction would run faster serially in cache resident mode or faster parallel in software transactional memory mode for the overall transaction. In the software transactional memory mode, cache resident mode is used for one or more hierarchically lower nested transactions. The method further includes continuing the transaction in the mode determined.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
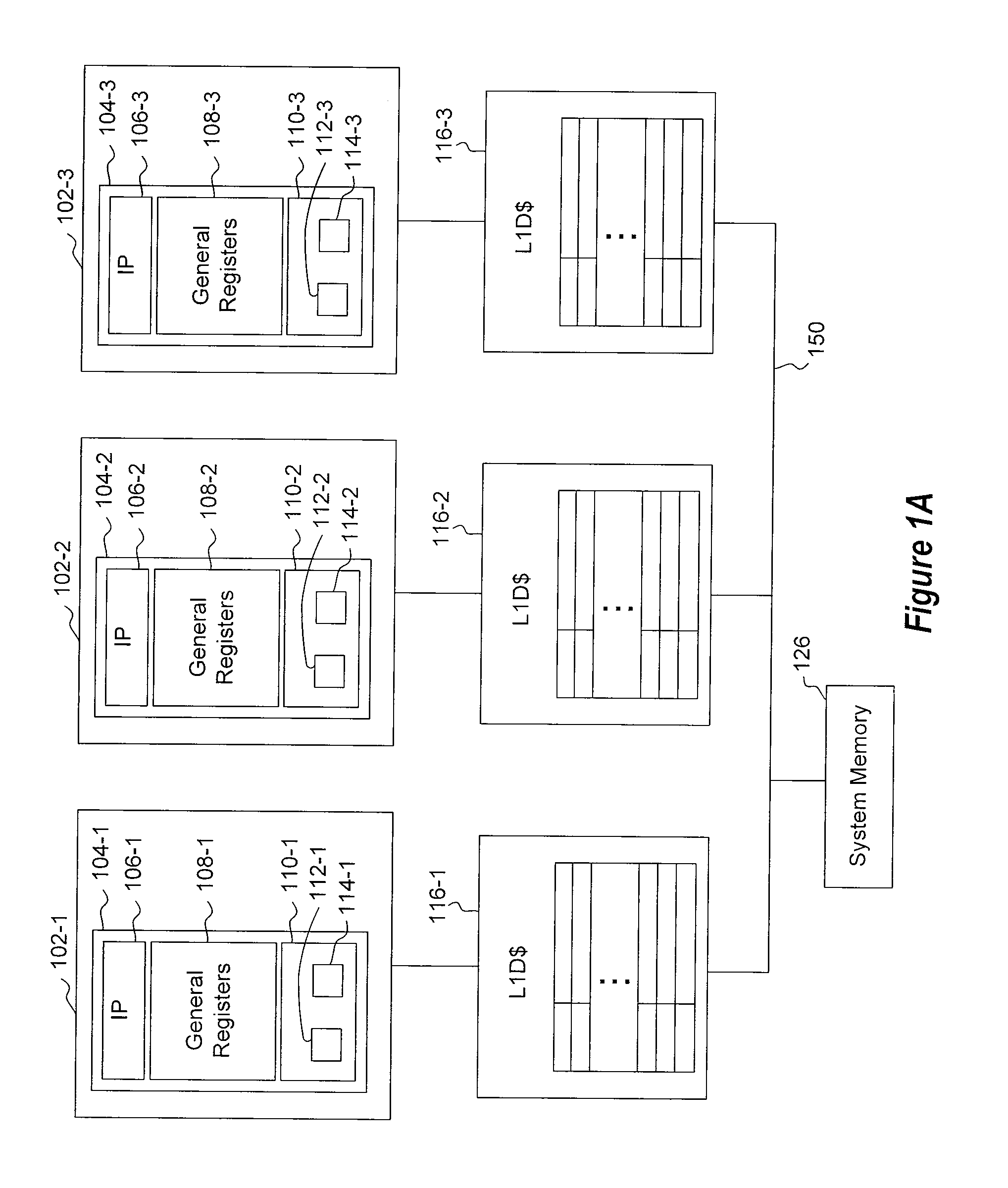
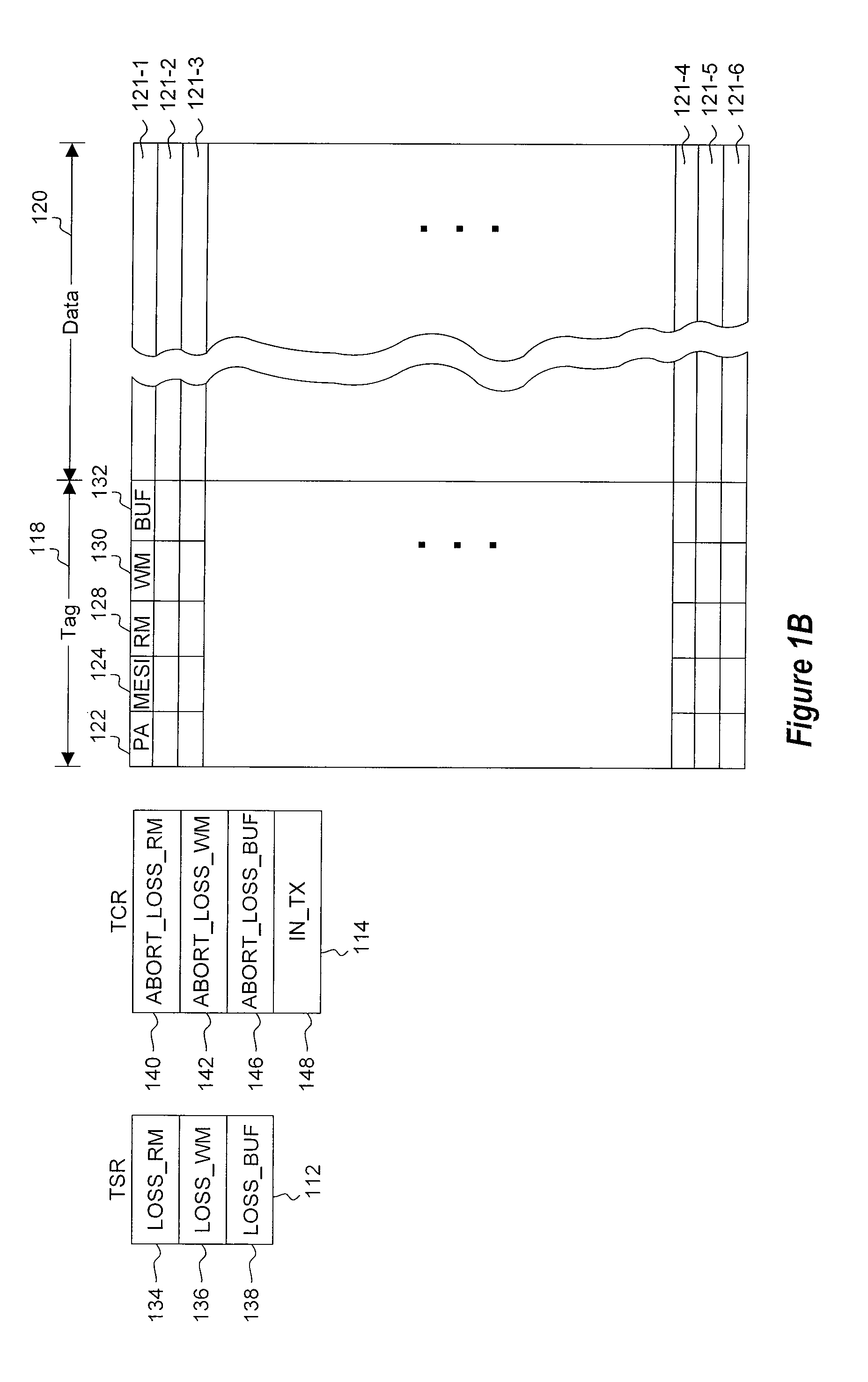
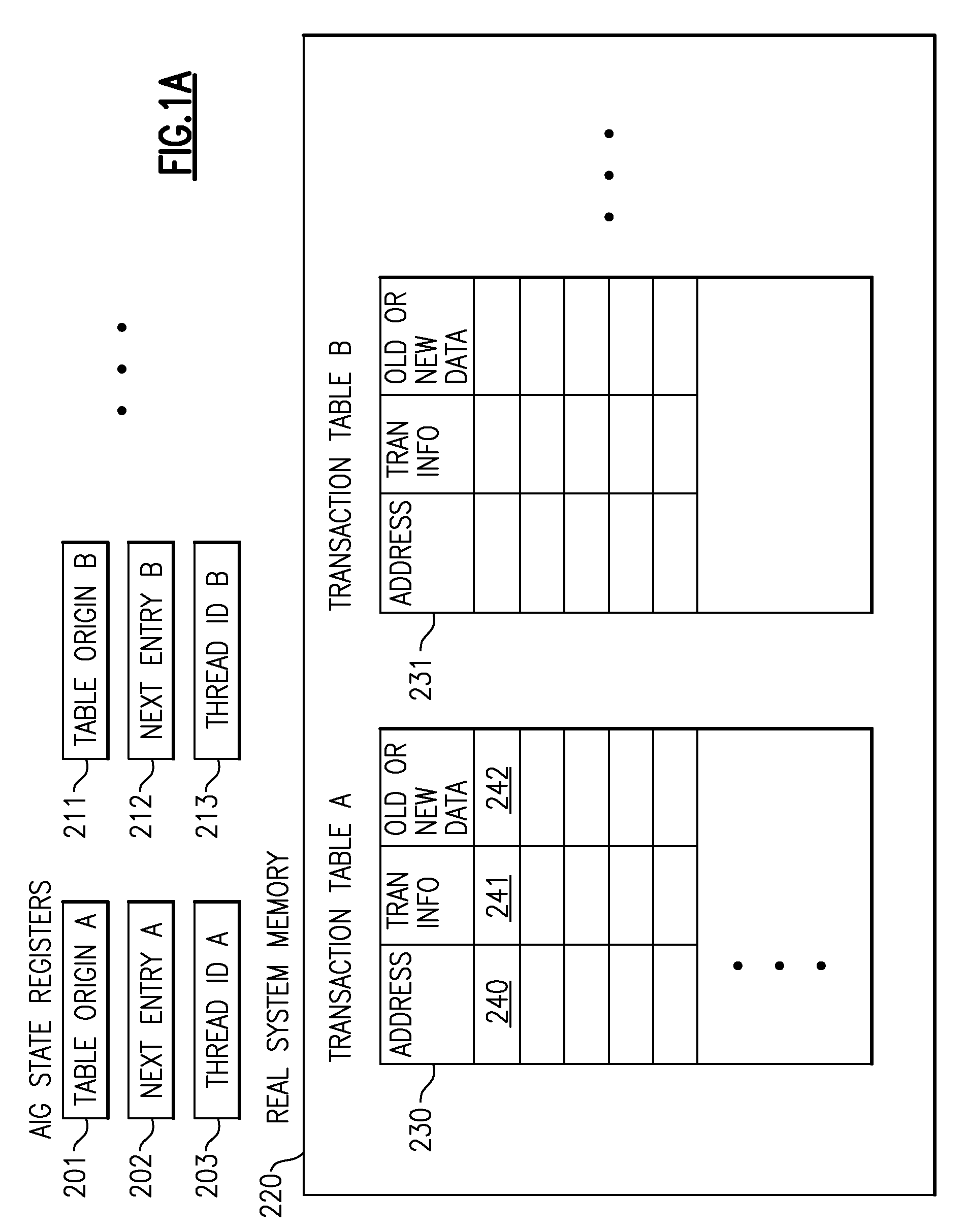
Transactional memory system which employs thread assists using address history tables
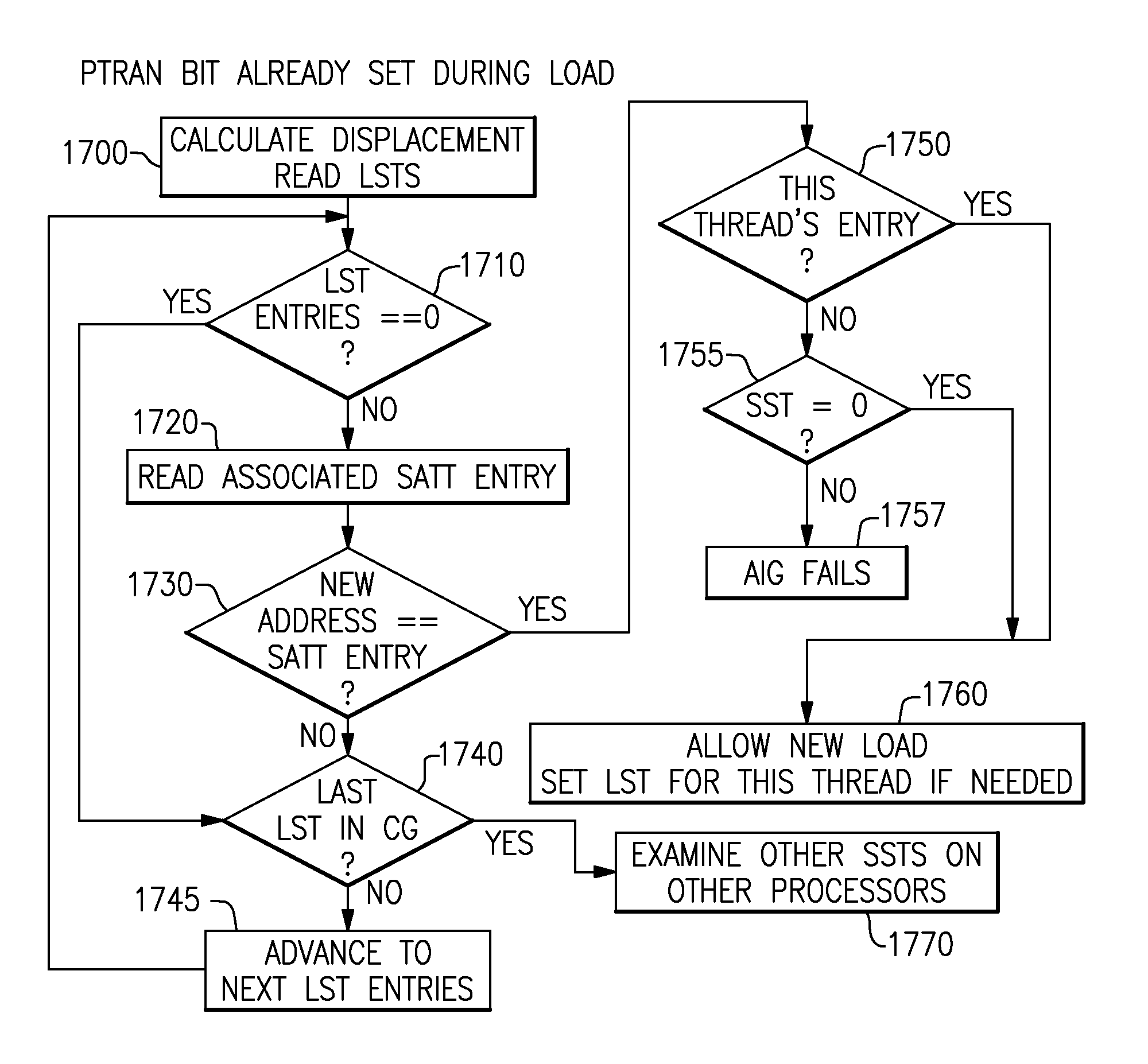
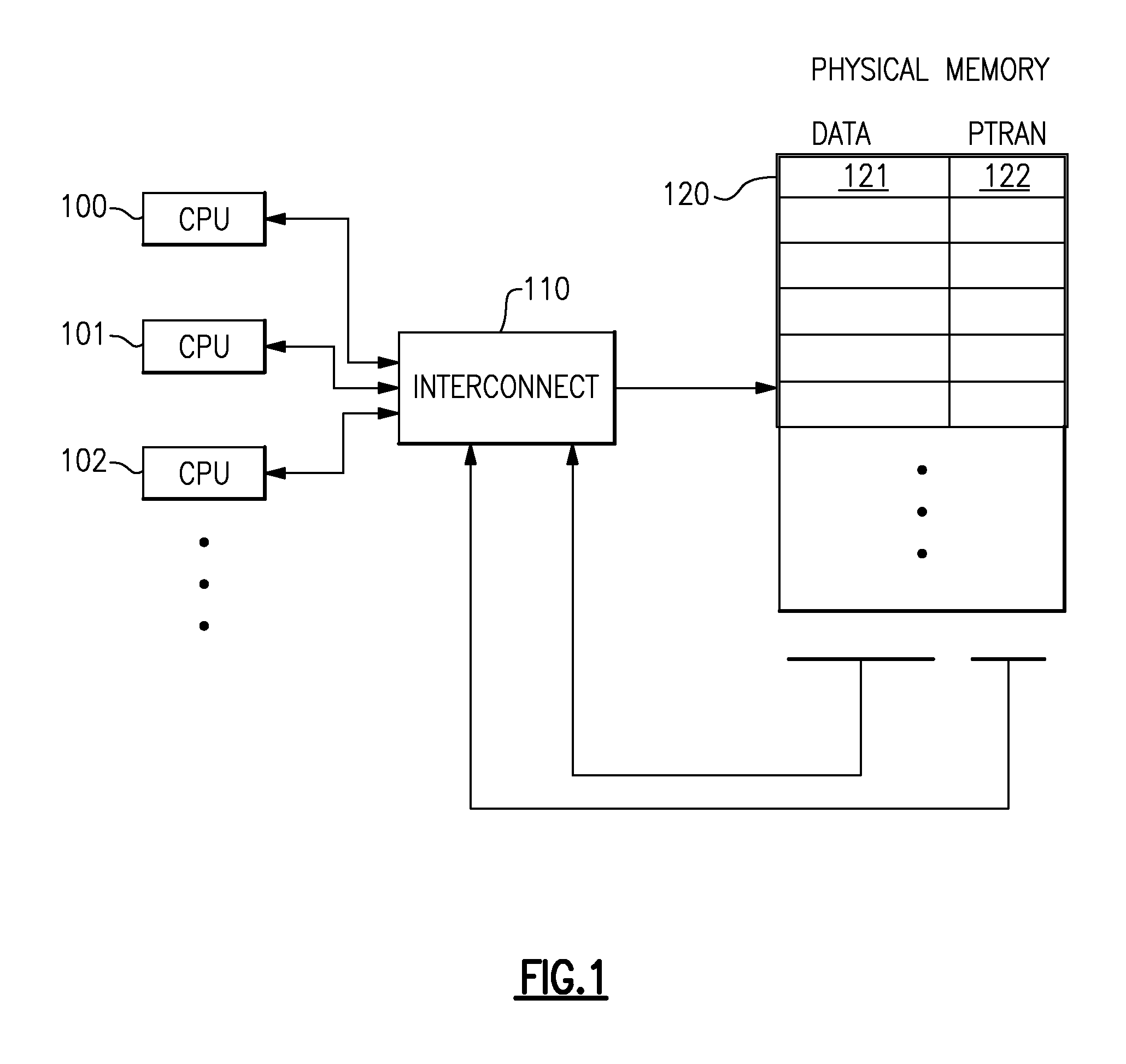
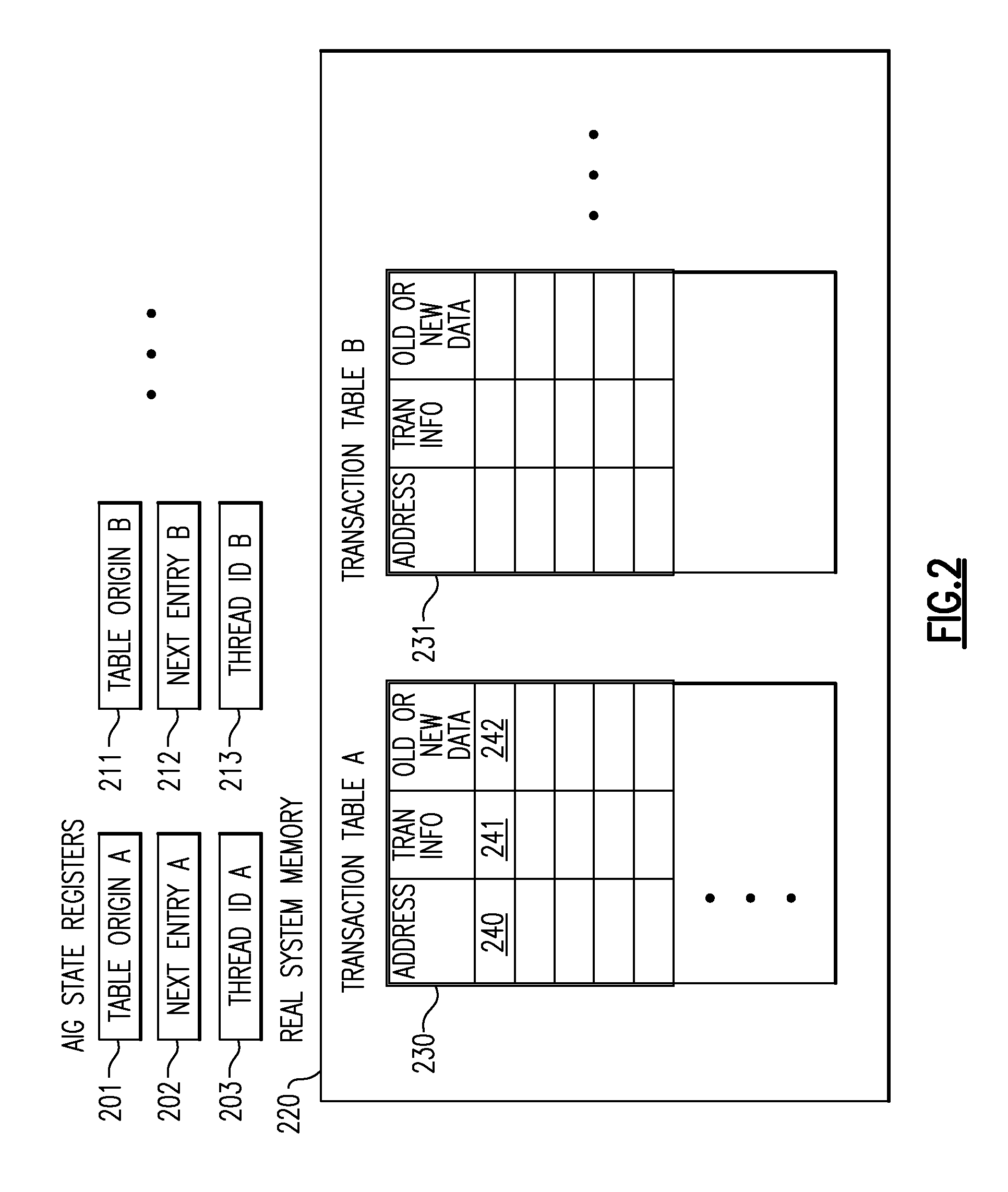
A computing system uses specialized “Set Associative Transaction Tables” and additional “Summary Transaction Tables” to speed the processing of common transactional memory conflict cases and those which employ assist threads using an Address History Table and processes memory transactions with a Transaction Table in memory for parallel processing of multiple threads of execution by support of which an application need not be aware. Special instructions may mark the boundaries of a transaction and identify memory locations applicable to a transaction. A ‘private to transaction’ (PTRAN) tag, directly addressable as part of the main data storage memory location, enables a quick detection of potential conflicts with other transactions that are concurrently executing on another thread of said computing system. The tag indicates whether (or not) a data entry in memory is part of a speculative memory state of an uncommitted transaction that is currently active in the system.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
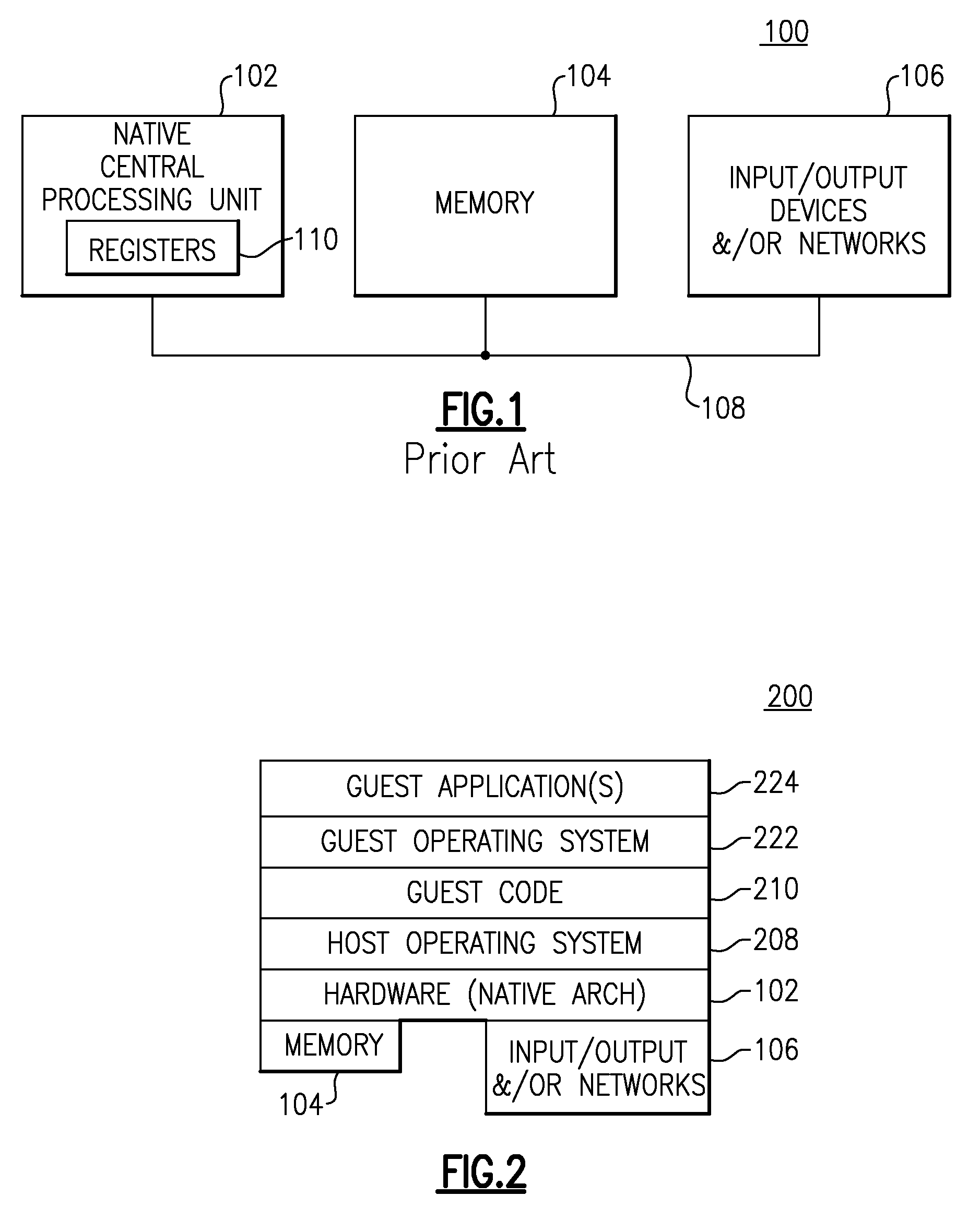
Computing System with Guest Code Support of Transactional Memory
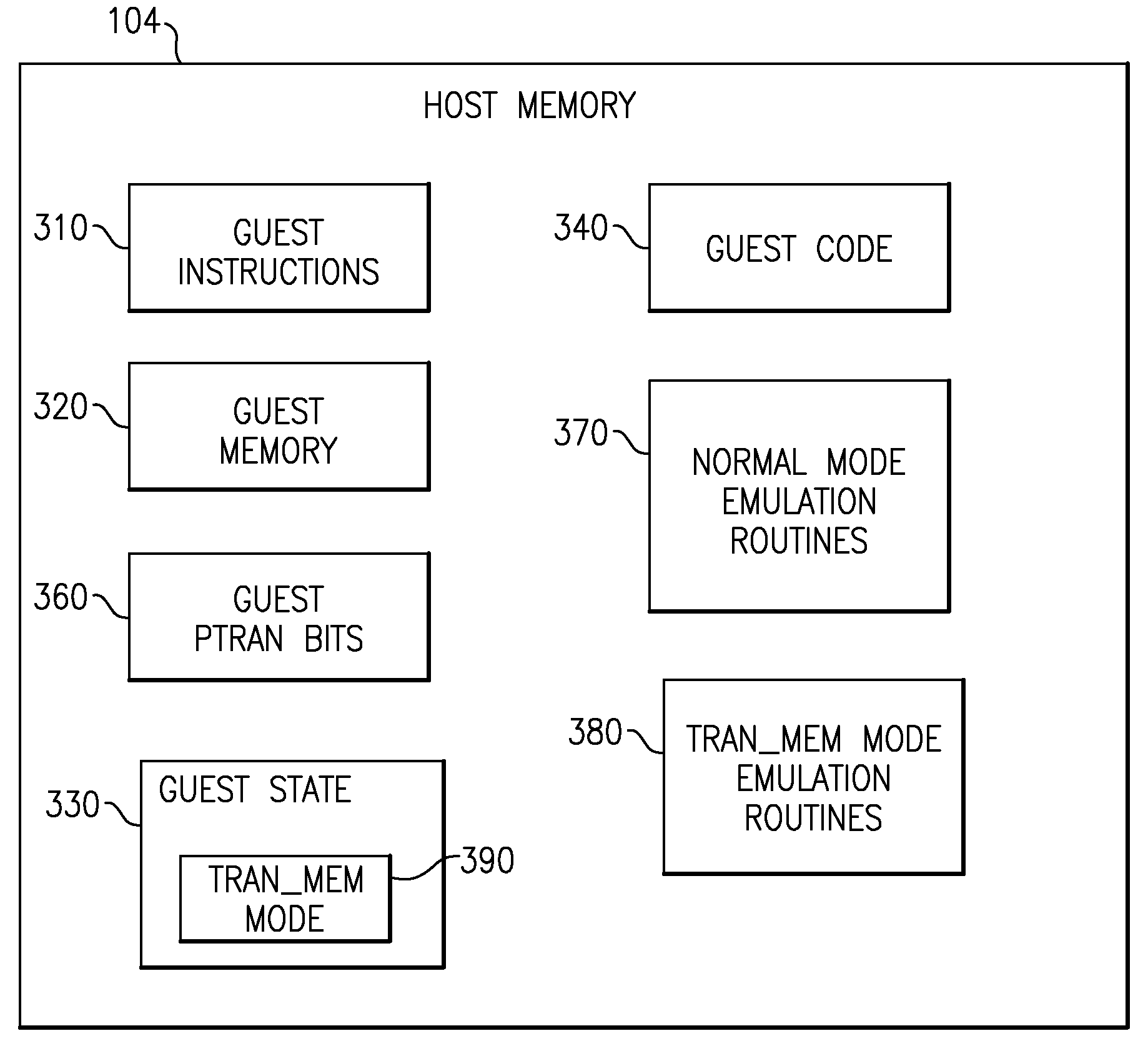
InactiveUS20080288238A1Slow performanceImprove performanceProgram synchronisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSoftware emulationComputing systems
A data structure of readily accessible units of memory is provided as computer useable media having computer readable program code logic providing information tables and a software emulation program to enable hardware to run new software that uses transactional memory and a bit associated with a transaction for executing transactional memory constructs. The data structure with Guest PTRAN bit is used in emulation of software written for a given computer on a different computer which executes a different set of instructions. The emulating instructions are used to provide transactional memory instructions on a computer which does not support those instructions natively
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com