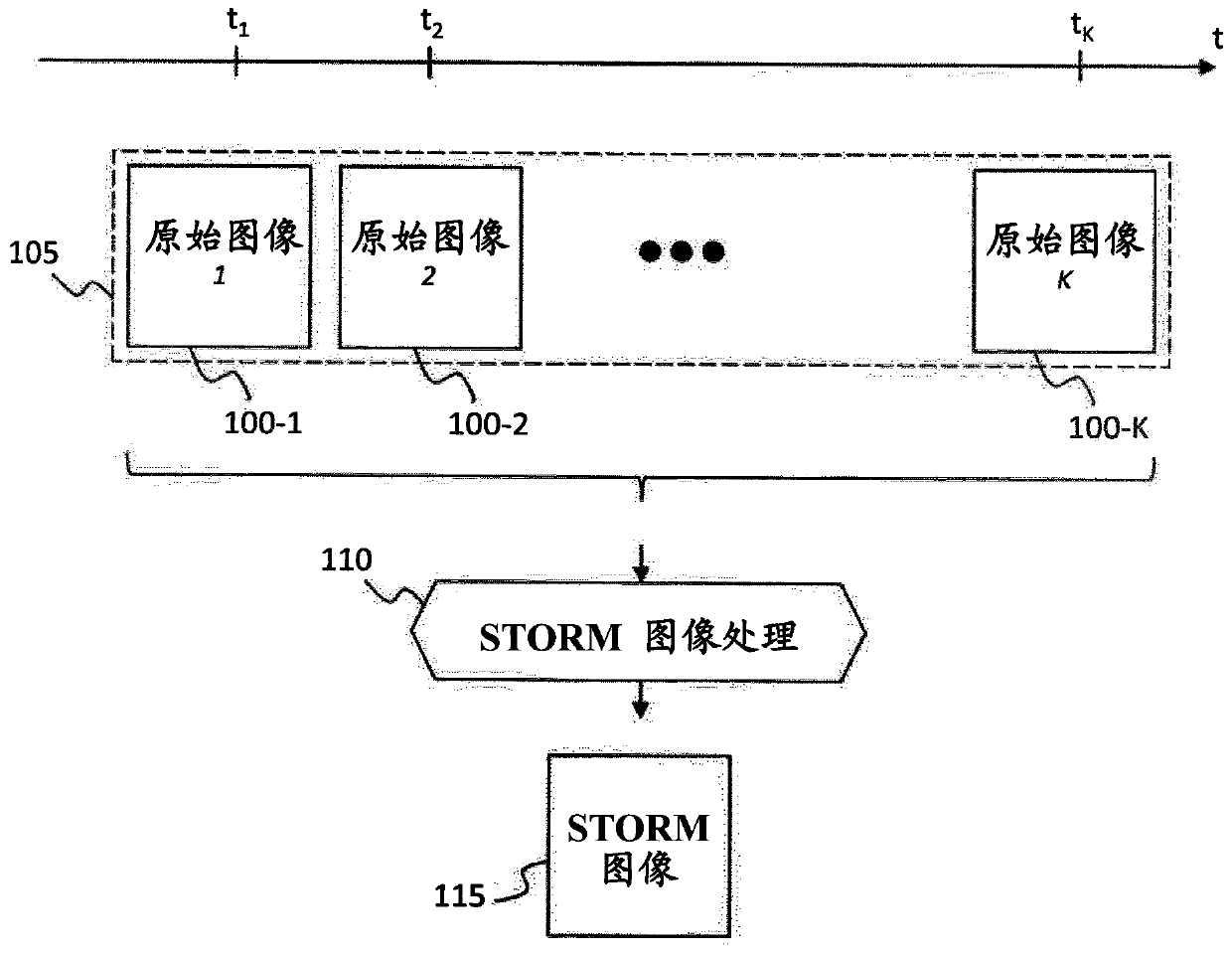
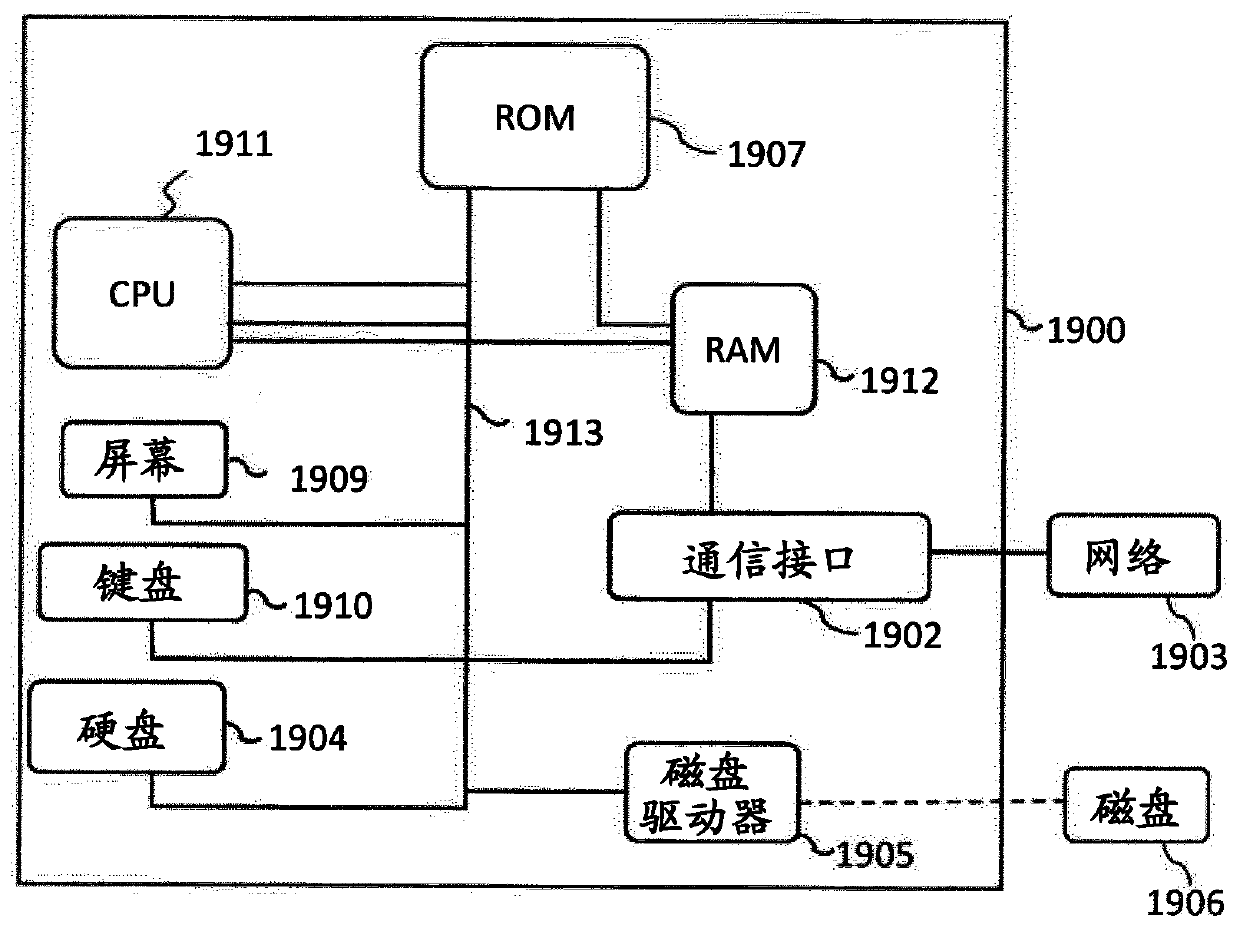
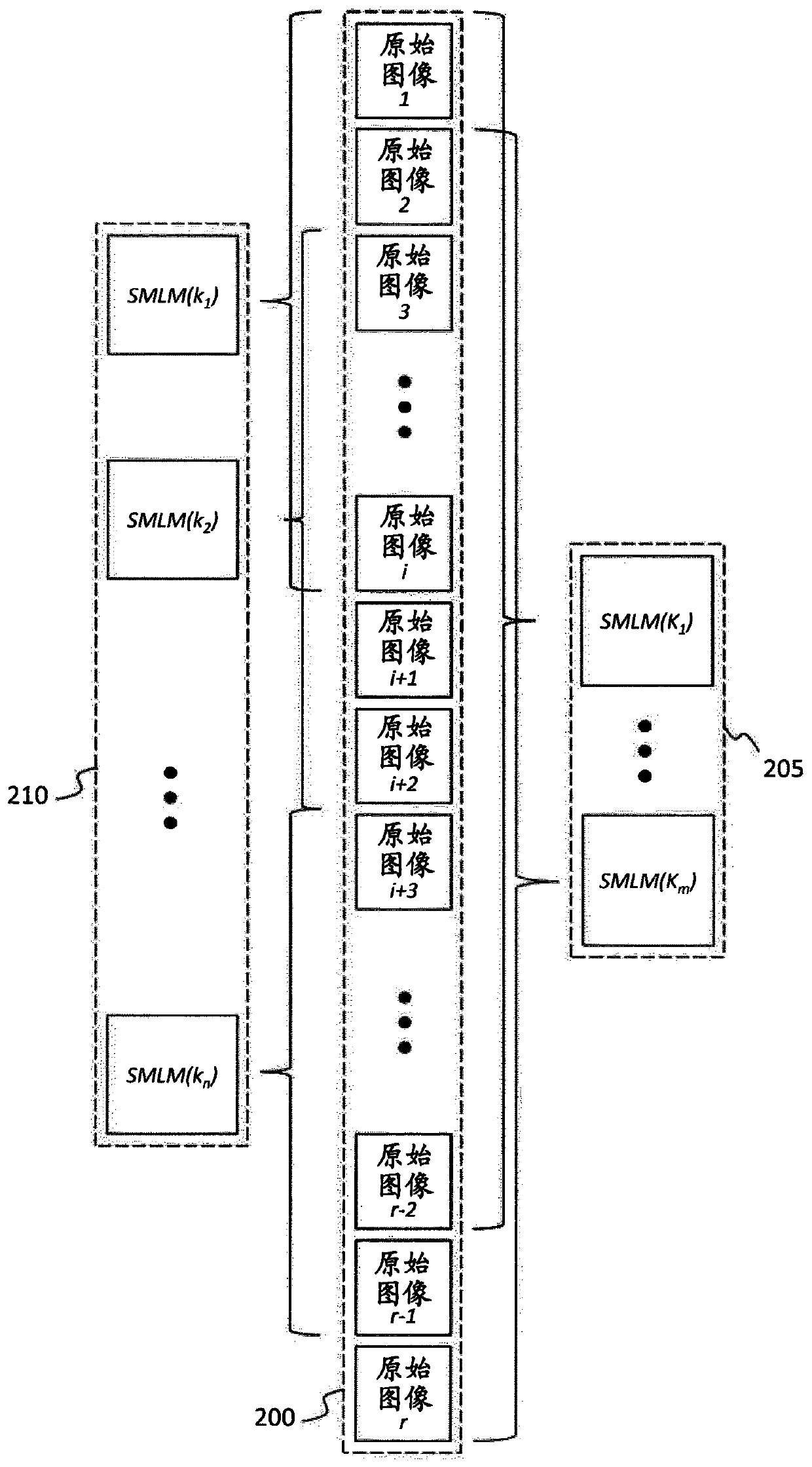
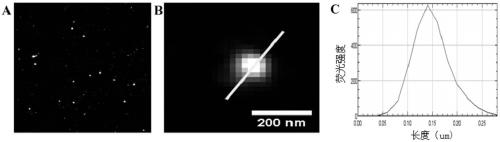
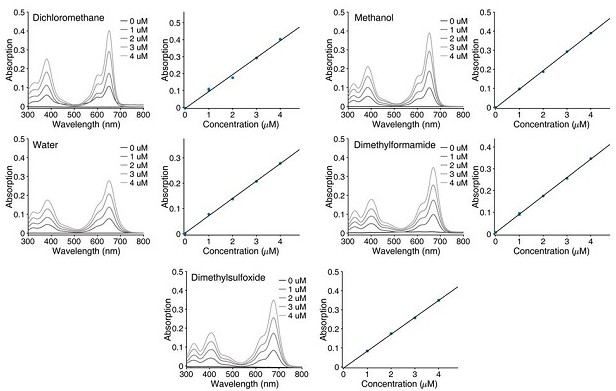
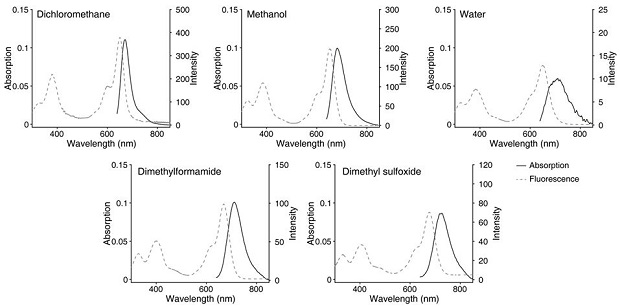
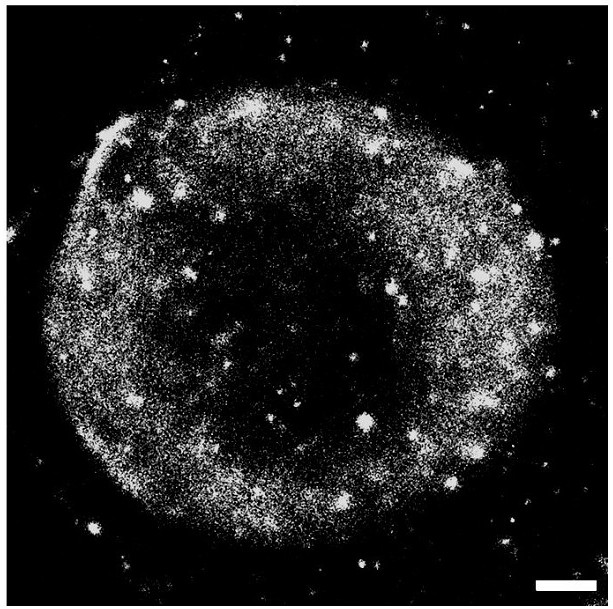
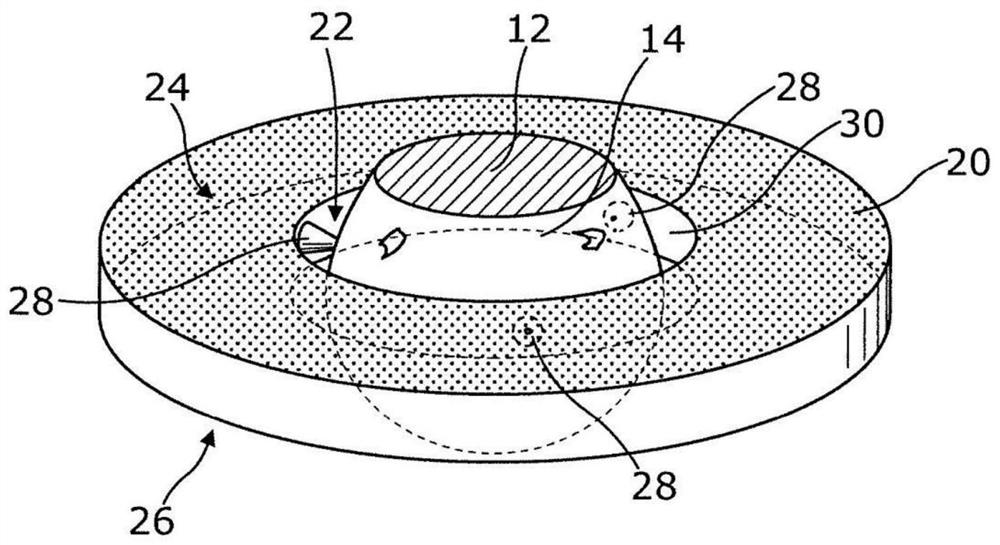
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Single molecule localization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
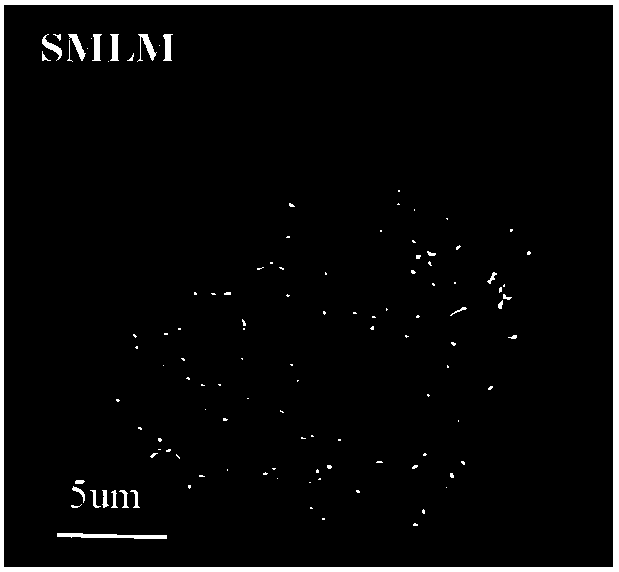
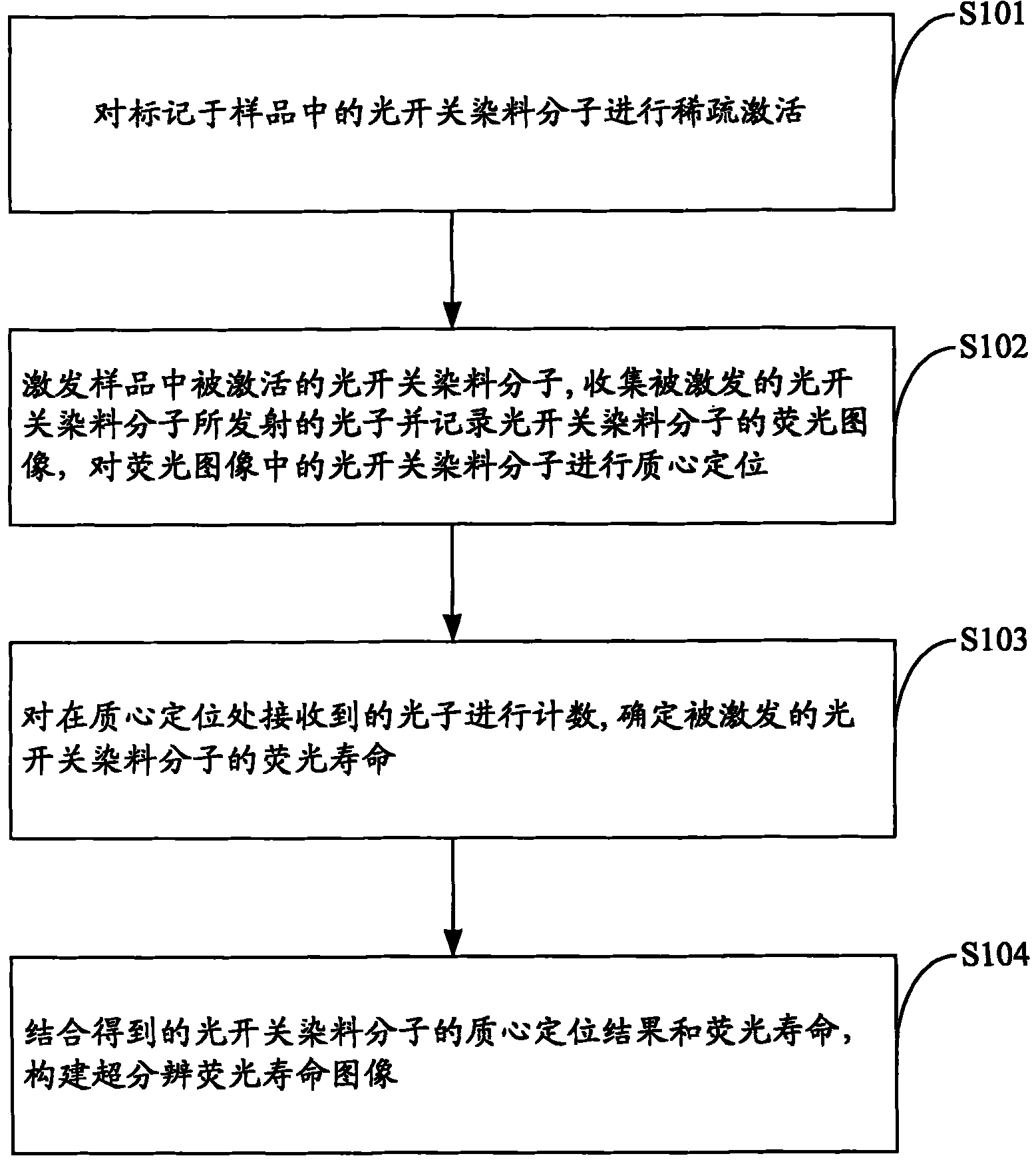
Super resolution fluorescence lifetime imaging method and system
ActiveCN102033058AFluorescence lifetime imaging realizedBreak through the limitation of optical diffraction limitFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical diffractionSingle molecule localization
The invention is applied to the fields of optics, biology, chemistry and the like and provides a super resolution fluorescence lifetime imaging method. The method comprises the following steps of: sparsely activating an optical switch dye molecule marked in a sample; exciting the activated optical switch dye molecule in the sample; collecting photons transmitted by the activated optical switch dye molecule and recording a fluorescent image of the optical switch dye molecule; carrying out the centroid positioning on the optical switch dye molecule in the fluorescent image; counting the photons received at the centroid positioning site and determining a fluorescence lifetime of the activated optical switch dye molecule; and constructing the super resolution fluorescence lifetime image by combining the centroid positioning result with the fluorescence lifetime of the obtained optical switch dye molecule. By combining the super resolution fluorescence microtechnique based on unimolecule positioning with the fluorescence lifetime imaging based on time relevant single photon counting, the invention realizes the super resolution fluorescence lifetime imaging, breaks through the traditional optical diffraction limit and has higher scientific significance and application value.
Owner:深圳市光科健康科技有限公司
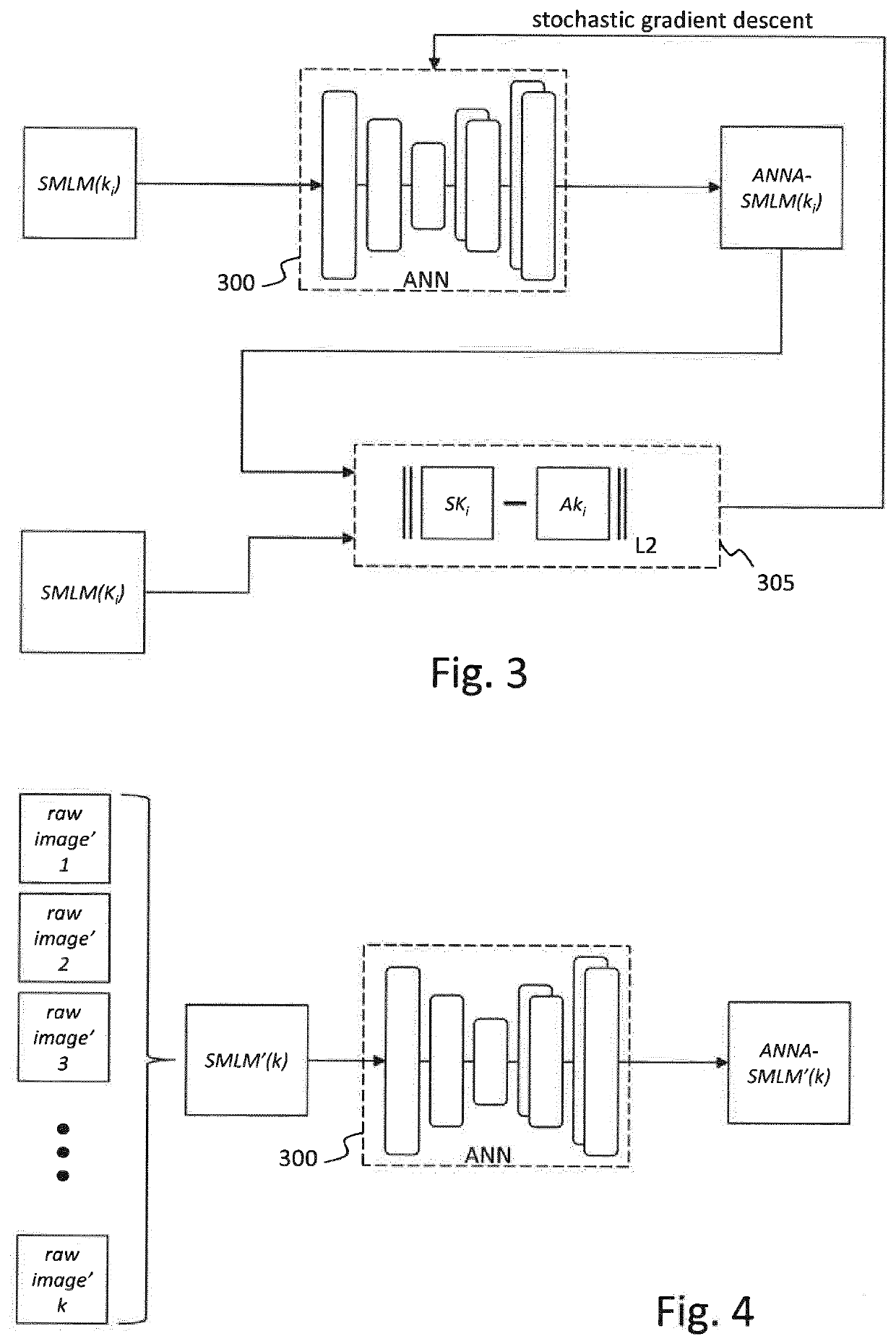
Method, device, and computer program for improving the reconstruction of dense super-resolution images from diffraction-limited images acquired by single molecule localization microscopy
ActiveUS20200250794A1Increase the number ofIncrease variabilityGeometric image transformationNeural learning methodsImaging processingImage resolution
The invention relates to reconstructing a synthetic dense super-resolution image from at least one low-information-content image, for example from a sequence of diffraction-limited images acquired by single molecule localization microscopy. After having obtained such a sequence of diffraction-limited images, a sparse localization image is reconstructed from the obtained sequence of diffraction-limited images according to single molecule localization microscopy image processing. The reconstructed sparse localization image and / or a corresponding low-resolution wide-field image are input to an artificial neural network and a synthetic dense super-resolution image is obtained from the artificial neural network, the latter being trained with training data comprising triplets of sparse localization images, at least partially corresponding low-resolution wide-field images, and corresponding dense super-resolution images, as a function of a training objective function comparing dense super-resolution images and corresponding outputs of the artificial neural network.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Random positioning super-resolution microscopy method and device based on fluorescence-emission kill mechanism
ActiveCN103592278AHigh resolution finenessSimple structureFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtensibilityWide field
The invention discloses a random positioning super-resolution microscopy method and device based on a fluorescence-emission kill mechanism. The method includes the following steps: coaxial and common-path exciting light and restraining light are simultaneously focused on a sample; the position on the sample, with the stimulated fluorescence-emission characteristic, randomly emits fluorescent light; fluorescent signals are collected to generated a sparse fluorescent distribution image; diffraction spots are positioned in a unimolecule manner, and the final product is obtained after different fluorescent light positioning images are synthesized. The device includes a first laser light source, a second laser light source, a reflector, a first dichroic mirror, a kohler mirror group, a second dichroic mirror, a microobjective, a sample, an optical filter, a field lens, an ocular, a wide field sensing element and a computer. The invention has the advantages that the resolution ratio and fineness are high, 20 nm crosswise super-resolution images can be obtained; the structure is simple, and the cost is low; irreversible damage of intensive laser or fluorescence photobleaching to samples is reduced, and repeating utilization ratio of samples is increased; the function extensibility is strong.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
A super-resolution optical imaging method based on a single-molecule positioning process
ActiveCN106053405AAchieving super-resolution optical imagingHigh-resolutionBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceNormal cellMembrane surface
A super-resolution optical imaging method based on a single-molecule positioning process is disclosed and used for observing an interaction process between a tumor cell exosome and a normal cell. The method includes (1) extracting the tumor cell exosome by utilizing a kit, (2) respectively labeling a membrane of the tumor cell exosome and a membrane surface receptor of the tumor cell exosome by using a first fluorescent molecule and a second fluorescent molecule, and staining the normal cell by using a third fluorescent molecule, and (3) observing the interaction process between the tumor cell exosome and the normal cell through a super-resolution optical microscope based on the single-molecule positioning process. The method overcomes the problem that exosomes cannot be observed carefully in the prior art due to a diffraction limit, and provides a novel technical means for researching exosome-mediated cancer metastasis mechanisms and for treating and researching cancer metastasis and spreading.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Real-time single-molecule positioning method guaranteeing precision and system thereof
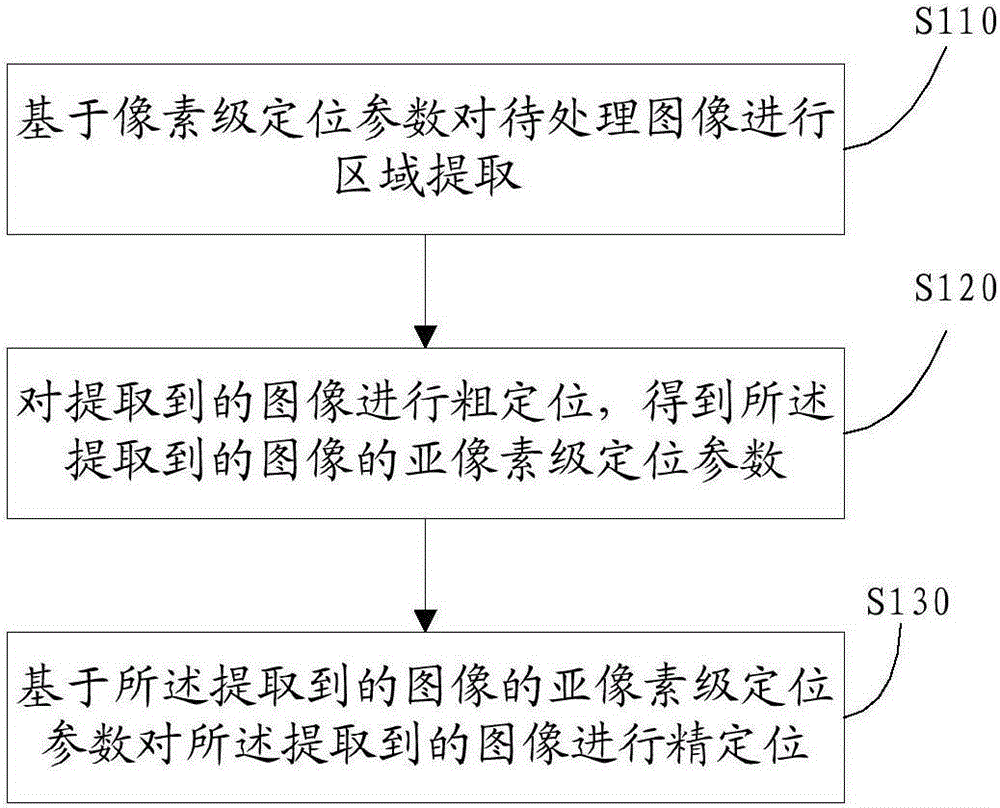
ActiveCN105243677AFast positioningReduce the number of iterationsImage analysis2D-image generationSingle molecule localizationComputer science
The invention discloses a real-time single-molecule positioning method guaranteeing precision and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps that region extraction is performed on an image to be processed based on pixel-level positioning parameters firstly; then coarse positioning is performed on the extracted image so that the subpixel-level positioning parameters of the extracted image are obtained; and then fine positioning is performed on the extracted image based on the subpixel-level positioning parameters of the extracted image. The initial value (the subpixel-level positioning parameters) obtained through coarse positioning is closer to a real value, based on which fine positioning calculation is performed so that the number of times of iteration in fine positioning is reduced, and thus positioning speed of a super-resolution image is accelerated. Therefore, positioning speed of the super-resolution image is accelerated under the condition of guaranteeing positioning precision.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-molecule positioning based fast super-resolution imaging method and system
ActiveCN102063730ASuper-resolution imaging real-timeFast super-resolution imaging2D-image generationImage data processing detailsImaging processingSingle molecule localization
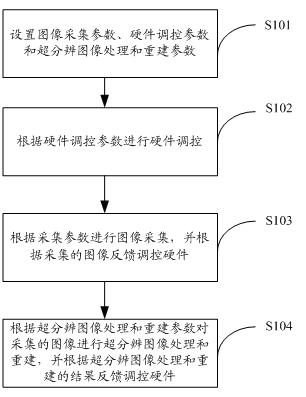
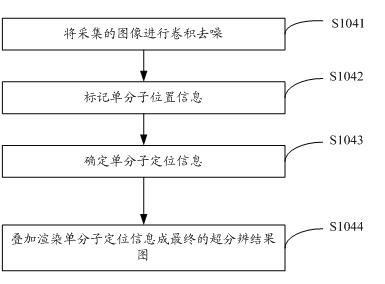
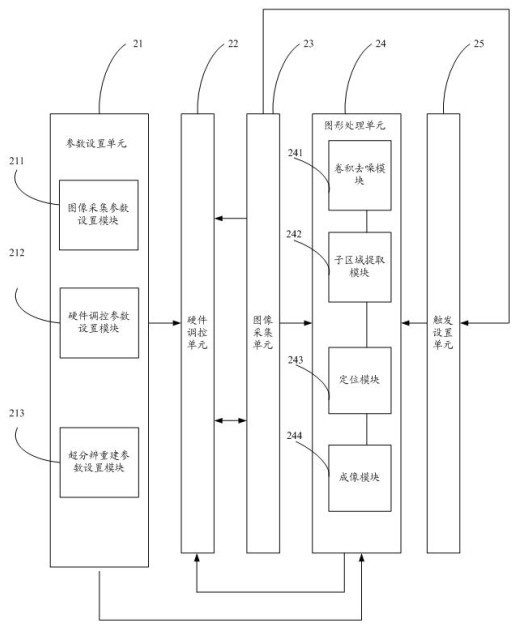
The invention discloses a single-molecular positioning based fast super-resolution imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: setting image acquisition parameters, hardware regulation and control parameters and super-resolution image processing and reconstruction parameters; performing hardware regulation and control according to the hardware regulation and control parameters; performing the super-resolution image processing and reconstruction on acquired images according to the super-resolution image processing and reconstruction parameters; and performing hardware regulation and control according to feedback results of super-resolution image processing and reconstruction. The single-molecular positioning based fast super-resolution imaging method adopts high algorithm precision, can be realized through parallel arithmetic of a graphic process unit (GPU), and can achieve higher image processing and reconstruction speed and automatically regulate and control the whole imaging system including a shutter, an electric bench and a step motor, thereby realizing fast super-resolution imaging.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-throughput super-resolution imaging system and method based on monomolecular positioning
InactiveCN102254331AImprove throughputSuper-resolution imaging real-time2D-image generationImage data processing detailsImaging processingSingle molecule localization
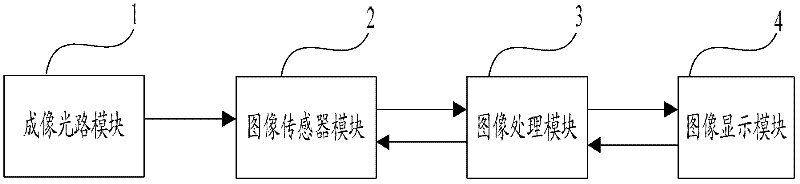
The invention discloses a high-throughput super-resolution imaging method and a high-throughput super-resolution imaging system based on monomolecular positioning. The system comprises an imaging light path module, an image sensor module, an image processing module and an image display module, wherein the imaging light path module maps an imaging viewing field into the image sensor module; the image sensor module images the imaging viewing field at a high speed; the image processing module acquires an image which is formed at the high speed and processes the image; and the image display module displays an image processing result in real time. The method comprises the following steps of: imaging the imaging viewing field at a high speed by the image sensor module; acquiring the image which is formed at the high speed by the image processing module, and processing the image; and displaying the image processing result in real time by the image display module. According to the high-throughput super-resolution imaging system and the method based on the monomolecular positioning provided by the invention, limit of an interface space on high-throughput super-resolution imaging is broken, and real-time, quick and high-throughput super-resolution imaging can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
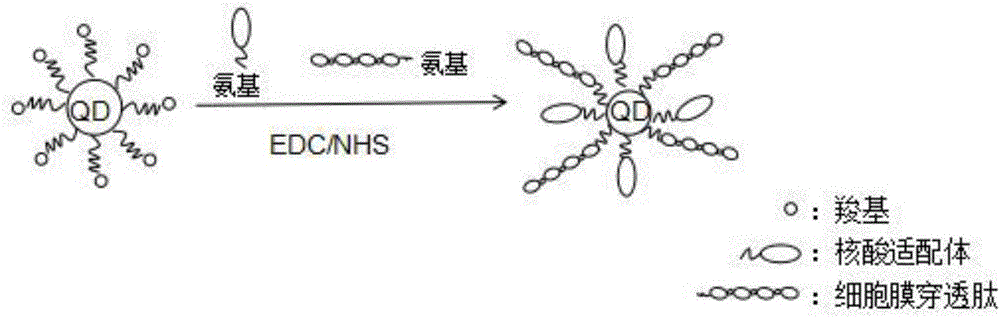
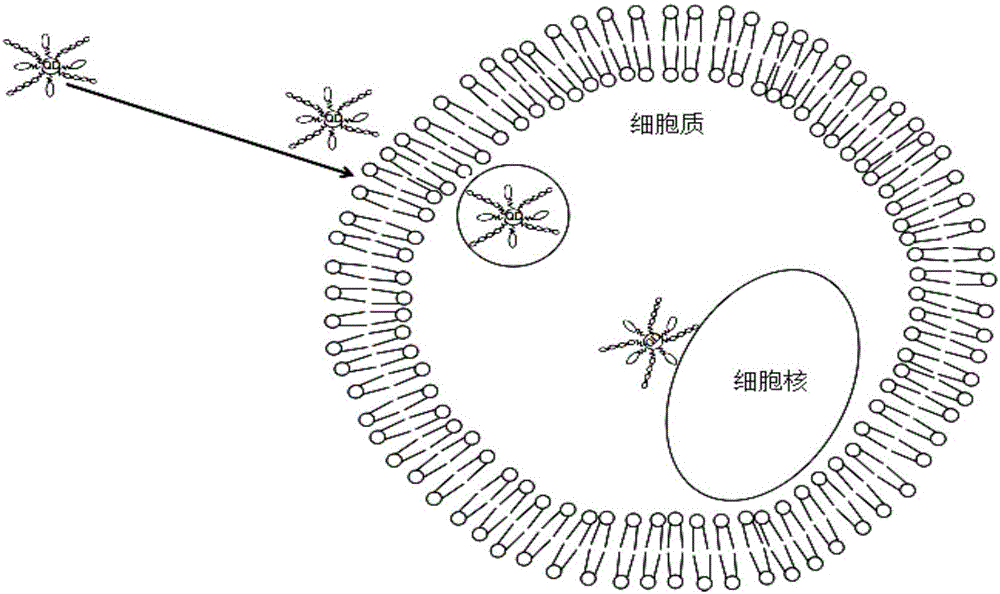
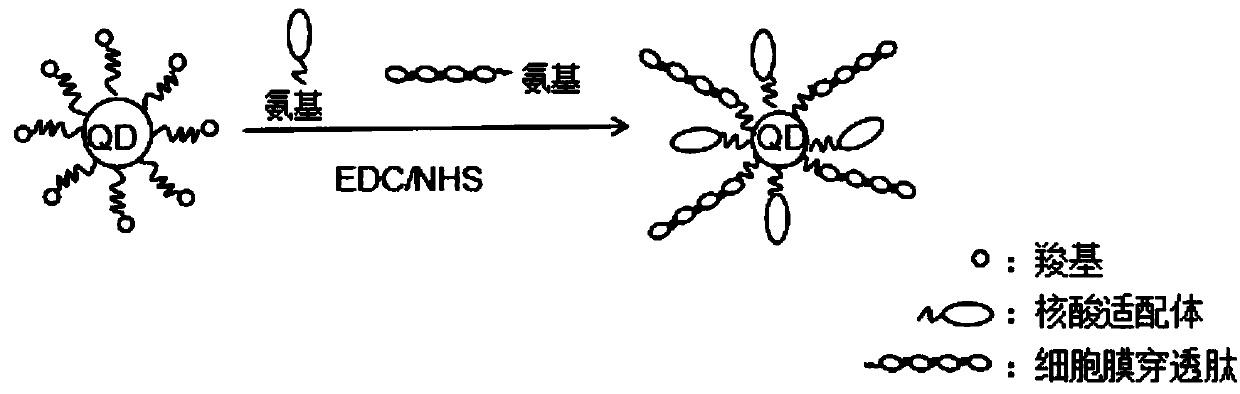
Super-resolution optical imaging probe for living cells and preparation method of super-resolution optical imaging probe
ActiveCN105950133AHigh luminous intensityExcellent luminous propertiesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsAptamerLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a super-resolution optical imaging probe for living cells and a preparation method of the super-resolution optical imaging probe. Quantum dots are taken as a fluorophore, cell membrane penetrating peptides and nucleic acid aptamers are coupled on the surfaces of the quantum dots, the cell membrane penetrating peptides are used for promoting the probe to penetrate through the living cells, the nucleic acid aptamers are used for specific binding with nuclear membrane receptor protein of the living cells, and cell nucleus positioning of the probe is realized. The quantum dots with scintillating effects are taken as the fluorophore and are adapted to super-resolution optical imaging based on a single-molecule positioning method by means of the high luminous intensity and the fluorescence scintillation characteristic; meanwhile, the quantum dots with scintillating effects are taken as the fluorophore, a special imaging buffering solution is not required, therefore, the probe is adapted to super-resolution imaging of the living cells; besides, the preparation method is simple and convenient to operate, the cost is low, and the time cost and the economic cost are effectively saved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
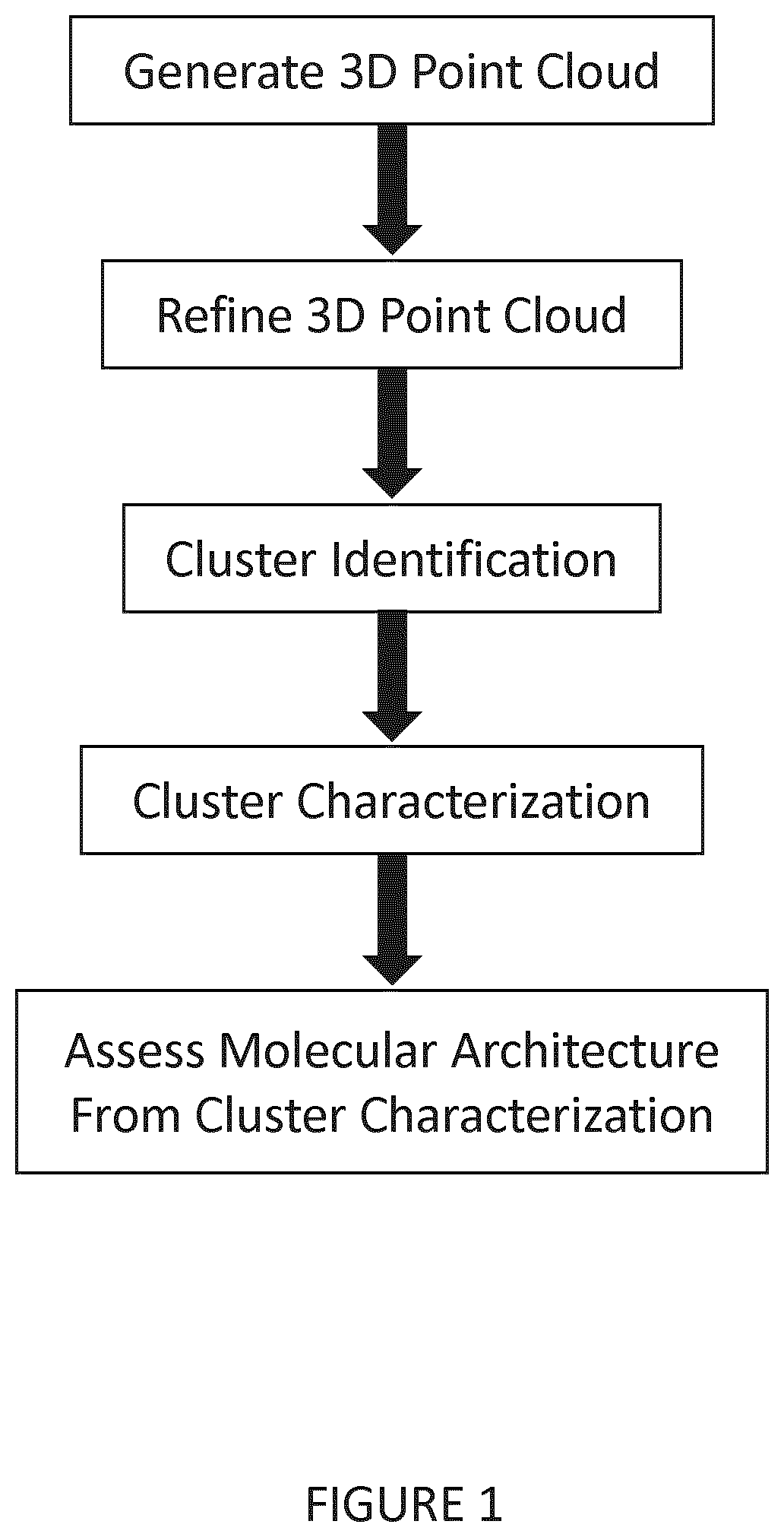
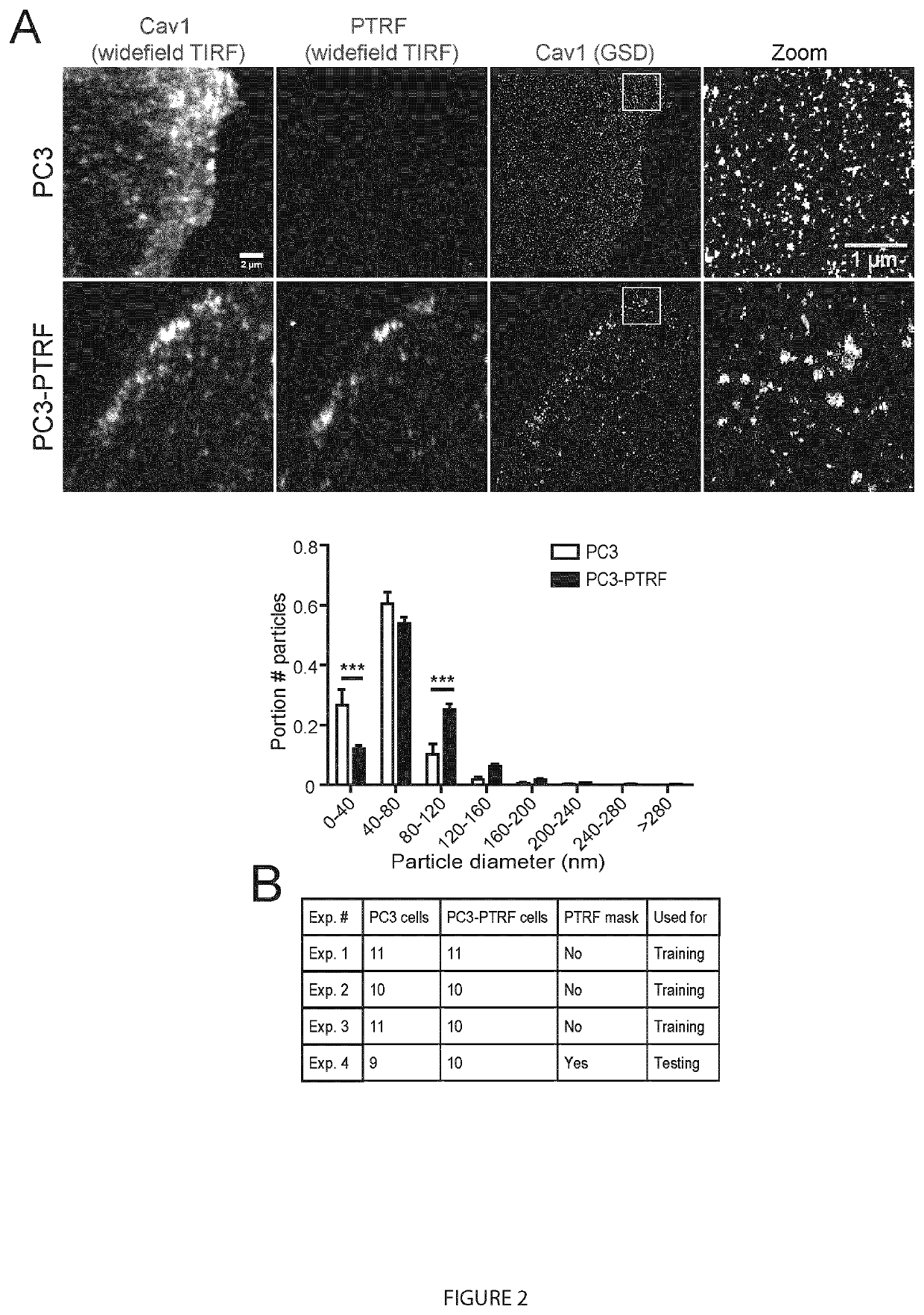
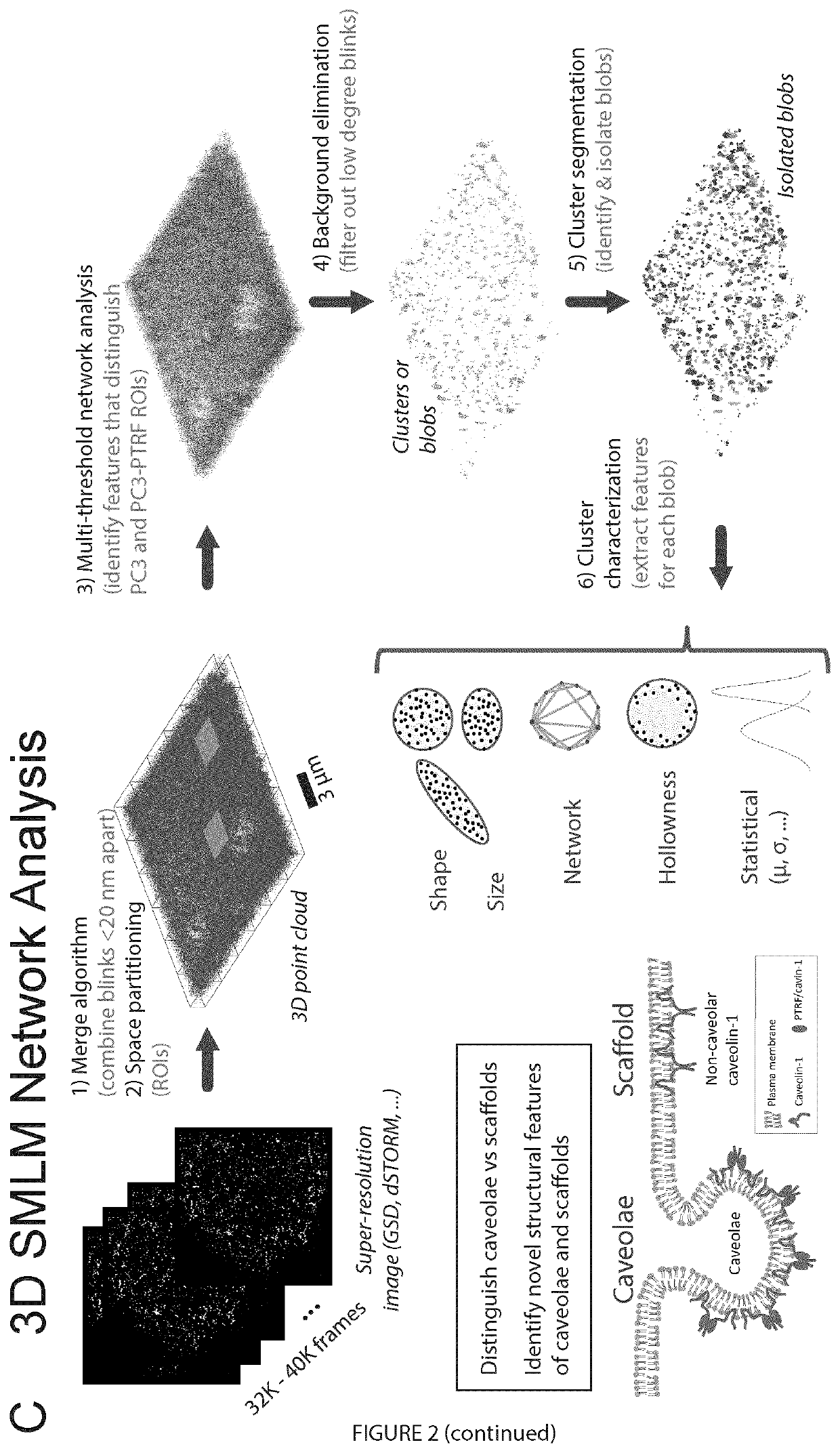
Methods for analysis of single molecule localization microscopy to define molecular architecture
A method of super-resolution microscopy is provided. The method includes mapping three-dimensional location of each single emission event in a plurality of single emission events from a series of optical images of a sample to create a point cloud. The point cloud is filtered or refined. Clusters within the point cloud are identified and characterized allowing for an assessment of molecular architecture.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY +1
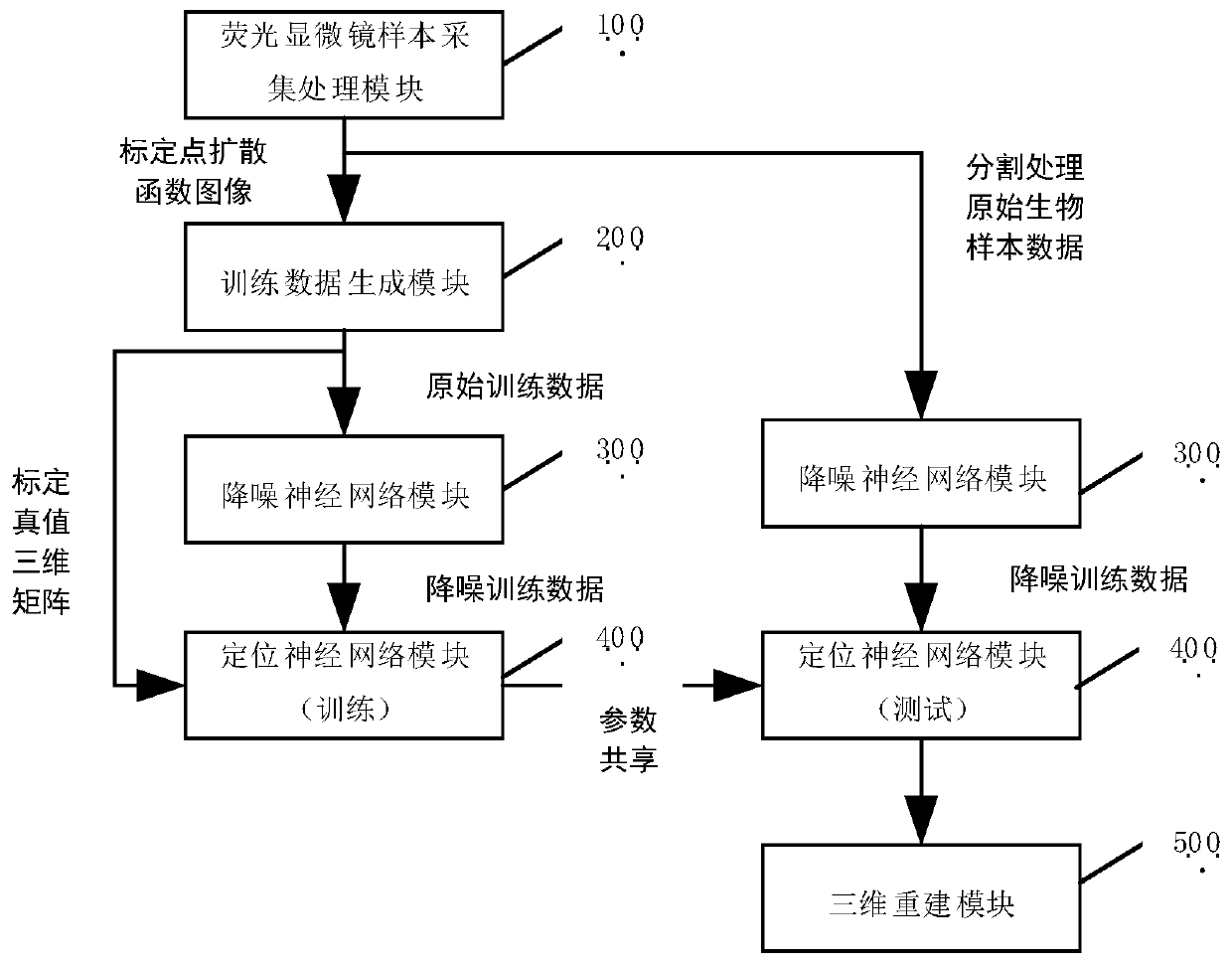
Three-dimensional single-molecule positioning system based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111310903AHigh positioning accuracyReduce signal to noise ratioNeural architecturesPhysical realisationFluorescence microscopeSingle molecule localization
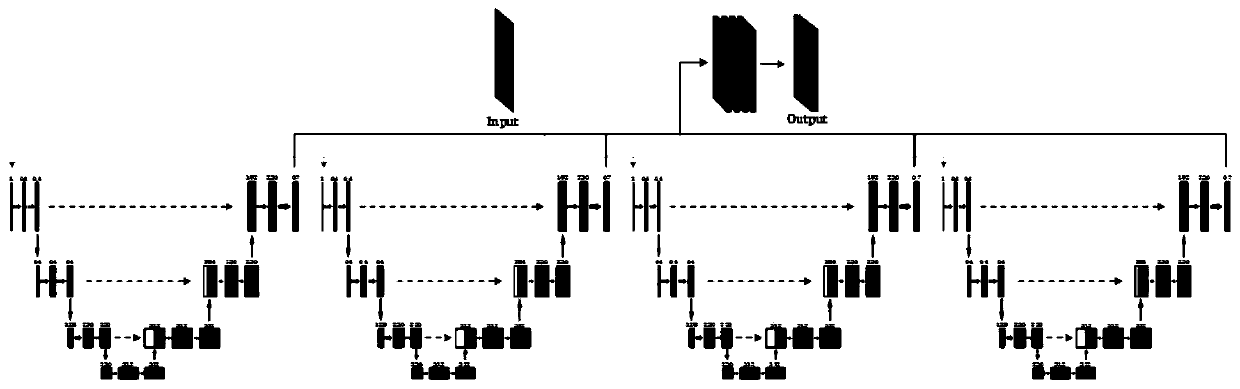
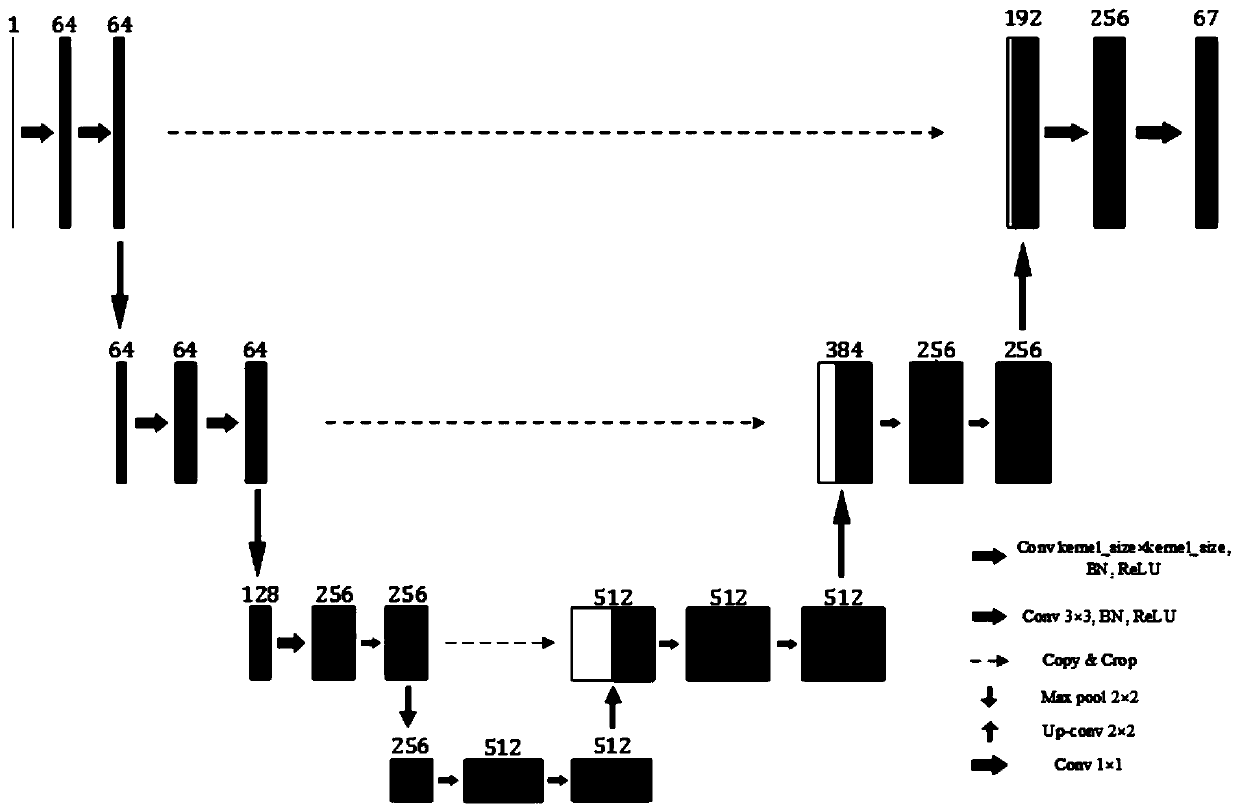
The invention discloses a three-dimensional single-molecule positioning system based on a convolutional neural network. According to the system, a point spread function is calibrated by using a smallfluorescent ball sample; utilizing the point spread function images and a camera noise model to simulate and excite to generate training samples, and generating a true value three-dimensional matrix corresponding to each training image; inputting the training sample into an unsupervised noise reduction network to obtain noise reduction model parameters; inputting the denoised training sample and the true value three-dimensional matrix into a positioning neural network for training to obtain positioning model parameters; imaging the sample to be observed through a fluorescence microscope, and segmenting the image into the same size as the training set; performing noise reduction on the processed image; inputting the denoised image into the trained positioning network for testing; and finally, performing super-resolution reconstruction on an output result through a sparse coding method to obtain a super-resolution image. The system can maintain high precision and high accuracy of axial positioning for a point spread function excited by high overlapping rate and high density.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Super-resolution microscopic scale based on quantum dot and DNA origami nano co-assembly structure
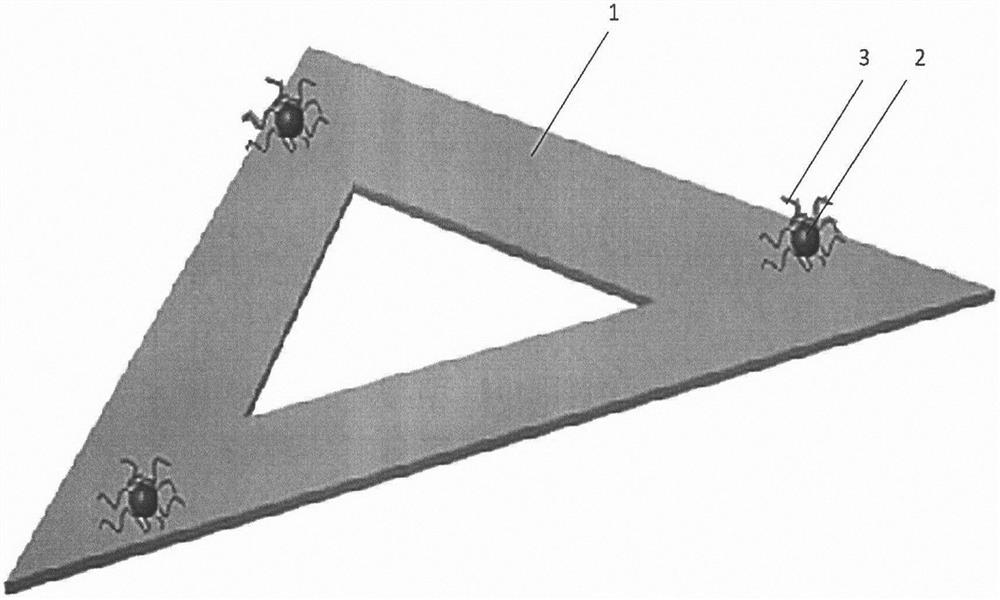
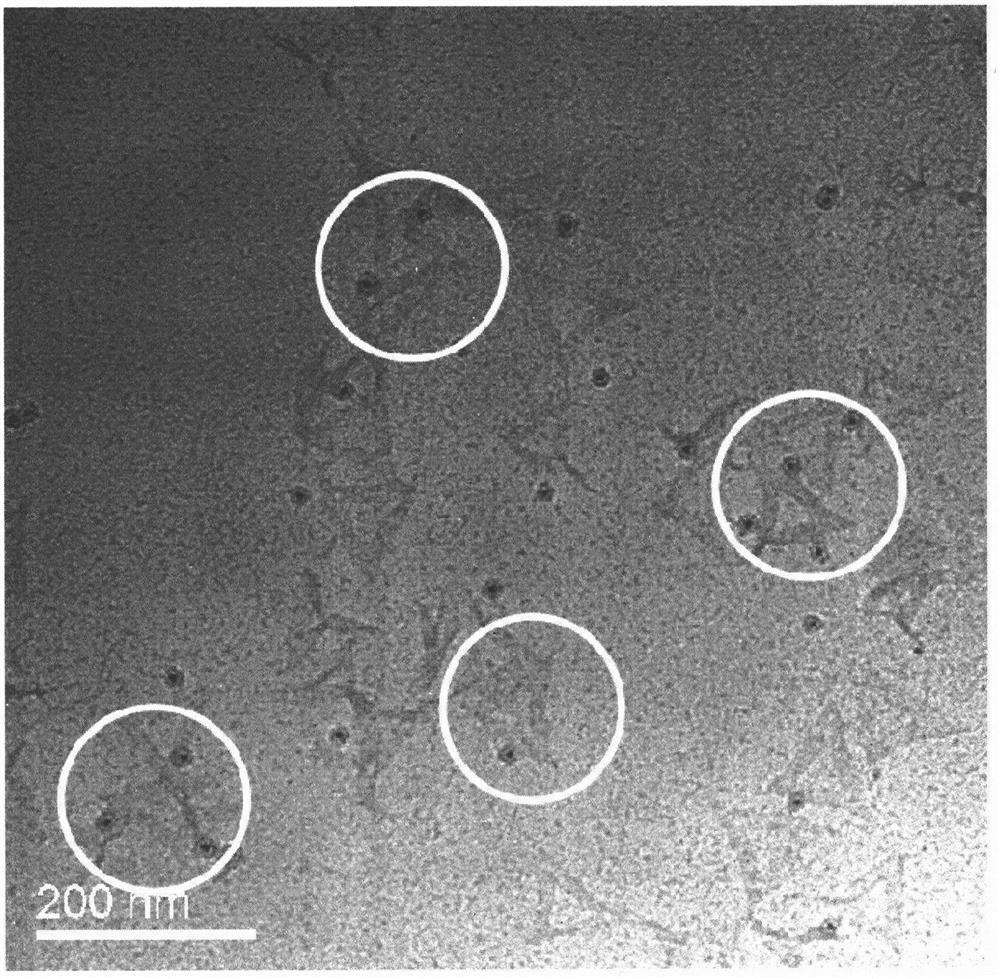
InactiveCN112129788AStable structureFluorescence stabilizationUsing optical meansFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic scale based on a quantum dot and DNA origami nano co-assembly structure, and belongs to the technical field of nano materials. The super-resolution microscopic scale is used for demarcating and calibrating the resolution of an ultrahigh-resolution fluorescence microscope system. According to the super-resolution microscopic scale based on thequantum dot and DNA origami nano co-assembly structure, quantum dots (2) and DNA single strands (3) are coupled and then modified to the fixed site of a DNA origami (1) (a triangle is taken as an example) to form the nano-scale with a fixed distance, so that the problem that the super-resolution microscopy lacks a high-precision scale to verify the accuracy of an obtained super-resolution image issolved. Through the super-resolution technology to break through the diffraction limit of light, the accuracy of the obtained super-resolution image is verified according to the fixed distance (20-200 nm) between the quantum dots on the same DNA origami structure. The super-resolution microscopic scale based on the quantum dot and DNA origami nano co-assembly structure is used for representing the imaging resolution of a positioning super-resolution monomolecular positioning microimaging technology (SMLM), and has the advantages of high brightness, stability, reusability and easiness in making different sizes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
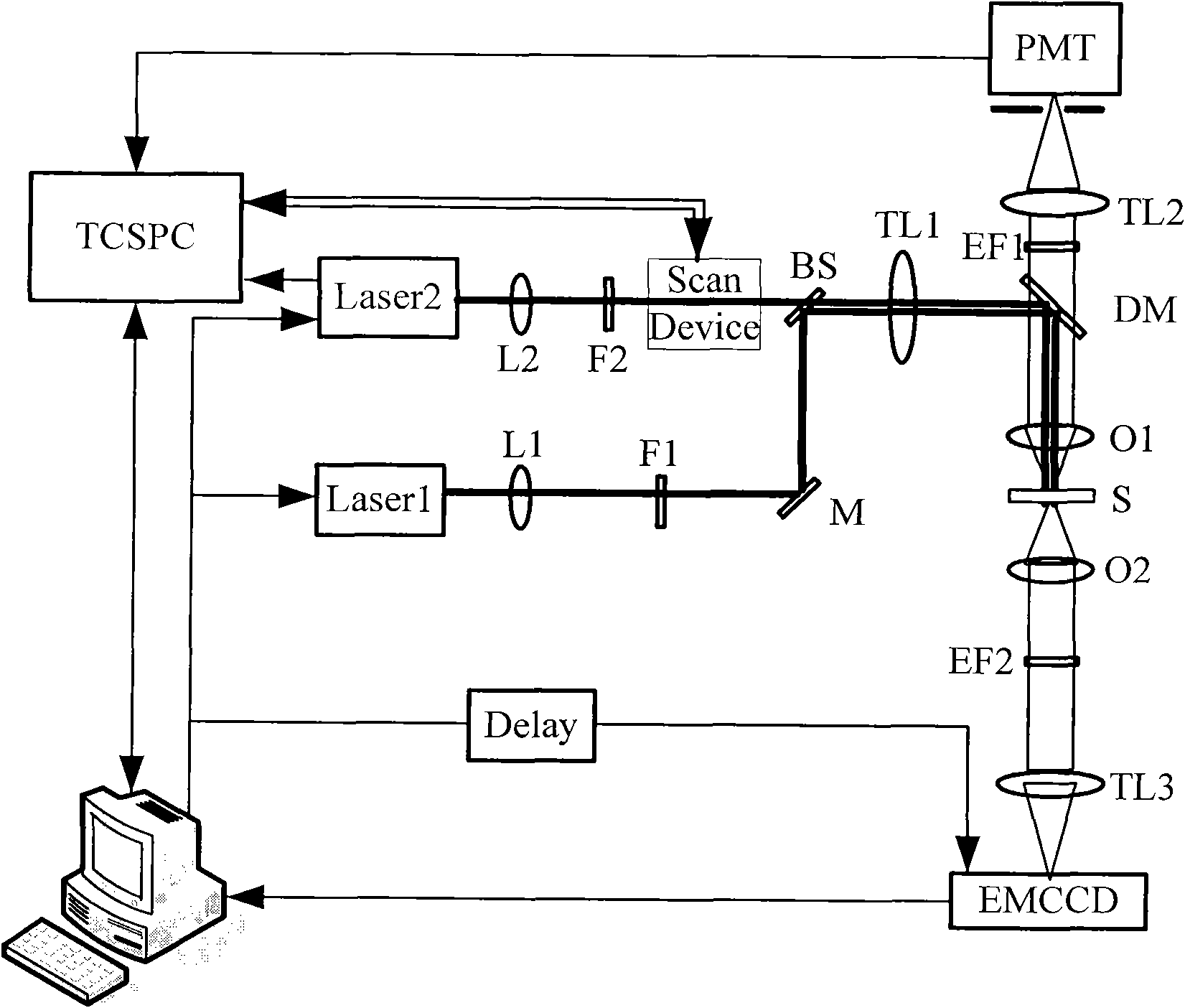
Anti-bleaching unimolecule positioning three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy system
InactiveCN107941777AMotivating realizationOvercoming fluorescence excitationFluorescence/phosphorescenceTime domainPhase grating
The invention discloses an anti-bleaching unimolecule positioning three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy system. The anti-bleaching unimolecule positioning three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy system comprises a first laser, a beam expanding and collimating unit, a phase grating, a third lens, a first dichroic mirror, an objective lens, a sample table, an optical filter, a fourth lens, a detector, a second dichroic mirror and a second laser. The anti-bleaching unimolecule positioning three-dimensional super-resolution microscopy system utilizes a time domain focusing characteristic, fluorescence excitation of a sample is generated only on a time domain focusing plane, and meanwhile, fluorescence excitation in the whole time domain focusing plane can be achieved. Therefore,compared with the prior art, bleaching of a sample in a non-focusing plane can be avoided, and the working efficiency of SMS fluorescence microscopy technology can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Manufacturing method and application of immunofluorescence co-localization imaging platform
PendingCN111077298AHas the characteristic of flickeringEnabling immunoassay researchBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerImaging chain
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and an application of an immunofluorescence co-localization imaging platform. A detection platform generates a gold nano array pattern through an electron beam lithography technology, and a surface is coupled with an HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) nucleic acid aptamer with a fluorophore FAM through a gold sulfur bond. The platform canspecifically capture exosomes secreted by HER2 high-expression tumor cells; an imaging chain is an HER2 nucleic acid aptamer probe with another fluorophore Cy5; and two probes have fluorescence scintillation characteristics and can be used for super-resolution monomolecular positioning imaging (SMLM). Through an SMLM imaging technology, the captured exosomes can be subjected to super-resolution optical imaging; in combination with a double-color fluorescence co-localization technology, a false positive event can be judged at a single molecular level, and accuracy of a sandwich immunoassay technology is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Telomere probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107723342ADosage controlAchieve conversionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationOptical diffractionSingle molecule localization
The invention discloses a telomere probe and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the telomere probe, a single stranded DNA is coupled onto the surface of the CdSSe / ZnS quantum dots, the telomere probe can be combined with the cell telomere by in-situ hybridization technique, and the telomere hybridized with the telomere probe is imaged by a single molecular positioning technique to realize the detection of the telomere. The telomere probe realizes the specific marking of the telomere, has higher resolution due to the adoption of the single molecule positioning microscopeimaging, and overcomes the limitation by the optical diffraction limit of the fluorescence microscopic technique. The telomere probe and the preparation method and the application thereof can be usedfor further study of the telomere structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method, device, and computer program for improving the reconstruction of dense super-resolution images from diffraction-limited images acquired by single molecule localization microscopy
ActiveCN111052173AGeometric image transformationNeural learning methodsImaging processingImage resolution
The invention relates to reconstructing a synthetic dense super-resolution image from at least one low-information-content image, for example from a sequence of diffraction-limited images acquired bysingle molecule localization microscopy. After having obtained such a sequence of diffraction-limited images, a sparse localization image is reconstructed from the obtained sequence of diffraction-limited images according to single molecule localization microscopy image processing. The reconstructed sparse localization image and / or a corresponding low-resolution wide-field image are input to an artificial neural network and a synthetic dense super-resolution image is obtained from the artificial neural network, the latter being trained with training data comprising triplets of sparse localization images, at least partially corresponding low-resolution wide-field images, and corresponding dense super-resolution images, as a function of a training objective function comparing dense super-resolution images and corresponding outputs of the artificial neural network.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Recombinant plasmid and cell line for monomolecular positioned super-resolution imaging of exosome and applications of recombinant plasmid and cell line
InactiveCN109182362AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetically modified cellsCD63Single molecule localization
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid and cell line for monomolecular positioned super-resolution imaging of exosome and applications of the recombinant plasmid and the cell line. The recombinant plasmid is formed by fusing and constructing a fluorescence protein gene with a photoactivation property and a marking CD63 protein gene on an exosome film; Hela cells are transfected through a liposome-mediated plasmid transfection technology; and the Hela cells capable of stably expressing the photoactivation fluorescence protein marked exosome are obtained through drug screening. Monomolecular positioned super-resolution imaging researches of the separated and purified exosome and CD63 protein distribution in cells are carried out, with the help of the photoactivation fluorescence protein. Compared with a traditional microscope, the monomolecular positioned super-resolution imaging provides a better space resolution ratio and the monomolecular positioned super-resolution imaging ofthe exosome with activity is realized; and meanwhile, monomolecular positioned imaging researches of the CD63 protein distribution in the cells are also realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
BSA-based super-resolution imaging probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108872172AGood light stabilityFlashing for a long timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSingle molecule localizationReceptor-mediated endocytosis
The invention discloses a BSA-based super-resolution imaging probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The super-resolution imaging probe is BSA nanometer balls coated with AlexaFluor 594 dye; in addition, HER2 antibodies are coupled on the surface. The probe has the fluorescence flickering features and can be used for super-resolution unimolecule imaging. In addition, the probe can be used for targeting high-EHR2-expression tumor cells and can enter the cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis; through an SMLM imaging technology, the tumor cells after the probe intakecan be subjected to super resolution optical imaging. The application of the super-resolution imaging probe in the cells to super-resolution imaging can be realized; an SMLM microscope is used; the distribution of the probe in the cells can be precisely positioned.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Single-molecule positioning micro-imaging method, optical assembly and imaging system
ActiveCN108956575AExpand the scope ofHigh resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingDiffusion function
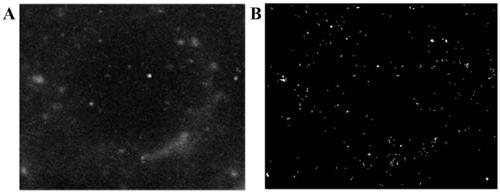
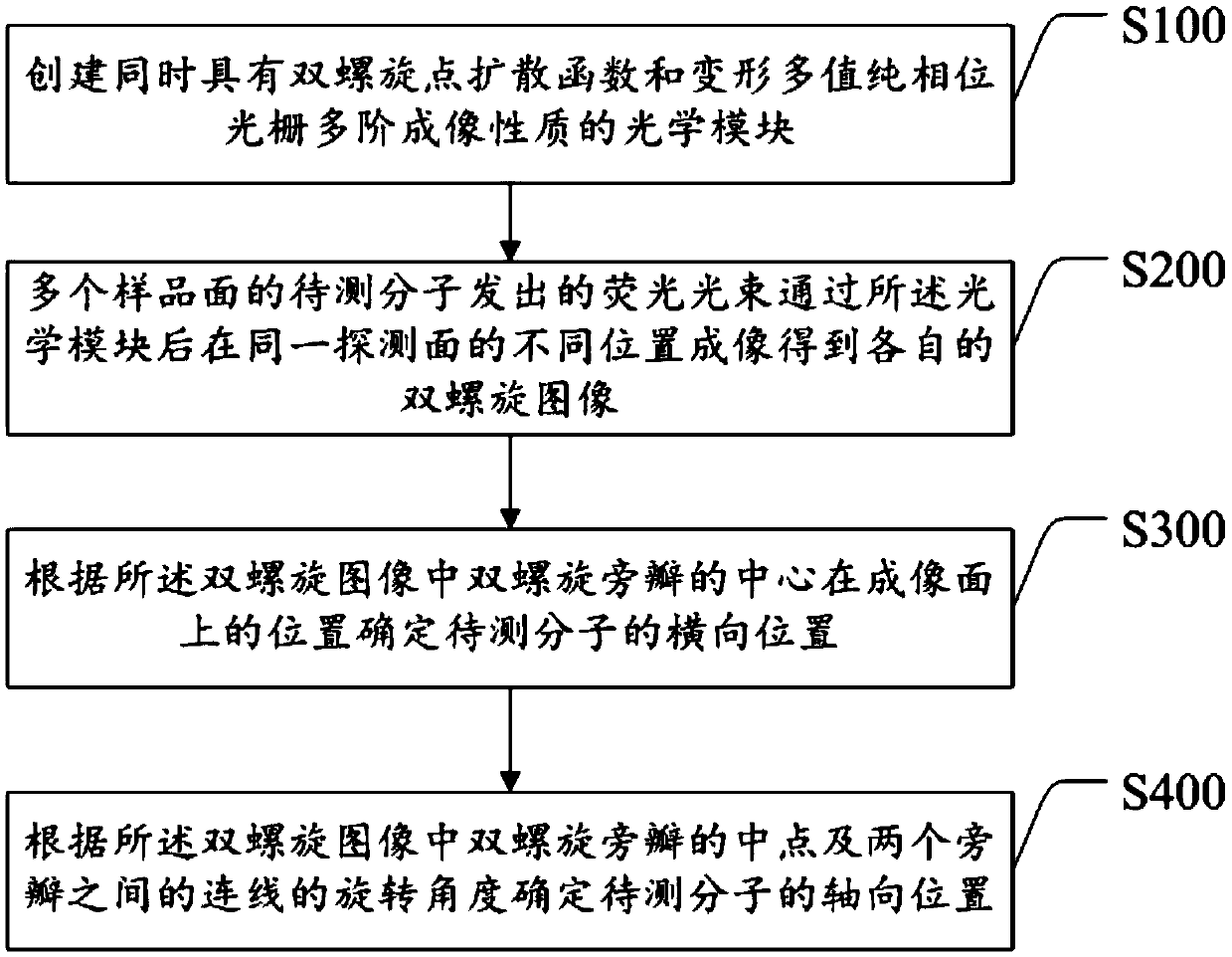
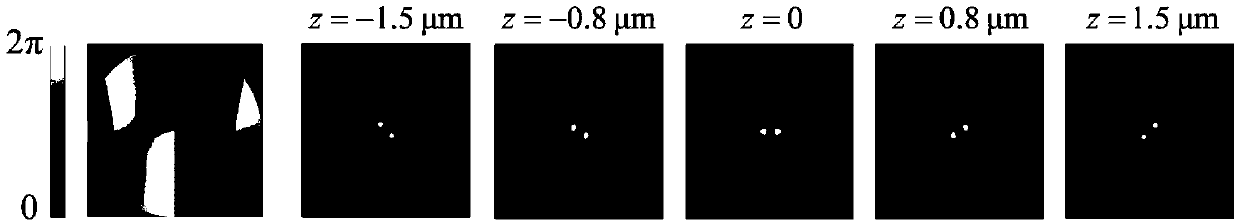
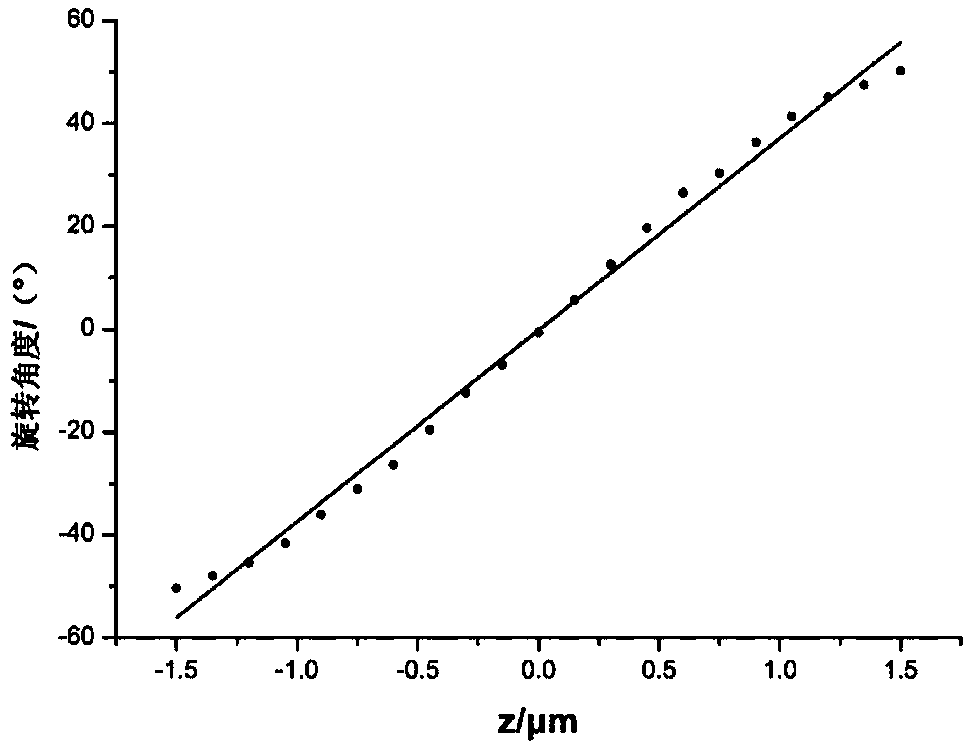
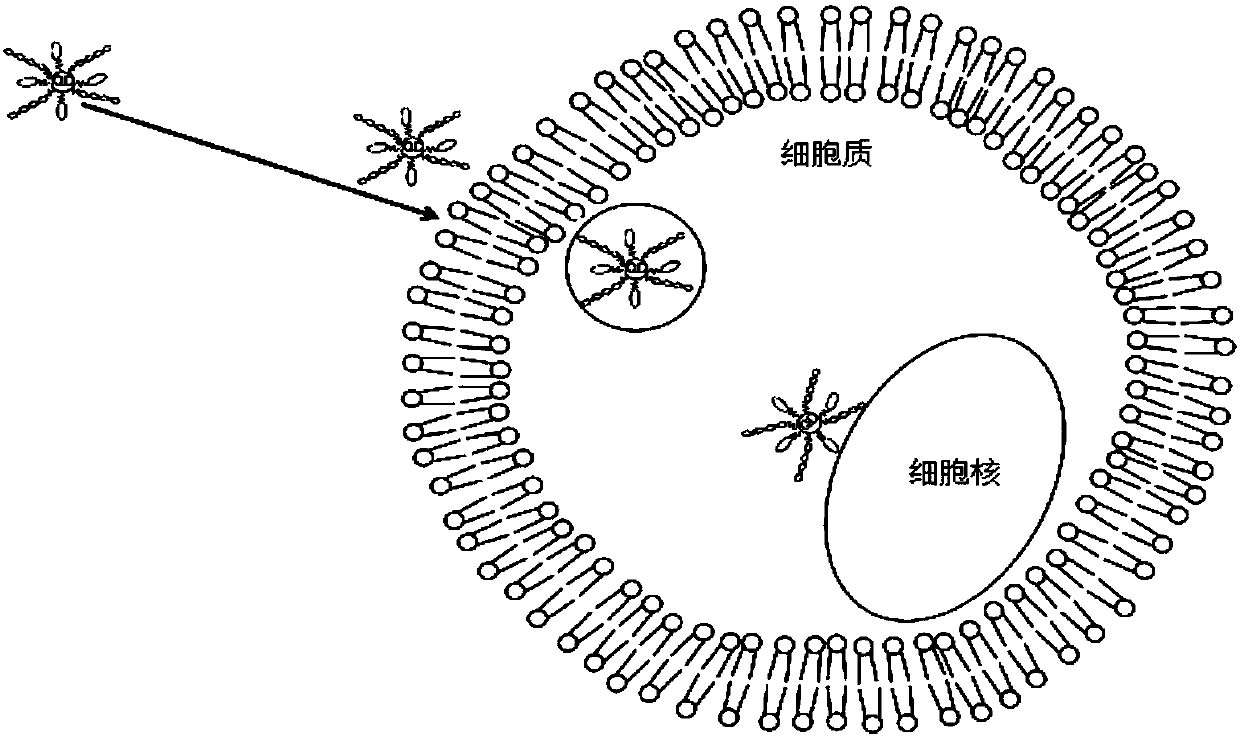
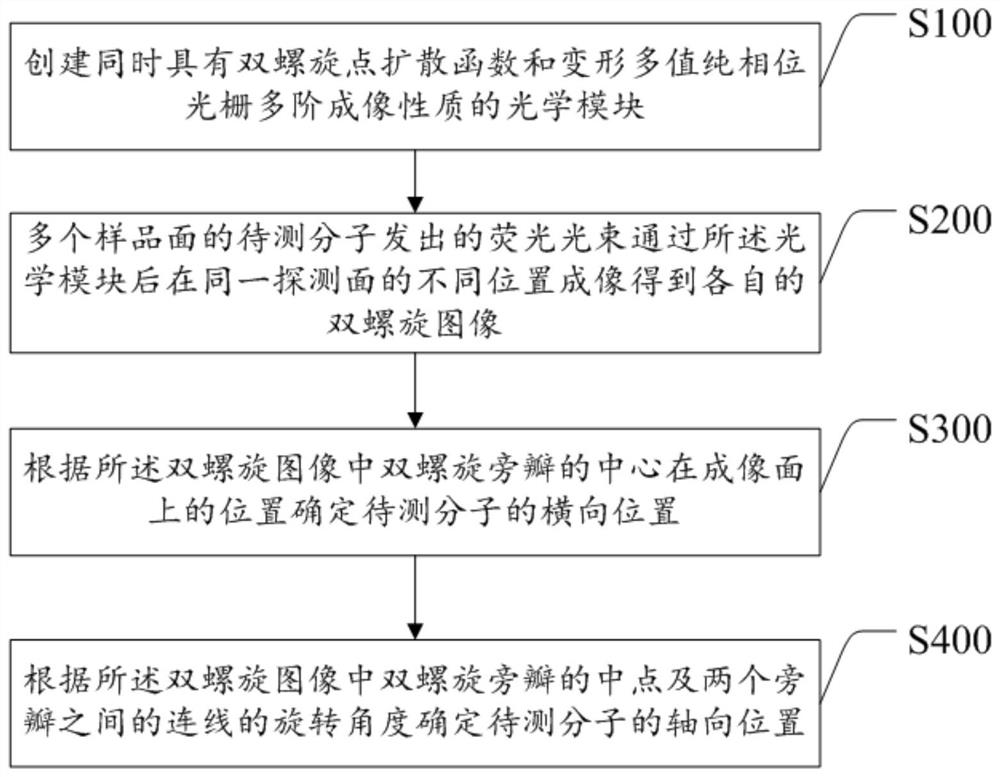
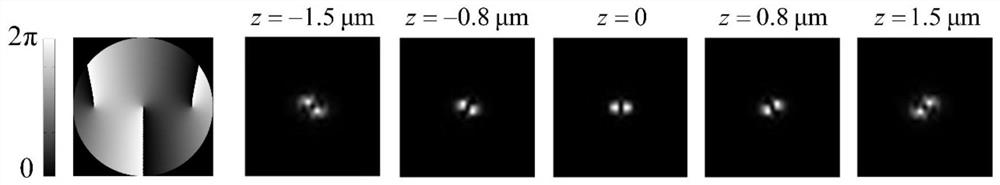
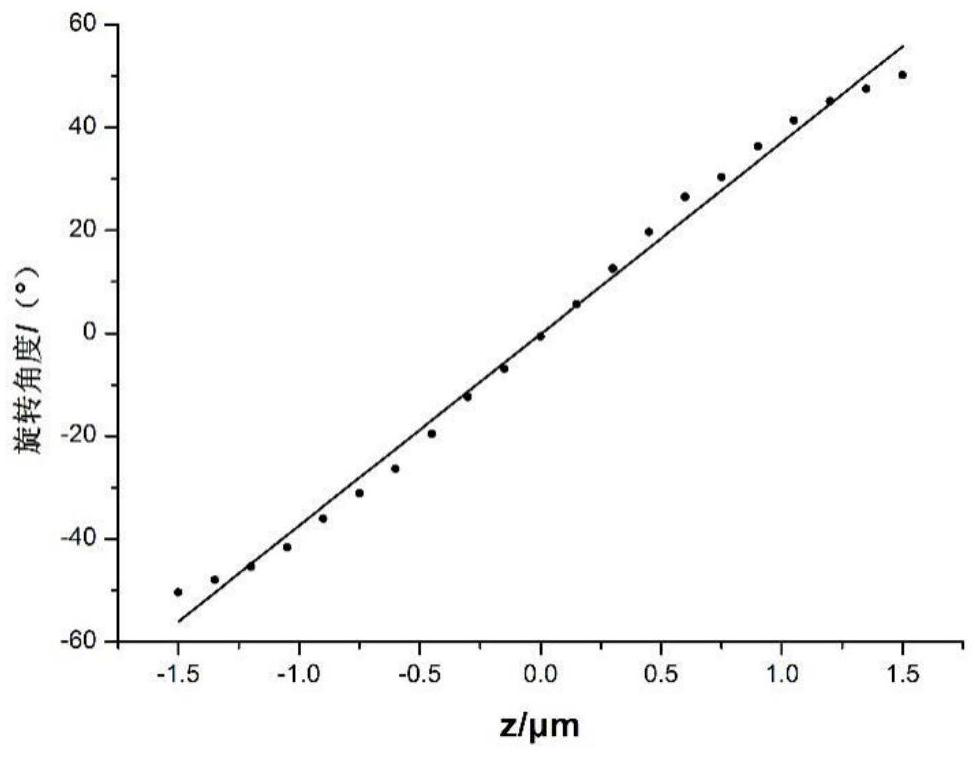
The invention discloses a single-molecule positioning micro-imaging method, an optical assembly and an imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an optical module with a double helix point dispersion function and a deformed multi-value pure phase grating multi-order imaging property; after fluorescence beams emitted by to-be-tested molecules of multiple sample surfacesare emitted through the optical module, carrying out imaging at different positions of the same detection surface, so as to respectively generate double helix images; determining transverse positionsof the to-be-tested molecules according to positions of the centers of double helix sidelobes in the double helix images on the imaging surfaces; and determining the axial positions of the to-be-tested molecules according to the middle points of the double helix sidelobes in the double helix images and a rotation angle of a connection line between the two sidelobes. The molecular information of multiple layers in the sample can be imaged at different positions of the same detection surface in a double helix manner, so that the axial positioning range and resolution ratio of a double helix point spread function can be improved without scanning, and the problem of large field depth detection in single molecule positioning and tracing techniques in living cells is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods for quantifying and enhancing accuracy in microscopy using measures of localization confidence
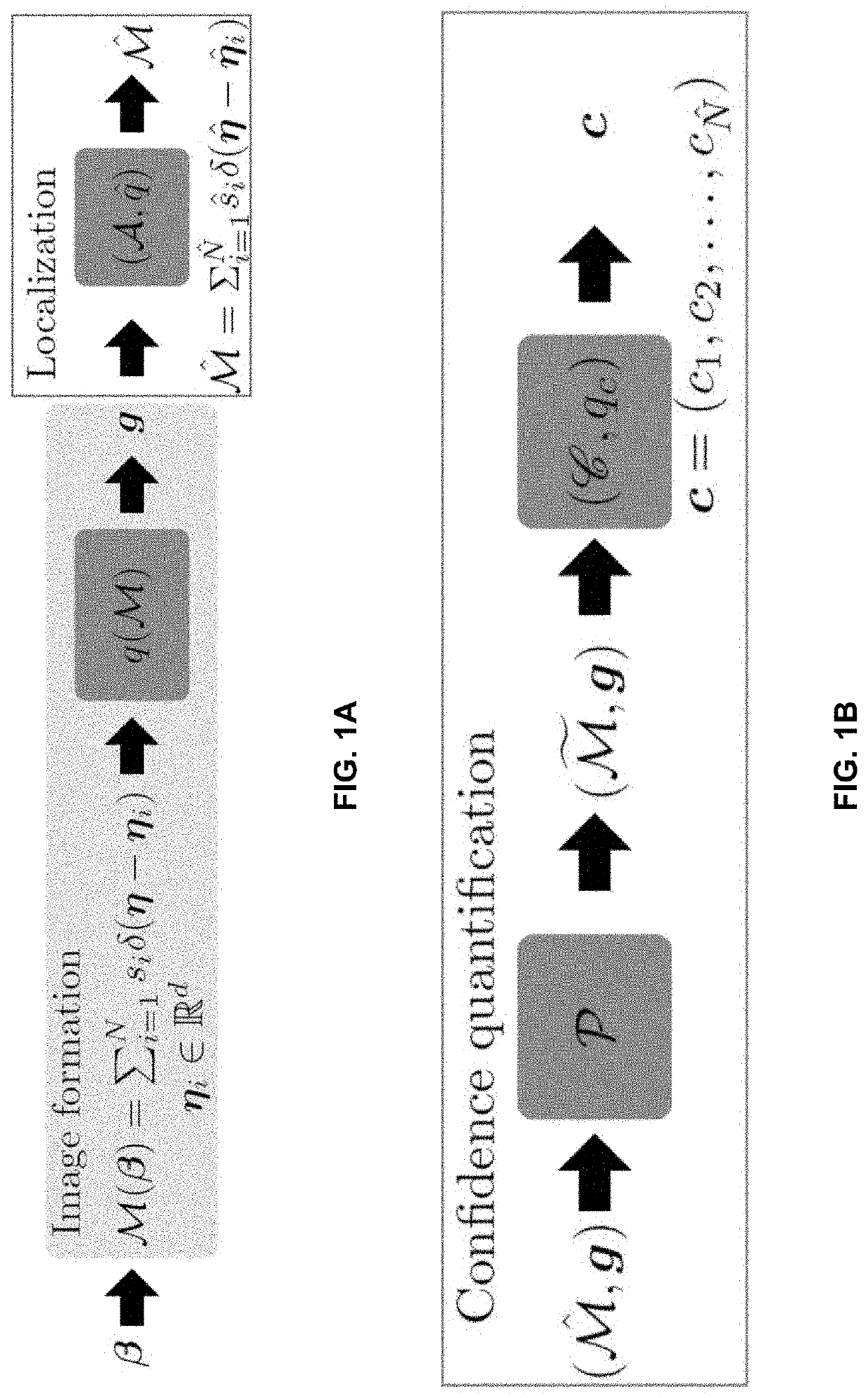
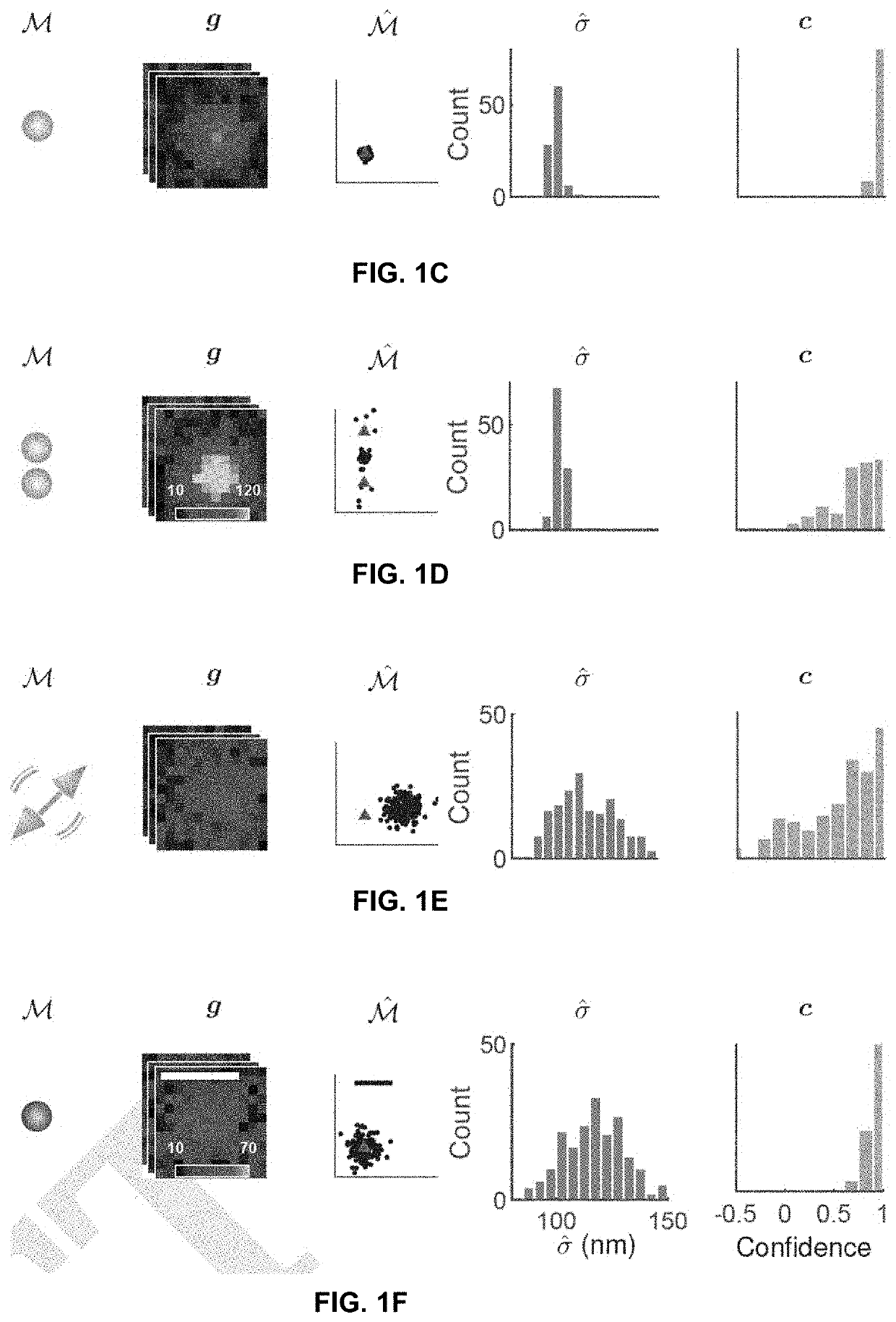
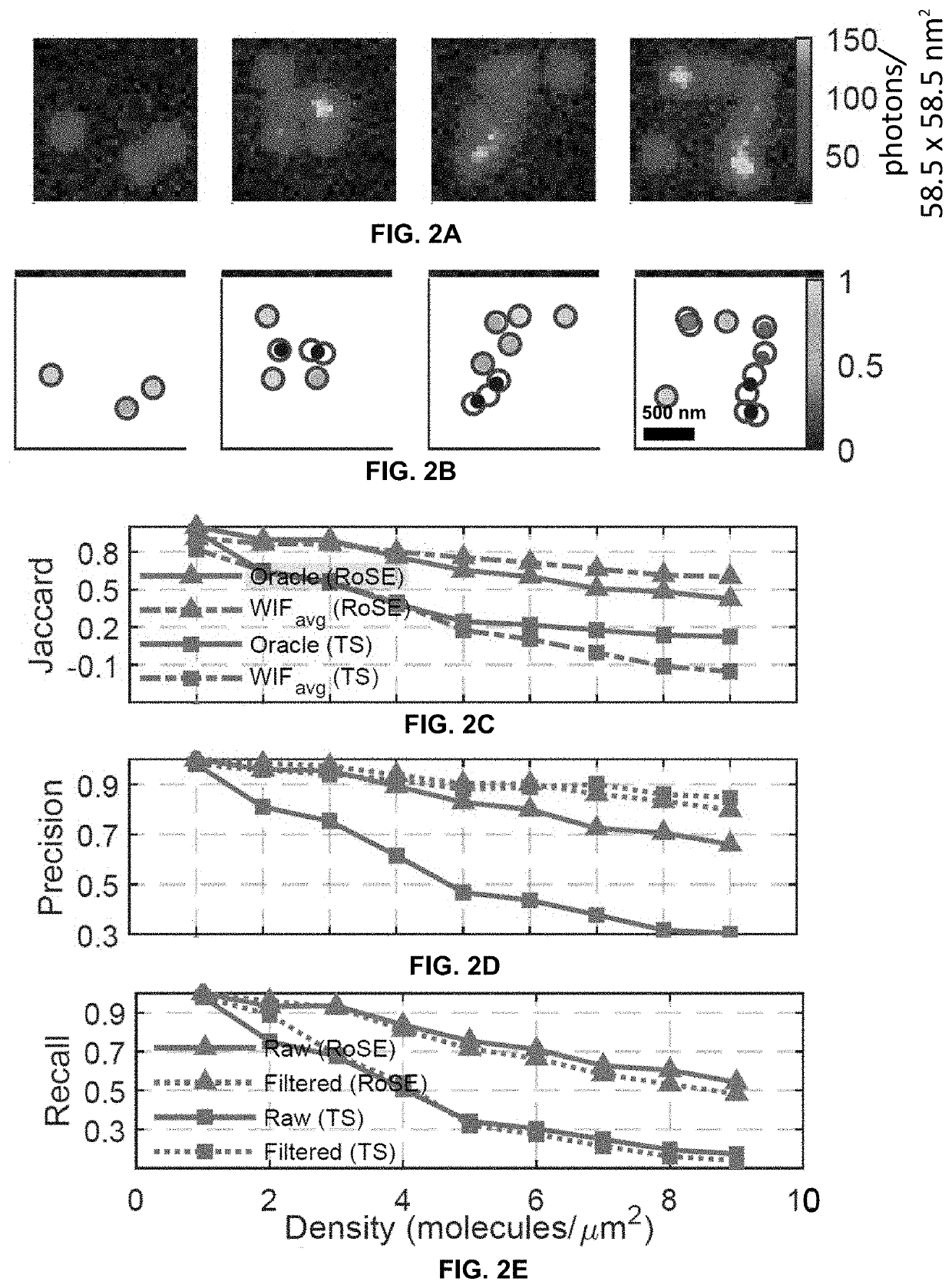
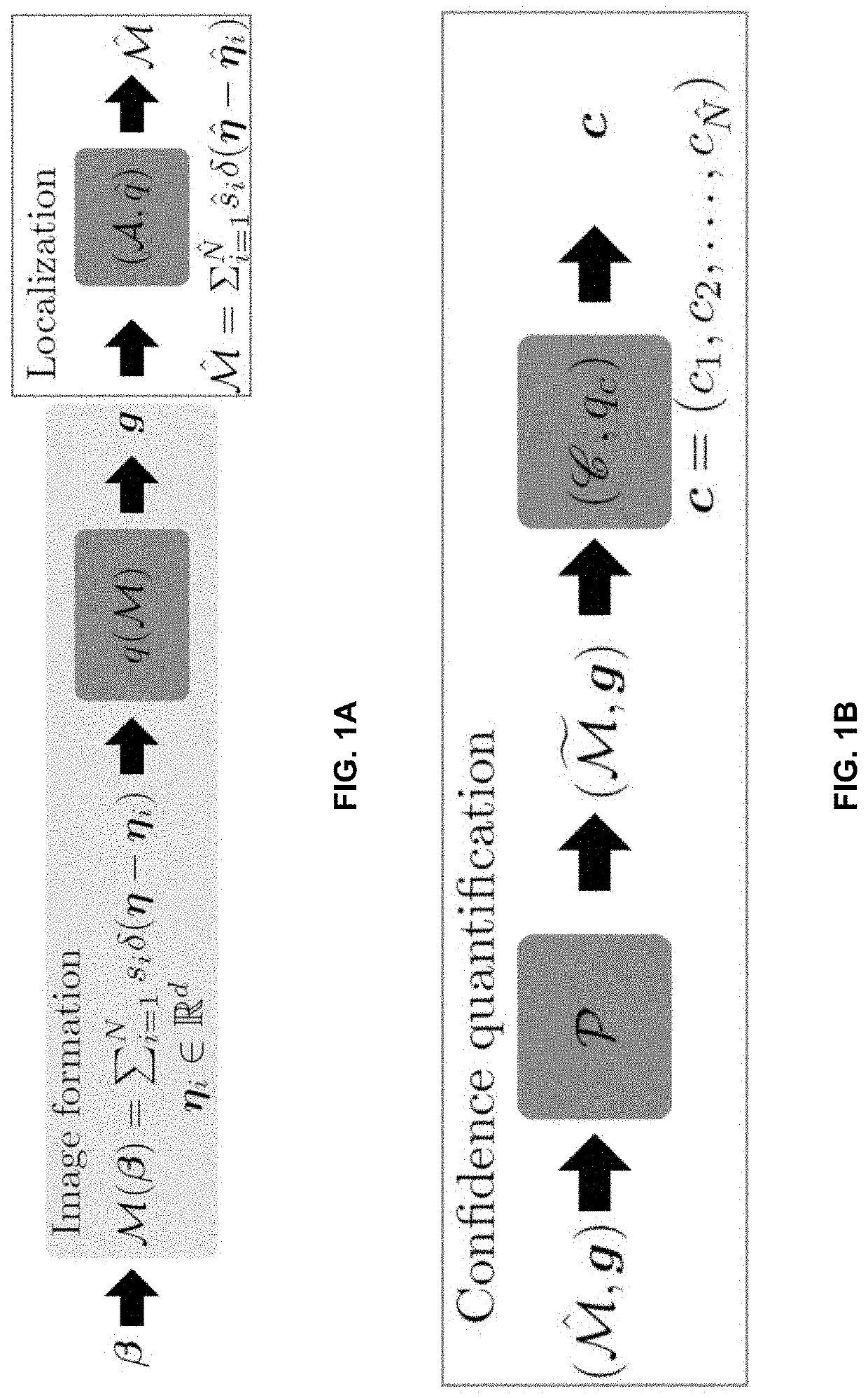
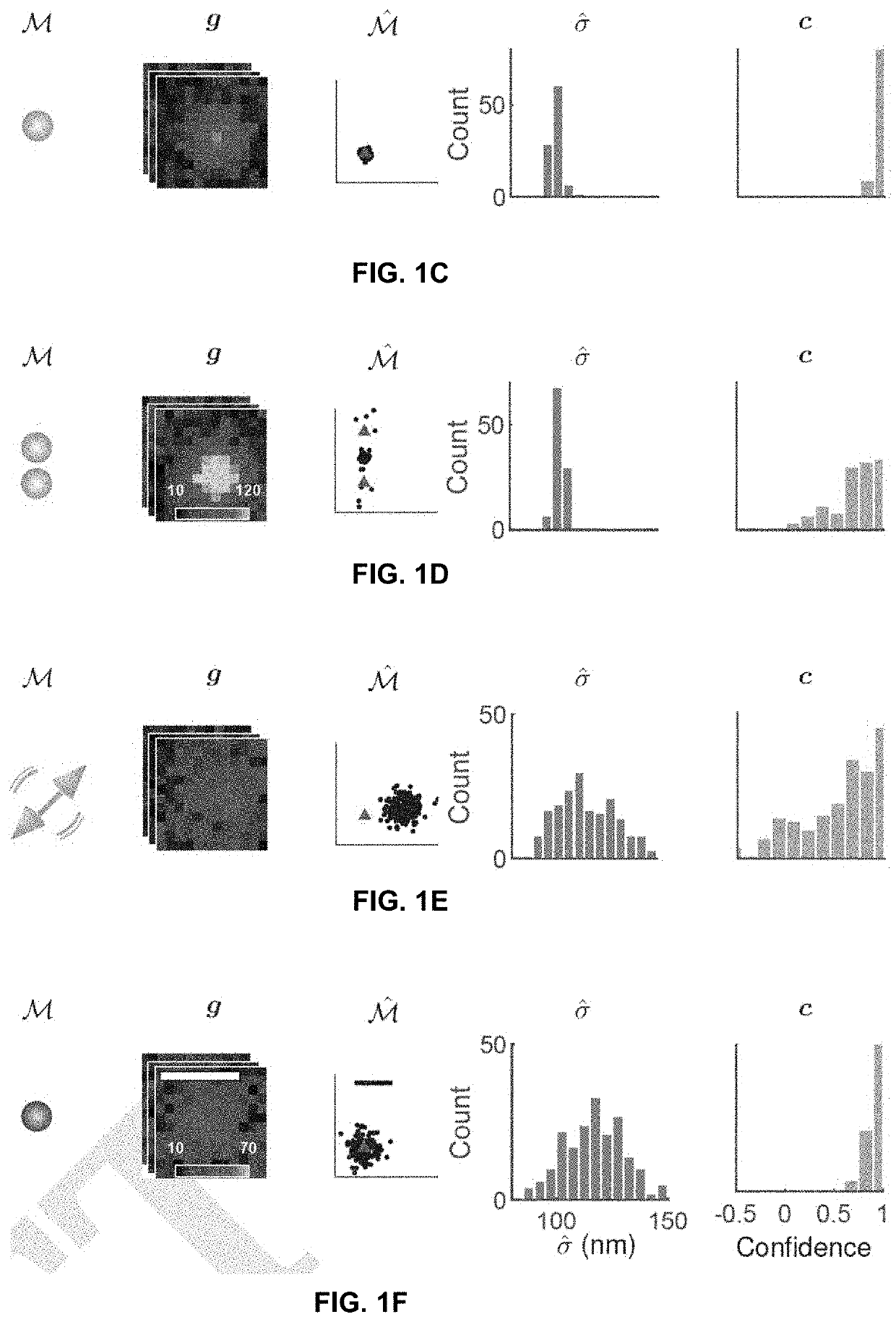
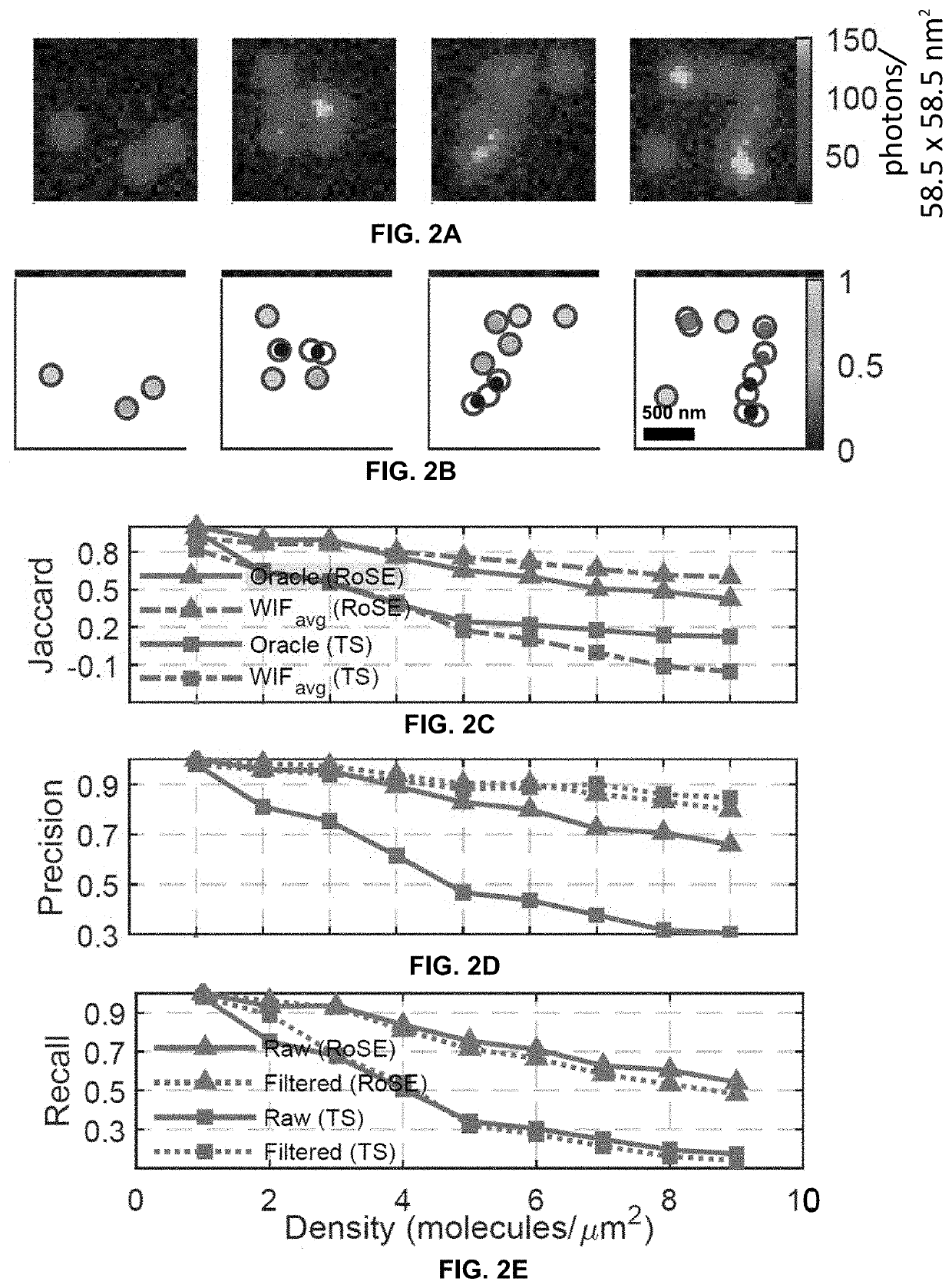
ActiveUS20210033536A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData setSingle molecule localization
Systems and methods assessing the accuracy of at least one localization from a single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) dataset containing a plurality of localizations are described. The systems and methods calculate a Wasserstein-induced flux (WIF) value indicative of a confidence in the accuracy of a localization within the SMLM data set.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
High-density three-dimensional single-molecule positioning super-resolution microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN113933277AImprove 3D positioning accuracyEnsure consistencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh densityBeam splitting
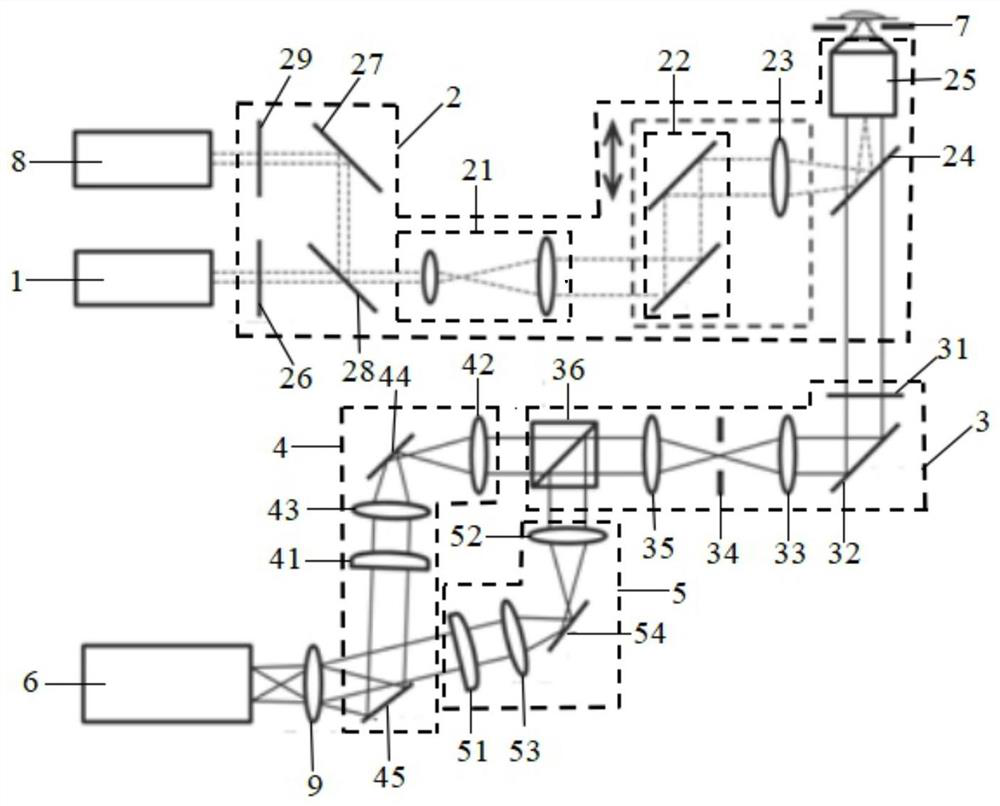
The invention provides a high-density three-dimensional single-molecule positioning super-resolution microscopic imaging system and method. The high-density three-dimensional single-molecule positioning super-resolution microscopic imaging system comprises a first laser, a fluorescence signal generation unit, a beam splitting unit, a first signal channel unit, a second signal channel unit, a detector and a control terminal. The first signal channel unit comprises a first cylindrical lens, the second signal channel unit comprises a second cylindrical lens, and the orientations of the first cylindrical lens and the second cylindrical lens are mutually orthogonal. The beam splitting unit is used for splitting a fluorescence signal into two beams of fluorescence signals with mutually vertical propagation directions. The first signal channel unit and the second signal channel unit are used for projecting the two beams of fluorescence signals to the detector for imaging respectively. The control terminal is used for performing three-dimensional positioning and super-resolution imaging according to a forward and reverse astigmatic point spread function image pair. According to the system, the three-dimensional positioning precision of defocused fluorescent molecules is improved on the premise of not sacrificing the original imaging depth, the three-dimensional positioning accuracy is high, and the effective detection range is large.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Super-resolution microscopic imaging system
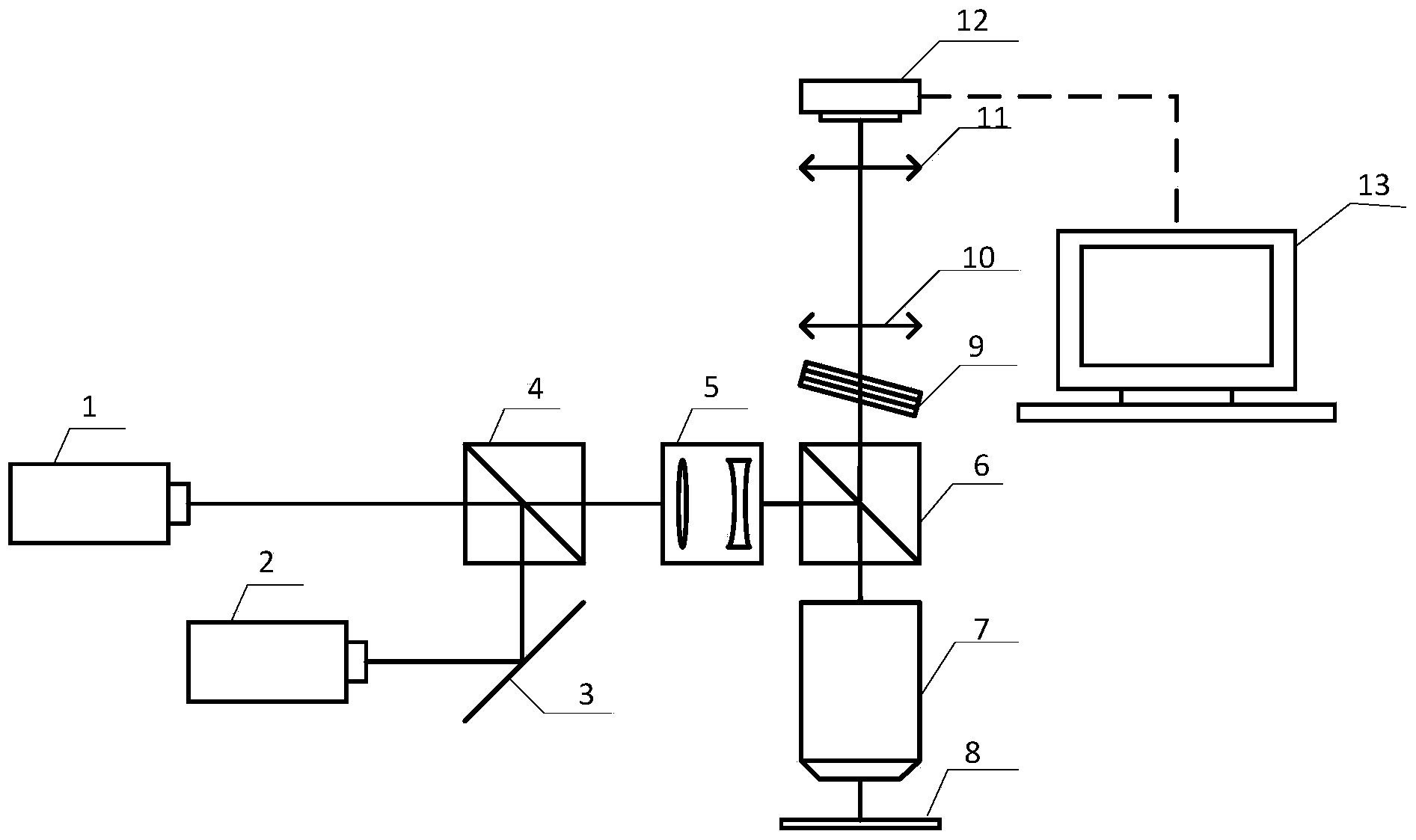
PendingCN112858250AMeet the experimental configuration requirementsHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMedicineSingle molecule localization
The embodiment of the invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic imaging system. The system comprises an excitation light source generation module, an imaging module, a focal plane locking module and a control and data acquisition module, wherein the excitation light source generation module is used for generating an excitation light source; the imaging module is used for receiving the excitation light source, enabling the excitation light source to irradiate a sample on the sample slide to enable a view field area of the sample to generate fluorescent light, and collecting the reflected fluorescent light through the camera; the focal plane locking module is used for emitting laser to the imaging module and receiving the laser reflected by the imaging module so as to lock the distance between an objective lens in the imaging module and a sample slide; and the control and data acquisition module is used for controlling and adjusting optical elements in the excitation light source generation module, the imaging module and the focal plane locking module, and acquiring fluorescence data obtained by the imaging module for data analysis. According to the system, a compact, adjustable and controllable single-molecule positioning microtechnique with high automation degree is realized, and the precision and the accuracy are improved.
Owner:山东迈科显微生物科技有限公司
Preparation method and application of super-resolution imaging probe based on silicon dioxide
InactiveCN111044496ASimple manufacturing methodSmall and uniform particle sizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerSingle molecule localization
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging probe based on silicon dioxide and a preparation method and application of the probe.The super-resolution imaging probe includes silicon dioxide nanoparticles connected with an Alexa Fluor 647 dye, and the surface of the super-resolution imaging probe is coupled with an HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) nucleic acid aptamer; the probe can be used for targeted recognition of HER2 overexpression cell exosomes, that is, the HER2 overexpression cell exosomes are subjected to fluorescence labeling; super-resolution optical imaging canbe carried out on the cell exosome which specifically recognizes the probe by utilizing an ultra-high resolution microscope; the probe is uniform in particle size, small in size, high in positioningprecision, excellent in scintillation performance and suitable for ultrahigh-resolution optical imaging based on a single-molecule positioning method; and the exosome is marked by the super-resolutionimaging probe, and the exosome of the cell can be accurately marked by using a single-molecule positioning microscope in a double-channel co-positioning mode.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Intra-cellular miRNA quantifying method based on unimolecule fluorescence imaging
InactiveCN110229870AMiRNA quantitative realizationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRNA extractionFiltration
The invention discloses an intra-cellular miRNA quantifying method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) fixing excised cells, and then performing cell nucleus dyeing; (2) adding a buffer solution containing fluorescent probes to the cells, and enabling the fluorescent probes and intra-cellular miRNA to be detected to generate reversible combination; (3) placing the cells on an objective table of a TIRF microscope, performing detection, recording the shape of the cells at a bright field, performing fluorescence recording of the position of a cell nuclei at a wide field, and recording unimolecule fluorescence intensity-time track in an HILO mode; and (4) performing signal filtration to obtain a unimolecule imaging graph in which the unimolecule fluorescence intensity-time track presenting ON-OFF alternate changes, namely an intra-cellular miRNA unimolecule imaging graph, and performing counting so as to obtain the quantity of intra-cellular miRNA. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an "in-situ quantifying imaging" manner is provided, high-identification degree unimolecule dynamics fingerprint signals are used, unimolecule positioning and pinpoint countingare performed on the intra-cellular miRNA, and the technical bottleneck that intra-cellular miRNA quantifying depends on RNA extraction is broken through.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
BODIPY derivative with cell membrane labeling function and used for single-molecule positioning super-resolution imaging and single-molecule tracking and application thereof
ActiveCN113214301AExcellent photophysical propertiesHigh spatio-temporal resolutionGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell membraneFluorophore
The invention discloses a BODIPY derivative with a cell membrane labeling function and used for single-molecule positioning super-resolution imaging and single-molecule tracking and application thereof, and belongs to the field of fine chemical engineering. The BODIPY derivative has excellent photo-physical properties, and has good brightness and stability. Meanwhile, due to introduction of double bonds, cis-trans isomerism change can occur under the condition of high laser irradiation, so that light conversion in bright and dark states is realized, and single-molecule positioning super-resolution imaging is facilitated. The dye is designed into an amphiphilic molecular structure and can be retained on a cell membrane for a long time, and meanwhile, a BODIPY fluorophore tends to enter the inner side of a phospholipid molecular layer, so that a long-range bright state can be realized, and tracking analysis of a single molecule is facilitated. The dye can be used for realizing simultaneous imaging of the ultra-structure and fluidity of living cells under a non-imaging liquid condition, and the imaging has ultrahigh temporal-spatial resolution and reveals important characteristics of a membrane, so that the derivative can be used for realizing molecular diagnosis of a cell membrane structure. The new diagnosis information can improve the diagnosis accuracy and precision, and has important application prospects in molecular-scale diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Lens assembly for super-resolution microscopy
PendingCN112888983AMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesImage resolutionSingle molecule localization
A lens assembly, for use in microscopy imaging of a sample in a cryogenic environment, is described. A solid immersion lens which has a planar surface for accepting a sample for imaging is mounted within an aperture provided through the plane of a planar mount. The microscopy imaging may include using super-resolution optical imaging techniques such as single molecule localisation techniques.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
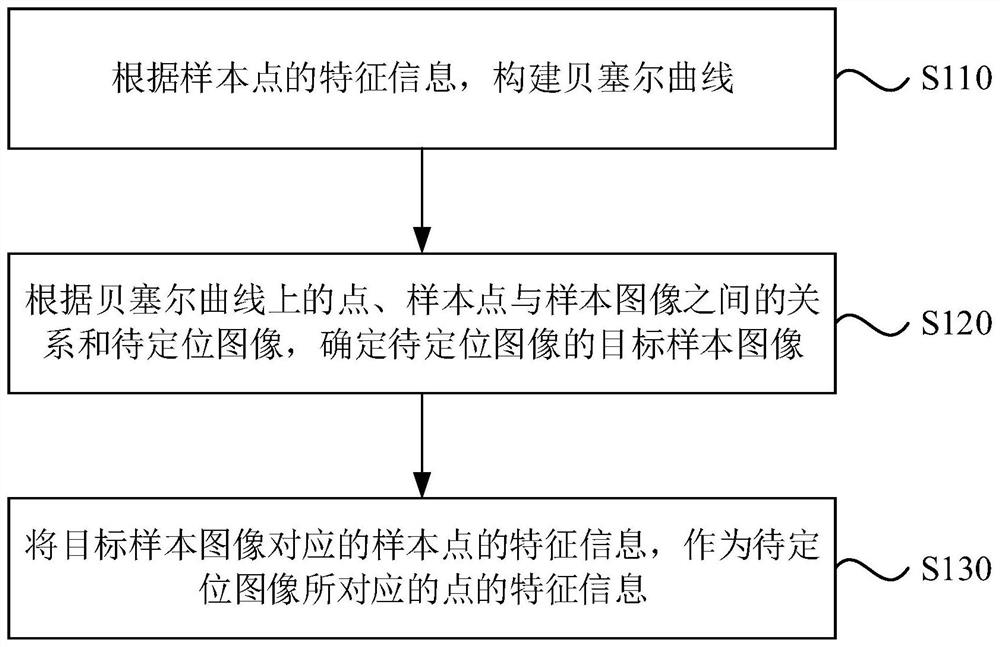
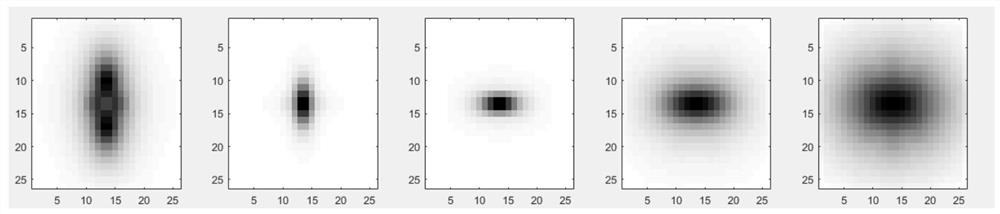
Feature determination method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
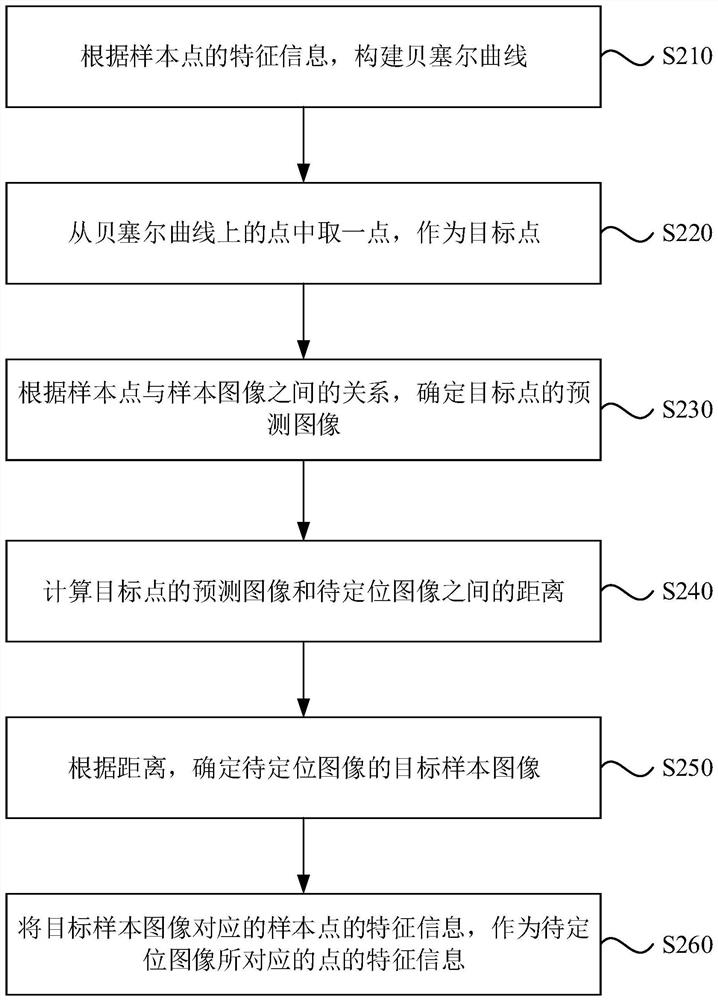
ActiveCN113112406ARich imaging informationSave memory resourcesGeometric image transformationMicroscopesComputer graphics (images)Sample image
The invention discloses a feature determination method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of single molecule positioning imaging. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a Bezier curve according to feature information of sample points; determining a target sample image of the to-be-positioned image according to the point on the Bezier curve, the relationship between the sample point and the sample image and the to-be-positioned image; and taking the feature information of the sample points corresponding to the target sample image as the feature information of the points corresponding to the to-be-positioned image. According to the technical scheme, compared with an existing Gaussian fitting and cubic spline interpolation method, more imaging information is obtained, meanwhile, memory resources are reduced, and a new thought is provided for multi-dimensional single-molecule positioning imaging.
Owner:山东迈科显微生物科技有限公司
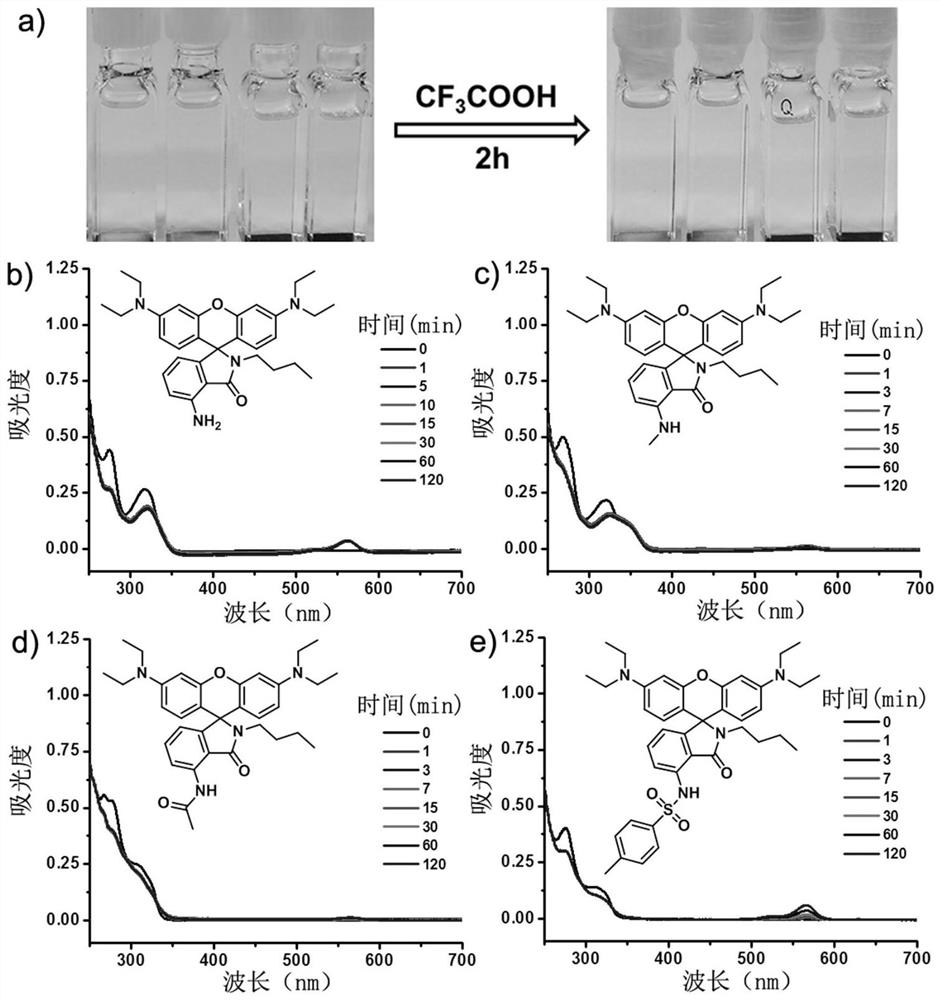
A kind of acid-resistant light-controlled fluorescent molecular switch and its synthesis method and application
ActiveCN110272637BHas acid resistancePreserve switch performanceOrganic chemistryDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesSingle molecule localizationMolecular fluorescence
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for quantifying and enhancing accuracy in microscopy using measures of localization confidence
ActiveUS11300515B2Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData setSingle molecule localization
Systems and methods assessing the accuracy of at least one localization from a single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) dataset containing a plurality of localizations are described. The systems and methods calculate a Wasserstein-induced flux (WIF) value indicative of a confidence in the accuracy of a localization within the SMLM data set.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
A living cell super-resolution optical imaging probe and its preparation method
ActiveCN105950133BHigh luminous intensityExcellent luminous propertiesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsNuclear membraneLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a super-resolution optical imaging probe for living cells and a preparation method of the super-resolution optical imaging probe. Quantum dots are taken as a fluorophore, cell membrane penetrating peptides and nucleic acid aptamers are coupled on the surfaces of the quantum dots, the cell membrane penetrating peptides are used for promoting the probe to penetrate through the living cells, the nucleic acid aptamers are used for specific binding with nuclear membrane receptor protein of the living cells, and cell nucleus positioning of the probe is realized. The quantum dots with scintillating effects are taken as the fluorophore and are adapted to super-resolution optical imaging based on a single-molecule positioning method by means of the high luminous intensity and the fluorescence scintillation characteristic; meanwhile, the quantum dots with scintillating effects are taken as the fluorophore, a special imaging buffering solution is not required, therefore, the probe is adapted to super-resolution imaging of the living cells; besides, the preparation method is simple and convenient to operate, the cost is low, and the time cost and the economic cost are effectively saved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A single-molecule positioning microscopic imaging method, optical component and imaging system
ActiveCN108956575BHigh resolutionSolve the problem of large depth of field detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingPhase grating
The invention discloses a single-molecule positioning micro-imaging method, an optical assembly and an imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an optical module with a double helix point dispersion function and a deformed multi-value pure phase grating multi-order imaging property; after fluorescence beams emitted by to-be-tested molecules of multiple sample surfacesare emitted through the optical module, carrying out imaging at different positions of the same detection surface, so as to respectively generate double helix images; determining transverse positionsof the to-be-tested molecules according to positions of the centers of double helix sidelobes in the double helix images on the imaging surfaces; and determining the axial positions of the to-be-tested molecules according to the middle points of the double helix sidelobes in the double helix images and a rotation angle of a connection line between the two sidelobes. The molecular information of multiple layers in the sample can be imaged at different positions of the same detection surface in a double helix manner, so that the axial positioning range and resolution ratio of a double helix point spread function can be improved without scanning, and the problem of large field depth detection in single molecule positioning and tracing techniques in living cells is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com