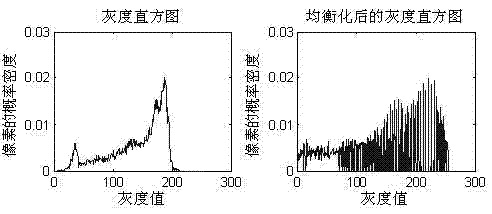
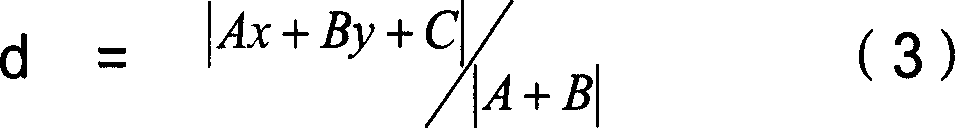Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
572 results about "Projection distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Projection Distance. The distance at which you place the projector from the screen determines the approximate size of the image. The image size increases the farther the projector is from the screen, but can vary depending on the zoom factor, aspect ratio, and other settings.
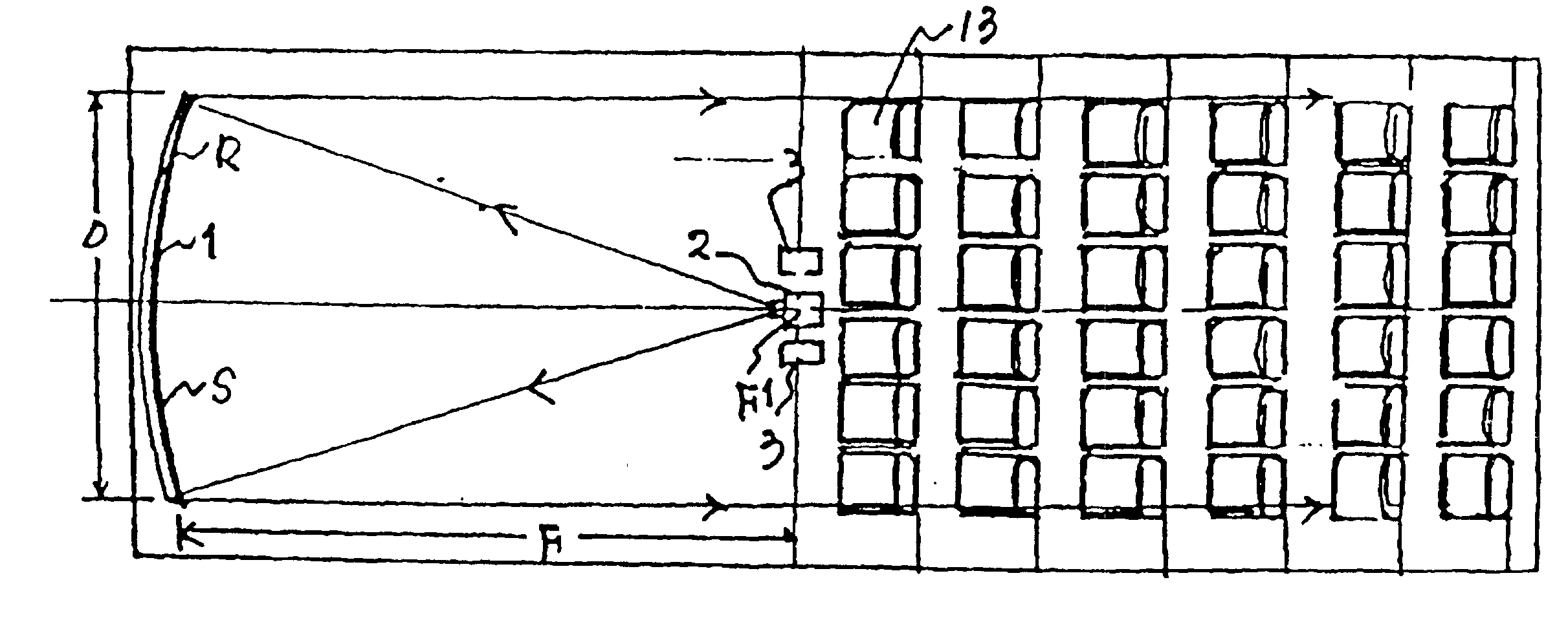
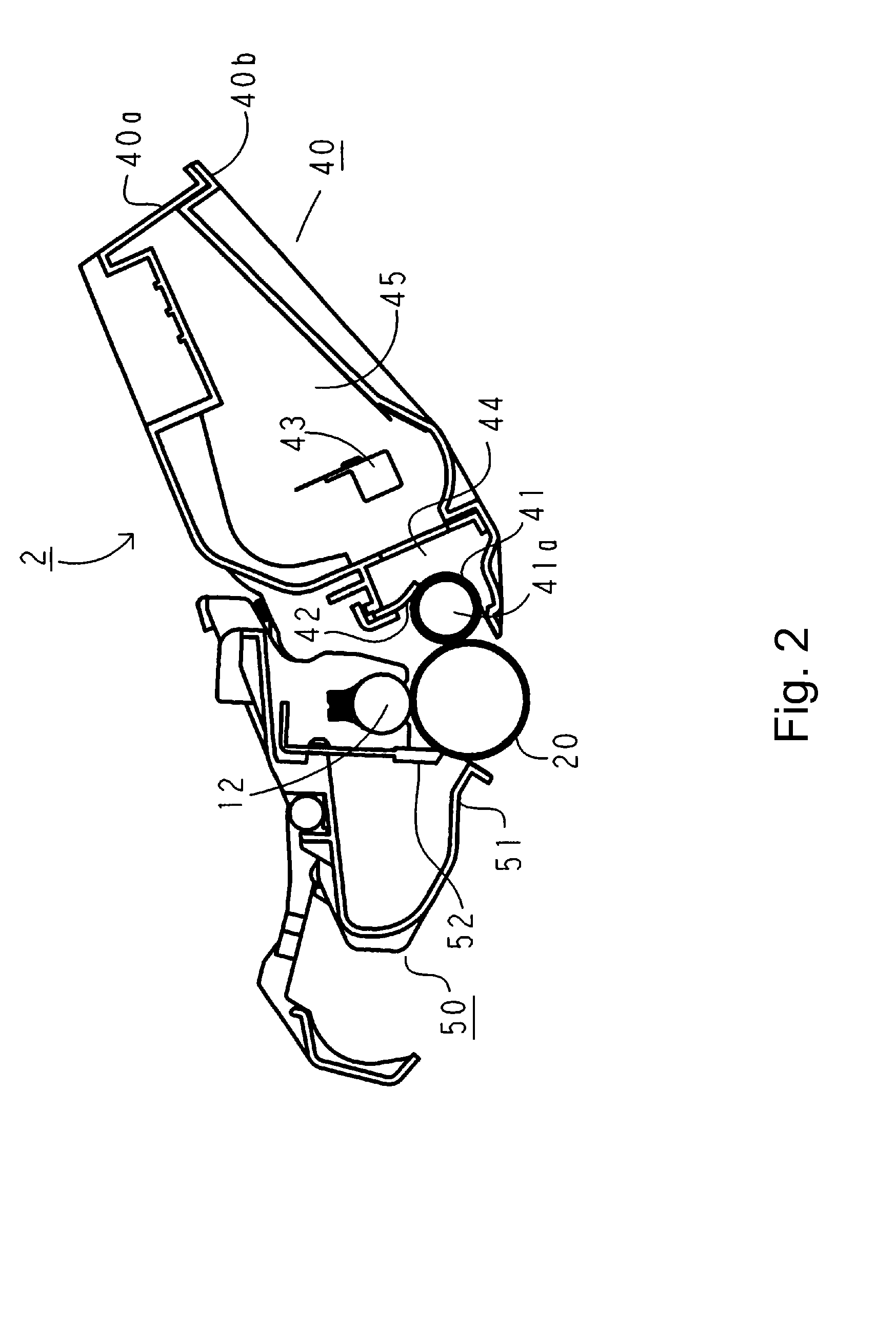
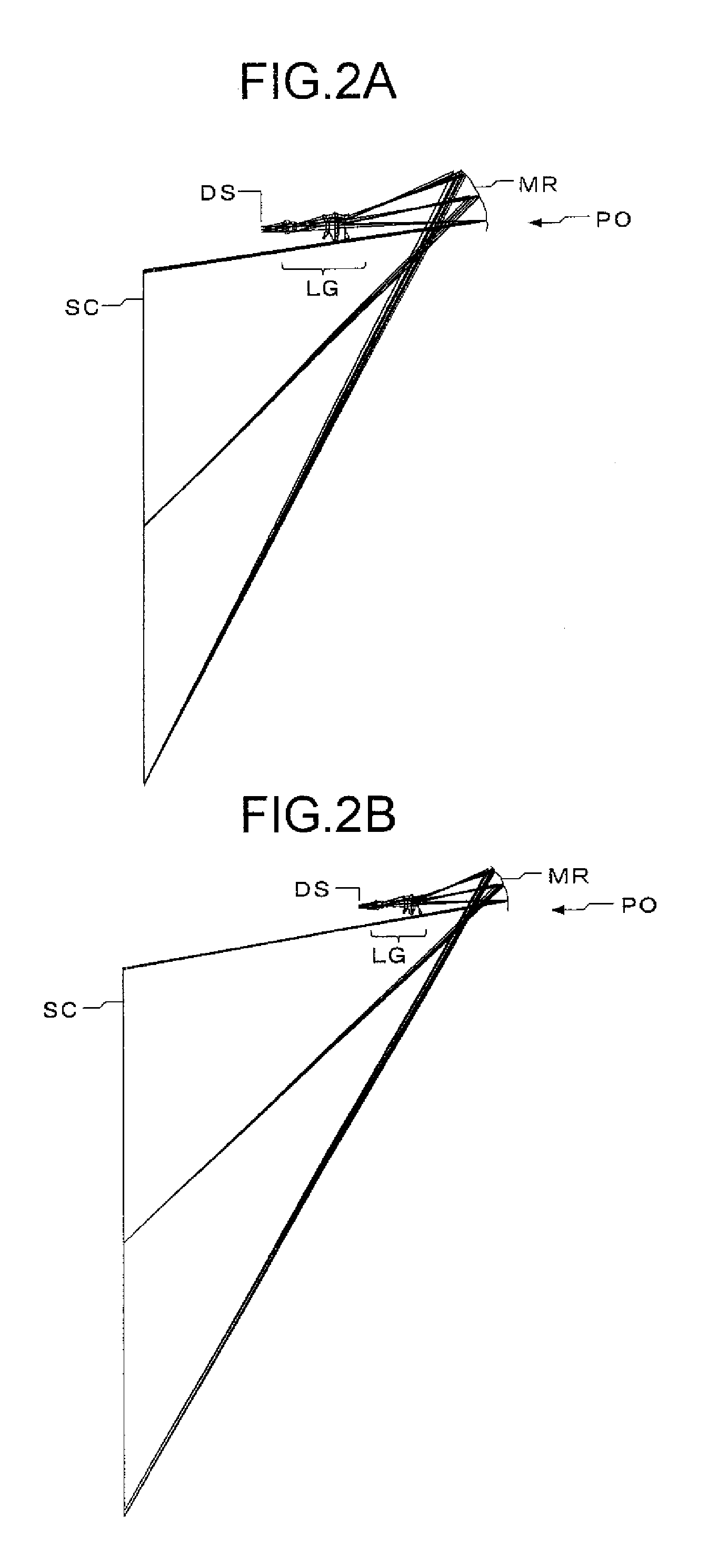
Visual and audio system for theaters
Disclosed is a visual and audio system for theaters including a spherical screen having a desired radius of curvature while having a surface reflectivity of 5-50%, and a projector located at a focal point of the spherical screen. The curvature radius of the spherical screen corresponds to the projection distance of the projector. The image projected from the projector at the focal point of the spherical screen is reflected from the spherical screen in a horizontal direction. Accordingly, viewers can view images projected on the screen corresponding to 5-50 times the brightness of conventional cases. Central speakers are arranged at the focal point of the spherical screen, so that viewers perceive the sound effect as coming directly from the spherical screen. This visual and audio system can be effectively used in theaters for stereoscopic movies, theaters for high resolution images, and theaters for viewing of images at a higher brightness such as theaters for sports broadcasts, and restaurant theaters, etc.
Owner:CHOI HAE YONG
Distance measuring device
ActiveUS7474388B2Improve measurement reliabilityOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansPhotodetectionDistance measuring equipment
Owner:KK TOPCON
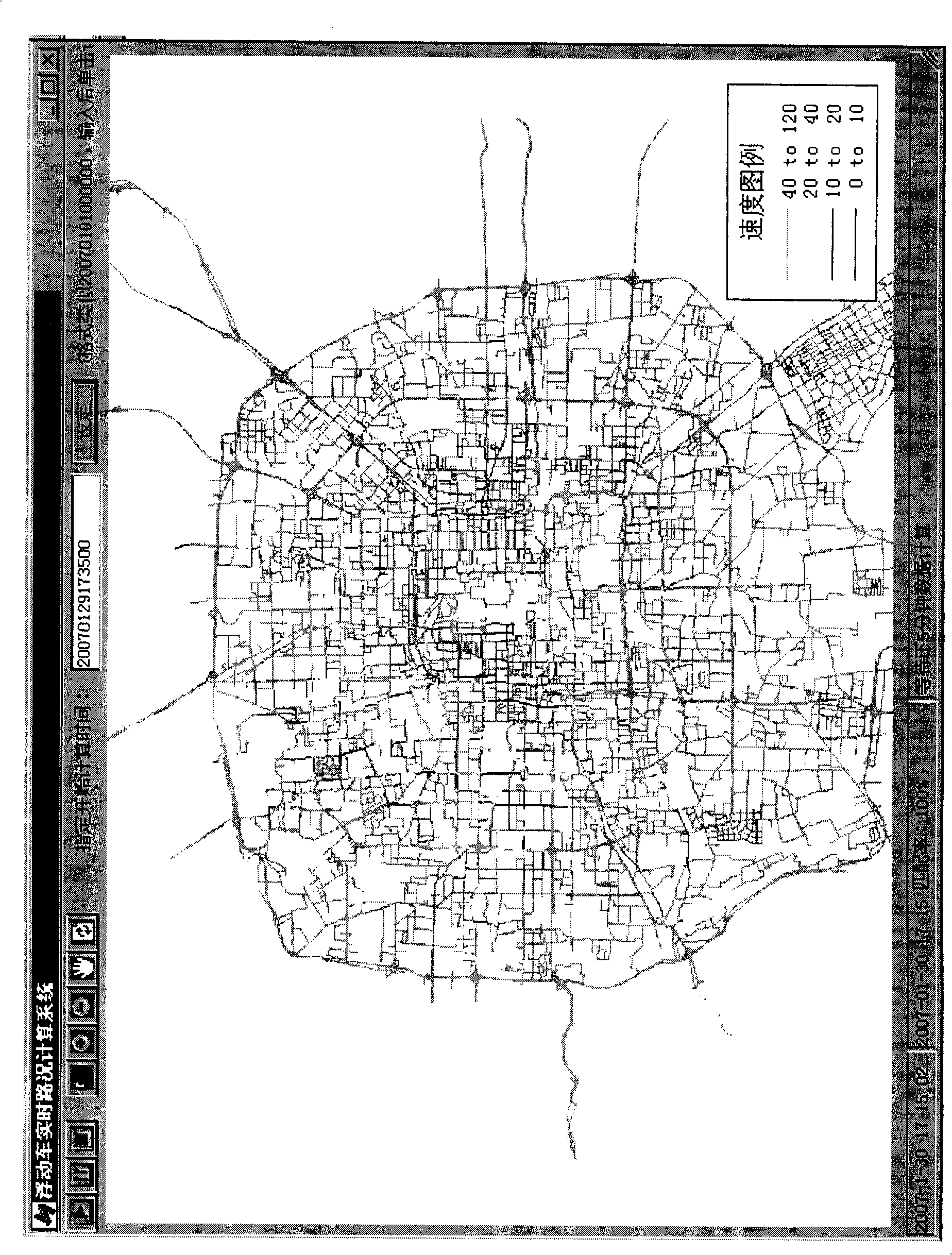
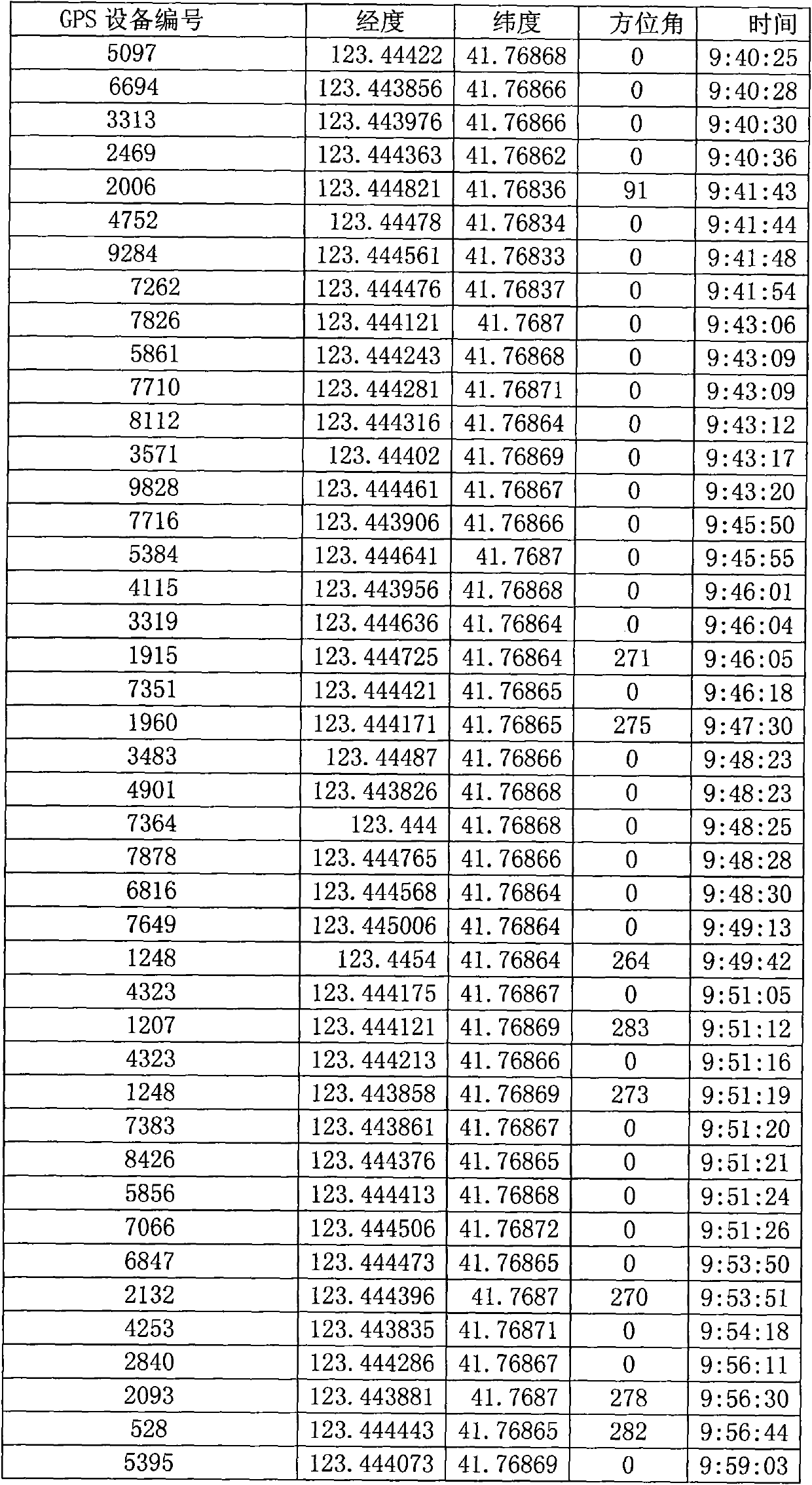
Floating car dynamic real-time traffic information processing method based on GPS data
ActiveCN101270997AMeet the speed performance requirements of real-time computingImprove matching accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationInformation processingSimulation
The invention discloses a floating car state real-time traffic information processing method based on GPS data, which includes the following steps: 1. GPS point data pre-processing and map pre-processing measures; 2. conduct point matching and select alternative road section sets according to projection distance and azimuth angles; 3. determine correct matching road sections and find out travel routes according to an improved optical route selection method considering topological relation between front and rear points (including a special regional node processing method for urban complicate road network); 4. calculate the route average travel speed, and conduct statistics in a speed formula to generate a road network speed thematic map. The floating car state real-time traffic information processing method based on GPS data of the invention is well applicable the modern complicated urban road network full of overpasses and staggered main and side roads, which can not only meet the speed requirement for large-data-quantity GPS data real-time calculation, but also obtain quite high matching precision.
Owner:北京交通发展研究院
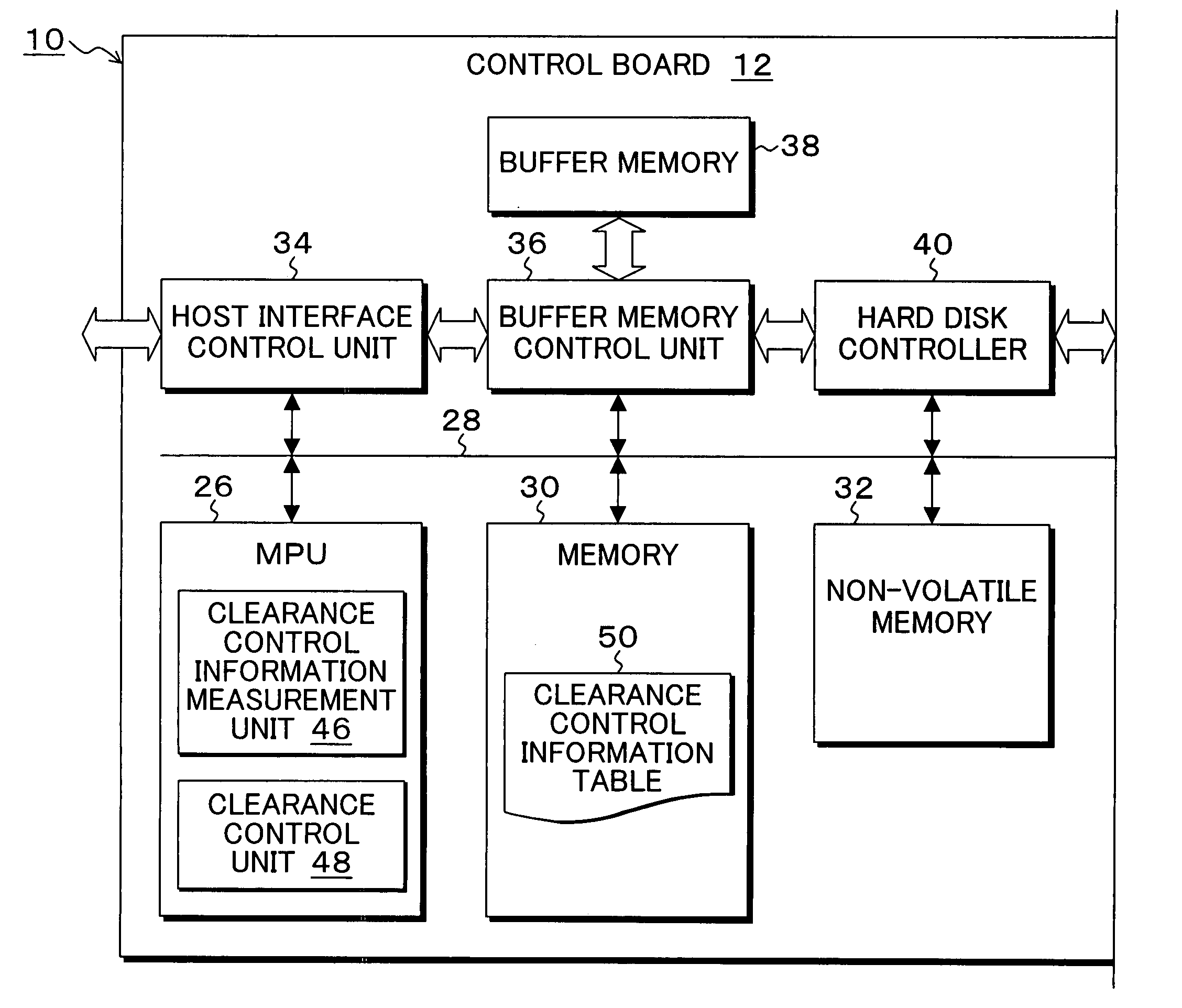
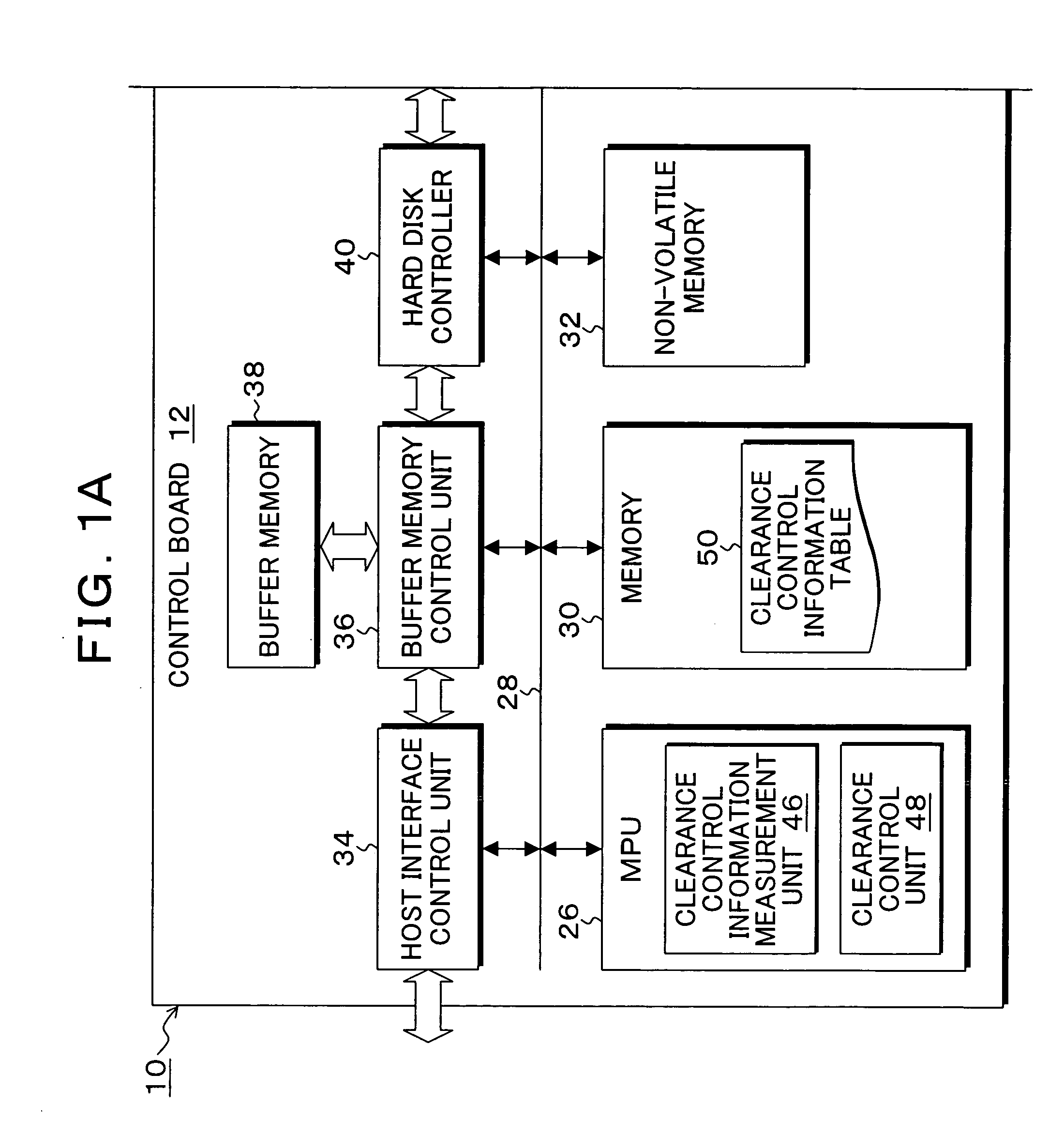
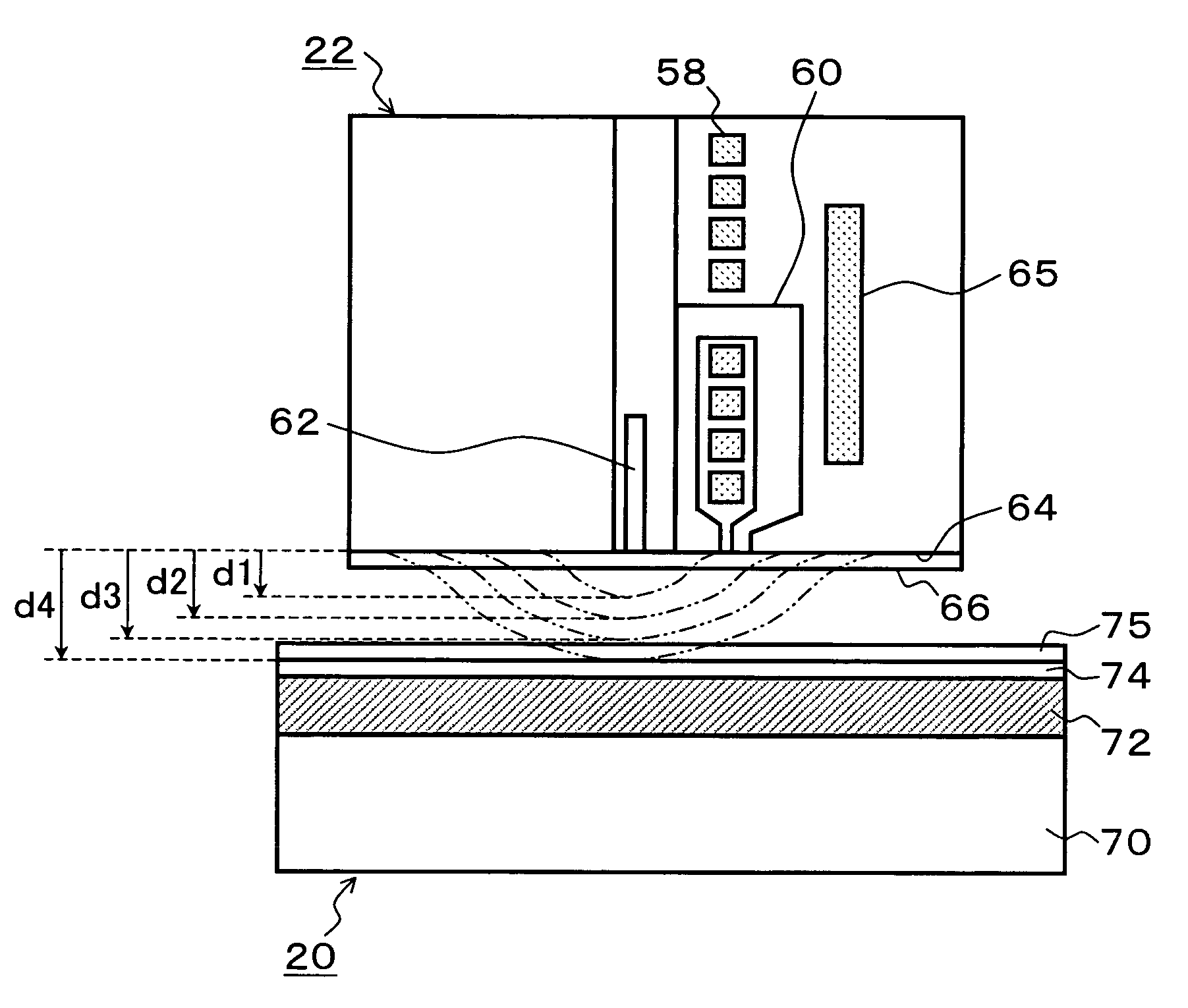
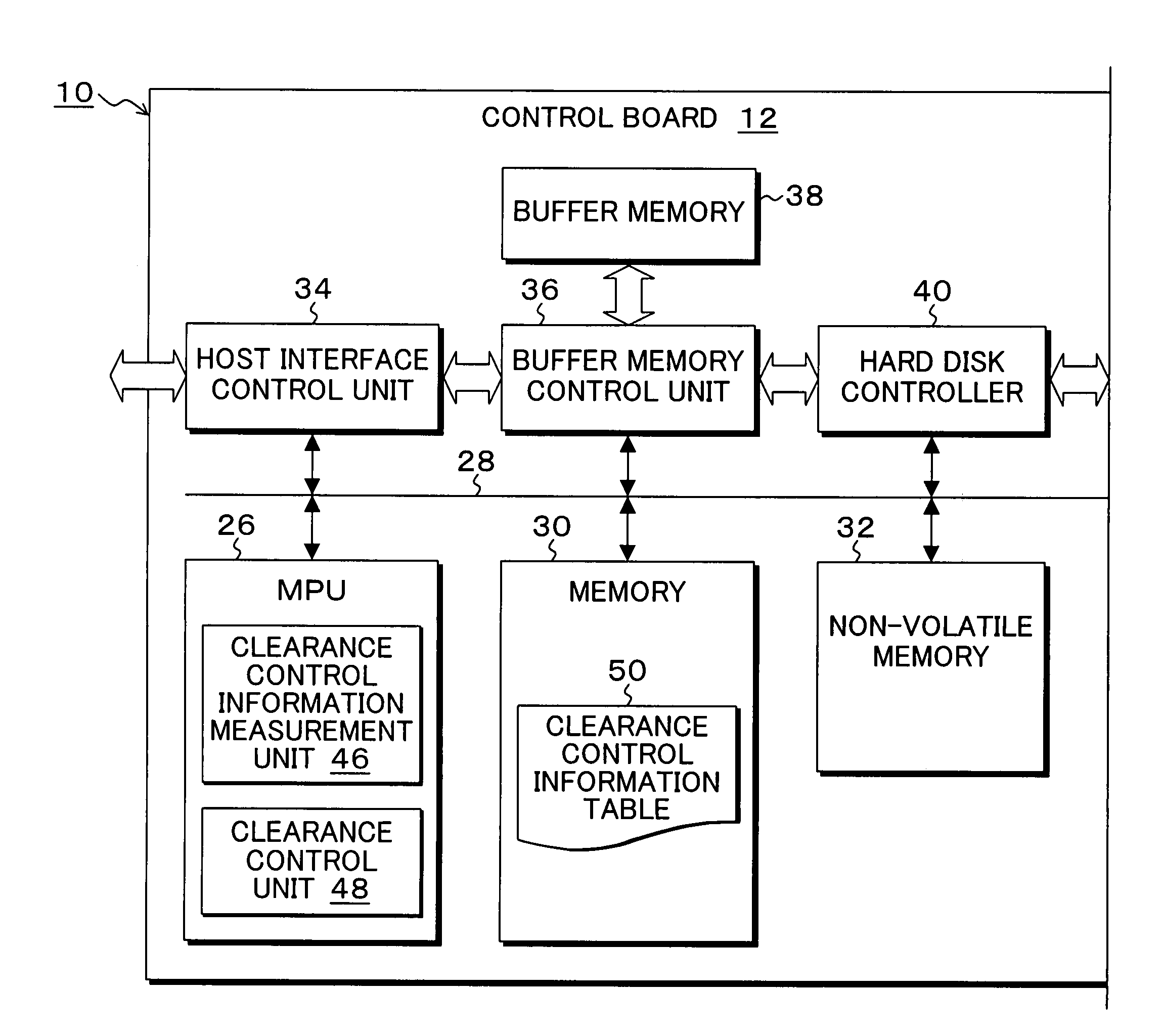
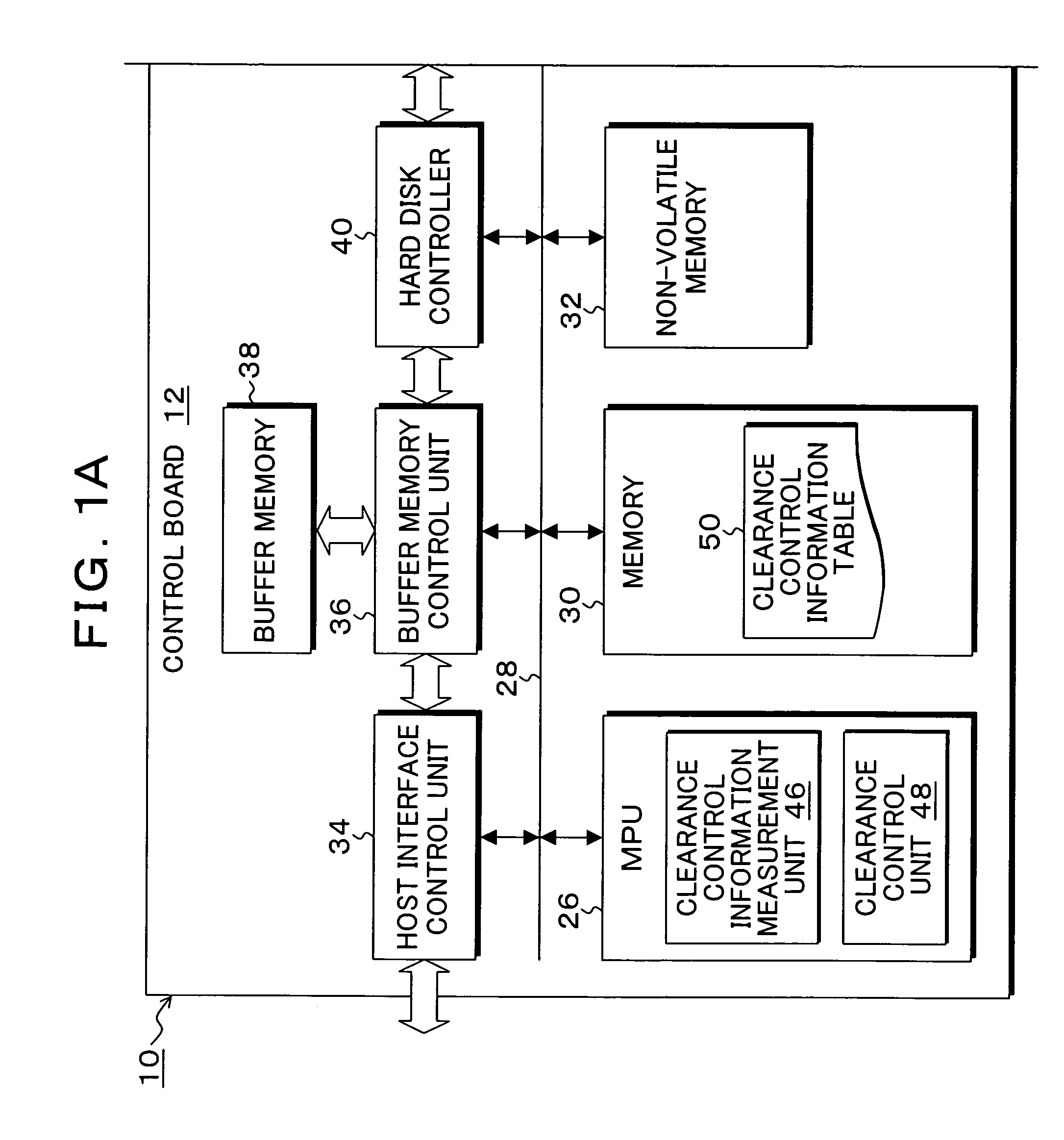
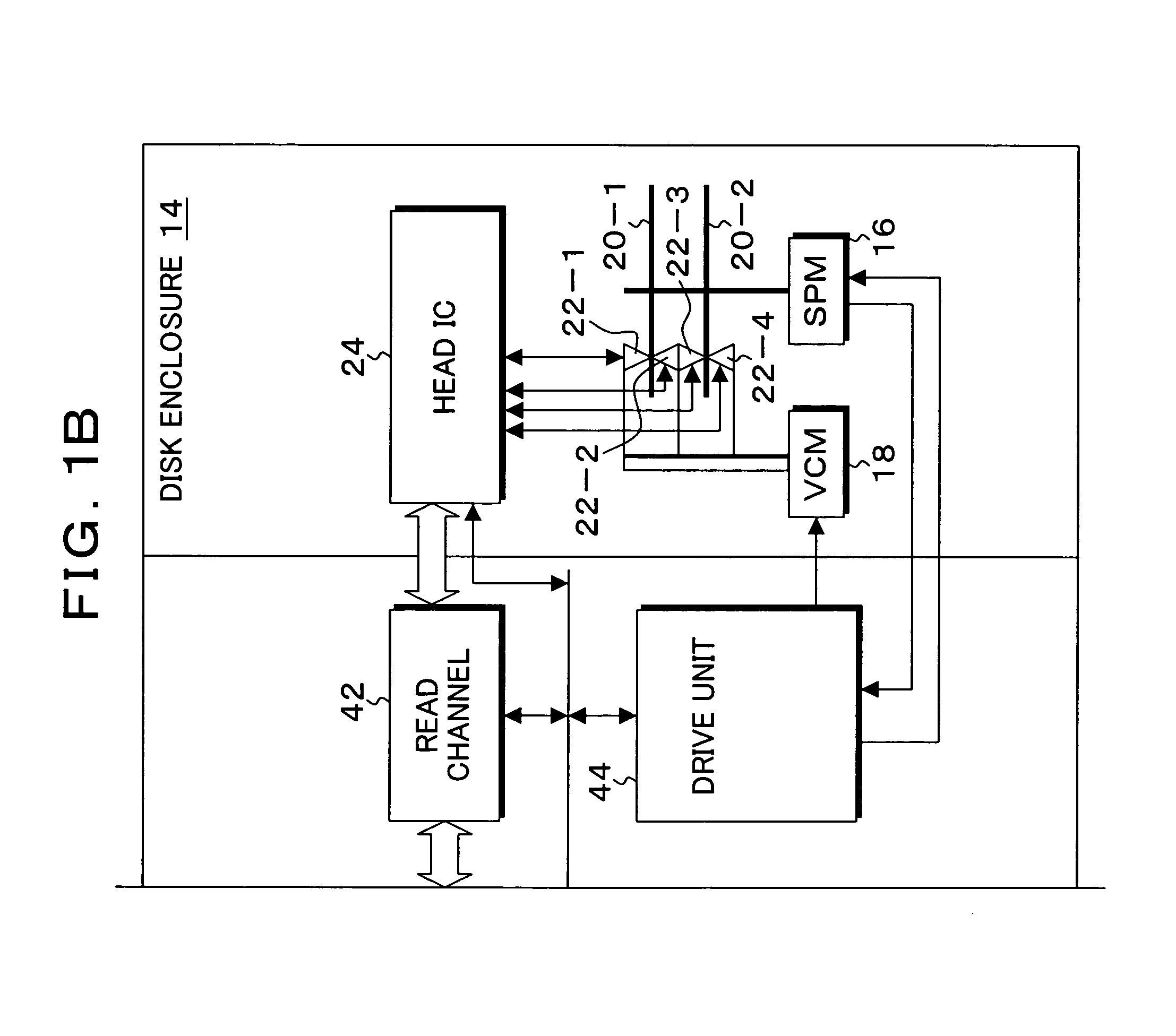
Storage device, control method, control device, and program
InactiveUS20070230015A1Easy to controlAccurate measurementDriving/moving recording headsFluid-dynamic spacing of headsDistance detectionThermal expansion
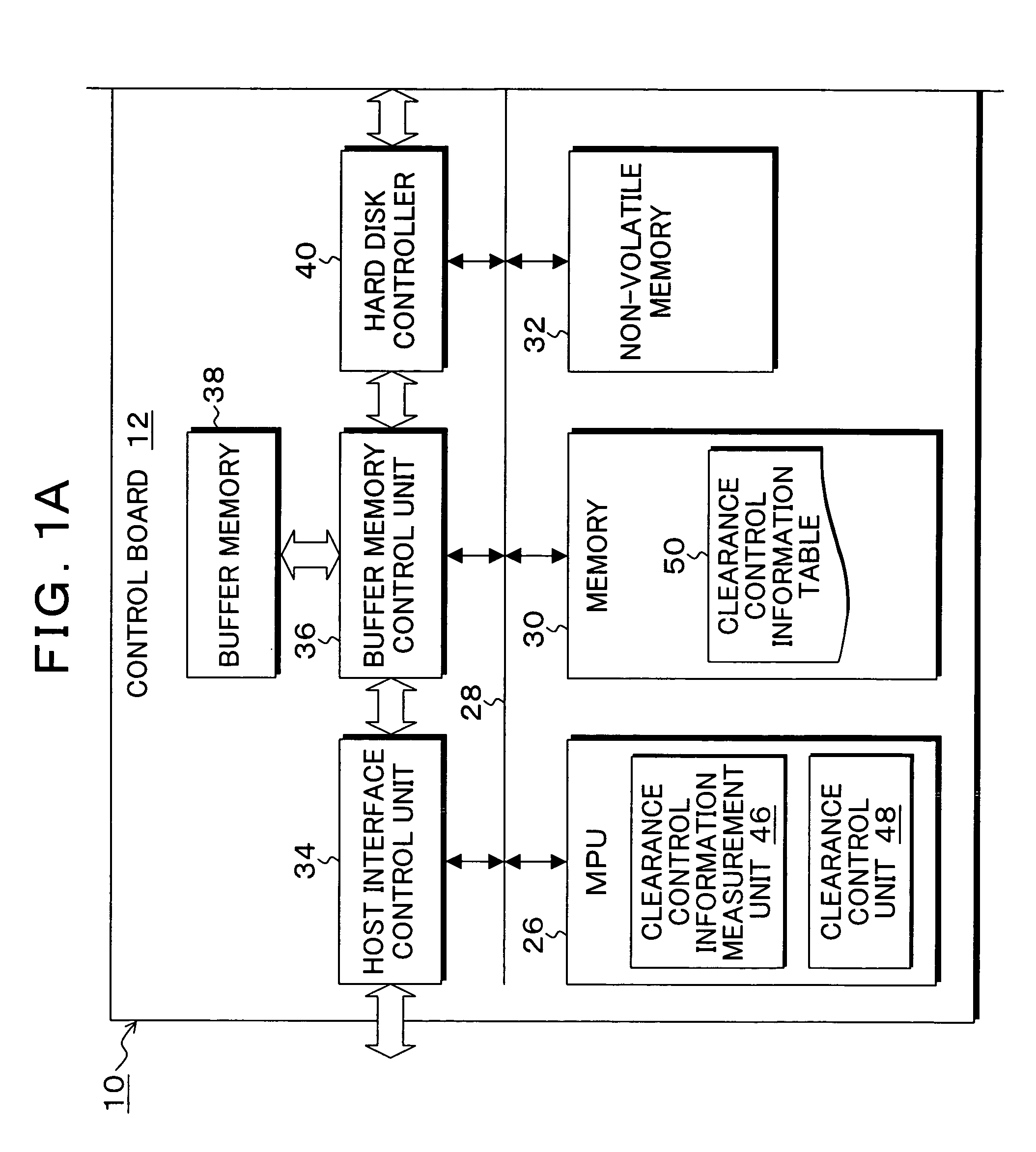
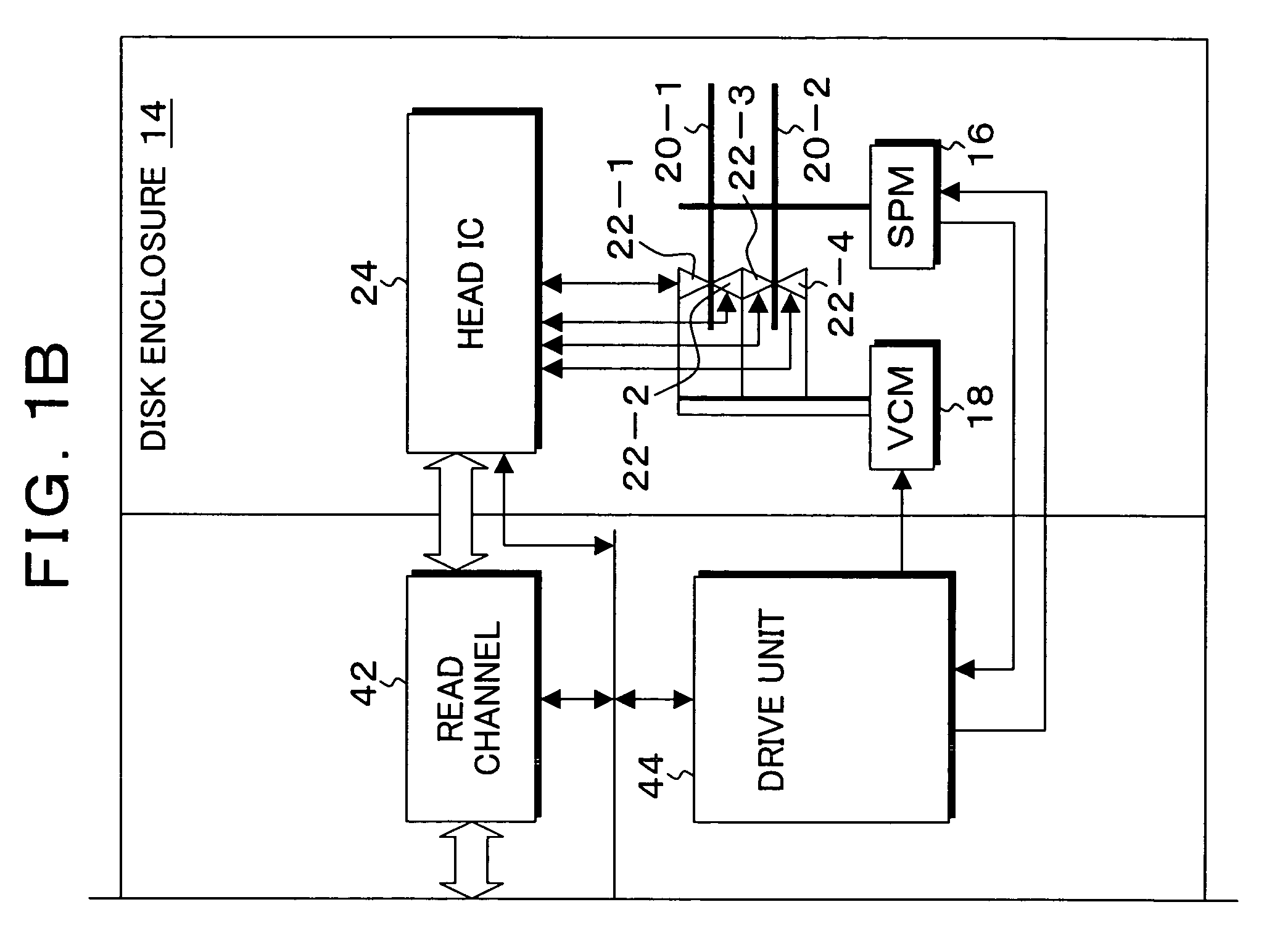
A heater for changing a projection distance protrusion value by thermal expansion accompanying electric-power-distributed heating is provided in a head having at least a reading element. At desired correction timing, a changed distance detection unit measures a clearance changed distance in a state in which the head is positioned to a track on the recording medium while increasing the amount of electric power distributed to the heater. A contact determination unit determines that the head is brought into contact with the recording medium when a derivative value of the clearance changed distance is below a predetermined threshold value. A measurement output unit outputs the clearance changed distance detected by the changed distance detection unit at the time of contact determination of the contact determination unit as a measurement result of the clearance between the reading element and the recording medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
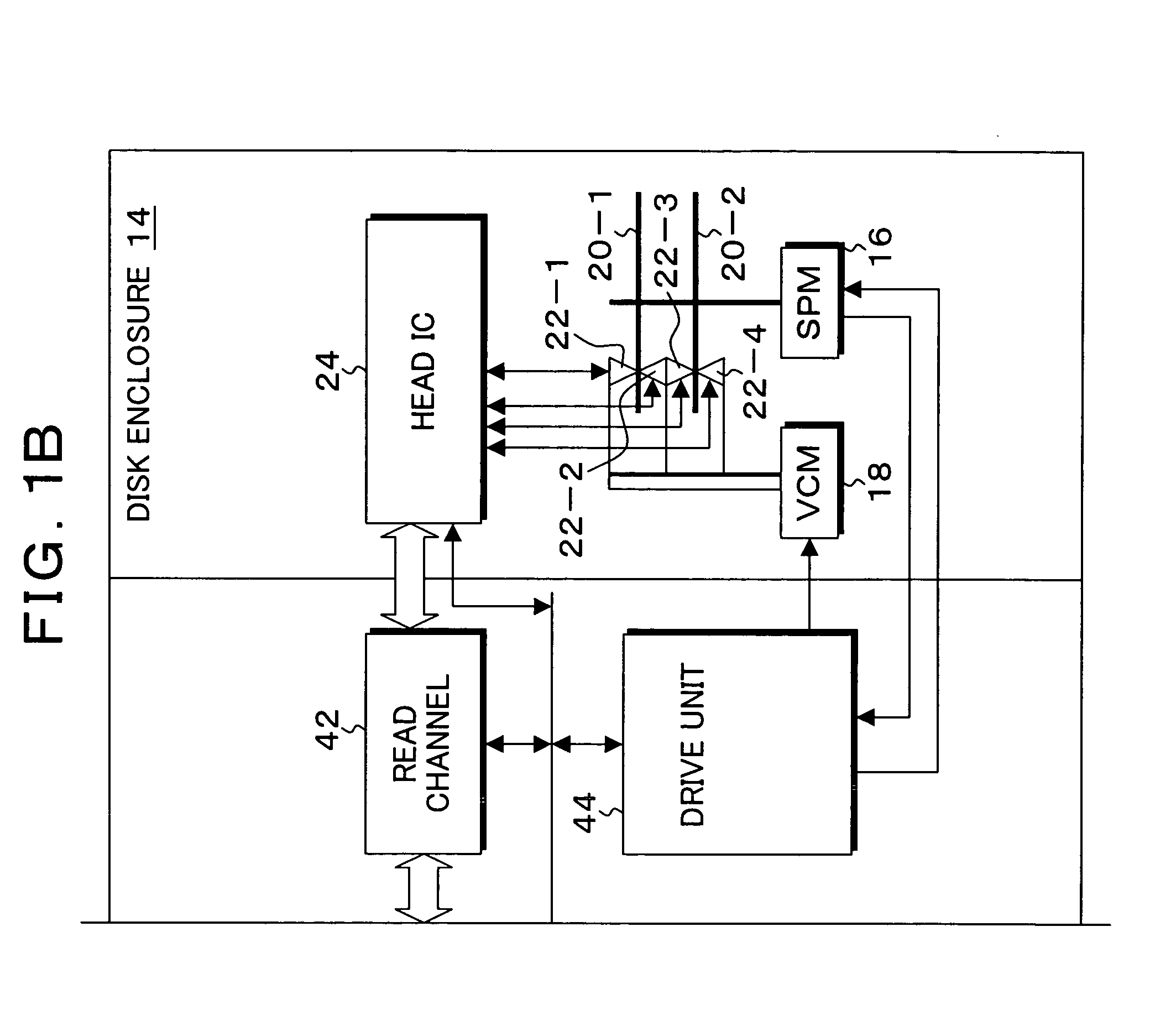
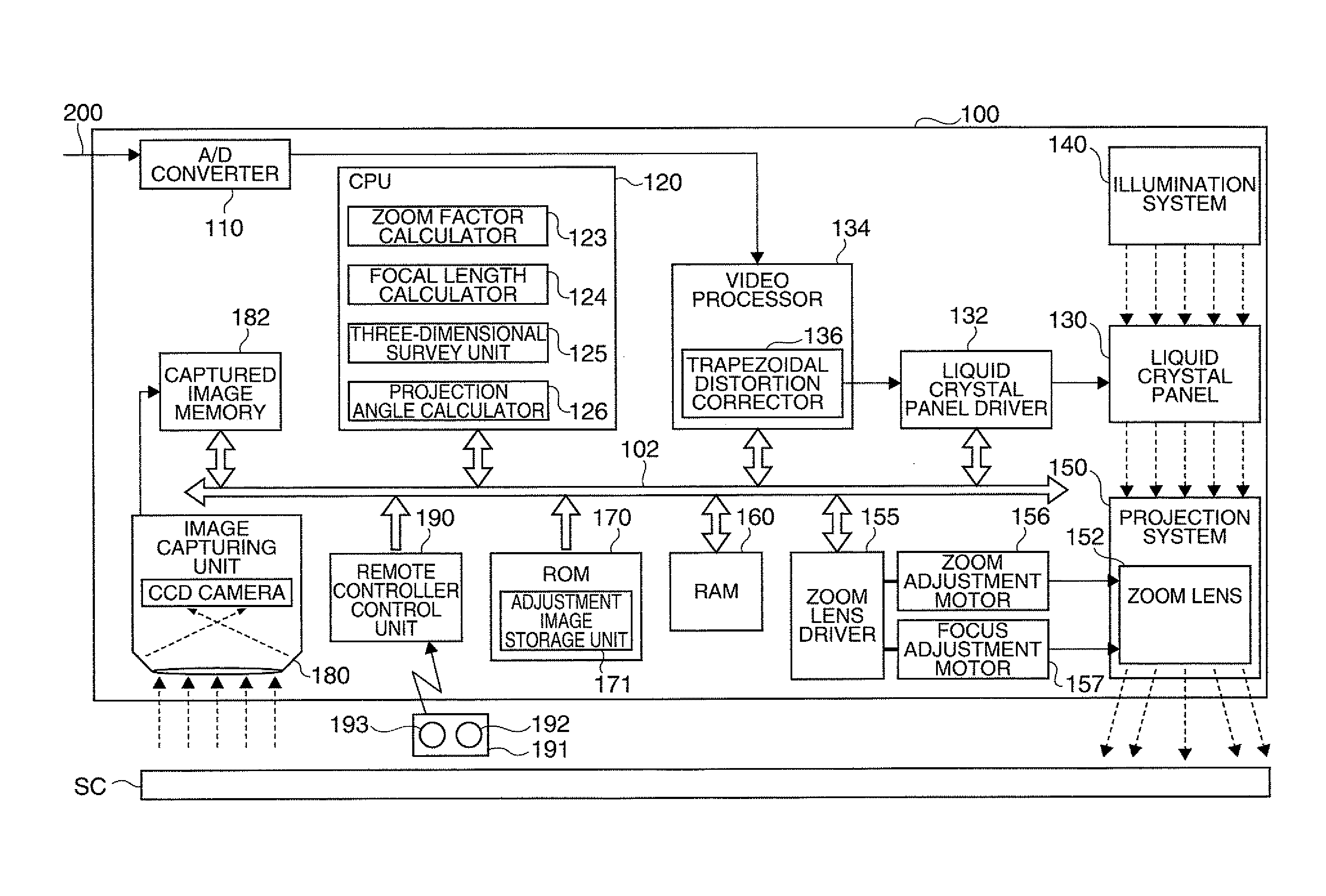
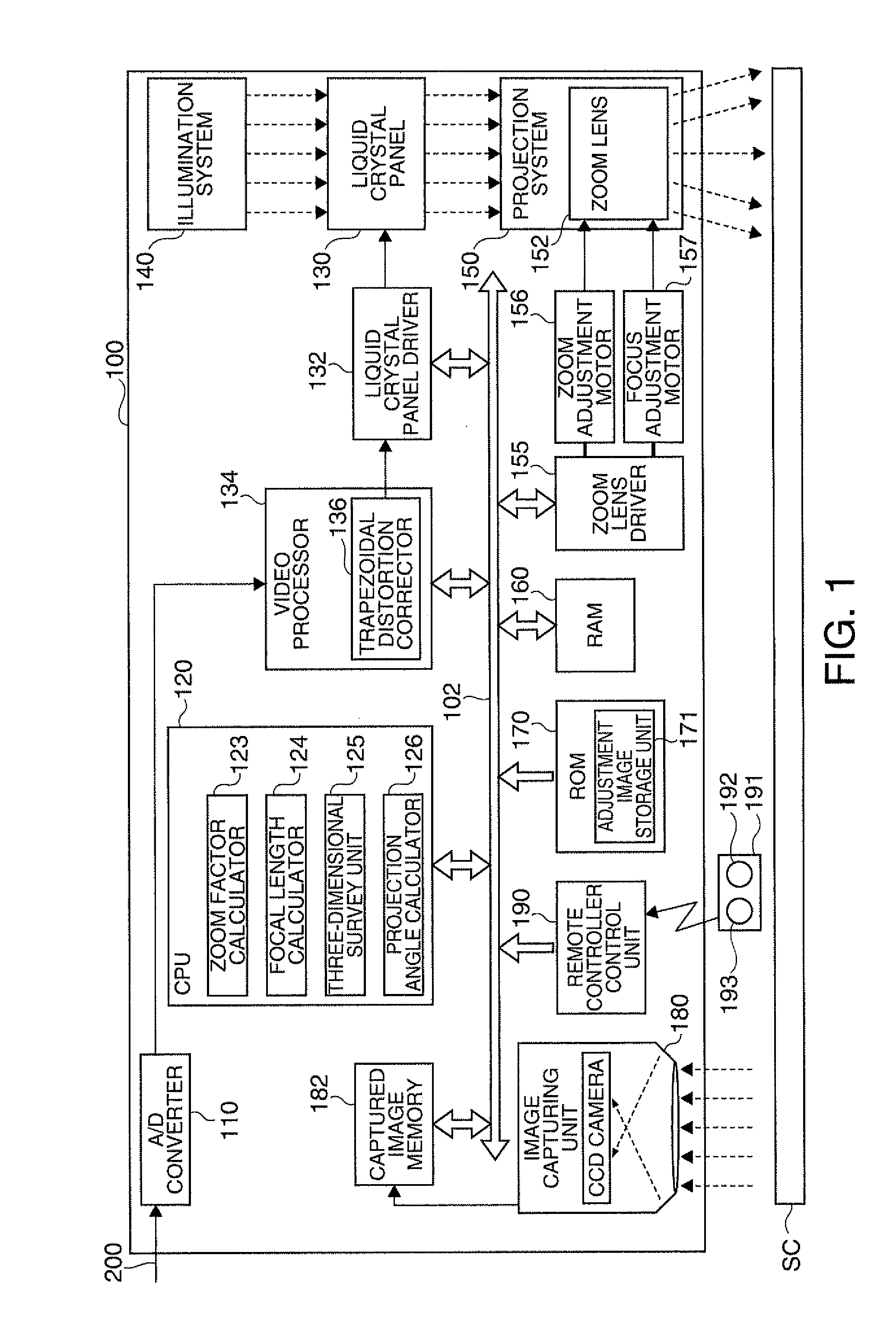
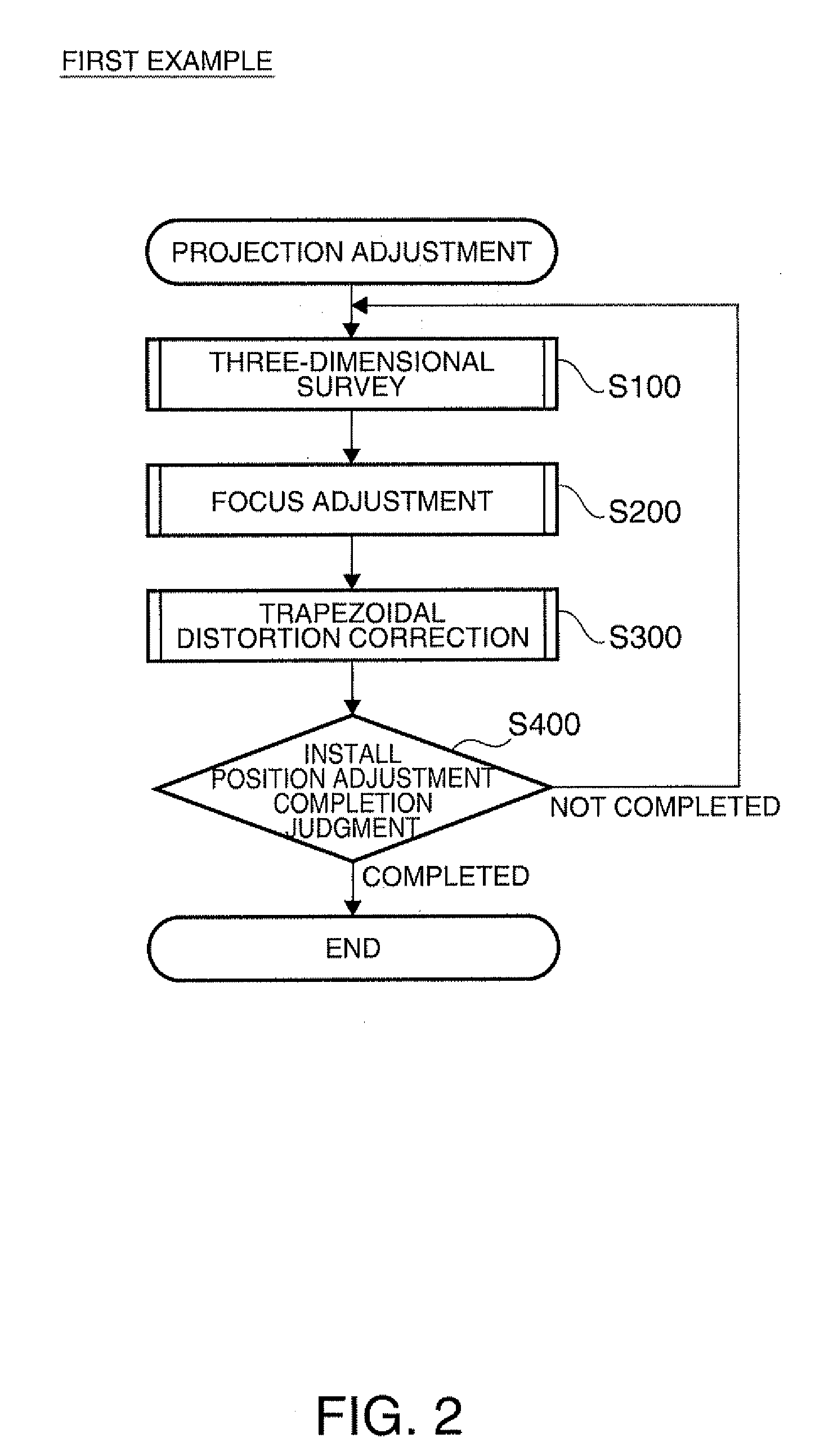
Projection-type display apparatus and method for performing projection adjustment
ActiveUS20100128231A1Easily allowTesting/calibration apparatusProjector focusing arrangementComputer graphics (images)Projection distance
A projection-type display apparatus that projects an image toward a projection surface and displays the image thereon, the apparatus includes: a projecting section that includes a focal length adjusting mechanism and projects an image; an adjustment image controlling section that uses the projecting section to project a guide display image suggesting how to adjust the position where the projection-type display apparatus is installed and uses the projecting section to project a calibration image having a predetermined shape when the guide display image is projected; a projection distance measuring section that measures a projection distance that is the distance to the projection surface based on a captured image obtained by capturing the calibration image; and a focus adjusting section that operates the focal length adjusting mechanism based on the projection distance to perform focus adjustment so that the displayed guide display image is brought into focus.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
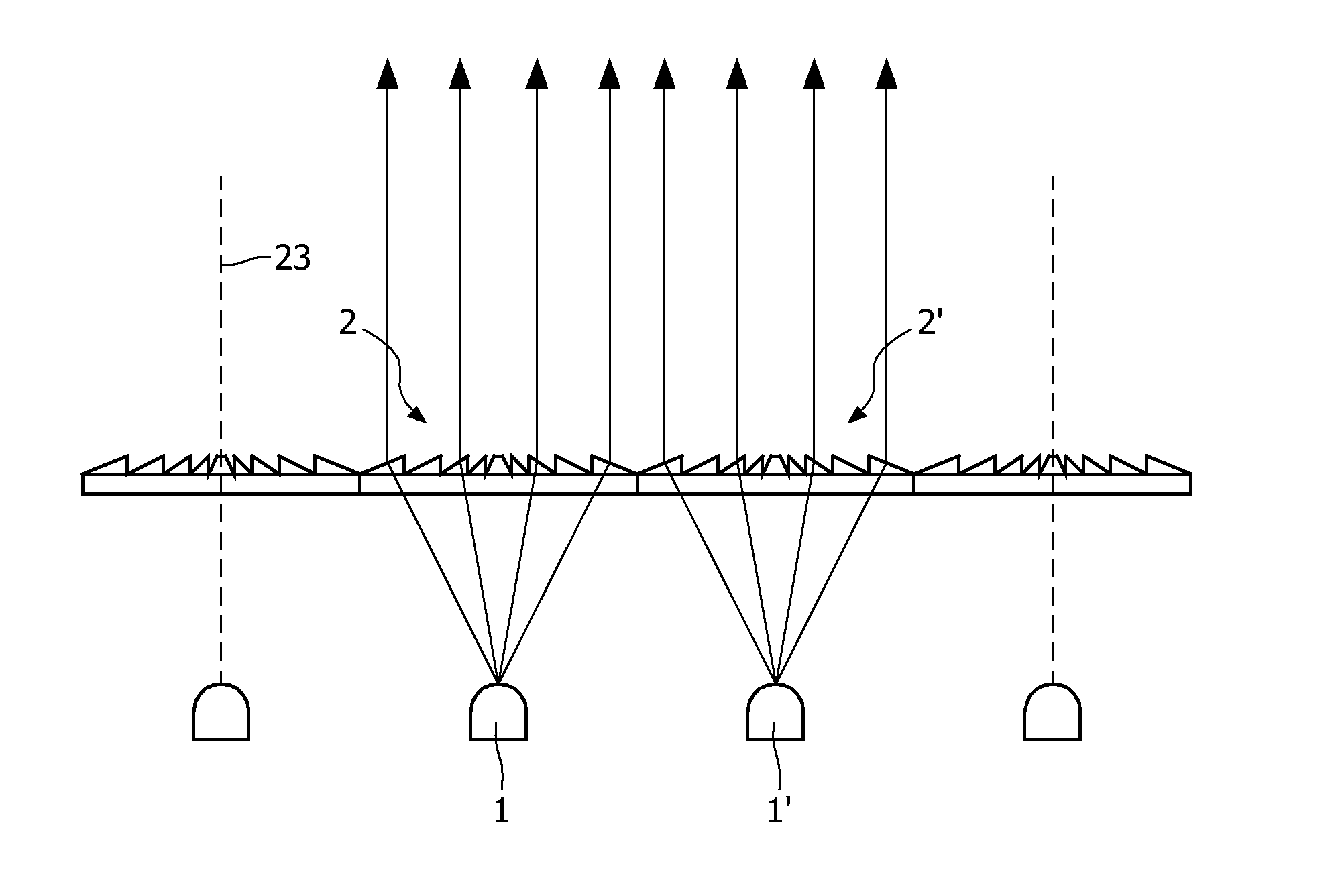
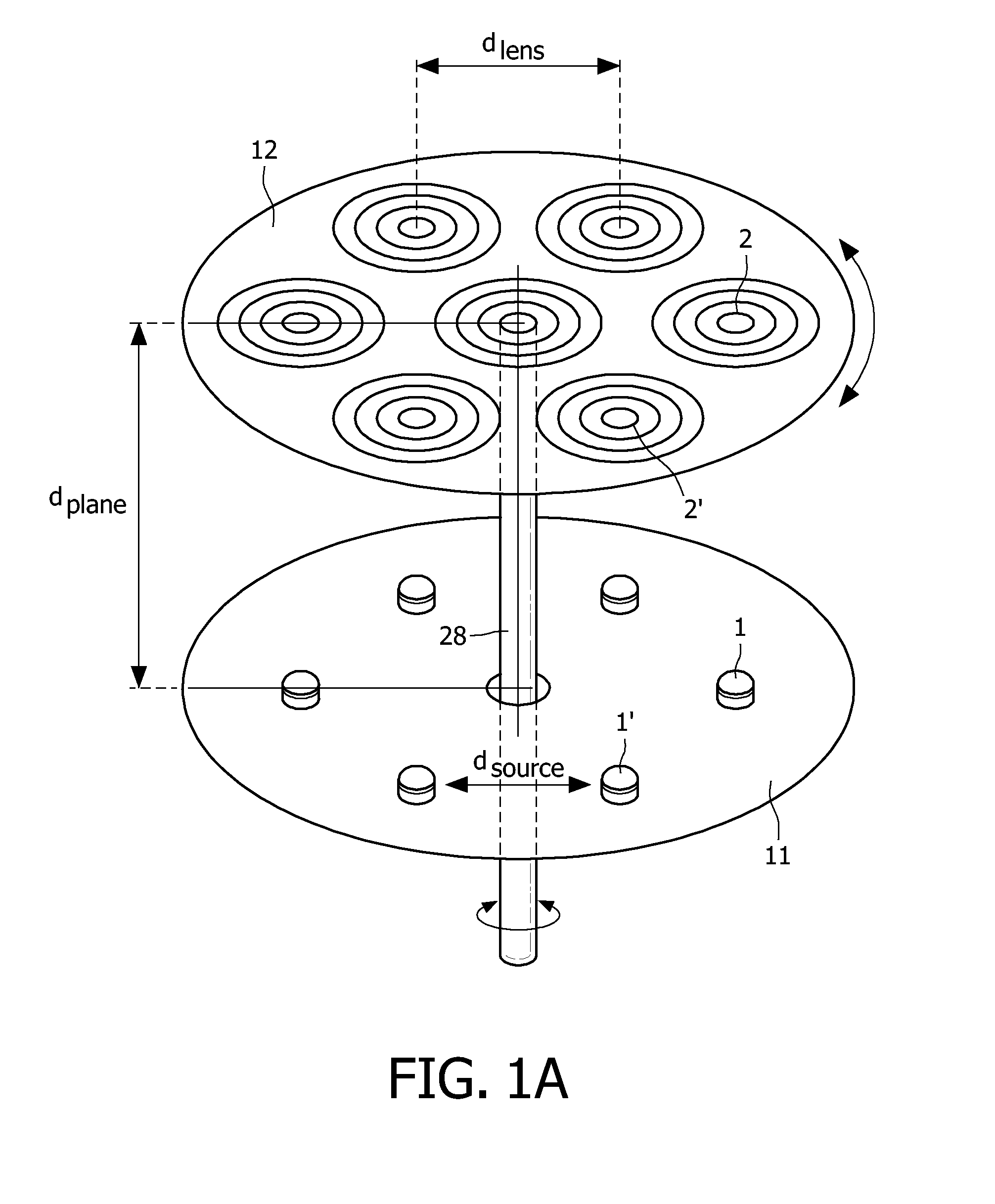
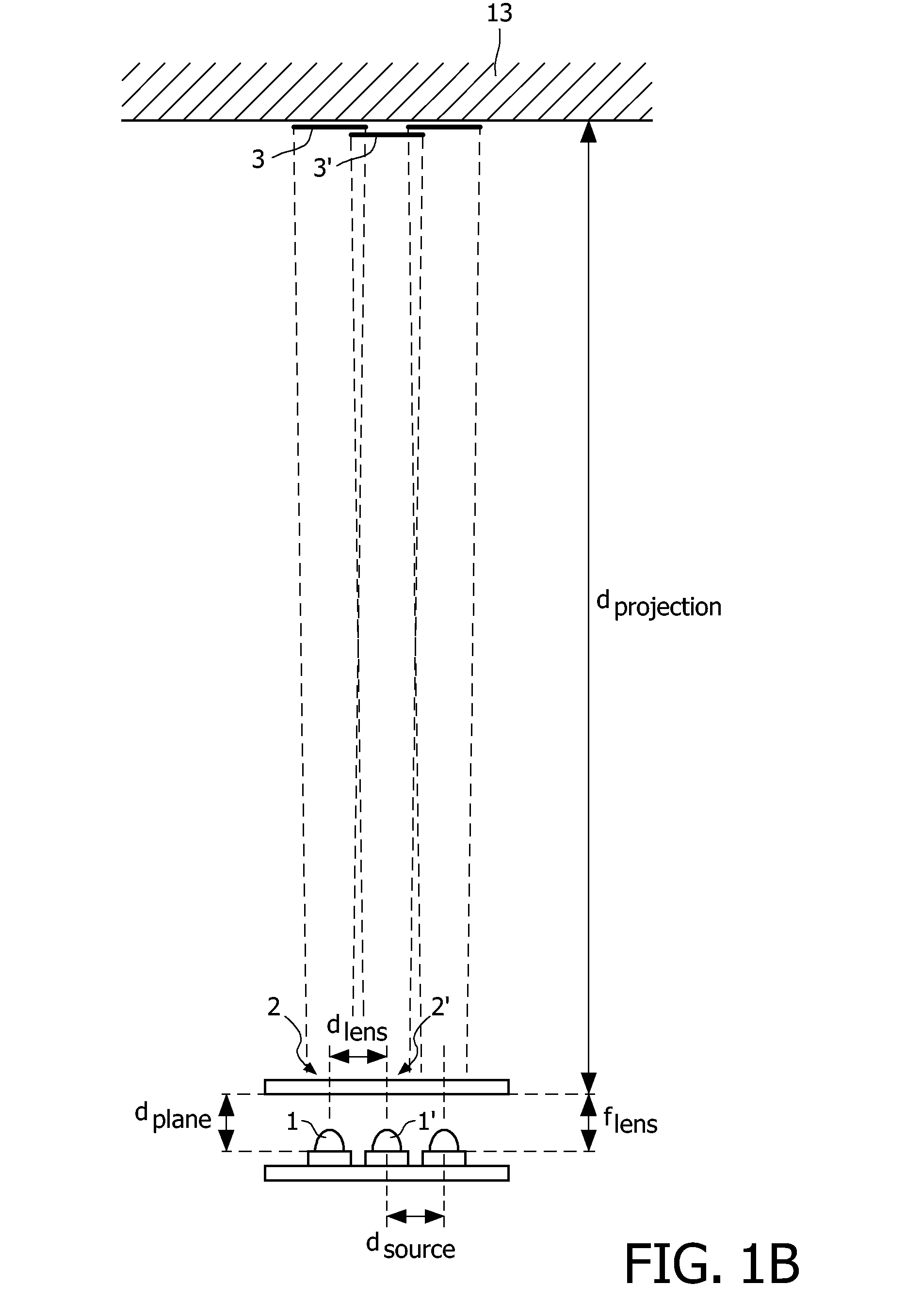
Illumination system
InactiveUS8262252B2Easy to manufactureEasy to useMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLight beamProjection plane
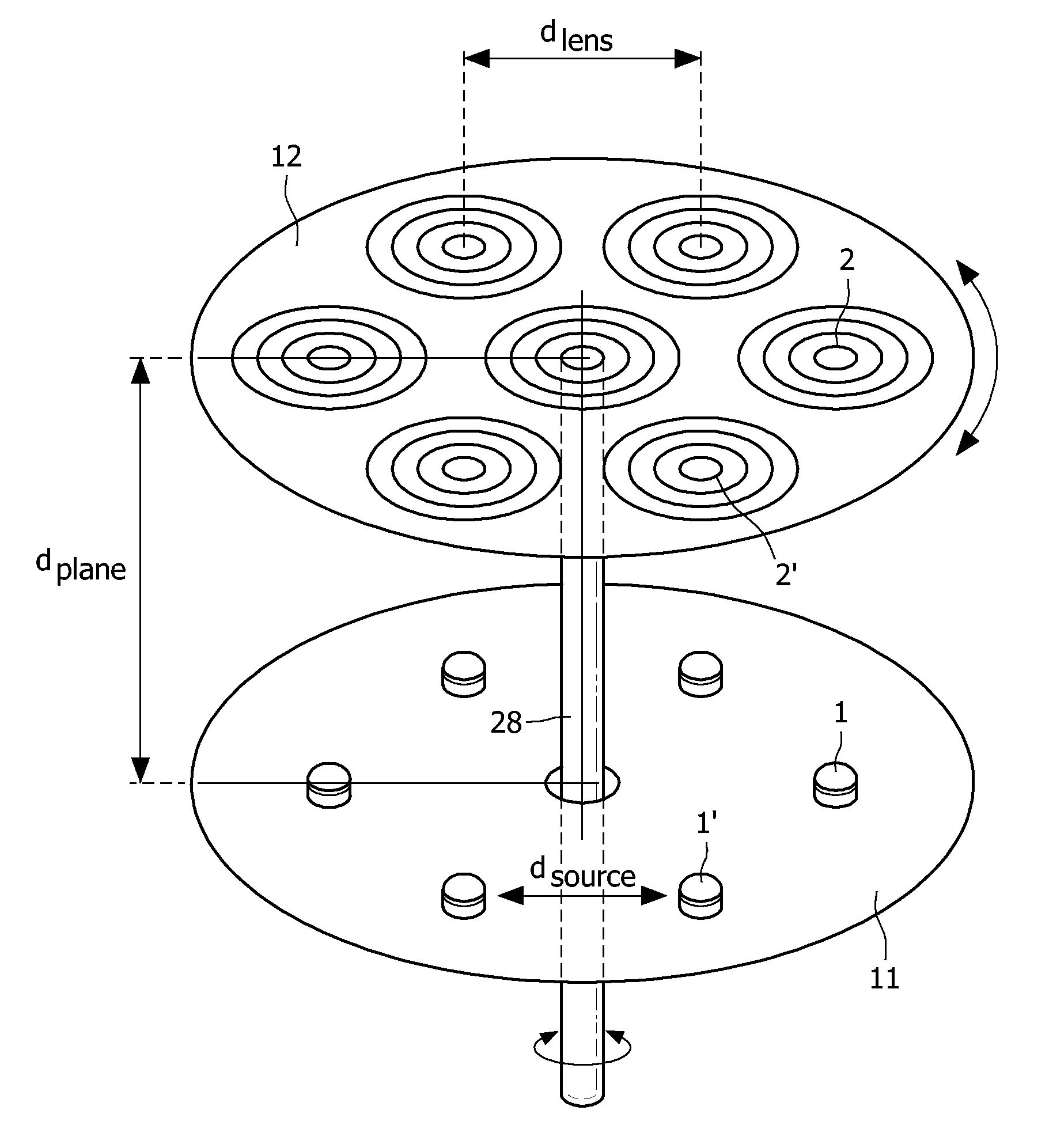
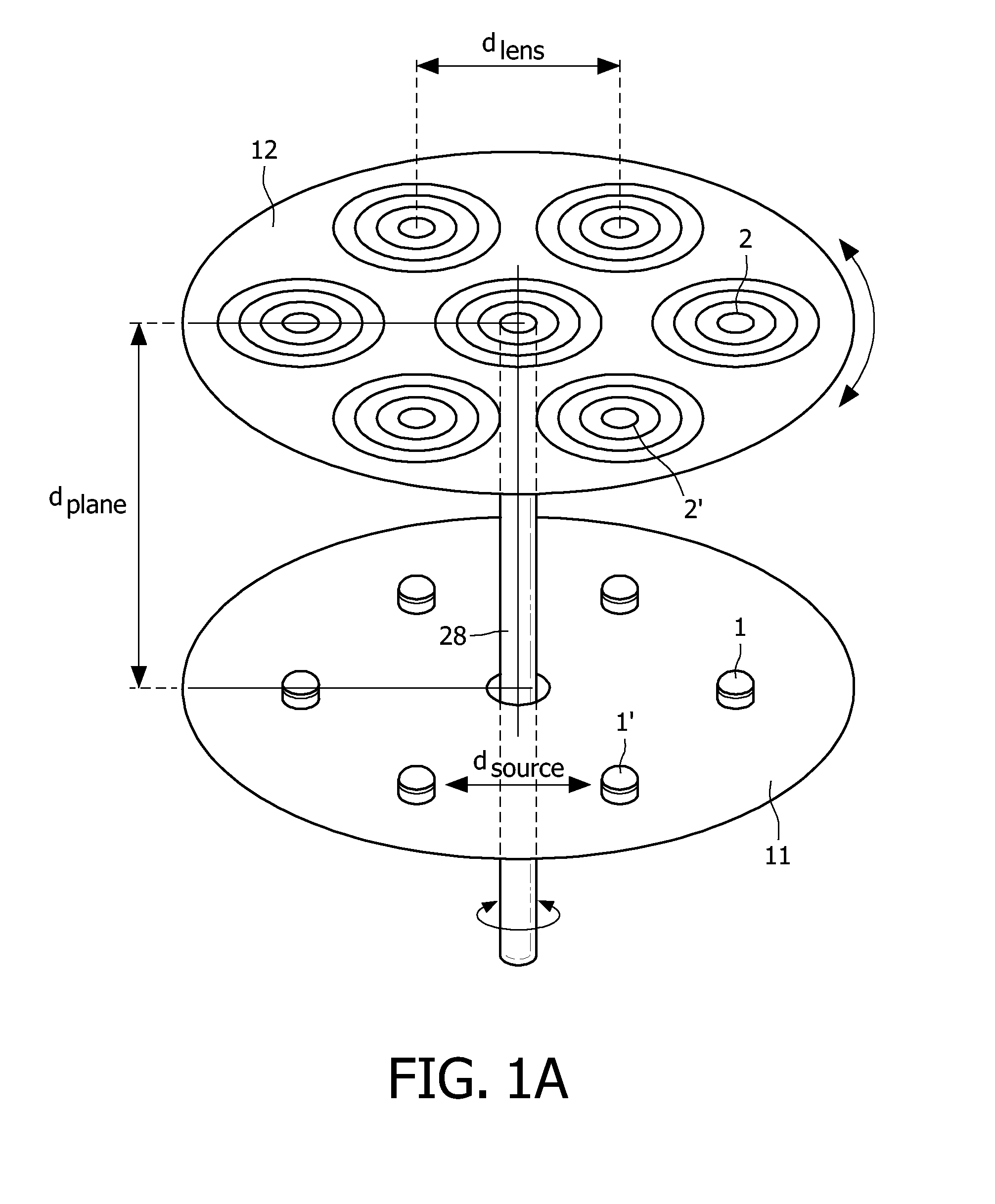
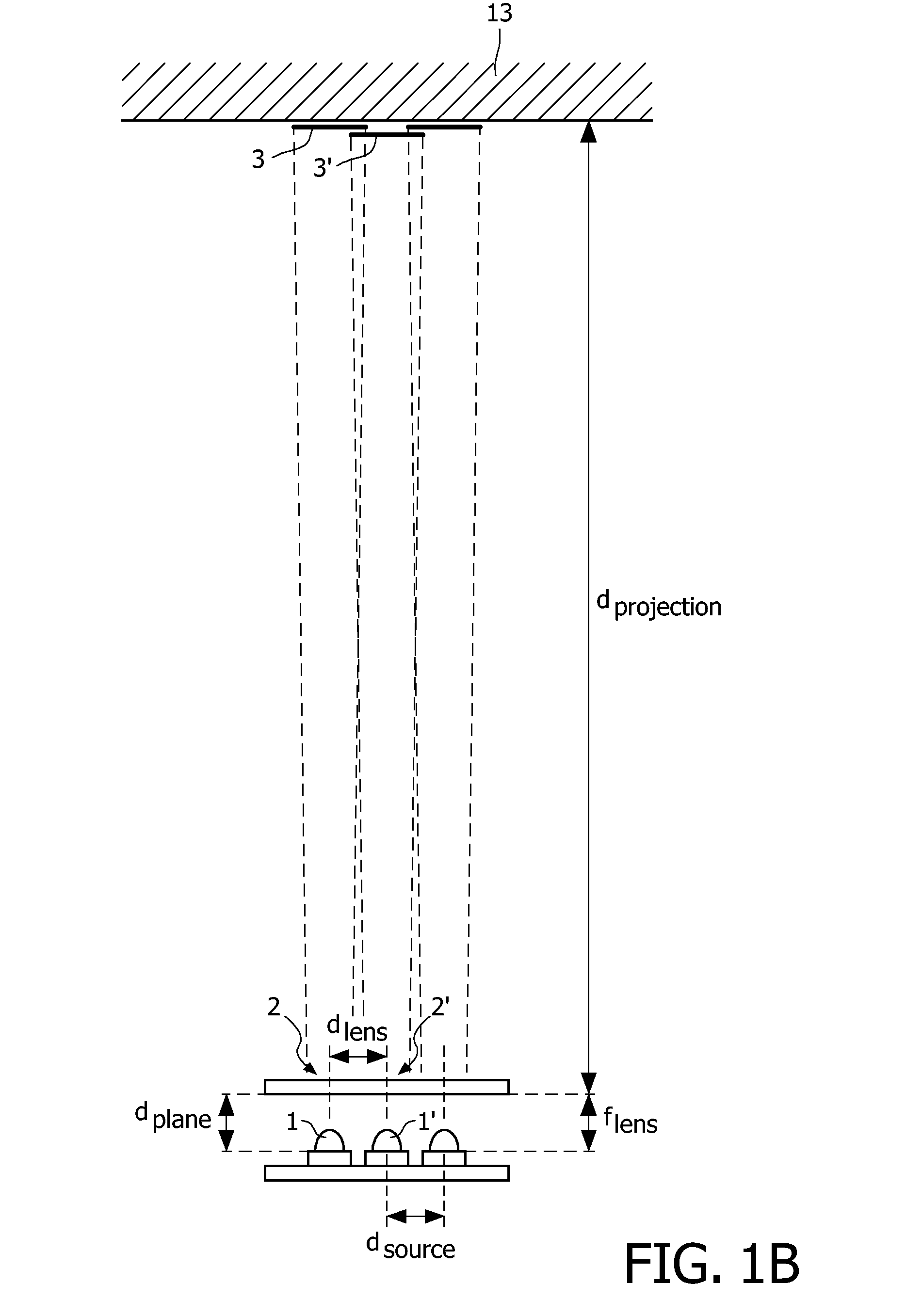
The illumination system has an array of light sources (1, 1′, . . . ) such as an array of light emitting diodes arranged in a pre-determined manner in a first plane (11), wherein dsource is a characteristic dimension of the spatial arrangement of the light sources in the first plane. An array of associated lenses (2, 2′, . . . ) is arranged in substantially the same pre-determined manner in a second plane (12). Each lens has substantially the same focal distance flens. The array of lenses is provided at a plane distance dplane from the array of light sources. The plane distance dplane is substantially equal to the focal distance flens of the lenses. The illumination system has displacement means for displacing the array of lenses with respect to the array of light sources so as to obtain a plurality of directional light beams projecting spots on a projection plane arranged at a projection distance dprojection from the illumination system, wherein dprojection≧10×dsource and dprojection≧10×dplane.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Optical micro-projection system and projection method
InactiveUS20120120375A1Provide protectionProjectorsColor television detailsComputer moduleOptical power
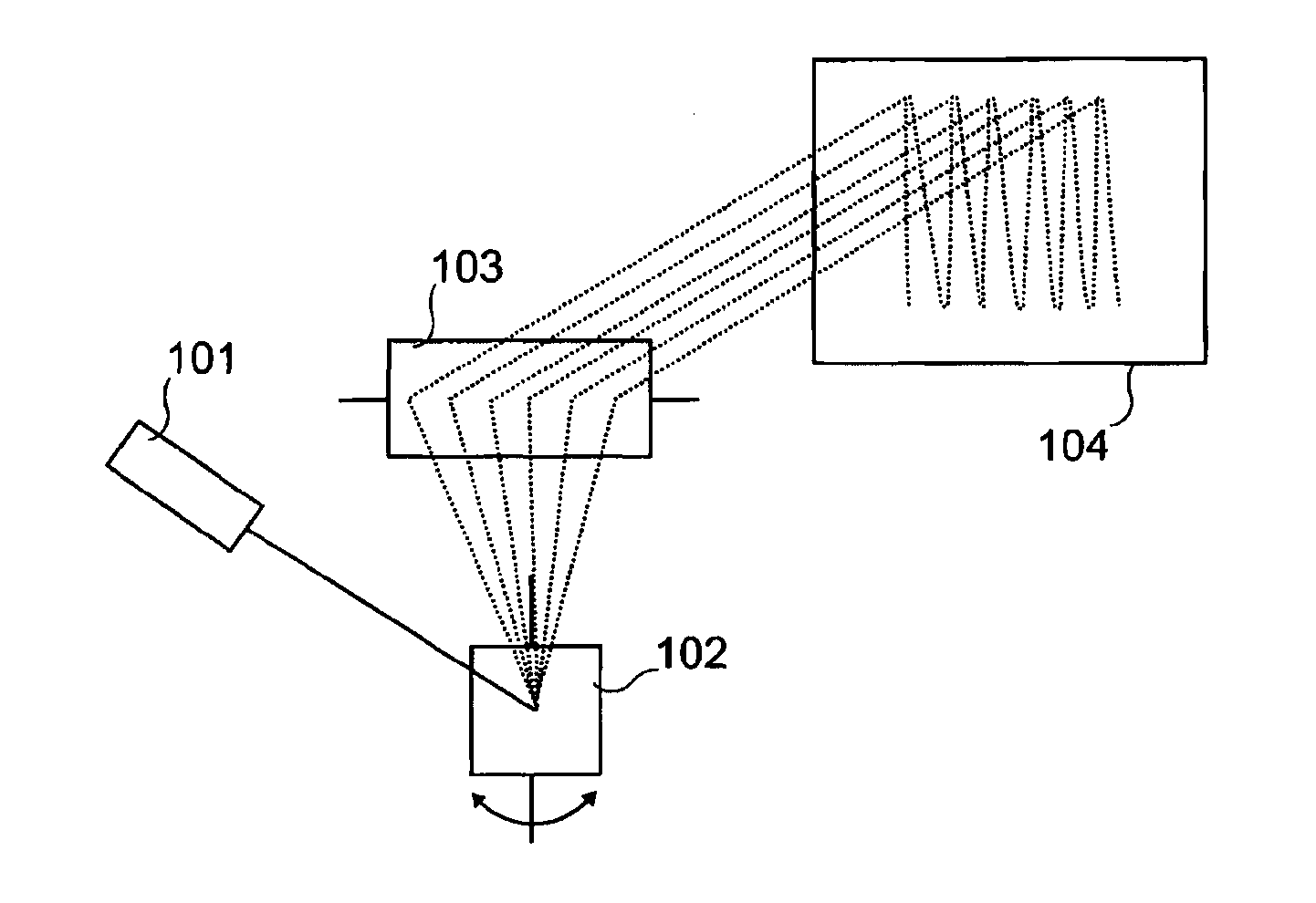
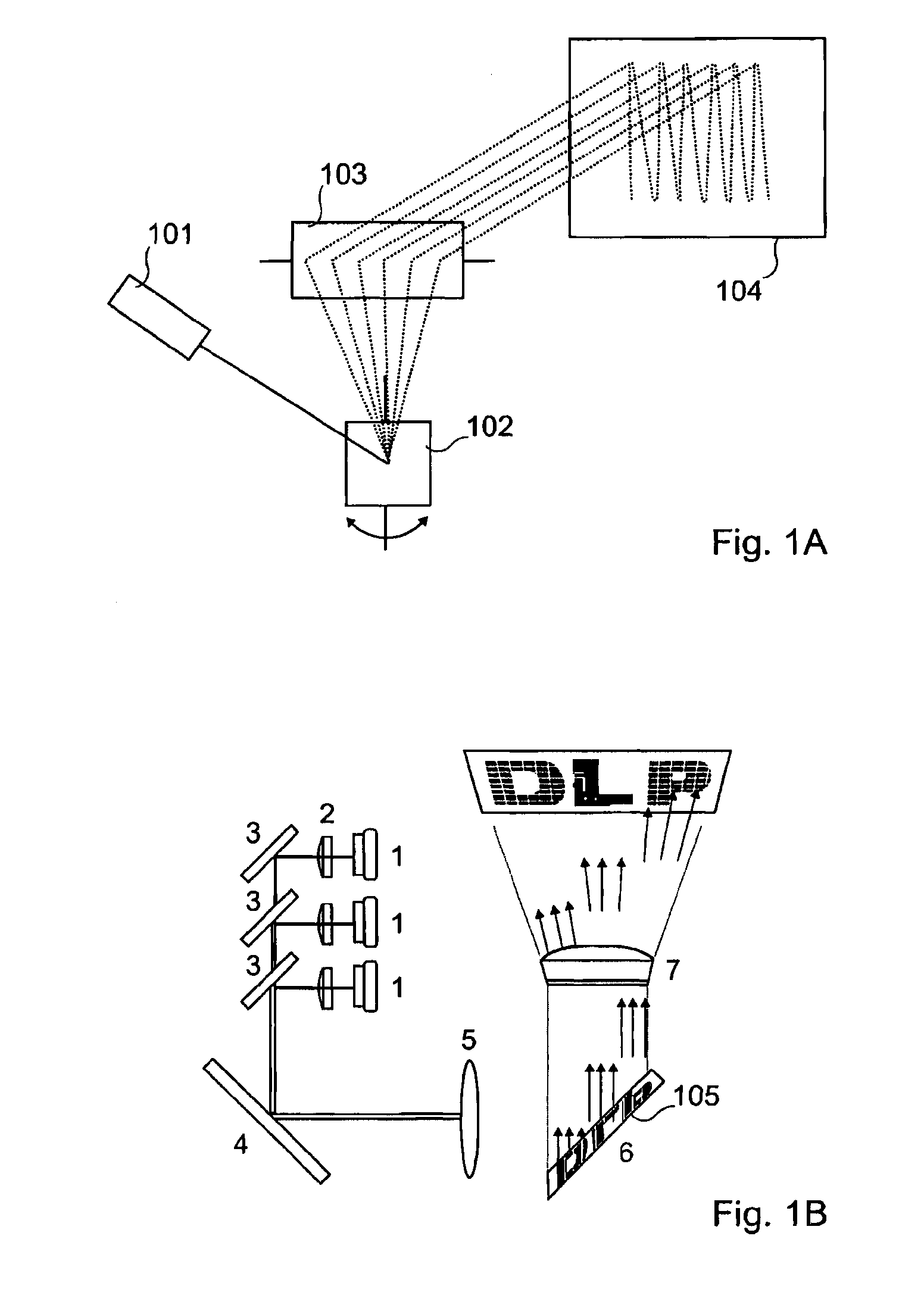
An optical micro-projection system comprising the following components: at least one laser light source (200, 400, 402, 600); at least one movable mirror (102, 103, 203) for deviating light from said light source to allow generation of images on a projection surface (104, 301, 303, 306, 603); a self mixing module for measurement of the distance (604) between the projection source and a projection surface, said self mixing module comprising:—at least one photodiode (401, 601) for monitoring the light emission power of the laser light source;—an optical power variation counter for counting optical power variations (605); successive displacements of said mirror allowing the self mixing module providing successive projection distance measurements of a plurality of points of said projection surface. A projection method for optical micro-projection system and a distance measurement method are also provided.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
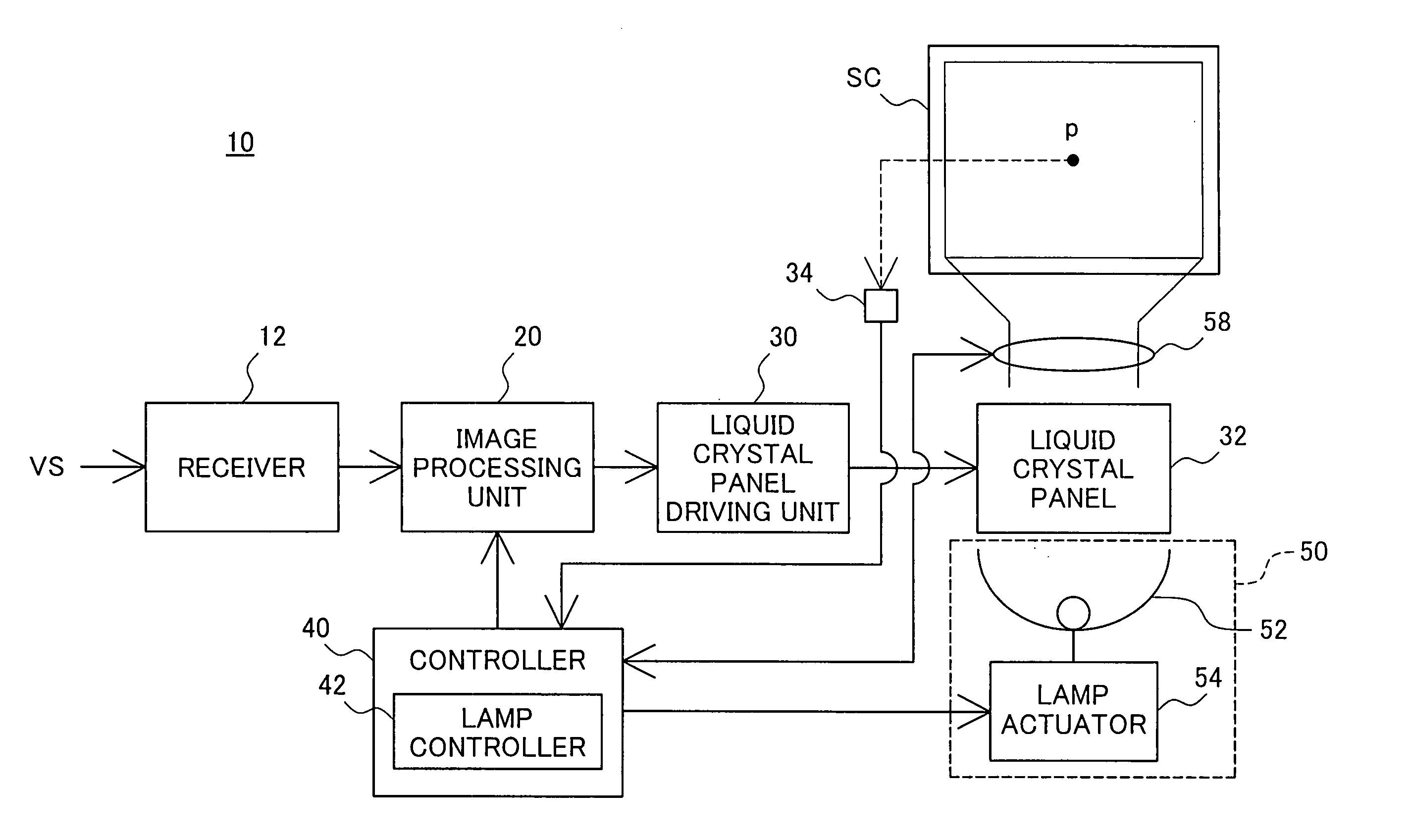
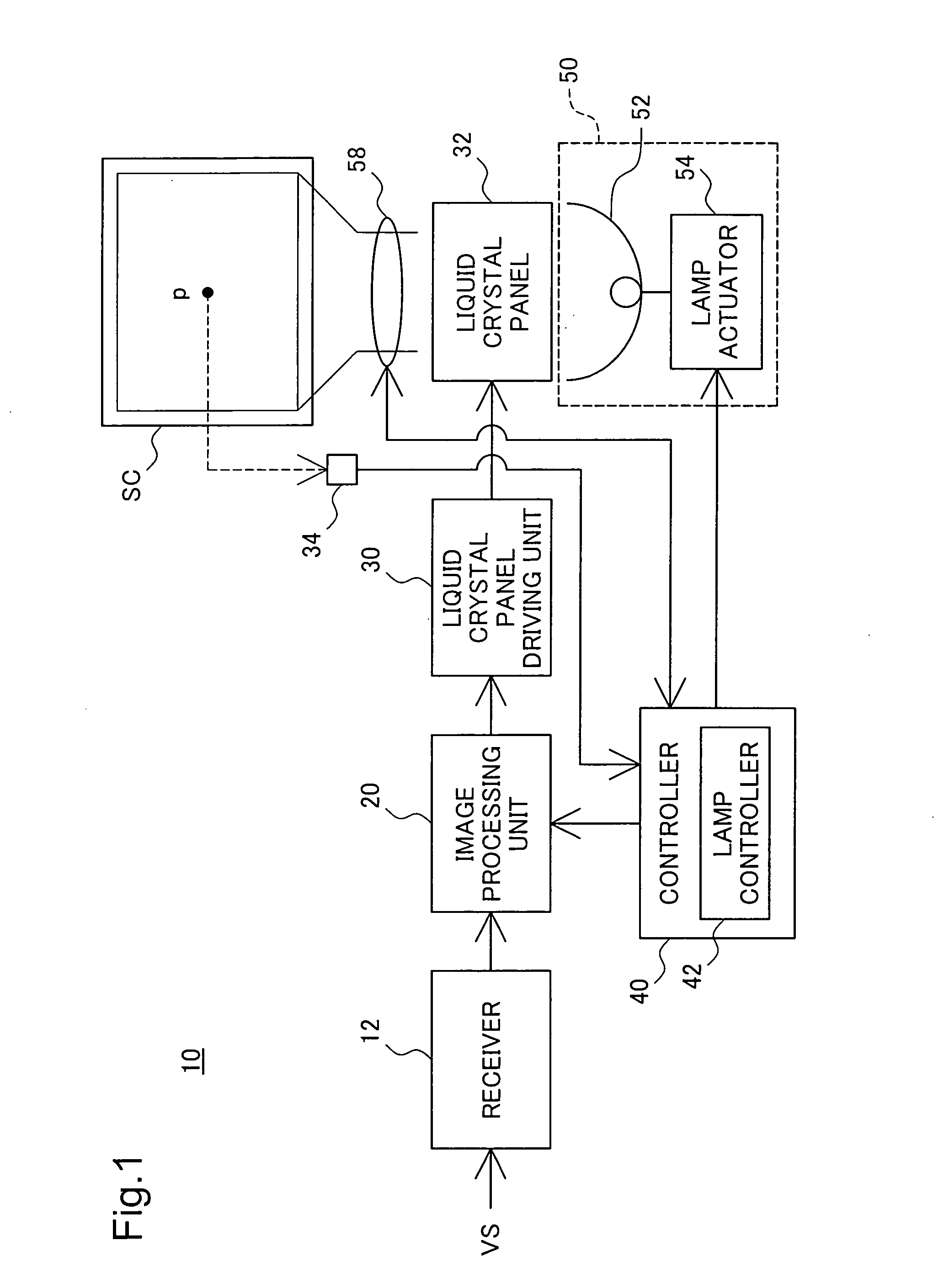
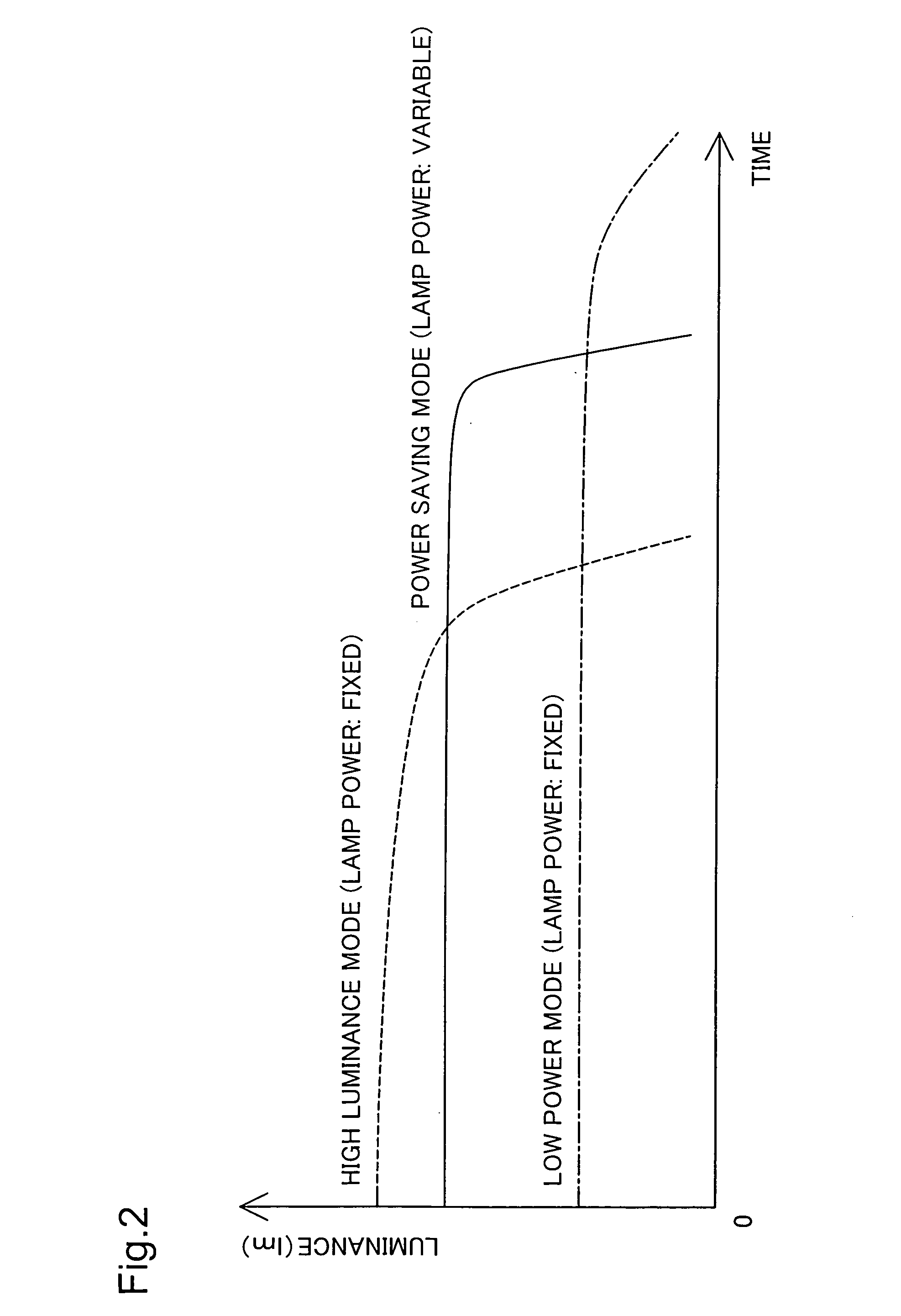
Projector and drive control of light source lamp for projector
ActiveUS20050094110A1Reduce adverse effectsTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesProjection imageProjection lens
A projector 10 of the invention measures the brightness of an image projected on a screen SC and corrects the measured brightness of the projected image with an input zoom ratio of a projection lens and an input projection distance. The projector 10 compares the corrected brightness of the projected image with a preset target value and sets a driving power of a light source lamp 52 to compensate for a difference between the normalized brightness and the preset target value. This arrangement effectively restrains potential adverse effects of a variation in luminance of illumination light emitted by the light source lamp of the projector on the brightness and the contrast of a resulting projected image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Illumination system
InactiveUS20100061090A1Low costEasy to manufactureMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLight beamProjection plane
The illumination system has an array of light sources (1, 1′, . . . ) such as an array of light emitting diodes arranged in a pre-determined manner in a first plane (11), wherein dsource is a characteristic dimension of the spatial arrangement of the light sources in the first plane. An array of associated lenses (2, 2′, . . . ) is arranged in substantially the same pre-determined manner in a second plane (12). Each lens has substantially the same focal distance flens. The array of lenses is provided at a plane distance dplane from the array of light sources. The plane distance dplane is substantially equal to the focal distance flens of the lenses. The illumination system has displacement means for displacing the array of lenses with respect to the array of light sources so as to obtain a plurality of directional light beams projecting spots on a projection plane arranged at a projection distance dprojection from the illumination system, wherein dprojection≧10×dsource and dprojection≧10×dplane.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
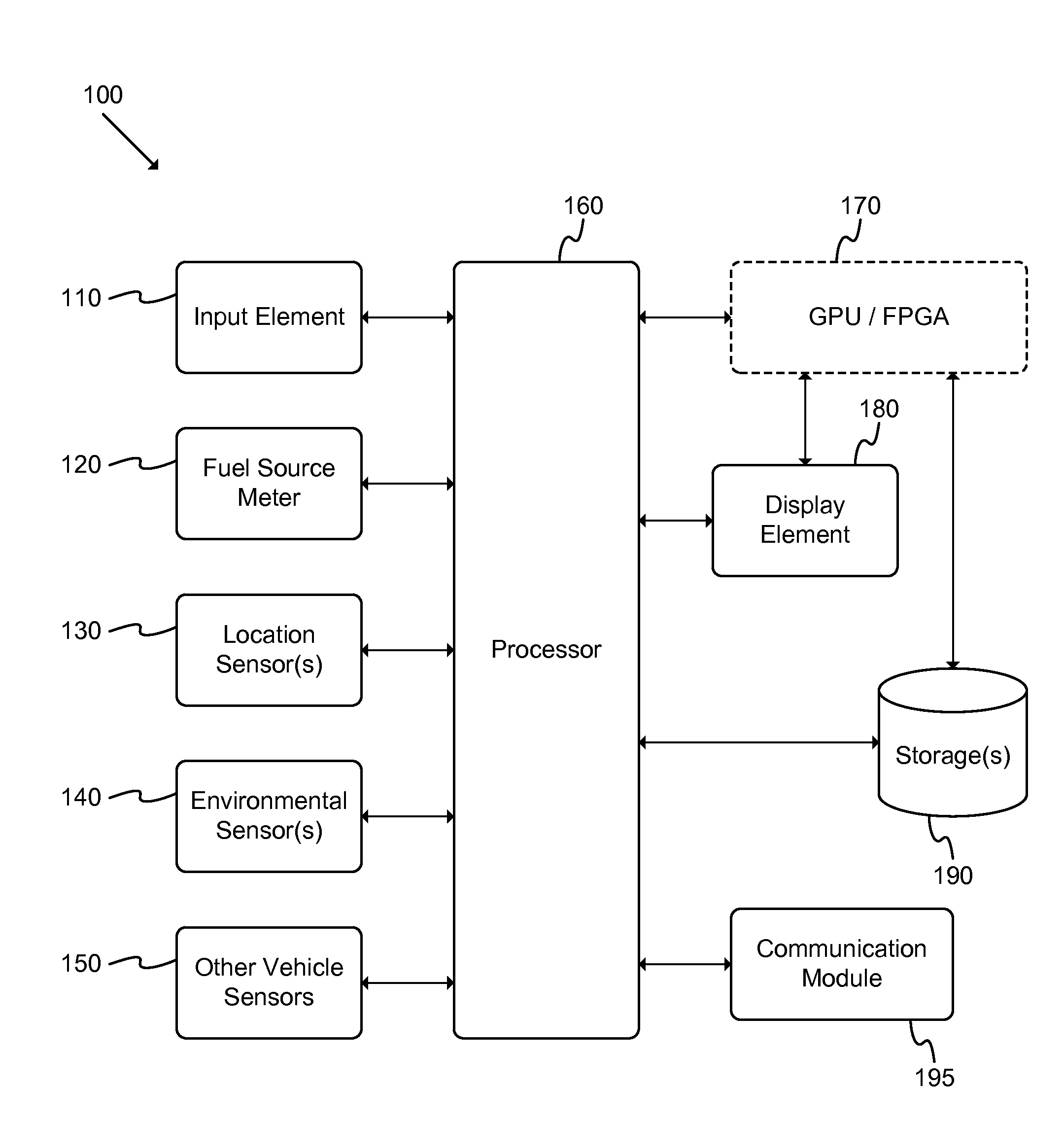
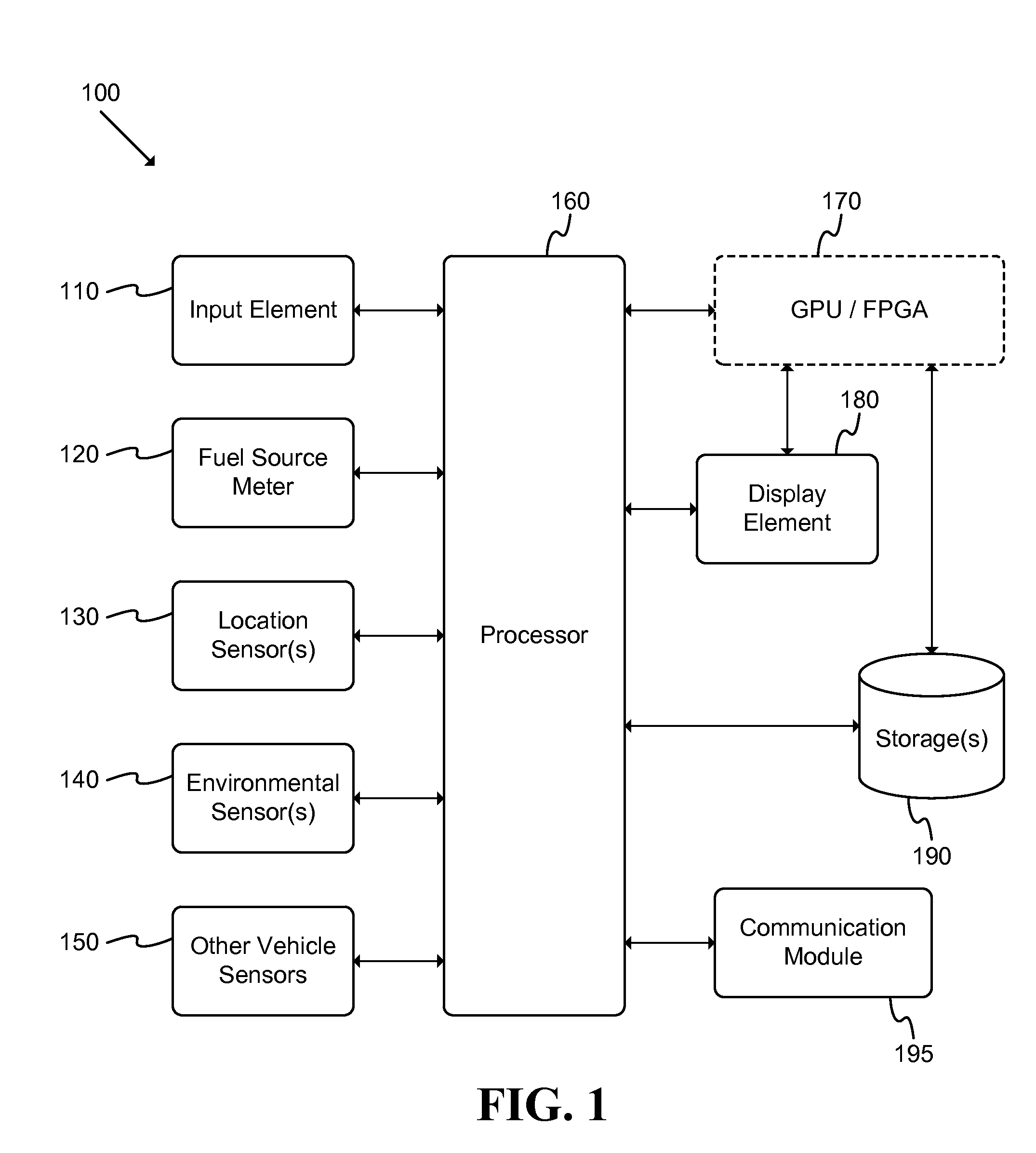
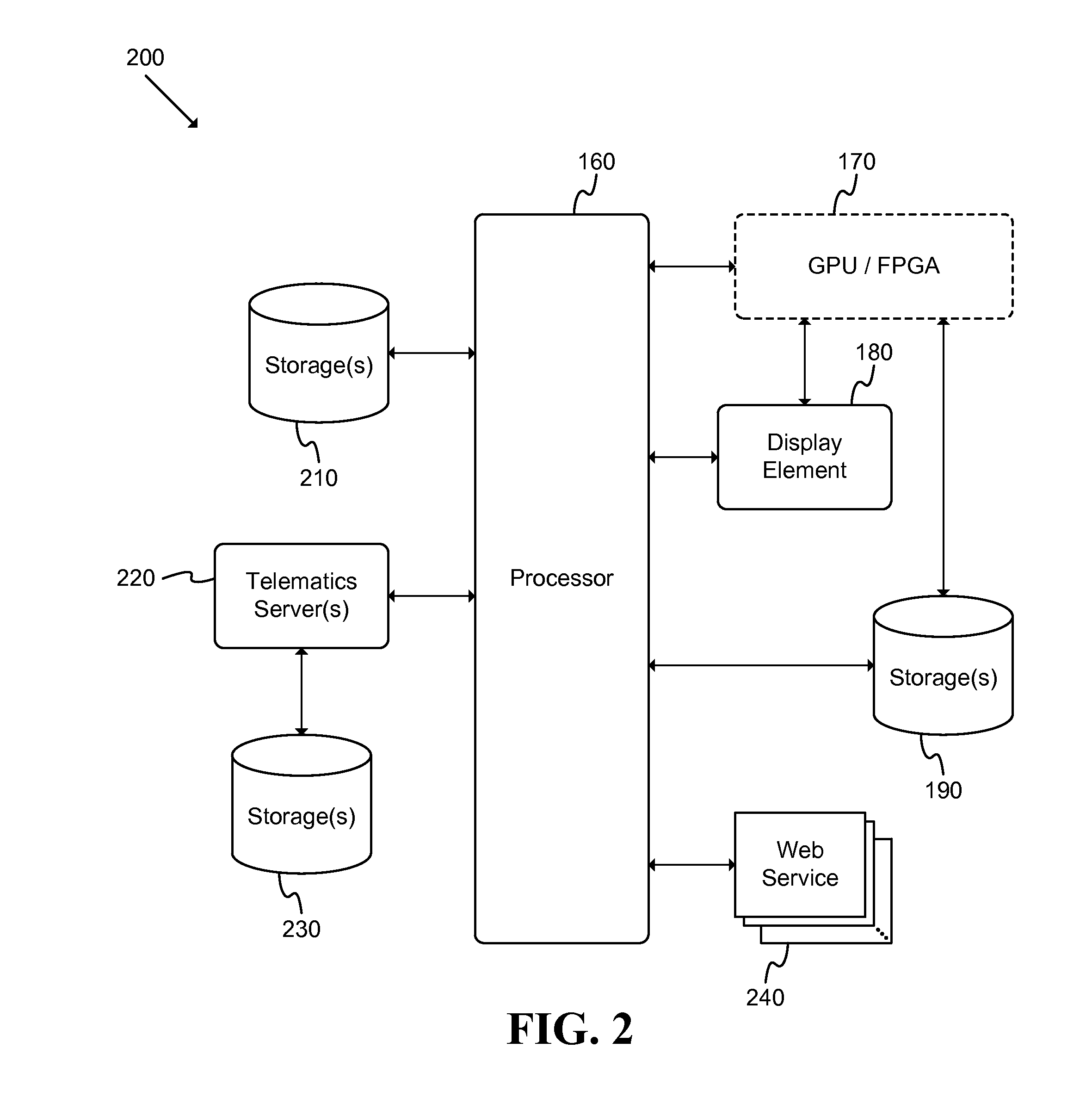
Vehicle Range Projection
ActiveUS20140278038A1Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationPosition dependentProcessing element
A system adapted to determine a projected range of a vehicle is described. The system includes: a storage element adapted to store a set of parameters associated with a vehicle; a map evaluation element adapted to retrieve information regarding a geographic area associated with a position of the vehicle; and a processing element adapted to determine the projected range of the vehicle based at least partly on the set of parameters and the retrieved information. An automated method of projecting a range of a vehicle includes: generating a set of range projection links; generating a monochrome bitmap based at least partly on the set of range projection links; rendering the set of range projection links within the monochrome bitmap; and tracing the rendered links to generate a polygon outline of the range of the vehicle. An automated method of caching map data for vehicle range projection is described.
Owner:ABALTA TECH
Metasurface lens
The invention provides a metasurface lens, including a plurality of sub-structures. Each sub-structure comprises a microstructure and a partial substrate supporting the microstructure. Sizes of each sub-structure on any direction are the same. The partial substrates of all sub-structures form a substrate of the metasurface lens. The microstructures of all sub-structures form a microstructure arrayof the metasurface lens. Phase corresponding to the central position of each microstructure included in the microstructure array can be determined by incident light wavelength, metasurface lens focallength, and projection distances of the center of the microstructure and the center of the metasurface lens on a phase modulation direction. The lens can effectively improve focusing efficiency of incident light in visible bands.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Storage device, control method, control device, and program
InactiveUS7835104B2Easy to controlAccurate measurementDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDistance detectionThermal expansion
A heater for changing a projection distance protrusion value by thermal expansion accompanying electric-power-distributed heating is provided in a head having at least a reading element. At desired correction timing, a changed distance detection unit measures a clearance changed distance in a state in which the head is positioned to a track on the recording medium while increasing the amount of electric power distributed to the heater. A contact determination unit determines that the head is brought into contact with the recording medium when a derivative value of the clearance changed distance is below a predetermined threshold value. A measurement output unit outputs the clearance changed distance detected by the changed distance detection unit at the time of contact determination of the contact determination unit as a measurement result of the clearance between the reading element and the recording medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
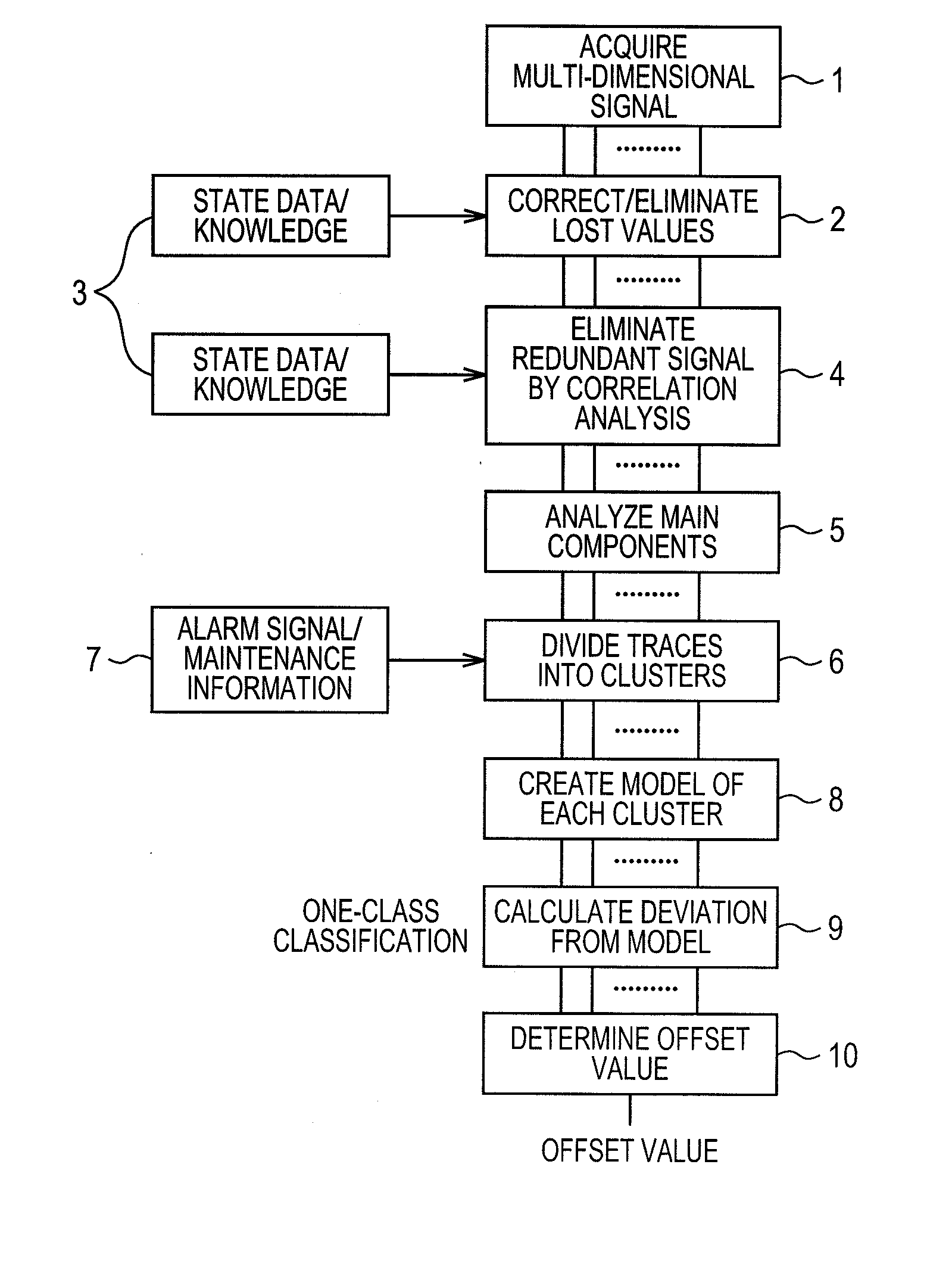
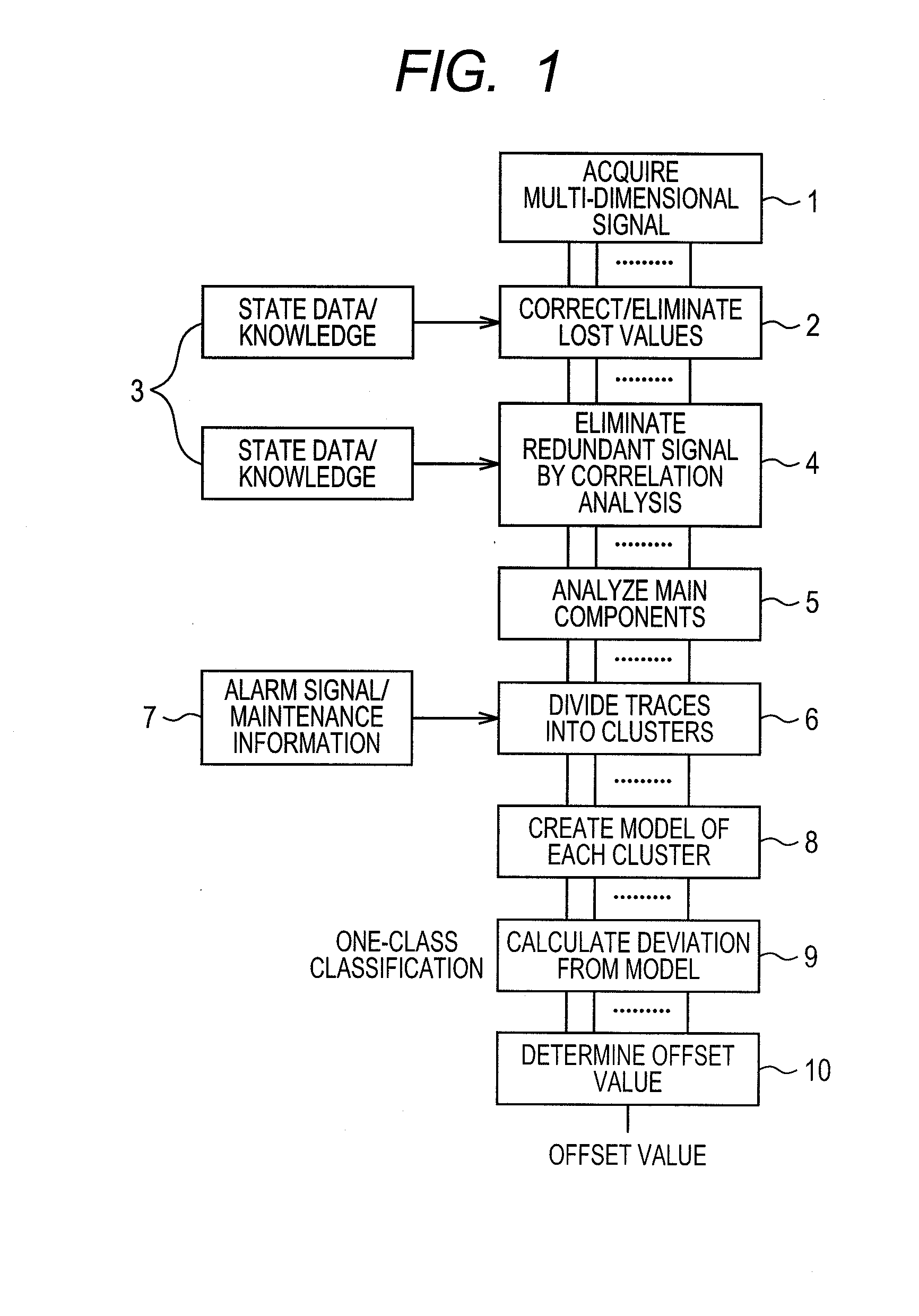
Error detection method and system
InactiveUS20110191076A1Early and accurate discoveryData processing applicationsElectric testing/monitoringRegression analysisCluster group
Provided are a method which permits complete training data and data with added errors, and enables the early and accurate discovery of errors in facilities such as a plant, and a system thereof. To achieve the objectives, (1) the behavior of temporal data is observed over time, and the trace is divided into clusters; (2) the divided cluster groups are modeled in sub spaces, and the discrepancy values are calculated as errors candidates; (3) the training data are used (compare, reference, etc.) for reference to determine the state transitions caused by the changes over time, the environmental changes, the maintenance (parts replacement), and the operation states; and (4) the modeling is a sub space method such as regression analysis or projection distance method of every N data removing N data items, (N=0, 1, 2, . . . ) (for example, when N=1, one error data item is considered to have been added, this data is removed, then the modeling is performed), or a local sub space method. Linear fitting in regression analysis is equivalent to the lowest order regression analysis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Cartridge and electrophotographic image forming apparatus
A cartridge mountable and dismountable by moving in the direction crossing with an axial direction of the drive shaft of a main assembly of the apparatus, includes a rotatable member; a coupling including a coupling member, a first receiving portion, provided at one end portion of said coupling member; a rotational force transmission member engaged with the other end portion of said coupling member and having opposite ends projected out in a crossing wherein said coupling member is pivotable between a transmitting angular position for transmitting the rotational force from the driving shaft to said rotatable member and a mounting-and-dismounting angular position which is inclined relative to the axis of said rotatable member; a flange mounted to said rotatable member and rotatable about an axis, said flange including an opening accommodating said transmission member with a gap, a regulating portion, provided in said opening, for regulating movement of said transmission member in the crossing direction when said coupling takes the transmitting angular position, a second rotational force receiving portion for being abutted by said transmission member to receive the rotational force from said coupling, an opposing portion opposing to said second receiving portion, wherein in a state that said coupling is in the transmitting angular position and that one end of said transmission member contacts to said regulating portion to be confined in movement, when said coupling inclines relative to said flange such that a side in which a projection distance of said rotational force transmission member is relatively smaller moves away from said first receiving portion, an engagement depth between said side of said transmission member and said second receiving portion and an engagement depth between said side of said transmission member and said opposing portion are larger than zero. The invention also relates to an electrophotographic image forming apparatus.
Owner:CANON KK
Storage device, control device, control method, and program
InactiveUS7426090B2Easy to controlAccurate measurementDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageThermal expansionEngineering
A heater for changing a projection distance protrusion value by thermal expansion accompanying electric-power-distributed heating is embedded in a head having a reading element and a recording element. A clearance control information measurement unit measures and saves, at desired correction timing, clearance control information including a clearance required for controlling the clearance between the reading element and the recording medium, heater projection sensitivity protrusion sensitivity, projection distance protrusion value transition time, recording current projection distance protrusion value, and a temperature correction coefficient. The clearance control unit varies the electric power distributed to the heater and changes the projection distance protrusion value of the head, thereby controlling the clearance to a target clearance upon reproduction and recording.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
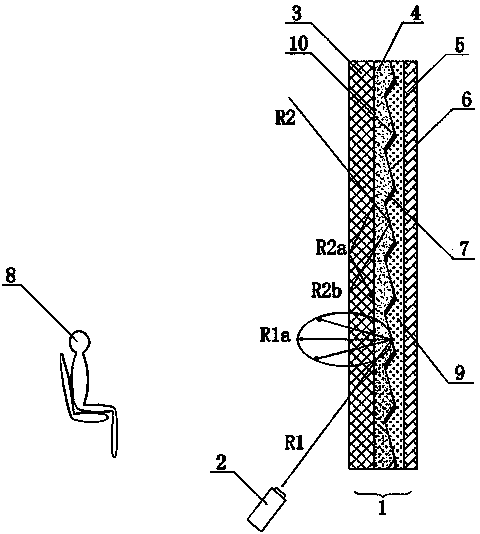
Positive projection optical screen projection system short in projection distance
The invention relates to a positive projection optical screen projection system short in projection distance, which comprises a positive projection screen (1) and a projector (2), wherein the projector (2) is arranged on one side of the positive projection screen (1); the positive projection screen (1) comprises an optical filtering layer (3), a diffusion layer (4), a micro prism array structure (10) and a substrate layer (5); the diffusion layer (4) is arranged on one face, deviating from the projector (2), of the optical filtering layer (3); the micro prism array structure (10) is arranged on one side, deviating from the projector (2), of the diffusion layer (4); a zonal micro prism array light reflection surface layer (6) and a zonal micro prism array light absorption surface layer (7) are respectively arranged on the two sides of the micro prism array structure (10); the zonal micro prism array light reflection surface layer (6) faces one side of the projector (2). The system has the advantage that under a bright environment, the positive projection optical screen projection system short in the projection distance has high gain, high contrast and high color revivification.
Owner:CHENGDU FSCREEN SCI TECH
Cartridge and electrophotographic image forming apparatus
A cartridge mountable and dismountable by moving in the direction crossing with an axial direction of the drive shaft of a main assembly of the apparatus, includes a rotatable member rotatable by receiving a rotational force from the apparatus; a coupling engageable with the rotational force applying portion to receive a force for rotating said rotatable member, said coupling including a coupling member rotatable about an axis, a first rotational force receiving portion, provided at one end portion of said coupling member, for receiving the rotational force from the driving shaft, a rotational force transmission member engaged with the other end portion of said coupling member and having opposite ends projected out in a crossing wherein said coupling member is pivotable between a transmitting angular position for transmitting the rotational force from the driving shaft to said rotatable member and a mounting-and-dismounting angular position which is inclined relative to the axis of said rotatable member; a flange mounted to said rotatable member and rotatable about an axis, said flange including an opening accommodating said transmission member with a gap, a regulating portion, provided in said opening, for regulating movement of said transmission member in the crossing direction when said coupling takes the transmitting angular position, a second rotational force receiving portion for being abutted by said transmission member to receive the rotational force from said coupling, an opposing portion opposing to said second receiving portion, wherein in a state that said coupling is in the transmitting angular position and that one end of said transmission member contacts to said regulating portion to be confined in movement, when said coupling inclines relative to said flange such that a side in which a projection distance of said rotational force transmission member is relatively smaller moves away from said first receiving portion, an engagement depth between said side of said transmission member and said second receiving portion and an engagement depth between said side of said transmission member and said opposing portion are larger than zero.
Owner:CANON KK
Projection control system, projector and projection control method
InactiveUS20060152682A1Quality improvementProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementInformation controlControl system
A projector includes a projection angle deriving section which generates projection angle information indicating an angle formed by a projection target area and projection light projected onto the projection target area; a projection distance deriving section which generates projection distance information indicating a distance from an aim area in the projection target area to a projection section which projects the projection light; a control information generation section which generates direction control information for aligning a projection direction of the projection light with a normal direction of the projection target area based on the projection angle information, and generates projection section control information for controlling the projection section so that the projection light is projected onto the aim area based on the projection distance information; a pedestal driver section which drives a pedestal which adjusts the projection direction of the projection light based on the direction control information; a control section which controls the projection section based on the projection section control information; and the projection section.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
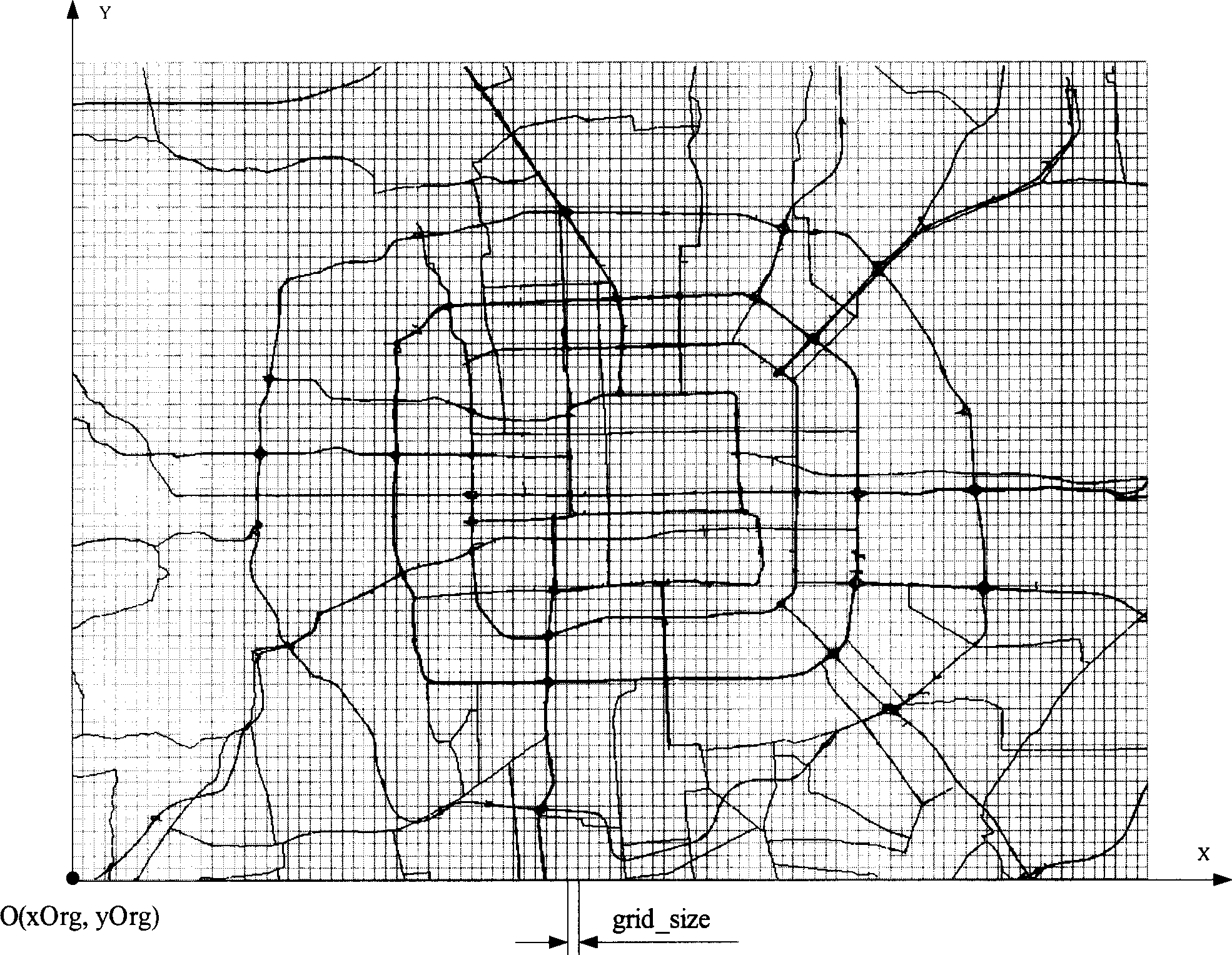
Fast map matching method based on small lattice road network organization and structure
InactiveCN1908588ALess sectionsHigh speedInstruments for road network navigationSpecial data processing applicationsMesh routingLongitude
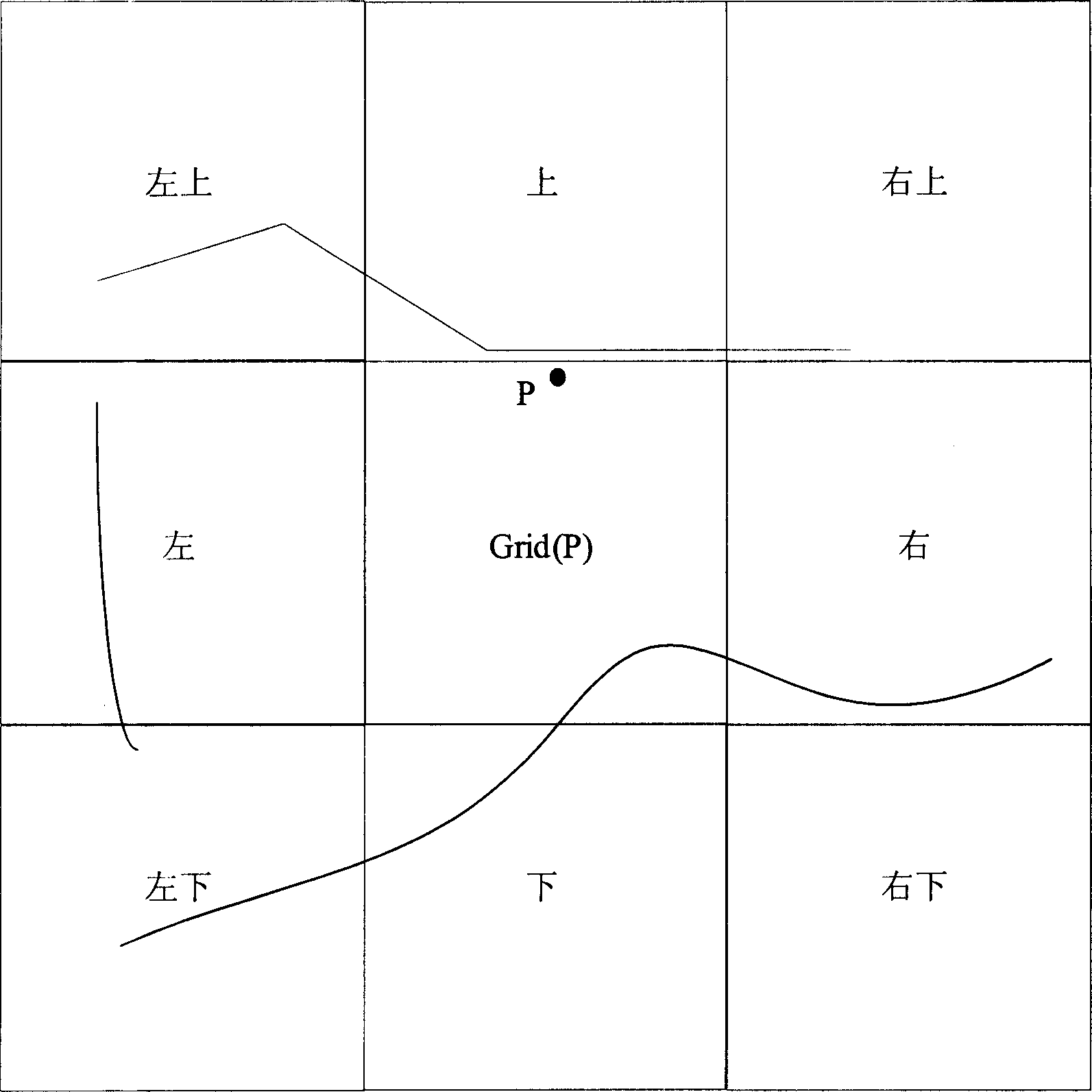
The fast map matching method based on small-mesh route network organization structure comprises: (1) creating and storing the route network organization structure; (2) given point P(x, y) on map (x for longitude and y for latitude), finding out all routes of this point, and defining the grid with P as Grid(P); (3) finding out all routes in grids near Grid(P); (4) combining the results in (2) and (3); (5) to every combined route, calculating the projection distance d of P to the route, and selecting the one with minimal d as the final result. This invention improves efficiency and speed greatly and reduces grid number to 9 for searching.
Owner:深圳市千方航实科技有限公司
Method for splicing and fusing image in multi-projection display system
InactiveCN102881006ASmall sizeEnhance layeringImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImage resolution
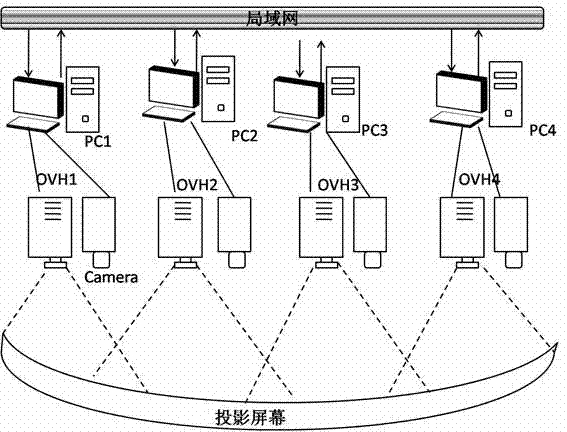
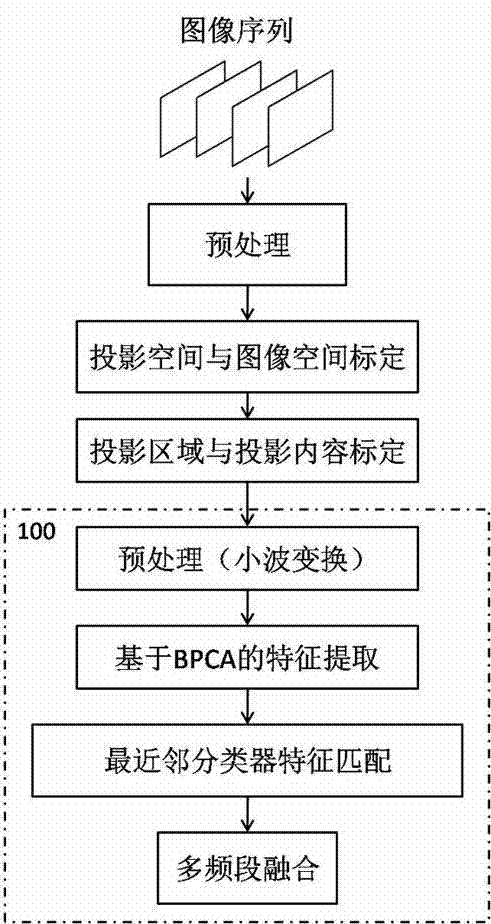
The invention discloses a method for splicing and fusing images in a multi-projection display system and relates to a method for processing images. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing an image sequence; geometrically calibrating; spatially splicing images; carrying out preprocessing by using wavelet transform; extracting features; and extracting features of adjacent images and fusing the images. With the adoption of the method, an overlapped part of the images can be eliminated, the sizes of the images are increased, the completeness of frames are guaranteed to a large extent, the revealed image resolution is increased, the projection distance is shortened, and the layering of the frames is increased. The invention provides a registering algorithm which can be used for matching rapidly and stably based on feature points so as to carry out the projection splicing and fusion, so that the method is applicable to various screen types.
Owner:吉林禹硕动漫游戏科技股份有限公司
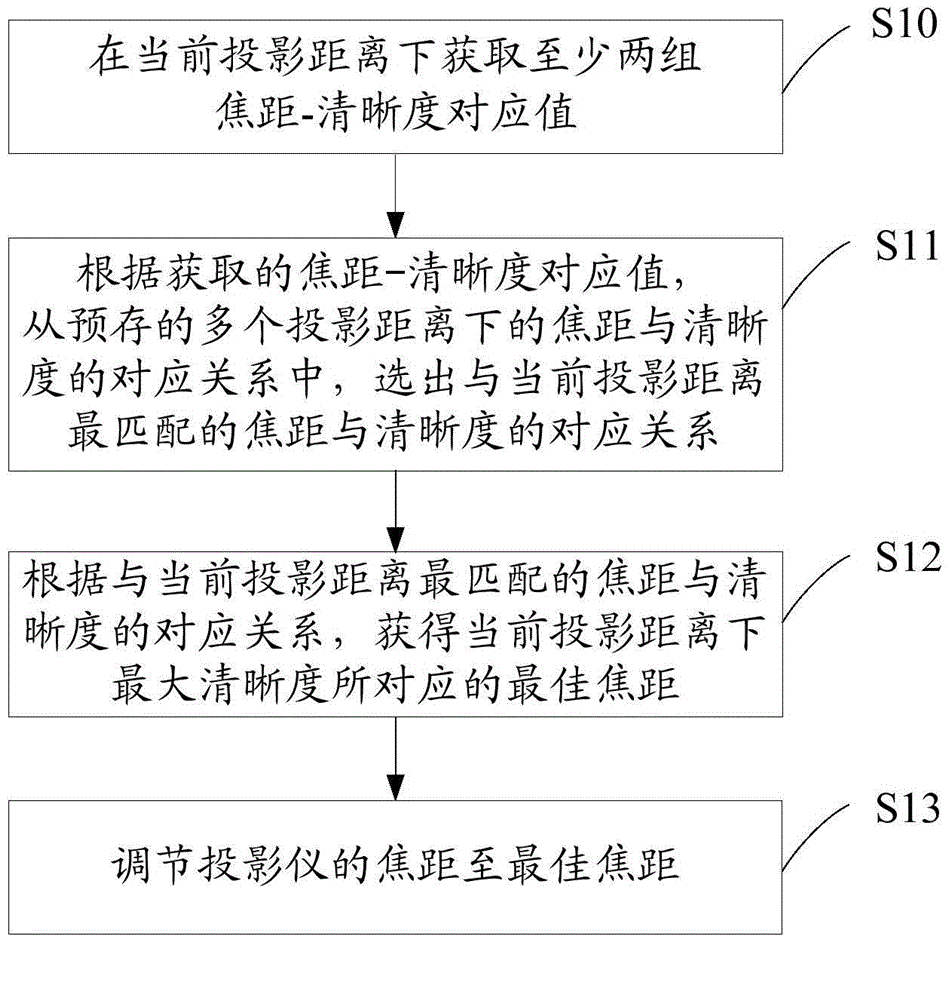
Method and device for regulating focal length of projector
ActiveCN104536249AImprove experienceRealize automatic adjustmentProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesComputer graphics (images)Physics
The invention discloses a method and device for regulating the focal length of a projector. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring the current projecting distance, or acquiring at least two groups of corresponding values of focal length and definition at the current projecting distance; selecting a corresponding relation between the focal distance and the definition, which is most matched with the current projecting distance, from the plurality of pre-stored corresponding relations between the focal length and the definition at the projecting distance according to the corresponding value of the current projecting distance or the focal length and the definition; acquiring the optimal focal length corresponding to the maximum definition at the current projecting distance according to the corresponding relation between the focal length and the definition which are most matched with the current projecting distance; and regulating the focal length of the projector to the optimal focal length to obtain a clear projected image. Therefore, the automatic regulation of the focal length of the projector is realized, the projector is more intelligent and humanized, the operation of manually regulating by a user is not needed, the user experience is improved, and the efficiency is increased.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Magnetic anomaly sensing system for detection, localization and classification of a magnetic object in a cluttered field of magnetic anomalies
InactiveUS7603251B1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsPhysicsProjection distance
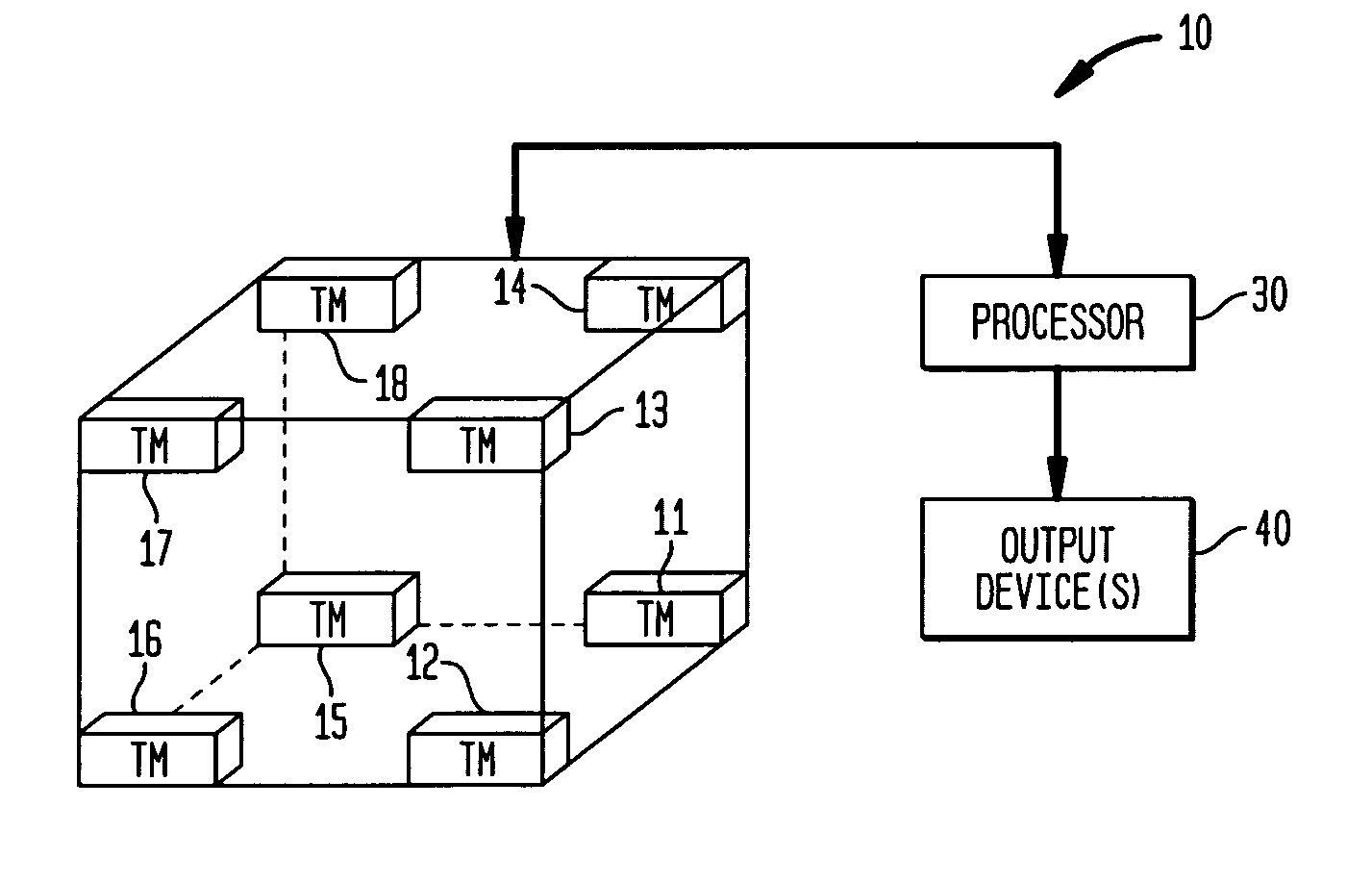
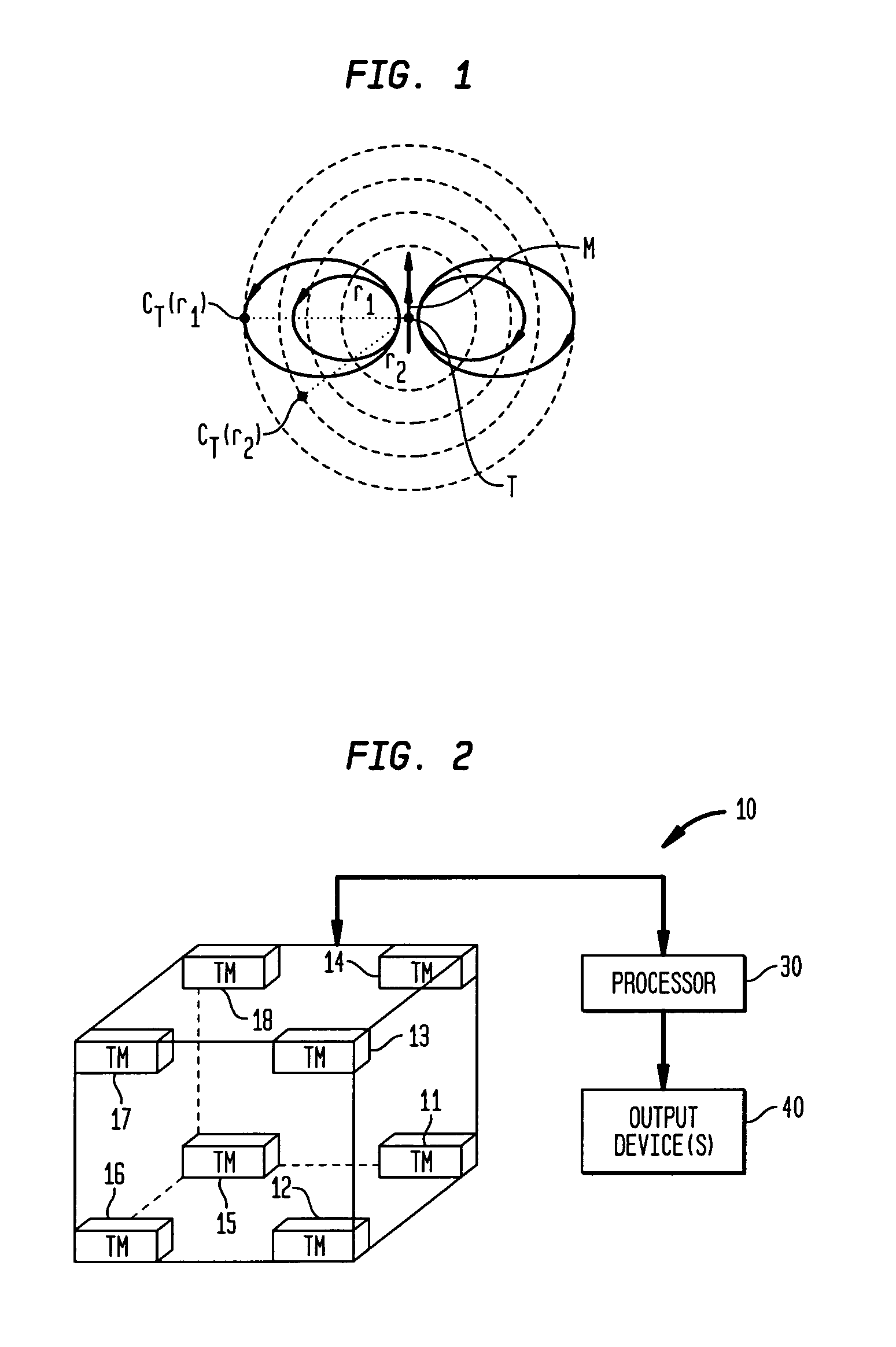
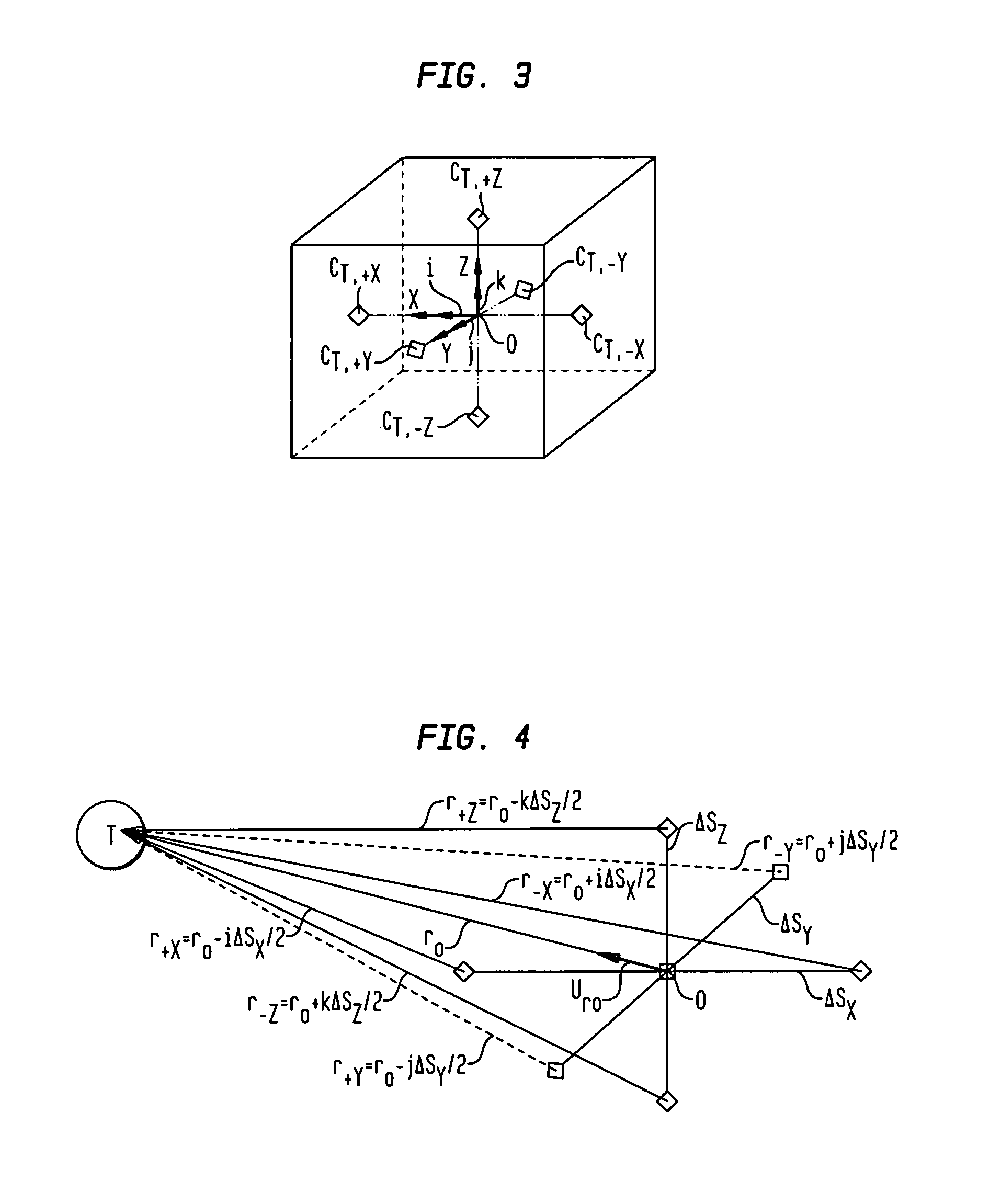
A magnetic anomaly sensing system and method uses at least eight triaxial magnetometer (TM) sensors arranged to define a cubic space. Each TM sensor measures a local magnetic field associated with a target region and generates magnetic field data indicative thereof. The magnetic field data is processed in accordance with a magnetic scalar triangulation and ranging (STAR) processing scheme to determine a plurality of gradient contractions CT,I at a corresponding plurality of measurement points I to include at least at the center of each face of the cubic space. Gradient contraction pairs are defined for each sensors' X, Y, Z magnetic sensing axes. A directional derivative ∇CT is determined using the gradient contraction pairs and the baseline distances therebetween. A unit vector, calculated using the directional derivative ∇CT, is used in determining a projection distance from each of the measurement points toward the target region.
Owner:USA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
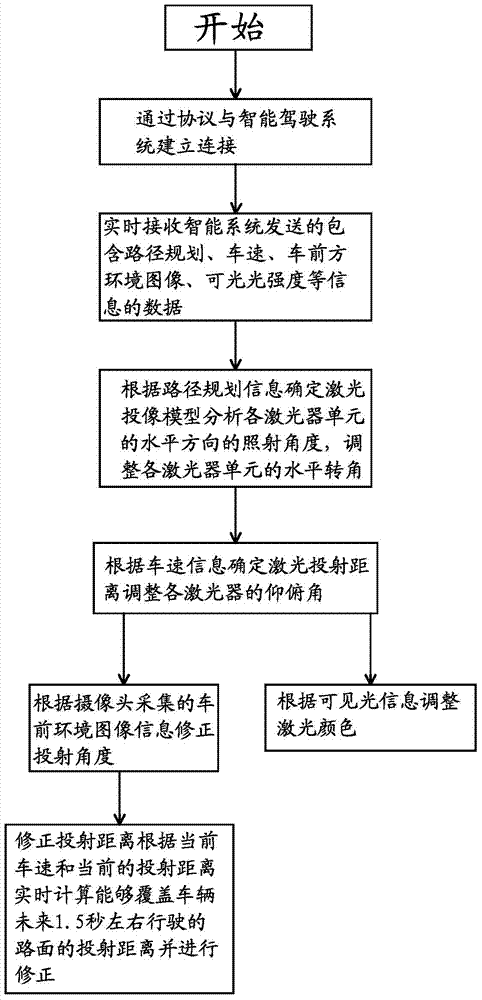
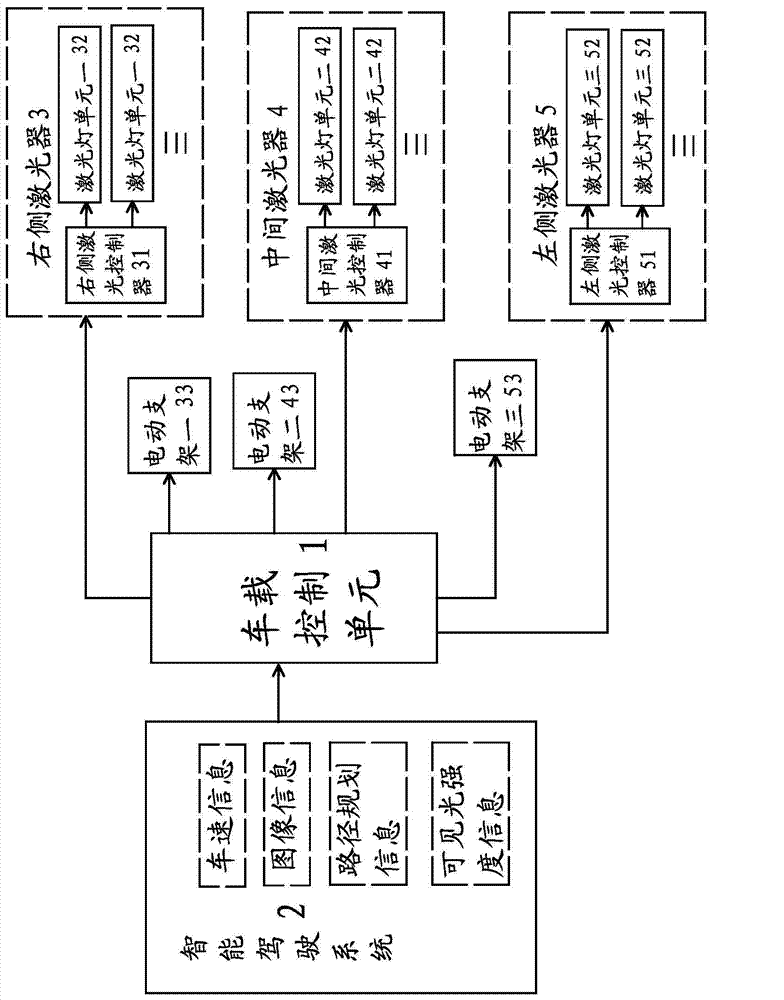
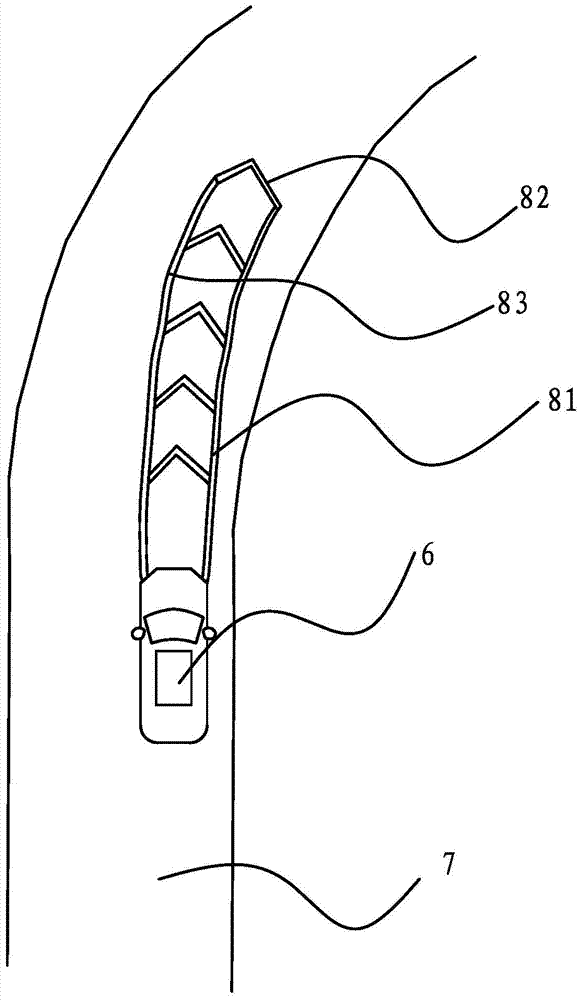
Driving route indicating method and system applied to intelligent driving vehicles
ActiveCN104842860APath instructions are clearClear directionsOptical signallingNetwork packetOn board
The invention provides a driving route indicating method and system applied to intelligent driving vehicles and belongs to the technical field of vehicles with an aim to solve the problem about how to efficiently indicate routes that the vehicles are about to drive on in the prior art. The method includes: A, establishing connection; B, receiving and analyzing a data packet; C, controlling and adjusting horizontal rotational ranges of laser lamp units according to route planning information; D, determining laser projection distance and controlling and adjusting pitching angles of lasers according to vehicle speed information. The system comprises a plurality of lasers, a plurality of electric supports used for adjusting the pitching angles of the lasers and an on-board control unit used for receiving the information, each laser comprises laser controllers and a plurality of laser lamp units correspondingly connected with the laser controllers, the electric supports and the laser controllers are respectively connected with the output end of the on-board control unit, and the on-board control unit performs adjustment on the beam angle and projection distance according to the route planning information and vehicle speed. By the method and the system, the capability of the vehicles in avoiding risks can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY AUTOMOBILE RES INST CO LTD +1
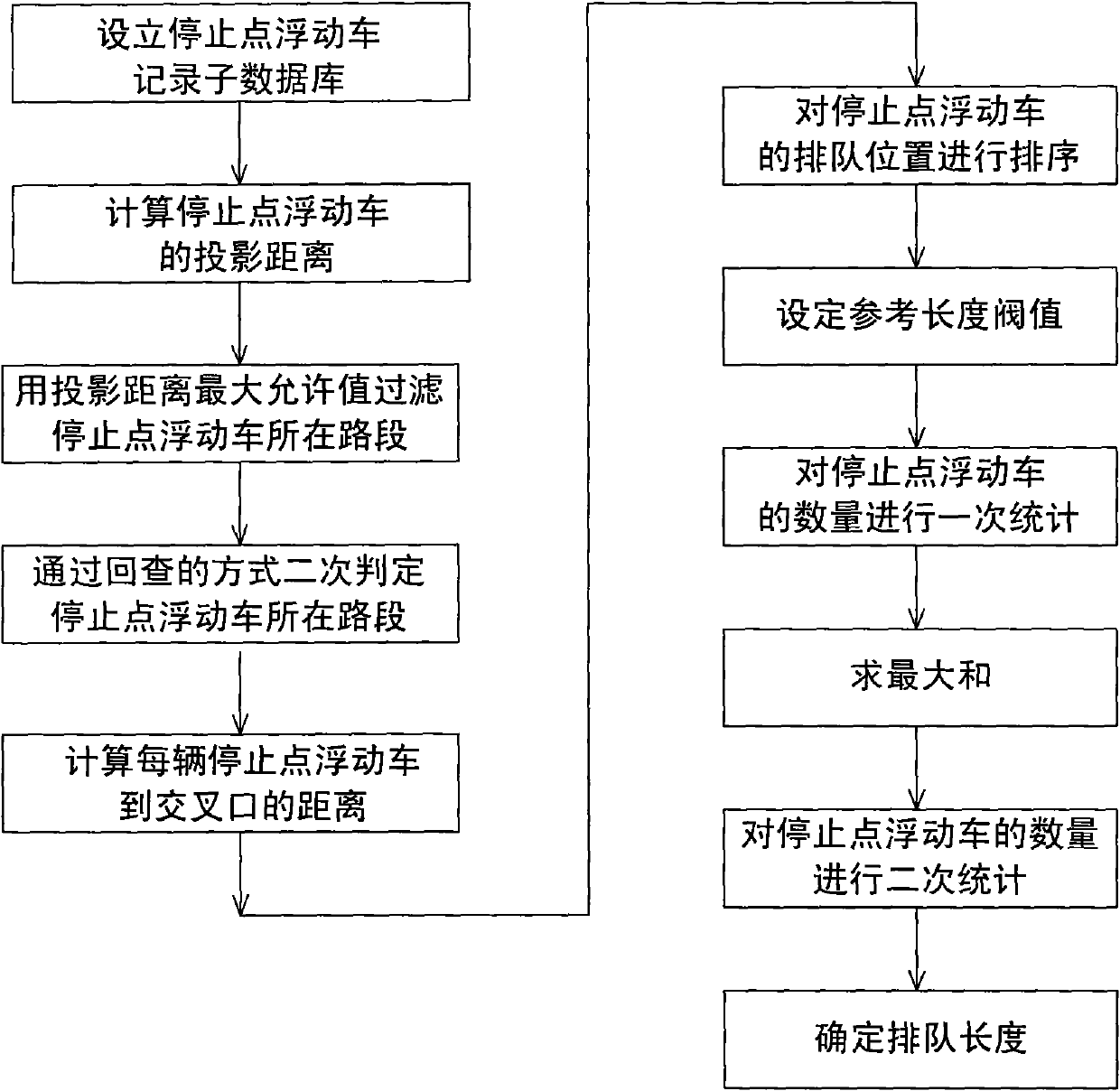
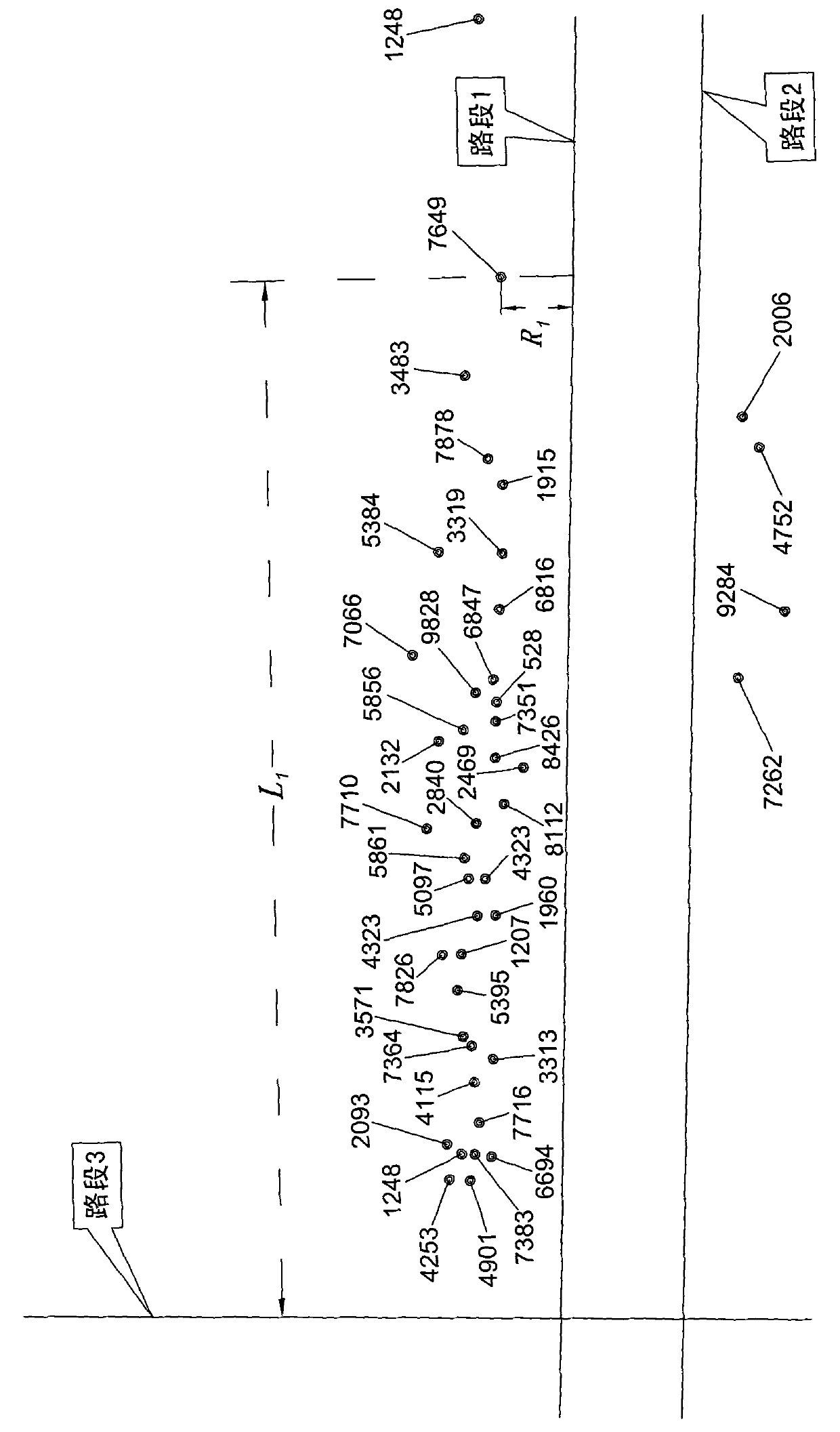
Method for extracting vehicle queue length based on floating vehicle data
ActiveCN102024323AAvoid detectionAvoid insufficiency of field measured dataRoad vehicles traffic controlData ingestionEconomic shortage
The present invention relates to a method for extracting vehicle queue length based on floating vehicle data, which comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a stop point floating vehicle record subdatabase; step 2, calculating the projection distance of the stop point floating vehicle; step 3, filtering the road where the stop point floating vehicle stays with the maximum allowable value of the projection distance; step 4, secondarily determining the road where the stop point floating vehicle stays in a check-back manner; step 5, calculating the distance from each stop point floating vehicle to the crossing; step 6, sorting the queuing position of the stop point floating vehicle; step 7, setting a reference length threshold value; step 8, carrying out a primary statisticsfor the number of the stop point floating vehicles; step 9, obtaining the maximum sum; step 10, carrying out a secondary statistics for the stop point floating vehicle; step 11, determining the queue length. The method can estimate the queue length of the vehicles in the crossing on the road by employing the floating vehicle data, thereby avoiding the shortage in the prior art which use video detecting devices and on-site actual measurement data.
Owner:RES INST OF HIGHWAY MIN OF COMM
Method and apparatus for a wide field of view display
ActiveUS20090201430A1Inefficient utilizationTelevision system detailsCosmonautic condition simulationsWide fieldImage resolution
A method and apparatus for a uniform resolution display screen. In one embodiment, the uniform resolution display screen comprises a surface of the uniform resolution display screen having a curvature configured to display images with a uniform resolution across the display screen. The curvature is based on a projection distance from a projector to the uniform resolution display screen and a viewing distance from an eyepoint of an observer to the uniform resolution display screen. The geometry of the display screen is configured to display images associated with a high definition imaging format.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
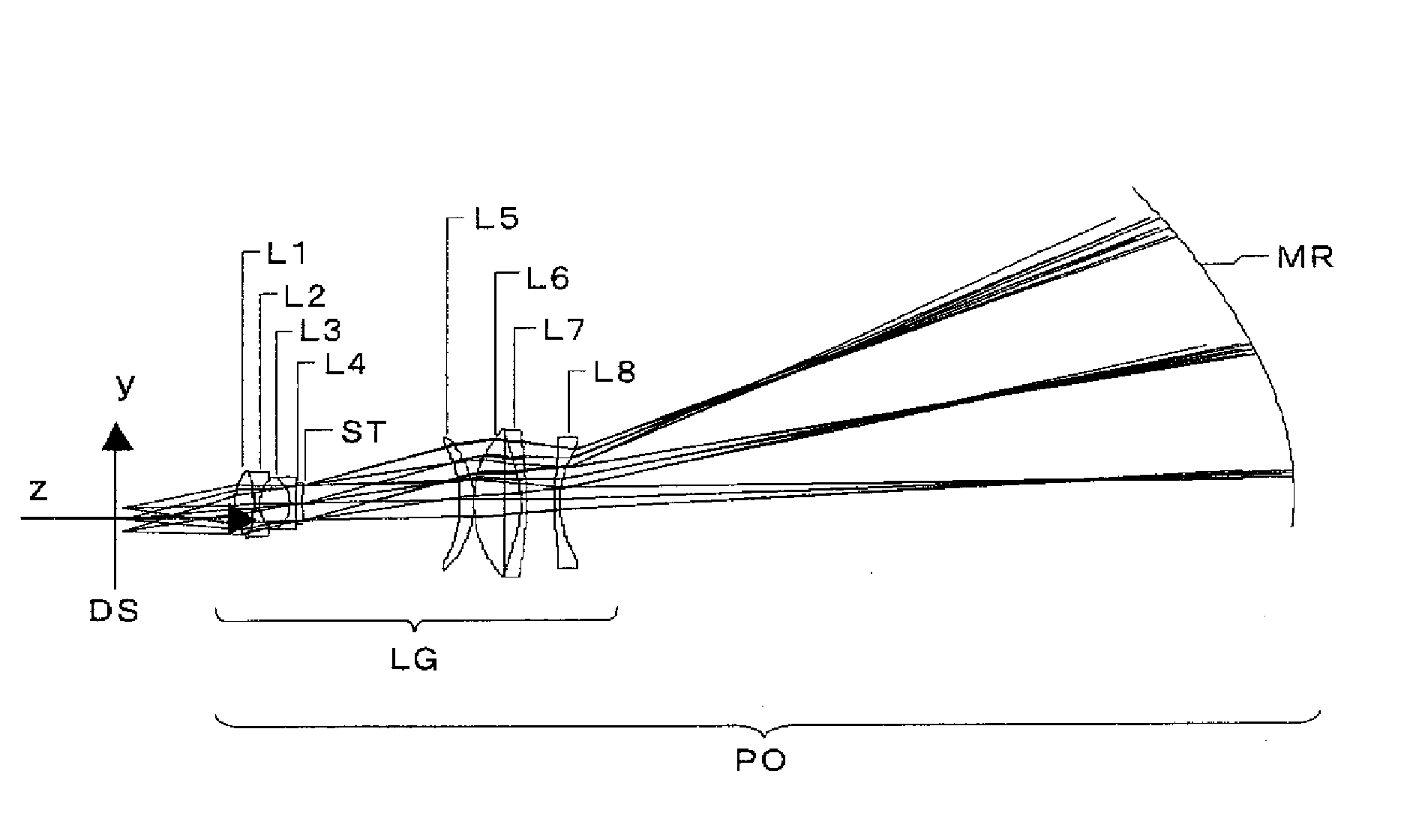
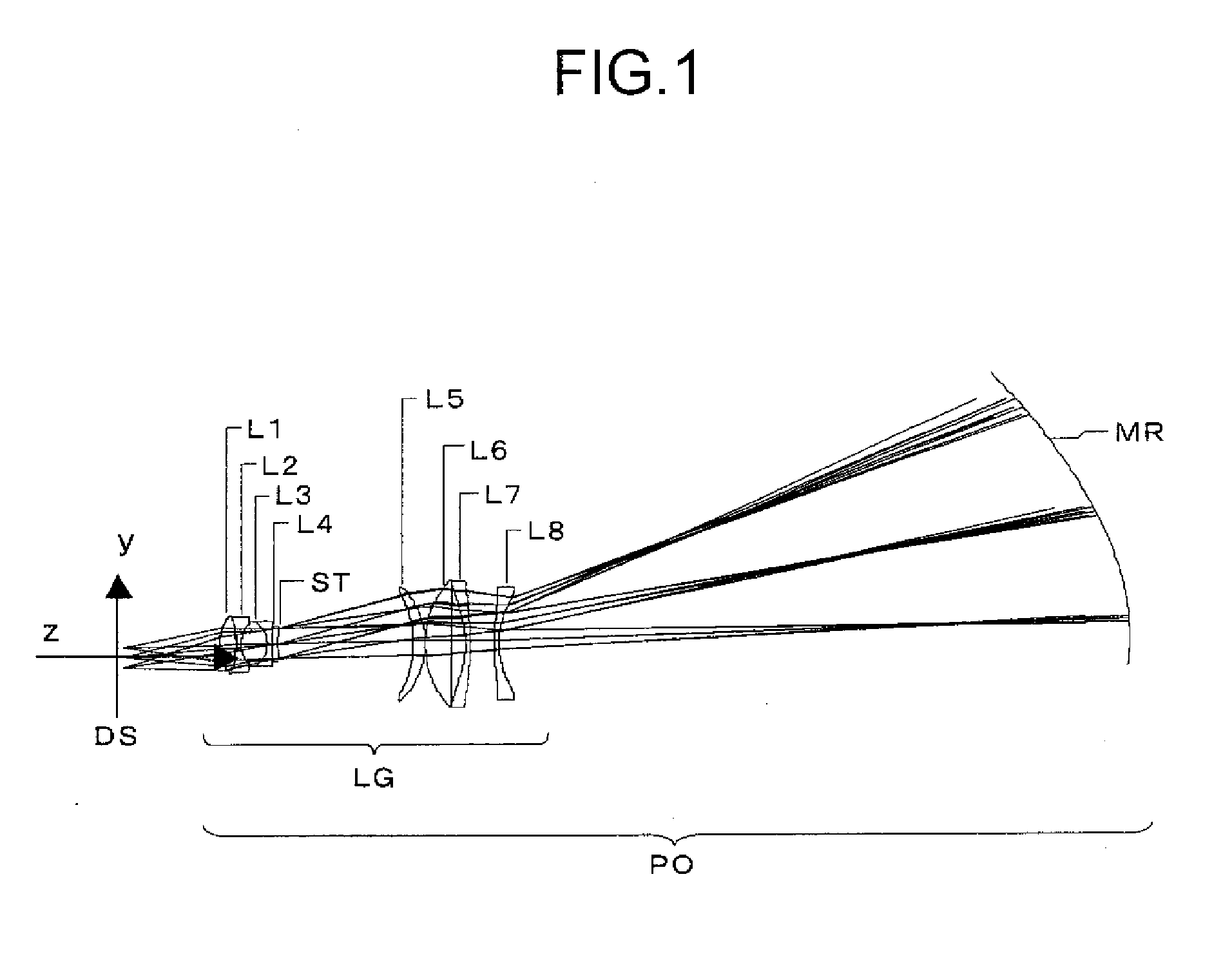
Projection optical system
ActiveUS20080192336A1Minimal movementMirrorsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsProjection opticsIntermediate image
A projection optical system that receives light from a display element to project an image displayed by the display element onto a screen with enlargement at a varying magnification achieved by varying the projection distance to the screen has: a refractive optical system composed of one or more refractive lenses and having a positive optical power; and a concave-surfaced mirror disposed to the screen side of the refractive optical system and having a plane-symmetric reflective surface. The projection optical system includes at least one optical element designed to be movable for focusing. The projection optical system forms an intermediate image between the refractive optical system and the concave-surfaced mirror. Moreover, a prescribed conditional formula is fulfilled.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
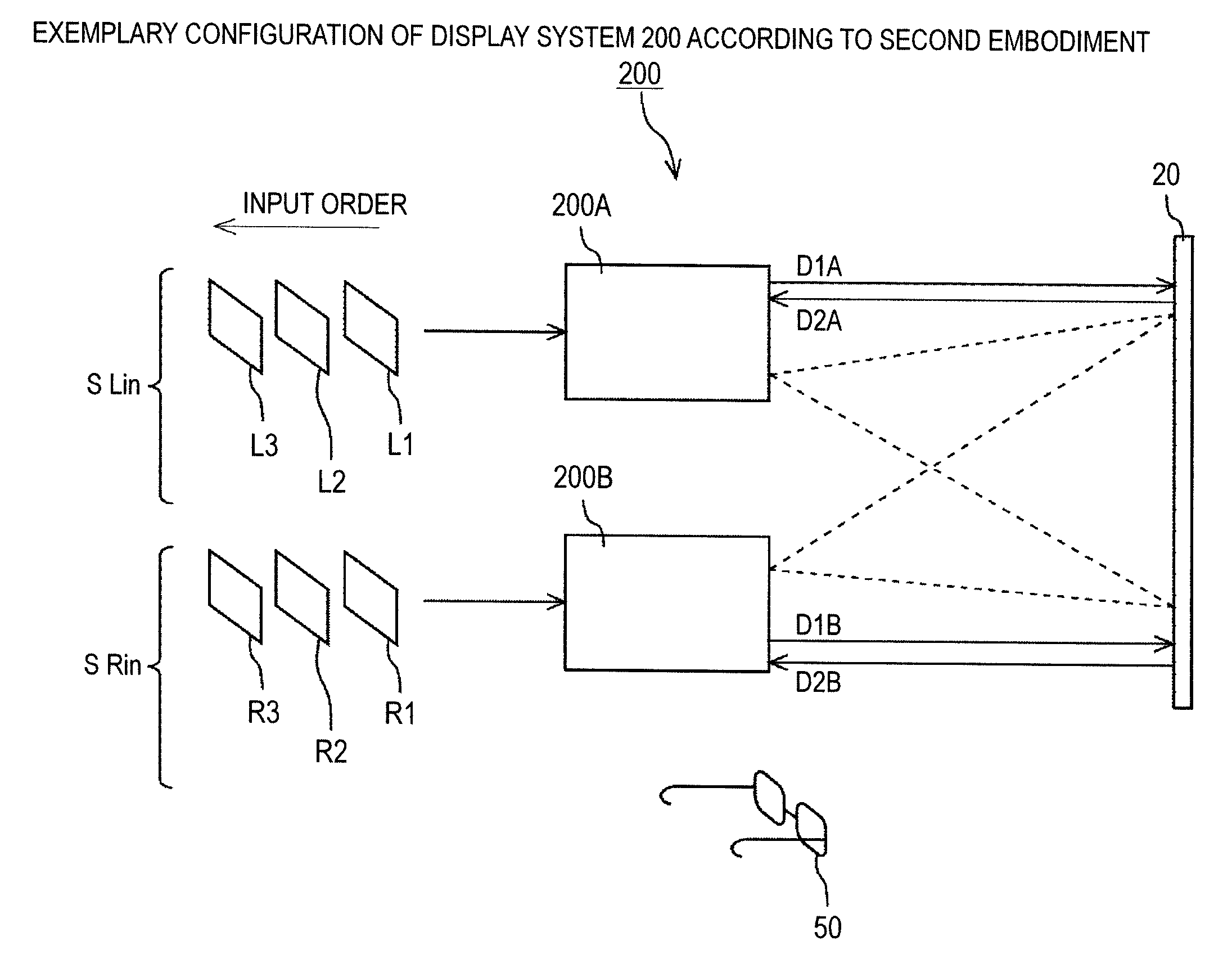
Display apparatus, display method, and display system
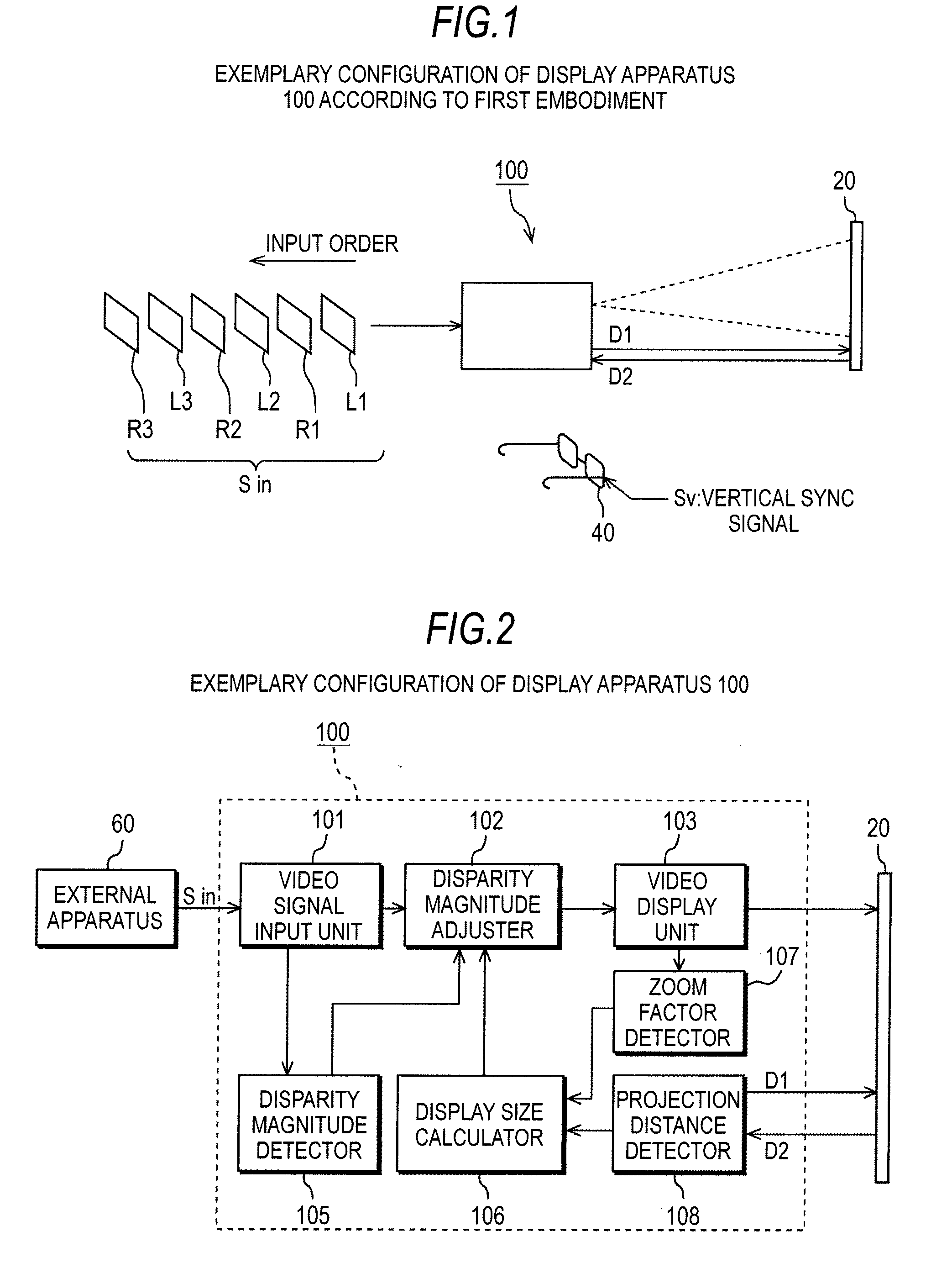
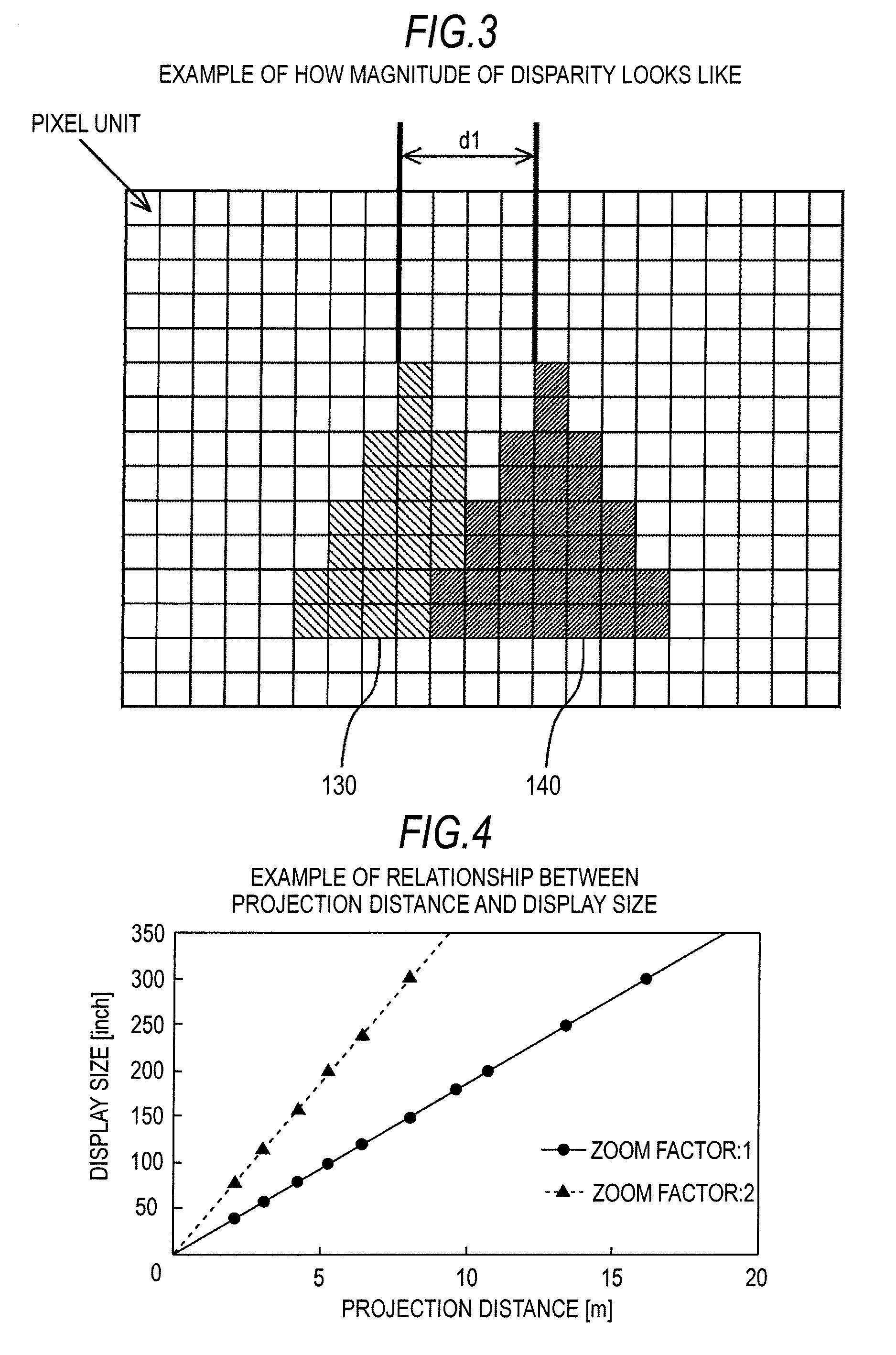
InactiveUS20100091098A1Reduce the burden onRealize automatic adjustmentColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsProjection distanceCalculator
A display apparatus includes: a video display unit that converts a video signal containing information indicating the magnitude of disparity between left-eye and right-eye video images into video images and displays the video images on a screen; a projection distance detector that detects a projection distance that is the distance between the video display unit and the screen; a display size calculator that calculates the size of the video images displayed on the screen using the projection distance detected by the projection distance detector; a disparity magnitude detector that detects the information indicating the magnitude of disparity from the video signal; and a disparity magnitude adjuster that adjusts the magnitude of disparity using the size of the video images displayed on the screen and the information indicating the magnitude of disparity detected by the disparity magnitude detector.
Owner:SONY CORP
Error detection method and its system for early detection of errors in a planar or facilities
InactiveUS8630962B2Early and accurate discoveryData processing applicationsElectric testing/monitoringRegression analysisState switching
Provided are a method which permits complete training data and data with added errors, and enables the early and accurate discovery of errors in facilities such as a plant, and a system thereof. To achieve the objectives, (1) the behavior of temporal data is observed over time, and the trace is divided into clusters; (2) the divided cluster groups are modeled in sub spaces, and the discrepancy values are calculated as errors candidates; (3) the training data are used (compare, reference, etc.) for reference to determine the state transitions caused by the changes over time, the environmental changes, the maintenance (parts replacement), and the operation states; and (4) the modeling is a sub space method such as regression analysis or projection distance method of every N data removing N data items, (N=0, 1, 2, . . . ) (for example, when N=1, one error data item is considered to have been added, this data is removed, then the modeling is performed), or a local sub space method. Linear fitting in regression analysis is equivalent to the lowest order regression analysis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
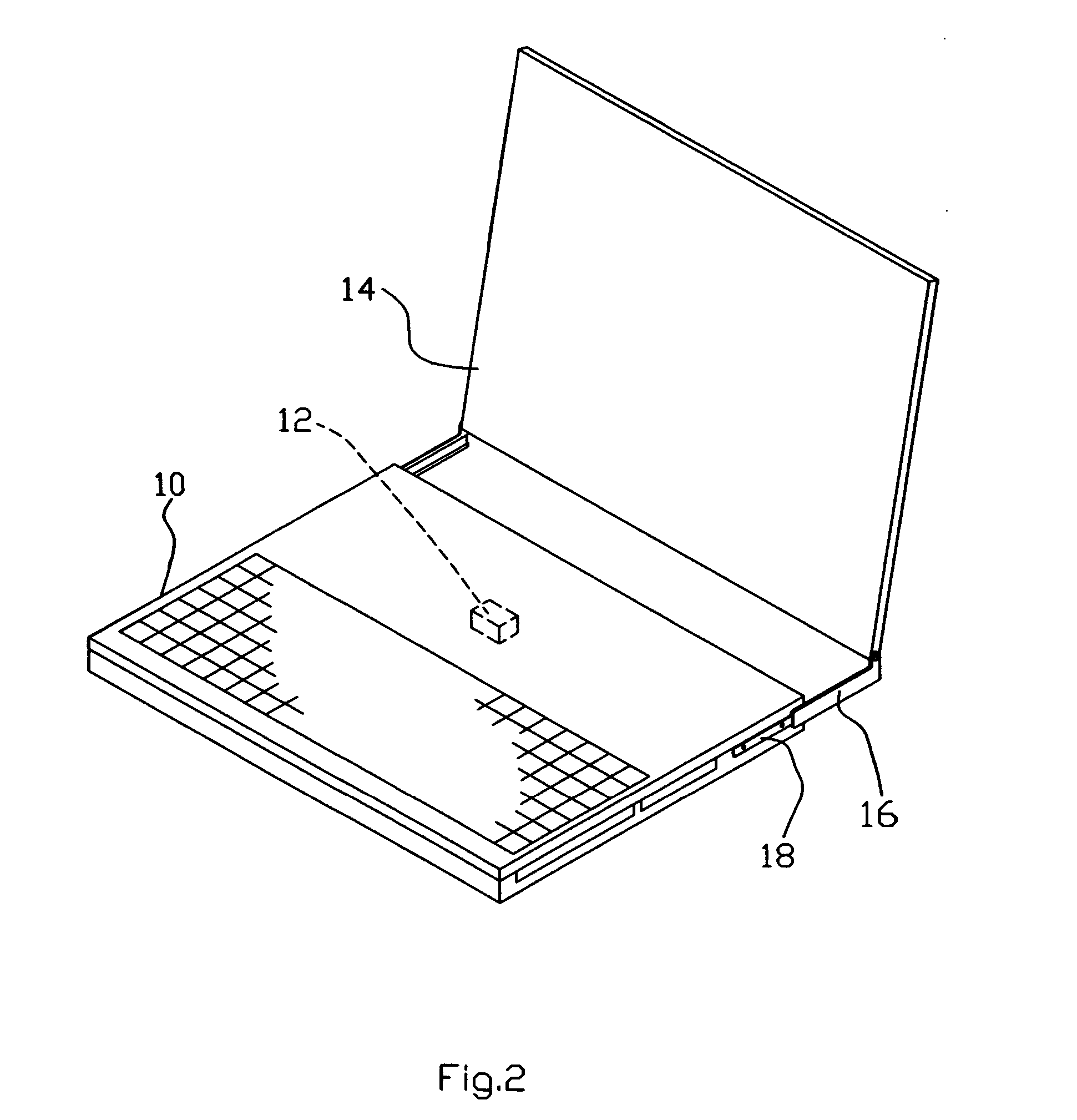
Portable computer with image-projecting function
InactiveUS20060256144A1Avoid pollutionLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersComputer graphics (images)Display device
A portable computer includes a main computer body having a micro-projector built therein, and a projection panel attached to the main computer body to constitute a portable computer displaying images in a projecting manner. The micro-projector includes an opto-mechanical system and a projecting system. The opto-mechanical system receives an image signal from the main computer body and outputs a light signal to the projecting system. The projecting system then convents the light signal into a digital image signal and projects the digital image to a projection panel in a manner of front or rear projection. The projecting distance between the projection panel and the micro-projector may be adjusted. The projection panel may also separate from the main computer body and supported by a support base. Increasing the projecting distance can enlarge the projecting image size. A portable computer system integrated with the micro-projector and having a large display is thus achieved.
Owner:CHUNG CHENG HUAN
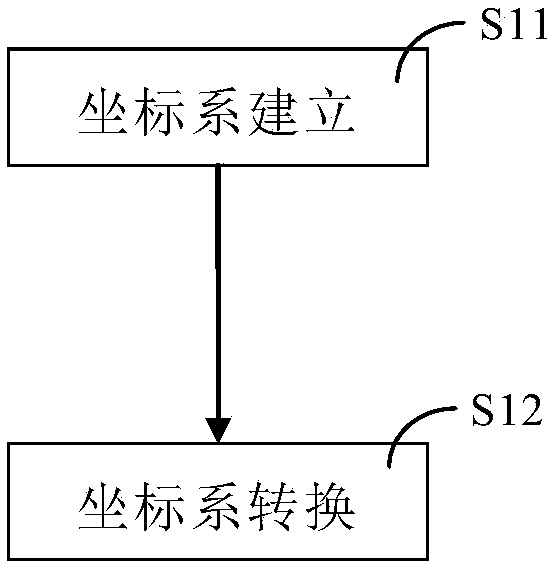
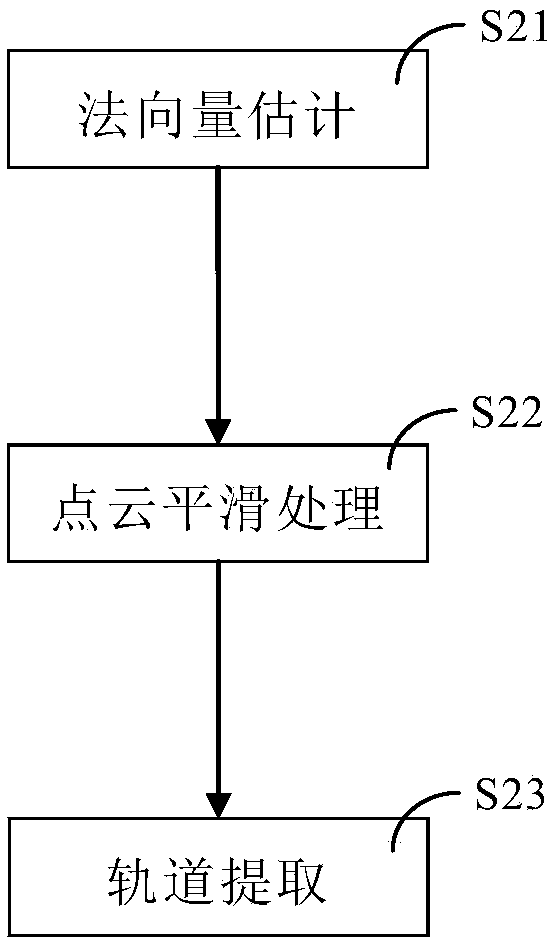
Online detection method based on laser radar
ActiveCN108549087AAchieving real-time limit violation detectionGuaranteed detection accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationPoint cloudRadar
The invention discloses an online detection method based on a laser radar, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, point cloud acquisition: establishing a global coordinate system, a vehiclebody coordinate system and a measurement coordinate system at an initial position of an intelligent inspection robot, and converting detection point coordinates, measured by a lidar, into position coordinates in the global coordinate system; S2, point cloud preprocessing: calculating an orbital plane by point cloud data of all the detection points located in the global coordinate system; S3, early warning judgment: projecting a real-time measured scanning point of the lidar to the orbital plane extracted at step S2, and calculating the projection distance from the scanning point to the orbital plane, determining that a foreign object invades the boundary if the projection distance is less than a set threshold value, or determining that the foreign object does not invade the boundary if the projection distance is greater than the set threshold value. The method provided by the invention enables a problem of a three-dimensional space into a one-dimensional space for judgment, reduces the calculation burden under the condition that the detection precision is guaranteed, and achieves the real-time boundary invasion detection in a tunnel of rail traffic.
Owner:BEIJING RUITU TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com