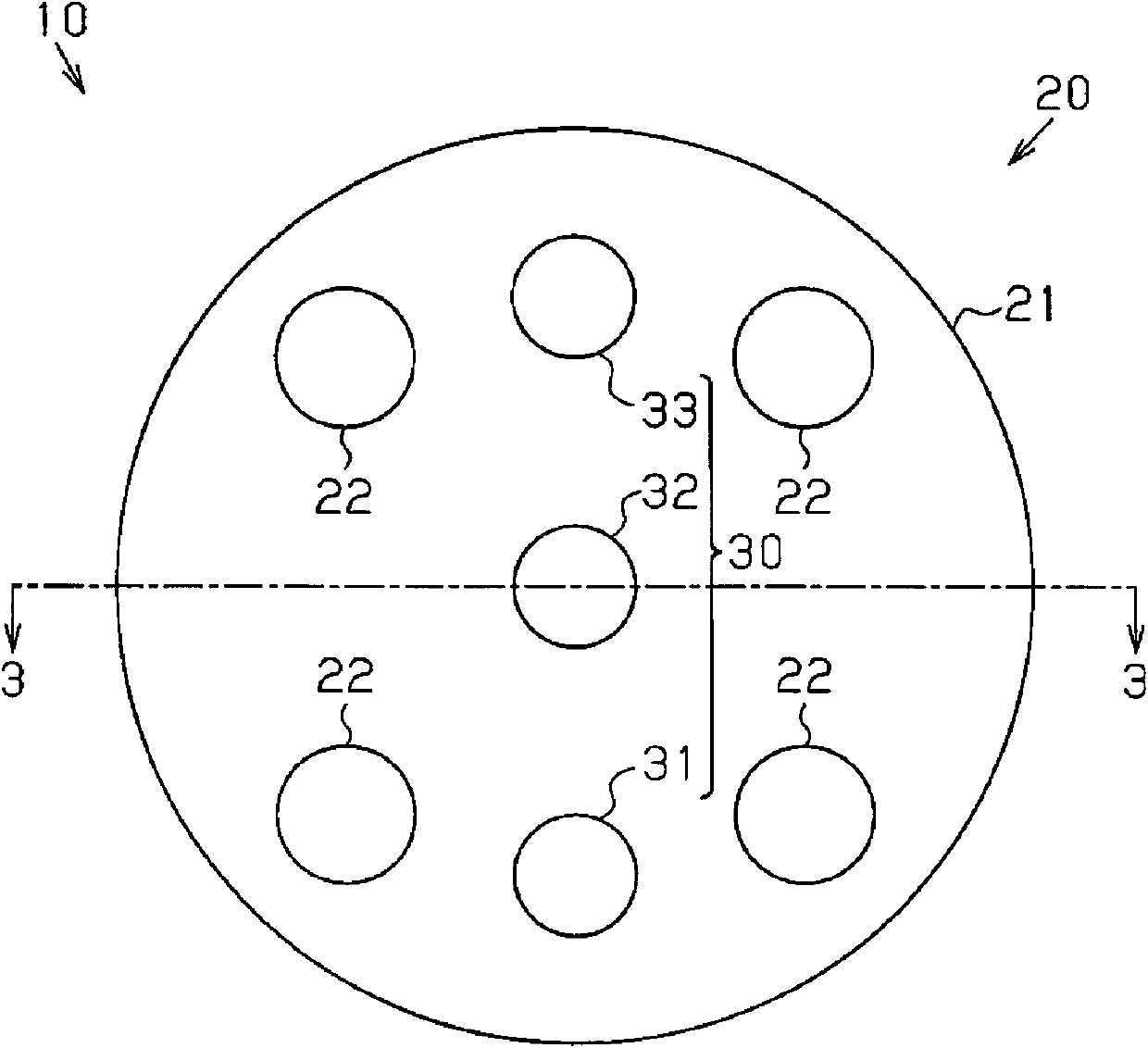
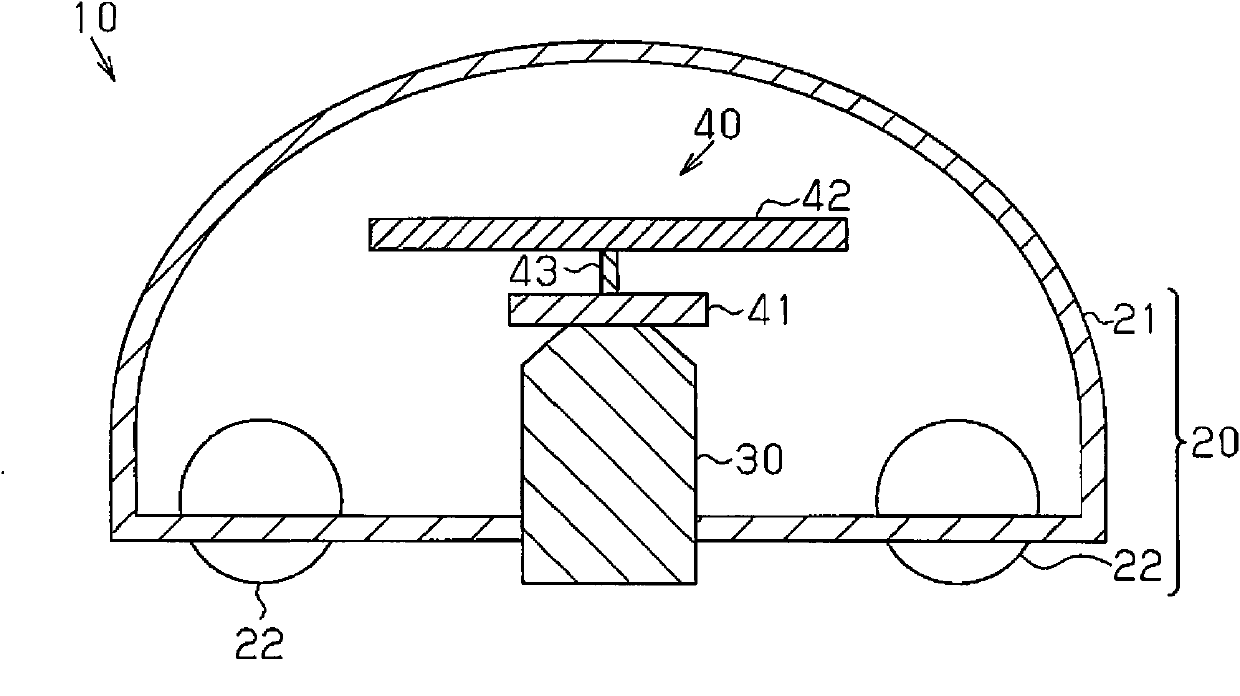
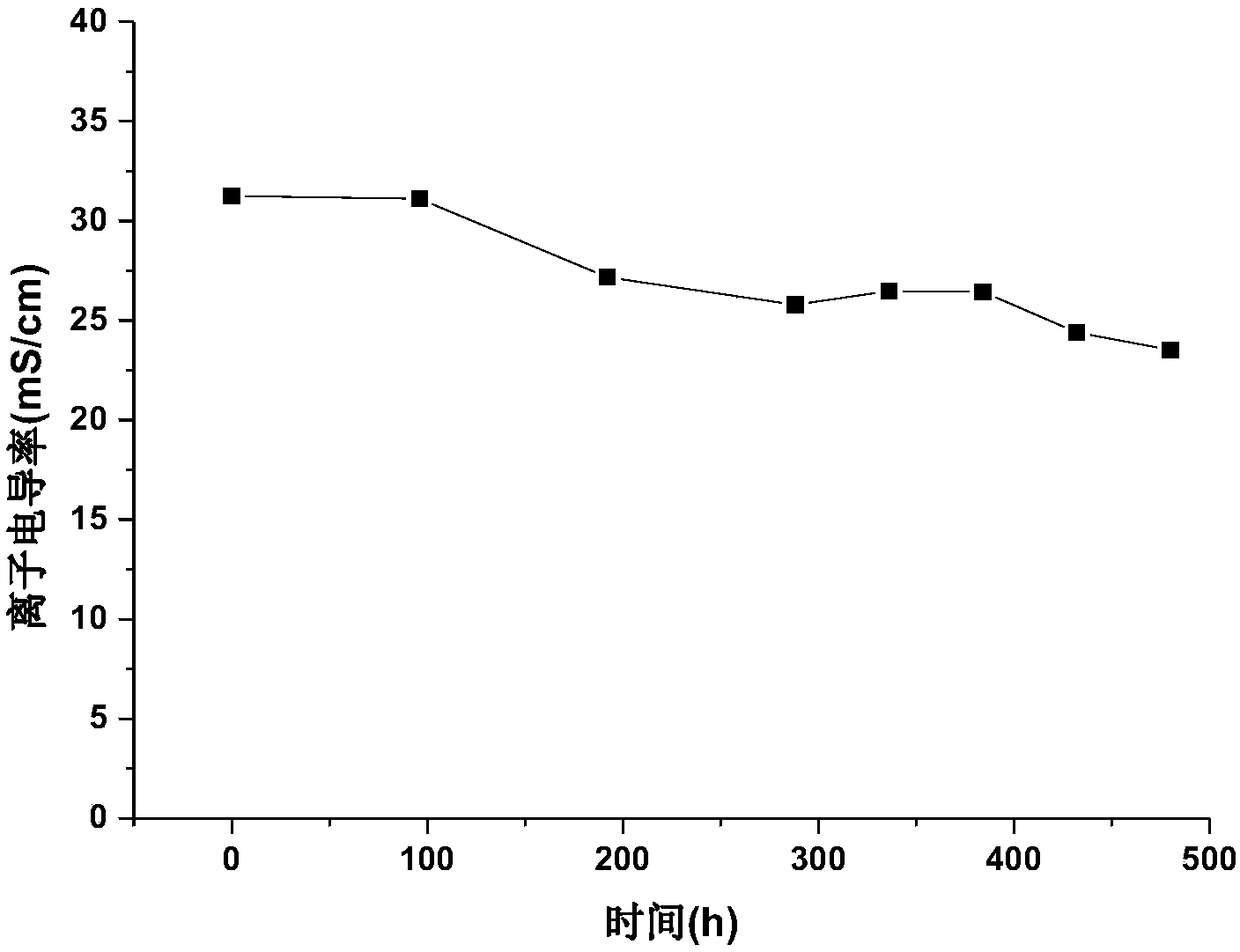
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Physical Composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The individual components that are required to comprise both the physical and structural elements of matter. The arrangement of these elements defines the final geometry of the resulting construct.
Classifying objects with additional measurements
ActiveUS20190317217A1Improve accuracyImprove classification efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionAuxiliary system
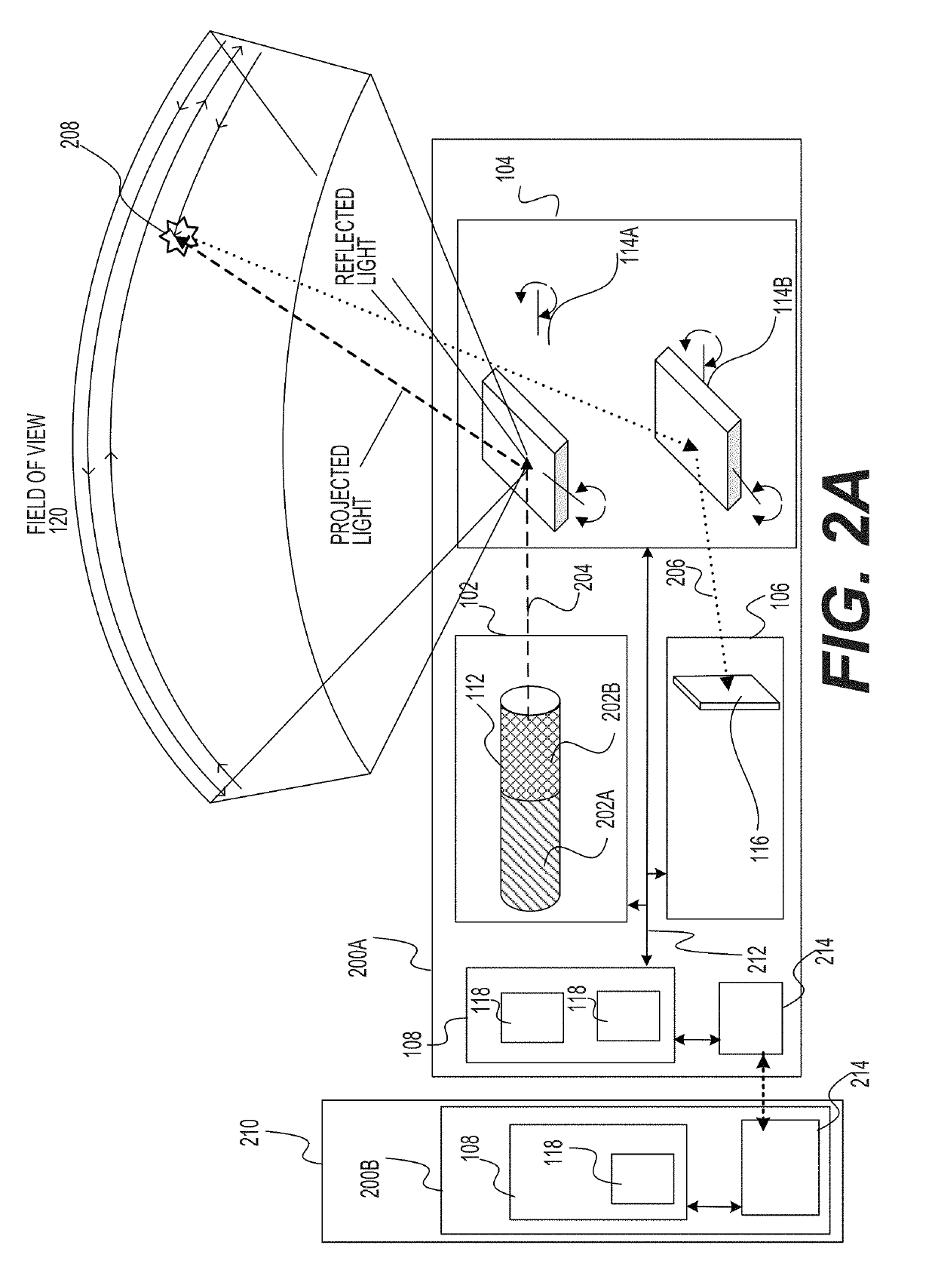
A vehicle-assistance system for classifying objects in a vehicle's surroundings is provided. The system may include at least one memory configured to store classification information for classifying a plurality of objects and at least one processor configured to receive, on a pixel-by-pixel basis, a plurality of measurements associated with LIDAR detection results. The measurements may include at least one of: a presence indication, a surface angle, object surface physical composition, and a reflectivity level. The at least one processor may also be configured to receive, on the pixel-by-pixel basis, at least one confidence level associated with each received measurement, and access the classification information. The at least one processor may further be configured to, based on the classification information and the received measurements with the at least one associated confidence level plurality, identify a of pixels as being associated with a particular object.
Owner:INNOVIZ TECH LTD
Method for preparing anode material of lithium ion battery in series of phosphate of olivine type
InactiveCN101049922AAchieve hybridEvenly distributedCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsAluminium-ion batteryPhosphate
This invention relates to a method for preparing olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method comprises: mixing one or more of ferrous salt solution, cobalt salt solution and manganese salt solution with oxalic acid or oxalate (precipitating agent) aqueous solution to obtain composite oxalate precursor, uniformly mixing with lithium source and phosphorus source by ball milling, and reacting in inert or weak-reductive atmosphere to obtain olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material. The method utilizes co-precipitation method for metal ion doping, and realizes molecular level uniform mixing among different ions. The obtained olivine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has uniform chemical and physical compositions. The average particle size can be controlled within 0.3-10 mu.m. The first charge and discharge cycle specific capacity can reach 150 mAh / g at 0.1 C rate and room temperature. The livine-type phosphate-series lithium ion battery anode material has such advantages as high cycle performance and high charge / discharge performance.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
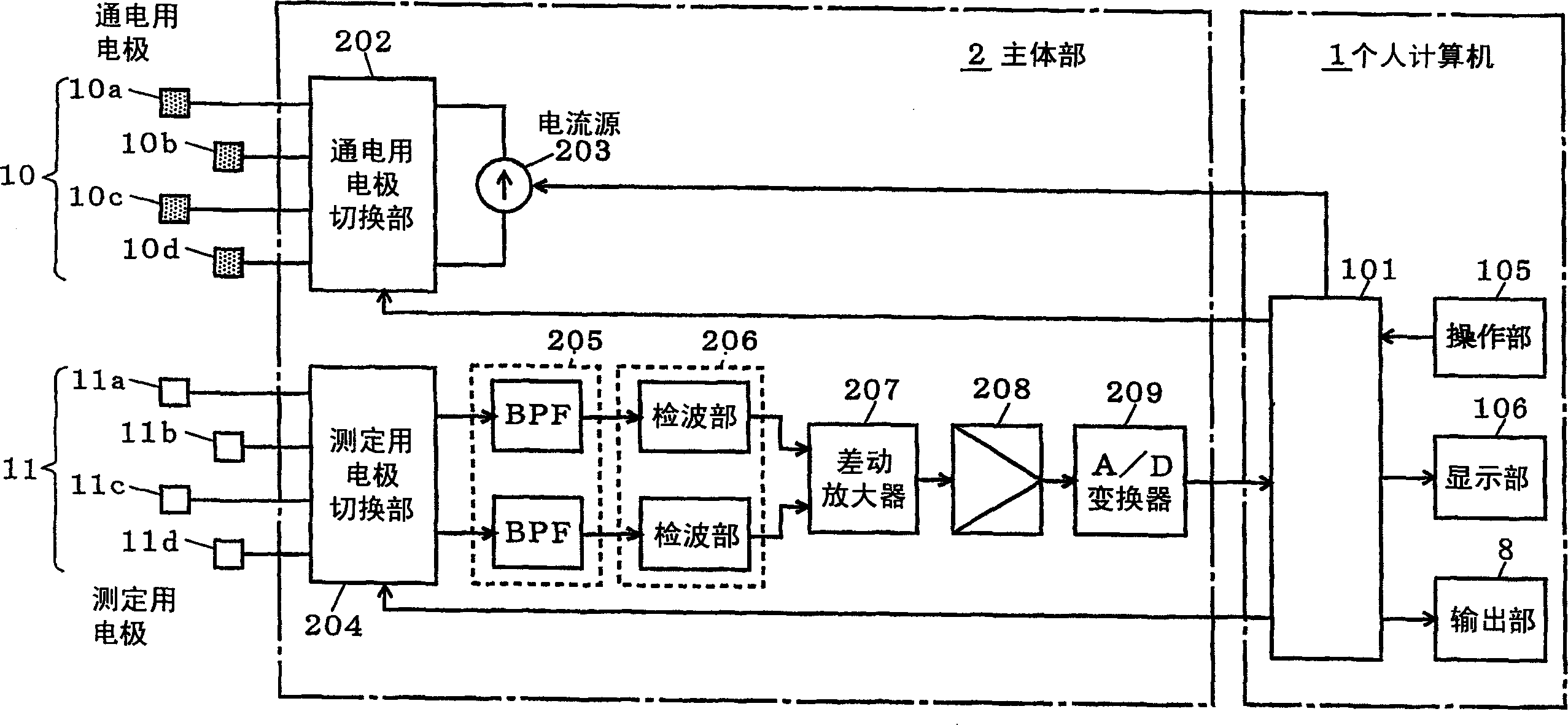
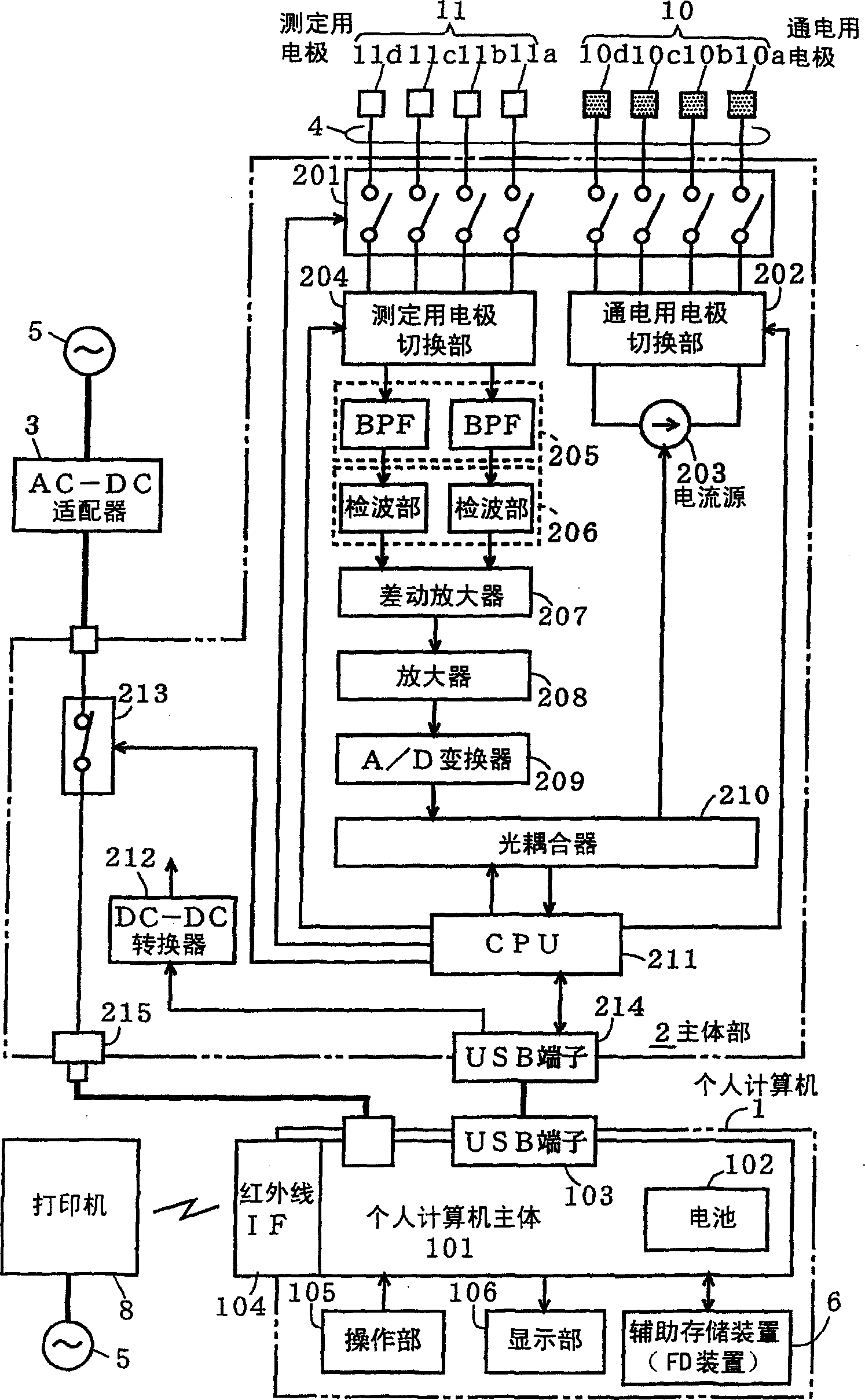
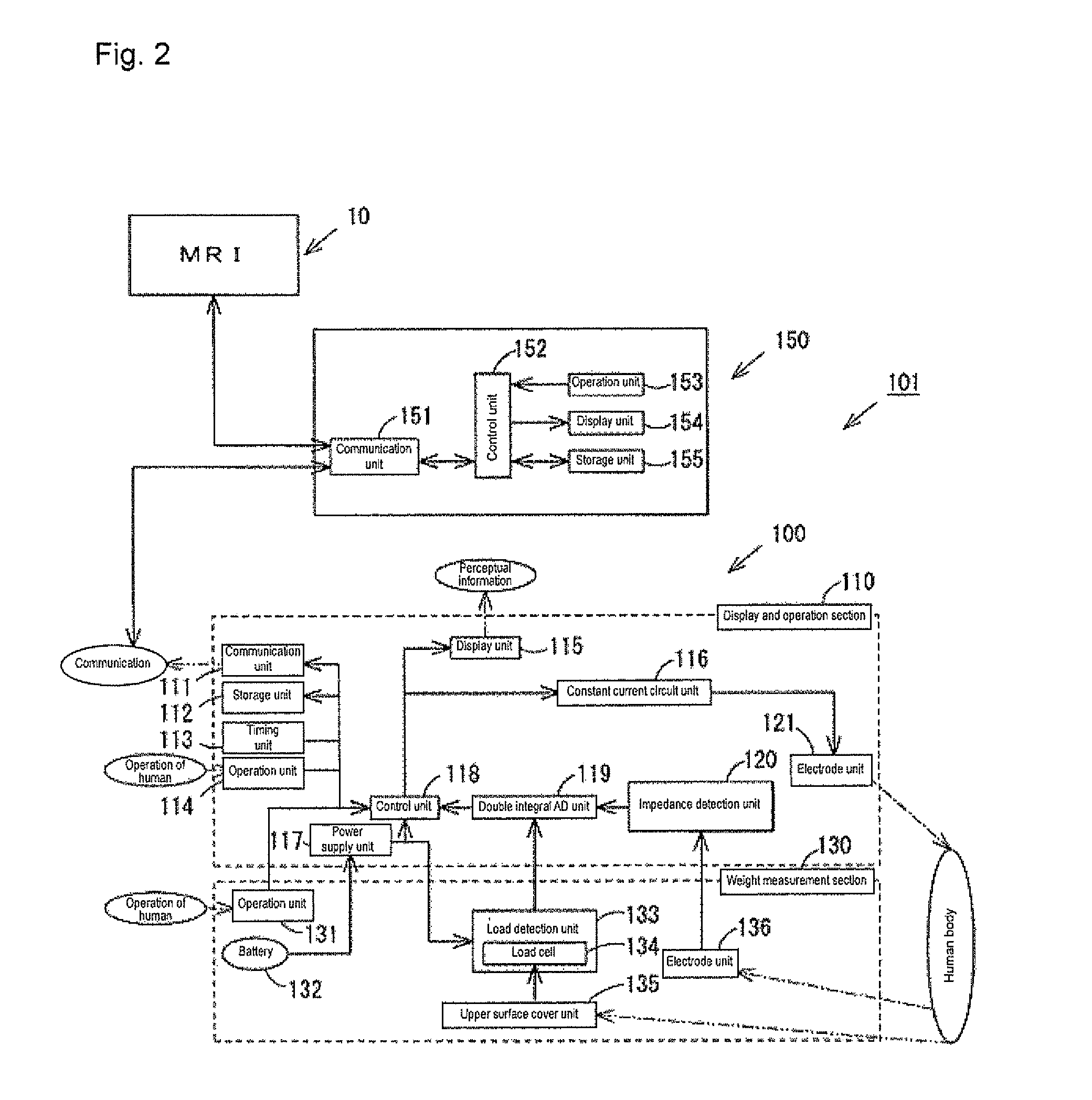
Biological information measurement device, biological information measurement method, and body composition measurement device
ActiveUS20120004570A1Accurate collectionImprove satisfactionPerson identificationSensorsBiological bodyCommunication unit
To accurately acquire body composition information using data acquired by another device. Thus, there is provided a body composition monitor with scale including a communication unit for allowing input of biological component information (cross-sectional area, site length, subcutaneous fat percentage, visceral fat percentage, etc.) of a living body measured with another device such as an MRI, where step of calculating the body composition of the living body based on the biological component information, an impedance detected by an impedance detection unit, and a weight measured by a load detection unit is executed.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Method and device for measuring body composition
InactiveCN1489447AHigh precisionCorrect feature deviationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProximal pointRegression analysis
To accurately measure the muscle mass, body-fat ratio and / or other information of the subject, the human body is divided into nine segments including the trunk, right and left forearms, right and left upper arms, right and left thigh, and right and left crura. Four distal voltage-measuring points Pv are determined at the wrists and ankles, and four proximal voltage-measuring points Pv are determined at the elbows and knees. Four current-carrying electrodes and four measuring electrodes are used. First, the measuring electrodes are attached to distal points, and the impedances of four limbs and the trunk are measured. Then, the measuring electrodes are moved to proximal points, and the impedances of four limbs and the trunk are measured. From the measurement result, the measurement value is calculated for each segment. Then, using estimation formulae created by a regression analysis based on the data collected with an MRI, the body composition such as a muscle mass is estimated from the measurement values of the impedances and body specific information including the height, weight, etc.
Owner:フィジオン
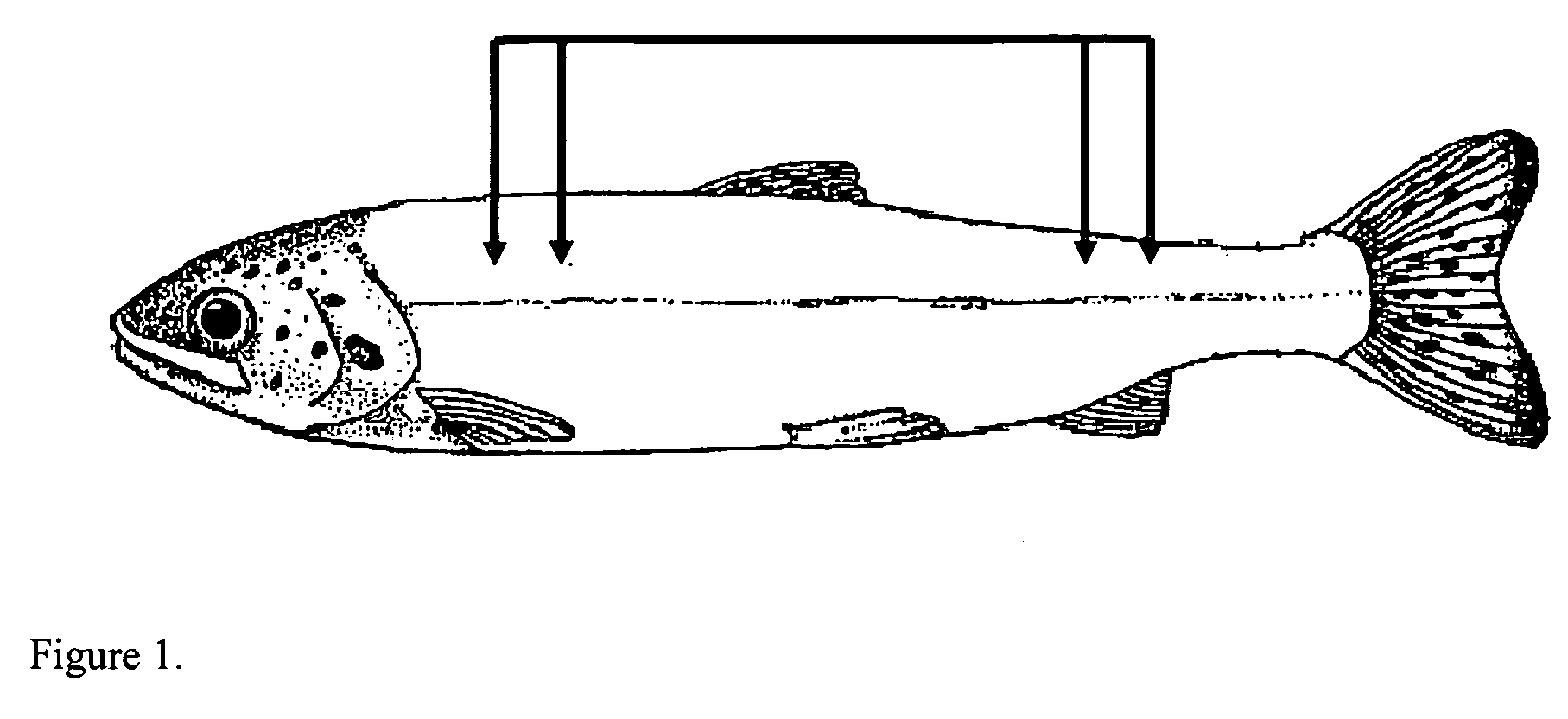
Method for evaluating the health status, gender, energy content and body composition of living and dead fish, and time of death of dead fish to better describe, evaluate and manage like fish populations using bioelectrical impedance analysis
InactiveUS20100081961A1Easy to useLow costPisciculture and aquariaDiagnostic recording/measuringBioelectrical impedance analysisMeasurement device
A method and an apparatus are described for testing the health status, gender, and body composition of living fish as well as time of death for dead fish. The apparatus consists of two series of needles that are mounted to a measuring device that is capable of simultaneously measuring the distance between the two sets of needles and the impedance of a whole fish. The method includes applying needles to the fish, passing an electrical current between the needles, determining impedance for tissue of the fish between the needles, measuring the distance between the two needles and correlating the determined impedance and needle distance measurement with the health status, gender and body composition of living fish and dead fish and time of death of dead fish.
Owner:COX MARLIN KEITH
Article With Health-Benefit Agent Delivery System
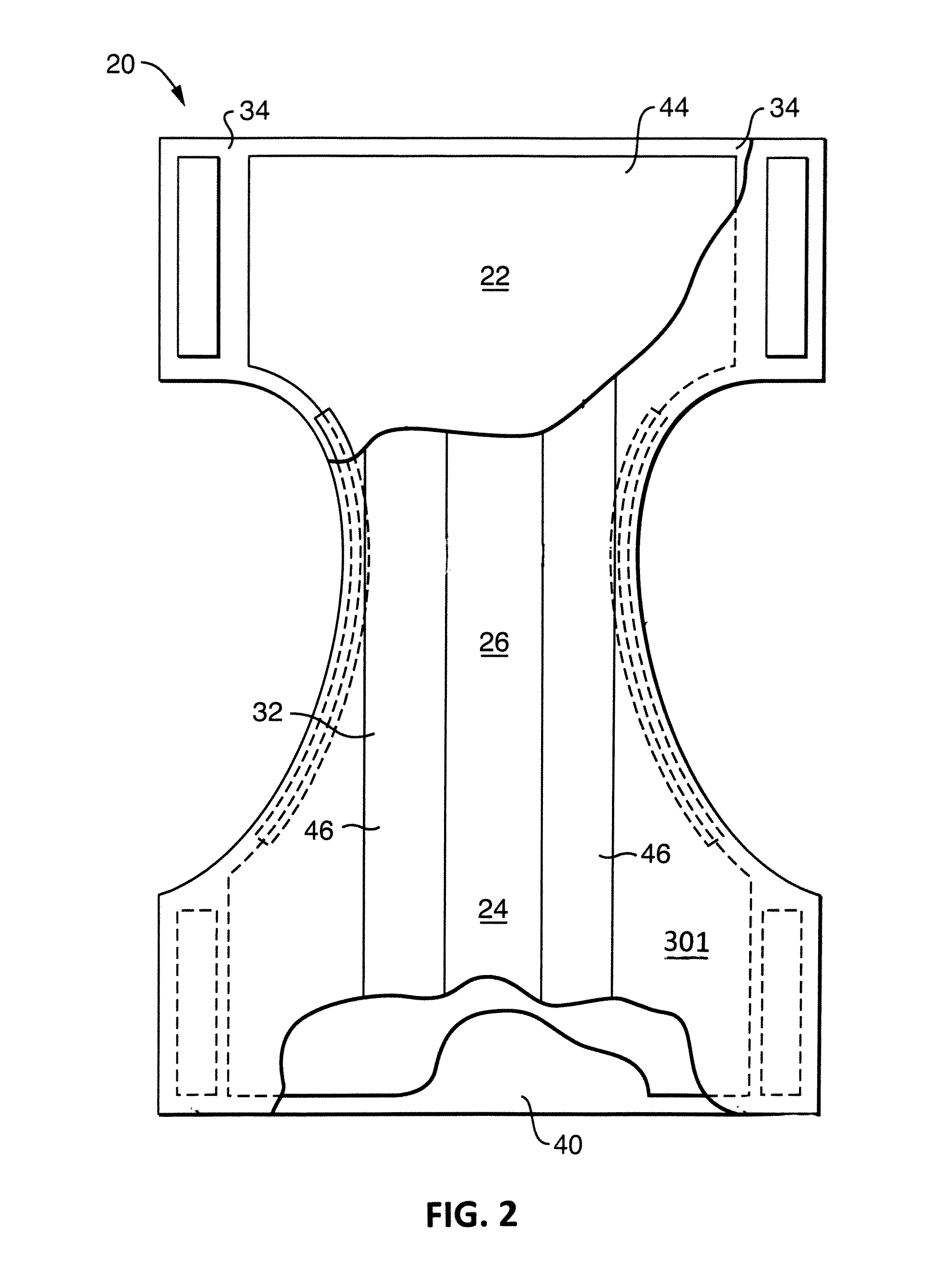
A laminate having health-benefit agents therein is made by particle stabilization within the lamination process. By changing the substrate type (tissue, nonwoven, film) and / or the physical composition and / or attributes of the laminate layers, the release of the health-benefit agents can be controlled. The laminate, sometimes referred to as a liner, may be used in personal absorbent articles such as diapers, feminine pads, bandages, bed pads, and the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method using native landscape plant to restore return-land-to-lake wetland soil
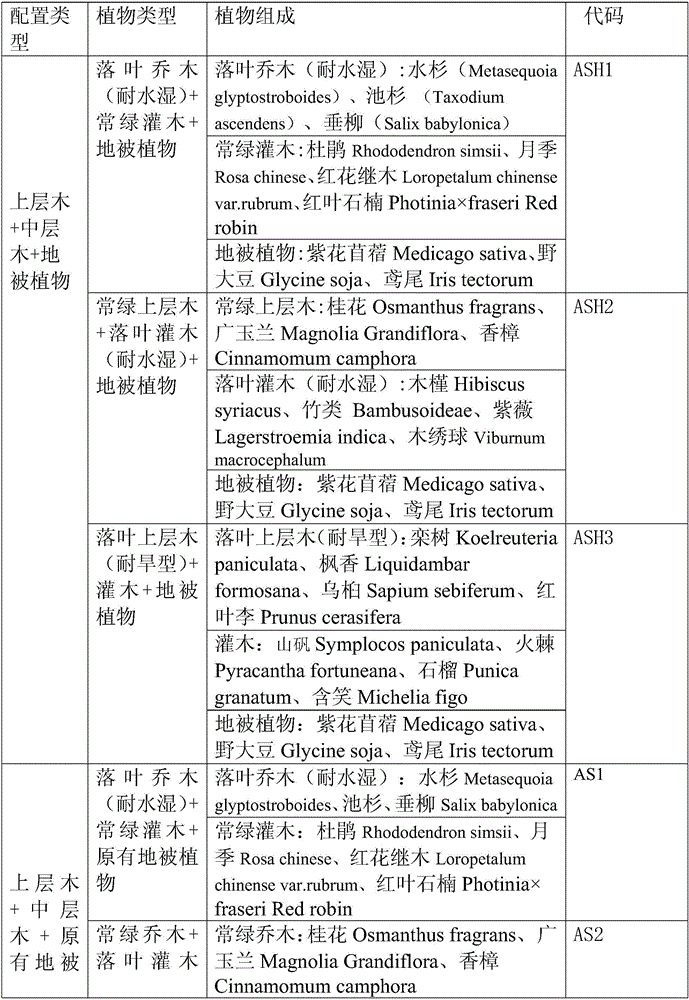
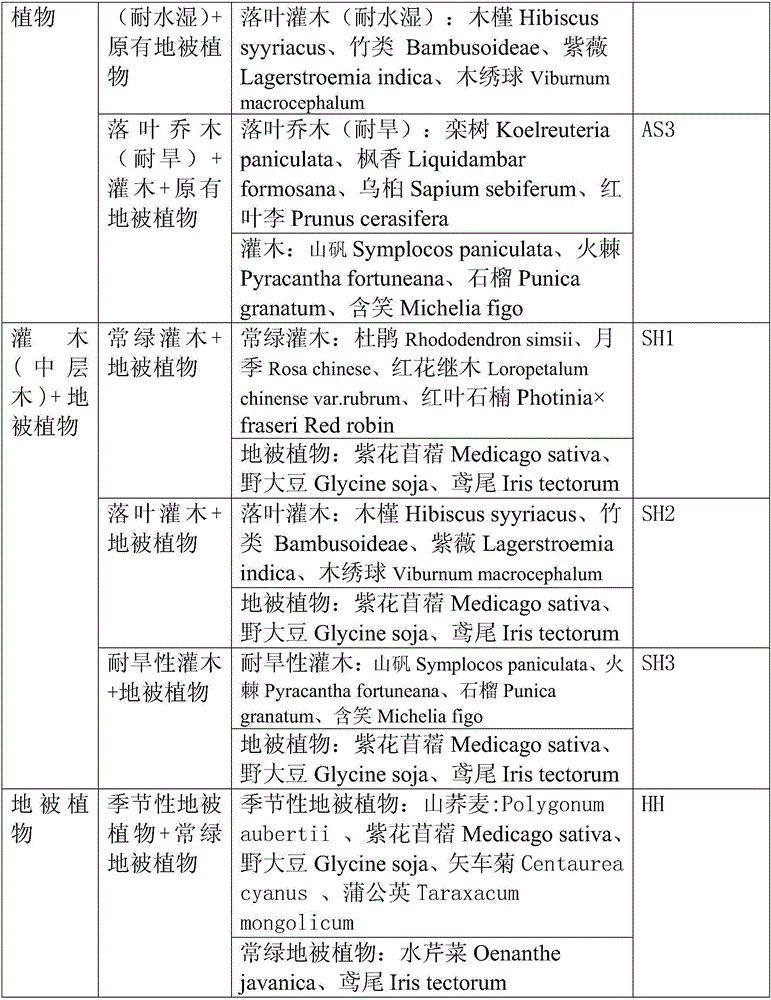
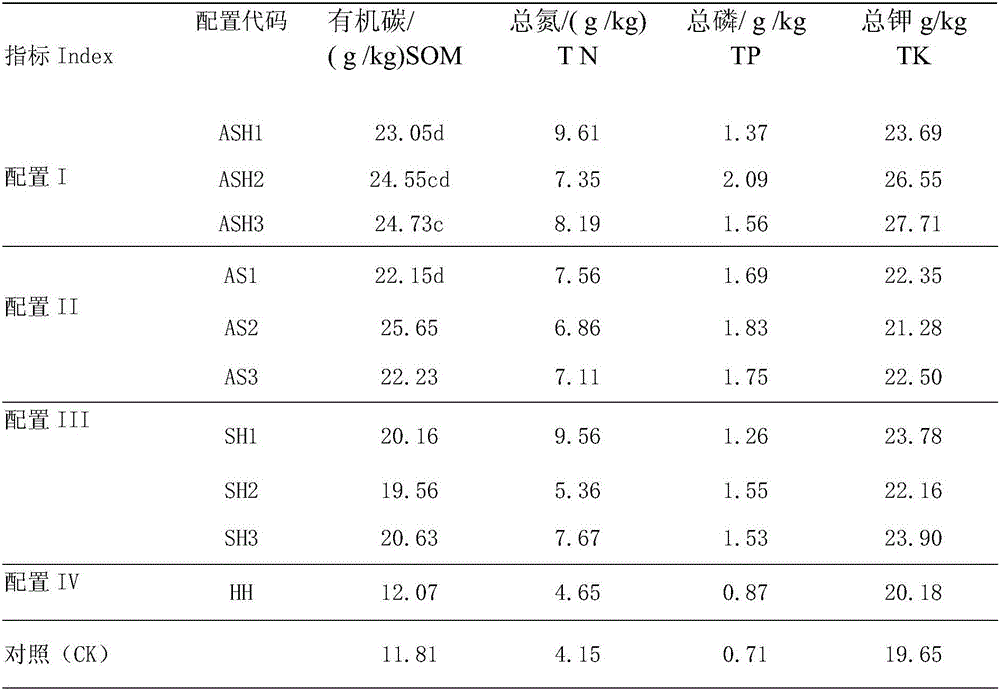
InactiveCN105960878AThe configuration method is scientific and reasonableIncrease plant diversityInvasive species monitoringSoil-working methodsNutritional statusPlant community
The invention relates to a method using native landscape plants to restore return-land-to-lake wetland soil; phytocoenosis main collocation methods comprise the following 4 modes: 1, landscape plant arbor-shrub-grass interbreed mode, i.e., overstory arbor+middle lamella arbor+ground cover plants; 2, landscape plant arbor-shrub interbreed mode, i.e., overstory arbor+middle lamella arbor+original ground cover plants; 3, shrub-grass interbreed mode, i.e., middle lamella arbor+ground cover plants; 4, ground cover plant single mode, introduction ground cover plants+original ground cover plants. The method introduces fast-growing native landscape tree species so as to fast adapt to the growing environment, thus forming landscape, becoming colony advantage species, and controlling alien species invasion; the method can improve farmland soil physical composition and nutrition status, can eliminate (degrade) residual poisonous and harmful pollutants, thus realizing soil pollution purification under nature conditions, realizing self-restoration, i.e., expressing soil-plant system degrading purifying effect.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Quantum dot and graphene photosensitive field-effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103943713ARealize transmissionIncrease concentrationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesResponsivityQuantum dot
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Apparatus and method for assessing body composition
InactiveUS20080039708A1Avoid necessityReliable and accurate and precise and specific non-invasiveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRadio frequency
A method for analyzing composition of a human body includes inducing a substantially homogeneous static magnetic field in the entire body. A substantially homogeneous radio frequency magnetic field is induced in the entire body so as to induce nuclear magnetic resonance effects in the body. Nuclear magnetic resonance signals emanating from the entire body are analyzed to determine body composition.
Owner:ECHO MEDICAL SYST
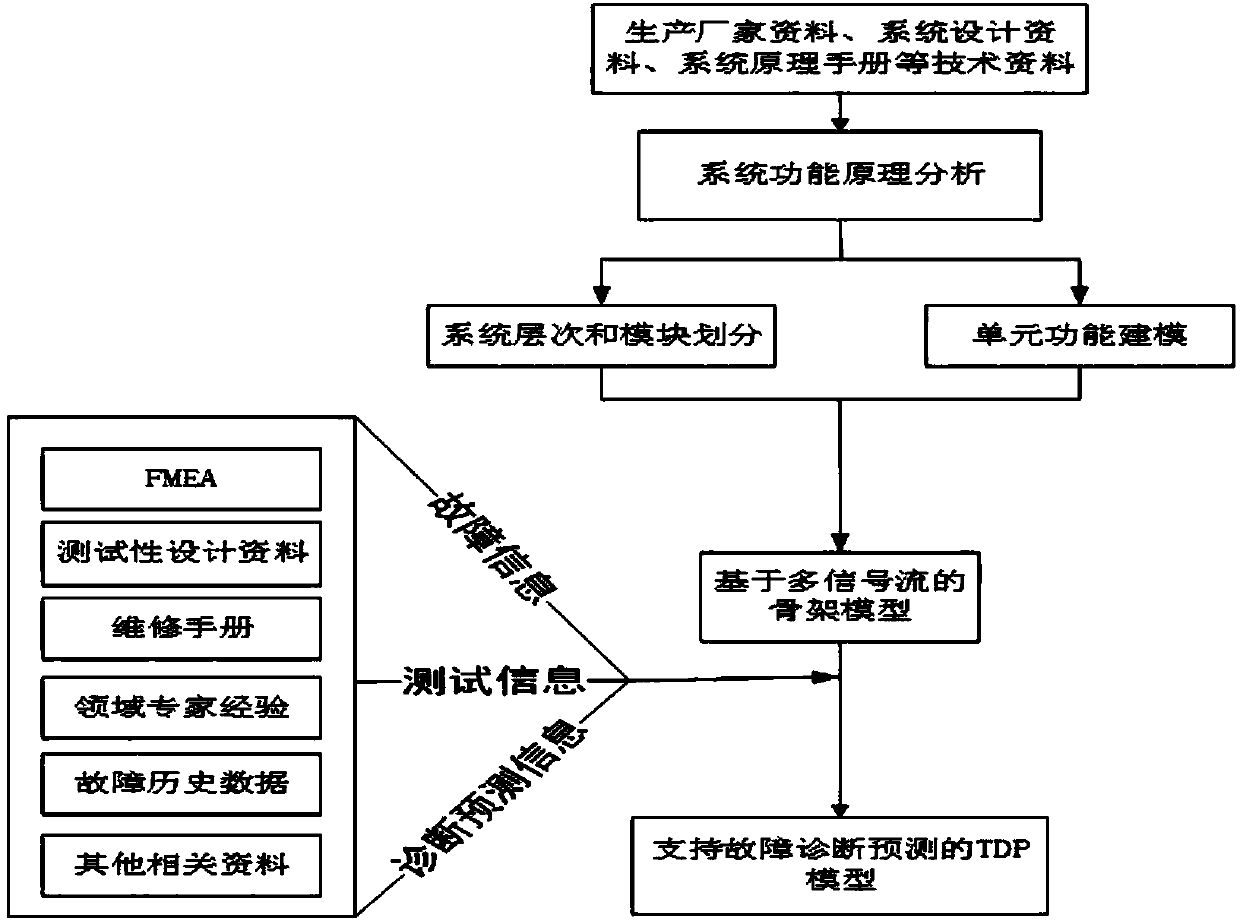
Diagnostic prediction method based on TDP model
InactiveCN108304661AImprove diagnostic efficiencyMachine part testingDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmFault analysis
The invention discloses a diagnostic prediction method based on a TDP model. TDP modeling includes the steps of 1, firstly, deeply analyzing the physical composition of a system and the connection relations of all the parts, and establishing a structure model based on a system working principle; 2, through functional principle analysis, forming a skeleton model; 3, using FMEA and other fault analysis methods to find key components and key faults which affect system performances; 4, analyzing test items at each test point, signals and behavior which can be observed in each test and prediction information of each test, and adding corresponding diagnosis prediction information obtained through analysis to the TDP skeleton model. The diagnostic prediction method for achieving the TDP model includes the steps of 1, TDP modeling based on the system principle and multi-signal flow, 2, diagnosis strategy optimization based on the TDP model, and 3, fault state identification and fault prediction based on the TDP model. According to the method, not only can the model evaluate the fault diagnosis and prediction ability of the system, but also model information can support fault prediction ofthe system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and process for weight management
A weight management method and system measures and utilizes an individual's specific body composition and metabolic rates to provide a nutritional plan designed to the individual's specific weight management goals, including weight loss, weight gain or weight control. The system is composed of four primary components: 1) body composition testing; 2) metabolic rate testing; 3) Registered Dietitian counseling; and 4) message therapy. These components are utilized to provide a system that utilizes behavior modification and stress management to allow the individual to meet his or her weight management goals through a healthy, stable process.
Owner:ON TARGET HEALTH LLC
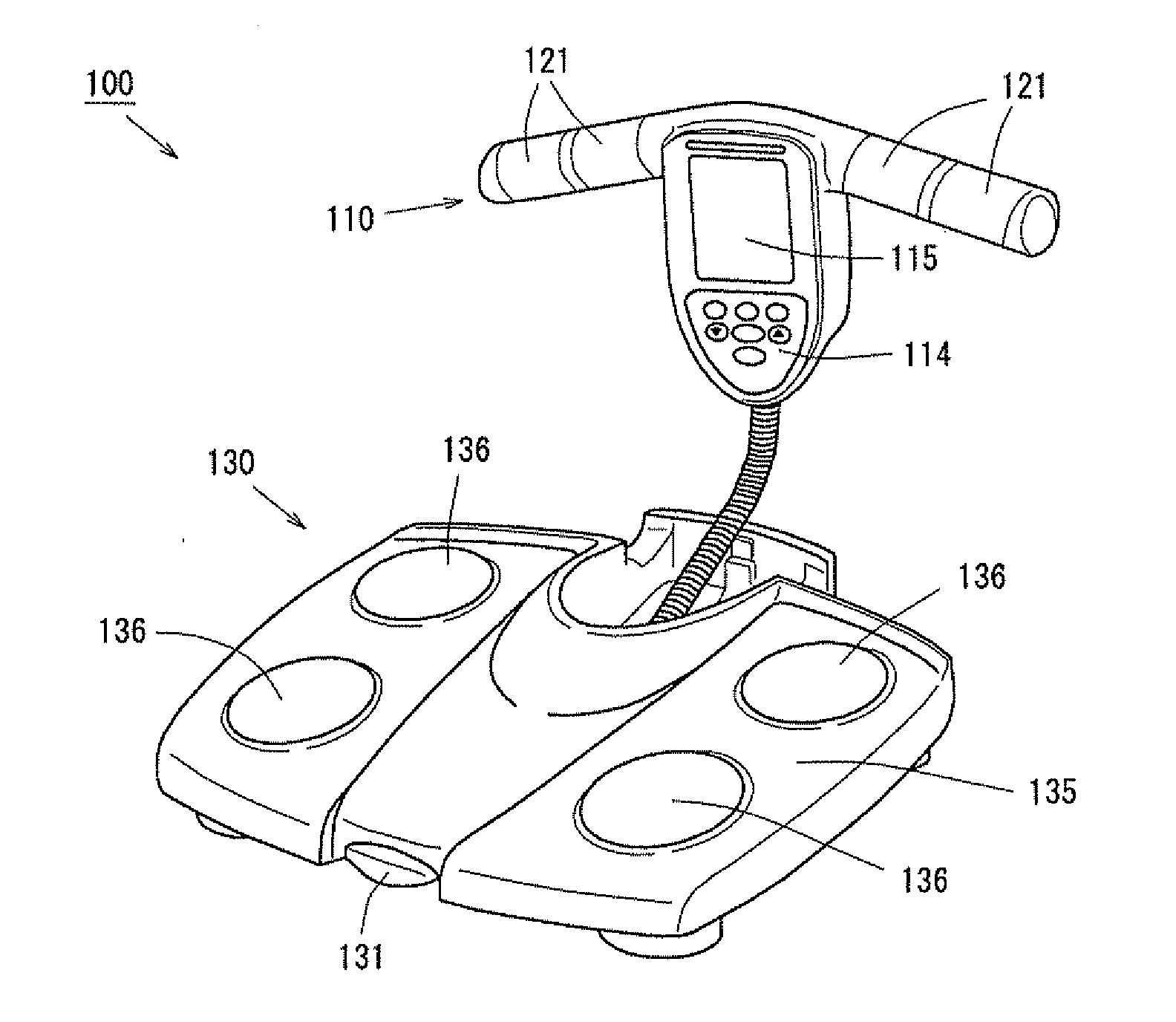
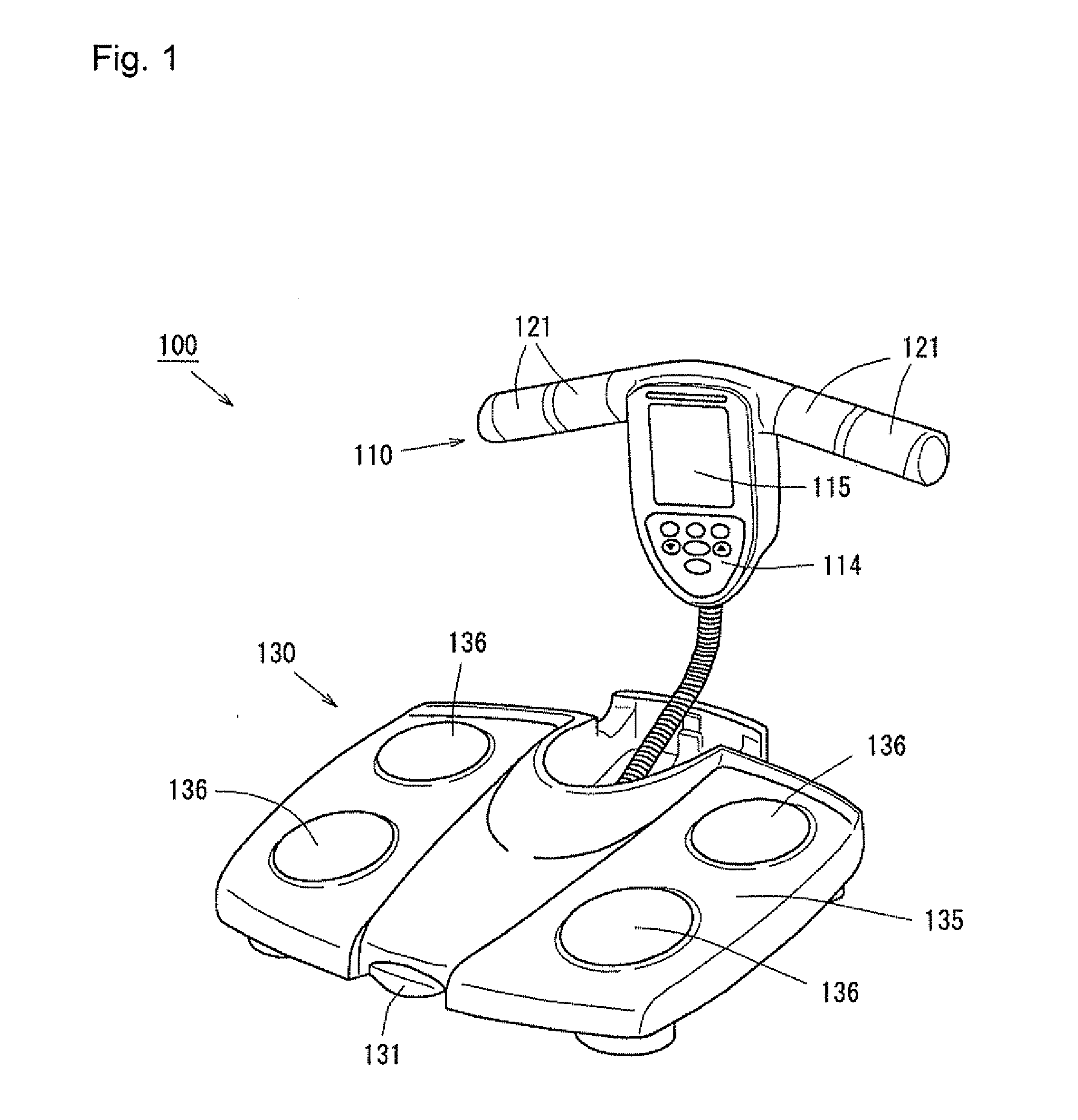
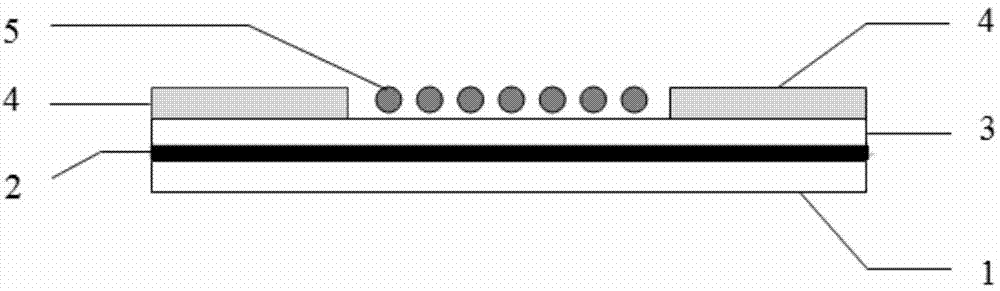
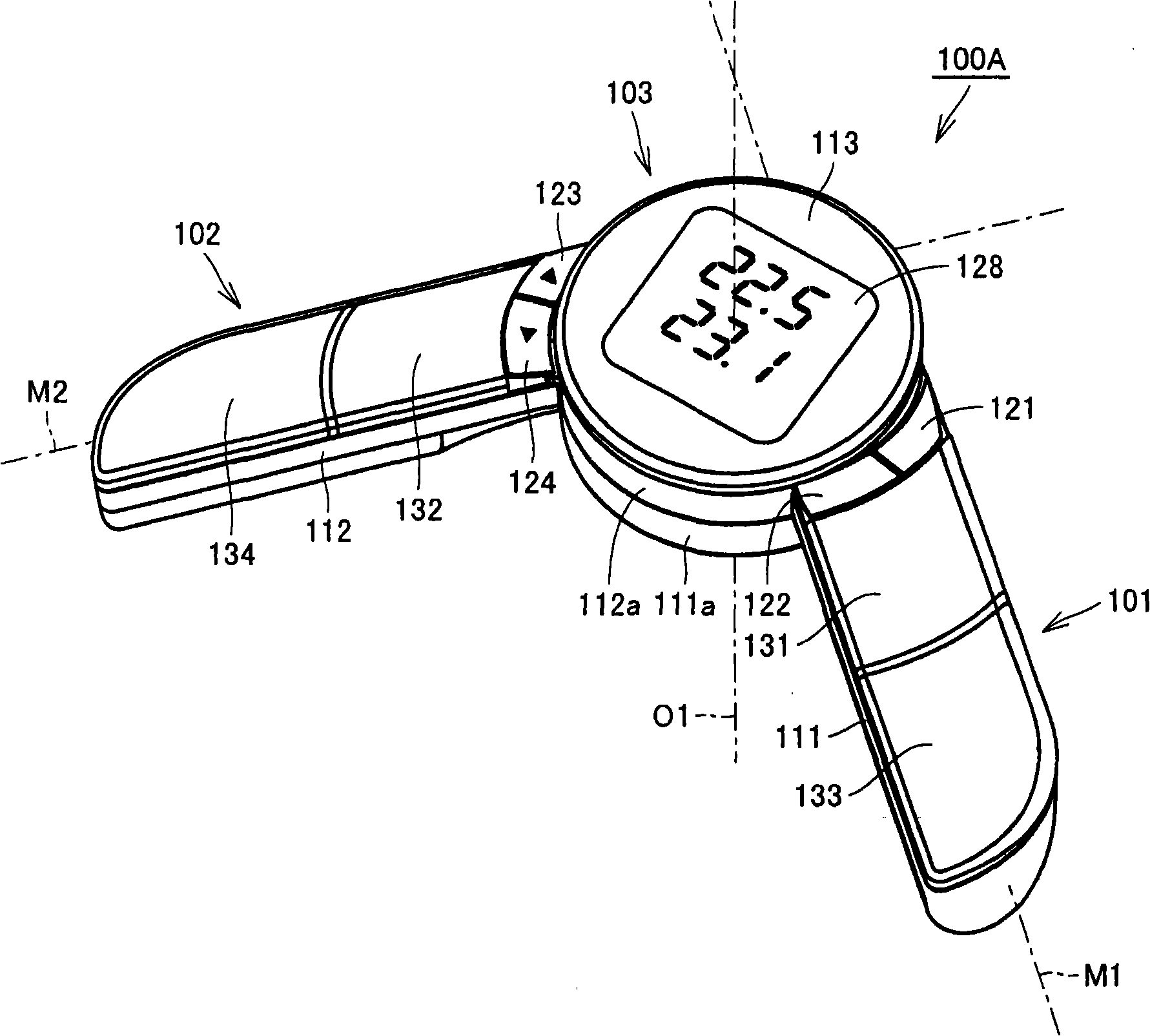
Body composition measuring device
InactiveCN101299961ADiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBody composition measurePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
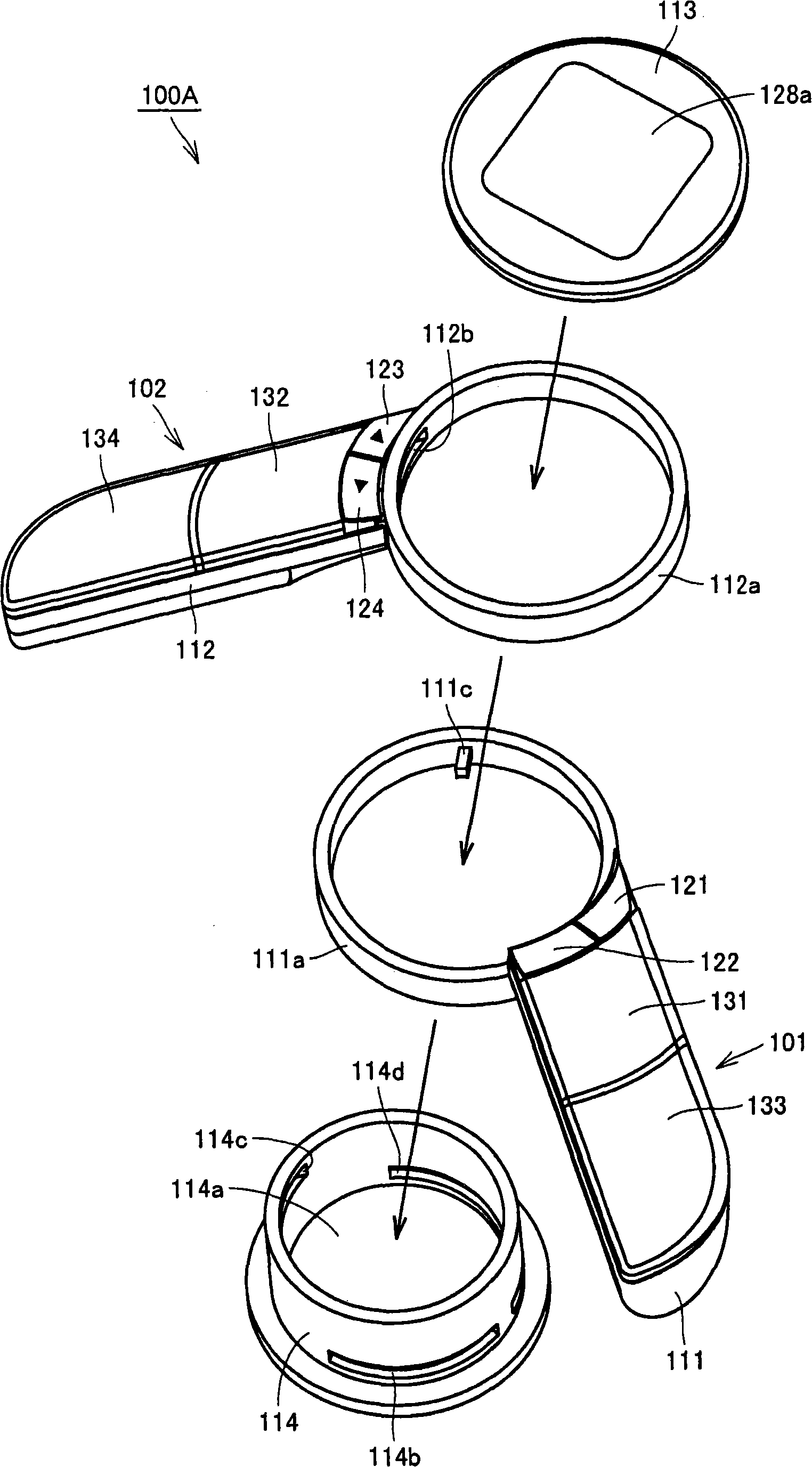
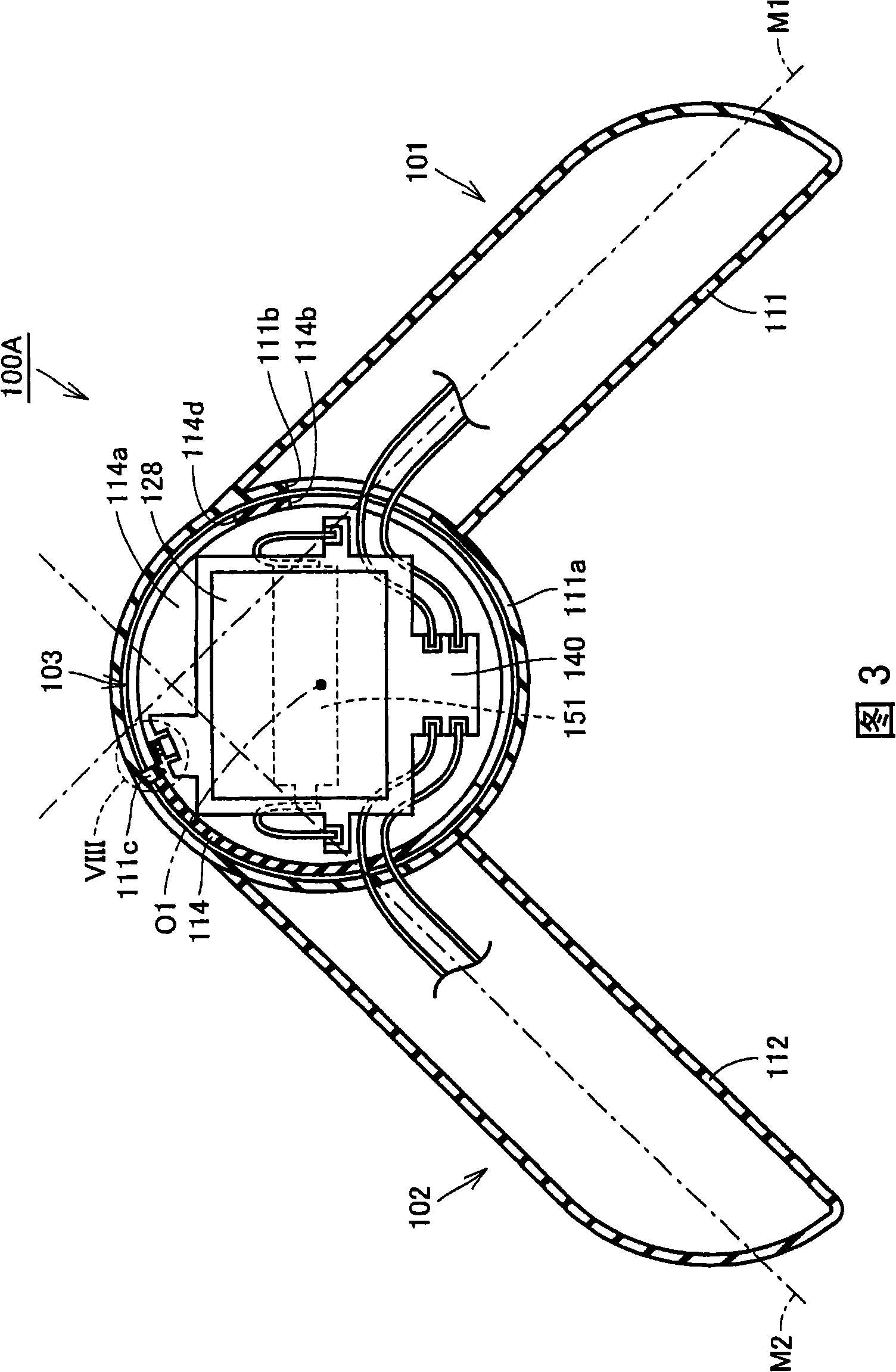
The invention provides a body composition measuring device (100A) having electrodes (131, 133) for a right hand, made to be in contact with the right hand of a subject, and also has electrodes (132, 134) for a left hand, made to be in contact with the left hand of the subject so to measure the body impedance of the subject. The device body has a rod-like grip portion (111) provided with the electrodes (131, 133) for a right hand, a rod-like grip portion (112) provided with the electrodes (132, 134) for a left hand, and a base portion (103) to which the grip portion (111) for a right hand and the grip portion (112) for a left hand are fixed. The grip portion (111) for a right hand is rotatablely fixed to the base portion (103), and the extending direction of the grip portion (111) for a right hand is differentiated from the extending direction of the rotating shaft thereof. Consequently, a small and thin portable body composition measuring device can be achieved.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Fitness test system
The present invention relates to a fitness test system for determining a fitness test result indicative of a user's fitness, for a plurality of components of physical fitness such as endurance, strength, flexibility, balance, and body composition. The fitness test system comprises a computing module (1) for accessing a collection of fitness tests and one or more peripheral devices (20-23), the one or more peripheral devices being communicatively connected to the computing module, and the one or more peripheral devices being adapted to measure one or more input parameters. The computing module is programmed for upon selection of a fitness test to determine the group of input parameters associated with the fitness tests and based on the determined input parameters to calculate and / or present a fitness test result indicative of a user's fitness related to the associated component of physical fitness.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
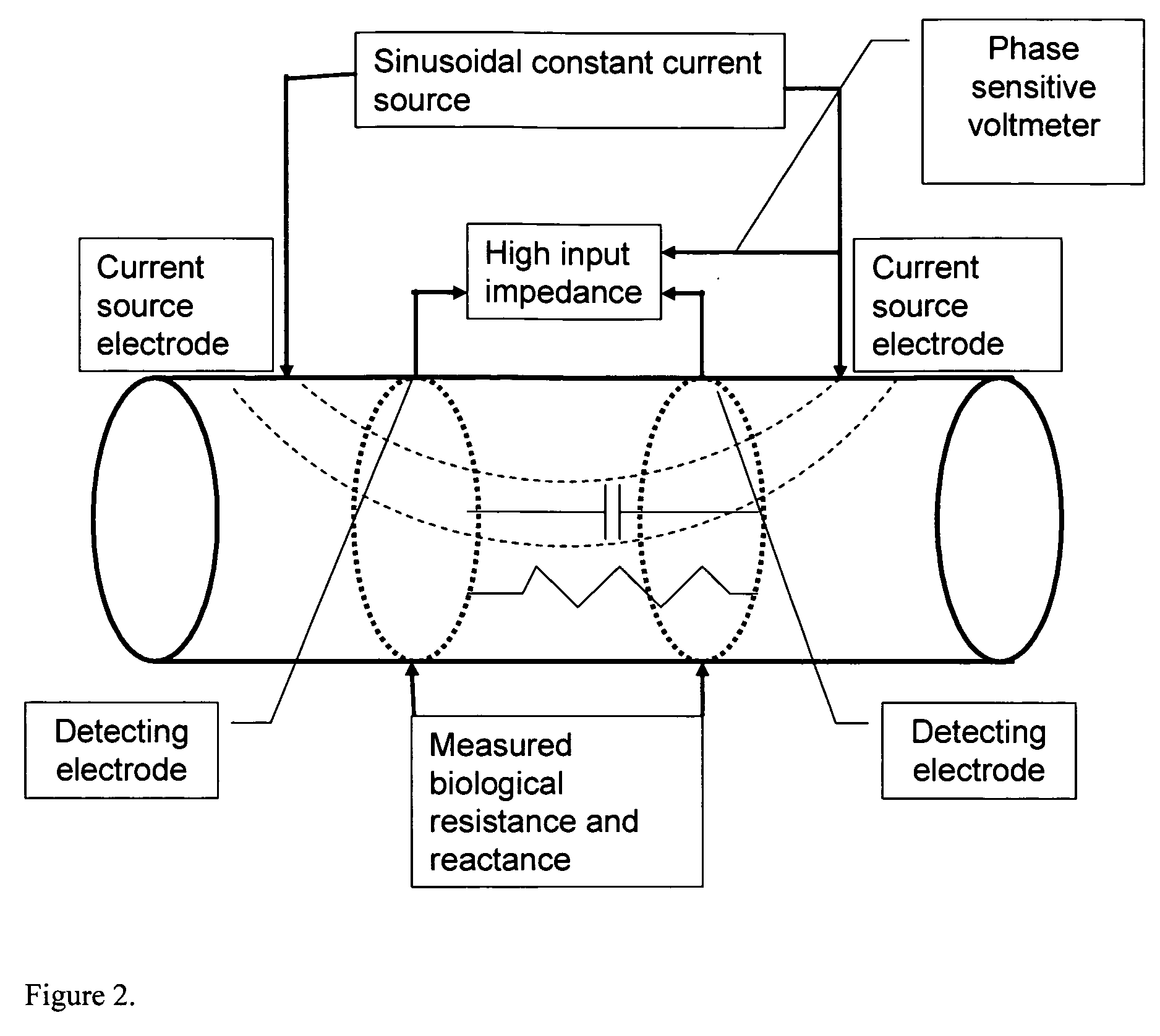
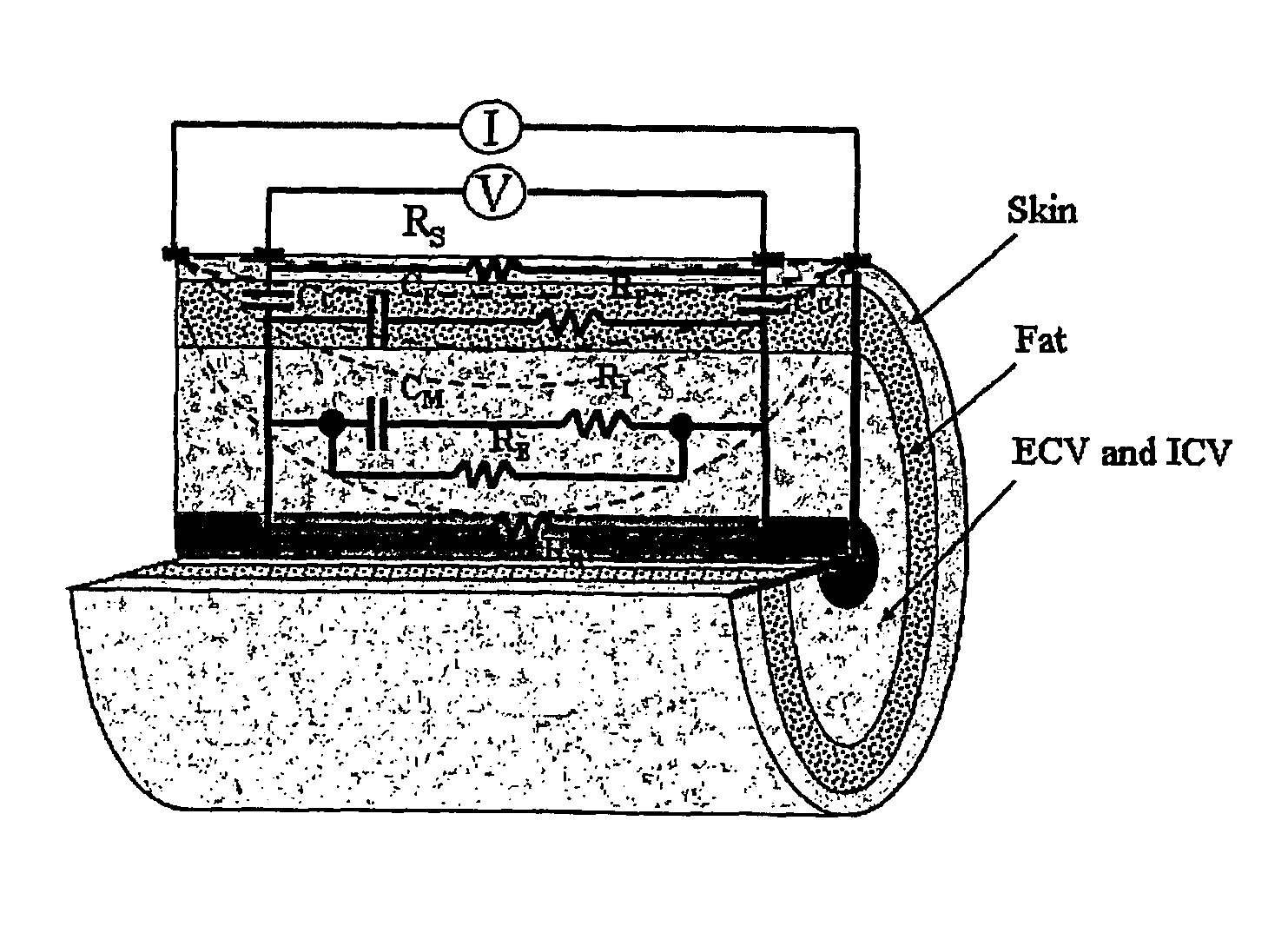
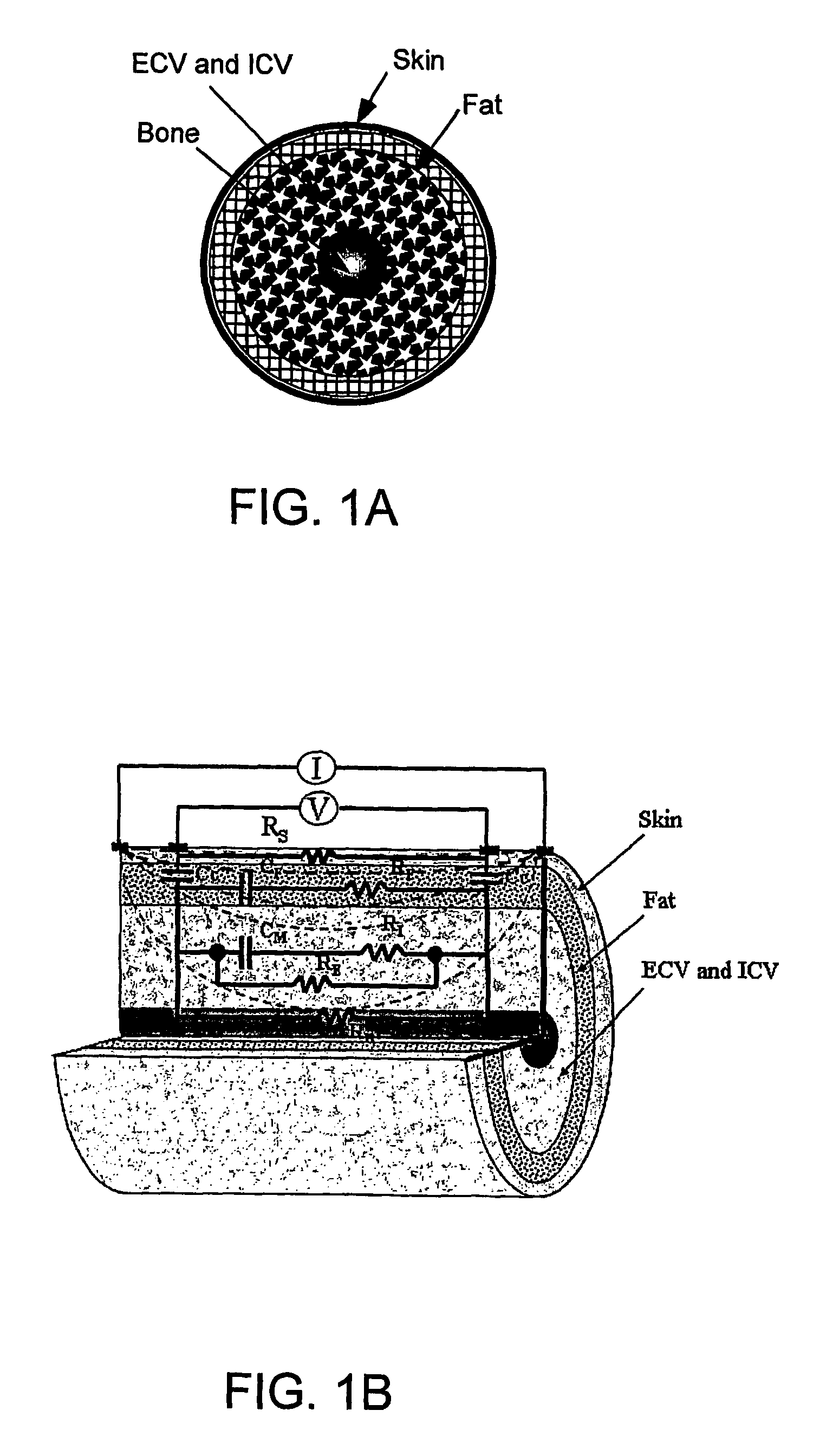
Bioimpedance methods and apparatus
Methods and apparatus for providing bioimpedance analysis are provided. In certain aspects, an equivalent circuit frequency response model is provided, resulting in improved correlation with MRI data. The frequency response model takes into account body composition, including fat composition of body segments. Data obtained by Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS) and MRI analysis on the subject's calf demonstrate improved correlation compared to single frequency analysis at 50 kHz and analysis with the conventional Cole-Cole model .
Owner:肾脏研究所有限公司
Body composing meter
InactiveCN101088458AEasy accessAccurate contactDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationThigh part
The present invention provides a body component meter which can easily and correctly measure the thickness of the subcutaneous fat at the abdomen, the thigh part, the upper arm part and the like measured parts. It is composed of the following components: a weight machine (2) which measures the body weight of the testee standing on the upper side; and a measuring unit (3) which is independent from the weighting machine (2); the measuring unit (3) is provided with the following components: a measuring used electrode (9) which contacts with the body of the testee and is used to measure the body impedance; and a sebum depth measuring part (12) which is used to measure the subcutaneous fat of the measuring part (20) of the testee. It is provided with a communication mechanism which does communication between the weighting machine (2) and the measuring unit (3). And it is also provided with a control part which simultaneously displays the measuring result on the display part (10) according to the test result which is tested by the weighting machine (2) or measuring unit (3) and is relative to the body composition.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Body forming and body weight detecting apparatus
InactiveCN102379696ALower impedanceShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyBody part weight
The present invention provides a body forming and body weight detecting apparatus, capable of shortening the time of detecting the resistance and body weight of users. The body forming and body weight detecting apparatus is provided with a first detecting portion provided with a carrying portion, wherein the first detecting portion is carried on the resistor of the organism of the carrying portion; a second detecting portion for detecting the body weight of the organism; and a control portion enabling the first detecting portion to detect the resistance in the stable pre-detection period from the time point of carrying the organism on the carrying portion to the time point of enabling the body weight change of the organism to be stable.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Body composition measuring device
InactiveCN102028452ADiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBody composition measureClassical mechanics
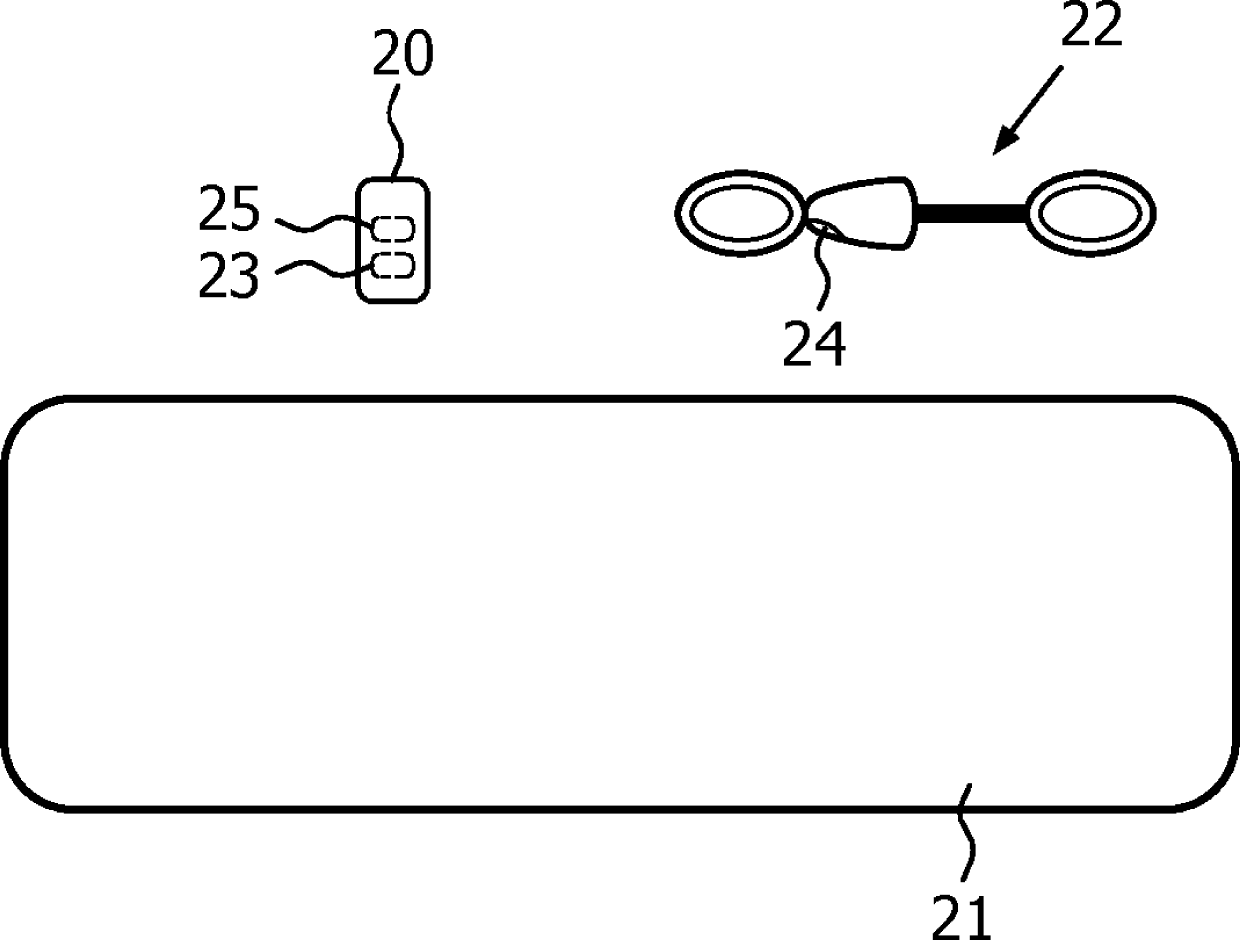
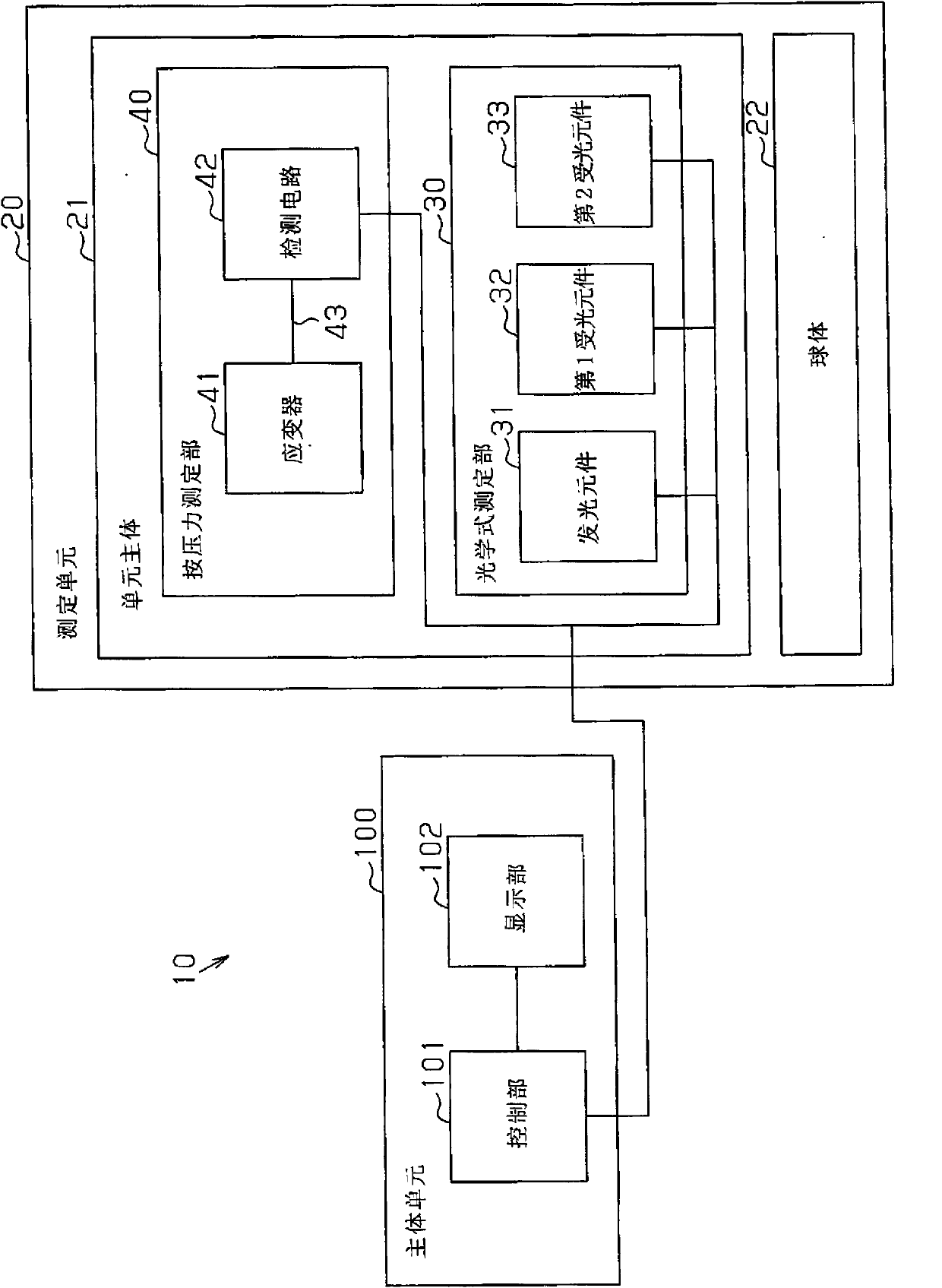
The present invention relates to a body composition measuring device (10) which can measure the body composition in a large area continuously and accurately. The body composition measuring device is provided with the following components: an optical type measuring part (30) which measures subcutaneous fat, a sphere (22) which is used for moving on the body surface, and a pressing force measuring part (40) which is used for measuring the pressing force of the optical type measuring part (30) to the body surface.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
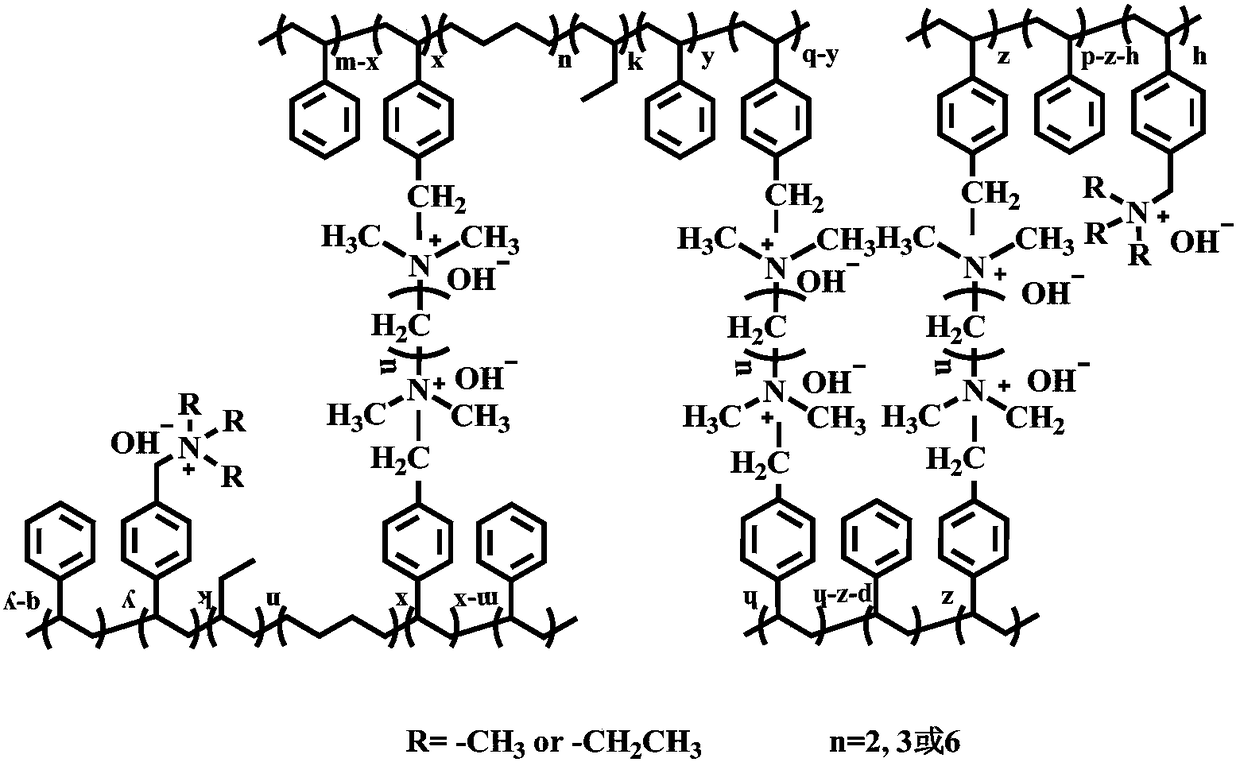
Styrenic thermoplastic elastomer/polystyrene composite membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109265715AImprove mechanical propertiesGood dimensional stabilityFuel cellsElastomerThermoplastic elastomer
The invention relates to a styrenic thermoplastic elastomer / polystyrene composite membrane and a preparation method thereof. The membrane material is prepared from styrenic thermoplastic elastomer andpolystyrene as matrices by the following steps: functionalizing and blending the styrenic thermoplastic elastomer and the polystyrene in form of solutions of different proportions, adding a cross-linking agent, preparing the membrane, and performing quaternary ammoniating and alkalifying under a non-homogeneous phase state to obtain a series of anion exchange membranes. The prepared styrenic thermoplastic elastomer / polystyrene composite membrane has the following advantages: 1) the ion transmission efficiency is obviously improved by effectively adjusting and controlling a microphase separation structure in the membrane by a simple and easy physical composition technique; and 2) the toughness of the styrenic thermoplastic elastomer and high strength of the polystyrene are combined, so thecomposite membrane has good mechanical properties and dimensional stability.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
SSD data physical backup method and device, electronic device and storage medium
ActiveCN110275800AImprove reliabilityMeet the needs of special scenariosInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionFault analysisComputer science
The invention relates to an SSD data physical backup method and device, an electronic device and a storage medium. The method comprises: acquiring a first command; returning physical composition information of the SSD according to the first command; obtaining a second command; processing the internal data of the SSD according to the second command to obtain to-be-backed-up data; feeding back the to-be-backed-up data to a file corresponding to the host; judging whether the internal data of the SSD is backed up or not; and if not, returning to obtain the second command. According to the method, physical backup is carried out on the internal data of the SSD, so that the requirement of a special scene is met, fault analysis or debugging can be carried out, subsequent failure analysis, fault reproduction and other applications can be carried out based on the backup data, and the reliability of the SSD is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YILIAN INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
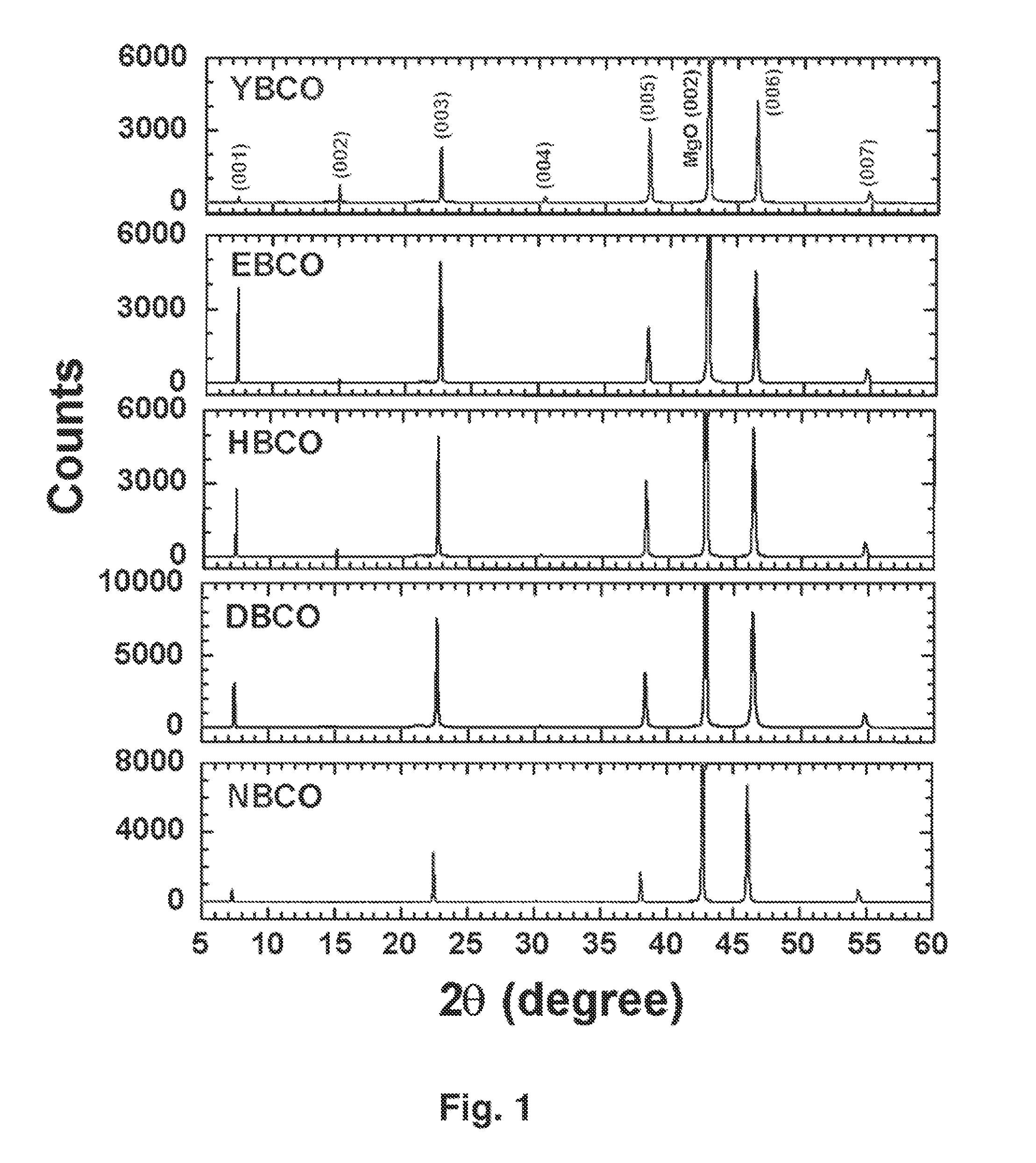
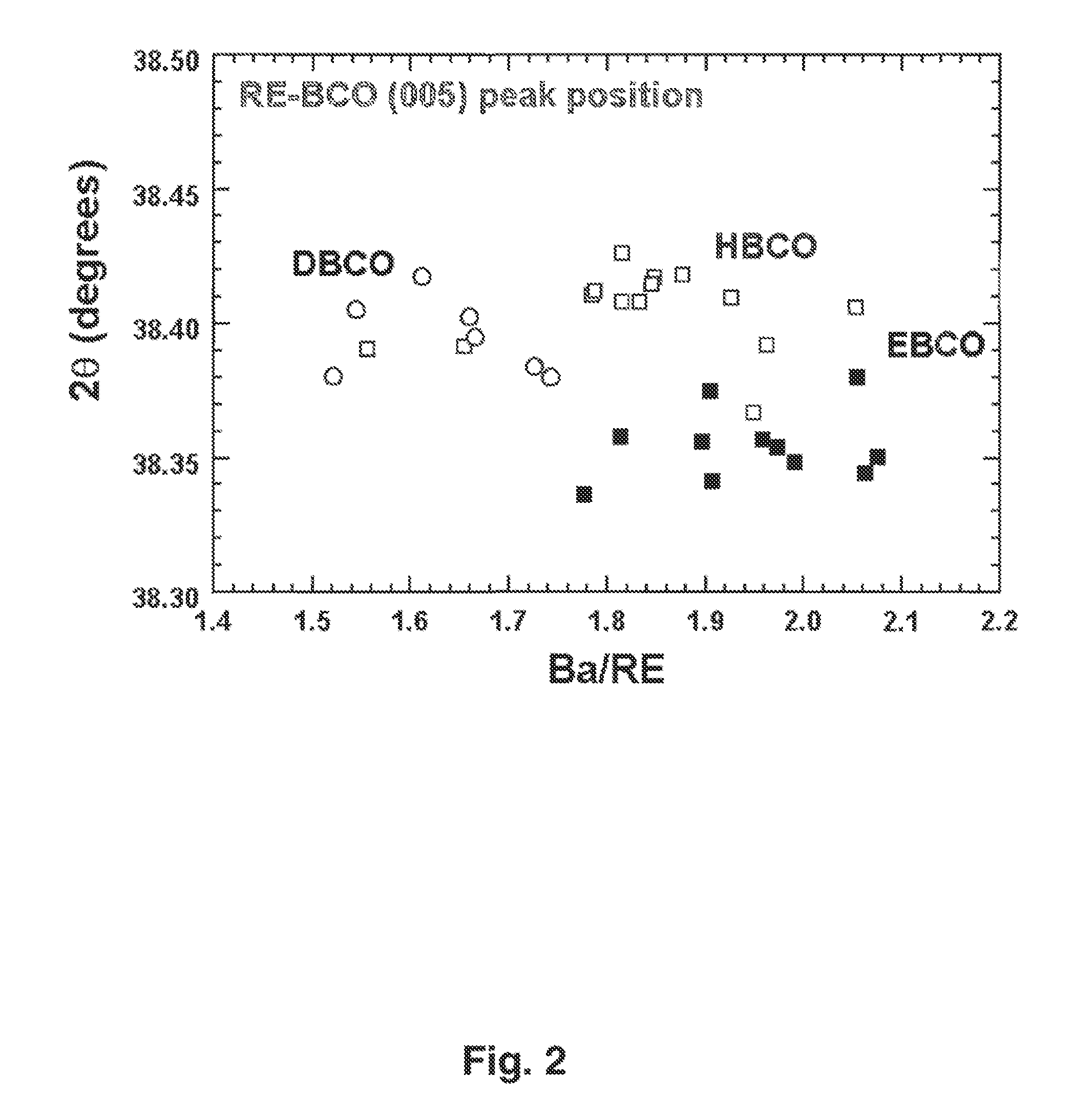
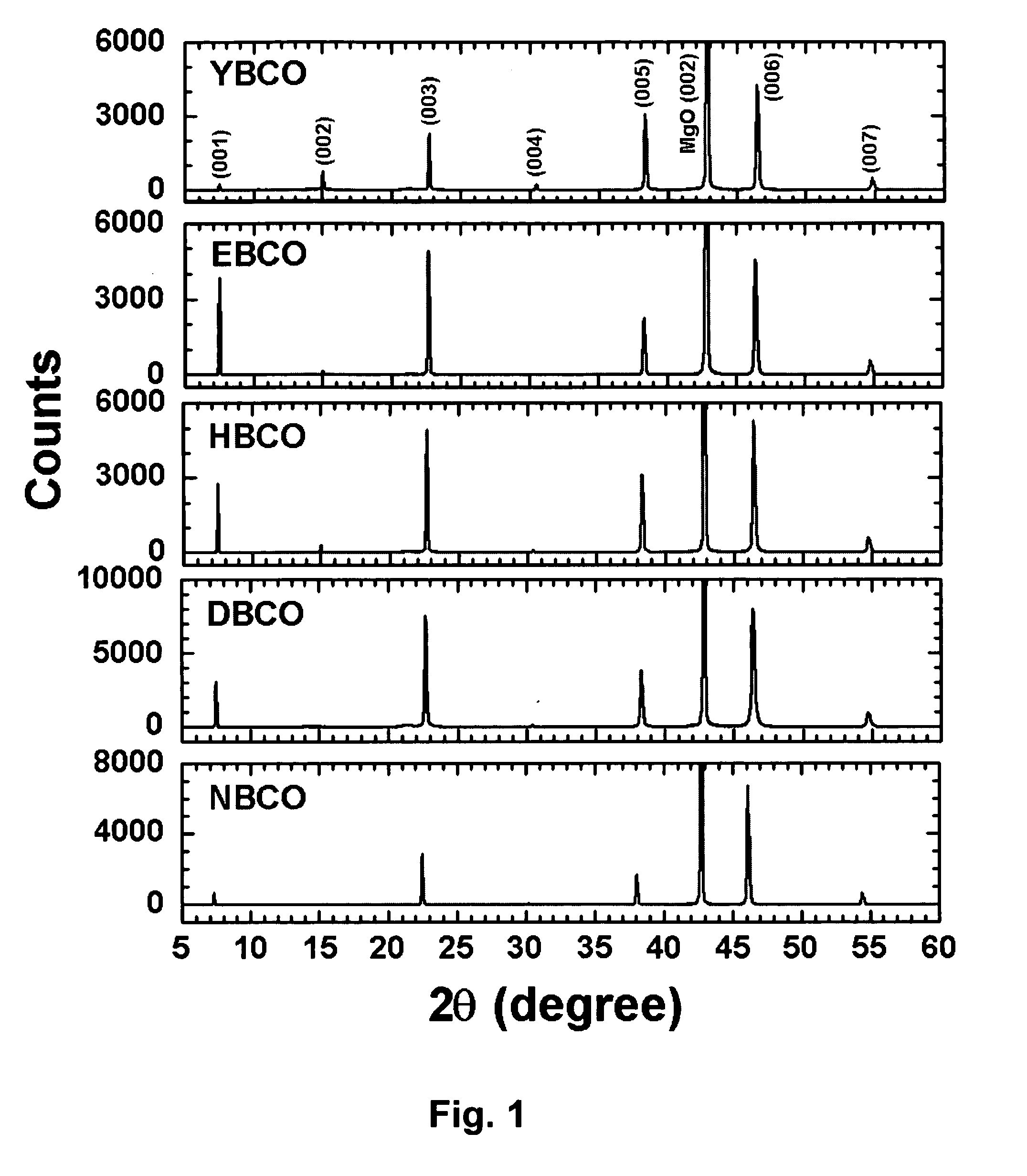
RF-PROPERTIES-OPTIMIZED COMPOSITIONS OF (RE) Ba2Cu3O7-8 THIN FILM SUPERCONDUCTORS
ActiveUS20110230356A1Optimized microwave and RF propertyReduce surface resistanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh-temperature superconductivity
The films of this invention are high temperature superconducting (HTS) thin films specifically optimized for microwave and RF applications. In particular, this invention focuses on compositions with a significant deviation from the 1:2:3 stoichiometry in order to create the films optimized for microwave / RF applications. The RF / microwave HTS applications require the HTS thin films to have superior microwave properties, specifically low surface resistance, Rs, and highly linear surface reactance, Xs, i.e. high JIMD. As such, the invention is characterized in terms of its physical composition, surface morphology, superconducting properties, and performance characteristics of microwave circuits made from these films.
Owner:HIGH TEMPERATURE SUPERCONDUCTORS INC
Seafood spoilage indicator
InactiveUS7560271B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCadaverineColor changes
An enzyme based nondestructive sensor for the qualitative detection of spoilage in seafood is provided wherein the sensor does not alter the physical composition of the seafood specimen. The sensor comprises a sampling matrix, at least three or more enzymes in contact with the sampling matrix, and at least one indicator compound in contact with the sampling matrix. The enzymes are capable of interacting with four target chemicals comprising putrescine, cadaverine, histamine and tyramine, which are located on the surface of the seafood specimen. The indicator compound is capable of changing the color of the sampling matrix thereby indicating a qualitative visually detectable color change. A method for the nondestructive detection of the quality of a seafood specimen at any given time and for determining the remaining usable shelf life of the seafood specimen is disclosed.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Bioimpedance methods and apparatus
Methods and apparatus for providing bioimpedance analysis are provided. In certain aspects, equivalent circuit frequency response models are provided which lead to improved correlations with MRI data. The frequency response models take account of body composition, including the fat component of a body segment. Data obtained by performing bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and MRI on the calves of subjects illustrates the improved correlations achieved compared to single frequency analyses at 50 kilohertz and analyses performed using the conventional Cole-Cole model.
Owner:RENAL RES INST +1
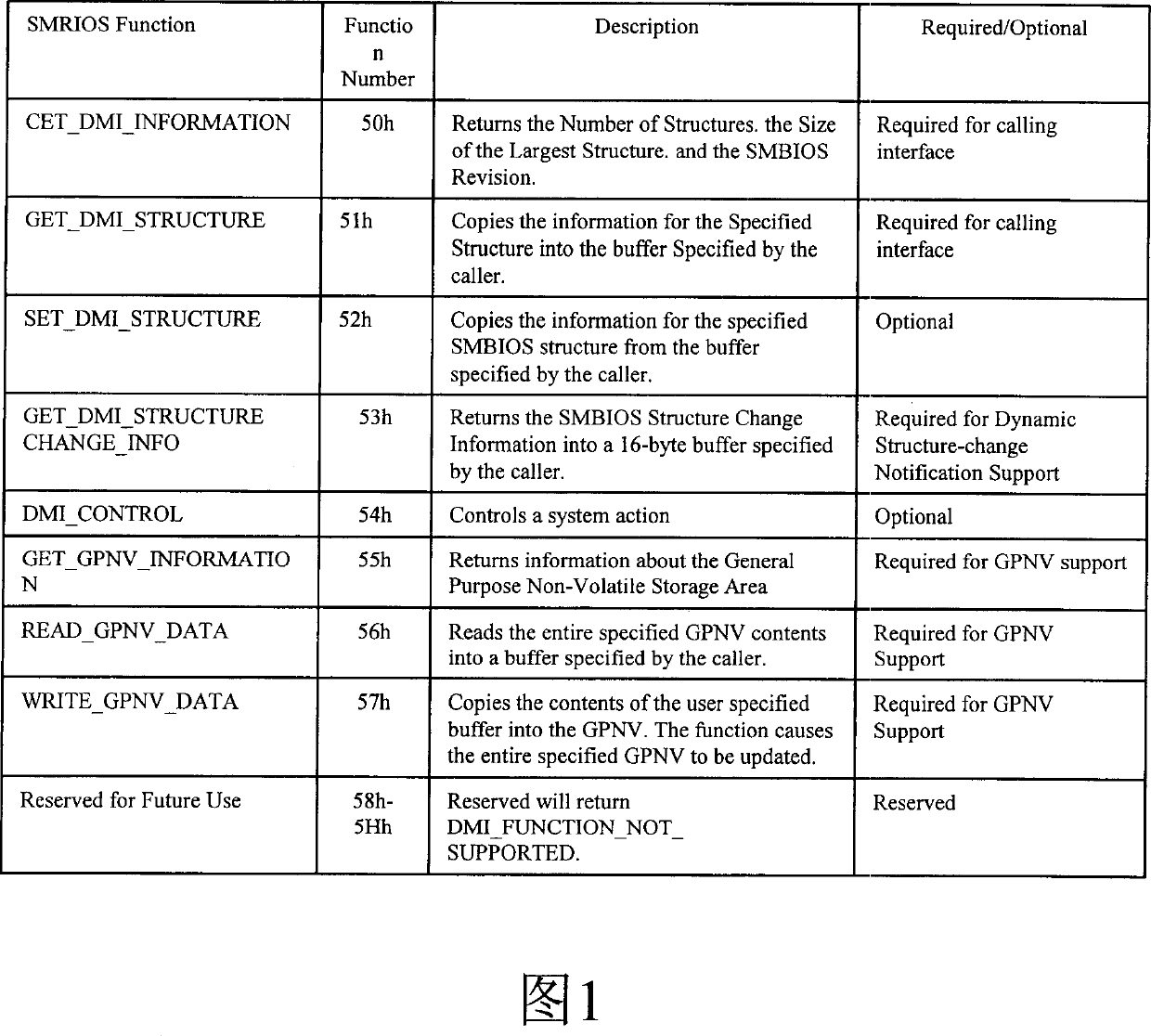
Multi adaptive internal-memory detecting method
InactiveCN1508688AImprove the content of the memory testRich contentFunctional testingInternal memoryOperational system
The invention refers to a detecting method for multi-adaptability memory, which applies to a system supporting Plug and Play, it detects and records the head information of PnP BIOS series, and gets the version number of SMBIOS, then searches the DMI structure body, finally, derives the memory information through the special structure body. The invention can apply to several main operation systems such as DOS, Windows, and Windows NT, and it can detect the memory information, includes the memory size, physical composition, the capacity of each physical unit, physical position and memory bank information.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
RF-properties-optimized compositions of (RE)Ba2Cu3O7-delta thin film superconductors
ActiveUS20060229211A1Efficient use ofImprove Microwave PerformanceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsOxide conductorsHigh-temperature superconductivityLinearity
The films of this invention are high temperature superconducting (HTS) thin films specifically optimized for microwave and RF applications. In particular, this invention focuses on compositions with a significant deviation from the 1:2:3 stoichiometry in order to create the films optimized for microwave / RF applications. The RF / microwave HTS applications require the HTS thin films to have superior microwave properties, specifically low surface resistance, Rs, and highly linear surface reactance, Xs, i.e. high JIMD. As such, the invention is characterized in terms of its physical composition, surface morphology, superconducting properties, and performance characteristics of microwave circuits made from these films.
Owner:HIGH TEMPERATURE SUPERCONDUCTORS LLC
Method for defining a standardized procedure for a haircut, a code for defining a haircut, and a method for giving a haircut
A method for defining a standardized procedure for a predetermined haircut comprises defining two or more sections of hair on a subject, defining two or more geographic checkpoints on the group consisting of the face, head, neck, and body, wherein each of the geographic checkpoints is generic to a large number of subjects, and defining at least one vector hairway, wherein the at least one vector hairway corresponds to one of the sections of hair and two or more of the geographic checkpoints, further wherein the at least one vector hairway defines a path upon which hair is cut. A code for use in defining a standardized procedure for a predetermined haircut and a method for giving a haircut based upon a standardized procedure are also disclosed.
Owner:GARRELL PATRICK
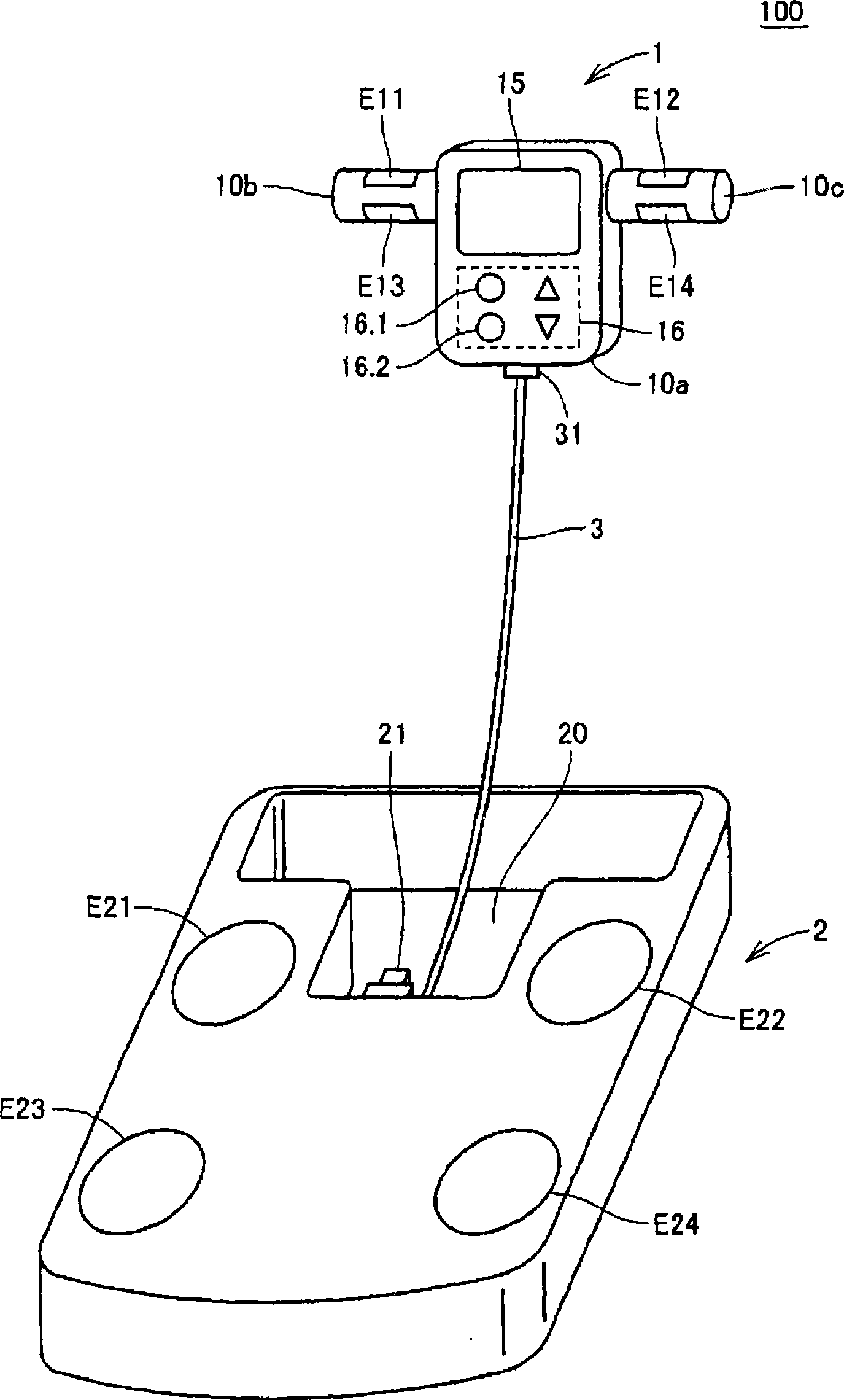
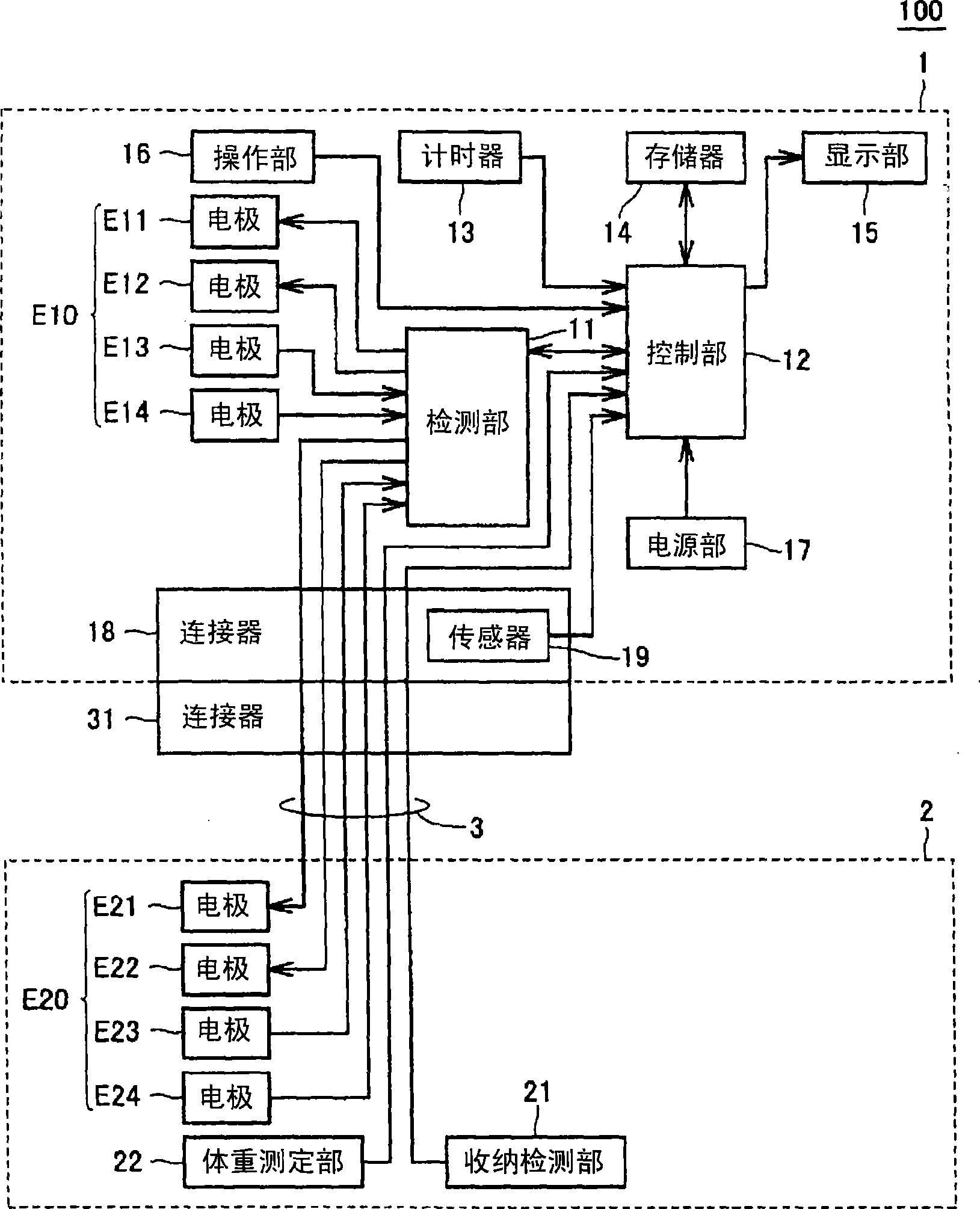
Body composition monitor capable of accurately measuring whole-body composition and achieving facilitated manipulation
ActiveCN101389269AImprove reliabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPotential difference
The invention provides a body composition meter comprising a detecting section (11) for detecting a first potential difference between a hand and a leg of subject by applying a current between the hand and leg through a hand electrode and a leg electrode and a second potential difference between the hands or the legs of the subject by applying a current between the hands or the legs through either the hand electrodes or the leg electrodes, a first body composition calculating section (103) for calculating a first whole-body composition by using the whole-body impedance based on the detection result of the first potential difference, a correcting section (104) for correcting the two-limb impedance according to the detection result of the second potential difference, and a second body composition calculating section (105) for calculating a second whole-body composition by using the corrected two-limb impedance.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Compositions comprising galactomannan and a process thereof
The present invention relates to a novel botanical galactomannan, obtained from the plant Trigonella foenum graecum, as provided in structural formula I, optionally along with excipients for improving body composition and the factors related to the pre-diabetic and diabetic conditions, and a process of manufacture of the same. The present invention also relates to the use of the novel botanical galactomannan for improving body composition, reducing body fat, increasing muscle mass, enhancing strength and improving impaired glucose metabolism. The present invention also relates to the use of the novel botanical galactomannan for the improvement of factors related to the pre-diabetic and diabetic conditions.
Owner:INDUS BIOTECH PVT
Body composition analysis apparatus
A wearable device for performing a plurality of functions including a first function to measure a body composition parameter of a user wearing the device and one or more second functions requiring aninput from the user. The device comprises a first electrode arranged, when the device is worn by a user, to contact the body of the user, a second electrode arranged to be touched by the user, a touchcontroller arranged to detect when a user touches the second electrode, a body composition parameter measurement device arranged, when the user is in contact with the second electrode, to measure a body impedance of the user by passing a current between the first and second electrodes and detecting a voltage generated between the first and second electrode in response to the current, and to use the measured body impedance to determine a body composition parameter.
Owner:TOMTOM INT BV
Biological information measurement device, biological information measurement method, and body composition measurement device
ActiveUS8554316B2Accurate collectionImprove satisfactionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyMeasurement device
To accurately acquire body composition information using data acquired by another device. Thus, there is provided a body composition monitor with scale including a communication unit for allowing input of biological component information (cross-sectional area, site length, subcutaneous fat percentage, visceral fat percentage, etc.) of a living body measured with another device such as an MRI, where step of calculating the body composition of the living body based on the biological component information, an impedance detected by an impedance detection unit, and a weight measured by a load detection unit is executed.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
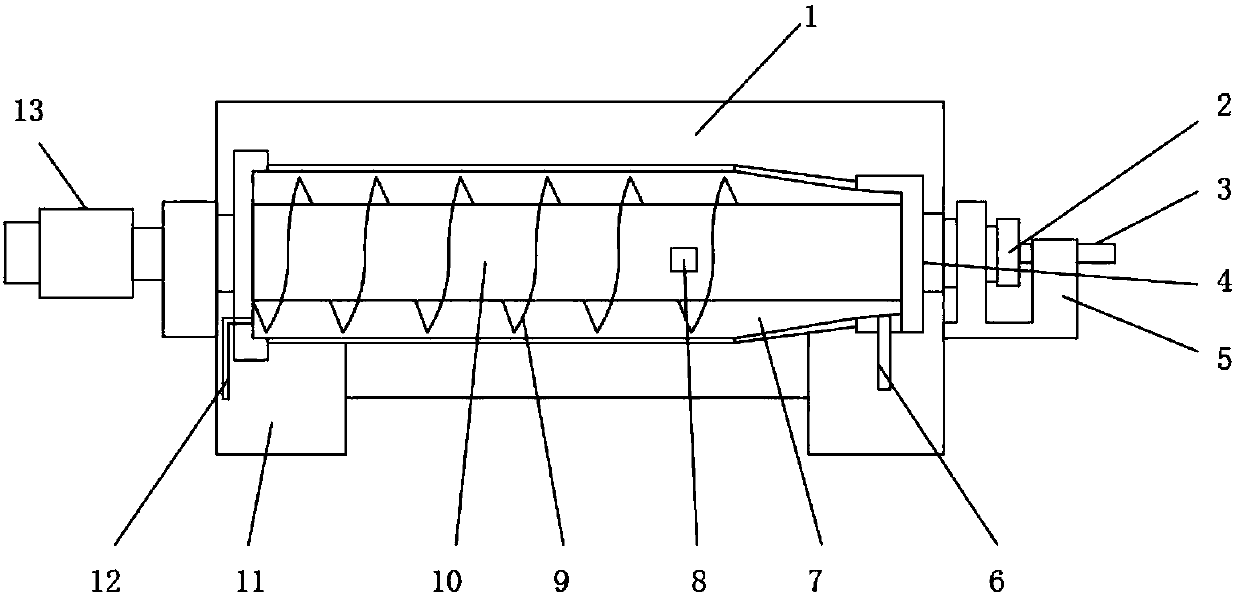
Novel oily sludge water treatment device
PendingCN107935352AReduce pollutionZero pollutionWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningChemical compositionSludge
The invention discloses a novel oily sludge water treatment device which comprises a horizontal screw machine and a disc separator, wherein the horizontal screw machine is electrically connected withthe disc separator; a feeding hole is formed in the surface on one side of the horizontal screw machine; a bearing seat is welded at the bottom of the feeding hole; the feeding hole is connected witha machine body by a connecting pipe. In the device, a chemical method is abandoned in a novel process, so that physical compositions and chemical compositions in oily sludge water treated by the novelprocess and the device are not changed, and the production requirements of the subsequent process can be completely achieved. Therefore, according to the novel process and the device, settlement, separation and use can be realized on the spot, and harmless and reduction requirements can be achieved on the spot, in order that reduction and harmless treatment can be performed on the oily sludge water, and pollution and harm cannot be caused again by the oily sludge water in the processes of storage, transportation, stacking and treatment.
Owner:天津绿业石化环保装备有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com