Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Peak velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Peak velocity is a specific point in the movement at which velocity of the measured object (center of mass, barbell, projectile…) is at its highest. Depending on the type of movement being performed, peak velocity will occur at different regions within the movement.
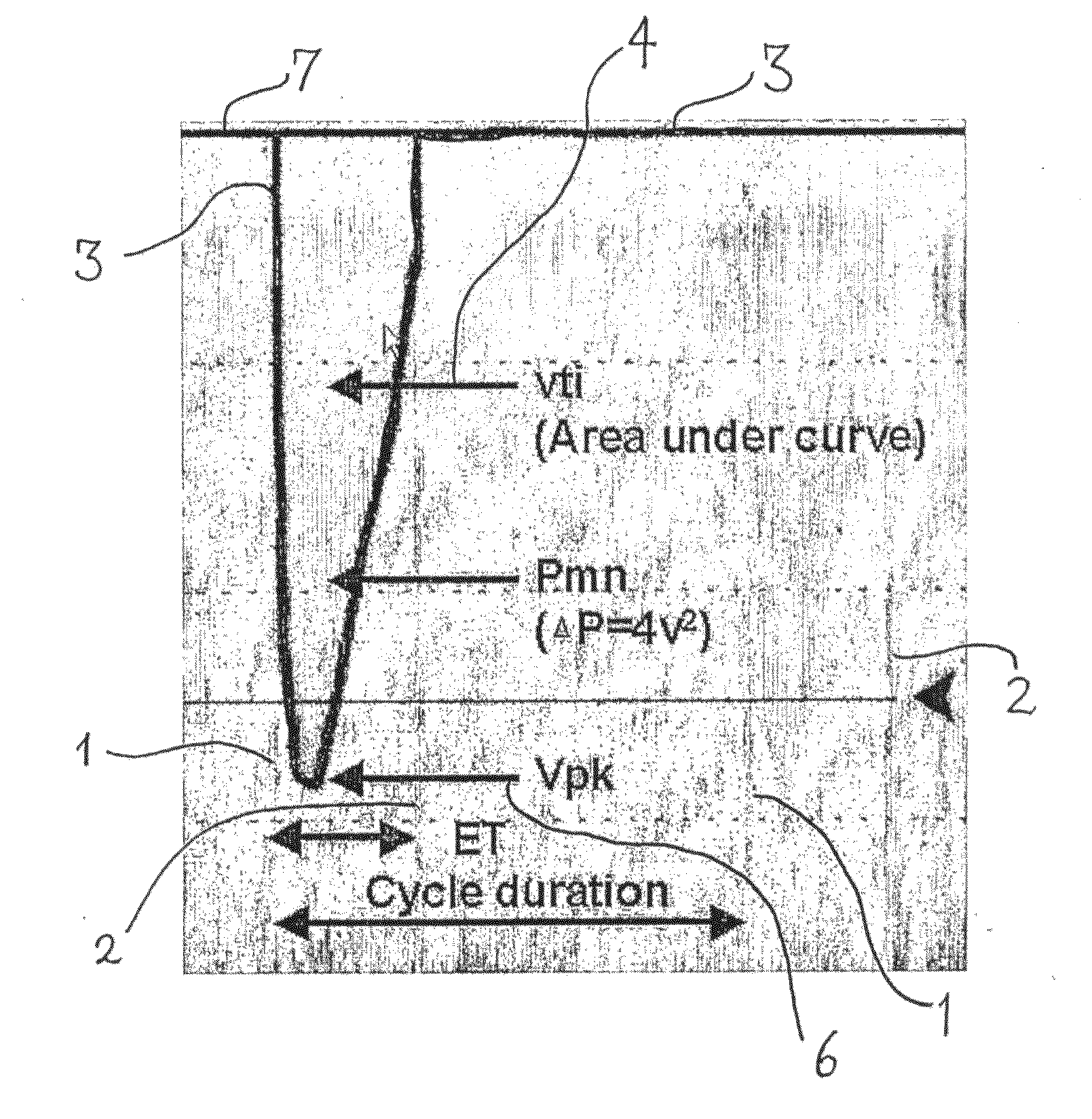
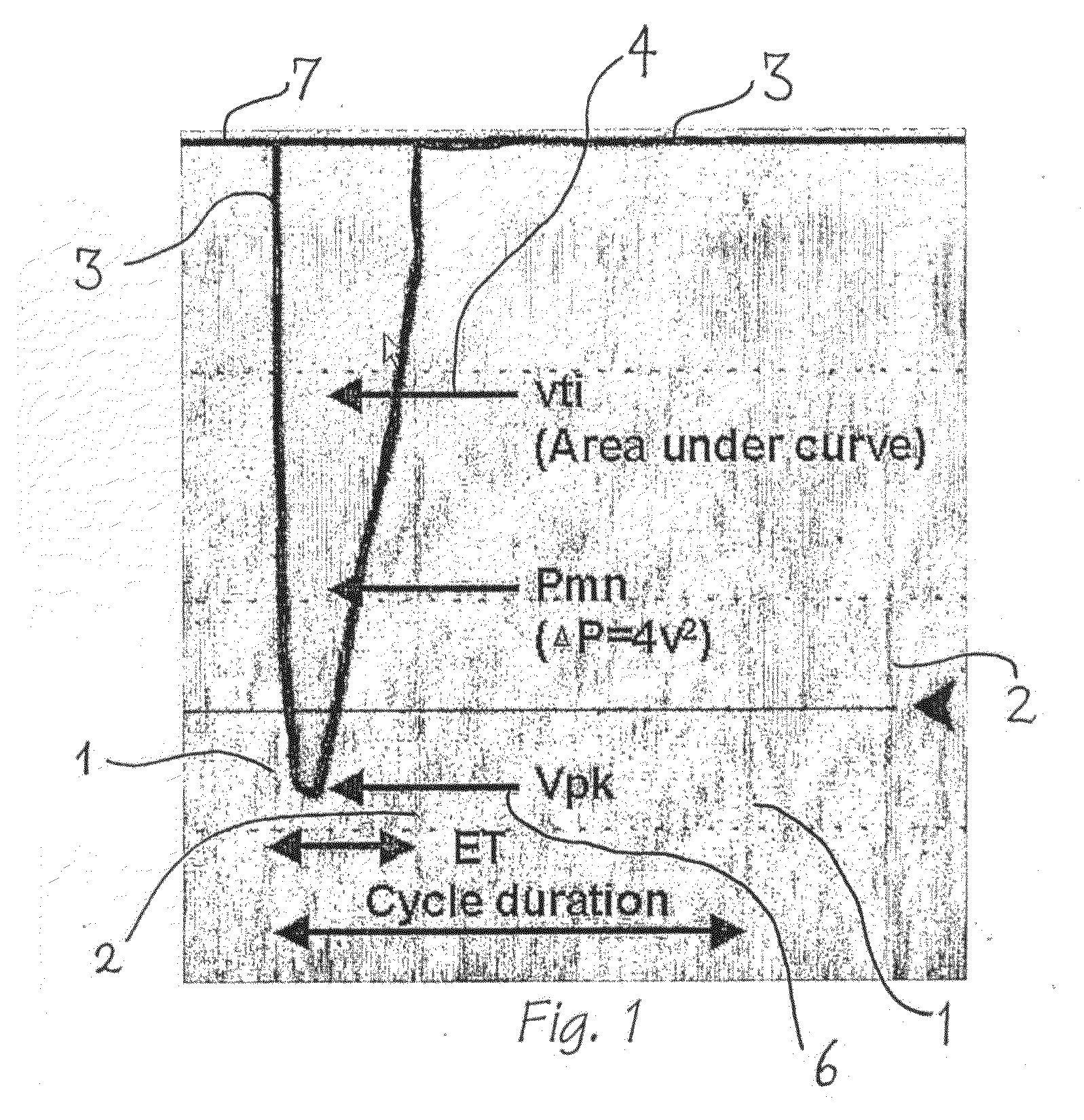
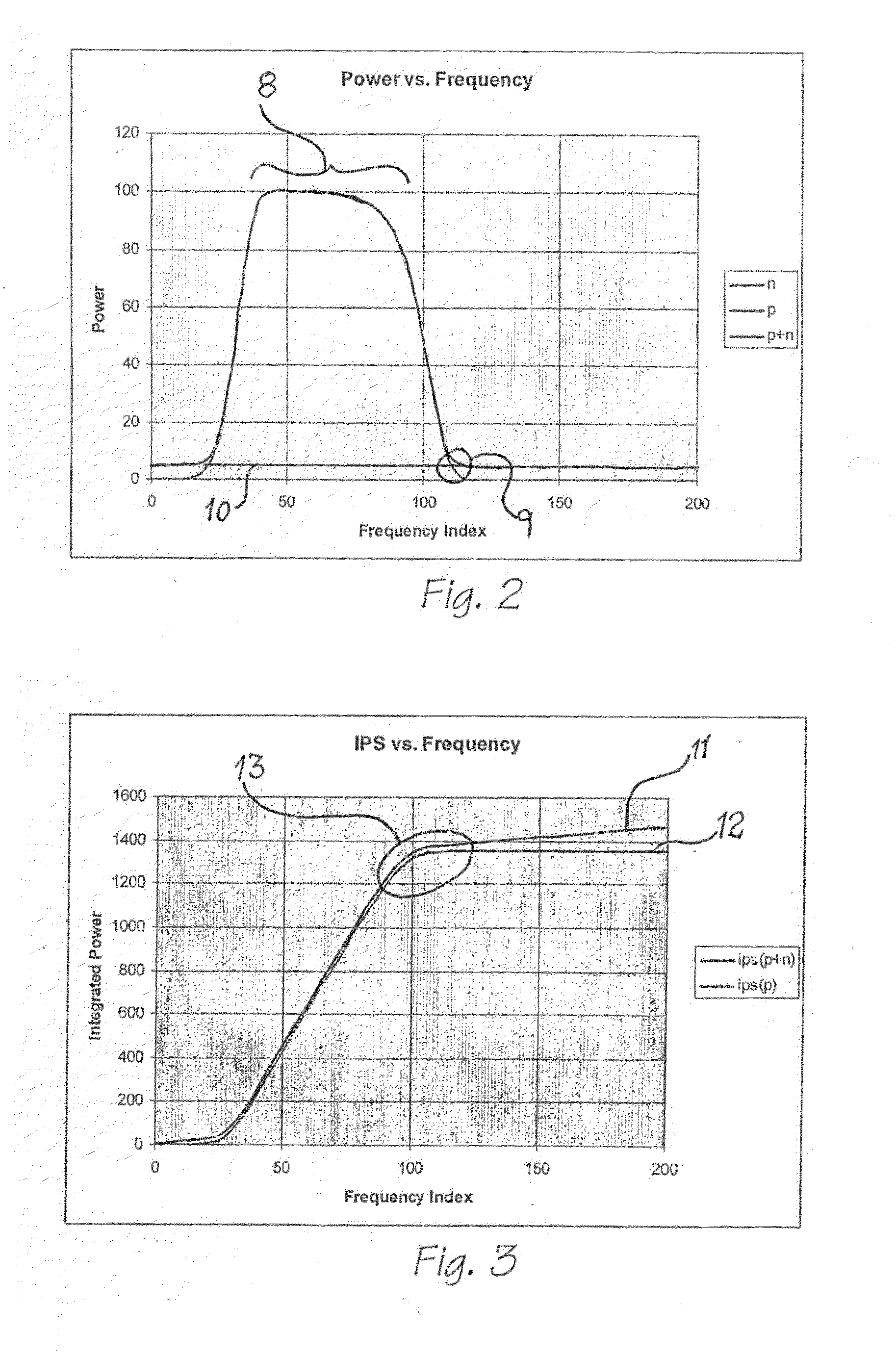
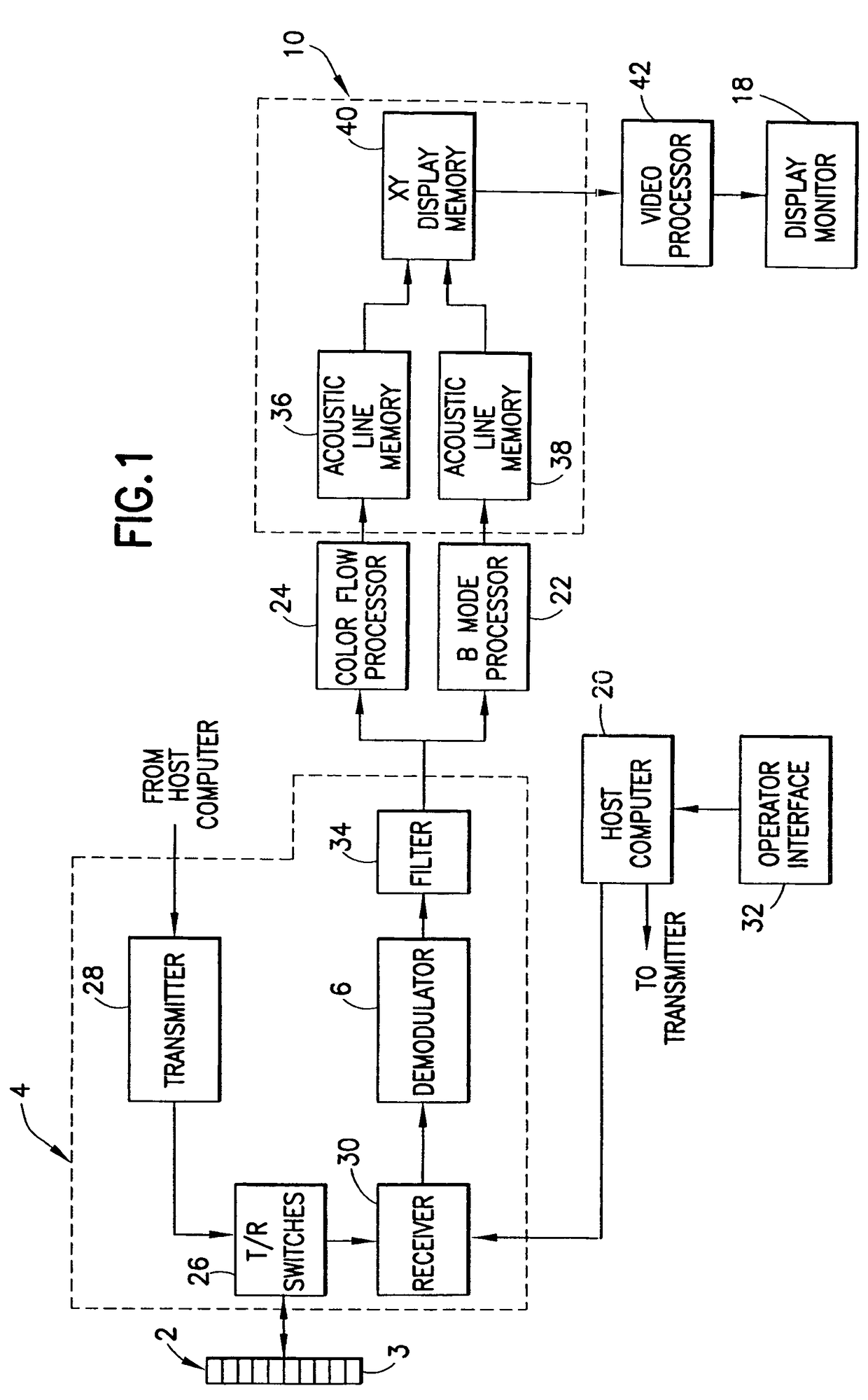
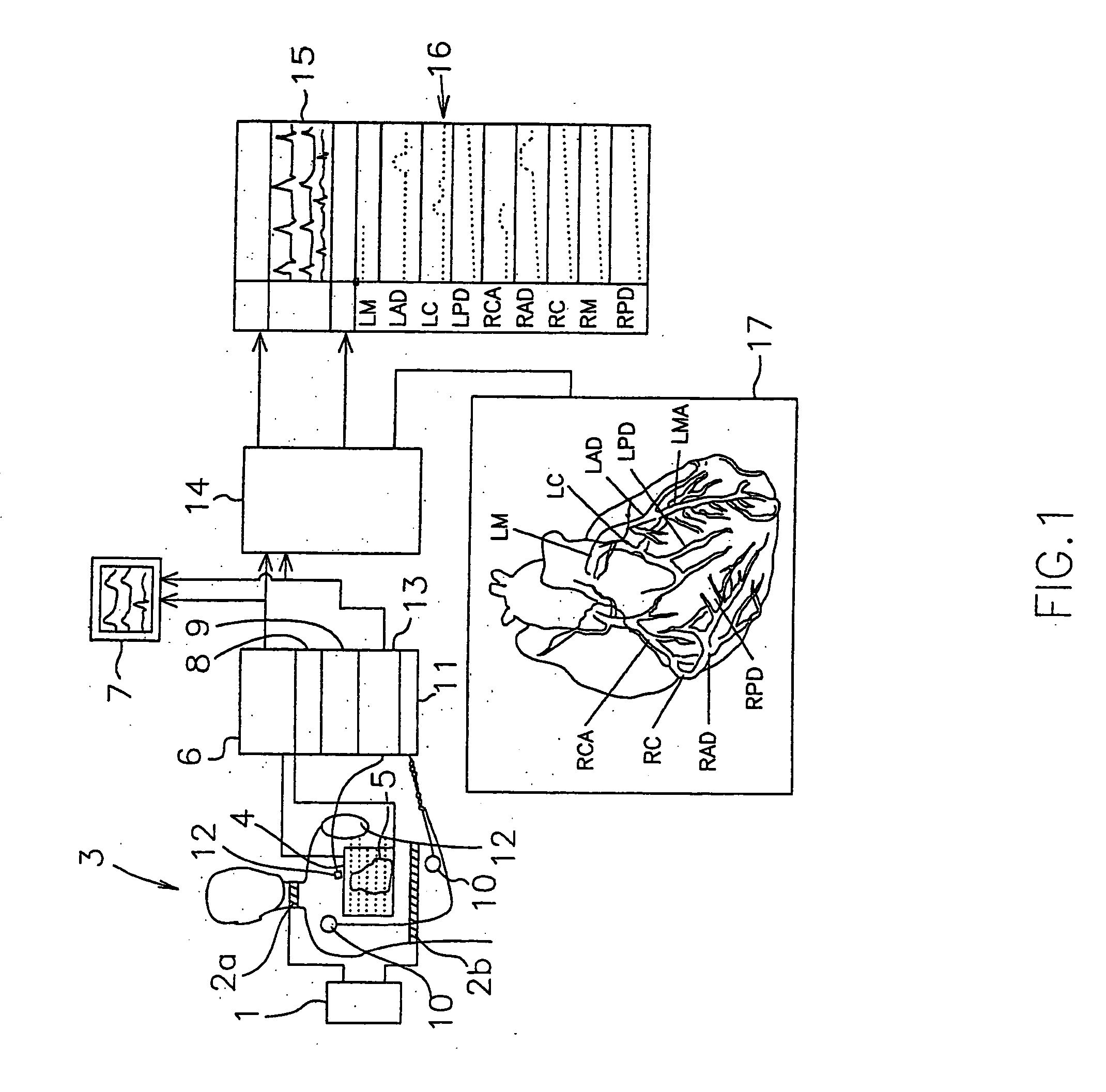
Viewing system having means for processing a sequence of ultrasound images for performing a quantitative estimation of flow in a body organ
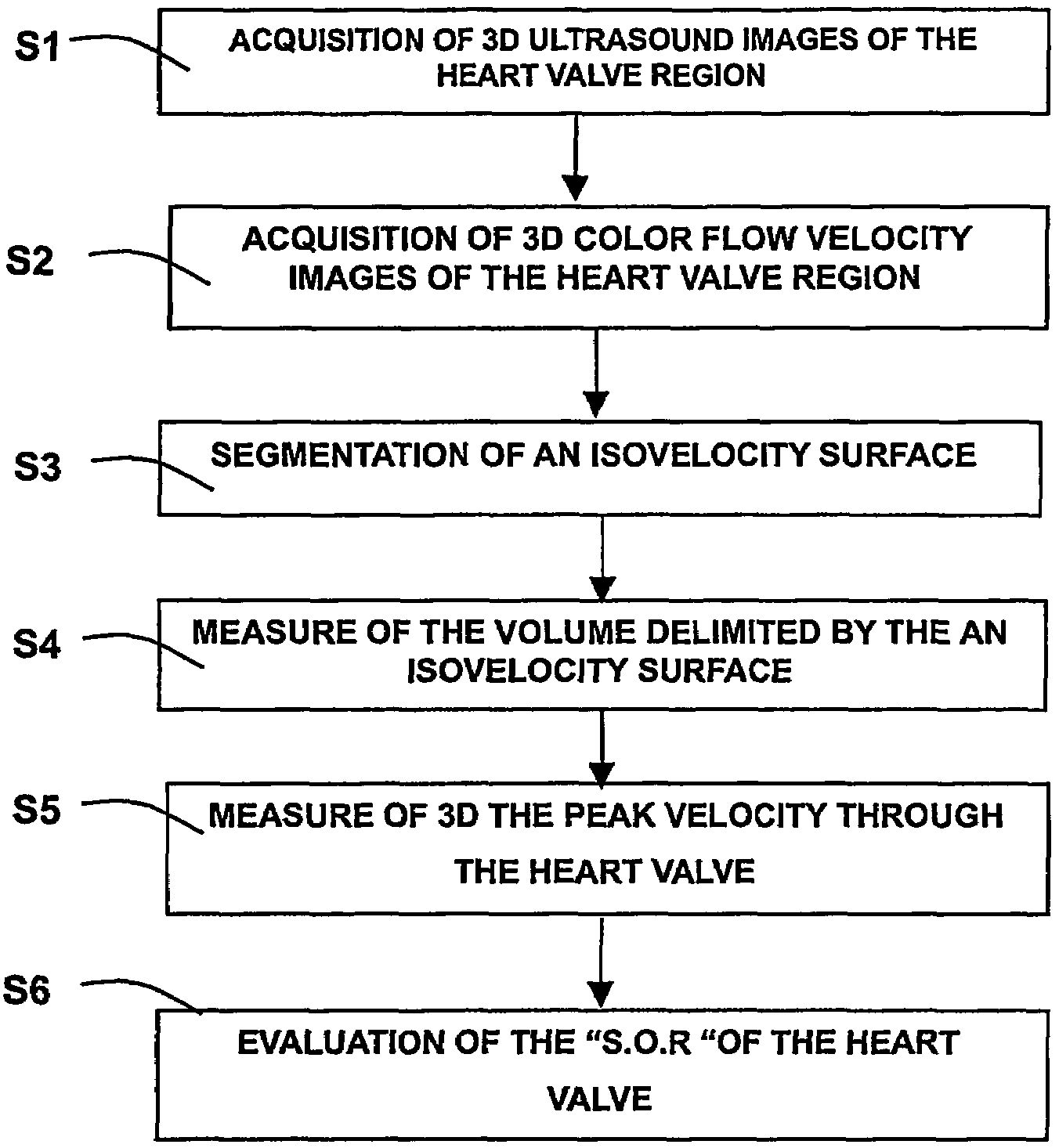
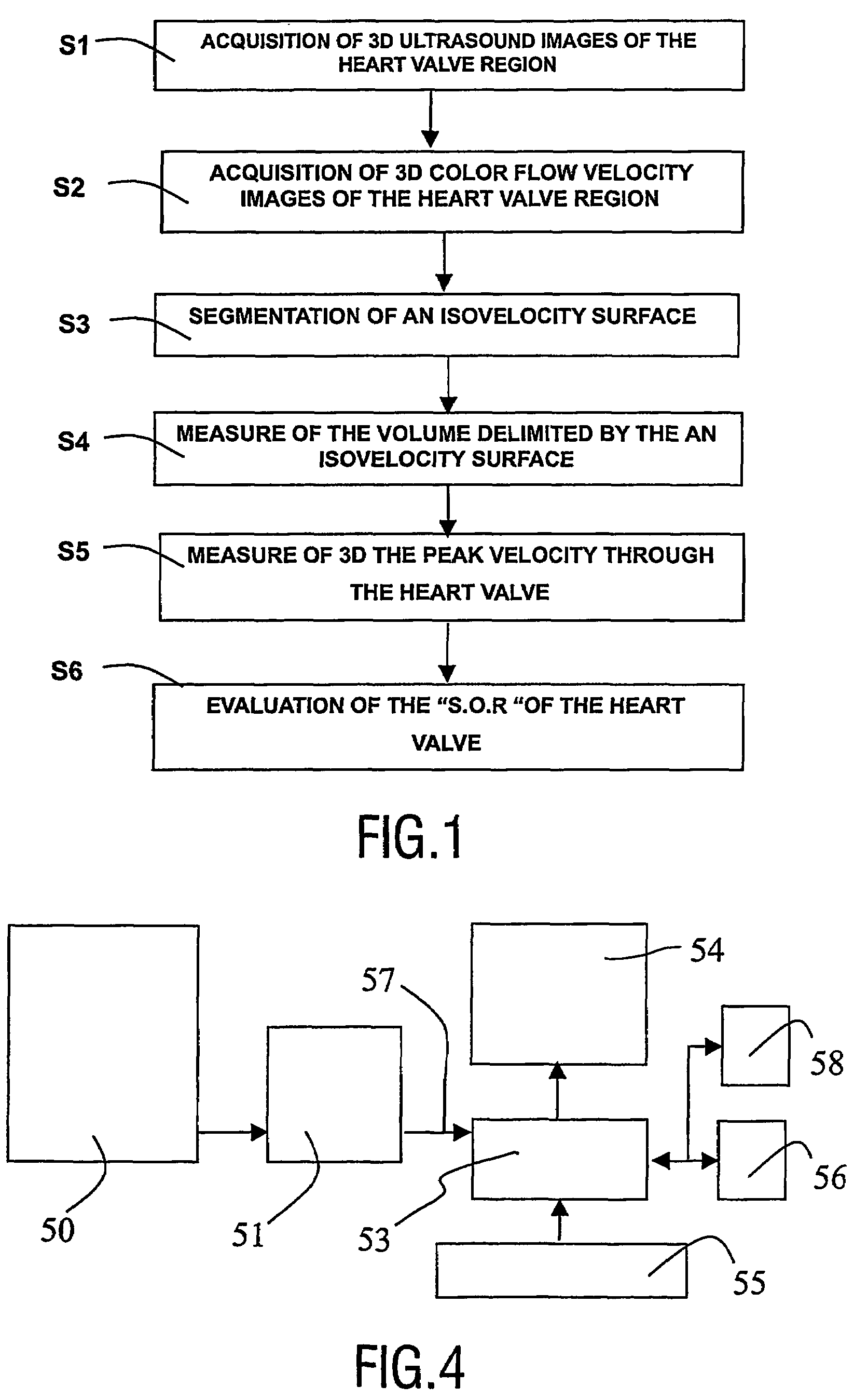
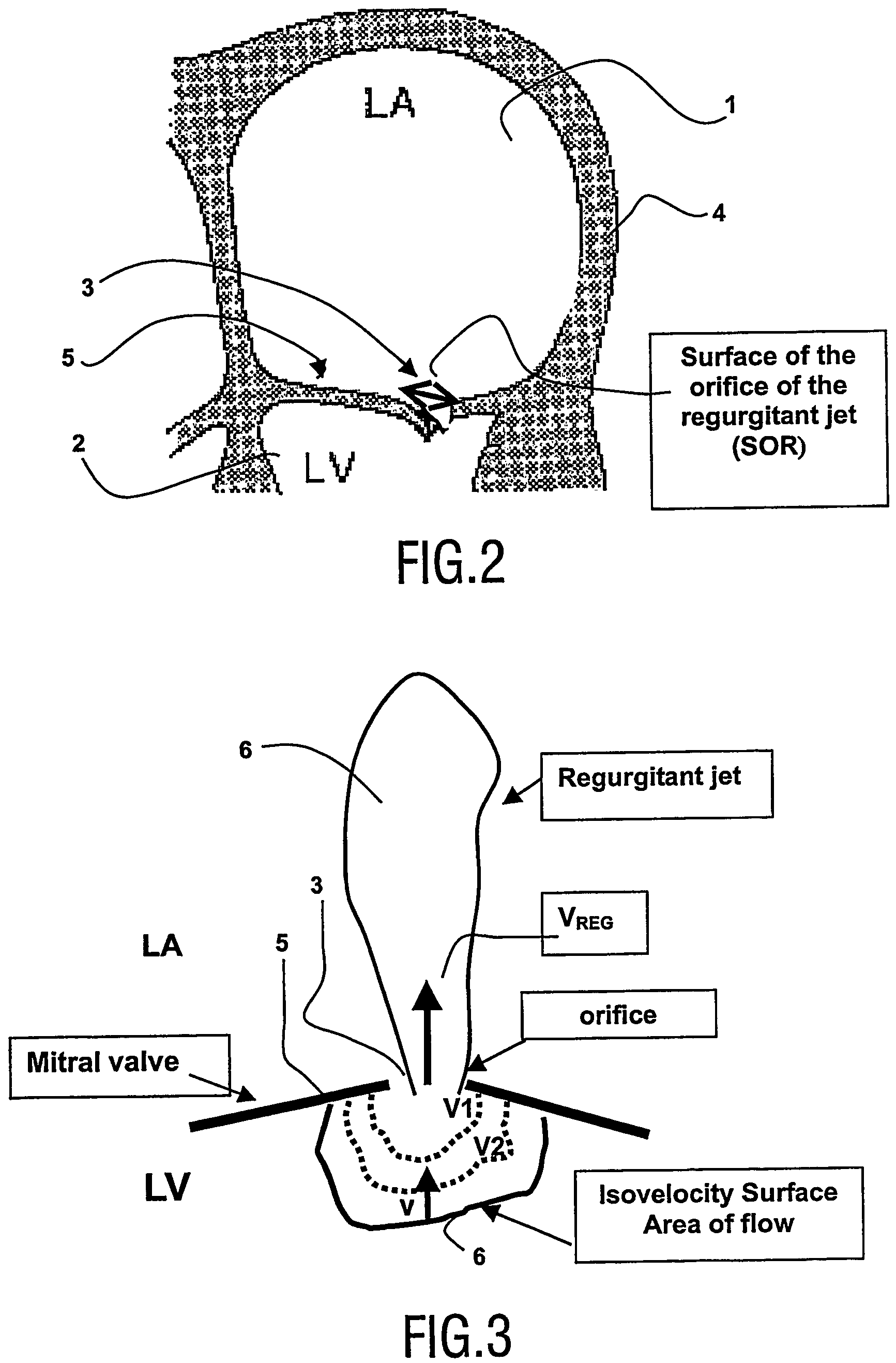
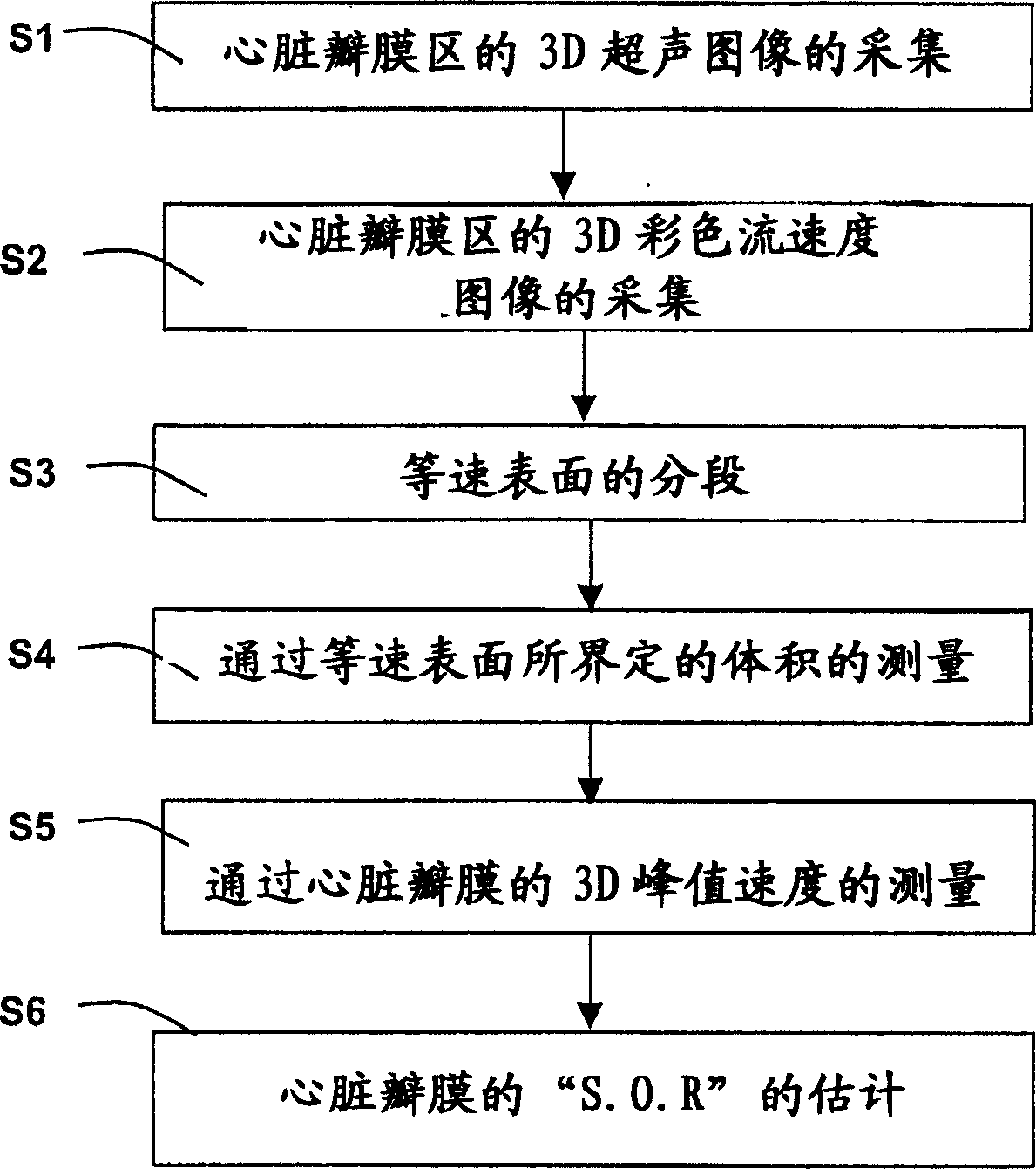
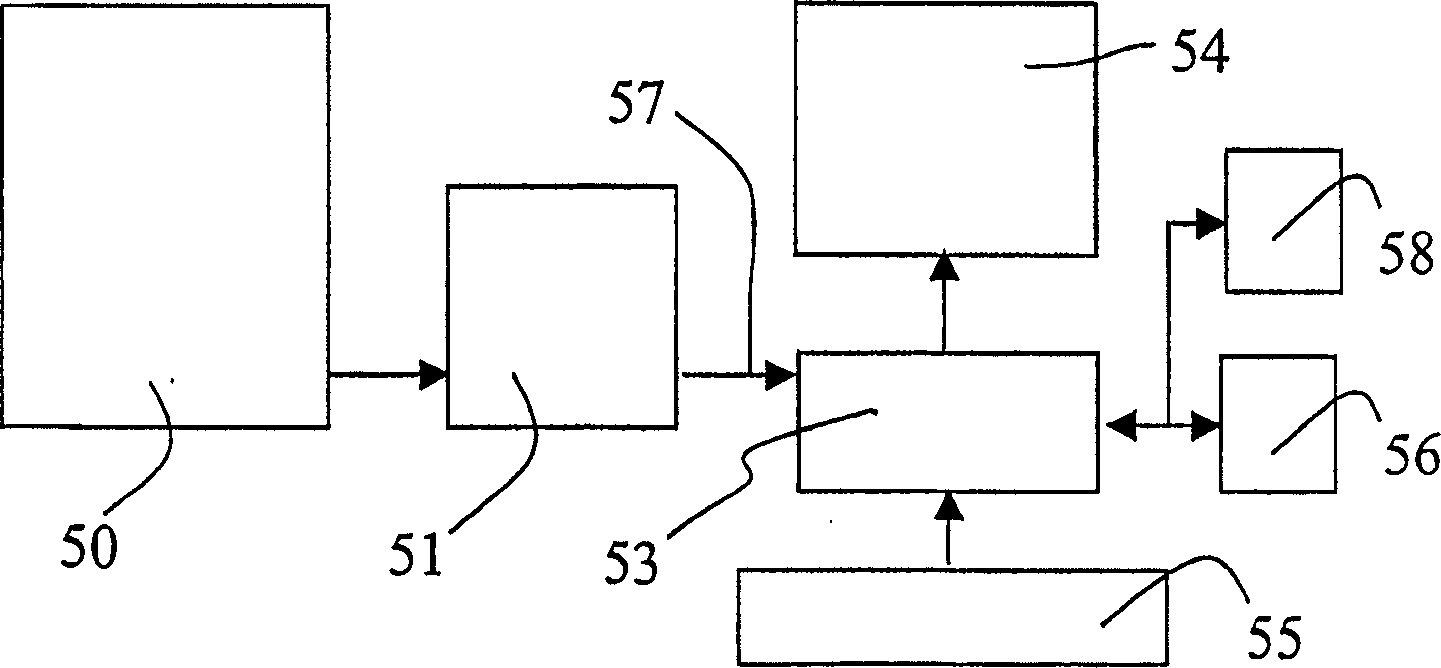
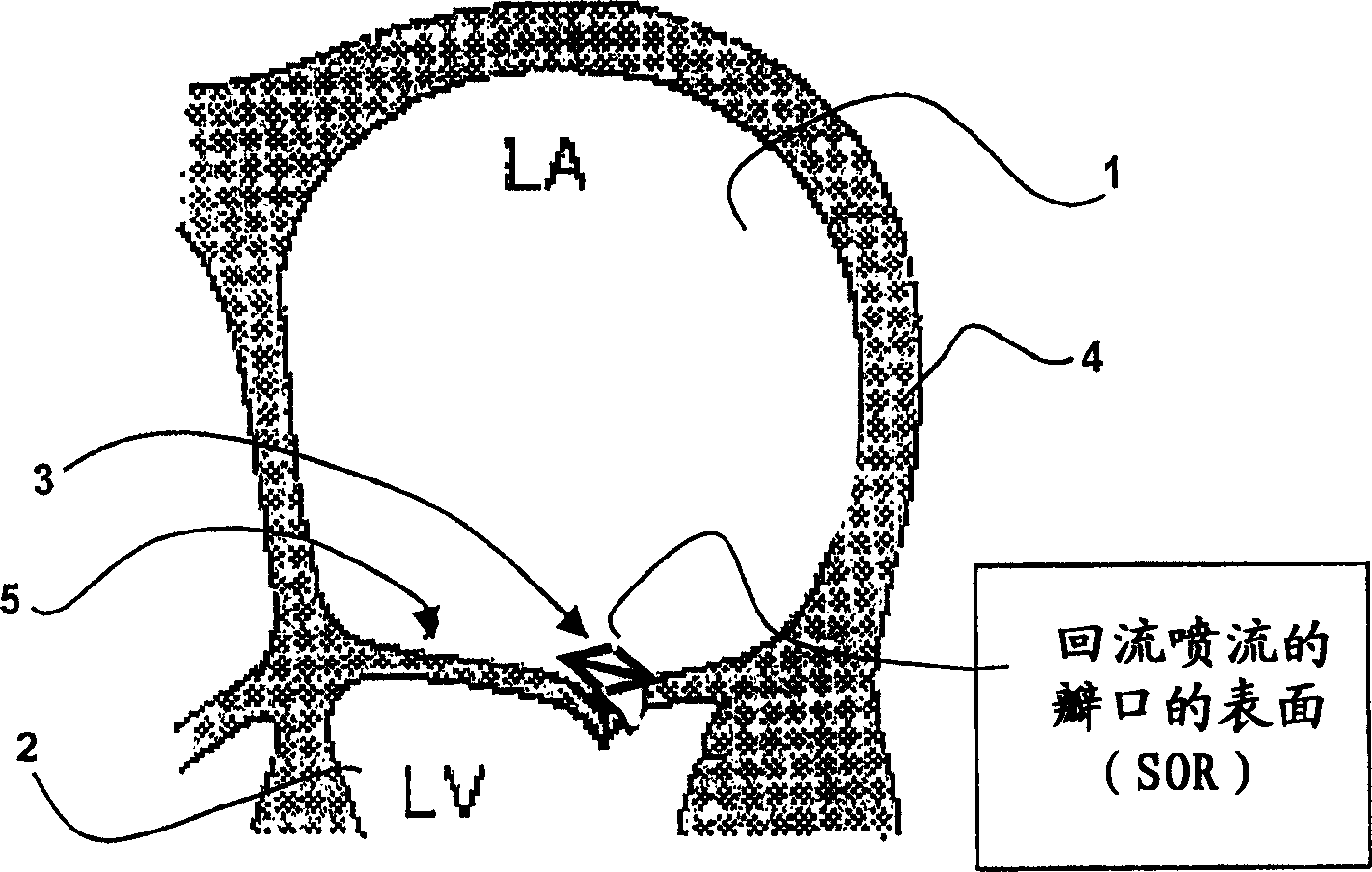
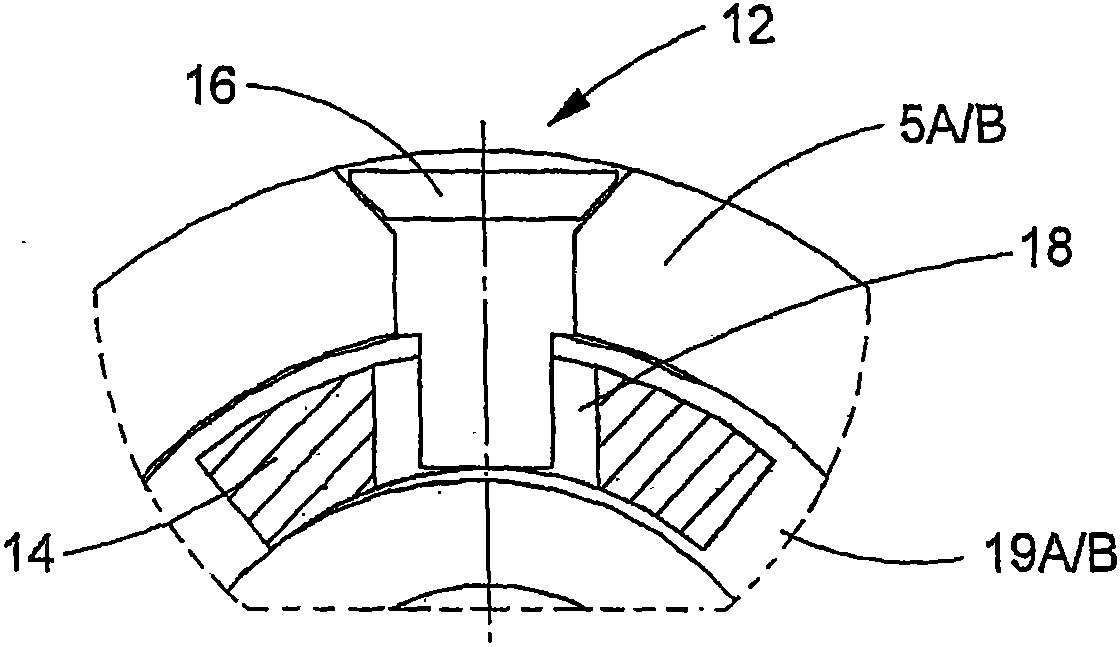
A medical ultrasound viewing system for processing a sequence of three-dimensional (3-D) ultrasound images far performing a quantitative estimation of a flow through a body organ comprising means for performing steps of acquiring a sequence of 3D color flow images, of said flow; assessing the flow velocity values in the 3D images, constructing isovelocity surfaces (6) by segmentation of the flow velocity values; computing the volume (Vol) delimited by the isovelocity surfaces; and using the flow velocity value (V) and the volume (Vol) computed from a segmented surface for computing the surface of an orifice (3) of the organ through which the flow propagates. The viewing system further comprises means for performing steps of measuring the peak velocity (VREG) of said flow through said orifice; computing the surface of the orifice (SOR) through which the flow propagates as a function of the flow velocity value (V) at an isovelocity surface upstream the flow propagation with respect to said orifice, the volume (Vol) computed from said segmented isovelocity surface, and the peak velocity of the flow through said orifice. The surface is given by the formula: SOR=Vol. V / VREG. The system can be applied to the assessment of the surface of regurgitation of the mitral jet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
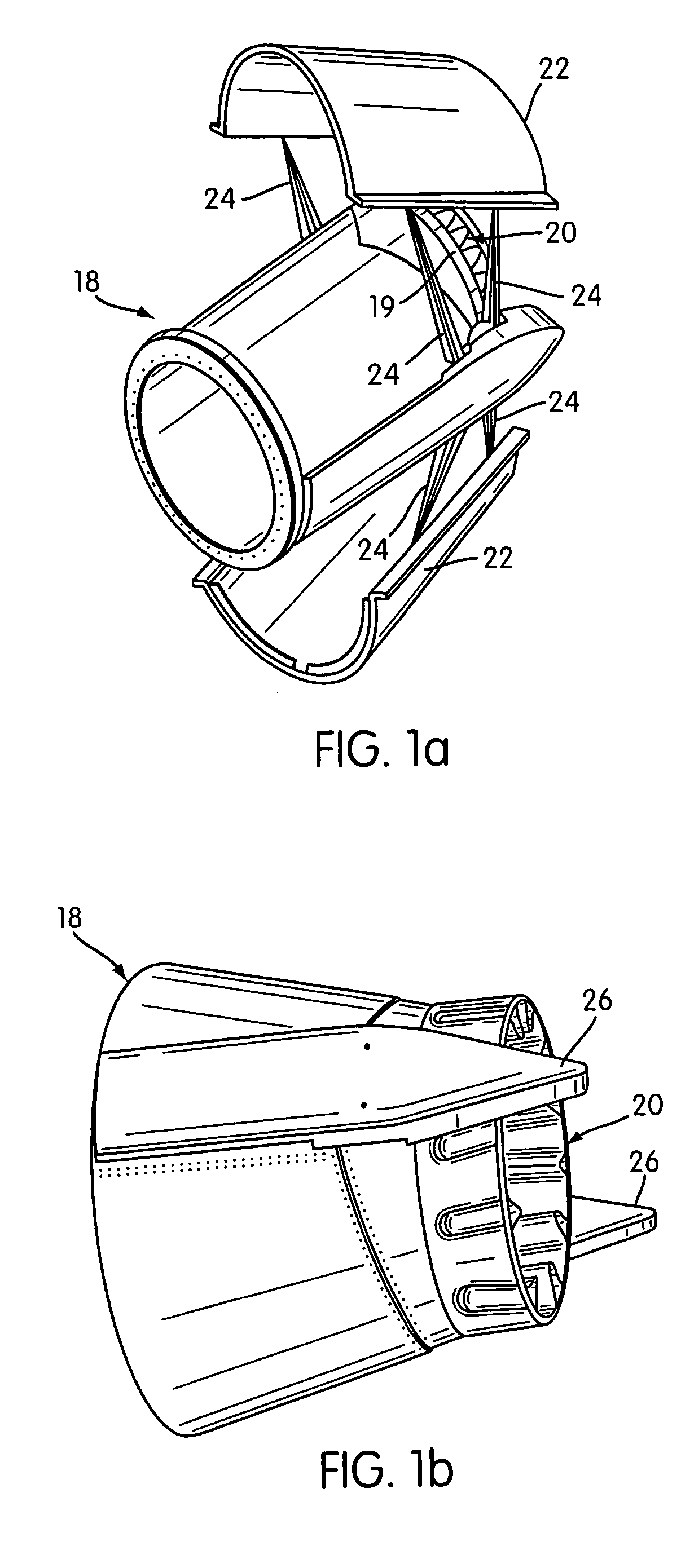
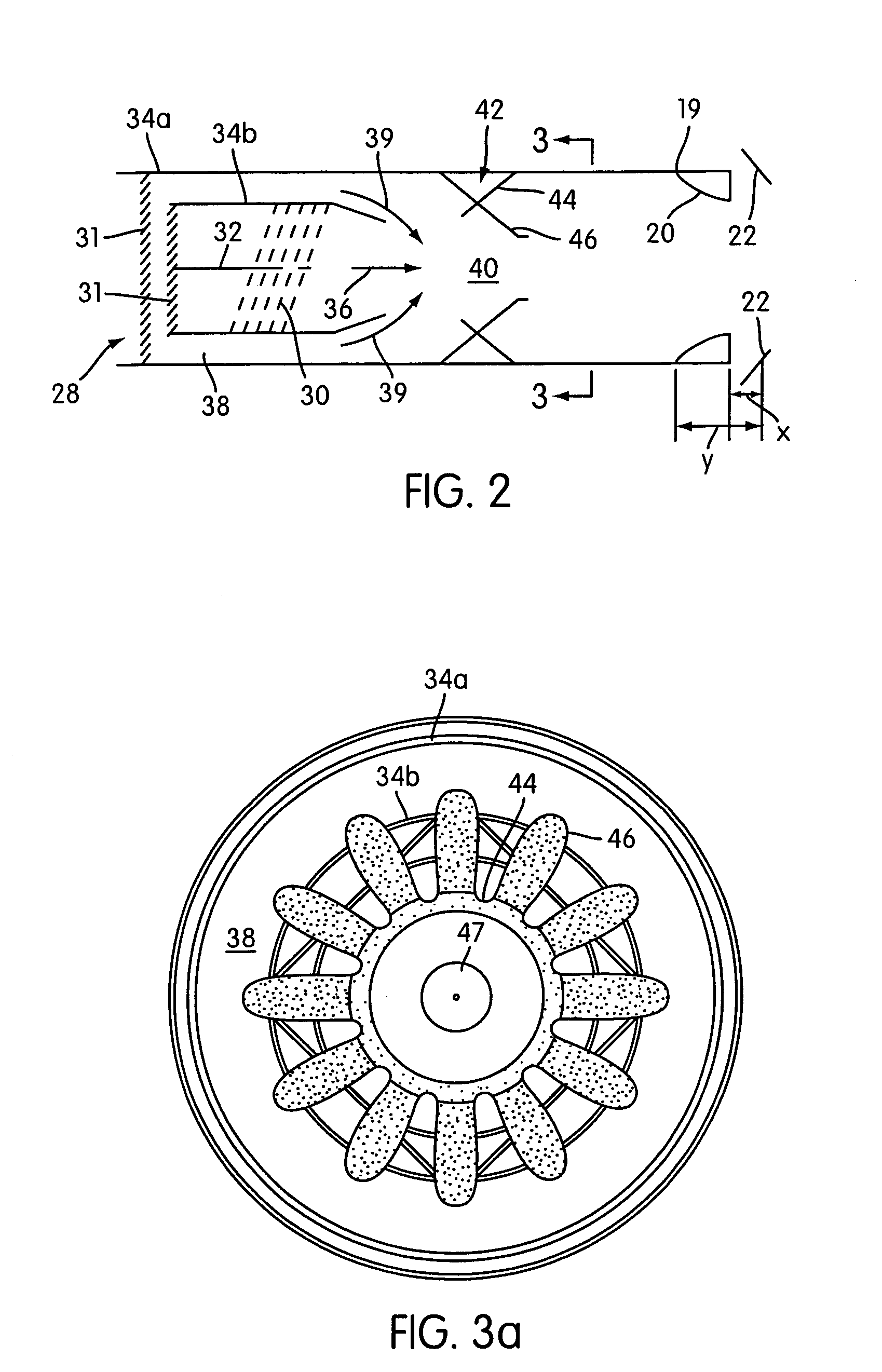
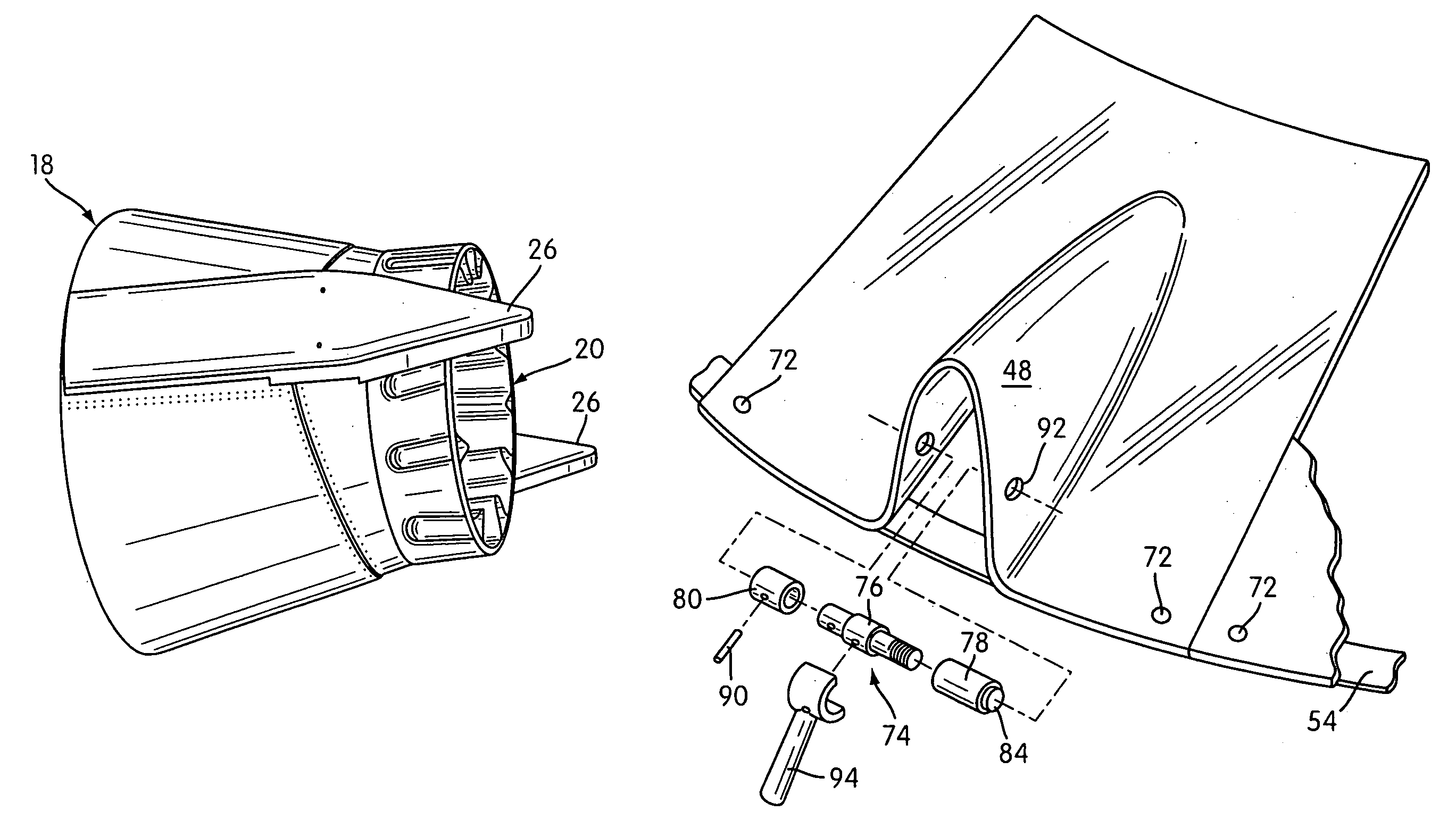
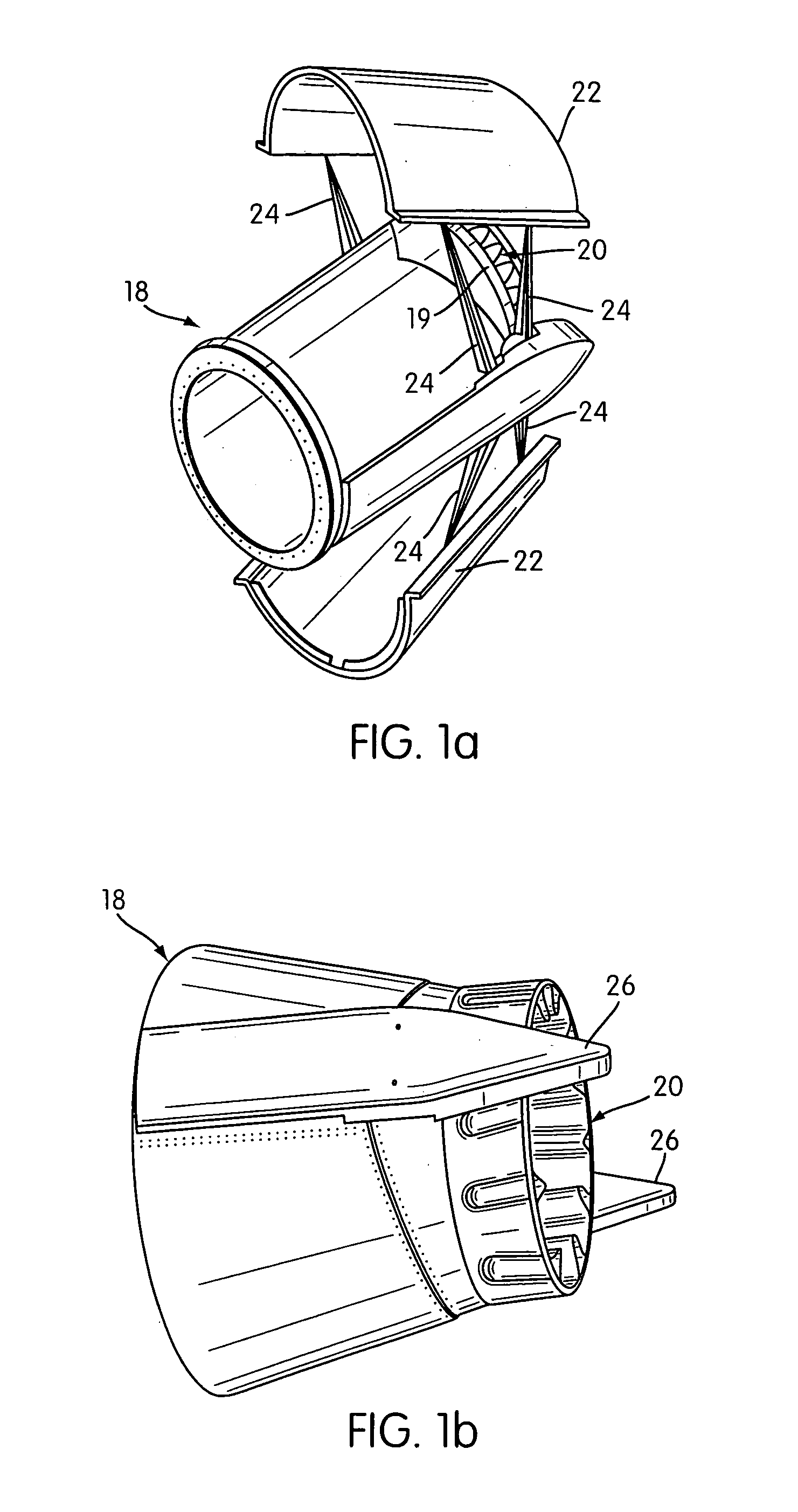
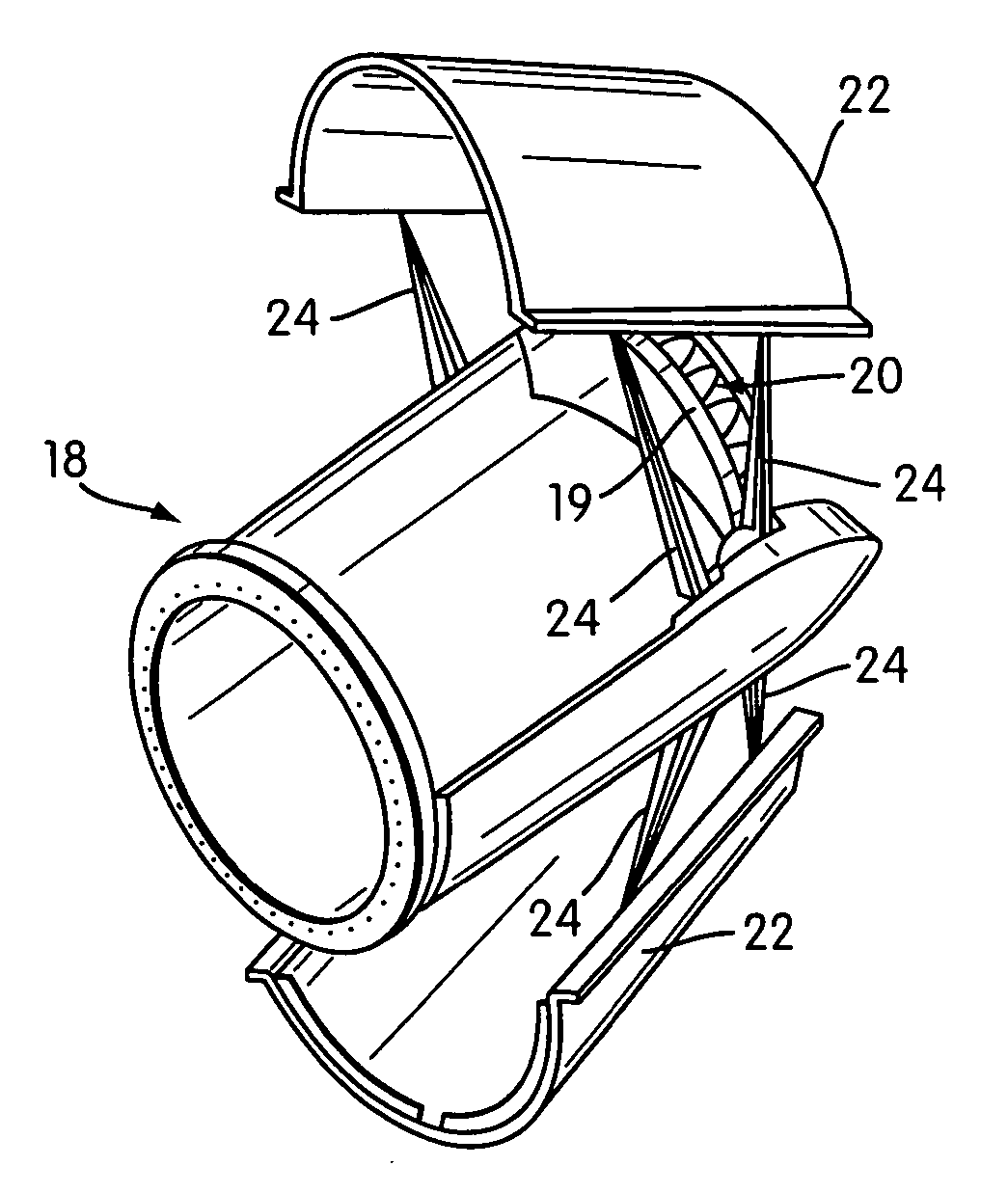
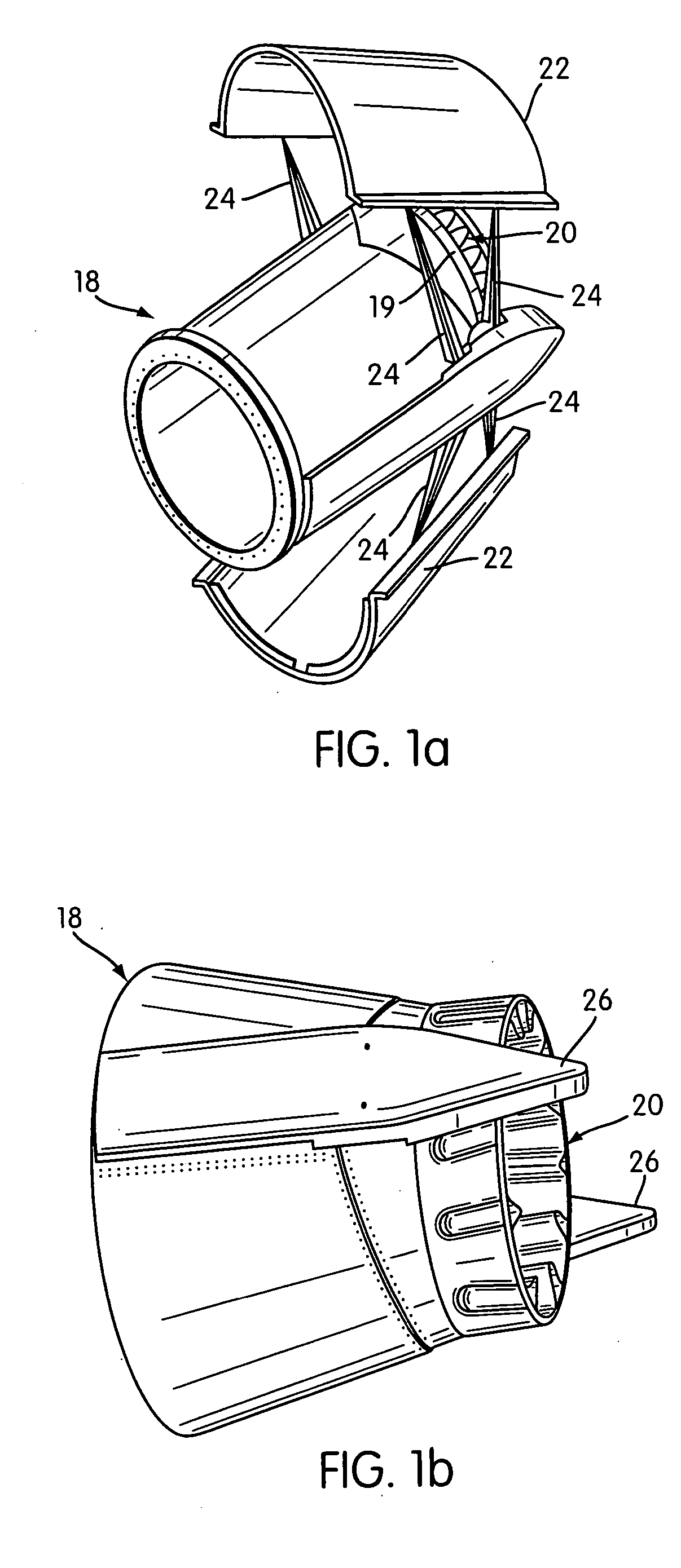
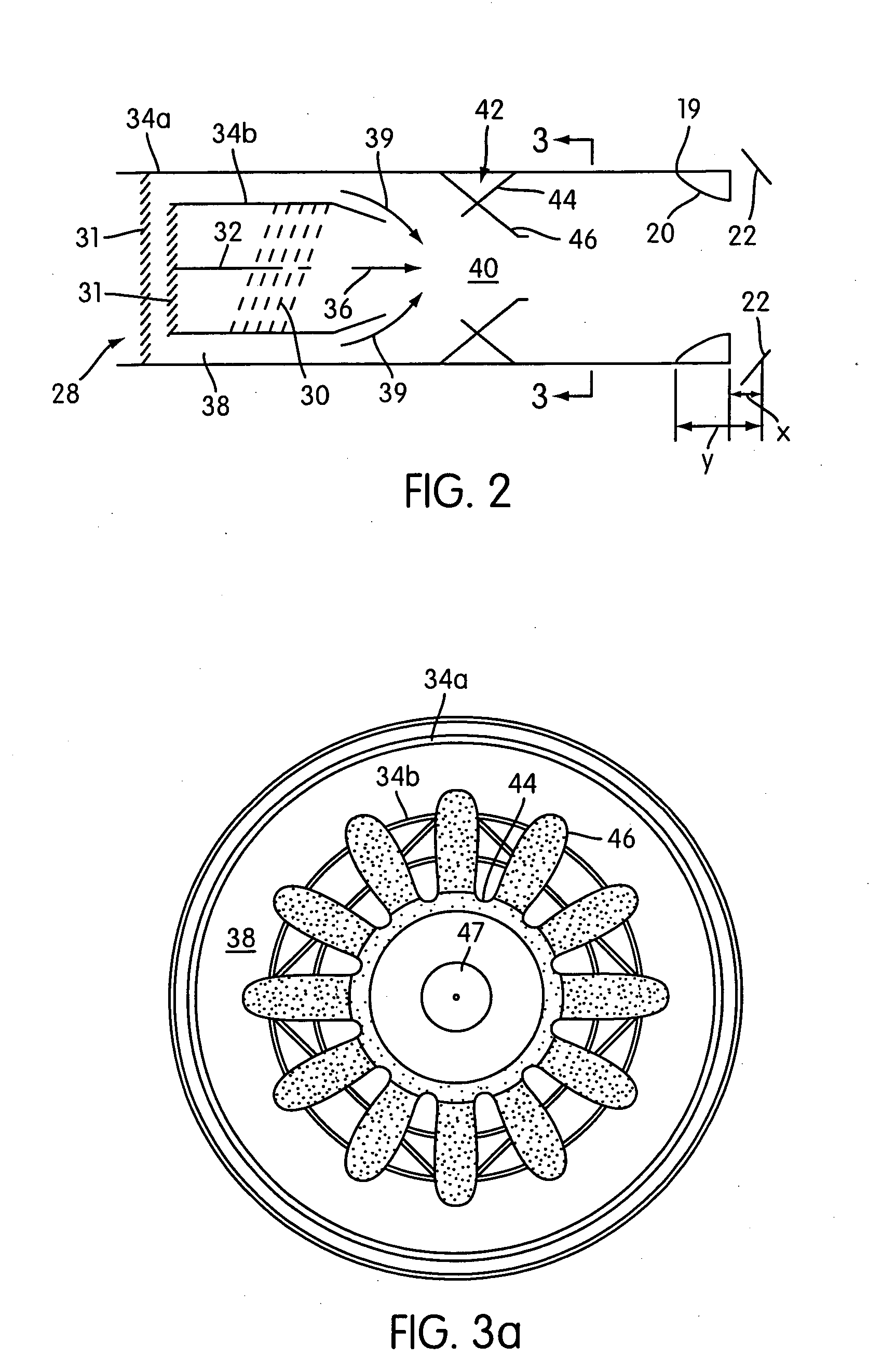
Jet nozzle mixer
InactiveUS7251927B2Reduce noiseWell mixedCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusJet engineNoise level
A second stage external jet nozzle mixer (20) includes identically formed lobes which equal in number the lobes of the first stage internal mixer. The external mixer works with the internal mixer, and furthers the mixing of the jet engine internal bypass flow with the internal jet engine core flow. This mixing levels the disparate flow velocities attendant with the jet engine exhaust, reduces the peak velocities from the jet engine core and increases the lower bypass velocities of the jet engine internal bypass flow. The lobes include complex curvatures that greatly enhance mixing of the gases and ambient cooling air, and thereby reduce noise. At the lobe terminus, the lobe dimensional characteristics may be adjusted to thereby adjust the total terminus area to achieve a match to a jet engine to cause that jet engine to run at a determined RPM and noise level. Noise attenuation may also be adjusted by changing lobe dimensions. Prior existing second stage exhaust jet nozzle mixers may be retrofitted to allow alteration of their total terminus area by employing the disclosed device and method.
Owner:COMTRAN LTD
Jet nozzle mixer
InactiveUS7017331B2Reduce noiseAvoid problemsAircraft navigation controlCosmonautic vehiclesJet engineNoise level
A second stage external jet nozzle mixer (20) includes identically formed lobes which equal in number the lobes of the first stage internal mixer. The external mixer works with the internal mixer, and furthers the mixing of the jet engine internal bypass flow with the internal jet engine core flow. This mixing levels the disparate flow velocities attendant with the jet engine exhaust, reduces the peak velocities from the jet engine core and increases the lower bypass velocities of the jet engine internal bypass flow. The lobes include complex curvatures that greatly enhance mixing of the gases and ambient cooling air, and thereby reduce noise. At the lobe terminus, the lobe dimensional characteristics may be adjusted to thereby adjust the total terminus area to achieve a match to a jet engine to cause that jet engine to run at a determined RPM and noise level. Noise attenuation may also be adjusted by changing lobe dimensions. Prior existing second stage exhaust jet nozzle mixers may be retrofitted to allow alteration of their total terminus area by employing the disclosed device and method.
Owner:COMTRAN LTD
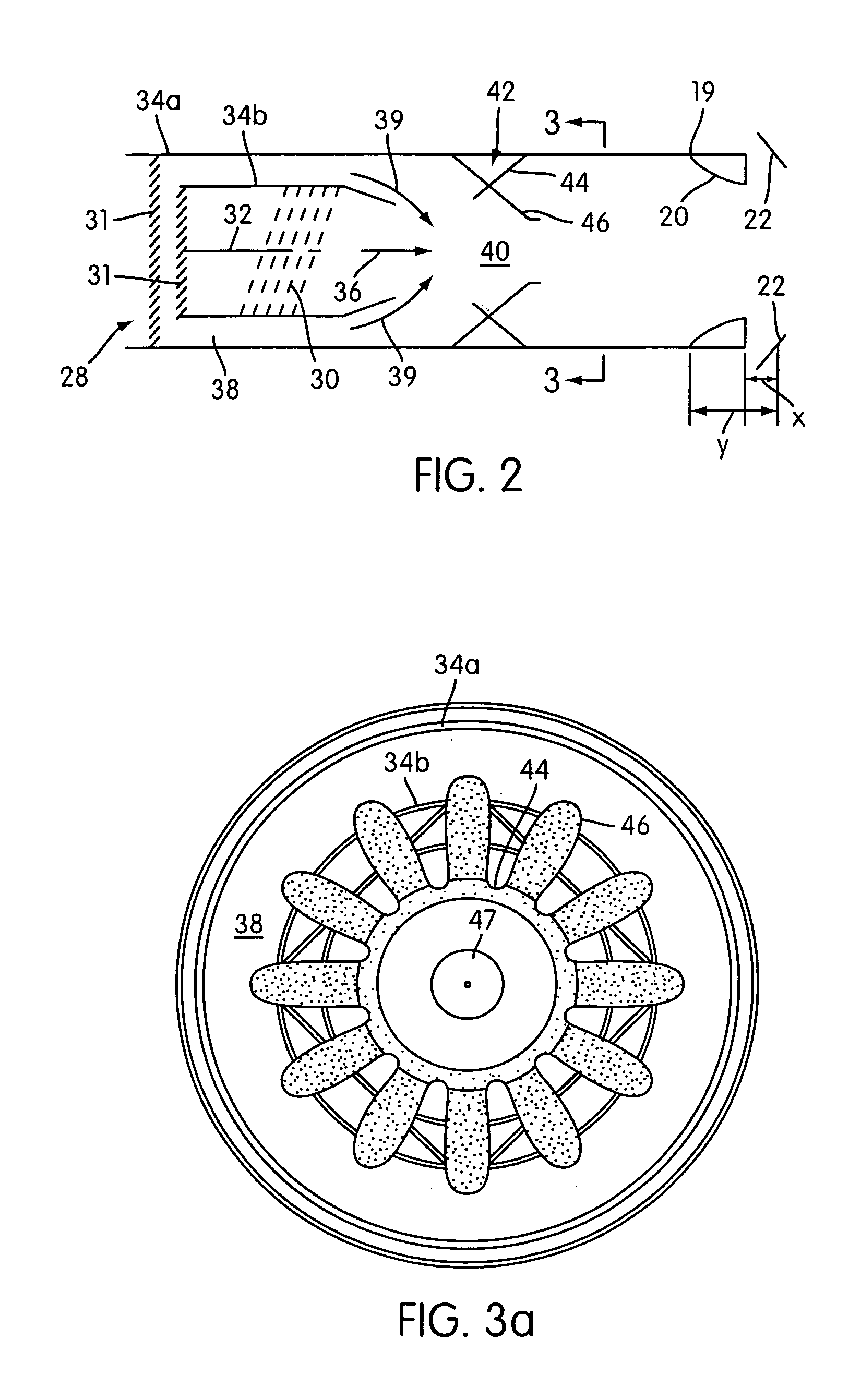
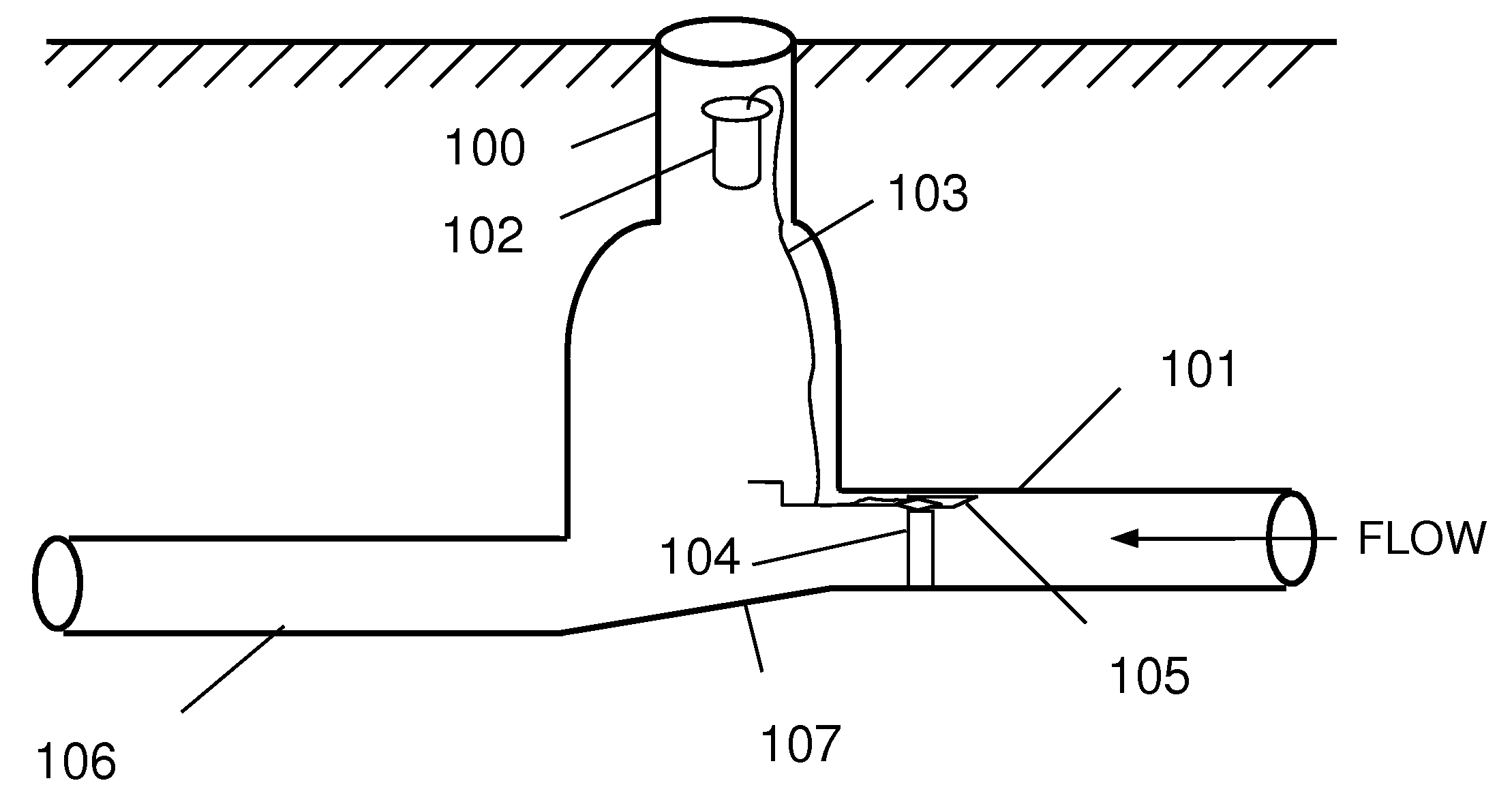
Augmented Surface Sensor for Measuring Flow Velocity
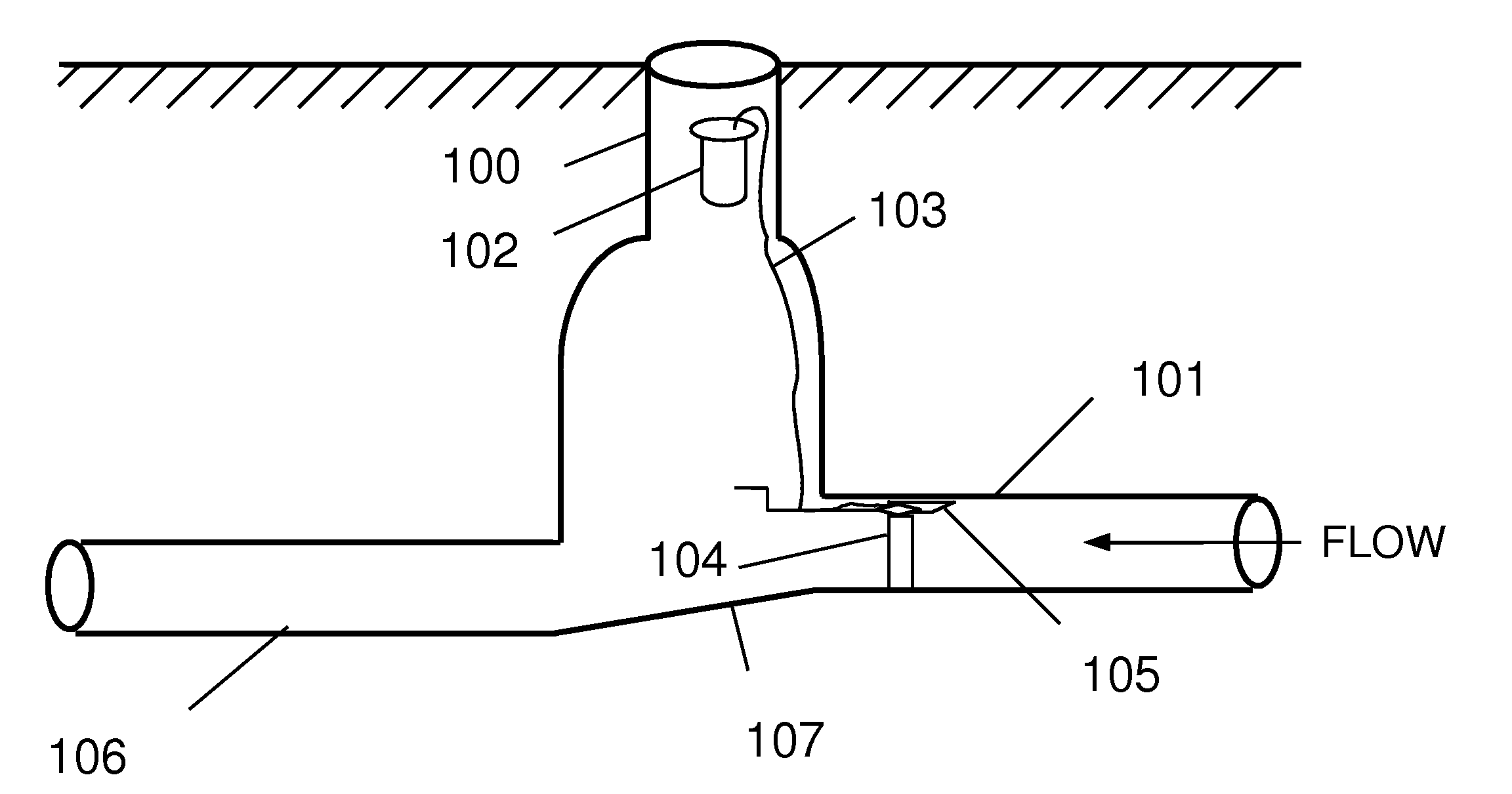
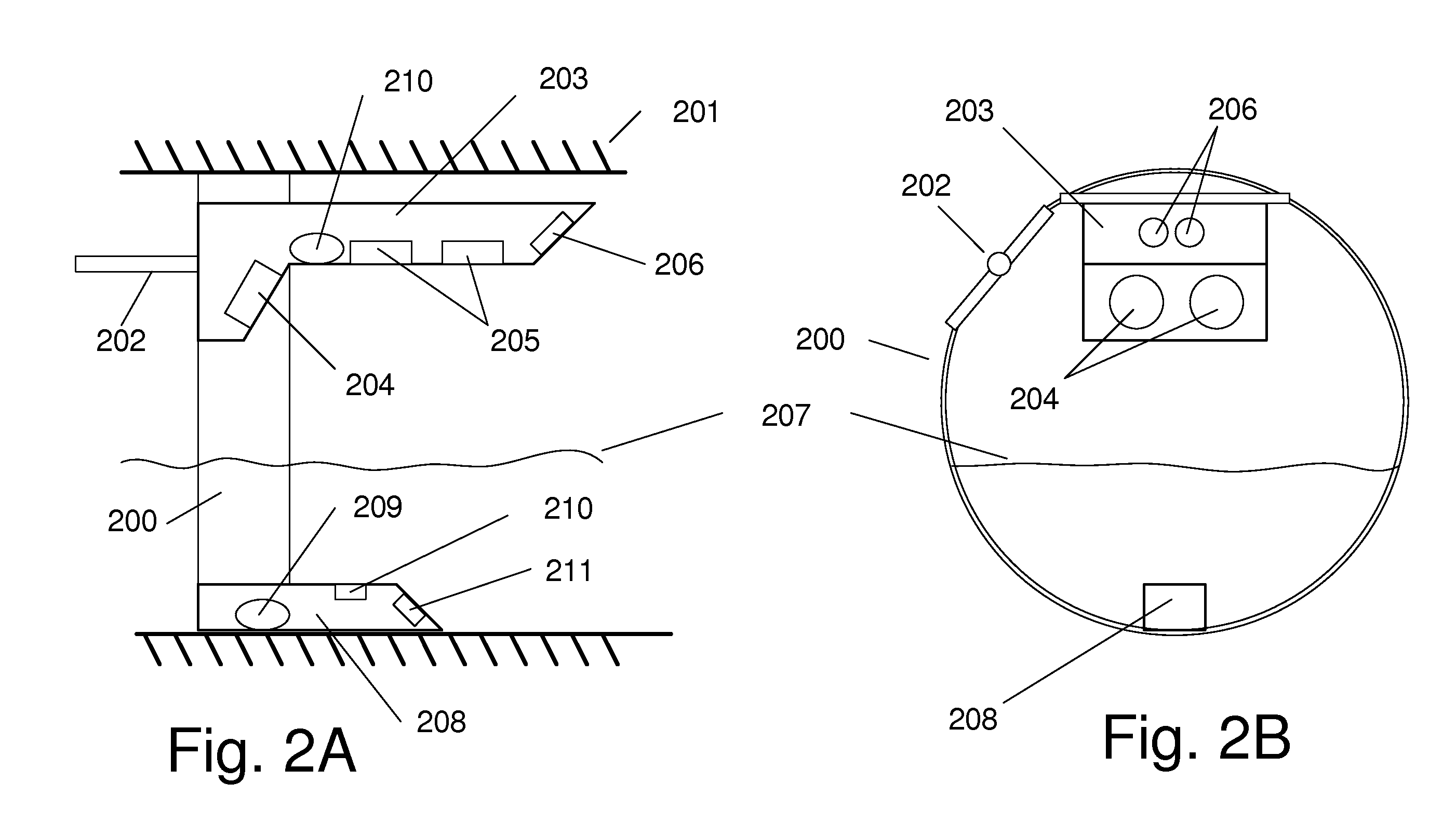
A system and method for measurement of flow parameters in a sewer pipe that may be partially or completely filled. Flow parameters may include flow velocity, flow volume, depth of flow and surcharge pressure. Measurements are taken from a sensor head installed on the inside of the pipe at the top of the pipe approximately the larger of at least 1 foot or 1 pipe diameter upstream of a pipe opening. Flow velocity may be measured by two different technologies. The technology employed depends on whether or not the pipe is full. If the pipe is not full then flow velocity may be measured, for example, using a wide beam, ultrasonic, diagonally downward looking Doppler signal that interacts with the surface of the flow. If the pipe is full, then flow velocity may be measured using, for example, an average velocity Doppler sensor, a peak velocity Doppler sensor or an ultrasonic velocity profiler.
Owner:ADS
Augmented surface sensor for measuring flow velocity
ActiveUS8215183B2Small sensor sizeFlow on effectVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringUltrasonic velocity
Owner:ADS
Flow measurement in partially filled pipes using pulsed peak velocity doppler
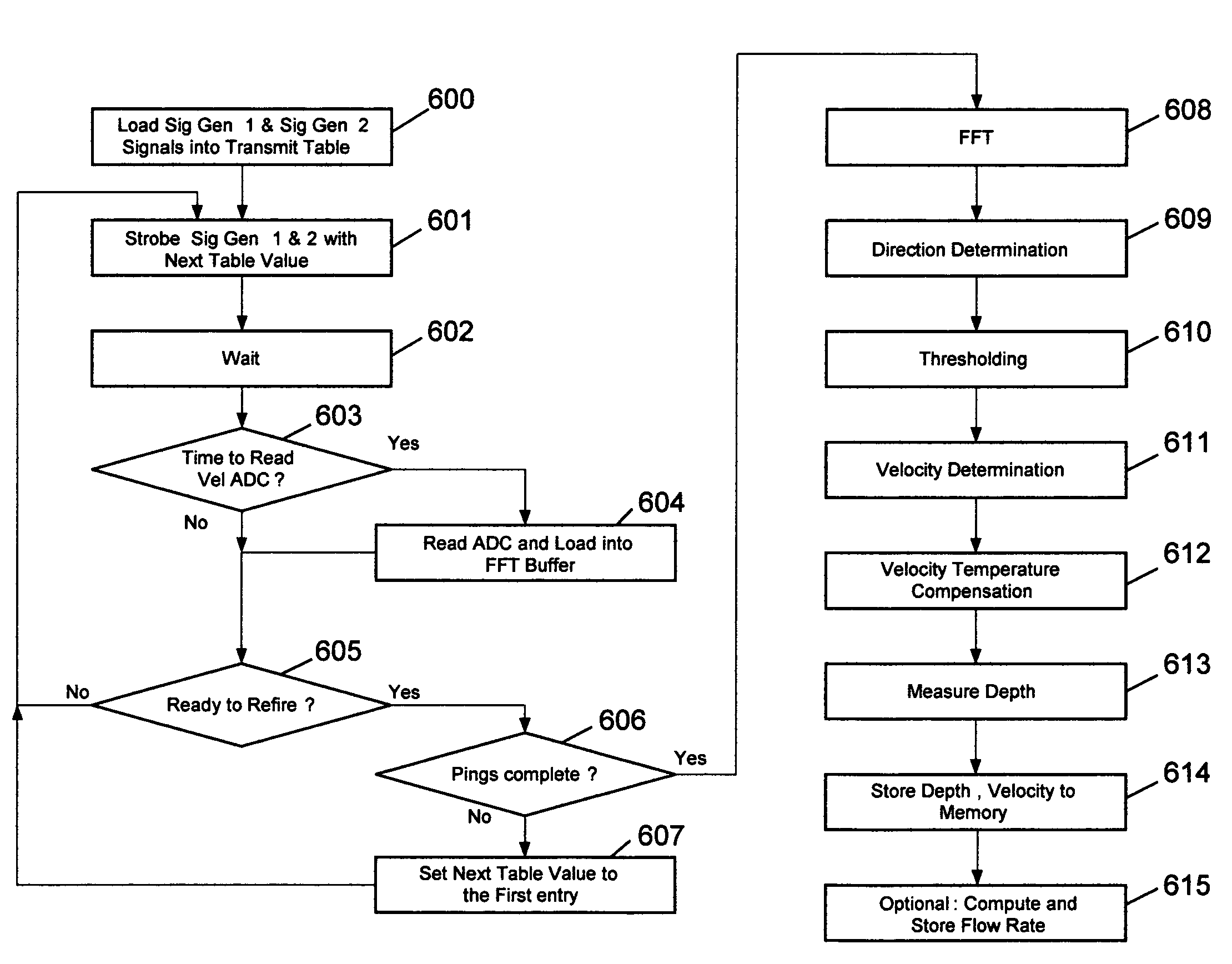
ActiveUS7672797B2Improve dynamic rangeEasy to distinguishTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementFrequency spectrumData set
The present invention relates to a system and method for measurement of flow velocity using the transmission of a sequence of coherent pulsed ultrasonic signals into the flow, and sampling the received response signal at a predetermined delay time relative to the pulse transmission that does not correspond to the signal transmission time. The sampling may be coherent with a frequency offset from the coherency frequency of the pulses. The received signal samples are then spectrally processed, typically by a Fourier process, to generate a frequency domain data set. A threshold technique is used on the frequency domain data set to determine a peak Doppler shift. Average velocity is then obtained by multiplying the peak Doppler shift by a factor, for example, 0.90. In one embodiment, the transmit pulse and receive samples are interleaved by alternating between transmitting a pulse and, after a delay, sampling the received signal.
Owner:ADS
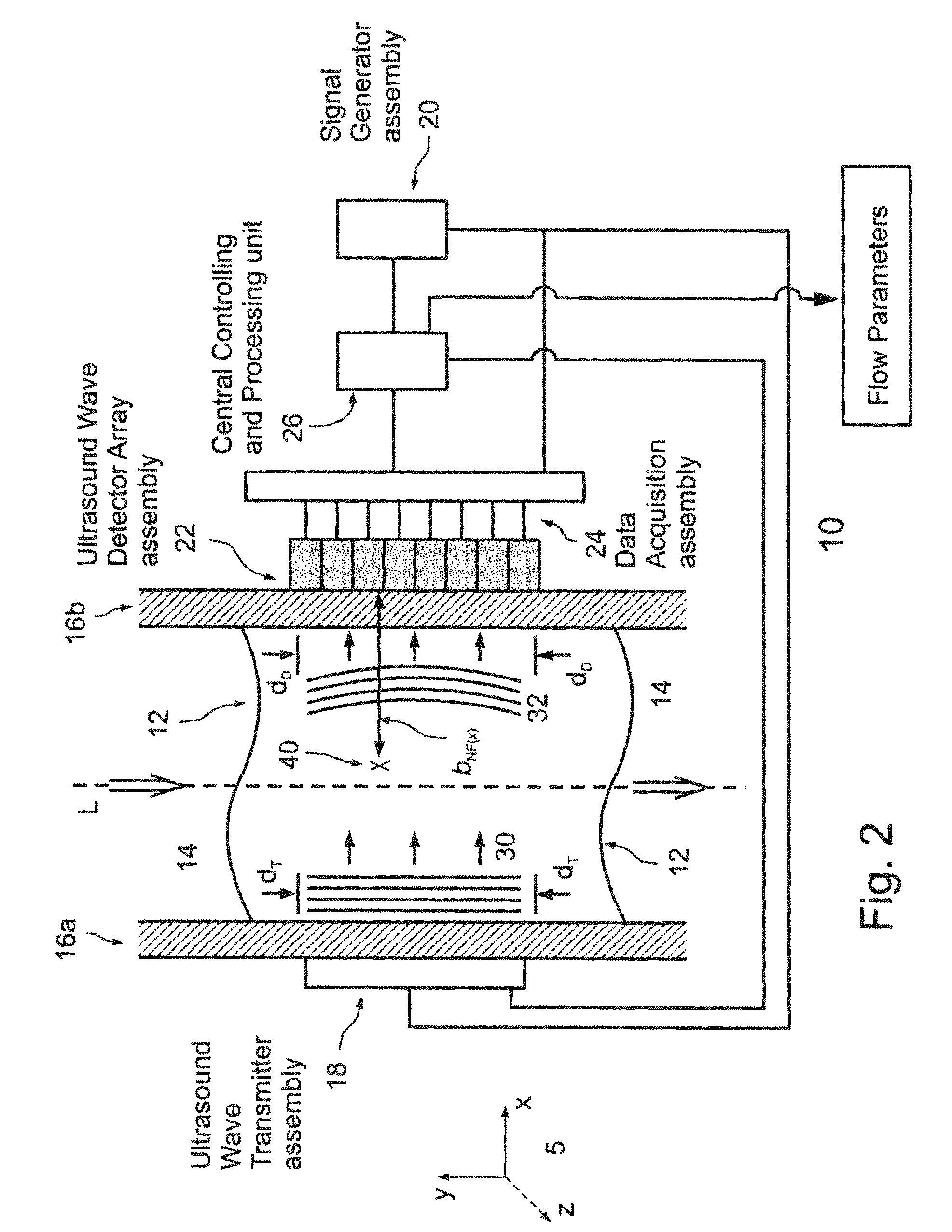
Ultrasonically determining flow parameters of a fluid flowing through a passage, by using far-field analysis
InactiveUS20110009745A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVolume/mass flow measurementDetector arrayEngineering
Ultrasonically determining flow parameters of a fluid (12) flowing through a passage (14), using far-field analysis. Includes: (a) acquiring near-field amplitude and phase change values of ultrasound waves transmitted (30) into, propagating through, and scattered (32) by, the flowing fluid; (b) determining far-field scattering amplitude distribution, A(θ, Δf), as two-dimensional function of scattering angle, θ, and Doppler frequency shift, Δf, from the acquired near-field amplitude and phase change values; and (c) determining flow parameters (peak velocity, velocity distribution, flow rate) of the flowing fluid, from the scattering amplitude distribution. Implementable using ‘clamp-on’ techniques including ultrasound wave transmitter and ultrasound wave detector array, clamped on, in an oppositely facing configuration, to the passage, for transmitting and detecting ultrasound waves propagating perpendicular to net flow direction of the flowing fluid. Applicable to different fluids (liquid or / and gas) flowing through different passages (channels, conduits, or ducts) of different types and sizes of processes.
Owner:SEIFER SHAHAR DR
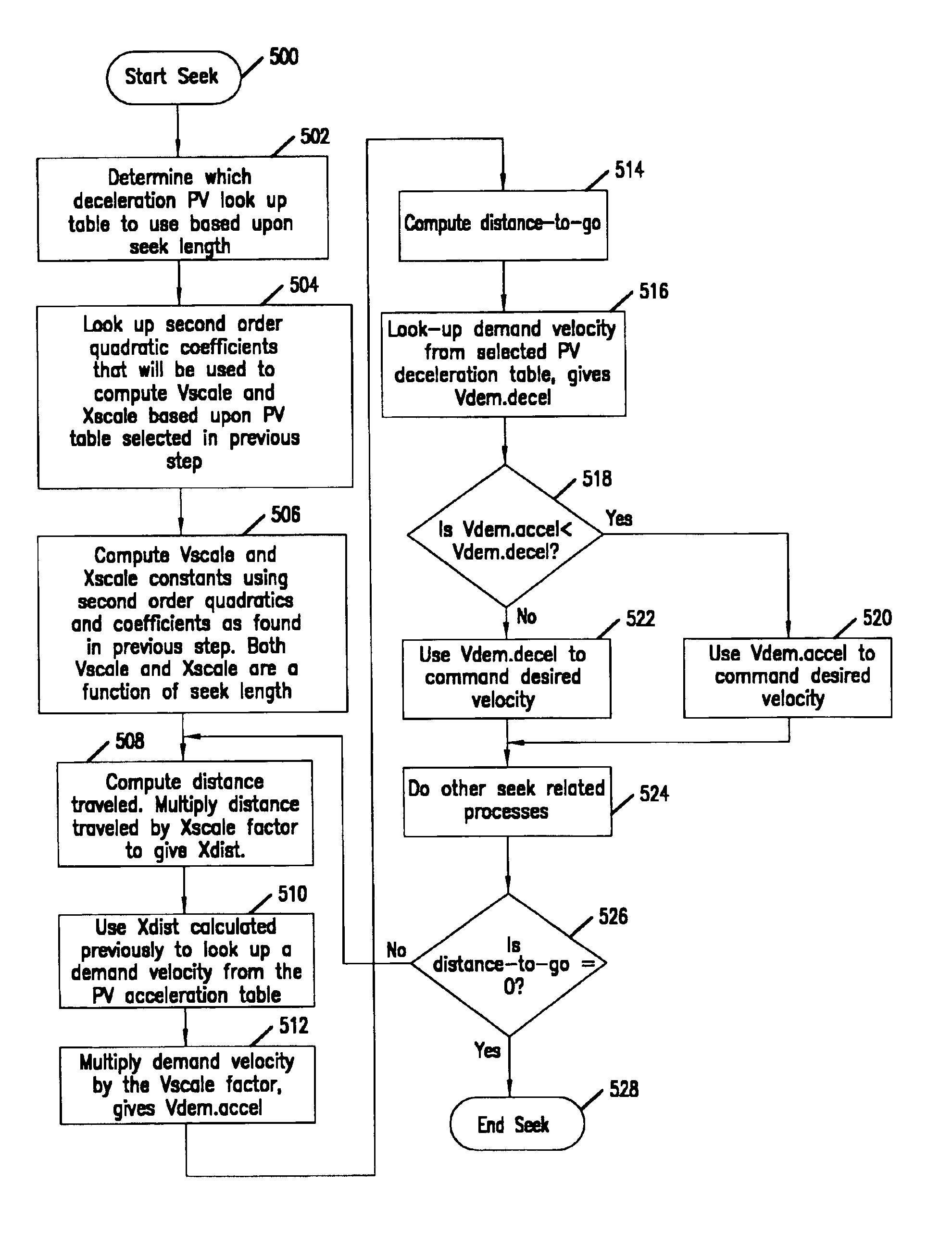
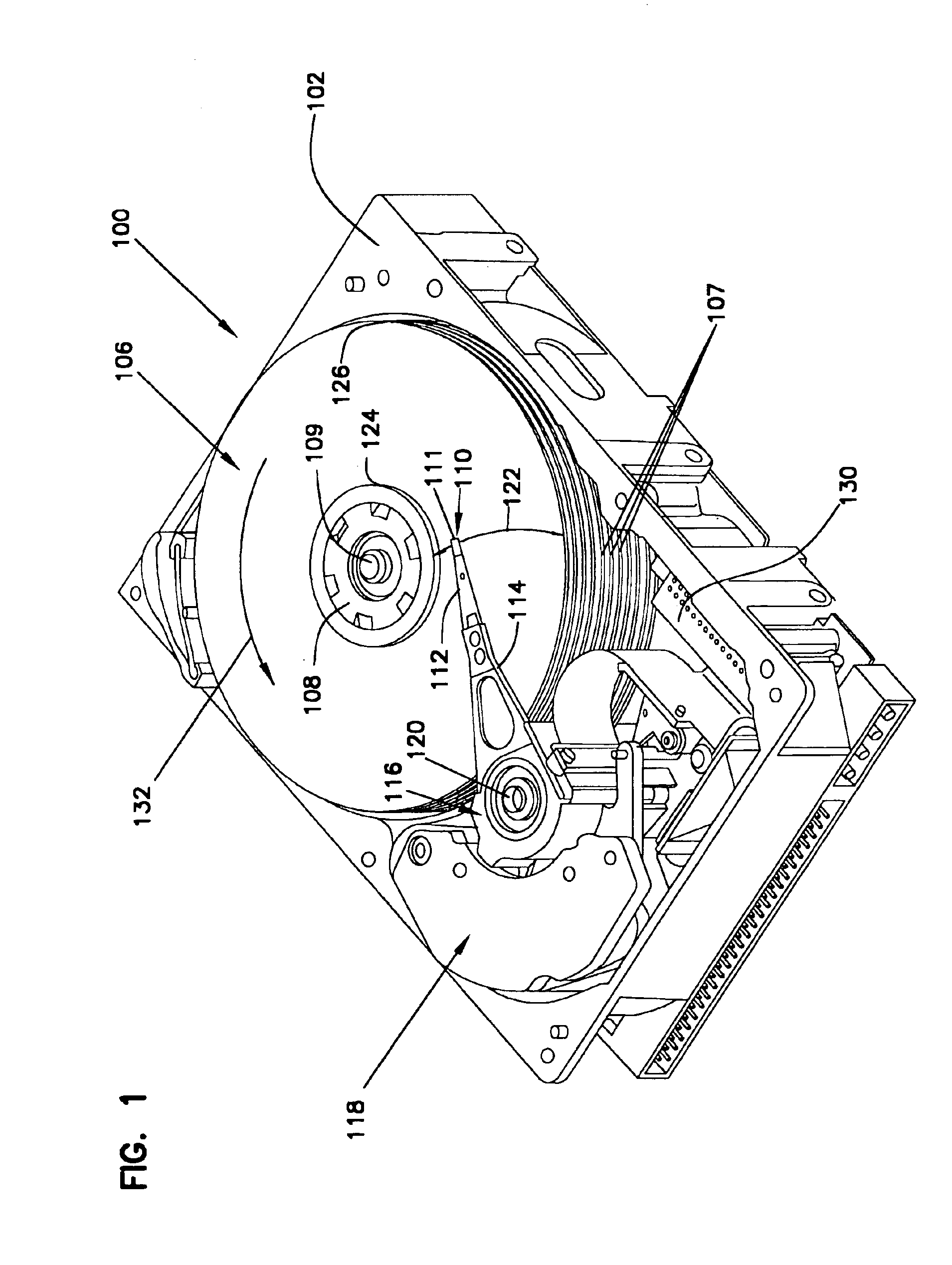
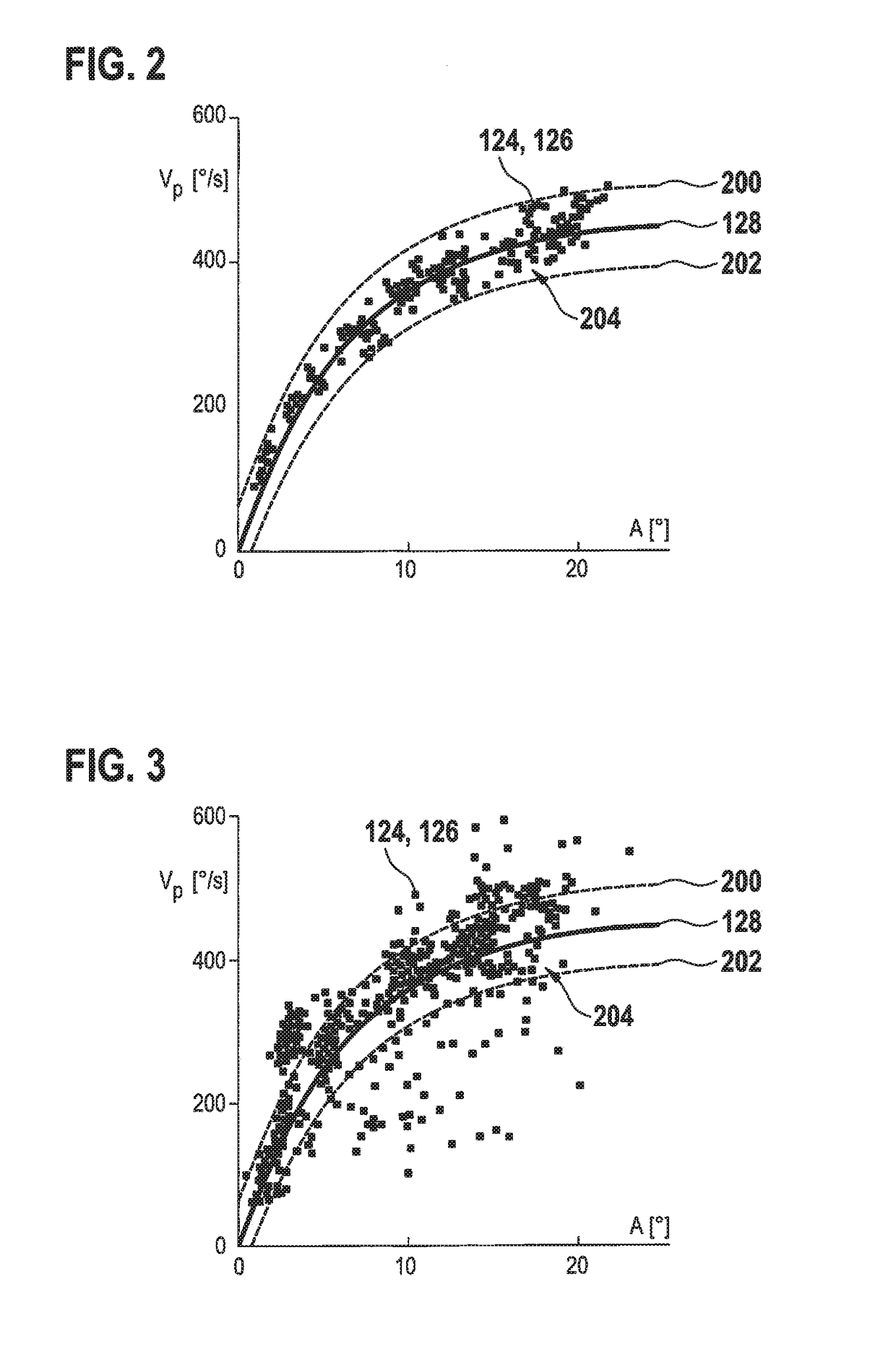
Matching peak velocities of acceleration and deceleration seek profiles in a disc drive
InactiveUS6937431B2Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksPeak valueEngineering
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
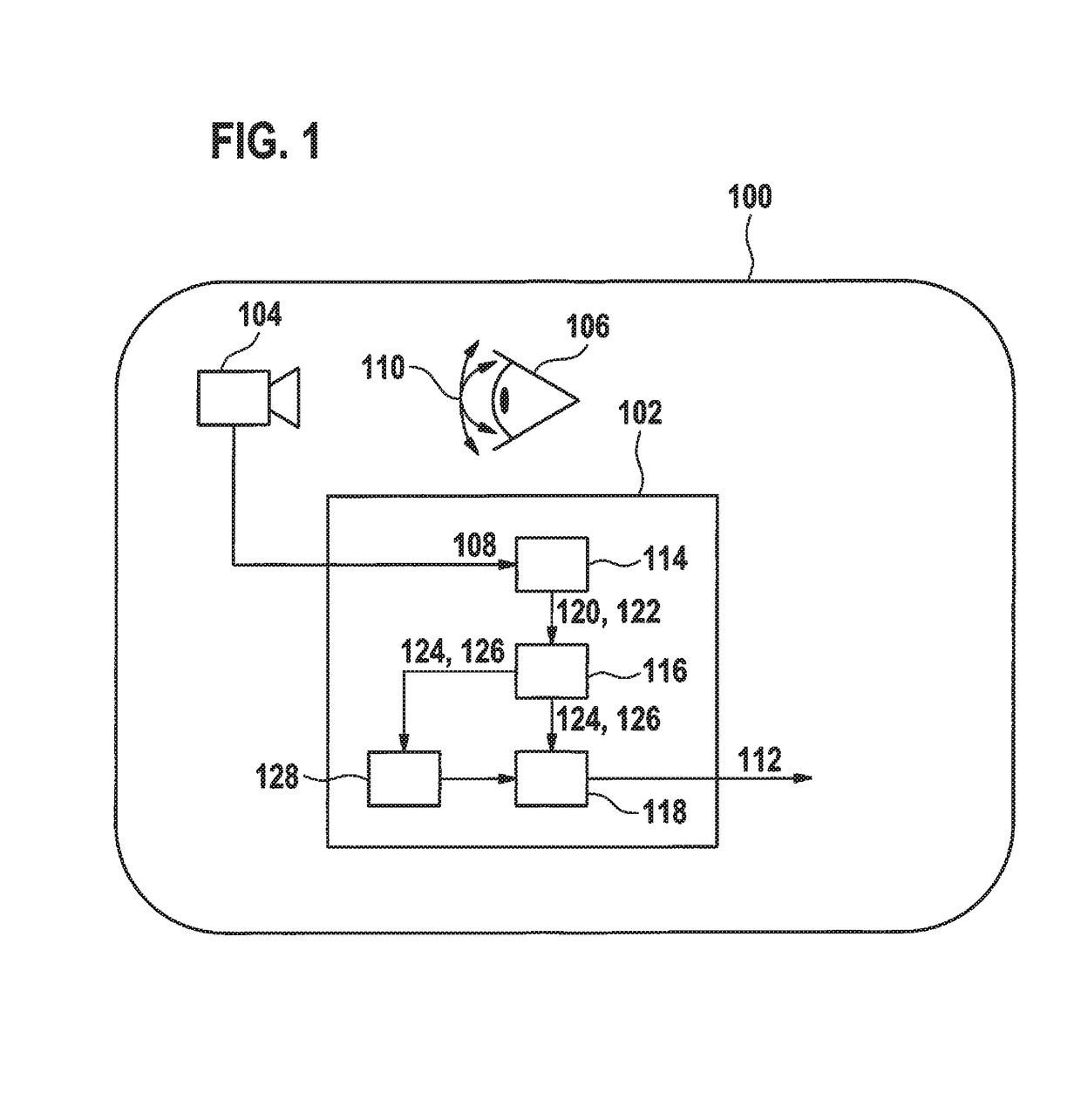
Method and apparatus for recognizing fatigue affecting a driver
InactiveUS20170215784A1Achieved quickly and efficientlyReliably recognizeAcquiring/recognising eyesDiagnostic recording/measuringPattern recognitionDriver/operator
A method is described for recognizing fatigue, the method comprising an ascertaining step, a determining step, and a comparing step. In the ascertaining step a first saccade and at least one further saccade of an eye movement of a person are ascertained using a gaze direction signal that models the eye movement. In the determining step, a first data point representing a first amplitude of the first saccade and a first peak velocity of the first saccade, and at least one further data point representing a further amplitude of the further saccade and a further peak velocity of the further saccade, are determined using the gaze direction signal. In the comparing step, the first data point and at least the further data point are compared with a saccade model. The person is recognized as fatigued if the data points have a predetermined relationship to a confidence region of the saccade model.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
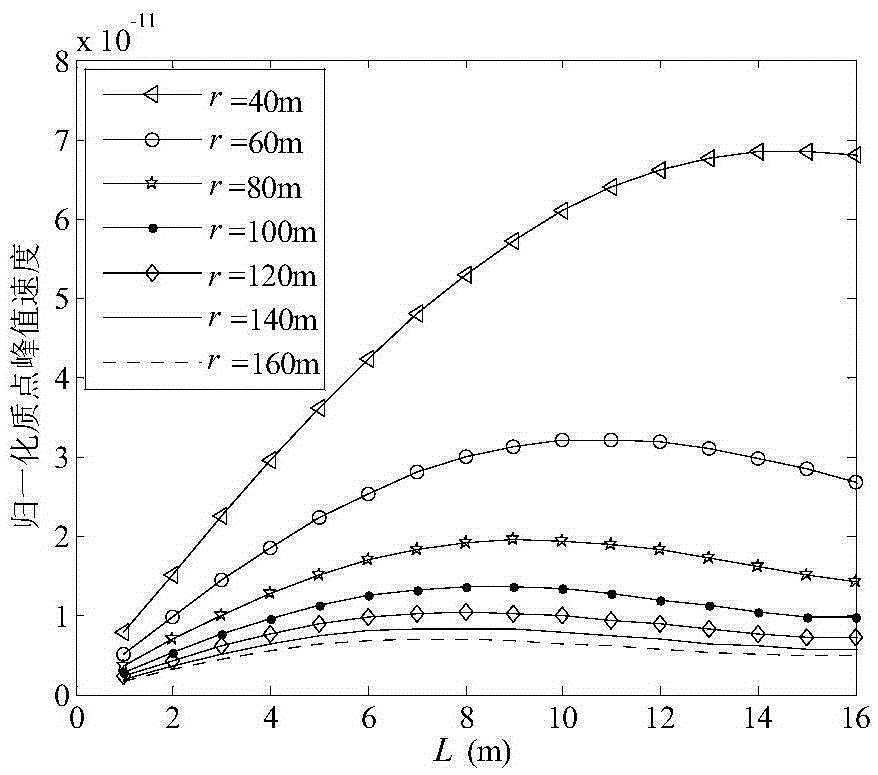
Prediction method for peak particle vibration velocity of column charge blasting
ActiveCN105389415AFacilitate discussionDescribe wellGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsPeak value
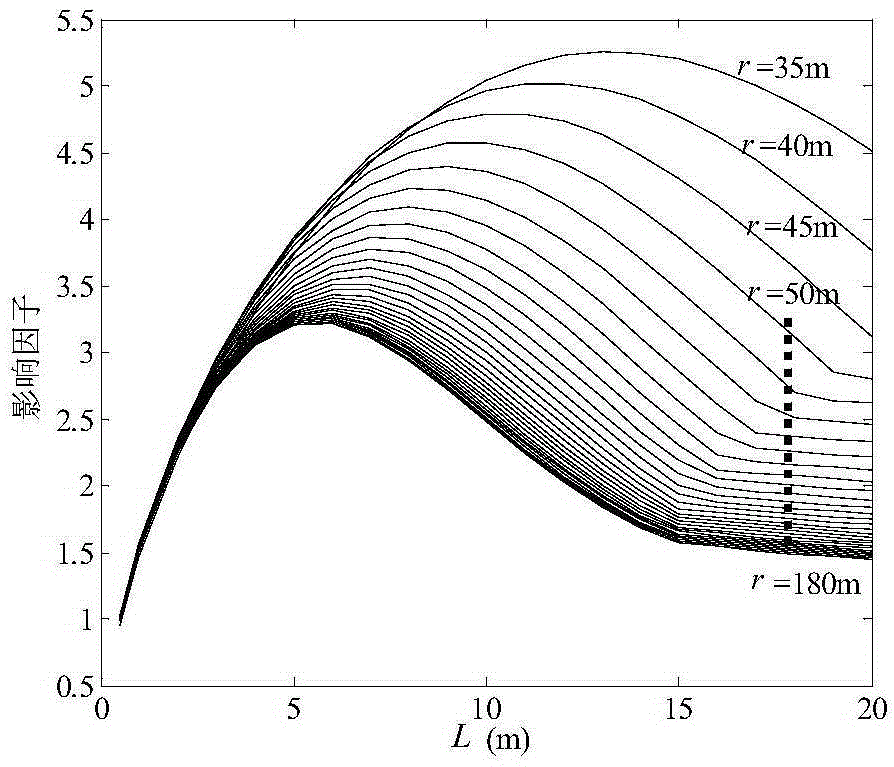
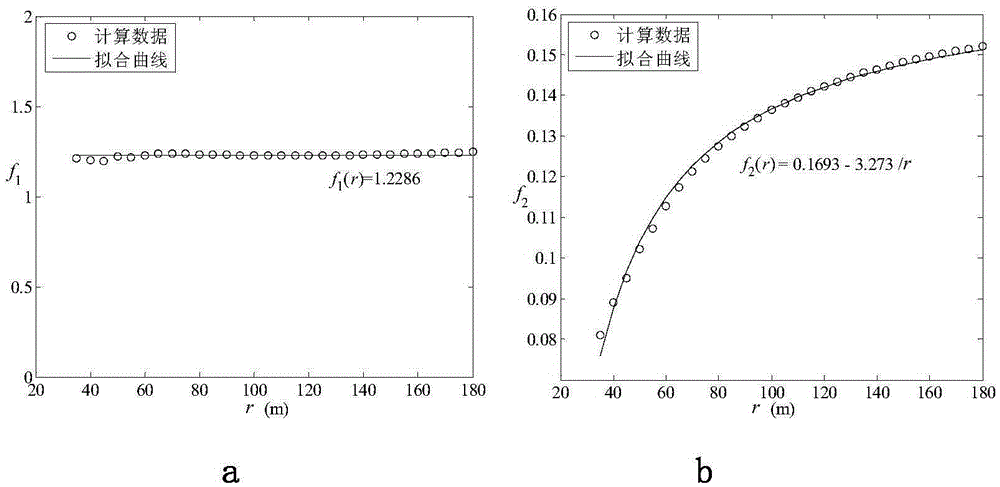
The invention discloses a prediction method for peak particle vibration velocity of column charge blasting. On the basis of existing spherical charge blasting vibration theory and stress wave superposition principle, axial detonation velocity influence of charge blasting is considered; a column charge is decomposed into a short column charge with the axial length of d; blasting vibration characteristics of the short column charge are mainly obtained through an Heelan solution; a theoretical solution of blasting vibration of a long column charge is compared with a Sadaovsk formula; and a length influence factor of the charge is introduced in the Sadaovsk formula to calculate the peak particle vibration velocity of column charge blasting. According to the method, the influence of the charge length in column charge blasting on the peak particle vibration velocity is considered, an attenuation relationship of the peak velocity along with a horizontal distance is given out, and the prediction and control of column charge blasting vibration can be realized; and corresponding charge length capable of maximizing the peak particle velocity can be obtained through a calculation model, so that the column charge blasting design can be subjected to peak velocity safety evaluation.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Automatic Flow Tracking System and Method
InactiveUS20100137717A1Diagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesEngineeringValve opening
A method of determining the blood flow characteristics from a monitoring signal indicative of blood flow in the vicinity of a heart, the method including the steps of: (a) extracting a flow envelope from the monitoring signal; (b) extracting a series of temporal markers from the flow envelope. (c) removing extraneous flows such as valve opening and closing flows from the flow envelope; (d) extracting features from the flow envelope and monitoring signal, such as peak velocity; (e) Producing cardiac parameters based on said monitoring signal.
Owner:USCOM LTD
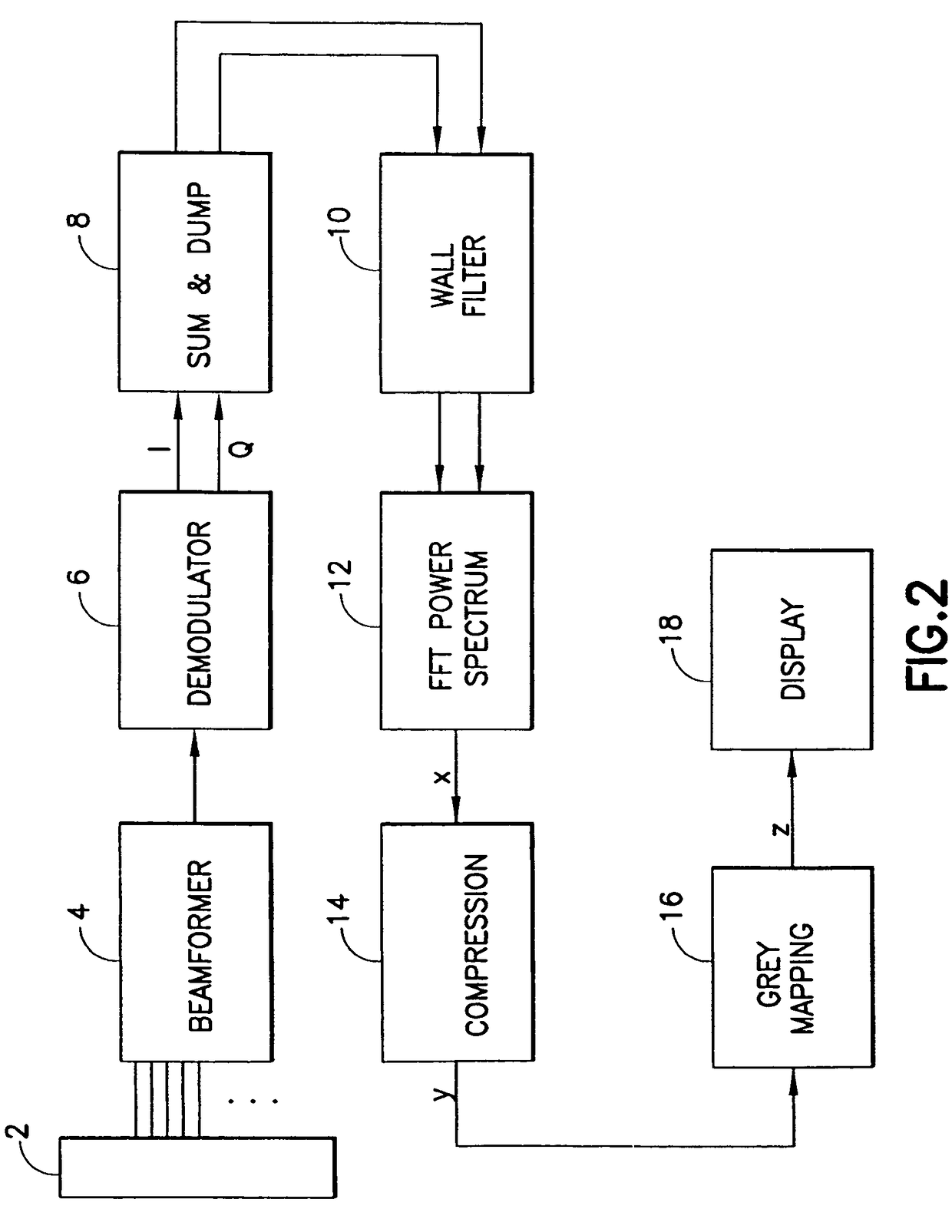
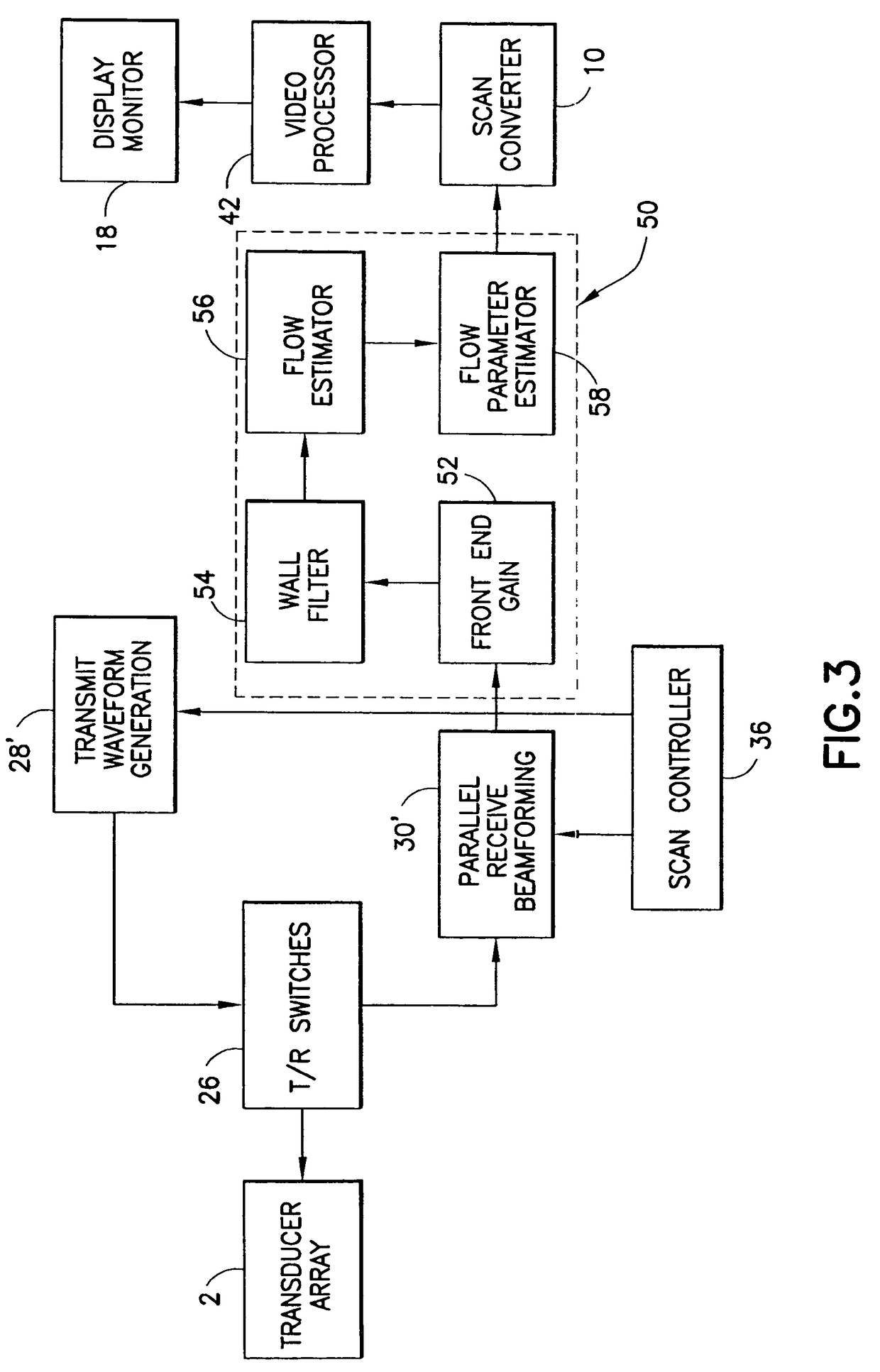
Method and apparatus for flow parameter imaging
A method and an apparatus for performing pulsed-wave spectral Doppler imaging at every color flow range gate location in a two-dimensional (or three-dimensional) region of interest. Spectral processing is necessary to determine the flow parameters. Performing this processing at every color flow range gate location creates the two-dimensional image. The method generates two-dimensional images of flow parameters such as peak velocity, pulsatility index, resistance index, etc. With the two-dimensional image, the user immediately observes where the most critical value of the flow parameter occurs and what that value is.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Viewing system having means for processing a sequence of ultrasound images for performing a quantitative estimation of a flow in a body organ
A medical ultrasound viewing system for processing a sequence of three-dimensional (3-D) ultrasound images far performing a quantitative estimation of a flow through a body organ comprising means for performing steps of acquiring a sequence of 3D color flow images, of said flow; assessing the flow velocity values in the 3D images, constructing isovelocity surfaces (6) by segmentation of the flow velocity values; computing the volume (Vol) delimited by the isovelocity surfaces; and using the flow velocity value (V) and the volume (Vol) computed from a segmented surface for computing the surface of an orifice (3) of the organ through which the flow propagates. The viewing system further comprises means for performing steps of measuring the peak velocity (VREG) of said flow through said orifice; computing the surface of the orifice (SOR) through which the flow propagates as a function of the flow velocity value (V) at an isovelocity surface upstream the flow propagation with respect to said orifice, the volume (Vol) computed from said segmented isovelocity surface, and the peak velocity of the flow through said orifice. The surface is given by the formula: SOR=Vol. V / VREG. The system can be applied to the assessment of the surface of regurgitation of the mitral jet.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Deeply-buried rock blasting excavation induced vibration prediction method based on energy principle
ActiveCN104537195AEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy balancingVibration control
The invention provides a deeply-buried rock blasting excavation induced vibration prediction method based on the energy principle. The method comprises a first step of establishing a peak vibration velocity prediction formula based on the energy balance principle through a dimension analysis method; a second step of arranging a vibration monitor on the wall of a deeply-buried underground tunnel to be blasted and excavated so as to record rock vibration waveform in blasting to acquire surrounding rock vibration response; and a third step of computing explosion energy of the explosive contained in each blast hole and strain energy of the to-be-excavated rock according to blasting parameters of the deeply-buried underground tunnel and site environment, and computing unknown coefficients of the prediction formula by a multivariate regression analysis method according to measured blasting vibration peak velocity so as to predict deeply-buried rock blasting excavation induced vibration. The method greatly improves the prediction precision of deeply-buried rock blasting excavation induced vibration, and can be widely used in prediction of blasting excavation induced vibration of deeply-buried underground engineering like communication, water and electricity, mine and so on.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
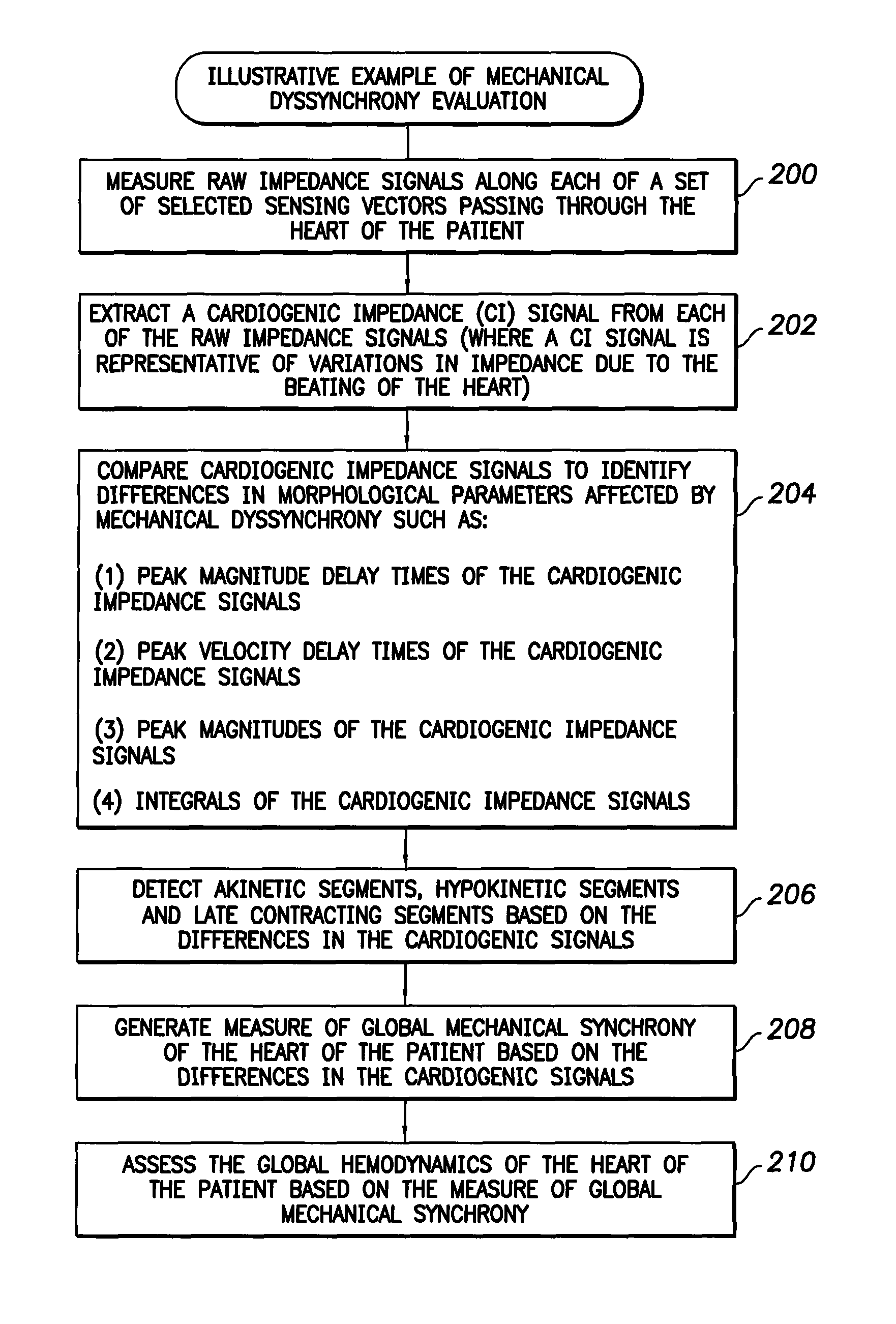
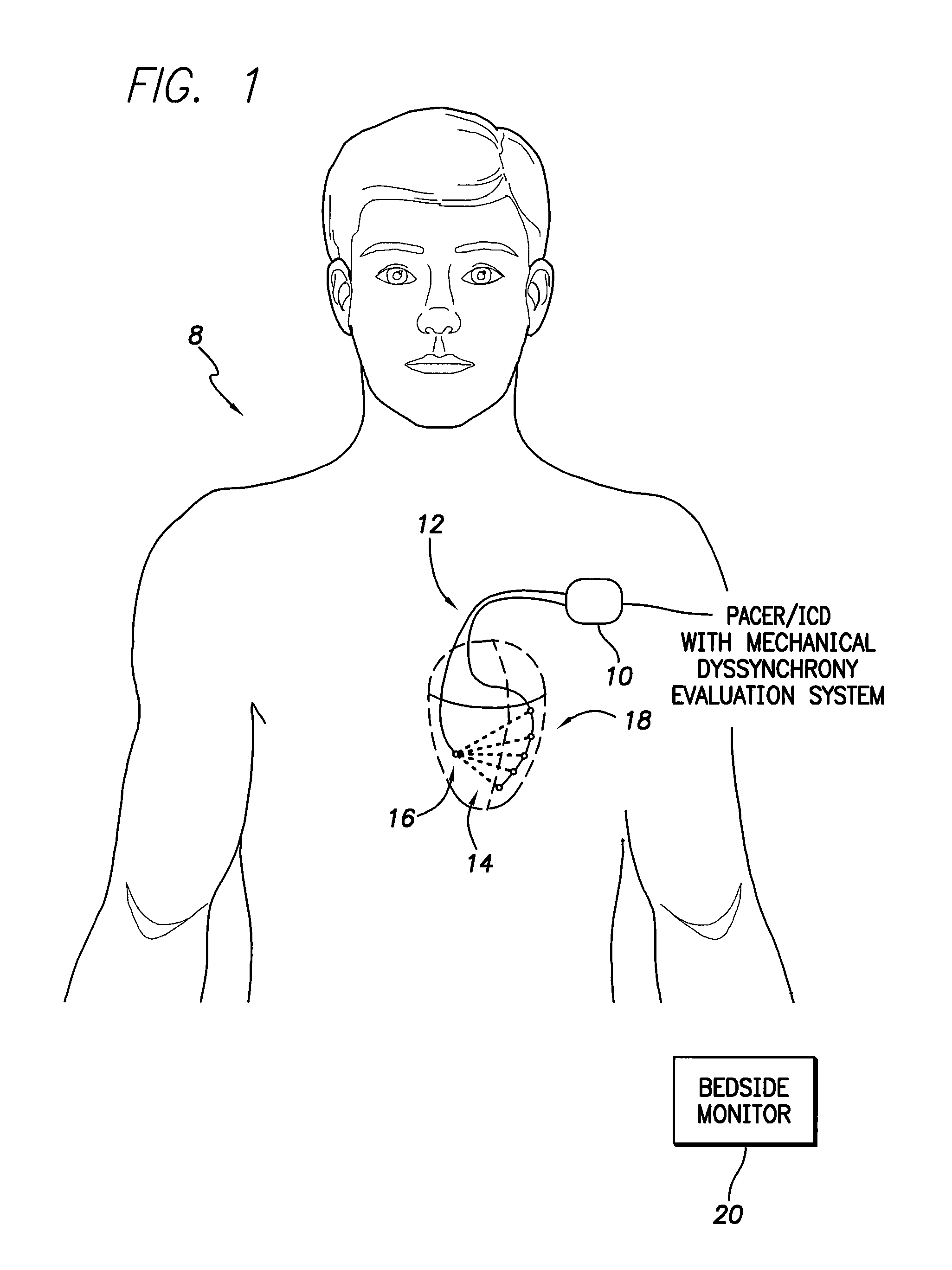
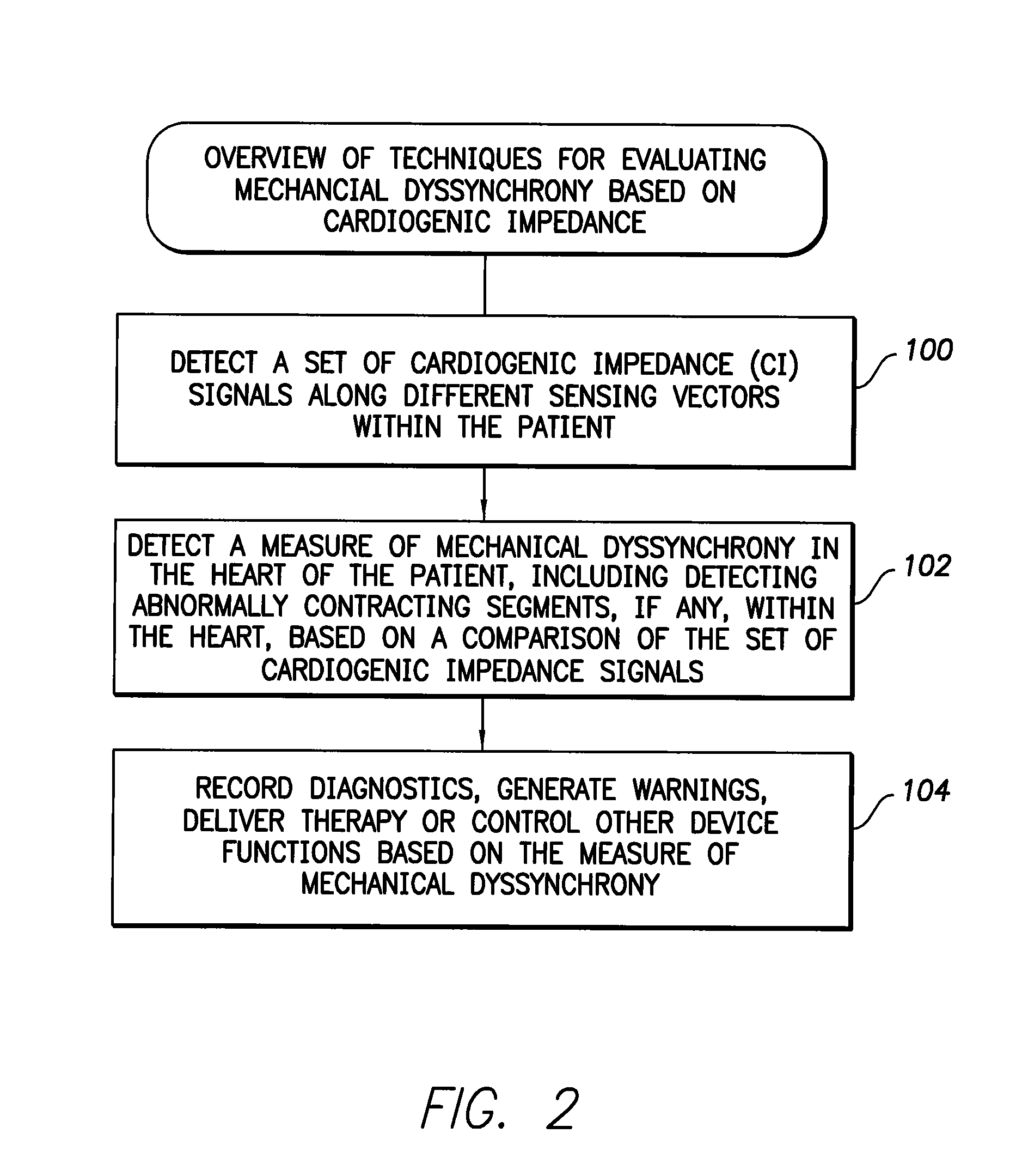
System and method for evaluating mechanical cardiac dyssynchrony based on multiple impedance vectors using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS8050760B2ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular myocardiumCardiac pacemaker electrode
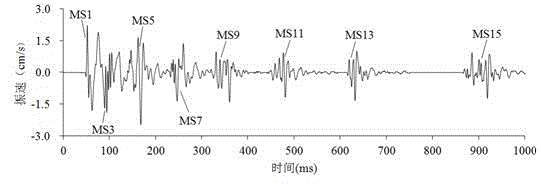
Techniques are provided for evaluating mechanical dyssynchrony within the heart of patient in which a pacemaker, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or other medical device is implanted. In one example, a set of cardiogenic impedance signals are detected along different sensing vectors passing through the heart of the patient, particularly vectors passing through the ventricular myocardium. A measure of mechanical dyssynchrony is detected based on differences, if any, among the cardiogenic impedance signals detected along the different vectors. In particular, differences in peak magnitude delay times, peak velocity delay times, peak magnitudes, and waveform integrals of the cardiogenic impedance signals are quantified and compared to detect abnormally contracting segments, if any, within the heart of the patient. Warnings are generated upon detection of any significant increase in mechanical dyssynchrony. Diagnostic information is recorded for clinical review. Pacing therapies such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) can be activated or controlled in response to mechanical dyssynchrony to improve the hemodynamic output of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Stenosis detection device
InactiveUS20050203427A1Improve automationReduces fiddlingElectrocardiographyStethoscopeCoronary arteriesPeak value
The present invention provides a method and a device for determining a peak blood flow signal of a blood flow through at least a section of a selected coronary artery of a beating heart of a mammal, in particular a human being, wherein said device comprises a bioimpedance measuring device. The method and device selects part of a bioimpedance signal, and calculates a peak velocity from it. This may e.g. be used to map the peak blood flow velocity along a coronary artery, in order to find possible stenoses in the vessel.
Owner:IMPEDANCE VASCULAR IMAGING PROD
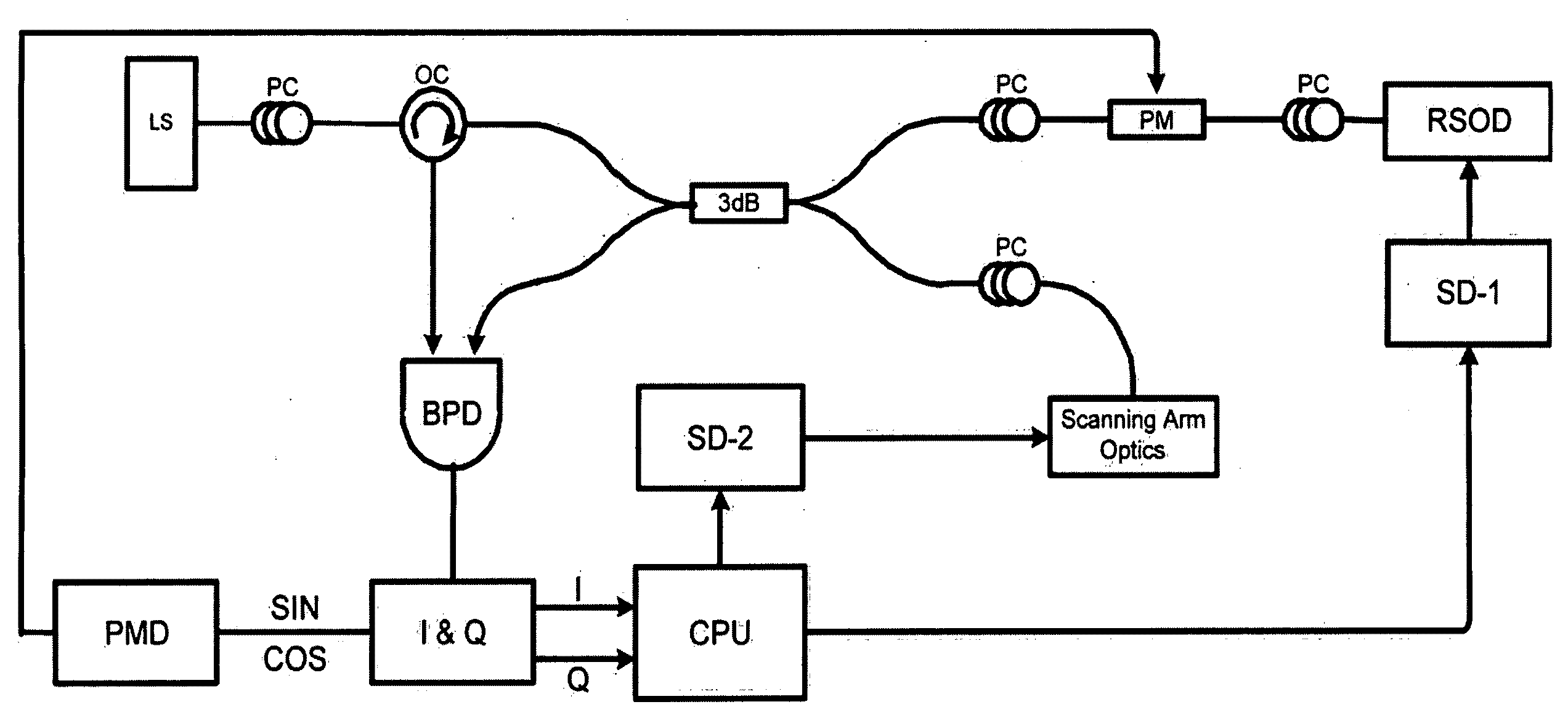
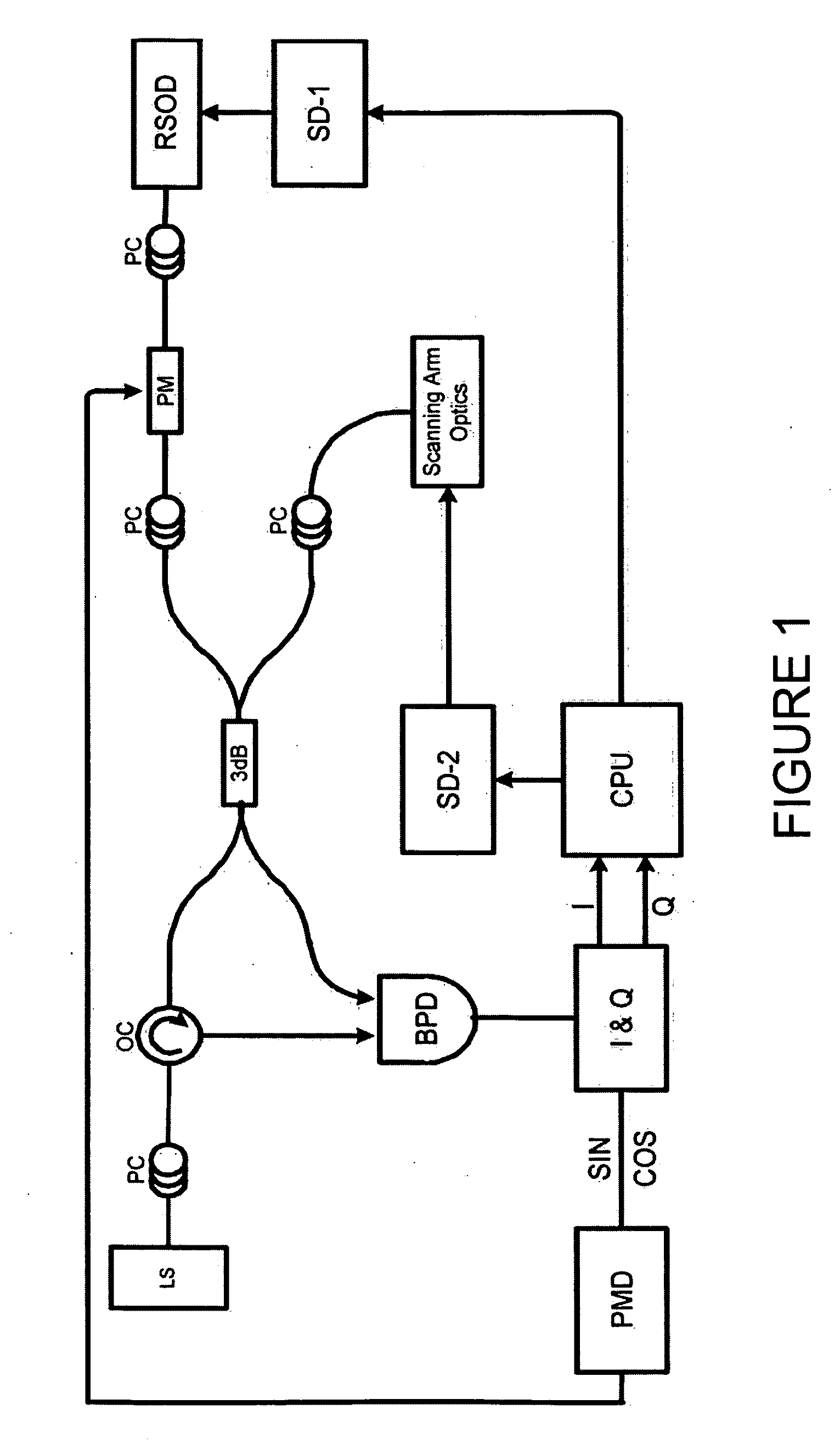
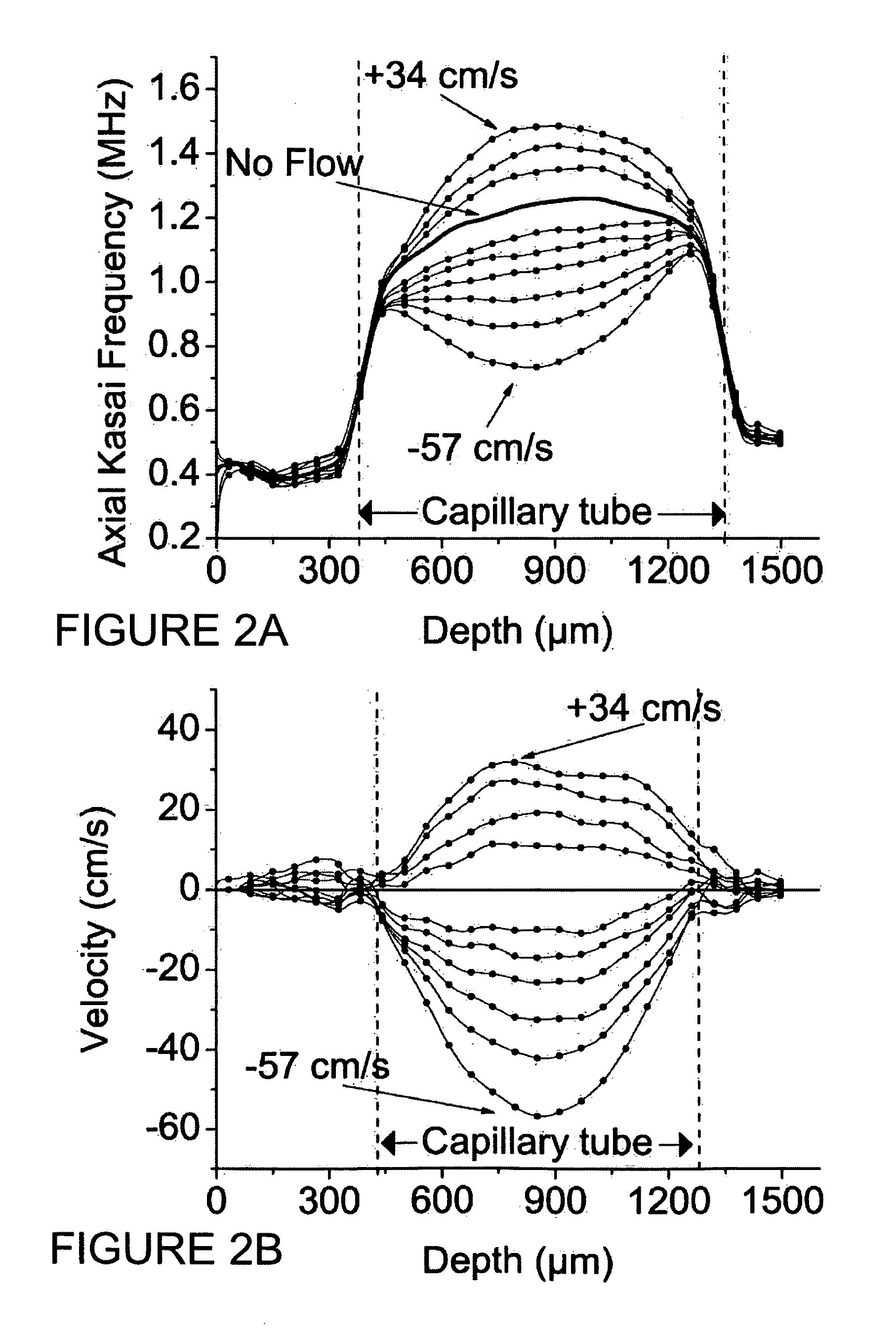
Two-dimensional estimation technique for doppler optical coherence tomography (oct)
InactiveUS20090225301A1Devices using optical meansFluid speed measurementIn-phase and quadrature componentsPeak value
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a high-resolution, non-invasive technique to image subsurface tissue and tissue functions. A broadband light source illuminates an object and the reflected photons are processed using an interferometer, demodulated into inphase and quadrature components and then digitized. The captured data contains information about the velocity of the moving scatterers but current Doppler estimation algorithms have a limited velocity detection range. Using a two dimensional velocity estimation, Doppler OCT (DOCT) can be used for the detection of in vivo aortic blood flow rates of over 1 m / s peak velocity through an esophageal DOCT probe. Previous methods have used a transverse Kasai (TK) autocorrelation estimation to estimate the velocity which is good for slow velocities, such as in the microvasculature. By calculating the Kasai autocorrelation with a lag in the depth or axial direction, backscattered frequency information is obtained which yields high velocity rate information. Through subtraction with stationary backscattered information, the Doppler shift is obtained by the axial Kasai (AK) technique. Through utilizing information from two dimensions, velocities can be resolved which spans rates from the microcirculation to cardiac blood flow velocities.
Owner:MOROFKE DARREN ROSS +2
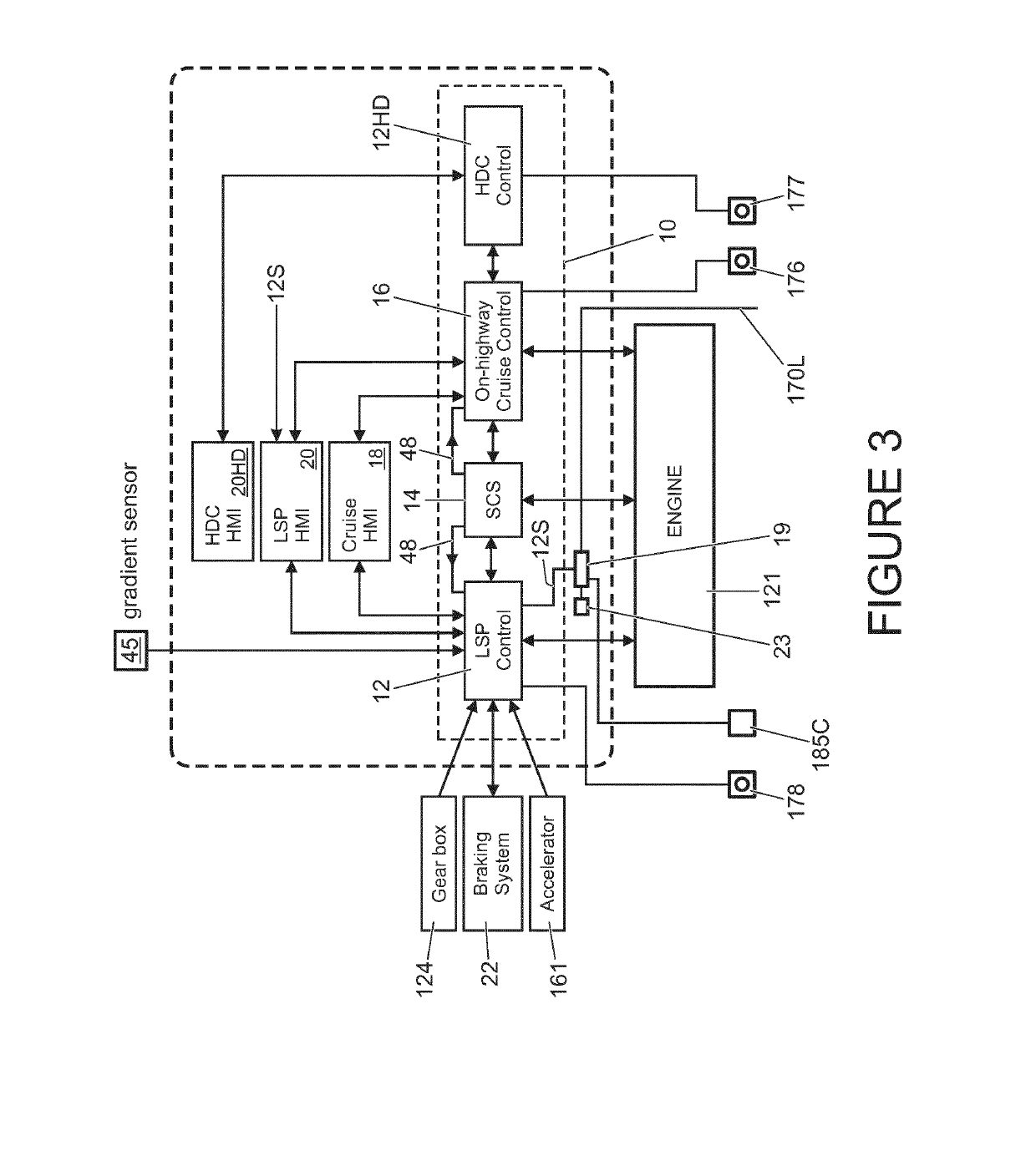
Vehicle speed control
ActiveUS20190161082A1Improve vehicle stabilityConfidenceCruise controlExternal condition input parametersTerrainHigh speed control
A speed control system (12) for a vehicle (100), the speed control system (12) being configured to: automatically cause application of positive and negative torque, as required, to one or more wheels of a vehicle (100) to cause a vehicle to travel in accordance with a target speed value, the target speed value being stored in a memory of the control system (12); and detect a crest of a slope ahead of the vehicle (100); wherein the speed control system (12) is configured automatically to attempt to adjust a speed of the vehicle (100) to cause the vehicle (100) to travel at a predetermined crest speed value when a crest of a slope is detected ahead of the vehicle (100), the predetermined crest speed value being determined in dependence at least in part on terrain gradient information respect of terrain prior to the crest.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
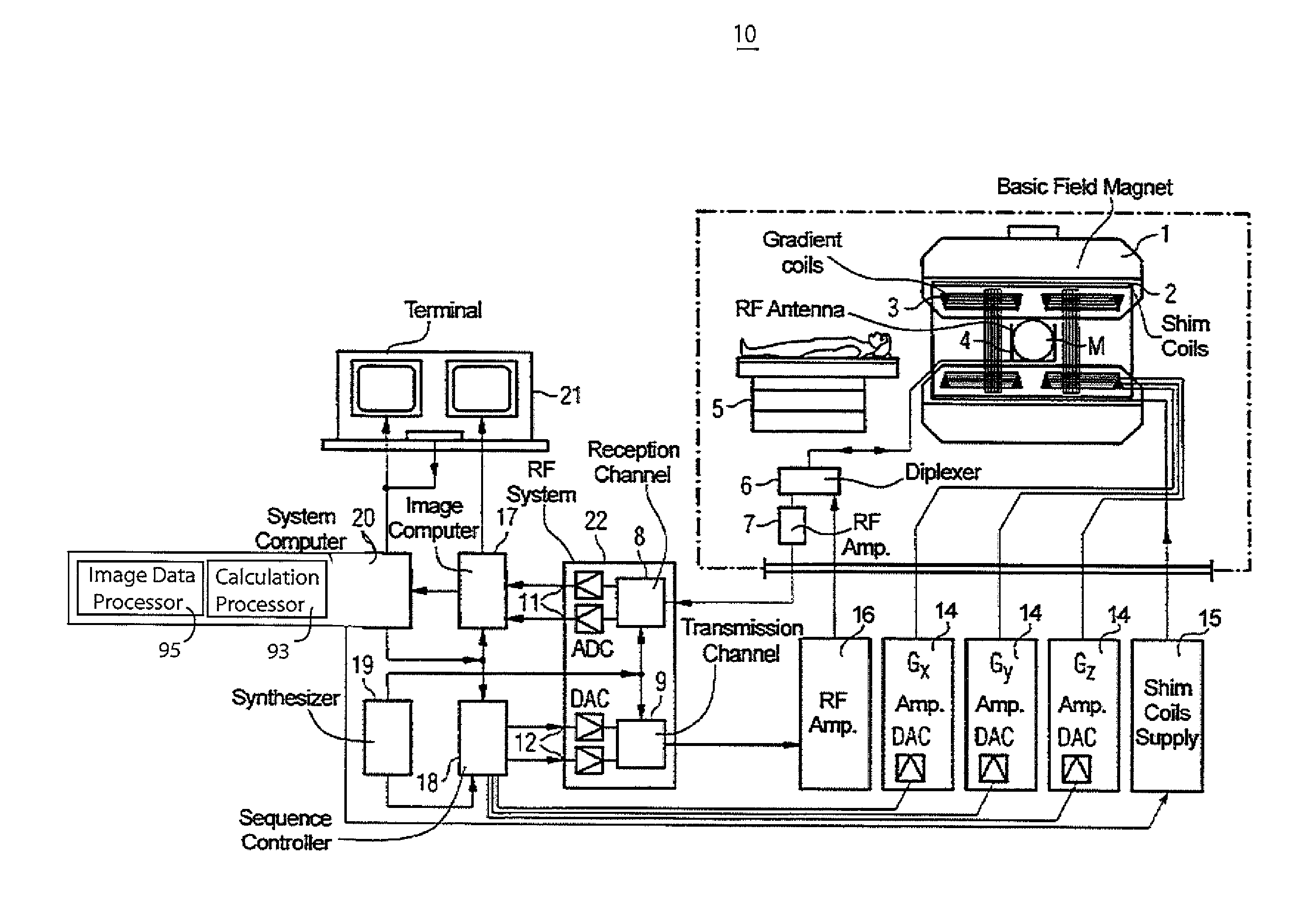
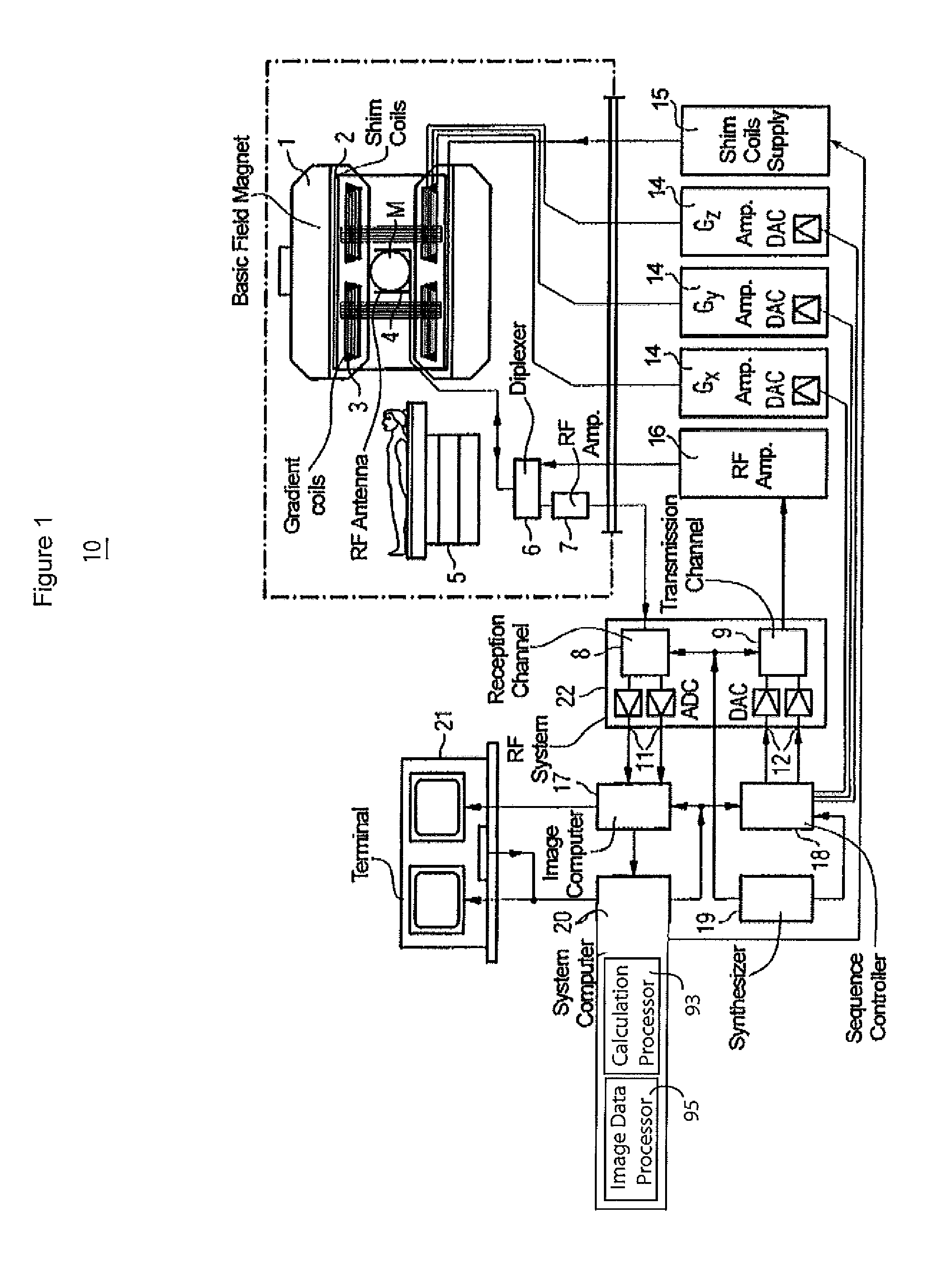
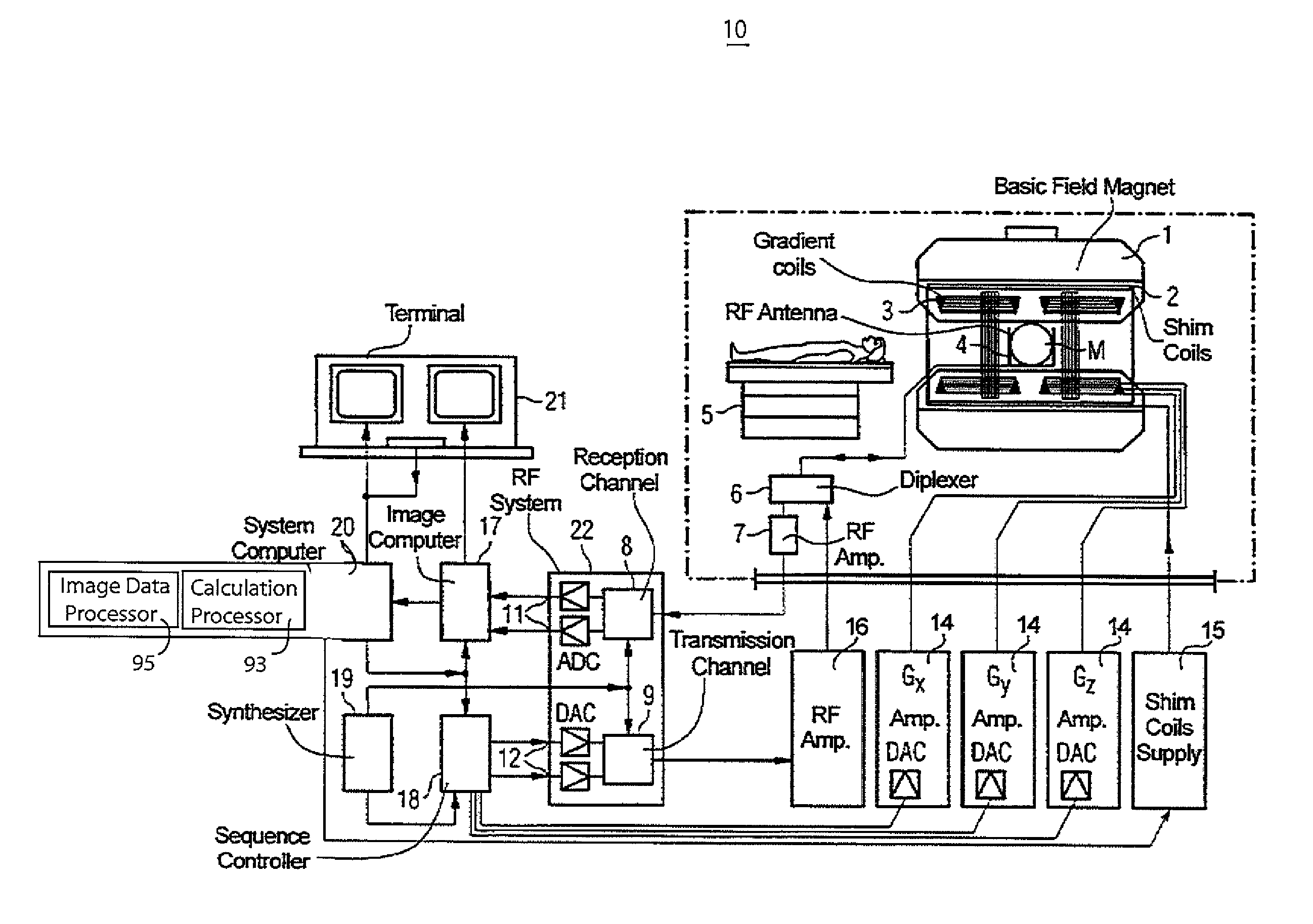
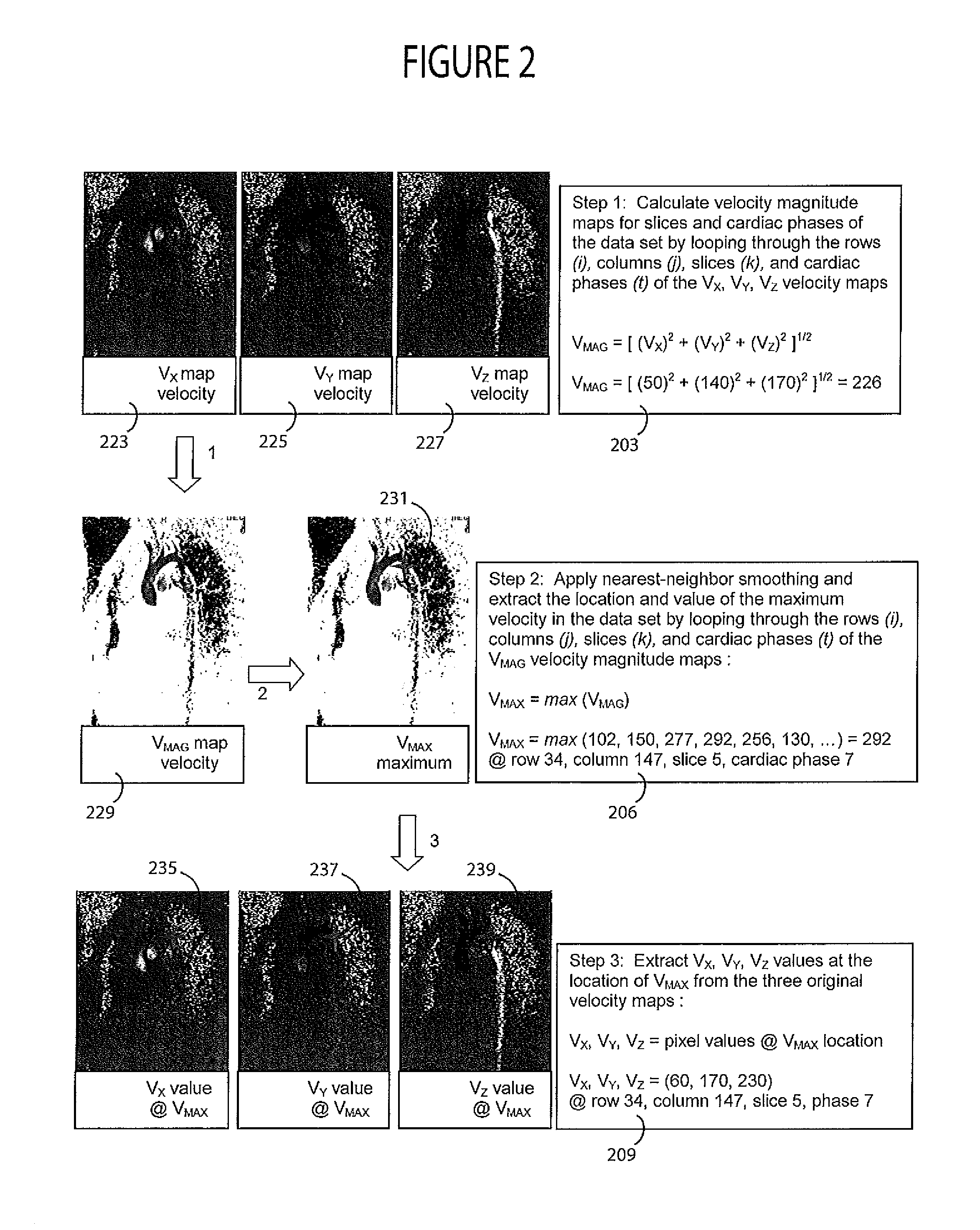
System for Blood Flow Velocity Determination using MR Imaging
ActiveUS20110175608A1Improve accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setData acquisition
A system improves accuracy of blood flow peak velocity measurements as well as the speed and precision of an MR data acquisition workflow. A system for blood flow velocity determination in MR imaging comprises an MR imaging system. The MR imaging system acquires a three dimensional (3D) MR imaging dataset of a patient anatomical volume of interest and a one dimensional (1D) MR imaging dataset within the volume of interest automatically aligned in response to 3D vector directional information. An image data processor derives the 3D vector directional information by, deriving velocity magnitude data using the acquired 3D MR imaging dataset, identifying maximum velocity data using the derived velocity magnitude data and transforming the identified maximum velocity data to provide the 3D vector directional information. A calculation processor uses the acquired 1D MR imaging dataset to calculate a blood flow velocity in a direction determined by the 3D vector directional information.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
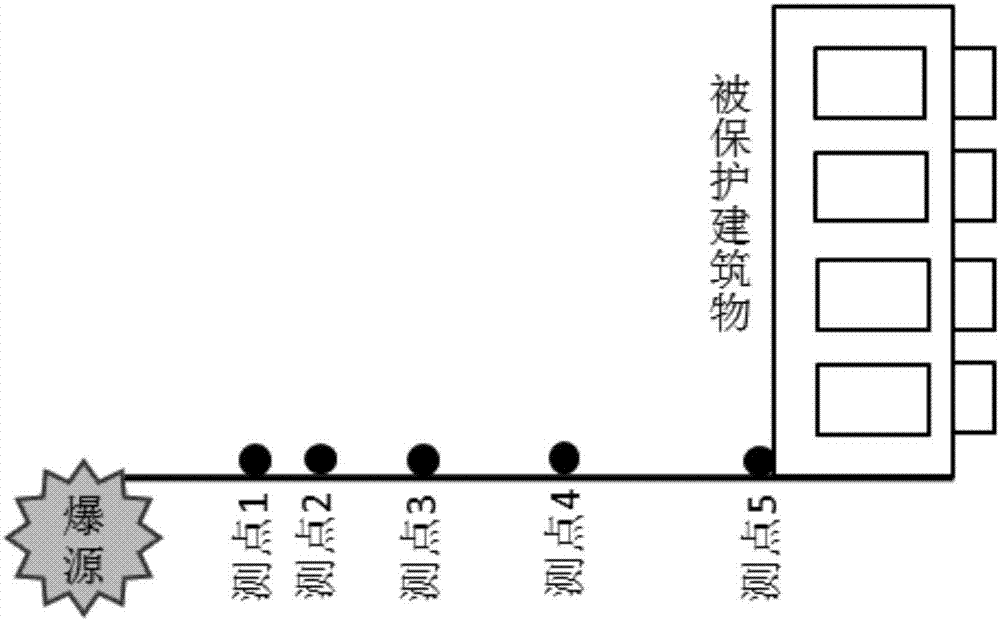
Blasting parameter optimization method capable of guaranteeing safety of above-ground structures
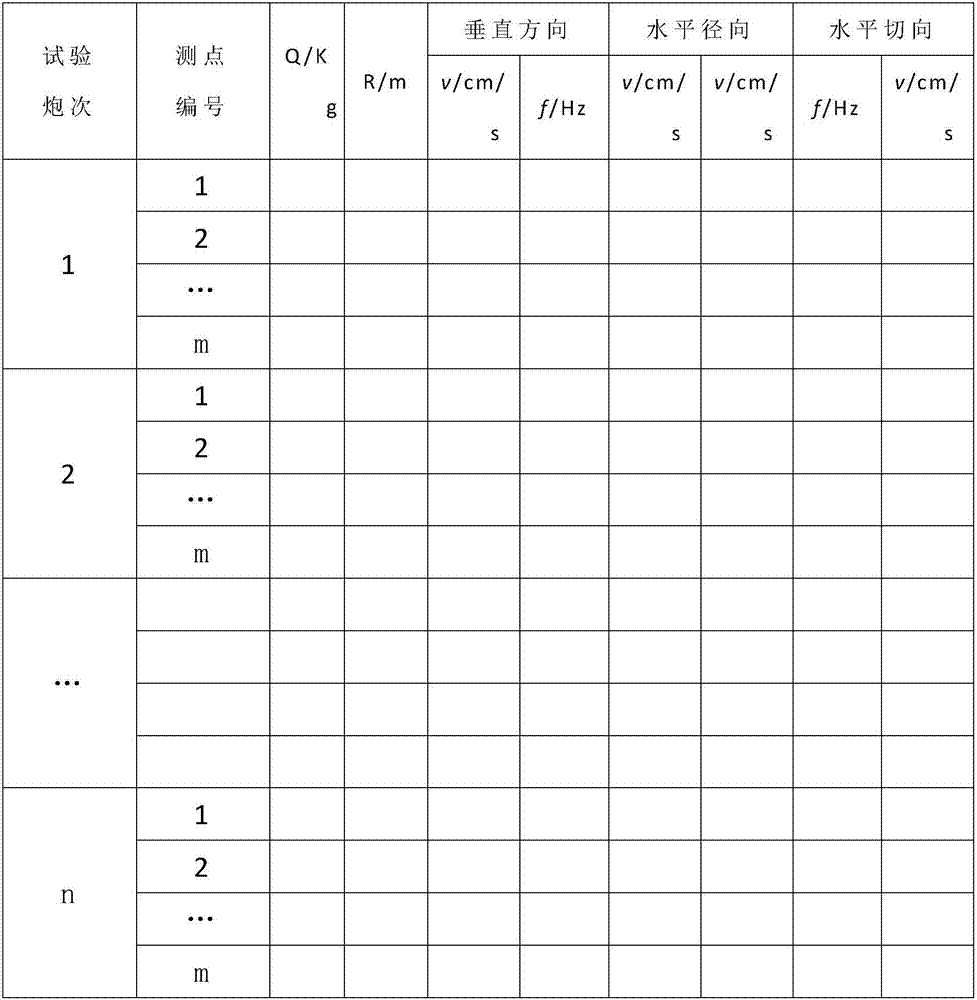
The invention discloses a blasting parameter optimization method capable of guaranteeing safety of above-ground structures. The blasting parameter optimization method comprises the steps that a blasting testing program is formulated; blasting is carried out according to the testing program, three sets of testing data of all measuring points in the vertical direction, horizontal radial direction and horizontal tangential direction are obtained, and the set of testing data which the maximum peak velocity arithmetic mean value corresponds to are taken as analyzing data; a v-f calculation model and a blasting vibration velocity model of a blasting zone are solved; the peak value vibration velocity and the main frequency in the initial blasting design program are solved; the peak value vibration velocity and the main frequency contrast with an existing blasting vibration safe and permitted standard point by point, the initial blasting design program corresponding to the peak value vibration velocity and the main frequency which do not conform a safety regulation for blasting is adjusted until the blast vibration safety allowance standard is met. The method is high in applicability, operation is simple, civil and economic disputes and construction delay caused by blasting vibration damage to the above-ground structures can be avoided, and the economical benefits of construction sides are greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
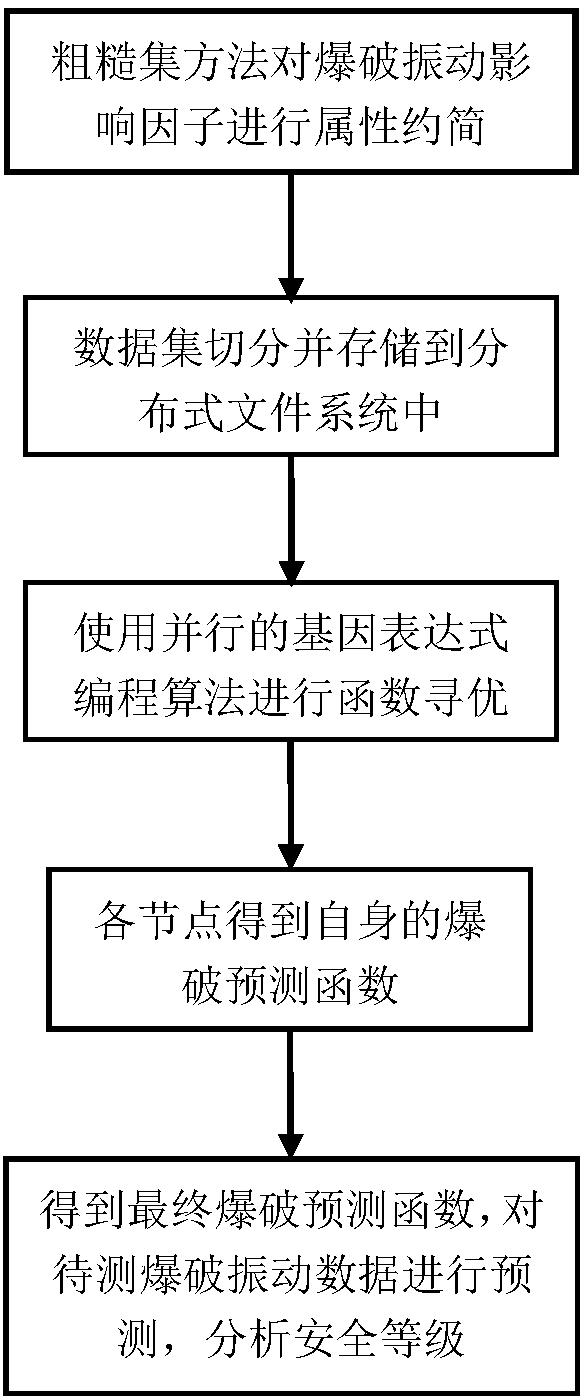
Blasting vibration prediction method based on Spark gene expression optimization
ActiveCN108154003ASolve the problem of training efficiencyFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsNODALData set
The invention provides a blasting vibration prediction method based on Spark gene expression optimization, and involves the field of machine learning. The data preprocessing technology is used for processing blasting data, and a sample data set is obtained; by calculating the incoordination rate of each condition attribute, condition attributes with the incoordination rate lower than a threshold value are deleted from an original data set, and then a new data set is generated to serve as an input data set; on each node, an improved gene expression method is used for function optimization, a blasting vibration effect prediction function can be obtained, and then the prediction value of the blasting vibration peak velocity is obtained. The method can better solve the training efficiency problem under the condition of mass data, the new-generation parallel computing technology is adopted, the genetic expression programming algorithm is improved for the global function optimization of theblasting data, the convergence speed can be largely improved, and the training efficiency is improved without affecting the training precision.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Jet nozzle mixer
InactiveUS20060242944A1Reduce noiseWell mixedCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusJet engineNoise level
A second stage external jet nozzle mixer (20) includes identically formed lobes which equal in number the lobes of the first stage internal mixer. The external mixer works with the internal mixer, and furthers the mixing of the jet engine internal bypass flow with the internal jet engine core flow. This mixing levels the disparate flow velocities attendant with the jet engine exhaust, reduces the peak velocities from the jet engine core and increases the lower bypass velocities of the jet engine internal bypass flow. The lobes include complex curvatures that greatly enhance mixing of the gases and ambient cooling air, and thereby reduce noise. At the lobe terminus, the lobe dimensional characteristics may be adjusted to thereby adjust the total terminus area to achieve a match to a jet engine to cause that jet engine to run at a determined RPM and noise level. Noise attenuation may also be adjusted by changing lobe dimensions. Prior existing second stage exhaust jet nozzle mixers may be retrofitted to allow alteration of their total terminus area by employing the disclosed device and method.
Owner:COMTRAN LTD
Velocity measurement signal processing method for Doppler velocimeter
InactiveCN102680958ASolve the problem of difficult speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationCurrent velocityClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a velocity measurement signal processing method for a Doppler velocimeter, comprising the following steps of: (A) preprocessing a received velocity measurement signal by using a filter; (B) carrying out Fourier analysis on the frequency of the signal obtained in the step (A) to obtain a reference velocity; (C) respectively solving the sine and a plurality of peak frequencies of the reference velocity obtained in the step (B) to respectively obtain a sine velocity curve and a peak velocity curve; and (D) comparing the reference velocity obtained in the step (B) with the sine velocity curve and the peak velocity curve obtained in the step (C) to obtain a corrected velocity curve. Three solving methods including a frequency Fourier analysis method, a sine solving method and a multi-peak frequency solving method are used in the velocity measurement signal processing method, so that the signal processing method is suitable for all the speed ranges, and the problem that the current velocity measurement method is difficult in velocity measurement in a region with low velocity smaller than 1000m / s, and particularly a region with the velocity close to 100m / s, is solved.
Owner:COMP APPL RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Subsurface intelligent cluster of current energy converters
ActiveUS8981585B2Increase capacityIncrease power generationMachines/enginesEngine componentsPeak valueEngineering
A subsurface floating cluster of current energy converters is disclosed. A cluster consists of many nodes on a single mooring cable. Two converters, rotating in opposite direction, are connected as a pair. At least two pairs, four converters, are connected to each node. Each converter consists of a rotor with curved blades, a transmission, and an electrical generator. A computer on the mother ship, that tows the cluster, controls the rotating rate of every rotor in the cluster. Each node moves vertically or horizontally according to the rotation-rate-differential in each pair of rotors. Each node seeks and remains in peak velocity region, or at a predetermined water depth, to convert kinetic energy to electricity with an optimal efficiency. This invention has characteristics of simplicity in design, using artificial intelligence to achieve high efficiency in peak speed region of an ocean current, incremental capacity, and mobility.
Owner:SOONG YIN SHANG
Automated biplane-pw workflow for ultrasonic stenosis assessment
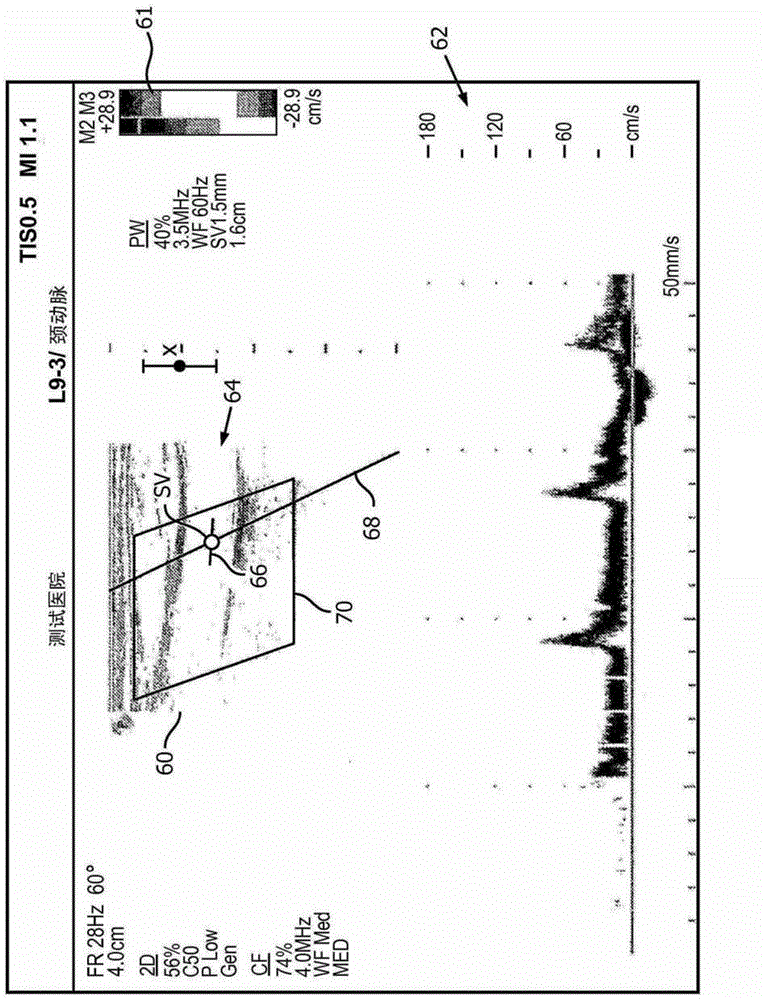
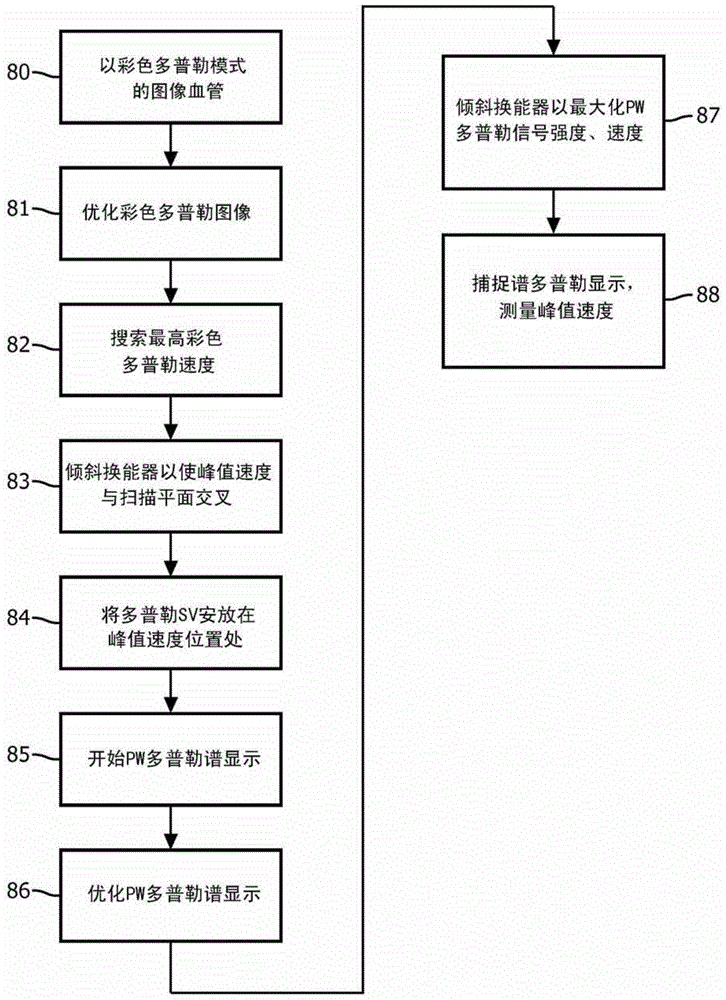
An ultrasound system with a matrix array (500) probe (10) operable in the biplane mode is used to assess stenosis of a blood vessel by simultaneously displaying two color Doppler biplane images (60a, 60b) of the vessel, one a longitudinal cross-sectional view (60a) and the other a transverse cross-sectional view (60b). The two image planes intersect along a Doppler beam line (68) used for PW Doppler. A sample volume graphic (SV) is positioned over the blood vessel at the peak velocity location in one image, then positioned over the blood vessel at the peak velocity location in the other image. As the sample volume location is moved in one image, the plane and / or sample volume location of the other image is adjusted correspondingly. Spectral Doppler data (62) is then acquired and displayed from the sample volume location.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Improved bone resector
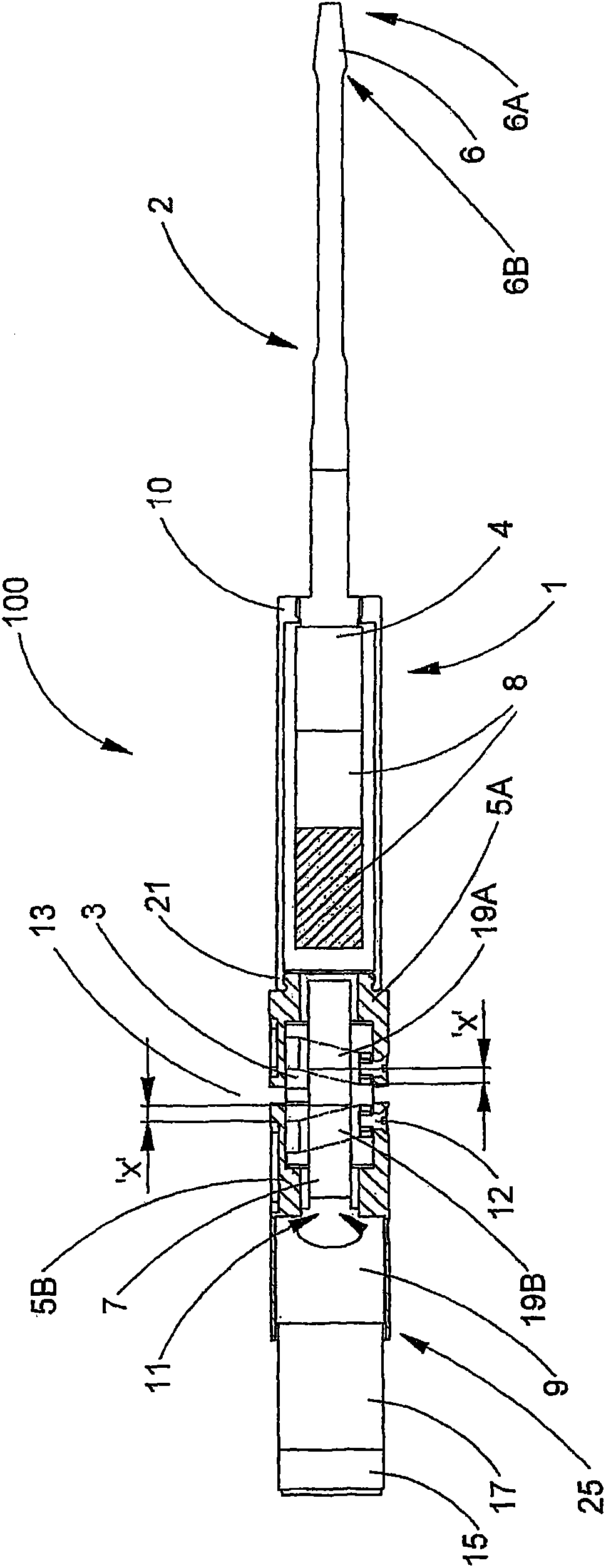
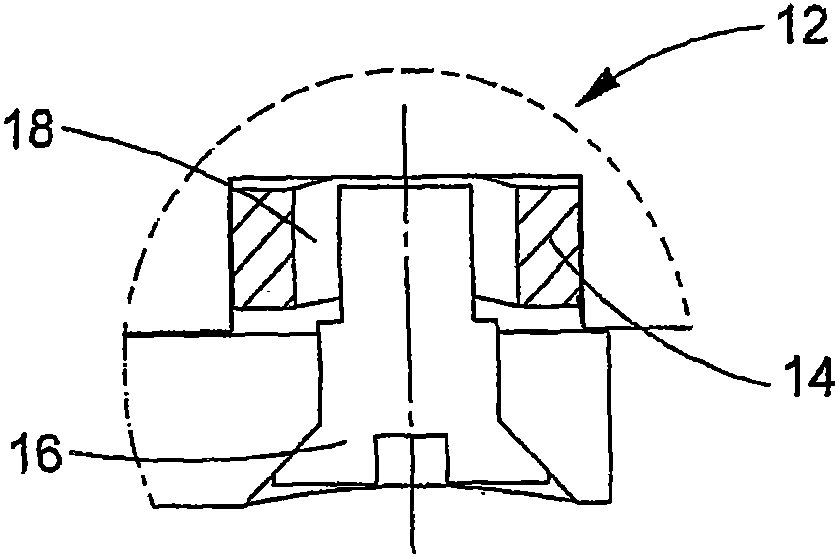
A bone resector tool (100) comprises an ultrasonic transducer (8), typically generating longitudinal mode vibrations at around 40 kHz, and having an elongate blade portion (2) mounted thereto. The transducer (8) and blade portion (2) are mounted to a rotatably- drivable converter element (3). Rotation of the converter element (3) produces reciprocal longitudinal motion of the transducer (8) and blade portion (2). A counterweight (5B) is also mounted to the converter element (3), moving exactly out of phase with the transducer (8) and blade portion (2), such that a centre of mass of the whole system is stationary, reducing vibration of the tool (100) in a user's hand. The peak velocity due to the ultrasonic vibrations of a distal tip (6A) of the blade portion (2) is up to seven times greater than its peak velocity due to the reciprocal longitudinal motion. This permits rapid, low-effort cutting of bone with easy removal of cut debris and minimal consequent necrosis.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
Two-dimensional estimation technique for doppler optical coherence tomography (OCT)
InactiveUS7894046B2Devices using optical meansFluid speed measurementIn-phase and quadrature componentsAortic flow
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a high-resolution, non-invasive technique to image subsurface tissue and tissue functions. A broadband light source illuminates an object and the reflected photons are processed using an interferometer, demodulated into inphase and quadrature components and then digitized. The captured data contains information about the velocity of the moving scatterers but current Doppler estimation algorithms have a limited velocity detection range. Using a two dimensional velocity estimation, Doppler OCT (DOCT) can be used for the detection of in vivo aortic blood flow rates of over 1 m / s peak velocity through an esophageal DOCT probe. Previous methods have used a transverse Kasai (TK) autocorrelation estimation to estimate the velocity which is good for slow velocities, such as in the microvasculature. By calculating the Kasai autocorrelation with a lag in the depth or axial direction, backscattered frequency information is obtained which yields high velocity rate information. Through subtraction with stationary backscattered information, the Doppler shift is obtained by the axial Kasai (AK) technique. Through utilizing information from two dimensions, velocities can be resolved which spans rates from the microcirculation to cardiac blood flow velocities.
Owner:MOROFKE DARREN ROSS +2
System and method for using microsaccade peak velocity as a measure of mental workload and fatigue
A system and method for determining a subject's level of fatigue. The method includes measuring microsaccadic eye movement dynamics of the subject, calculating a current microsaccade peak velocity from the measured microsaccadic eye movement dynamics, and comparing the current microsaccade peak velocity to a baseline microsaccade peak velocity. The method further includes determining the level of fatigue based on a difference between the current microsaccade peak velocity and the baseline microsaccade peak velocity.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Method and apparatus for recognizing fatigue affecting a driver
InactiveUS10159436B2Reliably recognizeGreat weightAcquiring/recognising eyesEye diagnosticsPattern recognitionDriver/operator
A method is described for recognizing fatigue, the method comprising an ascertaining step, a determining step, and a comparing step. In the ascertaining step a first saccade and at least one further saccade of an eye movement of a person are ascertained using a gaze direction signal that models the eye movement. In the determining step, a first data point representing a first amplitude of the first saccade and a first peak velocity of the first saccade, and at least one further data point representing a further amplitude of the further saccade and a further peak velocity of the further saccade, are determined using the gaze direction signal. In the comparing step, the first data point and at least the further data point are compared with a saccade model. The person is recognized as fatigued if the data points have a predetermined relationship to a confidence region of the saccade model.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
System for blood flow velocity determination using MR imaging
ActiveUS8487613B2Improve accuracyMagnetic property measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionData acquisitionBlood velocity
A system improves accuracy of blood flow peak velocity measurements as well as the speed and precision of an MR data acquisition workflow. A system for blood flow velocity determination in MR imaging comprises an MR imaging system. The MR imaging system acquires a three dimensional (3D) MR imaging dataset of a patient anatomical volume of interest and a one dimensional (1D) MR imaging dataset within the volume of interest automatically aligned in response to 3D vector directional information. An image data processor derives the 3D vector directional information by, deriving velocity magnitude data using the acquired 3D MR imaging dataset, identifying maximum velocity data using the derived velocity magnitude data and transforming the identified maximum velocity data to provide the 3D vector directional information. A calculation processor uses the acquired 1D MR imaging dataset to calculate a blood flow velocity in a direction determined by the 3D vector directional information.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com