Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
263 results about "Packaging Tank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
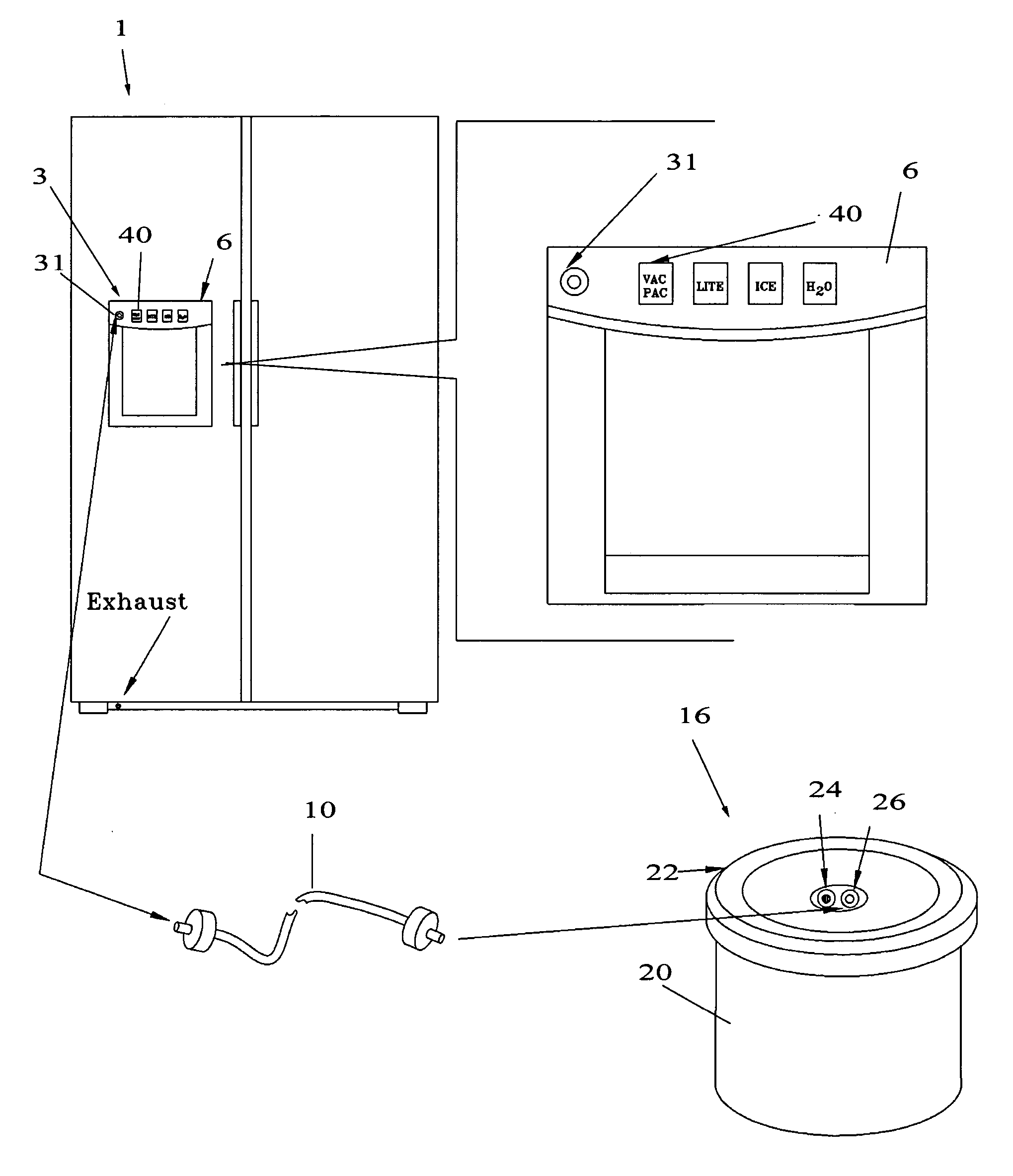
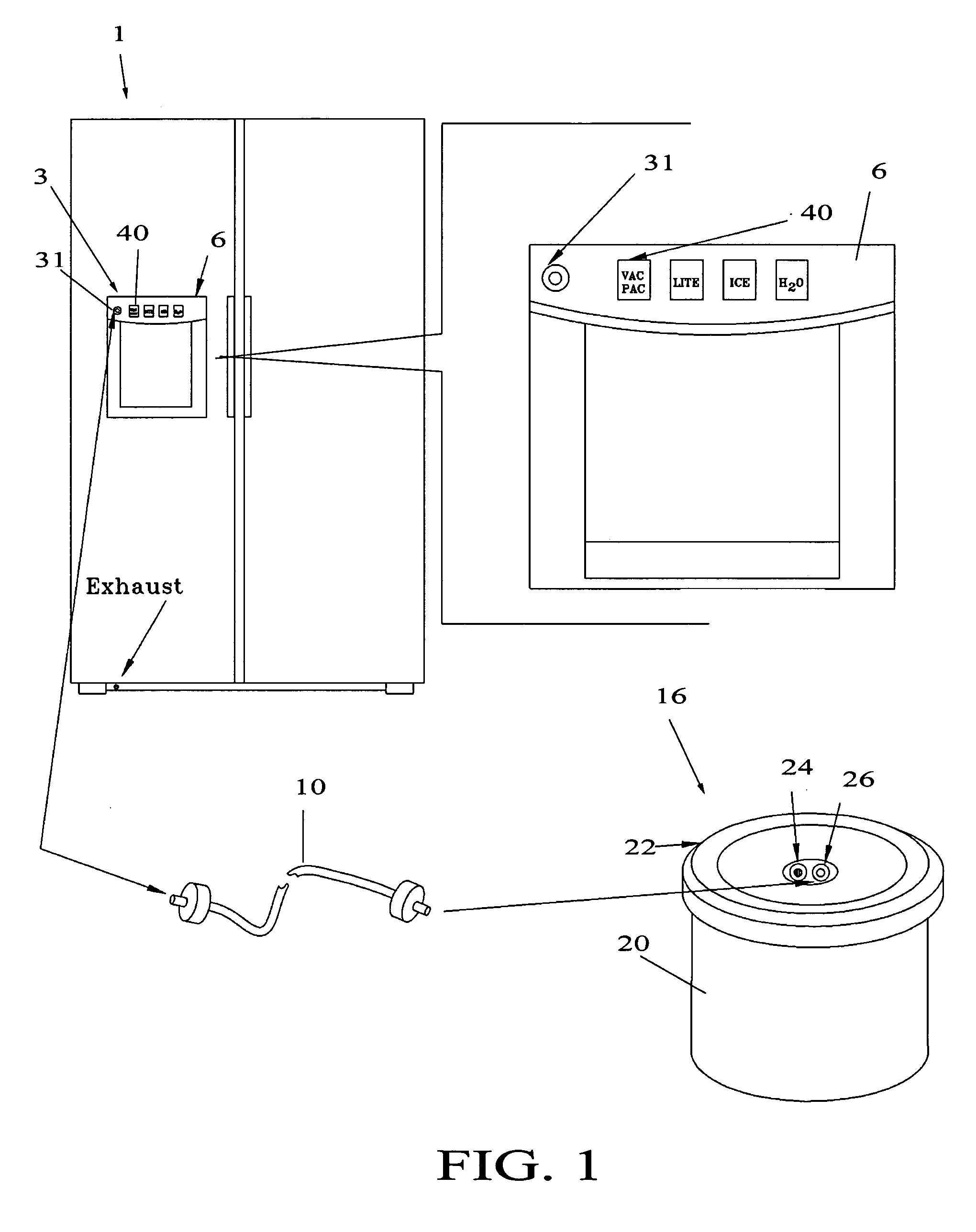
Refrigerator with integral vacuum sealer
InactiveUS20060090427A1Easy to useEasy accessLighting and heating apparatusPackaging under vacuum/special atmosphereEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
The present invention is a vacuum packaging system that is comprised of a very convenient vacuum pump and canister-sealing device that is an integral component of a refrigerator. The device is comprised of: 1) one or more external vacuum hose input ports or retractable combination hose / input ports, for applying a vacuum for packaging canisters, bottles or jars, or a remote bag sealing unit; 2) an internal configuration comprised of one or more vacuum hose input ports or retractable combination hose / input ports, canister lid storage attachments and / or carousel storage attachments; and / or 3) an external, integral or removable bagging unit (recessed into the refrigerator door) for vacuum sealing and cutting plastic bagging material.
Owner:HAU JOSEPH A +1
Heat shrinkable polyester film
InactiveUS20050196563A1Improve seismic performanceHigh adhesive retentionEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsPolyesterPolymer science
A heat shrinkable polyester film of the present invention has a transverse tear defect percentage of about 20% or less as determined in the following vibration test: the film is rolled into a tubular shape, two of its opposite edges bonded together, and then the tubular film is placed around a vertical stack (total weight: 660 g) of three food container cans each having a diameter of 72 mm and a height of 55 mm; the can stack with the tubular film placed therearound is passed through a shrink tunnel to shrink the tubular film onto the can stack; a total of 18 packs of such can stacks are placed into a cardboard box having a length of 455 mm, a width of 230 mm and a height of 165 mm (6 packs in the length direction by 3 packs in the width direction), and the cardboard box is sealed; the cardboard box is vibrated along the width direction for 30 min by a stroke of 50 mm and at a vibration rate of 180 reciprocations / min, after which the transverse tearage of the tubular film is visually observed; and the transverse tear defect percentage (%) is determined based on the number of defective packs per 18 packs, wherein the defective pack is any pack having a tear flaw of 30 mm or longer along a can periphery. The heat shrinkable polyester film of the present invention has a good shock resistance during shipping especially under low temperatures, with a good finish after shrinkage and a sufficient solvent adhesiveness. Thus, the heat shrinkable polyester film of the present invention is suitable for use in a multi-packaging label for packaging, inter alia, a stack of cans.
Owner:ITO HIDEKI +4
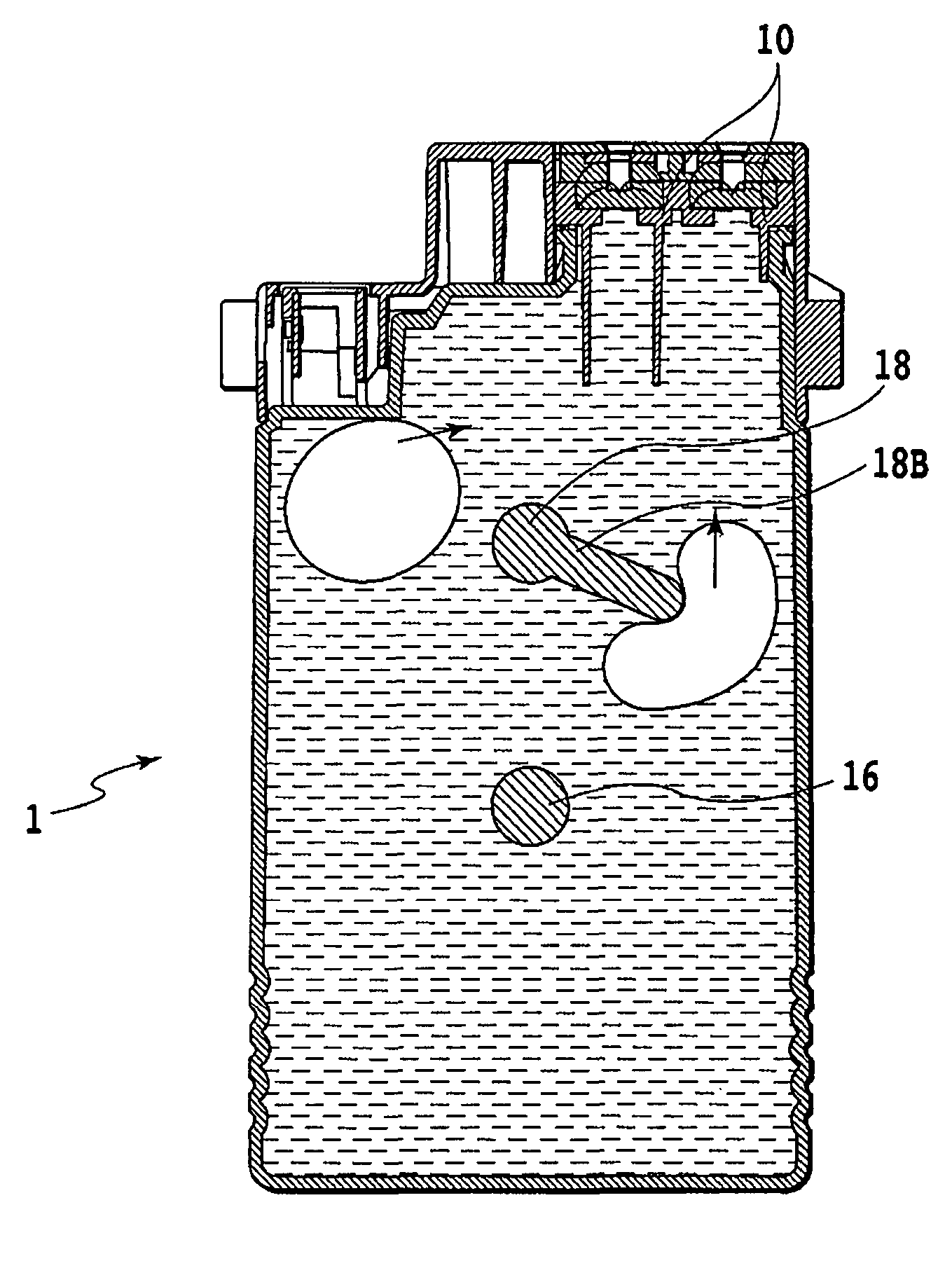
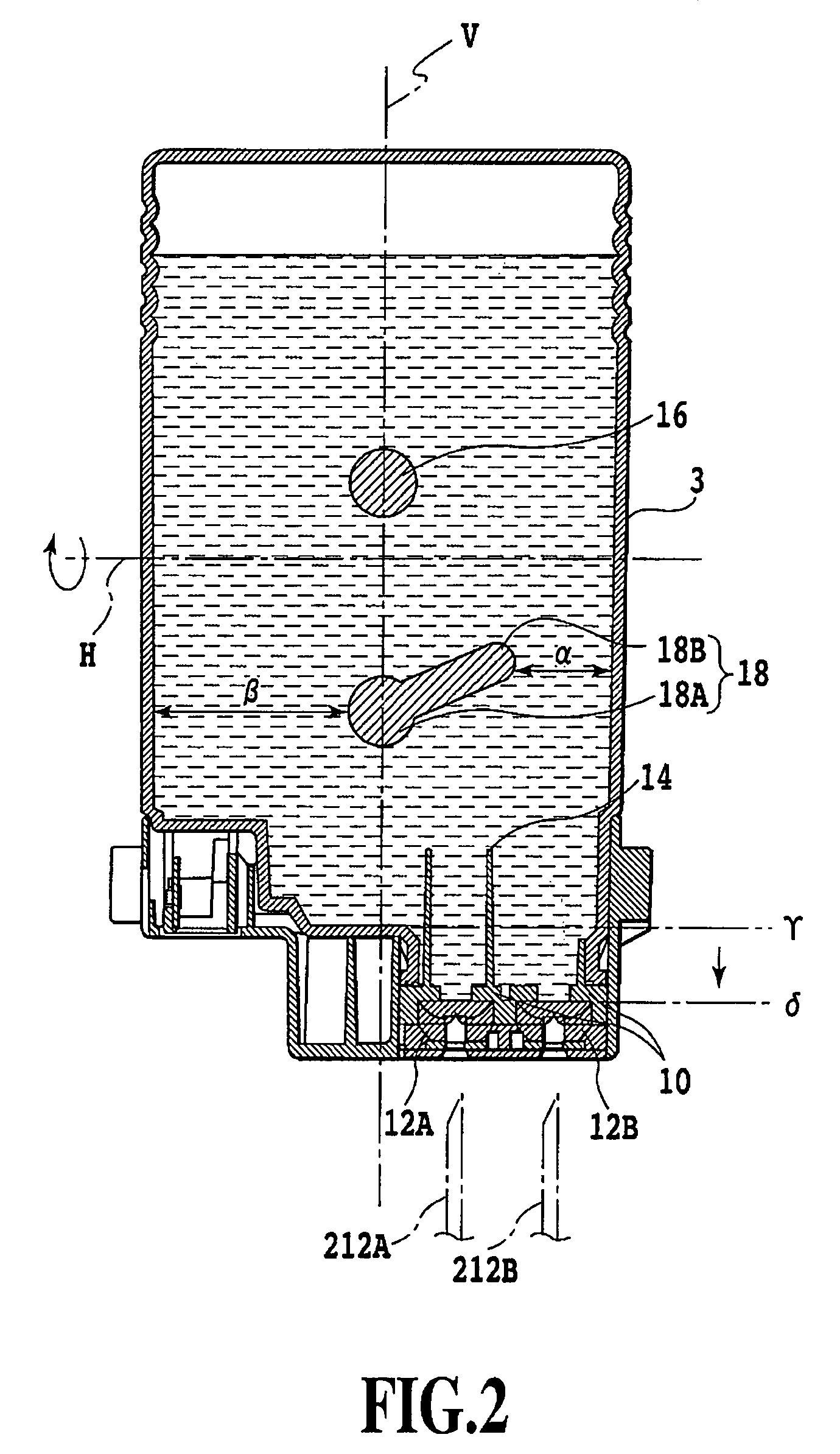
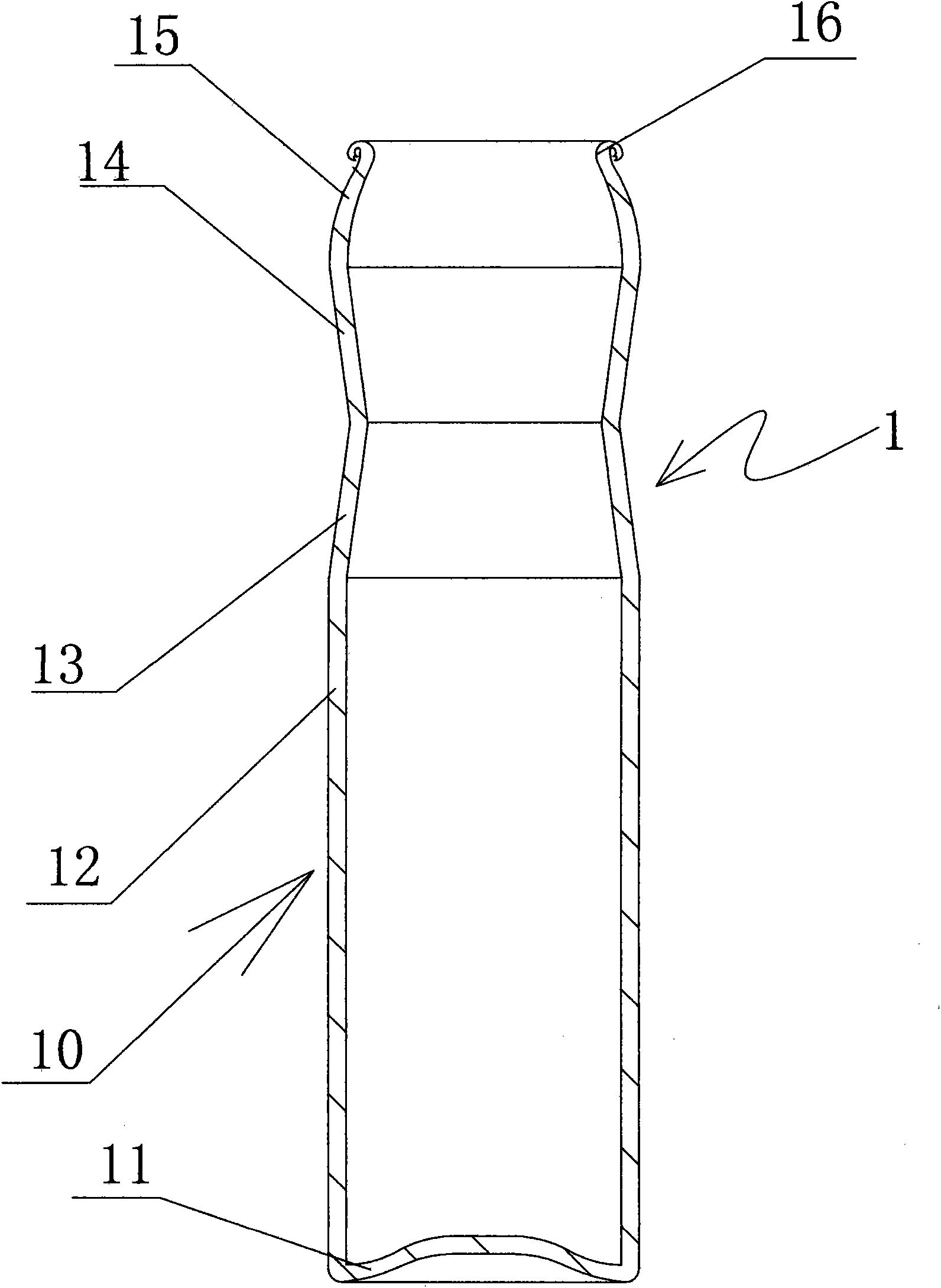
Liquid container and liquid container package
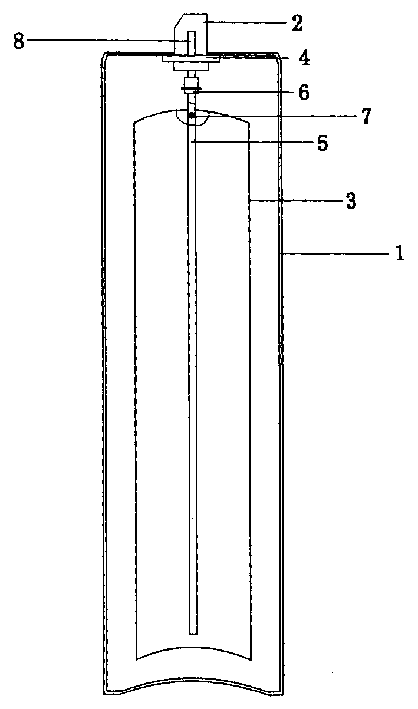
When a package in which a tank 1 is wrapped is opened, caused is an action of reversing vertical positions of an end face of the tank 1 having an ink supply portion 10, and an end face opposite to the foregoing end face. Along with this action, air existing inside the tank 1 ascends, and then is separated by air separating portions. Thus, a coloring material component inside the tank is stirred.
Owner:CANON KK
Powder material packaging machine
ActiveCN109335113AEvenly stackedQuick unloadingRotary stirring mixersSolid materialPackaging TankEngineering
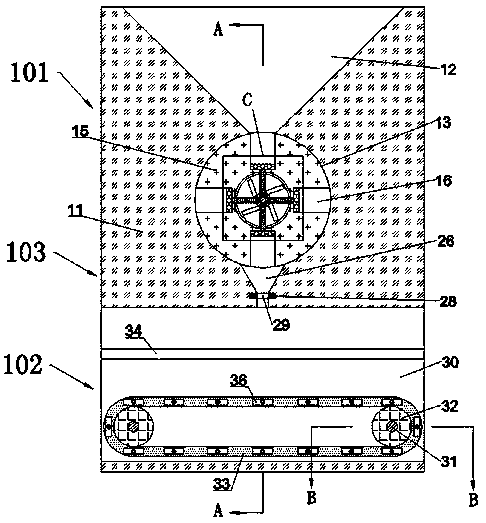
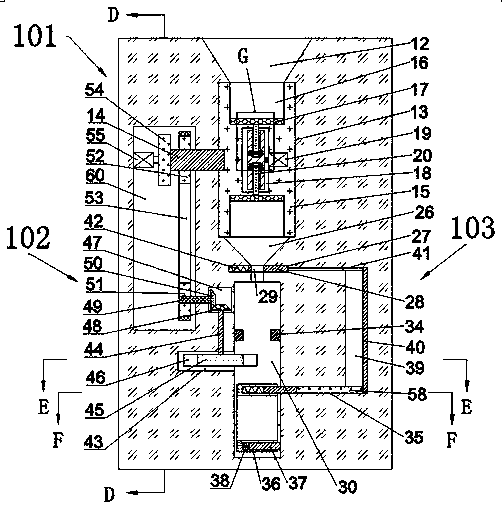
The invention relates to the technical field of food processing equipment, in particular to a powder materials packaging machine. The powder material packaging machine comprises a conveying mechanism,a lifting mechanism, a material storage cylinder, a sealing mechanism, a flattening mechanism, a rotating mechanism, a stirring mechanism and a feeding mechanism. According to the machine, a discharging pipe can be driven to move upwards gradually from the bottom layer in a packaging tank through the lifting mechanism, so that the materials are gradually accumulated from bottom to top, and the accumulation is more uniform; meanwhile, the rotating mechanism can drive the flattening mechanism to rotate, a shifting rod can shift and scatter the materials, a flattening plate can flatten the materials, so that the powder materials can fully fill the whole packaging tank; in the discharging process, stirring blades can stir the top area of the packaging tank, stirring rods which are distributedin a funnel shape can stir the outlet area of the packaging tank, so that the discharging is more rapid and the blockage is prevented; and automatic feeding and packaging can be realized.
Owner:台州佑辅机械实业有限公司
Intelligent powdering and selling robot and method
The invention discloses an intelligent powdering and selling robot and method. The intelligent powdering and selling robot mainly comprises a material bin device, a collecting hopper, a powdering device, a feeding device, a feeding hopper, a storing tank device, a sealing device, a packaging tank, a tank cover, a discharging box, a noiseless air pump, an air pressure sensor, a vacuum pump and a vacuum sensor. The intelligent powdering and selling method of the intelligent powdering and selling robot comprise the steps that the intelligent powdering and selling robot completes online charging according to materials and weight needed by users, and the intelligent powdering and selling robot processes the materials automatically. With requirements of current human cost and food processing safety and health degrees increasing, the intelligent powdering and selling robot can automatically complete selecting, weighing, powdering and packaging of grains without person, remote management and control such as online statistics, online charging, online maintenance and online early warning is achieved through the network, and remote management and control can also be achieved through mobile phone APPs.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Quantitatively-adjustable powder quantitative filling machine
The invention discloses a quantitatively-adjustable powder quantitative filling machine. The quantitatively-adjustable powder quantitative filling machine comprises a filling machine body, a materialcavity opened upwards is formed in the upper end face of the filling machine body, a filling device is mounted on the lower side of the material cavity, the filling device comprises a groove wheel cavity formed in the lower wall of the material cavity in a communicating manner, a conveying device is mounted in the filling machine, a filling control device is mounted in the filling machine, and comprises a hopper cavity mounted between the lower wall of the groove wheel cavity and the upper wall of the conveying channel in a communication manner, through the filling device, each packaging tankcan be filled with powder amounts of same volume stably, filling is stable, filling is quantitatively adjustable, according to different specifications of packaging tanks, the amount can be relativelyadjusted to the proper powder amount, due to fixing of a transmission ratio between the filling device and the conveying device, the position state of each packaging tank is ensured during filling, and through the filling control device, the condition that during replacing of the filled packaging tanks, powder is spilled can be effectively avoided.
Owner:WENZHOU ANPA TECH CO LTD
Two-component polyurethane resin for metal packaging tanks, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104449531AGood adhesionGood deep drawing resistancePolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyesterSolvent
The invention relates to a two-component polyurethane resin for metal packaging tanks, and a preparation method thereof. The host of the two-component polyurethane resin comprises, by mass, 25-50% of polyester polyol, 5-15% of epoxy resin, 0.2-1.0% of a coupling agent and 35-65% of a solvent; a curing agent is polyisocyanate, and the host is mixed with the curing agent according to a mass ratio of 100:5-20; and the hydroxy group of the host reacts with isocyanate in the curing agent to generate polyurethane. The polyester polyol is prepared through ester interchange of dimetyl terephthalate, dicarboxylic acid, acid anhydride, dihydric alcohol and polyol, esterification and a condensation polymerization reaction, or is prepared through esterification of the dicarboxylic acid, the acid anhydride, the dihydric alcohol and the polyol, and the condensation polymerization reaction. The preparation method has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simplicity and reliability. The two-component polyurethane resin can be well bonded with a metal substrate and a film, has good deep punching, corrosion and boiling resistance, and can be widely used in the metallic tank industry.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECHNOLOGY
Ship for removing aquatic plants in riverways
InactiveCN104831697AQuick clearImprove cleaning efficiencyWater cleaningWaterborne vesselsPackaging TankMarine engineering
The invention discloses a ship for removing aquatic plants in riverways, which relates to the field of shipbuilding technology. The ship comprises a ship body and a bridge, a treatment tank is arranged in the ship body, a rotary shaft is arranged at the front of the ship body, rowed teeth are arranged on the rotary shaft, conveyer belts which are longitudinally arranged are arranged in the ship body and close to the rowed teeth, a chopping device is arranged close to the output ends of the conveyer belts, and a cleaning and packaging tank is arranged at the output end of the chopping device. The ship can solve the problems of low removing efficiency and unsafety which exist in manual aquatic plant salvage at present.
Owner:GUANGXI WUZHOU YUNLONG PORT & SHIP MACHINERY MFG
Heating type paste-like material quantitative packing machine
InactiveCN101456527AAvoid condensationAvoid cloggingLiquid fillingPackaging TankReciprocating motion
The invention discloses a heat tracing type quantitative paste material split packaging machine, which comprises a split packaging tank body with a feeding inlet and a discharging outlet and a group of split packaging heads; the discharging outlet of the split packaging tank body is communicated to the split packaging heads through the inlet end and the outlet end of a rotary reversing valve; the direction reversal of the rotary reversing valve is controlled through a cam reversing device; a plunger case is communicated with a third port of the rotary reversing valve, and a plunger in the plunger case is driven by a driving device to move to and fro; and electric heat tracing systems are at least arranged at the split packaging tank body, the rotary reversing valve which is passed through by a discharged material and the plunger case. The heat tracing type quantitative paste material split packaging machine can overcome the defects in the prior art, and the material which is easy to cause blocking or is condensable can be processed with split packaging by the mechanical method; and the heat tracing type quantitative paste material split packaging machine is suitable for not only paste material, but also liquid or fluid containing particles with the diameter lower than 3 millimeters.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY +2
Fruit jam flexible packaging can and its processing technology
InactiveCN102293237AFast penetrationLow heating temperatureFruit and vegetables preservationFood preparationCanned fruitPackaging Tank
The invention discloses a soft-packed can of fruit jam and its processing technology. The technology includes the following steps: 1) raw material pretreatment; 2) mixing ingredients; 3) vacuum cooking: sucking the raw materials and ingredients into a vacuum concentration tank and starting to stir and heat. to 60-70℃, then evacuate the vacuum concentration tank and keep the temperature at 60-70℃ for heating; 4) sterilization and filling; 5) cooling. The processing technology of the fruit jam soft packaging canning of the present invention uses vacuum cooking to replace the traditional pre-cooking process, so that the ingredients can quickly penetrate into the raw material tissue, and the food can be eaten immediately without placing it, so that the eater can feel the sweet and sour taste. Compared with the traditional process, the heating temperature of the raw materials is greatly reduced and the heating time is shortened, so that the raw materials will not be affected by the loss of nutrients in the raw materials and the taste of the raw materials due to excessive heating temperature or long heating time.
Owner:北京海泰食品有限公司
Fully-automatic thermostatic magnetic stirring sterile liquid medicine preparing and packaging device
InactiveCN101830420AReduce volumeNo disturbanceTemperatue controlBottle-handling machinesMagnetic tension forceTemperature control
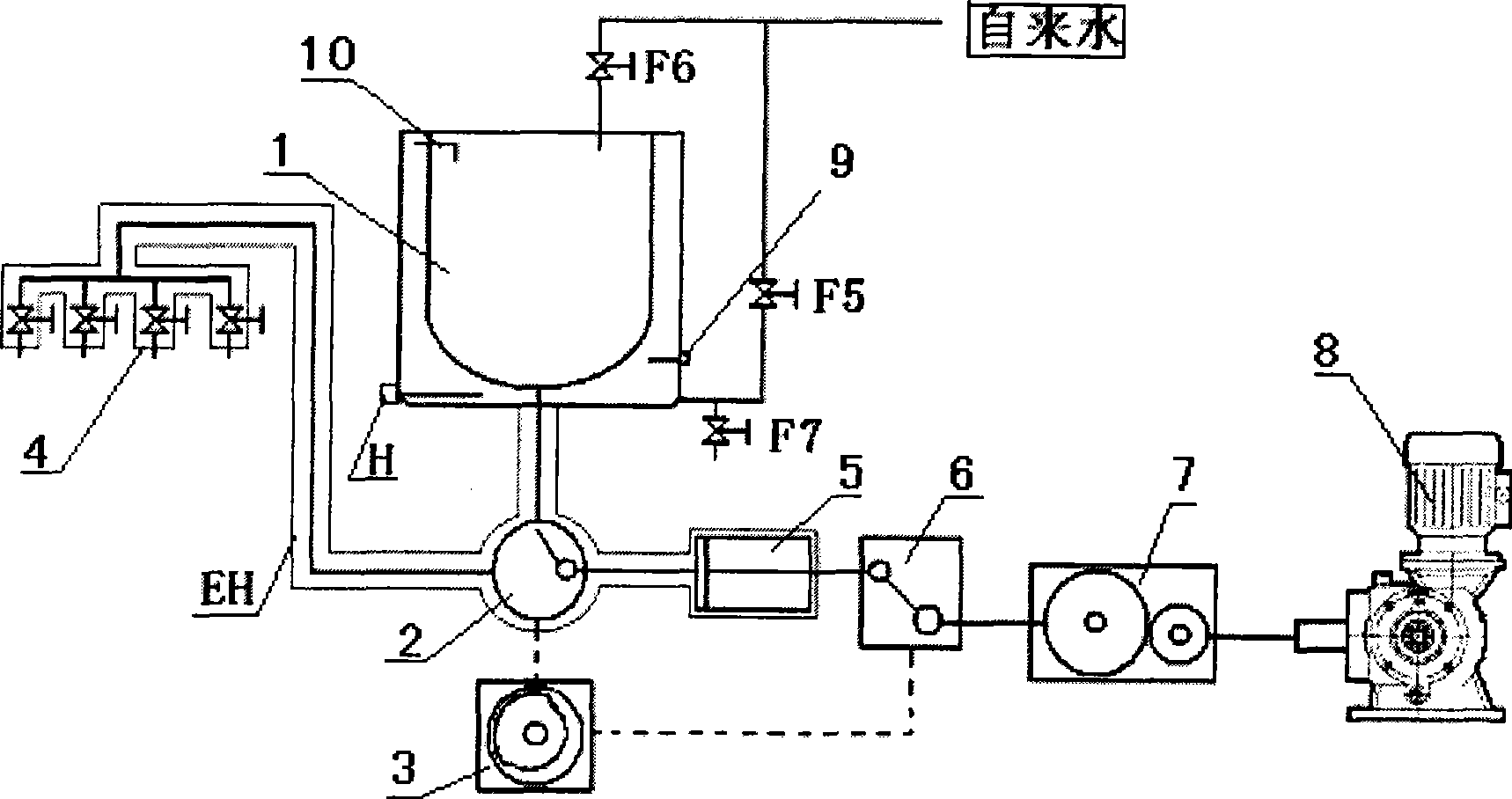
The invention discloses a fully-automatic thermostatic magnetic stirring sterile liquid medicine preparing and packaging device. The device comprises a worktable (1) and a packaging tank (2). Due to the adoption of the technical scheme of combining the worktable (1) which has the functions of automatic thermostatic control, semiconductor refrigeration element refrigeration and magnetic isolated type stirring with the packaging tank (2), the problems and the advantages of unreliable system tightness, low temperature control precision, lack of standardization, easy destruction of clean environment of a filling area by a mechanical stirrer and an ice bath in the prior art are solved and overcome. The provided fully-automatic thermostatic magnetic stirring sterile liquid medicine preparing and packaging device ensures that the liquid medicine in the packaging tank does not pollute the environment or is polluted by the environment by controlling the temperature of the liquid medicine in the packaging tank through the automatic thermostatic refrigeration of the worktable (1) and stirring the liquid medicine in the packaging tank by using non-contact magnetic force, enables the packaging of the liquid medicine to meet the requirements of a new edition of pharmacopoeia and the GMP, and fulfils the aim of ensuring safe, reliable and stable system tightness, constant temperature of the liquid medicine and uniform liquid medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG VACIN BIO PHARMA LTD
Novel aluminium packaging can and production method thereof
InactiveCN101683915AAvoid influenceFree choice of eating speedDispensing apparatusJarsEngineeringAutomation
The invention discloses a novel aluminium packaging can and a production method thereof. The novel aluminium packaging can comprises a can bottom, a can cylinder, a can shoulder and a can opening, andthe design key points are as follows: a gasket which can slide along the axis of the cylinder wall is sheathed inside the can cylinder; the inner cavity of the can cylinder is divided into an upper cavity and a lower cavity which are divided by the gasket; the upper cavity is communicated with the can opening; the can bottom is provided with a through hole which is used for communicating the lower cavity and the outside of the packaging can; the inner surface of the can shoulder is a conical surface; the upper part of the gasket is provided with a projection which can lean against the inner side of the can shoulder in an overlaying manner; and the projection is a conical body which can be matched with the conical surface at the inner side of the can shoulder. The invention aims at providing the production method of the novel aluminium packaging can with easy processing method and high degree of automation, and the novel aluminium packaging cans with simple structure, low cost and convenient use which are manufactured by adopting the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG EURO ASIA PACKAGING
Post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste temporary-storage processing system and method
InactiveCN106875998ARelieve temporary storage pressureTransportation safetyRadioactive decontaminationPackaging TankHandling system
The invention discloses a post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste temporary-storage processing system and method. The post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste temporary-storage processing method comprises the steps of loading a stainless steel packaging tank which is filled with high-radioactivity solid waste into a transferring container; adopting a transportation vehicle to transport the transferring container to a placing position of a storage container; adopting a crane to unload the stainless steel packaging tank in the transferring container into the storage container; adopting the crane to deliver the storage container to a temporary-storage area. By means of the post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste temporary-storage processing system and method, the processing method of the post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste is changed into the processing method of storing the waste in boxes on the ground, the temporary-storage pressure of the post-radiation high-radioactivity solid waste can be relieved, the operation procedures can be simplified, and the risks that operation personnel may be harmed by radiation are reduced.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Environment-protecting pesticide aerosol preparation and two-component packaging method
InactiveCN1476754ANo pollution in the processNo corrosionBiocideAnimal repellantsPackaging TankEngineering
The present invention relates to an insecticidal aerosol and its two-component packaging tank. The composition of the aerosol includes pyrethrin, synergist, surfactant, anti-oxidant, solvent, alakli-resisting material, high-temp.-resisting agent, essence, water photostabilizer and UV ray absorbent, and said invented packaging tank includes tank body, valve, bag sealing cover and liquid-transferring tube. Said liquid-transferring tube is inserted into the bag, a small hole is opened on the liquid-transferring tube.
Owner:李君
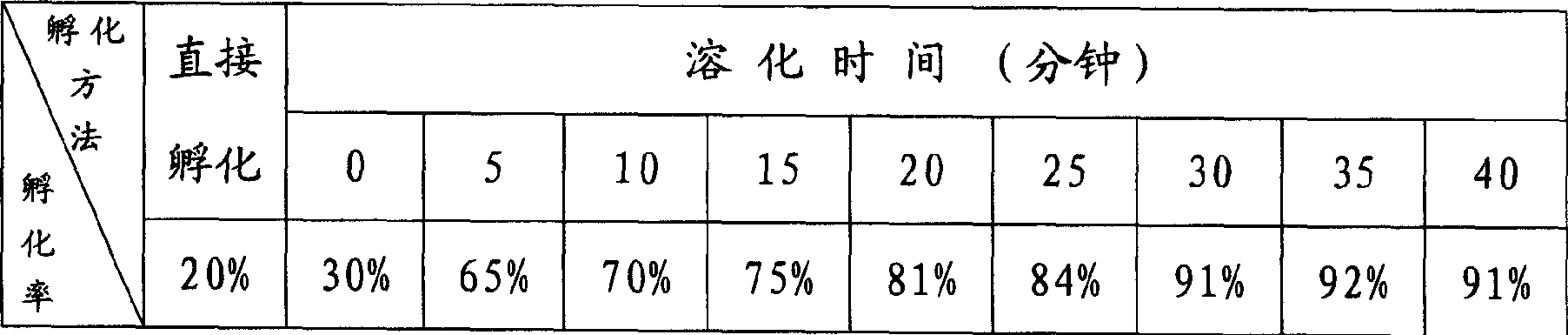
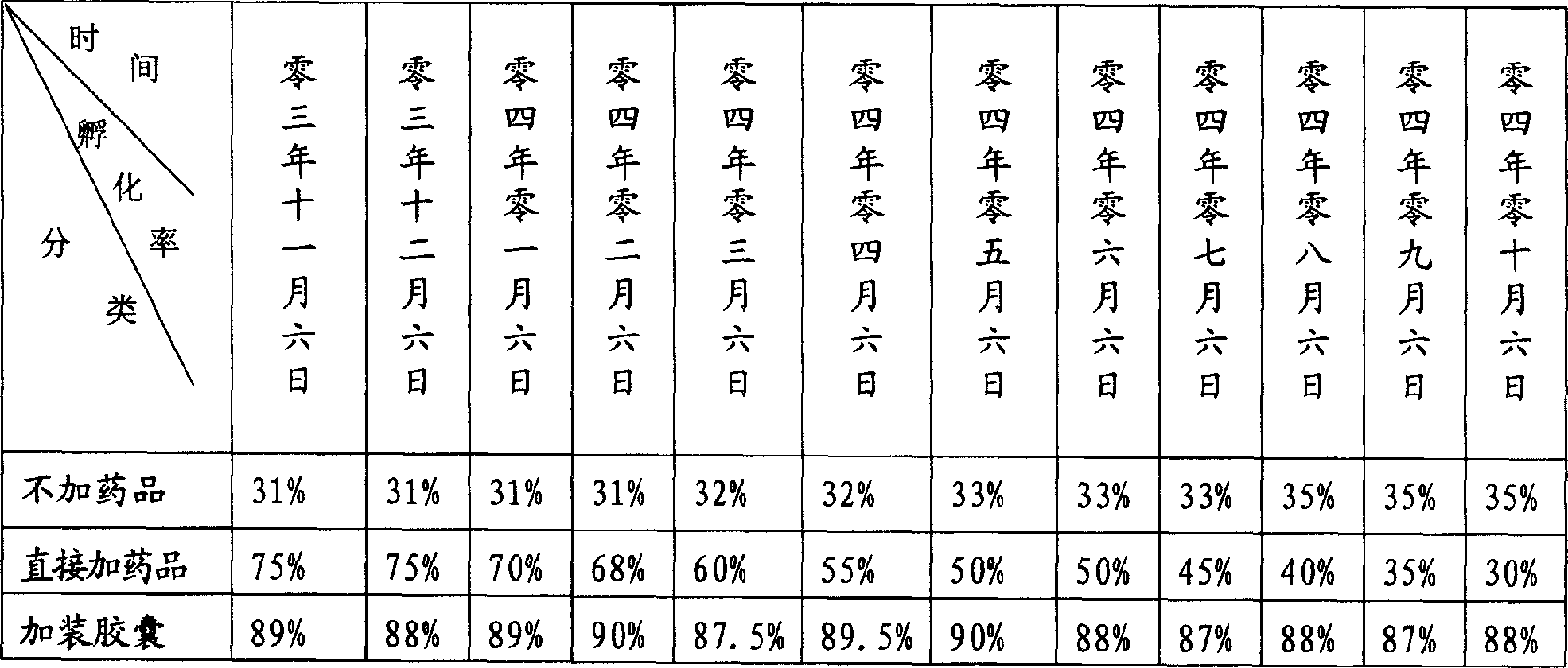
Artemia ovum hatching method with high hatchability rate
InactiveCN1631131AImprove hatchabilityAvoid deathClimate change adaptationOther angling devicesPackaging TankHatching
The invention discloses an Artemia ovum hatching method with high hatchability rate which comprises the steps of, freezing the collected insect ovum, drying directly, charging capsule with chemicals into the packaging tank, packaging together with the insect ovum, the chemicals include solids capable of generating hydrogen peroxide, during the using process, the insect ovum and capsule are poured into the hatching pool for hatching. The method can substantially increase hatching rate, the quality period can be extended for over 6 months.
Owner:付瑞岭
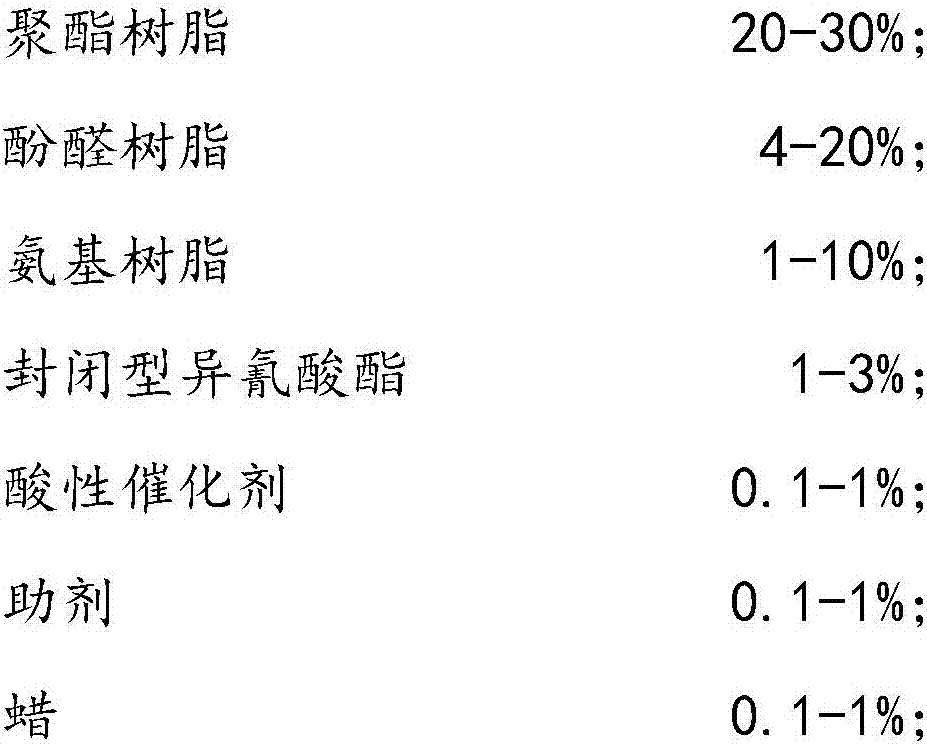
Application, preparation method and coating method of polyester type paint
InactiveCN107022286AEnvironmental recyclingImprove ductilityPretreated surfacesAnti-corrosive paintsPolyesterFood industry
The invention provides application of polyester type paint. The polyester type paint is applied to coating of an inner wall of a three-piece type packaging can for packaging acidic functional beverage. The invention further provides a preparation method and a coating method of the polyester type paint. By adopting the polyester type paint, the corrosion resistance of the packaging can is better than that of the prior art; the problem of a point which easily adsorbs furnace ash impurities is solved and requirements on bisphenol-A-free substances of partial national food industry standards are met.
Owner:SUZHOU SANXIN PACKAGING MATERIAL TECH CO LTD +1
Environmentally-friendly automatic building stone packaging equipment
The invention discloses environmentally-friendly automatic building stone packaging equipment. The environmentally-friendly automatic building stone packaging equipment comprises a rack, wherein a transmission shaft mounting hole is formed in the outer wall of one side of the rack; the inner wall of the transmission shaft mounting hole is connected to a transmission shaft by a bearing; the outer wall of one side of the transmission shaft is connected to a transmission belt pulley, a cam and a conveying belt pulley by keys; the outer walls of the transmission belt pulley and the conveying belt pulley are in sleeve connection with a transmission belt and a conveying belt; a second motor is fixed on the outer wall of one side of the rack by bolts; an output shaft of the second motor is fixed on the outer wall of one end of the transmission shaft by bolts; a weighing table is welded at one side, close to the conveying belt, of the outer wall of the top of the rack; and a packaging tank is put on the outer wall of the top of the weighing table. The environmentally-friendly automatic building stone packaging equipment has the beneficial effects that building stones can be sieved through matching of spiral blades and a first motor; the building stones fall along the spiral blades, so that the packaging tank can be prevented from being smashed up; and a blanking shaft can be pulled through matching of the first motor and a sliding plate, so that a discharging port is prevented from being blocked, and the improvement of the discharging efficiency is facilitated.
Owner:FOSHAN SHENYAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Closed continuous aftertreatment system for metal powder
PendingCN107321996ARealize airtightnessEffective connectionSolid materialPackaging TankProcess engineering
The invention discloses a closed continuous aftertreatment system for metal powder. The system comprises a metal powder drying device, a screening device, a fine metal powder collecting tank, a weight loss scale and a fine powder packaging tank. The screening device is arranged below the metal powder drying device and is connected with a discharging port of the metal powder drying device in a sealed mode through a first discharging pipe, and the fine metal powder collecting tank is arranged below a fine powder discharging port of the screening device and is connected with the fine powder discharging port of the screening device in a sealed mode through a second discharging pipe; and the weight loss scale is arranged below the fine metal powder collecting tank and is connected with a discharging port of the fine metal powder collecting tank in a sealed mode through a third discharging pipe, and the fine powder packaging tank is arranged below the weight loss scale and is connected with a feeding port of the weight loss scale in a sealed mode through a fourth discharging pipe. According to the closed continuous aftertreatment system, the gravity feeding mode is adopted, and the problems that as for a conventional powder transferring mode, the loss quantity is a large, and adhering is prone to occurring to the pipe wall are solved; and additionally, through closing and automation of different working procedures, the problem of powder flying is solved, the production efficiency is improved, and the powder quality is ensured.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH BAZHOU SPECIAL POWDER CO LTD +1
Automatic cover pressing and screwing device for gift packaging tins
ActiveCN111573581ANo rotationPlay the role of clamping and fixing positioningCapsThreaded caps applicationPackaging TankBevel gear
The invention relates to a cover pressing and screwing device, in particular to an automatic cover pressing and screwing device for gift packaging tins. Through the automatic cover pressing and screwing device for the gift tins, the gift tins and covers are placed by multiple times, and automatic cover pressing and screwing can be realized. According to a technical scheme, the automatic cover pressing and screwing device for the gift packaging tins comprises a base, a first bearing seat, a first rotary shaft, a first bevel gear, a limiting rotary disk, a telescopic clamping device, a supporting frame, a shell, a second bearing seat, a second rotary shaft, a second gear, a charging tray, a telescopic stop lever device, a strut, a hole disk, a guide sleeve and a press-down device, wherein the first bearing seat is fixed to the top of the base, and the first rotary shaft is rotationally connected to the top of the first bearing seat. According to the device, the gift tins can be clamped through the telescopic clamping device on the limiting rotary disk, the phenomenon that the gift tins still rotate after the covers are pressed cannot occur, and the functions of clamping, fixing and locating are achieved.
Owner:上海鲸初科技有限公司
Collecting box for coin packaging tank
ActiveCN105173301AThere will be no movementAvoid damageBoxesInternal fittingsPackaging TankEngineering
The invention discloses a collecting box for a coin packaging tank and belongs to the technical field of collectable packaging containers. The collecting box comprises a box body and a box cover. The collecting box is characterized in that a coin packaging tank limiting flange is formed in a box cavity; a left stop block and a right stop block are arranged on the front wall of the box body; the side, facing the left stop block, of the right stop block extends to form a buckling plate; the side, back to the box cavity, of the bottom wall of the box cavity forms a strengthening rib of the bottom wall of the box cavity; a pressing ring and a tank cover side face limiting flange are formed on the top wall of a box cover cavity; a left stop block of the box cover and a right stop block of the box cover are formed on the front side wall of the box cover; a buckling plate sliding cavity is formed by the space between the left stop block of the box cover and the right stop block of the box cover; a box cover buckling plate is formed in the buckling plate sliding cavity; a locking buckling plate sliding fit cavity is formed by the space between the box cover buckling plate and the front side wall of the box cover; and a sliding locking buckling plate is arranged on the box cover buckling plate in a matched manner. The collecting box has good concentrated storing, keeping, temporary carrying and durable collecting functions and is convenient and flexible to use; the coin packaging tank can be well limited; the coin packaging tank can be prevented from being damaged, and the strength of the box body is improved.
Owner:常熟市教育工艺品有限公司
Preparation method of nutritional eight-ingredient porridge
InactiveCN103070341AHigh in proteinMake up for the shortcomingsFood preparationTremellaAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nutritional eight-ingredient porridge. The method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing materials, wherein raw materials comprise a main material and auxiliary materials of lotus seeds and longan pulps; the main material comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 20-32 % of sticky rice, 10-16 % of red kidney bean, 18-28 % of soybean, 10-20 % of red bean, 1-4 % of tremella and 15-27 % of highland barley; and 1-5 lotus seeds and 1-5 longan pulps are used for every 43-47 g of main material; (2), washing; (3), filling the washed raw materials into a packaging tank; (4), injecting a boiled mixed solution containing both white granulated sugar and sodium tripolyphosphate into the packaging tank; (5), sterilizing and steaming the raw materials, wherein the raw materials in the packaging tank are cooked in the sterilizing process; and (6), cooling the materials obtained in the step (5) to room temperature so as to obtain the nutritional eight-ingredient porridge. The nutritional eight-ingredient porridge prepared by using the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of richer proteins and more balanced amino acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Aluminium packaging can and production method
The invention discloses an aluminum packaging tank which comprises a tank cylinder, a tank bottom, tank shoulders, a tank neck and a tank port. An inward concave part which is inward concave arc shape and can be held in hands conveniently shrinks in the middle part of the tank cylinder. The tank cylinder on the lower part of the inward concave part is cylindrical, and a longitudinal cross section of the tank cylinder on the upper part is arc shape extruding outwards. Due to the inward concave part, the tank can be held conveniently and comfortably. As the friction force is added, the aluminum packaging tank can not creep down from hands easily.
Owner:GUANGDONG EURO ASIA PACKAGING
Multipath stirrer for aluminum paste packaging tanks
InactiveCN103432937AImprove processing efficiencyNo wasteRotating receptacle mixersTransportation and packagingPackaging TankDrive motor
The invention relates to a multipath stirrer for aluminum paste packaging tanks. The multipath stirrer comprises a bottom plate, a driving motor, a transmission box, a fixed plate and rotary shafts, wherein the transmission box and the fixed plate are respectively fixed at two ends of the bottom plate; the fixed plate is connected with the transmission box through the rotary shafts; a plurality of first belt wheels, pressing wheels, a second belt wheel and a regulating wheel are arranged in the transmission box; the driving motor drives the second belt wheel to rotate; the rotary shafts are parallel to one another; the distance between each two adjacent rotary shafts is equal; an interval between the inner sides of the two adjacent rotary shafts is smaller than the diameter of each aluminum paste packaging tank. The multipath stirrer for the aluminum paste packaging tanks has the advantages that a plurality of groups of aluminum paste packaging tanks can be placed between the two adjacent rotary shafts; a large number of aluminum paste packaging tanks can be stirred during once processing; the processing efficiency is greatly improved; in the stirring process, the aluminum paste packaging tanks do not need to be opened; the phenomenon of waste caused by scattering of aluminum paste out of the tanks is avoided, and the phenomenon of oxidation caused by exposing of the aluminum paste in air during stirring is avoided.
Owner:EGING PHOTOVOLTAIC TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine based on three-axis ball screw sliding table and work method of chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine
PendingCN106956792AQuick and precise positioning and arrangementMeet needsIndividual articlesPackaging fruits/vegetablesPackaging TankBall screw
The invention relates to a chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine based on a three-axis ball screw sliding table and a work method of the chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine. The chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine is characterized in that the chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine comprises a horizontal machine base and a first horizontal sliding base arranged on the horizontal machine base; a first vertical base is vertically arranged on the first horizontal sliding base; a first sliding vertical base capable of rising and falling along the first vertical base is arranged on the first vertical base; a second horizontal base is arranged on the first sliding vertical base; the horizontal movement sliding table capable of moving along the second horizontal base is arranged on the second horizontal base; an intermittent discharge mechanism is arranged on the horizontal movement sliding table; and a packaging tank is arranged on the portion, beside the horizontal machine base, of the intermittent discharge mechanism. According to the chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine and the work method, control over the horizontal movement sliding table in three axes is convenient and accurate, and rapid and precise positioning and arranging of chestnut kernels can be achieved; and compared with existing manual packaging, much labor is saved, the packaging efficiency is improved, the production cost is reduced, the chestnut kernel arrangement and placement machine and the work method are more sanitary and reliable, and the requirement for packaging chestnuts is met.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Inflatable packaging structure for plastic product
PendingCN109484768ARegular shapePlace stableContainers to prevent mechanical damagePackaging TankEngineering
The invention relates to an inflatable packaging structure for a plastic product. The inflatable packaging structure comprises an inner bag body for holding the plastic product and an outer bag body arranged outside the inner bag body in a sleeving mode, a sealed space is formed between the inner bag body and the outer bag body, and the inner bag body and the outer bag body are connected through aplurality of inflatable bubbles; and gas bags are arranged in the positions, on the inner surface of the outer bag body, of the inflatable bubbles, the gas bags are filled with compressed gas, openings of the gas bags are provided with valves, and touch switches corresponding to the valves of the gas bags are arranged in the positions, on the outer surface of the inner bag body, of the inflatablebubbles. Compared with the prior art, the inflatable packaging structure is provided with the gas bags filled with the compressed gas, when the outer bag body is damaged or subjected to gas leakage,the inflatable bubbles can act as a first layer of protection, when excessively-large external compression force squeezes the inflatable bubbles, the compressed gas of the gas bags is released, and the inflatable bubbles bulge to form a second layer of protection; and the outer bag body is cuboid, is regular in shape, can be stably placed, can achieve multi-layer stacking, can be directly loaded into a packaging tank or a packaging box, and does not need to be adjusted many times, and the packaging efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHIEF LAND ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Tank cleaning machine
ActiveCN107252805AClean thoroughlyPrevent recontaminationHollow article cleaningElectrostatic cleaningLow speedPackaging Tank
The invention discloses a tank cleaning machine used for cleaning away dust on the surface of a tank body. A machine frame of the tank cleaning machine is provided with a conveying system, a sweeping cleaning system and a dust sucking collecting system. The conveying system comprises a conveying belt used for conveying the tank body. The conveying belt comprises a low-speed belt body and a high-speed belt body, and the low-speed belt body and the high-speed belt body are arranged side by side and have a speed difference. The sweeping cleaning system comprises cleaning brushes, brushing discs and nozzles, wherein the cleaning brushes are arranged on the two sides of the conveying belt and used for rotationally brushing away dust on the side surface of the tank body, the brushing discs are arranged above the conveying belt and used for rotationally brushing away the dust on the top of the tank body, and the nozzles are used for blowing away the dust on the surface of the tank body by using compressed air. The dust sucking collecting system comprises a dust sucking branch pipe. The dust sucking branch pipe is provided with a main sucking nozzle with a sucking opening facing the upper portion of the conveying belt. The dust sucking branch pipe is connected to a dust sucking header pipe. The dust sucking header pipe is connected to a dust removing device. According to the tank cleaning machine, plenty of tank bodies can be continuously processed without stop, cleaning of the surface of the tank body is thorough, the dust content in the environment surrounding the machine is low, and the tank cleaning machine can be applied to cleaning for all kinds of powder packaging tanks.
Owner:江苏永兴长和智能科技有限公司
Punch forming device for metal cover of food packaging tin
ActiveCN112207199AAvoid stickingSave human resourcesMetal-working feeding devicesPositioning devicesPunchingPackaging Tank
The invention discloses a punch forming device for a metal cover of a food packaging tin, and belongs to the technical field of punching devices. The punch forming device solves the defects that in the prior art, a to-be-punched part of a traditional punch forming device is prone to adhering to an upper punching die and a lower punching die, the punching quality is affected as the to-be-punched part is prone to shaking in the punching process. A main structure of the punch forming device comprises a worktable and a to-be-punched part, wherein a guide groove is formed in the worktable, a communicating groove is formed in the upper end of the worktable, a storage mechanism opposite to the communicating groove is fixedly connected to the upper end of the worktable, the to-be-punched part is placed in the storage mechanism, and a pushing mechanism is fixedly connected to the side wall of the worktable. The pushing mechanism penetrates through the side wall of the guide groove and extends into the guide groove, the lower punching die is arranged at the inner bottom of the guide groove, a punching groove communicating to the guide groove is formed in the upper end of the worktable in a penetrating mode, and a discharging groove communicating to the guide groove is formed in the bottom of the worktable. The punch forming device is mainly used for punching the metal cover of the food packaging bin.
Owner:SHANDONG HUANQIU TINPLATE CAN MAKING
Tea packaging tin manufacturing method
ActiveCN111229973AImprove the stabilityHigh forming precisionMetal-working feeding devicesPositioning devicesPackaging TankPortal frame
The invention relates to a tea packaging tin manufacturing method, which uses a tea packaging tin manufacturing device. The tea packaging tin manufacturing device comprises a portal frame, a workbench, auxiliary lapping devices and an edge lapping device, wherein the workbench is arranged on the lower side of the portal frame, and the auxiliary lapping devices are installed on the upper end face of the workbench from left to right at equal intervals; and a lapping device is arranged on the left side of the auxiliary lapping devices, wherein the lower end of the lapping device is in sliding fitwith the upper end of the workbench, and the upper end of the lapping device is connected with the upper end of the portal frame in a sliding fit mode. According to the tea packaging tin manufacturing method, tea packaging tin manufacturing is carried out according to a multi-clamping design principle, the stability degree of a iron sheet in the winding drum landing edge forming process is improved, and forming precision of a iron sheet tank body is further improved; and meanwhile, iron sheet pre-bending, overall winding drum landing edge forming and edge sealing treatment can be continuouslyoperated on the same working line, and accordingly working efficiency is improved.
Owner:安徽中联茶叶进出口有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine decocting device and traditional Chinese medicine decocting method
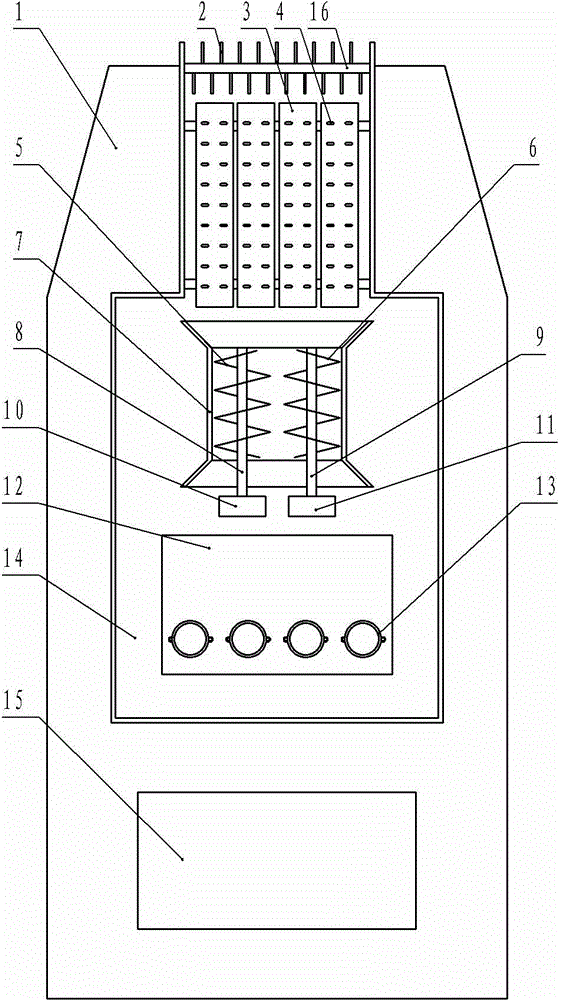
InactiveCN106074162AEnsure safetyShorten the timePharmaceutical product form changePackaging TankEngineering
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine decocting device and a traditional Chinese medicine decocting method. The device comprises a supporting frame, a soaking tank, two extraction tanks, a concentration tank, a storage tank, a packaging tank and a cleaning tank. The soaking tank, the extraction tanks, the concentration tank, the storage tank, the packaging tank and the cleaning tank are respectively connected with a control cabinet on the supporting frame through an electromagnetic valve. The traditional Chinese medicine decocting device is characterized in that the soaking tank, the extraction tanks, the concentration tank, the storage tank and the packaging tank are sequentially communicated through a pipeline and respectively communicated with the cleaning tank. Compared with the prior art, the traditional Chinese medicine decocting device has advantages that by adoption of the two extraction tanks, more required traditional Chinese medicines can be decocted, and time saving and work efficiency improvement are realized; by the cleaning tank, all tank bodies and pipelines of the medicine decocting device can be cleaned orderly, convenience and cleanness in cleaning are realized, negligence caused by manual operations is avoided, and property safety of traditional Chinese medicines is guaranteed.
Owner:泽望自动化设备(上海)有限公司
Aluminum packaging can and production method thereof
InactiveCN101683902ACompact structureStrong three-dimensional senseJarsLinings/internal coatingsEngineeringVertical cylinder
The invention discloses an aluminium packaging can and a production method thereof. The design key points of the aluminium packaging lie in comprising a can bottom which extends upwards to form a hollow cylindrical vertical cylinder; the opening at the upper end of the vertical cylinder shrinks upwards to form a conical part; the opening at the upper end of the conical part expands upwards to forman inverted conical part; the conical degree of the longitudinal section of the inverted conical part is equal to that of the conical part; the opening at the upper end of the inverted conical part shrinks upwards to form a can shoulder and turns up to form a can opening with a lip. The invention aims at providing a production method of the aluminium packaging can with simple processing method and high degree of automation and an aluminium packaging can with strong tank body stereoscopic impression and simple structure manufactured by the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG EURO ASIA PACKAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com