Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
241 results about "Muscle material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
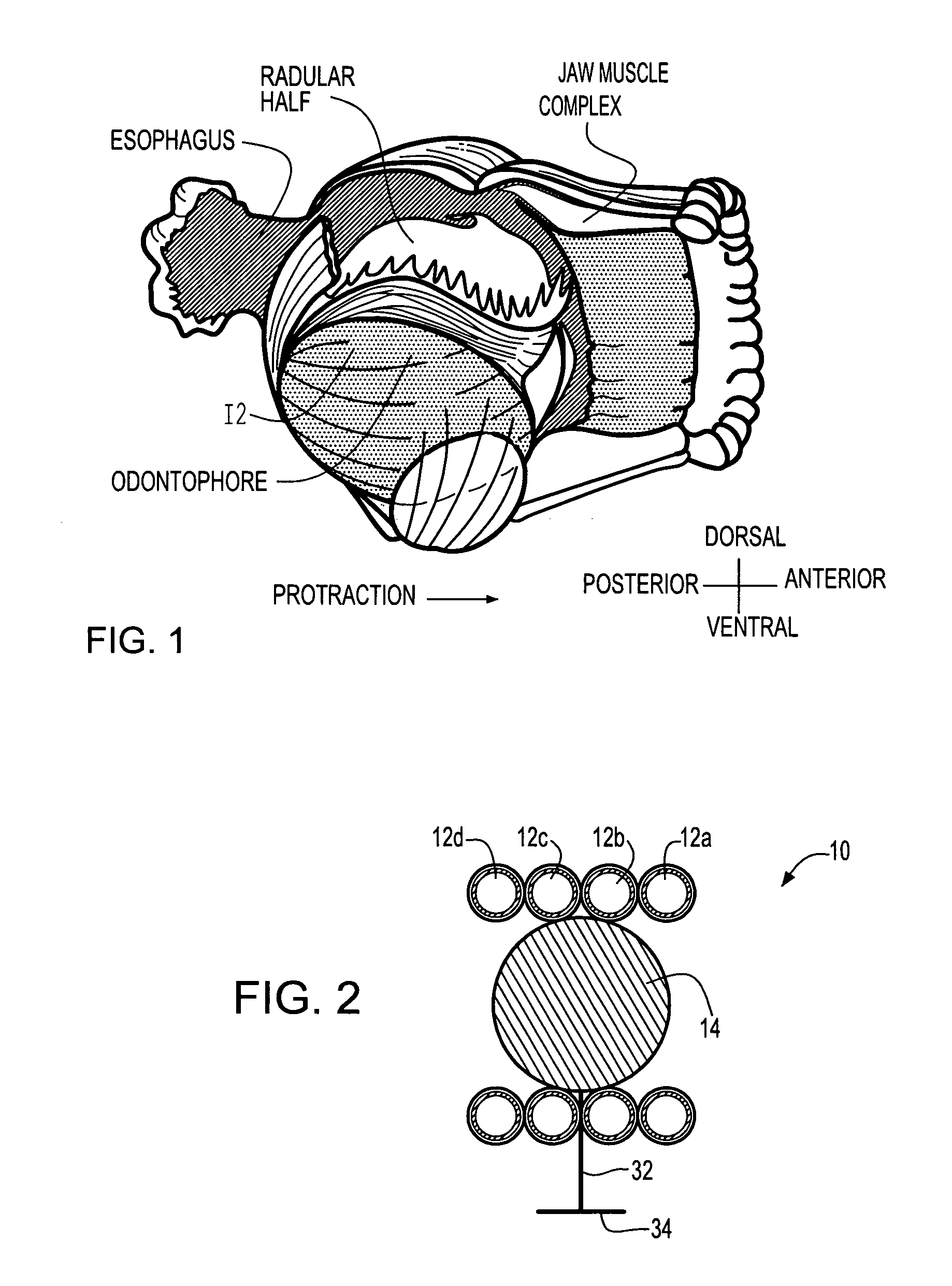
Artificial muscle is a generic term used for actuators, materials or devices that mimic natural muscle can reversibly contract, expand, or rotate within one component due to an external stimulus (such as voltage, current, pressure or temperature).
Electromechanical machine-based artificial muscles, bio-valves and related devices
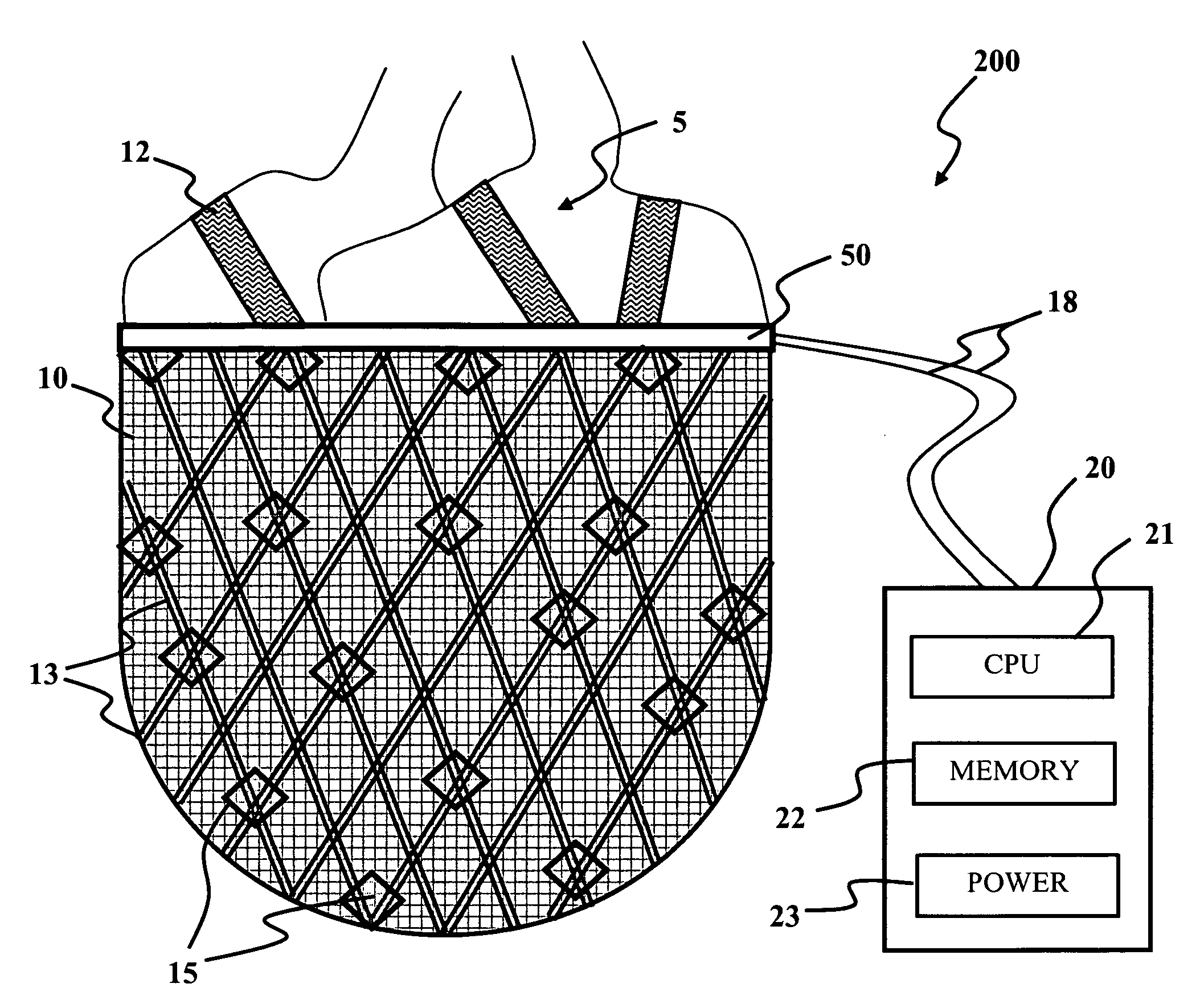
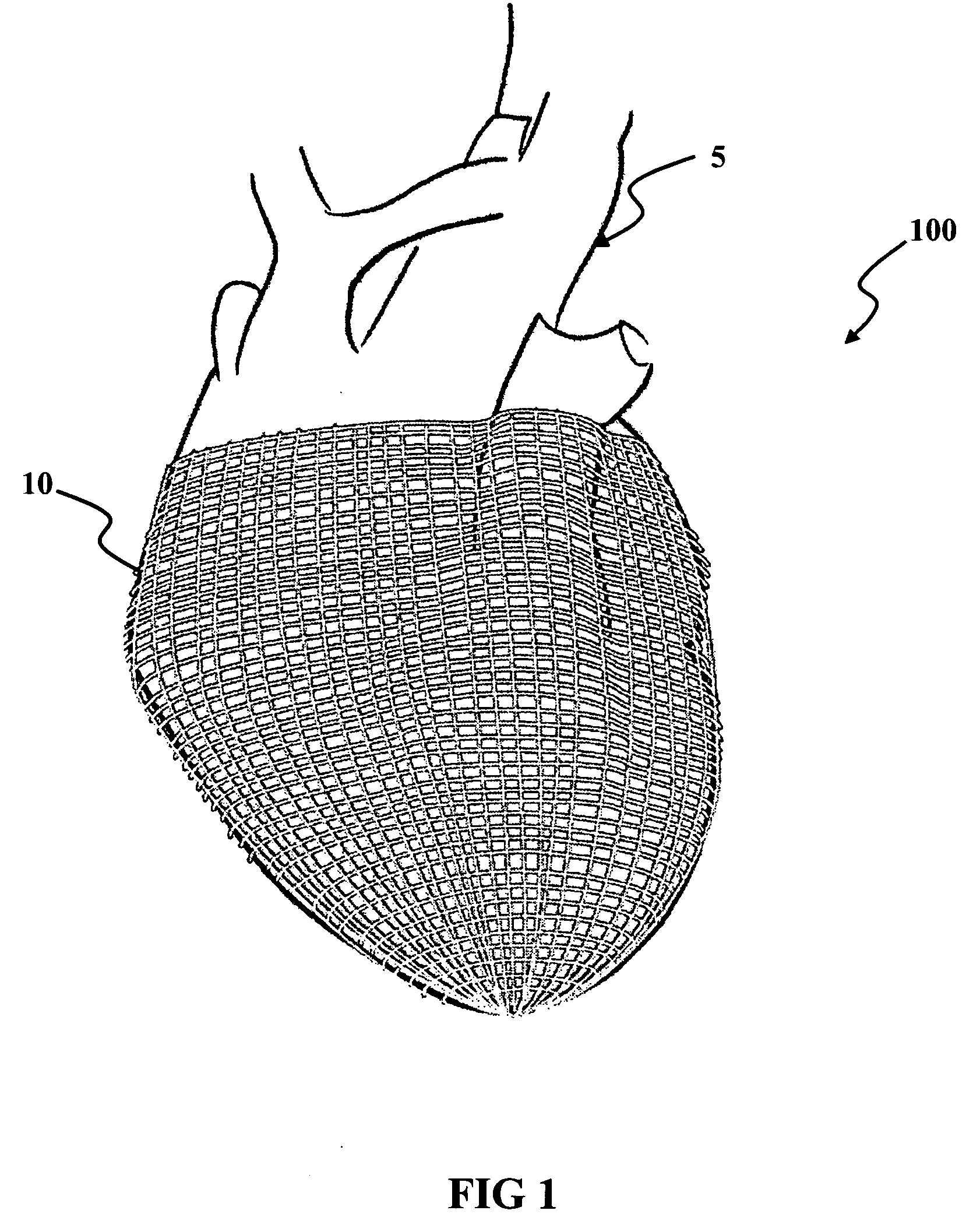
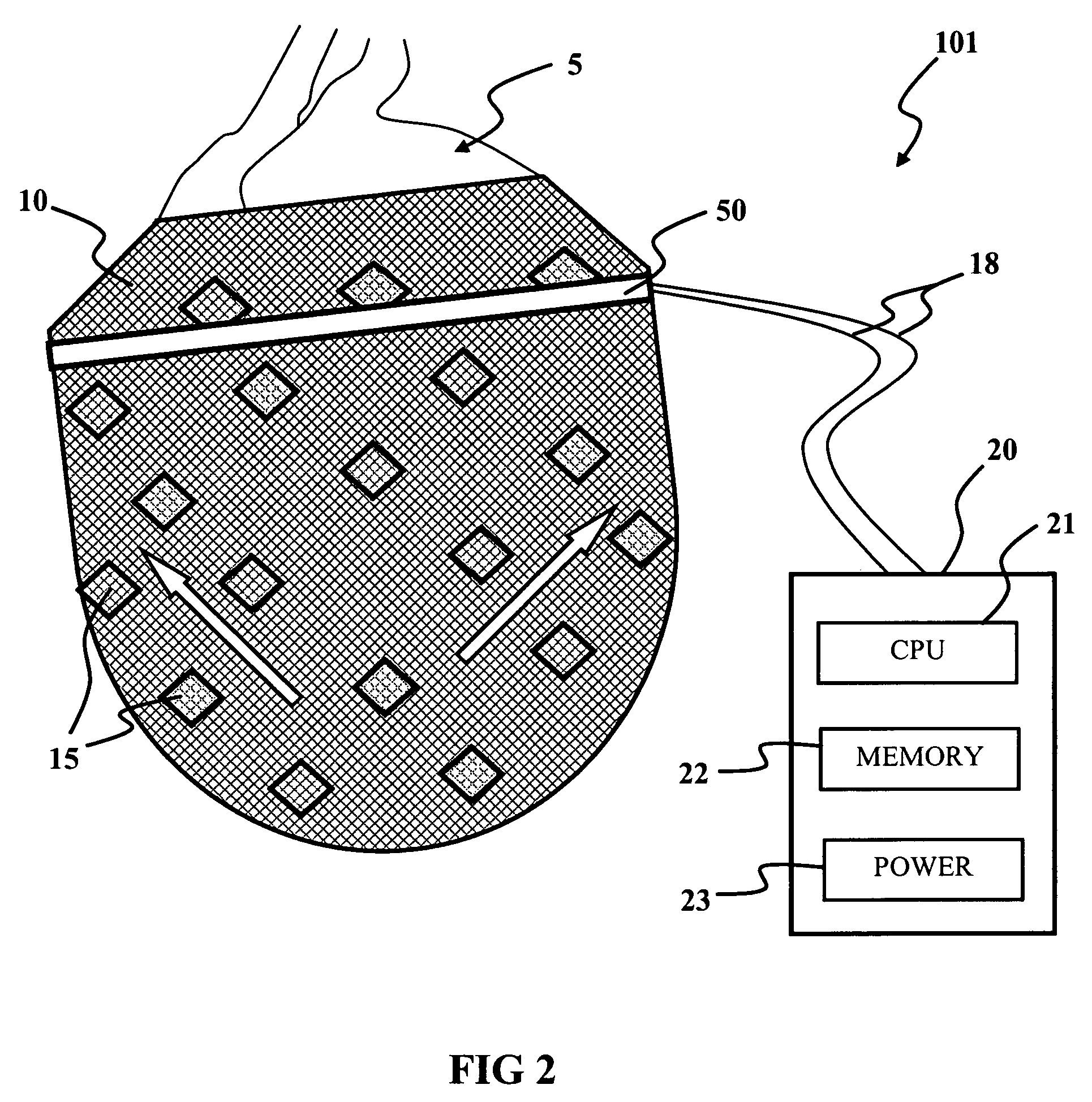
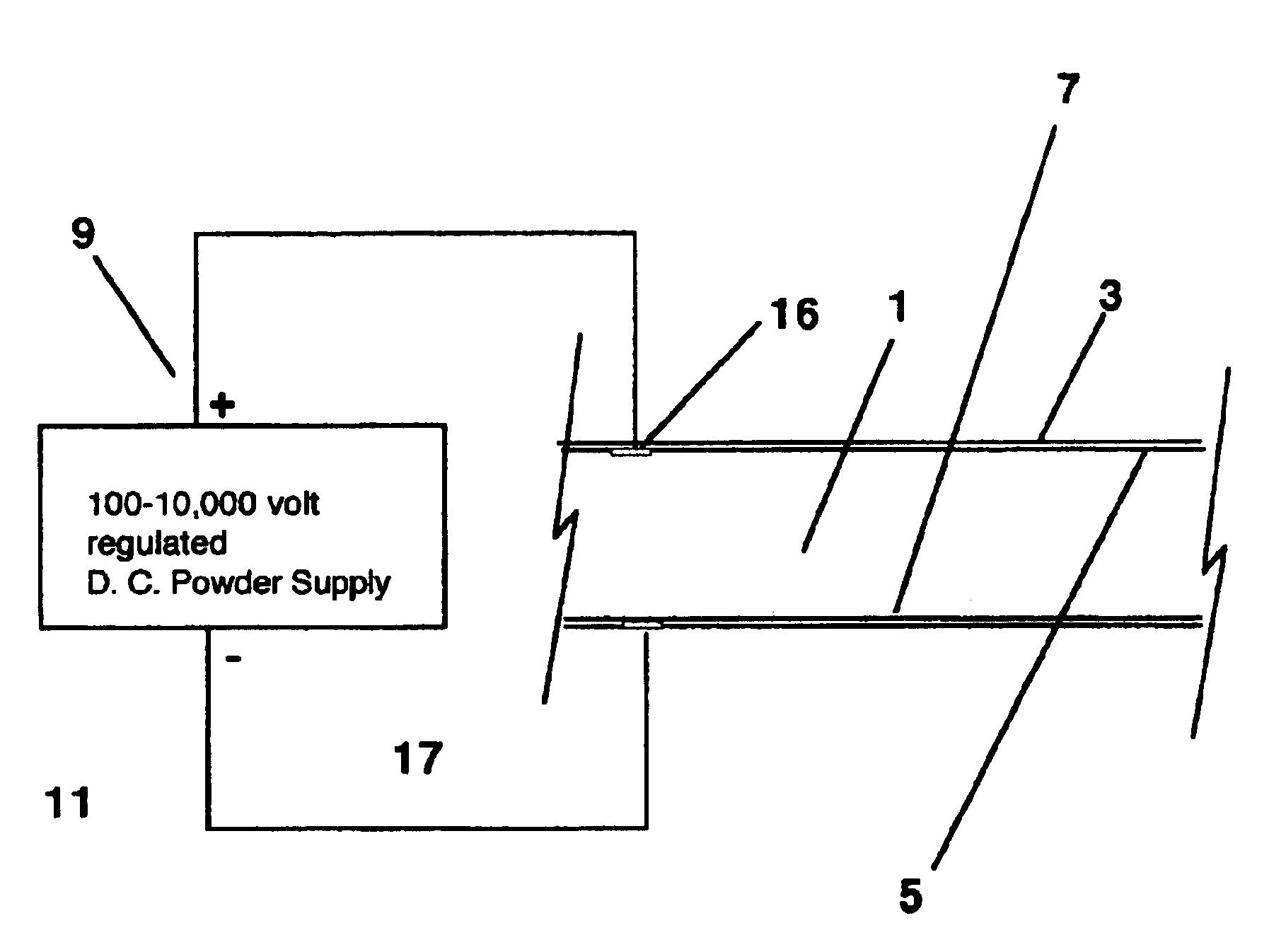
InactiveUS20060041183A1Easy to understandAnti-incontinence devicesHeart valvesSphincterFailing heart
A biological function assist apparatus composed an electromechanically-based system wrapped in protective coating and controlled by a controller, which also provides power to the electromechanically-based system. The electromechanically-based system can be formed as a mesh using MEMS or a larger electromechanically grid and wrapped around a failing heart, or the electromechanical system can be formed in a circle forming an artificial valve (e.g., sphincter). The electromechanically-based system can operate as a bone-muscle interface, thereby functioning in place of tendons.
Owner:ORSEN
High strain tear resistant gels and gel composites for use as artificial muscle actuators
InactiveUS6909220B2Improve propertiesImprove tear resistanceCellsSludge treatmentPolymer sciencePlasticizer
Novel gels and articles are formed from one or more copolymers having at least one poly(ethylene) components and high levels of one or more plasticizers, said gels having an amount of crystallinity, glassy components, and selected plasticizers sufficient to achieve improvements in one or more physical properties including improved crack propagation resistance, improved tear resistance, improved resistance to fatigue, resistance to catastrophic failure, and exhibiting high strain under elongations not obtainable in amorphous gels which high strain making the gel suitable for use as film layers for artificial muscles.
Owner:APPLIED ELASTOMERICS
Video-game console for allied touchscreen media
PendingUS20160030835A1Facilitate comprehensive mapping coverageInput/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHolographic imaging
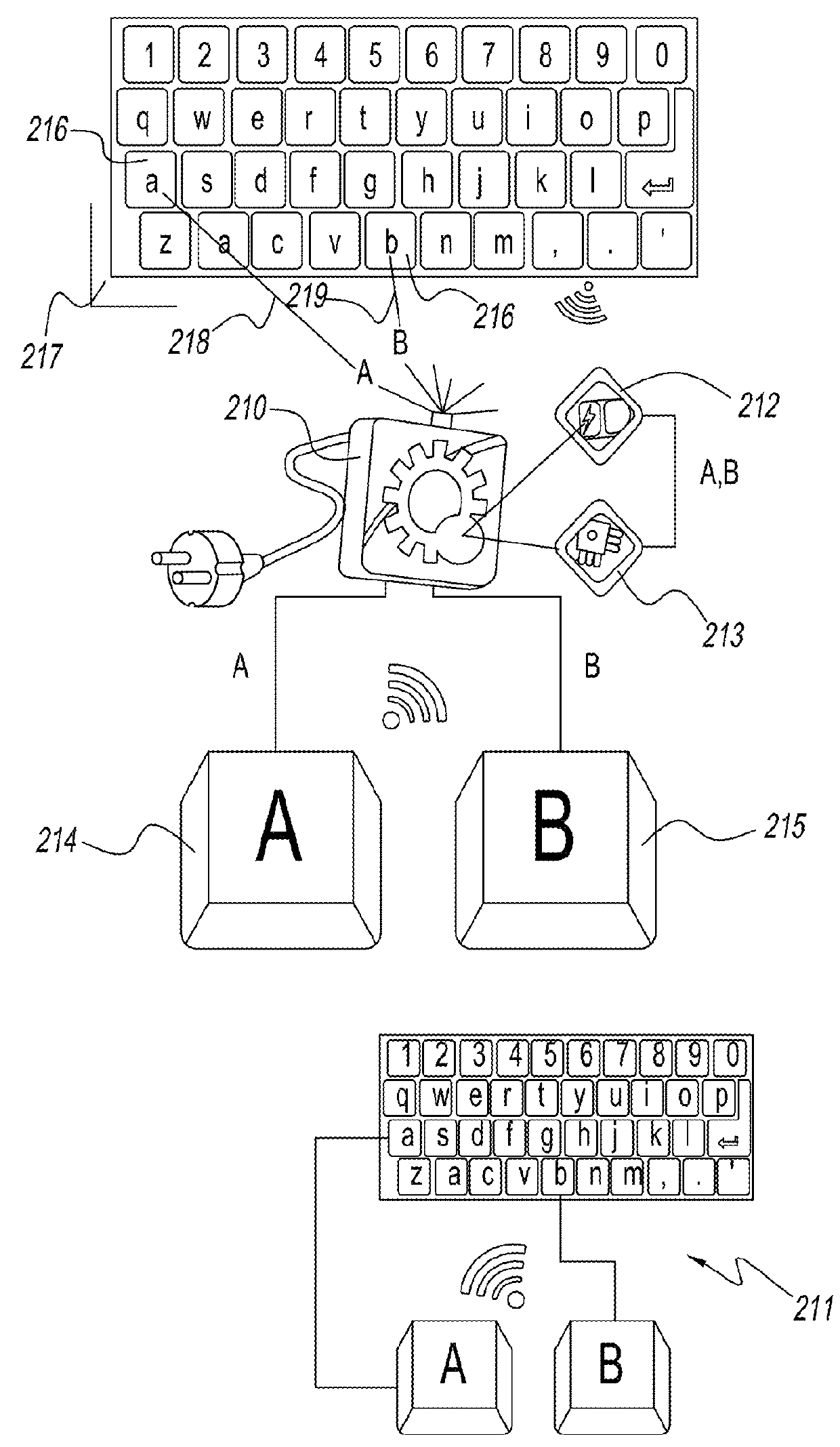
The present invention seeks to introduce a new delivery system, interactive platform and controller compliment for an allied touchscreen media; with said media particularly comprising repository-sourced mobile game applications configured for native operation. Mapping systems are dynamic and include an interface for user manipulation of immersive, 3-D holographic imaging modalities to advance input in a video-game environment. A series of specialty-input controllers for interaction with said touchscreen media are also advanced by the inventor; including those designed for remote and mappable manipulation of an actionable sensor input where salient to the input dynamics of an engaged gaming title. A user worn artificial muscle interface that reacts to game events are also advanced by the inventor.
Owner:ARGIRO CHRIS
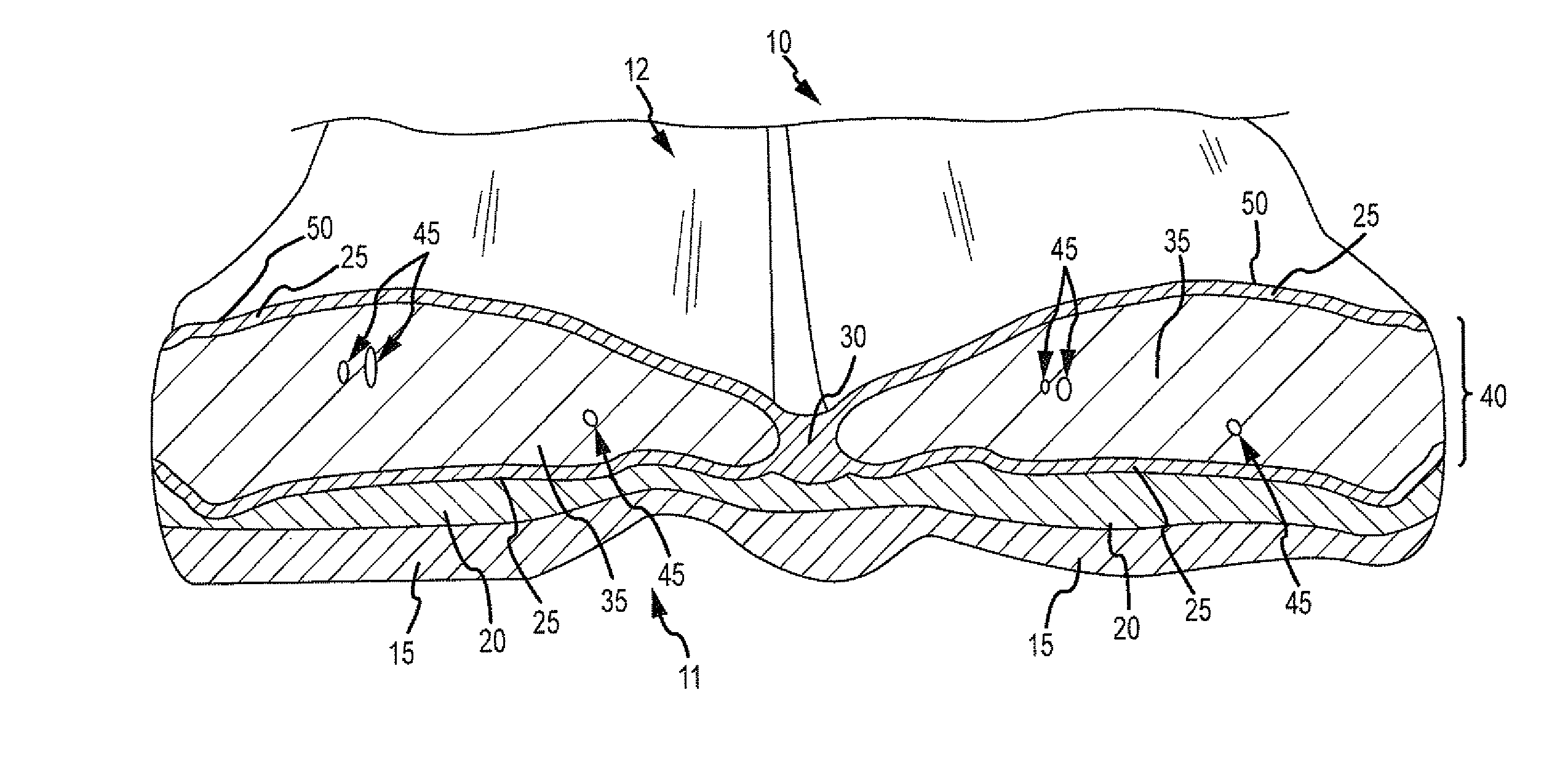
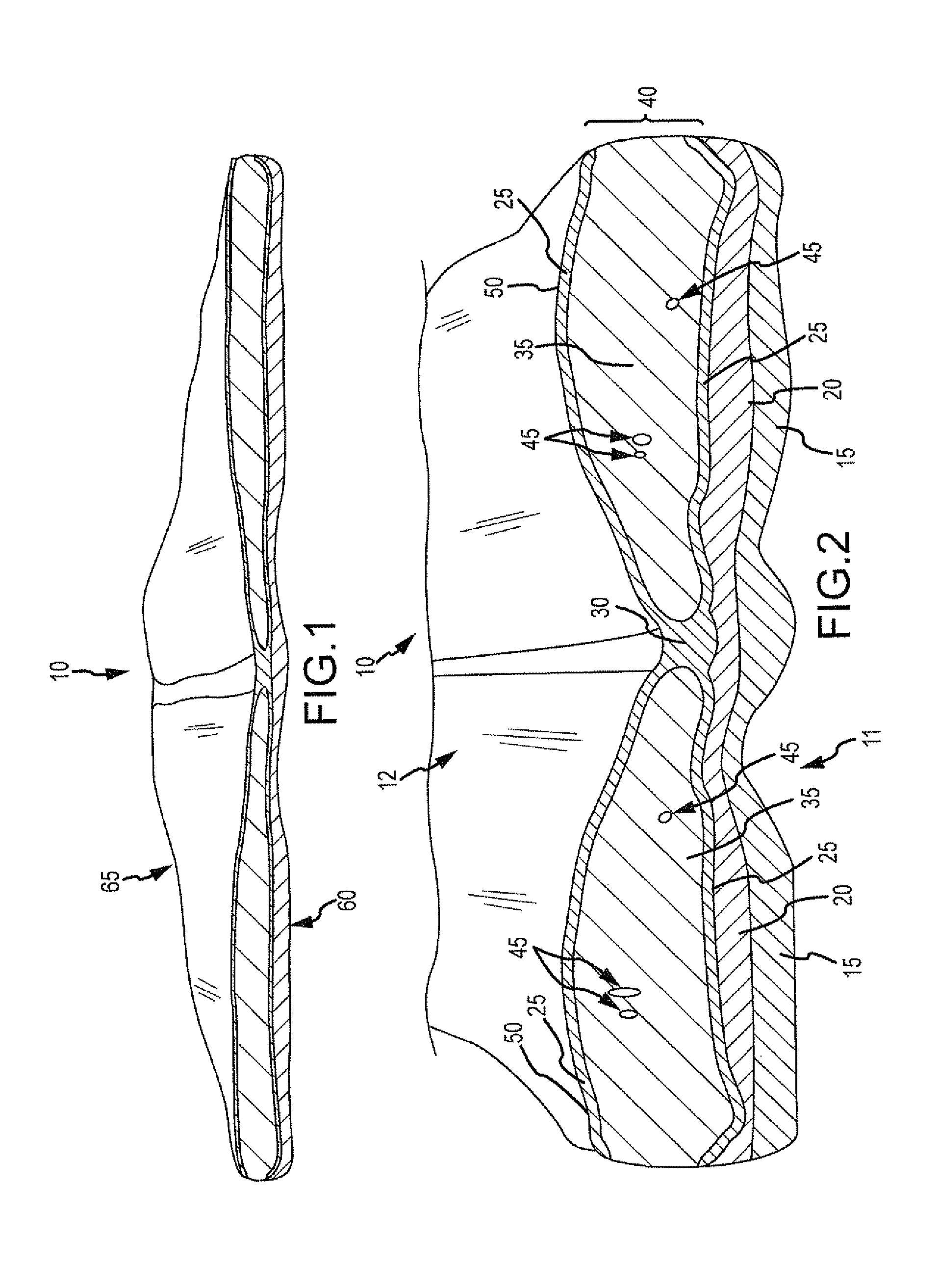
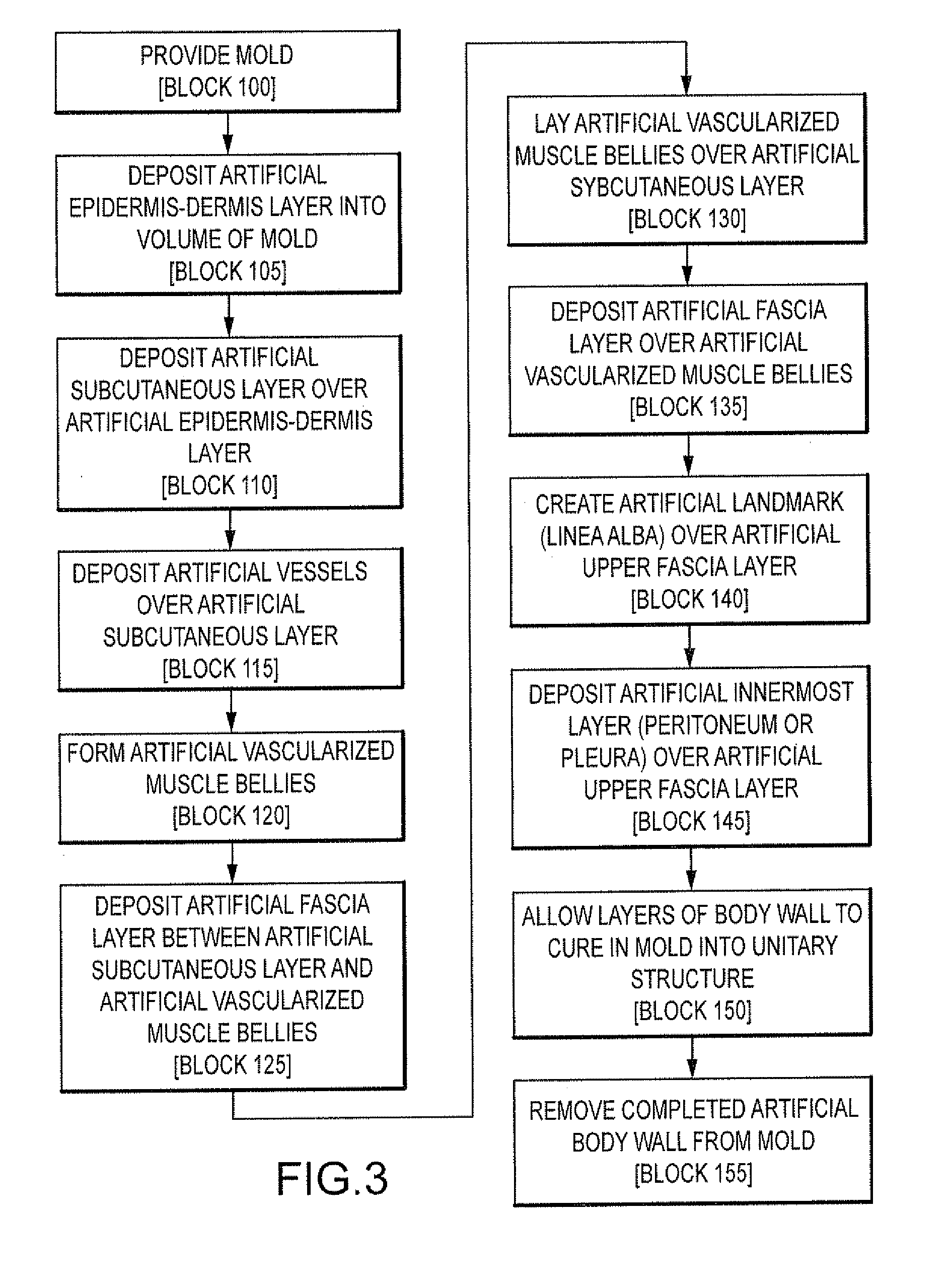
Simulated tissue, body lumens and body wall and methods of making same
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Biologically inspired gripping device
ActiveUS20060004395A1Clean plumbingPliable materialCannulasSurgical veterinaryBiological activationBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a gripping device that consists of four artificial muscle rings arranged in parallel. A grasper is placed in the middle of the rings. Sequential activation of the rings produces a peristaltic motion that moves the grasper back and forth within the rings. By activating the grasper appropriately, it can grab, ingest, and move soft and irregular material from one side of the lumen formed by the rings to the other side.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Implementation of electronic muscles in a portable computer as user input/output devices
InactiveUS7034802B1Improve ergonomicsInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsKey pressingUser input
A portable computer system contained within a housing that comprises an electronic muscle material for performing a plurality of functions. The electronic muscle can be used to replace buttons or keys used in many PDAs. The movement of the electronic muscle material can charge the battery. When handled, the electronic muscle material can further detect the left- or right-handedness of the user and, based on the handedness, can generate function buttons or other alterations to accommodate the user's hand preference and finger placement. The electronic muscle can change shape to accommodate the user's hand for comfort and, further, as a security function to identify and authorize the user. Additionally, the electronic muscle material in the housing can be caused to vibrate at given frequencies so that it can generate an alarm and can function as a speaker or a dynamically directional microphone.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
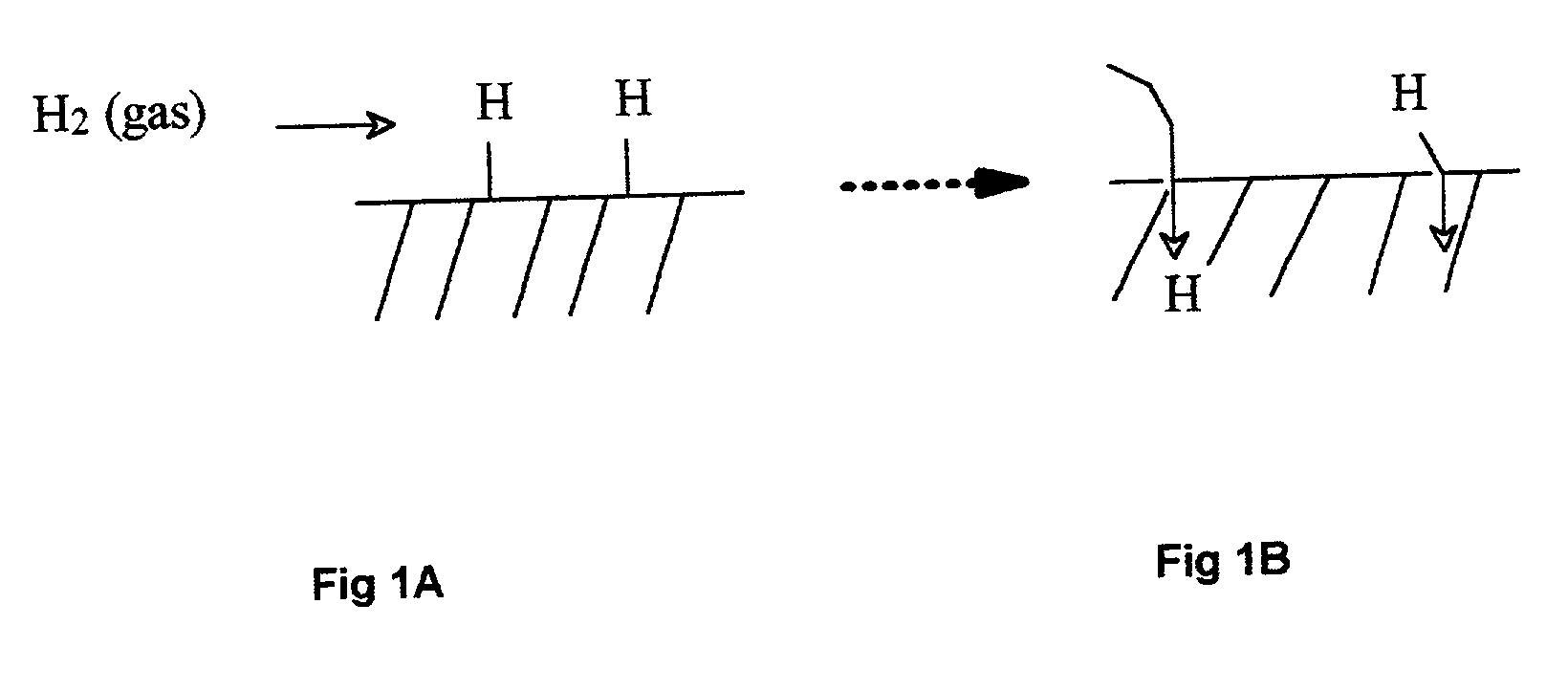
Novel metal hydride artificial muscles
InactiveUS20020026794A1Guaranteed uptimeLong stroke capabilities of actuationProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpace suitsEngineeringArtificial muscle
New artificial muscles and actuators, that are operated by hydrogen gas as working fluid stored interstitially in metal hydrides as a hydrogen sponge. These artificial muscles and actuators are operated both electrically and thermally. The artificial muscles and actuators have fast response, are compact / light-weight, are noiseless, and produce high-power density. They can be used for biomedical, space, defense, micro-machines, and industrial applications.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
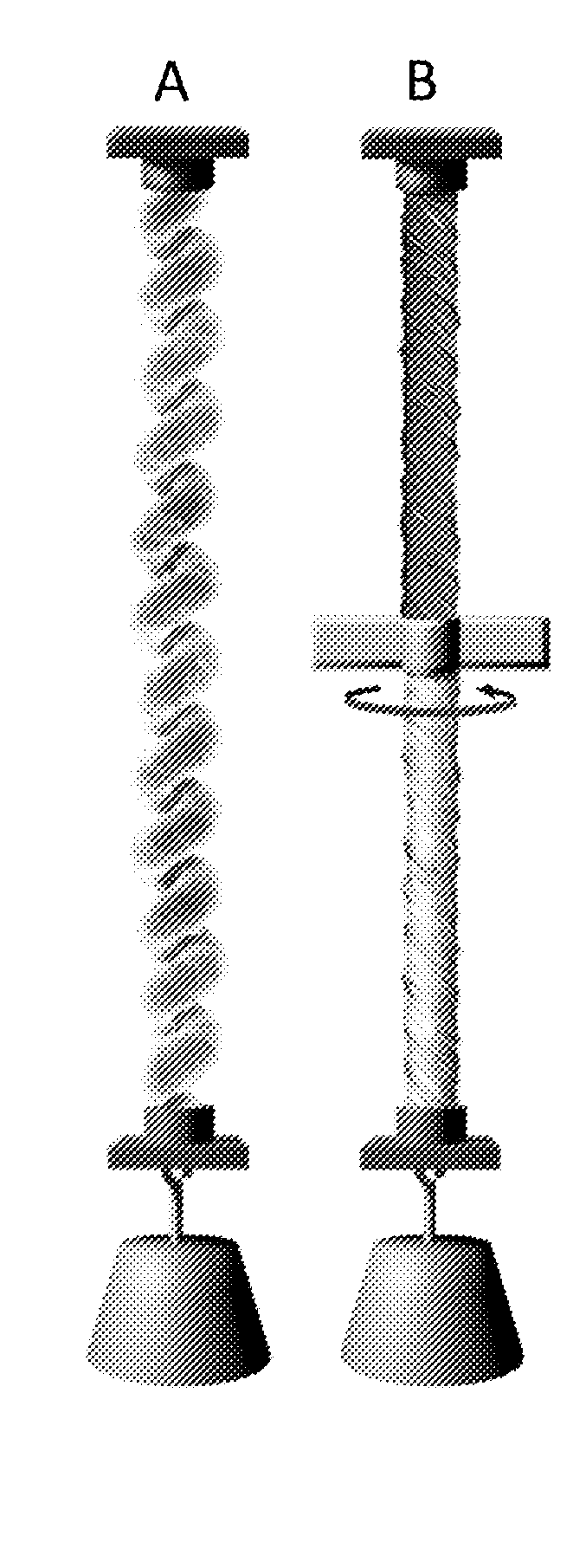
Coiled and non-coiled twisted polymer fiber torsional and tensile actuators
Actuators (artificial muscles) comprising twist-spun nanofiber yarn or twist-inserted polymer fibers generate torsional and / or tensile actuation when powered electrically, photonically, chemically, thermally, by absorption, or by other means. These artificial muscles utilize non-coiled or coiled yarns and can be either neat or comprising a guest. Devices comprising these artificial muscles are also described.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Fluid-driven artificial muscles as mechanisms for controlled actuation
InactiveUS20080035798A1AdaptableEasily interchangeableFlexible wall reciprocating enginesAircraft stabilisationBiomedical engineeringArtificial muscle
A fluid contact surface actuation system for a vehicle, including a first fluid contact surface constructed and arranged to act against a first fluid passing over the first fluid contact surface; and a first fluid actuator coupled to the first fluid contact surface to move the first fluid contact surface between a first position and a second position to enable control of the vehicle in a predetermined manner, the first fluid actuator having a first resilient bladder that receives a second fluid such that pressure of the second fluid moves the first bladder between a contracted configuration and an expanded configuration.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +2
Follow Robot
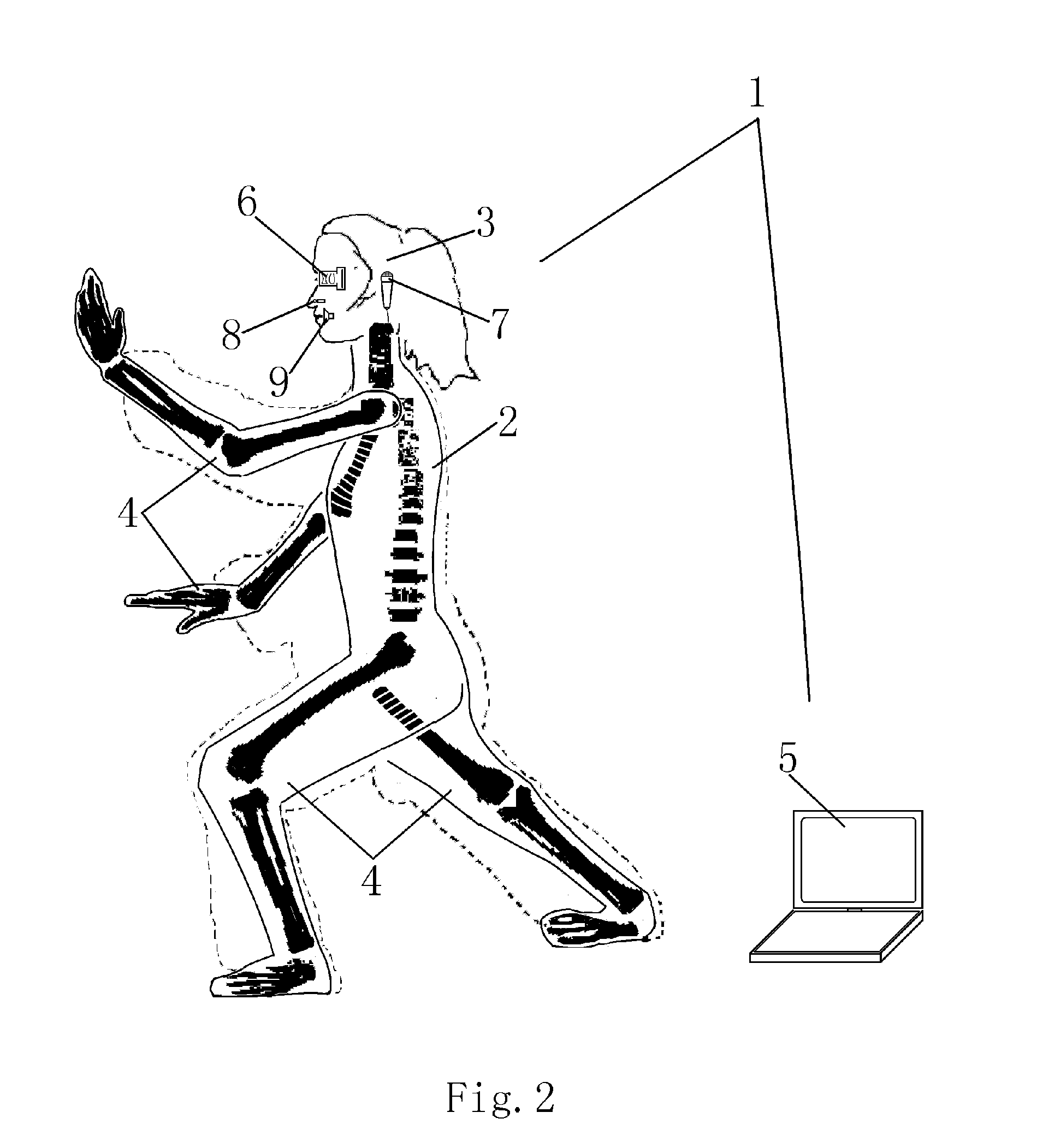
InactiveUS20070233318A1Reduce design difficultyFollow robotArtificial lifeVehicle position/course/altitude controlHuman bodyNose
A follow robot is disclosed. The follow robot comprises body, head, limbs and muscles same as or proportional with human's body, head, limbs and muscle in shape, size, Specific Gravity (SG) and Center of Gravity (CG). The follow robot's joints are same as or proportional with human's joints and can turn around to reach same angle as human's joints. The follow robot's head, body, limbs, bones and joints possess the same or proportional support ability as human's head, body, limb, bones and joints, and are droved by artificial muscle, step motor, hydraulic pressure component. Many position and distance sensors are mounted on or around a man, which measure any action of the man continuously. These movement signals are collected by a Personal computer (PC) and transmitted to the follow robot. Following these signals, the follow robot repeats every movement of the man, acts exactly same as the man. Many sensors are also mounted on the follow robot; they are eyes, ears, skin and noses of the follow robot. Any thing the follow robot seeing, hearing, feeling and smelling will be converted to digital signal and transmitted to the man by the PC. The man can see, hear, feel and smell any thing around the fellow robot real timely, and respond to it immediately.
Owner:LEI TIANMO
Multi-combination push type flexible bionic robotic fish
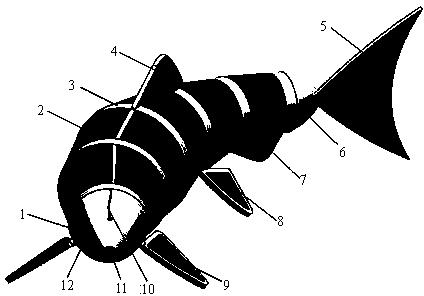
InactiveCN104015904AIncrease energy densityQuick responsePropulsive elements of non-rotary typePropulsive transmissionShape changeMuscle contraction
A multi-combination push type flexible bionic robotic fish comprises a head, a body, a tail and fins. The multi-combination push type flexible bionic robotic fish is characterized in that the body comprises a flexible shaft, flexible skeletons and body artificial muscles with a flexible electrode, the flexible skeletons are of an annular frame structure and is fixed to the flexible shaft, the body artificial muscles are symmetrically arranged between the flexible skeletons in a tensioning state, when the artificial muscles on one side are powered on, the tensile stress is reduced, and the artificial muscles on the other side contracts, so that the flexible shaft and the body bends continuously, and are matched with the tail and the fins to form the body / fin push mode; the head and the tail are arranged at the two ends of the flexible shaft respectively and are connected with the first flexible skeleton and the last flexible skeleton respectively. The flexible structure and flexible drive are adopted, the multi-combination push type flexible bionic robotic fish simulates the motion function of bionic fishes to form gradient flexible shape changing of the whole robotic fish, the flexible body / tail fin push mode and the flexible middle fin / pair-fin push mode are achieved, and movement is flexible.
Owner:王跃成
Human lower limb performance enhancement outfit
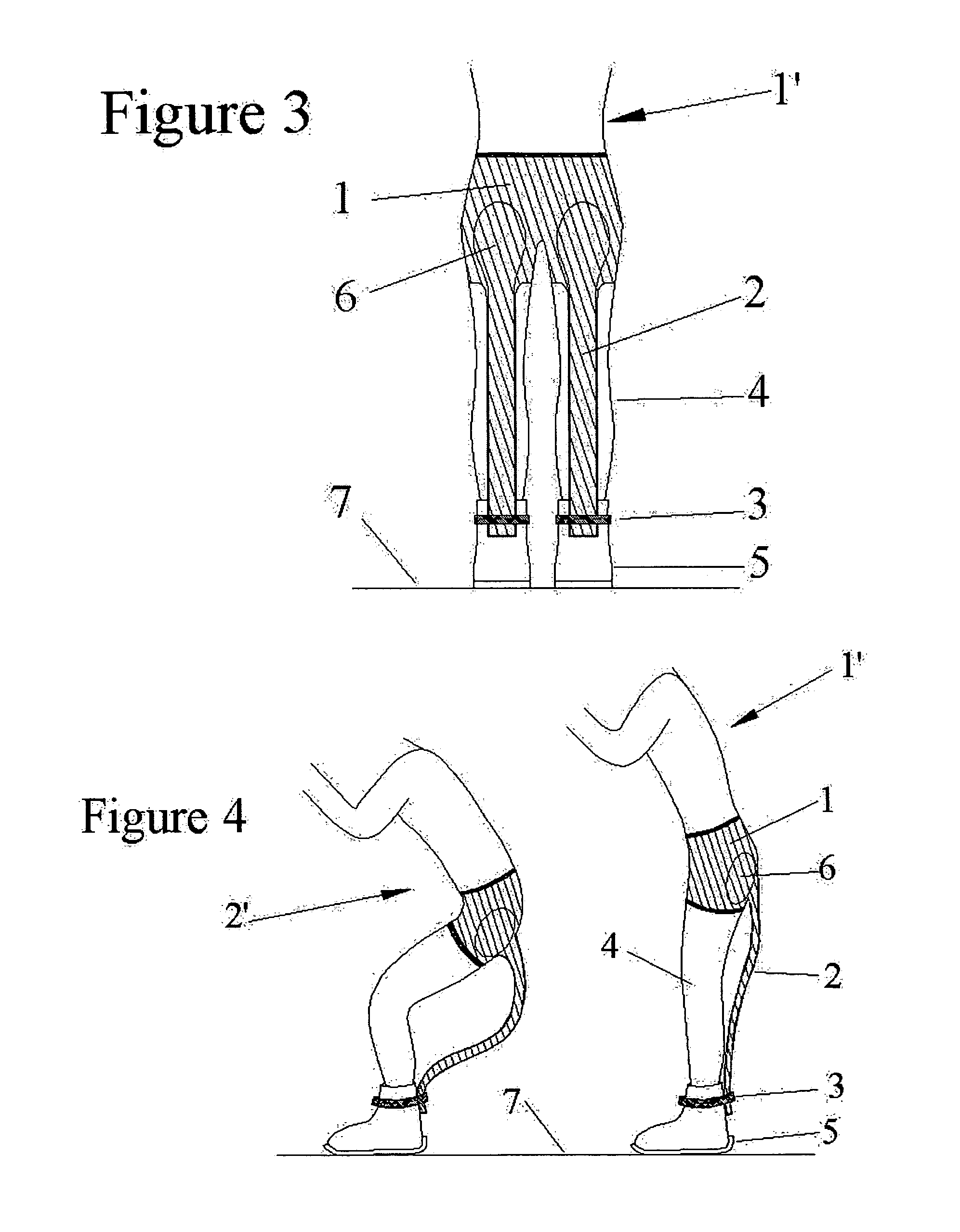
InactiveUS20060240953A1Easy to useControllable forceResilient force resistorsStiltsButtocksPerformance enhancement
The present invention comprises a user-friendly, soft and resilient, biomimetic (mimicking biological entities) lower limb support outfits that can be worn externally by people to improve and enhance lower limb, legs and knees performance in sports, daily dynamic activities and medical rehabilitation / physical therapy. More specifically, the present invention relates to an outfit, which allows a portion of the upper limb's quasi-static weight and dynamic weight due to impact forces to be excluded from being transmitted to the lower limb, legs, quadriceps and hamstrings muscles and knees by directly transmitting them to the ankles, footwear and / or the ground, through soft elastic columnar quasi-legs that are equipped with smart biomimetic materials such as shape memory materials and artificial muscles such as synthetic and / or ionic polymeric muscles and provide lower limb support function by buckling and bending in accordance with the dynamic maneuvering of the user. The said lower limb performance enhancing outfit is encapsulated by user-friendly fabric means for easy wear. The upper portion of the outfit can be in the form of a sports short worn by the user and encapsulating the buttocks support plates.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN
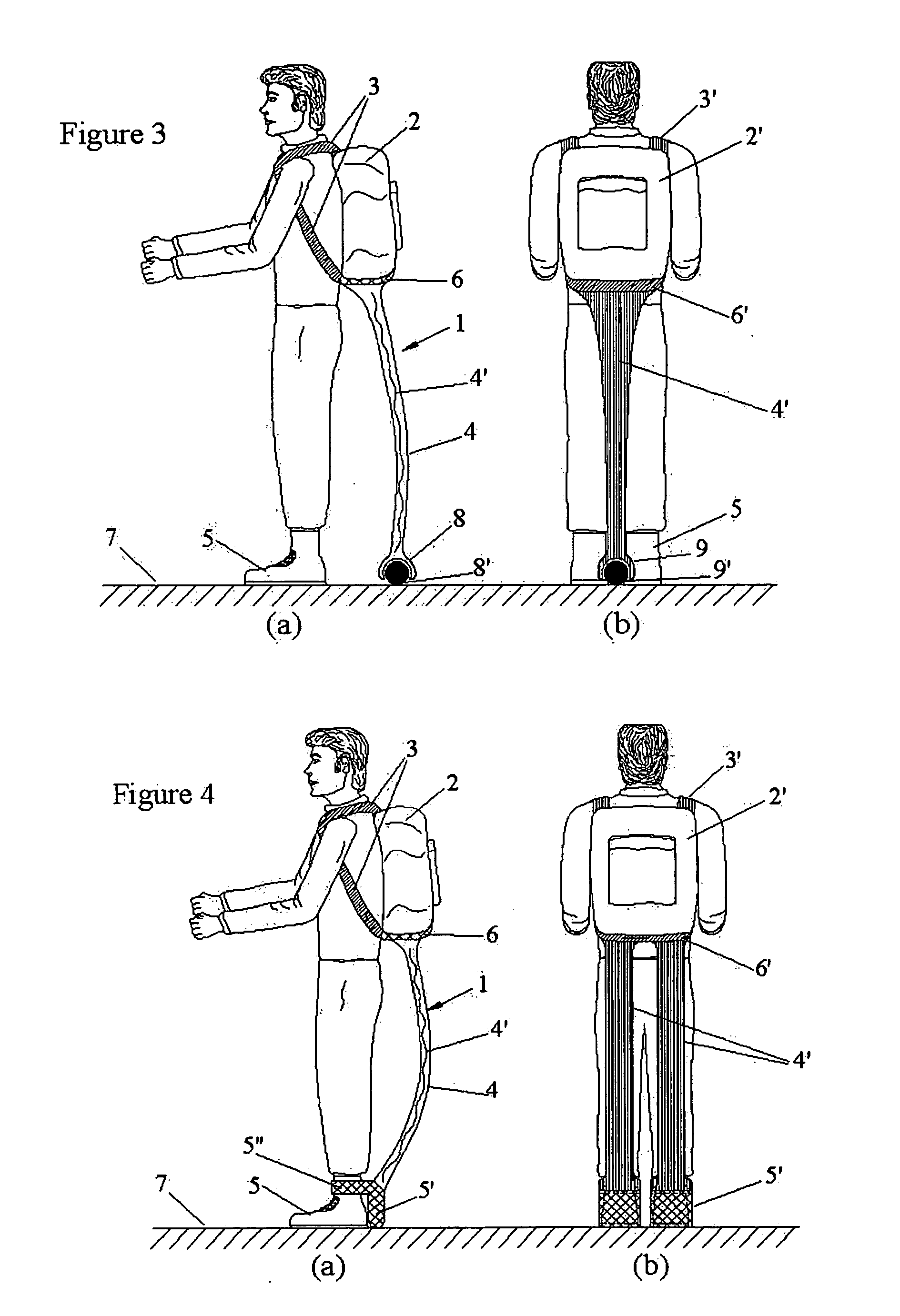
Backpack support apparatus
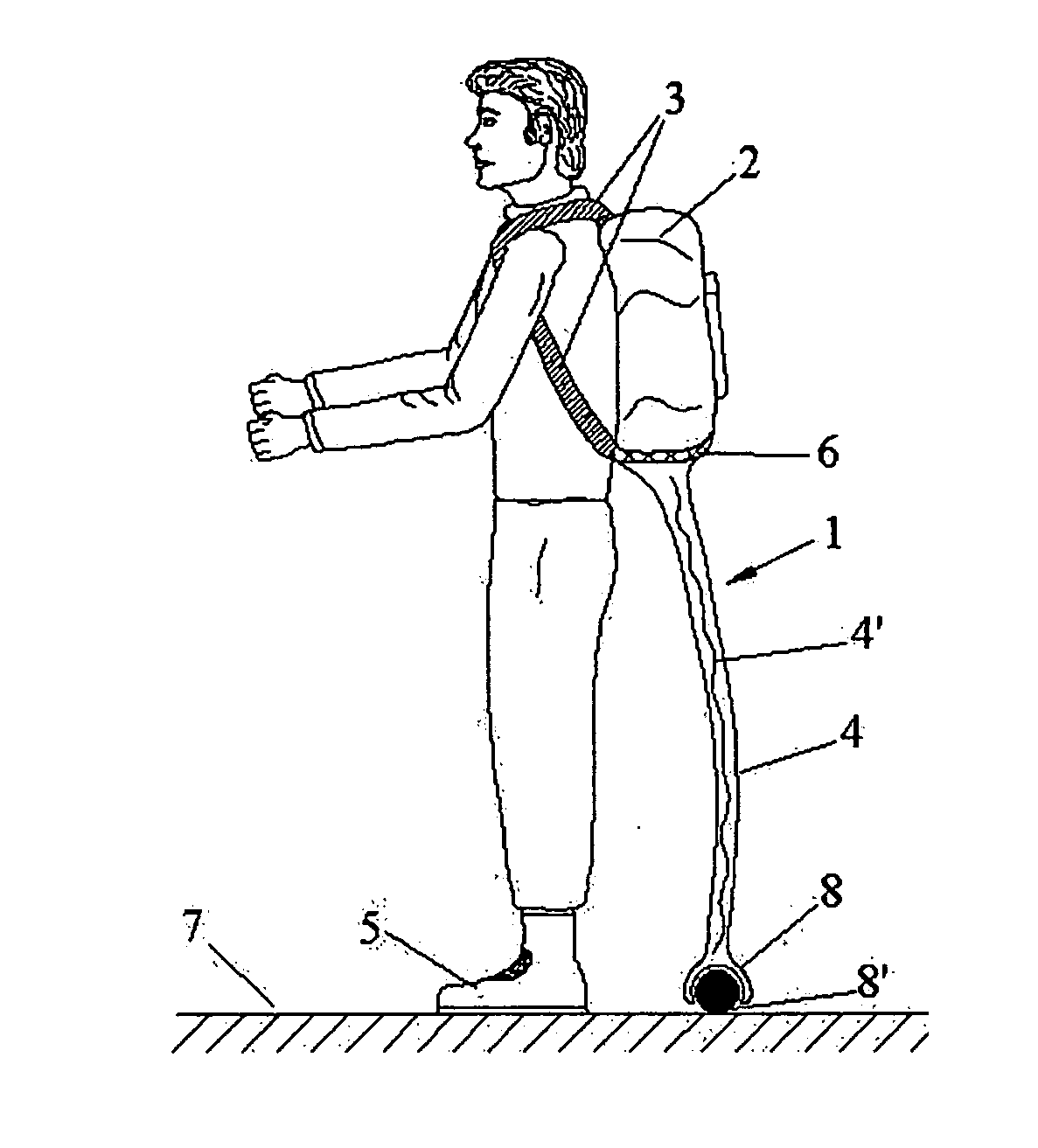
InactiveUS20060240960A1Enhance shoulder, back, upper body, abdomen, waistEliminate transmissionResilient force resistorsPursesEngineeringBiomimetic materials
The present invention comprises a user-friendly, soft and resilient, biomimetic (mimicking biological entities) back pack weight support and mobility enhancement system that can function like a caddie and can be worn externally by people carrying a back pack to improve and enhance shoulder, back, upper body, abdomen, waist, hips, lower limb, legs, knees, calves, quadriceps and hamstrings muscles performance in all dynamic activities while carrying a back pack. The present invention can comprise an outfit, allowing a portion of the back pack's weight to be excluded from being transmitted to the shoulder, back, upper body, abdomen, waist, hips, lower limb, legs, knees, calves, quadriceps and hamstrings muscles; instead directly transmitting the weight to the footwear and / or the ground, through soft elastic columnar quasi-legs equipped with smart biomimetic materials such as shape memory materials and artificial muscles such as synthetic and / or ionic polymeric muscles and provide support function by buckling and bending in accordance with the dynamic maneuvering of the user. The outfit can be encapsulated by user-friendly fabric means for easy wear. The upper portion of the outfit can be in the form of a pouch equipped with fastening portions to be attached to the bottom of the back pack worn by the user while the lower portion of the outfit can be attached to the footwear while transmitting the weight of the back pack to the ground or attached to a ball and socket wheel on the ground right behind the user.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN
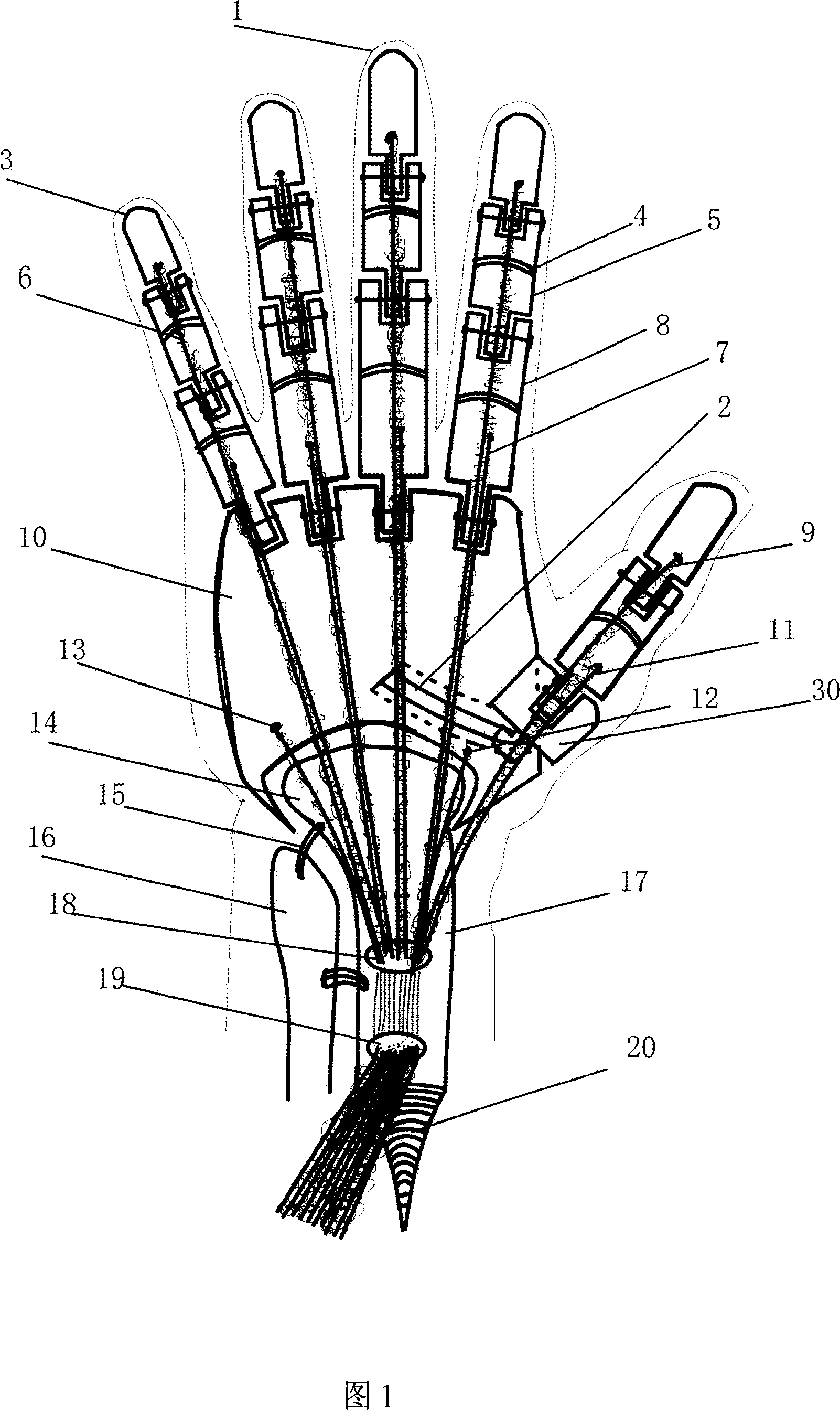
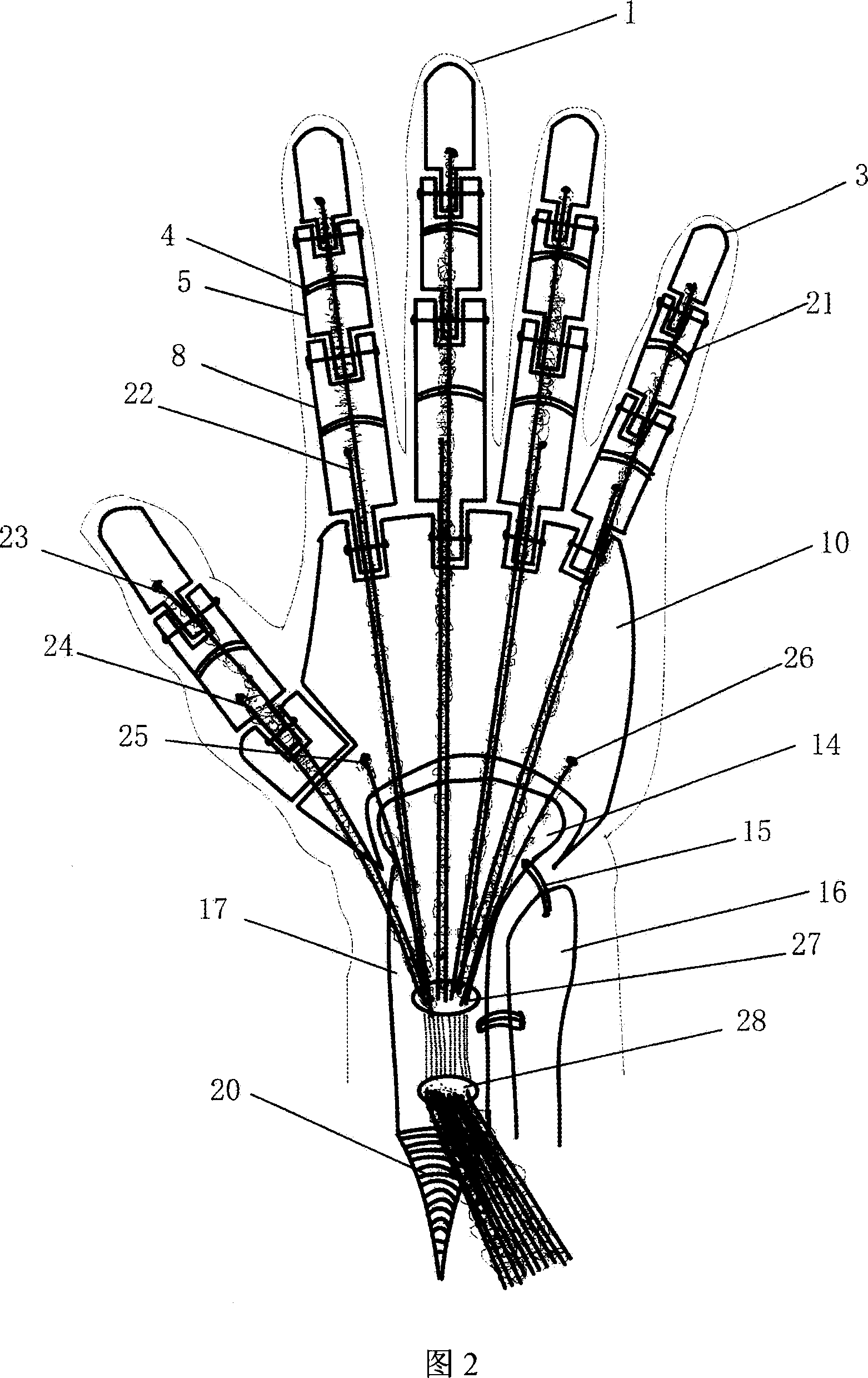
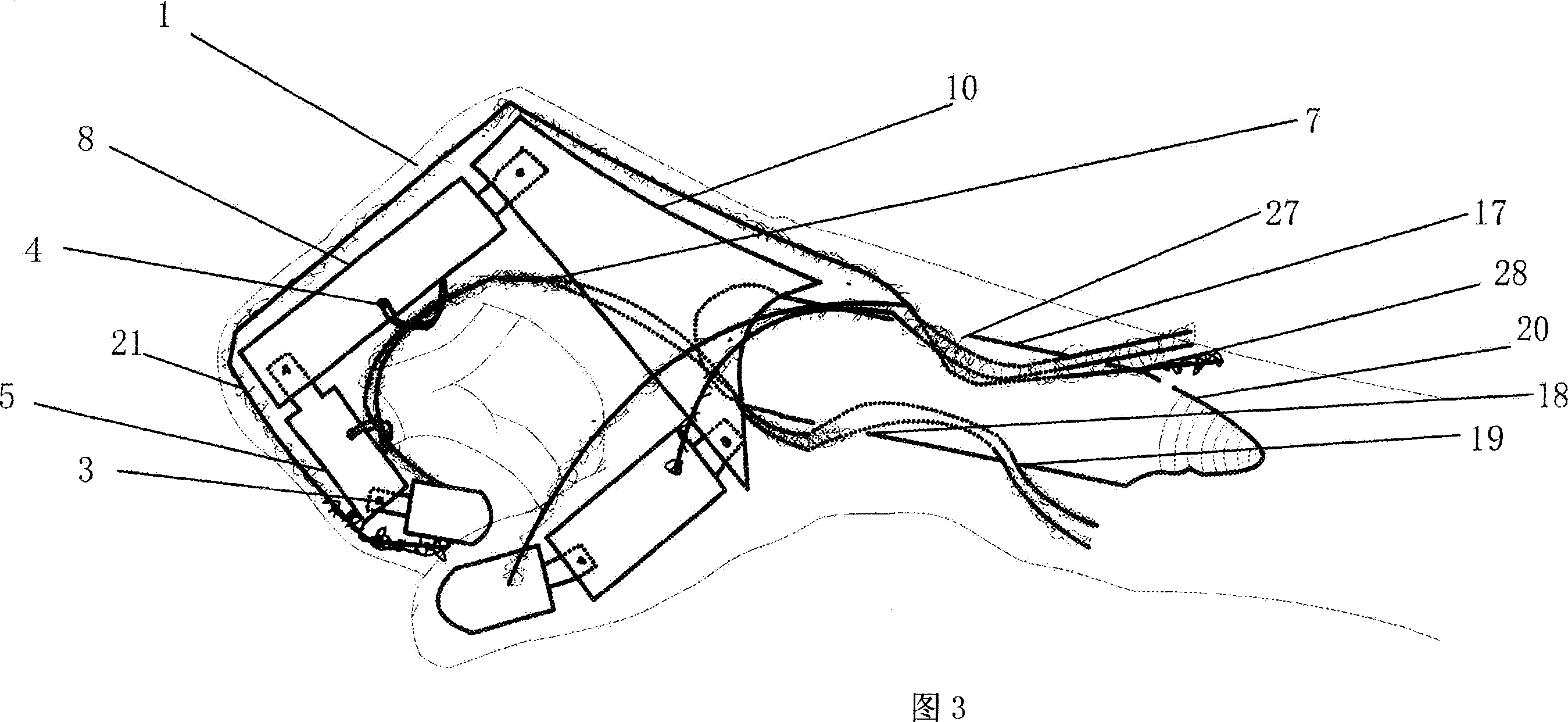
Artificial simulation arm
InactiveCN100998527AMeet the requirements of mechanical transmissionFunctional Movement FlexibilityArtificial handsHuman bodyTendon sheath
An artificial hand with multiple functions, no error operation and no complication is composed of such artificial units as finger bones, metacarpal bones, ulna, radius, muscle tendons, tendon sheaths, slide mechanism, muscles and skin. It can be connected to the crippled end of human radius by screw and its artificial muscle tendons can be linked with relative ones of human body by stitch.
Owner:张为众
Actuator, optical apparatus using actuator, and method of manufacturing actuator
An actuator includes a holder having a movement hole, a lens barrel which moves within the movement hole, and driving means for driving the lens barrel. Each of the driving means is provided with driving members composed of an artificial muscle. The lens barrel can be suitably moved within the movement hole by making the driving members perform a predetermined operation.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Fuel-powered actuators and methods of using same
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Electroactive materials and electroactive actuators that act as artificial muscle, tendon, and skin
ActiveUS8088453B1Improve metal-polymer interfaceIncreased durabilityMachines/enginesSpecial surfacesCross-linkWrinkle skin
This invention describes a method for producing a novel, superior electroactive material and electroactive actuator, which act as artificial muscle, tendon, fascia, perimysium, epimysium, and skin that wrinkles and with the preferred movement of contraction, comprising ion-containing, cross-linked electroactive material(s); solvent(s); electrolyte(s); plasma treated electrode(s); attachments to levers or other objects; and coating(s). The composition and electrode configuration of the electroactive material of the electroactive actuator can be optimized so that contraction occurs when activated by electricity, when allowed to relax back to its original conformation, when the polarity of the electrodes is reversed, or a combination of these movements, such as antagonistic pairs. The electroactive material itself or the electroactive actuator may be used individually or grouped to produce movement when activated by electricity. This invention can provide for human-like motion, durability, toughness, and strength.
Owner:RAS LABS
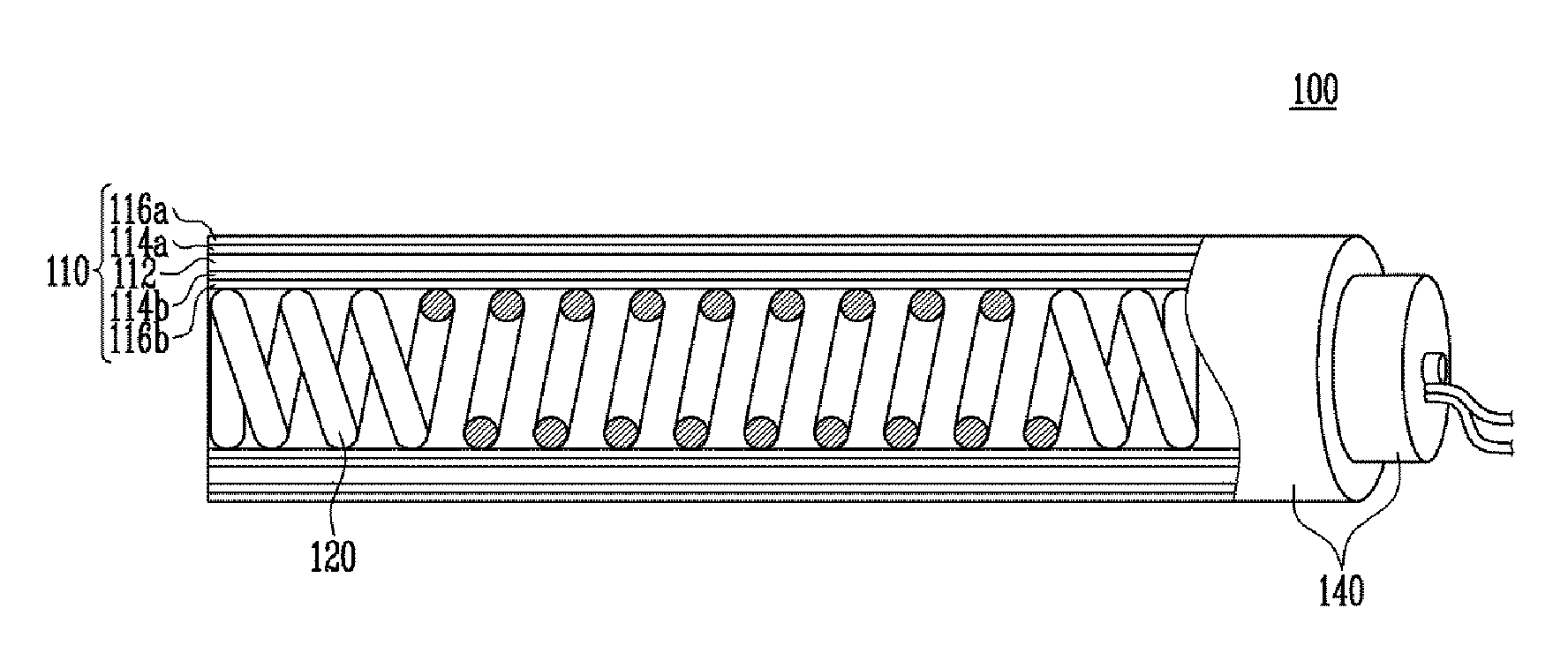
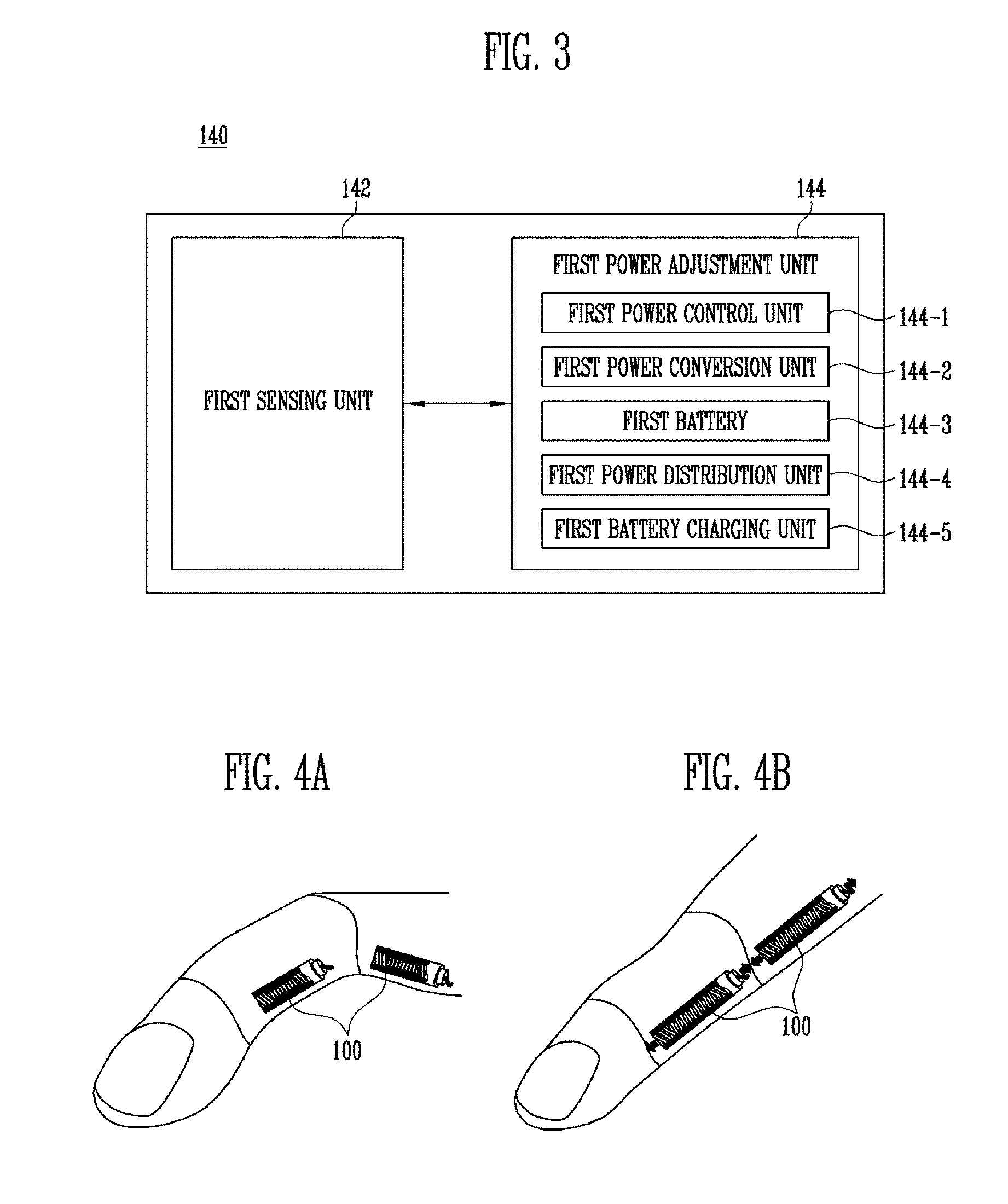
Artificial muscle
ActiveUS20160206420A1Increase flexibilityIncrease elasticityProgramme-controlled manipulatorLigamentsActive polymerYarn
Provided herein is an artificial muscle capable of being miniaturized, realizing precision movement, and performing selective relaxation / contraction deformation according to the power output necessary in the muscle, the muscle including a first operation unit that includes electro-active polymer where relaxation-deformation occurs based on electric energy being applied; a heating unit that generates heat energy based on the electric being applied; a second operation unit that has a yarn structure and where contraction-deformation occurs based on the heat energy generated in the heating unit; and a control unit that applies electric energy to the first operation unit and the heating unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Reprogrammable shape change sheet, uses of the sheet and method of producing a shaped surface
The invention relates to a reprogrammable shape change sheet, a method of shaping a surface and a reprogrammable injection molding machine. The sheet comprises a plurality of muscle elements capable of changing shape upon electric stimulation, the elements being arranged in an array to define a surface. According to the invention, the muscle elements comprise two muscle material layers capable of changing shape upon electric stimulation and a flexible wiring layer sandwiched between the muscle material layers, the wiring layer being electrically connected to said muscle material layers for delivering electric stimulation signals to the muscle material layers for changing the shape of the muscle elements and further the topology of the surface. The invention provides a new shape change sheet structure, which can be made thin, accurate and durable for various uses.
Owner:ALLEN
Fuel-powered actuators and methods of using same
ActiveUS20090021106A1Avoid damageCombustion enginesMechanical power devicesCompound (substance)Engineering
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Preparation method of sulfamethoxazole residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle
The invention discloses a preparation method of sulfamethoxazole residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle, which takes the carp as a research object to research a carp muscle material object standard sample containing sulfamethoxazole of certain concentration in a breeding mode of adding sulfamethoxazole. The key production control technology of the material object standard sample disclosed by the invention is mastered and comprises content level, evenness, stability, constant value and the like control, and the standard sample is produced and prepared in a standardization and scale mode. The standard sample is used for detection quality control and detection capability evaluation for residue of veterinary drug in animal-derived food and has an important meaning for food safety detection.
Owner:时文春
Fluidic artificial muscle actuator and swaging process therefor
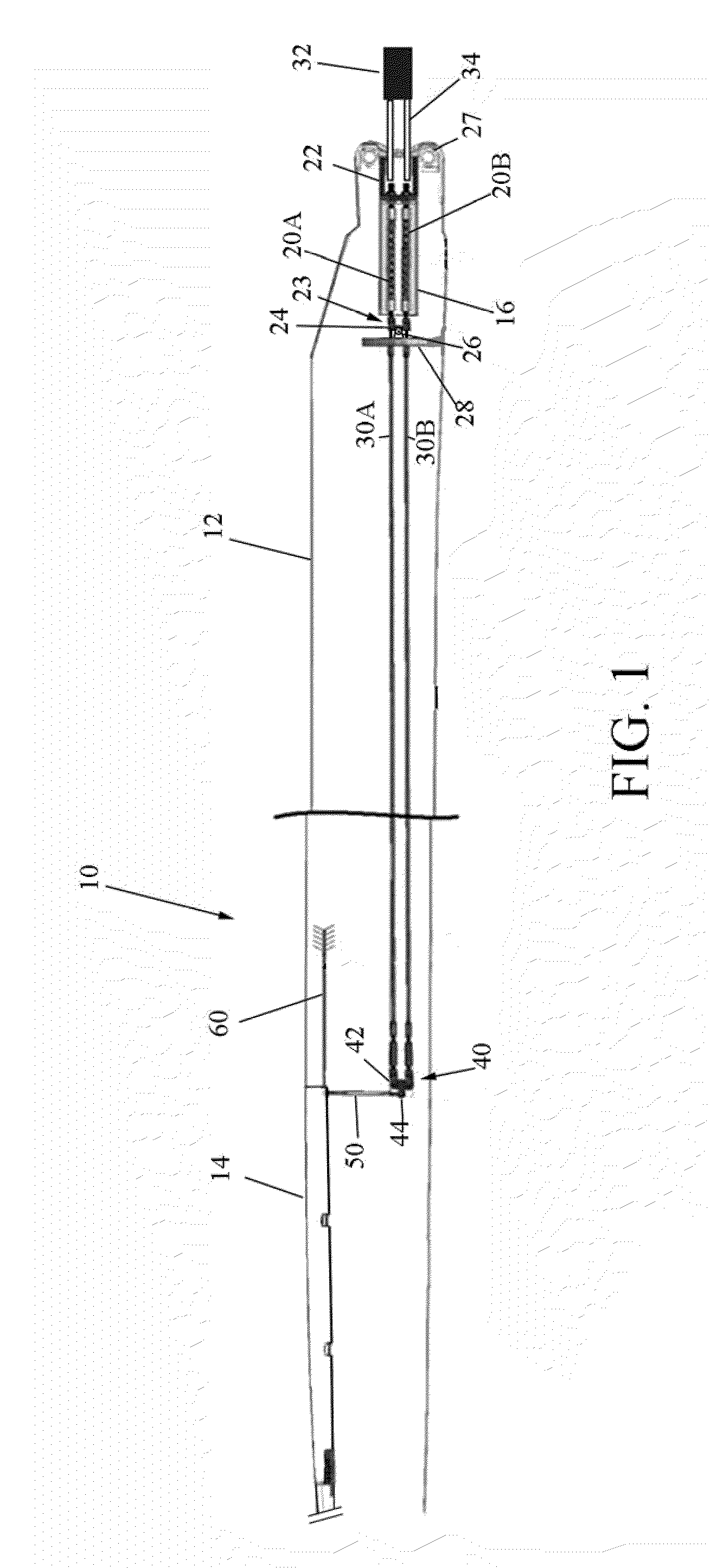
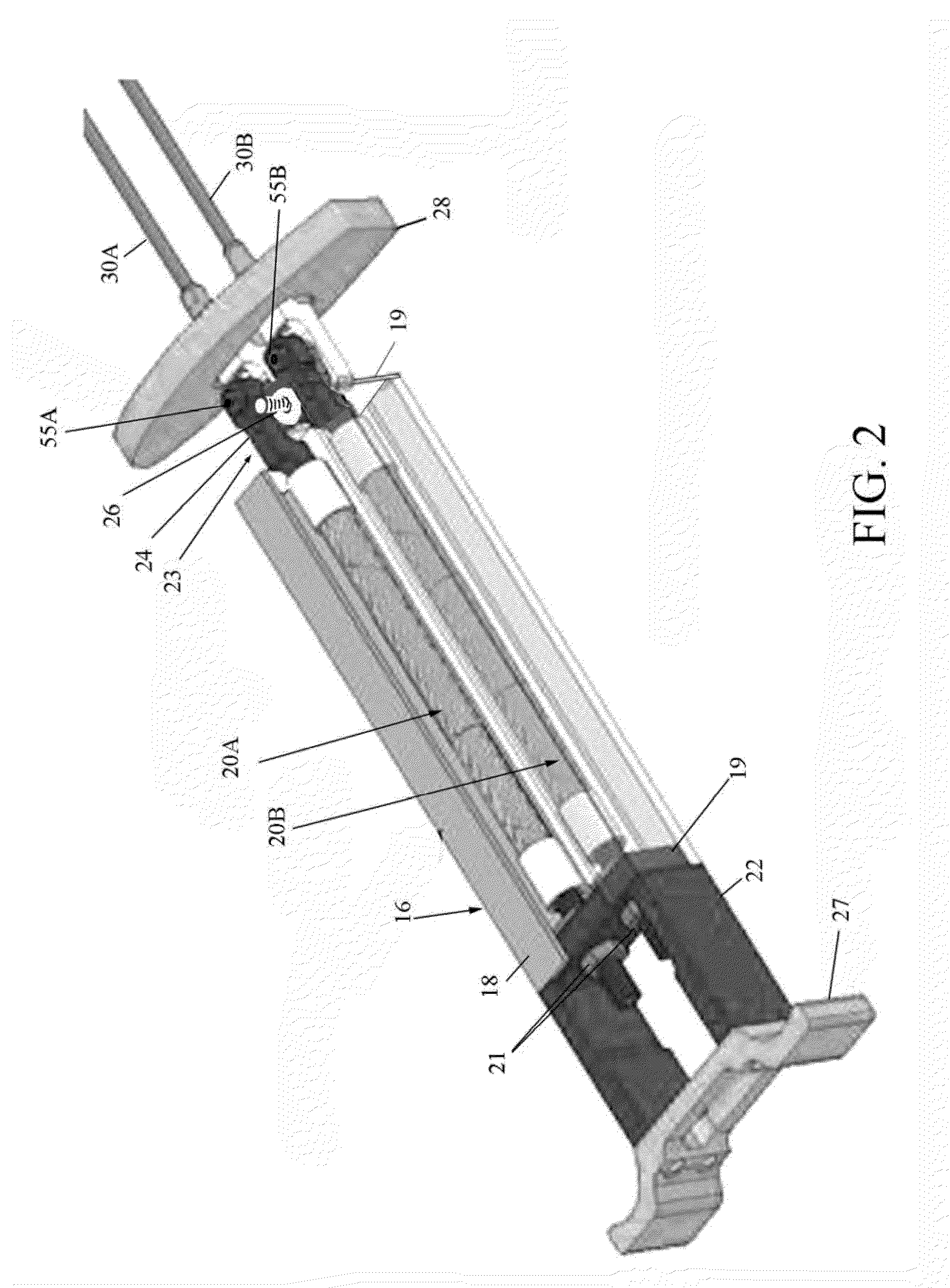
ActiveUS20090301292A1Simple and robust connectionHigh tensile strengthShaping toolsFlexible wall reciprocating enginesEngineeringSwaging
A fluidic artificial muscle actuator consisting of an inner elastic bladder surrounded by a braided filament sleeve and sealed off on either end with end fittings. Pressurization of the actuator produces force and / or motion through radial movement of the bladder and sleeve which forces the sleeve to move axially. Both contractile and extensile motions are possible depending on the geometry of the braided sleeve. The fluidic artificial muscle actuator is manufactured using a swaging process which plastically deforms swage tubes around the end fittings, braided sleeve, and pressure bladder, creating a strong mechanical clamping action that may be augmented with adhesive bonding of the components. The swaging system includes the swaging die and associated components which are used to plastically deform the swage tube during assembly of the actuator.
Owner:INNOVITAL LLC +1
Fluidic Artificial Muscle Actuation System For Trailing-Edge Flap
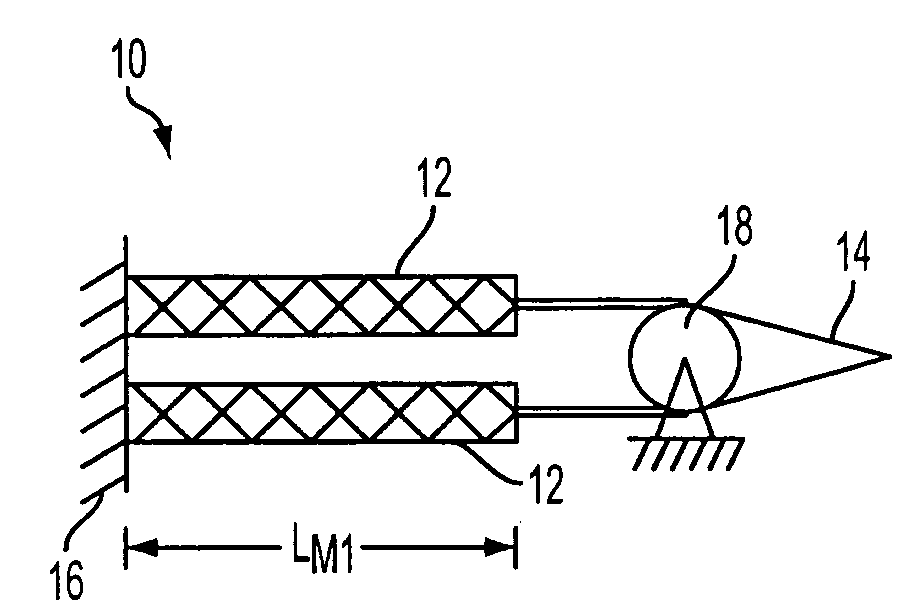
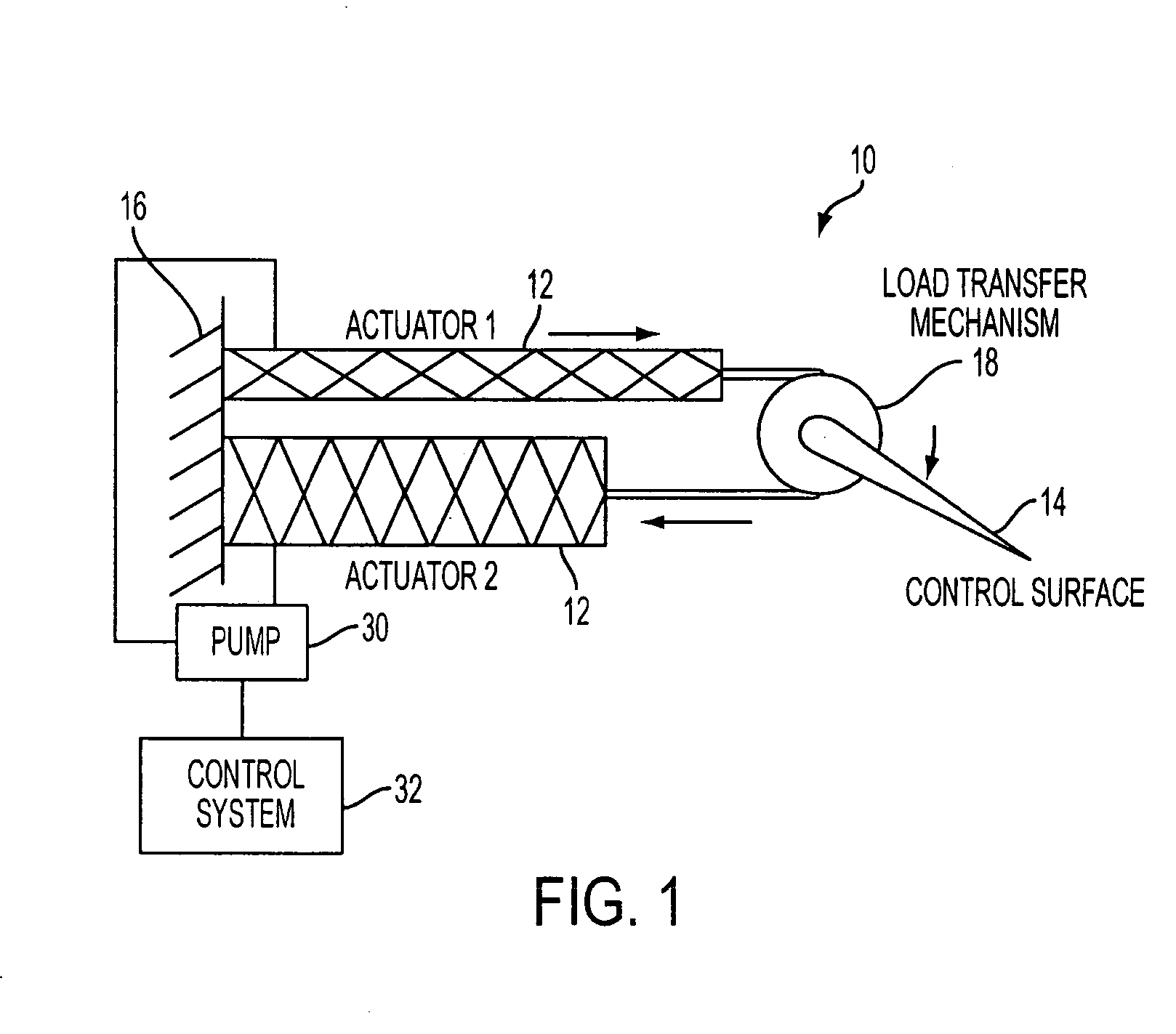
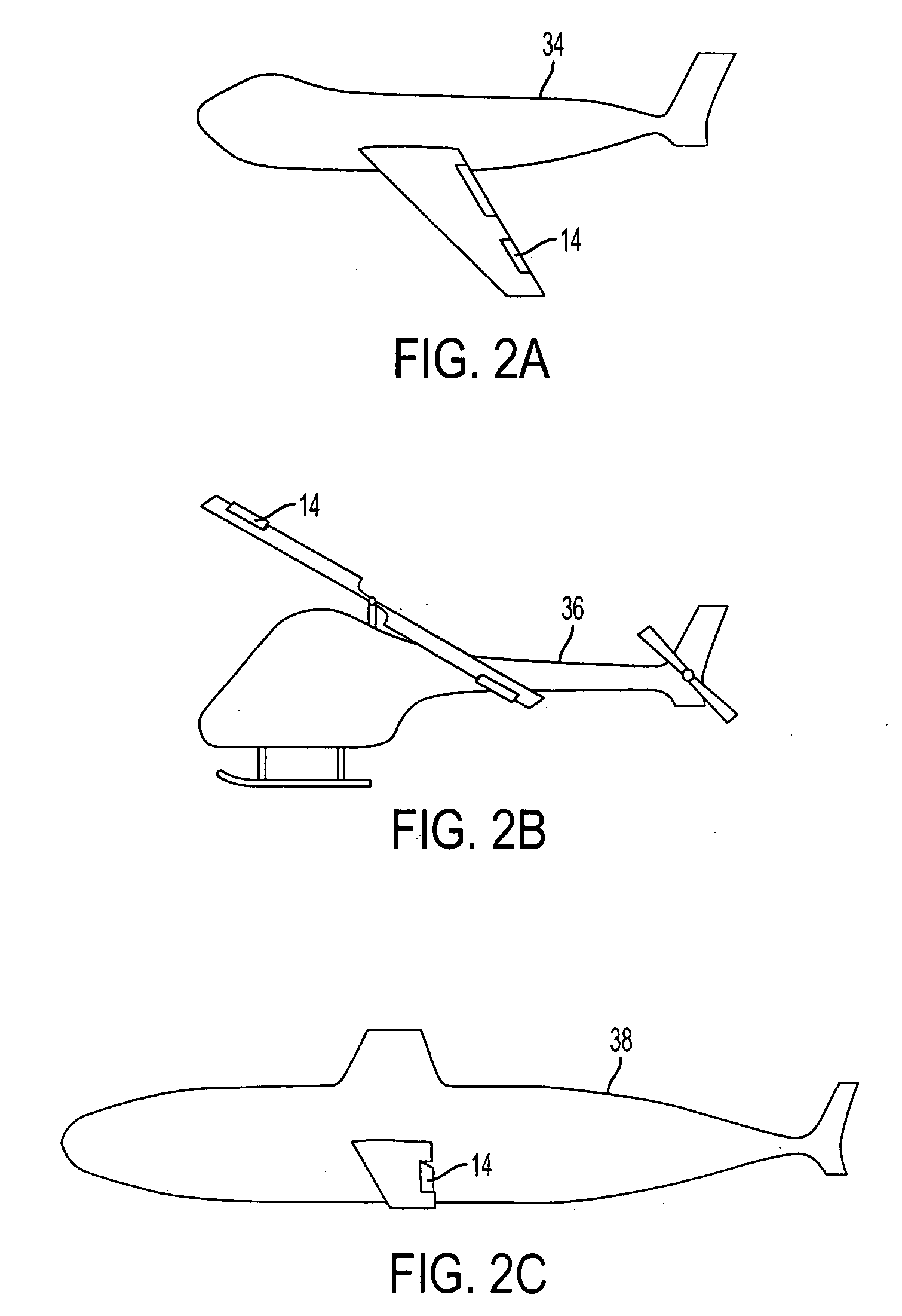
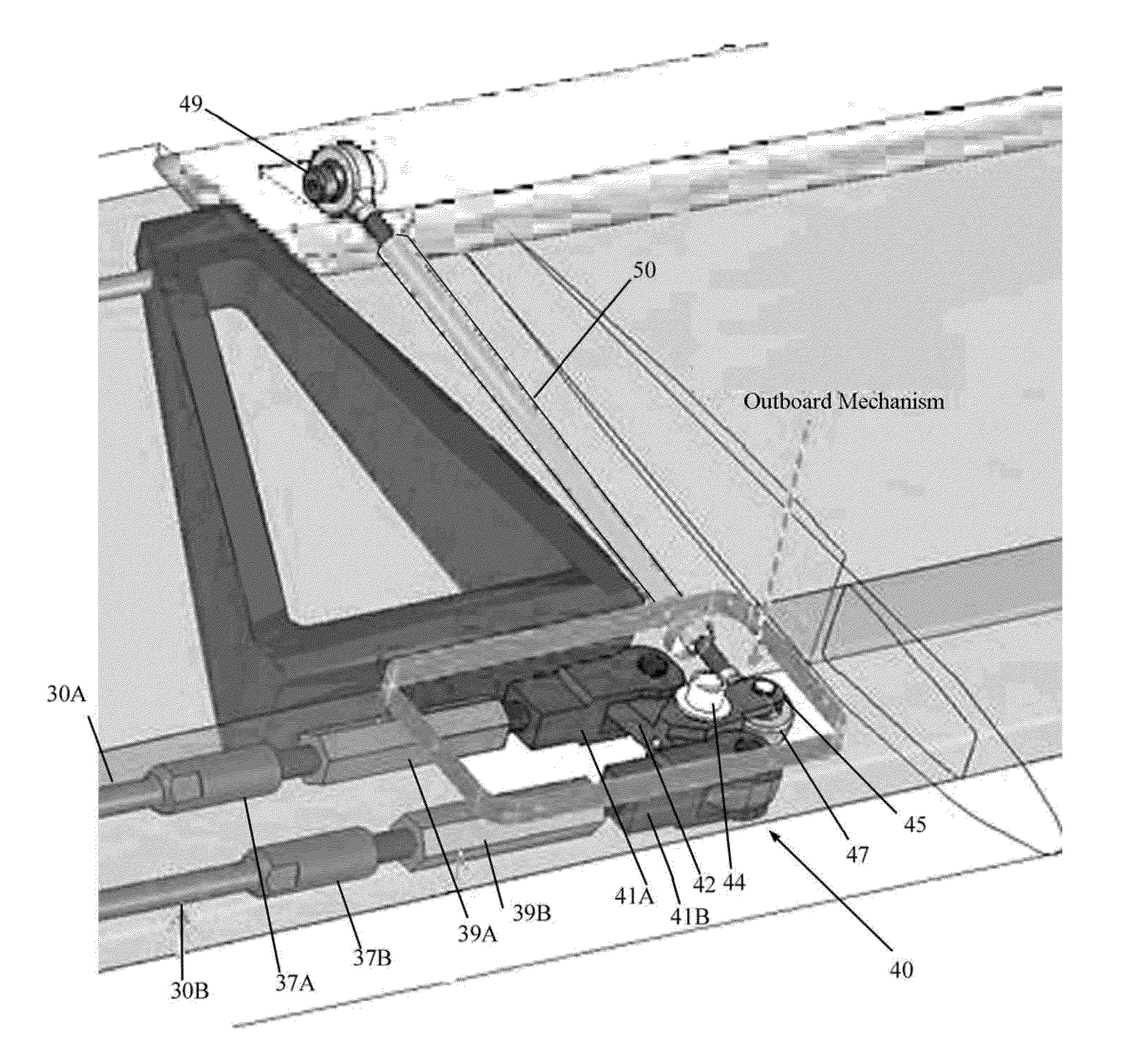
InactiveUS20110266391A1Reduce vibrationLarge deflectionFlexible wall reciprocating enginesAircraft stabilisationEngineeringTransfer mechanism
An actuation system for trailing-edge flap control suitable for use in reducing vibration in rotorcraft blades as well as primary flight control and noise mitigation employing an antagonistic pair of fluidic artificial muscles (FAMs) located and operated inside the rotor blade. The FAMs are connected to a force transfer mechanism such as an inboard bellcrank and engaged to an outboard bellcrank by one or more linkages running spanwise out through the spar. The outboard mechanism translates the spanwise linkage motion into chordwise motion of a flap control rod which is connected to the trailing-edge flap. A torsion rod flexure (TRF) device is included connecting the trailing-edge flap to the blade. The actuation system can produce large flap deflections at relatively high operating frequencies for vibration reduction and noise cancellation and is capable of larger flap deflections at lower operating frequencies for embedded primary control of the rotorcraft.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Artificial muscle stent model as well as preparation device and method thereof
ActiveCN107320773AEvenly distributedImprove survival rateAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationHigh cellInsertion stent
The invention discloses an artificial muscle stent model as well as a preparation device and method thereof. The model comprises a lower stent, an upper stent and a cellular bundle layer, wherein the cellular bundle layer, the upper stent and the lower stent are distributed from top to bottom sequentially. The artificial muscle stent model prepared by the preparation device with the preparation method has the advantages of uniform cell arrangement, high cell survival rate and high printing precision.
Owner:深圳协同创新高科技发展有限公司
Preparation method of large-strain quick-response electrothermal driving artificial muscles
ActiveCN112391831AEasy to operateLarge strainProgramme-controlled manipulatorCarbon fibresFiberPolymer science
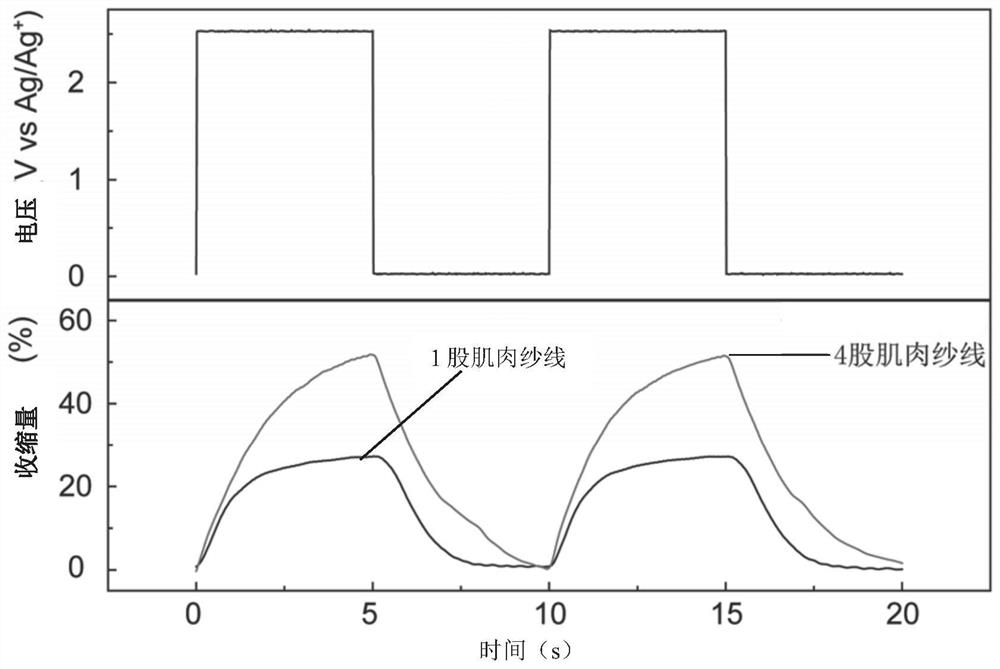
The invention belongs to the technical field of material science and soft robot driving, and particularly relates to a preparation method of large-strain quick-response electrothermal driving carbon nanotube fiber artificial muscles. The invention provides a preparation method of fiber artificial muscles by mixing a variable hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer and carbon nanotube fibers, and the method is applied to the field of intelligent robots. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing spinnable carbon nanotube fibers, and compounding the spinnable carbon nanotube fibers with thevariable hydrophilic-hydrophobic polymer through a composite doping method to prepare quick-response composite carbon nanotube fiber artificial muscles; and controlling the stretching and retractingof the quick-response composite carbon nanotube fiber artificial muscles in an electric heating driving mode, and introducing water mist into the quick-response composite carbon nanotube fiber artificial muscles, so that the purpose of large-strain quick response is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle
InactiveCN102323123AGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed stabilityPreparing sample for investigationResearch ObjectFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin residue freeze-dried powder standard sample in carp muscle, which takes the carp as a research object to research a carp muscle material object standard sample containing ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin of certain concentration in a breeding mode of adding target medicine. The key production control technology of the material object standard sample disclosed by the invention is mastered and comprises the control of content level, evenness, stability, constant value and the like, and the standard sample is produced and prepared in a standardization and scale mode. The standard sample is used for detection quality control and detection capability evaluation for residue of veterinary drug in animal-derived food and has an important significance on food safety detection.
Owner:时文春
Modular flexible artificial muscle joint
The invention provides muscle joint, in particular to a modular flexible artificial muscle joint, and belongs to the technical field of flexible robots. By adoption of the modular flexible artificialmuscle joint, the problems that existing flexible drive joints are complex in structure and large in size and cannot be combined easily are solved. The modular flexible artificial muscle joint comprises a front module port, a rear module port, an elastic supporting beam, two installation flange assemblies and N artificial muscles, wherein N is an integer greater than or equal to three, one installation flange assembly is fixedly installed at one end of the front module port, and the other installation flange assembly is fixedly installed at one end of the rear module port; the two ends of theelastic supporting beam are fixedly installed on the two installation flange assemblies correspondingly; and the N artificial muscles are arranged between the two installation flange assemblies, and the two ends of each artificial muscle are fixedly connected with the two installation flange assemblies correspondingly.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Electrochemically-driven artificial muscle fiber as well as preparation method and application thereof
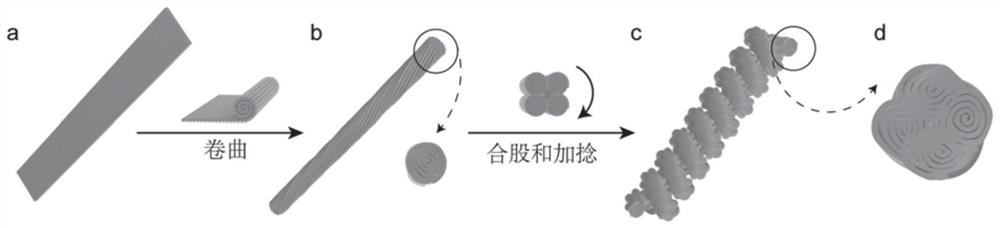
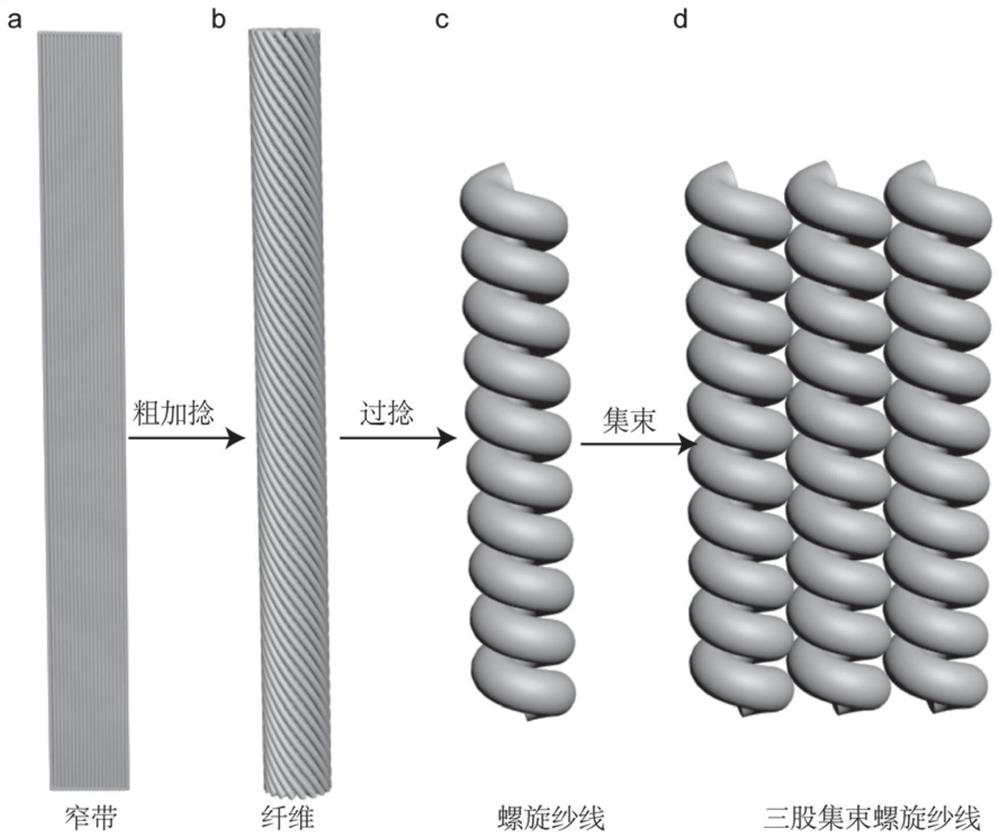
The invention discloses an electrochemically-driven artificial muscle fiber as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The electrochemically-driven artificial muscle fiber comprises at least one strand of muscle yarn, wherein the muscle yarn is at least obtained by sequentially pre-crimping, stranding and twisting a plurality of carbon nanotube narrow bands until a uniform spiral structure is formed, or the muscle yarn is at least obtained by twisting a single carbon nanotube narrow band until the uniform spiral structure is formed. According to the preparation method of the electrochemically-driven artificial muscle fiber, the plurality of carbon nanotube narrow bands are pre-crimped, stranded and twisted to obtain the muscle yarn, or the carbon nanotube narrow bands are directly twisted to obtain the muscle yarn; the obtained muscle yarn has a spiral or threaded structure, so that the specific surface area of the carbon nanotube narrow bands is increased; a large numberof micro-nano pore passages are introduced into the artificial muscle fiber, and the energy density and the driving stroke of the artificial muscle fiber are improved in a bunching or stranding mode.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Bio-Potential Activation of Artificial Muscles
The invention relates to the general field of electrical activation of non-biological artificial muscles, such as ionic polymeric synthetic artificial muscles, by means of action potentials produced by a biological nerve, such as mammalian sciatic nerve. This invention demonstrates how to stimulate and activate a non-biological muscle such as an ionic polymeric metal composite (IPMC) electro-active artificial muscle with the biological action potential generated by a mammalian nerve such as a rat sciatic nerve. The said invention further presents settings to generate optimal movement and force in artificial muscle due to the application of a nerve action potential. The invention uses the sciatic nerve to generate an action potential, which is subsequently amplified and applied to a cantilever sample of an electro-active ionic polymeric artificial muscle to cause it to bend, flex, and twitch. The sciatic nerve, in this invention, is stimulated by a separate signal to cause it to generate an action potential in the range of hundreds of μV, which is recorded by the electrodes attached to the nerve. These electrodes carry the action potential to an amplifier to amplify it to between 10's of Volts and subsequently are attached to the ionic polymeric artificial muscle to cause it to flex and twitch. Different frequencies of stimulation are tried to optimize the motion and force generated by the polymeric artificial muscles.
Owner:SHAHINPOOR MOHSEN
Double-acting hydraulic artificial muscle linear reciprocating actuator
ActiveCN110695981AProtect the loadCompact designProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a double-acting hydraulic artificial muscle linear reciprocating actuator which comprises hydraulic artificial muscles, a pressure-isolating sealing linkage device and a guidingdeflector; each hydraulic artificial muscle comprises a closed end connector, a rubber pipe and a water passing end connector; the center of an inverted cone tooth surface portion of the closed end connector is provided with a cylindrical blind hole in an axial direction; the center of the water passing end connector is sequentially provided with a water passing hole A and a water passing hole Bin the axial direction from outside to inside; the pressure-isolating sealing linkage device comprises a cylinder linkage device, a pressure-isolating sealing main body and a sealing ring; the cylinder linkage device extends into a through hole of the pressure-isolating sealing main body; each of the two ends of the pressure-isolating sealing linkage device is connected with one hydraulic artificial muscle; the guide deflector is provided with a diversion trench, a diversion hole A, a diversion hole B, a diversion hole C and a diversion hole D; the diversion hole A, the diversion hole B, the diversion hole C and the diversion hole D communicate with each other; and the two ends of the cylinder linkage device extend into the diversion hole D of the guide deflector through clearance fit. Thedouble-acting hydraulic artificial muscle linear reciprocating actuator provided by the invention solves various problems caused by a complex structure of a hydraulic system of an existing hydraulicactuator.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com