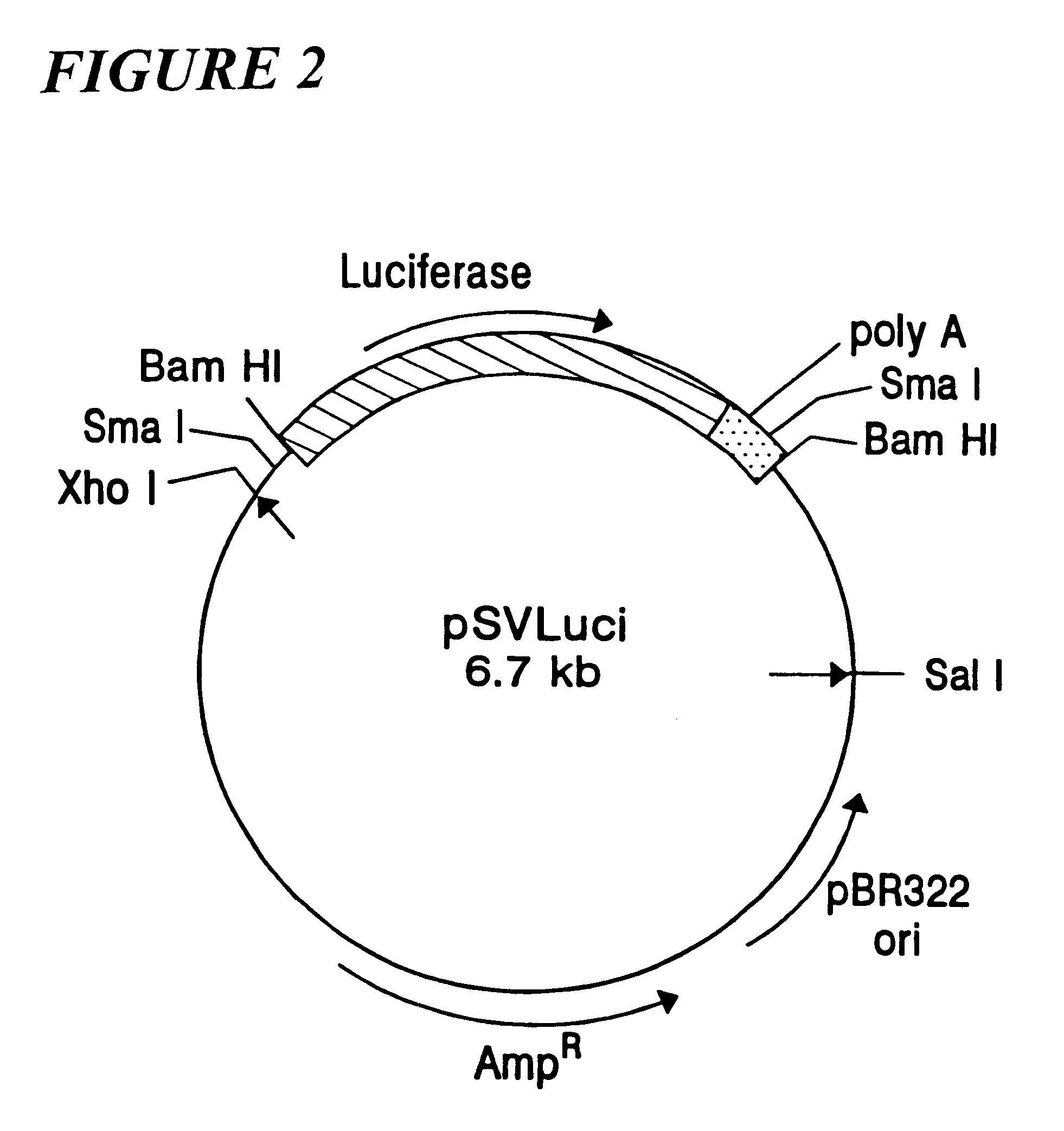
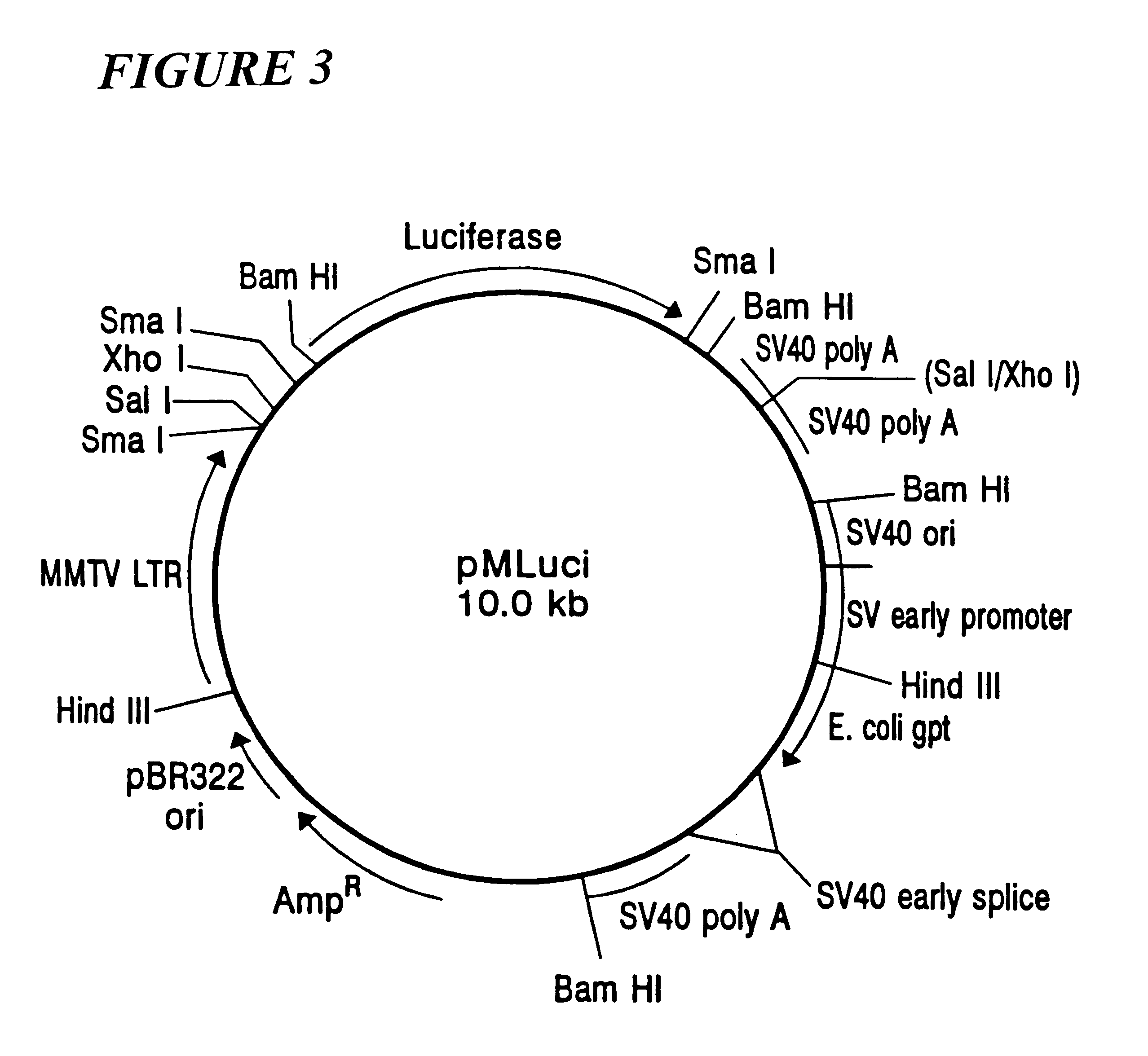
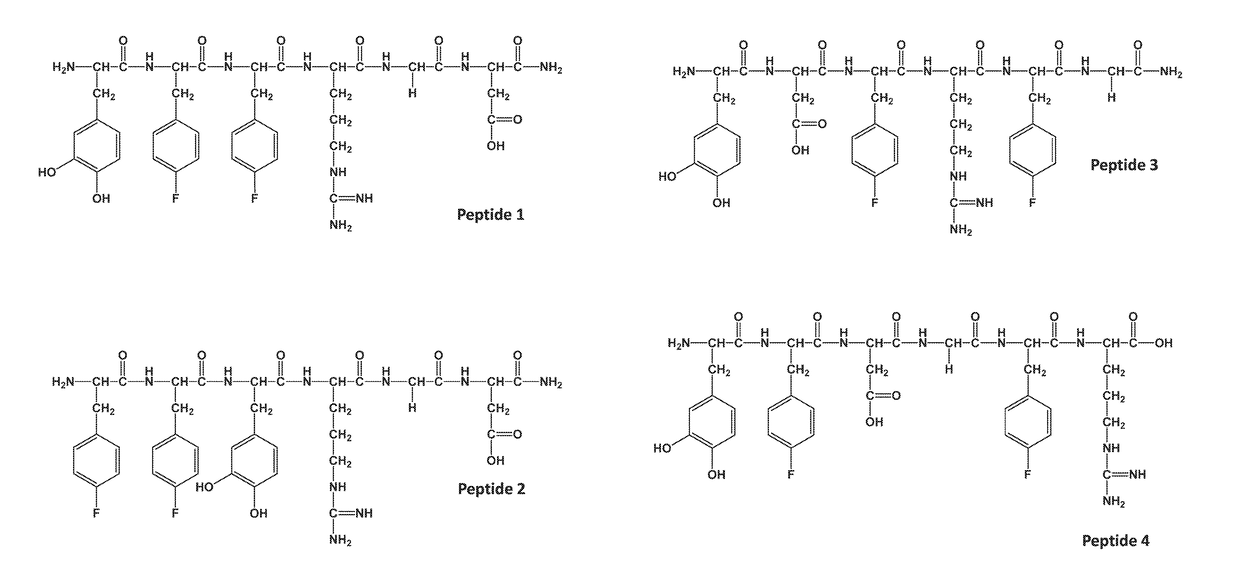
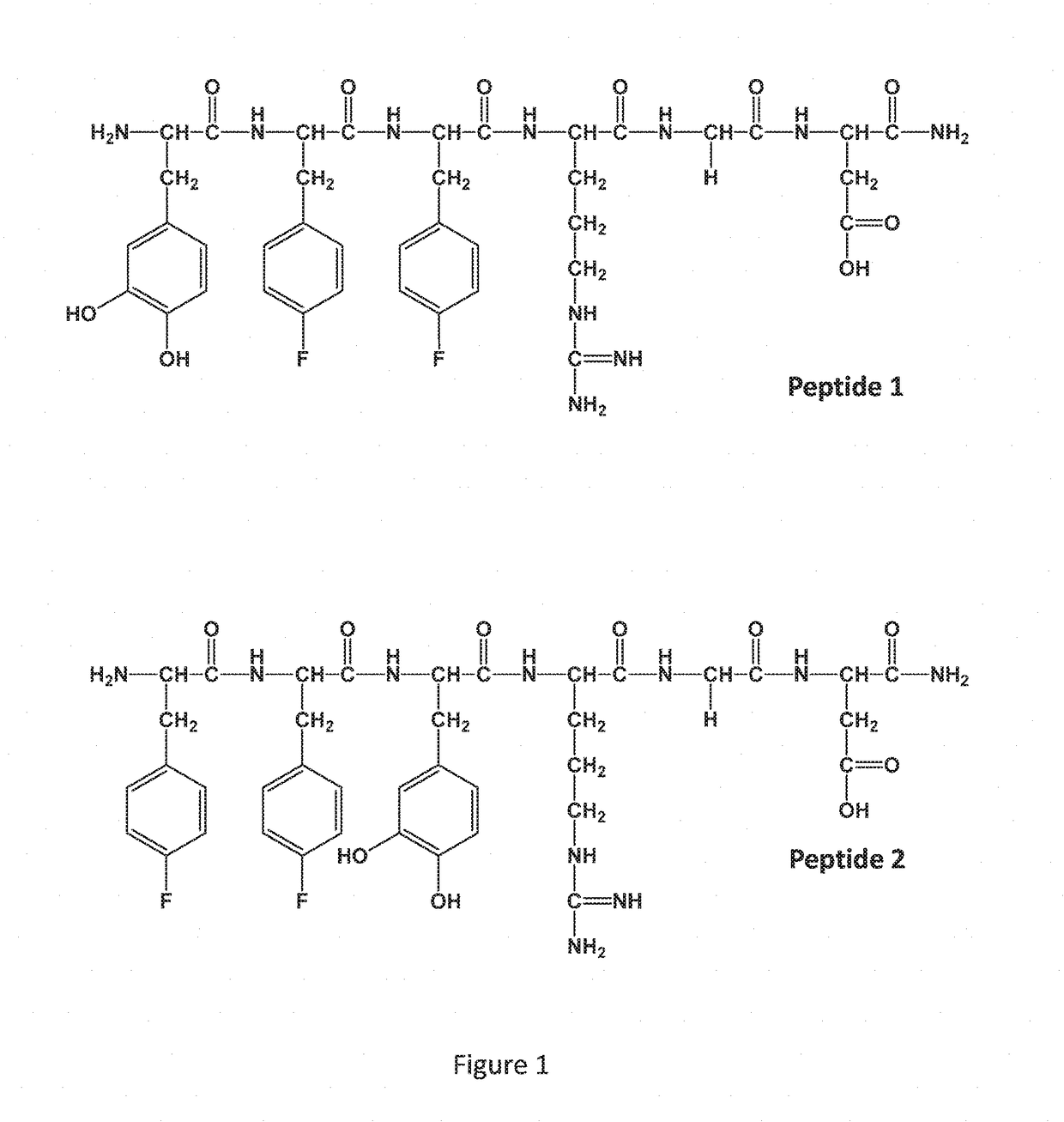
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Multicellular animals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social amoebae such as the genus Dictyostelium.
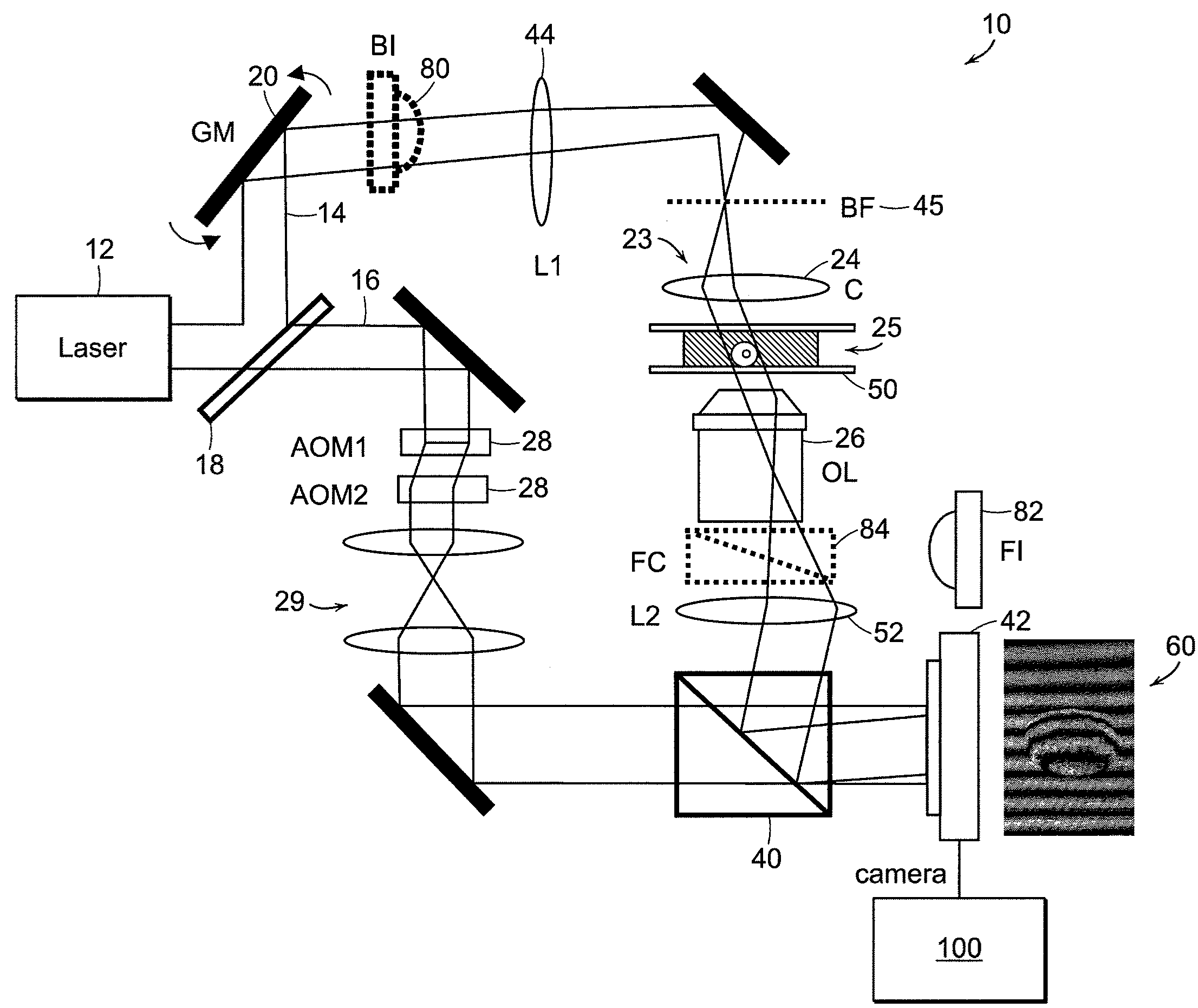
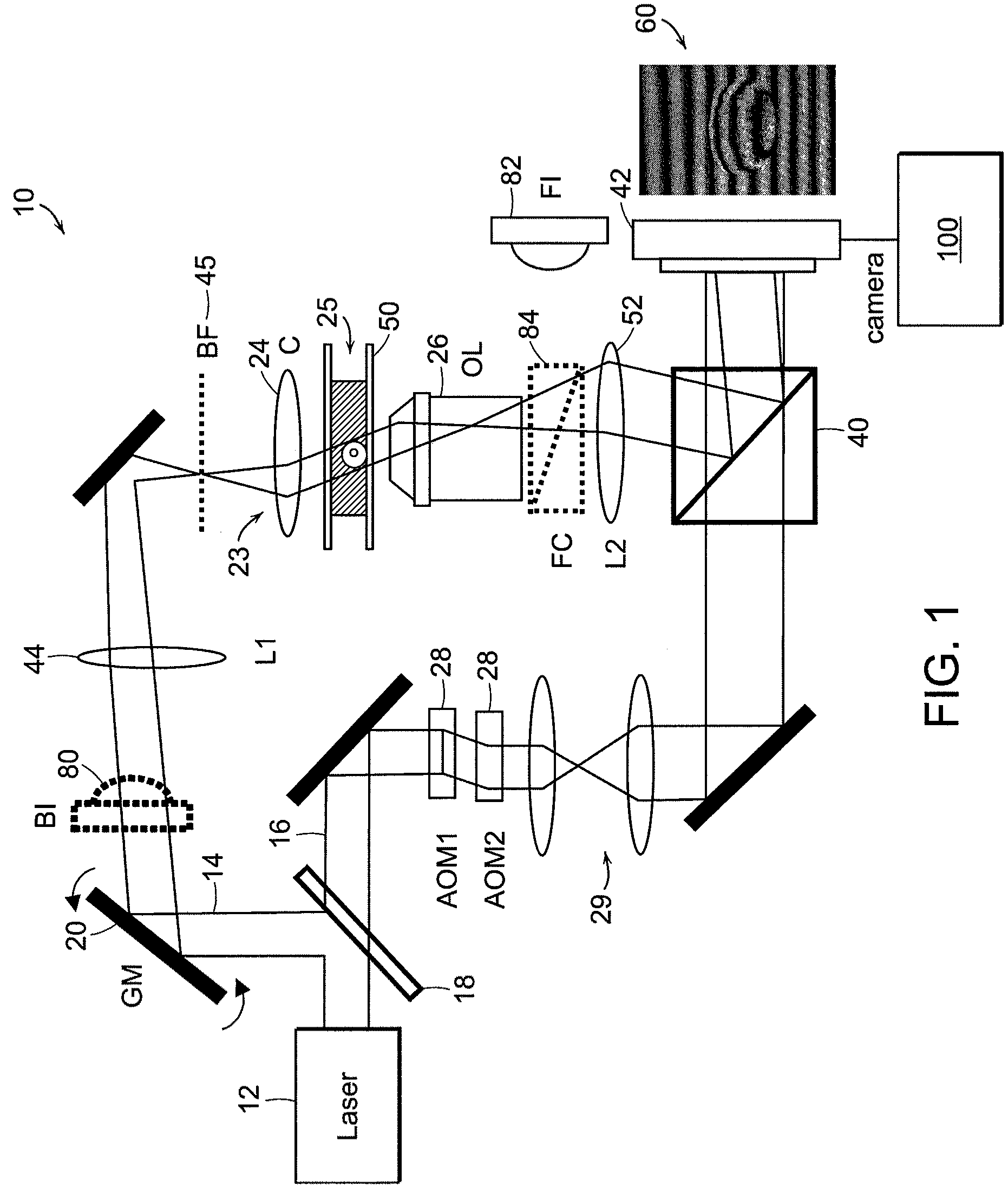
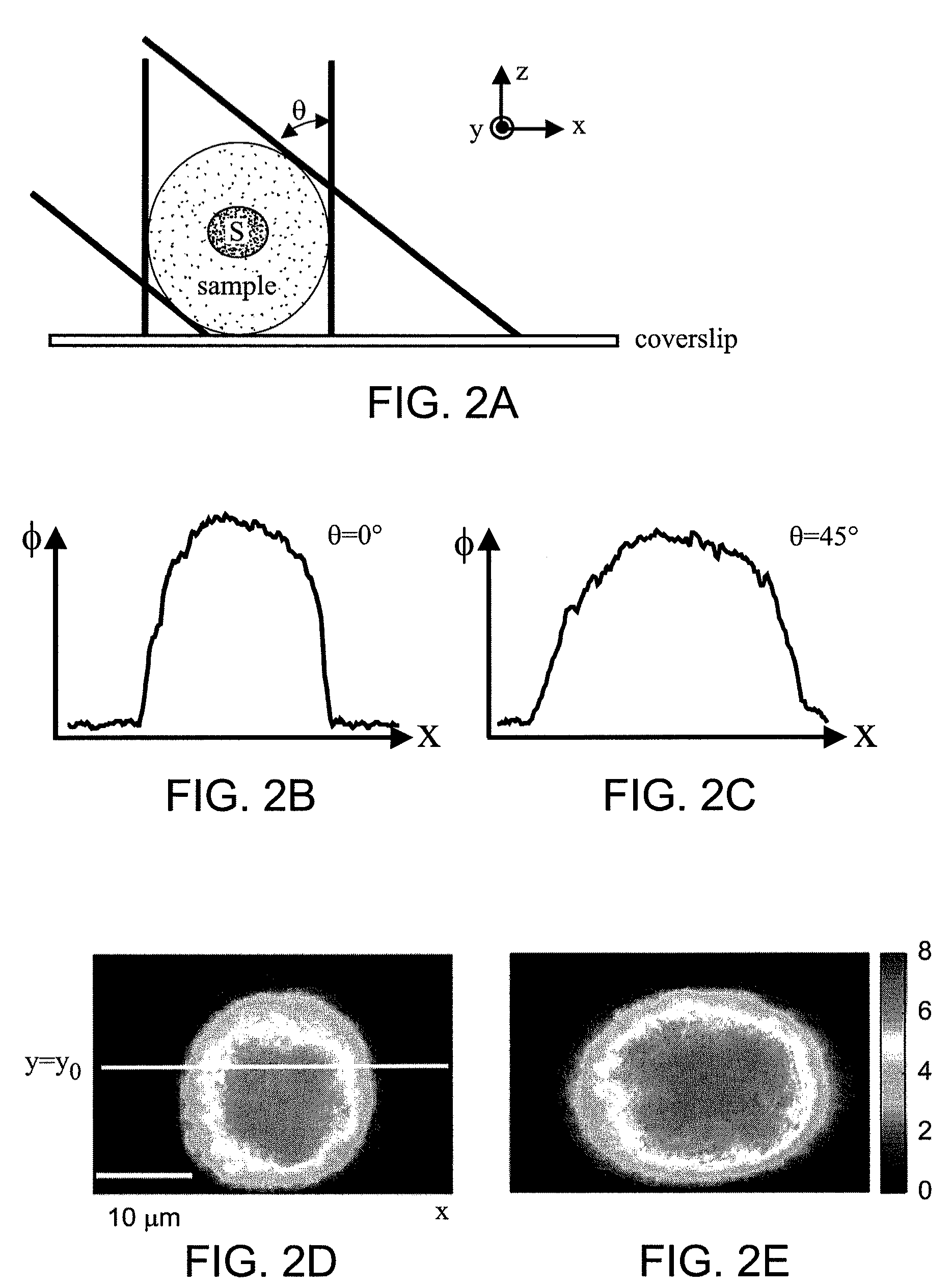
Tomographic phase microscopy
ActiveUS20090125242A1Phase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsRefractive indexOrganism
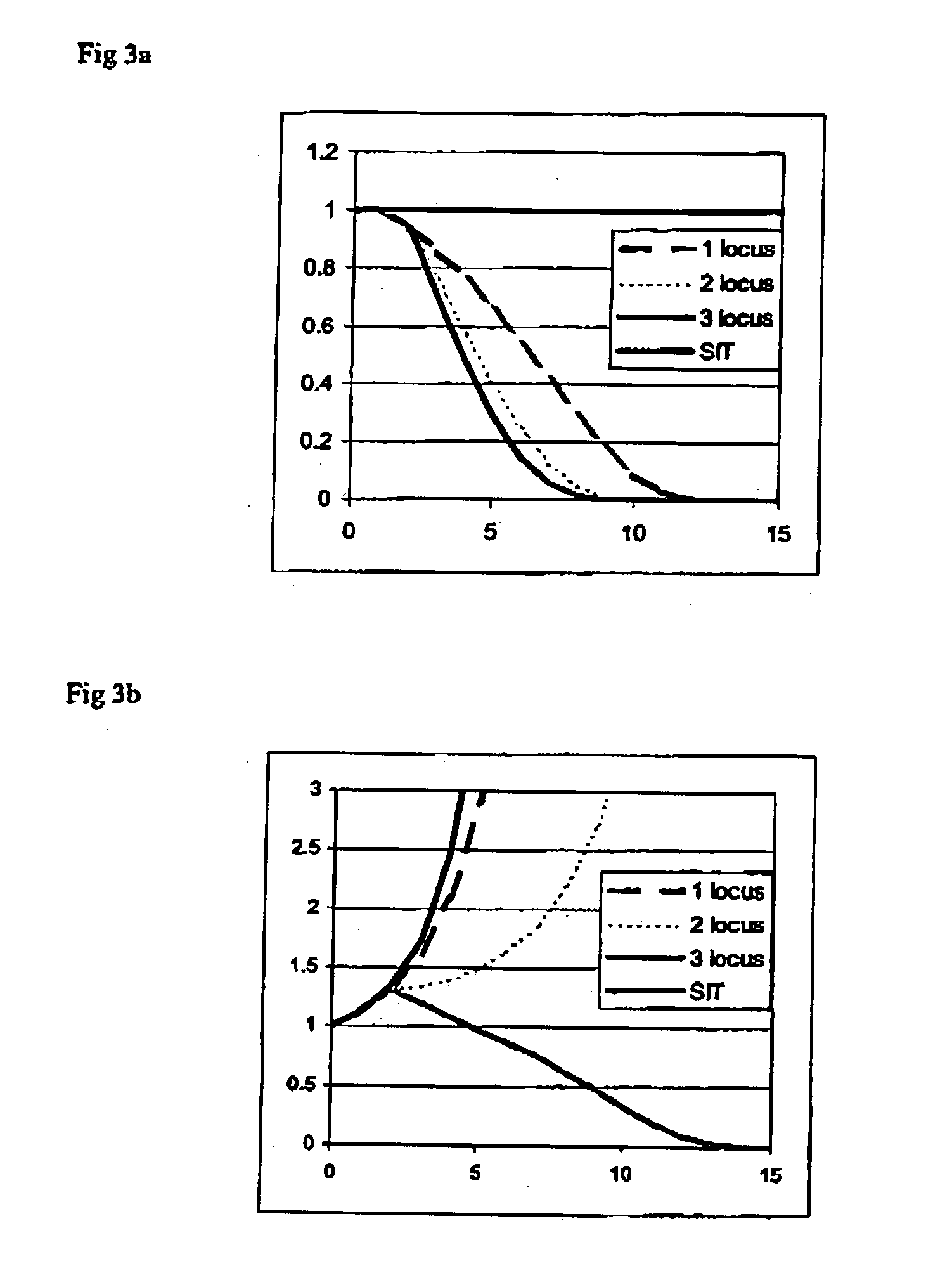
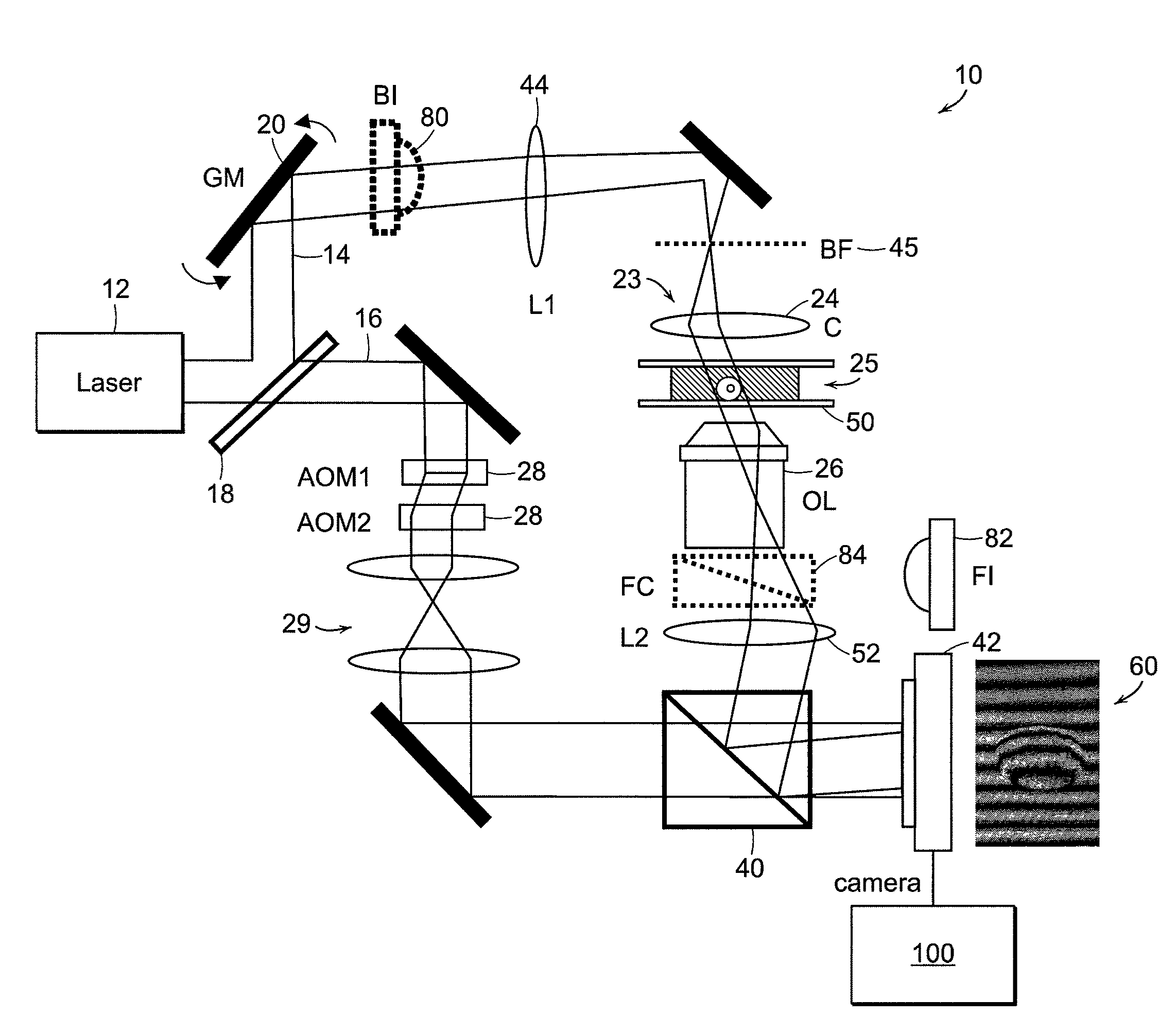
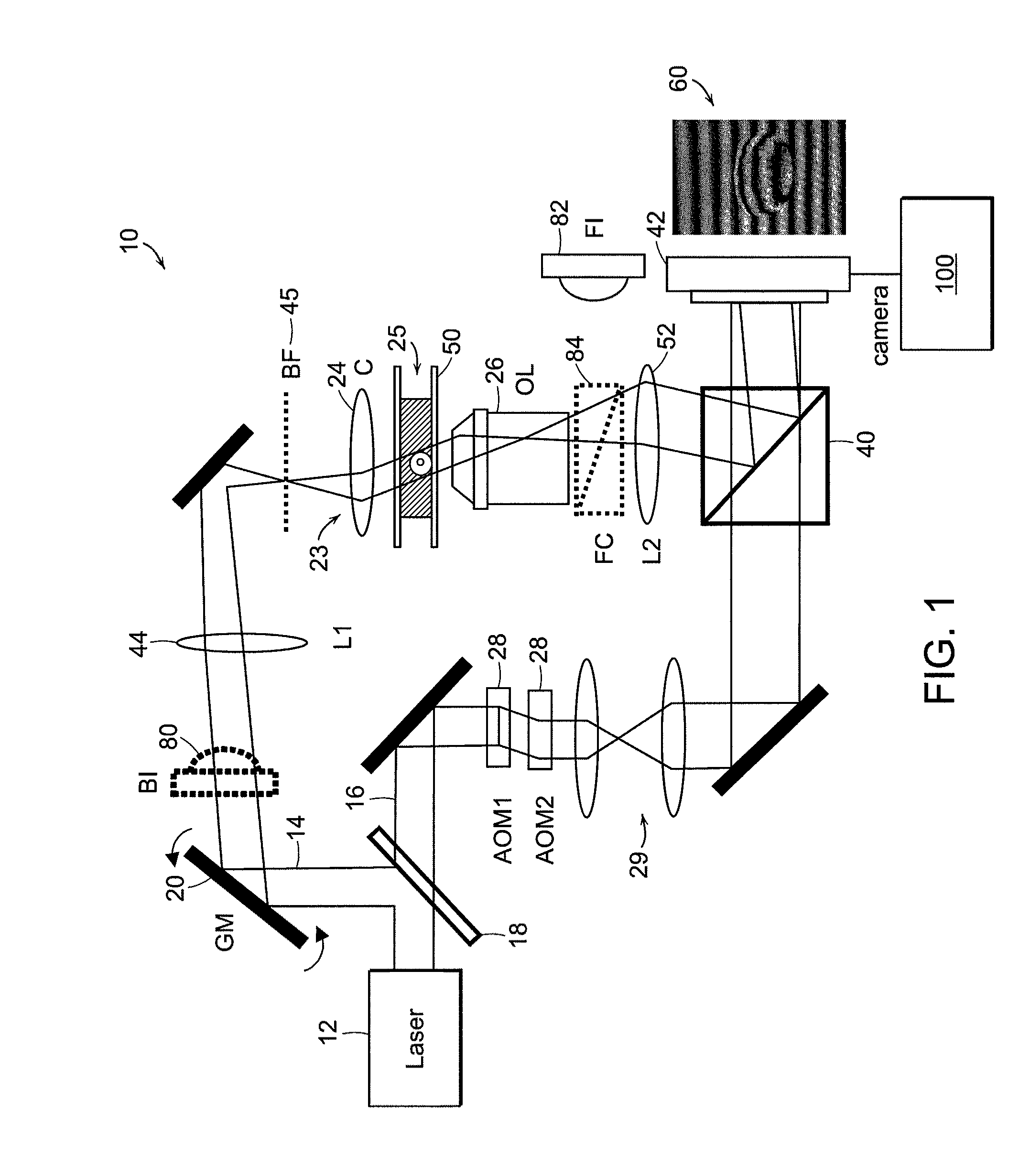
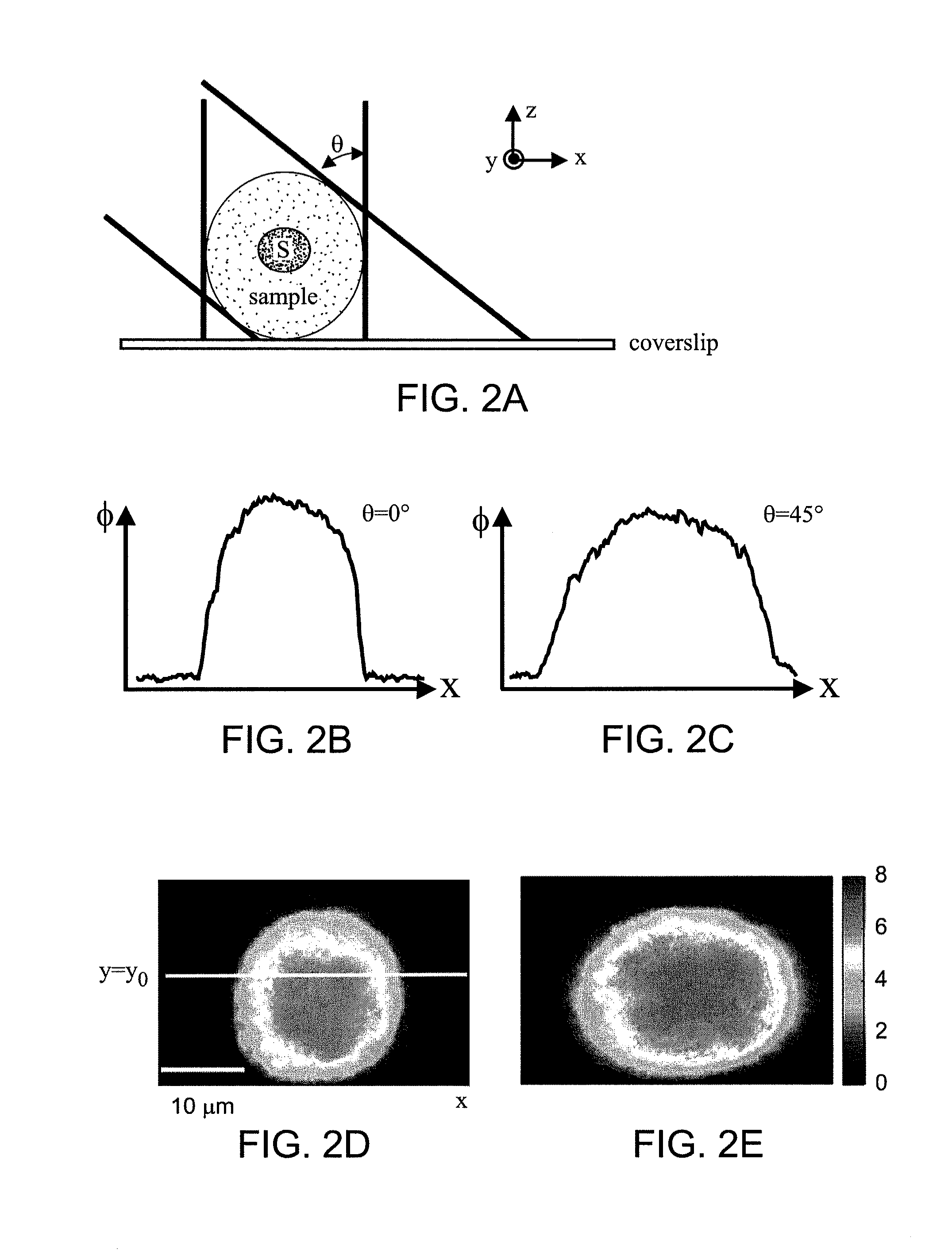
The present invention relates to systems and methods for quantitative three-dimensional mapping of refractive index in living or non-living cells, tissues, or organisms using a phase-shifting laser interferometric microscope with variable illumination angle. A preferred embodiment provides tomographic imaging of cells and multicellular organisms, and time-dependent changes in cell structure and the quantitative characterization of specimen-induced aberrations in high-resolution microscopy with multiple applications in tissue light scattering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
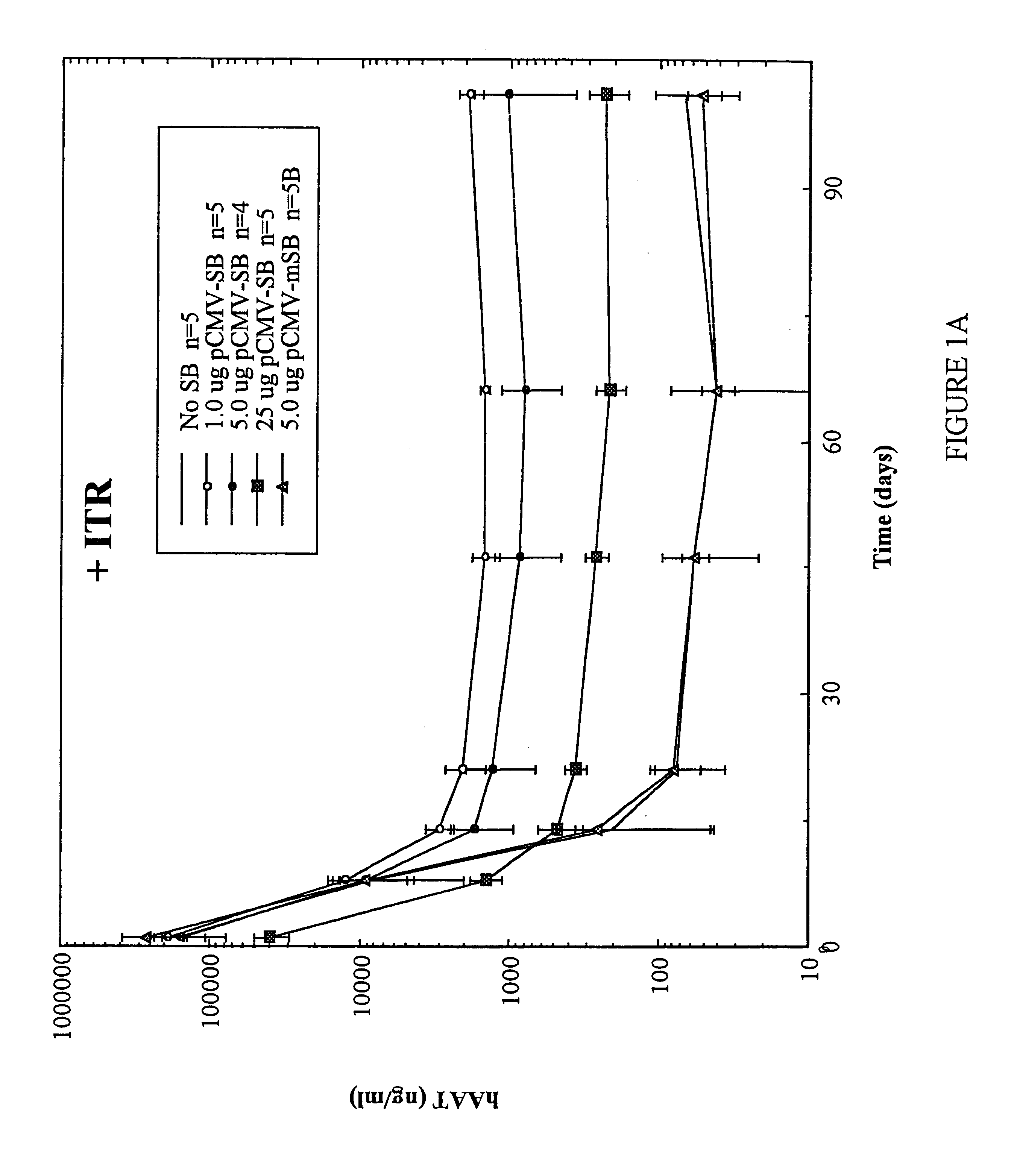
Methods of in vivo gene transfer using a sleeping beauty transposon system
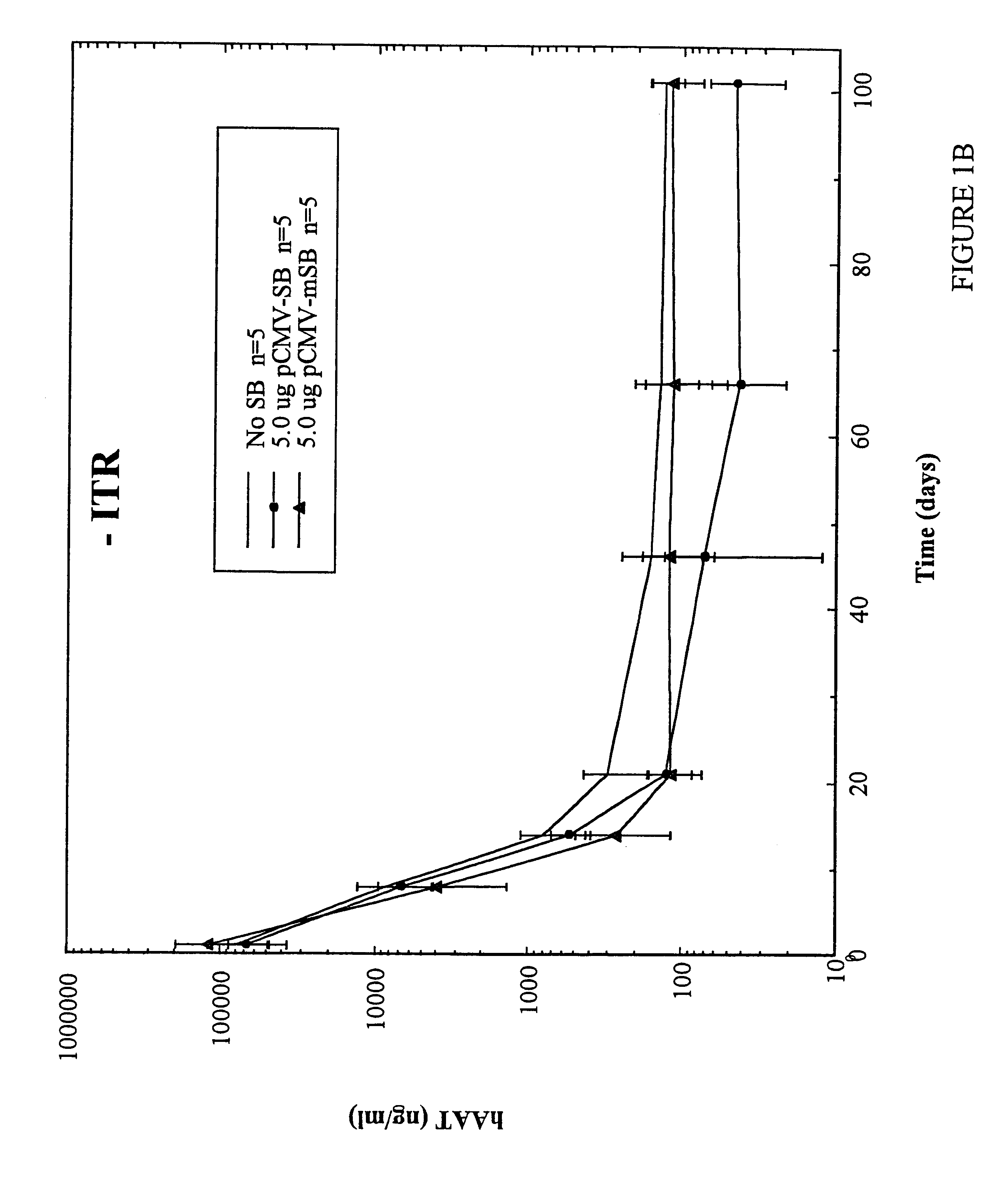
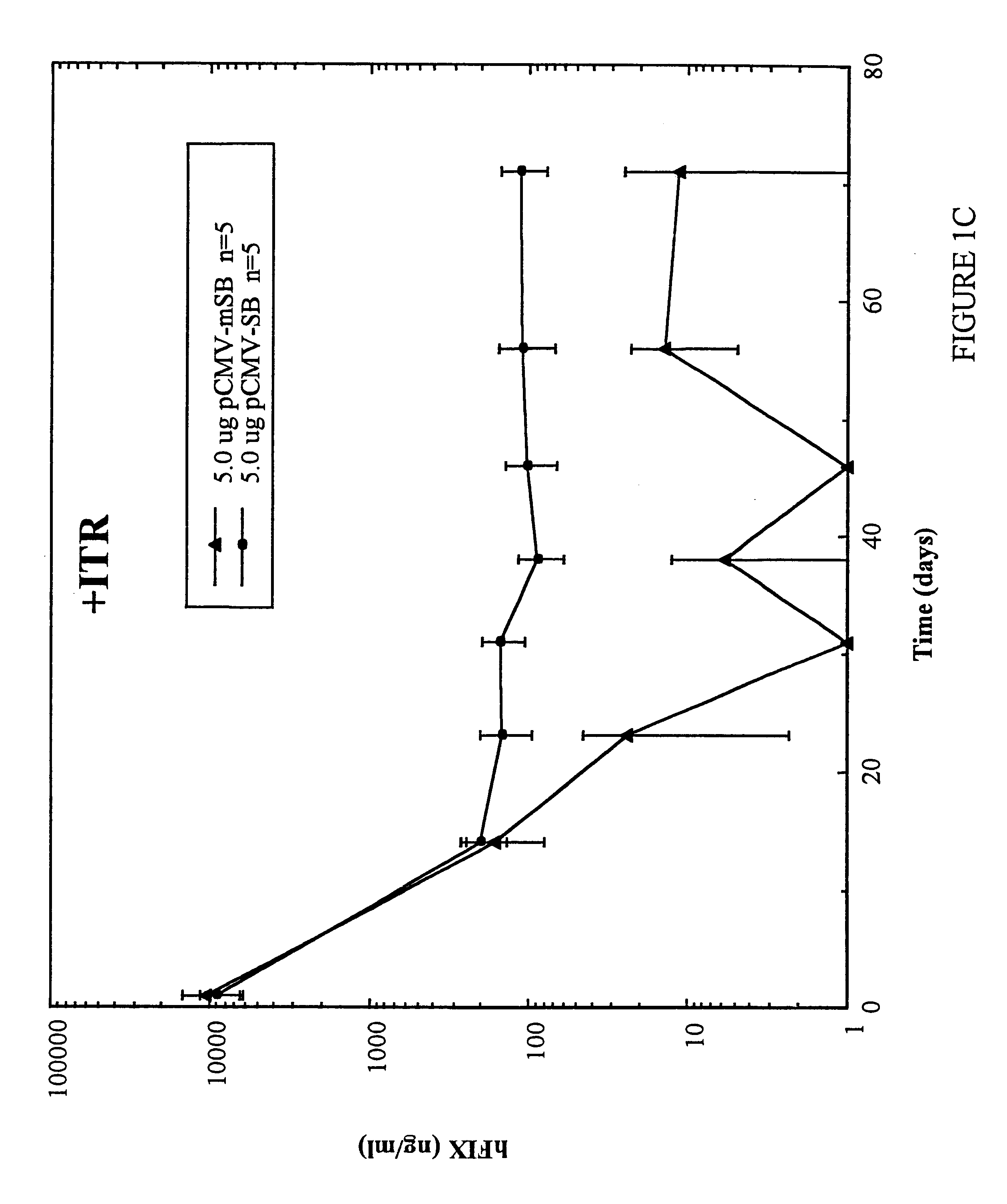
InactiveUS6613752B2Observed effectPromote cloningBiocideHydrolasesSleeping Beauty transposon systemMulticellular organism
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of at least one cell of a multicellular organism are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is administered to the multicellular organism along with a source of a Sleeping Beauty transposase activity. Administration of the transposon and transposase results in integration of the transposon, as well as the nucleic acid present therein, into the genome of at least one cell of the multicellular organism The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the in vivo transfer of genes for use in, among other applications, gene therapy applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biological control
InactiveUS20030213005A1Not affectAvoidance of sterilisationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyBiological body
The invention relates to a non-human multicellular organism carrying a dominant lethal genetic system, the lethal effect of which is conditional, wherein the lethal effect of the lethal system occurs in the natural environment of the organism.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Tomographic phase microscopy
ActiveUS8848199B2Phase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsRefractive indexOrganism
The present invention relates to systems and methods for quantitative three-dimensional mapping of refractive index in living or non-living cells, tissues, or organisms using a phase-shifting laser interferometric microscope with variable illumination angle. A preferred embodiment provides tomographic imaging of cells and multicellular organisms, and time-dependent changes in cell structure and the quantitative characterization of specimen-induced aberrations in high-resolution microscopy with multiple applications in tissue light scattering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
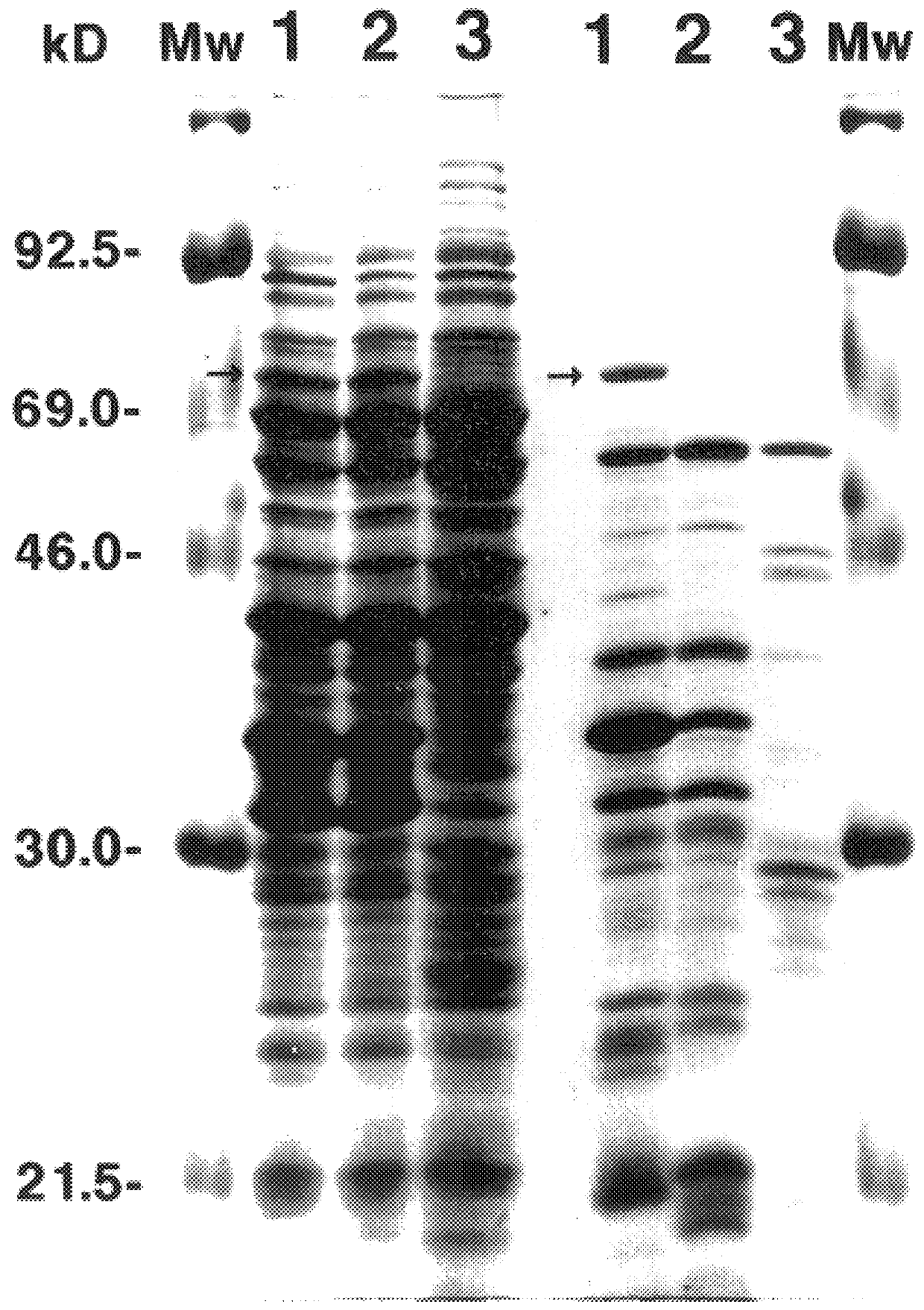
66 kDa antigen from Borrelia
InactiveUS6054296AReduce sensitivityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtozoaAntigen
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides encoded by the same, antibodies directed thereto and a method of preparing such polypeptides including: (a) inserting an isolated DNA molecule coding for a polypeptide which is immunoreactive with a 66 kDa polypeptide derived from Borrelia garinii IP90 into an expression vector; (b) transforming a host organism or cell with the vector; (c) culturing the transformed host cell under suitable conditions; and (d) harvesting the polypeptide. The isolated DNA molecule is preferably at least 10 nucleotides in length, and the method may optionally include subjecting the polypeptide to post-translational modification. The host cell can be a bacterium, a yeast, a protozoan, or a cell derived from a multicellular organism such as a fungus, an insect cell, a plant cell, or a mammalian cell.
Owner:SYMBICOM
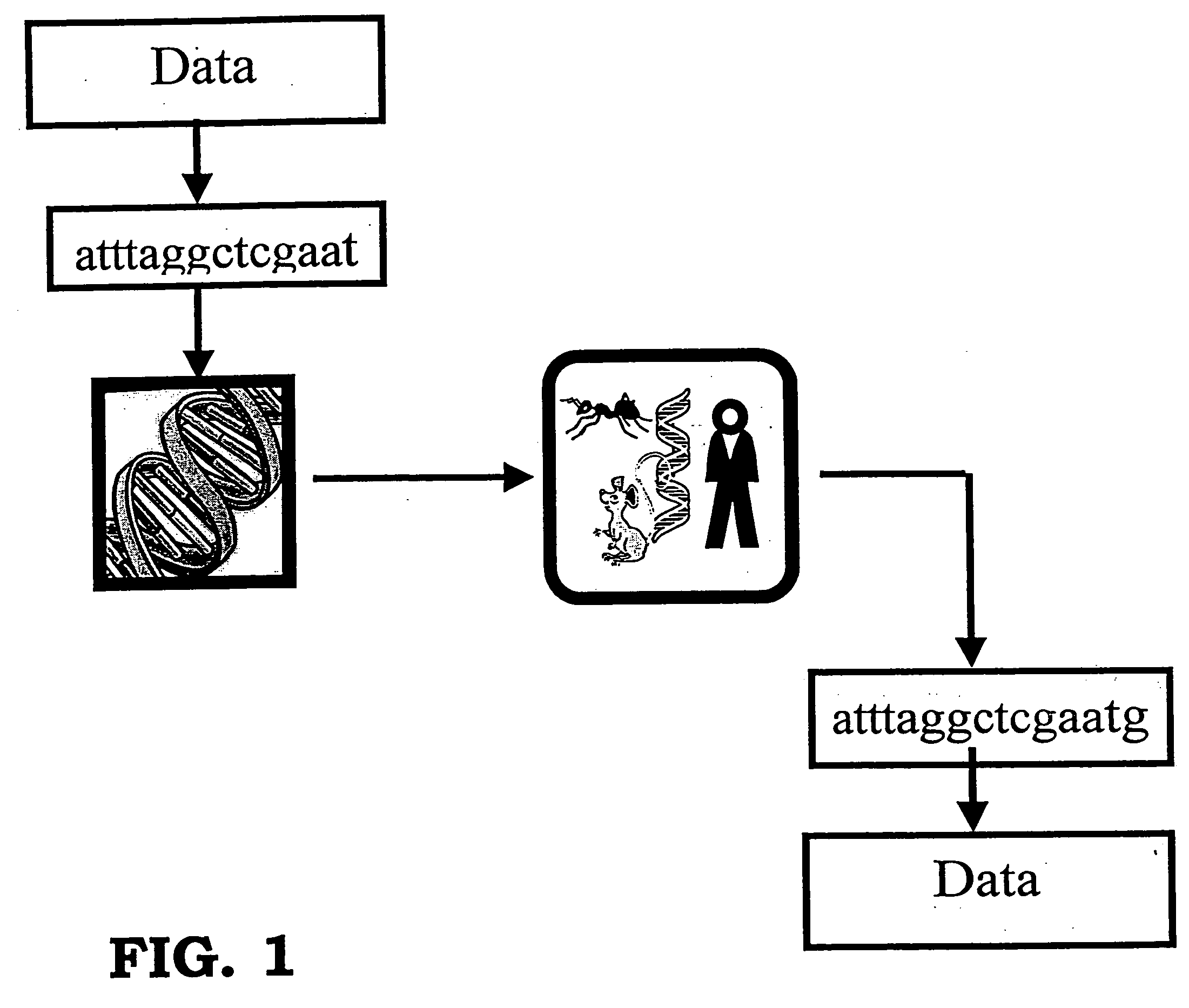
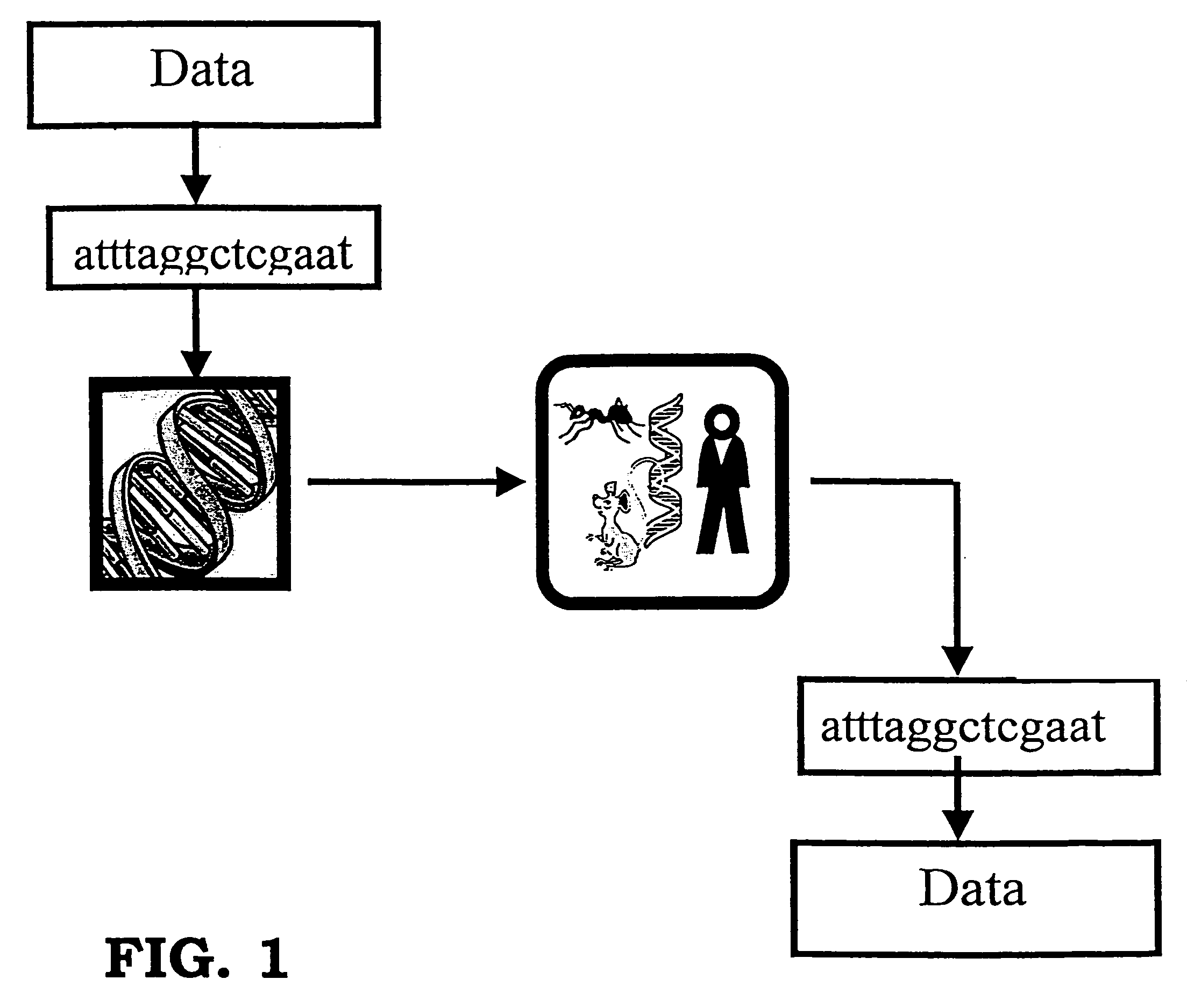
Storing data encoded DNA in living organisms
Current technologies allow the generation of artificial DNA molecules and / or the ability to alter the DNA sequences of existing DNA molecules. With a careful coding scheme and arrangement, it is possible to encode important information as an artificial DNA strand and store it in a living host safely and permanently. This inventive technology can be used to identify origins and protect R&D investments. It can also be used in environmental research to track generations of organisms and observe the ecological impact of pollutants. Today, there are microorganisms that can survive under extreme conditions. As well, it is advantageous to consider multicellular organisms as hosts for stored information. These living organisms can provide as memory housing and protection for stored data or information. The present invention provides well for data storage in a living organism wherein at least one DNA sequence is encoded to represent data and incorporated into a living organism.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
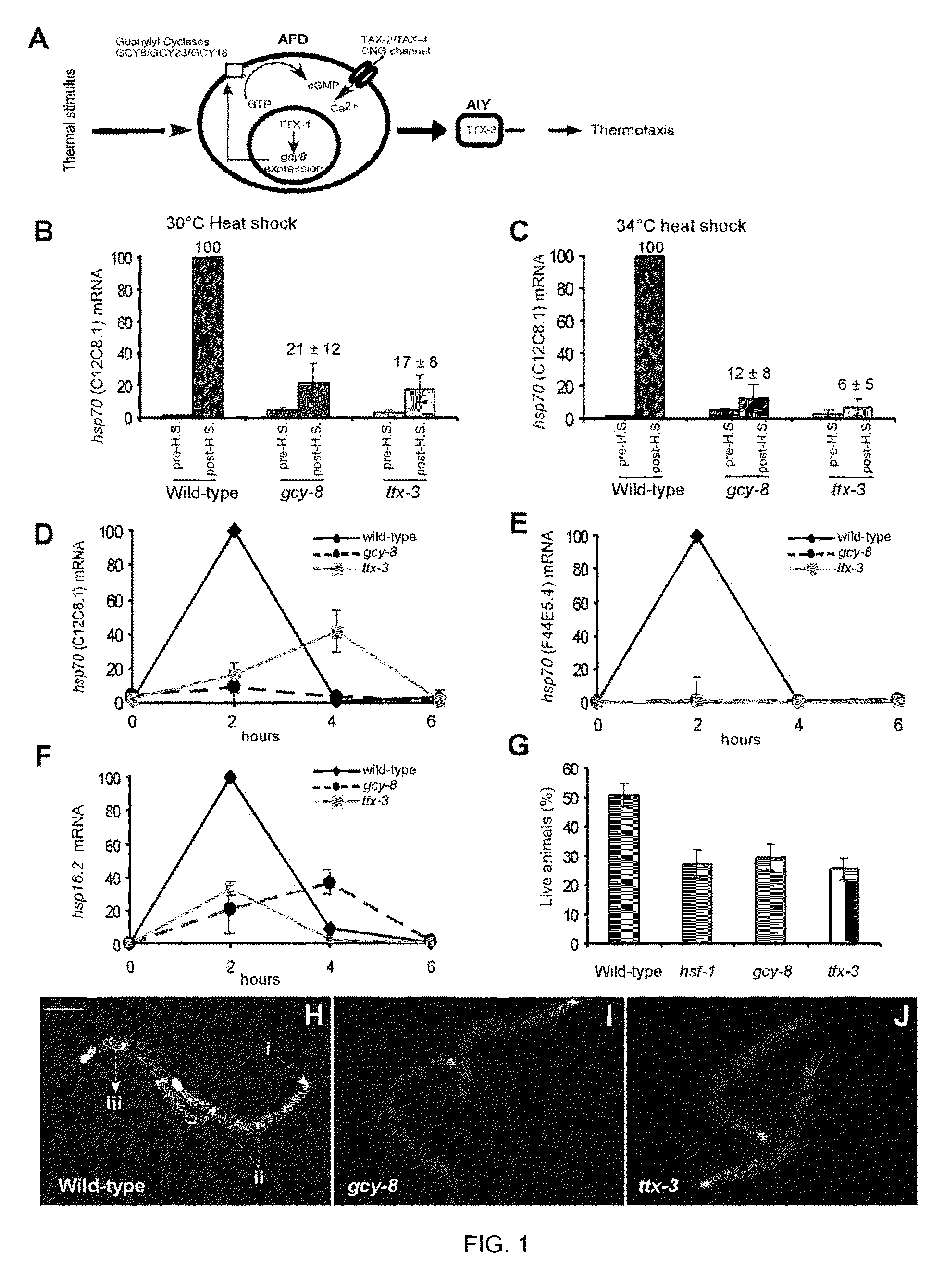
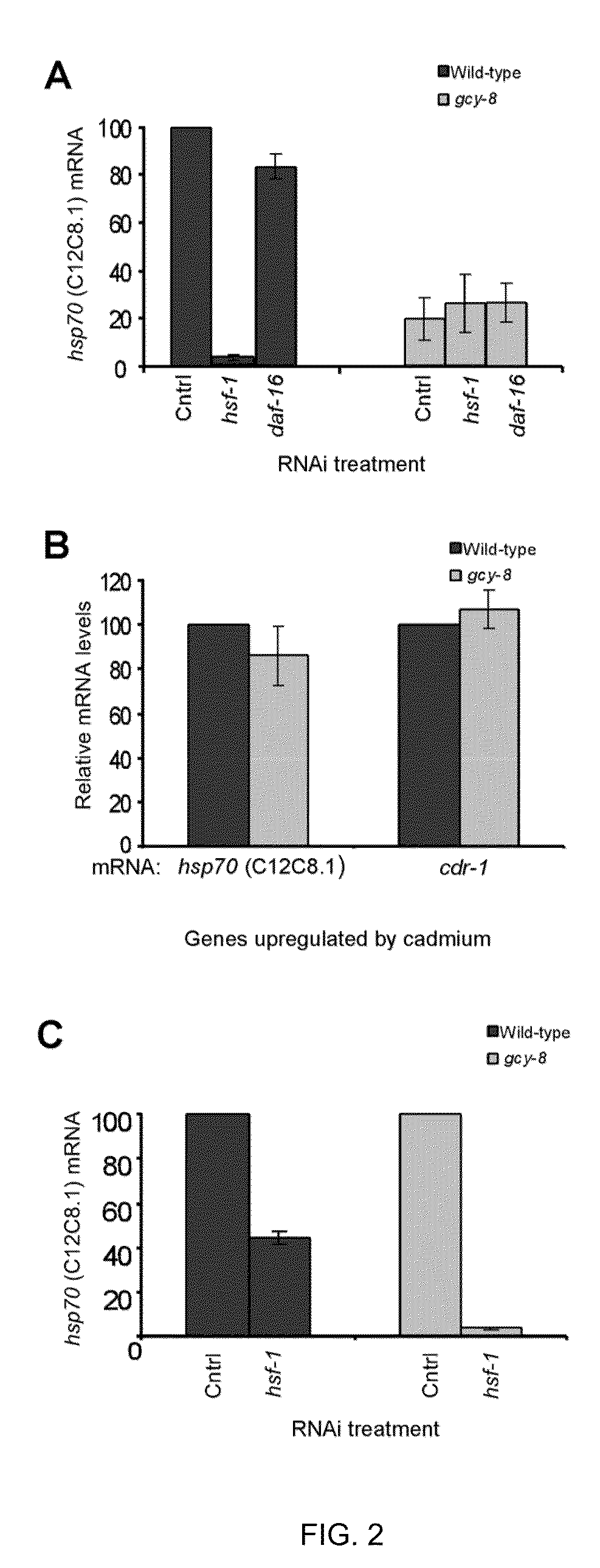
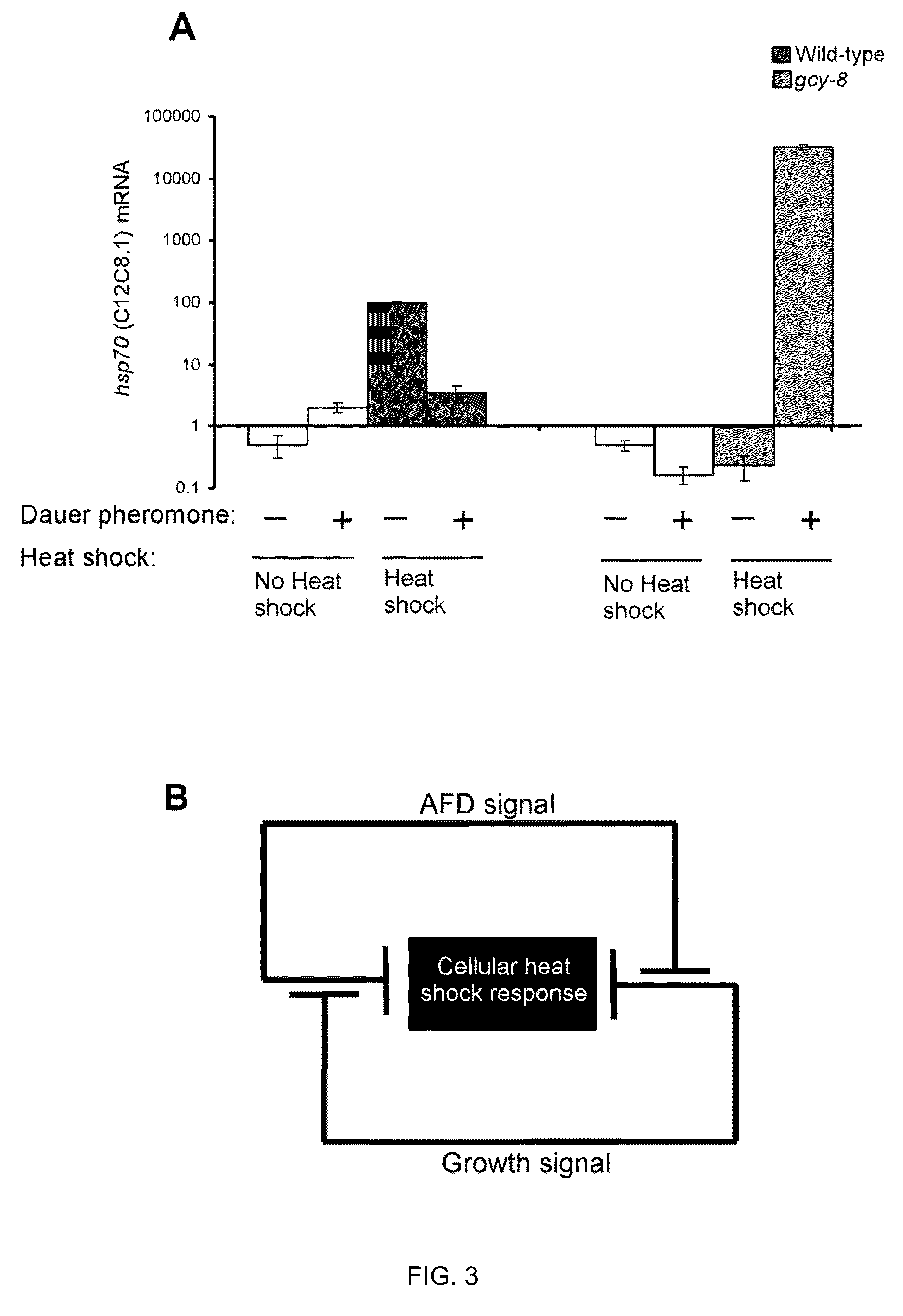
Method of regulating the heat shock response
The present invention is directed to method of modulating a heat shock response in a first cell of a multicellular organism comprising stimulating or inhibiting an HSR signaling activity of a second cell, wherein the second cell is a neuronal cell that regulates heat shock response activation in the first cell and that does not directly innervate the first cell.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Storing data encoded DNA in living organisms
Current technologies allow the generation of artificial DNA molecules and / or the ability to alter the DNA sequences of existing DNA molecules. With a careful coding scheme and arrangement, it is possible to encode important information as an artificial DNA strand and store it in a living host safely and permanently. This inventive technology can be used to identify origins and protect R&D investments. It can also be used in environmental research to track generations of organisms and observe the ecological impact of pollutants. Today, there are microorganisms that can survive under extreme conditions. As well, it is advantageous to consider multicellular organisms as hosts for stored information. These living organisms can provide as memory housing and protection for stored data or information. The present invention provides well for data storage in a living organism wherein at least one DNA sequence is encoded to represent data and incorporated into a living organism.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
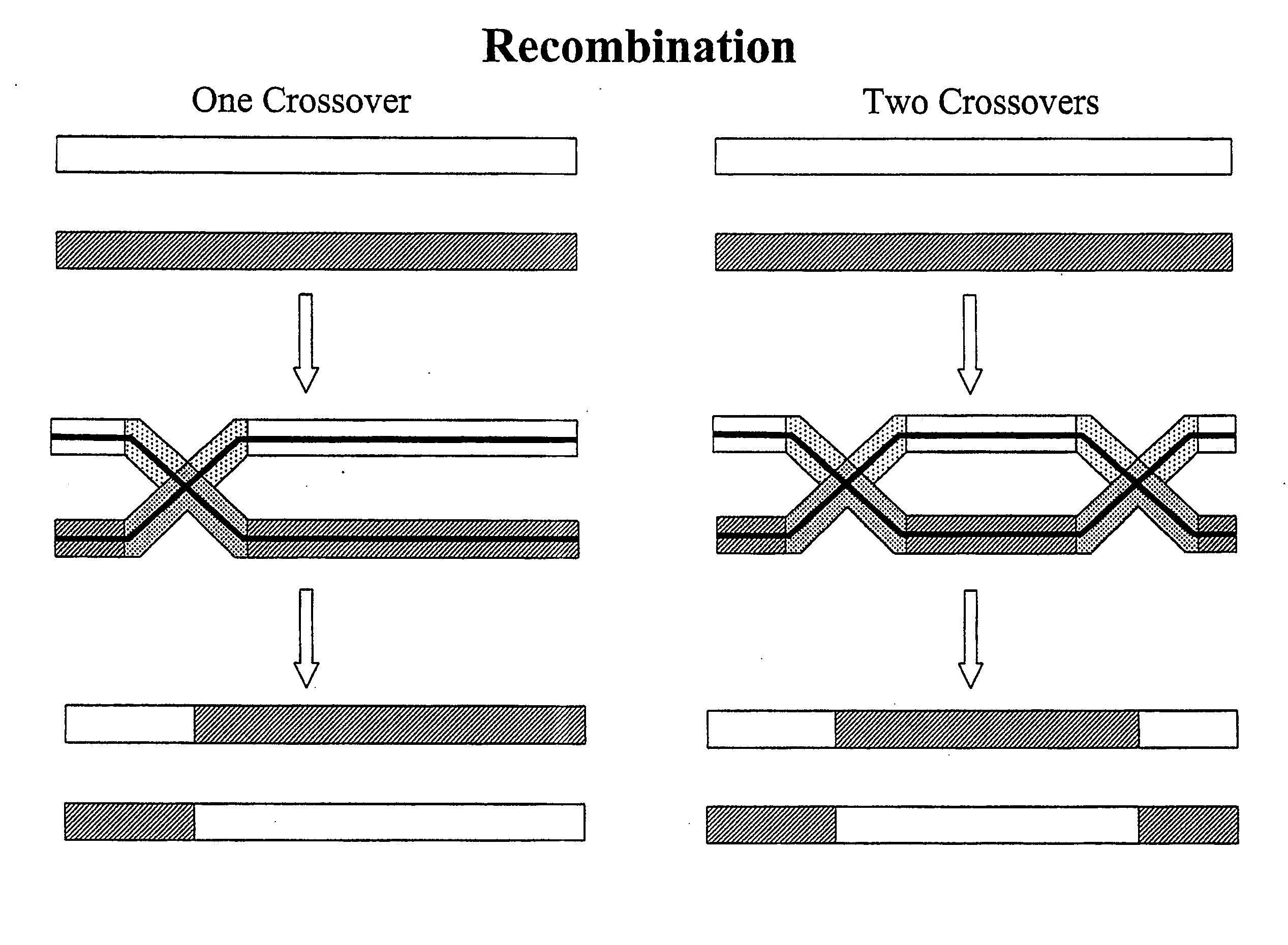
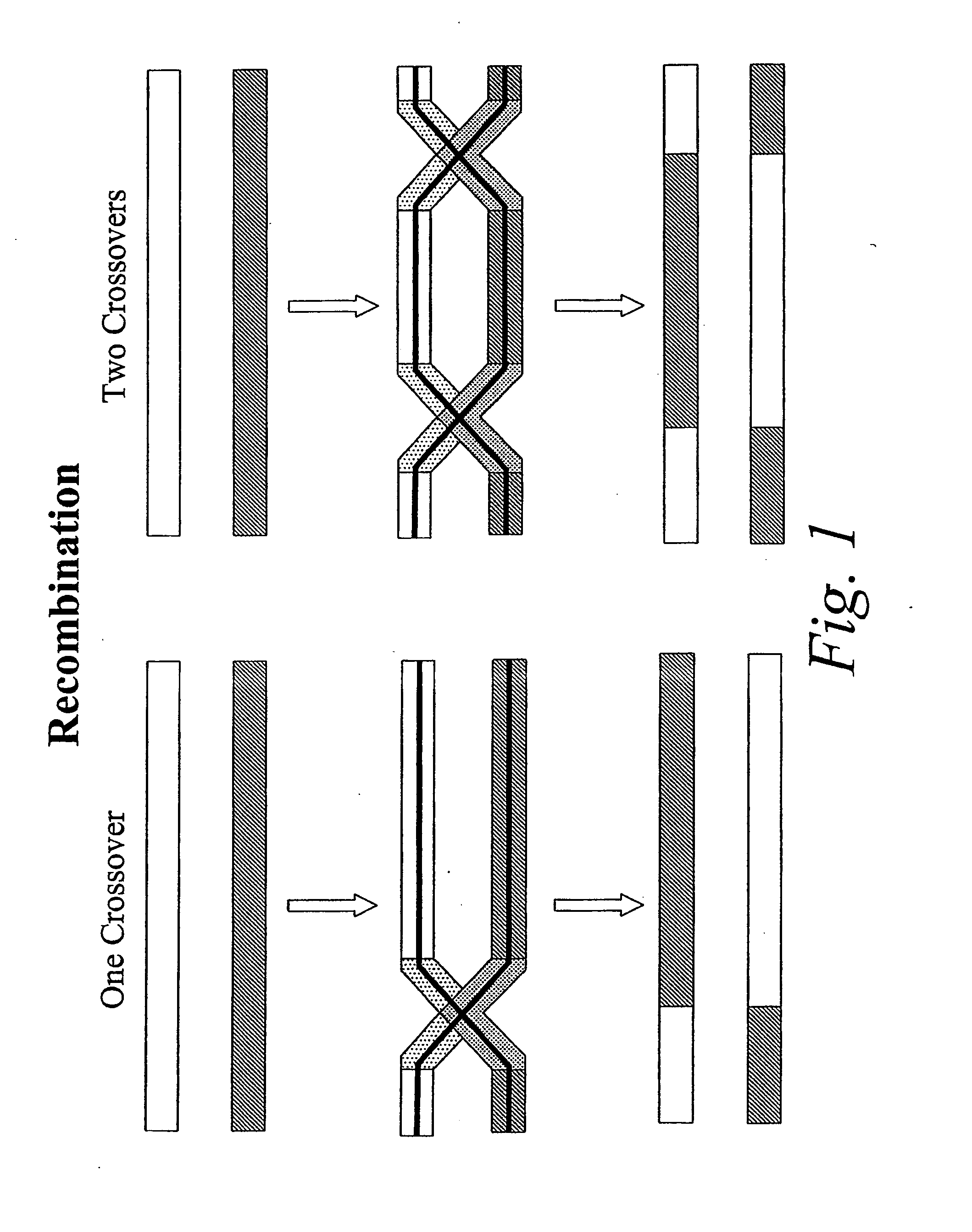
Copy choice recombination and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070253978A1Improve humanImprove animal healthSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMulticellular organismAnimal health
The instant invention provides methods for determining, predicting and characterizing the genetic variability of a range of organisms, including, e.g., viruses, microbes, cells and multicellular organisms. Accordingly, the invention provides methods for identifying virulent pathogens, genetic mutations within pathogens that are relevant to animal health, and methods and compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic intervention against such pathogens.
Owner:NIMAN HENRY L
Transgenic reporter system that reveals expression profiles and regulation mechanisms of alternative splicing in living organisms
ActiveUS20080095712A1Accurate detectionEfficient screeningDrug compositionsIn-vivo testing preparationsBiological bodyReporter gene
An object of the present invention is to develop a new alternative splicing reporter system and to provide a method for detecting alternative splicing patterns in a multicellular organism more precisely, a method for identifying efficiently substances and gene regions that affect alternative splicing in a multicellular organism, and the like by utilizing the alternative splicing reporter system. Specifically, the present invention relates to a method for detecting alternative splicing in a multicellular organism, and a method for identifying substances and gene regions that affect alternative splicing in a multicellular organism, which use a DNA construct in which at least two different reporter genes are inserted into a specific gene that undergoes alternative splicing, or a combination of DNA constructs (a combination of at least two different DNA constructs) in which DNA construct a reporter gene is inserted into a specific gene that undergoes alternative splicing.
Owner:KINOPHARMA
Capsules Containing Transiently Transfected Cells, Method for Preparing Same and Uses Thereof
The invention concerns a capsule containing cells that are transiently transfected with a gene of interest and entrapped within a biocompatible polymer membrane, a method of preparing those capsules, a method for in vivo assessing an activity of the protein secreted by the gene of interest, which comprises administering to a multicellular organism the capsule and detecting an activity, a pharmaceutical composition comprising such a capsule, and the use thereof for the administration of a protein of interest to a subject.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Compositions and methods for cell killing
A method of generating a change in a cellular process of a target cell is disclosed. The method comprises contacting the target cell with a solid buffer, so as to alter an intracellular pH value in at least a portion of the cell, thereby generating the change in a cellular process of a target cell of a multicellular organism. The method may be used to kill either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells. Pharmaceutical compositions and devices are also enclosed.
Owner:OPLON
Molecular control of transgene segregation and its escape by a recoverable block of function (RBF) system
InactiveUS6849776B1Avoid environmentAvoid separationSugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructMolecular motor
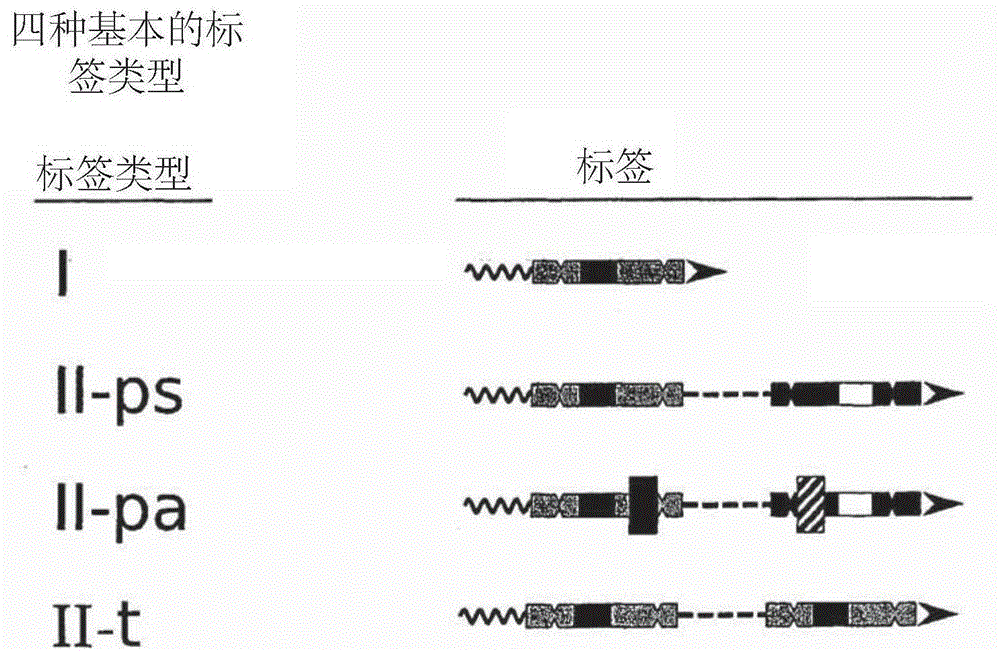
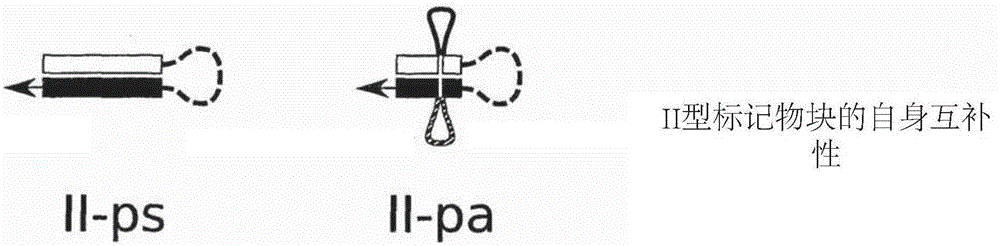
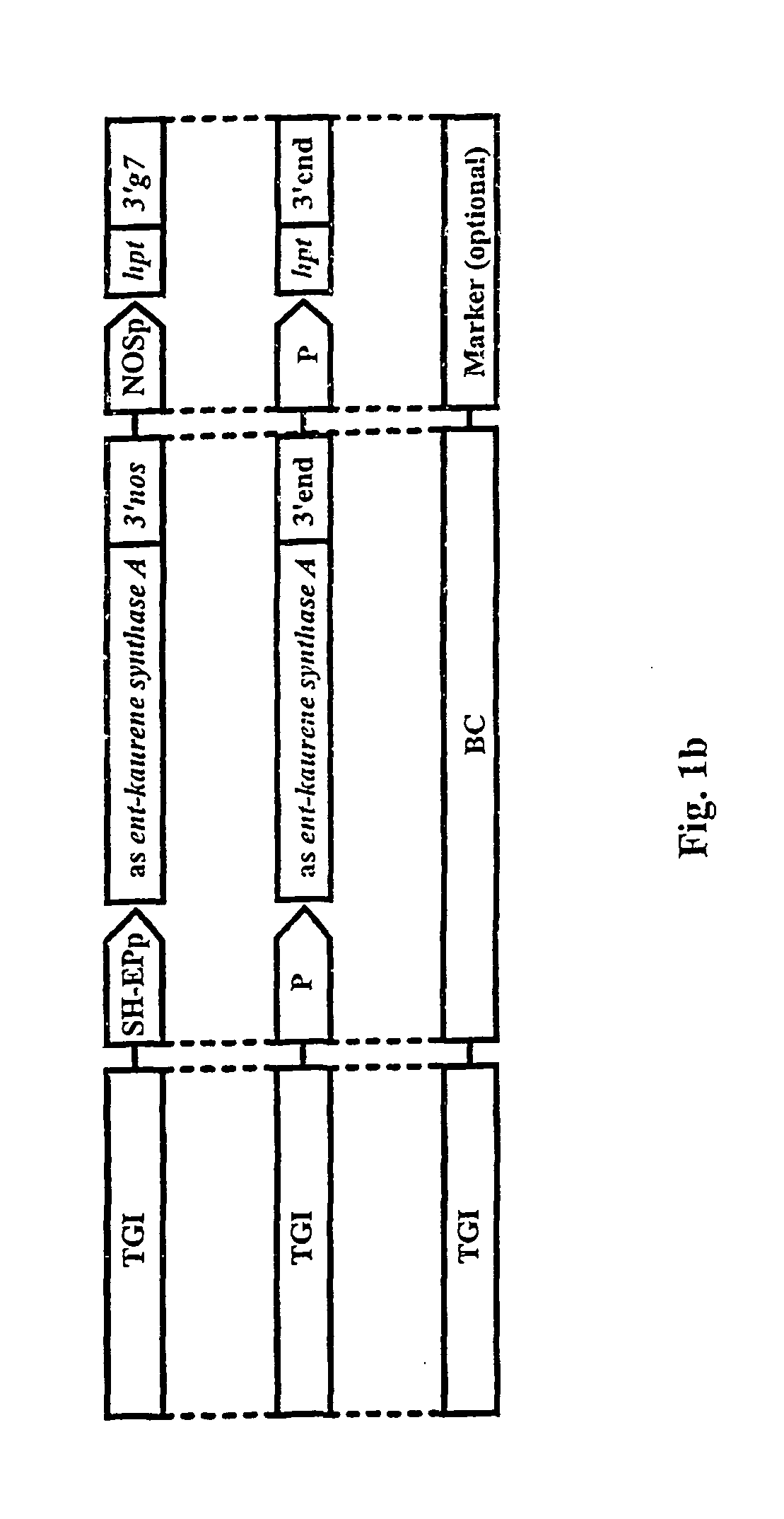
The invention is related to a method and a DNA construct for controlling transgene segregation in a sexually reproducing multicellular organism (SRMO), especially in such SRMOs which are susceptible of interbreeding with their cultured or wild-type relatives. The method and construct allows the farmer to reuse the transgenic crop without risk for escape of the transgene into the environment. The DNA construct is a recoverable block of function (RBF) system comprising at least one blocking construct (BC), and at least one means for recovering the blocked functions. The BC has a capacity of blocking at least one molecular or physiological function essential for the development and / or reproductive cycle of the SRMO. The BC is closely linked to the transgene of intereset (TGI). The blocked function is recoverable by an external treatment or intervention, which is optionally combined with one or more recovering constructs (RC). Different types of RBFs, including single, full, delayed, double, multiple and reversed delayed RBF are disclosed.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
High surface cultivation system with surface increasing substrate
InactiveCN101646762ATissue/virus culture apparatusSolid phase fermentation bioreactorsMulticellular organismCell organisation
The present invention is directed culture vessel suitable for cultivation of cells and / or tissues comprising at least one reversibly clo sable aperture in the vessel wall, and at least one surface-increasing substrate within the vessel, said substrate being made of a single mold. The invention further provides a system comprising at least two vessels being interconnected via at least one aperturein their vessel wall, and a cultivation process using such a vessel or system, in which at least one type of cells, tissue, tissue-like cell cultures, organs, organ- like cell cultures, or multicellular organisms are cultivated in the presence of at least one fluid or solid medium necessary for growing and / or cultivating the aforesaid culture.
Owner:CINVENTION AG
Methods and compositions for use in homologous recombination
Methods for homologously recombining an exogenous nucleic acid into a target cell genome of a multicellular organism, e.g., an animal, are provided. In the subject methods, a targeting vector that includes a linearizing endonuclease site, e.g., a recombinase recognition site, and a homologous recombination integrating element, is contacted with the multicellular organism, e.g., via systemic or local administration, such that the target cell(s) of the multicellular organism takes up the targeting vector. The targeting vector is one that has been linearized by a linearizing endonuclease, e.g., a recombinase, at some point prior to the homologous recombination event, e.g., prior to or after contact with the multicellular organism. Following uptake by the target cell(s), the integrating element then homologously recombines into the target cell genome from the linearized targeting vector. Also provided are targeting vectors, systems and kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:TOSK INC
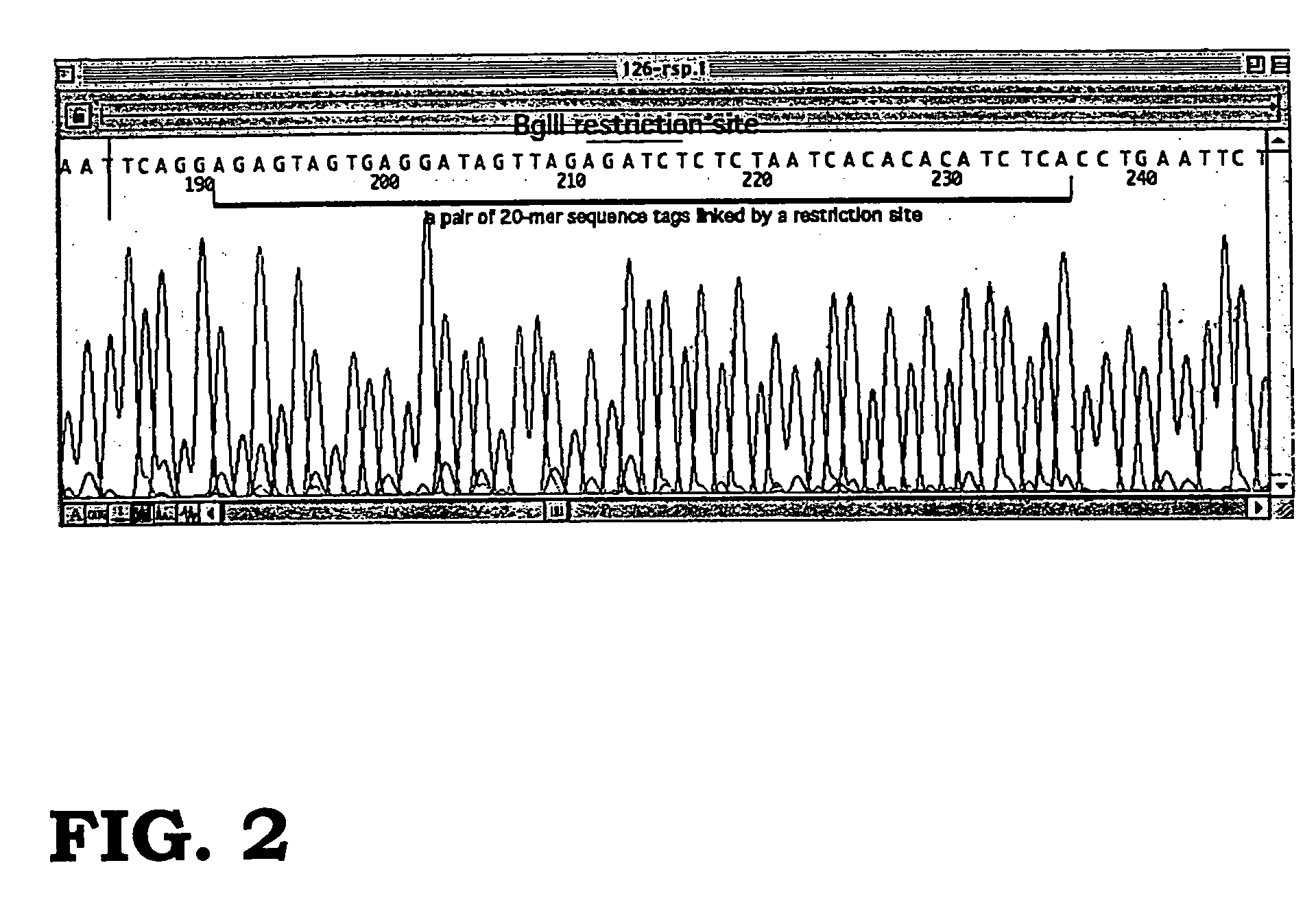
Methods of sequencing nucleic acids in mixtures and compositions related thereto
This disclosure relates to analyzing the end-to-end sequence and the relative distributions in heterogeneous mixtures of polynucleotides and methods and enabling reagents related thereto. In certain embodiments this method relates to the complete full length sequencing and quantitative profiling of mRNAs present in the transcriptomes of cells or tissues of, but not limited to, higher multicellular organisms that possess interrupted genes subject to complex post-transcriptional RNA processing.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Molecular control of transgene segregation and its escape by a recoverable block of funtion (rbf) system
InactiveUS20040025200A1Leak to environmentInhibition of segregationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructWild type
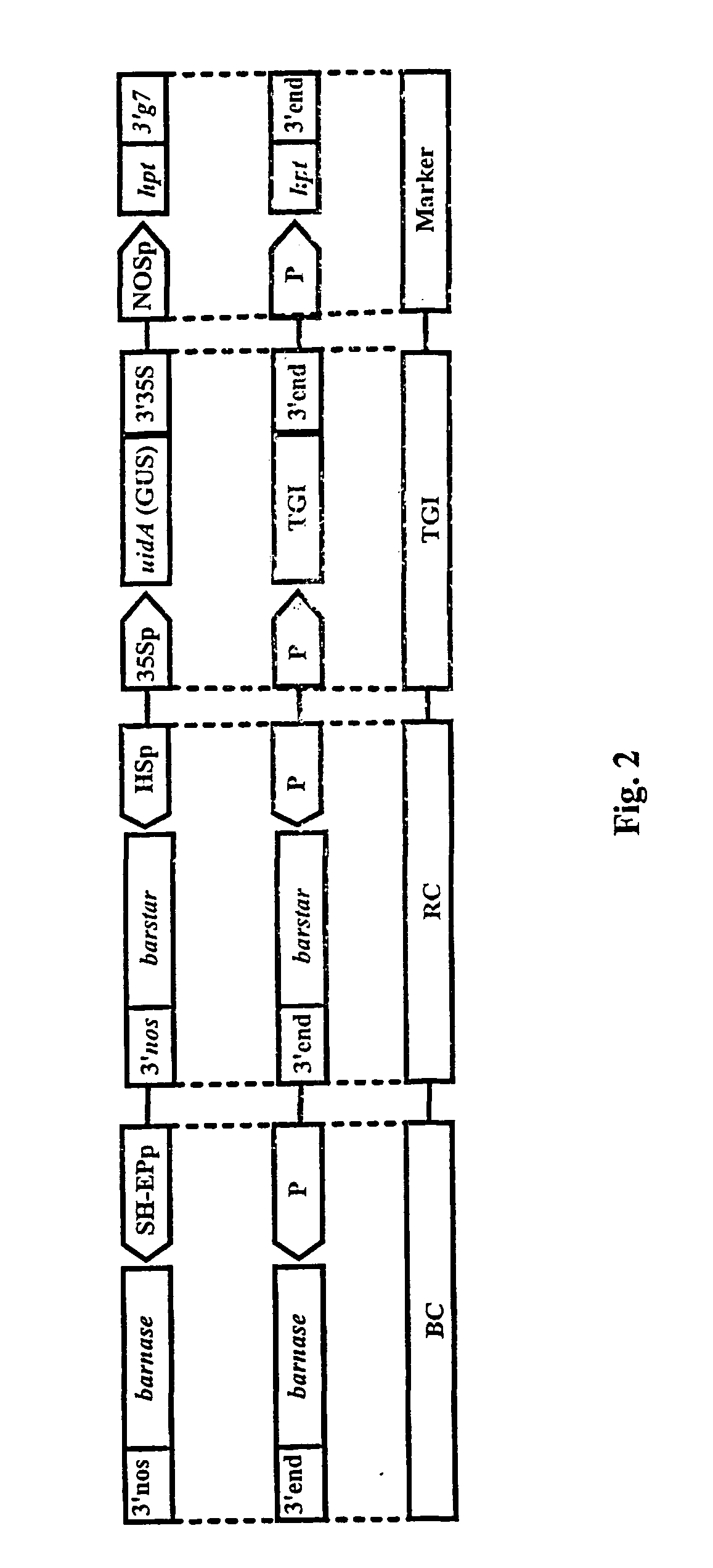
The invention is related to a method and a complex of DNA constructs for providing an increased level of control of transgene segregation in Sexually Reproducing Multicellular Organisms (SRMOs), which are prone to out-crossing with their wild-type or cultivated relatives. The method and constructs allow the farmer to reuse the transgenic crop. without risk. The RBF system comprises one or more Transgenes of Interest (TGIs) encoding desired gene products, one or more Blocking Constructs (BC), and one or more user-controlled means for recovering the blocked functions. The BC has the capacity of blocking at least one function essential for the survival and / or reproduction of the SRMO. Preferably more than one BC flanking the TGIs are used. The BC may be located in close proximity to the TGI, preferably in an intron or flanking the TGIs. The blocked function is recoverable by user-controlled interventions preferably applicable under confined conditions. The intervention is combined with one or more Recovering Constructs (RC). Different types of RBF systems are disclosed. The Double and Triple and Segregating RBF systems and intron-inserted BC are the preferred embodiments of the present invention. The Transgenic Inserts (TI) of the Triple RBF system and their interactions are shown in FIG. 10.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
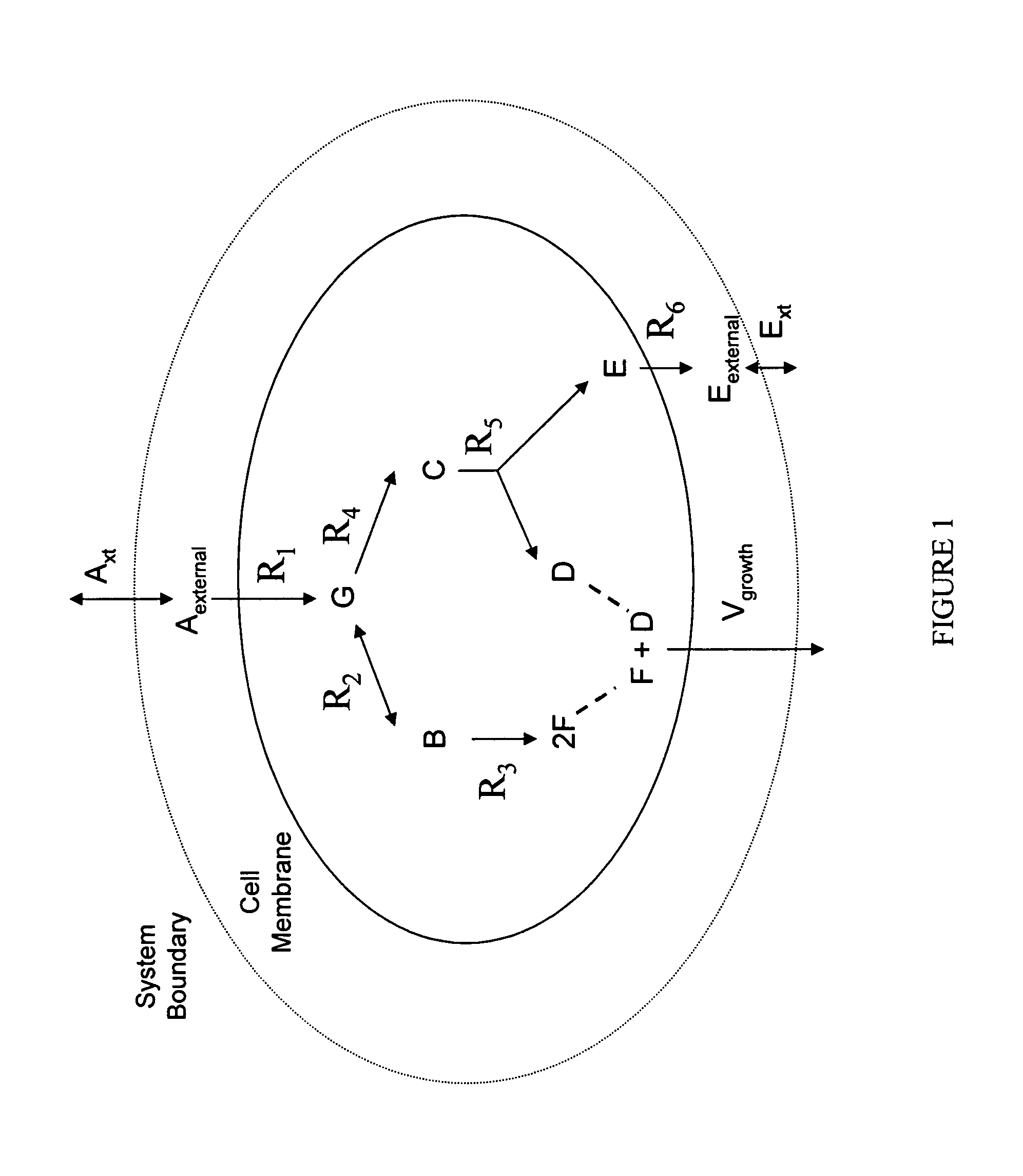
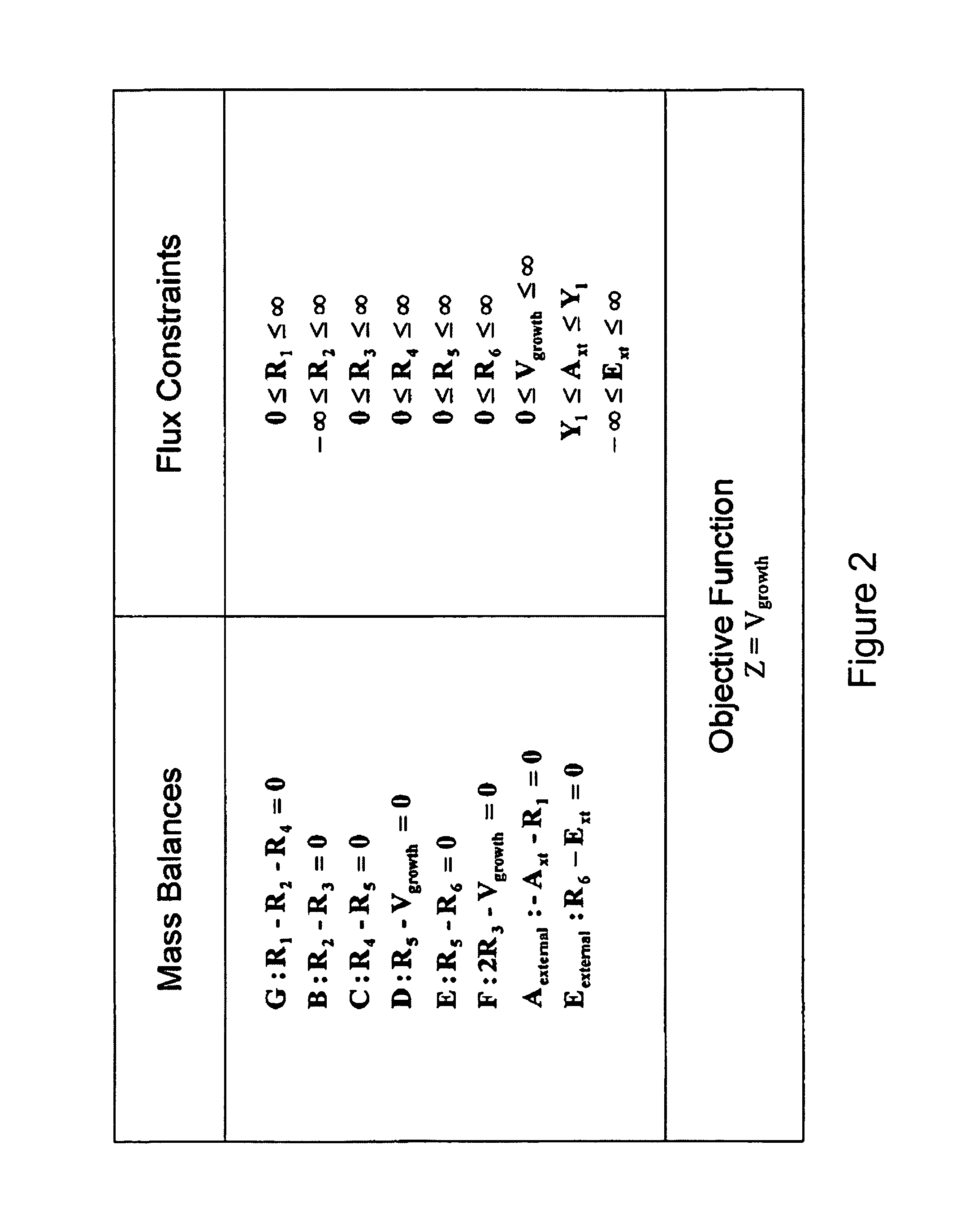
Multicellular metabolic models and methods
ActiveUS8949032B2Chemical property predictionCompound screeningMulticellular organismMetabolic Model
The invention provides a computer readable medium or media, having: (a) a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures, and (e) commands for determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells. The first, second and third data structures also can include a plurality of data structures. Additionally provided is a method for predicting a physiological function of a multicellular organism. The method includes: (a) providing a first data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a first cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (b) providing a second data structure relating a plurality of reactants to a plurality of reactions from a second cell, each of said reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (c) providing a third data structure relating a plurality of intra-system reactants to a plurality of intra-system reactions between said first and second cells, each of said intra-system reactions comprising a reactant identified as a substrate of the reaction, a reactant identified as a product of the reaction and a stoichiometric coefficient relating said substrate and said product; (d) providing a constraint set for said plurality of reactions for said first, second and third data structures; (e) providing an objective function, and (f) determining at least one flux distribution that minimizes or maximizes an objective function when said constraint set is applied to said first and second data structures, wherein said at least one flux distribution is predictive of a physiological function of said first and second cells.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Methods for Purifying Polysaccharides and Pharmaceutical Compositions and Medical Devices Containing the Same
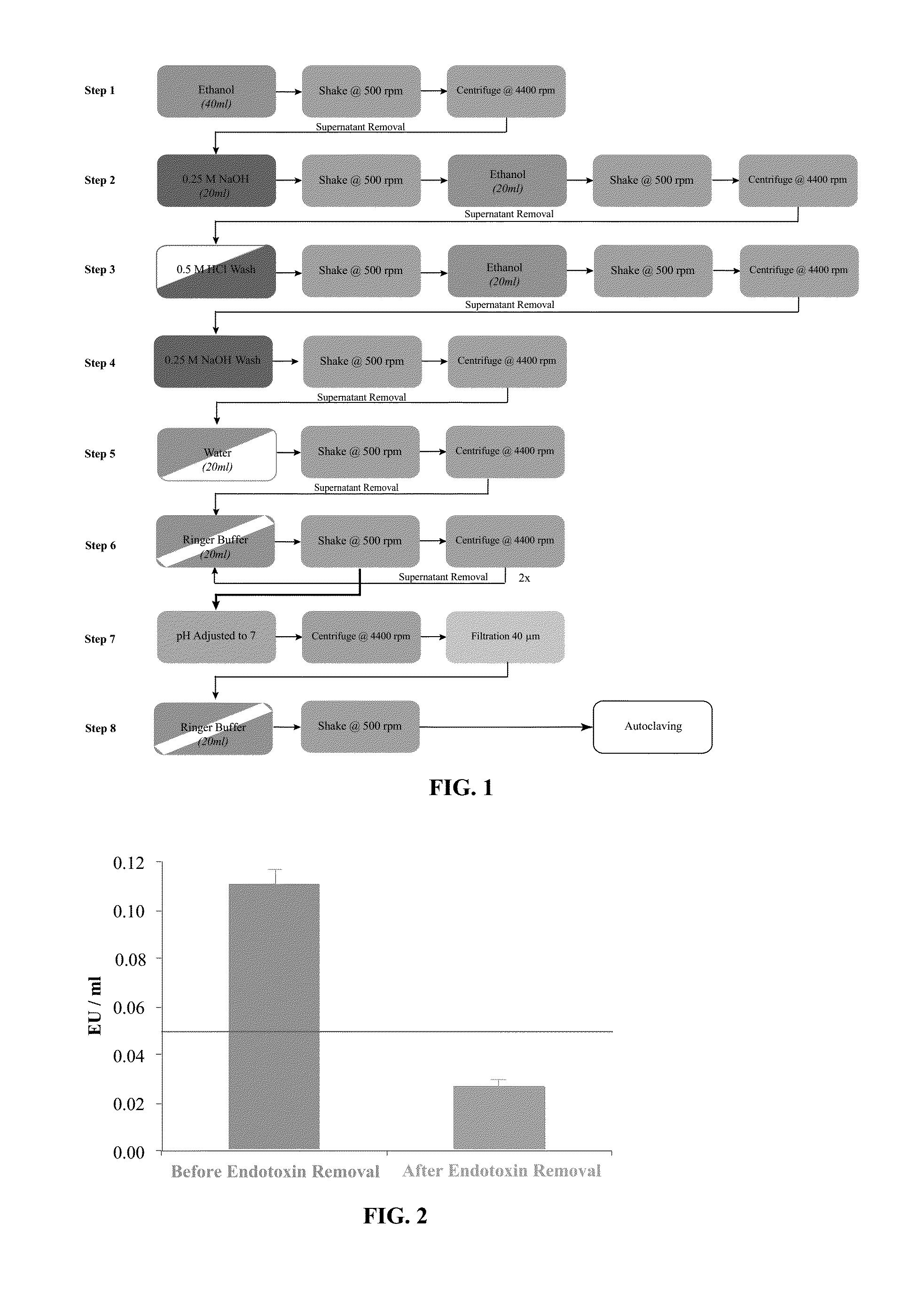
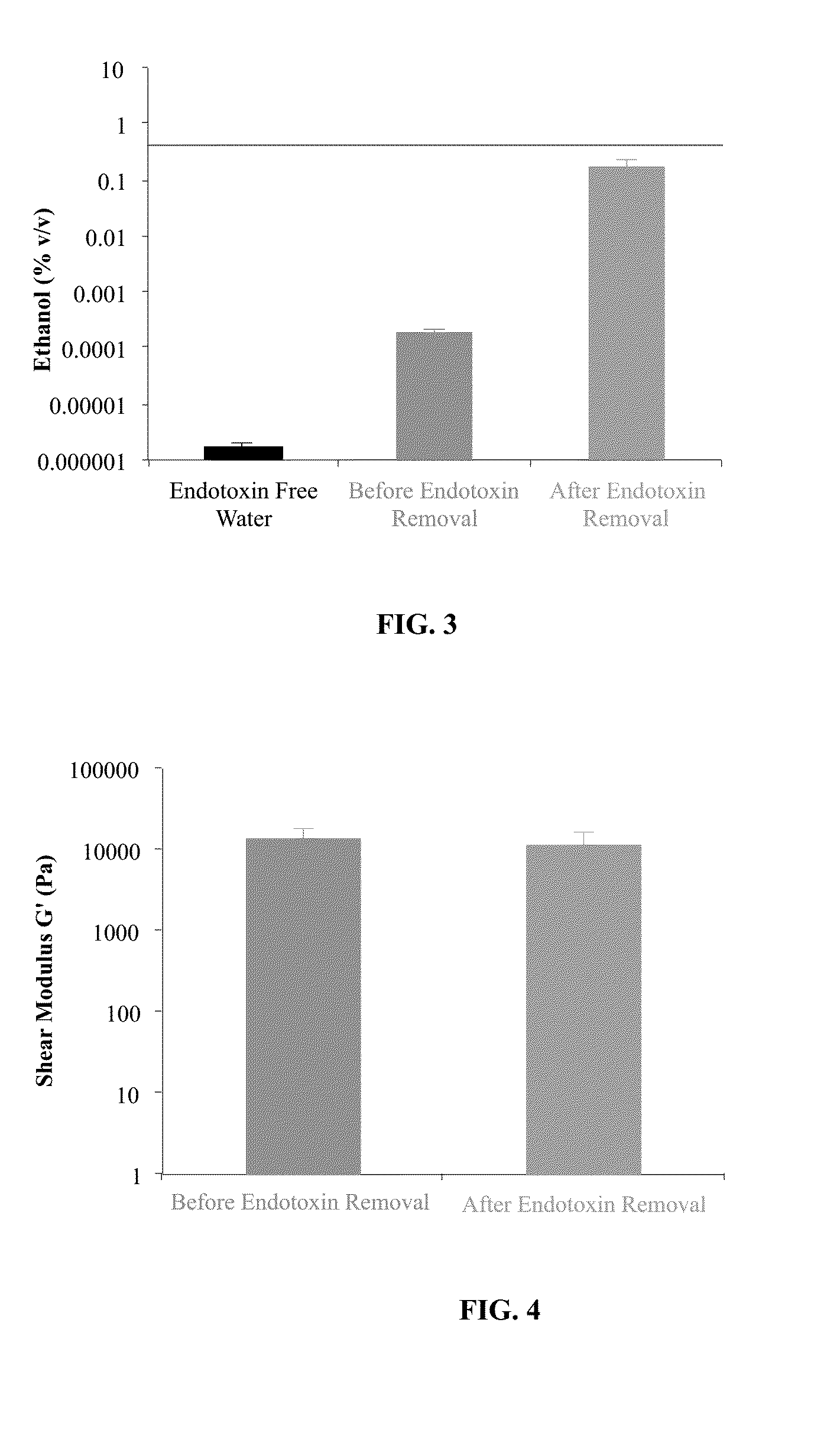
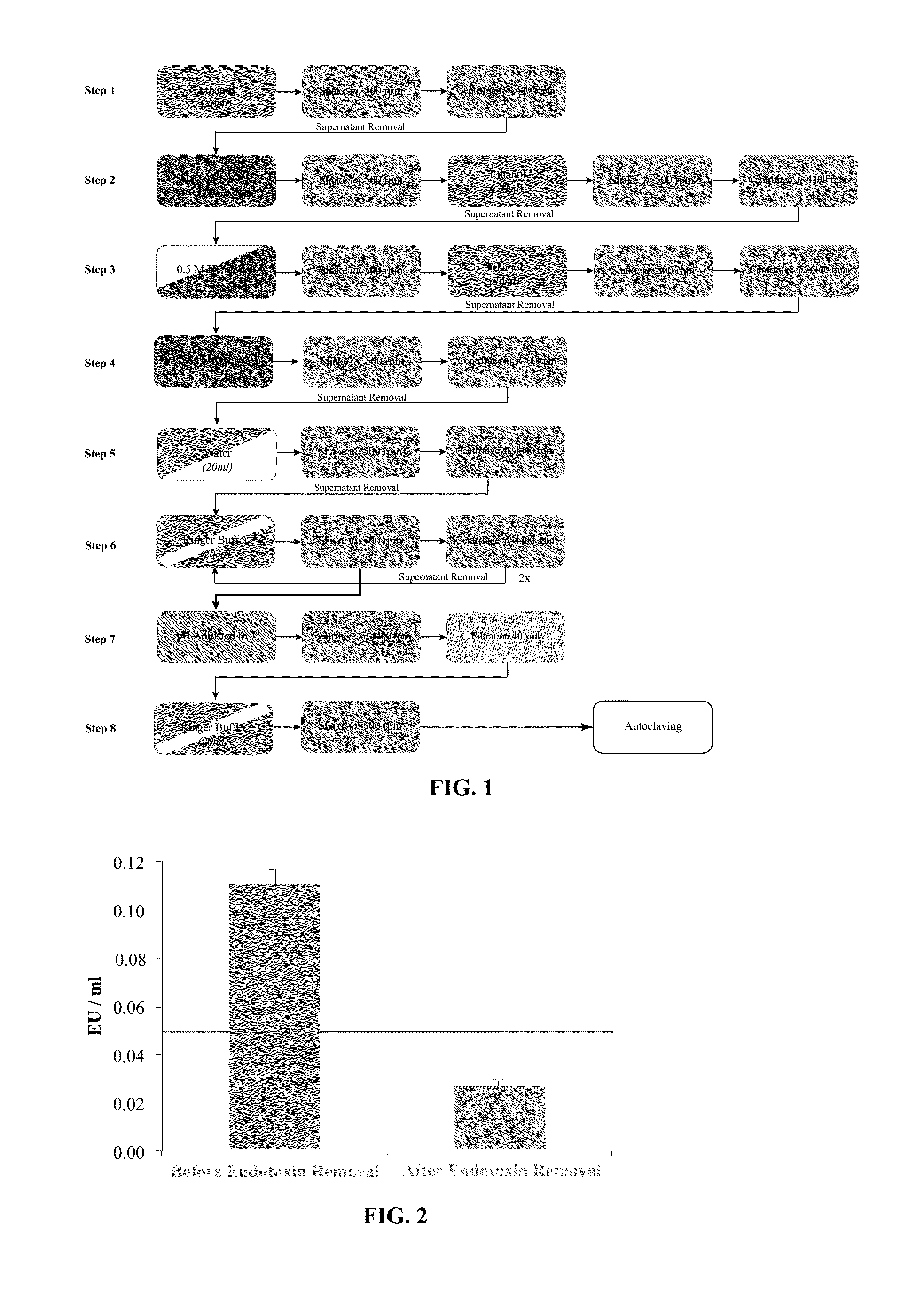
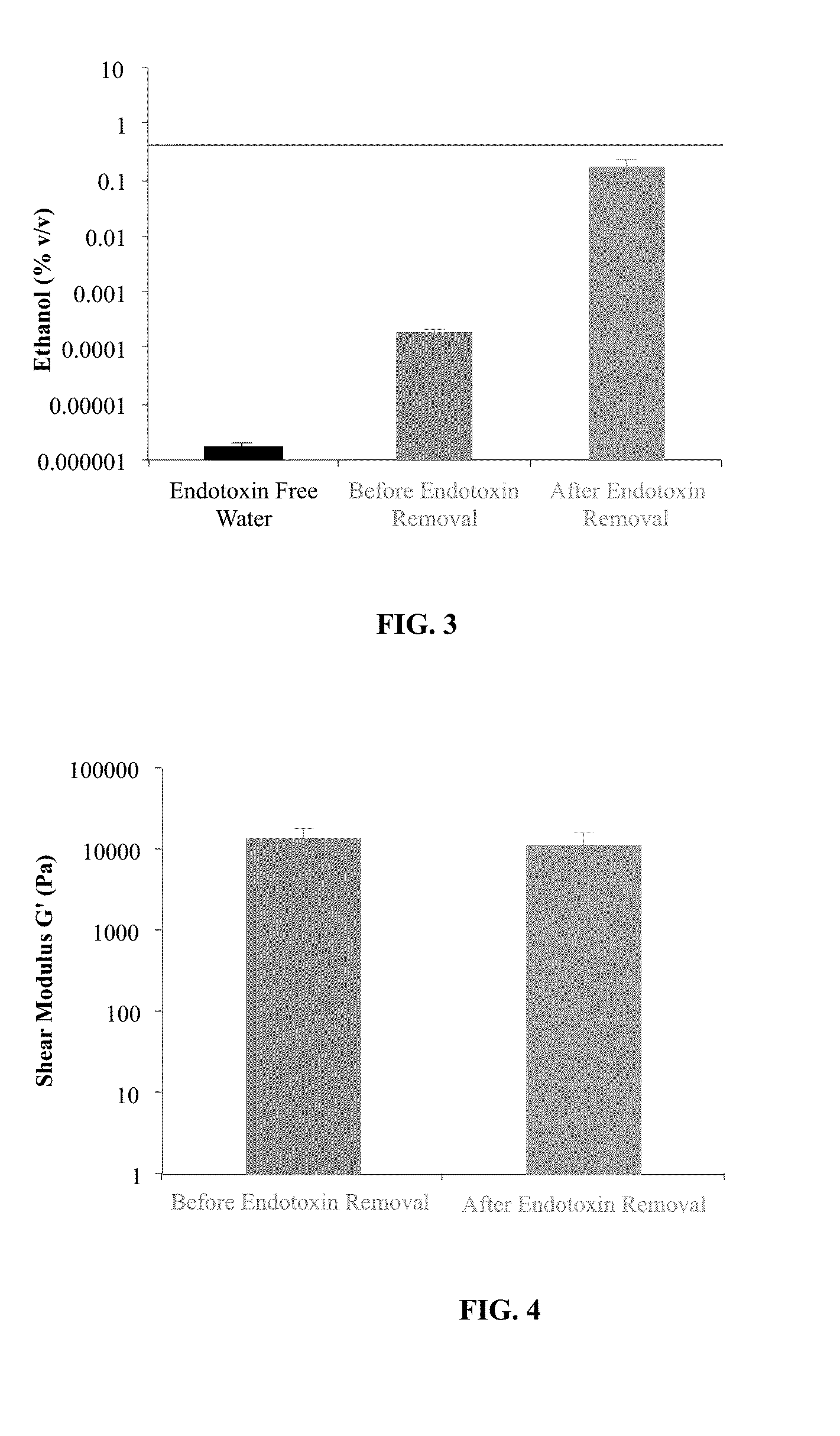
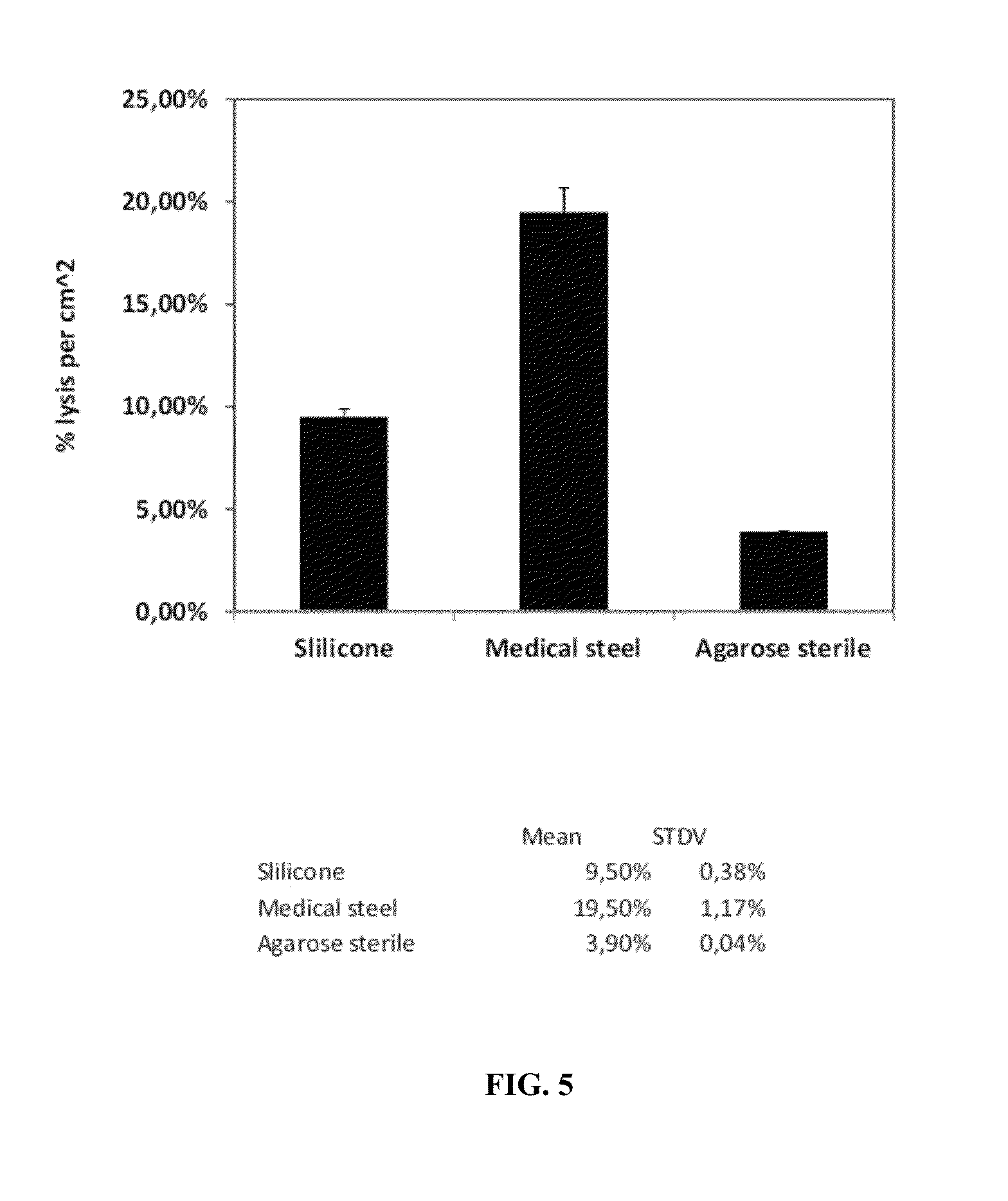
Methods for removing endotoxin from naturally occurring materials, such as polysaccharides (e.g., agarose and / or carrageenan) are described herein. Polysaccharides that are substantially free of endotoxins and uses thereof are also described. The polysaccharide materials can be isolated from microorganisms, multicellular organisms, such as, algae, plants, seaweed, etc. The method involves the use of acidic and basic solutions to hydrolyze the lipid-polysaccharide bond in endotoxins. Cleaving the fatty acid from the polysaccharide reduces the water-solubility of the fatty acid and enables its removal with an organic solvent such as ethanol. The polysaccharide component can also undergo acidic or basic hydrolysis due to the weak glycosidic bond between the sugar rings.
Owner:MAPTECH HLDG UG
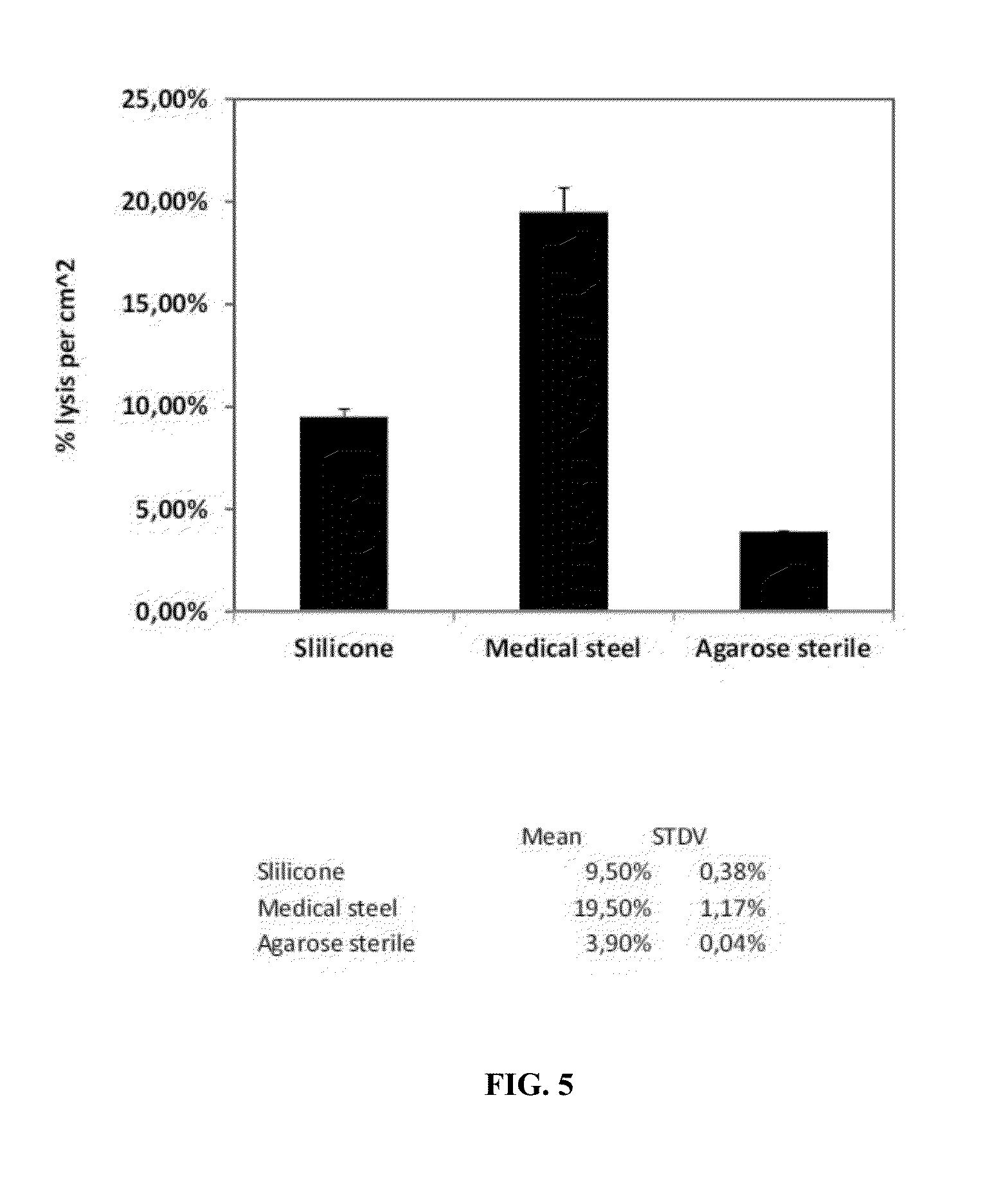
Deep-sea multicellular organism pressure-maintaining capture and long-term culture device
ActiveCN114081010ASimple structureSimple and fast operationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaInterference fitDeep sea creature
The invention relates to a deep-sea organism capturing and culturing technology, and aims to provide a deep-sea multicellular organism pressure-maintaining capturing and long-term culture device. The two ends of a pressure maintaining cavity of the device are open, and movable end covers are arranged on the inner side for sealing; a spring sleeve mechanism is arranged in the pressure maintaining cavity in parallel, an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve are in coaxial interference fit, and the two ends of a spring are fixed to a movable end cover. The outer side of the movable end cover is connected with a damping release mechanism; the pressure maintaining cavity is further connected with an energy accumulator system, a fresh seawater conveying system and a food feeding system. By adopting a sealed triggering structure, the structure of the biological pressure-maintaining sampling equipment is simplified, the weight is reduced, and the operation is simple and convenient. The two ends of the pressure maintaining cabin are sealed by the movable end covers, and the movable end covers are powered by the spring sleeves, so that the design of a motor, an oil cylinder and a transmission structure which are possibly added is omitted, the overall structure is simplified, and the cost is saved. The matched culture system can provide seawater circulation renewal, oxygen supply and physical nutrition supply for multicellular organisms.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for purifying polysaccharides and pharmaceutical compositions and medical devices containing the same
Methods for removing endotoxin from naturally occurring materials, such as polysaccharides (e.g., agarose and / or carrageenan) are described herein. Polysaccharides that are substantially free of endotoxins and uses thereof are also described. The polysaccharide materials can be isolated from microorganisms, multicellular organisms, such as, algae, plants, seaweed, etc. The method involves the use of acidic and basic solutions to hydrolyze the lipid-polysaccharide bond in endotoxins. Cleaving the fatty acid from the polysaccharide reduces the water-solubility of the fatty acid and enables its removal with an organic solvent such as ethanol. The polysaccharide component can also undergo acidic or basic hydrolysis due to the weak glycosidic bond between the sugar rings.
Owner:MAPTECH HLDG UG
Methods of preparing compositions comprising chemicals capable of transcriptional modulators
InactiveUS6589733B1Effect is affectedOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMulticellular organismADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides a method of transcriptionally modulating the expression of a gene of interest, the expression of which is associated with a defined physiological or pathological effect within a multicellular organism. The method comprises contacting a cell which is capable of expressing the gene with an amount of a molecule effective to transcriptionally modulate expression of the gene and thereby affect the level of the protein encoded by the gene which is expressed by the cell. Molecules useful in the practice of the invention are characterized as follows (a) do not naturally occur in the cell, (b) specifically transcriptionally modulate expression of the gene of interest, and (c) bind to DNA or RNA or bind to a protein through a domain of such protein which is not a ligand binding domain of a receptor which naturally occurs in the cell, the binding of a ligand to which ligand binding domain is normally associated with the defined physiological or pathological effect.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
Novel compounds with dual activity
PendingUS20180296727A1Promote and encourage adherencePreventing antifoulingDental implantsAntifouling/underwater paintsUnicellular organismMulticellular organism
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Composition and methods for cell killing
A method of generating a change in a cellular process of a target cell is disclosed. The method comprises contacting the target cell with a solid buffer, so as to alter an intracellular pH value in at least a portion of the cell, thereby generating the change in a cellular process of a target cell of a multicellular organism. The method may be used to kill either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells. Pharmaceutical compositions and devices are also enclosed.
Owner:OPLON
MGAL: A GAL Gene Switch-Based Suite of Methods for Protein Analyses and Protein Expression in Multicellular Organisms and Cells Therefrom
InactiveUS20080249045A1Reduce the amount requiredInduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsAgonistRegulator gene
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Transgenic reporter system that reveals expression profiles and regulation mechanisms of alternative splicing in nematodes
InactiveUS7928283B2Accurate detectionEfficient screeningDrug compositionsIn-vivo testing preparationsBiological bodyDNA construct
Owner:KINOPHARMA
MicroRNAome
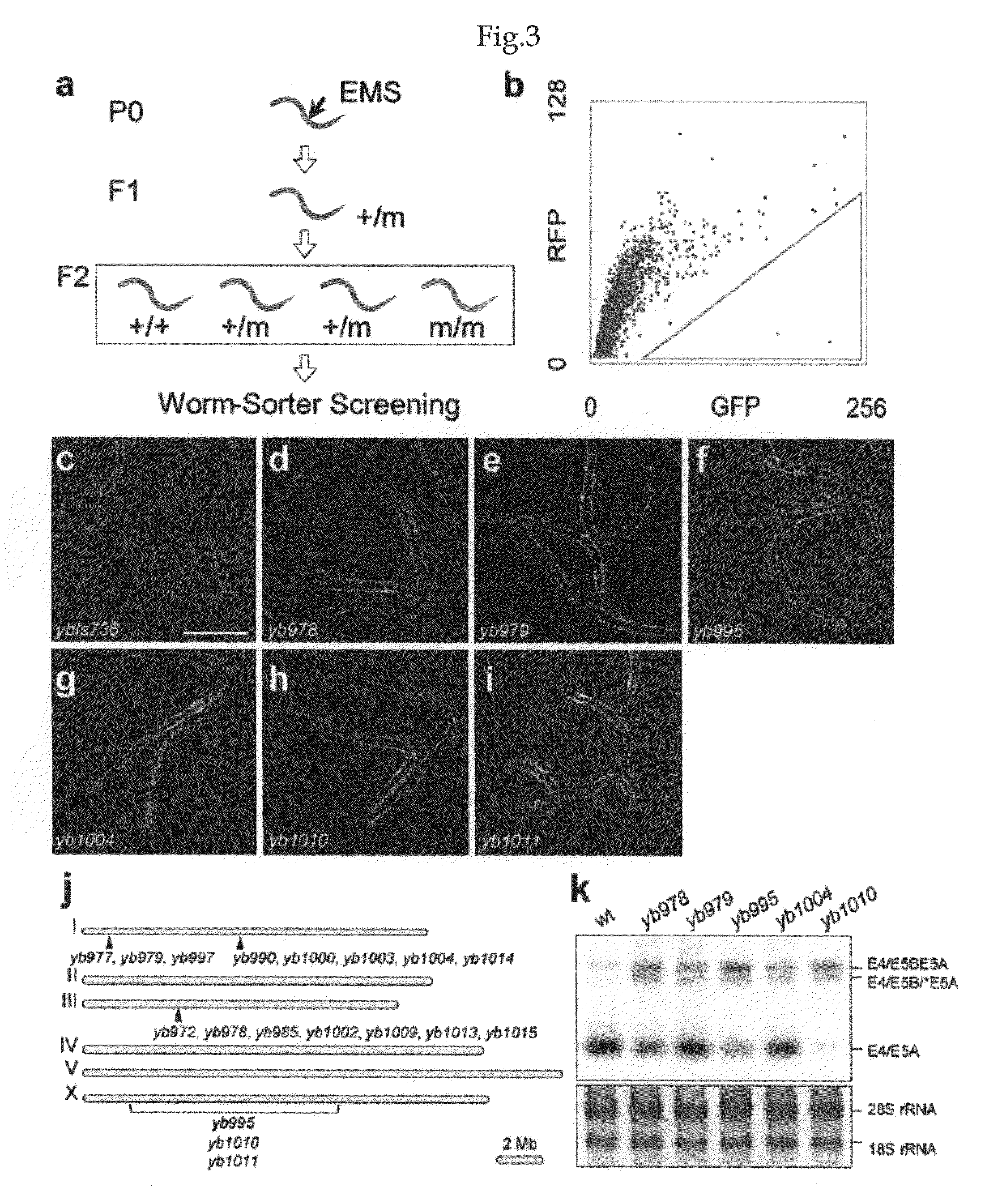
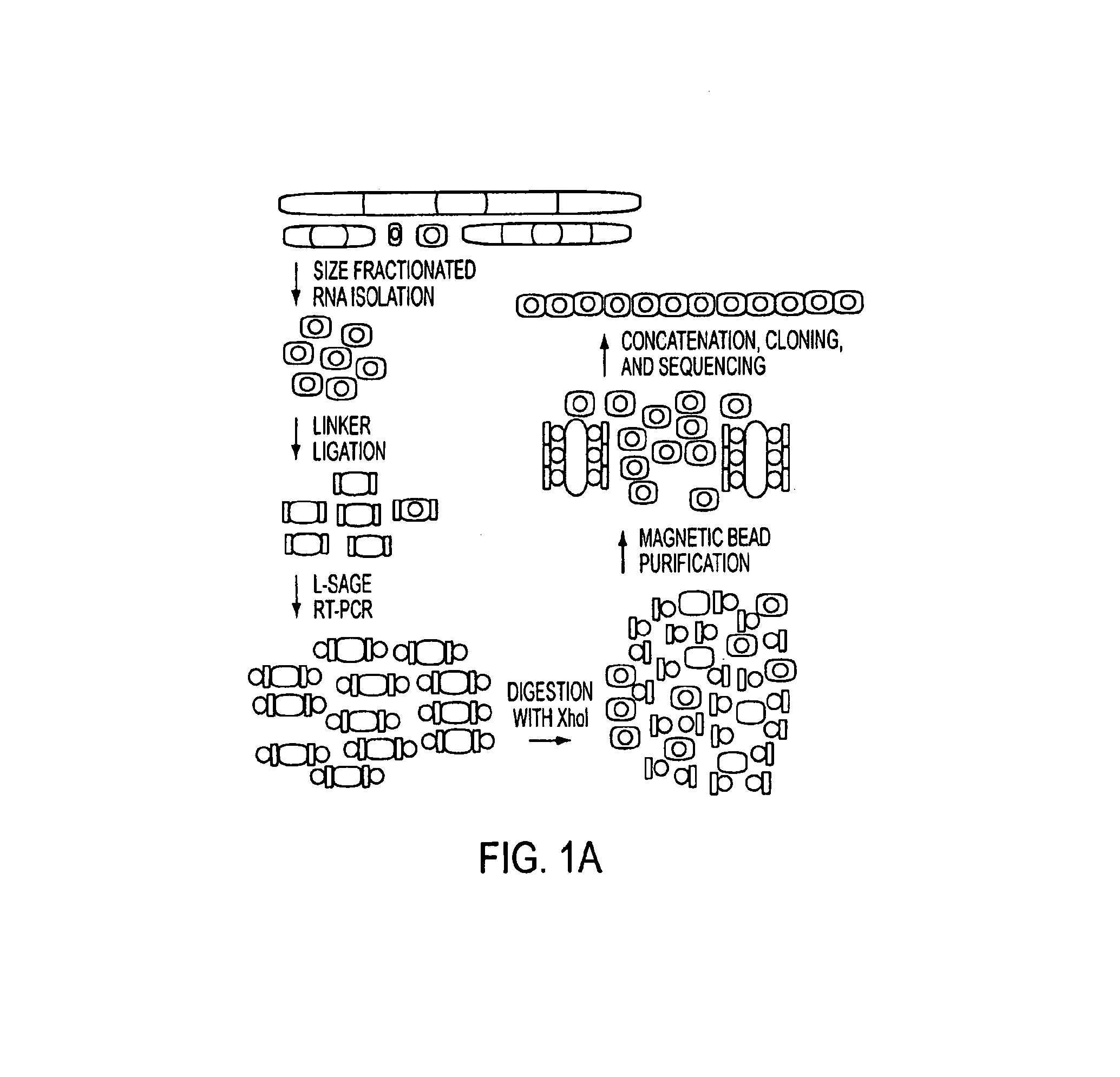
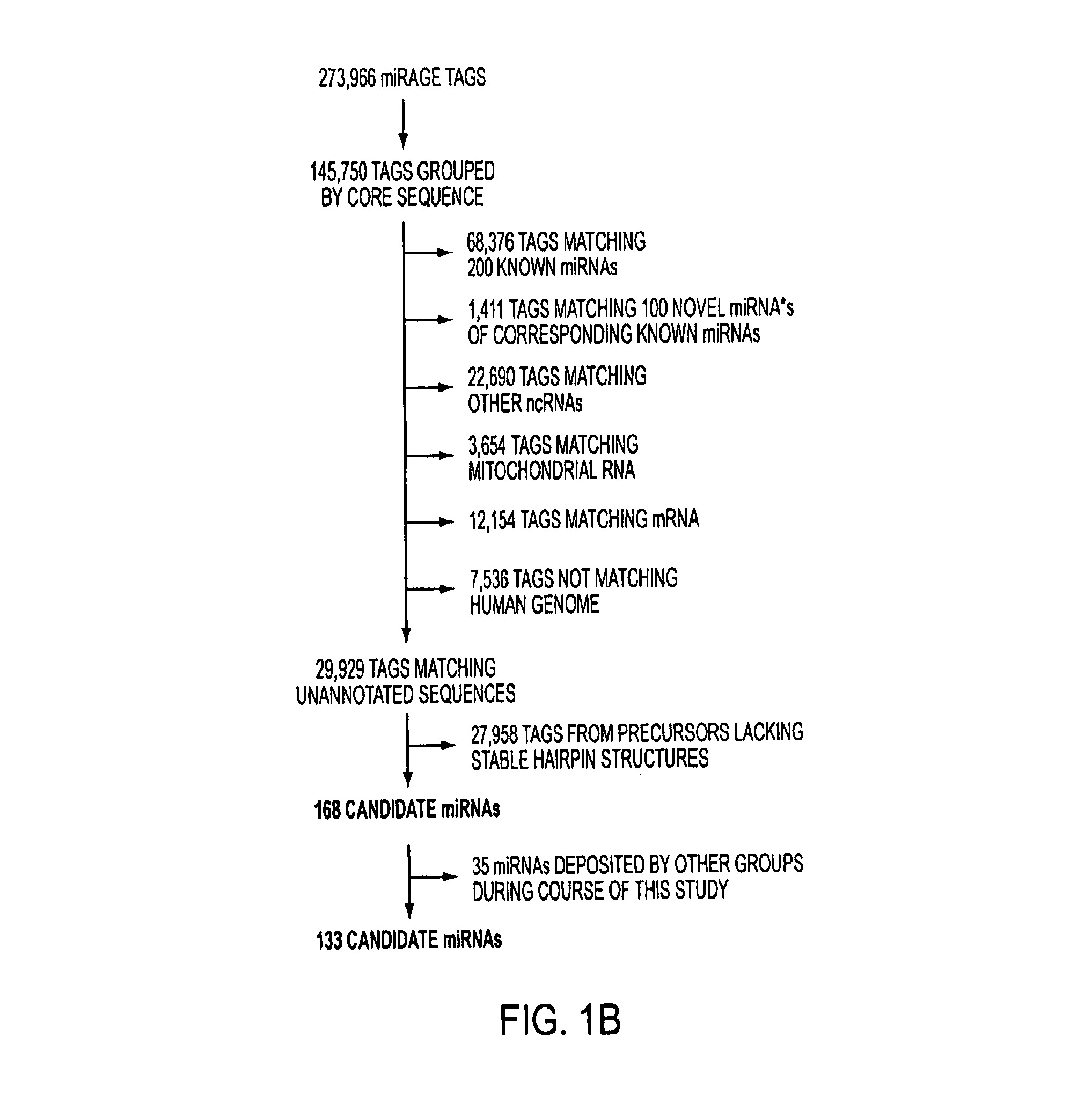
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small noncoding RNAs that have important regulatory roles in multicellular organisms. The public miRNA database contains 321 human miRNA sequences, 234 of which have been experimentally verified. To explore the possibility that additional miRNAs are present in the human genome, we have developed an experimental approach called miRNA serial analysis of gene expression (miRAGE) and used it to perform the largest experimental analysis of human miRNAs to date. Sequence analysis of 273,966 small RNA tags from human colorectal cells allowed us to identify 200 known mature miRNAs, 133 novel miRNA candidates, and 112 previously uncharacterized miRNA* forms. To aid in the evaluation of candidate miRNAs, we disrupted the Dicer locus in three human colorectal cancer cell lines and examined known and novel miRNAs in these cells. The miRNAs are useful to diagnose and treat cancers.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Insecticidal and Nematicidal Compositions and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20080188564A1Inhibit growthInhibition of reproductionBiocideMaterial thermal conductivityNematodeToxicology
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Covalently binding imaging probes
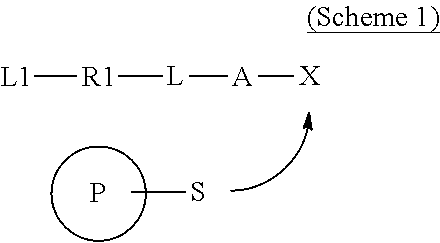
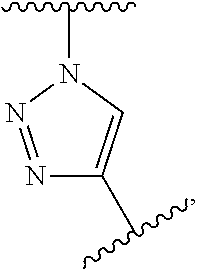
The present invention relates to molecular probes of the formula (I)L1-R1-L-A-X (I)as defined herein that allow for the observation of the catalytic activity of a selected caspase, cathepsin, MMP and carboxypeptidase in in vitro assays, in cells or in multicellular organisms, a method for their preparation and the use thereof.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Caspase imaging probes
InactiveUS20100303728A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsMulticellular organismCaspase
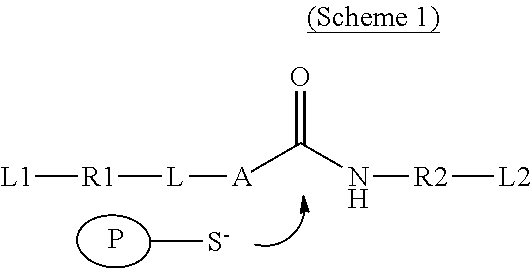
The present invention relates to molecular probes of formula (I){L1-R1-L}n-A-CO—NH—R2-L2 (I)as defined herein that allow for the observation of the catalytic activity of a selected caspase in in vitro assays, in cells or in multicellular organisms, a method for their preparation and the use thereof.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com