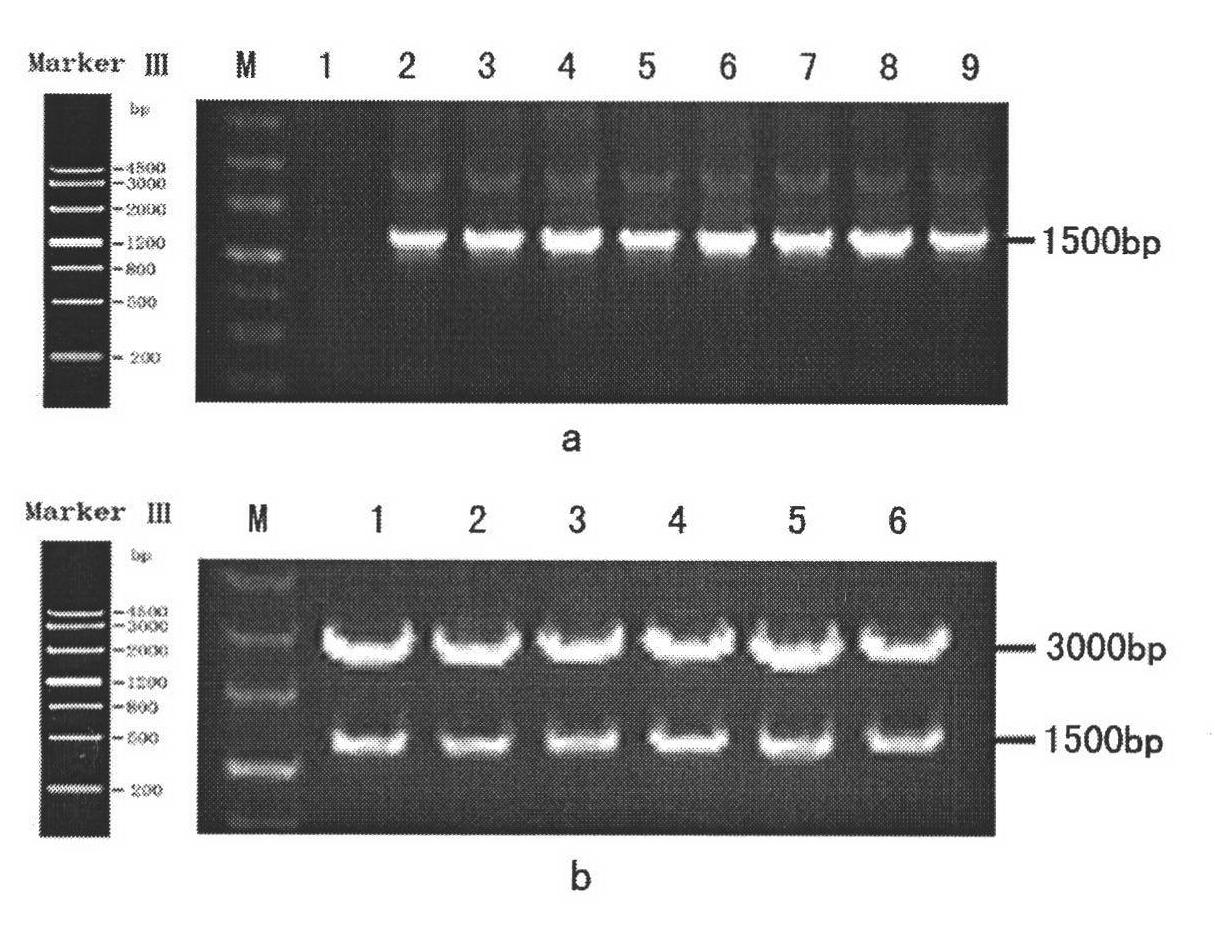
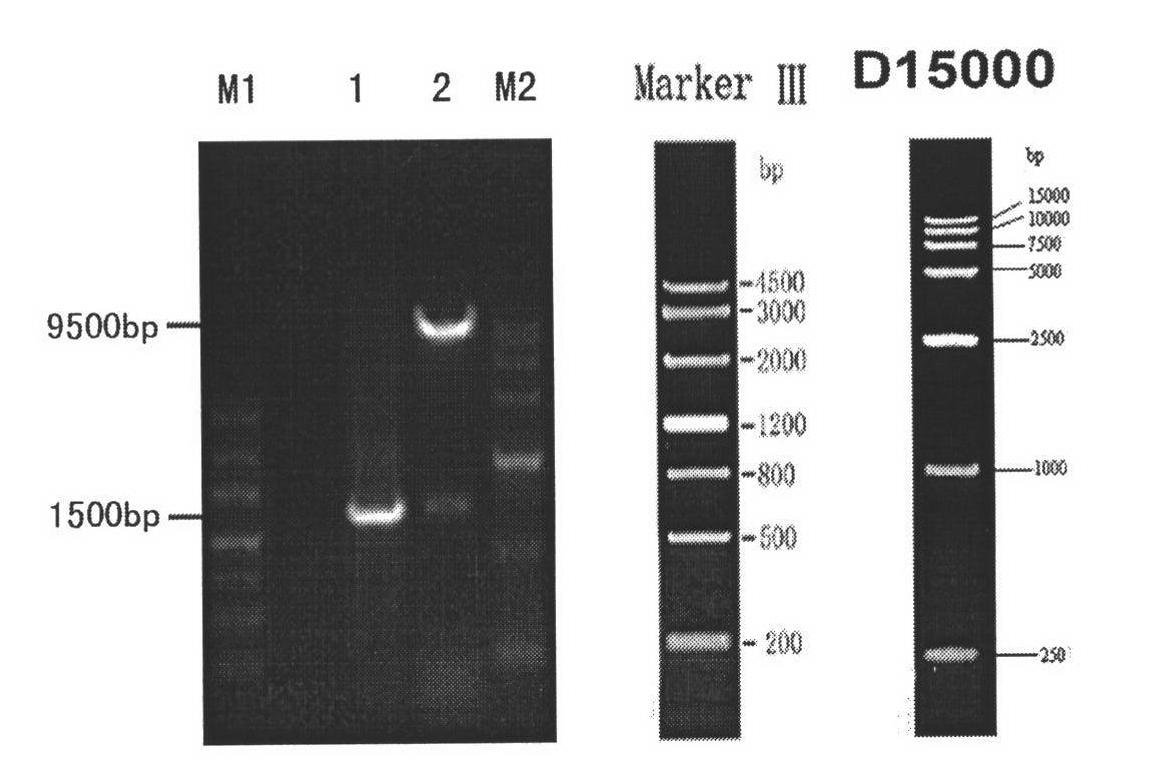
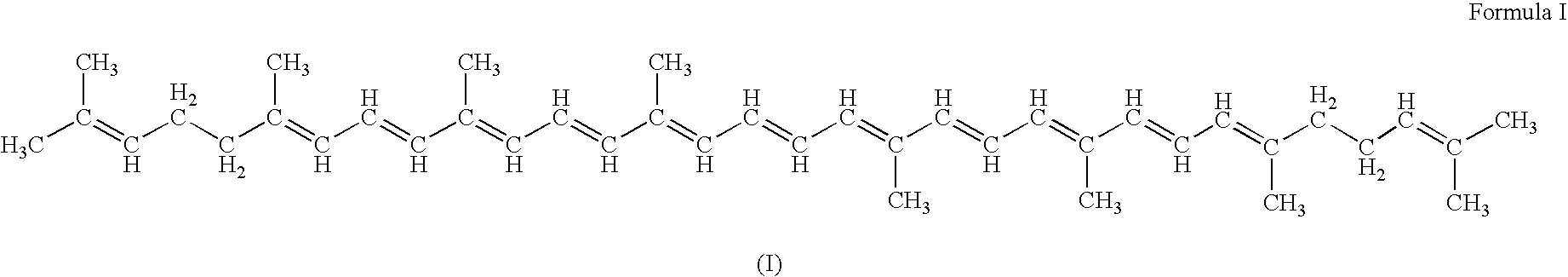
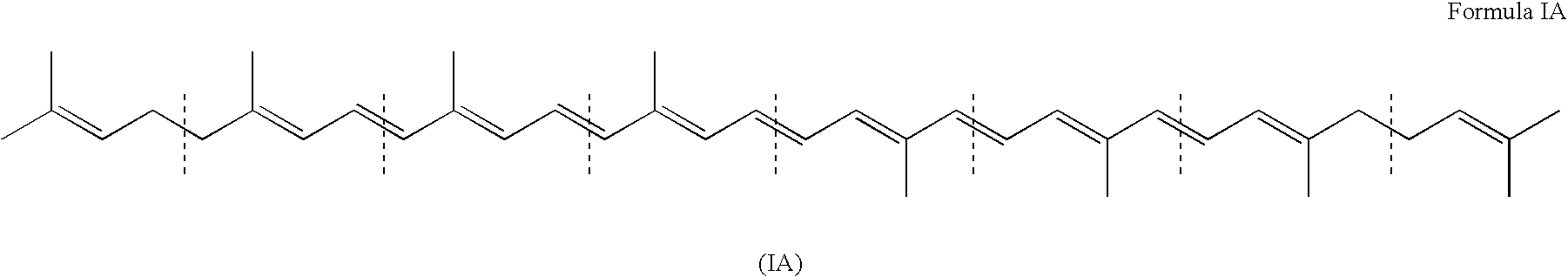
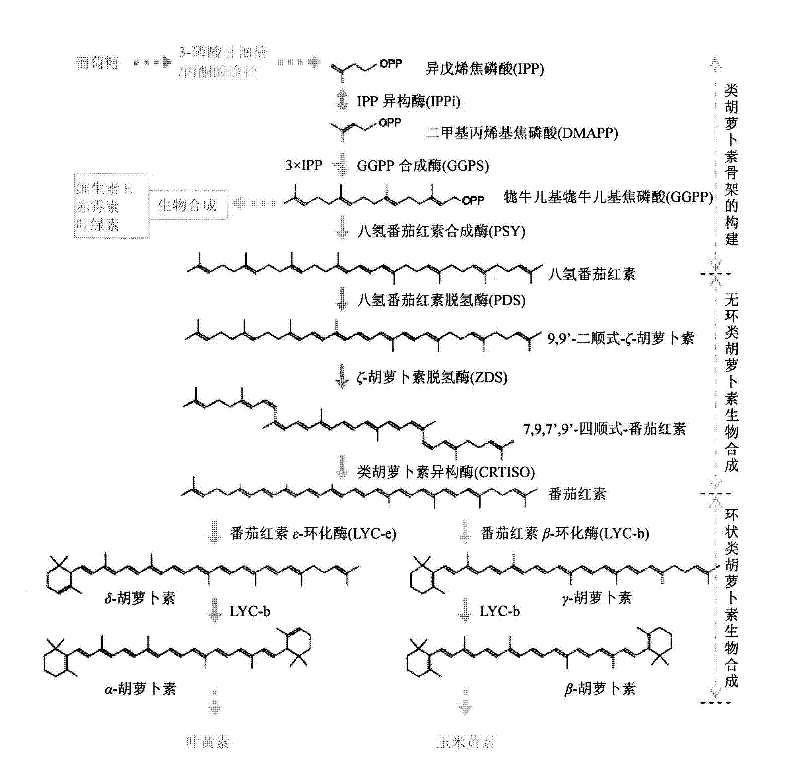
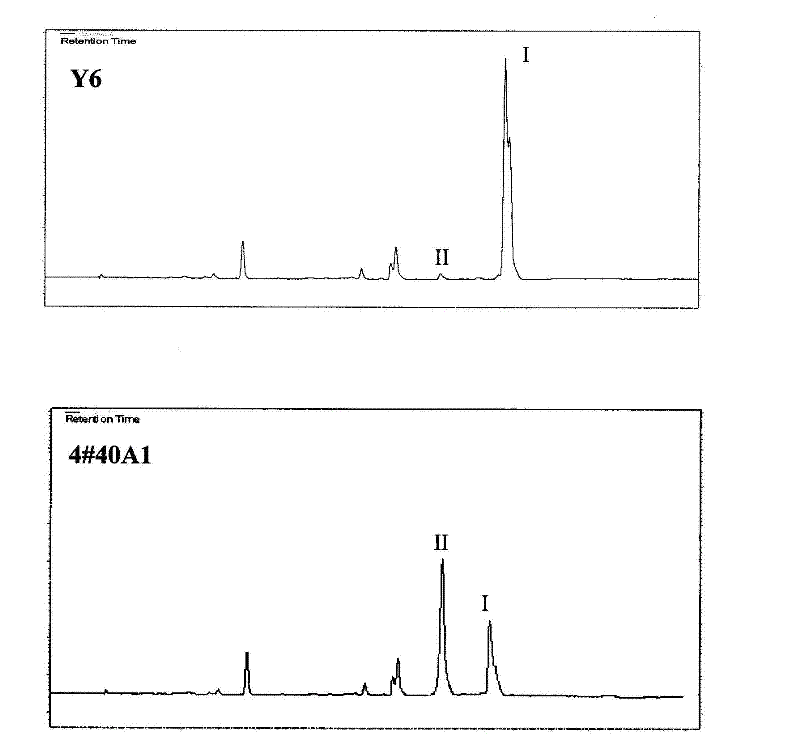
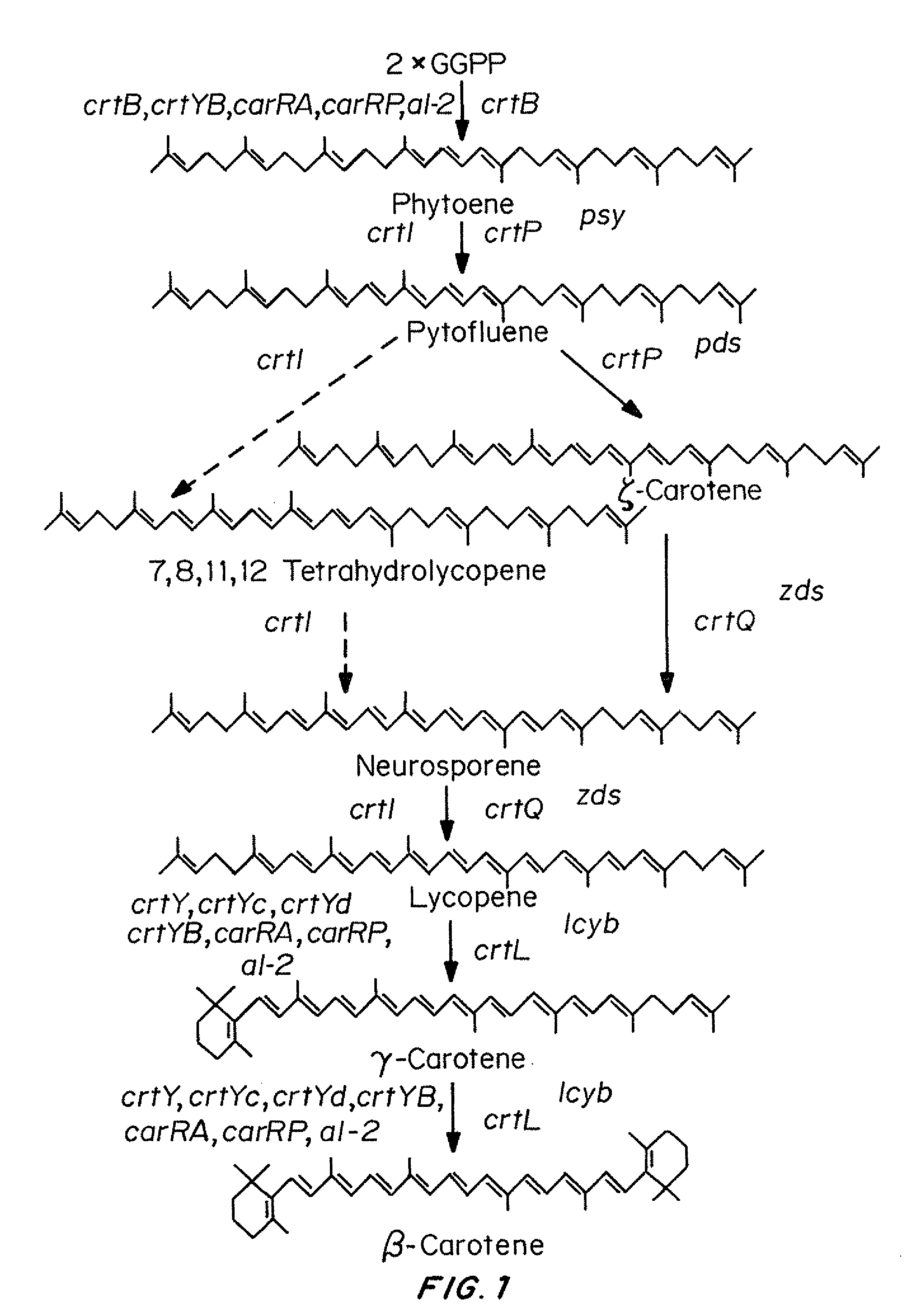
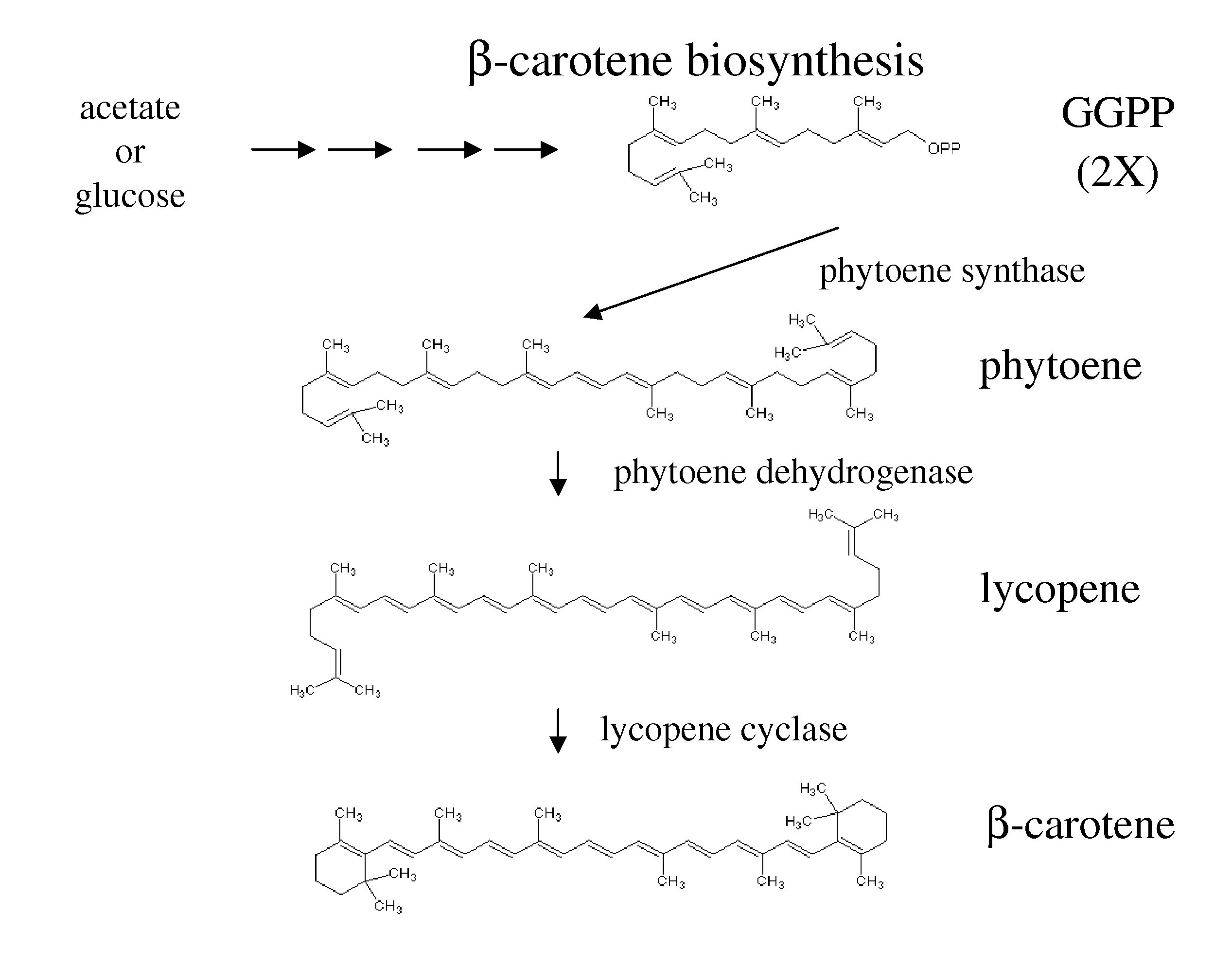Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Lycopene cyclase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
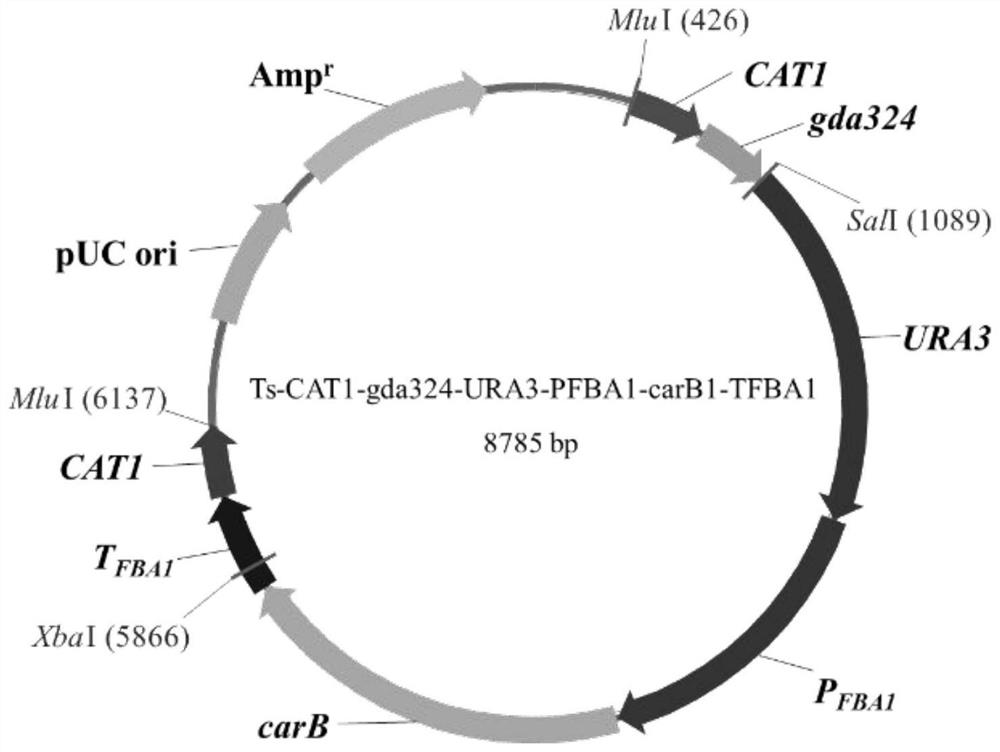
Recombinant yeast strain, and construction method and application thereof
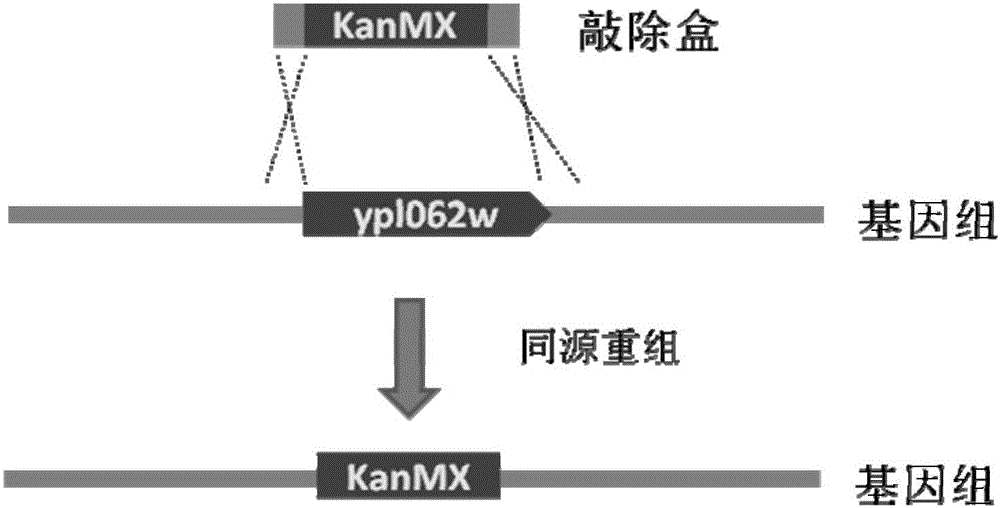
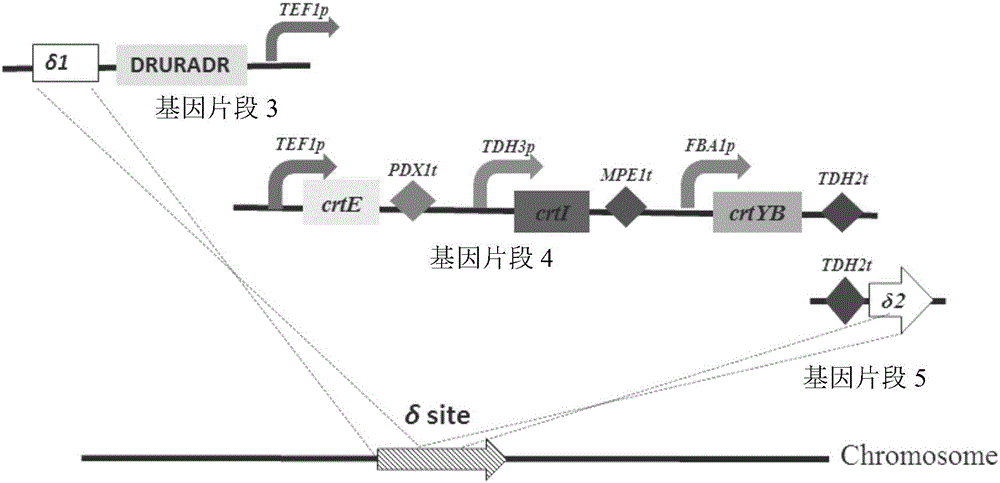
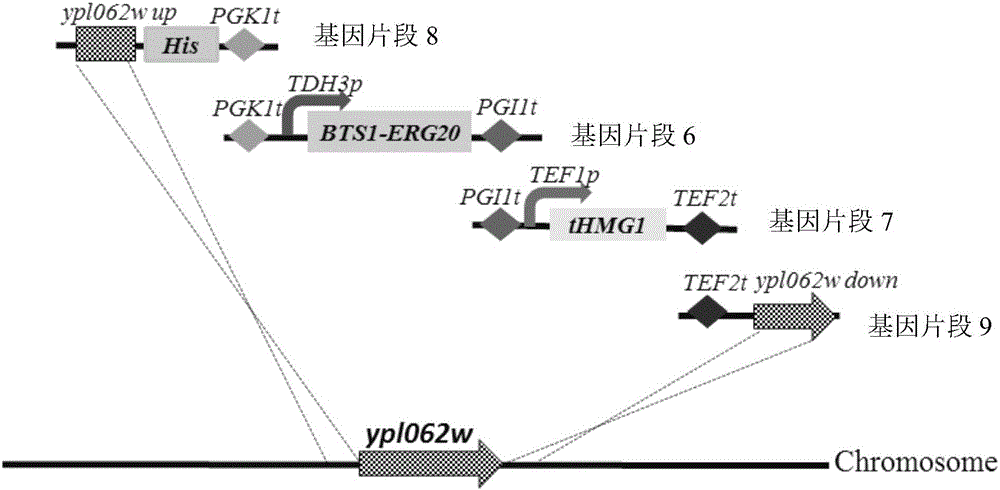
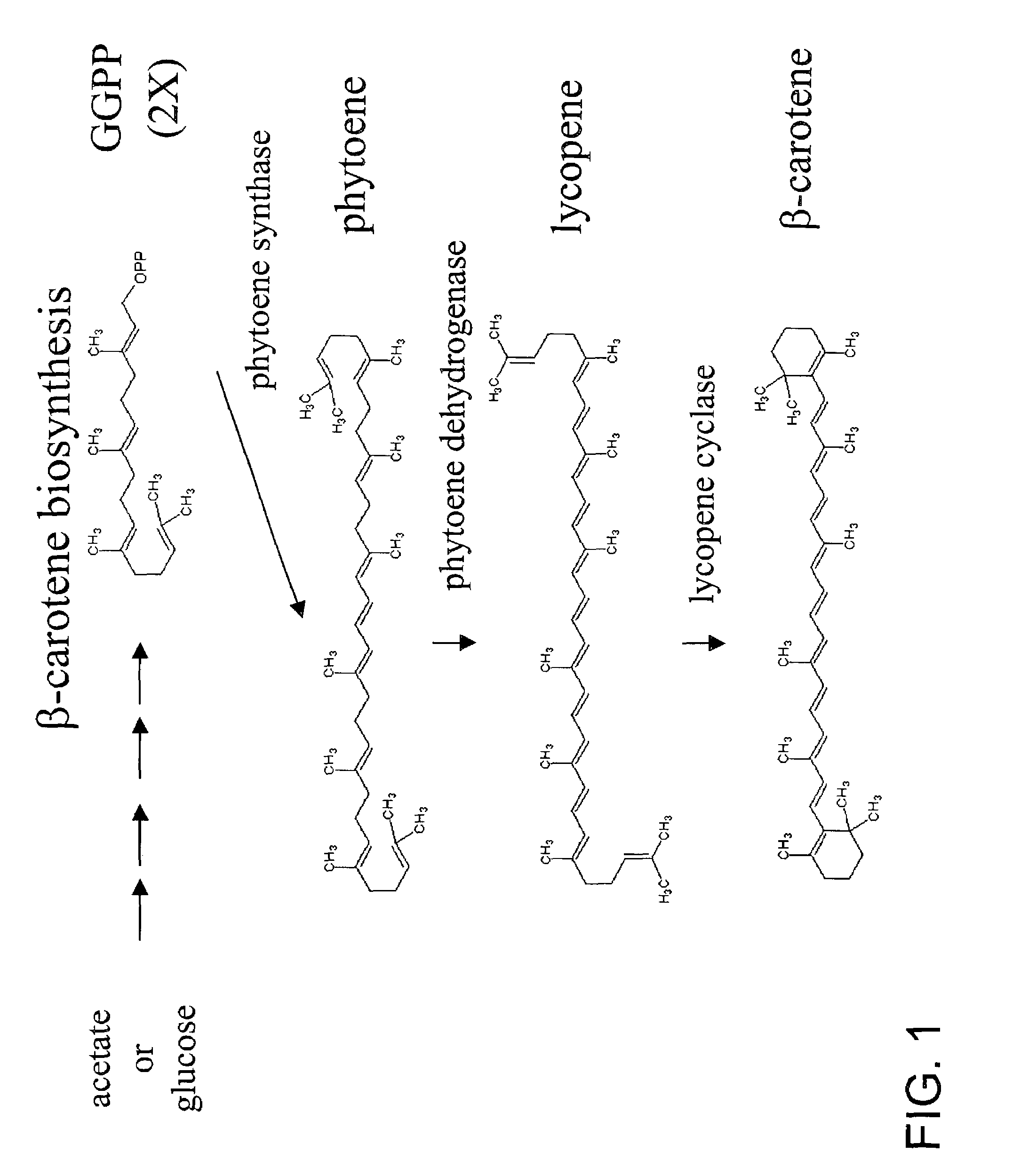
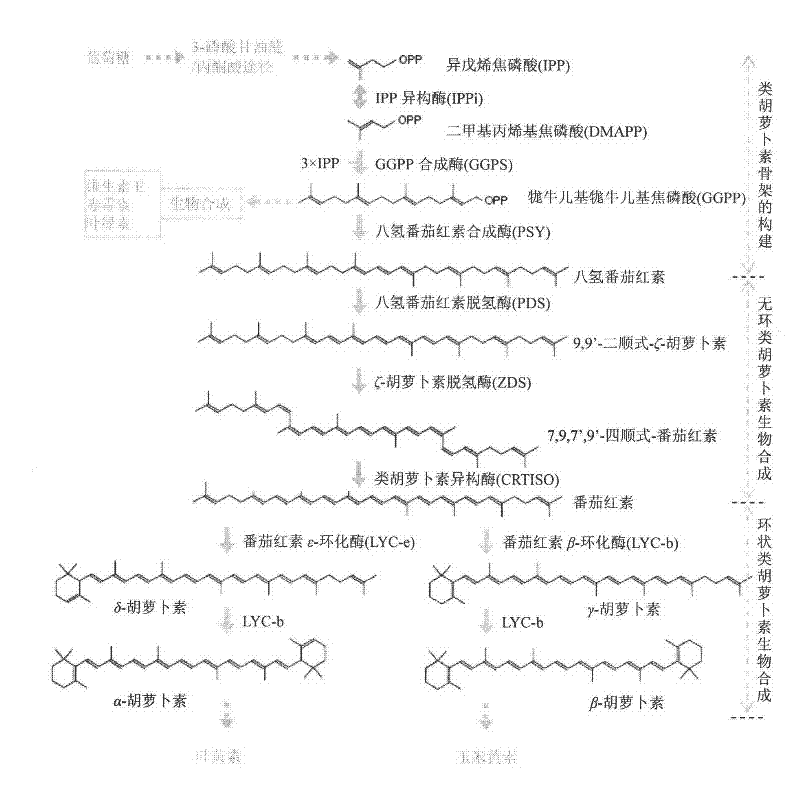
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a construction method and application thereof. In the recombinant yeast strain, gal1, gal7, gal10 and ypl062w genes are knocked out, and the recombinant yeast strain comprises 9 gene segments which are integrated to the genome by yeast homologous recombination. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing a four-knock-out yeast strain to provide an optimized host cell for producing beta-carotin, selecting lycopene cyclases crtY from different sources, and carrying out modular design to integrate functional genes crtE crtB and crtI of the specific-source synthetic lycopene, specific yeast endogenous genes and the like to the four-knock-out yeast strain genome, thereby obtaining a brand-new recombinant strain capable of producing beta-carotin at high yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
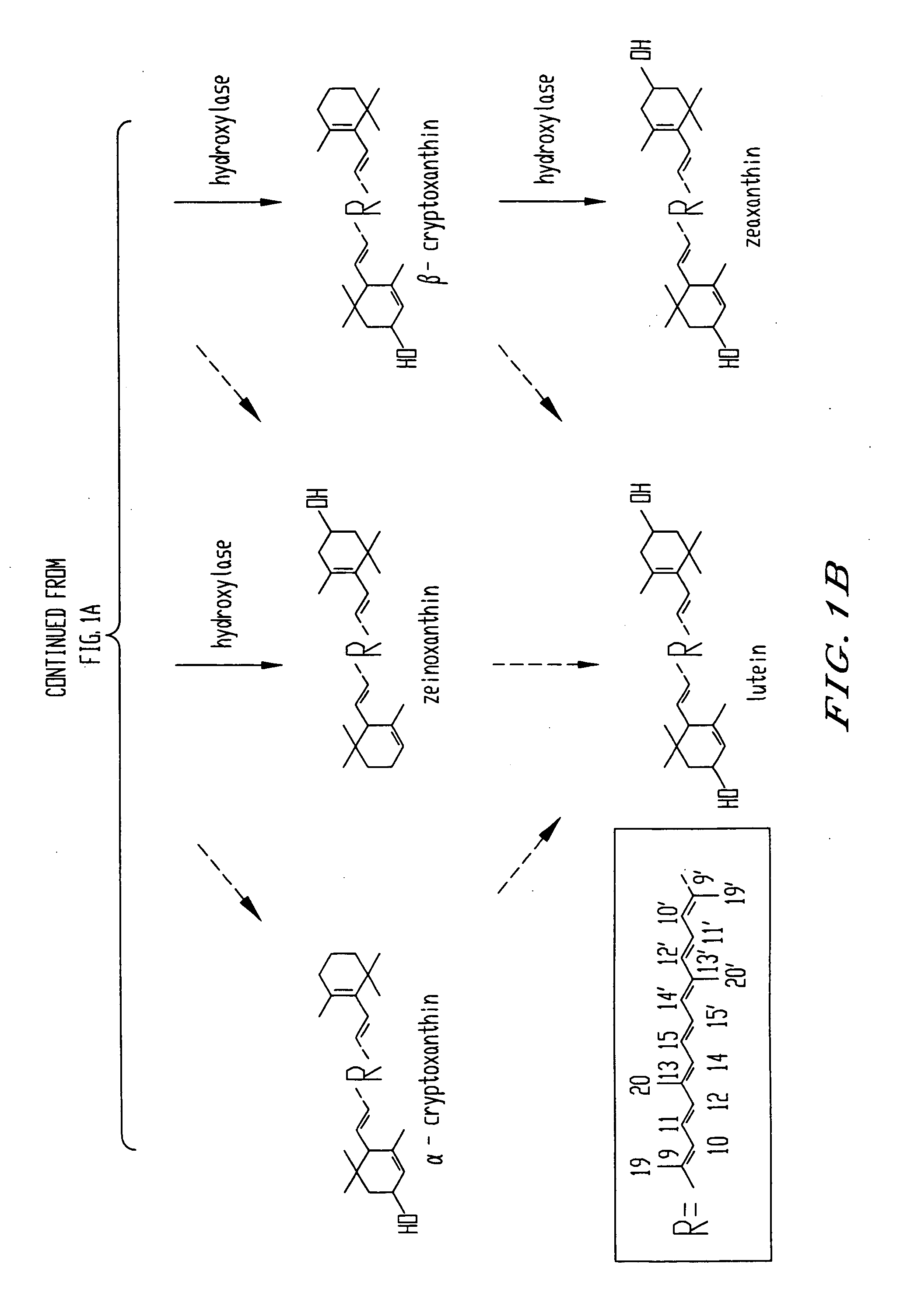
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
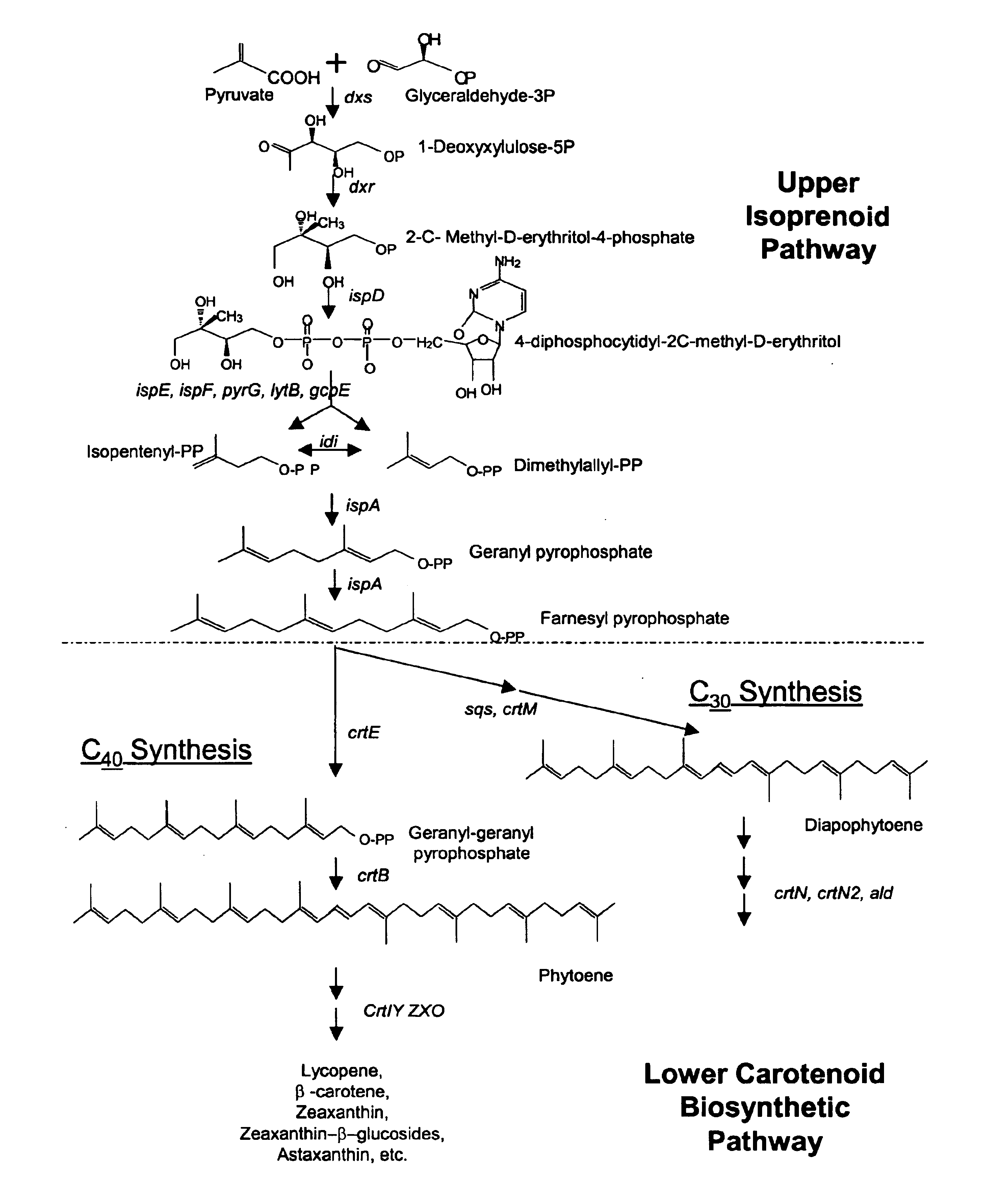
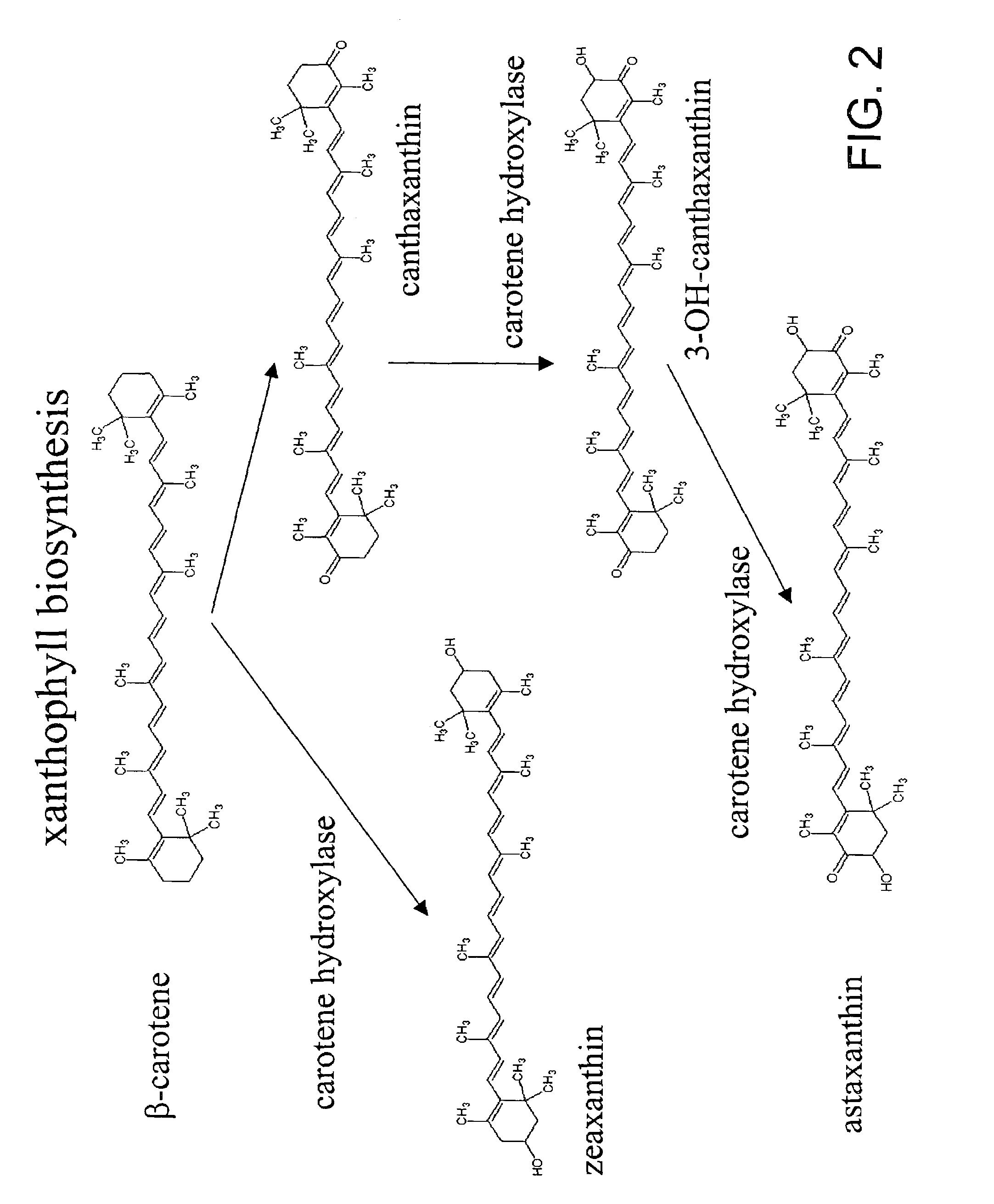
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
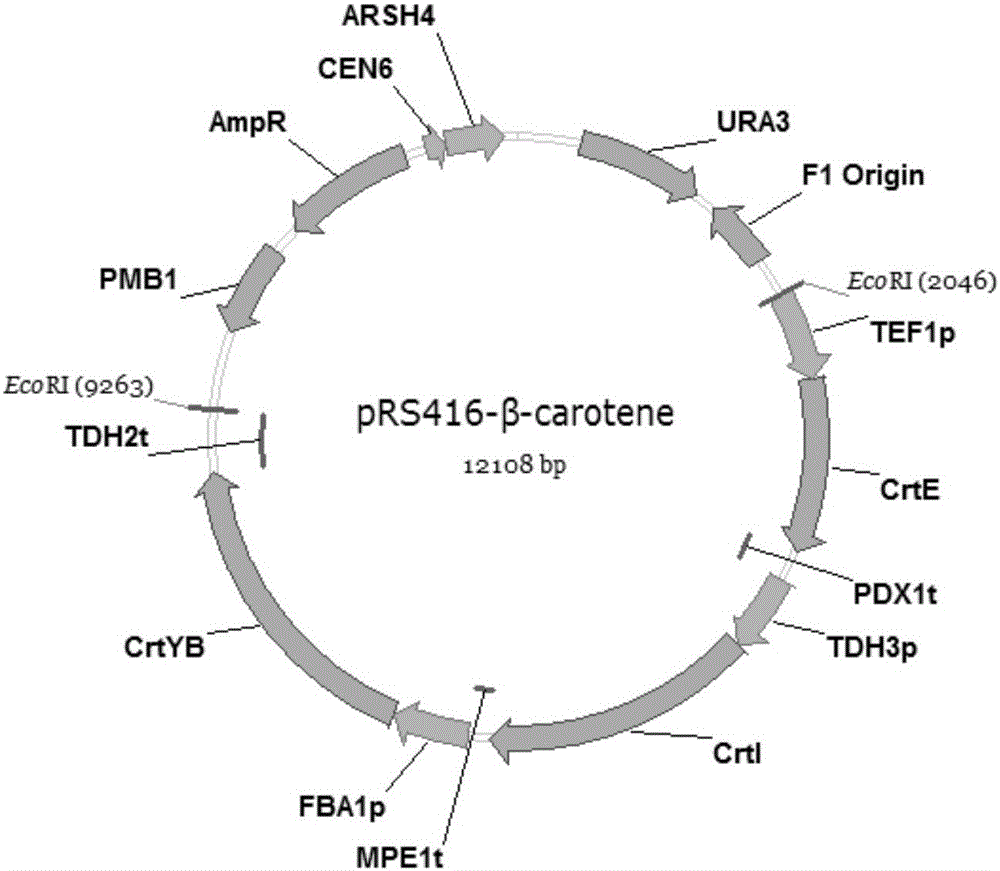
Recombinant yeast strain, and building method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses a recombinant yeast strain, and a building method and application thereof. The recombinant yeast strain includes two specific gene segments recombined and integrated onto a genome in a homologous way through yeast. By selecting the specific group for forming a promoter combination and matching phaffia rhodozyma sourced phytoene synthetase and lycopene cyclase dual-function enzyme gene CrtYB, GGPP synthase CrtE, phytoene desaturase CrtI and specific yeast endogenous gene and the like, the substances are integrated onto the yeast strain genome through modular design; the yp1062w gene is knocked away through homologous recombination; one strain of fire-new recombinant yeast without an inducing agent is obtained; the high yield of the beta-renieratene is ensured.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
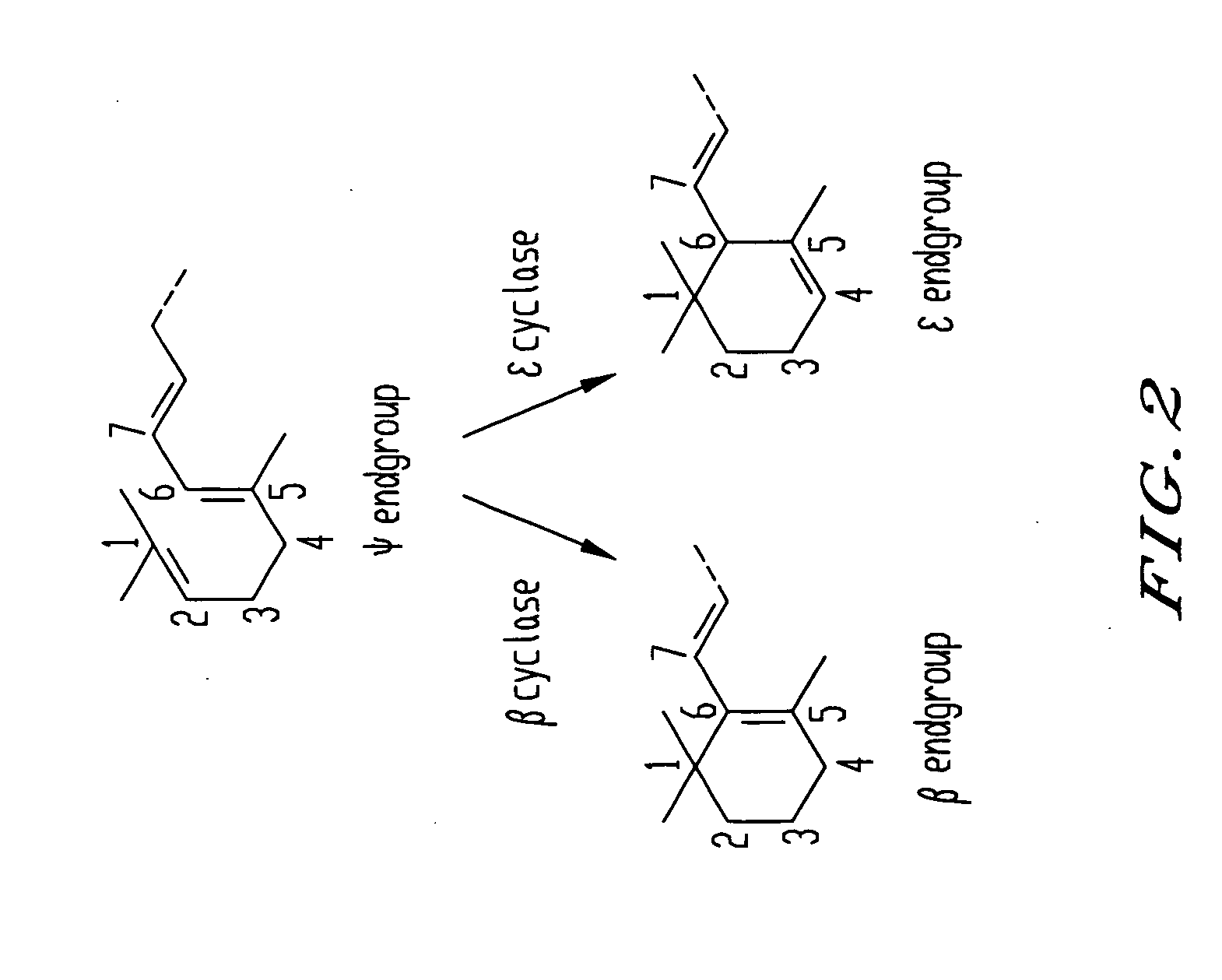
Genes encoding epsilon lycopene cyclase and method for producing bicyclic carotene
The present invention relates to the DNA sequence for eukaryotic genes encoding epsi cyclase isolated from romaine lettuce as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with said vectors. The present invention provides methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and to the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for treating disease by administering carotenoids obtained from transformed hosts, or by administering a composition containing the transformed hosts.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Genes encoding epsilon lycopene cyclase and method for producing bicyclic epsilon carotene
The present invention relates to the DNA sequence for eukaryotic genes encoding ε cyclase isolated from romaine lettuce as well as vectors containing the same and hosts transformed with said vectors. The present invention provides methods for controlling the ratio of various carotenoids in a host and to the production of novel carotenoid pigments. The present invention also provides a method for treating disease by administering carotenoids obtained from transformed hosts, or by administering a composition containing the transformed hosts.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
Genes have been isolated from strain DC260, a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family, encoding geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), phytoene synthase (CrtB), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ), and zeaxanthin glucosyl transferase (CrtX) activity. The genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Lycium chinense miller lycopene beta-cyclase gene, recombinant vector containing gene, host cell and application
InactiveCN102321649AIncrease biosynthesisIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a lycium chinense miller lycopene beta-cyclase gene, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a host cell and application. Total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of fresh lycium chinense miller leaf is extracted, and lycopene beta-cyclase gene LmLycB is cloned by using 3' RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology to obtain a complete gene sequence of 1,506bp. An Escherichia coli expression vector pMON-LmLycB is constructed; an escherichia coli heterogenous expression system is applied; the activity of cloned LmLycB gene-coded enzyme is identified; and two beta-lonone rings can be added at the tail end of lycopene by LmLycB to produce beta-carotene. A maize inbred line immature embryo genetic transformation system is optimized; a plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-LmLycB-Bar containing a target gene is transformed into maize callus to finally obtain a transgenic positive plant; through HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection, the total carotinoid content of transgenic maize leaf is 165.70mug / g FW and is 12.76 percent greater than that of a wild maize; and beta-carotene content is 80.17mug / g FW and is 54.83 percent greater than that of the wild maize.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genes of strain DC413 encoding enzymes involved in biosynthesis of carotenoid compounds
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
Genes have been isolated from Pectobacterium cypripedii encoding geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthase (CrtE), phytoene synthase (CrtB), phytoene desaturase (Crtl), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ), and zeaxanthin glucosyl transferase (CrtX) activity. The genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
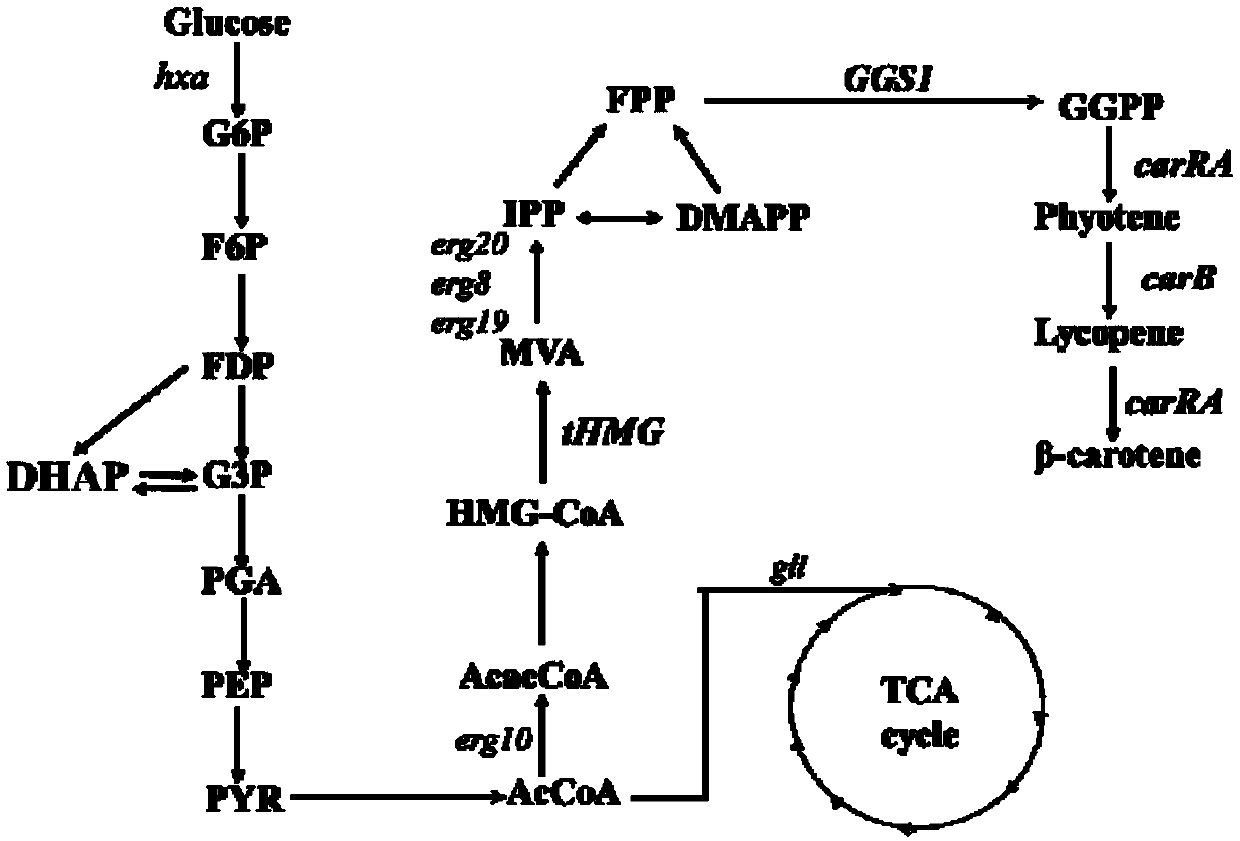
Recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and construction method utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology
PendingCN109666596AIncrease the efficiency of homologous recombinationImprove stabilityFungiStable introduction of DNABeta-CaroteneKu70
The invention discloses recombinant bacteria used for producing beta-carotene and a construction method utilizing a Crispr-Cas9 technology. A Ku70 gene is subjected to knockout from yarrowia lipolytica, and then phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA), phytoene desaturase (carB), geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and a 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene take snfas a target point and are integrated in a yarrowia lipolytica gene set after knockout of the ku70 gene, wherein the phytoene synthase / lycopene cyclase (carRA) and phytoene desaturase (carB) are from blakeslea trispora, and the geranyl pyrophosphate synthetase (GGS1) and the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (tHMG) gene are from the yarrowia lipolytica; the Crispr-Cas9 technology isutilized for regulating the copy number of the carRA, the carRA, the GGS1 and the tHMG, and the recombinant bacteria capable of producing the high-yield beta-carotene is constructed. After the recombinant bacteria is fermented, cultured, extracted and separated, the content of the beta-carotene can reach the dry cell weight of 35 mg / g, and the bacterial strain stability is high.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Carotene Synthase Gene and Uses Therefor
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Tomato gene B polynucleotides coding for lycopene cyclase
An isolated complementary and genomic DNA segment encoding lycopene cyclase of the B locus of tomato are provided.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Lycopene Cyclase Gene of Sphingomonas paucimobilis and Its Application
The invention provides the DNA sequence of a lycopene cyclase gene (crtY) in sphingomonas sp., a recombinant strain lacking lycopene cyclase and use thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the crtY gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The DNA sequence of the lycopene cyclase gene (crtY) in sphingomonas sp., which is provided by the invention, lays a foundation for the genetic modification of a sphingomonas sp. carotenoid biological synthesis means. In addition, compared with a wild strain, the sphingomonas sp. recombinant strain lacking the lycopene cyclase gene, which is constructed by a gene knockout method, has the advantages that: the gellengum yield is basically unchanged; and lycopene can be produced in the production of gellengum by fermentation. And the strain can be used for further gene knockout or metabolic engineering modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fermentative carotenoid production
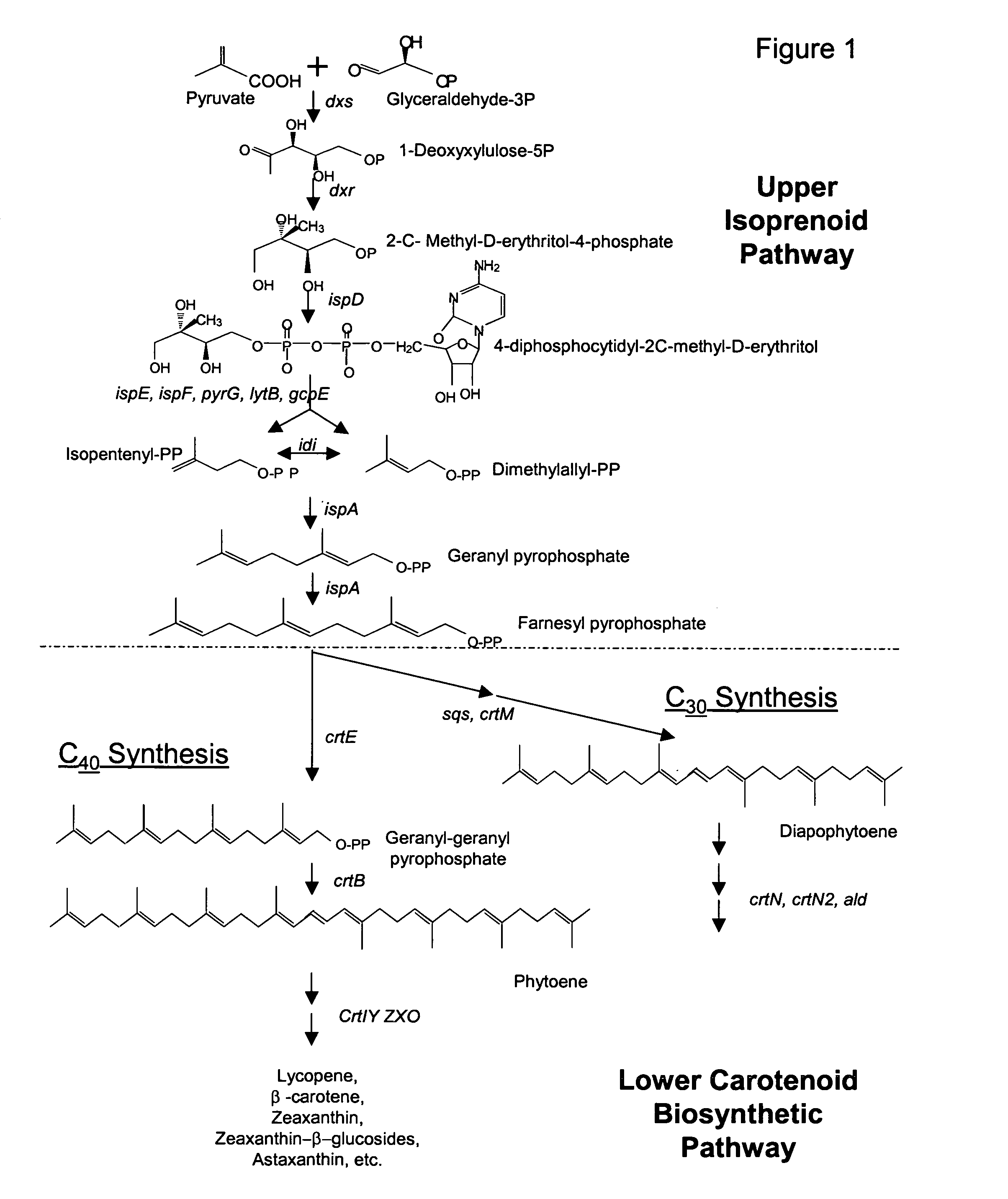
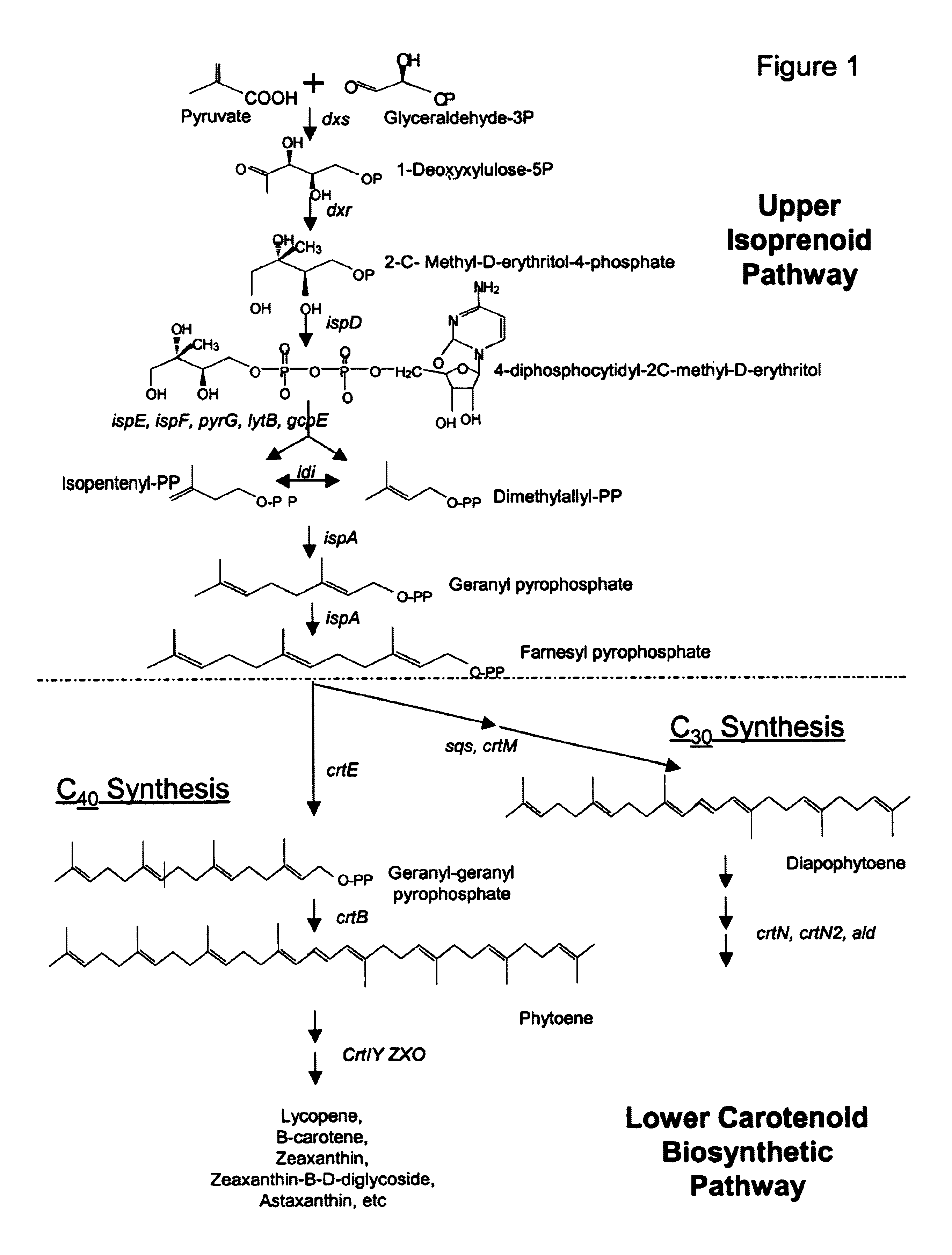
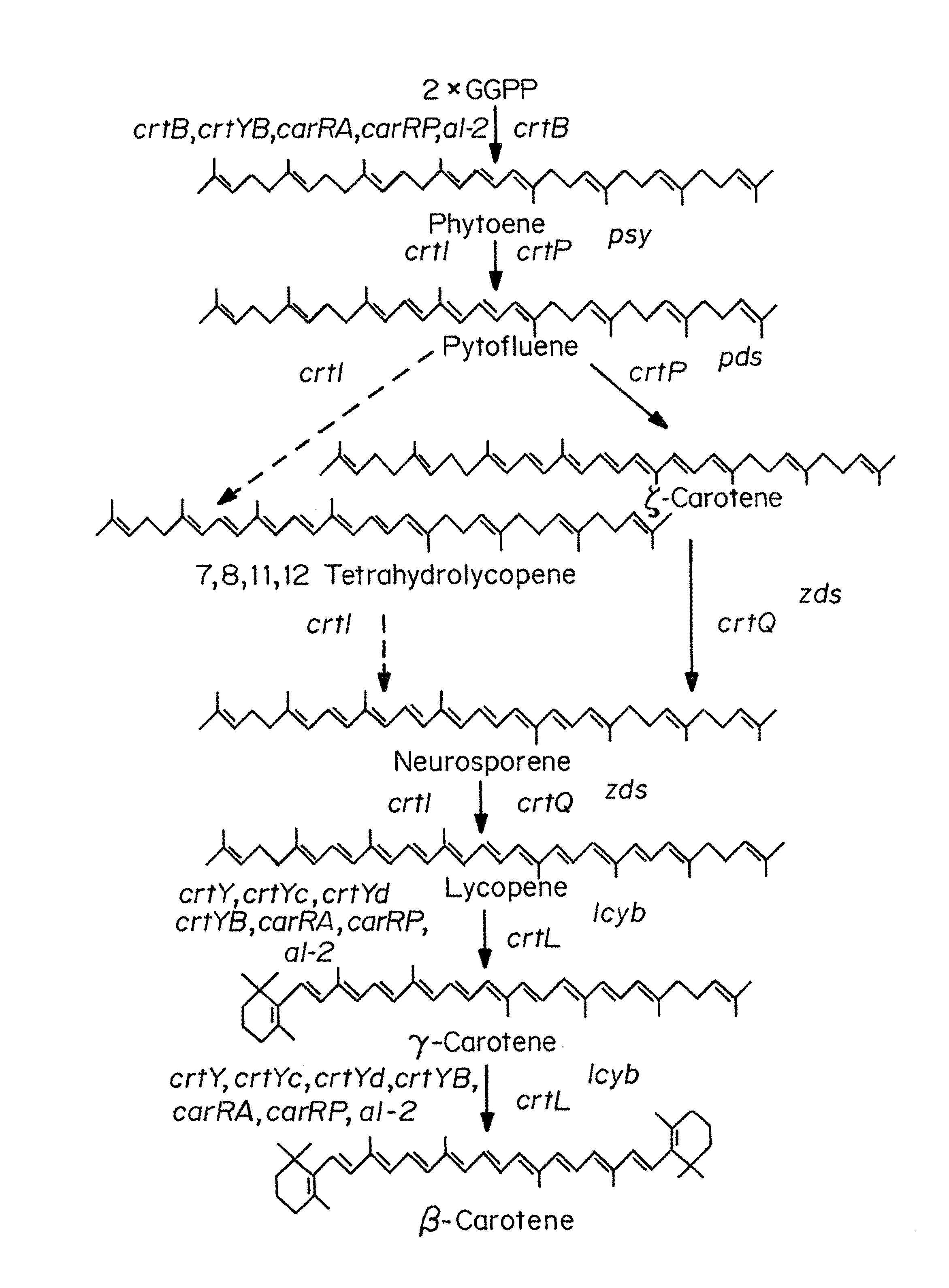
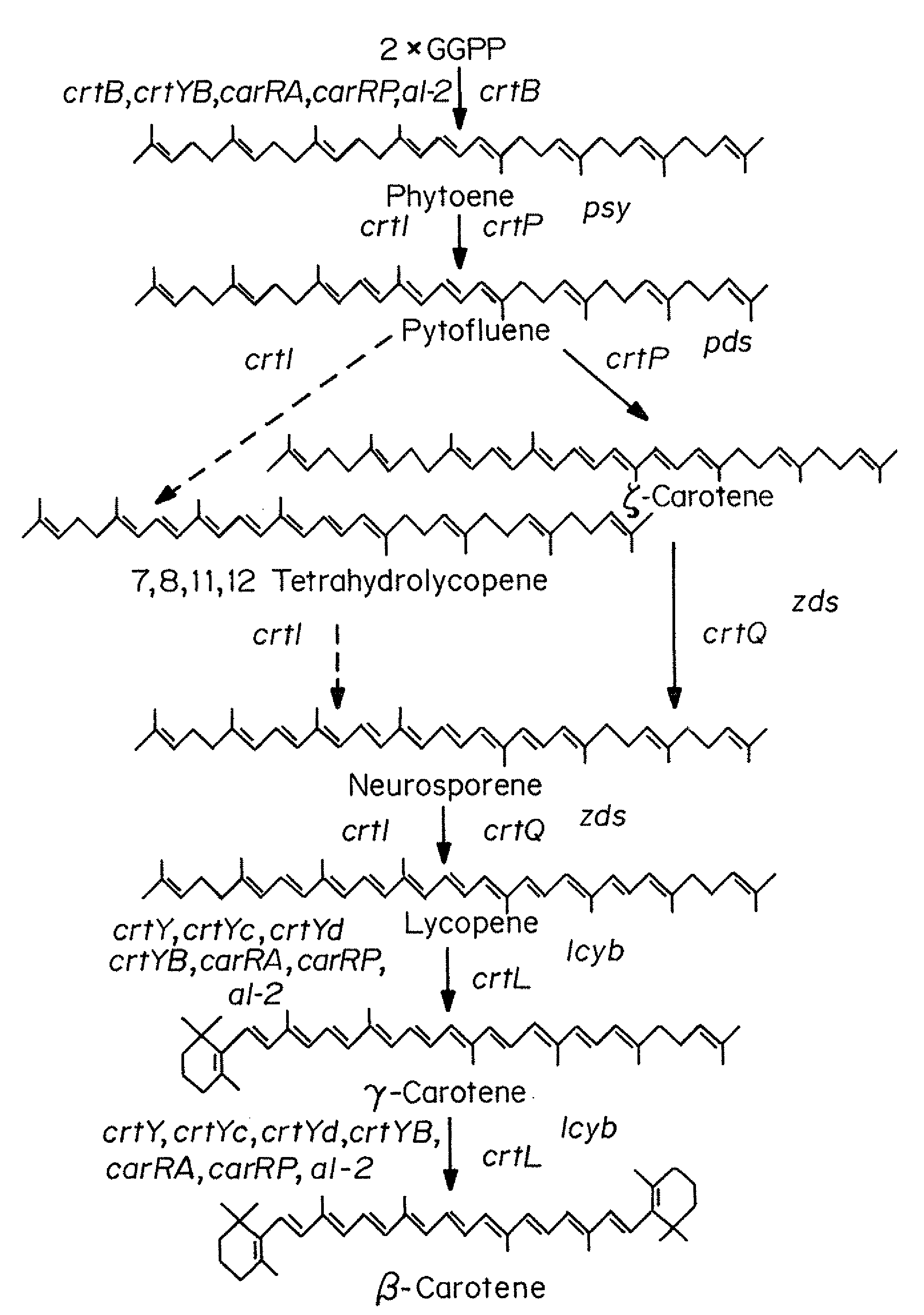
The present invention is directed to a DNA sequence comprising one or more DNA sequences selected from the group consisting of a DNA sequence which encodes the GGPP synthase of Flavobacterium sp. R1534 (crtE), a DNA sequence which encodes the prephytoene synthase of Flavobacterium sp. R1534 (crtB), a DNA sequence which encodes the phytoene desaturase of Flavobacterium sp. R1534 (crtI), a DNA sequence which encodes the lycopene cyclase of Flavobacterium sp. R1534 (crtY) or a DNA sequence which encodes the beta -carotene hydroxylase of Flavobacterium sp. R1534 (crtZ) or DNA sequences which are substantially homolgous, vectors comprising such DNA sequences and / or a DNA sequence which encodes the beta -carotene beta 4-oxygenase of Alcaligenes strain PC-1 (crt W) or a DNA sequence which is substantially homologous, cells which are transformed by such DNA sequences and / or vectors, a process for the preparation of a desired carotenoid or a mixture of carotenoids by cultering such transformed cells and a process for the preparation of a food or feed composition. <IMAGE>
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
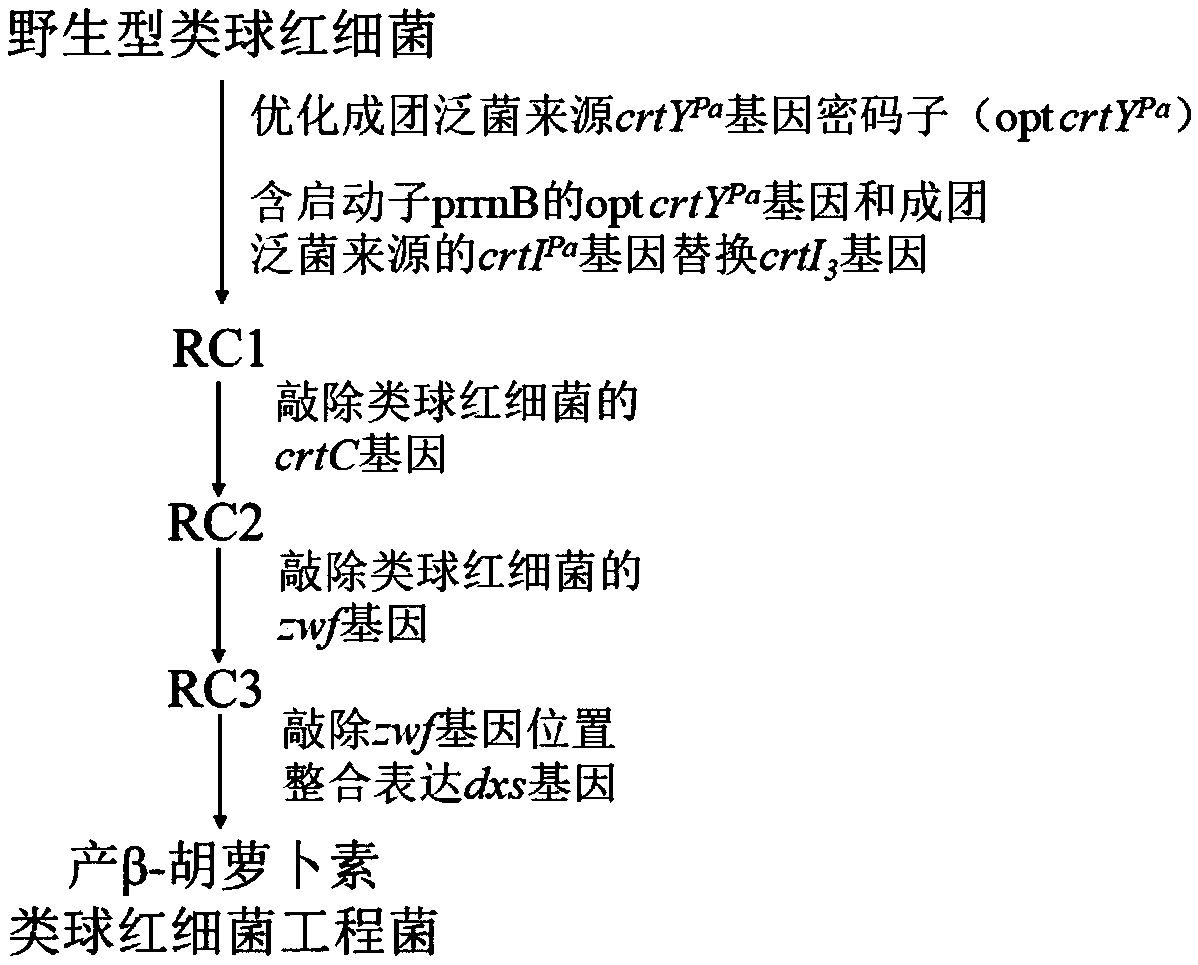
Rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing beta-carotene and a construction method thereof. The method includes first optimizing a codon of a lycopene cyclase gene crtYPa derived from pantoea agglomerans to obtain an opt crtYPa gene, then replacing an endogenous phytoene three-step dehydrogenase gene crtI3 of rhodobacter sphaeroides with the opt crtYPa genecontaining a promoter prrnB and a phytoene four-step dehydrogenase gene crtIPa gene derived from the pantoea agglomerans in a traceless mode, then knocking out an endogenous neurosporene hydroxylase gene crtC of the rhodobacter sphaeroides and a 6-phosphoglucose dehydrogenase gene zwf and finally knocking out an endogenous 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene dxs of the rhodobacter sphaeroides with integration expression at zwf position to obtain the rhodobacter sphaeroides engineering strain for producing the beta-carotene. The strain is cultured by fermentation, and the content of the beta-carotene can reach 30mg / g DCW.
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
Carotene synthase gene and uses therefor
Described herein is a novel three domain gene from Schizochytrium, denoted carotene synthase, that encodes a protein with three different enzymatic activities: phytoene dehydrogenase (PD), phytoene synthase (PS), and lycopene cyclase (LC). Also described is the isolated gene encoding the carotene synthase, homologues thereof, the enzyme encoded by such gene, biologically active portions and homologues thereof, recombinant nucleic acid molecules, microorganisms and plants that have been genetically modified to increase or decrease the action of such gene, and methods of producing carotenoids and derivatives thereof or methods of producing microorganisms and lipid products lacking pigmentation using the knowledge of the carotene synthase described herein.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Dunaliella gene knockout vector and application thereof
InactiveCN102191265AReduce accessIncrease contentMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionLycoperseneCyclase
The invention relates to Dunaliella gene engineering, in particular to a Dunaliella lycopene-beta-cyclase (LycB) gene knockout vector and application thereof. The LycB gene knockout vector comprises a selection marker gene and is connected to a 3' end homologous recombination region and a 5' homologous recombination region of the LycB gene. The LycB gene knockout vector is applied to culturing LycB gene knockout Dunaliella. The process of biologically synthesizing beta-carotene by using LycB gene knockout Dunaliella is stopped at the lycopene stage; and under the stress condition, high-content lycopene can be accumulated and the accumulation quantity is 3 to 4 percent of the dry weight of the Dunaliella.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for enabling Dunaliella to accumulate high-content lycopene
InactiveCN102191266AIncrease contentReduce accessMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionDry weightBeta-Carotene
The invention relates to a method for biologically synthesizing lycopene, in particular to a method for enabling Dunaliella to accumulate high-content lycopene. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting Dunaliella genome DNA; cloning a lycopene-beta-cyclase (LycB) gene of the DNA; constructing an LycB gene knockout vector and transforming the vector into a Dunaliella salina cell; and screening and identifying to obtain LycB gene knockout Dunaliella, wherein the LycB gene expression of the Dunaliella is inhibited; the process of biologically synthesizing beta-carotene by using the cell is stopped at the lycopene stage; and under the stress condition, a large amount of lycopene can be accumulated in an organism and the lycopene content is 3 to 4 percent of the dry weight of the Dunaliella. The method is a new way of obtaining a large amount of natural lycopene with low price.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Regulatory gene for reducing total protein of tobacco leaves and phenol content in smoke
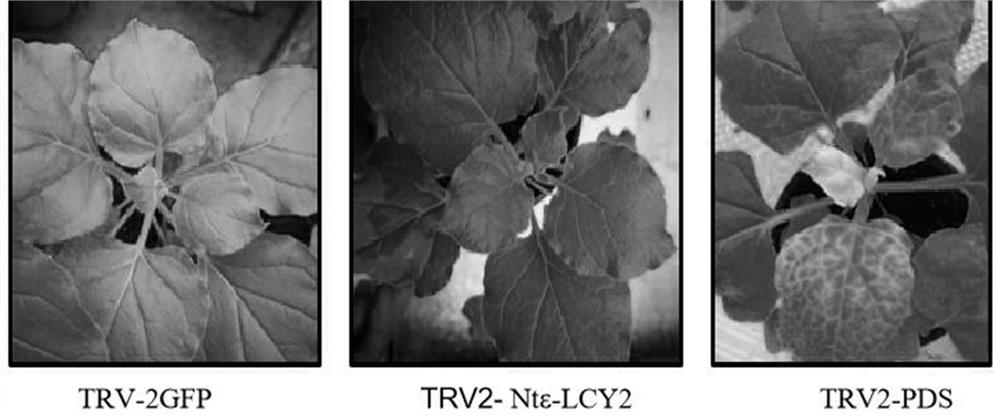
The invention belongs to the field of tobacco gene engineering, and particularly relates to a regulatory gene tobacco lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene Nt epsilon-LCY2 for reducing total protein of tobacco leaves and phenol content in smoke. The base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The tobacco lycopene epsilon-cyclase Nt epsilon-LCY2 is composed of 498 amino acid residues, wherein the 105 to 287 amino acid and the 290 to 475 amino acid are conservative transport protein structural domains. The protein is related to the total protein content in plant leaves, and after the gene expression is reduced, the total protein content in the leaves is obviously reduced. Preliminary research on the specific Nt epsilon-LCY2 shows that the specific Nt epsilon-LCY2 is highly related to the total protein content of the tobacco, and after the gene is mutated, the total protein content of the tobacco is obviously reduced. On the basis of the characteristic, a certain application basis and reference can be provided for the cultivation of new varieties of low-phenol-content tobaccos.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
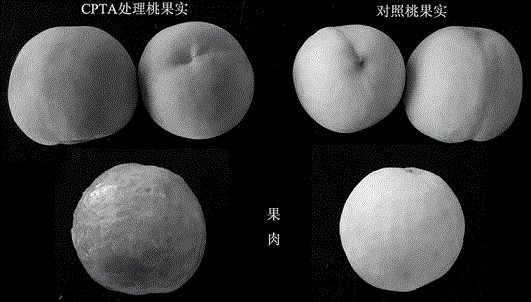
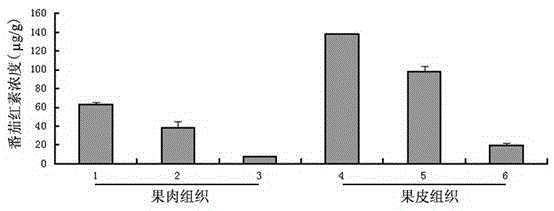
Method for detecting synthesis capability of carotenoid in fruit
The invention discloses a method for detecting the synthesis capability of carotenoid in a fruit. According to the method, lycopene cyclase inhibitor, namely CPTA, is adopted for treating the fruit to be detected, degradation of the carotenoid in the fruit is blocked so that the carotenoid can be accumulated in the form of lycopene, and the capability of the fruit for synthesizing the carotenoid can be evaluated objectively by detecting the lycopene. The method is generally applicable to various fruits such as peaches, apricots and apples.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing compound carotenoids as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacteria
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria for producing compound carotenoids (including [alpha]-carotene, [beta]-carotene, [delta]-carotene and lycopene) as well as a construction method and an application of the genetically engineered bacteria. The genetically engineered bacteria for producing the compound carotenoids are obtained by linking a musa nana luor. lycopene [epsilon]-cyclase gene to an expression vector and then transforming the gene linked with the expression vector into engineering bacteria containing LYC-LCYB1 plasmids, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the musa nana luor. lycopene [epsilon]-cyclase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. With the application of the genetically engineered bacteria provided by the invention, the compound carotenoids, which are high in proportion of the [alpha]-carotene, can be directly obtained from the bacterium body; and the genetically engineered bacteria have a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A gene encoding lycopene dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a gene that can be used for encoding lycopene dehydrogenase, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the gene of the present invention is shown in SEQ ID NO.24; this gene is integrated into the co-expressed gene encoding lycopene cyclase and lycopene synthase (nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.12 Shown) in Candida tropicalis, can make Candida tropicalis can highly express β-carotene; Ferment this Candida tropicalis for 96h, can make the output of β-carotene up to 4.24g L ‑1 .
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production of provitamin A carotenoids in mushrooms and uses thereof
Owner:MEDICINE & NEED CORP
Method for production of asymmetric carotenoids
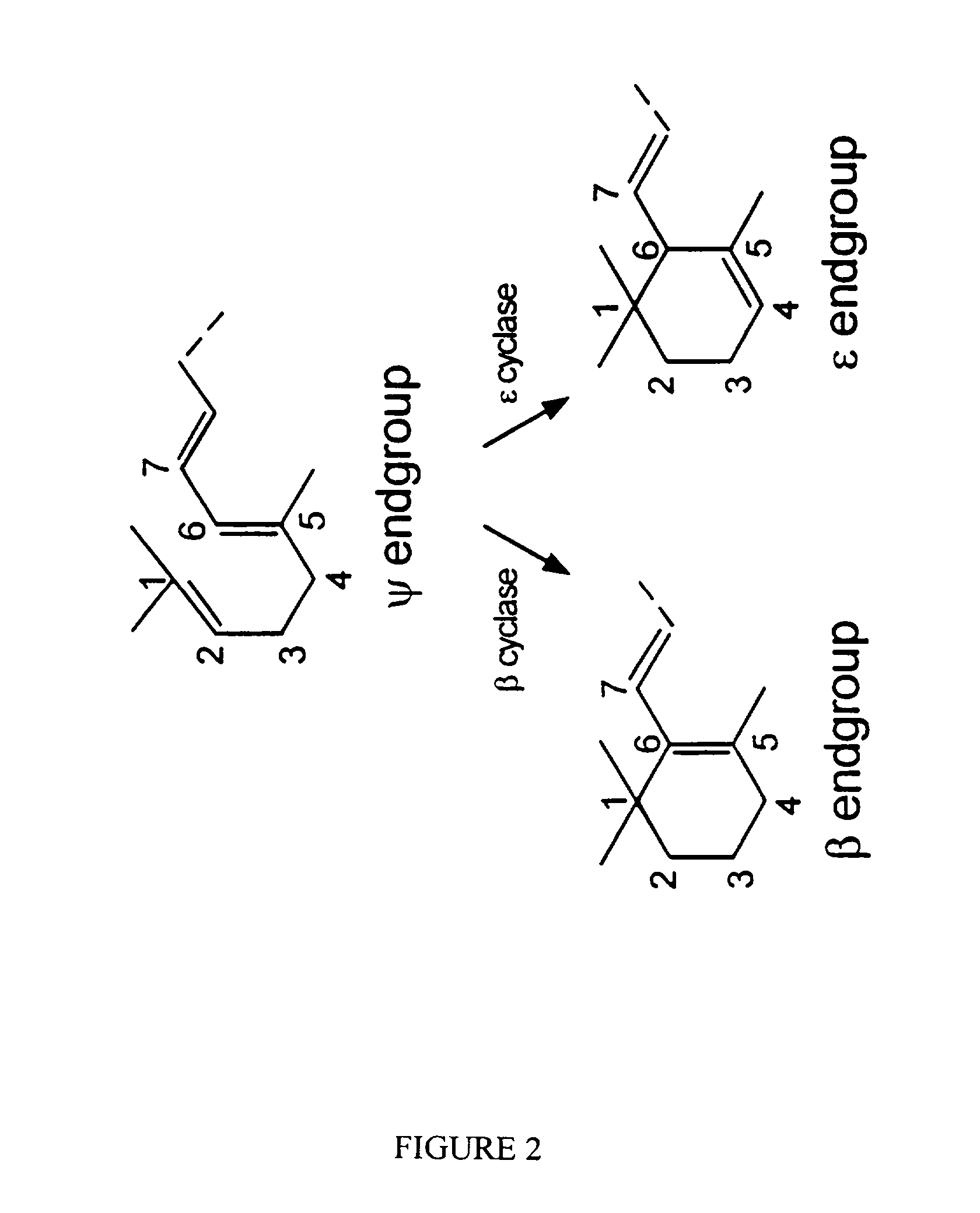
Genes have been isolated from Rhodococcus and Deinococcus which encode a specific lycopene β-cyclase capable of converting acyclic carotenoids with at least one ψ-end group to the corresponding asymmetric carotenoid containing a single β-ionone ring end group. The genes are new. Transformed host cells expressing the present genes and methods for the bio-conversion of acylic carotenoid substrates to corresponding asymmetric carotenoid are also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Methods of production of products of metabolic pathways
A plurality of isolated polynucleotide sequences encoding enzymes of the astaxanthin pathway is disclosed. The polynucleotides include:(i) a polynucleotide which encodes Phytoene dehydrogenase (crtI) and a first transcriptional regulatory sequence;(ii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-lycopene cyclase (lcy-B) and a second transcriptional regulatory sequence;(iii) a polynucleotide which encodes Beta-carotene ketolase (crtW) and a third transcriptional regulatory sequence; andwherein the first, second and third regulatory sequence are selected such that the expression of the Icy-B and the crtW is greater than a level of expression of the crtI. Methods of generating astaxanthin using the plurality of polynucleotide are also disclosed as well as bacterial cells comprising high levels of astaxanthin.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for identifying tobacco product by using lycopene epsilon cyclase gene ILP marker
The invention belongs to the field of research of molecular biology, and in particular relates to a method for identifying a tobacco product by using a lycopene epsilon cyclase gene ILP marker. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a sample to be detected by using a cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method; and carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplified reaction by taking CTGATGTGTTGCTGTGCTAGG and AATGCACTTCGCAAGCTCTA as upstream and downstream primers respectively, detecting an amplified product through gel electrophoresis after reaction, and judging that the sample is the tobacco product if electrophoretic bands exist at the positions of 450bp and 550bp. Compared with the traditional identification method, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being more objective, more accurate, more reliable and the like.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Production of provitamin a carotenoids in mushrooms and uses thereof
Mushrooms genetically engineered to produce provitamin A carotenoids including α-carotene, β-carotene, γ-carotene, and β-cryptoxanthin are provided. In some embodiments, mushrooms are transformed with genes that encode enzymes that have phytoene synthase, pyhtoene dehydrogenase and lycopene cyclase activities and function to convert GGPP to one or more provitamin A carotenoids. Mushrooms are transformed using known methods, including Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Transgenic mushrooms producing provitamin A carotenoids are useful to treat, alleviate, reduce, and / or inhibit one or more symptoms of a disease or disorder associated with vitamin A deficiency (VAD).
Owner:MEDICINE & NEED CORP
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing alpha-carotene and construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
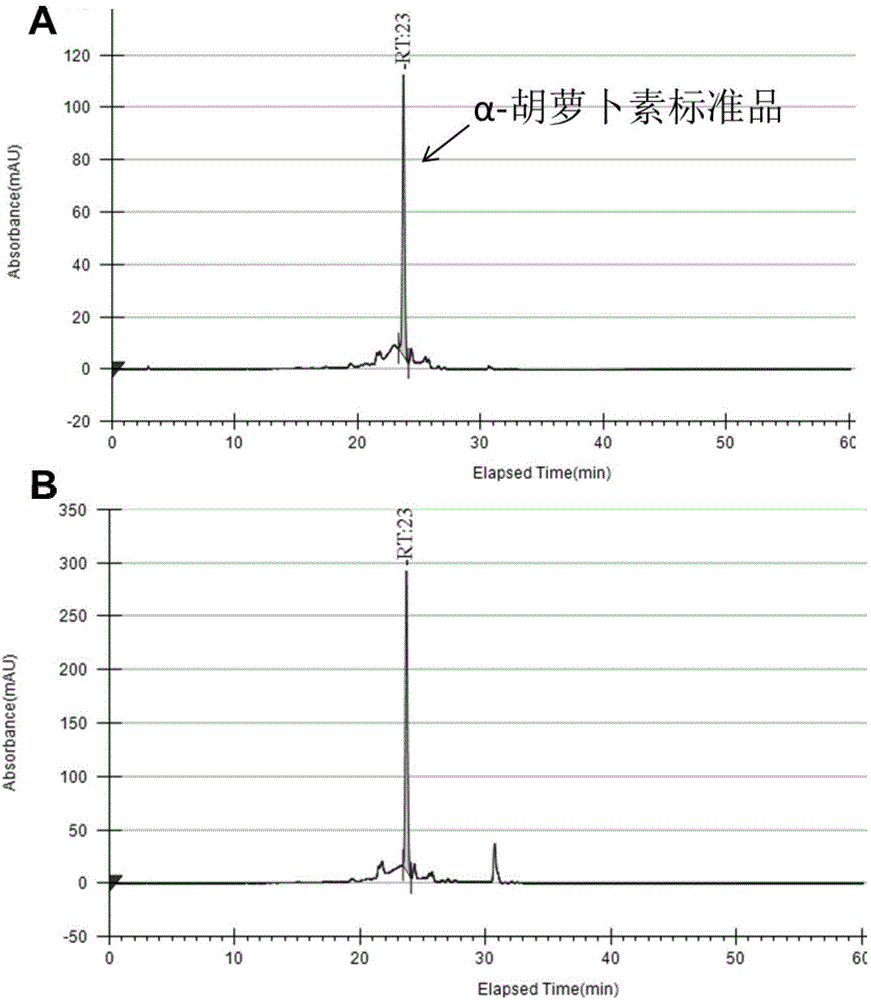
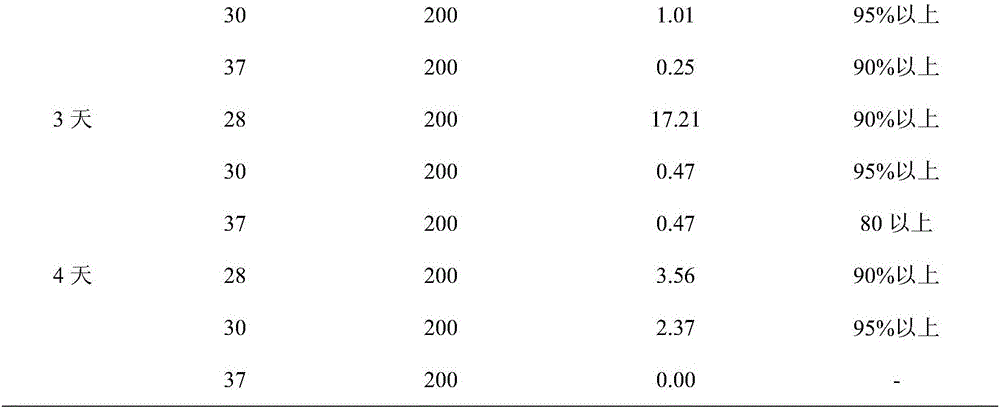
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing alpha-carotene and a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The construction method includes the steps that a banana lycopene beta-cyclase gene is connected with an expression carrier and then converted into an engineered bacterium containing pAC-Delta plasmids, and the genetically engineered bacterium for producing alpha-carotene is obtained, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the banana lycopene beta-cyclase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The yield of alpha-carotene can reach up to 17.21 mg / L after the genetically engineered bacterium is subjected to fermentation culture for 3 days. High-purity and high-yield alpha-carotene can be directly obtained from thalli of the genetically engineered bacterium, mass production of high-pruity alpha-carotene can be achieved, and the genetically engineered bacterium has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com