Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Logical block number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
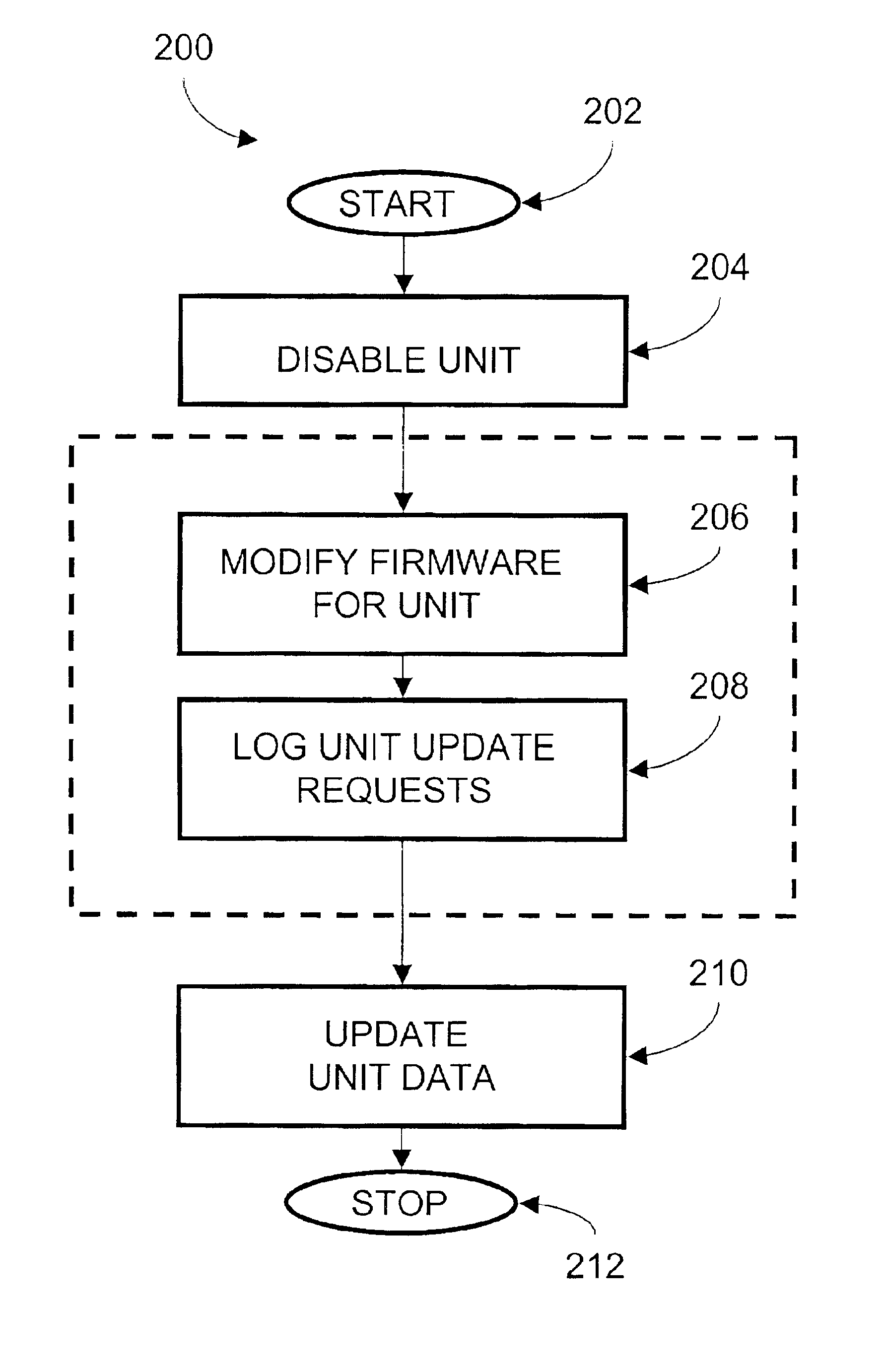
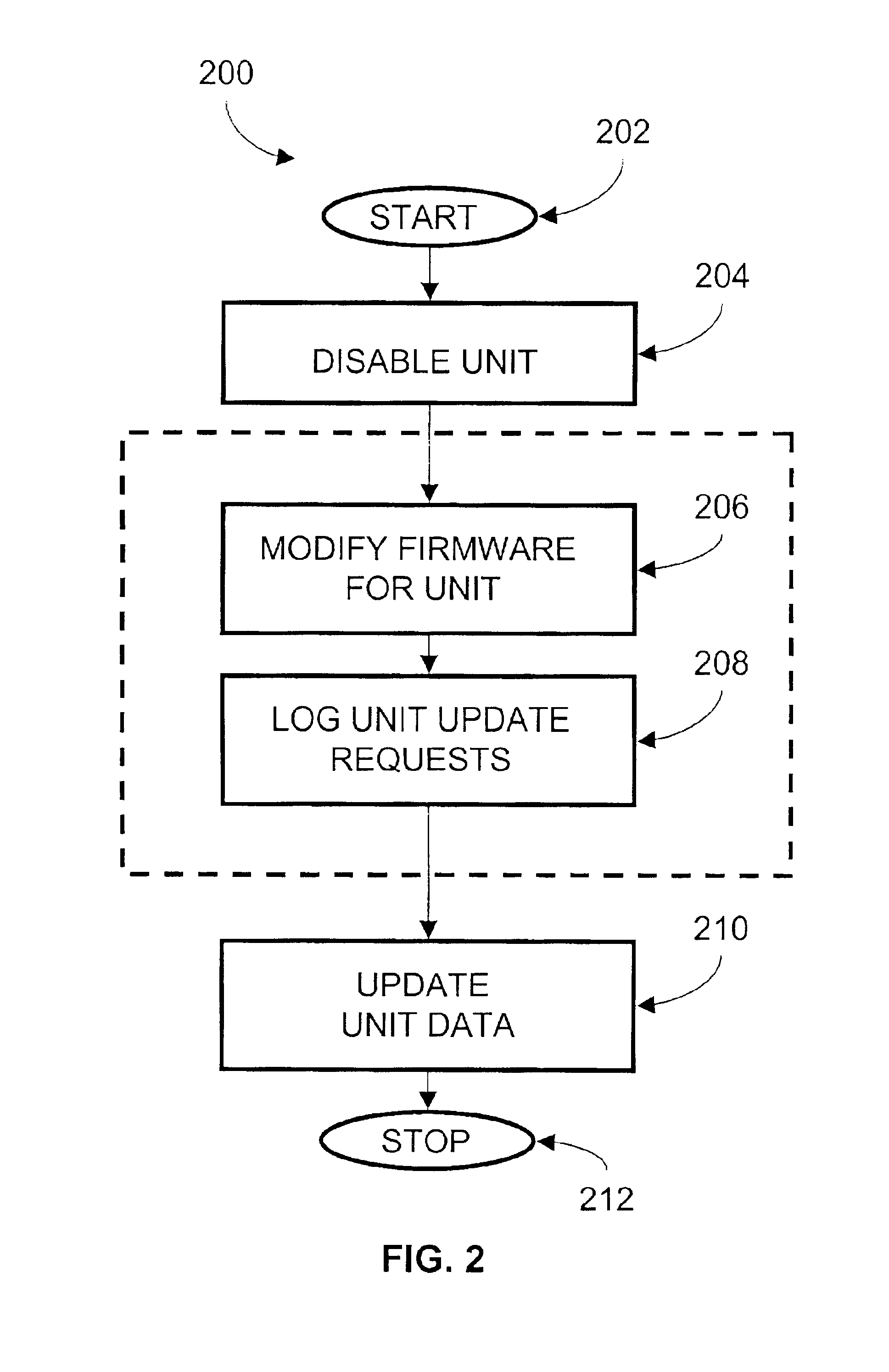
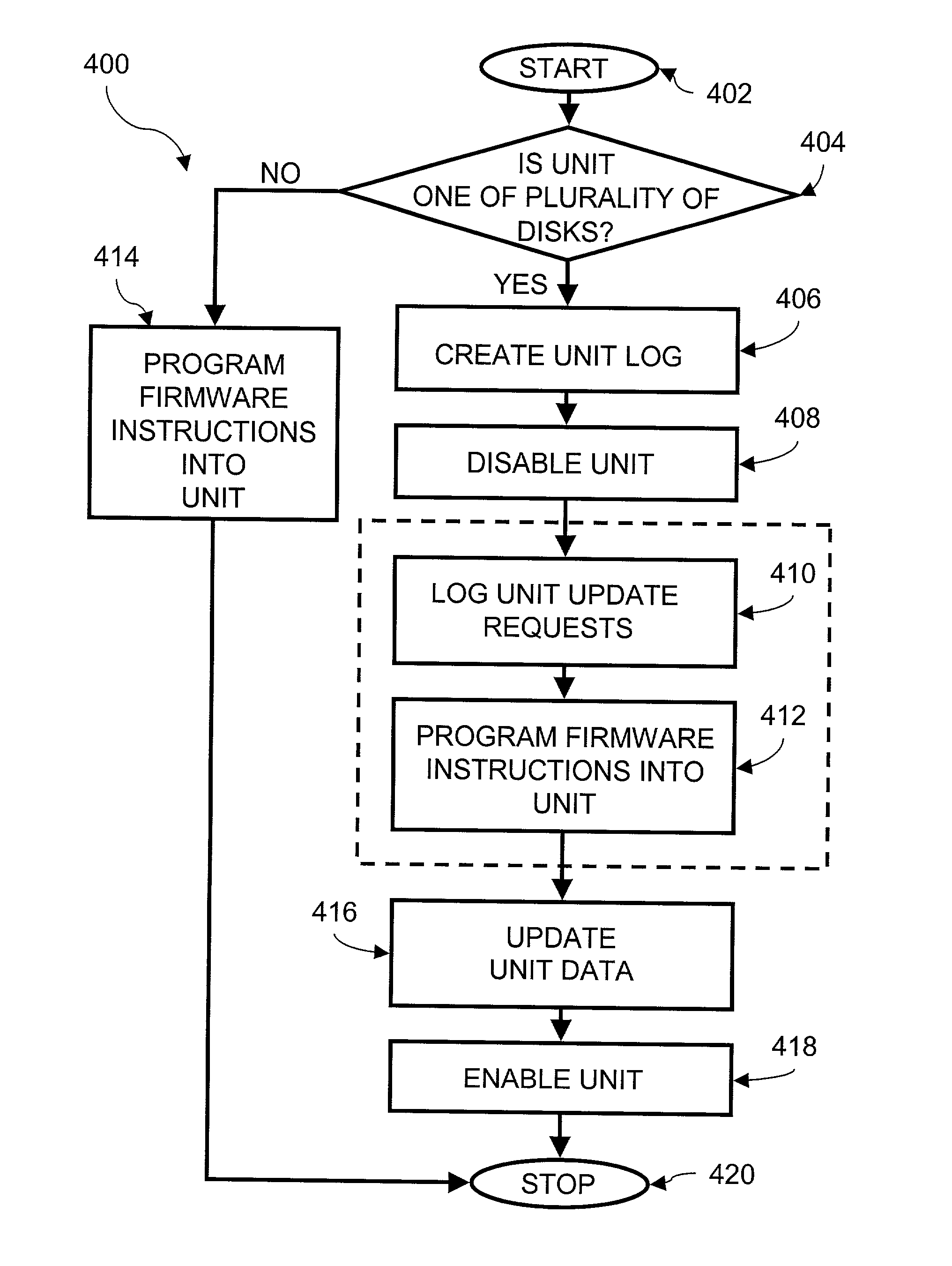
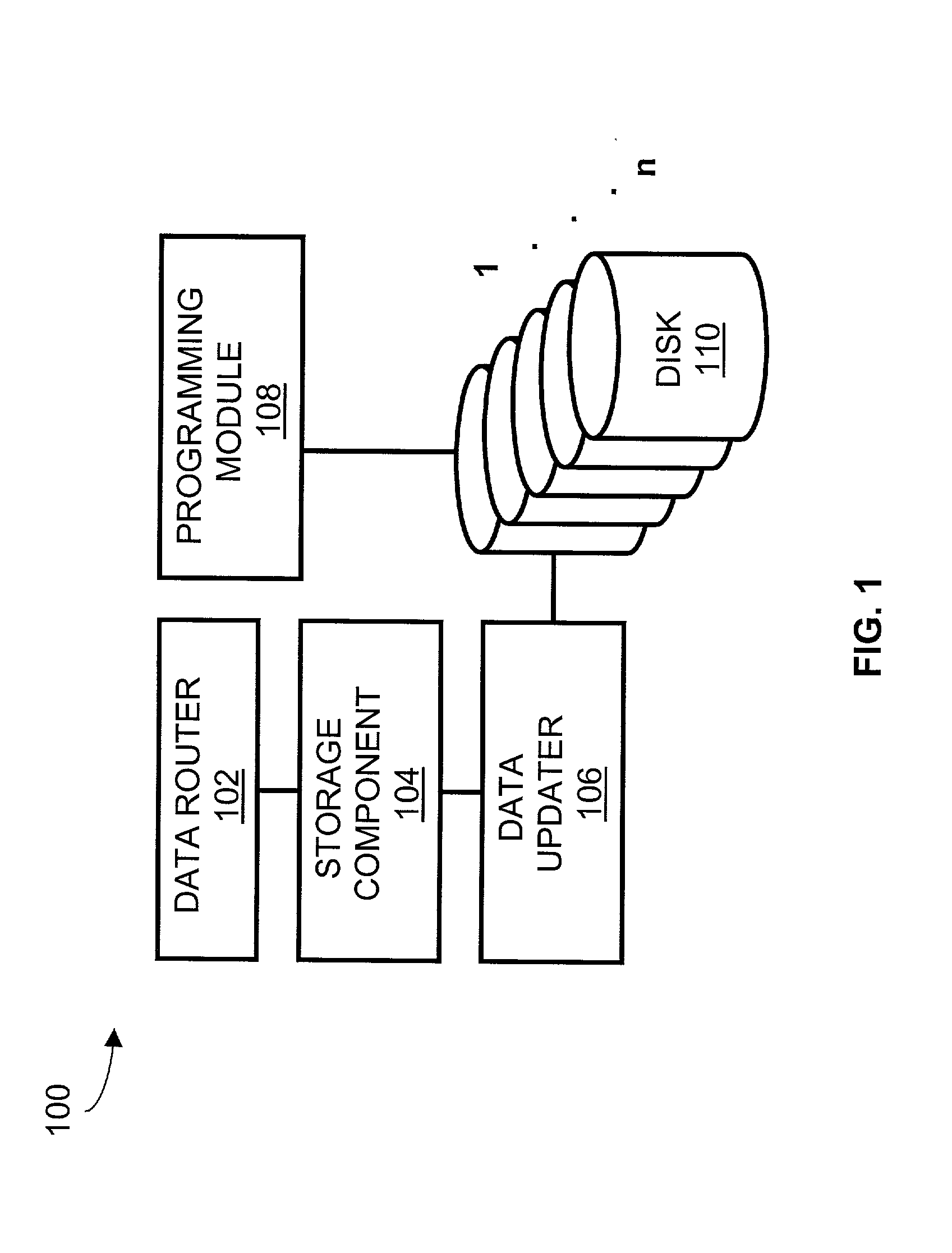
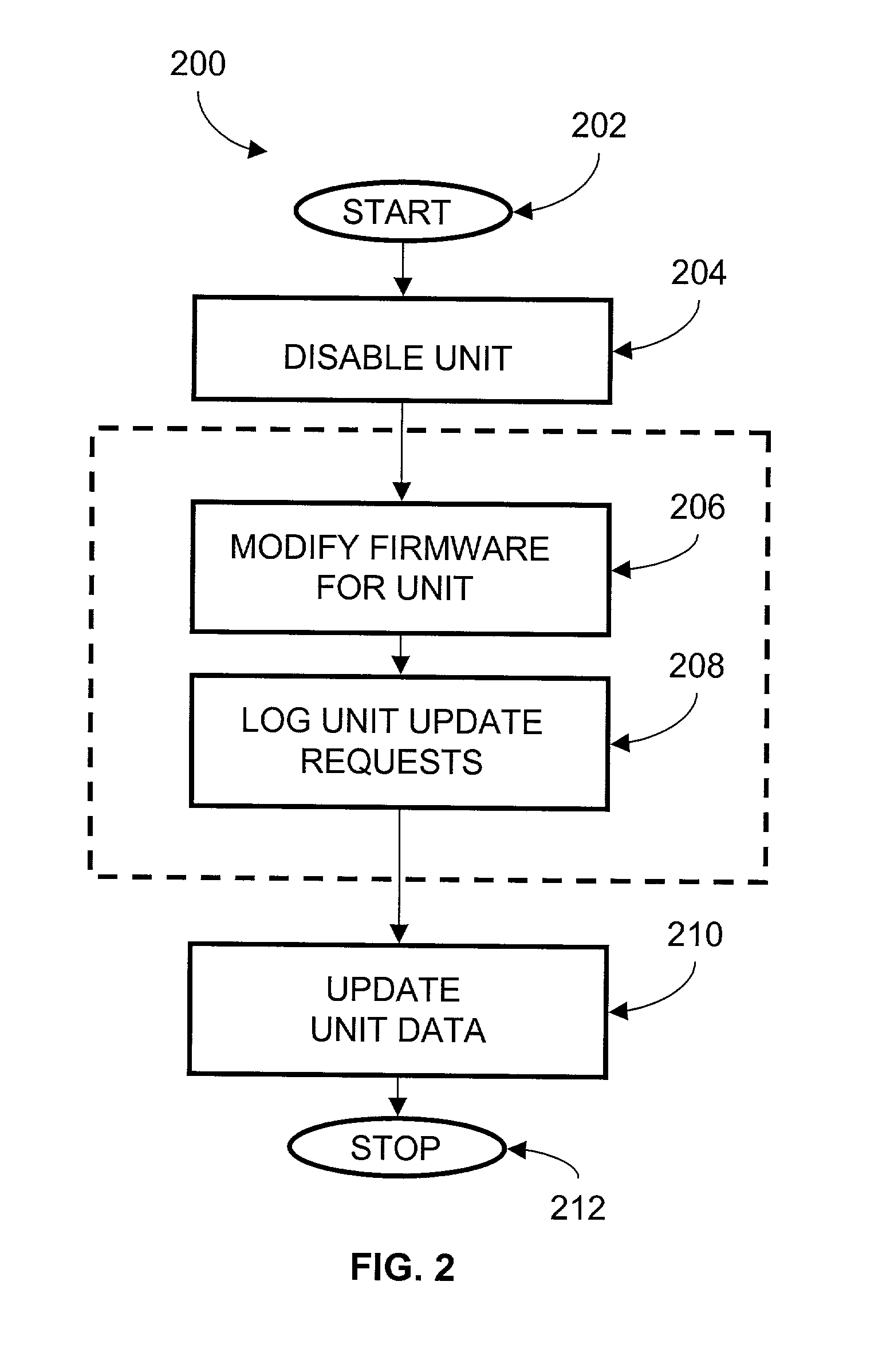
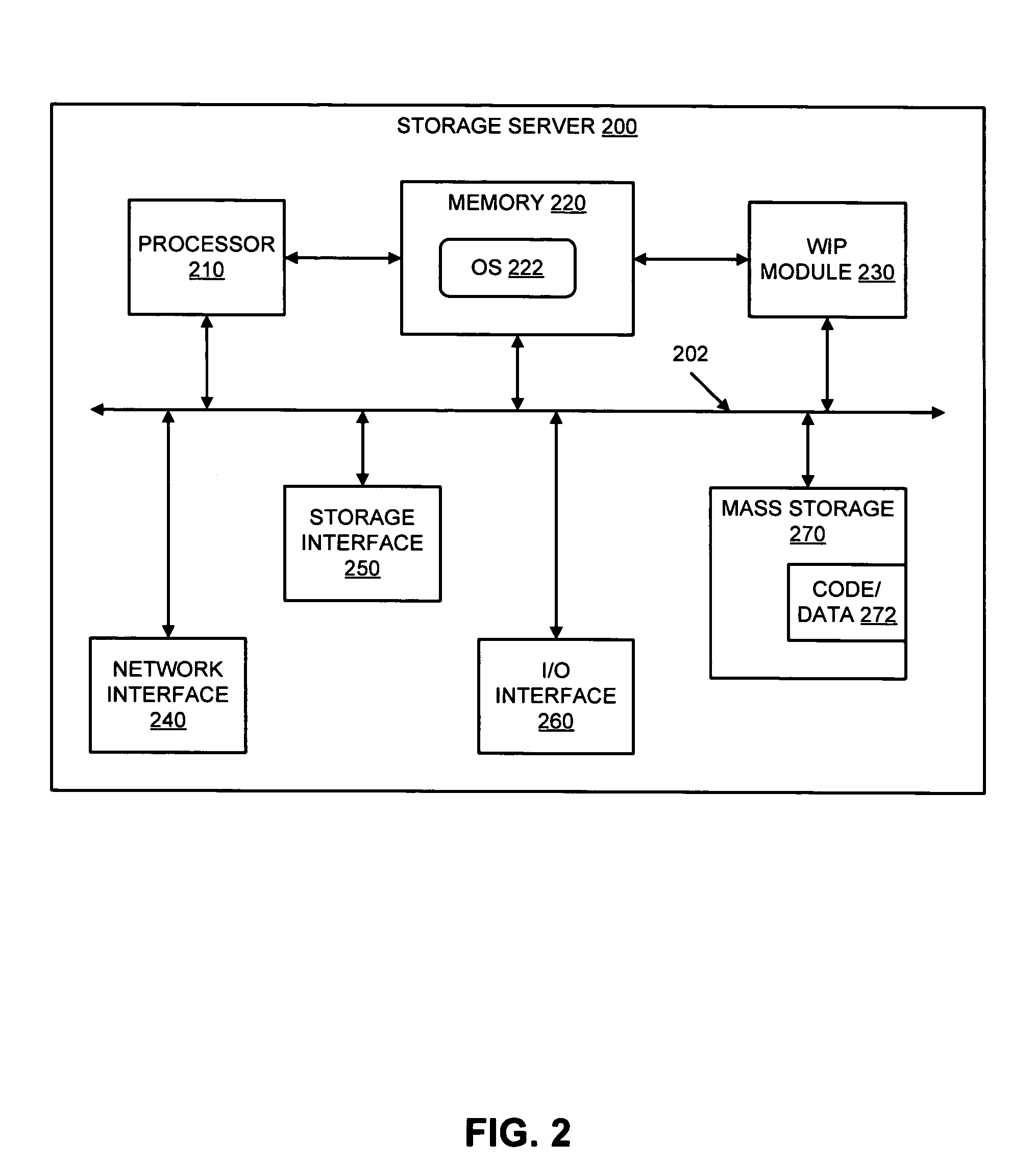
Method and apparatus for upgrading disk drive firmware in a RAID storage system
InactiveUS6816950B2Shorten the timeEliminate needData processing applicationsProgram loading/initiatingRAIDData reconstruction
The present invention provides systems and methods for logging information regarding write operations directed to the disk being upgraded while the single disk is inoperable during the upgrade process. When the upgrade of the disk is complete, the logged information is used to update the information stored on the upgraded disk. The logged information is sufficient to update the disk contents without requiring a time consuming total reconstruction of the entire content of the disk. In one exemplary preferred embodiment, the logged information identifies a logical block numbers of the disk that are impacted by write operations processed while the disk firmware was being upgraded. Only the data corresponding to the logged logical block numbers needs be reconstructed from the redundant data on other disks of the array. This method of data reconstruction is a less time consuming process than a total reconstruction of all data on the upgraded disk.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for flash memory wear-leveling using logical groups
ActiveUS7797481B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionRandom access memoryParallel computing
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
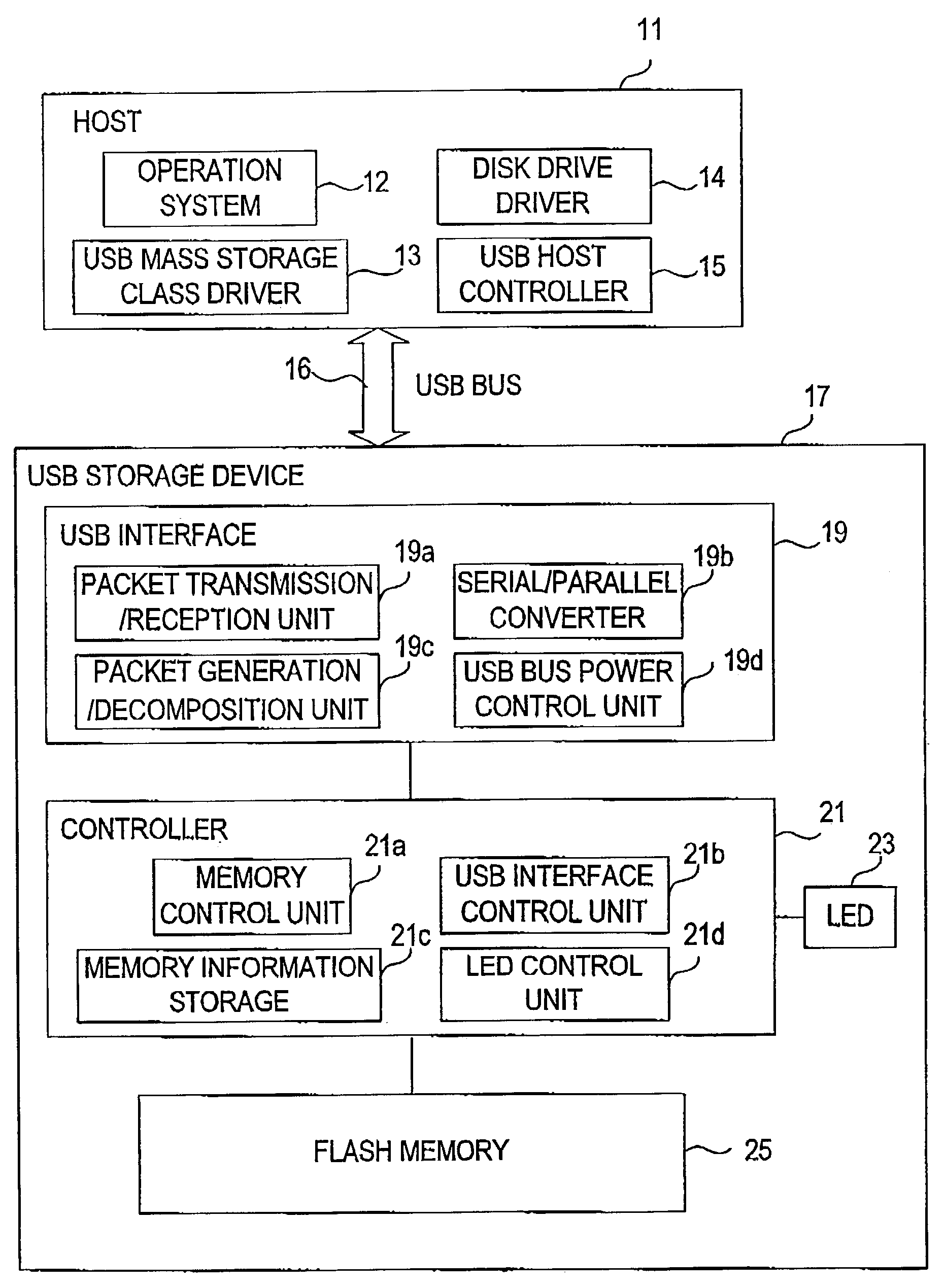
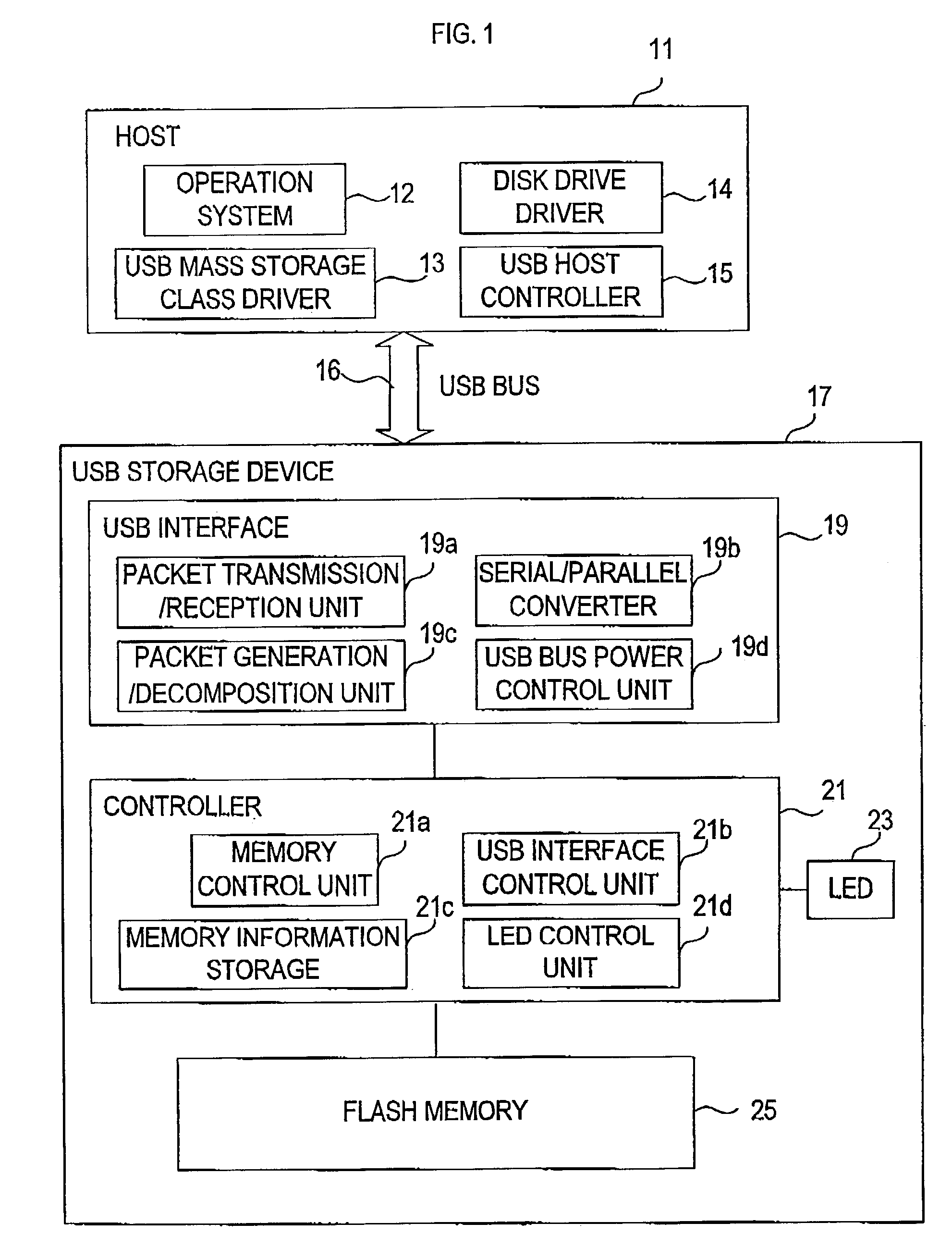
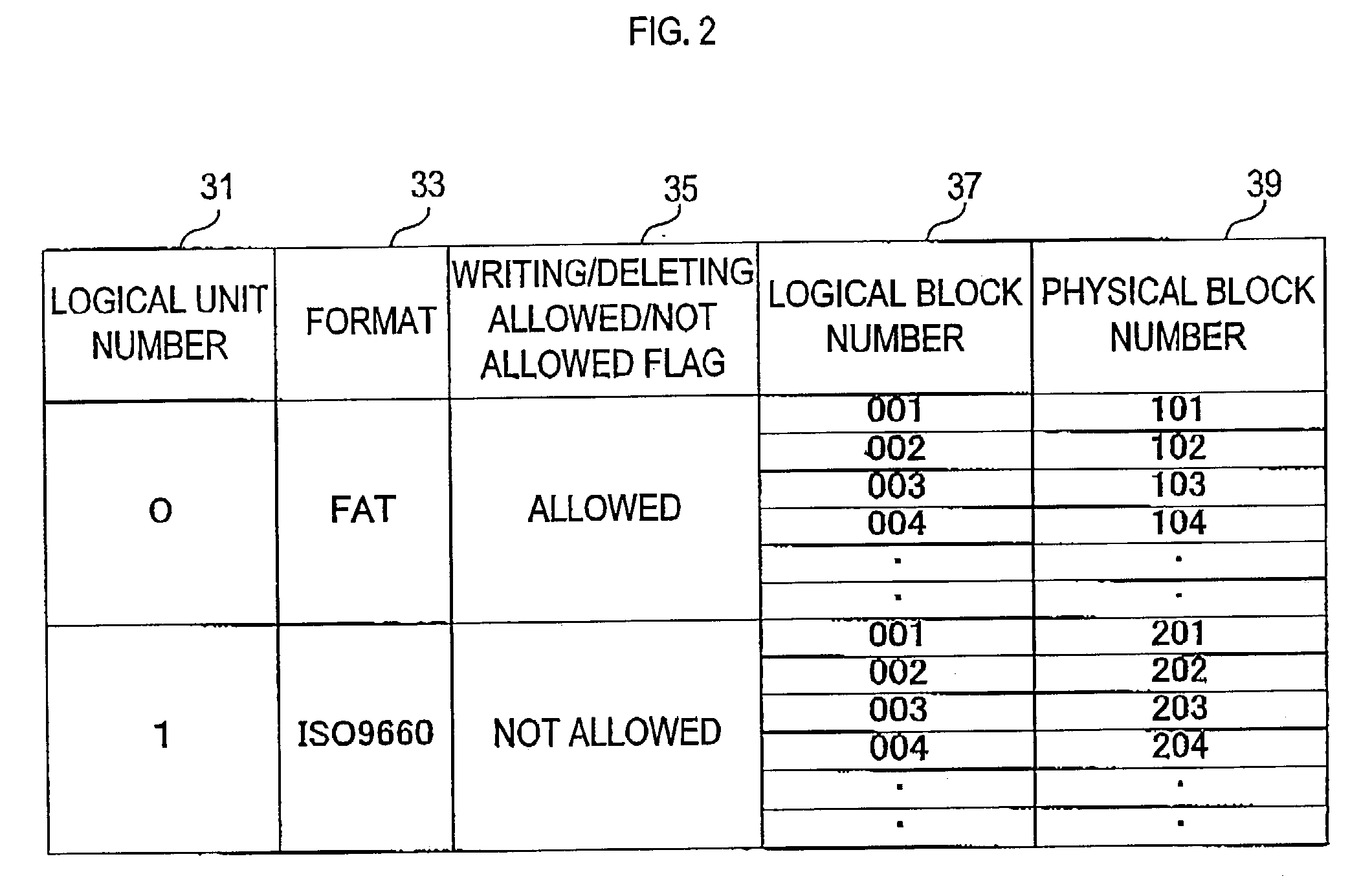
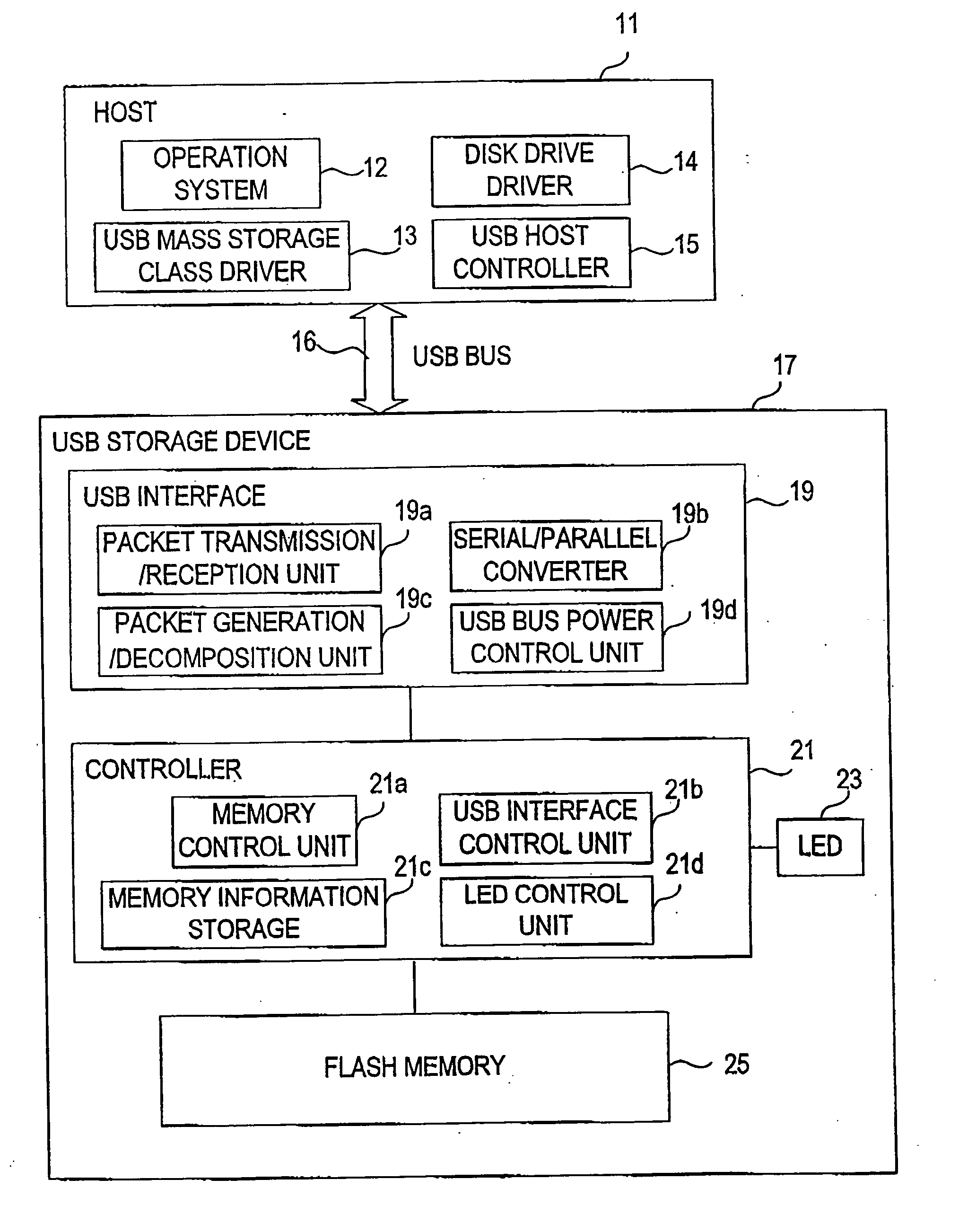
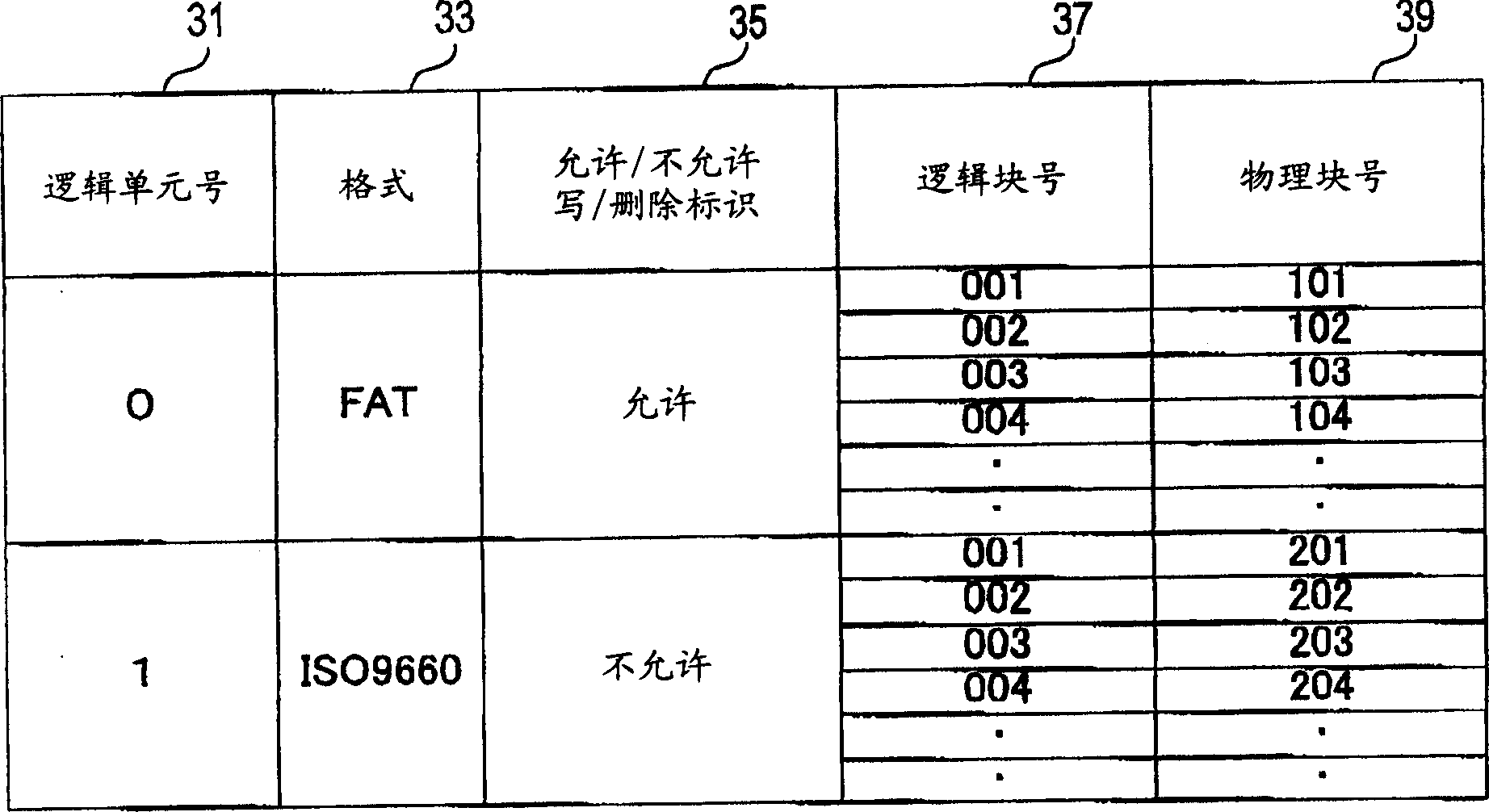
USB storage device and program
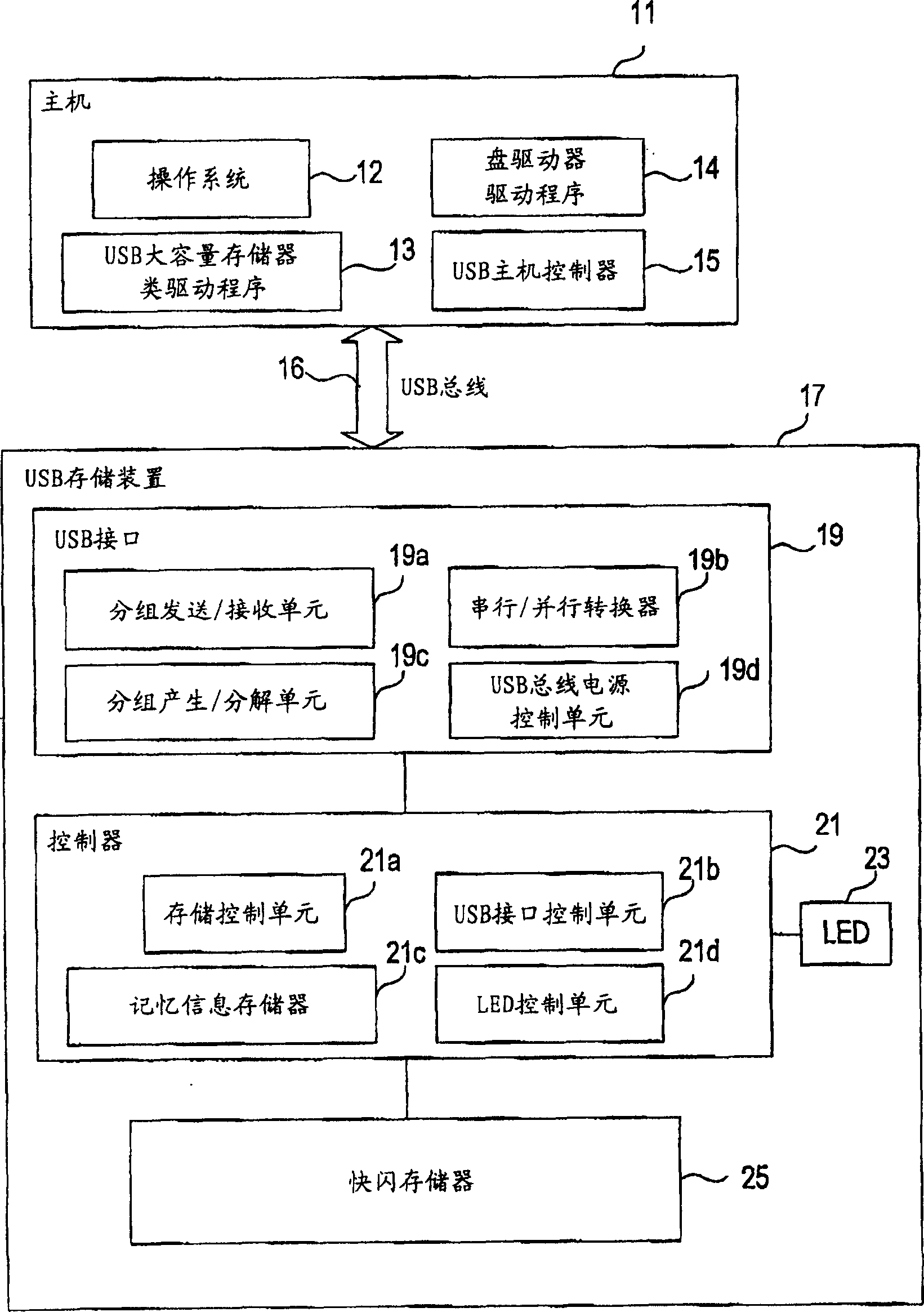
InactiveUS7111121B2Controller of the USB storage device can be simplifiedSimple controllerInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionMass storageSCSI
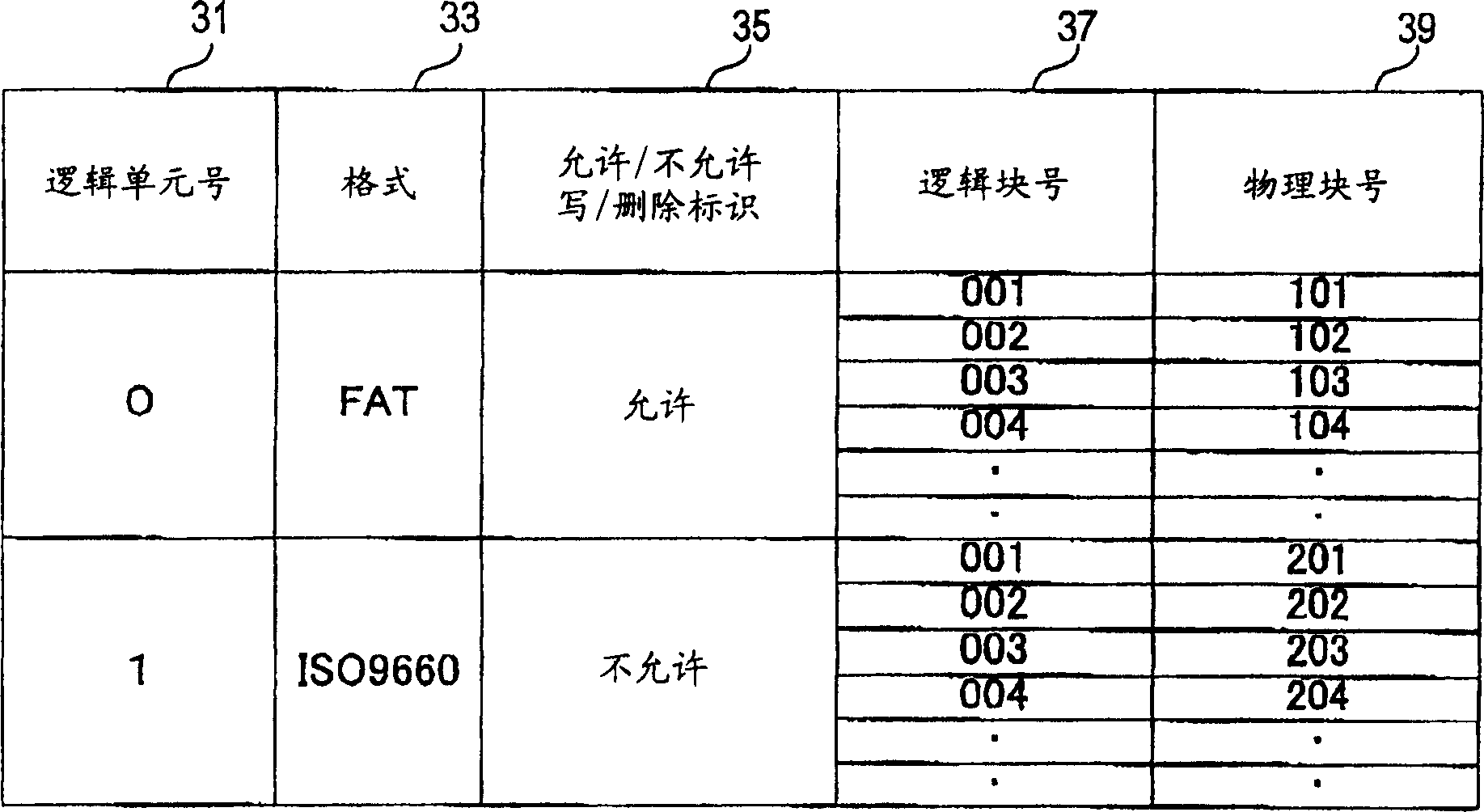
A USB storage device having the function of preventing stored software from being deleted by mistake achieved with as simple a structure as possible. In the USB storage device, the storage area is divided into an area in which execution of reading, writing and deleting is allowed and an area in which only execution of reading is allowed. Information to make a USB mass storage class driver recognize these areas as areas corresponding, respectively, to logical unit numbers defined in the SCSI command set of the USB mass storage class driver owned by the host is stored in the USB storage device. The information includes logical unit numbers, formats, writing / deleting allowed / not allowed flag, logical block numbers and physical block numbers. By this, the USB mass storage class driver recognizes the USB storage device as a SCSI device having two logical units.
Owner:HAGIWARA SOLUTIONS CO LTD
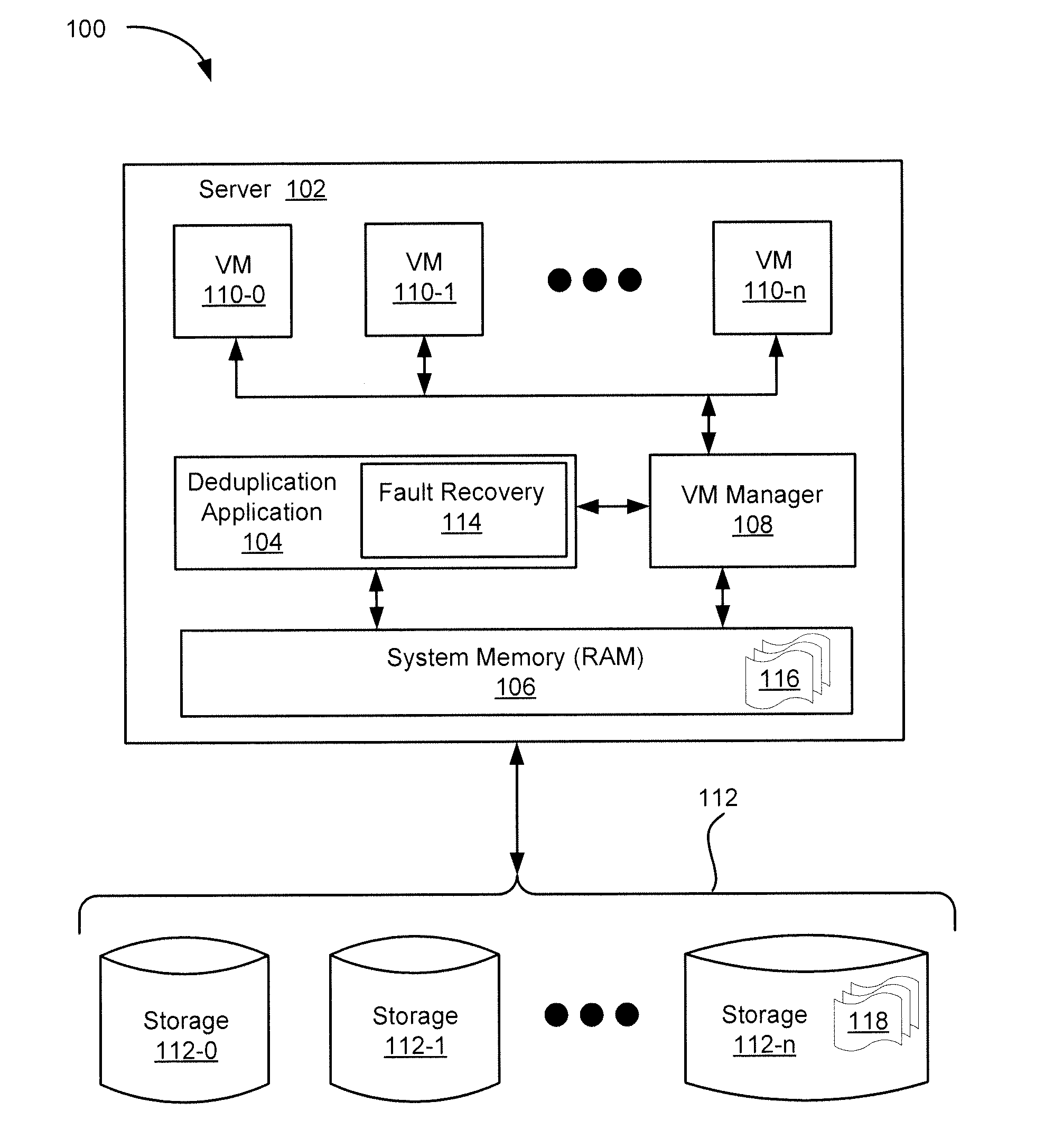
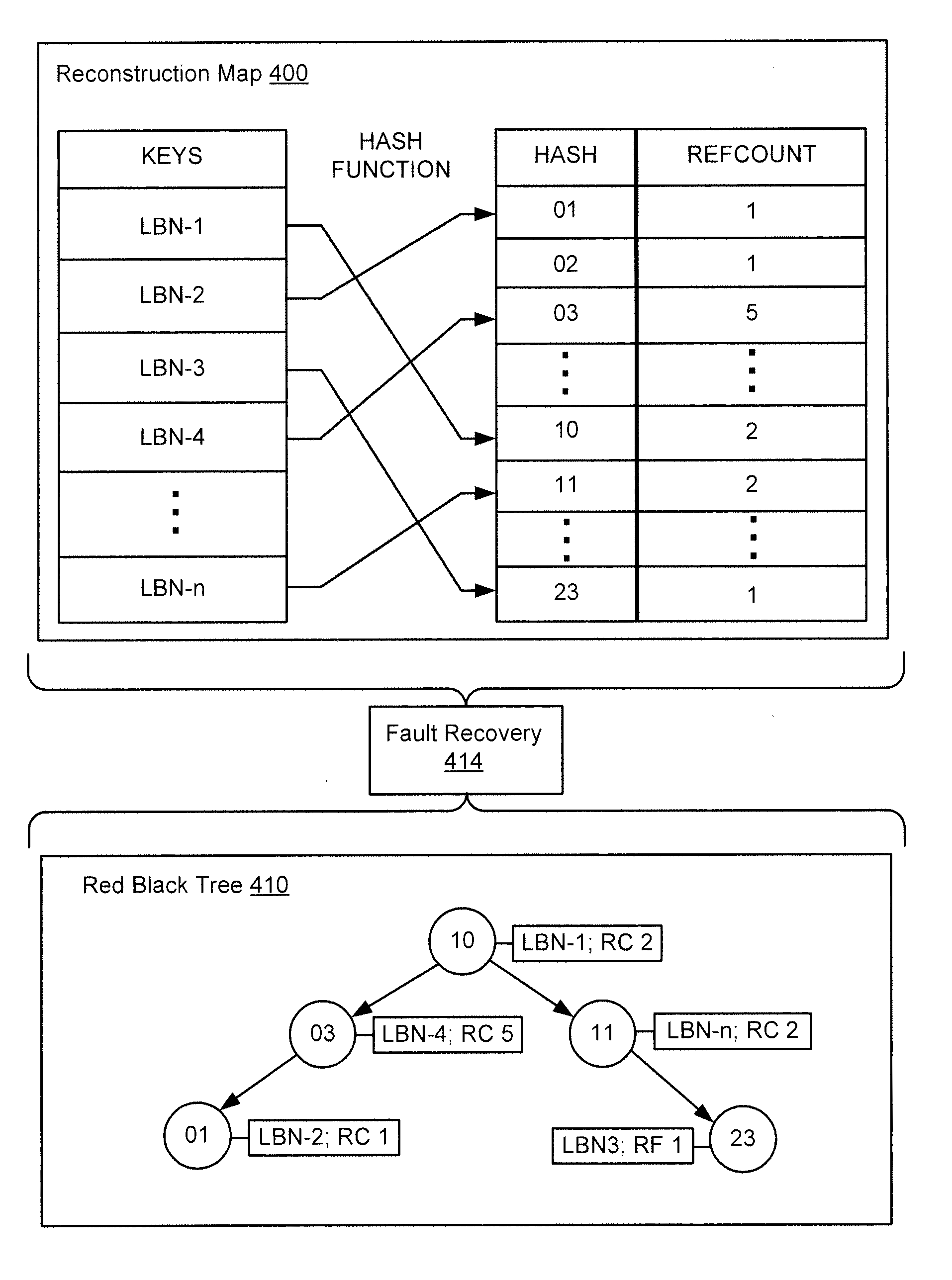
Deduplication metadata access in deduplication file system
ActiveUS20140229451A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile systemData access
Techniques associated with deduplication metadata access in a deduplication file system are described, including determining a state of a file system, reading a table associated with the file system, including reading block numbers associated with files in the file system, the table being stored in a storage,wherein the block numbers include a block number and logical block number, determining whether each of the block numbers exists in a reconstruction map, modifying the reconstruction map, obtaining a hash value associated with each of the block numbers, reading data blocks from a disk using the plurality of block numbers, and constructing deduplication metadata in system memory (i.e., RAM) using a read of the data blocks.
Owner:ATLANTIS COMPUTING HLDG LLC
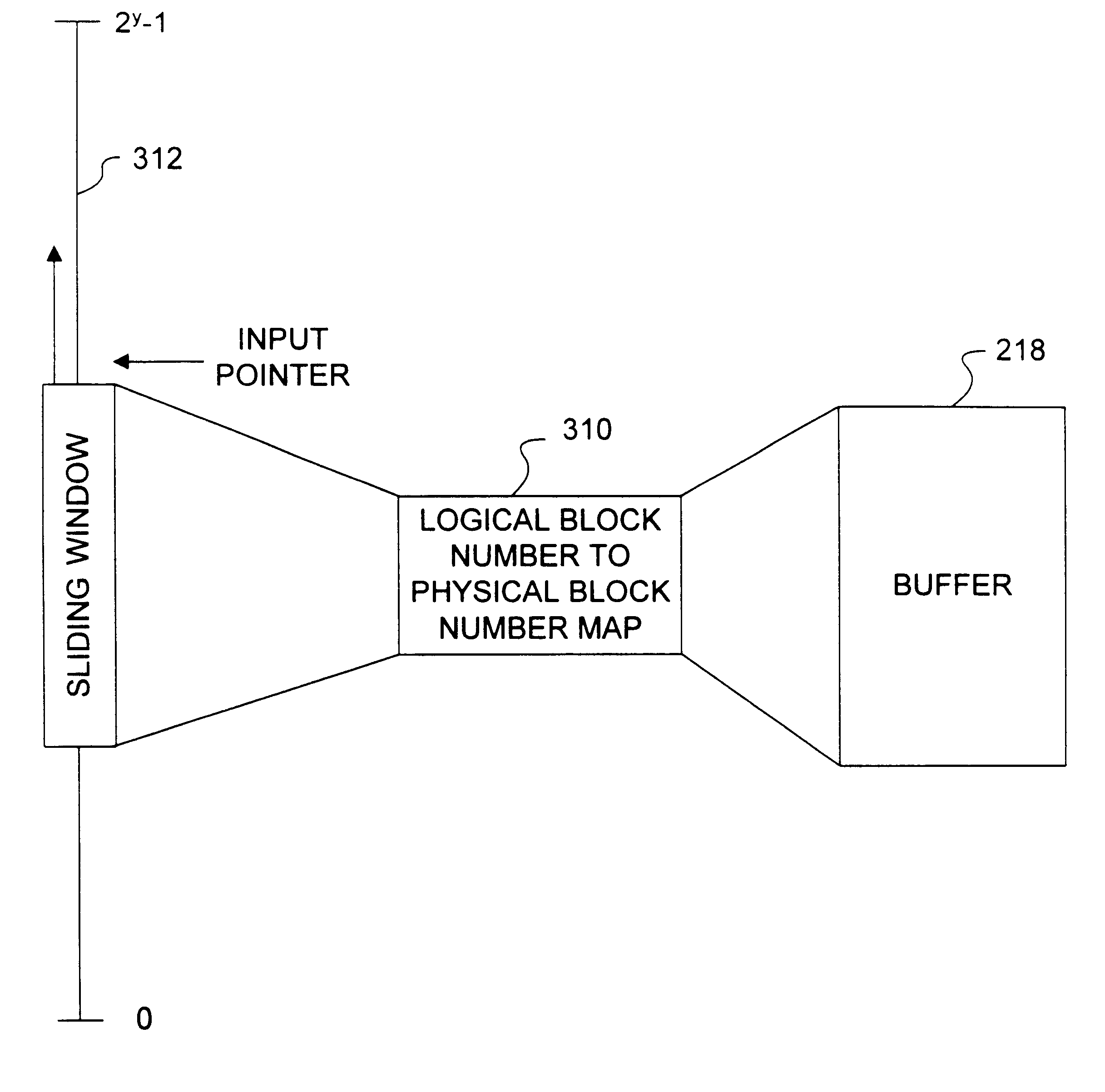
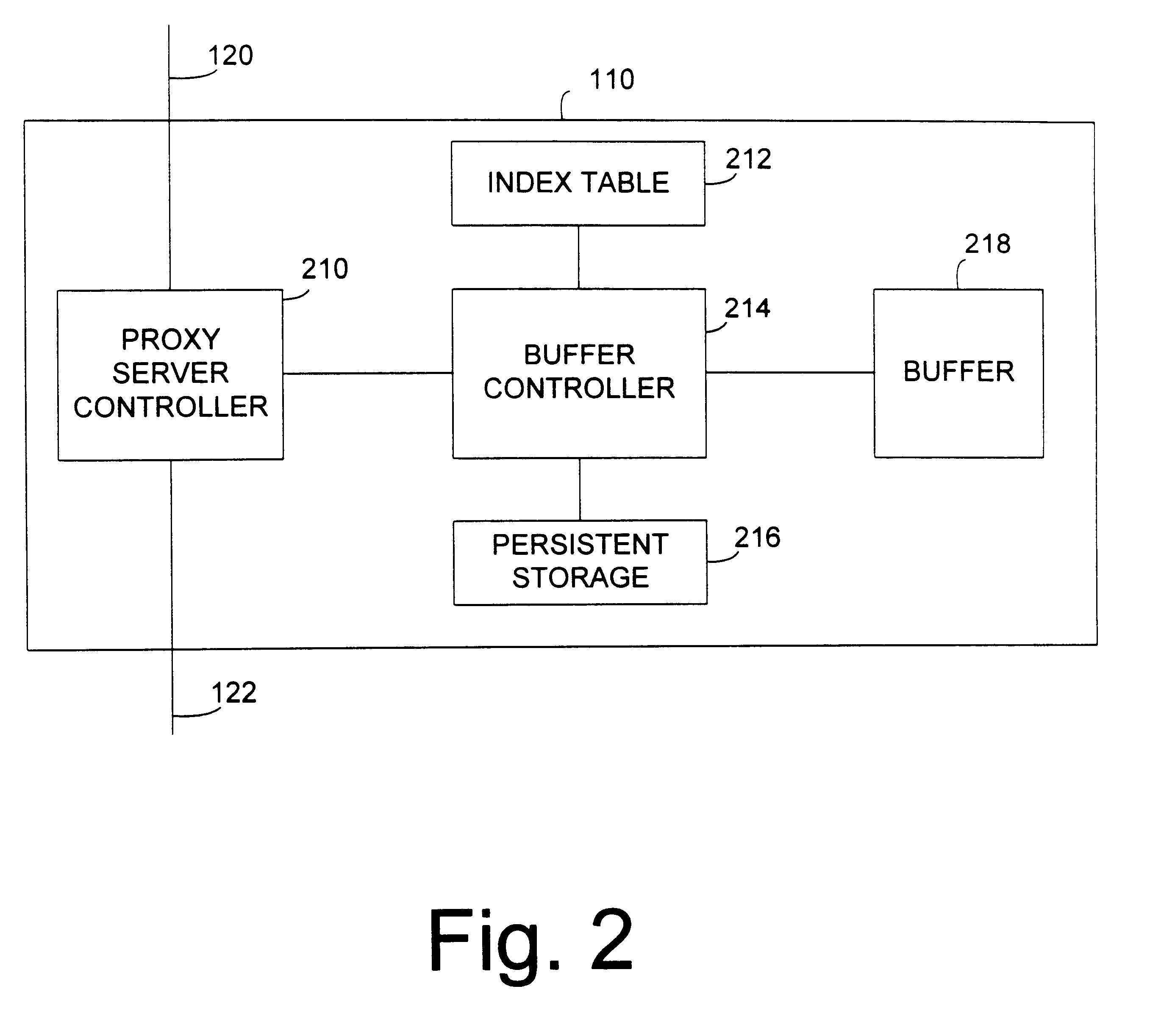
Apparatus and method for providing a cyclic buffer using logical blocks
InactiveUS6807615B1Overcome problemsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingCircular bufferData buffer
An apparatus and method for creating and maintaining a cyclic or circular buffer are implemented using logical blocks corresponding to the physical blocks of the buffer. The logical blocks are mapped to the physical blocks of the cyclic buffer, and are used to create an index table for the buffer. Each entry in the index table corresponds to one or more blocks in the buffer, and has a logical block number respectively associated with a buffer block. When information from the buffer is accessed, the index table is consulted to determine if the requested information is stored in the buffer. If the information is stored in the buffer, the logical block number corresponding to the information is retrieved from the entry and translated into a corresponding physical block number. Using logical block numbers allows simple determination of whether the buffer block is valid, and how new or fresh the buffer block is without requiring a generation or cycle number.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
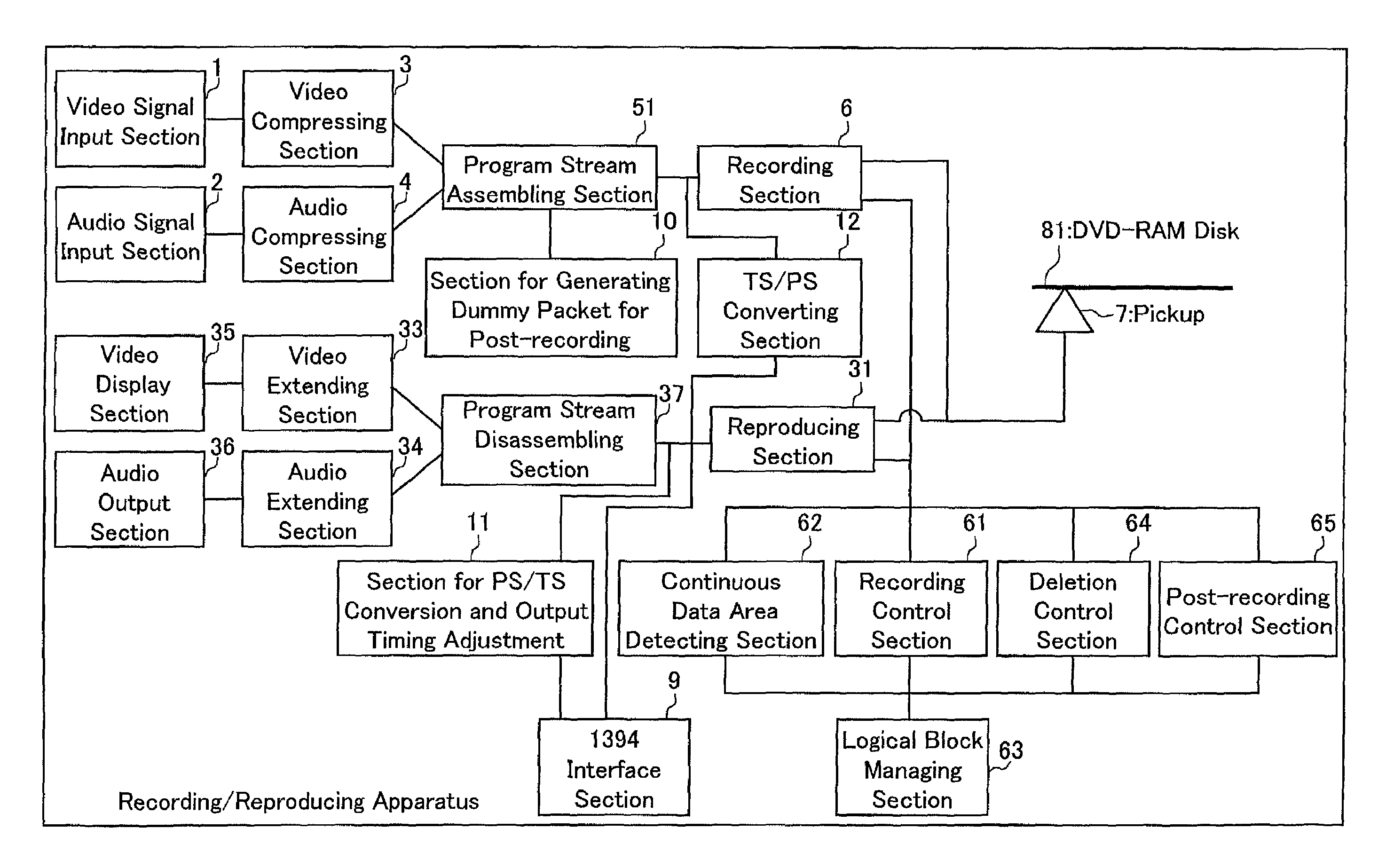
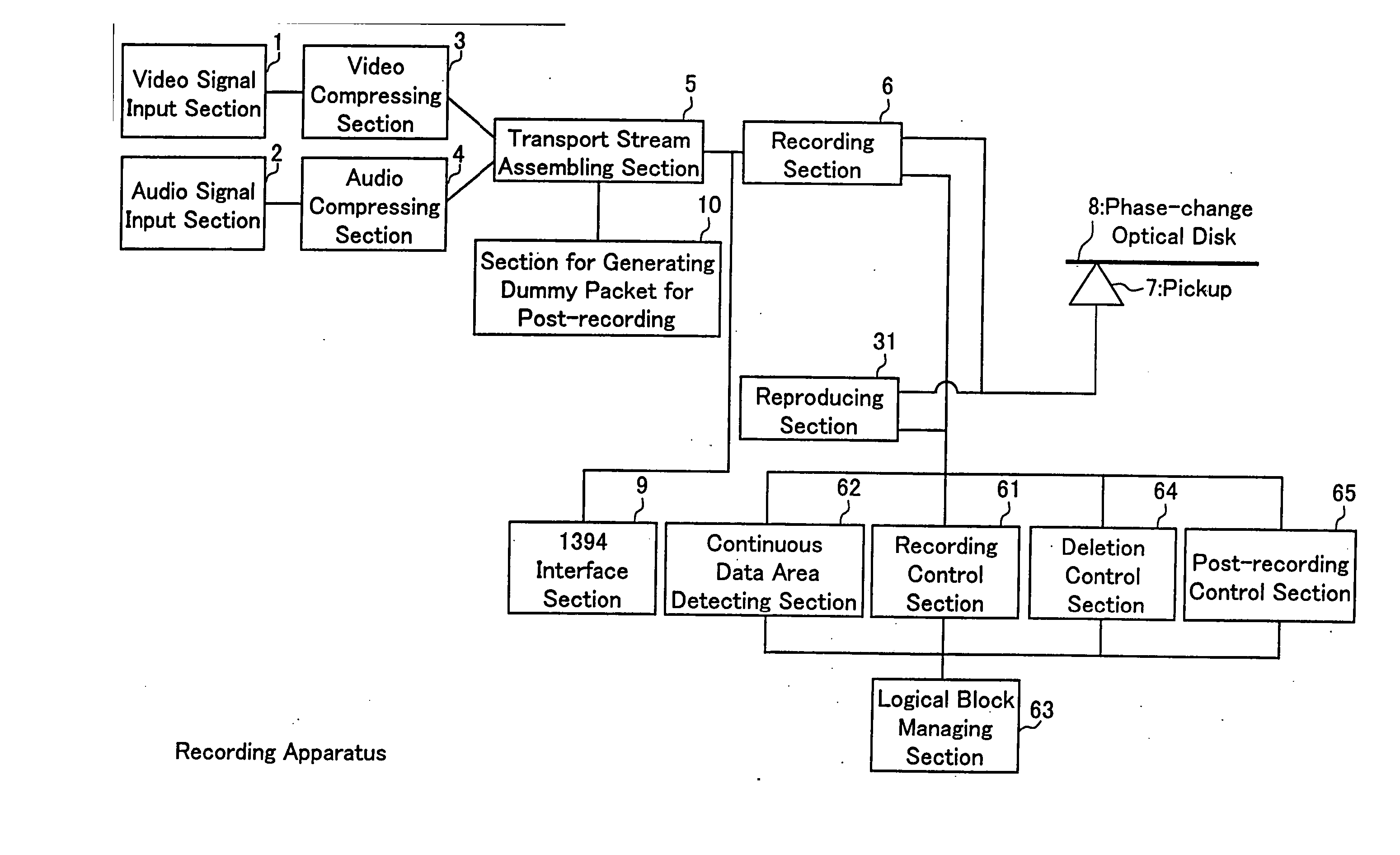
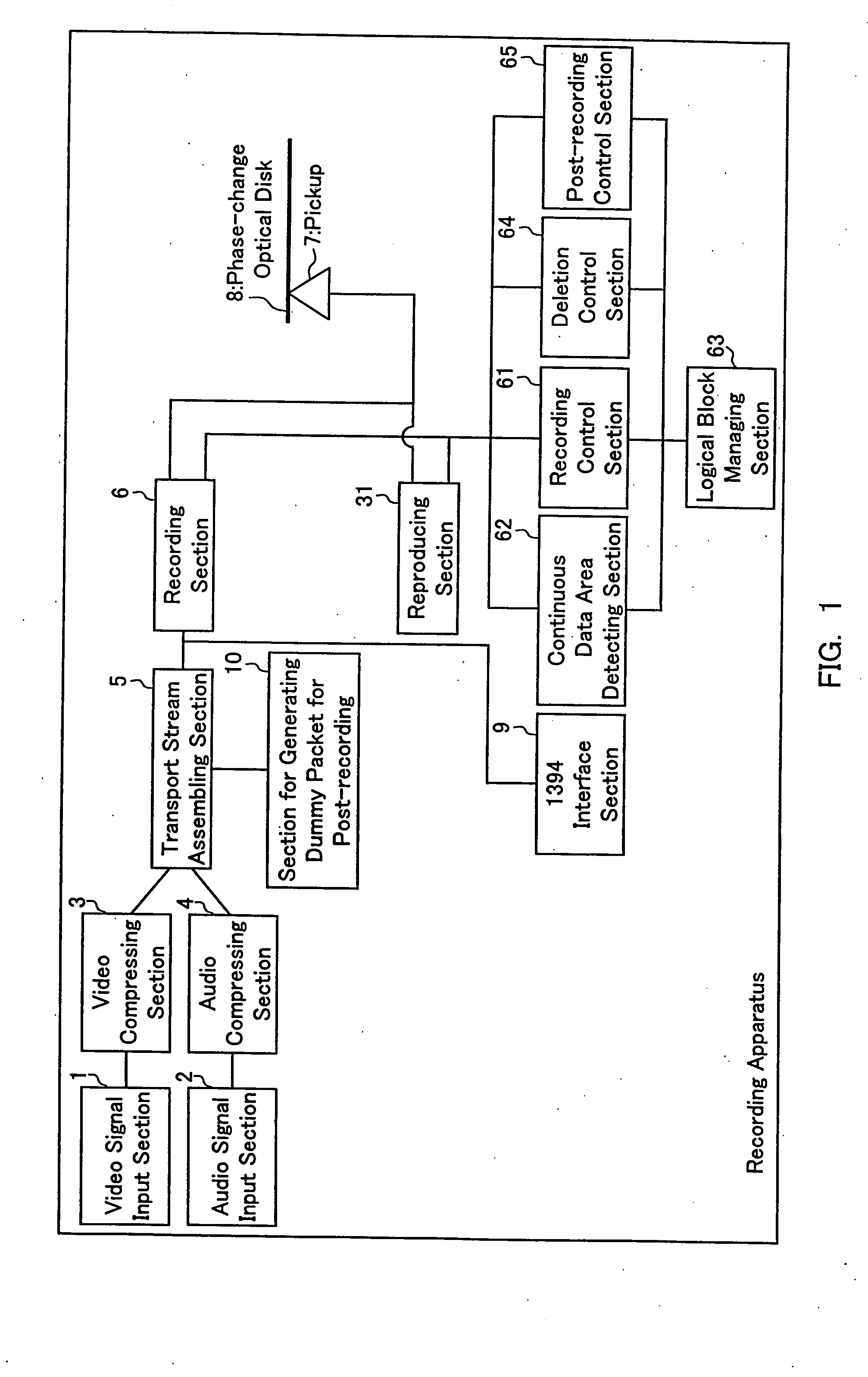
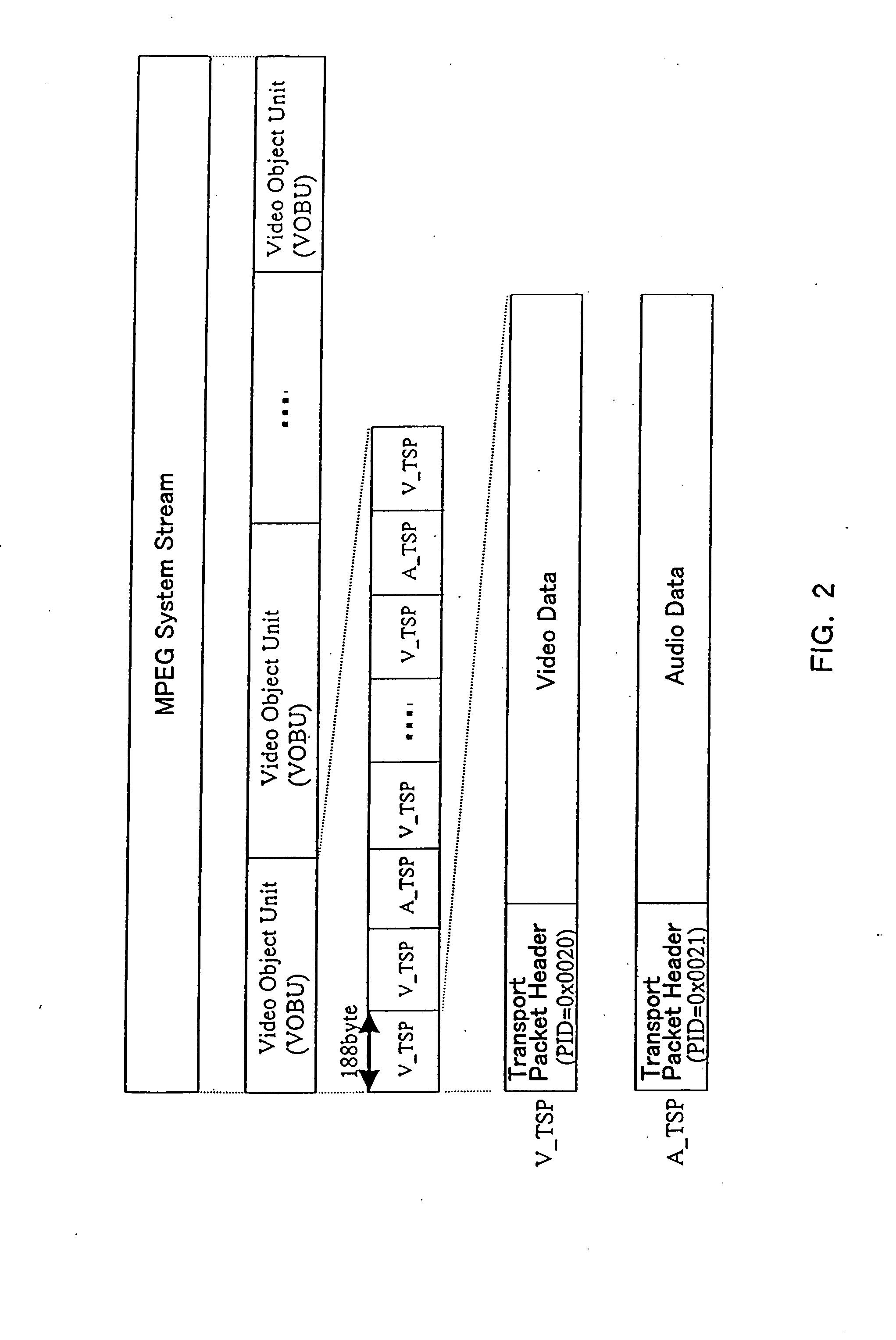
AV data recording device and method, disk recorded by the AV data recording device and method, AV data reproducing device and method therefor
InactiveUS7292781B1Easy to copyReduce wasteTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsData recordingAudio frequency
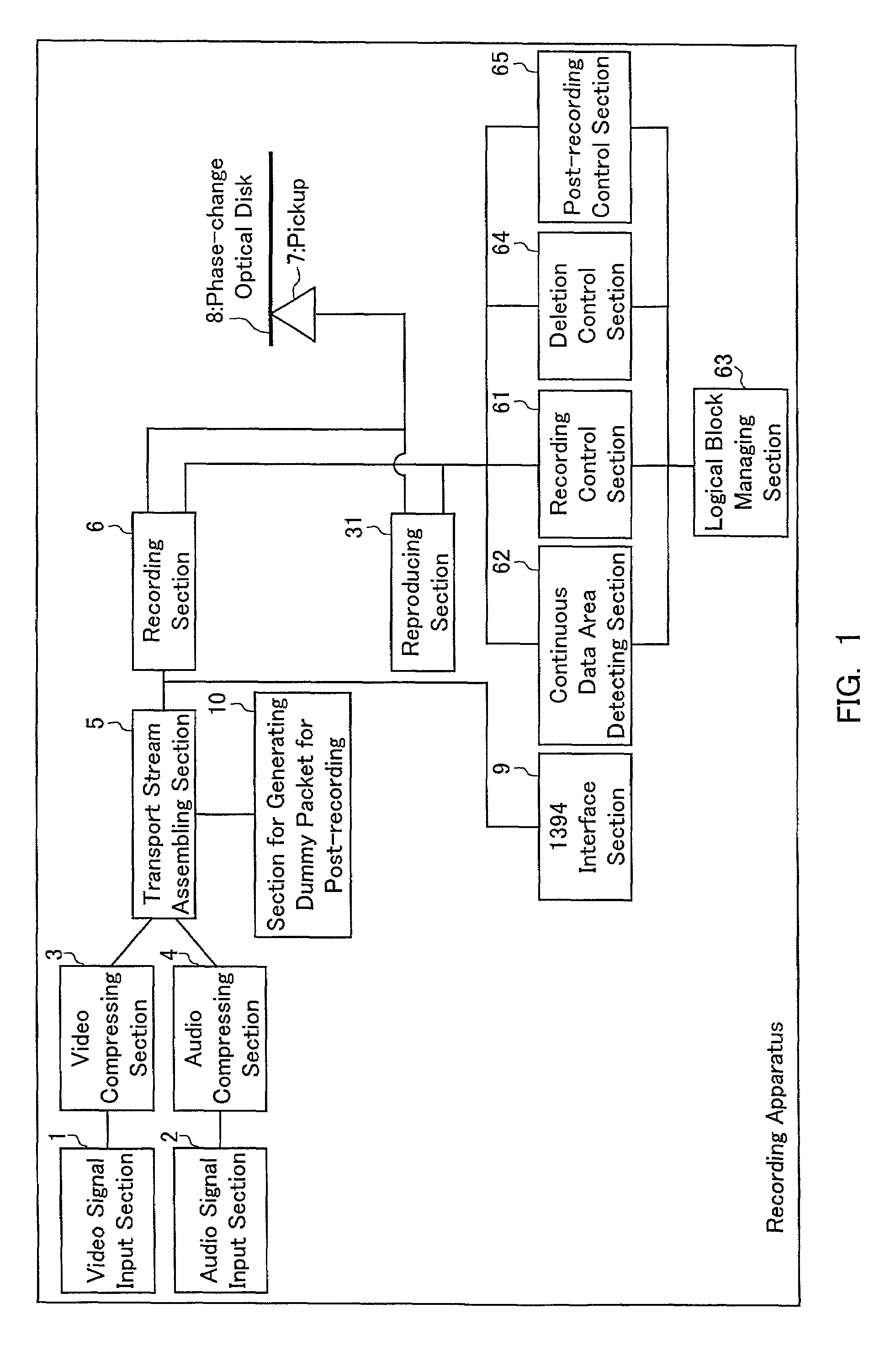
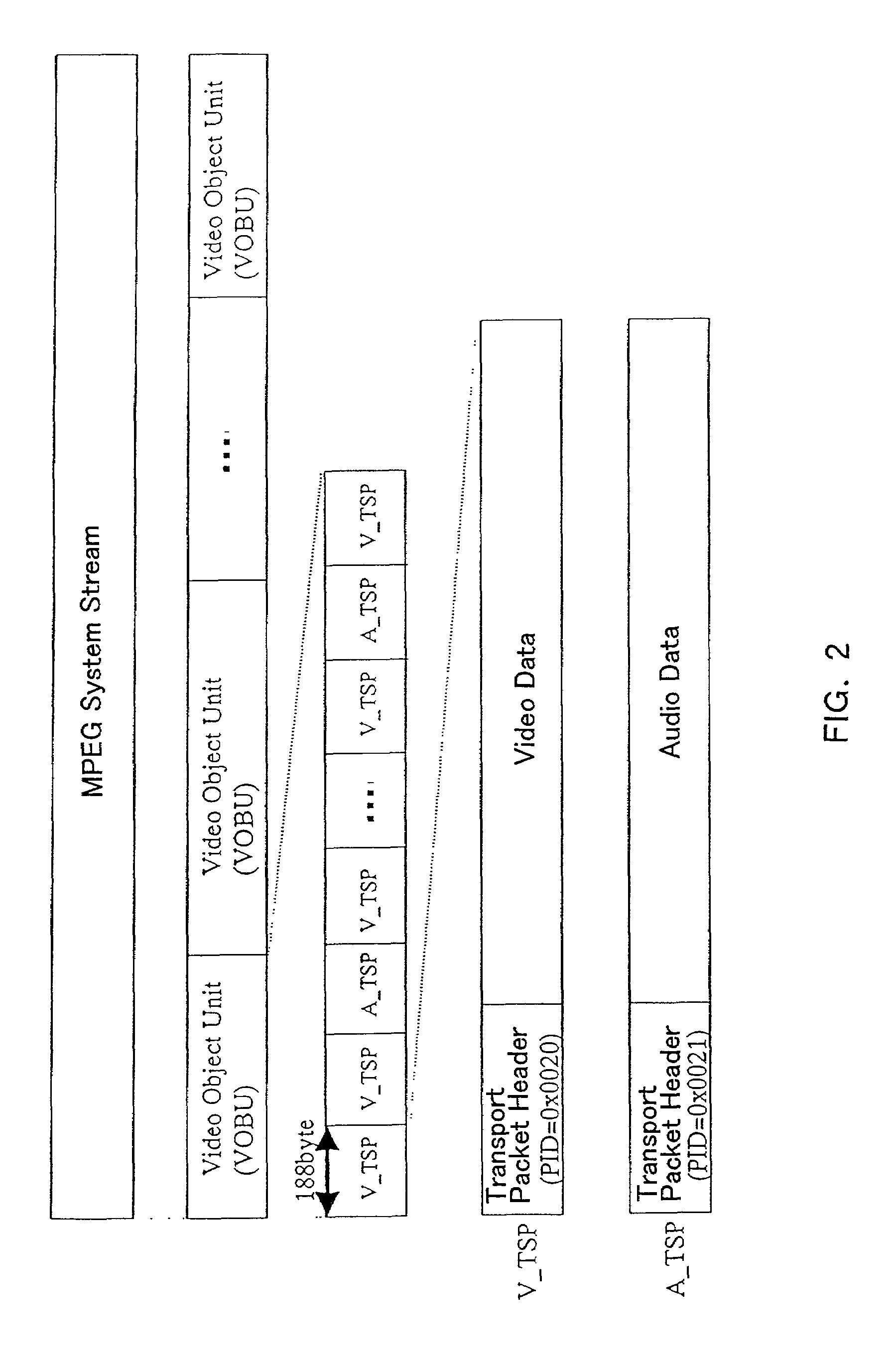
The present invention provides an AV data recording apparatus and method that facilitate various processes concerning a recorded video, including continuous reproduction, digital transmission, file operation, partial deletion, and post-recording. The AV data recording apparatus divides an audio signal and a video signal into transport packets having a predetermined unit length, assembles a plurality of transport packets as one transport stream and executes recording. Accordingly, this invention enables managing whether a logical block is used or not, detecting a continuous data area comprising plural logical blocks that ensure realtime continuous reproduction, and determining logical block numbers of continuous data areas to be recorded. As a result, the transport stream is recorded continuously on a plurality of detected continuous data areas.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
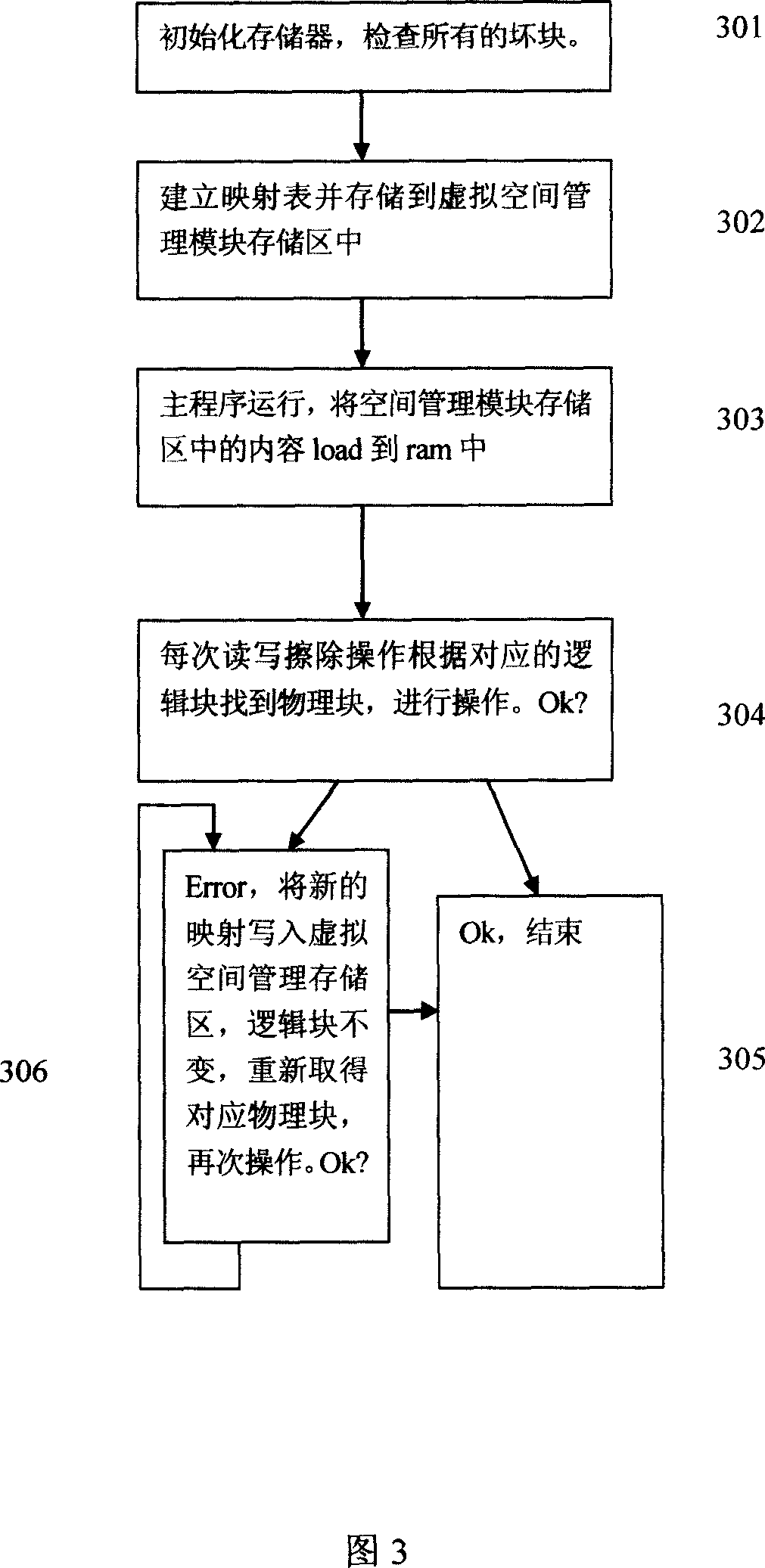
Method for conducting virtual space management to NAND FLASH memory
InactiveCN1932778ASolve downloadSolve storage problemsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual spaceSpace management
The invention is concerned with the method that processes the virtual space management to the NAND flash memorizer: establishes mapping table, maps the virtual series useable logical block on the non-series useable physical block, saves the mapping table in the managing module of the virtual space, elides the error block managing part of every non-correlated programming module in order to get the better logical block, the logical space managing module provides the corresponding error block mapping mechanism and finds out the corresponding physical block number function according to the logical block number. The invention can avoid the error block processing problem of several software modules in the mobile phone terminal repeatedly, and also avoid the complex processing when two terminal programs that can not run synchronously both can visit the error block.
Owner:HISENSE +1
USB storage device and program
InactiveUS20060200629A1Easy to storeController of the USB storage device can be simplifiedInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionMass storageSCSI
A USB storage device having the function of preventing stored software from being deleted by mistake achieved with as simple a structure as possible. In the USB storage device, the storage area is divided into an area in which execution of reading, writing and deleting is allowed and an area in which only execution of reading is allowed. Information to make a USB mass storage class driver recognize these areas as areas corresponding, respectively, to logical unit numbers defined in the SCSI command set of the USB mass storage class driver owned by the host is stored in the USB storage device. The information includes logical unit numbers, formats, writing / deleting allowed / not allowed flag, logical block numbers and physical block numbers. By this, the USB mass storage class driver recognizes the USB storage device as a SCSI device having two logical units.
Owner:HAGIWARA SYS COM
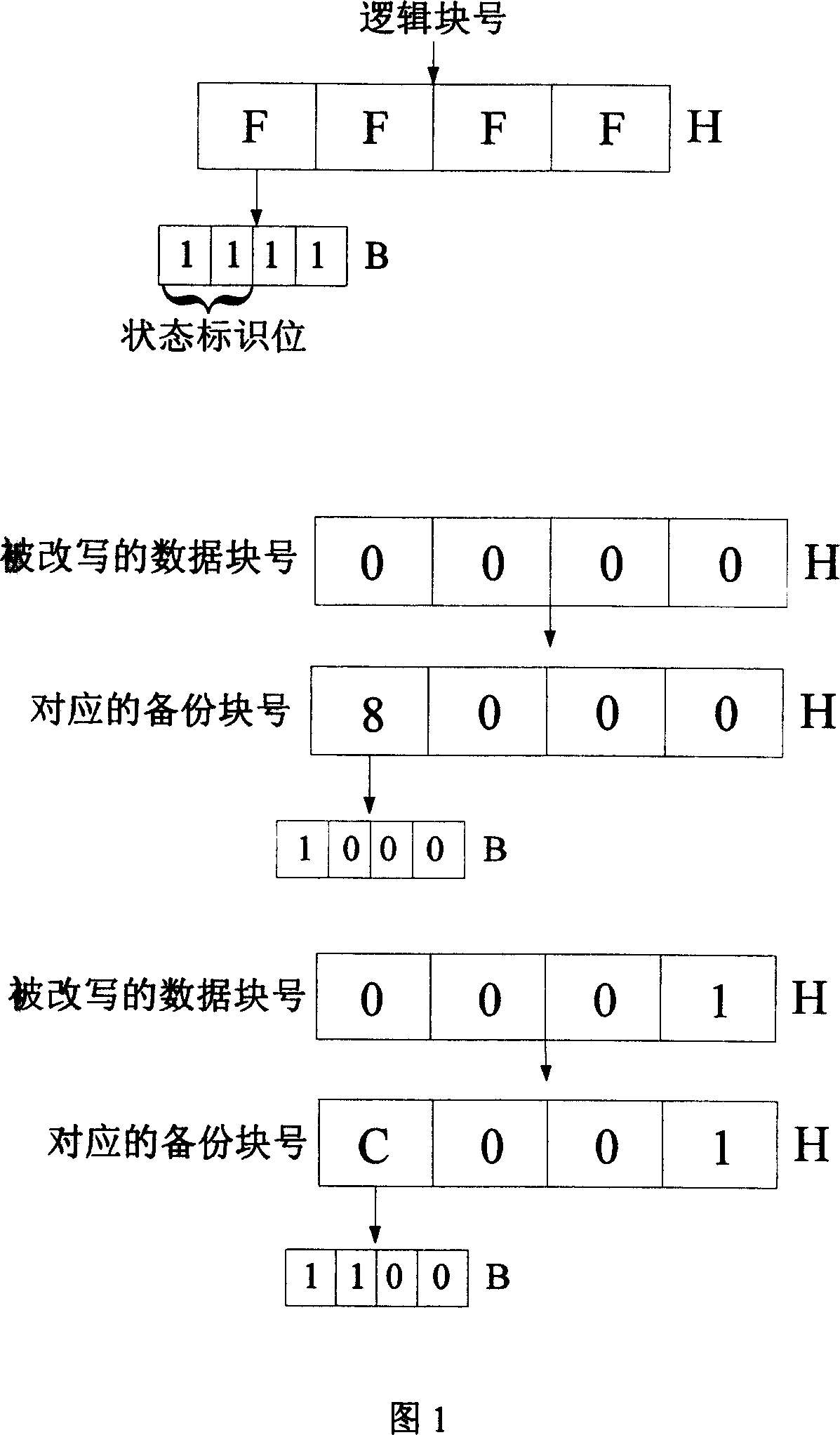
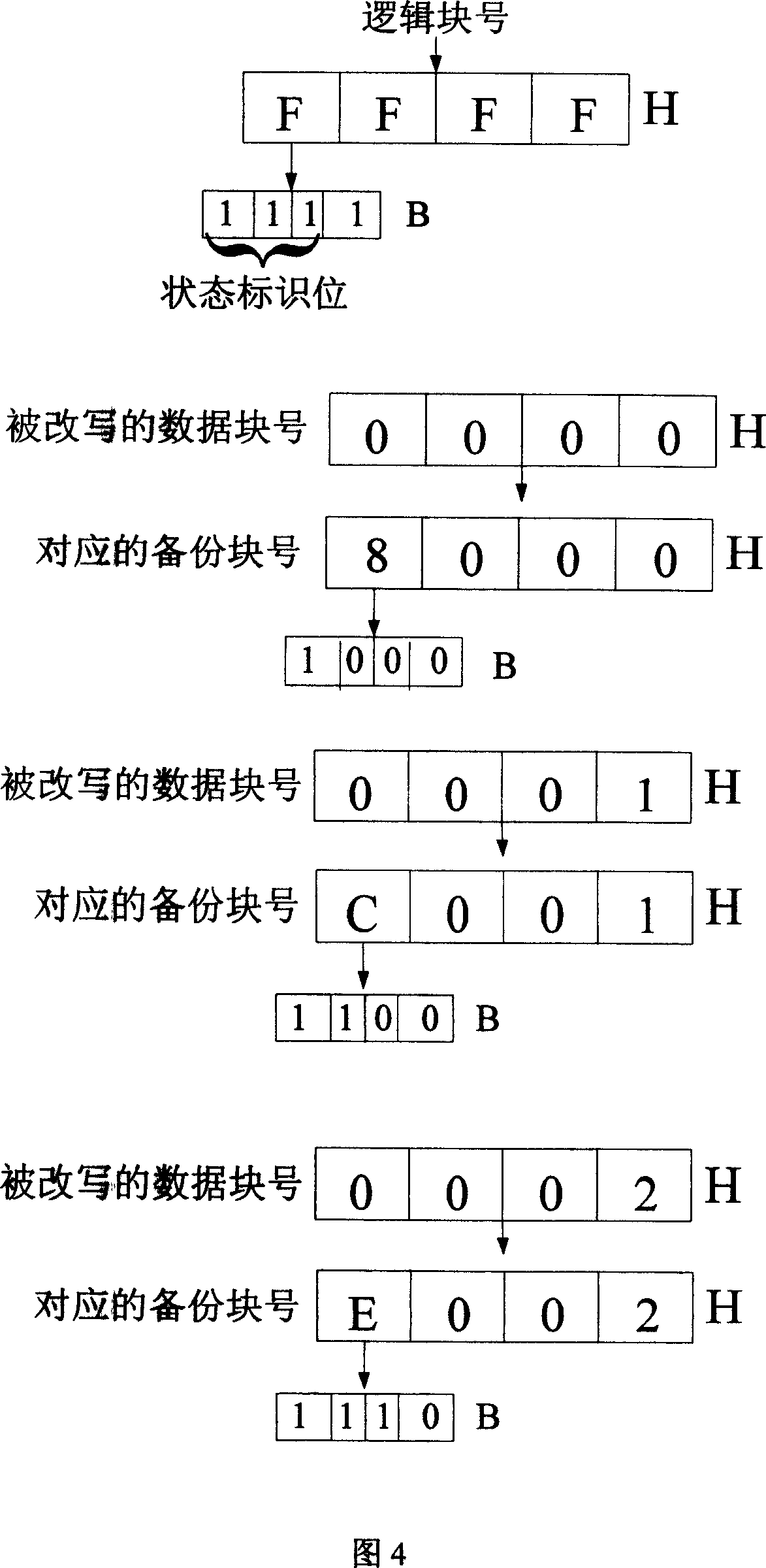
Power-fail protection method based on two continuous logical blocks for non-volatile memory
ActiveCN101025715AAchieve protectionAchieve the purpose of recoveryMemory loss protectionRedundant operation error correctionElectricityData store
The invention relates to a data power-off protection method, especially relating to a power-off protection method based on two continuous logic blocks in a nonvolatile memory, adding one or more backup blocks in a memory area and on the basis of the original logic block number, adding state flag bit of logic block, and comprising trans-block data power-off safety rewrite course and after-power-on data recovery course. By adding backup blocks, the invention assures the data is uneasy to lose at power off while rewriting multiple data blocks, largely improving data storage reliability and safety, and effectively avoiding frequently erasing some erase block so as to prolong Flash memory service life.
Owner:FEITIAN TECHNOLOGIES
Usb storage device and program
ActiveCN1542630AImprove protectionSimple controllerInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionMass storageSCSI
A USB storage device having the function of preventing stored software from being deleted by mistake achieved with as simple a structure as possible. In the USB storage device, the storage area is divided into an area in which execution of reading, writing and deleting is allowed and an area in which only execution of reading is allowed. Information to make a USB mass storage class driver recognize these areas as areas corresponding, respectively, to logical unit numbers defined in the SCSI command set of the USB mass storage class driver owned by the host is stored in the USB storage device. The information includes logical unit numbers, formats, writing / deleting allowed / not allowed flag, logical block numbers and physical block numbers. By this, the USB mass storage class driver recognizes the USB storage device as a SCSI device having two logical units.
Method and apparatus for upgrading disk drive firmware in a RAID storage system
InactiveUS20030212856A1Shorten the timeEliminate needData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionRAIDData reconstruction
The present invention provides systems and methods for logging information regarding write operations directed to the disk being upgraded while the single disk is inoperable during the upgrade process. When the upgrade of the disk is complete, the logged information is used to update the information stored on the upgraded disk. The logged information is sufficient to update the disk contents without requiring a time consuming total reconstruction of the entire content of the disk. In one exemplary preferred embodiment, the logged information identifies a logical block numbers of the disk that are impacted by write operations processed while the disk firmware was being upgraded. Only the data corresponding to the logged logical block numbers needs be reconstructed from the redundant data on other disks of the array. This method of data reconstruction is a less time consuming process than a total reconstruction of all data on the upgraded disk.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Caching system capable of supporting zero copy on the basis of flash memory array, and method
InactiveCN107256196AImprove reading and writing efficiencyReduce erasureMemory adressing/allocation/relocationZero-copyData path
The invention discloses a caching system capable of supporting zero copy on the basis of a flash memory array, and a method. The system comprises a main control module, a physical caching module, a read address and write address conversion module, an idle block management module, a metadata recording table and a rear side flash memory module. The method comprises the following the following steps that: receiving a command request sent from a front side, converting a logic block number in the command request into a corresponding physical block number, carrying out a Hash operation on a rear-side address in the command request to obtain a corresponding metadata address index; according to the metadata address index, inquiring a metadata state table and a metadata record chart, processing the data of a corresponding table item in the metadata record chart according to the state information of the corresponding table item of the state table, and updating the corresponding table item of the metadata state table, and updating a mapping table in the read address and write address conversion module; and returning a completion command to the front side. By use of the system, a contradiction that the read-write access size of a traditional cache and a flash memory page size are not matched is solved, meanwhile, the zero copy on a caching read-write data path is realized, an unnecessary middle copy process is eliminated, cache read-write efficiency is improved, meanwhile, erasing for Flash can be reduced, and the service life of the Flash is prolonged.
Owner:北京中航通用科技有限公司
Flash memory access apparatus and method
InactiveUS7664906B2Process can be minimizedMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerLogic block
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for processing data of flash memory equipment
InactiveCN101231617ASimplify the logical address mapping relationshipExtended service lifeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesData stabilityLogic mapping
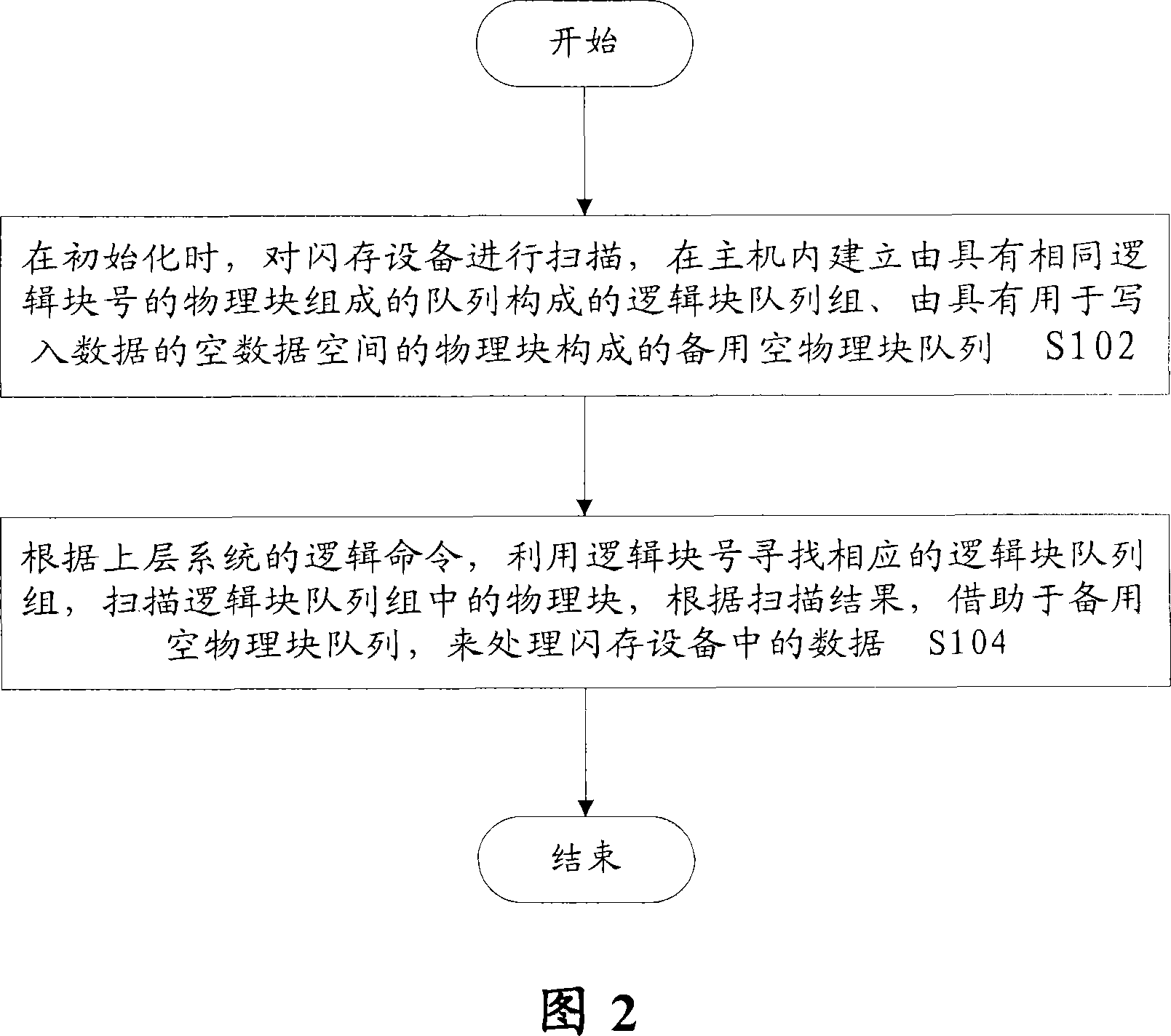
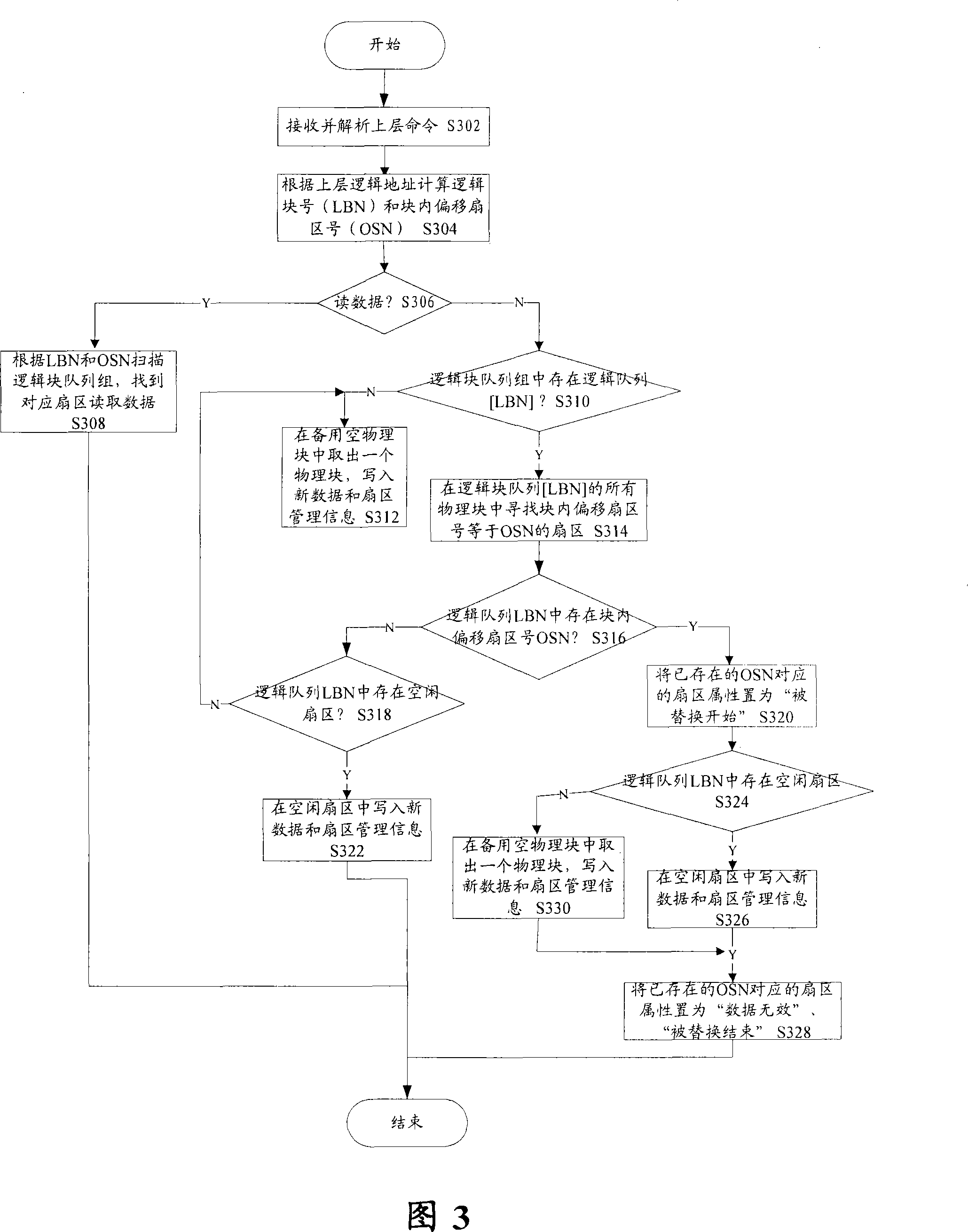
The invention provides a data processing method for a flash memory device. The method comprises the following steps that: step S102, the flash memory device is scanned during the initialization, a logical block queue group and a spare empty physical block queue are established in a host computer, the logical block queue group is formed by queues composed of physical blocks with the same logical block number, and the spare empty physical block queue is composed of physical blocks with empty data spaces, in which data can be written; step S 104, the corresponding logical block queue group is searched by utilizing the logical block number according to the logical order of an upper-level system, the physical blocks in the logical block queue group are scanned, and the data in the flash memorydevice is processed by dint of the spare empty physical block queue according to the scanning result. Through the technical proposal of the invention, the logical mapping relation is simplified, the efficiency is improved, the data stability is ensured, and the service life of the flash memory is prolonged.
Owner:ZTE CORP
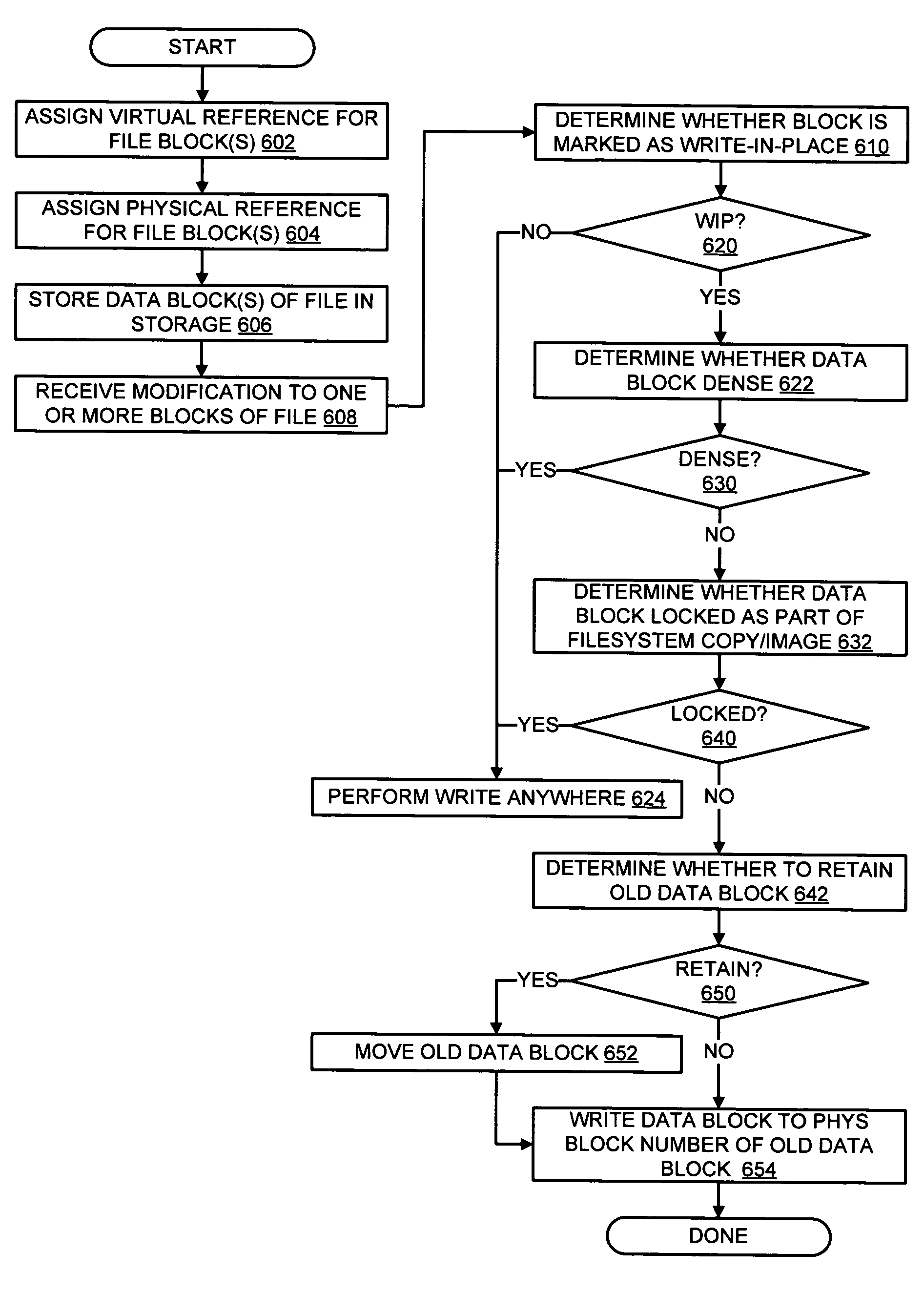
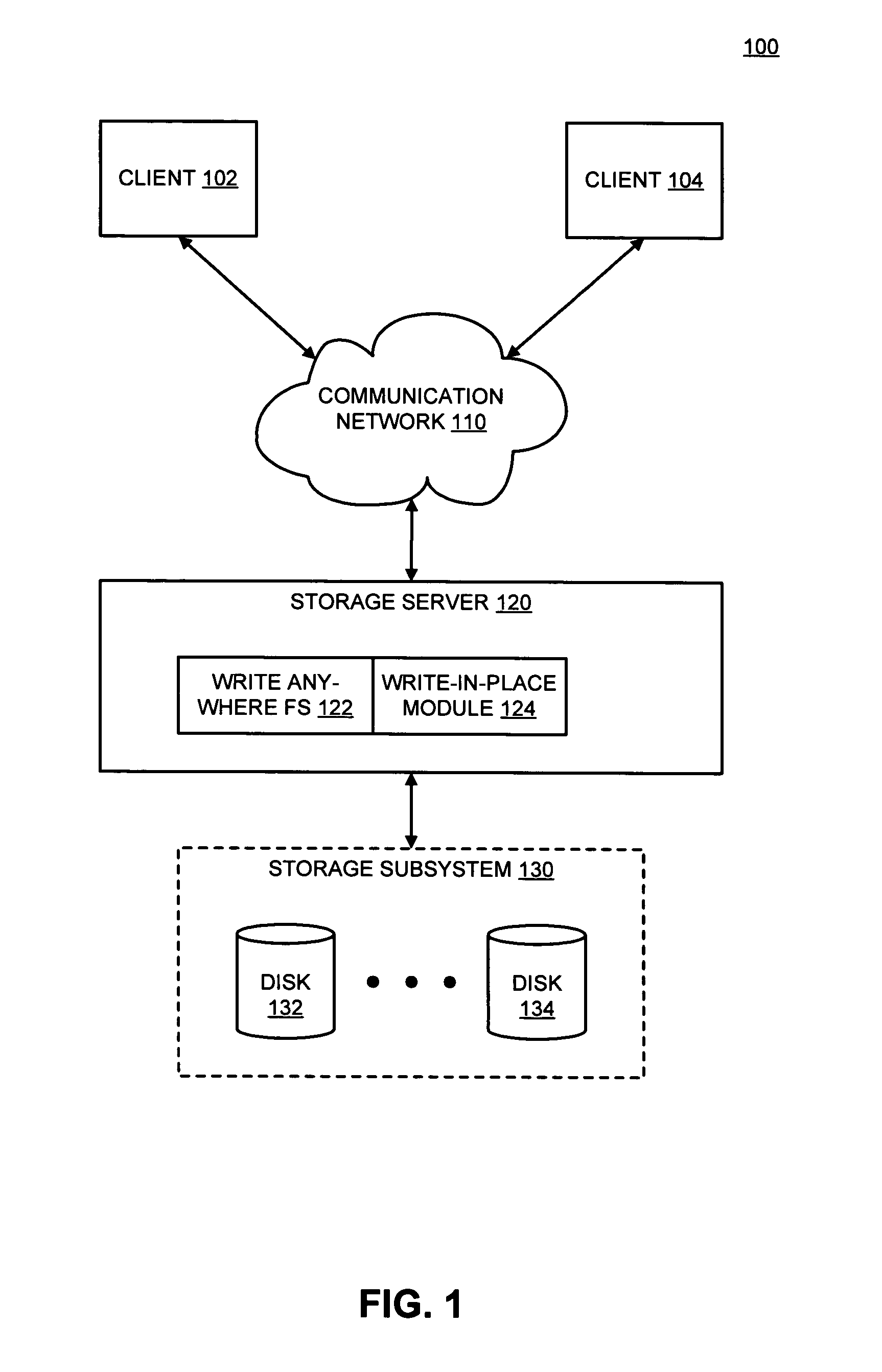
Write-in-place within a write-anywhere filesystem
In a write-anywhere filesystem, a write-in-place property allows the write-anywhere filesystem to selectively perform write-in-place processing for write allocation to selected data blocks. The filesystem stores a data block in a storage, and references the data block with both physical and virtual or logical block number references. The block number references allow the filesystem to manage storage of the data blocks through indirection. The data block may be modified, which generates an updated data block in memory having the new data. The filesystem performs write allocation to store the updated data block to the storage. Write-in-place within the write-anywhere filesystem allows the write-anywhere filesystem to write the data block to the same physical location and thus maintain the same physical block number reference while modifying the virtual block number reference.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Storage of data blocks of logical volumes in a virtual disk storage subsystem
ActiveUS20060129785A1Reduce probabilityRemove correlationInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsData elementData store
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method for processing address discontinuity in MTD design of NAND flash memory
ActiveCN101470663ANot changing effectsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMapping algorithmLogical block number
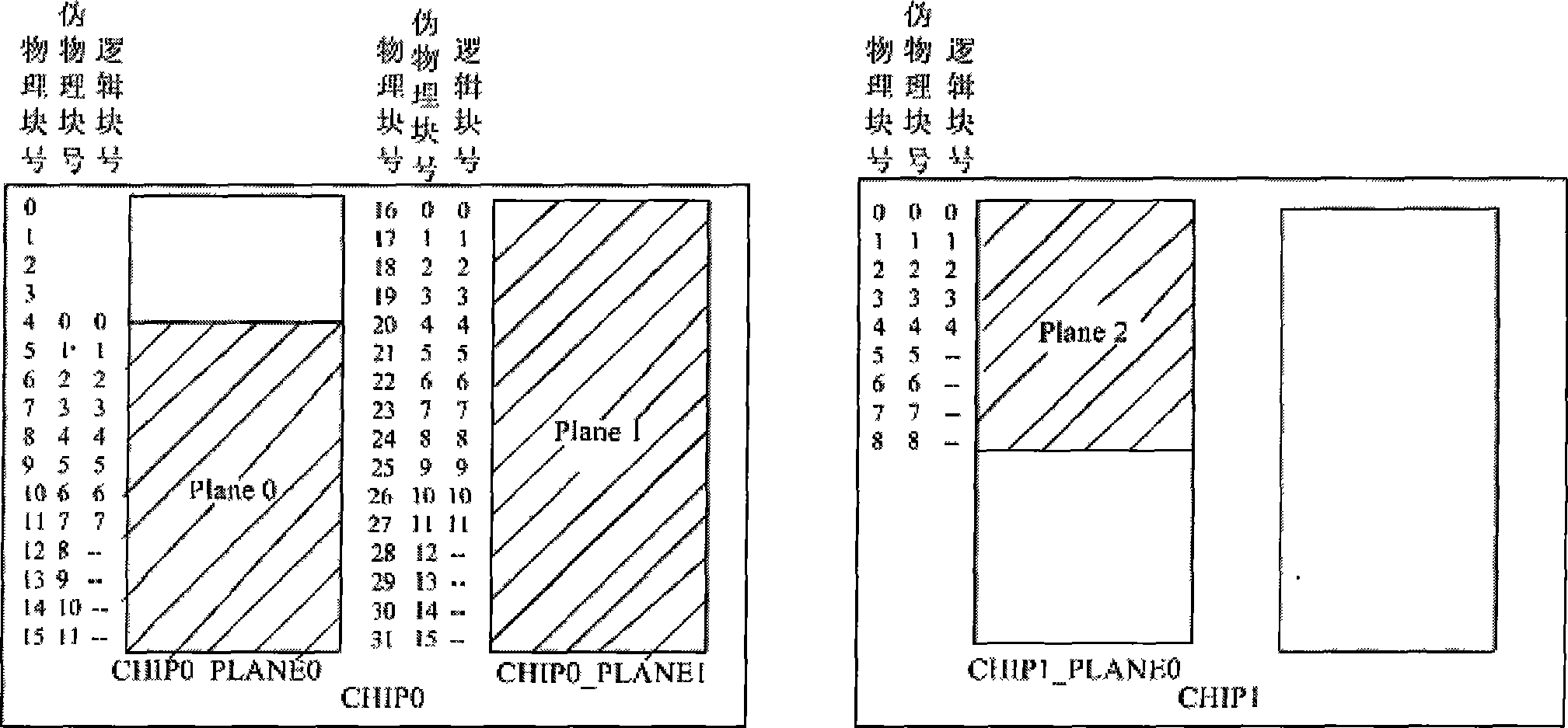
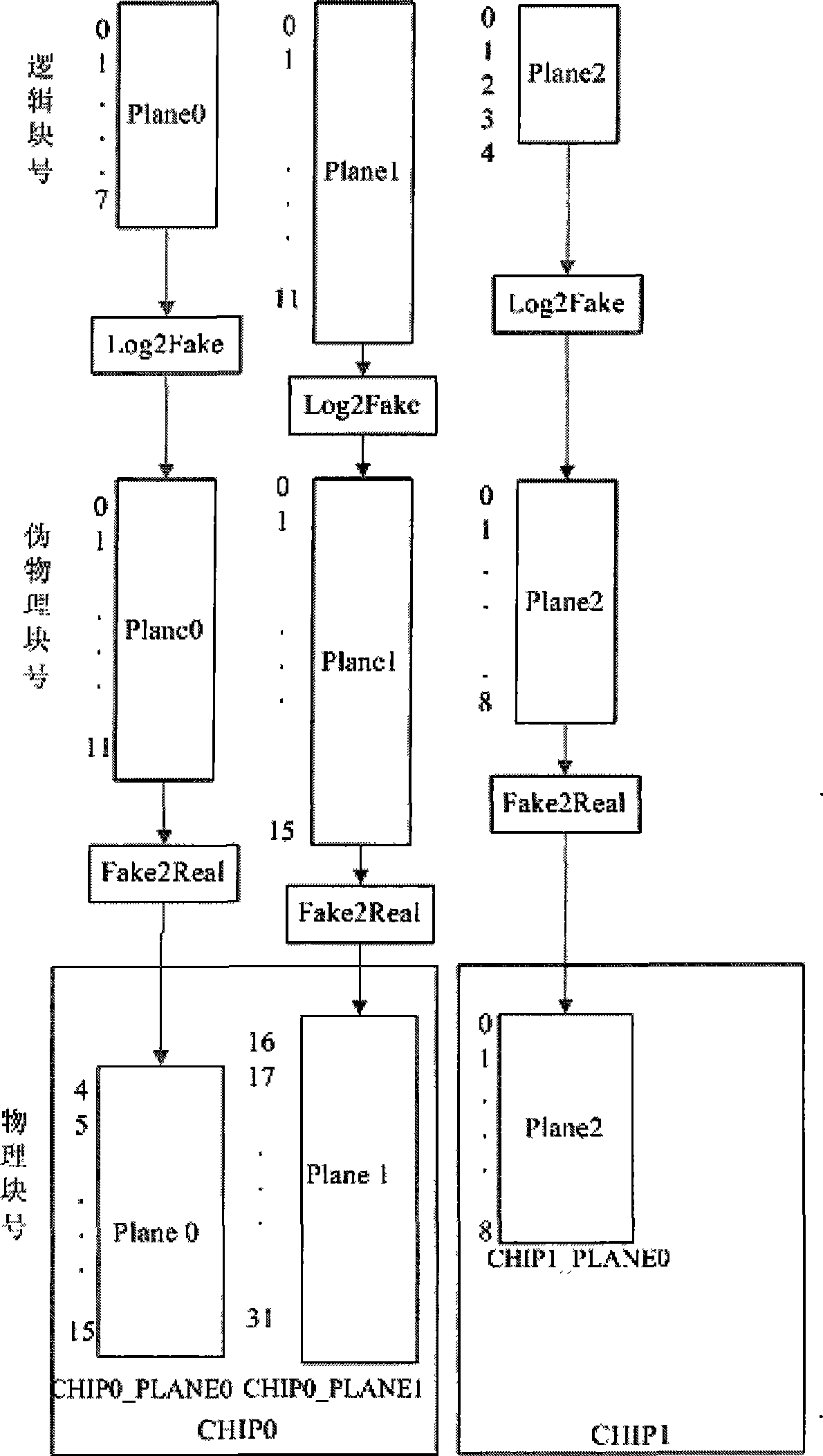
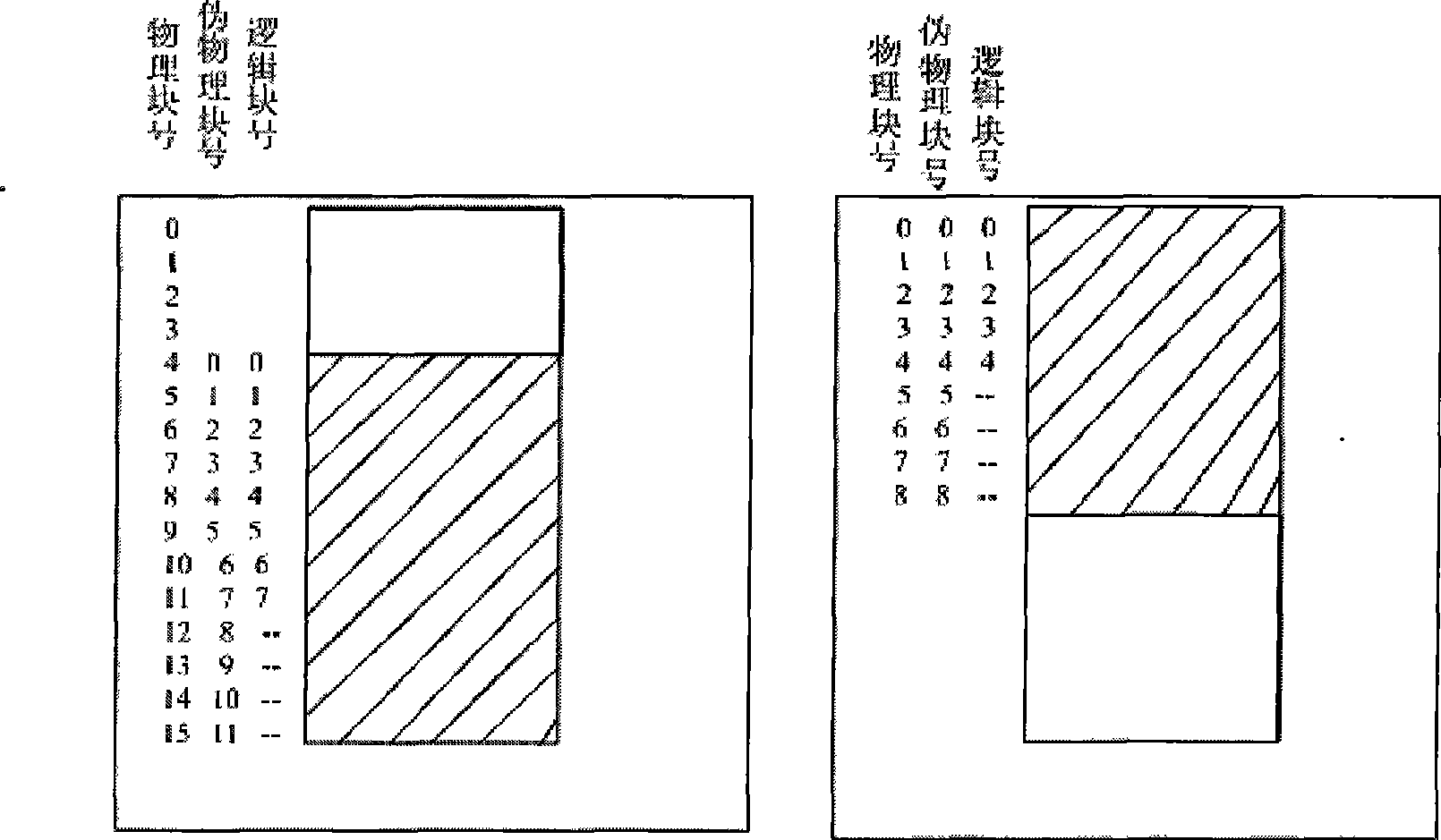
The invention discloses a method of unconsciously processing addresses in an MTD design which supports a multi-plane type NAND flash memory, which comprises dividing the whole NAND flash memory space into a plurality of regions, managing each region according to an MTD, abstracting each physical plane in each region into a logical plane, calculating the related logical block numbers by the MTD according to logical sector numbers transmitted from the upper application, then addressing according to the logical block numbers, corresponding the logical block numbers to false physical block number one by one through a mapping table, and finally realizing the access of MTD to a physical block number through related algorithm according to the false physical block numbers. The method facilitates the MTD to support an NAND flash memory comprising a plurality of physical planes, and to be independent from a changing MLC.
Owner:ANYKA (GUANGZHOU) MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Data storage structure analyzing method of NAND FLASH memory chip
ActiveCN106201774AAchieve data recoveryRealize forensicsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant operation error correctionData segmentControl circuit
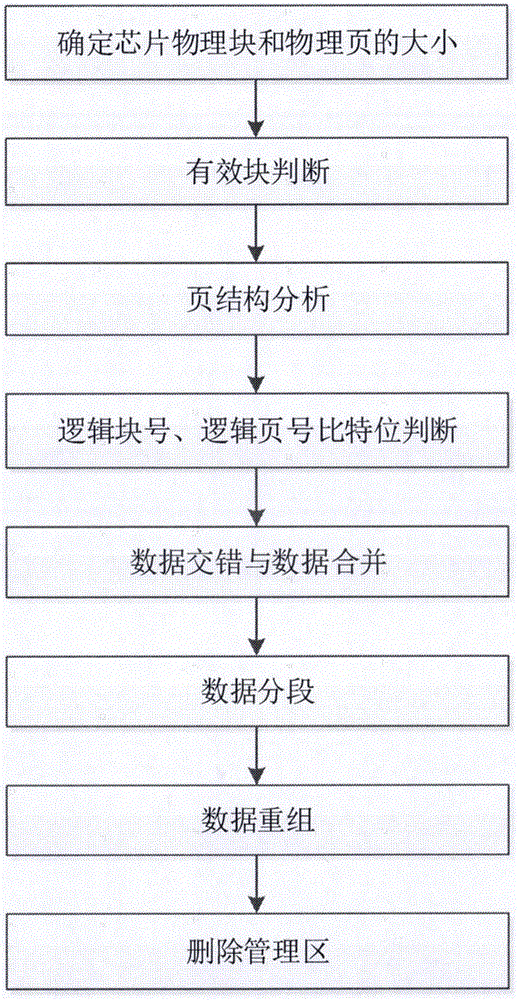
The invention discloses a data storage structure analyzing method of a NAND FLASH memory chip. The method comprises: determining the size of physical blocks and the size of physical pages of the chip, and opening a physical image as read-only; carrying out valid block judgement; analyzing the structure of the pages by utilizing the physical pages where continuous data exists; determining the positions of logical block numbers and the positions of logical page numbers according to the changes over bits of each physical page admin area; conducting data interleave analyzing and data merging according to the data continuity condition of a data volume which can reflect the continuity about data; judging whether or not to conduct data segmenting according to the duplication of the logical block numbers; conducting data reorganizing; and deleting the admin area data, and finally obtaining a logical image file. According to the data storage structure analyzing method of the NAND FLASH memory chip, the conversion from the physical image to the logical image of the storage chip is realized on the premise that an NAND FLASH control circuit is not used, thus the aim that conducting data recovering and obtaining evidence after this class of devices are damaged is achieved.
Owner:中国人民解放军61660部队
Recombination method for irrelevant mirror images of file system
ActiveCN105183383AQuick searchReasonable result of restructuringInput/output to record carriersFile systemPhysical address
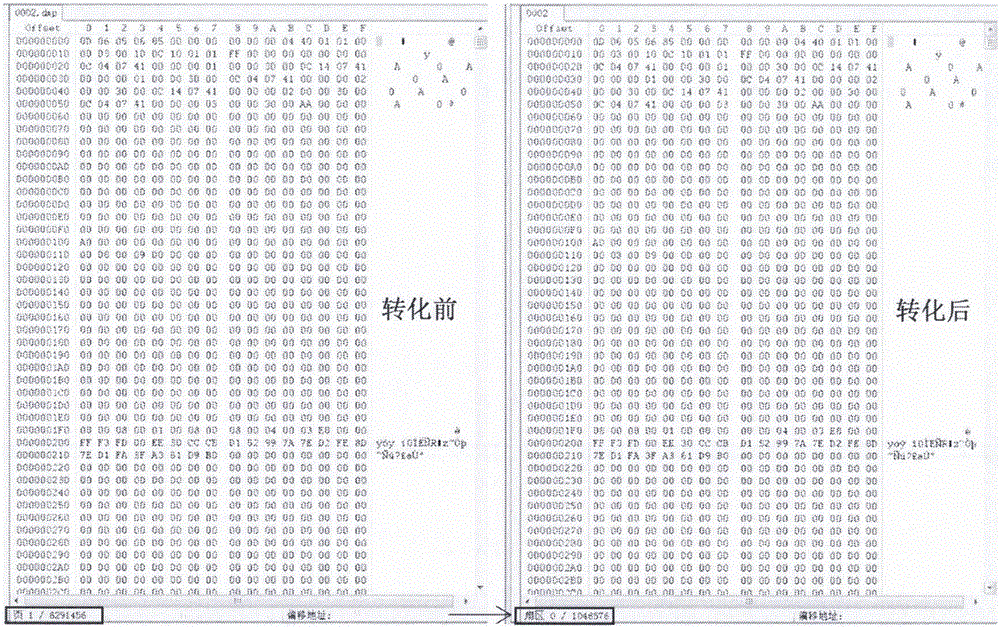
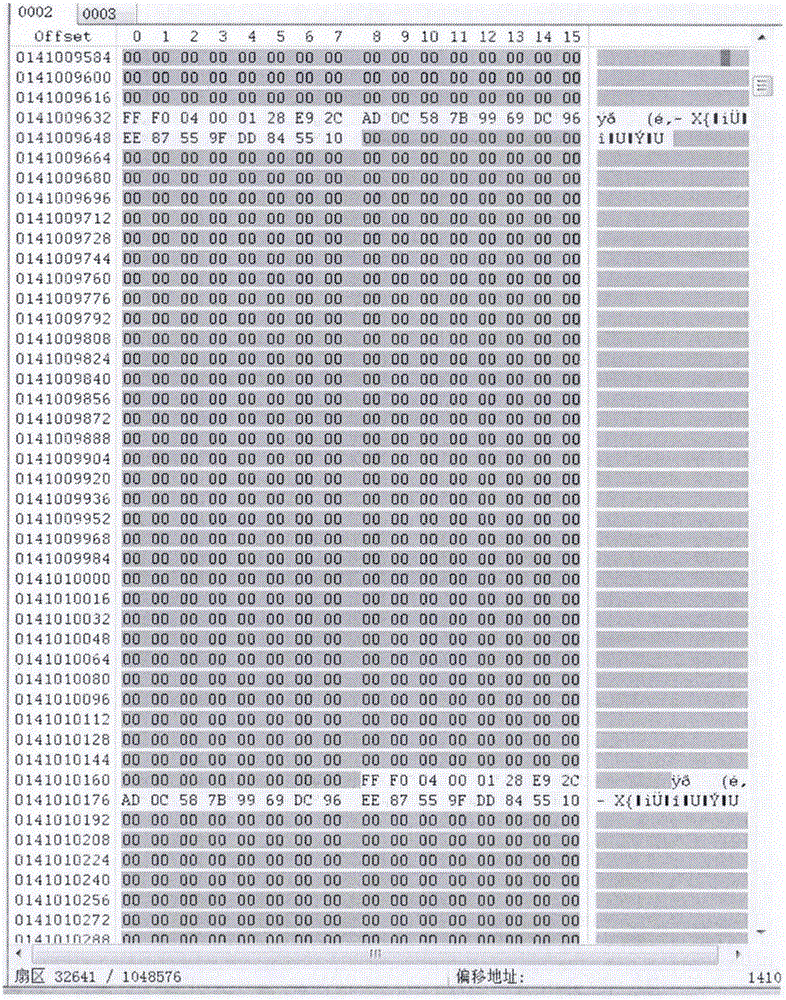
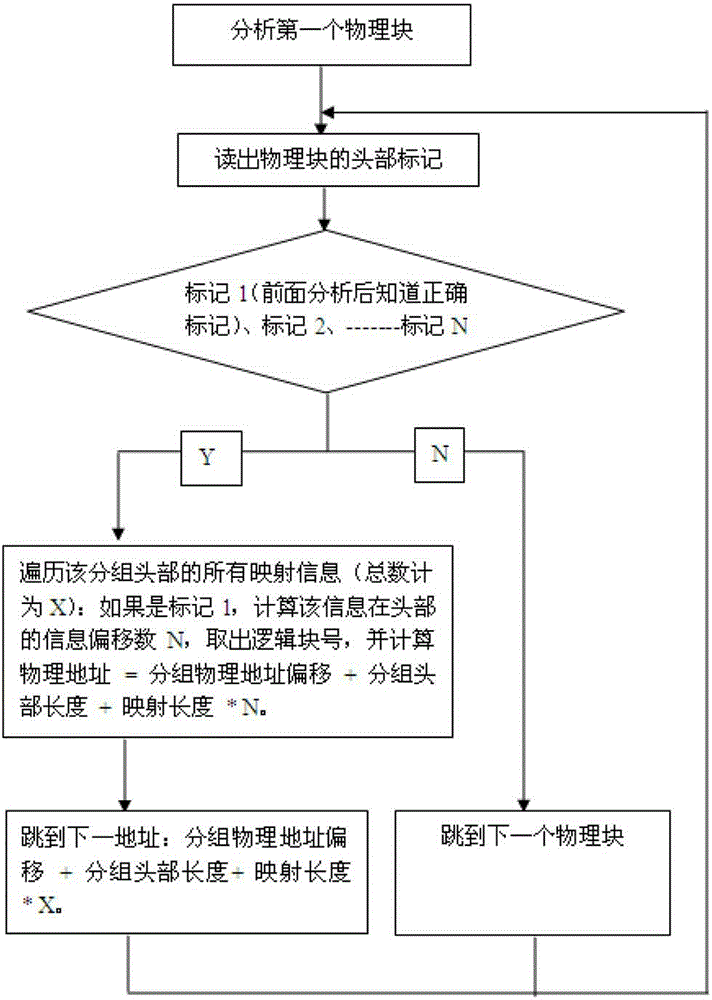
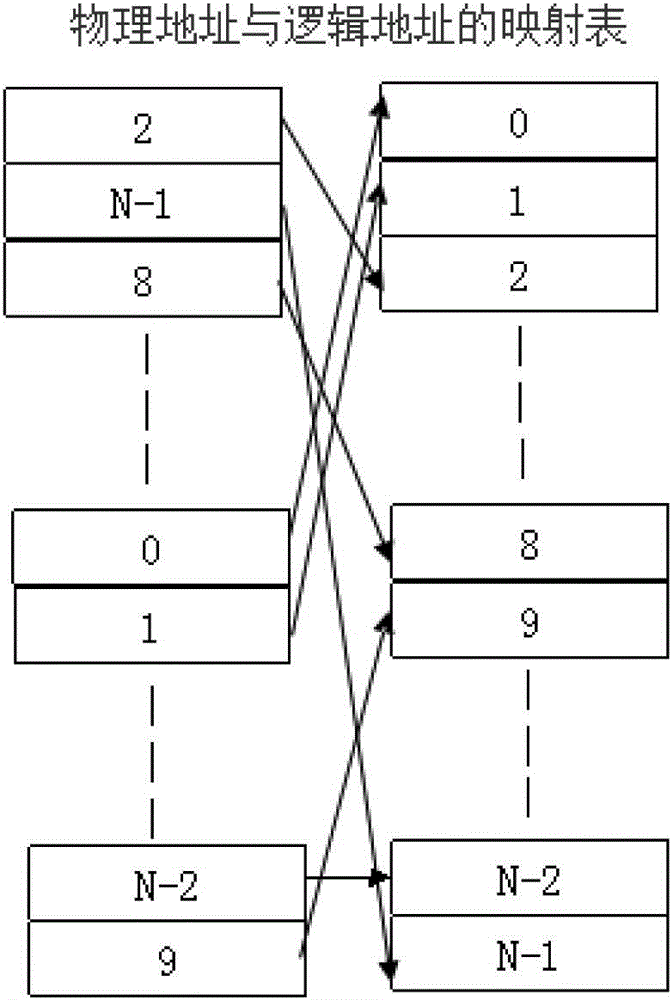
The invention relates to the technical field of information security and mobile phone applications, in particular to a recombination method for irrelevant mirror images of a file system. The method includes the mirror image acquisition step, the head mark taking step, the mark confirming step and the group type and head length confirming step. In the mirror image acquisition step, physical mirror images of a mobile terminal are acquired, and physical structures of the physical mirror images are analyzed. In the head marker taking step, front N bytes of each physical block are taken as head marks of the physical block. In the mark confirming step, data of one physical block where the head marks are located are read, whether the physical block is a mapping table or not is judged, if yes, the next step is executed, and if not, the next physical block is skipped, and the head mark taking step is executed again. In the group type and head length confirming step, all mapping information of the heads of one group is traversed, one logical block number is taken out according to the marks, a physical address is calculated according to the formula that the physical address=group physical address offset + group head length + mapping length * marker serial number, the next physical block address is skipped, the head mark taking step is returned, and the process continues to be executed till all the physical block addresses are traversed. Recombination efficiency is high.
Owner:XIAMEN MEIYA PICO INFORMATION
Usb storage device and control device
ActiveCN1300711CImprove protectionSimple controllerInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionMass storageSCSI
A USB storage device having the function of preventing stored software from being deleted by mistake achieved with as simple a structure as possible. In the USB storage device, the storage area is divided into an area in which execution of reading, writing and deleting is allowed and an area in which only execution of reading is allowed. Information to make a USB mass storage class driver recognize these areas as areas corresponding, respectively, to logical unit numbers defined in the SCSI command set of the USB mass storage class driver owned by the host is stored in the USB storage device. The information includes logical unit numbers, formats, writing / deleting allowed / not allowed flag, logical block numbers and physical block numbers. By this, the USB mass storage class driver recognizes the USB storage device as a SCSI device having two logical units.
Methods for accessing data in a circular block mode and apparatuses using the same
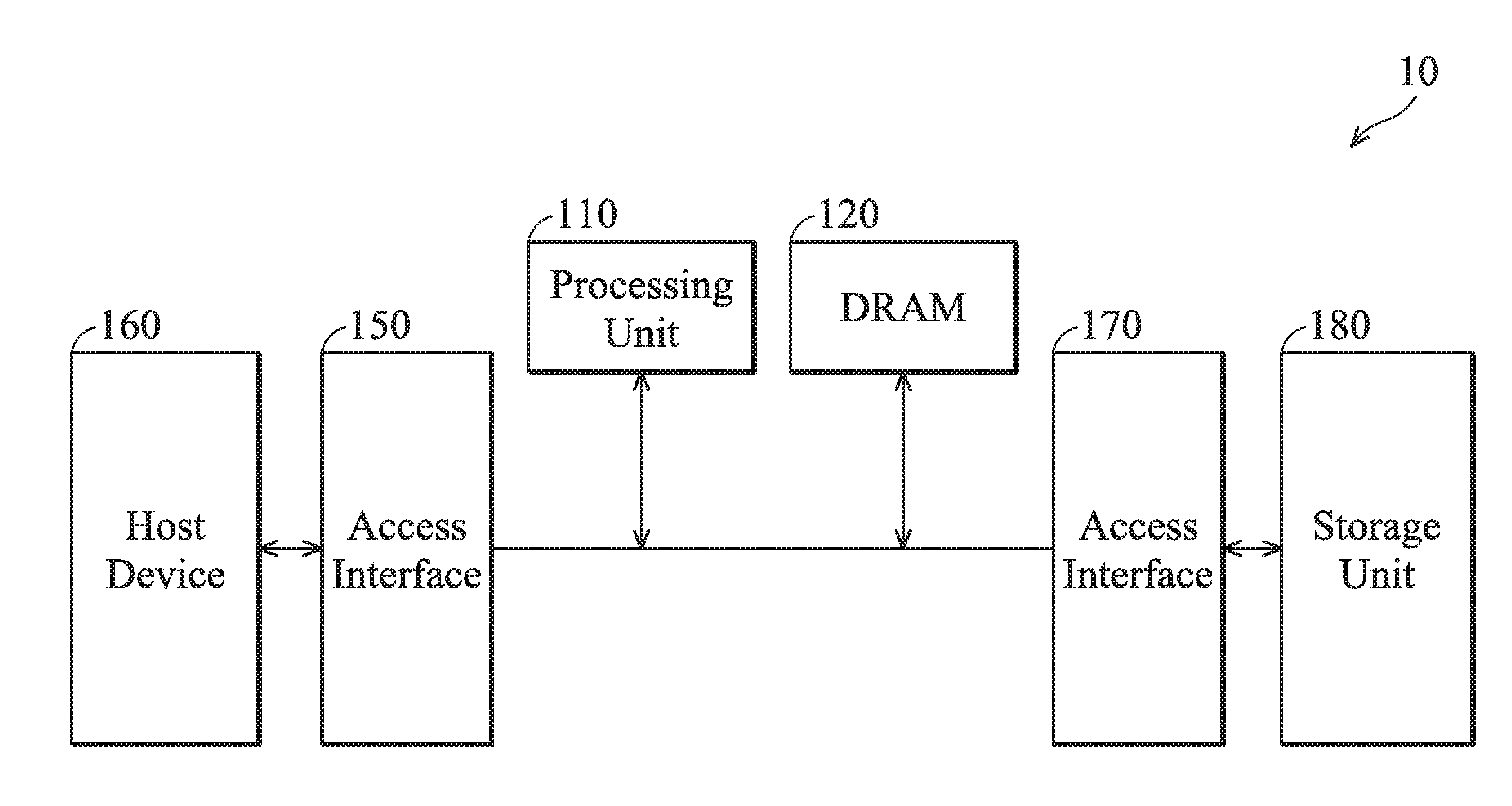
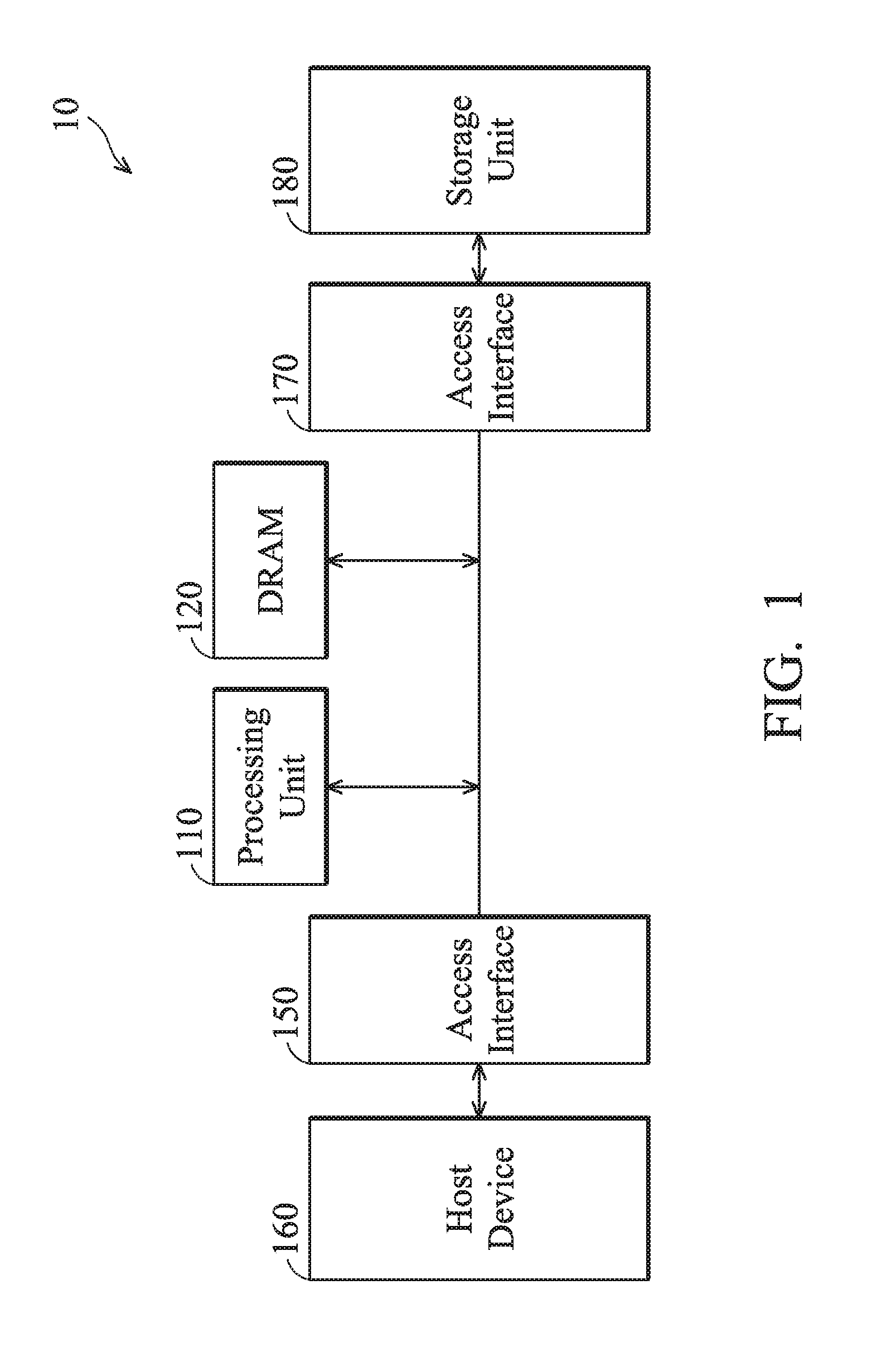
ActiveUS20160328183A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersLogical block addressingProcessing element
A method for accessing data in a circular block mode, executed by a processing unit, is introduced to contain the following steps. A read command and an LBA (Logical Block Address) are obtained from a host device through a first access interface. Logical block and page numbers are calculated according to the LBA, and a record associated with the logical block number is read from a storage mapping table, where the record contains a physical block number and a circular index. A physical page number is calculated according to the logical page number and the circular index. A read command is issued to a storage unit through a second access interface for reading data of the LBA from a region associated with the physical block number and the physical page number, and the data is replied to the host device through the first access interface.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Information processing method and apparatus having data locations accessible by different devices in accordance with different permissions
InactiveUS7437526B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersInformation processingWrite buffer
Memory corruption can be suppressed. When data stored in a random access area are read, the read data (physical block) are retrieved by a logic block number and newest data are read by referring to an incremental counter of data having that logic block number. When data are stored in the random access area, the incremental counter and the logic block number of data already stored in the random access area are referred and a physical block set to be unnecessary is set to a writer buffer, and then the data are written to this write buffer.
Owner:SONY CORP
AV data recording apparatus and method, disk recorded with the AV data recording apparatus or method, and AV data reproducing apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080025700A1Easy to copyReduce wasteTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsData recordingAudio frequency
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
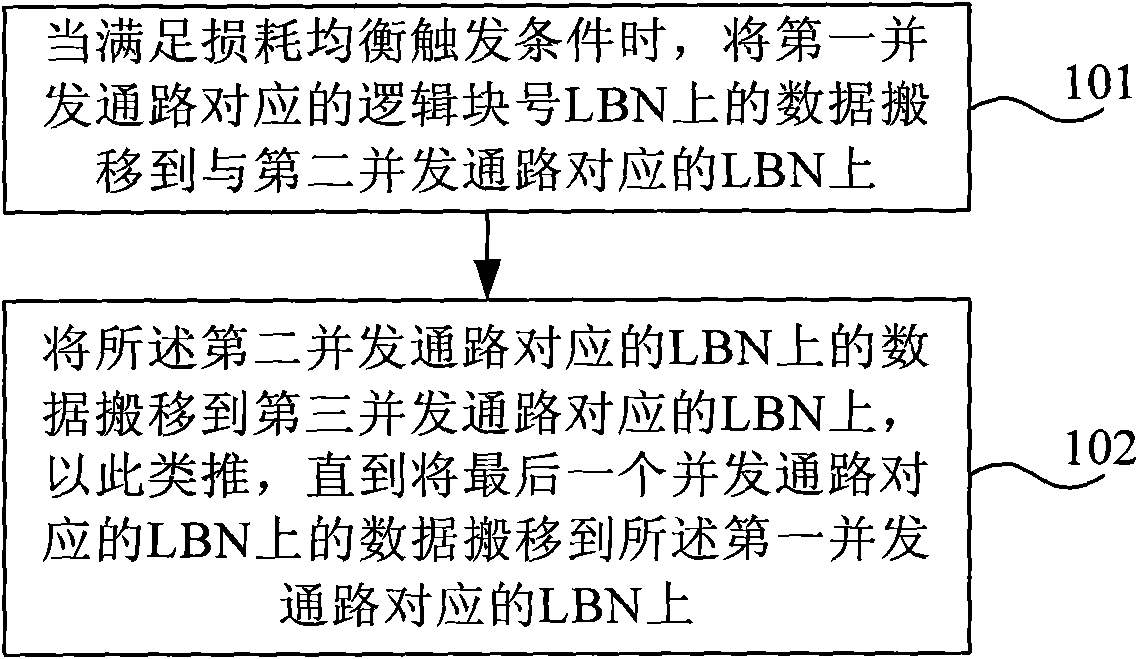
Consumption balance processing method and system as well as solid hard disk
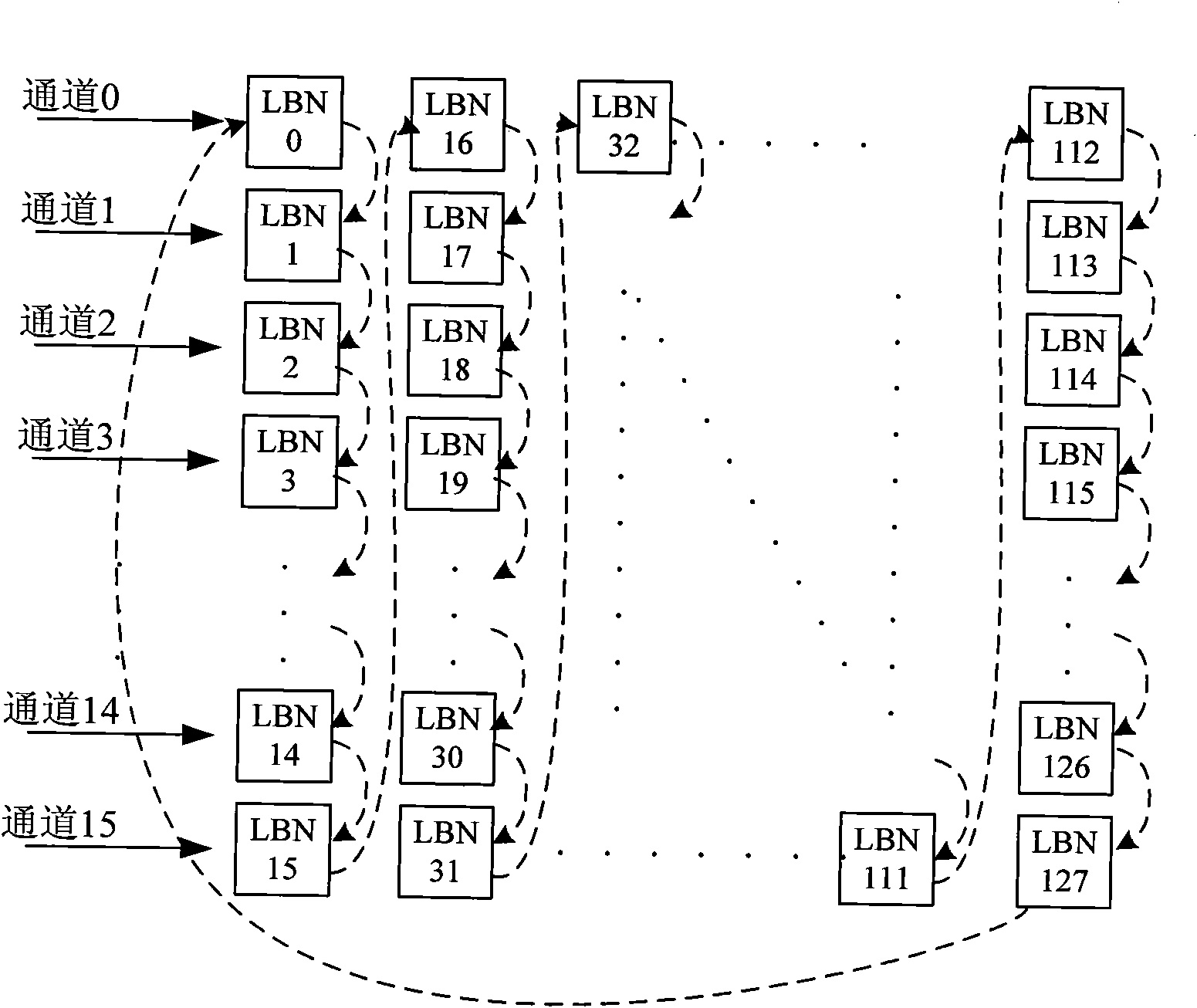
InactiveCN102375693AWill not cause aggregationDoes not affect concurrencyInput/output to record carriersDigital storageDistributed computingLogical block number
The embodiment of the invention provides a consumption balance processing method and a system as well as a solid hard disk. The method comprises the following steps that: a data on logical block number (LBN) corresponding to a first concurrency passage is moved to the LBN corresponding to a second concurrency passage, in addition, the data on the LBN corresponding to the second concurrency passage is moved to the LBN corresponding to a third concurrency passage, and in the same manner, the data on the LBN corresponding to a final concurrency passage is moved onto the LBN corresponding to the first concurrency passage. The embodiment of the invention can realize the full disk balance.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL TECH (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Flash memory access apparatus and method
InactiveCN1538456AMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerLogic block
A flash memory access apparatus and method improves the overall performance of a flash memory system by minimizing the deterioration of performance of a flash memory due to repeated write operations through a minimized process of a write operation and the process of a recovery operation in consideration thereof and by allowing a stable recovery even though an error occurs. The flash memory access apparatus comprises a flash memory with regions divided on the basis of a unit that consists of predetermined blocks; and a flash memory controller. When a write operation is requested for a specific logical block number of the flash memory, the flash memory controller writes data and meta-information in a physical block corresponding to a logical block with the logical block number in the absence of a previous write operation for the logical block, but performs a write operation for writing the data and the meta-information allocated to the logical block in a new physical block without changing flash memory state information written in a previous physical block corresponding to the logical block in case of the presence of the previous write operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
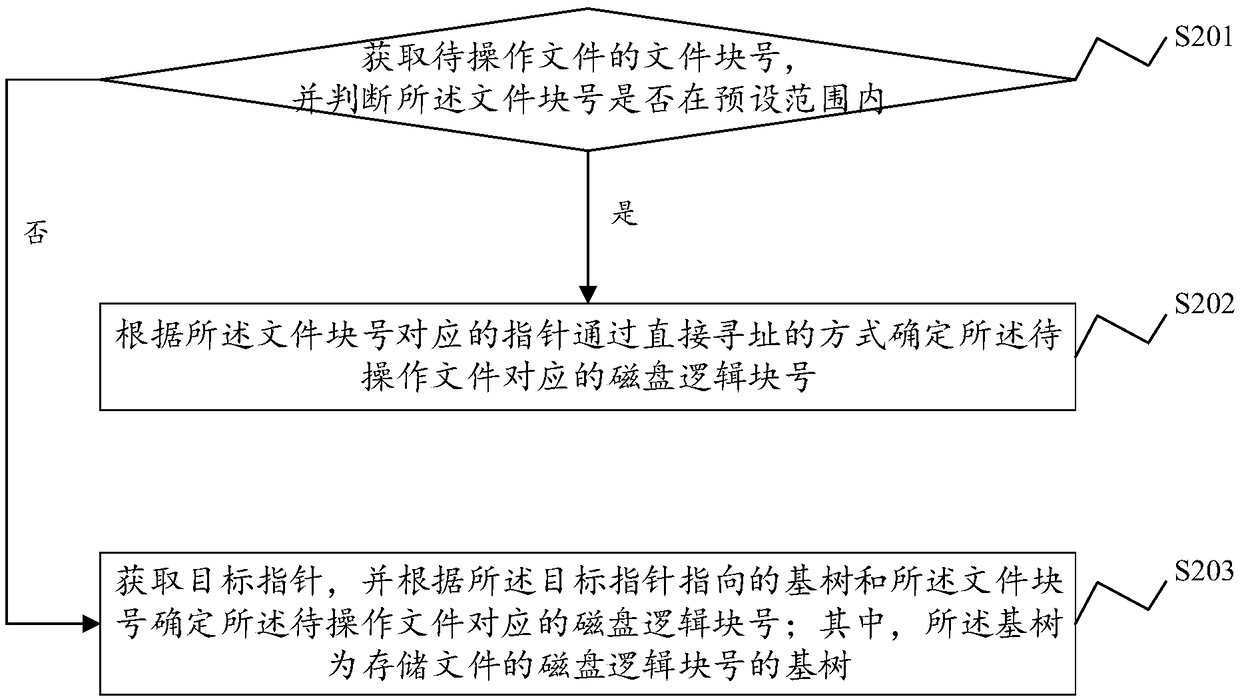
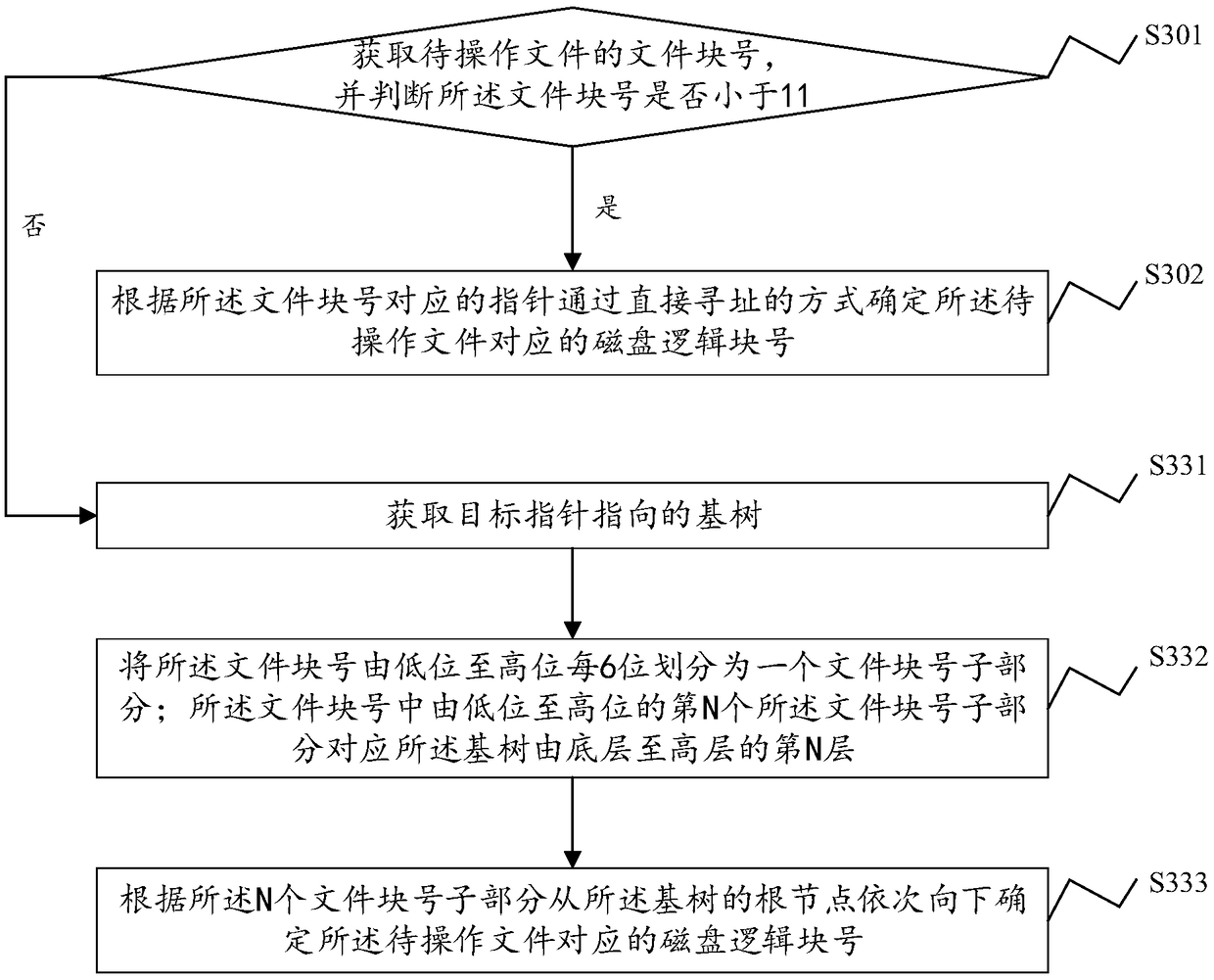
File data block addressing method, system, device and storage medium
ActiveCN108897698AReduce the number of operationsReduce occupancyMemory systemsSmall filesTree mapping
The present application discloses a file data block addressing method, system, and device and computer readable storage medium. The file data block addressing method comprises obtaining a file block number of a file to be operated, and determining whether the file block number is within a preset range; if yes, according to a pointer corresponding to the file block number, a disk logical block number corresponding to the file to be operated is determined by directly addressing; if not, a target pointer is acquired, and according to the base tree pointed by the target pointer and the file blocknumber, a disk logical block number corresponding to the file to be operated is determined; the base tree is a base tree of a disk logical block number storing the file. The file data block addressingmethod uses a direct mapping and a base tree mapping to map a file block number to a disk logical block number. Through a direct index of a preset range of the file block number, small files can complete the disk request by accessing the disk twice, and the base tree mapping is adopted for sparse files and large files, thereby effectively reducing the disk occupation of the index block.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
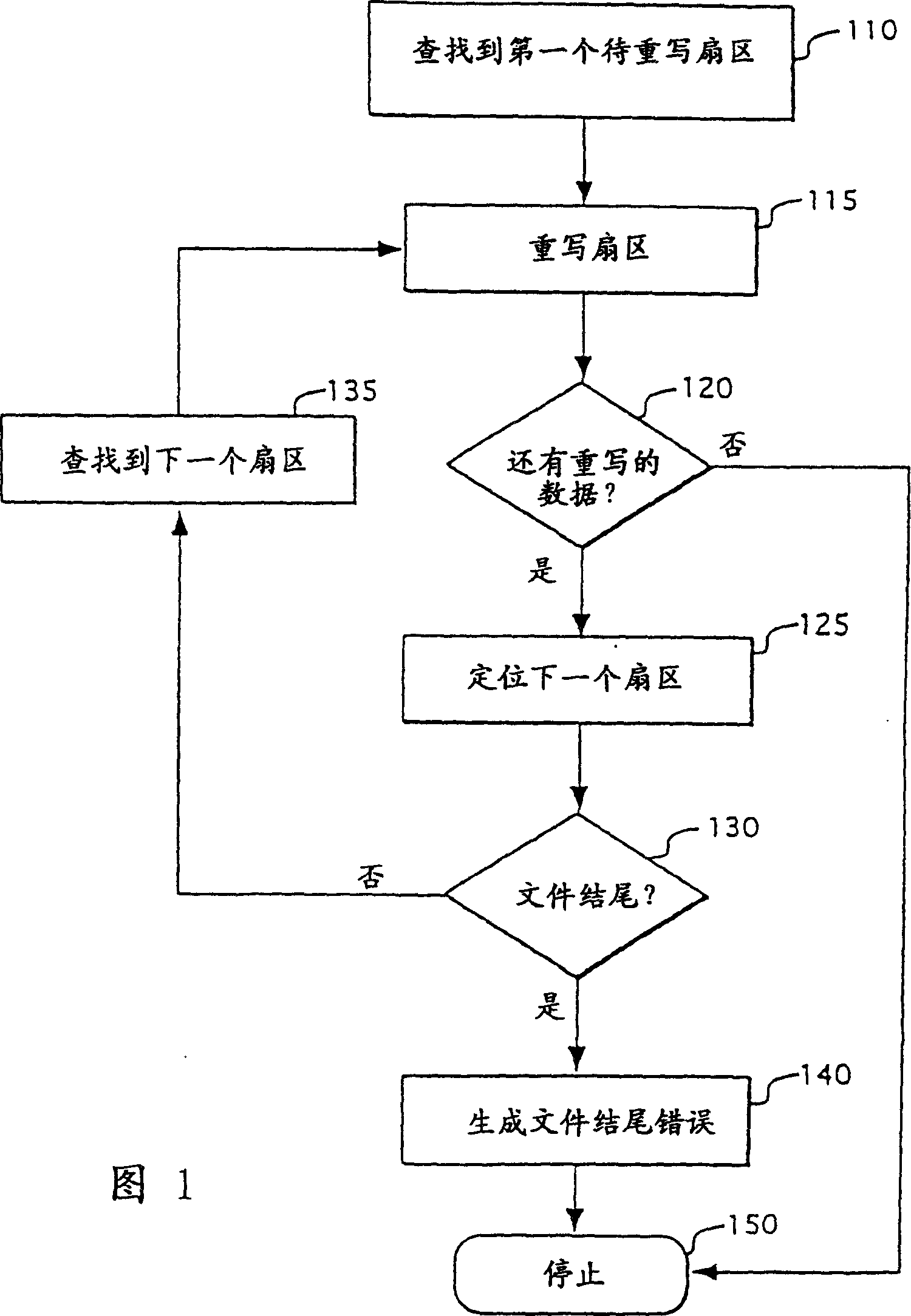
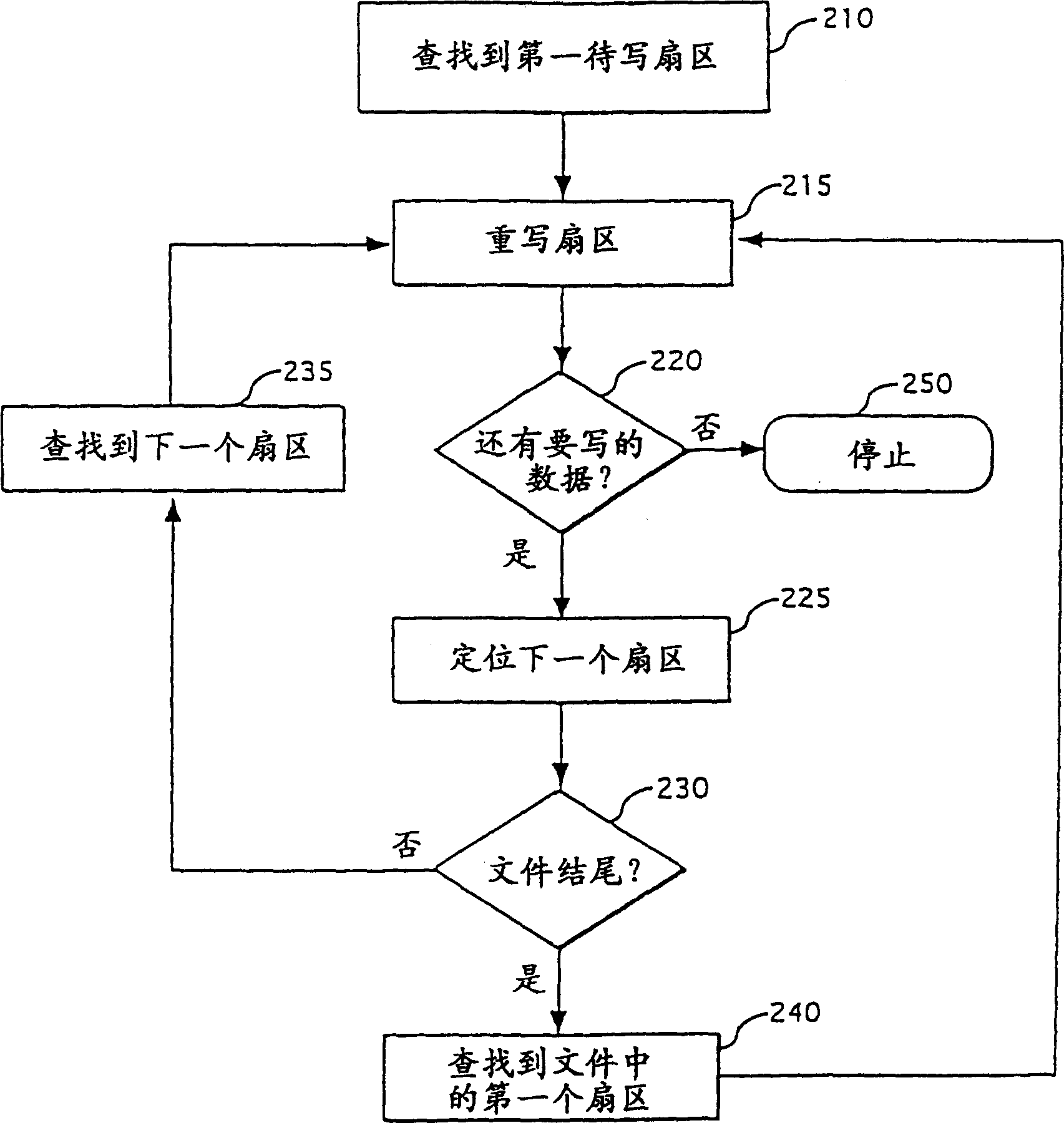
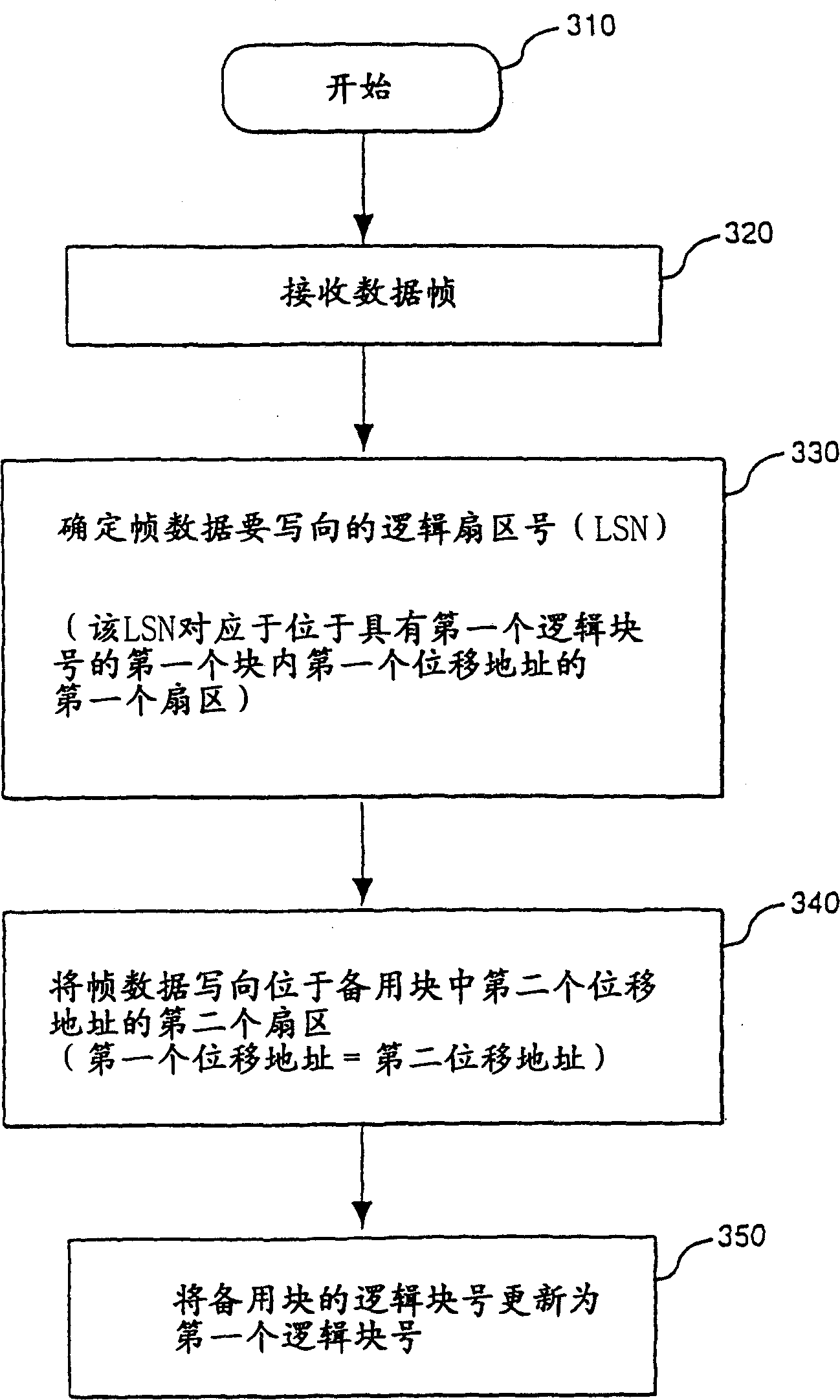
Method for performing continuous over write of file in nonvolatile memory
InactiveCN1129848CMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersComputer scienceOperating system
A nonvolatile memory having a plurality of individually erasable blocks is used to store sectors of a file. A method of overwriting the file includes the step of receiving a frame of data (320). The logical sector that the frame is to be written to is determined (330). The logical sector corresponds to a first sector located at a first offset in a first block of the nonvolatile memory (330). The first block also has an associated first logical block number (330). The frame of data is written to a second sector (240). The second sector is located at a second offset in a spare block (340). The first and second offsets are identical (340). The logical block number of the spare block is updated to be the same as the first logical block number.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Storage of data blocks of logical volumes in a virtual disk storage subsystem
ActiveUS7685400B2Adversely affecting system performanceReduce close associationInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsData elementData store
When data is stored in many storage subsystems, metadata, such as a sequence number, is also generated and stored with the data. When the data is accessed, the metadata is checked to ensure that the desired data element has been accessed. In conventional storage subsystems, data elements, such as logical blocks, are stored sequentially in logical pages of each logical volume. Consequently, sequence numbers closely correlate with block positions within the physical pages and sequence number / position patterns tend to repeat frequently and access errors may not be detected. Algorithms are provided to calculate new, offset, physical block positions which reduce the close association of sequence numbers and physical positions, thereby reducing such aliasing. The algorithms incorporate the logical volume number, the logical page number, or both, in addition to the logical block number. As a result, detection of access errors becomes more likely.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Deduplication metadata access in deduplication file system
ActiveUS9372865B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemData access
Techniques associated with deduplication metadata access in a deduplication file system are described, including determining a state of a file system, reading a table associated with the file system, including reading block numbers associated with files in the file system, the table being stored in a storage, wherein the block numbers include a block number and logical block number, determining whether each of the block numbers exists in a reconstruction map, modifying the reconstruction map, obtaining a hash value associated with each of the block numbers, reading data blocks from a disk using the plurality of block numbers, and constructing deduplication metadata in system memory (i.e., RAM) using a read of the data blocks.
Owner:ATLANTIS COMPUTING HLDG LLC
Flash memory data control method and system
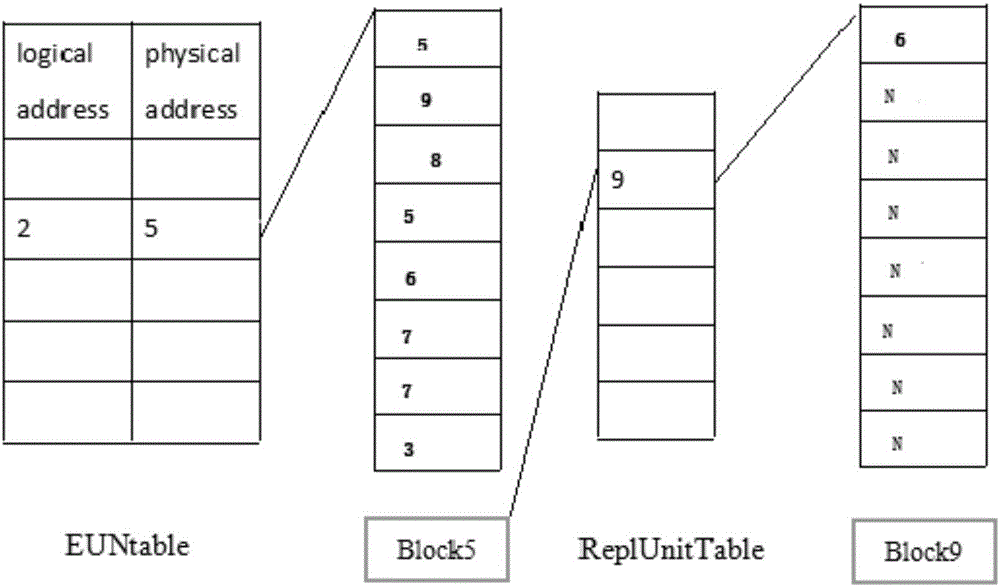
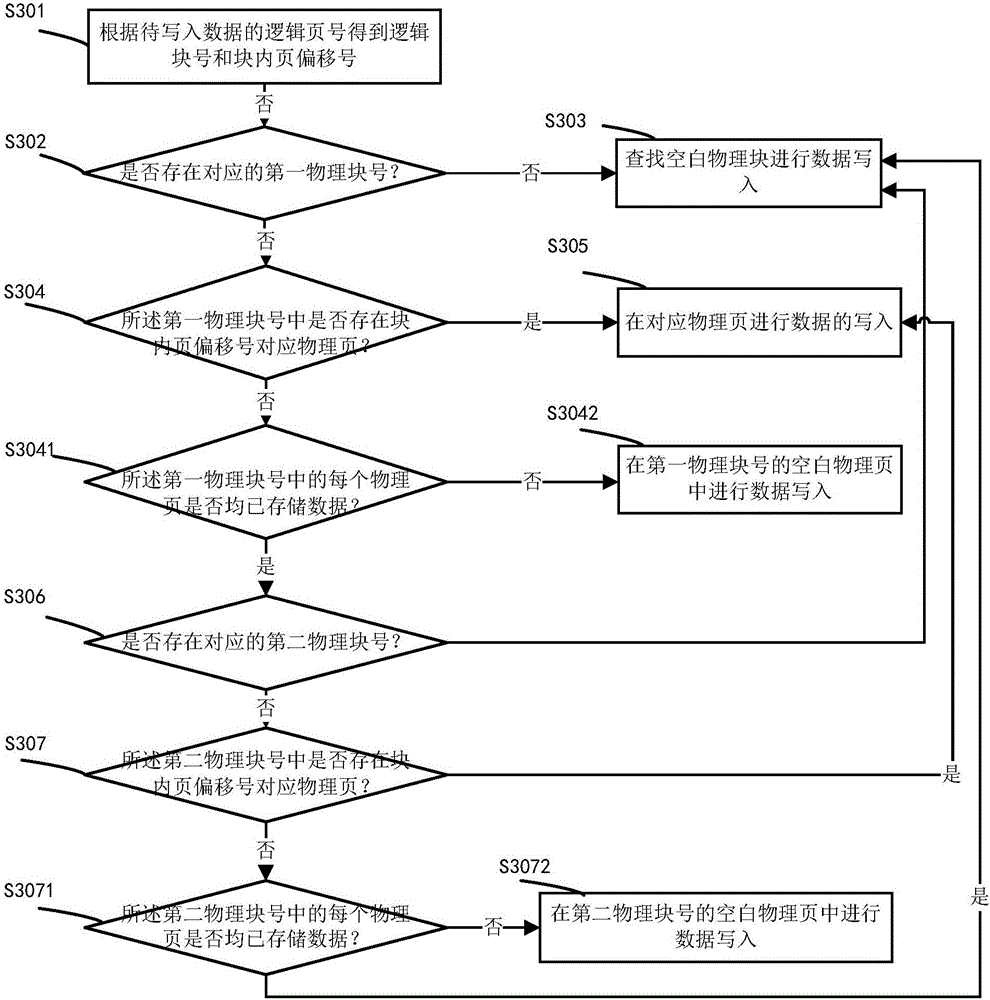
ActiveCN106528446AReduce the number of wipesEfficient use ofMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData controlControl system
The invention provides a flash memory data control method and system. The control method includes the following steps that the logical block number and deviation number of pages in a block are obtained according to logic page number of read / write data; whether a corresponding first physical block number exists or not is judged according to the logical block number and a first preset mapping table, and if not, a blank physical block is searched for to carry out operation of data writing or read finishing; if yes, physical page tables in the first physical block number are sequentially read to determine whether the physical page corresponding to the deviation number of the pages in the block exists or not, and if yes, data writing or reading is carried out on the corresponding physical page; if not, whether a corresponding second physical block number exists or not is determined according to the first physical block number and a second preset mapping table, and if yes, physical page tables of the second physical block number are sequentially read to determine whether the physical page corresponding to the deviation number of the pages in the block exists in the second physical block number or not.
Owner:深圳市先天海量技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com