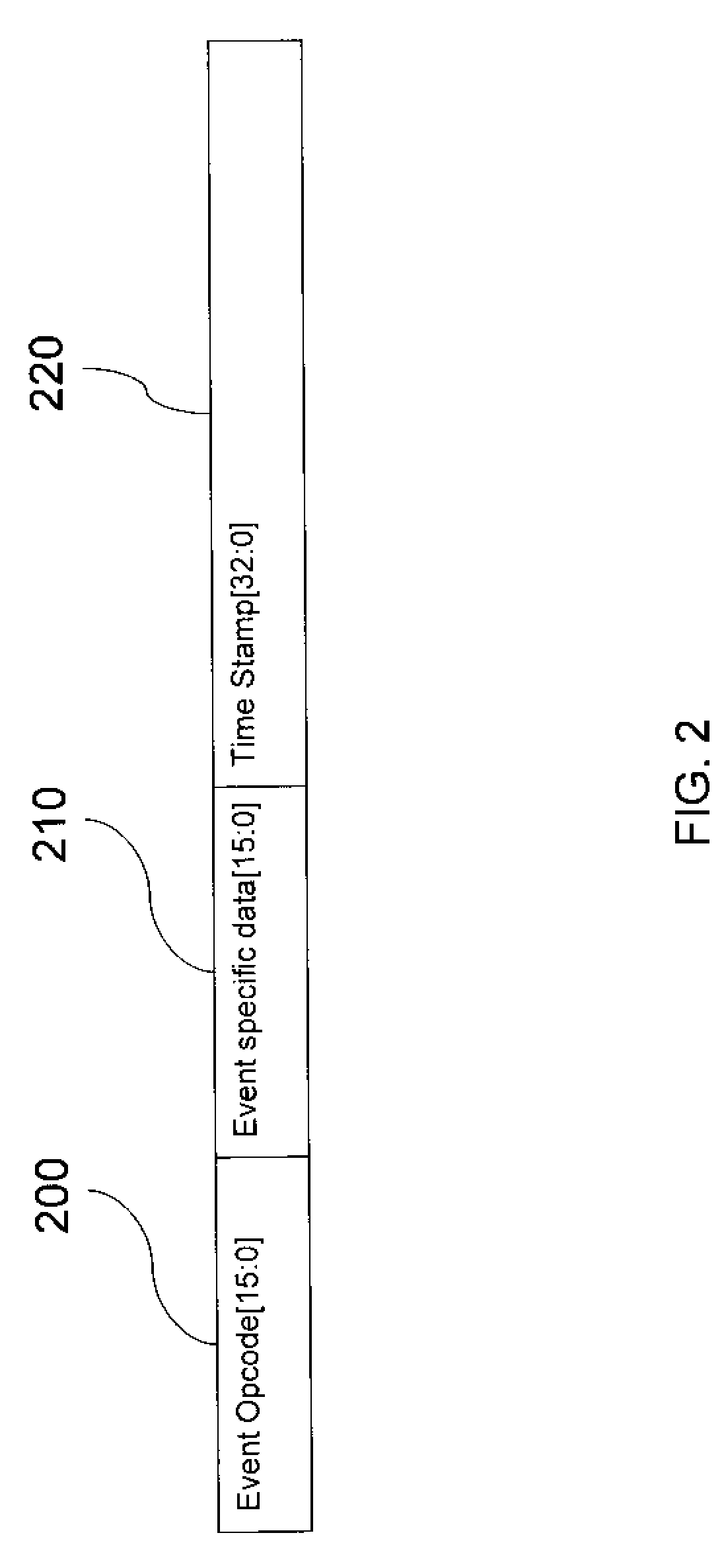
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "High speed serial link" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
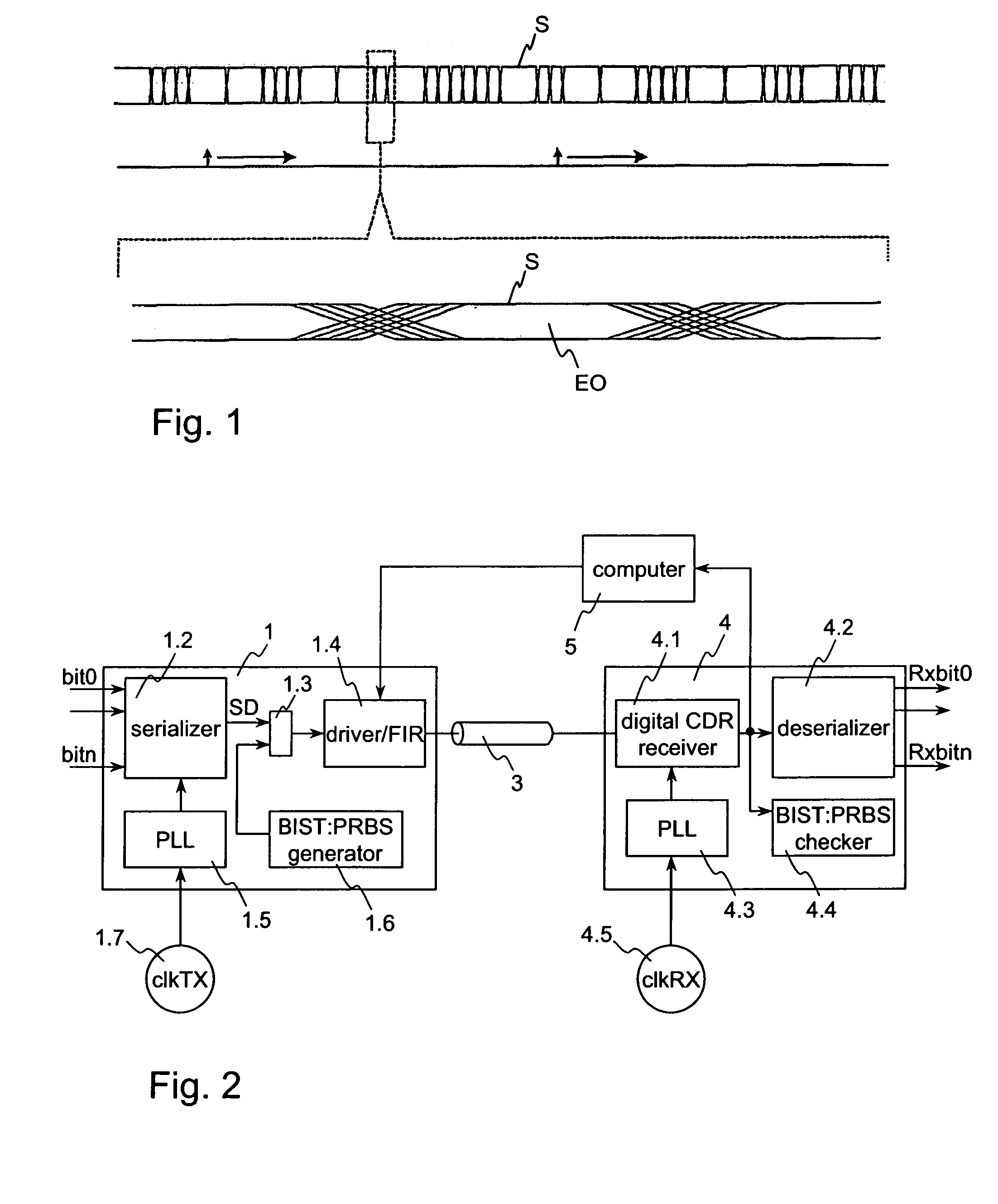
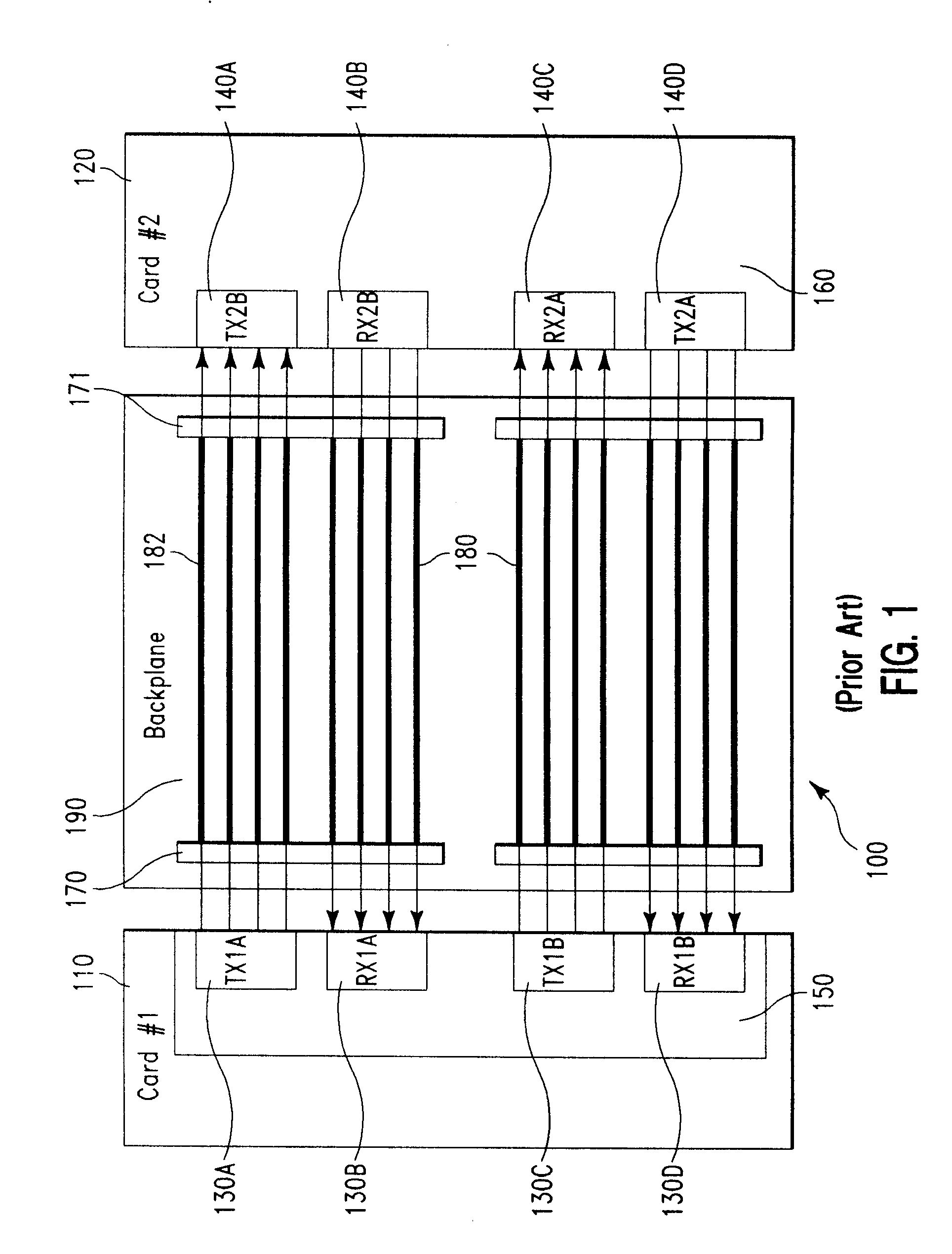
High Speed Serial Link (HSSL) is a proprietary communications protocol and was primarily developed by Alcatel. It is now owned by Alcatel-Lucent. Capable of transmitting data at rates up to 10 Gbit/s, HSSL is chiefly used in electronic system backplanes for inter-board communication.
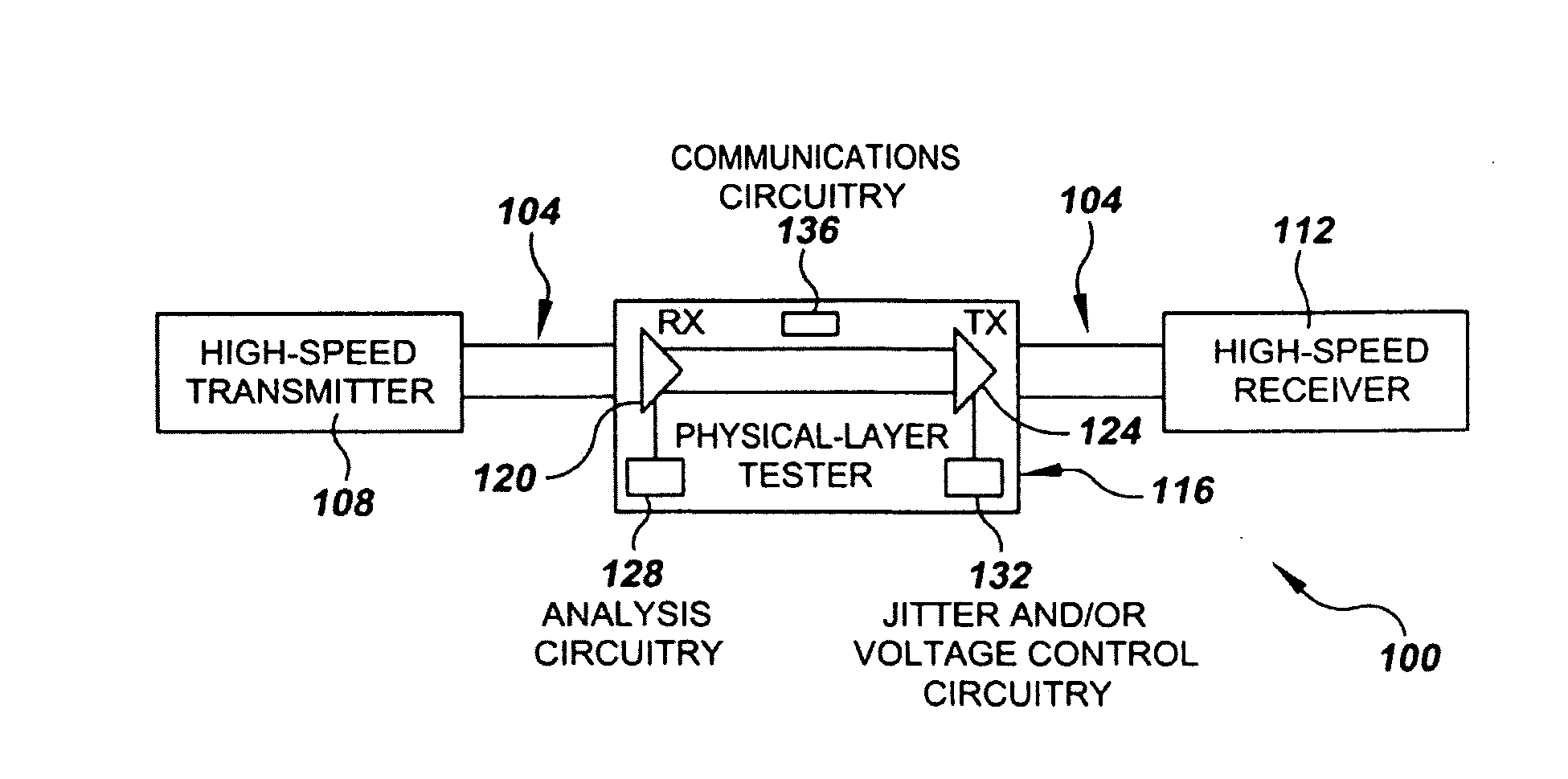
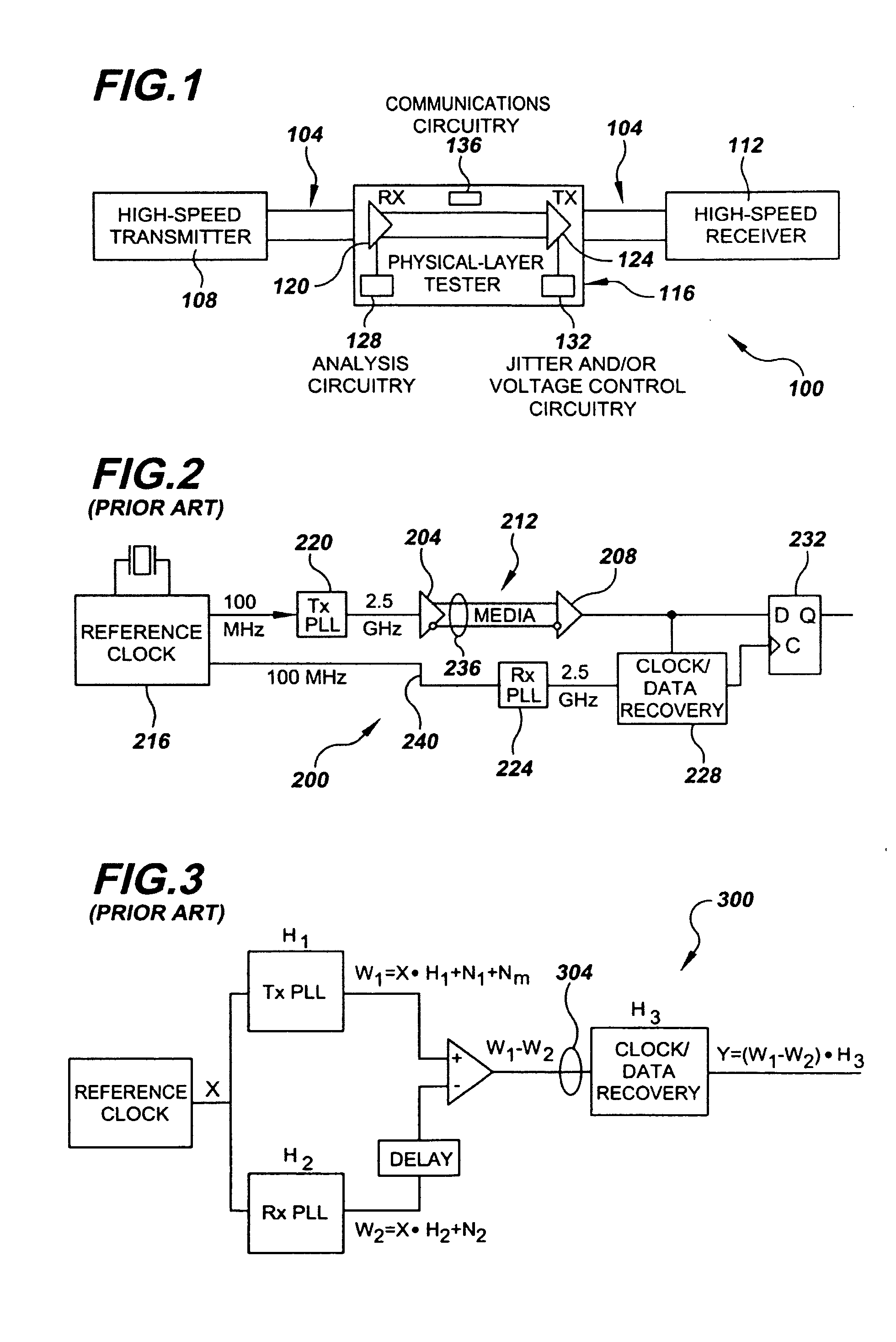
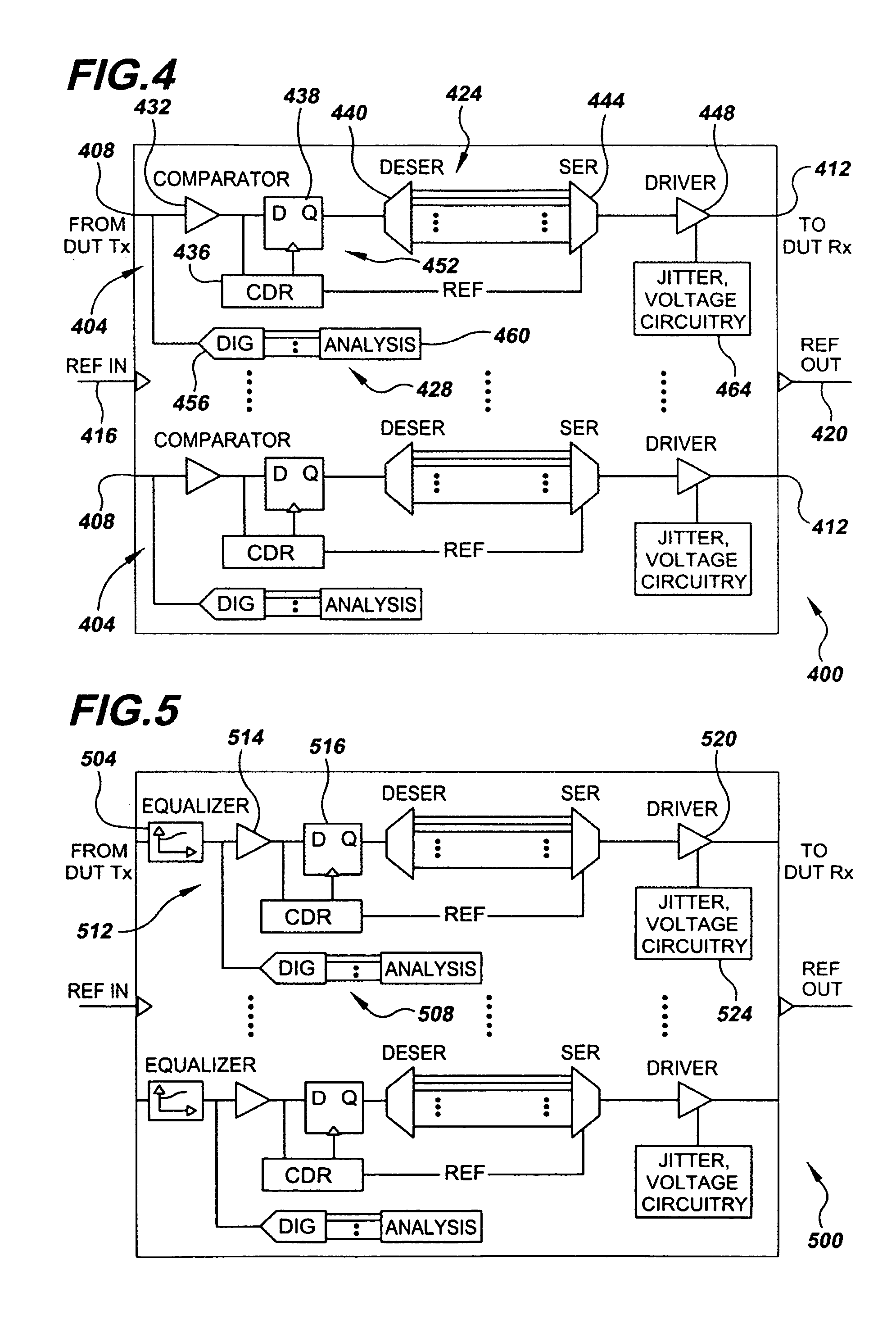
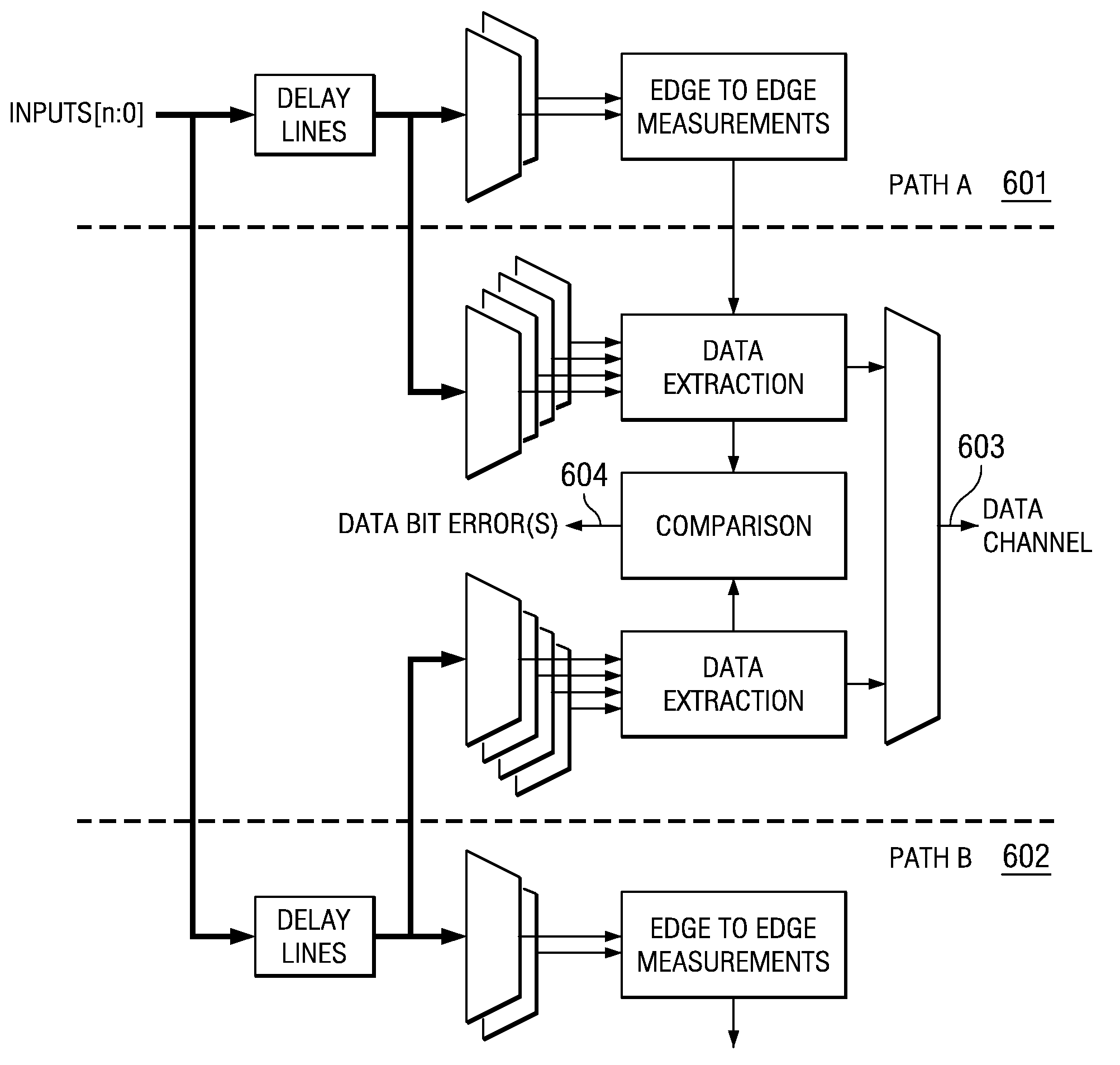
System and Method for Physical-Layer Testing of High-Speed Serial Links in their Mission Environments
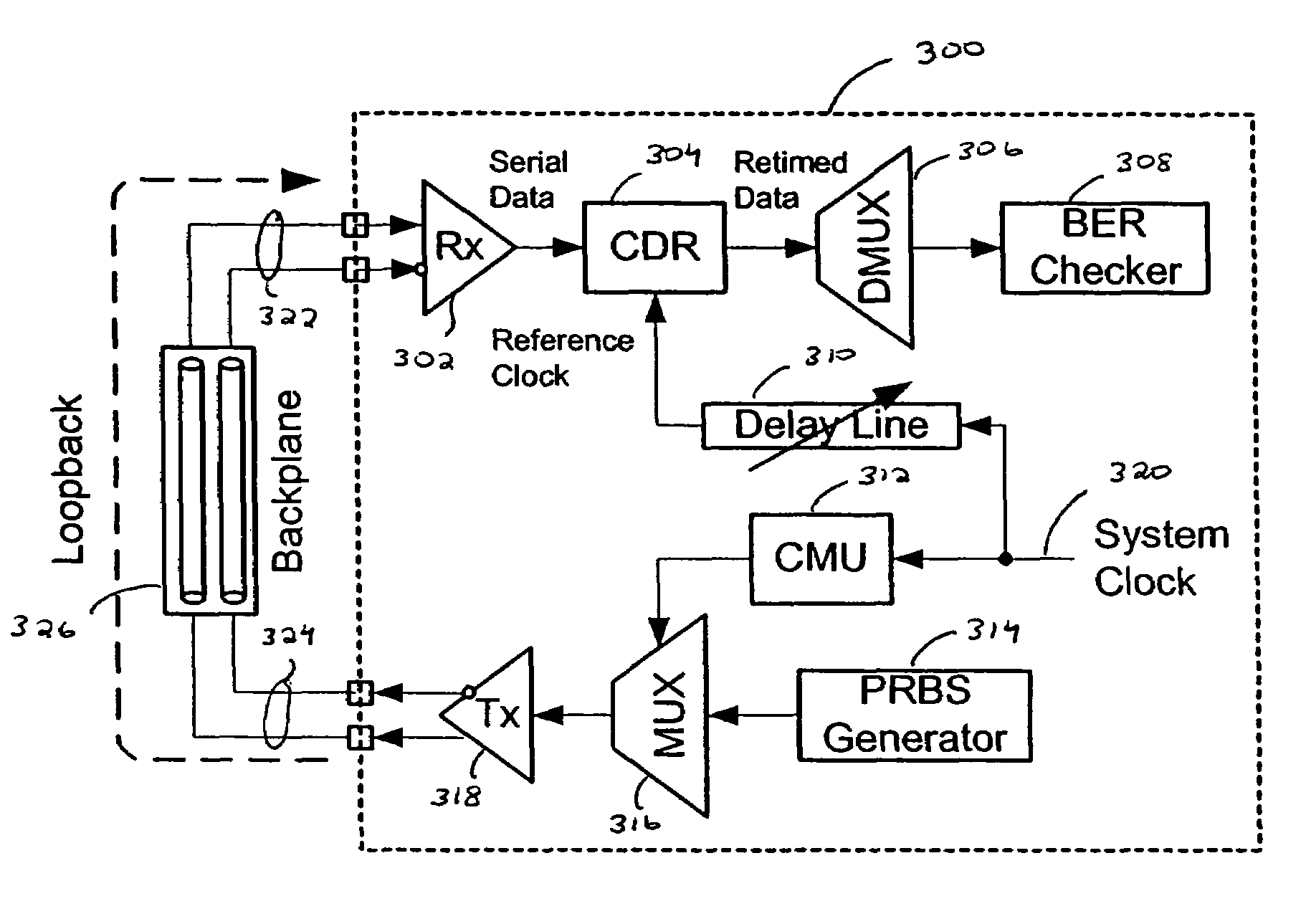
A physical-layer tester for testing a high-speed serial link between a mission-environment transmitter and a mission-environment receiver. The tester includes a data path and a measurement path. The data path allows a data signal transmitted from the mission-environment transmitter to be passed through the tester to the mission-environment receiver. The measurement path includes circuitry for use in analyzing characteristics of the high-speed serial data traffic on the high-speed serial link. The tester is placed in the high-speed serial link and allows the link to be tested while live, mission-environment data is present on the link. Methods for implementing in-link testing are also disclosed.
Owner:DFT MICROSYST
Method and system for configuring high-speed serial links between components of a network device
ActiveUS20060075175A1Low-latency communicationMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingLatency (engineering)
A system for selectively forming high-speed serial connections between various components of a network device that includes a multiplexing switch coupled a GE slot and to the high speed serial interfaces of a PHY and at least two network devices. The switch can be programmed to connect the serial interfaces of the two network modules to provide a high-speed, low-latency serial link between the two network modules. Alternatively, the serial interface of a network module can be connected to the GE slot to provide a high-speed, low-latency serial link between the network module and the GE slot.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Built-in at-speed bit error ratio tester
InactiveUS7743288B1Low-cost solutionEfficient testingError preventionTransmission systemsEqualizationBuilt-in self-test
A built-in, at-speed BERT is provided that may be part of high-speed serial interface circuitry implemented on an integrated circuit. The built-in, at-speed BERT takes advantage of an existing clock data recovery (CDR) dual-loop architecture and built-in self test (BIST) circuitry. The built-in, at-speed BERT provides a low-cost solution for production testing of high-speed serial links, facilitating jitter analysis and evaluation of pre-emphasis and equalization performance. This further allows adaptation of pre-emphasis and equalization.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
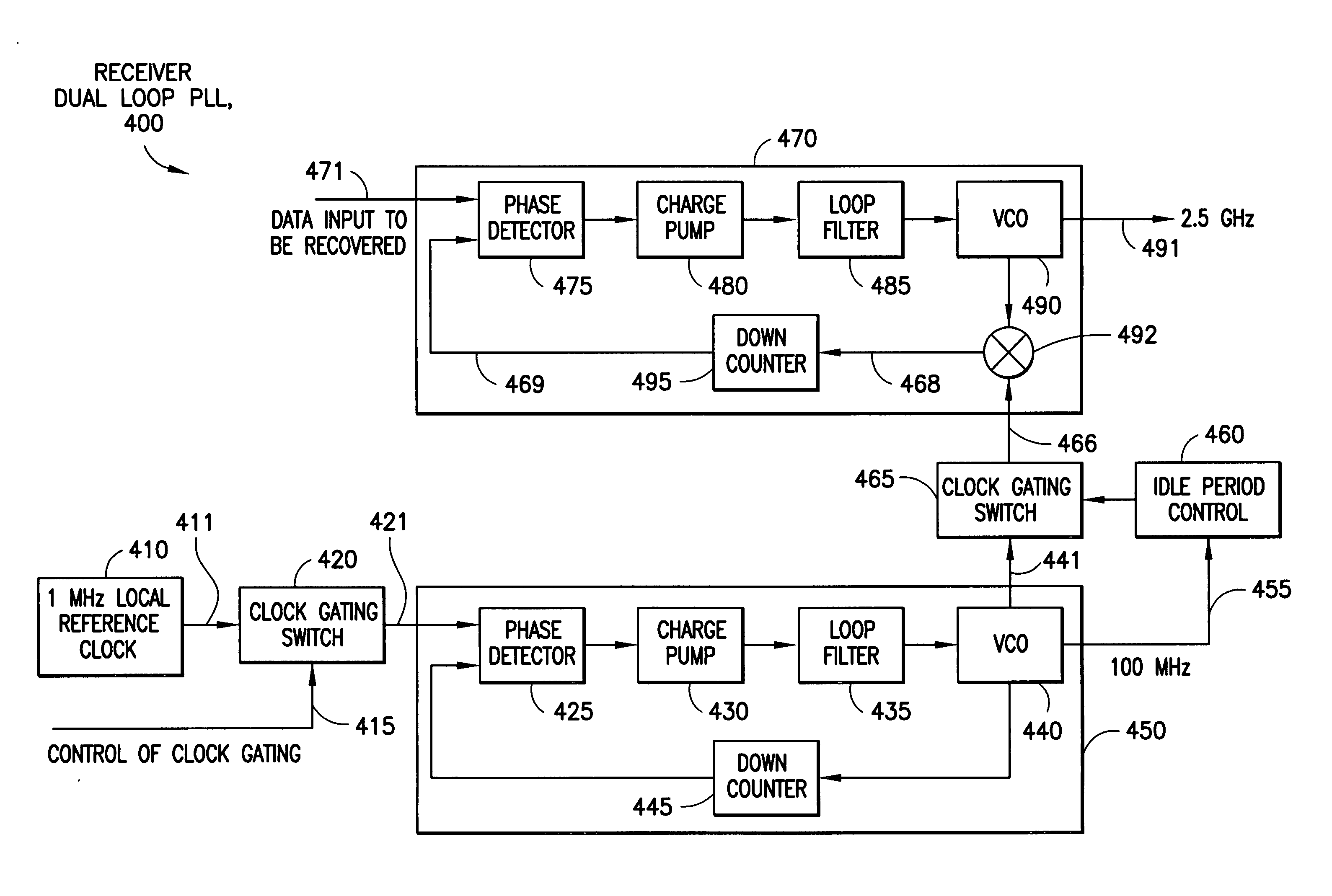
System and method for pre-defined wake-up of high speed serial link
A system and method for transmitting and receiving through a high speed serial link with power up and power down capability. The exemplary embodiments of this invention involves a method of power up and power down the high-speed serial link without using high voltage swing control and signaling. Both the transmitter and the receiver wake up only during pre-defined burst cycles. During each burst cycle, data will be transmitted and received in burst mode. Outside each burst cycle, the transmitter and receiver will be powered off or partially powered off. Various phase-locked loop based circuit ensure the transmitter and the receiver can be locked in frequency and phase quickly at the time of power-up. The duration of the burst cycle and the interval between two adjacent burst cycles can be either fixed or changed by upper level protocol.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
High Speed Serial Link In-Band Lane Fail Over for RAS and Power Management
ActiveUS20150278040A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission link error control systemTelecommunicationsTelecommunications link
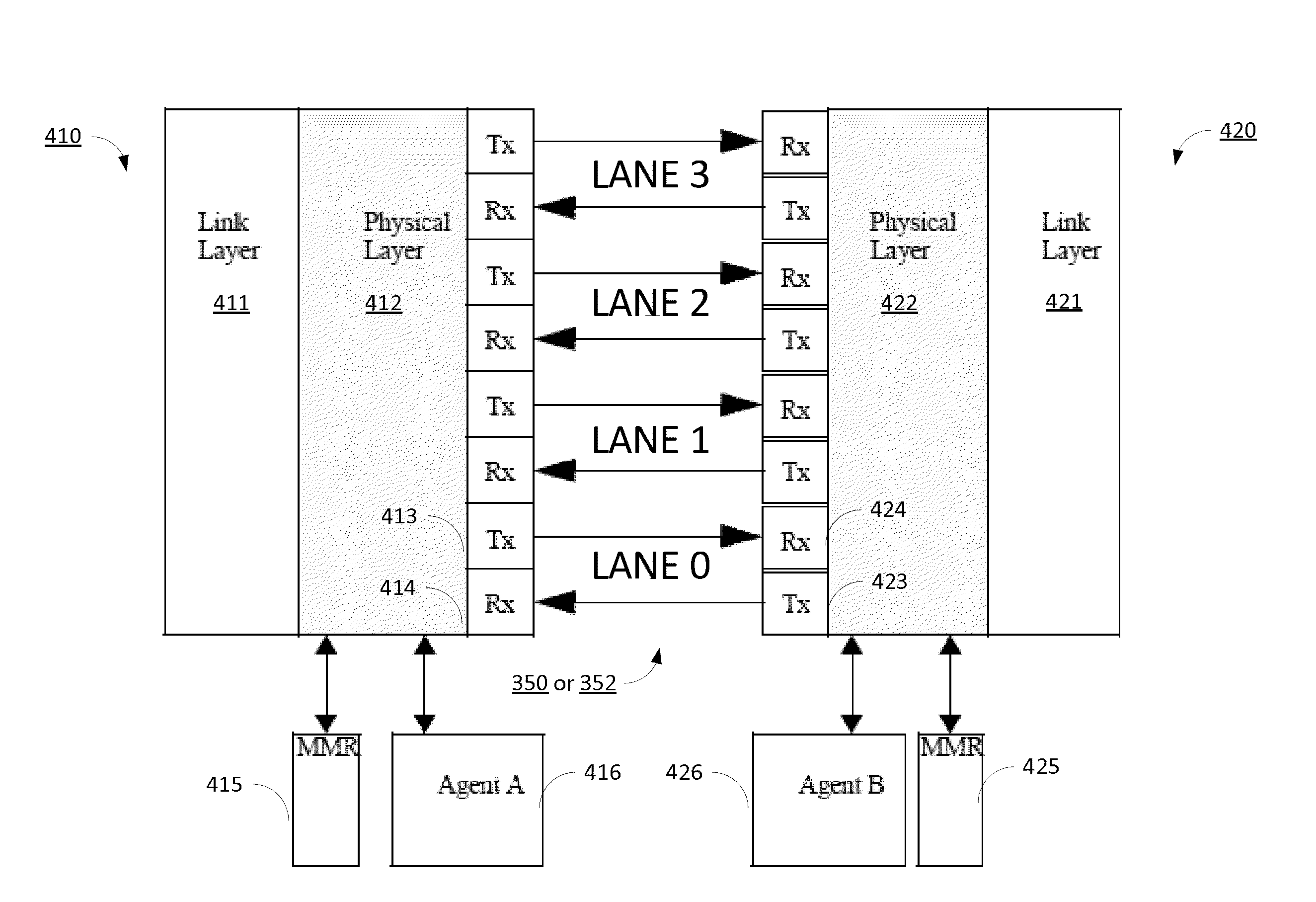
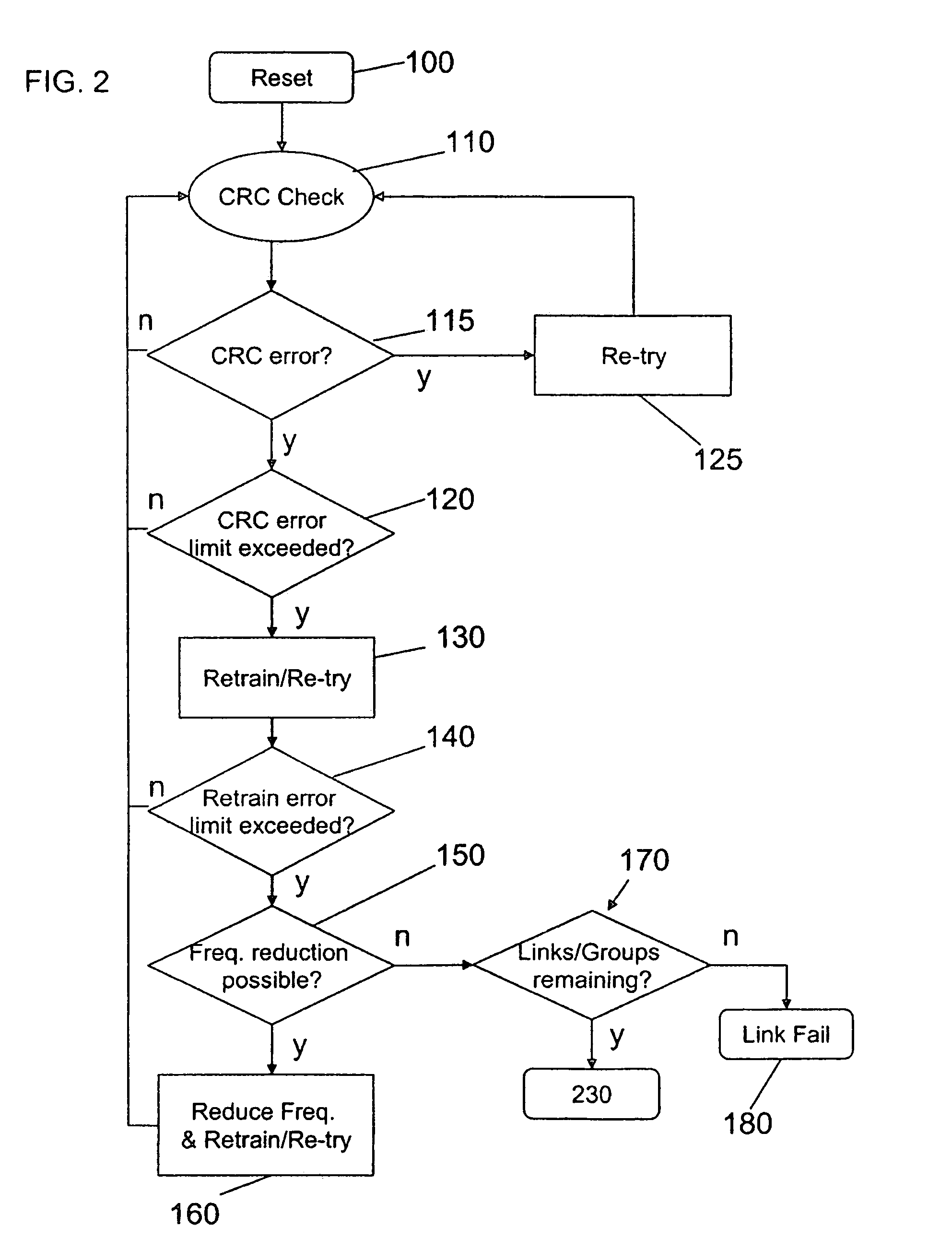
A system and method provide a communications link having a plurality of lanes, and an in-band, real-time physical layer protocol that keeps all lanes on-line, while failing lanes are removed, for continuous service during fail over operations. Lane status is monitored real-time at the physical layer receiver, where link error rate, per lane error performance, and other channel metrics are known. If a lane failure is established, a single round trip request / acknowledge protocol exchange with the remote port completes the fail over. If a failing lane meets an acceptable performance level, it remains on-line during the round trip exchange, resulting in uninterrupted link service. Lanes may be brought in or out of service to meet reliability, availability, and power consumption goals.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
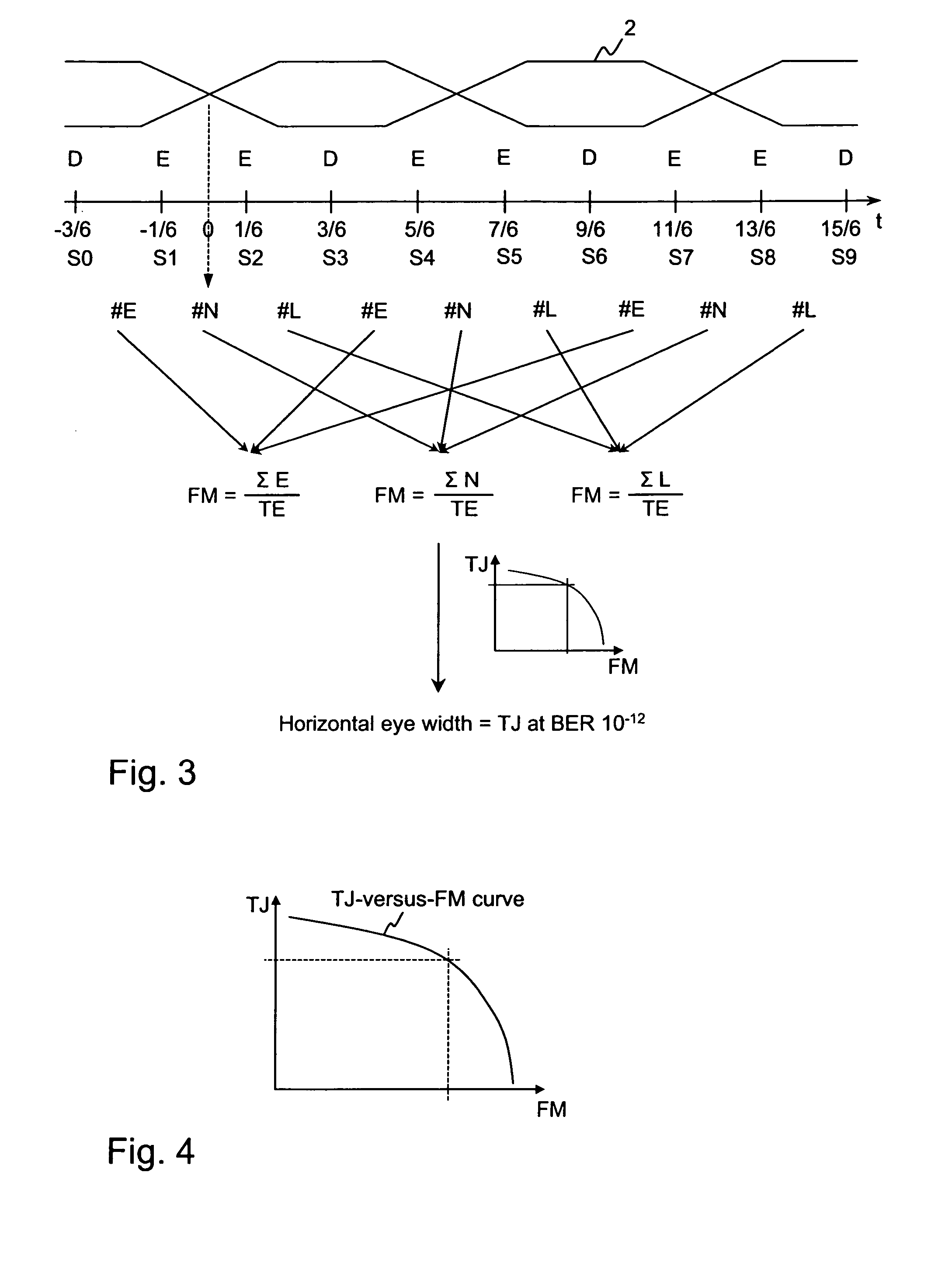
Method for determining jitter of a signal in a serial link and high speed serial link
ActiveUS7295604B2Easy to implementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTransmission channelFigure of merit
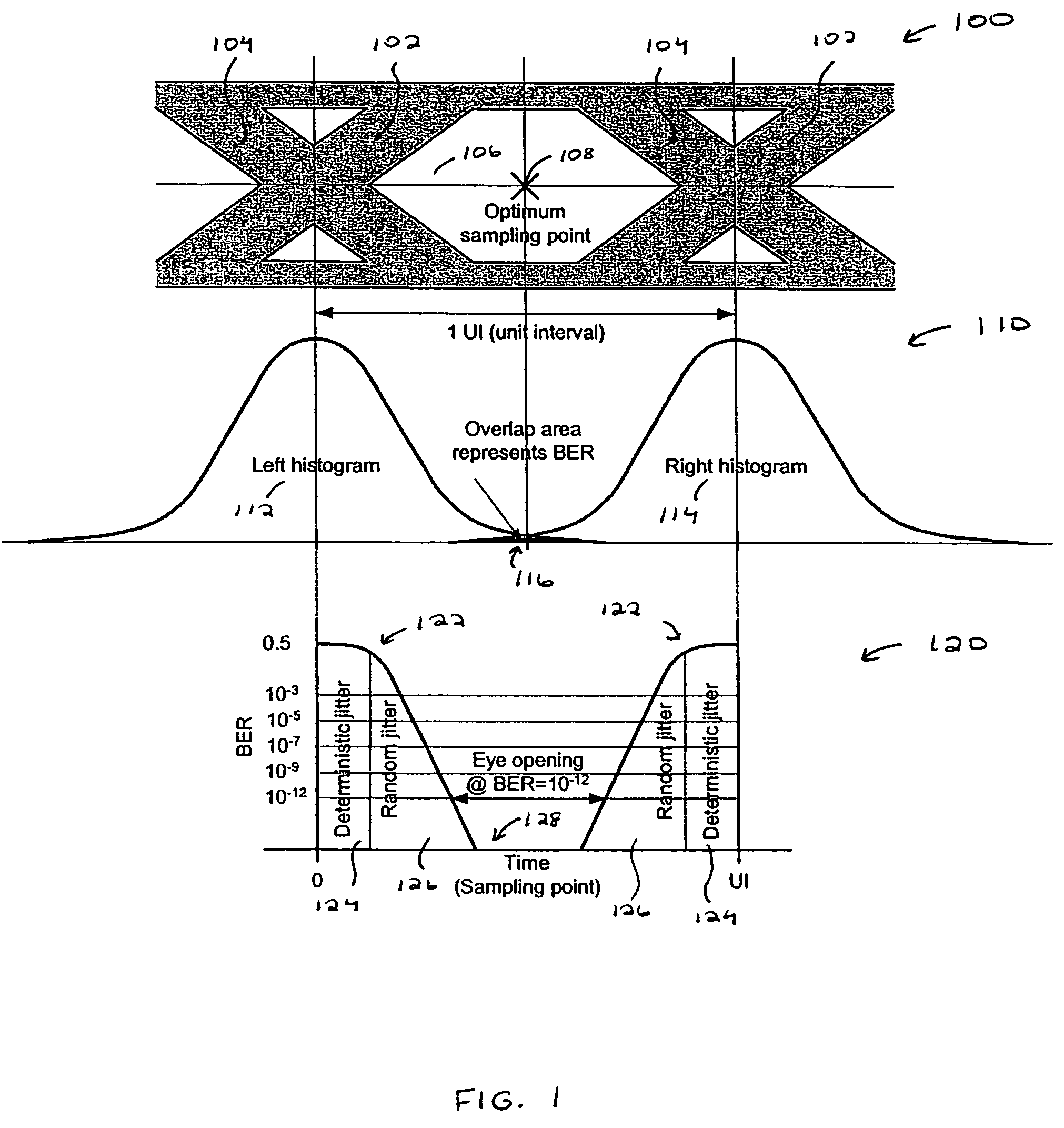
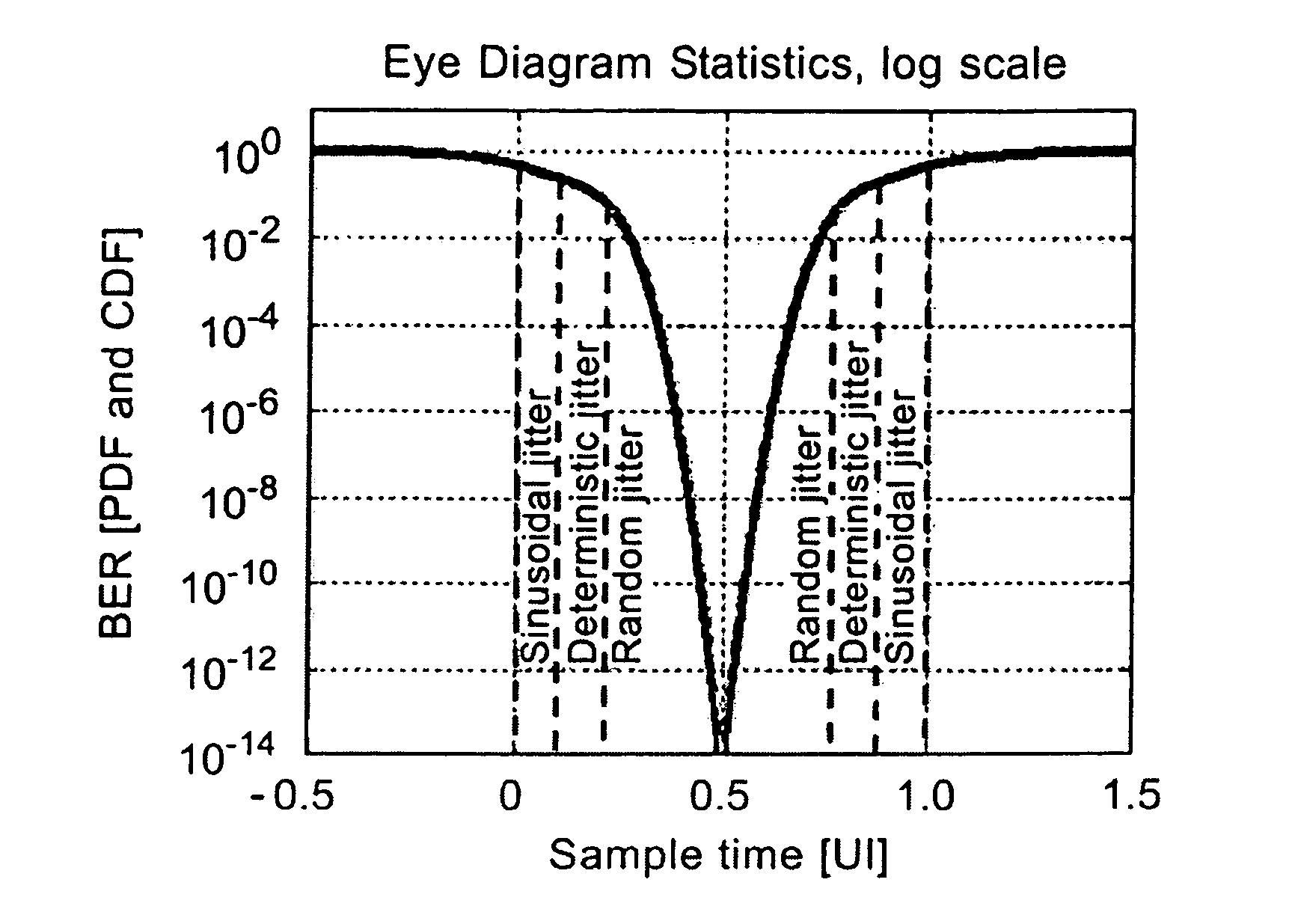
The method for determining jitter of a signal in a serial link according to the invention comprising the following steps: First, a section of the signal transmitted via a transmission channel is sampled at different sampling times. The total number of edges in the section is determined. The neighboring sample values are analyzed and from that a statistical value is formed. From the statistical value and the total number of edges a figure of merit is determined. Finally, by means of a look-up table or a jitter-versus-figure of merit curve, the total jitter corresponding to the figure of merit is derived.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
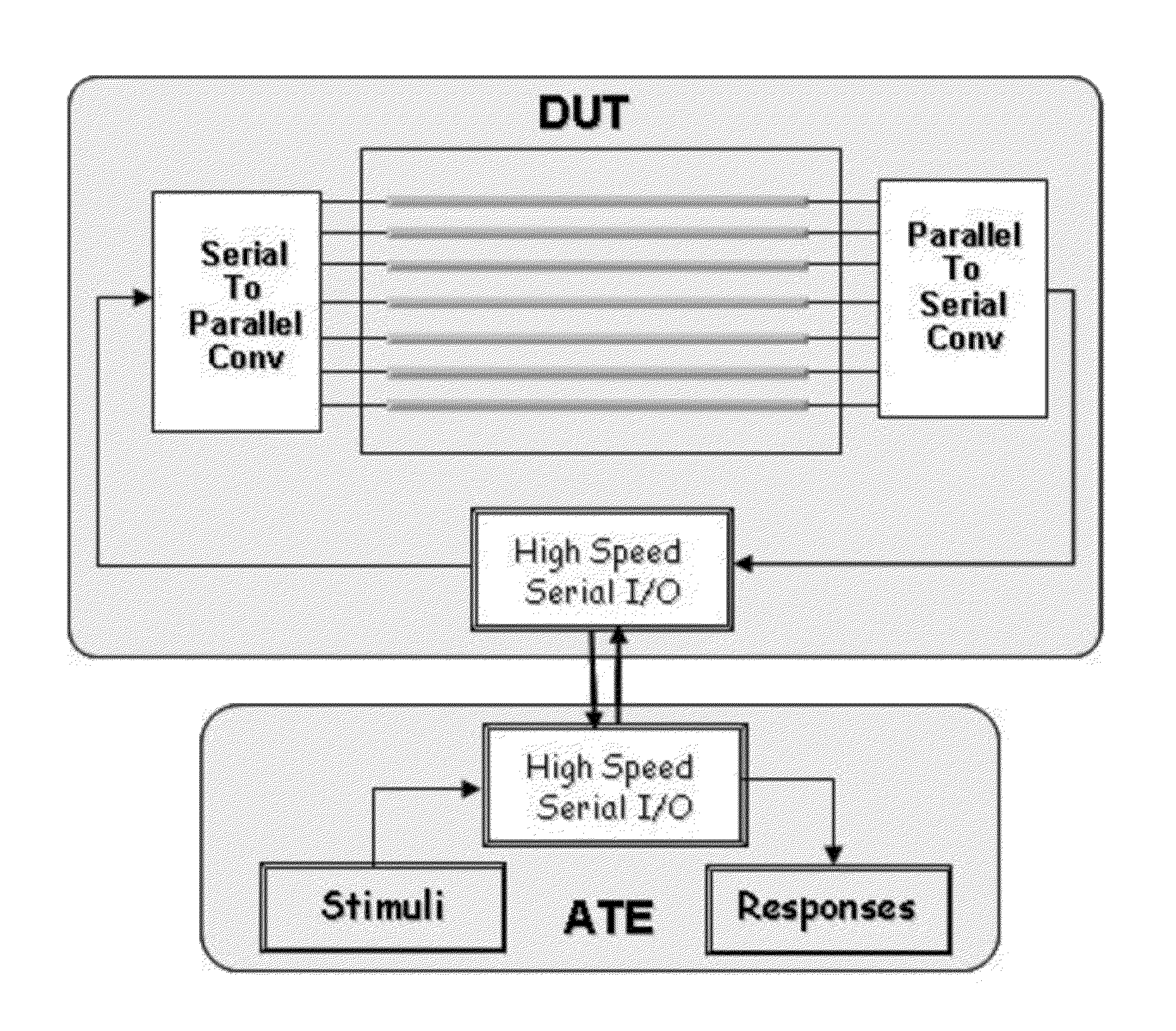
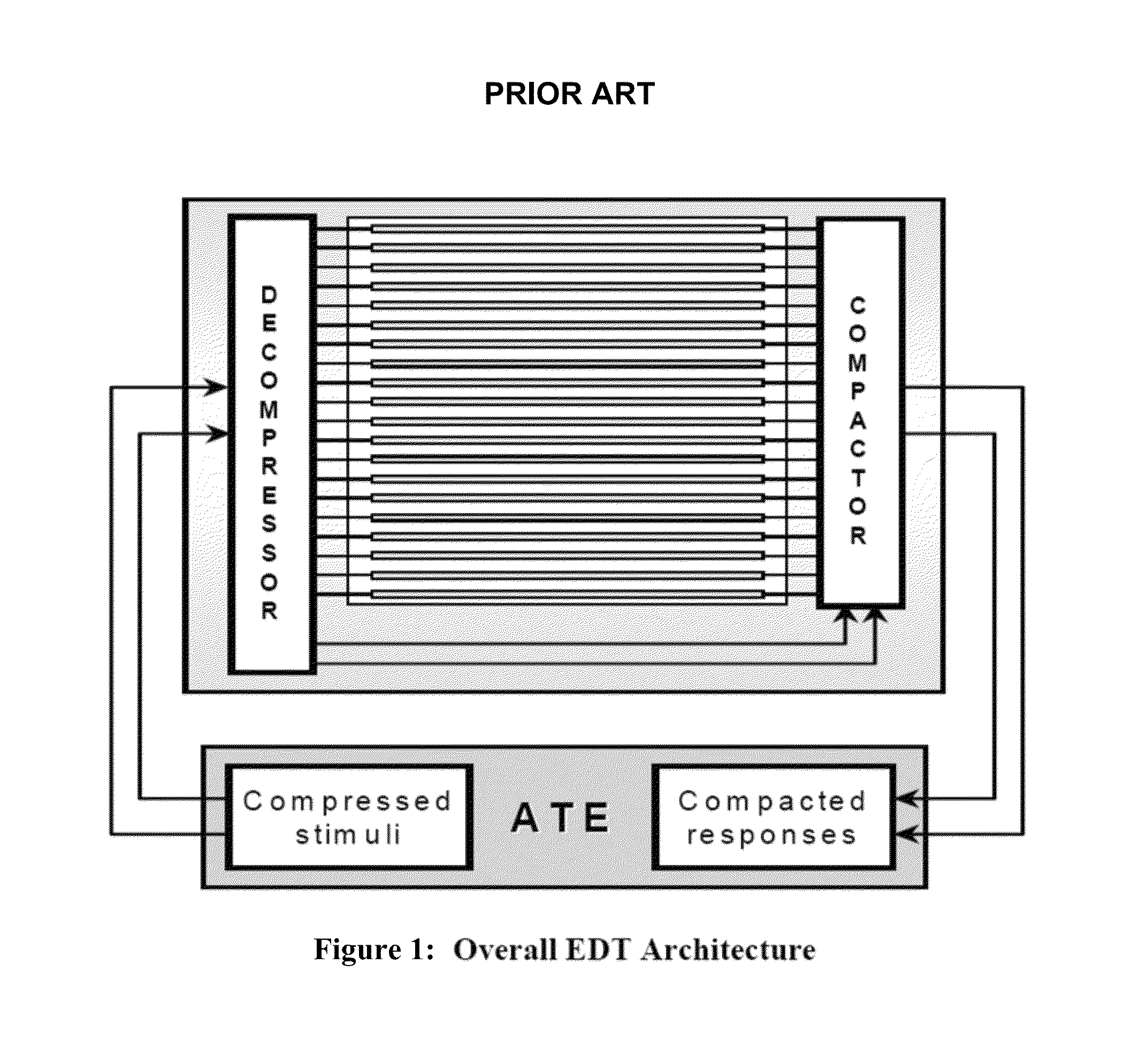
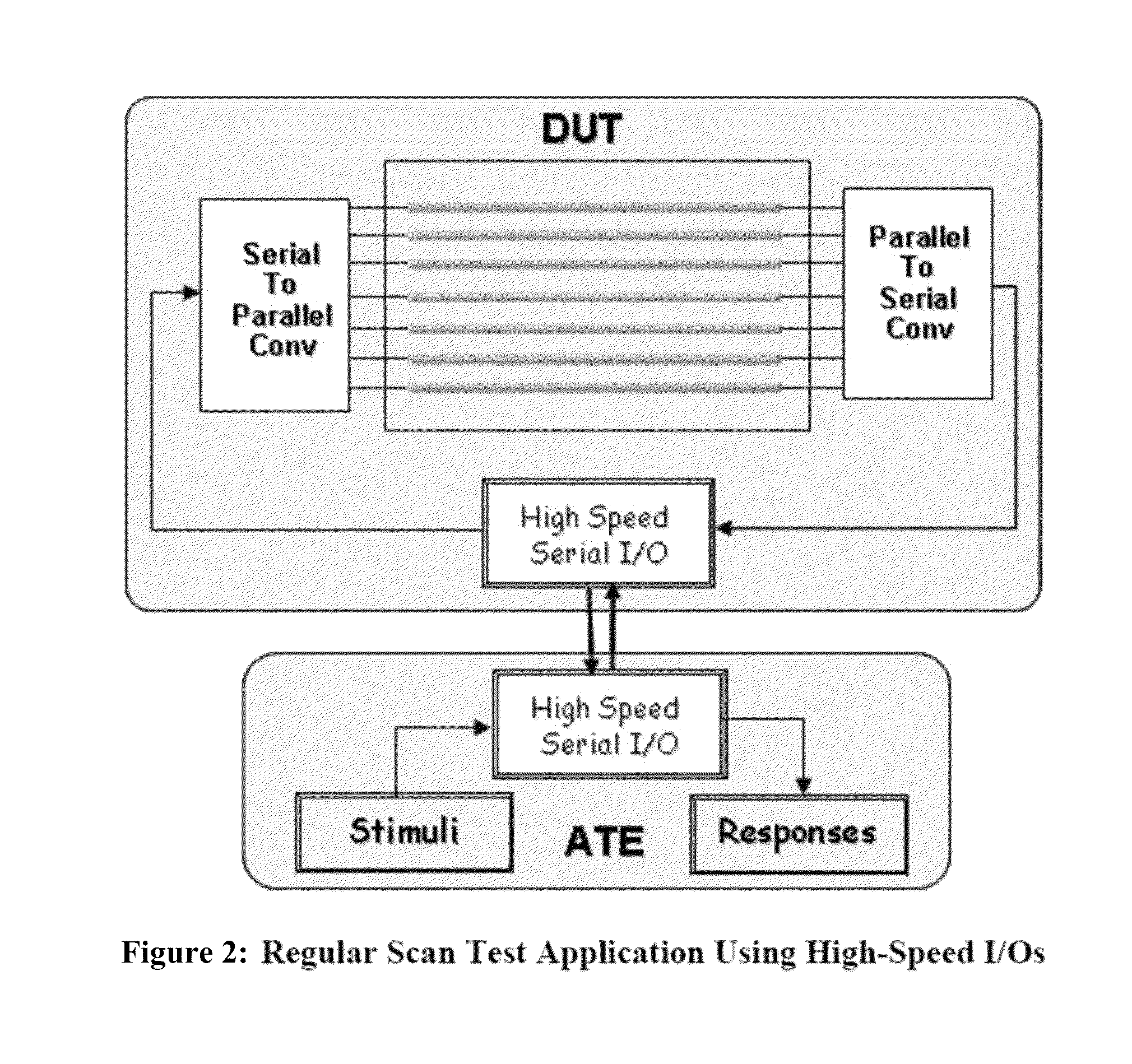
Scan test application through high-speed serial input/outputs
ActiveUS8726112B2Reduce test data volumeMinimize timeElectronic circuit testingData compressionAsynchronous operation
Methods and devices for using high-speed serial links for scan testing are disclosed. The methods can work with any scheme of scan data compression or with uncompressed scan testing. The protocol and hardware to support high speed data transfer reside on both the tester and the device under test. Control data may be transferred along with scan data or be partially generated on chip. Clock signals for testing may be generated on chip as well. In various implementations, the SerDes (Serializer / Deserializer) may be shared with other applications. The Aurora Protocol may be used to transport industry standard protocols. To compensate for effects of asynchronous operation of a conventional high-speed serial link, buffers may be used. The high-speed serial interface may use a data conversion block to drive test cores.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
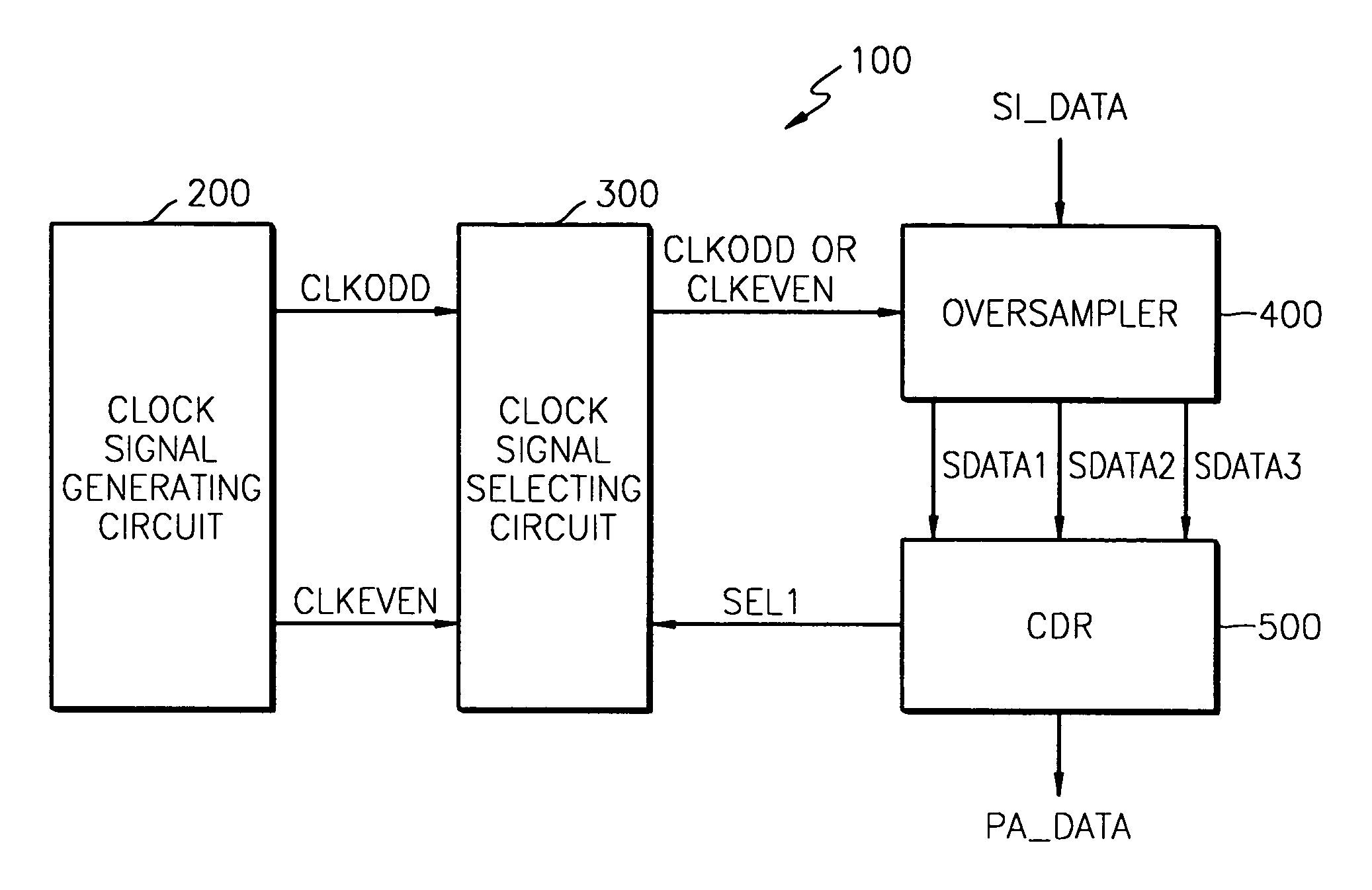
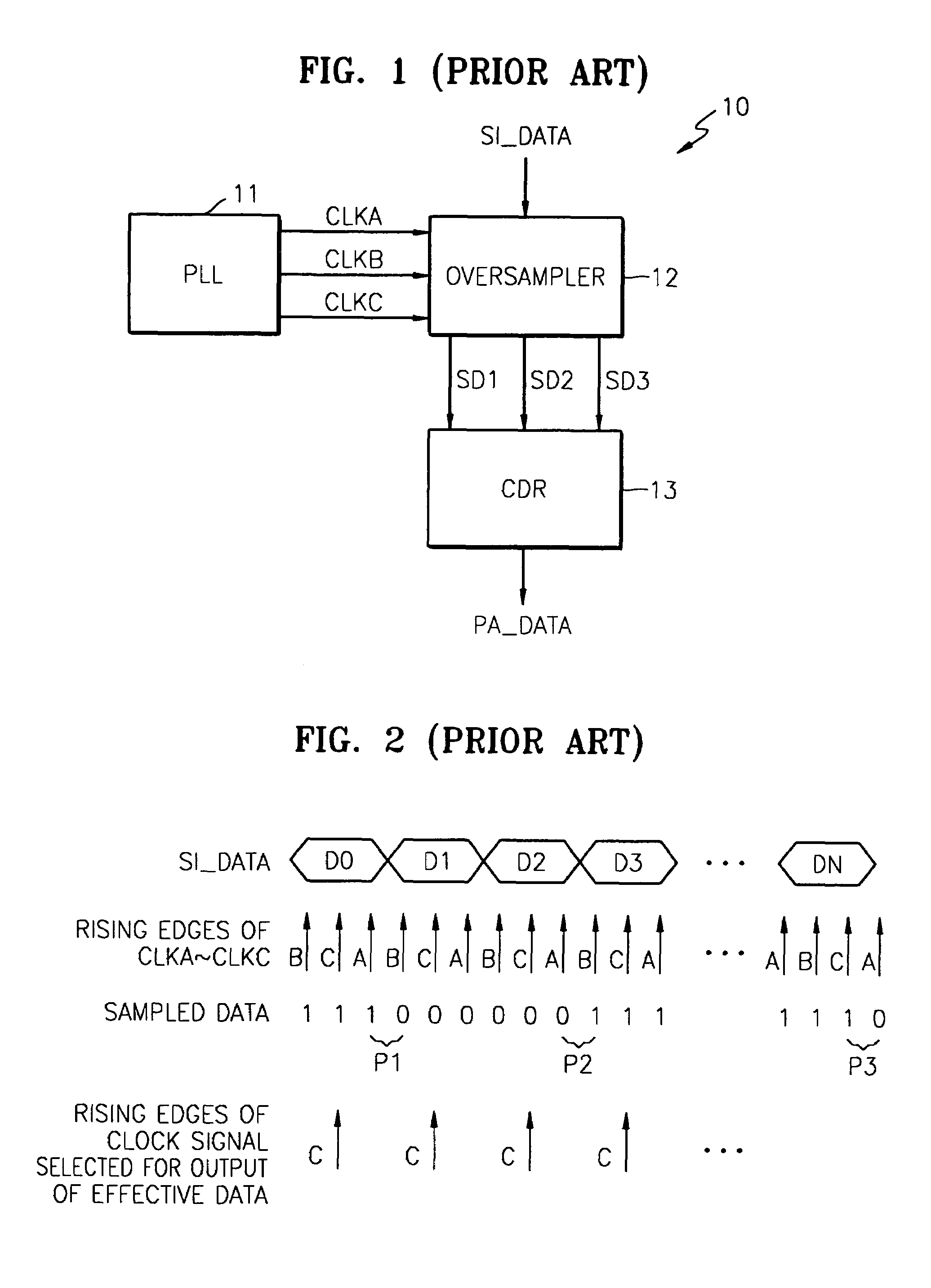
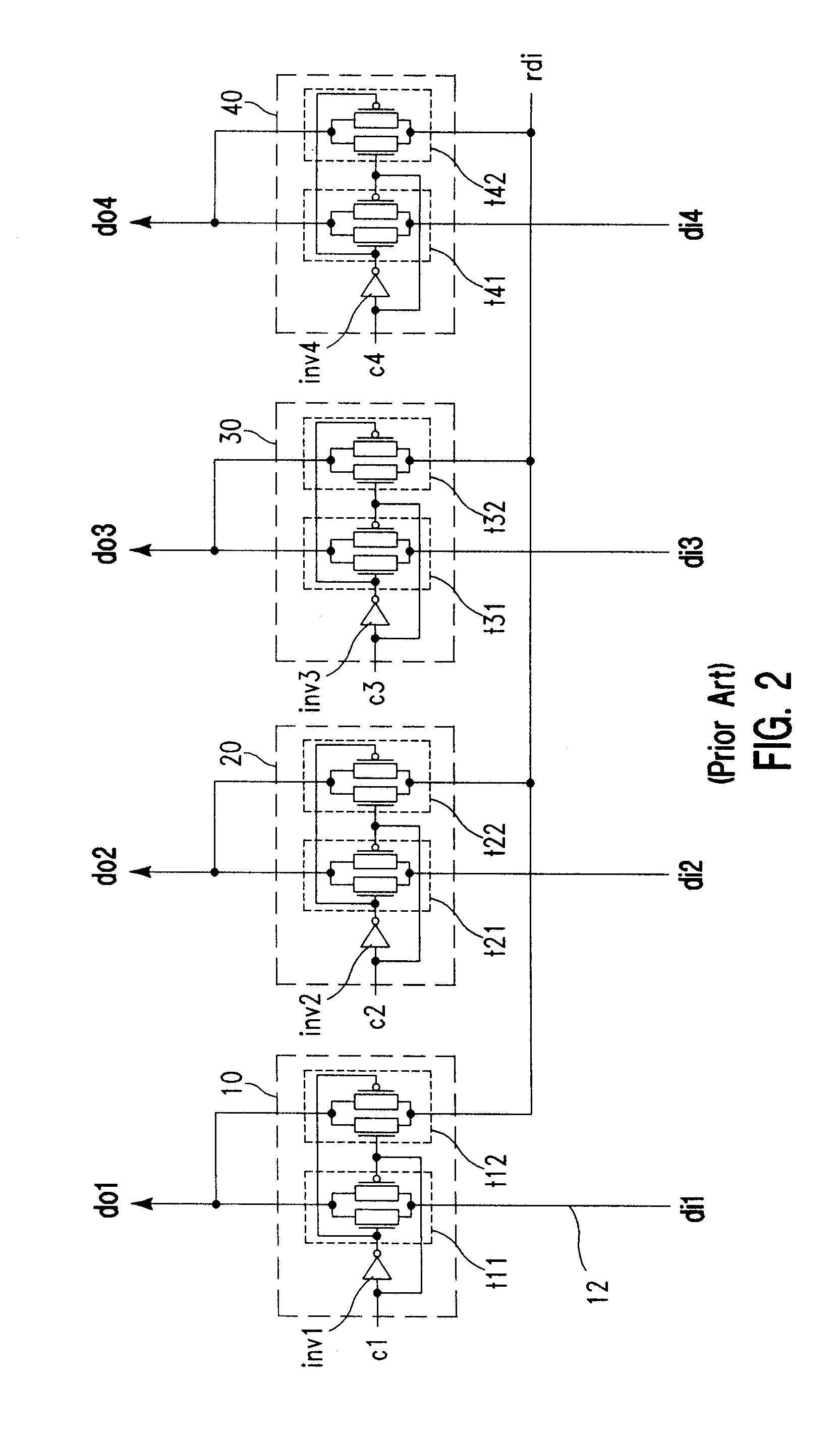
Data recovery apparatus and method for decreasing data recovery error in a high-speed serial link
ActiveUS7436904B2Degrades data recoveryReduce dataError preventionModulated-carrier systemsData recovery circuitHigh speed serial link
Provided are a data recovery apparatus and method for recovering (parallel) data from serial data received via a high-speed serial link with a reduced data recovery error rate. The data recovery apparatus includes a clock signal generating circuit and a data recovery circuit. The clock signal generating circuit generates at least two clock signal groups including first and second clock signal groups with different phases for alternate use in the data recovery circuit. The data recovery circuit recovers the data from the serial data by oversampling the serial data using one of the at least two clock signal groups selected based on the number of rising edges of sampling clock signals of the selected clock signal group being within an eye open region of the serial data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
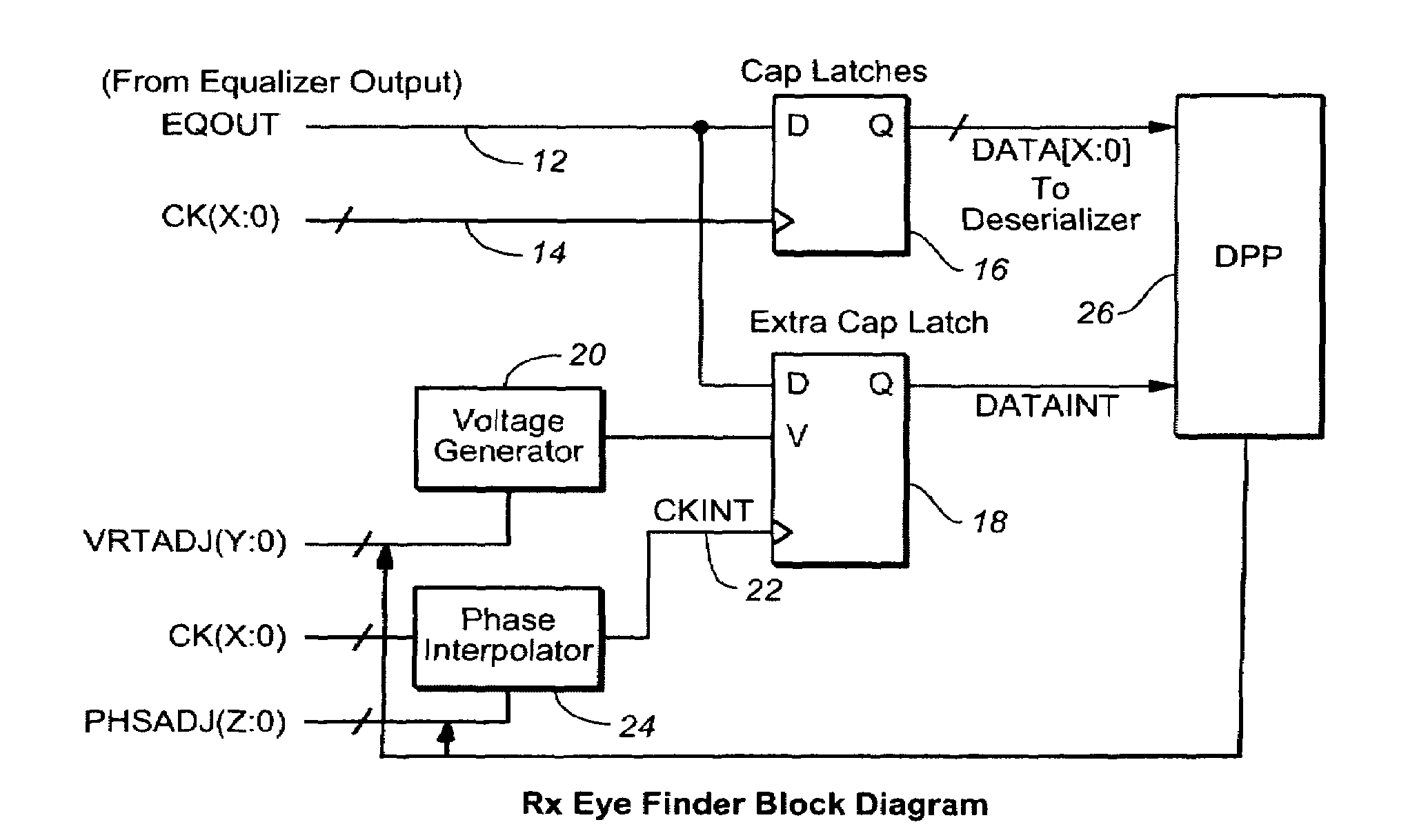
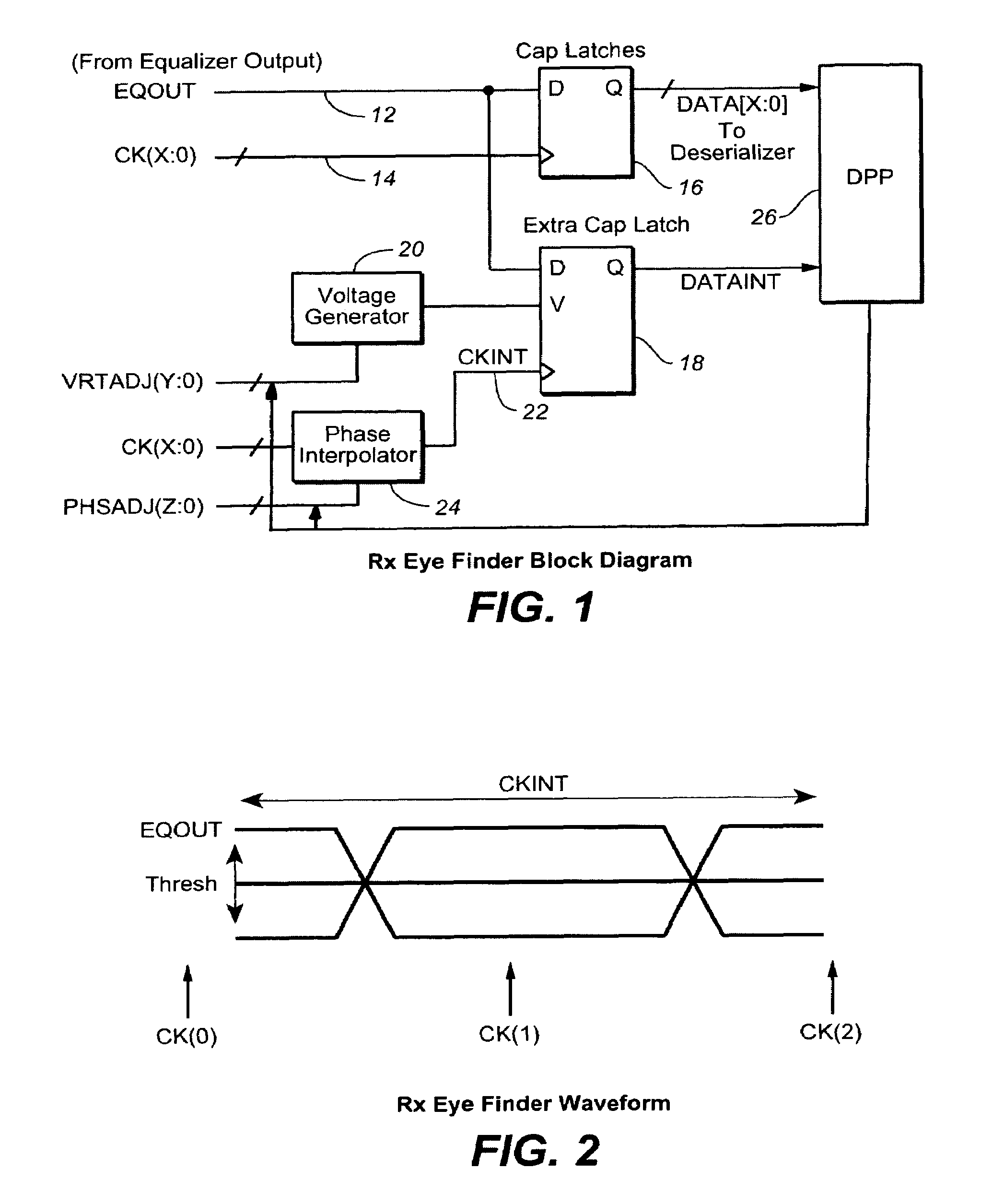
On-chip receiver eye finder circuit for high-speed serial link
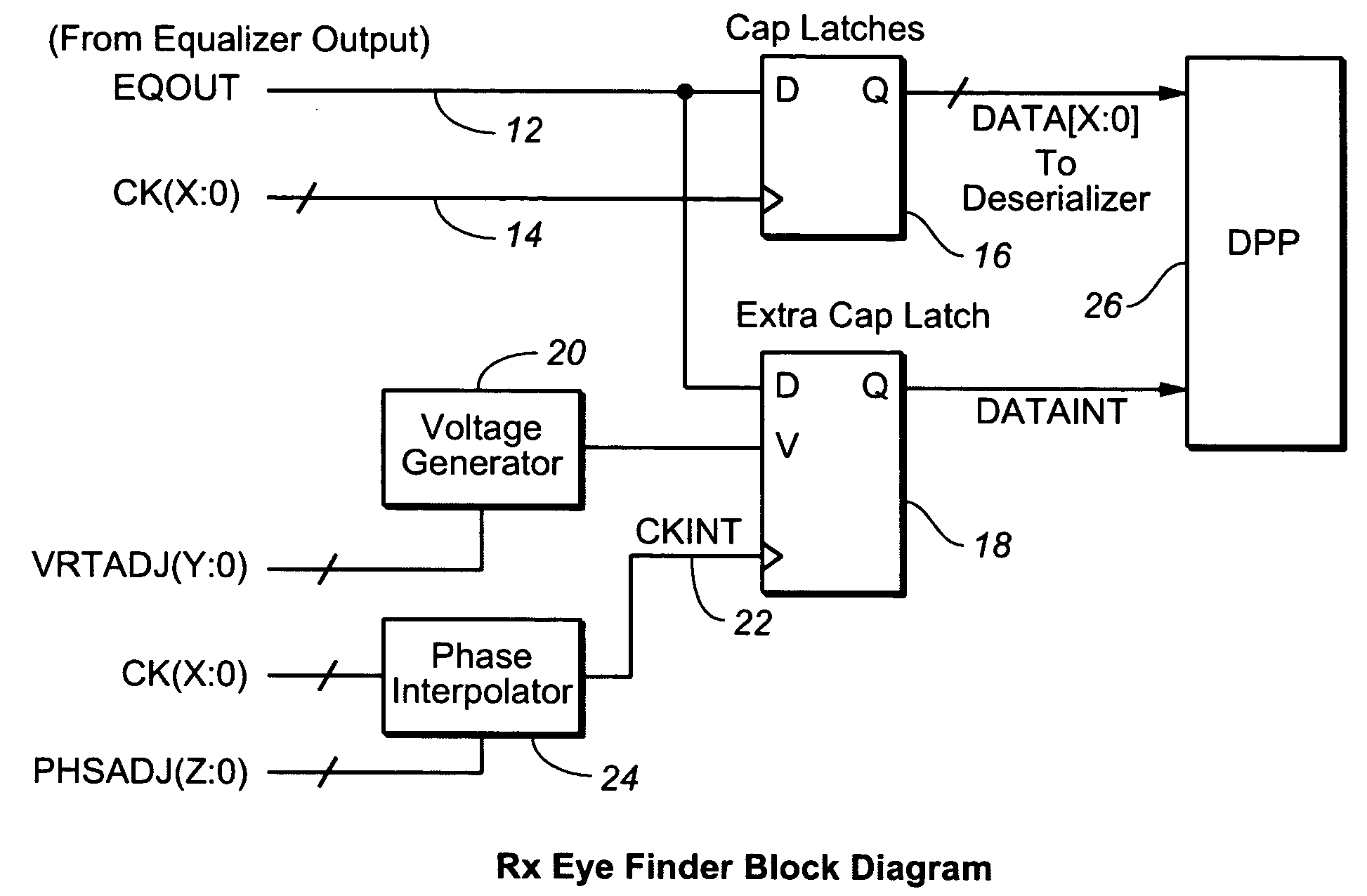
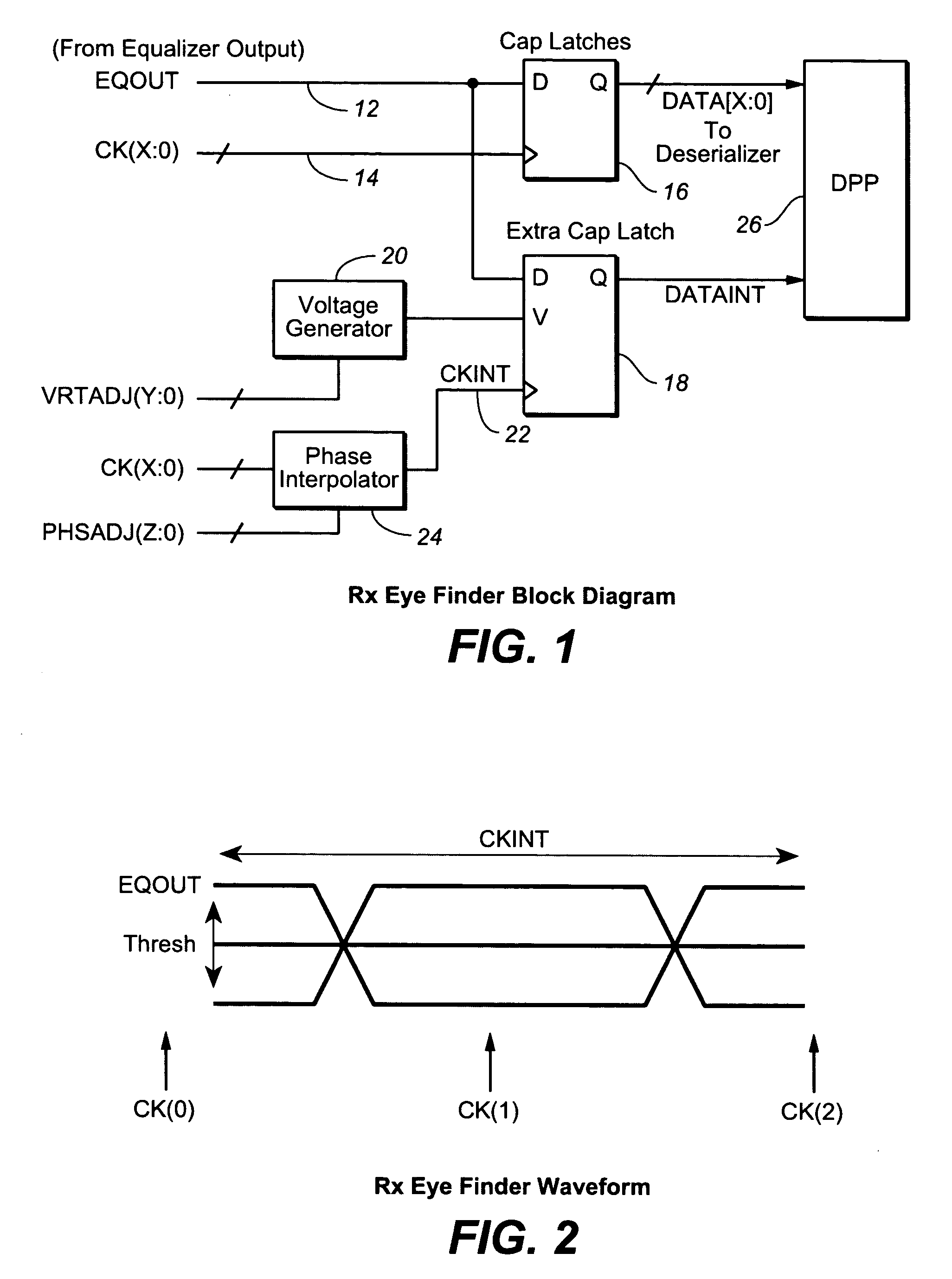
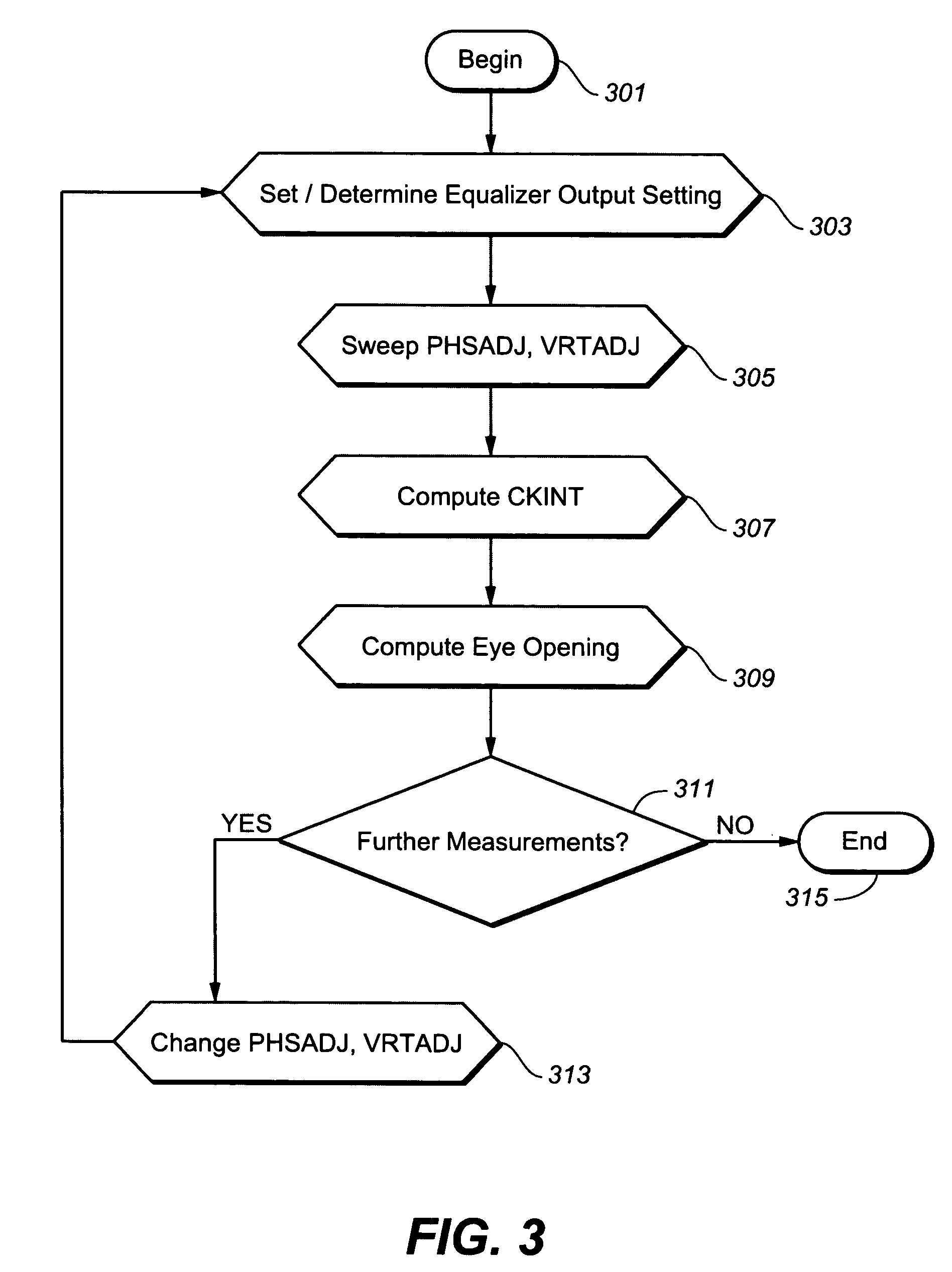
ActiveUS20080005629A1Minimize the numberArea minimizationTelevision system detailsElectrical testingVoltage generatorVoltage reference
In a high-speed serial link, an eye finder diagnostic circuit has improved performance by being on-chip with the existing capture latch(es) of a receive equalizer. The eye finder circuit employs an additional capture latch with its input tied to the same input node as the existing capture latch(es) of a receive equalizer. The additional capture latch has a clock input and reference voltage input. The clock input is adjusted through a phase interpolator (or variable delay line) while the reference voltage input is adjusted by a voltage generator. A digital post processing circuit then compares the output of the additional capture latch with the output of the other existing capture latch(es), in order to determine the receive eye opening. The horizontal eye opening is measured by changing the phase of the additional capture latch through the phase interpolator, while the vertical eye opening is measured by changing the reference voltage of the voltage generator of the additional capture latch. The eye finder circuit, being on-chip and in-line with existing capture latch(es), employs a minimum of power, minimum of area, and minimizes the extra loading to the existing equalizer output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Rapid I/O traffic system
ActiveUS7710969B2Preventing Head-Of-Line blockingSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityExchange network
High speed networking systems such as PCI-Express and Serial Rapid I / O are based on the exchange of packets across switched networks of high speed serial links. Information in the headers of these packets indicate the kind of transaction they represent. Queuing all received packets in a single queue will cause interactions between transaction types. Indirection can be used create the effect of multiple independent queues from a shared memory. This provides efficient centralized packet storage, while allowing independent processing of different transactions types.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for sequential testing of high speed serial link core
ActiveUS7191371B2Minimize test timeMinimized in sizeCorrect operation testingTransmission systemsEngineeringHigh speed serial link
A testing circuit for testing a series of at least three alternating transmitter and receiver links. The testing circuit including a built-in-self-test (BIST.) macro for generating test data and transmitting the test data to a first link of the series of transmitter and receiver links, and for receiving processed test data from a last link of the series of transmitter receiver links; and at least one test transmission line for transmitting test data received by a link of the series of transmitter and receiver links to a next link of the series of transmitter and receiver links, wherein the at least one test transmission line connects the at least three transmitter and receiver links. A method for testing a series of links having at least three alternating transmitter and receiver links of a plurality of transmitter and receiver links in a SerDes core including generating at least one test data signal; transmitting the at least one test data signal sequentially through the transmitter and receiver links of the series of links; receiving the at least one test data signal from a last link of the series of transmitter and receiver links; and checking the at least one test data signal received.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
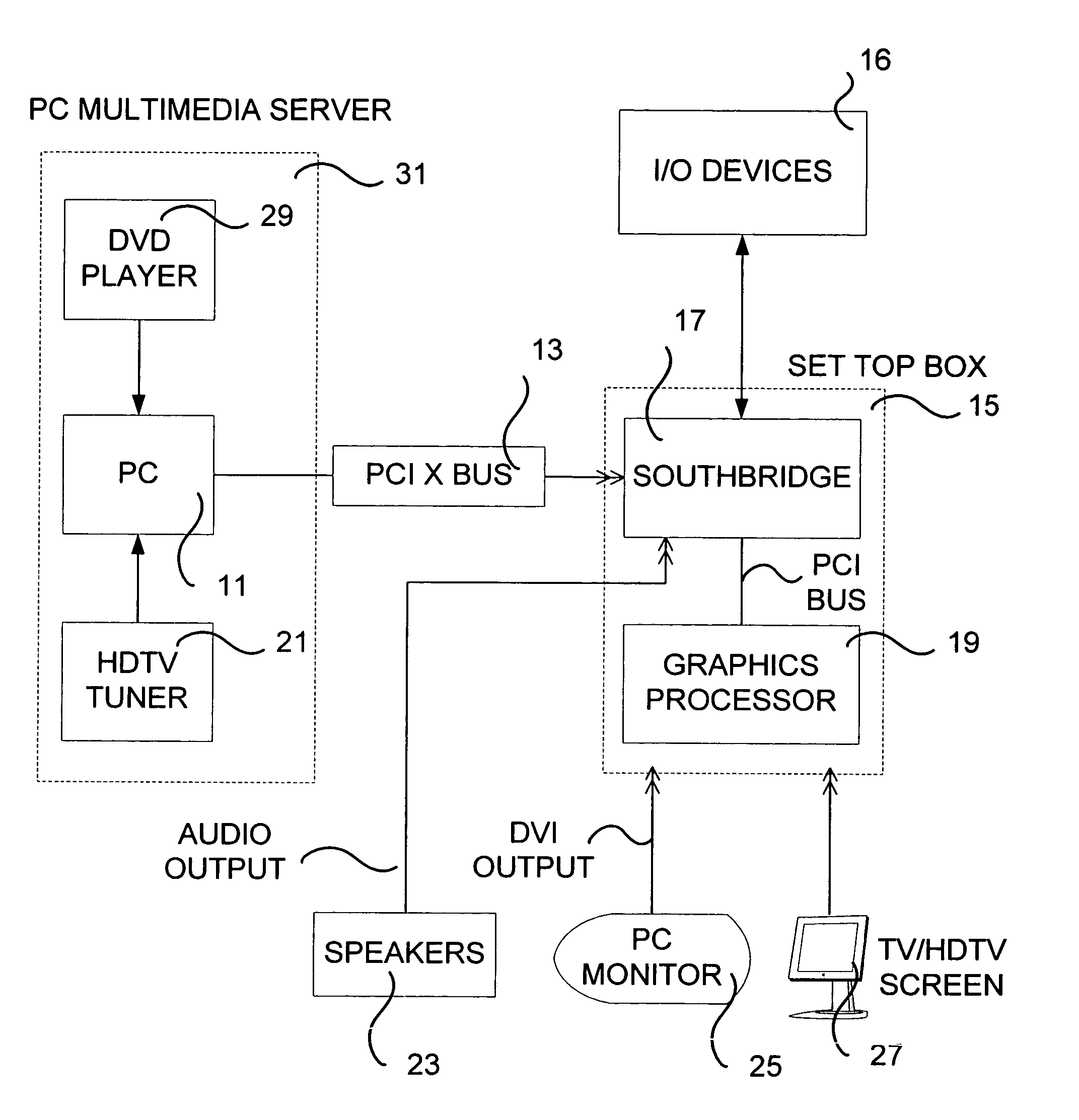
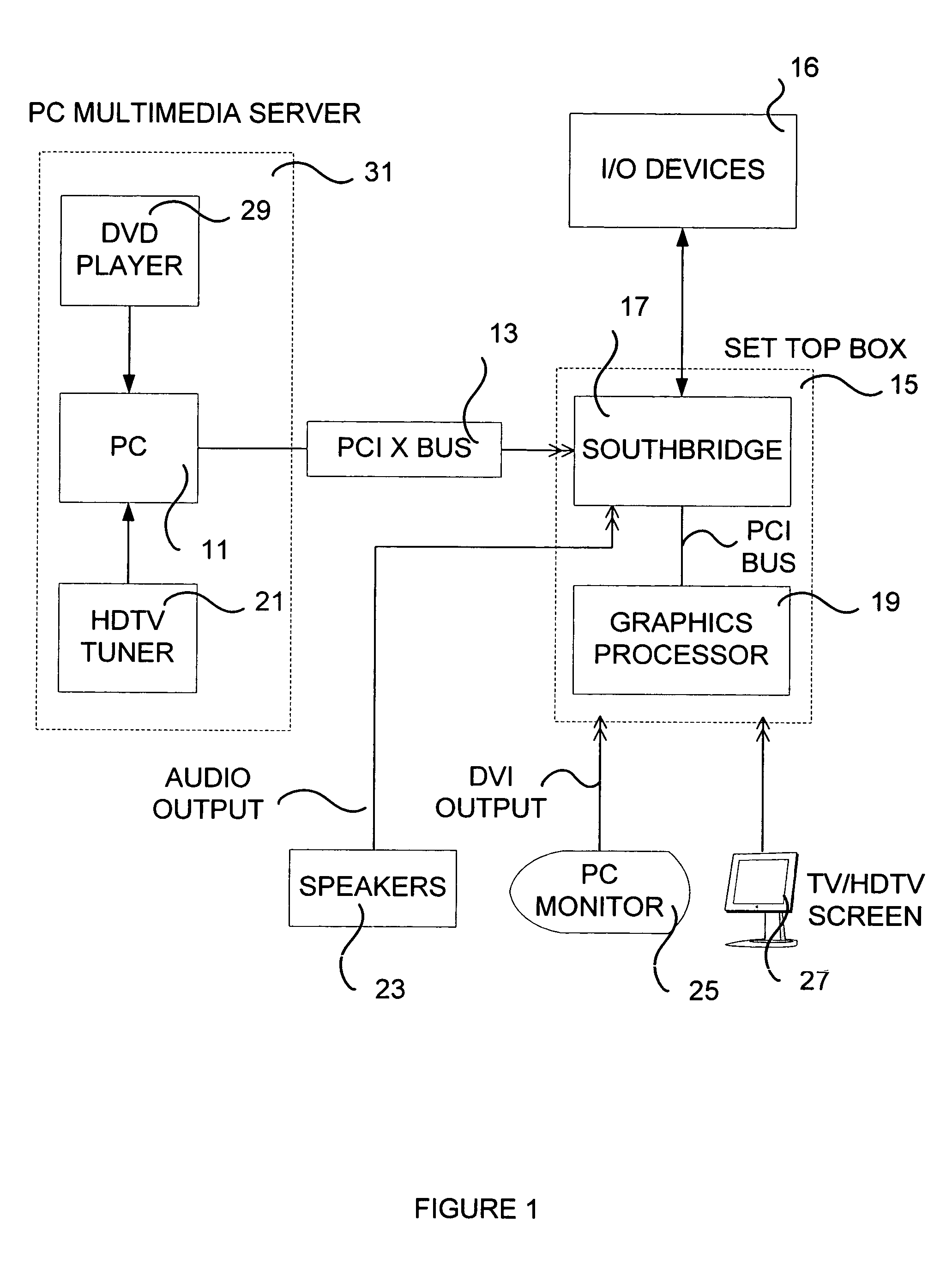
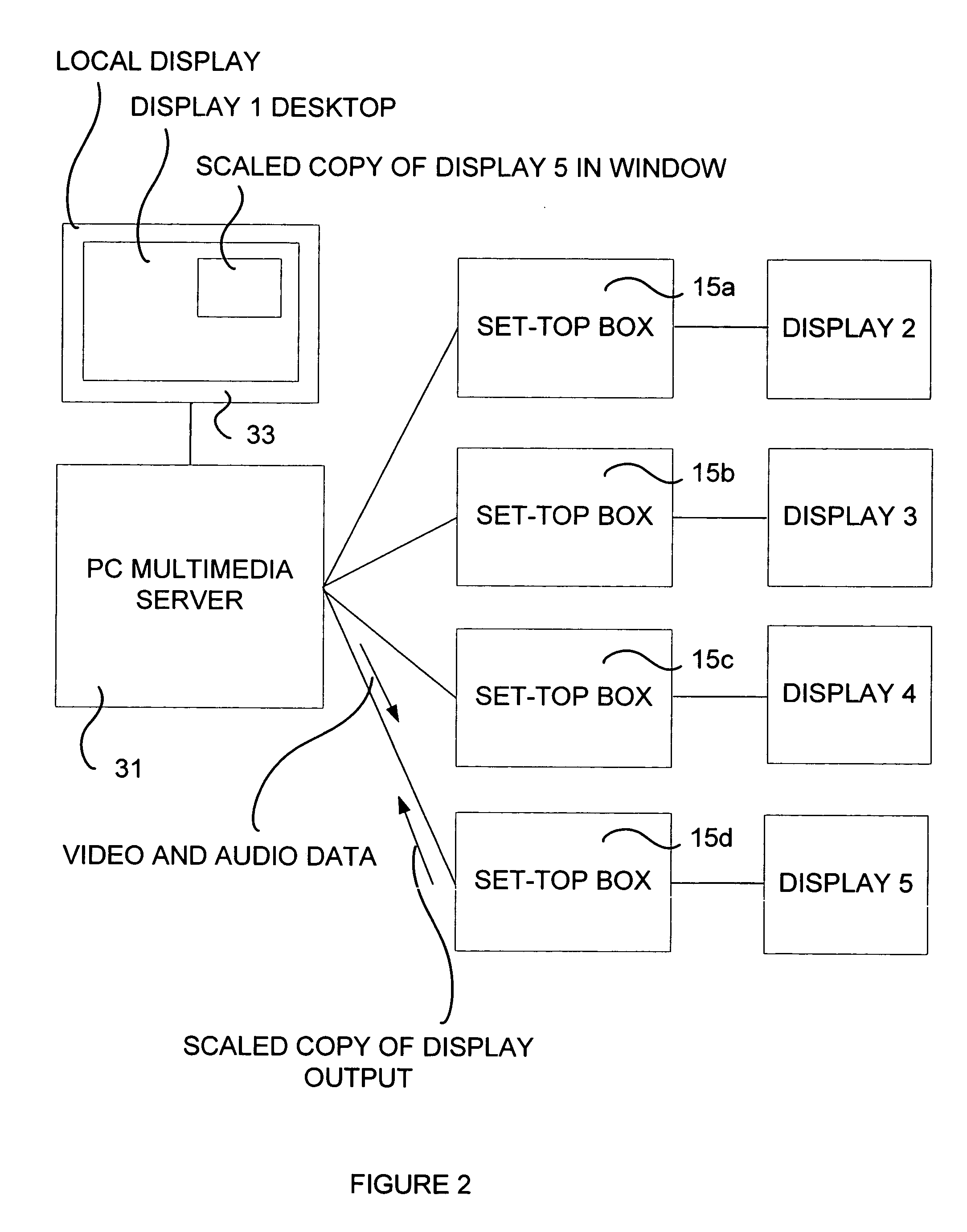
Set top box for PC/HDTV multimedia center
ActiveUS20050273824A1Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsGraphicsDisplay device
A multimedia system is provided, comprising a computer for receiving audio data and video data from a source and transmitting the data serially over a high speed serial link, a set-top box connected through the link to the computer for receiving the audio data and video data, the set-top box having a southbridge module with a link interface connected to the link and providing a local parallel data bus output and at least one audio playback channel receiving the audio data; and a graphics processor receiving from the southbridge module the video data over the bus, processing the video data and providing a video output in at least one display format. At least one display device is connected to the graphics processor for receiving and displaying the video output; and at least one speaker is connected to the audio playback channel.
Owner:MATROX
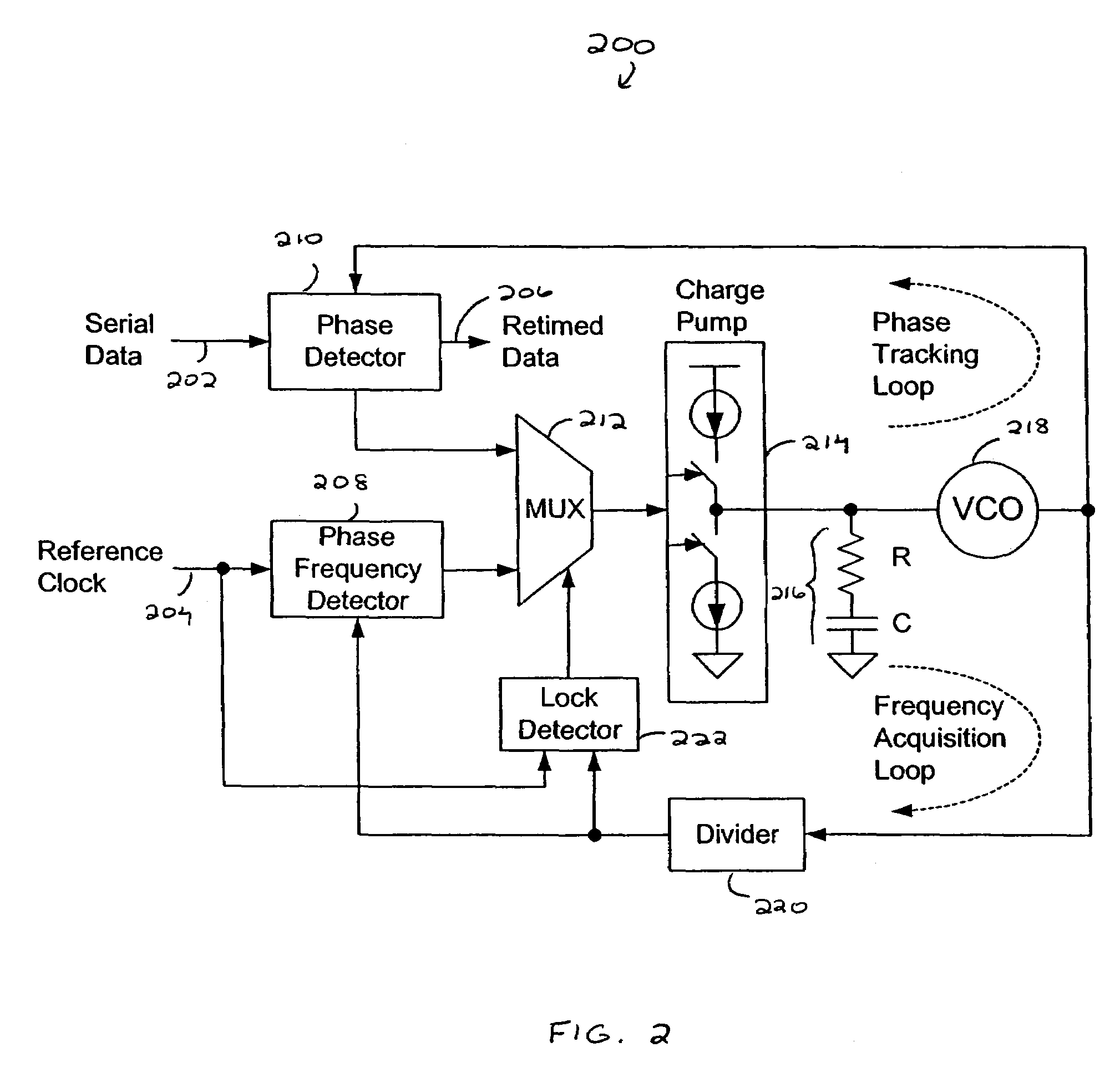
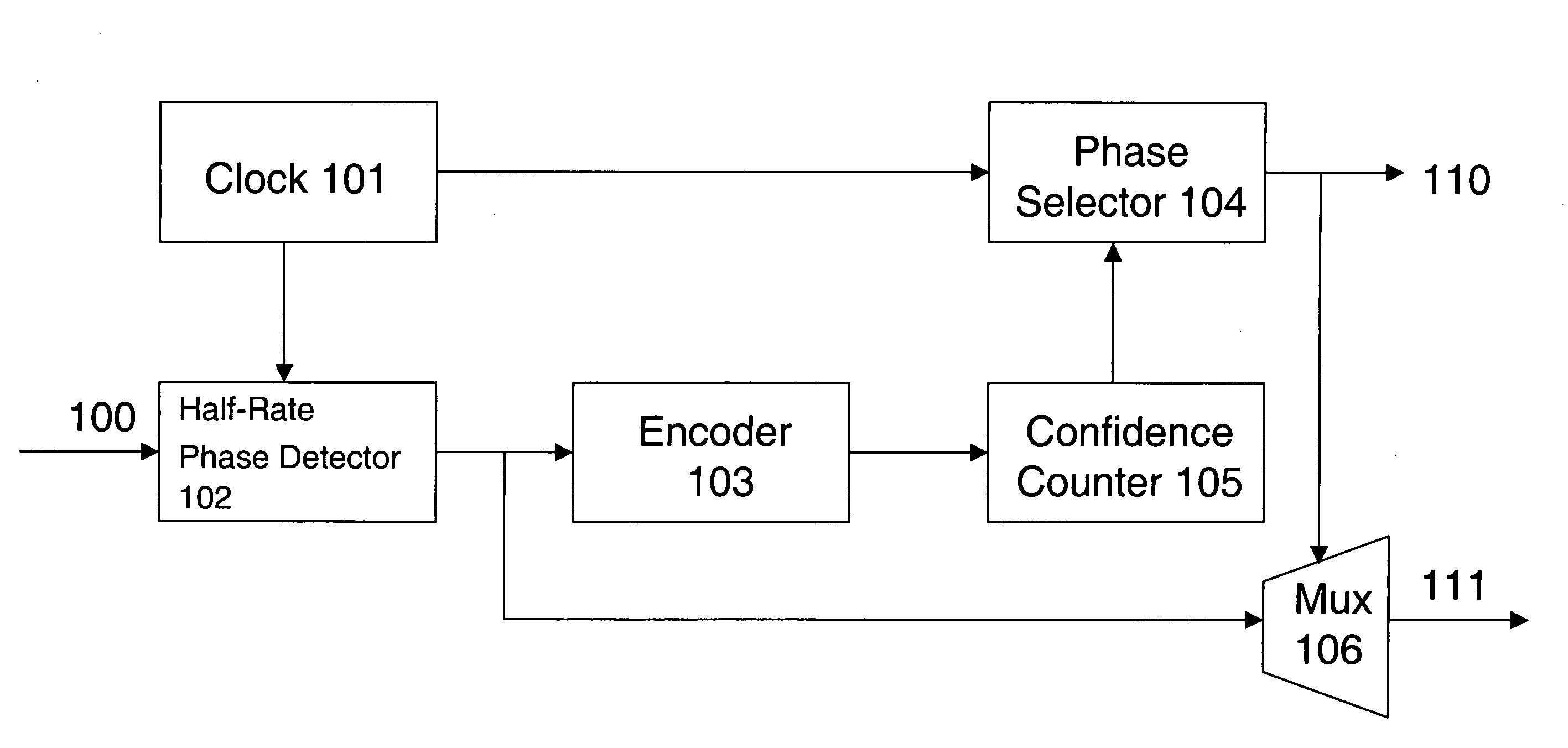
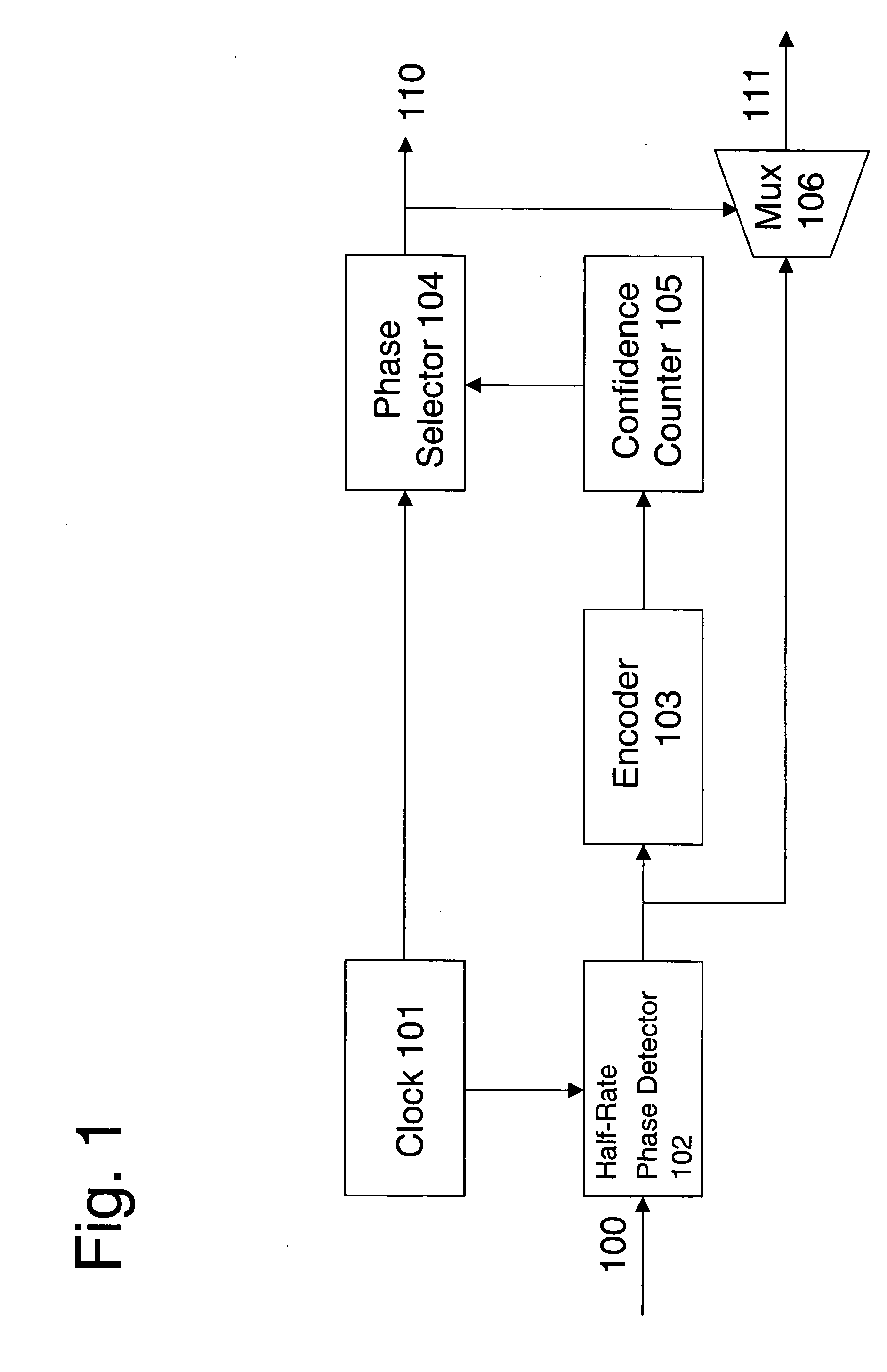
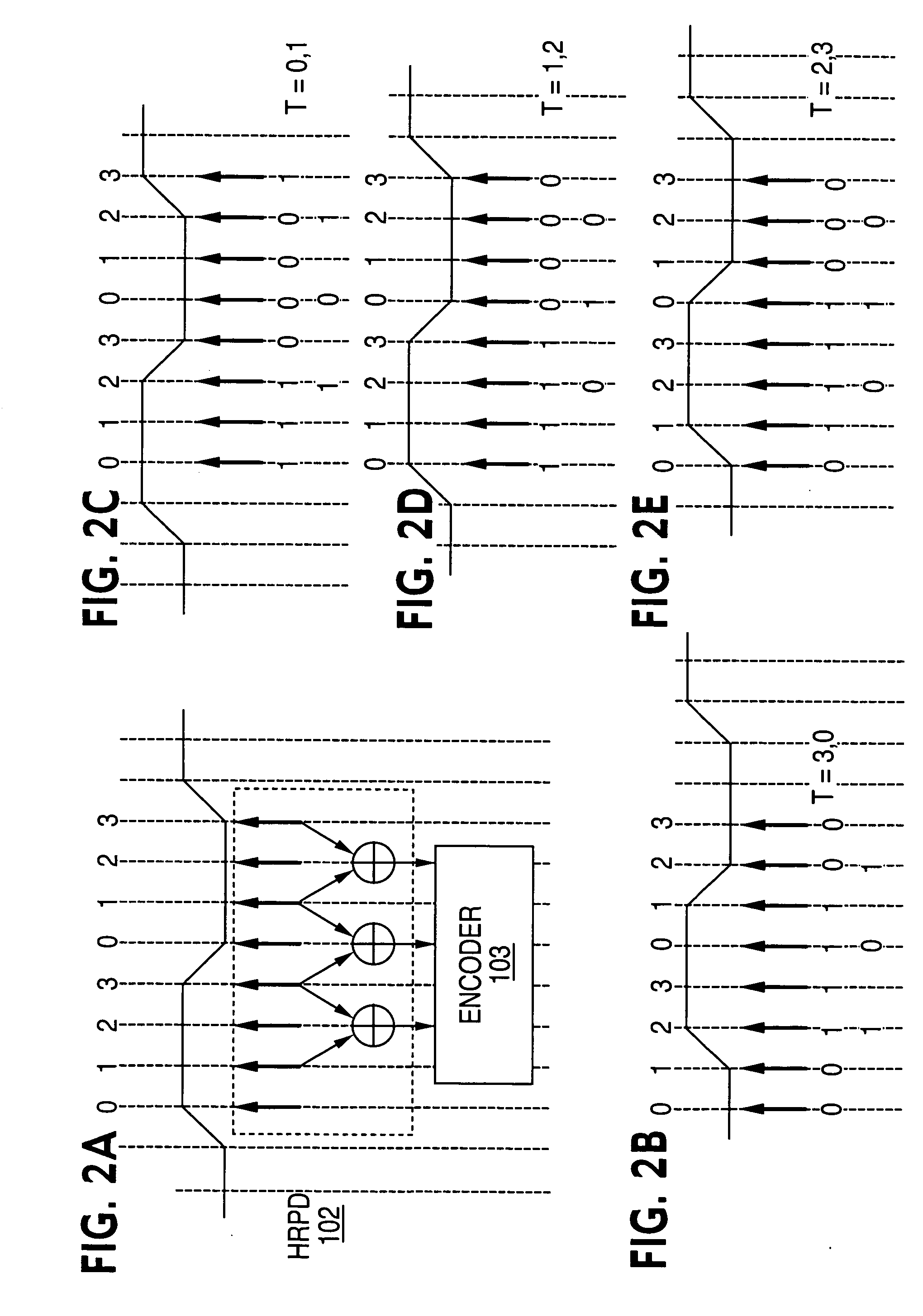
High-speed serial link clock and data recovery
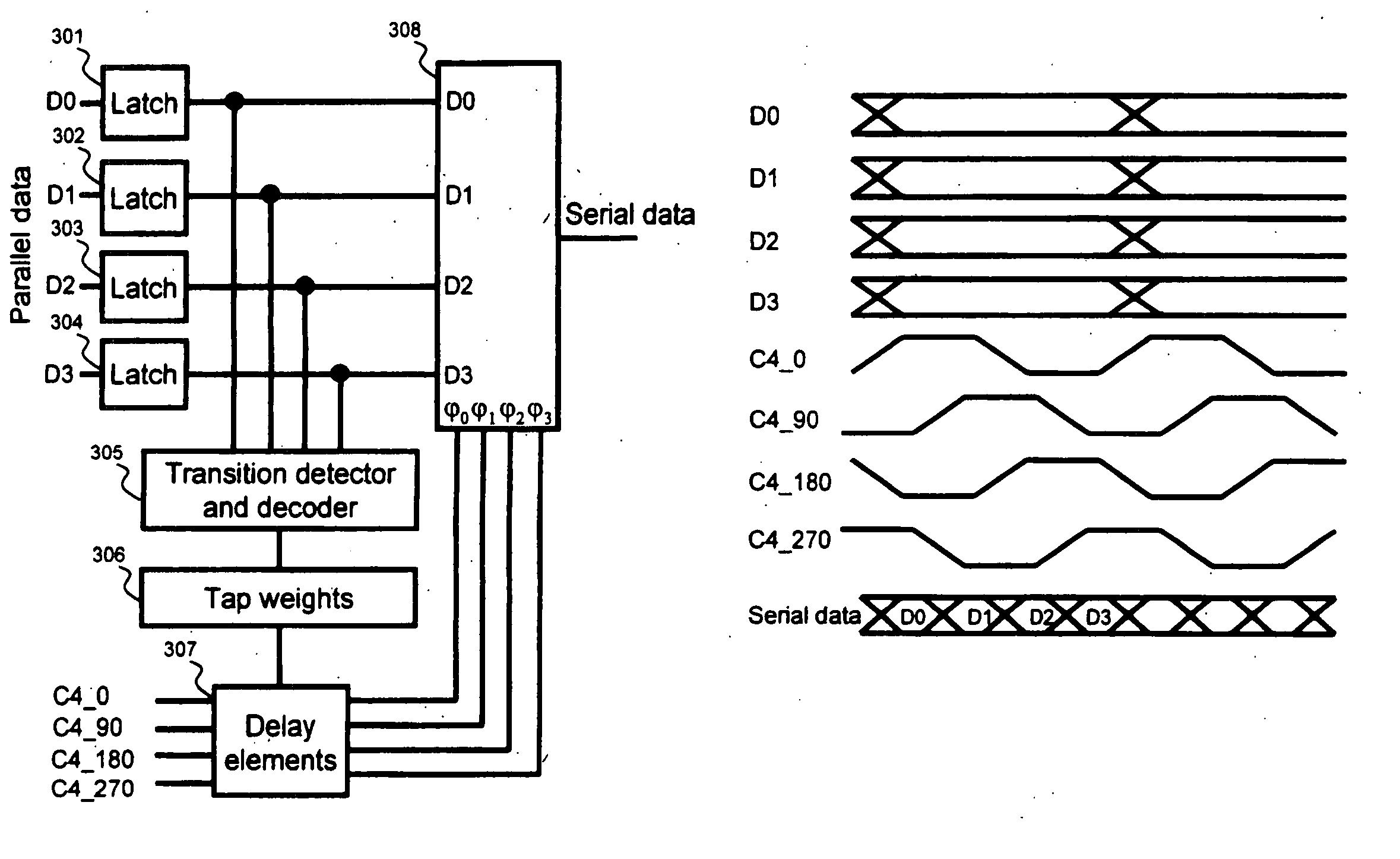
A system for clock and data recovery (“CDR”) includes a clock generator, a half-rate phase detector for receiving the input data, an encoder, a phase selector outputting recovered clock, a confidence counter, and a multiplexer outputting recovered data. The clock generator generates an 8-phase clock signal at half a rate of the transmitted serial data. The phase detector samples input data at four times the standard sampling rate, takes the oversampled data and detects phase transitions therein, i.e., phase lead and lag. The encoder encodes the phase transition data. The confidence counter receives the phase transition data and generates a signal representing the accumulated net effect of the phase transitions. The phase selector receives the confidence counter signal and the 8-phase clock from the clock generator, and determines the optimum phase for data sampling.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
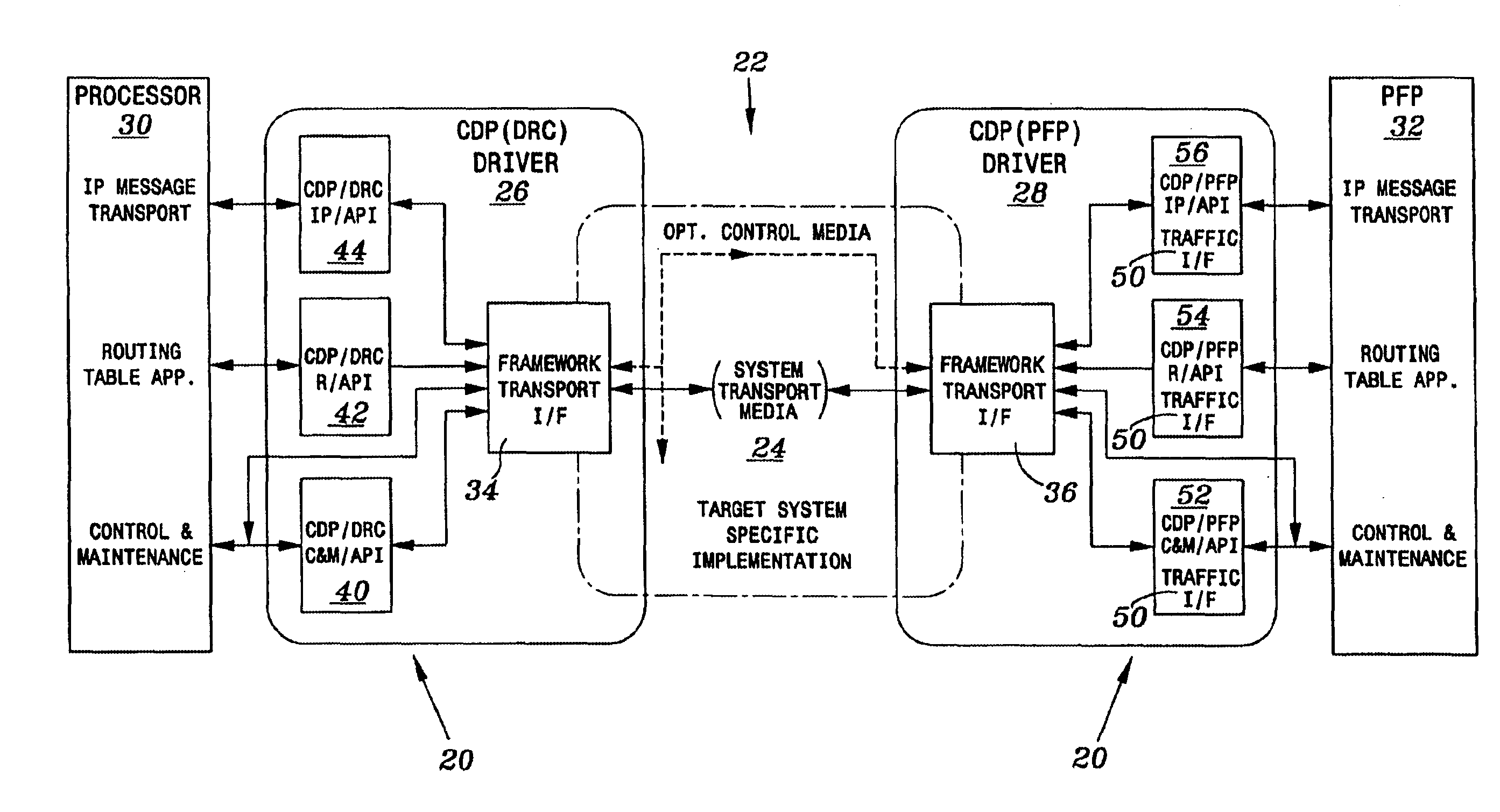
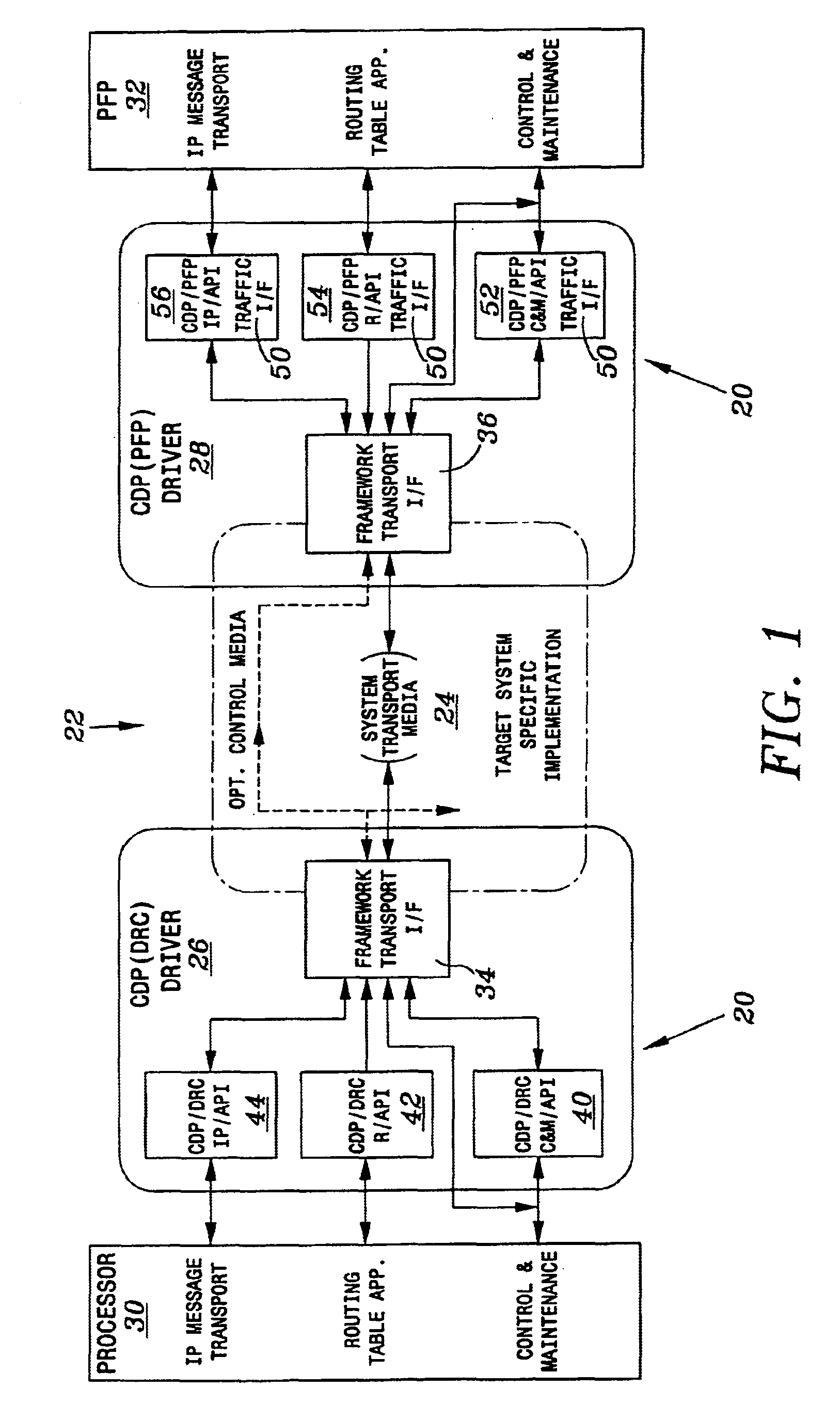
Control and distribution protocol for a portable router framework
InactiveUS6977924B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityStructure of Management Information
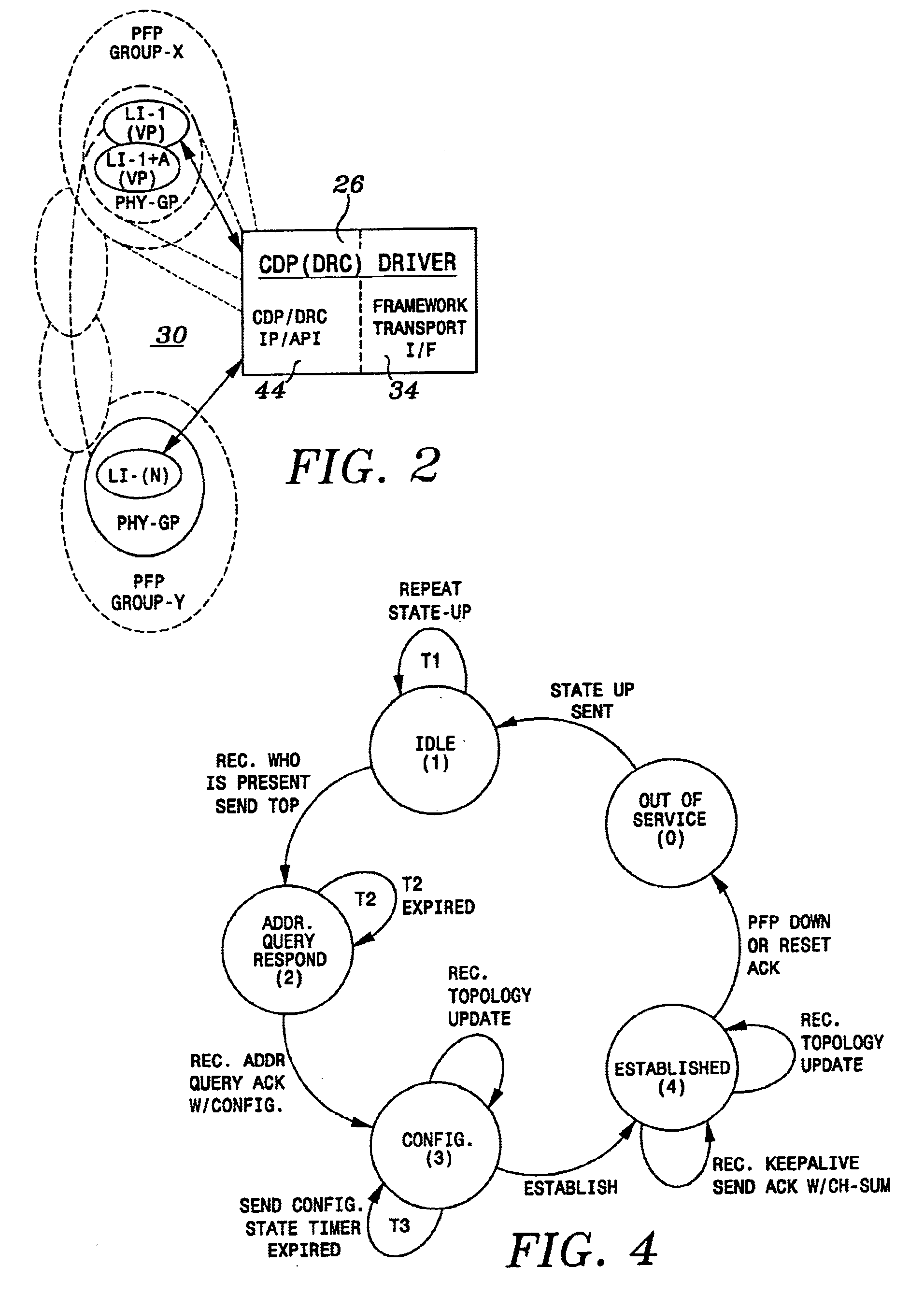
A control and distribution protocol (CDP) is implemented for transport across a backplane bus, through a high-speed serial link or through a switching fabric connection. The protocol includes an intra-system transport of dynamic routing protocol (DRP) IP messages, the distribution of routing information within the router, the transport of control and maintenance messages, and the transport of IP and multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) traffic between ingress and egress ports. The protocol further includes a dynamic routing and control driver which interacts with dynamic routing control applications to exchange messages that are to be transmitted to packet flow processors and to handoff messages received from packet flow processors. A packet flow processor driver which services messages carried between the dynamic routing control and packet flow processors. An IP traffic interface provides transfer of IP L3 / L2 protocol data unit (PDU) header primitive from the packet flow processors. Both the DRC driver and PFP driver include a framework transport interface.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Implantable medical device configured for diagnostic emulation through serial communication
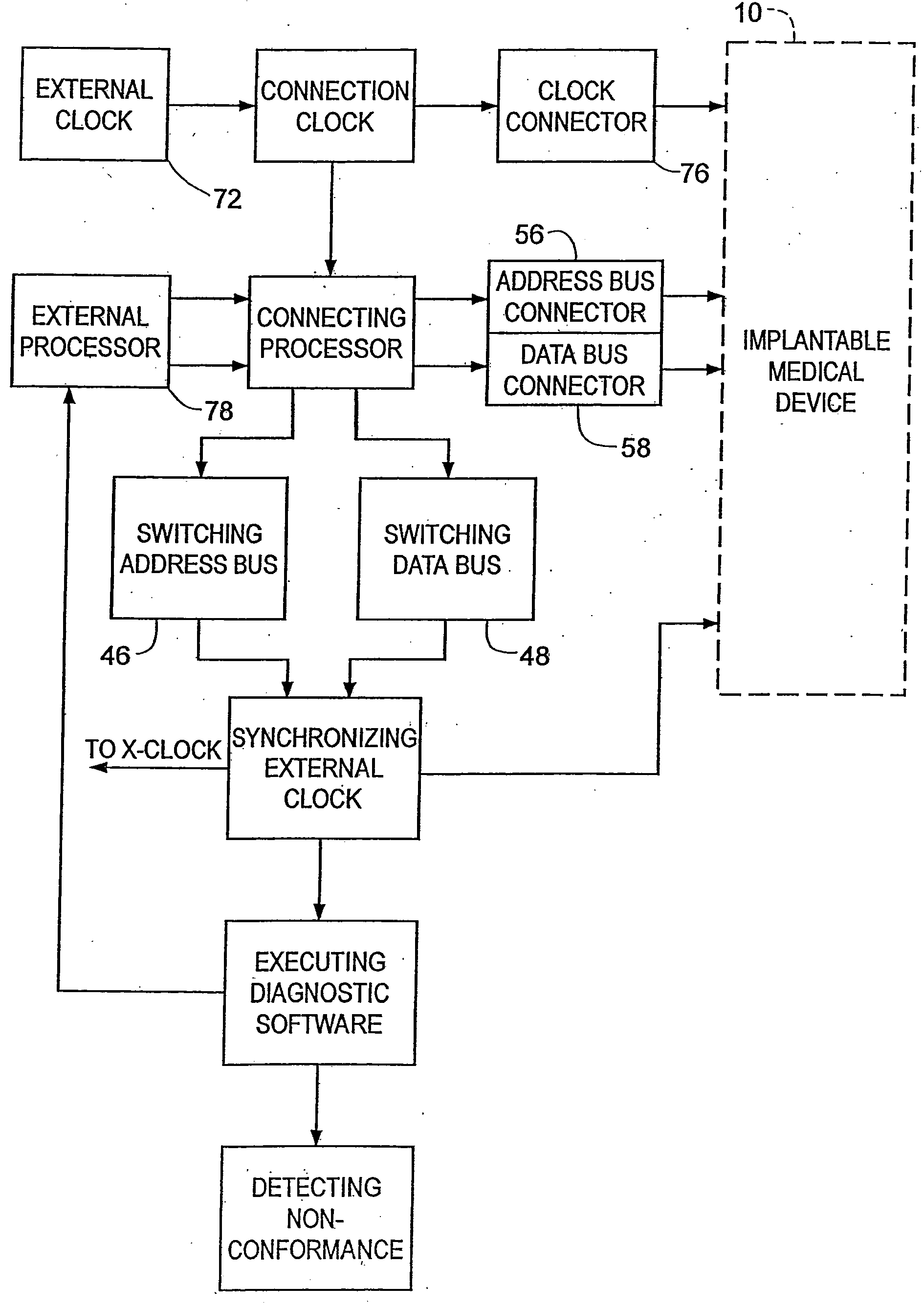
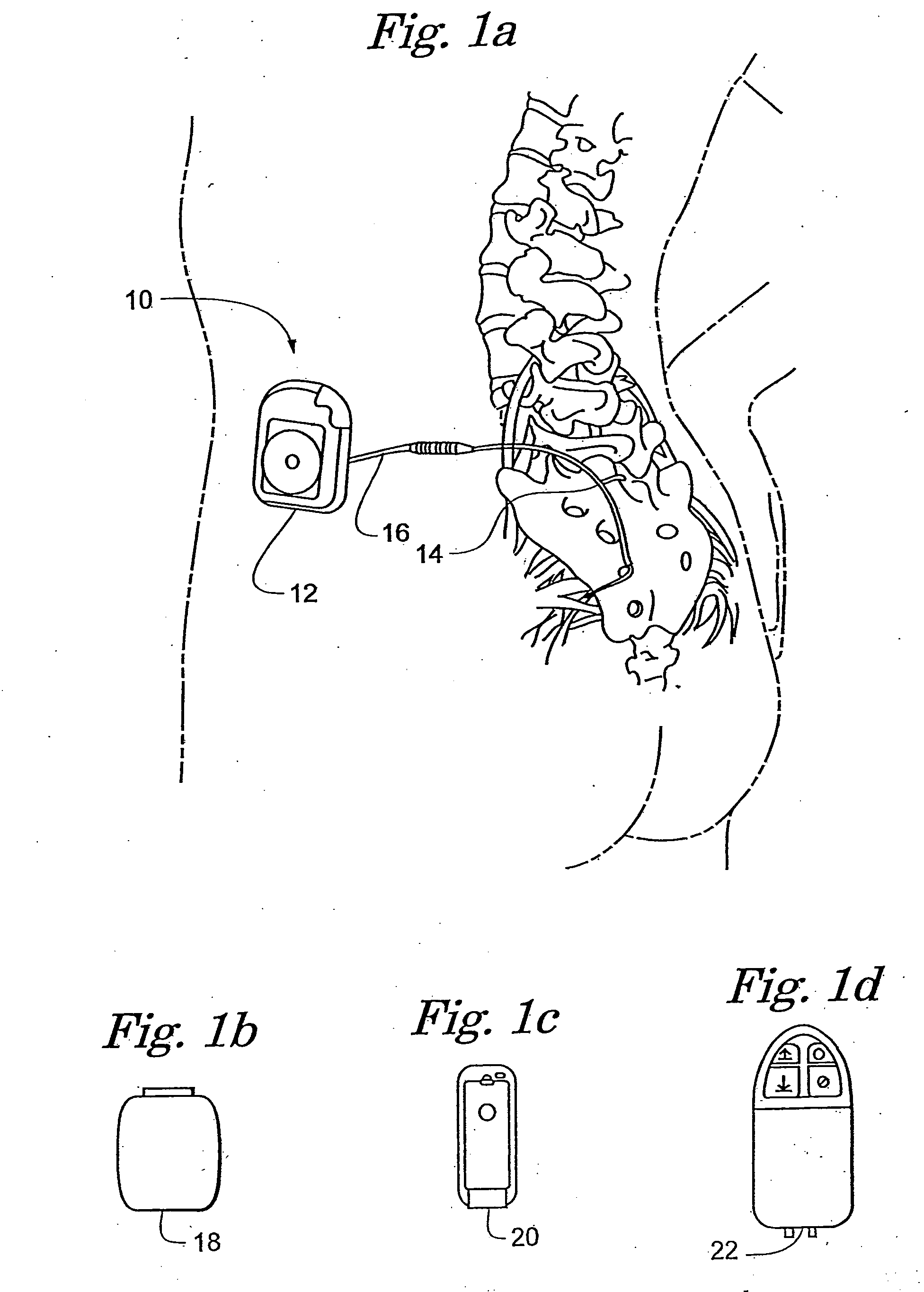
InactiveUS20050066088A1Reduce the numberFast executionMedical devicesPressure infusionElectricityContact pad
An implantable medical device (IMD) with internal processor is configured for diagnostic emulation using an external processor coupled to the internal processor through a high speed serial link. The native external processor parallel data and address bus content can be converted to a serial communications stream, sent into the device, converted back to parallel address and data bus formats, and used to drive the device in place of the internal processor. The serial communication allows use of a small number of contact pads, conductors, or feed-throughs, depending on the device. Some devices allow serialized communication through the feed-through typically used for electrical stimulation. The devices can be used to enhance diagnostic testing with capabilities such as faster testing and more realistic testing. The IMD can be a wide variety of implantable devices such as neuro stimulators, pace makers, defibrillators, drug delivery pumps, diagnostic recorders, cochlear implants, and the like. The device can have a bus switch, which when activated, decouples the internal processor, and couples address and data buses containing information and commands provided by the external emulator through the serial communication channel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Redundancy structure and method for high-speed serial link
InactiveUS20050180521A1Error preventionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingData sourceEngineering
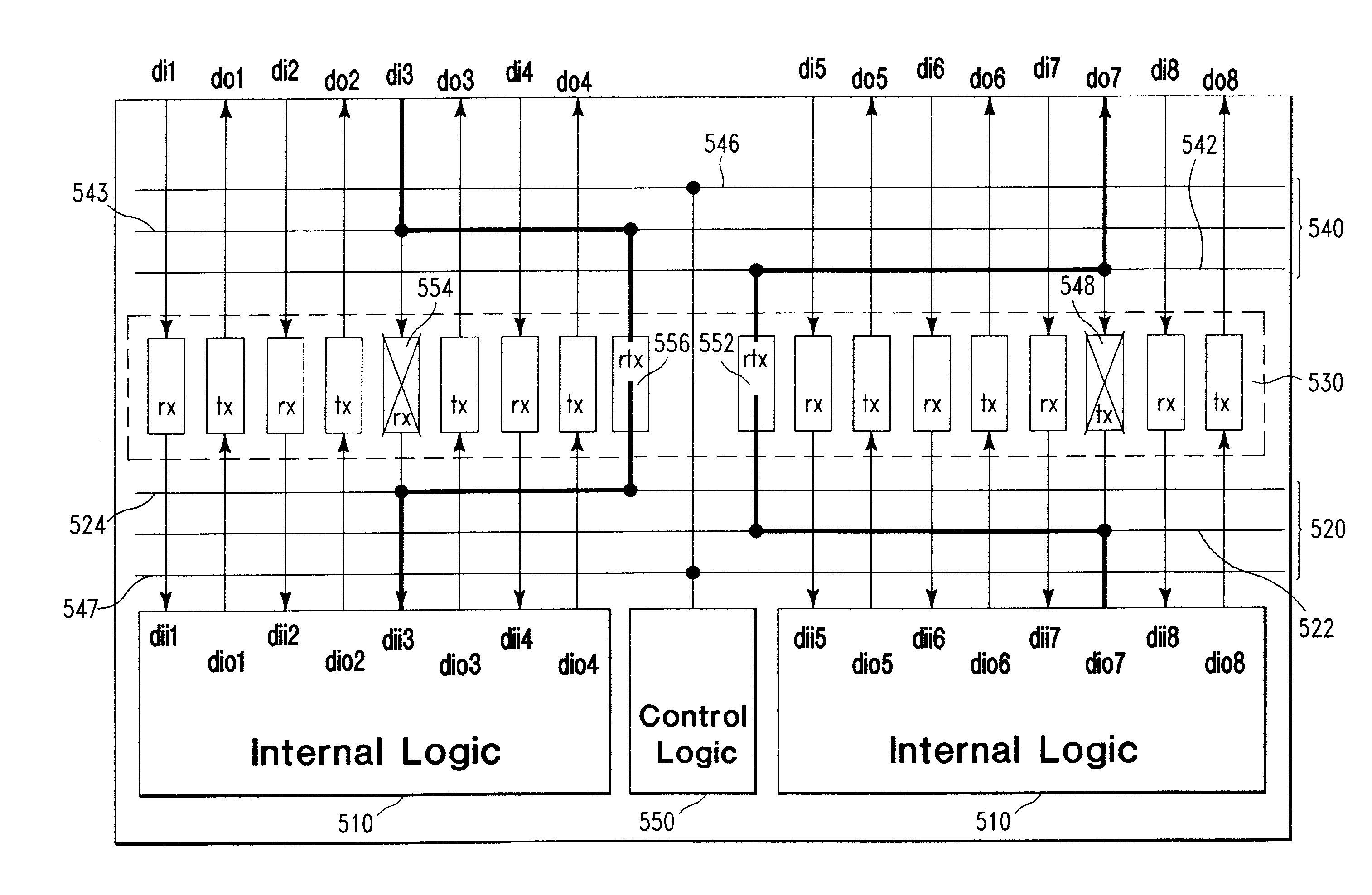
An integrated circuit is provided having a plurality of data transmitters, including a plurality of default data transmitters for transmitting data from a plurality of data sources and at least one redundancy data transmitter. A plurality of connection elements are provided having a first, low impedance connecting state and having a second, high impedance, disconnecting state. The connection elements are operable to disconnect a failing data transmitter from a corresponding output signal line and to connect the redundancy data transmitter to that output signal line in place of the failing data transmitter. In one preferred form, the connection elements include a fuse and an antifuse. In another form, the connection elements include micro-electromechanical (MEM) switches. The connecting elements preferably present the low impedance connecting state at frequencies which include signal switching frequencies above about 500 MHz.
Owner:IBM CORP
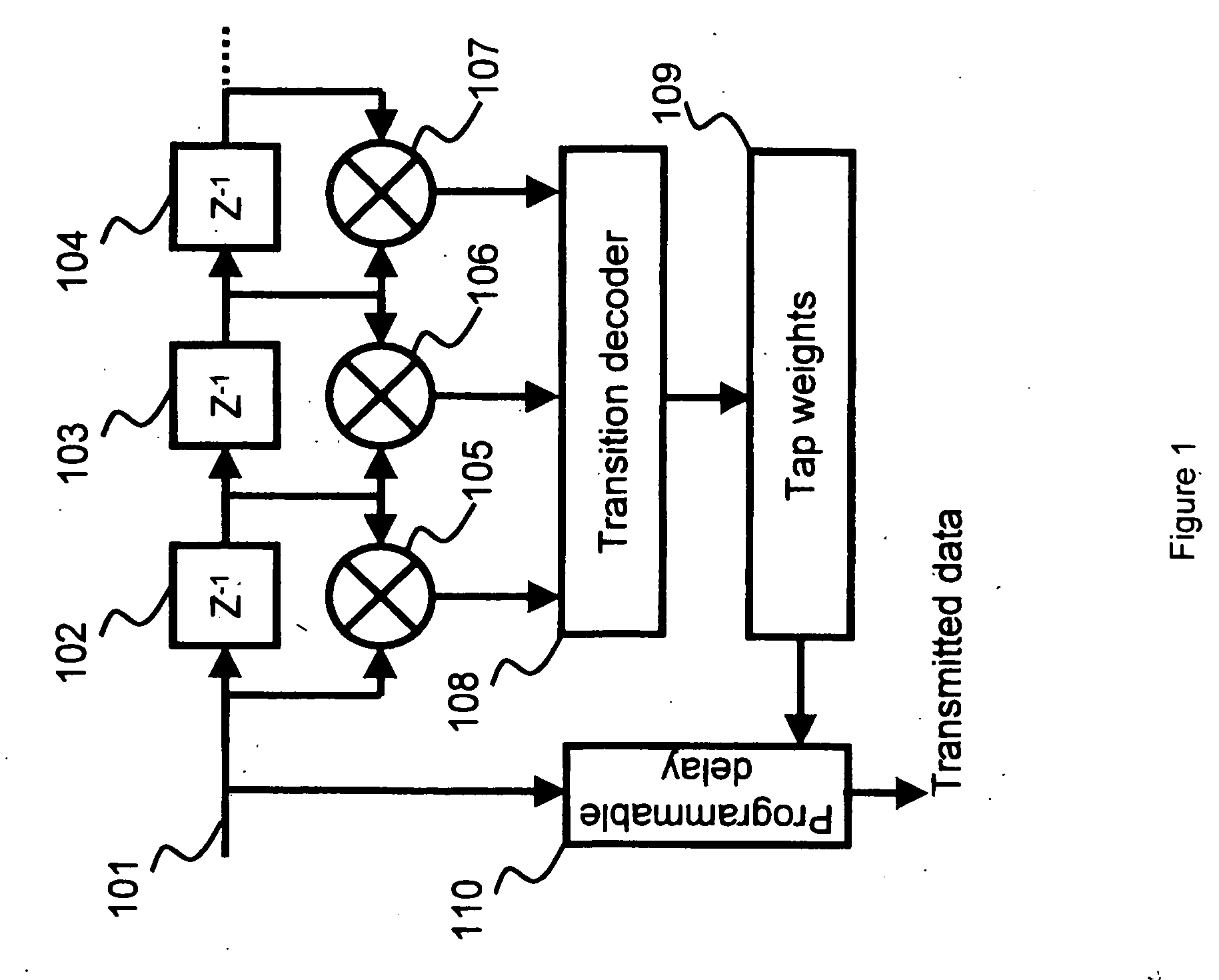
High-speed serial linking device with de-emphasis function and the method thereof
ActiveUS20050018778A1Increase speedDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationComputer hardwareHigh speed serial link
Owner:VIA TECH INC
High speed on-chip serial link apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070079025A1Control performanceAvoid the needGenerating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple usePower-on resetElectricity
A converter apparatus and method are provided that transforms an external low speed industry standard interface into an on-chip high speed serial link (HSSL). The converter of the present invention is preferably placed in close vicinity of the external interface. The HSSL operates at the system clock speed and, as a result, the HSSL interface signals can be readily treated like any other timed signal facilitating the physical design process. Because synchronization is performed once in the converter near the external interface and the signals along the HSSL of the present invention may be treated like any other timed signal, the need for interface units in each processing element of the chip to perform synchronization is eliminated. Thus, the complexity and silicon area used by the present invention is reduced. The converter enables the maximum speed for the serial interface, which is crucial in power-on-reset, manufacturing testing, and chip debugging.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
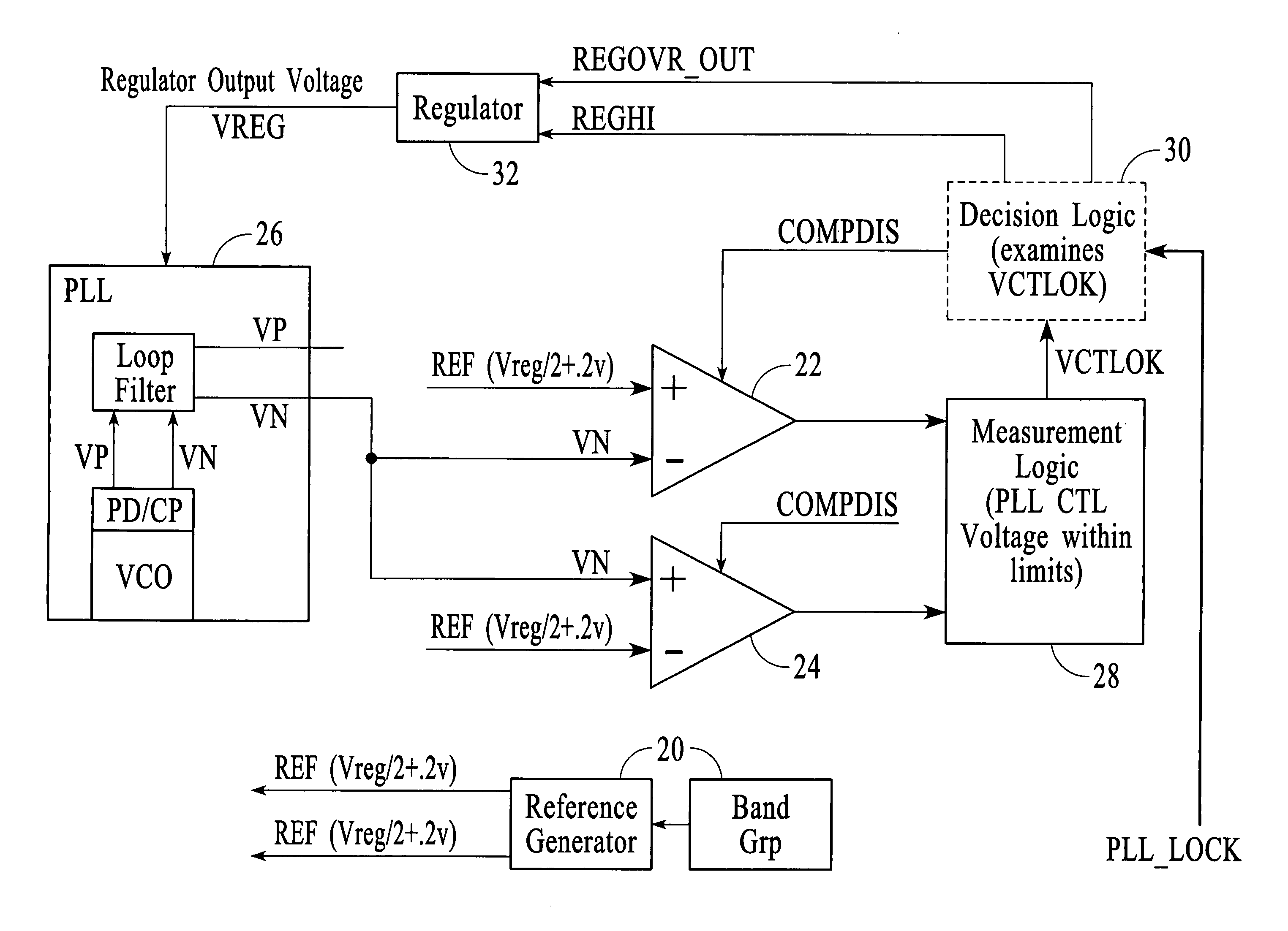
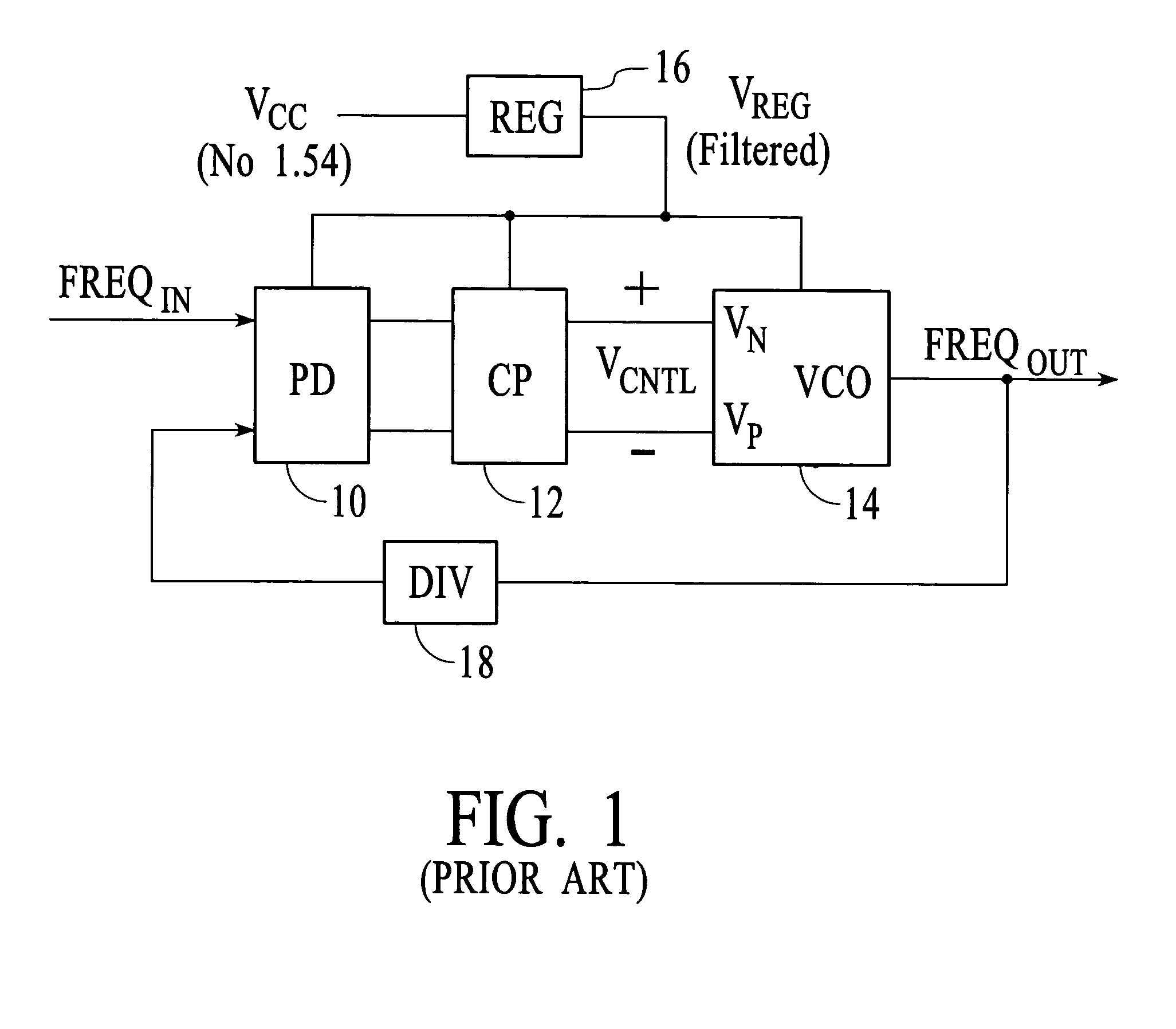
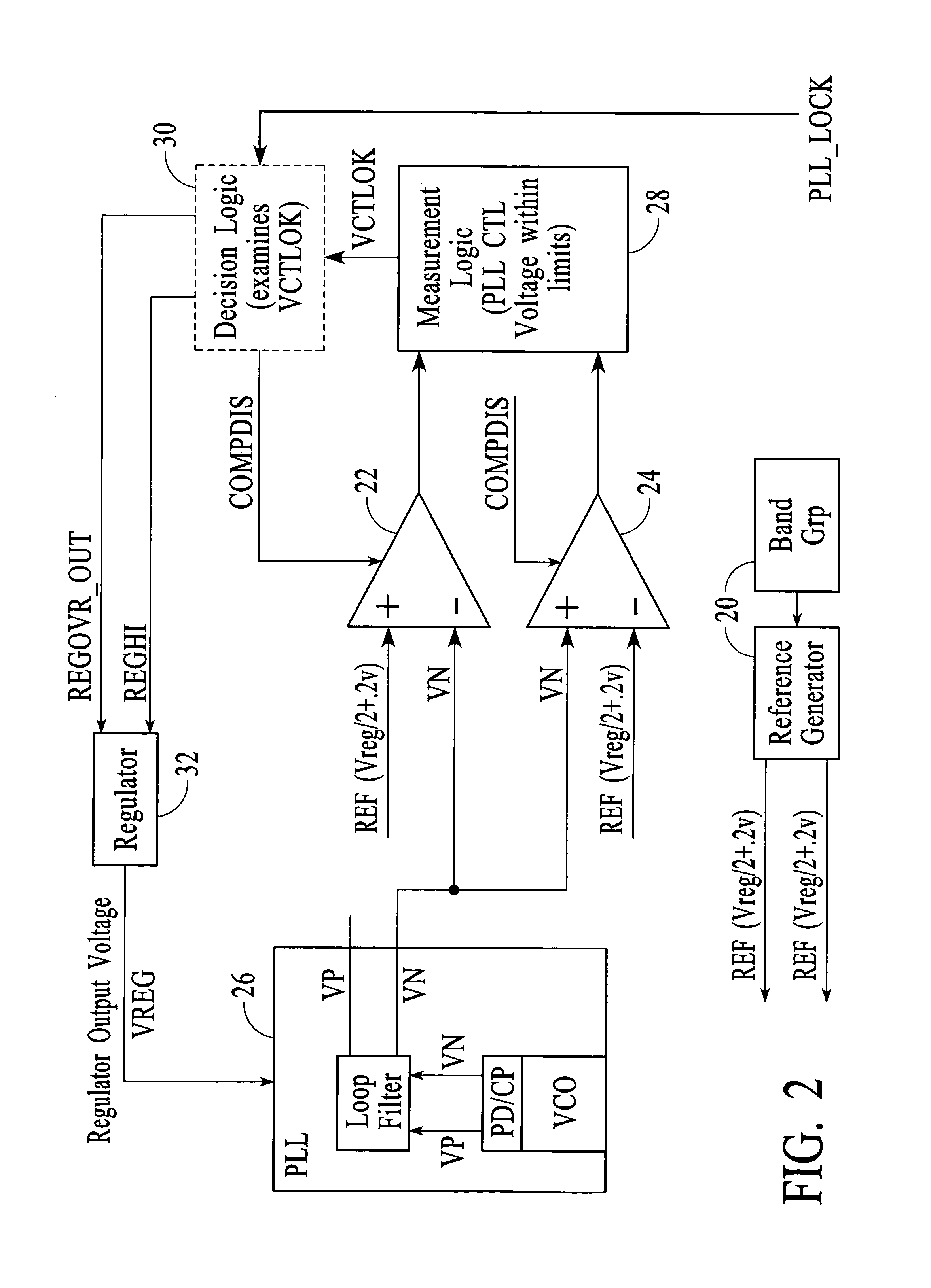
Circuit and method for reducing jitter in a PLL of high speed serial links
InactiveUS7042277B2Flexible and efficient approachLower success ratePulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow by mechanical effectsEngineeringControl circuit
Aspects for reducing jitter in a PLL of a high speed serial link include examining at least one parameter related to performance of a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) in the PLL, and controlling adjustment of a supply voltage to the VCO based on the examining. A regulator control circuit performs the examining and controlling.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
On-chip receiver eye finder circuit for high-speed serial link
ActiveUS7640463B2Minimize the numberArea minimizationTelevision system detailsElectrical testingVoltage generatorVoltage reference
In a high-speed serial link, an eye finder diagnostic circuit has improved performance by being on-chip with the existing capture latch(es) of a receive equalizer. The eye finder circuit employs an additional capture latch with its input tied to the same input node as the existing capture latch(es) of a receive equalizer. The additional capture latch has a clock input and reference voltage input. The clock input is adjusted through a phase interpolator (or variable delay line) while the reference voltage input is adjusted by a voltage generator. A digital post processing circuit then compares the output of the additional capture latch with the output of the other existing capture latch(es), in order to determine the receive eye opening. The horizontal eye opening is measured by changing the phase of the additional capture latch through the phase interpolator, while the vertical eye opening is measured by changing the reference voltage of the voltage generator of the additional capture latch. The eye finder circuit, being on-chip and in-line with existing capture latch(es), employs a minimum of power, minimum of area, and minimizes the extra loading to the existing equalizer output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High Speed On-Chip Serial Link Apparatus
ActiveUS20080133800A1Control performanceAvoid the needGenerating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple usePower-on resetLow speed
A converter apparatus and method are provided that transforms an external low speed industry standard interface into an on-chip high speed serial link (HSSL). The converter of the present invention is preferably placed in close vicinity of the external interface. The HSSL operates at the system clock speed and, as a result, the HSSL interface signals can be readily treated like any other timed signal facilitating the physical design process. Because synchronization is performed once in the converter near the external interface and the signals along the HSSL of the present invention may be treated like any other timed signal, the need for interface units in each processing element of the chip to perform synchronization is eliminated. Thus, the complexity and silicon area used by the present invention is reduced. The converter enables the maximum speed for the serial interface, which is crucial in power-on-reset, manufacturing testing, and chip debugging.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
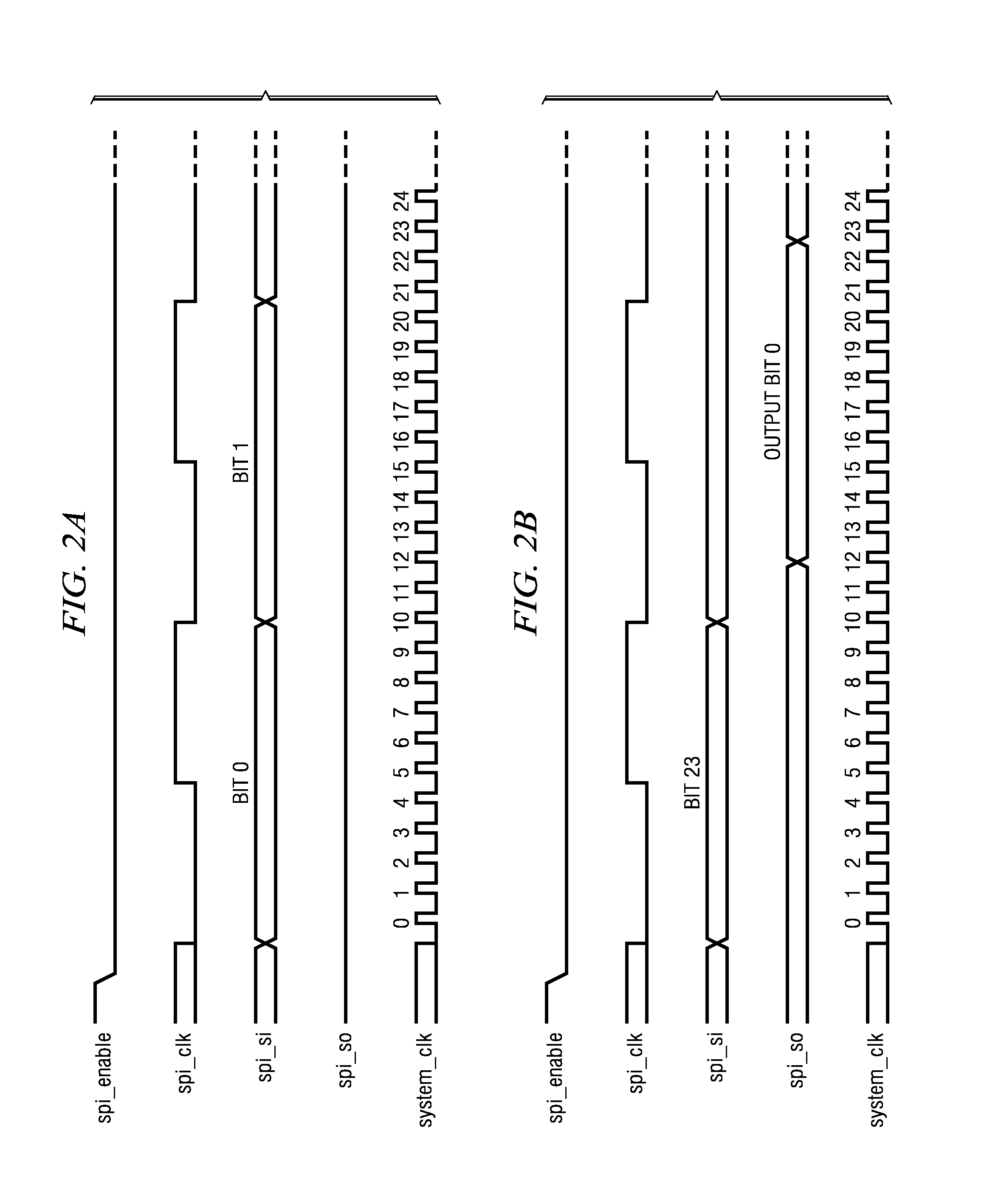
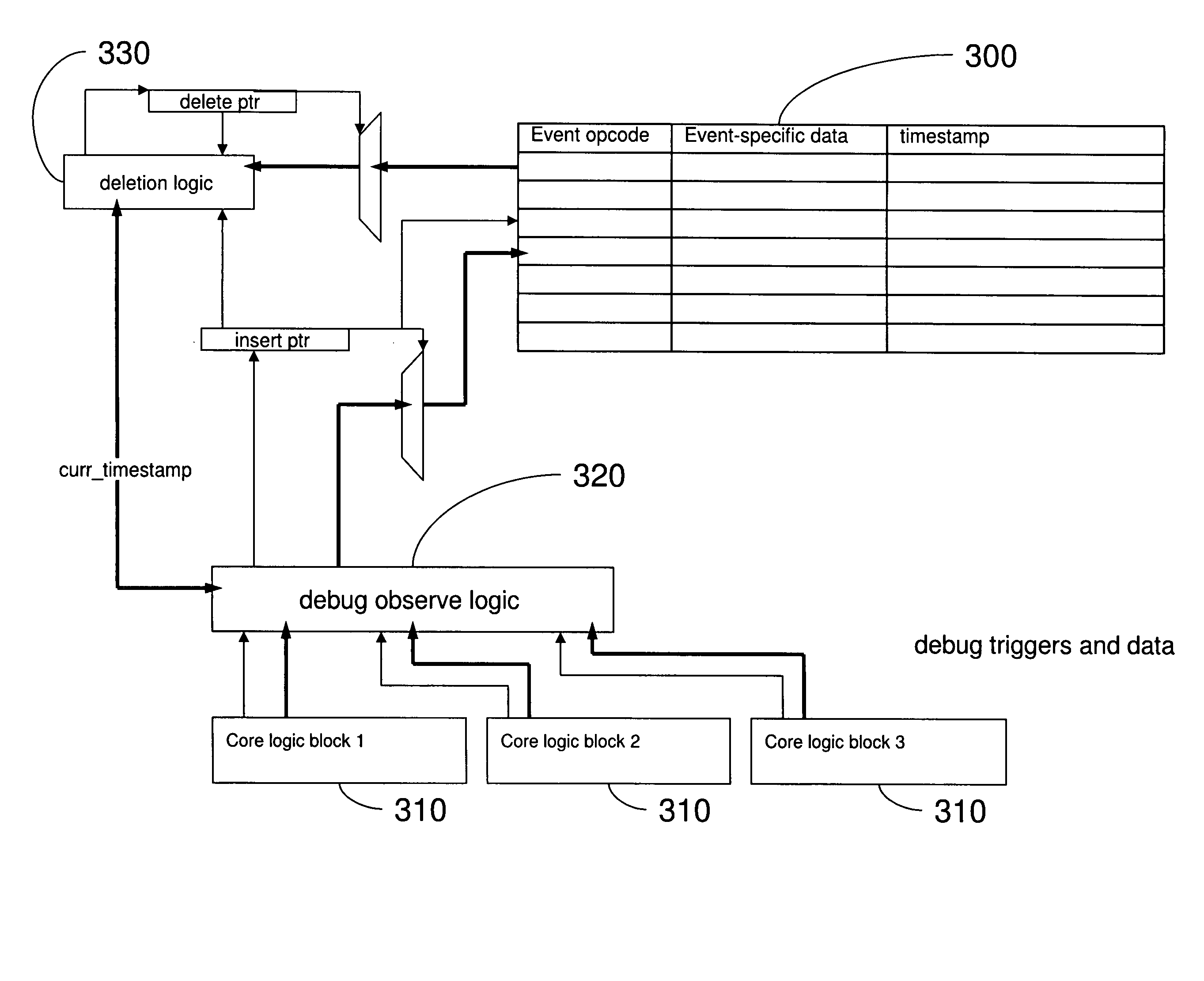
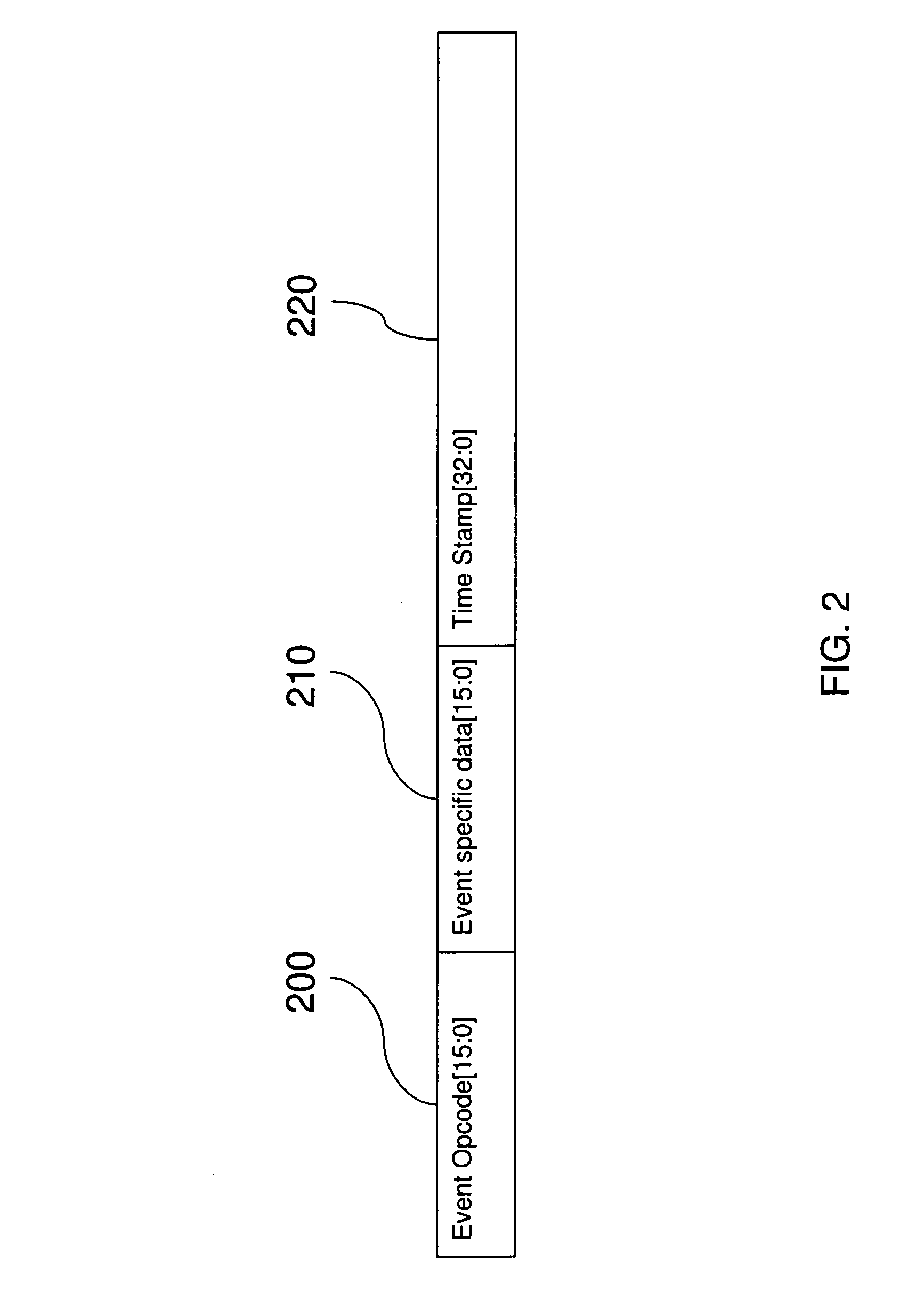
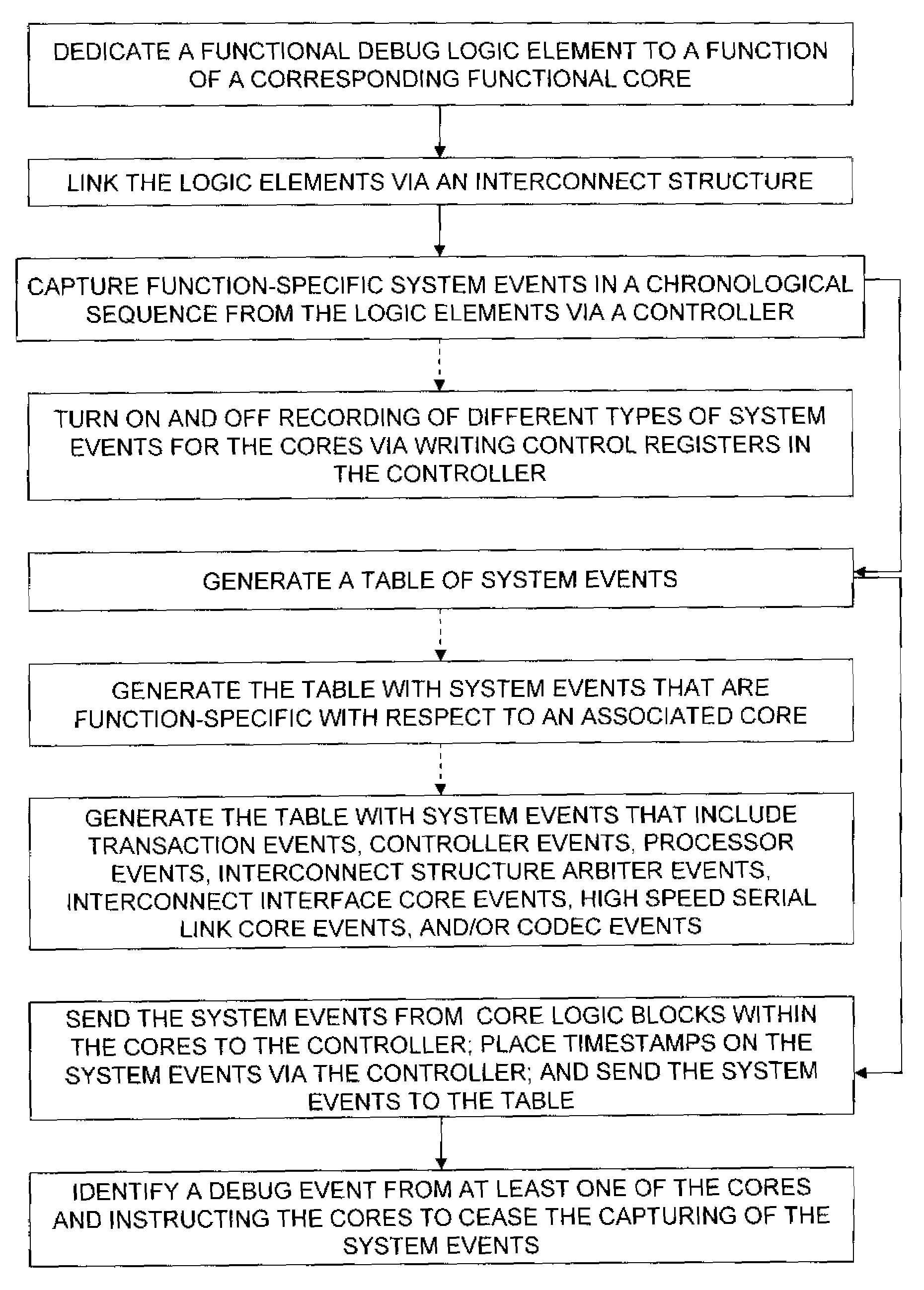
Design structure for task based debugger (transaction-event -job-trigger)
Disclosed is a design structure for an apparatus for a task based debugger (transaction-event-job-trigger). More specifically, an integrated event monitor for a SOC comprises functional cores each having a functional debug logic element. The cores are connected to an interconnect structure that links the functional debug logic elements. Each functional debug logic element is specifically dedicated to a function of its corresponding core, wherein the functional debug logic elements generate a table of function-specific system events. The system events are function-specific with respect to an associated core, wherein the system events include transaction events, controller events, processor events, interconnect structure arbiter events, interconnect interface core events, high speed serial link core events, and / or codec events.
Owner:IBM CORP
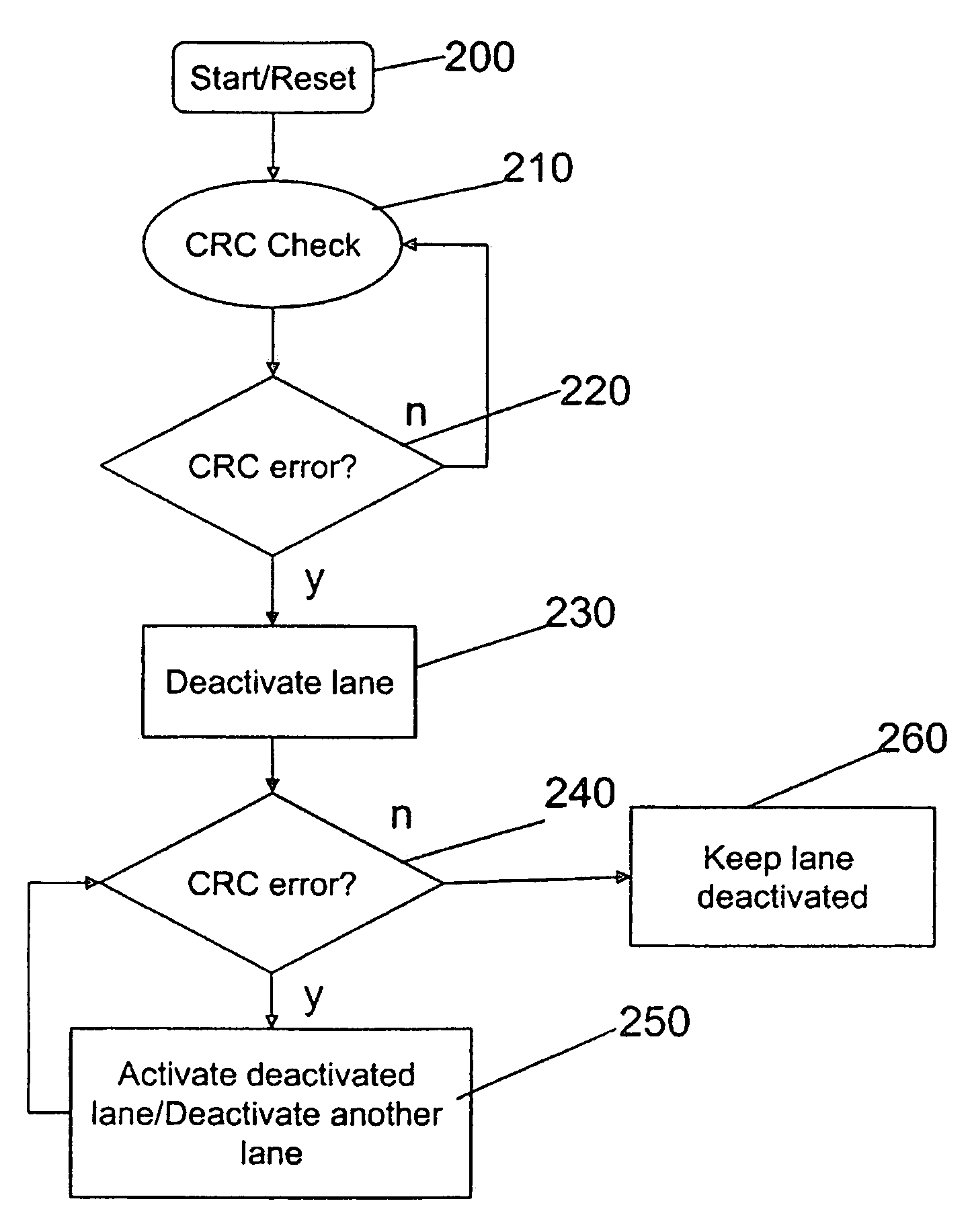
Repairing high-speed serial links
ActiveUS20100083030A1Reduce generationError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsElectronic componentData transmission
A method and system for repairing high speed serial links is provided. The system includes a first electronic components, connected to at least a second electronic component via at least one link. At least one of the first or second electronic components has a link controller. The link controller is configured to repair serial links by detecting a link error and mapping out individual lanes of a link where the link error is detected. The link controller resumes operation, i.e., transmission of data and continues to monitor the lanes for errors. If and when additional link errors occur, the link controller identifies the lanes in which the link error occurs and deactivates those lanes. The deactivated lane(s) can not be used in further transmissions which, in turn, reduces the occurrence of intermittent link errors.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
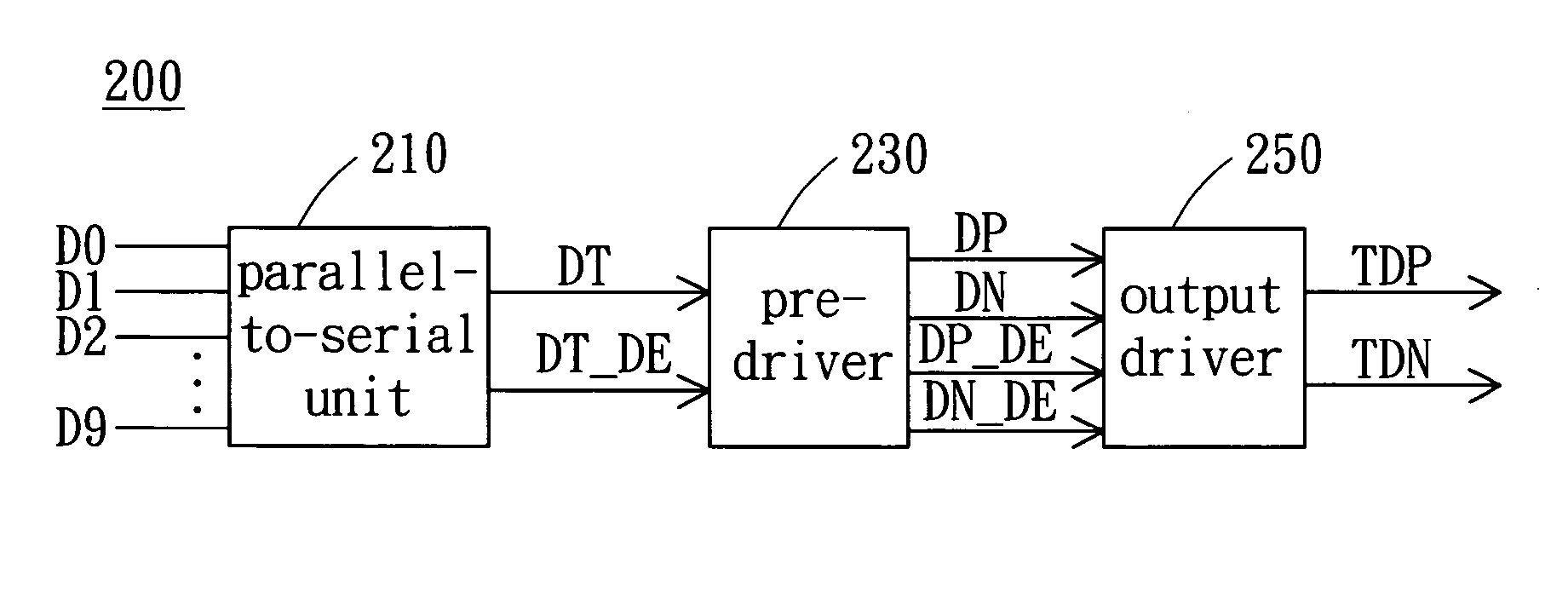
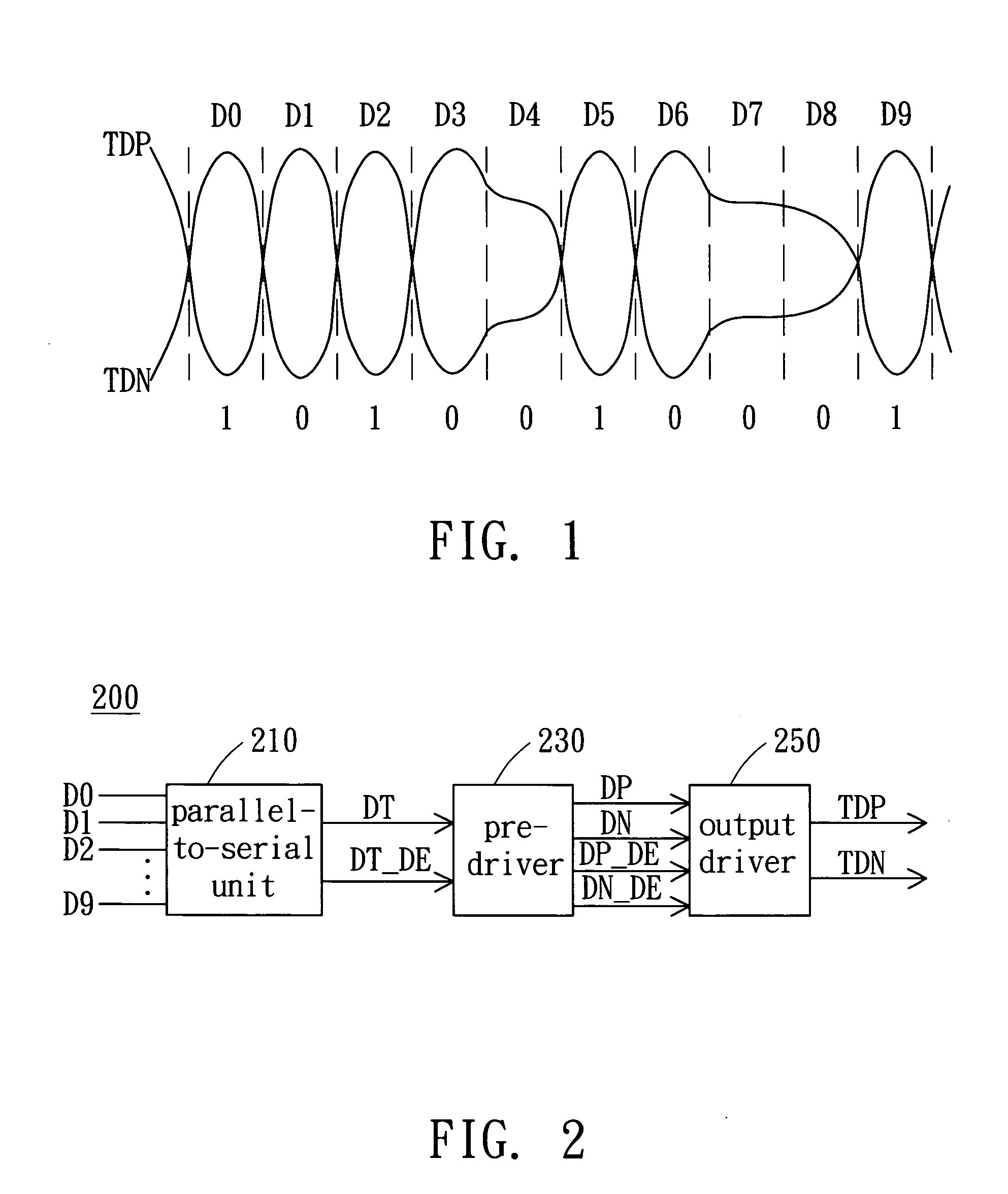
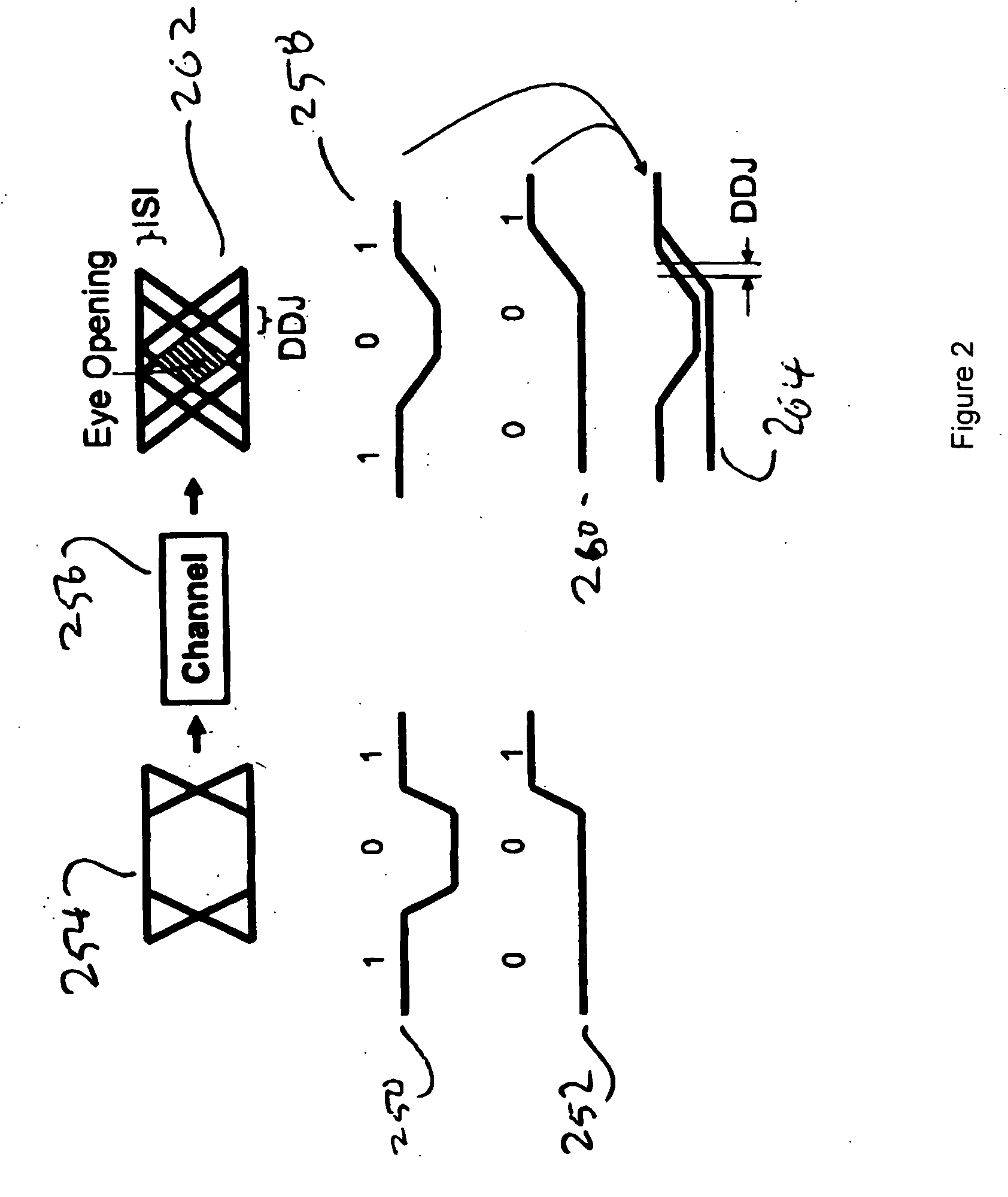
Data-dependent jitter pre-emphasis for high-speed serial link transmitters
InactiveUS20070177663A1Improve signal integrityLittle additional power consumptionMultiple-port networksParallel/series conversionData dependentComputer science
In the context of high-speed serial links, data-dependent jitter compensation techniques performed using phase pre-distortion. Broadly contemplated is an expansion of the notion of pre-emphasis beyond conventional amplitude compensation of ISI, whereby phase pre-emphasis for compensating data-dependent jitter (DDJ) is introduced. DDJ can be addressed by exploiting the relationship between the data sequence and the timing deviation. Phase pre-emphasis improves the signal integrity with little additional power consumption in the transmitter and with no cross-talk penalty.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Task based debugger (transacation-event-job-trigger)
InactiveUS20080127216A1Digital computer detailsCAD circuit designHigh velocityHigh speed serial link
The embodiments of the invention provide an apparatus, method, etc. for a task based debugger (transaction-event-job-trigger). More specifically, an integrated event monitor for a SOC comprises functional cores each having a functional debug logic element. The cores are connected to an interconnect structure that links the functional debug logic elements. Each functional debug logic element is specifically dedicated to a function of its corresponding core, wherein the functional debug logic elements generate a table of function-specific system events. The system events are function-specific with respect to an associated core, wherein the system events include transaction events, controller events, processor events, interconnect structure arbiter events, interconnect interface core events, high speed serial link core events, and / or codec events.
Owner:IBM CORP
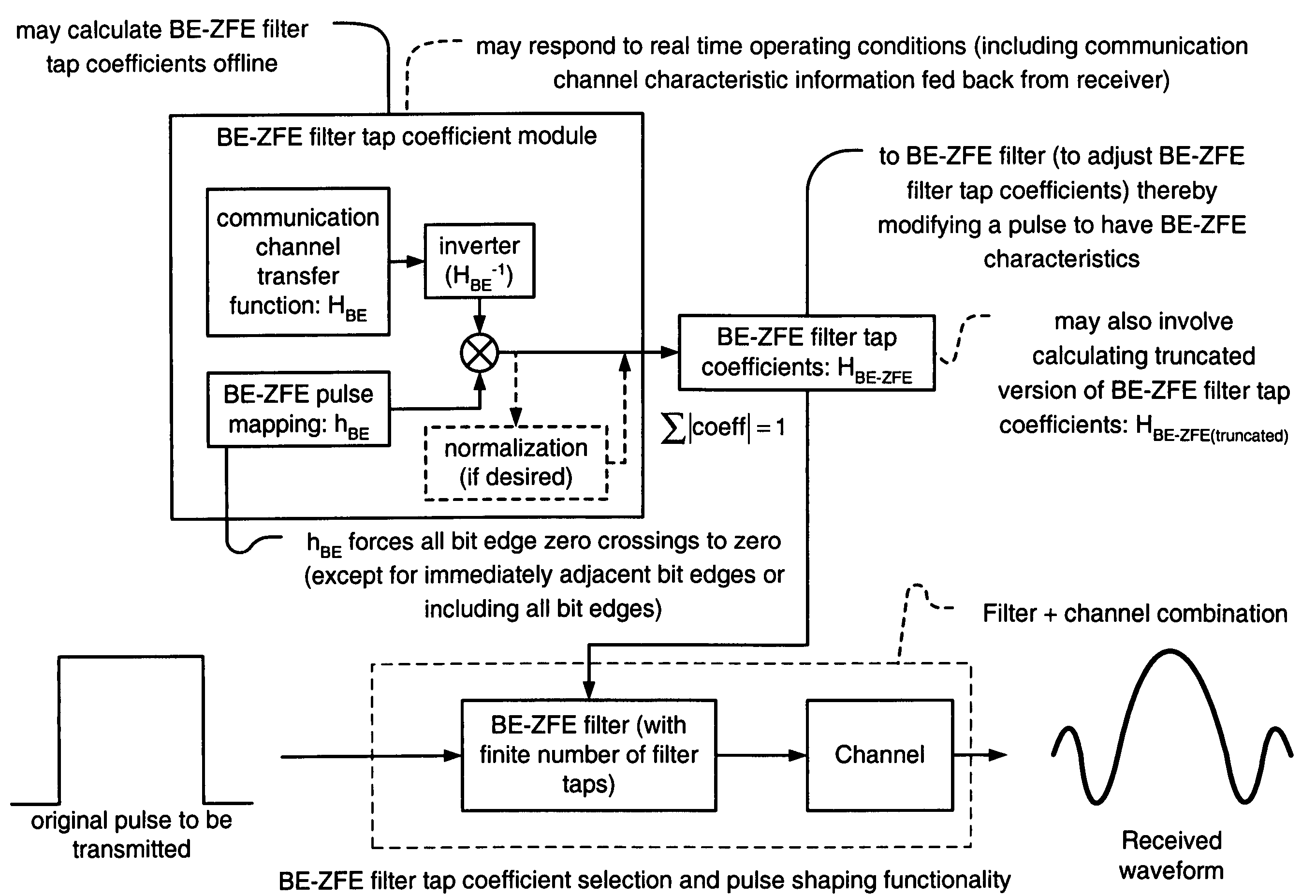
Bit-edge zero forcing equalizer
Bit-Edge Zero Forcing Equalizer. A novel solution is presented by which a BE-ZFE (Bit-Edge Zero Forcing Equalizer) is employed to drive an error term within a data signal to an essentially zero value. This new BE-ZFE looks at values of data that occur at the bit edges of a data signal and drives the associated error term to zero. The new BE-ZFE is appropriately implemented within communication systems that are phase (or jitter) noise limited. Some examples of such communication systems include high-speed serial links one type of which serviced using a SERDES (Serializer / De-serializer) where data that is originally in a parallel format is serialized into a serial data stream and then subsequently de-serialized back into a parallel data stream.
Owner:XILINX INC
Data transmission device and data transmission method with self-adapting link
ActiveCN103488596AGuaranteed to be correctWill not cause overflowElectric digital data processingComplete dataComputer hardware
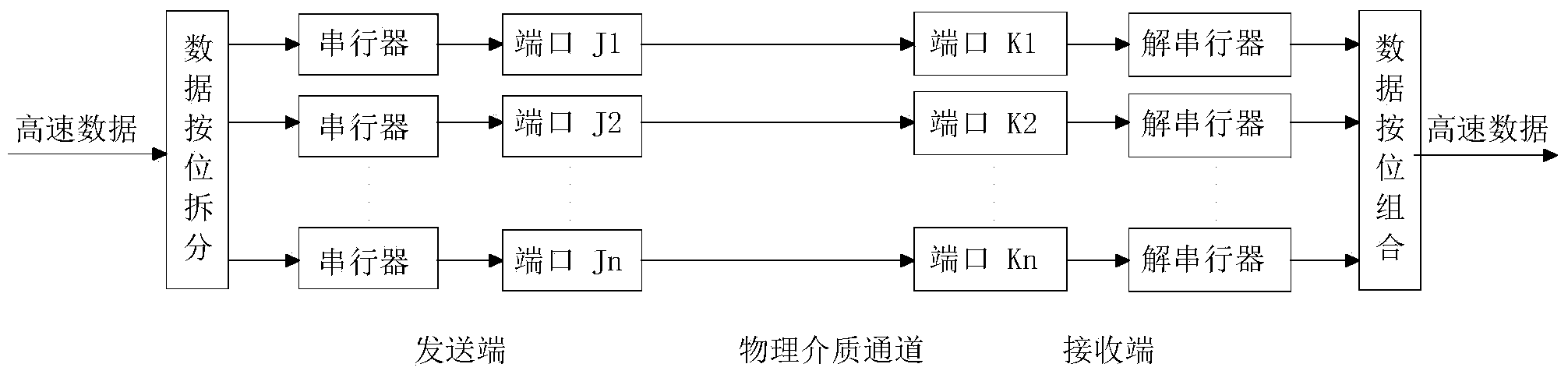
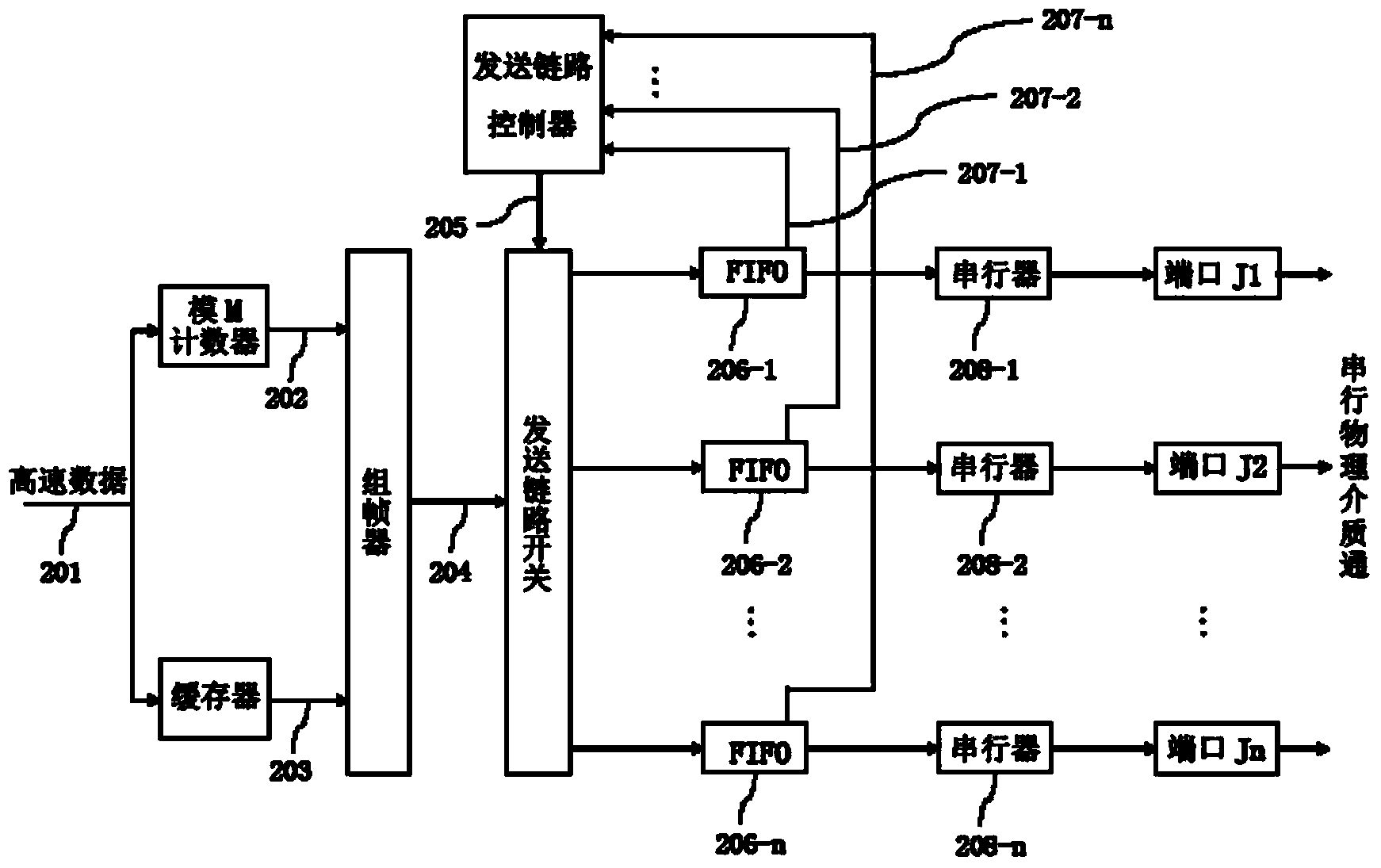
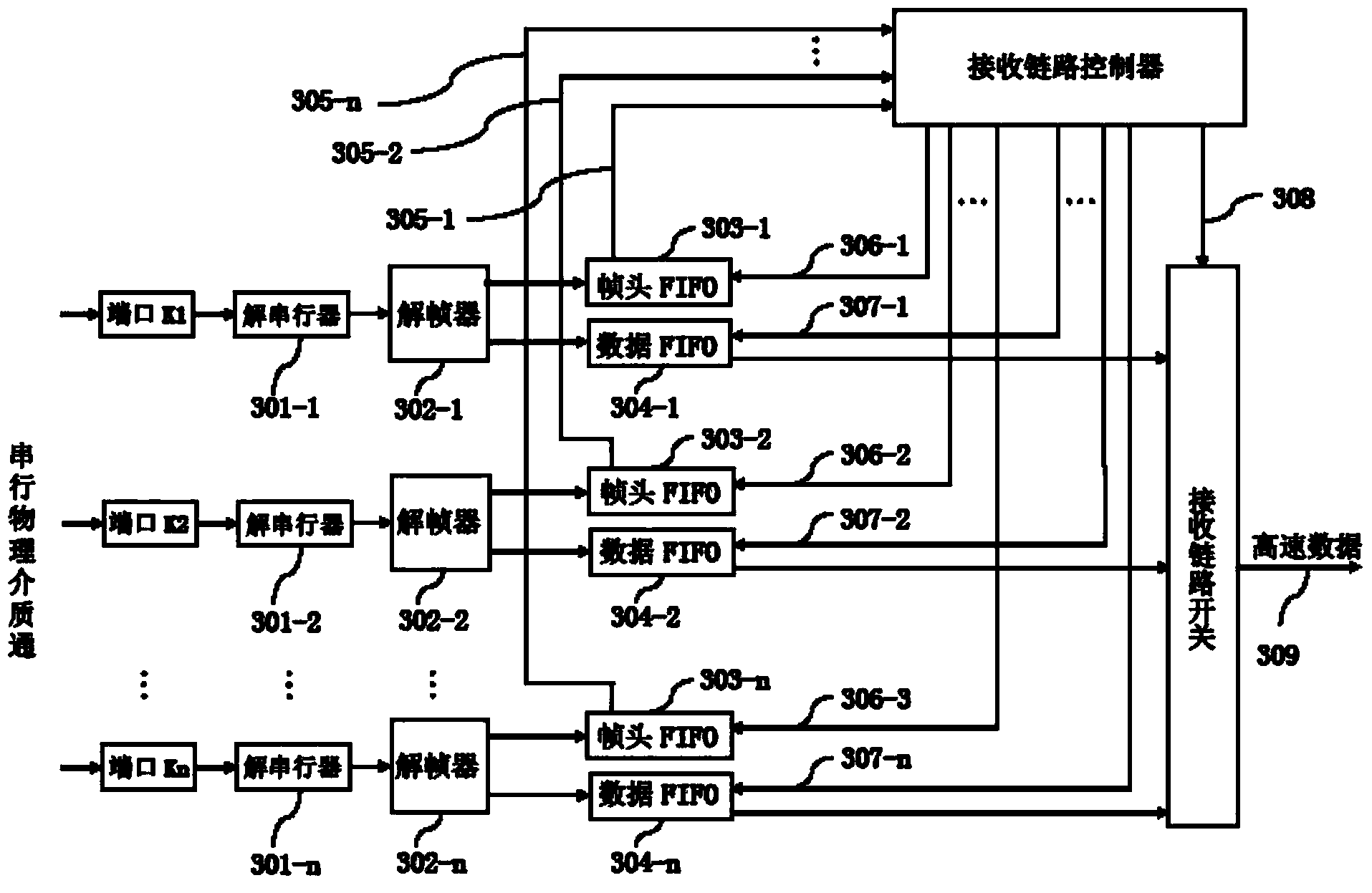
The invention discloses a data transmission device and a data transmission method with a self-adapting link. At a sending end, high-speed data to be sent is divided into data units according to a fixed length, cycle count is carried out on the data units, count values of the data units are taken as frame headers which constitute data frames with the current data units, and each data frame selects an appropriate high-speed serial link for transmission; at a receiving end, after each high-speed serial link completes data serial-parallel conversion by a respective deserializer, a de-framer is used for de-framing the data frames, the data units are written into a data FIFO (First In First Out) of the corresponding link, the frame headers are written into a frame header FIFO of the corresponding link, a receiving logic judges the frame header FIFO value of each high-speed serial link at regular time, an appropriate data FIFO is selected according to the cycle increasing sequence of the count values, one corresponding data unit is read, and data combination is thus realized. The connecting mode of the serial link is flexible, and the physical line length is not constrained.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Method and system for testing system-on-chip chip
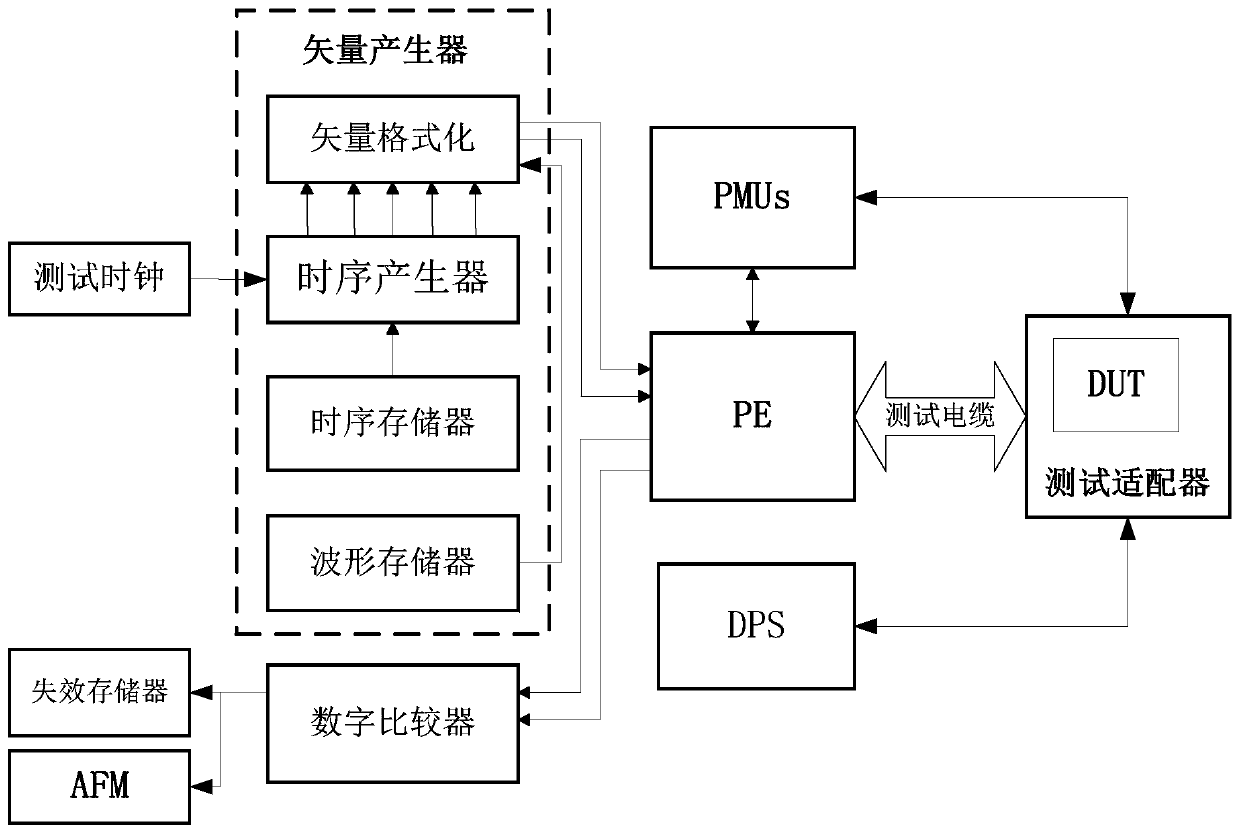
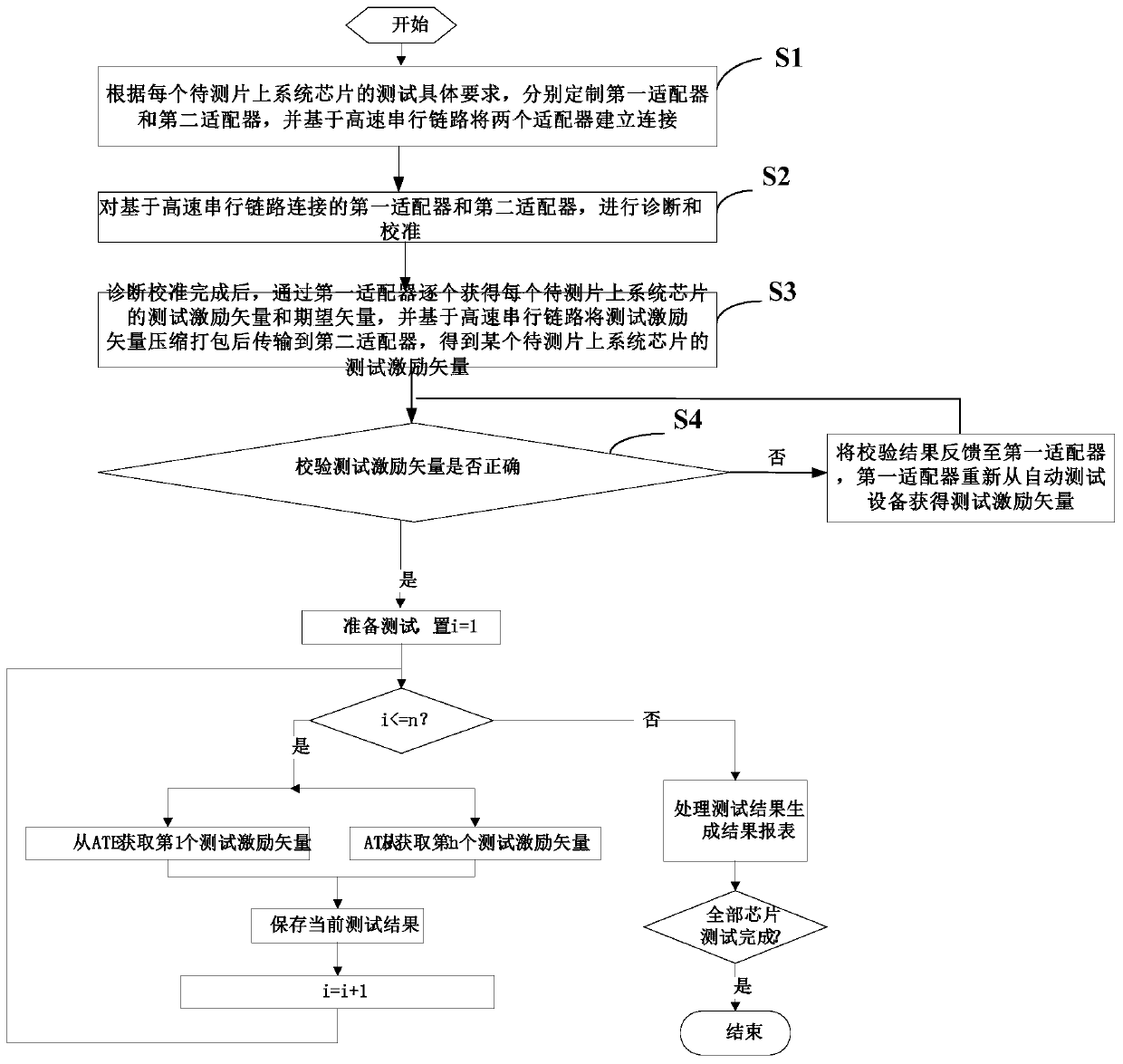
PendingCN111025134AEasy to batch testImprove test efficiencyElectrical testingSystem on a chipHigh speed serial link
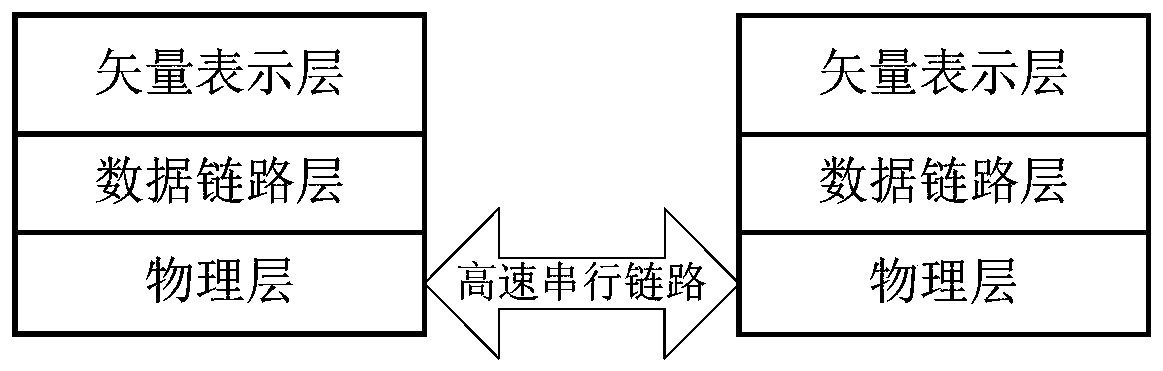
The invention discloses a method and a system for testing a system-on-chip chip. The method comprises the following steps: diagnosing and calibrating a first adapter and a second adapter which are connected based on a high-speed serial link; after the diagnosis and calibration are completed, obtaining test excitation vectors and expected vectors of to-be-tested system-on-chip chips one by one through the first adapter, compressing and packaging the test excitation vectors based on the high-speed serial link, and transmitting the compressed and packaged test excitation vectors to the second adapter to obtain a test excitation vector of a certain to-be-tested system-on-chip chip; and verifying the obtained test excitation vector, and if the vector passes verification, correspondingly transmitting the test excitation vector to the input pin of the corresponding to-be-tested system-on-chip chip so as to complete the test. According to the method, a traditional test cable is replaced by a high-speed serial transmission medium, a test excitation vector is serialized and then compressed and added to a verification mechanism, so that mapping from the test excitation vector to an input pinof a to-be-tested system-on-chip chip is completely programmable, and the accuracy of a test result is guaranteed.
Owner:北京自动测试技术研究所有限公司
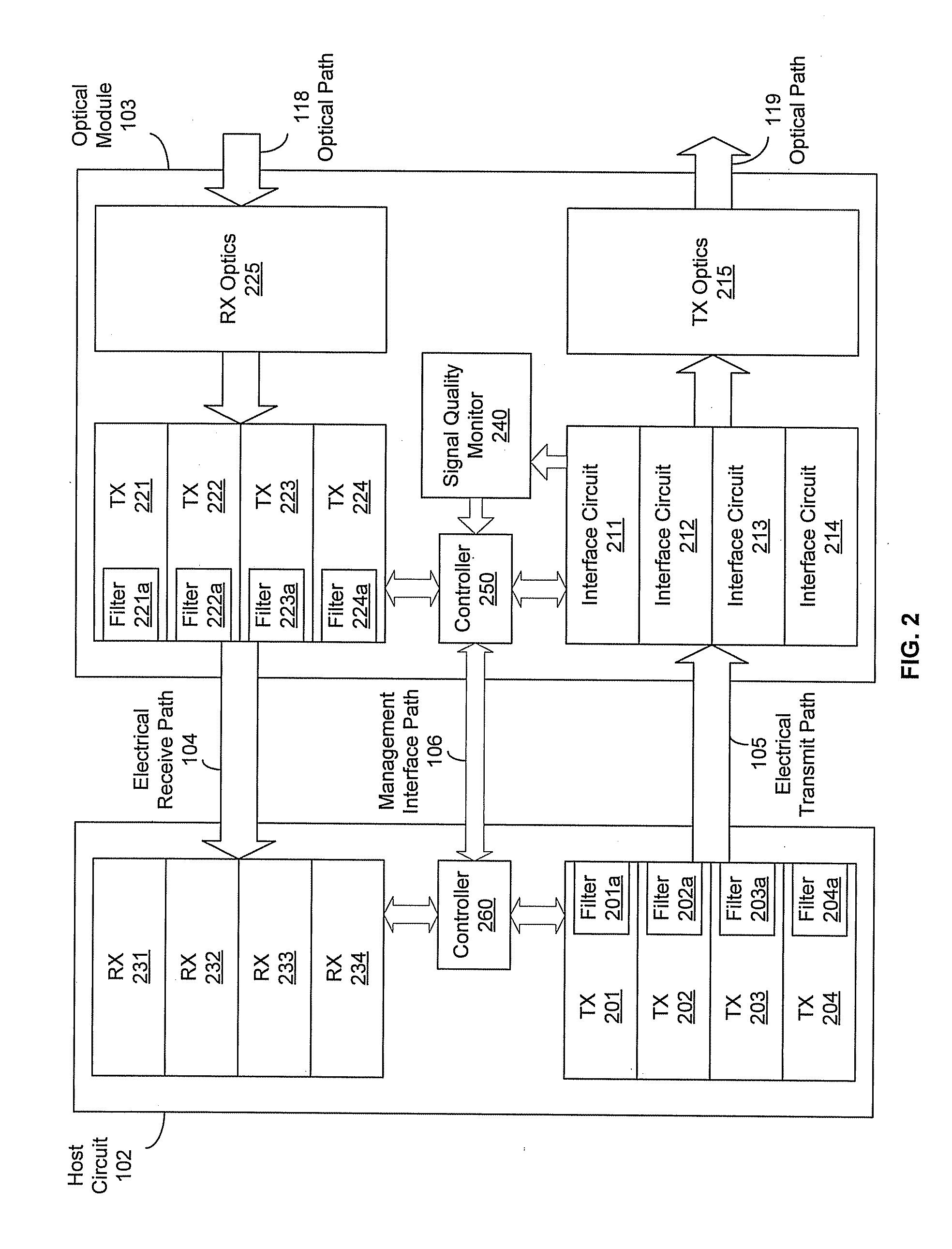
Method and System for Adaptively Setting a Transmitter Filter for a High Speed Serial Link Transmitter
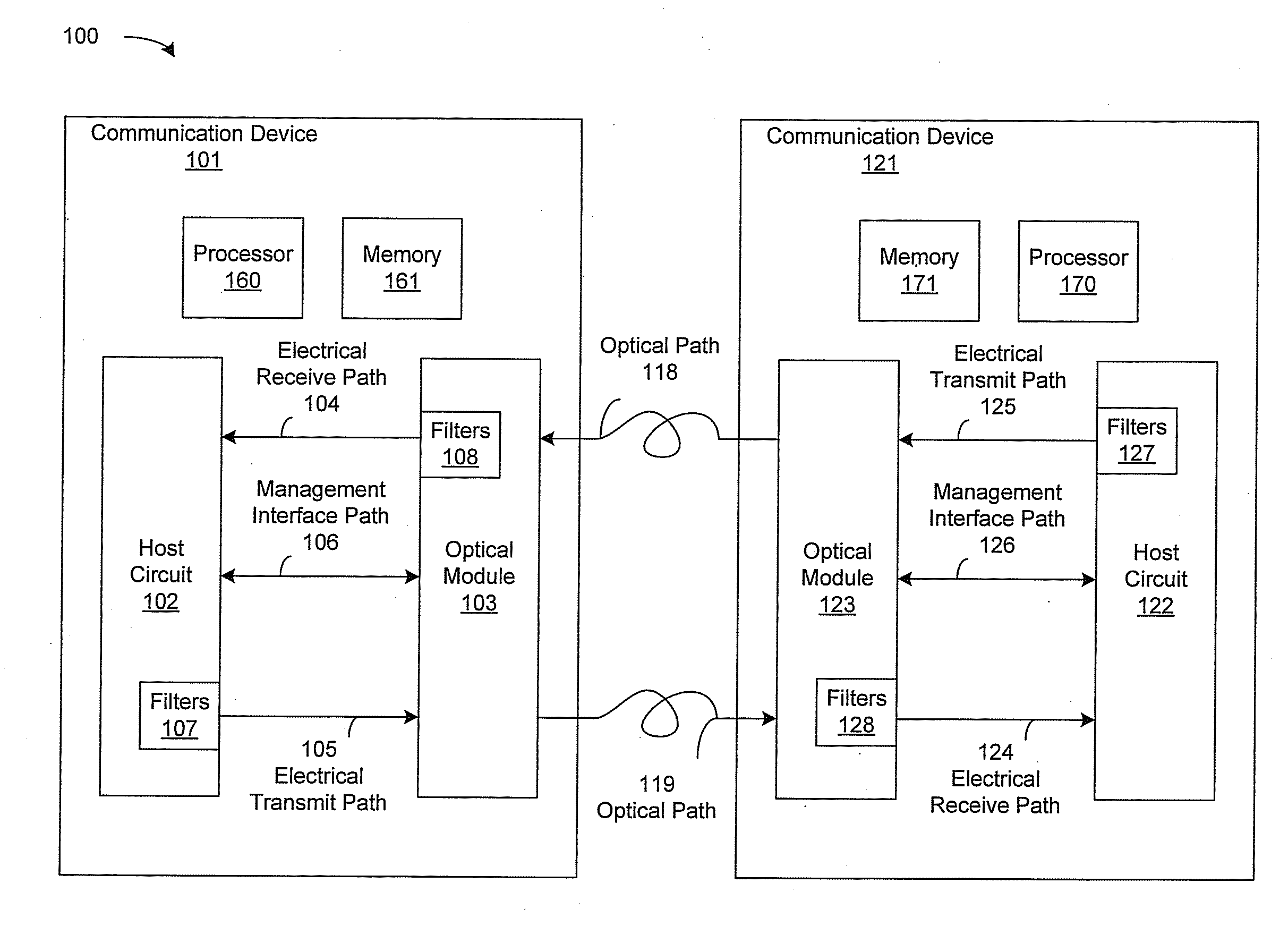
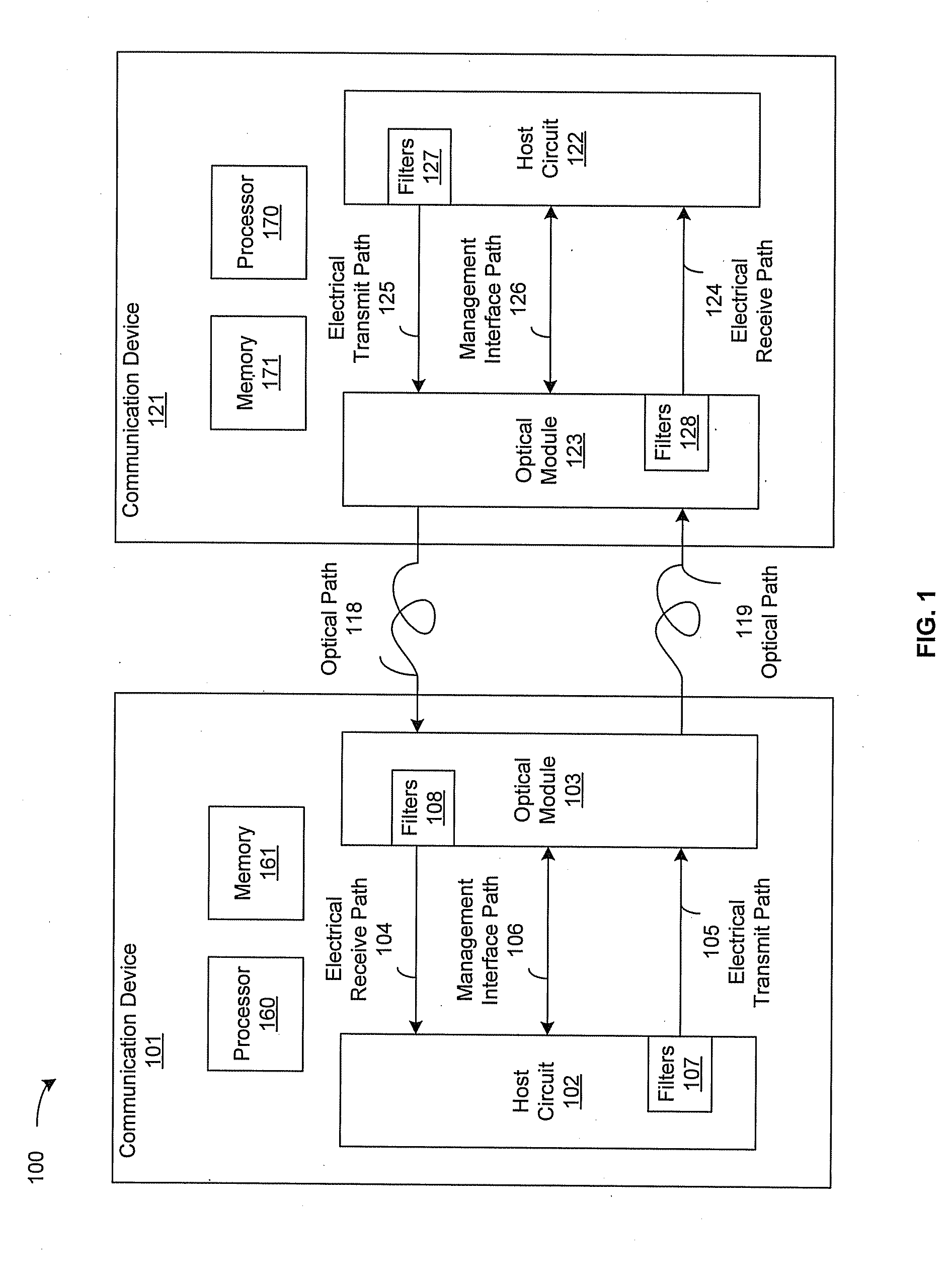
InactiveUS20110249967A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsOptical ModuleSignal quality
A communication device may be operable to determine, in an optical module, a signal quality associated with each of one or more host transmitter filters in a host circuit. The signal quality may be communicated from the optical module to the host circuit via a management interface. The communication device may control, in the host circuit, configuration of each of the host transmitter filters based on the signal quality. The communication device may be operable to determine, in the host circuit, a signal quality associated with each of one or more module transmitter filters in the optical module. The signal quality associated with each of the module transmitter filters may be communicated from the host circuit to the optical module via the management interface. The communication device may control, in the optical module, configuration of each of the module transmitter filters based on the signal quality.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
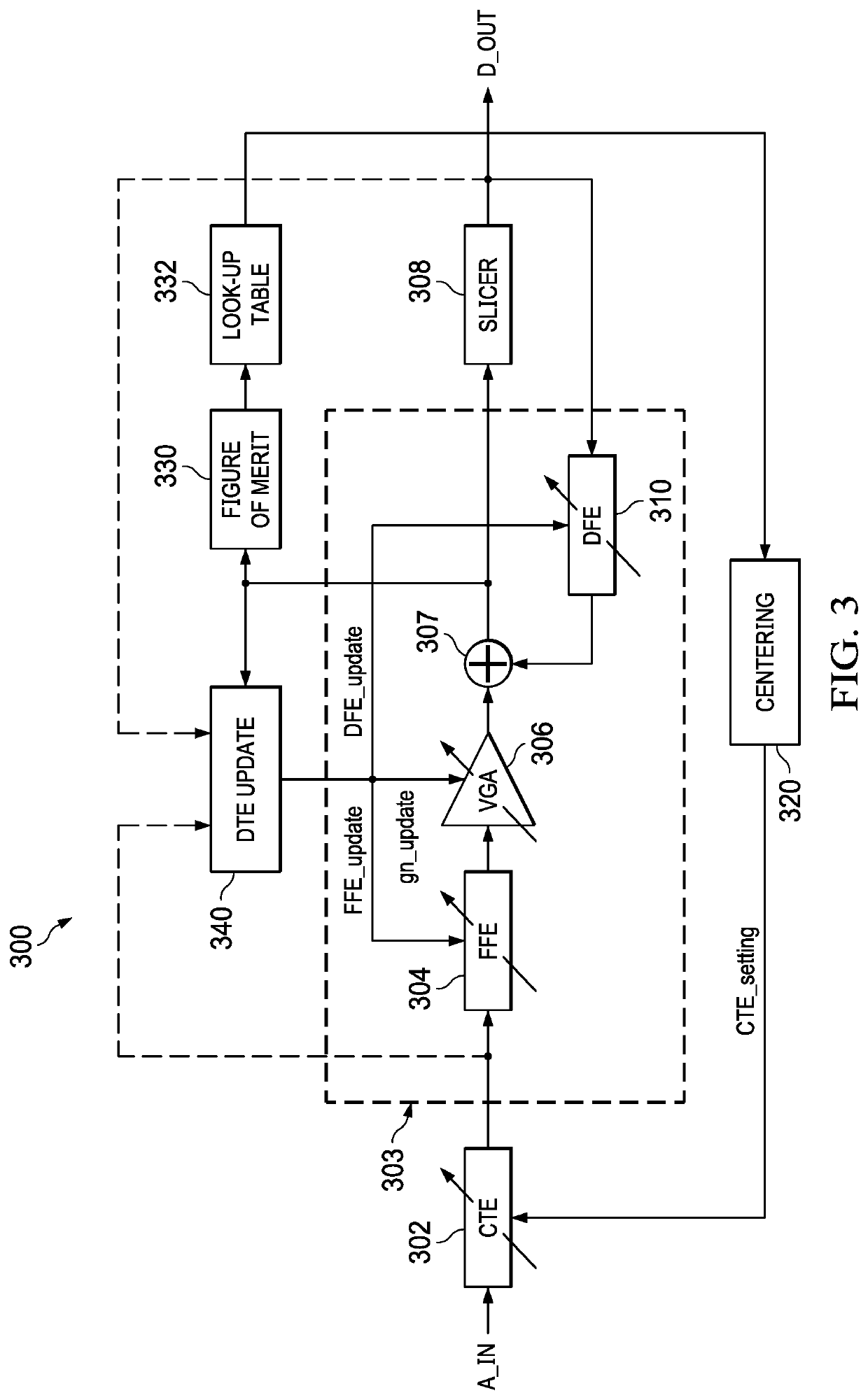
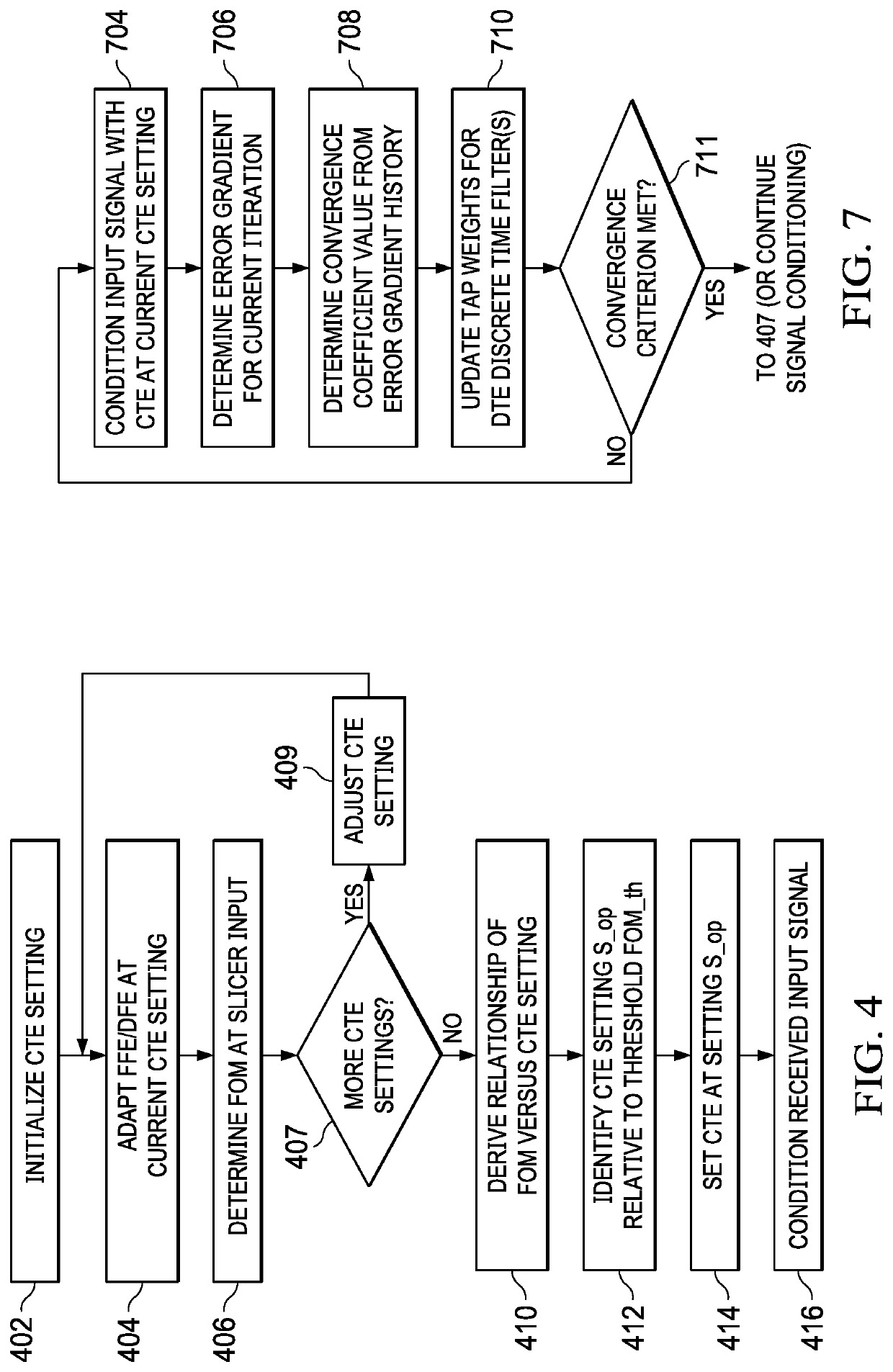
Lane adaptation in high-speed serial links
ActiveUS11177986B1Reduced lane adaptation timeRapid post-initialization re-adaptationEqualisersTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAlgorithmHemt circuits
Adaptive equalizer circuitry including both a continuous time equalizer (CTE) and a discrete time equalizer (DTE) and a method of jointly adapting the CTE and DTE in lane adaptation. Jointly adaptation of the CTE and DTE is performed by adapting the DTE at each of a plurality of filter characteristic settings of the CTE and determining a figure of merit for signals filtered by the CTE and DTE at that condition. Adaptation of the DTE may be performed by dynamically adjusting a convergence coefficient based on a history of error gradients. After a figure of merit is determined for each of the plurality of CTE filter characteristics, a CTE filter characteristic setting is then selected based on those figure of merit values, for example at a CTE setting near a midpoint of an acceptable region of figure of merit values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com