Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Feed forward equalizer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
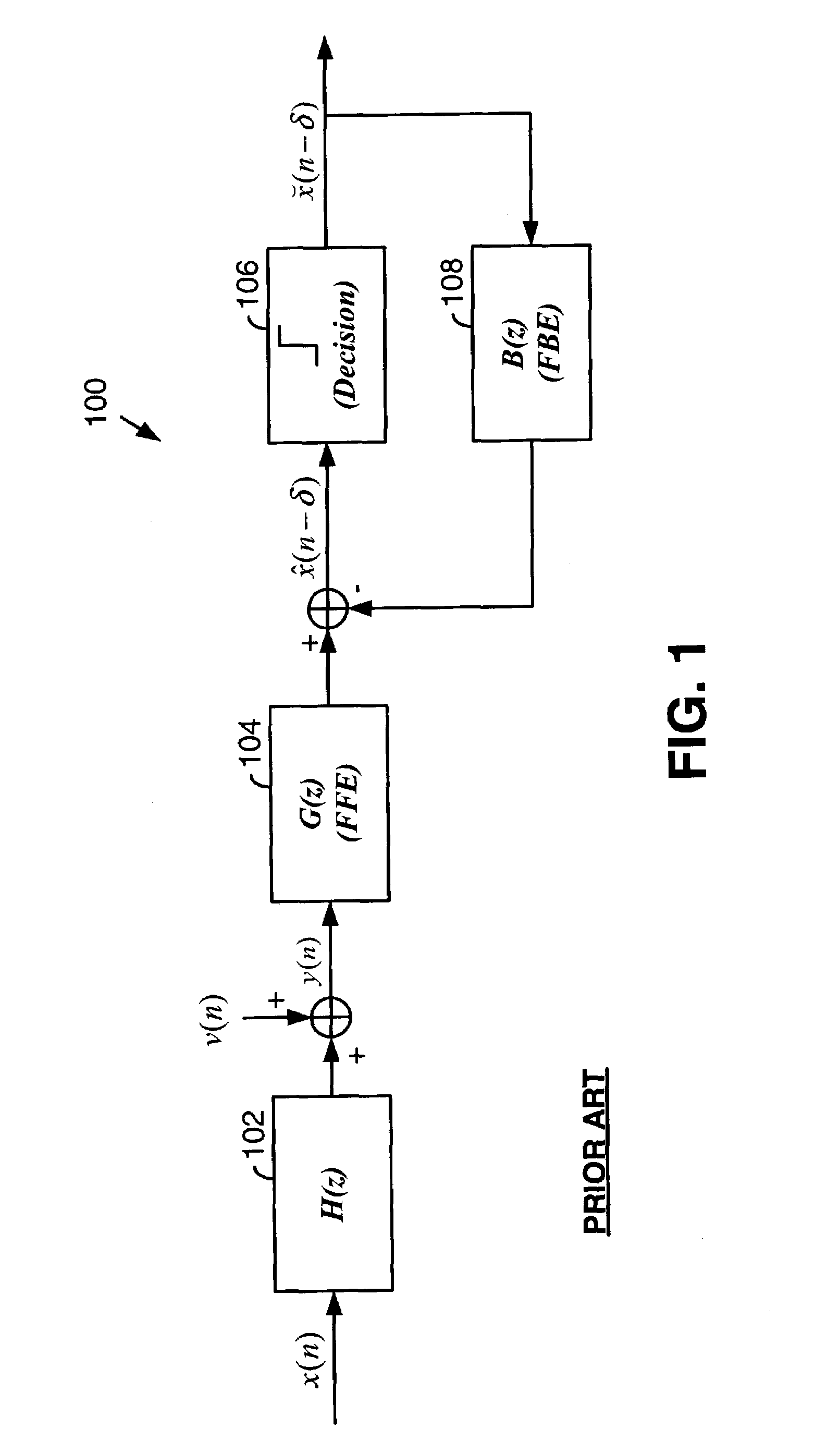
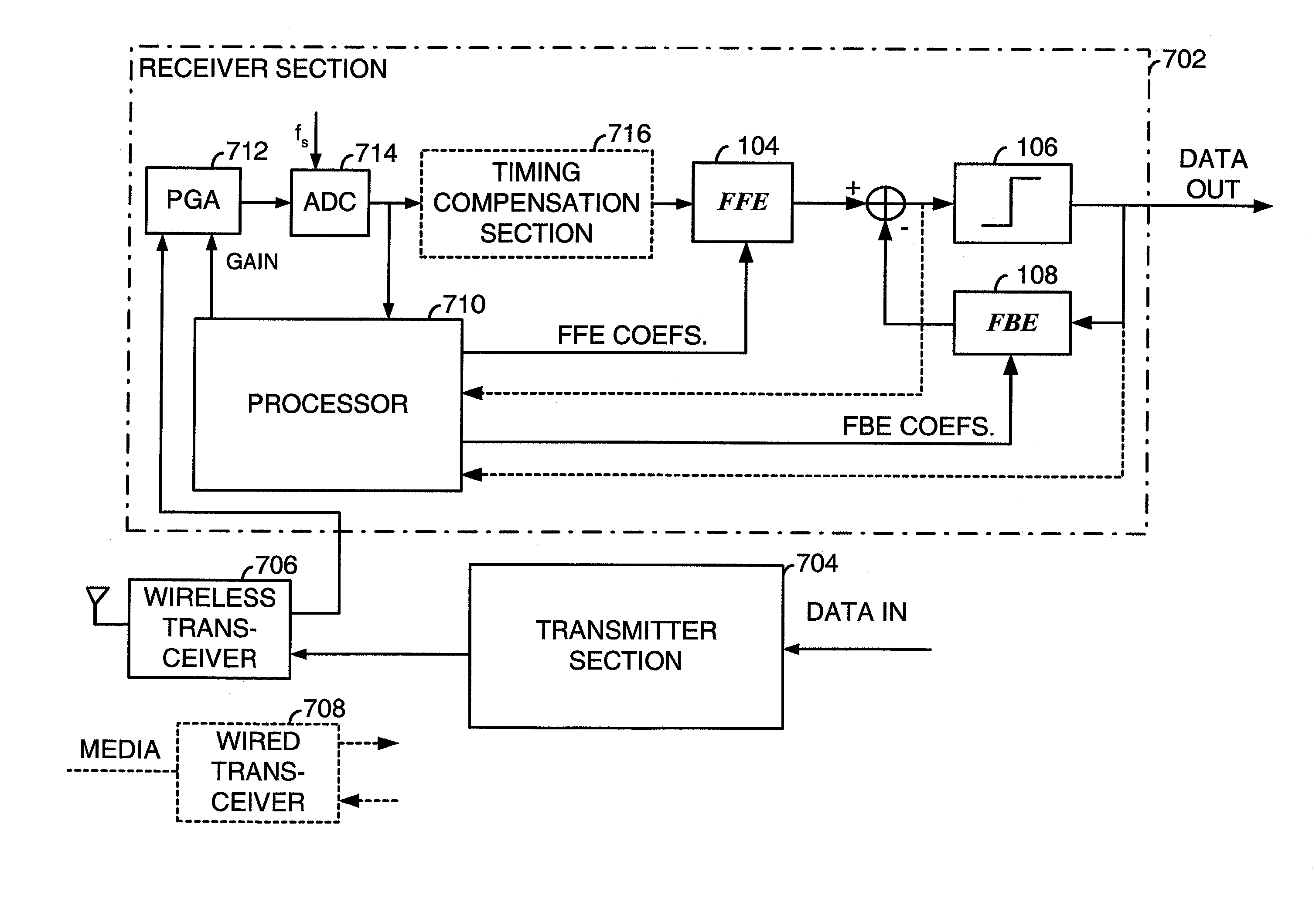
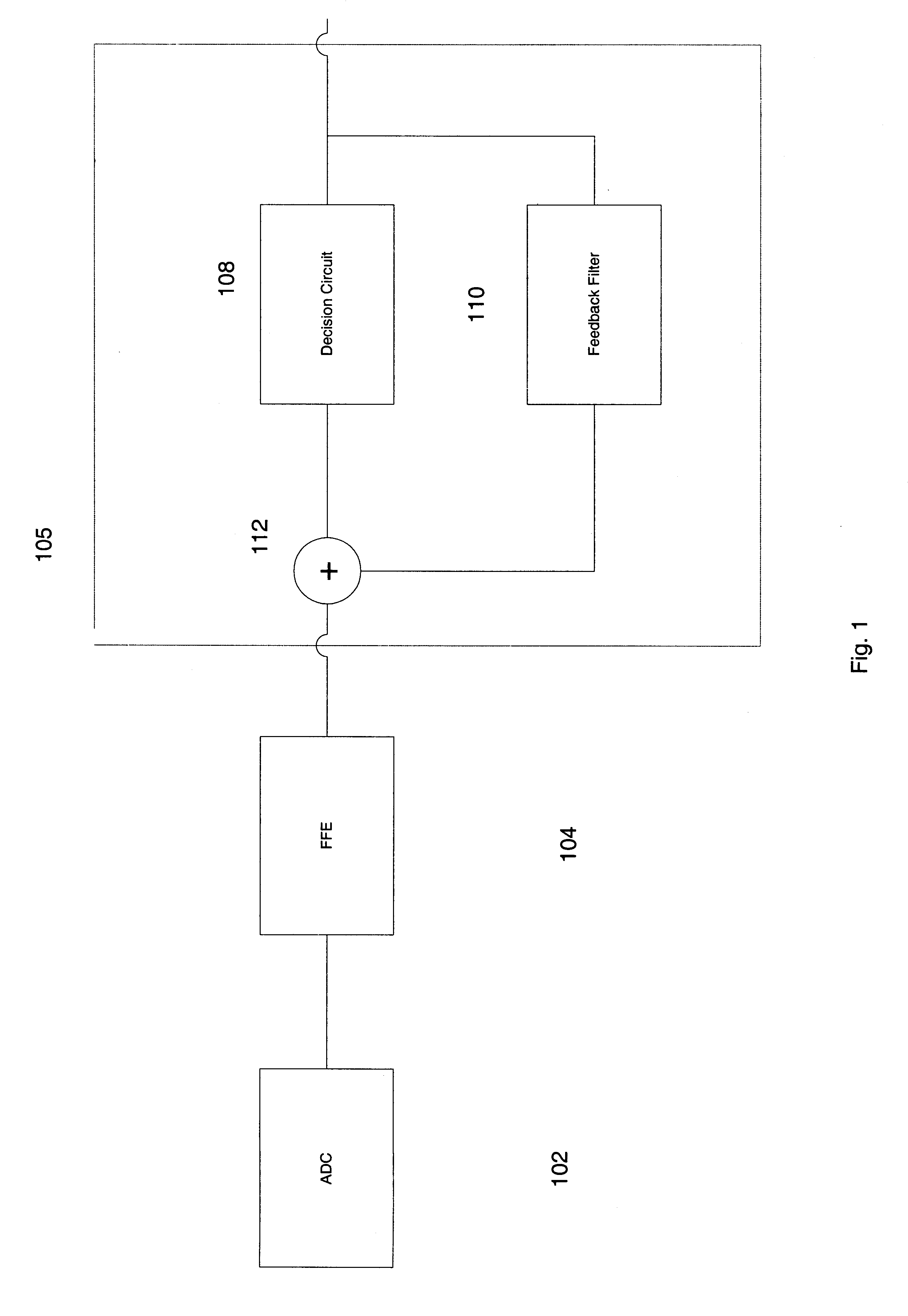
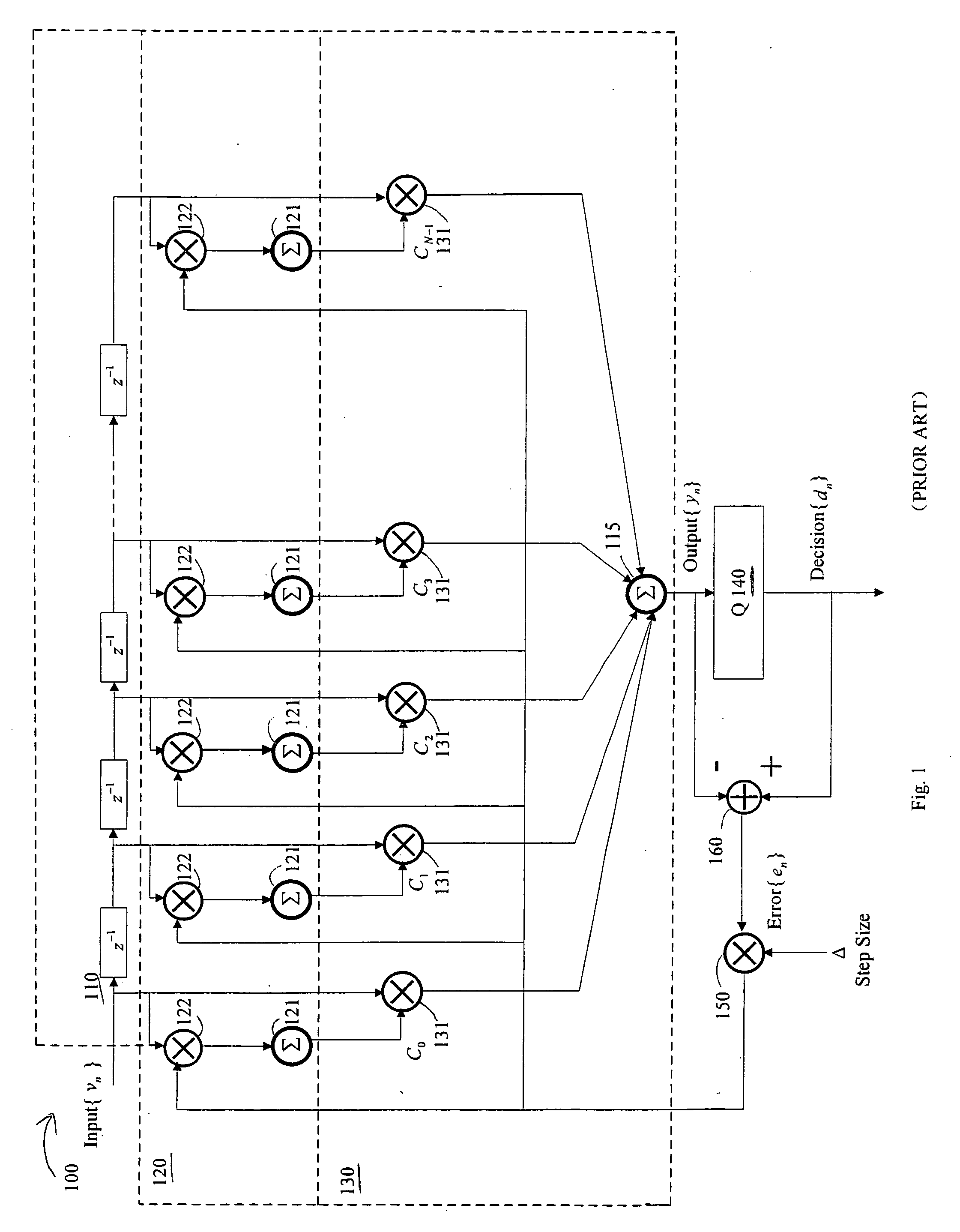
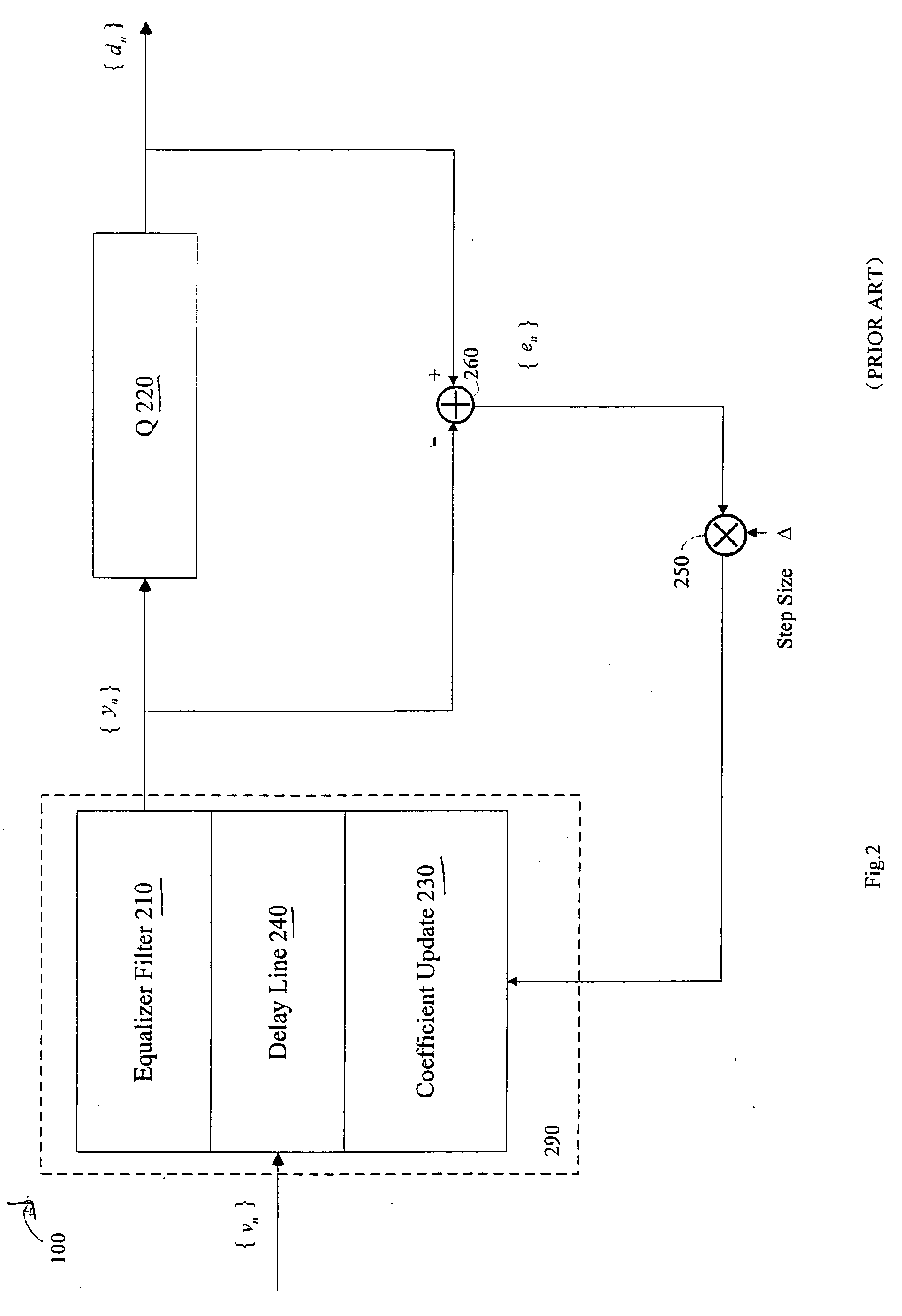
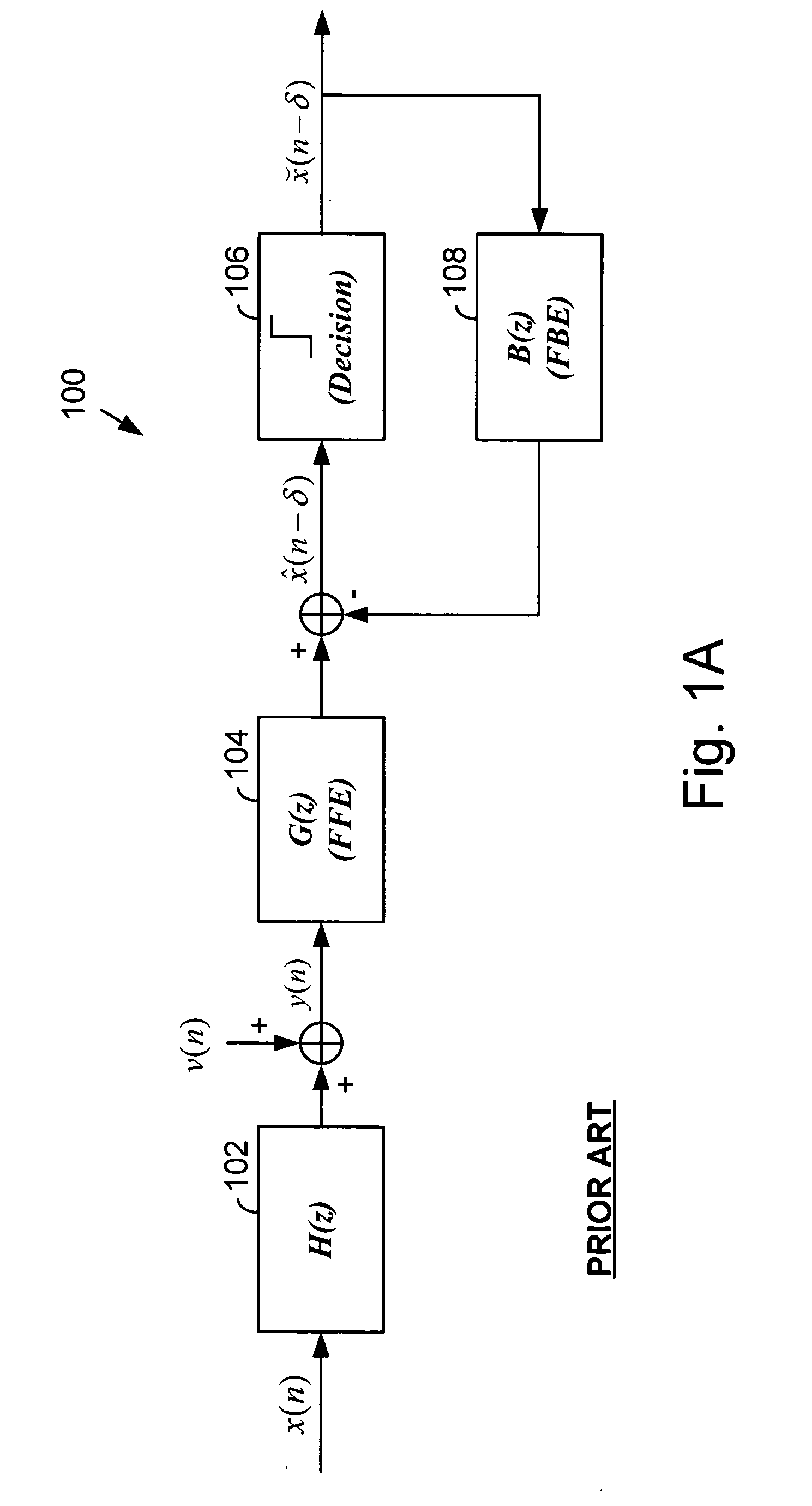
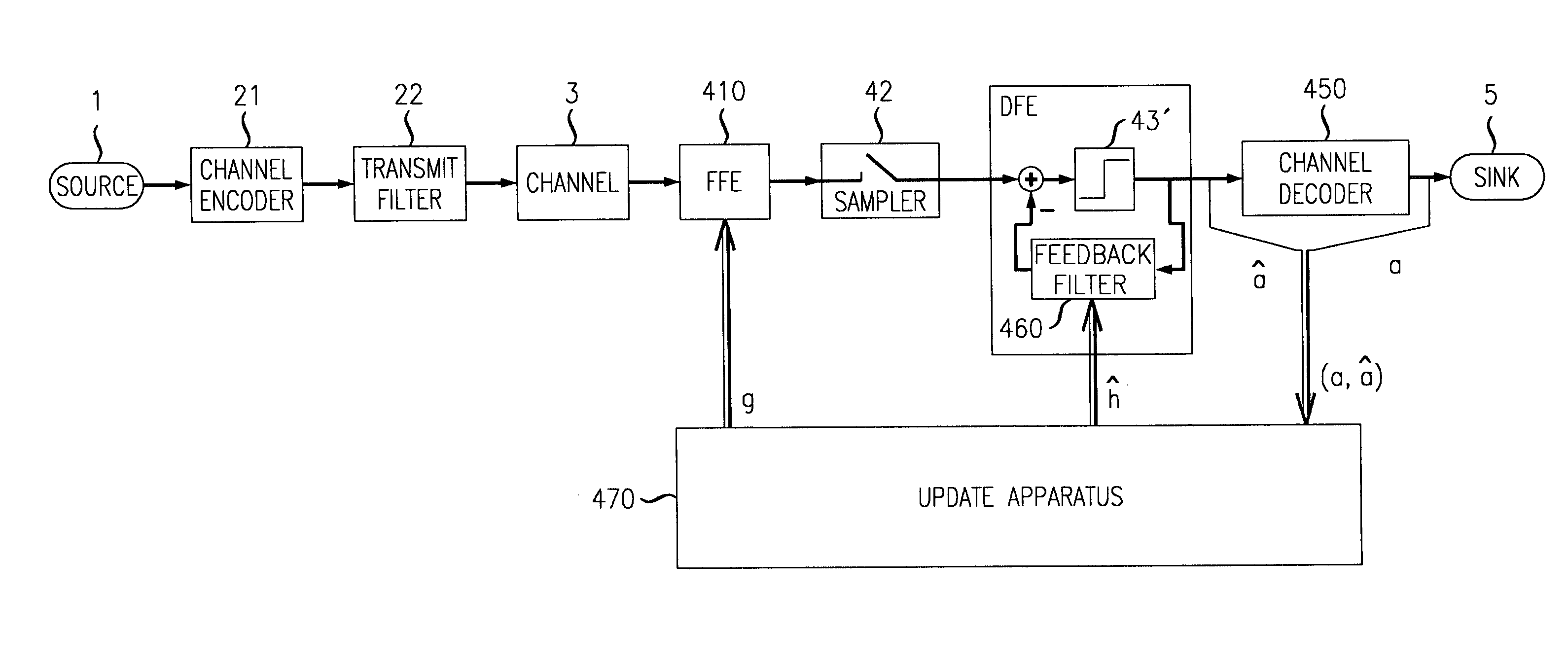
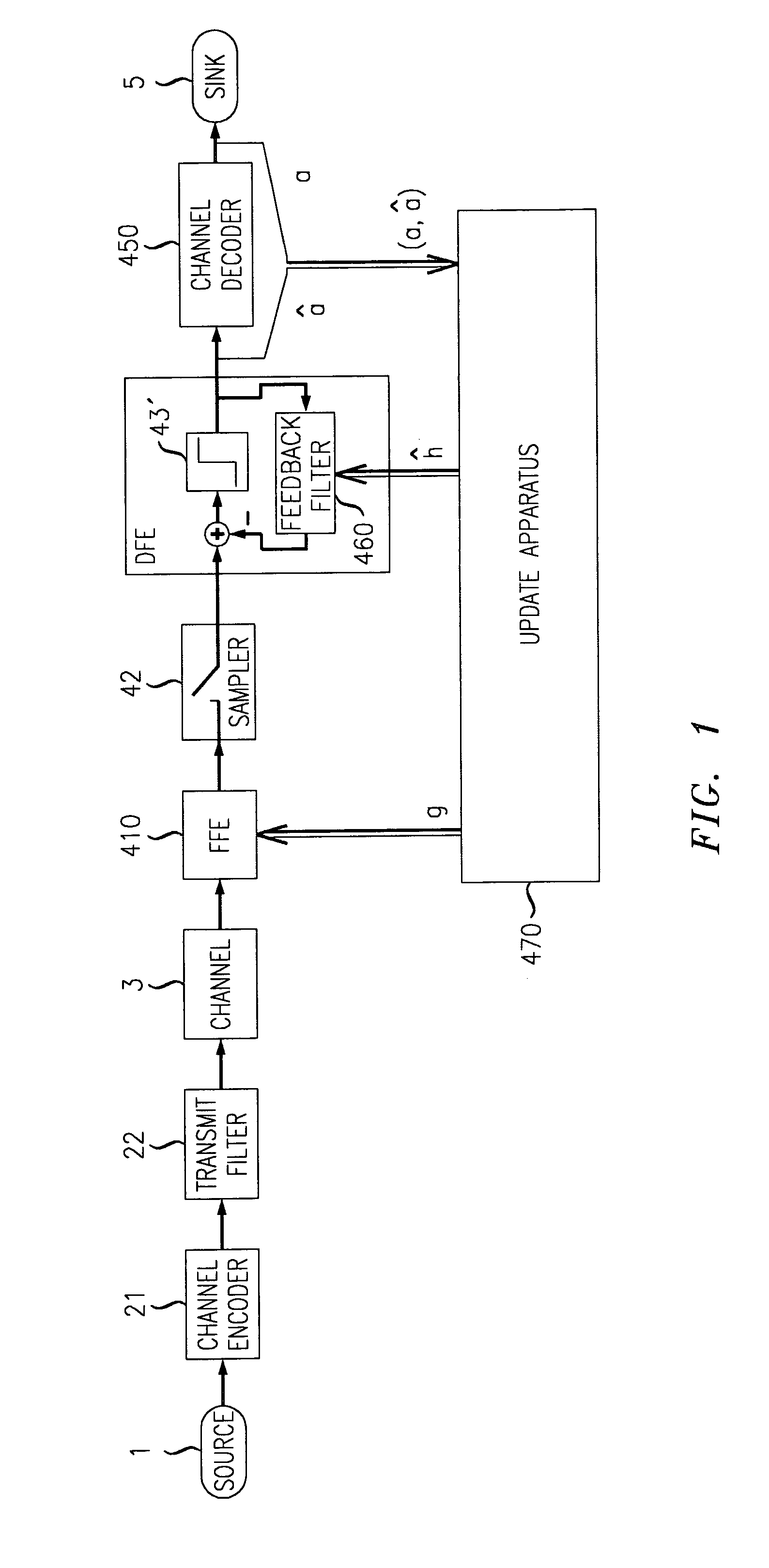
Adaptive equalizers and methods for carrying out equalization with a precoded transmitter
InactiveUS6167082AEliminateEliminate interferenceMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationDecision circuitEqualization
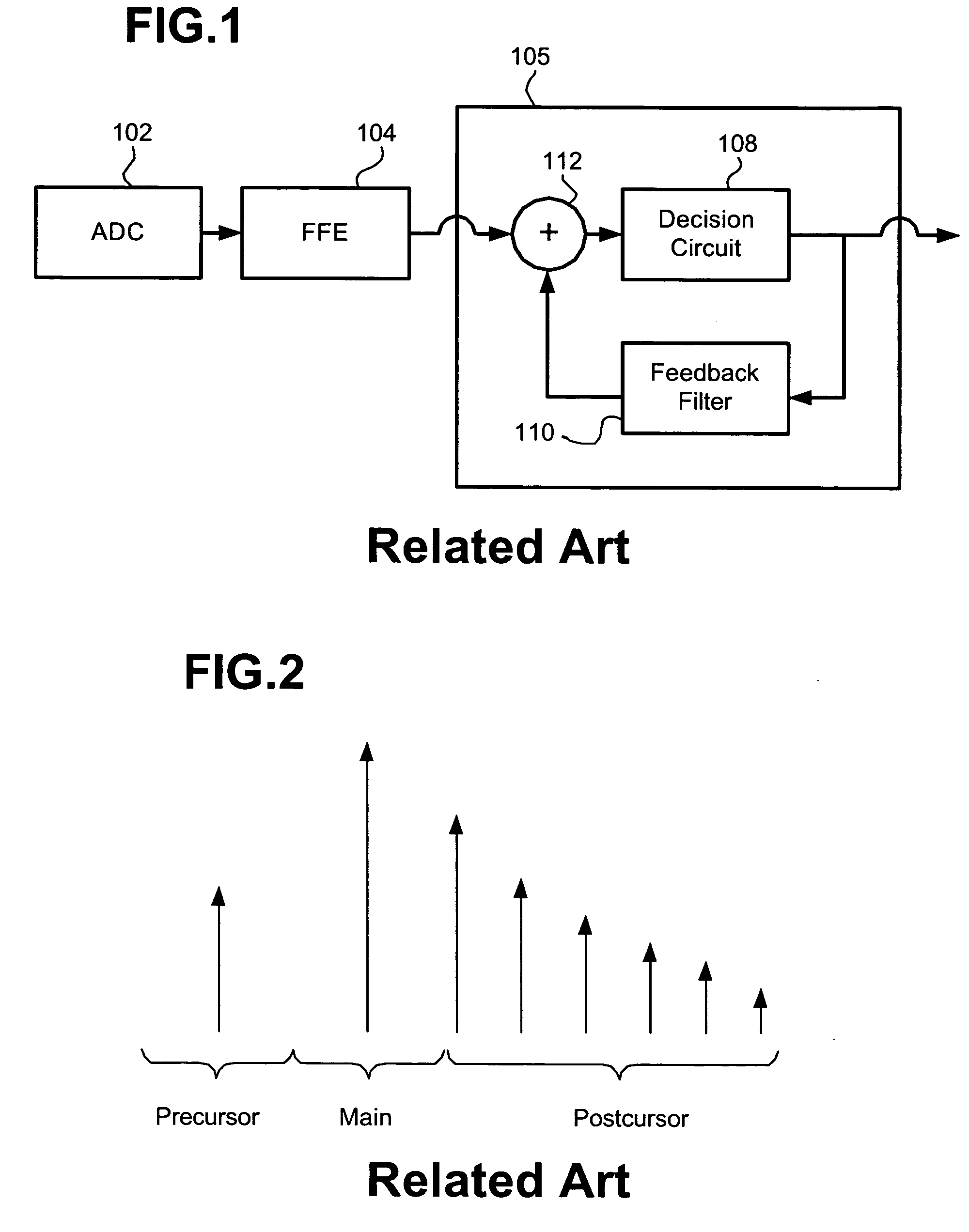
Adaptive equalization methods and adaptive equalizers used with precoded systems dominated by intersymbol interference (ISI) monitor the output of a DFE and compare it to a reference for updating a precoder in response to the comparison. To accomplish this, an adaptive equalizer includes a feed forward equalizer receiving a signal from a communication channel, the feed forward equalizer equalizing variations in pre-cursor intersymbol interference resulting from changes in characteristics of the channel and providing an output signal to an error correction decoder, a decision circuit, coupled to the feed forward equalizer, for generating error vectors in response to the output signal of the feed forward equalizer and a decision feedback equalizer, coupled to the decision circuit, the decision feedback equalizer monitoring the pre-cursor intersymbol interference of the channel, determining when the transmitter coefficients to the precoder warrant updating, and generating a signal indicating that an update to the transmitter coefficients to the precoder is warranted. The adaptive equalizer farther includes a comparison circuit, the comparison circuit receiving an output from the decision feedback equalizer and comparing the output from the decision feedback equalizer to a reference, the comparison circuit generating the signal indicating that an update to the transmitter coefficients to the precoder is warranted in response to the comparison.
Owner:LEVEL ONE COMM
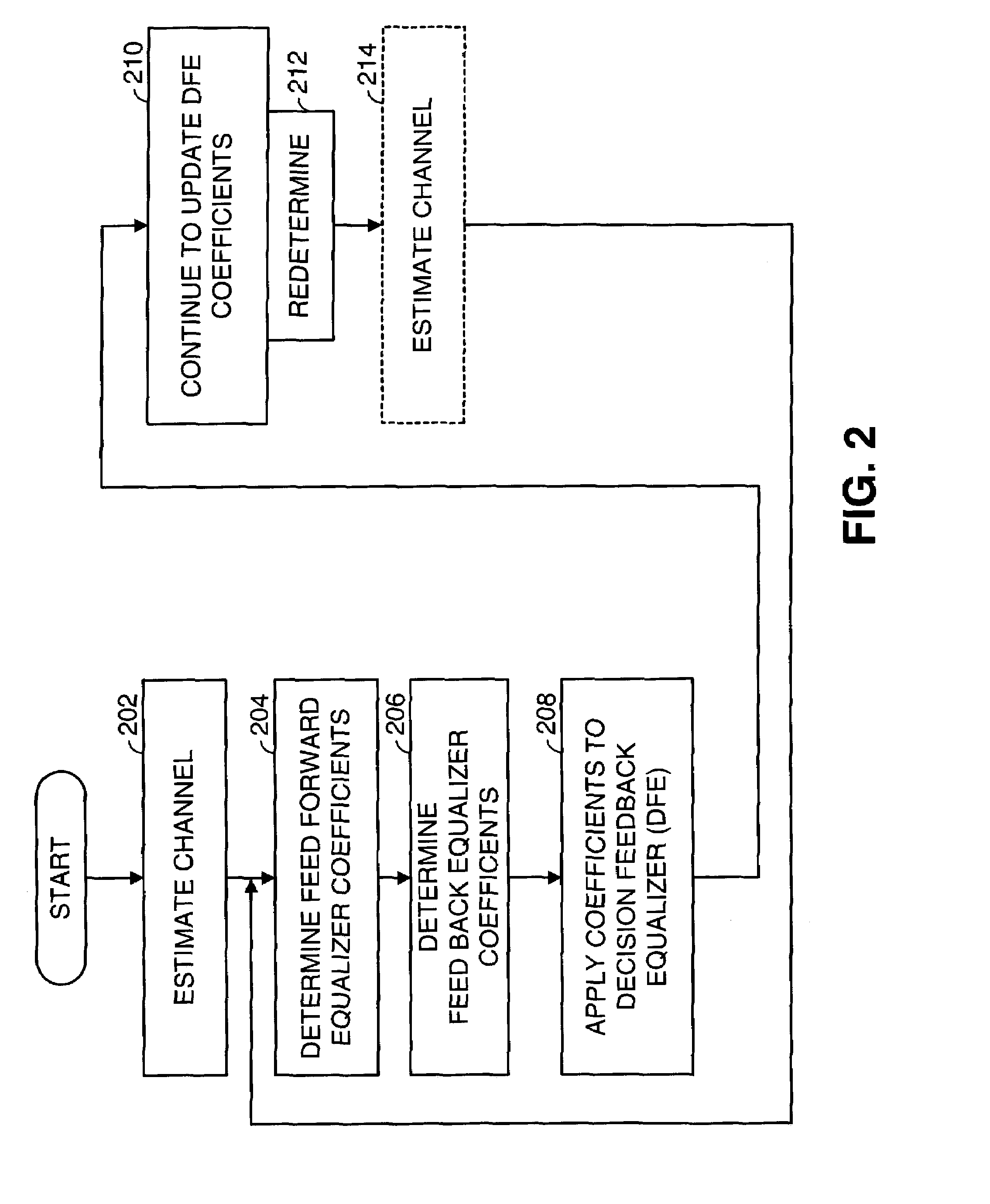
Fast computation of coefficients for a variable delay decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7263123B2Reduce computational complexityIncrease computing speedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsOptimal decisionComputational problem
Optimal Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) coefficients are determined from a channel estimate by casting the DFE coefficient problem as a standard recursive least squares (RLS) problem and solving the RLS problem. In one embodiment, a fast recursive method, e.g., fast transversal filter (FTF) technique, is used to compute the Kalman gain of the RLS problem, which is then directly used to compute MIMO Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) coefficients. The FBE coefficients are computed by convolving the FFE coefficients with the channel impulse response. Complexity of a conventional FTF algorithm may be reduced to one third of its original complexity by selecting a DFE delay to force the FTF algorithm to use a lower triangular matrix. The length of the DFE may be selected to minimize the tap energy in the FBE coefficients or to ensure that the tap energy in the FBE coefficients meets a threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
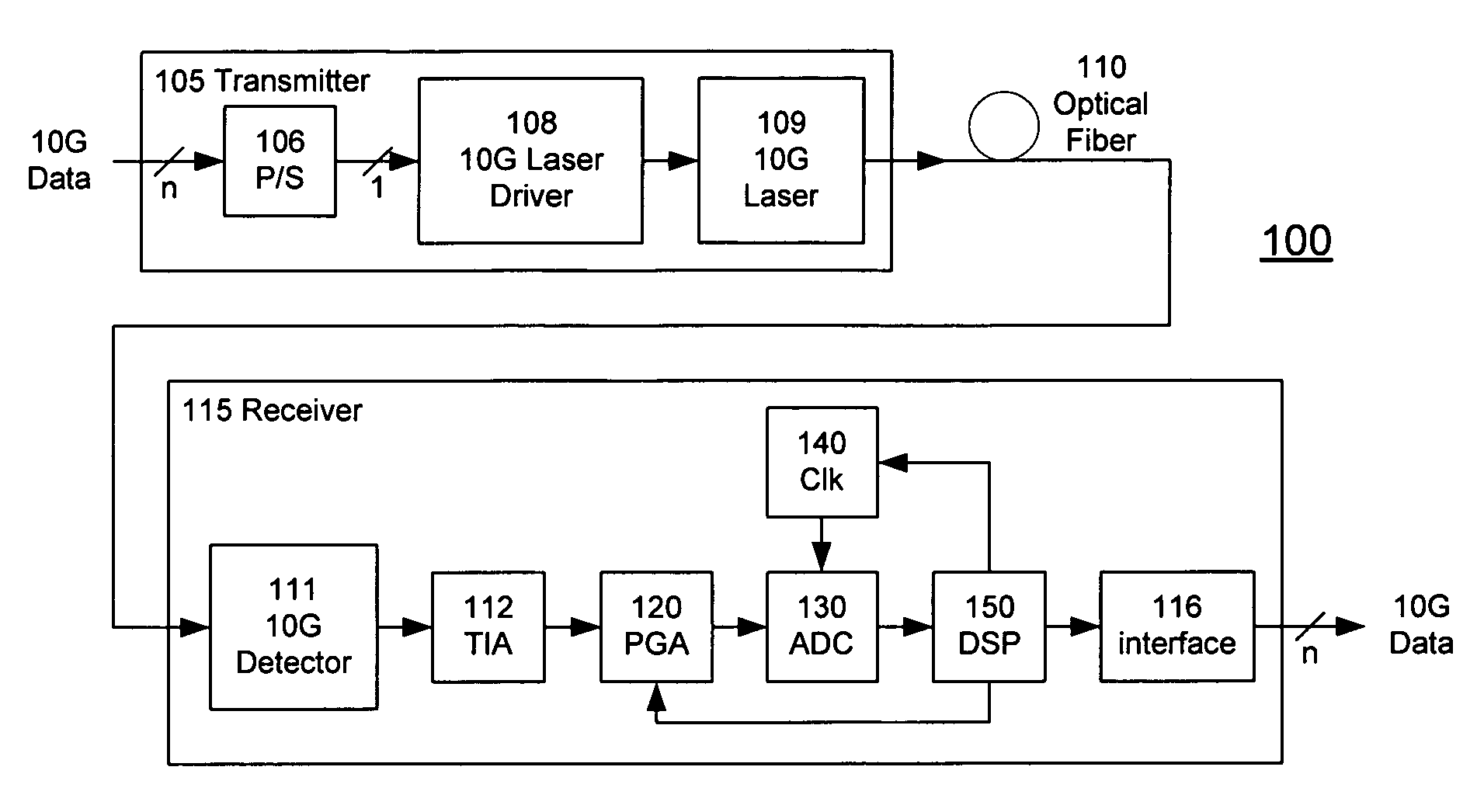
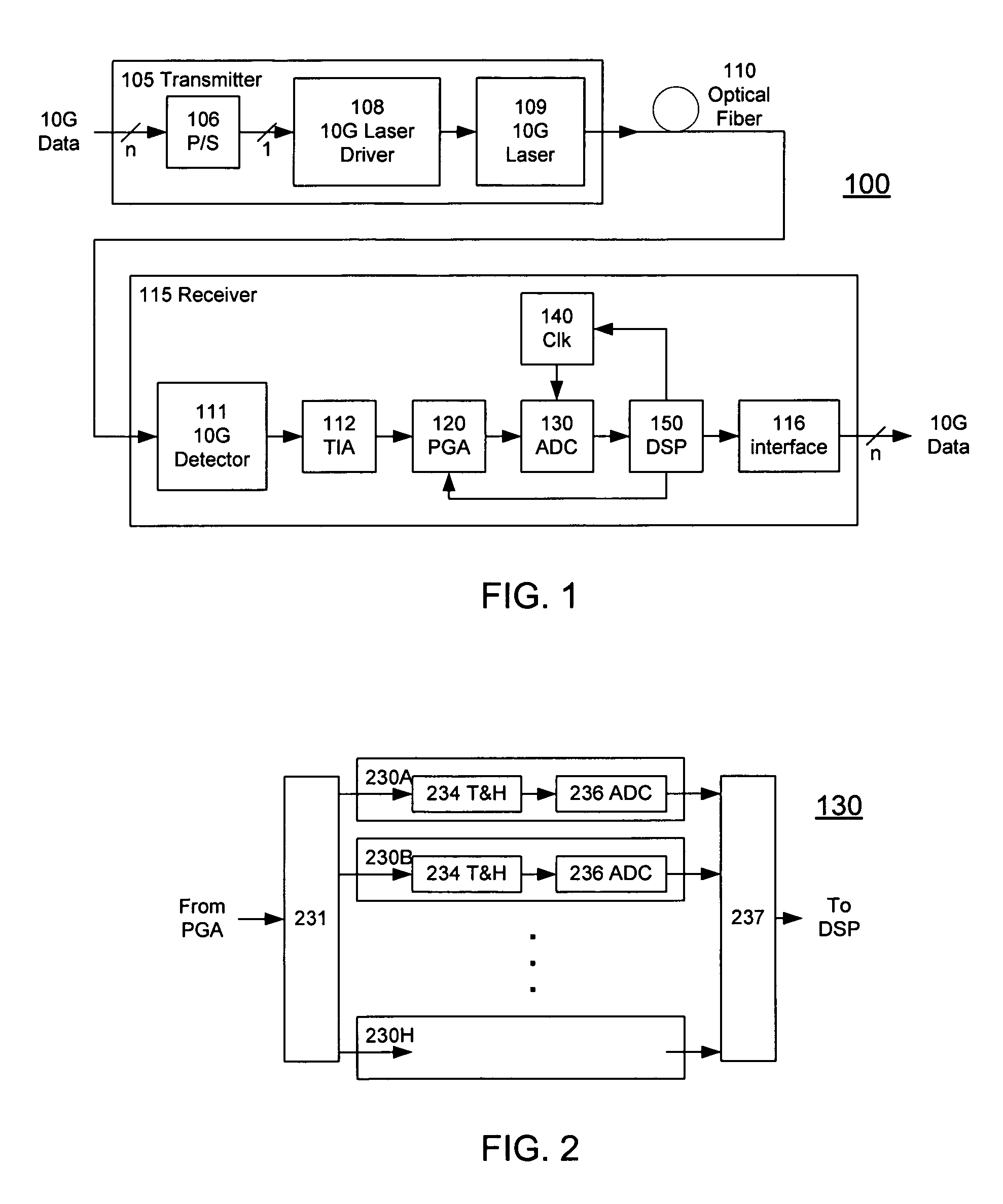
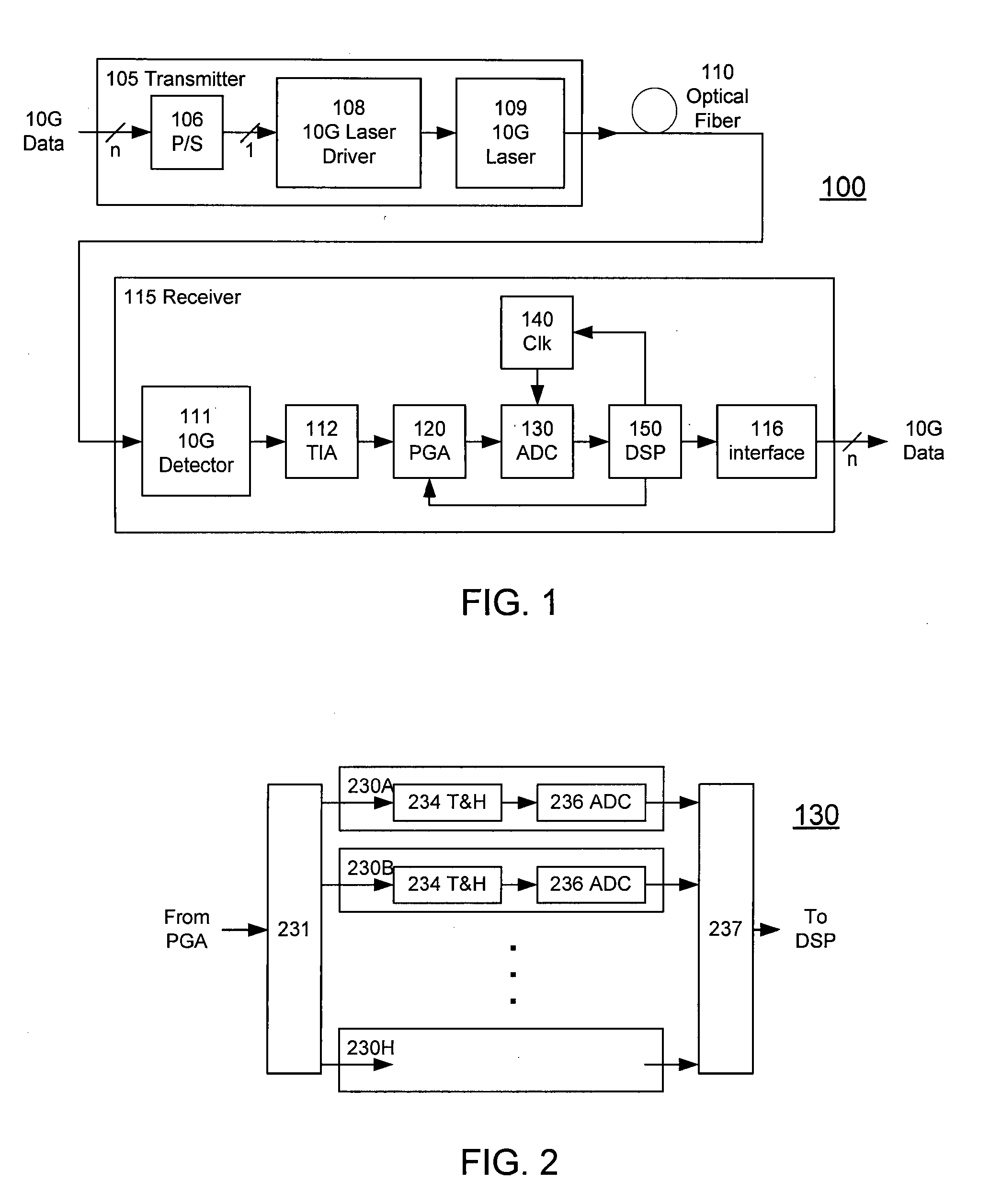
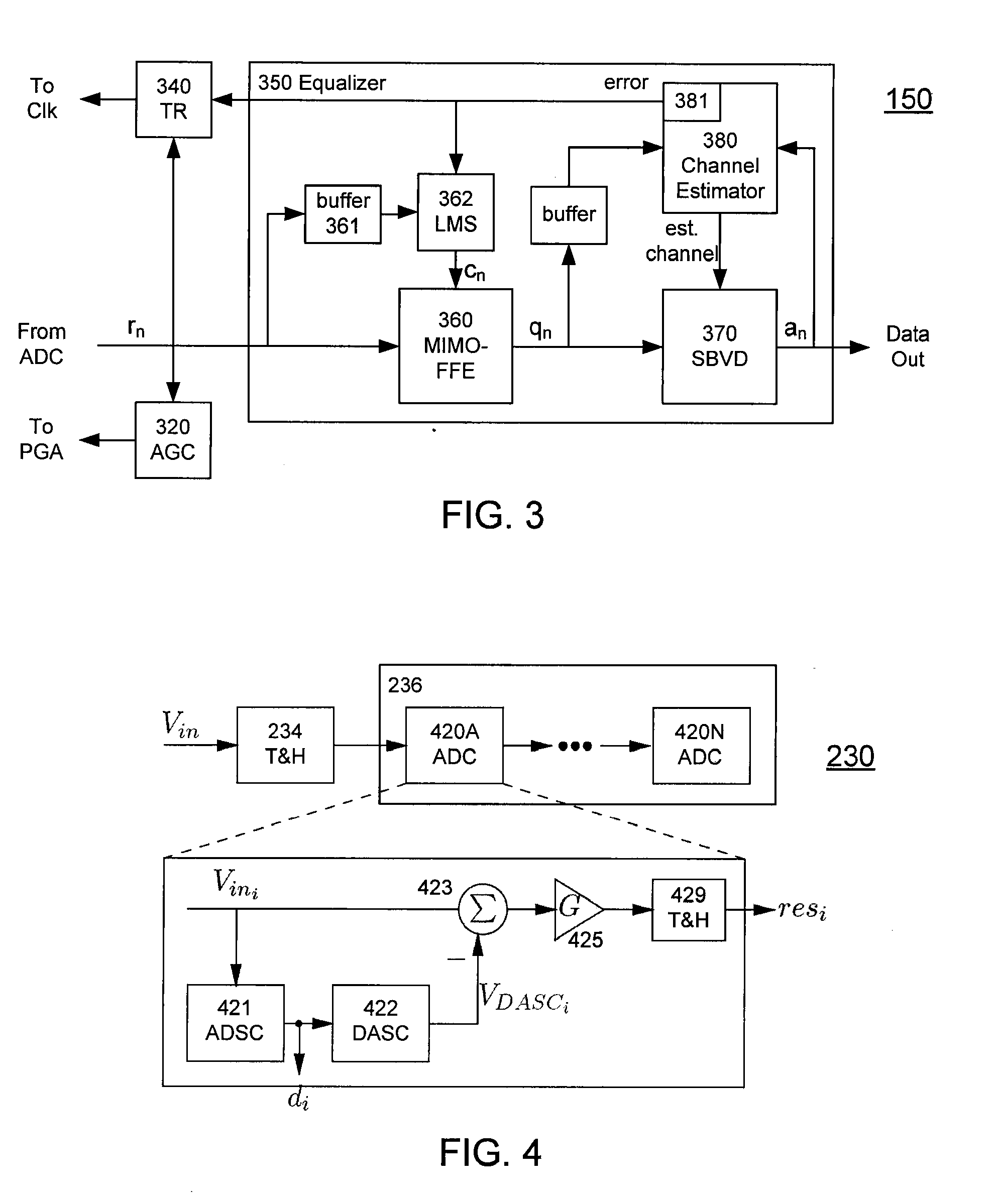
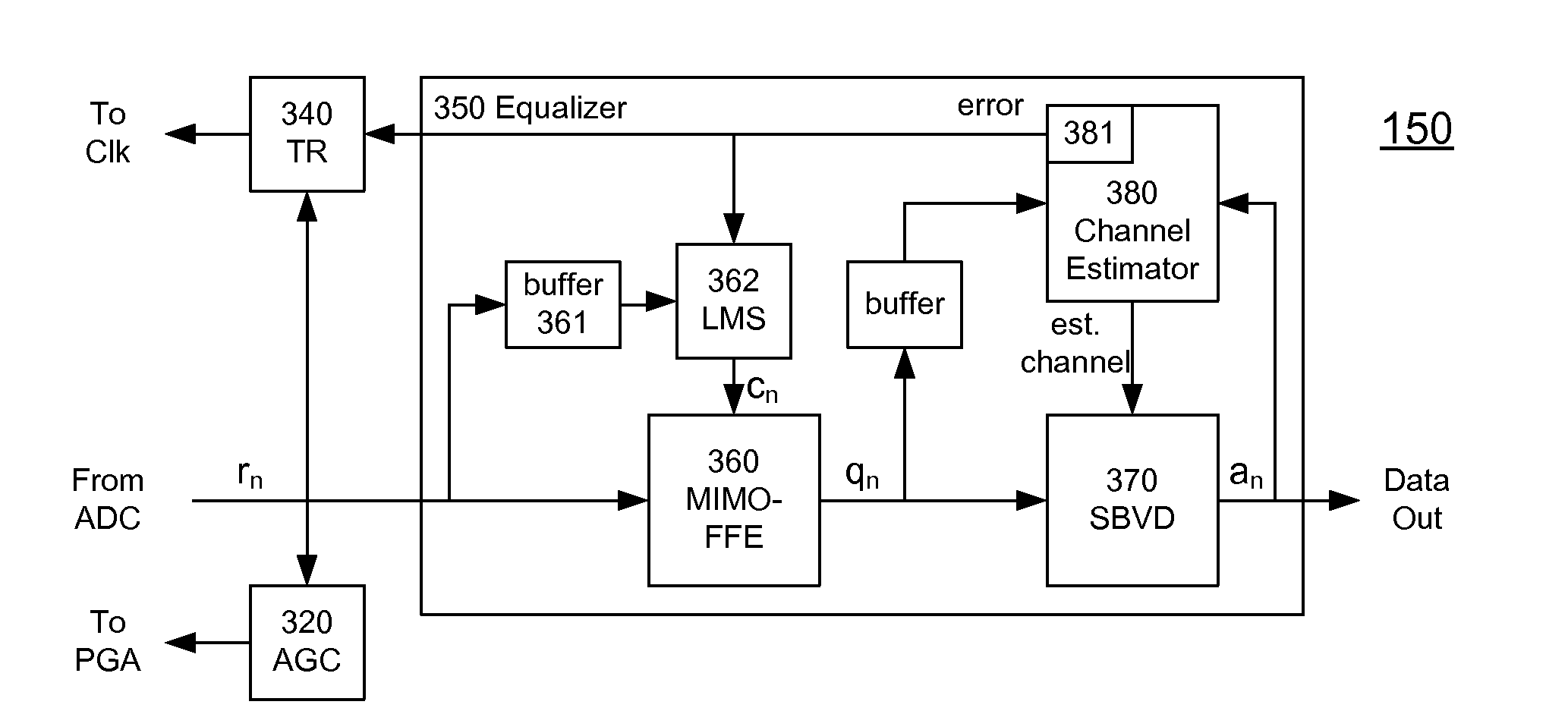
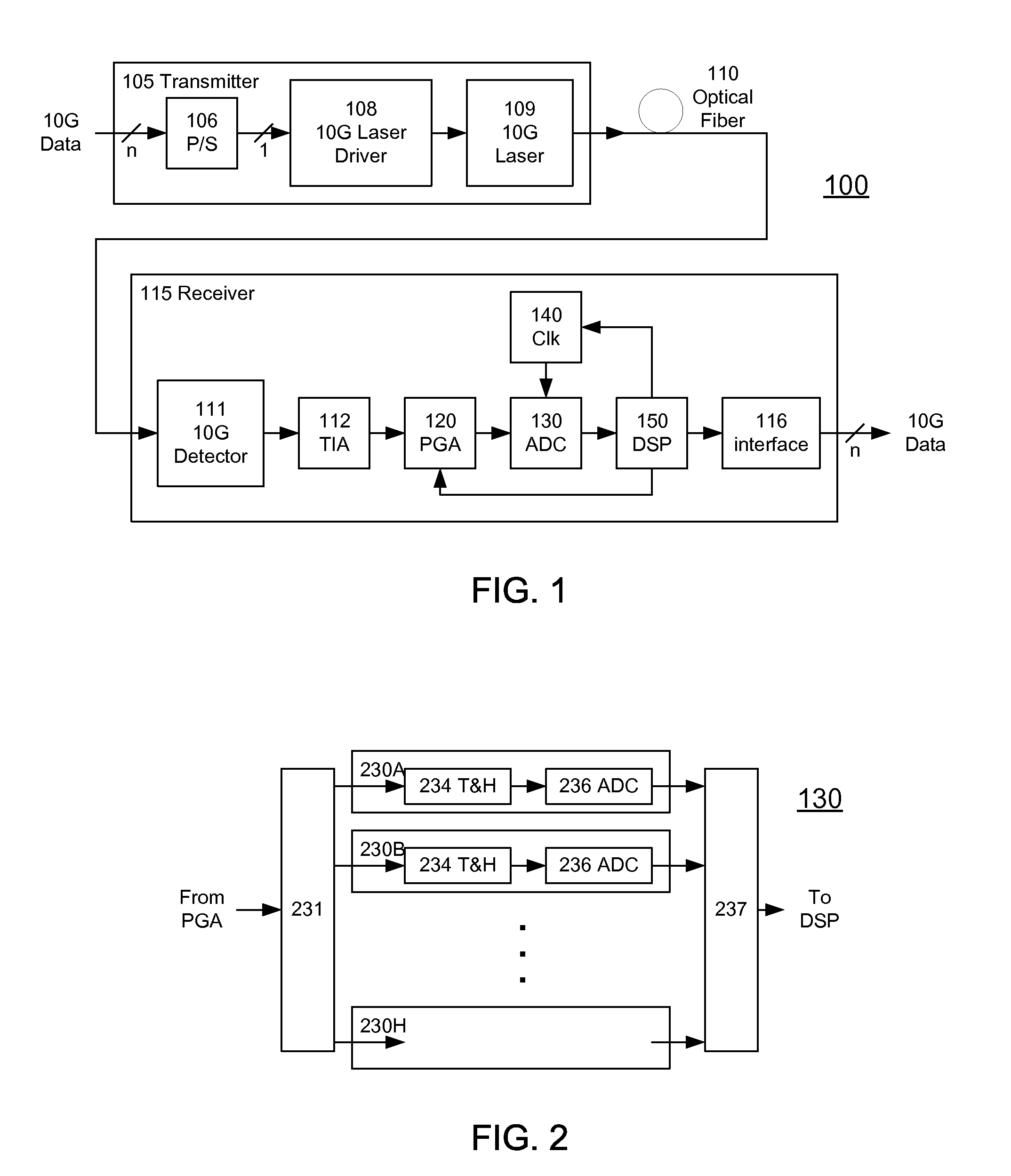
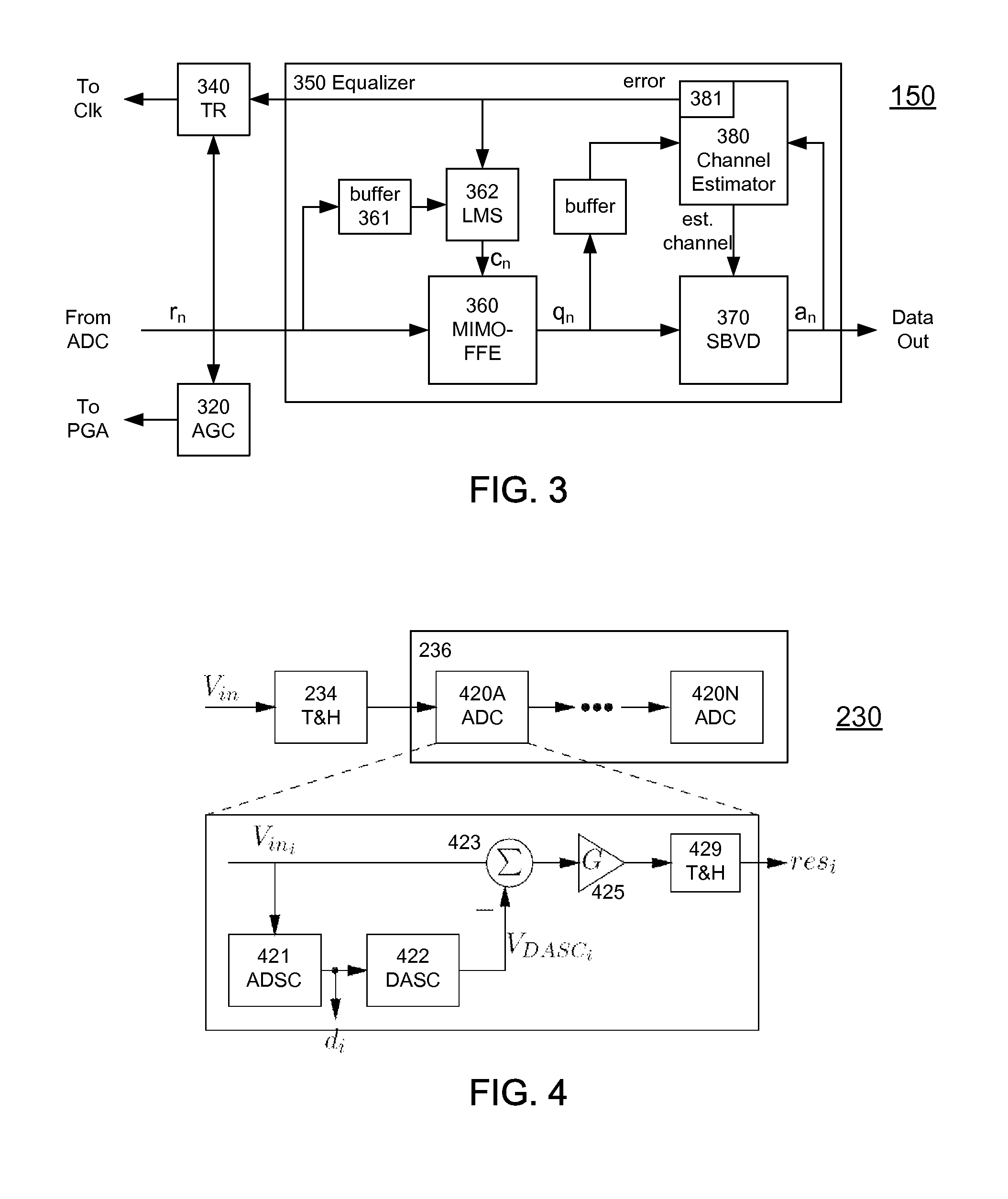
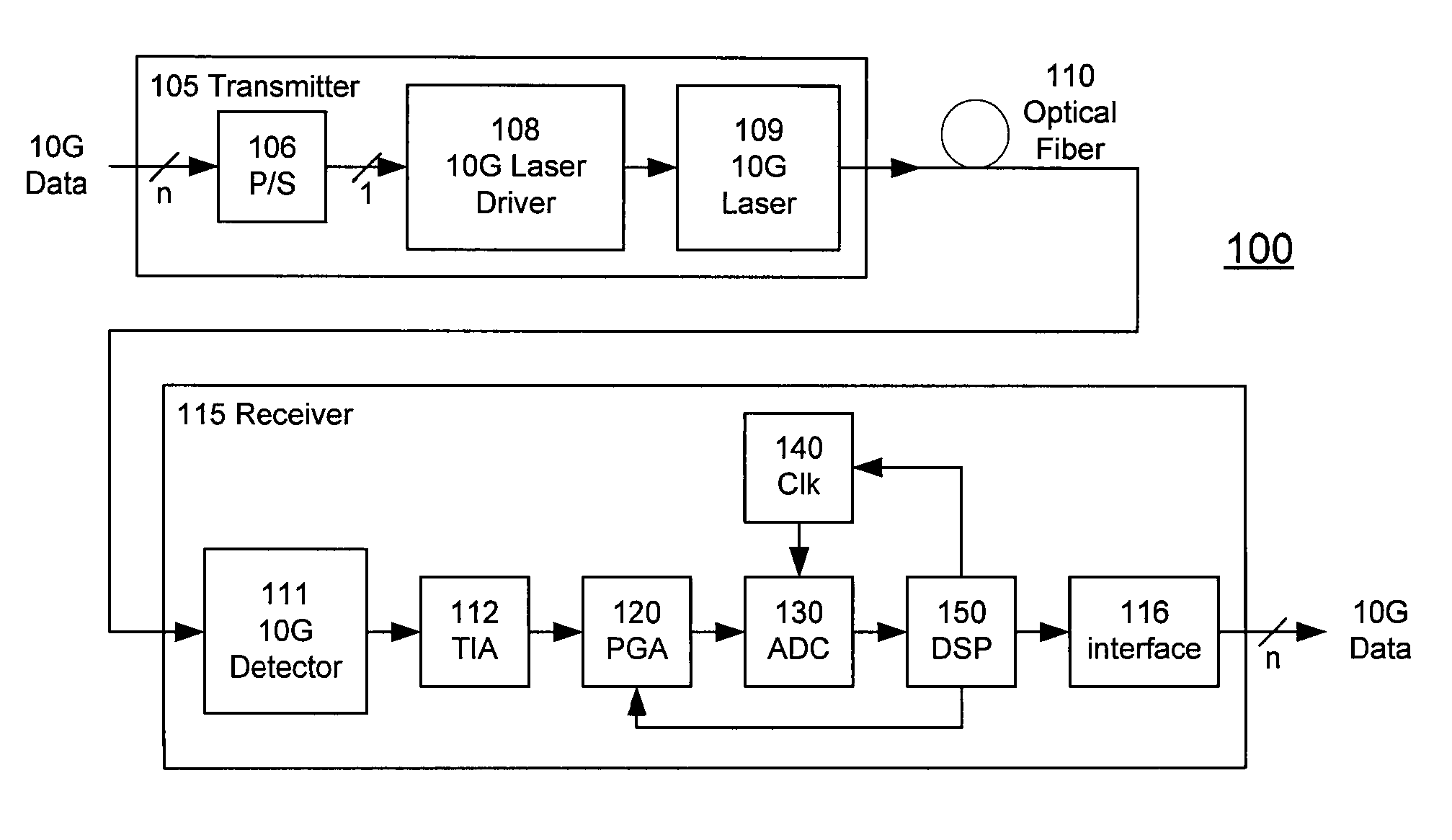
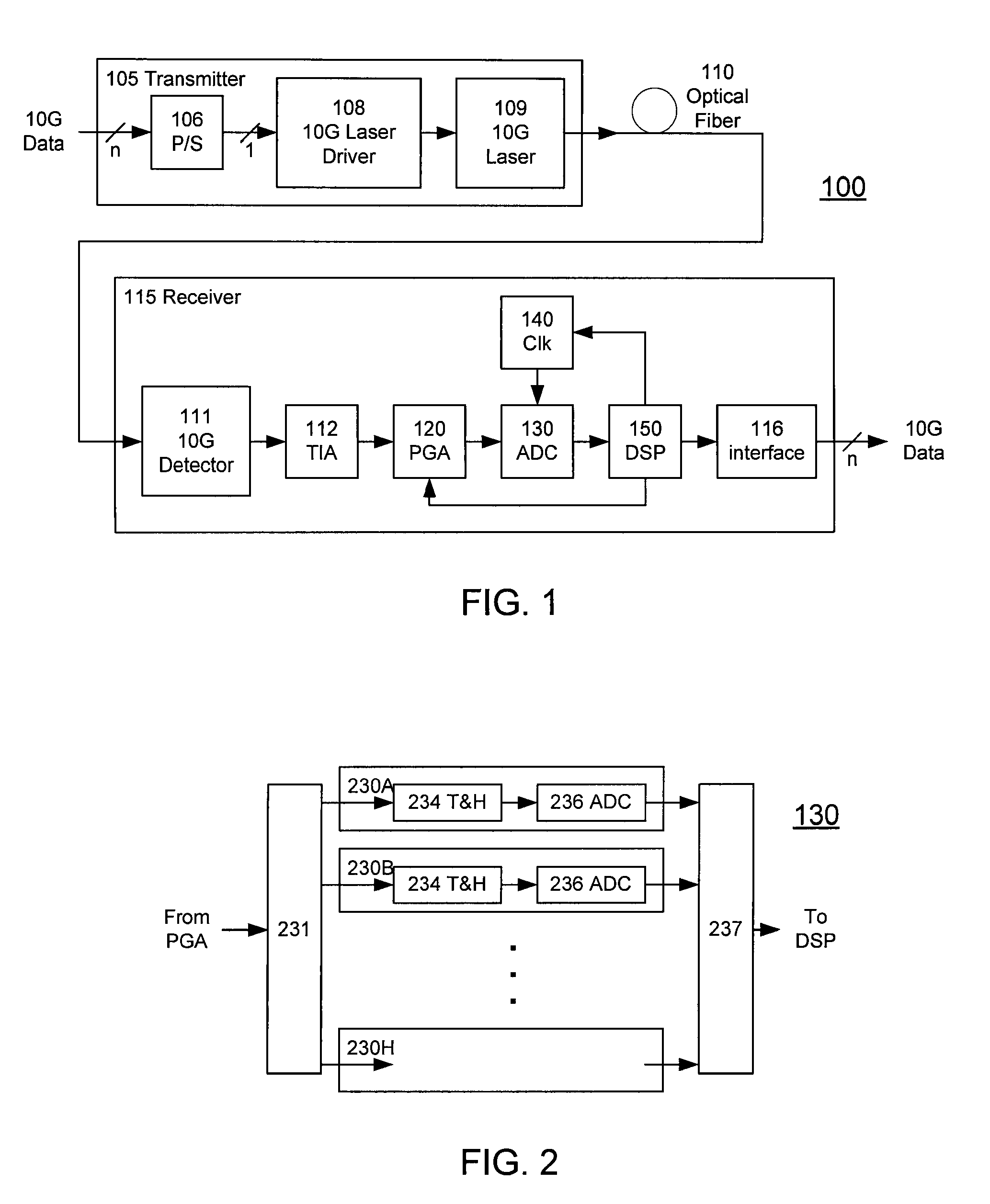
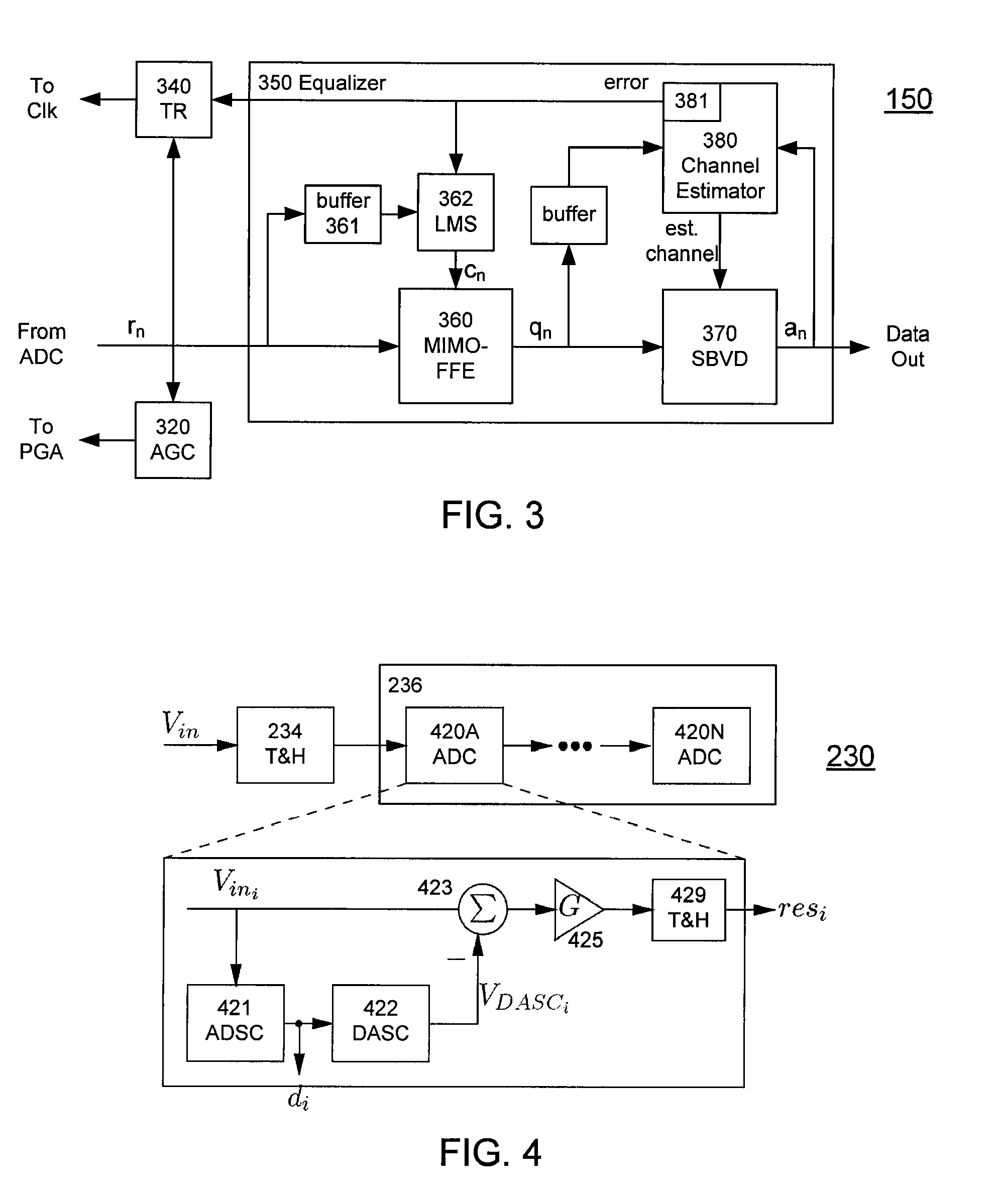
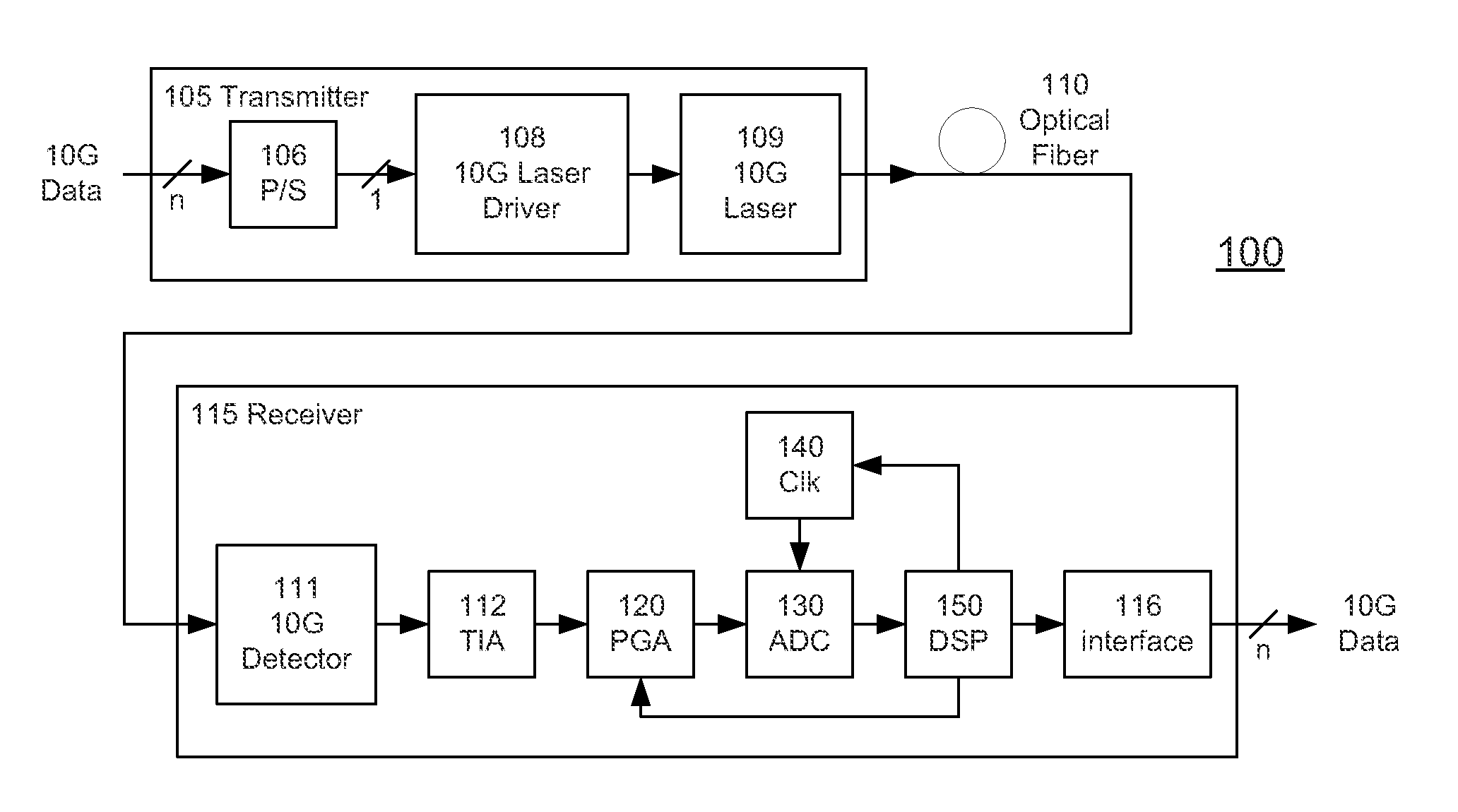
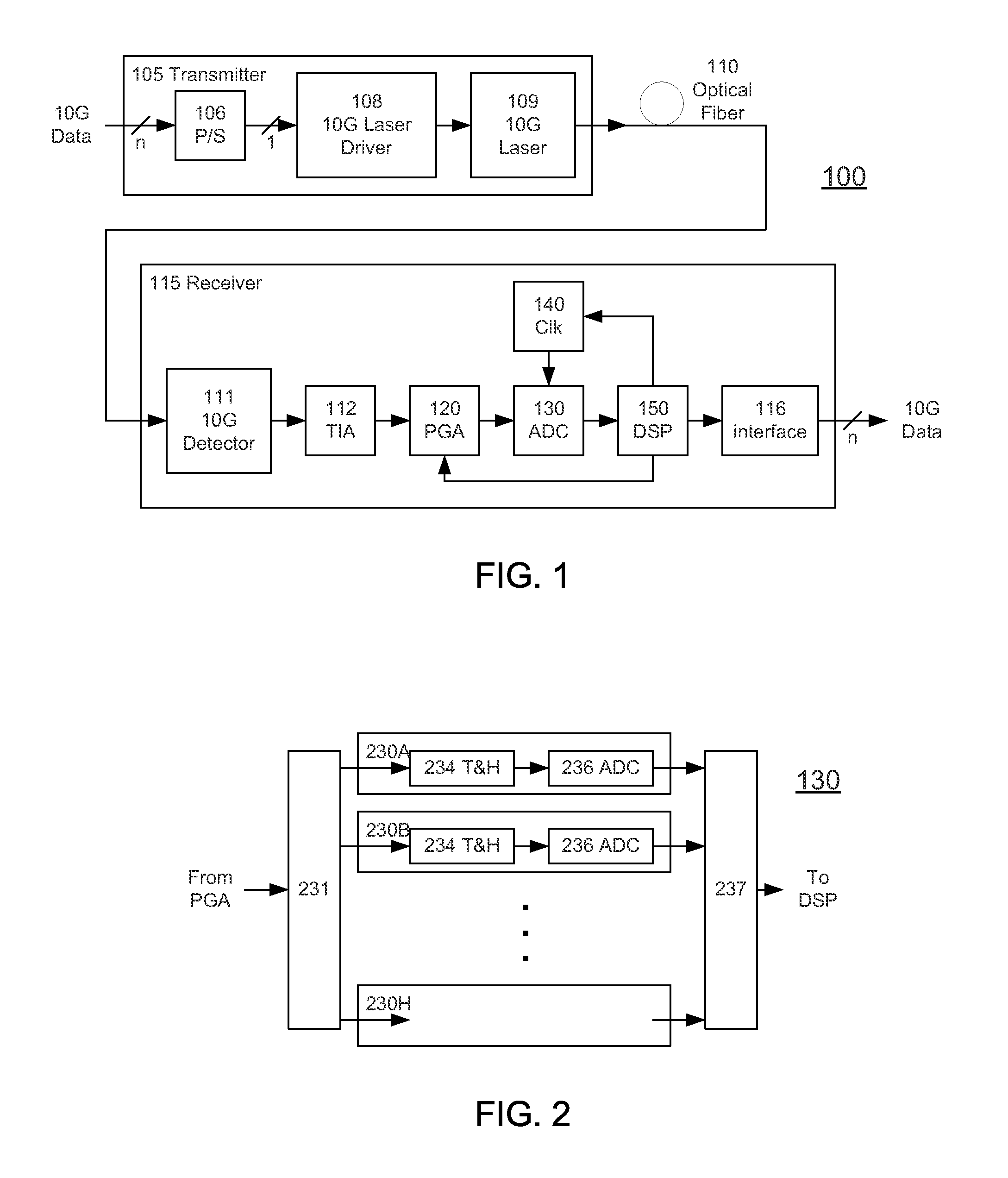
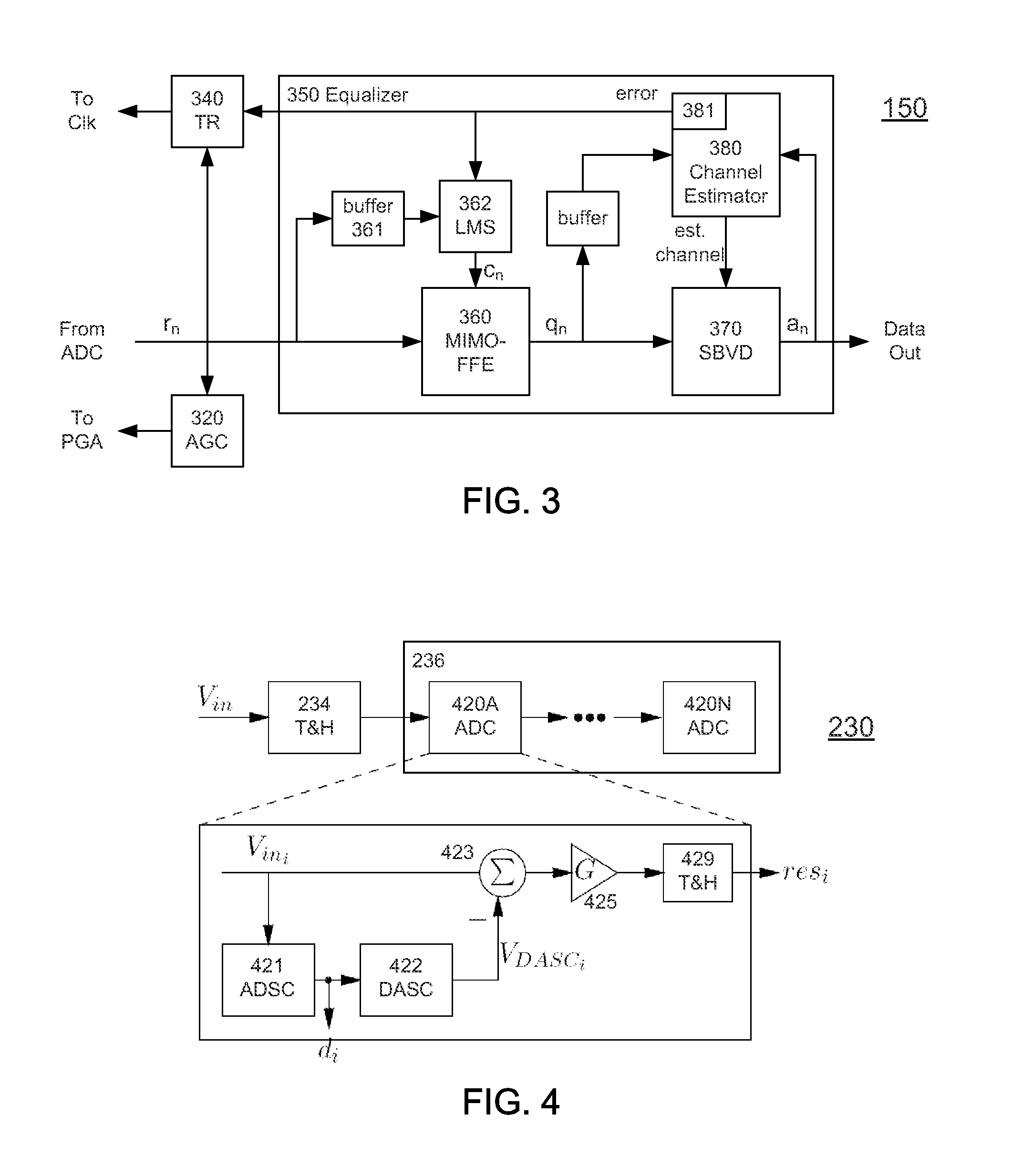
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
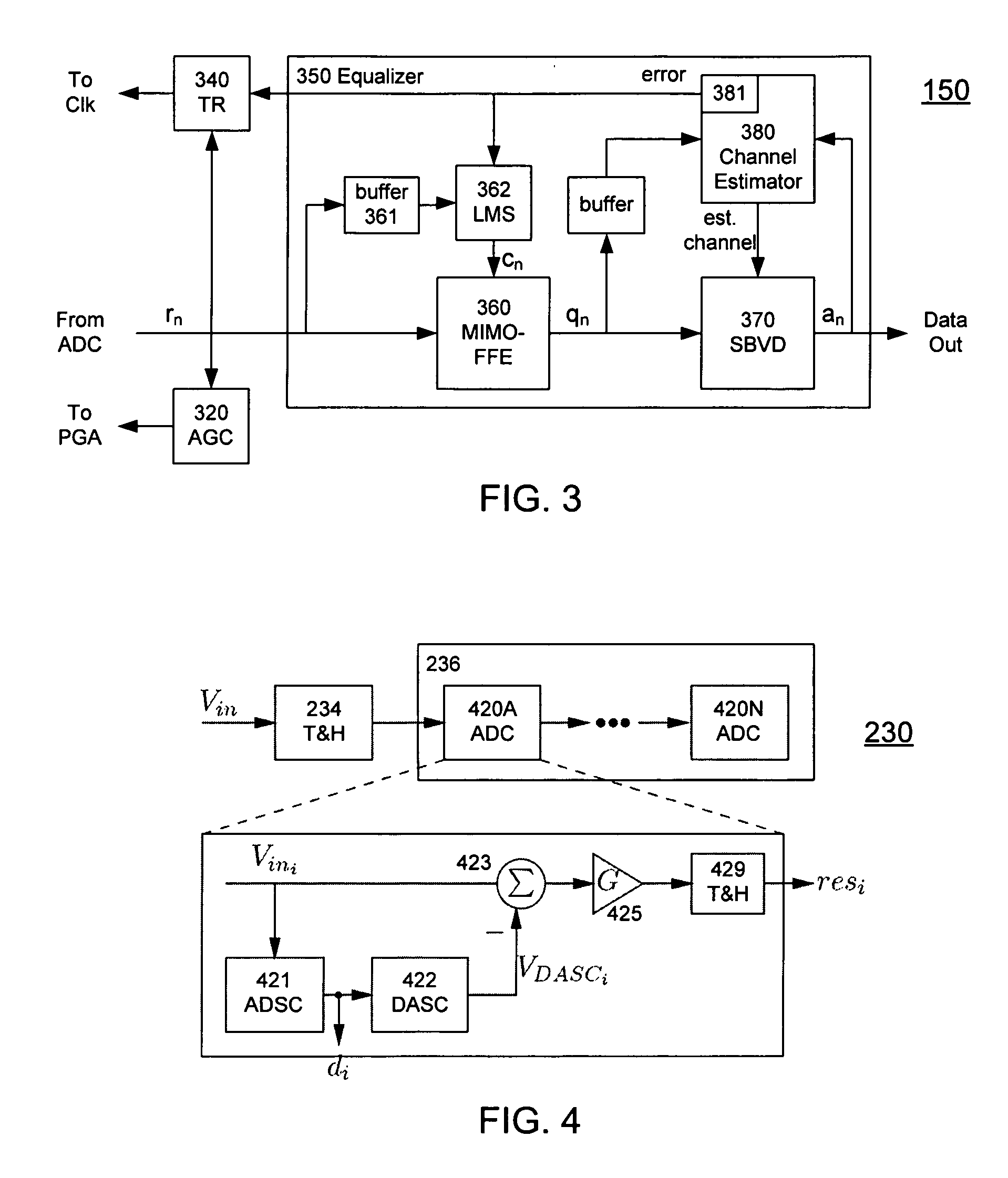
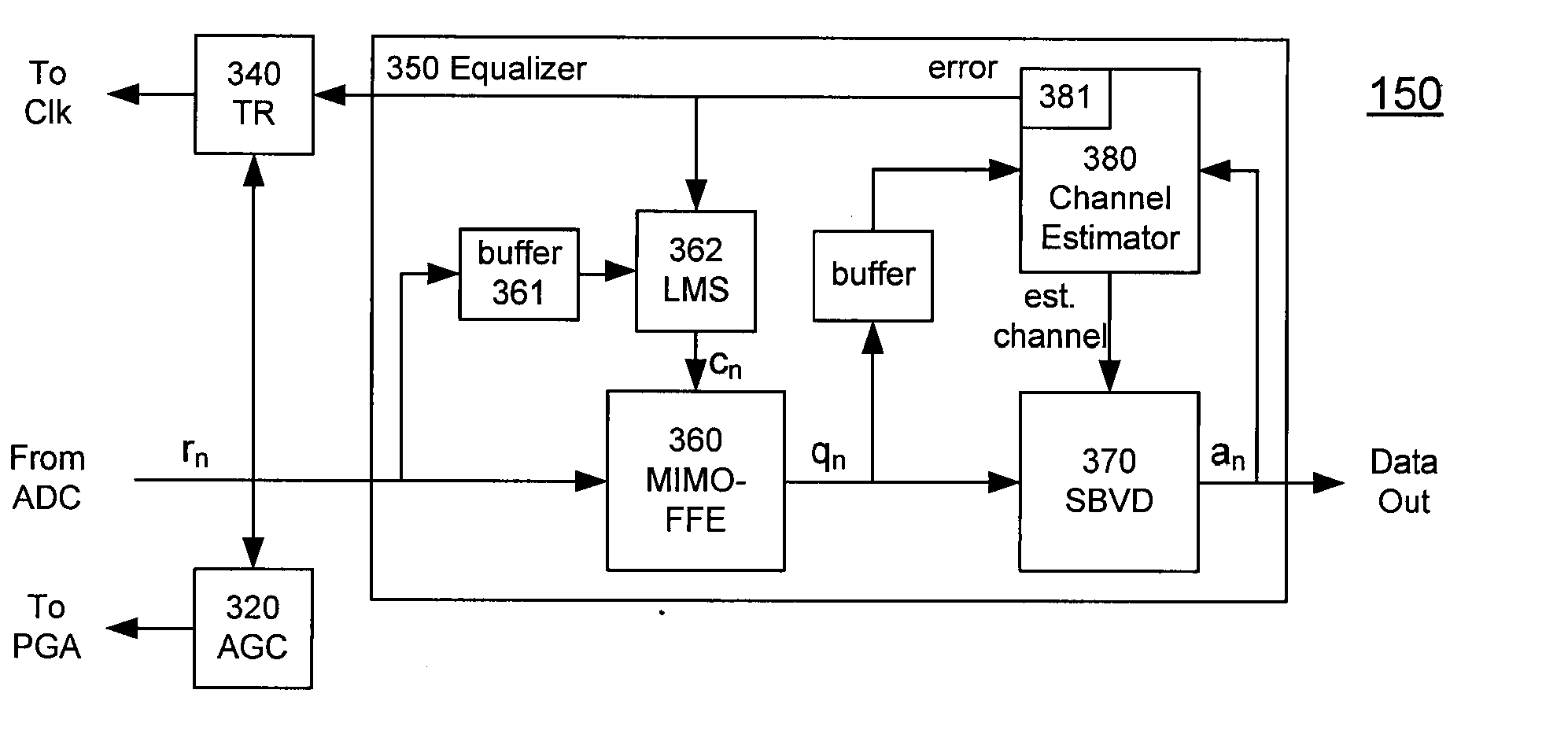
ActiveUS20080240325A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyAnalogue/digital conversionReceiver initialisationViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Fast computation of multi-input-multi-output decision feedback equalizer coefficients
InactiveUS7113540B2Lower requirementRapid productionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputOptimal decision
Multi-Input-Multi-Output (MIMO) Optimal Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) coefficients are determined from a channel estimate h by casting the MIMO DFE coefficient problem as a standard recursive least squares (RLS) problem and solving the RLS problem. In one embodiment, a fast recursive method, e.g., fast transversal filter (FTF) technique, then used to compute the Kalman gain of the RLS problem, which is then directly used to compute MIMO Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) coefficients gopt. The complexity of a conventional FTF algorithm is reduced to one third of its original complexity by choosing the length of a MIMO Feed Back Equalizer (FBE) coefficients bopt (of the DFE) to force the FTF algorithm to use a lower triangular matrix. The MIMO FBE coefficients bop are computed by convolving the MIMO FFE coefficients gopt with the channel impulse response h. In performing this operation, a convolution matrix that characterizes the channel impulse response h extended to a bigger circulant matrix. With the extended circulant matrix structure, the convolution of the MIMO FFE coefficients gopt with the channel impulse response h may be performed easily performed in the frequency domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Feedforward equalizer for DFE based detector
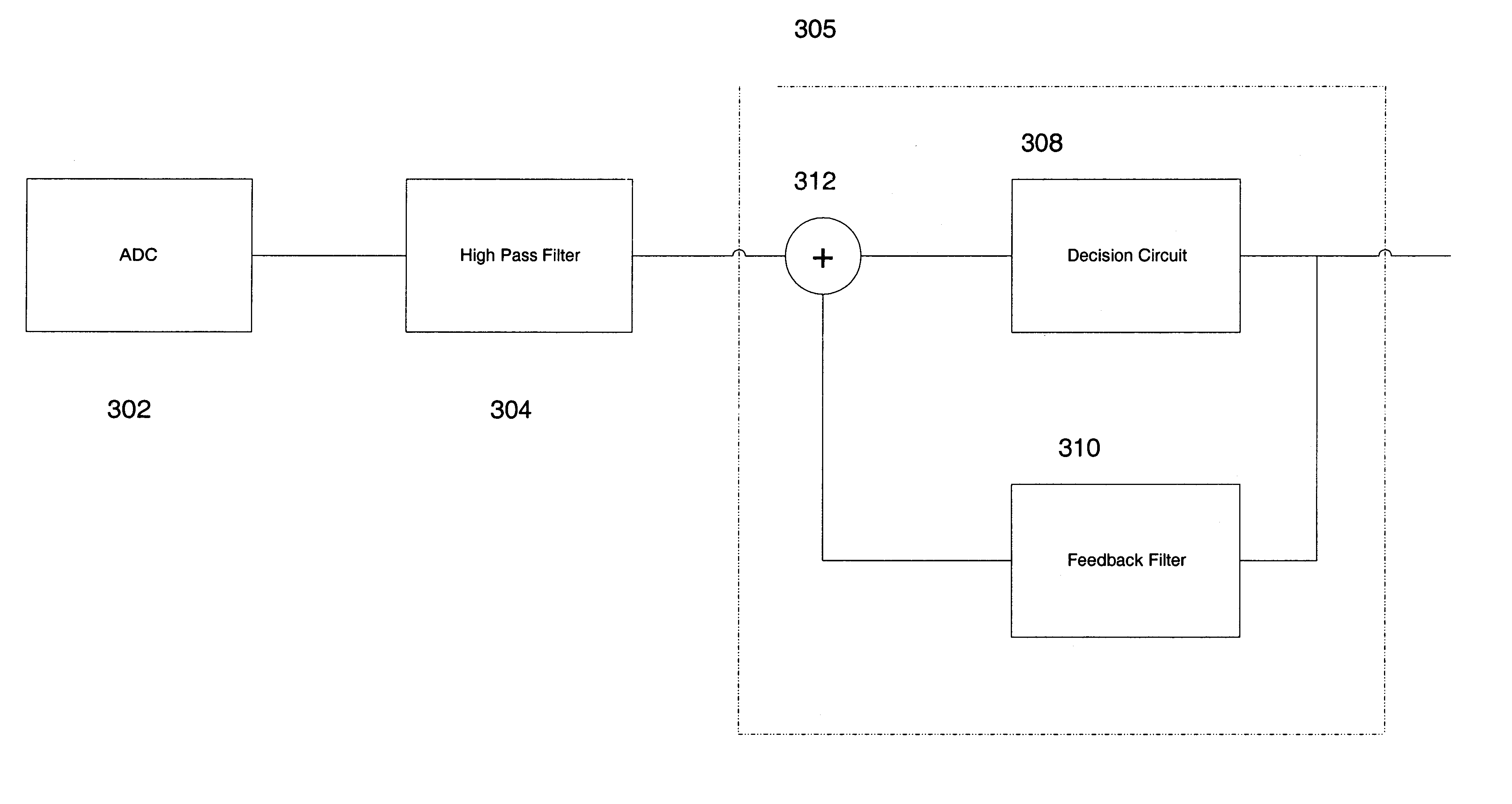
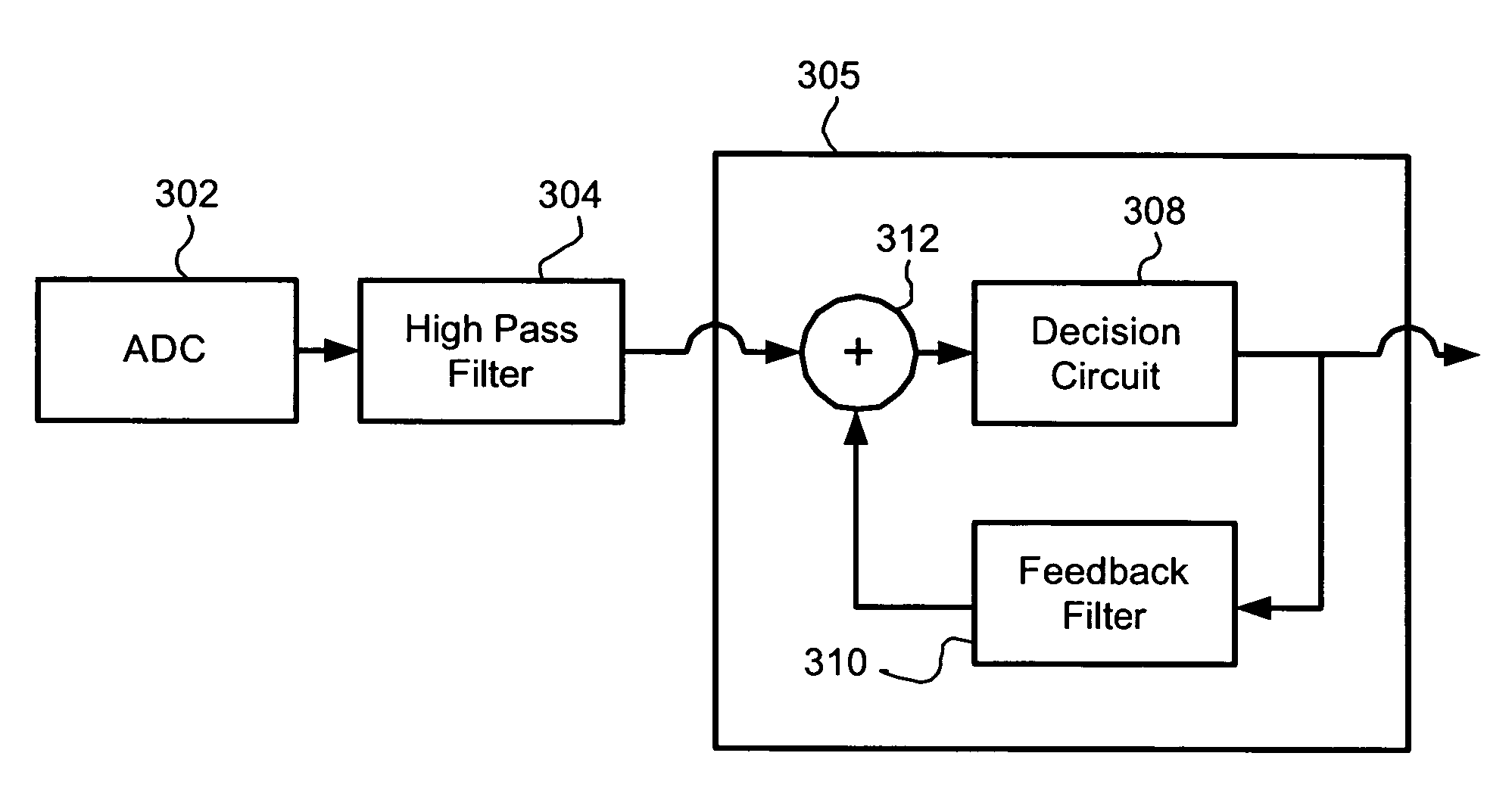
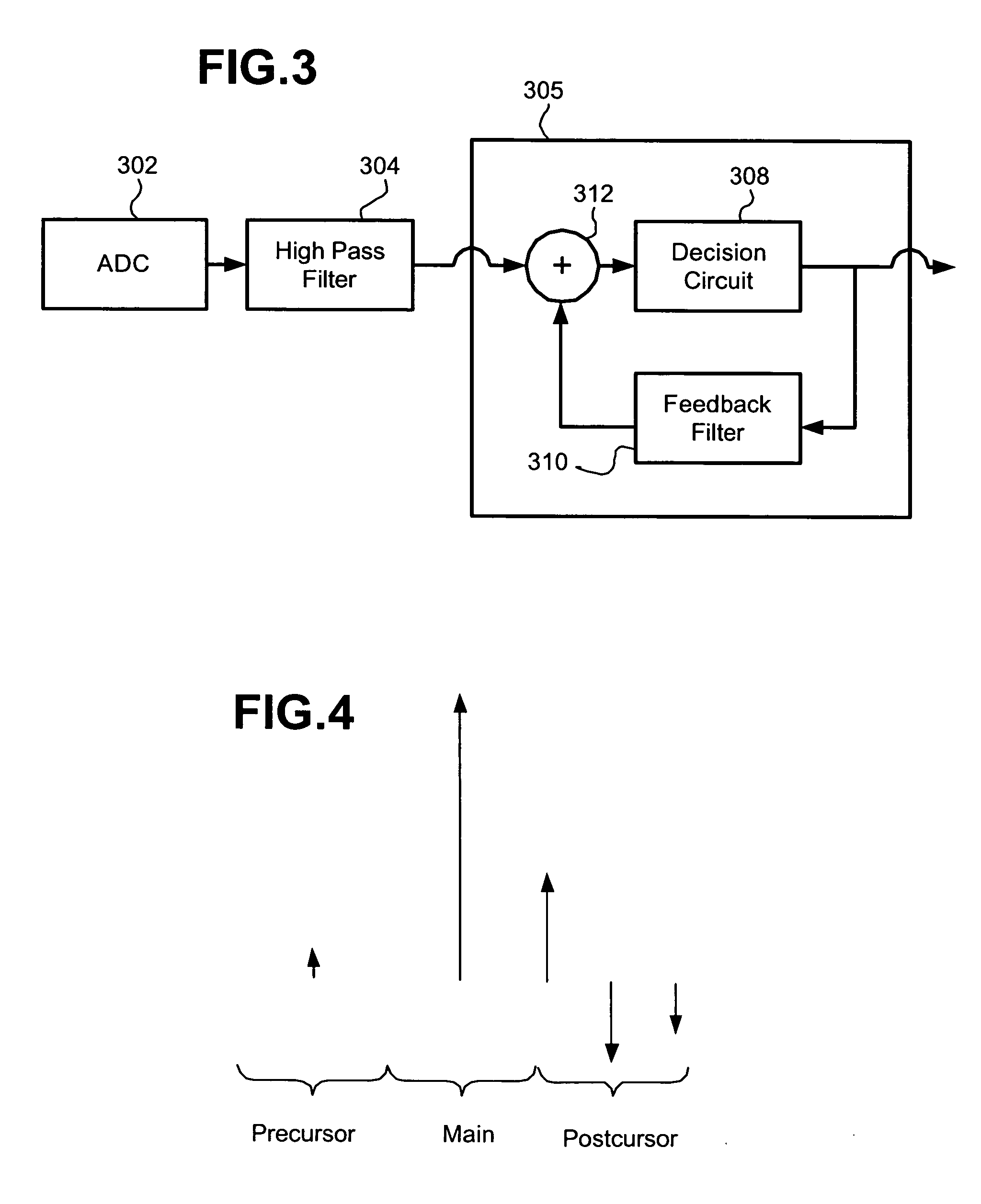
InactiveUS6870881B1Low cutoff frequencySpeed up the descentMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsDecision circuitAnalog signal
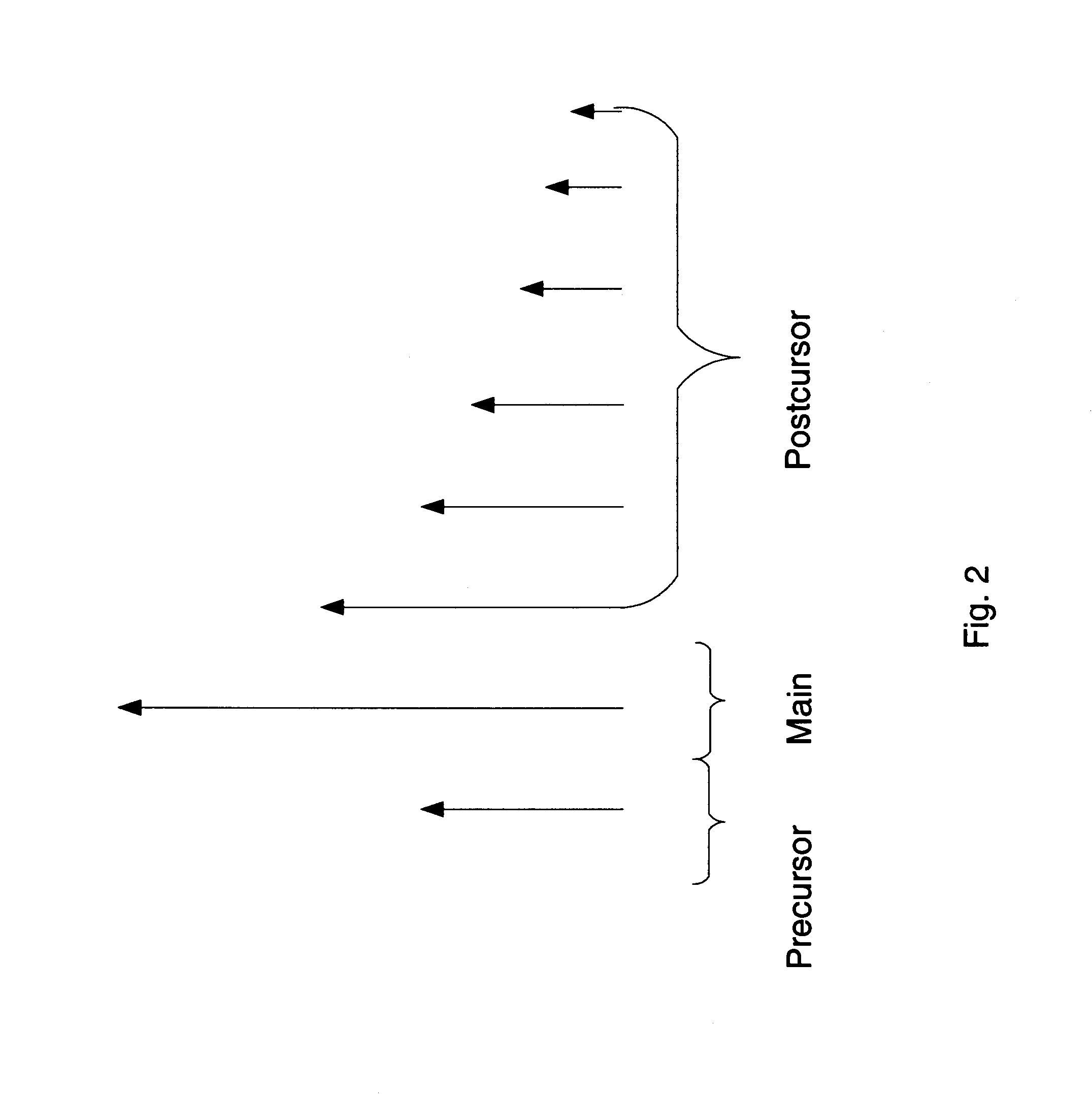
A feedforward equalizer for DFE based detector is provided comprising a digital to analog converter to convert an analog signal to a digital signal. A feedforward equalizer comprises a high-pass filter and is responsive to the input circuit. The high-pass filter has a low cutoff frequency, has a relatively flat response and has high attenuation at low frequencies. A decision feedback equalizer comprises a decision circuit responsive to the feedforward equalizer, and a feedback filter is responsive to the decision circuit. The decision circuit is also responsive to the feedback filter.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS20070133719A1Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderFiber
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
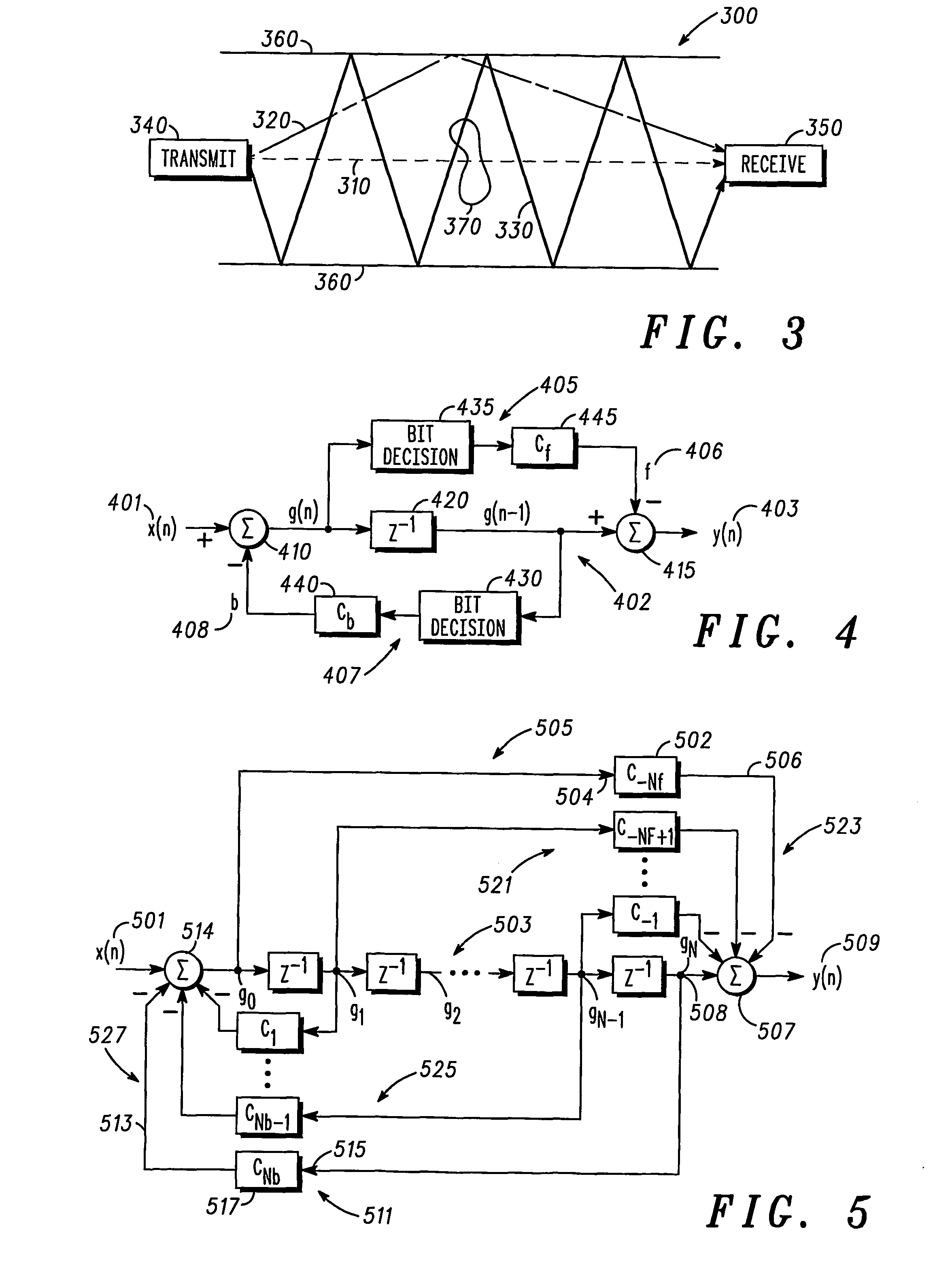
Decision feed forward equalizer system and method
An equalizer and corresponding methods is arranged and constructed to mitigate adverse effects of a wireless channel (300). The equalizer includes a delay line (503) coupled to an input signal (501) and comprising a delay circuit coupled to an output combiner (507) that is operable to provide an interim signal (g0 . . . gN) and a feed forward circuit (505) coupled to the delay line and operable to provide a feed forward signal (506) that comprises a hard decision scaled according to a scaling factor corresponding to an estimate of channel parameters, wherein the output combiner is operable to combine the feed forward signal and the interim signal to provide an output signal (509) that is compensated for an adverse effect of the wireless channel on the input signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20090185613A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Feedforward equalizer for DFE based detector
InactiveUS7426236B1Low cutoff frequencySpeed up the descentMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsDecision circuitEngineering
A signal processing apparatus includes an input circuit to receive an input signal, and a high-pass filter responsive to the input circuit. The high-pass filter includes M taps to filter precursor intersymbol interference (ISI), one main tap and N taps to filter postcursor ISI. Each of n taps of the N taps is limited to a range of between −1 and 0. The signal processing apparatus includes a decision feedback equalizer. The decision feedback equalizer includes a decision circuit responsive to the high-pass filter, and a feedback filter responsive to the decision circuit. The decision circuit is responsive to the feedback filter.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
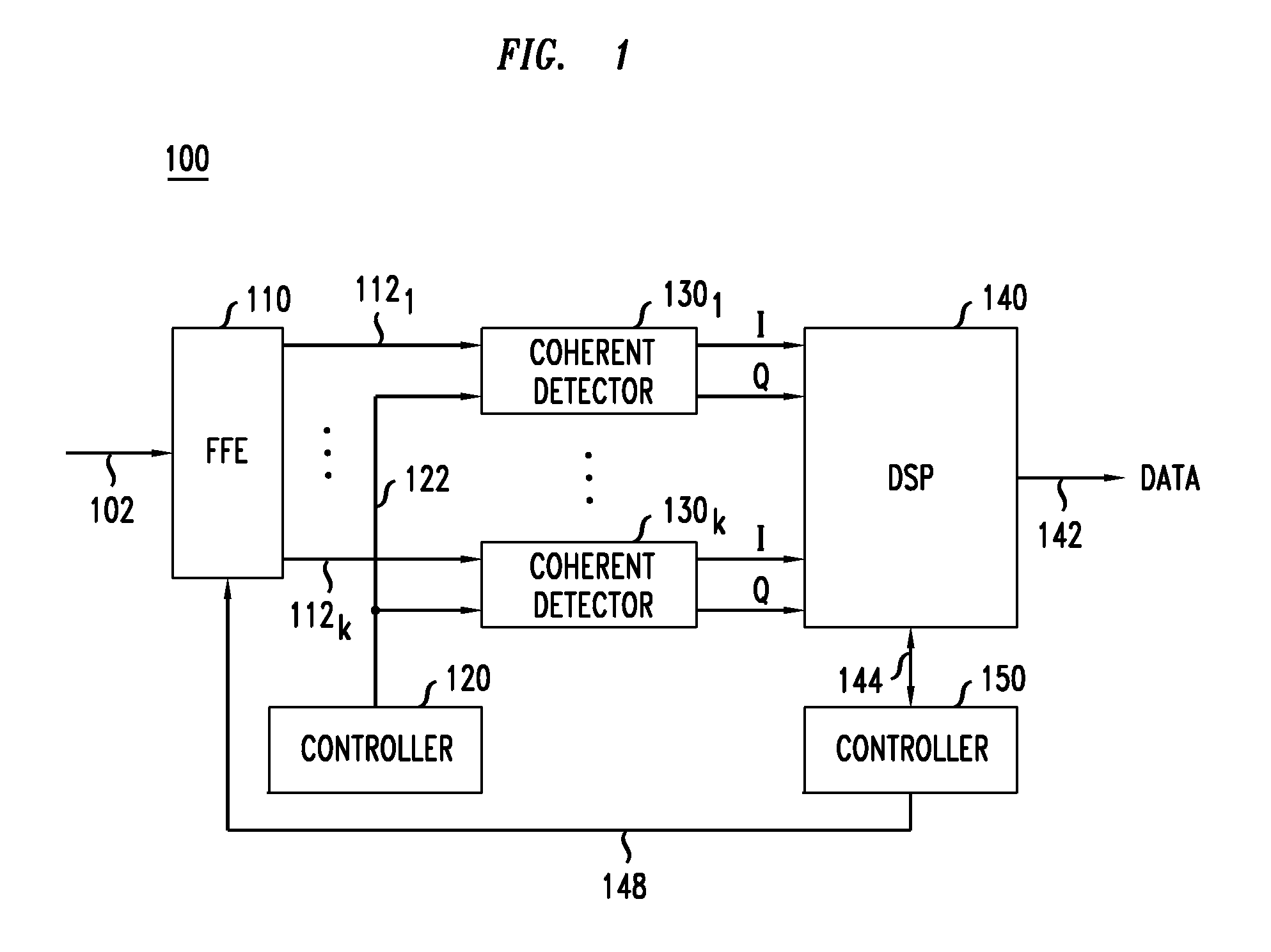
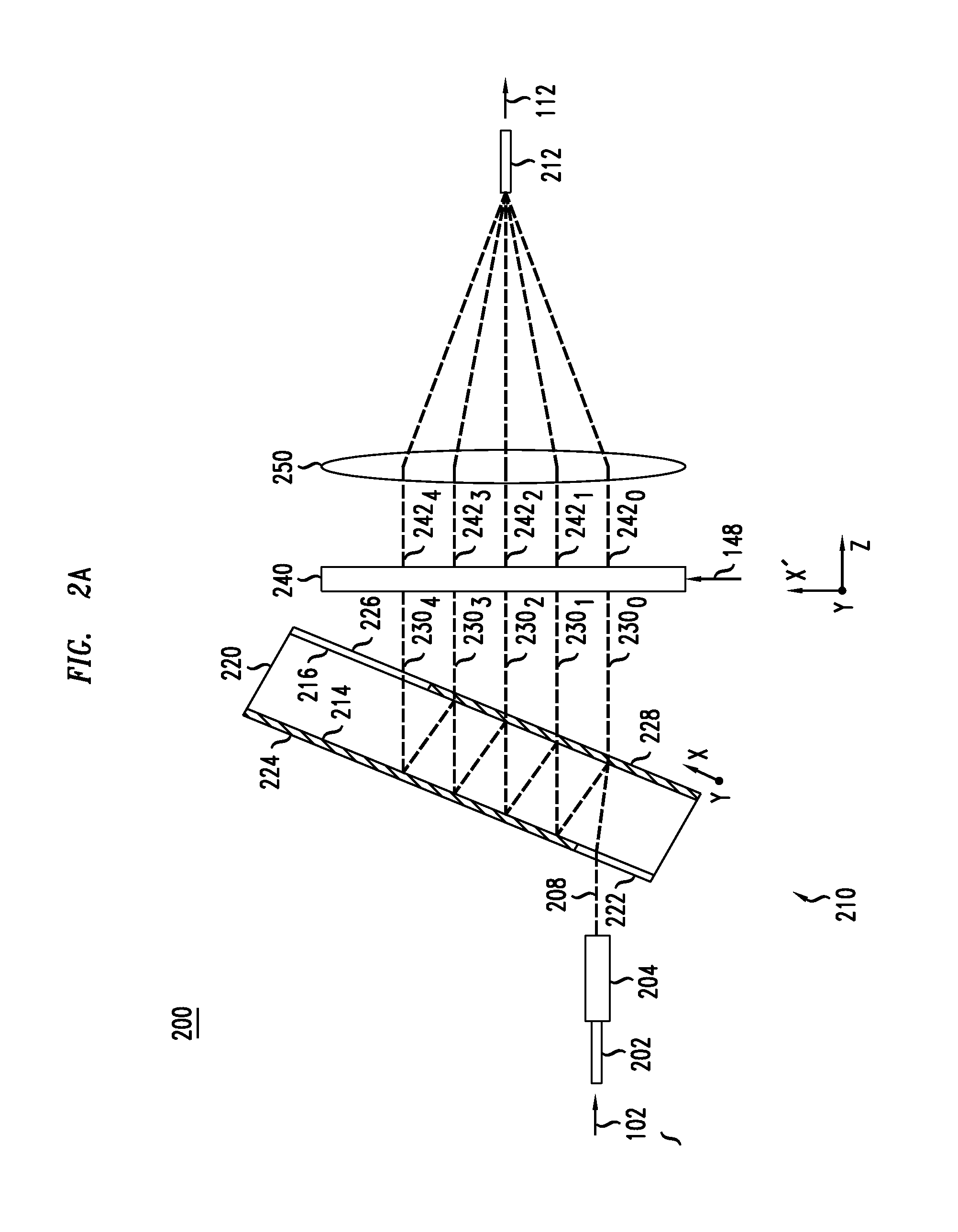
Optical feed-forward equalizer for MIMO signal processing
ActiveUS20130236195A1Reduce loadMeet cutting requirementsElectromagnetic receiversOptical light guidesSoftware engineeringLight signal
A feed-forward equalizer can be used in the host optical receiver to perform at least some of the desired signal processing in the optical domain, e.g., prior to coherently detecting and digitizing the received optical signal(s). In some embodiments, the signal processing implemented in the feed-forward equalizer can at least partially compensate the adverse effects of chromatic dispersion, polarization-mode dispersion, and / or spatial-mode mixing / crosstalk imparted on the received optical signal(s) in the optical transport link. This reduces the signal-processing load of and the signal-processing requirements to the receiver's electrical DSP.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
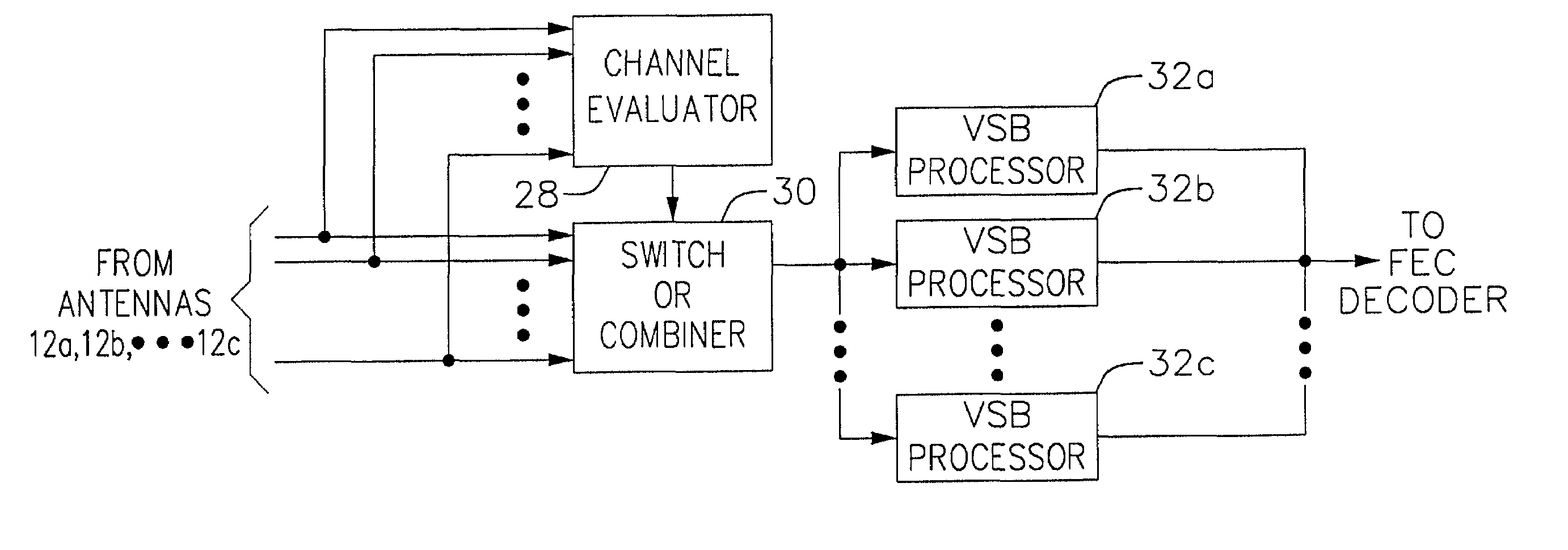
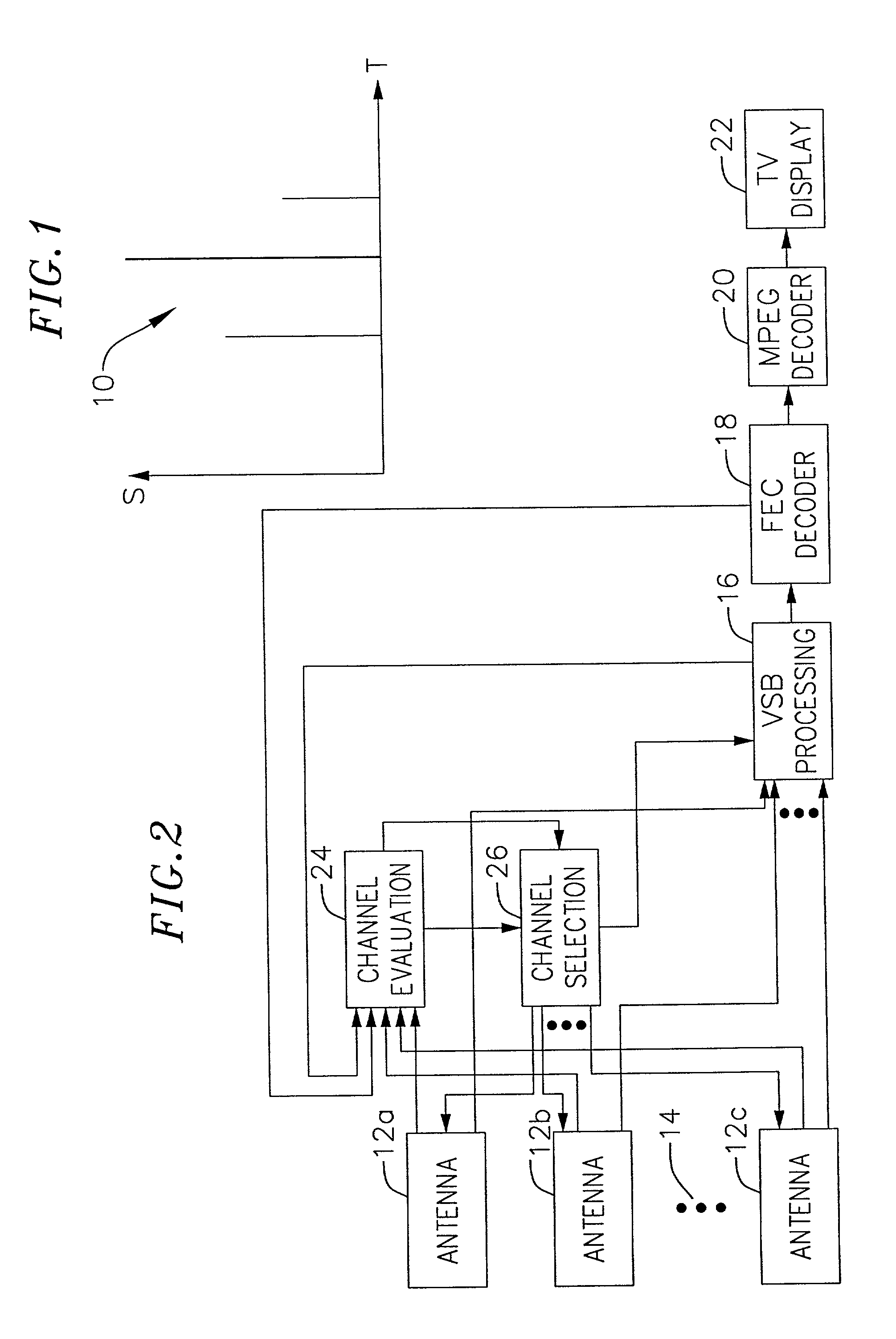
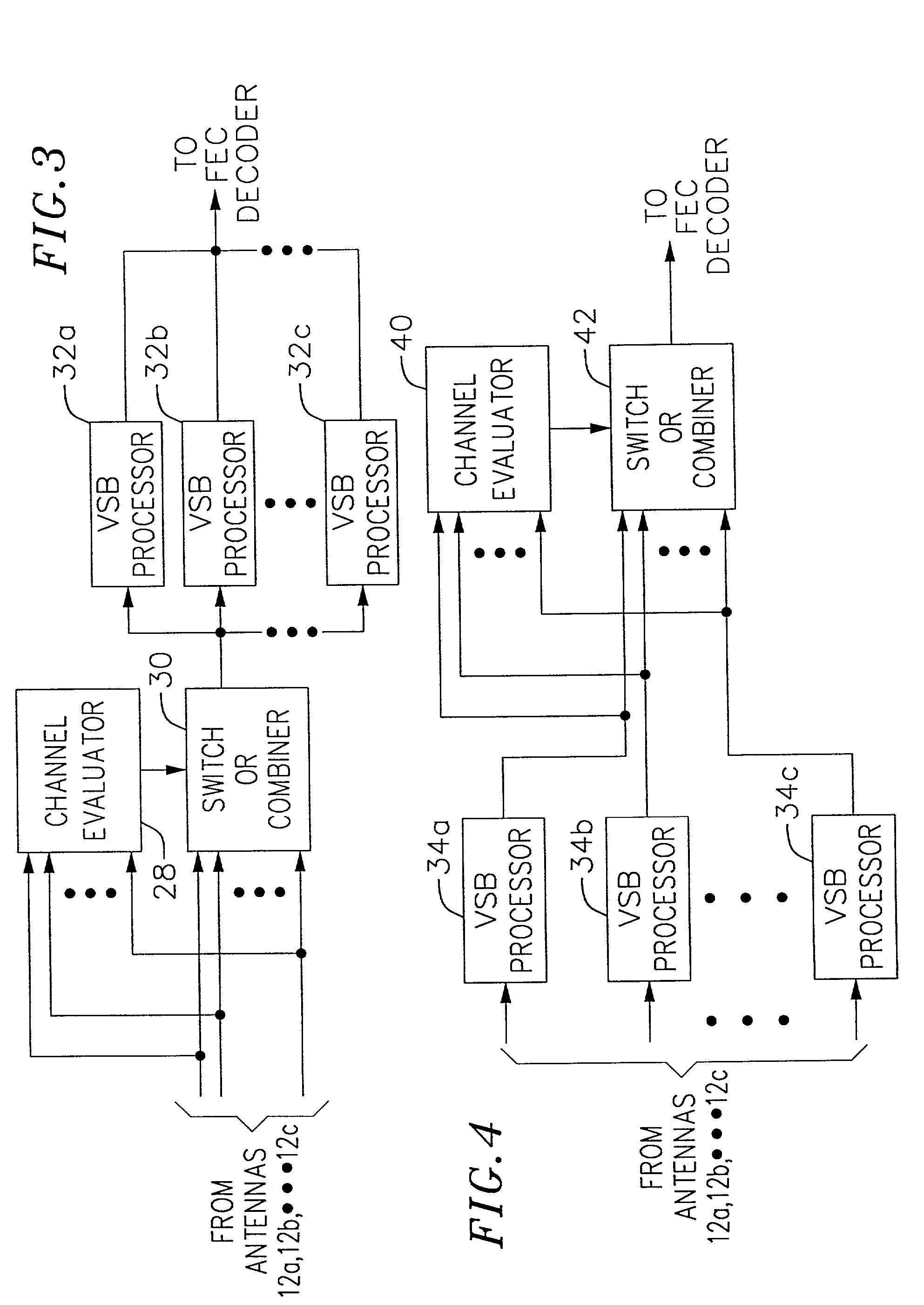
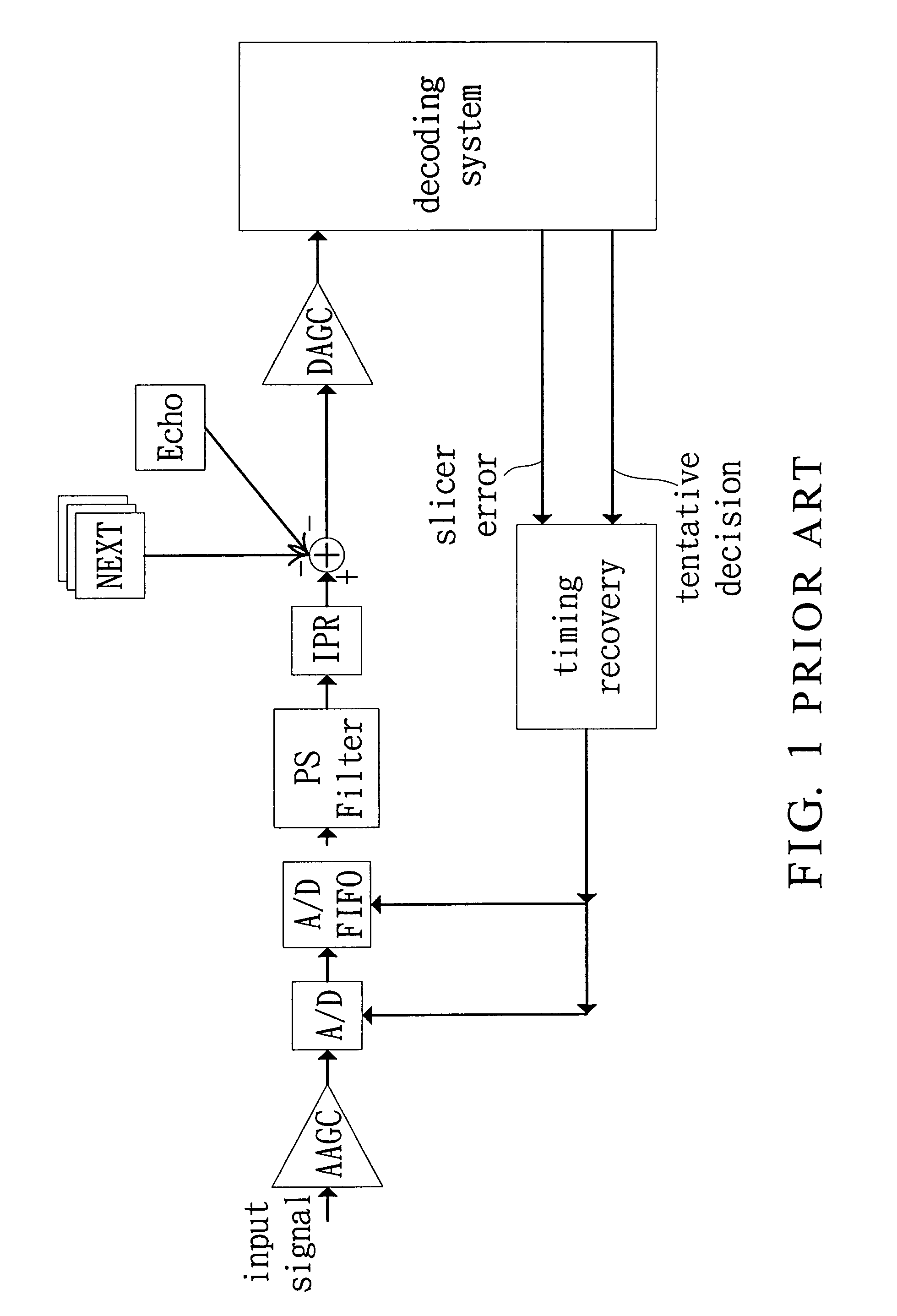
Method and apparatus for reception of terrestrial digital television signals
InactiveUS7034893B2Quality improvementTelevision system detailsError preventionForward error correctionSideband
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
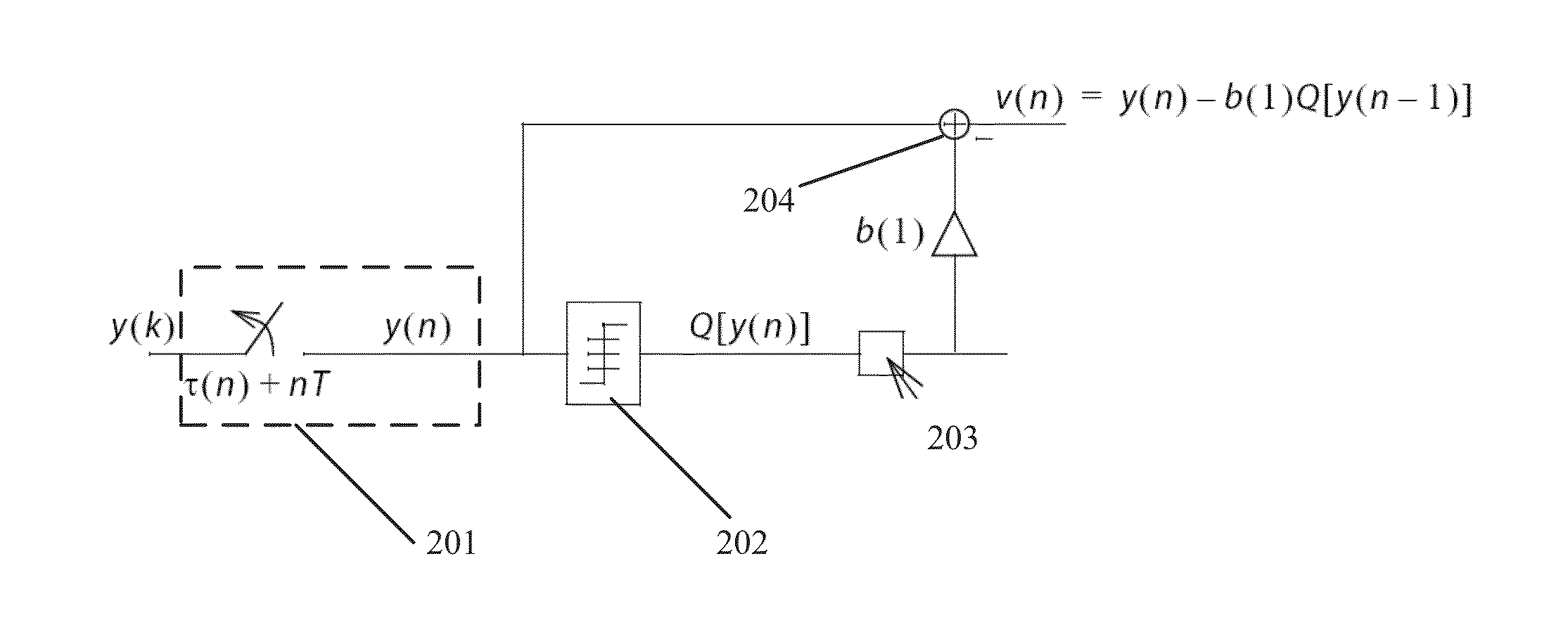
Decision feedforward equalization
InactiveUS20130243066A1Well formedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPathPingSoftware engineering
In described embodiments, a Decision Feed Forward Equalizer (DFFE) comprises a hybrid architecture combining features of a Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) and a Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE). An exemplary DFFE offers relatively improved noise and crosstalk immunity than an FFE implementation alone, and relatively lower burst error propagation than a DFE implementation alone. The exemplary DFFE is a relatively simple implementation due few or no critical feedback paths, as compared to a DFE implementation alone. The exemplary DFFE allows for a parallel implementation of its DFE elements without an exponential increase in the hardware for higher numbers of taps. The exemplary DFFE allows for cascading, allowing for progressive improvement in BER, at relatively low implementation cost as a solution to achieve multi-tap DFE performance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
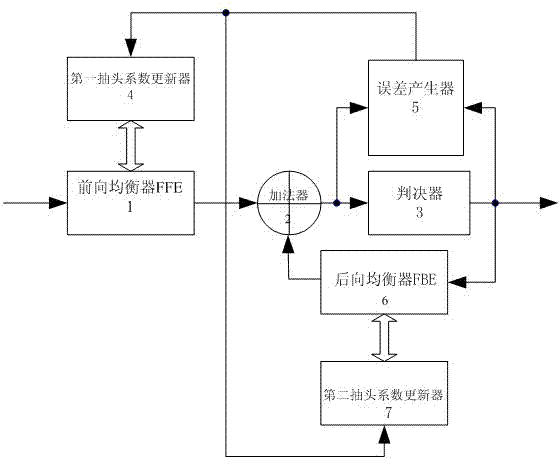
Adaptive equalizer of Bluetooth 4.0 low-power receiver and implementation method of adaptive equalizer
ActiveCN103401821AHighlight substantive featuresSignificant progressNear-field transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBluetoothSelf adaptive
The invention relates to an adaptive equalizer of BT4.0 (Bluetooth 4.0) low-power receiver and an implementation method of the adaptive equalizer. A feed-forward equalizer (FFE) is connected with a decision device by a summator; the output end of the decision device is connected with a feed-backward equalizer (FBE); the input end of an error generator is connected with the input end and the output end of the decision device; the output end of the error generator is connected with the input end of a first tap coefficient updater and the input end of a second tap coefficient updater; the output end of the first tap coefficient updater is connected with the FFE; the output end of the second tap coefficient updater is connected with the FBE; the output end of the FBE is connected with the summator. The optimization and the improvement are made in the aspects of eliminating ISI (inter symbol interference) and tolerating symbol timing phase errors, and the ascertained ISI introduced by originating is eliminated by using a decision feedback equalizer of symbol intervals, and therefore, PER can be favorably reduced by a BT 4.0 signal receiving end, and the stability of the receiver is improved.
Owner:ARKMICRO TECH
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS7852913B2Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderFiber
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Equalizer circuit, data transmission system and equalization method
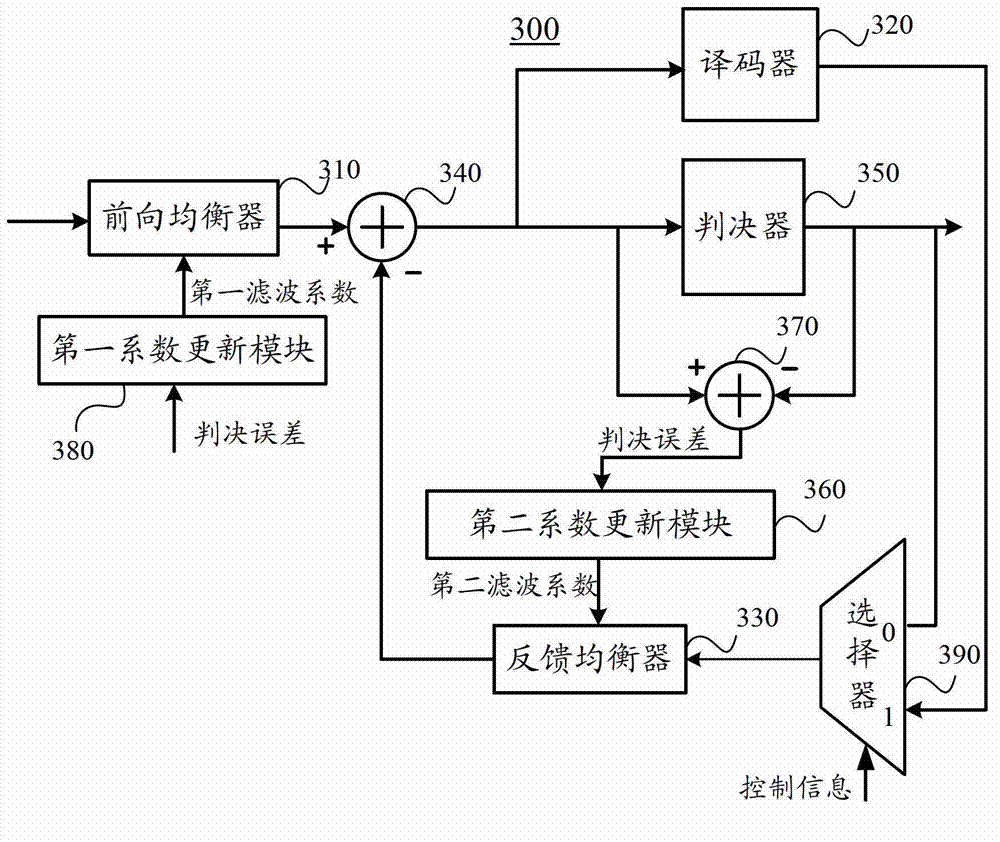
ActiveCN102882817AEliminate distractionsNo error deliveryTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime lagEqualization
The invention provides an equalizer circuit, a data transmission system and an equalization method. The equalizer circuit comprises a first adder, a decoder and a decision feedback equalizer, wherein the first adder receives a feedback signal and first input data which are output by a feed forward equalizer circuit, and is used for adding the first input data and the feedback signal to acquire an equalization output result; the decoder receives the equalization output result, and is used for decoding the equalization output result to acquire a decoding result; and the decision feedback equalizer receives the decoding result, and is used for filtering the decoding result on the basis of a first filter coefficient to acquire the feedback signal and outputs the feedback signal to the first adder, so that time-lag inter-symbol interference is eliminated. By the circuit, the system and the method, the decision feedback equalizer for filtering the output of a decision device to eliminate the inter-symbol interference is eliminated, so that error propagation can be avoided in the decision feedback equalizer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Timing recovery method and device for combining pre-filtering and feed-forward equalizing functions
InactiveUS20050249275A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsRecovery methodCommunications system
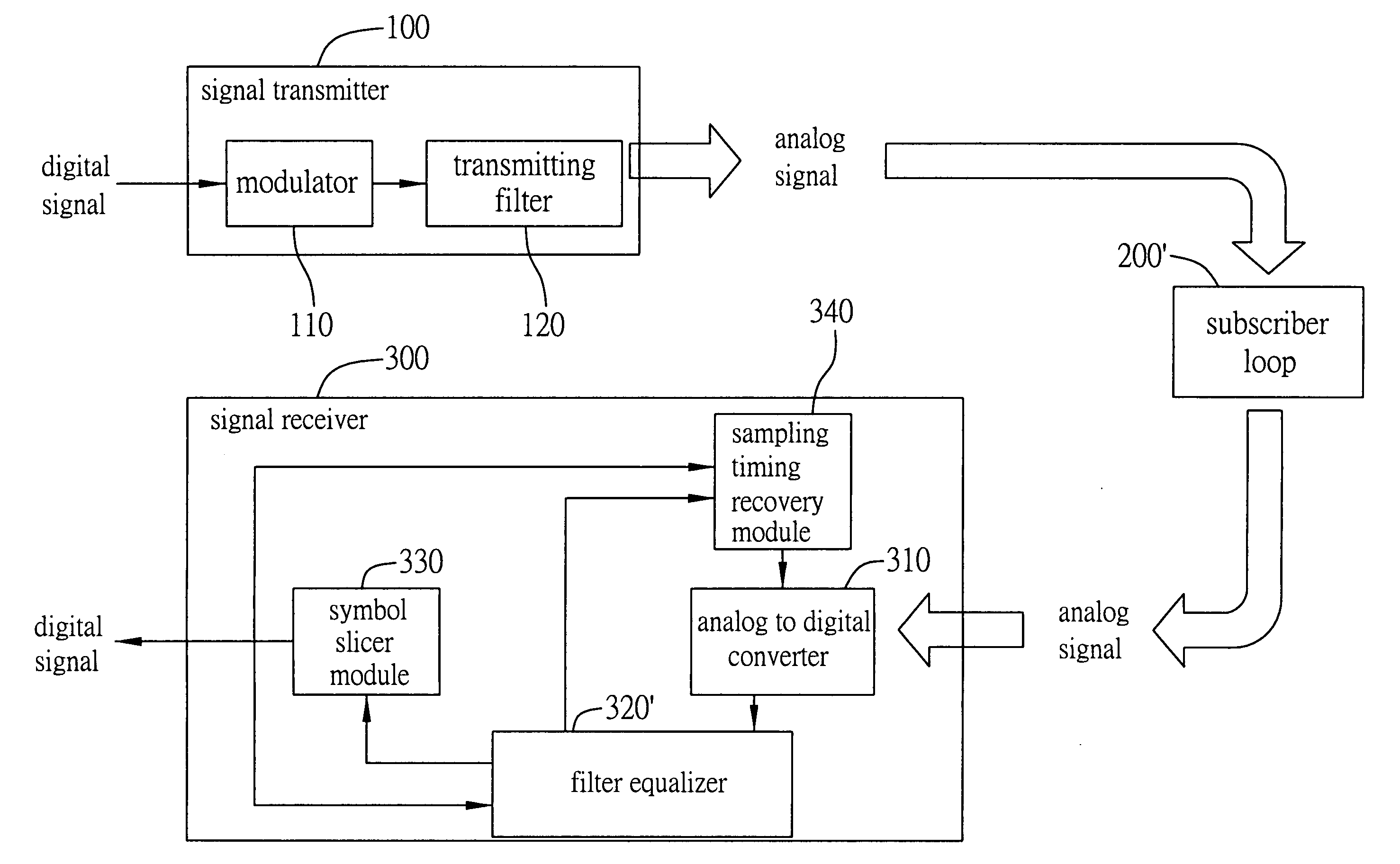
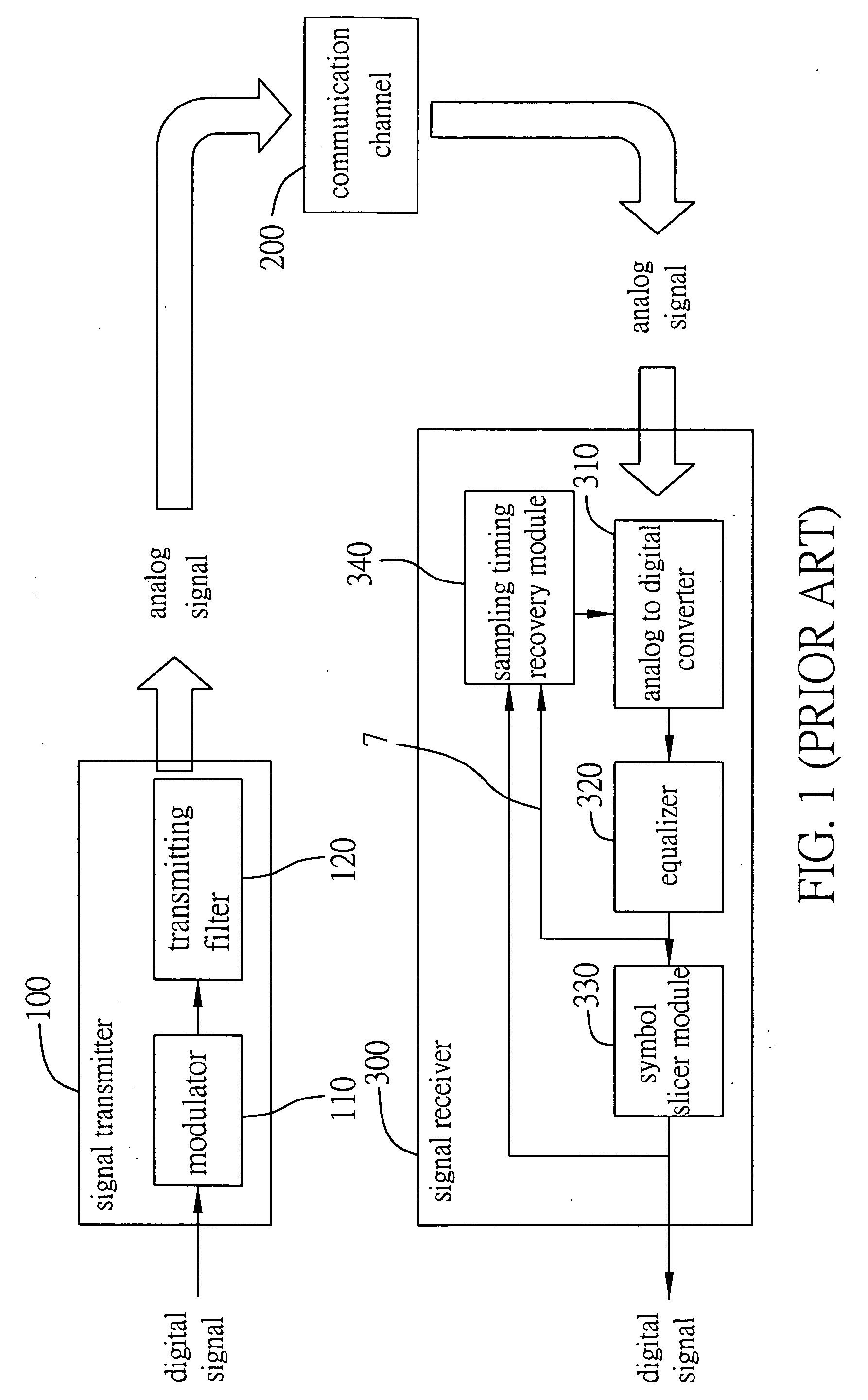
Timing recovery method and device for combining pre-filtering and feed-forward equalizer functions are proposed and used in a digital communication system. A signal receiver is provided to receive a signal transmitted from a signal transmitter in the communication system, and recovers a sampling clock phase of the received signal to the phase of the signal transmitted from the signal transmitter. The method is used to control the signal receiver to transform the received signal to a signal similar to a Nyquist pulse after the pre-filtering and feed-forward equalizing operations are performed on the received signal, thereby improving the performance of the following sampling timing recovery process and increasing the signal noise ratio (SNR) of the received signal.
Owner:RDC SEMICON CO LTD
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20110211842A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyOther decoding techniquesTransmission control/equalisingFiberViterbi decoder
A receiver (e.g., for a 10G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
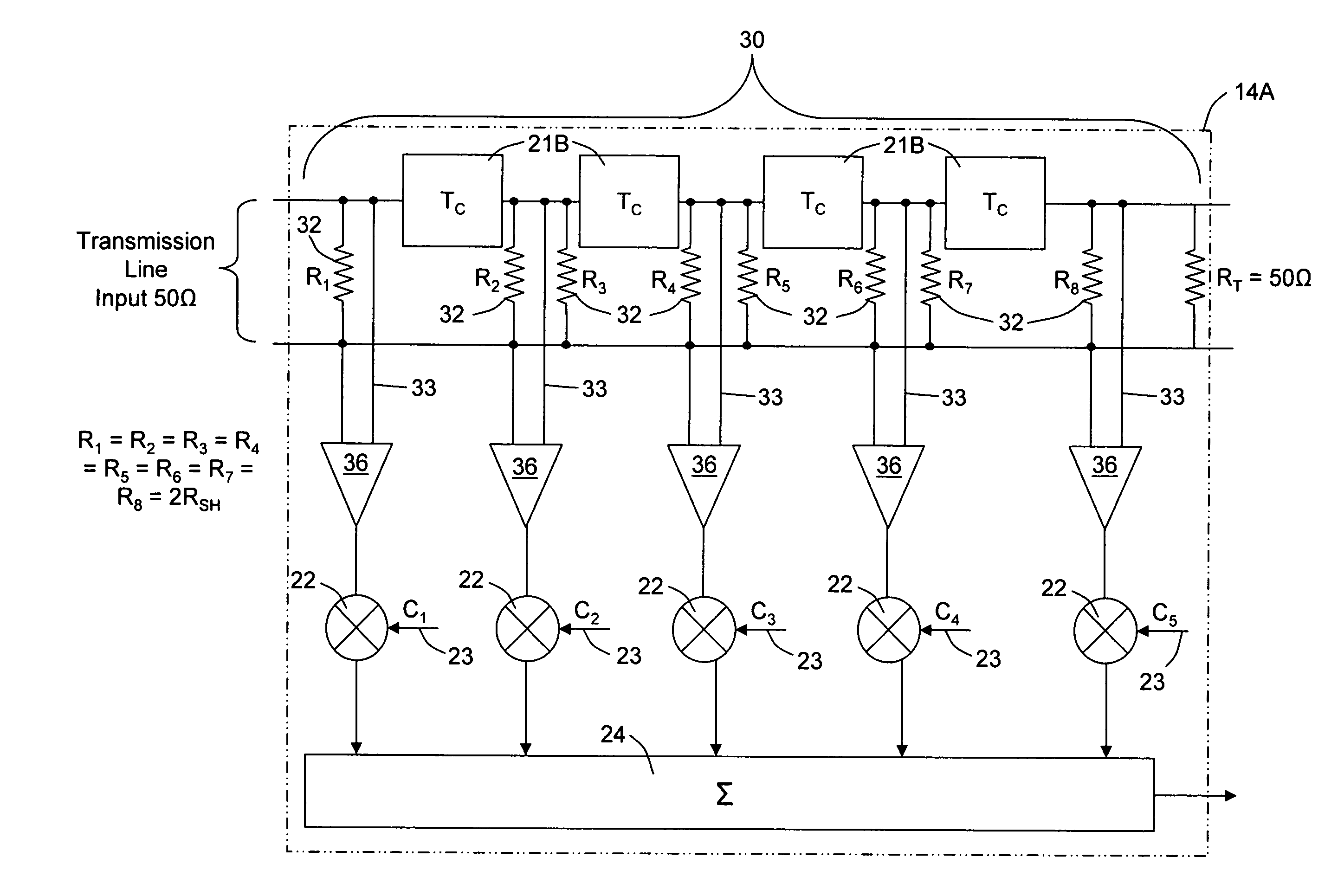
Transmission line with low dispersive properties and its application in equalization
ActiveUS7446622B2Transmission control/equlisationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksElectrical resistance and conductanceAnalog delay line
A transmission line is provided with added shunt resistance, RSH, distributed along the length of the micro transmission line permitting the extension of constant characteristic impedance to the transmission line to lower signal frequencies. The loss in gain to the signal propagating the transmission line due to the added resistance can be compensated for by amplification provided at the output of the transmission line or at output taps provided along the length of the transmission line such as in cases where the line is utilized as a circuit delay line. An exemplified application disclosed is an analog delay line formed as a metal microstrip in an IC chip circuit provided, for example, in a feed forward equalizer (FFE).
Owner:INFINERA CORP
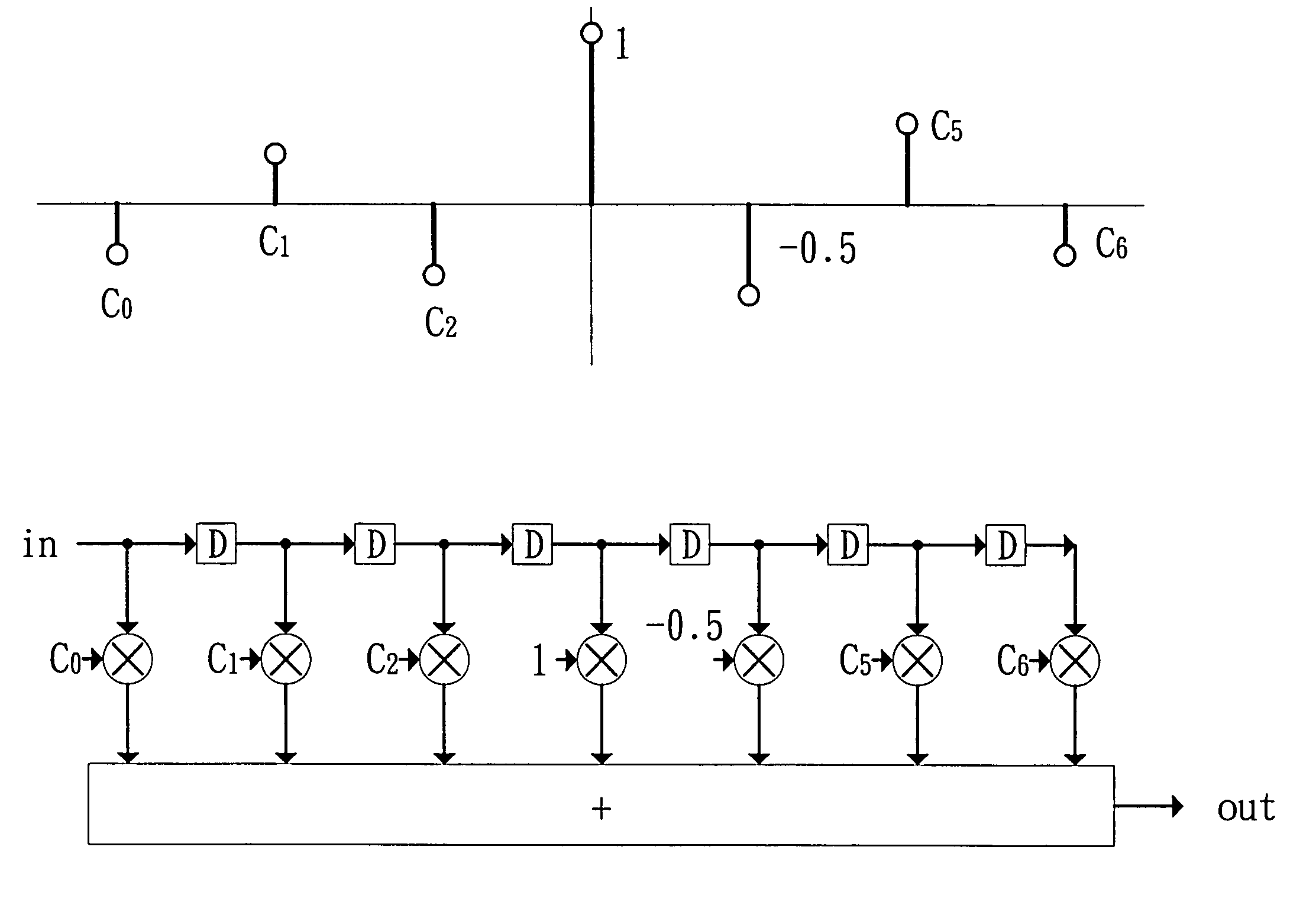
Sparse and reconfigurable floating tap feed forward equalization
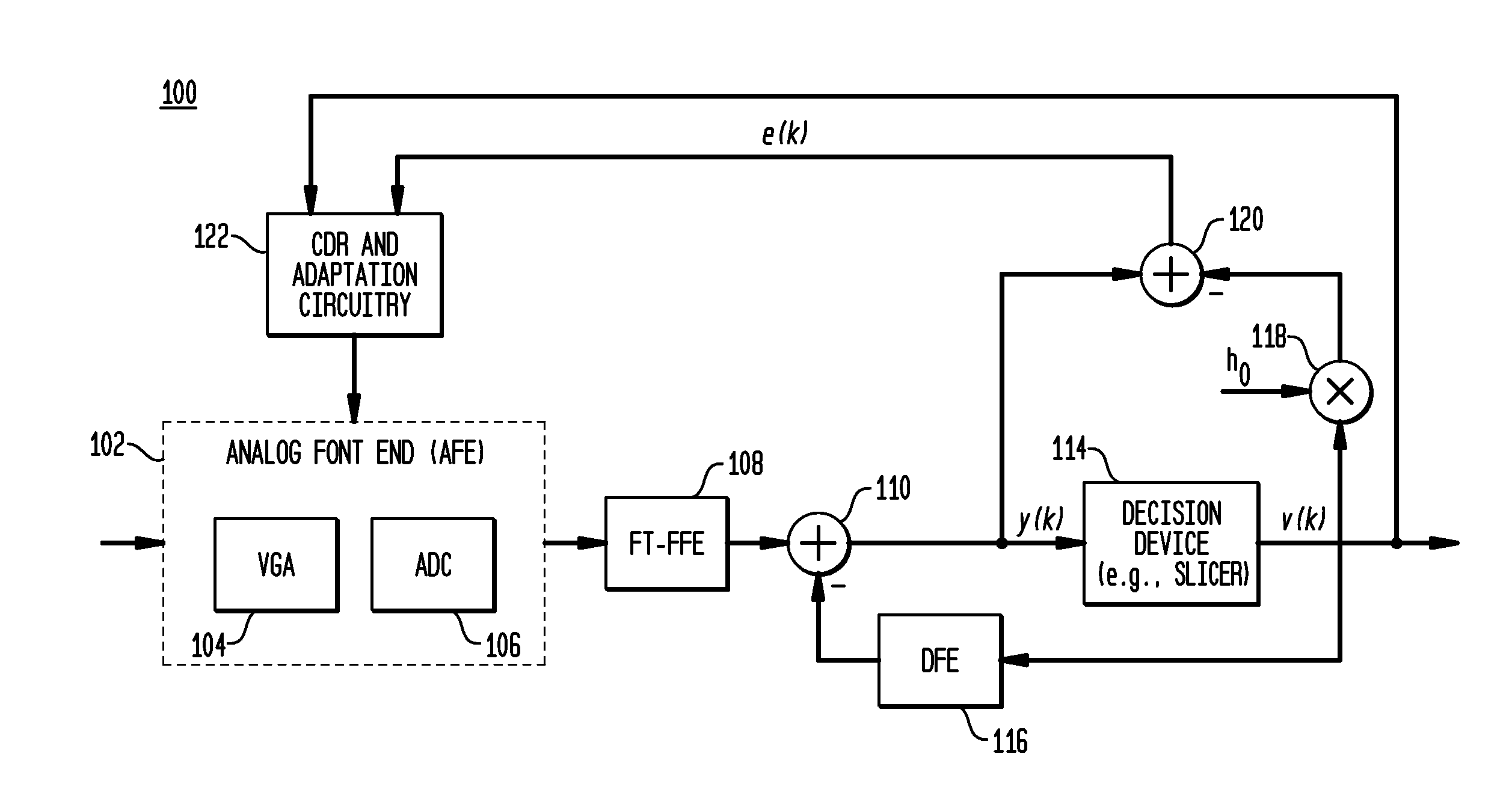
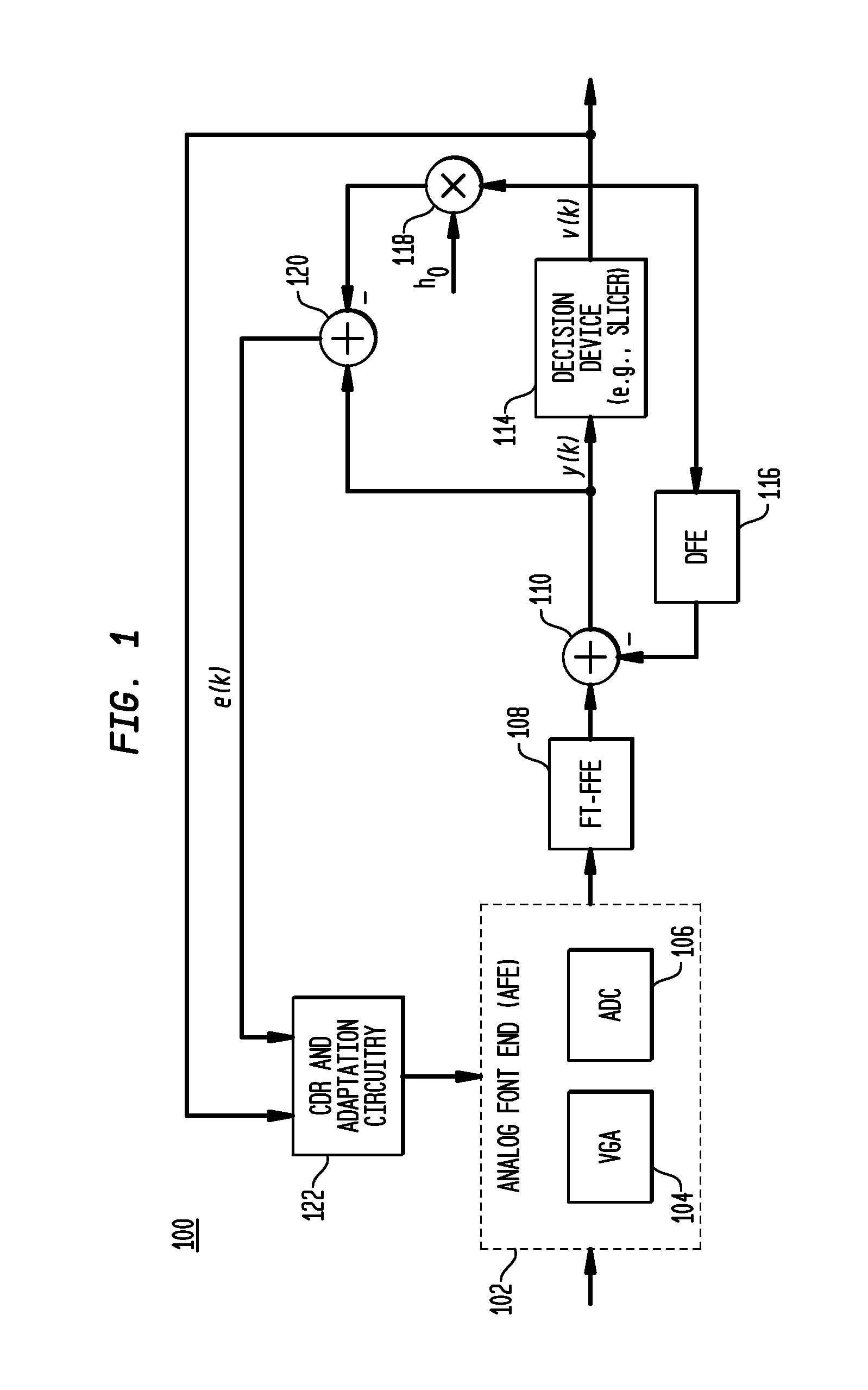
In described embodiments, a Floating Tap, Feed Forward Equalizer (FT-FFE) achieves performance comparable to a full size, long FFE when equalizing wire line channels in, for example, SerDes receivers. A FT-FFE might be employed as a standalone datapath equalizer, or might be employed in conjunction with other equalization techniques.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Novel high-speed serial interface transmitter
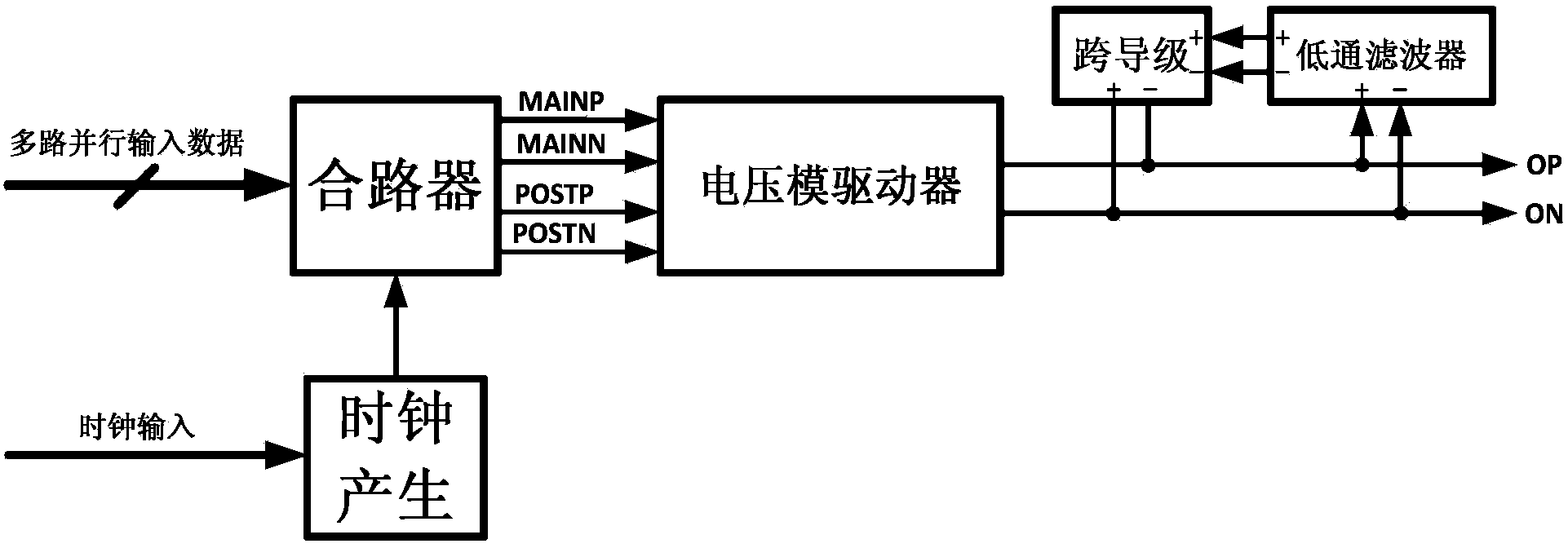
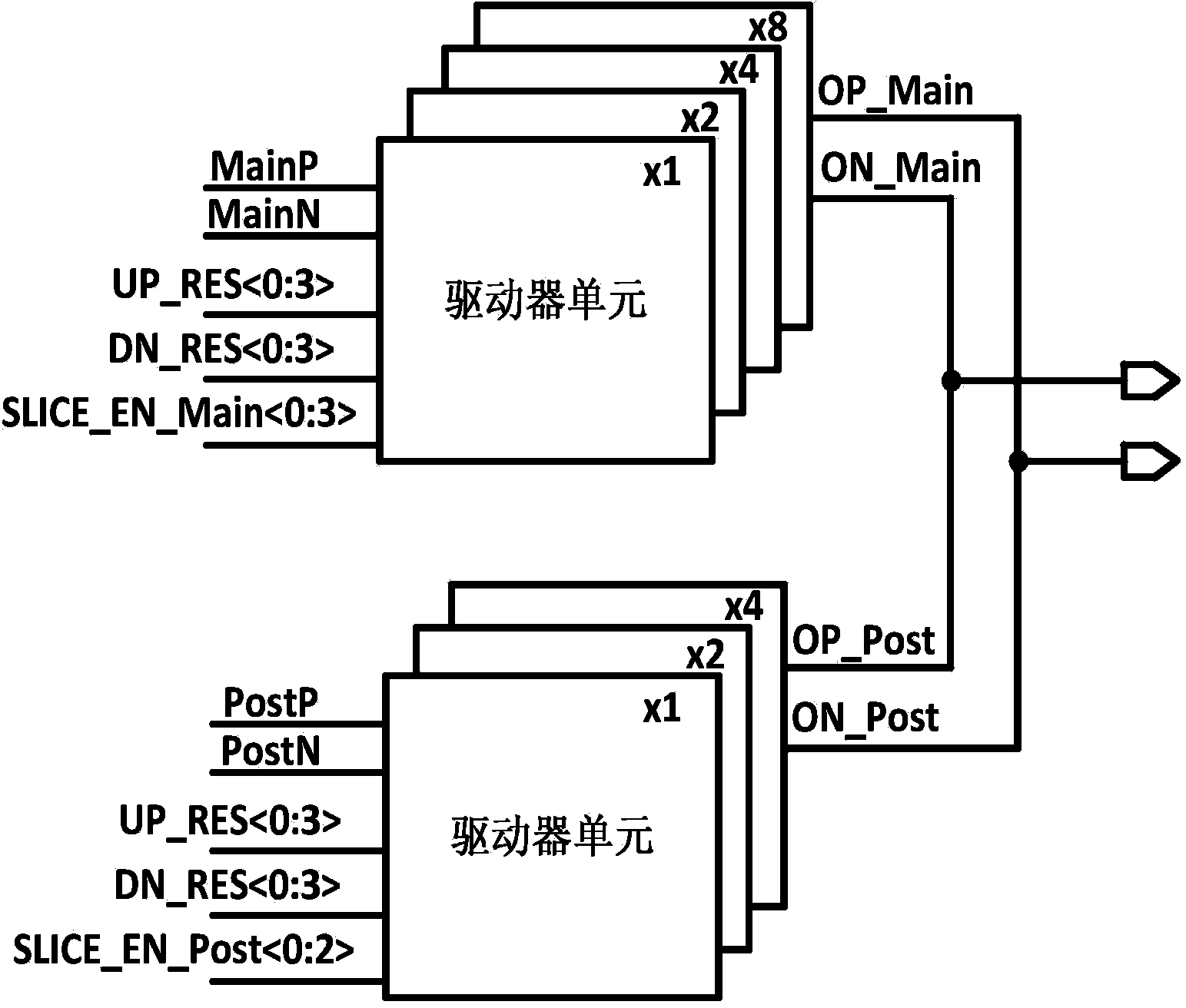
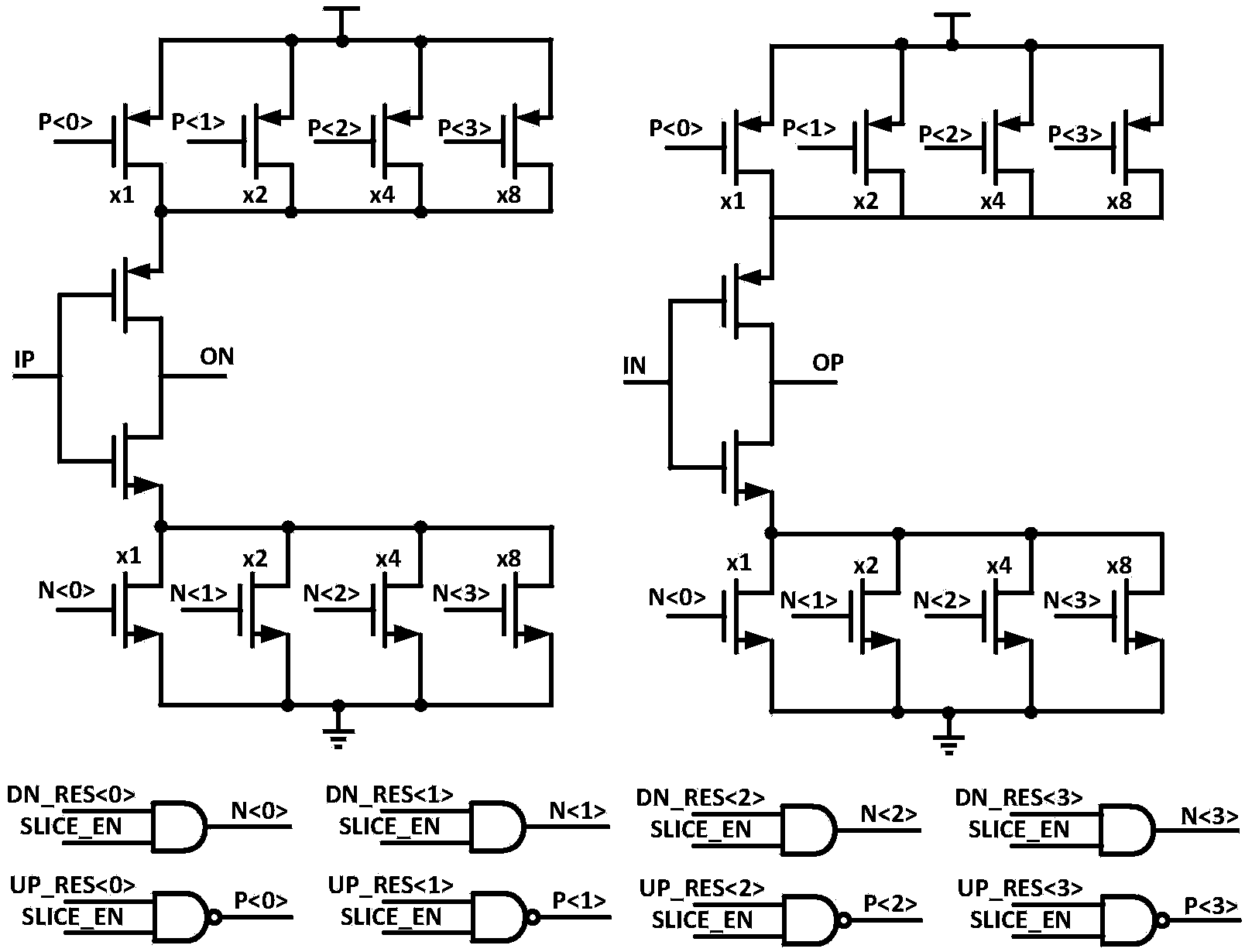
ActiveCN104333524AReduce power consumptionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksHigh level techniquesBand-pass filterEngineering
The invention discloses a novel high-speed serial interface transmitter. The transmitter comprises a combiner, a voltage-mode driver, a feed-forward equalizer and a feedback equalizer, wherein the feed-forward equalizer is integrated in the voltage-mode driver, an input end is connected with high-speed code stream serial data output by the combiner, and output impedance and an equilibrium factor can be independently adjusted; the feedback equalizer comprises a low-pass filter and a transconductance stage circuit which are both connected with an output end of the voltage-mode driver; the low-pass filter is used for extracting a low-frequency component of the high-speed data code stream output by the voltage-mode driver; the transconductance stage is simultaneously connected with the output of the low-pass filter; output voltage of the low-pass filter is converted into current, and the current and the output current of the voltage-mode driver are summated. The feed-forward equalizer is combined with the feedback equalizer, so that the skin effect attenuation and the dielectric loss attenuation are compensated through feedback and feed-forward respectively, meanwhile equilibrium is realized, and the power consumption of the transmitter is greatly reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Segmented equalizer
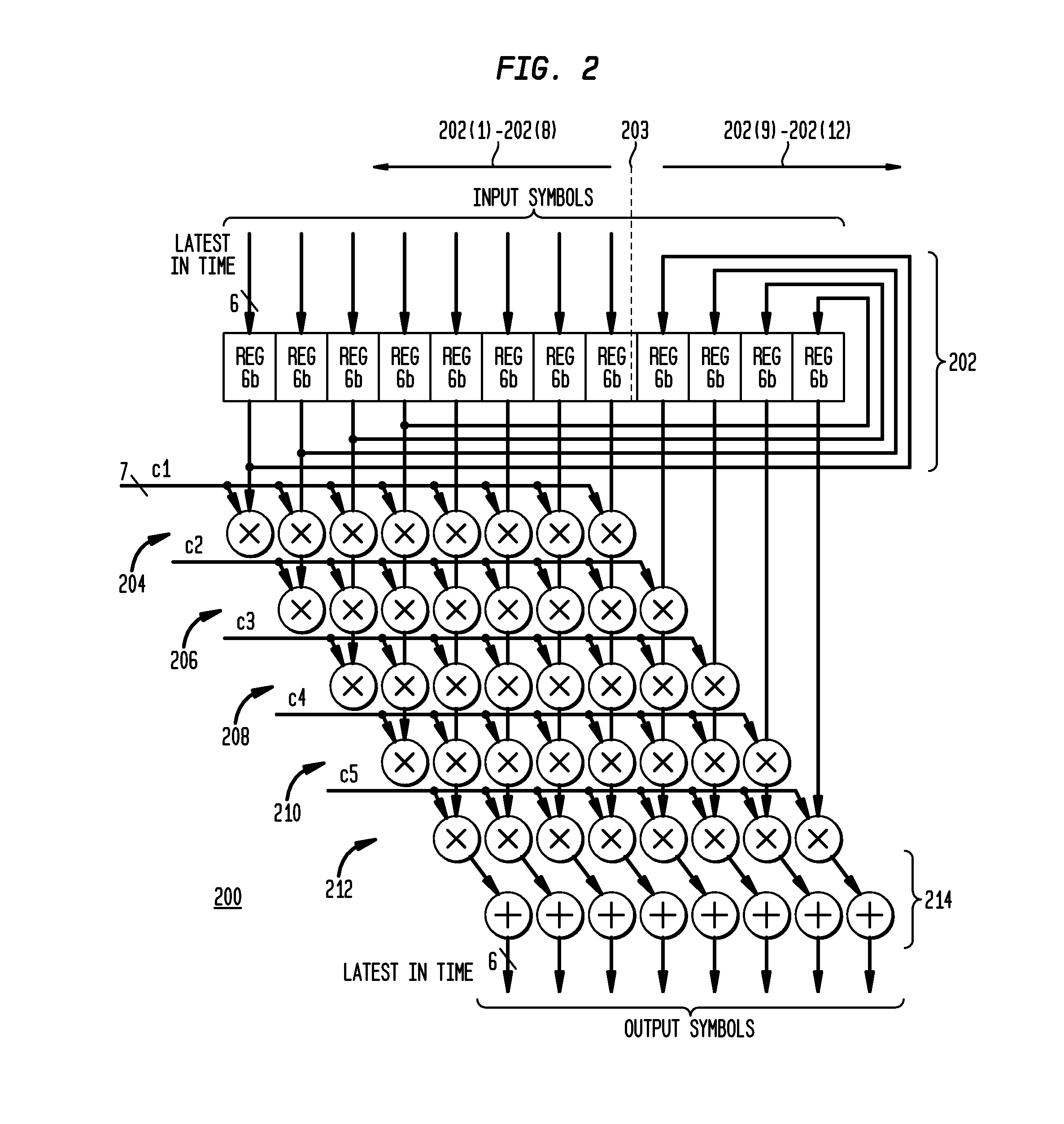
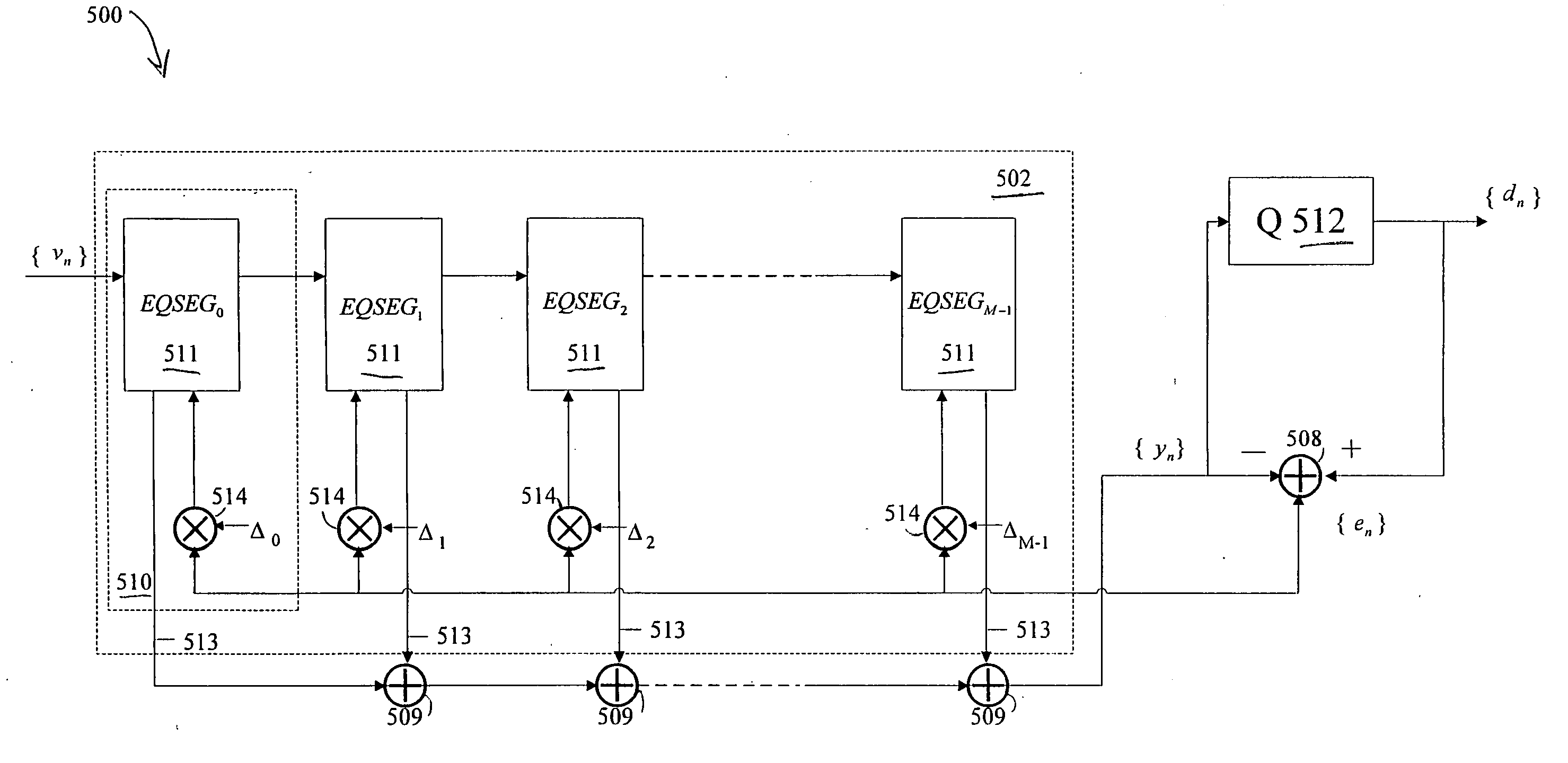
InactiveUS20070121717A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationEngineeringFeed forward equalizer
In one embodiment of the present invention, a segmented equalizer includes a plurality of feedforward equalizer segments, each feedforward equalizer segment responsive to delayed samples of an input signal {vn}, wherein n is the index of samples, and including a filter block for filtering the delayed samples by using coefficients which are updated based on a step size generated for each equalizer segment.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
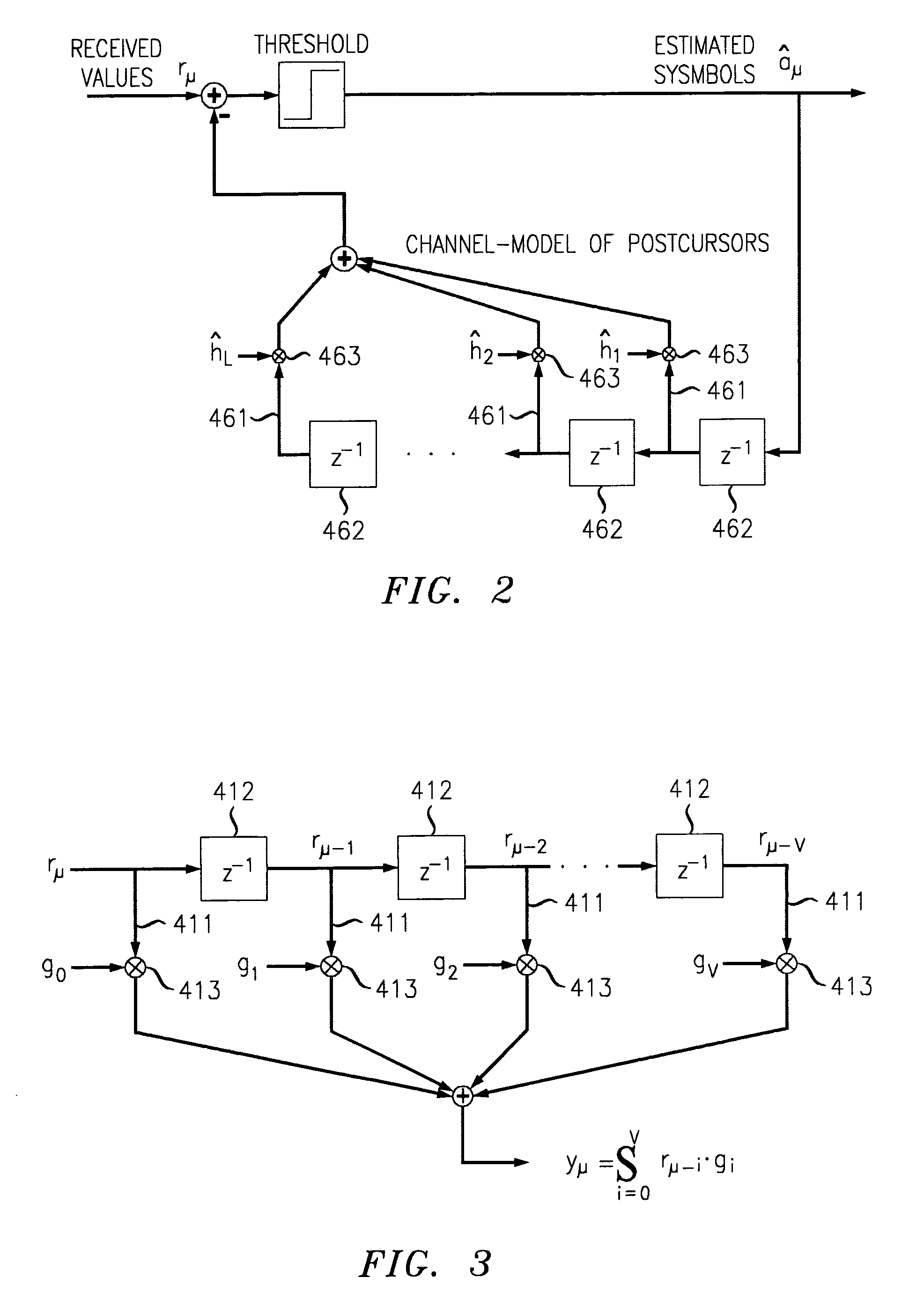
Computation of decision feedback equalizer coefficients with constrained feedback tap energy
Directly computing Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) coefficients and Feed Back Equalizer (FBE) coefficients of a Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) from a channel estimate. The FBE coefficients have an energy constraint. A recursive least squares problem is formulated based upon the DFE configuration, the channel estimate, and the FBE energy constraint. The recursive least squares problem is solved to yield the FFE coefficients. The FFE coefficients are convolved with a convolution matrix that is based upon the channel estimate to yield the FBE coefficients. A solution to the recursive least squares problem is interpreted as a Kalman gain vector. A Kalman gain vector solution to the recursive least squares problem may be determined using a Fast Transversal Filter (FTF) algorithm.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Demodulation apparatus for a network transceiver and method thereof
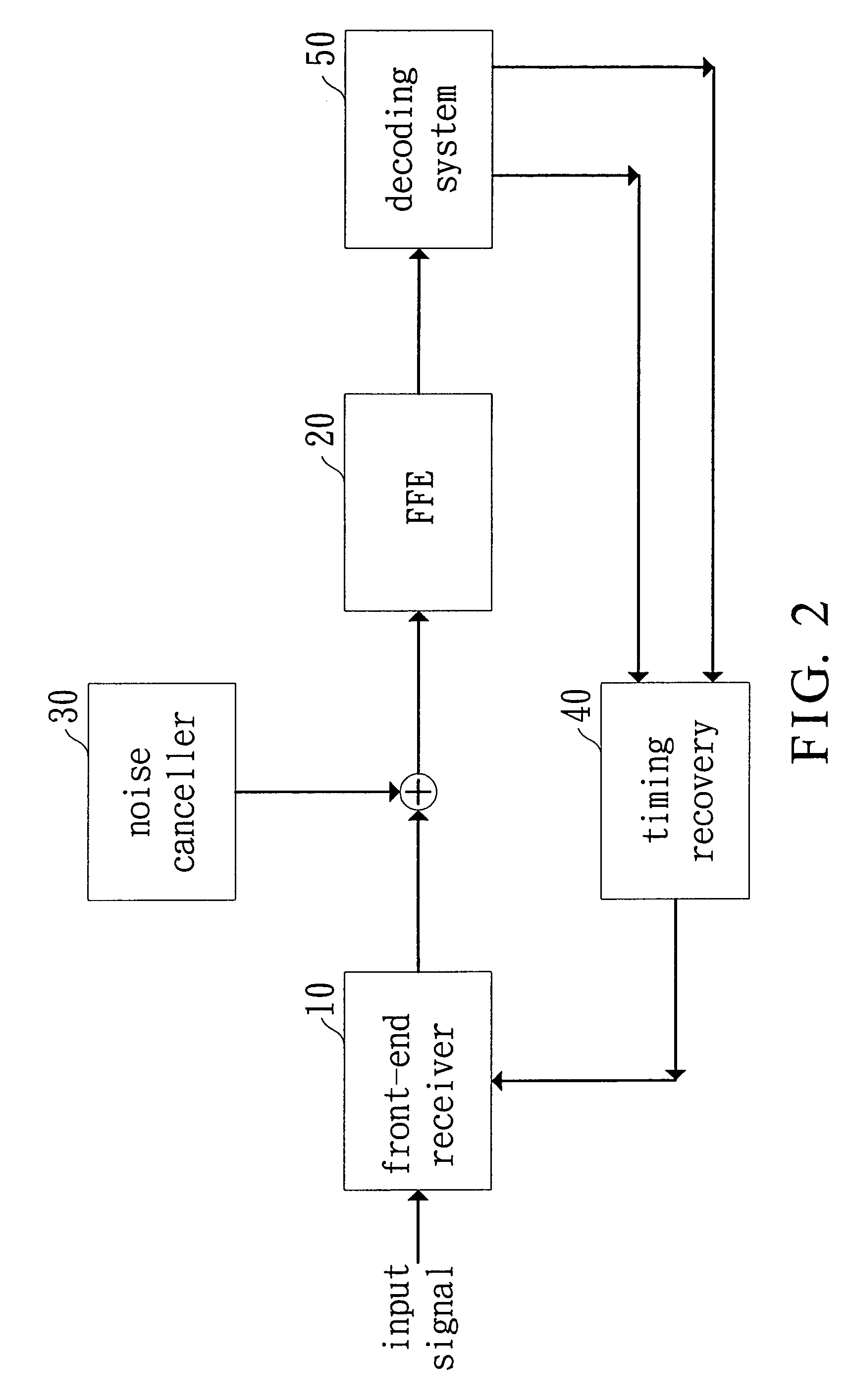
ActiveUS7272177B2Poor divergenceImprove performanceMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCommunications systemTransceiver
A transceiver of a communication system is disclosed. The transceiver comprises a front-end receiver for receiving a receiving signal and converting to a first signal with a pre-cursor component and a post-cursor component, a noise canceller coupled to the front-end receiver 10 for generating a second signal through eliminating the noise of the first signal, a Feed-Forward Equalizer (FFE) coupled to the noise canceller for generating a third signal through eliminating the pre-cursor component in the second signal according to a transfer function including a plurality of adjustable constants, wherein the adjustable constants includes a main-tap and the value of the main-tap is predetermined, and a decoding system coupled to the FFE for decoding the third signal and eliminating the post-cursor component in the third signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
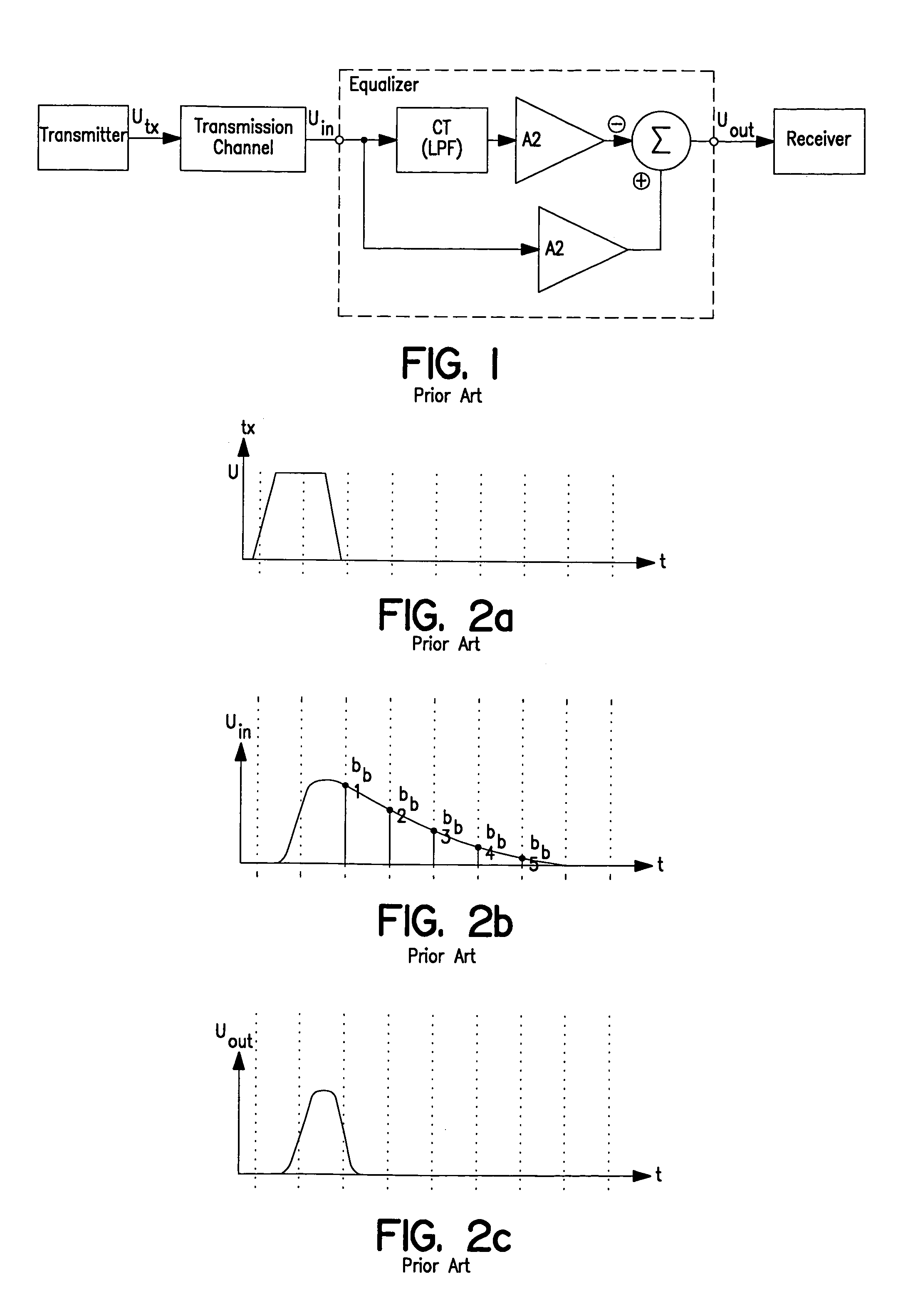
Feed forward equalizer and a method for analog equalization of a data signal
InactiveUS7292631B2Easy to implementReduce complexityMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
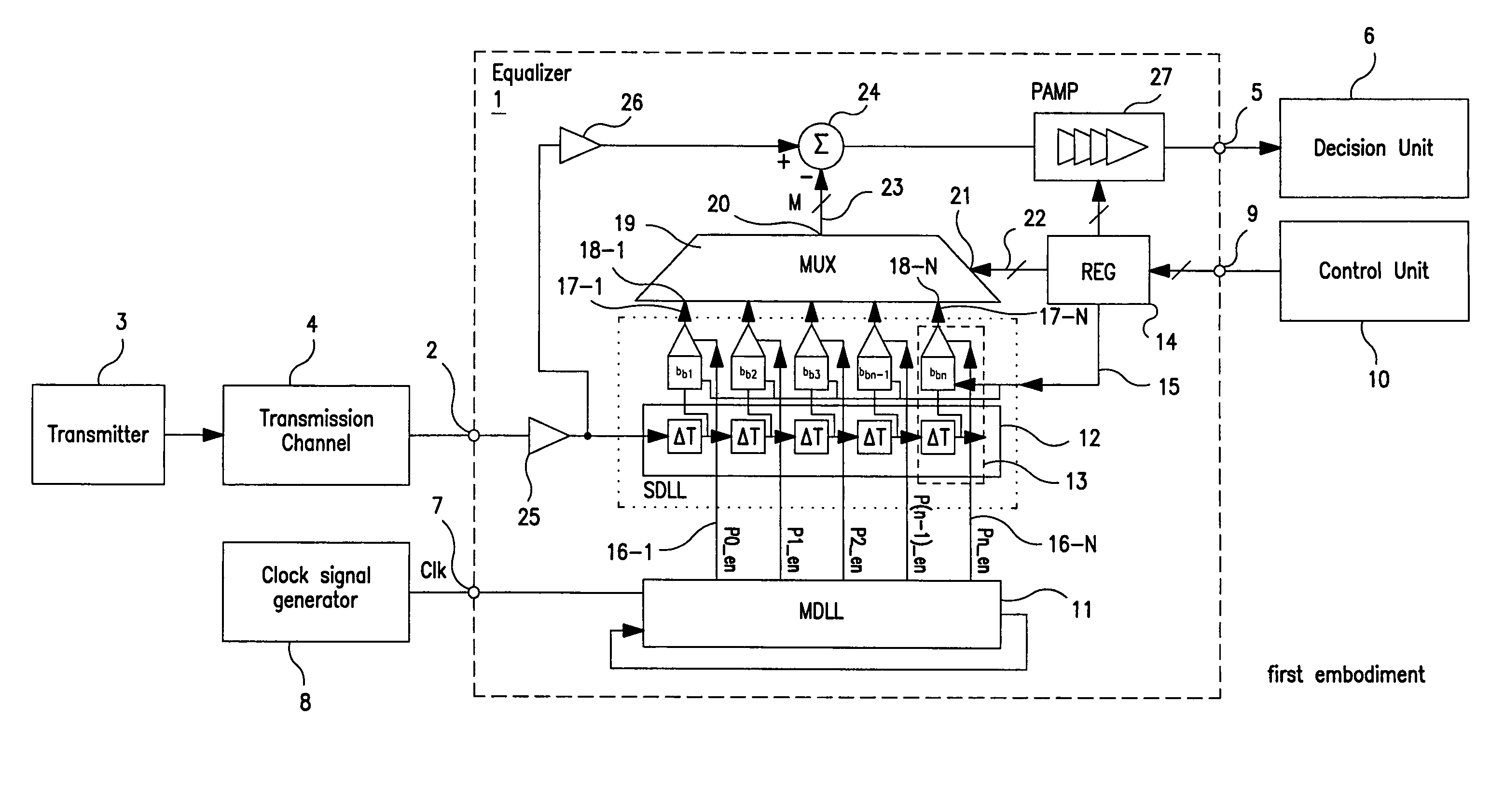
A feed forward equalizer for analog equalization of a data signal received over a data transmission channel comprising a Master Delay Locked Loop (MDLL) for generating equidistant reference phase signals; a Slave Delay Line (SDL) formed by serial connected Slave Delay Units (SDU), wherein each Slave Delay Unit (SDU) has a Slave Delay Element (SDE) to delay the received data signal with a predetermined delay time (ΔT) and an analog amplifier which amplifies the delayed output signal of the Slave Delay Element (SDE) with a respective weighting coefficient to generate a weighted delay signal, wherein the analog amplifier is switched transparent in response to a corresponding reference phase signal generated by said Master Delay Locked Loop (M-DLL); and subtracting means for subtracting the weighted delay signals which are selected by means of a multiplexer from the received data signal to generate an equalized output data signal.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
Feed forward equalizer controlled by FEC correction rates
InactiveUS7130341B2Optimization parametersReduce parameterMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringEqualization
A method of signal equalization of a transmitted bit stream by means of a feed forward equalizer is provided, whereby the signal is decomposed into at least two components and the components are multiplied with equalization parameters to form equalized components, which are superposed to form an equalized signal, and whereby conditional bit error rates by counting faulty transmitted bits in dependence of preceding and succeeding bits are determined and the equalization parameters are tuned dependent on the determined conditional bit error rates.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
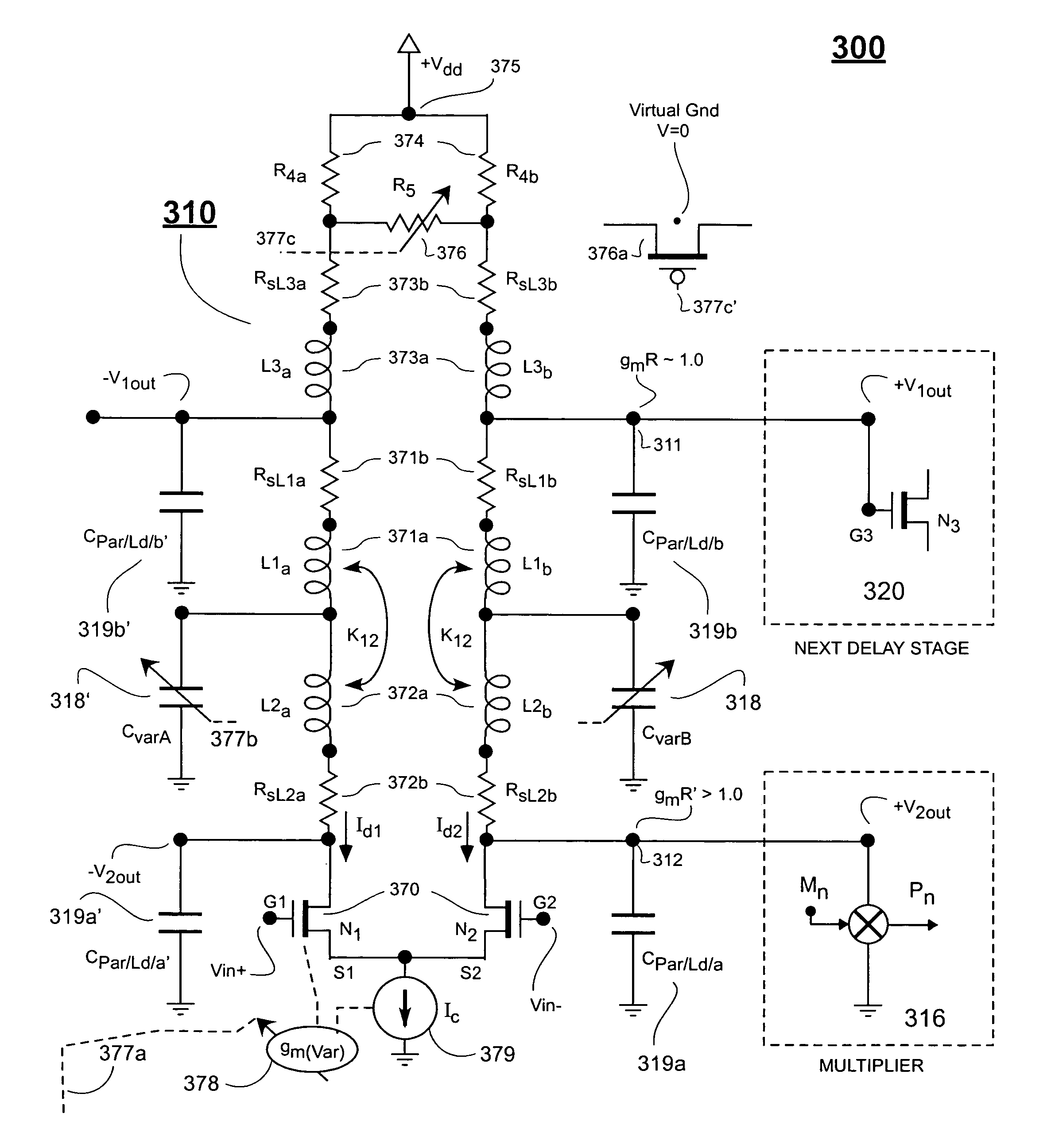
Communications receiver equalizer
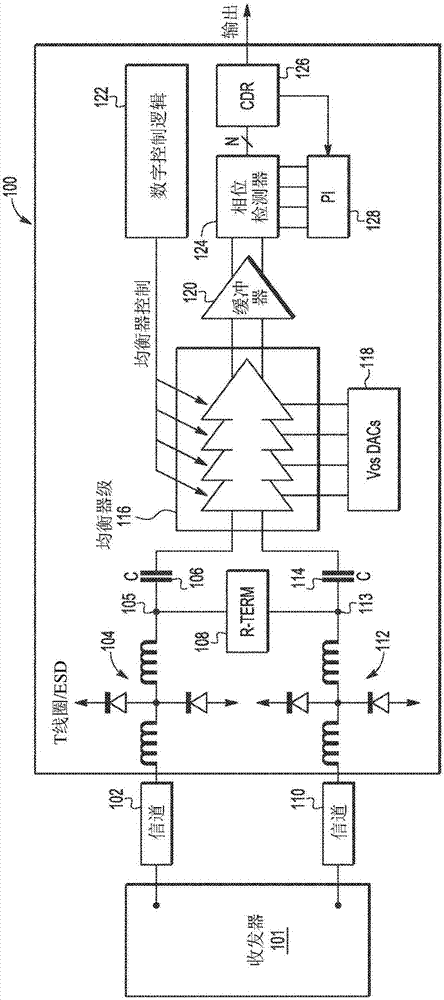
ActiveCN107070824ATransmitter/receiver shaping networksPulse manipulationDelayed timeTransimpedance amplifier
A continuous-time linear equalizer implementing enhanced analog delay cells with gain-peaking characteristics and a constant delay time is provided. A receiver feed-forward equalizer architecture implements a gain-stage chain, analog multipliers for correcting coefficients, and a linear combiner as an analog summation circuit. Each of the gain stages produces linear gain peaking and presents a constant delay-time (through calibrations) at each stage. Each delay cell includes a transconductance stage configured to convert a differential input voltage signal to a differential output current signal, wherein the transconductance stage includes a differential pair of first and second transistors coupled in a source degeneration configuration, a negative resistance network coupled in parallel with a tunable resistor network, and shunt inductive circuitry coupled in parallel with the negative resistance network. The delay cells also include a transimpedance stage configured to convert the differential output current signal received from the transconductance stage to a differential output voltage signal, wherein the transimpedance stage implements a first transimpedance amplifier coupled in series with a first shunt inductive circuit. The shunt inductive circuits may include inductorless inductor circuit elements.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Arrangement for initializing digital equalizer settings based on comparing digital equalizer outputs to prescribed equalizer outputs
ActiveUS7233616B1Reliable receptionEnhance layeringMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverPhysical layer
A physical layer transceiver, configured for retrieving signal samples from a prescribed network medium having an undetermined length, includes a digital feedforward equalizer, configured for generating equalized signal samples from the retrieved signal samples and based on supplied equalizer settings, and an equalizer controller. The equalizer controller is configured for supplying selected equalizer settings that overcome intersymbol interference encountered by transmission of the signal samples across the prescribed network medium. The equalizer controller is configured for supplying prescribed initial equalizer settings to the digital feedforward equalizer, receiving equalized signal samples from the digital feedforward equalizer, and selectively changing the prescribed initial equalizer settings based on comparing the equalized signal samples to a prescribed equalization threshold. The equalizer controller is configured for selectively repeating the changing of the equalizer settings until the equalized signal samples reach the prescribed equalization threshold.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Feed forward equalizer tap weight adaptation based on channel estimation
ActiveUS20140064352A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsSelf adaptiveFeed forward equalizer
An apparatus including a receiver having a feed forward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a communication channel. The receiver may be configured to adjust the FFE using information based on an estimate of one or more characteristics of the communication channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
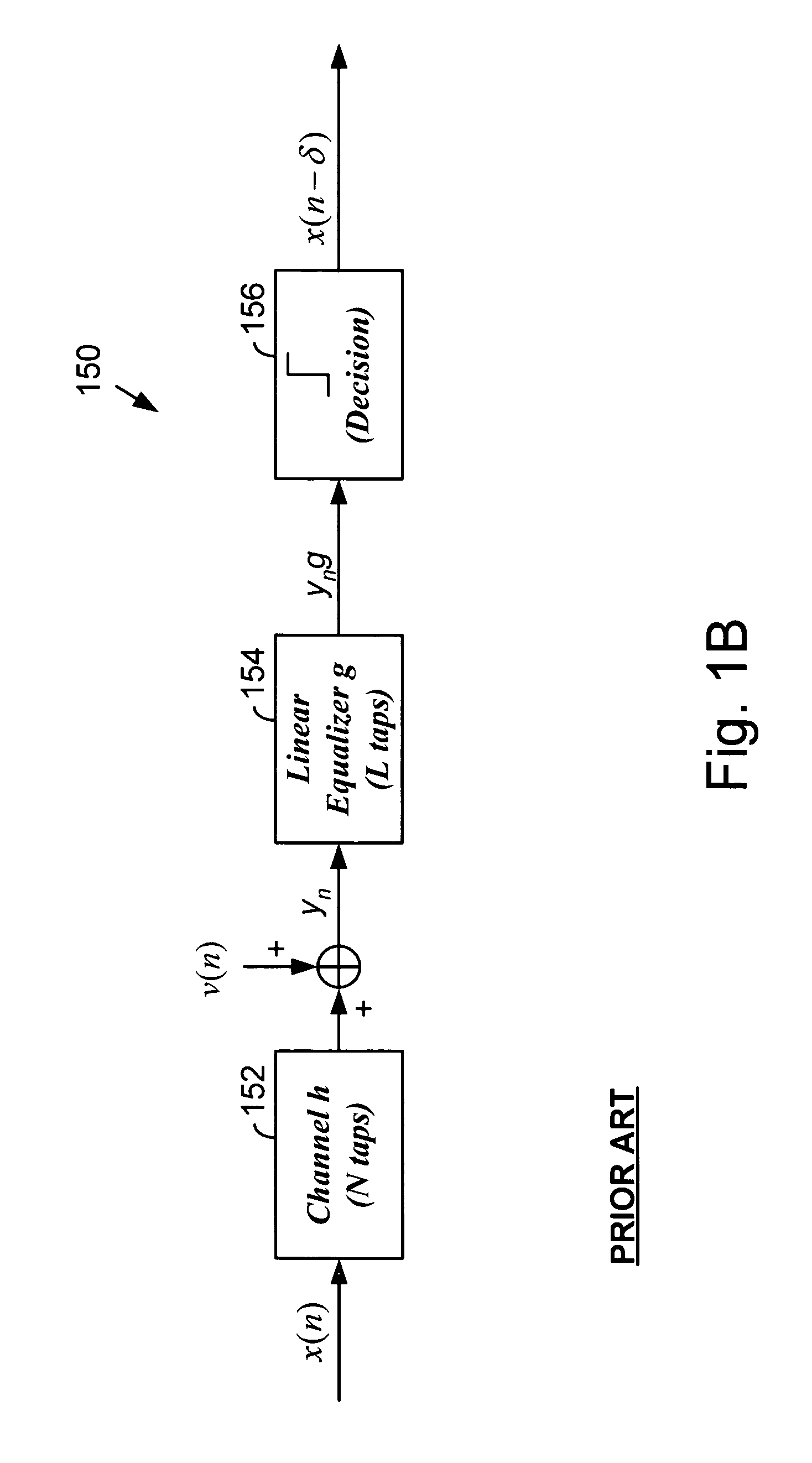
Receiver for high rate digital communication system
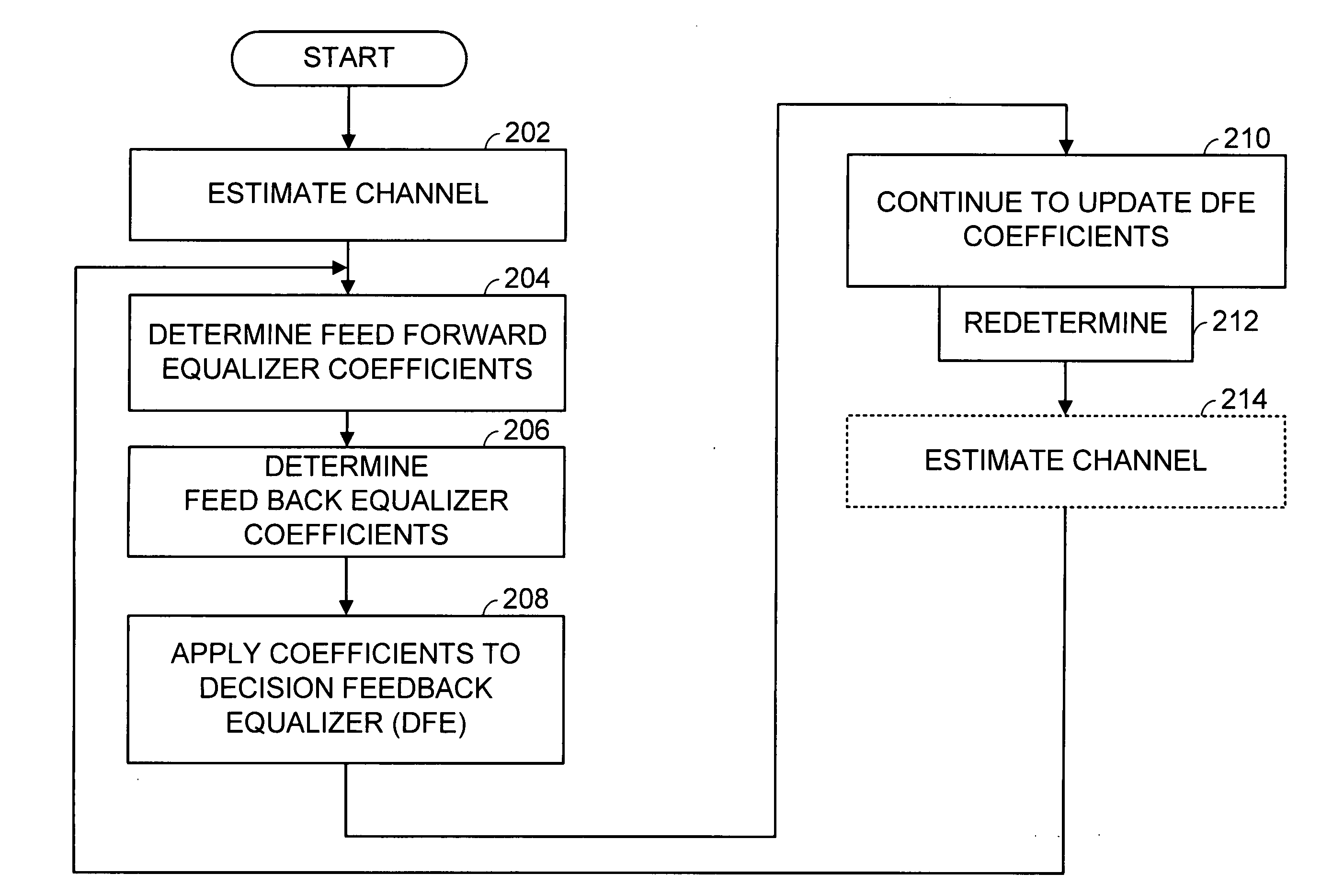
InactiveUS7161980B2Without impairing the received signal's energyMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkHigh rateCommunications system
A system and method for processing received transmission signal(s) adapted to be used in high rate communication systems without impairing the received signal energy and without additional expensive components. The system and method are adapted to transmission system(s) having at the receiver-side a compound system of a feed-forward equalizer (FFE) and a subsequent decision feedback equalizer (DFE). A feed forward equalization and / or a decision feedback equalization is performed on the received high rate signal by deriving adaptation information from the equalized signal after a signal decision is performed for adjusting all intended feed forward equalization and / or decision feedback equalization coefficients and / or table entries in dependence on said information.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Analog delay chain having more uniformly distributed capacitive loads and analog delay cell for use in chain
InactiveUS20060044061A1Wide frequency response rangeReduce load capacitanceAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceEngineering
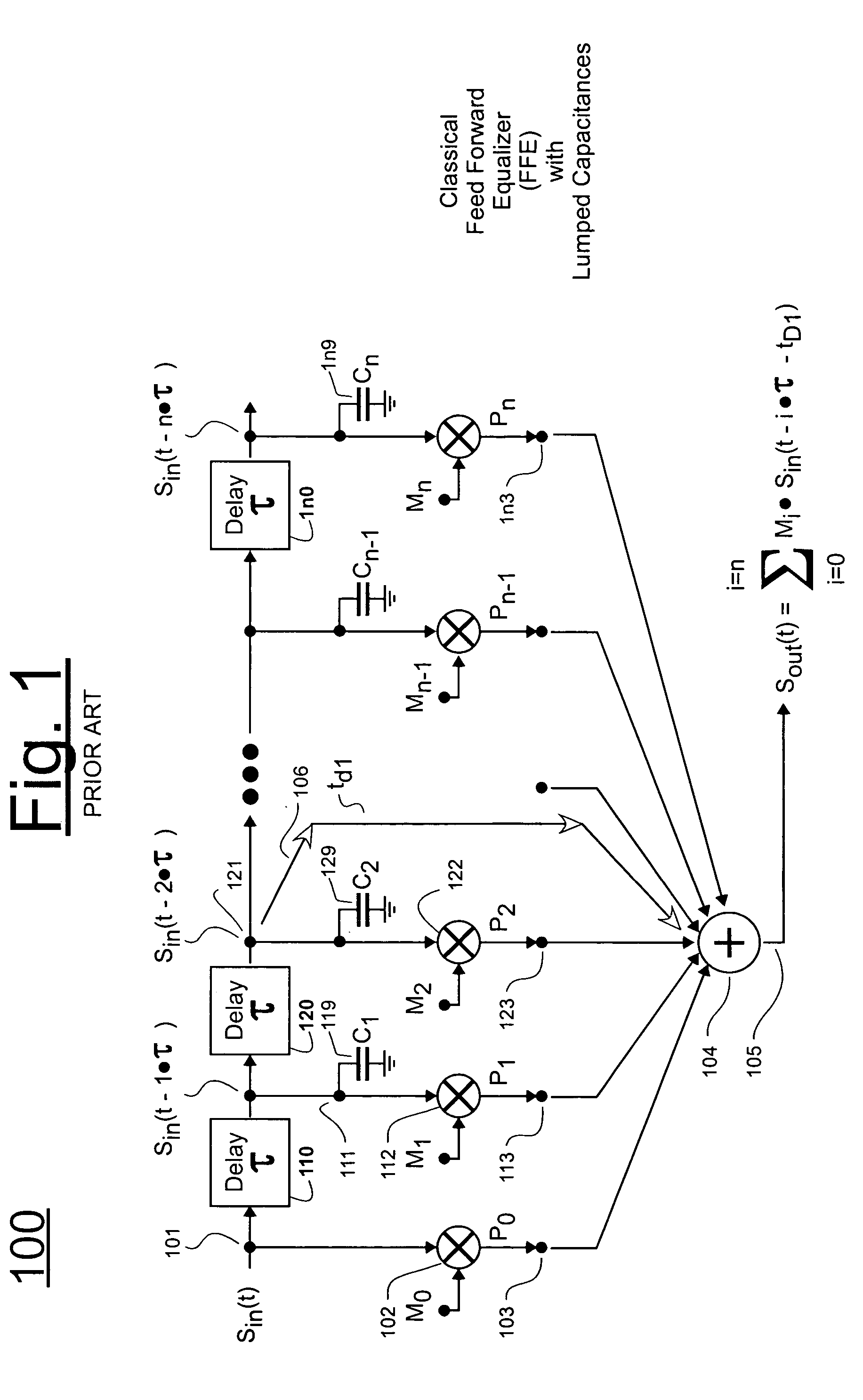
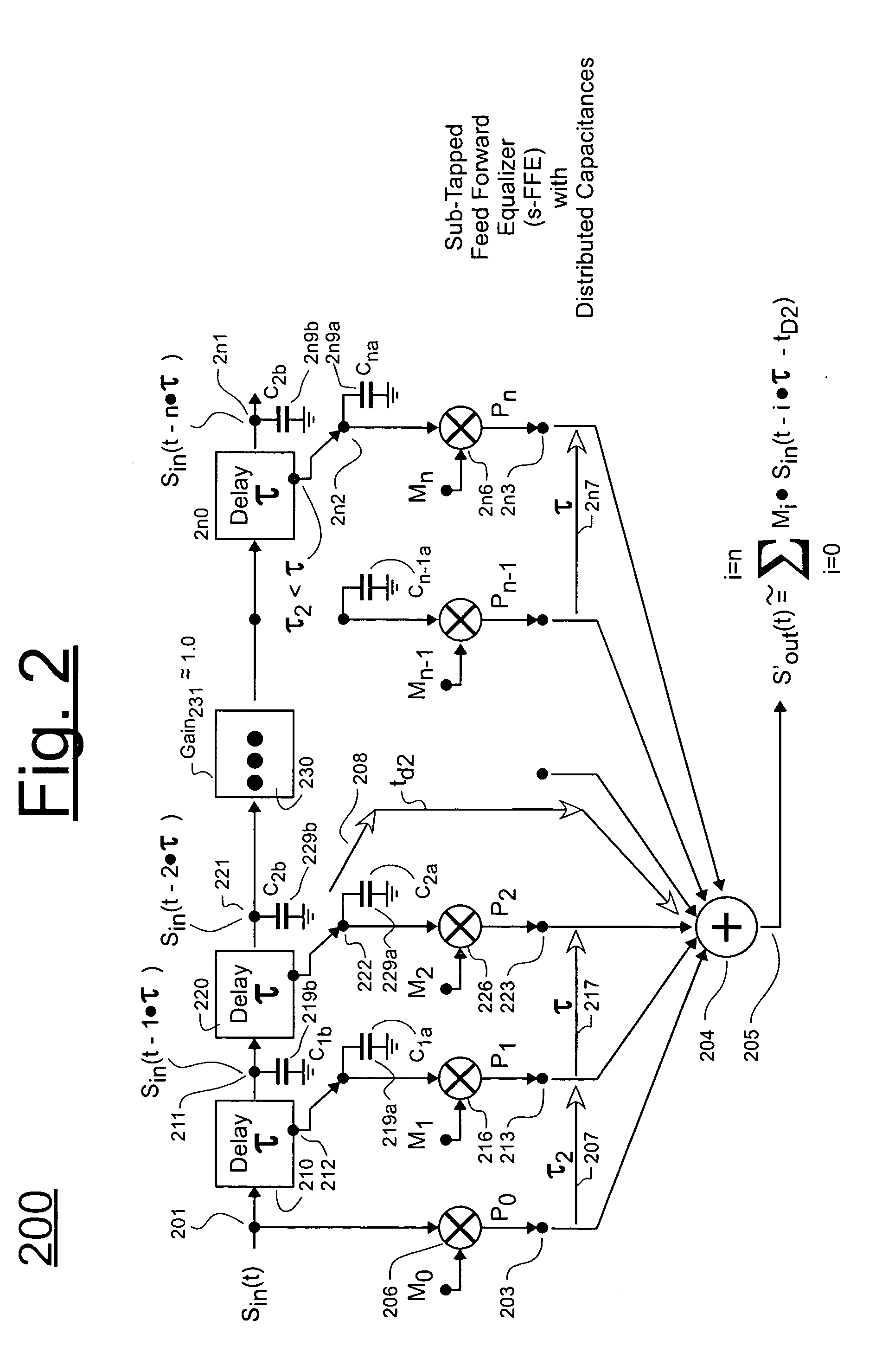
A tapped delay chain comprises a plurality of delay cells where each cell has at least two output taps: a primary one for feeding forward a delayed signal to a next cell in the chain, and a secondary output tap for feeding a slightly-differently delayed signal to a multiplier unit so that the slightly-differently delayed signal can be multiplied by a weighting coefficient. The split of output taps in each delay cell allows for a corresponding split of loading capacitance. Each output tap of the delay cell is loaded by a smaller capacitance than it would have had to otherwise drive had the split taps been instead lumped together as a common node. The reduced loading capacitance at each of the split taps allows for a wider frequency response range. The tapped delay chain may be used to form a feed-forward equalizer (FFE) which further comprises an adder, and a plurality of multipliers each respectively receiving a delayed input signal (Sin(delayed)) from a secondary output tap of a respective delay cell in the chain and each outputting a correspondingly delayed and weighted, product signal (Pi) to the adder.
Owner:SCINTERA NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com