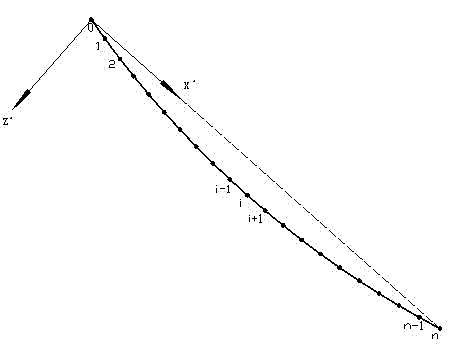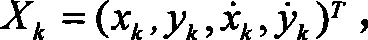Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
566 results about "Equations of motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a physical system in terms of its motion as a function of time. More specifically, the equations of motion describe the behaviour of a physical system as a set of mathematical functions in terms of dynamic variables: normally spatial coordinates and time are used, but others are also possible, such as momentum components and time.
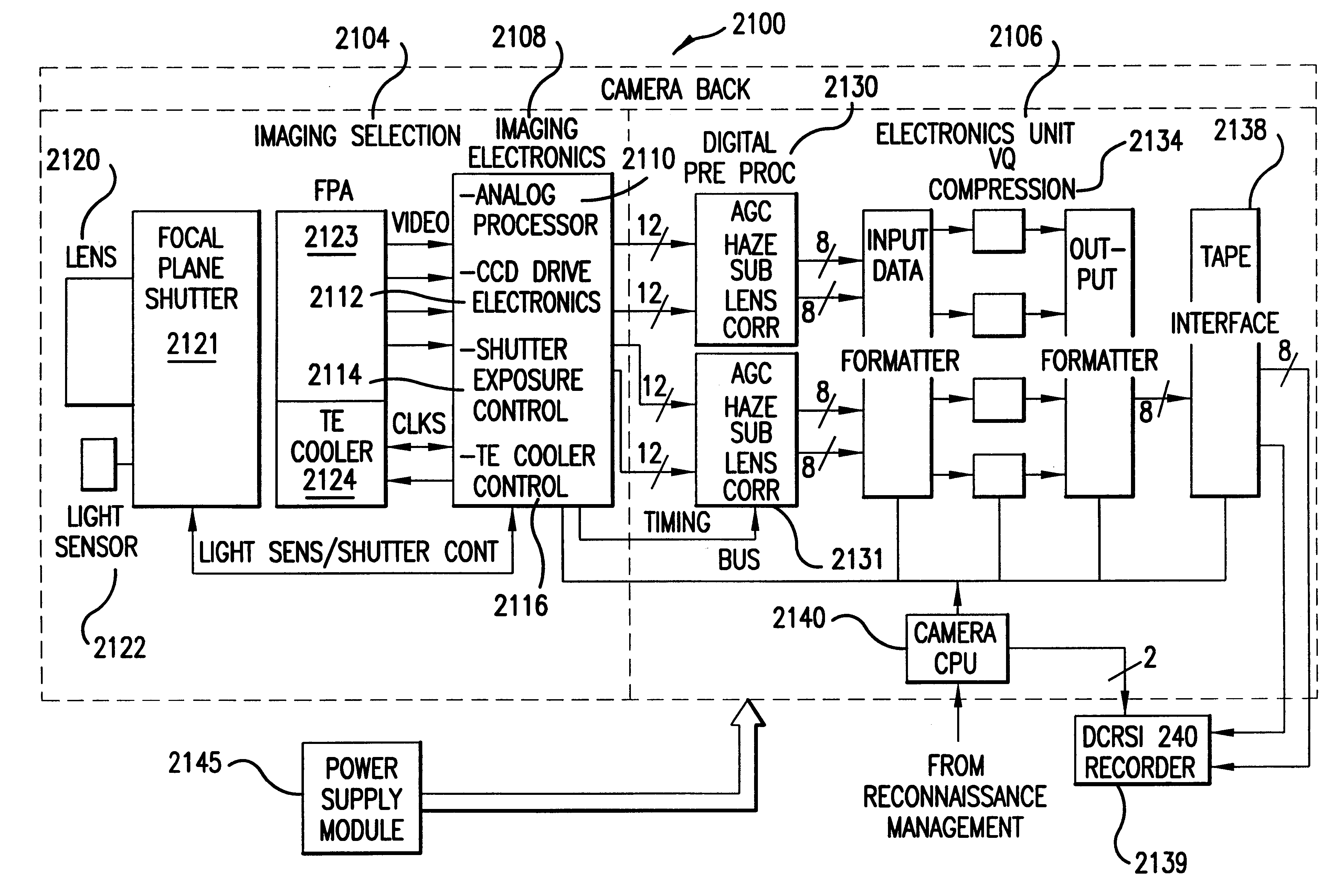
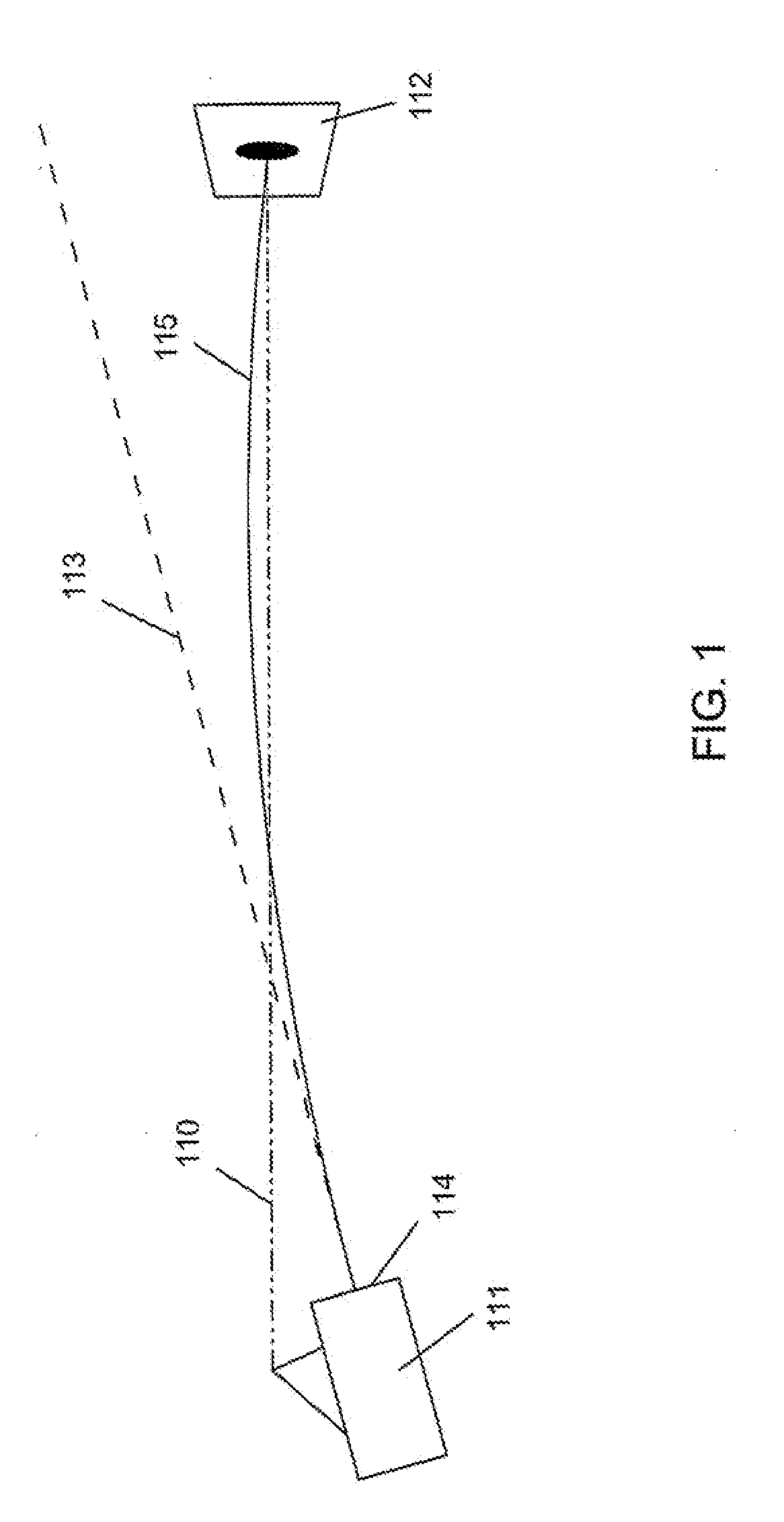
Electro-optical reconnaissance system with forward motion compensation
InactiveUS6256057B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferImage motion
An electro-optical framing camera forward motion compensation (FMC) reconnaissance system comprising a moving shutter and a full frame focal plane array detector is designed to minimize the variation of image motion from a target scene across the focal plane array. The full frame focal plane array, such as a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), is designed to transfer and add the image from pixel to pixel at a predetermined rate of image motion corresponding to the region exposed by the focal plane shutter. The focal plane shutter aperture and velocity are set to predetermined values coordinated with the available illumination. The CCD image transfer rate is set to minimize the smear effects due to image motion in the region of the scene exposed by the focal plane shutter. This rate is variable with line of sight depression angle, aircraft altitude, and aircraft velocity / altitude ratio. Further, a method of FMC utilizes a comparison of a measured light level to a standard value in order to determine the appropriate exposure time and shutter motion rate. An optimal FMC clocking signal is calculated based on image motion equations incorporated in the processing unit of the reconnaissance system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Predictive virtual reality display system with post rendering correction
ActiveUS20170018121A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEffectively approximatesInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Biomechanical model
A virtual reality display system that generates display images in two phases: the first phase renders images based on a predicted pose at the time the display will be updated; the second phase re-predicts the pose using recent sensor data, and corrects the images based on changes since the initial prediction. The second phase may be delayed so that it occurs just in time for a display update cycle, to ensure that sensor data is as accurate as possible for the revised pose prediction. Pose prediction may extrapolate sensor data by integrating differential equations of motion. It may incorporate biomechanical models of the user, which may be learned by prompting the user to perform specific movements. Pose prediction may take into account a user's tendency to look towards regions of interest. Multiple parallel pose predictions may be made to reflect uncertainty in the user's movement.
Owner:LI ADAM
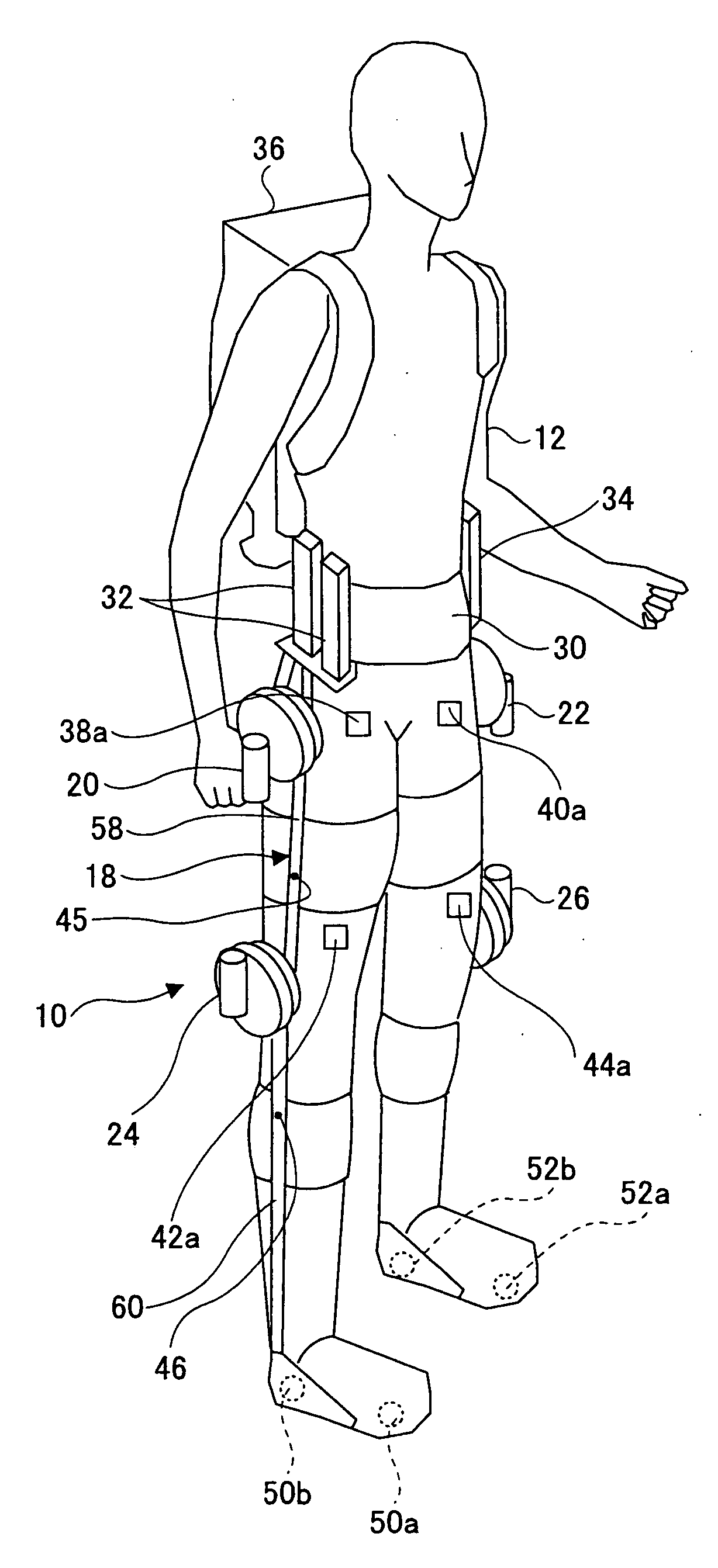
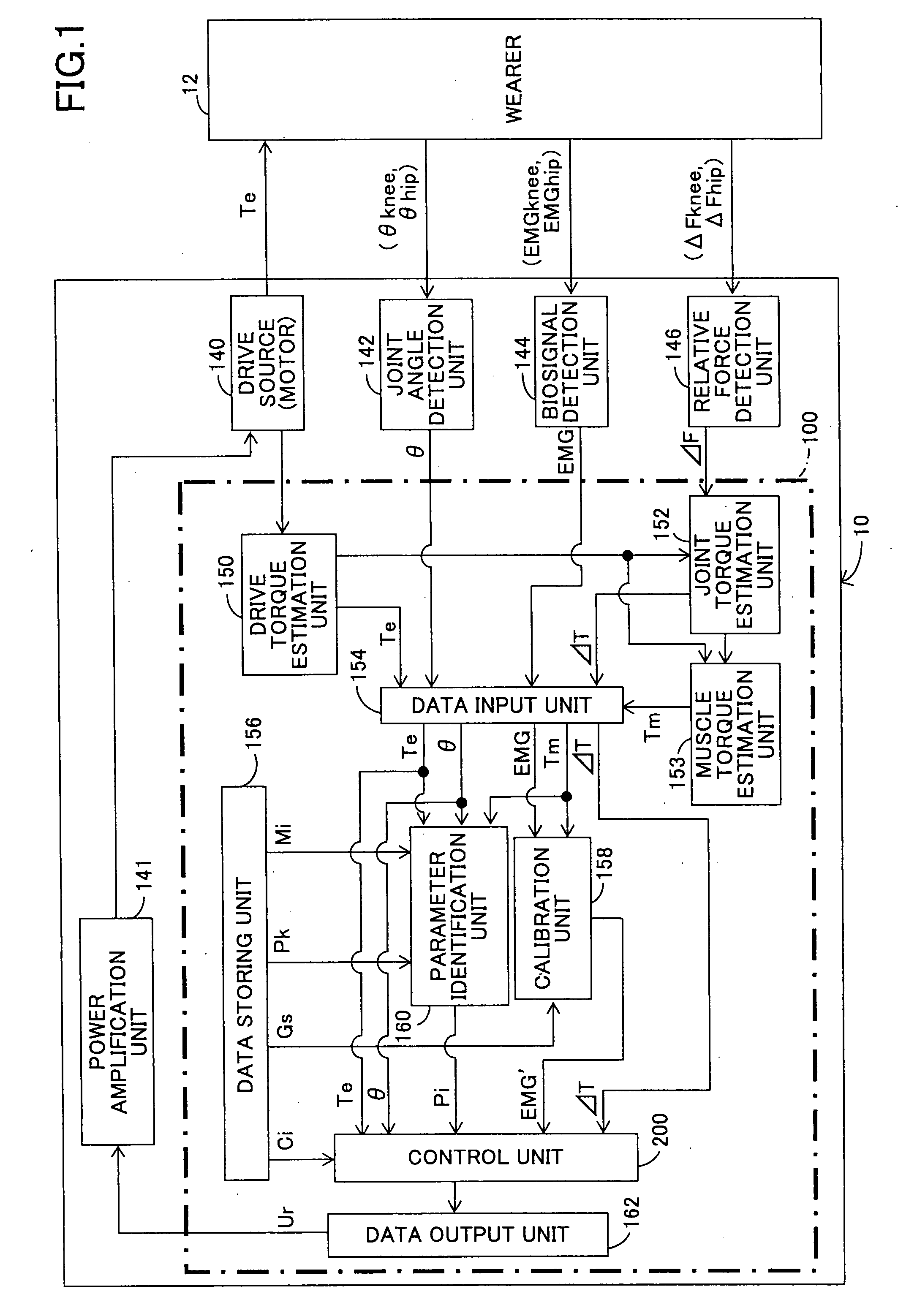
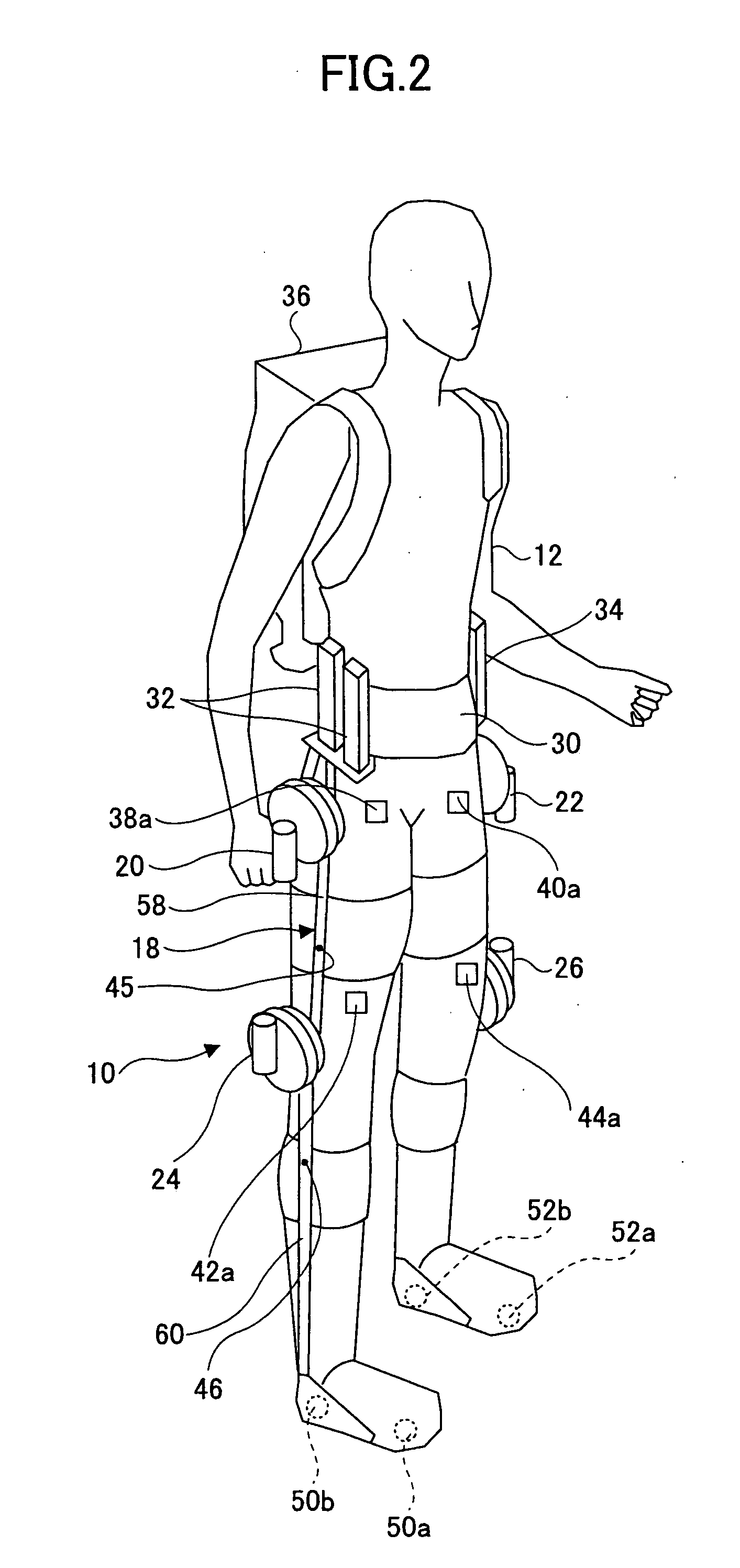
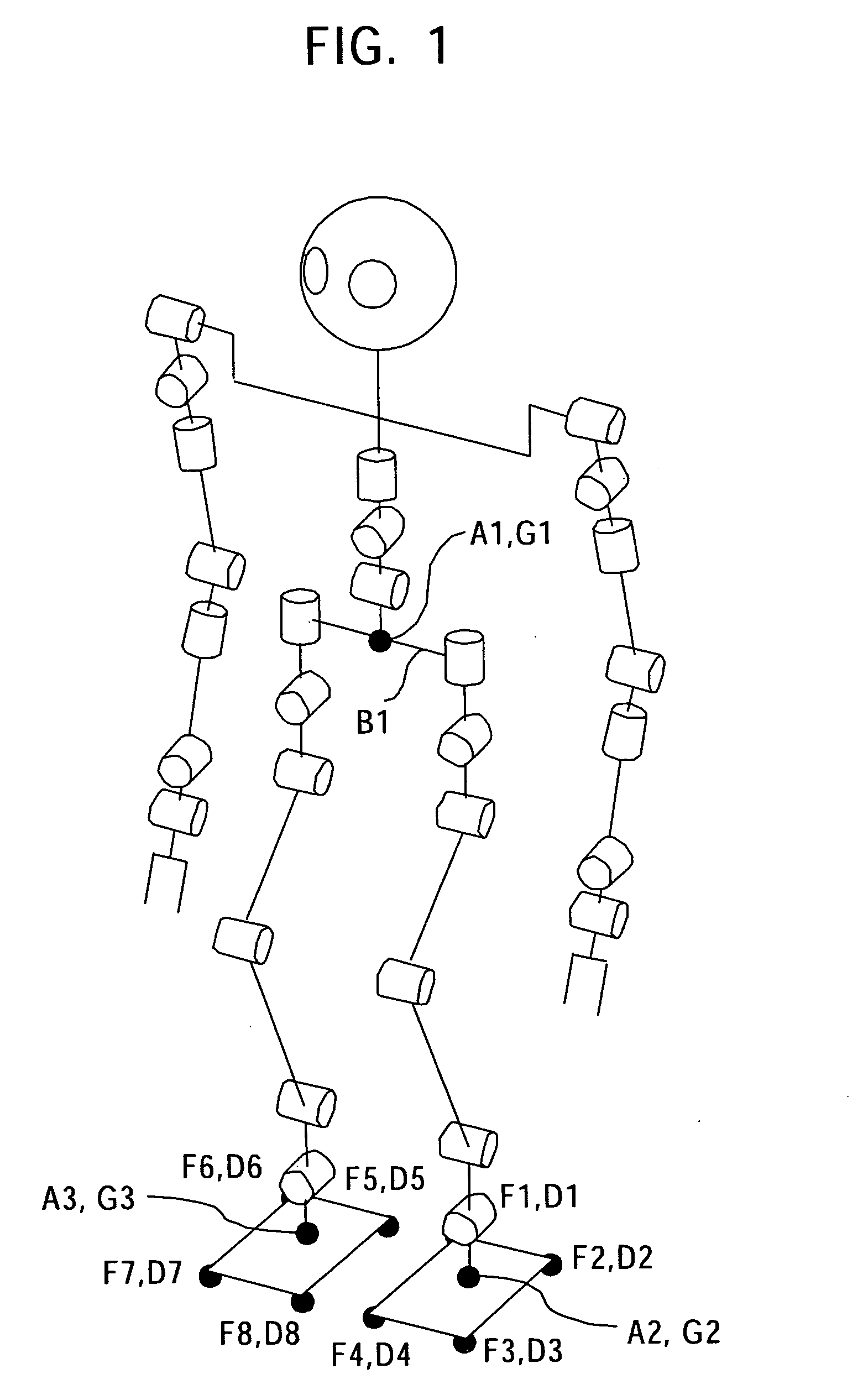
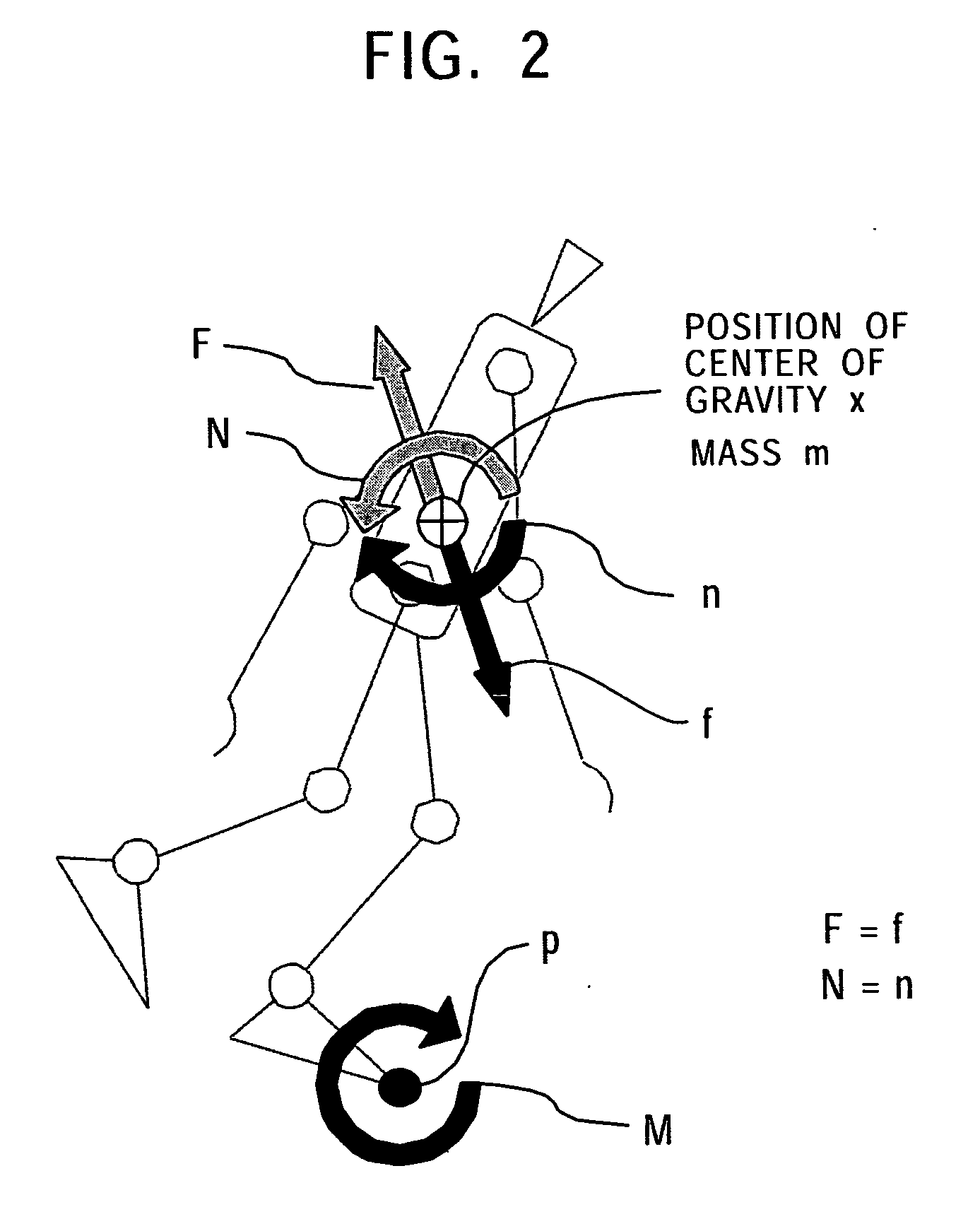
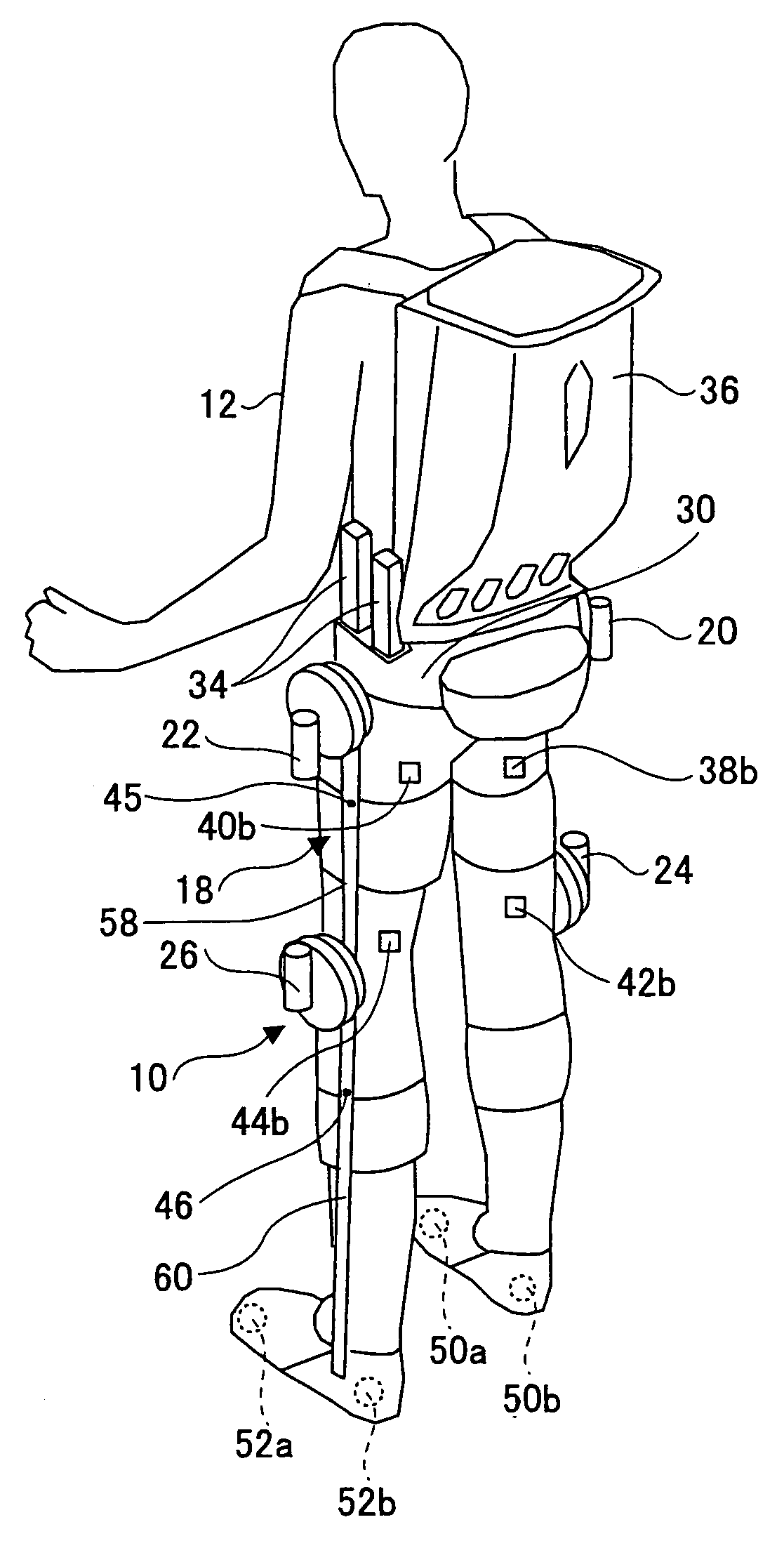
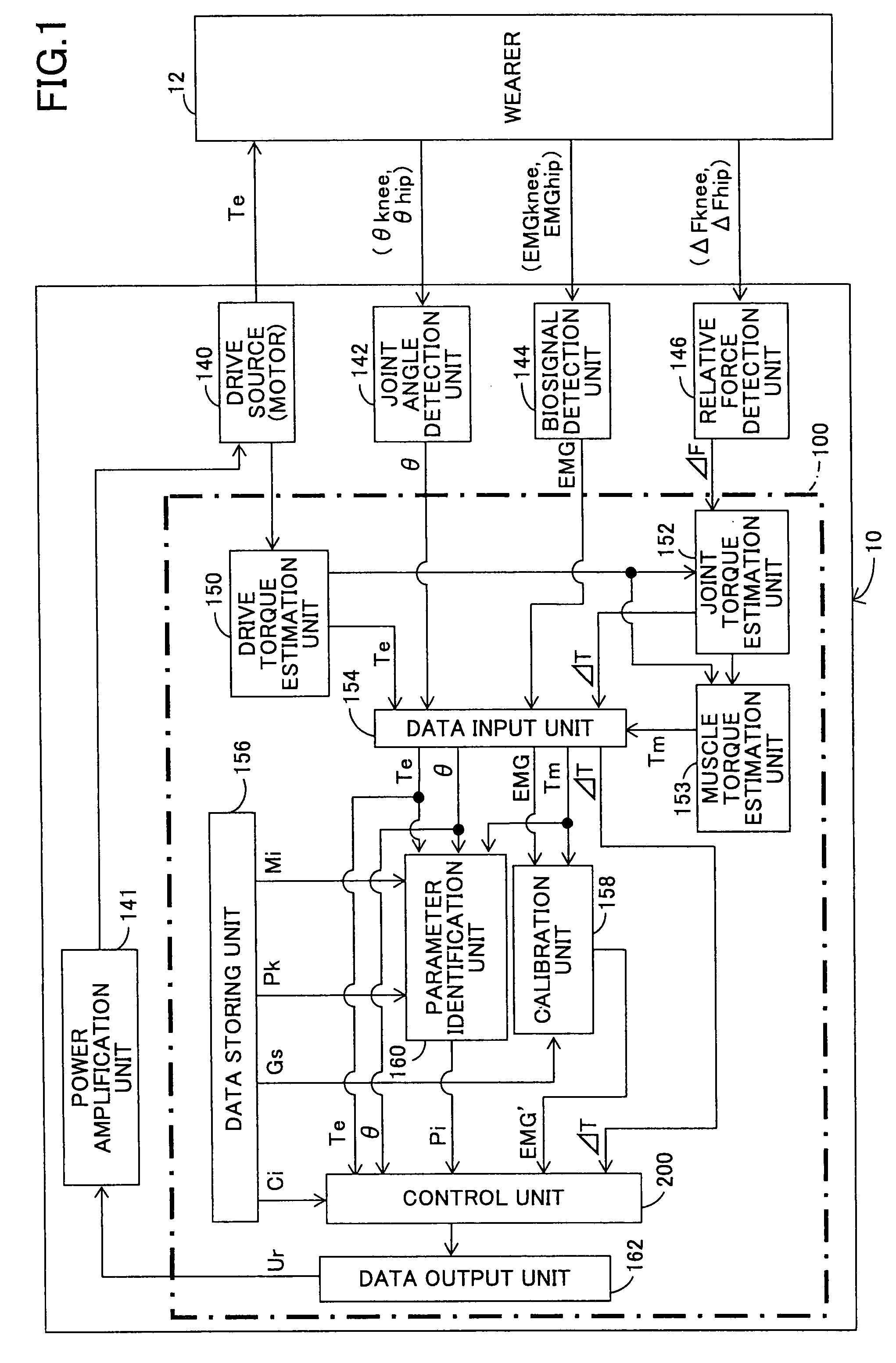
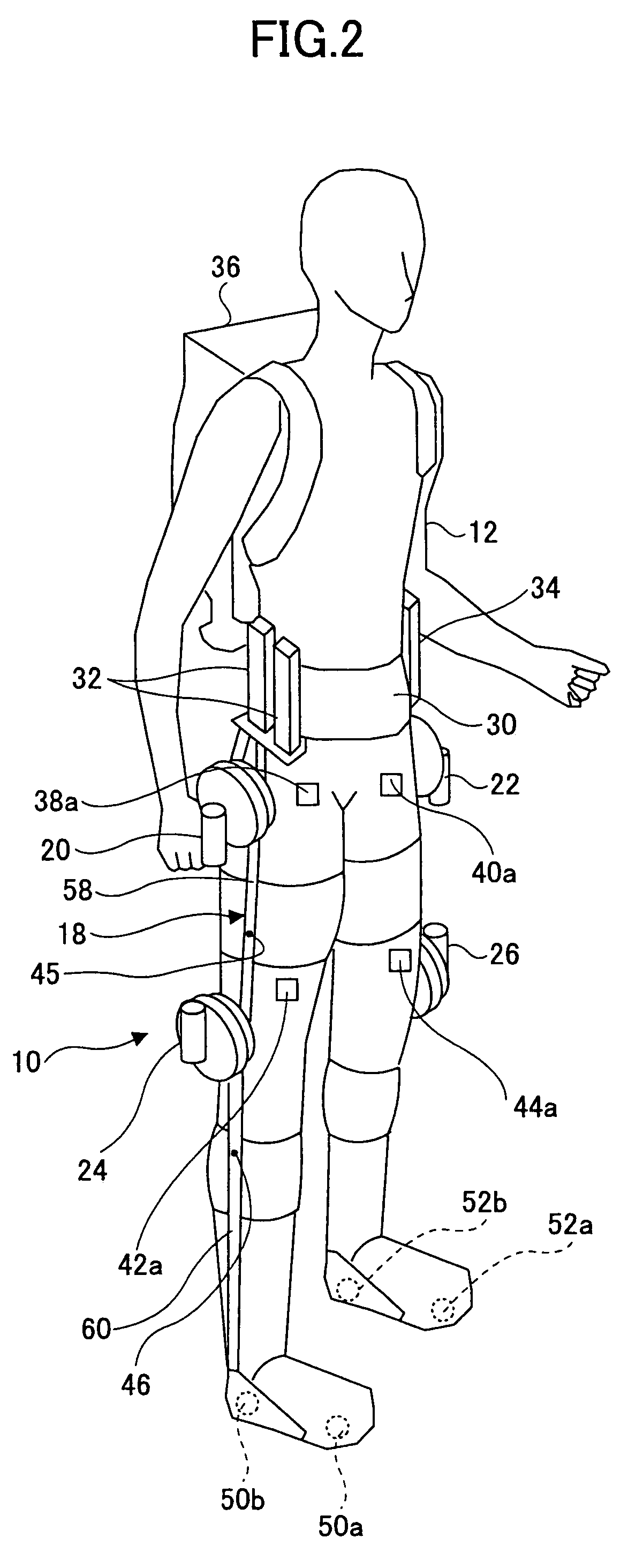
Wearing-Type Motion Assistance Device and Program for Control
ActiveUS20080161937A1Sufficient effect in conformityAvoid it happening againProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingEngineeringParametric identification
A motion assistance device has a biological signal detection means for detecting a biological signal from the wearer of the device; a motion assistance device installation member having a drive source for applying torque acting to the wearer by use of each joint of the wearer as a rotating shaft; a control means for controlling the drive source to generate torque corresponding to the biological signal detected by the biological signal detection mean; a drive torque estimation means for estimating the drive torque generated by the drive source; a joint angle detection means for detecting angular displacement of a joint; and a parameter identification means for substituting the drive torque estimated by the drive torque estimation means and the angular displacement detected by the joint angle detection means into an equation of motion to specify the wearer-specific dynamics parameter, the equation relating to the entire system and including wearer-specific dynamics parameter. The control means controls the drive source according to a predetermined control method, based on the equation of motion into which the dynamics parameter identified by the parameter identification means is substituted.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC
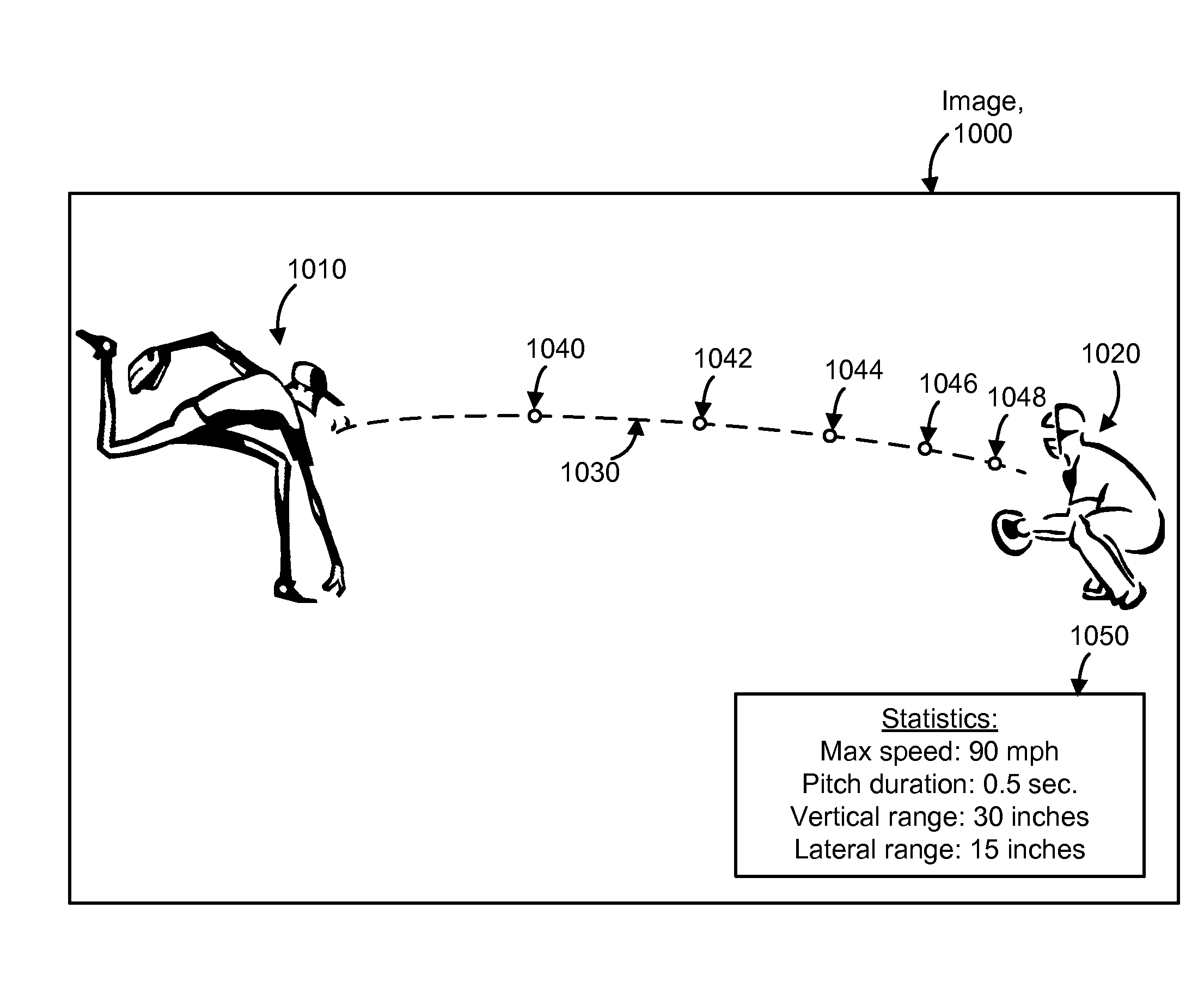
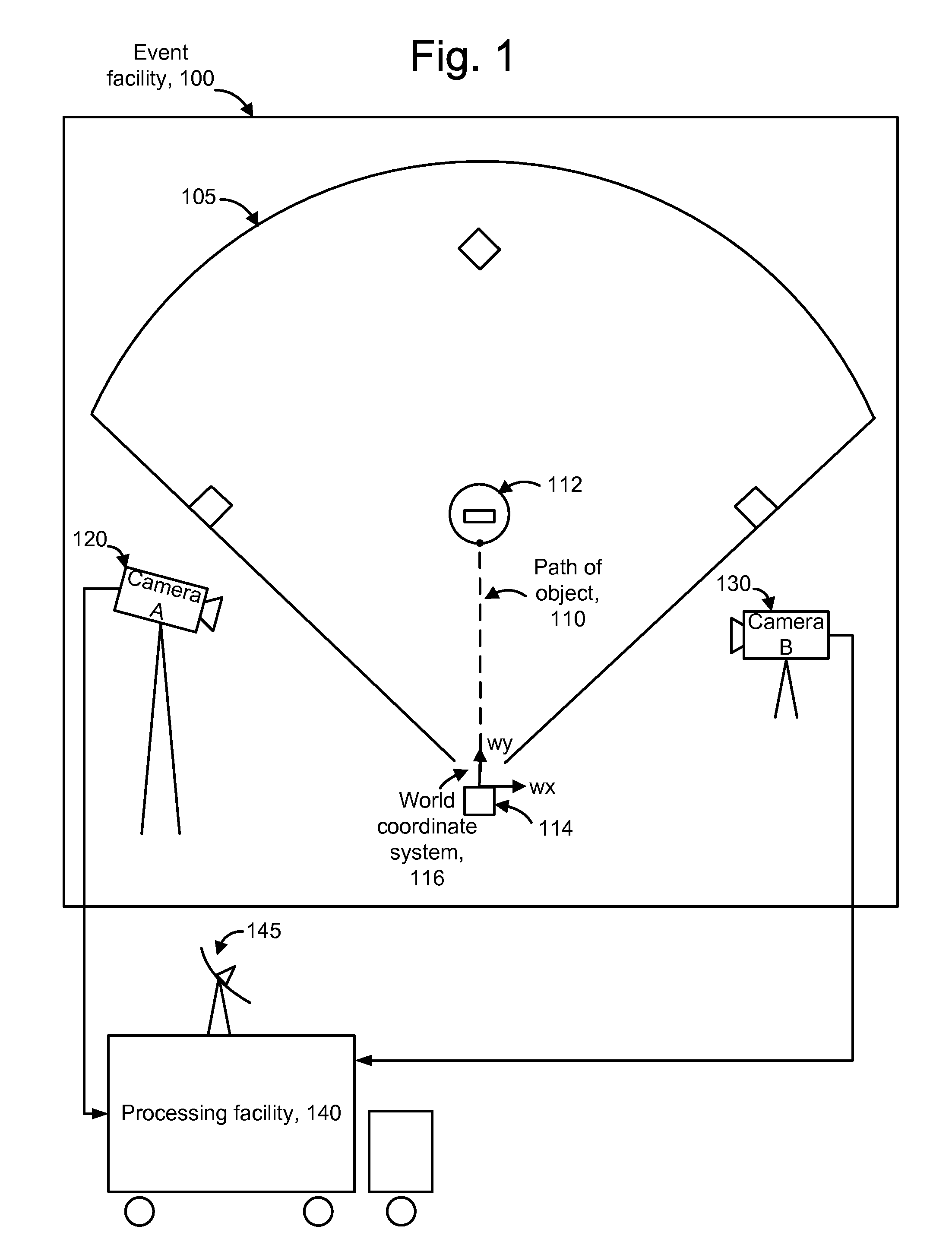
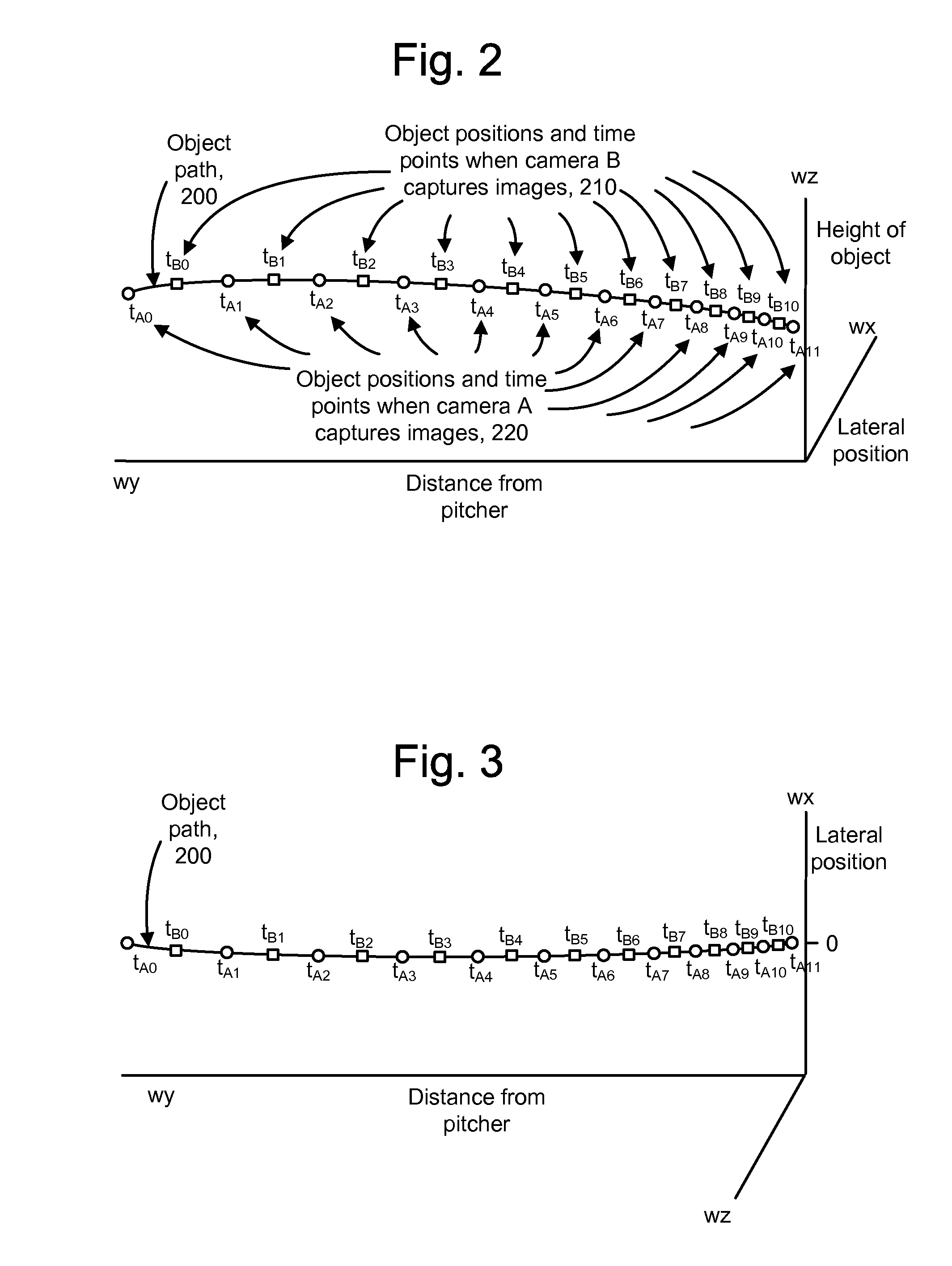
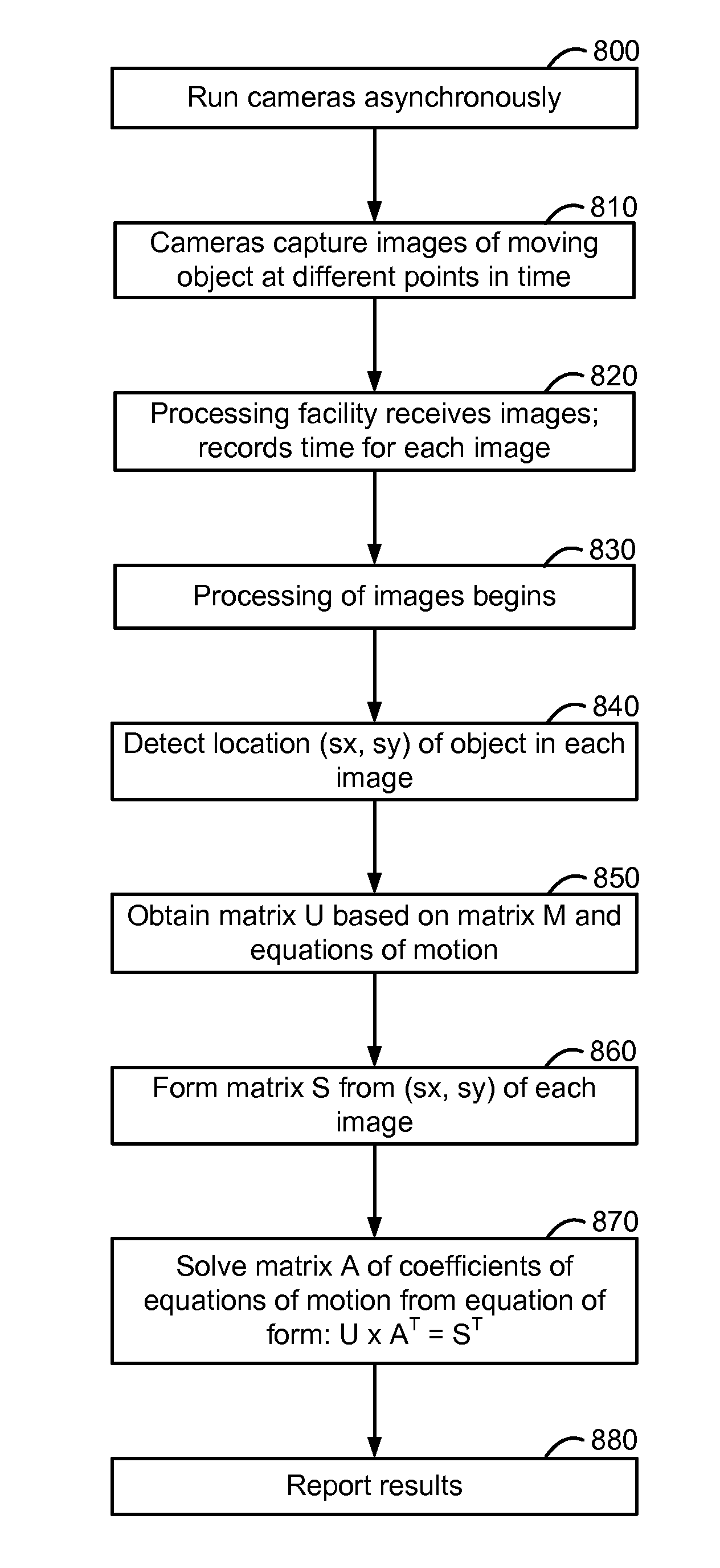
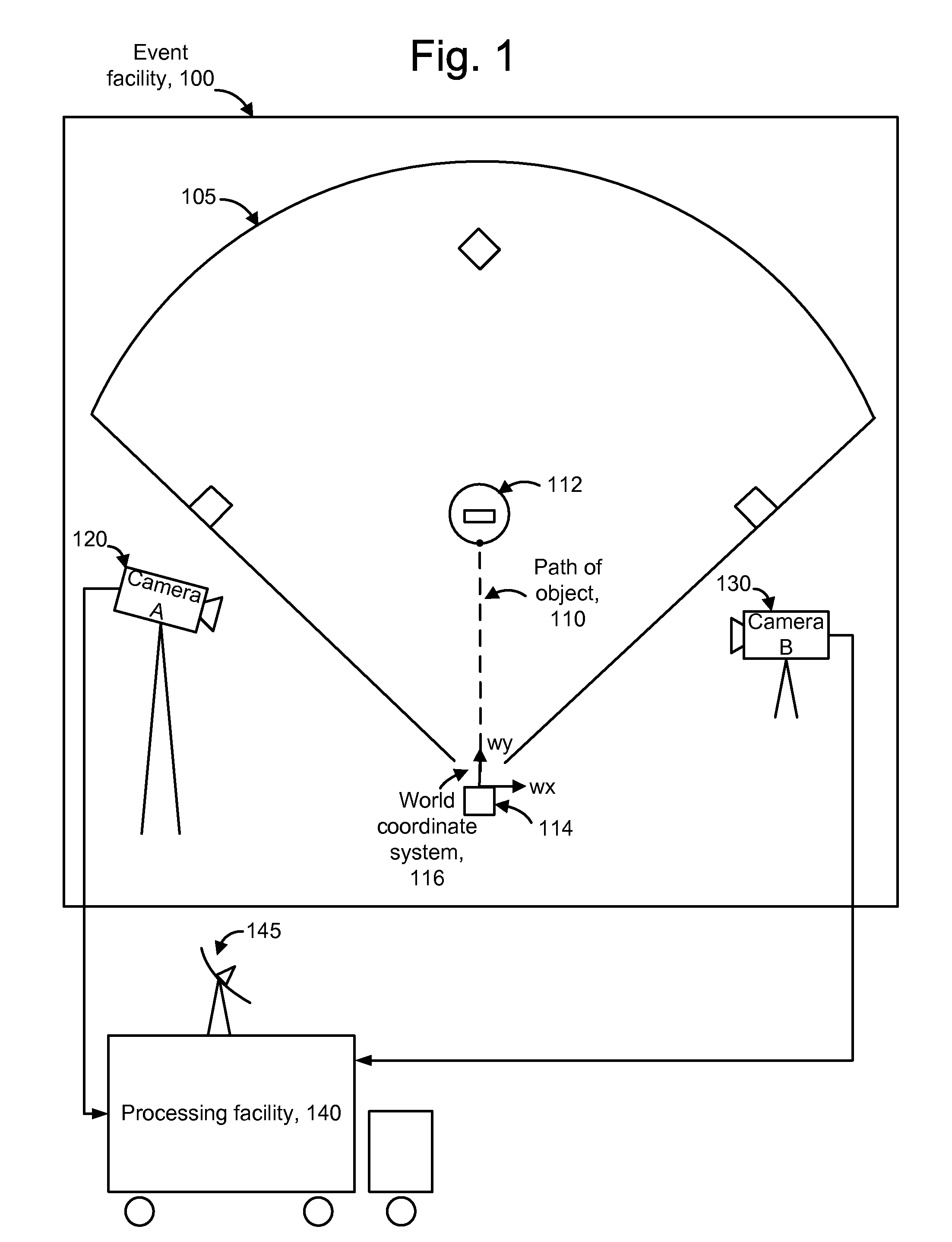
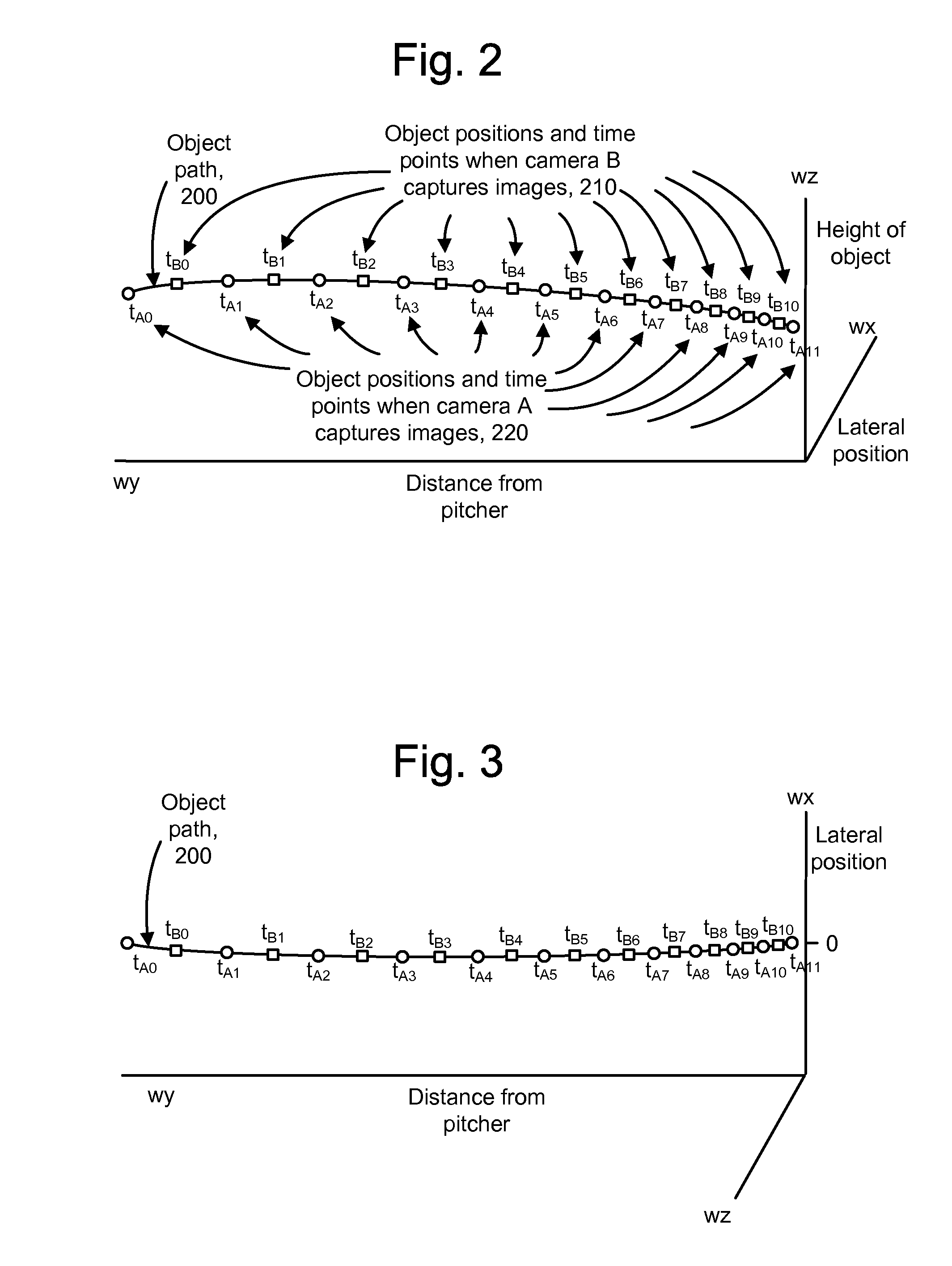
Tracking an object with multiple asynchronous cameras
The path and / or position of an object is tracked using two or more cameras which run asynchronously so there is need to provide a common timing signal to each camera. Captured images are analyzed to detect a position of the object in the image. Equations of motion for the object are then solved based on the detected positions and a transformation which relates the detected positions to a desired coordinate system in which the path is to be described. The position of an object can also be determined from a position which meets a distance metric relative to lines of position from three or more images. The images can be enhanced to depict the path and / or position of the object as a graphical element. Further, statistics such as maximum object speed and distance traveled can be obtained. Applications include tracking the position of a game object at a sports event.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
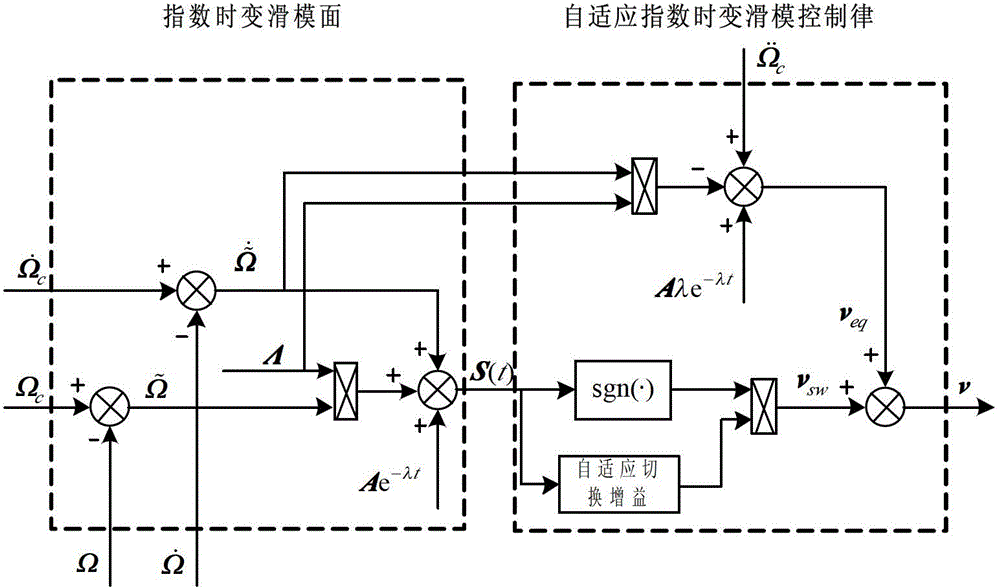
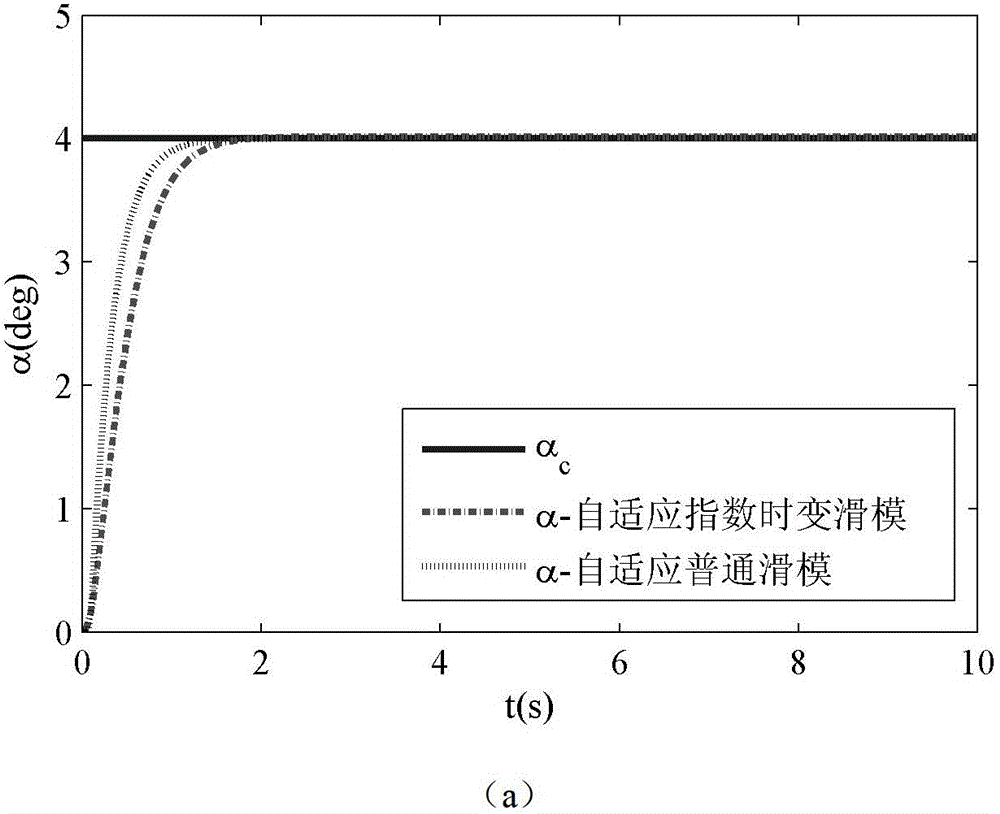
Self-adaptive index time varying slip form posture control method of reentry flight vehicle
InactiveCN102880060ASolve non-robust problemsImprove robustnessVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlAttitude controlFlight vehicle
The invention relates to a self-adaptive index time varying slip form posture control method of a reentry flight vehicle, belonging to the technical field of flight vehicles. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a posture motion equation in a mode that a powerless reentry flight vehicle model is used as an object; secondly modifying the equation into the mode of an MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) affine non-linear system, further applying a feedback linearization principle to carry out linearization processing so as to obtain a three-channel linearization model of pitching, rolling and yawing; aiming at the obtained linearization system, designing a modified self-adaptive index time varying slip form controller; and subsequently obtaining a control moment instruction for the posture control of the reentry flight vehicle, and inputting the control moment instruction into the reentry flight vehicle so as to control the posture. By combining the index time varying slip form control with a self-adaptive method, the problem of excessive adaptation of switch gain in the self-adaptive slip form control is solved to a certain extent, the uncertainty of system parameters and the influence of external disturbance can be suppressed effectively, and the precise posture control is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
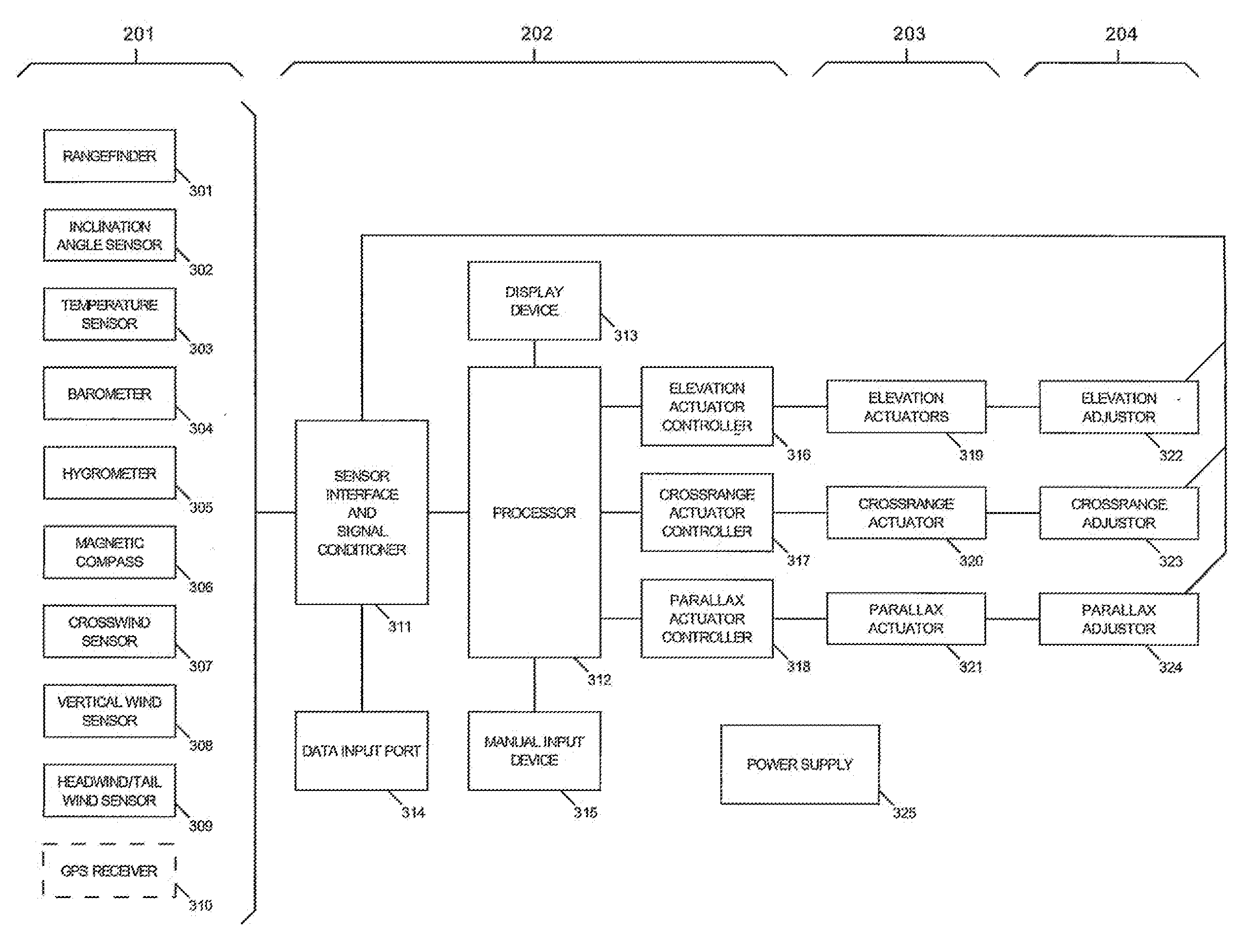
Optical Sighting System
ActiveUS20090266892A1Facilitate rapid aimingControlling membersMechanical apparatusDynamic modelsEngineering
An automatic optical sighting system generates at least one adjustment for an adjustable optical system based on at least one detected condition, an appropriate dynamic model of a projectile in flight, and a solution of the equations of motion in flight, so that the projectile will have a trajectory between an origin and a selected target that helps the projectile to hit the target.
Owner:WINDAUER BERNARD T +1
Tracking an object with multiple asynchronous cameras
The path and / or position of an object is tracked using two or more cameras which run asynchronously so there is need to provide a common timing signal to each camera. Captured images are analyzed to detect a position of the object in the image. Equations of motion for the object are then solved based on the detected positions and a transformation which relates the detected positions to a desired coordinate system in which the path is to be described. The position of an object can also be determined from a position which meets a distance metric relative to lines of position from three or more images. The images can be enhanced to depict the path and / or position of the object as a graphical element. Further, statistics such as maximum object speed and distance traveled can be obtained. Applications include tracking the position of a game object at a sports event.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
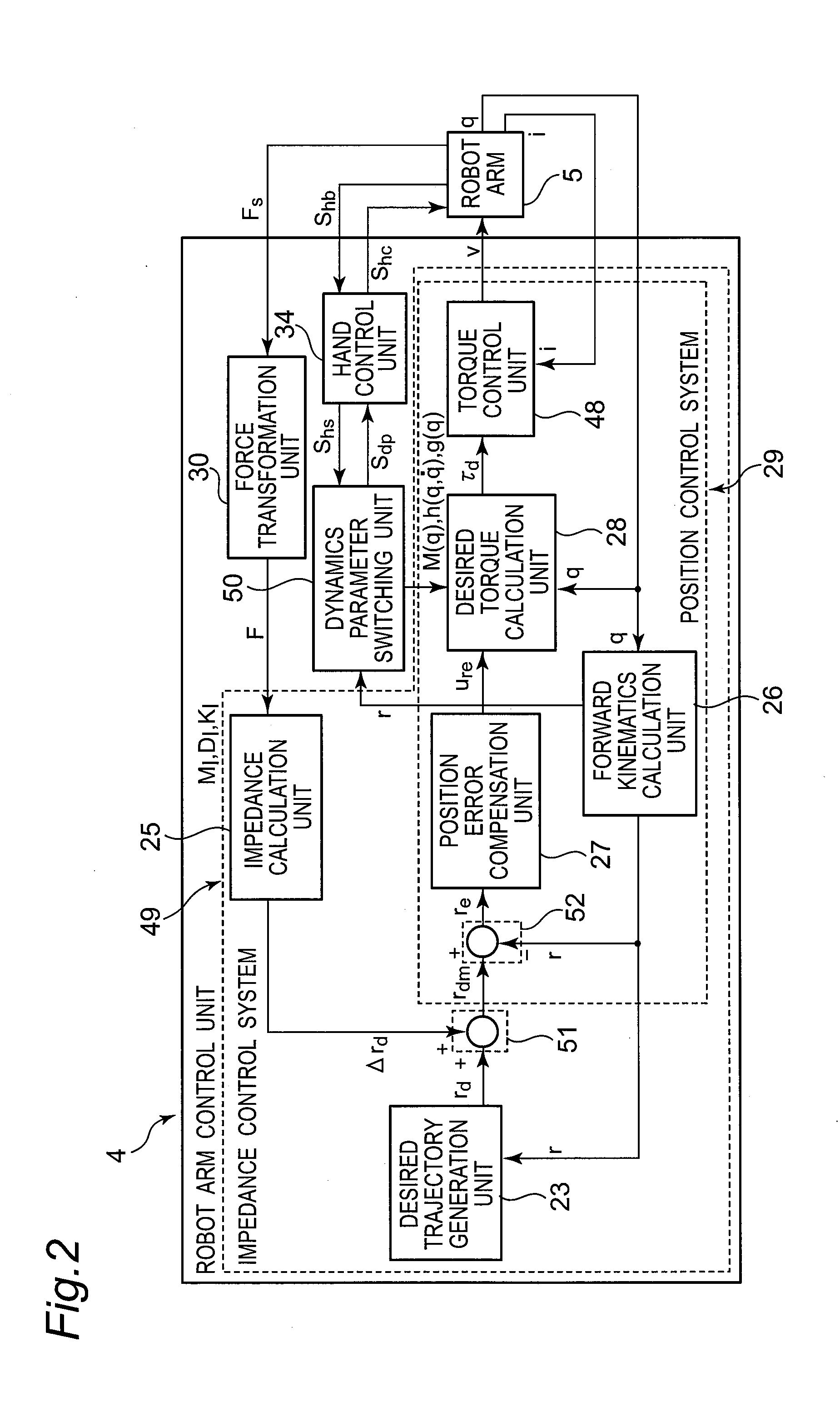
Robot, robot control device, robot control method, and robot control program
A robot having joints includes a position information acquiring section that acquires time series information about a robot position, speed information, or acceleration information, a dynamics parameter switching section that switches a gravity term component and an inertia force term component of a motion equation separately between dynamics parameters including dynamics parameter of the robot gripping no object and dynamics parameter including the object gripped by the robot which robot arm gripping the object, and a desired torque calculation section that outputs a desired robot joint torque value as a desired joint torque based on the motion equation after the dynamics parameter switching section switches the dynamics parameters and the time series information about the robot position, the speed information, or the acceleration information acquired by the position information acquiring section. The robot controls an operation of the robot based on an output from the desired torque calculation section.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
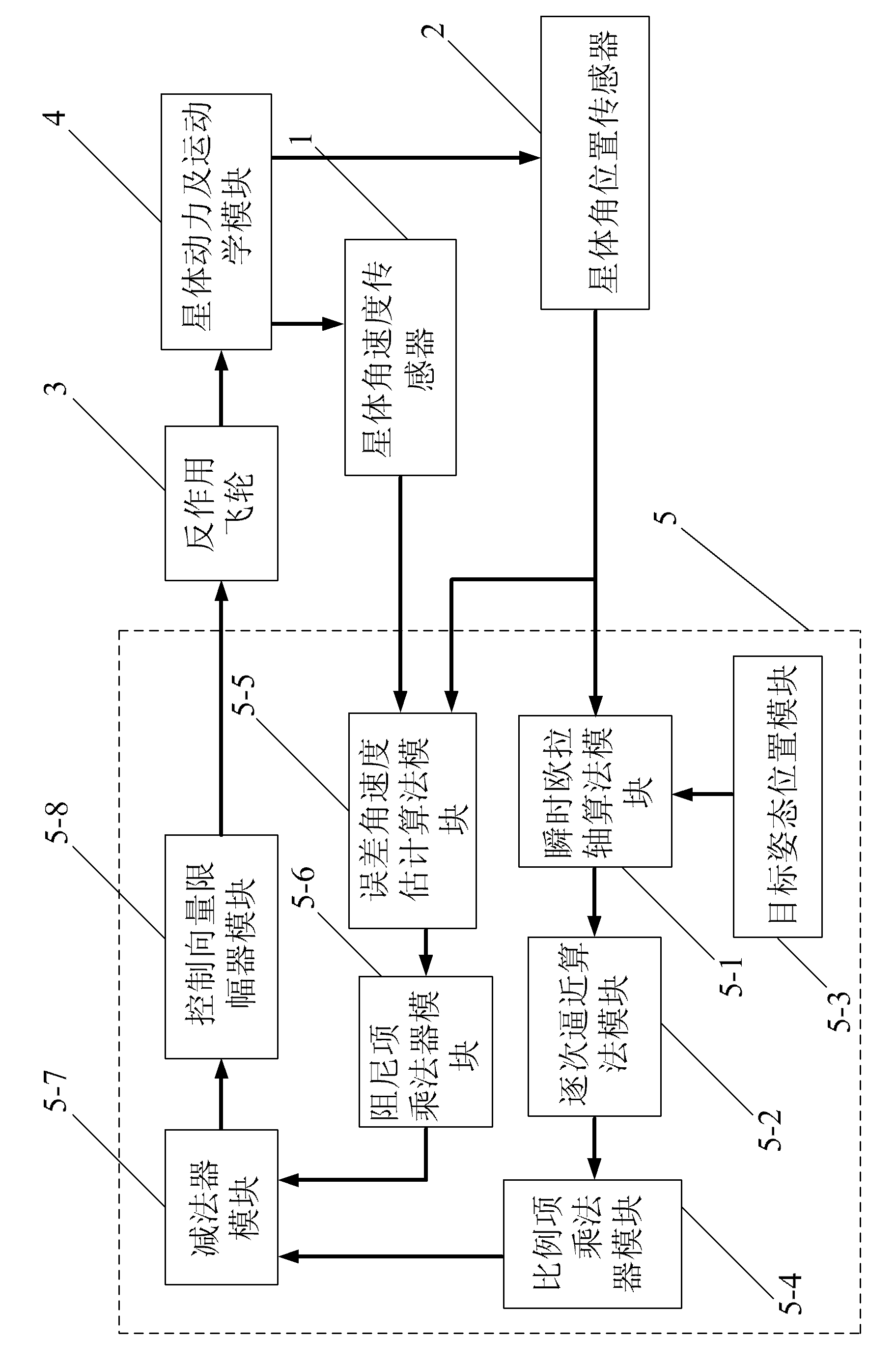
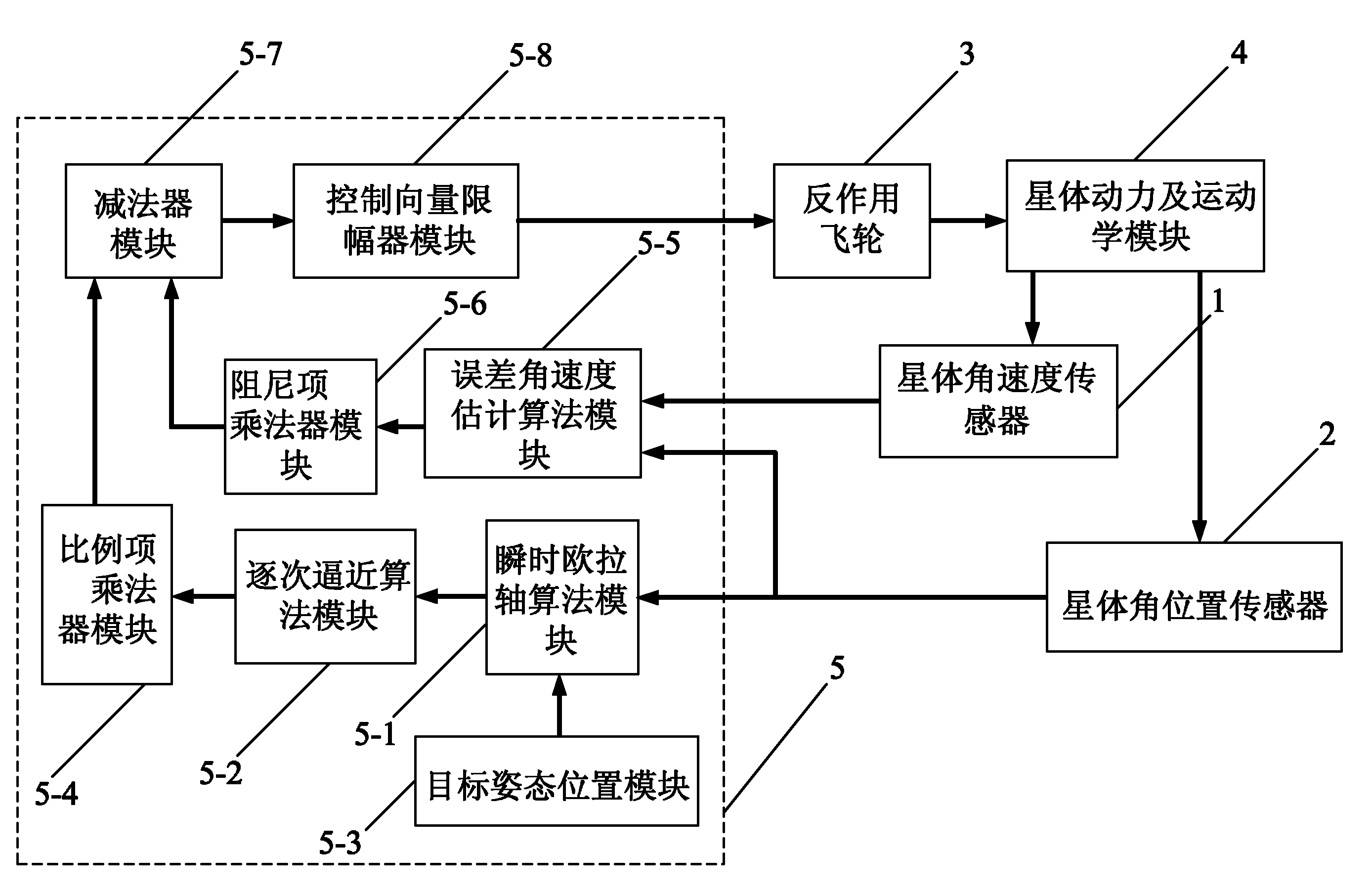
Flywheel based attitude maneuvering control device and method for successive approaching of satellite rounding instantaneous Euler shaft
InactiveCN101941528AExtended service lifeLow costSpacecraft guiding apparatusData controlSystem requirements
The invention discloses flywheel based attitude maneuvering control device and method for successive approaching of a satellite rounding an instantaneous Euler shaft and relates to control device and method for satellite attitude adjustment. The invention is provided for solving the problems of great fuel consumption, short service life of a satellite, complex configuration of an air injecting control system and difficult reduction of size and weight of the satellite existing in the realization of satellite wide-angle attitude maneuvering by adopting air injecting control. The method comprises the following steps of: setting a parameter of the control device according to the system requirement of the control device and obtaining attitude deviation angular velocity according to a motion equation; and expressing a relationship of the instantaneous Euler shaft and a deviation angle of the current attitude and a target attitude of the satellite by an attitude error quaternion to obtain a control signal, calculating to obtain a flywheel control input moment vector calculated by a satellite controller, to be used as a data control command as a basis for generating moment by a back action flywheel. The invention does not consume other resources on the satellite or consume fuel, prolongs the service life of the satellite and can be widely suitable for various satellites needing attitude maneuvering.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
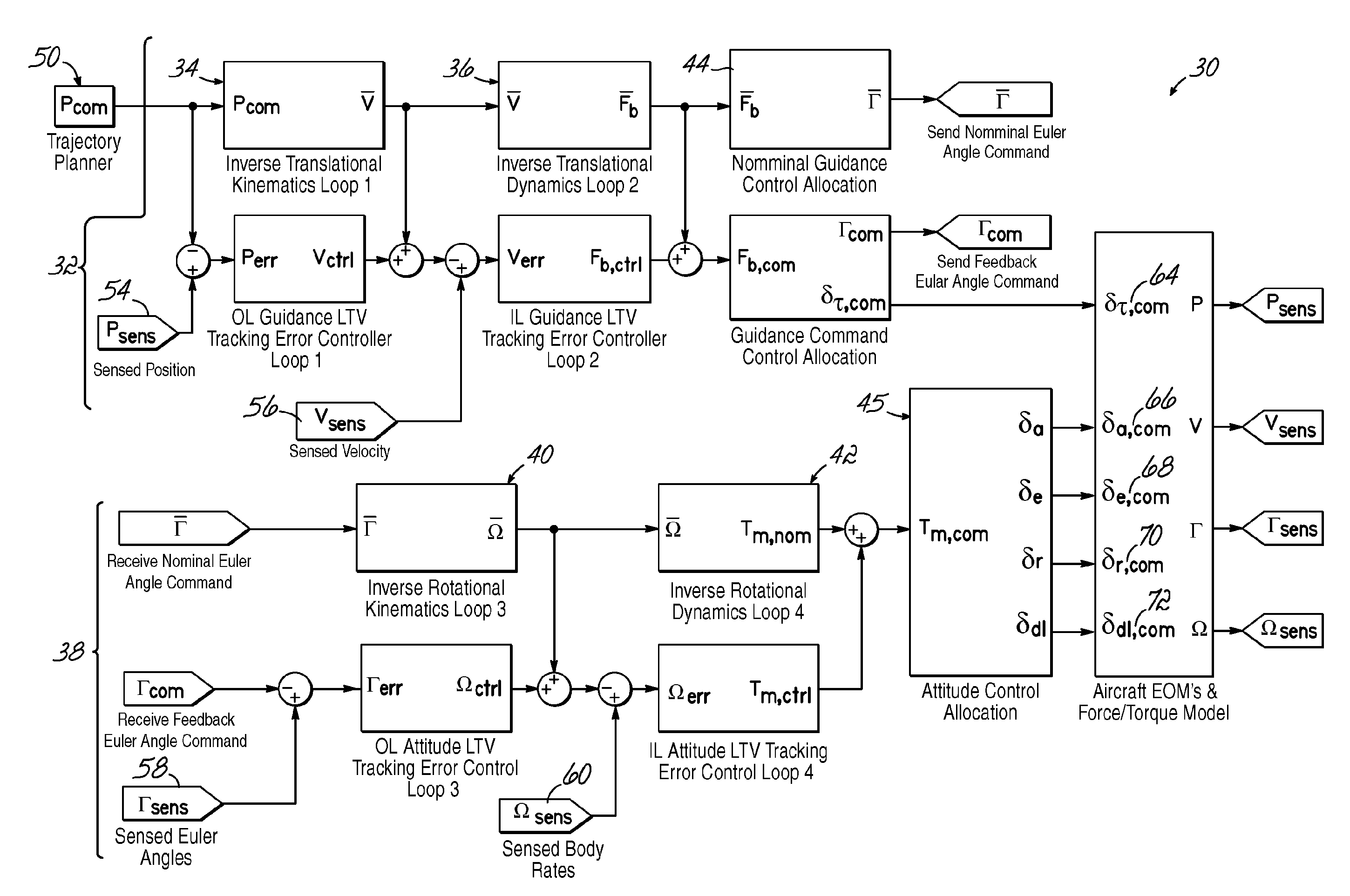
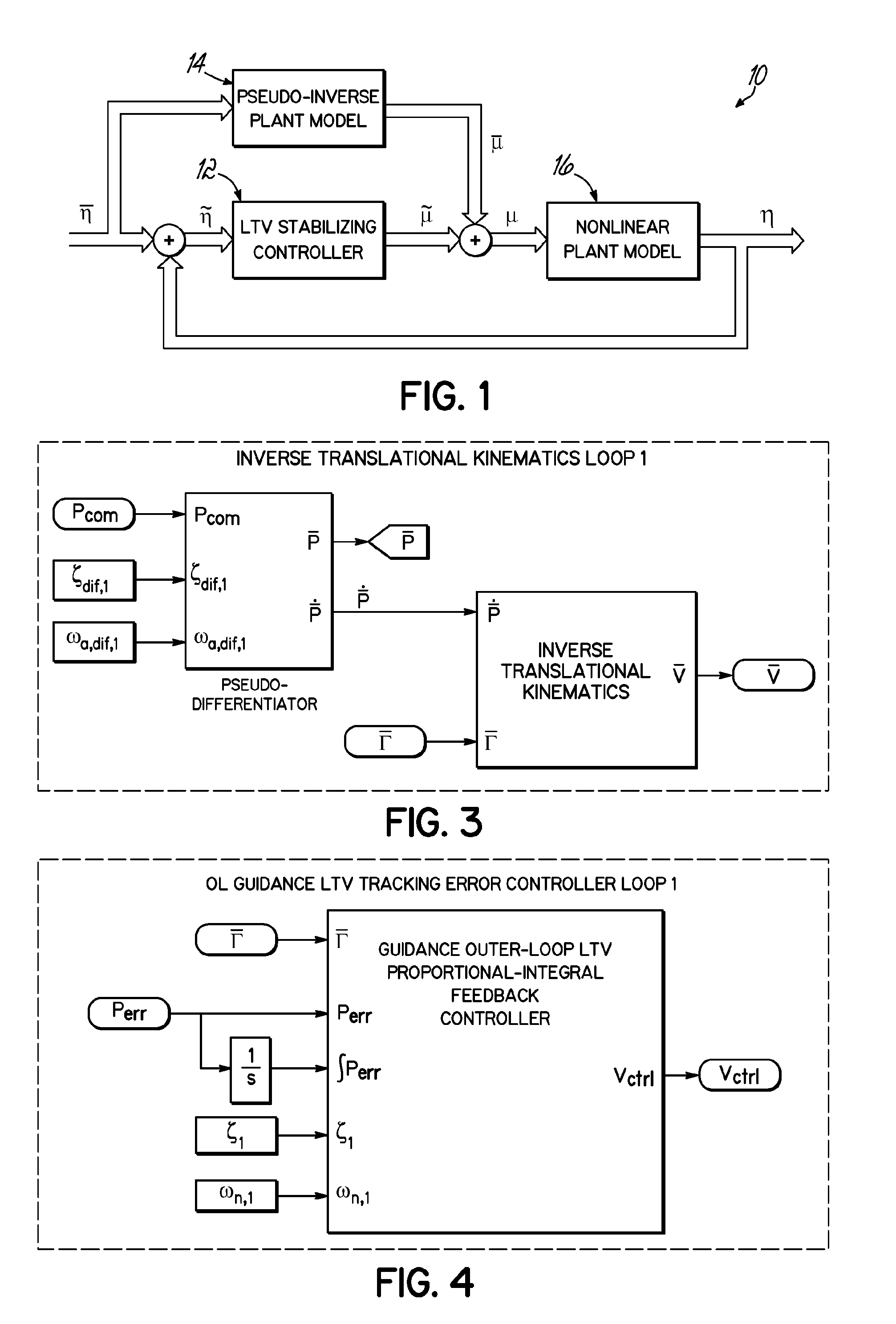
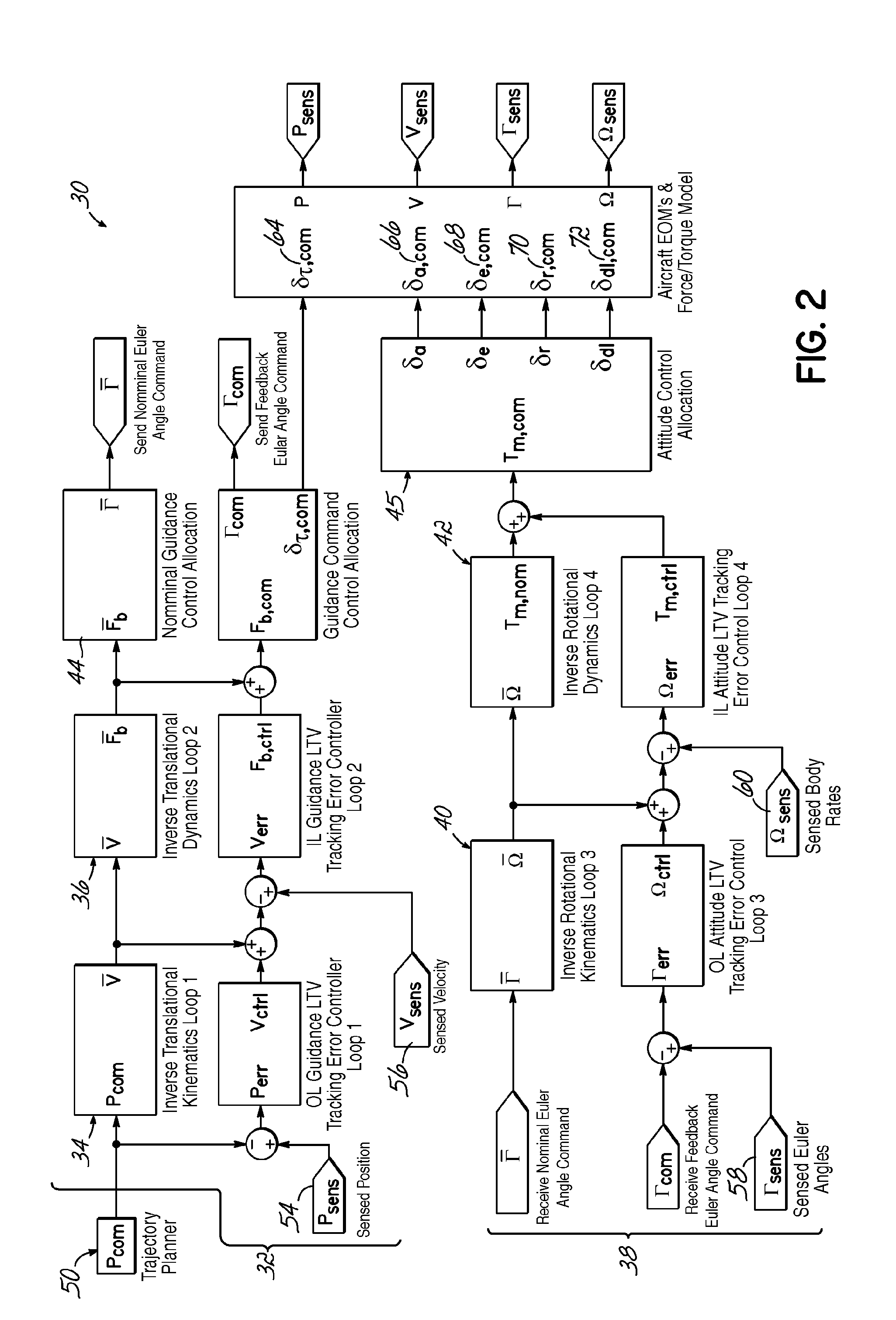
Trajectory tracking flight controller
ActiveUS20120095621A1Navigational calculation instrumentsDigital data processing detailsClosed loopNonlinear Dirac equation
A six degree-of-freedom trajectory linearization controller (TLC) architecture (30) for a fixed-wing aircraft (46) is set forth. The TLC architecture (30) calculates nominal force and moment commands by dynamic inversion of the nonlinear equations of motion. A linear time-varying (LTV) tracking error regulator provides exponential stability of the tracking error dynamics and robustness to model uncertainty and error. The basic control loop includes a closed-loop, LTV stabilizing controller (12), a pseudo-inverse plant model (14), and a nonlinear plant model(16). Four of the basic control loops (34, 36, 40, 42) are nested to form the TLC architecture (30).
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Image matching method and image interpolation method using the same
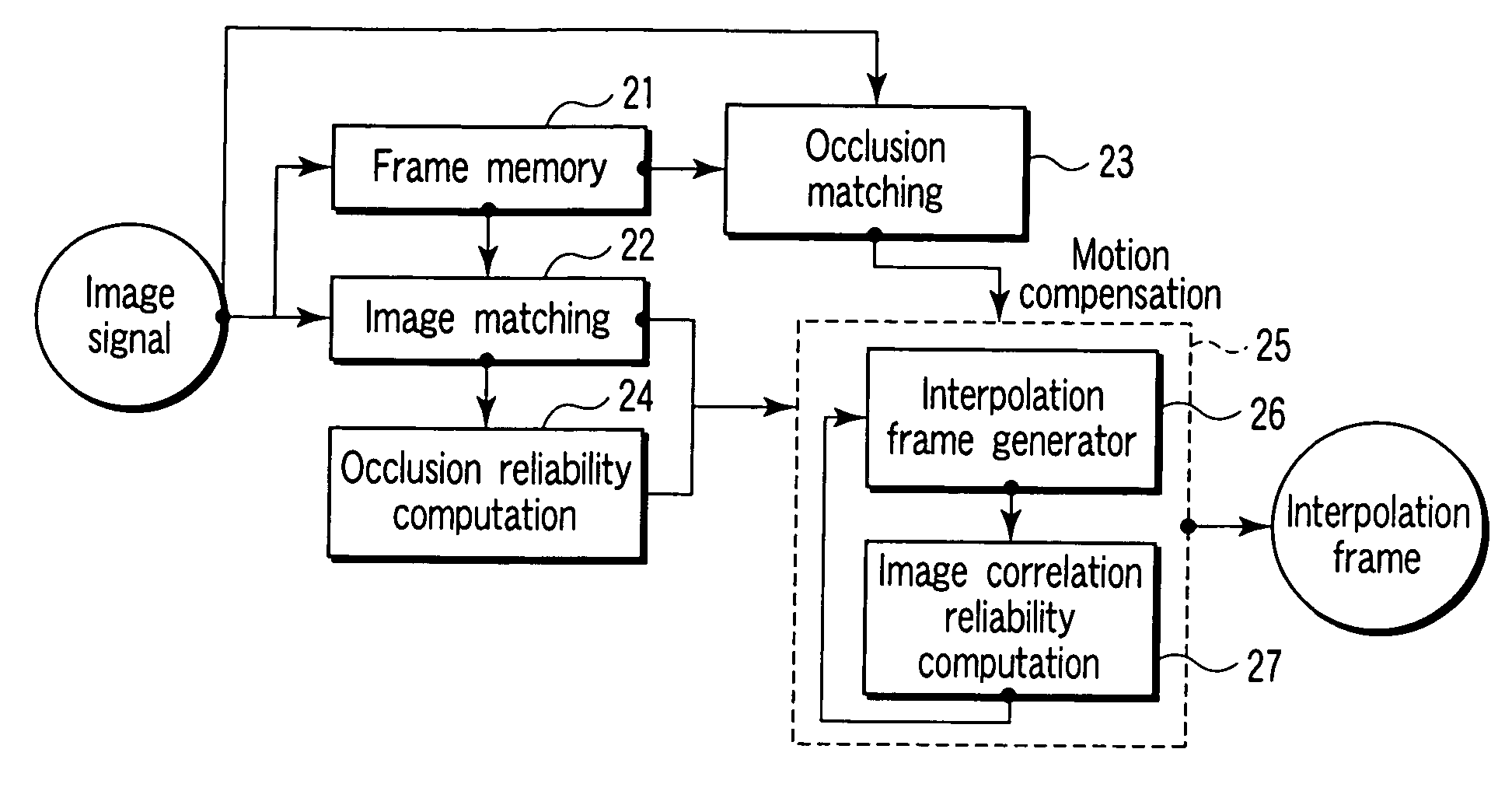
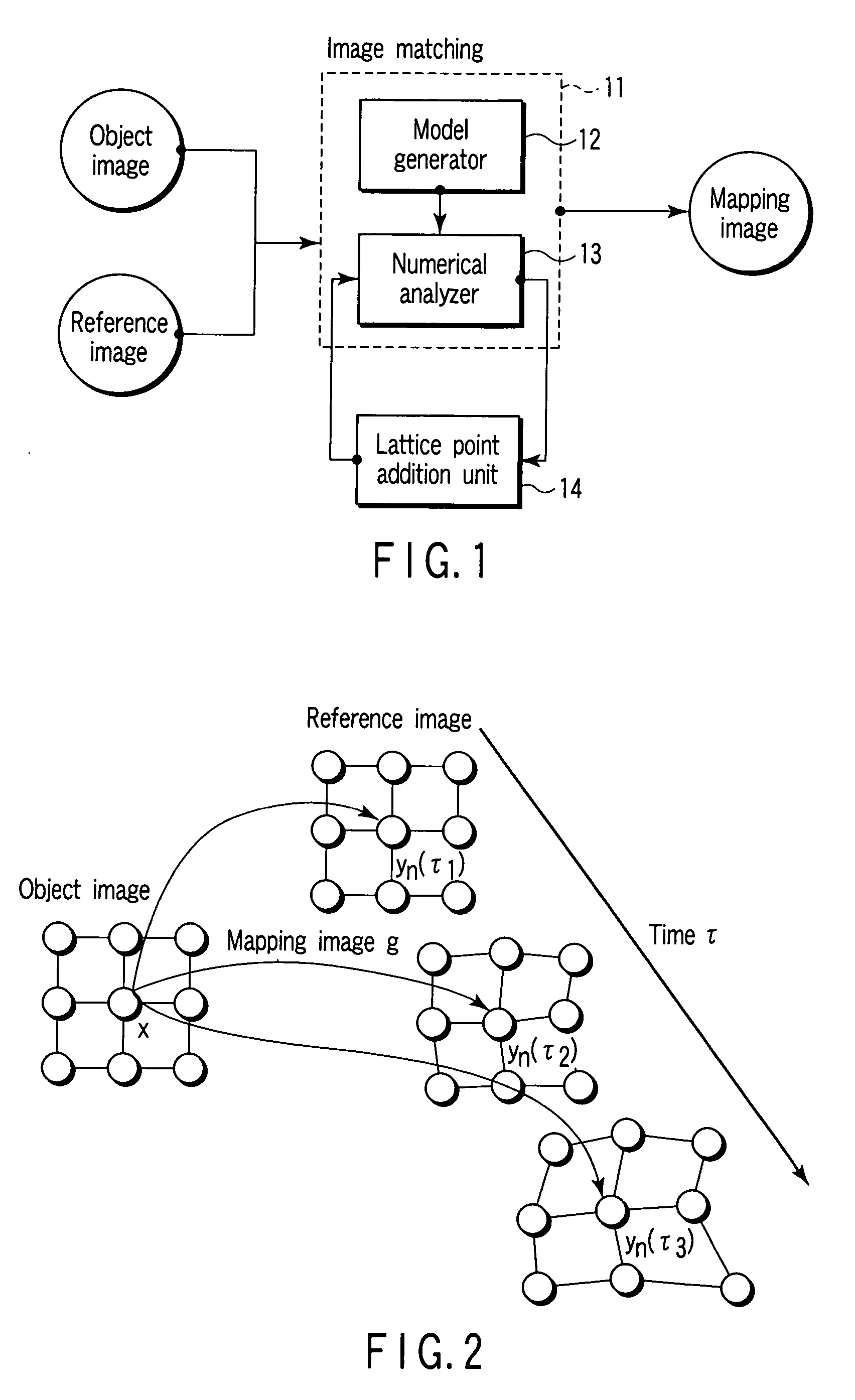
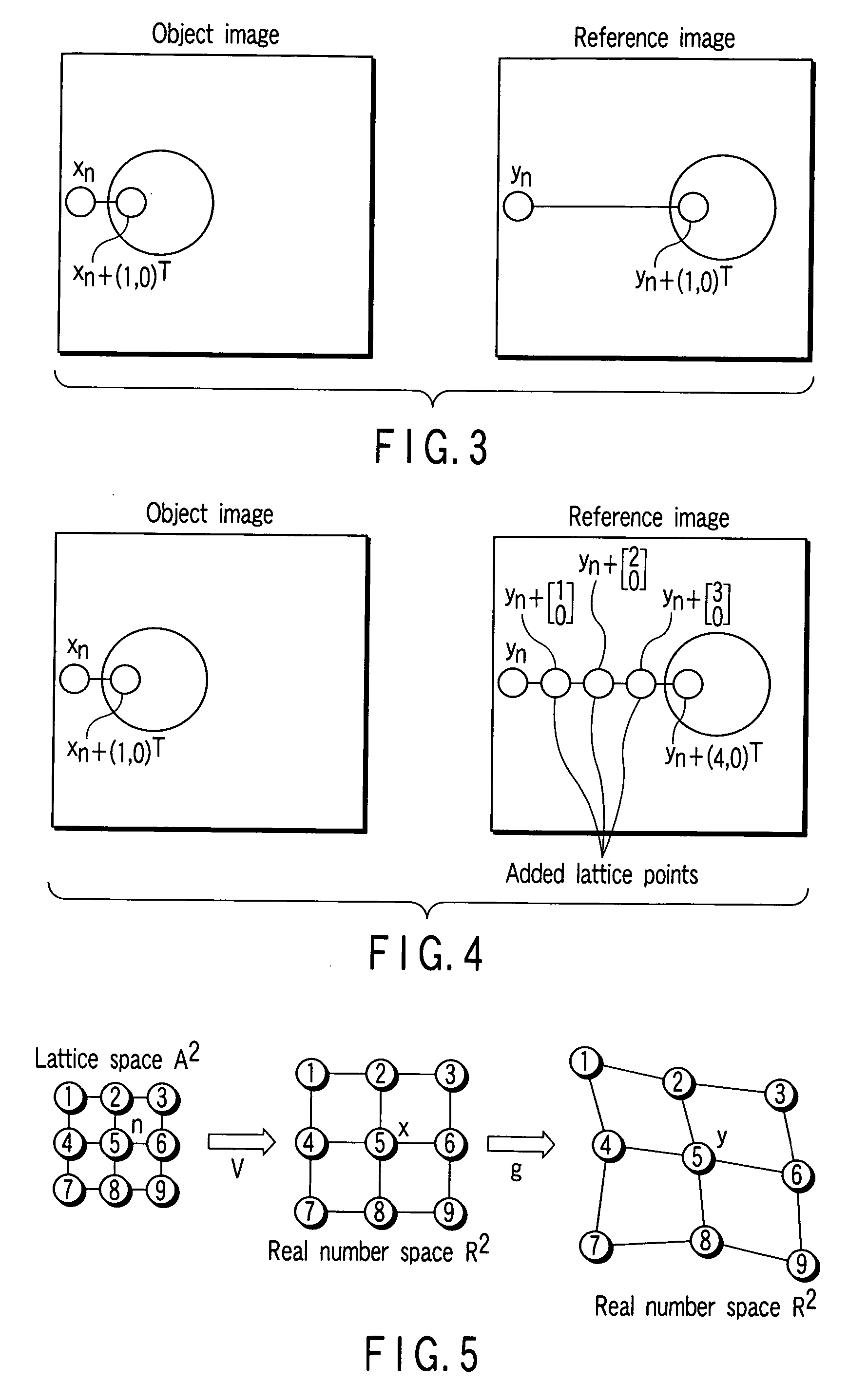
An image matching method includes setting first and second lattices to first and second images respectively, computing potential force to each second lattice point of the second lattice by a gradient of an image correlation potential energy based on a position of each first lattice point and pixel thereof and a position of the second lattice point and pixel thereof, computing elasticity force to the second lattice point from elasticity energy between the second and adjacent lattice points, computing frictional force occurring at the second lattice point, performing a numerical analysis of an equation of motion regarding the second lattice point and based on the potential force, elasticity force and frictional force to obtain a convergence state of the second lattice points, and adding a new lattice point between an adjacent lattice point pair of second lattice points according to a distance between the adjacent lattice point pair.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Robot device, motion control device for robot device and motion control method
ActiveUS20050038560A1Force be exertAccurate balanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlHorizontal axisEngineering
A motion equation with a boundary condition regarding a future center-of-gravity horizontal trajectory of a robot is solved so that the moment around a horizontal axis at a point within a support polygon is zero when the robot is in contact with a floor or so that horizontal translational force is zero when the robot is not in contact with the floor and so that connection is made to a current horizontal position and speed of the center of gravity. In addition, a motion equation with a boundary condition regarding a future center-of-gravity vertical trajectory of the robot is solved so that vertical translational force acting upon the robot other than gravity is zero when the robot is not in contact with the floor and so that connection is made to a current vertical position and speed of the center of gravity. A motion state of a next time is determined so that, when the robot is not in contact with the floor, the moment around the center of gravity is zero, and the determined center-of-gravity position is achieved. Therefore, a stable motion pattern which allows transition between a floor contact period and a floor non-contact period is generated in real time.
Owner:SONY CORP
Wearing-type motion assistance device and program for control
ActiveUS7857774B2Sufficient in conformityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGymnastic exercisingRotational axisEngineering
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC
Multi-sensor guidance system for extreme force launch shock applications
InactiveUS20050040280A1Direction controllersDigital data processing detailsGuidance systemControl signal
A projectile navigation system operable within an extremely high G-shock loading environment during the launch phase may include a set of Kalman filters configured to repeatedly calculate a navigational solution by solving a set of non-linear equations of motions of the projectile utilizing a current parameter vector, position, velocity, and attitude of the projectile. The system may include a suite of solid state sensors to calibrate the Kalman filter equations. If desired, the system may also include a satellite based positioning-determining (SBPD) attitude determination system configured to update the state of the host projectile by making real time attitude measurements of the projectile, and a parameter estimator configured to estimate and update a parameter vector of the host projectile. An external guidance and control processor may be used to generate guidance and control signals, enabling real time navigation of the host projectile.
Owner:HUA CUONG TU
Optimal track planning method for space robot for capturing rolling target
ActiveCN106625671ADoes not encounter kinetic singularitiesReduce collision forceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorOptimal controlSimulation
The invention discloses an optimal track planning method for a space robot for capturing a rolling target. The method comprises the steps that a motion equation of the space robot and the rolling target is set up; a solution algorithm of the work space of the space robot and a determining rule of the optimal capturing opportunity are provided; the optimal capturing track of a mechanical arm end effector is obtained, finally, the effectiveness of the method is verified through examples. According to the determining rule of the optimal capturing opportunity, it can be guaranteed that capturing occurs in the path-independent work space of the space robot, and therefore a dynamics singular problem is avoided. According to the optimal capturing track, obtained based on the optimal control theory, of the mechanical arm end effector, it can be guaranteed that the end effector and a capturing point on the target reach the same position at the identical speed, and therefore collision force generated during capturing is minimum.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
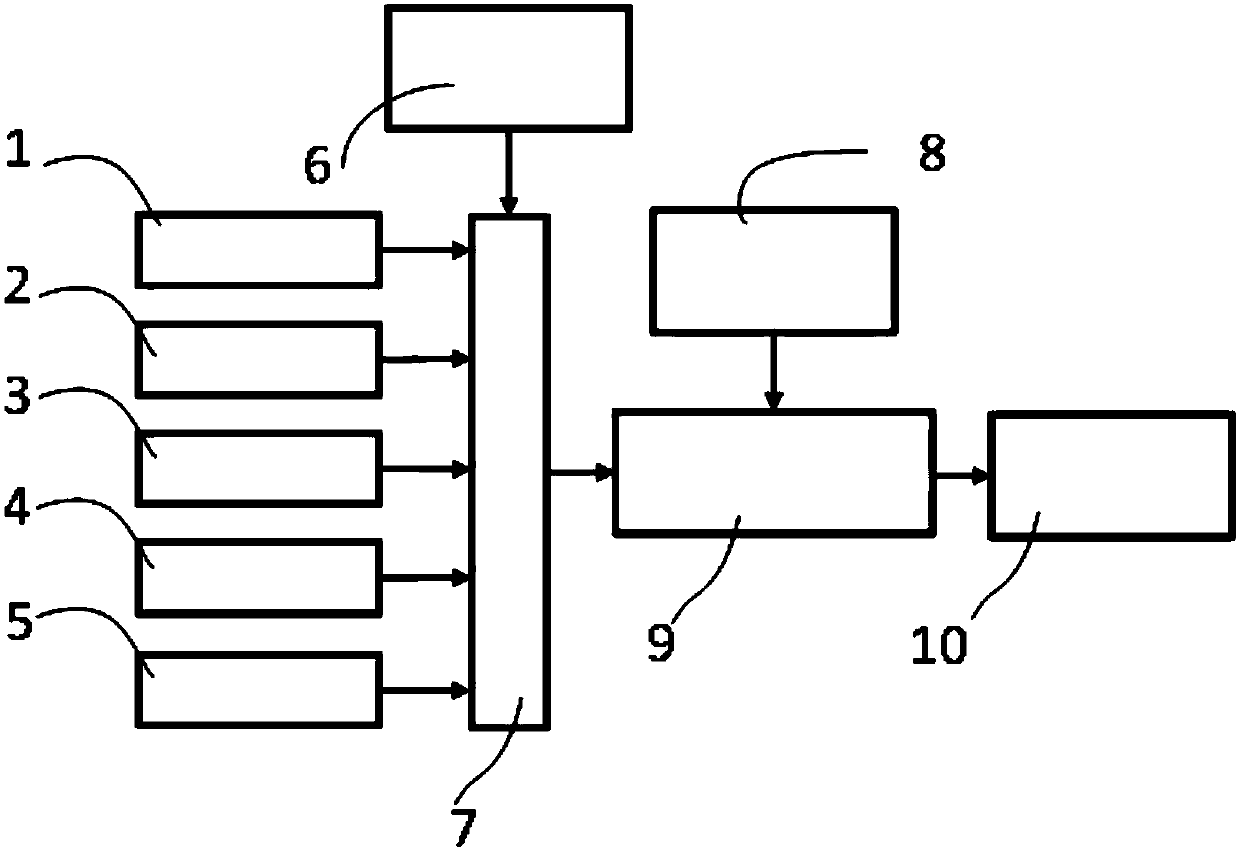
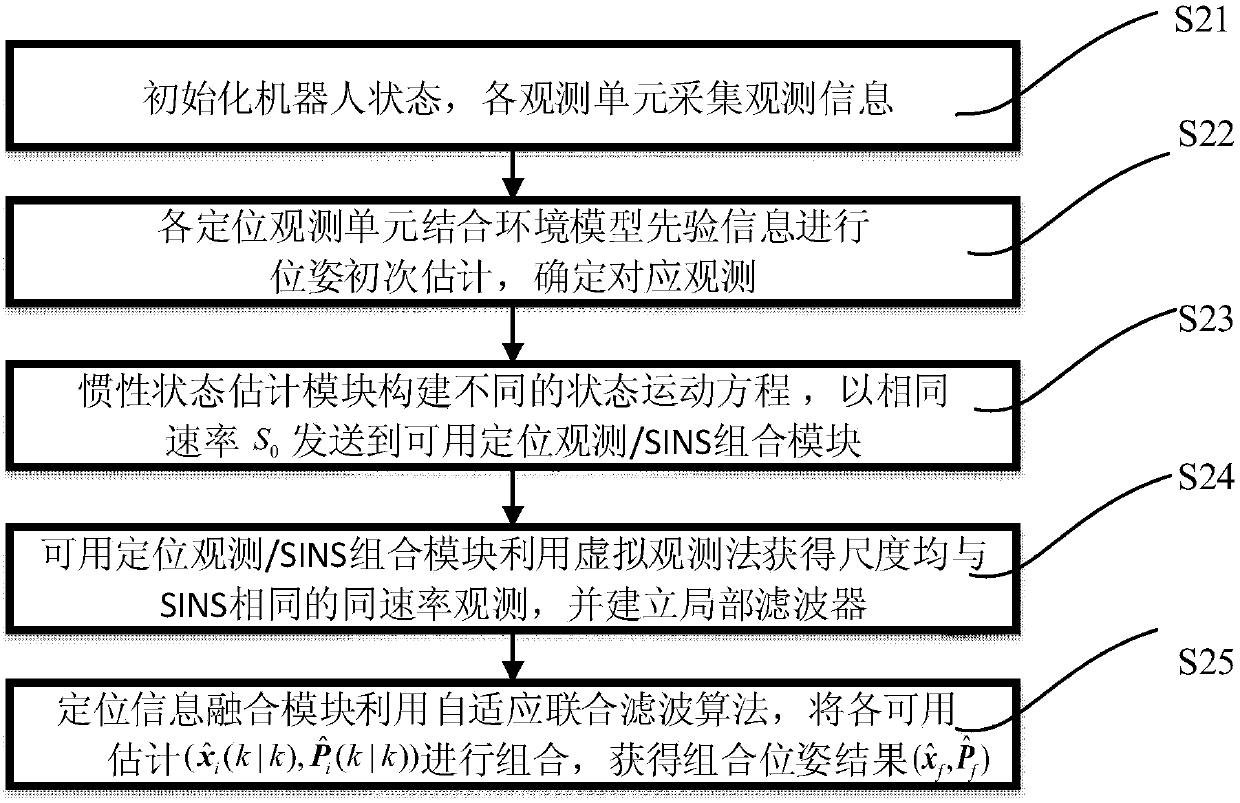
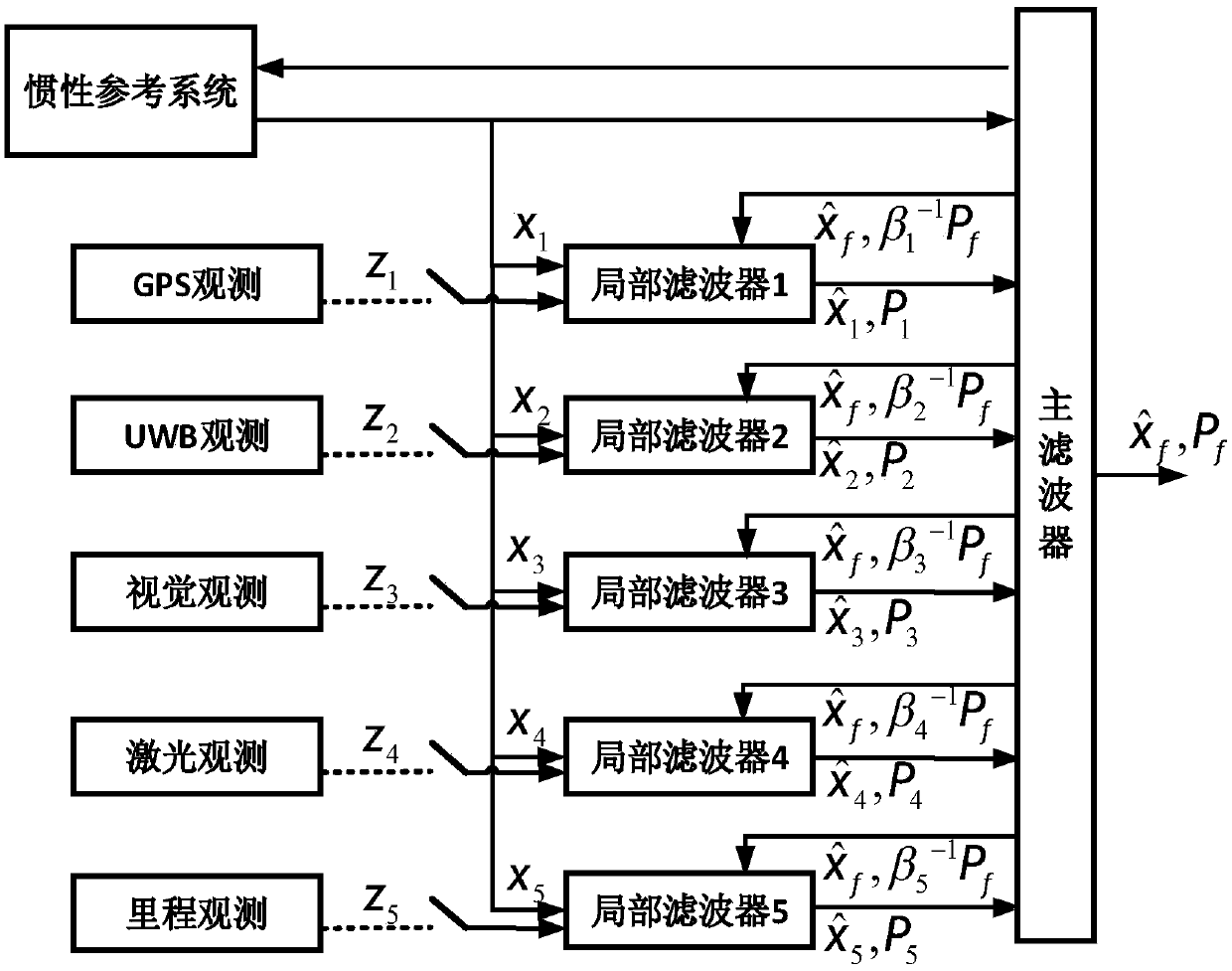
System and method for locating inspection robot in petrochemical plant
ActiveCN108225302AGuaranteed seamless positioningObservation synchronizationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingPetrochemicalGlobal Positioning System
The invention discloses a system and a method for locating an inspection robot in a petrochemical plant. The system comprises a global positioning system (GPS) observation unit, an ultra-wide bandwidth (UWB) observation unit, a visual observation unit, a laser observation unit, a mileage observation unit, a combination decision module, an inertial state estimation module, an available positioningobservation / strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) combination module, and a positioning information fusion module. The GPS observation unit, the UWB observation unit, the visual observation unit, the laser observation unit and the mileage observation unit acquire the respective observation data and send same to the combination decision module; the combination decision module performs multi-layer map-based positioning by combining an environmental map model stored in an environmental model prior information module so as to determine available observation types; the available positioning observation / SINS combination module combines available observation data with a corresponding motion equation established by an inertial state estimation module, and the combined result is sent to the positioning information fusion module for carrying out final integrated pose estimation. The system and the method solve the problem of seamless positioning of the inspection robot which runs in various complicated regions of the petrochemical plant, and guarantee the continuity of a positioning process and the stability of the positioning result.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Accurate track tracking control method based on finite time expansion state observer
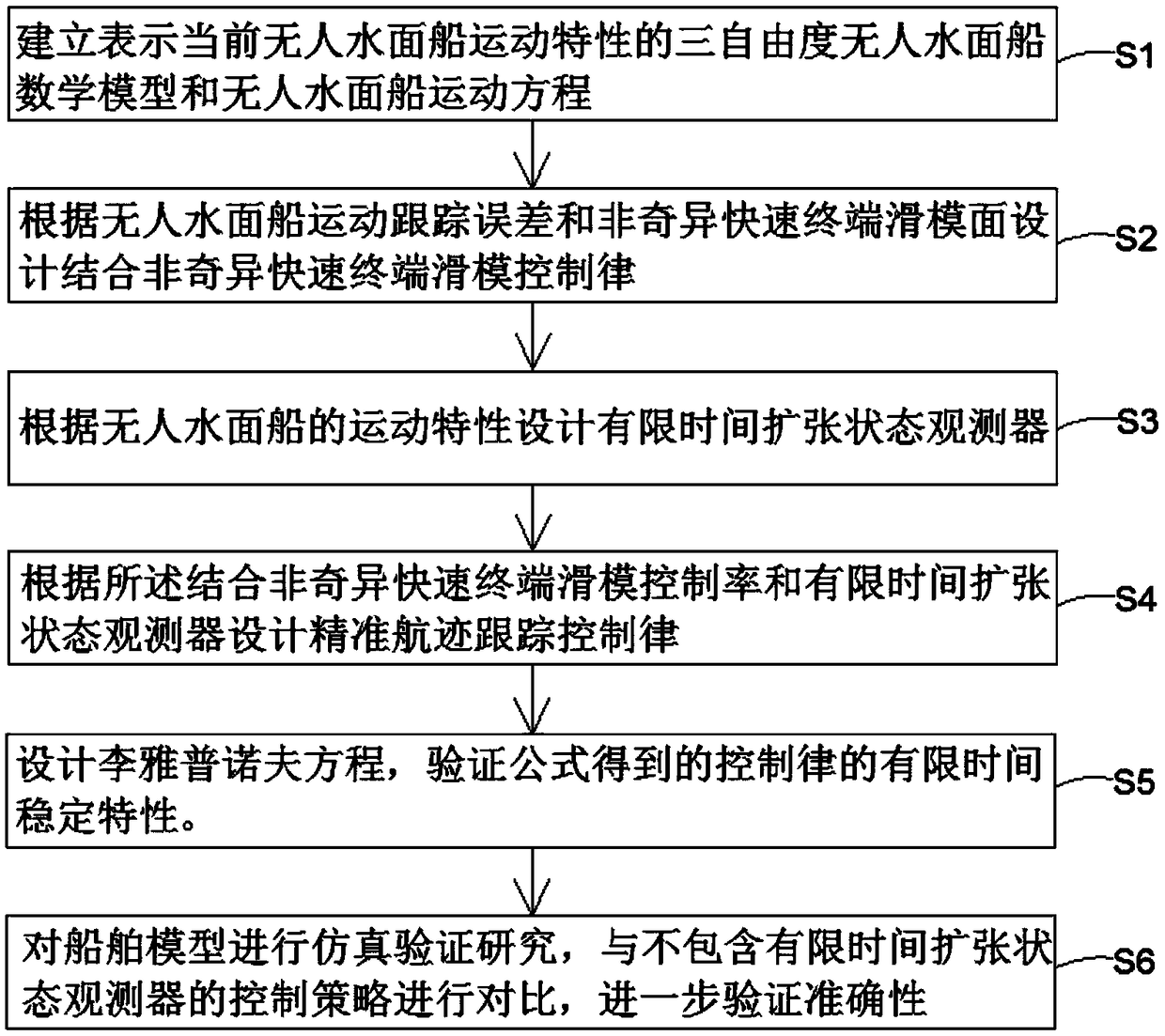
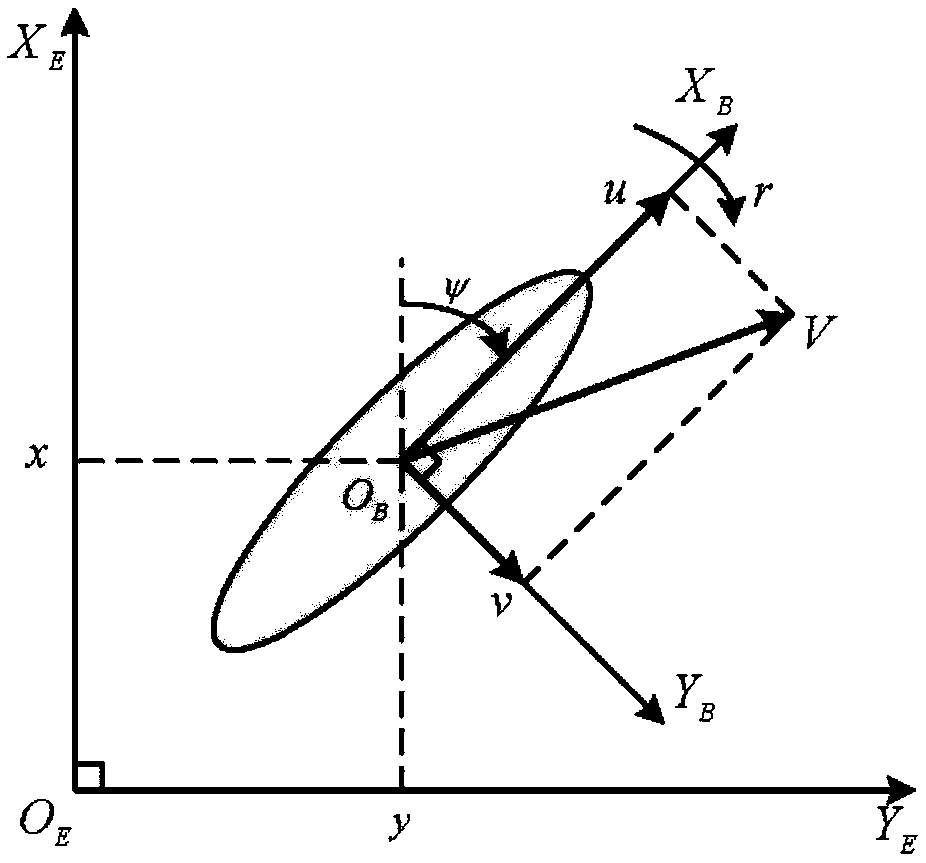
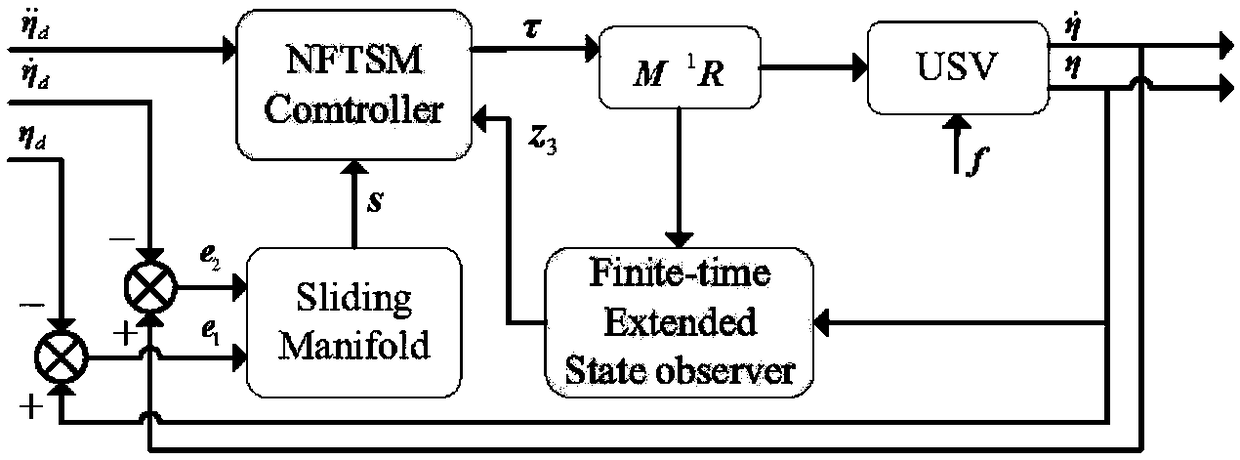
ActiveCN108828955AOvercome limitationsPrecise track tracking control performanceAdaptive controlKinematics equationsMathematical model
The present invention provides an accurate track tracking control method based on a finite time expansion state observer. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a mathematical modeland a kinematic equation representing current unmanned ship motion features, designing a combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law according to the unmanned surface ship motion tracking errors and a nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode surface, designing a finite time expansion state observer according to the unmanned ship motion features, and designing an accurate track tracking control law according to the combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law and the finite time expansion state observer. Through design of the finite time expansion state observer, the lump interference comprising external interference and a complex nonlinear term can be observed by the finite time to a small enough range to avoid the limitation of the approximation observation. Through the designed combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law and the nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode unmanned ship track tracking controller, the accurate track tracking control method achieves the accurate track tracking control performance in a complex external interference.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
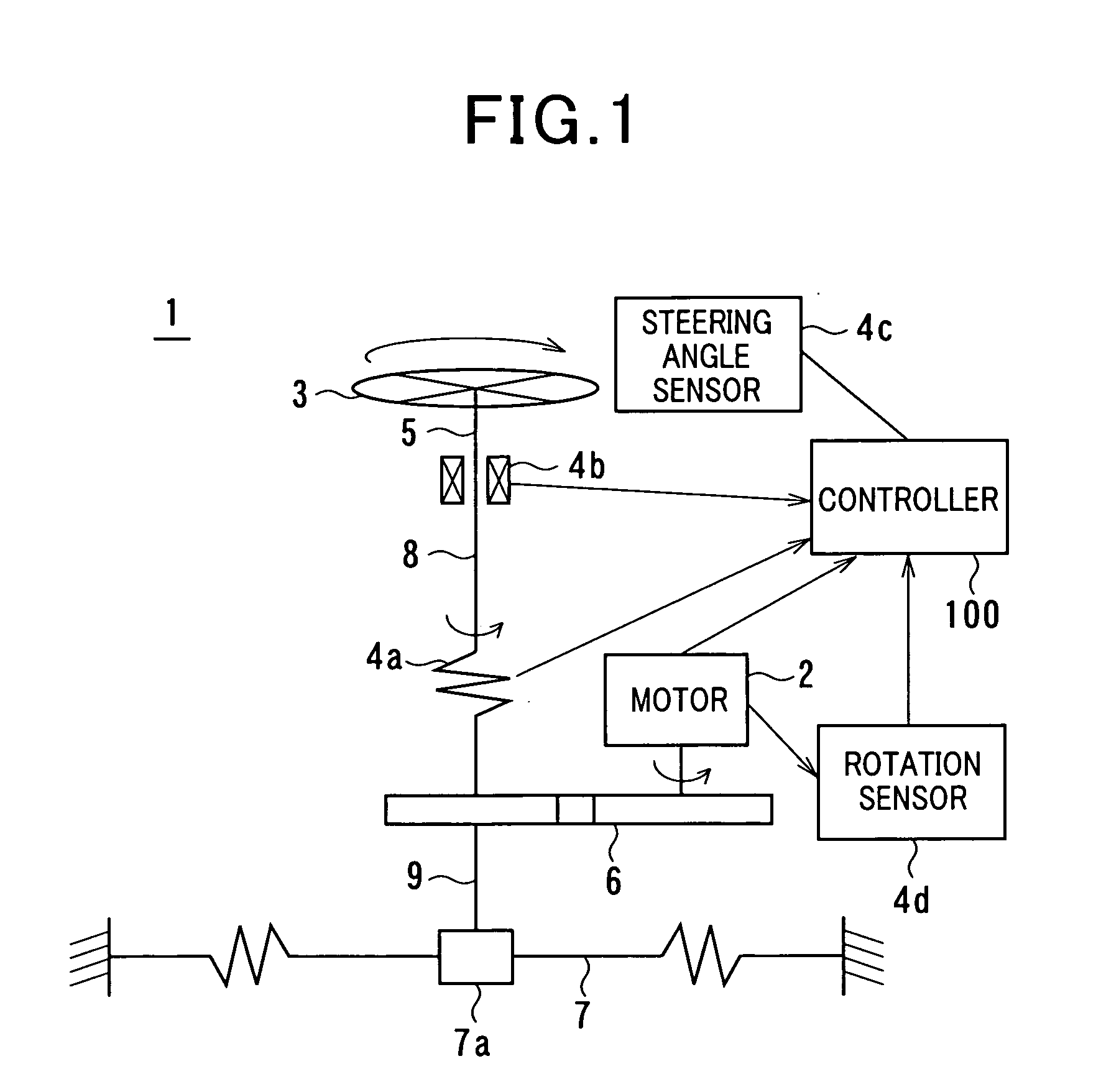
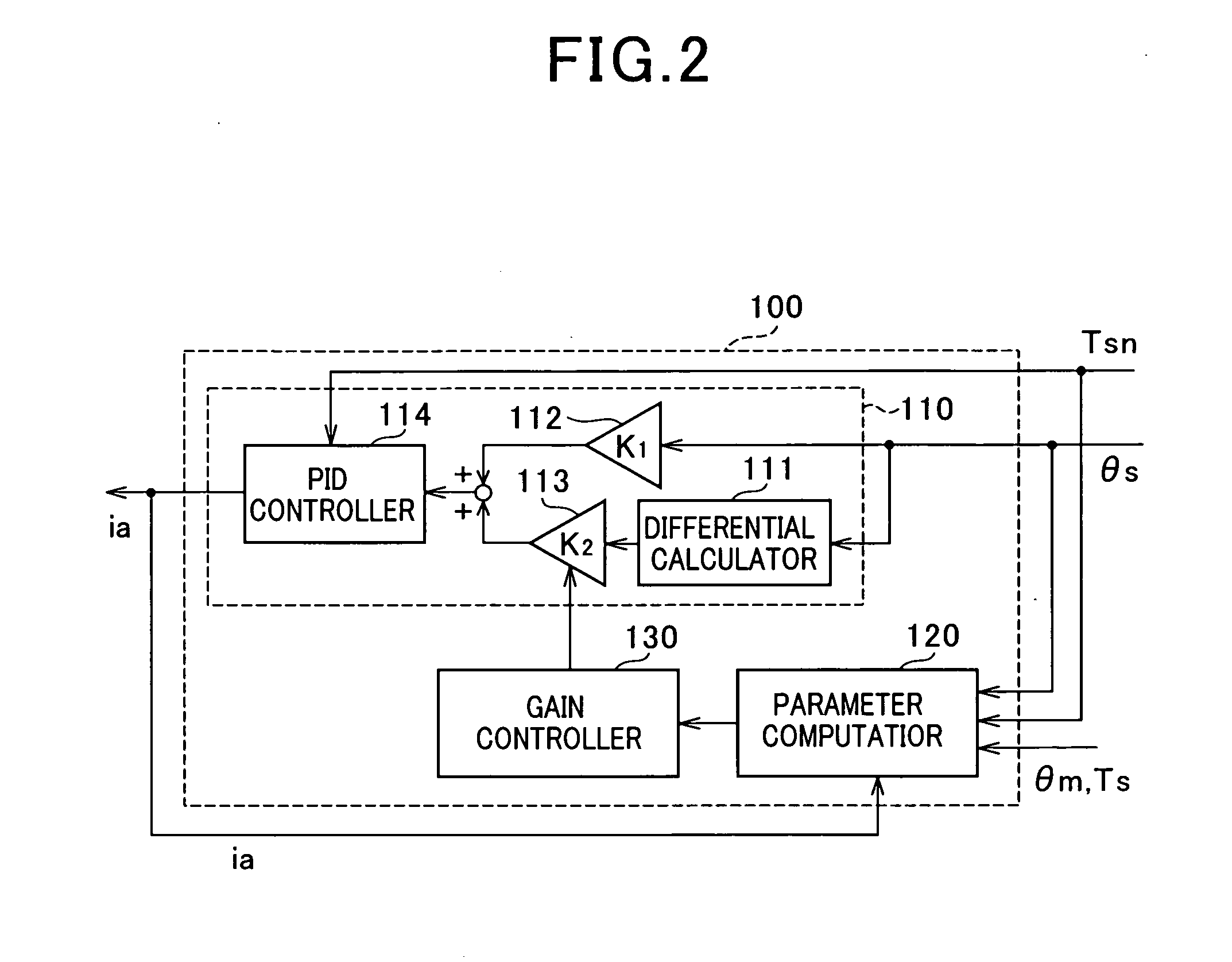
Control apparatus for electric power steering system
InactiveUS20080306655A1Feel goodSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringMotor drive
There is provided a control apparatus that controls a motor of an electric power steering system to assist a steering effort of an operator. The control apparatus includes a sensor, a parameter computer, a difference computer, a target torque computer, and a motor driver. The parameter computer computes a current value of one of physical parameters of one of constituents of the electric power steering system based on a steering parameter determined by the sensor referring to an equation of motion. The difference computer computes a difference between the current value of the one of the physical parameters computed by the parameter computer and a predetermined value of the one of the physical parameters. The target torque computer computes a target torque of the motor which compensates for the difference between the current value and the predetermined value of the one of the physical parameters.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
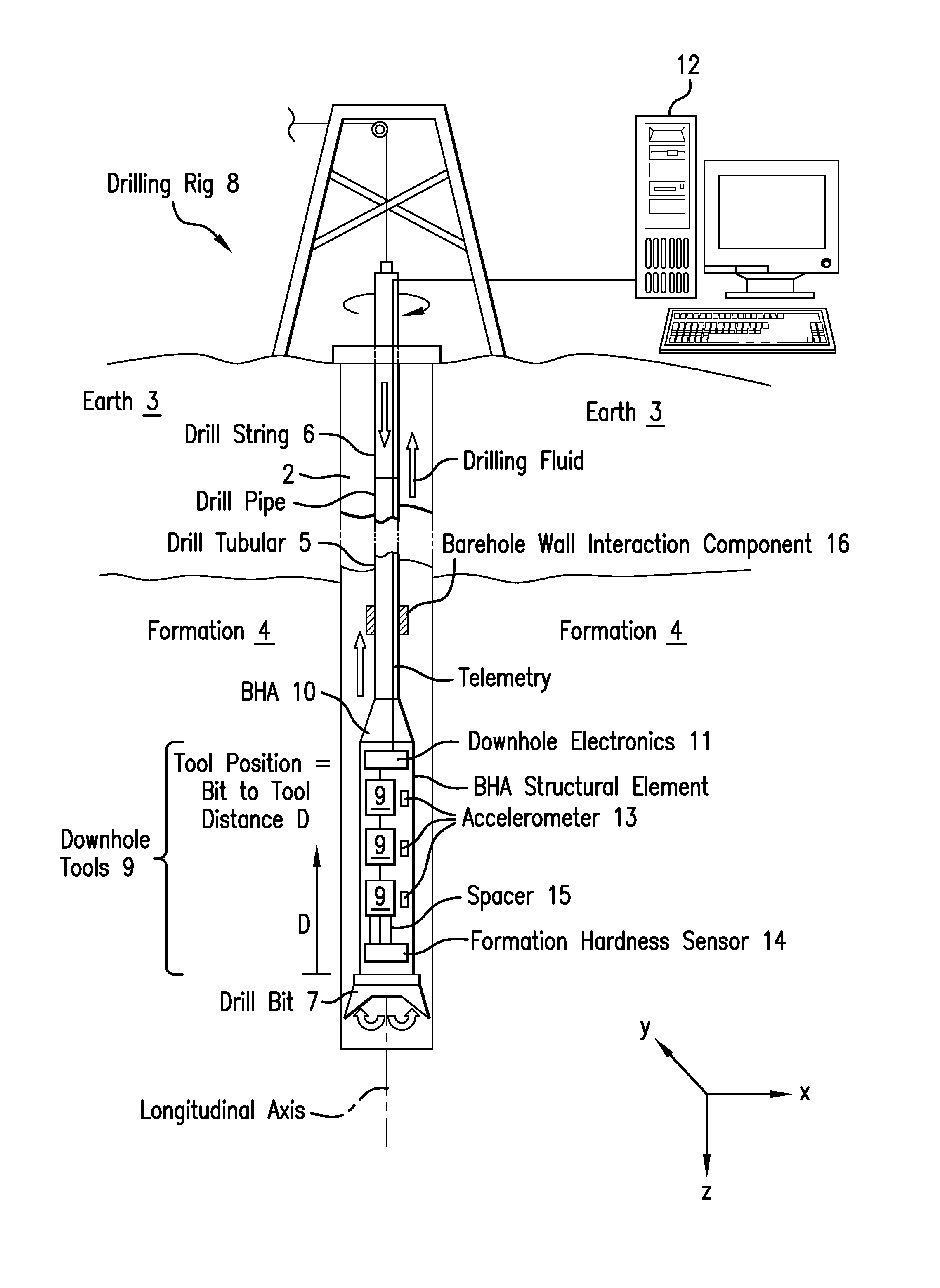
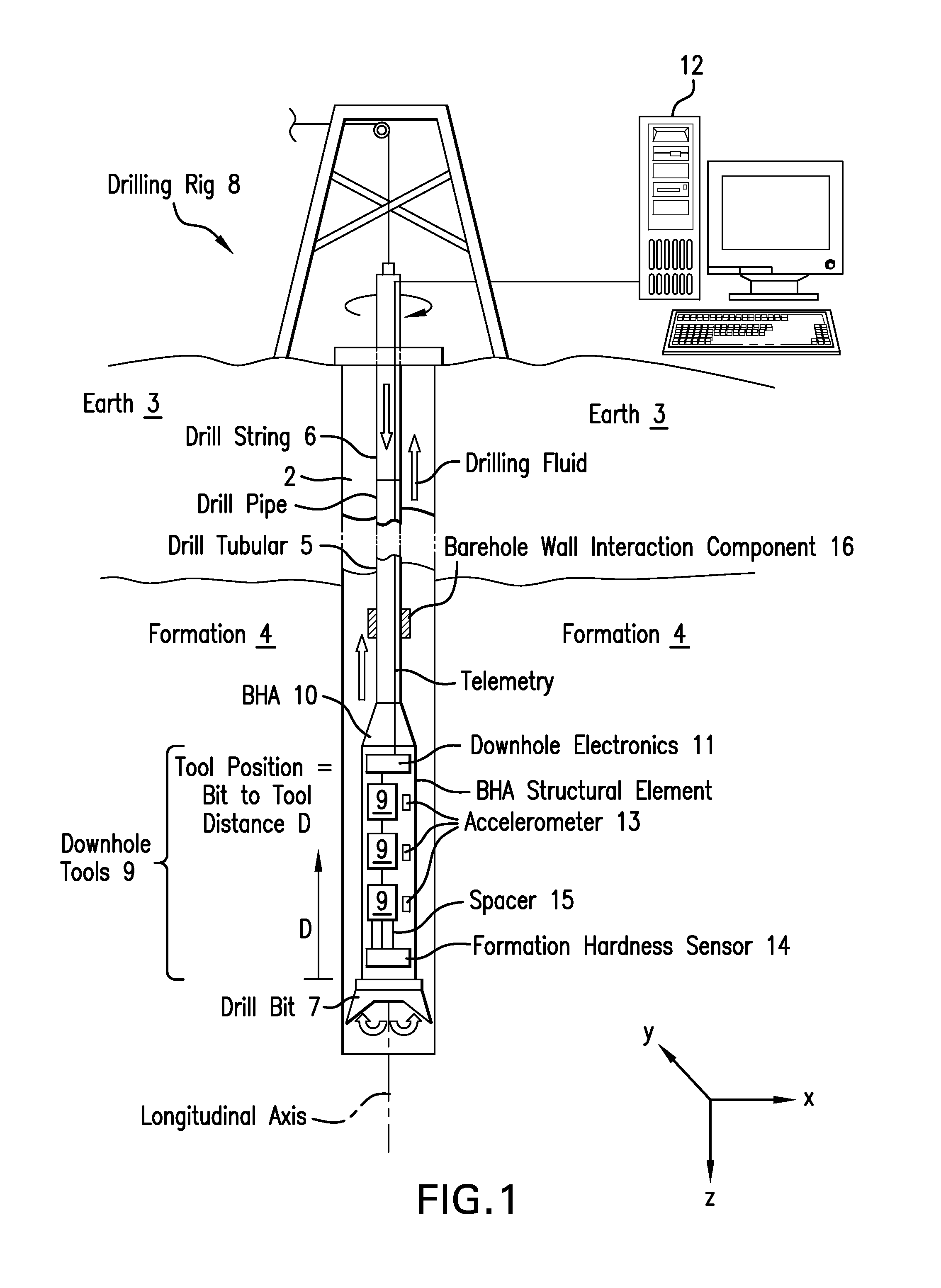
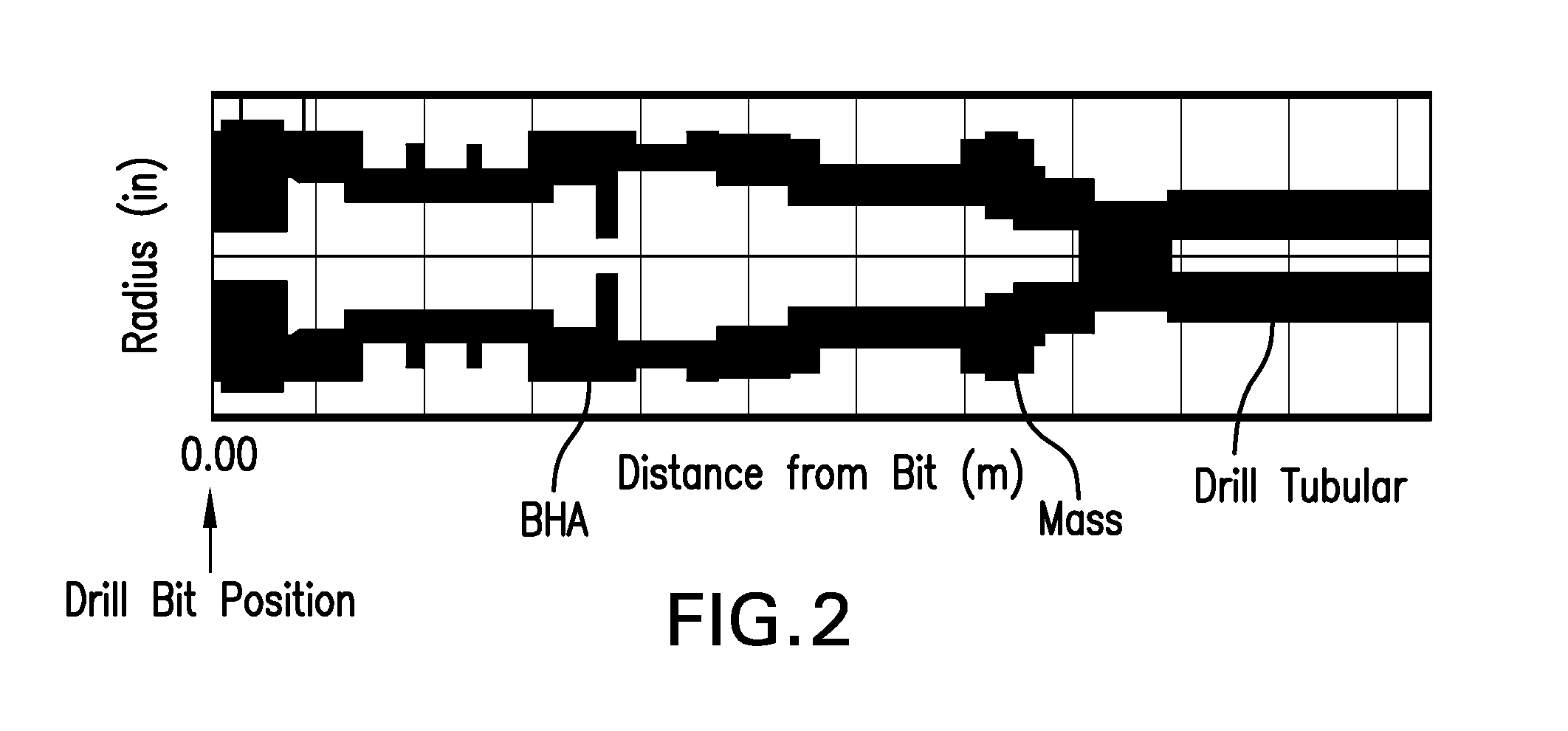
Method to mitigate bit induced vibrations by intentionally modifying mode shapes of drill strings by mass or stiffness changes
A method for reducing drill tubular vibrations includes: constructing a mathematical model the drill tubular having mass distribution, material stiffness and material damping; constructing an equation of motion of the drill tubular in one of a time domain and frequency domain; transforming the equation of motion into a modal domain equation of motion to provide a mode shape of the drill tubular at an eigenfrequency, the mode shape providing an amplitude at a position along the drill tubular; comparing the amplitude at the position along the drill tubular to a threshold amplitude value; modifying at least one of the mass distribution, material stiffness and material damping if the amplitude exceeds the threshold value; and iterating the above step until at least one of the amplitude of the latest mode shape at the position is less than or equal to the threshold amplitude value and a predetermined constraint limits the modifying.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
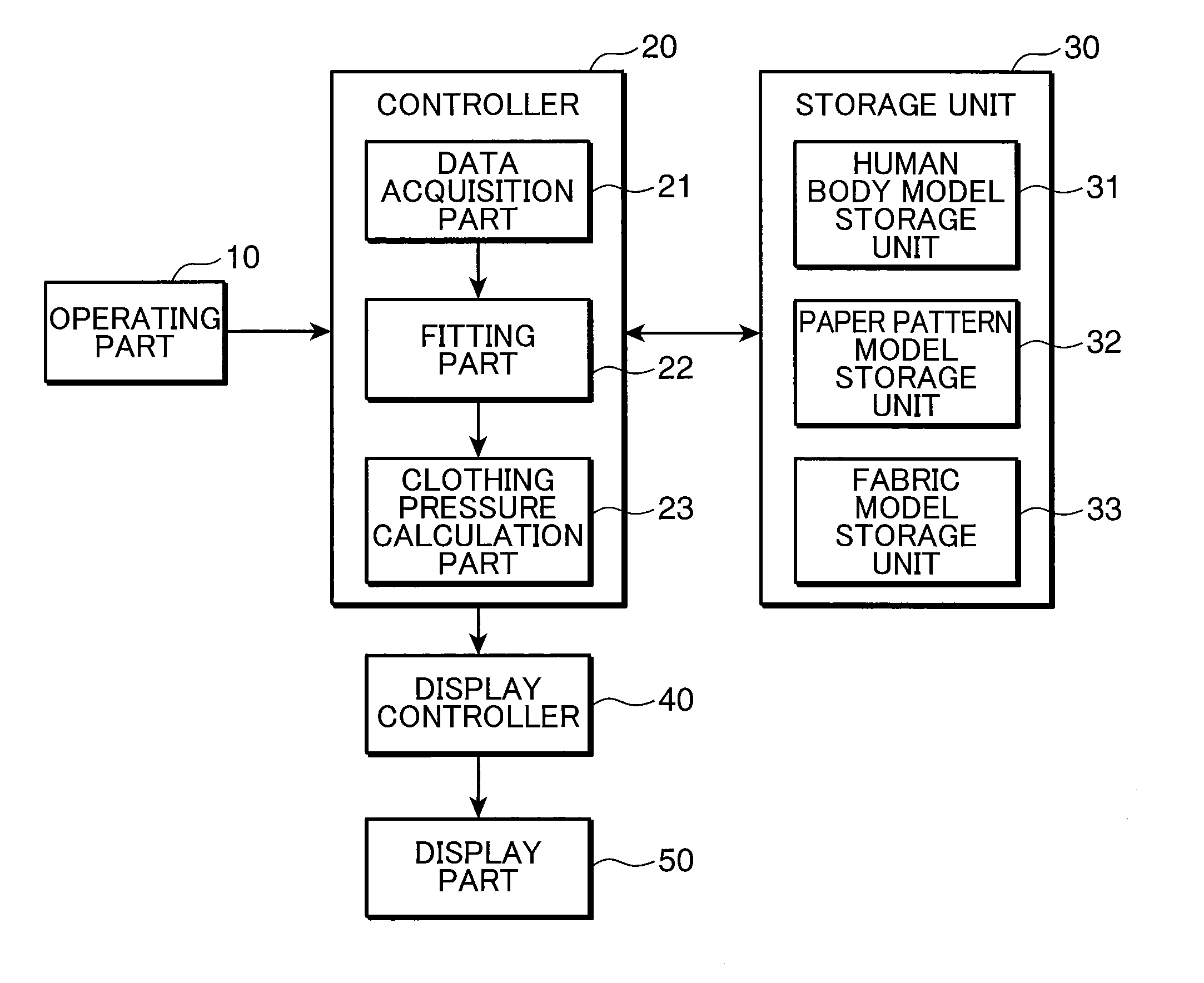
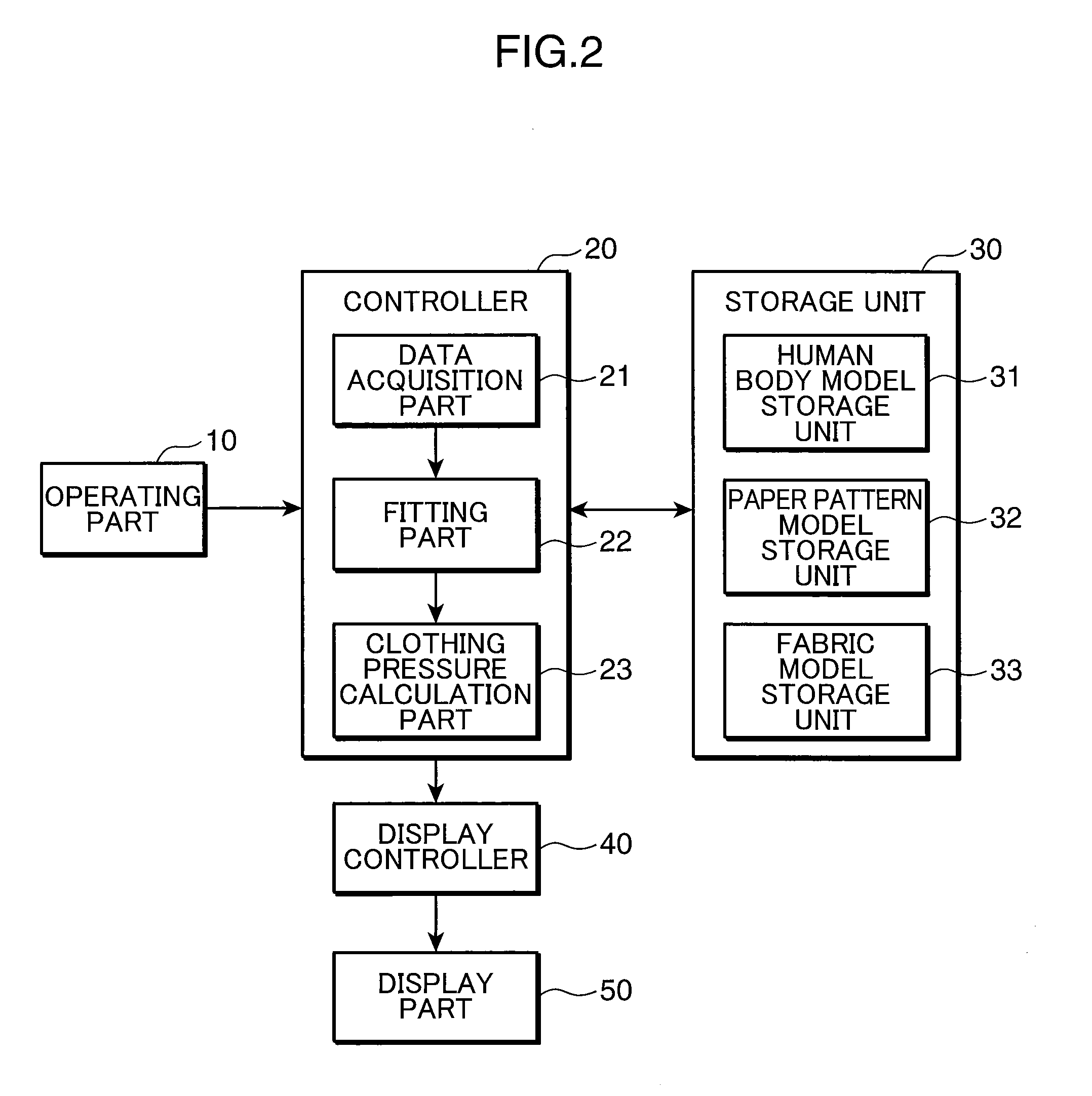
Clothing simulation apparatus, clothing simulation program, and clothing simulation method
InactiveUS20110022372A1Accurate acquisitionClothing pressureAnalogue computers for chemical processesDesign optimisation/simulationHuman bodyFinite element method
A clothing simulation apparatus precisely determines clothing pressure for bringing a clothing into tight contact with a human body. A fitting part 22 divides a paper pattern model into a plurality of elements, imparts dynamic characteristics shown by a fabric model to each element, deforms the paper pattern model by solving the motion equation of each element using a finite element method, and then fits the clothing virtually to a human body model. The fitting part 22 sets a temporary model to cover a predetermined section of the human body model, deforms the paper pattern model to bring the paper pattern model into contact with the temporary model, and thereafter deforms the paper pattern model to bring the paper pattern model into contact with the human body model.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Recognition method of critical geometrical error source of machine tool
The invention discloses a recognition method of a critical geometrical error source of a machine tool and belongs to the technical field of machine precision designing. The recognition method of the critical geometrical error source of the machine tool is characterized by comprising the steps that the machine tool is abstracted into a multi-body system according to the structure and motion characteristics of the machine tool, relevance of parts of the machine tool is described by a topological structure and a low-order body array, a generalized coordinate system is built in the multi-body system, coupling relationship of error amounts of parts of the machine tool is described by a homogeneous transformation matrix, a characteristic matrix and a motion equation of the relative movement between two adjacent bodies of the machine tool are elicited, a precision model of a machining center is built, an ordinary mathematical model used for error sensitivity analysis of a four-shaft machine tool is built with a matrix differential method according to the precision model of the precision horizontal machining center, influence degrees on the whole space error of all error elements are compared by calculating the geometrical error sensitivities of all parts, and finally the critical error source influencing the machining precision of the machine tool is recognized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
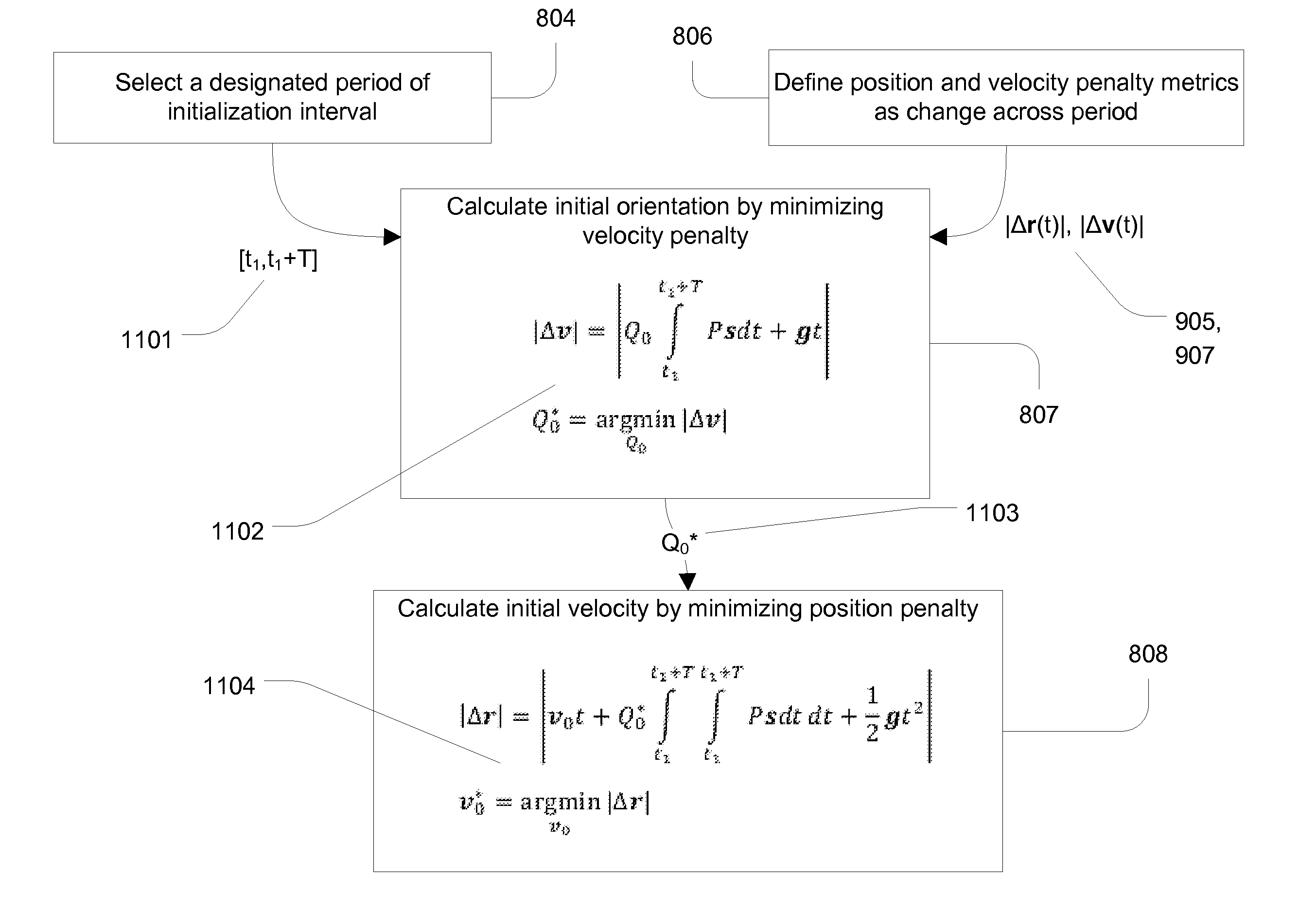
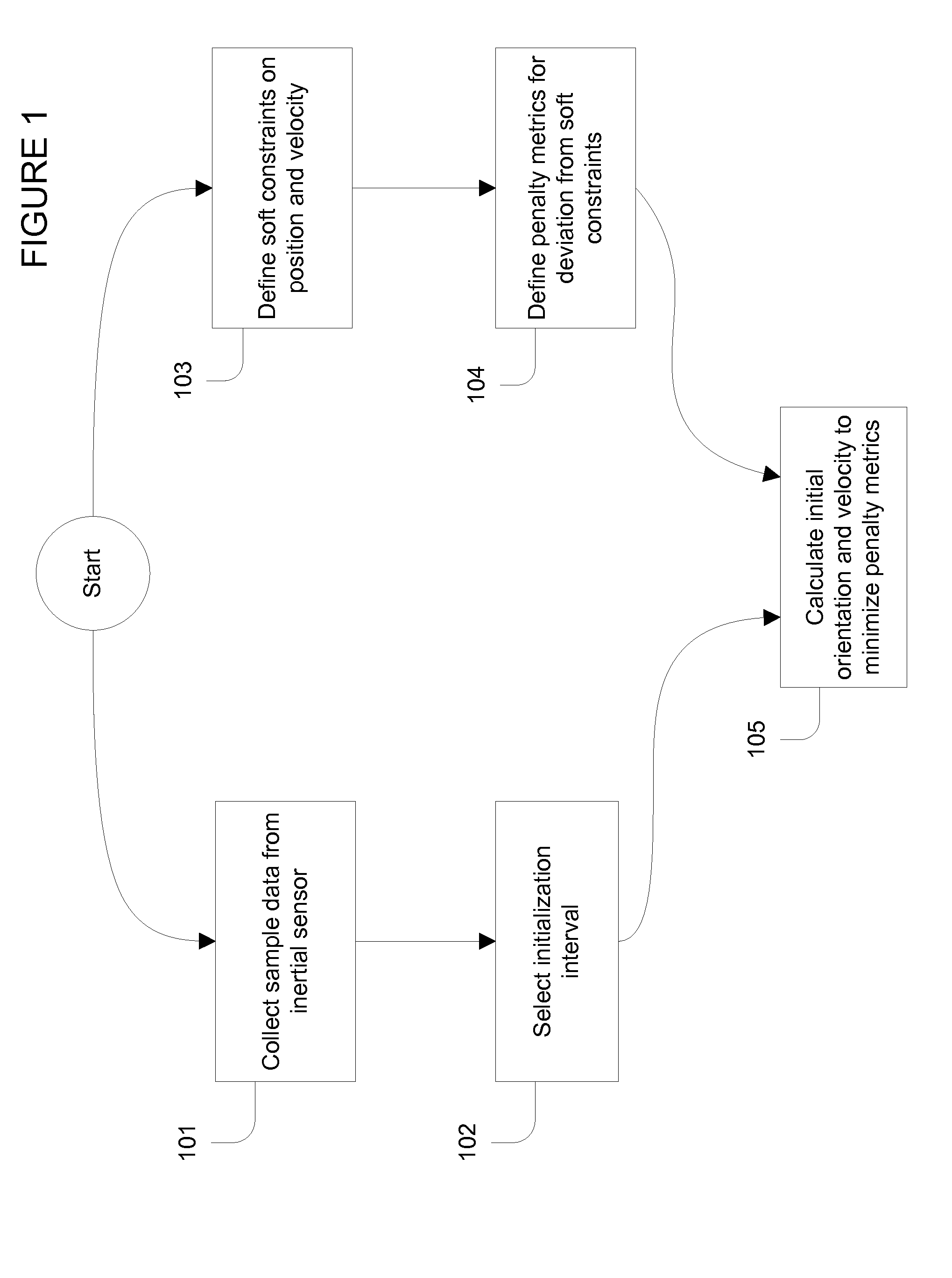
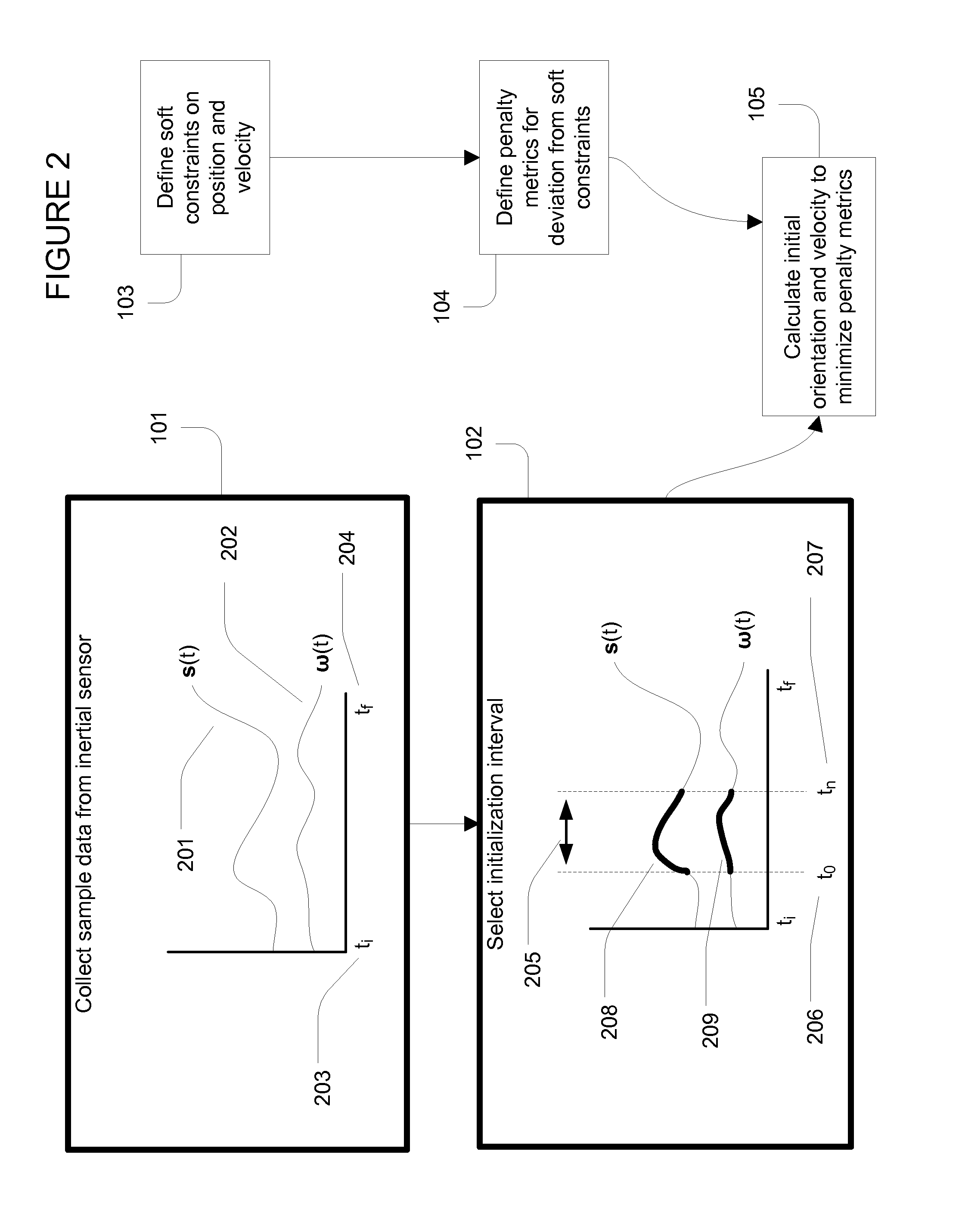
Initializing an inertial sensor using soft constraints and penalty functions
ActiveUS20140229138A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesDigital computer detailsComputer scienceDifferential equation
An initialization method for an inertial sensor that estimates starting orientation and velocity without requiring the sensor to start at rest or in a well-known location or orientation. Initialization uses patterns of motion encoded as a set of soft constraints that are expected to hold approximately during an initialization period. Penalty metrics are defined to measure the deviation of calculated motion trajectories from the soft constraints. Differential equations of motion for an inertial sensor are solved with the initial conditions as variables; the initial conditions that minimize the penalty metrics are used as estimates for the actual initial conditions of the sensor. Soft constraints and penalty metrics for a specific application are chosen based on the types of motion patterns expected for this application. Illustrative cases include applications with relatively little movement during initialization, and applications with approximately periodic motion during initialization.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
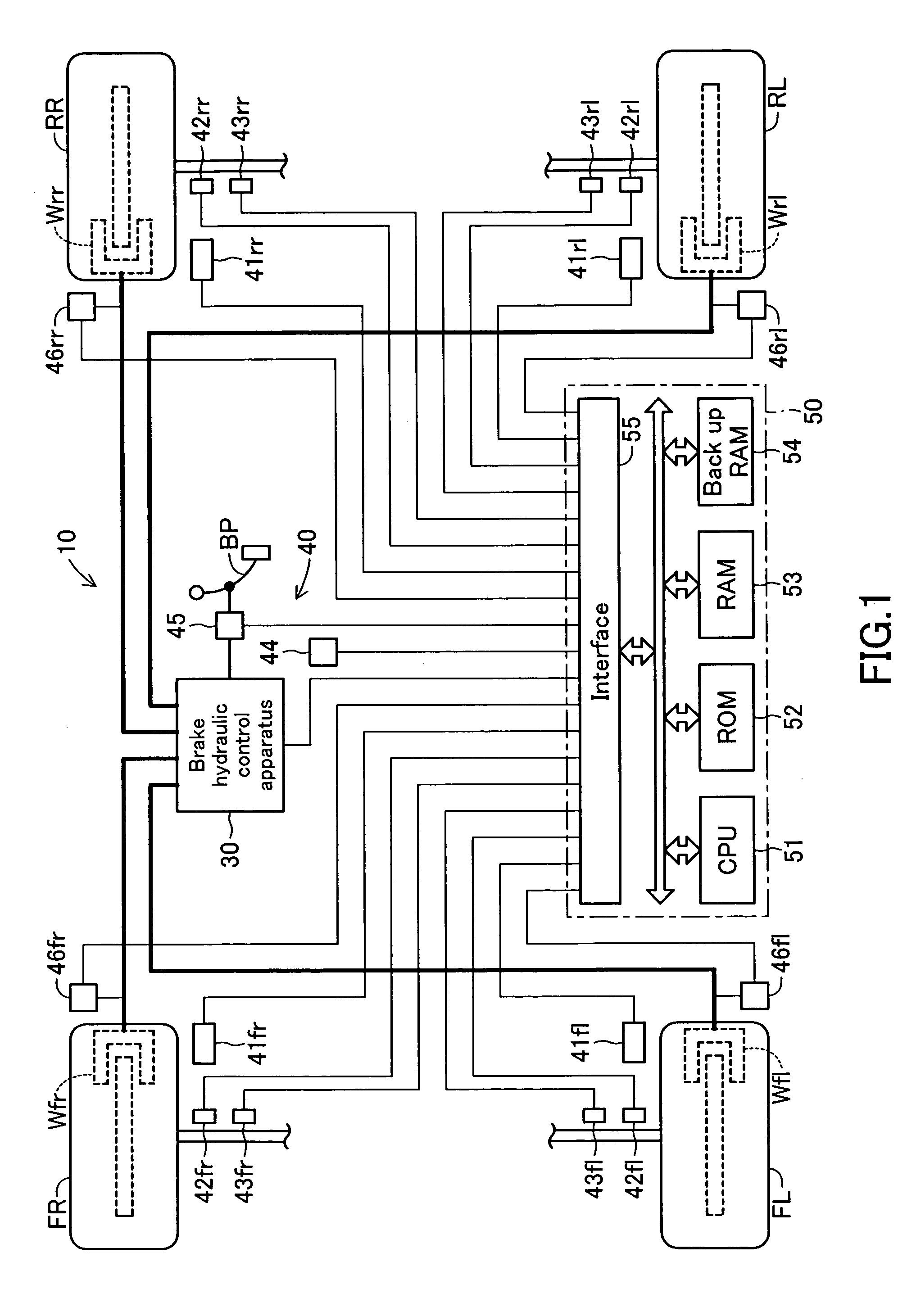
Maximum road friction force estimating device and brake torque control device
InactiveUS20050012386A1Accurate estimateBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesBrake torqueRoad surface
A brake torque control device obtains inertia torque Tine based upon an equation of motion (Tine=Tw−Ft·Rt) about the rotation of a tire based upon a wheel torque Tw according to a brake torque exerted on the tire, road friction force Ft and a radius Rt of the tire. When the inertia torque Tine exceeds a predetermined reference value, road friction force Ft at this time is set as estimated maximum road friction force Fmax. The instructed brake torque is calculated under the condition that the value that is obtained by adding the predetermined value corresponding to the inertia torque Tine to the torque Fmax·Rt based upon this estimated maximum road friction force Fmax is set as an upper limit value of the instructed brake torque. This allows to clearly set, as one value, the target value of the instructed brake torque upon an ABS control, thereby being capable of more accurately executing the pressure-increasing control and pressure-reducing control of the brake fluid pressure.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
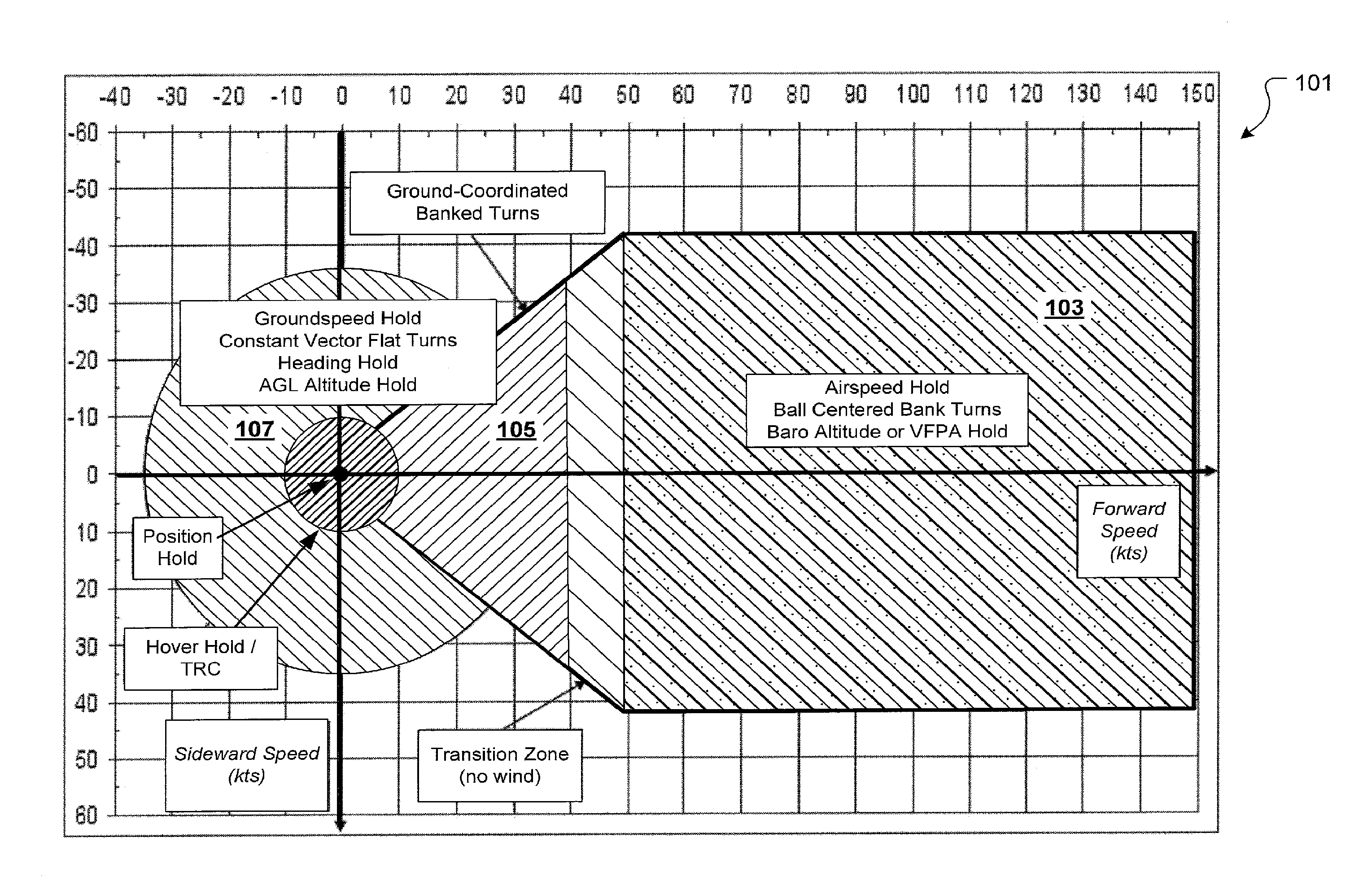
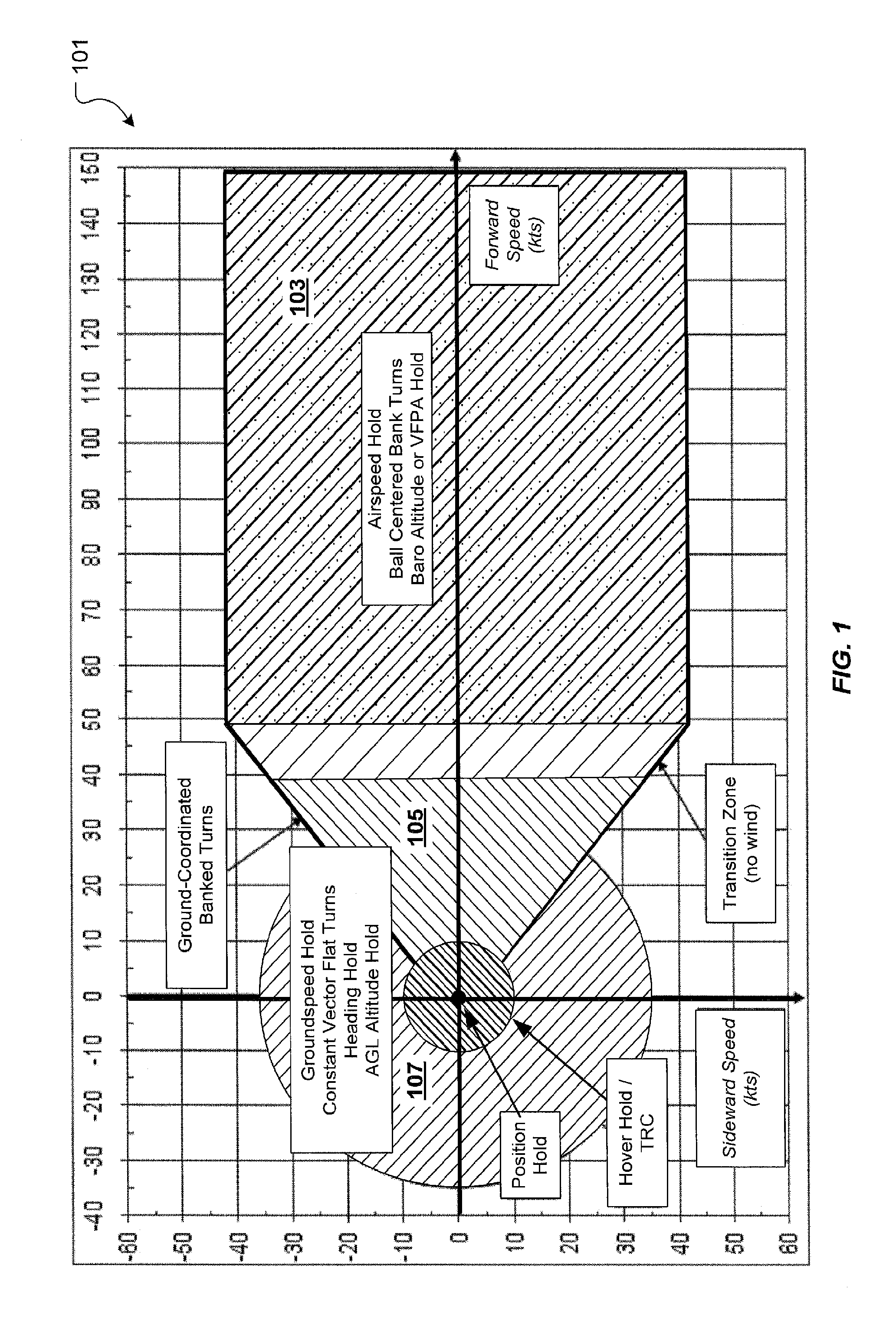
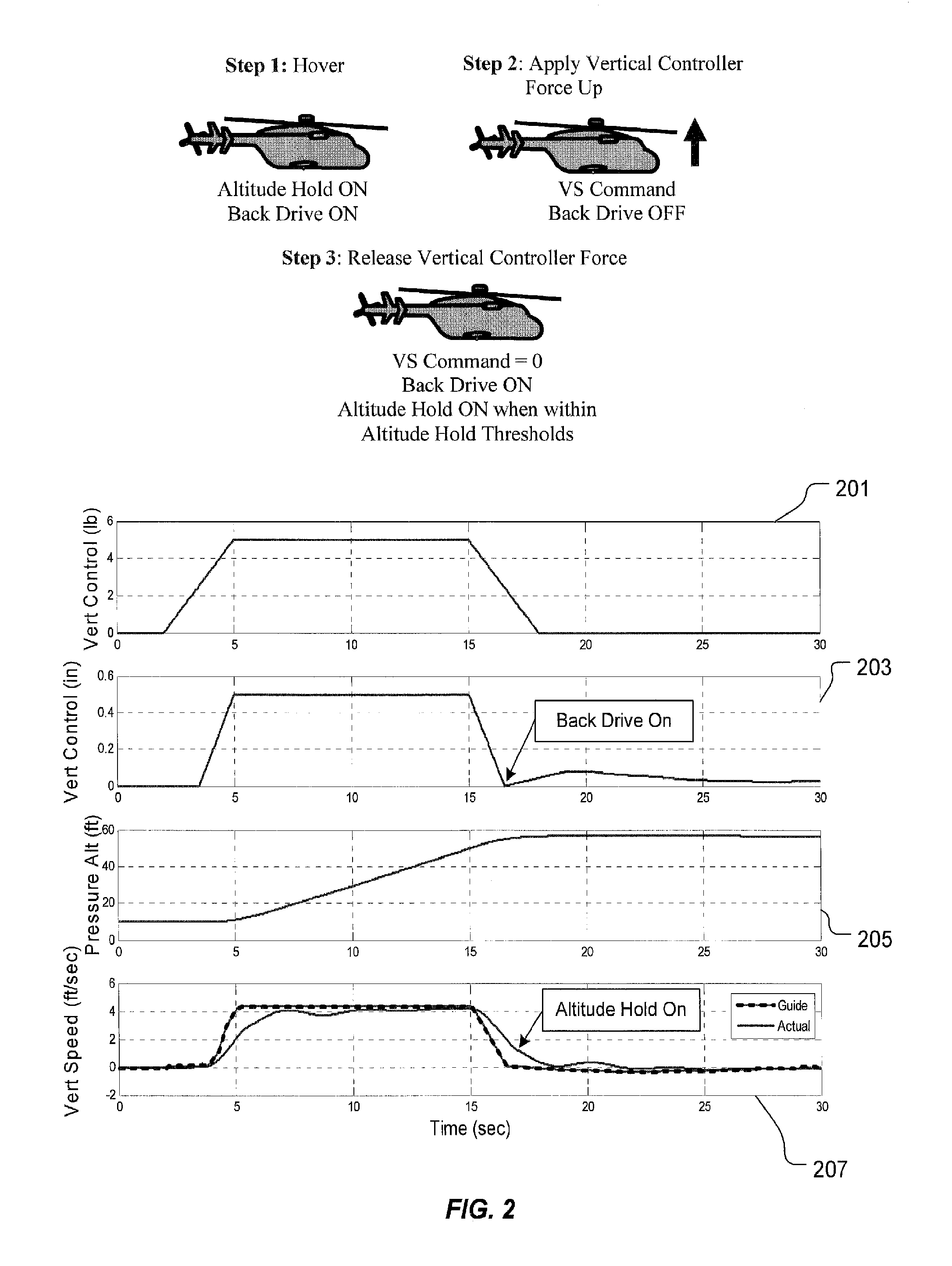
Flight Control Laws for Vertical Flight Path
ActiveUS20130060406A1Aircraft controlDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleFlight control modes
A flight control system and method for controlling the vertical flight path of an aircraft, the flight control system includes a stable decoupled model having a decoupled lateral equation of motion and a decoupled longitudinal equation of motion and a feedback command loop operably associated with the stable decoupled model. The feedback command loop includes a vertical flight path angle control law; an altitude control law; and a vertical speed control law.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Bending stiffness-considered numerical computation method for stay cable forces
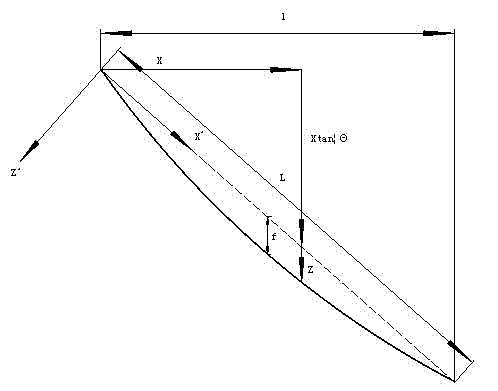
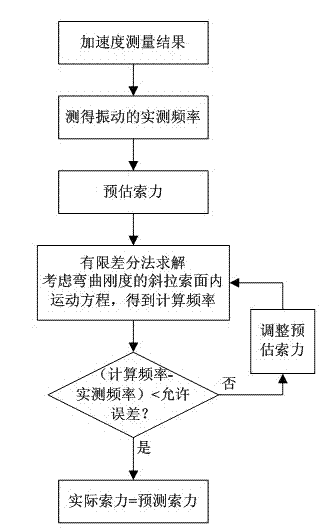
ActiveCN102735386AImprove accuracyHigh precisionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTension measurementIn planeEngineering
The invention relates to a bending stiffness-considered numerical computation method for stay cable forces, comprising the following steps of: 1, measuring the vibration of a stay cable to obtain the vibration frequency which are actually measured, and estimating the force of the stay cable to obtain the estimated force value; 2, putting the characteristic value of the stay cable and the estimated force value to an in-plane equation of motion of the stay cable based on the flexural rigidity, and utilizing a limited difference value method to solve, and then obtaining the vibration computing frequency of the stay cable; 3, computing the difference between the computing frequency and the really measured frequency of the vibration of the stay cable, if the difference is in the allowed error range, judging the estimated force value to be the actual force value of the stay cable and ending up the algorithm, if the difference is not in the allowed error range, adjusting the estimated force value, performing the loop iteration until that the difference between the computed frequency and the actual frequency is located in the allowed error range, and adopting the estimated force value after being adjusted as the actual force value. The method is in favor of improving the accuracy of the force measurement result of the stay cable.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
PSD range finding-based AGV accurate positioning method
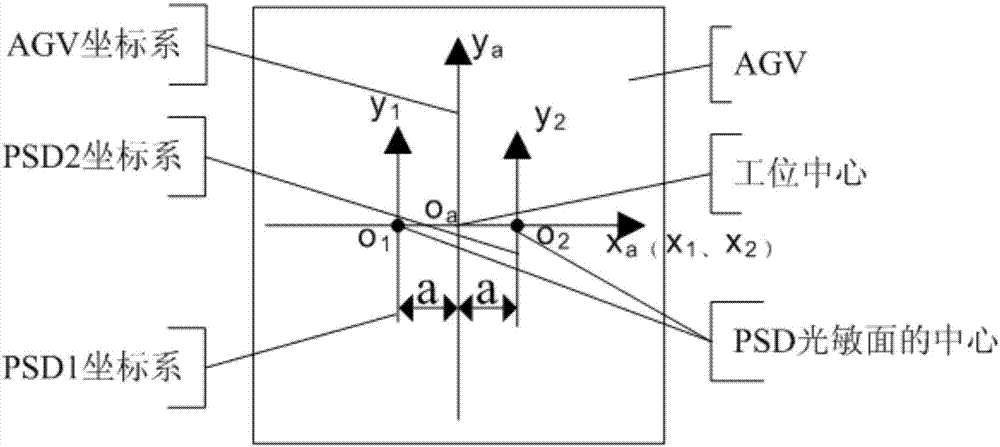
ActiveCN106940183AGuaranteed accuracyHigh positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansOffset distanceAutomated guided vehicle
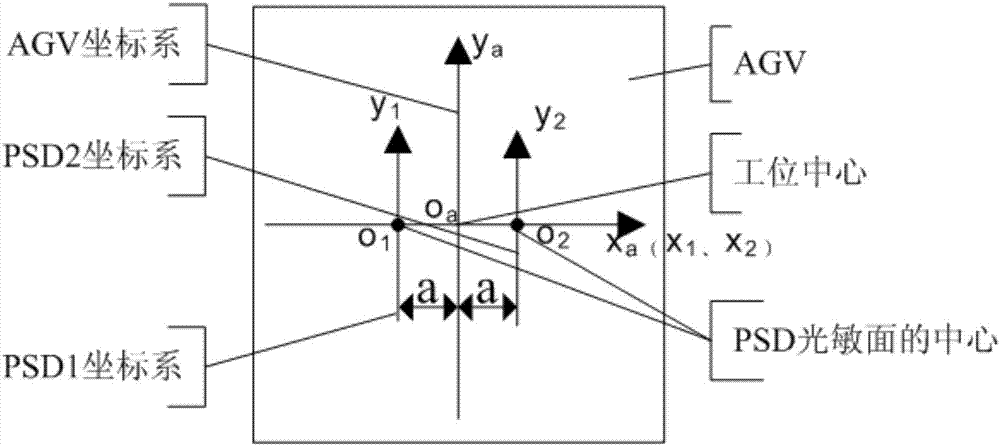
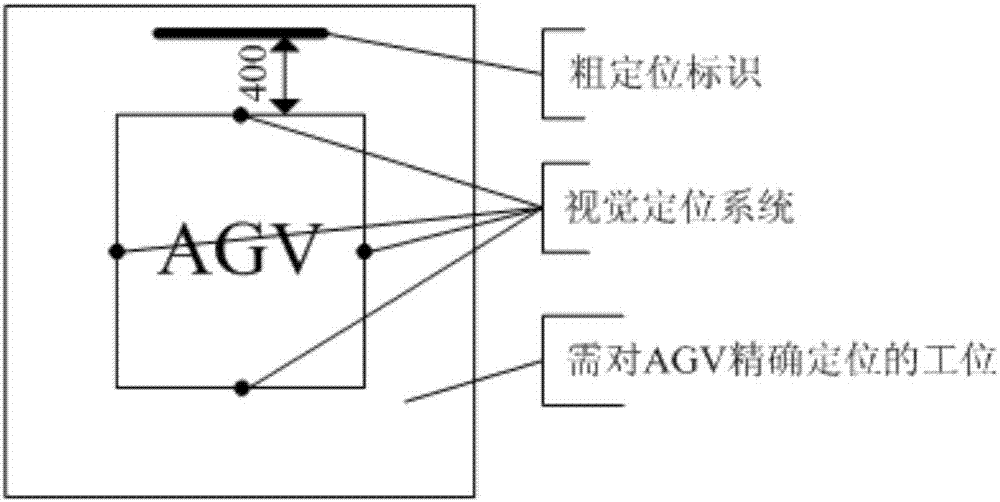
A PSD (position sensitive detector) range finding-based AGV (automated guided vehicle) accurate positioning method comprises the following steps: (1) allowing the positioning precision of the AGV to be in + / - 10 mm in a visual guidance manner; (2) using PSD range finding to measure the coordinates of two reference points after the coarse positioning of the AGV is completed, and determining the current transverse and longitudinal offset distance and the offset angle of the AGV according to a linear equation in order to obtain the current pose of the AGV; (3) inputting the current pose and the target pose of the AGV, establishing the motion equation of the AGV, and calculating the yaw angle and the rotating angle of the AGV; (4) realizing the pose adjustment through the Mecanum wheel-based omnidirectional movement (forward and backward straight movement, leftward and rightward traverse movement, oblique movement at any angle, 0-revolution radius in-place rotation, and combination of all above movements) of the AGV; and (5) resolving the pose of the AGV in real-time in the AGV pose adjustment process until the positioning accuracy reaches up to + / - 0.3mm. The method has the advantages of high positioning accuracy, simplicity in calculation, and easiness in engineering realization.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
Motion-estimation-based road video stabilization method
InactiveCN102202164AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyTelevision system detailsImage analysisDynamic motionImage sequence
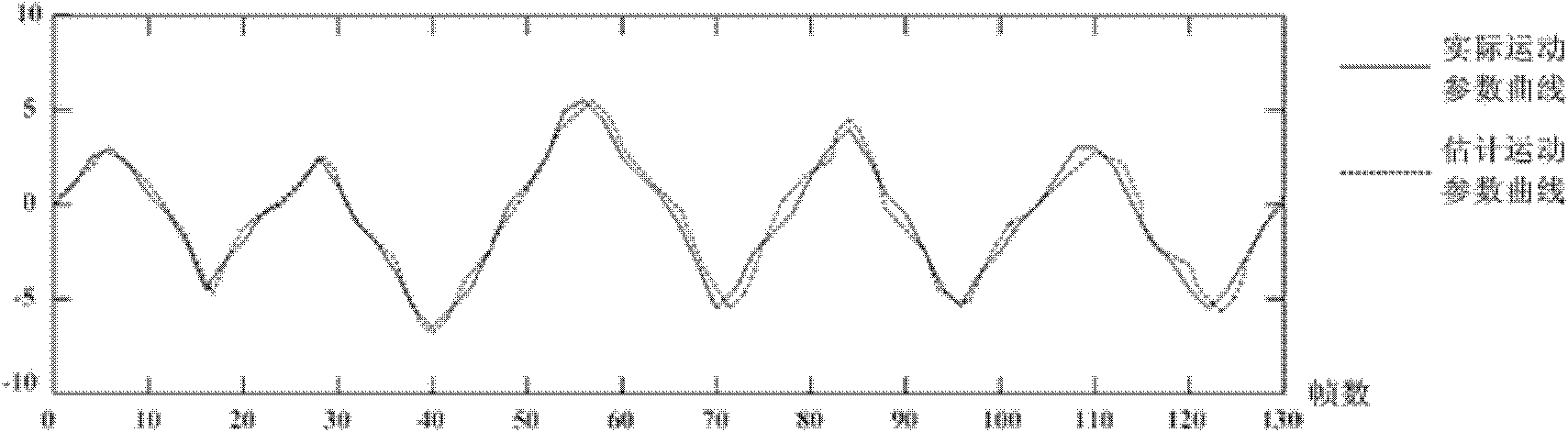
The invention relates to a motion-estimation-based road video stabilization method, which comprises the following steps of: performing nonlinear smooth denoising on an input image; determining a characteristic searching range according to the requirements of a system on accuracy, and acquiring optimal characteristic information; performing cross grayscale projection on a template and a block to be matched, and finding an optimal matched area according to a difference; constructing a dynamic motion model in a recursion way by adopting a Kalman filter with a uniform motion equation, obtaining motion parameters of a camera for describing inter-frame motions caused by the motions of the camera, and identifying and filtering random jitter in an offset sequence obtained by motion estimation; and filling an area losing an image due to the video jitter, and reconstructing adjacent frames by adopting a hybrid Gaussian model and utilizing time relativity between image sequences.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV +2
Wireless positioning method under visual distance and non-visual distance mixed environment
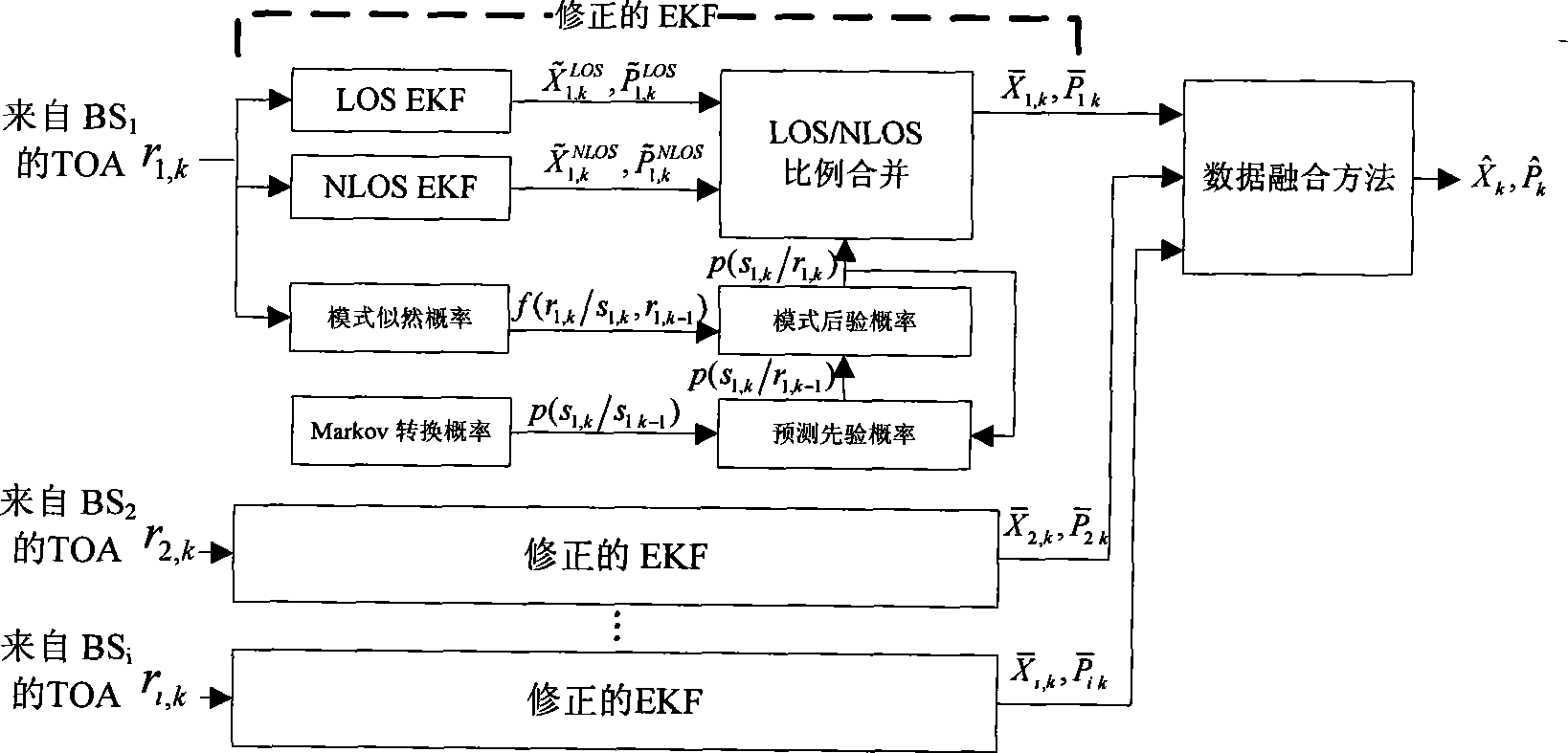
InactiveCN101483805AEffective positioningReduce the estimated varianceLocation information based serviceBase stationEquations of motion
The invention relates to a wireless locating method which can be used for location with high degree of accuracy in a mixed environment of sight distance and non-line of sight. The method first sets up motion equations and observation equations of wireless location and then expresses state transition probability model of the non-line of sight and the sight distance, which can make use of rectified extended Kalman filter (EKF) to estimate the motion state and the non-line of sight state according to measured values obtained by every base station and then blends the motion state and the non-line of sight state together through the use of a data fusion method to get the estimation of the motion state at the present moment and at last on-line wireless device position solutions can be realized through loop iteration. The method of the invention can effectively solve the non-line of sight influence in wireless location so as to effectively improve the motion state estimation of wireless devices, which has robustness to LOS / NLOS transition probability in different environments. At the same time, the method is suitable for VLSI parallel processing, operand can meet real time requirements, and the method is suitable for different signal measuring methods such as TOA, RSS, etc.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
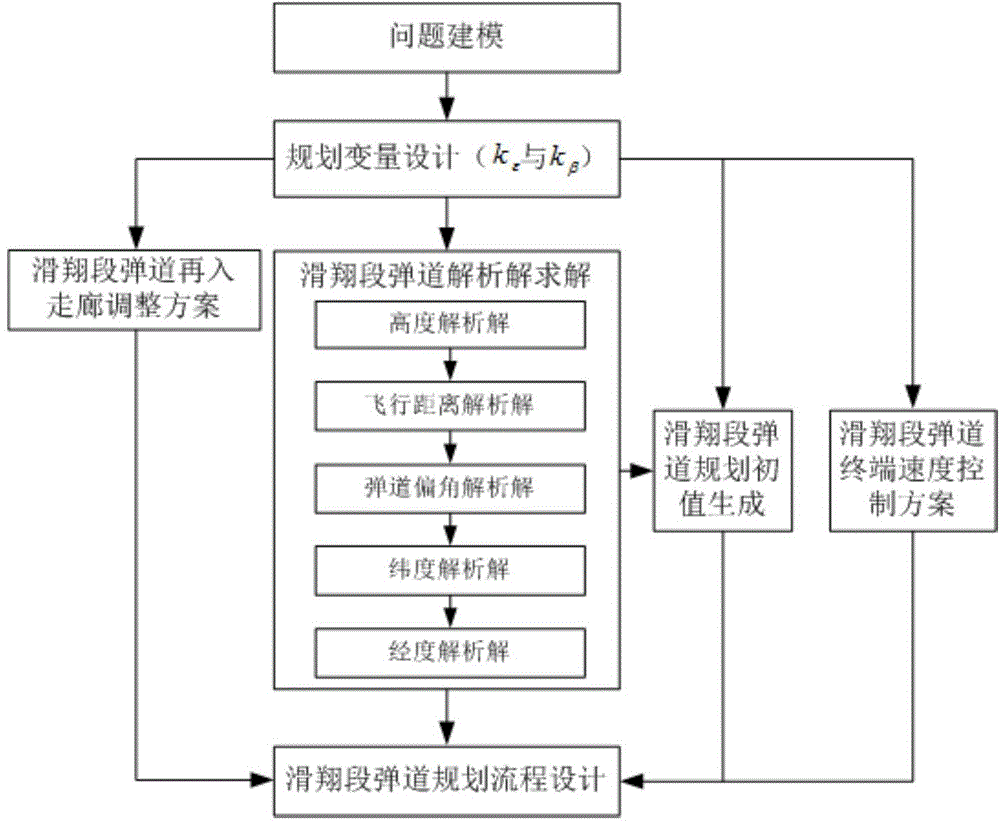
Quick trajectory programming method based on smooth glide trajectory analytic solution
The invention discloses a quick trajectory programming method based on a smooth glide trajectory analytic solution. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution includes that step 1, modeling glide trajectory programming problems; step 2, designing glide trajectory programming variables; step 3, calculating a glide trajectory analytic solution; step 4, designing a glide trajectory terminal speed control scheme; step 5, designing a glide trajectory re-entry corridor regulating proposal; step 6, generating initial values of glide trajectory programming; step 7, designing a glide trajectory programming flow. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution uses longitudinal maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficients and transverse maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficients as the glide trajectory programming variables so that differential equations of the trajectory inclination angle, trajectory deflection angle, height, longitude and latitude in motion equations do not comprise a speed item. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution obtains the glide trajectory analytic solution corresponding to a fixed longitudinal maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficient and a fixed transverse maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficient.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Collaborative path planning method for kinematic redundant two-arm space robot
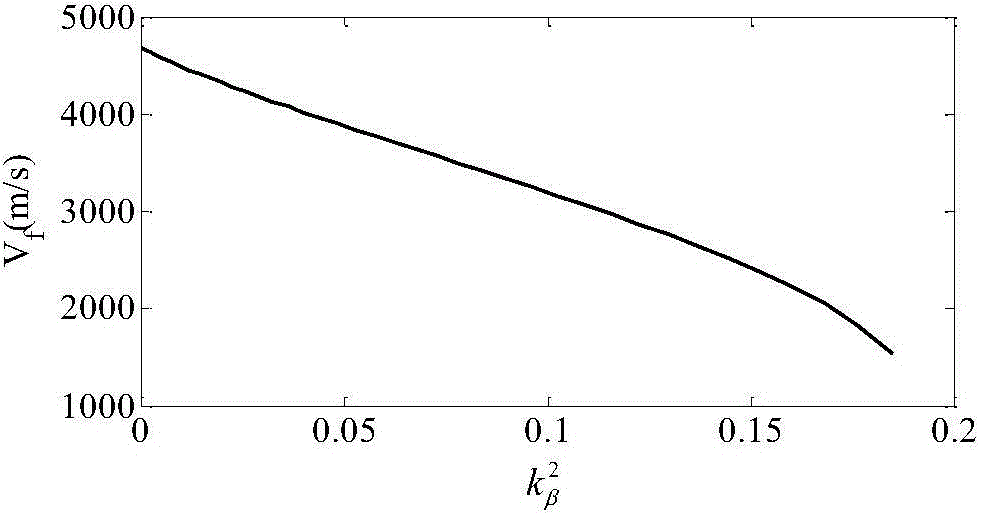
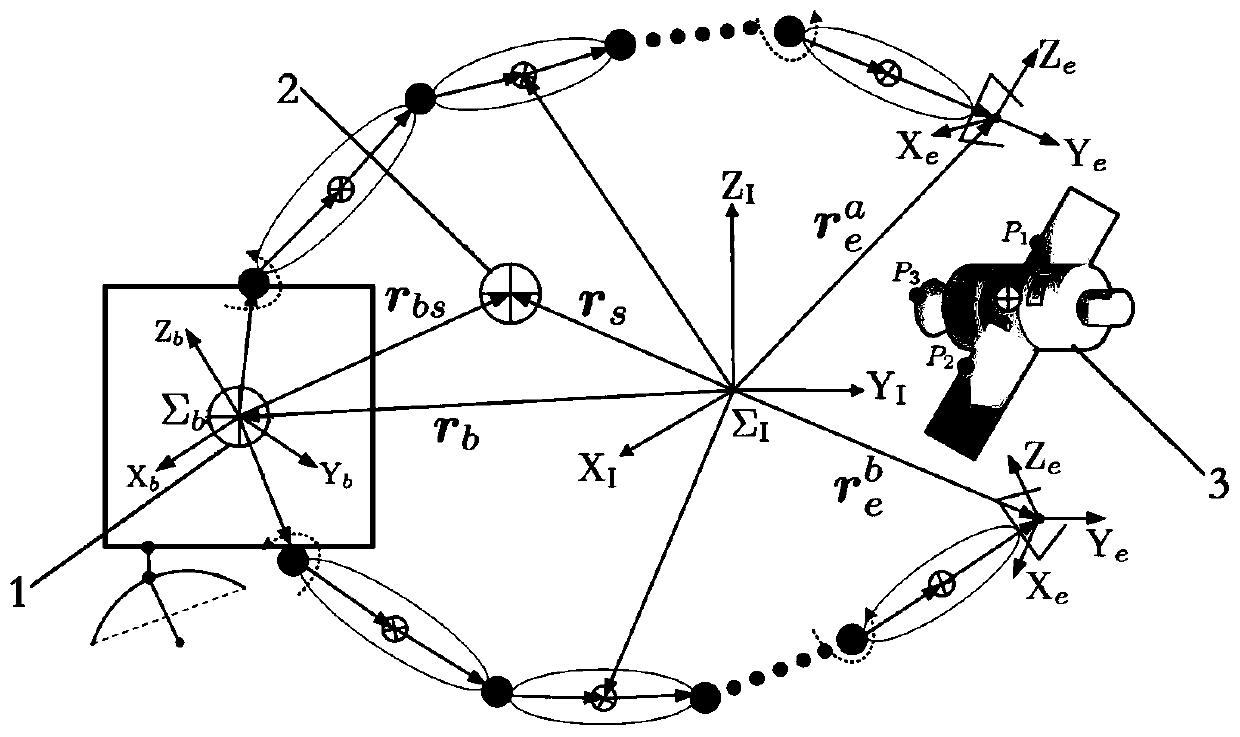
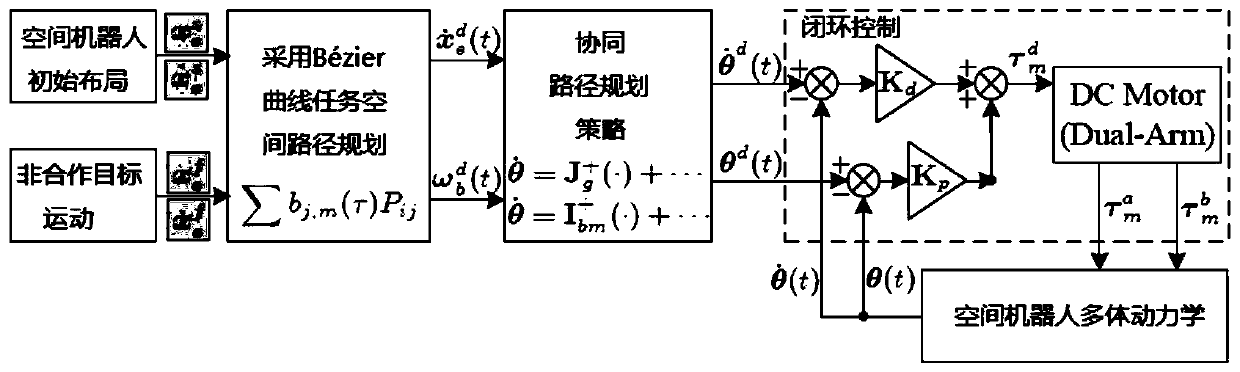
ActiveCN110104216AImplementing a collaborative path planning methodSmall attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic vehiclesKinematics equationsDynamic balance
The invention discloses a collaborative path planning method for a kinematic redundant two-arm space robot. The collaborative path planning method for the kinematic redundant two-arm space robot comprises the following steps that a dynamic equation and a kinematic equation of a space robot system are established; a redundant solution of an inverse kinematics equation of an end-effector is solved,and a system non-holonomic constraint equation is obtained through a momentum conservation equation; a task space constraint equation of the relationship between the end-effector motion and the attitude of a base is obtained through the system non-holonomic constraint equation; the path planning of the end-effector in a task space is obtained by using a quintic bezier curve, and path execution time is determined by the velocity and acceleration boundary of the end-effector; and the joint motion trajectory planning corresponding to different task priorities is obtained through the end-effectormotion equation and the task space constraint equation. The collaborative path planning method of the space two-arm robot is implemented, various tasks can be performed according to the priorities ofthe tasks such as a multi-arm collaborative task and a dynamic balancing task, and the operation ability of a space manipulator is greatly expanded.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com