Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Enhance the virtual reality experience" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
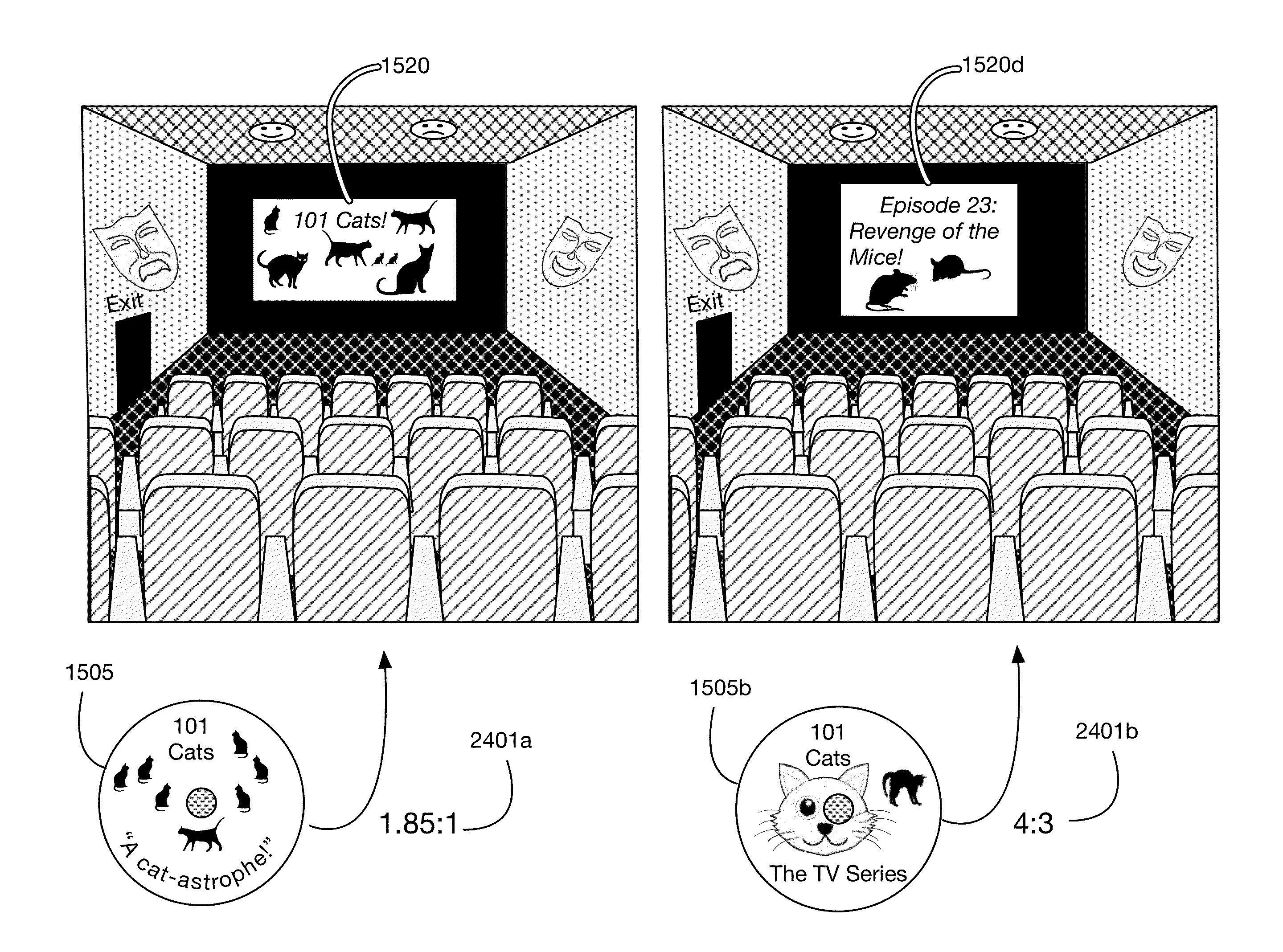
Virtual reality virtual theater system
InactiveUS9396588B1Latency display updateEfficient rerenderingGeometric image transformationStereophonic systemsLoudspeakerVirtual theater
A virtual reality virtual theater system that generates or otherwise displays a virtual theater, for example in which to view videos, such as movies or television. Videos may be for example 2D or 3D movies or television programs. Embodiments create a virtual theater environment with elements that provide a theater-like viewing experience to the user. Virtual theaters may be for example indoor movie theaters, drive-in movie theaters, or home movie theaters. Virtual theater elements may include for example theater fixtures, décor, and audience members; these elements may be selectable or customizable by the user. One or more embodiments also render sound by placing virtual speakers in a virtual theater and projecting sounds from these virtual speakers onto virtual microphones corresponding to the position and orientation of the user's ears. Embodiments may also employ minimal latency processing to improve the theater experience.
Owner:LI ADAM
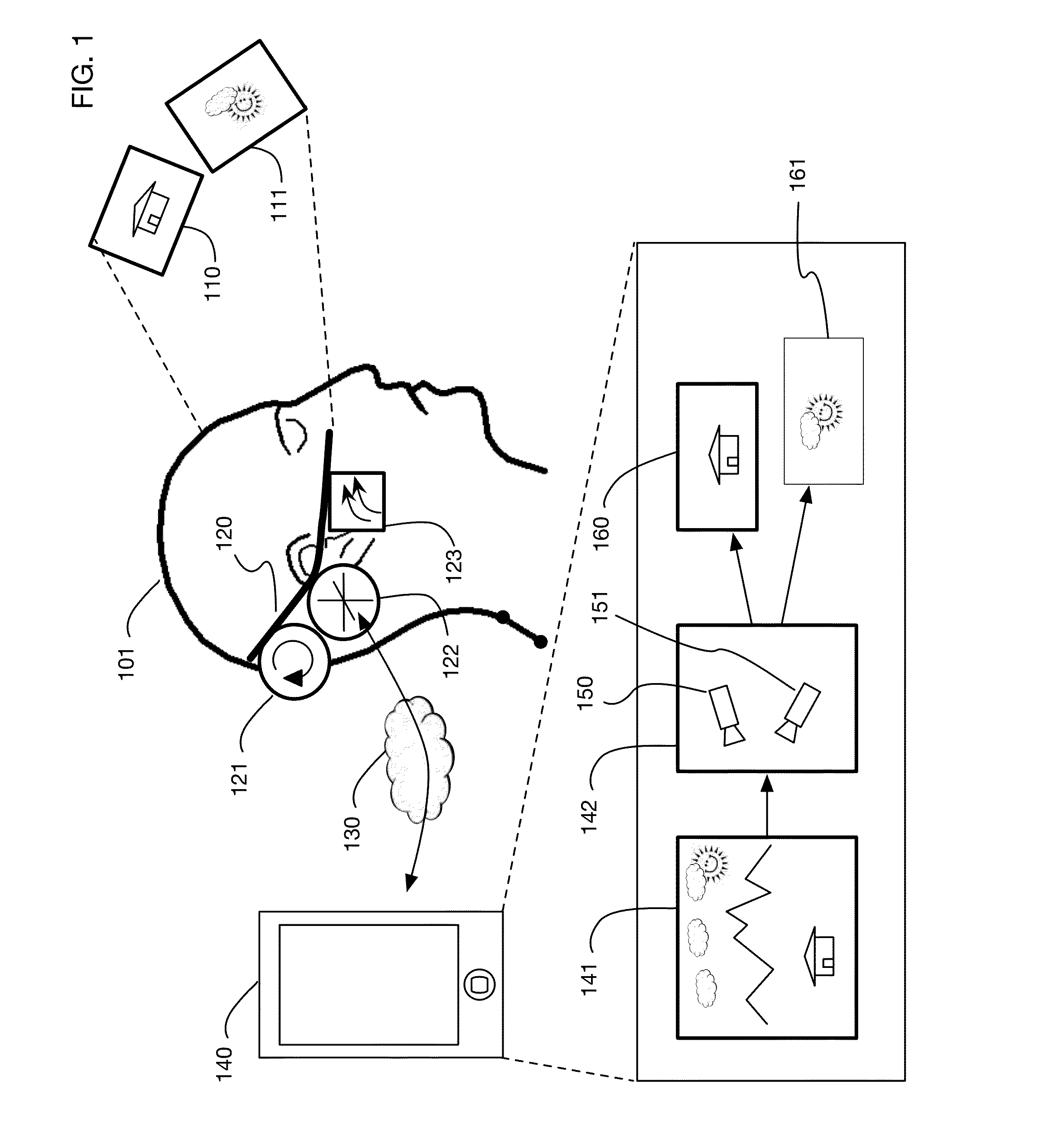
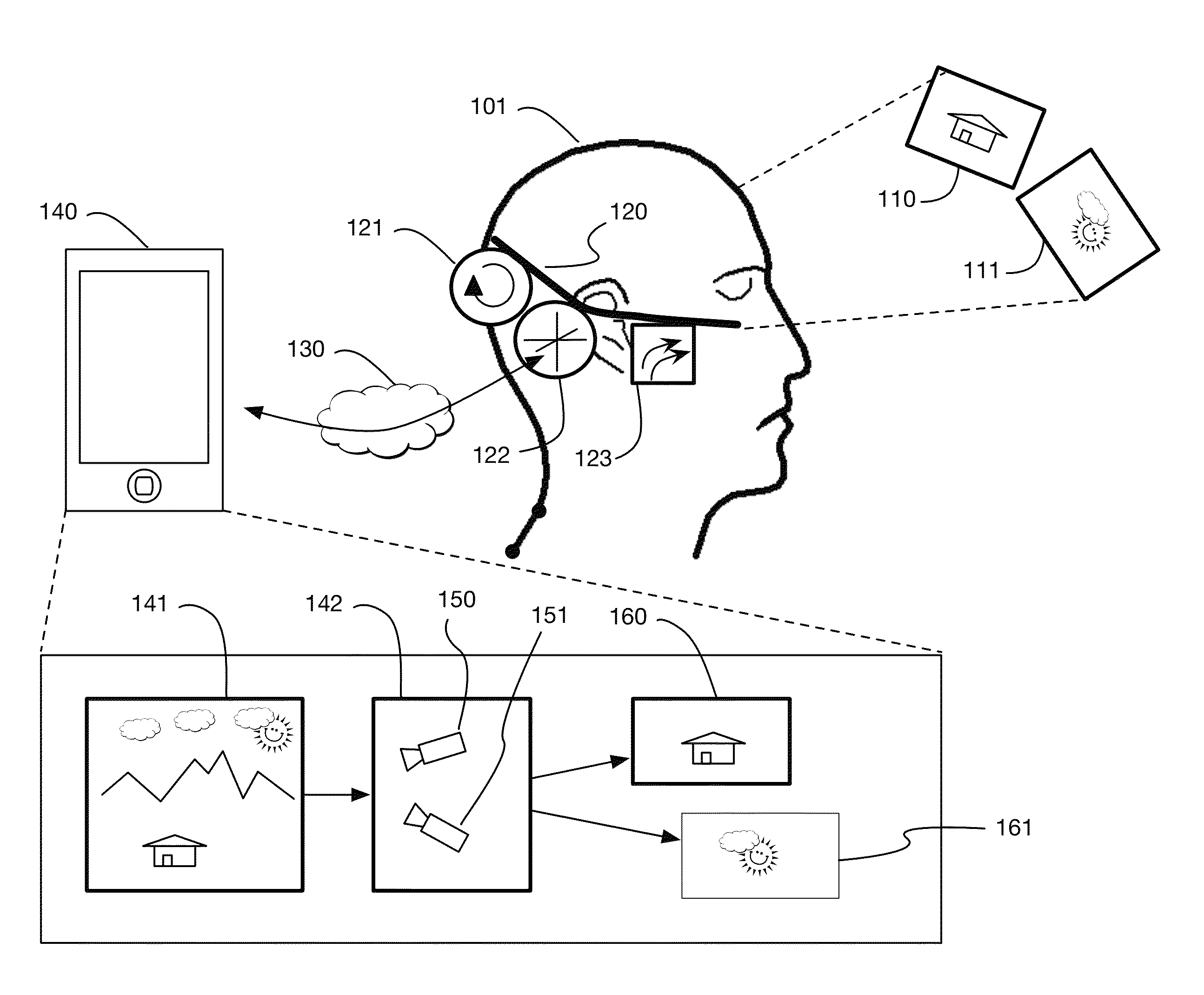
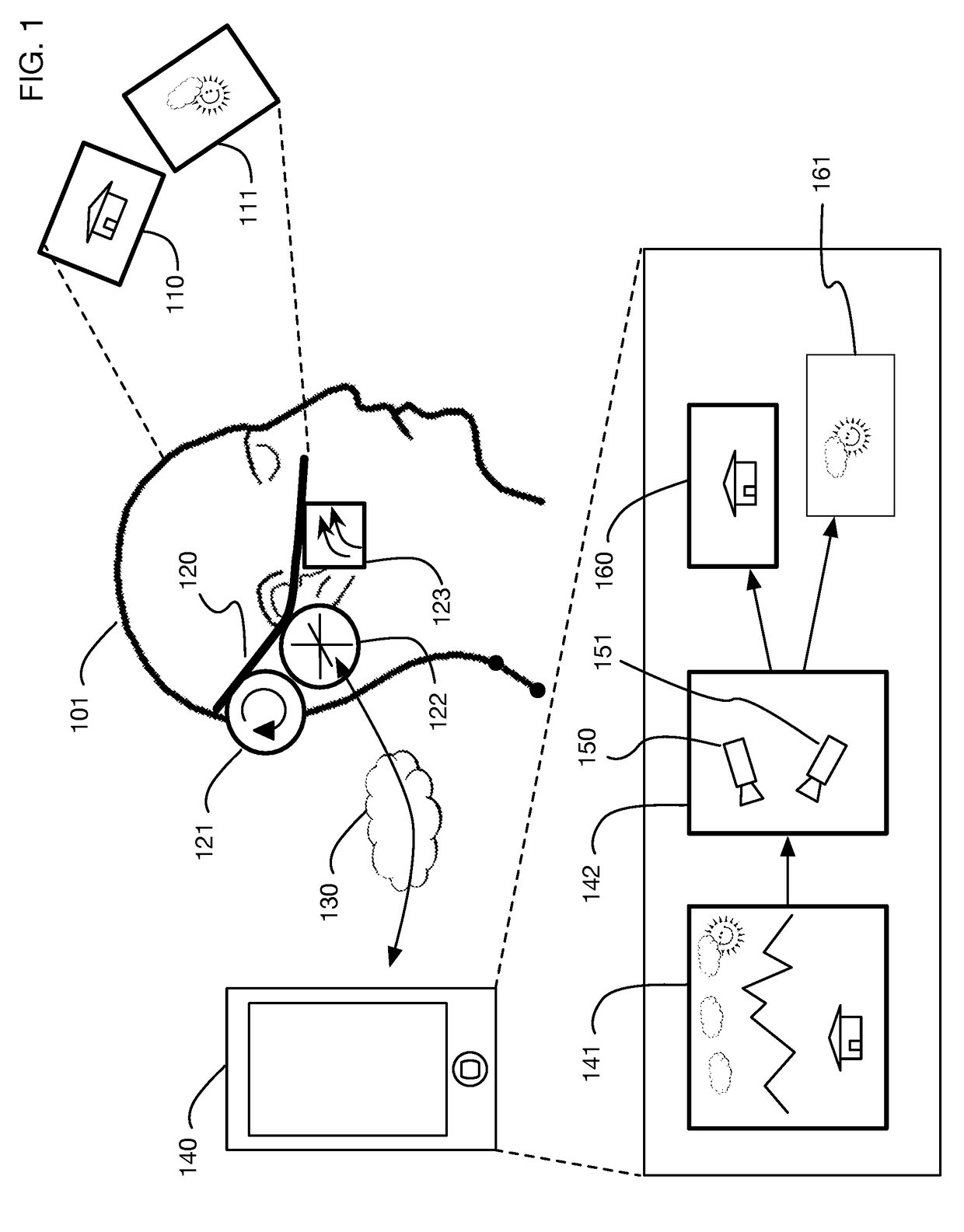
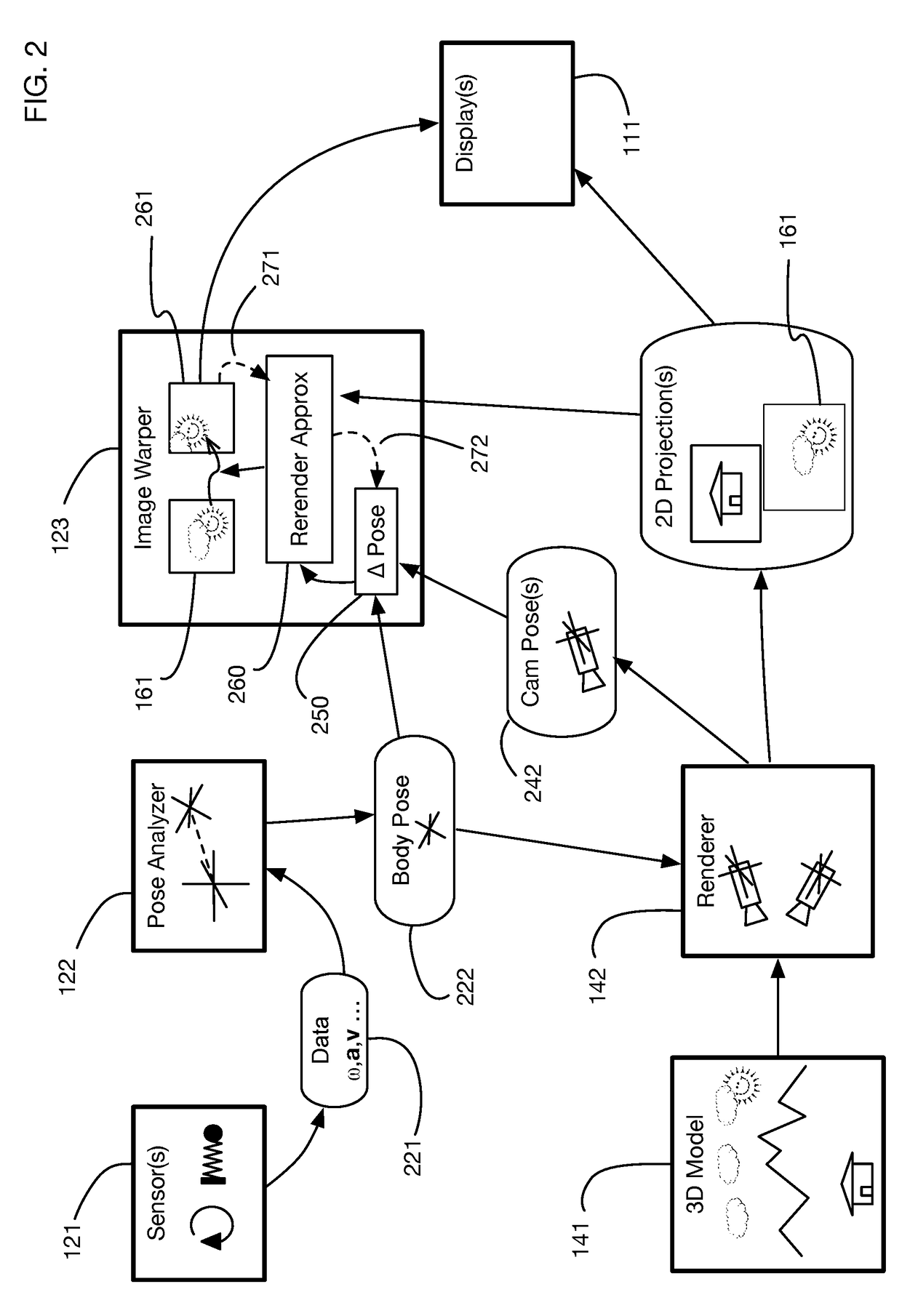
Low-latency virtual reality display system
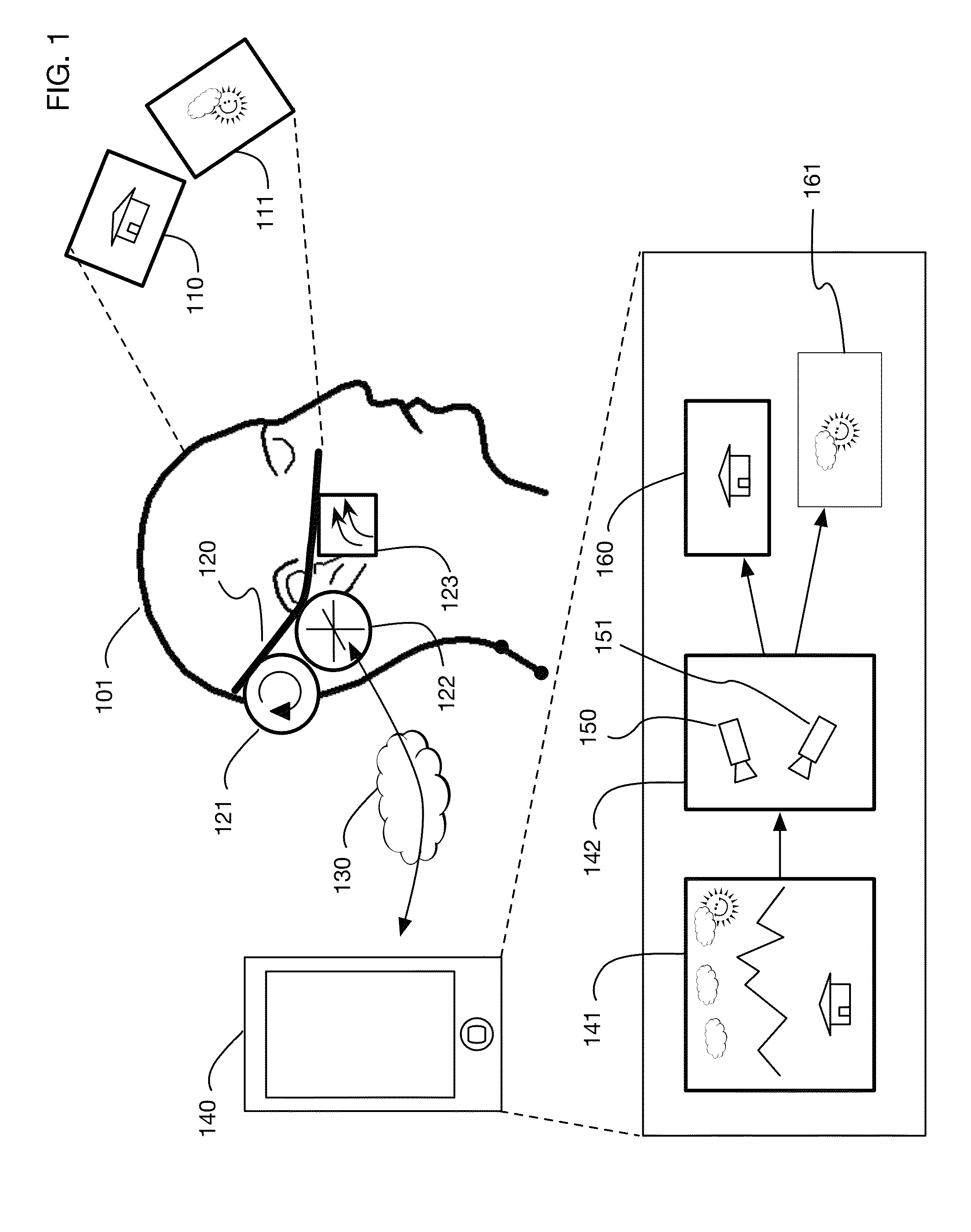
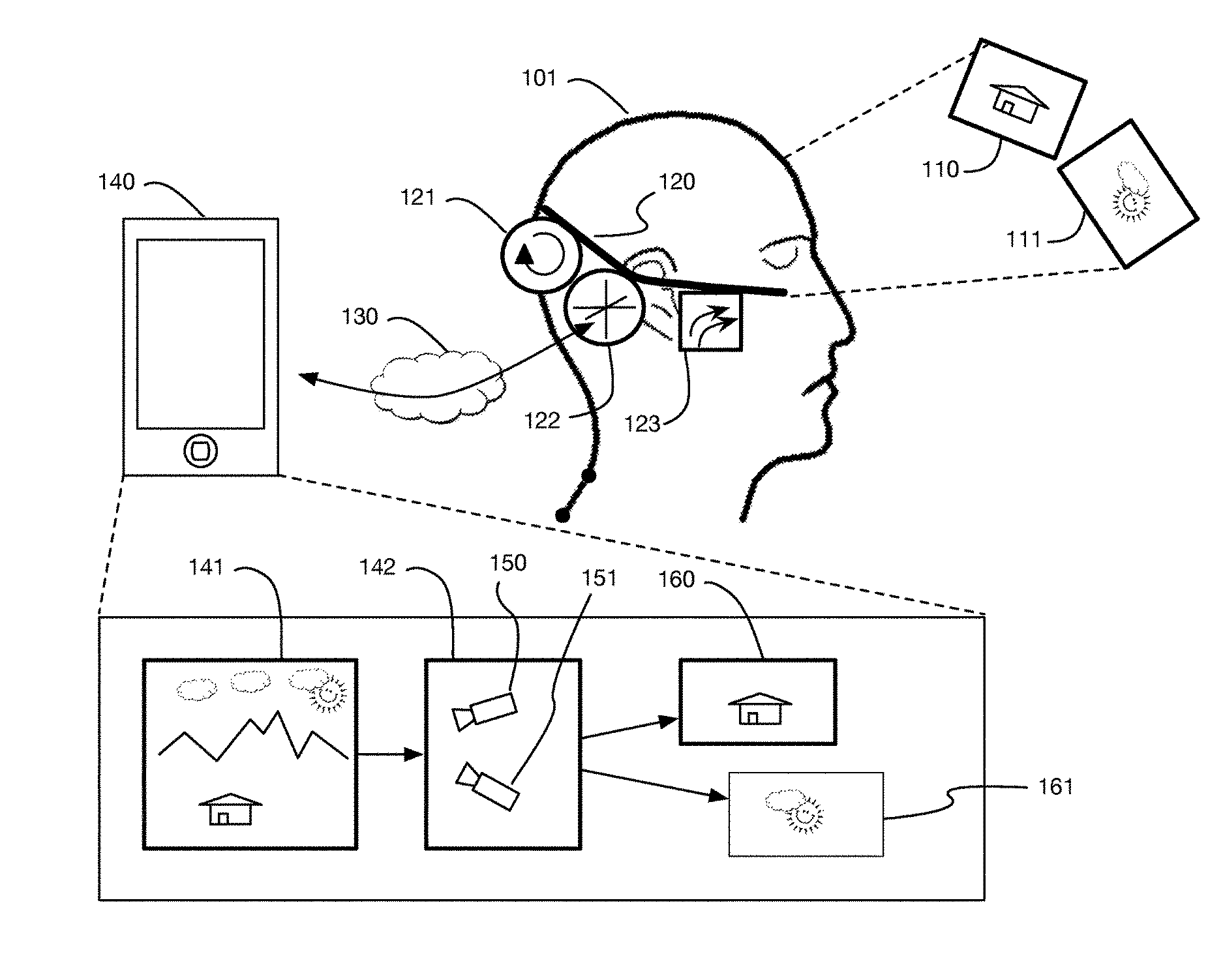
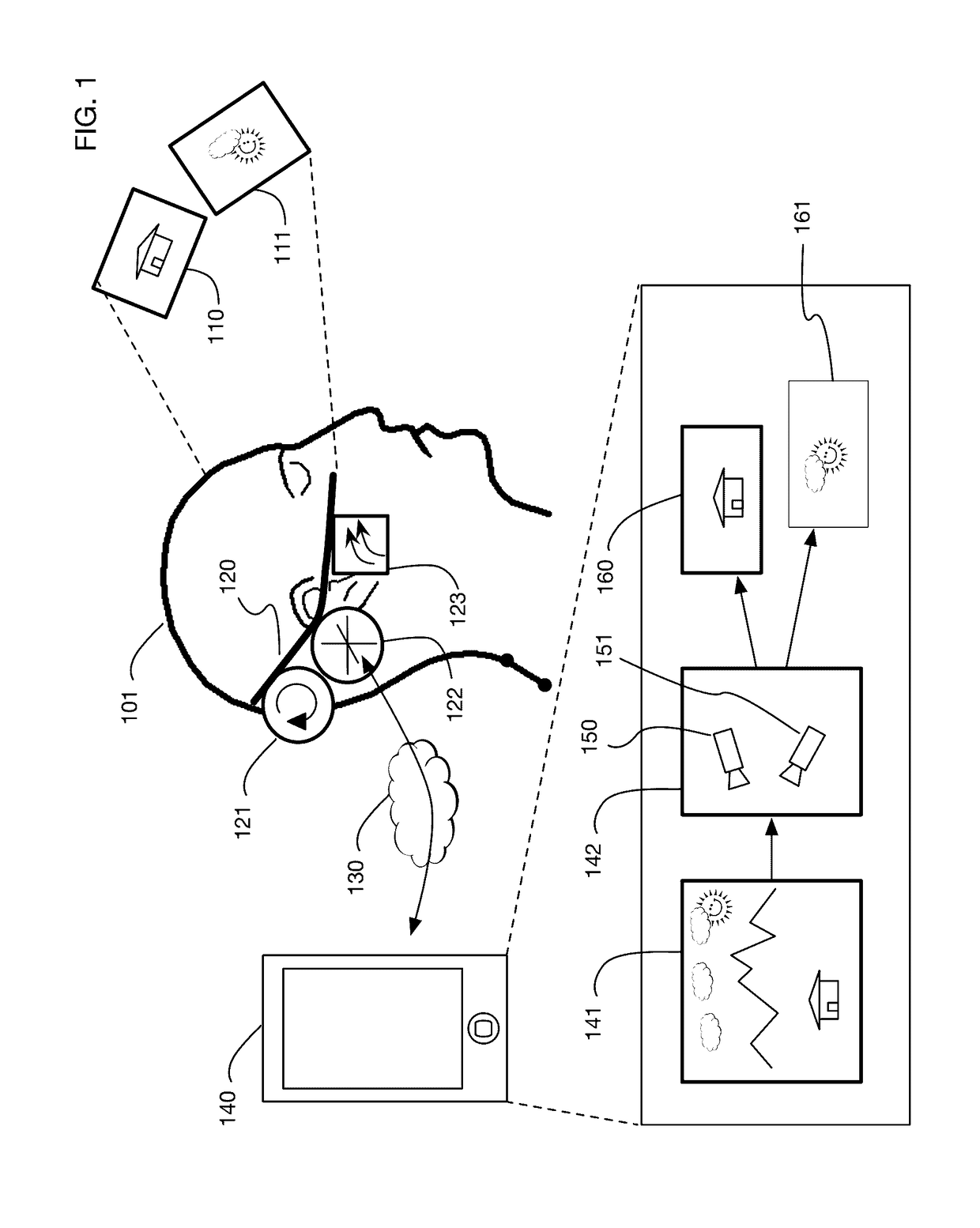
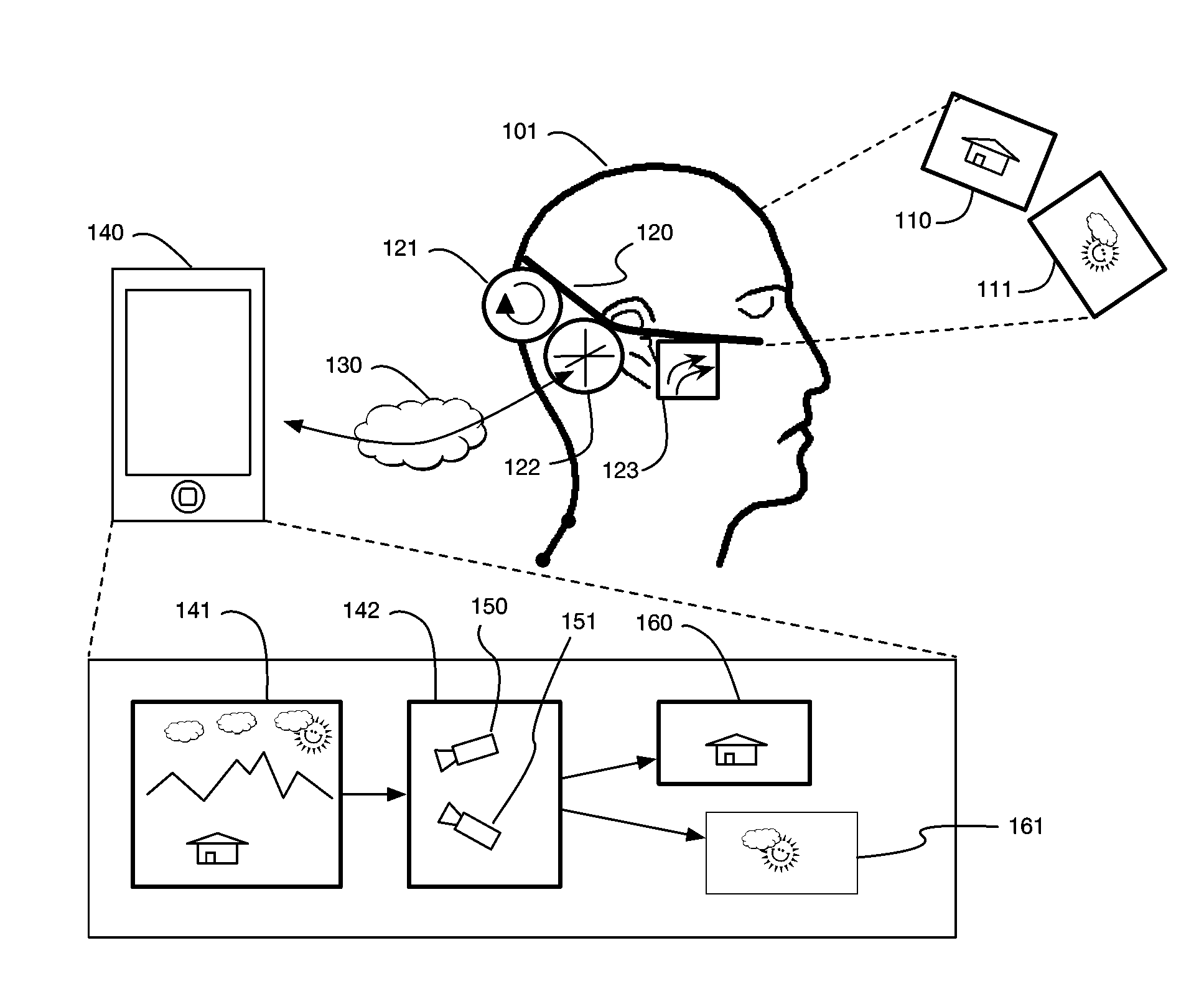
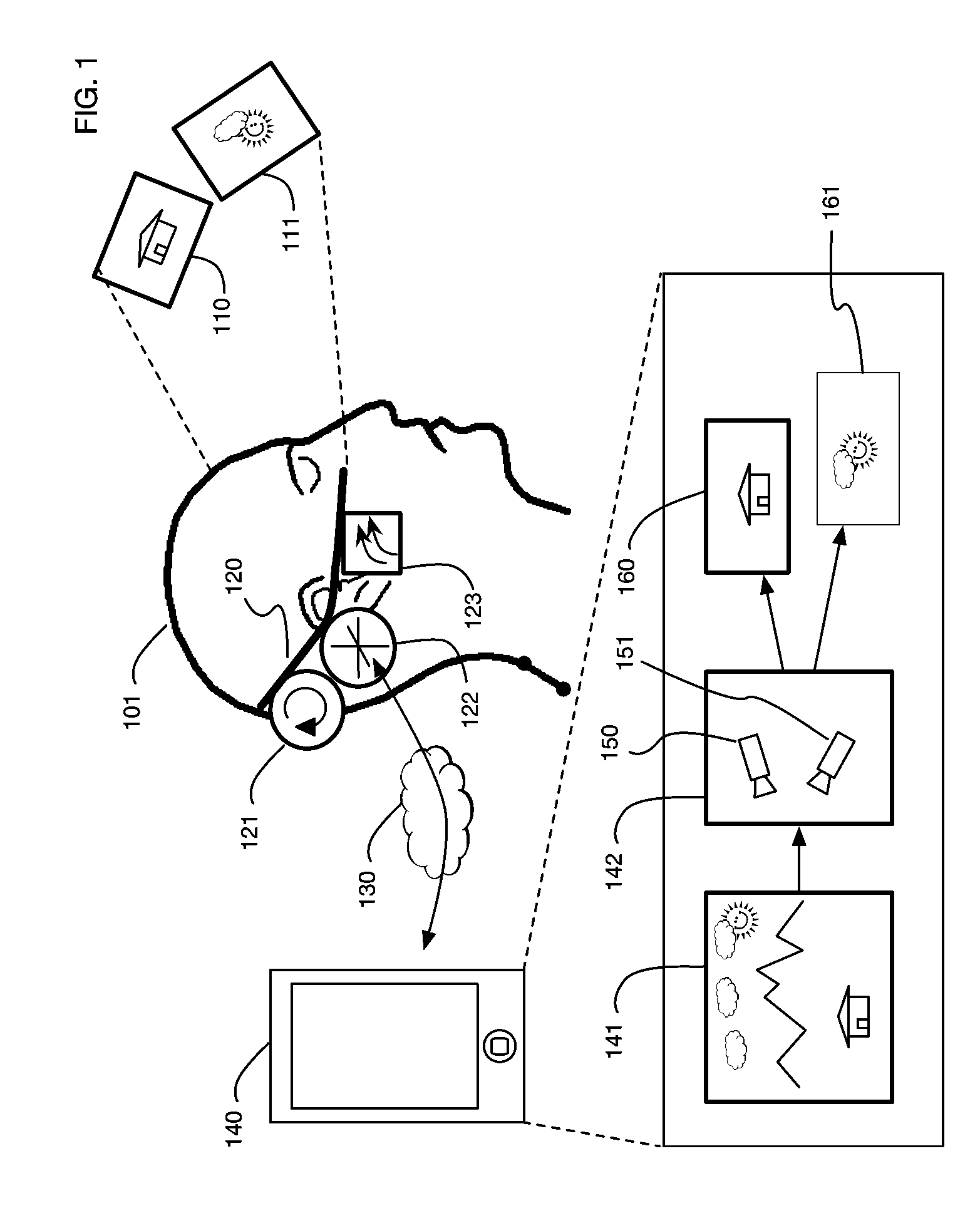
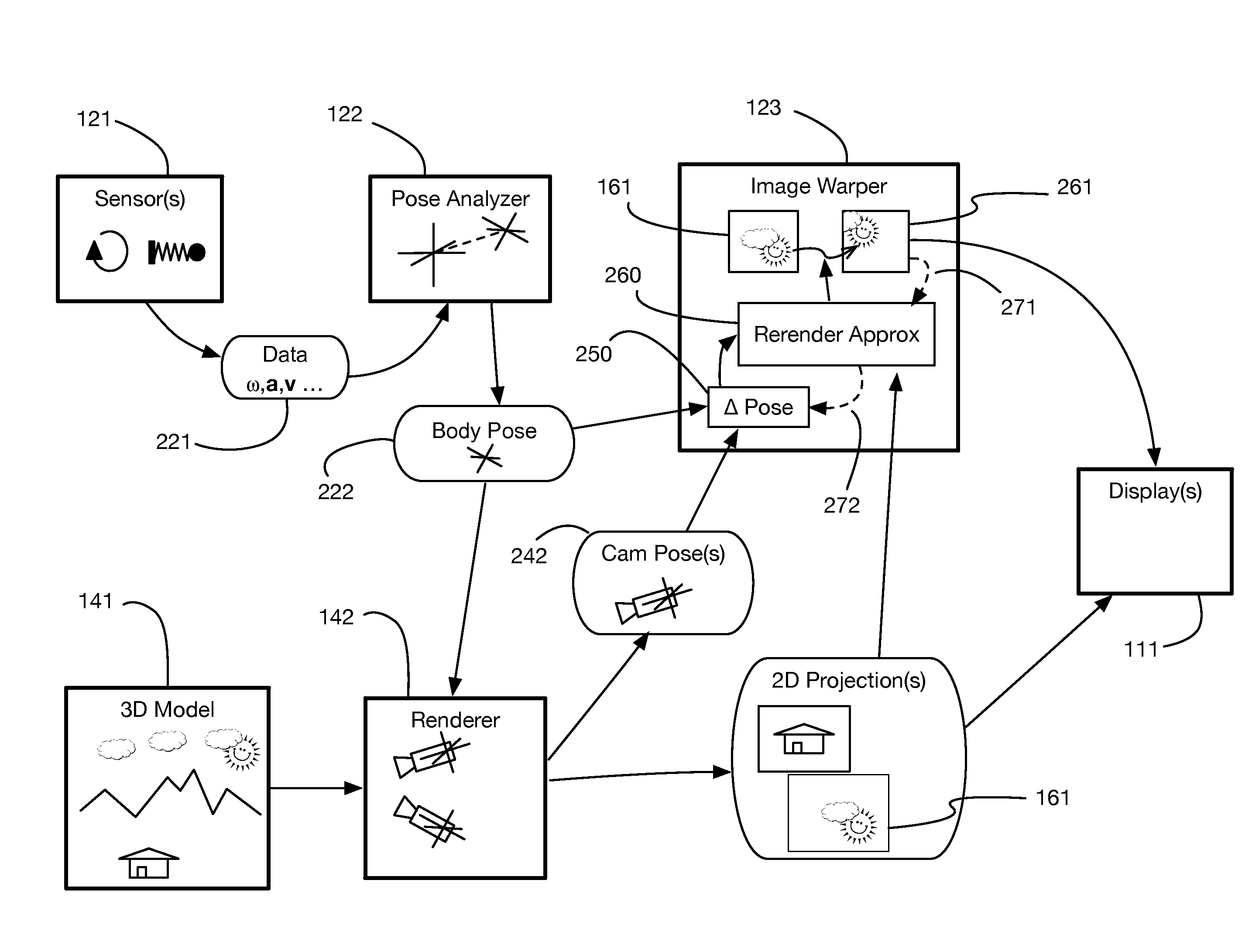
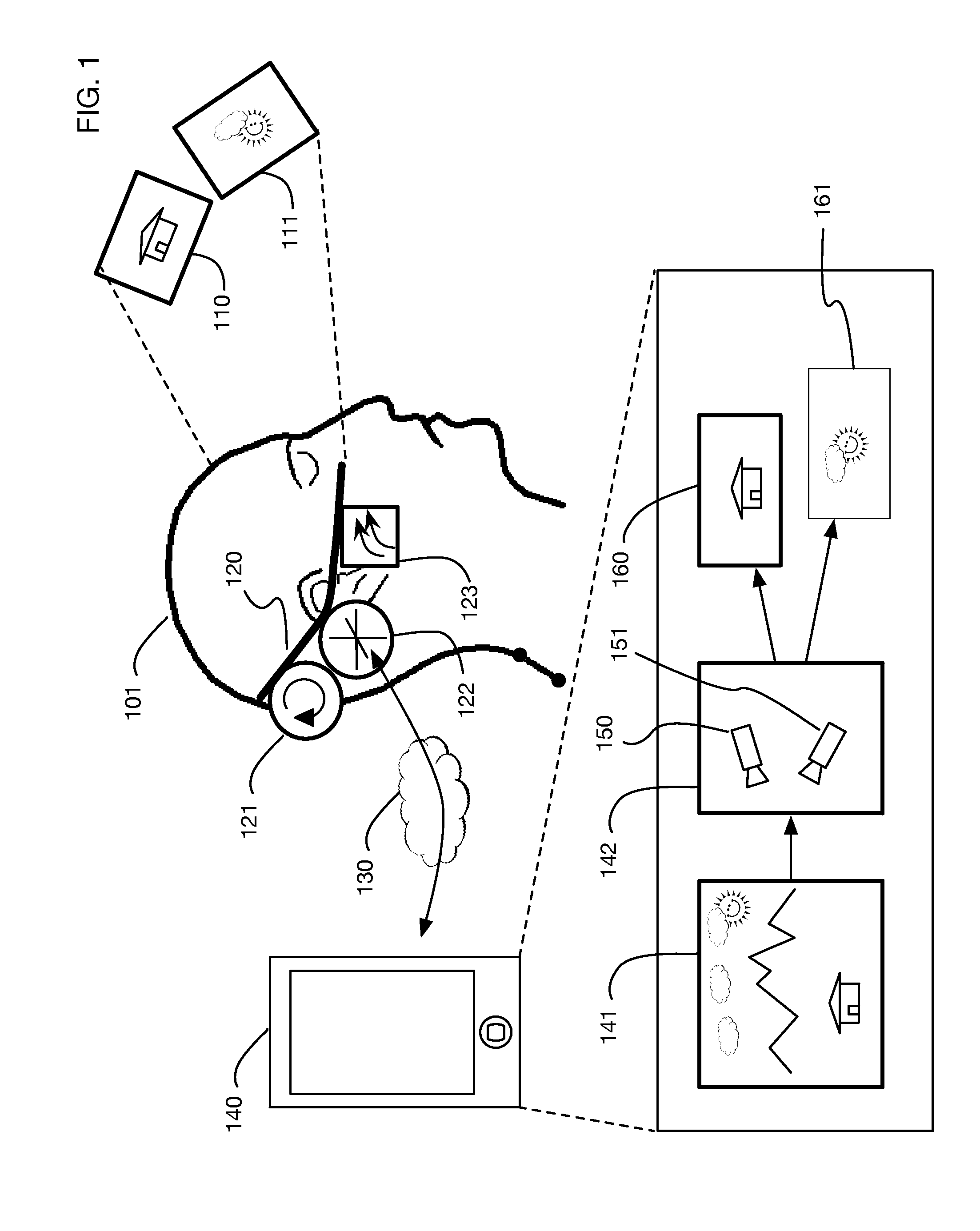
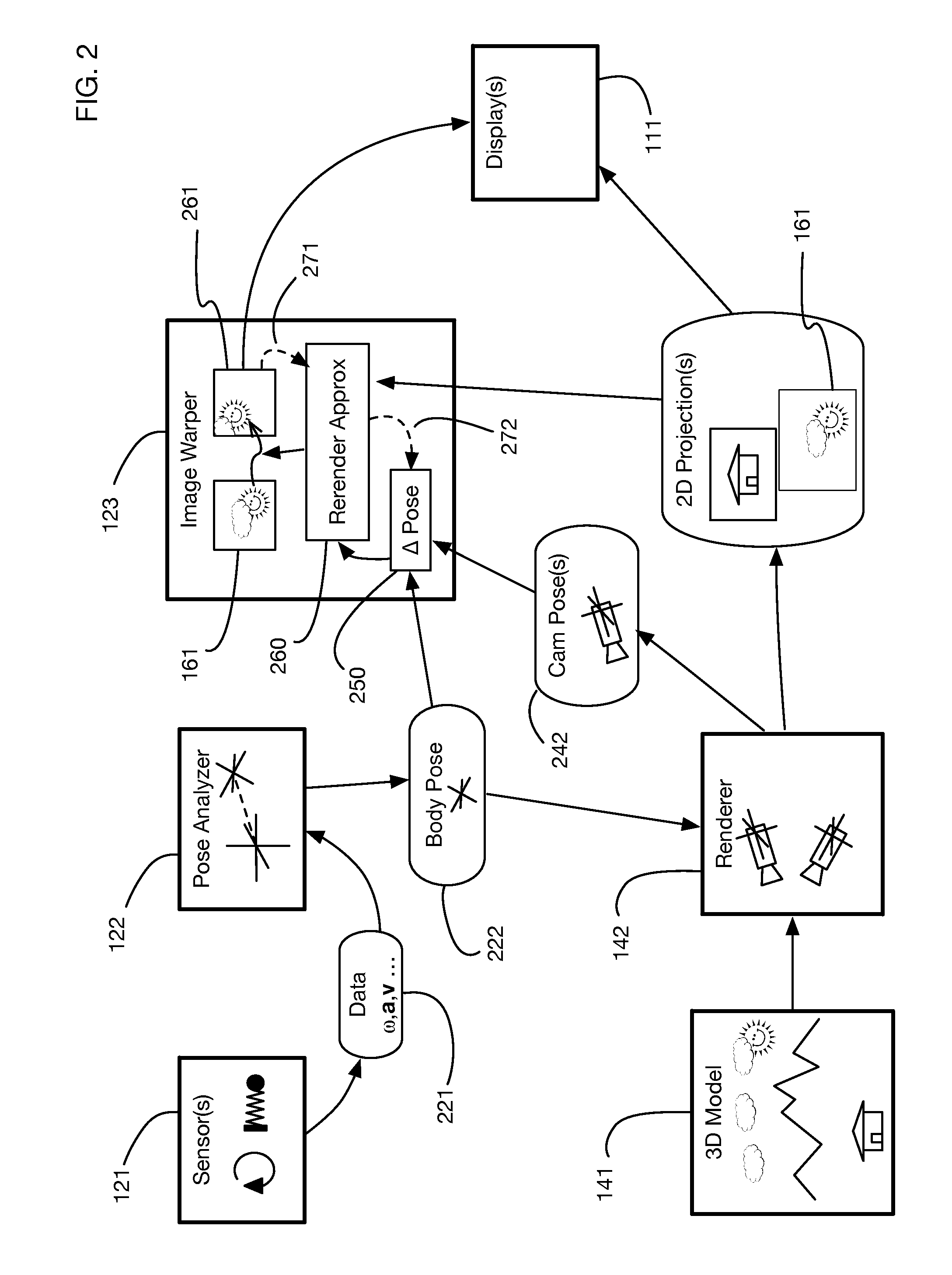
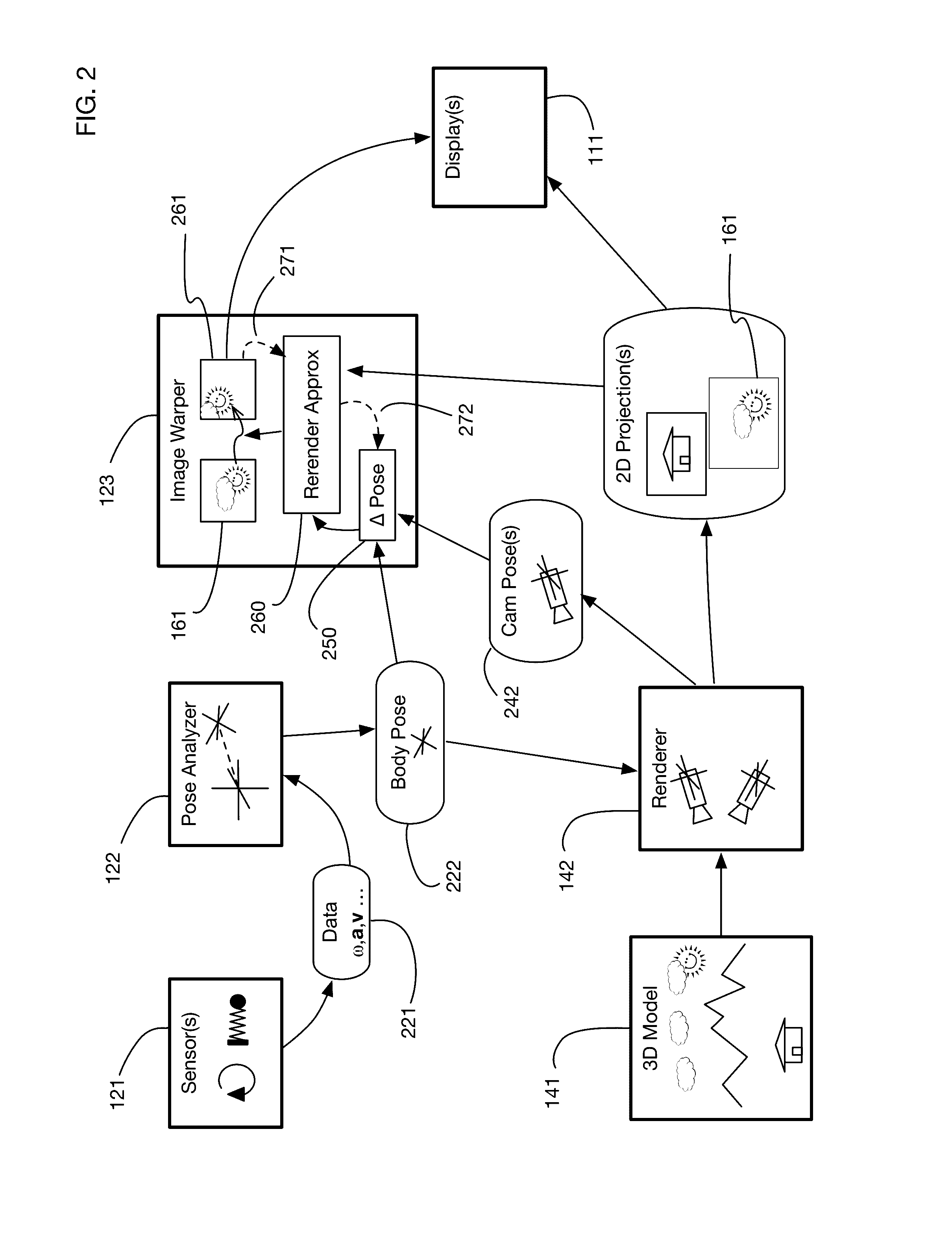
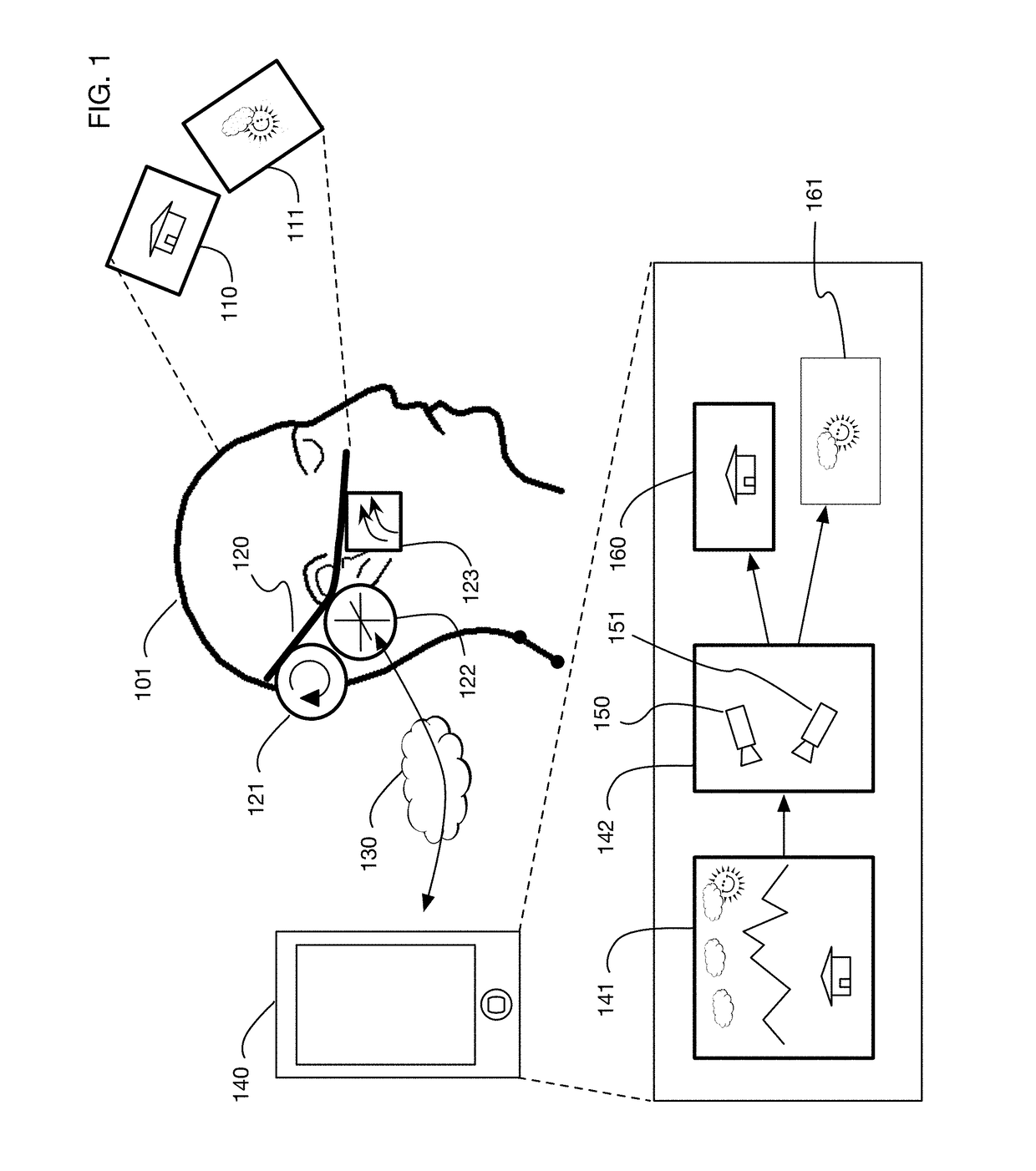
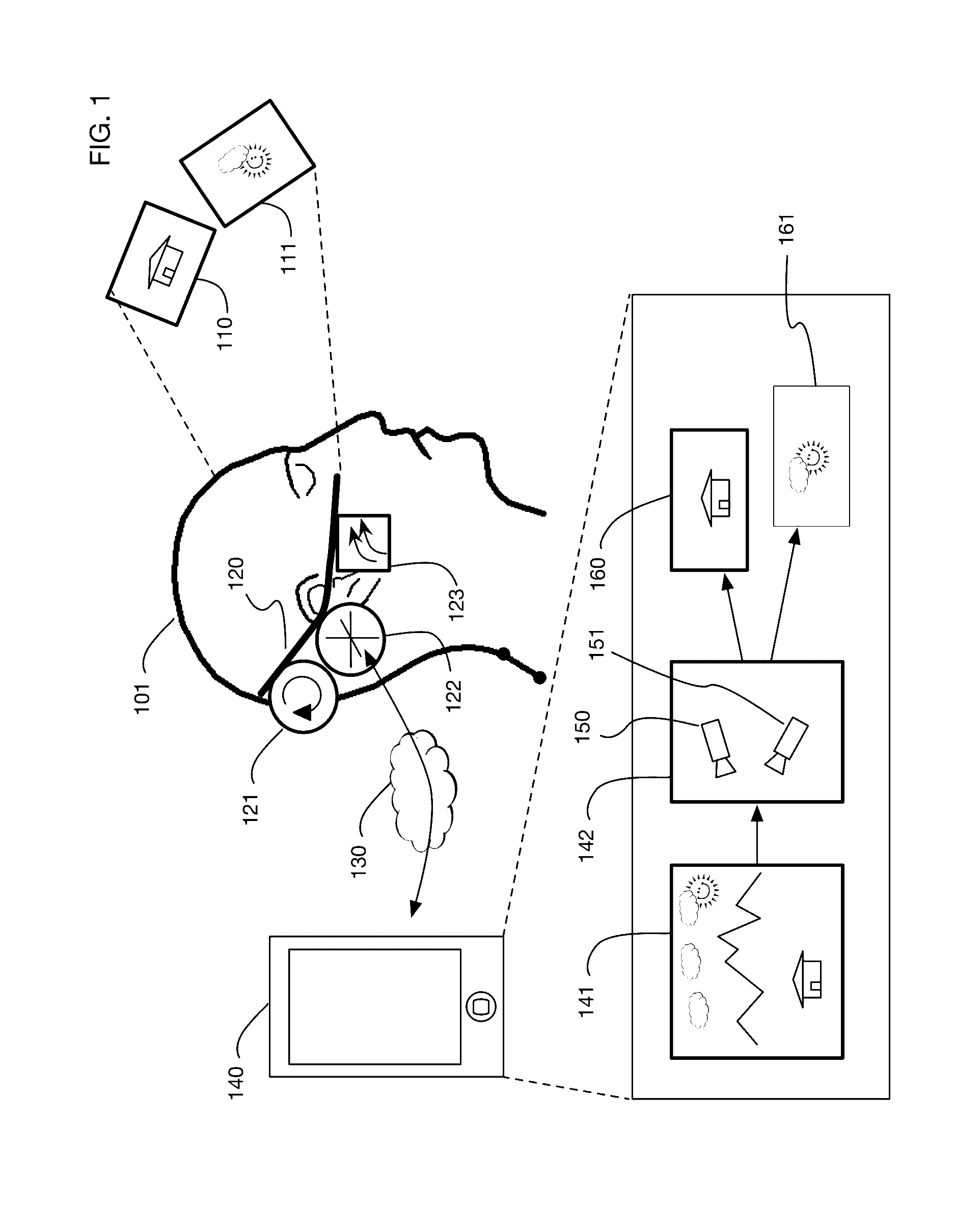
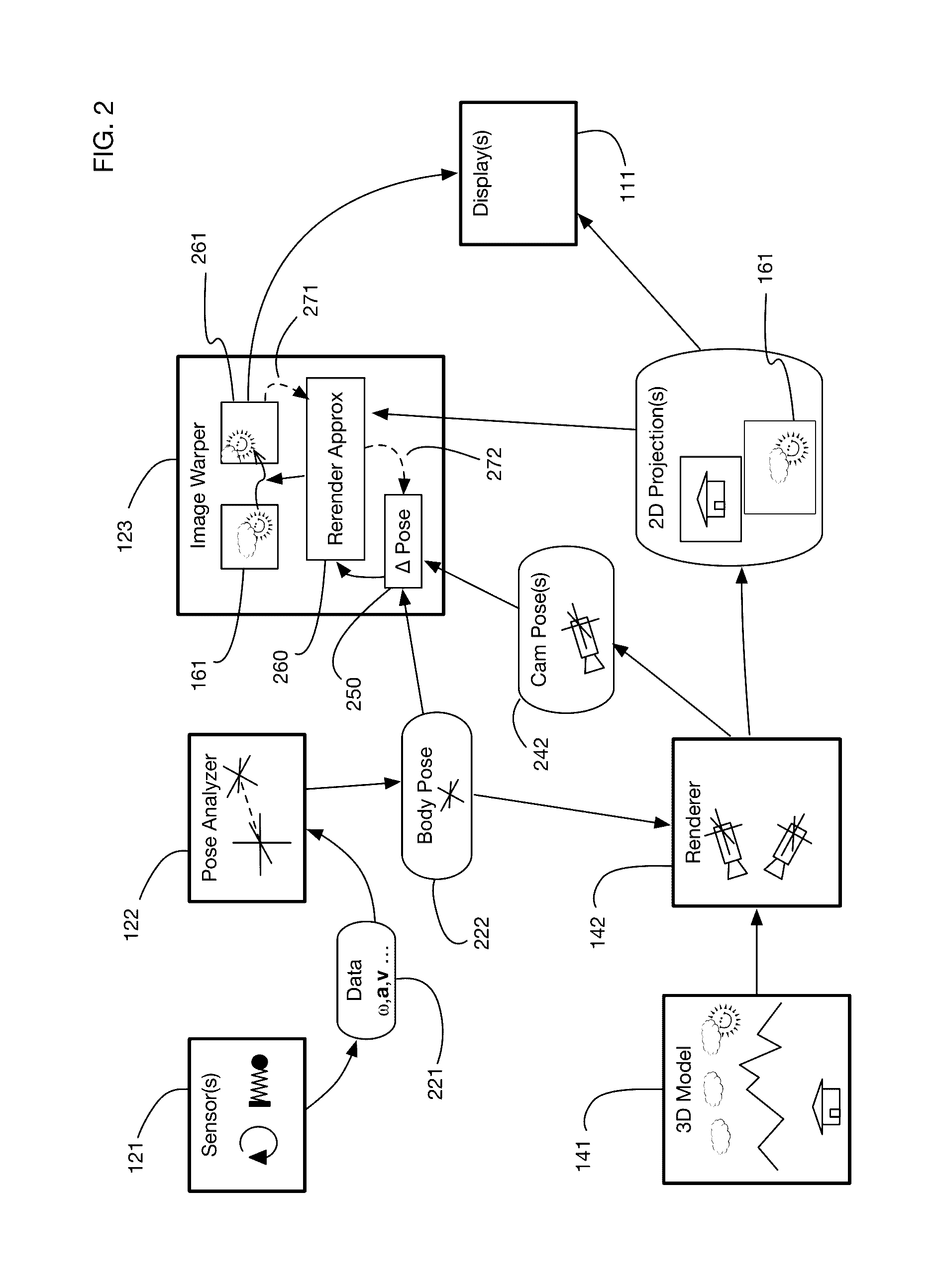
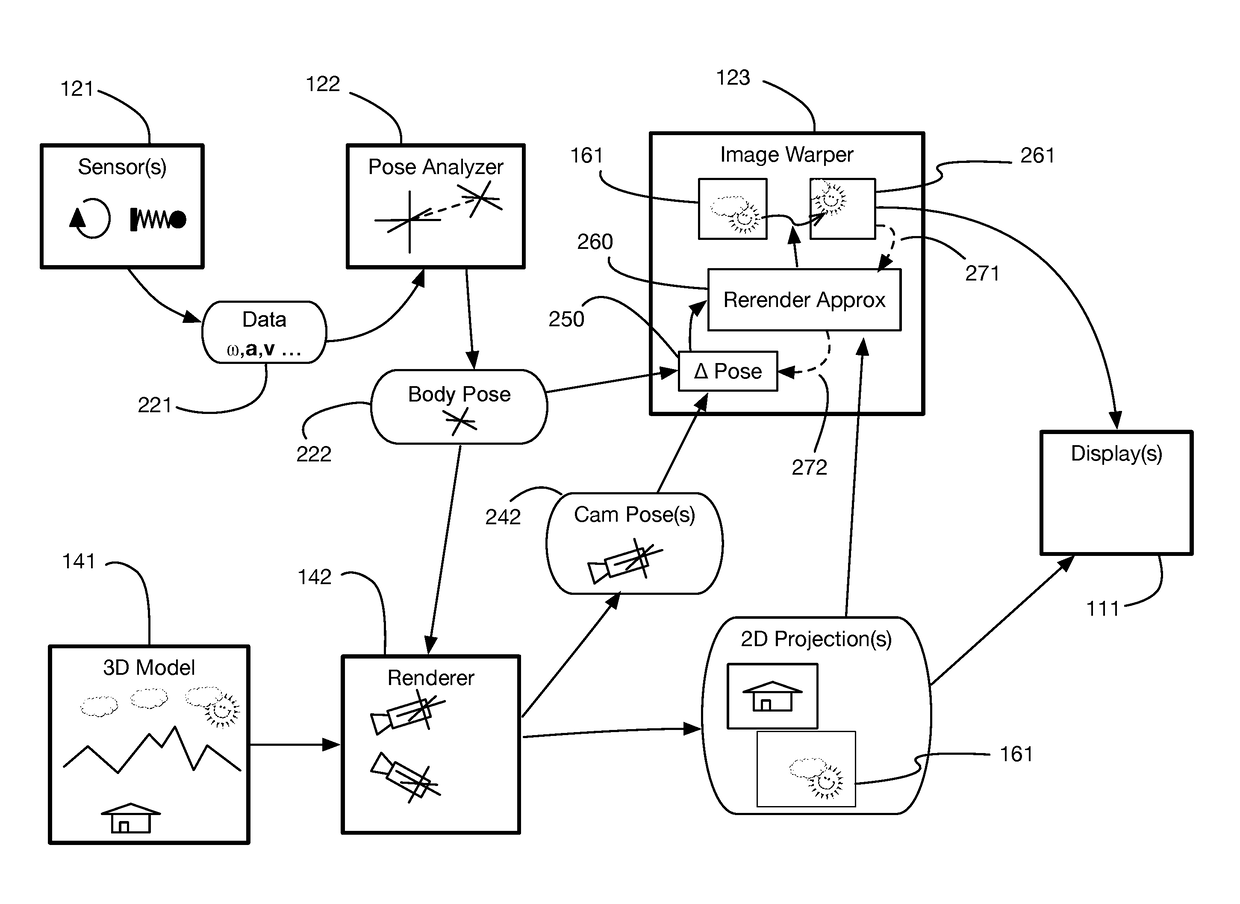
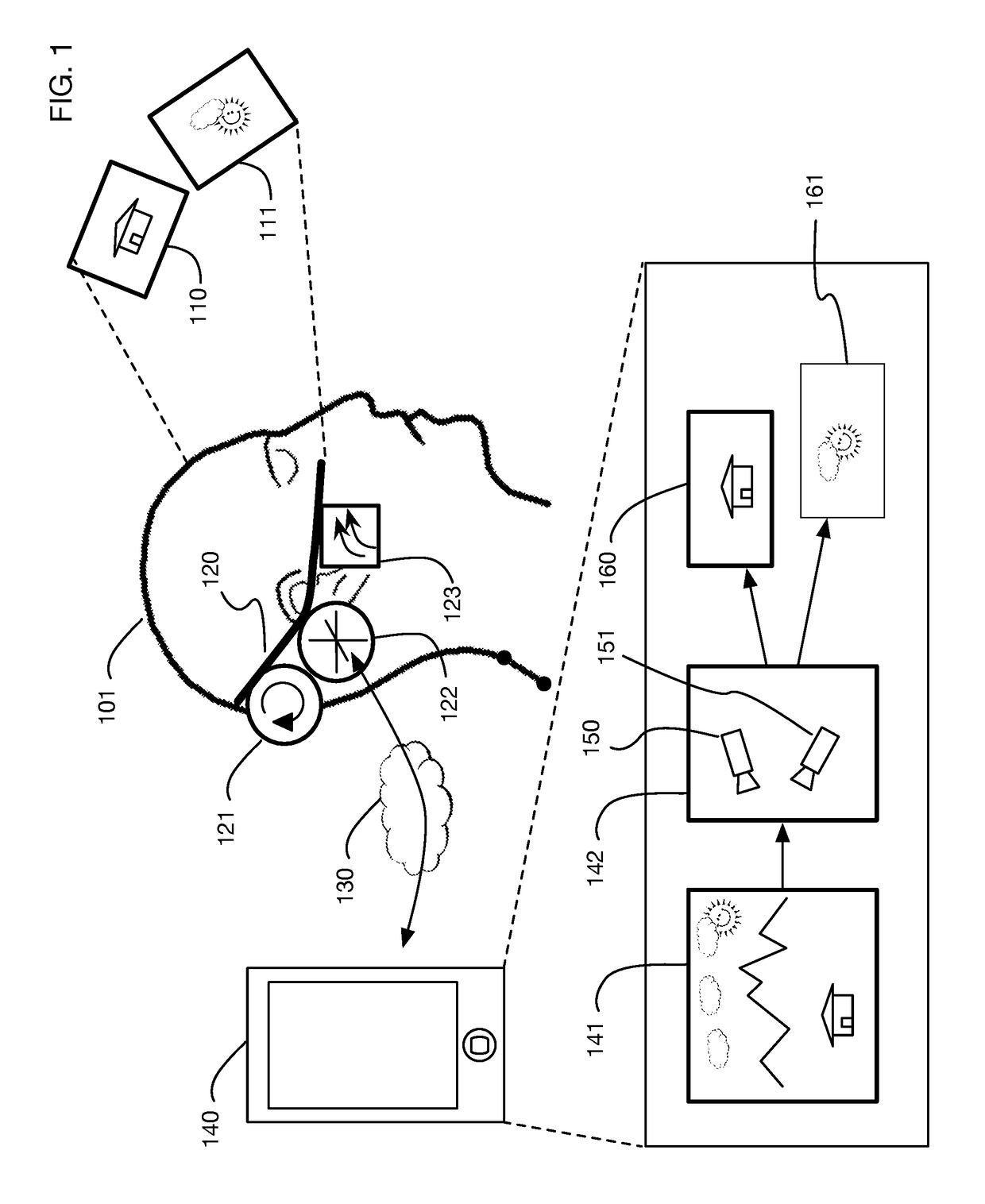
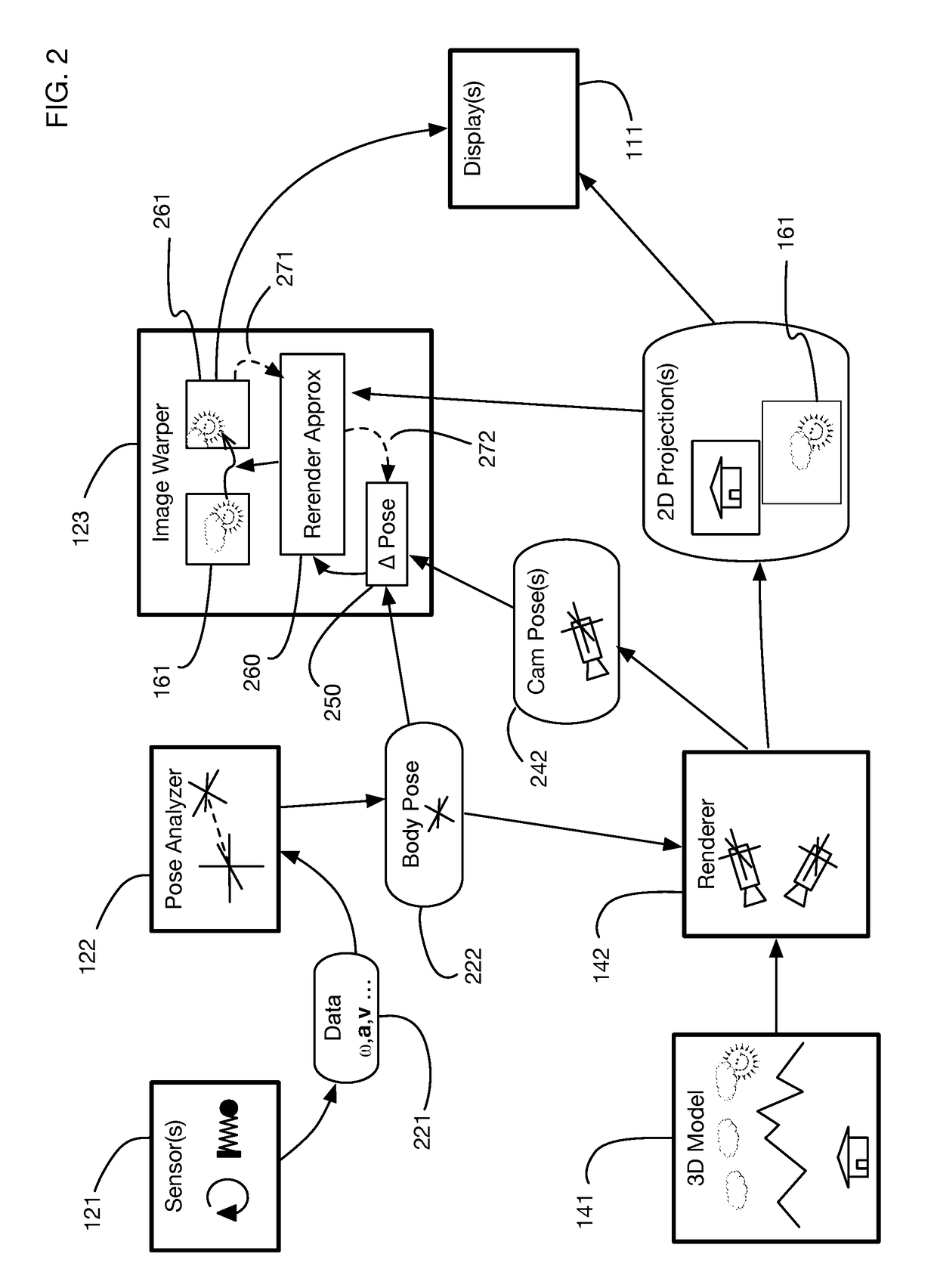
InactiveUS9240069B1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyImage renderingInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Display device
A low-latency virtual reality display system that provides rapid updates to virtual reality displays in response to a user's movements. Display images generated by rendering a 3D virtual world are modified using an image warping approximation, which allows updates to be calculated and displayed quickly. Image warping is performed using various rerendering approximations that use simplified 3D models and simplified 3D to 2D projections. An example of such a rerendering approximation is a shifting of all pixels in the display by a pixel translation vector that is calculated based on the user's movements; pixel translation may be done very quickly, possibly using hardware acceleration, and may be sufficiently realistic particularly for small changes in a user's position and orientation. Additional features include techniques to fill holes in displays generated by image warping, synchronizing full rendering with approximate rerendering, and using prediction of a user's future movements to reduce apparent latency.
Owner:LI ADAM
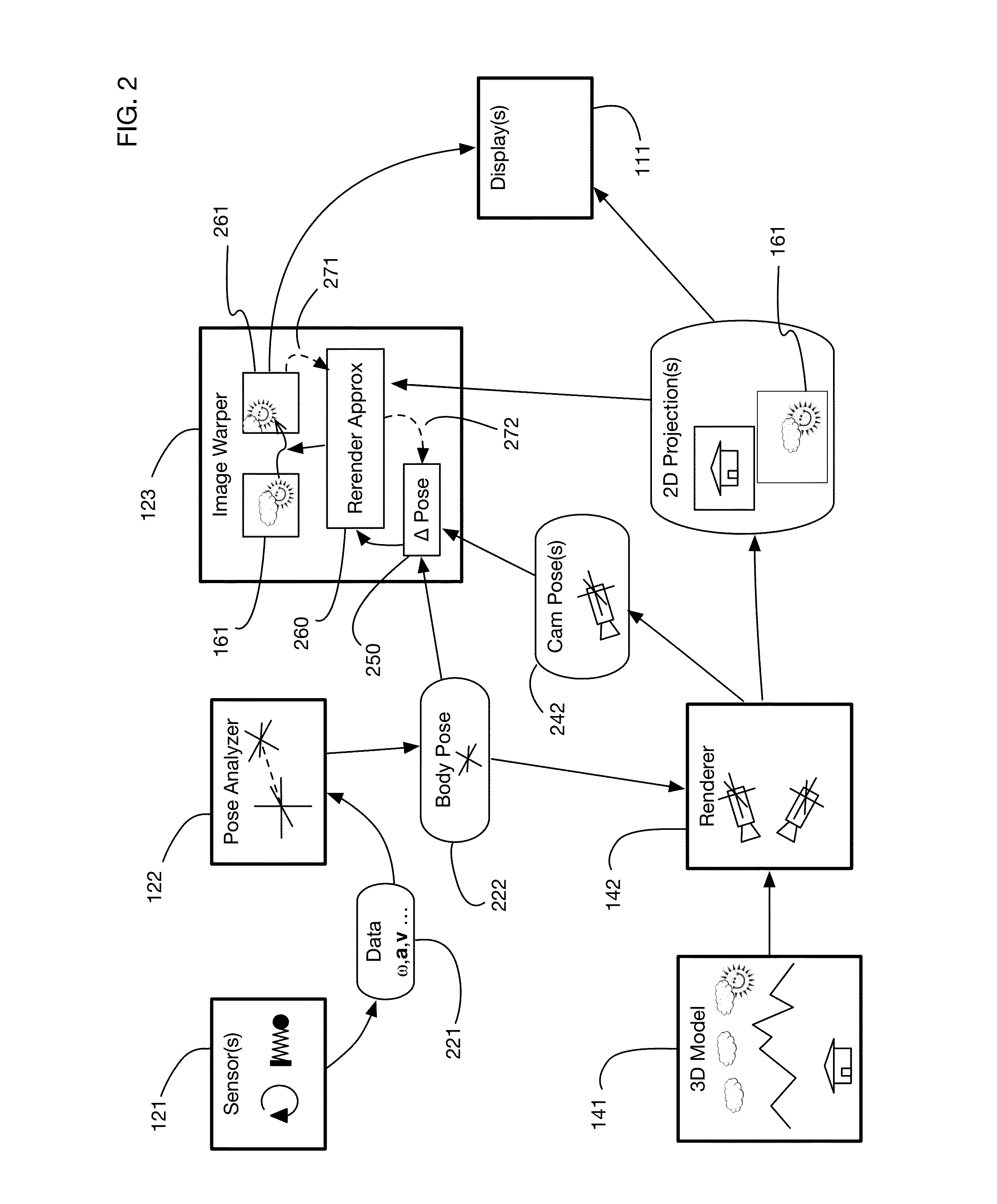
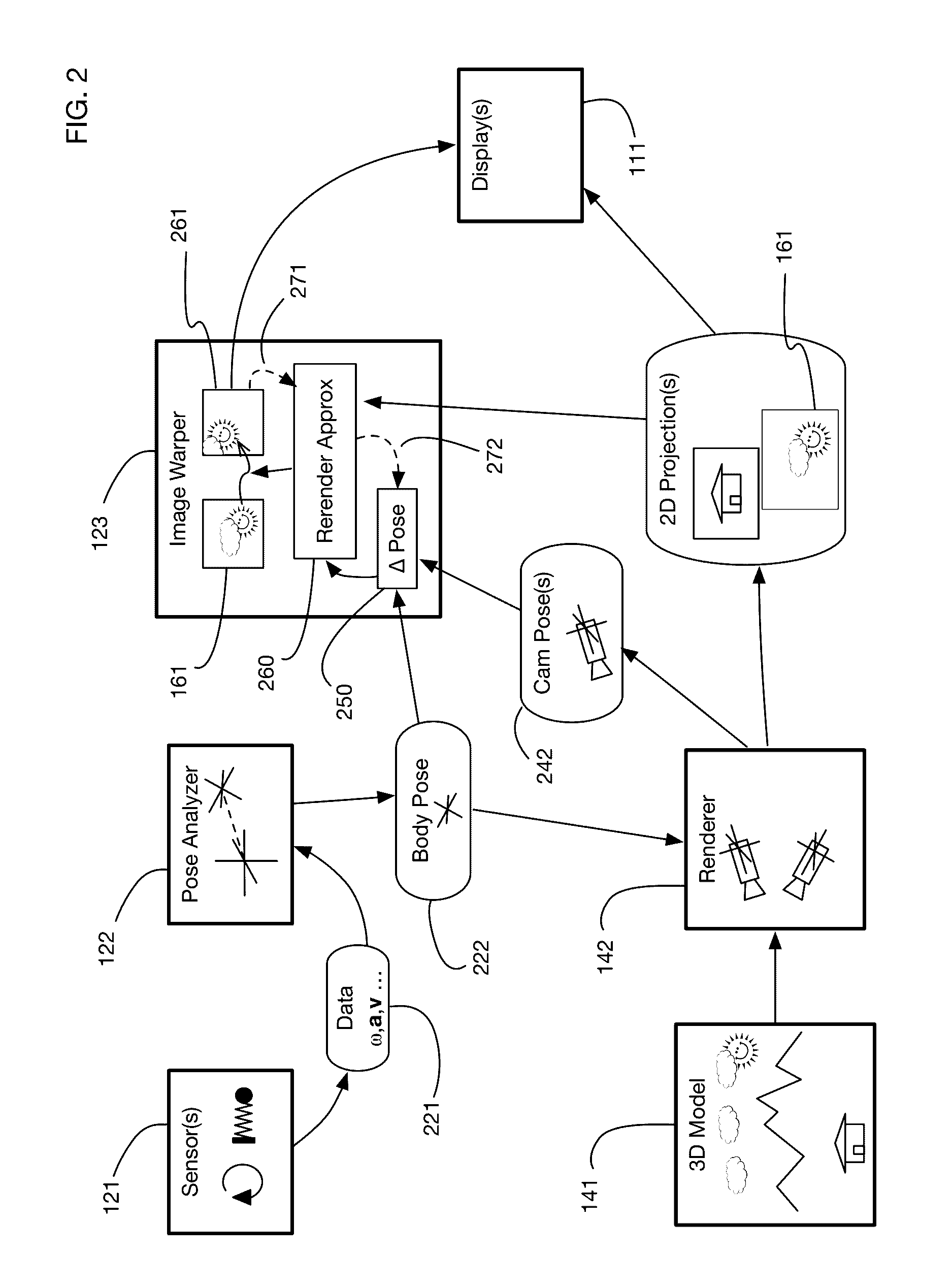
Predictive virtual reality display system with post rendering correction
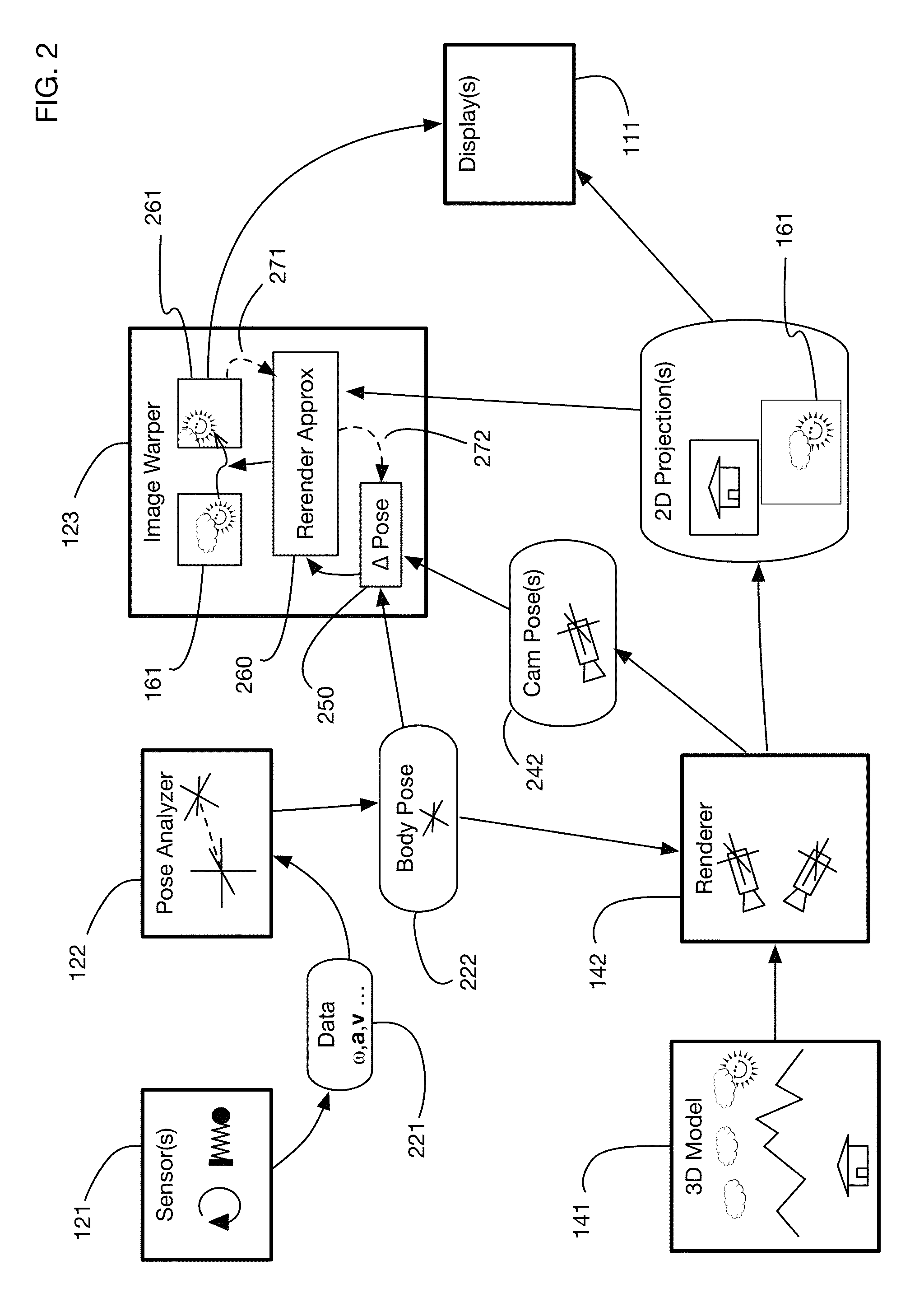
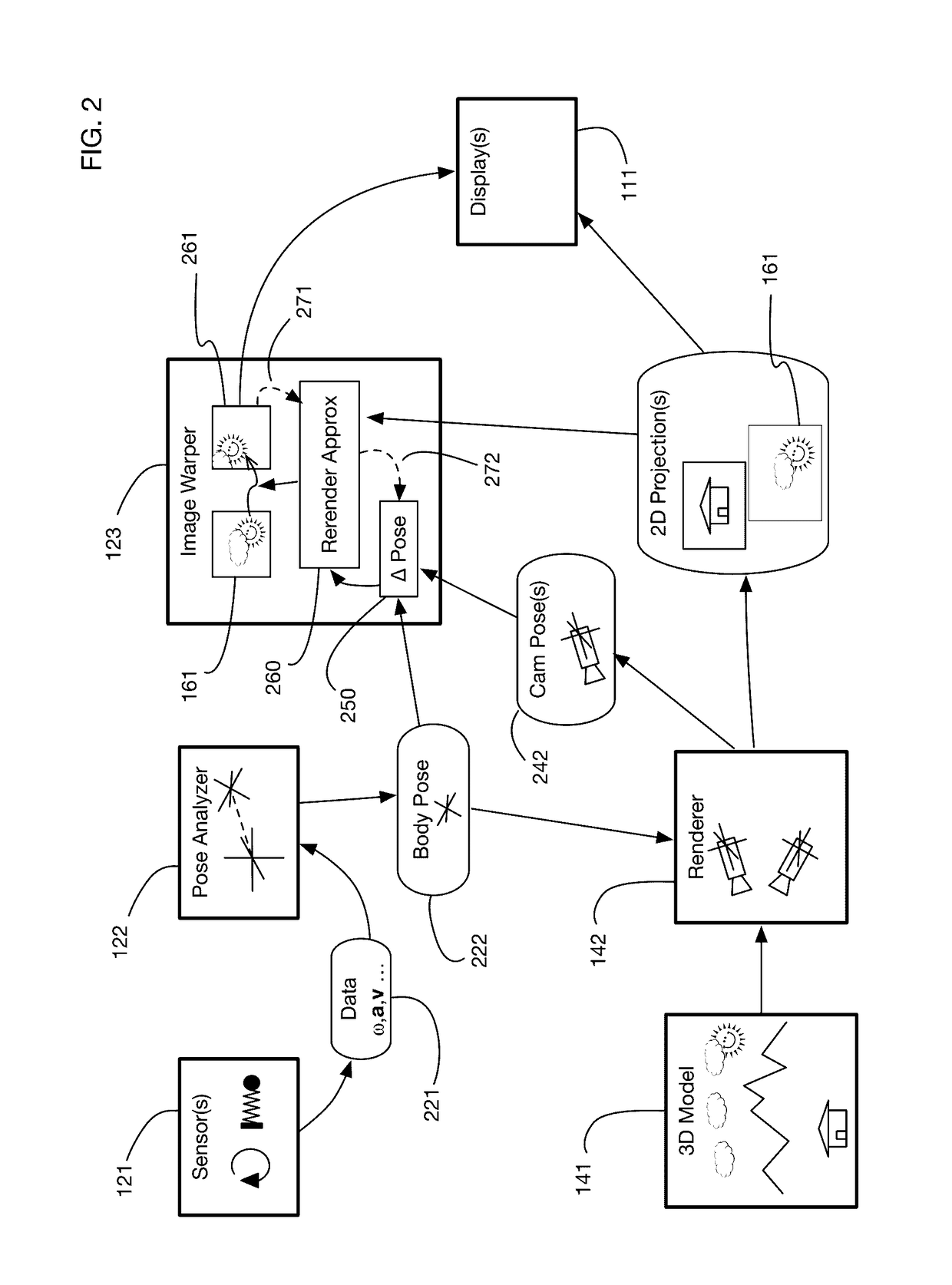
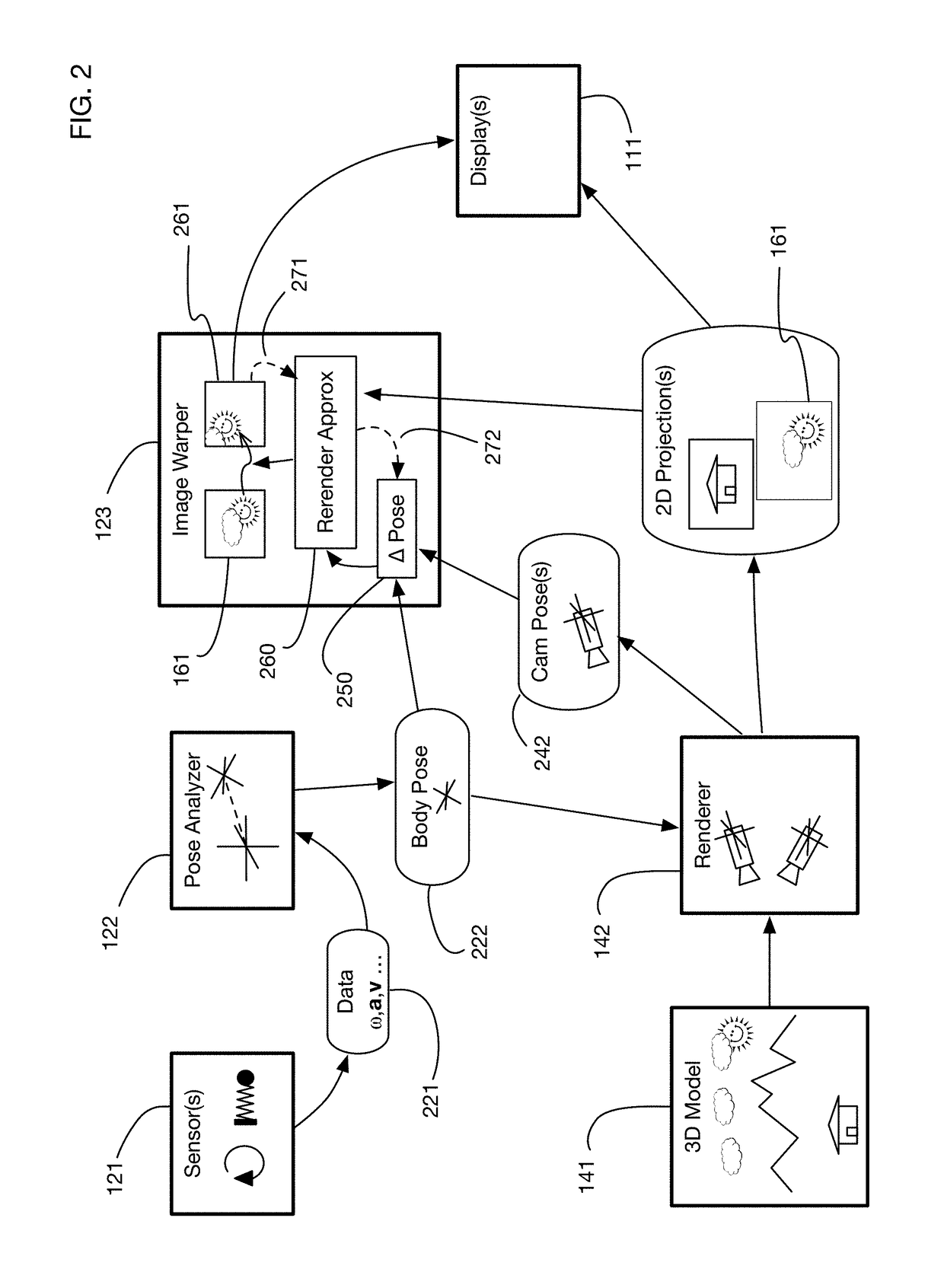
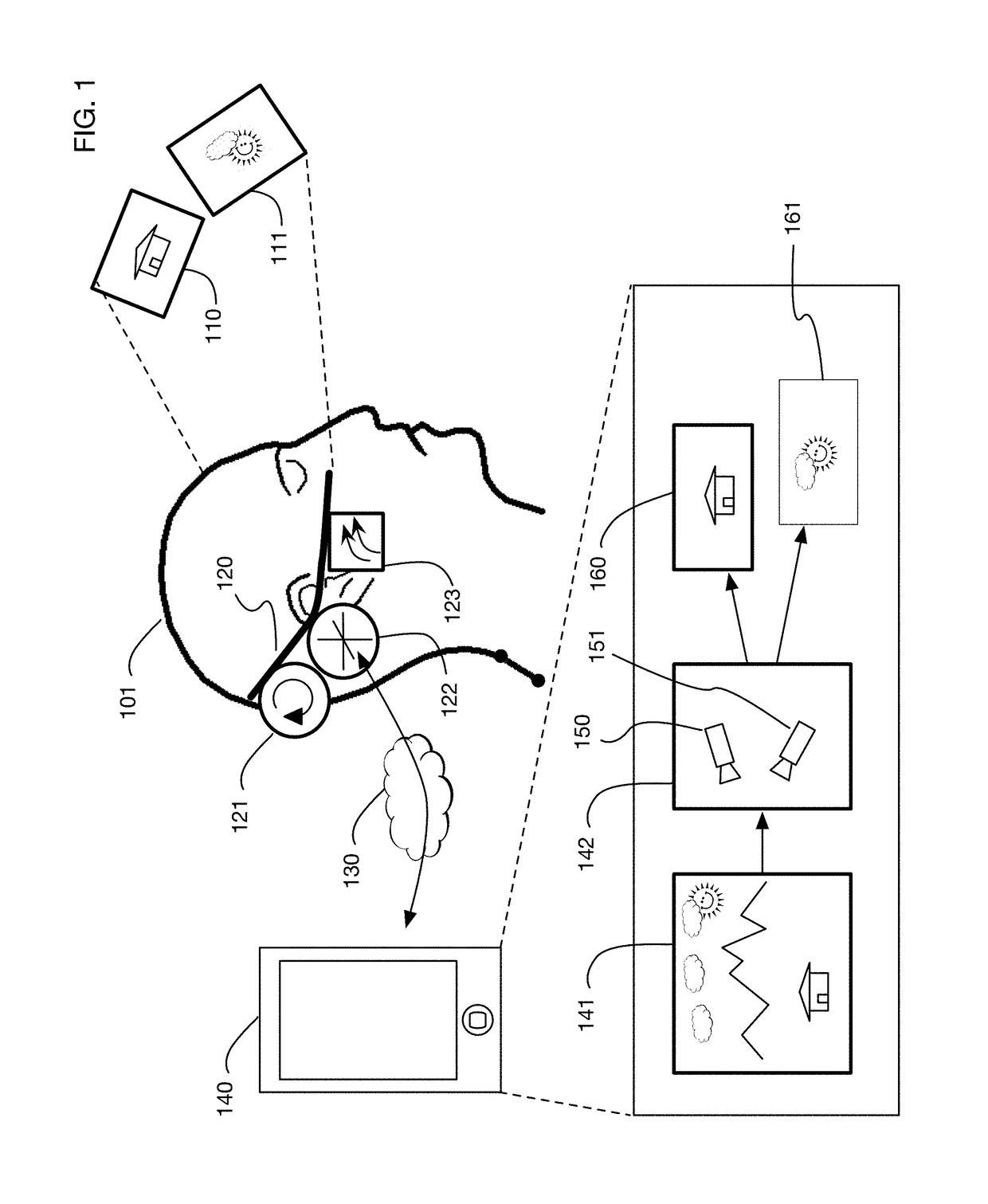
ActiveUS20170018121A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEffectively approximatesInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Biomechanical model
A virtual reality display system that generates display images in two phases: the first phase renders images based on a predicted pose at the time the display will be updated; the second phase re-predicts the pose using recent sensor data, and corrects the images based on changes since the initial prediction. The second phase may be delayed so that it occurs just in time for a display update cycle, to ensure that sensor data is as accurate as possible for the revised pose prediction. Pose prediction may extrapolate sensor data by integrating differential equations of motion. It may incorporate biomechanical models of the user, which may be learned by prompting the user to perform specific movements. Pose prediction may take into account a user's tendency to look towards regions of interest. Multiple parallel pose predictions may be made to reflect uncertainty in the user's movement.
Owner:LI ADAM
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
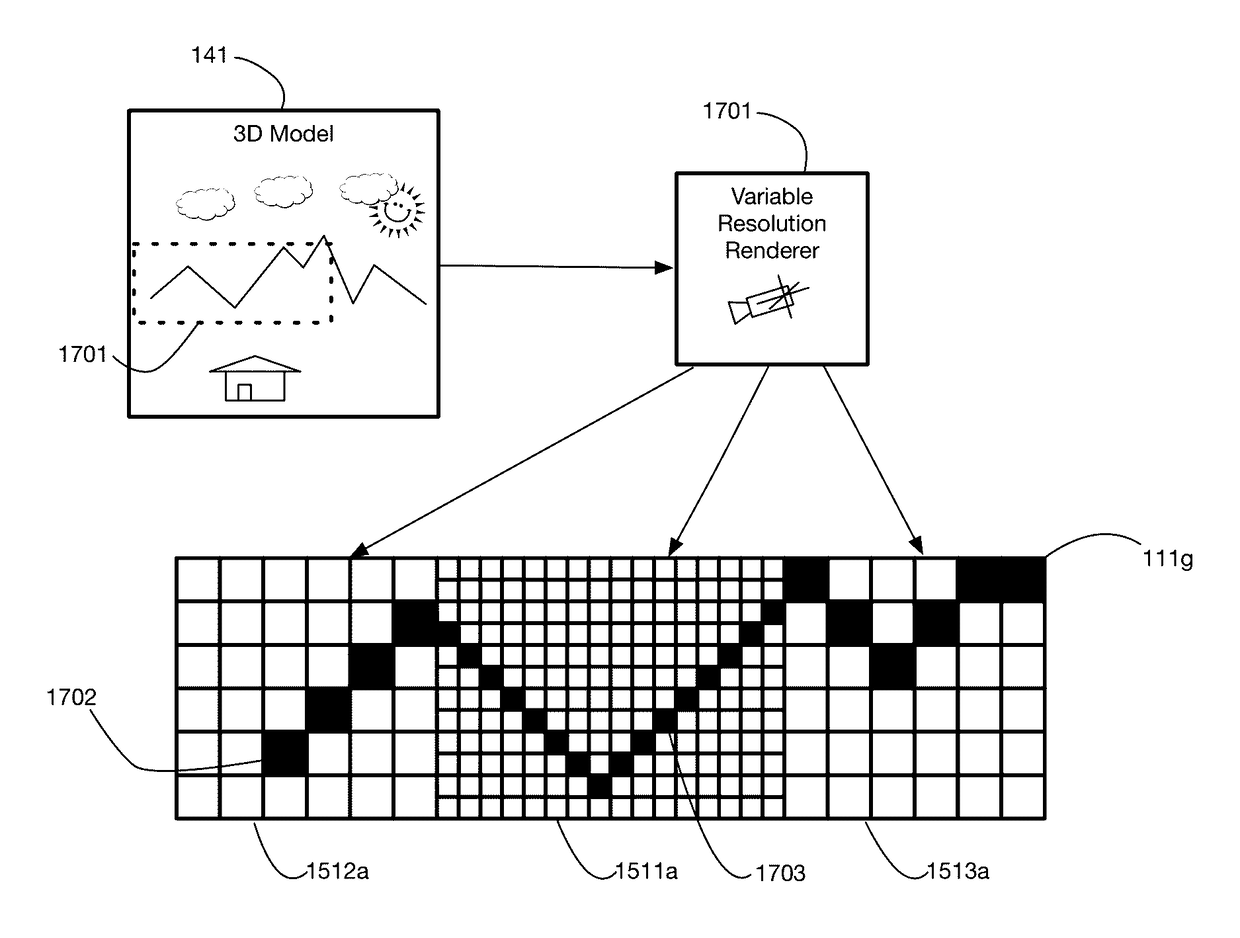
ActiveUS9607428B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
Owner:LI ADAM
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
ActiveUS20170004648A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
A virtual reality display system that renders images at different resolutions in different parts of a display. Reduces rendering latency by rendering at a lower resolution in selected regions, for example on the sides of a display where human vision has lower resolution than in the center. Pixels in low resolution regions are combined into grid elements, and rendering may generate grid element values rather than individual pixel values. Rendering may use ray casting, rasterization, or both. Variable resolution rendering may be combined with variable level of detail geometry models to further reduce rendering time. Selected objects may be designed as high resolution objects that are rendered at a high resolution even in low resolution display regions.
Owner:LI ADAM
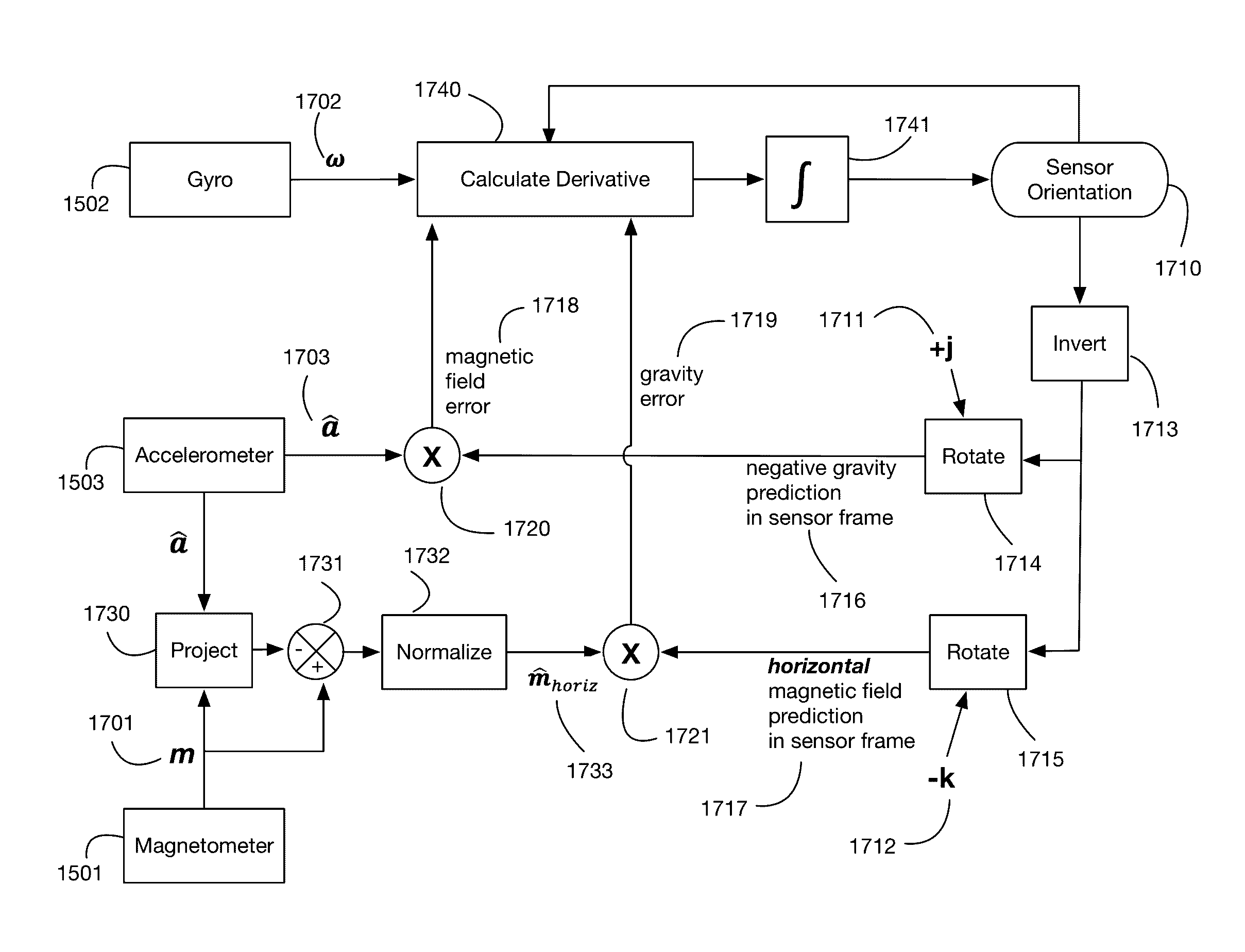
Efficient orientation estimation system using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors
ActiveUS20170003764A1Effective estimateEnhance the virtual reality experienceImage data processingInput/output processes for data processingKaiman filterLatency (engineering)
A system that efficiently estimates an object's orientation using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors. The object may be for example a virtual reality headset or a user in a virtual reality environment. Magnetic and gravity data are used to correct errors that accumulate from integrating angular velocity. Unlike systems that use Kalman filter approaches, embodiments of the system apply a simple, highly efficient technique to generate magnetic and gravity error vectors; these error vectors are added directly to the angular velocity prior to integration. Error calculations are performed in the sensor reference frame rather than in the Earth reference frame. Magnetic error correction uses only the horizontal component of the magnetic field, which is efficiently calculated by subtracting off the projection of the magnetic field onto the measured gravity vector. Sensors and processors for calculating orientation may be integrated into a low-latency virtual reality display system.
Owner:LI ADAM
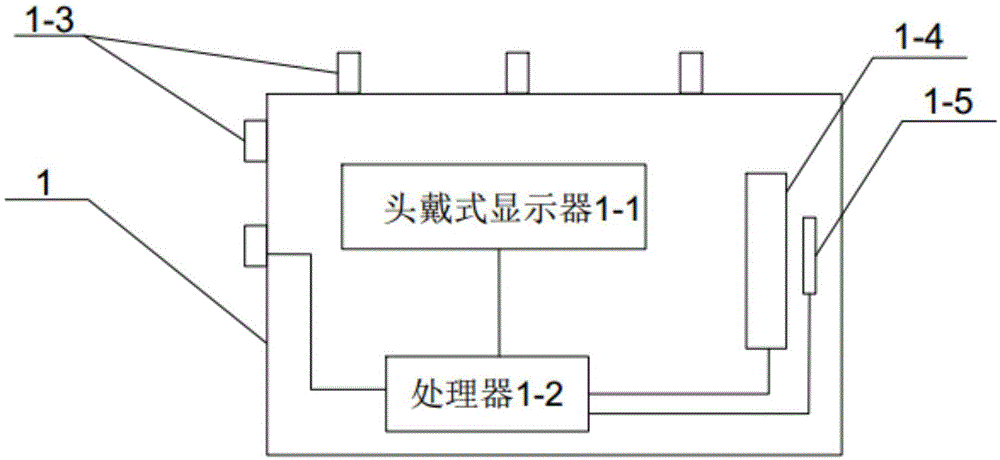
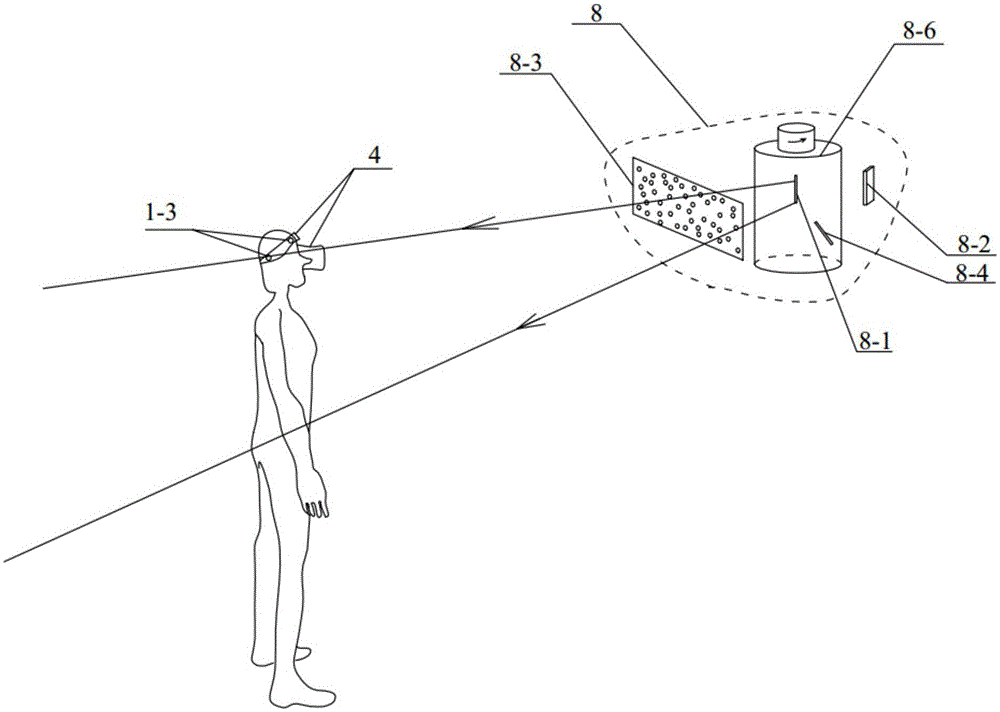
Head-mounted type virtual reality device and virtual reality system
ActiveCN105138135AEnhance the virtual reality experienceAchieve interactionInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingDisplay deviceLight beam
The invention discloses a head-mounted type virtual reality device. The device comprises a shell, a head-mounted display, a plurality of positioning light beam receivers and a processor. The head-mounted display is located in the shell and used for displaying a three-dimensional virtual scene. The positioning light beam receivers are embedded in the outer surface of the shell and used for receiving positioning light beams which conduct sweeping in a laser positioning base station according to a preset sweeping period. The relative space position relations between the positioning light beam receivers are fixed. The processor is located in the shell and used for determining the position of the head-mounted type virtual reality device according to the times when the four positioning beam receivers receive the positioning light beams respectively, the sweeping period, the relative space position relations and a preset position of the positioning light beam emitting device. Therefore, when a three-dimensional virtual image is shown to a user through the head-mounted type virtual reality device, position information of the user can be determined. Therefore, the position information of the user can be displayed in the virtual scene through the head-mounted type virtual reality device, and interaction between the user and the virtual reality scene can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING G WEARABLES INFORMATION SCI & TECH
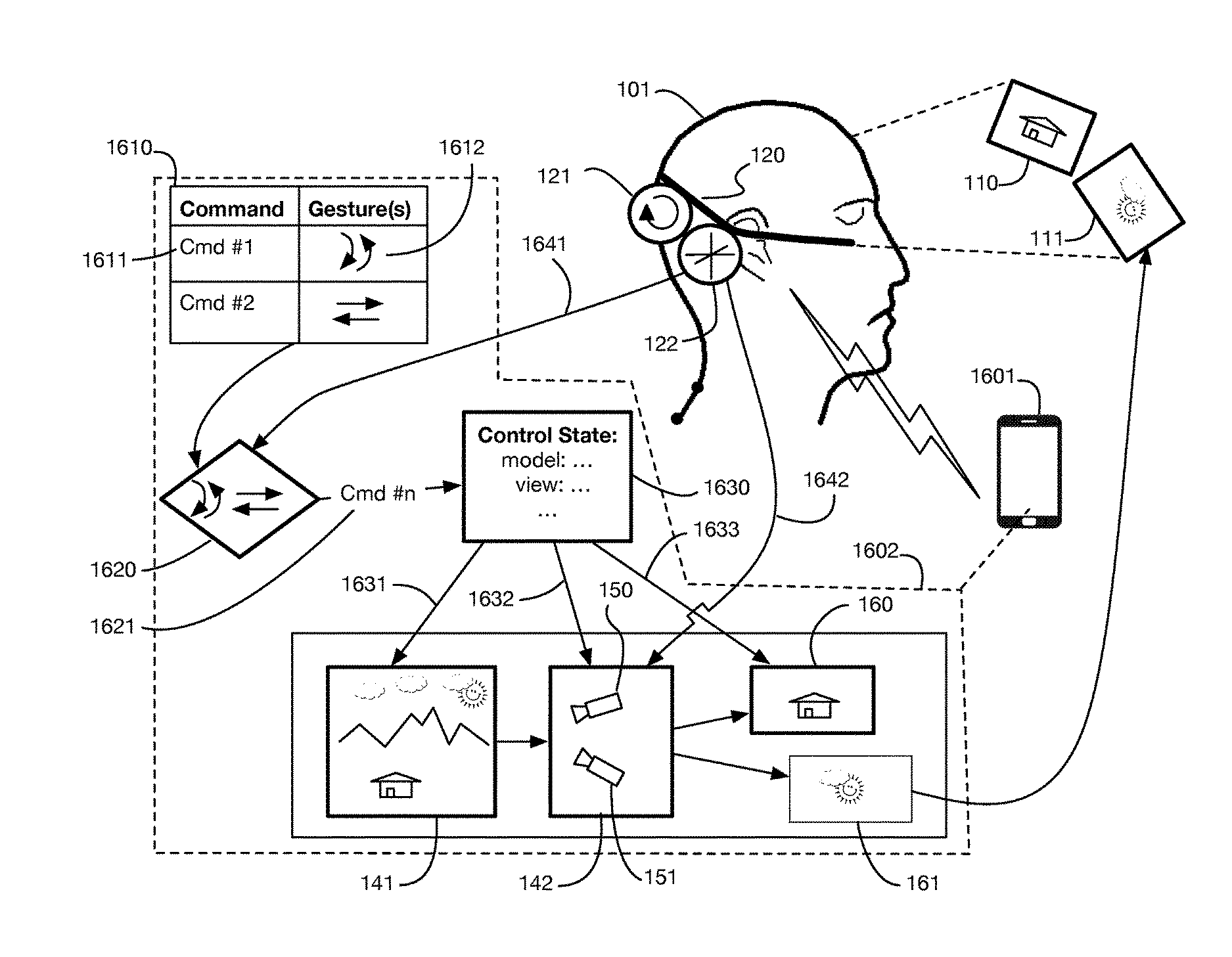
Virtual reality system with control command gestures
ActiveUS20170003750A1Latency display updateEfficient rerenderingInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementHead movementsViewpoints
A virtual reality system that uses gestures to obtain commands from a user. Embodiments may use sensors mounted on a virtual reality headset to detect head movements, and may recognize selected head motions as gestures associated with commands. Commands associated with gestures may modify the user's virtual reality experience, for example by selecting or modifying a virtual world or by altering the user's viewpoint within the virtual world. Embodiments may define specific gestures to place the system into command mode or user input mode, for example to temporarily disable normal head tracking within the virtual environment. Embodiments may also recognize gestures of other body parts, such as wrist movements measured by a smart watch.
Owner:LI ADAM
Controlled dynamic multi-axis virtual reality system
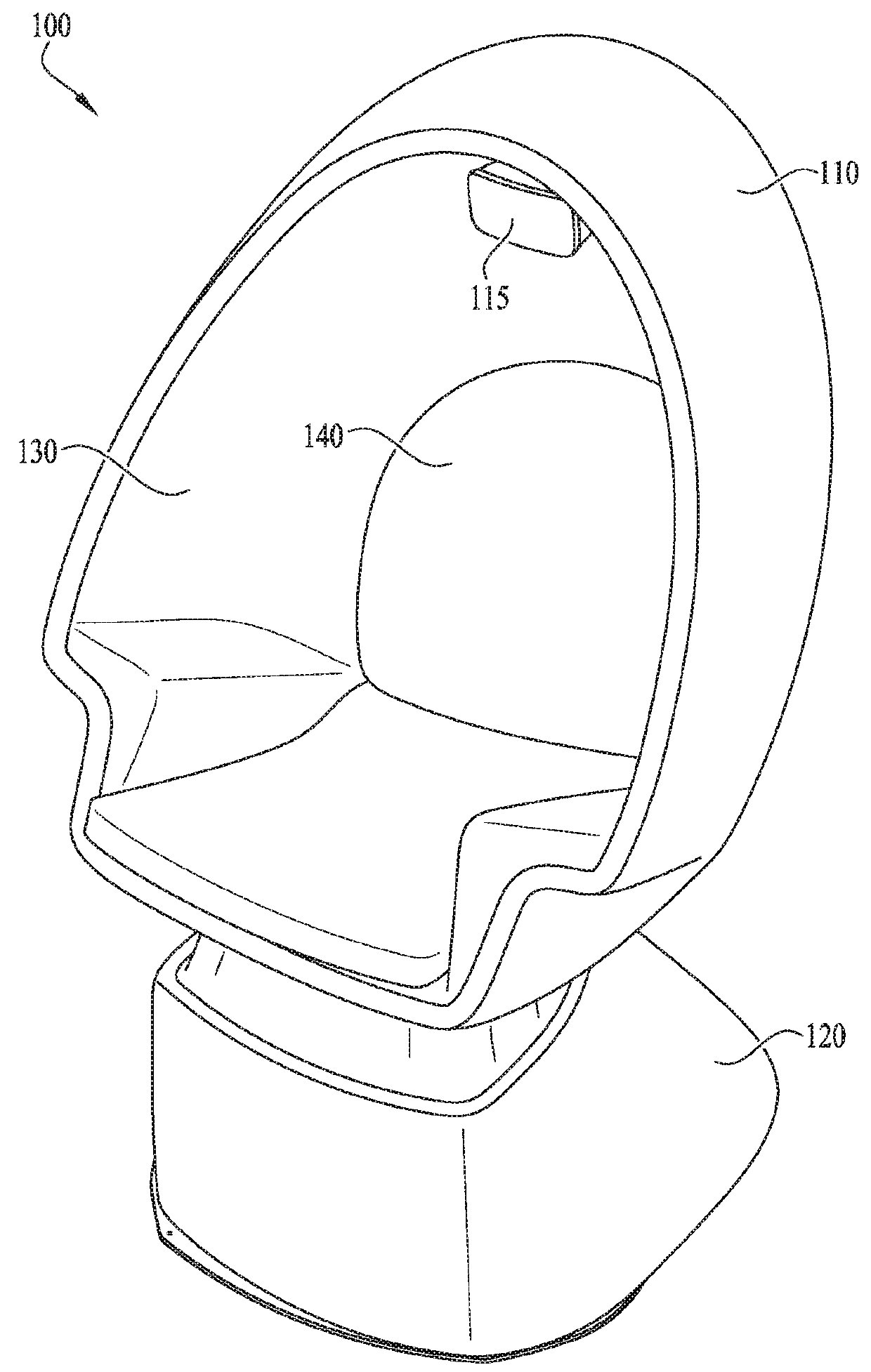
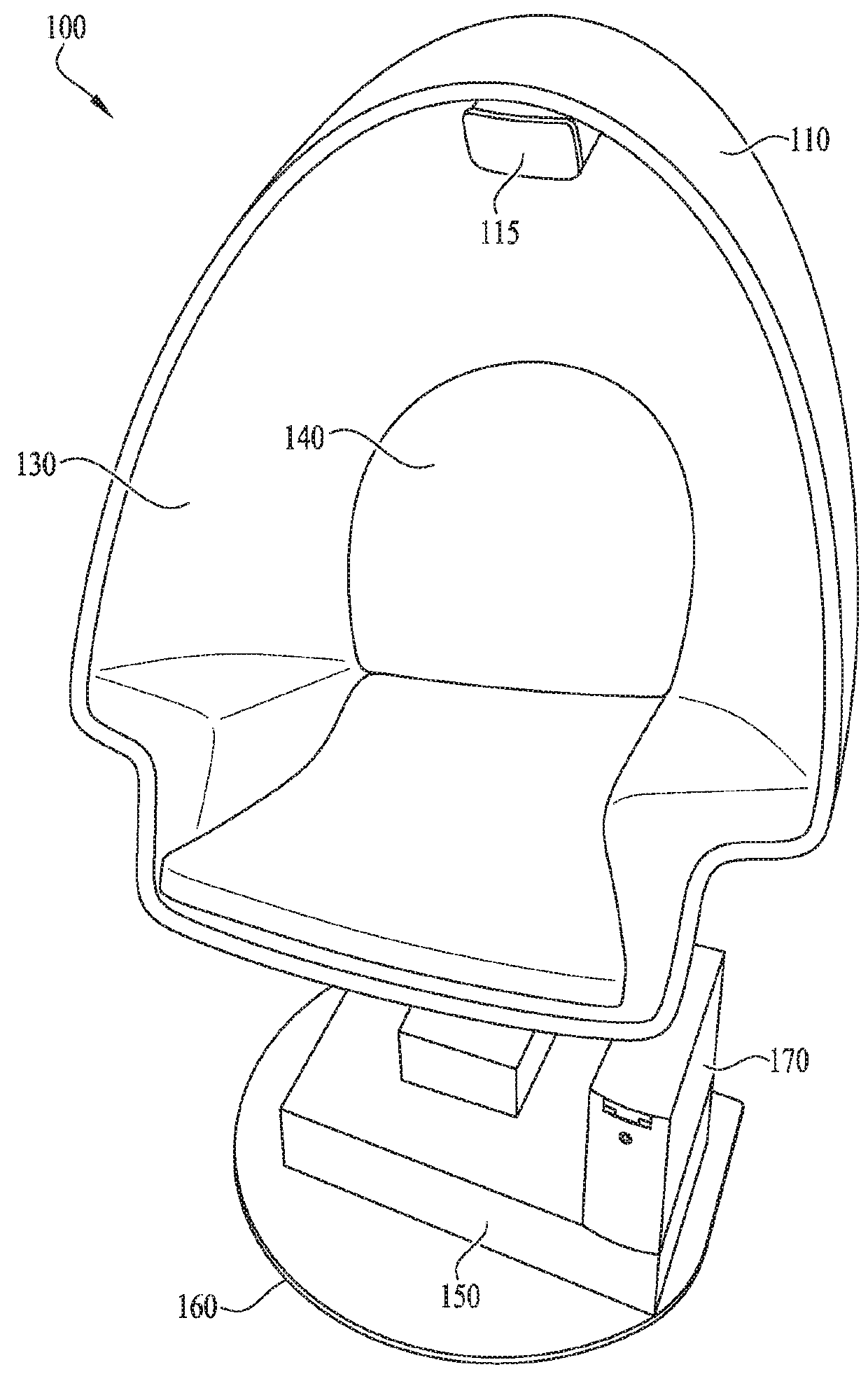
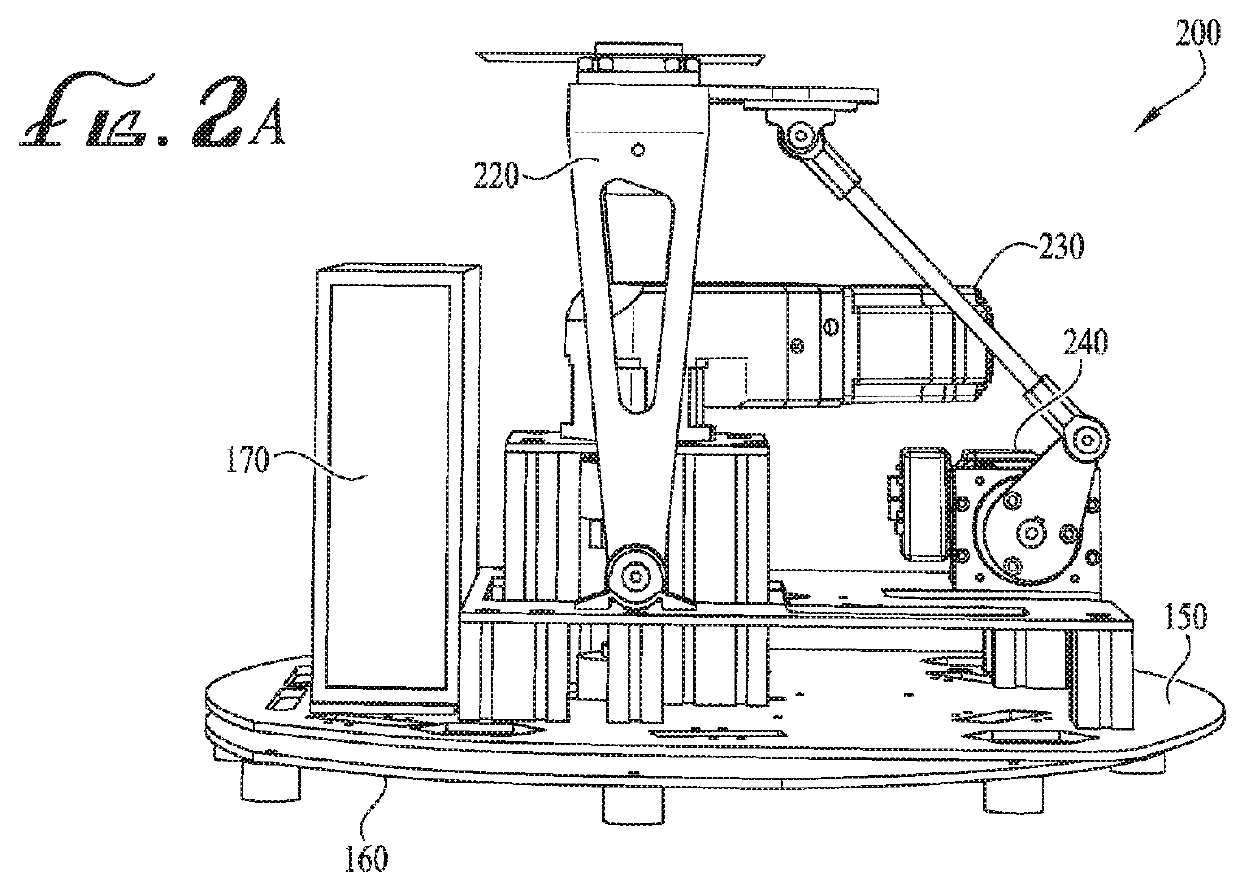
ActiveUS20180104578A1Eliminate needImprove user experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionAmusementsAs DirectedControl theory
An improved virtual reality system comprises a chair 110 integrated with a pedestal 120, which contains a motion platform 150 and base 160. The chair 110 can be rotated continuously in the yaw axis by a stepper motor 230 and substantially in the pitch axis by an additional stepper motor 240 in coordination with the content of the VR display as directed by a chair controller located on the motion platform 150.
Owner:POSITRON VOYAGER INC
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
ActiveUS20170200304A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyGeometric image transformationImage renderingImage resolutionLevel of detail
A virtual reality display system that renders images at different resolutions in different parts of a display. Reduces rendering latency by rendering at a lower resolution in selected regions, for example on the sides of a display where human vision has lower resolution than in the center. Pixels in low resolution regions are combined into grid elements, and rendering may generate grid element values rather than individual pixel values. Rendering may use ray casting, rasterization, or both. Variable resolution rendering may be combined with variable level of detail geometry models to further reduce rendering time. Selected objects may be designed as high resolution objects that are rendered at a high resolution even in low resolution display regions.
Owner:LI ADAM
Virtual reality system with control command gestures
ActiveUS9588593B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementHead movementsViewpoints
A virtual reality system that uses gestures to obtain commands from a user. Embodiments may use sensors mounted on a virtual reality headset to detect head movements, and may recognize selected head motions as gestures associated with commands. Commands associated with gestures may modify the user's virtual reality experience, for example by selecting or modifying a virtual world or by altering the user's viewpoint within the virtual world. Embodiments may define specific gestures to place the system into command mode or user input mode, for example to temporarily disable normal head tracking within the virtual environment. Embodiments may also recognize gestures of other body parts, such as wrist movements measured by a smart watch.
Owner:LI ADAM
Predictive virtual reality display system with post rendering correction
ActiveUS10089790B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEffectively approximatesInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationComputer graphics (images)Biomechanical model
A virtual reality display system that generates display images in two phases: the first phase renders images based on a predicted pose at the time the display will be updated; the second phase re-predicts the pose using recent sensor data, and corrects the images based on changes since the initial prediction. The second phase may be delayed so that it occurs just in time for a display update cycle, to ensure that sensor data is as accurate as possible for the revised pose prediction. Pose prediction may extrapolate sensor data by integrating differential equations of motion. It may incorporate biomechanical models of the user, which may be learned by prompting the user to perform specific movements. Pose prediction may take into account a user's tendency to look towards regions of interest. Multiple parallel pose predictions may be made to reflect uncertainty in the user's movement.
Owner:LI ADAM
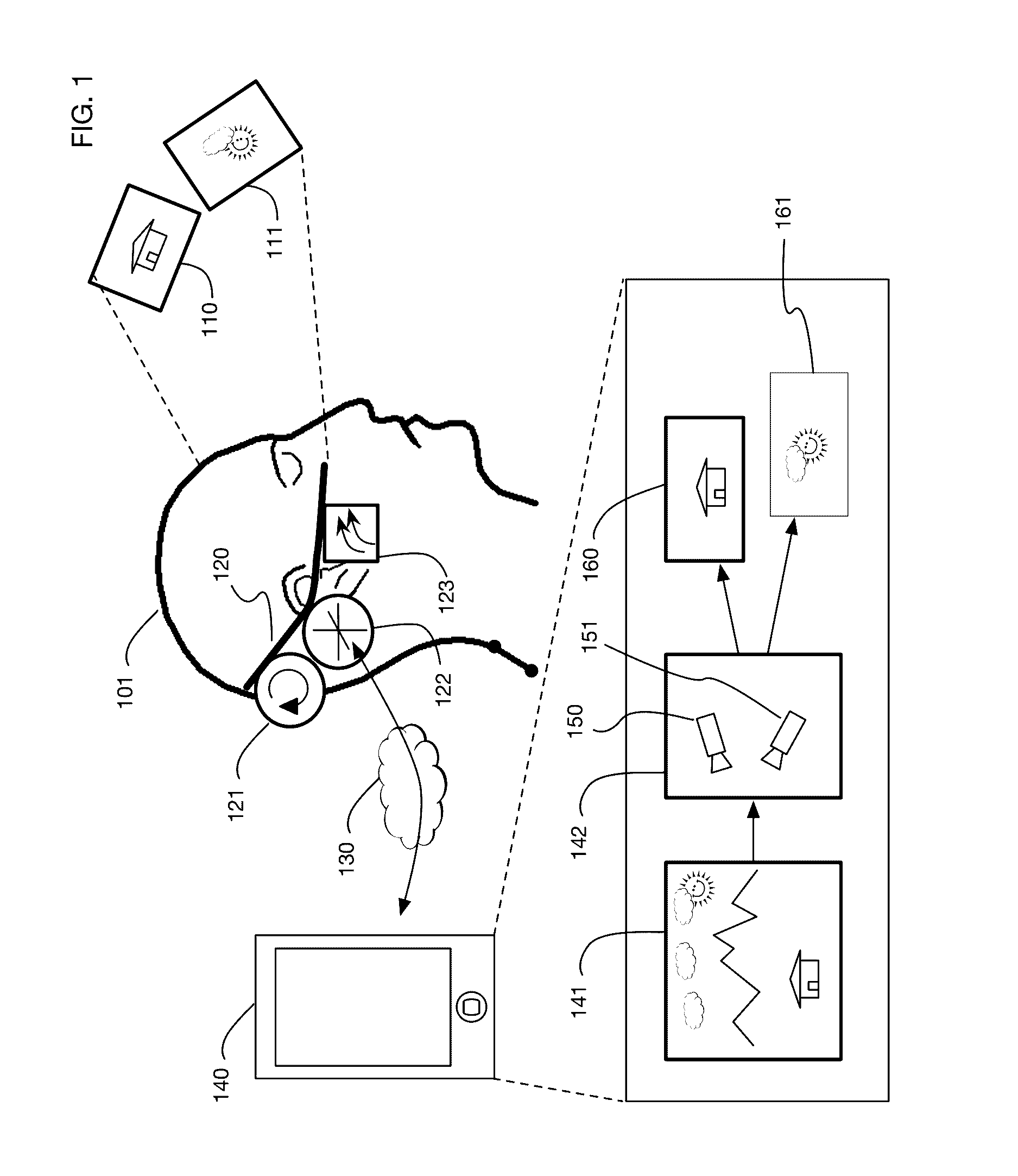
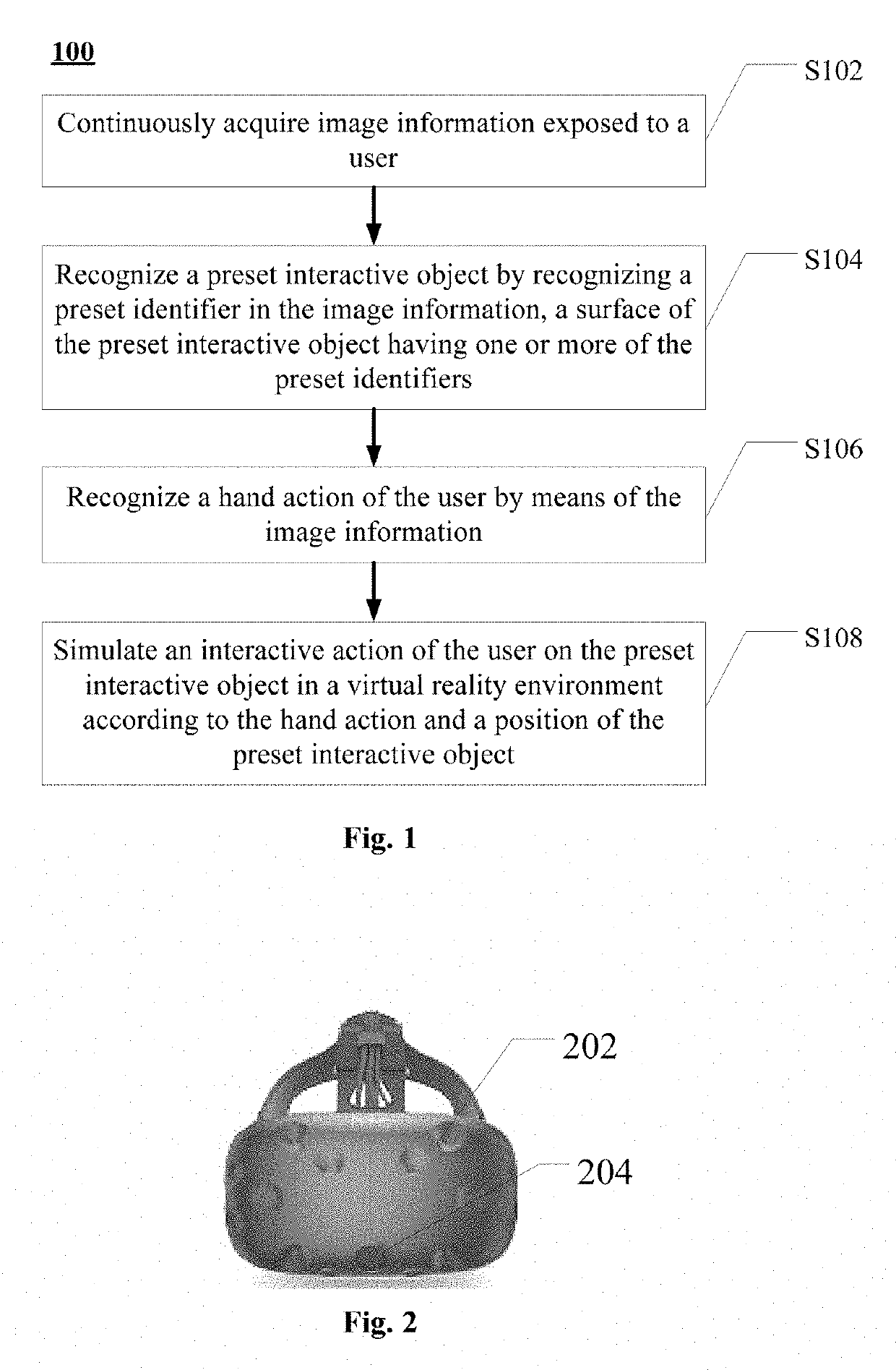
Virtual reality interaction method, apparatus and system
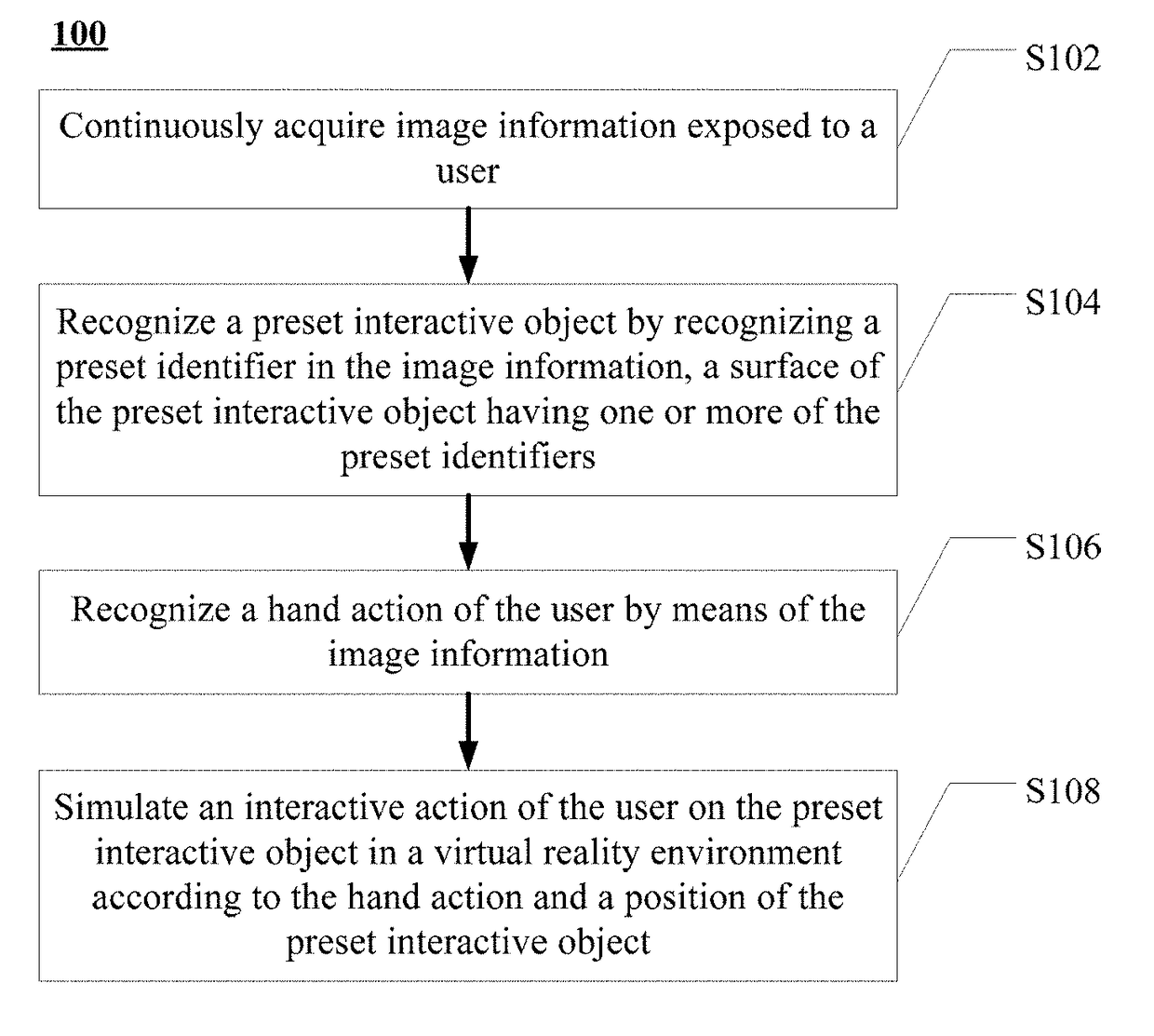
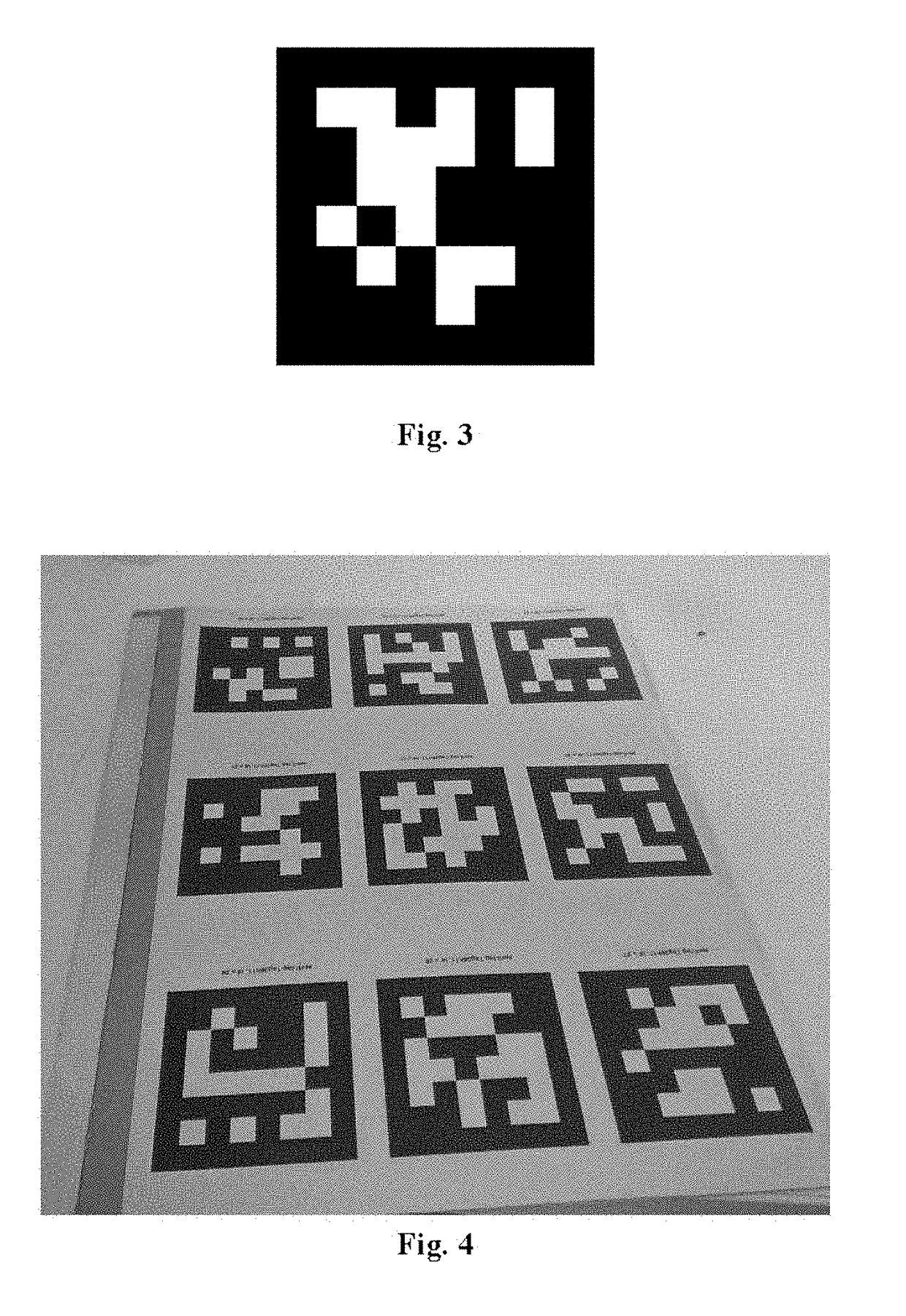
ActiveUS20180113505A1Precise positioningEnhance the virtual reality experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionImage data processingComputer graphics (images)Virtual reality
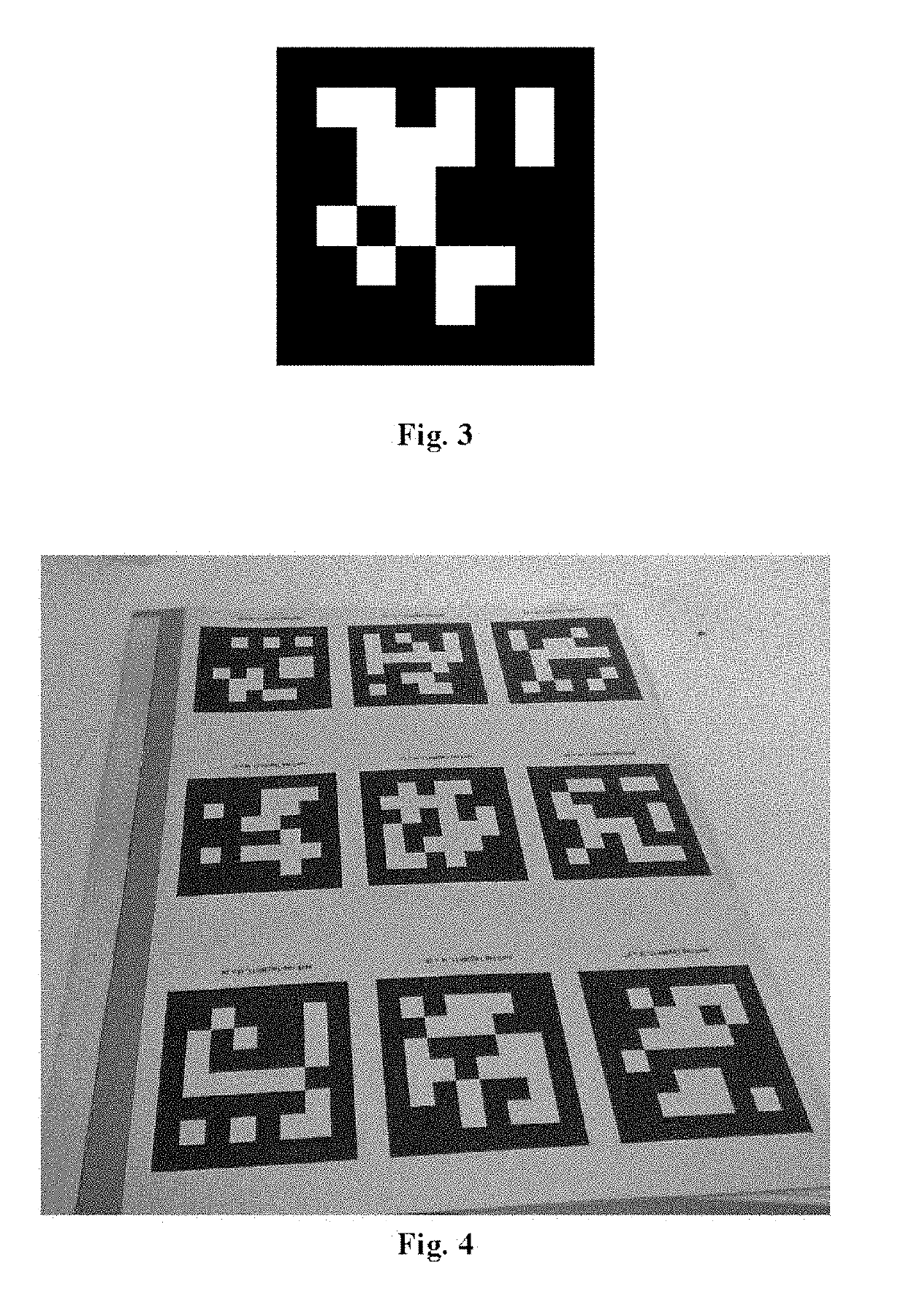
A virtual reality interaction method comprises: continuously acquiring image information in front of a user; recognizing a preset interactive object by recognizing a preset identifier in the image information, a surface of the preset interactive object having one or more of the preset identifiers; recognizing a hand action of the user according to the image information; and simulating an interactive action of the user on the preset interactive object in a virtual reality environment according to the hand action and a position of the preset interactive object. The virtual reality interaction method provided by the present disclosure can accurately simulate an interactive action of the user on a real object in a virtual reality environment, thereby improving user experience of virtual reality.
Owner:HTC CORP
Virtual reality system with control command gestures
ActiveUS20170185144A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementHead movementsViewpoints
A virtual reality system that uses gestures to obtain commands from a user. Embodiments may use sensors mounted on a virtual reality headset to detect head movements, and may recognize selected head motions as gestures associated with commands. Commands associated with gestures may modify the user's virtual reality experience, for example by selecting or modifying a virtual world or by altering the user's viewpoint within the virtual world. Embodiments may define specific gestures to place the system into command mode or user input mode, for example to temporarily disable normal head tracking within the virtual environment. Embodiments may also recognize gestures of other body parts, such as wrist movements measured by a smart watch.
Owner:LI ADAM
Wireless virtual reality (VR) helmet
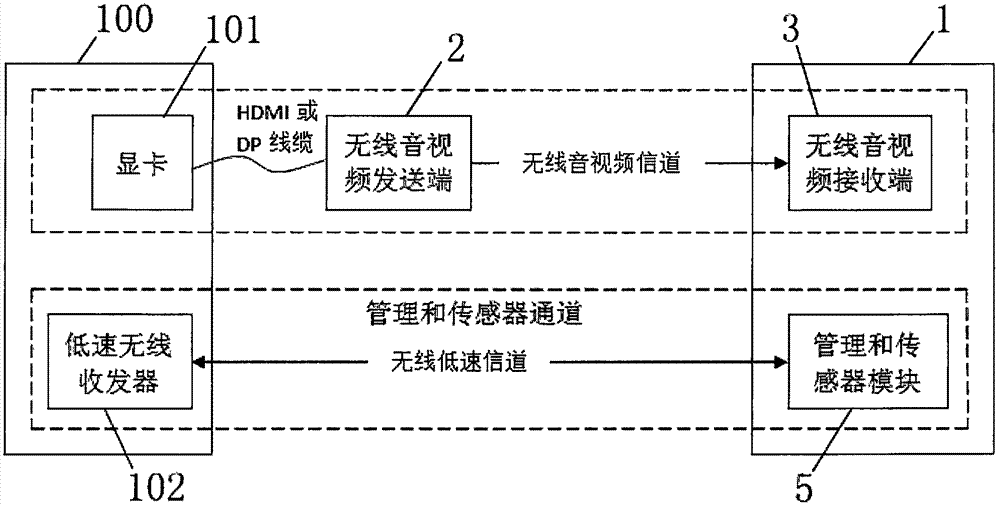
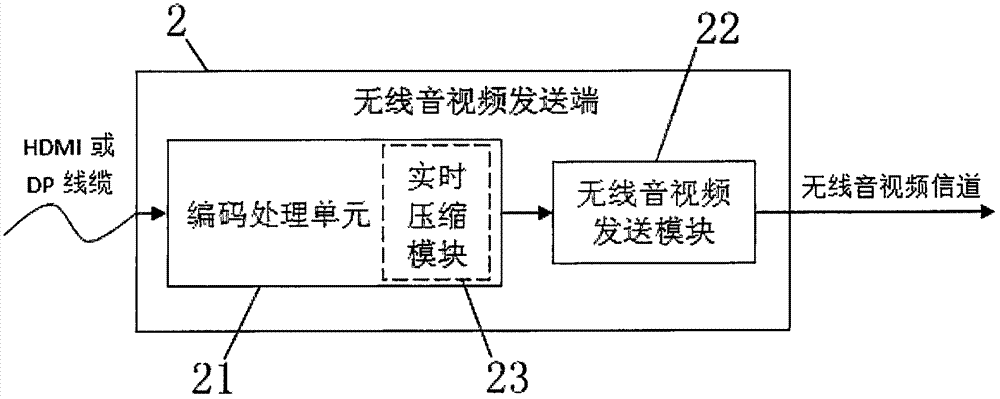
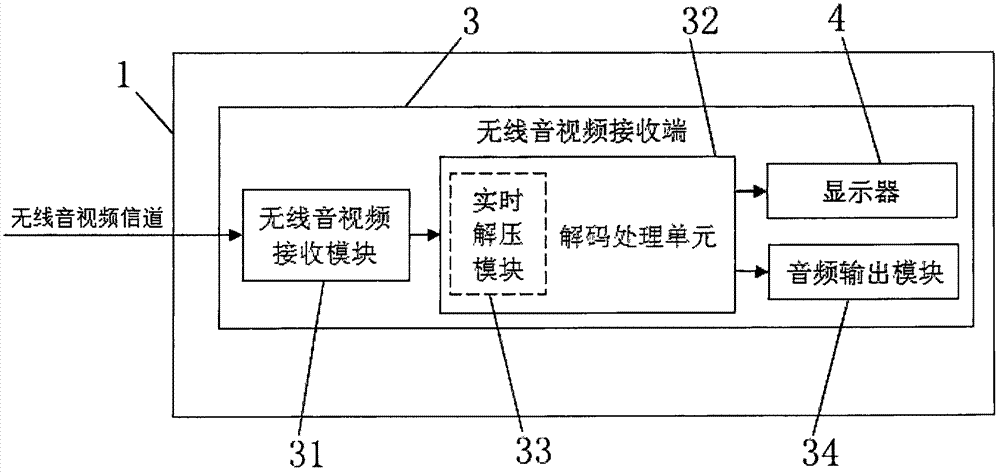
ActiveCN106888372AEnhance the virtual reality experienceEnsure real-time communicationSteroscopic systemsOptical elementsGraphicsComputer module
The invention relates to the technical field of VR, especially to a wireless VR helmet based on a high-performance host. The wireless VR helmet comprises a helmet body, a wireless audio-video sending end, a wireless audio-video receiving end and a display screen, the wireless audio-video sending end comprises a coding unit and a wireless audio-video sending module, the wireless audio-video receiving end comprises a wireless audio-video receiving module and a decoding unit, and the decoding unit is connected with the display screen via an MIPI or LVDS interface. According to the invention, the VR helmet is no longer connected with the host in a wired manner due to use of a wireless communication technology, a user can walk freely in a larger space without limit of cables when using the wireless VR helmet, and the VR experience is improved; and graphs and computing resources in the host are fully utilized, signals of a signal source is decompressed in a compression-free or real-time compression manner, the communication instantaneity is ensured, and thus, dazzling caused by time delay is reduced.
Owner:北京轻威科技有限责任公司
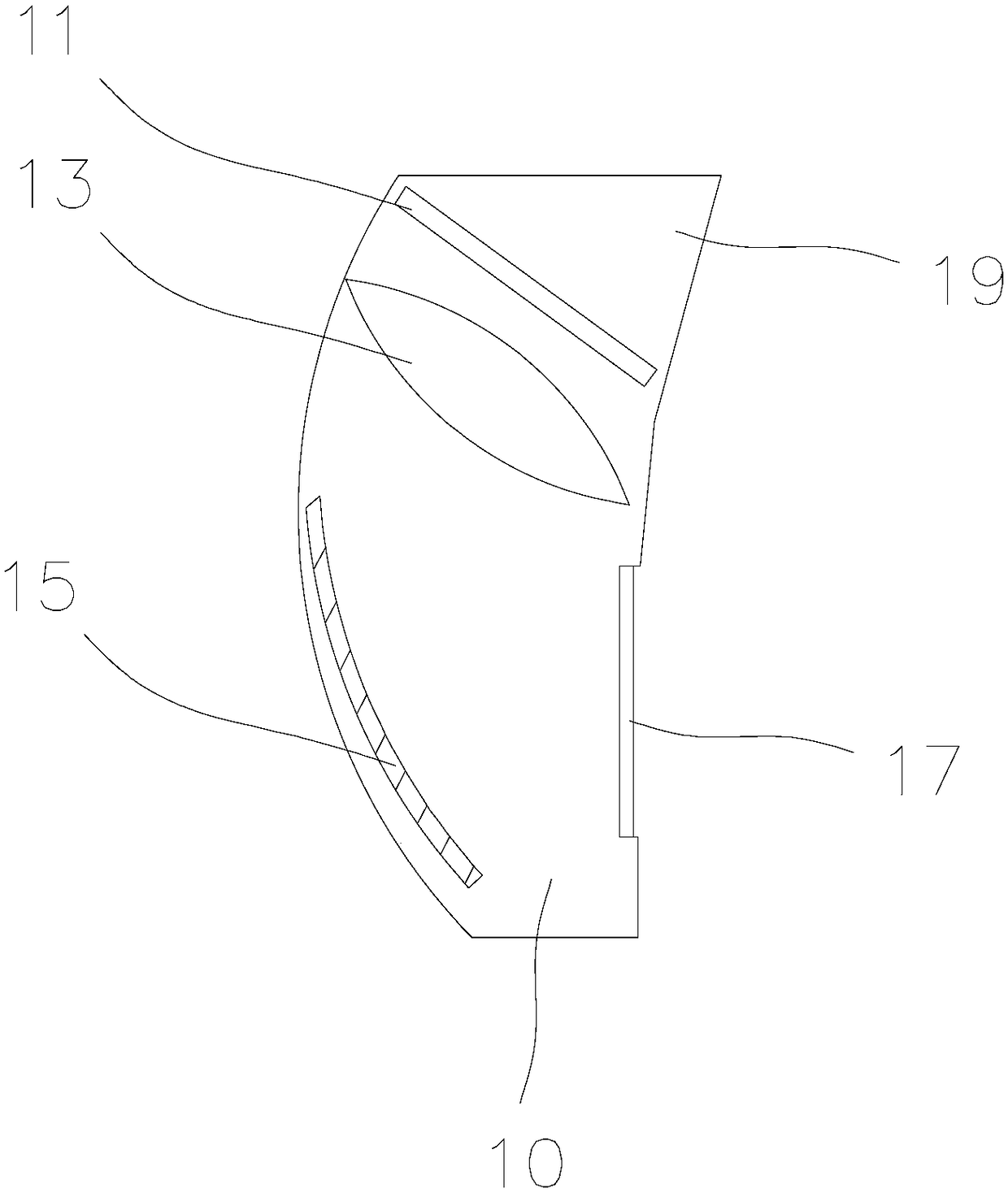
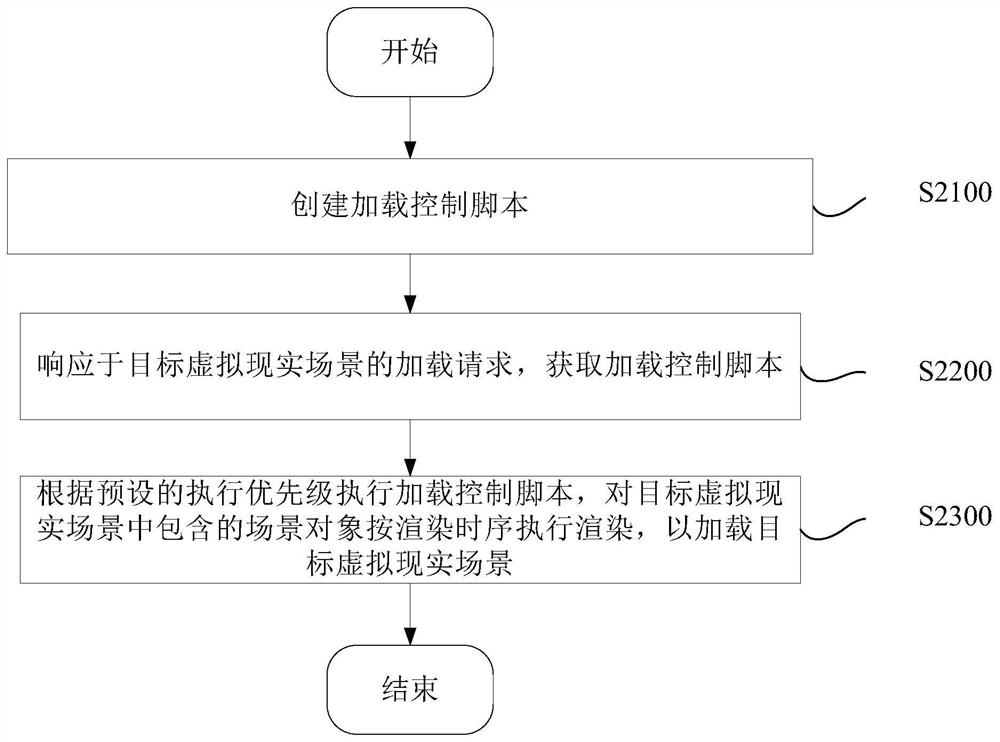
Loading method and device for virtual reality scene and virtual reality device
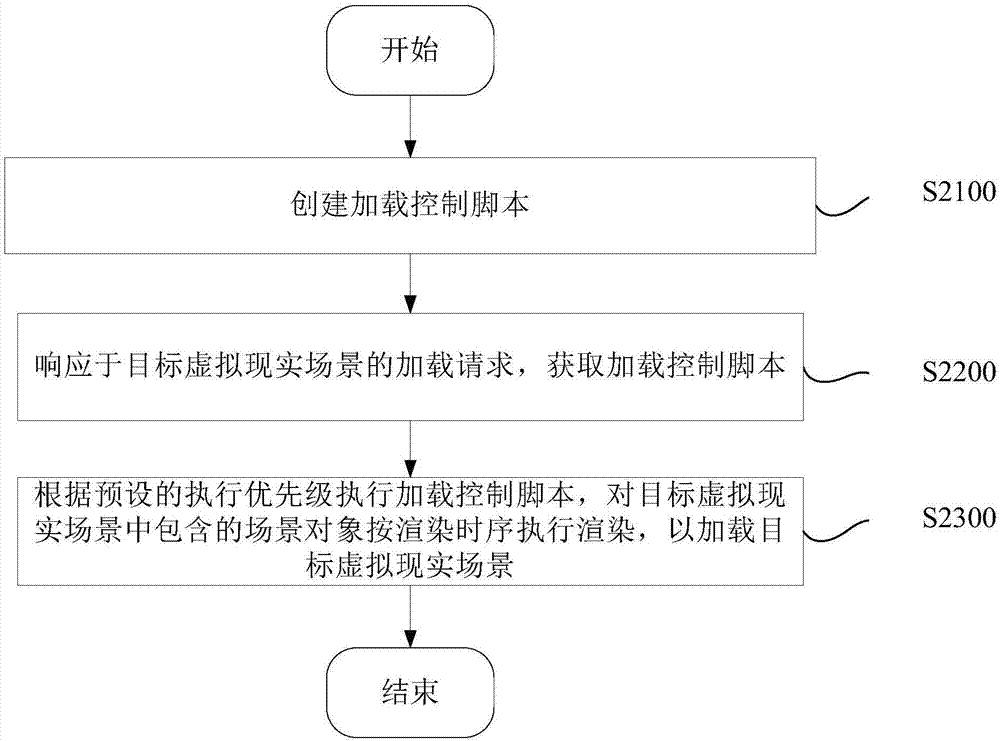
ActiveCN107168780AAvoid loading failuresEnhance the virtual reality experienceProgram initiation/switching3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Virtual reality
The present invention discloses a loading method and device for a virtual reality scene, and a virtual reality device. The loading method comprises: creating a loading control script; in response to a loading request of a target virtual reality scene, acquiring the loading control request; and executing the loading control script according to a preset execution priority, and rendering scene objects in the target virtual reality scene in a rendering sequence, so as to load the target virtual reality scene. According to the method, loading of the virtual reality scene will not limited to the version of the scene development platform, so as to avoid failure in loading the virtual reality scene caused by incompatibility of the version of the scene development platform, and improve virtual reality experience of the users.
Owner:BEIJING PICO TECH
Efficient orientation estimation system using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors
ActiveUS20170185171A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyImage data processingInput/output processes for data processingComputational scienceKaiman filter
A system that efficiently estimates an object's orientation using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors. The object may be for example a virtual reality headset or a user in a virtual reality environment. Magnetic and gravity data are used to correct errors that accumulate from integrating angular velocity. Unlike systems that use Kalman filter approaches, embodiments of the system apply a simple, highly efficient technique to generate magnetic and gravity error vectors; these error vectors are added directly to the angular velocity prior to integration. Error calculations are performed in the sensor reference frame rather than in the Earth reference frame. Magnetic error correction uses only the horizontal component of the magnetic field, which is efficiently calculated by subtracting off the projection of the magnetic field onto the measured gravity vector. Sensors and processors for calculating orientation may be integrated into a low-latency virtual reality display system.
Owner:LI ADAM
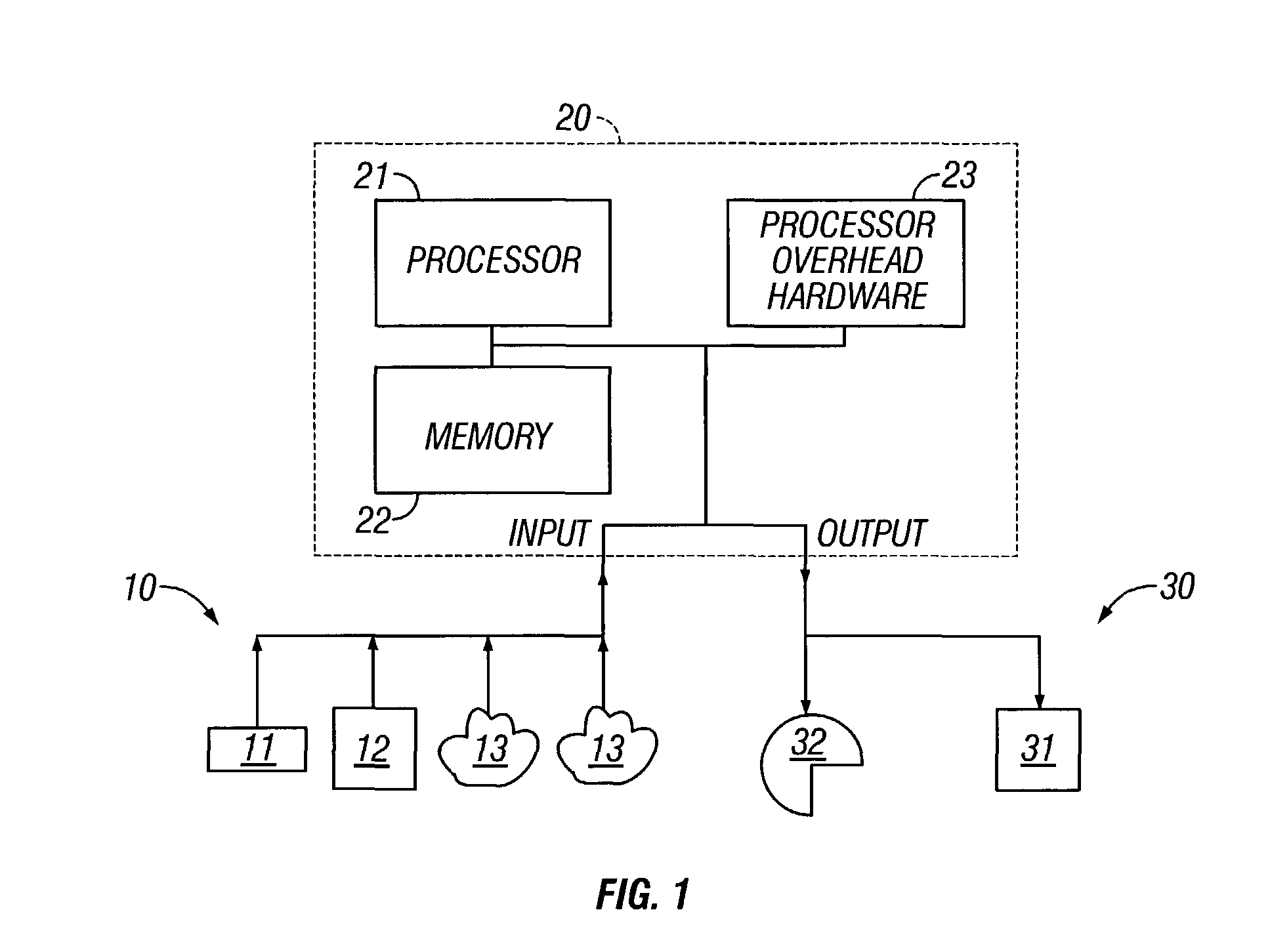
Virtual Reality Interface for Show Control
InactiveUS20100287487A1Facilitate entryThree dimensional problemInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingReal-time simulationDisplay device
A system for designing light and sound systems for use in stage productions. Virtual reality interfaces facilitate the selection and location of lighting and sound displays by providing a real-time simulation of the devices and the display produced thereby. The system also calculates parameters with respect to structural elements used for mounting the lighting and sound equipment. In addition, the virtual reality interface permits the simulation of the packing of the lighting and sound equipment and the automatic calculation of parameters relating to packing space, package weight, preferred location, and order of packing.
Owner:PRODN RESOURCE GROUP L L C
Virtual reality enhancement device
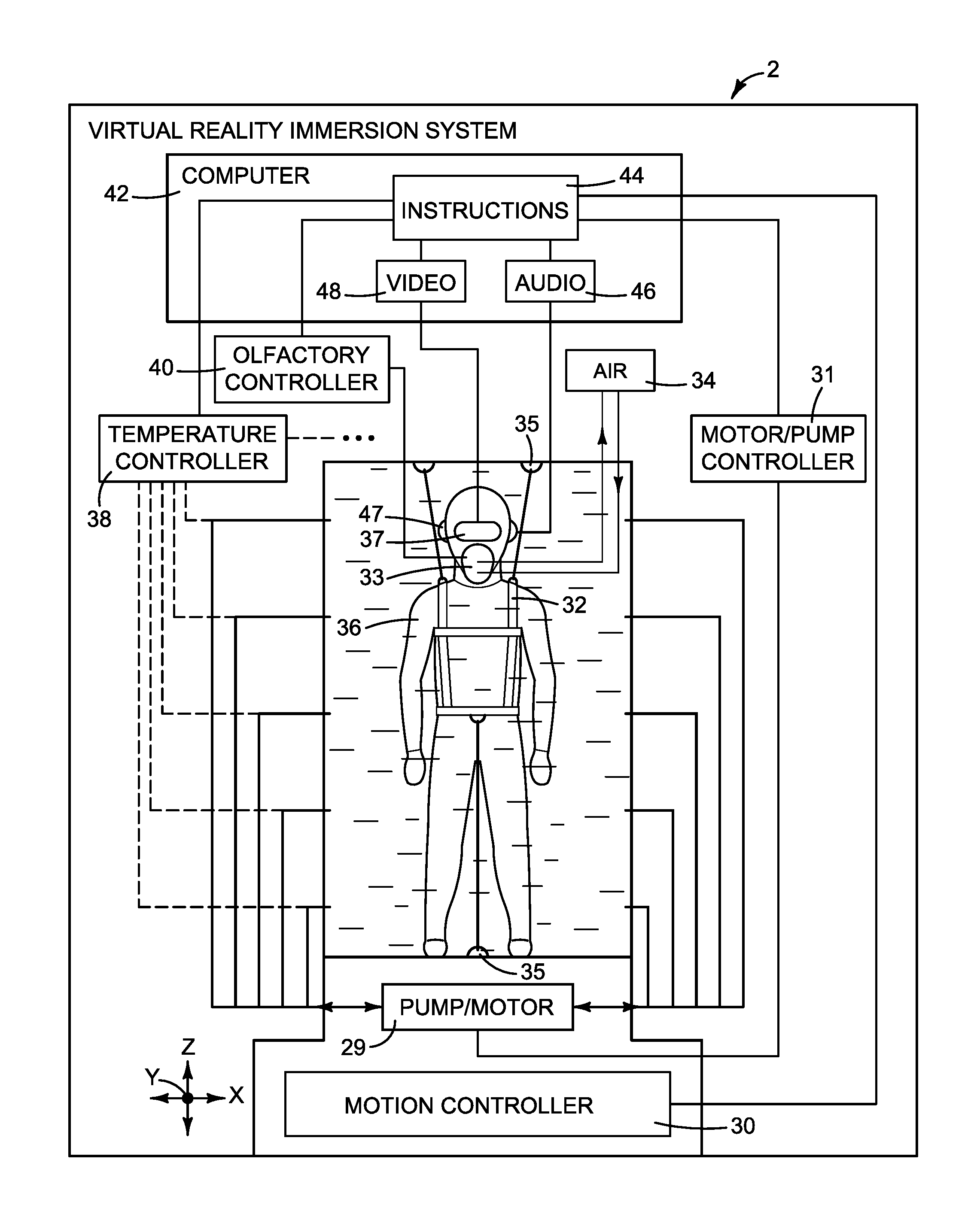
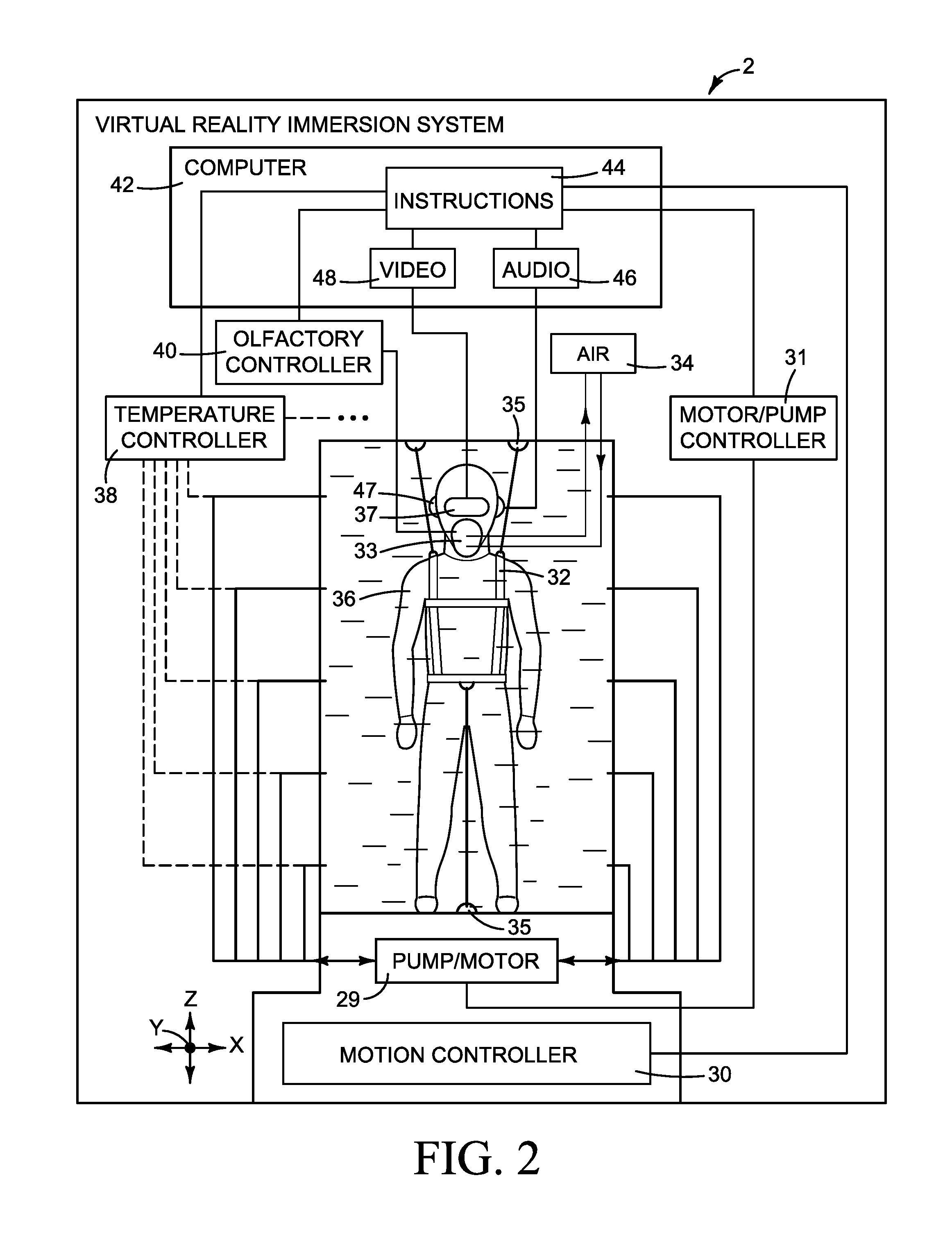
ActiveUS9573068B1Increasing and decreasing oxygen percentageEnhance the virtual reality experienceAmusementsAnimationEngineeringVirtual reality
What is disclosed is a virtual reality enhancement device that has a chamber in which a user is located, one or more pumps for pumping a fluid into and / or out of the chamber, and a series of ports for allowing the fluid to flow into and out of the chamber. The fluid circulates into and out of the chamber around the user in coordination with the 3-D visual and auditory experience provided to the user in order to enhance the user's haptic experience. The chamber can be used, for example, to simulate a user swimming or flying.
Owner:MARTIN KIPLING
Virtual reality interface for show control
InactiveUS7761803B2Facilitate entryThree dimensional problemInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsReal-time simulationDisplay device
A system for designing light and sound systems for use in stage productions. Virtual reality interfaces facilitate the selection and location of lighting and sound displays by providing a real-time simulation of the devices and the display produced thereby. The system also calculates parameters with respect to structural elements used for mounting the lighting and sound equipment. In addition, the virtual reality interface permits the simulation of the packing of the lighting and sound equipment and the automatic calculation of parameters relating to packing space, package weight, preferred location, and order of packing.
Owner:PRODN RESOURCE GROUP L L C
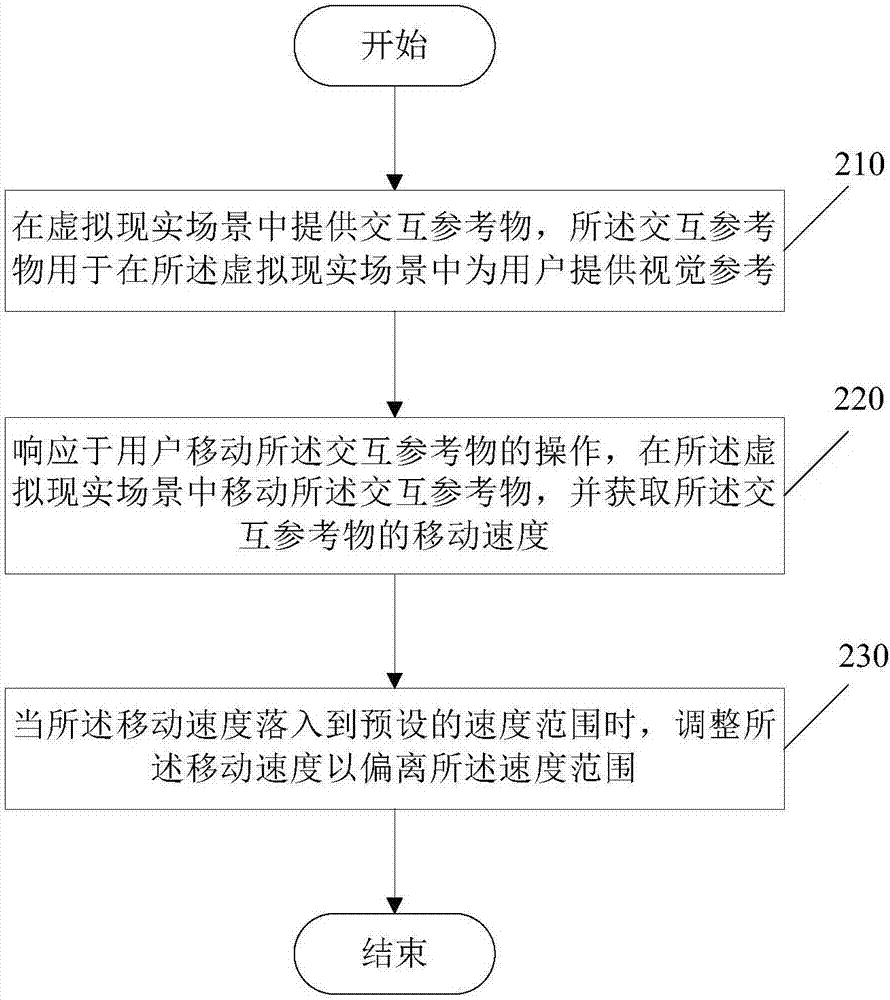
Virtual reality scene control method and device and virtual reality device
ActiveCN107479692AReduce dizzinessEnhance the virtual reality experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingVisual perceptionVirtual reality
The invention discloses a virtual reality scene control method and device and a virtual reality device. The method comprises the steps that an interaction reference substance is provided in a virtual reality scene, and the interaction reference substance is used for providing visual reference for a user in the virtual reality scene; by responding to the operation of the user for moving the interaction reference, the interaction reference substance is moved in the virtual reality scene, and the motion speed of the interaction reference substance is obtained; when the motion speed is within the preset speed range, the motion speed is adjusted to be out of the speed range. According to the virtual reality scene control method and device, the spinning sensation caused when the user watches the motion scene shown through high-speed motion of the scene frames in the virtual reality scene can be lowered, and the user's virtual reality experience is improved.
Owner:BEIJING PICO TECH
Image generation from video
ActiveUS20200045287A1Reduce biasReduce computing resource usageCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processingPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
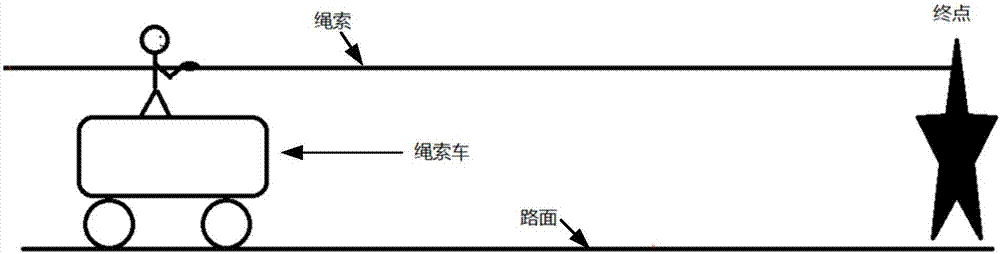
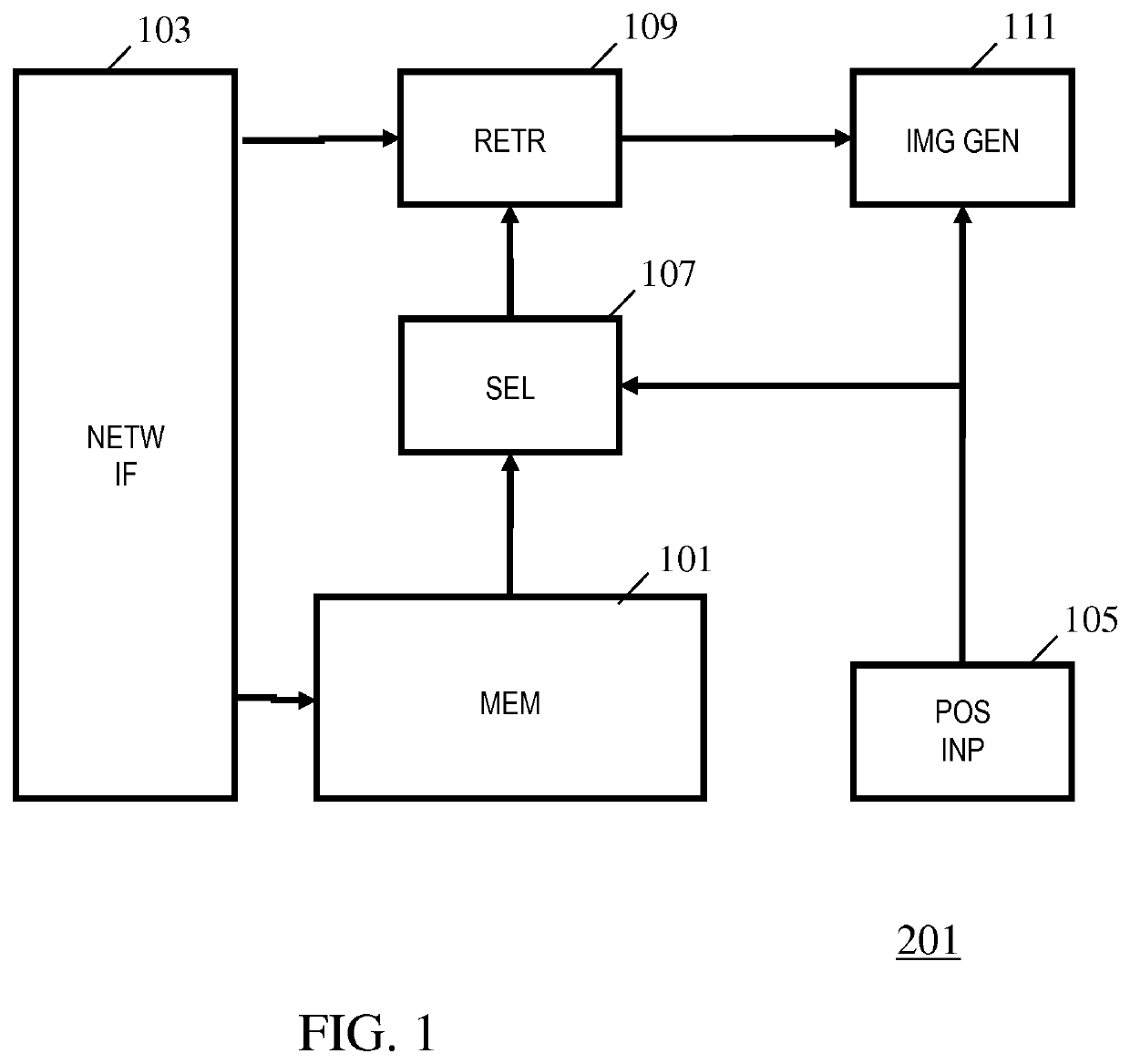
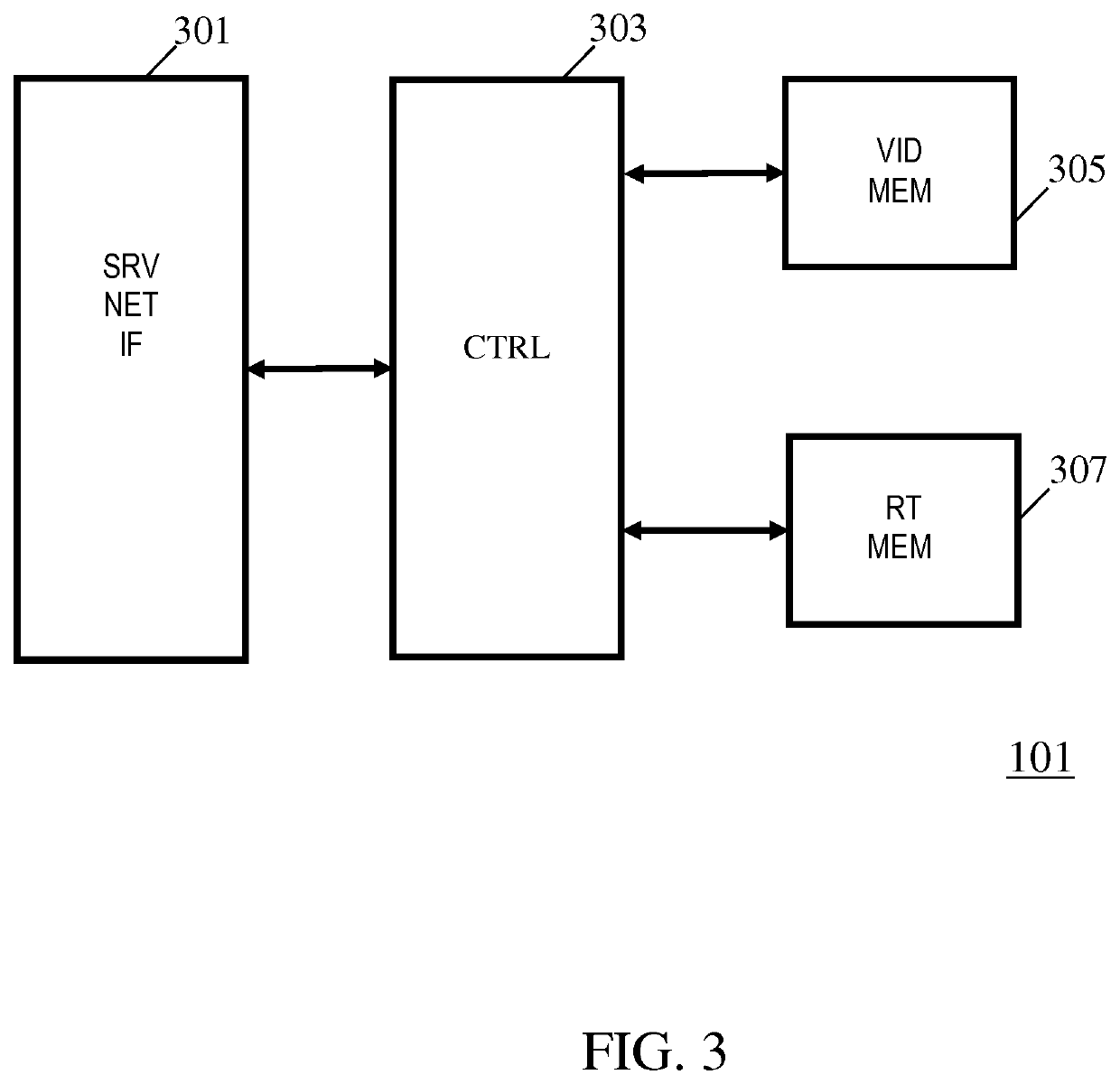
An apparatus comprising a store (101) for storing route data for a set of routes in an N-dimensional space where each route of the set of routes is associated with a video item including frames comprising both image and depth information. An input (105) receives a viewer position indication and a selector (107) selects a first route of the set of routes in response to a selection criterion dependent on a distance metric dependent on the viewer position indication and positions of the routes of the set of routes. A retriever (103, 109) retrieves a first video item associated with the first route from a video source (203). An image generator (111) generates at least one view image for the viewer position indication from a first set of frames from the first video item. In the system, the selection criterion is biased towards a currently selected route relative to other routes of the set of routes.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Efficient orientation estimation system using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors
ActiveUS9588598B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyImage data processingInput/output processes for data processingKaiman filterMagnetic tension force
A system that efficiently estimates an object's orientation using magnetic, angular rate, and gravity sensors. The object may be for example a virtual reality headset or a user in a virtual reality environment. Magnetic and gravity data are used to correct errors that accumulate from integrating angular velocity. Unlike systems that use Kalman filter approaches, embodiments of the system apply a simple, highly efficient technique to generate magnetic and gravity error vectors; these error vectors are added directly to the angular velocity prior to integration. Error calculations are performed in the sensor reference frame rather than in the Earth reference frame. Magnetic error correction uses only the horizontal component of the magnetic field, which is efficiently calculated by subtracting off the projection of the magnetic field onto the measured gravity vector. Sensors and processors for calculating orientation may be integrated into a low-latency virtual reality display system.
Owner:LI ADAM
Virtual reality interaction method, apparatus and system
ActiveUS20190302878A9Simulation is accurateOvercome problemsInput/output for user-computer interactionImage data processingVirtual realityInteraction method
A virtual reality interaction method comprises: continuously acquiring image information in front of a user; recognizing a preset interactive object by recognizing a preset identifier in the image information, a surface of the preset interactive object having one or more of the preset identifiers; recognizing a hand action of the user according to the image information; and simulating an interactive action of the user on the preset interactive object in a virtual reality environment according to the hand action and a position of the preset interactive object. The virtual reality interaction method provided by the present disclosure can accurately simulate an interactive action of the user on a real object in a virtual reality environment, thereby improving user experience of virtual reality.
Owner:HTC CORP
Virtual model rendering method, device, equipment and readable storage medium
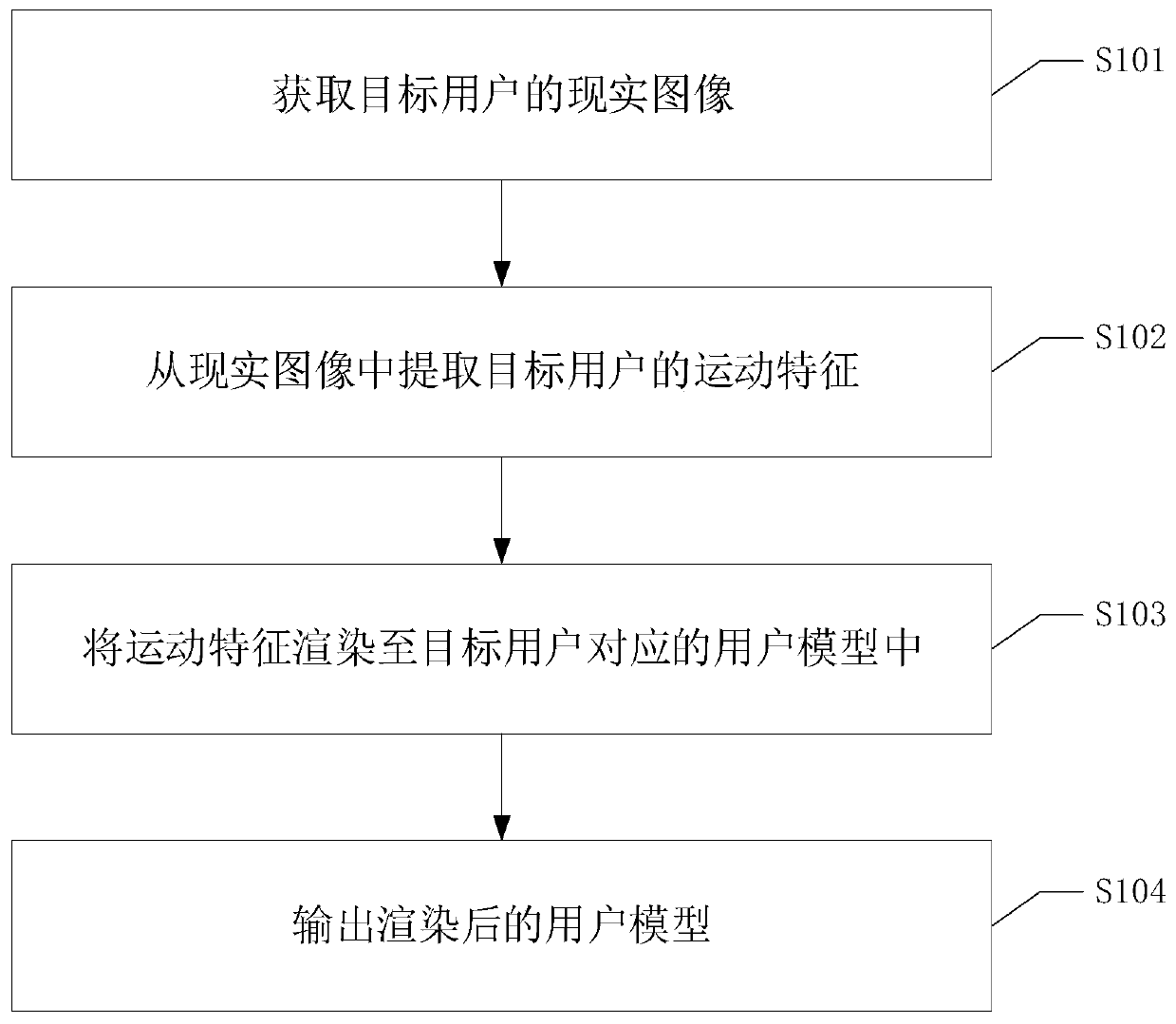
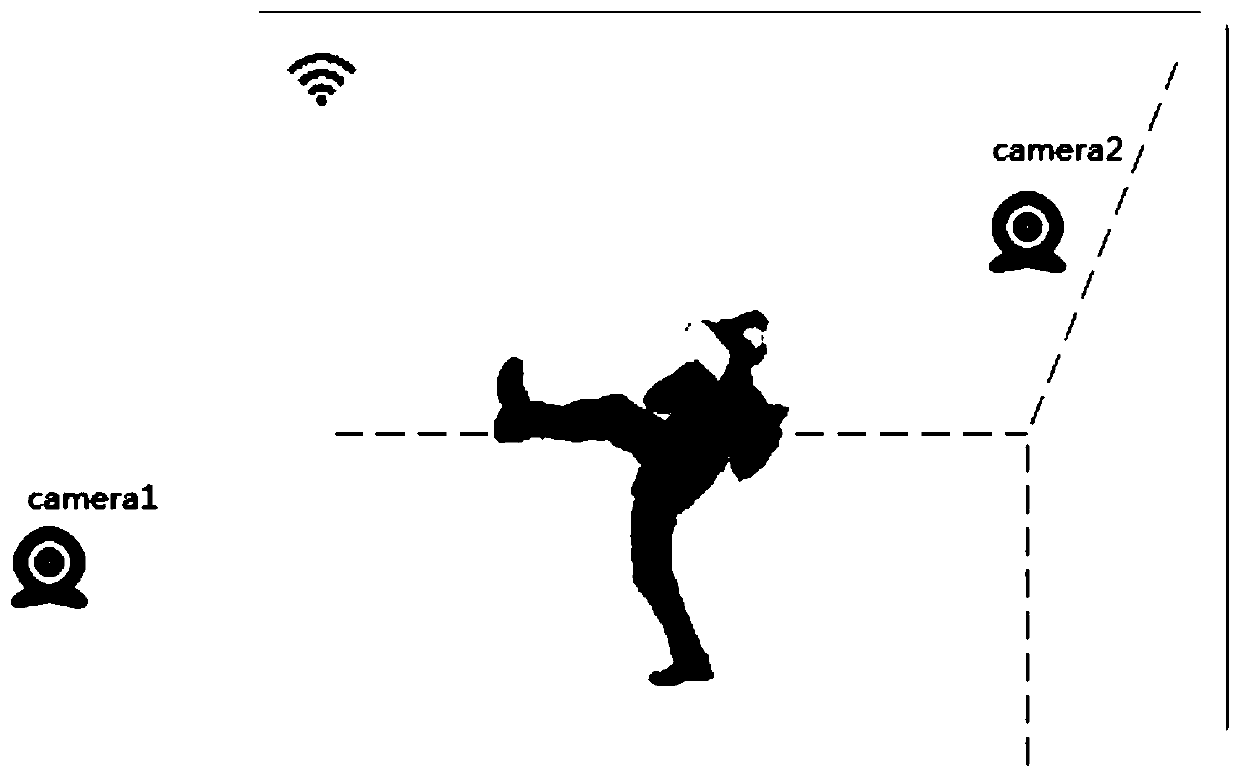
ActiveCN111383313AEnhance the virtual reality experienceImprove experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The invention discloses a virtual model rendering method, a device, equipment and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a real image of a target user; extracting motion features of the target user from the real image; rendering the motion features to a user model corresponding to the target user; and outputting the rendered user model. According to the method, thereal action of the target user can be rendered in the user model; that is to say, the user model obtained by rendering can display the real action, so that other users can observe the specific actionof the target user in the virtual world, the current state and information of the user in the virtual world can be better experienced, and the virtual reality experience of the user can be improved.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Flip type large-view-angle moving-end virtual-reality head-mounted display device
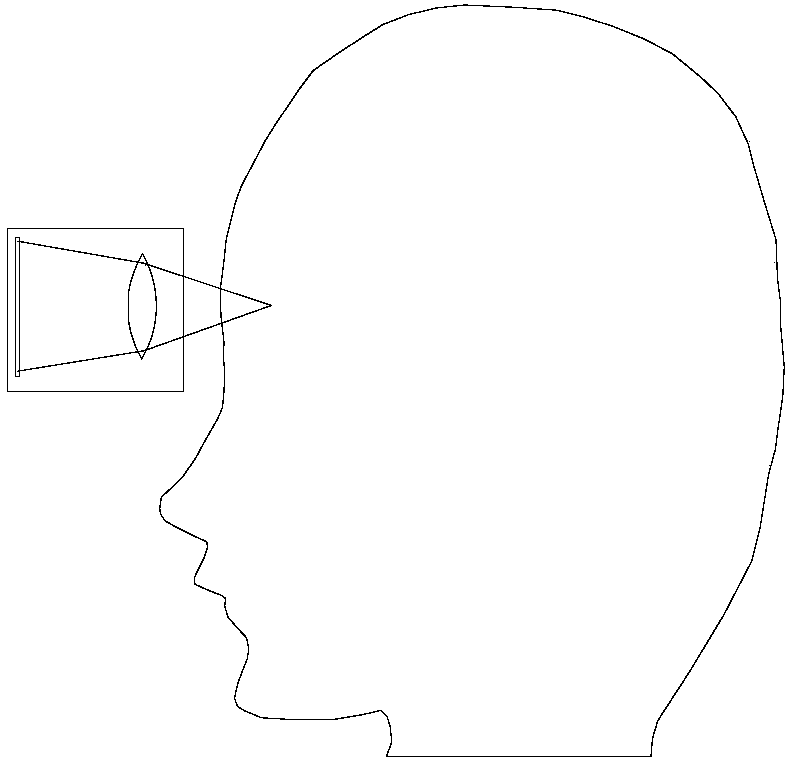
The invention provides a flip type large-view-angle moving-end virtual-reality head-mounted display device comprising an accommodating cavity, a bracket, an optical lens and a concave mirror. The accommodating cavity is arranged above the optical lens; the optical lens is arranged above the concave mirror and faces the accommodating cavity directly; and a mobile terminal can be placed in the accommodating cavity with the display screen down. Light emitted by the mobile terminal is refracted by the optical lens and enters eyes of an observer after reflection by the concave mirror. The virtual-reality head-mounted display device can slide on the bracket and can be fixed at the upper part of the bracket or the lower part of the bracket.
Owner:VR TECH (SHENZHEN) LTD
Method, device, and storage medium for virtual reality display
InactiveUS20190265481A1Improve clarityEnhance the virtual reality experiencePrismsSteroscopic systemsPrismComputer science
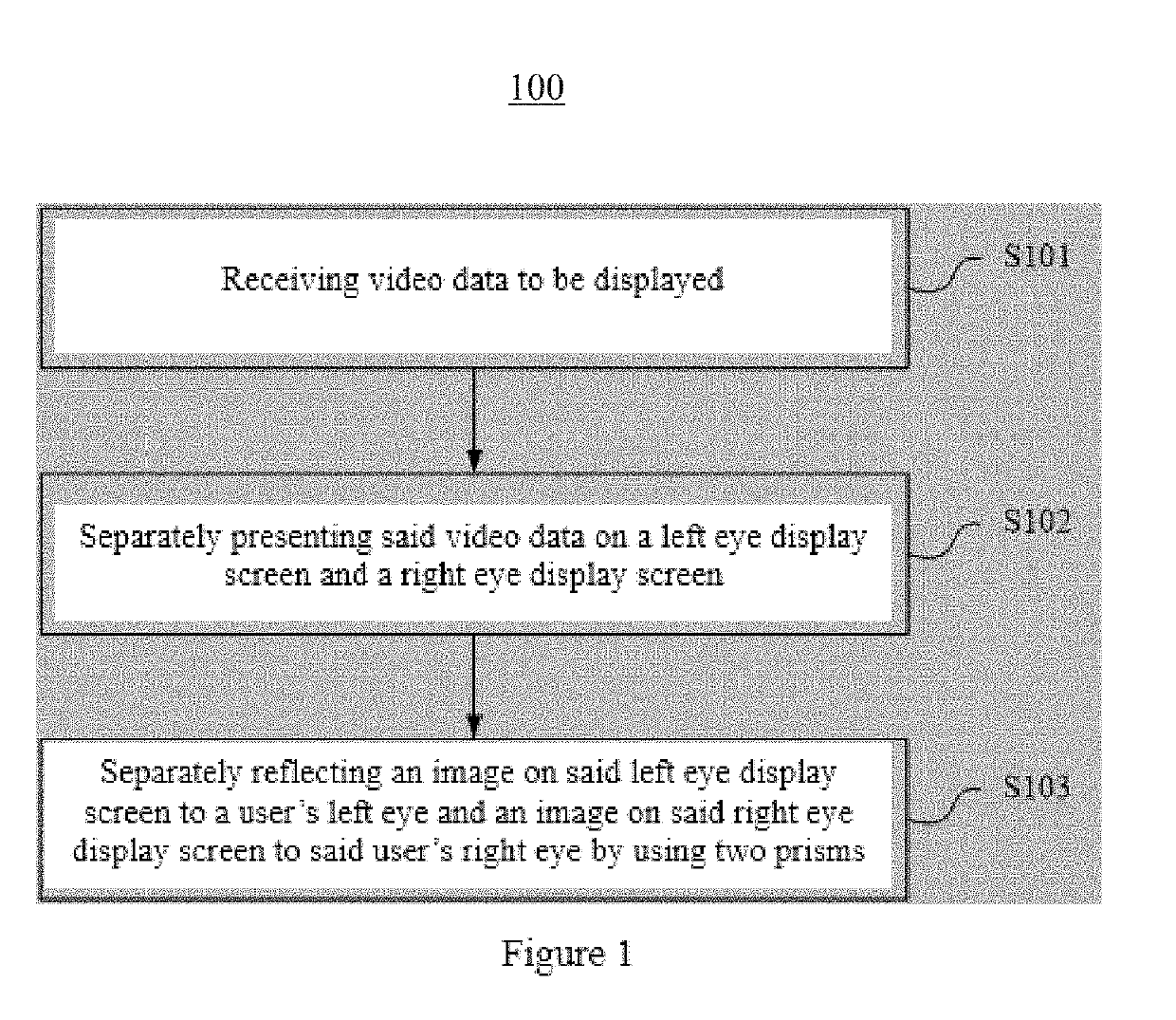
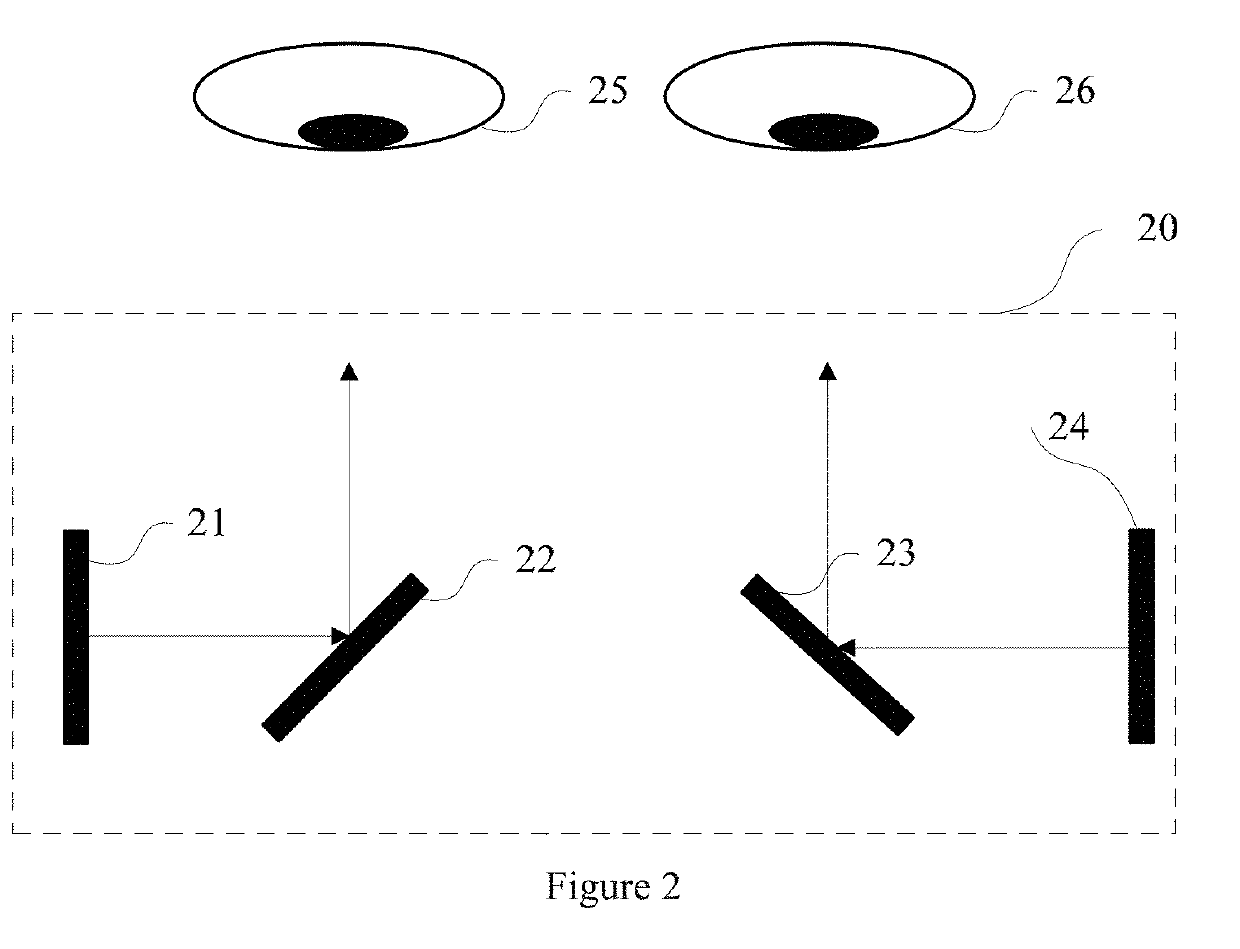
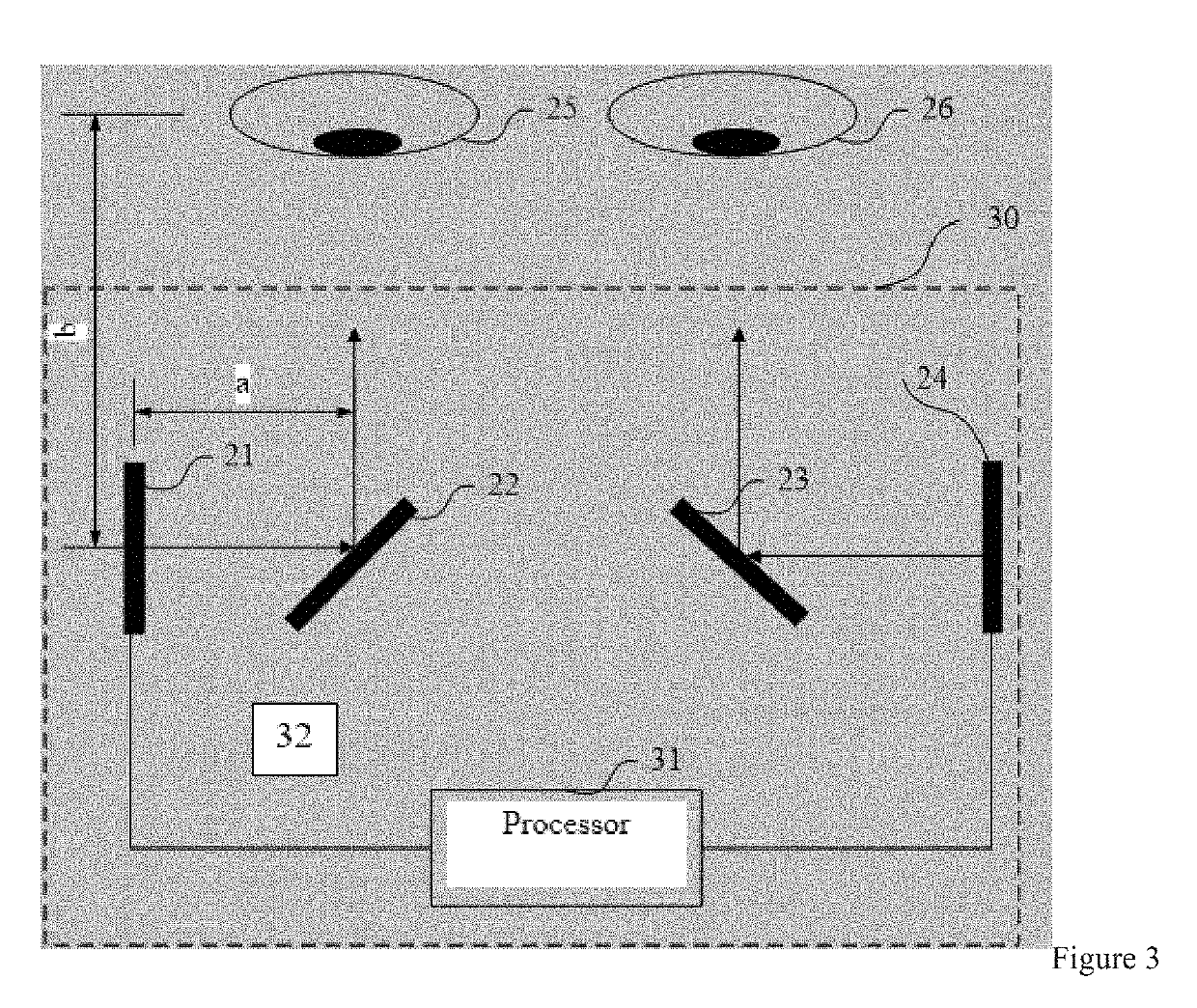
Virtual reality display methods and virtual reality glasses are disclosed. According to some disclosed embodiments, the method includes: receiving video data to be displayed; separately presenting the video data on a left eye display screen and a right eye display screen; and separately reflecting an image on the left eye display screen to a user's left eye and an image on the right eye display screen to the user's right eye by using two prisms.
Owner:SHANGHAI XIAOYI TECH CO LTD
Portable virtual reality headset
InactiveCN108227196AReduce areaEnhance the virtual reality experienceOptical elementsVirtual realityCurved mirror
The invention provides a portable virtual reality headset which comprises a display screen, an optical lens and a concave mirror, wherein the display screen is arranged above the optical lens; the optical lens is arranged above the concave mirror; the optical lens is aligned at the display screen; and light rays emitted by the display screen are refracted by the optical lens and then enter eyes ofan observer by virtue of reflection of a reflective device. Compared with the prior art, the portable virtual reality headset disclosed by the invention has the advantages that by utilizing positionarrangement of the display screen, the optical lens and the curved mirror, the light rays of the display screen enter the eyes by virtue of actions of the optical lens and the concave mirror. By virtue of a convergence effect of the optical lens on the rays and a convergence effect of the concave mirror on the light rays, the area of the display screen is greatly decreased, so that the portable virtual reality headset is portable.
Owner:VR TECH (SHENZHEN) LTD
Virtual reality display control method, device and related equipment
ActiveCN106095103BImprove display qualityEnhance the virtual reality experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingComputer graphics (images)Display device
The invention discloses a virtual reality display control method and device and relevant equipment and systems. Virtual reality control equipment can obtain the rotation information, in three directions (a first coordinate axis, a second coordinate axis and a third coordinate axis), of a virtual reality scene operation device and send the rotation information to displaying and processing equipment, so that the displaying and processing equipment determines the movement speed of a user in a virtual reality scene according to the rotation information and sends the virtual reality scene corresponding to a position determined according to the movement speed to a display device to be displayed. In this way, the user can control roaming direction and speed in virtual reality through the virtual reality control equipment. Compared with the prior art, human-machine interaction can be improved, virtual reality experience can be improved for the user, and virtual reality display quality can be improved.
Owner:S Y TECH ENG & CONSTR CO LTD
Virtual reality scene loading method, device and virtual reality device
ActiveCN107168780BAvoid loading failuresEnhance the virtual reality experienceProgram initiation/switching3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Engineering
The present invention discloses a loading method and device for a virtual reality scene, and a virtual reality device. The loading method comprises: creating a loading control script; in response to a loading request of a target virtual reality scene, acquiring the loading control request; and executing the loading control script according to a preset execution priority, and rendering scene objects in the target virtual reality scene in a rendering sequence, so as to load the target virtual reality scene. According to the method, loading of the virtual reality scene will not limited to the version of the scene development platform, so as to avoid failure in loading the virtual reality scene caused by incompatibility of the version of the scene development platform, and improve virtual reality experience of the users.
Owner:BEIJING PICO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com