Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
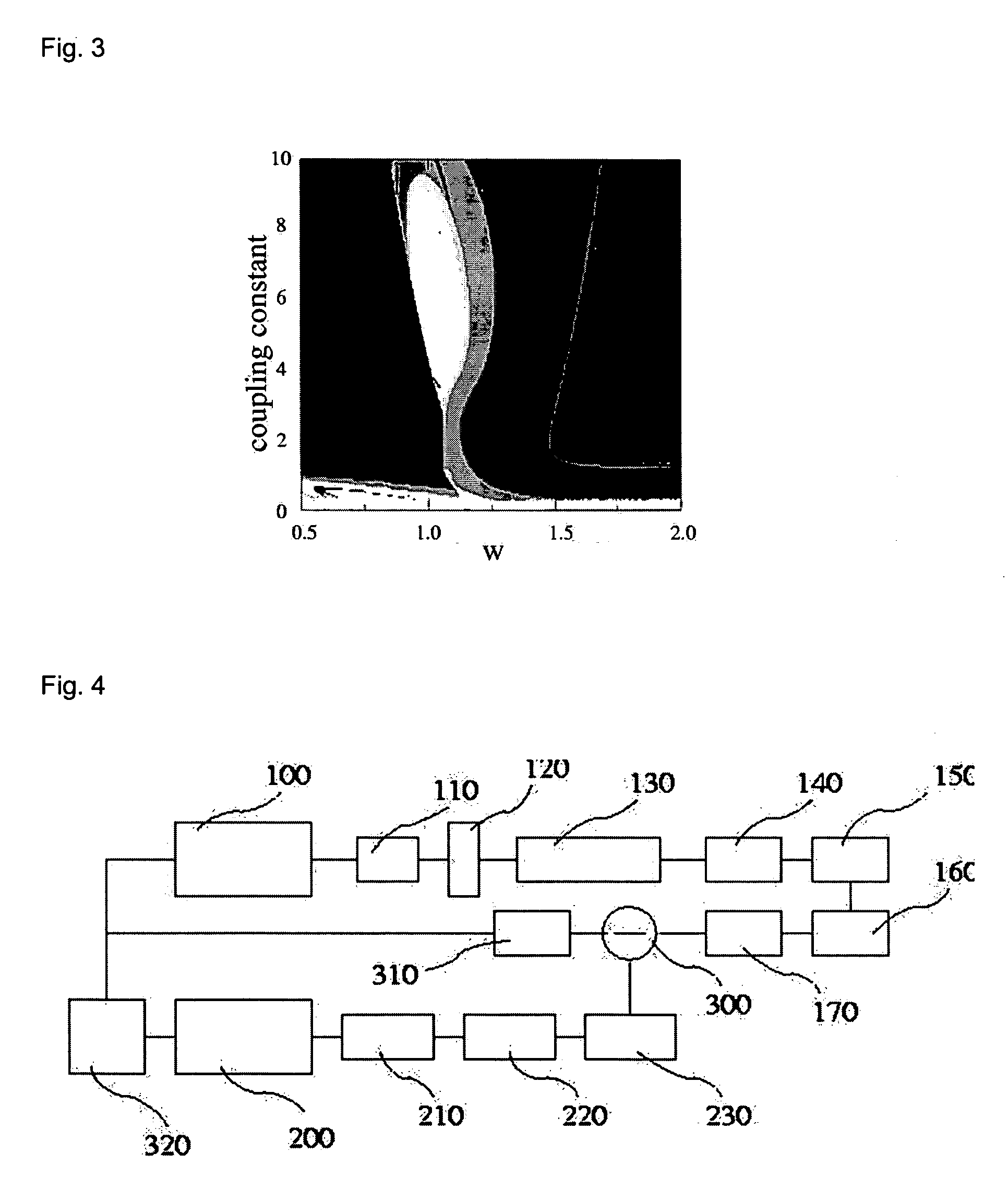
63 results about "Coupling constant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a coupling constant or gauge coupling parameter (or, more simply, a coupling), is a number that determines the strength of the force exerted in an interaction. Usually, the Lagrangian or the Hamiltonian of a system describing an interaction can be separated into a kinetic part and an interaction part. The coupling constant determines the strength of the interaction part with respect to the kinetic part, or between two sectors of the interaction part. For example, the electric charge of a particle is a coupling constant that characterizes an interaction with two charge-carrying fields and one photon field (hence the common Feynman diagram with two arrows and one wavy line). Since photons carry electromagnetism, this coupling determines how strongly electrons feel such a force, and has its value fixed by experiment.
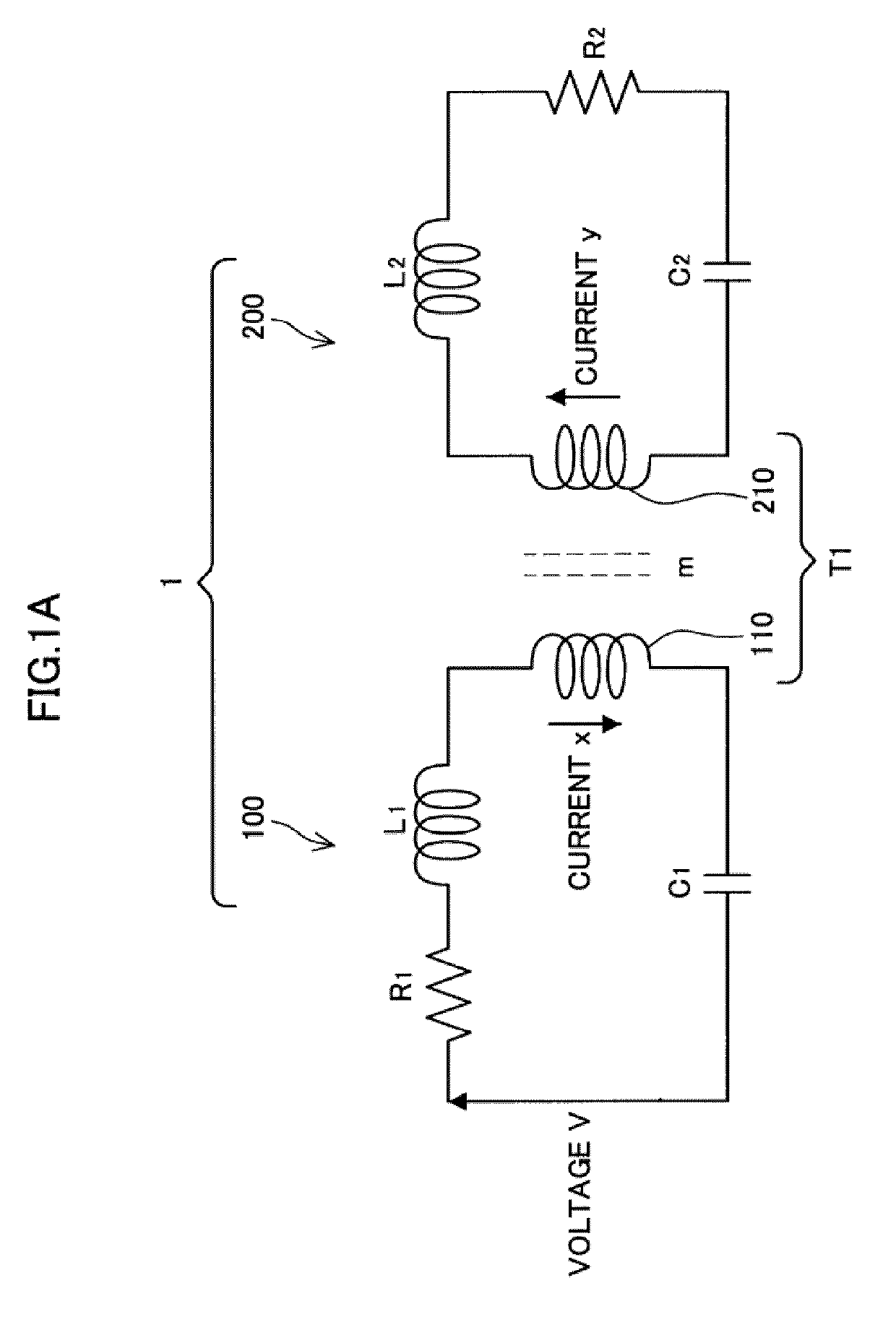
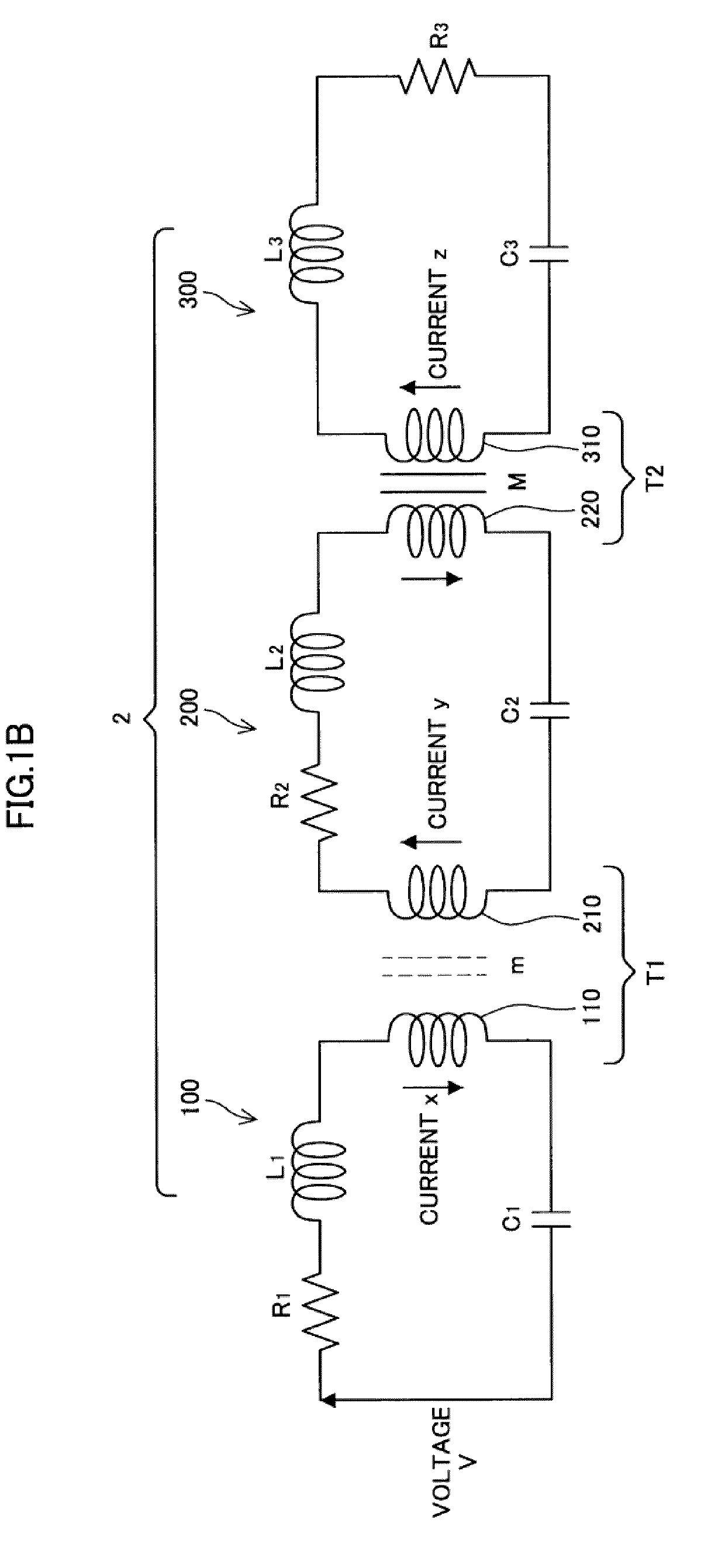
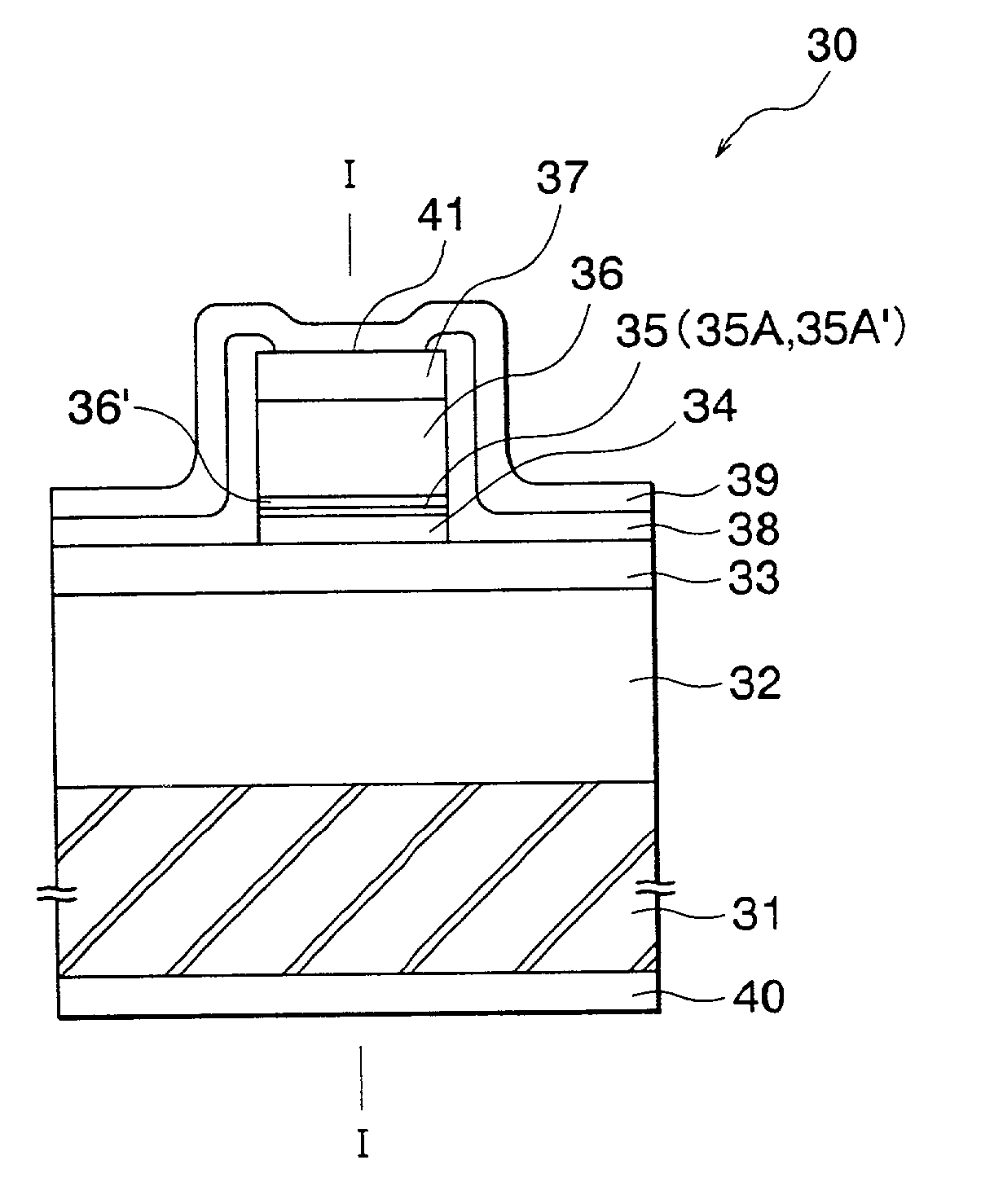
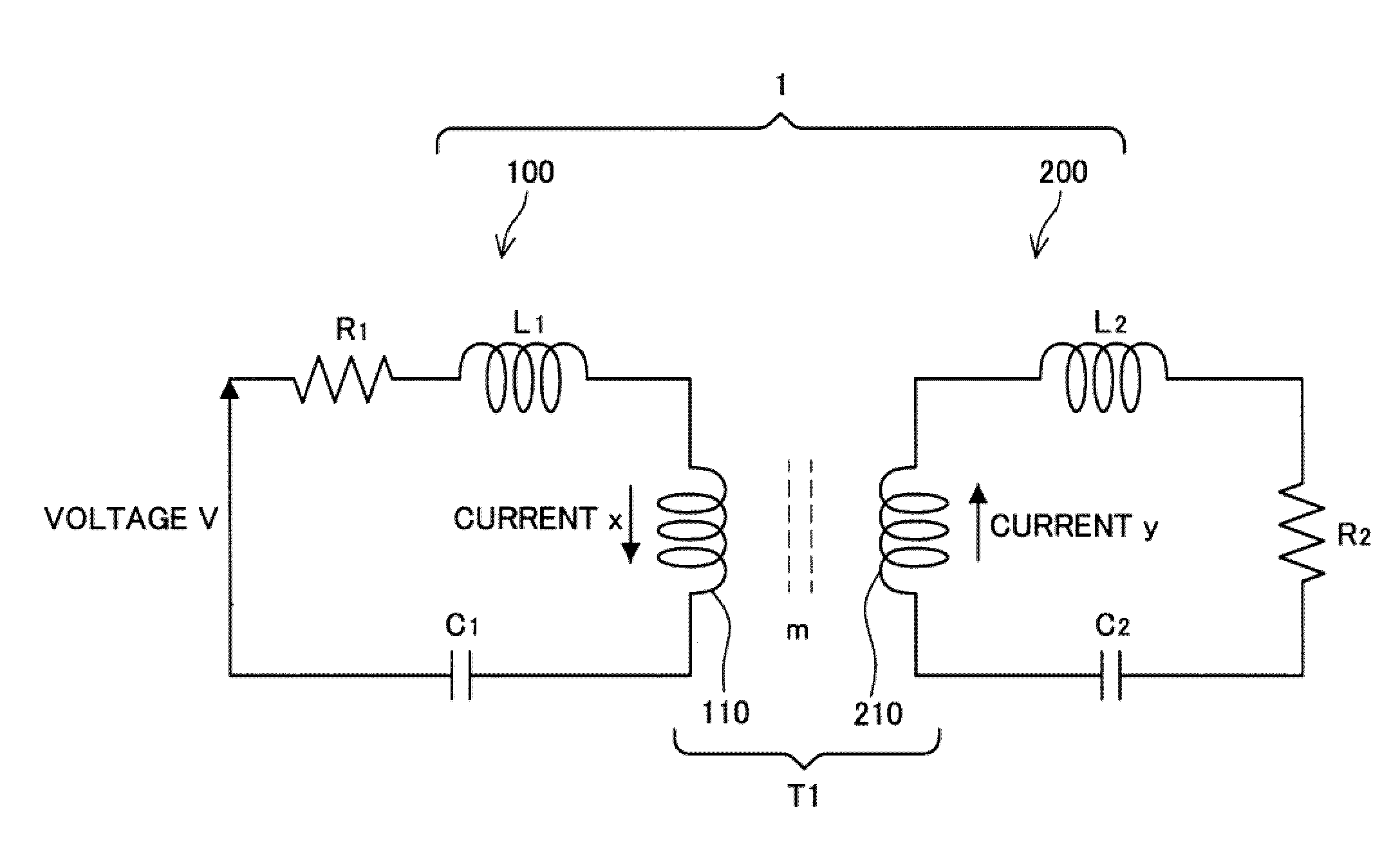
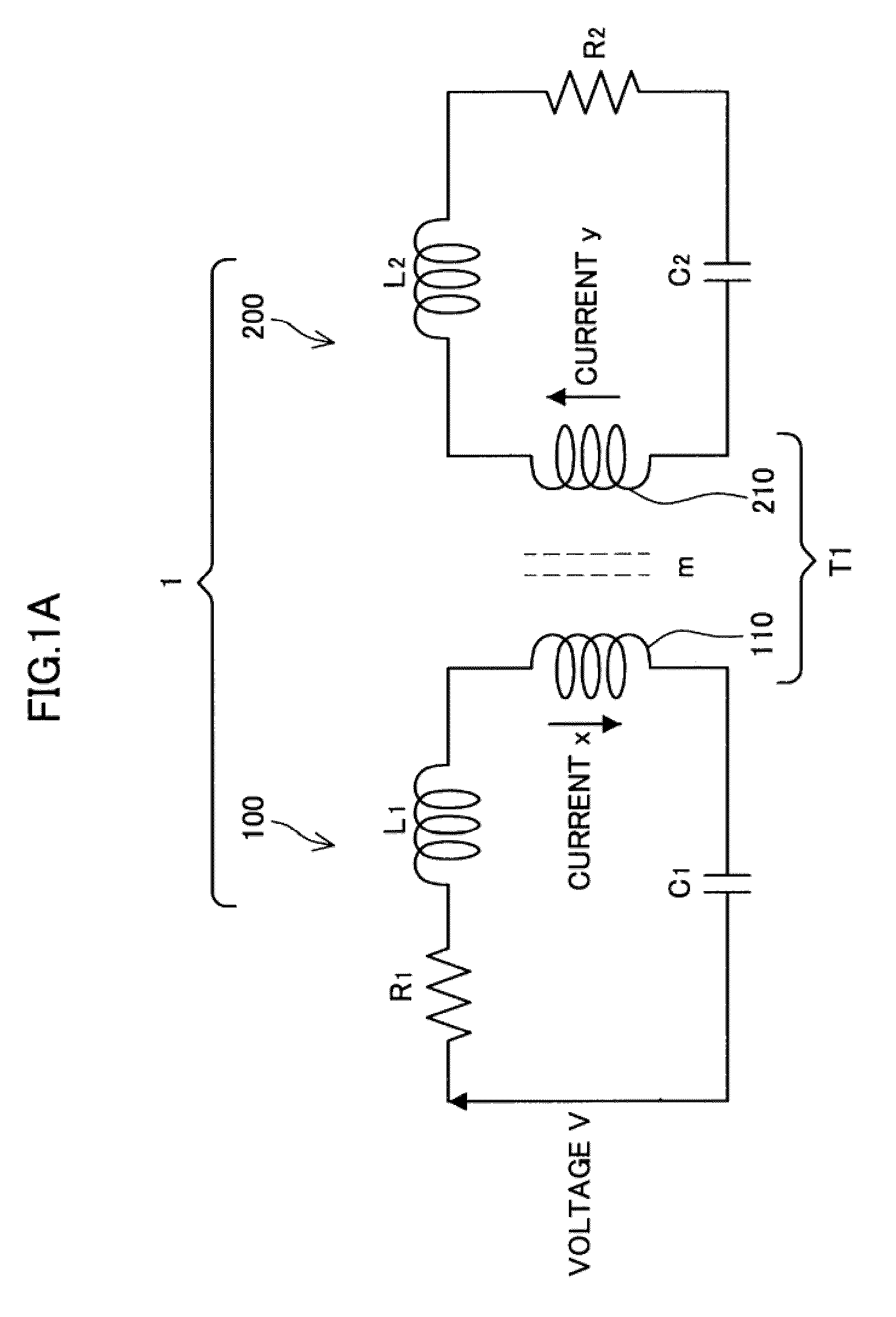
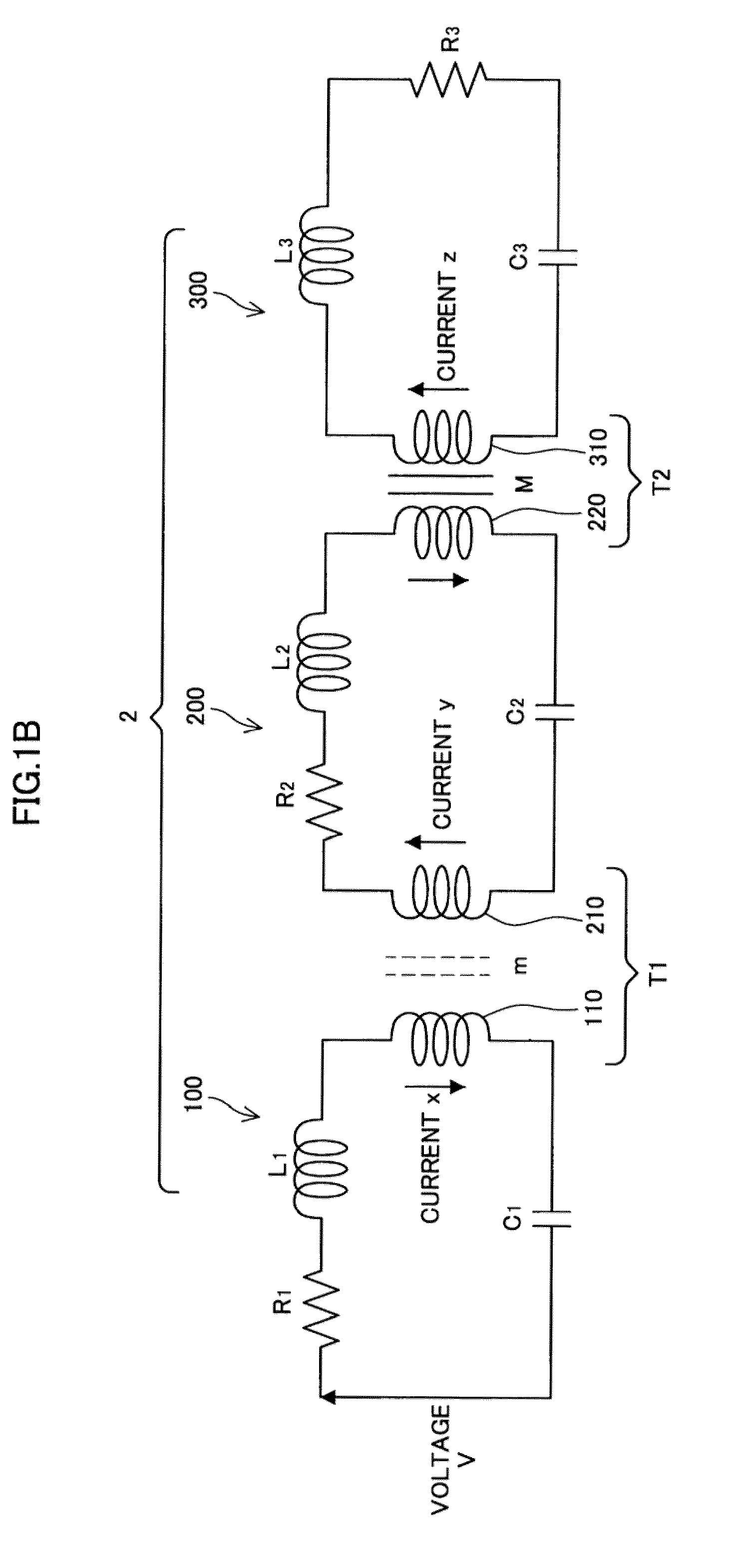
Power Transfer Device, Power Supply Device and Power Receiving Device
ActiveUS20090322307A1Reduce energy transferHigh power transmission efficiencyCircuit arrangementsVariable inductancesElectric power transmissionCapacitance
A power transfer device includes: a transformer that couples a primary circuit and a secondary circuit and has a coupling constant of less than 1; and capacitances that are respectively provided in the primary circuit and the secondary circuit, and connected in series with coils that form the transformer. Circuit constants of the primary circuit and the secondary circuit are set so that the primary circuit and the secondary circuit resonate at the same frequency and a product of the square of the coupling constant, a Q value of the primary circuit and a Q value of the secondary circuit is 1. The primary circuit transfers power to the secondary circuit by means of the transformer, using a carrier wave having the resonance frequency.
Owner:SONY CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance multi-spectral method for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of plurality of coupling networks
InactiveCN106706694ASimple and convenient NMR methodMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
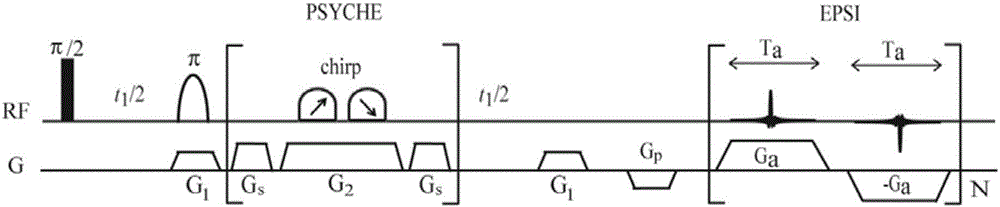
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-spectral method for measuring the hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of a plurality of coupling networks. The method comprises the following steps: applying a 90 DEG hard pulse to make a magnetization vector rotate to the XY plane from the Z direction; applying a selective 180 DEG soft pulse and a magnetic field gradient in the Z direction t1 / 2 time later in order to excite different nuclei in different space positions; applying a PSYCHE module; applying gradients with the same intensity and the same direction to two sides of the PSYCHE module to disperse unwanted signals; adopting an EPSI sampling module t1 / 2 time later to obtain chemical displacement information and space position information; coupling other nuclei obtained at different layers and the nuclei excited by he 180 DEG soft pulse in the same layer to make the couplings have split peaks in indirect dimension; and measuring a corresponding J coupling constant from the split peaks.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Magnetic memory device and write method of magnetic memory device
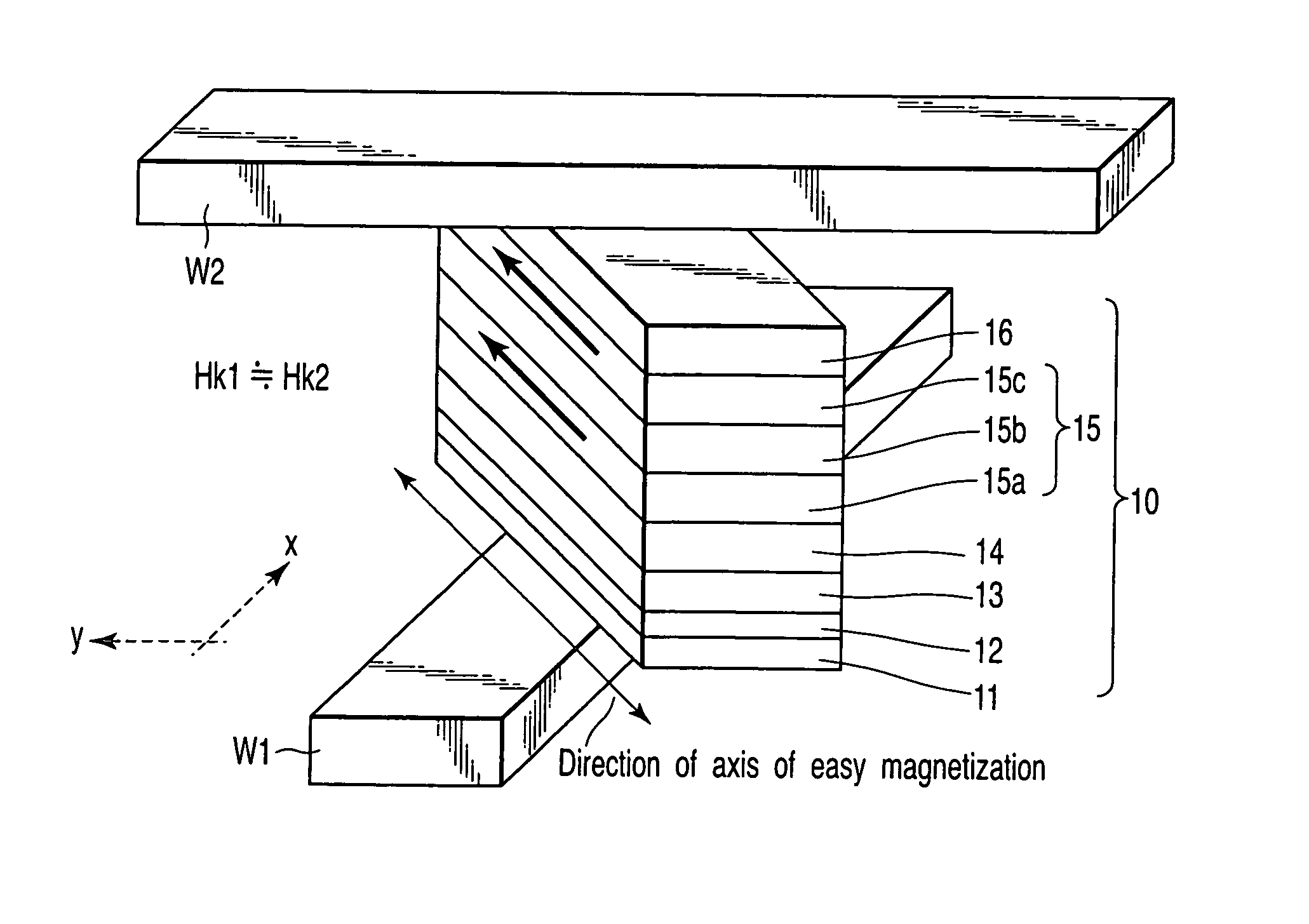
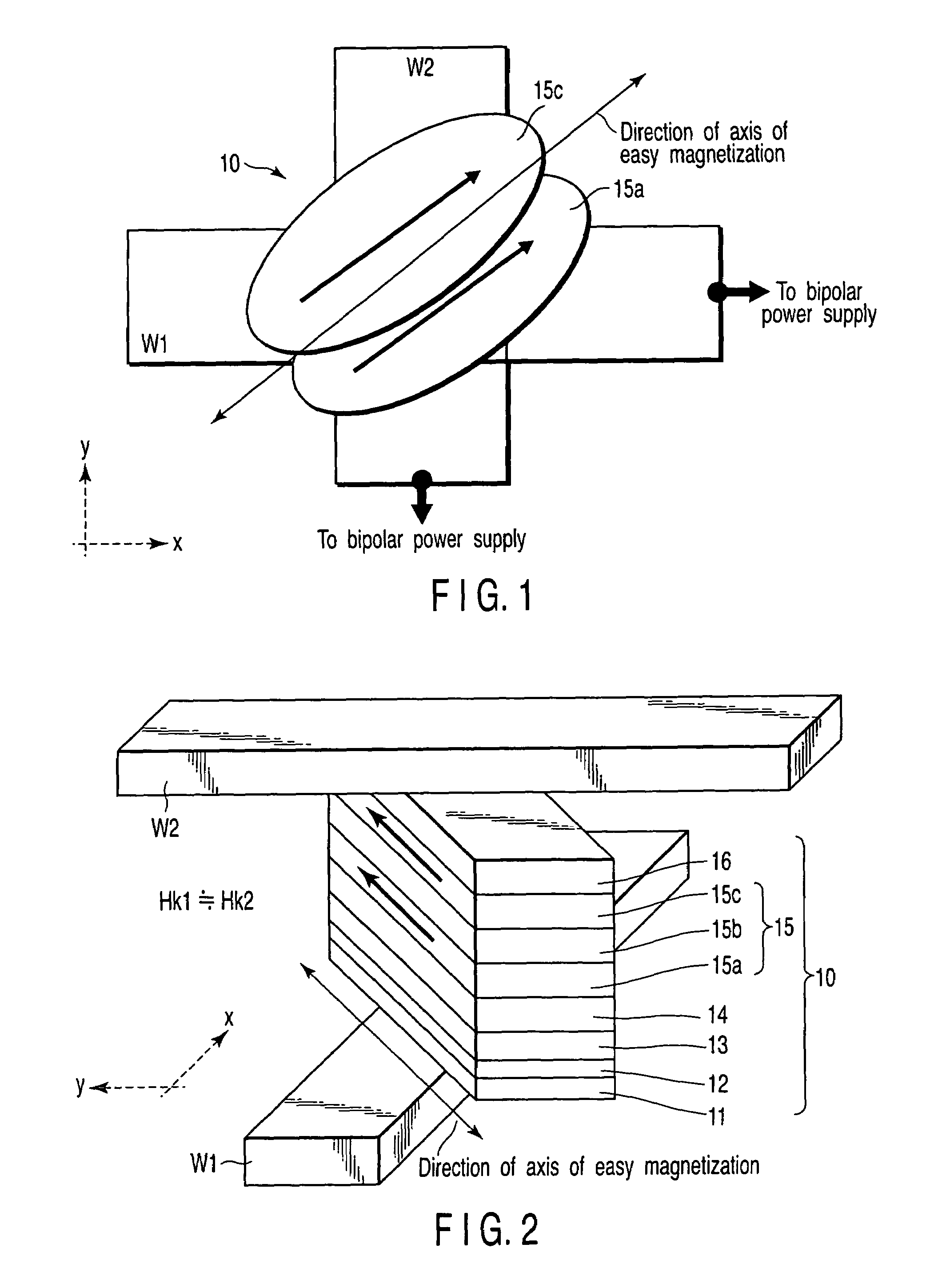
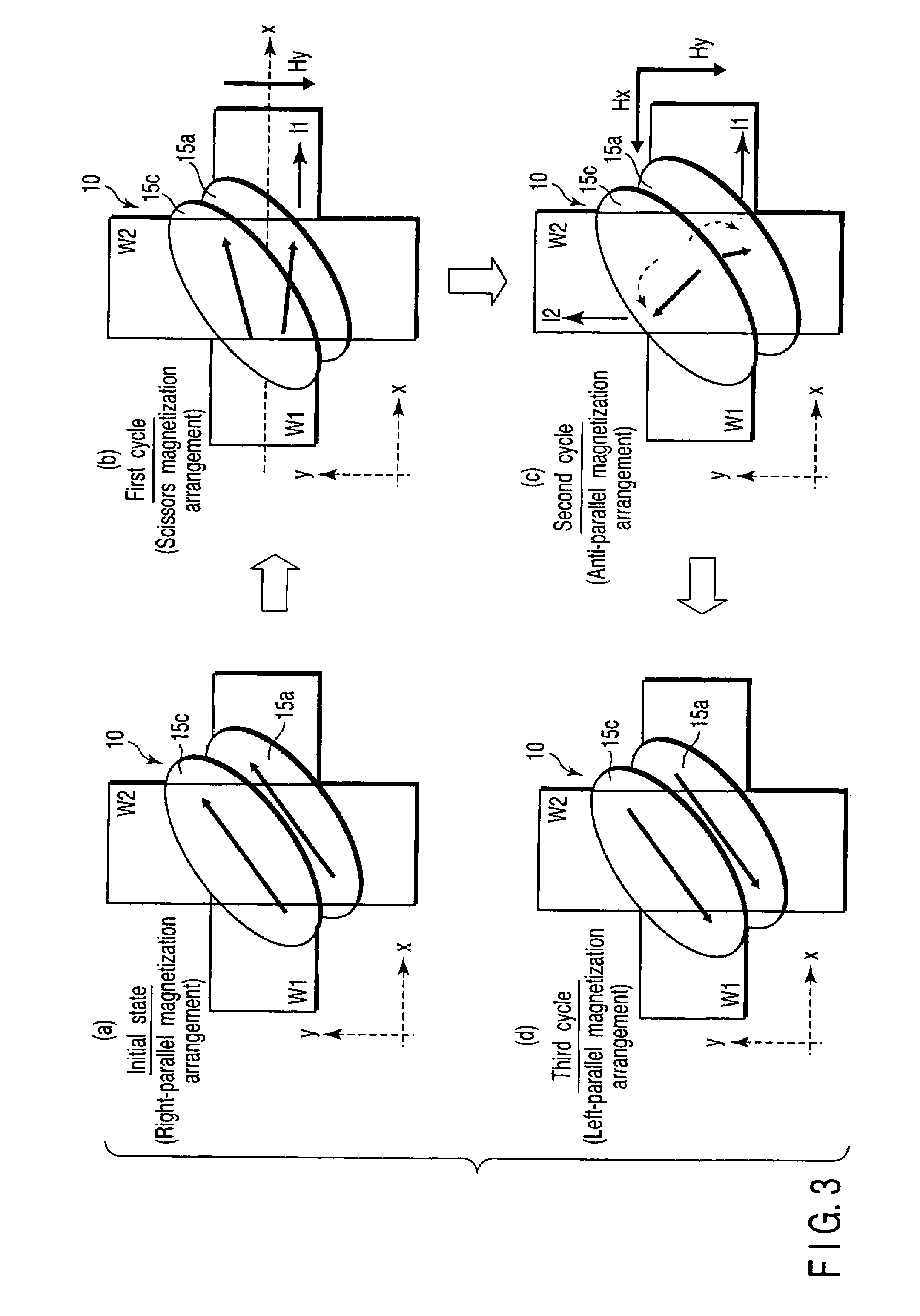
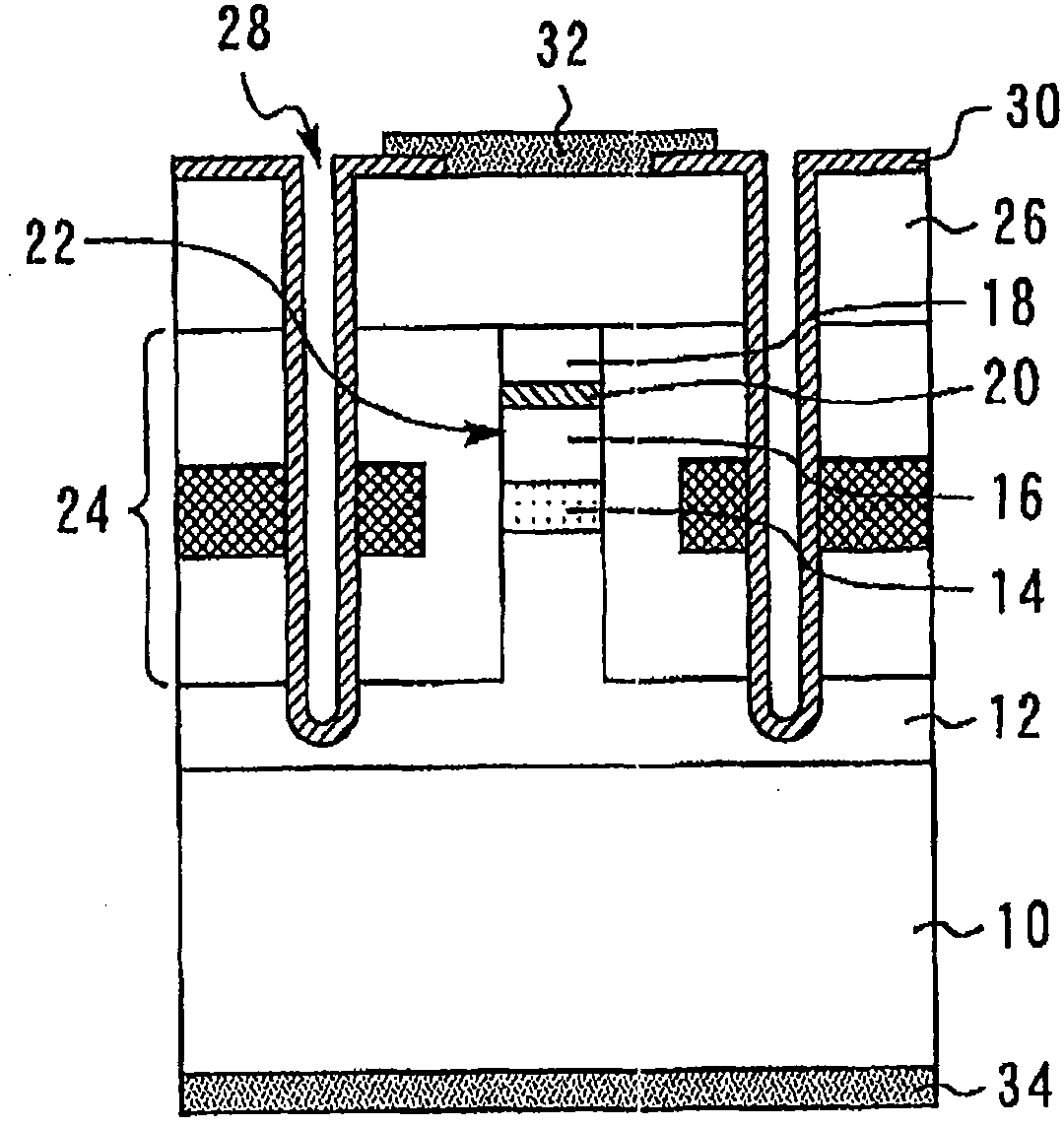
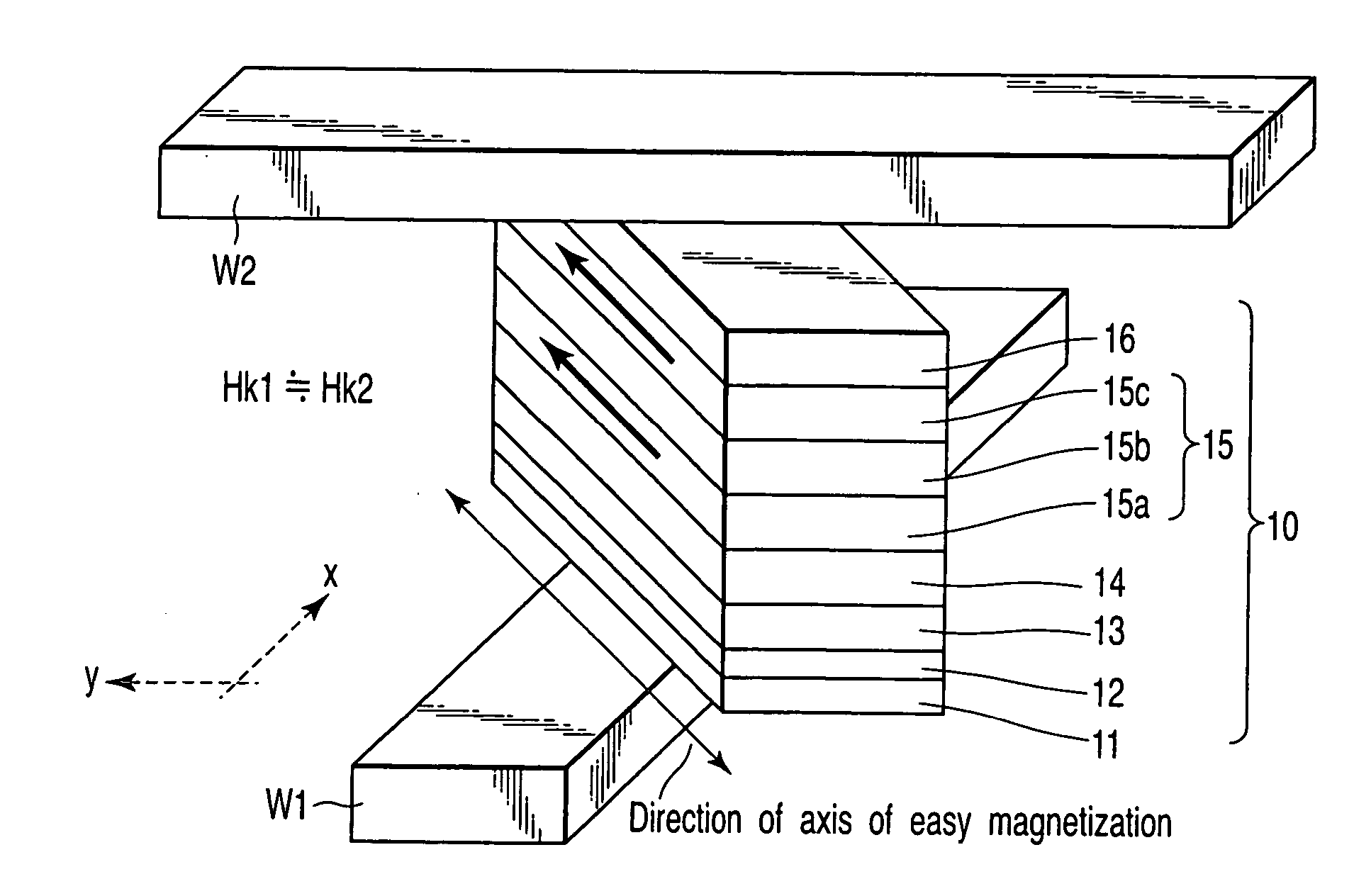
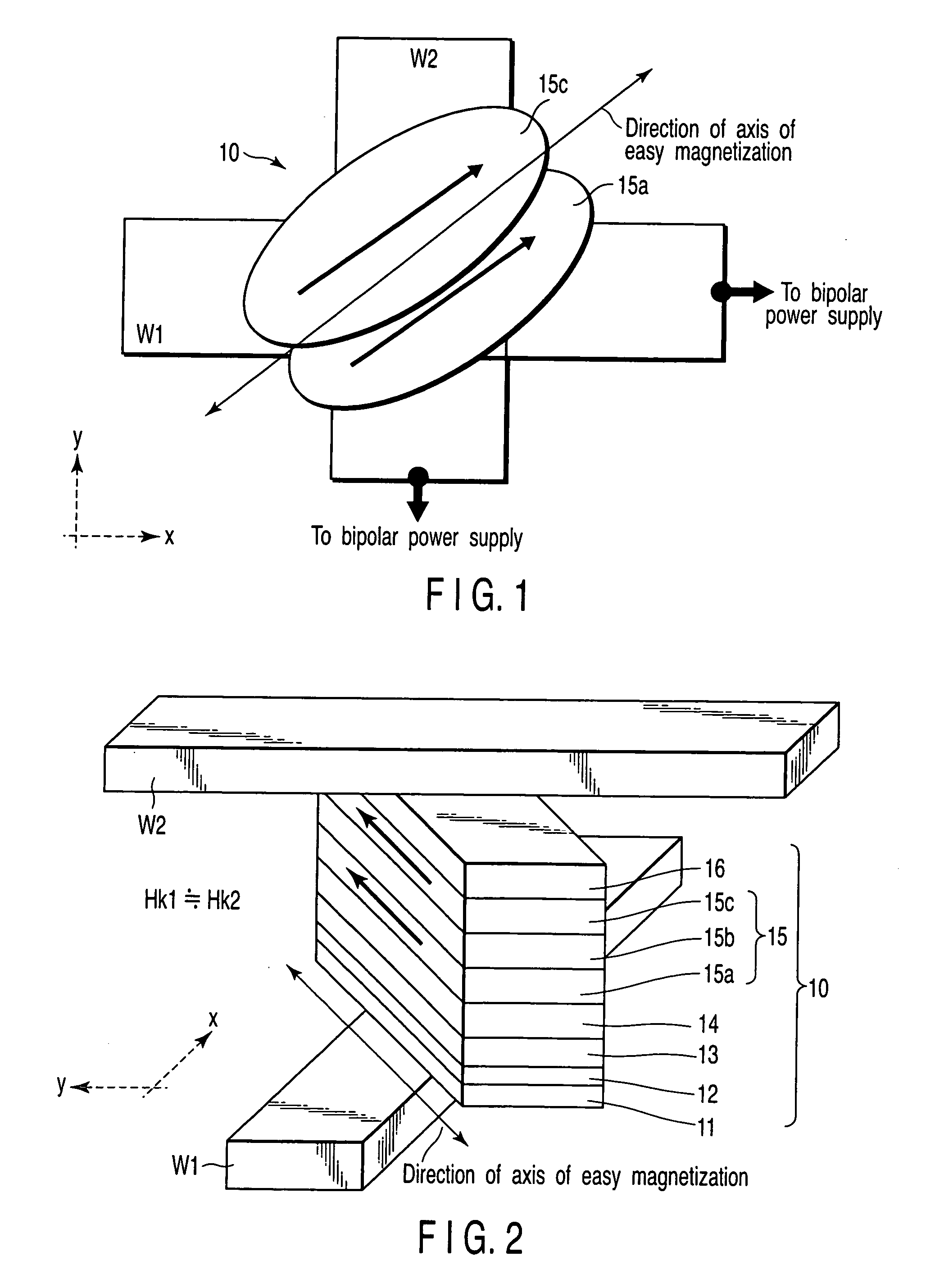
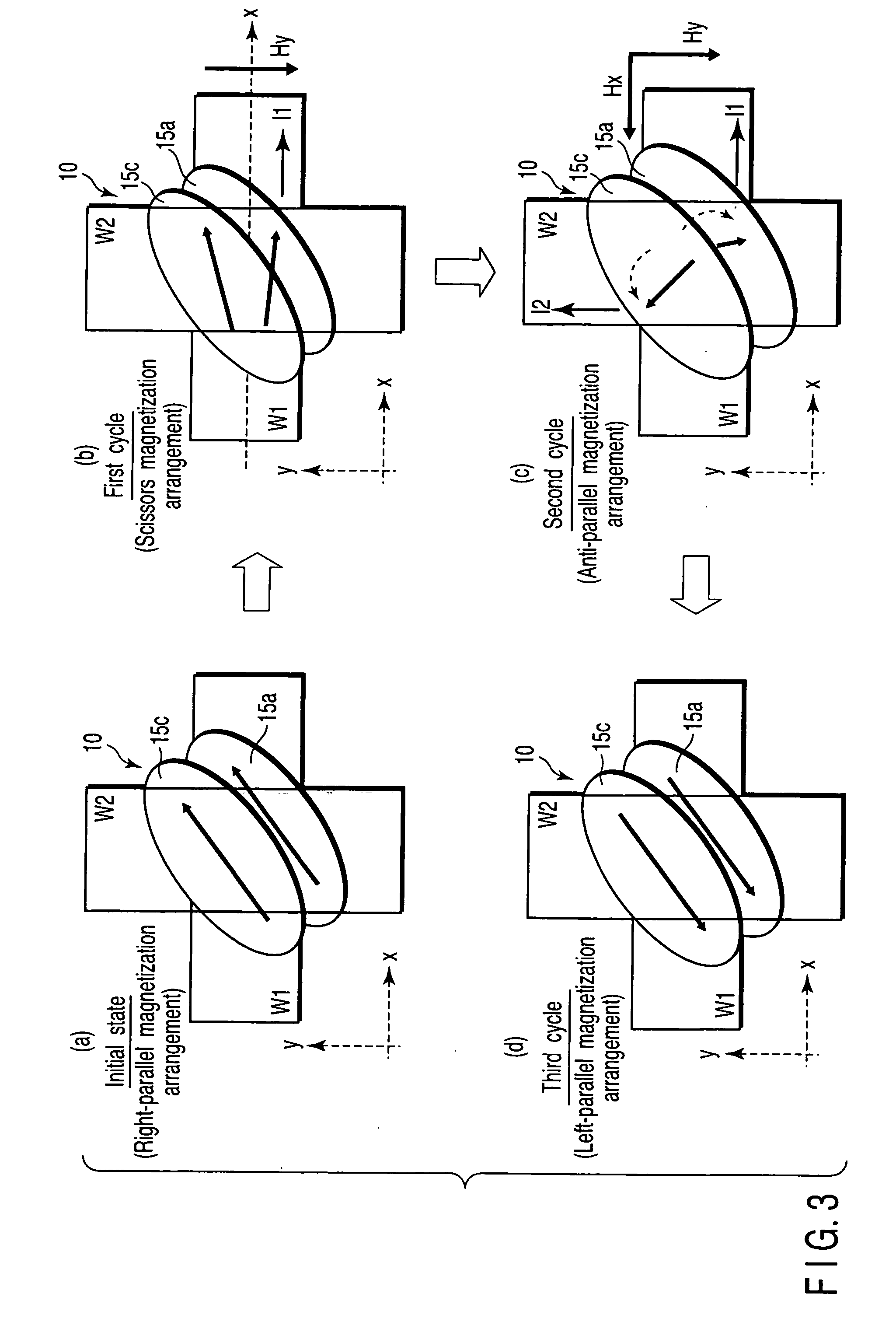
A magnetic memory device includes a first write wiring which runs in a first direction, a second write wiring which runs in a second direction different from the first direction, and a magnetoresistive element which is arranged at an intersection between the first and second write wirings, has a fixed layer, a recording layer, and a magnetoresistive layer sandwiched between the fixed layer and the recording layer, and has an axis of easy magnetization obliquely with respect to the first and second directions, the recording layer including a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, and a first nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the first and second ferromagnetic layers, in which first magnetization of the first ferromagnetic layer and second magnetization of the second ferromagnetic layer are ferromagnetically coupled, and a ferro-coupling constant C of a ferromagnetic coupling is 0.0001 erg / cm2≦C≦0.2 erg / cm2.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
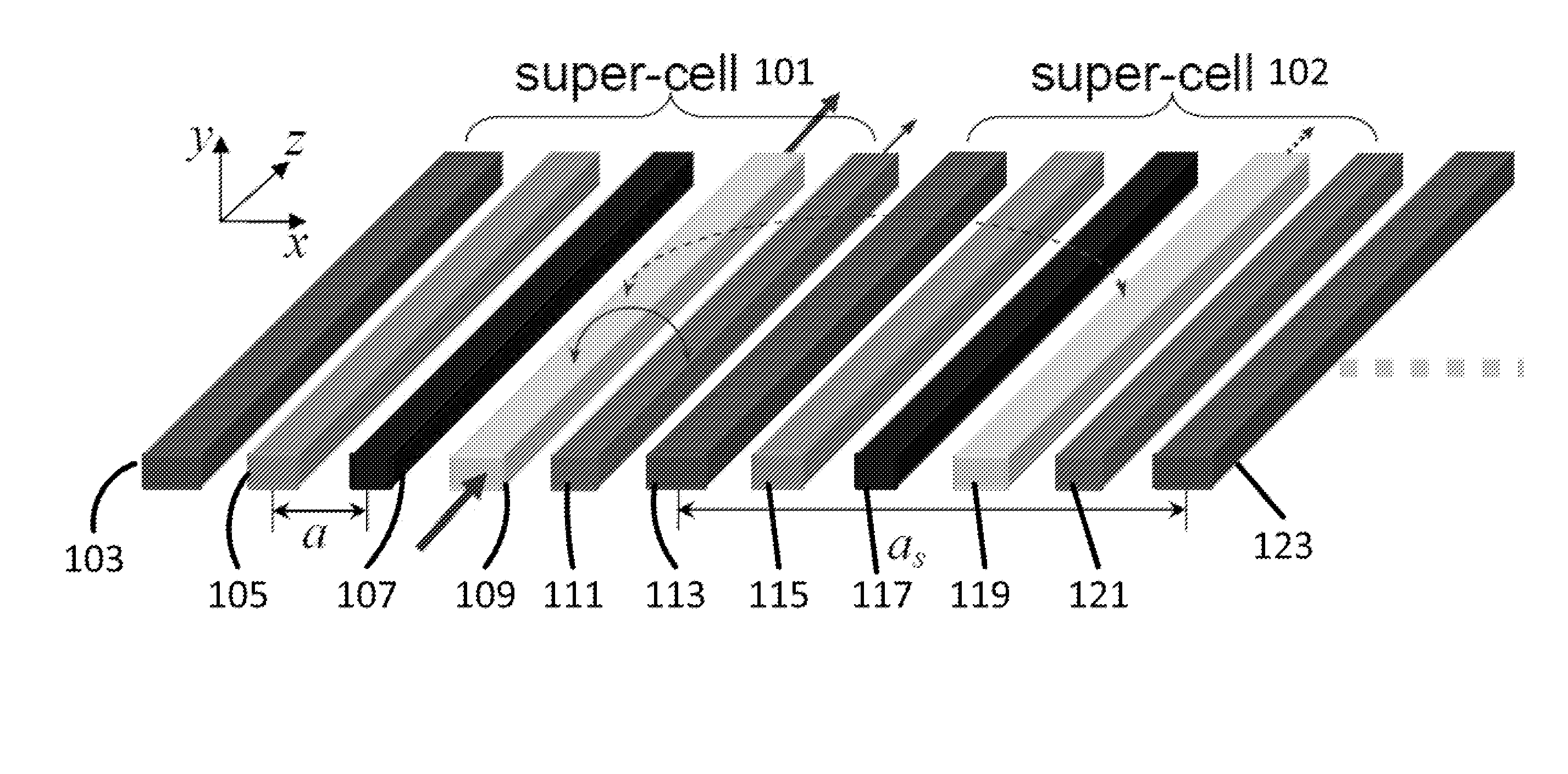
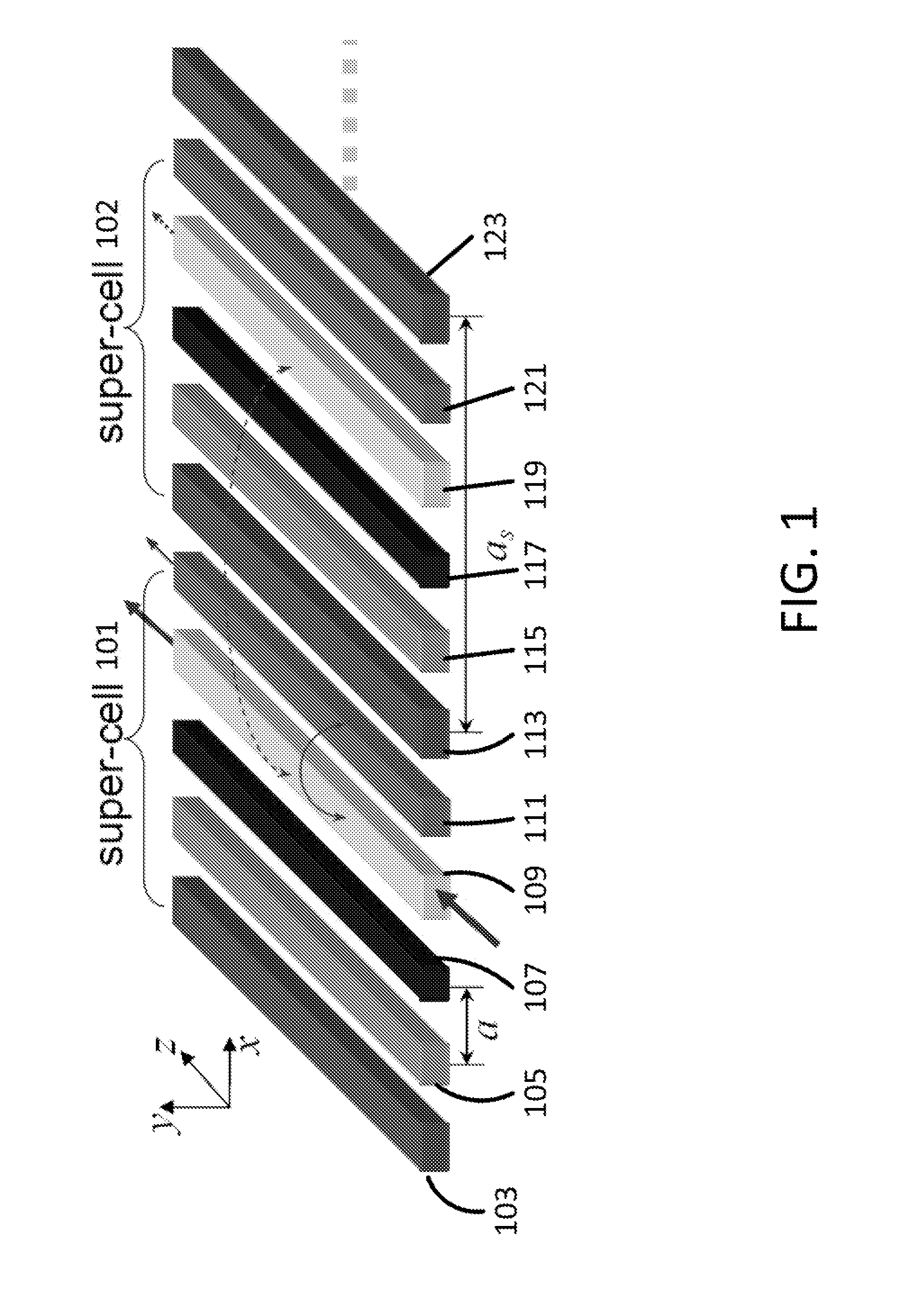
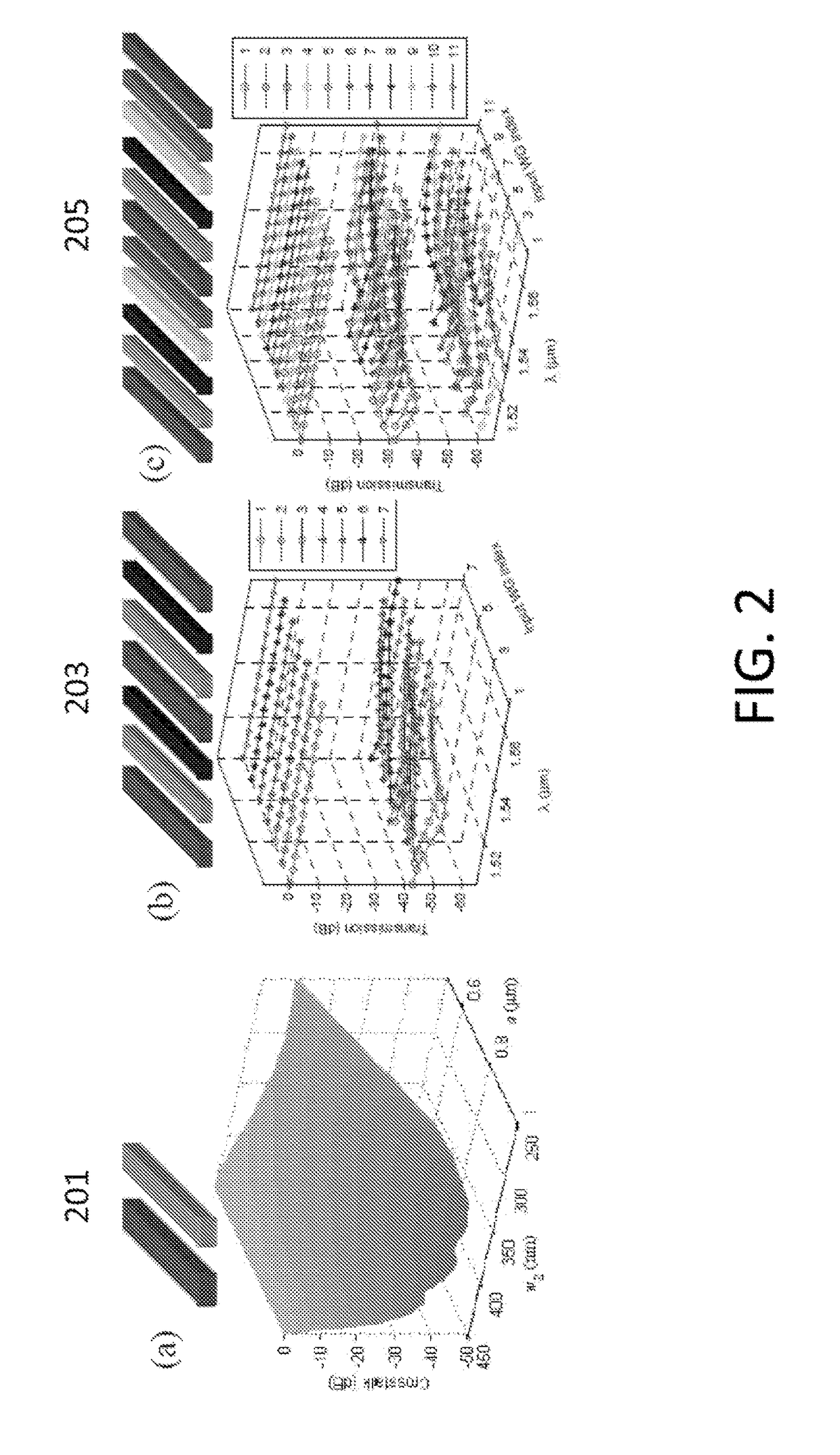
Waveguide superlattices for high density photonics integrations
An apparatus and method for transmitting a plurality of light signals is disclosed. The apparatus includes a splitter configured to split an incoming light signal into a plurality of light signals. Phase control units are included which modify the phase of the light signals. Waveguides are coupled to the phase control units. Each waveguide has a different propagation constant, that is different from adjacent waveguides and the difference between the propagation constants of any two adjacent waveguides is substantially larger than an effective coupling constant between said two adjacent waveguides. Coupling members couple the light signal in one of the plurality of waveguides to free space. The splitter may include output and / or input waveguides and a dispersion element splitting and / or combining: light.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
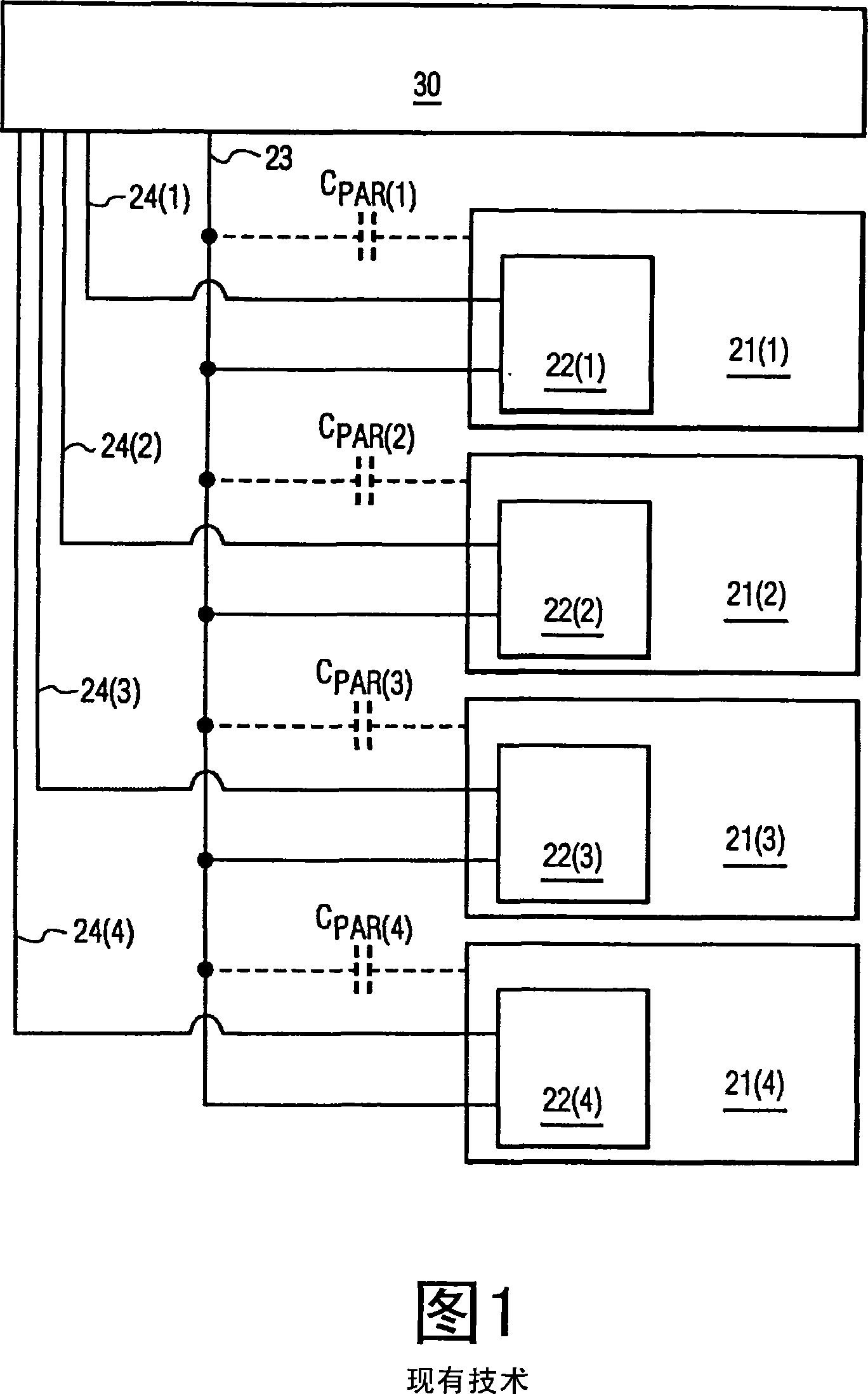
Cross-talk reduction for active matrix displays
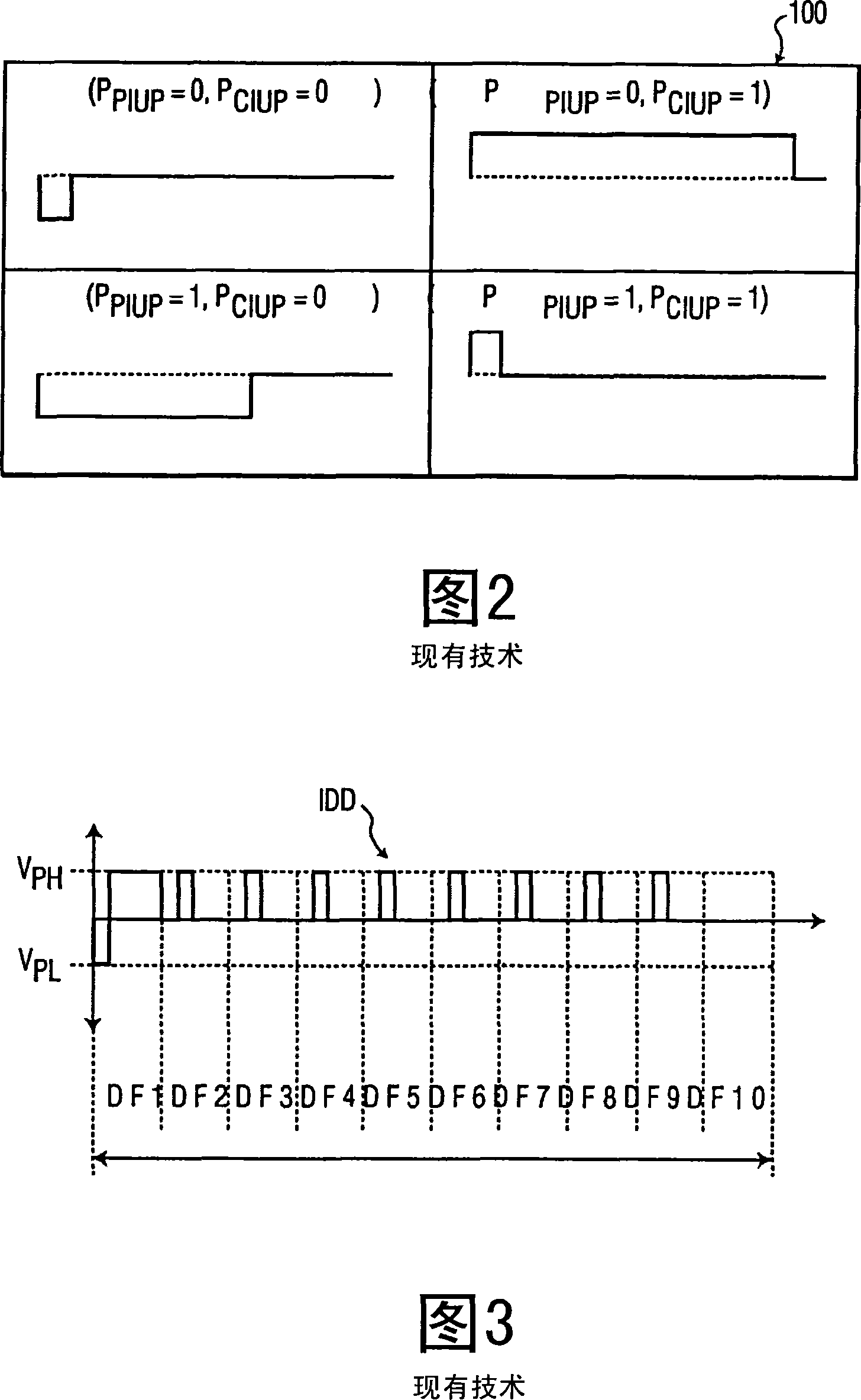
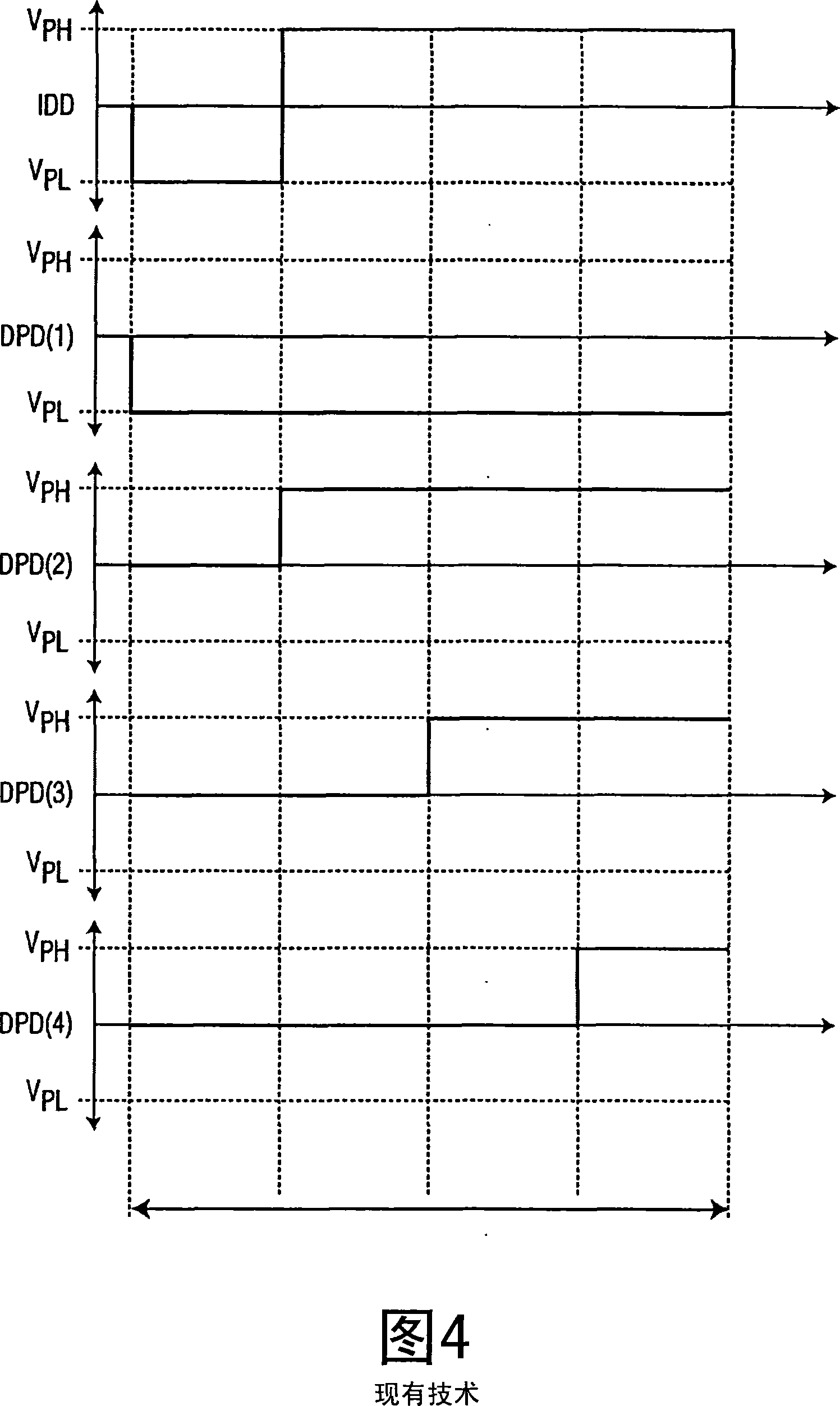
An image drive data system (40) applies cross-talk compensated image drive data (CIDD) to a data line (23) for driving each pixel (21) coupled to the data line (23) to a desired optical state during an image update period inclusive of a cross-talk between the pixels (21) and the data line (23). To reduce the cross-talk, the image drive data system (40) determines cross-talk uncompensated image drive data (IDD) for driving each pixel (21) to its respective desired image exclusive of the cross-talk between the pixels (21) and the data line (23), determines a time averaged pixel data shift based on the cross-talk uncompensated image drive data (IDD) and a cross-talk coupling constant between the pixels (21) and the data line (23), and determines the cross-talk compensated drive data (CIDD) based on the time-averaged pixel data shift.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of measuring dimensionless coupling constant of magnetic structure
In A method for measuring a dimensionless coupling constant of a magnetic structure includes the following steps. A step of applying an external vertical magnetic field is performed for enabling magnetic moments of a RE-TM (Rare Earth-Transition metal) alloy magnetic layer of the magnetic structure to be vertical and saturated. A step of measuring a compensation temperature is performed when the sum of the magnetization of the RE-TM alloy magnetic layer is zero. A step of applying an external parallel magnetic field to the RE-TM alloy magnetic layer is performed. A step of adjusting the temperature of the magnetic structure to the compensation temperature and measuring a hysteresis loop of the magnetic structure under the external parallel magnetic field is performed, wherein the inverse of the slope of hysteresis loop is a dimensionless coupling constant.
Owner:NATIONAL YUNLIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
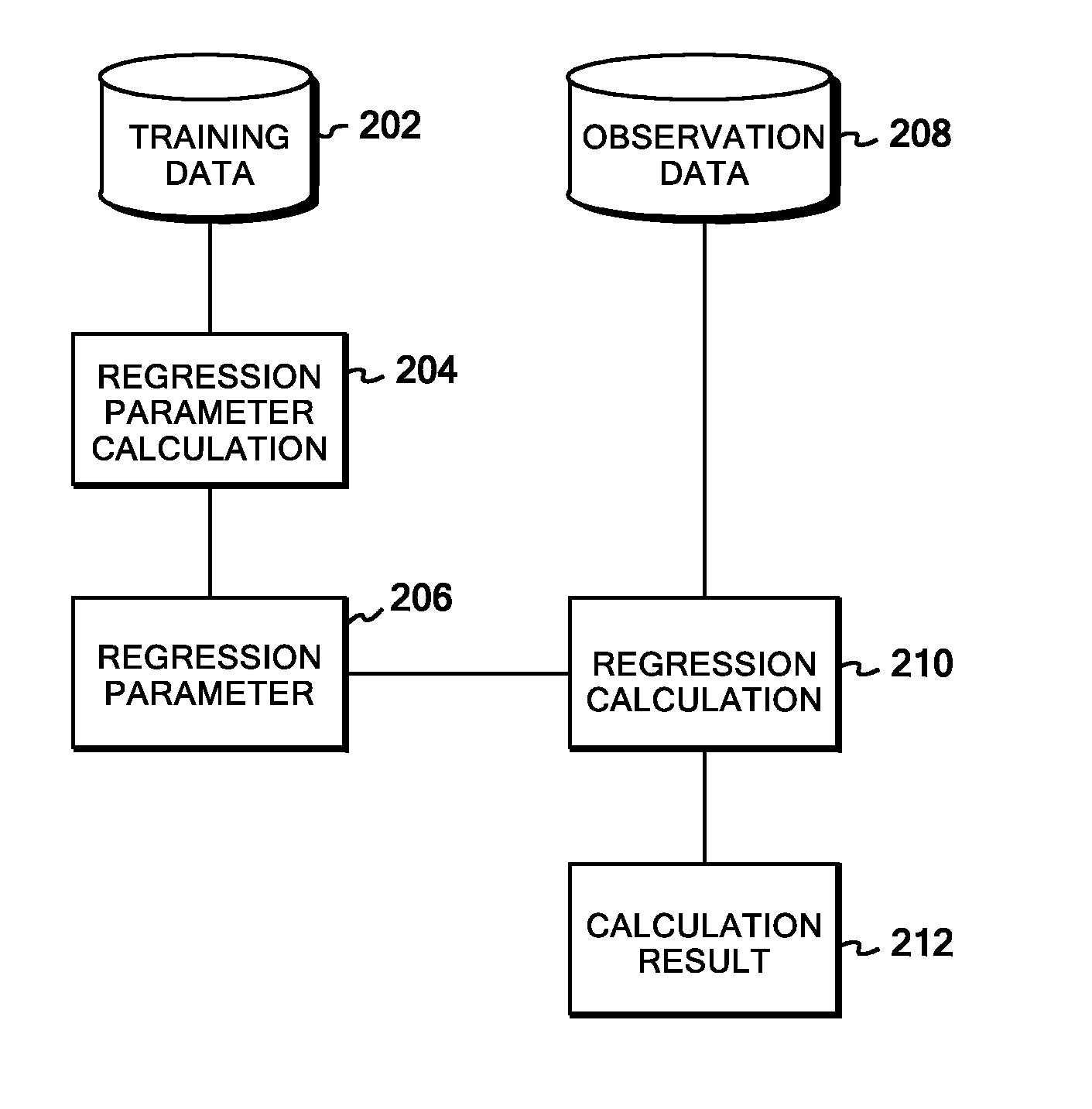
Kernel regression system, method, and program
InactiveUS20110238606A1Reduce computing costDigital computer detailsForecastingKernel regressionAlgorithm
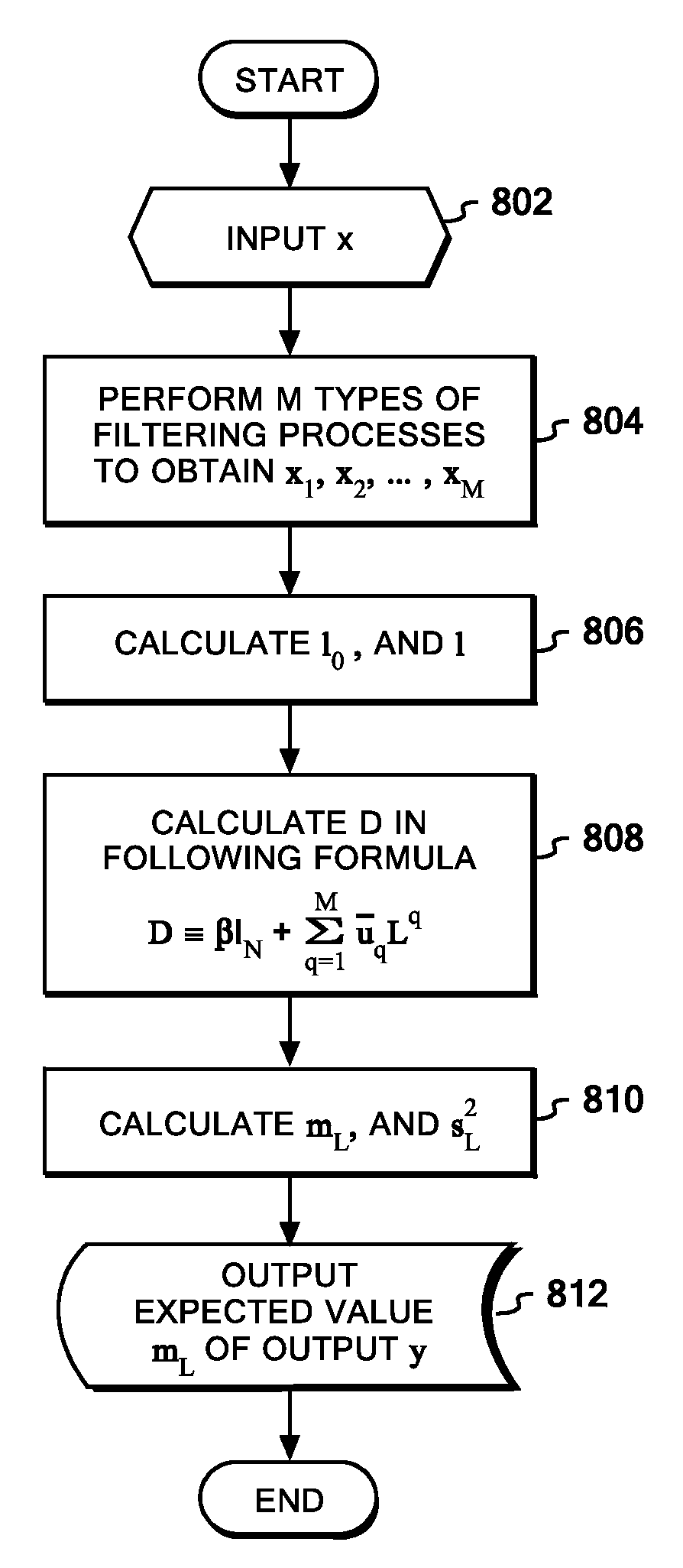
In training data, a similarity matrix is generated for each of types of data corresponding to different kernels, and graph Laplacians are formed individually from the similarity matrices. An entire graph Laplacian is defined as linear combination of the individual graph Laplacians with coupling constants. Observation variables and latent variables associated therewith are assumed to form normal distributions, and the coupling constants are assumed to form a gamma distribution. Then, on the basis of a variational Bayesian method, a variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants can be figured out with a reasonable computational cost. Once the variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants are figured out, a predictive distribution for any input data can be figured out by means of a Laplace approximation.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Apparatus and method for decoupling mr coils
An apparatus includes a first RF coil integrated into a first printed circuit board (PCB) and a second RF coil integrated into the first PCB. The apparatus also includes a tuning member positioned adjacently to the first PCB and inductively coupled to the first and second RF coils, the tuning member configured to minimize a mutual inductance formed between the first and second RF coils via modification of a coupling constant between the first and second RF coils.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for obtaining single voxel one-dimensional localization spectra capable of eliminating scalar coupling modulation
InactiveCN103645453APromote localizationGood signalMagnetic measurementsPhase distortionCoupling constant
The invention provides a method for obtaining single voxel one-dimensional localization spectra capable of eliminating scalar coupling modulation. A same-direction 90-degree radio-frequency pulse is added between two spin echo modules to form a hard pulse scalar coupling re-aggregation module and a soft pulse scalar coupling re-aggregation module, the interval t between the pulses in the re-aggregation modules is set according to the coupling system condition included in a sample, and when the t and scalar coupling constant J product is much smaller than 1, the scalar coupling re-aggregation modules can eliminate scalar coupling modulation effects caused by various coupling systems. The soft pulse scalar coupling re-aggregation module completes voxel selection by combining with selecting layers and destroy gradients. According to the method, by the aid of the obtained one-dimensional localization spectra, signal amplitude and phase distortions caused by scalar coupling modulation can be prevented, perfect signals are obtained, and spectrogram attribution analysis is facilitated.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Superconductor compositions operable at high temperatures
InactiveUS20080125323A1Increase temperatureConductive materialSuperconductor detailsElectron phonon couplingElectron phonon
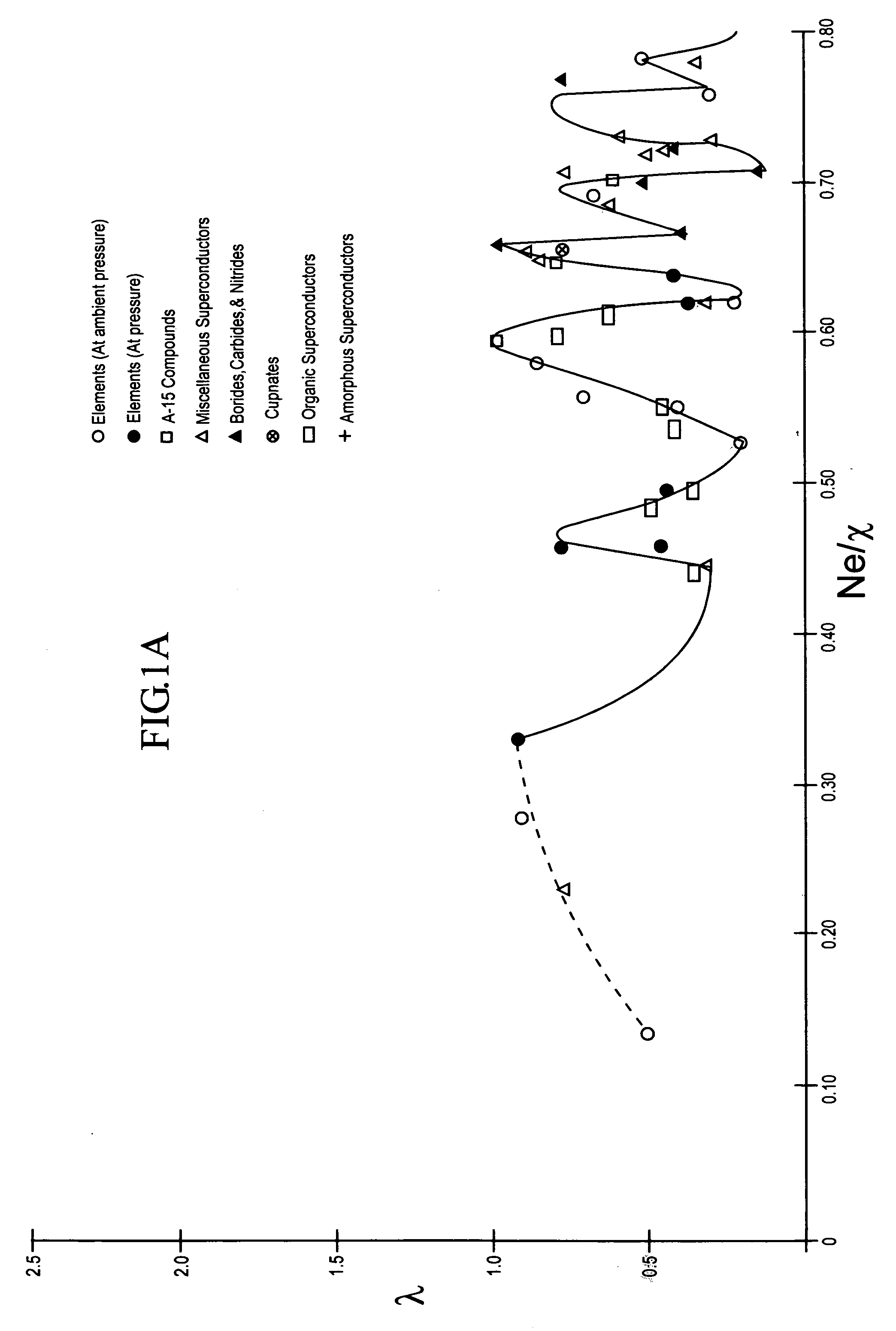
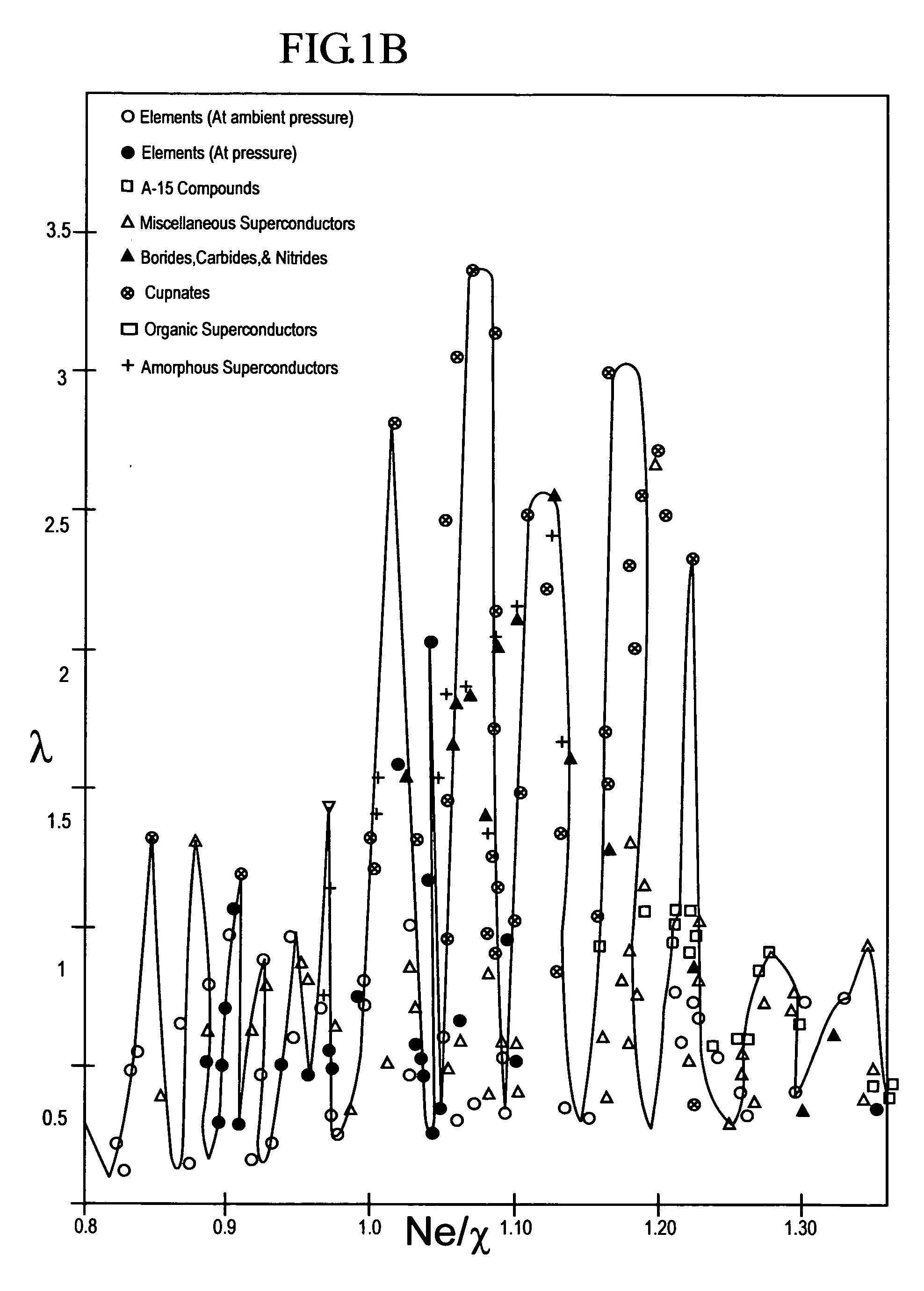
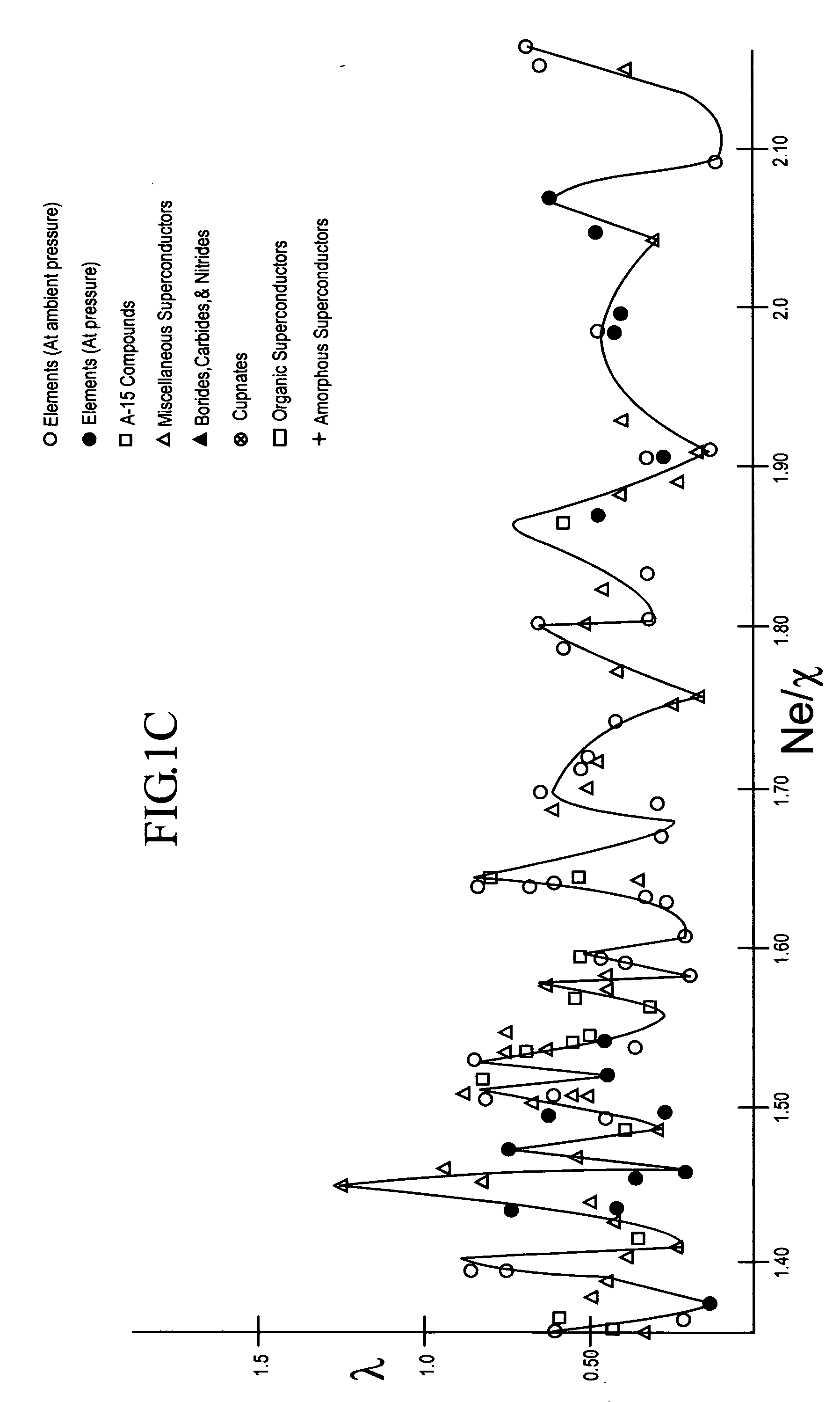
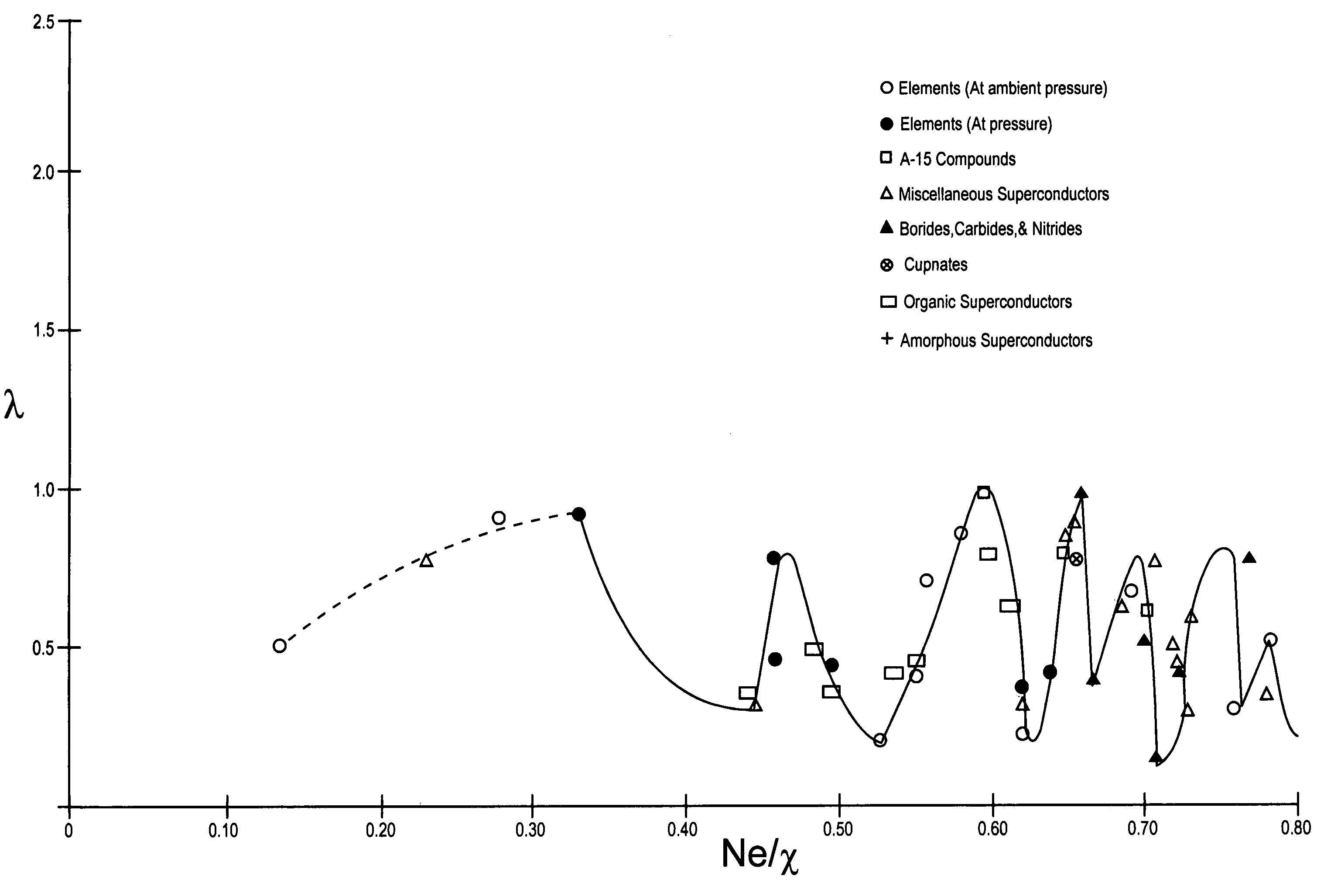
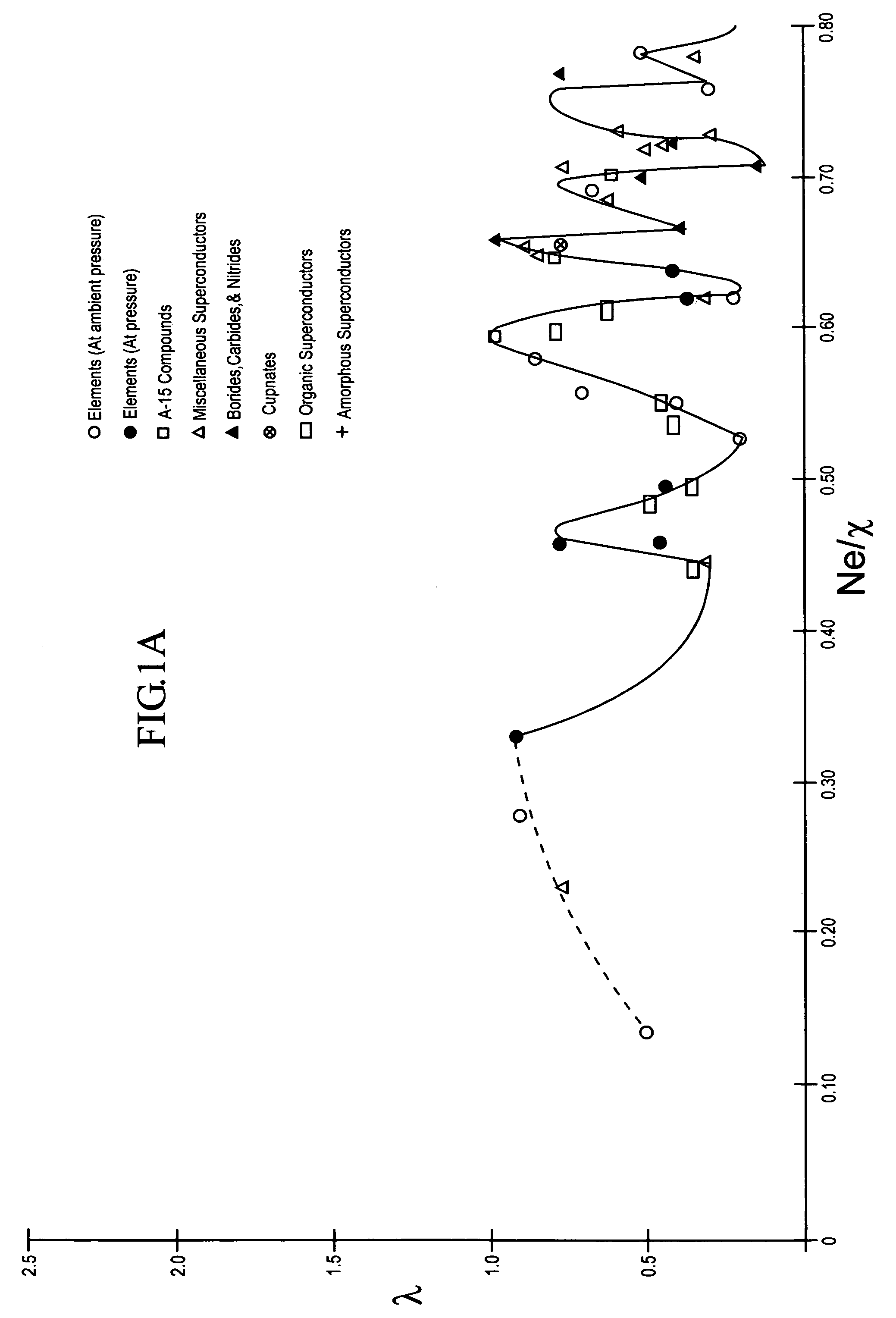
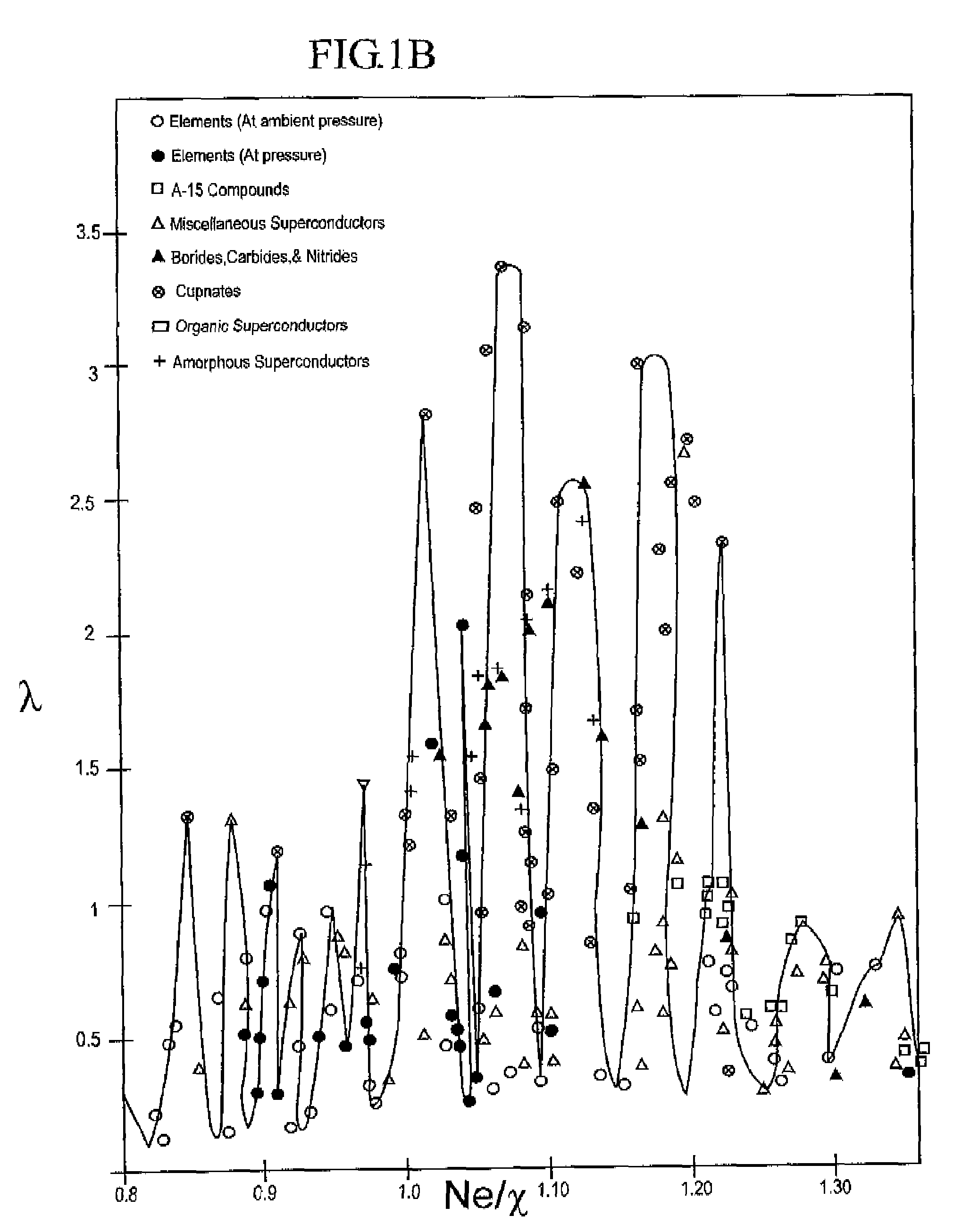
The composition of compounds containing a multiplicity of different elements are optimized in general by full or partial substitutions of one or more of the atoms in such compounds so as to effect an Ne / χ value which represents a peak or near peak value in λ (the electron-phonon coupling constant) so as to maximize Tc for such compositions of matter.
Owner:NEPELA DANIEL A
Nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of specific hydrogen nucleus
InactiveCN109187613AStrong spectrogram signalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method for measuring the hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of a specific hydrogen nucleus. The nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method comprises: applying a selective 90 DEG soft pulse while applying a Z-direction magnetic field gradient; applying a perfect echo module, and applying Z-direction magnetic field gradients with the same strength and the same direction on both sides of the selective 180 DEG soft pulse of the perfect echo; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of an S nucleus after the first t1 / 2 evolution time in the second echo of the perfect echo so as to retain the J-coupling information of the S nucleus; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of the S nucleus after the second t1 / 2 to compensate phase distortion; respectively applying the 180 DEG soft pulse of the selective S nucleus before the two t1 / 2 evolution times in the second echo so as to obtain a R type sequence corresponding toa N type sequence; and finally carrying out addition on a N type spectrum and a R type spectrum inverted along indirect dimension to obtain a phase-sensitive two-dimensional spectrum, and obtaining the corresponding J-coupling constant by measuring from the splitting of the peak in the indirect dimension.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Superconductor compositions operable at high temperatures
InactiveUS7482298B2Calcium/strontium/barium compoundsBoron/boridesElectron phonon couplingElectron phonon
The composition of compounds containing a multiplicity of different elements are optimized in general by full or partial substitutions of one or more of the atoms in such compounds so as to effect an Ne / χ value which represents a peak or near peak value in λ (the electron-phonon coupling constant) so as to maximize Tc for such compositions of matter.
Owner:NEPELA DANIEL A
Cylindrical electron paramagnetic resonance probe for detecting external sample
ActiveCN103033526ASimple structureEasy to processDentistryDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrowave cavityResonant cavity
The invention relates to a cylindrical electron paramagnetic resonance probe capable of locally detecting an external sample. The probe is rectangular; a cylindrical microwave cavity is formed inside the probe; a polygon sample detecting hole is formed in the center of the top surface of the probe; the detecting hole penetrates longitudinally to the interior of a microwave cavity body space in the wall thickness direction, and penetrates through in the cavity thickness direction; a long edge of the detecting hole cuts a microwave magnetic field component in a resonant cavity and is parallel to the current line direction of the detecting hole in the cavity wall; a pair of coils for providing a regulated magnetic field is placed on the both sides of the detecting hole, and generates the regulated magnetic field required by paramagnetic resonance at the detecting hole; a coupling is coupled with a tuning unit by a coupling hole; and a coupling constant of the resonant cavity and a microwave system is regulated by an adjusting bolt outside the coupling hole. The probe is mainly used for conducting local EPR (electron paramagnetic resonance) detection on the sample that a whole structure is inconvenient to damage.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Chlorinated 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3- distyryl benzene derivatives as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104016868AEasy to passAvoid decompositionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChemical structureOrtho position
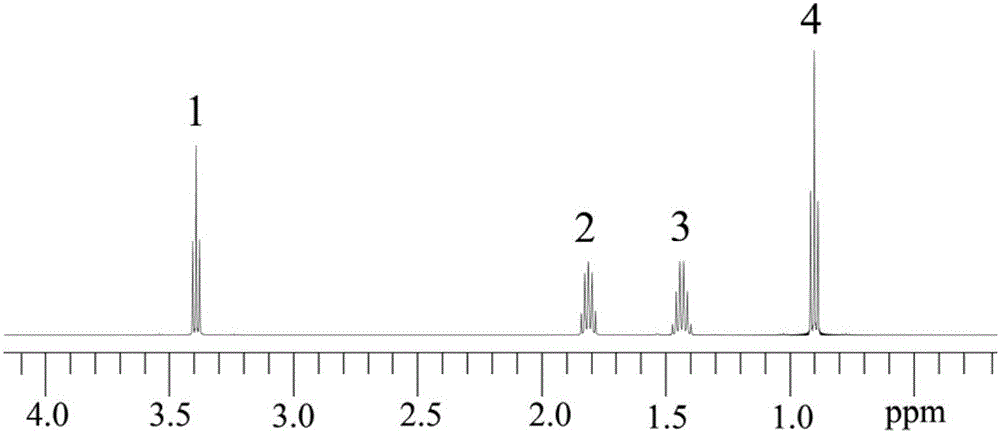
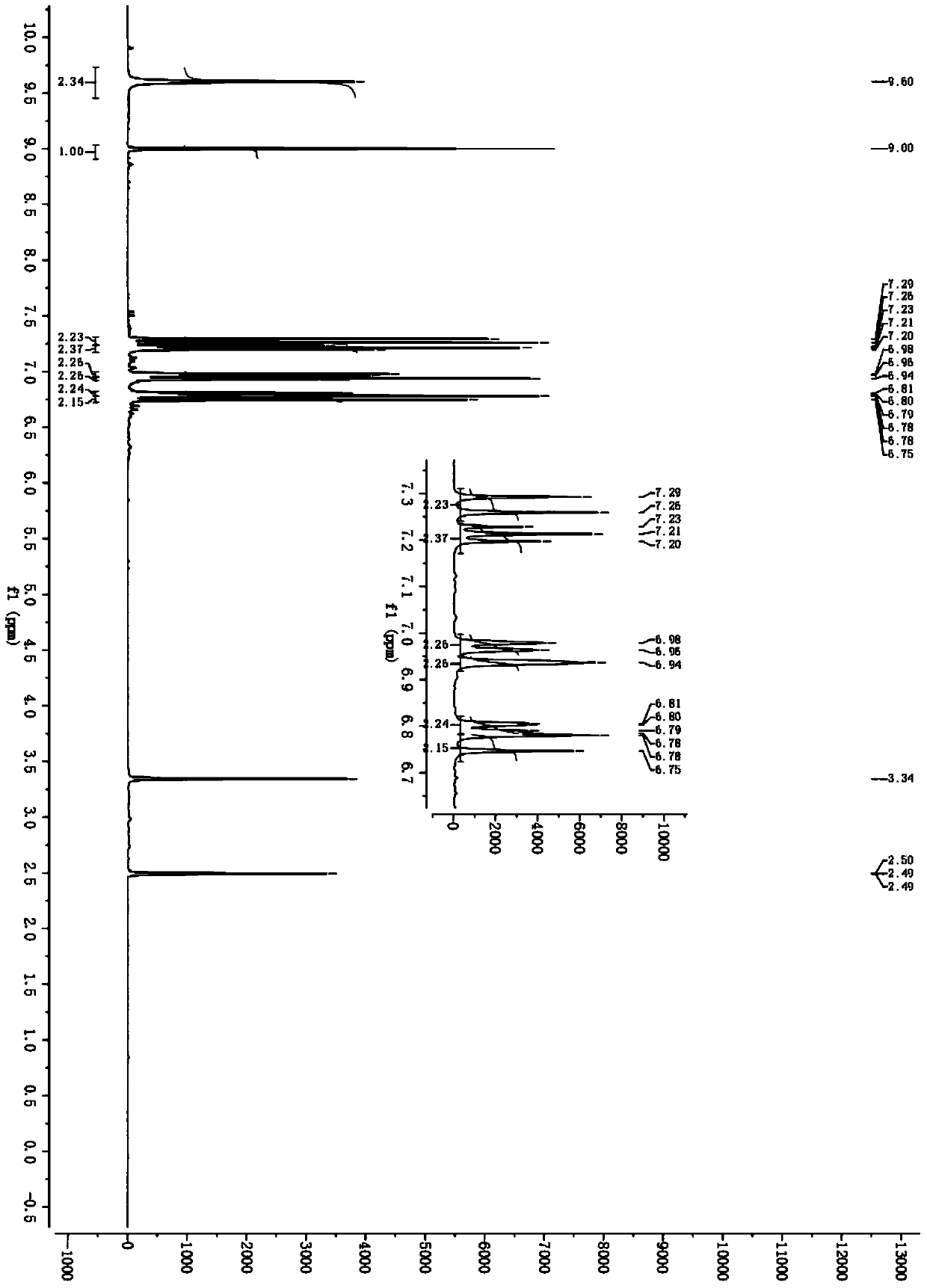
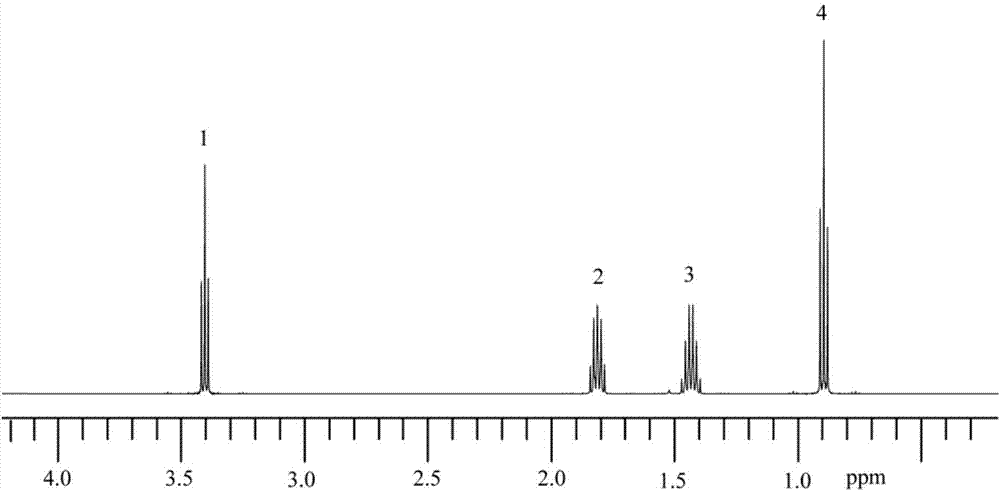
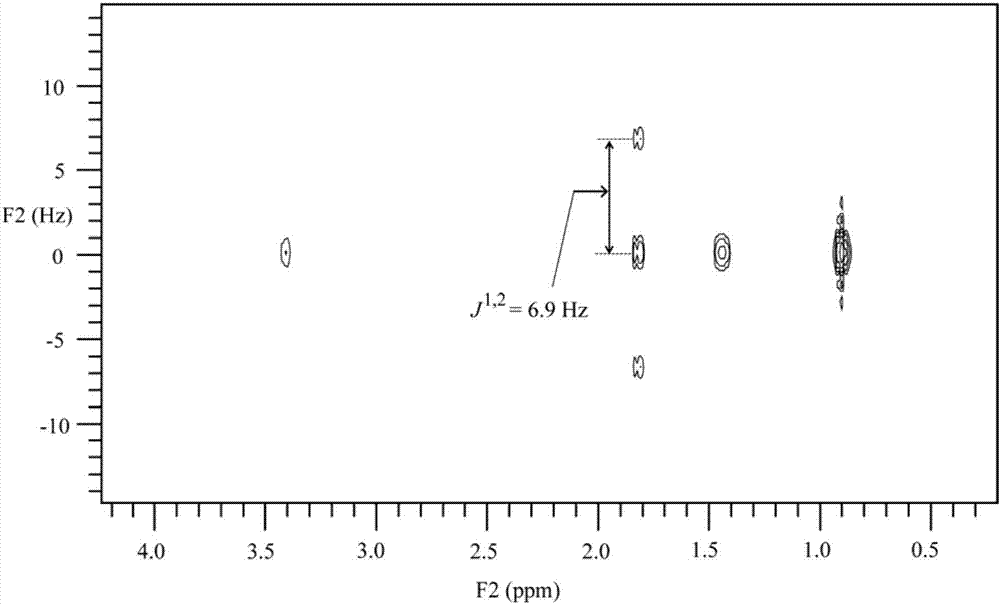
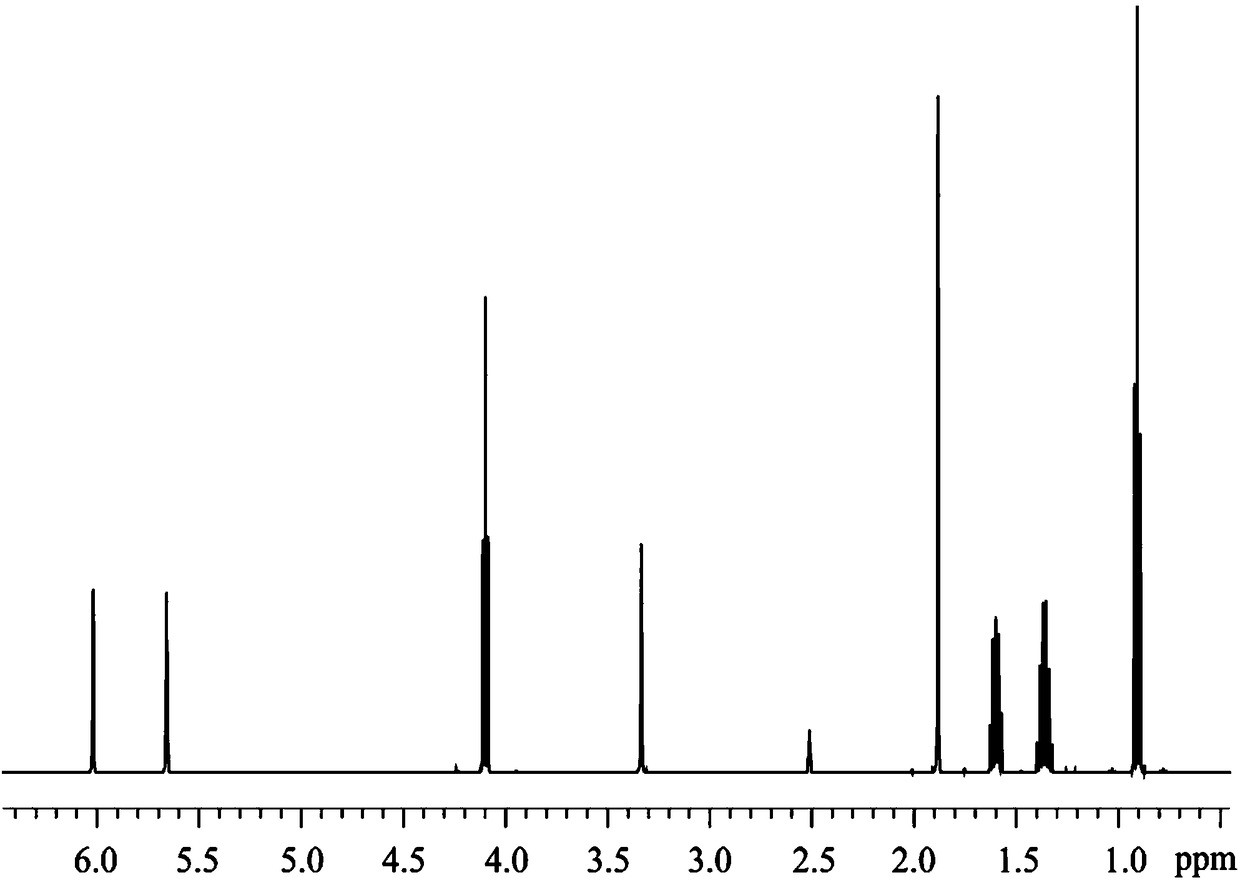
The invention discloses 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3-distyryl benzene derivatives containing chlorine substituent as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical structure of the compounds is characterized in that three nitryls exist at positions 2, 4, 6 of a middle benzene ring of 1, 3-distyryl benzene, and ortho-positions, meta-positions and para-positions of benzene rings at the two sides are connected to chlorine atoms, or the ortho-positions and the para-positions are simultaneously connected to the chlorine atoms. The chemical structure of the compounds is confirmed to be the trans-structure when the coupling constant of diphenylethene double bonds in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum is about 16.0Hz. The 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3-distyryl benzene derivatives containing chlorine substituent are synthesized through microwave assistance under a catalysis condition, are simple in a preparation technology, solvent-free, fast, green and safe and can be potentially applied to the field of luminescent devices and energetic materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rectangular electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) probe for exo-cavity sample detection
ActiveCN103018269ASimple structureEasy to processAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceMicrowaveResonance
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Waveguide superlattices for high density photonics integrations
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20020146050A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionRefractive indexCoupling constant
A semiconductor laser device comprising a substrate, a resonator overlying said substrate, a waveguide overlying said substrate and optically coupled to said resonator, and a diffraction grating formed on said resonator or said waveguide, said diffraction grating including slits or grooves formed on an Al-oxidized region of an Al-containing oxidized semiconductor layer, said Al-oxidized region being formed by selectively oxidizing Al in said Al-containing oxidized semiconductor layer. In the present invention, the difference between the refractive indices of the layer having the embedded grating and the Al oxide layer becomes larger to increase the coupling constant between laser beams and the grating. The decrease of the cavity length can increase the number of the devices obtainable from a single wafer.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Energetic salt based on 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3-di(2', 4', 6'-trinitro-3'-hydroxyl styryl) benzene, synthetic method and application thereof
ActiveCN103992227AHigh melting pointGuaranteed energyUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationChemical structureBenzene
The invention discloses an energetic salt based on a compound 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3-di(2', 4', 6'-trinitro-3'-hydroxyl styryl) benzene, and a synthetic method thereof. The chemical structure of the 2, 4, 6-trinitro-1, 3-di(2', 4', 6'-trinitro-3'-hydroxyl styryl) benzene is characterized in that 3 nitro groups are located on 2, 4 and 6 sites on an intermediate benzene ring of 1, 3-distyryl benzene, a nitro group is respectively connected to 2, 4, 6 sites on benzene rings on both sides of the 1, 3-distyryl benzene, and a hydroxyl is further connected to a meta-position. As the coupling constant of distyryl double bonds in a nuclear magnetic spectrogram is about 16.60Hz, the double bonds are in a trans-structure. As the compound has a structure similar to picric acid, a series of stable energetic salts are generated by hydroxyl functional groups and nitrogenous positive ions. The compound is synthesized by adopting a four-step reaction. The method is simple to operate, mild in reaction condition and relatively high in yield. The compound has good heat-resistant performance and detonation performance and belongs to the field of energetic materials.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Kernel regression system, method, and program
In training data, a similarity matrix is generated for each of types of data corresponding to different kernels, and graph Laplacians are formed individually from the similarity matrices. An entire graph Laplacian is defined as linear combination of the individual graph Laplacians with coupling constants. Observation variables and latent variables associated therewith are assumed to form normal distributions, and the coupling constants are assumed to form a gamma distribution. Then, on the basis of a variational Bayesian method, a variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants can be figured out with a reasonable computational cost. Once the variance of the observation variables and the coupling constants are figured out, a predictive distribution for any input data can be figured out by means of a Laplace approximation.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101814696AImprove featuresImprove long-term reliabilityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotoluminescenceCoupling
The invention provides a semiconductor laser including a p-type semiconductor layer, an active layer, and an n-type semiconductor layer sequentially laminated on a p-type semiconductor substrate; and a diffraction grating in the n-type semiconductor layer along the direction of an optical waveguide. The reflectance of light on two facing laser end surfaces is asymmetric; the length L of the active layer in the optical waveguide direction is 130 mum or shorter; the diffraction grating material has a photoluminescence wavelength of 1,200 nm or longer; and kappa L, which is the product of the length L and the coupling coefficient kappa of the diffraction grating, is at least 1.5 and smaller than 3.0.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
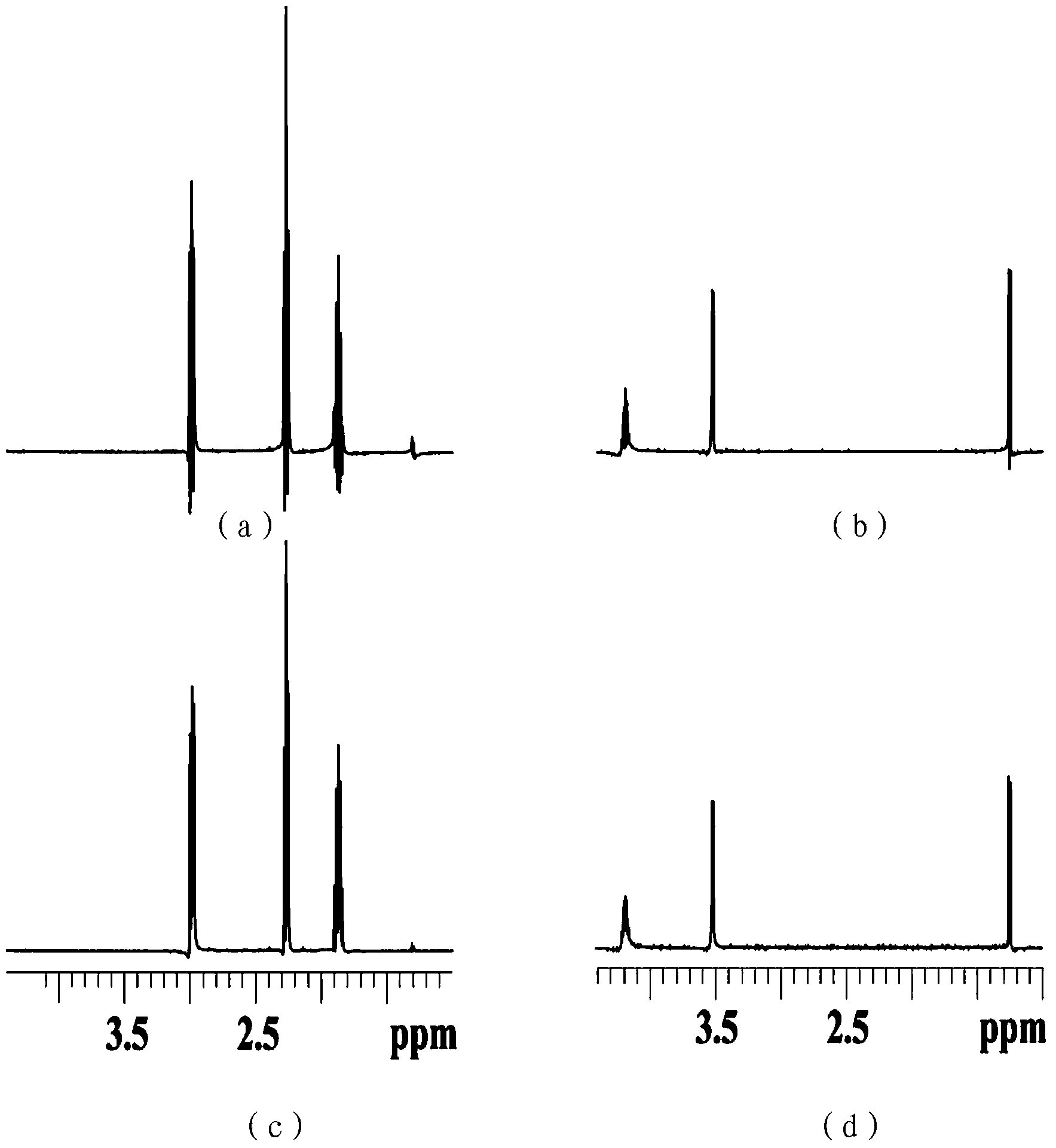
Construction method of 1H-NMR (1 hydrogen-nuclear magnetic resonance) fingerprint spectrum of hippocampus, and application
InactiveCN107102021AQuality Evaluation and ControlAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceChemical structureCoupling constant
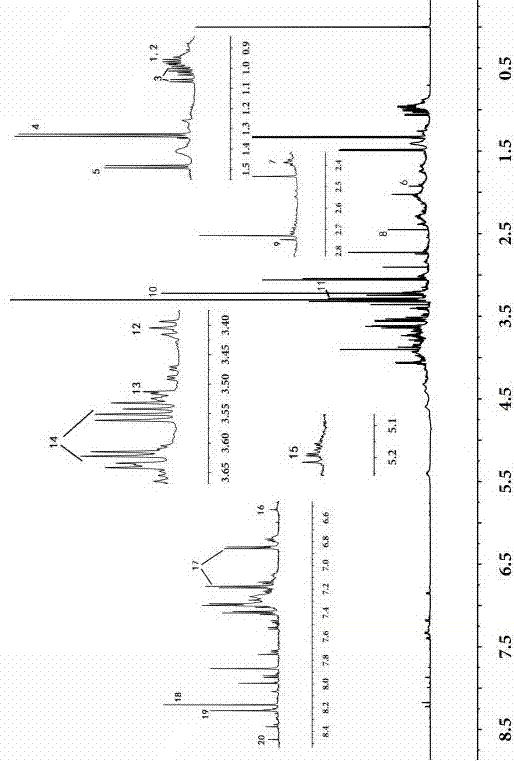
The invention discloses a construction method of a 1H-NMR (1 hydrogen-nuclear magnetic resonance) fingerprint spectrum of hippocampus. The method mainly comprises the steps of obtaining the 1H-NMR fingerprint spectrum of the animal medicine hippocampus by an NMR technique, identifying and discriminating chemical components, performing comparison by utilizing a comparison product, performing analysis by combining an NMR spectrum peak chemical shift and a coupling constant, determining a characteristic peak of the fingerprint spectrum of the hippocampus, and characterizing the chemical components contained in the fingerprint spectrum. The method can be used for quality evaluation and quality control of a hippocampus medicine. The method has the benefits that the 1H-NMR fingerprint spectrum of the hippocampus constructed by the NMR technique can simultaneously characterize 20 chemical components, including amino acid, organic acid, alkaloid and the like; the chemical components and the quality characteristic of the hippocampus are relatively comprehensively reflected; and the quality of the hippocampus can be accurately and effectively evaluated and controlled by measuring NMR spectra of different samples and performing analysis and comparison in a chemical structure composition aspect.
Owner:山西广誉远国药有限公司
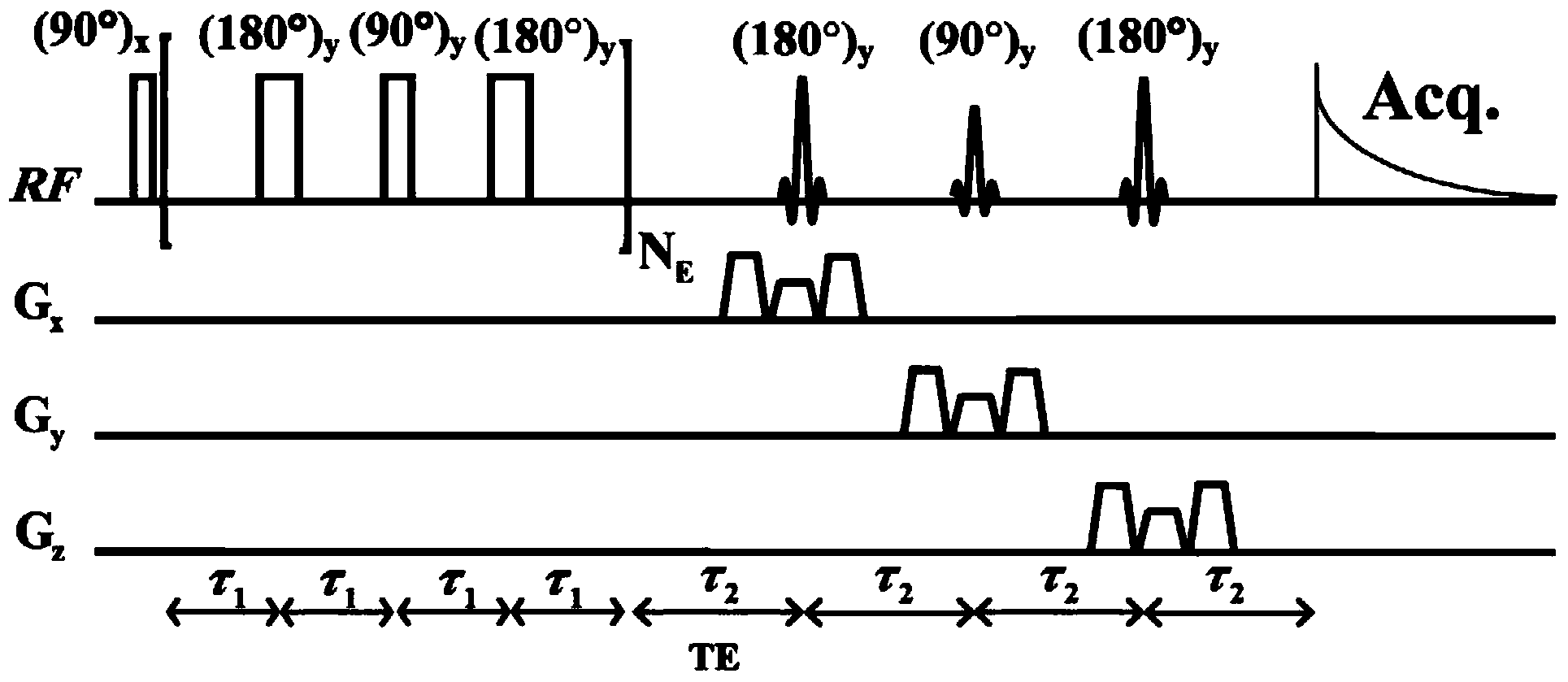
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring all hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constants in molecule
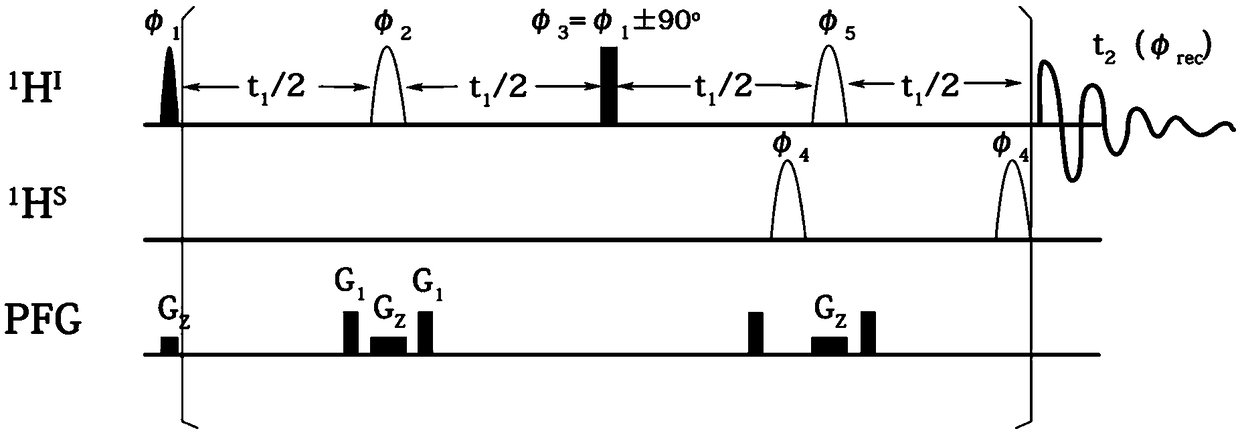
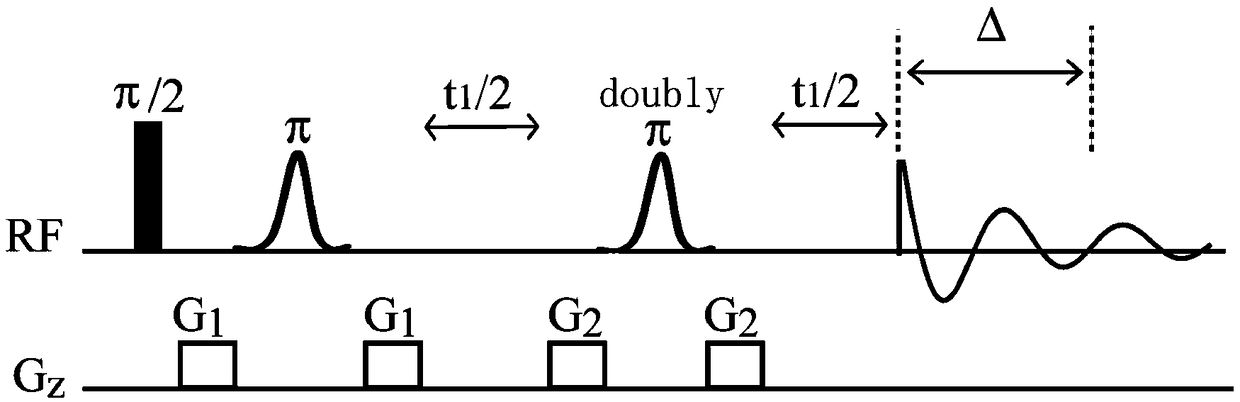
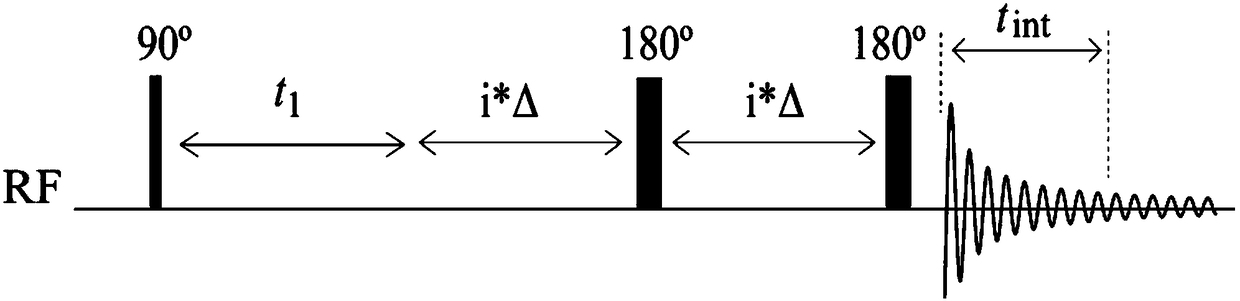
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring all hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constants in a molecule. The nuclear magnetic resonance method comprises the following steps: firstly applying one 90-degree hard pulse to rotate a magnetization vector to an XY plane from a Z direction, setting a sampling point at one fixed moment delta after the 90-degree hard pulse; enabling a selective 180-degree soft pulse applied at the same time with Z direction magnetic field gradient to move between the 90-degree hard pulse and the sampling point along with variation of indirect dimension evolution time t1; under the action of the magnetic field gradient, overturning different nucleuses at different spatial positions by the selective 180-degree soft pulse; acquiring chemical displacement information and spatial position information at the same time by adopting an EPSI sampling module, so that couplings of other nucleuses and the nucleus overturned by the 180-degree soft pulse at the same layer can be obtained at different layers, the couplings can show up split peaks at an indirect dimension, and corresponding J coupling constants can be measured from the split peaks.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
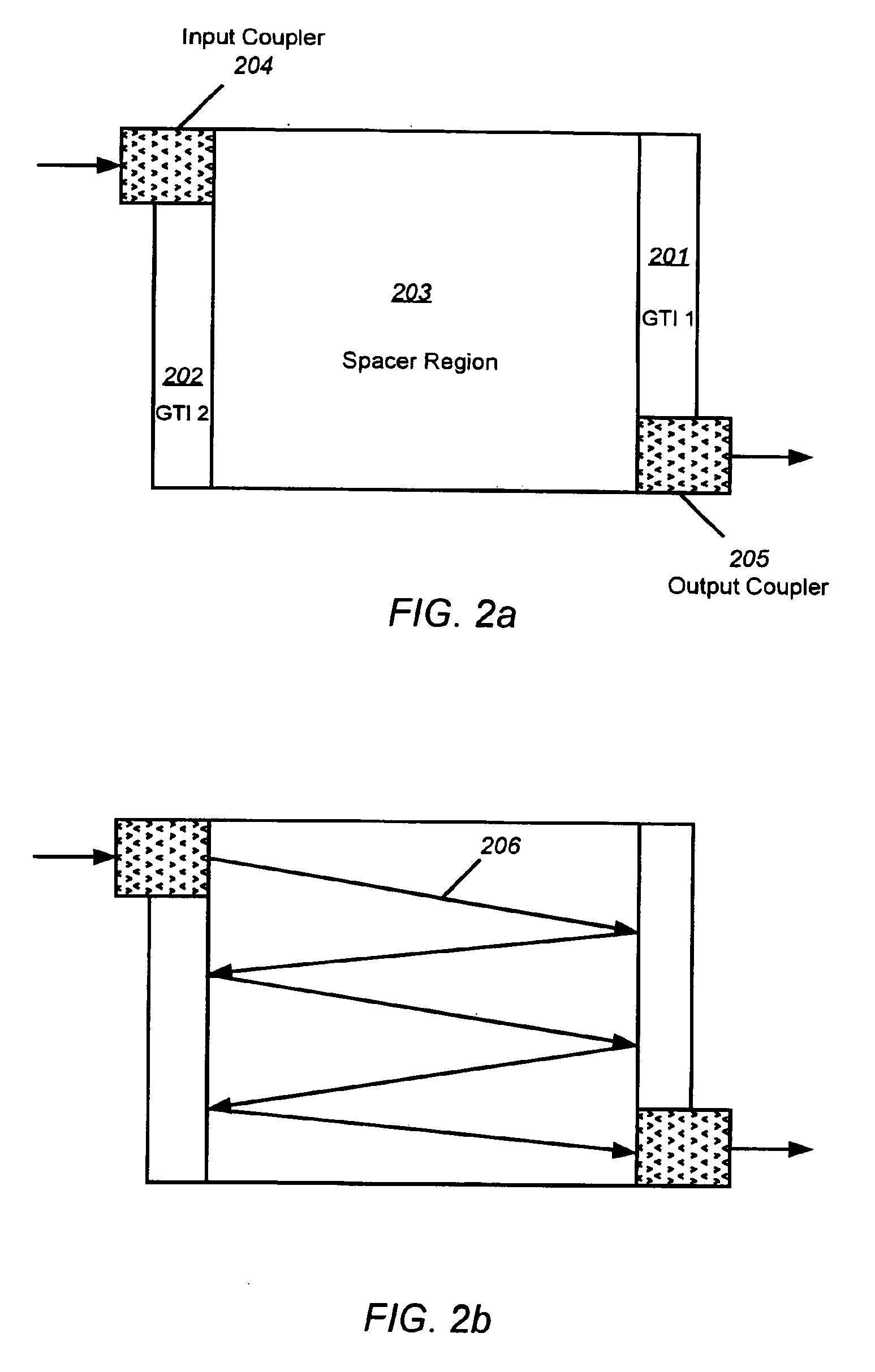
Dispersion compensation using resonant cavities
InactiveUS6859320B2High bandwidthGood dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryResonant cavityPath length
Multi-stage, all-pass optical filters used to make low-loss, multi-channel dispersion compensation modules are disclosed. The all-pass optical filters can be ring resonators in waveguides, Gires-Tournois Interferometers (GTIs) in free space form, and the like. The coupling constants and circulating path lengths may also be distinctively varied in each of the series of GTIs, tuning the net dispersion spectrum of the GTI set, such that the sum of the dispersions from the series of GTI's can provide a system with greater bandwidth than the same number of identical GTIs. The local dispersion slope can also be tuned in this manner. Multi-cavity GTIs can also be formed with similar performance enhancing properties.
Owner:OPLINK COMM
Power transfer device, power supply device and power receiving device
ActiveUS8319489B2Reduce energy transferHigh power transmission efficiencyCircuit arrangementsVariable inductancesCapacitanceElectric power transmission
A power transfer device includes: a transformer that couples a primary circuit and a secondary circuit and has a coupling constant of less than 1; and capacitances that are respectively provided in the primary circuit and the secondary circuit, and connected in series with coils that form the transformer. Circuit constants of the primary circuit and the secondary circuit are set so that the primary circuit and the secondary circuit resonate at the same frequency and a product of the square of the coupling constant, a Q value of the primary circuit and a Q value of the secondary circuit is 1. The primary circuit transfers power to the secondary circuit by means of the transformer, using a carrier wave having the resonance frequency.
Owner:SONY CORP
Ultrasonic sensor
InactiveCN101196415AImprove reliabilityImprove productivityVolume/mass flow measurementFluid speed measurementCouplingMetallurgy
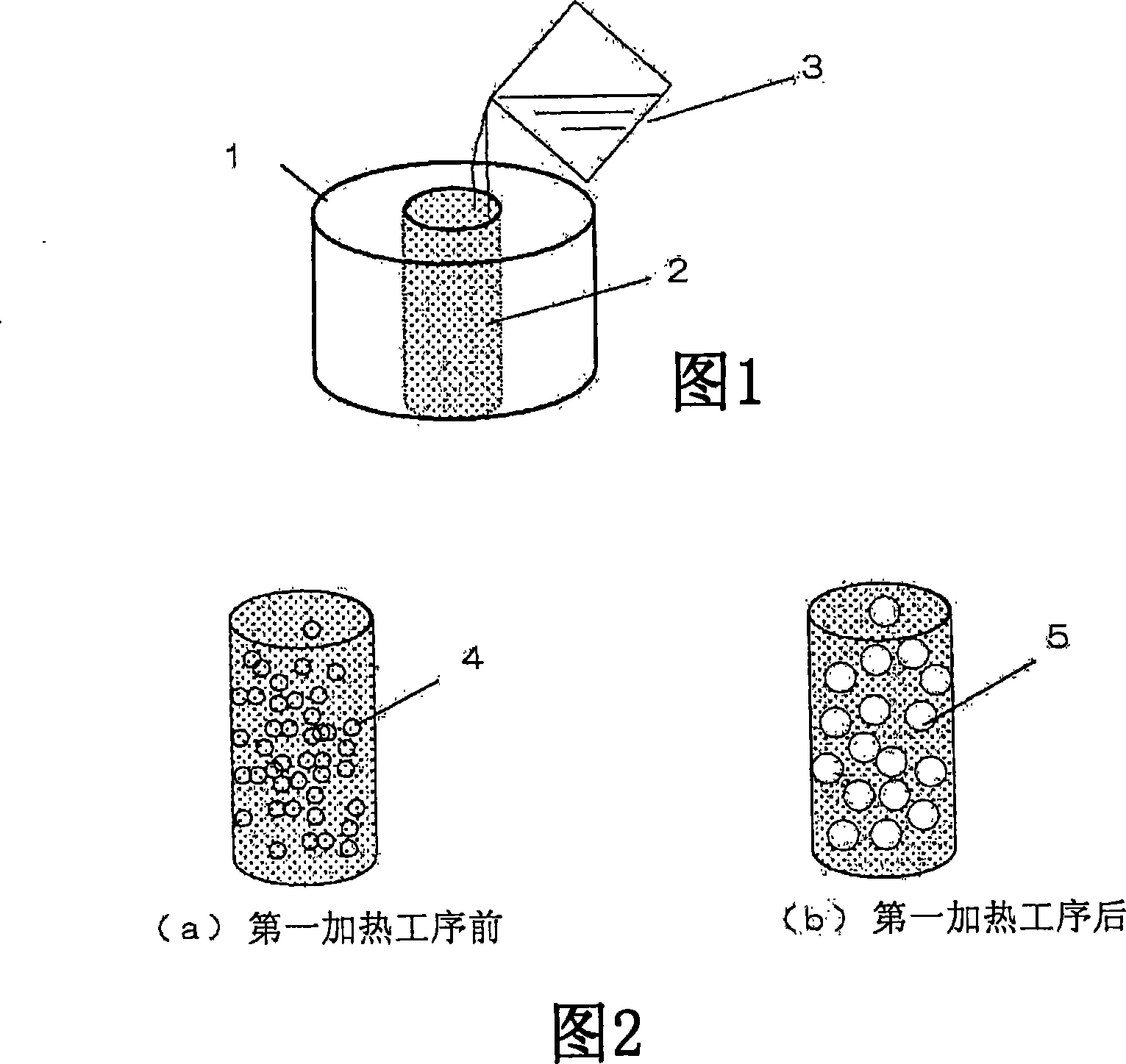
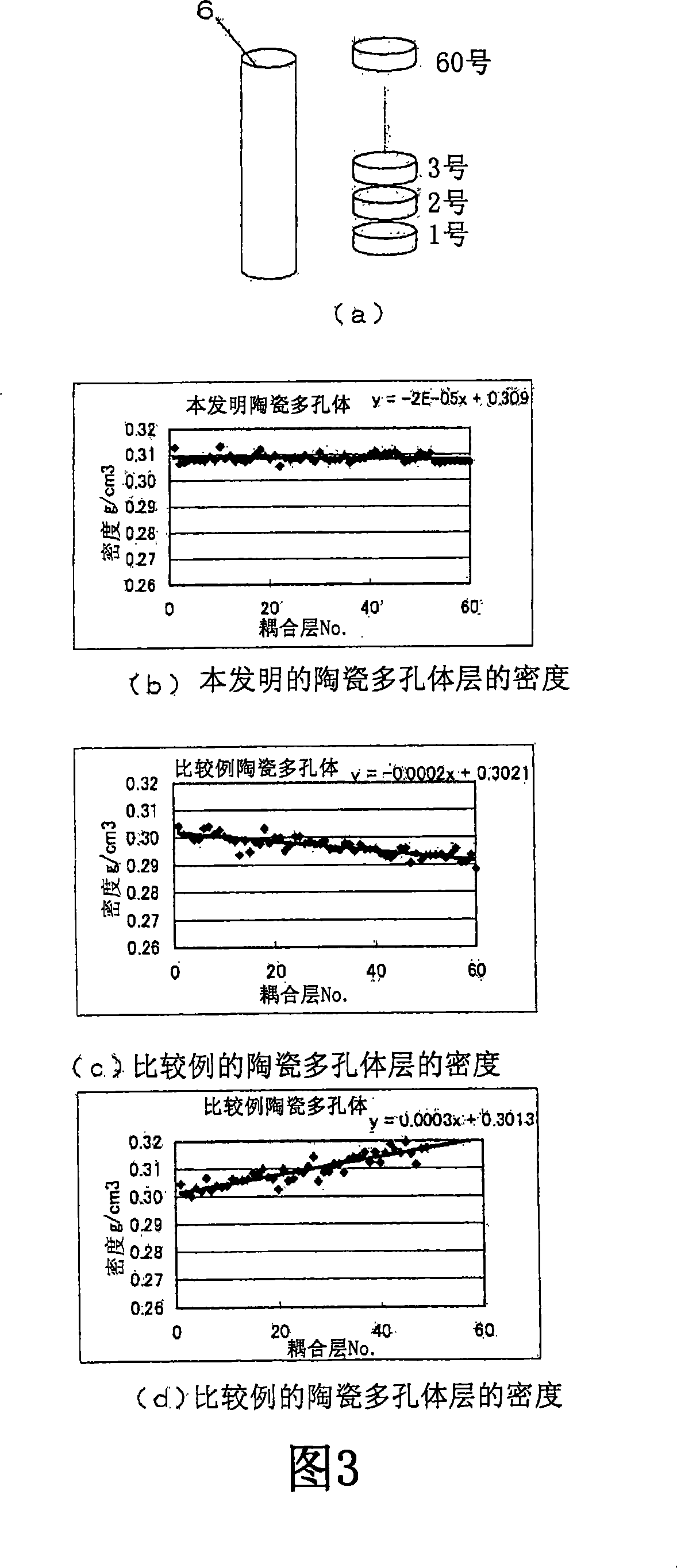
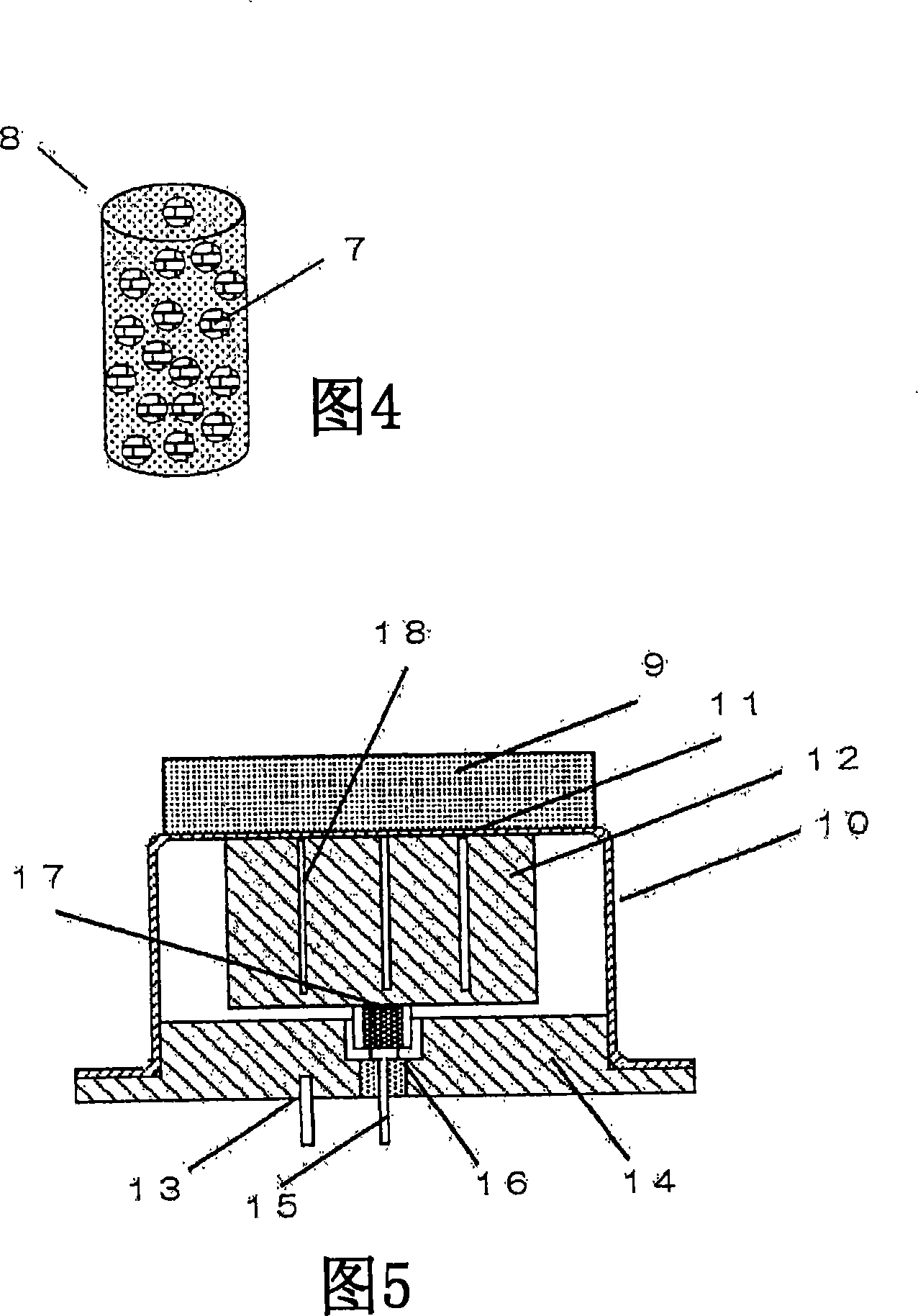
The object of the present invention is to control the diameter of pores in a coupling layer formed of a ceramic porous body and organic glass. An ultrasonic sensor is provided, comprising a piezoelectric body, a casing for containing the piezoelectric body, and a coupling layer arranged on the top of the casing, wherein the coupling layer is composed of a ceramic porous body with uniform glass spheres in the holes, and the The glass spheres are formed from a dried gel of plexiglass. In the ultrasonic sensor, resin particles (4) containing liquefied gas are added to a slurry (3) using an inorganic material, and the resin particles (4) are foamed in a first heating step to form hollow spherical particles (5) In the second heating step, the ceramic porous body is fired to form plexiglass (7) in the controlled pores, and a coupling layer (9) with stable internal density and constant acoustic impedance is produced, thereby providing a stable output Ultrasonic sensor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen J coupling constant
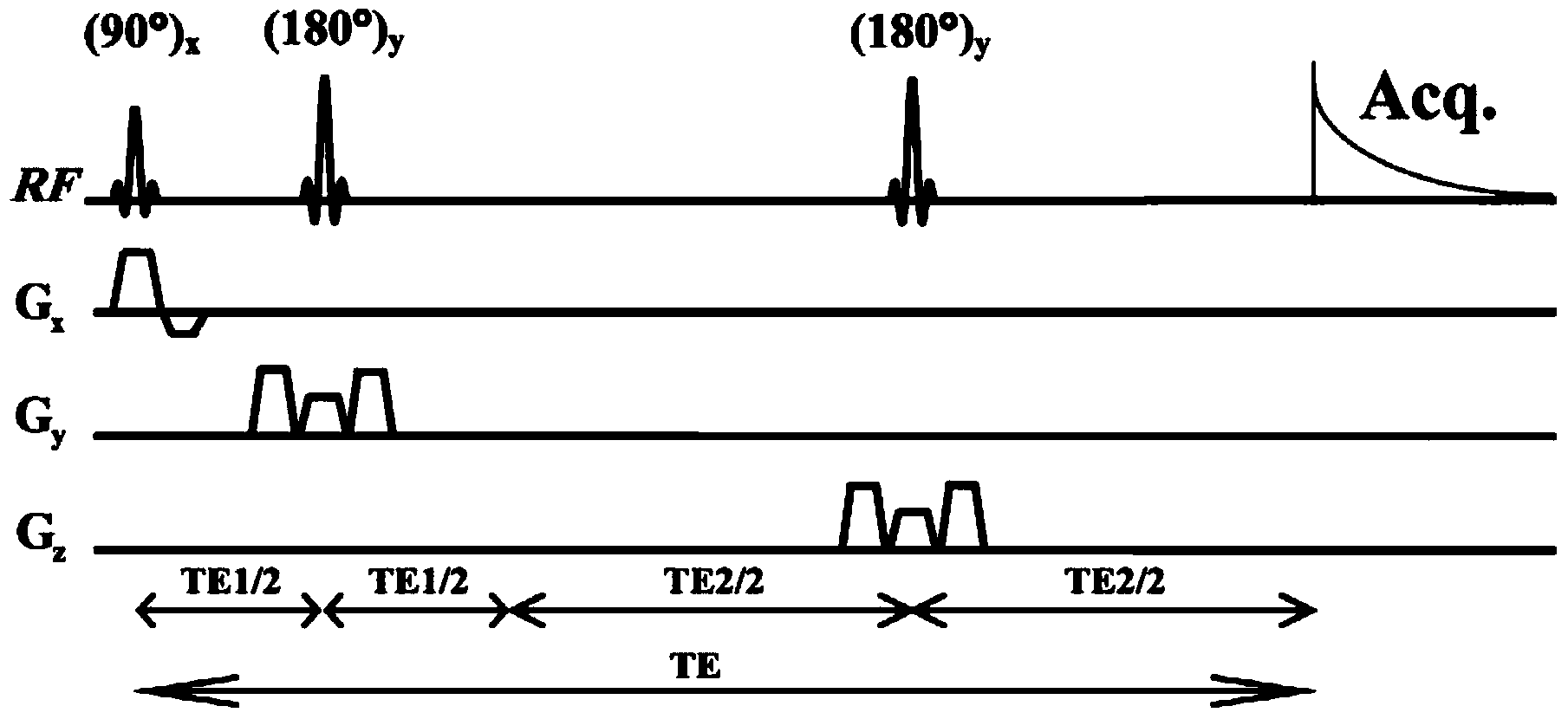
The invention provides a high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring a hydrogen-hydrogen J coupling constant. The method comprises the following steps: after a 90-degree excitation pulse is applied, applying a monochromatic selective 180-degree pulse to a to-be-detected proton, delaying for t1 / 2 time, applying a dichromatic selective 180-degree pulse to the to-be-detectedproton and another proton coupled with the to-be-detected proton, and delaying for t1 / 2 time; carrying out sampling after an evolution period; after the experiment is finished, extracting starting delta time length data from each group of data, and sequentially splicing the data into new one-dimensional data; and carrying out Fourier transform, so as to obtain a new one-dimensional spectrum required by a user, wherein only a signal for detecting the proton selected by the user is maintained, and only J coupling cracking between the proton and another selected proton is maintained. Therefore,the J coupling constant between the two protons can be accurately measured.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for acquiring J coupling constant amplified spectrogram
InactiveCN108279392AQuick measurementHigh-resolutionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance method for acquiring a J coupling constant amplified spectrogram. Firstly, a 90-degree hard pulse is applied to turn a magnetization vector from a Zdirection to an XY plane. After time t1, i*delta time is delayed, a 180-degree hard pulse is applied, i*delta time is delayed again, and then sampling is started. The t1 is increased at equal intervals in each time of sampling. The 'i*delta-180-egree pulse-i*delta' is a spin echo module, only J coupling evolution is performed in the meantime, and chemical displacement evolution is reunited. Therefore, in each time of sampling, J coupling evolution time is 2 delta longer than chemical displacement evolution time, so that a J coupling constant can be effectively amplified. After experiments, starting time tint data of data acquired by sampling in each time are extracted and sequentially spliced to obtain new one-dimensional data, and then Fourier transformation is performed to obtain the Jcoupling constant amplified spectrogram.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Apparatus for controlling chaos using oscillation quenching
InactiveUS20060002554A1Convenient and stableEasy to implementAnti-hunting elementsInternal feedback arrangementsChaotic systemsEngineering
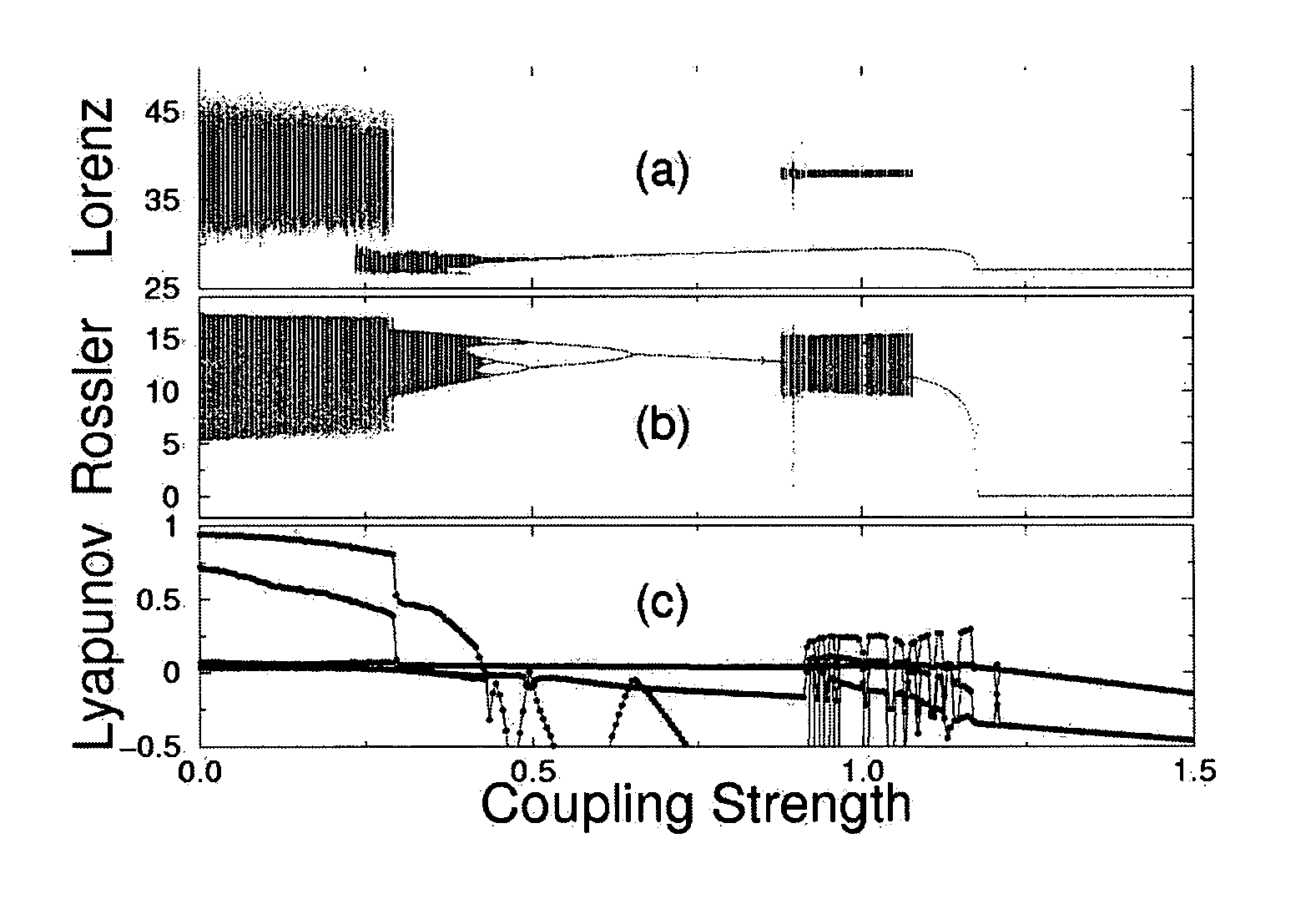
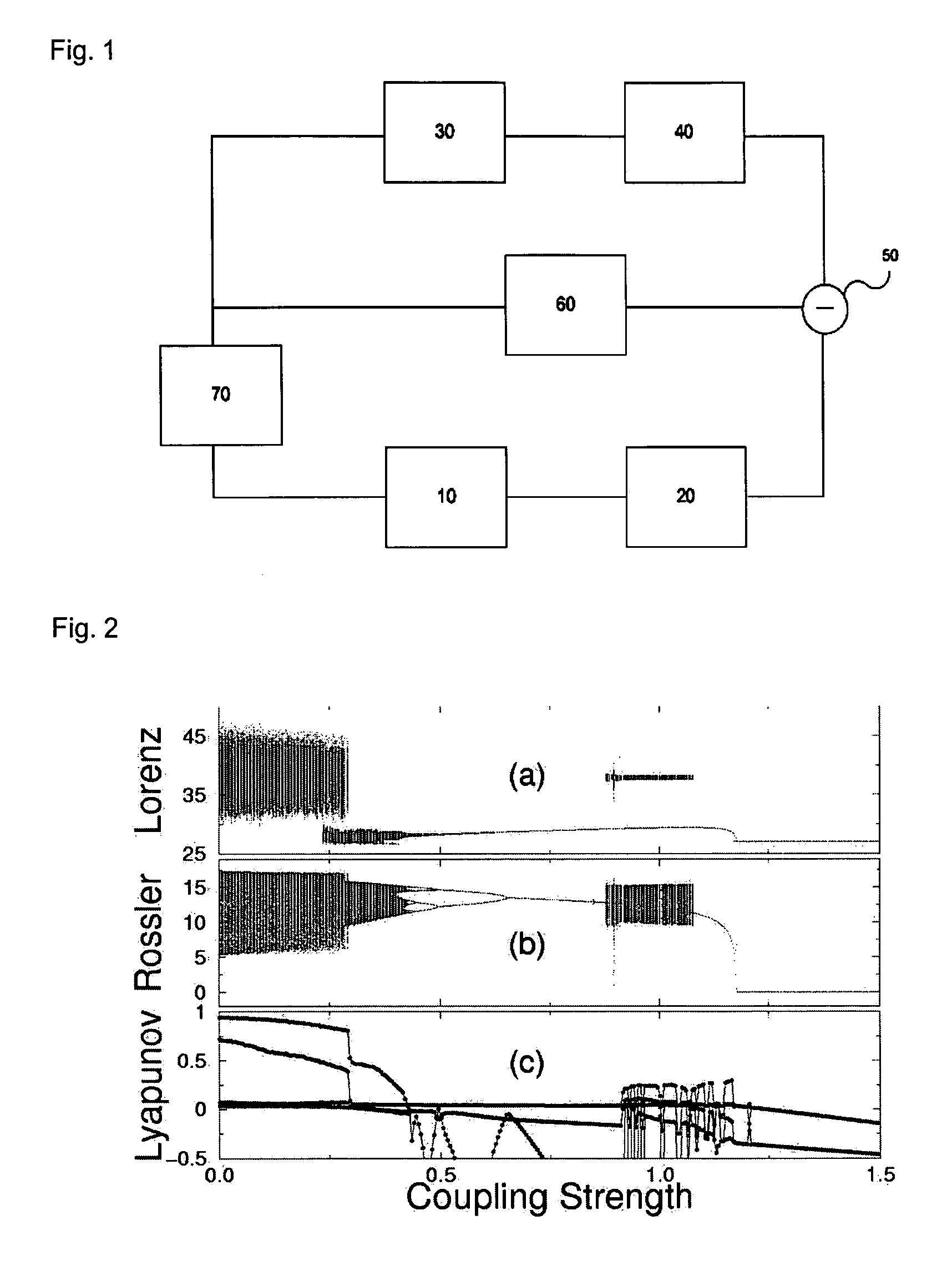
The present invention relates to an apparatus for controlling chaos using oscillation quenching, and more particularly, to an apparatus for controlling chaos using oscillation quenching, wherein a chaos system to be controlled can be easily stabilized by coupling the chaos system with another chaos system or a periodic system that can be easily implemented, using the concept of oscillation quenching. To this end, the present invention provides an apparatus for controlling chaos using oscillation quenching, comprising a chaos signal generating device 10 for generating a chaos signal; a first scaling means 40 for scaling an output signal from a controlled chaos device; a second scaling means 20 for scaling an output signal from the chaos signal generating device 10; a subtraction means 50 for performing a subtraction operation between the output signals of the first and second scaling means 40 and 20; an auxiliary scaling means 60 for scaling an output signal from the subtraction means 50 so that a coupling constant for the controlled chaos device 30 and the chaos signal generating device 10 is in a state where chaos is stabilized, and for feeding back the scaled signal to the controlled chaos device 30; and an inverting means 70 for inverting an output signal from the auxiliary scaling means 60 and feeding back the inverted signal to the chaos signal generating device 10.
Owner:PAICHAI UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
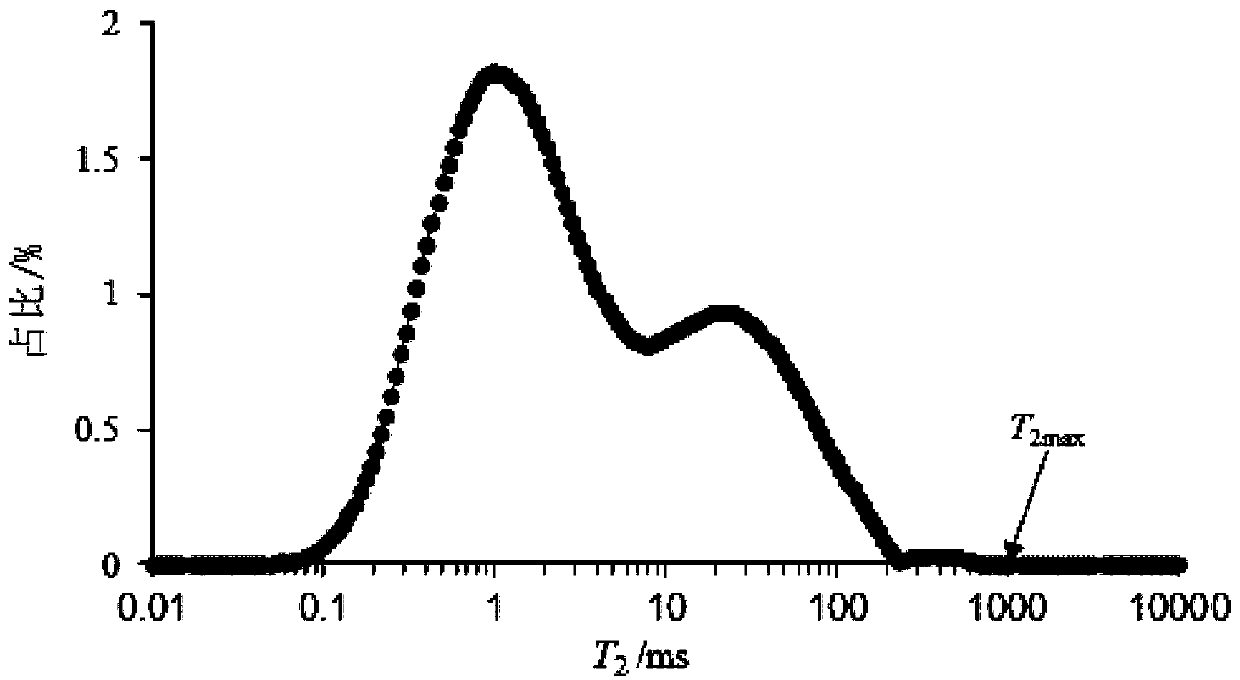
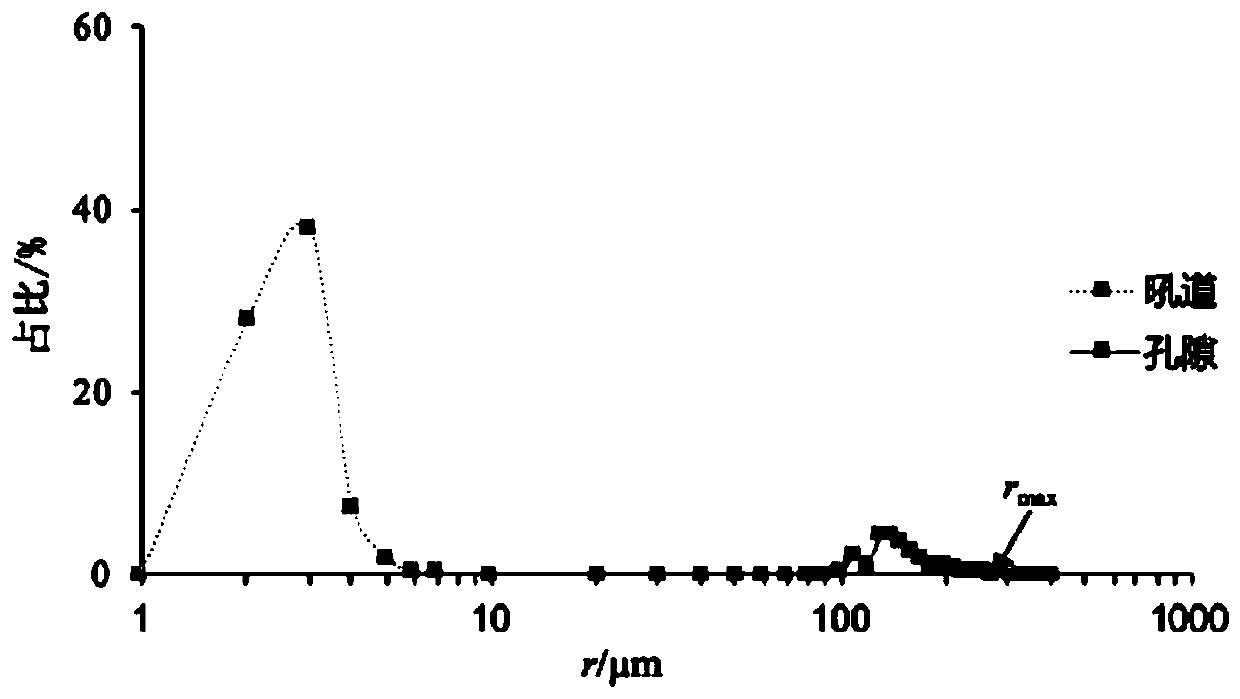
Method for quantitatively representing sandstone reservoir hole throat structure by nuclear magnetic resonance coupling constant-speed mercury injection
ActiveCN110133035ASimple methodFast wayWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCoupling constantTime distribution
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively representing a sandstone reservoir hole throat structure by nuclear magnetic resonance coupling constant-speed mercury injection. The method for quantitatively representing the sandstone reservoir hole throat structure by nuclear magnetic resonance coupling constant-speed mercury injection comprises the steps of selecting a full-size core of a target sandstone reservoir, drilling a small rock sample, and performing nuclear magnetic resonance experiment to obtain a T2 relaxation time duty ratio distribution curve; performing constant-speed mercury injection on the small rock sample to obtain a constant-speed mercury injection hole throat duty ratio distribution curve; coupling maximum relaxation time T<2max> and maximum hole throat radiumr<max> of the same small rock sample to obtain surface relaxation rate Phi of each small rock sample so that the surface relaxation rate Phi is used as the surface relaxation rate Phi of the target sandstone reservoir; and performing calculation to obtain complete effective hole throat radius duty ratio distribution map according to a nuclear magnetic resonance principle. By the method, thecomplete and effective hole throat relaxation time distribution characteristic can be non-destructively detected, the complete and effective hole throat radium duty ratio distribution map of the reservoir sandstone is obtained, and the quantitative representation of the effective hole throat structure distribution of the sandstone reservoir is achieved.
Owner:RES INST OF SHAANXI YANCHANG PETROLEUM GRP
Magnetic memory device and write method of magnetic memory device
A magnetic memory device includes a first write wiring which runs in a first direction, a second write wiring which runs in a second direction different from the first direction, and a magnetoresistive element which is arranged at an intersection between the first and second write wirings, has a fixed layer, a recording layer, and a magnetoresistive layer sandwiched between the fixed layer and the recording layer, and has an axis of easy magnetization obliquely with respect to the first and second directions, the recording layer including a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, and a first nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the first and second ferromagnetic layers, in which first magnetization of the first ferromagnetic layer and second magnetization of the second ferromagnetic layer are ferromagnetically coupled, and a ferro-coupling constant C of a ferromagnetic coupling is 0.0001 erg / cm2≦C≦0.2 erg / cm2.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com