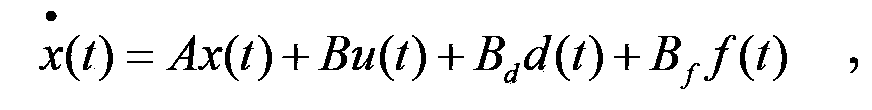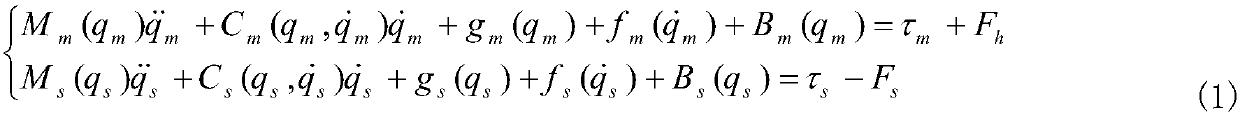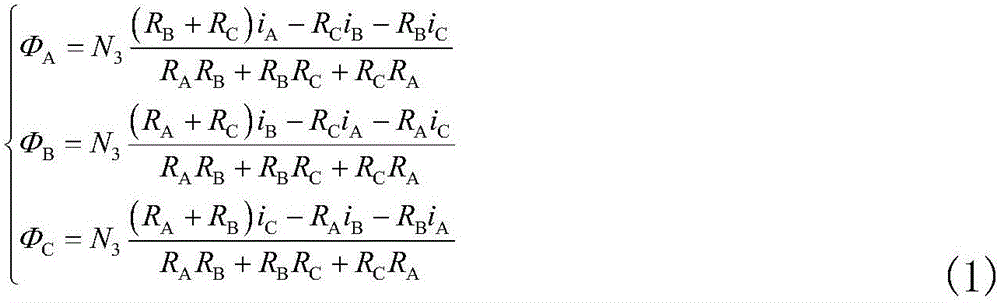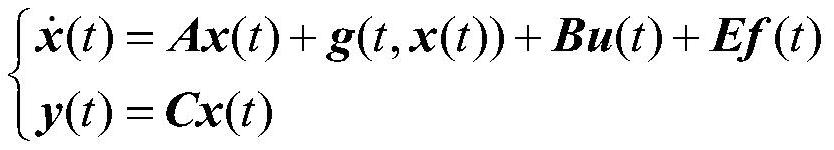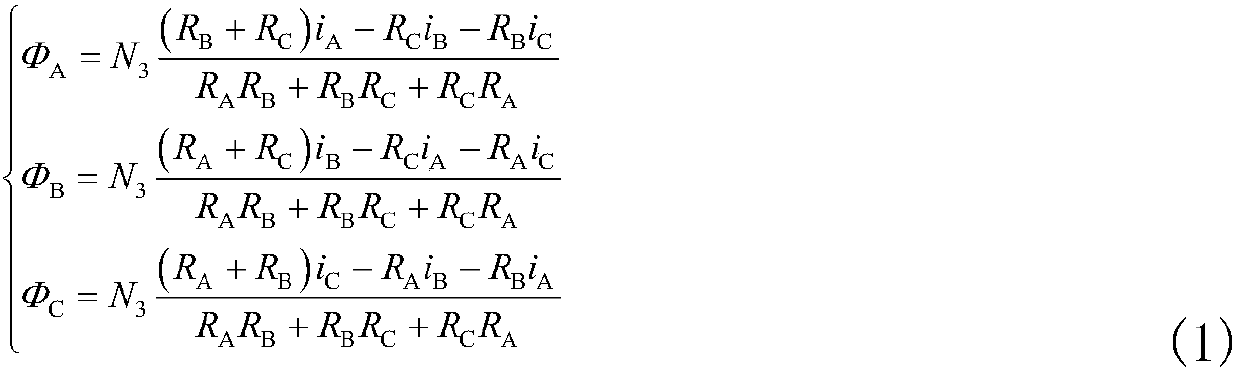Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Continuous time system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
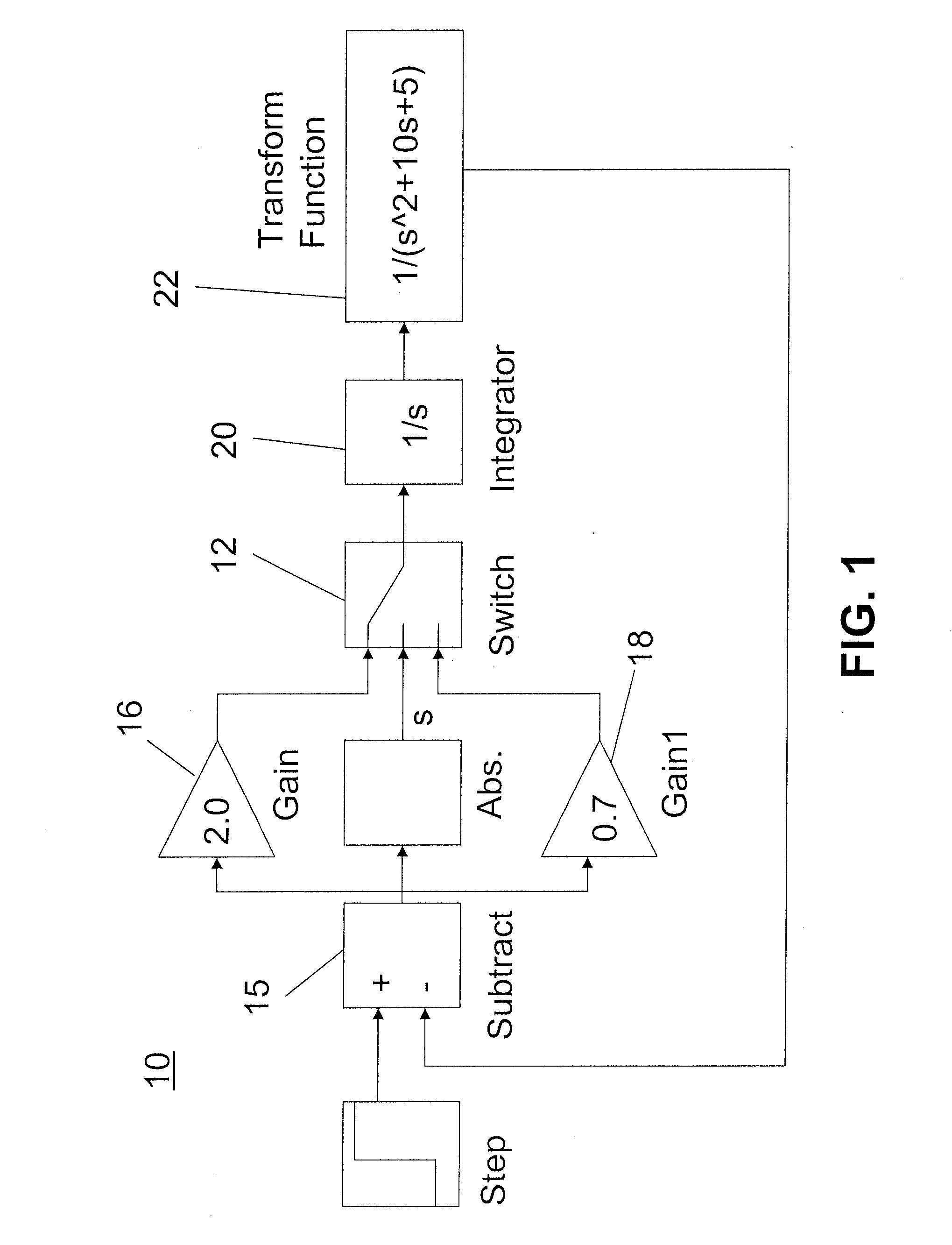
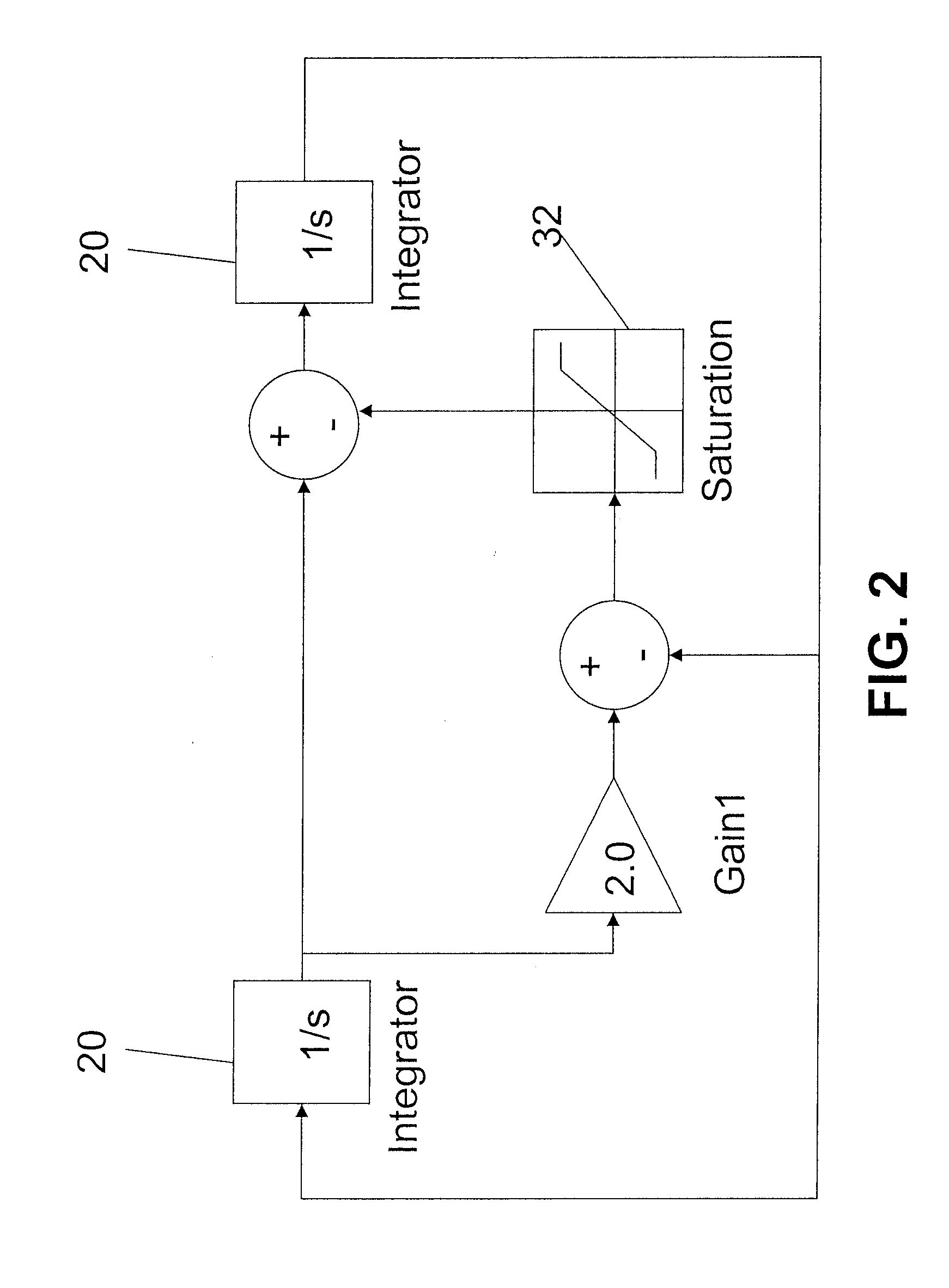
The class of continuous time systems that are both linear and time invariant, known as continuous time LTI systems, is of particular interest as the properties of linearity and time invariance together allow the use of some of the most important and powerful tools in signal processing.
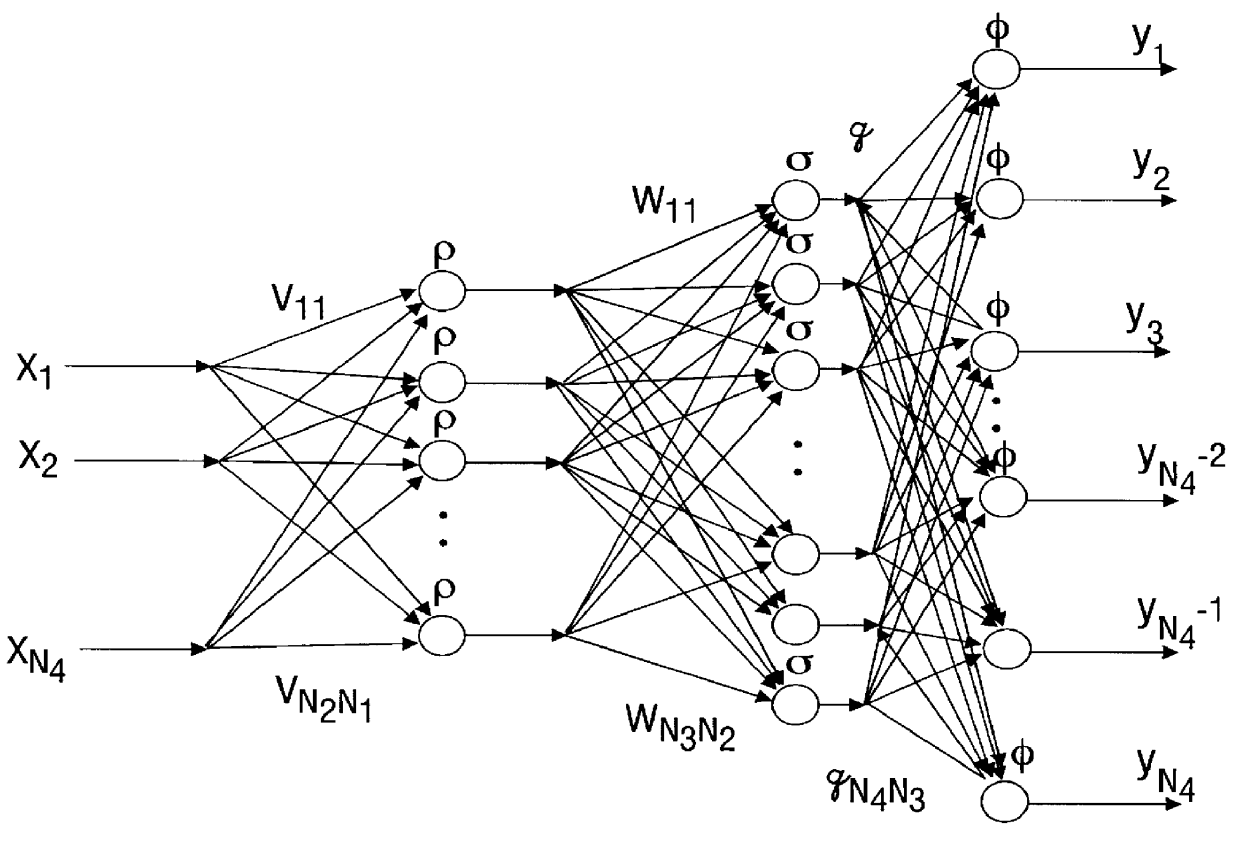
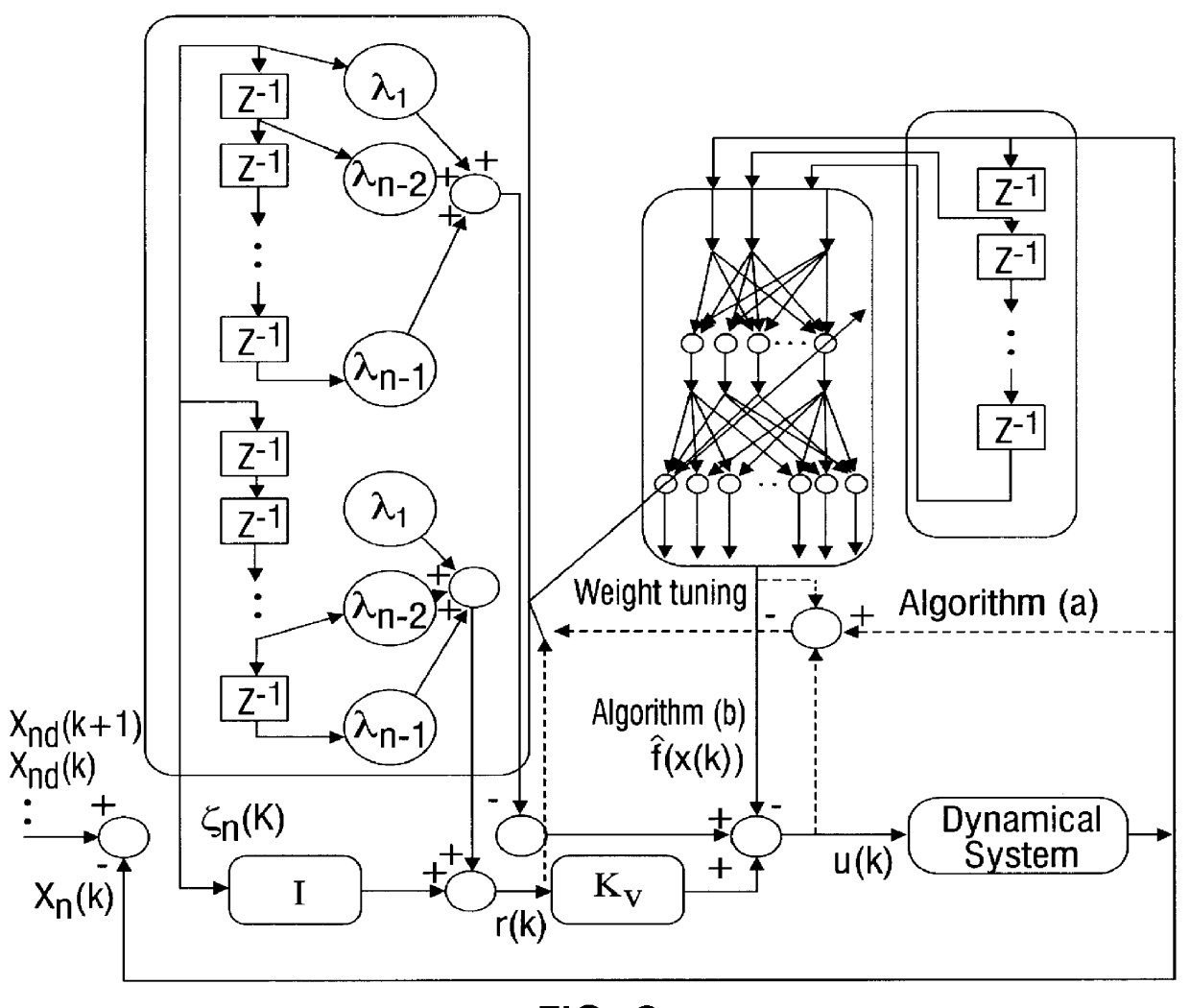
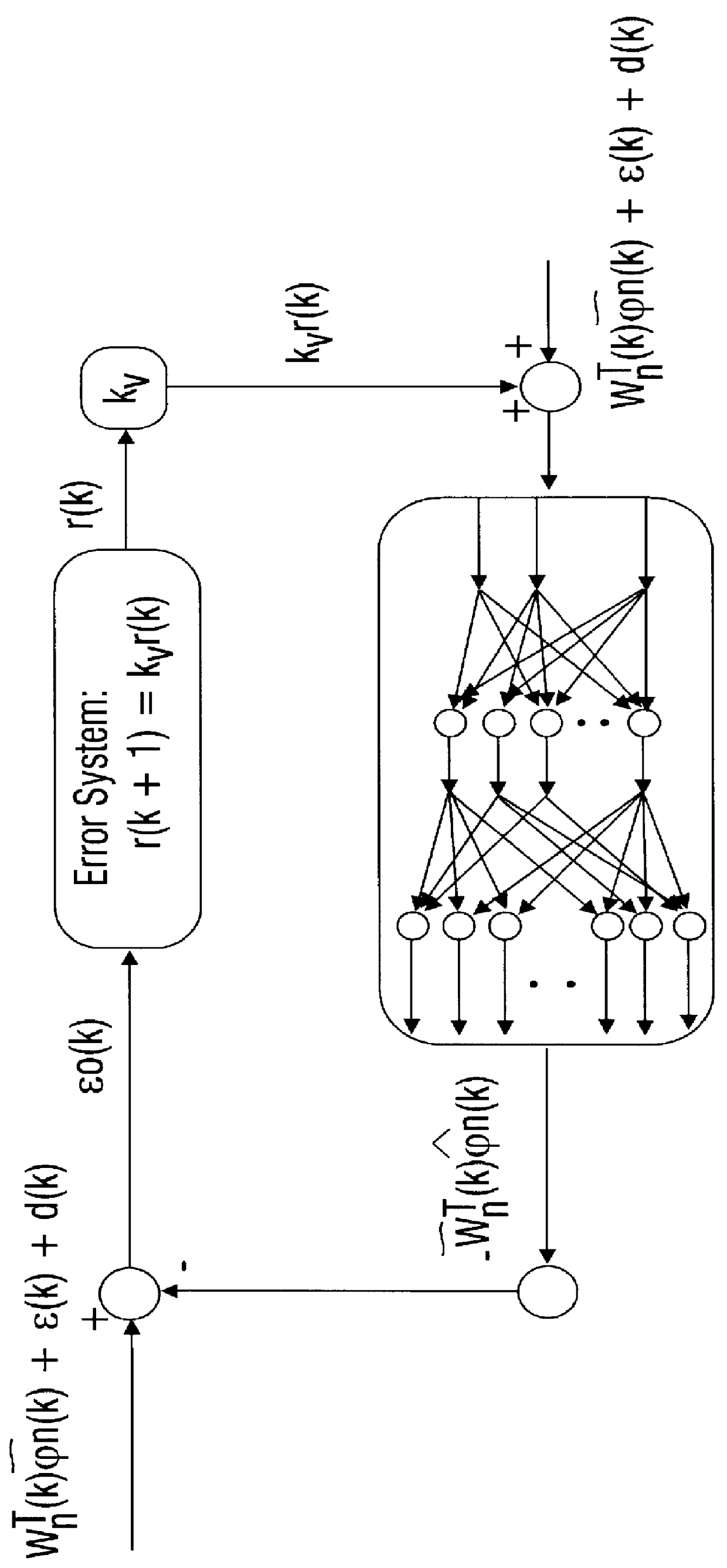
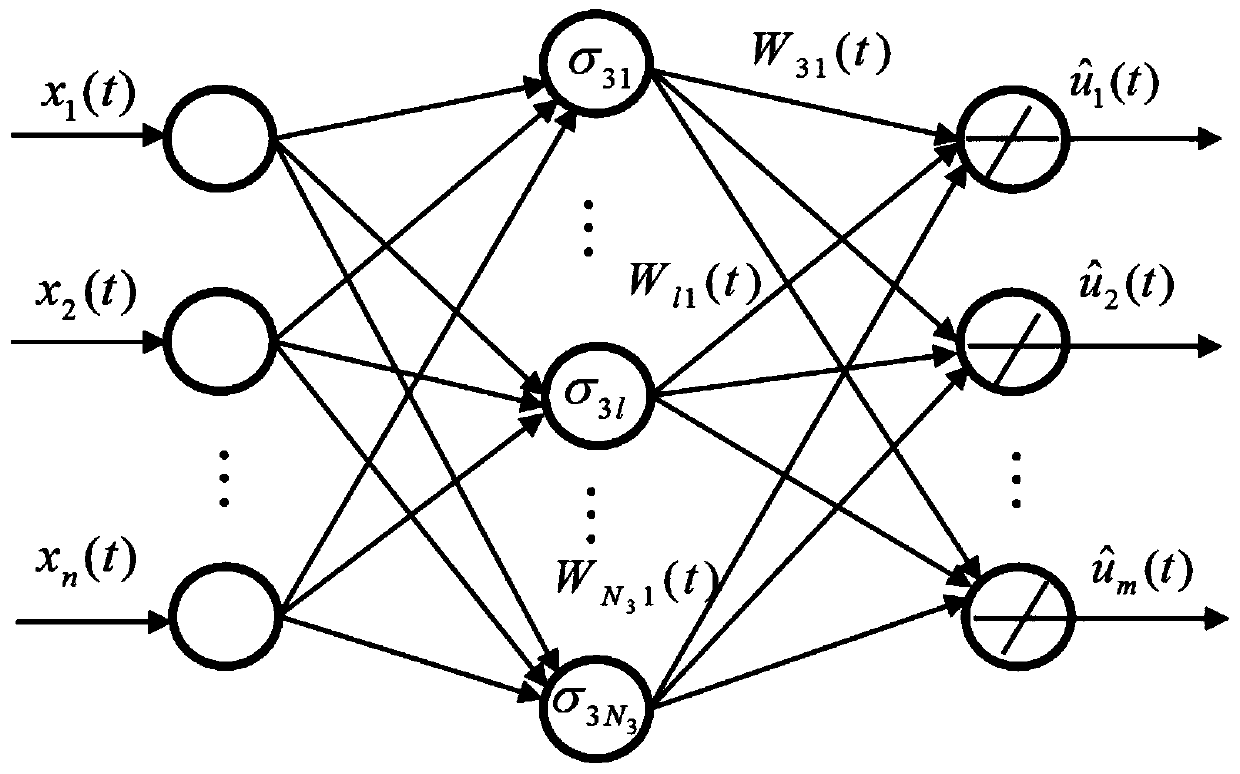
Discrete-time tuning of neural network controllers for nonlinear dynamical systems
A family of novel multi-layer discrete-time neural net controllers is presented for the control of an multi-input multi-output (MIMO) dynamical system. No learning phase is needed. The structure of the neural net (NN) controller is derived using a filtered error / passivity approach. For guaranteed stability, the upper bound on the constant learning rate parameter for the delta rule employed in standard back propagation is shown to decrease with the number of hidden-layer neurons so that learning must slow down. This major drawback is shown to be easily overcome by using a projection algorithm in each layer. The notion of persistency of excitation for multilayer NN is defined and explored. New on-line improved tuning algorithms for discrete-time systems are derived, which are similar to e-modification for the case of continuous-time systems, that include a modification to the learning rate parameter plus a correction term. These algorithms guarantee tracking as well as bounded NN weights. An extension of these novel weight tuning updates to NN with an arbitrary number of hidden layers is discussed. The notions of discrete-time passive NN, dissipative NN, and robust NN are introduced.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
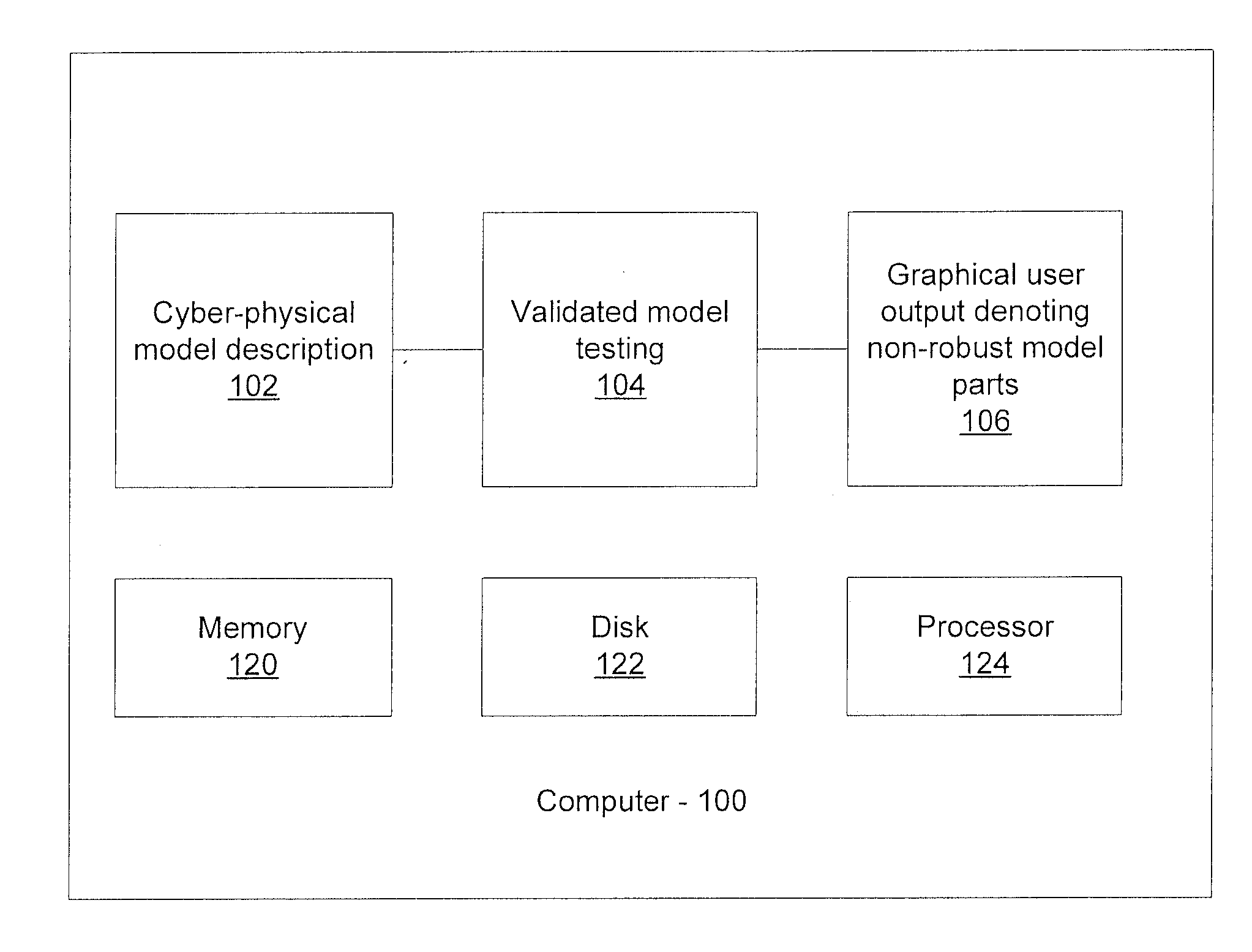
Robust testing for discrete-time and continuous-time system models
InactiveUS20100299651A1Error detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsRobustificationTest input
A system and method for testing robustness of a simulation model of a cyber-physical system includes computing a set of symbolic simulation traces for a simulation model for a continuous time system stored in memory, based on a discrete time simulation of given test inputs stored in memory. Simulation errors are accounted for due to at least one of numerical instabilities and numeric computations. The set of symbolic simulation traces are validated with respect to validation properties in the simulation model. Portions of the simulation model description are identified that are sources of the simulation errors.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
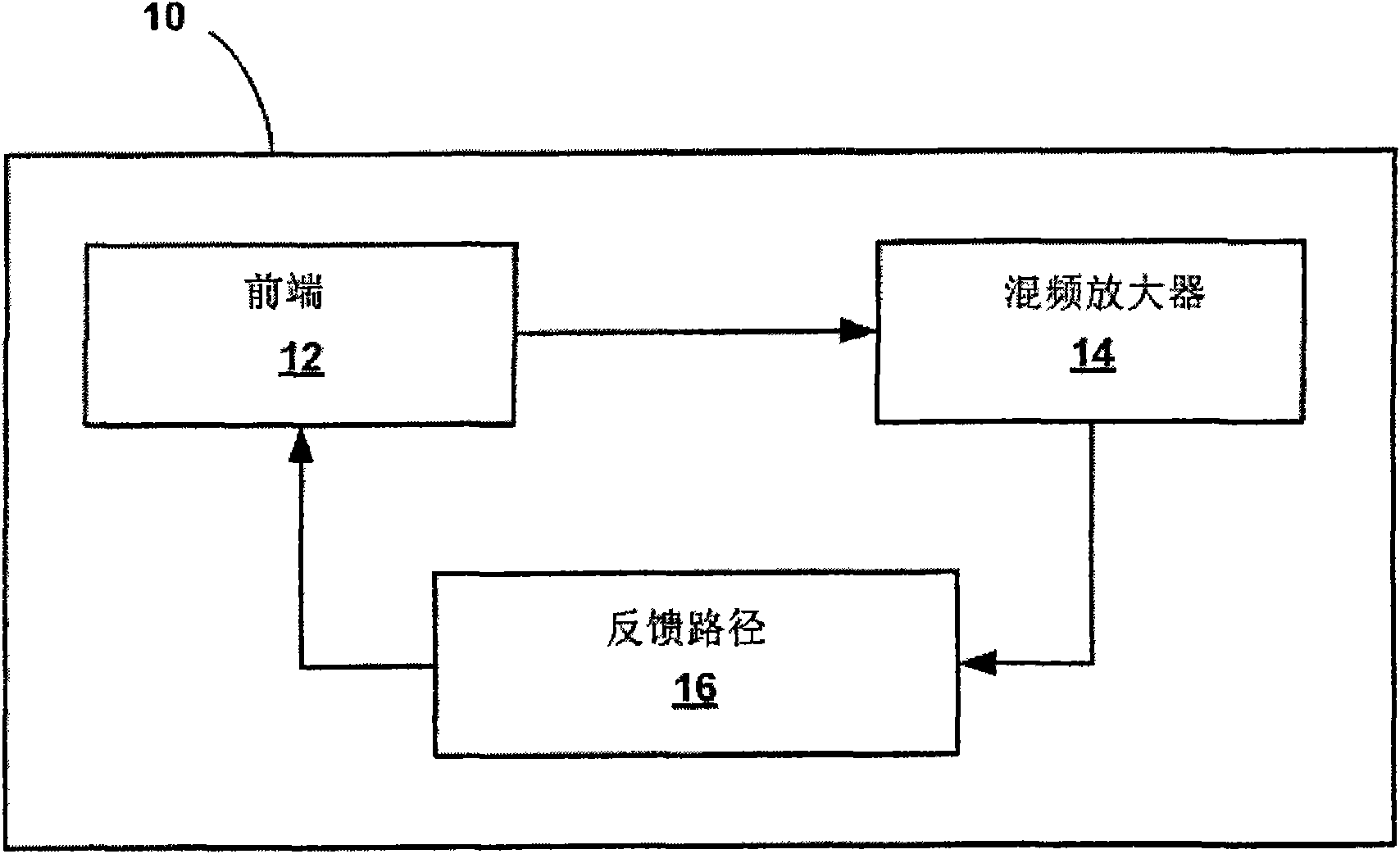
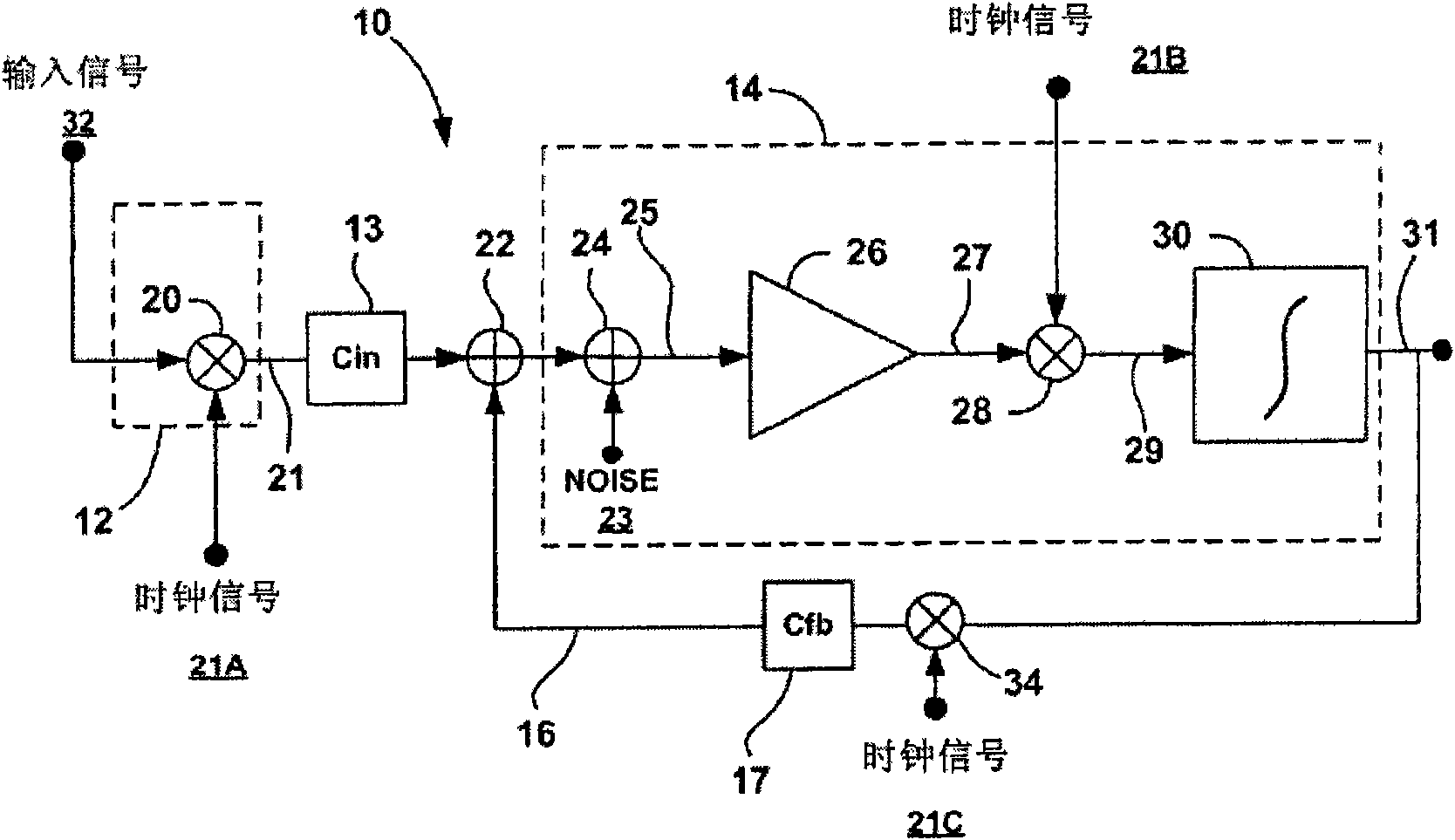
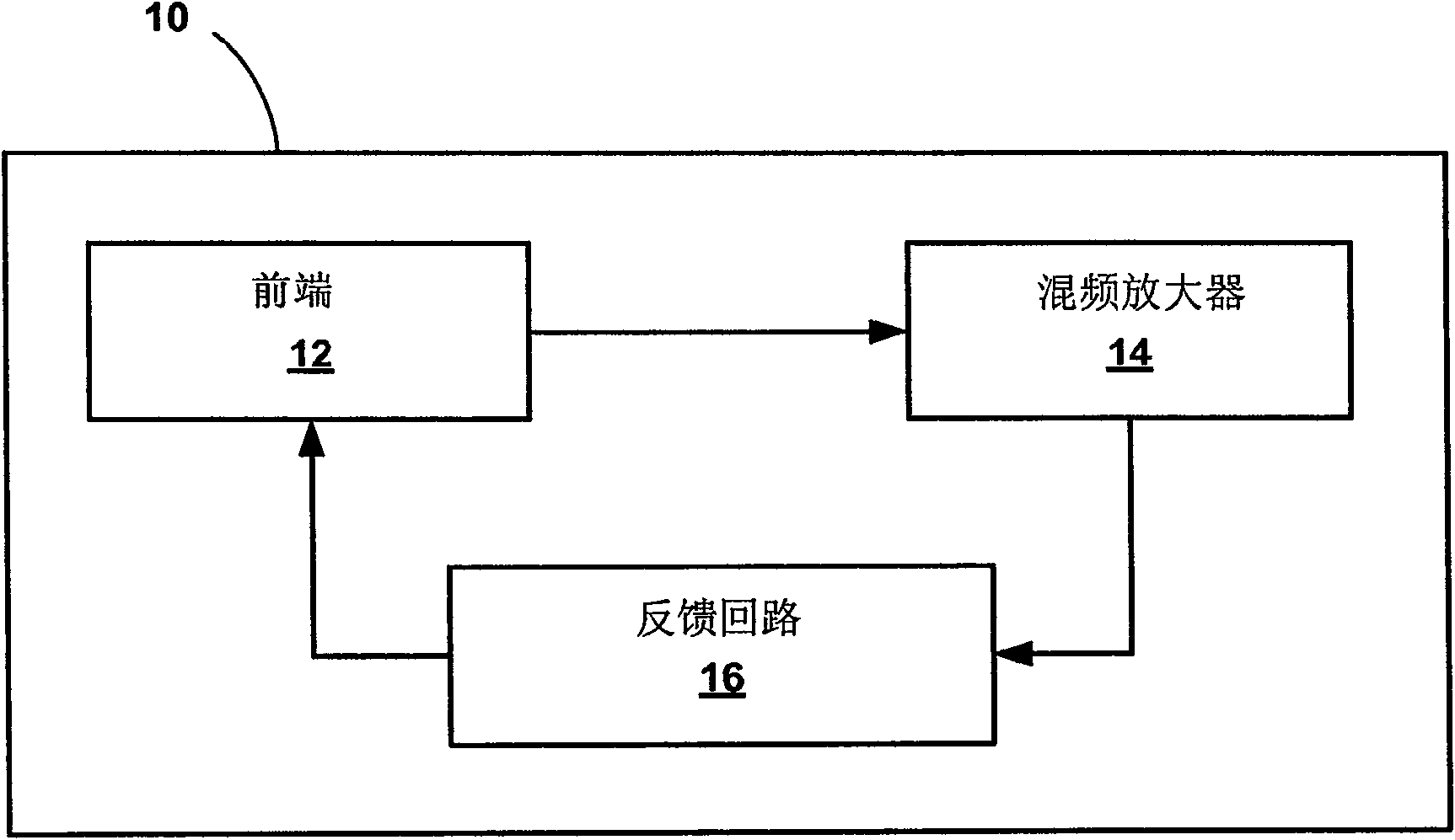
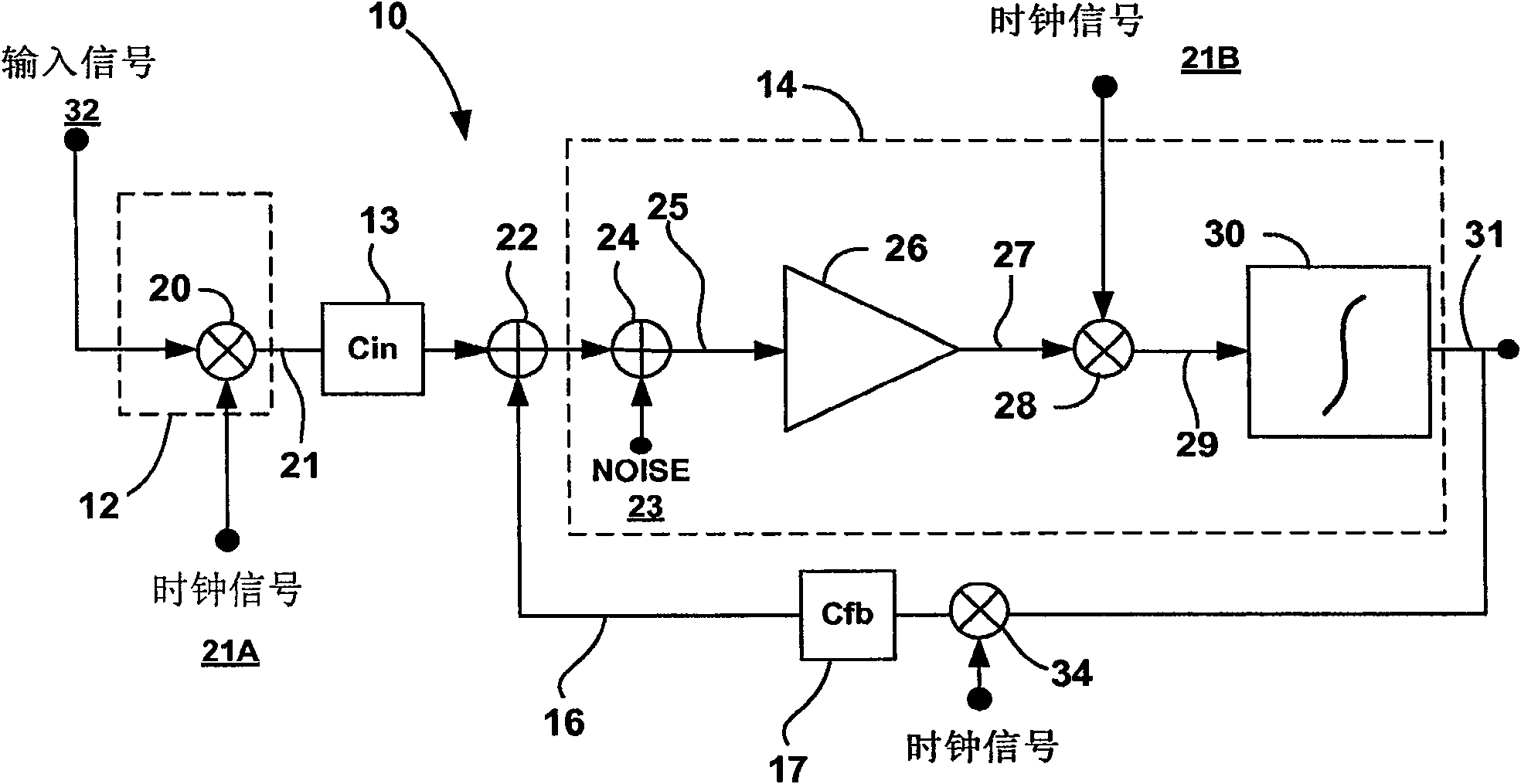
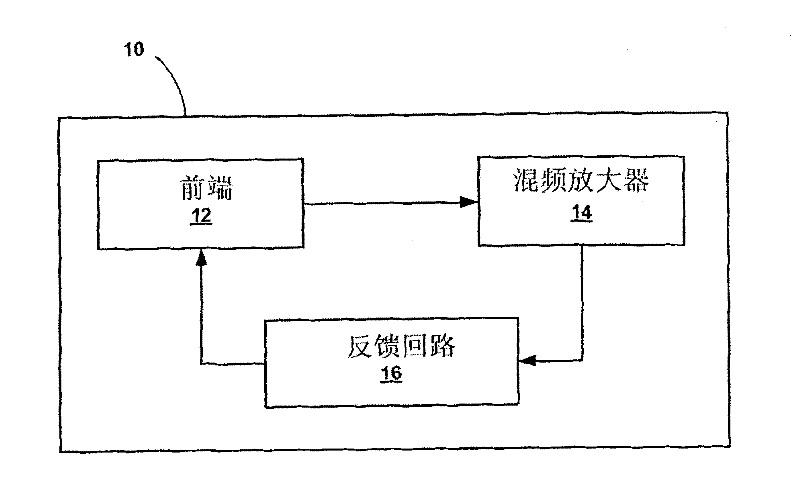
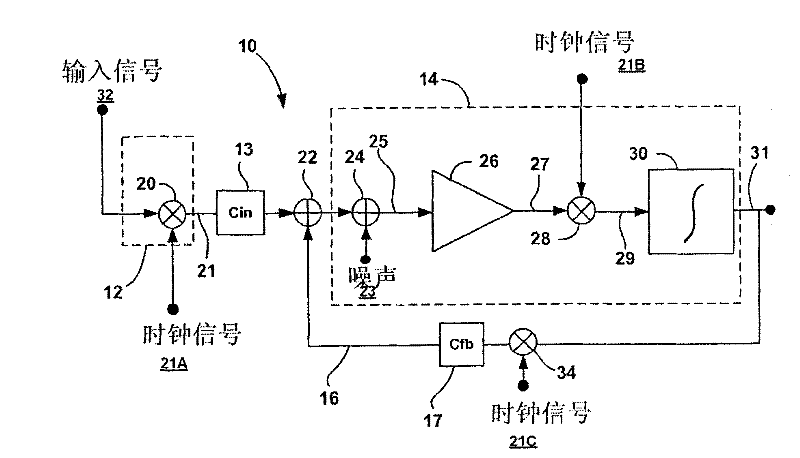
Chopper-stabilized instrumentation amplifier
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Chopper-stabilized instrumentation amplifier
ActiveUS20110068861A1Measurement stabilityRemove noiseBioelectric signal measurementAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyLow noiseInstrumentation amplifier
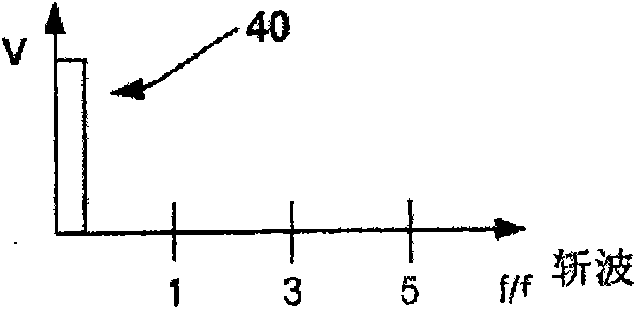
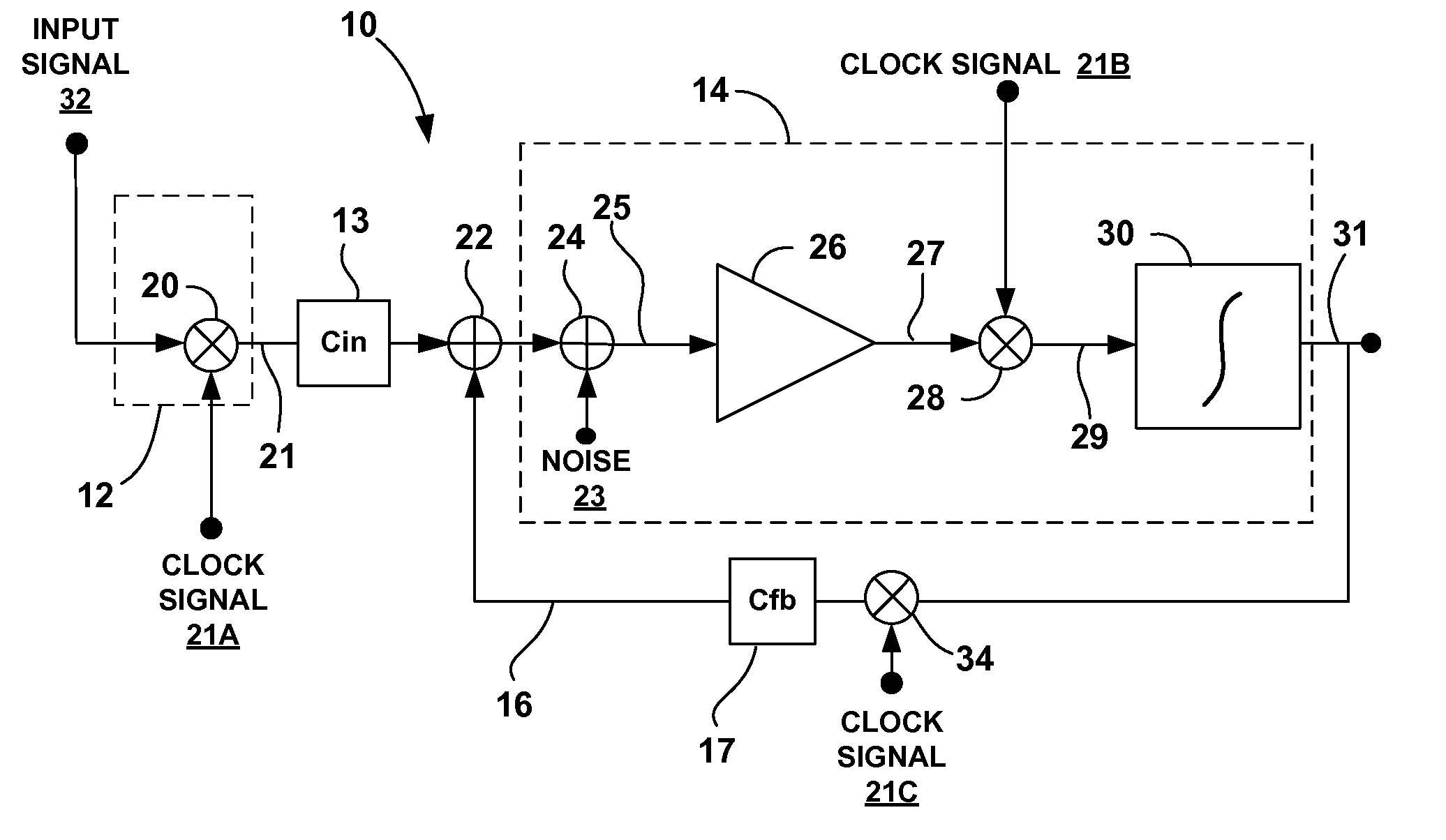
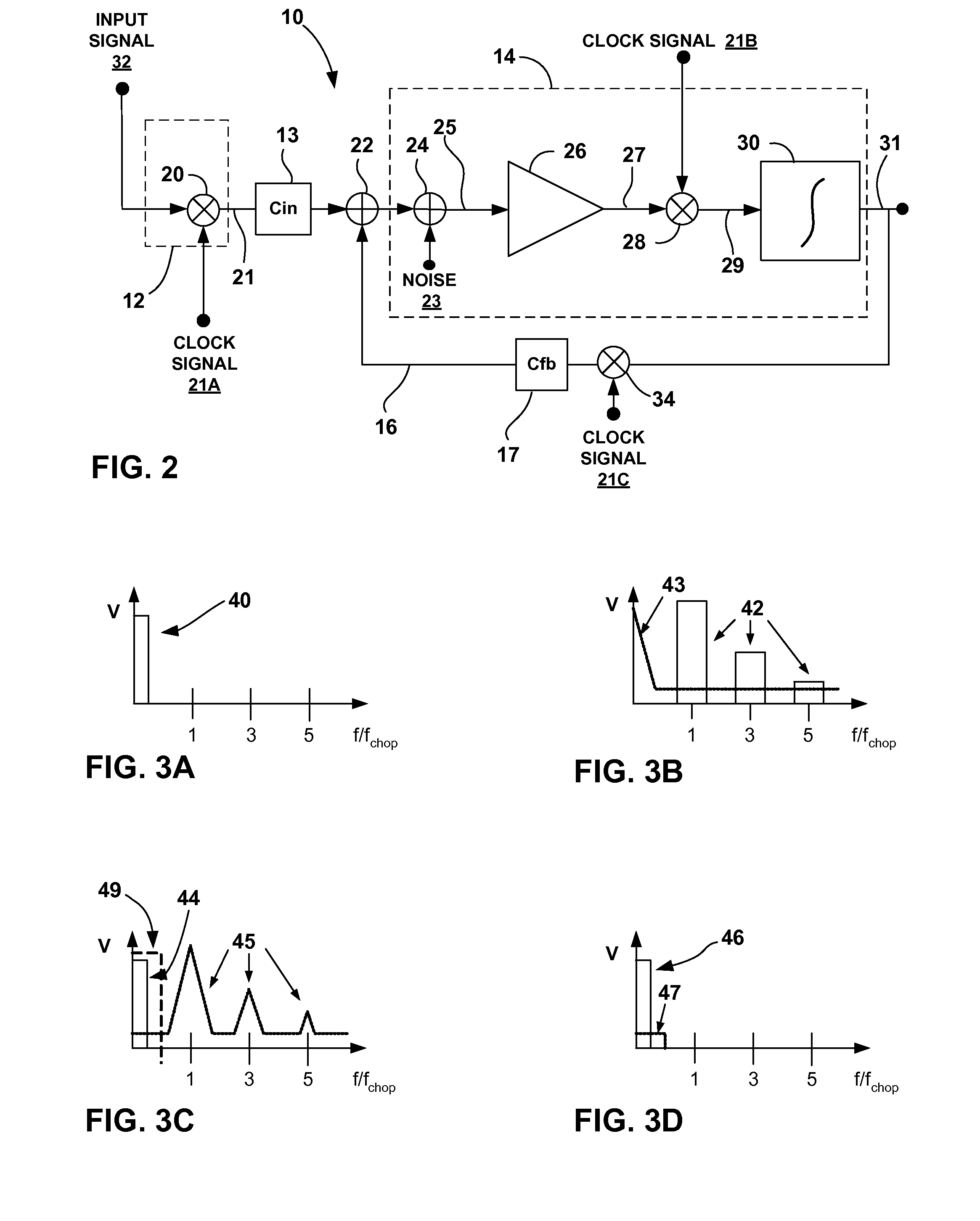
This disclosure describes a chopper stabilized instrumentation amplifier. The amplifier is configured to achieve stable measurements at low frequency with very low power consumption. The instrumentation amplifier uses a differential architecture and a mixer amplifier to substantially eliminate noise and offset from an output signal produced by the amplifier. Dynamic limitations, i.e., glitching, that result from chopper stabilization at low power are substantially eliminated through a combination of chopping at low impedance nodes within the mixer amplifier and feedback. The signal path of the amplifier operates as a continuous time system, providing minimal aliasing of noise or external signals entering the signal pathway at the chop frequency or its harmonics. The amplifier can be used in a low power system, such as an implantable medical device, to provide a stable, low-noise output signal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
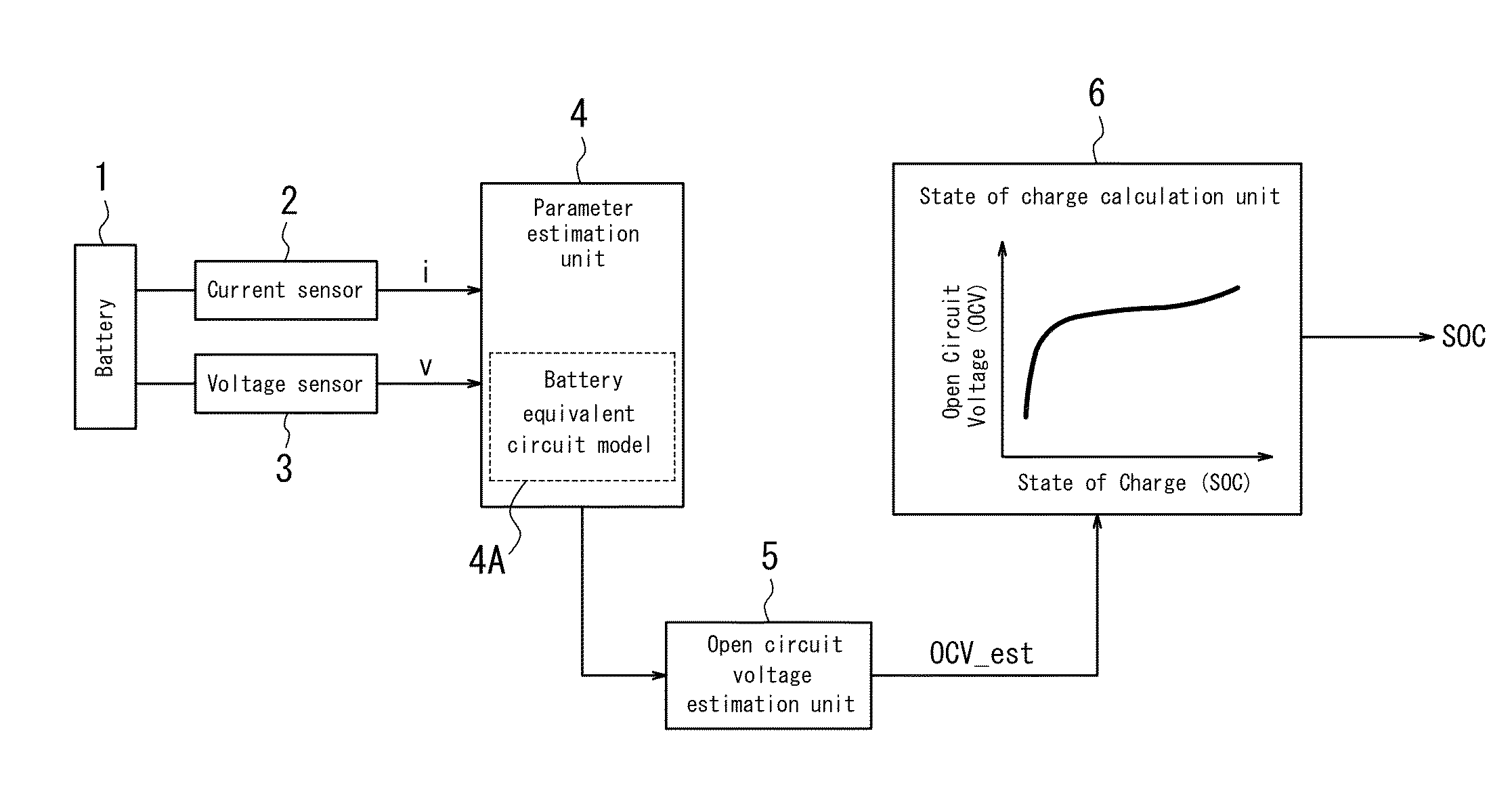
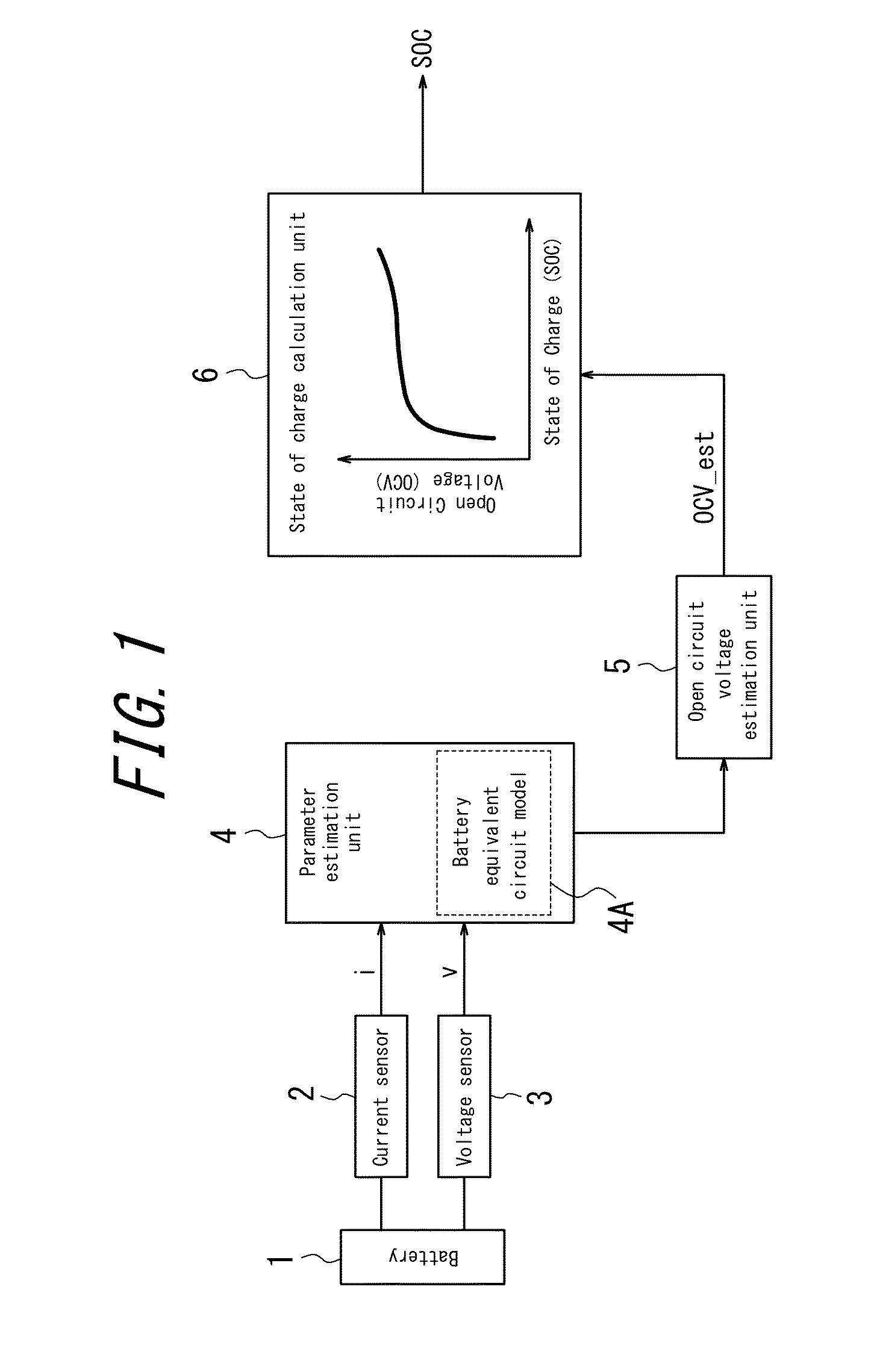
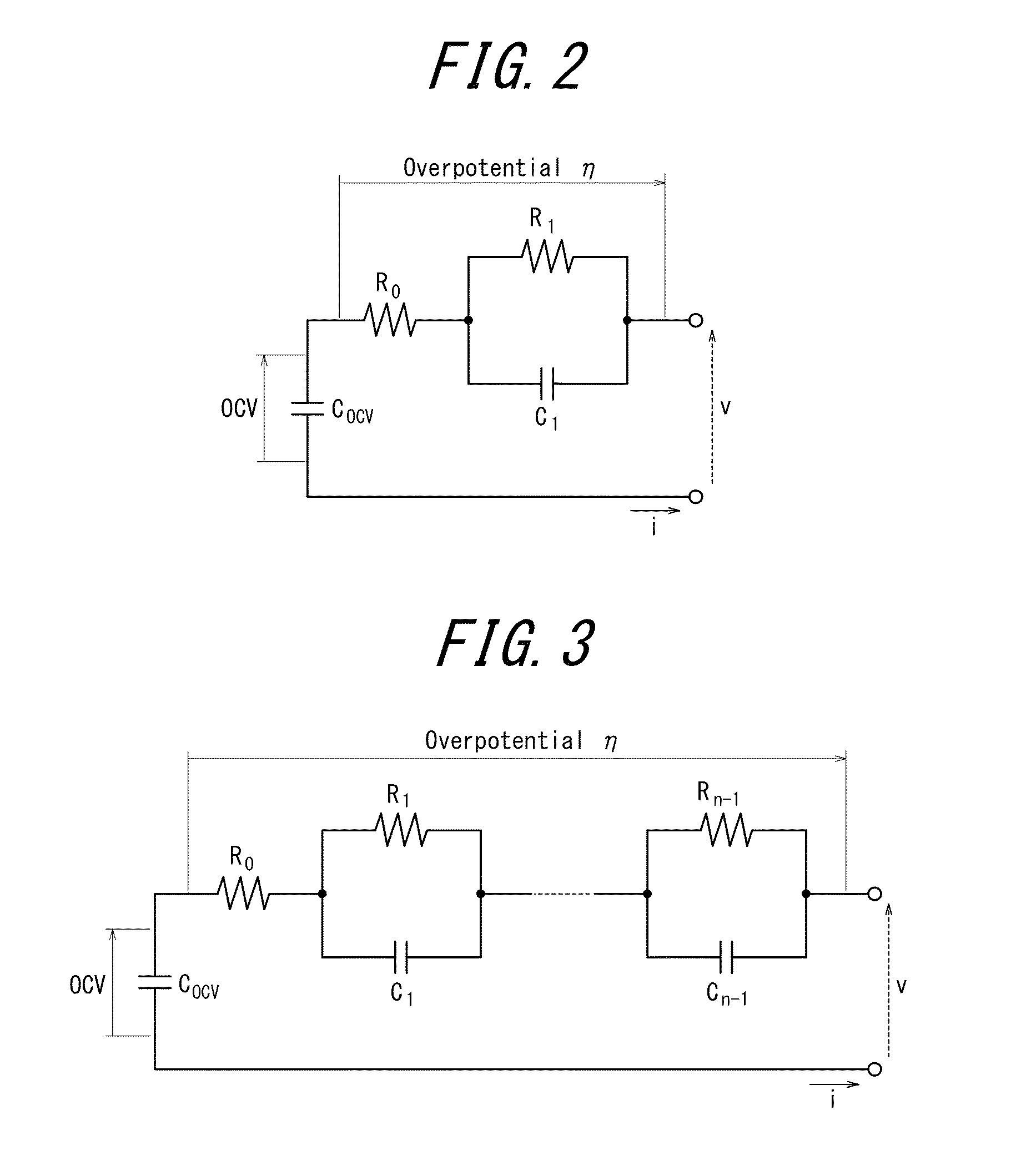
Apparatus for parameter estimation
InactiveUS20150051853A1Inaccurate estimationReduce errorsElectrical testingSecondary cellsMathematical modelGoal system
Provided is an apparatus for parameter estimation that, when performing parameter identification of a mathematical model expressing a target system as a differential equation, can reduce the estimation error of the parameters insofar as possible. The apparatus for parameter estimation includes a mathematical model expressing a target system as a differential equation, an input signal detection unit that detects an input signal to the target system, an output signal detection unit that detects an output signal from the target system, and a parameter identification unit that performs system identification by taking the input signal and the output signal as input and using these signals to identify parameters used in a transfer function of the mathematical model. The parameter identification unit performs, simultaneously with the system identification, continuous-time system identification of initial values of the transfer function based on the input signal and the output signal.
Owner:CALSONIC KANSEI CORP +1
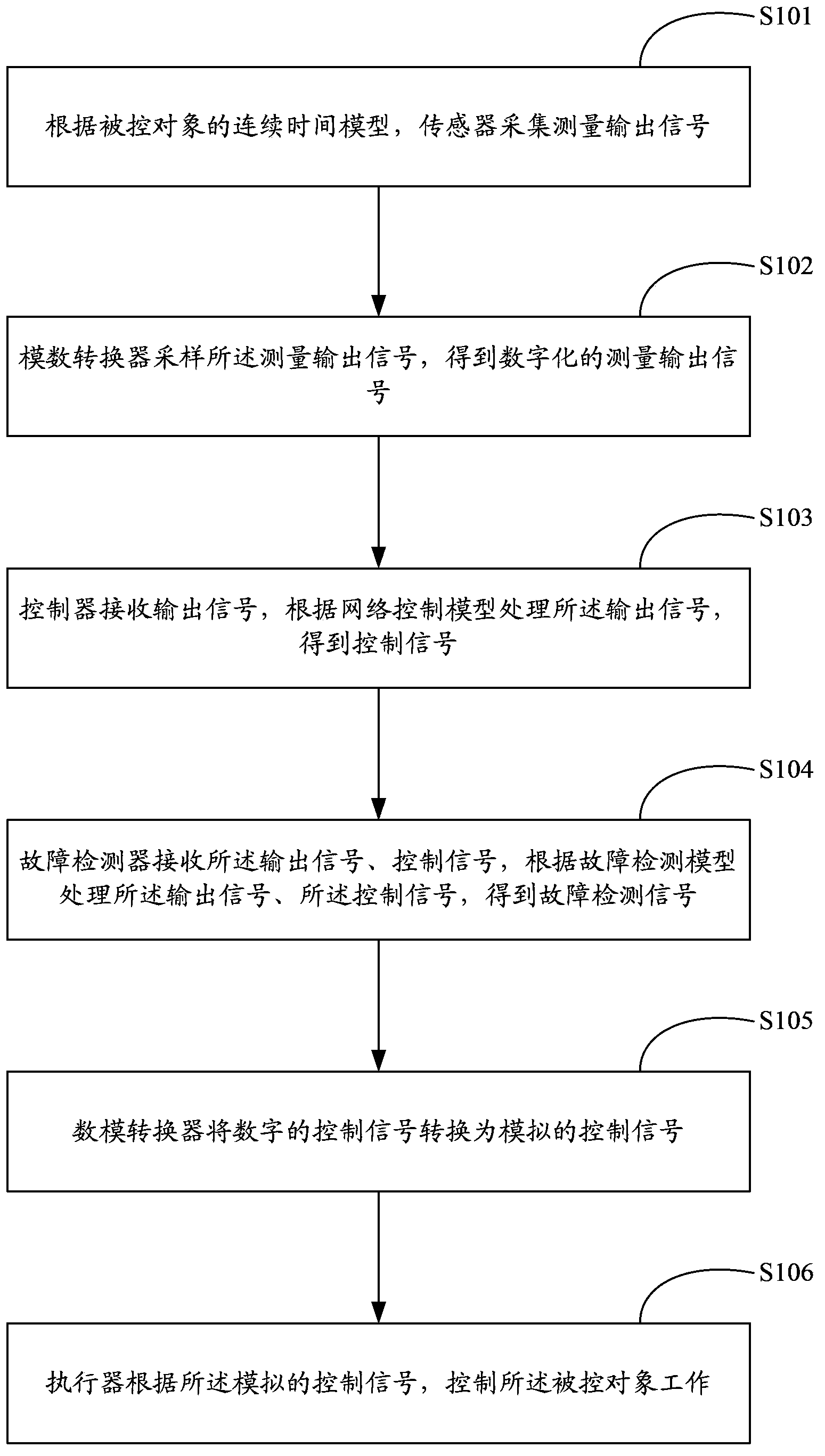
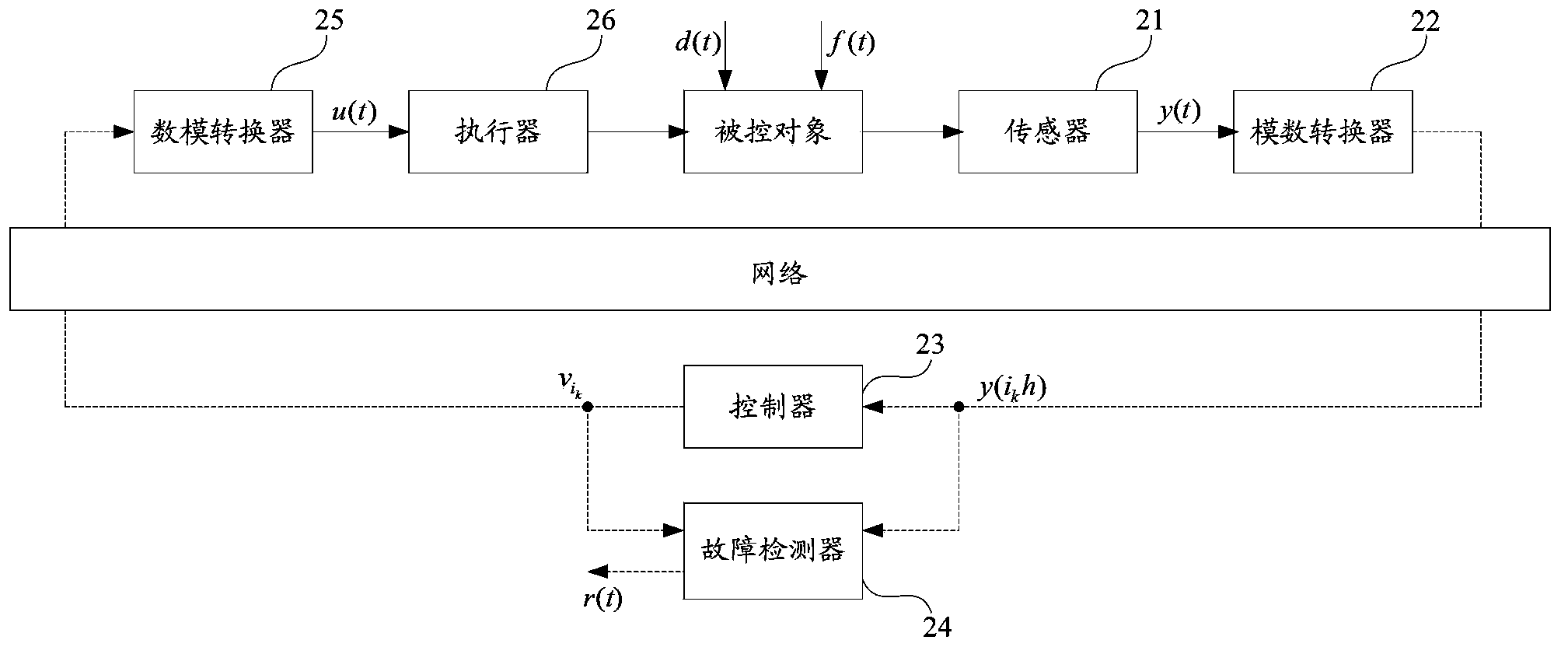
Method and system for detecting and controlling network control system
The invention belongs to the field of control, and provides a method and system for detecting and controlling a network control system. Based on a continuous time system model of a controlled object, a controller acquires output signals collected through a sensor and passing through an analog-digital converter and the sampling time delay of network transmission, and the controller and a fault detector are designed. The fault detector detects fault detection signals, and meanwhile the controller outputs control signals to achieve closed-loop control over the controlled object. Therefore, the method and system for detecting and controlling the network control system avoids the model error brought by discretization modeling, fault information is taken into consideration with the design of an initiative fault-tolerant controller, and the needs of detecting faults accurately of the fault detector are further taken into consideration. Preferably, a cone complementarity linearization technology is called in the integral design process of the fault detector and the controller depending on a time-lag network control system, the solution of designing the controller is translated into a nonconvex optimization problem under a linear matrix inequality, and conservative properties are reduced greatly compared with lag irrelevance. Therefore, the method and system for detecting and controlling the network control system achieves fault detection and fault tolerance control.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
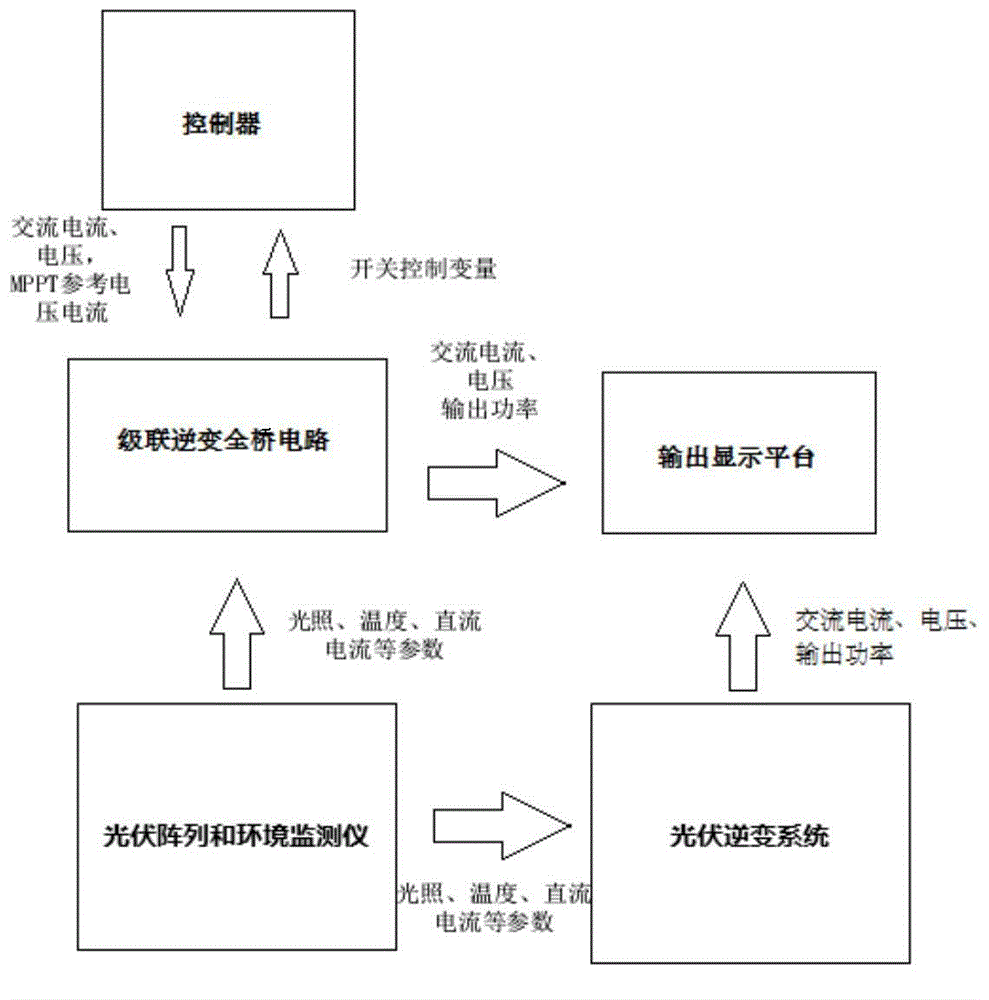
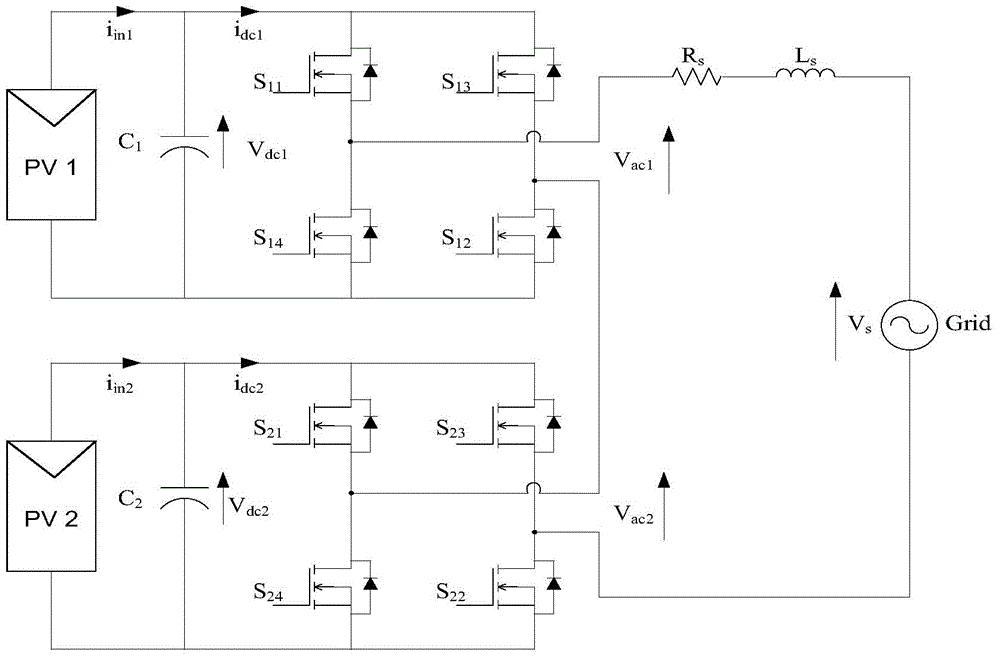
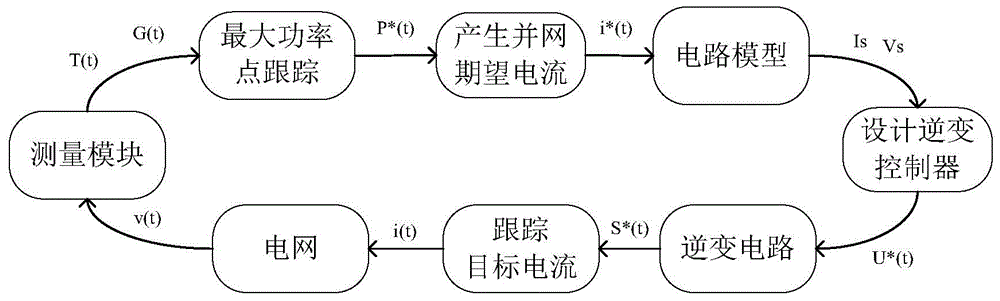
Model predictive control method based on grid-connection inversion of photovoltaic system
InactiveCN104135181AImprove protectionLess harmonics are introducedAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFull bridgeDynamic models
The invention relates to a model predictive control method based on grid-connection inversion of a photovoltaic system. The model predictive control method comprises the following steps: 1, building a cascade full-bridge inversion model, analyzing an output current and a DC side voltage according to an analysis result of a two-stable single-phase full-bridge inversion circuit, and acquiring an instantaneous dynamic model of a continuous time system by Kirchhoff laws; 2, building a simulation model according to the built instantaneous dynamic model by using PSIM simulation software, and performing simulation calculation based on the simulation model; 3, designing a model predictive controller based on three indexes such as expected power grid current tracking, an ideal voltage working point and switch switching frequency; and 4, determining the cascade comprehensive performance index of the model predictive controller according to the three indexes obtained in the step 3. By the model predictive control method, frequency and phase of grid-connected current and power grid voltage can be kept same, target current is traced, minimum harmonic wave is introduced, the minimum switch switching frequency is achieved, and device protection is promoted, and energy is saved.
Owner:上海紫竹新兴产业技术研究院
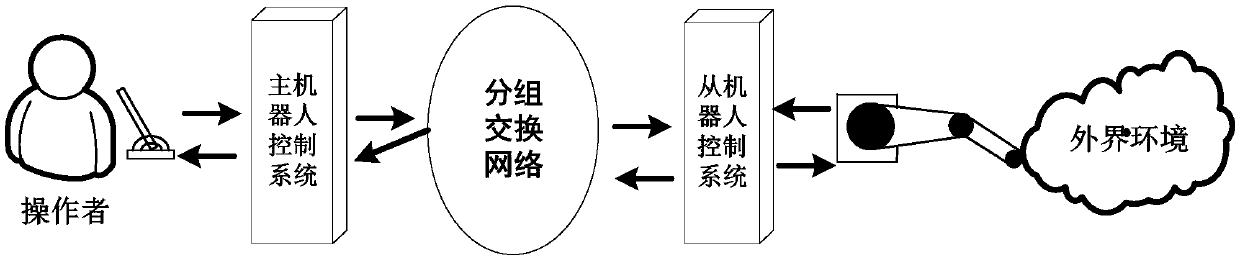
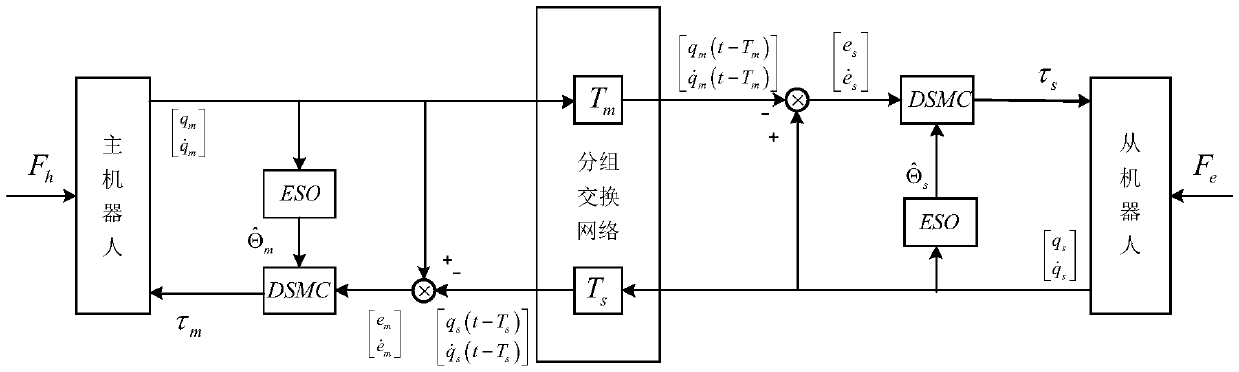
Control method of remote operation system in discrete time state
The invention discloses a control method of a remote operation system in a discrete time state. The method includes the following steps that a remote operating system model in an n-dimensional discrete time state is established; an expanded state observer is established on the basis of the established system model to estimate and compensate the total interference in the system; position synchronization errors of a master robot and a slave robot are defined under network communication time delay,and a discrete sliding mode control method with input time delay is designed; finally,stability conditions of the remote operation system are given on the basis of the Lyapunov theory,and the stability and synchronism of the remote operation system are guaranteed. According to the method,the controlmethod design of the remote operation system under the discrete time state is considered; compared with a remote operation system in a continuous time state,the discrete system state is considered inthe design stage of a controller,discrete errors caused by the design of the controller are avoided,and the method is more suitable for actual working environments,so that the method is more flexibleto use.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Chopper-stabilized instrumentation amplifier for wireless telemetry
InactiveCN101622784AHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringInstrumentation amplifierFeedback circuits
This disclosure describes a chopper stabilized instrumentation amplifier. The amplifier is configured to achieve stable measurements at low frequency with very low power consumption. The instrumentation amplifier uses a differential architecture and a mixer amplifier to substantially eliminate noise and offset from an output signal produced by the amplifier. Dynamic limitations, i.e., glitching, that result from chopper stabilization at low power are substantially eliminated through a combination of chopping at low impedance nodes within the mixer amplifier and feedback. The signal path of the amplifier operates as a continuous time system, providing minimal aliasing of noise or external signals entering the signal pathway at the chop frequency or its harmonics. The amplifier can be used in a low power system, such as an implantable medical device. The amplifier may be used for physiological signal sensing, impedance sensing, telemetry or other test and measurement applications.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
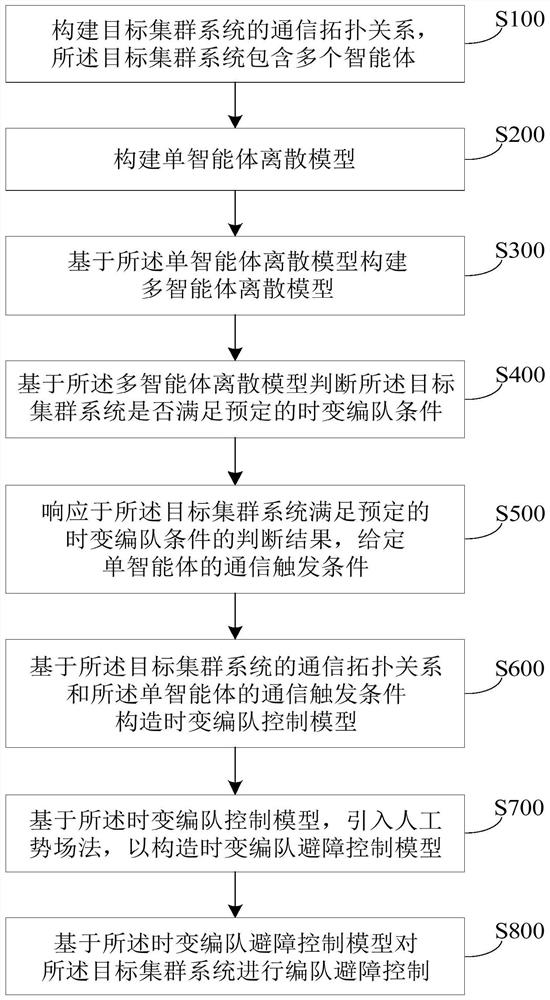
Cluster system formation obstacle avoidance control method
PendingCN113625747AReduce communication frequencyReduce the number of communicationsPosition/course control in three dimensionsContinuous time systemObstacle avoidance
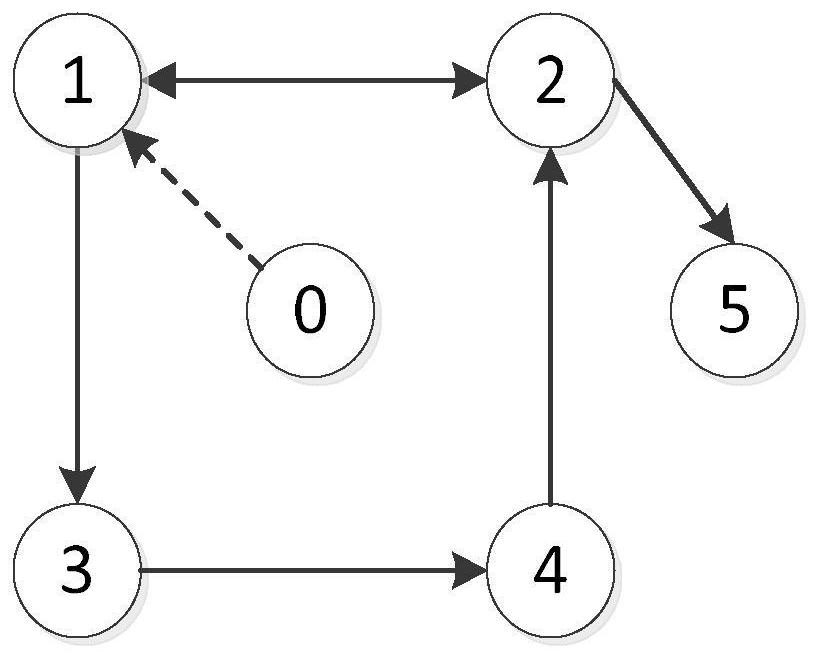
The invention discloses a cluster system formation obstacle avoidance control method. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a communication topological relation of a target cluster system comprising a plurality of agents; constructing a single agent discrete model; constructing a multi-agent discrete model based on the single-agent discrete model; judging whether the target cluster system meets a time-varying formation condition based on the multi-agent discrete model; if yes, giving a communication triggering condition of the single agent; constructing a time-varying formation control model based on the communication topological relation and the communication triggering condition; based on the time-varying formation control model, introducing an artificial potential field method to construct a time-varying formation obstacle avoidance control model; and performing formation obstacle avoidance control on the target cluster system based on the time-varying formation obstacle avoidance control model. According to the invention, the problem that an existing cluster system formation control method based on consistency cannot be applied to an actual system with discrete system time and obstacles in a task environment due to facing a continuous time system and an ideal task environment can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Online learning method for optimal controller of nonlinear system
ActiveCN111142383AGood exploration abilityInternal combustion piston enginesAdaptive controlUncrewed vehicleMotor control
The invention relates to an online learning method for an optimal controller of a nonlinear system. The method comprises the steps that: the initial state, system state and control input of a controlsystem are acquired, wherein the control system comprises a motion control system of a robot or a flight control system of an unmanned aerial vehicle; a continuous time system model is established; atarget function is defined; an optimal controller is established; a synchronization strategy iterative algorithm based on off-strategy learning is established; online training learning is performed onthe optimal controller; and the optimal controller obtained by training and learning is applied to an actual controlled object, wherein the controlled object comprises the control parameters of the motion control system of the robot or the control parameters of the flight control system of the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:INFORMATION SCI RES INST OF CETC
Discretization processing method of transfer function in continuous time systems, system and program therefor, and compensator and feedback control system using the same
InactiveUS6996592B2Easily approximatedReduce product manufacturing costsSampled-variable control systemsTrack finding/aligningControl systemSignal transfer function
A discretization processing method for transforming a transfer function in continuous time systems to a transfer function in discrete time systems is disclosed. To obtain the new transfer function, angular frequency ωa of the original transfer function in continuous time systems is transformed to angular frequency ωc using the bilinear z-transform of the inverse characteristic. In the discretion processing result, the equivalent characteristics of the original transfer function in continuous time systems can be obtained by performing the bilinear z-transform against the new transfer function in continuous time systems having been obtained by the angular frequency transformation of inverse characteristic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
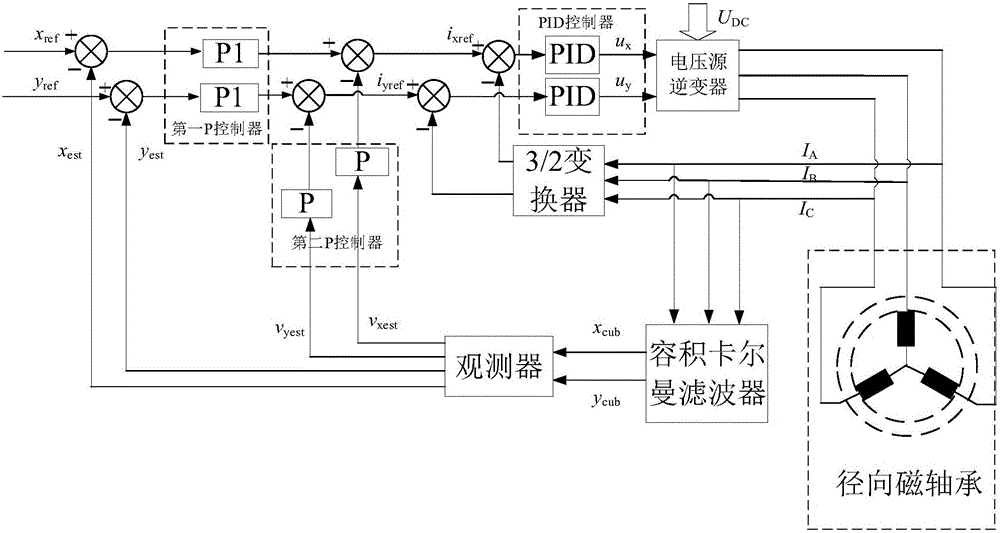
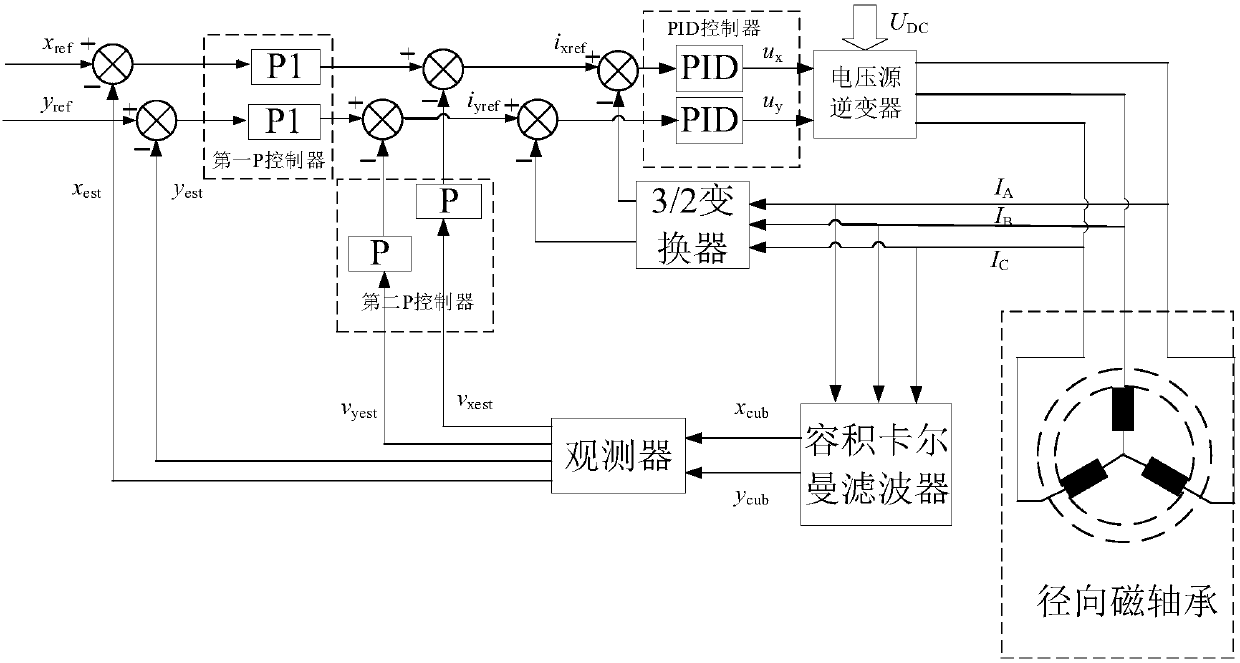
Volume kalman filter-based radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method and system
ActiveCN106026828APoor filtering performance or even divergenceMeet real-time requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsKaiman filterMagnetic bearing
The invention relates to a volume kalman filter-based radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method and system. The radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method comprises the steps of obtaining radial displacement output signals and rotating speed signals of a rotor in an x direction and a y direction according to a continuous time system and discretizing the continuous time system to achieve extraction of displacement information of the rotor by a volume kalman filter algorithm. According to the volume kalman filter-based radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method and system, linear processing of a radial magnetic bearing which is a nonlinear model essentially is avoided; operation of a displacement-free sensor is achieved; the detection system has very high interference rejection capability; the radial magnetic bearing displacement can be accurately detected; and the radial magnetic bearing displacement can also be detected when the exact nature of the system is unknown.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
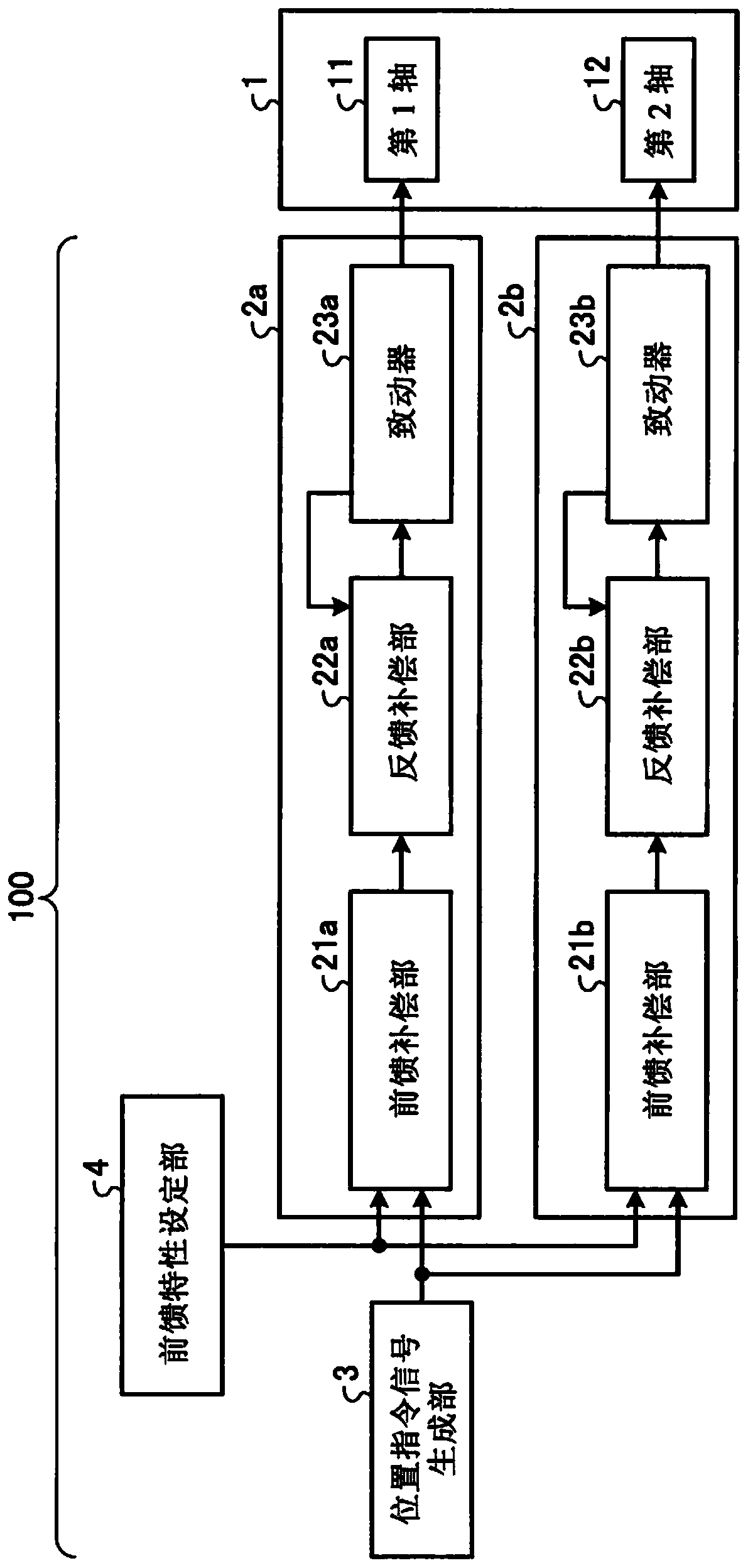
Servo control device
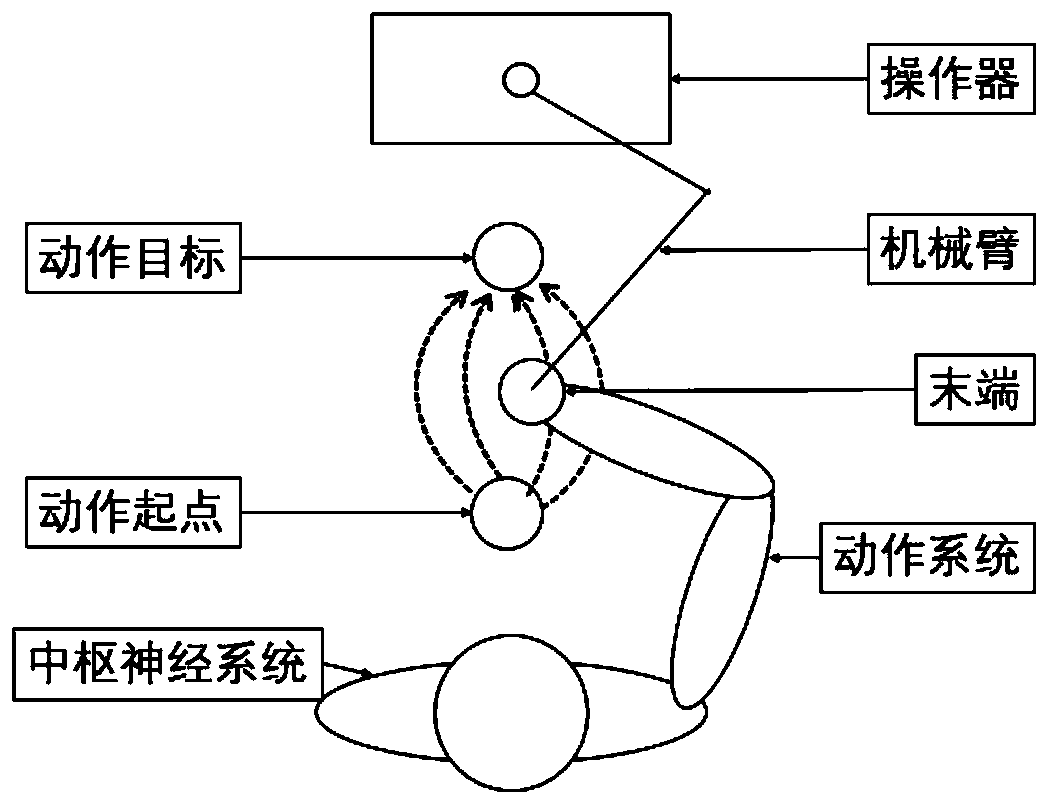
ActiveCN111095132ARealize the designImplement featuresProgramme-controlled manipulatorIgnition automatic controlControl engineeringMachine
The present invention provides a servo control device (100) which drives a machine (1) by means of actuators (23a, 23b) and thereby performs control such that an end of the machine (1) follows a set target trajectory. The servo control device (100) is provided with feedforward compensation units (21a, 21b) which output the feedforward signals for controlling the actuators(23a, 23b), on the basis of an input position command signal, and thereby perform feedforward compensation, wherein the input-to-output characteristics of the feedforward compensation units (21a, 21b) in a continuous-time system are represented by a transfer function having an unstable zero point, and the feedforward compensation units (21a, 21b) produce a step response having a reverse swing.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Longitudinal-column type double-rotor-wing helicopter model system based on nonlinear three freedom degrees
The invention discloses a longitudinal-column type double-rotor-wing helicopter model system based on nonlinear three freedom degrees, and the system is characterized in that the system employs the following steps: 1, selecting a height axis and a rotating axis from the three freedom degrees, adding a state and achieving decoupling in a system dynamic state, and knowing that a system model has a nonsingular decoupling matrix (shown in the description); 2, employing a PCGSHF multi-rate sampling signal retainer to achieve the Taylor power series approximate expansion of system output in each section, and obtaining an approximate discrete time model (shown in the description) of a double-rotor-wing helicopter model under the PCGSHF condition, so a local truncation error between one order output (shown in the description) of a deduced approximate discrete time system and the output of a corresponding original continuous time system is shown in the description; 3, enabling a discretization zero dynamic state to consist of a true dynamic state and a sampling zero dynamic state, wherein the approximate asymptotic expression of the true dynamic state of the system is shown in the description, and the sampling zero dynamic state is the root of a characteristic polynomial (shown in the description).
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Nonlinear system fault detection and estimation method and device based on adaptive iterative learning algorithm
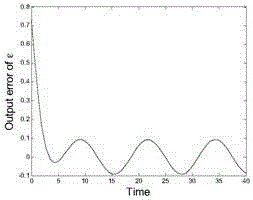
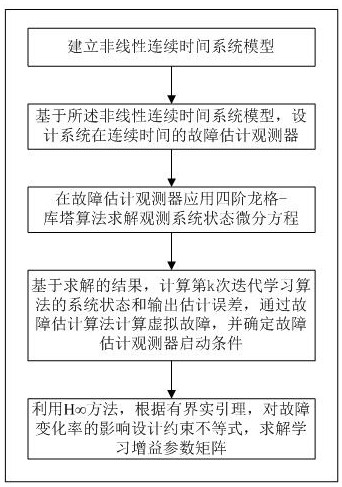
InactiveCN113625677AConvergence vs AccuracyGood precisionProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringIterative learning algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a nonlinear system fault detection and estimation method and device based on an adaptive iterative learning algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a nonlinear continuous time system model; based on the nonlinear continuous time system model, designing a fault estimation observer of the system in continuous time; applying a fourth-order Runge-Kutta algorithm to the fault estimation observer to solve an observation system state differential equation; calculating a system state and an output estimation error of the kth iterative learning algorithm based on the solving result, calculating a virtual fault through a fault estimation algorithm, and determining a starting condition of a fault estimation observer; and using an H infinity method, designing a constraint inequality according to the bounded real lemma and the influence on the fault change rate, and solving a learning gain parameter matrix. By means of the method, the fault estimation error is effectively reduced, and the convergence speed of the fault estimation observer is improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
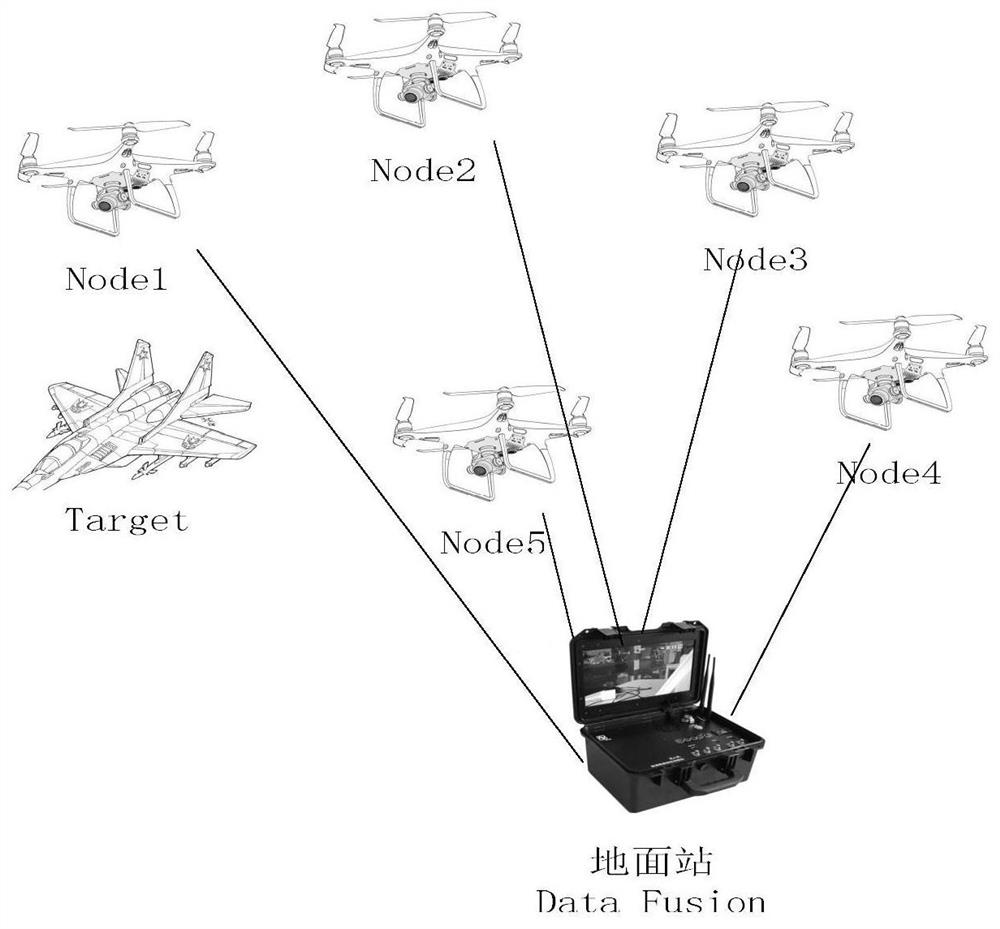
Multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative tracking and positioning method
PendingCN113534834ASolving State Estimation ProblemsSmall mean square errorPosition/course control in three dimensionsConnectivityGraph theoretic
The invention discloses a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative tracking and positioning method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a directed connected graph based on a graph theory method according to an unmanned aerial vehicle communication network topological structure graph, and obtaining connection information of unmanned aerial vehicle sensor nodes and adjacent nodes; establishing a linear continuous time system model; estimating unknown information of a target by using an IKCF filtering algorithm; and carrying out data fusion on the estimation result of each node by adopting a sequential fast covariance cross fusion algorithm to obtain a determined target position. According to the multi-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative tracking and positioning method of the invention, the estimation information of the adjacent unmanned aerial vehicle nodes is fully utilized, the real-time performance of the system is improved, and the target position estimation is more accurate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
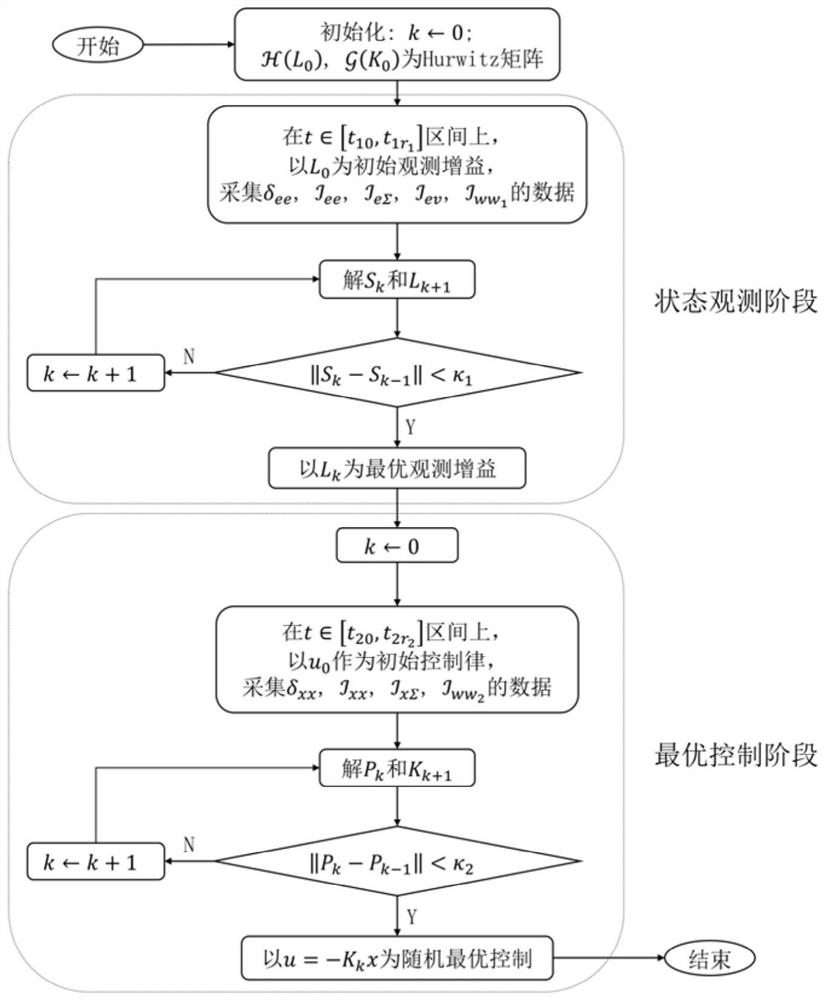
Data-driven adaptive optimization control method for random disturbance system and medium
The invention discloses a data-driven adaptive optimization control method for a random disturbance system and a medium. The method comprises a problem description part, a design part of a data-drivenoptimal state observer, and an off-policy data-driven ADP control part of a random disturbance system. The three parts are explained in detail in the invention. A data-driven optimal state observer is designed to carry out off-policy data-driven ADP control on a random disturbance system. The data-driven ADP method is used in a system with a completely unmeasurable state for the first time. Model-free LQG control is generalized to a continuous time system. In the ADP design, non-matching noise except a control signal channel and independent noise independent of the state and the control signal are considered. By using the novel off-policy data-driven ADP control method for a random disturbance system and the medium provided by the invention, the burden of repeatedly reading and updating acontrol signal is avoided, and the computation is remarkably reduced.
Owner:北京理工大学重庆创新中心 +1
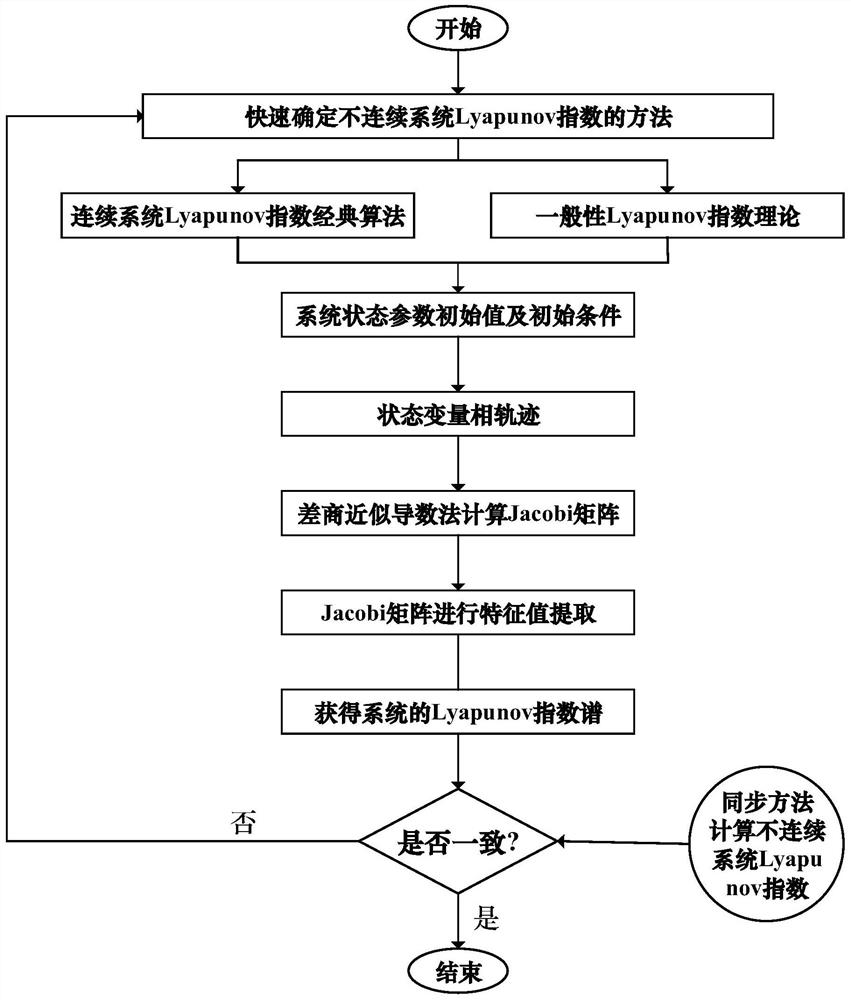
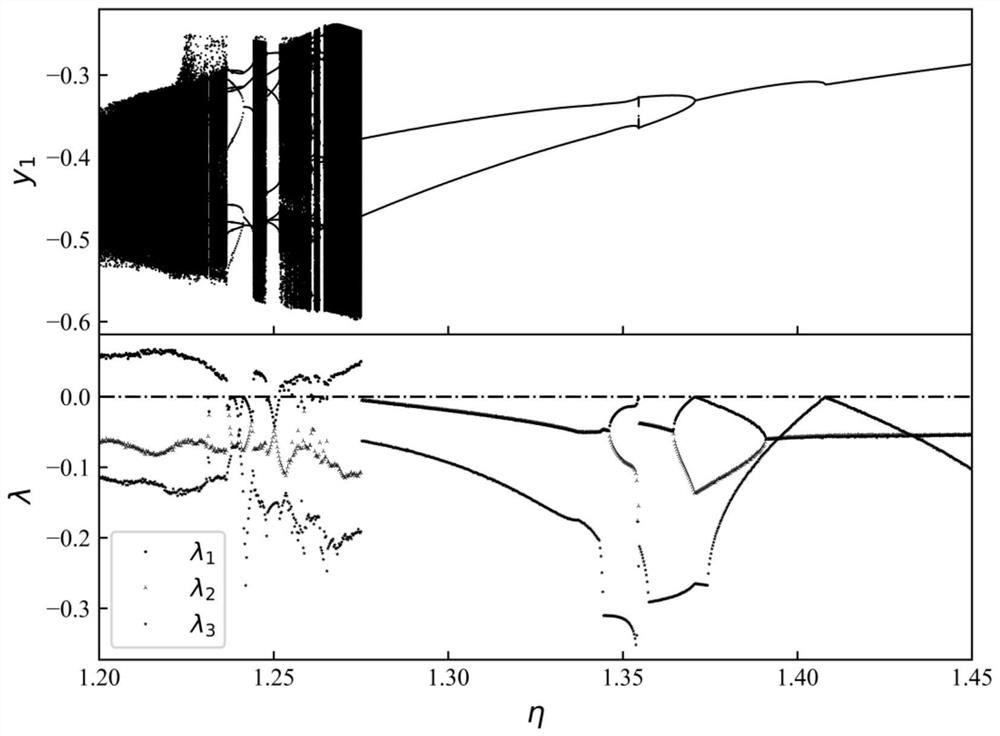
Method for rapidly determining Lyapunov index spectrum of discontinuous system
PendingCN113642119AGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsPhase spaceComputational physics
The invention discloses a method for rapidly determining a Lyapunov index spectrum of a discontinuous system, and the method comprises the steps of taking a state parameter initial value of the discontinuous system and a disturbance quantity of each basic vector along a phase space as initial conditions, and determining a phase trajectory; secondly, adopting a difference quotient approximate derivative method to obtain an approximate matrix of the Jacobi matrix; then, performing feature value extraction on the Jacobi matrix, and obtaining a Lyapunov index spectrum of a discontinuous system; finally, applying the new algorithm to a two-degree-of-freedom dry friction impact oscillator system example, comparing a calculation result with a calculation result of the synchronization method, and verifying the effectiveness of the new method. The method is not only suitable for a discrete system and a continuous time system, but also can quickly determine the Lyapunov index of the complex discontinuous system, and provides a new thought for determining the dynamic behavior of the complex discontinuous system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A high-precision controller for ultra-low speed control moment gyro frame servo system
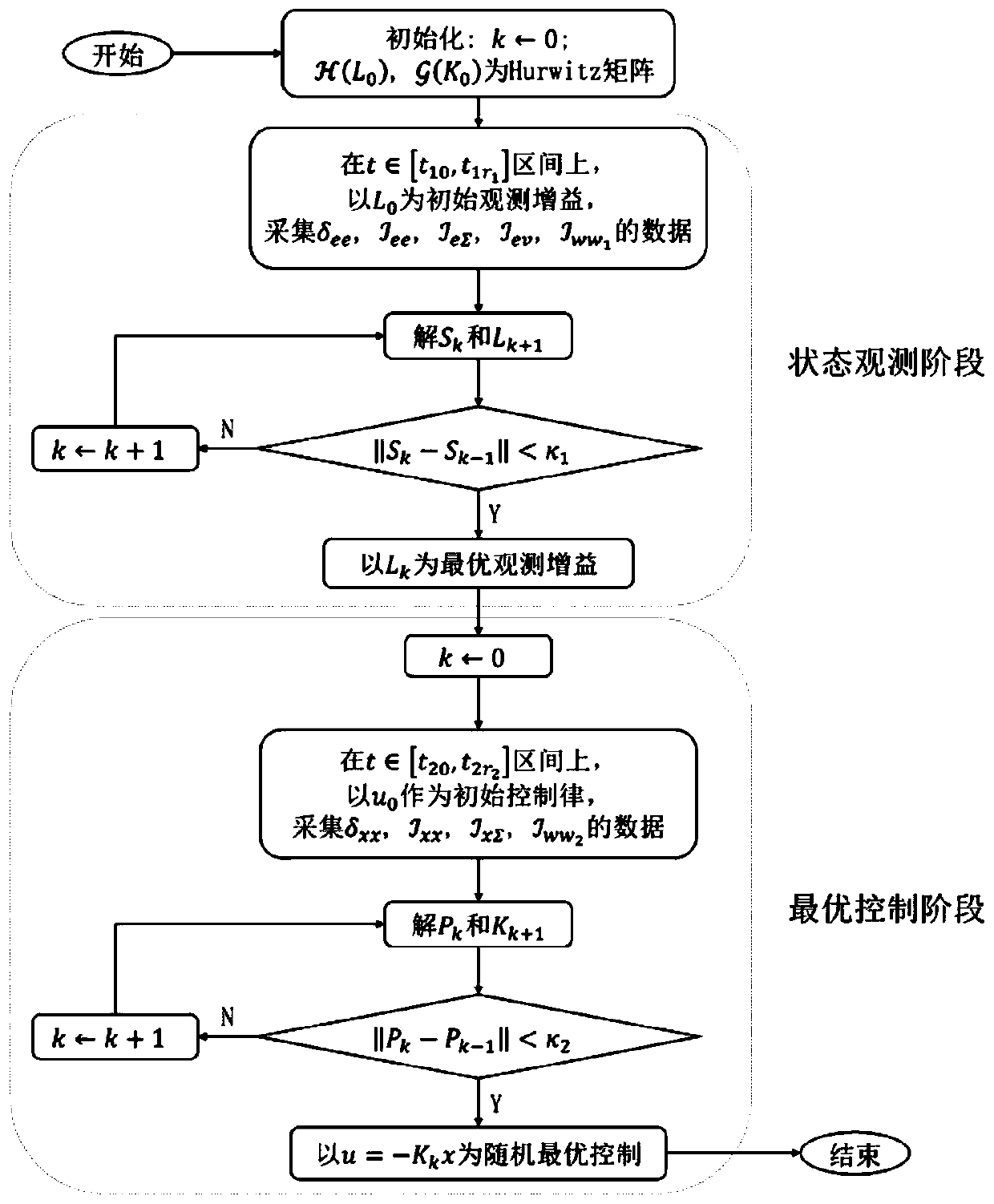
ActiveCN112859612BAddressing the issue of poor estimation performanceImplementing Instantaneous Velocity EstimationAdaptive controlState observerControl engineering
The invention provides a high-precision controller of an ultra-low speed control moment gyro frame servo system. Firstly, the discrete-time system state-space equation is obtained according to the continuous-time system state-space equation of the ultra-low-speed frame servo system, and then the precise estimation of the instantaneous velocity and "lumped disturbance" is realized by designing a double sampling rate expansion state observer, and finally in the velocity loop A compound sliding mode control algorithm based on sliding mode control and disturbance compensation is designed to suppress the "lumped disturbance". The high-precision controller of the ultra-low-speed control torque gyro frame servo system proposed by the present invention not only designs a double sampling rate expansion state observer to solve the estimation performance deterioration of the existing estimation method under the influence of factors such as changes in the model parameters of the ultra-low-speed frame servo system In order to solve the problem, a compound sliding mode control algorithm is also designed to enhance the disturbance suppression ability of the system; starting from two aspects of sensor detection and disturbance suppression, the angular rate control accuracy of the ultra-low speed frame servo system is comprehensively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Construction Method of Continuous Time System for Displacement Detection of Radial Magnetic Bearing
ActiveCN106026828BPoor filtering performance or even divergenceMeet real-time requirementsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsKaiman filterMagnetic bearing
The invention relates to a volume kalman filter-based radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method and system. The radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method comprises the steps of obtaining radial displacement output signals and rotating speed signals of a rotor in an x direction and a y direction according to a continuous time system and discretizing the continuous time system to achieve extraction of displacement information of the rotor by a volume kalman filter algorithm. According to the volume kalman filter-based radial magnetic bearing displacement detection method and system, linear processing of a radial magnetic bearing which is a nonlinear model essentially is avoided; operation of a displacement-free sensor is achieved; the detection system has very high interference rejection capability; the radial magnetic bearing displacement can be accurately detected; and the radial magnetic bearing displacement can also be detected when the exact nature of the system is unknown.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
A data-driven adaptive optimization control method and medium for random disturbance system
The invention discloses a data-driven adaptive optimization control method and medium for a random disturbance system. The method includes a problem description part, a design part of a data-driven optimal state observer, and a different-strategy data-driven ADP control part of a random disturbance system; for The above three parts, the present invention has been described in detail. The invention implements different-strategy data-driven ADP control of a random disturbance system by designing a data-driven optimal state observer. For the first time, the data-driven ADP method is used for the system whose state is completely unpredictable; the model-free LQG control is extended to the continuous time system; the non-matching noise outside the control signal channel is considered in the ADP design, and the independent state and control signal are not dependent Noise: A new type of different strategy data-driven ADP control method and medium for random disturbance systems is proposed, which avoids the burden of repeatedly reading and updating control signals, and significantly reduces the amount of calculation.
Owner:北京理工大学重庆创新中心 +1
High-precision controller for ultra-low-speed control moment gyroscope frame servo system
ActiveCN112859612AAddressing the issue of poor estimation performanceImplementing Instantaneous Velocity EstimationAdaptive controlState observerControl engineering
The invention provides a high-precision controller for an ultra-low-speed control moment gyroscope frame servo system. Firstly, a discrete time system state-space equation is obtained according to a continuous time system state-space equation of the ultra-low-speed frame servo system, then accurate estimation of instantaneous speed and lumped disturbance is achieved by designing a double-sampling-rate extended state observer, and finally, a composite sliding mode control algorithm is designed based on sliding mode control and disturbance compensation in a speed ring to suppress lumped disturbance. According to the high-precision controller for the ultra-low-speed control moment gyroscope frame servo system, provided by the invention, the double-sampling-rate extended state observer is designed to solve the problem that the estimation performance of an existing estimation method becomes poor under the influence of factors such as model parameter change of the ultra-low-speed frame servo system; the composite sliding mode control algorithm is further designed to enhance the disturbance suppression capability of the system; and starting from two aspects of sensing detection and disturbance suppression, the angular rate control precision of the ultra-low-speed frame servo system is comprehensively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
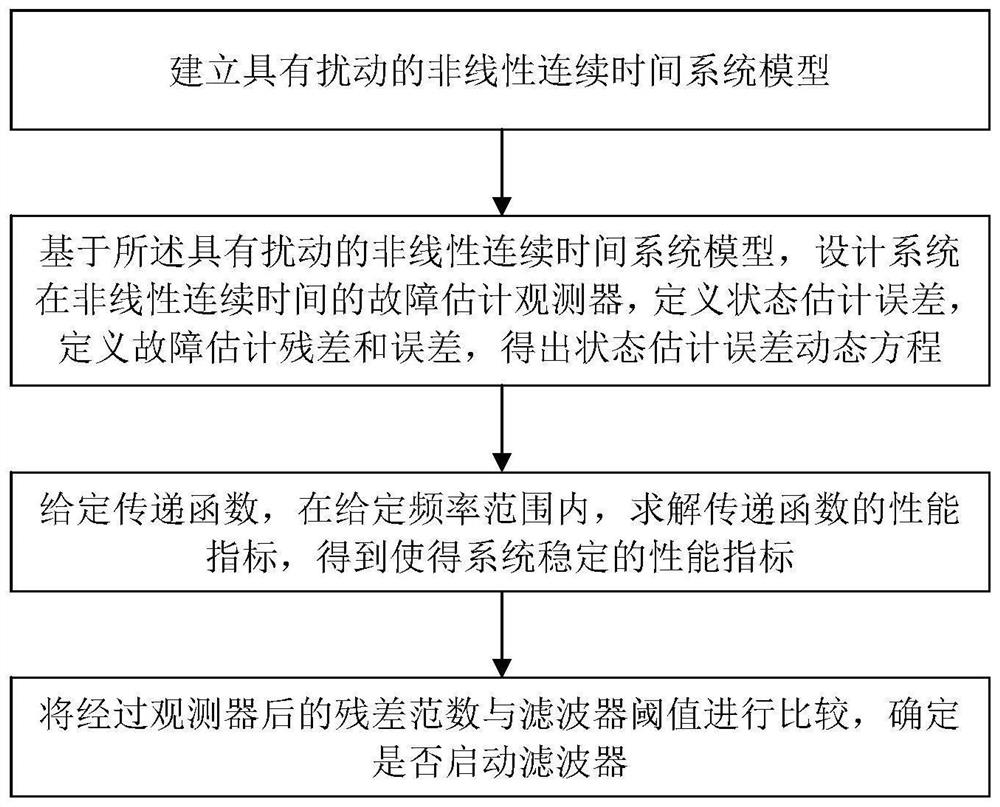
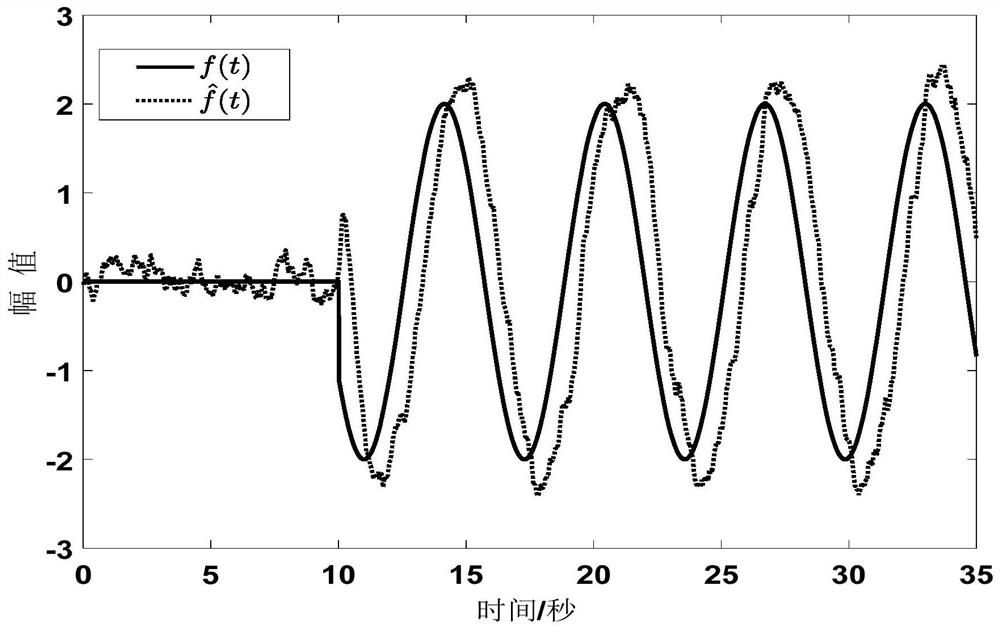
Fault estimation observation method and device for nonlinear system with disturbance
InactiveCN113721458ASuppresses failure rate of changeSuppress the effects of disturbancesAdaptive controlDynamic equationReconstruction method
The invention discloses a fault estimation observation method and device for a nonlinear system with disturbance. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a nonlinear continuous time system model with disturbance; s2, based on the nonlinear continuous time system model with disturbance, designing a fault estimation observer of the system in nonlinear continuous time, defining a state estimation error, defining a fault estimation residual error and an error, and obtaining a state estimation error dynamic equation; s3, giving a transfer function, and solving a performance index of the transfer function in a given frequency range to obtain a performance index enabling the system to be stable; and S4, comparing the norm of the residual error passing through the observer with a threshold value of the filter, and determining whether the filter is started or not. For the nonlinear disturbance system, the fault reconstruction method combining the robust observer and the fault estimation filter is designed, the rapidity and the robustness of fault estimation are improved, and accurate and rapid estimation of faults is realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
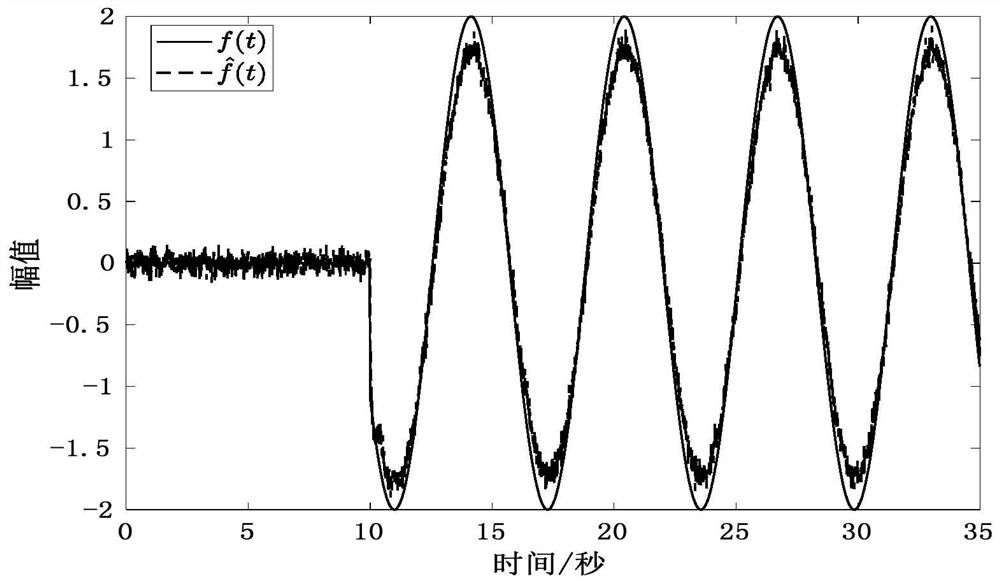
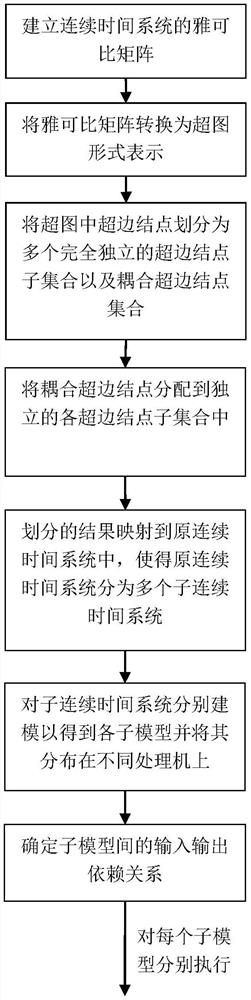
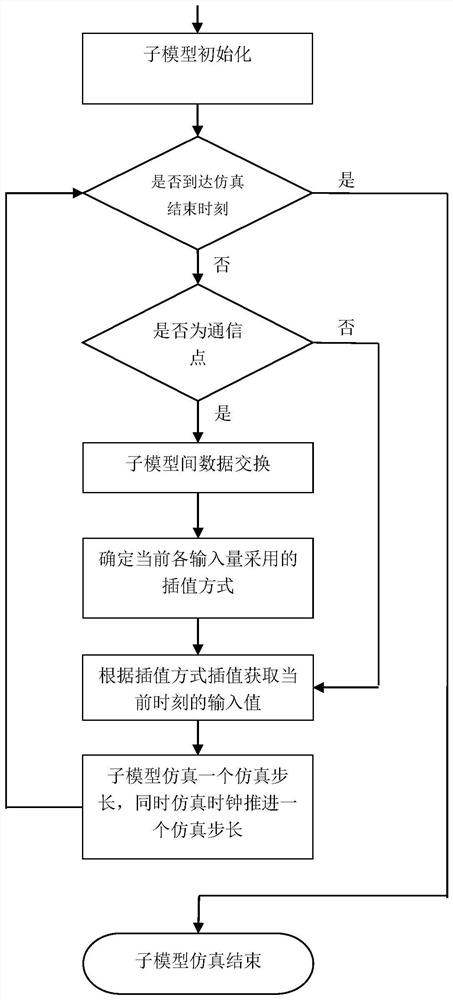
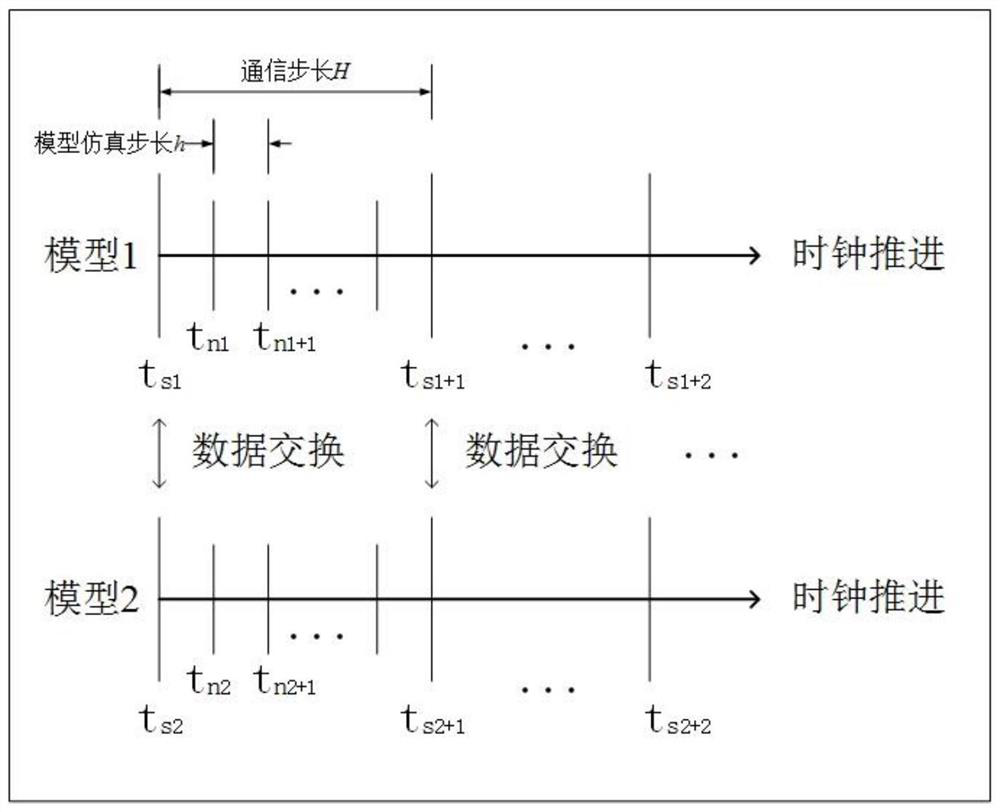
A Parallel Simulation and Error Compensation Method of Continuous Time System
ActiveCN108629136BReasonable Error Compensation StrategyReduce mistakesDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmContinuous time system
The invention discloses a continuous time system parallel simulation and error compensation method, which belongs to the technical field of complex system simulation. The present invention first establishes the Jacobian matrix of the continuous time system, then converts the Jacobian matrix into a hypergraph form expression, uses the hypergraph segmentation strategy to divide the hypergraph into multiple parts with as low coupling degree as possible, and then The result of hypergraph partitioning is mapped to the continuous time system to realize the division of the continuous time system into multiple sub-continuous time systems with low coupling between the sub-continuous time systems. Finally, each sub-continuous-time system is distributed on different processors for parallel simulation, and each sub-continuous-time system adopts a dynamically selected interpolation method to interpolate the input value to compensate the error during the simulation process. The invention has the advantages of good universality of the error compensation strategy, can shorten the time-consuming solution of the continuous time system, and can reduce the load of a single computer, and is suitable for the simulation of the continuous time system in the engineering field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
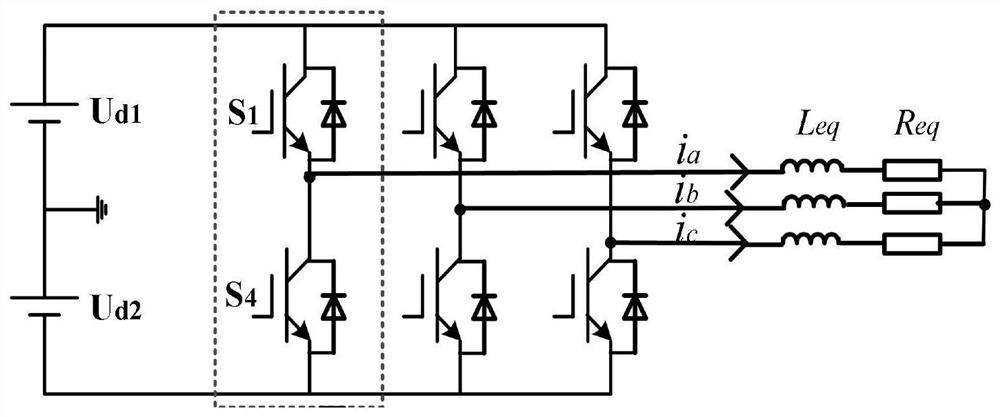
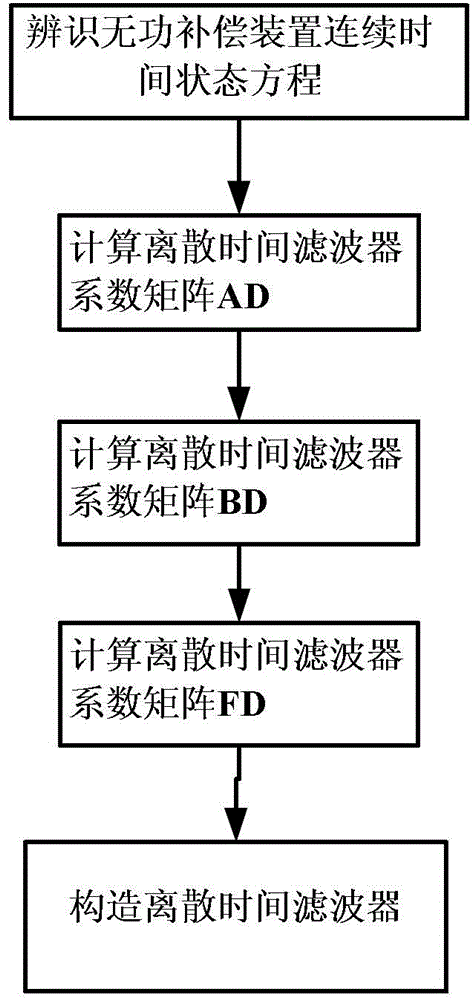
Method for transforming continuous-time filter to discrete-time filter
ActiveCN103176406AImprove performanceSuitable for engineering practical applicationAdaptive controlSystems designPartial differential equation
The invention provides a method for transforming a continuous-time filter to a discrete-time filter. The method includes: sampling input quantity and output quantity of a controlled system, and utilizing an identification algorithm for obtaining a continuous-time model of the system; constructing the continuous-time filter according to the continuous-time model; adopting a partial differential equation method to compute a coefficient matrix of the discrete-time filter according to coefficients in a continuous-time filter equation and adopted time of a discrete system; and constructing a discrete-time filter structure. The discrete-time filter is obtained by performing discrete transformation to the designed continuous-time filter. Compared with an existing discrete-time filter design method, the method has the advantages that discretization processes of a controlled object and filter designing processes based on the discrete system are decreased, and by utilizing advantages of a filter design theory based on a continuous-time system, the filter excellent in performances can be designed, system design and development time can be saved, and the method is particularly suitable for practical engineering application of digital control systems.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Chopper-stabilized instrumentation amplifier and method for impedance measurement
ActiveCN101589548BElectrocardiographyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseInstrumentation amplifier
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
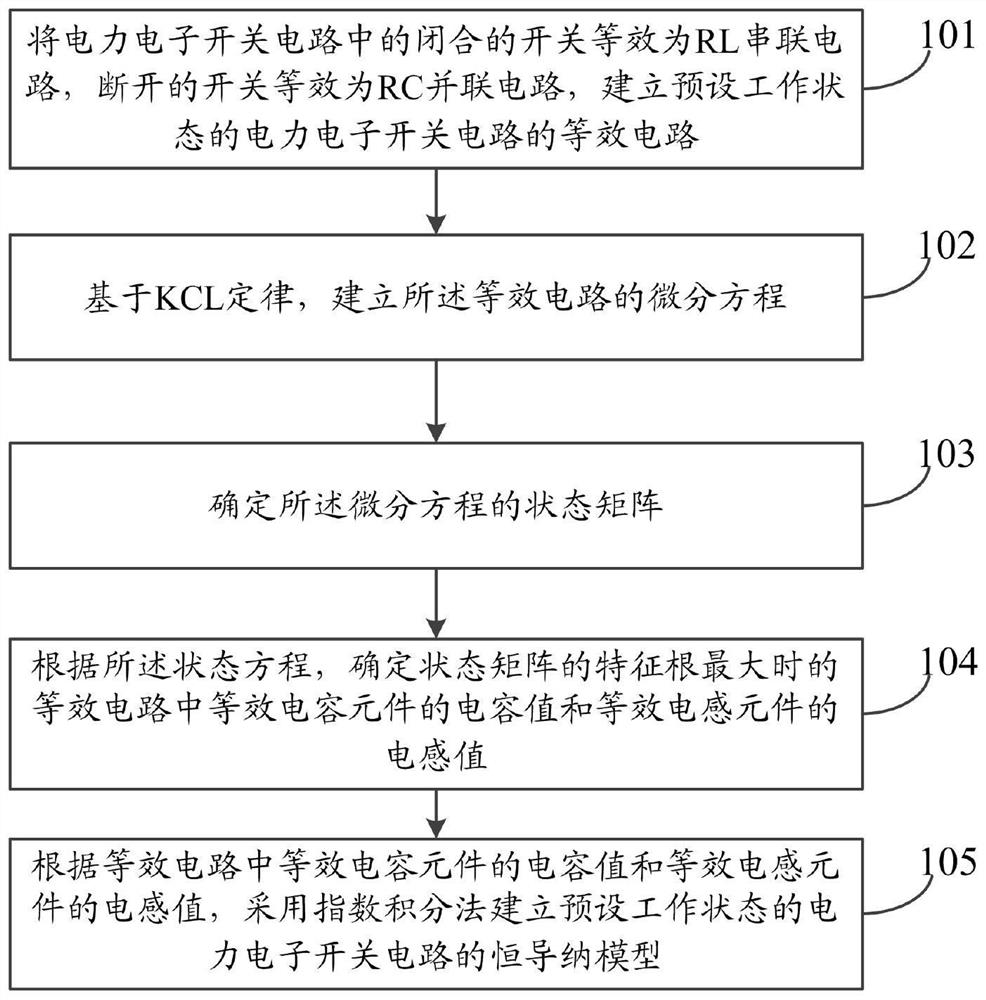
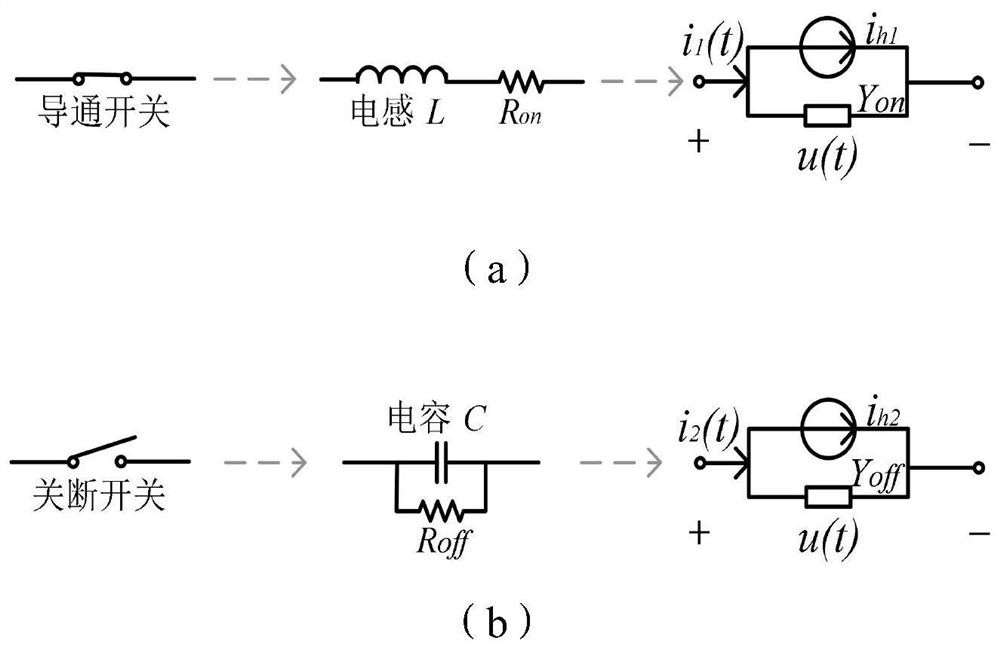
Method and system for establishing constant admittance model of power electronic switch
PendingCN112199914AHigh precisionSuppress numerical oscillationCAD numerical modellingComplex mathematical operationsDamping functionElectronic switch
The invention discloses a method and system for establishing a constant admittance model of a power electronic switch. According to the method, firstly resistors are introduced into a switching-on equivalent branch and a switching-off equivalent branch respectively, and a first-order dynamic circuit form with a damping function is formed; the optimal parameters of the equivalent circuits are determined through a final value theorem and the characteristic root analysis of a continuous time system, and the precision is improved; and finally, the constant admittance model of the power electronicswitching circuit in the preset working state is established through the exponential integration method, due to the fact that the exponential integration method has the L-stability, numerical oscillation during switching action can be effectively restrained. Because the exponential integral method has high-order precision, consistency of simulation algorithms before and after the switching actioncan be realized, and complexity caused by state switching is avoided. The invention provides the power electronic switch constant admittance switch model establishing method which is high in precision, small in numerical oscillation and simple in simulation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
A Method of Converting Continuous Time Filters to Discrete Time Filters
ActiveCN103176406BImprove performanceSuitable for engineering practical applicationAdaptive controlSystems designPartial differential equation
The invention provides a method for transforming a continuous-time filter to a discrete-time filter. The method includes: sampling input quantity and output quantity of a controlled system, and utilizing an identification algorithm for obtaining a continuous-time model of the system; constructing the continuous-time filter according to the continuous-time model; adopting a partial differential equation method to compute a coefficient matrix of the discrete-time filter according to coefficients in a continuous-time filter equation and adopted time of a discrete system; and constructing a discrete-time filter structure. The discrete-time filter is obtained by performing discrete transformation to the designed continuous-time filter. Compared with an existing discrete-time filter design method, the method has the advantages that discretization processes of a controlled object and filter designing processes based on the discrete system are decreased, and by utilizing advantages of a filter design theory based on a continuous-time system, the filter excellent in performances can be designed, system design and development time can be saved, and the method is particularly suitable for practical engineering application of digital control systems.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Laser mapping method and device based on hierarchical switchable sparse pose map optimization
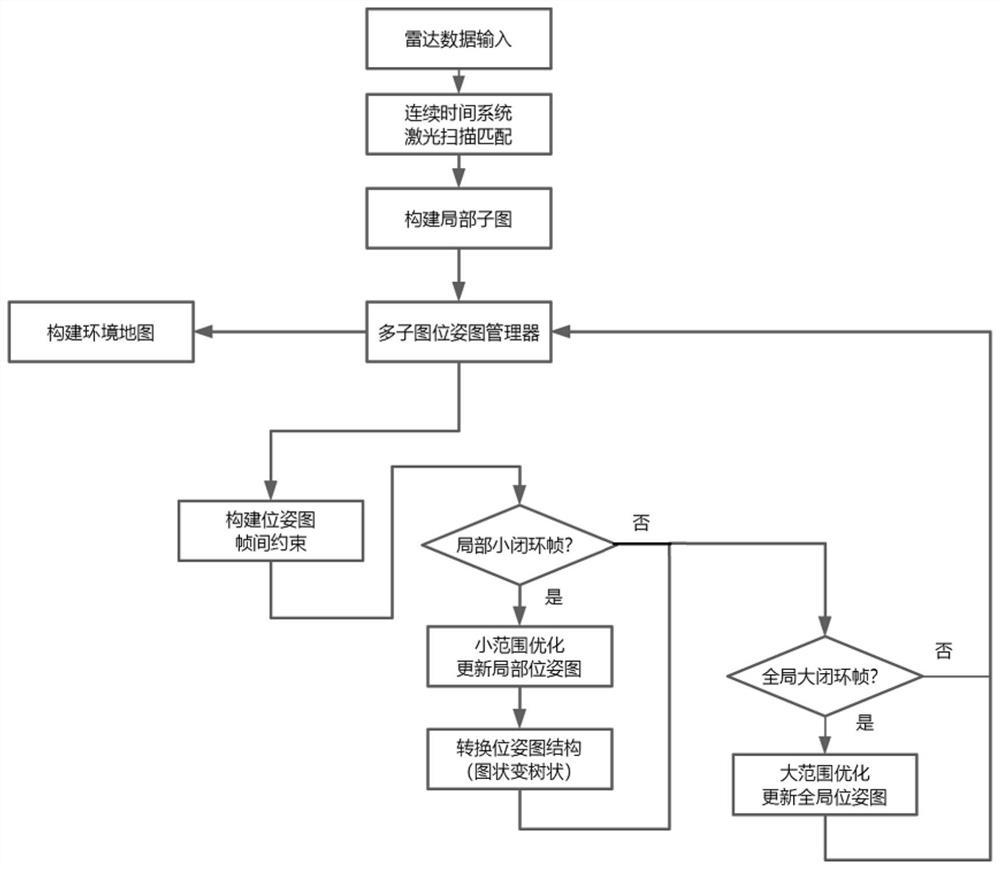
PendingCN113624239AImprove applicabilityHigh intelligenceNavigational calculation instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPattern recognitionEngineering
The invention provides a laser mapping method and device based on hierarchical switchable sparse pose map optimization. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring laser radar multi-frame scanning data; modeling the pose of the robot by using a continuous time system, and tracking the pose of the robot through laser matching; constructing local sub-graphs, calculating construction inter-frame motion constraints and closed-loop constraints among the local sub-graphs, and constructing a pose graph; and performing hierarchical pose map optimization according to the type of the inter-frame constraint, updating the position of each sub-map, and updating the environment map. According to the method, the efficiency, the precision and the anti-interference performance in the mapping process are improved by using pose map optimization, so that the adaptability of the algorithm to a low-performance computing resource plate can be improved, and the algorithm provides a more accurate environment model for motion planning control of autonomous navigation; and accurate positioning and motion planning control in the environment are facilitated, so that the intelligent degree of the autonomous navigation robot is improved.
Owner:火种源码(中山)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com