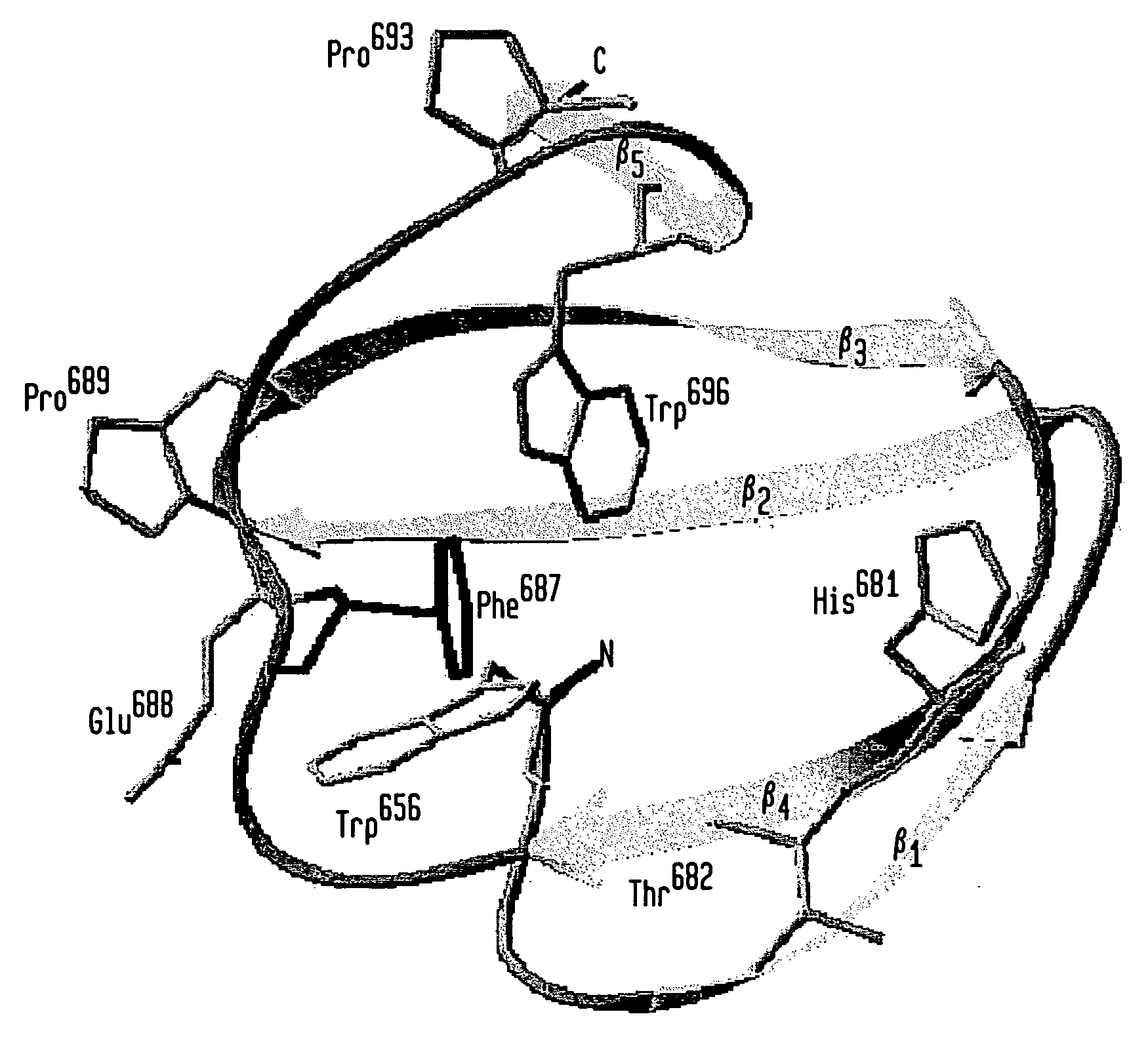
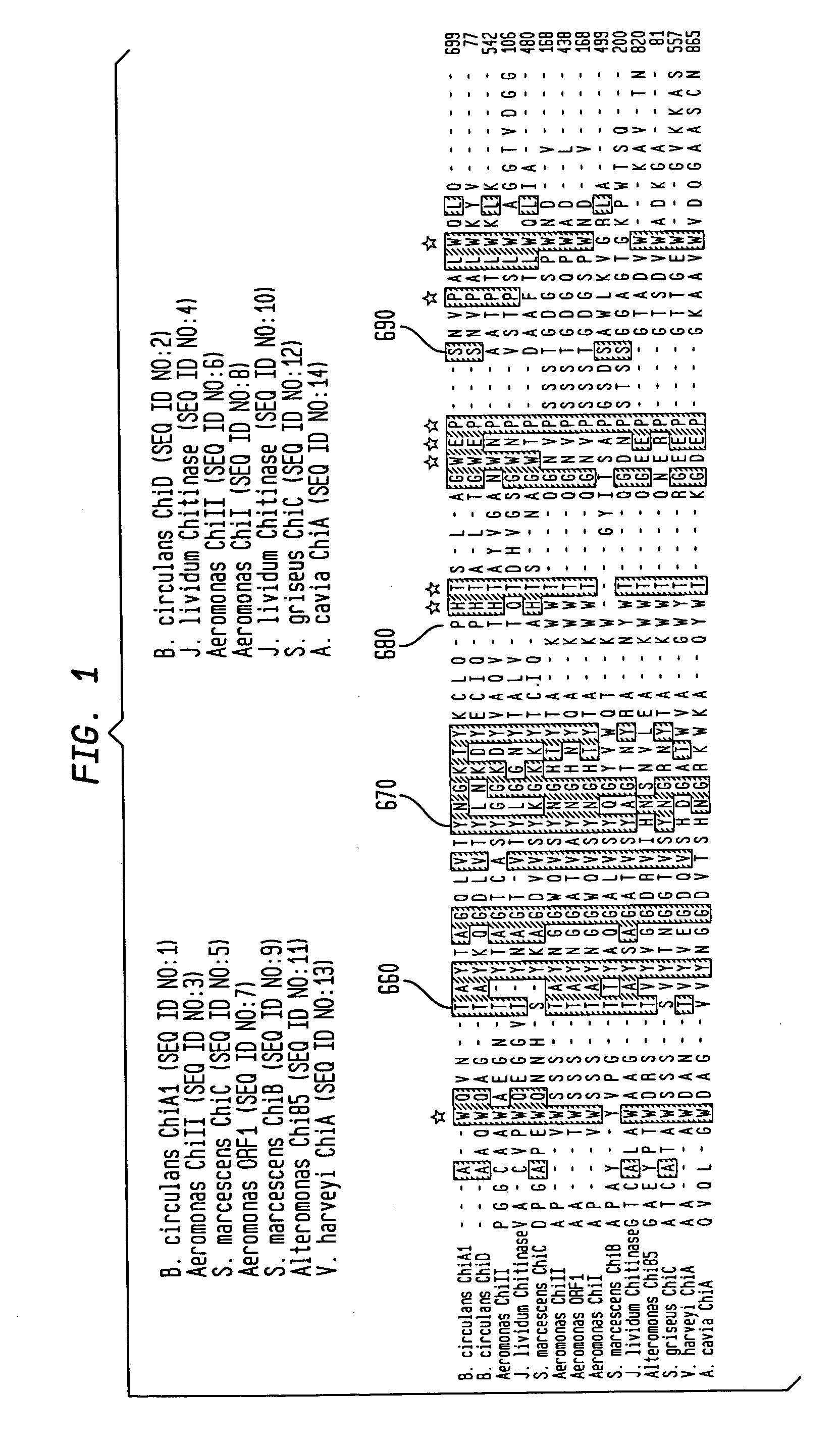
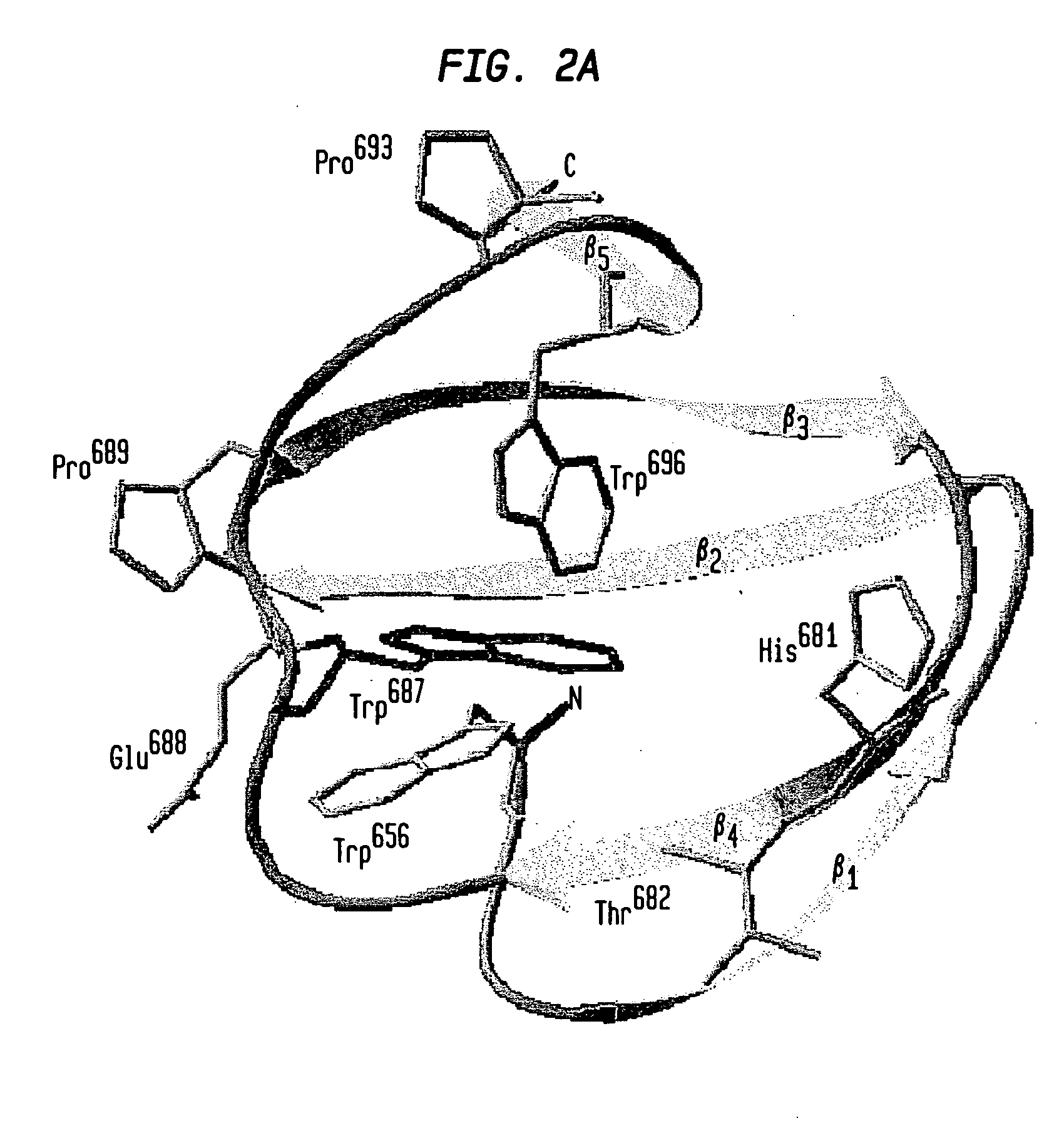
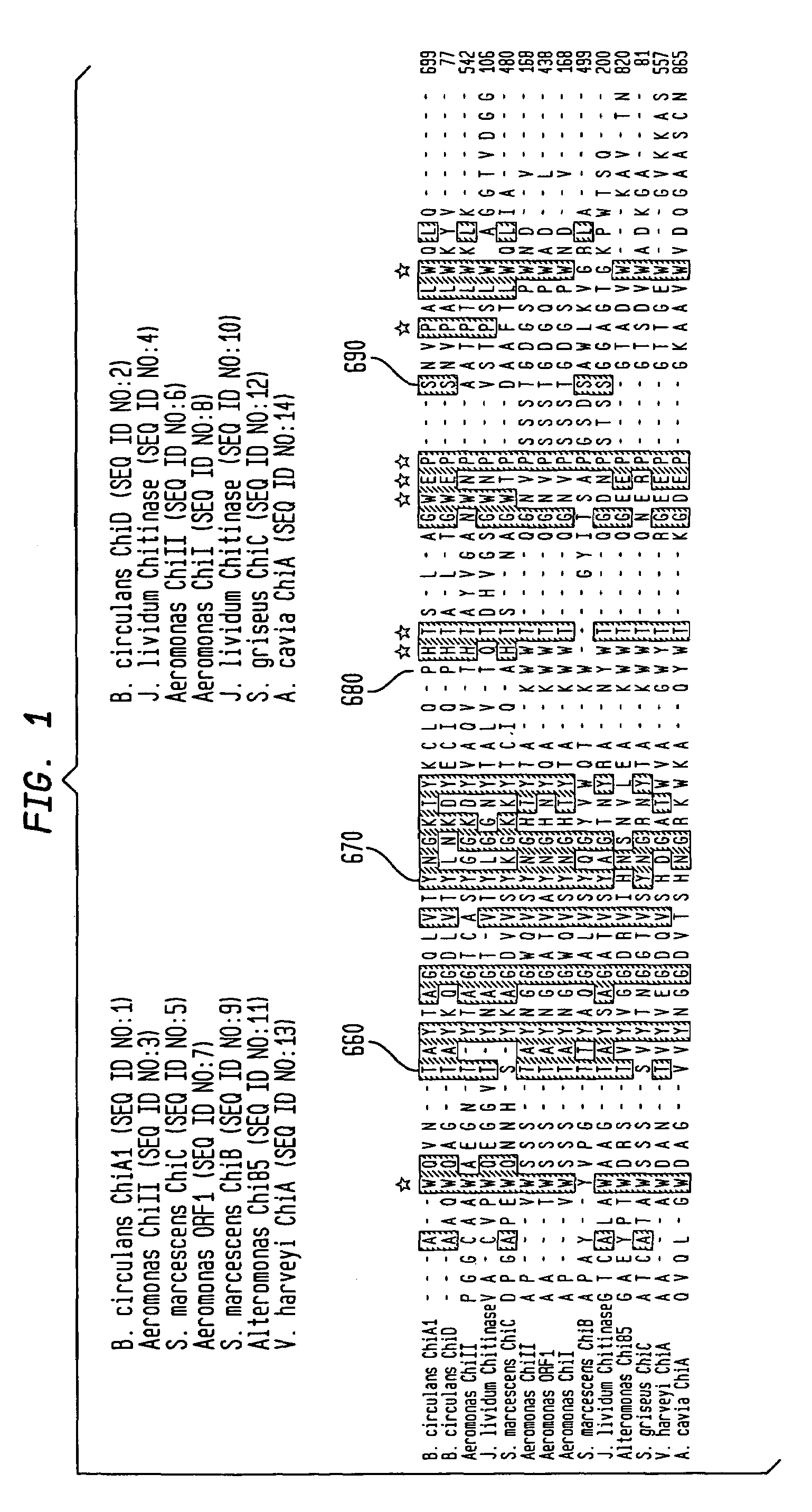
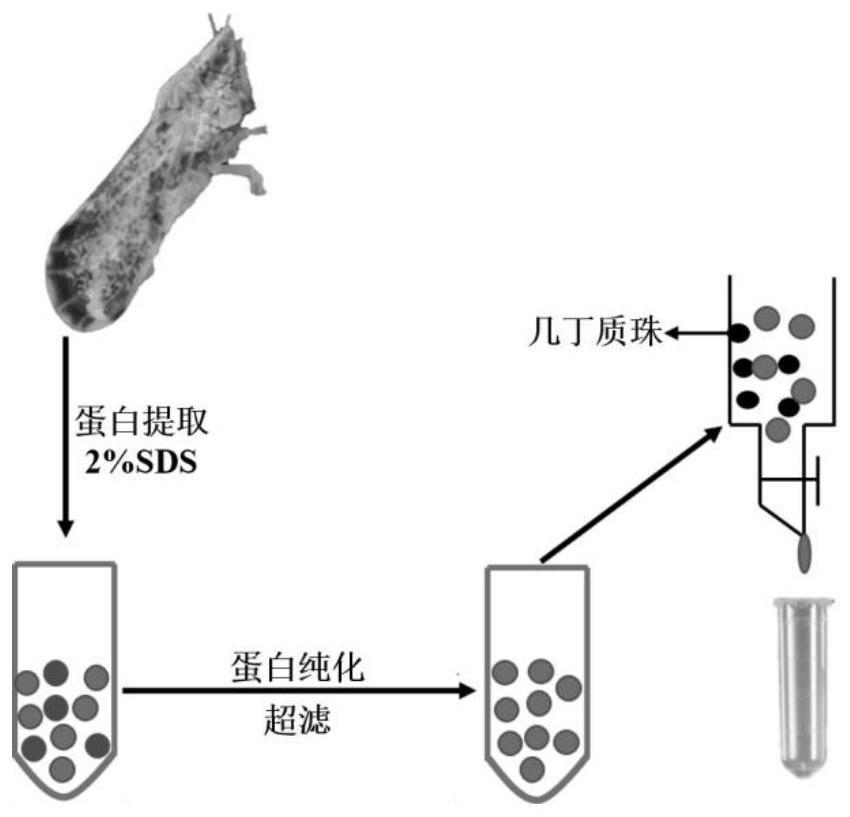
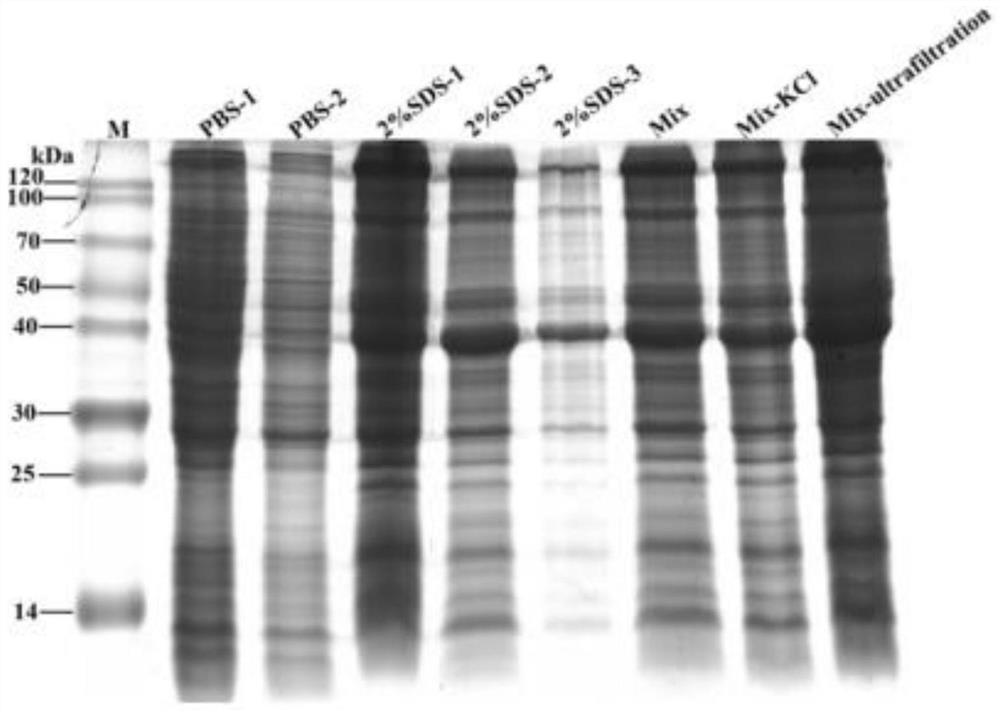
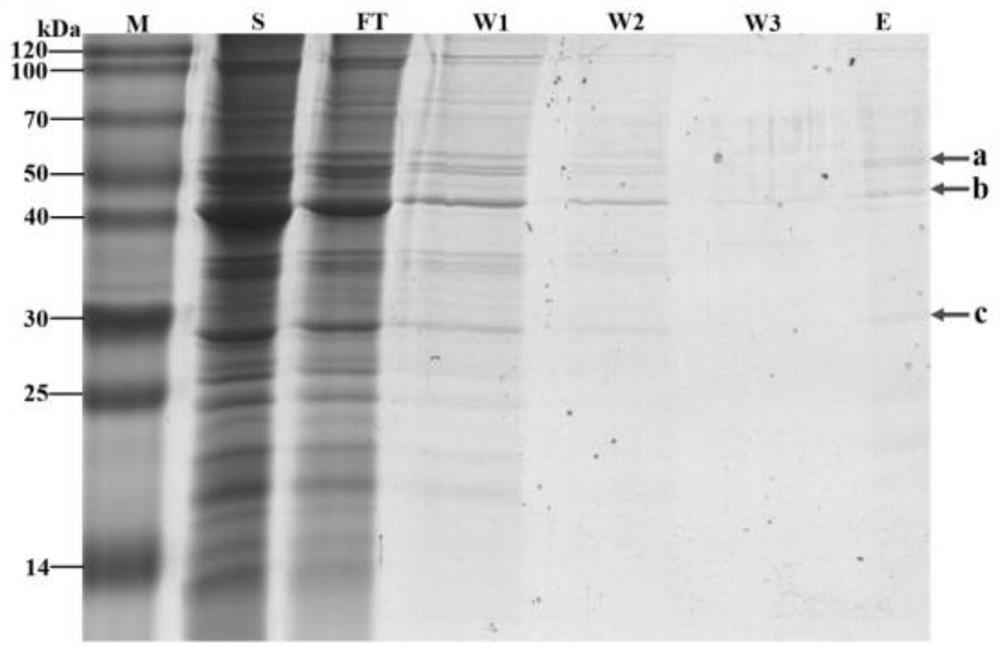
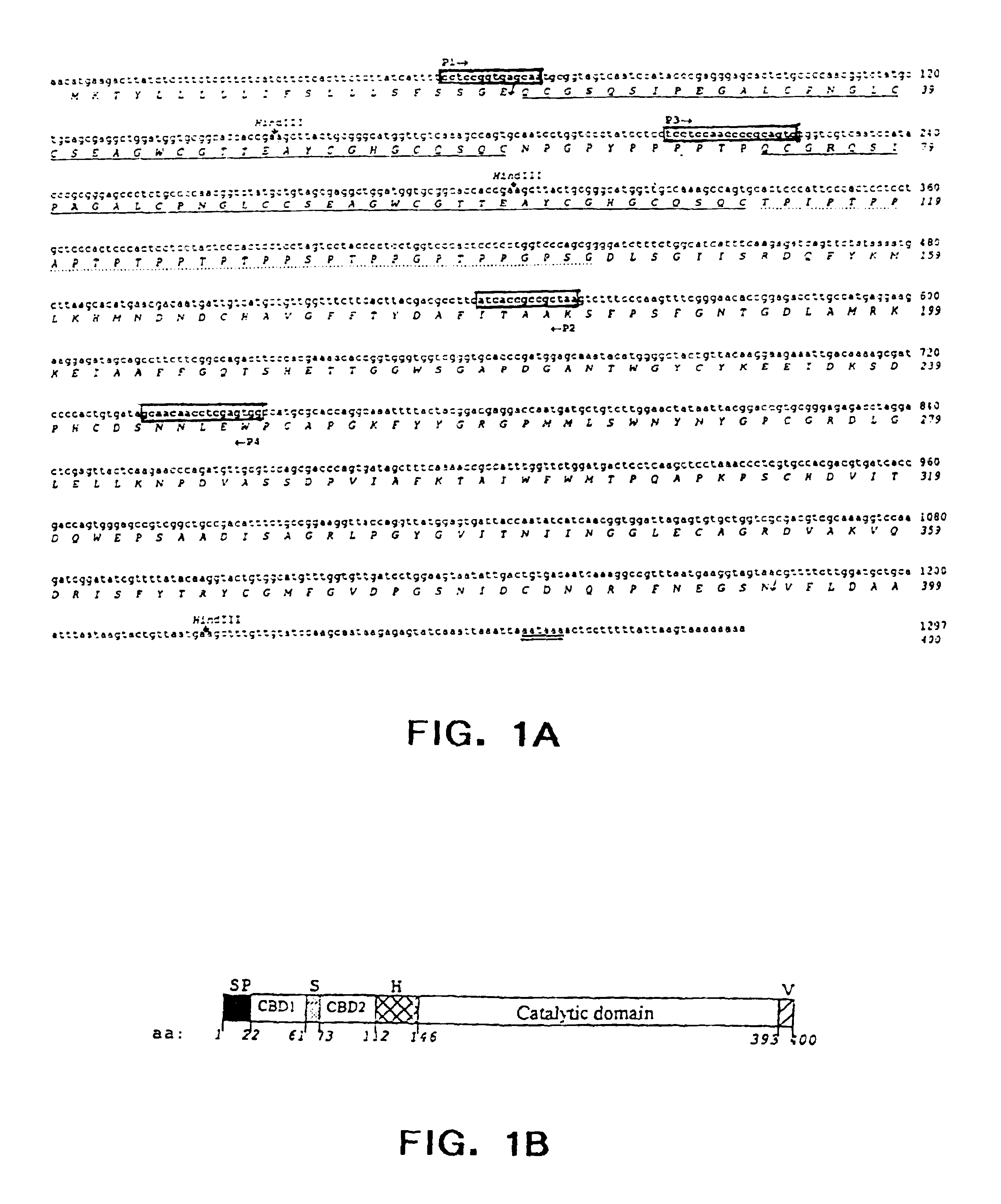
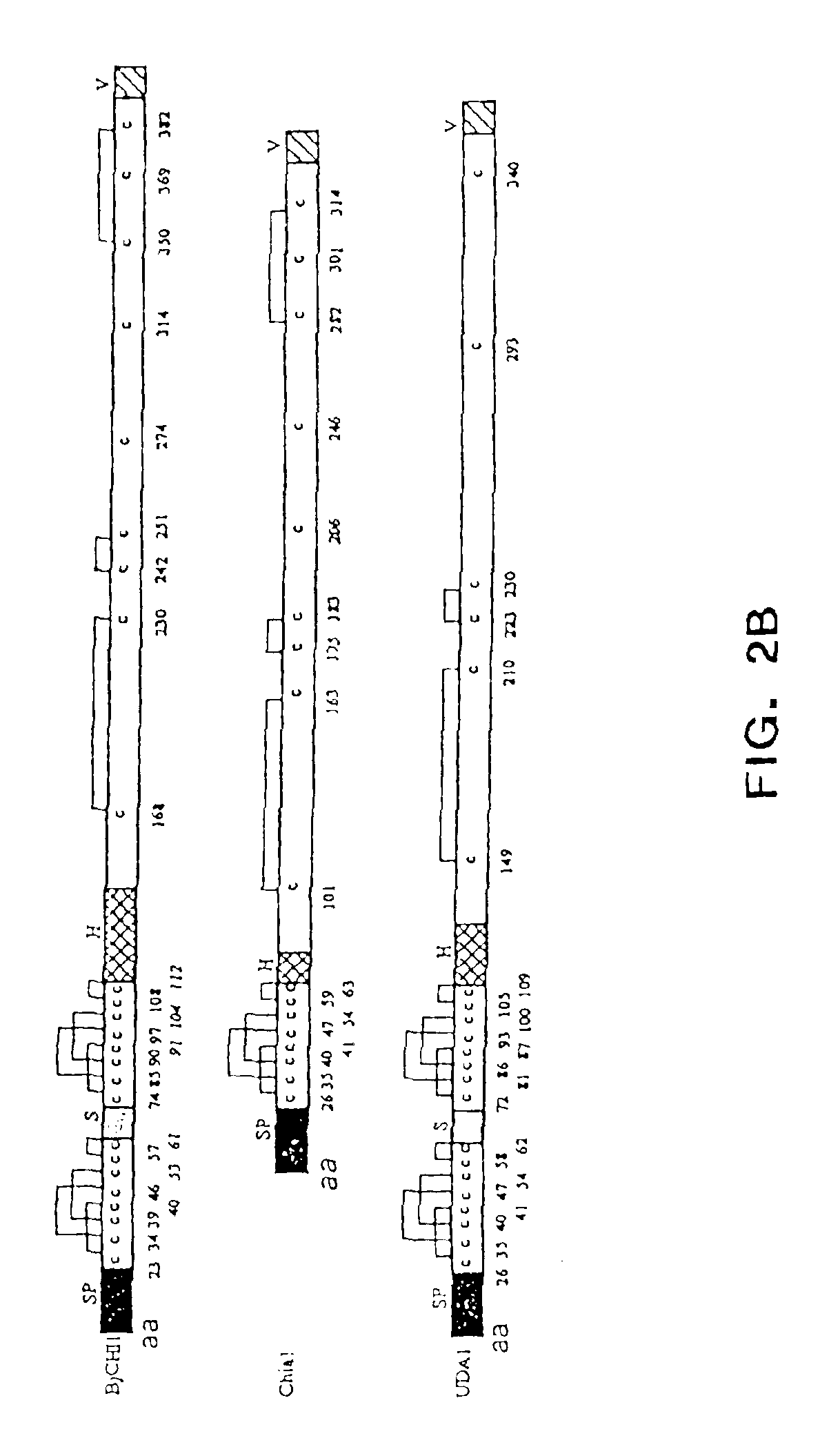
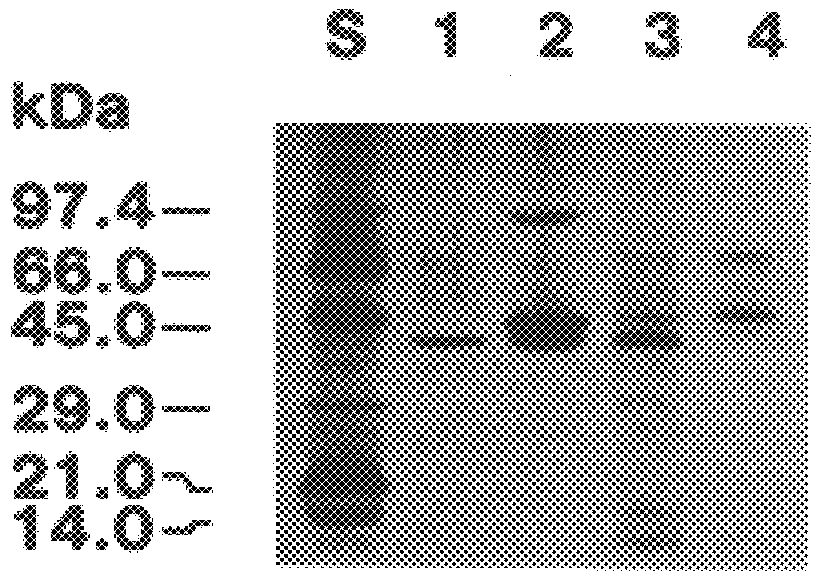
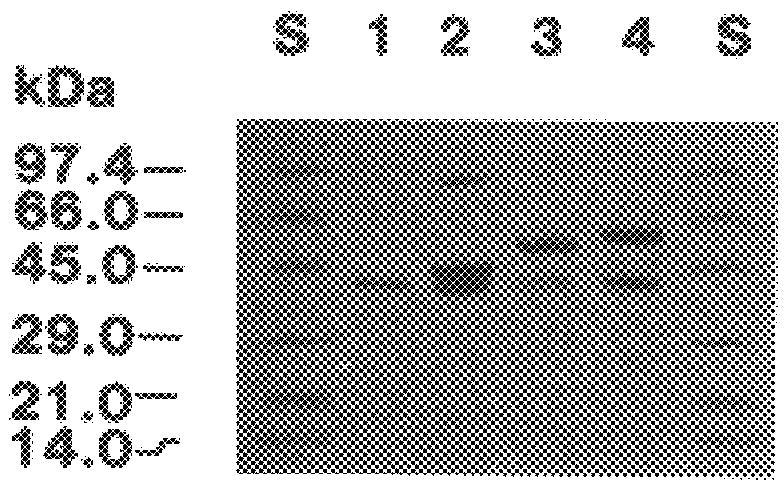
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Chitin binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
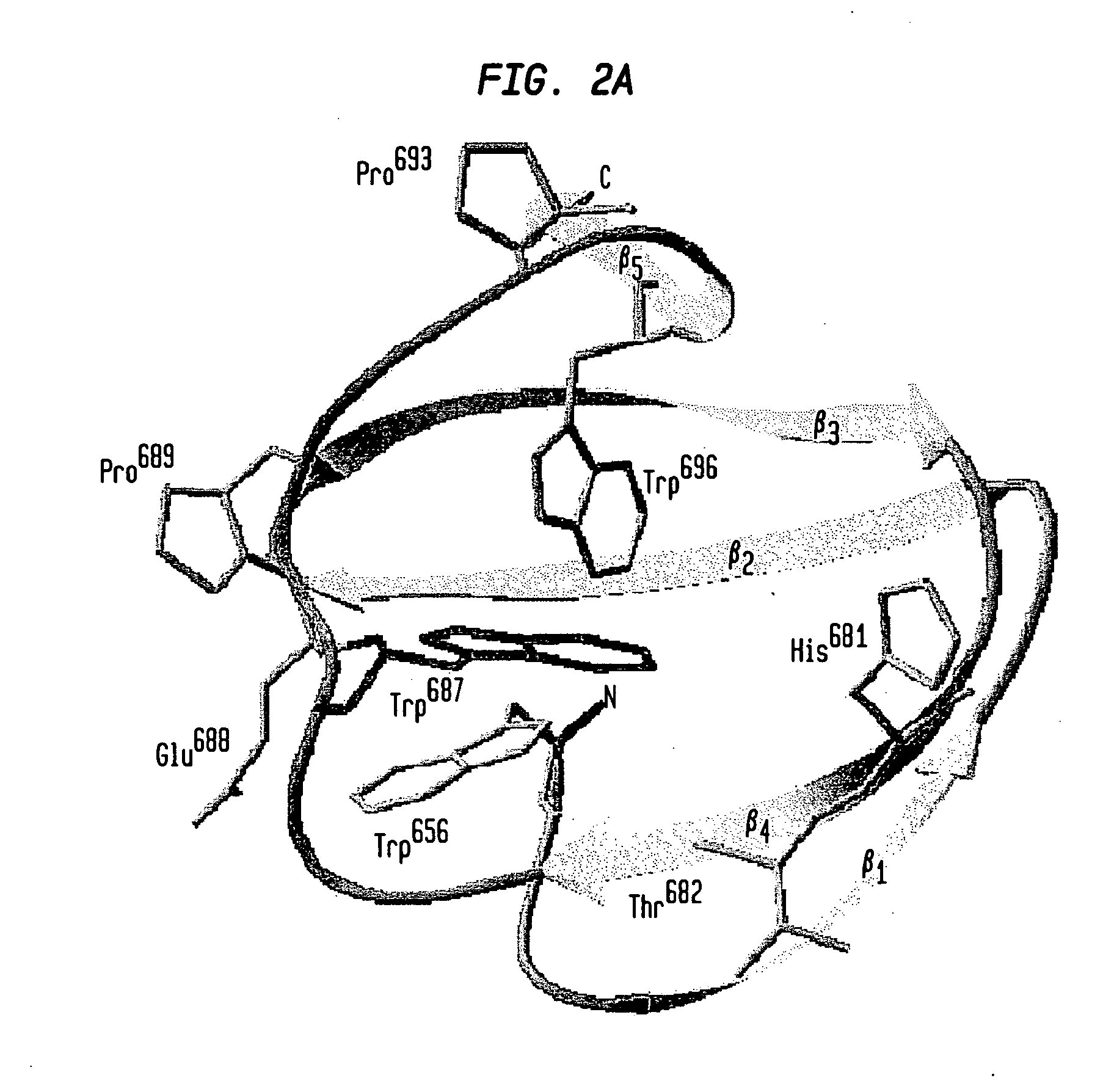
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with chitin, a linear polysaccharide consisting of beta-(1->4)-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues. [GOC:jl, ISBN:0198506732]
Modified chitin binding domain and uses thereof
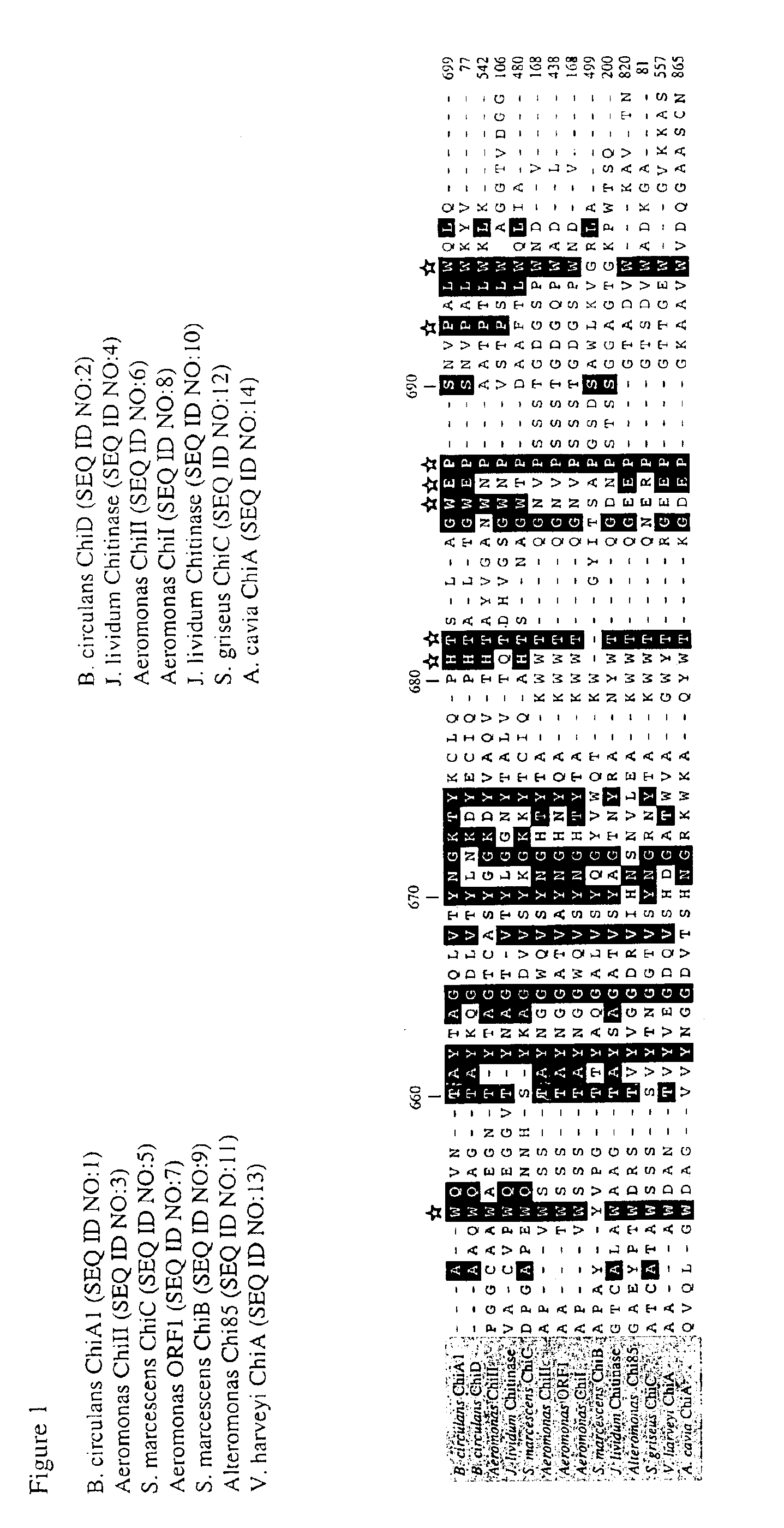
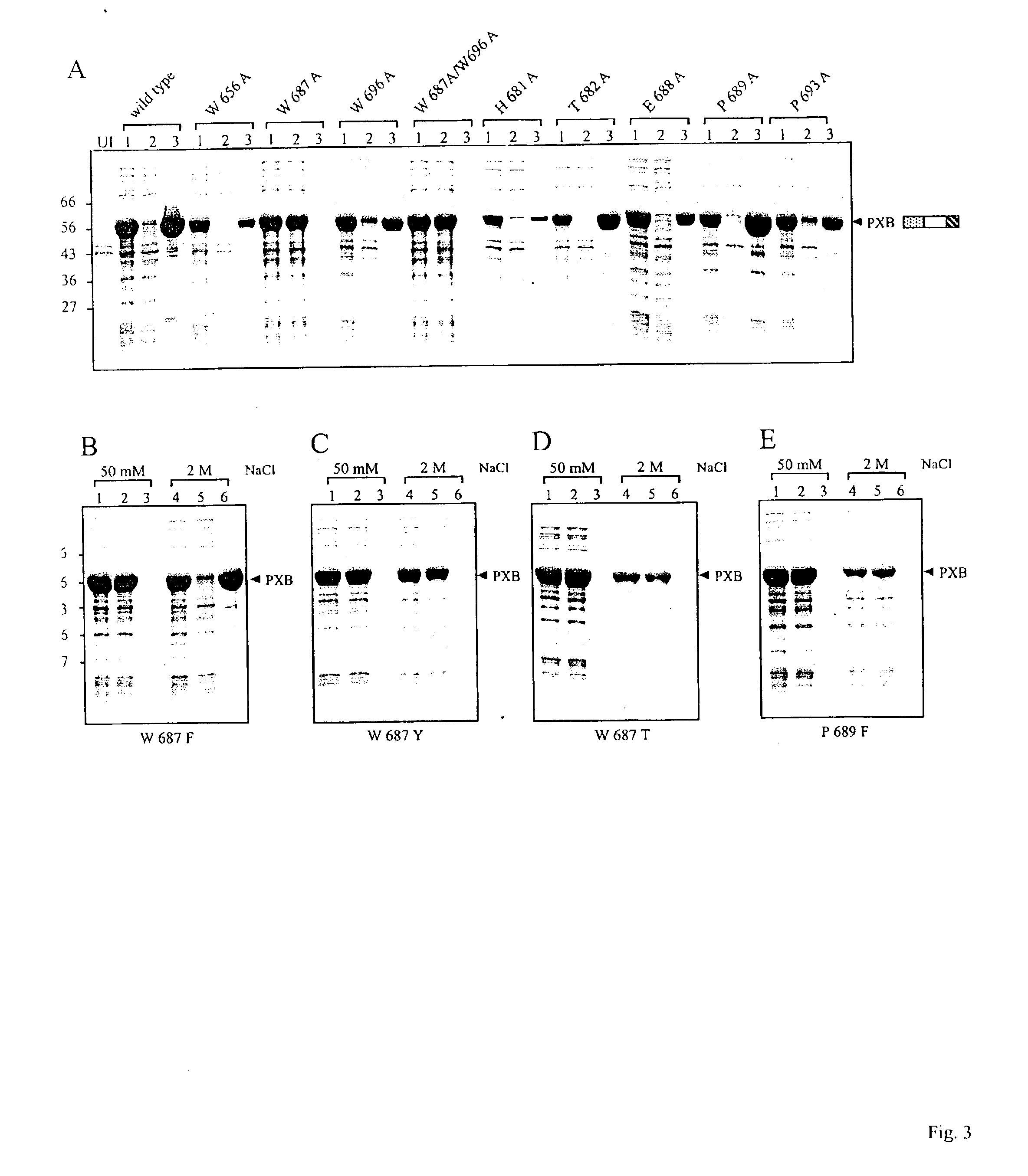
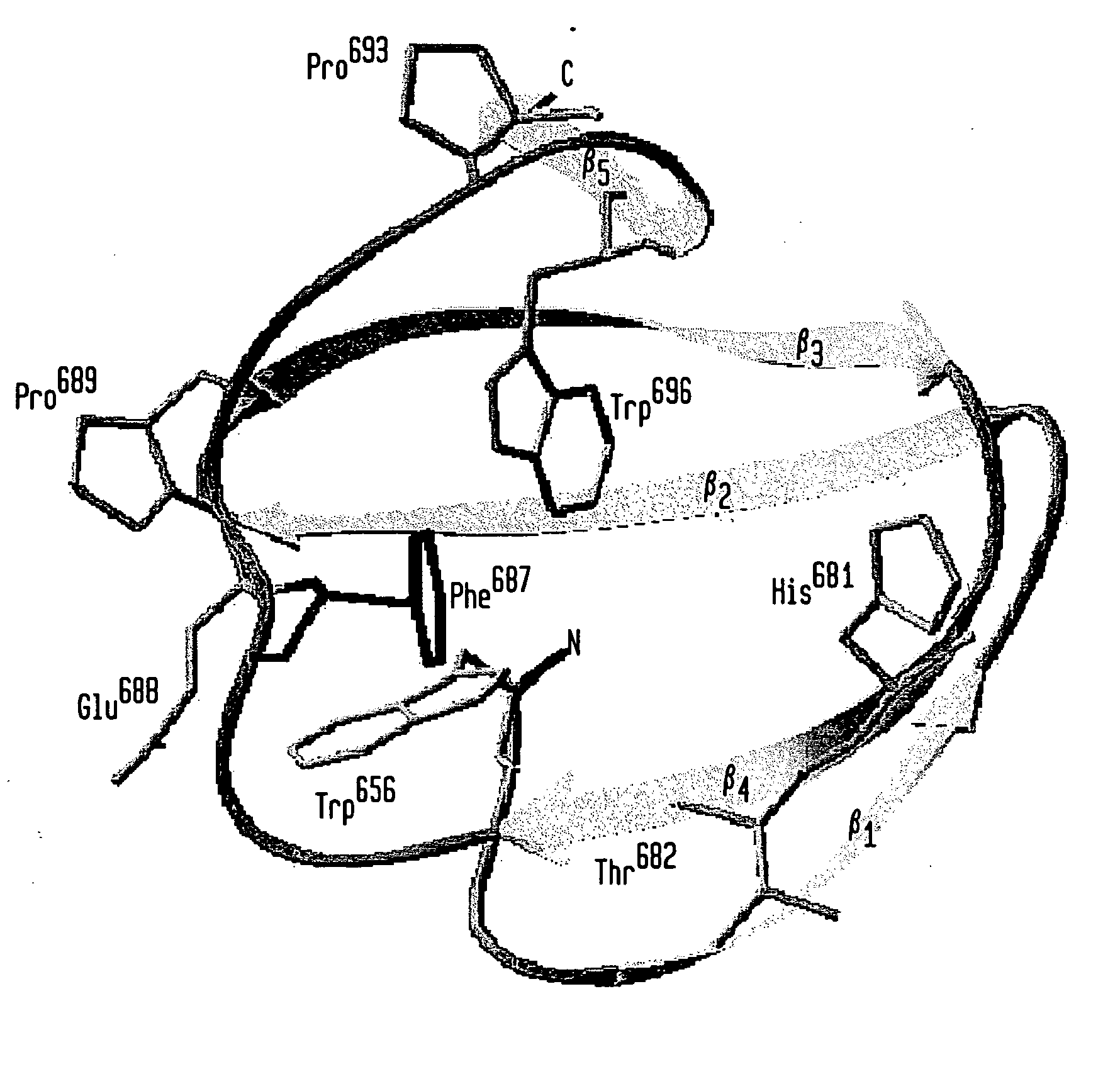
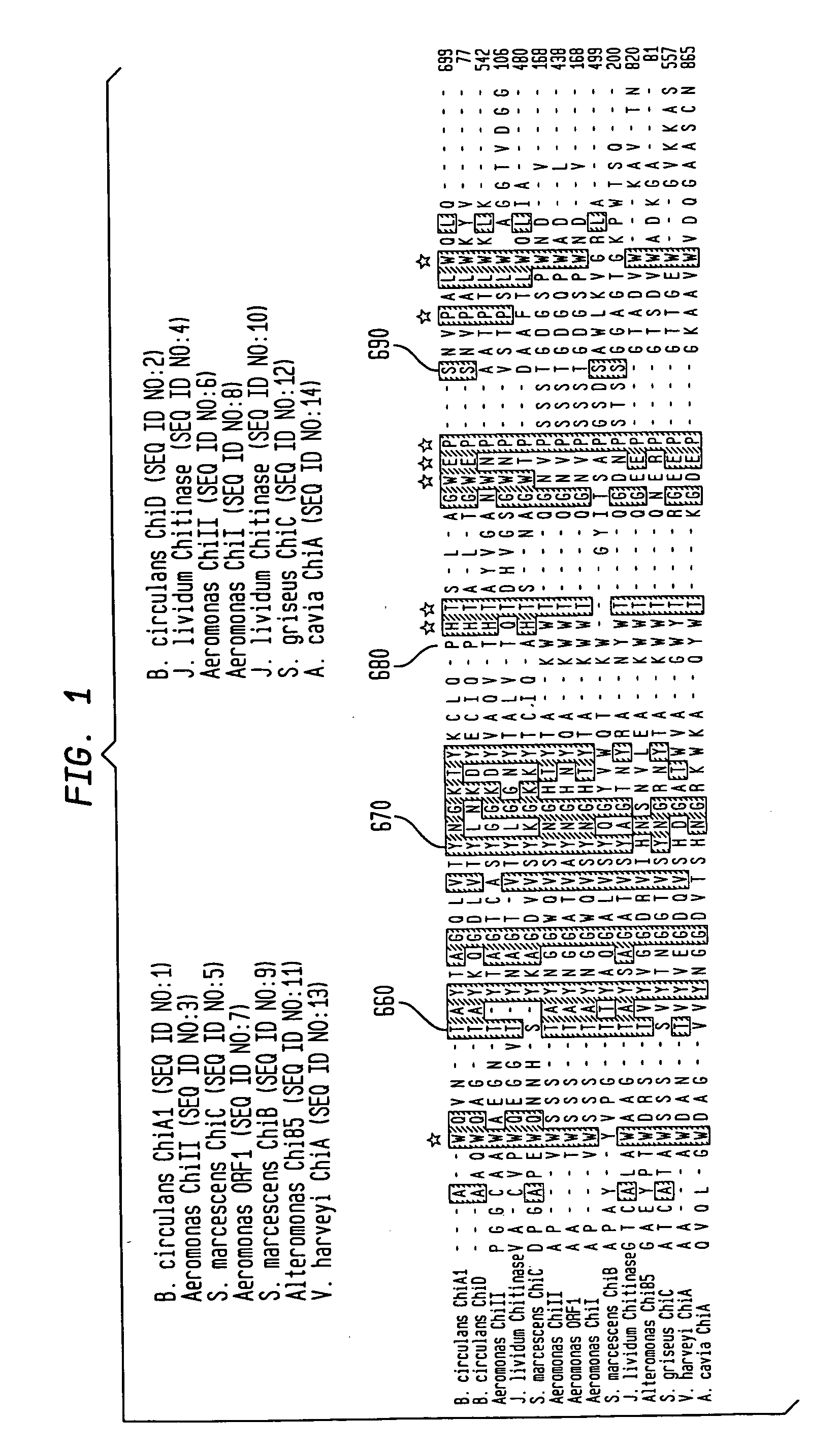
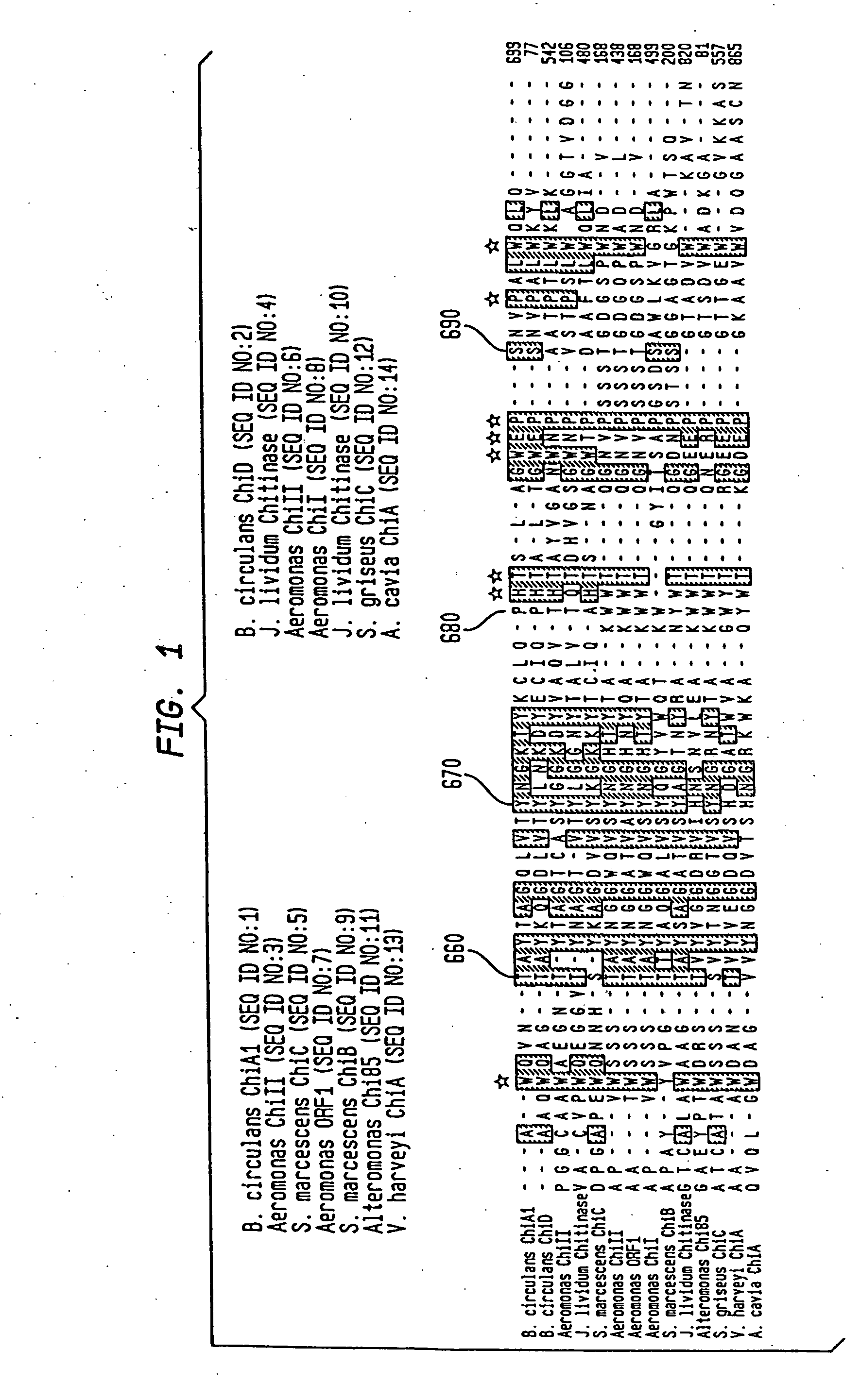
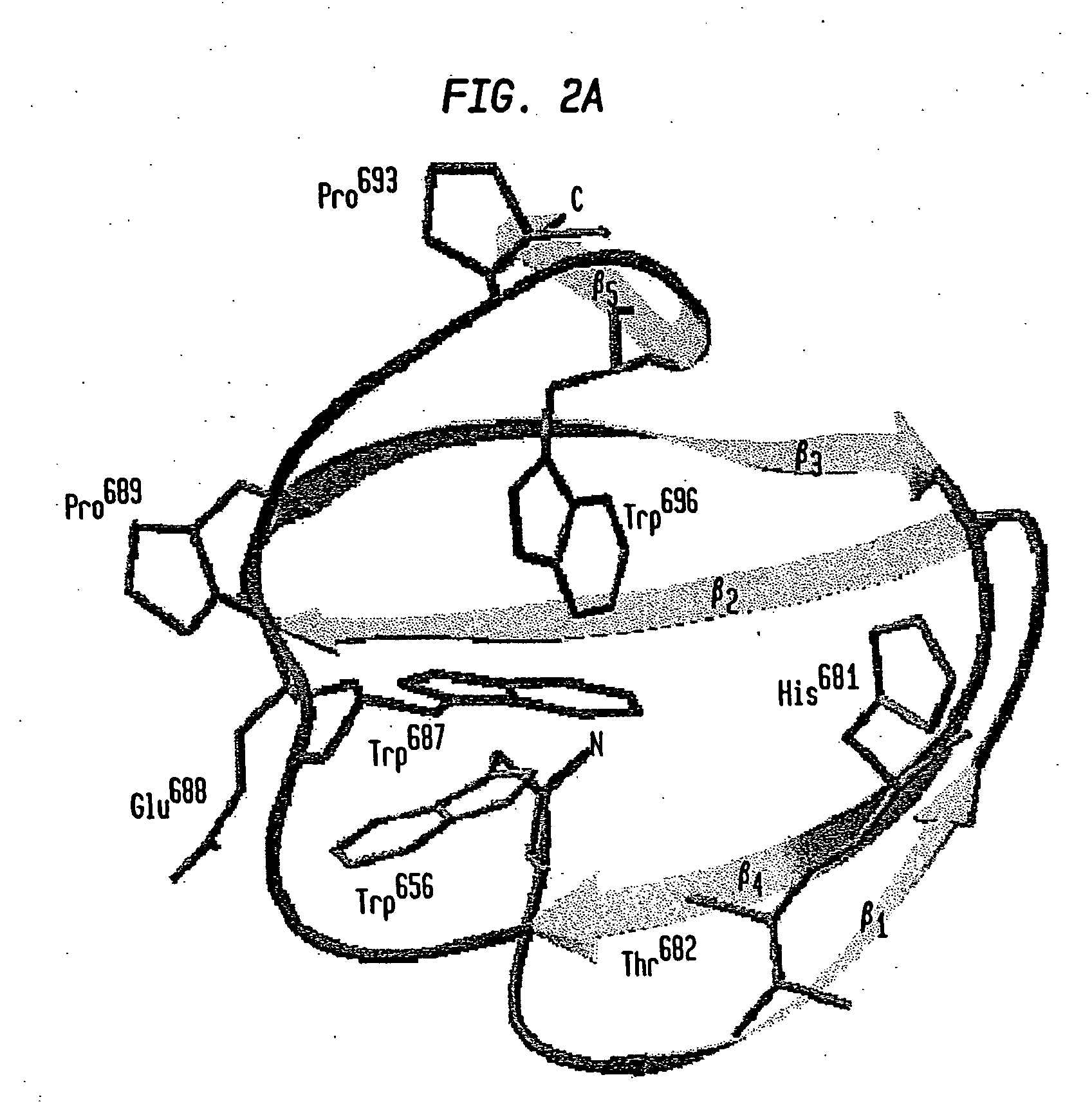
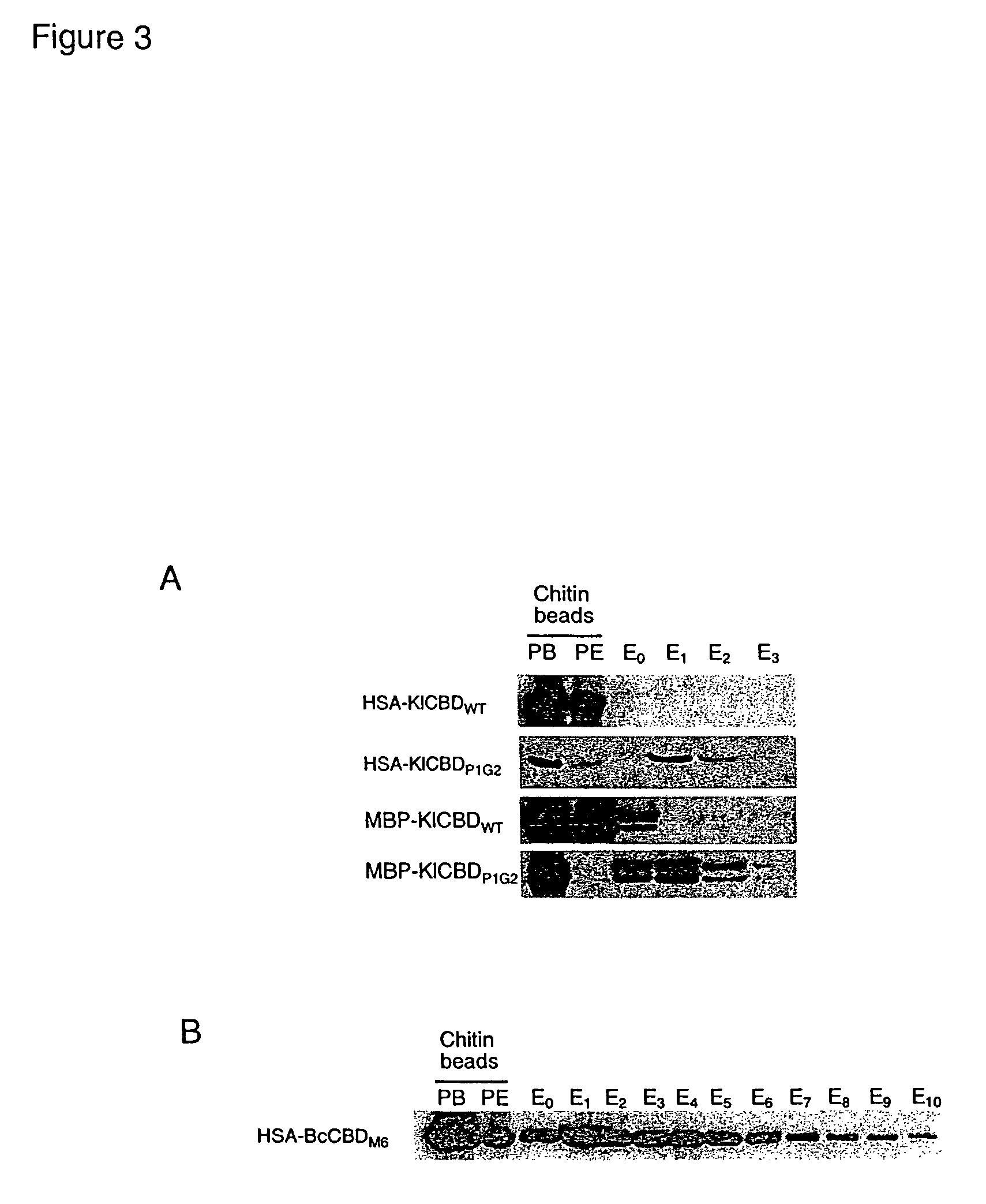
Compositions and methods are provided for reversibly binding chitin binding domain (CBD) to a chitin or equivalent substrate under non denaturing conditions. CBD is modified preferably by a mutation to achieve this change in properties. In one embodiment, an aromatic amino acid residue located in the binding cleft of the CBD was altered resulting in reversible binding affinity for substrate in select conditions. Creating a modified CBD with an altered binding affinity for substrate provides new uses for CBD not previously possible with unmodified CBD which binds irreversibly to chitin.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Cotton cells, plants, and seeds genetically engineered to express insecticidal and fungicidal chitin binding proteins (lectins)
Owner:MYCOGEN CORP
Cotton cells, plants, and seeds genetically engineered to express insecticidal and fungicidal chitin binding proteins (lectins)
Owner:MYCOGEN CORP
Bacillus velezensis ZJ20 strain and liquid preparations thereof
InactiveCN102703342AStrong stress resistanceImprove suitabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteHigh stress
The invention discloses a bacillus velezensis ZJ20 strain and liquid preparations thereof. The bacillus velezensis ZJ20 strain is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center in Chaoyang district, Beijing, China under the number of CGMCC NO.5995 on April 13 2012. A microbial biocontrol agent, namely the novel bacillus velezensis ZJ20 strain, prepared by screening has endospores with high stress resistance and long shelf life, is highly environmentally adaptive and can be produced into commercial biological agents. Metabolites of the bacillus velezensis ZJ20 strain have high bactericidal power, have high colonization ability and fast speed on plants, and can occupy the surface of hybrid bamboo effectively to prevent dieback. Antibacterial protein (chitin with protein) produced by the strain is antibacterial, can promote growth of hybrid bamboo and various types of bamboo branches and leaves, and have a novel effect of recovering posterior production capacity.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Application of type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA (double strand ribonucleic acid) of insect
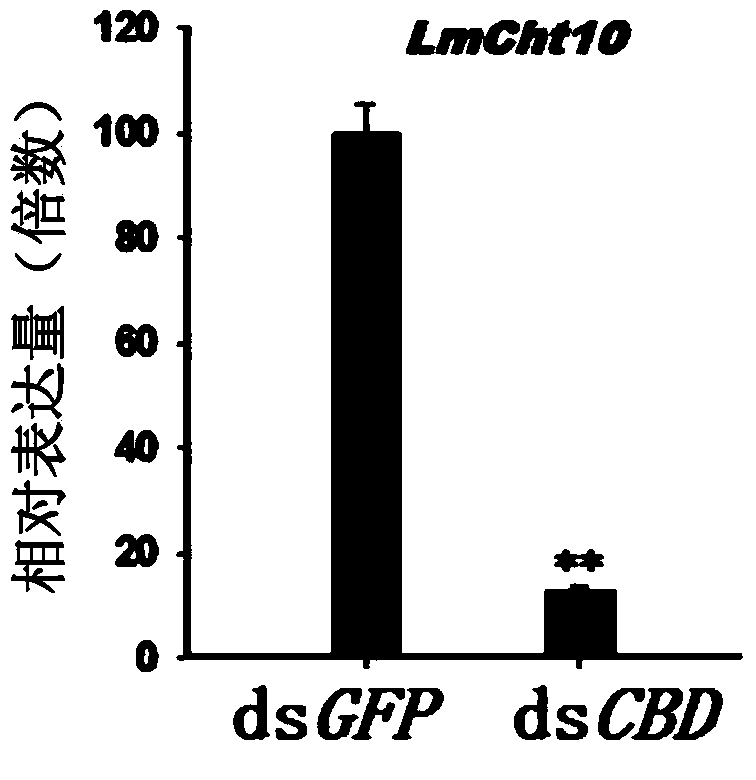
The invention provides application of a type II chitinase gene (Cht10) specificity dsRNA (double strand ribonucleic acid) of an insect. The type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA can silence the type II chitinase gene so as to allow a migratory locust to die without affecting other insects. The type II chitinase gene of the migratory locust is cloned and sequenced, then the functional domain is analyzed, unique chitin binding domains are selected, the gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 is designed for synthesis of specificity dsRNA. After the dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of the migratory locust, the migratory locust cannot exuviate smoothly to step into next instar and dies at the rate of 100%, but other insects injected with the dsRNA do not die. The invention provides a target for specific pest control based on RNA interference, and the type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA can be used for preventing and controlling specific insect-migratory locust.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Modified chitin-binding domain and use thereof
Compositions and methods are provided for reversibly binding chitin binding domain (CBD) to a chitin or equivalent substrate under non denaturing conditions. CBD is modified preferably by a mutation to achieve this change in properties. In one embodiment, an aromatic amino acid residue located in the binding cleft of the CBD was altered resulting in reversible binding affinity for substrate in select conditions. Creating a modified CBD with an altered binding affinity for substrate provides new uses for CBD not previously possible with unmodified CBD which binds irreversibly to chitin.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Recombinant serine protease and fungicide containing the same
The present invention relates to one kind of recombinant serine proteinase. The recombinant serine proteinase contains one kind of fusion protein comprising serine proteinase from fungus and chitin binding domain from insect chitinase fused together and contains one gene coding serine protein from fungus and one gene coding chitin binding domain from insect chitinase with separated nucleotide sequences. The recombinant serine proteinase of the present invention may be enriched in insect body wall to raise insect body wall degrading speed and raise pesticidal fungal virulence.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Modified chitin-binding domain and use thereof
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Modified chitin-binding domain and use thereof
Compositions and methods are provided for reversibly binding chitin binding domain (CBD) to a chitin or equivalent substrate under non denaturing conditions. CBD is modified preferably by a mutation to achieve this change in properties. In one embodiment, an aromatic amino acid residue located in the binding cleft of the CBD was altered resulting in reversible binding affinity for substrate in select conditions. Creating a modified CBD with an altered binding affinity for substrate provides new uses for CBD not previously possible with unmodified CBD which binds irreversibly to chitin.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
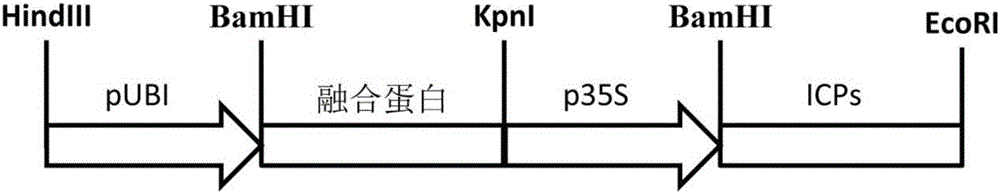
Insect-resistant fusion gene and encoded protein as well as application thereof
ActiveCN106834318AEasy to useBroad insecticidal spectrumBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOrder LepidopteraNucleotide
The invention discloses an insect-resistant fusion gene and an encoded protein as well as application thereof. The gene comprises a nucleotide sequence of encoding chitin binding protein and a nucleotide sequence of encoding Vip3 toxin in turn from 5' to 3'. The two nucleotide sequences are located in one opening reading frame. Compared with original chitin binding protein and by Vip3 protein, the artificial protein molecule formed by fusing one chitin binding protein and one Vip3 toxin designed by the invention has the advantages that the insecticidal spectrum is wide, various important pests (such as beet armyworm, armyworm and mealywing) in lepidoptera and hemiptera can be simultaneously prevented and controlled and the insecticidal efficiency reaches up to 50%-100%; the combined utilization of the proteins with different functions and other insect-resisting proteins (such as ICPs) is benefited, the insecticidal spectrum is further widened, and the generation of pest resistance is delayed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
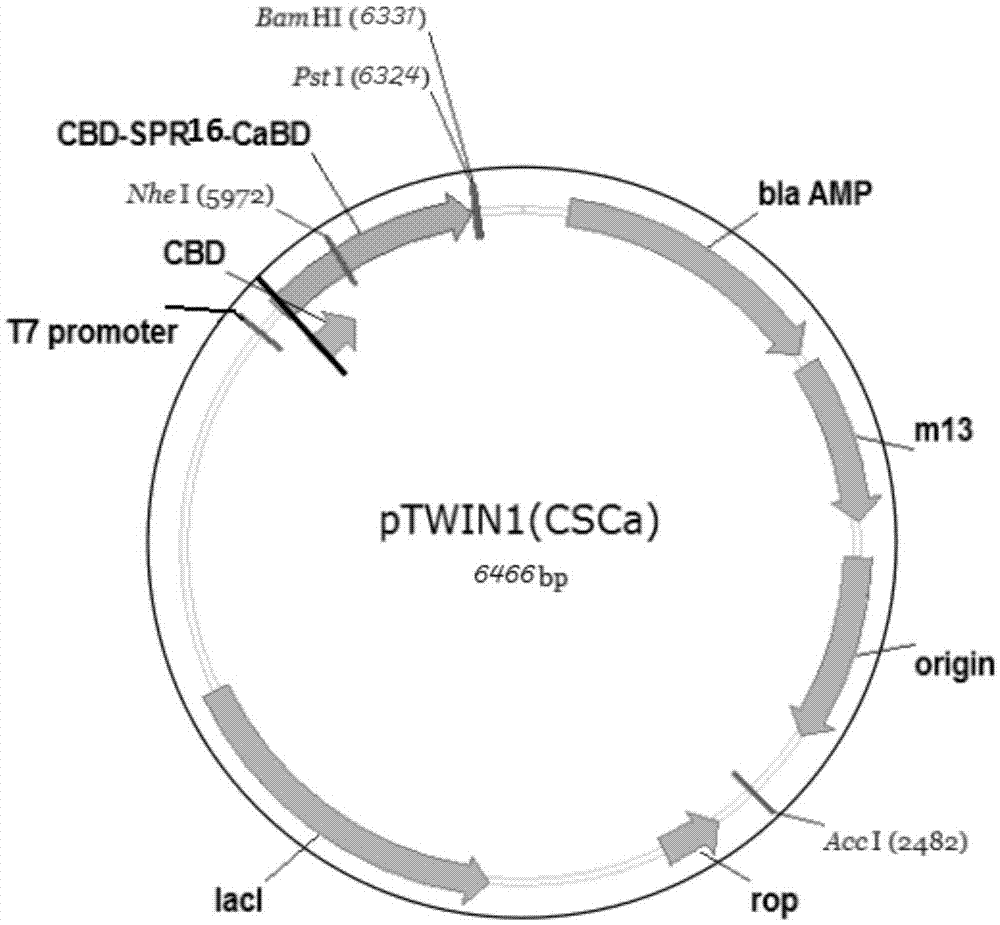
Shell nacre-like recombinant protein CSCa and method for regulating and preparing calcium carbonate by using same
ActiveCN105440140AEasy to prepareEasy to operateCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRepetitive SequencesMaterials preparation
The invention specifically relates to a shell nacre-like recombinant protein CSCa and a method for regulating and preparing calcium carbonate by using the same, belonging to the field of material preparation. The recombinant protein CSCa is composed of a chitin binding domain, a silk protein repetitive sequence and a calcium ion binding domain. The method for regulating and preparing calcium carbonate by using the same comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing chitin with a recombinant protein CSCa solution; adding a NaHCO3 solution when chitin and recombinant protein CSCa are fully combined together and carrying out uniform mixing under stirring; then adjusting a pH value to 8.5 to 9.5 and adding a CaCl2.2H2O solution; and carrying out a mineralization reaction under the condition of stirring so as to obtain mineralized calcium carbonate. Vaterite-phase calcium carbonate can be prepared by using the method provided by the invention and can be stably maintained for a period of time under the action of the recombinant protein CSCa, which is an unusual phenomenon in the process of mineralization and is of great promotion significance to deeper understanding of the mechanism of mineralization.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Modified chitin binding domain and uses thereof
Compositions and methods are provided for reversibly binding chitin-binding domain (CBD) to a chitin or equivalent substrate under non-denaturing conditions. CBD from either prokaryotes or eukaryotes are modified for example, by random mutation, and screened to identify mutants that achieve this change in properties. Creating a modified CBD with an altered binding affinity for substrate provides new uses for CBD not previously possible with unmodified CBD that binds irreversibly to chitin.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through immobilized lysine decarboxylase
InactiveCN109880859AImmobilizationImprove adsorption capacityOn/in organic carrierFermentationProtein CChitin binding
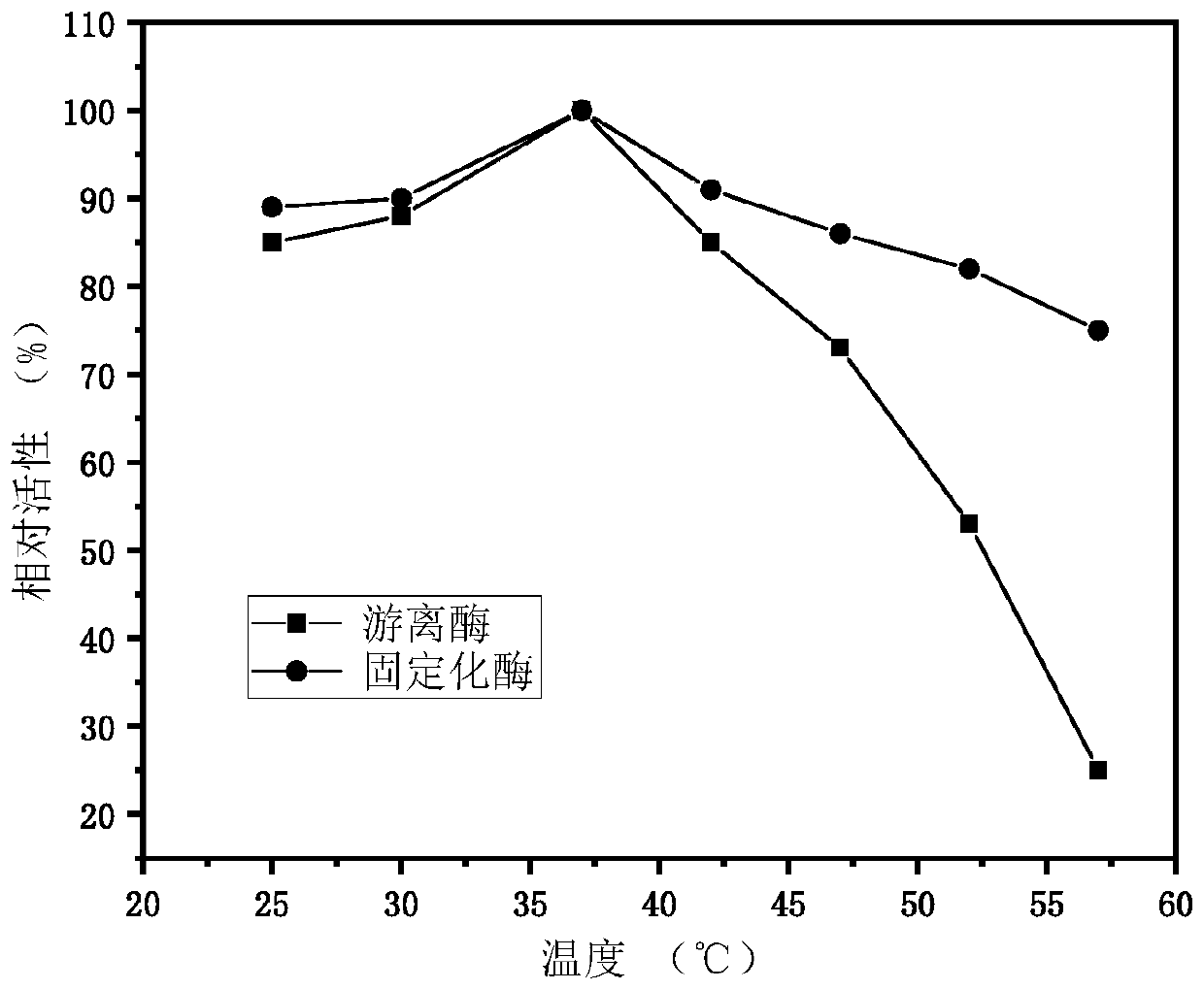
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through immobilized lysine decarboxylase. The method comprises the following steps of connecting a chitin binding domain (ChBD) gene to the N end of a lysine decarboxylase gene (CadA) to construct a fusion protein; fermenting the fusion protein to obtain a crude lysine decarboxylase enzyme solution; adding chitin into the crude enzyme solution to obtain immobilized lysine decarboxylase; finally, enabling the obtained immobilized lysine decarboxylase to participate in a decarboxylation reaction of L-lysine to prepare 1,5-1,5-pentanediamine. According to the method, the specific affinity effect of the substrate chitin and the fusion protein is skillfully utilized to adsorb the lysine decarboxylase, the cost of the immobilizedcarrier chitin is low, the immobilization efficiency is high, the activity stability of enzymes is high, and meanwhile, the procedure of protein purification can be omitted through specific affinity adsorption. The provided method achieves repeated production of 1,5-1,5-pentanediamine and can reduce the production cost, simplify the separation procedure of downstream products and enzymes and achieve remarkable economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
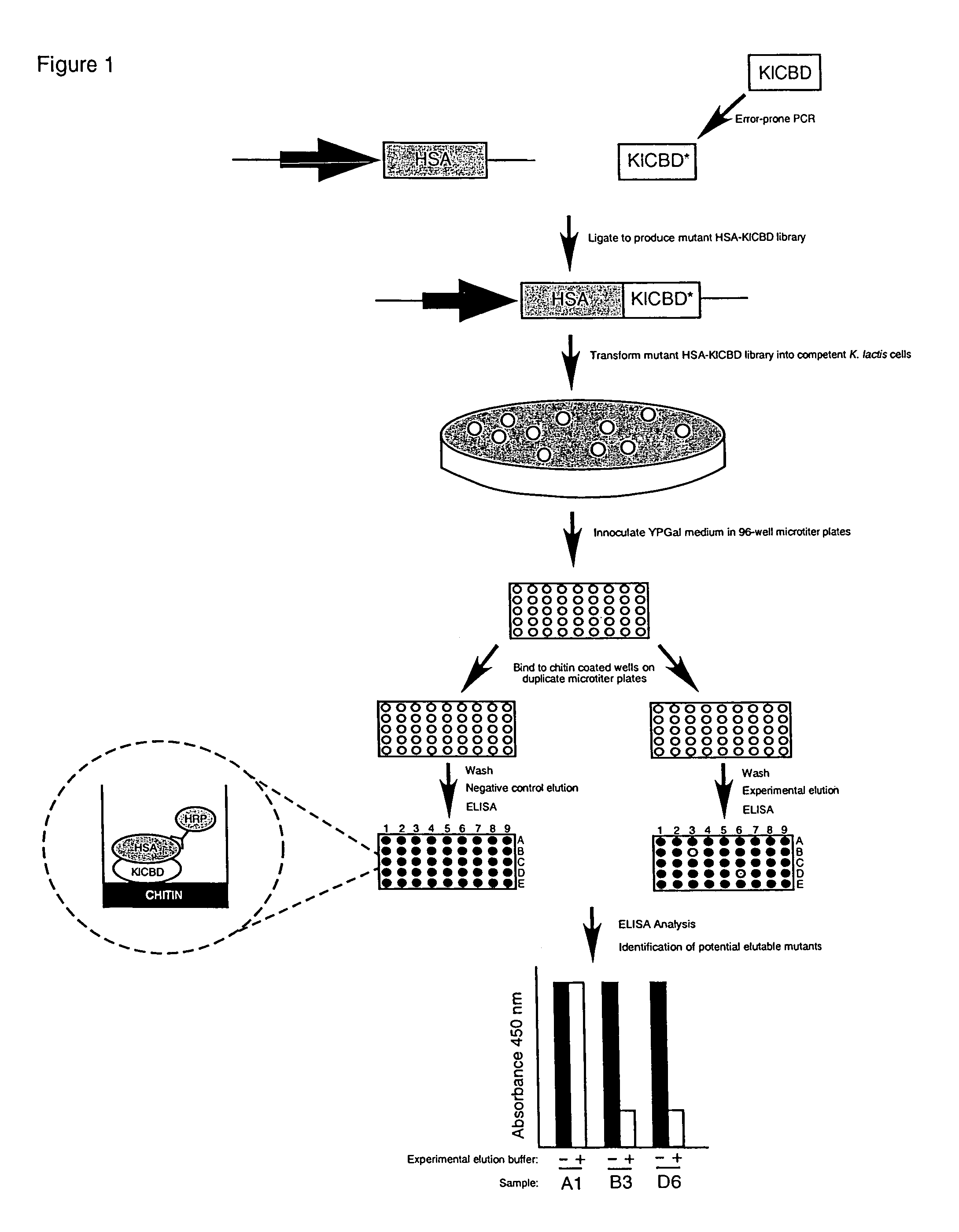
Compositions and methods relating to elutable carbohydrate-binding proteins
InactiveUS7732565B2Peptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningCarbohydrate-binding proteinChitin formation
Compositions and methods are provided for creating and identifying mutant carbohydrate-binding proteins that reversibly bind to carbohydrate substrates under conditions where the native protein remains bound. Examples of modified chitin-binding domains are provided which can be eluted from chitin in the presence of a reducing agent or at a pH within the range of 5-10.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Chitin binding protein CBP58, and encoding gene and application thereof
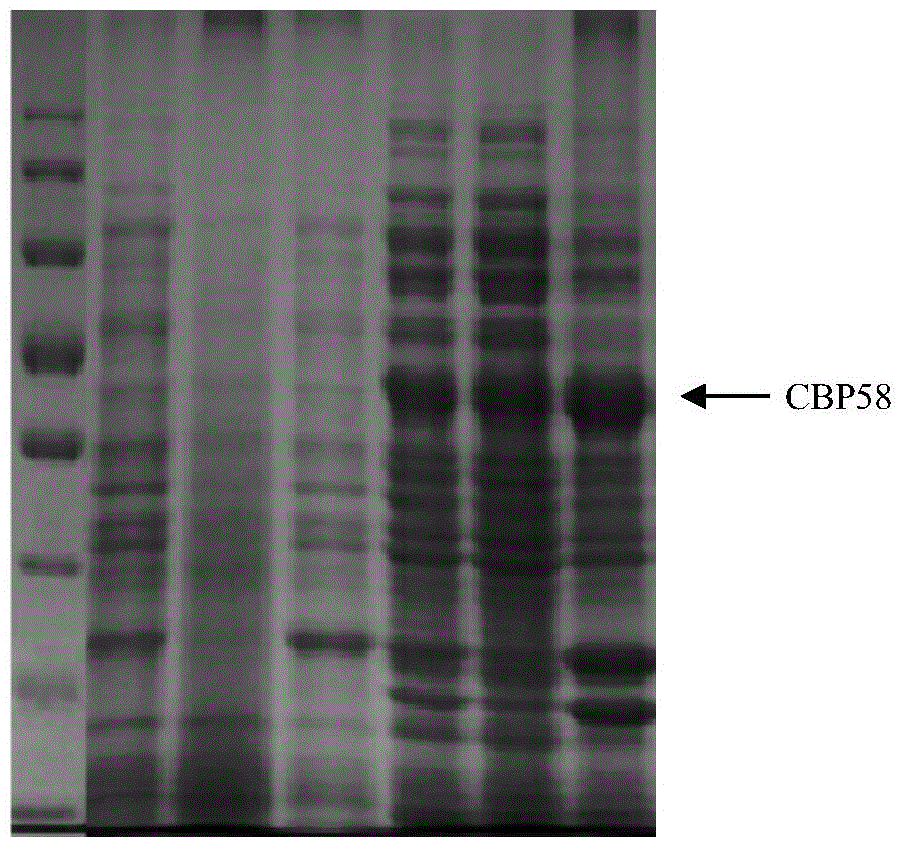
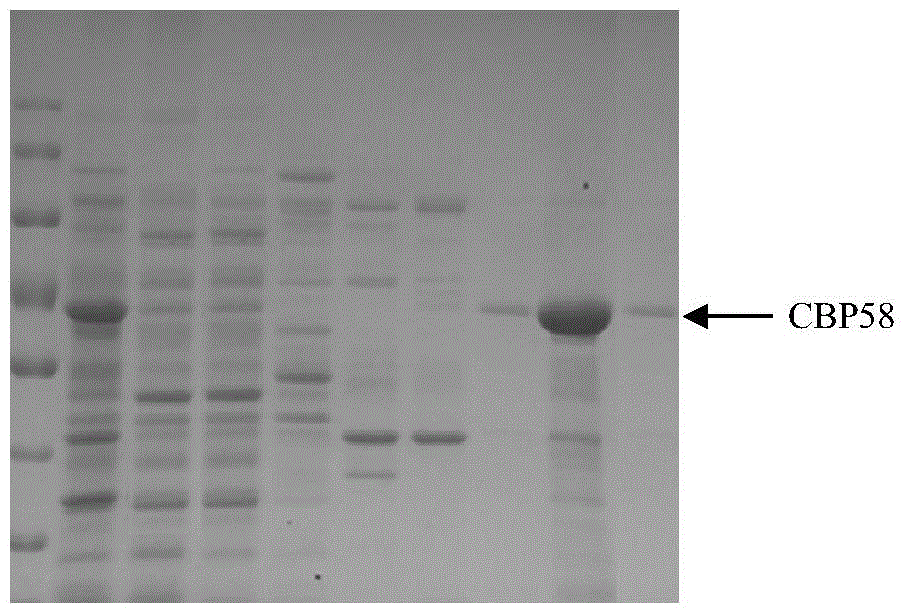
InactiveCN104877018AHigh activityEasy to makeMicroorganism based processesFungicidesAntifungalHigh activity
The invention relates to a chitin binding protein CBP58, and an encoding gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The encoding gene of the chitin binding protein CBP58 is cloned from a strain pseudoalteromonas sp.DL-6 for the first time; and a high-activity expression product is obtained by construction of a prokaryotic expression vector and imidazole elution. The preparation process is simple; a simple and convenient method is provided for subsequent research on the chitin protein CBP58; the chitin protein CBP58 is low in production cost and easy to store, has a chitin binding function, is applied to purification and auxiliary identification of chitin, has a good inhibiting effect on aspergillus niger (Aspergillus niger) and cytospora mandshurica miura (Cytospora mandshurica miura), has a potential biological control function and has wide application value; a novel research direction is provided for research and development of anti-fungal medicines in the field of agriculture; and great industrial benefits and economic value are generated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Chitin binding protein Bt-CBP, and coding gene and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107098953AHigh activityEasy to makeBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFusarium oxysporum
The invention relates to a chitin binding protein Bt-CBP, and a coding gene and a preparation method and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The coding gene of the chitin binding protein is cloned from bacillus thuringiensis for the first time, and an expression product with high activity is obtained by constructing a prokaryotic expression vector and expressing the gene in escherichia coli. The chitin binding protein Bt-CBP has a good inhibiting effect on cucumber gray mold and fusarium oxysporum. In addition, the chitin binding protein Bt-CBP has a synergic effect on catalytic activity of chitin ChiB, can promote ChiB to efficiently degrade chitin, can remarkably enhance the inhibiting effect of ChiB on cucumber gray mold, has a good biological control function, provides a novel research direction for research of antifungal drugs in the agricultural field, has wide application value and generates a huge industrial benefit and economical value.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Use of radish chitin-binding protein in preparing dental health product
InactiveCN101406435ANo side effectsEasy to cleanCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsToothpasteConjugated protein
The invention relates to application of radish chitin conjugated protein in preparing oral hygiene products such as toothpaste, dental floss, mouth wash, oral spray or inhalant, and chewing gum and so on The oral hygiene products are used for removing and / or reducing dental plagues and / or bacteria in the oral cavity, thereby reducing the incidence of odontopathies (decayed tooth, periodontal disease, etc.) and halitosis.
Owner:宋秋兰
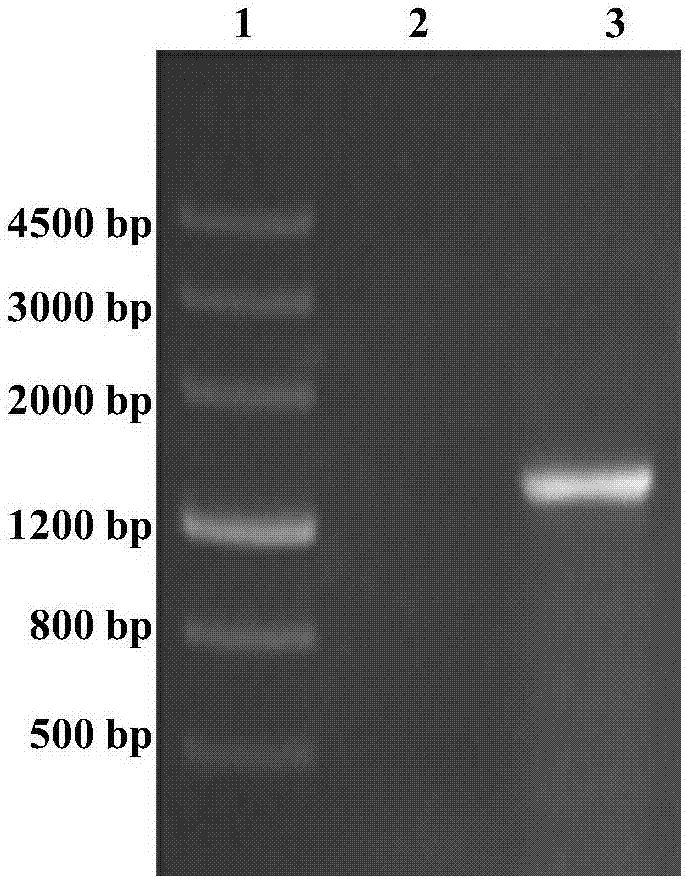
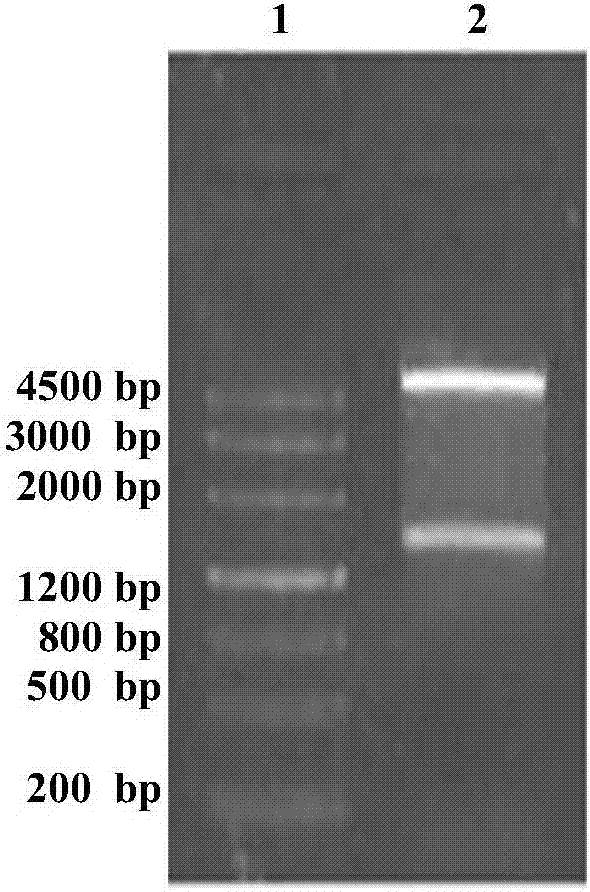
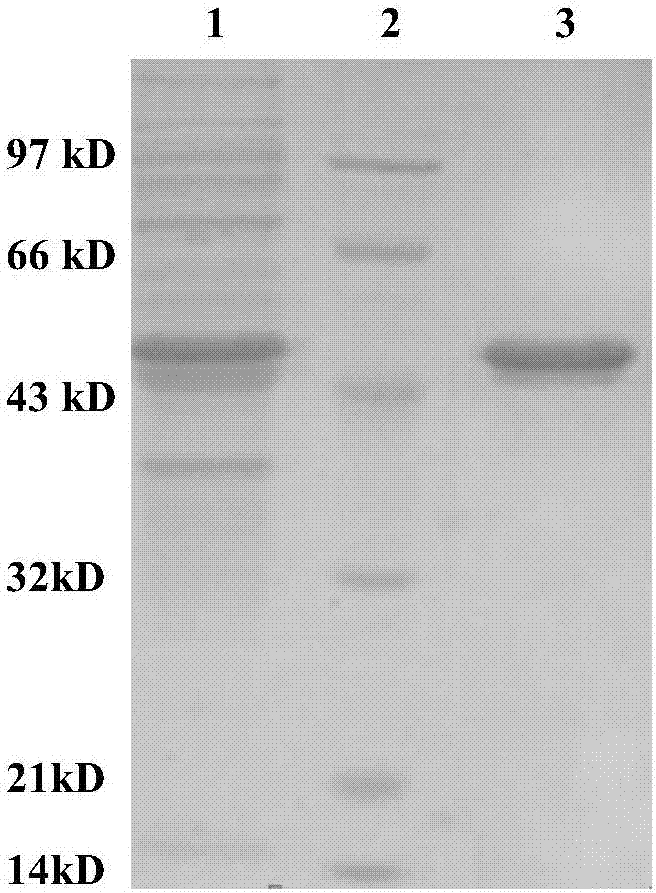
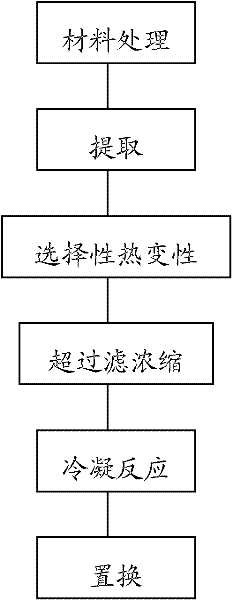
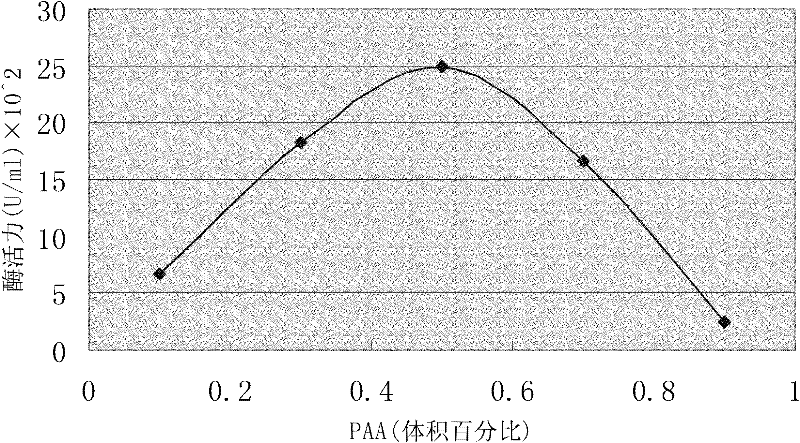
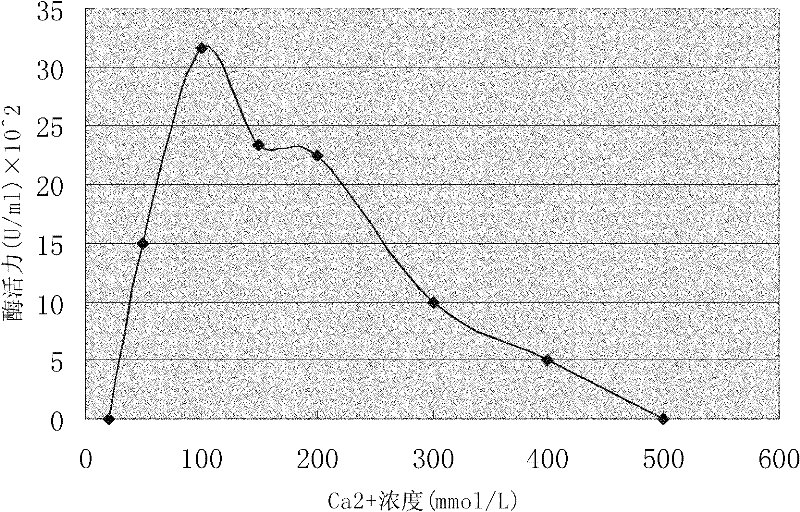
Method for preparing turnip chitin binding protein through macromolecular cold-condensation method
The invention relates to a method for preparing turnip chitin binding protein through a macromolecular cold-condensation method. The principles of PAA+R.CBP -> PAA-R.CBP and PAA-R.CBP+Ca<2+> -> PAA-Ca<2+>+R.CBP are utilized, turnip used as a material is purified to obtain R.CBP powder, wherein the purification step comprises induction, extraction, selective thermal denaturation, ultrafiltration concentration, condensation reaction and displacement. The technical production equipment has low investment, the technology is simple and easy to realize industrial production; and PAA can be recycled by adopting the reaction product PAA-Ca<2+> and using a H2SO4 solution, the cost can be reduced, and no environmental pollution is caused.
Owner:ZHUHAI YUPINTANG BIOLOGICAL TECH
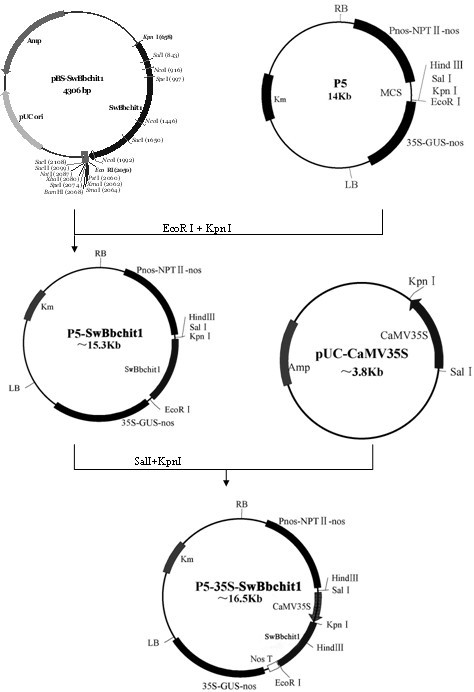
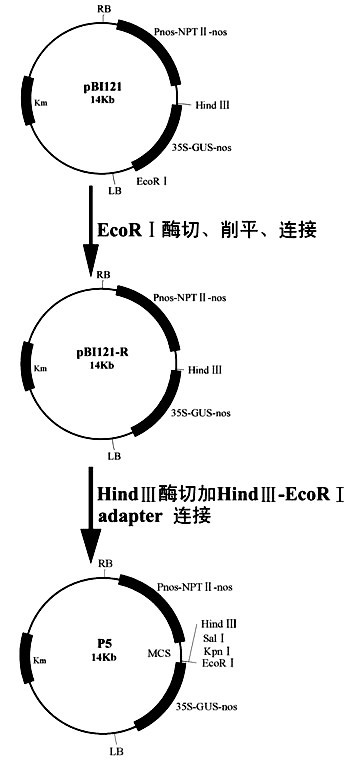
Method for improving beauveria bassiana chitinase gene disease resistance and culturing disease resistance plants adopting method
InactiveCN102533819AImprove disease resistanceIncrease resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
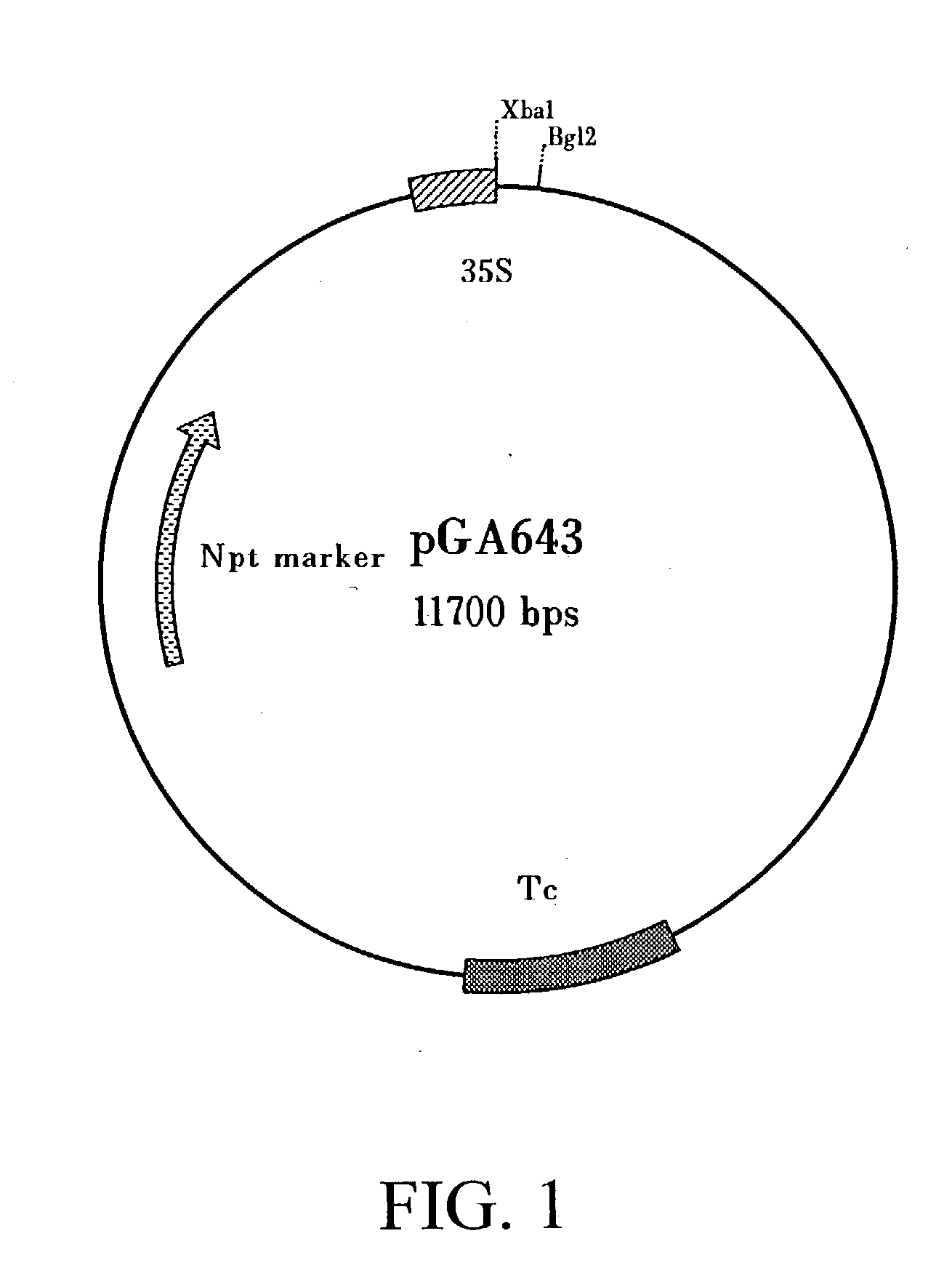
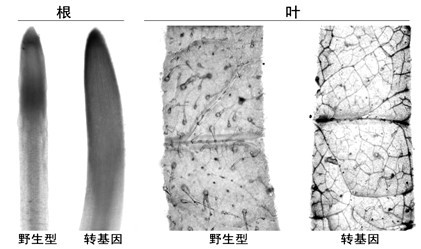
The invention provides a method for improving the beauveria bassiana chitinase gene disease resistance and culturing disease resistance plants adopting the method. The method is characterized in that a chitin binding structure domain of silkworm chitinase genes is fused with beauveria bassiana chitinase genes, and the disease resistance of the beauveria bassiana chitinase genes is improved. A 35S promoter is used for controlling fusion genes SwBbchit1, in addition, plant expression vectors are built and are respectively transferred into cotton and tomatoes, and the disease resistance of the transgenic cotton and tomatoes can be further improved. Compared with the disease resistance of the Bbchit1 transgenic cotton and tomatoes, the disease resistance of the SwBbchit1 cotton and tomatoes obtained by the method provided by the invention is obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Chitin degradative systems
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Method for improving antibacterial activity of antifungal protein
InactiveCN101921792AInhibitory effective concentrationImprove efficiencyHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAntifungal proteinAntibacterial activity
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and in particular relates to a method for improving the antibacterial activity of antifungal protein. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of a coding chitin binding domain with a cDNA (complementary DNA) sequence of coded antifungal protein by a correct reading frame; then cloning to a protein expression vector; expressing fused protein by using engineering bacteria; carrying out protein purification by further utilizing a commercialized medium; and detecting the chitin binding capacity of the purified protein and analyzing the antibacterial activity. The invention can improve the antibacterial efficiency of the antifungal protein. By applying the invention, the activity of the traditional antifungal protein and the targeted binding capacity of the protein on fungal cell walls are improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Glucoside hydrolase CmChi3 and application thereof in degradation of hydrolyzed colloid chitin
ActiveCN112553183AEfficient degradationIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenomic sequencingGlycoside
The invention discloses a glucoside hydrolase CmChi3 and an application thereof in degradation of colloid chitin. The invention comprises the following steps of performing genome sequencing analysis on a bacterial strain Chitinolyticbacter meiyuanensis SYBC-H1 screened from soil, cloning CmChi3, constructing a recombinant bacterial strain, expressing CmChi3 protein, purifying HIS-TAG, identifyingthat the recombinant protein has two catalytic structural domains and two chitin binding domains, has the properties of endonuclease and glucoside hydrolase, and can efficiently hydrolyze chitin and can take GlcNAc as a final chitin product. The research is expected to provide theoretical basis and basis for high-efficiency production of GlcNAc by a single-enzyme method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein and a preparation method thereof and relates to chitin binding protein. A ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein gene is a cbpA, cbpB, cbpC or cbpD gene. A method for obtaining a nucleotide sequence of the ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein gene comprises the following steps of: extracting RNA of ridgeia piscesae; reversely transcribing the RNA into cDNA; and performing recombinant expression in insect cells high5 by using the cDNA as a template and using a composition sequence as a primer through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification so as to prove that polypeptide encoded by the cbpA, cbpB, cbpC or cbpD gene has chitin binding activity. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: extracting the RNA of the ridgeia piscesae; performing cDNA reverse transcription on the ridgeia piscesae; performing PCR amplification and sequence analysis on the ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein gene; and performing expression on the ridgeia piscesae chitin binding protein.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Diaphorina citri chitin binding protein Chitinase-like EN03 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention provides a chitin binding protein Chitinase-like EN03 of diaphorina citri, and belongs to the technical field of pest control. The amino acid sequence of the chitin binding protein Chitinase-like EN03 of diaphorina citri is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the chitin binding protein Chitinase-like EN03 of diaphorina citri. The coding gene of the chitin binding protein Chitinase-like EN03 of diaphorina citri is silenced through RNA interference, so that the diaphorina citri can die due to incomplete ecdysis or unsuccessful ecdysis, and the effect of preventing and treating diaphorina citri is achieved.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Silica-based material for detection and isolation of chitin and chitin-containing microorganisms
InactiveUS20110053187A1High-precision detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiMicrobiologyChitin binding
The subject invention provides silica-based material that has high affinity to chitin, chitin derivatives and chitin-containing microorganisms at an acidic pH. In an embodiment, the silica-based material surface comprises glass. Also provided are methods for preparing the subject silica-based chitin-binding material. In addition, the subject invention provides rapid, specific, sensitive, accurate and convenient methods for detection, isolation and purification of chitin, chitin derivatives and chitin-containing microorganisms.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
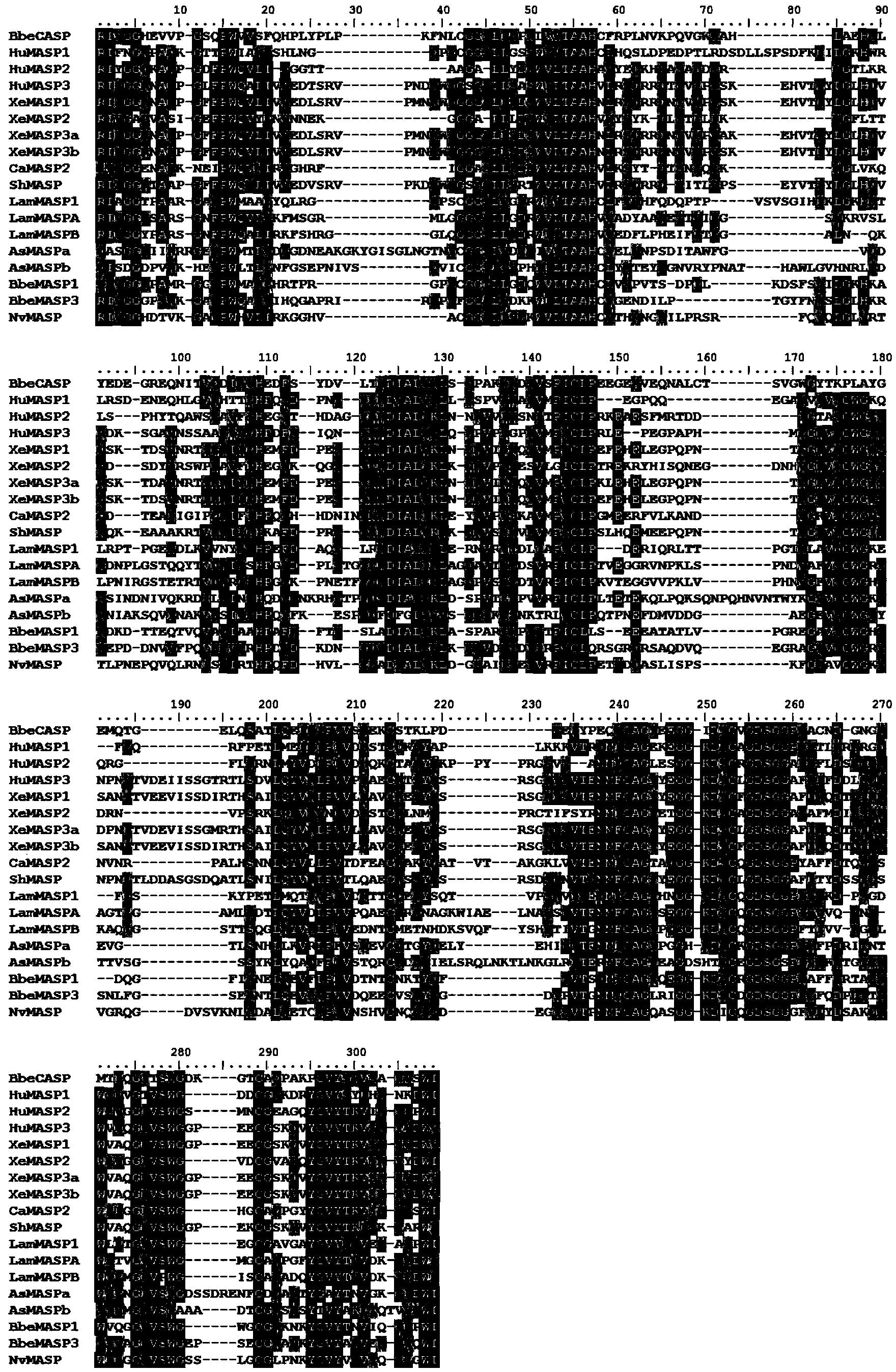
Branchiostoma belcheri chitin-binding associated serine protease CASP gene for identifying chitin and application thereof
InactiveCN103509809AHas serine protease activityEnhance phagocytosisAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention relates to a branchiostoma belcheri chitin-binding associated serine protease CASP gene for identifying chitin, a protein coded by the gene and an expression method and application of the protein. The CASP gene is aN MASP (Mbl Associated Serine Protease) similar gene obtained by cloning from a total RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) of branchiostoma belcheri by a method of combining primer amplification and RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) amplification. The protein coded by the CASP gene is expressed in an intracellular soluble form in escherichia coli by a recombinant expression vector PET-32a(+)-CASP. The protein coded by the CASP gene takes an important effect of resisting to foreign pathogen and has the development value of becoming a high-efficiency natural antibacterial medicament.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for separating and purifying fusion protein containing chitin binding domain
The invention provides application of a partially deacetylated chitin derivative in separation and purification of fusion protein containing a chitin binding domain. The principle used in the invention is that chitin undergoes deacetylation through NaOH alkali lye heating and then acetic acid treatment is carried out to acetylate the deacetylated chitin so as to obtain the partially deacetylated chitin derivative. The partially deacetylated chitin derivative is applied to separation and purification of fusion protein containing the chitin binding domain and has a better improved specific adsorption effect on fusion protein containing the chitin binding domain.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Application of basic chitinase from vibrio in fungus dyeing
The invention discloses application of basic chitinase from vibrio in fungus dyeing. The basic chitinase from the vibrio is applied to dye fungi, and can targetedly and specifically bind to chitin ofthe fungus cell wall, observation is conducted under a fluorescence microscope, ultraviolet light of 340-400 nm is used for activating, and the fungi can show blue or yellow-green color.
Owner:MERLIN BIOMEDICAL (XIAMEN) CO LTD
Genetically modified plants with enhanced resistance to fungal diseases and a method of production thereof
InactiveUS6956147B2Improve protectionProvide protectionBryophytesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePlant cell
The present invention discloses genetically modified plants, such as potato plants. The plants are more resistant to a pathogen of interest following transformation of plant cells with a chimeric gene comprising a chitinase gene and β-1,3-glucanase gene. The invention also provides a method of enhancing the resistance of plants to pathogens by introducing a Brassica chitinase gene encoding two or more chitin-binding domains and β-1,3-glucanase gene and expressing the chitinase gene and β-1,3-glucanase gene.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF
cDNA encoding a polypeptide including a hev ein sequence
InactiveUS6083687APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryEscherichia coli
A cDNA clone (HEV1) encoding hevein was isolated via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using mixed oligonucleotides corresponding to two regions of hevein as primers and a Hevea brasiliensis latex cDNA library as a template. HEV1 is 1018 nucleotides long and includes an open reading frame of 204 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence contains a putative signal sequence of 17 amino acid residues followed by a 187 amino acid polypeptide. The amino-terminal region (43 amino acids) is identical to hevein and shows homology to several chitin-binding proteins and to the amino-termini of wound-induced genes in potato and poplar. The carboxyl-terminal portion of the polypeptide (144 amino acids) is 74-79% homologous to the carboxyl-terminal region of wound-inducible genes of potato. Wounding, as well as application of the plant hormones abscisic acid and ethylene, resulted in accumulation of hevein transcripts in leaves, stems and latex, but not in roots, as shown by using the cDNA as a probe. A fusion protein was produced in E. coli from the protein of the present invention and maltose binding protein produced by the E. coli.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com