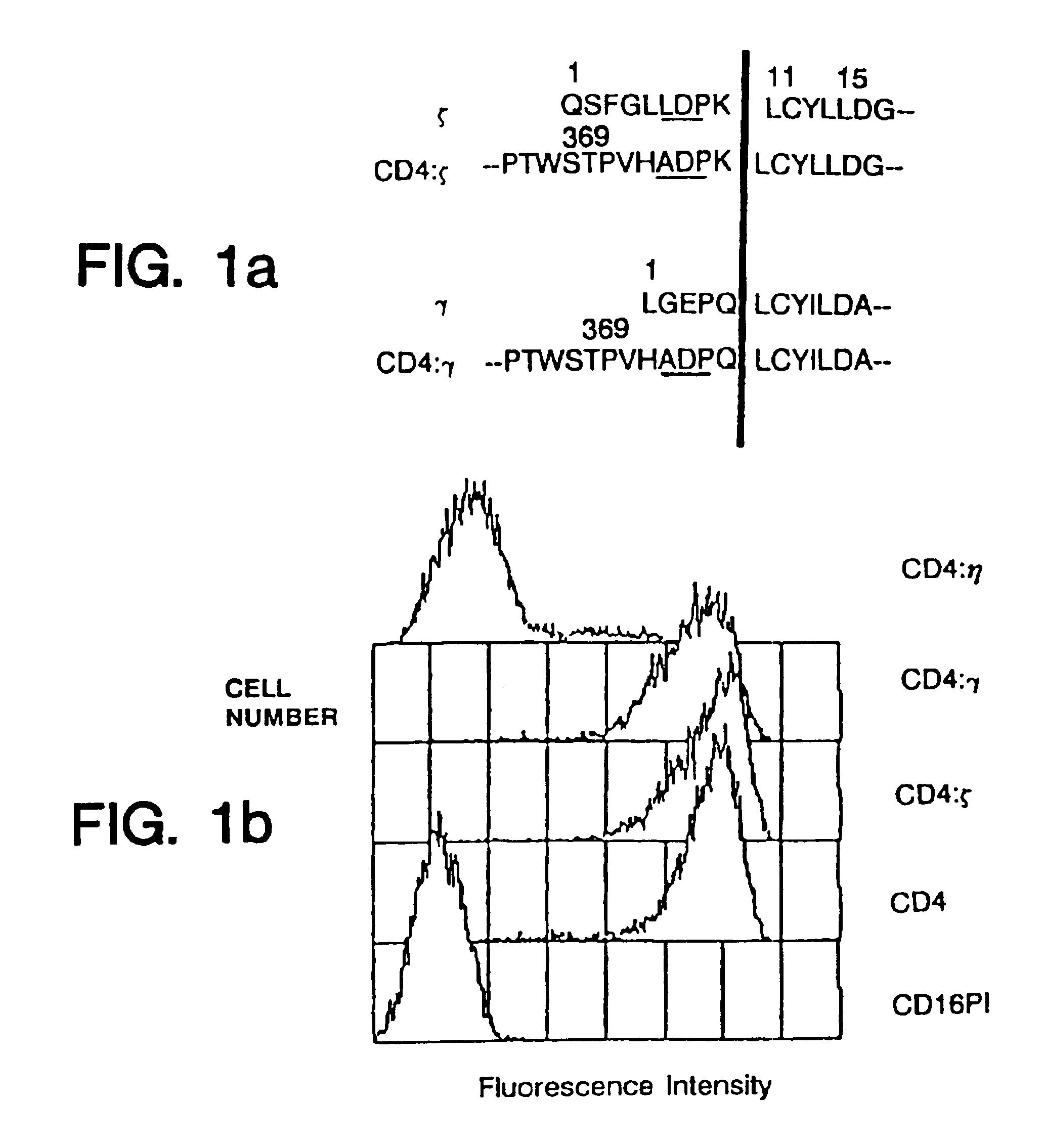
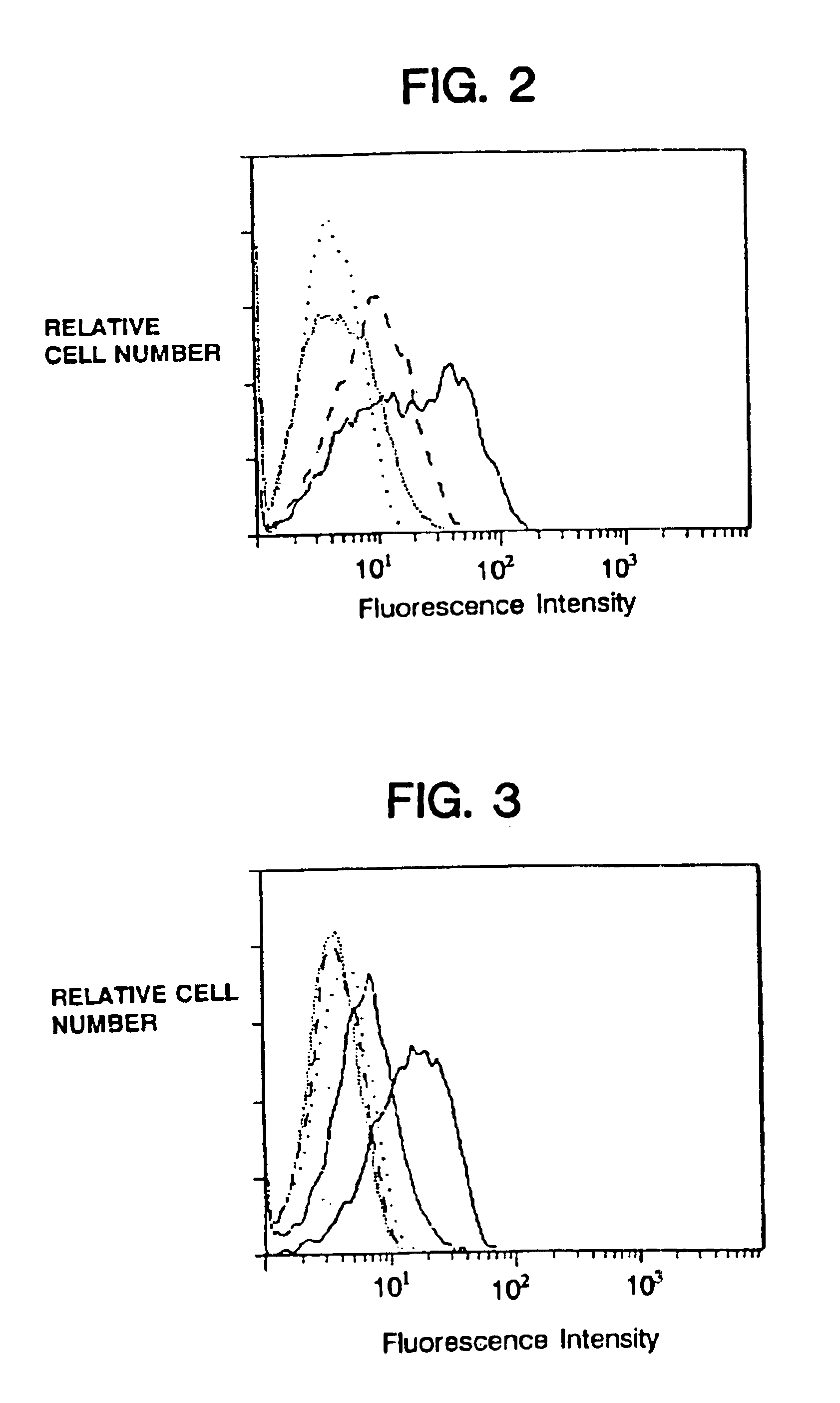
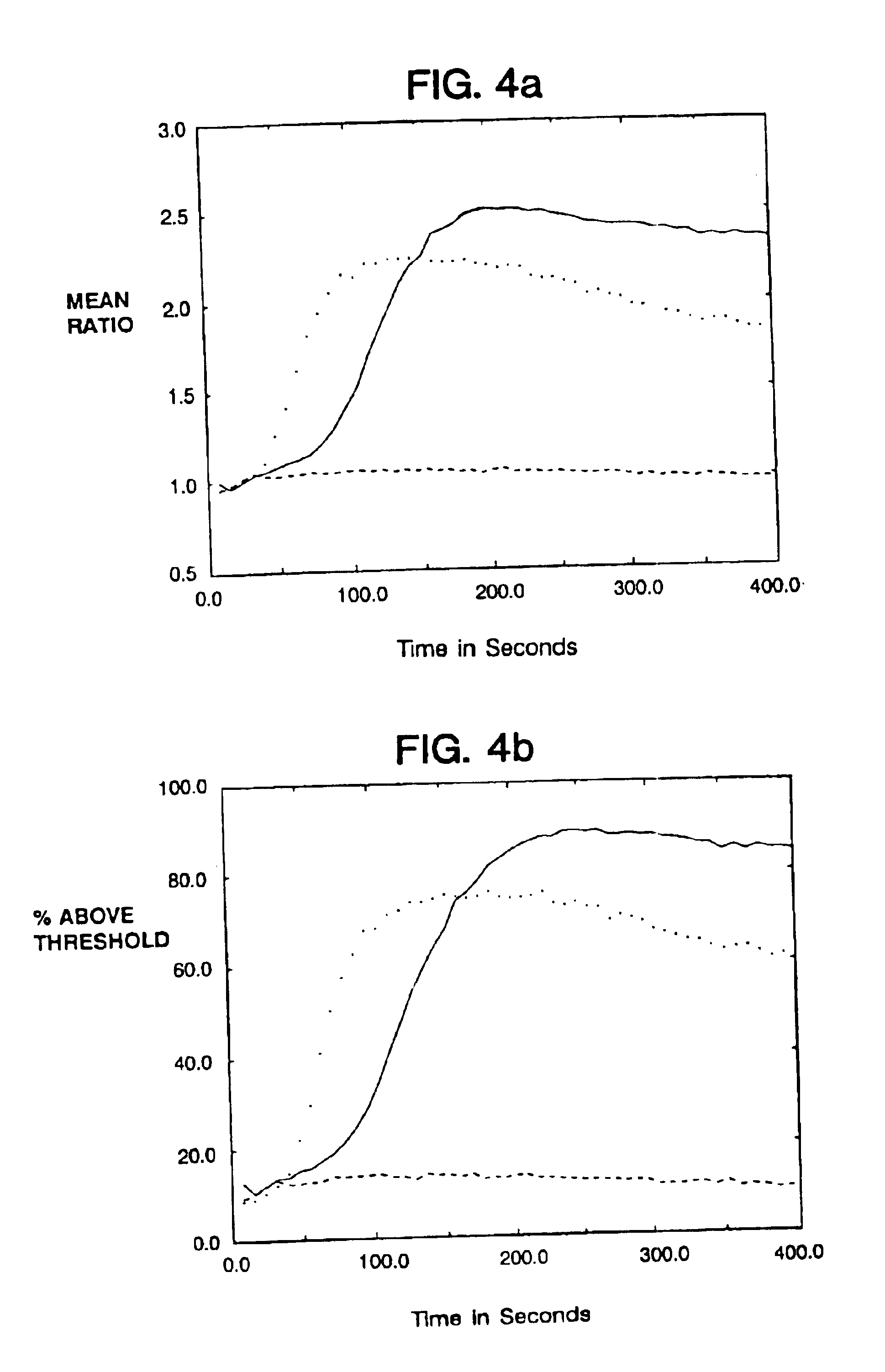
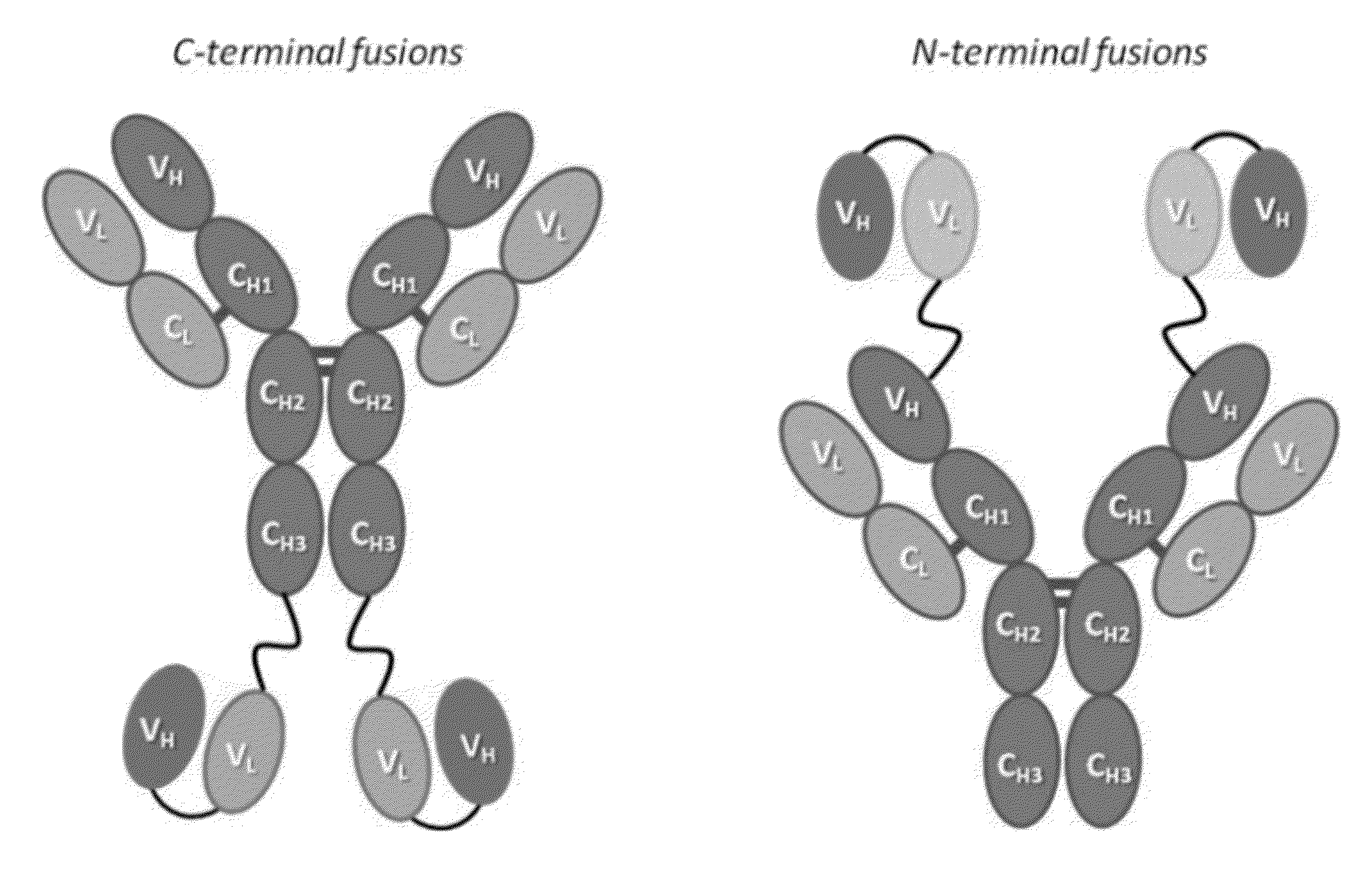
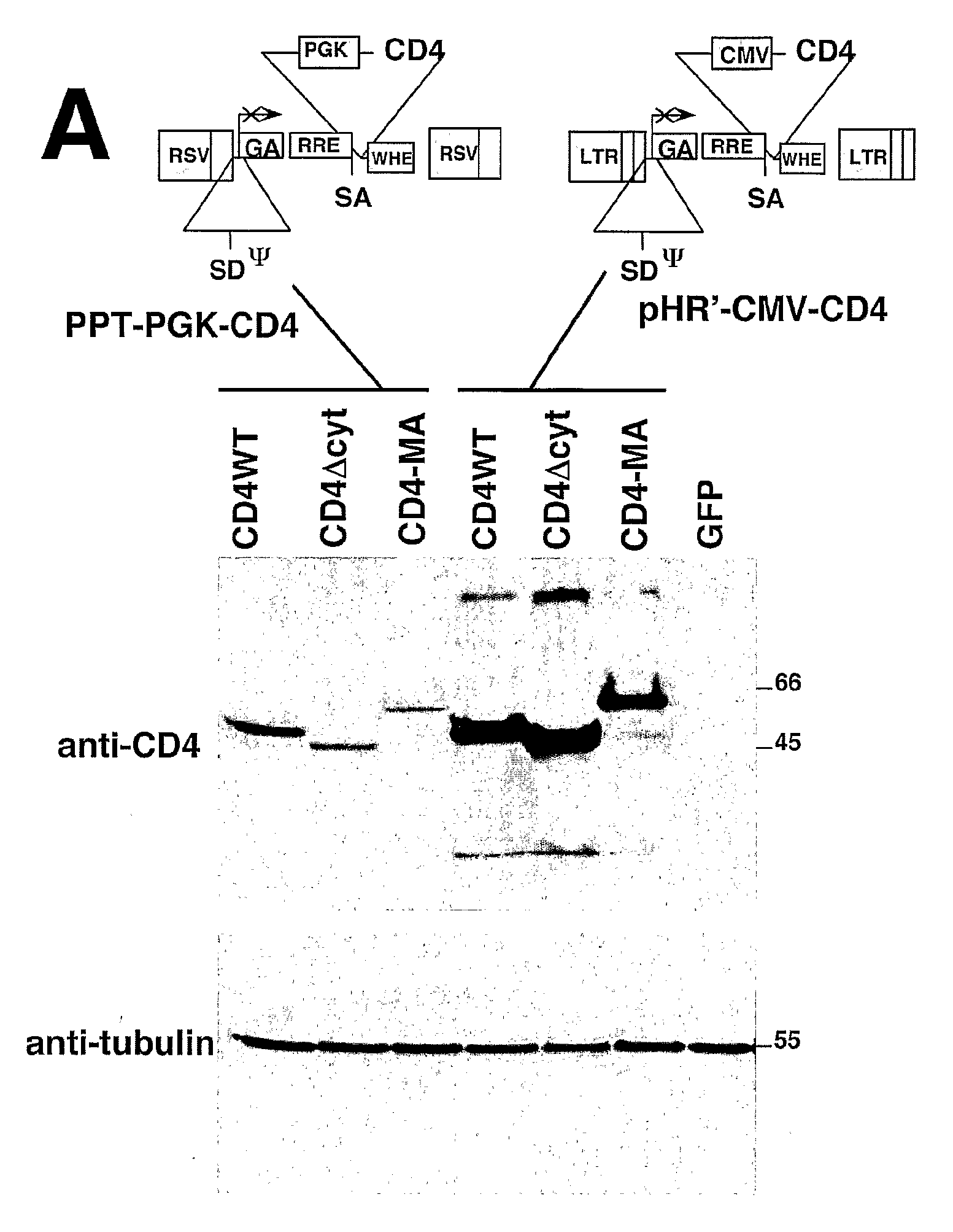
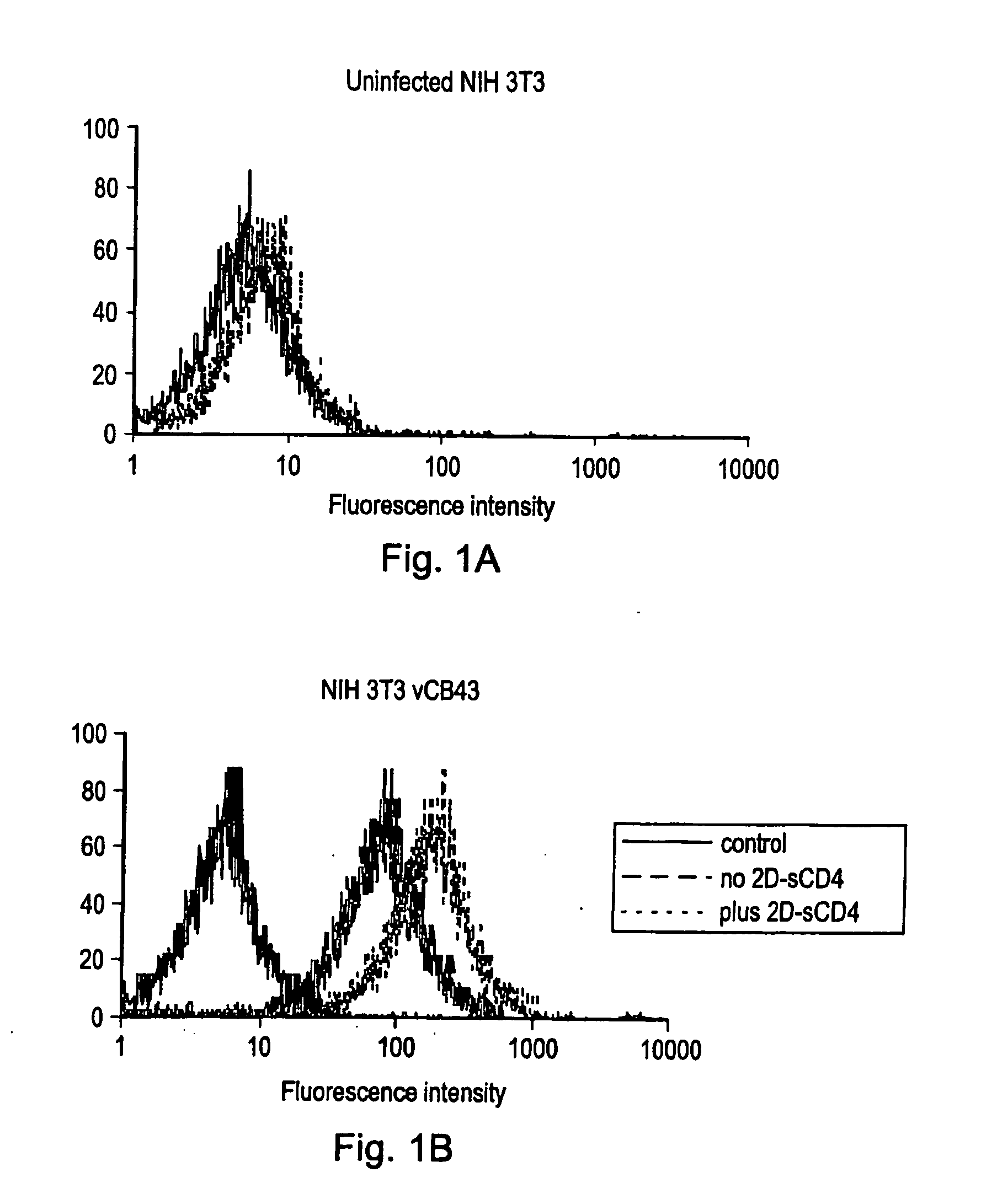
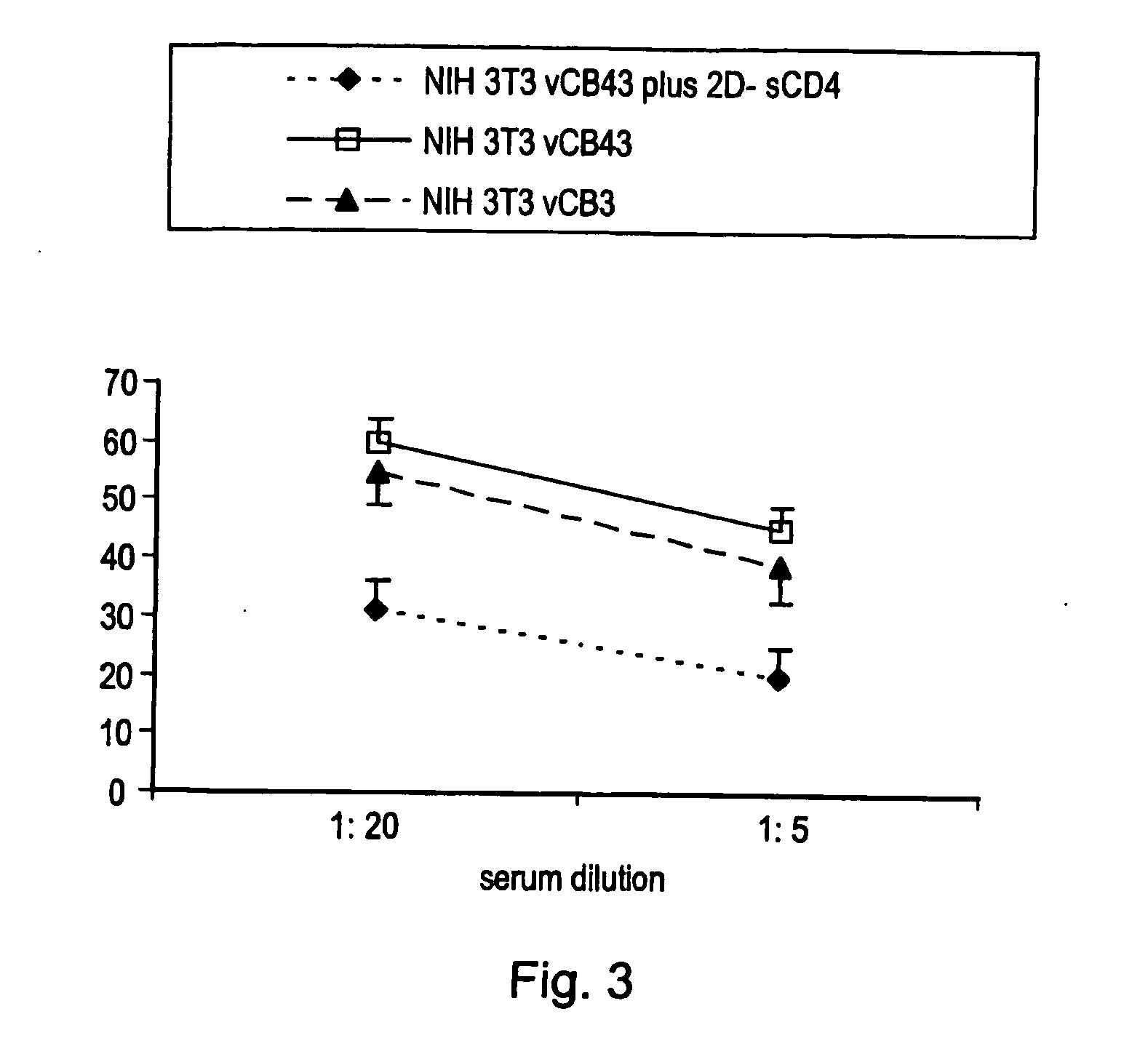
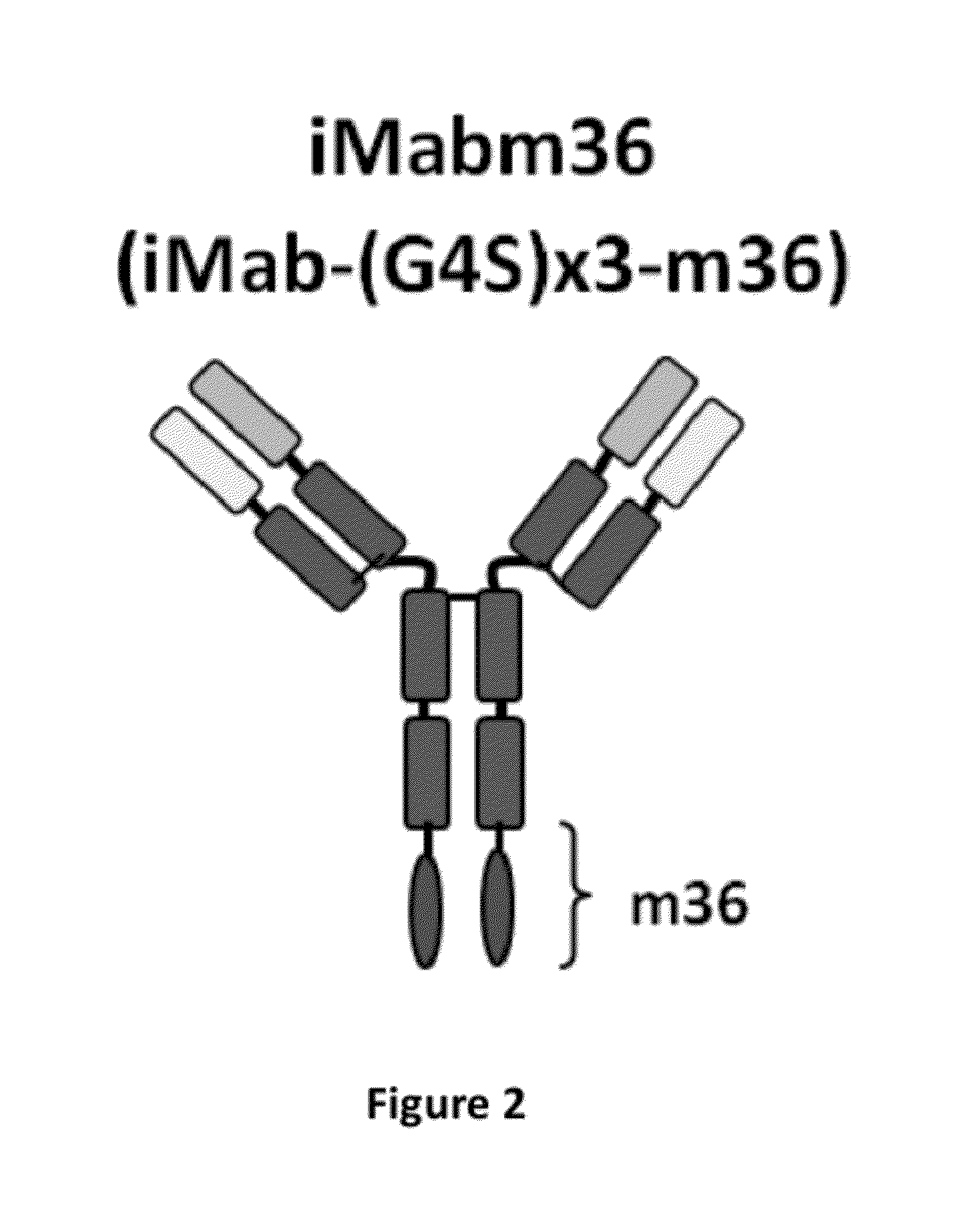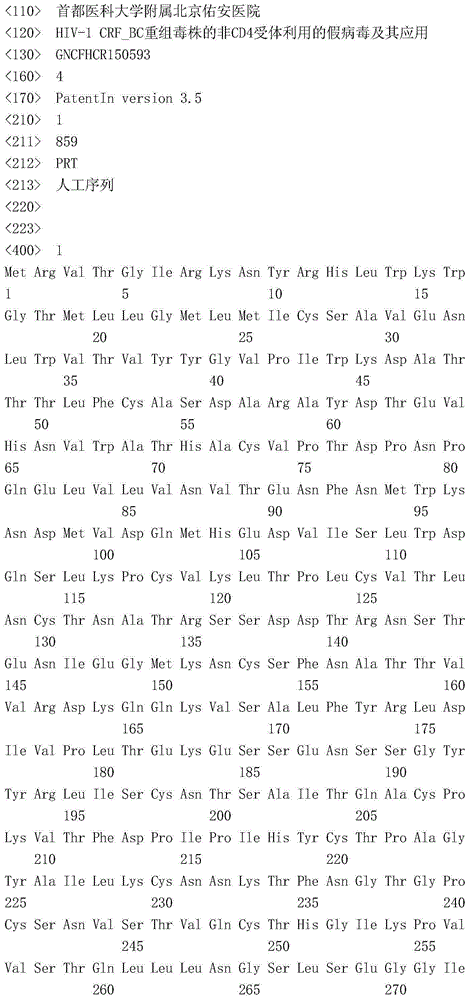Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Cd4 receptors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A protein found primarily on the surface of CD4 T lymphocytes (CD4 cells). To enter a host cell, HIV binds to a CD4 receptor and a coreceptor (either CCR5 or CXCR4) on the host cell.
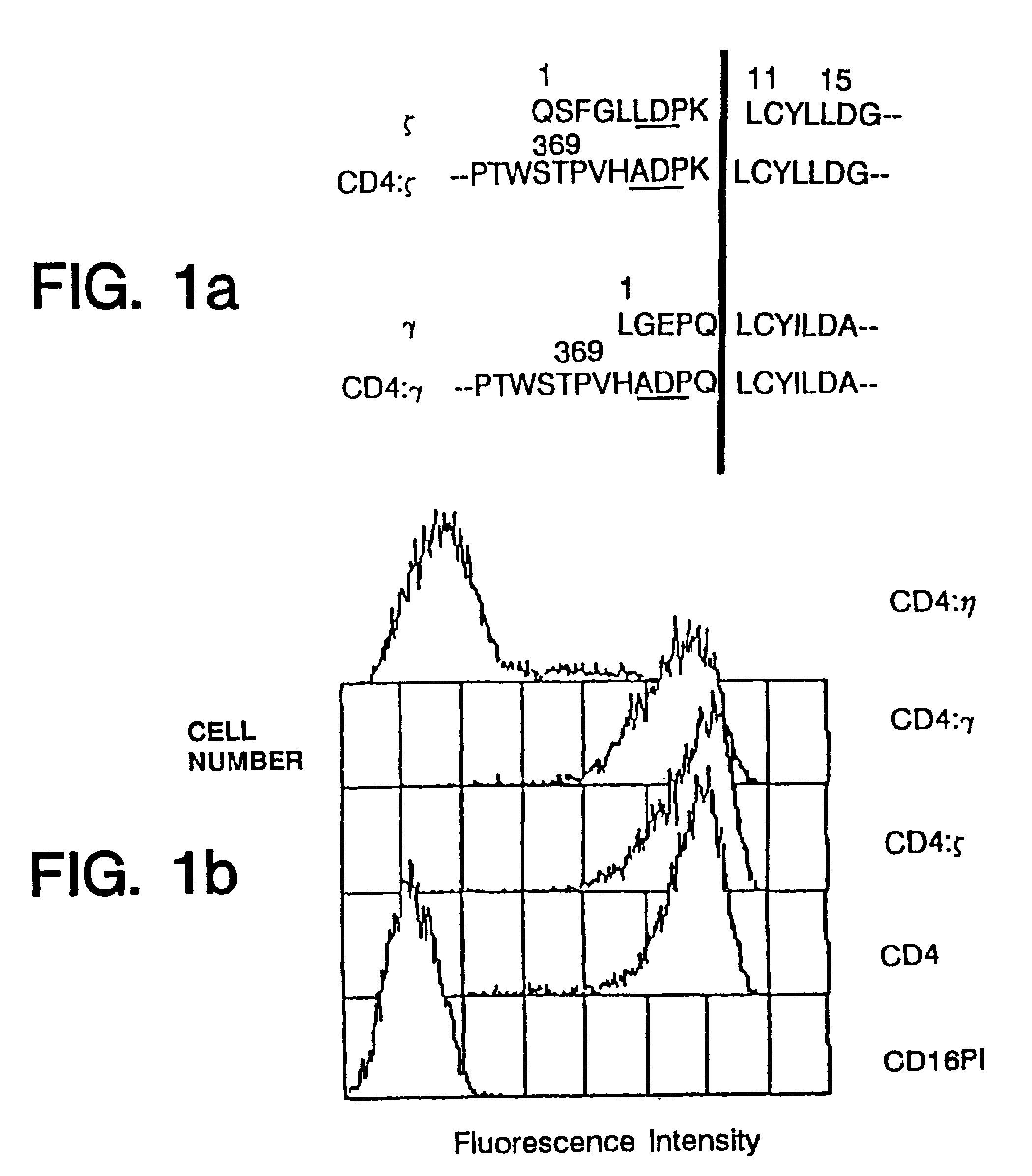
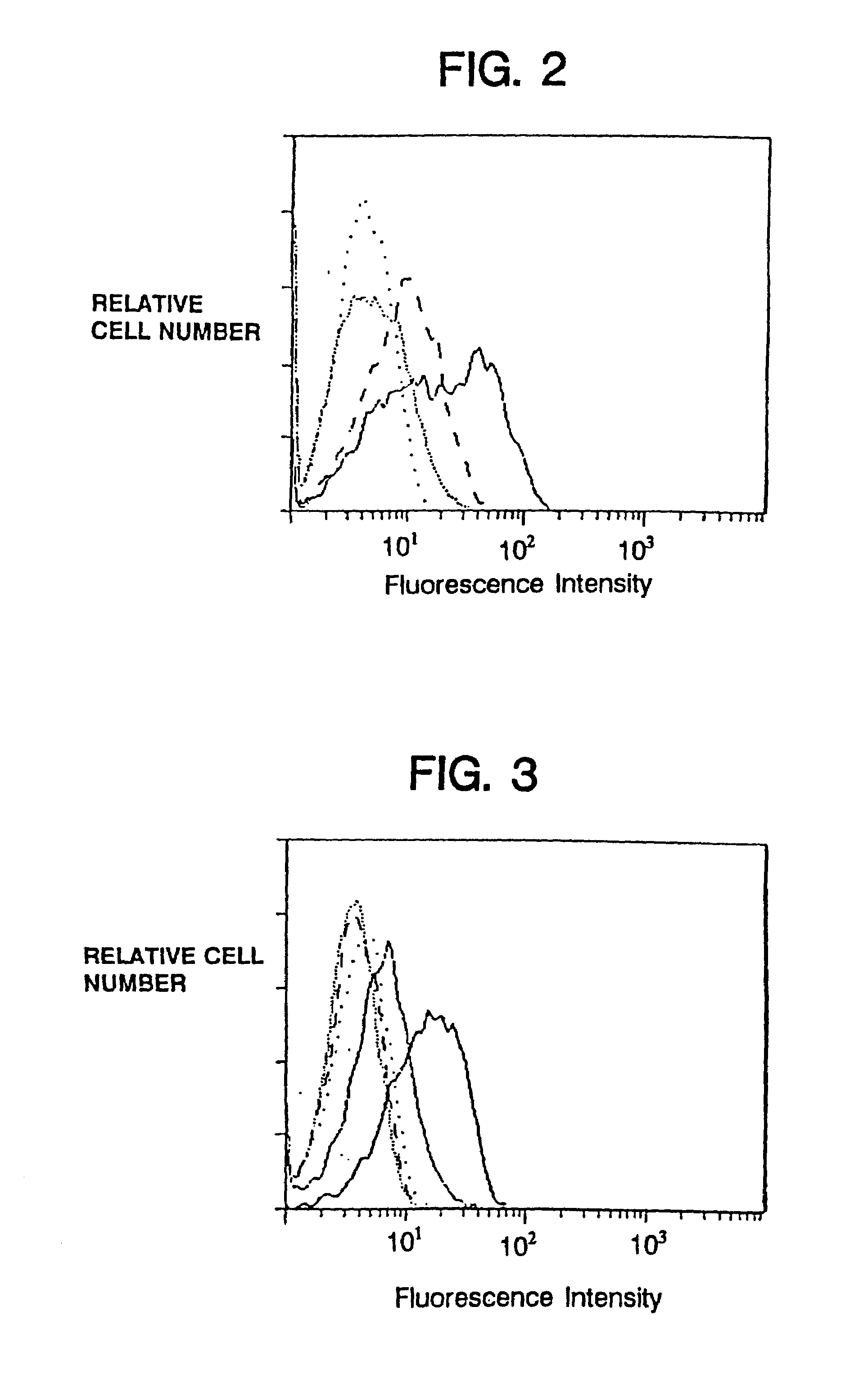
Targeted cytolysis of HIV-infected cells by chimeric CD4 receptor-bearing cells
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular immune response against an HIV-infected cell in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells which express a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising (a) an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection and (b) an intracellular portion which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy the receptor-bound HIV-infected cell. Also disclosed is a second method of treating HIV in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells expressing a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA and vectors encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Fusion proteins for HIV therapy
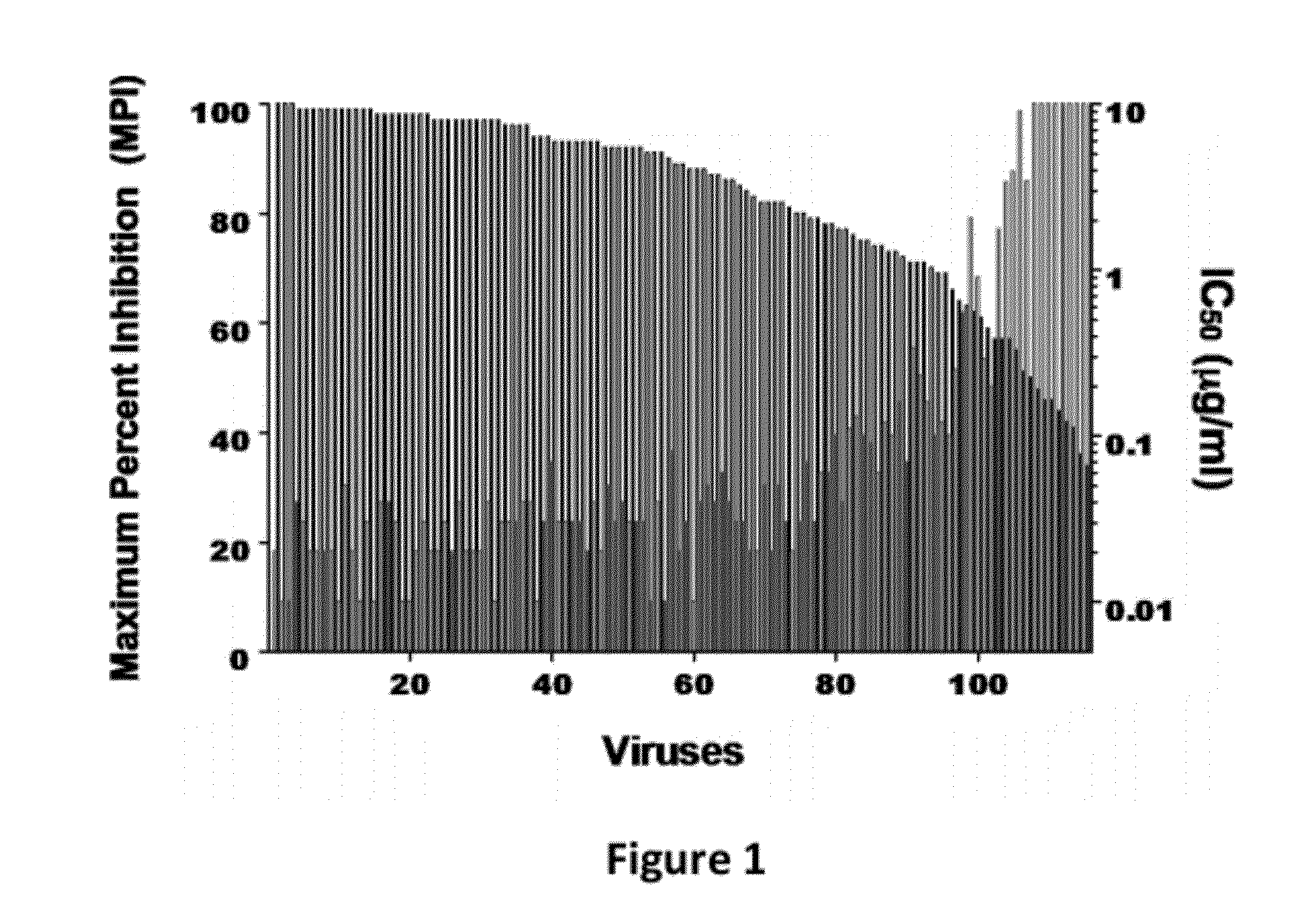
InactiveUS20120121597A1Improved potency and breadth against HIVImprove barrier propertiesHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHiv envelopeBinding site
Disclosed herein are fusion antibodies created to provide both an antigen-binding site that targets the CD4 receptor and an antigen-binding site that targets the HIV envelope. The fusion antibodies disclosed herein provide improved potency and breadth against HIV as compared to monospecific antibodies, and additionally provide high barrier against viral resistance. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical formulations and therapeutic methods utilizing such fusion proteins.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
InactiveUS6858400B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhagocyteBinding site
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by any one of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
Targeted cytolysis of HIV-infected cells by chimeric CD4 receptor-bearing cells
InactiveUS7094599B2Promote absorptionProlong lifeVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEphA Receptors
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular immune response against an HIV-infected cell in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells which express a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising (a) an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection and (b) an intracellular portion which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy the receptor-bound HIV-infected cell. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA and vectors encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Fusion antibodies for HIV therapy
InactiveUS8637024B2Improved potency and breadth against HIVImprove barrier propertiesHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsHiv envelopeBinding site
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Synergistic compositions for the prevention and treatment of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
InactiveUS20060121480A1Good curative effectLess drugPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAcquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)Synergistic combination
A method for preventing infection of helper T and other target cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (“HIV-1”) and for preventing or treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (“AIDS”) by exposing target cells to a synergistic combination of at least one attachment inhibitor and at least one fusion inhibitor. The attachment inhibitors are compounds that bind to the CD4 receptor on target cells or that bind to gp120 on HIV-1, e.g., antibodies, and the fusion inhibitors compounds that interact with gp41 to inhibit or prevent its interaction with target cells, e.g., pentafuside.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Starch-pomegranate juice complex as an HIV entry inhibitor and topical microbicide
A complex comprising a starch and an active anti-HIV-1 or anti-HIV-2 ingredient of pomegranate juice that is adsorbed on the starch when the starch is in a water insoluble form. The complex inhibits HIV-1 or HIV-2 infection and blocks the binding of HIV-1 or HIV-2 to the CD4 receptor and the CCR5 and CXCR4 coreceptors. The complex is used in a method of preventing HIV-1 or HIV-2 infection comprising administering to a mucous membrane of a human a pharmaceutically effective anti-HIV-1 or anti-HIV-2 amount of the complex.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
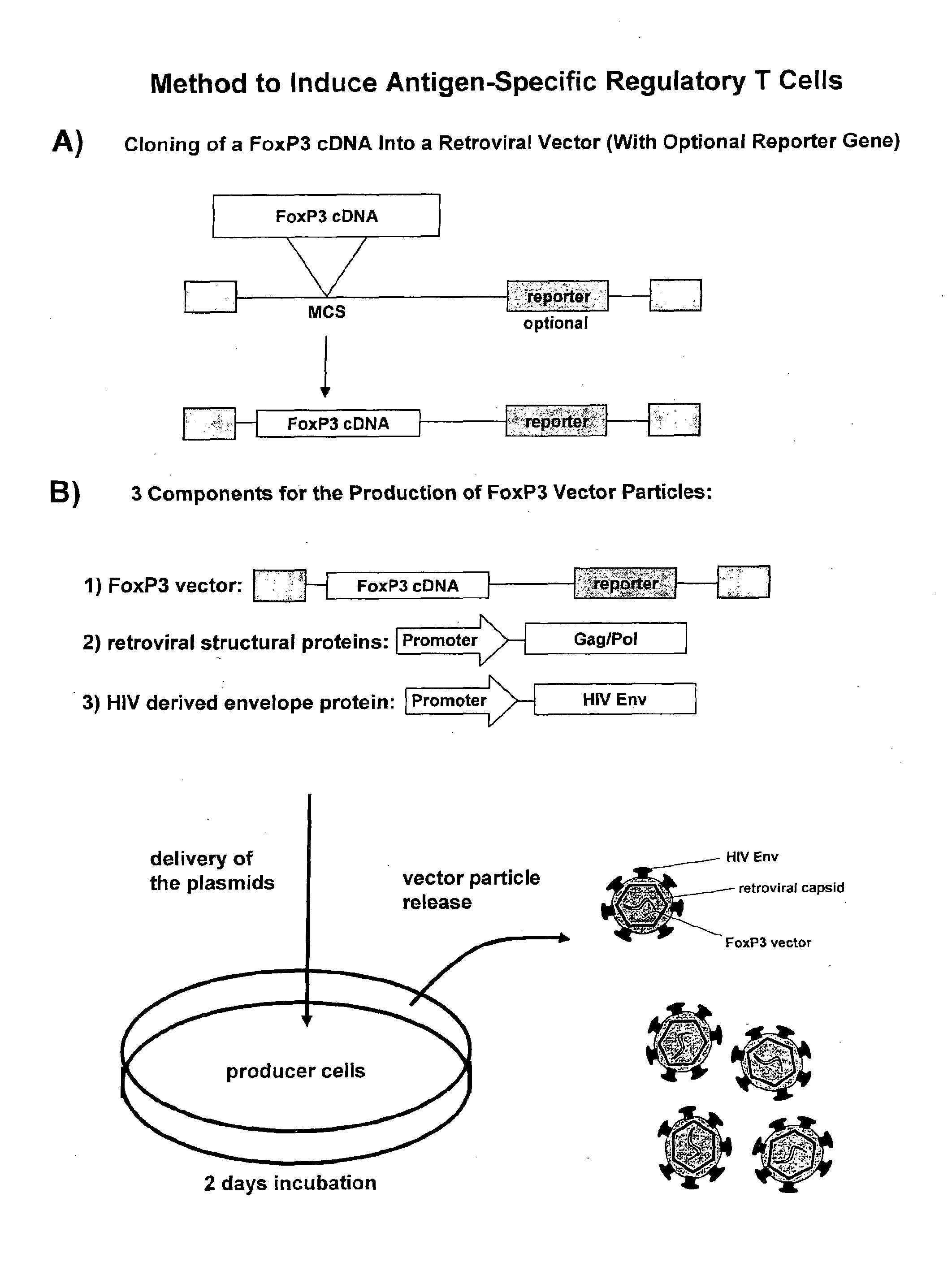
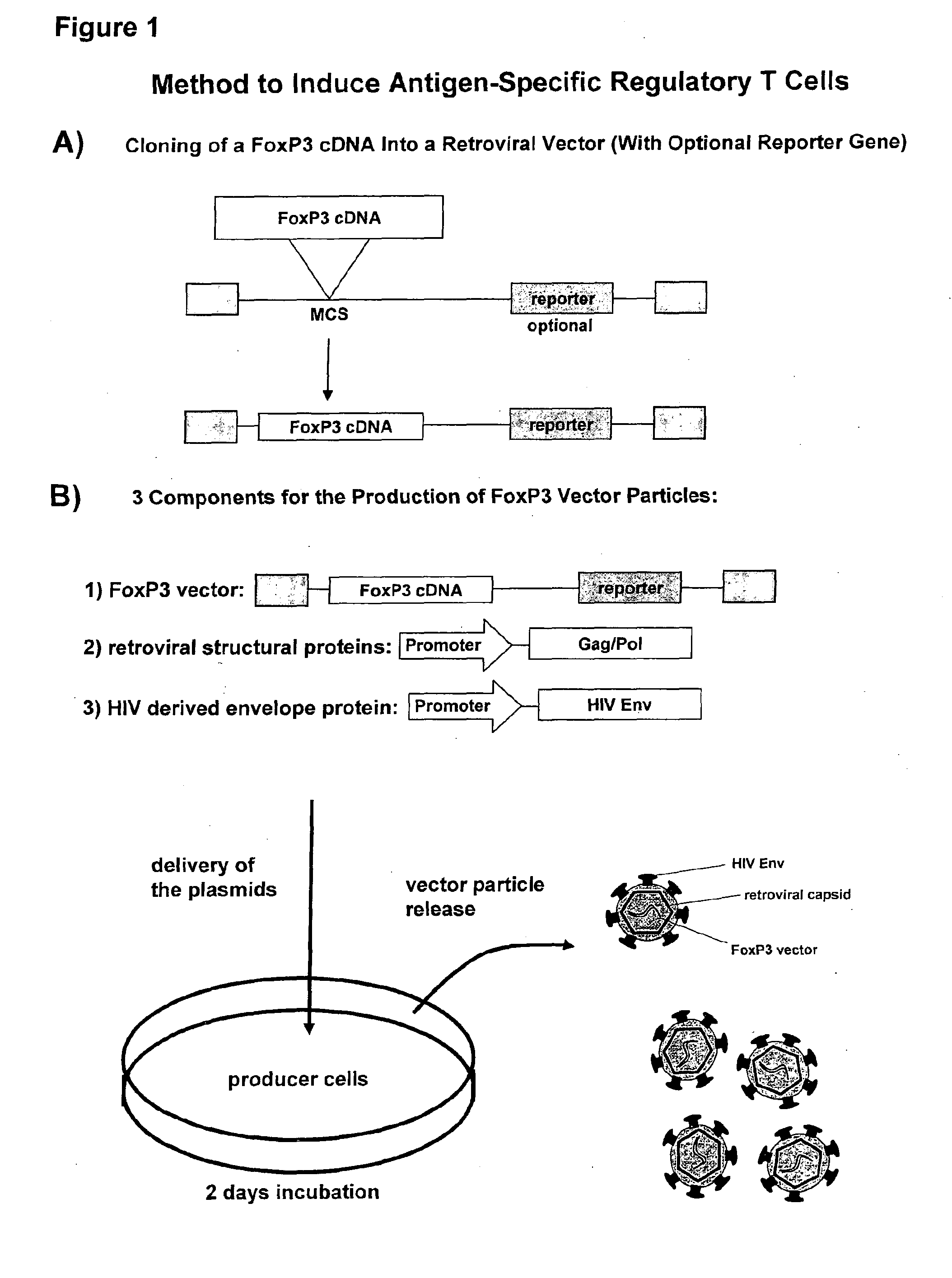
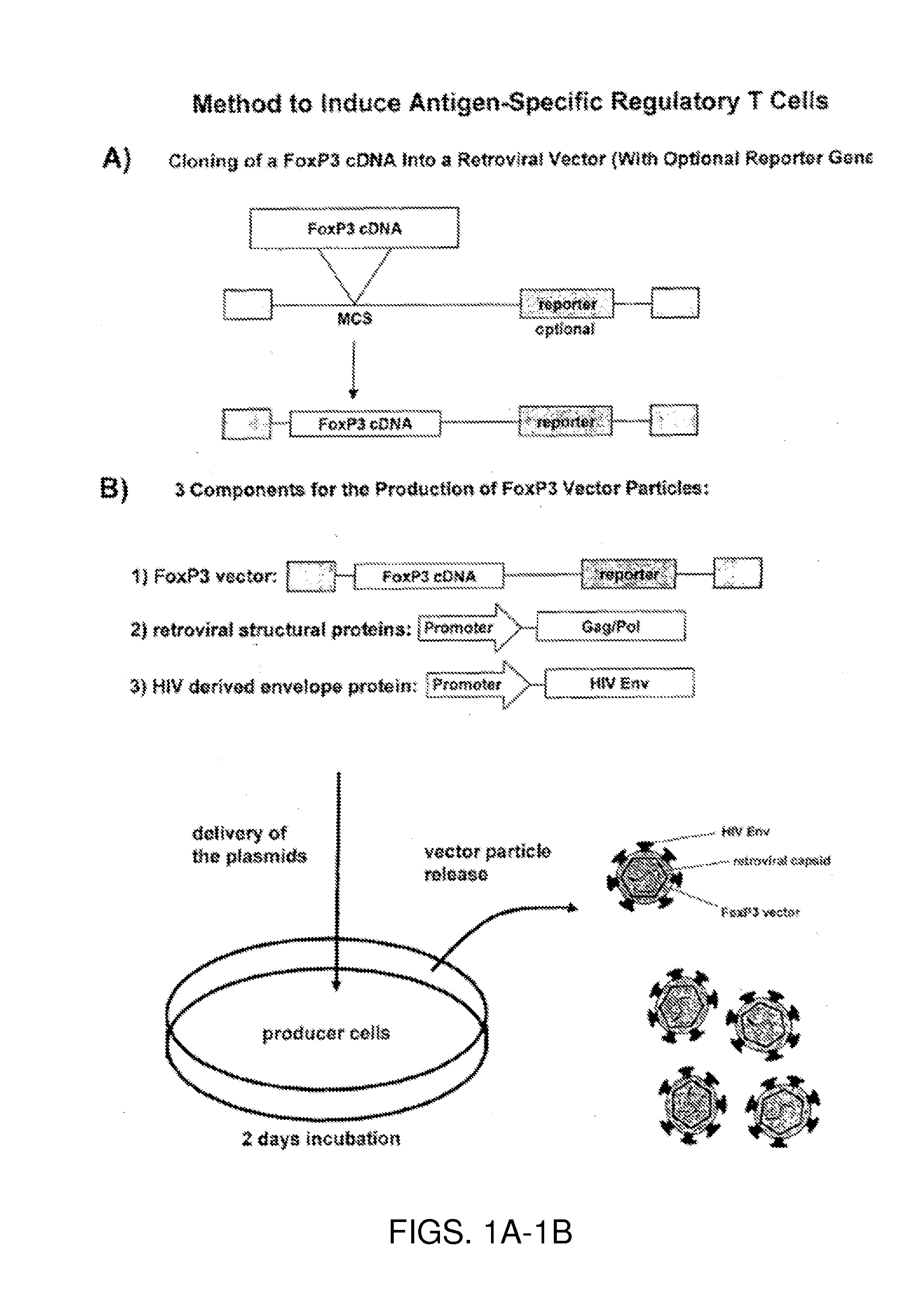
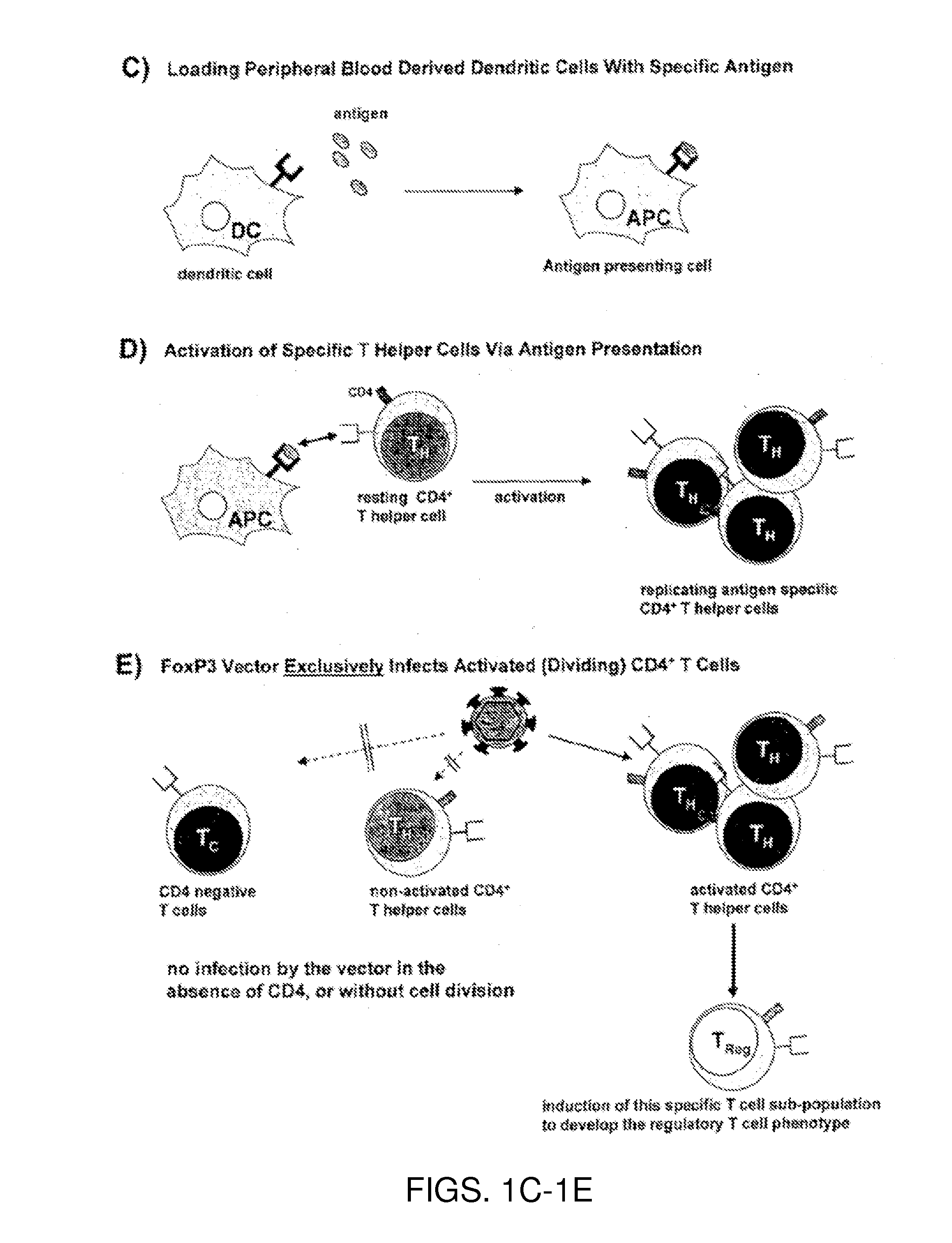
Antigen-specific regulatory t-cell induction
The present invention relates to an infectious particle having a surface displaying a ligand binding to a CD4 receptor for selectively infecting dividing CD4+ cells, said particle comprising: (a) one or more structural proteins, and (b) a vector containing a gene of interest functional in a CD4+ cell, said gene of interest encoding a Forkhead box protein 3 or a protein inducing expression of Forkhead box protein 3 in the CD4+ cell.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Chimeric immunoglobulin for CD4 receptors
Chimeric antibodies for CD4 receptor comprising a variable or antigen binding region of a non-human origin specific for CD4 receptor and a constant region of human origin are disclosed. These antibodies are useful as therapeutic agents for auto-immune disorders.
Owner:CENTOCOR
A32 Monoclonal Antibody Fusion Proteins For Use As Hiv Inhibitors And Vaccines
The invention provides a fusion protein, which comprises an antigen binding portion of an A32 human antibody, or variant thereof, and one of the following: (a) an antigen-binding portion of a second antibody or variant thereof, wherein the second antibody binds to an epitope of an envelope protein of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that is exposed upon the HIV binding to a CD4 receptor, (b) an immunogenic portion of an envelope protein of a HIV, or a variant thereof, or (c) a soluble CD4 (sCD4) polypeptide capable of binding to HIV, or a or variant thereof.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC
Methods of monitoring HIV drug resistance
InactiveUS6884576B2Genetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtein regulationReceptor degradation
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
HIV-Env gene DNA allosterism recombination envelope protein antigen for immunoresponsiveness of anti-HIV test and method
InactiveCN101002949AFighting Immunosuppressive StressAvoid infectionBiological testingIn-vivo testing preparationsHIV vaccineProtein antigen
A clinic human experiment of HIV envelope protein gp120 or gl160 antigen vaccine proves that it can not prevent the infection of HIV to human body, but can be used to research and screen the anti-HIV therapeutic vaccine and the vaccine for preventing the infection of HIV to human body.
Owner:叶新新
HIV-Env gene DNA allosteric recombinant envelope protein antigen immune response anti HIV experiment and method
InactiveCN101021539AEfficient removalIncrease variabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHIV ProteinsClinical trial
This invention is called: the experiment and method of the protein envelope which is allosteric restructuring of the HIV-Env gene DNA and its antigenic immunity responsive HIV. It relates to the domain of life sciences and medicine sciences. It is confirmed that gp120 of the HIV protein envelope or the gp160 of the antigenic vaccine combines with cell CD4+ that can induce the infirm immunogen of the alloantigen of the immune tolerant receptor CD4 and can not induce the HIV to infect the immune response of the parasitifer. It can also eliminate the multi-clone group of hill of the wild virus which is of fast copy the initial infection virus, high variability and sequence diversity. This invention can develop the non-spark human tolerant immunity HIV vaccine of the protein envelope which is allosteric restructuring of the HIV-Env gene DNA, the HIV preventive vaccine that can provide the scientific basis of the direct animal experiment and direct clinical trial of human being. It also provides the enforceable anti-HIV cell model, rodent model, non-human Primates model and the research program of human clinical trial.
Owner:叶新新
Synergistic compositions for the prevention and treatment of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
InactiveCN100341573CPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman immunodeficiency virus 1Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Owner:TANOX
Pseudoviruses for non-CD4 receptors of HIV-1 CRF_BC recombinant strain and application of pseudoviruses
The invention discloses pseudoviruses for non-CD4 receptors of an HIV-1 CRF_BC recombinant strain and application of the pseudoviruses. The invention successfully constructs the pseudoviruses CH120N197S and CH110N197S for the non-CD4 receptors of the HIV-1 CRF_BC recombinant strain, and the two pseudoviruses not only can infect a target cell with the CD4 receptor, but also can infect a target cell without the CD4 receptor. The infectivity of the pseudovirus CH120N197S infecting the target cell without the CD4 receptor is 73 / 100 of that of the pseudovirus CH120N197S infecting the target cell with the CD4 receptor and is higher than that of a reported pseudovirus e7adaN197S (60 / 100). The successfully-constructed pseudoviruses for the non-CD4 receptors of the HIV-1 CRF_BC recombinant strain greatly enrich the main HIV-1 pseudovirus resources in China so as to have very important significance for studying the structural characteristics of cell membrane proteins of the CRF_BC recombinant strain serving as a main epidemic strain in China and developing an HIV vaccine for the CRF_BC recombinant strain in China.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Methods of monitoring HIV drug resistance
InactiveUS20020132347A1Easy to produceEasy maintenanceGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtein regulationReceptor degradation
a method is provided for detecting a presence of HIV virus in a sample comprising: taking a culture of recombinant cells which (a) are capable of cell division, (b) express CD4 receptor and one or more additional cell surface receptors necessary to allow the HIV virus to infect, (c) enable the HIV virus to replicate and infect the noninfected cells in the cell culture, and (d) comprise a reporter sequence introduced into the recombinant cells comprising a reporter gene whose expression is regulated by a protein specific to HIV viruses which is expressed from a genome of an HIV virus upon infection of the recombinant cell by the HIV virus; contacting the cell culture with a sample to be analyzed for the presence of HIV virus in the sample; and detecting a change in a level of expression of the reporter gene in cells in the recombinant cell culture. The method can be used to detect the presence of HIV virus in a sample, detect the presence of different strains of HIV virus in a sample, detect HIV drug resistance in a sample, determine what combination of one or more anti-HIV agents would be effective in treating a patient, and screen compositions for anti-HIV activity.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Methods for Treating Hiv by Inhibiting Cd4 Down-Modulation
The present invention provides methods for inhibiting the ability of HIV genes products to bind to the cytoplasmic domain of a CD4 receptor. This domain is necessary to the ability of the HIV Nef and Vpu gene products to connect the CD4 receptor to cellular degradation pathways. The present invention provides a method for introducing a modified CD4 receptor into a cell, and inhibitors thereof, to treat HIV infection and CD4 receptor down-modulation. The present invention is also directed to a method for screening compounds for the ability to inhibit CD4 down-modulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
InactiveUS20020004212A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhagocyteBinding site
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also "binding sites") on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by any one of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
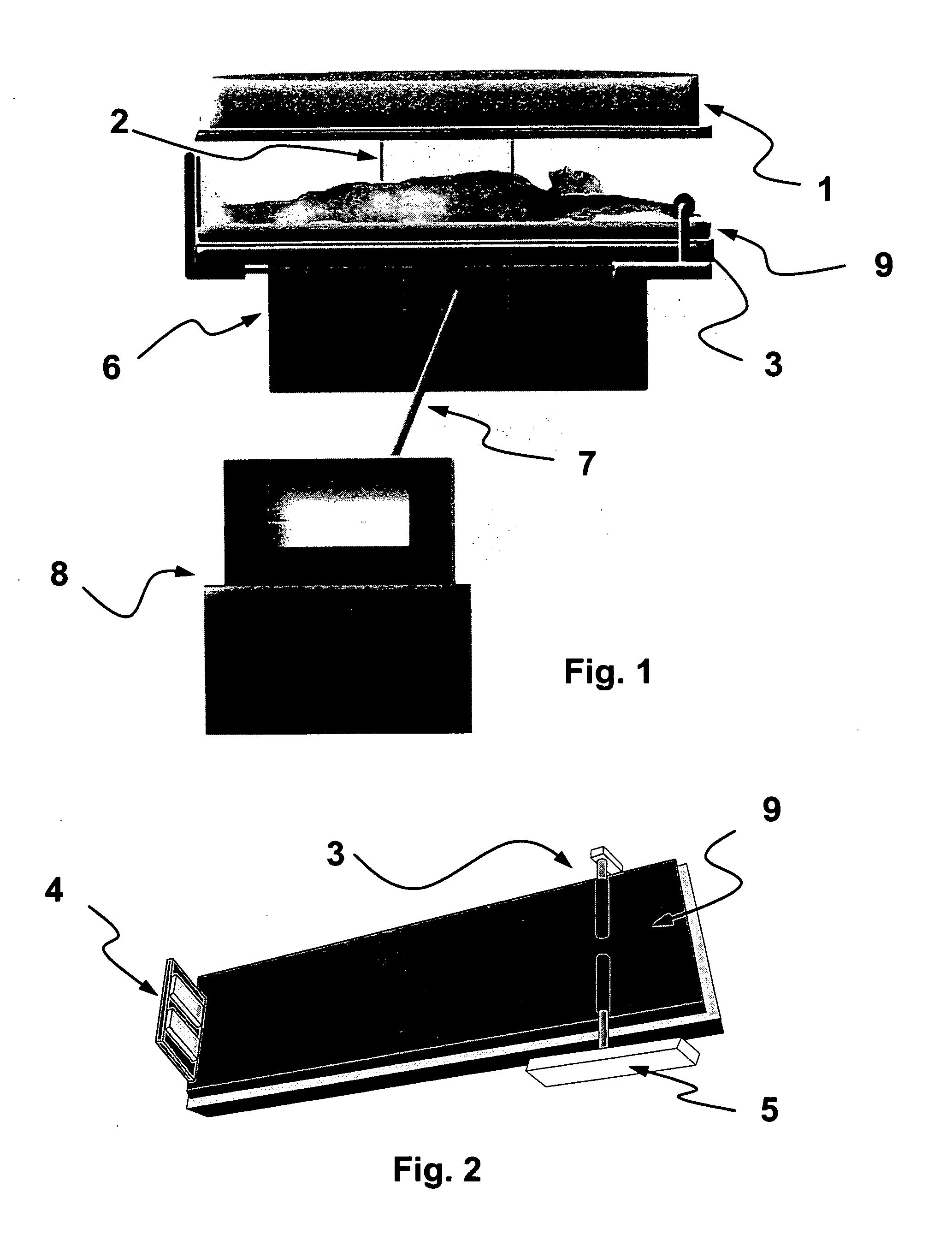
Electroimmunisation chamber
The invention relates to a horizontal chamber for treating patients suffering from the human immunodeficiency virus HIV. The patients position themselves in a supine decubitus position, and the chamber has a cover in the upper part thereof, at a variable height, comprising a magnetic pulse generator. Furthermore, electrodes are arranged in the area occupied by the patient, said electrodes being fixed in the lower area and variable in the upper area of the patient's body, generating electrical impulses complementing the magnetic impulses.; The control and regulation mechanisms of the chamber ensure a certain dosage of electromagnetic energy acting on the ionic channels of the protein GP120 present in the human immunodeficiency virus HIV, which open up and lose the necessary energy used to interact with the CD4 receptors that are marker molecules in the cellular surface and recognise certain antibodies.
Owner:欧内斯特·米格尔·冈萨雷斯 阿马斯 +1
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by anyone of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:RONALD WINSTON
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising an hiv envelope protein and cd4
InactiveUS20060142219A1Easy to manageEffectively prevent murine collagen-induced arthritisVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeNucleotide
Pharmaceutical composition for treating / preventing HIV comprising (i) a polynucleotide encoding HIV envelope protein and (ii) a polynucleotide encoding CD4 receptor protein or; (i) a polynucleotide encoding HIV envelope protein and (ii) a CD4 receptor protein or; a fixed cell expressing an HIV envelope protein complexed with a CD4 receptor protein. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions for treating / preventing HIV comprising an antibody immunospecific for a fixed cell expressing an HIV envelope protein complex with a CD4 receptor protein. The binding of the CD4 to the HIV envelope protein, i.e. gp120, exposes hidden epitopes that may be used as targets in immunotherapy; the presentation of the gp120 and CD4 in the present forms is said to overcome problems with prior art soluble gp120-CD4 complexes.
Owner:FOND CENT SAN RAFFAELE DEL MONTE TABOR
Conjugated molecules for the treatment of AIDS comprising a peptide derived from a CD4 receptor coupled to a polyanionic polypeptide
InactiveCN103429269BCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapy HIVCD4 antigen
The present invention relates to conjugated molecules comprising a peptide derived from the CD4 receptor coupled to an organic molecule via a linker and a method for their preparation. The organic molecules include anionic polypeptides of 5 to 21 amino acids. The conjugated molecule can be used for antiviral therapy, that is, for the treatment of AIDS.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +2
Detection of surface-associated human leukocyte elastase
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemoline receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by anyone of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:RONALD WINSTON
Detection of surface-associated human Leukocyte Elastase
In order to accurately and reliably quantitate HLE on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes, a test sample containing the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes is initially treated with a first antiserum specific for CD4 receptors on the plasma membrane or with a second antiserum specific for chemokine receptors on the plasma membrane. Once the CD4 or chemokine receptors have been rendered non-reactive (competitive) relative to the HLE receptors (also “binding sites”) on the plasma membrane, the test sample is contacted with an immunoreagent specific for interaction with one or more of the HLE receptors on the plasma membranes of the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes. The immunoreagent forms a complex with the HLE binding sites and produces a characteristic physical change in the lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes that can be monitored by any one of a number of standard techniques, (e.g., confocal laser scanning microscopy and flow cytometry).
Owner:BRISTOW CYNTHIA L
New conjugated molecules comprising peptide derived from CD4 receptor coupled to polyanionic polypeptide for treatment of AIDS
InactiveCN103429269ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapy HIVAmino acid anion
This invention relates to a conjugated molecule comprising a peptide derived from the CD4 receptor coupled to an organic molecule by means of a linker as well as a process for its preparation. Said organic molecule comprises a 13 amino acid anionic polypeptide. Such a conjugated molecule can be used in antiviral treatment, namely in the treatment of AIDS.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +2
Electroimmunization chamber
InactiveUS20110196437A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectricityEngineering
An electroimmunization chamber consists of a horizontal space designed for treatment of patients with HIV, who place themselves in supine lying position, and the upper part of which has a cover with adjustable height with a magnetic pulse generator. The patient rest area also contains fixed electrodes in the lower part and variable electrodes in the upper patient area, which generate electrical impulses that supplement the magnetic pulses. The mechanisms for control and regulation of the chamber ensure dosing of electro-magnetic energy that acts on the ionic channels of the GP120 protein that is present in HIV. These channels open and lose the necessary energy used for interacting with the CD4 receptors, which are marking molecules on the cell surface, which recognize certain antibodies.
Owner:GONZALEZ ARMAS ERNESTO MIGUEL +1
HIV-EnvHIV-Env gene DNA recombinant envelope protein antigen immune response experiment and method for resisting HIV
InactiveCN101210919AFighting Immunosuppressive StressImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVirus peptidesCell specificHuman body
The invention relates to an anti-HIV immune response apparatus of an HIV-Env DNA recombinant envelope protein antigen and a method thereof, belonging to life science and medicinal fields. The clinic experiment in human body prove that vaccines derived from HIV envelope protein gp120 or gp160 can not prevent HIV infection, because the HIV envelope protein gp120 or gp160 is a heterogeneous specific ligand that can specifically bind with CD4<+> cells-specific receptor CD4<+> receptor and induce immunological tolerance mechanism of human body but can not inducing immune response mechanism for effectively eliminating HIV. The invention can be used for searching a method for solving immunological tolerance mechanism of human body, developing an anti-HIV vaccine derived from HIV-Env DNA recombinant envelope protein antigen for preventing and treating HIV that does not induce immunological tolerance mechanism of human body, and providing sufficient scientific reference for direct animal model experiments and direct clinical human trials.
Owner:叶新新
Antigen-specific regulatory t-cell induction
The present invention relates to an infectious particle having a surface displaying a ligand binding to a CD4 receptor for selectively infecting dividing CD4+ cells, said particle comprising: (a) one or more structural proteins, and (b) a vector containing a gene of interest functional in a CD4+ cell, said gene of interest encoding a Forkhead box protein 3 or a protein inducing expression of Forkhead box protein 3 in the CD4+ cell.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Nucleic acid construct for AIDS gene therapy
PendingCN114645066AImprove expression efficiencyGood neutralizing activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against virusesIn vivoViral vector
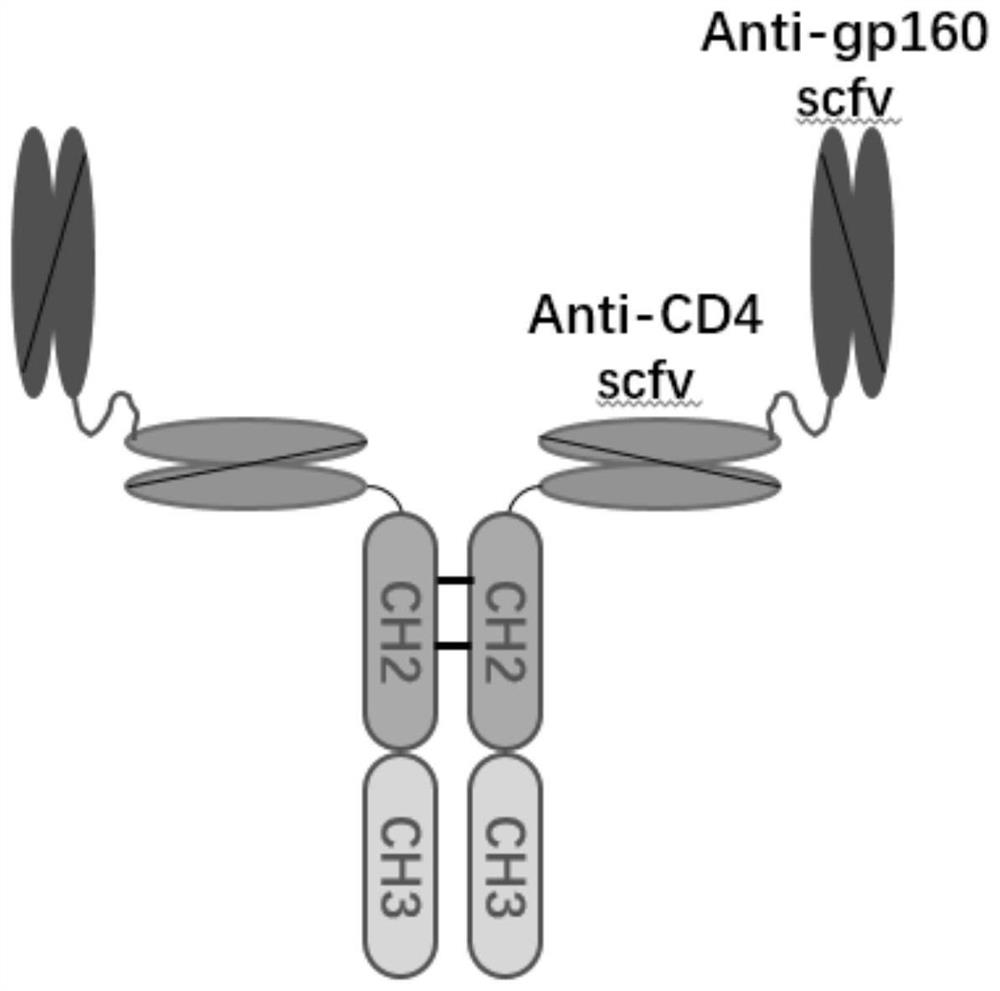
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, in particular to a nucleic acid construct for AIDS gene therapy, which comprises a plurality of polynucleotides for coding single-chain variable fragments of an anti-AIDS neutralizing antibody and polynucleotides for coding an immune globulin Fc fragment. The single-chain variable region fragment of the anti-AIDS neutralizing antibody comprises a single-chain variable region fragment capable of being specifically combined with HIV and a single-chain variable region fragment capable of being specifically combined with a CD4 receptor. The construction body can be used for gene therapy of AIDS caused by HIV virus infection, can be used for expressing an amphiphilic / polyphilic neutralizing antibody with broad-spectrum and high-efficiency neutralizing activity in vivo and in vitro, and can be used for clinical research and new drug research and development of AIDS gene therapy drugs delivered by recombinant viruses or non-viral vectors.
Owner:KANGLIN BIOTECHNOLOGY (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Cell-based method and assay for measuring the infectivity and drug sensitivity of immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20050032046A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisImmunodeficiency virusHIV receptor
Methods and reagents for the capture of primary HIV are provided. A cell line expressing CCR5, CXCR4 and CD4 receptors binds and is infected by primary HIV. The cell line contains a marker gene sequence, the marker gene sequence expressed in near linear quantities over at least two orders of magnitude in response to HIV infection. Primary HIV is amplified to create a primary virus stock through insertion of an amplicon gene into the receptor expressing cell line. HIV amplification occurs rapidly and is operative with noninfectious HIV through amplification in the presence of an infectivity complement. The present invention is useful in determining host HIV titer, drug sensitivity, HIV amplification, gene sequencing and co-receptor utilization.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com