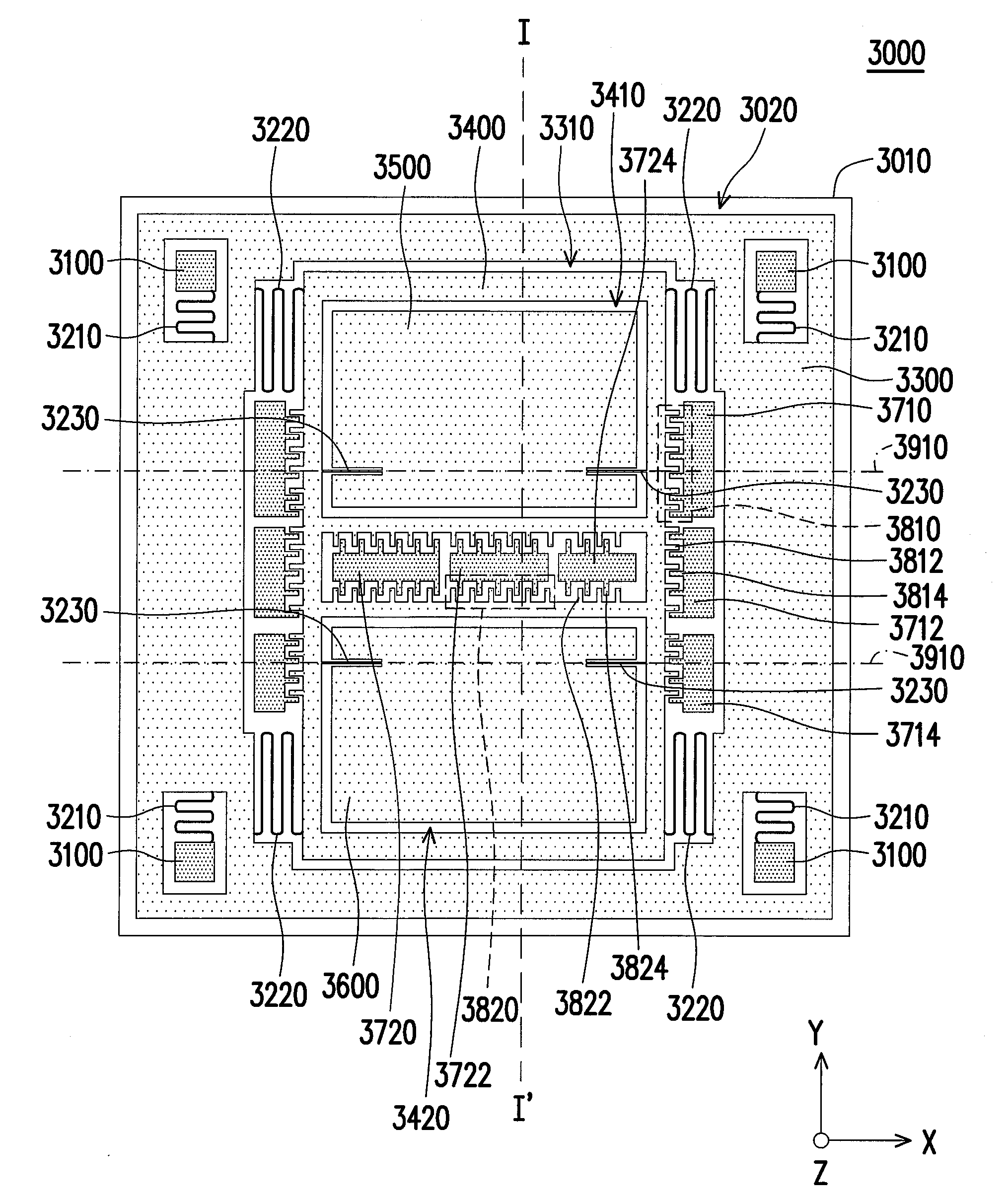
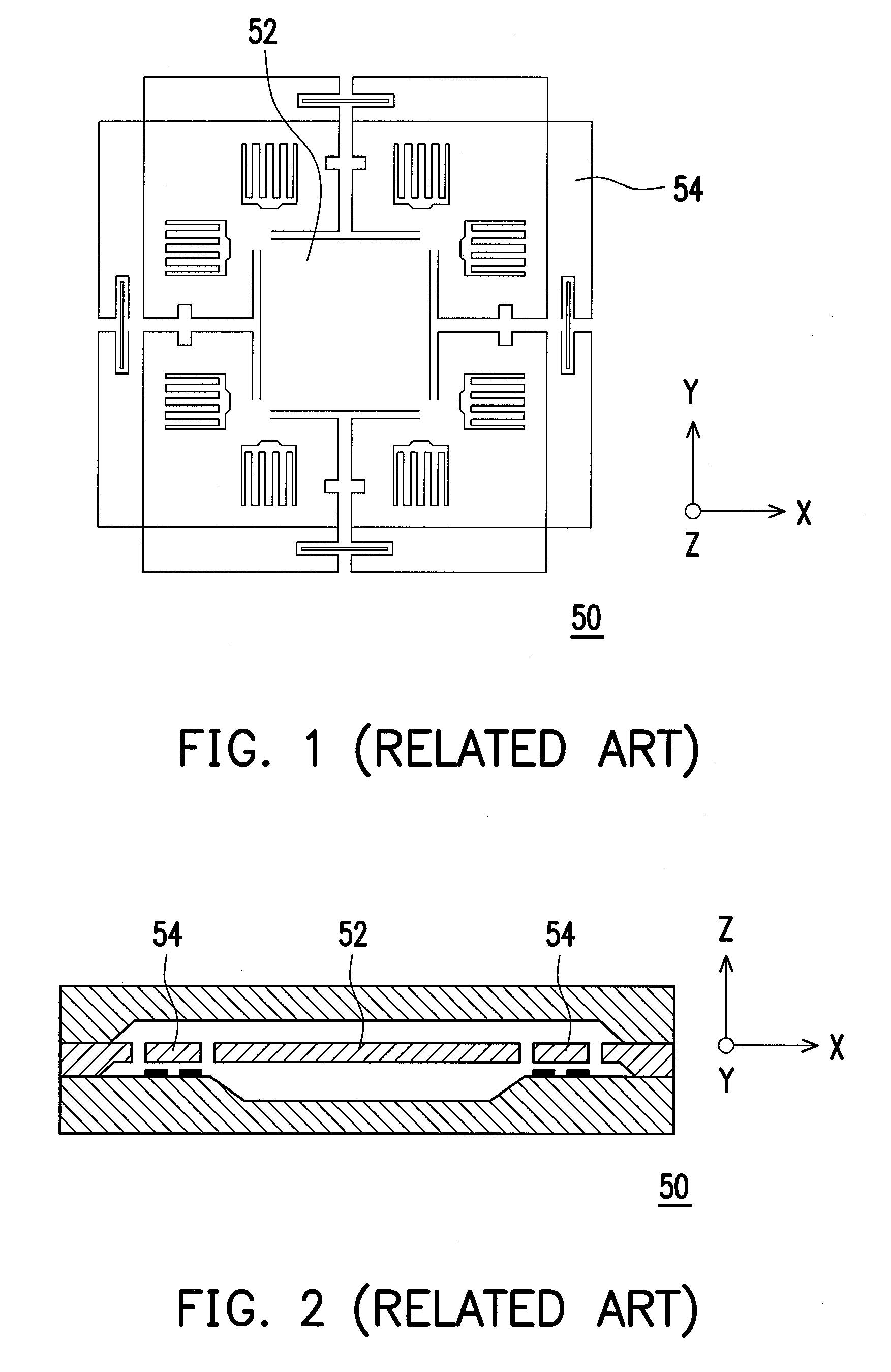
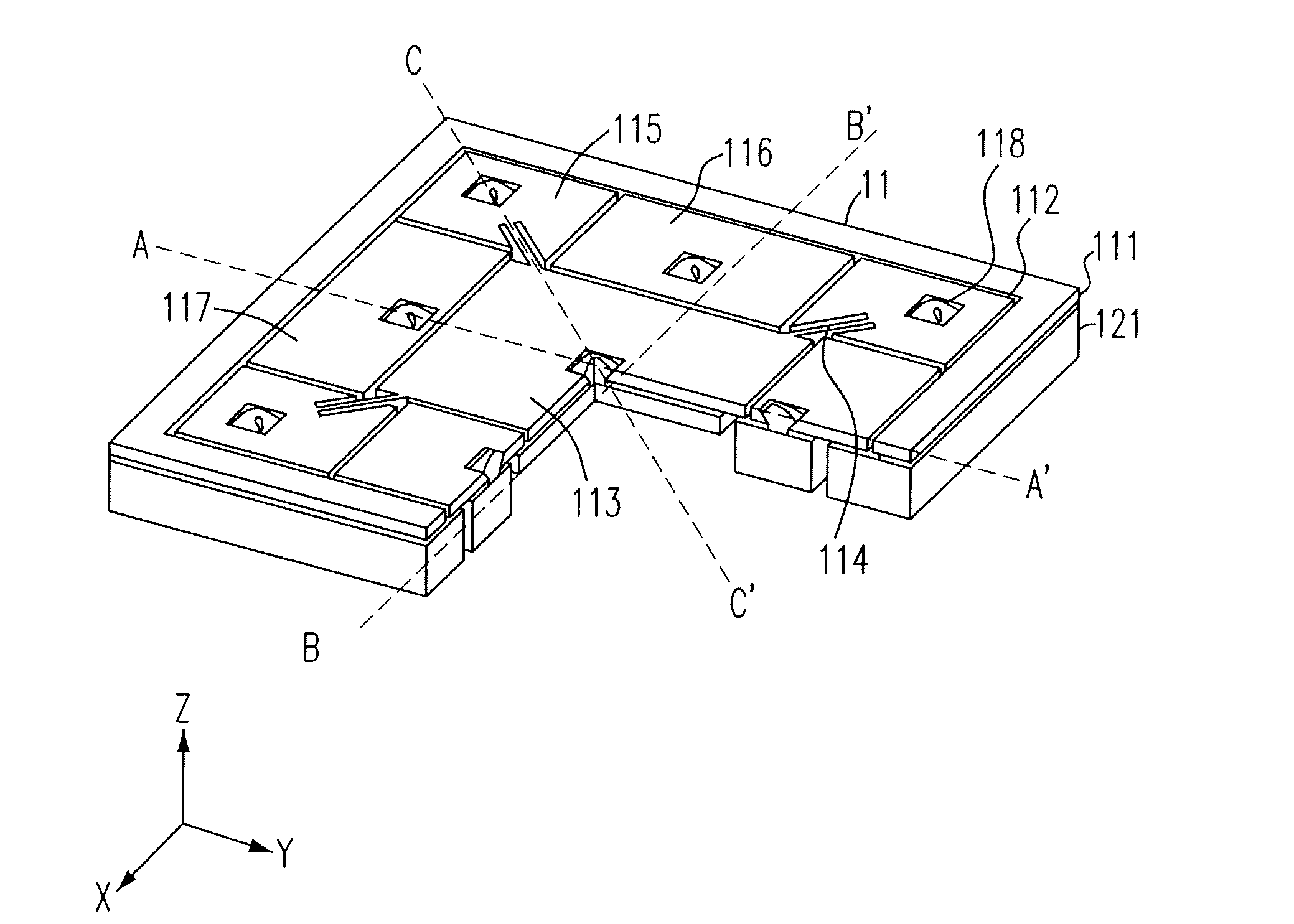
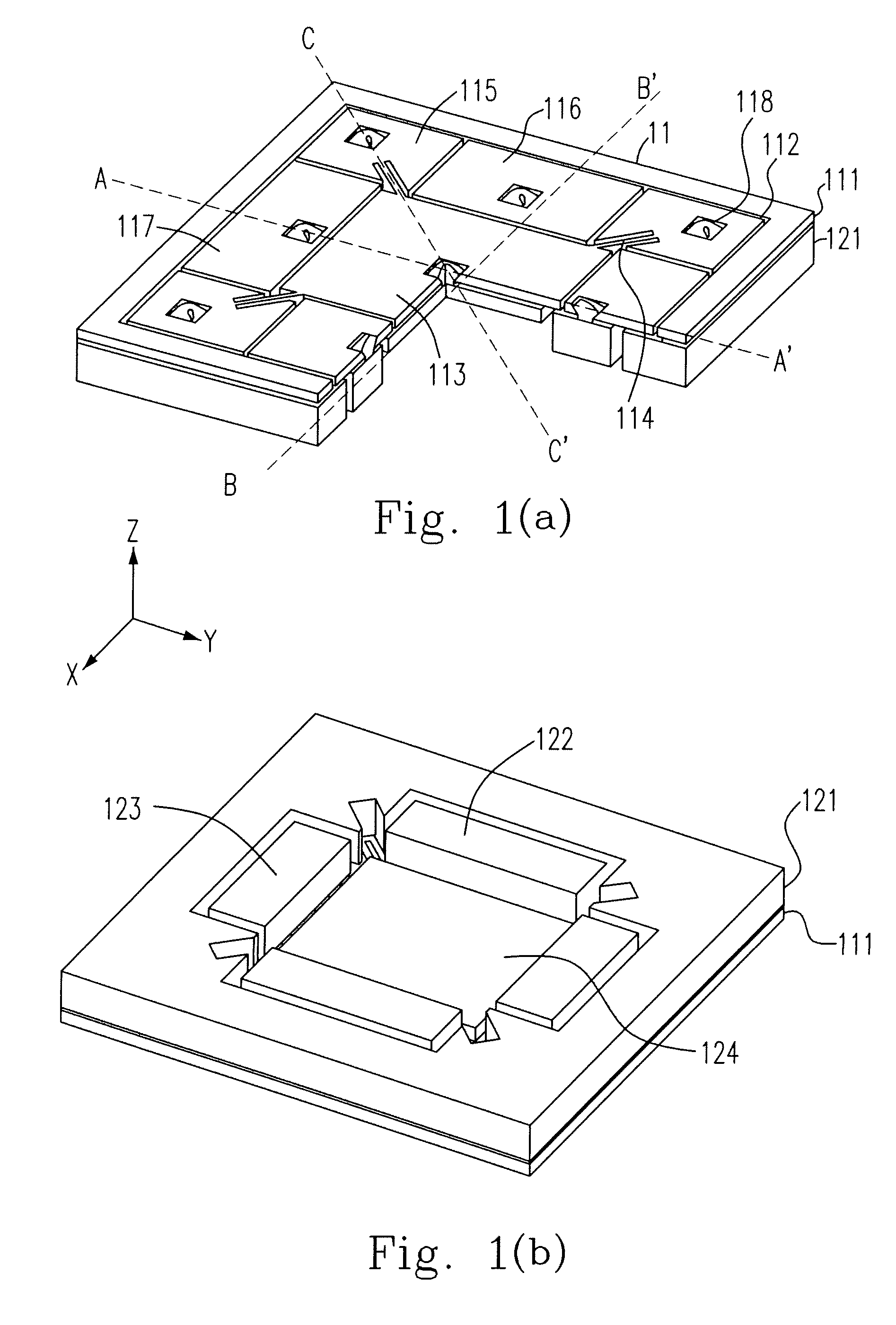
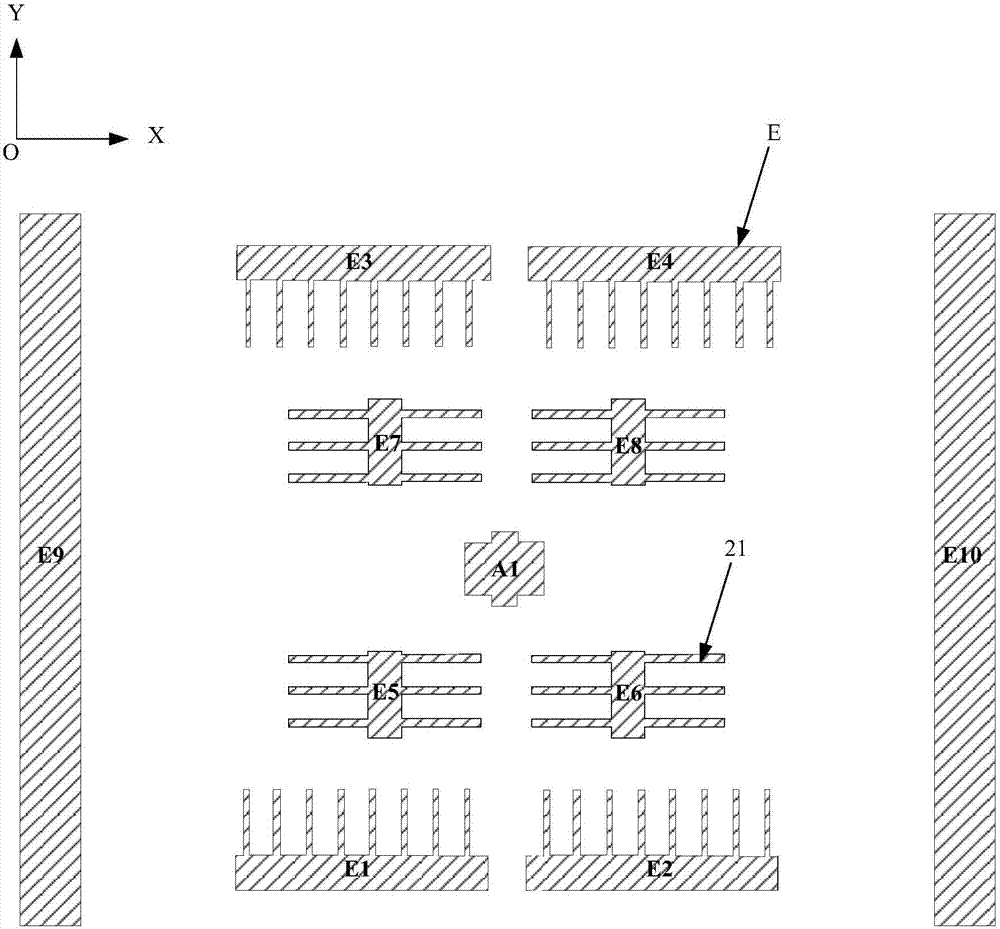
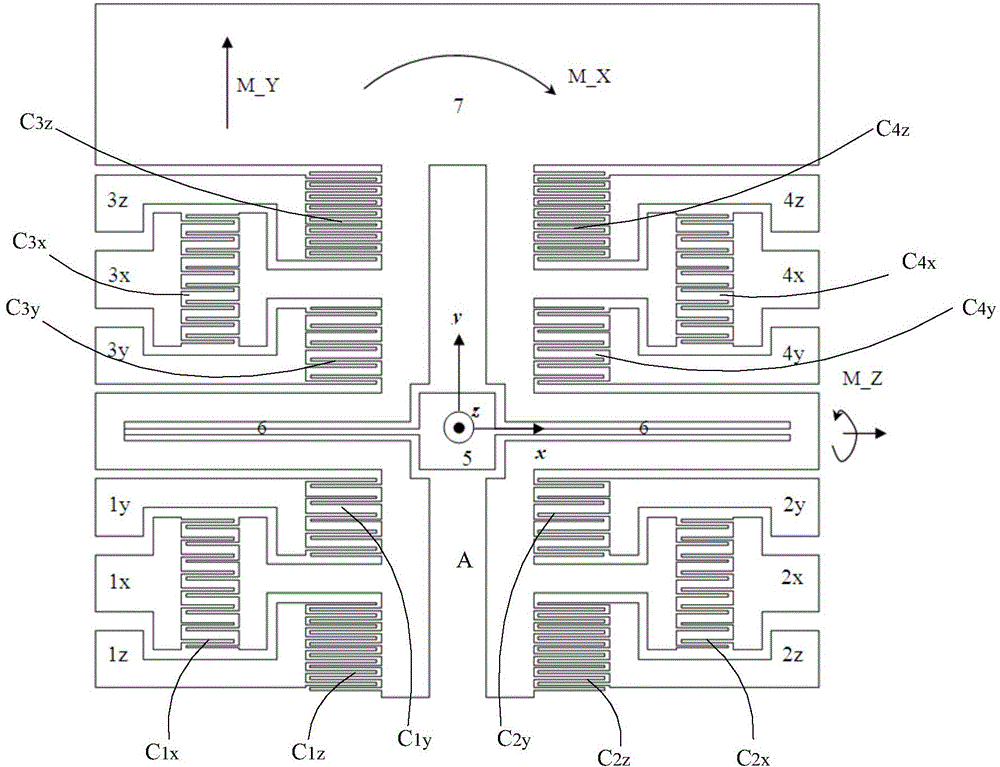
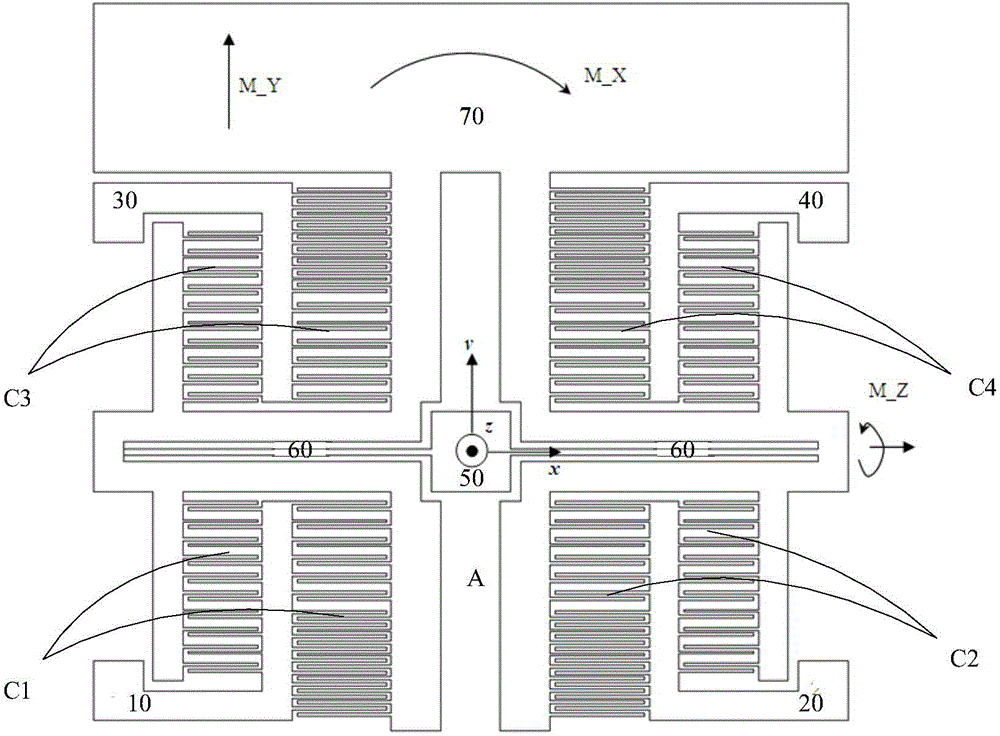
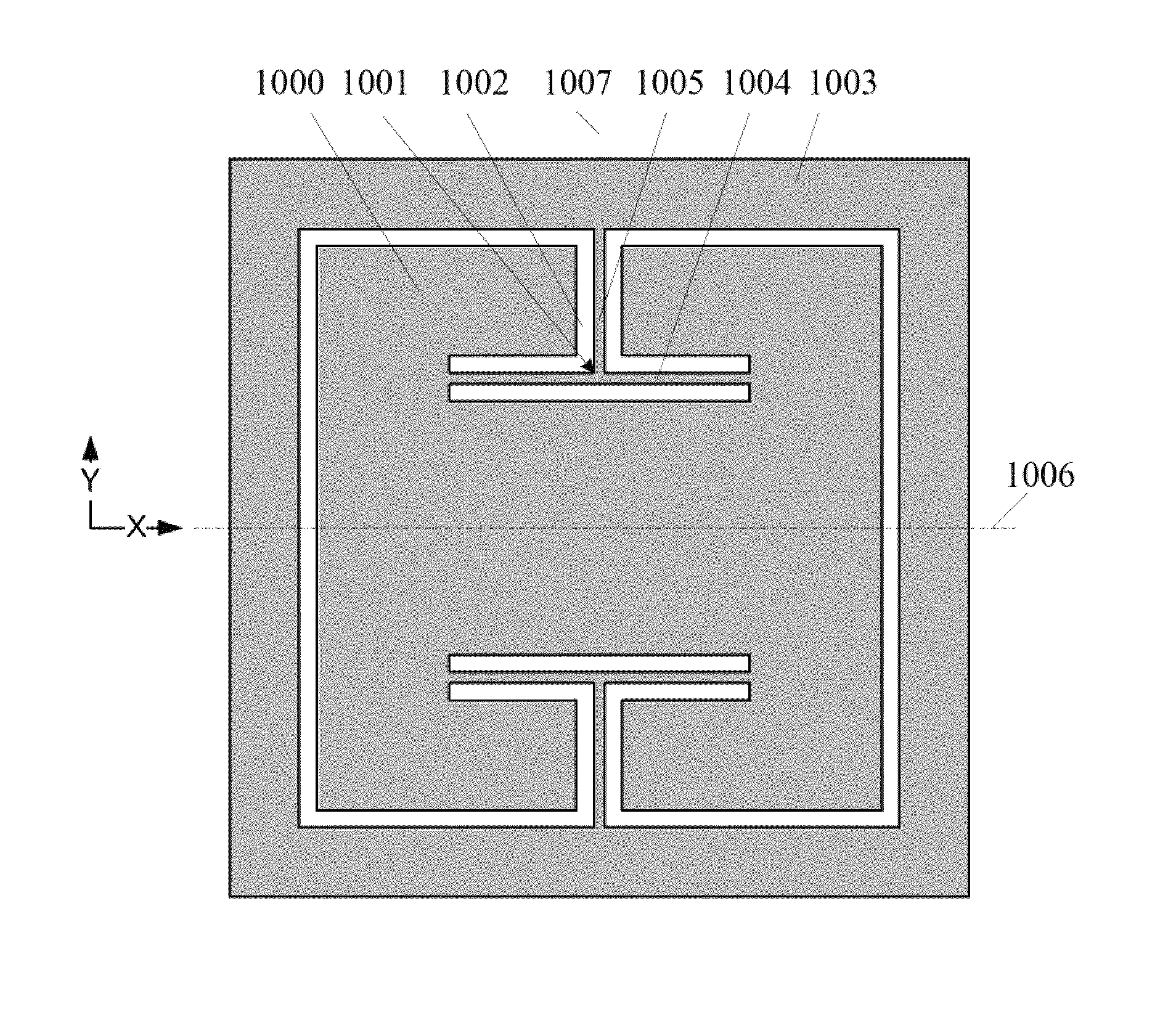
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117 results about "Capacitive accelerometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A capacitive accelerometer is a type of accelerometer device that measures the acceleration on a surface using capacitive sensing techniques. It has the ability to sense static and dynamic acceleration on equipment or devices - enforced by human or mechanical forces - and converts this acceleration into electrical currents or voltage.
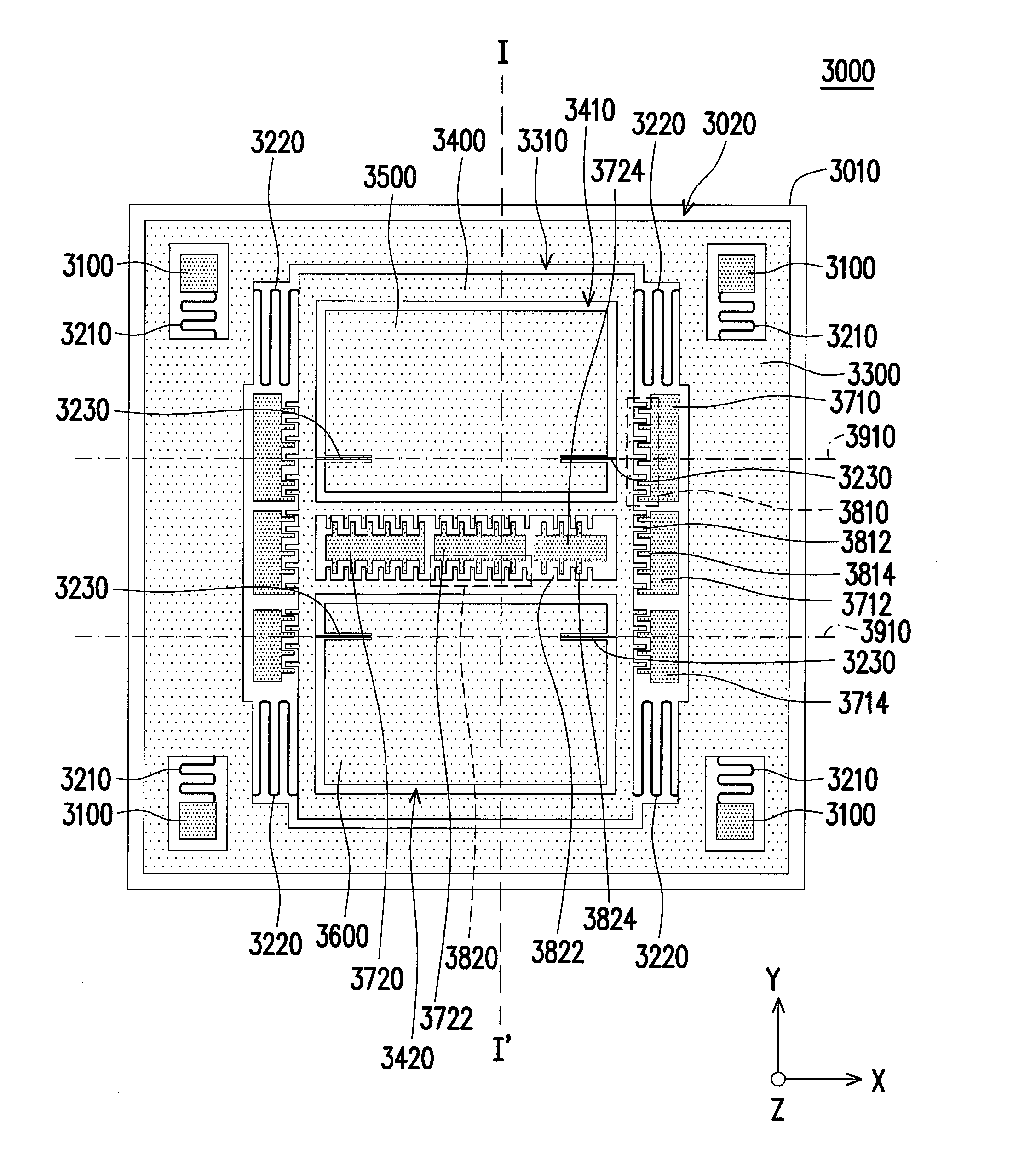
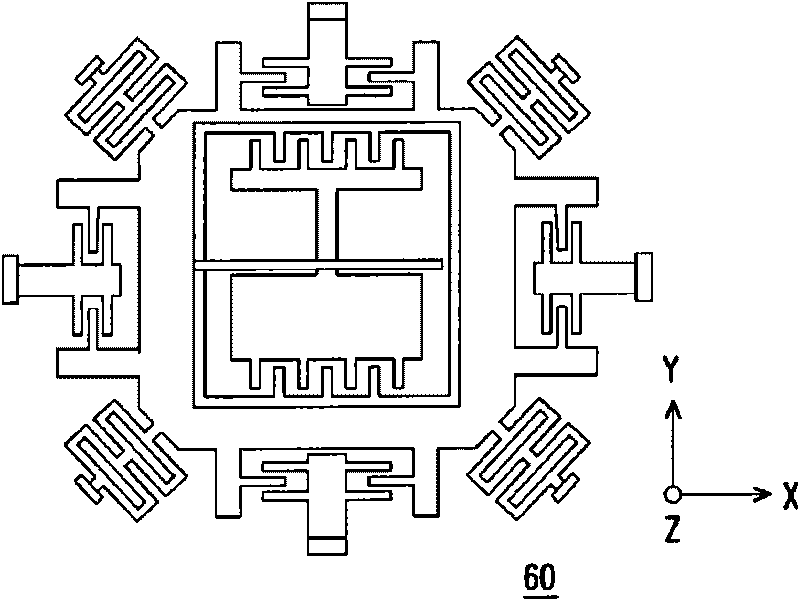
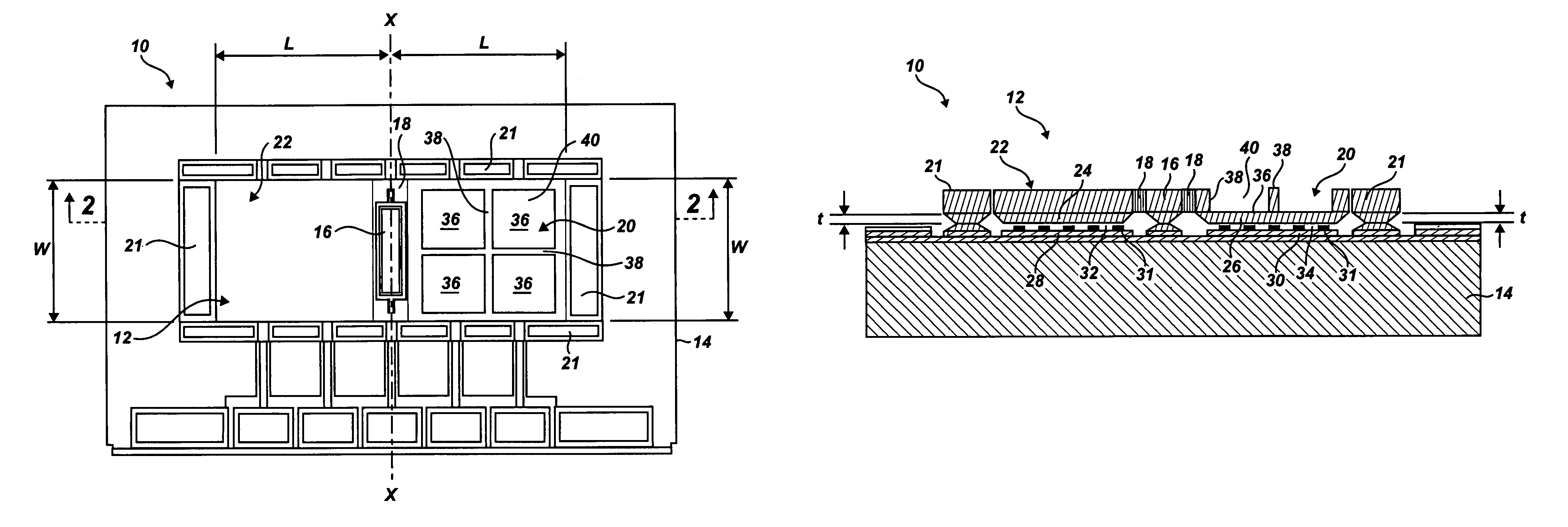
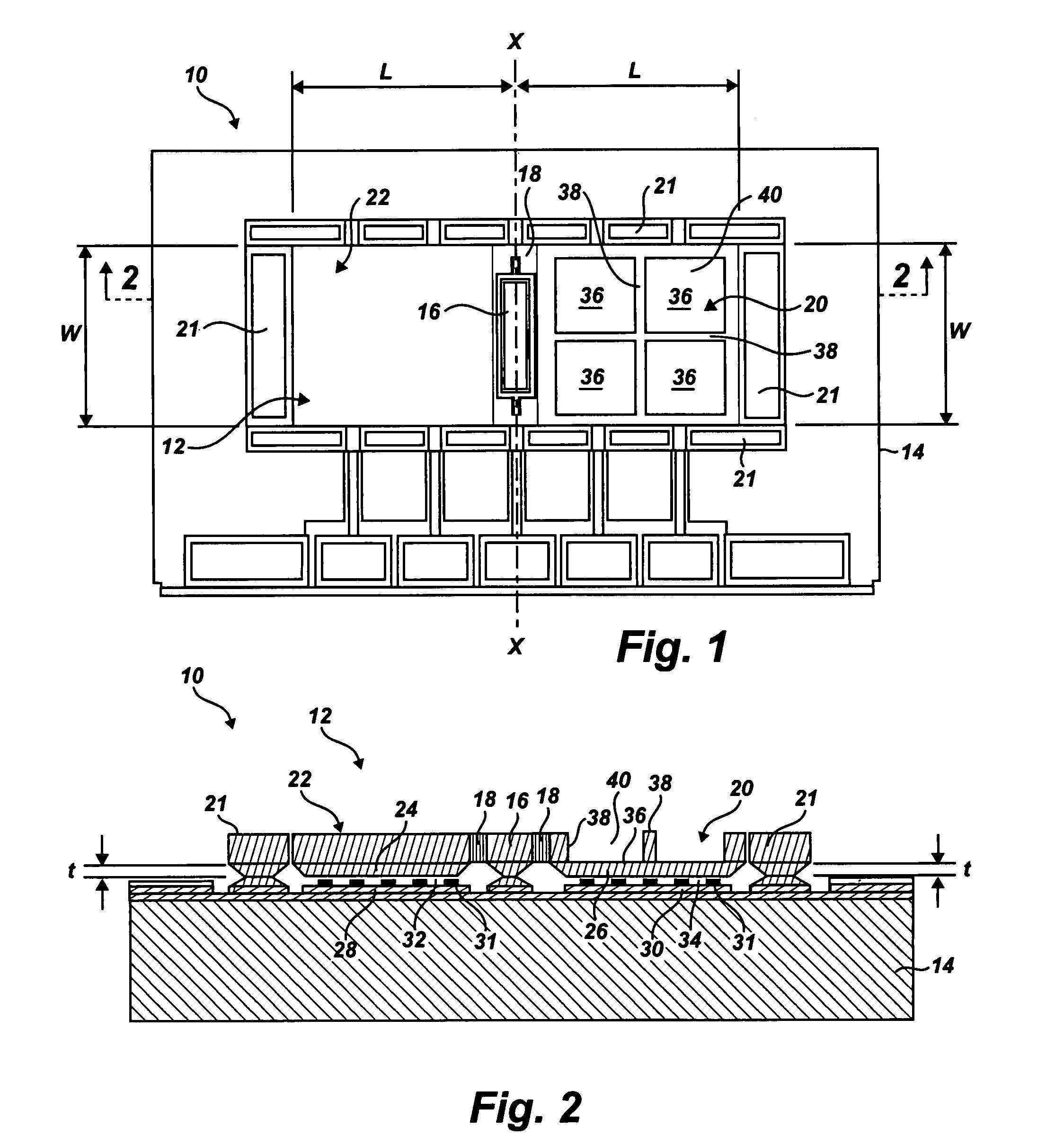
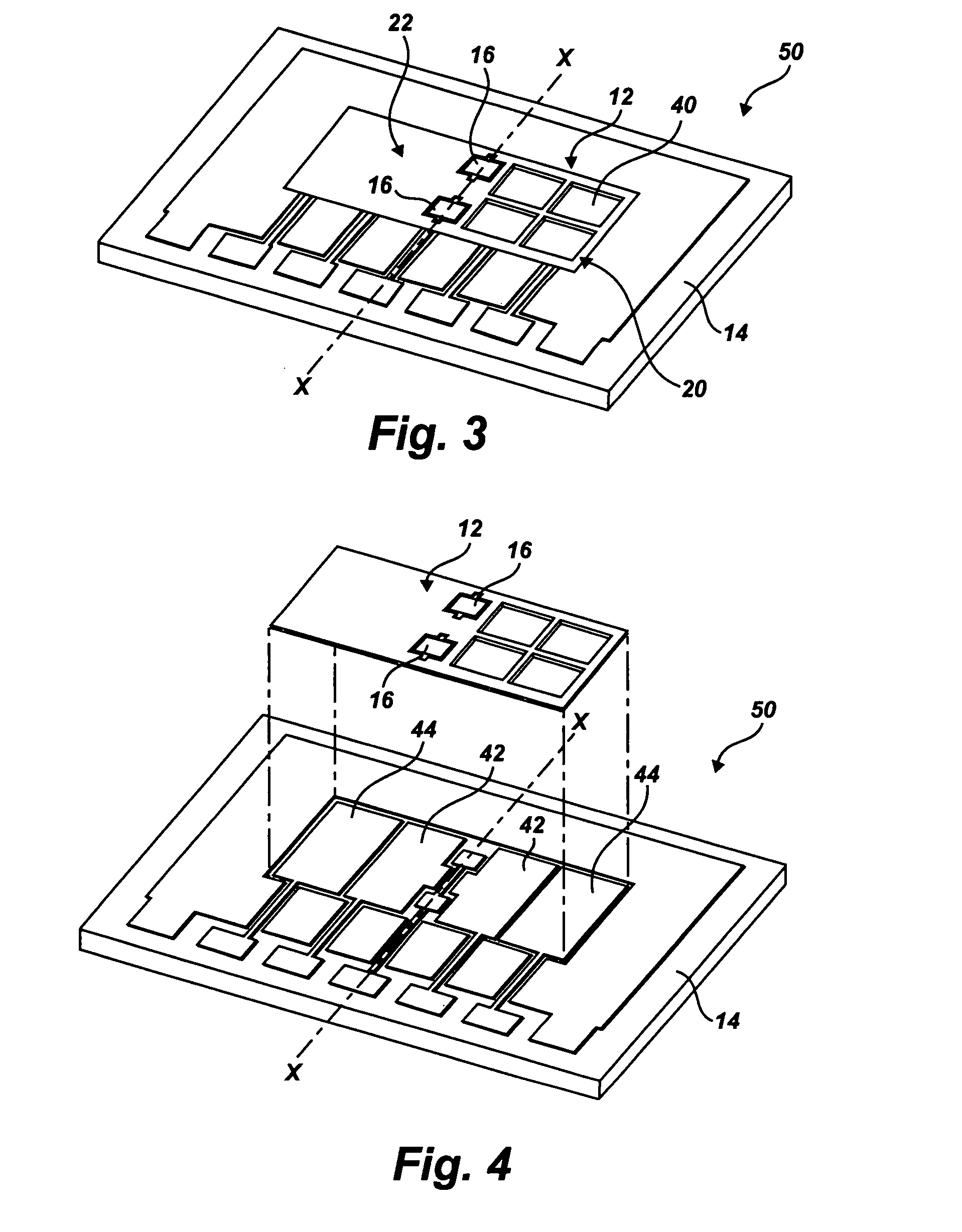
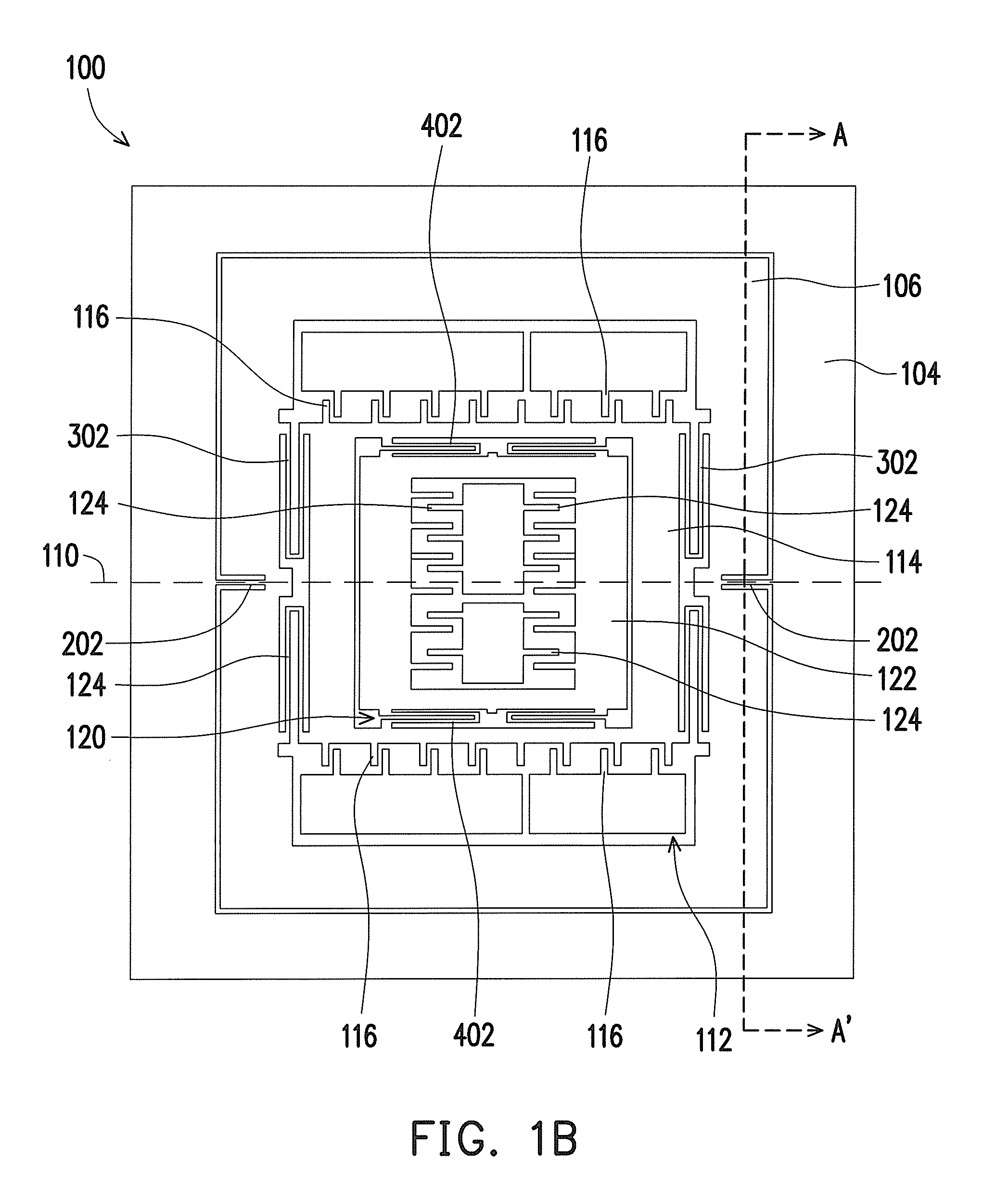
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS20100122579A1Improve linearityEliminate relative rotationAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
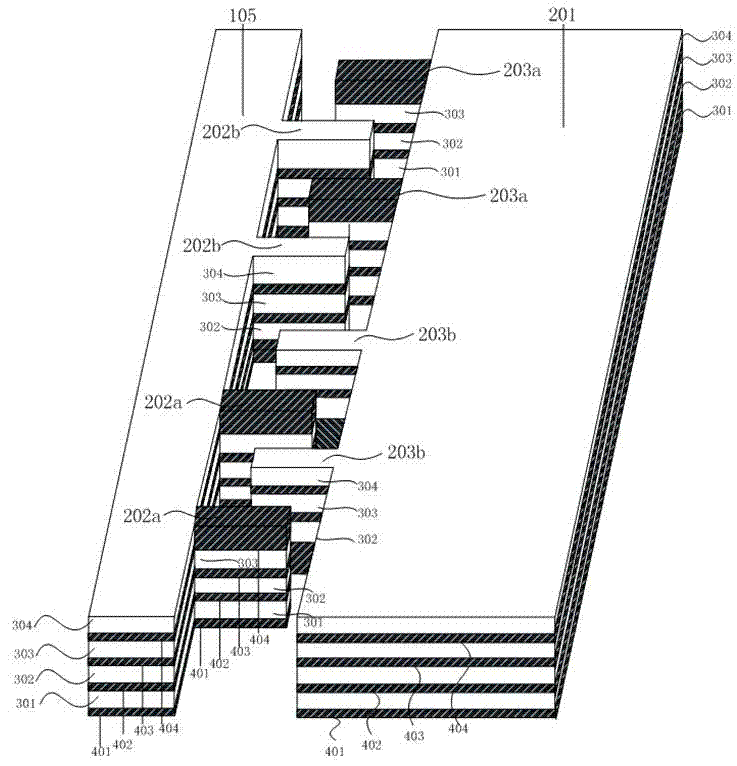
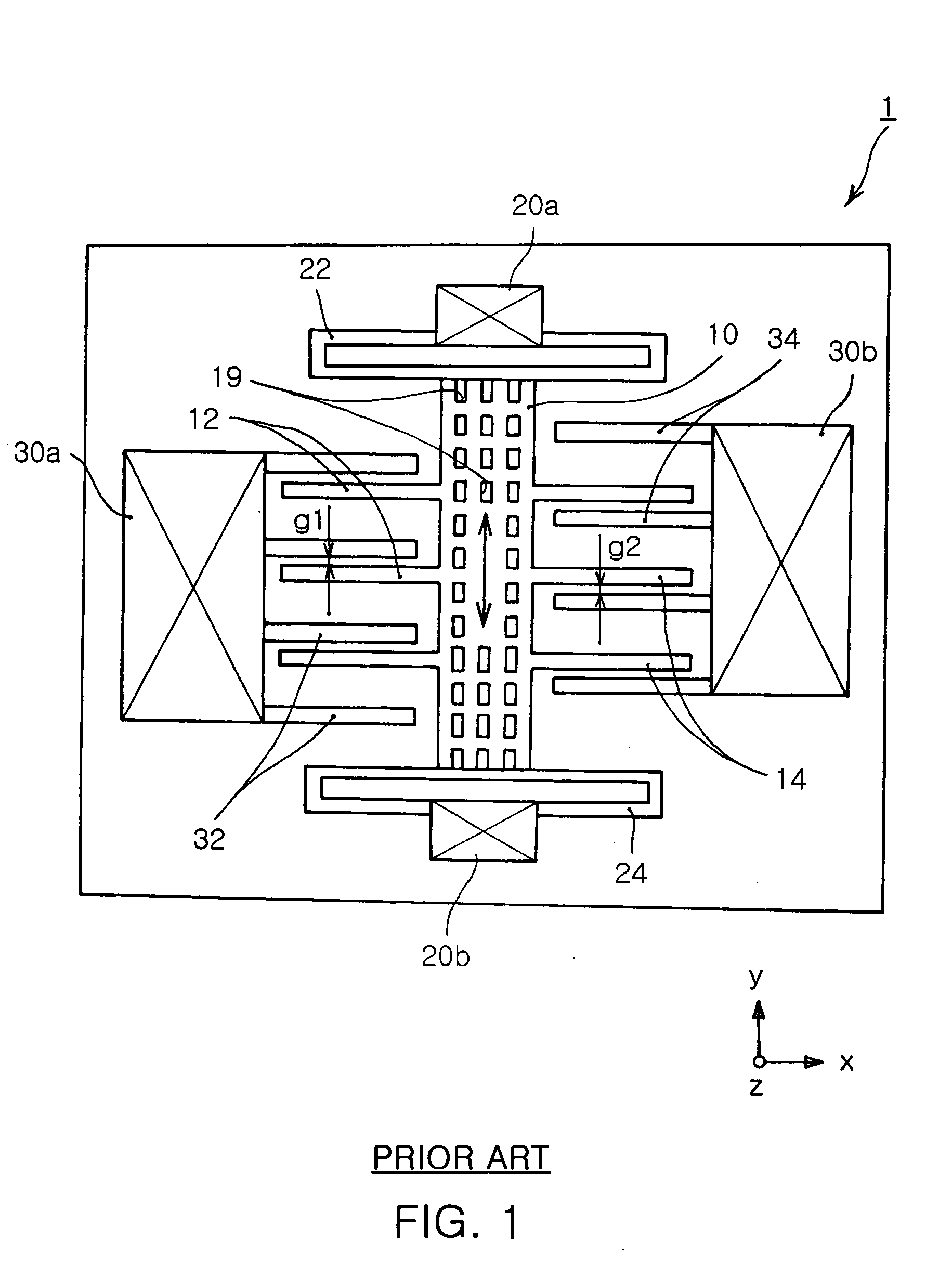
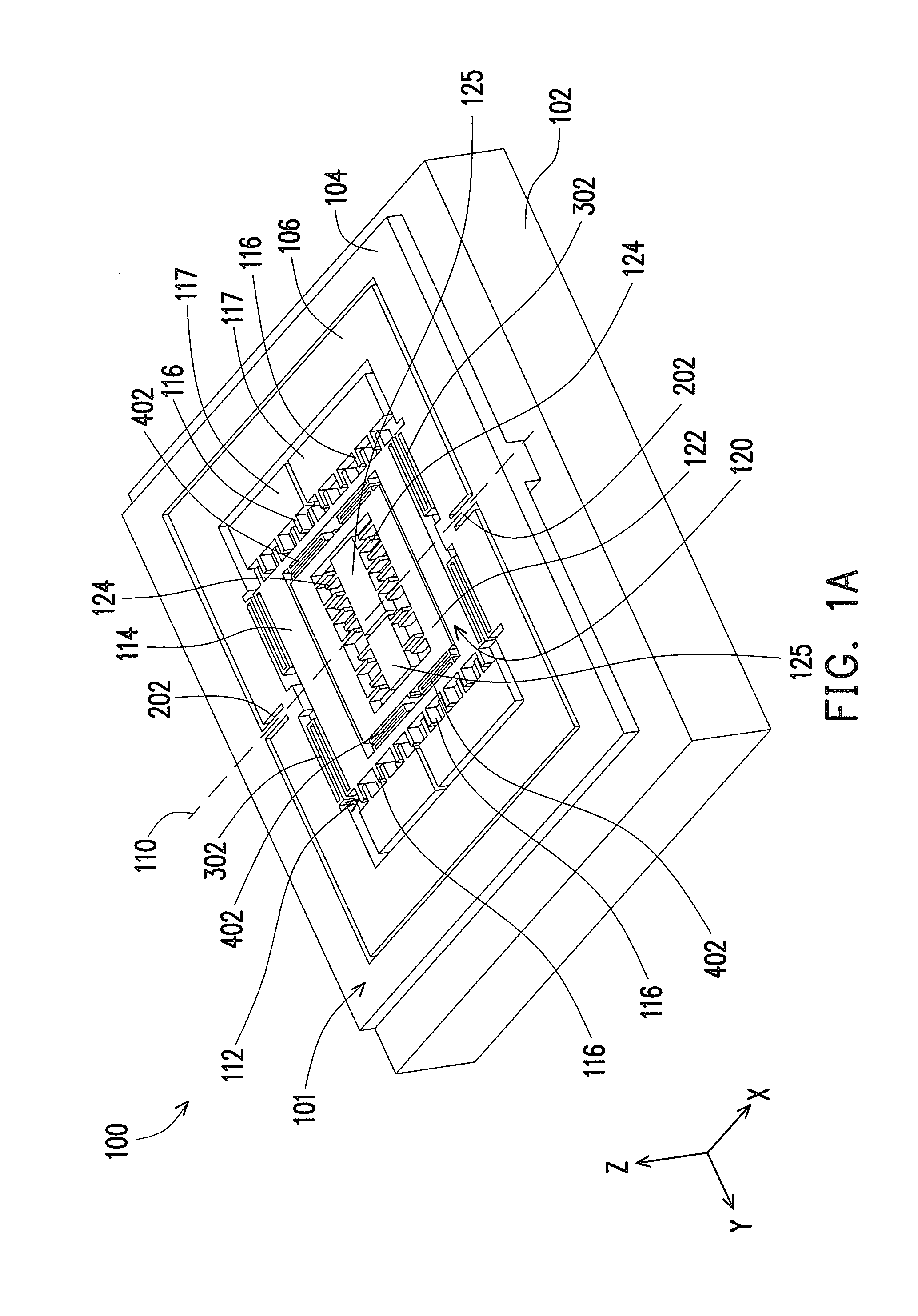
A multi-axis accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate. A first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The first proof mass is suspended to the anchor bases. Fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. A second proof mass and a third proof mass are disposed in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveCN101738496AAvoid influencePreferred linearityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
A multi-axis capacitive accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate, a movable first proof mass, a group of first flexible structures, a plurality of fixed sensing blocks, a second proof mass, a third proof mass, a second flexible structure and a third flexible structure. The first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The flexible structures are connected with the anchor bases and the first proof mass. The fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. The second proof mass and the third proof mass are disposed over the substrate and in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended over the first proof mass respectively by the second flexible structure and the third flexible structure. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS20100058864A1Reduce distractionsImprove linearityAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsClassical mechanicsMulti axis
A multi-axis capacitive accelerometer is disclosed. A first mass is disposed and held by an anchor supported by a substrate, wherein the first mass is asymmetrically suspended on the anchor by means of two cantilevers, so that the first mass rotates about a rotation axis, for sensing the acceleration in a first direction perpendicular to the substrate. A second mass is disposed in the first mass and suspended on the first mass by means of a set of springs to sense the acceleration in a second direction parallel to the substrate. Furthermore, a third mass can be disposed in the second mass, wherein the third mass is suspended on the second mass by means of another set of springs to sense the acceleration in a third direction. The first direction, the second direction and the third direction are mutually orthogonal to each other.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Monolithic integrated CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) MEMS (Micro-electromechanical Systems) multilayer metal three-axis capacitive accelerometer and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102955046AReduce areaReduce Interconnect Parasitic CapacitanceTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLow noiseManufacturing technology
The invention provides a monolithic integrated three-axis accelerometer and a manufacturing method thereof so as to solve the defects in structure and manufacturing technology of the existing structural capacitive accelerometer. Three layers of metal Al thin films are deposited in the direction of an axis Z so as to form a comb pair sensitive electrode; four layers of metal Al / SiO2 thin films are deposited in the directions of an axis X and an axis Y so as to form comb pair sensitive electrodes, and the accelerations of the three axis directions are detected simultaneously by a single integrated structure. The accelerometer and the manufacturing method thereof have the following positive technical effects: the interconnection stray capacitance among accelerator devices in three axis directions is lowered remarkably, and high detection accuracy and lower noise performance are realized; since the accelerometer is provided with the multiple metal layers, compared with a microaccelerometer manufactured from the same material, namely polycrystalline silicon, the accelerometer is more flexible in wiring; a foldable beam is used in the structure of the accelerometer, so that the own stress of the accelerometer is released better, and therefore the influence of the stress on the system can be reduced effectively.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
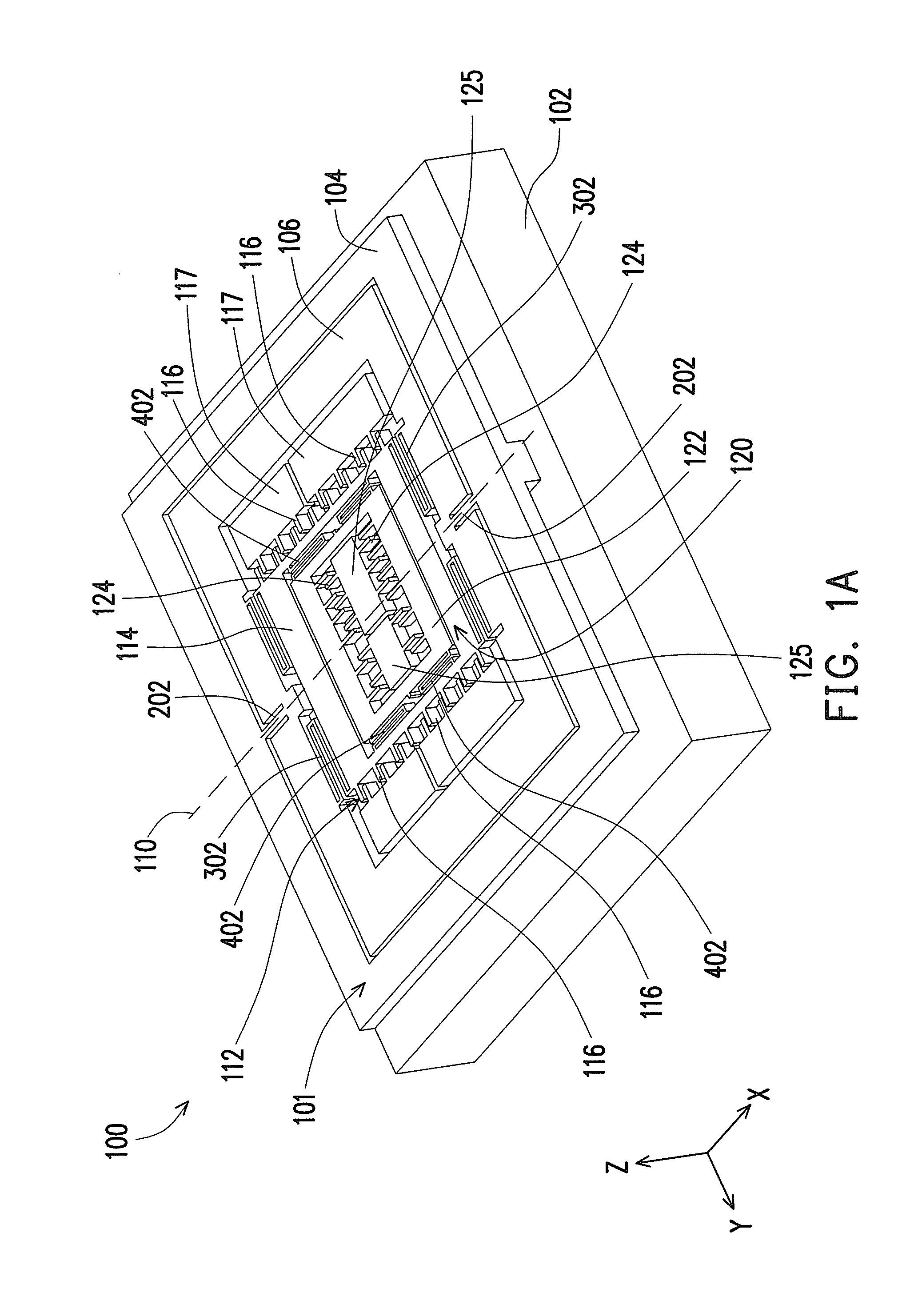
Microelectromechanical three-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS20120000287A1Reduced dimensionDesired characteristicAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsInertial massCapacitive accelerometer
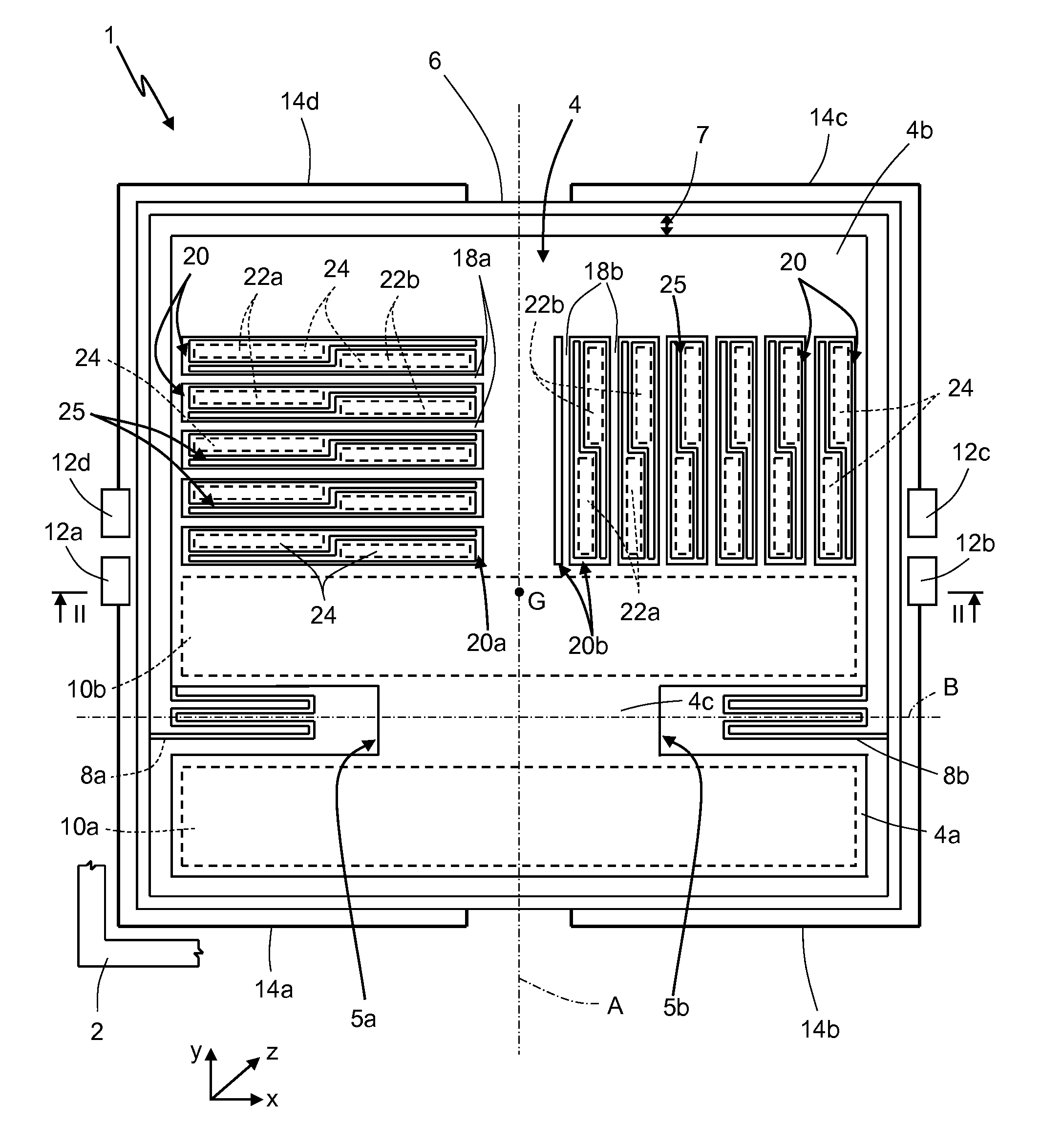
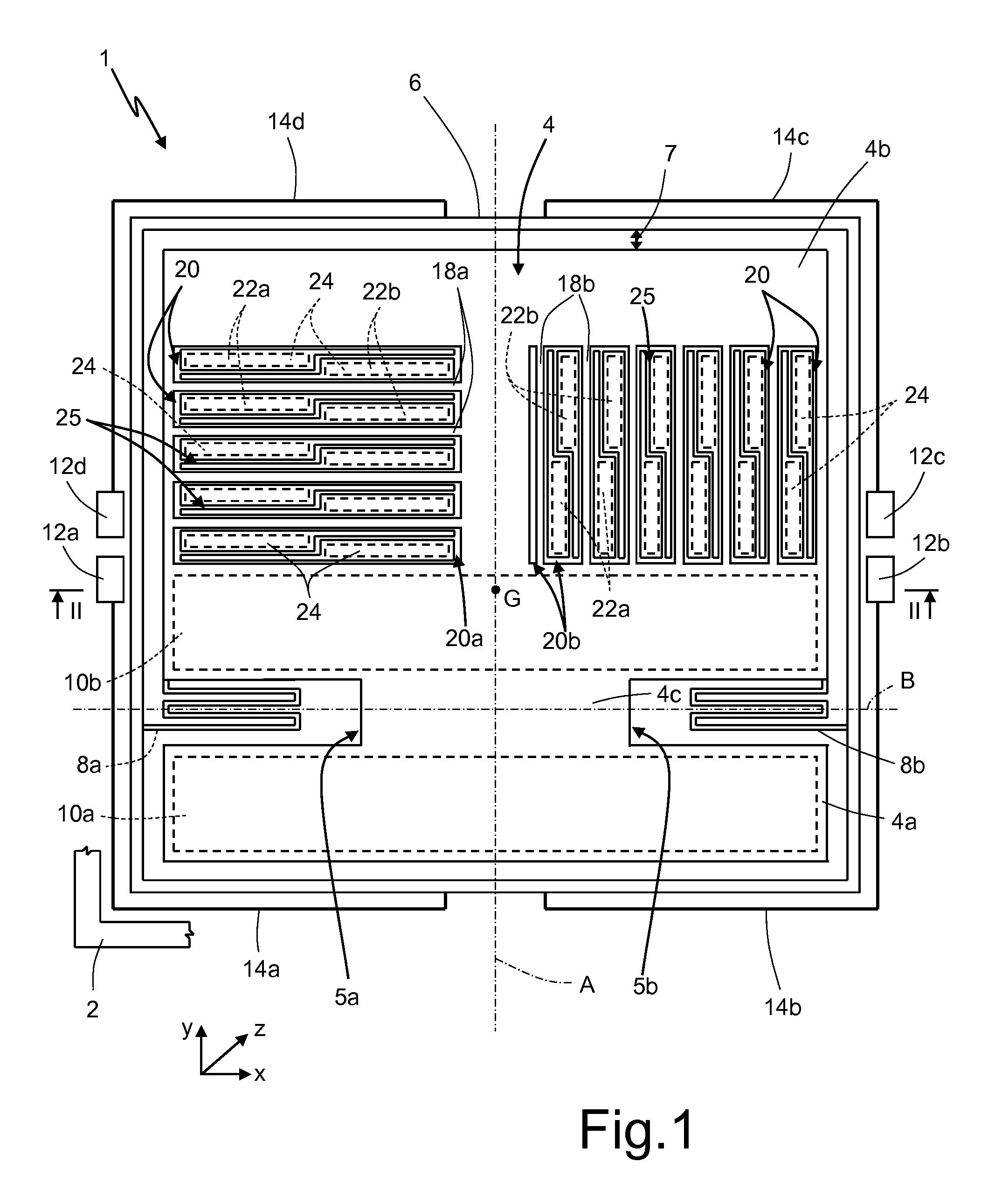
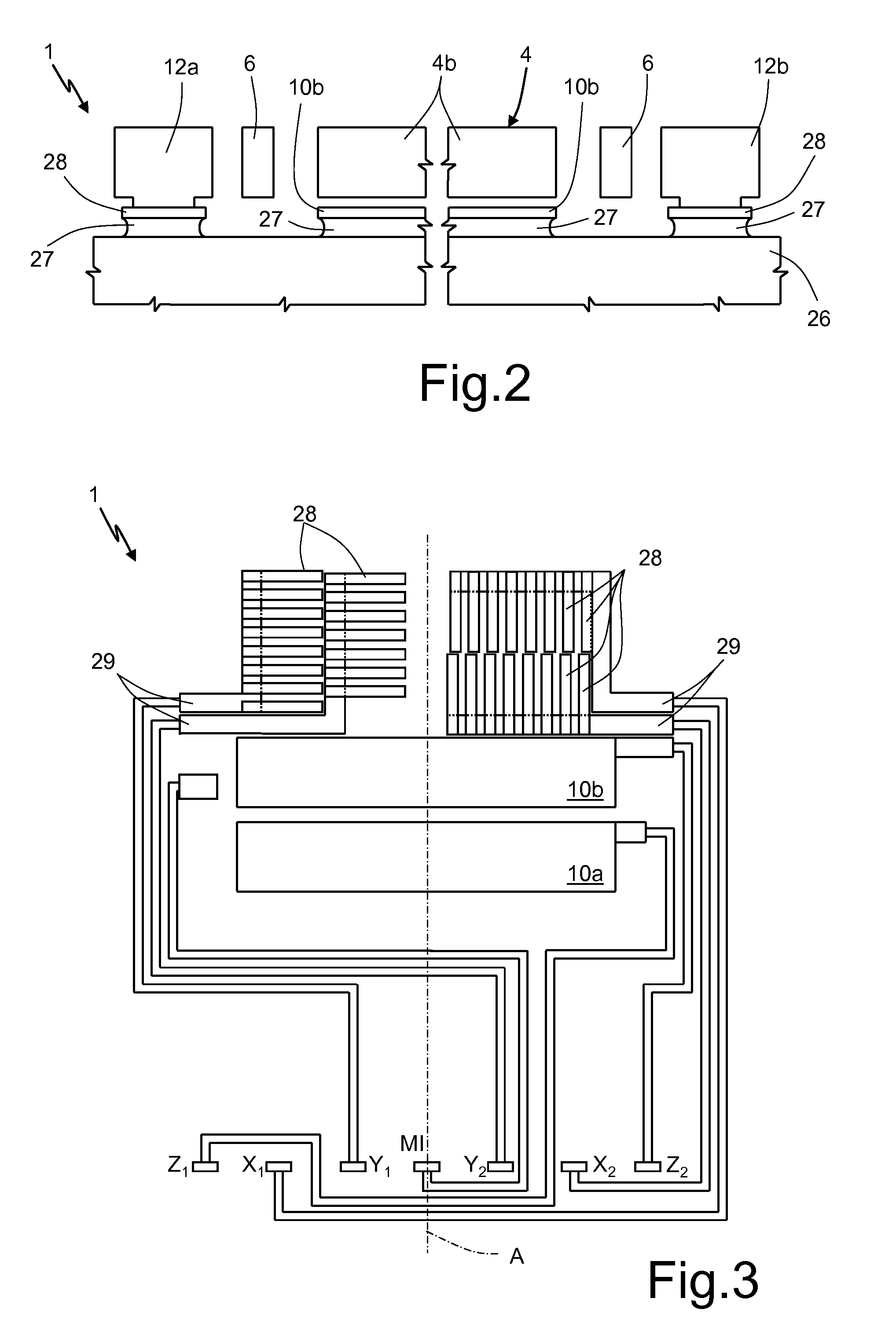
A micromechanical structure for a MEMS three-axis capacitive accelerometer is provided with: a substrate; a single inertial mass having a main extension in a plane and arranged suspended above the substrate; and a frame element, elastically coupled to the inertial mass by coupling elastic elements and to anchorages, which are fixed with respect to the substrate by anchorage elastic elements. The coupling elastic elements and the anchorage elastic elements are configured so as to enable a first inertial movement of the inertial mass in response to a first external acceleration acting in a direction lying in the plane and also a second inertial movement of the inertial mass in response to a second external acceleration acting in a direction transverse to the plane.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS8205498B2Improve linearityEliminate relative rotationAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
A multi-axis accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate. A first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The first proof mass is suspended to the anchor bases. Fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. A second proof mass and a third proof mass are disposed in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
3-Axis Accelerometer With Gap-Closing Capacitive Electrodes
ActiveUS20100212425A1Precise definitionAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsElectricityThree axis accelerometer
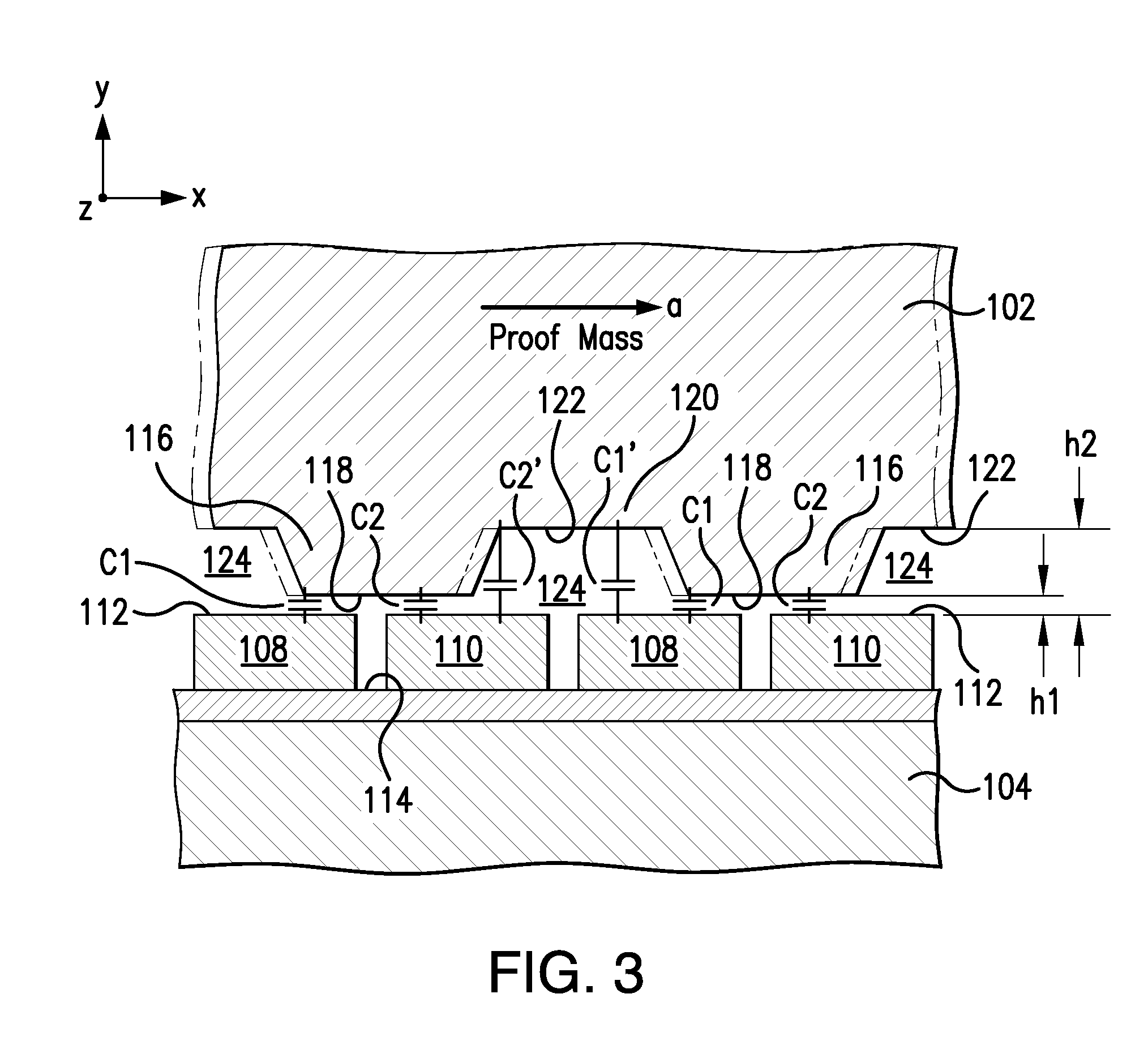
Disclosed is a novel three-axis capacitive-type accelerometer implemented on SOI wafer. The accelerometer consists of four springs, one proof mass, four pairs of gap-closing sensing electrodes (each pair of gap-closing sensing electrode containing one movable electrode and one stationary electrode), and several metal-vias as the electrical interconnections. The movable electrodes are on the proof mass, whereas the stationary electrodes are fixed to the substrate. The three-axis accelerometer has five merits. (1) The sensitivity of the accelerometer is improved since the proof-mass is increased by containing both device and handling silicon layers; (2) The sensitivity is also improved by the gap-closing differential capacitive sensing electrodes design; (3) The parasitic capacitance at bond pad is reduced by the existing of metal-vias between the device Si layer and handling Si layer; (4) The sensing gap thickness is precisely defined by the buried oxide of SOI wafer; (5) The stationary sensing electrodes anchored to the substrate also act as the limit stops to protect the accelerometer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
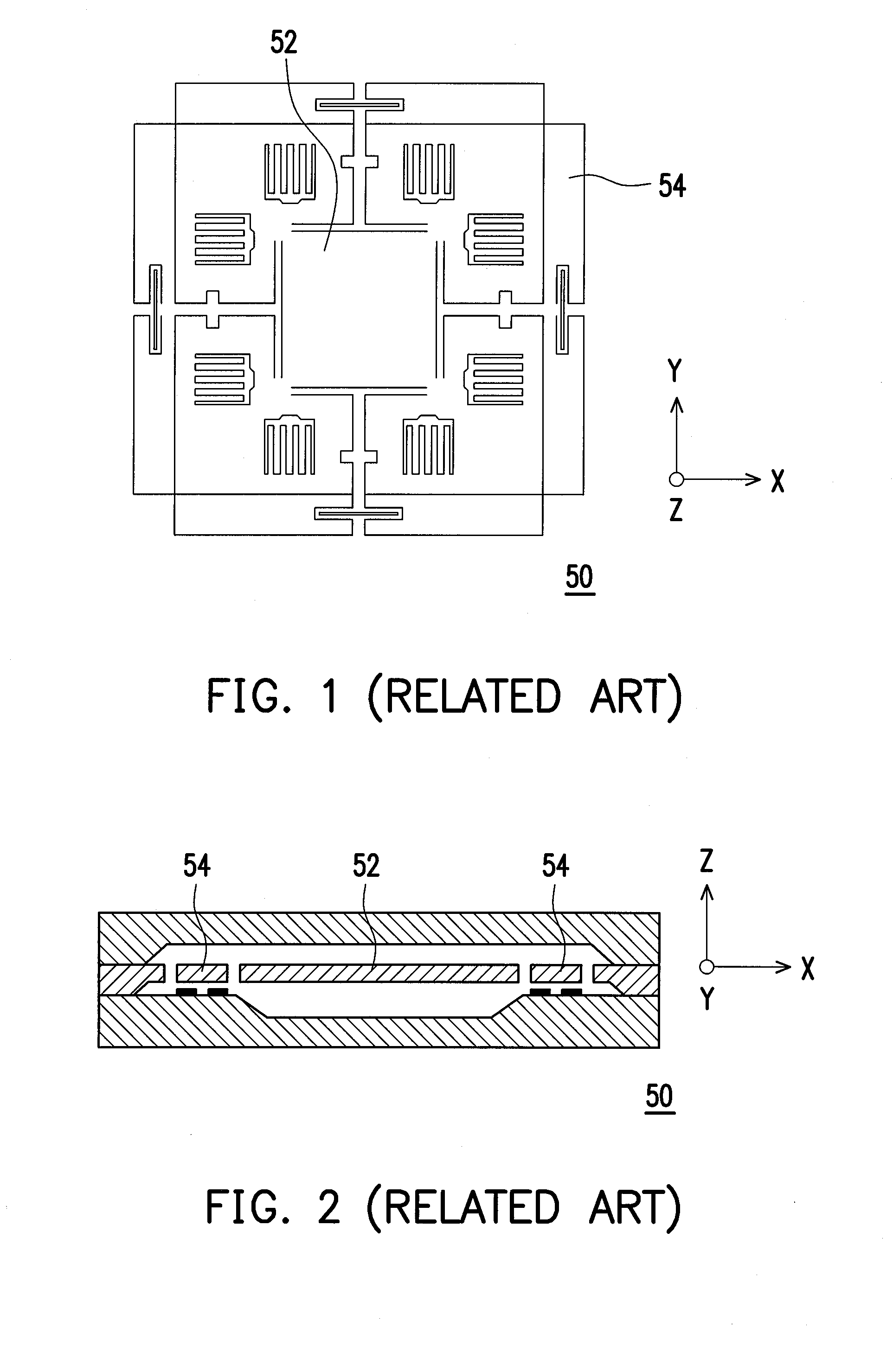
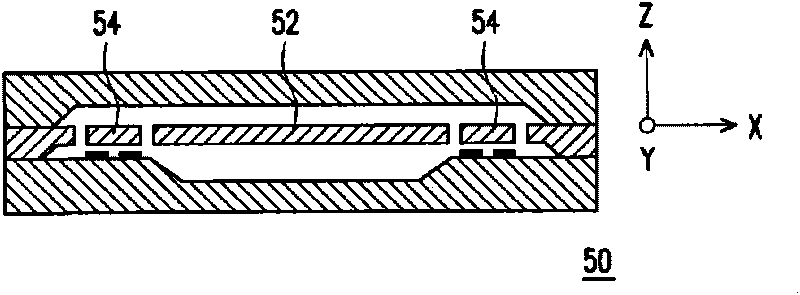
Pendulous accelerometer with balanced gas damping
A pendulous capacitive accelerometer including a substrate having a substantially planar upper surface with an electrode section, and a sensing plate having a central anchor portion supported on the upper surface of the substrate to define a hinge axis. The sensing plate includes a solid proof mass on a first side of the central anchor portion and a substantially hollow proof mass on a second side of the central anchor portion, providing for reduced overall chip size and balanced gas damping. The solid proof mass has a first lower surface with a first electrode element thereon, and the substantially hollow proof mass has a second lower surface with a second electrode element thereon. Both the solid proof mass and the hollow proof mass have the same capacitive sensing area. The sensing plate rotates about the hinge axis relative to the upper surface of the substrate in response to an acceleration.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Pendulous accelerometer with balanced gas damping
InactiveUS20090107238A1Balanced gas dampingHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurementChip sizeEngineering
A pendulous capacitive accelerometer including a substrate having a substantially planar upper surface with an electrode section, and a sensing plate having a central anchor portion supported on the upper surface of the substrate to define a hinge axis. The sensing plate includes a solid proof mass on a first side of the central anchor portion and a substantially hollow proof mass on a second side of the central anchor portion, providing for reduced overall chip size and balanced gas damping. The solid proof mass has a first lower surface with a first electrode element thereon, and the substantially hollow proof mass has a second lower surface with a second electrode element thereon. Both the solid proof mass and the hollow proof mass have the same capacitive sensing area. The sensing plate rotates about the hinge axis relative to the upper surface of the substrate in response to an acceleration.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Wireless passive capacitive accelerometer
InactiveCN103293337ARealize measurementSimple structureTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityPunching
The invention discloses a wireless passive capacitive accelerometer comprising a substrate with a closed cavity inside. A mass is fixed in the closed cavity through a cantilever; a first capacitor is arranged above the mass in the closed cavity, and a second capacitor is arranged below the mass in the closed cavity; a plane spiral inductor is arranged on the bottom surface of the substrate, electric connecting lines are sputtered on the substrate and the mass through TSV (through silicon via) technique punching, and the first capacitor, the second capacitor and the plane spiral inductor are in series connection to form a closed loop circuit through the electric connecting lines. The wireless passive capacitive accelerometer is skillful in design, simple in structure, high in sensitivity and accurate in test results, is wireless and passive, and can be used in severe environment; non-contact measurement is adopted during measuring, so that the range of application of the sensor is greatly broadened.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Built-in self test circuit and self test method for parallel plate capacitive MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System) accelerometer
ActiveCN105823907AReduce usage costsSimple structureAcceleration measurementTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesParallel plateParasitic capacitance
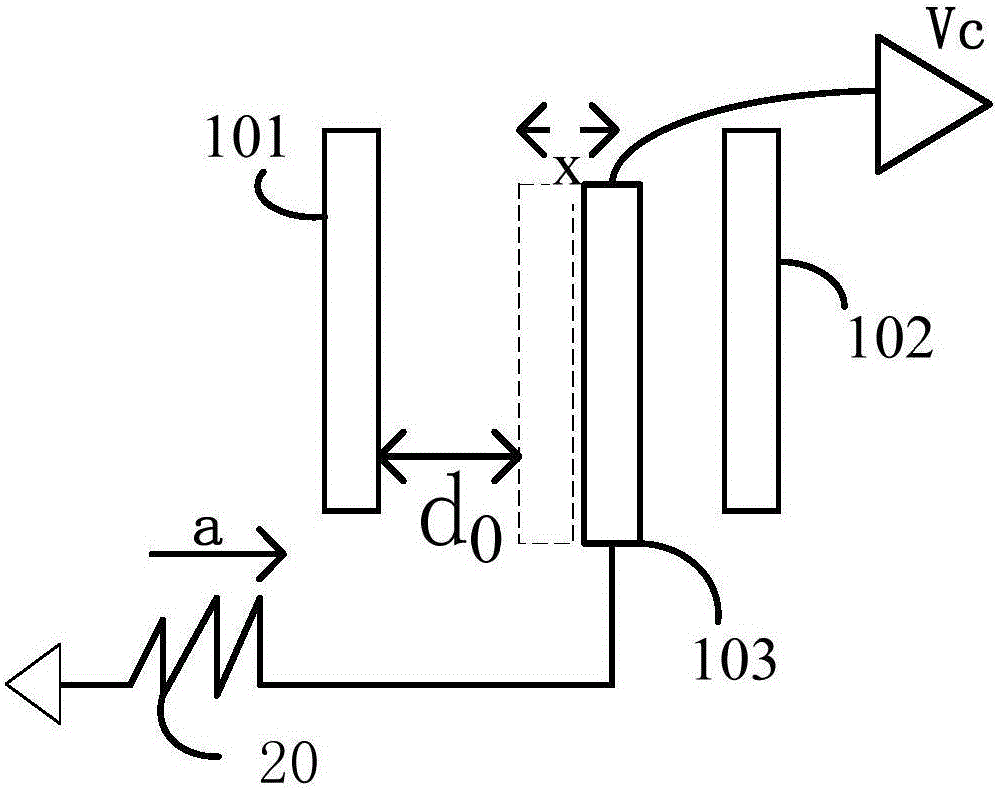
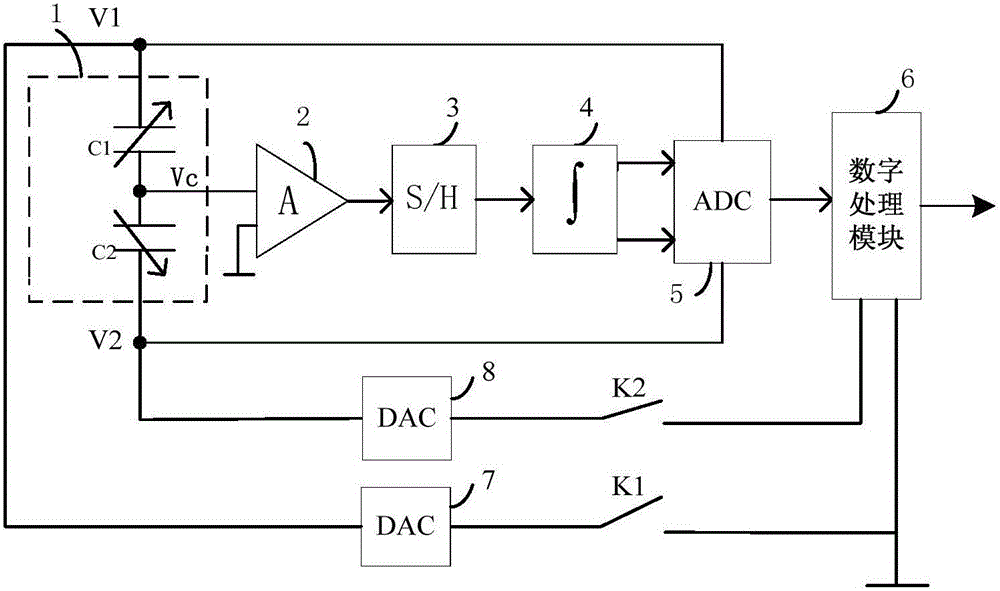
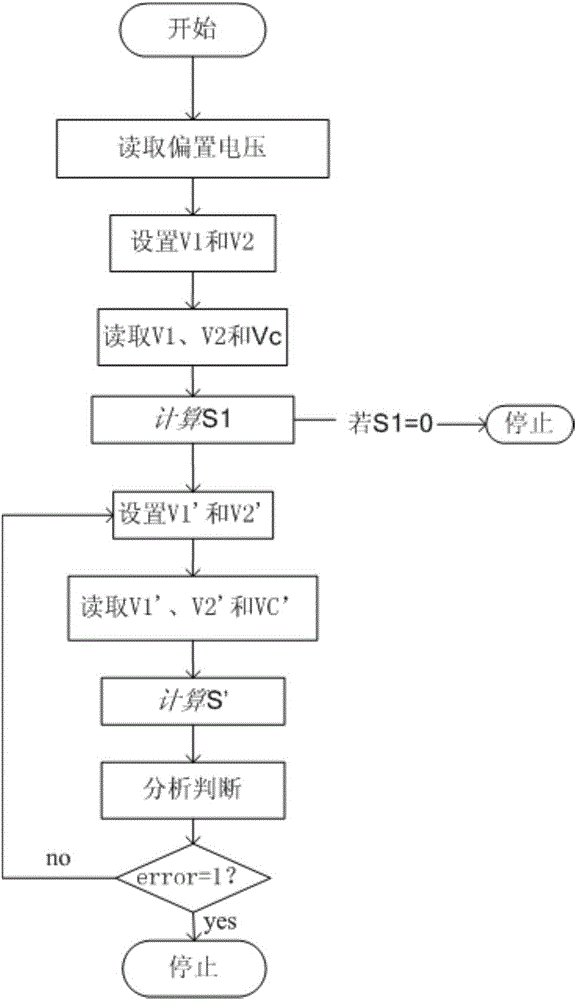
The invention provides a built-in self test circuit for a parallel plate capacitive MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-System) accelerometer and a self test method. Electric excitation is provided for the parallel plate capacitive accelerometer, signals outputted by a capacitive sensing module are simplified and subjected to analog-to-digital conversion and digital processing, the sensitivity S is analyzed according to self test power supply voltages V1 and V2 in different conditions and an output response Vc of the capacitive sensing module, technical defects of the parallel plate capacitive MEMS accelerometer are then diagnosed, and built-in self test is carried out on the sensitivity S of the capacitive accelerometer. Influences on output signals by the external environment and parasitic capacitance are optimized, the test standardization degree is improved, dependence on a complicated test instruction is reduced, and the test cost and the product cost are effectively reduced.
Owner:北京中科微知识产权服务有限公司
Temperature compensating device for micro-machined capacitive accelerometer
ActiveCN101858930ASimple structureLow costAcceleration measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceLow-pass filter
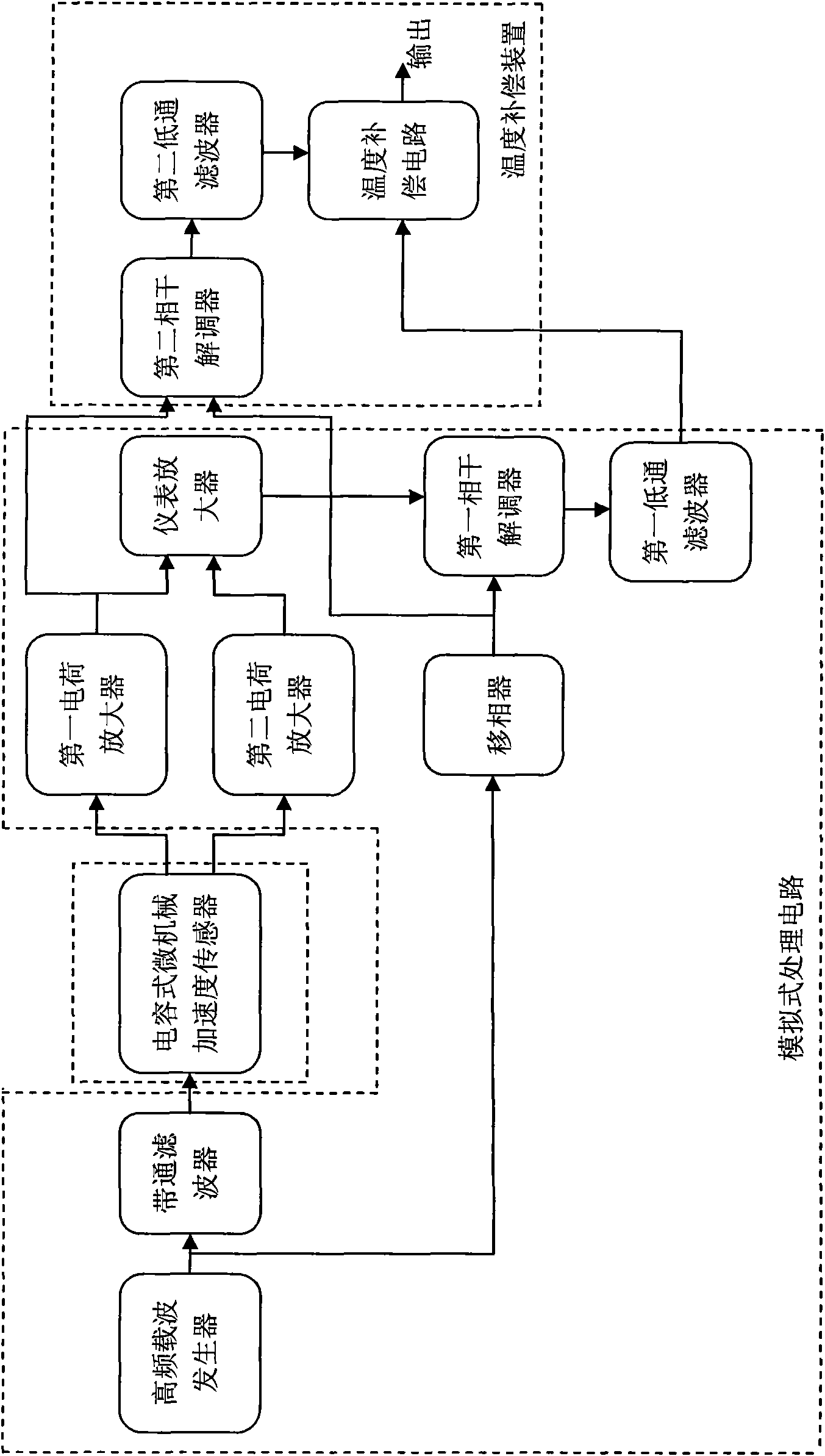
The invention discloses a temperature compensating device for a micro-machined capacitive accelerometer. The temperature compensating device mainly comprises a coherent demodulator, a low pass filter and a temperature compensating circuit, wherein an output end of the coherent demodulator is connected with an input end of the low pass filter; and the output end of the low pass filter is connectedwith the input end of the low temperature compensating circuit. By taking the internal capacitance which changes with the temperature of the micro-machined capacitive accelerometer as a compensating reference signal of an output signal of the accelerometer, the temperature compensating device does not need a thermistor or an integrated temperature sensor for measuring the temperature of an acceleration sensor, so the structure of the temperature compensating device is simplified, and the cost is reduced; the influence on compensating precision due to temperature measurement error is eliminated, and the temperature compensating precision is improved; and no temperature sensor is needed to be arranged and used on the micro-machined capacitive accelerometer, so a temperature measurement error due to a temperature gradient of a metal pipe shell of the acceleration sensor is avoided, and the temperature compensating precision is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Capacitance z-axis accelerometer
InactiveUS20050132804A1Small sensor sizeMaximize changeAcceleration measurementAudio power amplifierSingle chip
Disclosed is a capacitance accelerometer comprising a fixed electrode, a movable electrode and support beams. The fixed electrode has rectangular fixed electrode plates arranged parallel with a top surface of an insulation board. The fixed electrode plates are placed one above another via posts, and arranged on an electrode-fixing section of the insulation board. The movable electrode has rectangular movable electrode plates alternating with the fixed electrode plates. The movable electrode plates are placed one above another via connector posts placed within guide holes perforated through the fixed electrode plates. The support beams connect the movable electrode with beam-fixing sections to elastically support the movable electrode. The capacitance z-axis accelerometer can be integrated together with x- and y-axis accelerometers into a single chip, maximize the change of capacitance to achieve excellent acceleration sensitivity, and utilize an amplifier and a filter of low cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
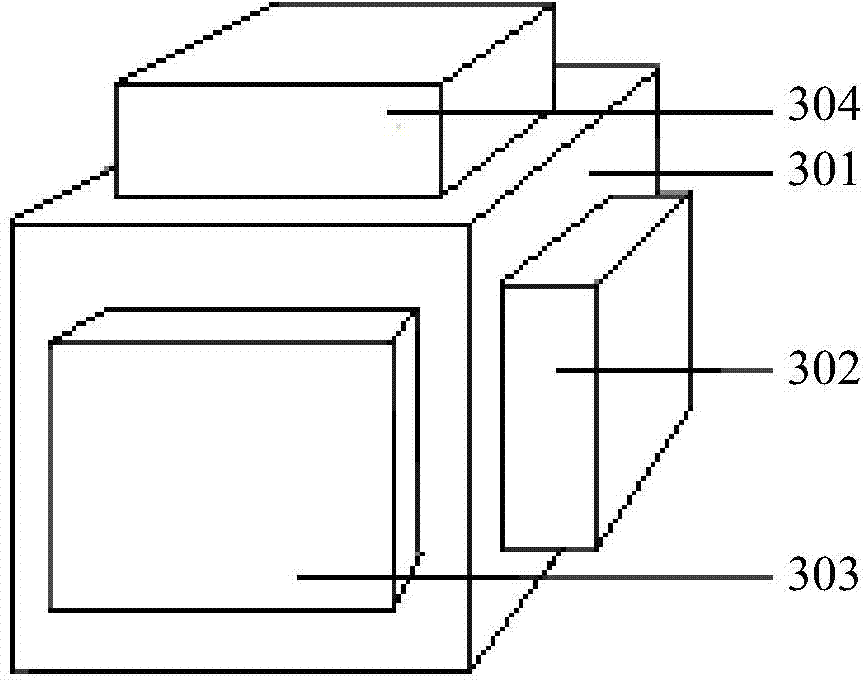
Micromachined comb capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS7444873B2Improve rigidityHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcceleration measurementEngineeringCapacitive accelerometer
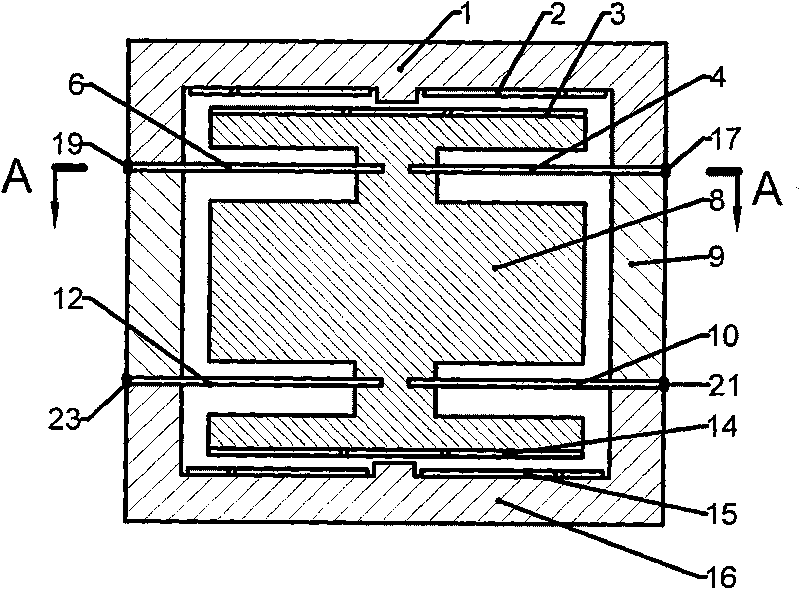
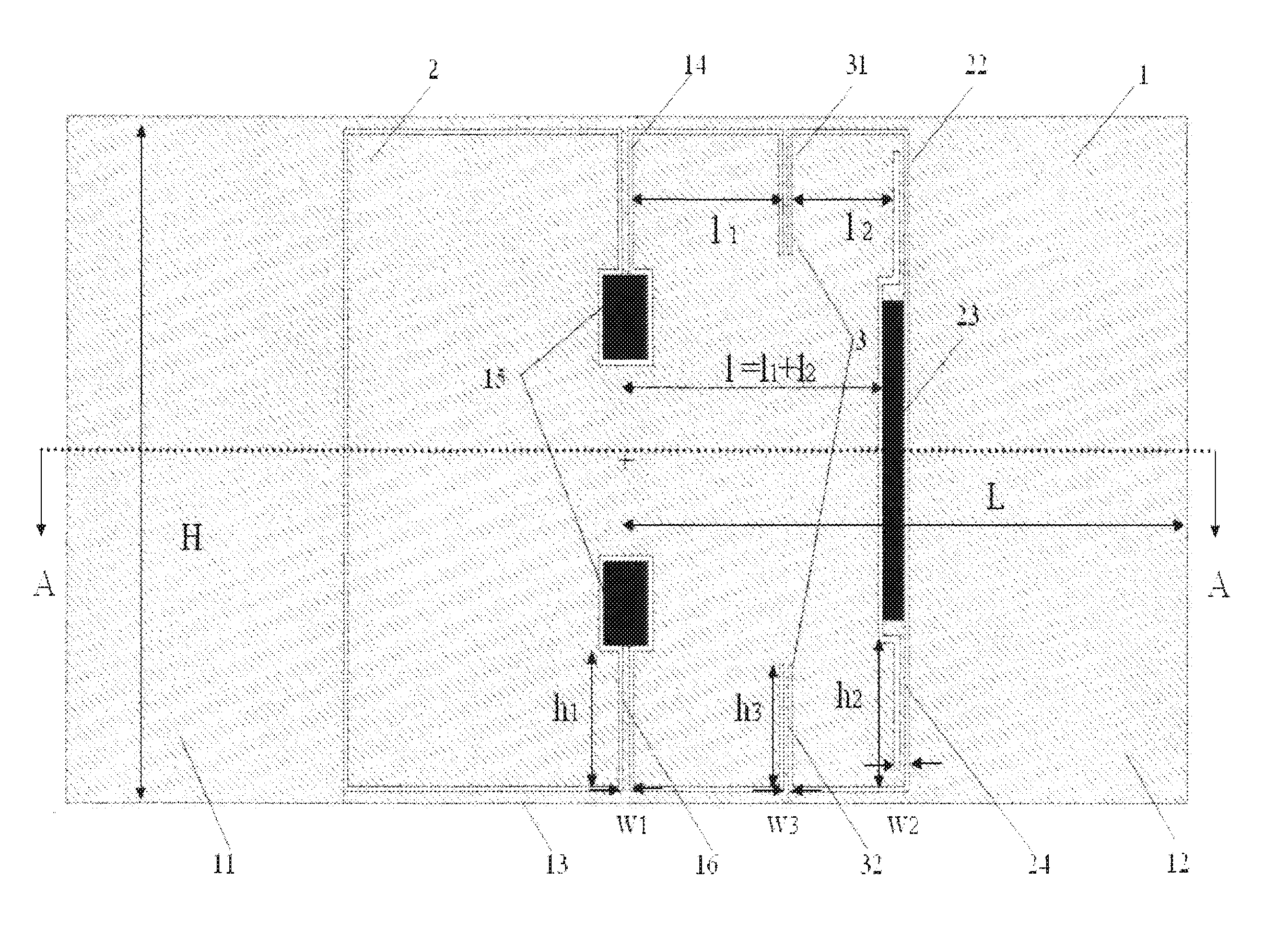
A comb capacitive accelerometer comprising a substrate, a mobile electrode relative to said substrate fitted with a plurality of mobile fingers, an electrode fixed relative to said substrate fitted with a plurality of fixed fingers, each of said mobile fingers being positioned between two contiguous fixed fingers so as to form a microstructure with interdigital combs. According to the invention the mobile fingers are connected to one another by at least a first connecting beam etched directly into the substrate, and / or the fixed fingers are connected to one another by at least a second connecting beam etched directly in the substrate.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
In-plane capacitive MEMS accelerometer
A system for determining in-plane acceleration of an object. The system includes an in-plane accelerometer with a substrate rigidly attached to an object, and a proof mass—formed from a single piece of material—movably positioned a predetermined distance above the substrate. The proof mass includes a plurality of electrode protrusions extending downward from the proof mass to form a gap of varying height between the proof mass and the substrate. The proof mass is configured to move in a direction parallel to the upper surfaces of each of the plurality of substrate electrodes when the object is accelerating, which results in a change in the area of the gap, and a change in capacitance between the substrate and the proof mass. The in-plane accelerometer can be fabricated using the same techniques used to fabricate an out-of-plane accelerometer and is suitable for high-shock applications.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Capacitive accelerometer
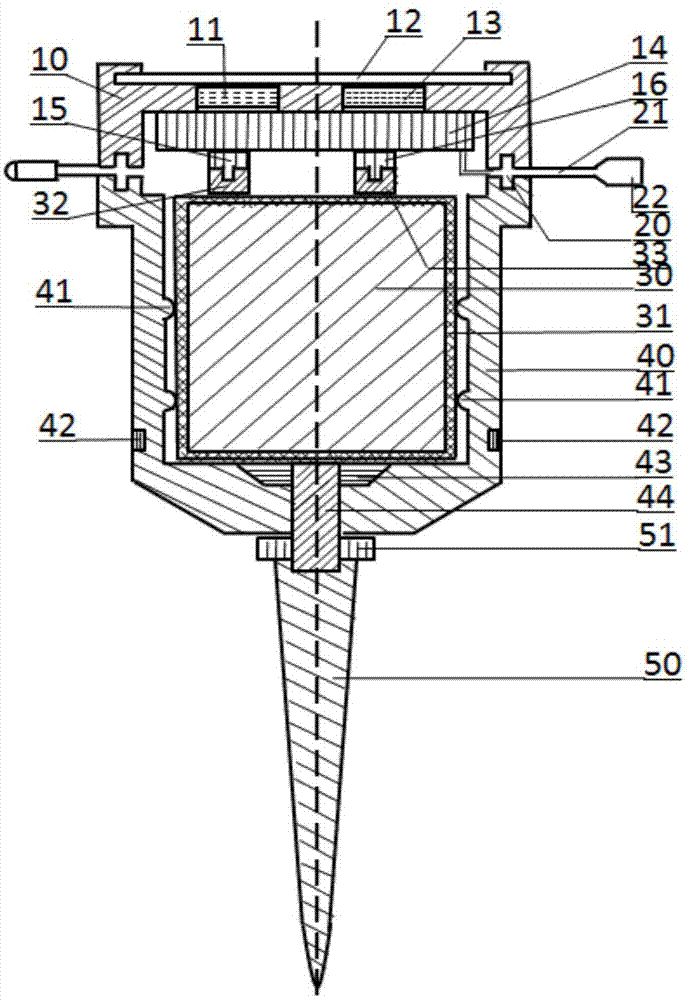
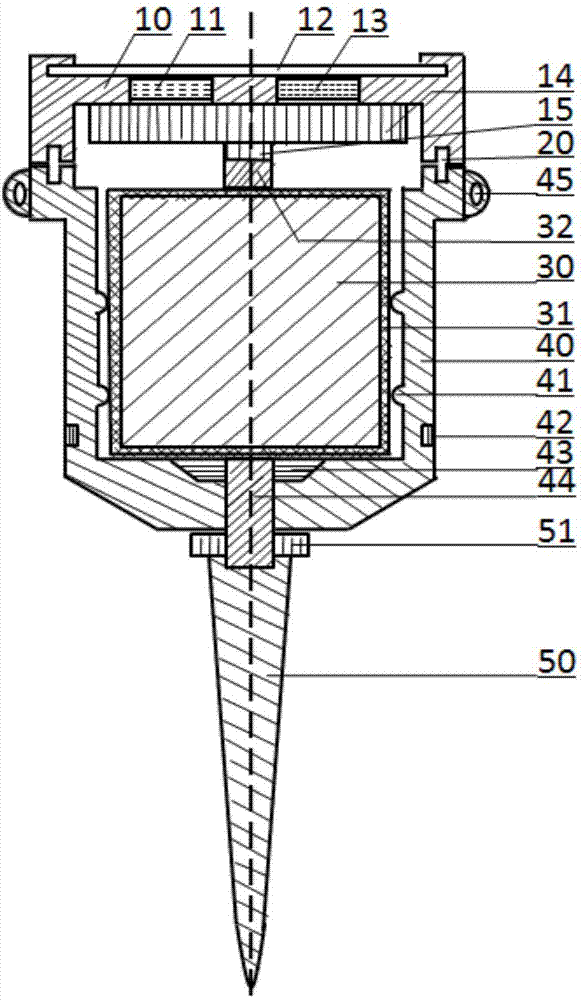
InactiveCN101710133ASmall radiusIncrease stiffnessAcceleration measurementEngineeringAngular acceleration
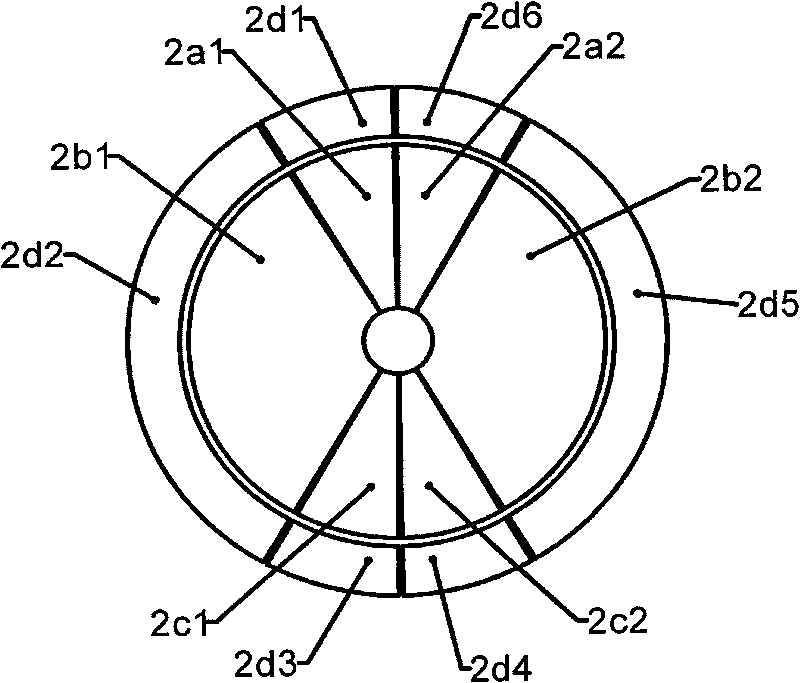
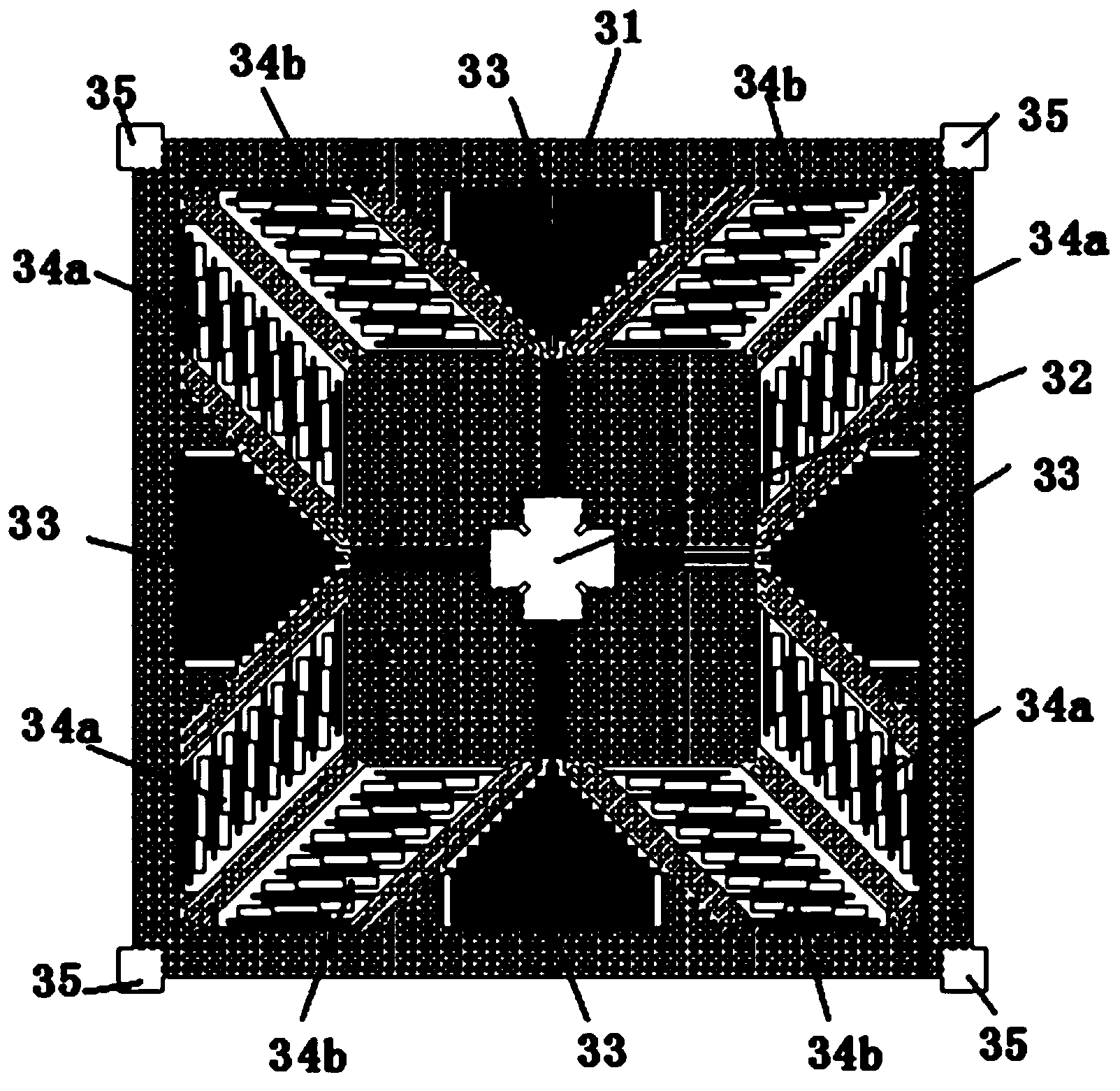
The invention relates to a capacitive accelerometer which comprises an upper end cover with an upper end cover polar plate, a lower end cover with a lower end cover polar plate, a mass block with a mass block upper polar plate and a mass block lower polar plate, a cylinder and eight elastic supporting rods. The upper end cover and the lower end cover are combined with the cylinder to fix the elastic supporting rods; the mass block is connected with the cylinder through the elastic supporting rods to form a sensitive motion mechanism; the upper end cover polar plate, the lower end cover polar plate, the mass block upper polar plate and the mass block lower polar plate are provided with a plurality of sector sub-electrodes which are spaced between each other; and the sector sub-electrodes ensure that the upper end cover polar plate and the lower end cover polar plate form differential capacitive structures with the mass block upper polar plate and the mass block lower polar plate respectively. The capacitive accelerometer can be used for measuring longitudinal acceleration and angular acceleration simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS8459114B2Small sizeImprove performanceAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsClassical mechanicsMulti axis
A multi-axis capacitive accelerometer is disclosed. A first mass is disposed and held by an anchor supported by a substrate, wherein the first mass is asymmetrically suspended on the anchor by means of two cantilevers, so that the first mass rotates about a rotation axis, for sensing the acceleration in a first direction perpendicular to the substrate. A second mass is disposed in the first mass and suspended on the first mass by means of a set of springs to sense the acceleration in a second direction parallel to the substrate. Furthermore, a third mass can be disposed in the second mass, wherein the third mass is suspended on the second mass by means of another set of springs to sense the acceleration in a third direction. The first direction, the second direction and the third direction are mutually orthogonal to each other.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for manufacturing monolithic polysilicon cantilever structure
InactiveCN102086019ASolve stickingAchieve monolithic integrationDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingGyroscopeSignal processing circuits
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a monolithic polysilicon cantilever structure. In the invention, a processing step of the polysilicon cantilever structure is inserted in a conventional BiCMOS (Bipolar Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technical process, the deposition and the annealing of polysilicon are finished and an MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) high-temperature process is prevented from influencing on the metalation process before the metalation process. In the release process of the polysilicon cantilever structure, a special etching solution is adopted, and a negative photoresist is used as a post of the polysilicon cantilever structure so as to effectively avoid the problem of substrate adhesion in the cantilever structure release process by using a wet method. The method provided by the invention solves the technical problems of compatibility between a manufacture process of the polysilicon cantilever structure and a processing process of a BiCMOS circuit, realizes the monolithic integration of the polysilicon cantilever structure and a BiCMOS signal processing circuit, and can be widely applied to the monolithic integration manufacture field of MEMS sensors, such as capacitive accelerometers, gyroscopes, and the like.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
MEMS geophone
The invention discloses an MEMS geophone which comprises a protection shell provided with an upper cover, an MEMS machine core arranged in the protection shell, and a tail cone arranged outside the protection shell. The MEMS machine core comprises a machine core shell fixed into the protection shell, a supporting frame arranged in the machine core shell, and a plurality of MEMD accelerometers arranged on the supporting frame. The supporting frame is cuboid. The MEMS accelerometers are capacitive accelerometers and include the X accelerometer, the Y accelerometer and the Z accelerometer, wherein the three accelerometers are vertically arranged on three adjacent side faces of the supporting frame respectively, and the side face where the Z accelerometer is located is the top face, facing towards the upper cover, of the supporting frame. The tail cone is arranged on a screw which penetrates through a base plate of the protection shell and abuts against the machine core shell. A coil with the fixed frequency is not used in the MEMS geophone, the recordable dynamic range is large, the response bandwidth is wide, the resolution ratio is high, and detection of all broadband elastic waves generated by an artificial seismic source is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
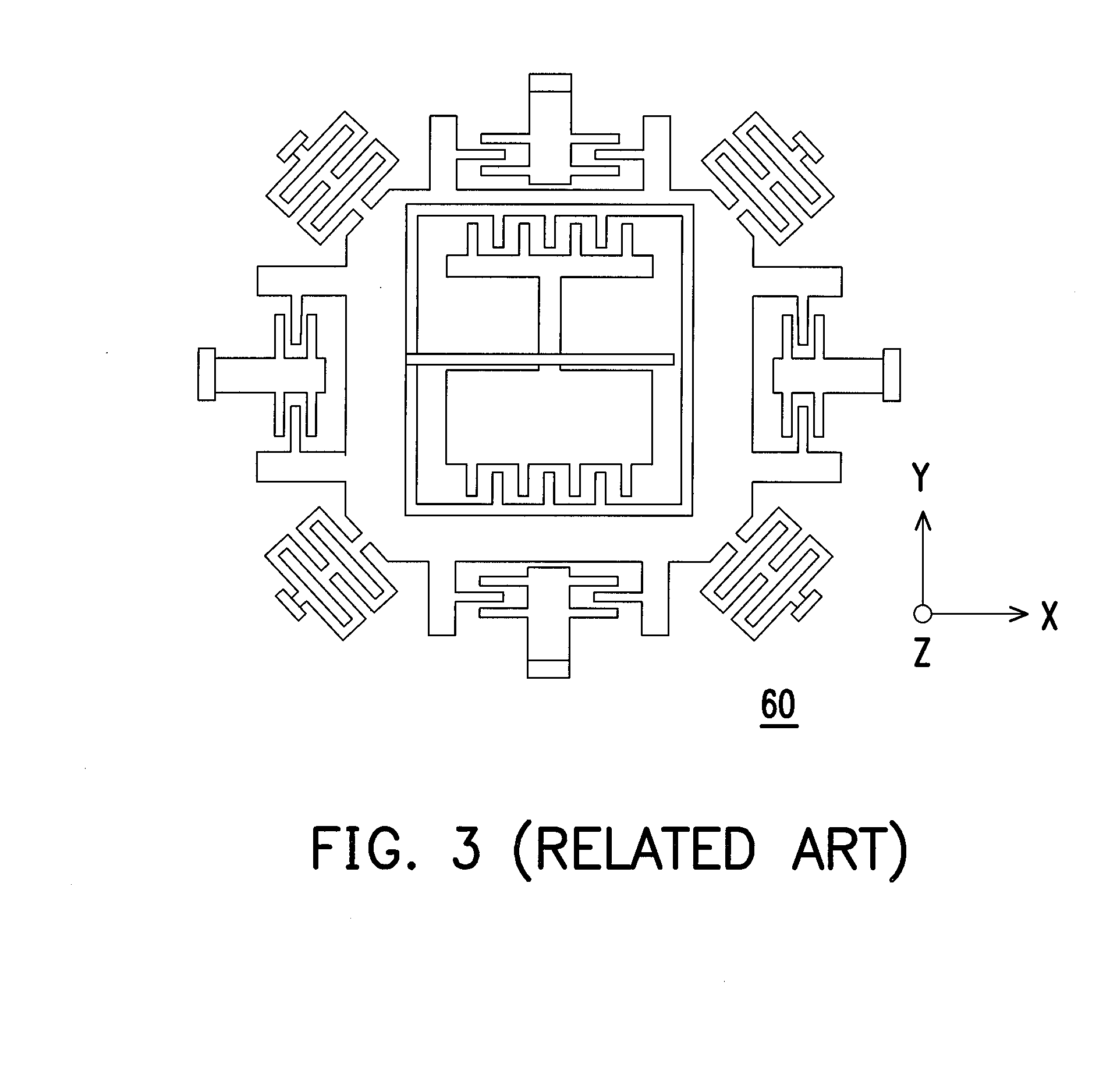
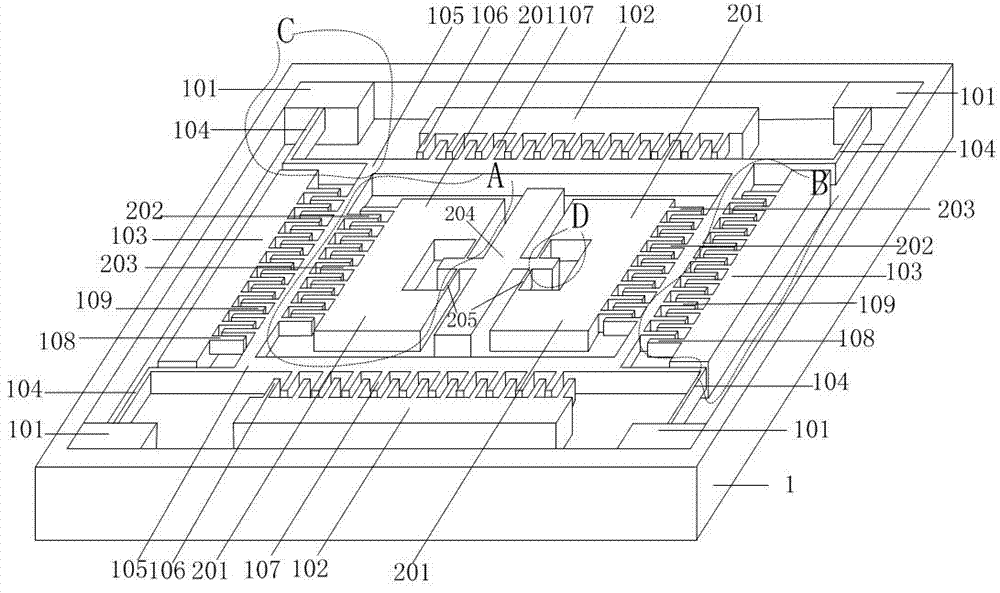
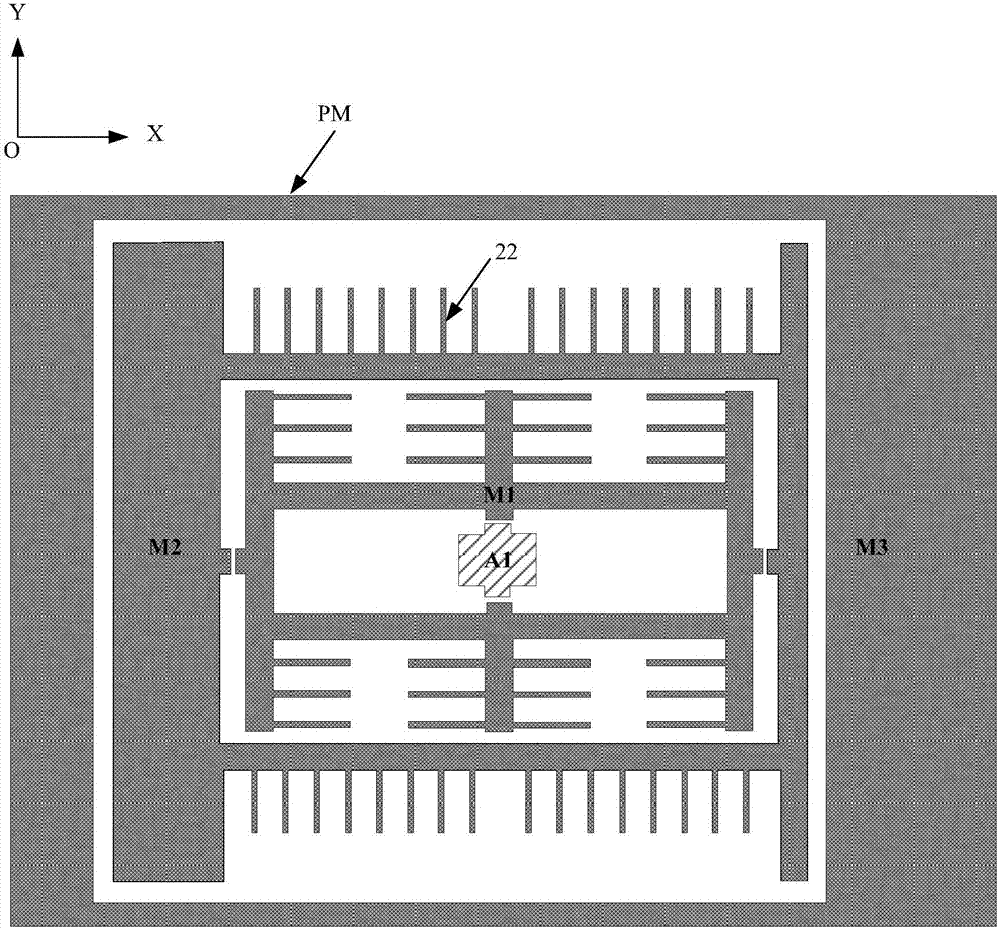
Three-axis capacitive accelerometer
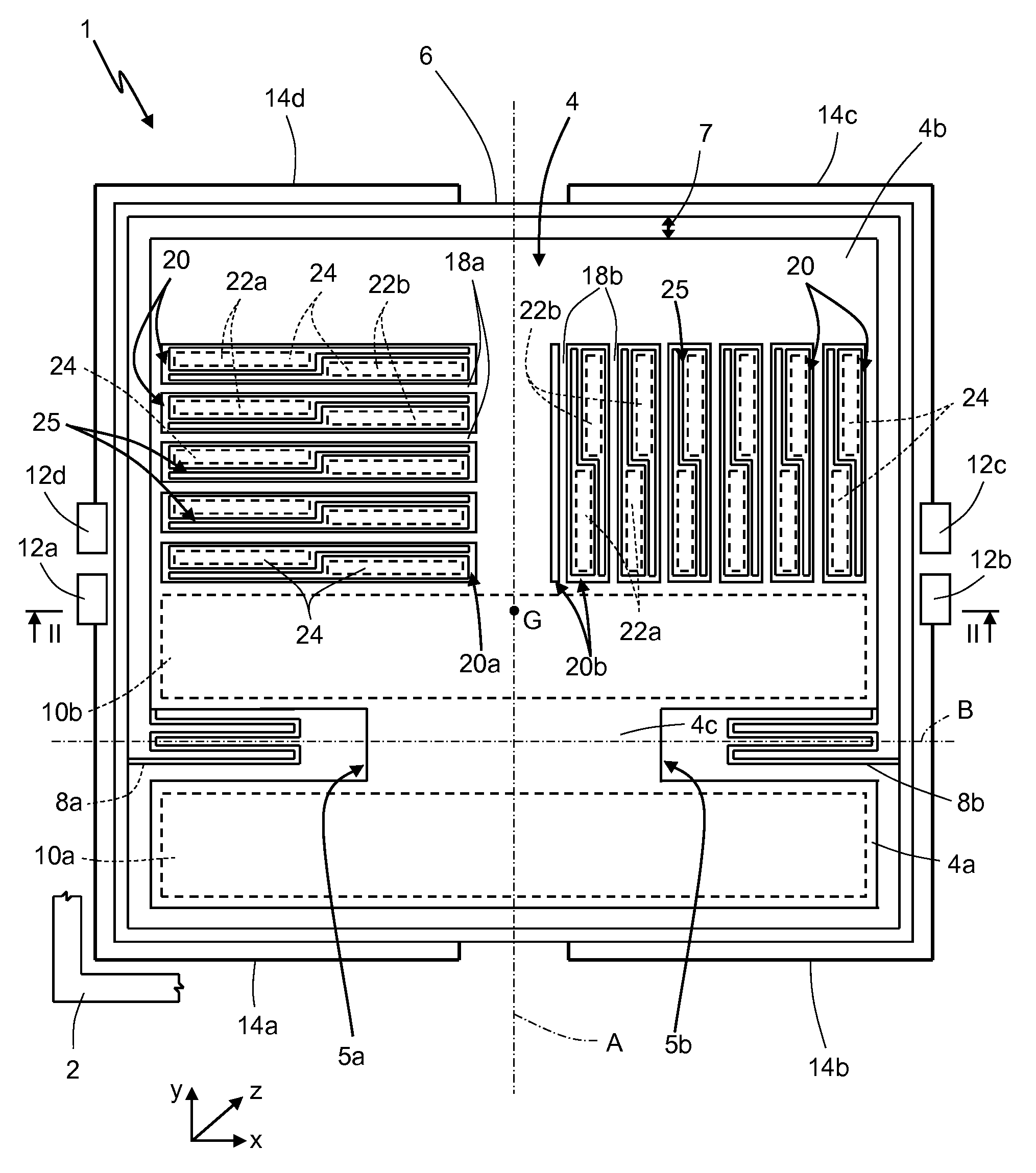
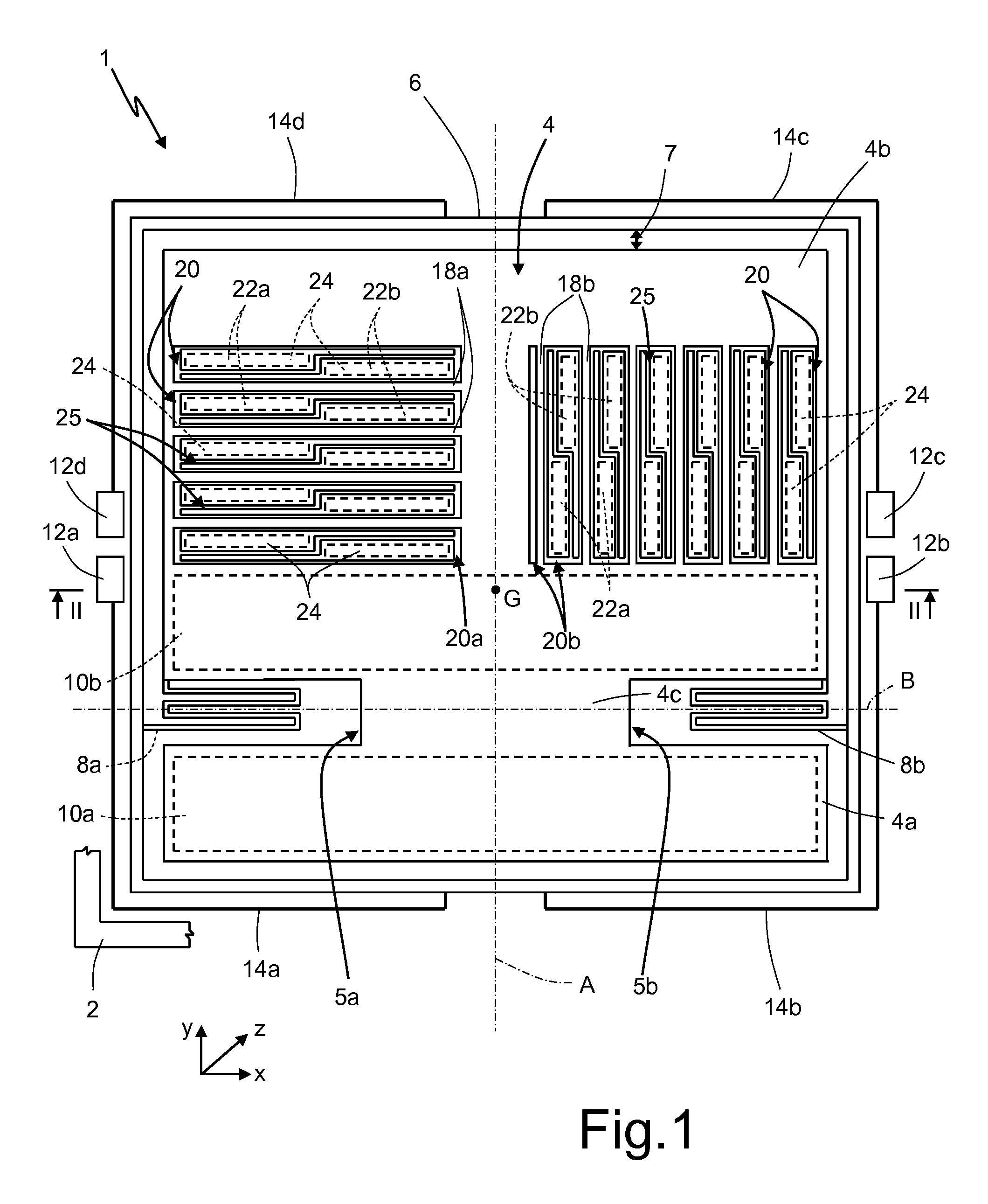
The invention discloses a three-axis capacitive accelerometer. The three-axis capacitive accelerometer comprises a substrate, a movable part and multiple fixed electrodes, wherein a surface of the substrate has a fixed anchor point, the movable part is arranged on the fixed anchor point and has a first mass block, a second mass block and a third mass block, the multiple fixed electrodes are a first electrode set, a second electrode set and a third electrode set, the first electrode set is used for forming an X-axis detection capacitor together with the second mass block to detect acceleration input along an X axis, the second electrode set is used for forming a Y-axis detection capacitor together with the first mass block to detect acceleration inputted along the Y axis, and the third electrode set is used for forming a Z-axis detection capacitor together with the third mass block to detect acceleration inputted along the Z axis. The three-axis capacitive accelerometer is advantaged in that detection on acceleration in the X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis directions in a right angle coordinate system can be realized, through arranging motion dimensions of the mass blocks, a problem of axis cross coupling can be avoided.
Owner:SENODIA TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
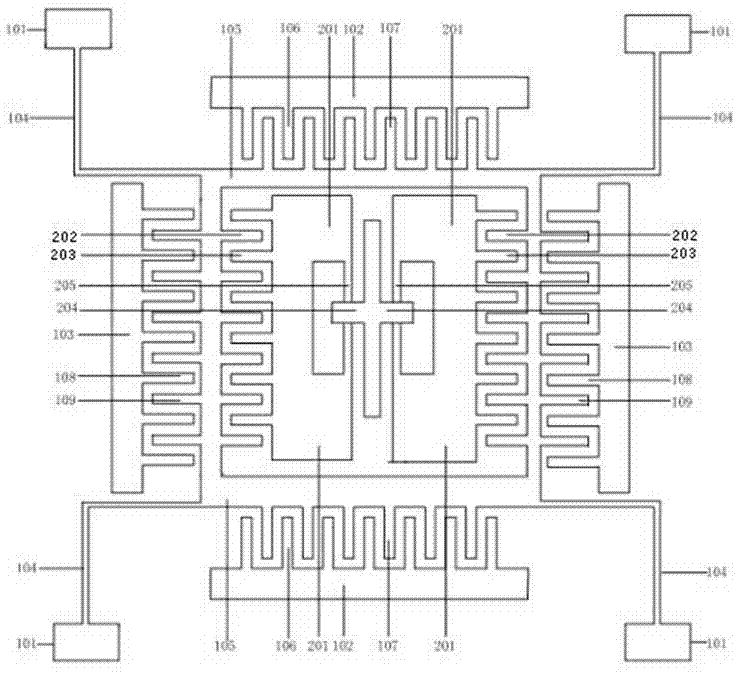
Triaxial capacitive accelerometer with sharing of detection capacitors
ActiveCN105823906AThe detection method is simpleReduce areaAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsClassical mechanicsCapacitive accelerometer
The invention discloses a three-axis capacitive accelerometer with shared detection capacitance, which includes a mass block, a fixed anchor point, a base, and four detection capacitances, wherein each detection capacitance includes fixed comb teeth and movable comb teeth The mass block is fixed to the base through the corresponding fixed anchor point, and is used to generate a motion corresponding to the acceleration when an axial acceleration is applied; the movable comb teeth of the four detection capacitors are connected To the mass block, when an axial acceleration is applied, the movable comb teeth move with the mass block to generate a specific capacitance value change for the axial acceleration. The three-axis capacitive accelerometer with shared detection capacitance involved in the present invention can achieve the purposes of reducing the area of the micro-electromechanical chip, simplifying the detection mode of the detection capacitance and improving the sensitivity of the accelerometer.
Owner:SENODIA TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Micromachined accelerometer with monolithic electrodes and method of making the same
ActiveUS8322216B2Improves reliability and lifespanReduce mold sizeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingClassical mechanicsAngular acceleration
A capacitive accelerometer having one or more micromachined acceleration sensor assembly is disclosed. The acceleration sensor assembly comprises a spring-mass-support structure, a top cap and a bottom cap. The proof mass plate of the spring-mass-support structure has cutout spaces and is supported by a pair of branched torsional beams which are substantially located in the cutout spaces. The torsional axis of the proof mass plate is offset from the mass center in direction perpendicular to the proof mass plate. The acceleration sensor assembly further comprises multiple coplanar electrodes for differential capacitive sensing and electrostatic forcing. The capacitive accelerometer according to the present invention may comprise one, two or six micromachined acceleration sensor assemblies with electronic signal detection, conditioning and control circuits in different configurations and applications to detect and measure linear and angular accelerations. Methods to fabricate the micromachined acceleration sensor assembly are disclosed.
Owner:YU DULI +2
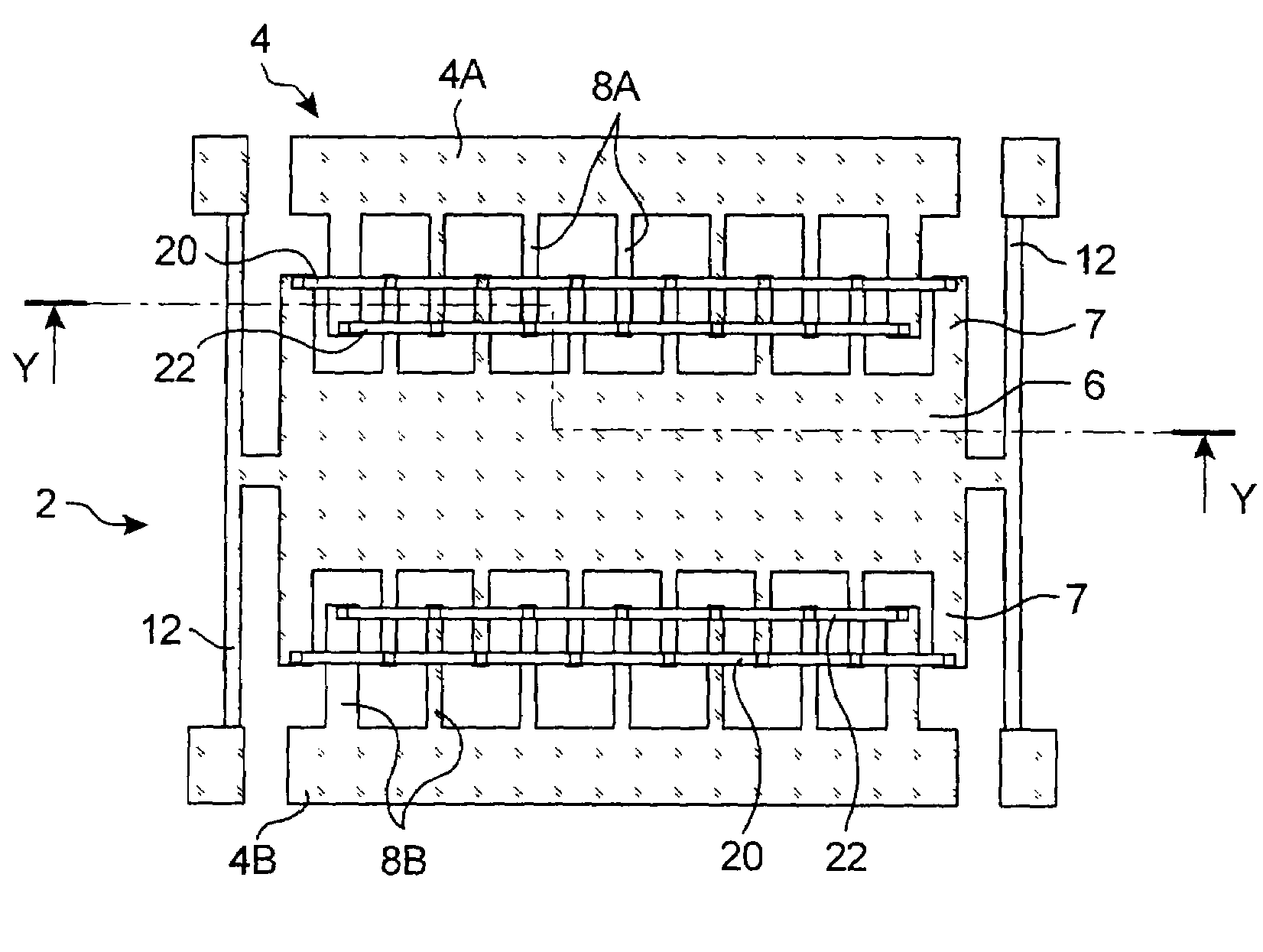
Microfactory comb capacitive accelerometer
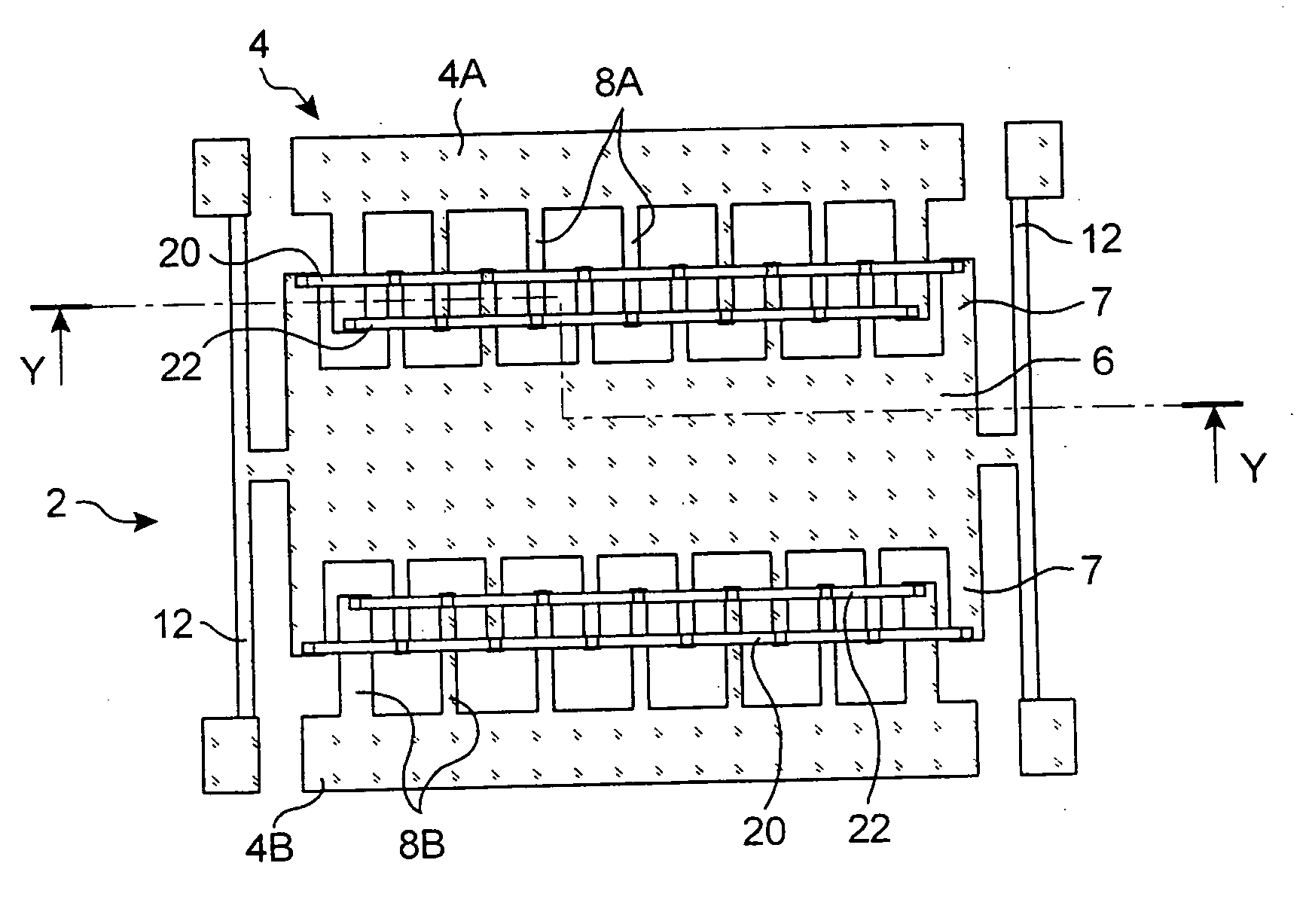
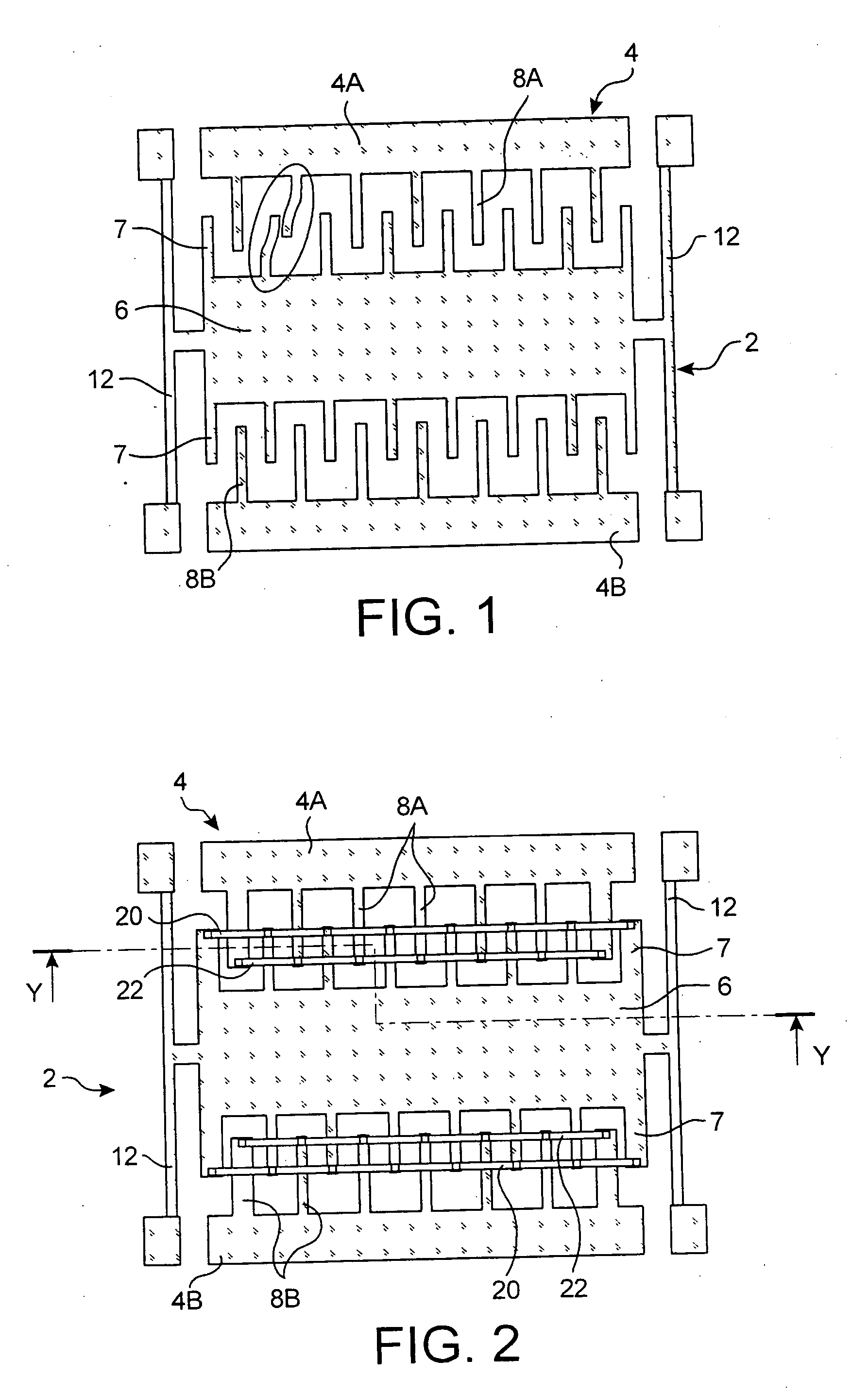
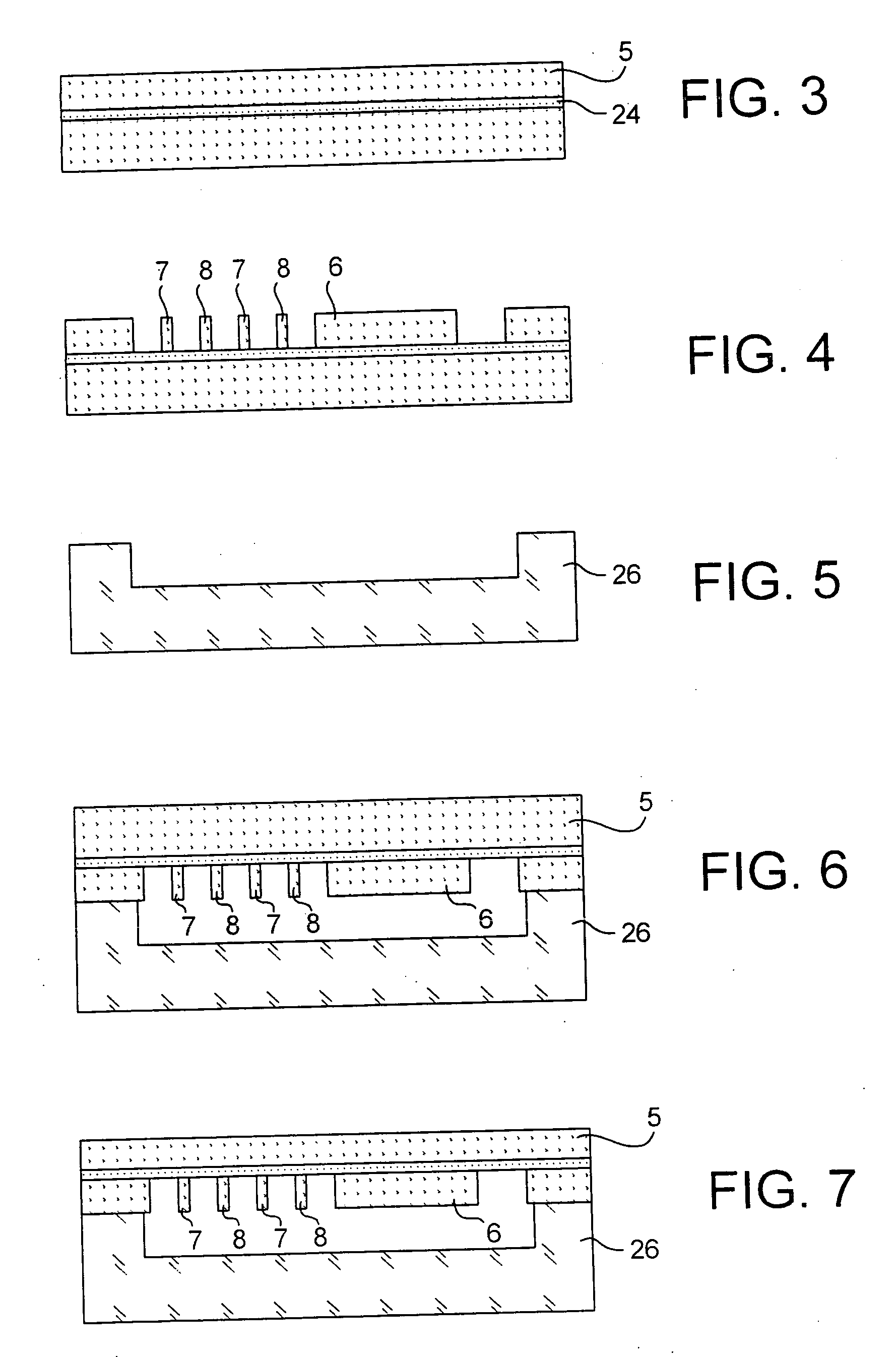
ActiveUS20070012110A1Improve rigidityHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcceleration measurementCapacitive accelerometerElectrical and Electronics engineering
A comb capacitive accelerometer comprising a substrate (5), a mobile electrode (2) relative to said substrate (5) fitted with an ensemble of mobile fingers (7), an electrode (4) fixed relative to said substrate (5) fitted with an ensemble of fixed fingers (8A, 8B), each of said mobile fingers (7) being positioned between two contiguous fixed fingers (8A, 8B) so as to form a microstructure with interdigital combs. According to the invention the mobile fingers (7) are connected to one another by at least a first connecting beam (20) etched directly into the substrate (5), and / or the fixed fingers (8A, 8B) are connected to one another by at least a second connecting beam (22) etched directly in the substrate (5).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
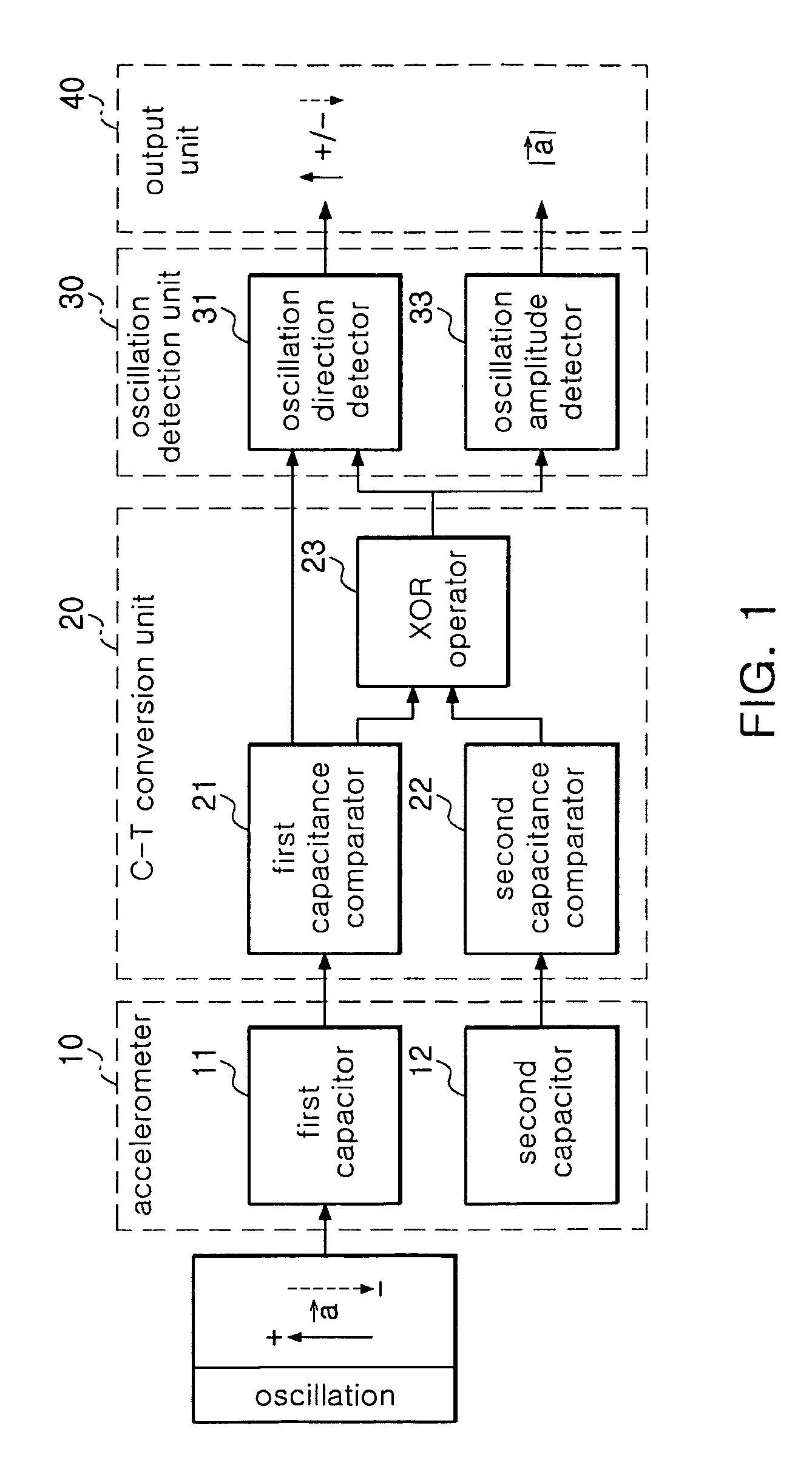
Bidirectional readout circuit for detecting direction and amplitude of capacitive MEMS accelerometers
InactiveUS7997137B2High resolutionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementTime changesMems sensors
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Test device and test method for thermal sensitivity drift of impact accelerometer
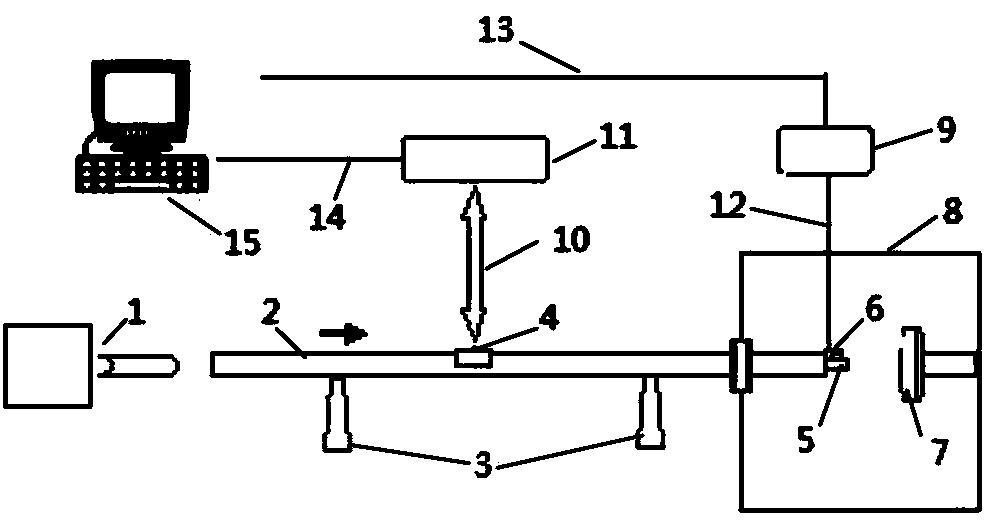
InactiveCN108427015AHigh impact accelerationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTemperature controlAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a test device for testing the change of the sensitivity output of an impact accelerometer with temperature. The test device comprises a temperature control box, a metal rod, apneumatic system, an accelerometer signal amplifier, a laser interferometric speed measuring device, and a computer for data sampling and data processing; the metal rod is horizontally supported by asupporting structure and can move freely axially; one end of the metal rod is aligned with the pneumatic system; the other end of the metal rod fixes an accelerometer to be tested and is arranged inthe temperature control box; the output signals of the accelerometer are inputted to the signal amplifier through a wire; the laser interferometric speed measuring device emits laser onto the metal rod and receives reflected laser; the output signals of the accelerometer signal amplifier and the laser speed measuring device are connected with the computer through data wires; and a relationship between the sensitivity output of the accelerometer to be tested and temperature is obtained by means of an absolute method. The test device of the invention has the advantages of large impact acceleration, directness and relatively high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Manufacturing method for quartz comb teeth capacitive accelerometer
ActiveCN104133079AIncrease temperatureCTE matchingAcceleration measurementImage resolutionThermal expansion
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for a quartz comb teeth capacitive accelerometer. The accelerometer comprises an upper cover plate, a lower cover plate and sensitive components. The manufacturing method refers to manufacturing of the sensitive components, manufacturing of the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate and bonding between the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate. According to the method, quartz materials are adopted in manufacturing of the teeth capacitive accelerometer for the first time, the manufacturing method aiming at the specific structure of the accelerometer is innovatively designed, and new purposes of the quartz materials are achieved. The whole structure of the capacitive accelerometer is made of the quartz materials, thermal expansion coefficient is matched with the accelerometer, temperature performance of sensors can be improved, great sensing masses and initial capacitance values can be obtained, sensitivity and resolution of the sensors can be obviously improved, and it is ensured that manufactured comb teeth have large depth-to-width ratios.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF TELEMETRY +1
Multiaxial capacitive accelerometer and acceleration detection method
ActiveCN103645342AHigh sensitivityReduce mistakesAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsClassical mechanicsCapacitive accelerometer
The invention provides a multiaxial capacitive accelerometer and an acceleration detection method. Two Z axis structure layers of a Z axis accelerometer of the multiaxial capacitive accelerometer are placed on two sides of an X and Y axis accelerometer respectively. By using the above structure, an error caused by packaging deformation can be reduced so that sensitivity of the multiaxial capacitive accelerometer is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
Microelectromechanical three-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS8863575B2Reduced dimensionDesired characteristicAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsInertial massCapacitive accelerometer
A micromechanical structure for a MEMS structure is provided with: a substrate; a single inertial mass having a main extension in a plane and arranged suspended above the substrate; and a frame element, elastically coupled to the inertial mass by coupling elastic elements and to anchorages, which are fixed with respect to the substrate by anchorage elastic elements. The coupling elastic elements and the anchorage elastic elements are configured so as to enable a first inertial movement of the inertial mass in response to a first external acceleration acting in a direction lying in the plane and also a second inertial movement of the inertial mass in response to a second external acceleration acting in a direction transverse to the plane.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Z-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS8701490B2Increase distanceCapacitance change increasesAcceleration measurementEngineeringCapacitive accelerometer
A Z-axis capacitive accelerometer includes a substrate, a capacitance sensing plate, a proof mass and at least one pair of spring beams. The capacitance sensing plate includes two symmetrical sense areas to create differential capacitive measurement. A decoupling structure separates the proof mass and the capacitance sensing plate and their rotational motions from each other. In the proposed Z axis capacitive accelerometer, the distance of the capacitance sensing plate relative to its rotation axis is considerably increased, thereby effectively enhancing the sensitivity when measuring the Z-axis acceleration.
Owner:MEMSIC
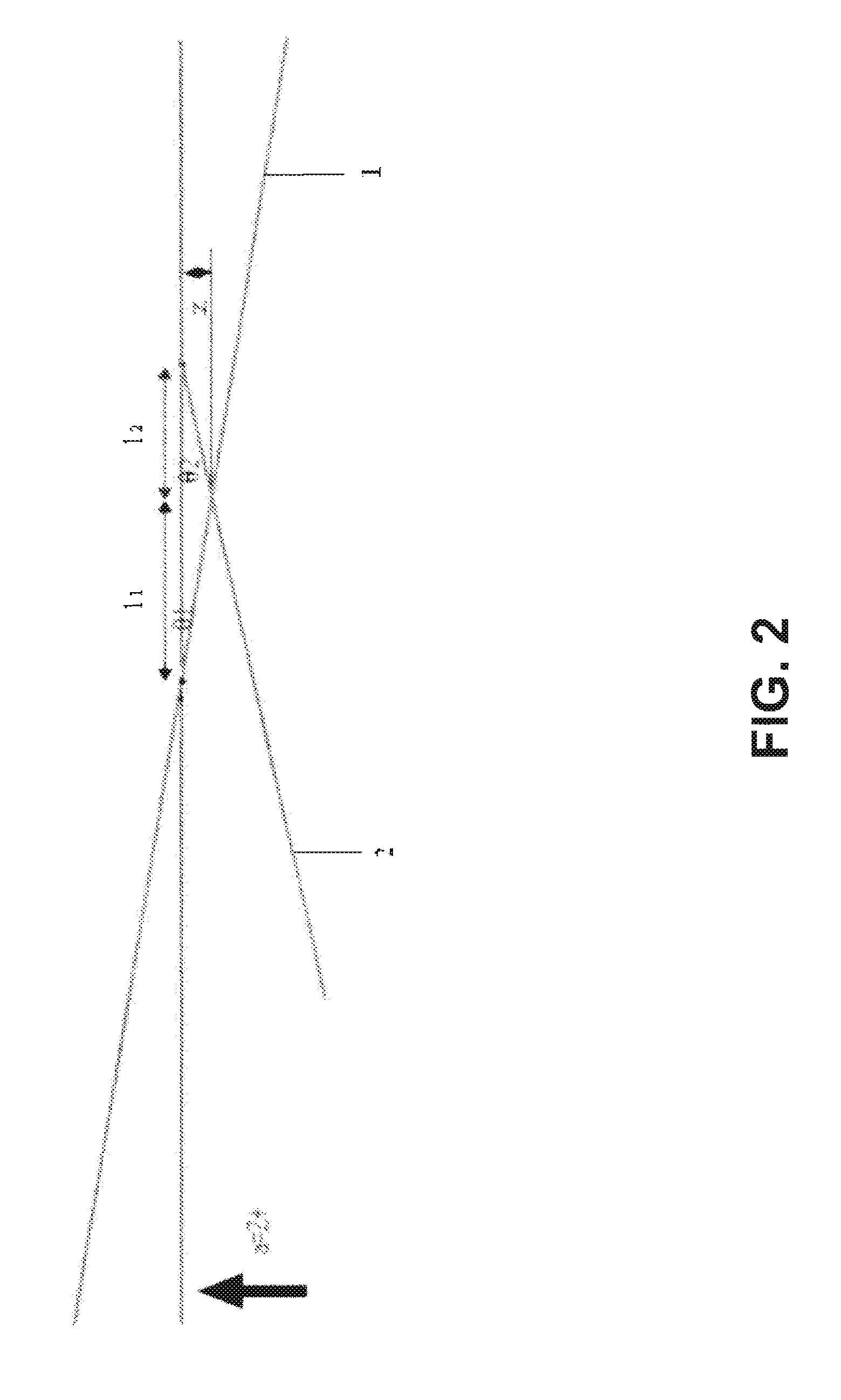
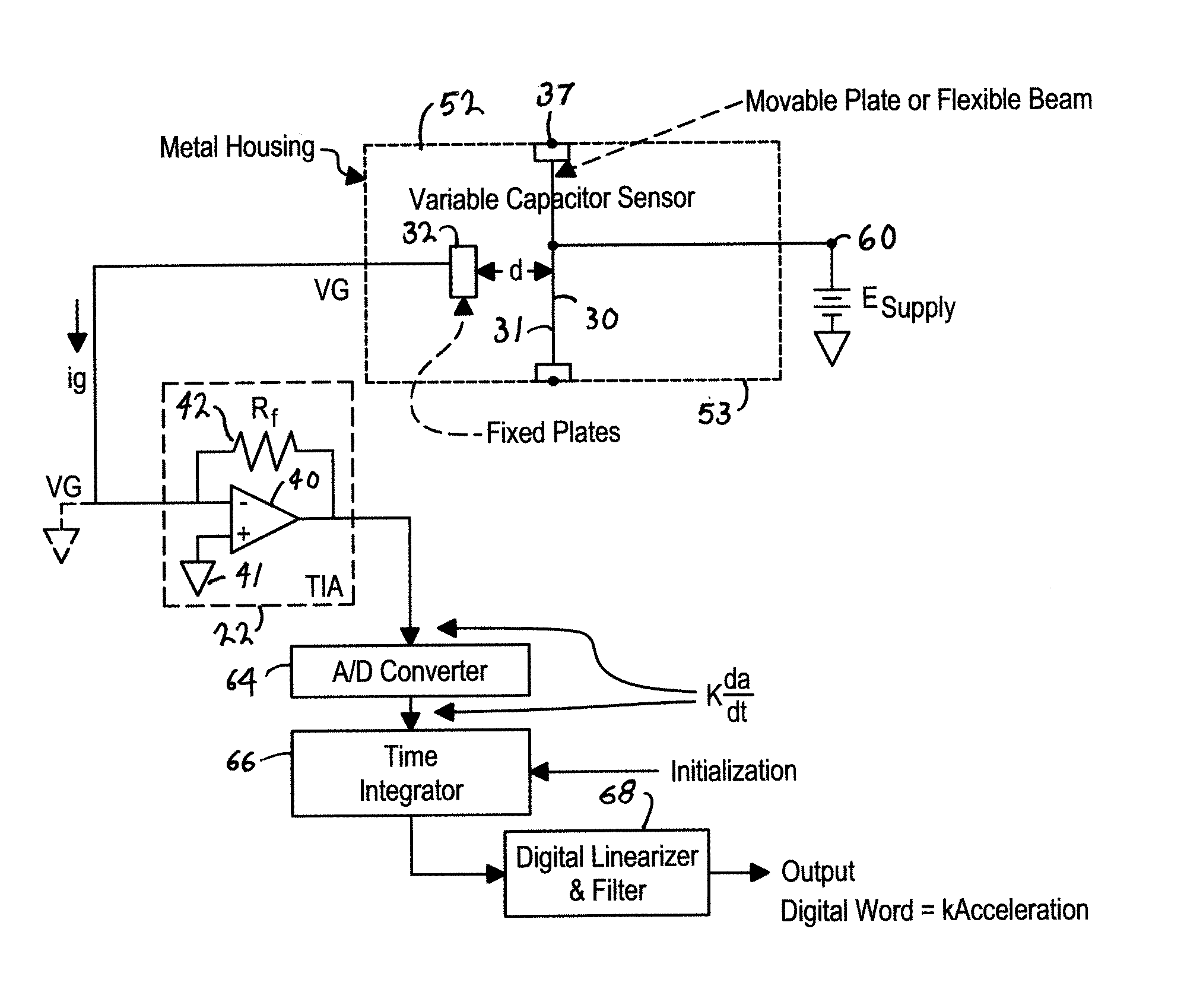
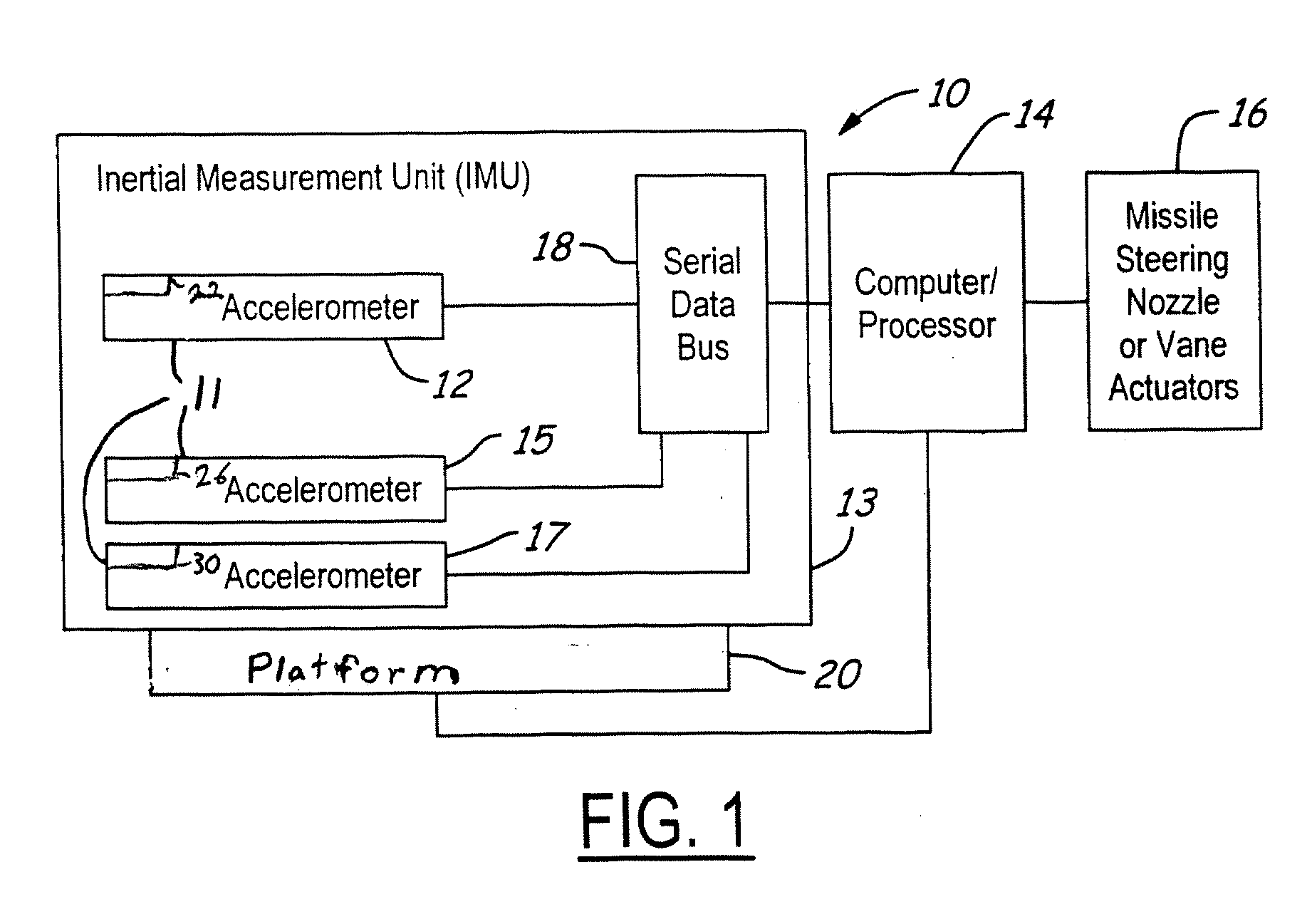
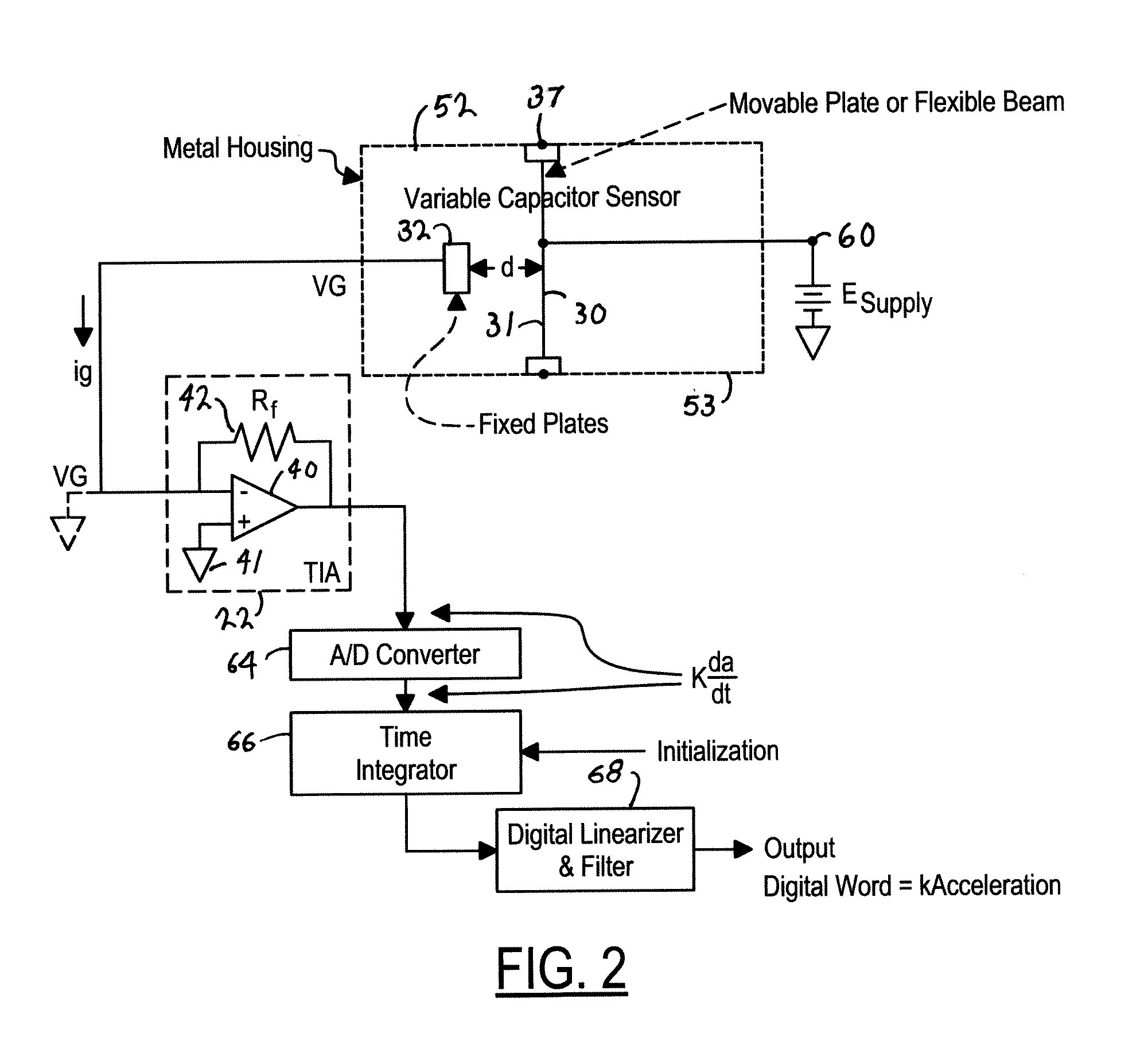
Single Plate Capacitive Acceleration Derivative Detector
InactiveUS20050022598A1Less powerImprove reliabilityBiocideAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAudio power amplifierSingle plate
A capacitance accelerometer includes a housing, and a plate fixed within the housing. A moveable plate is disposed in substantially parallel relation to the fixed plate and is coupled to the housing along at least an edge. The moveable plate and the fixed plate define a distance. The distance varies in response to acceleration forces acting upon the moveable plate, and wherein the moveable plate and the fixed plate generate a charge displacement capacitance signal. A transimpedance amplifier receives the charge displacement capacitance signal and generates a scaled voltage signal therefrom. An acceleration signal is generated from the scaled voltage signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com