Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
136 results about "Bit manipulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bit manipulation is the act of algorithmically manipulating bits or other pieces of data shorter than a word. Computer programming tasks that require bit manipulation include low-level device control, error detection and correction algorithms, data compression, encryption algorithms, and optimization. For most other tasks, modern programming languages allow the programmer to work directly with abstractions instead of bits that represent those abstractions. Source code that does bit manipulation makes use of the bitwise operations: AND, OR, XOR, NOT, and bit shifts.
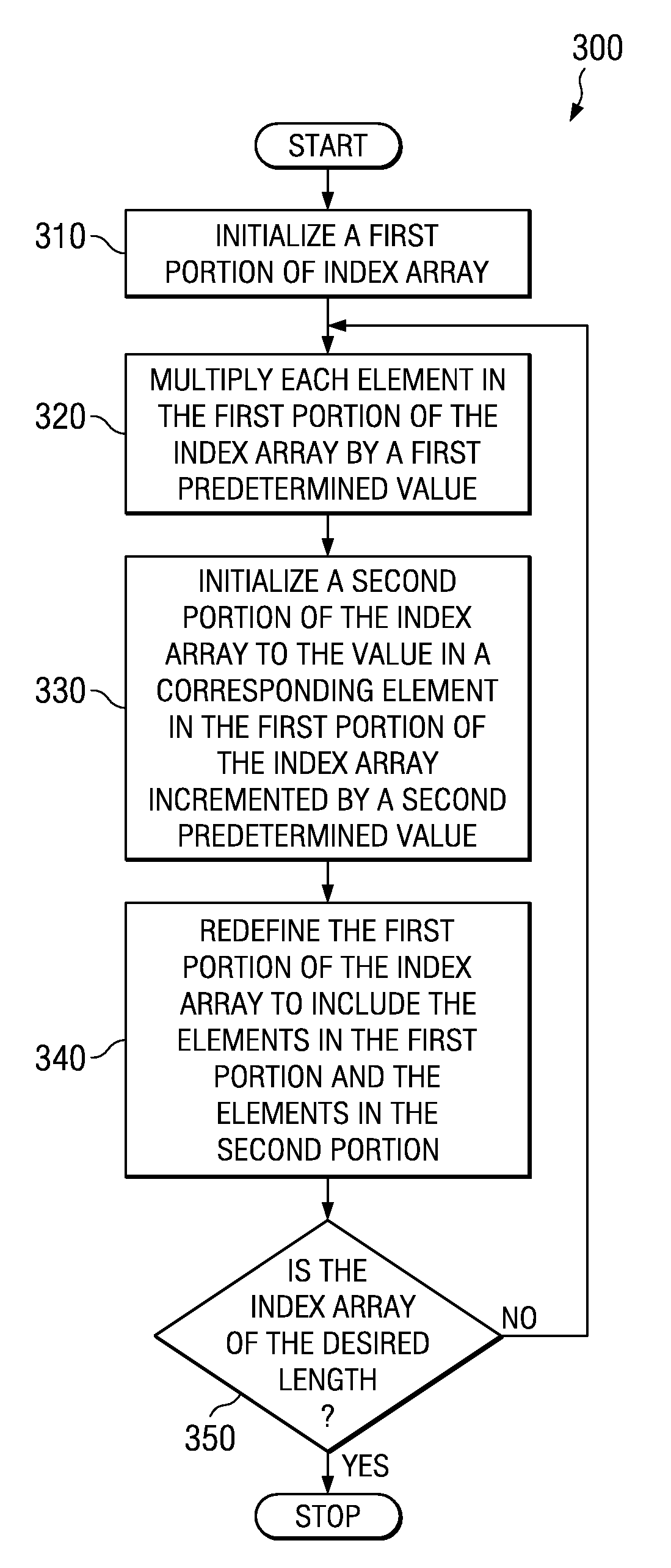
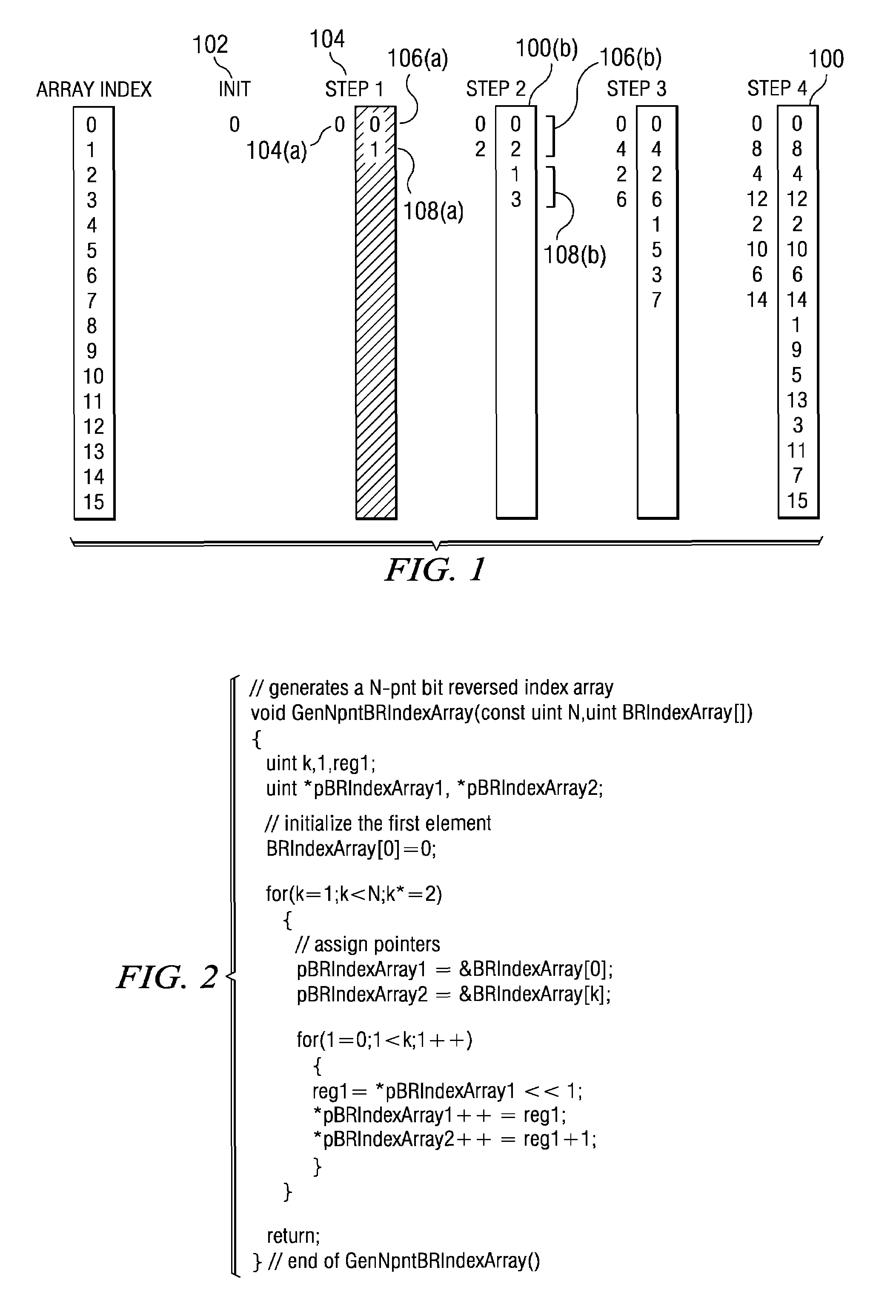
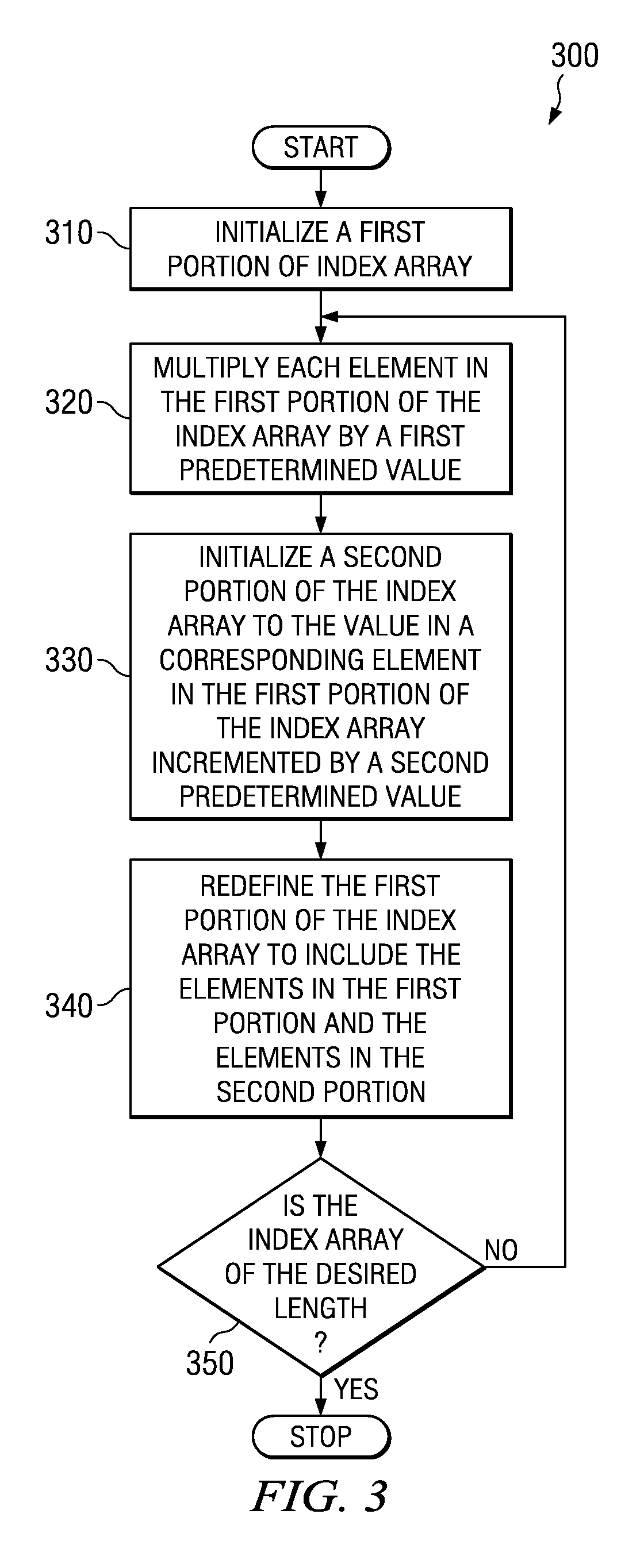
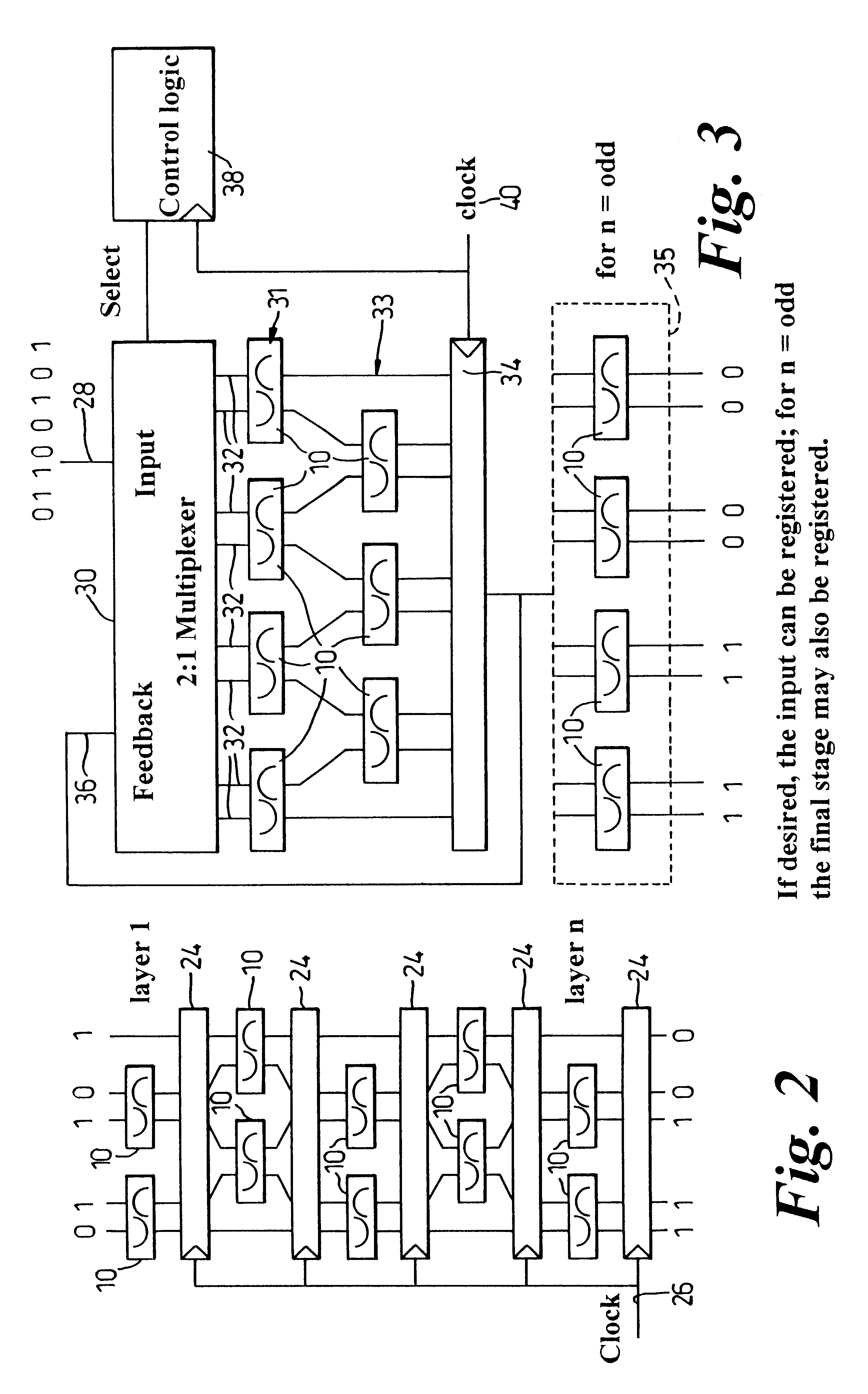
Method of generating a cycle-efficient bit-reverse index array for a wireless communication system
ActiveUS7406494B2Efficient hardwareGenerate efficientlyDigital computer detailsHandling data according to predetermined rulesCommunications systemReverse index
An efficient method of generating a bit-reverse index array in real time without performing any bit manipulation for a wireless communication system.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
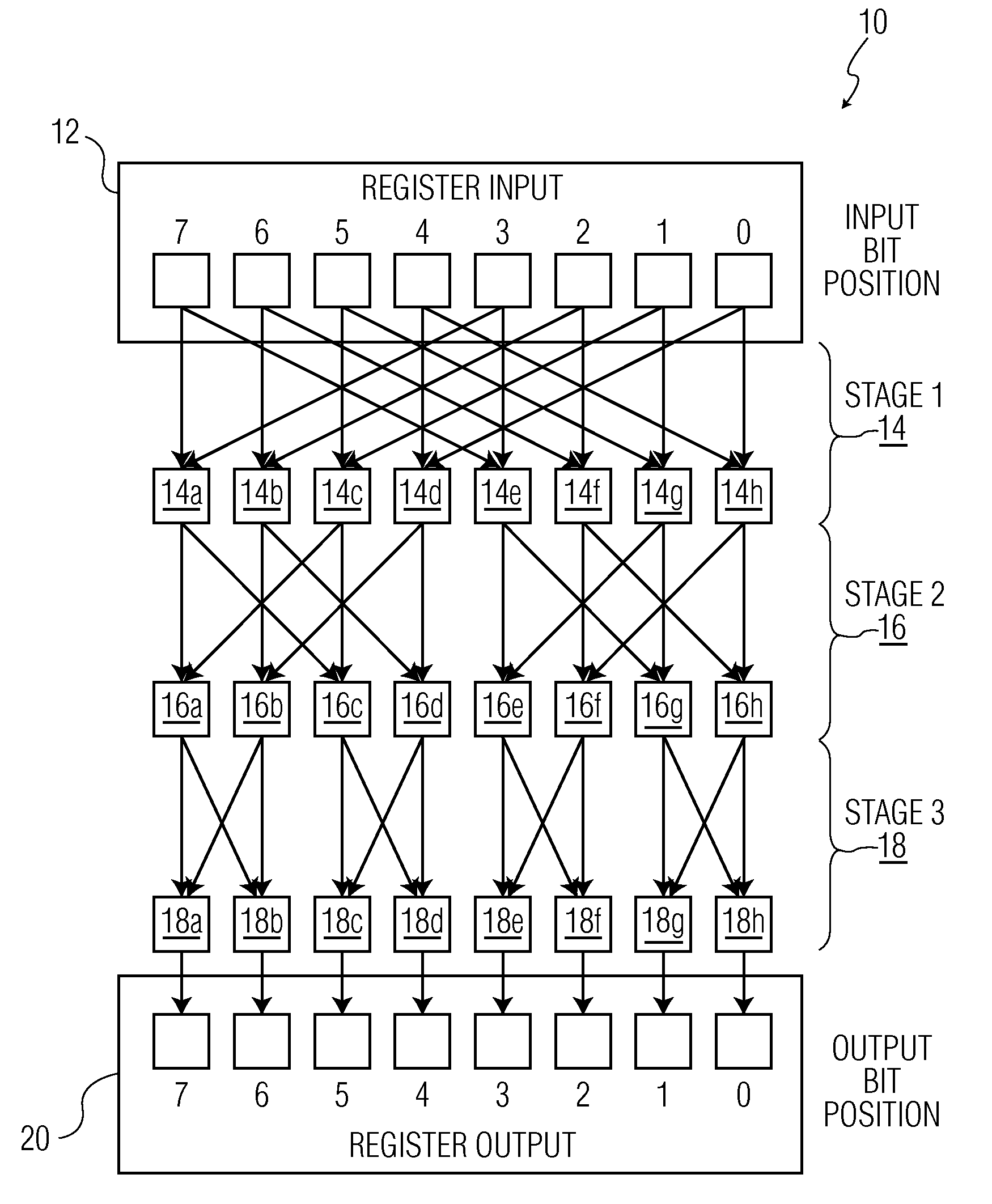
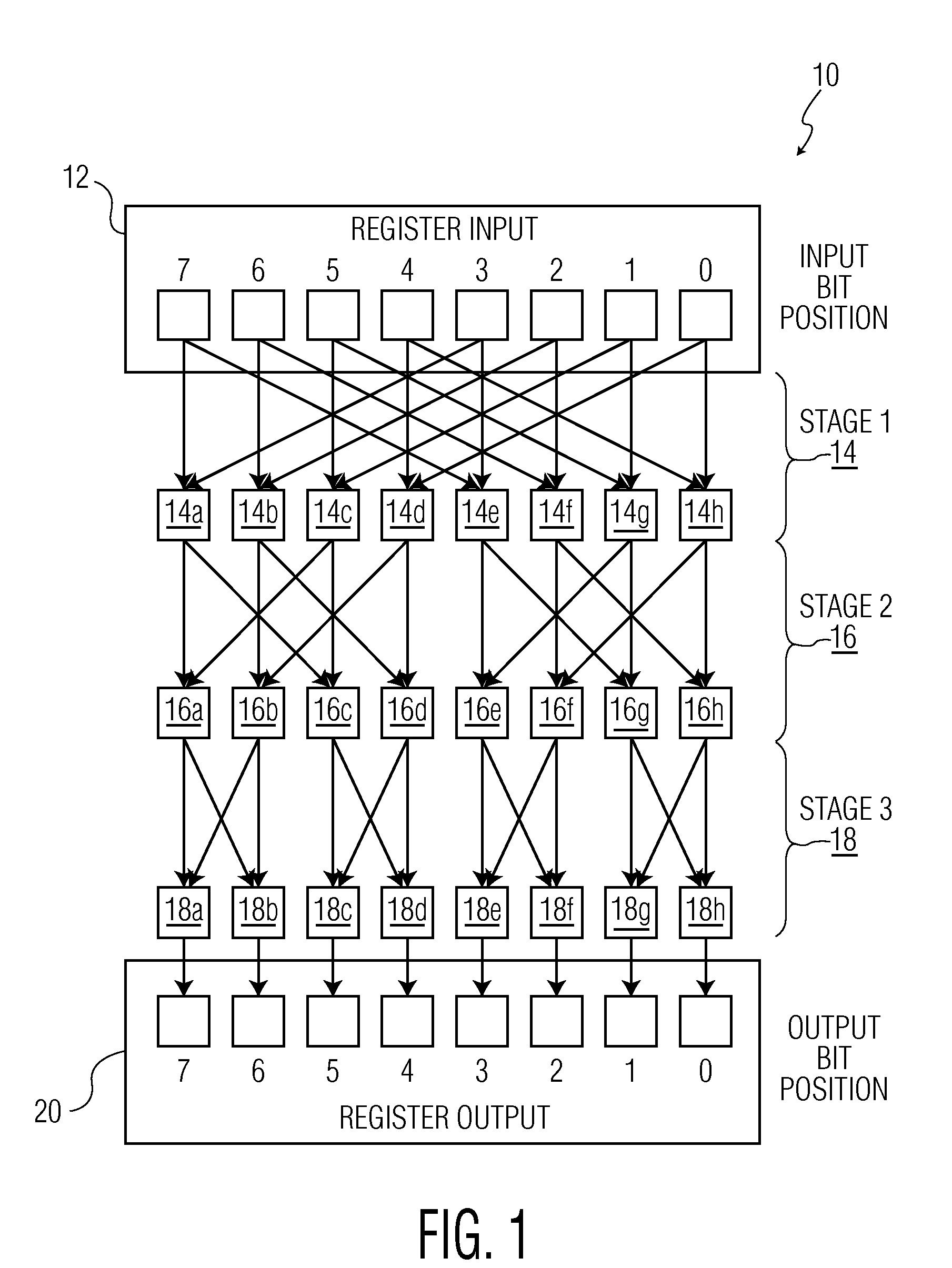
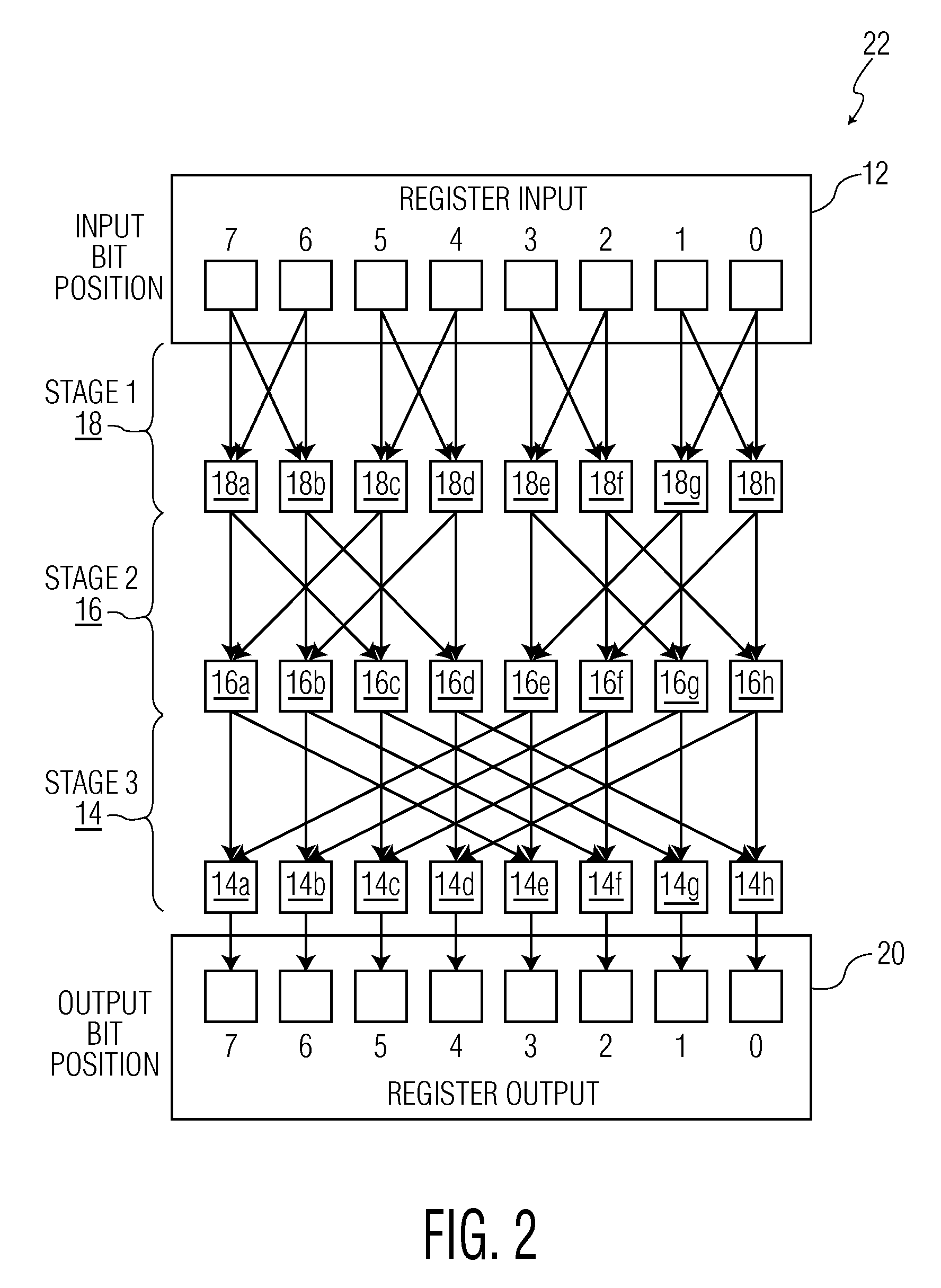
Microprocessor Shifter Circuits Utilizing Butterfly and Inverse Butterfly Routing Circuits, and Control Circuits Therefor
ActiveUS20090138534A1Saving chip spaceReduce the amount requiredDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsGroup operationControl circuit
Microprocessor shifter circuits utilizing butterfly and inverse butterfly circuits, and control circuits therefor, are provided. The same shifter circuits can also perform complex bit manipulations at high speeds, including butterfly and inverse butterfly operations, parallel extract and deposit operations, group operations, mix operations, permutation operations, as well as instructions executed by existing microprocessors, including shift right, shift left, rotate, extract, deposit and multimedia mix operations. The shifter circuits can be provided in various combinations to provide microprocessor functional units which perform a plurality of bit manipulation operations.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
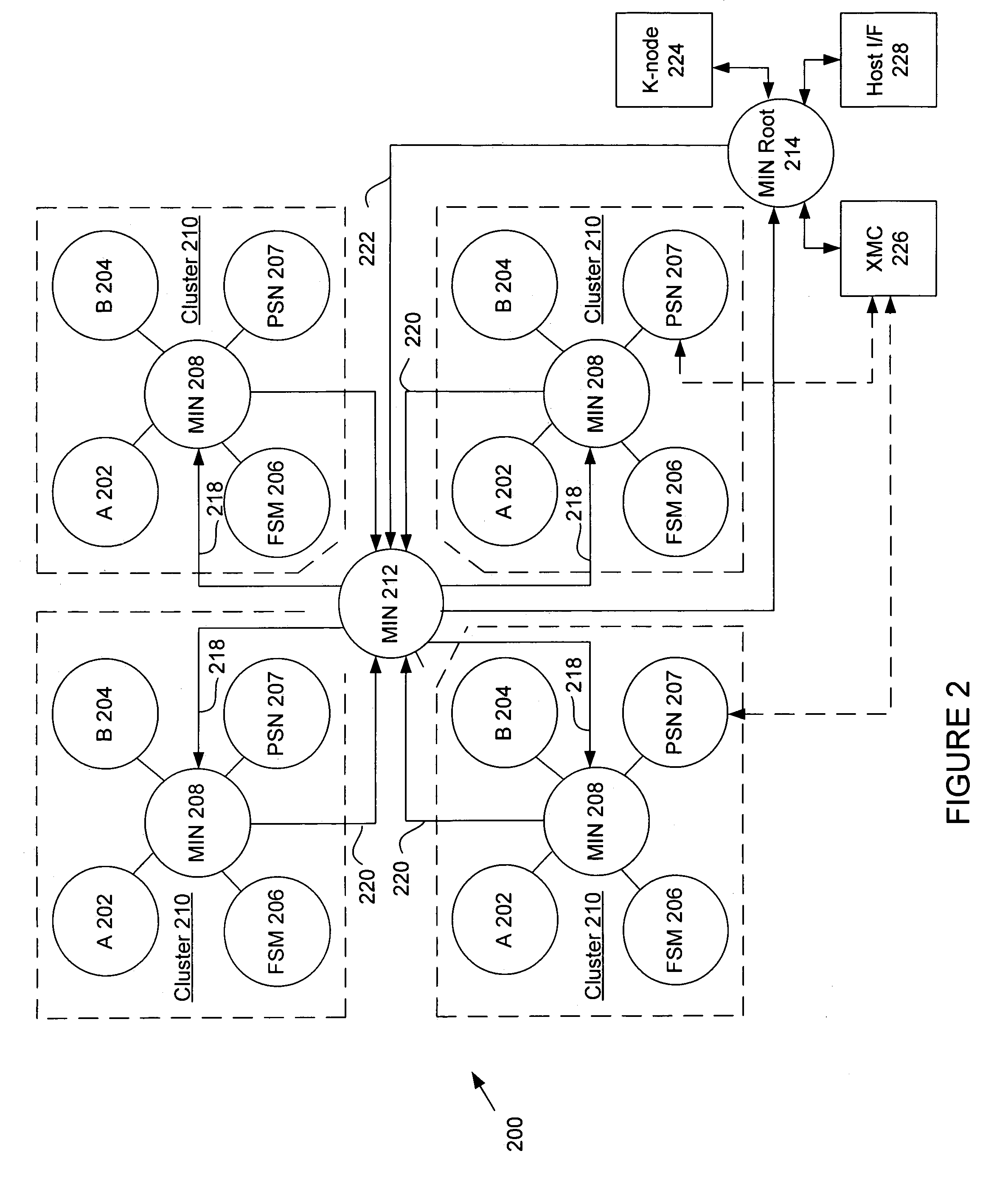
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
ActiveUS7194598B2Easy to useInherent adaptabilitySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGeneral purposeFinite-state machine
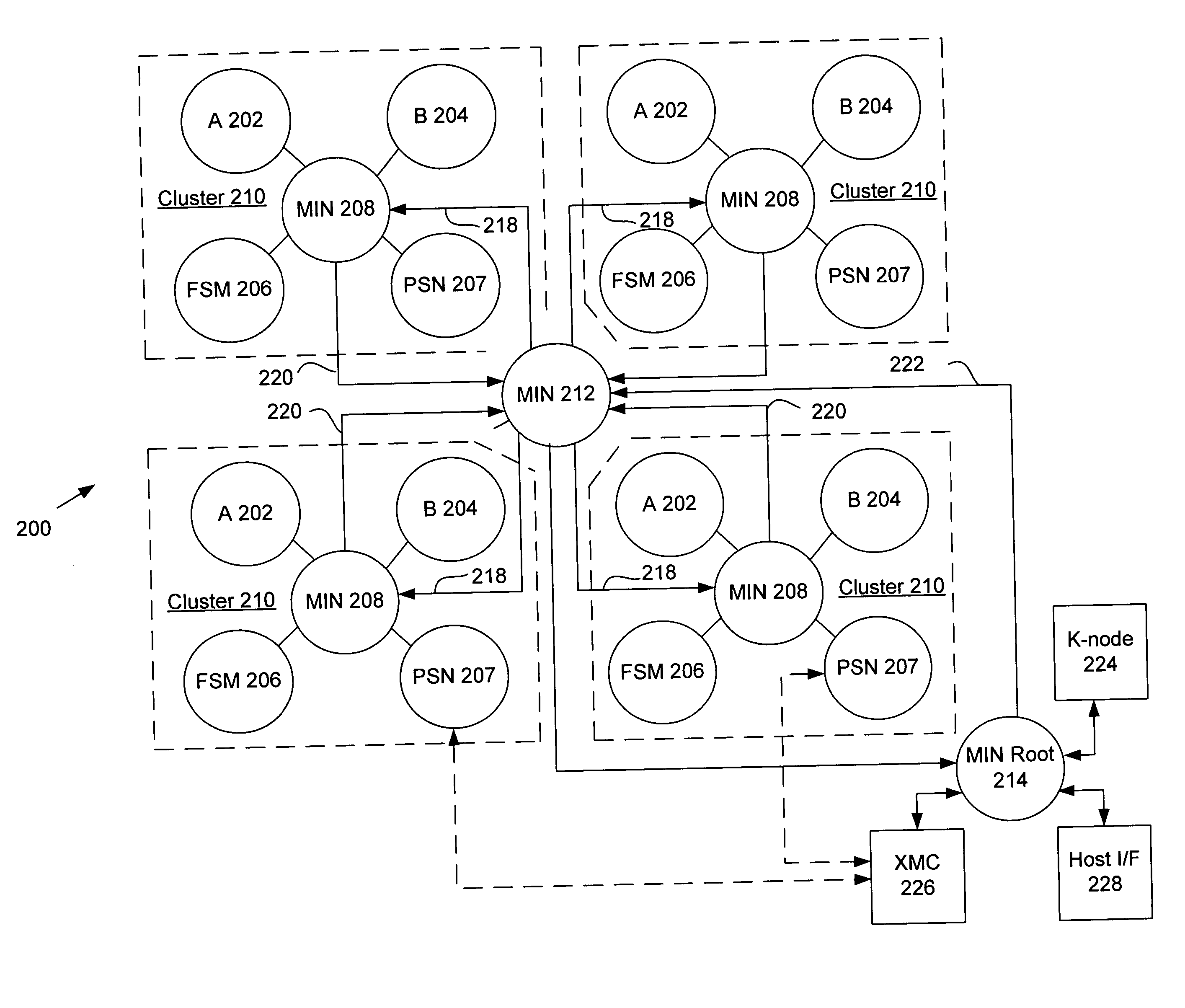
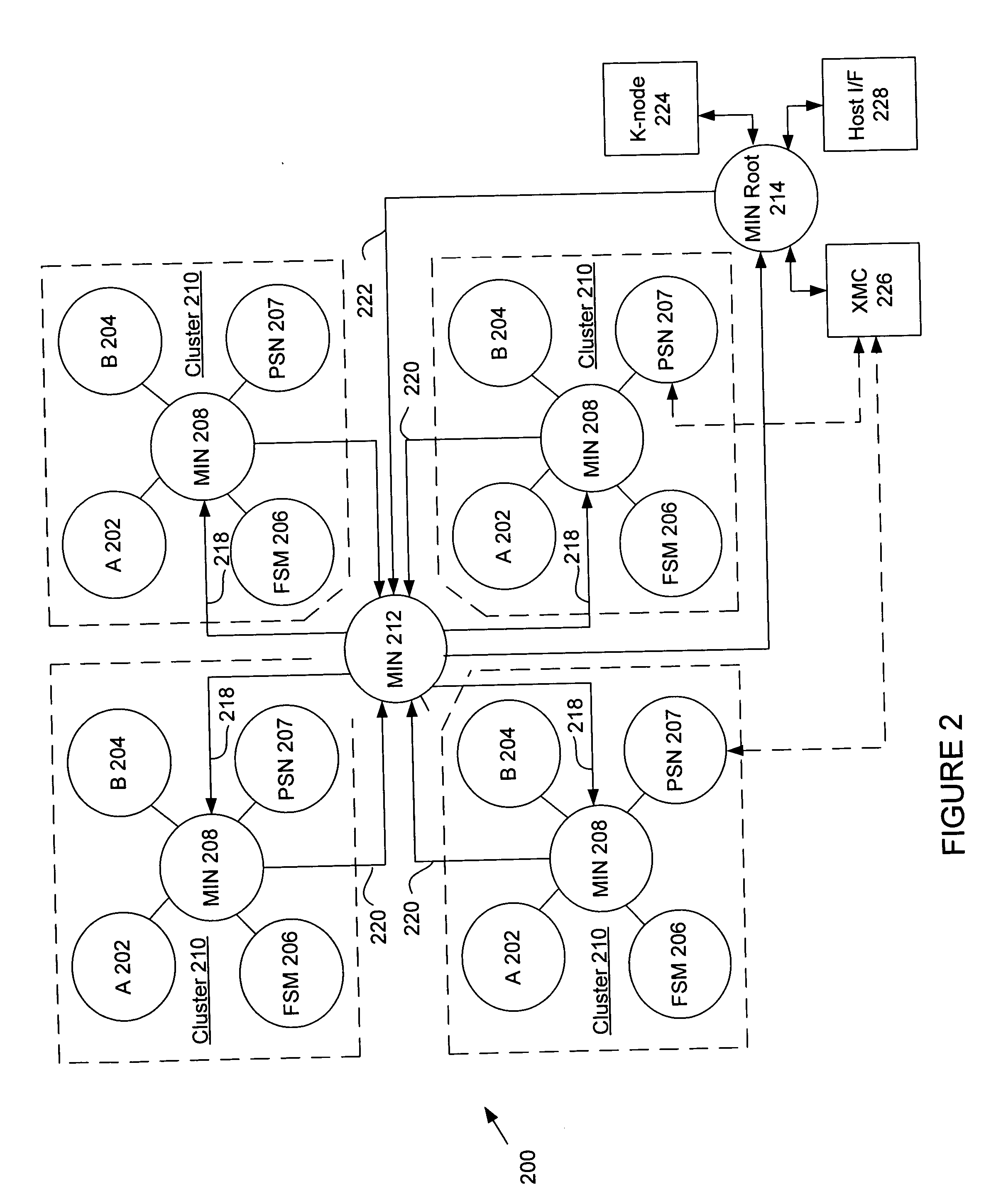
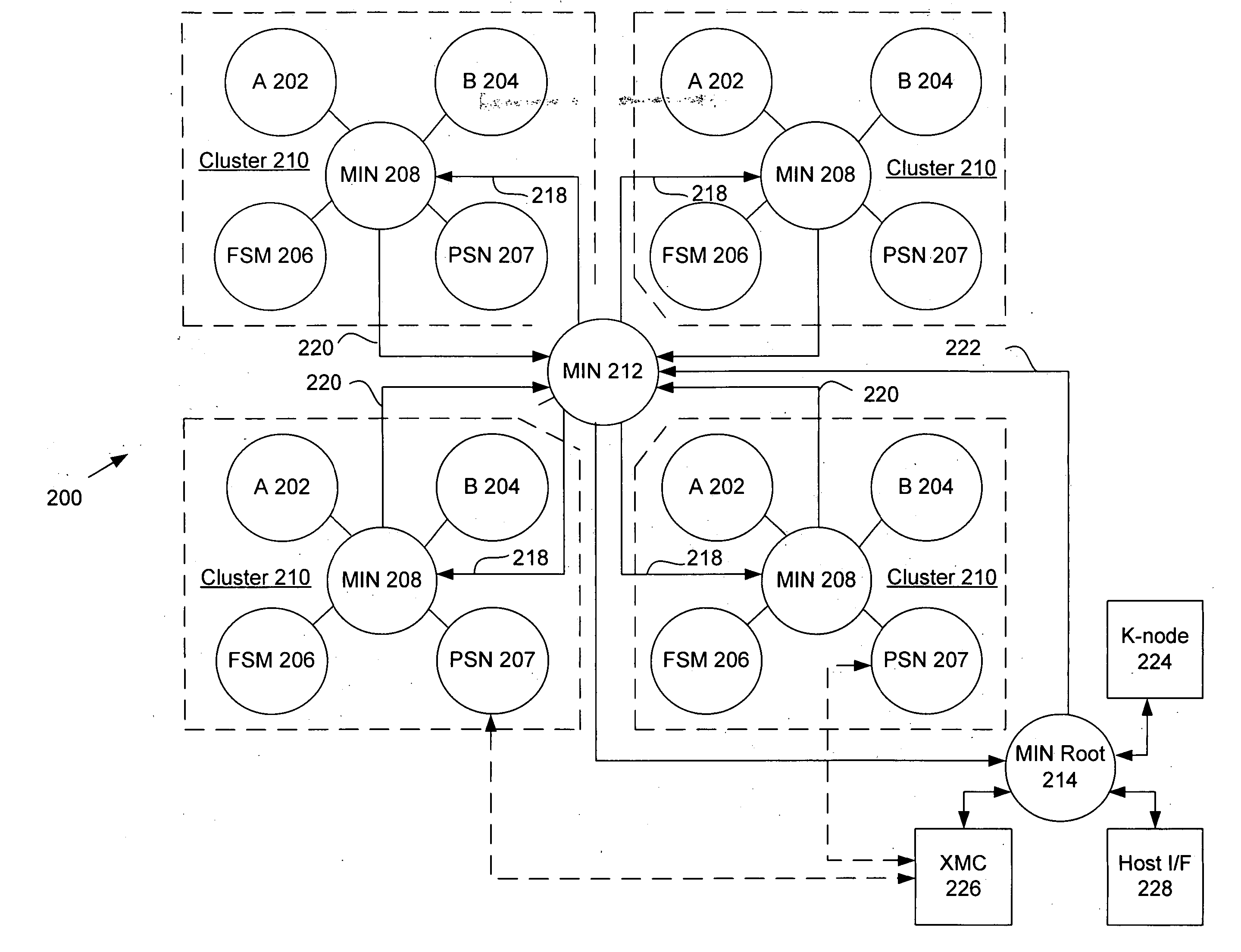
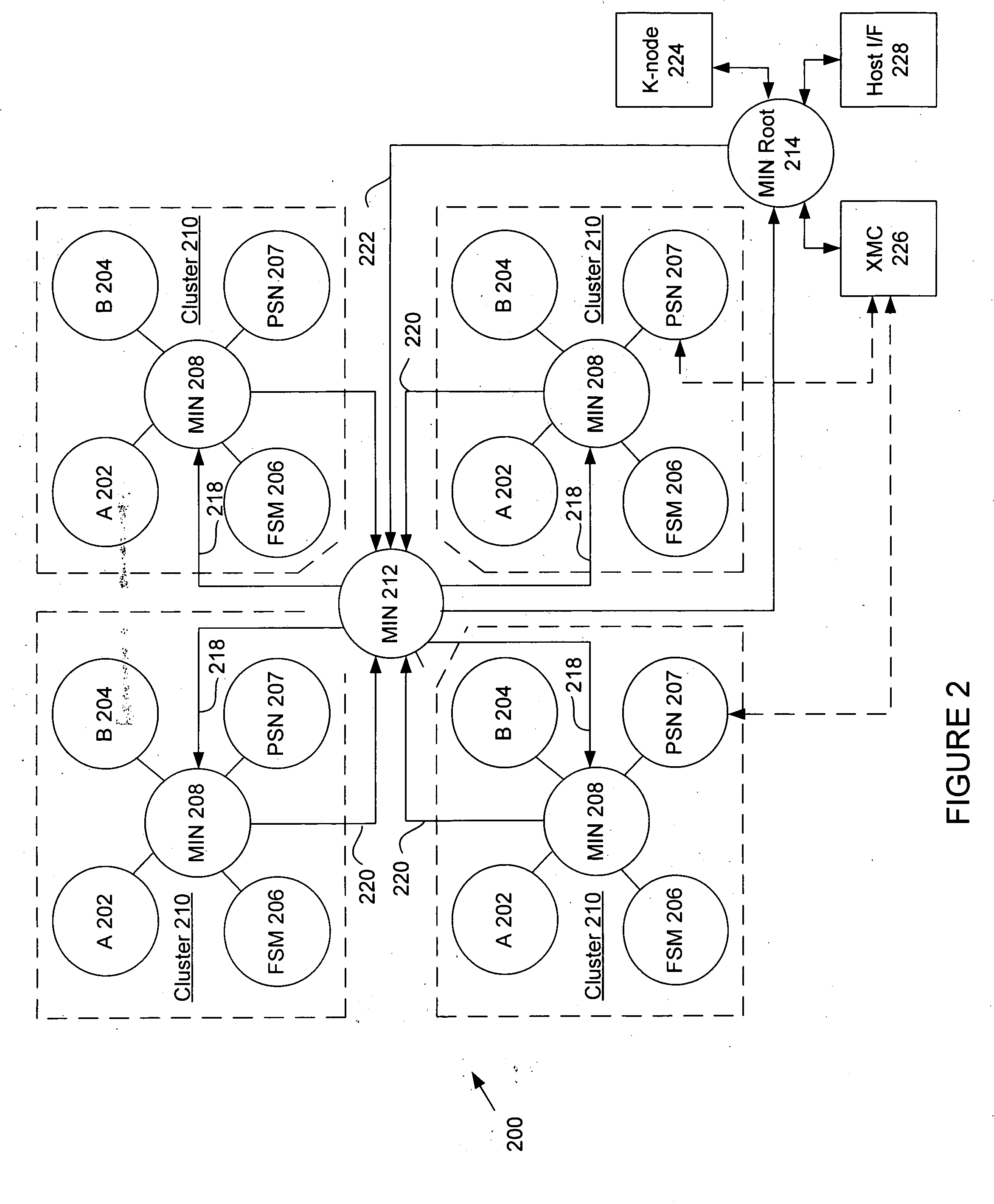
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing. The present invention further provides an interconnection scheme so that a plurality of ACE devices operates under the control of a single k-node.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
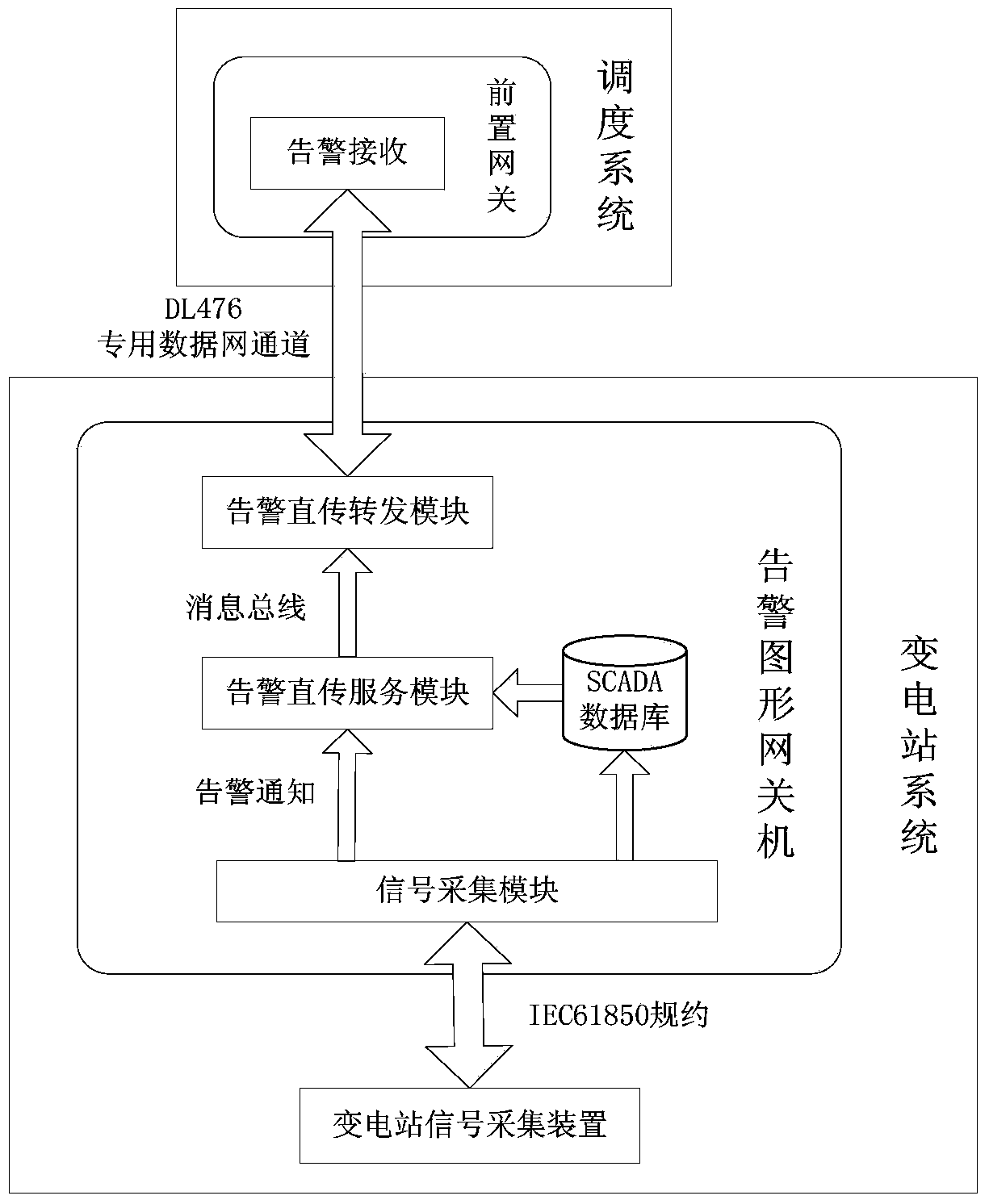
Transformer substation alarming graph gateway minimizing system and achieving method thereof
ActiveCN103729806AClear divisionReduce couplingData processing applicationsOperational systemTransformer
The invention relates to a system and an achieving method of the system in the technical field of power system automation, in particular to a transformer substation alarming graph gateway minimizing system and an achieving method of the system. The minimizing system utilizes an embedded industrial personal computer as a hardware platform and a RedHat Linux 64 bit operation system as a software platform, and acquires data sources of the whole substation through data of an IEC61850 MMS protocol collection device, a shared memory real-time base and a file memory with a Harsh algorithm as the index serve as data storage media, a message bus runs through the applications for data interaction between different threads, alarming direct transmission service and picture refreshing service for alarming direct transmission and remote browsing are arranged on the base to provide a standard data source for the alarming forwarding and the remote browsed data forwarding. The system and the method solve the transmission and processing problems of a main station and caused by the fact that the access data of the transformer substation increase severely, and a new data interaction mode of the alarming direct transmission and the remote browsing is provided.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
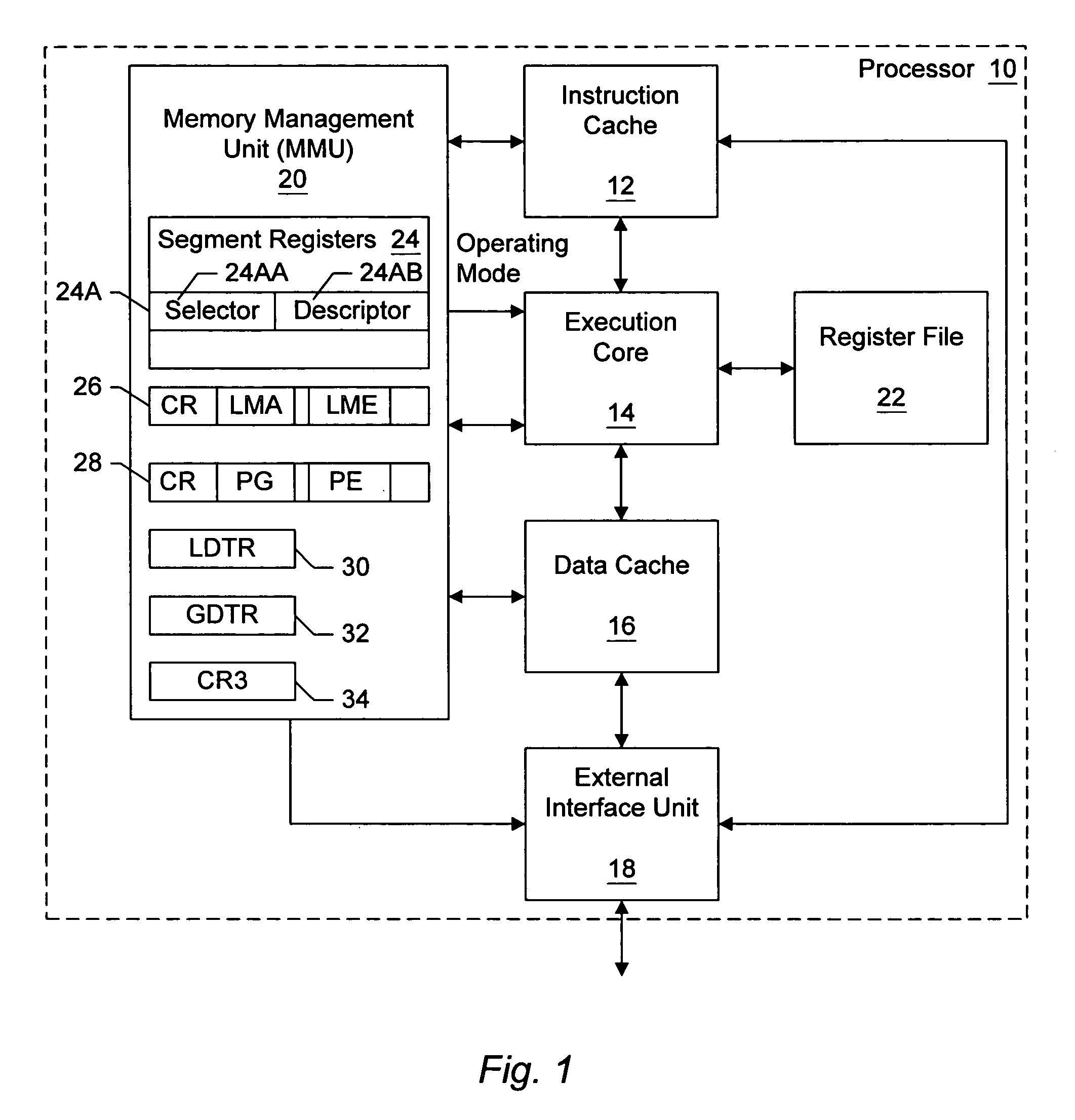
Establishing a mode indication responsive to two or more indications
ActiveUS7058791B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationGeneral purpose stored program computerLong mode16-bit
A processor generates a mode indication based on two or more other indications. The mode indication is indicative of whether or not a particular mode is active in the processor. Each indication is stored in a storage location which is addressable via a different instruction. In one embodiment, a long mode in which a 64 bit operating mode is selectable in addition to 32 bit and 16 bit modes may be activated via a long mode active indication. The long mode active indication may be generated by the processor, and may indicate that long mode is active if paging is enabled and a long mode enable indication indicates that long mode is enabled. In this manner, long mode may be activated after paging is enabled (with a set of long mode page tables indicated by the page table base address).
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
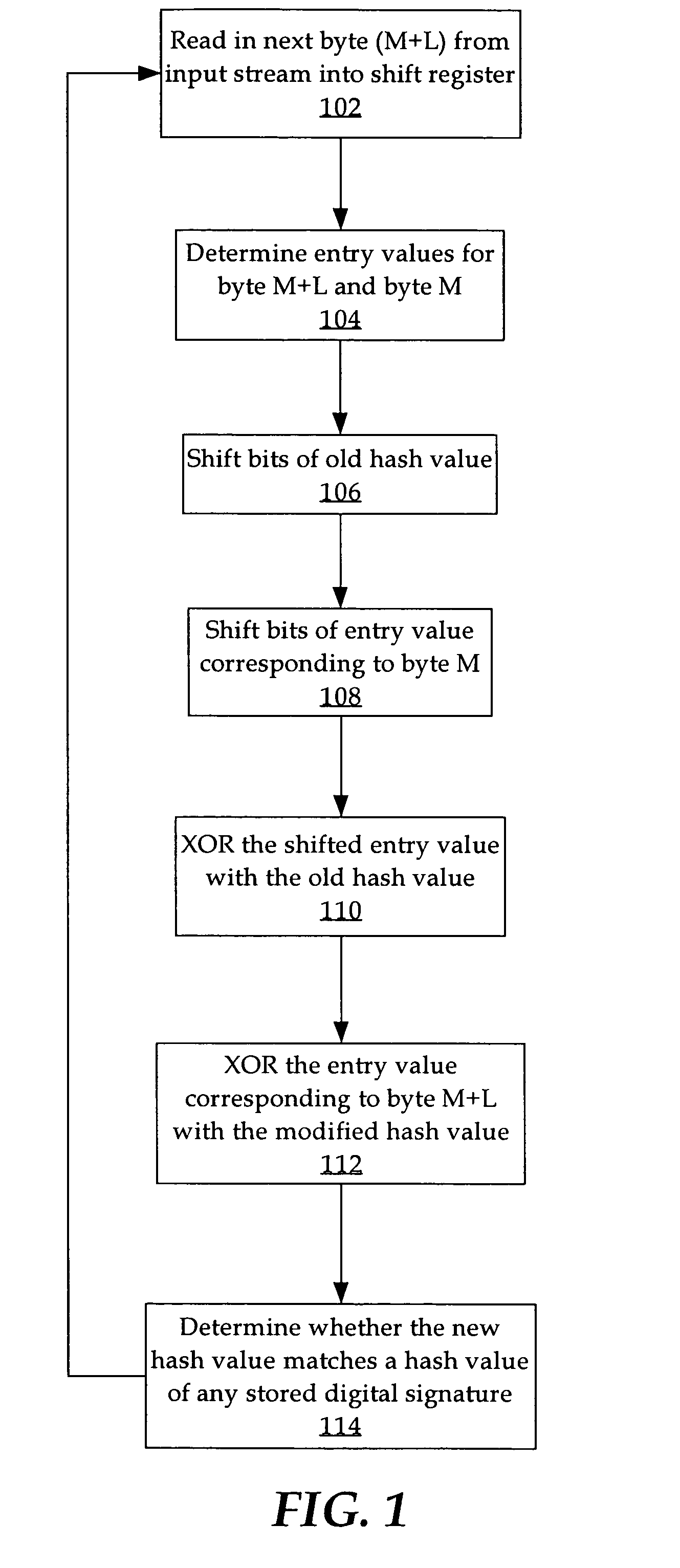
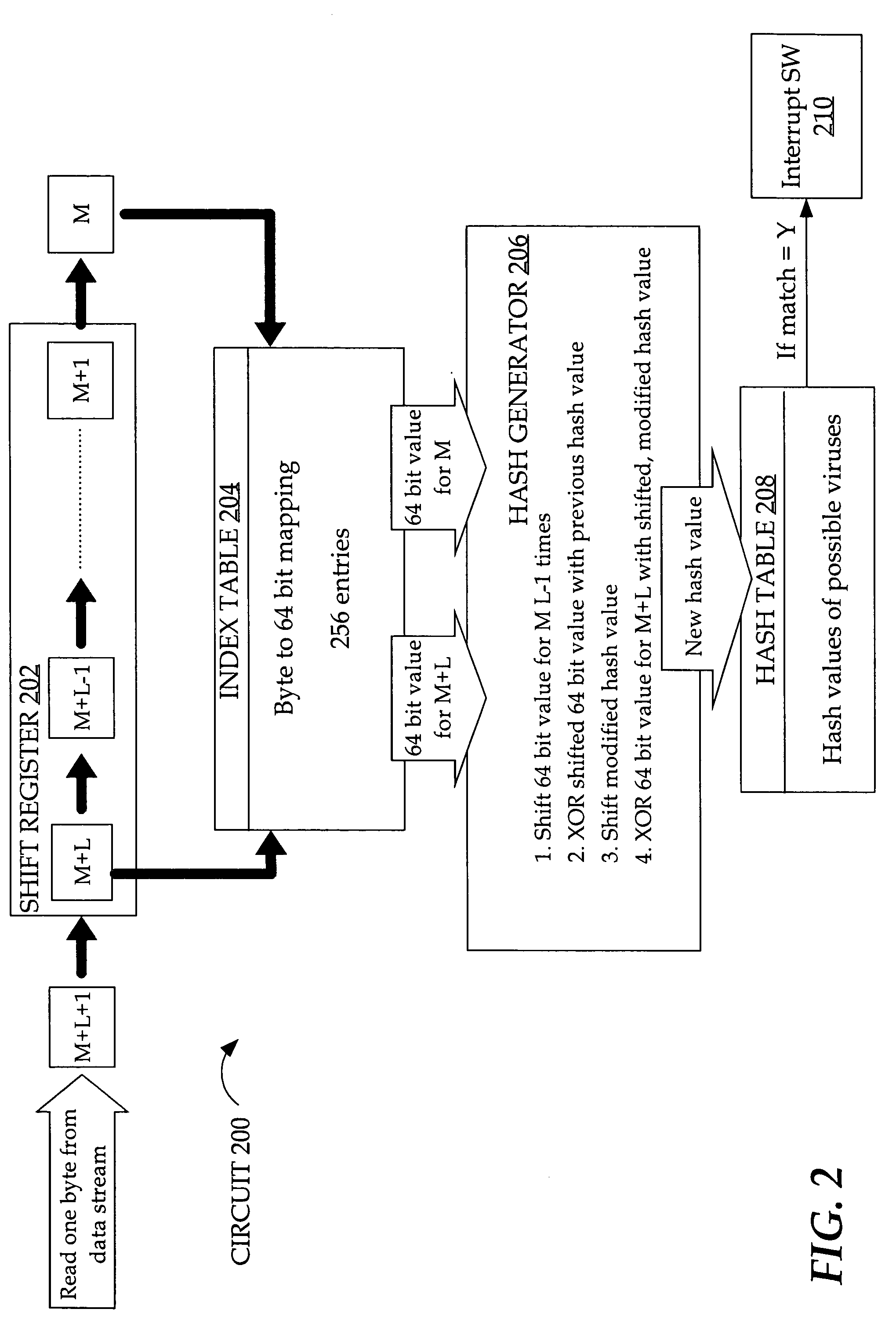
Substring search algorithm optimized for hardware acceleration
ActiveUS7941435B2Digital data information retrievalRandom number generatorsData streamTheoretical computer science
Techniques are provided for generating a hash value for searching for substrings in a data stream without reading more than one element (e.g. one byte) at a time. According to one technique, a before a next element is added to an old hash value, the old hash value is circularly shifted one or more bits. The first original element is shifted a number of bits and XOR'ed against the old hash value. The next element is added to the old hash value. In one embodiment, an entry value is retrieved for each element from an index table and the XOR and shift operations are performed on the entry values. According to another technique, each Linear Feedback Shift Register (LFSR) of a plurality of LFSRs read in one element at a time beginning at different offsets. Each LFSR uses the same state machine. The result of reading a number of elements into an LFSR is used as the hash value.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
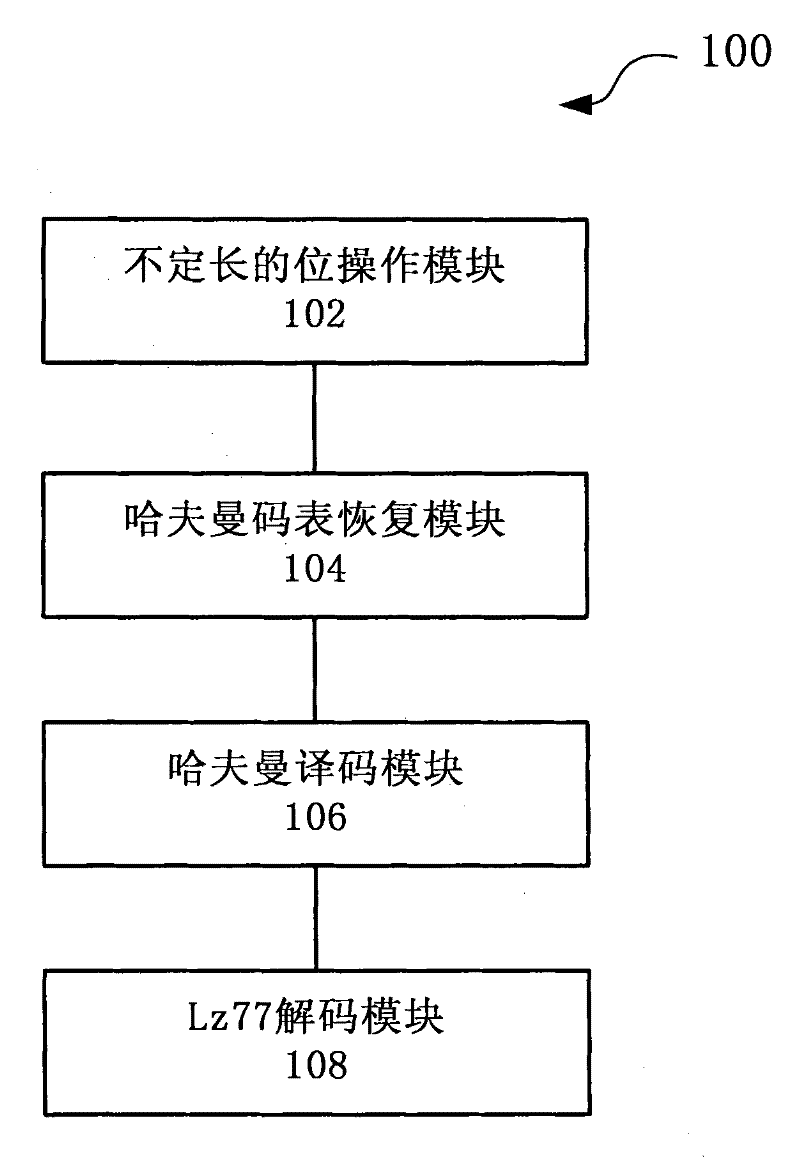
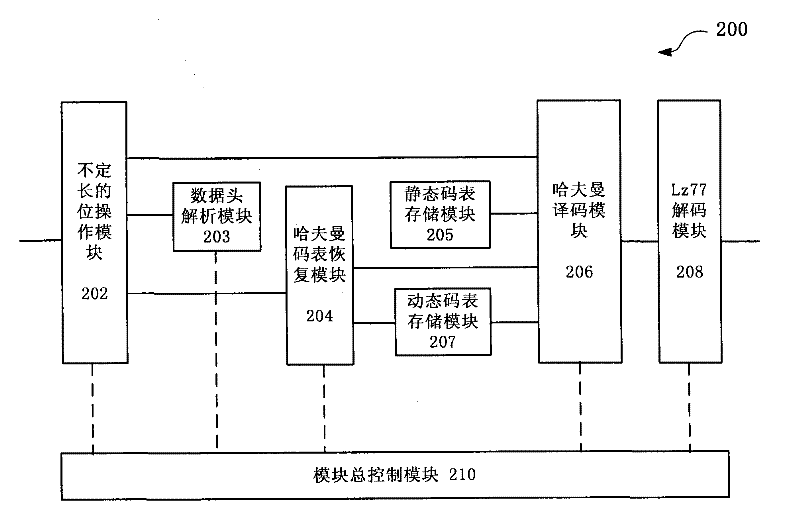
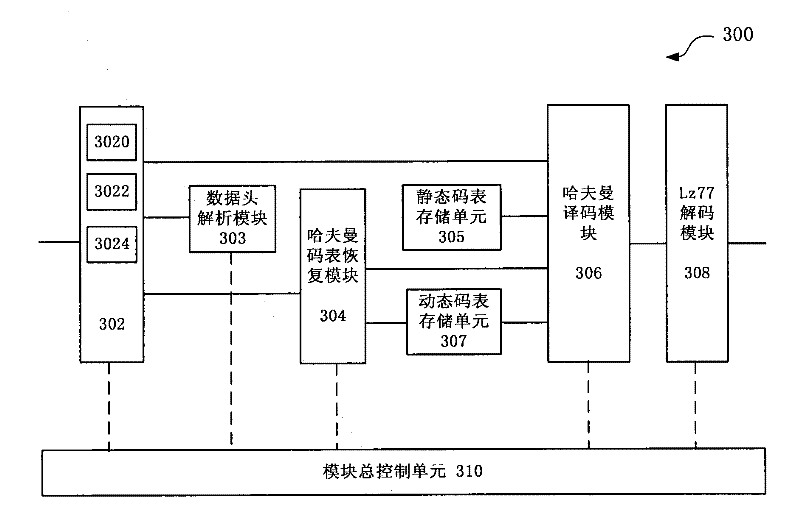
System and method for realizing parallel decompression of hardware
The invention discloses a system and method for realizing parallel decompression of hardware. The system comprises a variable-length bit manipulation module, a Huffman table recovery module, a Huffman coding module and a decoding module, wherein the variable-length bit manipulation module is used for carrying out variable-length bit manipulation on to-be-decompressed data to acquire variable-length data; the Huffman table recovery module is used for recovering a Huffman table in accordance with the variable-length data; the Huffman coding module is used for executing Huffman coding in parallel in accordance with the Huffman table; and the decoding module is used for carrying out decoding in accordance with the Huffman coding result. According to the system and method for realizing the parallel decompression of hardware, an FPGA (field programmable gate array) is utilized to realize a Gzip decompressing function, a parallel decompression algorithm is utilized and a hardware circuit structure suitable for the algorithm is designed, thus improving the processing efficiency of the decompression greatly.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
ActiveUS20040143724A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecific program execution arrangementsGeneral purposeFinite-state machine
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Processor for executing highly efficient VLIW
InactiveUS20020129223A1Efficiently constructHighly efficient code structureInstruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computer4-bit12-bit
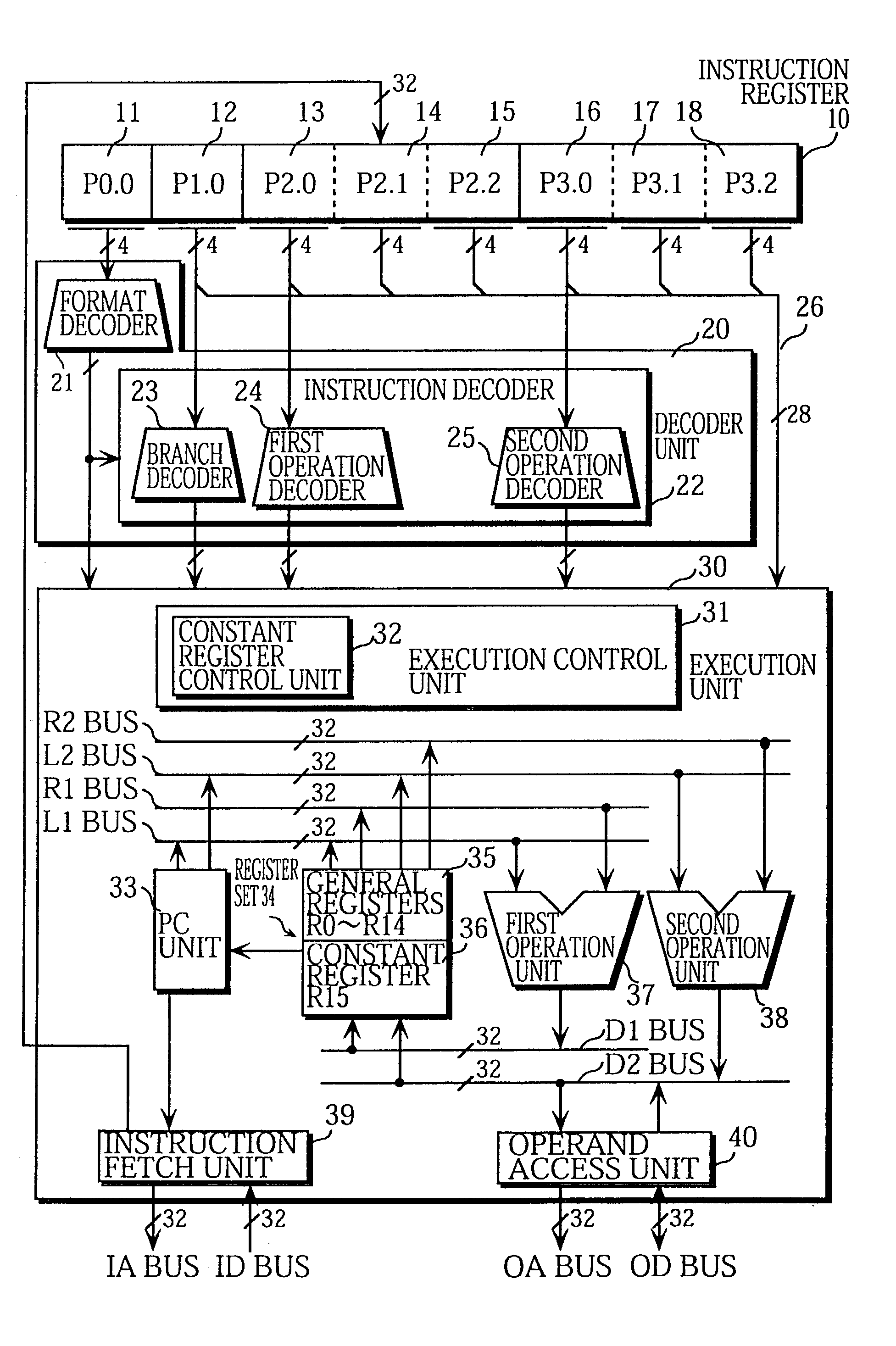
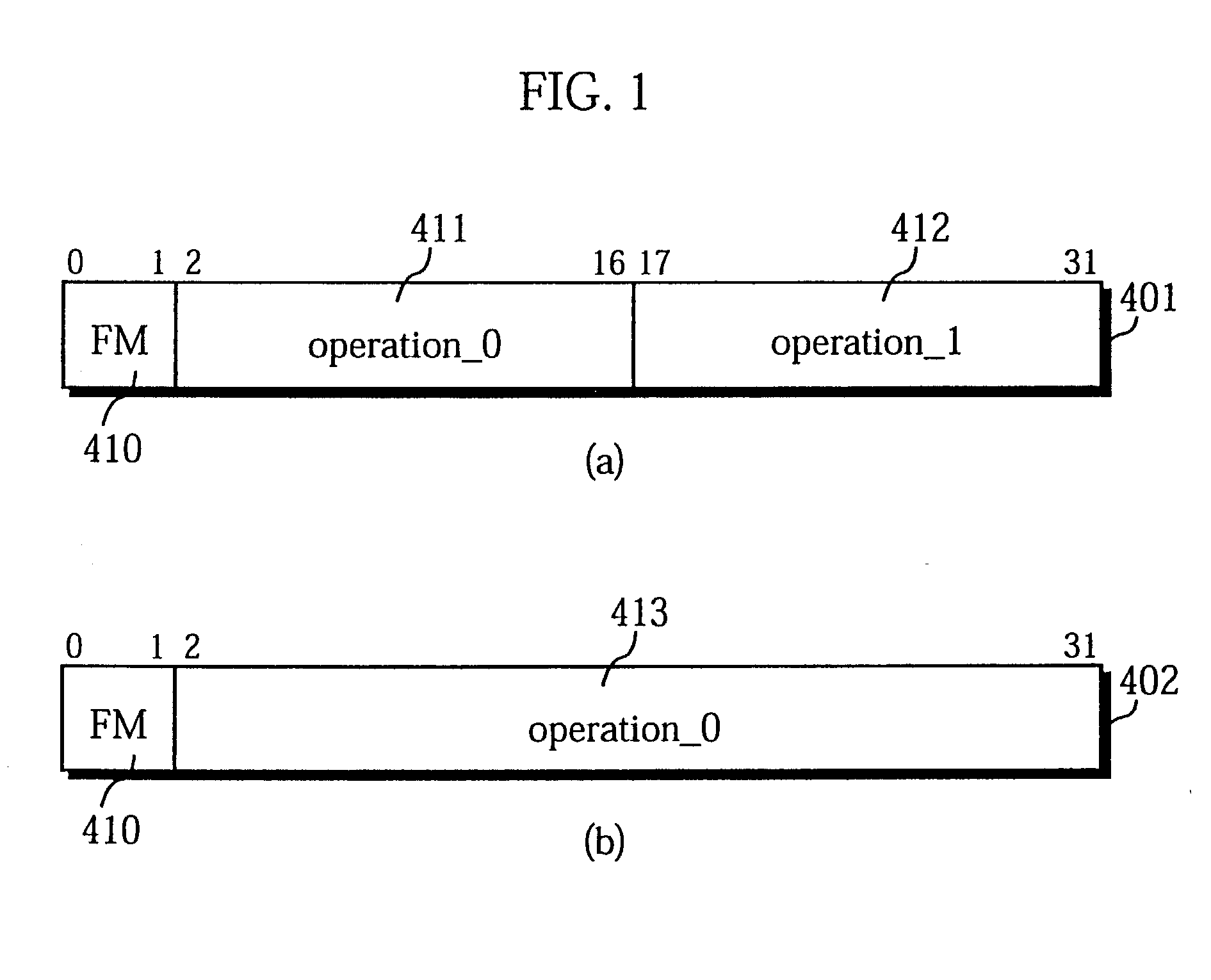
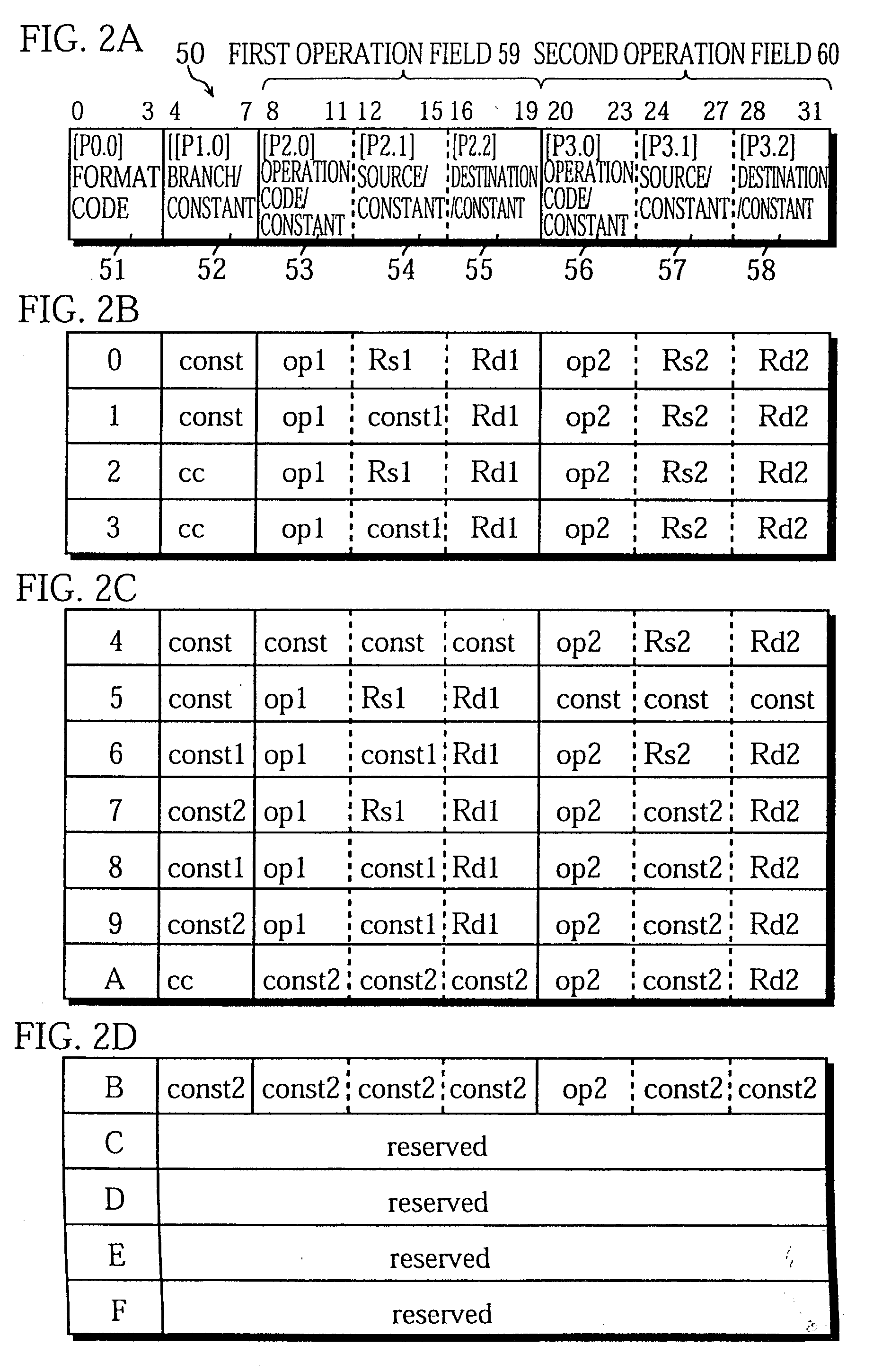
A 32-bit instruction 50 is composed of a 4-bit format field 51, a 4-bit operation field 52, and two 12-bit operation fields 59 and 60. The 4-bit operation field 52 can only include (1) an operation code "cc" that indicates a branch operation which uses a stored value of the implicitly indicated constant register 36 as the branch address, or (2) a constant "const". The content of the 4-bit operation field 52 is specified by a format code provided in the format field 51.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
ActiveUS20050166033A1Increase the number ofHigh speed communicationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsElectric digital data processingGeneral purposeParallel computing
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing. The present invention further provides an interconnection scheme so that a plurality of ACE devices operates under the control of a single k-node.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Apparatus and method for uniformly performing comparison operations on long word operands
InactiveUS6742013B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsAlgorithmOperand
Using a subtraction without borrow operation, the first operand lowest order word is subtracted from a second operand lowest order word. If the result of the subtracting is not zero, then a zero (Z) flag is cleared such that a Z flag status is not set. If, however, the result of the subtracting is zero, then the Z flag is set as usual. Next, a first operand next higher order word is subtracted from a second operand next higher order word using a subtraction with borrow and a sticky not Z flag (SBBZ) instruction and, based upon the subtracting, the Z flag is updated accordingly such that it represents the result of the whole multi-word subtraction until the first operand highest order word is subtracted from the second operand highest order word. The comparing of the first operand and the second operand is then based upon the Z flag status, if needed, after the subtraction of the first operand highest order word is subtracted from the second operand highest order word.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Bit field manipulation
InactiveUS7013302B2Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsExternal storageBit field
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
Method and apparatus for bit vector array
InactiveUS7284260B2Controls contentionGeneral purpose stored program computerStar/tree networksVector elementParallel processing
A bit vector array apparatus provides a high speed method for processing network transmission controls. Complex data structures for controlling network access are represented in the simplest possible form as single bit vector elements. The bit vector elements are combined into bit vectors comprised of 32 single bit vector elements. The bit vectors are processed in parallel in the bit vector array apparatus, which is comprised of special-purpose bit manipulation functions to expedite the processing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Montgomery multiplication circuit
ActiveUS20120265794A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsMuxponderMultiplexer
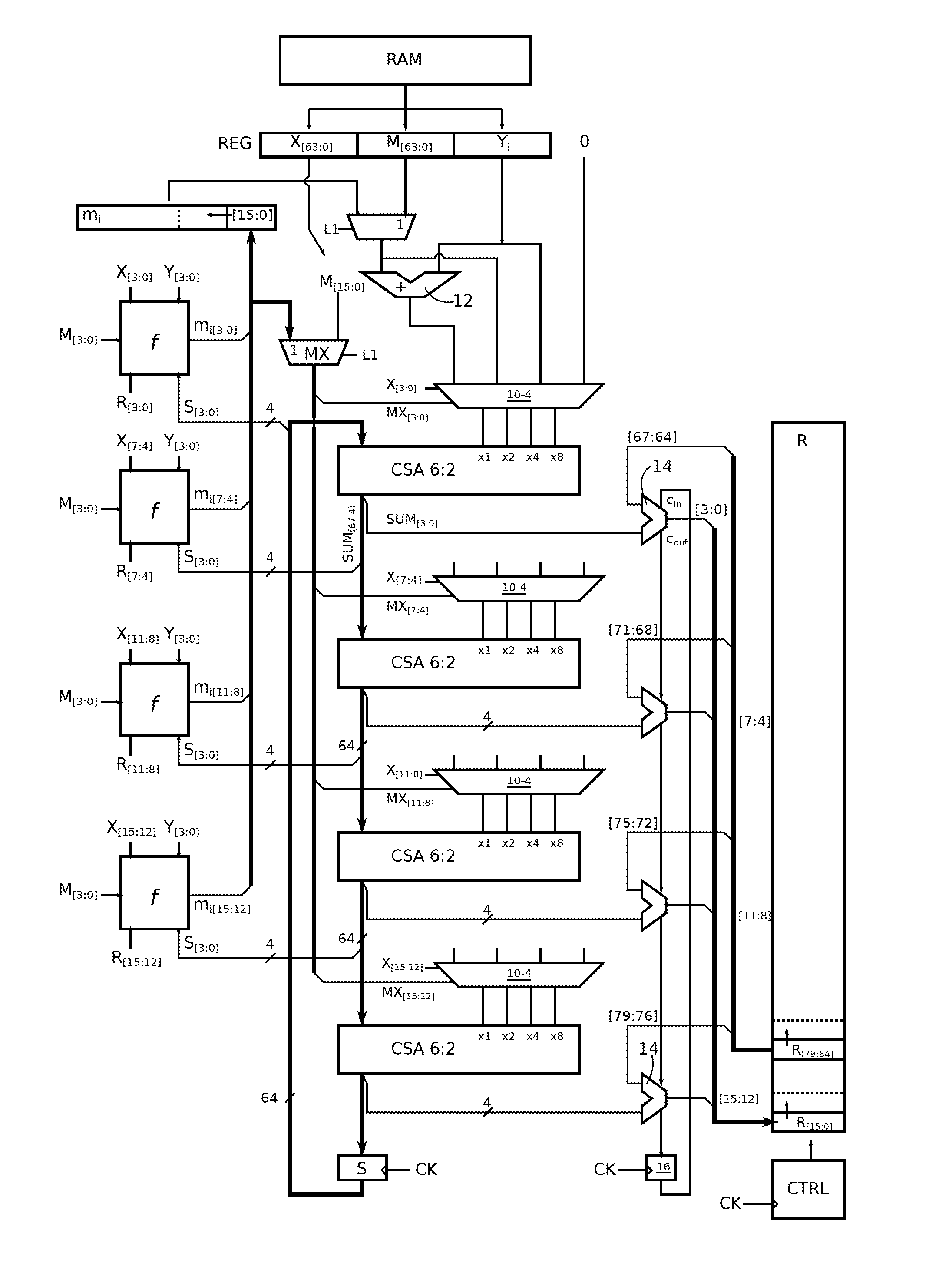
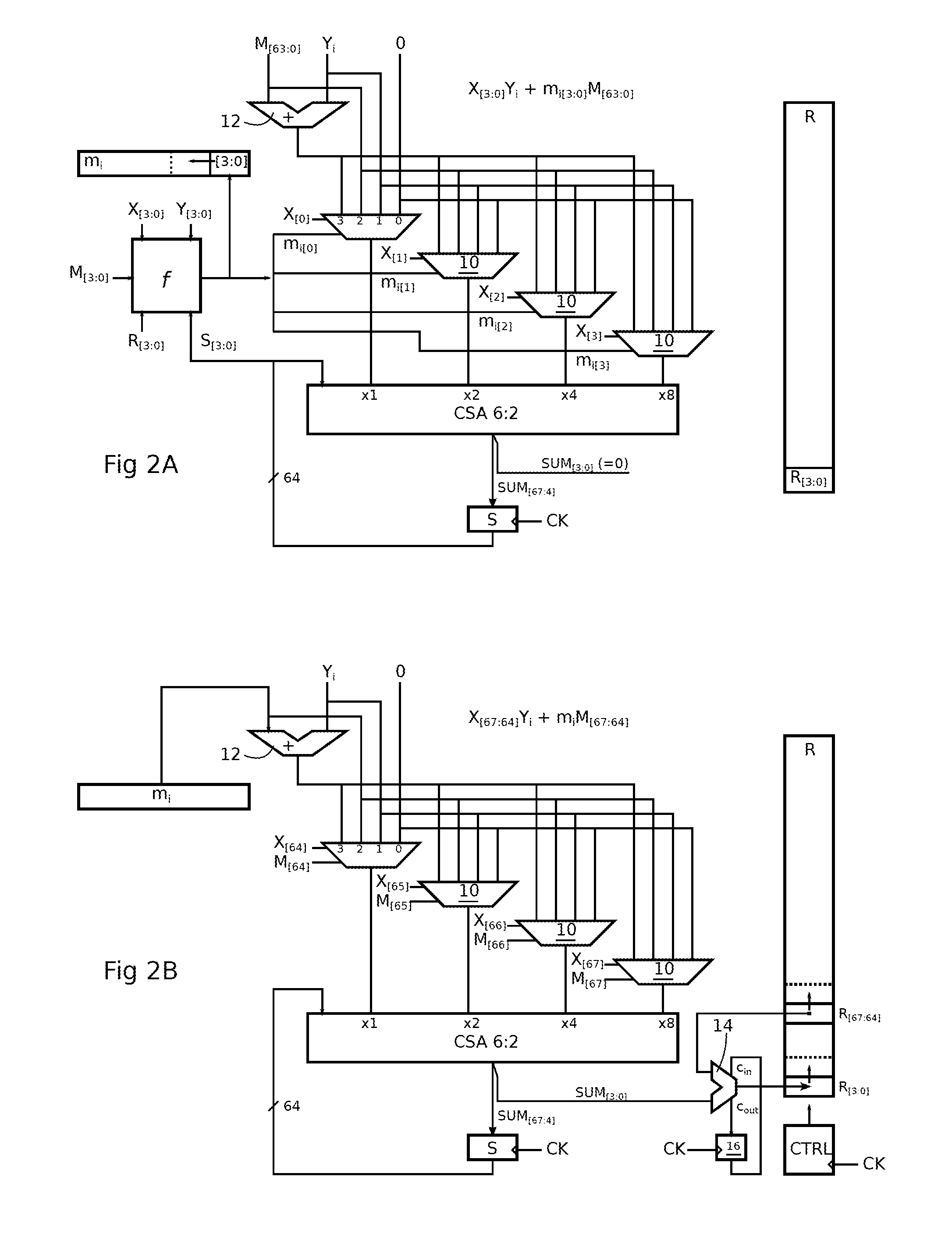
A circuit for calculating a sum of products, each product having a q-bit binary operand and a k-bit binary operand, where k is a multiple of q,includes a q-input carry-save adder (CSA); a multiplexer (10) by input of the adder, having four k-bit channels respectively receiving the value 0, a first (Yi) of the k-bit operands, the second k-bit operand (M[63:0], mi), and the sum of the two k-bit operands, the output of a multiplexer of rank t (where t is between 0 and q−1) being taken into account by the adder with a t-bit left shift; and each multiplexer having first and second path selection inputs, the bits of a first of the q-bit operands being respectively supplied to the first selection inputs, and the bits of the second q-bit operand being respectively supplied to the second selection inputs.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Combined floating point adder and subtractor
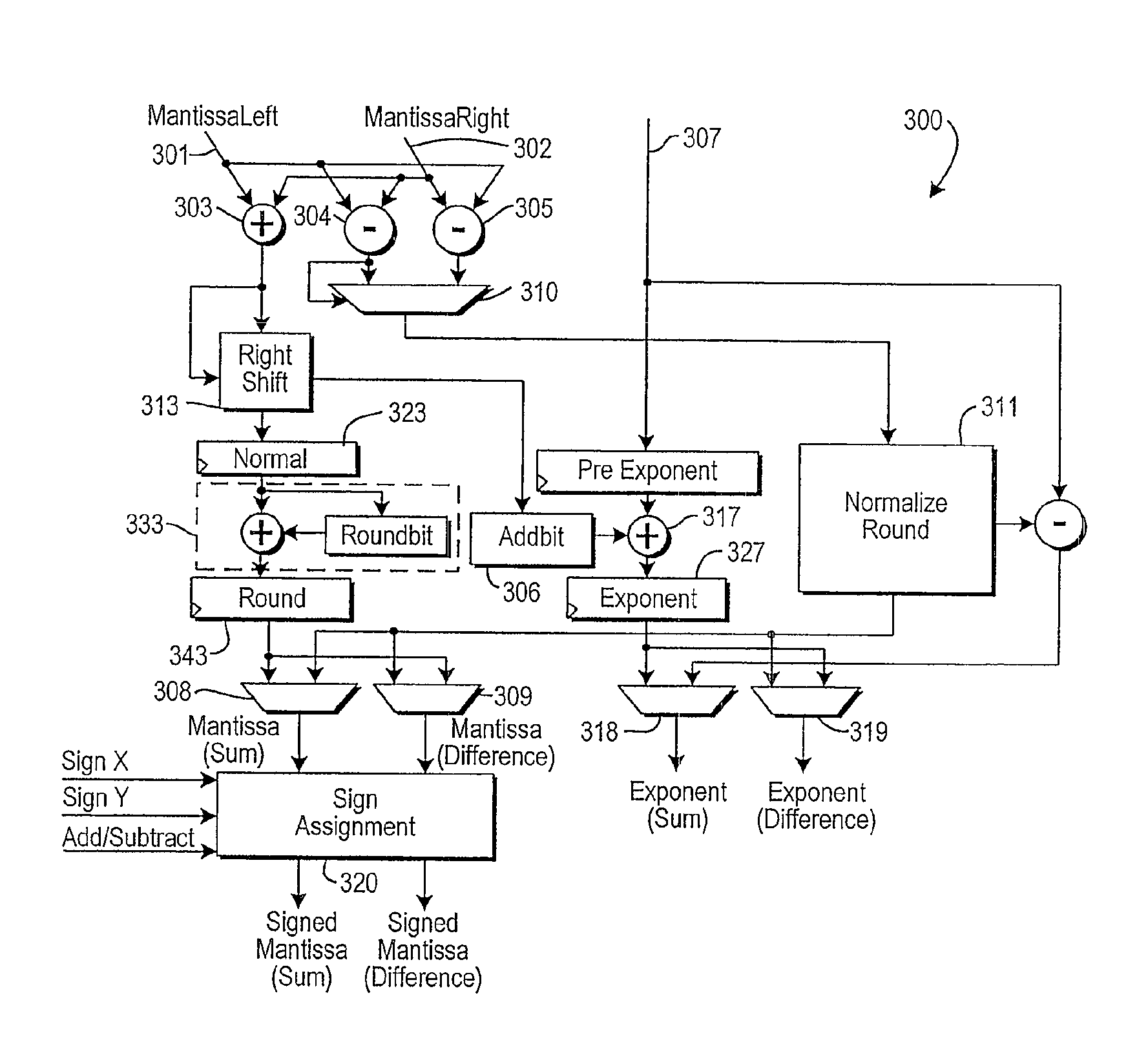
InactiveUS8645449B1Reduced resourceComputations using contact-making devicesFloating pointComputer science
Circuitry (fixed or configured in a programmable device) for performing floating point addition and subtraction uses approximately the same resources as required for either operation separately. The circuitry is based on a recognition that when adding or subtracting two numbers, the two resulting mantissa values will be two out of three possibilities, and will involve either a one-bit shifting operation, or a shifting operation involving a large number of bits. Therefore, one mantissa path—a subtraction path—can be provided with full add / normalize / round circuitry, while a second mantissa path—an addition path—can be provided with a simple one-bit shifter and simplified rounding circuitry. Because the input numbers are signed, the “addition path,” which only adds the mantissas, may provide the mantissa for the subtraction result, depending on the signs of the input numbers. Similarly, the “subtraction path” may provide the mantissa for the addition result.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Spatial decomposition methods using bit manipulation
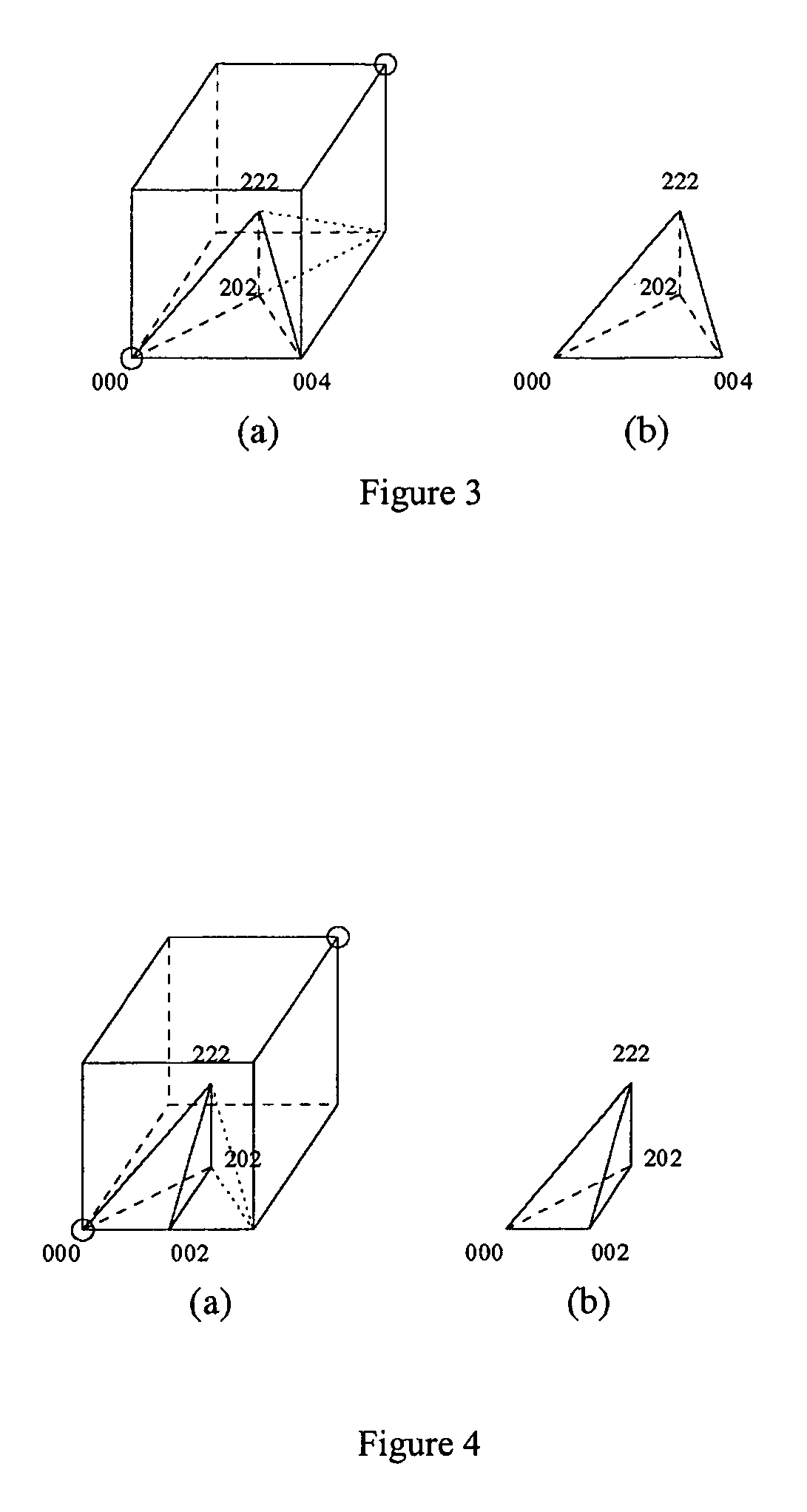
InactiveUS7777740B2Increase speedQuick and easy manipulation3D-image rendering3D modellingDecompositionPseudo-code
Owner:BINARY SIMPLEX
Spatial decomposition methods using bit manipulation
InactiveUS20120038640A1Increase speedQuick and easy manipulation3D modellingDecompositionComputer vision
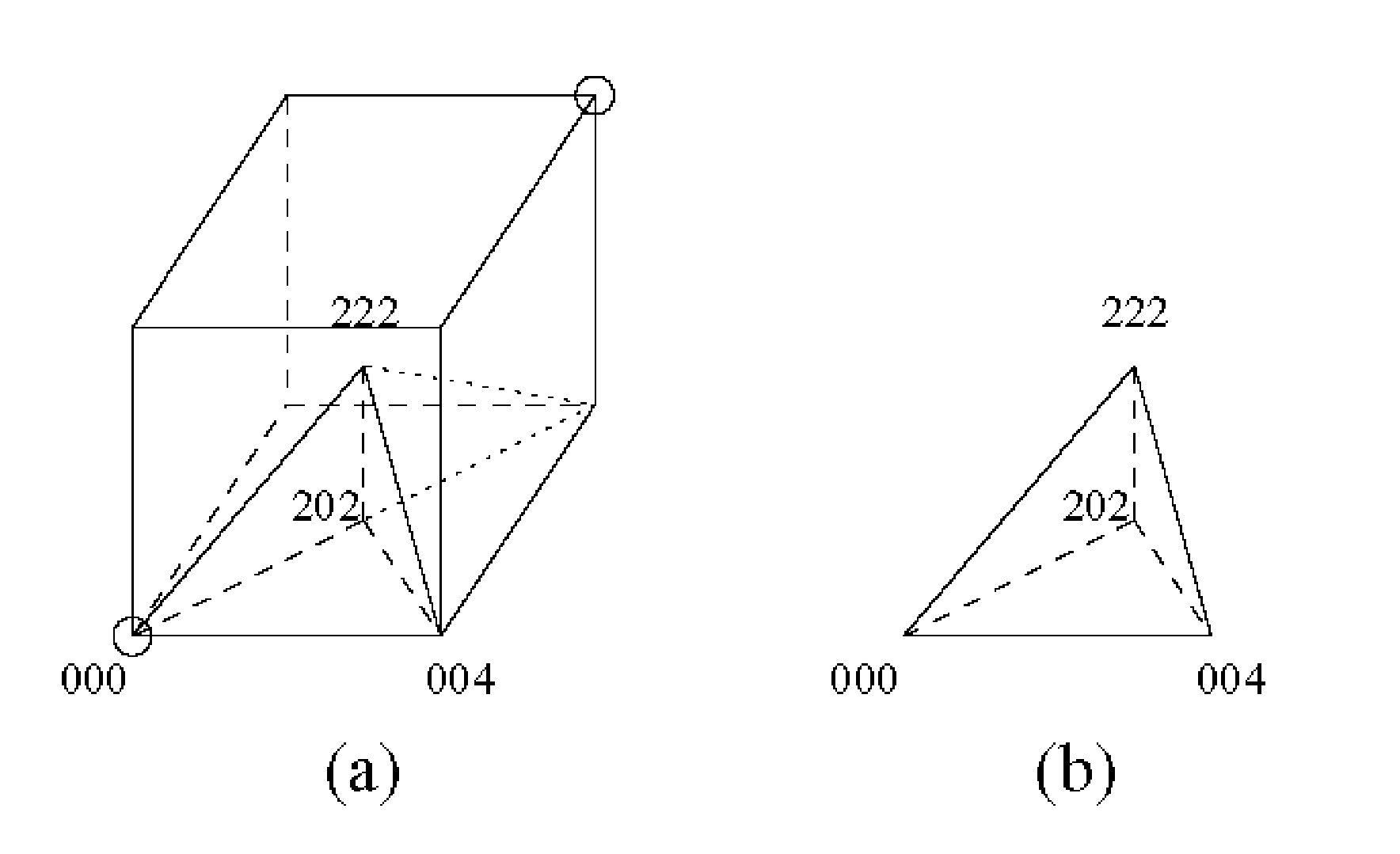
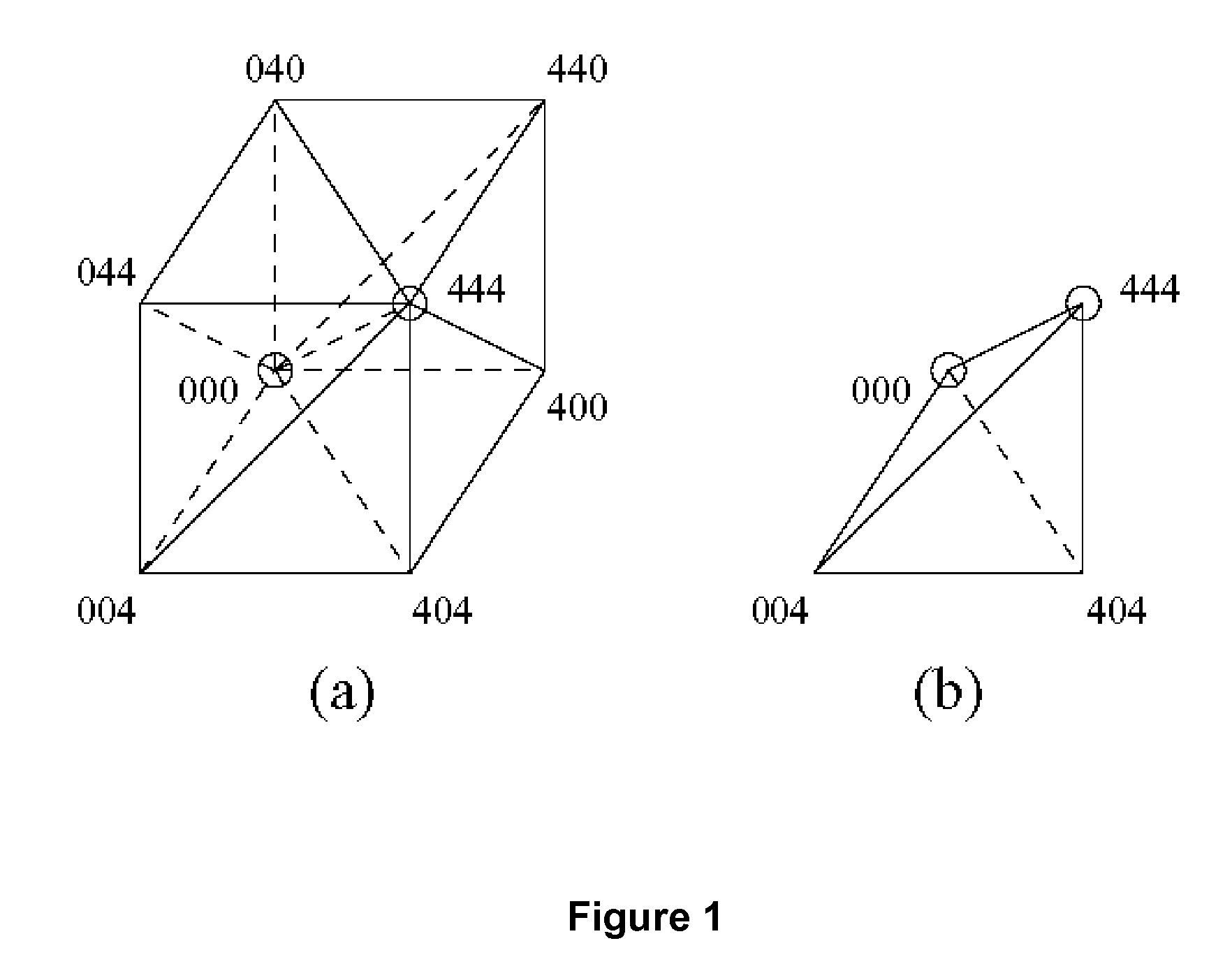
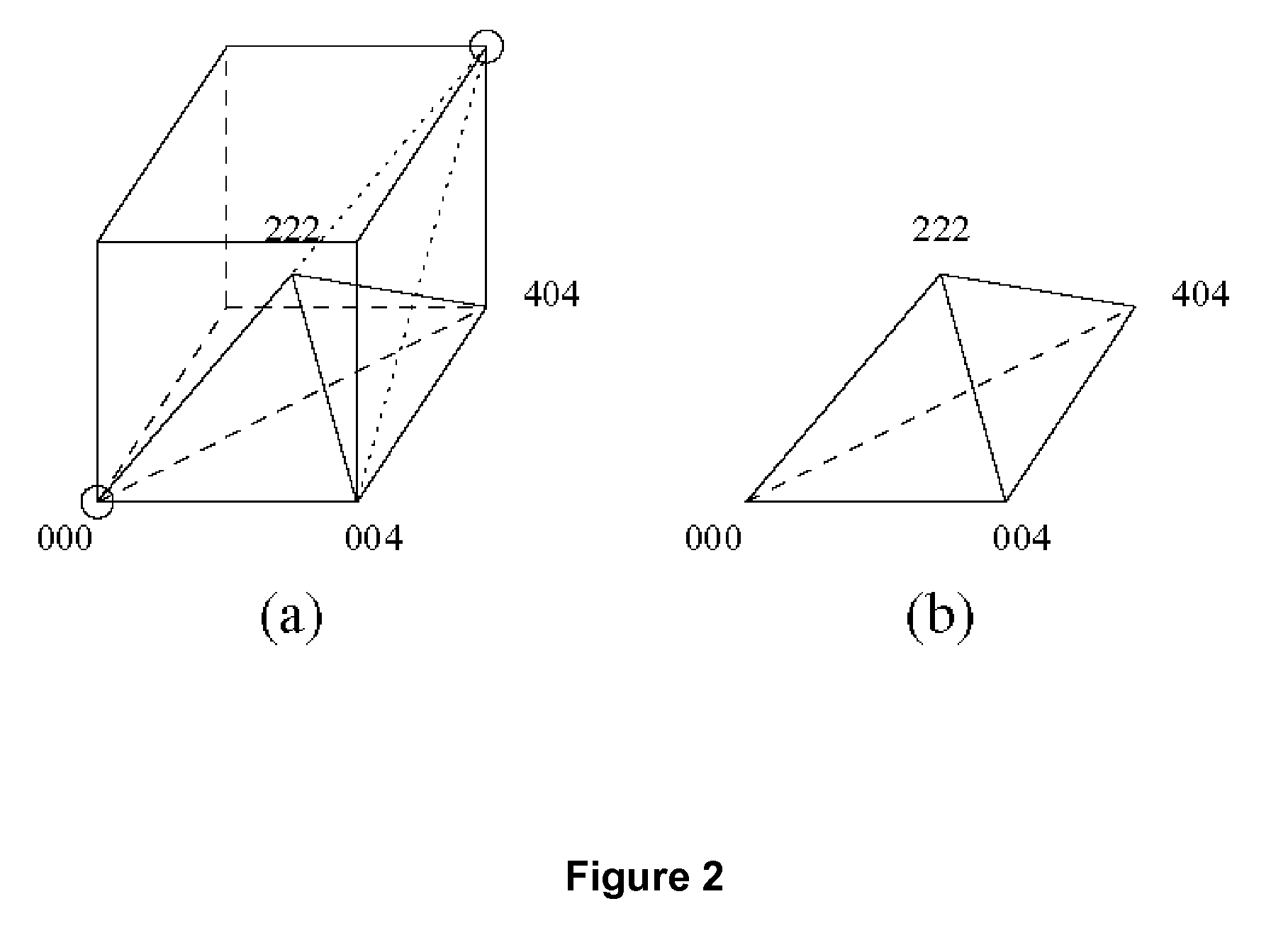
The invention relates to image decomposition strategies and computer-based methods for implementing them. In one method of the invention, the ordering of tetrahedral shapes that define or approximate an image is performed in such a way that neighboring tetrahedral shapes can be identified, located and efficiently used. In one aspect, binary location code array is used to represent an image and the method for identify the neighbor shape employs a bit manipulation step in code or psuedo-code for operating a computer. In this aspect, the invention allows one to move between adjacent tetrahedra, and any data corresponding to the tetrahedra, in constant time.
Owner:BINARY SIMPLEX
Binary code converters and comparators
A thermometer code converter for converting weightless binary tuples of 2 or higher dimensional arrays into a thermometer or aggregate code comprises a series of layers (16, 18) each made up of bit manipulation cells (10) which collectively cause set bits to be shifted towards a required bit position. The bit manipulation cells are made up of logic elements (12, 14) and the entire converter may be asynchronous. Also disclosed is a sum and threshold device which employs a thermometer code converter and a bit selector device.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
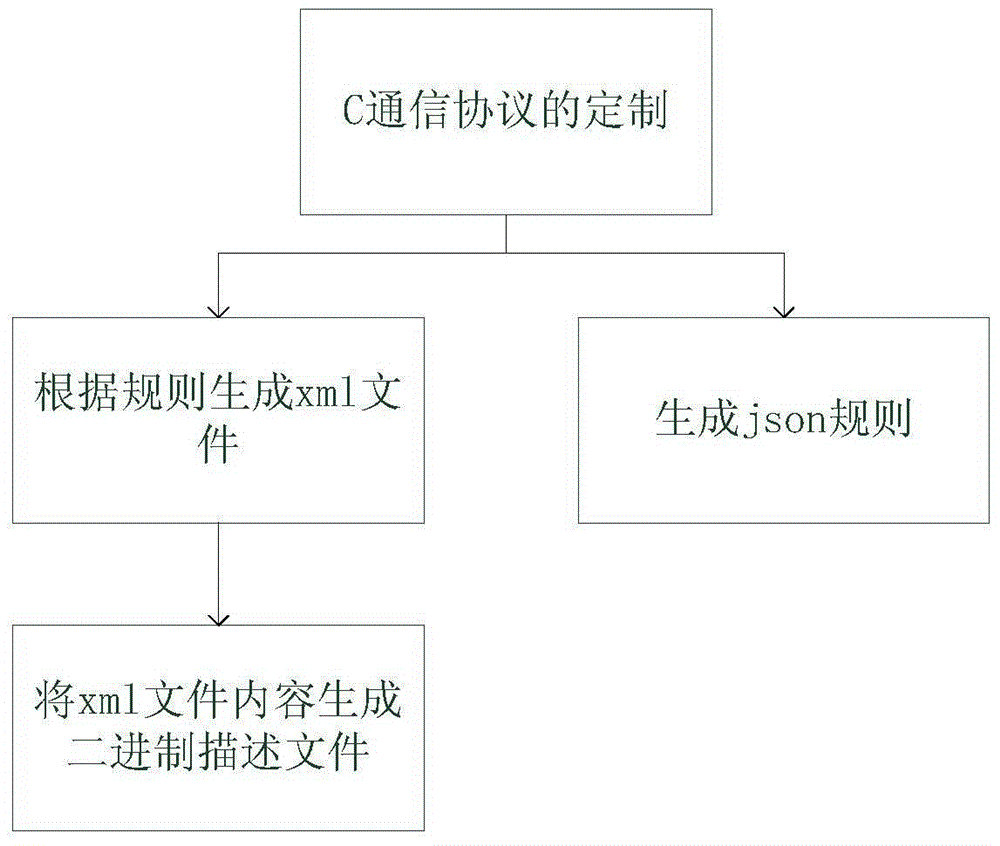
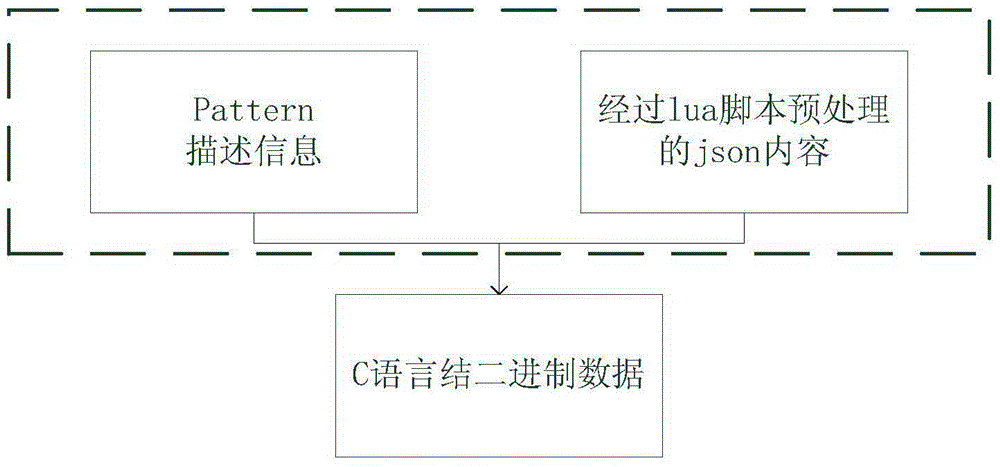
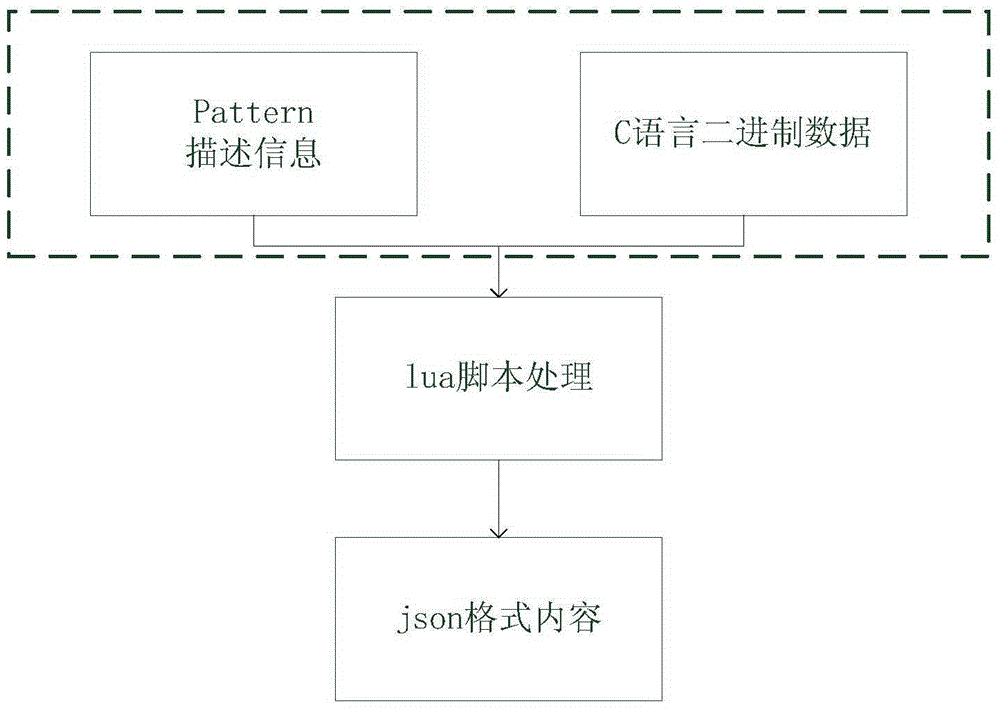
Method for controlling different products by using same rule
The invention relates to a method for controlling different products by using a same rule and aims at solving the deficiency in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: I, firstly generating a pattern file of a conversion rule and analyzing a communication protocol of target hardware which is defined by adopting C language; II, describing structure information of the C language in the communication protocol of the target hardware by using an xml file; III, converting the structure information described by the xml into description information; IV, setting a conversion rule of json according to the step III so as to form a binary description file; V, converting a function rule of the target hardware through an lua script and carrying out conversion supplementation on bit manipulation content in the communication protocol of the target hardware through the lua script at the same time so as to form a character string in a json format; VI, converting the character string in the json format into binary data of the C language through the pattern file; and VII, executing corresponding functions by the target hardware according to the binary data of the C language.
Owner:HANGZHOU BROADLINK ELECTRONICS TECH
Hamming value determination and comparison
The comparators described herein comprise bit manipulation cells of a number of logic cells each built up of AND, OR etc. logic gates interconnected in parallel to make up one or more layers and do not rely on clocks, instead operating asynchronously. This makes the comparators highly robust and fault tolerant, and well suited for use as binary neurons in high integrity systems. They are less susceptible to radio frequency interference induced data corruption than alternative register-based implementations. Planar Hamming comparators capable of comparing two dimensional input arrays are also described.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Image compression method and device based on run-length encoding (RLE)
ActiveCN103124350AAvoid disadvantagesIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImage compressionRun-length encoding
The invention provides an image compression method and device based on run-length encoding (RLE). The image compression method includes that whether pixel values of adjacent pixels in an image to be compressed are identical is sequentially compared and judged, the zone bit in the pixel format is set to be the value adopting RLE and RLE is performed on yes judgment, otherwise the zone bit is set to be the value not adopting RLE and RLE is not performed; during decoding, whether RLE is adopted is judged according to the zone bit in the pixel format of a pixel to be decoded, and RLE is adopted on yes judgment; and the zone bit is the bit with the smallest color display influence caused by G in the red, green and blue (RGB) pixel format. The image compression method and device can solve the problem of the traditional RLE algorithm of data quantity increasing after coding on some conditions, reach a compression ratio larger than that of the RLE algorithm only by losing little pixel accuracy, and are simple and convenient due to the fact that only shifting and bit manipulation are adopted in the whole encoding and decoding processes.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
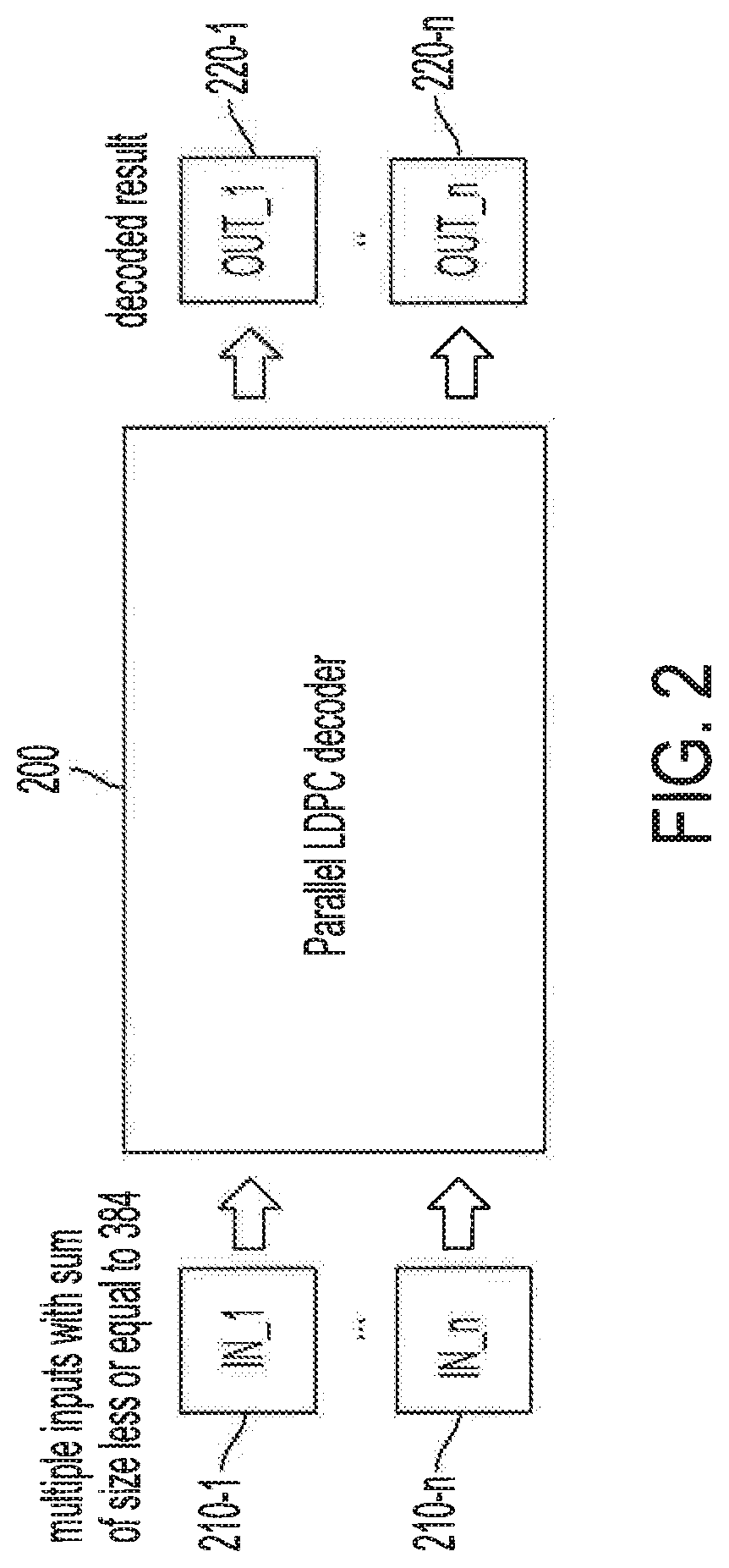
Parallel LDPC decoder
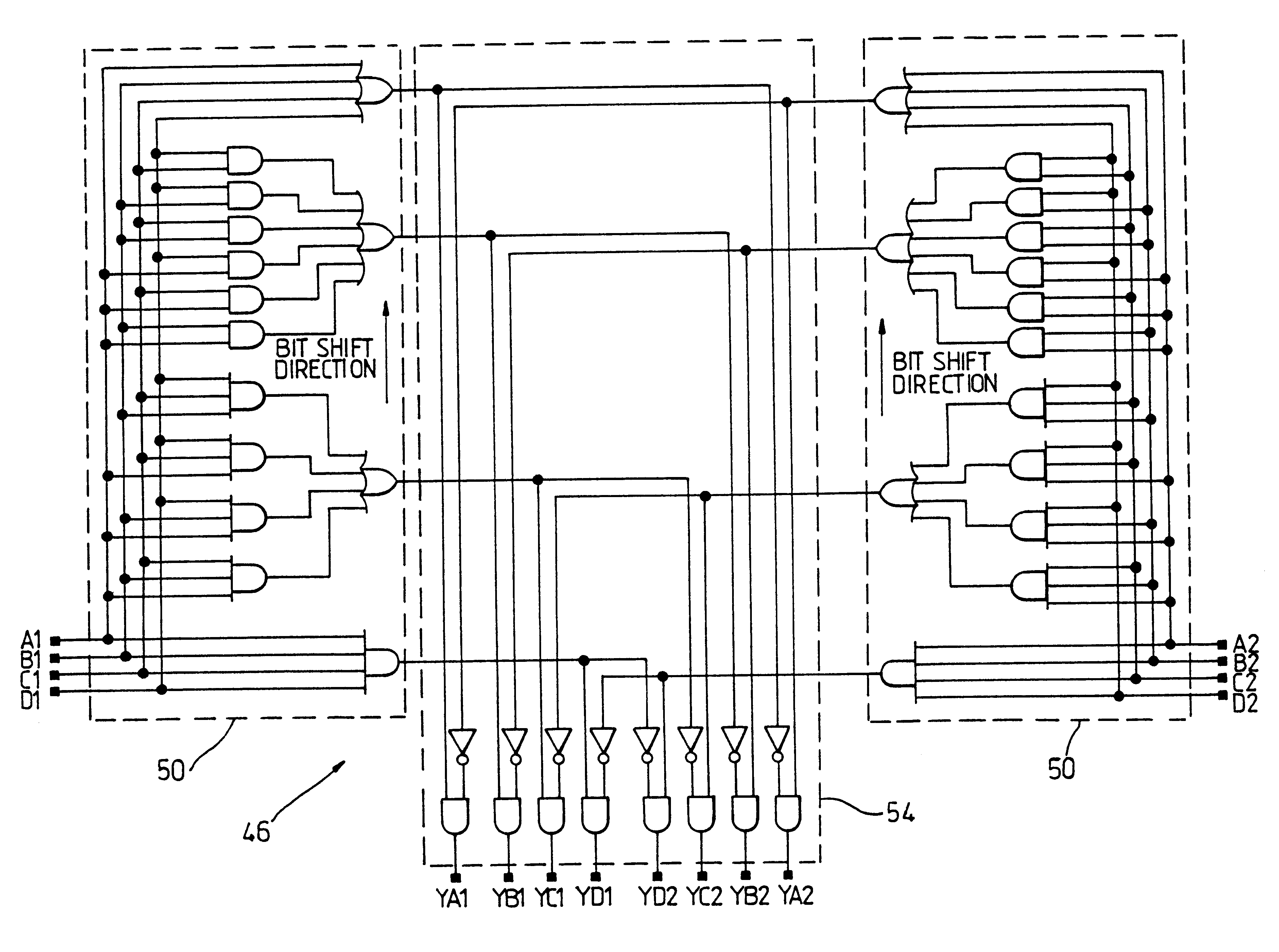
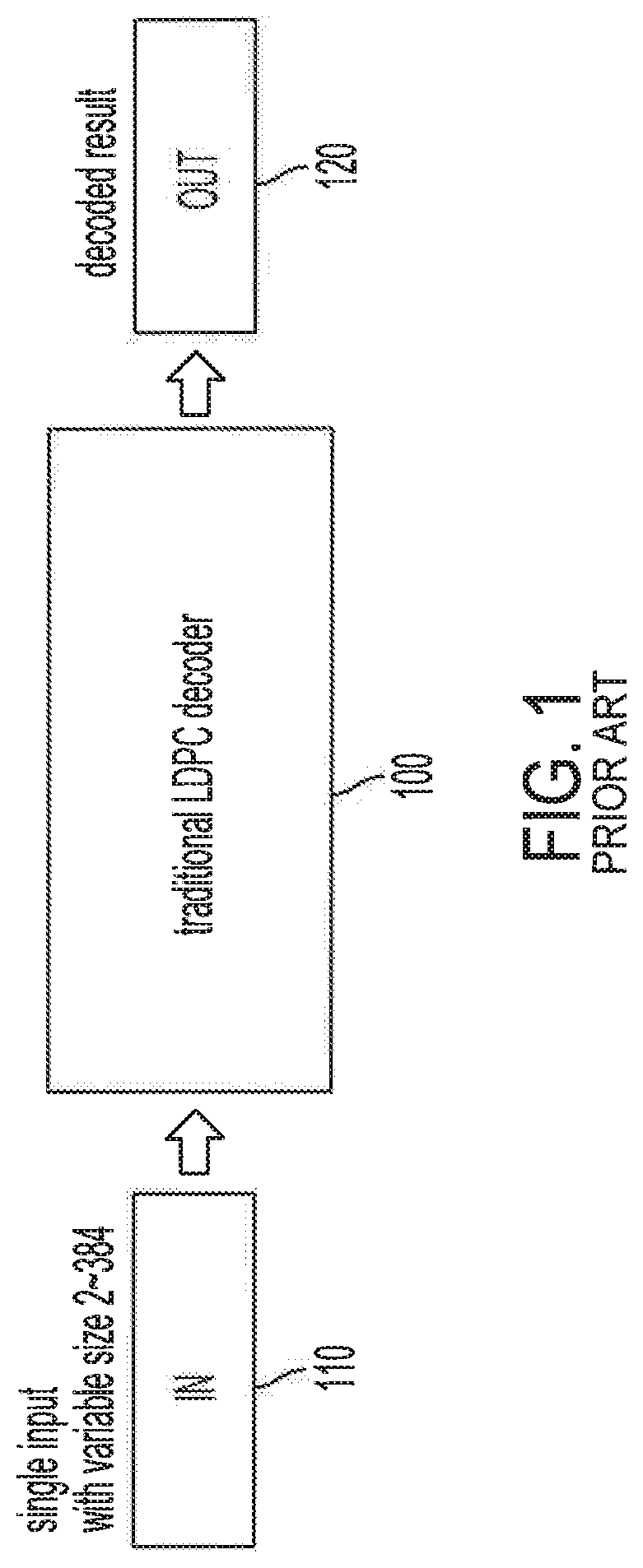
ActiveUS20200252080A1Efficient and flexible designEnhanced operational aspectError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCoding blockComputer architecture
Systems and methods providing low-density parity-check (LDPC) decoder configurations capable of decoding multiple code blocks in parallel are described. Parallel LDPC decoders of embodiments can be reconfigured to simultaneously decode multiple codewords with reconfigurable size. In operation of embodiments of a parallel LDPC decoder, a plurality of active portions of the decoder logic are configured for parallel processing of a plurality of code blocks, wherein each active region processes a respective code block. The decoder logic active portions of embodiments are provided using a reconfigurable segmented scalable cyclic shifter supporting multiple instruction, multiple data (MIMD), wherein multiple individual different data shifts are implemented with respect to a plurality of code blocks in an instance of data shifting operation. Multiple data shift commands may be utilized such that the plurality of code blocks have an individual shifting command to thereby implement different data shifting with respect to each code block.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
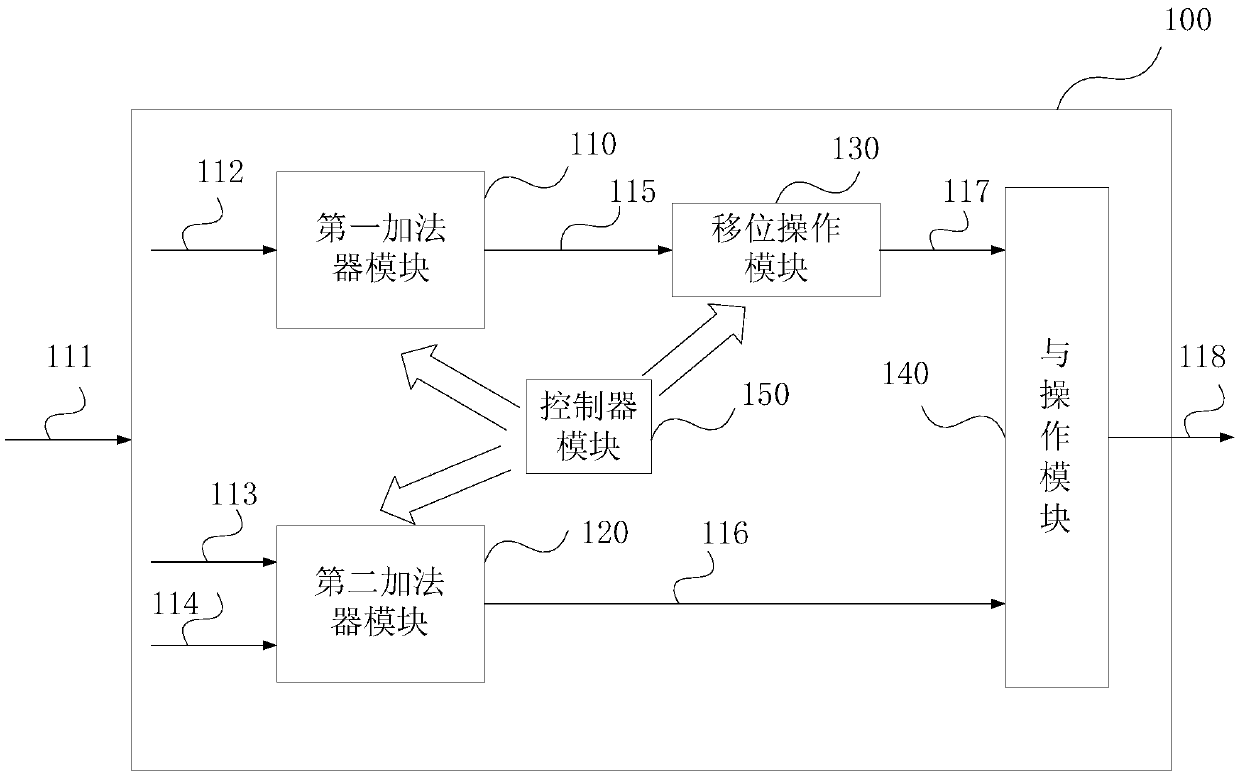
Adder device, data accumulation method, and data processing device
ActiveCN105512724ADoes not affect execution speedHigh precisionComputation using non-contact making devicesPhysical realisationControl signalControl cell
The invention discloses an adder device, a data accumulation method, and a data processing device. The adder device comprises a first adder module which is provided with an addition tree unit composed of a multi-stage adder array, and also provided with a first control unit, wherein the addition tree unit accumulates the data in a mode of step-by-step accumulation based on a control signal of the first control unit; a second adder module which comprises two input addition and subtraction operation units and a second control unit, and is used for the addition or subtraction operation of the input data; a shift operation module which is used for the left shift operation of the output data of the first adder module; an AND operation module which is used for the AND operation of the output data of the shift operation module and the output data of the second adder module; and a controller module which is used for controlling the data input of the first and second adder modules, controlling the shift operation of the shift operation module, and controlling the transmission of control signals of the first and second control units. Therefore, the adder device achieves the quick accumulation of data.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spatial decomposition methods using bit manipulation
ActiveUS20040201584A1Increase speedEnhance analytical option3D-image rendering3D modellingDecompositionPseudo-code
The invention relates to image decomposition strategies and computer-based methods for implementing them. In one method of the invention, the ordering of tetrahedral shapes that define or approximate an image is performed in such a way that neighboring tetrahedral shapes can be identified, located and efficiently used. In one aspect, a binary location code array is used to represent an image and the method for identifying the neighbor shape employs a bit manipulation step in code or pseudo-code for operating a computer. In this aspect, the invention allows one to move between adjacent tetrahedra, and any data corresponding to the tetrahedra, in constant time.
Owner:BINARY SIMPLEX
Multiple-Symbol Polarization Switching for Differential-Detection Modulation Formats
InactiveUS20120321303A1Enabling detectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsOriginal dataLaser source
An inventive method for multi-symbol polarization switching for differential detection optical systems includes modulating a laser source by a DQPSK modulator, driving the DQPSK modulator with a data block configured for generating multi-symbol polarization-switched DQPSK differential-encoded signals, and polarizing the multi-symbol polarization-switched DQPSK signals with a polarizing modulator whose modulation speed is based on how often polarization states vary, wherein the data block provides a bits manipulation to provide the multi-symbol polarization switching thereby enabling differential detection for recovering correct original data by a receiver.
Owner:NEC CORP
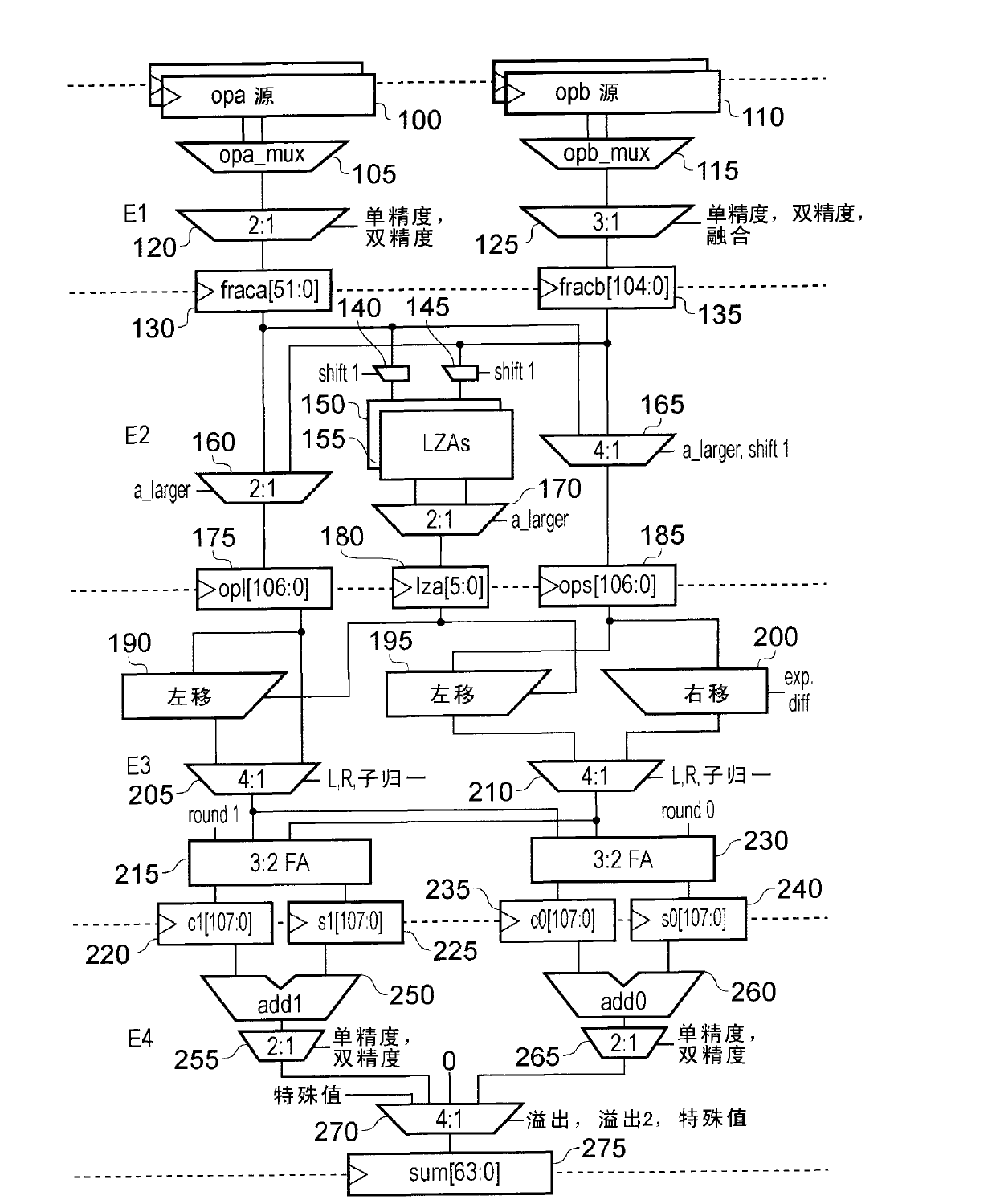
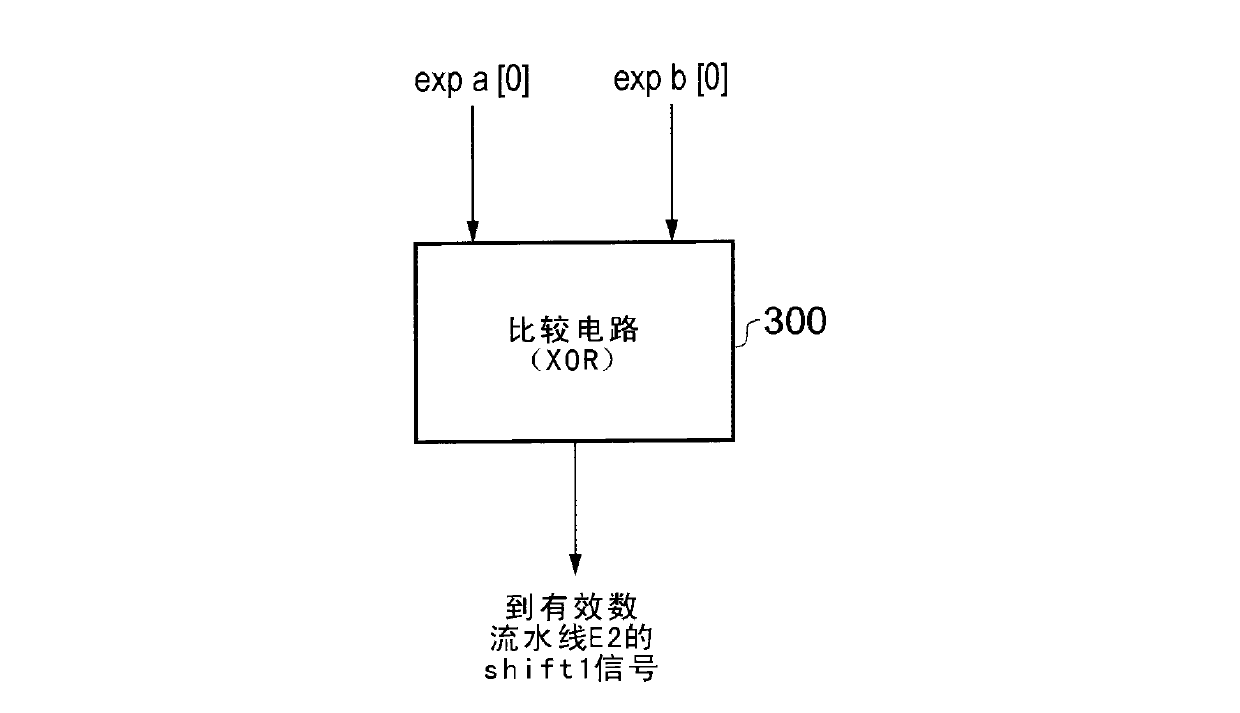
Leading zero prediction in floating point addition
An apparatus and method are provided for performing an addition operation on operands A and B in order to produce a result R, the operands A and B and the result R being floating point values each having a significand and an exponent. The apparatus comprises prediction circuitry for generating a shift indication based on a prediction of the number of leading zeros that would be present in an output produced by subjecting the operands A and B to an unlike signed addition. Further, result pre-normalization circuitry performs a shift operation on the significands of both operand A and operand B prior to addition of the significands, this serving to discard a number of most significant bits of the significands of both operands as determined by the shift indication in order to produce modified significands for operands A and B. Operand analysis circuitry detects, with reference to the exponents of operands A and B, the presence of a leading bit cancellation condition, and addition circuitry is configured, in the presence of the leading bit cancellation condition, to perform an addition of the modified significands for operands A and B, in order to produce the significand of the result R. Such an approach provides a particularly simple and efficient apparatus for performing addition operations.
Owner:ARM LTD +1
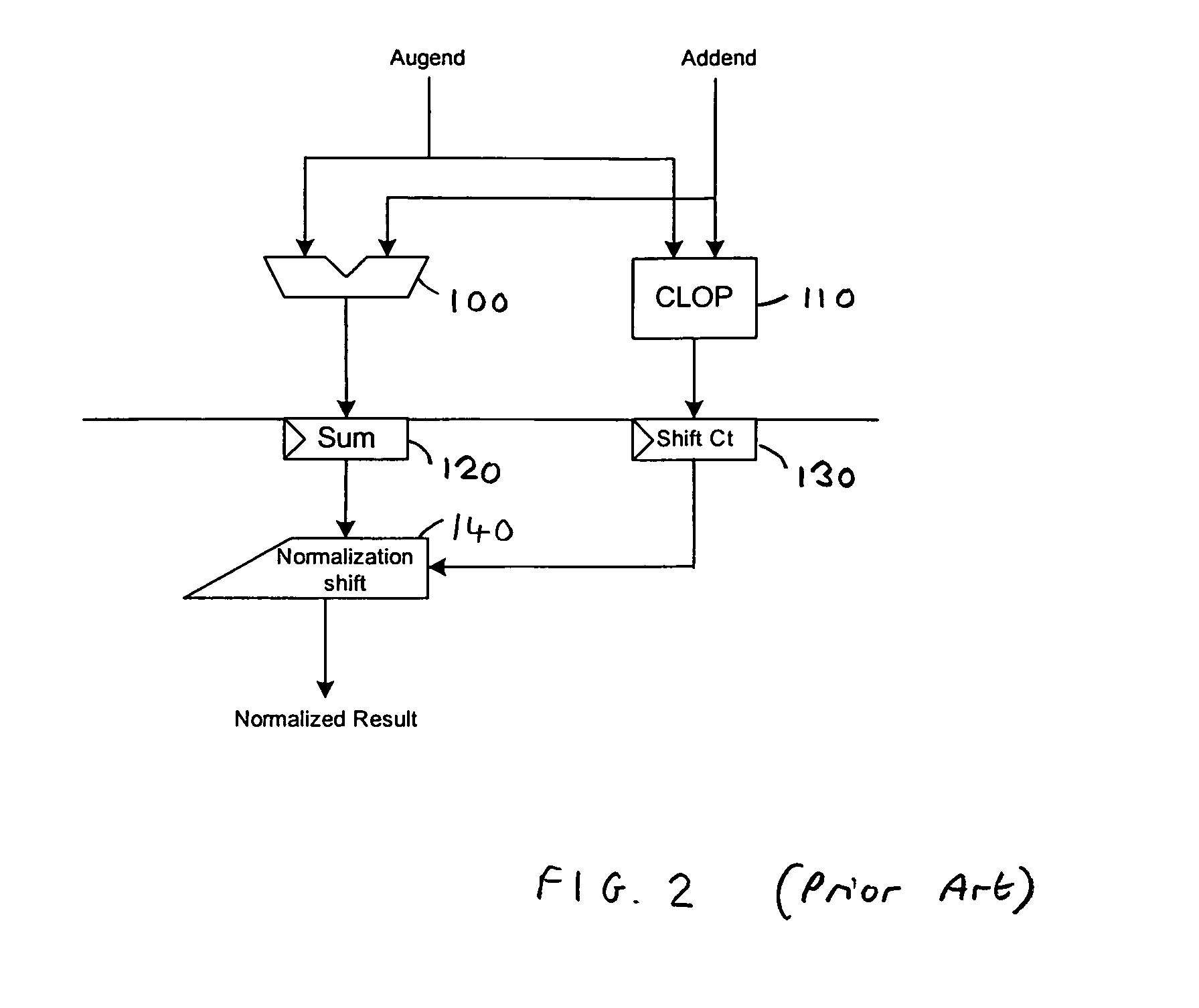
Data processing apparatus and method for normalizing a data value
ActiveUS20070050434A1Avoid complex processExtension of timeComputations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsAlgorithmLeast significant bit
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for normalizing a data value to produce a result value. The data processing apparatus includes prediction logic for generating a shift indication based on a prediction of the number of bit positions by which the data value needs to be shifted in order to normalize the data value. Further, normalizer logic is used to apply a shift operation to the data value based on the shift indication. In addition, correction logic is operable in parallel with the normalizer logic to determine from the data value and a least significant bit of the shift indication whether the shift indication has correctly predicted the number of bit positions by which the data value needs to be shifted in order to normalize the data value, or whether instead the prediction is incorrect, and to generate an output signal dependent on that determination. Shift logic is then used, if the output signal indicates that the prediction is incorrect, to apply a correction shift such that the result value is the normalized data value.
Owner:ARM LTD
Colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code generating method
ActiveCN105354717AThe generation method is simpleImprove securityCommerceChaotic systemsTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code generating method. The colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code generating method comprises the following steps: converting a commodity identification code for representing the unique identity information of a certain commodity into a binary data; obtaining an initial value and parameters of a chaotic system based on the commodity identity information and an external secret key through calculation, and performing iteration on a chaotic mapping to generate two groups of chaotic signal binary sequences; performing bit manipulation taking 2bits as a unit on the commodity identification code by the chaotic binary signals to generate an anti-counterfeiting number overlapped with a colorful background, and further combining the anti-counterfeiting number into the colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code. The colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code generating method provided by the invention is simple, feasible, high in safety, and difficult to be cracked; and in addition, the generated colorful commodity anti-counterfeiting code is has the uniqueness and unforgeability.
Owner:礼何科技(上海)有限公司
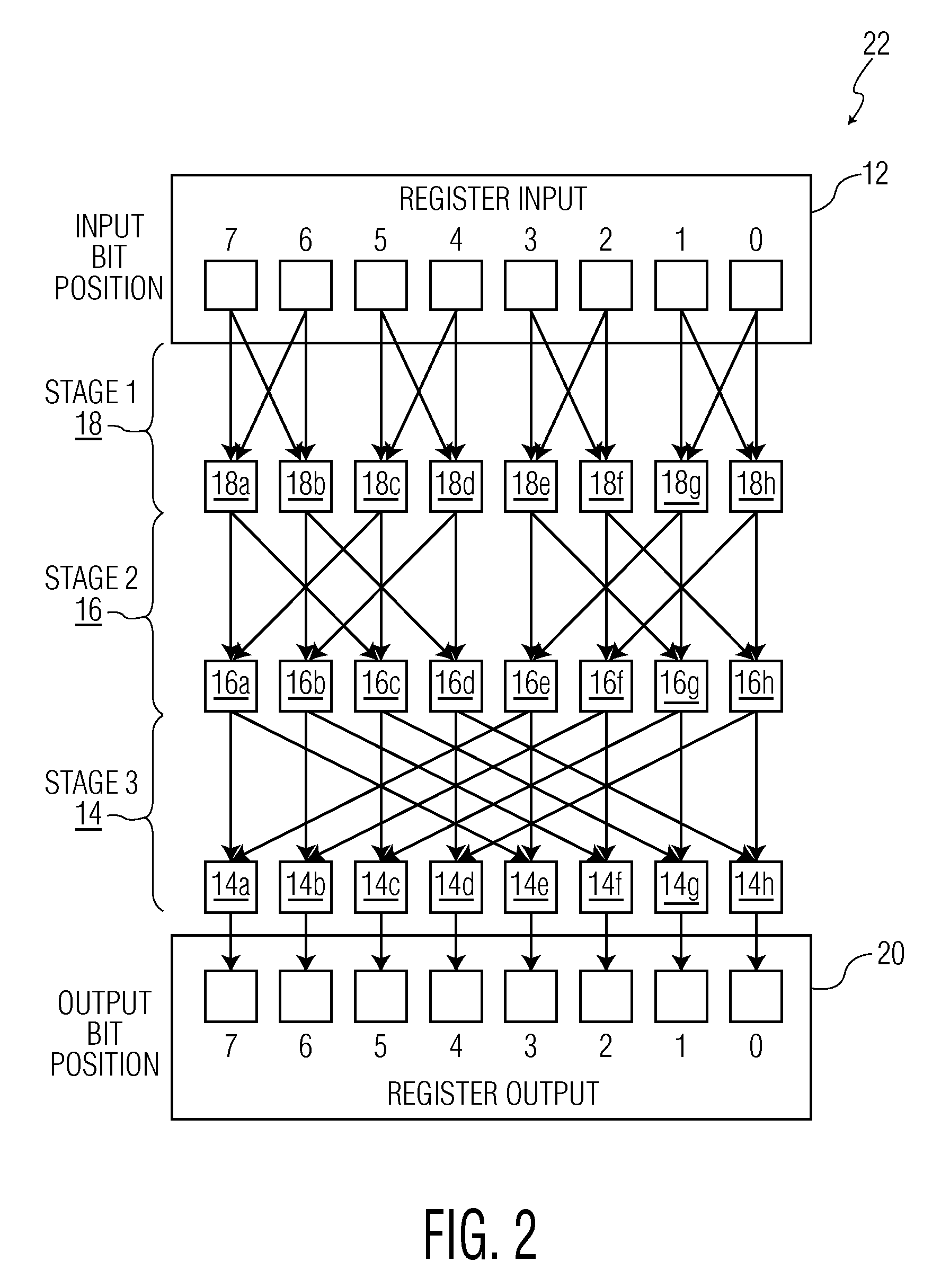
Microprocessor shifter circuits utilizing butterfly and inverse butterfly routing circuits, and control circuits therefor
ActiveUS8285766B2Reduce the amount requiredSave spaceDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsGroup operationControl circuit
Microprocessor shifter circuits utilizing butterfly and inverse butterfly circuits, and control circuits therefor, are provided. The same shifter circuits can also perform complex bit manipulations at high speeds, including butterfly and inverse butterfly operations, parallel extract and deposit operations, group operations, mix operations, permutation operations, as well as instructions executed by existing microprocessors, including shift right, shift left, rotate, extract, deposit and multimedia mix operations. The shifter circuits can be provided in various combinations to provide microprocessor functional units which perform a plurality of bit manipulation operations.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
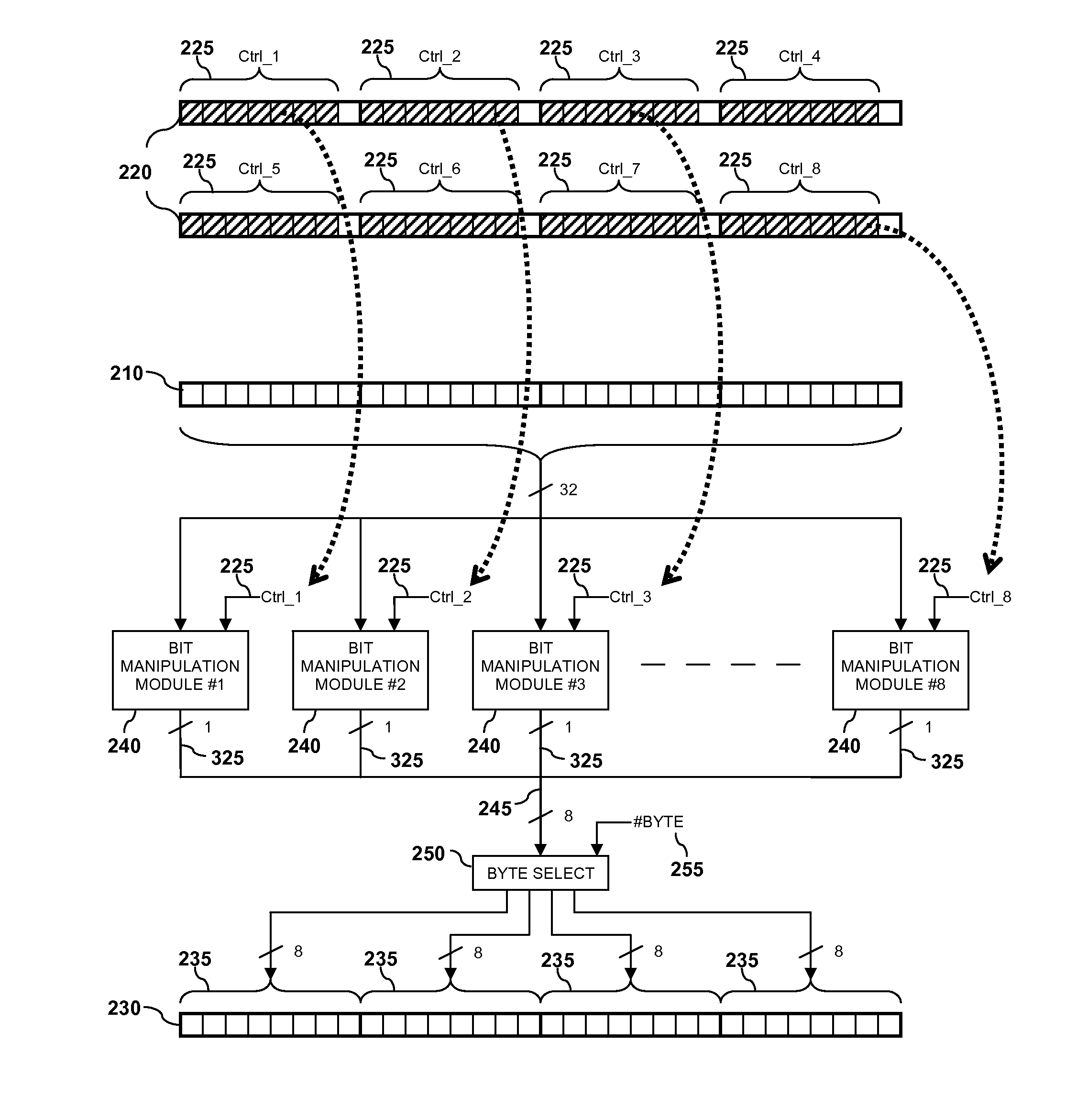
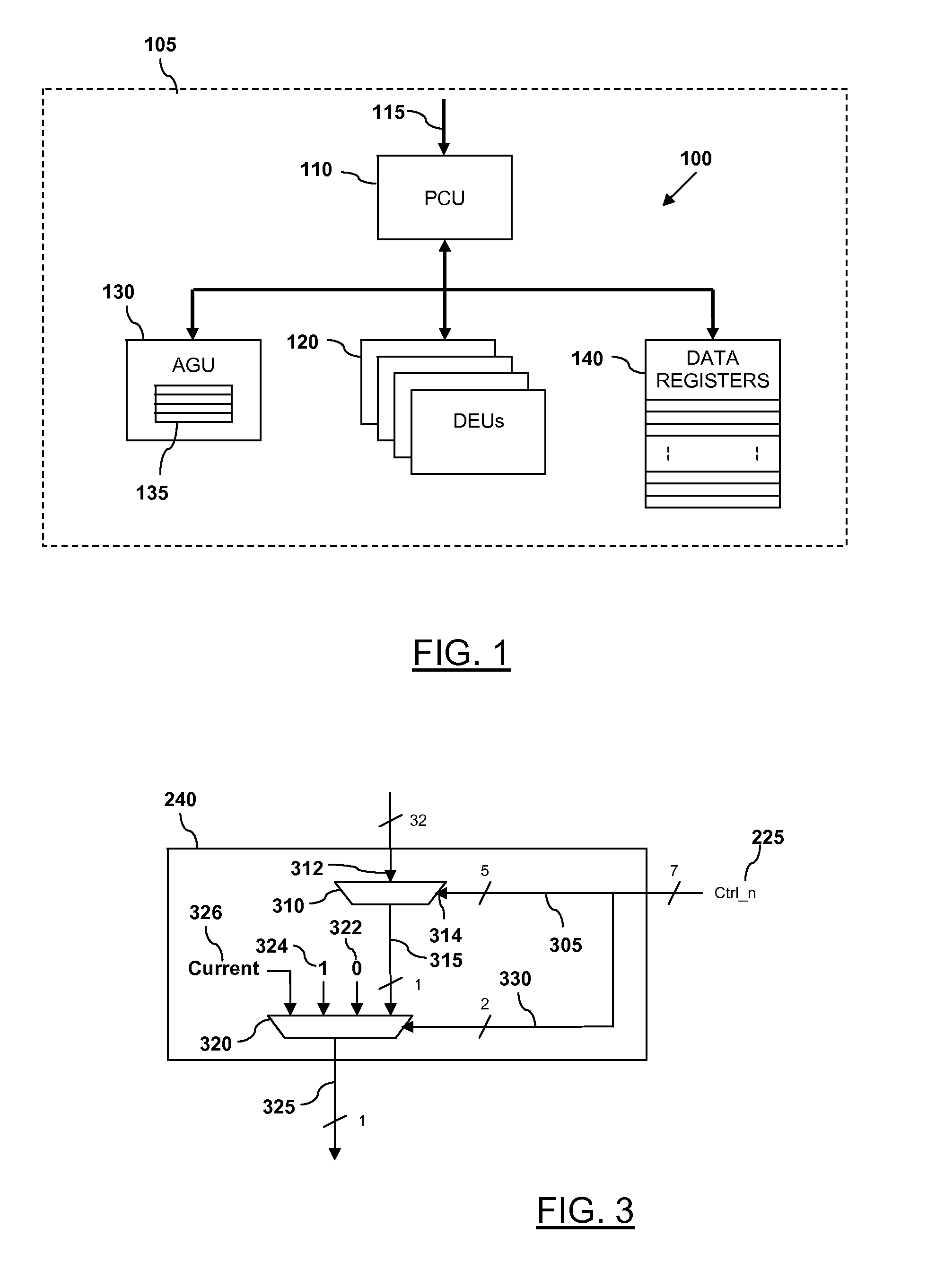
Integrated circuit device and methods of performing bit manipulation therefor
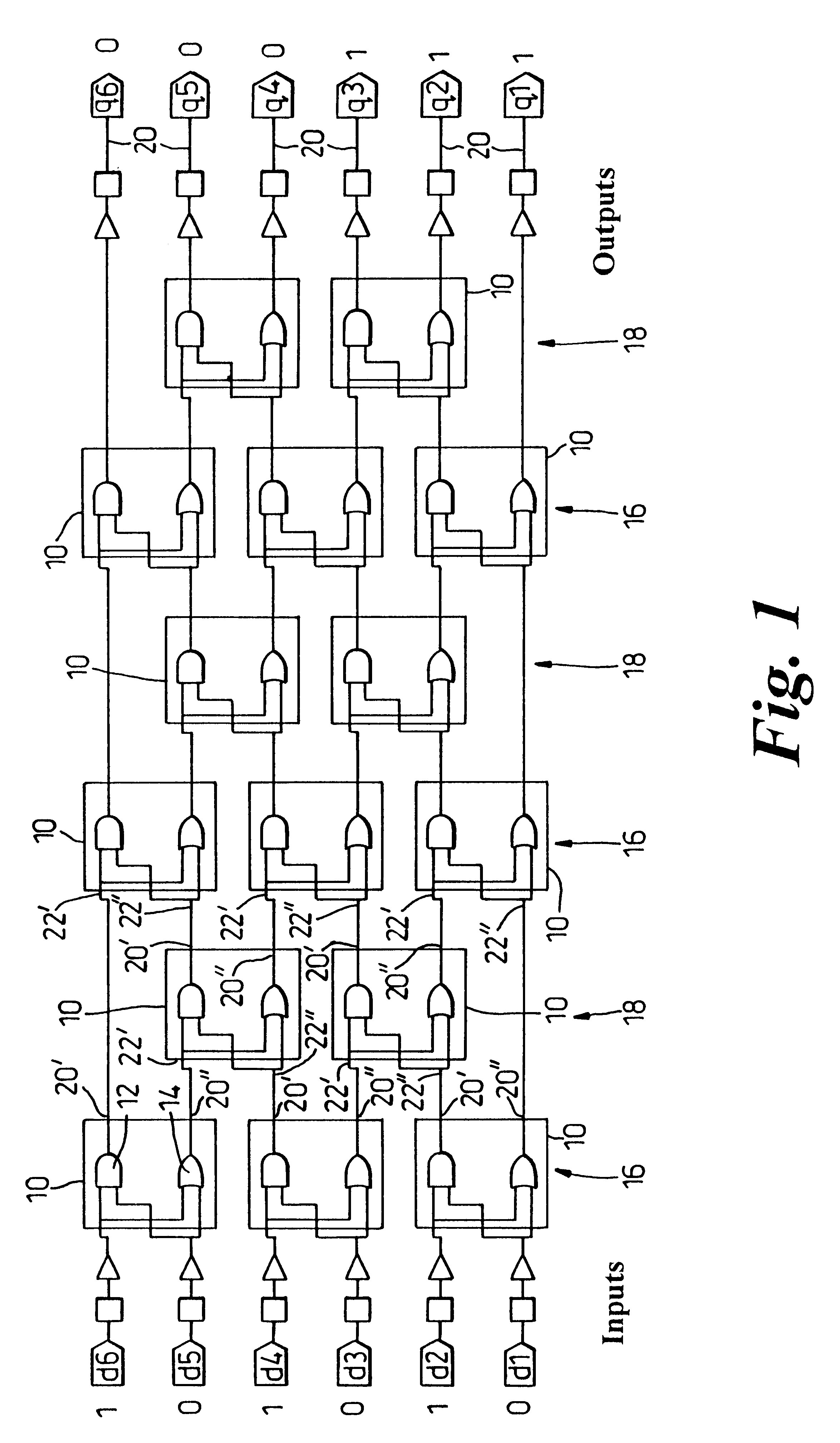
ActiveUS20140013088A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsComputer moduleComputer science
An integrated circuit device comprising at least one instruction processing module arranged to receive a bit-manipulation instruction, and in response to receiving the bit-manipulation instruction to select at least one bit from at least one source data register in accordance with a value of at least one control bit, select from candidate values a manipulation value for the at least one selected bit in accordance with a value of at least one further control bit, and store the selected manipulation value for the at least one selected bit in at least one output data register.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com