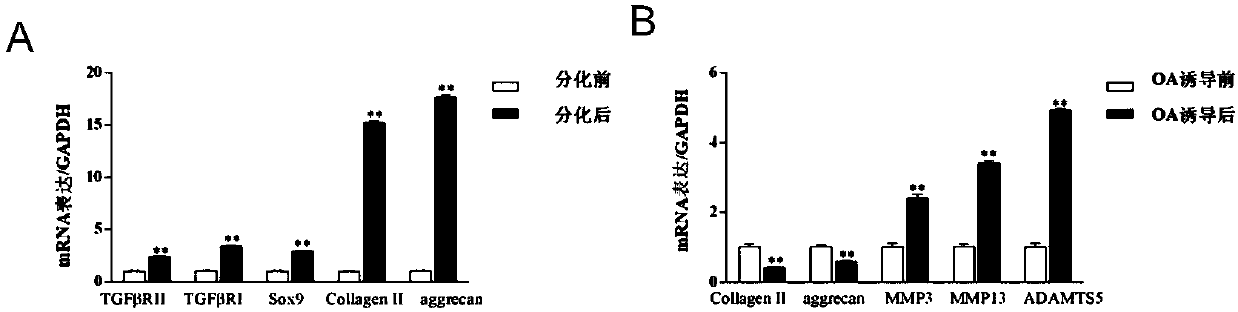
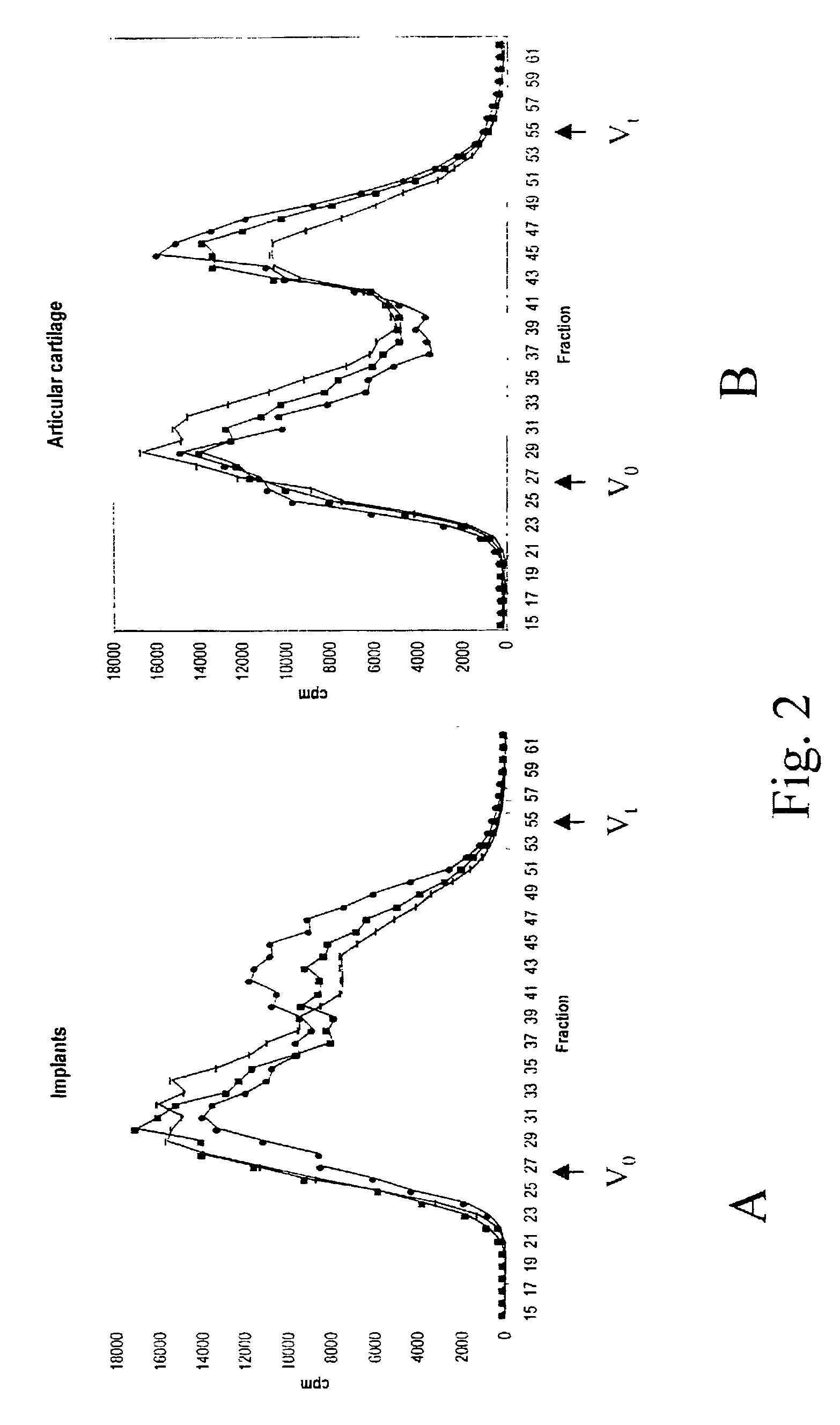
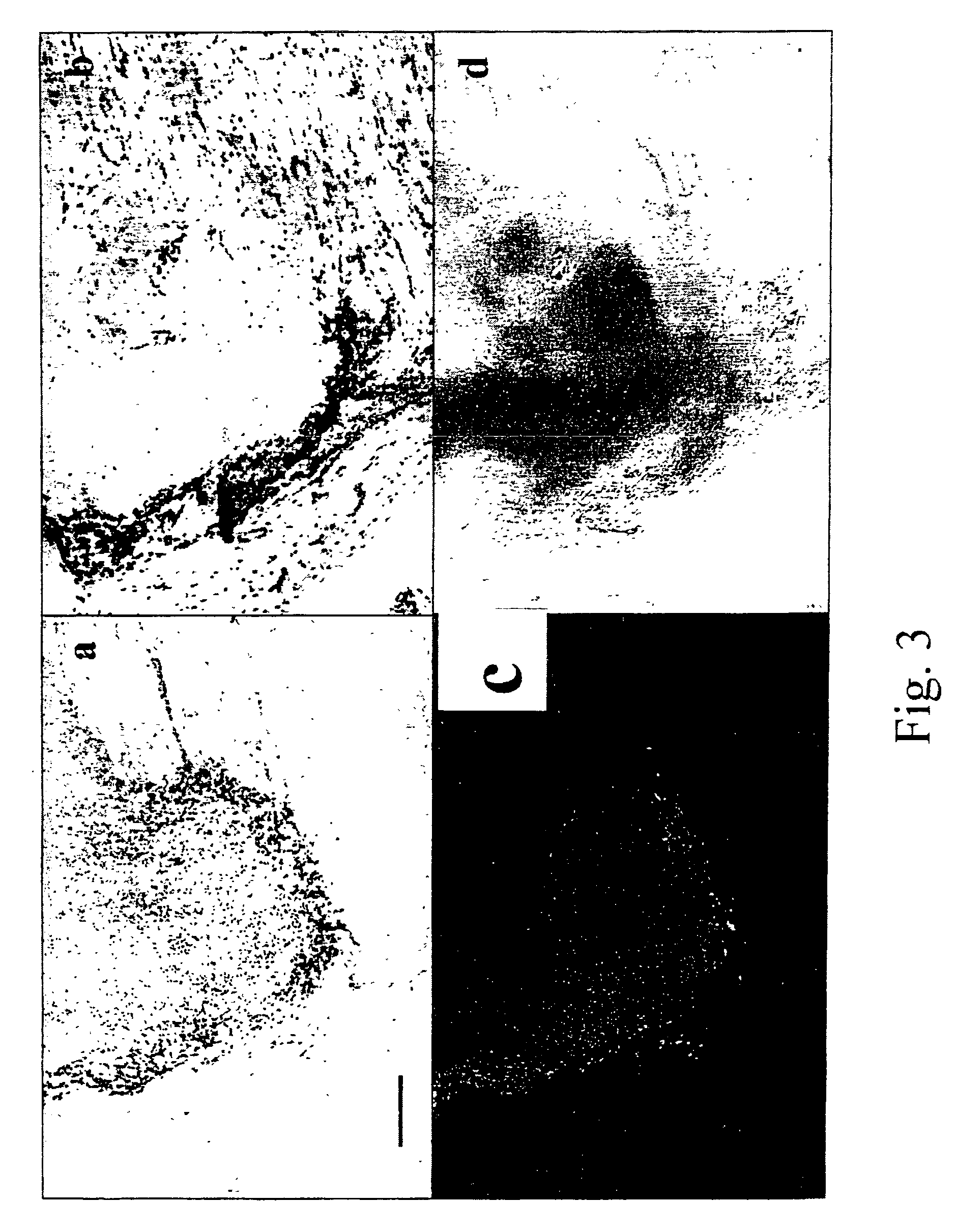
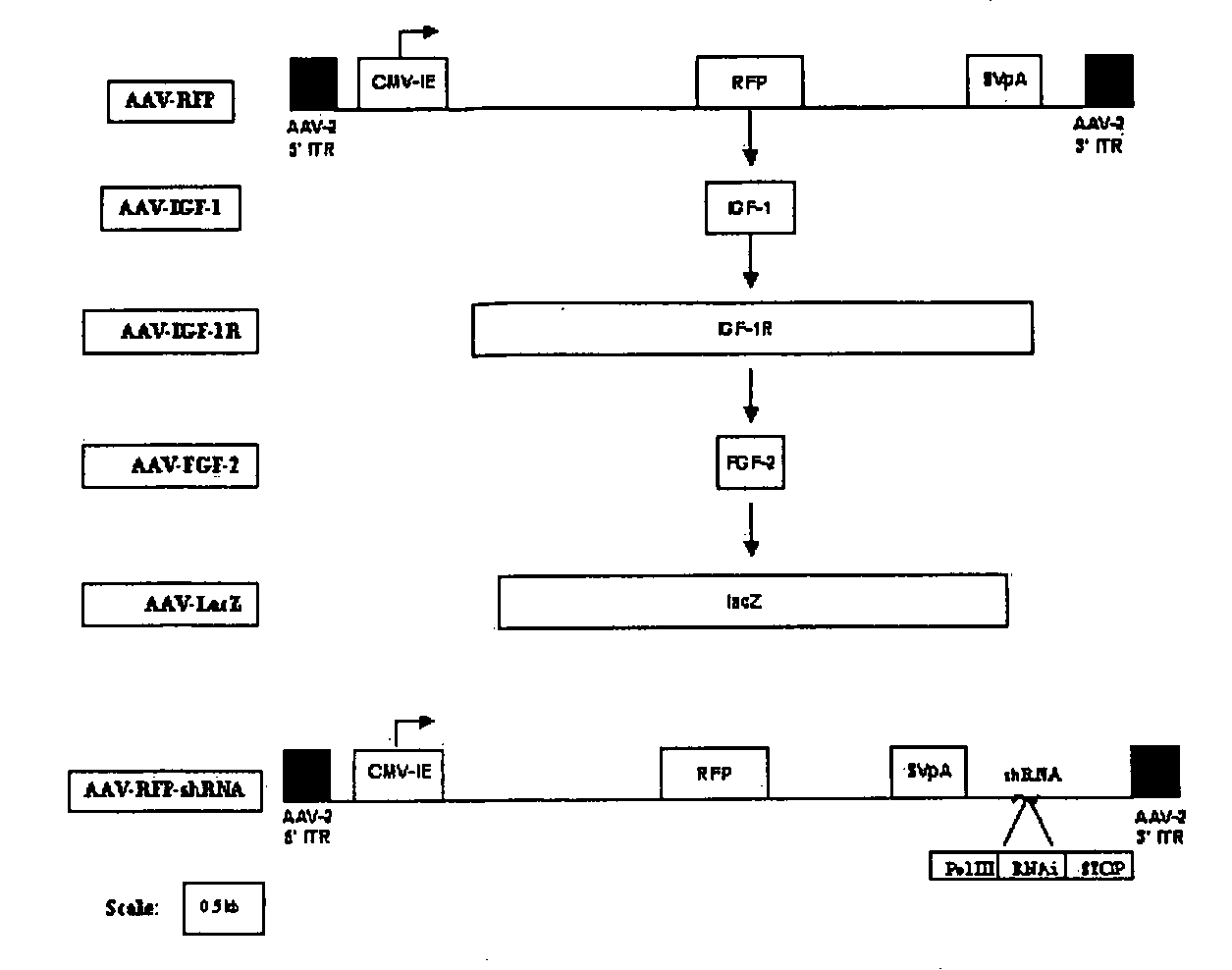
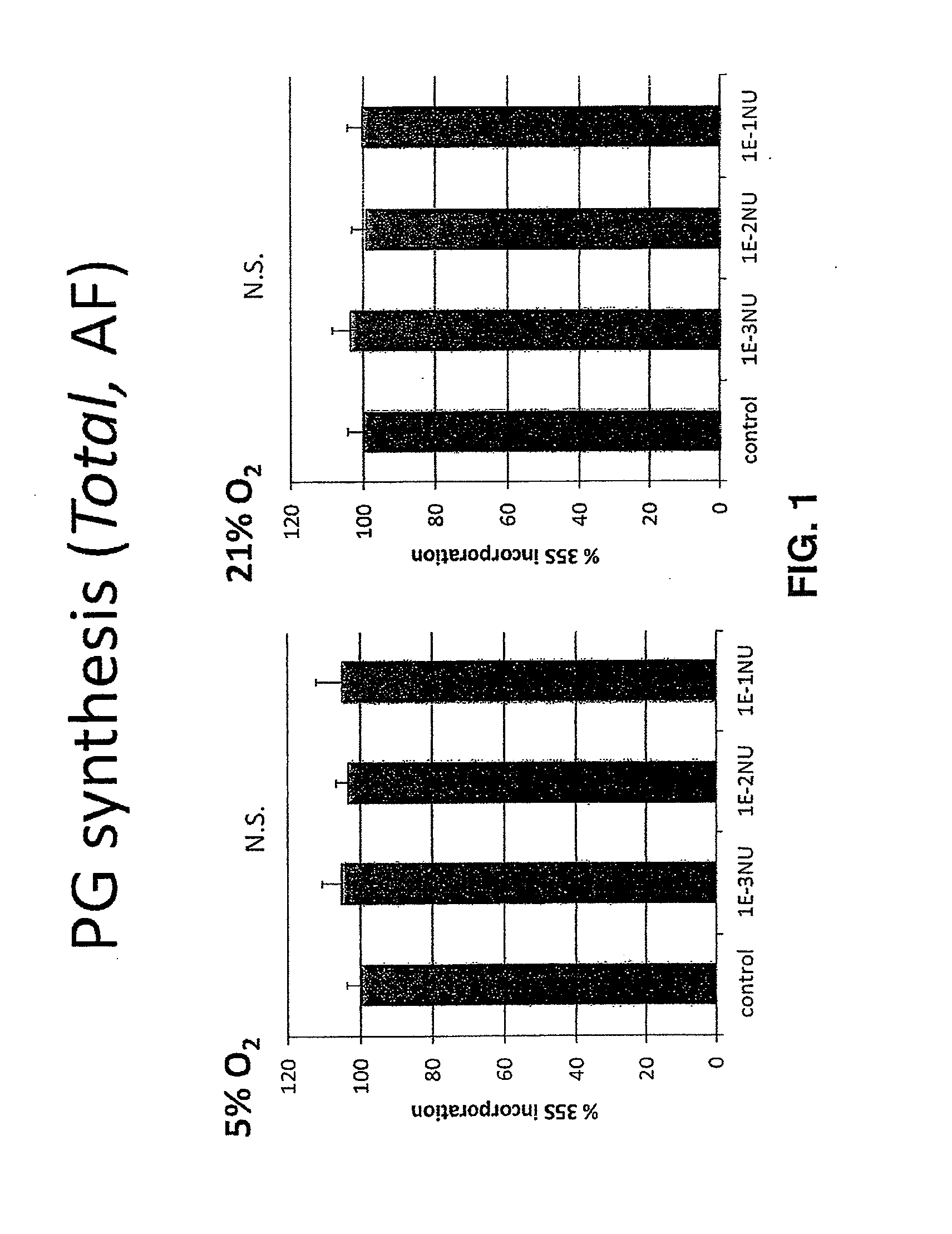
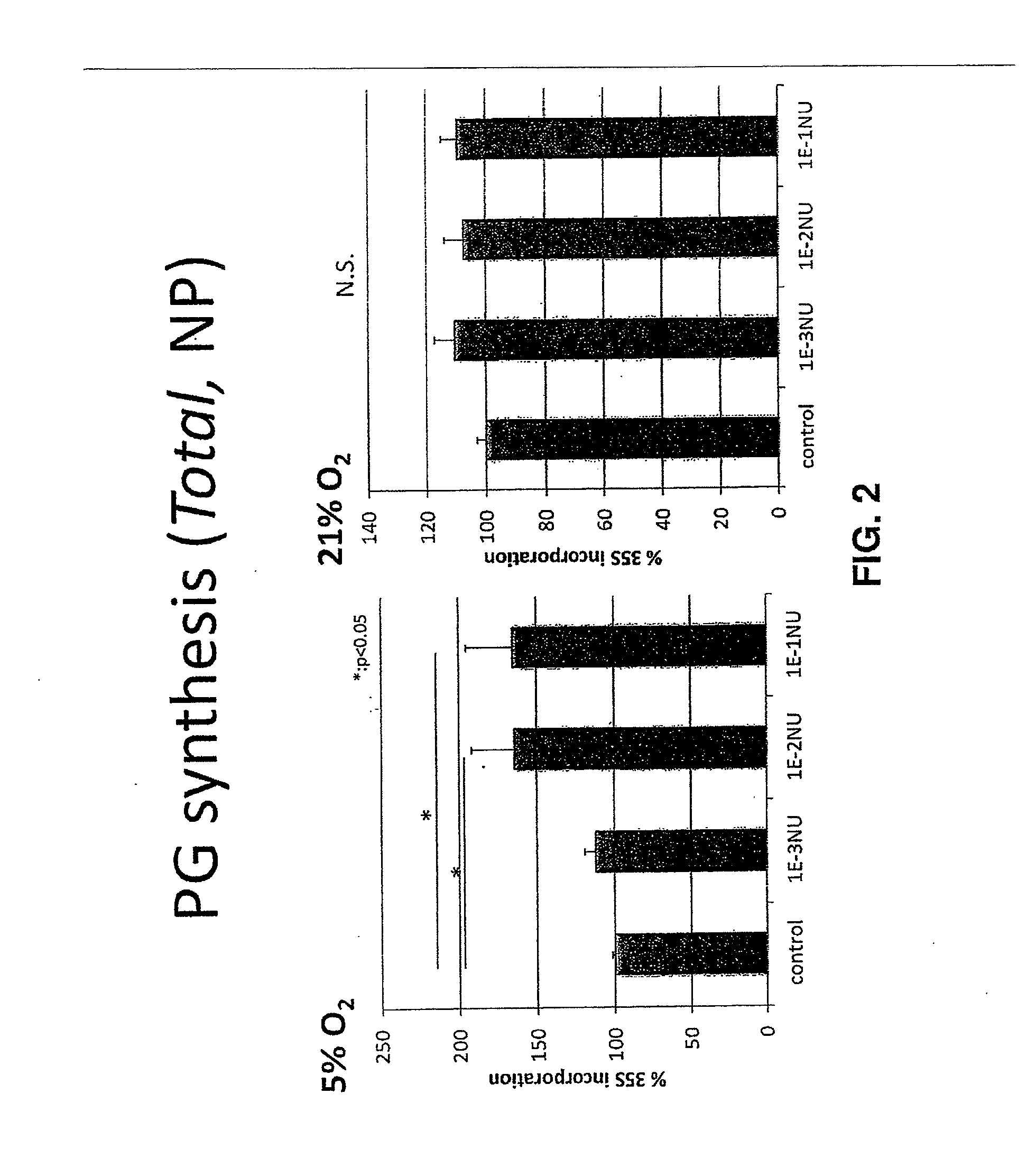
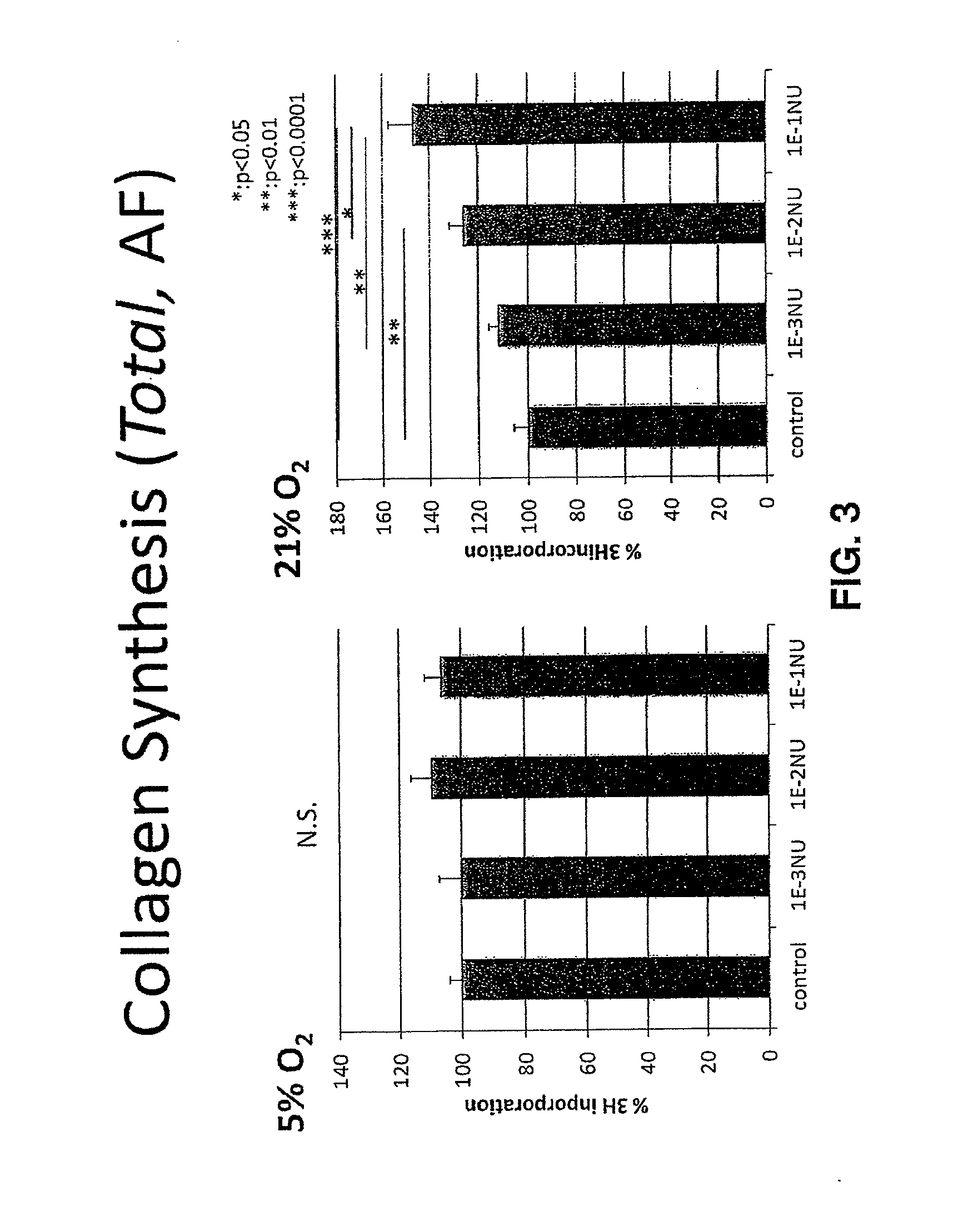
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Articular chondrocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
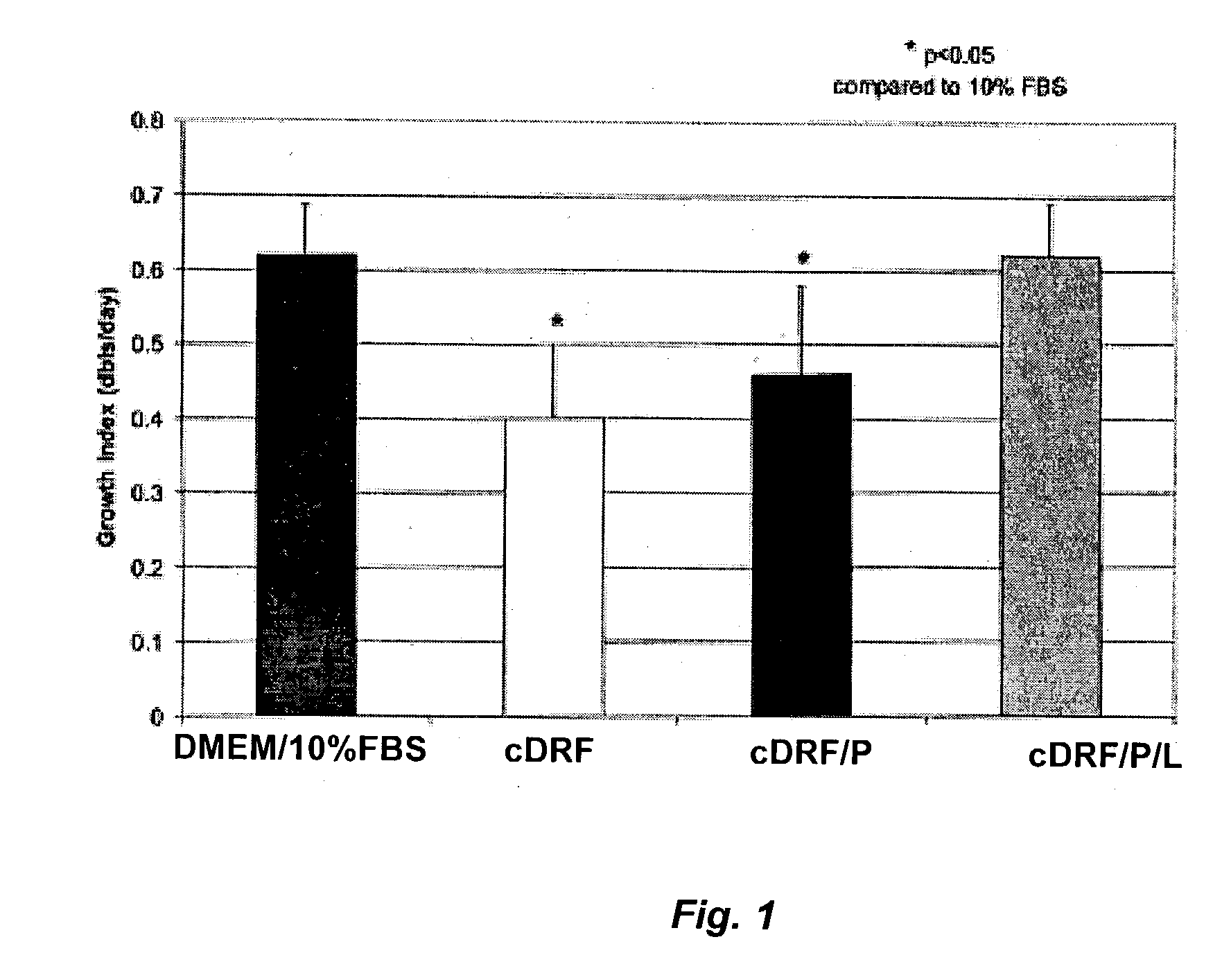
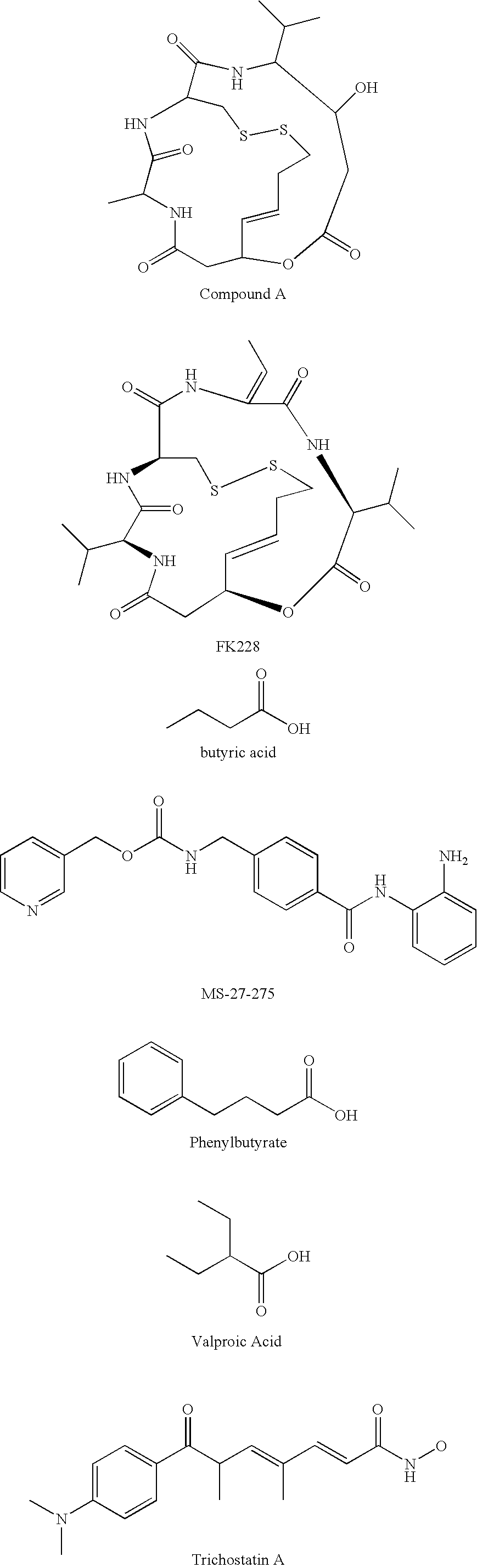
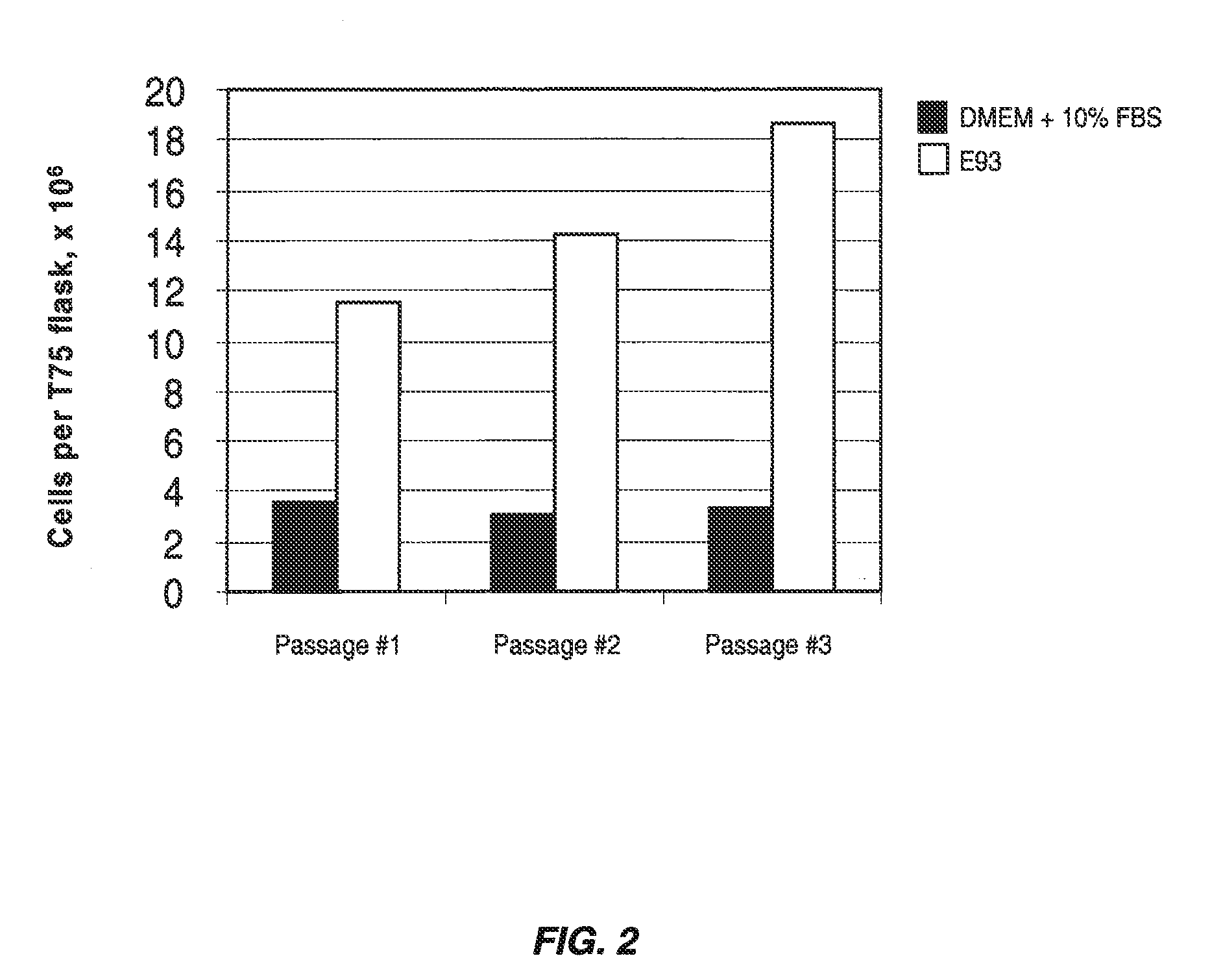
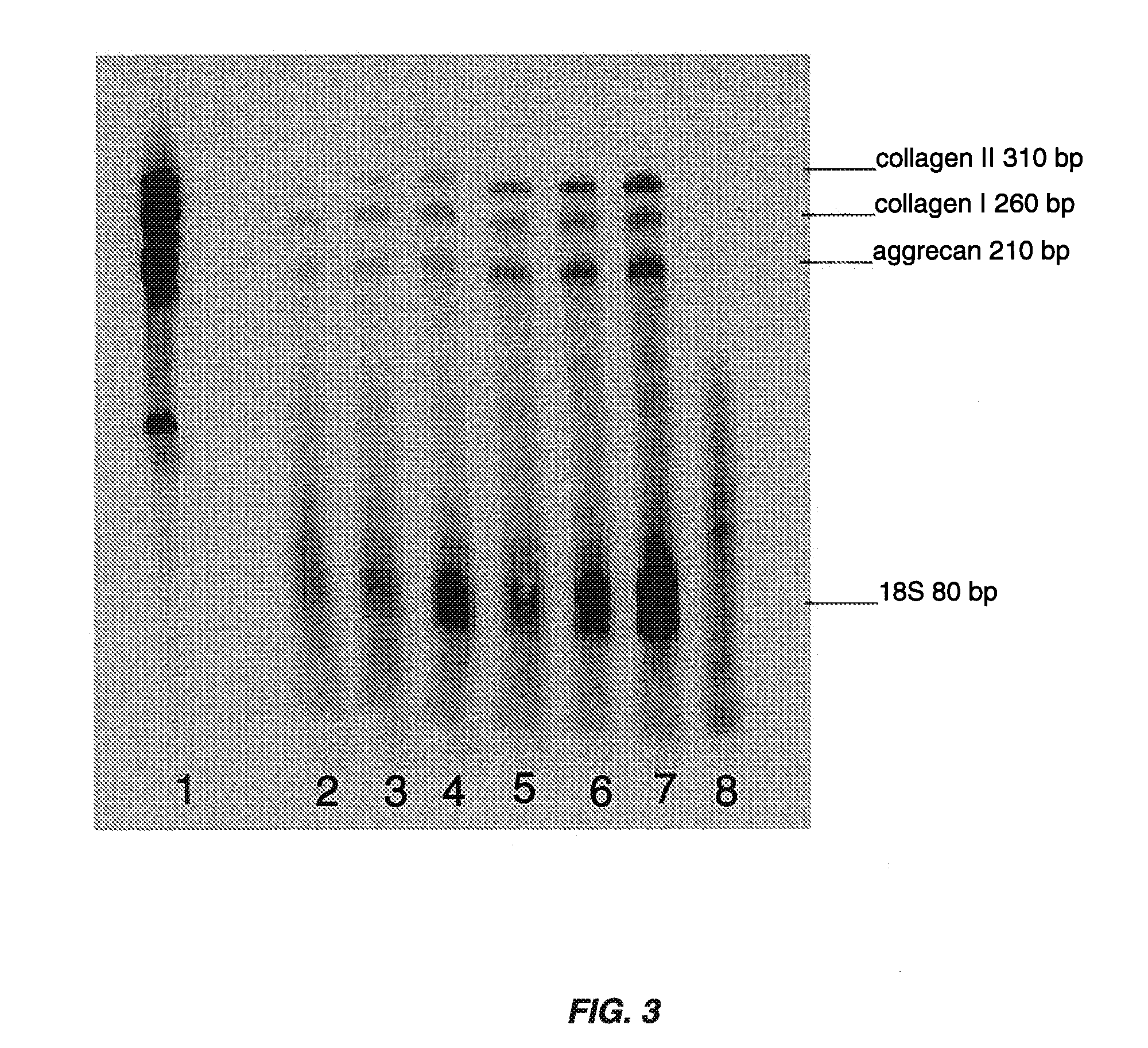
Serum-free media for chondrocytes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7169610B2Safe effective inexpensiveSafe and effective and inexpensiveCulture processArtificial cell constructsLipid formationSerum free media
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoids problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and chemically defined lipids, or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Theurapeutic or prophyiactic agent for arthritis
ActiveUS20070197434A1Slow changeIncrease the number ofAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCyclaseArthritis therapy
This invention provides a new therapeutic or prophylactic agent for arthritis such as osteoarthritis. Specifically, it provides a therapeutic or prophylactic agent for arthritis such as osteoarthritis, or an agent for promoting the growth of articular chondrocyte, comprising a guanyl cyclase B (GC-B) activator as an active ingredient; or a method for inhibiting arthritis or for promoting the growth of articular chondrocyte by activating GC-B; or a method for screening an agent for promoting the growth of articular chondrocyte or an agent capable of treating arthritis using the GC-B activity as an indication.
Owner:KAZUWA NAKAO +1
Methods of promoting healing of cartilage defects and method of causing stem cells to differentiate by the articular chondrocyte pathway
InactiveUS20060111778A1Promote healingBone implantSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixArticular chondrocyte
Methods of promoting healing of a cartilage defect in a region of cartilage, which comprises the defect and which may further comprise stem cells, and methods of promoting healing of a cartilage defect in a region of cartilage, which comprises the defect and an implant comprising cartilage scaffold or a cartilage graft, which methods comprise contacting the region with various combinations of cartilage fragments, a growth factor, a partially synthesized extracellular matrix, a scaffold, an implant comprising cartilage scaffold, an implant comprising a cartilage graft, stem cells, chondrocytes, a proteoglycan, an anti-oxidant, a collagen precursor, a vitamin, a mineral, and / or a cartilage-degrading enzyme; and a method of causing stem cells to differentiate by the articular chondrocyte pathway comprising contacting the stem cells with a compound comprising an active alcohol moiety.
Owner:MICHALOW ALEXANDER E
Method of treating arthritis and promoting growth of articular chondrocytes
ActiveUS7642243B2Increase the number ofReduce degradationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCyclaseArticular chondrocyte
Owner:KAZUWA NAKAO +1
Injection-type cartilage bionic matrix for regenerative repair of cartilage and method for using same
InactiveCN101934092AReduce dwell timeSolve the problem of excessive degradationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
The invention discloses an injection-type cartilage bionic matrix for the regenerative repair of cartilage and a method for using the same. The materials, of which the main components are the same as those of the extracellular matrix of the normal articular cartilage, are used as a raw material, and the raw materials undergo dissolution and pH adjustment to form the injection-type cartilage bionic matrix which is in a sol state at the low temperature and at a gel state at the body temperature; and by using the injection-type cartilage bionic matrix as a carrier, the injection-type cartilage bionic matrix is mixed with seed cells at the low temperature and then injected in cartilage deficiency parts, the injected materials undergo phase change by raising the temperature of the deficiency area to turn into the gel, so that the seed cells are fixed in the deficiency parts to conduct the regenerative repair function. The method is simple and easily implemented, the product is conveniently used, the operation injury is small, and the repair effect of the deficiency parts is good; the raw material has high biocompatibility and safety, all components undergo intermolecular bonding under the preparation conditions of the invention, so that the problem that the single bionic material is degraded too fast is solved; and the seed cells are directly mixed with the raw materials, and the culture in vitro is unnecessary so that the detention time in vitro of the seed cells are shortened, and the clinical application is safer.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Arthrodial cartilage extracellular matrix degradation inhibitor
InactiveUS20050272647A1Strong inhibitory activityBiocideAntipyreticCell-Extracellular MatrixHistone deacetylase
An agent for inhibiting articular cartilage extracellular matrix degradation of the present invention, comprising a histone deacetylase-inhibiting compound as an active ingredient, is effective for the prevention and treatment of diseases and pathological conditions involving the degradation and degeneration of the articular cartilage extracellular matrix, in particular, arthrosteitis, rheumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, and the like.
Owner:ASTELLAS PHARMA INC
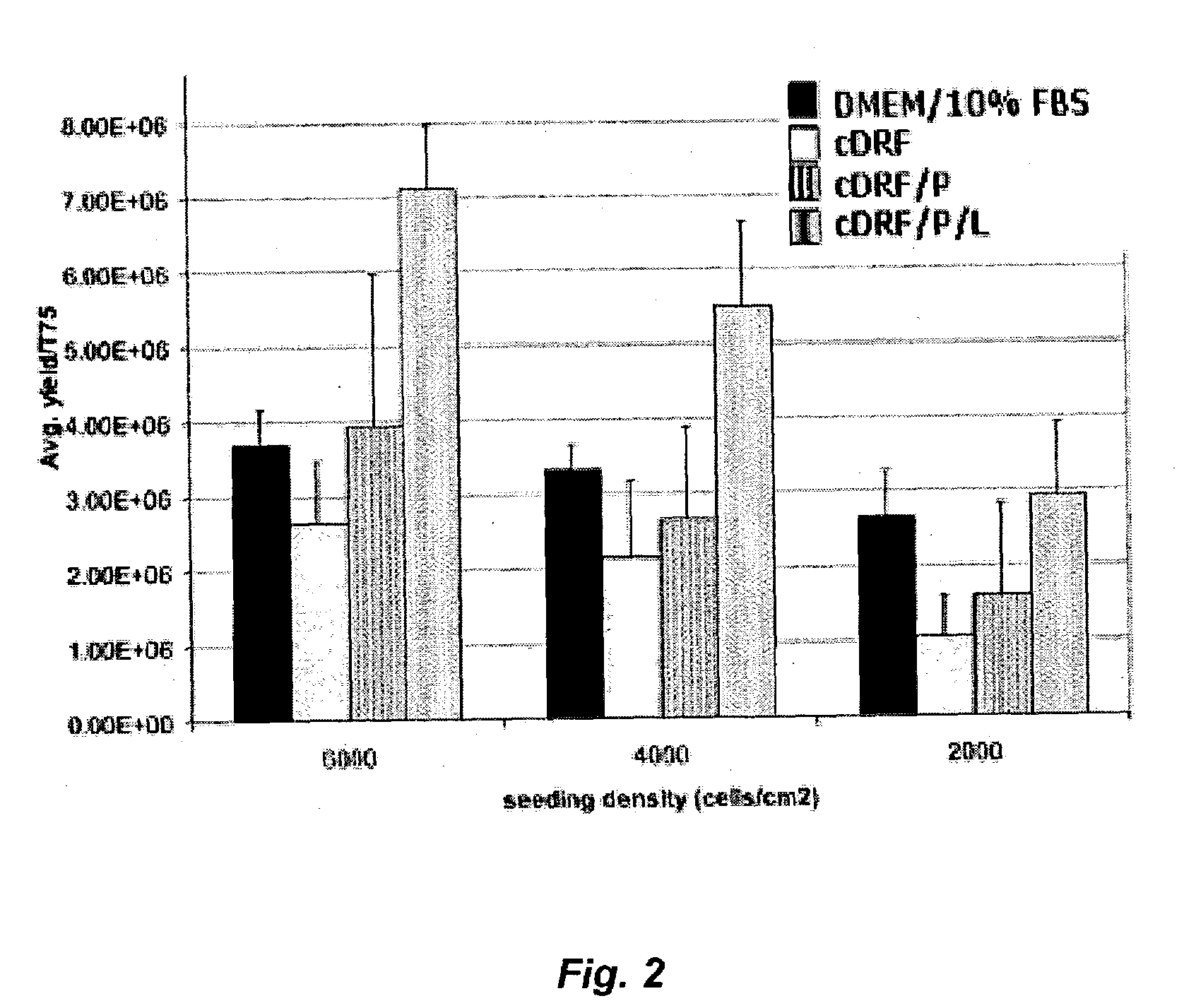
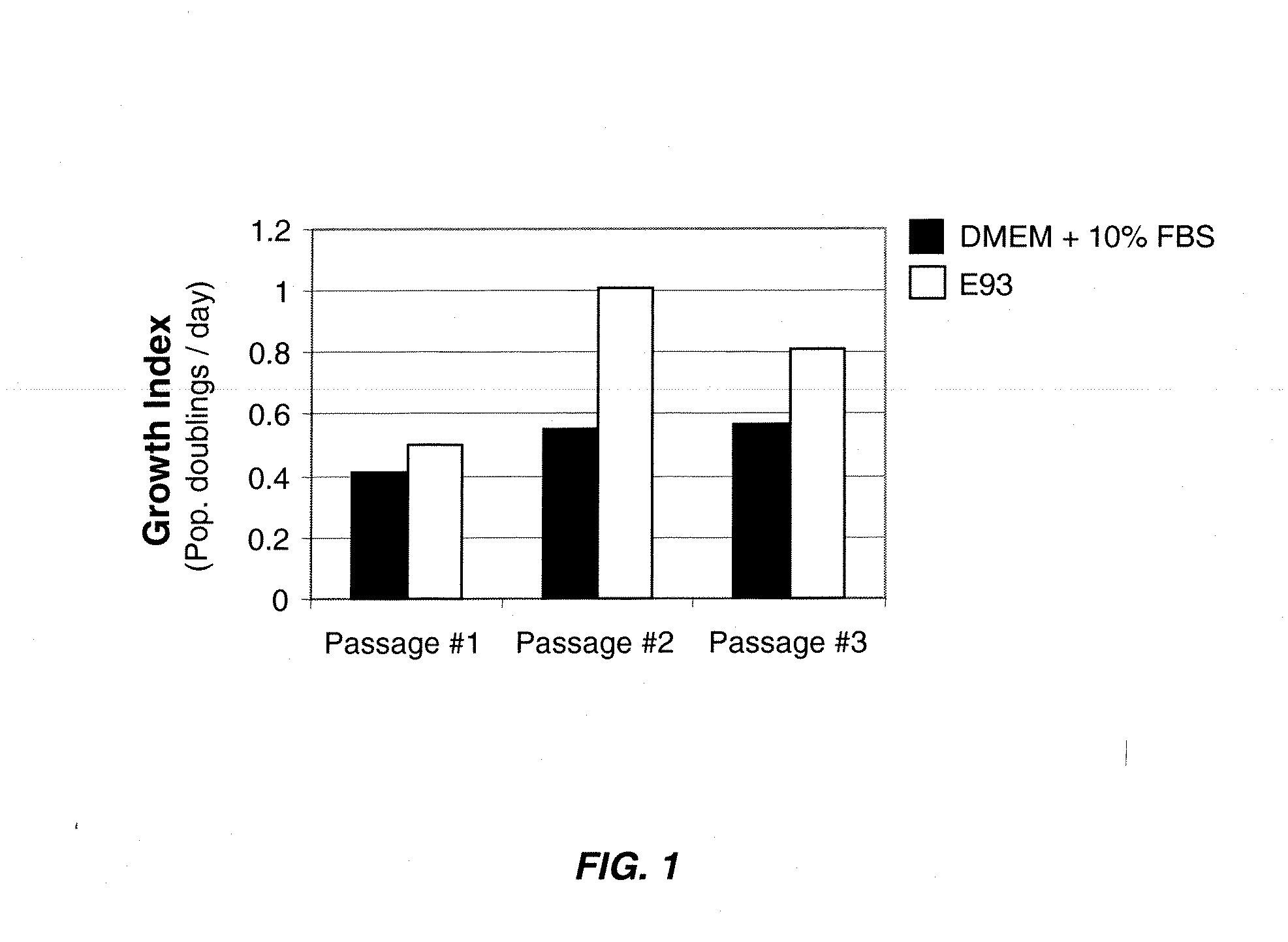
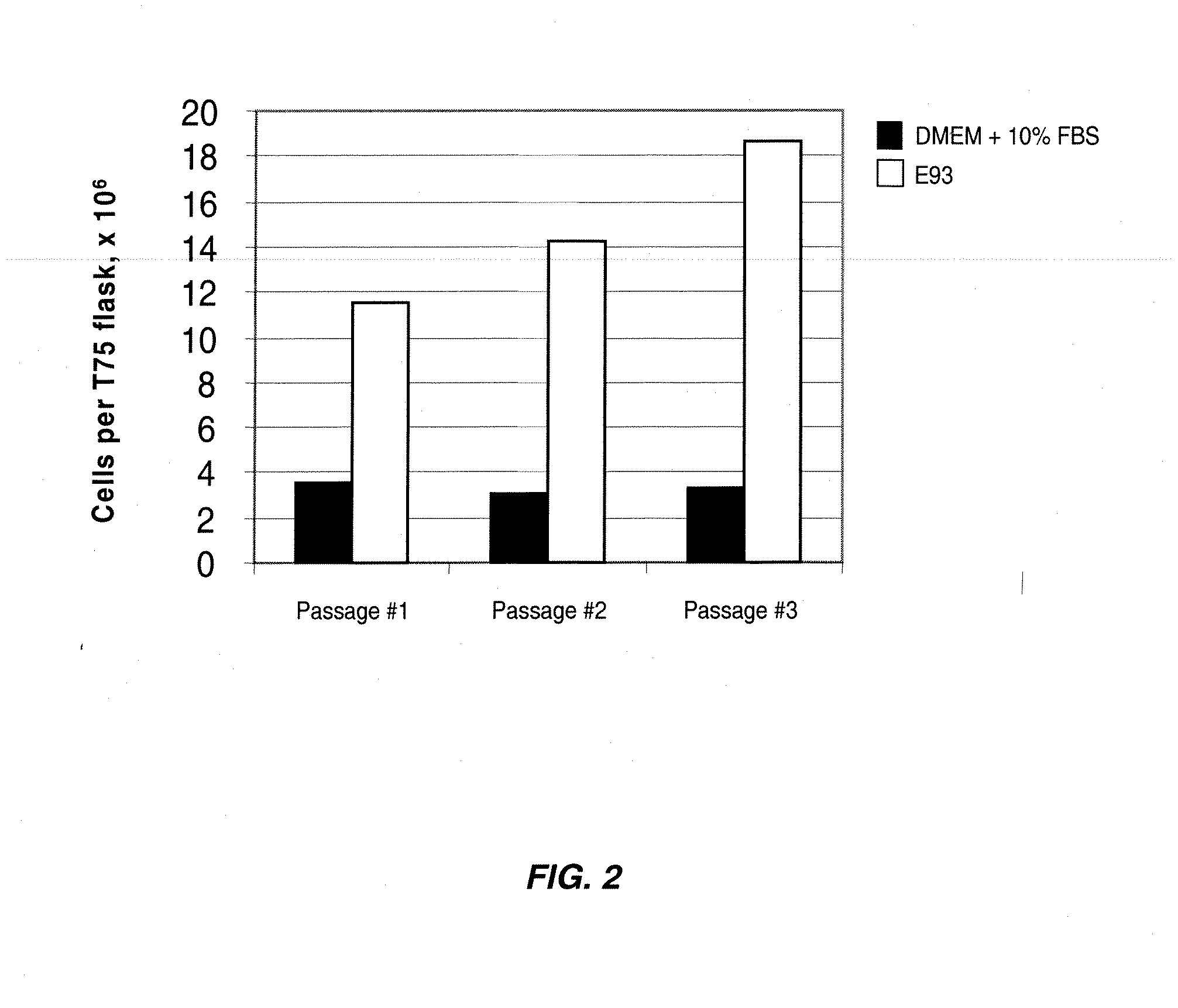
Serum-free media and their uses for chondrocyte expansion
InactiveUS20070292949A1Enhance cell attachmentIncreased proliferationCulture processSkeletal disorderInterleukin 6Lipid formation
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoid problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), chemically defined lipids, oncostatin M (OSM), interleukin-6 (IL-6), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum-free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
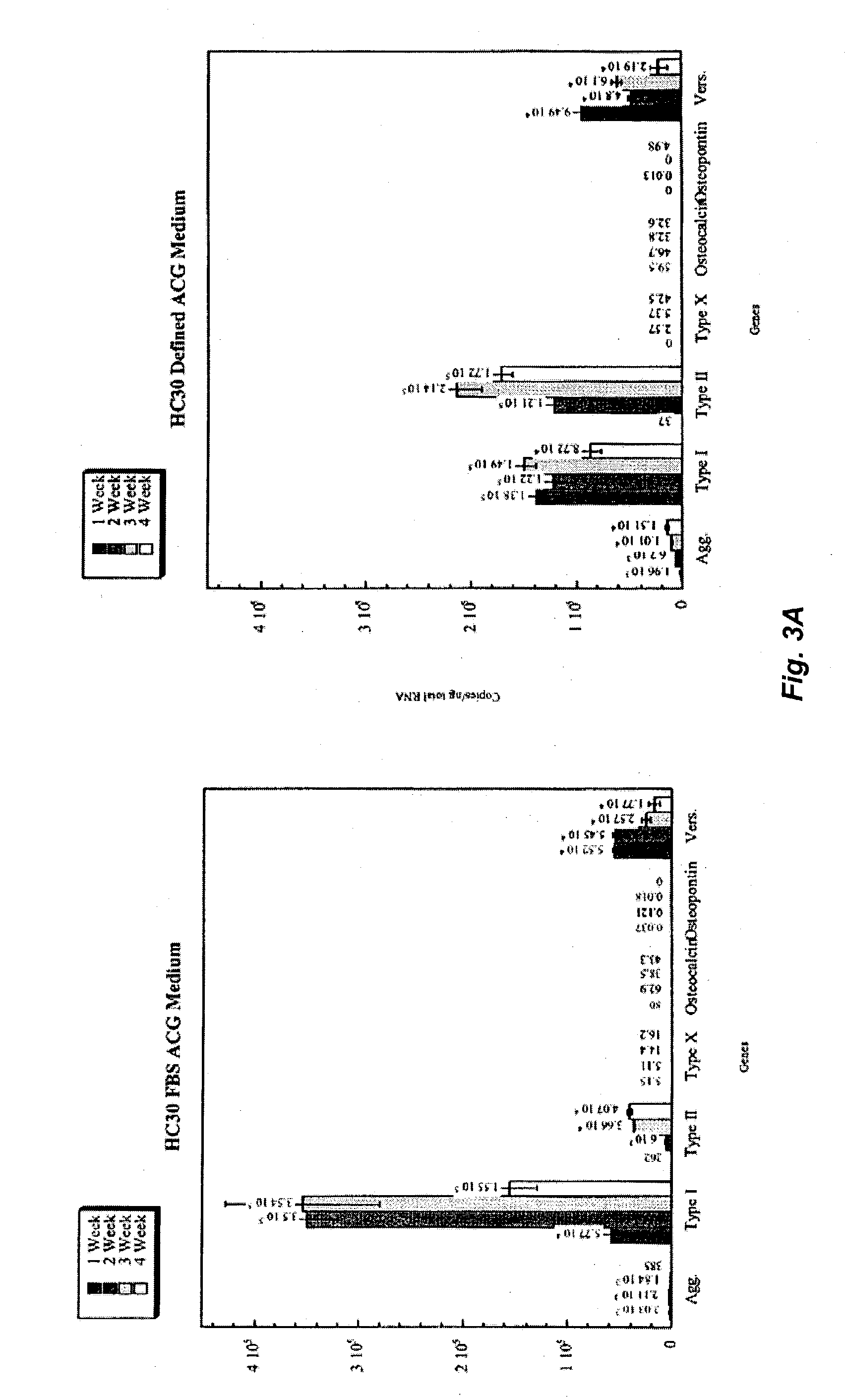
Three-dimensional culture containing human articular chondrocytes with induced terminal differentiation changes, and preparation process and uses of the same
ActiveUS20080026362A1Induce changeMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsDiseaseBiological property
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Non-virus nano nucleic acid transferring composite for curing gristle defection by injecting in joint cavity and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101085357AGood biocompatibilityLow viscosityGenetic material ingredientsSkeletal disorderSolubilityNucleic acid transport
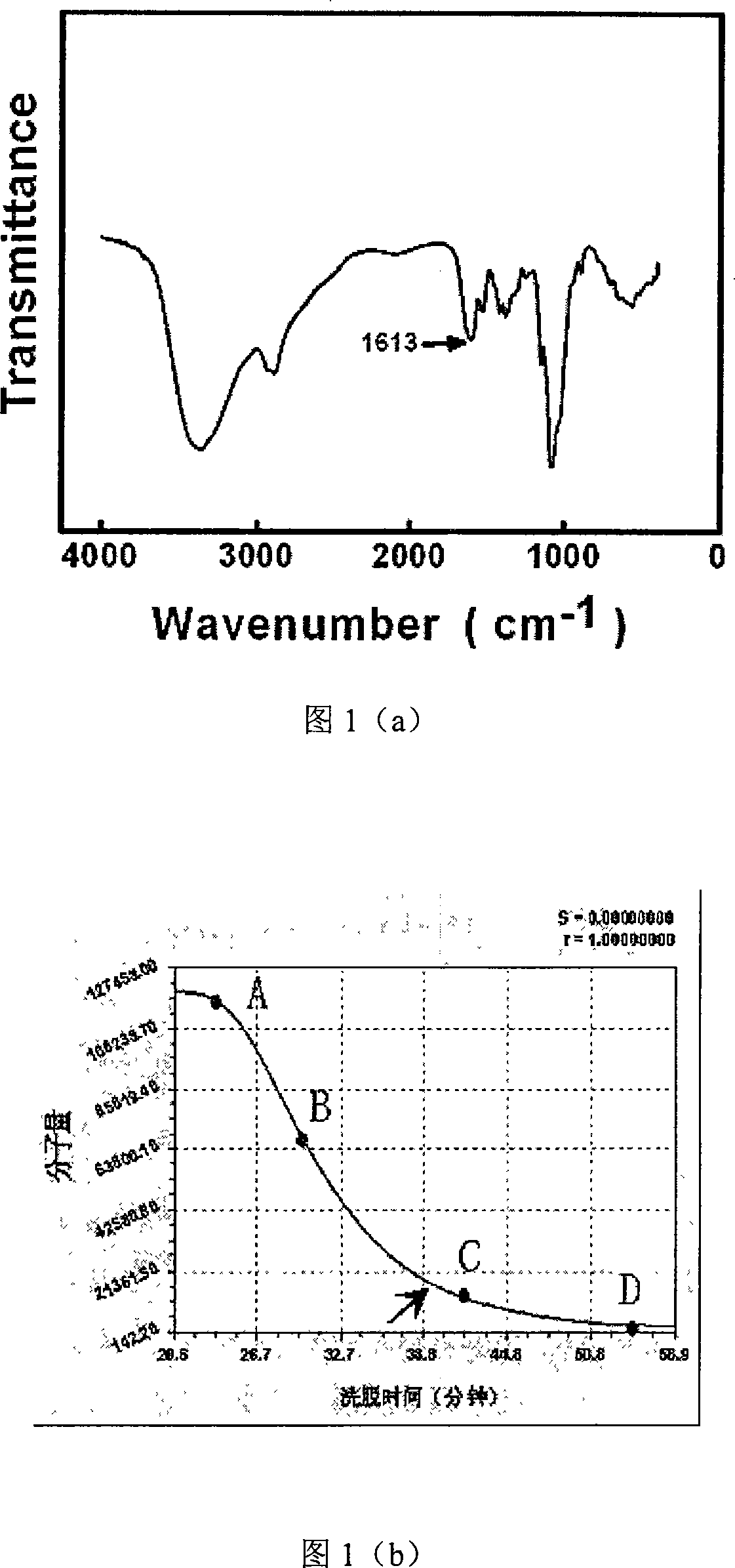
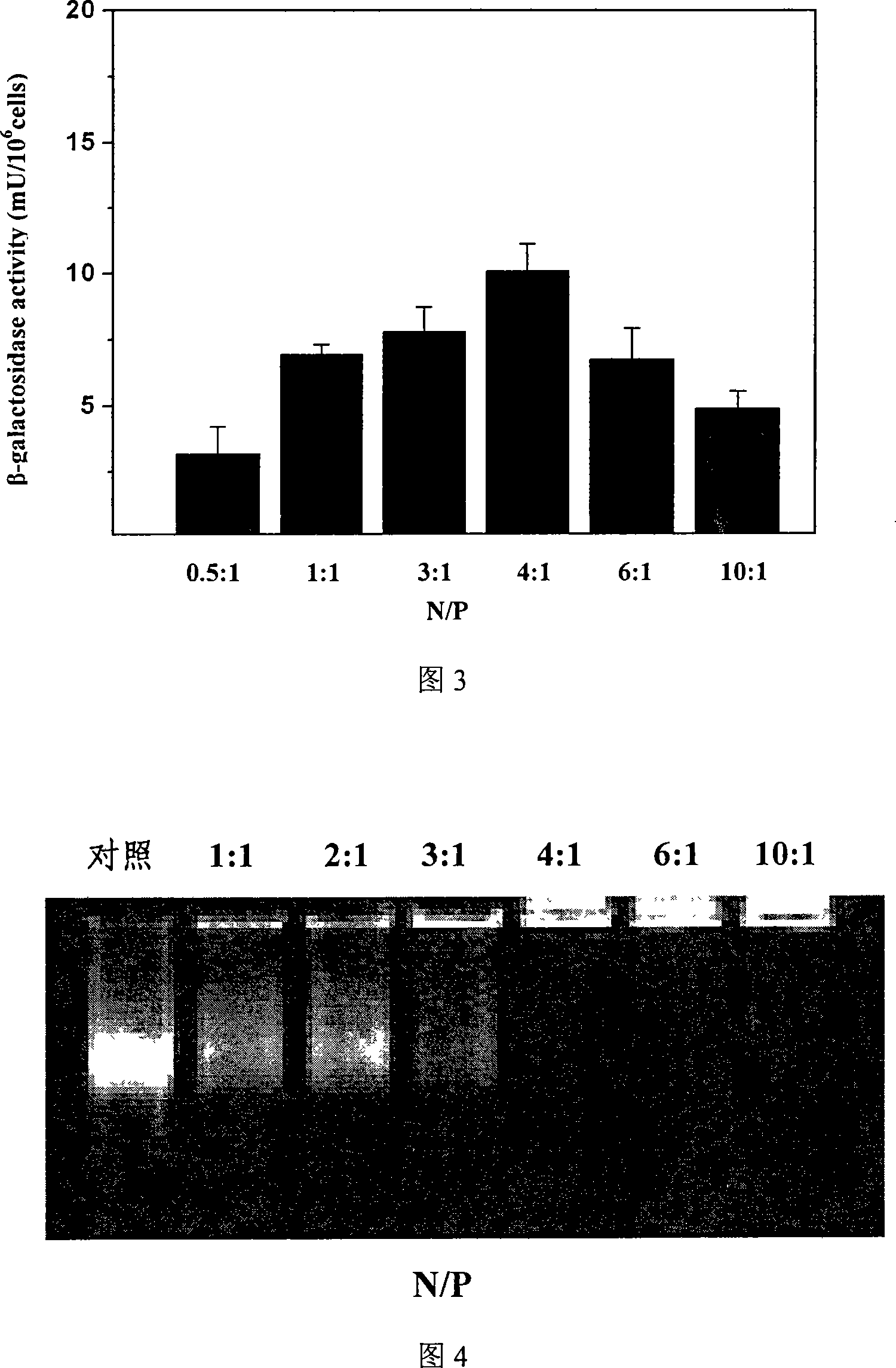
The invention discloses a non-viral nanometer nucleic acid transportation compound used for treating cartilage defect through intra-articular injection which comprises low-molecular chitosan with molecular weight of 5KD-100KDand percentage composition of amino group of 30-70%, and nucleic acid, wherein N / P of the compound is 0.2:1-10:1.The invention degrades high molecular chitosan to low molecular chitosan, increases water solubility of material, reduces viscosity of solution, reduces influence of sour environment of solvent to cell, improves compound size with nanometer, is in favor of performing genetic transmission to cartilago articularis cell, and protects target nucleic acid from neutralizing with synovial fluid and being degrade by nuclease in lysosome. The invention has simple preparation and abroad application scope; can solve engineering roadblock of cartilage repair with no requirement of operation, complex device and bracket material.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
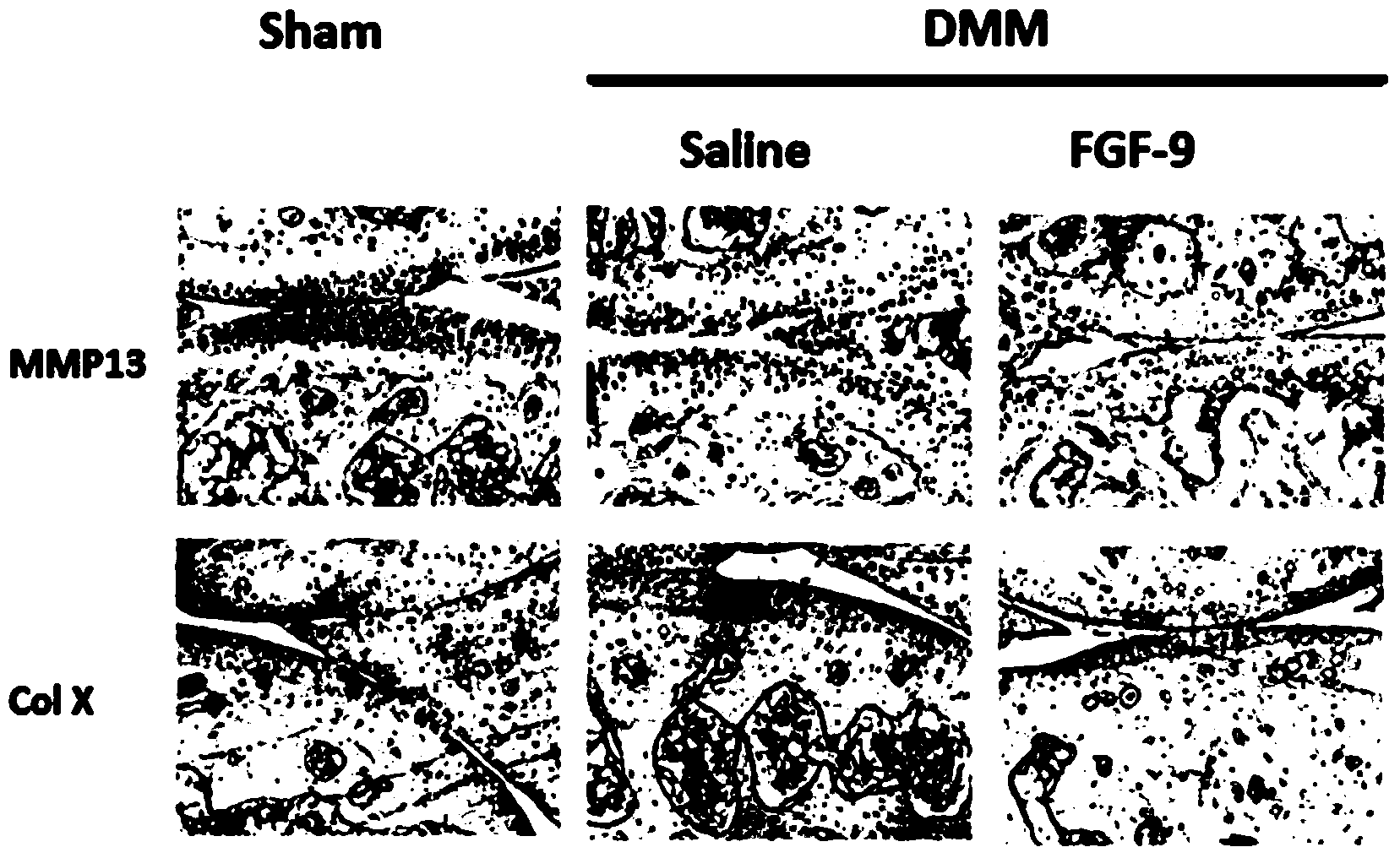
Application of FGF (fibroblast growth factor) 9 in preparation of osteoarthritis cartilage repair promotion medicine
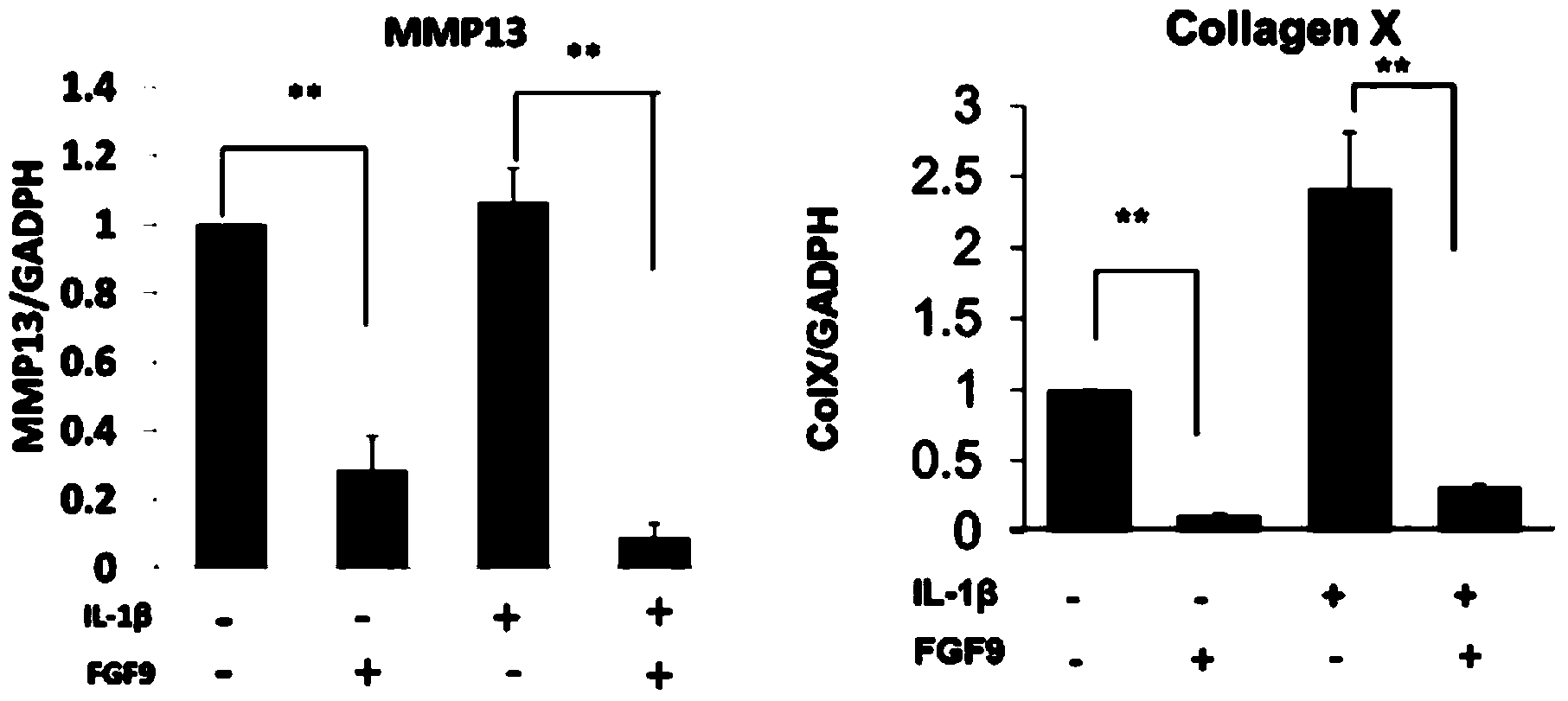
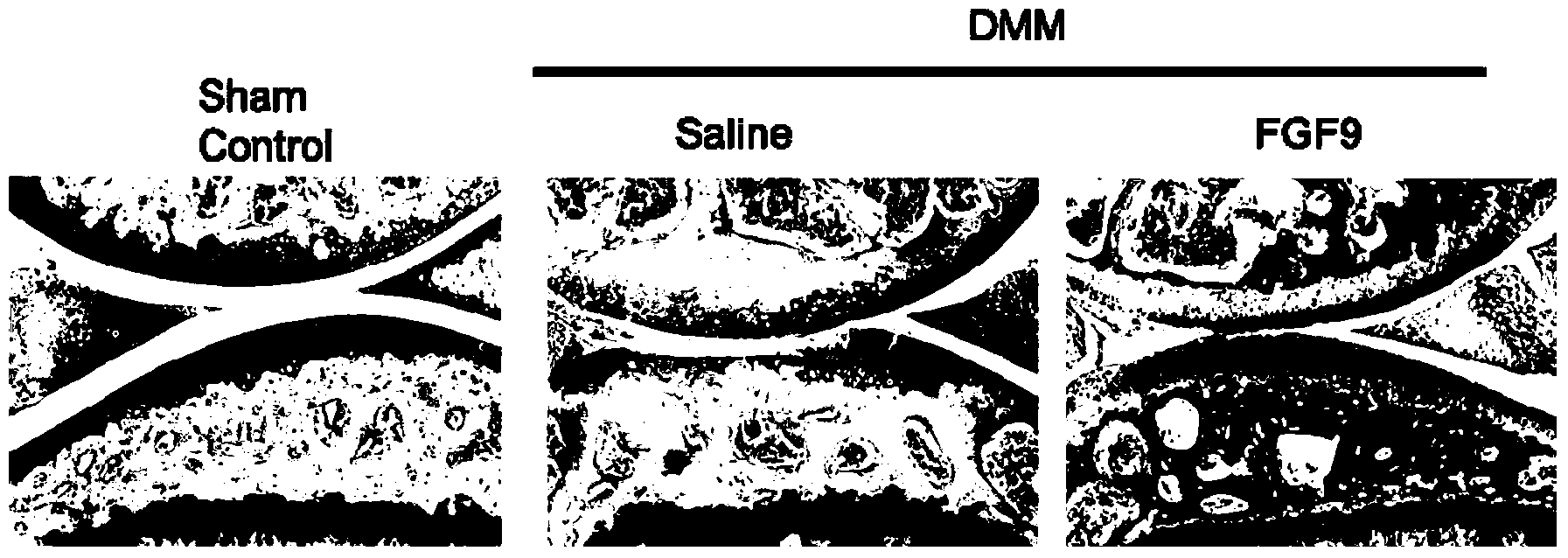
InactiveCN104162148AReduce degradationSlow down the hypertrophy processPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderEccentric hypertrophyMedicine
The invention discloses application of FGF (fibroblast growth factor) 9 in preparation of osteoarthritis cartilage repair promotion medicines, researches find the FGF9 can play the role of retardation of abnormal differentiation of articular cartilage cells in the articular cartilage cells in the inflammatory environment, the FGF9 can alleviate the articular cartilage degradation in an osteoarthritis model in mice, can inhibit key enzyme MMP-13 of articular cartilage degradation, can slow down the hypertrophy process of articular cartilage, can be use for preparation of the osteoarthritis cartilage repair promotion medicines, and has good potential application prospect in the osteoarthritis treating field.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Serum-free media for chondrocytes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070275463A1Safe and effective and inexpensiveSimple methodCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLipid formationSerum free media
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoids problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and chemically defined lipids, or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
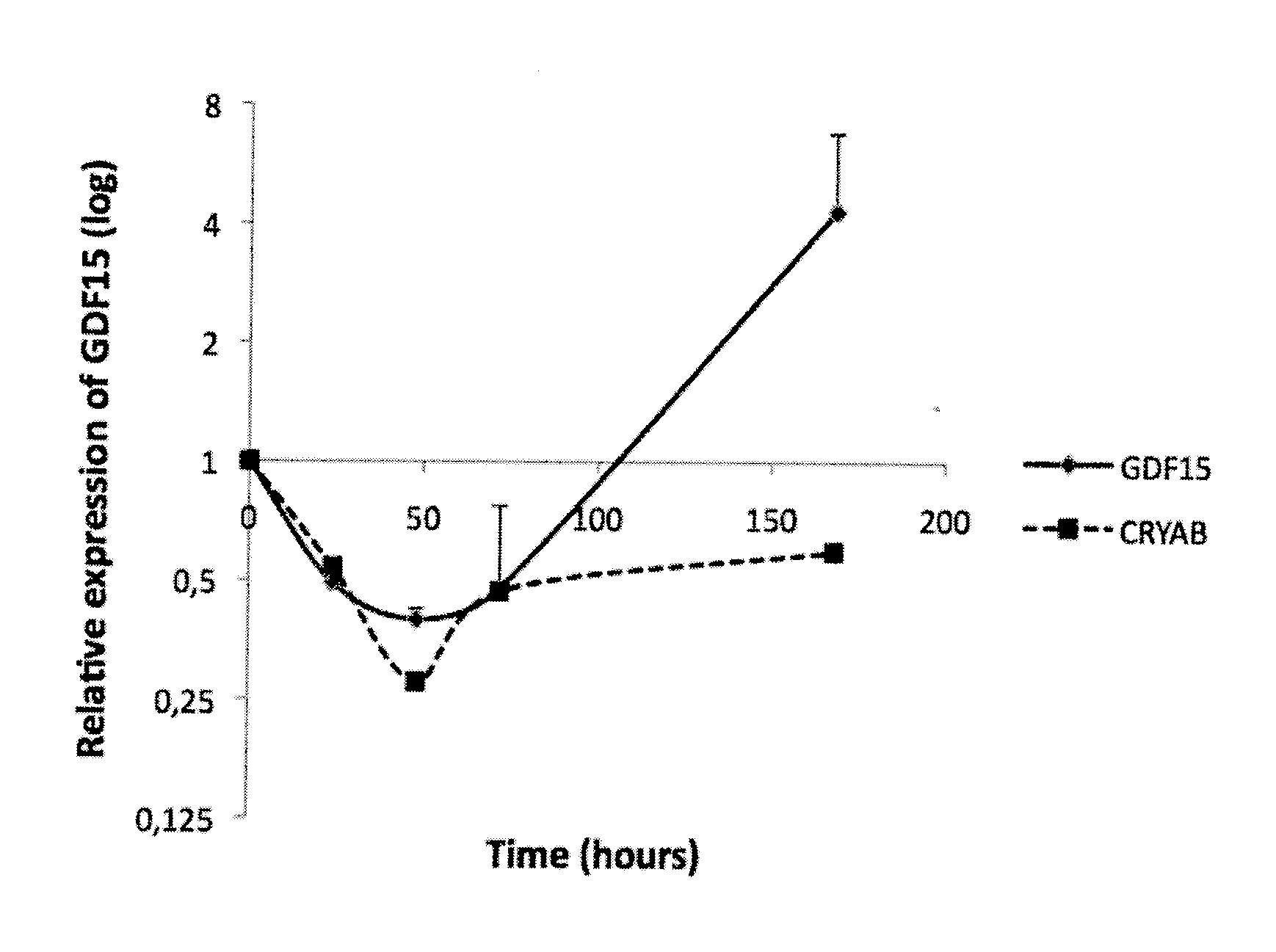
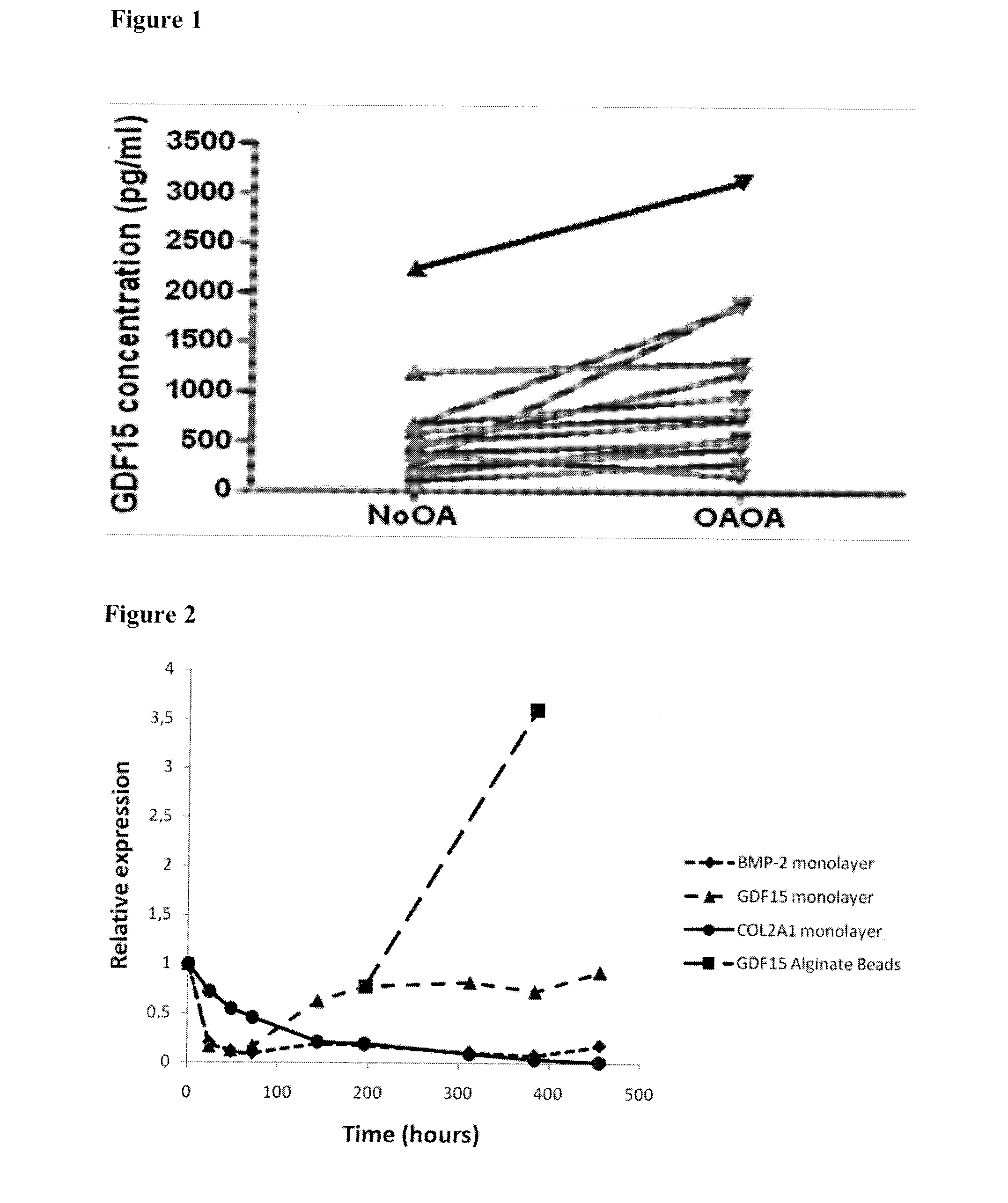
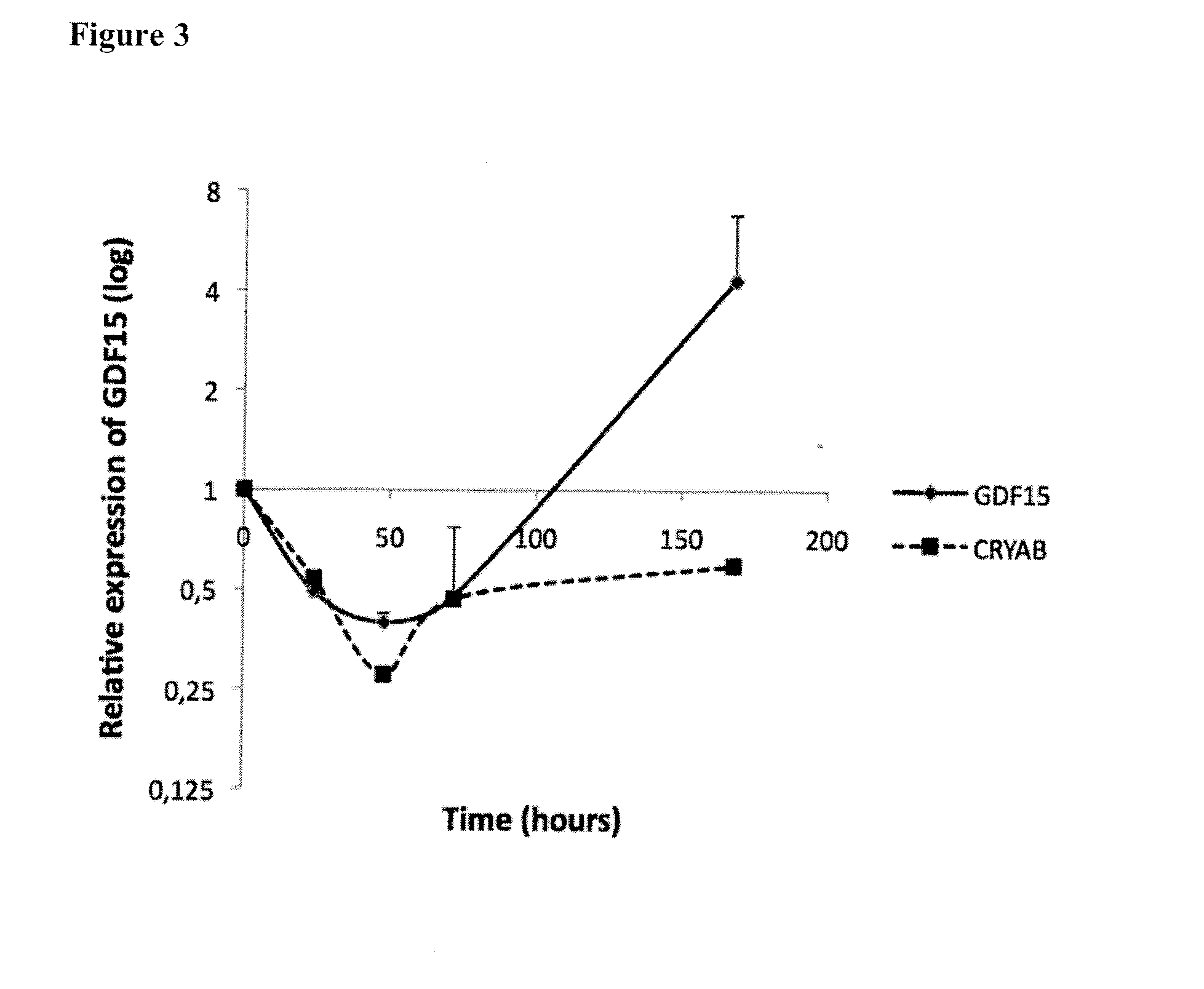
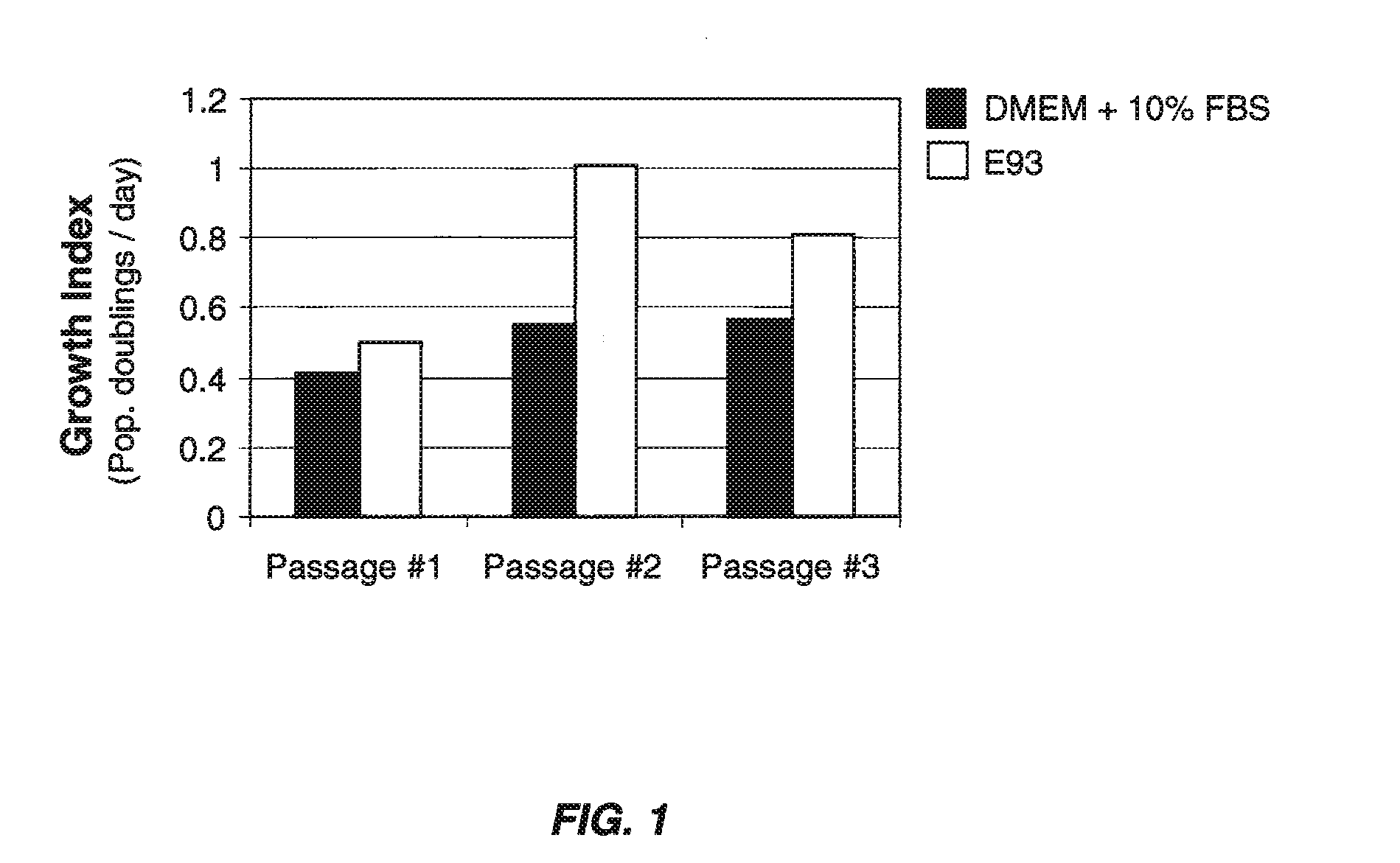
Gdf15 as molecular tool to monitor and enhance phenotypic stability of articular chondrocytes
InactiveUS20110300548A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsArticular chondrocyteGDF15
The present invention relates to GDF15 as a molecular marker in in vitro assays determining phenotypic stability of articular chondrocytes and predicting the outcome of chondrocyte transplantation.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Preparation method of bionic cartilage extracellular matrix for tissue engineering
ActiveCN101690830ASimple processGood reproducibilityProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bionic cartilage extracellular matrix for tissue engineering, which comprises the following steps of: selecting a raw material having the same main components as the normal articular cartilage extracellular matrix as a bionic raw material to prepare the bionic cartilage extracellular matrix for the tissue engineering; fully dissolving the selectedbionic raw material in organic acid; and then carrying out hole making processing, curing processing and strengthening processing in sequence to the selected bionic raw material. The method makes thematerial structure of the finally obtained bionic cartilage extracellular matrix for the tissue engineering have physical structure characteristics suitable for biological behavior requirements such as vaccination, survival, multiplication and the like of a cartilage seed cell and have good biocompatibility, appropriate degradation rate and biomechanical strength at the same time. The preparationmethod has the advantages of wide material source, low cost, simple and easy process and good reproducibility, and the prepared product can be widely used to repair a large area of articular cartilage defect and has fewer clinical complications.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Cartilage preserving fluid and utilization method thereof
InactiveCN109566601AGuaranteed ingredient shipmentReduce mortalityDead animal preservationDegenerative changePenicillin
The invention provides cartilage preserving fluid and a utilization method thereof. The cartilage preserving fluid is prepared from monopotassium phosphate, histidine or histidine salt, lactobionic acid, saccharose, allopurinol, low-molecular dextran-40, NaCl, KCl, magnesium sulfate, penicillin, reduced glutathione, adenosine, trehalose, catechin, vitamin E and chondroitin sulfate, deionized waterserves as a solvent, a pH value is 7.35-7.52, and the cartilage preserving fluid is used for cartilage preservation at a temperature of 0-4 DEG C. The cartilage preserving fluid and the utilization method thereof have advantages that bioactivity of articular cartilage cells can be kept, degenerative changes of articular cartilages can be delayed, and assistances are provided for clinical treatment of large-area articular cartilage defects and cartilage tissue transplantation.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Serum-free media and their uses for chondrocyte expansion
InactiveUS20120213745A1Promote cell proliferationIncreased proliferationBiocideCulture processInterleukin 6Lipid formation
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoid problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), chemically defined lipids, oncostatin M (OSM), interleukin-6 (IL-6), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum-free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for cltivating cartilage cells in knee joint of BALB/c chmice
InactiveCN1539963ALow antigenicityExpand sourceSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCartilage cellsBALB/c
A method for culturing the cartilage cells of BALB / c mouse knee joint is disclosed. Its advantage is high surviral rate (80-90%).
Owner:刘健
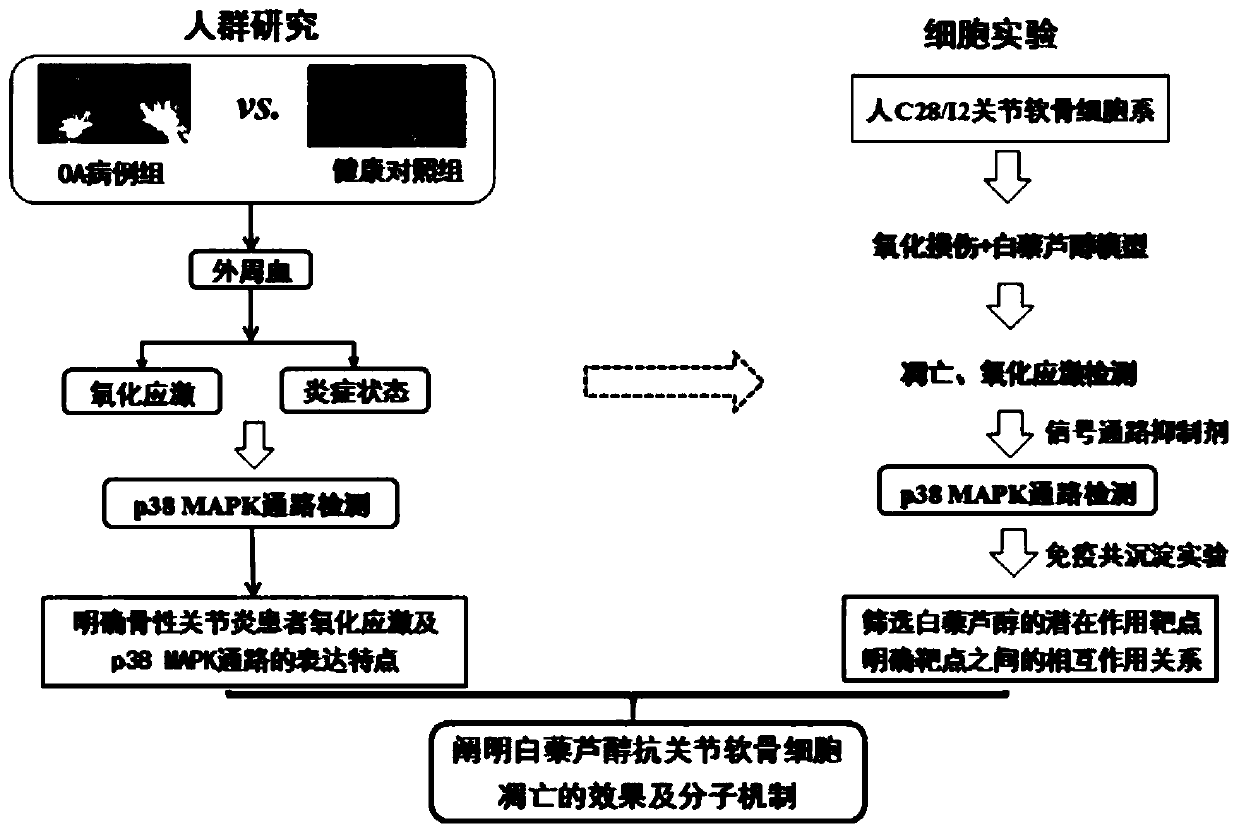
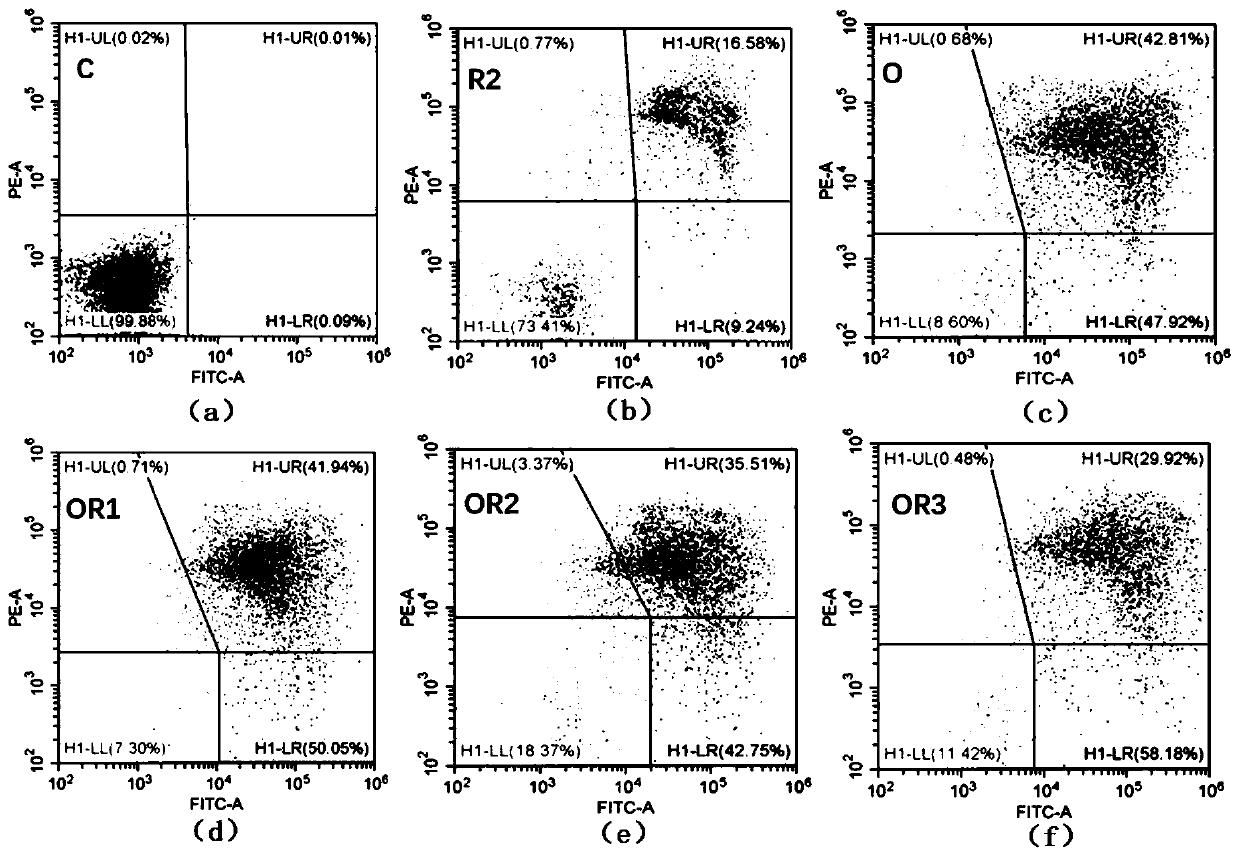
Experimental method for researching anti-articular cartilage cell apoptosis of resveratrol
ActiveCN111455043AAbility to inhibit apoptosisRegulatory effect is clearCompound screeningApoptosis detectionP38 MAPK Signaling PathwayArticular chondrocyte
The invention discloses an experimental method for researching anti-articular cartilage cell apoptosis of resveratrol. The ability of resveratrol to inhibit articular cartilage cell apoptosis is verified by establishing crowd research, in vivo experiments and in vitro experiments, and the mechanism of action of resveratrol to inhibit articular cartilage cell apoptosis is discussed to verify the 'effect axis hypothesis' of resveratrol-p38 MAPK signal pathway down-regulation-anti-apoptosis, which proves that the potential action targets of resveratrol in the screened p38 MAPK pathway have a targeting relationship, and further defines the overall regulation effect of resveratrol on a plurality of targets in the pathway. Experiments prove that resveratrol has the ability to inhibit articular cartilage cell apoptosis, and provides experimental basis for clinical practice of resveratrol in treating osteoarthritis.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method of Three-Dimesionally Culturing Chondrocytes
It is intended to provide a method of three-dimensionally culturing normal joint chondrocytes; the production and supply of chondrocytes; and a transplantation material to be used in an injured site in a joint tissue.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
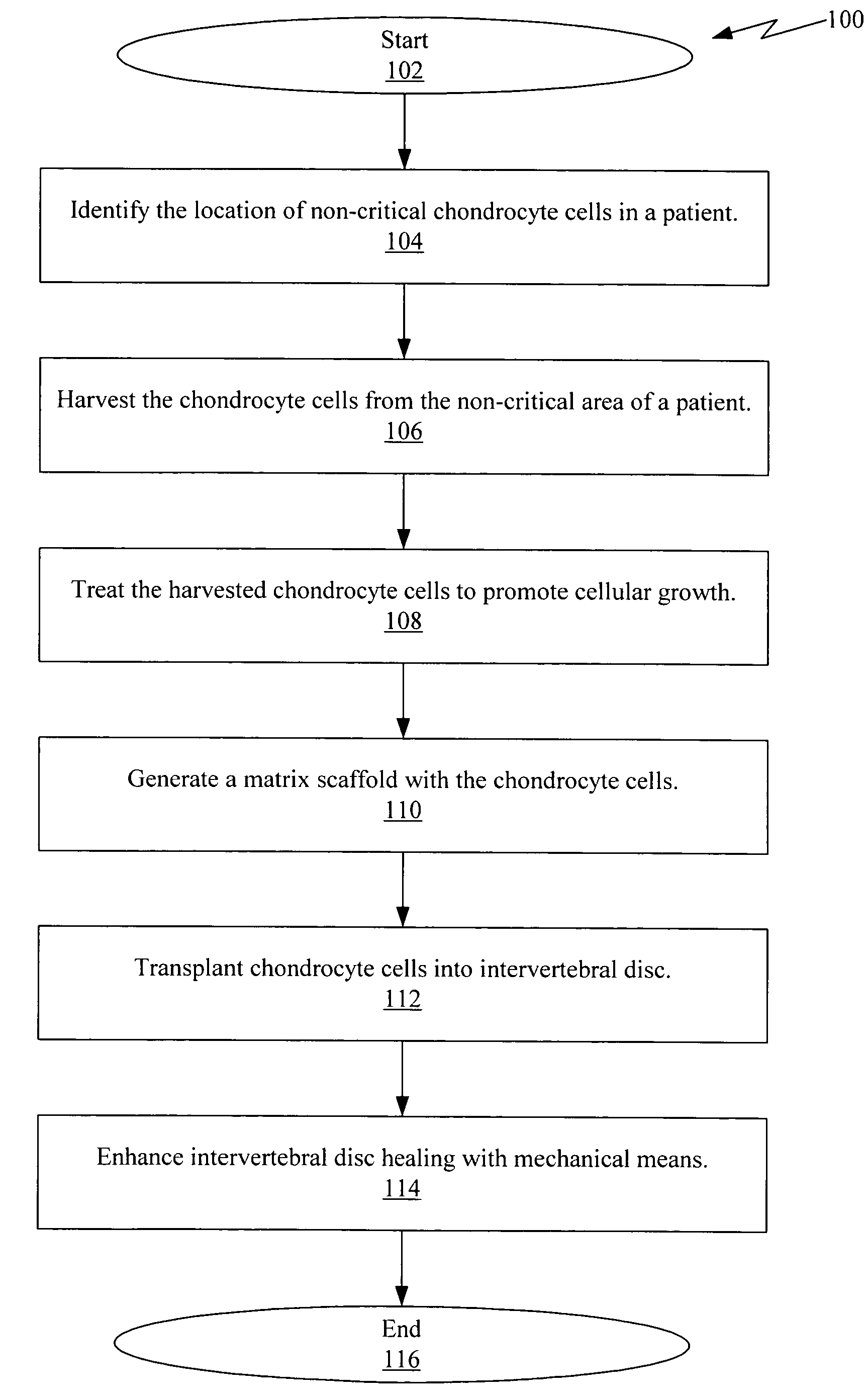
Method of intervertebral disc treatment using articular chondrocyte cells
InactiveUS8697139B2Improve efficiencyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsIntervertebral discArticular chondrocyte
Harvesting articular chondrocyte cells from a non-critical location of a patient and growing additional cells for transplantation into a damaged or diseased disc of the patient.
Owner:PHILLIPS FR M
Serum-free media and their uses for chondrocyte expansion
InactiveUS20130273010A1Promote cell proliferationIncreased proliferationBiocideCulture processLipid formationInterleukin 6
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoid problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), chemically defined lipids, oncostatin M (OSM), interleukin-6 (IL-6), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum-free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for establishing osteoarthritis osteoclast-like cell model of mesenchymal stem cells after cartilage differentiation through two-step method
ActiveCN108048394ALow costShort cycleCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDirected differentiationArticular chondrocyte
The invention discloses a method for establishing an osteoarthritis osteoclast-like cell model of mesenchymal stem cells after directional cartilage differentiation through a two-step method. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the mesenchymal stem cells are induced to be subjected to directional differentiation into articular cartilage cells, and then the articular cartilage cells are induced by adopting IL-1beta in-vitro induction to establish the osteoarthritis model. According to the method, the two-step method is used for establishing the osteoarthritis model after directional cartilage differentiation for the first time, and by exploring the cartilage cell morphology and expression change of phenotype genes aggrecan and Co12alpha1, the optimal use concentration and cell induction time of a solution are determined. The method is easy to operate and low in cost and can be applied to related studies such as cell quality evaluation of the mesenchymal stem cells after directional cartilage differentiation, early warning of easy infection of adult osteoarthritis, verification of osteoarthritis drug action targets and screening of drug toxicity / drug functions.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for treating a mammal having damaged articular cartilage tissue
A method for treating a mammal having damaged articular cartilage tissue includes harvesting a tissue sample from the mammal, growing articular cartilage cells from the tissue sample, and transplanting the articular cartilage cells into the damaged tissue. Growing the articular cartilage cells from the tissue sample can be accomplished by breaking the tissue sample into fragments, placing the fragments into a culture vessel, inducing at least some of the fragments to adhere to the culture vessel, and supplying the fragments with nutrients so that articular cartilage cells contained therein divide and grow.
Owner:CASEY PATRICK J +2
Culture method for improving differentiation from peripheral blood multipotent cells to cartilage cells
InactiveCN109112102AReduce the number of proliferating passagesReduce in quantityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsArticular chondrocyteRegenerative medicine
The invention relates to a culture method for improving differentiation from peripheral blood multipotent cells to cartilage cells, and belongs to the technical field of cytobiology and regenerative medicine. The culture method comprises the following steps: carrying out primary culture on peripheral blood multipotent mesenchymal matrix cells to obtain third-generation cells; co-culturing the third-generation passed-down peripheral blood multipotent mesenchymal matrix cells and human articular chondrocytes in an induction culture medium. According to the culture method for improving the differentiation from the peripheral blood multipotent cells to the cartilage cells, the peripheral blood multipotent stem cells and the chondrocytes are co-cultured and the two types of cells mutually promote proliferation and the differentiation; the number of times of chondrocyte proliferation and passage and the quantity of the chondrocytes can be reduced, and the differentiation is improved; an efficient method is provided for establishing a seed cell source, and a new medical experiment evidence is also provided for enlarging a cell source of cartilage tissue engineering.
Owner:丰泽康生物医药(深圳)有限公司
In vivo assay and molecular markers for testing the phenotypic stability of cell populations and selected cell populations for autologous transplantation
An in vivo assay to measure anchorage-independent growth and phenotypic stability of a certain cell population comprising subcutaneous or intramuscular injection in a mammal of a cell suspension of articular chondrocytes in an iso-osmotic liquid, the same suspension comprising articular chondrocytes in an amount equivalent to at least 1×106 chondrocytes as applied to immune-deficient mice. The outcome is linked to molecular markers. The present invention further relates to DNA chips and diagnostic tools comprising the latter to predict the outcome of ACT. Antibodies raised against positive and negative markers of chondrocyte stability can also be used for quality control on the chondrocytes. Therapeutical composition comprising stable chondrocytes are very useful for tissue repair.
Owner:TIGENIX NV
Compositions and Methods that Enhance Articular Cartilage Repair
InactiveUS20080031819A1Facilitates cell proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesisPromote healingPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
In general, this invention relates to compositions and methods useful in enhancing articular cartilage repair by providing for the sustained release of growth factors to articular cartilage cells to induce cell proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method for promoting the synthesis of collagen and proteoglycan in chondrocytes
The synthesis of collagen and proteoglycan in chondrocytes, such as intervertebral disc cells, articular chondrocytes and meniscal cells is promoted by administration of an extract from inflamed tissue inoculated with vaccinia virus.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Three-dimensional culture containing human articular chondrocytes with induced terminal differentiation changes and preparation process and uses of the same
ActiveUS8470522B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsDiseaseBiological property
Disclosed herein is a three-dimensional culture containing human articular chondrocytes with induced terminal differentiation changes, as well as a process for preparing the same. The three-dimensional culture, which was found to mimic the biological characteristics of articular chondrocytes that undergo terminal differentiation in vivo, can be used as a tool in the studies of the molecular and cellular mechanisms of osteoarthritis, and in the screening of candidate drugs for use in treatment of a disorder associated with articular chondrocytes.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
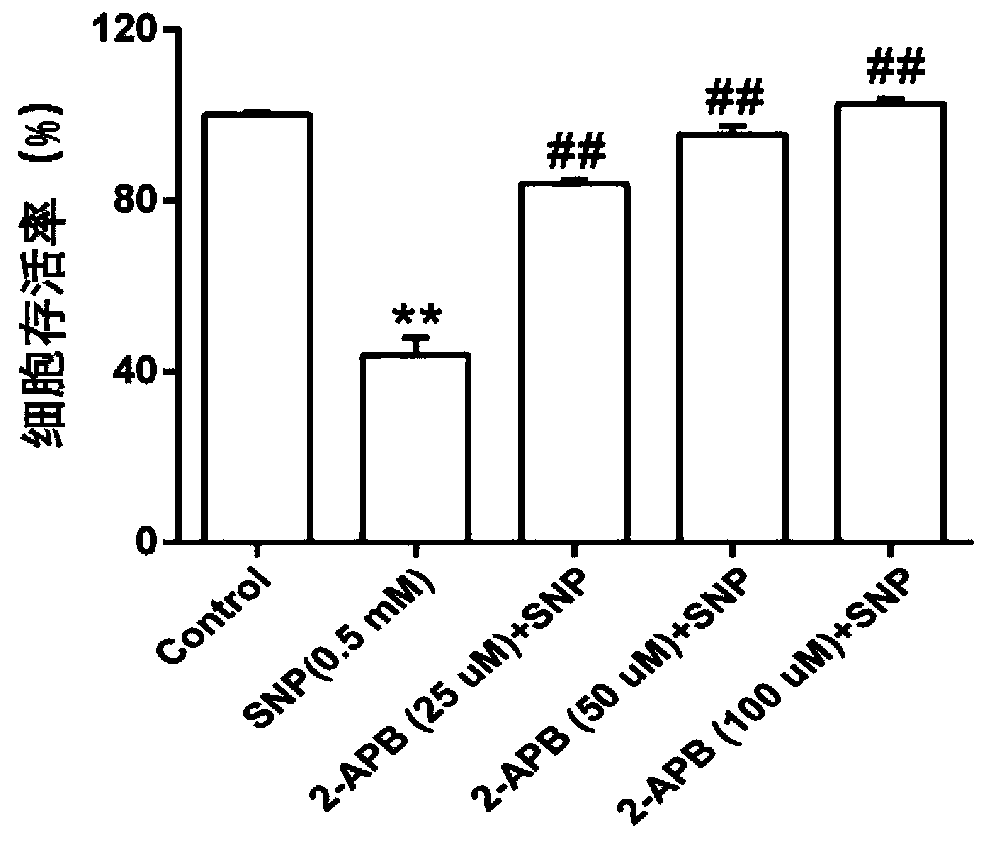
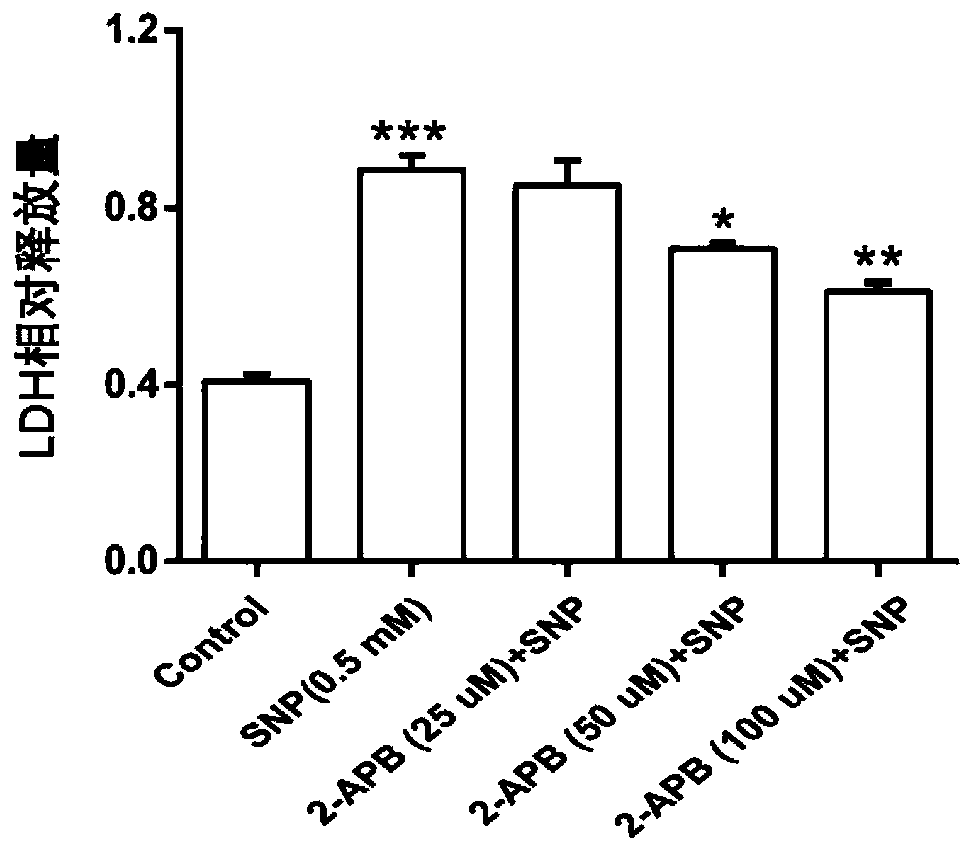
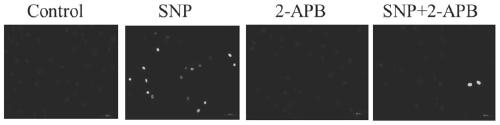
Application of 2-APB in preparation of medicine for treating osteoarthritis
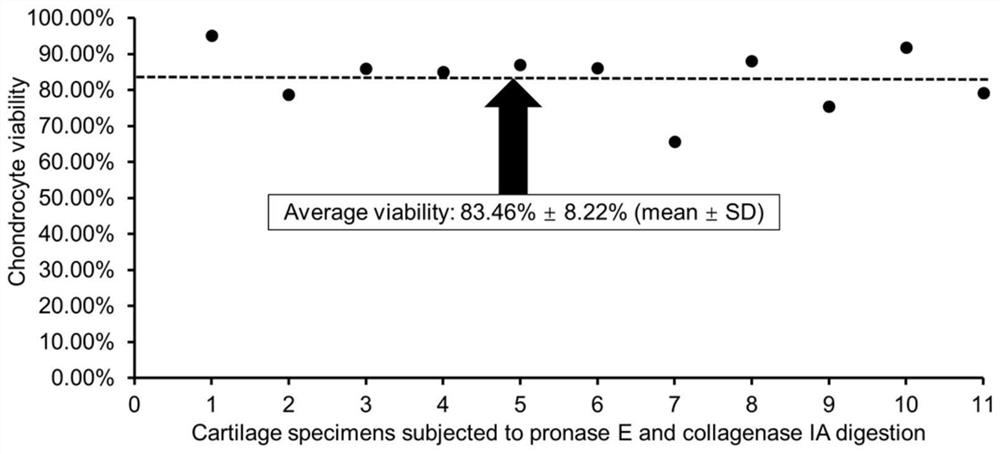
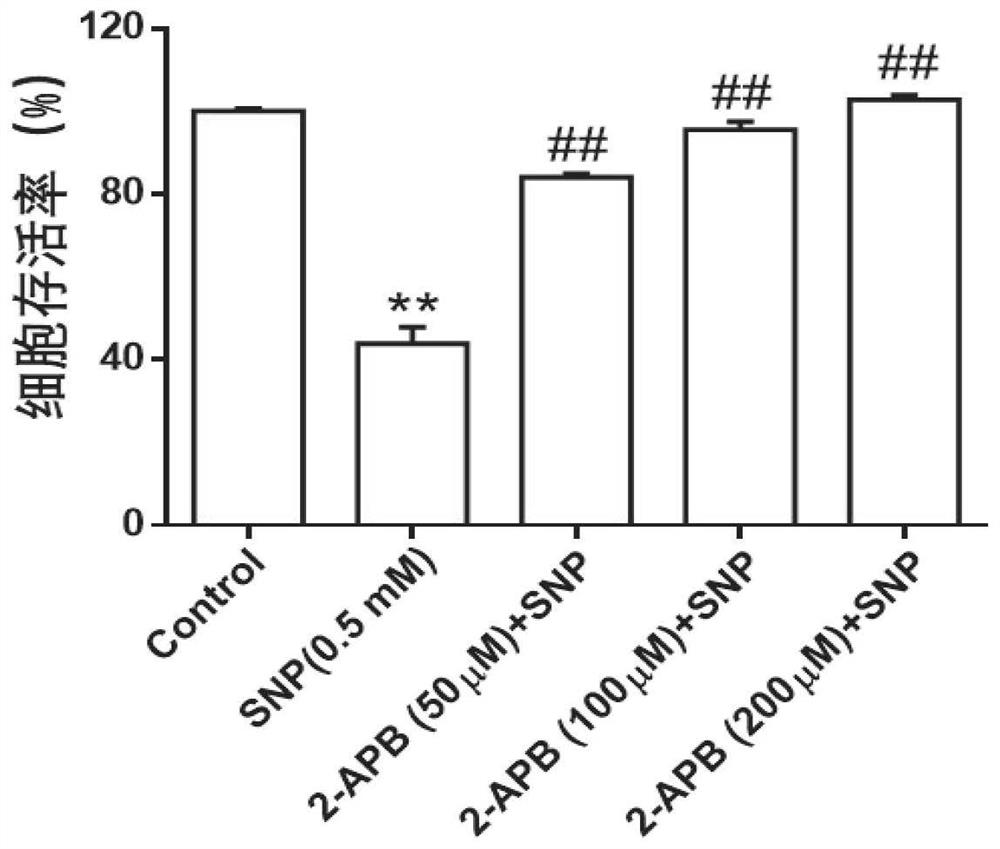
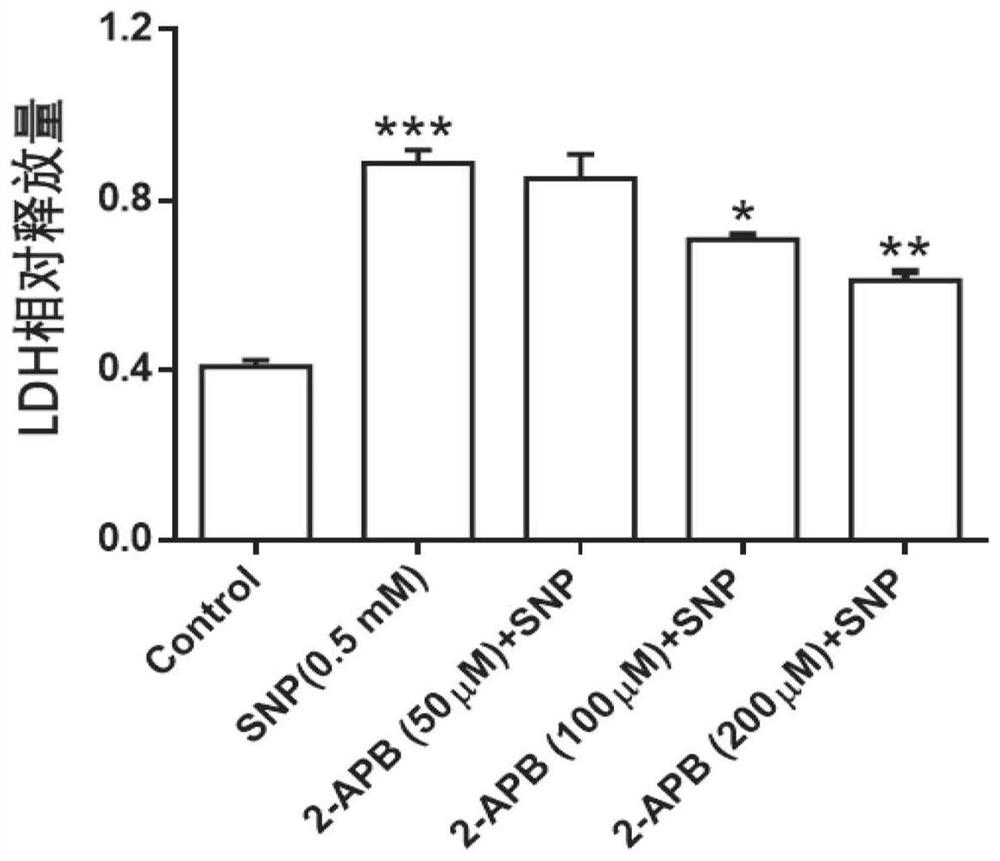
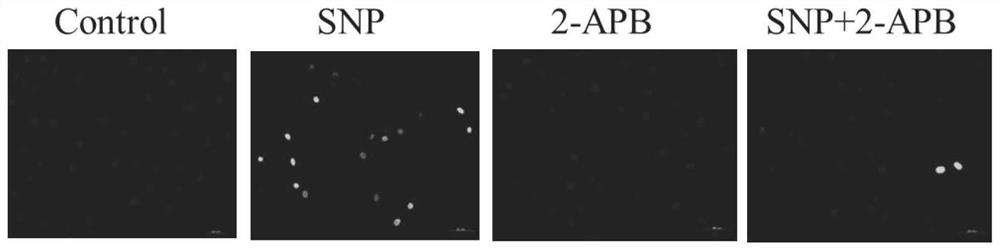
ActiveCN111388485AReduce apoptosisEnhance cell viabilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsNew medicationsArticular chondrocyte
The invention relates to application of 2-aminoethoxy diphenyl borate in preparation of a medicine for treating osteoarthritis, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines. According tothe invention, an apoptosis model is constructed on primary rat articular cartilage cells to simulate cartilage cell damage after osteoarthritis. The invention finds that 2-APB with different concentrations can obviously recover the cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential level of apoptotic chondrocytes and reduce LDH leakage rate and ROS release, and can reduce the cartilage cell apoptosis by inhibiting IHH / Bcl-2 / Bax signal transduction pathway, such that the related research on the cartilage cell protection mechanism is further supplemented and enriched, and the more scientificbasis is provided for the research and the development of new drugs for treating osteoarthritis.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
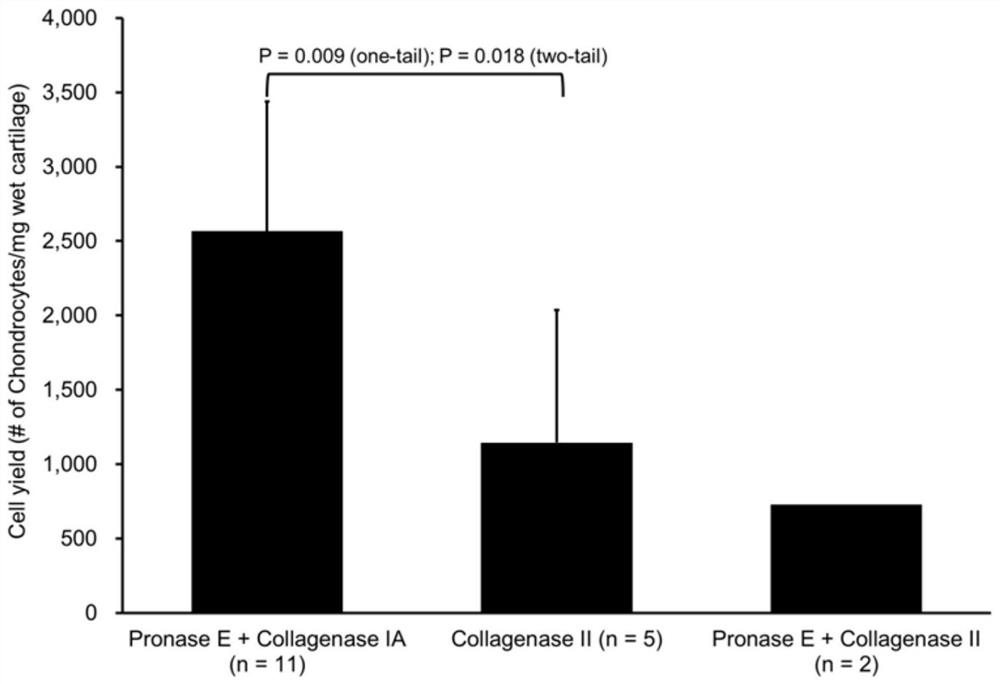
A method for isolating and culturing cells from aged human synovial articular cartilage
ActiveCN110484495BFully contactedIncrease productionCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to a method for separating and culturing cells from synovial articular cartilage of old people, and belongs to the technical field of human tissue engineering. A large number ofcells with metabolic activity are obtained from senile articular cartilage, and the method is applied to molecular pathology and biological treatment fundamental researches for repairing cartilage tissue defects and cartilage degenerative changes through clinical autologous cartilage cell transplantation. The invention discloses a chondrocyte separation method. According to the method, mechanicalcutting and enzymatic hydrolysis of cartilage tissues are combined. Cartilage fragments are in full contact with degradable cartilage extracellular matrix protein specific protease in a tissue decomposition bottle (Spiner flasK) sterilized at high temperature and high pressure and in a cell incubator, thus achieving the purpose of completely dissolving a matrix to release cartilage cells to the maximum extent. Compared with an existing human load-bearing synovial articular cartilage cell separation method, the method has the advantages that the yield of cartilage cells is higher, the proportion of living cartilage cells is larger and the pollution probability is lower.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of 2-apb in preparation of medicine for treating osteoarthritis
ActiveCN111388485BReduce apoptosisEnhance cell viabilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsNew medicationsSacroiliitis
The invention relates to the application of 2-aminoethoxy diphenyl borate in the preparation of medicines for treating osteoarthritis, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The present invention simulates chondrocyte damage after osteoarthritis by constructing an apoptosis model on primary rat articular chondrocytes, and finds that different concentrations of 2-APB can significantly restore the cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential level of apoptotic chondrocytes, reduce LDH leakage rate, ROS release, and can reduce chondrocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the IHH / Bcl‑2 / Bax signal transduction pathway, which further complements and enriches the research on the protection mechanism of chondrocytes, and provides a basis for the research and development of osteoarthritis The new drug provides more scientific basis.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com